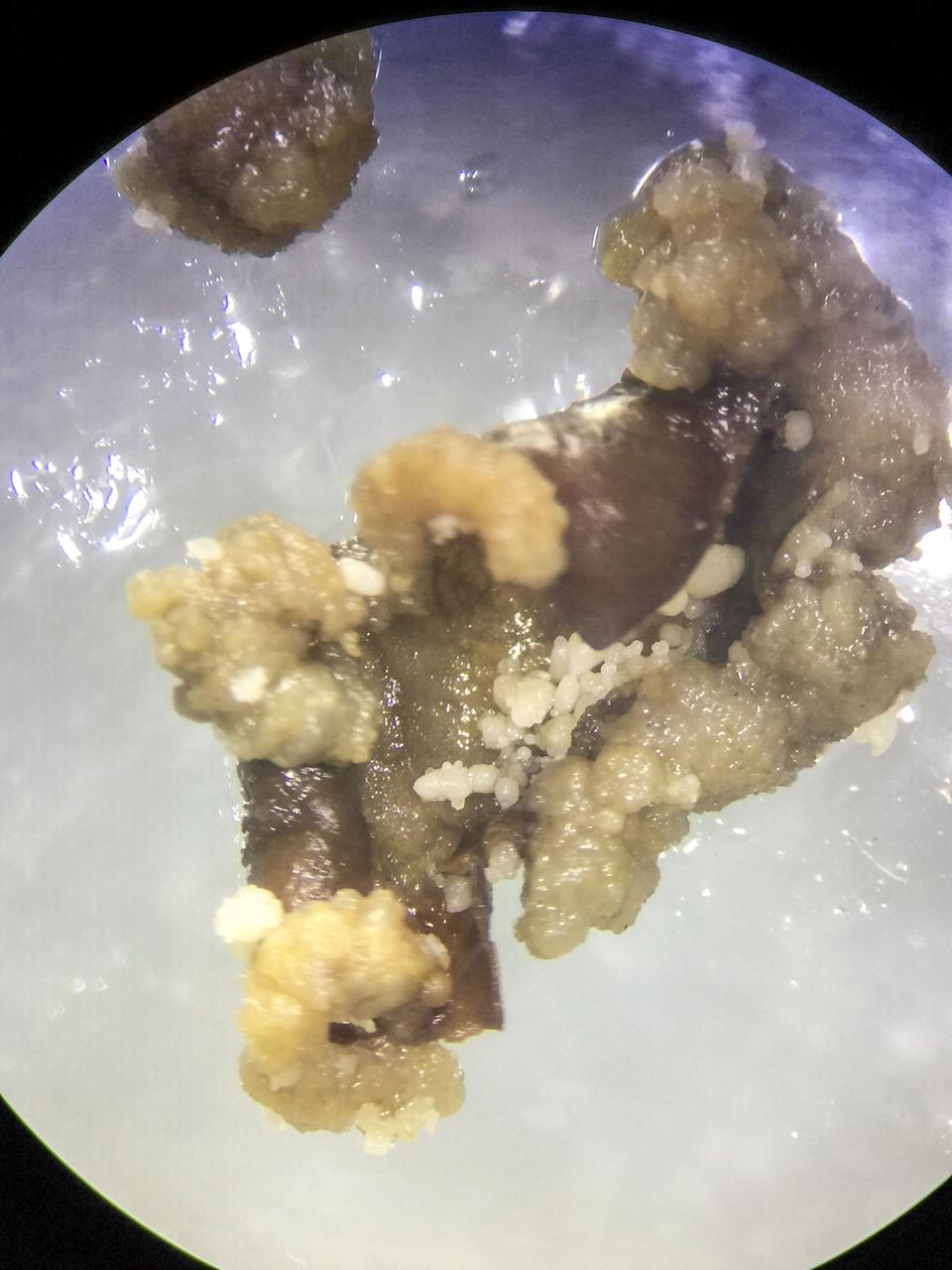

jsc2020e003413 (12/4/2019) --- Preflight imagery of space Cells-01. Space Cells-01 examines gene expression changes and genetic mutations in hemp and coffee plant cells in microgravity. Cell cultures spend approximately one month on the space station then return to Earth for analysis of their physical structure and gene expression and are compared to preflight parameters. Results could help identify new varieties or chemical expressions in the plants and improve understanding of how plants manage the stress of space travel.
