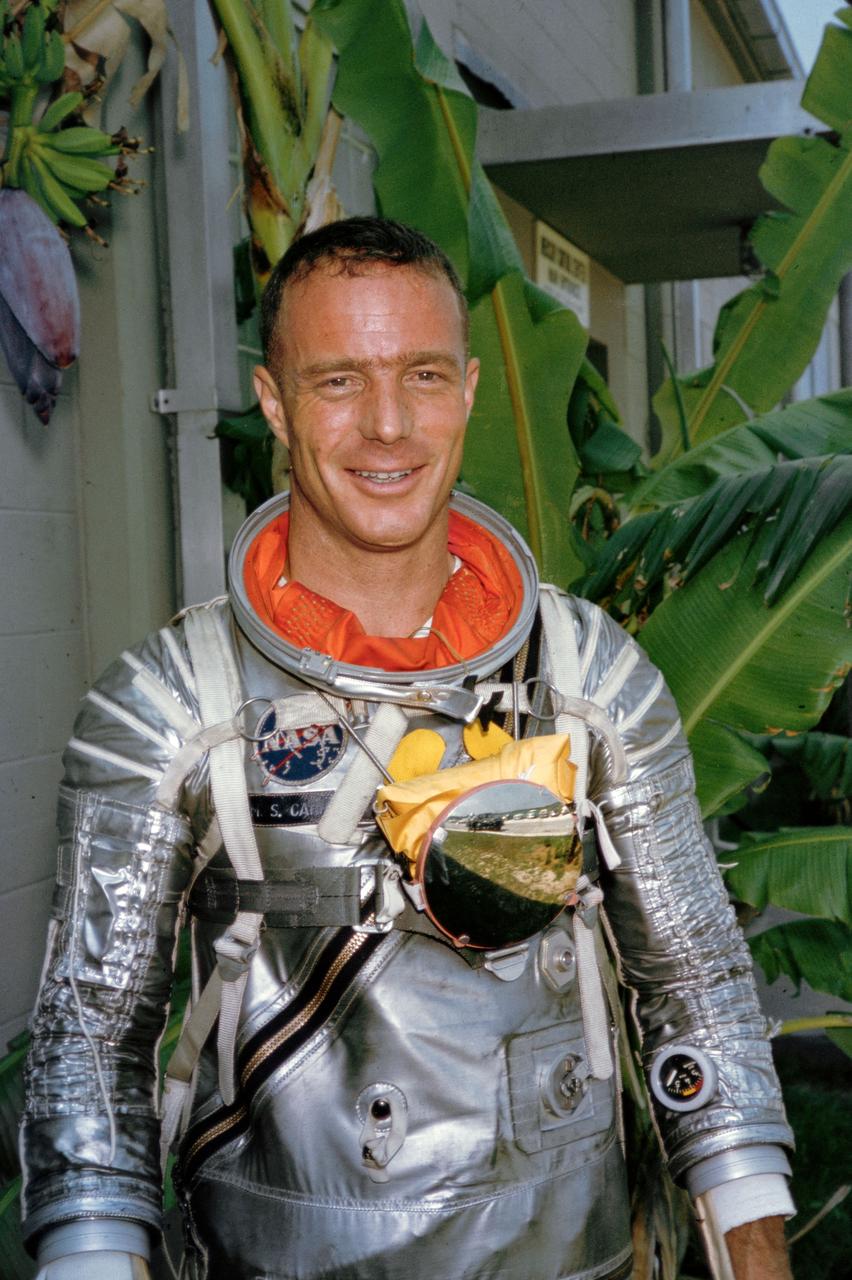

S64-36908 (1962) --- Portrait view of astronaut M. Scott Carpenter, wearing Mercury pressure suit, posing for pictures during astronaut training at the Cape Canaveral, Florida. Photo credit: NASA
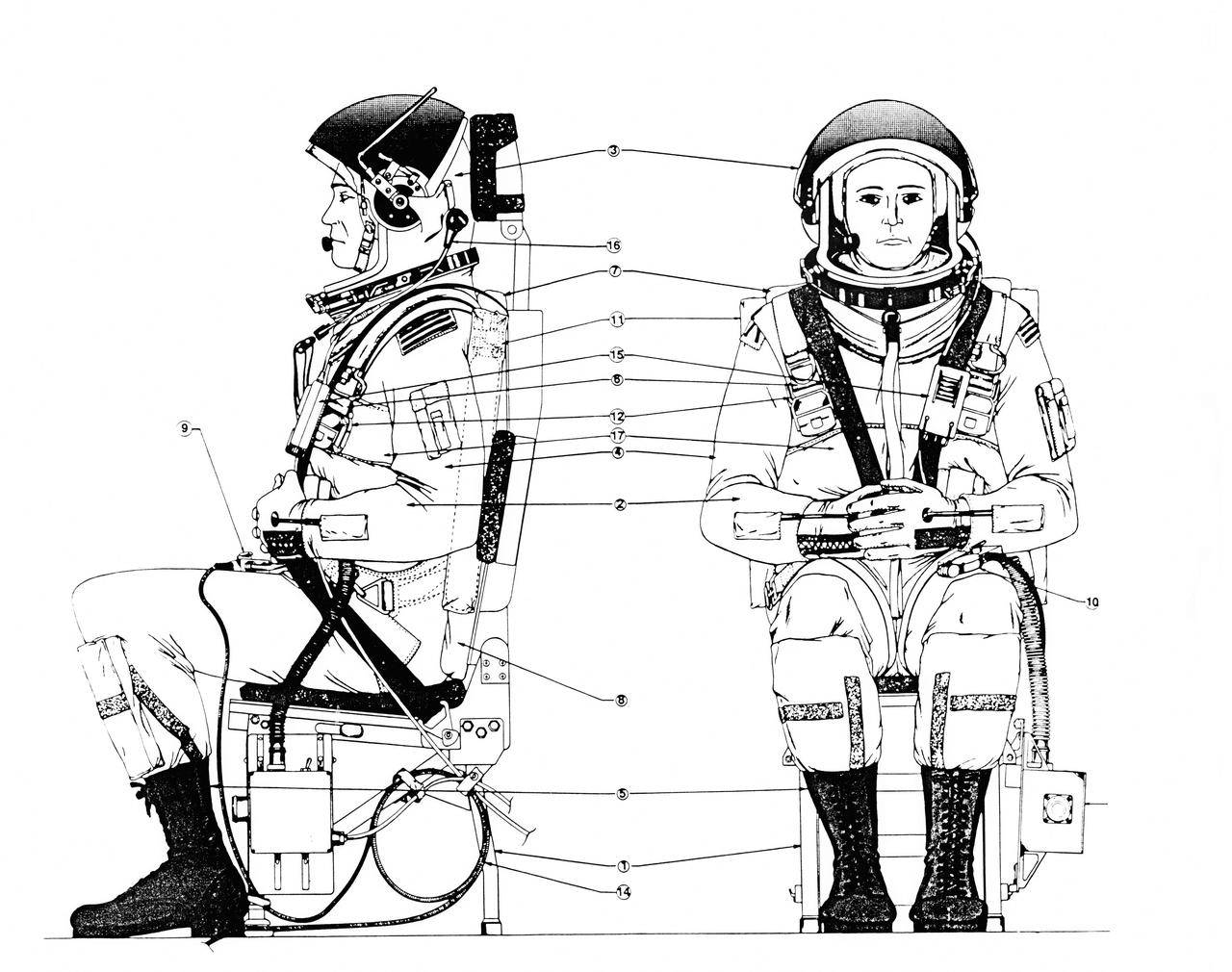
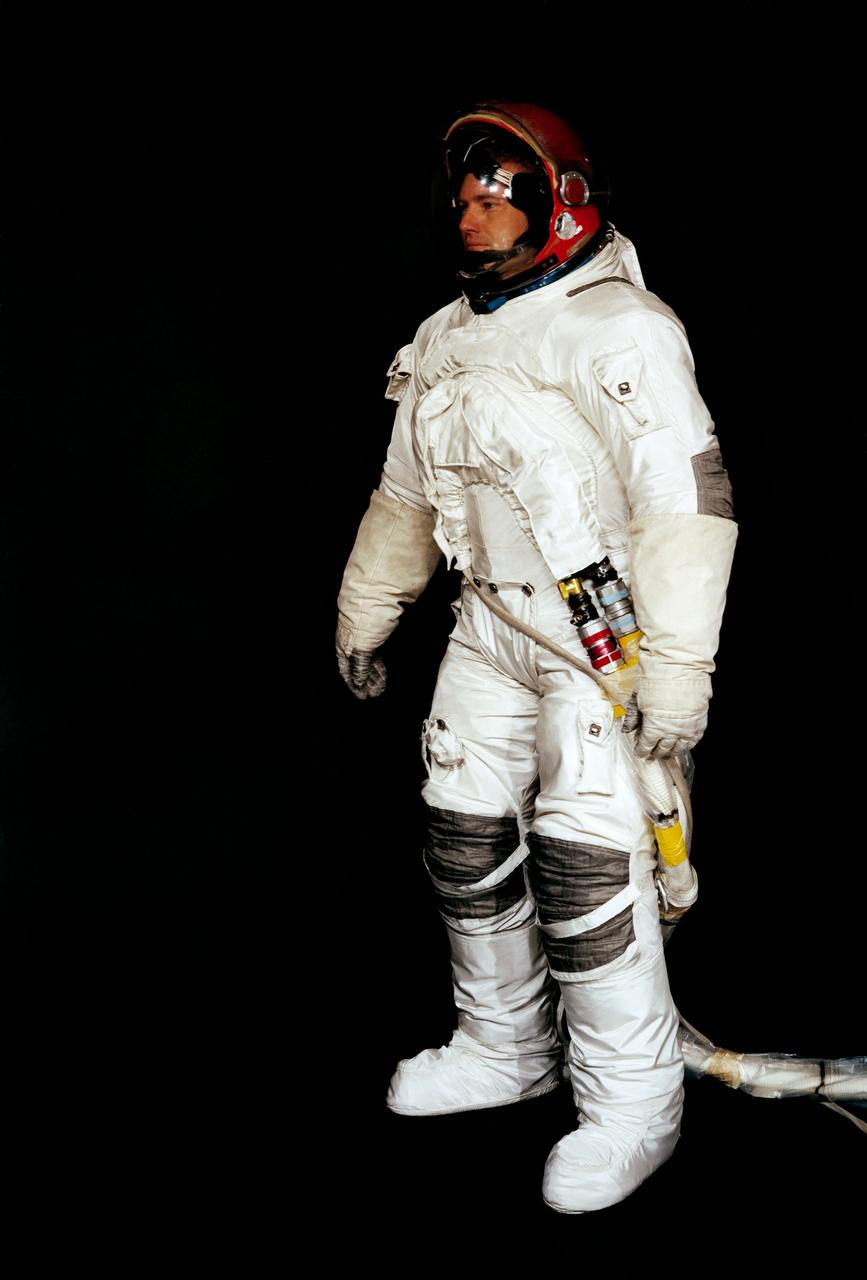
Diagrams of Crew Escape System Partial Pressure Suits, dated July, 1988.
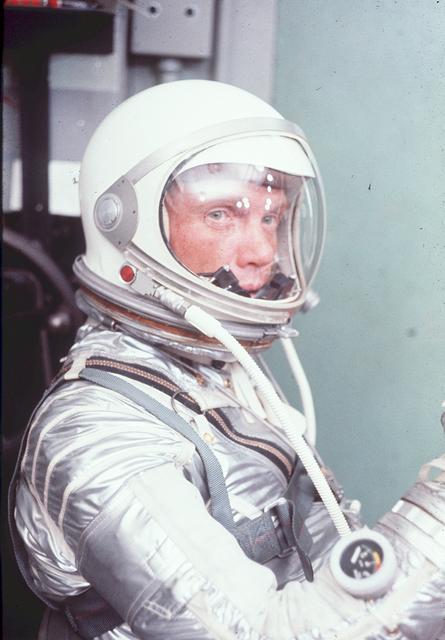

S64-36910 (February 1962) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., wearing a Mercury pressure suit, was the pilot of the Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) mission. Glenn made America's first manned Earth-orbiting spaceflight on Feb. 20, 1962. This photograph was taken at Cape Canaveral, Florida, during MA-6 preflight training activities. Photo credit: NASA
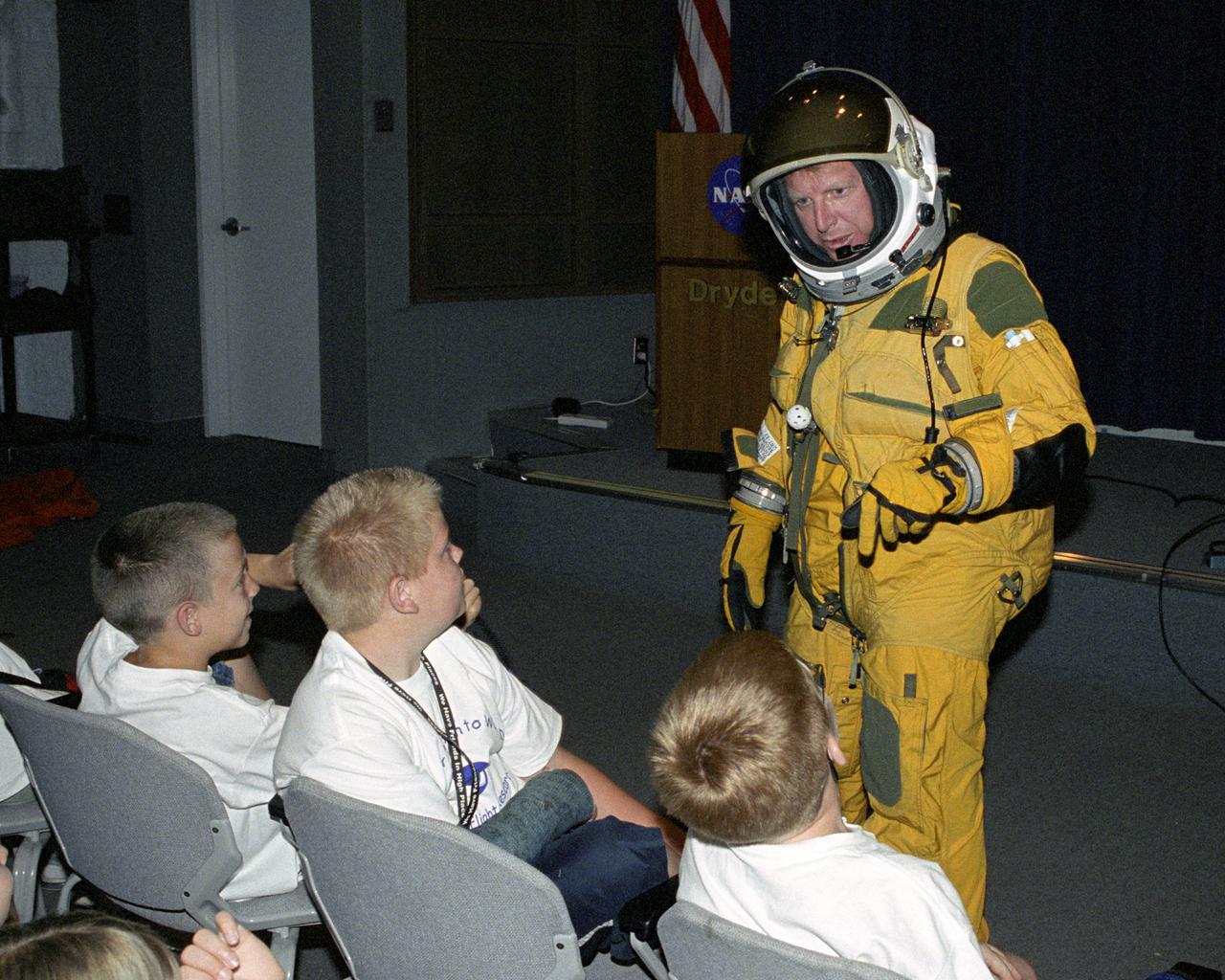

NASA Dryden historian Christian Gelzer explains functions of the high-altitude pressure suit he is wearing to (left to right) Brandon Blankenship and Garrett Clay of Lancaster and Eddie Patterson of Tehachapi during Take Your Children to Work Day activities at NASA Dryden Flight Research Center June 22.
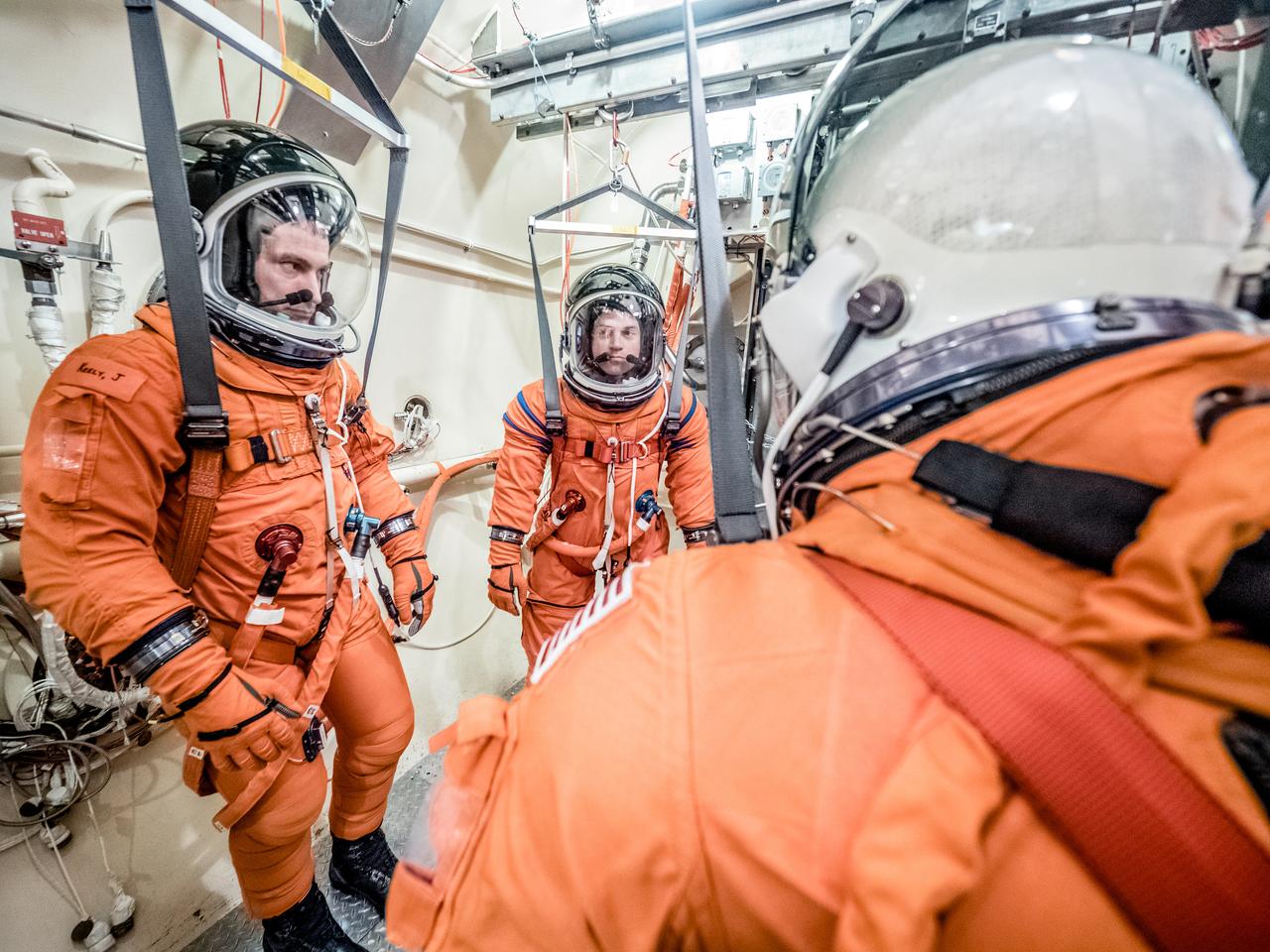