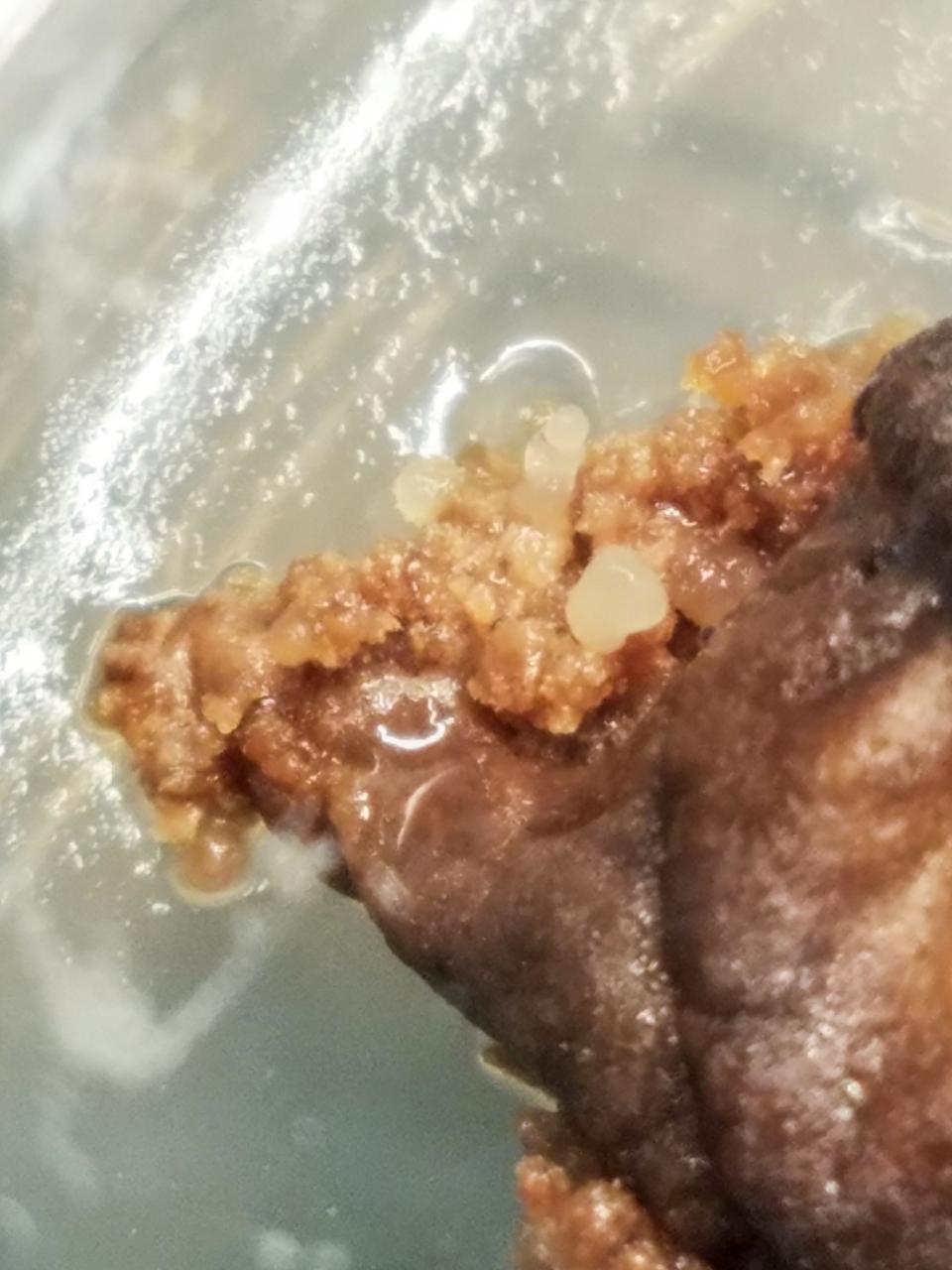
jsc2020e003414 (12/20/2019) --- Preflight imagery of Space Cells-01. Space Cells-01 examines gene expression changes and genetic mutations in hemp and coffee plant cells in microgravity. Cell cultures spend approximately one month on the space station then return to Earth for analysis of their physical structure and gene expression and are compared to preflight parameters. Results could help identify new varieties or chemical expressions in the plants and improve understanding of how plants manage the stress of space travel.
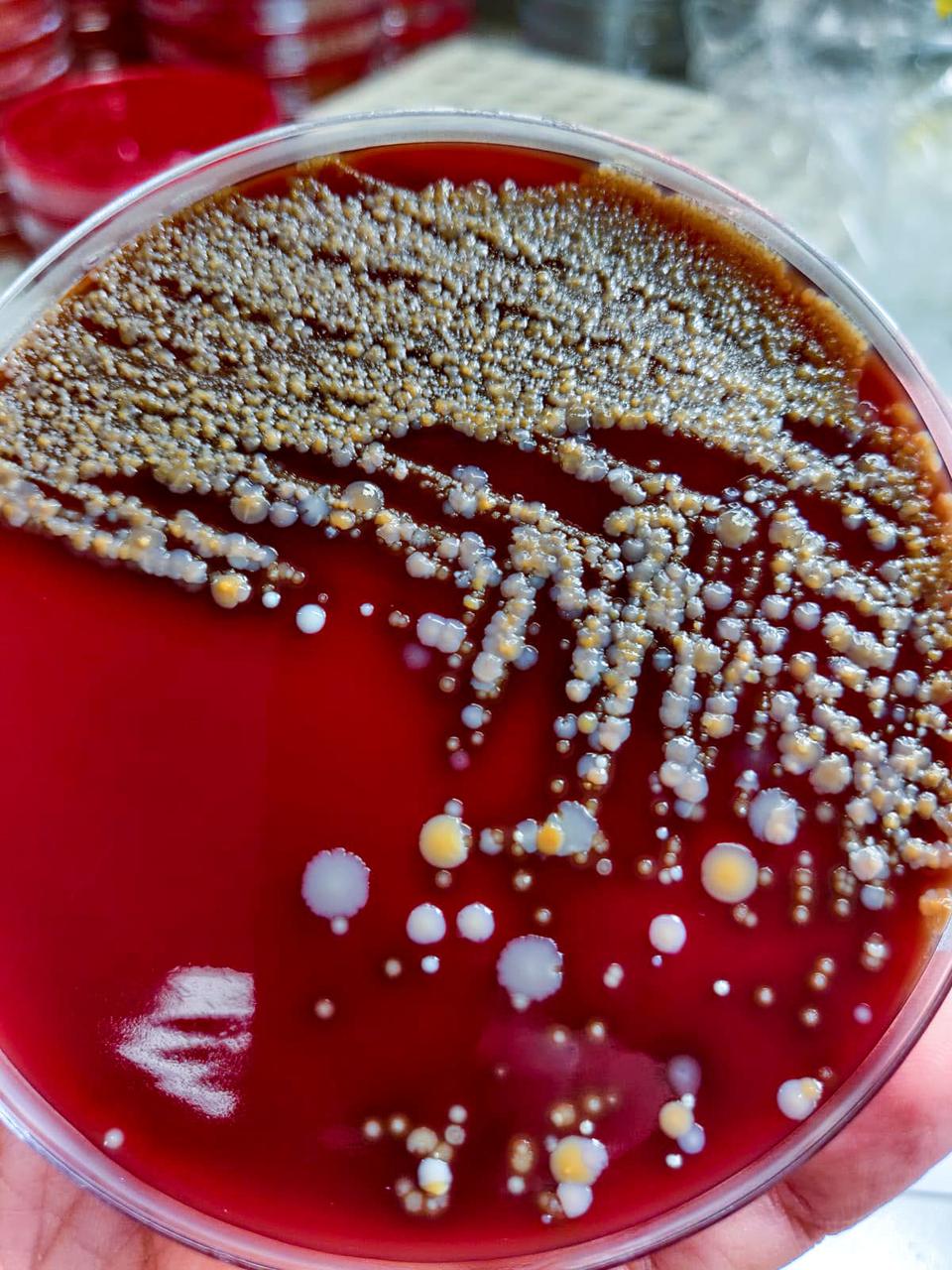
sc2021e033545 (8/4/2021) --- A preflight view the Ice Cubes #9 – Project Maleth (Space Omics Analysis of the Skin Microbiome of Diabetic Foot Ulcers, or SpaceOMIX) The investigation studies Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFU) using genetics and space biosciences is new and innovative research. Image credit: DOI: Ministry for Foreign and European Affairs, Malta
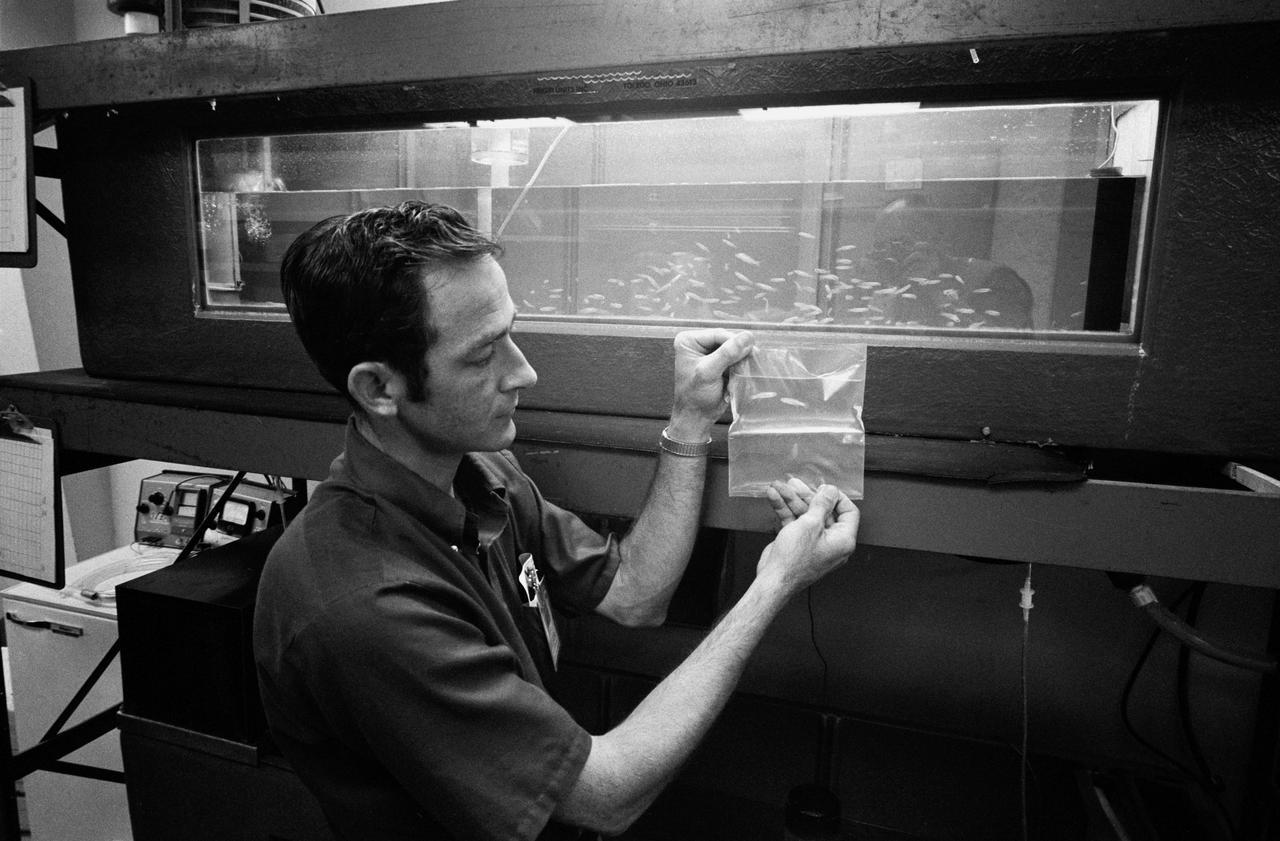

S73-30856 (29 June 1973) --- John Boyd observes a bag with two ?brackish water? minnows known as ?Mummichog Minnows? which will be onboard Skylab 3 with