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
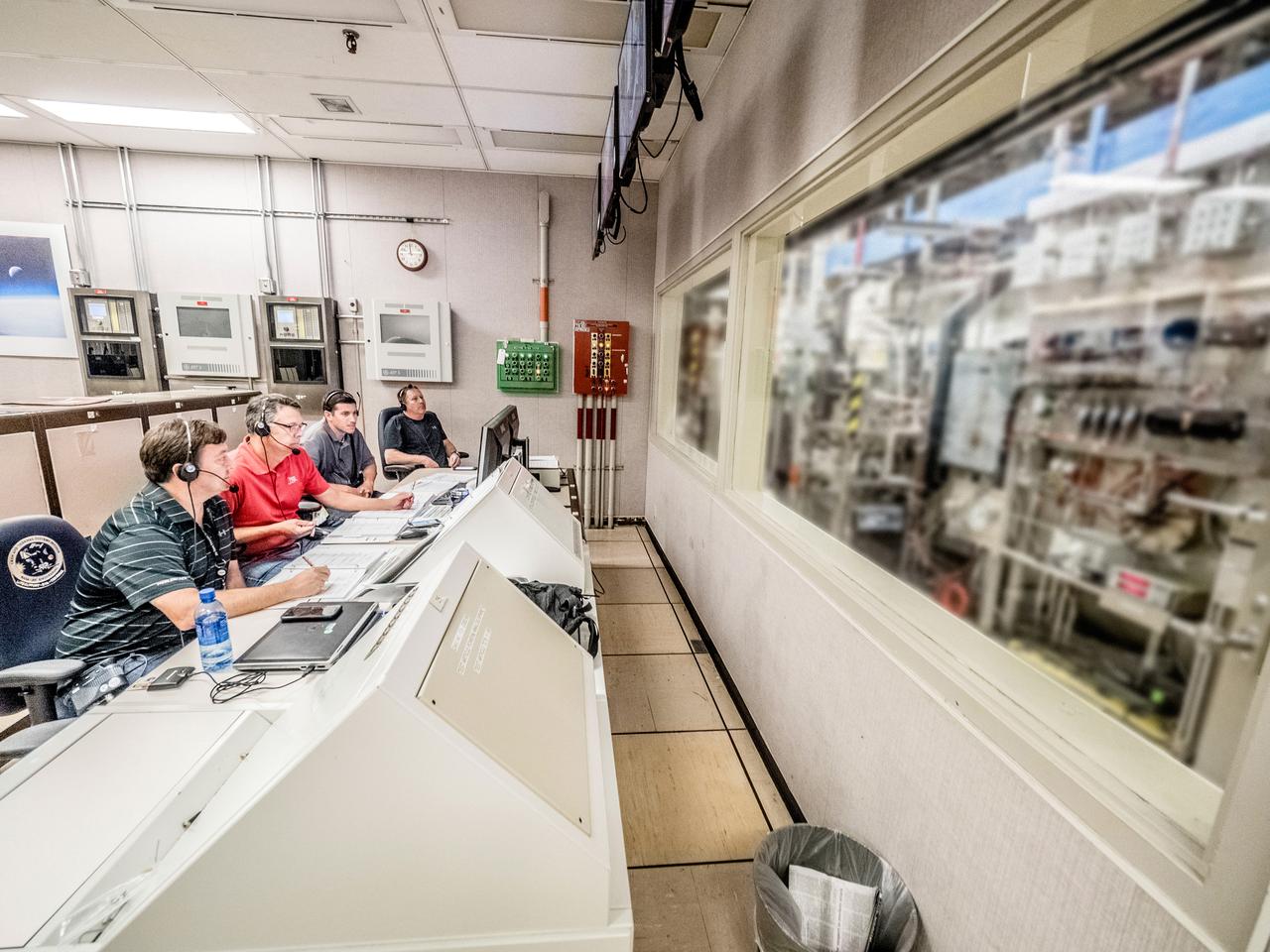

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
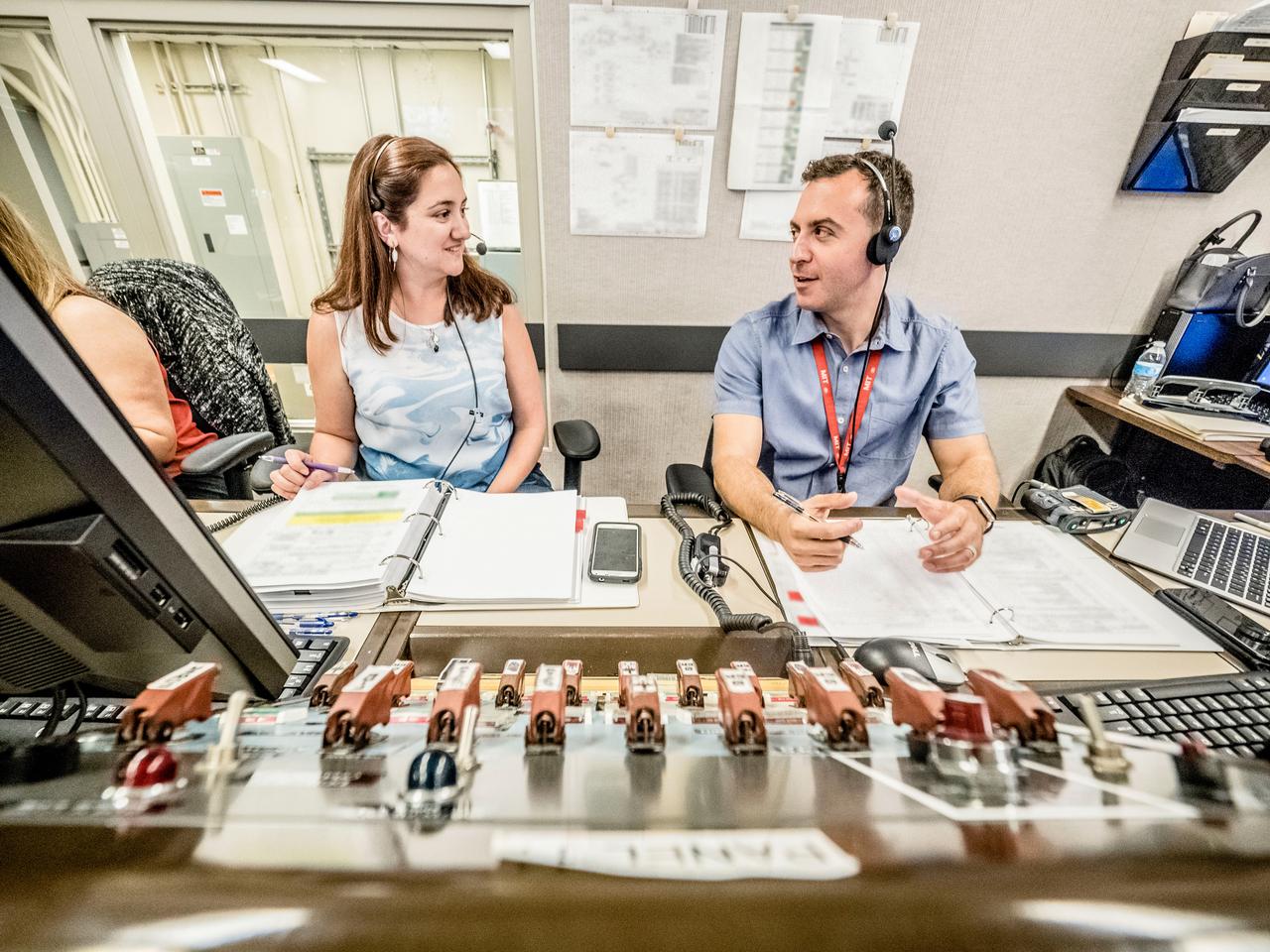

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
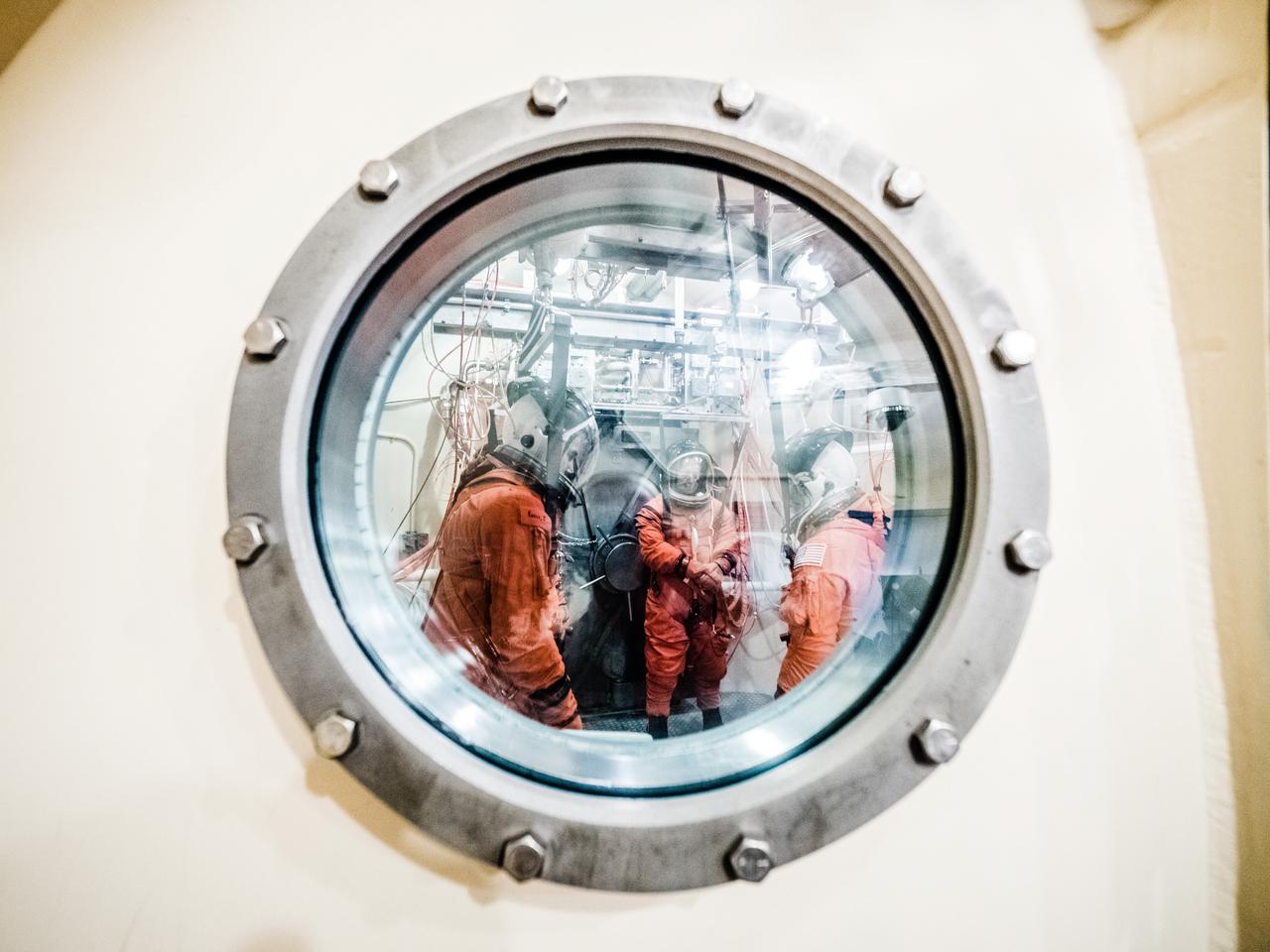

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
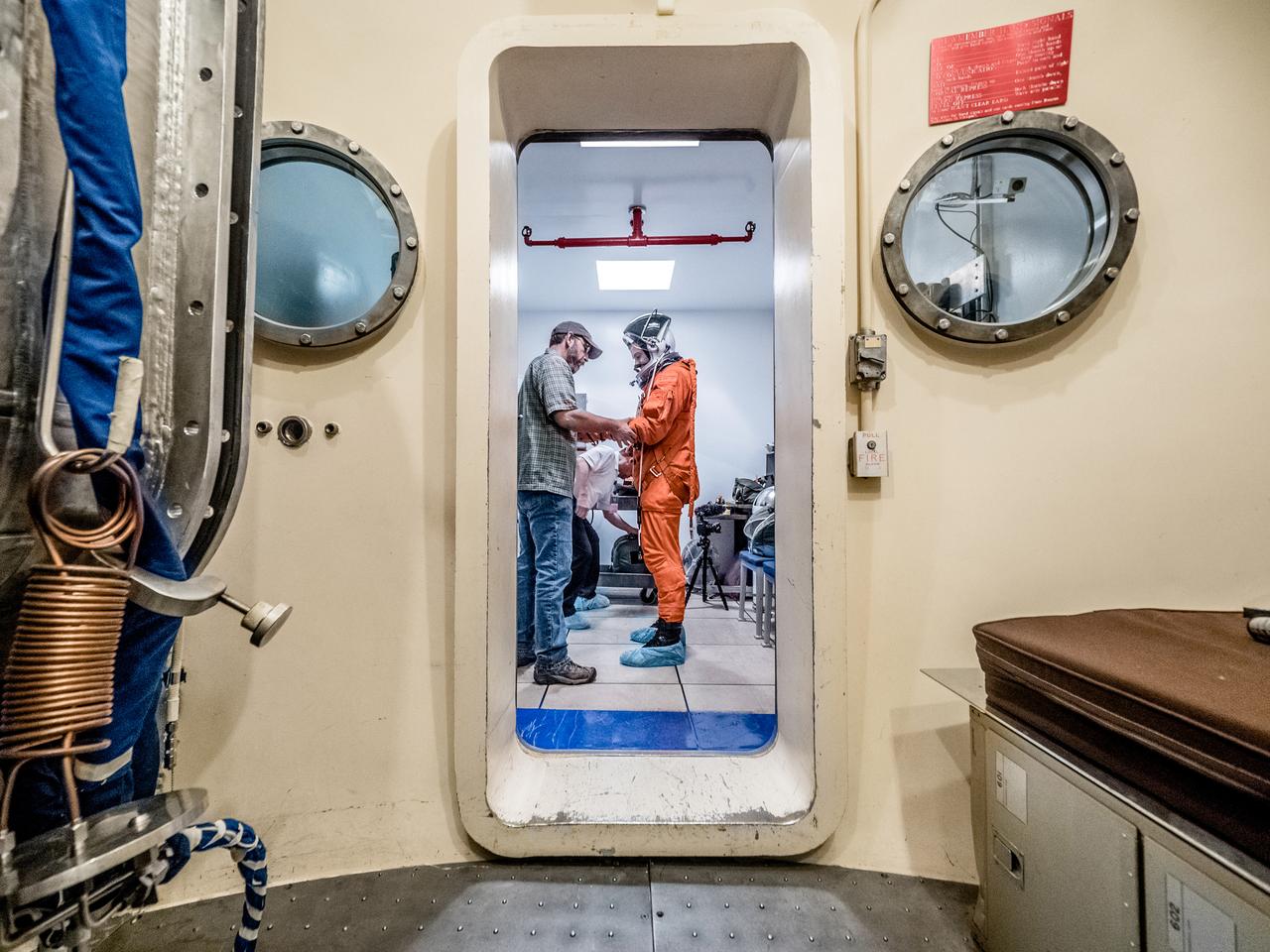

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
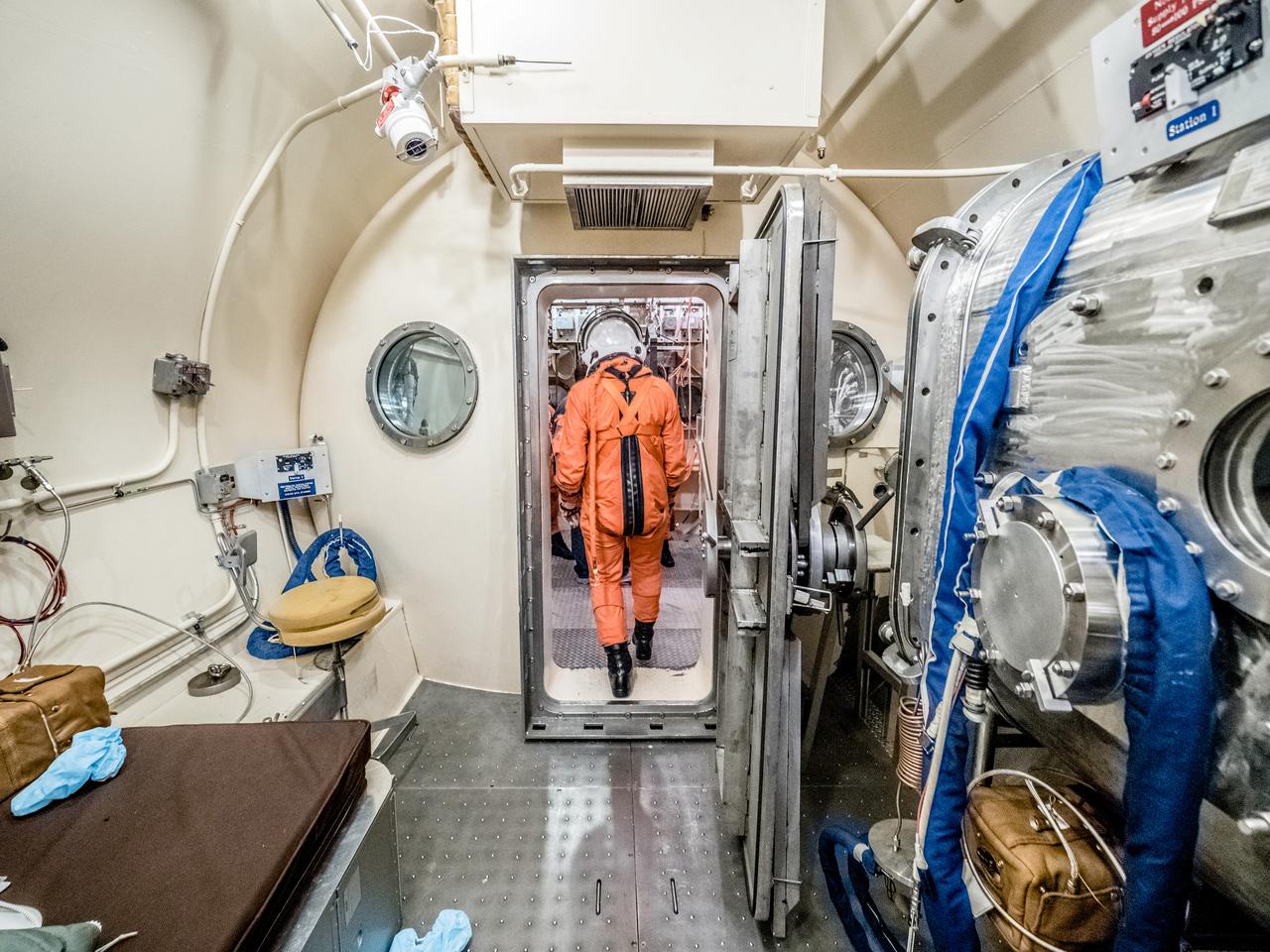

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
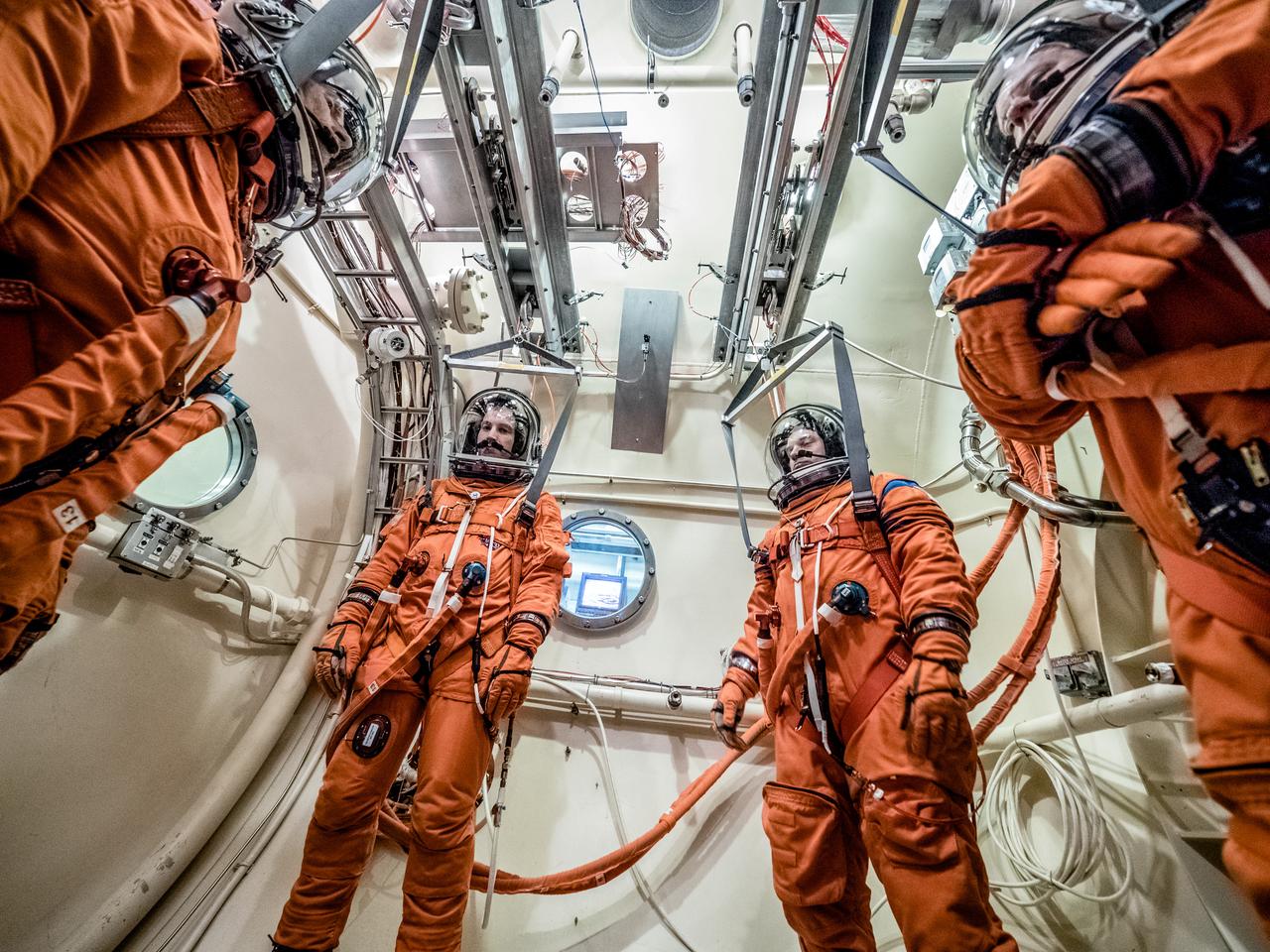