astronauts Alan L. Bean, Owen K. Garriott and Jack R. Lousma. The fish were added to the flight at the request of scientist-astronaut Dr. Owen K. Garriott, science pilot. Fifty eggs from the minnows will also be included in the bag. The objective of this experiment is to show what disorientation the fish will experience when exposed to weightlessness. Many fish have vestibular apparatus quite similar to man. Even though they live in an environment usually considered to resemble weightlessness, they do perceive a gravity vector. An aquarium of the minnows, caught off the coast of Beaufort, North Carolina, is in the background. Photo credit: NASA
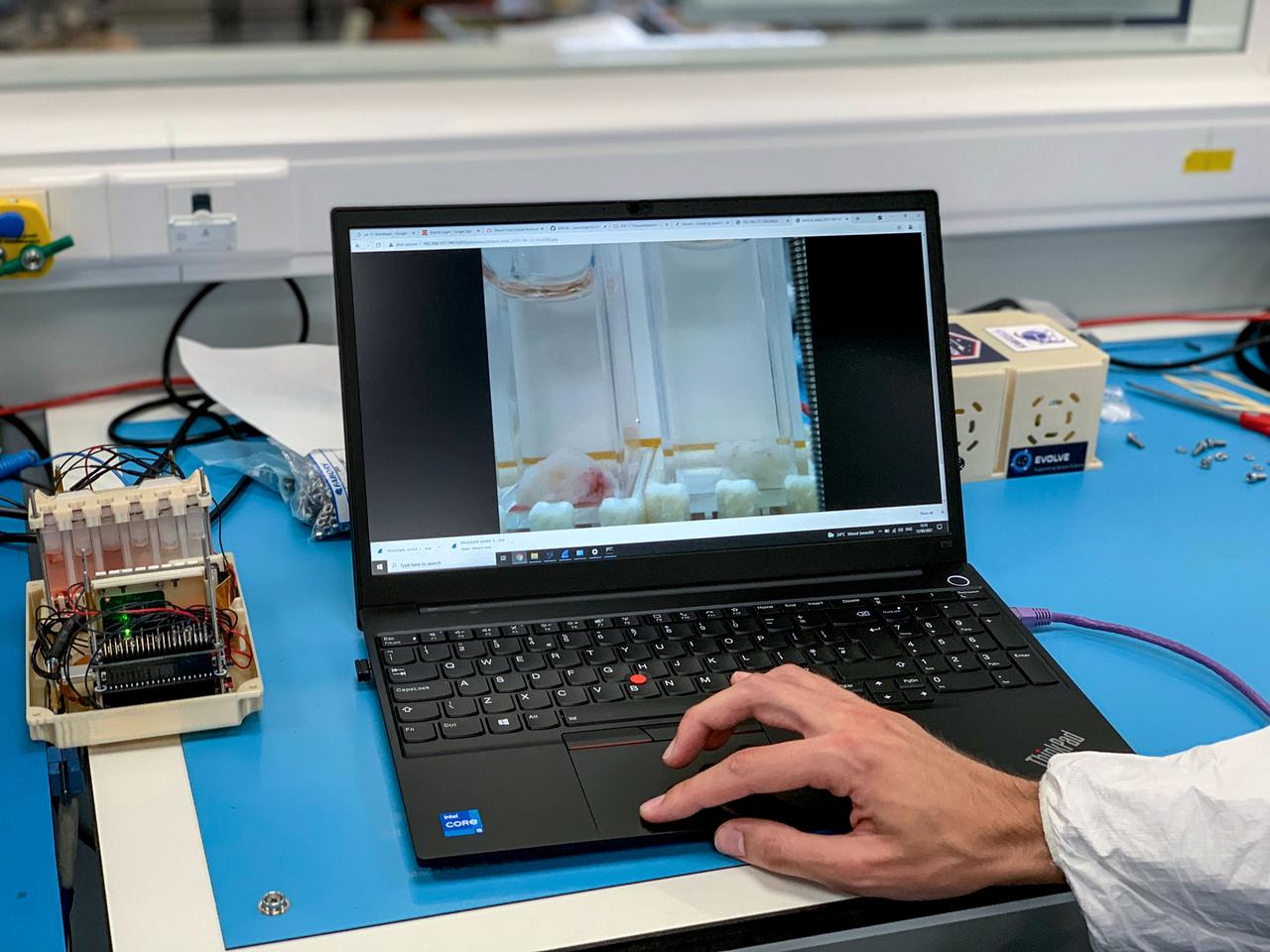

jsc2021e037898 (8/12/2021) --- A preflight image shows a zoomed up picture of two sample cuvettes containing human skin samples taken by the raspberry Pi video feed. Videos of up to 60 FPS can be recorded and saved for remote use. The Ice Cubes #9 – Project Maleth (Space Omics Analysis of the Skin Microbiome of Diabetic Foot Ulcers, or SpaceOMIX) investigation that studies Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFU) using genetics and space biosciences is new and innovative research. Image courtesy Space Applications Services.
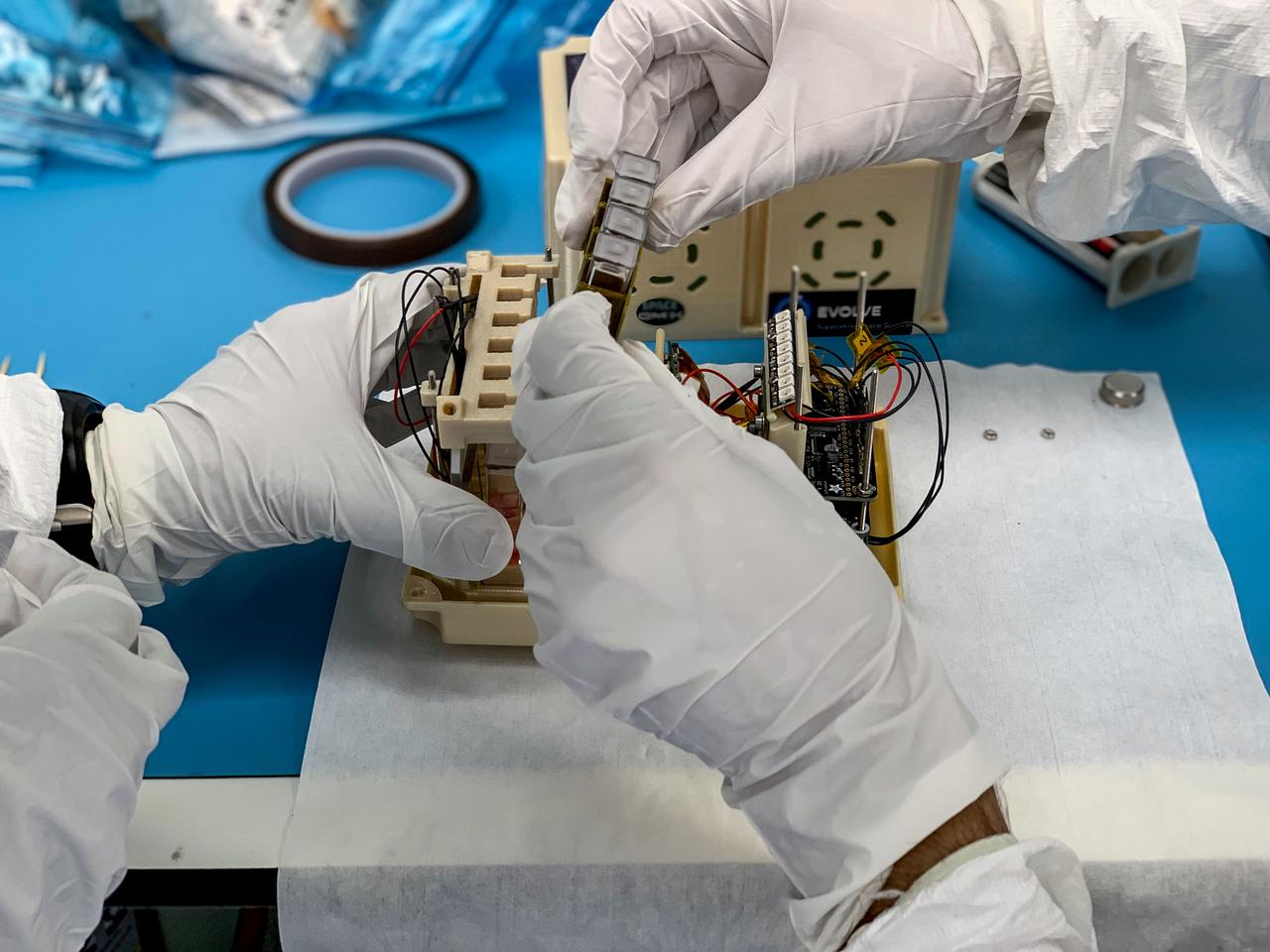
jsc2021e037896 (8/12/2021) --- A preflight imagevshows integration of 2nd to 5th sample cuvettes to fit between the first and last samples cuvettes. The sample cuvettes are securely fastened in place using tools and under strict clean room preparations. The Ice Cubes #9 – Project Maleth (Space Omics Analysis of the Skin Microbiome of Diabetic Foot Ulcers, or SpaceOMIX) investigation that studies Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFU) using genetics and space biosciences is new and innovative research. Image courtesy Space Applications Services.

jsc2021e037900 (8/12/2021) --- A preflight image shows the two cameras facing the six cuvettes. A set of soft RGB led lights are also present that will illuminate to varying levels the lighting inside the cube. The top cover is shown alongside the base together with the prominent logos of the misson. The Ice Cubes #9 – Project Maleth (Space Omics Analysis of the Skin Microbiome of Diabetic Foot Ulcers, or SpaceOMIX) investigation that studies Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFU) using genetics and space biosciences is new and innovative research. Image courtesy Space Applications Services.