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
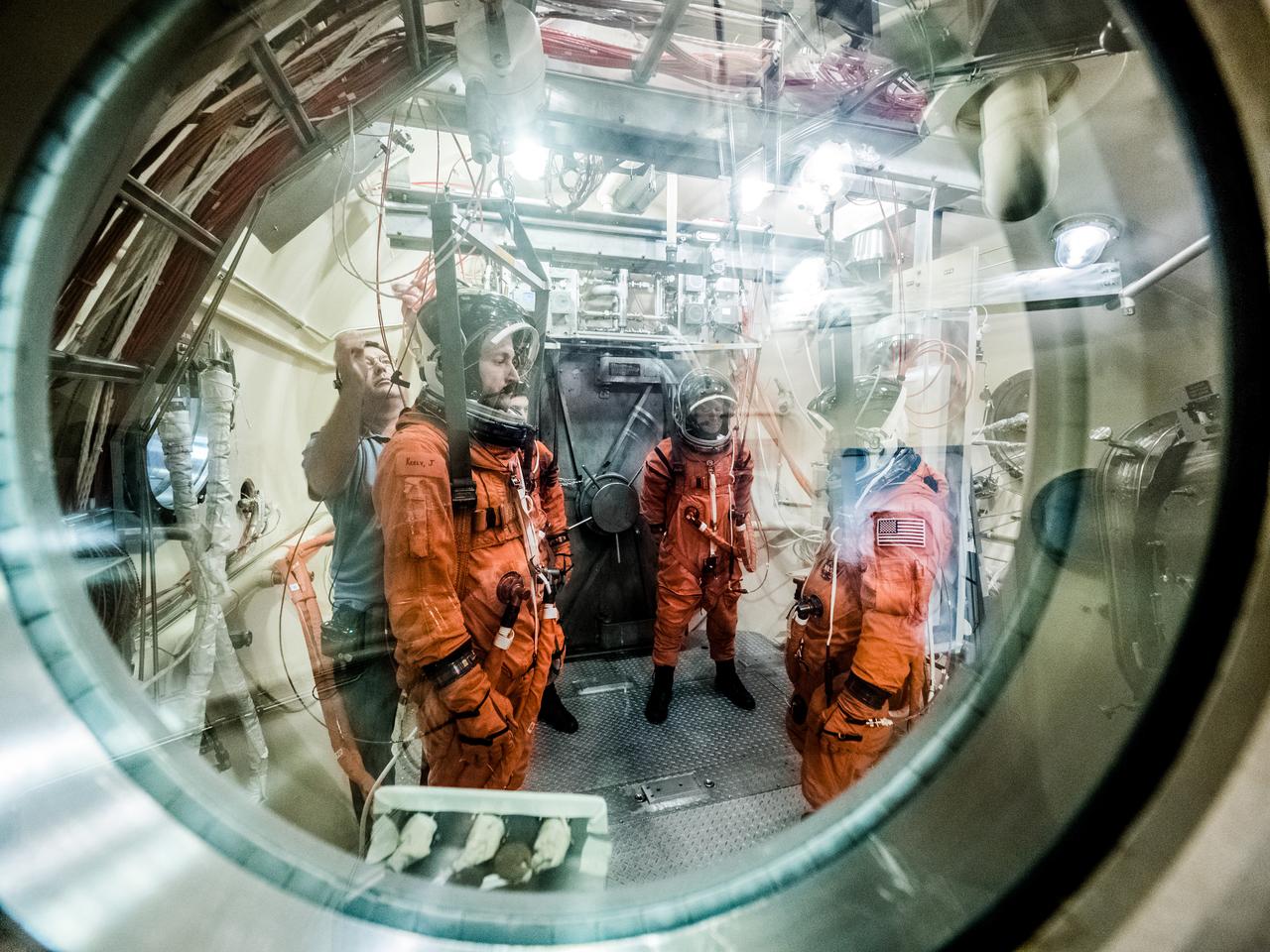

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
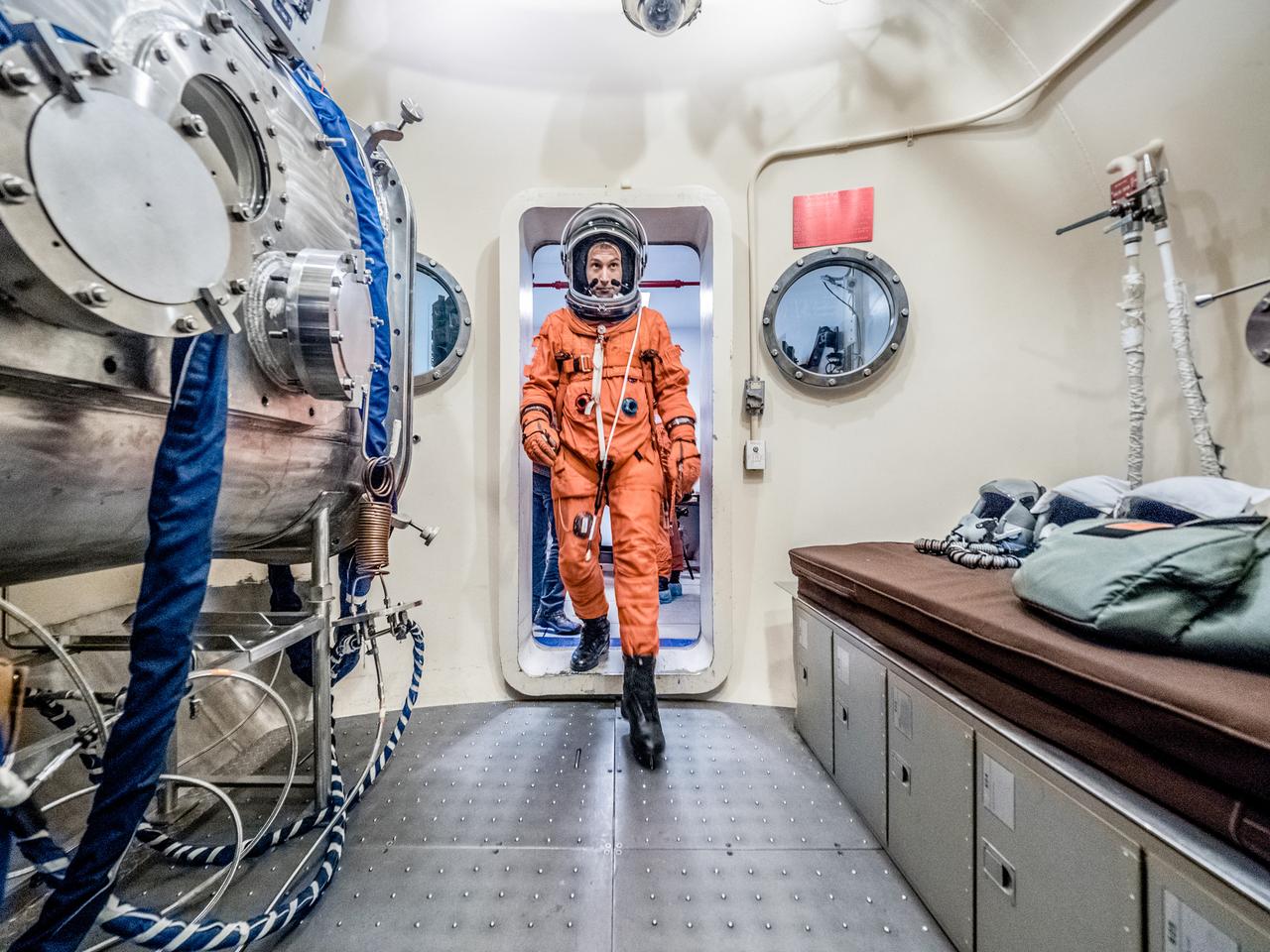

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
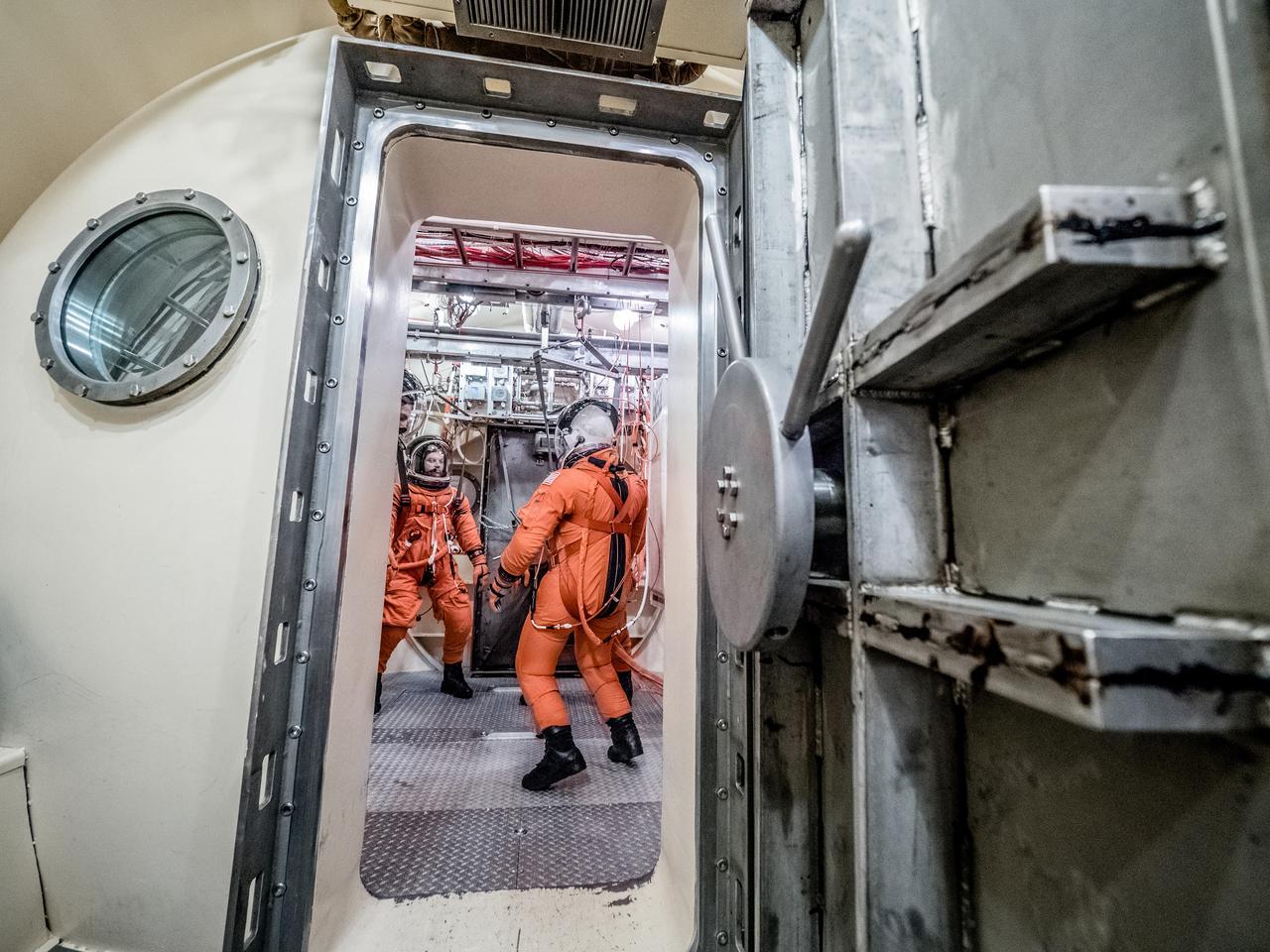

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
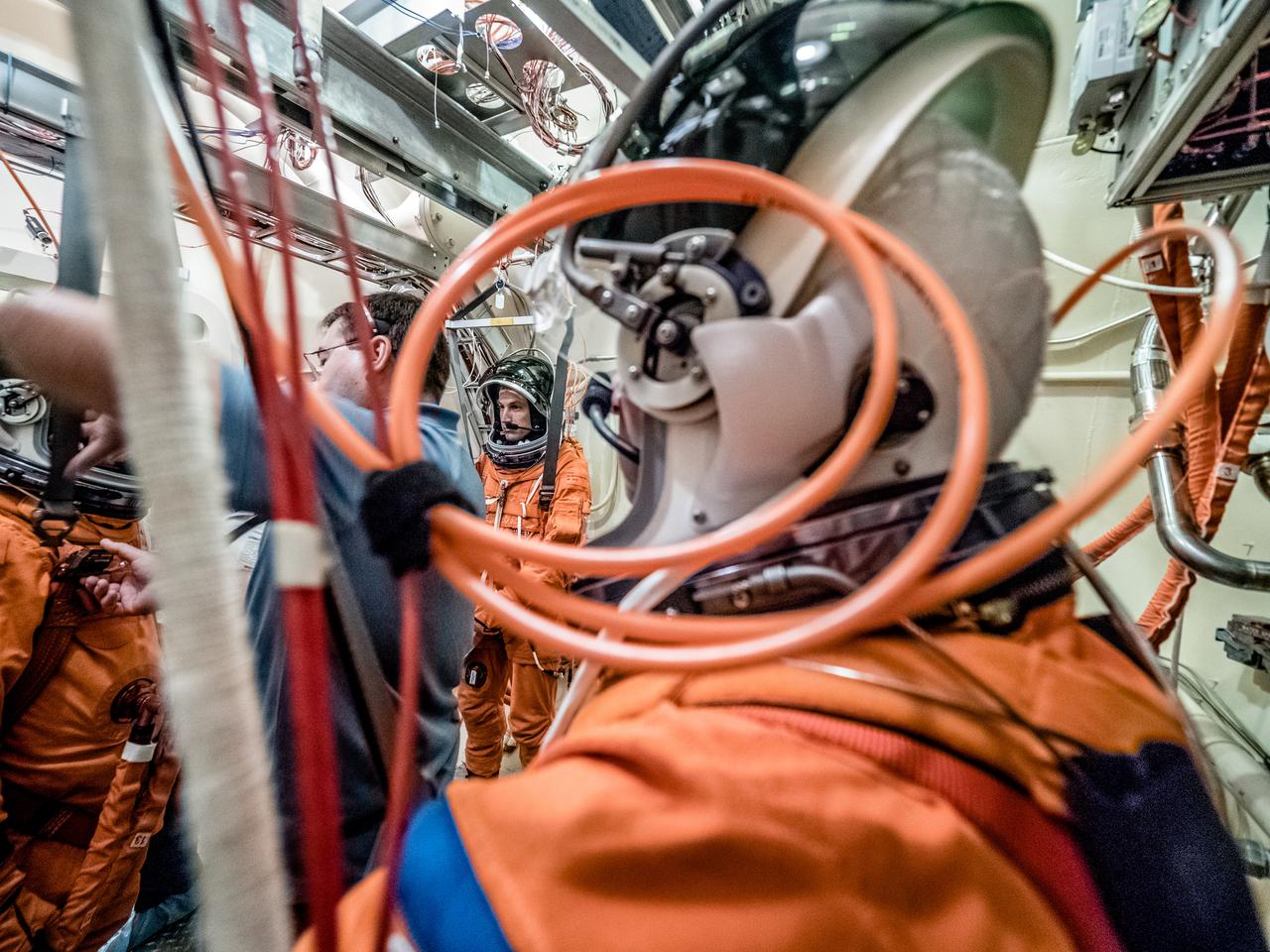

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
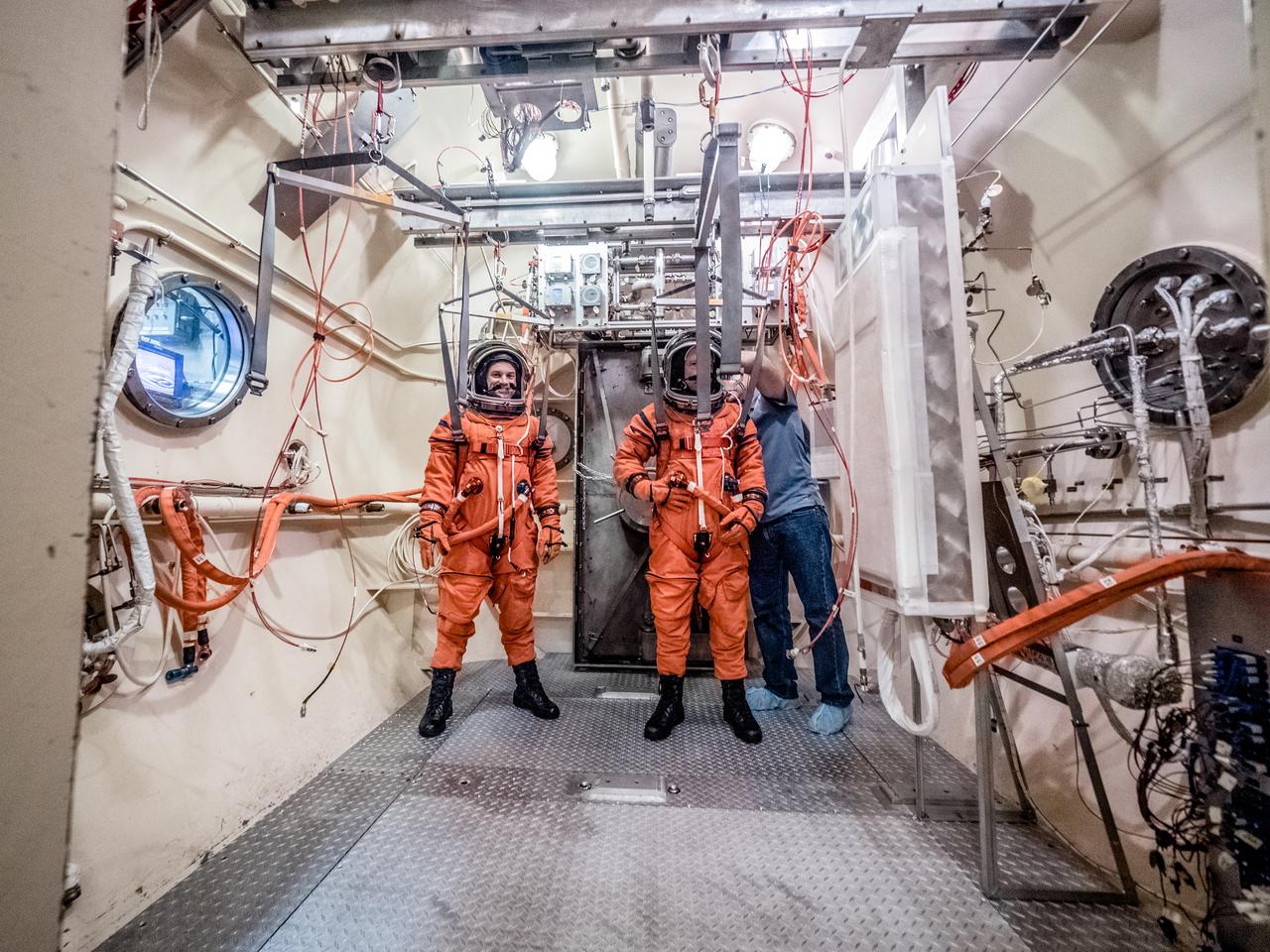

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
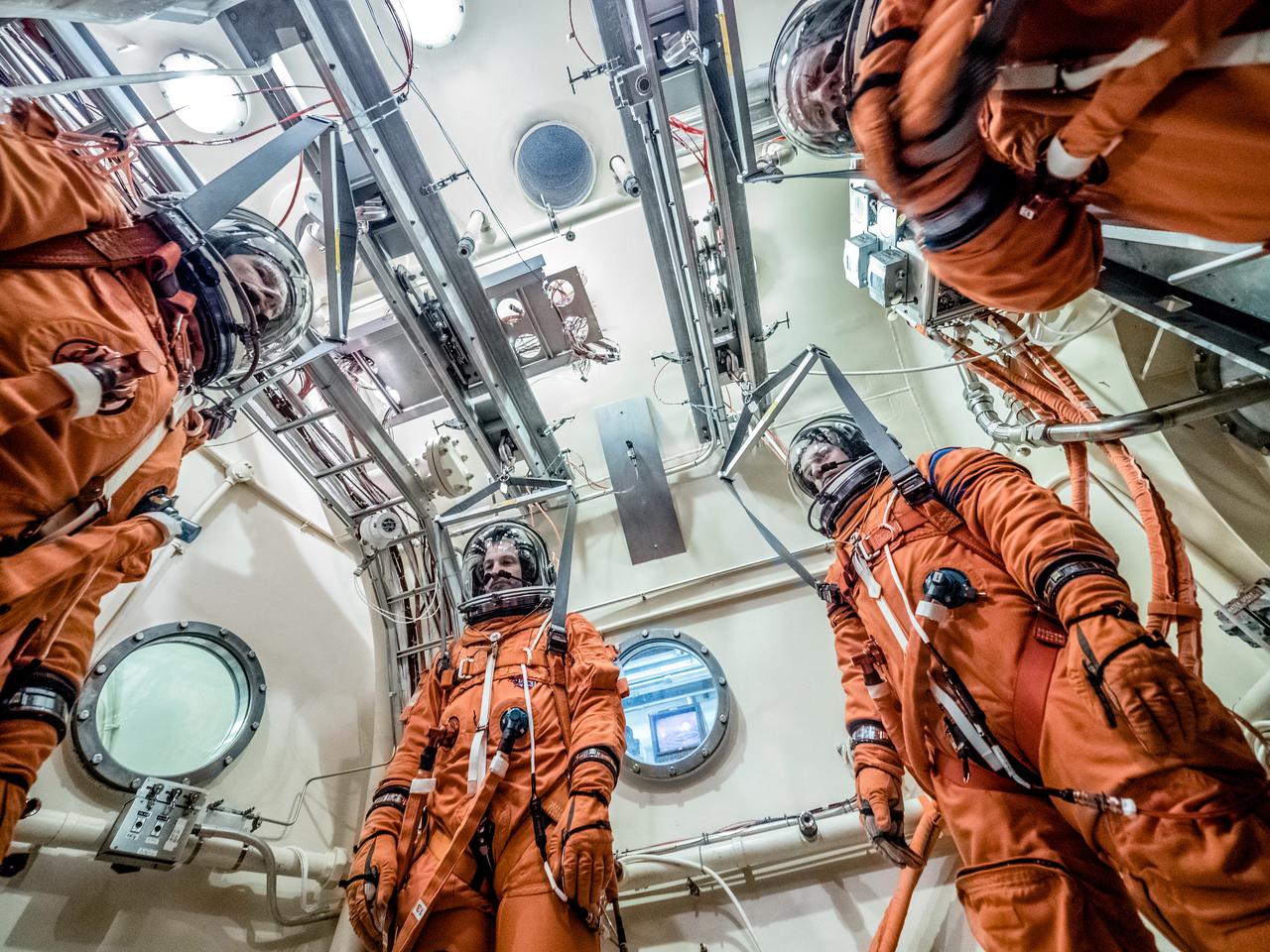

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
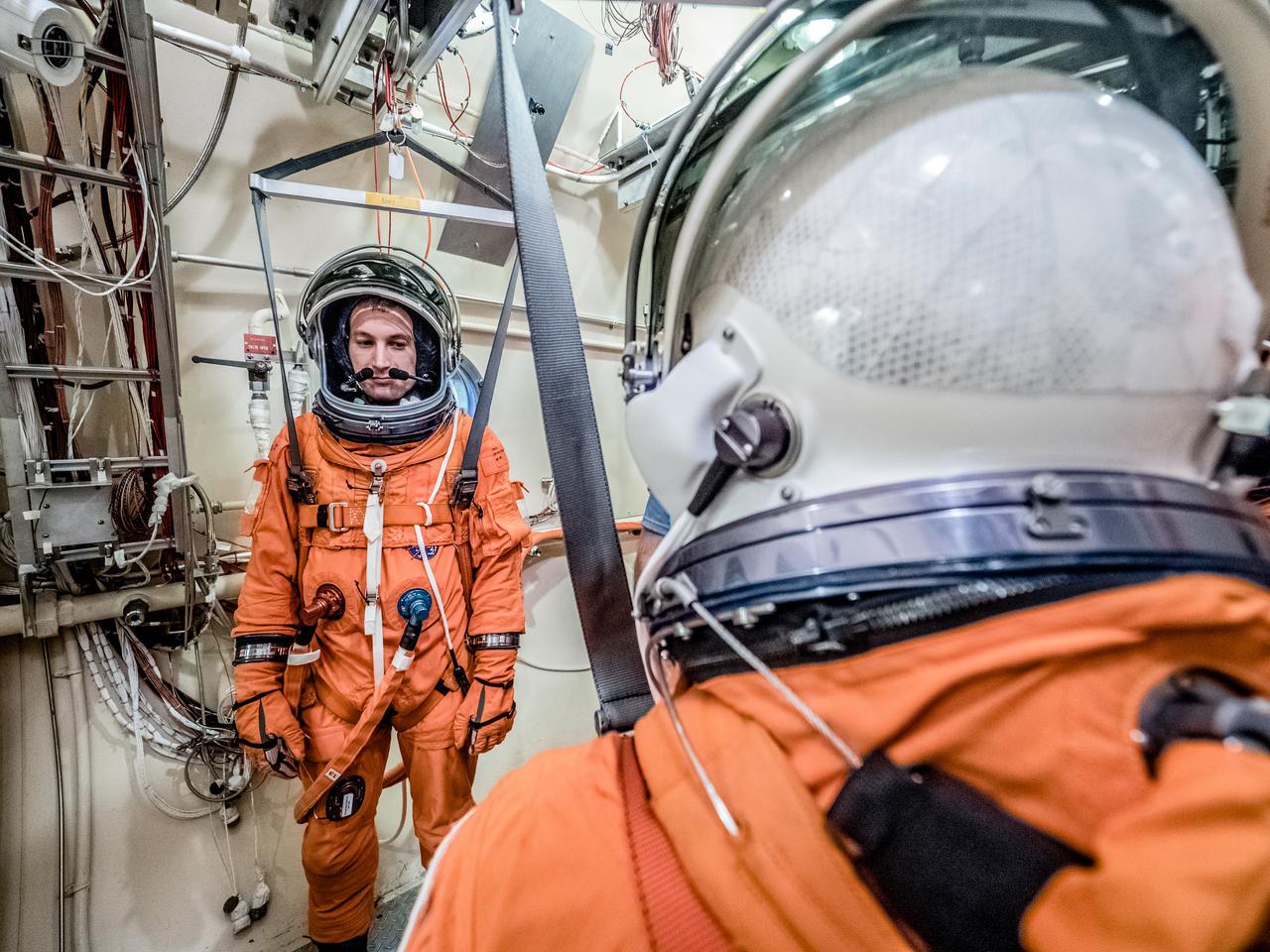

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
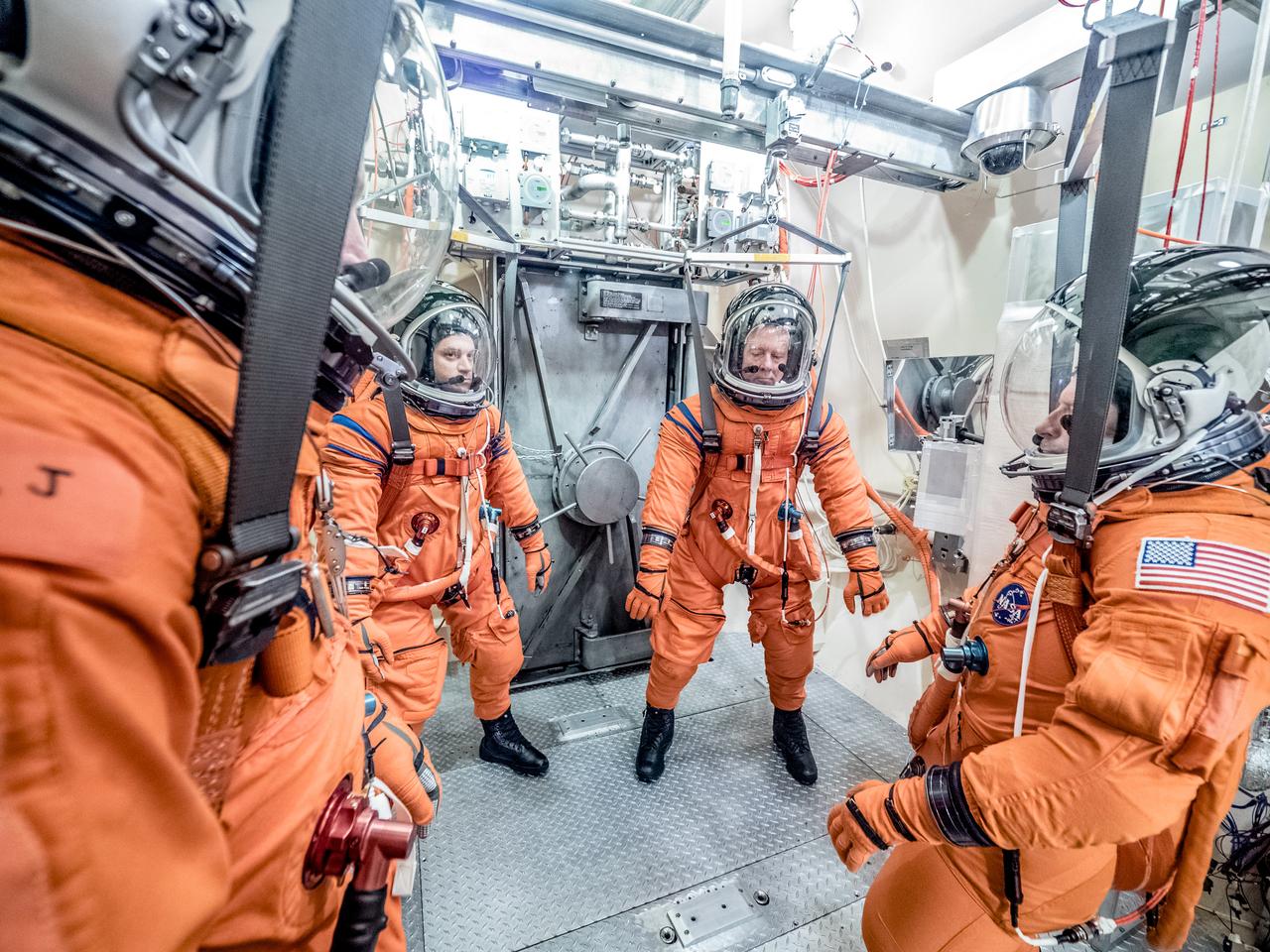

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
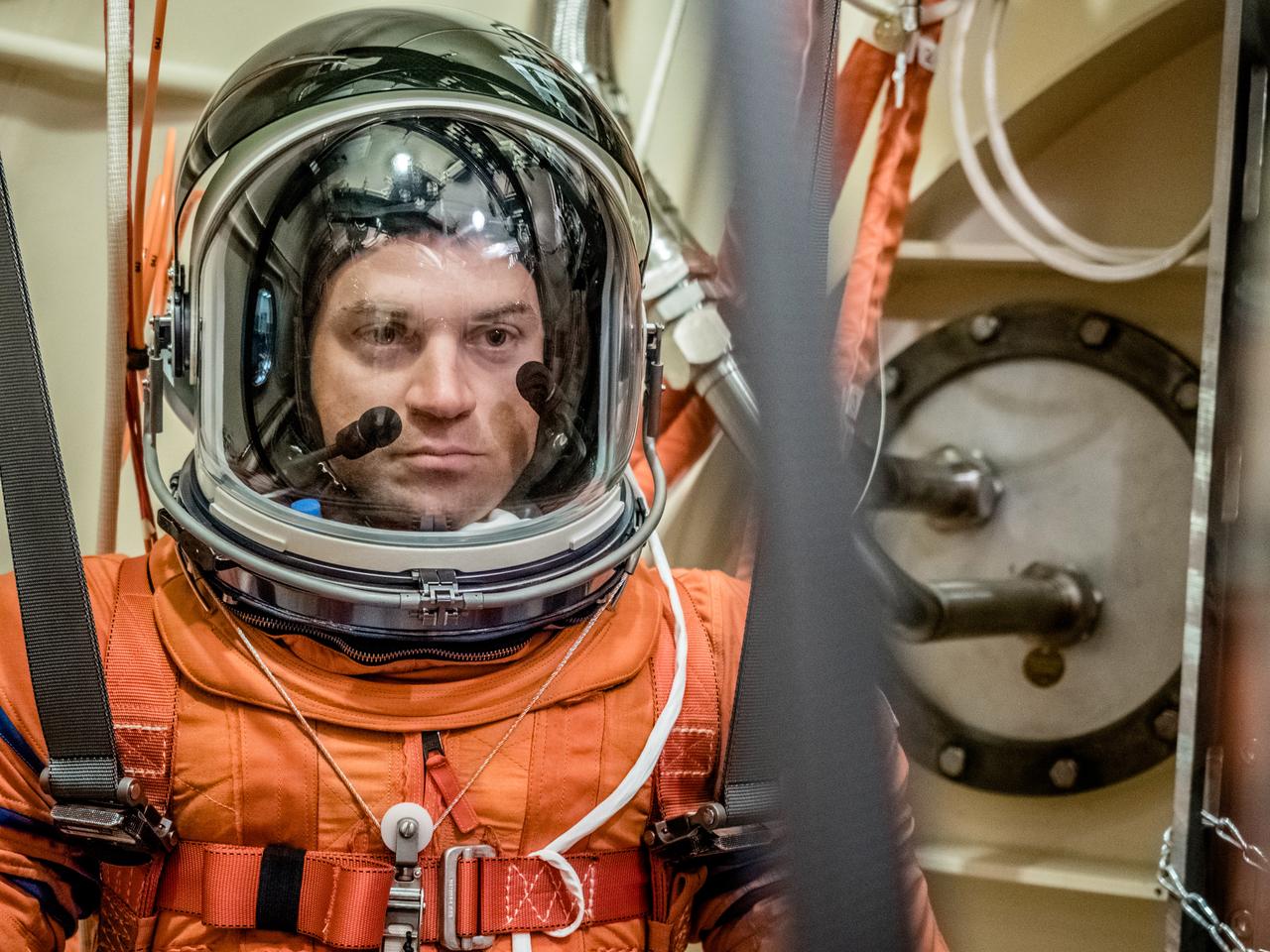

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
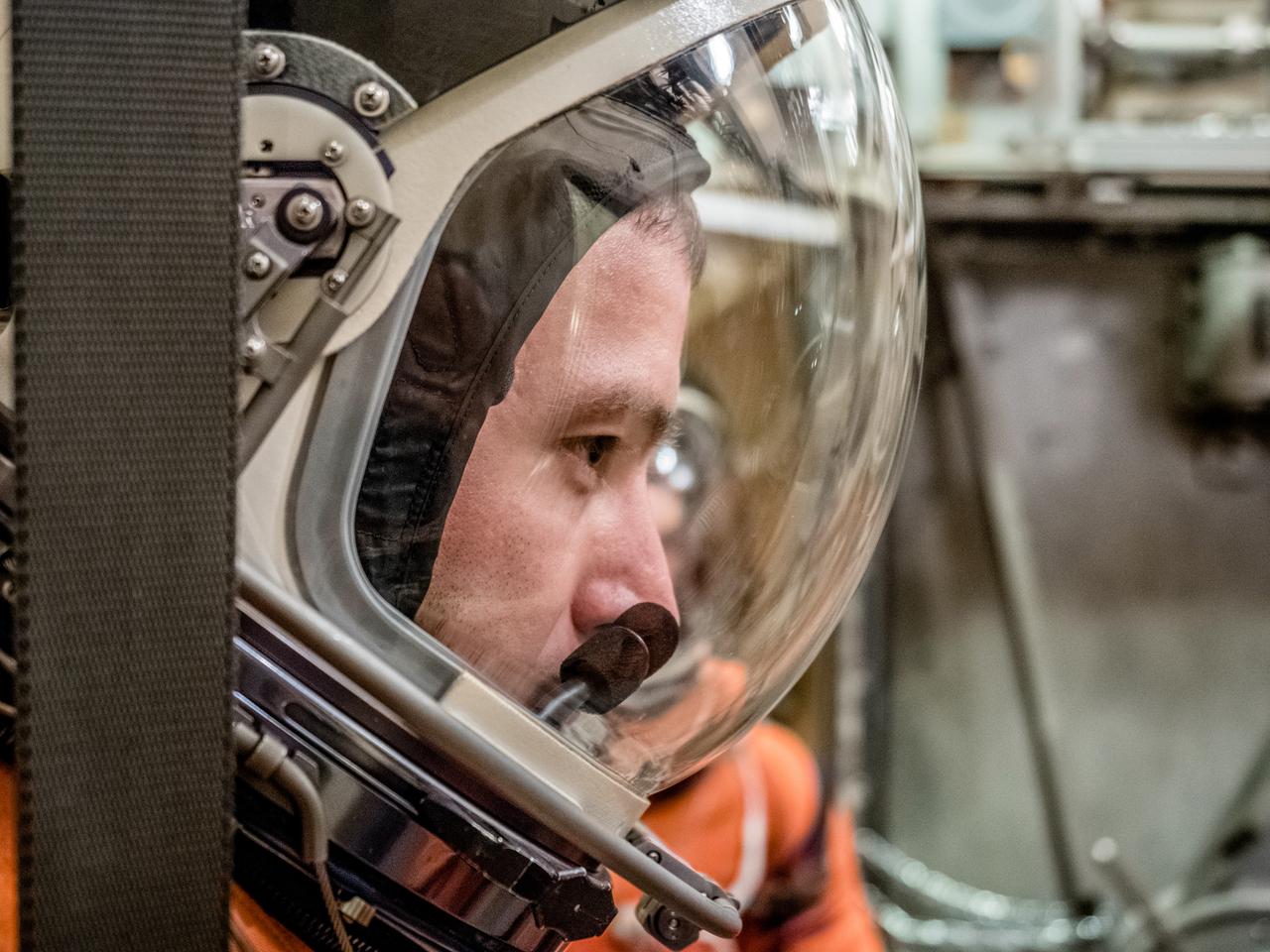

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
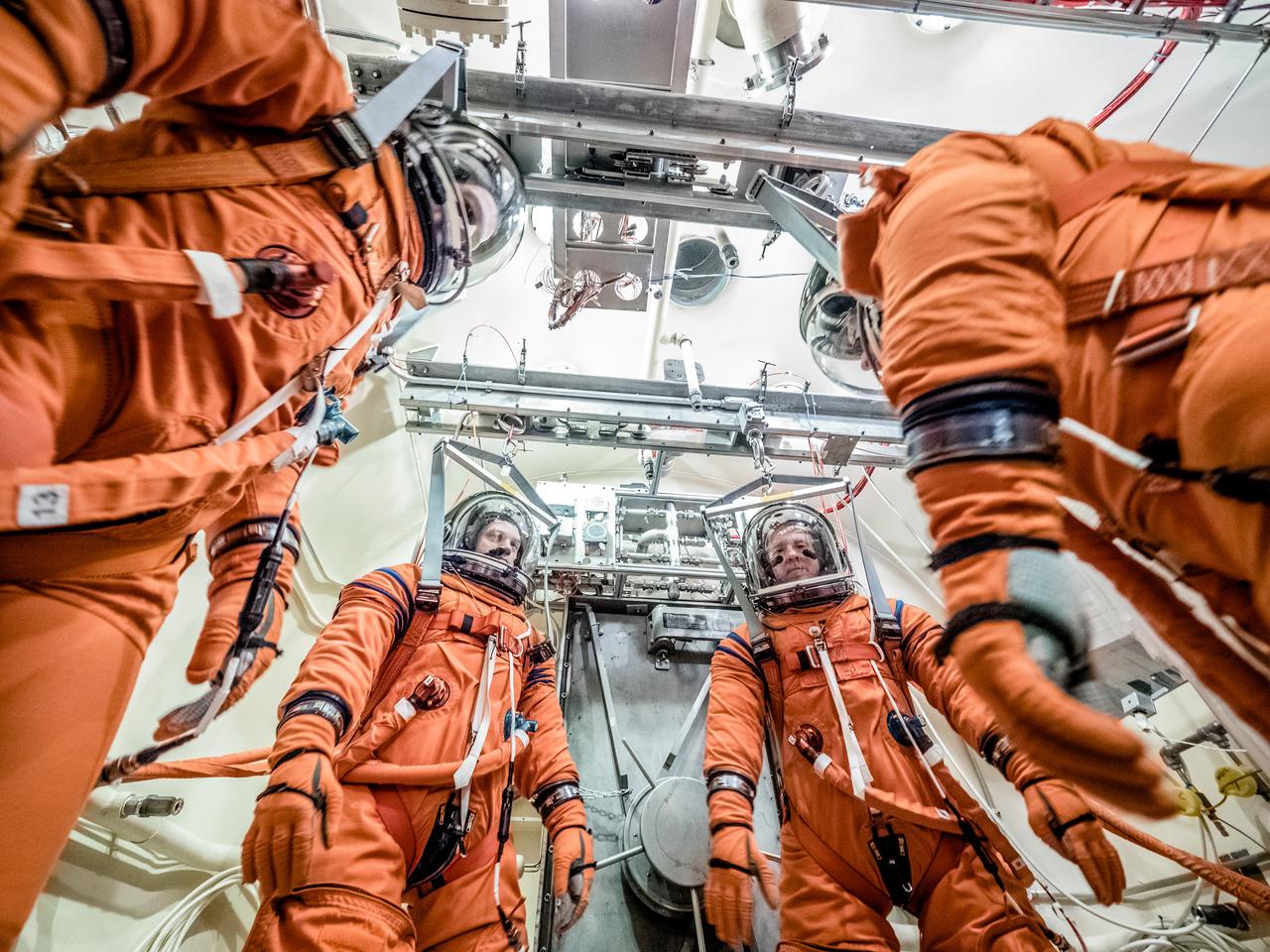

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
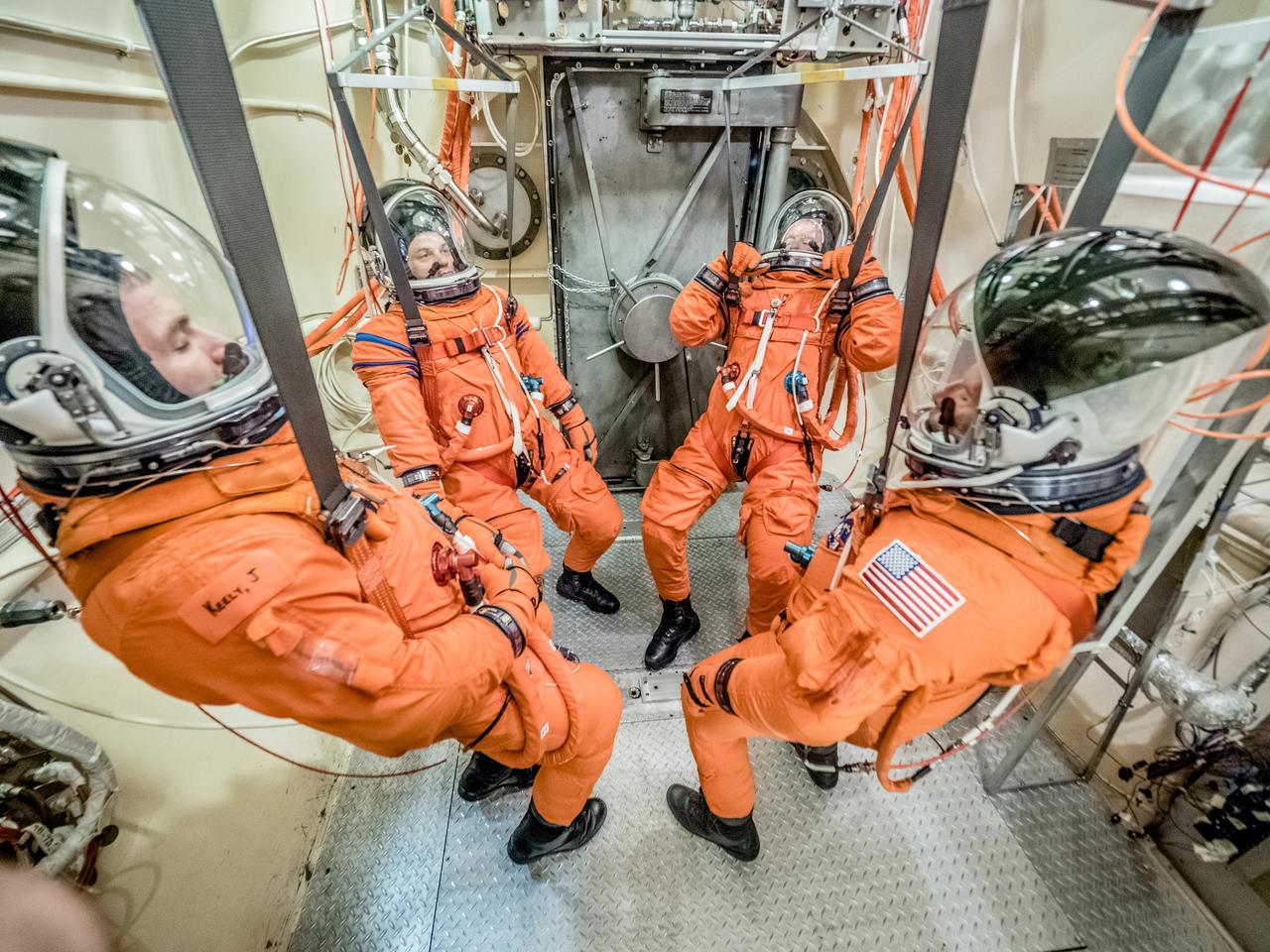

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
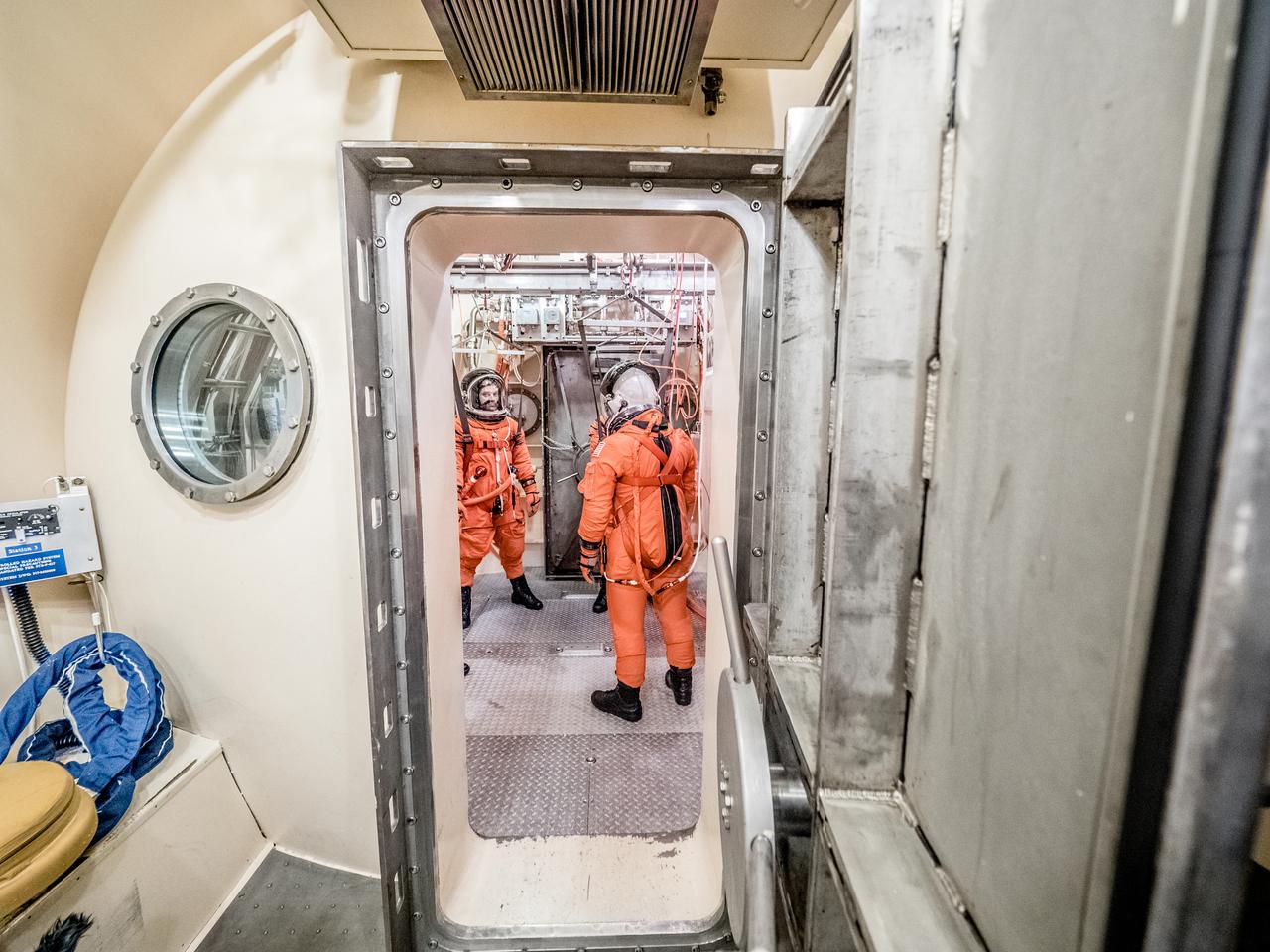

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
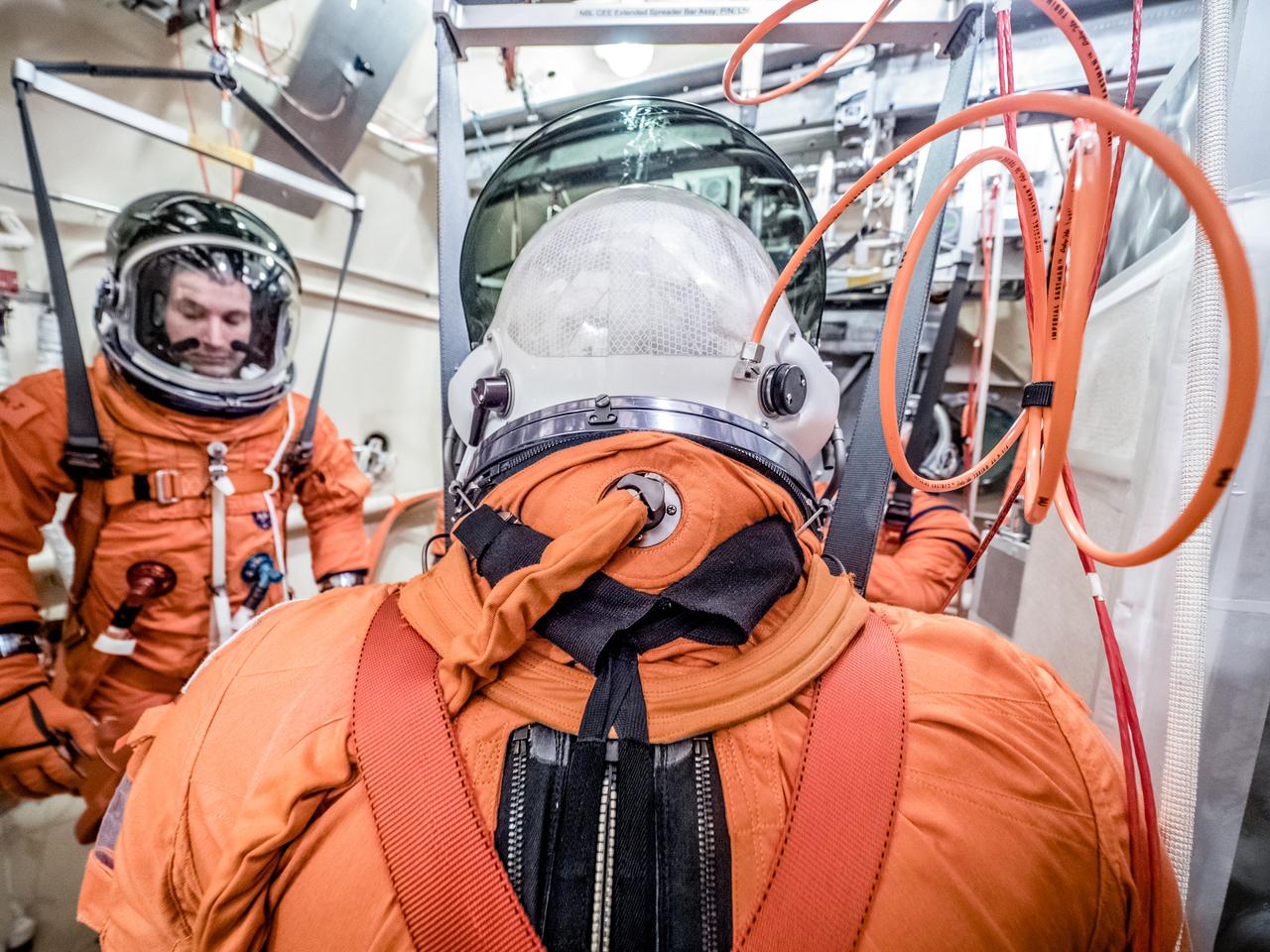

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
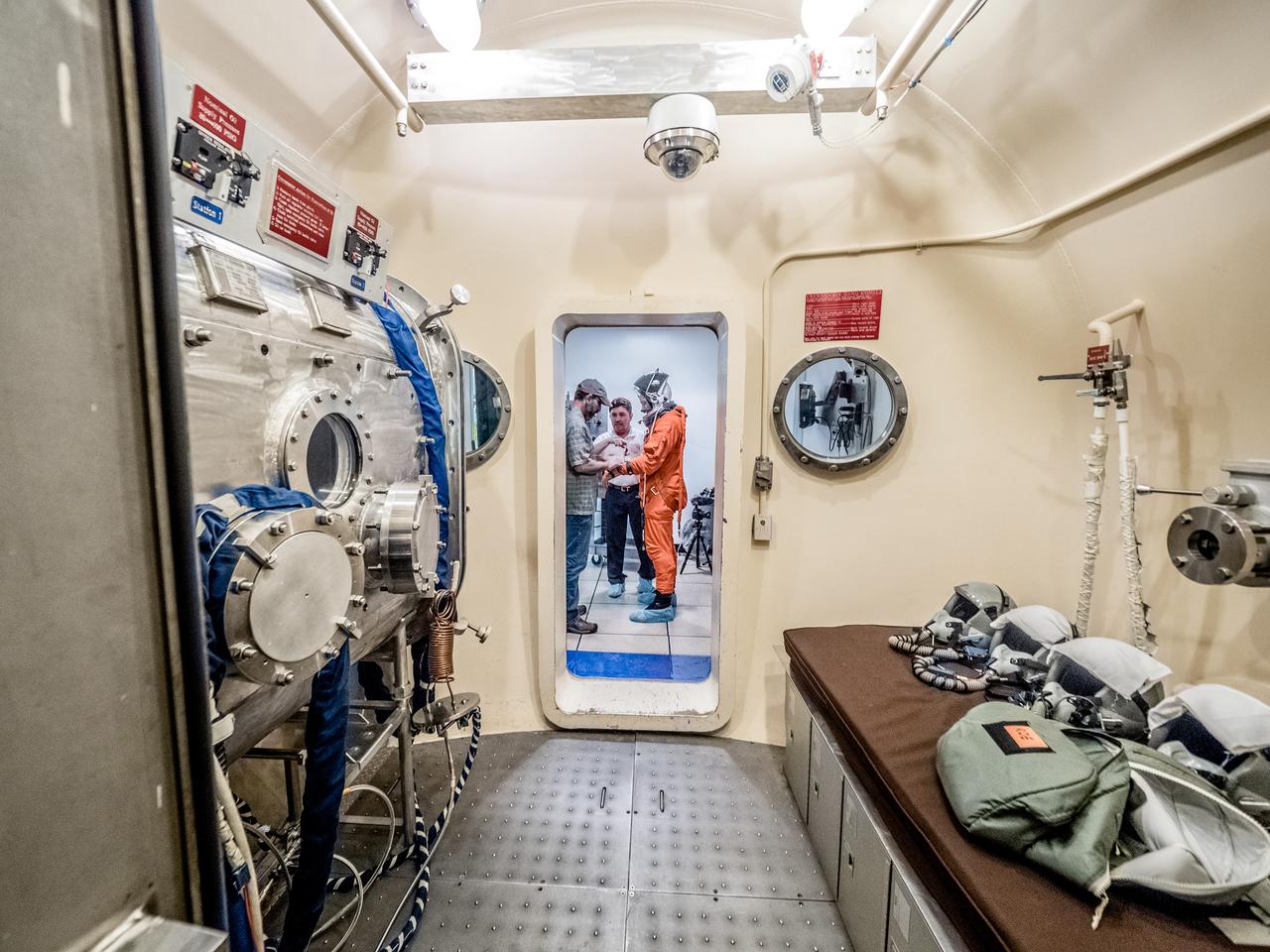

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
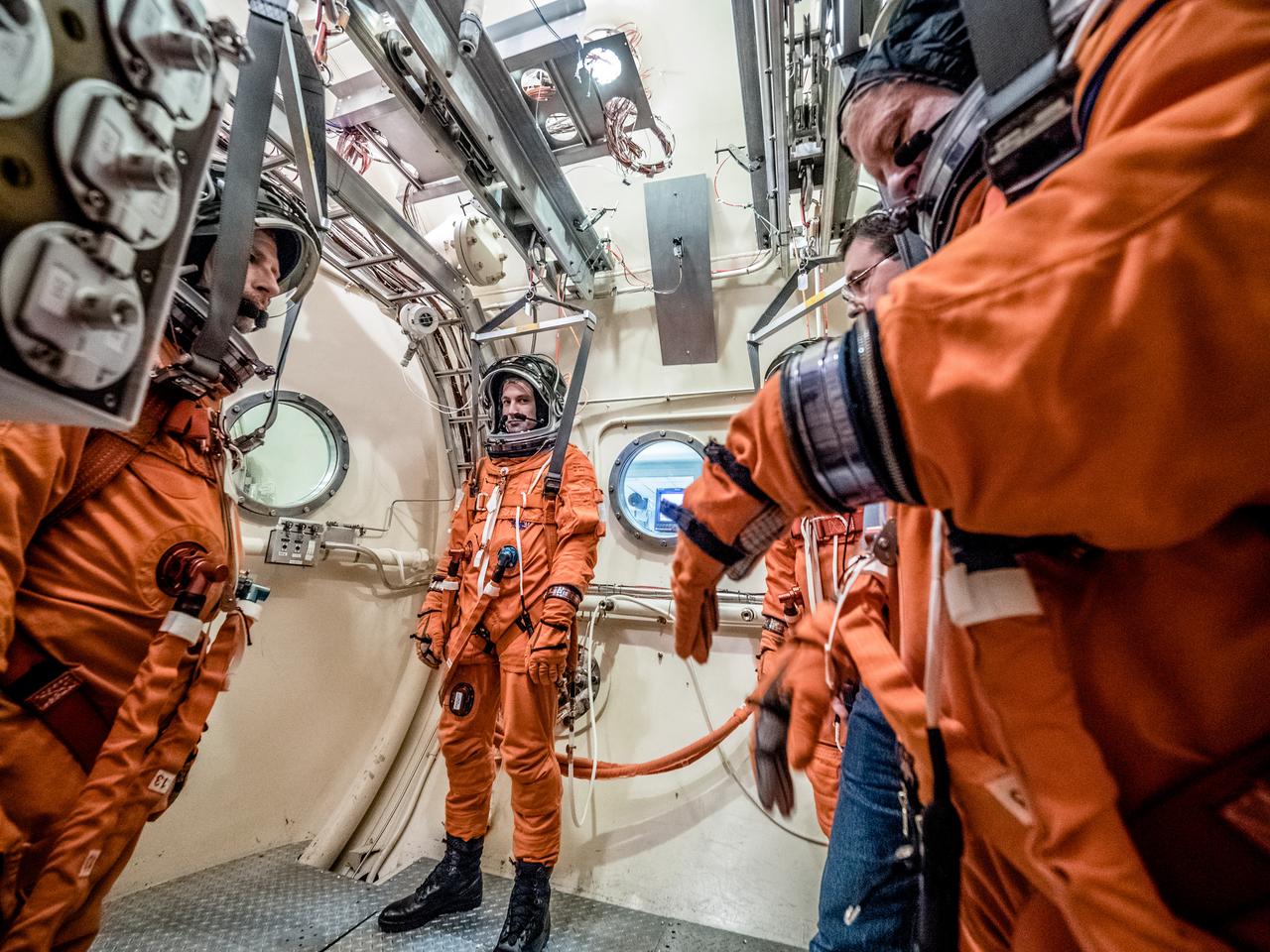

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
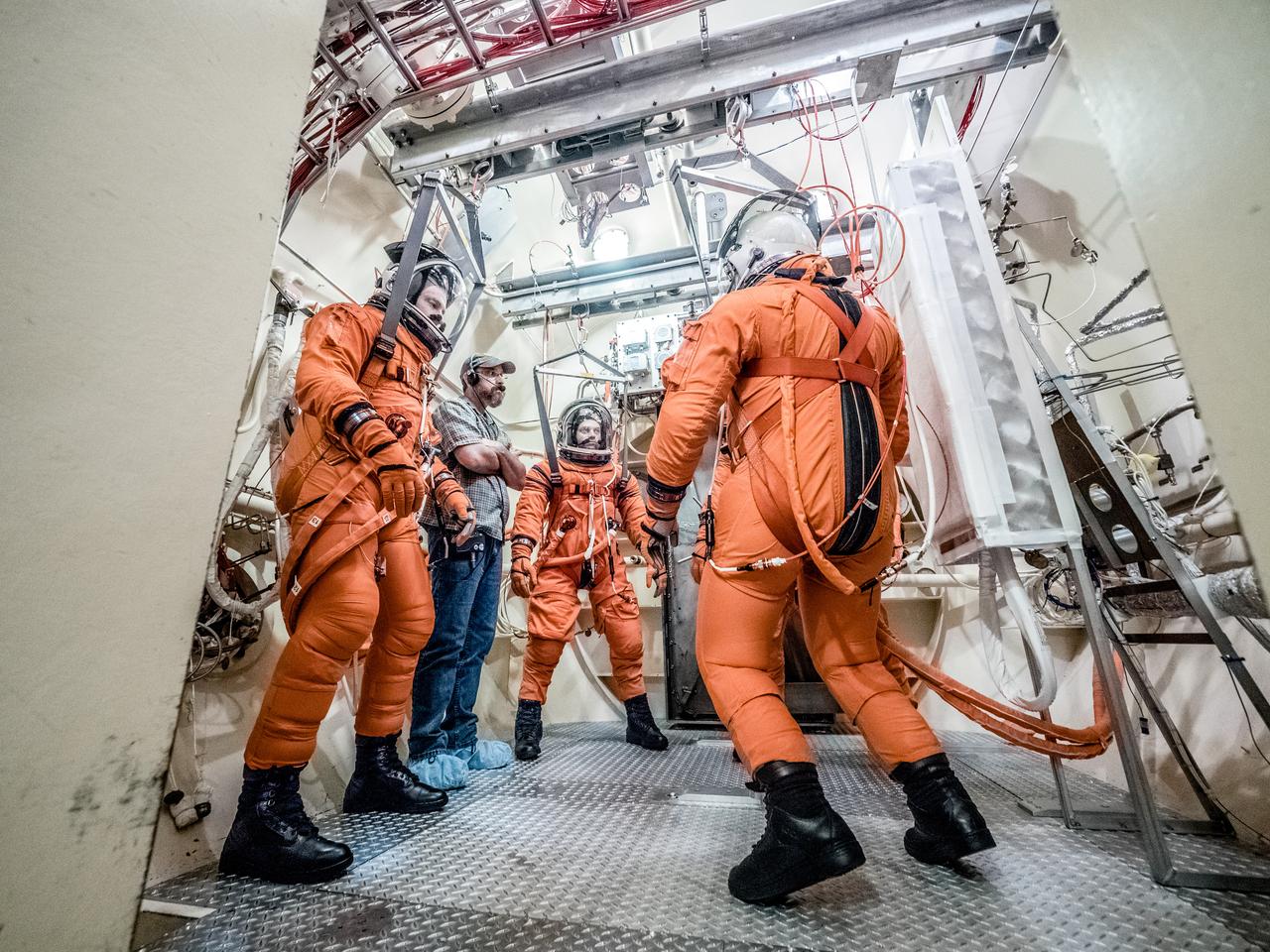

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston are testing the spacesuit astronauts will wear in the agency’s Orion spacecraft on trips to deep space. On June 22, 2017, members of the Johnson team participated in a Vacuum Pressure Integrated Suit Test to verify enhancements to the suit will meet test and design standards for the Orion spacecraft. During this test, the suit is connected to life support systems and then air is removed from Johnson’s 11-foot thermal vacuum chamber to evaluate the performance of the suits in conditions similar to a spacecraft. The suit will contain all the necessary functions to support life and is being designed to enable spacewalks and sustain the crew in the unlikely event the spacecraft loses pressure. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
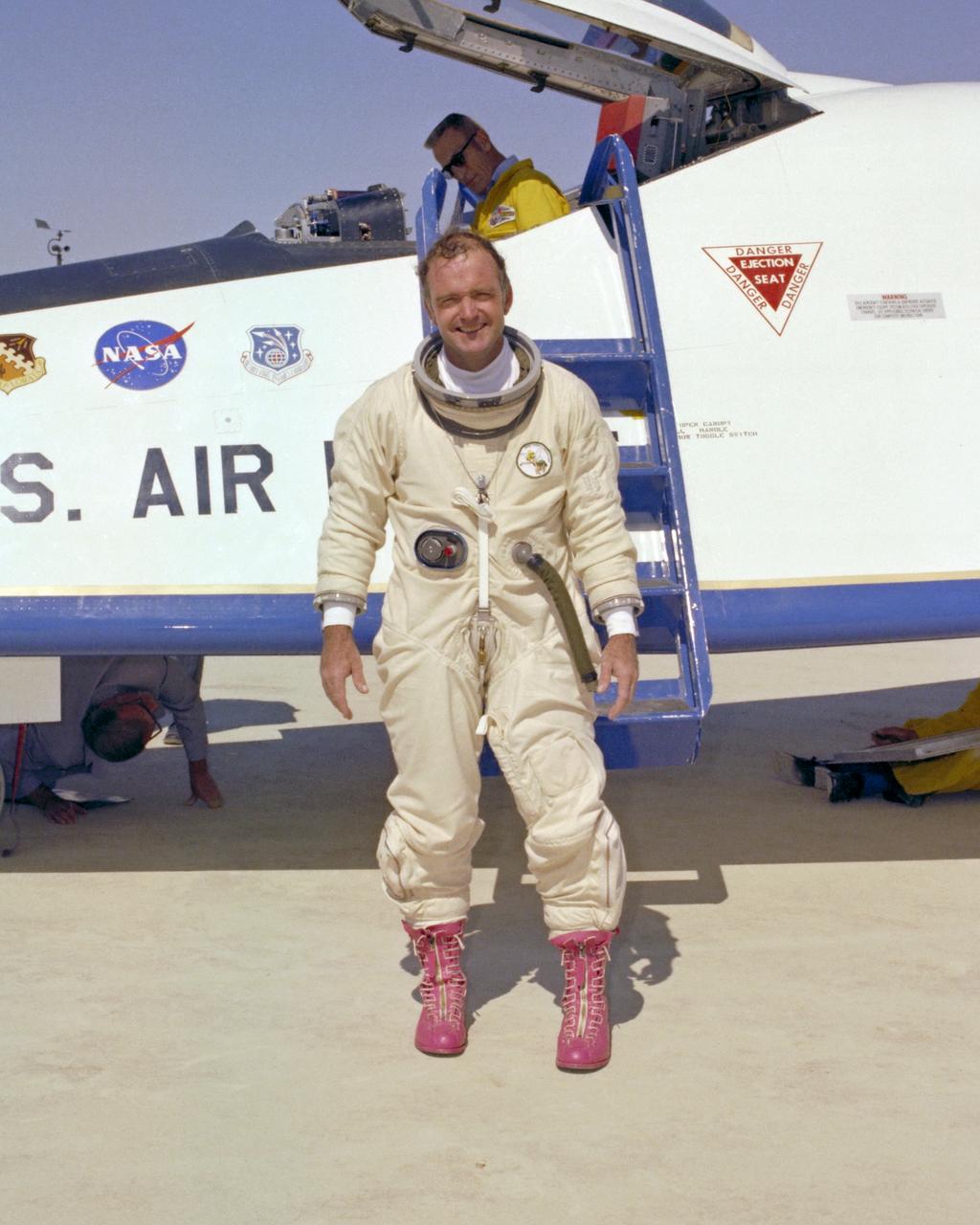

NASA test pilot Bill Dana, resplendent in pink boots and pressure suit, was all smiles following the last powered flight of the X-24B on Sept. 23, 1975.
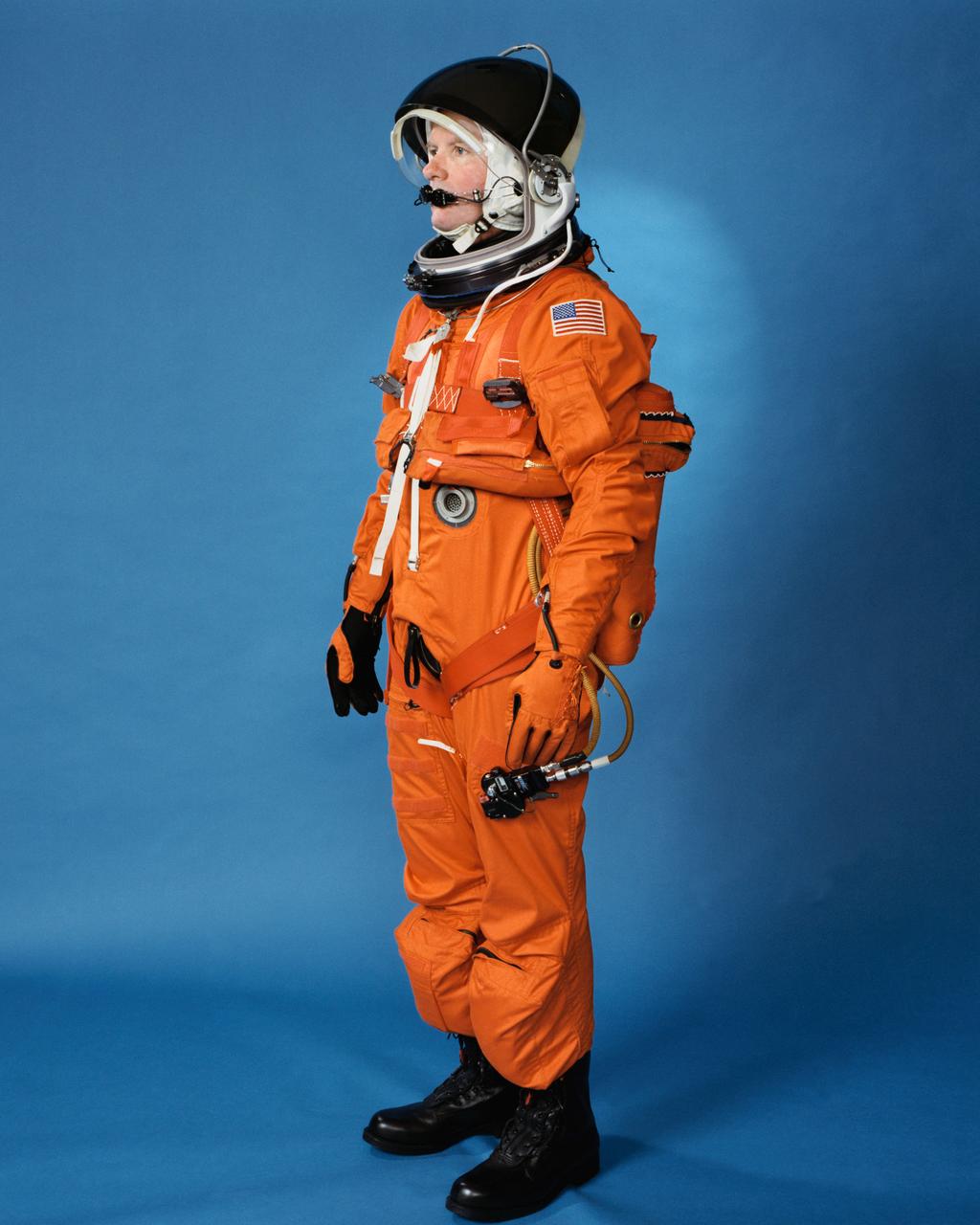

Space shuttle orange launch and entry suit (LES), a partial pressure suit, is modeled by a technician. LES was designed for STS-26, the return to flight mission, and subsequent missions. Included in the crew escape system (CES) package are launch and entry helmet (LEH) with communications carrier (COMM CAP), parachute pack and harness, life raft, life preserver unit (LPU), LES gloves, suit oxygen manifold and valves, boots, and survival gear.
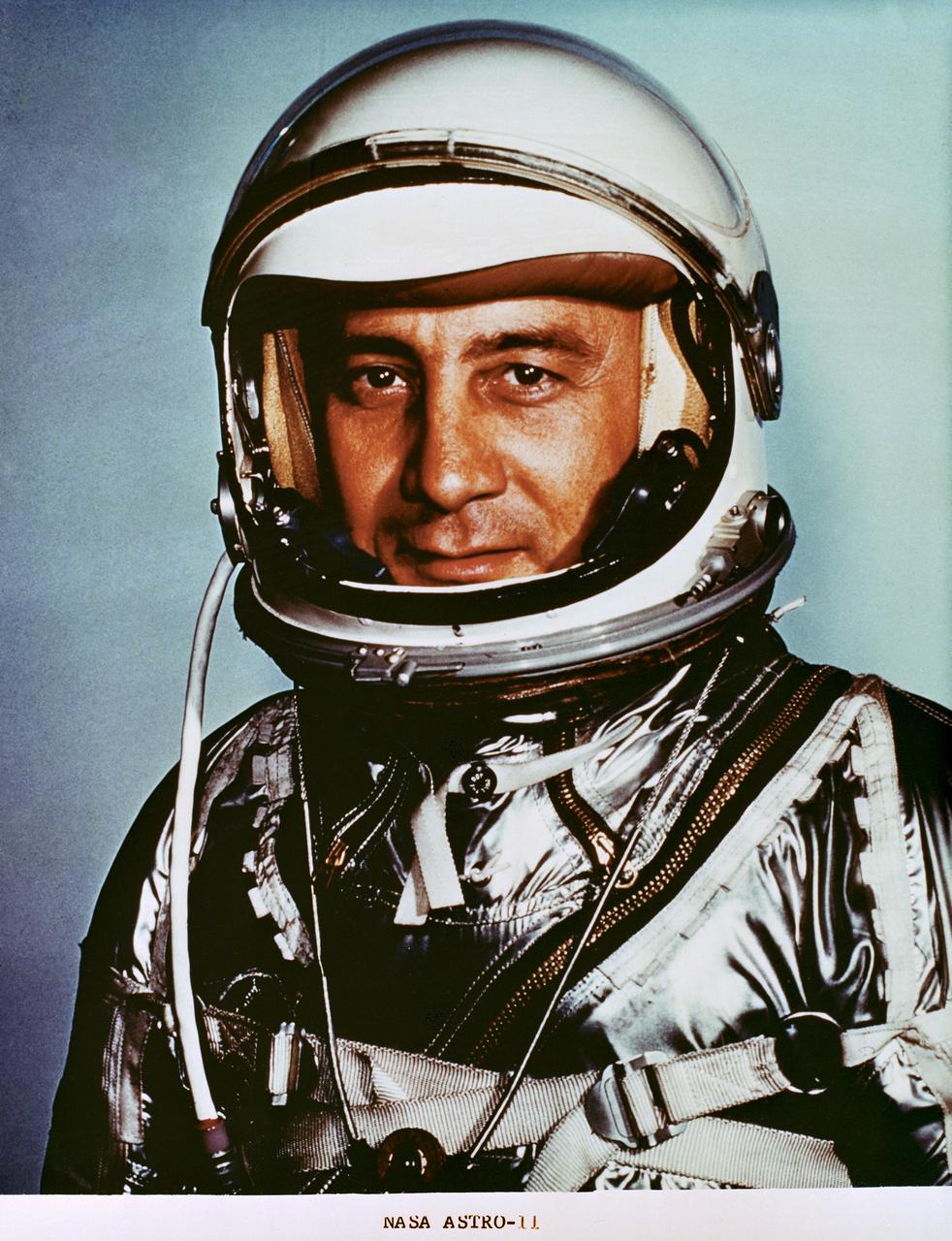

S88-55873 (1961) --- Astronaut Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, pilot of the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) spaceflight. (NOTE: Astronaut "Gus" Grissom, one of the original seven astronauts, died Jan. 27, 1967, at NASA?s John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Cape Canaveral Florida, in the Apollo 1 spacecraft fire.) Photo credit: NASA
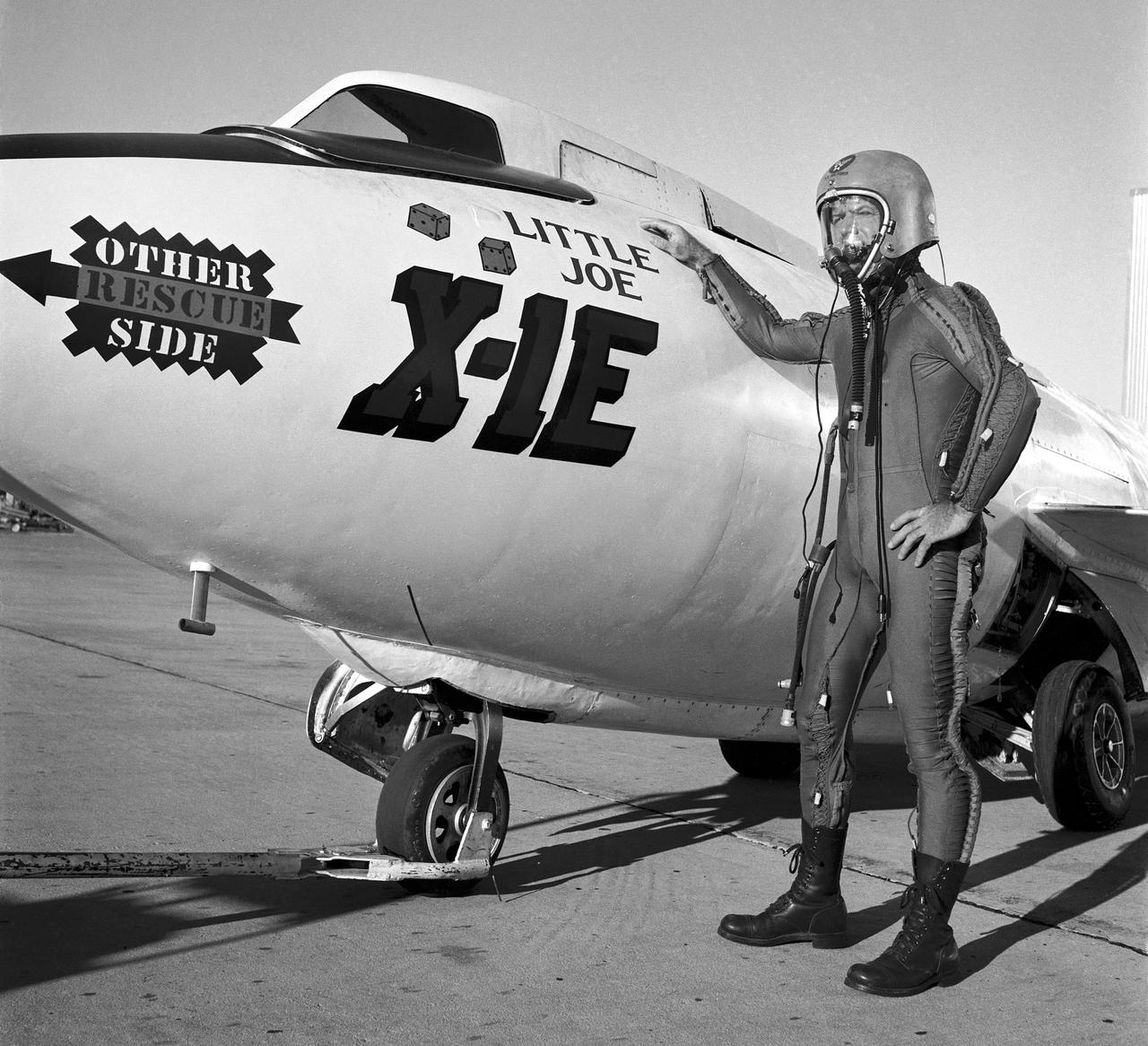

Joe Walker in a pressure suit beside the X-1E at the NASA High-Speed Flight Station, Edwards,California. The dice and "Little Joe" are prominently displayed under the cockpit area. (Little Joe is a dice players slang term for two deuces.) Walker is shown in the photo wearing an early Air Force partial pressure suit. This protected the pilot if cockpit pressure was lost above 50,000 feet. Similar suits were used in such aircraft as B-47s, B-52s, F-104s, U-2s, and the X-2 and D-558-II research aircraft. Five years later, Walker reached 354,200 feet in the X-15. Similar artwork - reading "Little Joe the II" - was applied for the record flight. These cases are two of the few times that research aircraft carried such nose art.
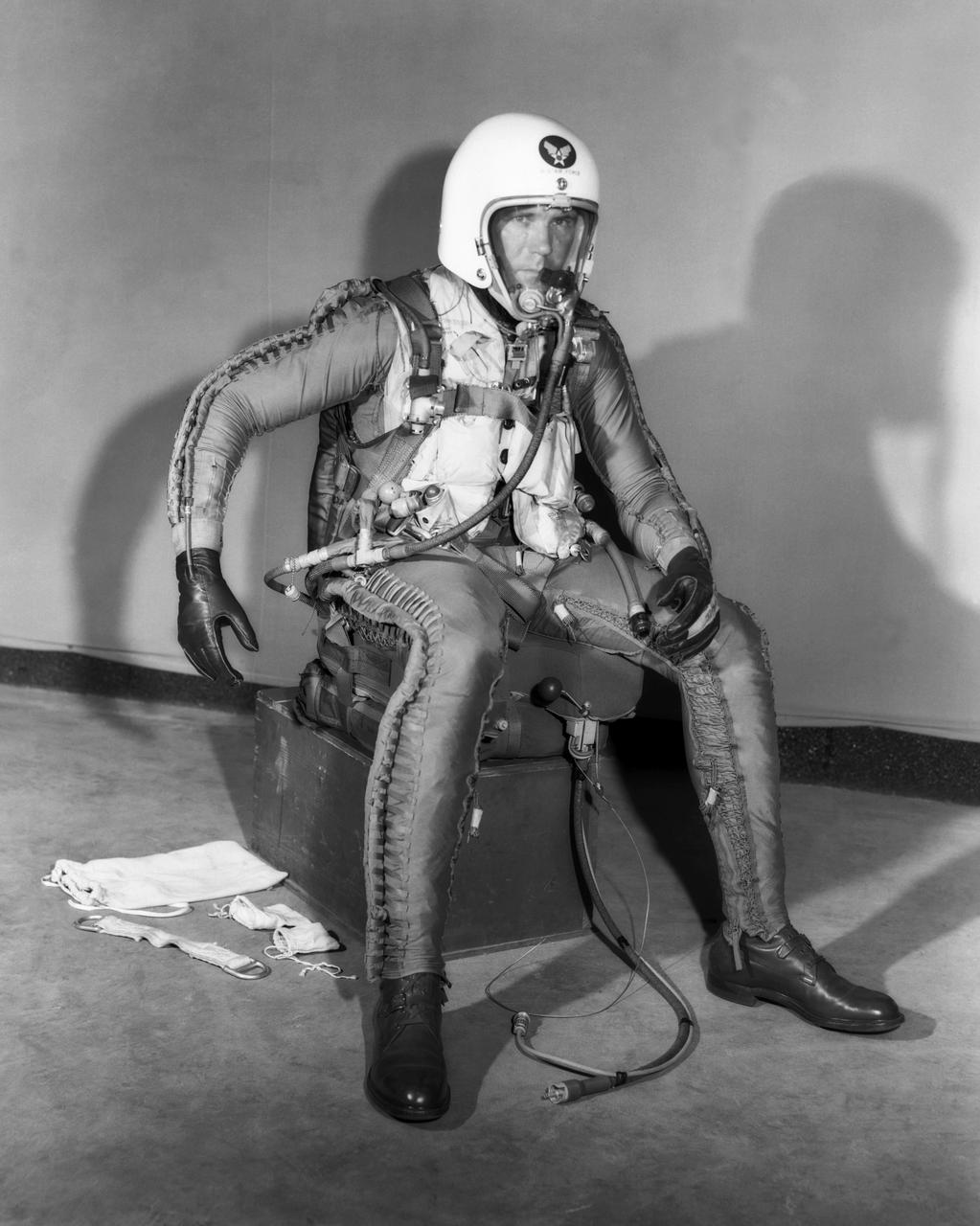

Robert Champine in X-Series Pressure Suit. Photograph published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen. Page 305.
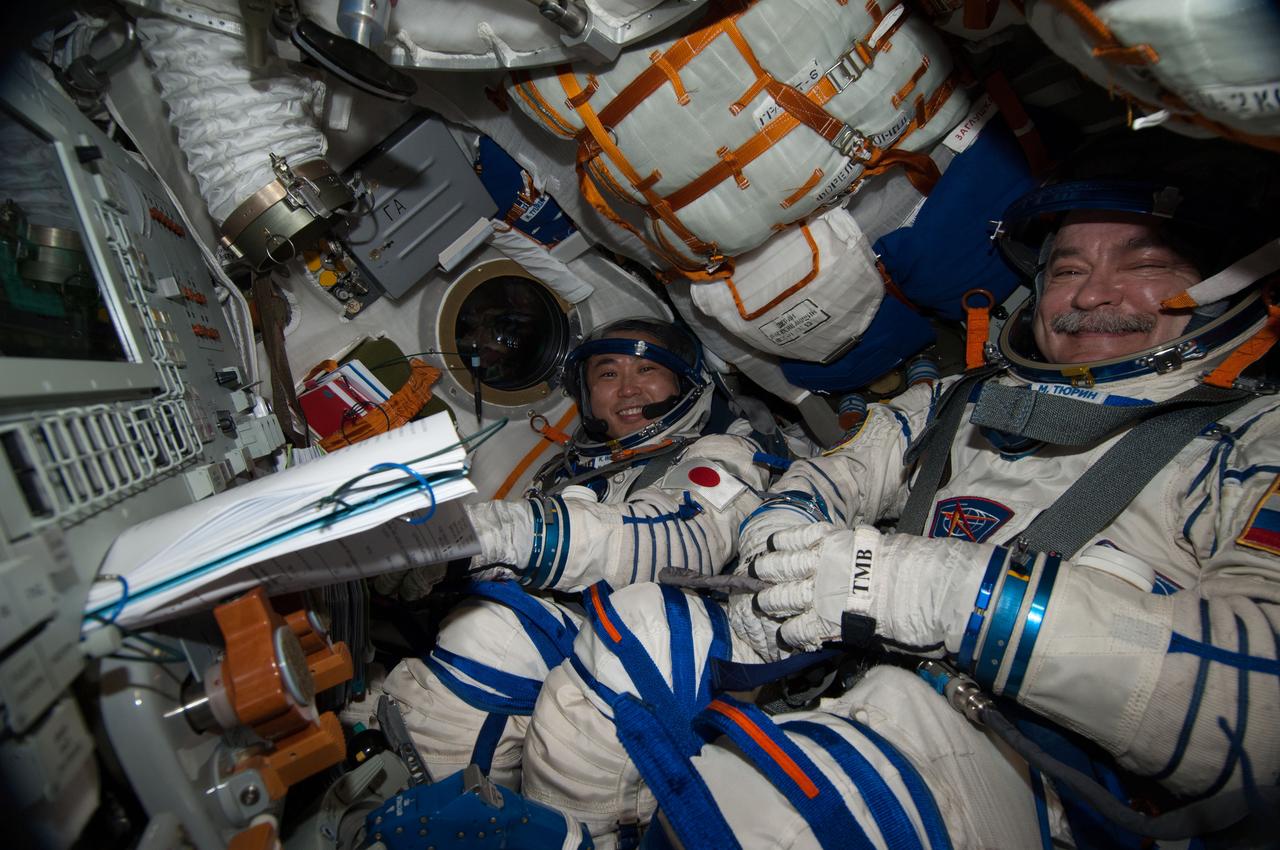

Expedition 39 commander Koichi Wakata and flight engineer Mikhail Tyurin, wearing Sokol pressure suits, are photographed in the Soyuz TMA-11M spacecraft during a Sokol leak check. Wakata is a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut; Tyurin is a Roscosmos cosmonaut. Image was released by the commander on Twitter.
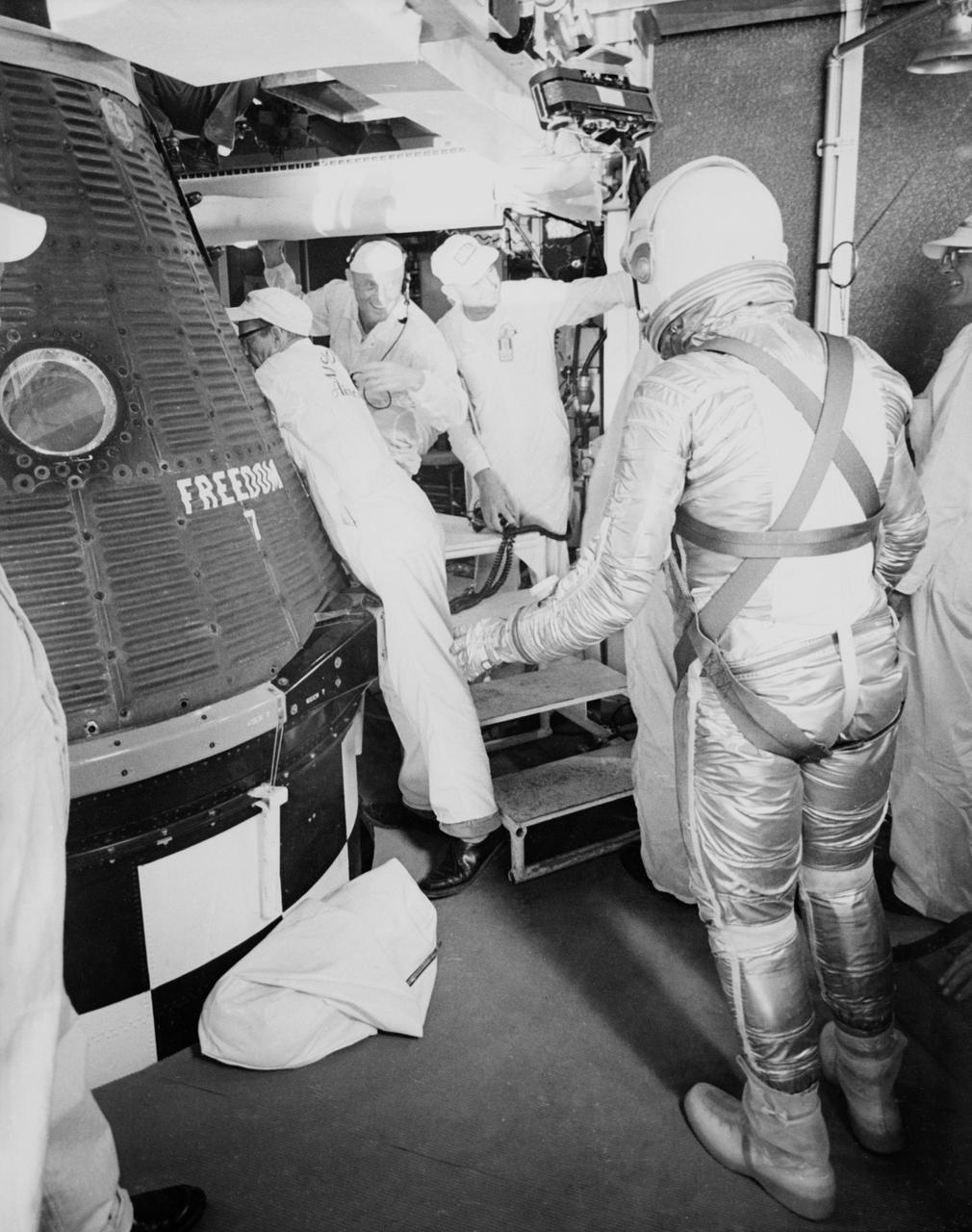

S61-02792 (5 May 1961) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., in his pressure suit and helmet, approaches the Freedom 7 capsule in preparation for insertion before the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) mission. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

Expedition 18 Commander Michael Fincke has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked prior to launching in the Soyuz TMA-13 spacecraft with Expedition 18 Flight Engineer Yuri V. Lonchakov and American spaceflight participant Richard Garriott, Sunday, Oct. 12, 2008 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The three crew members are scheduled to dock with the International Space Station on Oct. 14. Fincke and Lonchakov will spend six months on the station, while Garriott will return to Earth Oct. 24 with two of the Expedition 17 crew members currently on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
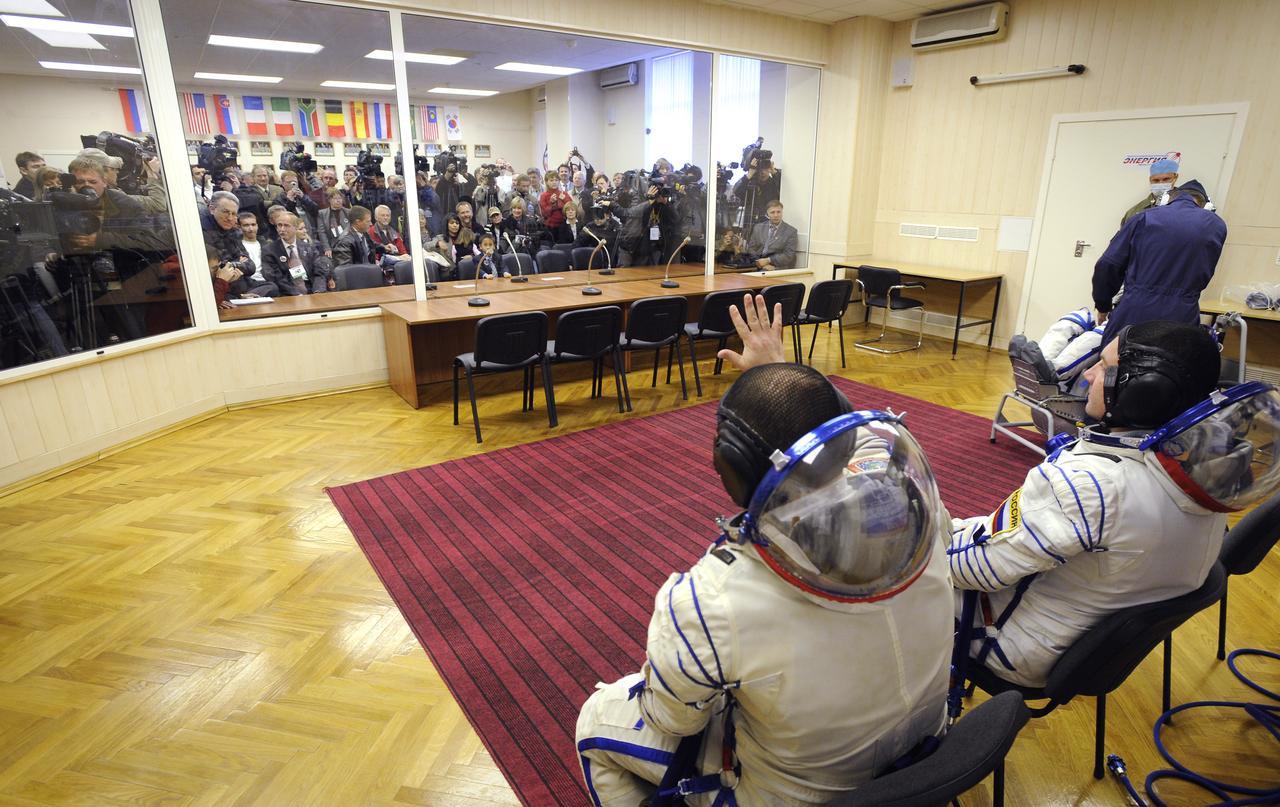

Expedition 18 Commander Michael Fincke waves hello to his family as he and Expedition 18 Flight Engineer Yuri V. Lonchakov and American spaceflight participant Richard Garriott have their Russian Sokol suits pressure checked prior to launching in the Soyuz TMA-13 spacecraft, Sunday, Oct. 12, 2008 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The three crew members are scheduled to dock with the International Space Station on Oct. 14. Fincke and Lonchakov will spend six months on the station, while Garriott will return to Earth Oct. 24 with two of the Expedition 17 crew members currently on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
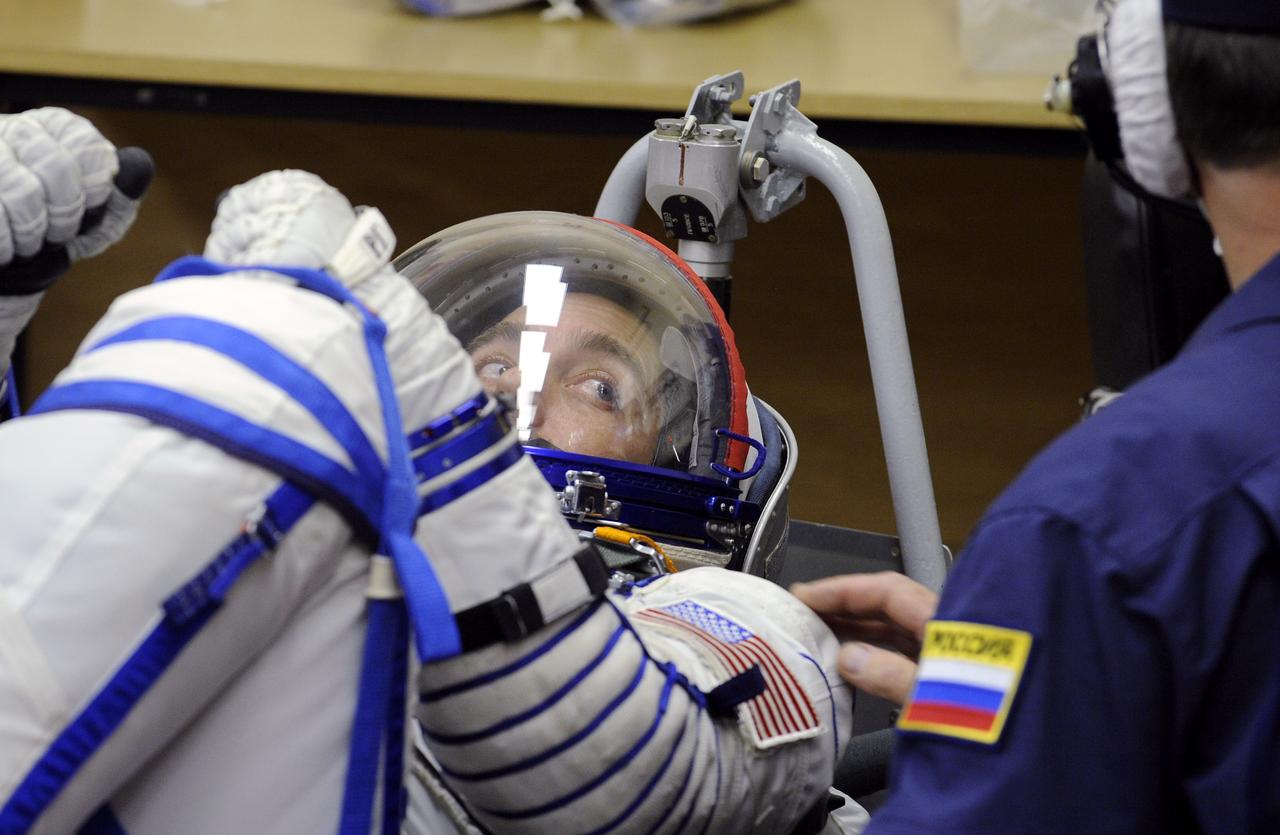

American Spaceflight Participant Richard Garriott has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked prior to launching in the Soyuz TMA-13 spacecraft with Expedition 18 Commander Michael Fincke and Flight Engineer Yury V. Lonchakov, Sunday, Oct. 12, 2008 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The three crew members are scheduled to dock with the International Space Station on Oct. 14. Fincke and Lonchakov will spend six months on the station, while Garriott will return to Earth Oct. 24, 2008 with two of the Expedition 17 crewmembers currently on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
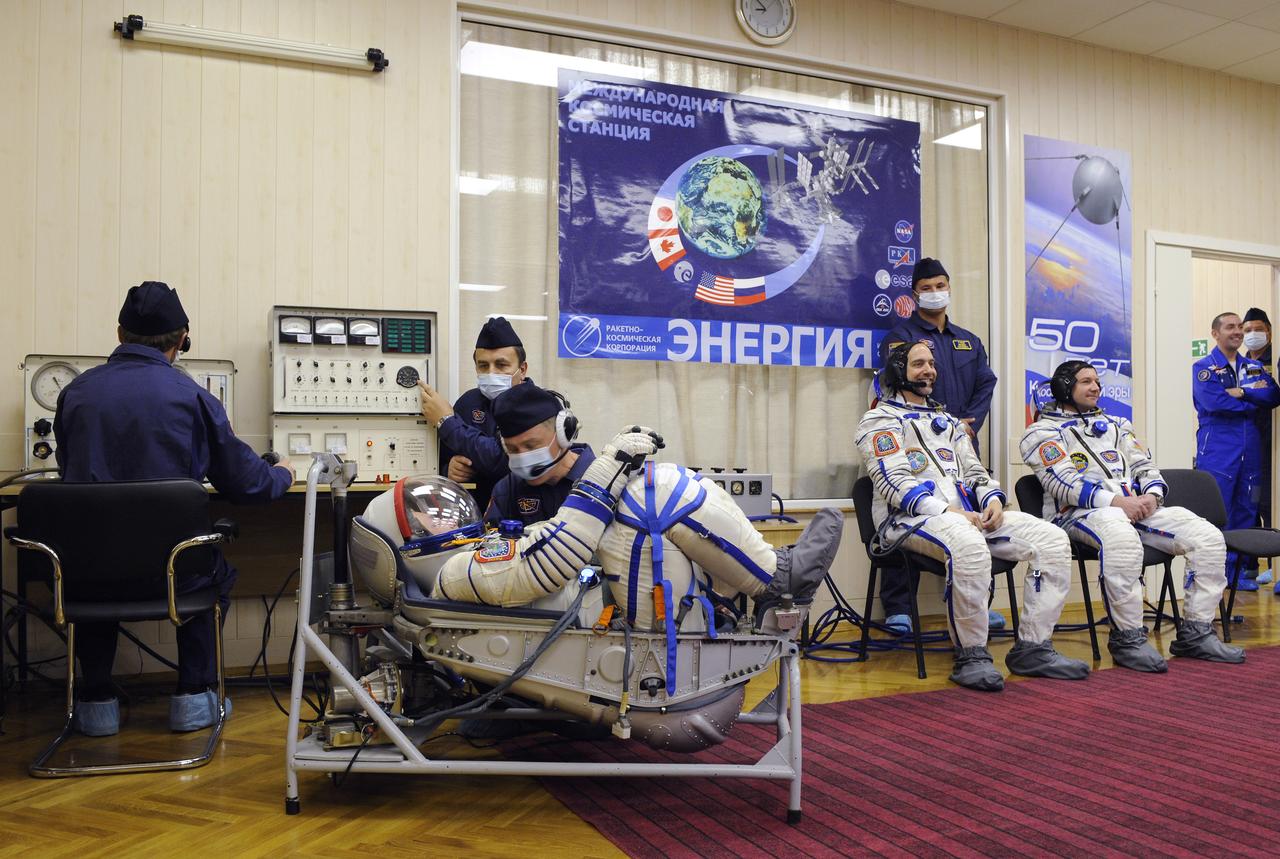

Expedition 18 Commander Michael Fincke, foreground, has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked prior to launching in the Soyuz TMA-13 spacecraft with American spaceflight participant Richard Garriott and Expedition 18 Flight Engineer Yuri V. Lonchakov, right, Sunday, Oct. 12, 2008 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The three crew members are scheduled to dock with the International Space Station on Oct. 14. Fincke and Lonchakov will spend six months on the station, while Garriott will return to Earth Oct. 24 with two of the Expedition 17 crew members currently on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
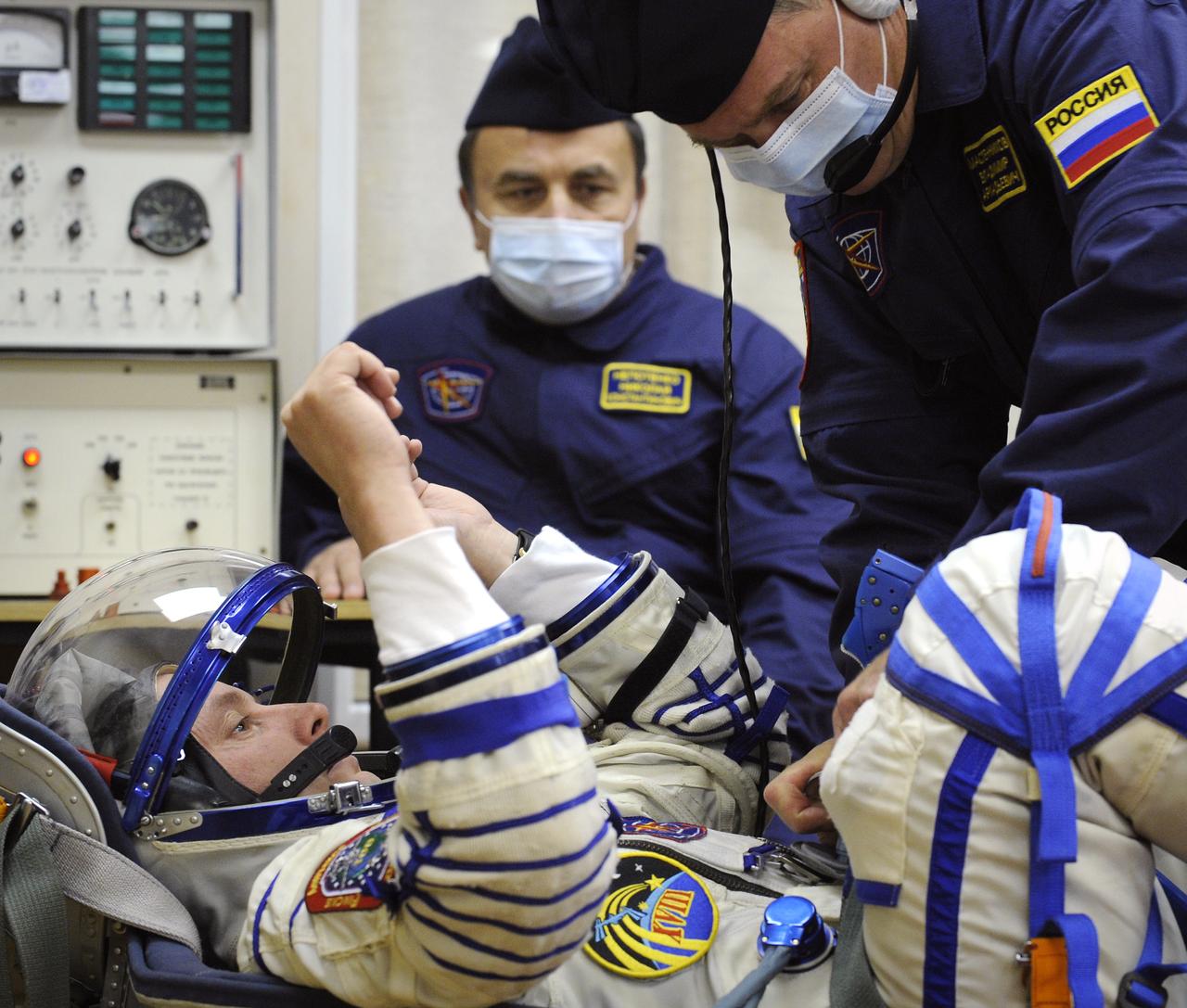

Expedition 18 Commander Michael Fincke has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked prior to launching in the Soyuz TMA-13 spacecraft with Expedition 18 Flight Engineer Yuri V. Lonchakov and American spaceflight participant Richard Garriott, Sunday, Oct. 12, 2008 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The three crew members are scheduled to dock with the International Space Station on Oct. 14. Fincke and Lonchakov will spend six months on the station, while Garriott will return to Earth Oct. 24 with two of the Expedition 17 crew members currently on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
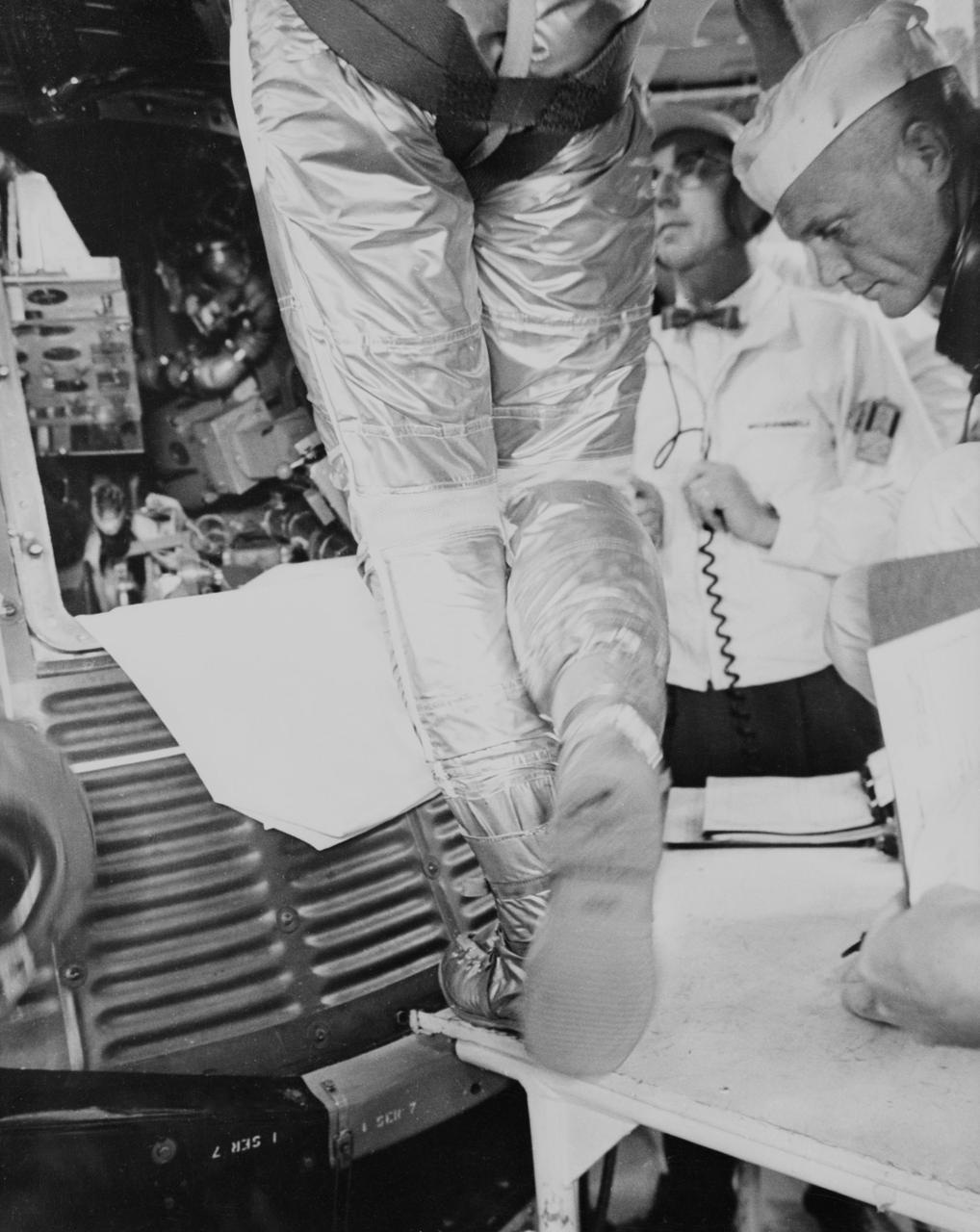

S61-02796 (5 May 1961) --- Rear view of astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., in his pressure suit and helmet, as he approaches the Freedom 7 capsule in preparation for ingress before the Mercury-Redstone 3 mission. All that can be seen of the astronaut is his legs. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
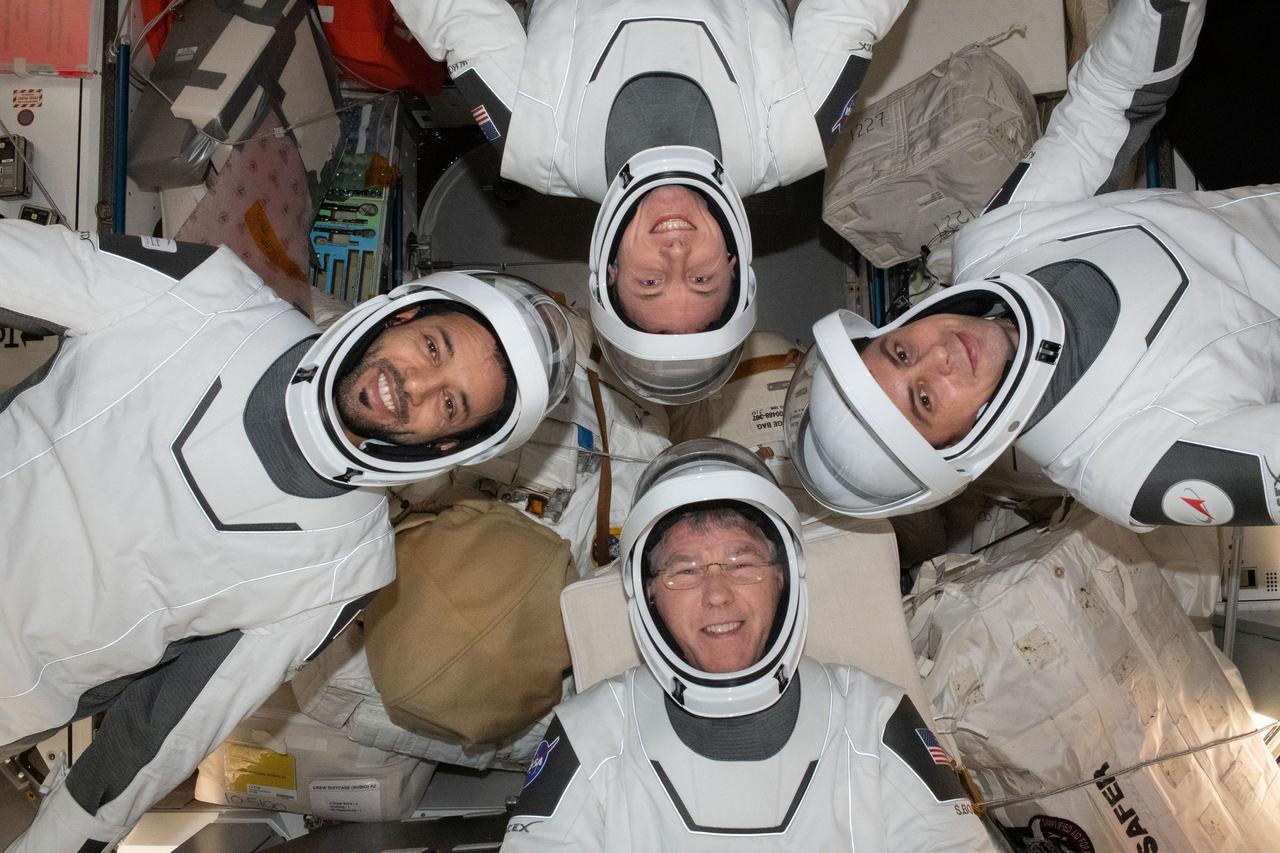

iss069e008444 (May 2, 2023) --- Four Expedition 69 flight engineers aboard the International Space Station pose for a portrait in the pressure suits they will wear when they relocate the SpaceX Dragon Endeavour crew ship from the Harmony module's space-facing port to Harmony's forward port on Saturday May 6, 2023. Clockwise from bottom, are NASA astronaut Stephen Bowen; UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut Sultan Alneyadi; NASA astronaut Woody Hoburg; and Roscosmos cosmonaut Andrey Fedyaev.
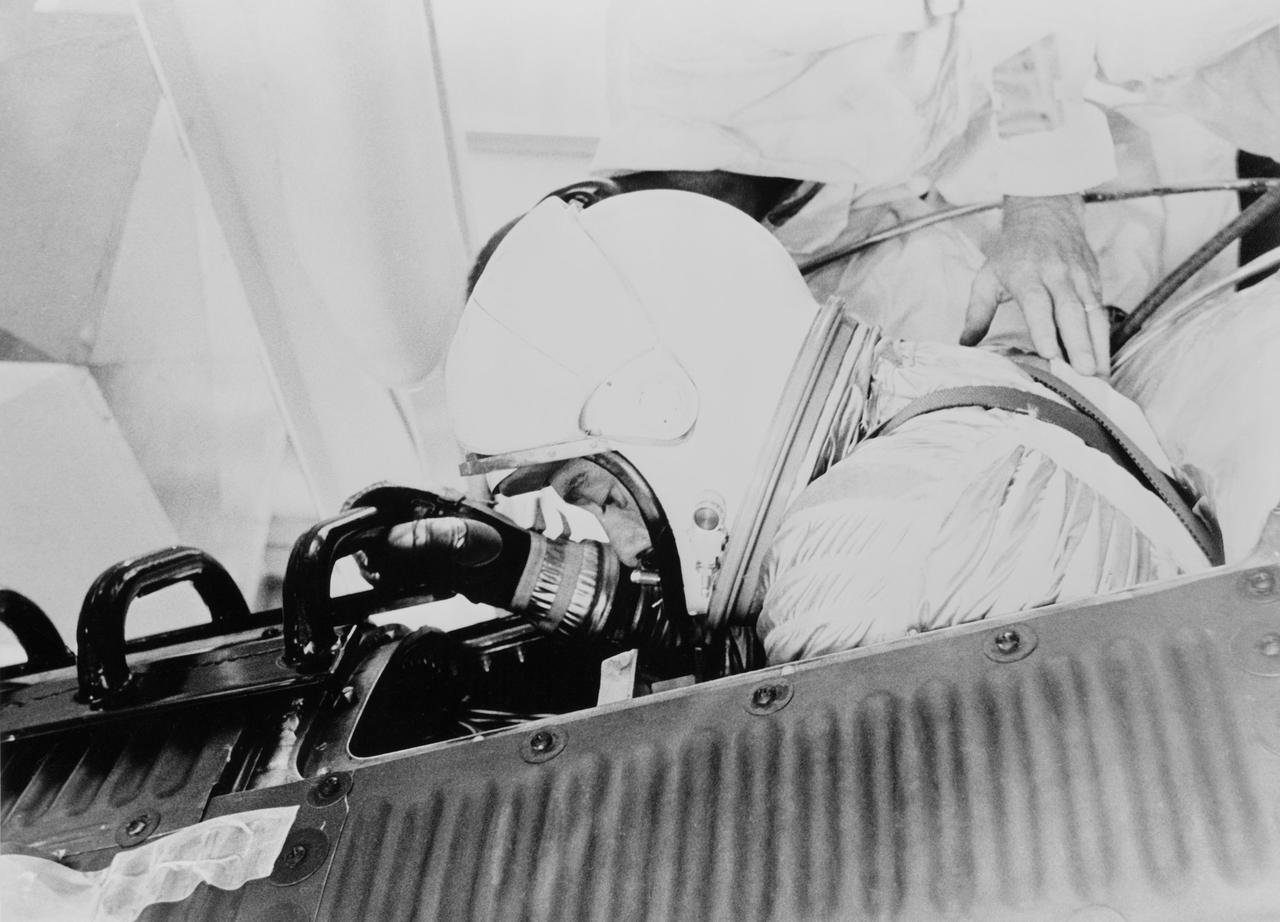
S61-03645 (5 May 1961) --- Close-up of astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., in his pressure suit and helmet, ingressing into the Freedom 7 capsule in preparation for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) mission. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
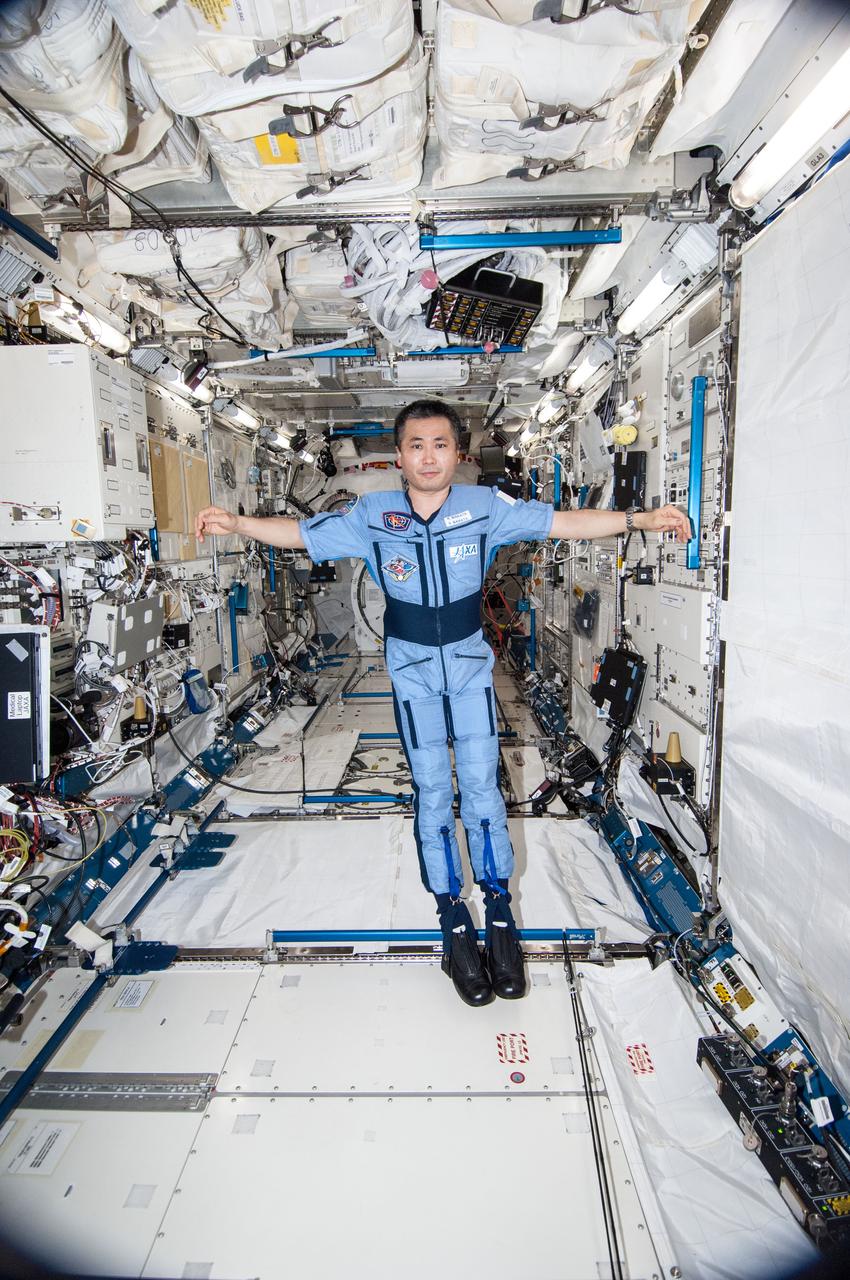

ISS038-E-035473 (24 Jan. 2014) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 38 flight engineer, is pictured wearing the Penguin-3 antigravity pressure/stress suit in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
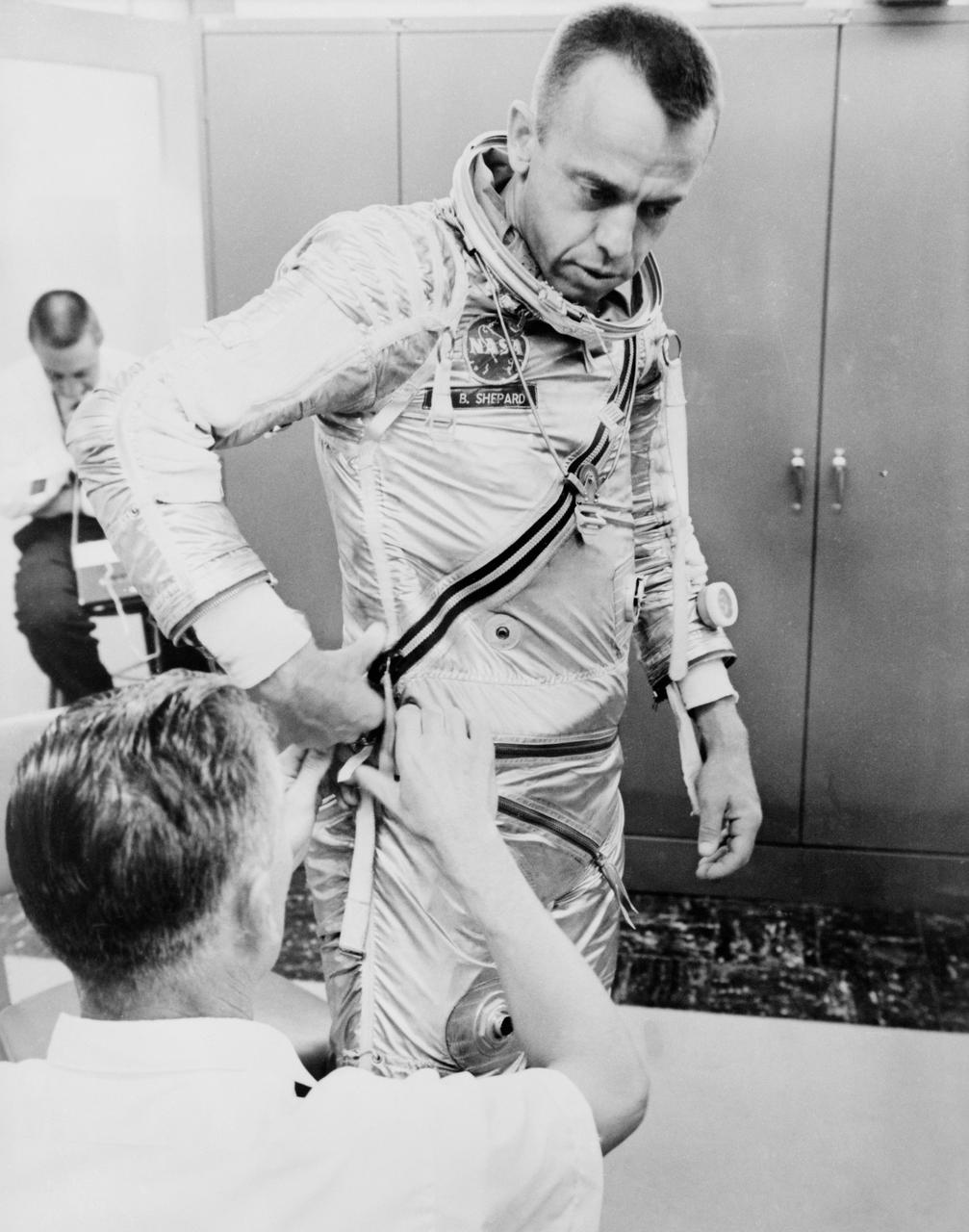

S61-02757 (5 May 1961) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr. is being helped into his pressure suit for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) flight, the first American manned spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