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this video of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter's 54th flight on Aug. 3, 2023. After performing a preflight "wiggle check" with its rotors, the helicopter takes off, hovers at an altitude of 16 feet (5 meters), and rotates to the left, before touching back down. The mission conducted the short pop-up flight to check Ingenuity's navigation system. The video was captured by the rover's Mastcam-Z imager from a distance of about 180 feet (55 meters). Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25970
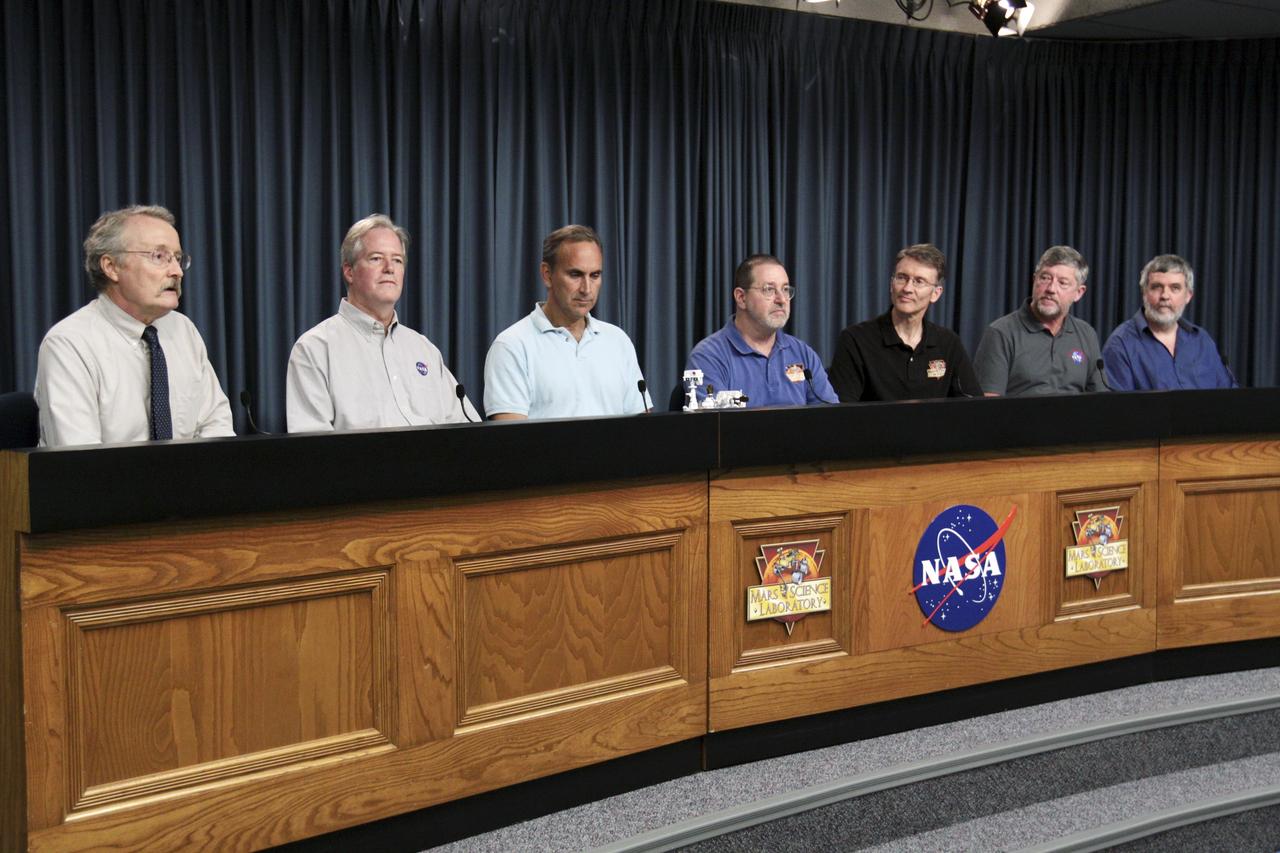

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is host to a Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) science briefing as part of preflight activities for the MSL mission. From left, NASA Public Affairs Officer Guy Webster moderates the conference featuring Michael Meyer, lead scientist for NASA Mars Exploration Program; John Grotzinger, project scientist for Mars Science Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif.; Michael Malin, principal investigator for the Mast Camera and Mars Descent Imager investigations on Curiosity, Malin Space Science Systems; Roger Wiens, principal investigator for Chemistry and Camera investigation on Curiosity, Los Alamos National Laboratory; David Blake, NASA principal investigator for Chemistry and Mineralogy investigation on Curiosity, NASA Ames Research Center; and Paul Mahaffy, NASA principal investigator for Sample Analysis at Mars investigation on Curiosity, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
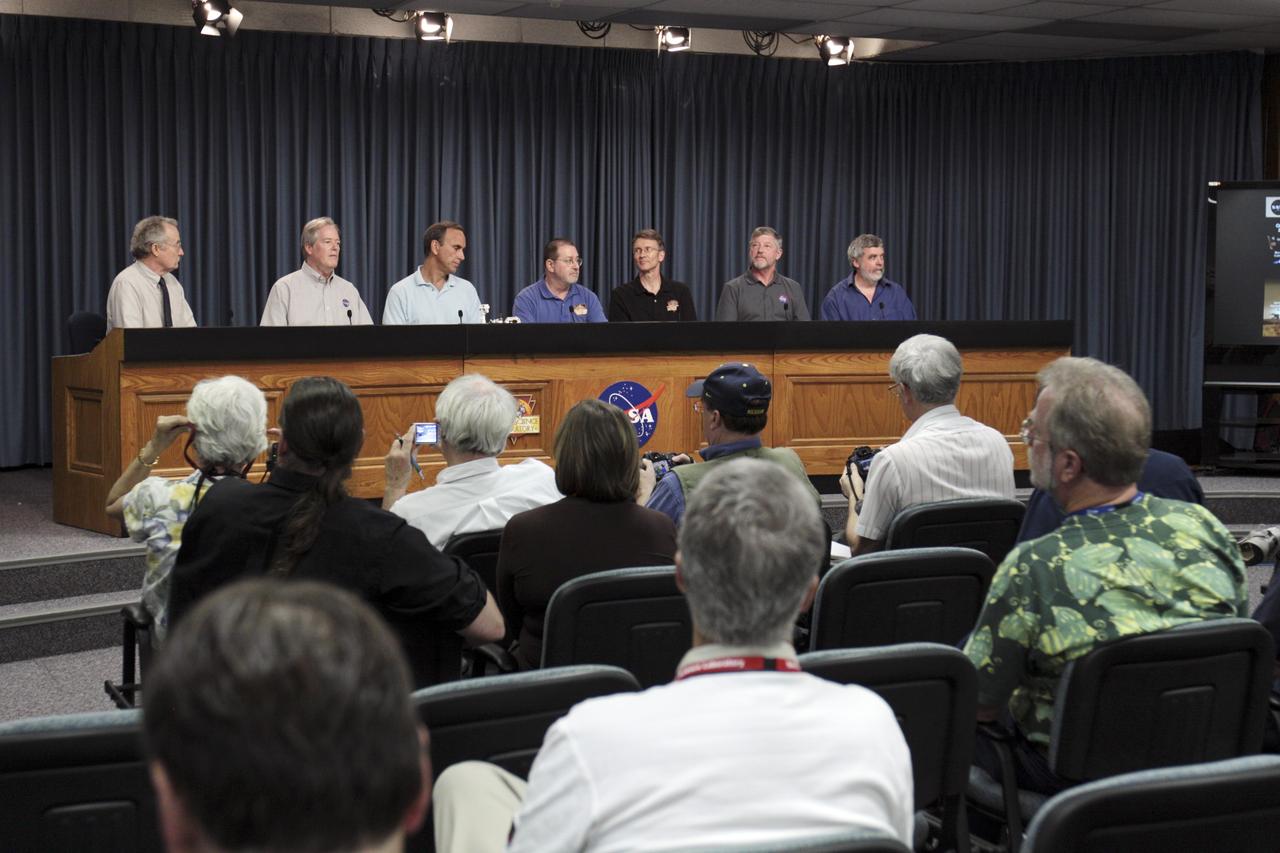

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is host to a Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) science briefing as part of preflight activities for the MSL mission. From left, NASA Public Affairs Officer Guy Webster moderates the conference featuring Michael Meyer, lead scientist for NASA Mars Exploration Program; John Grotzinger, project scientist for Mars Science Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif.; Michael Malin, principal investigator for the Mast Camera and Mars Descent Imager investigations on Curiosity, Malin Space Science Systems; Roger Wiens, principal investigator for Chemistry and Camera investigation on Curiosity, Los Alamos National Laboratory; David Blake, NASA principal investigator for Chemistry and Mineralogy investigation on Curiosity, NASA Ames Research Center; and Paul Mahaffy, NASA principal investigator for Sample Analysis at Mars investigation on Curiosity, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett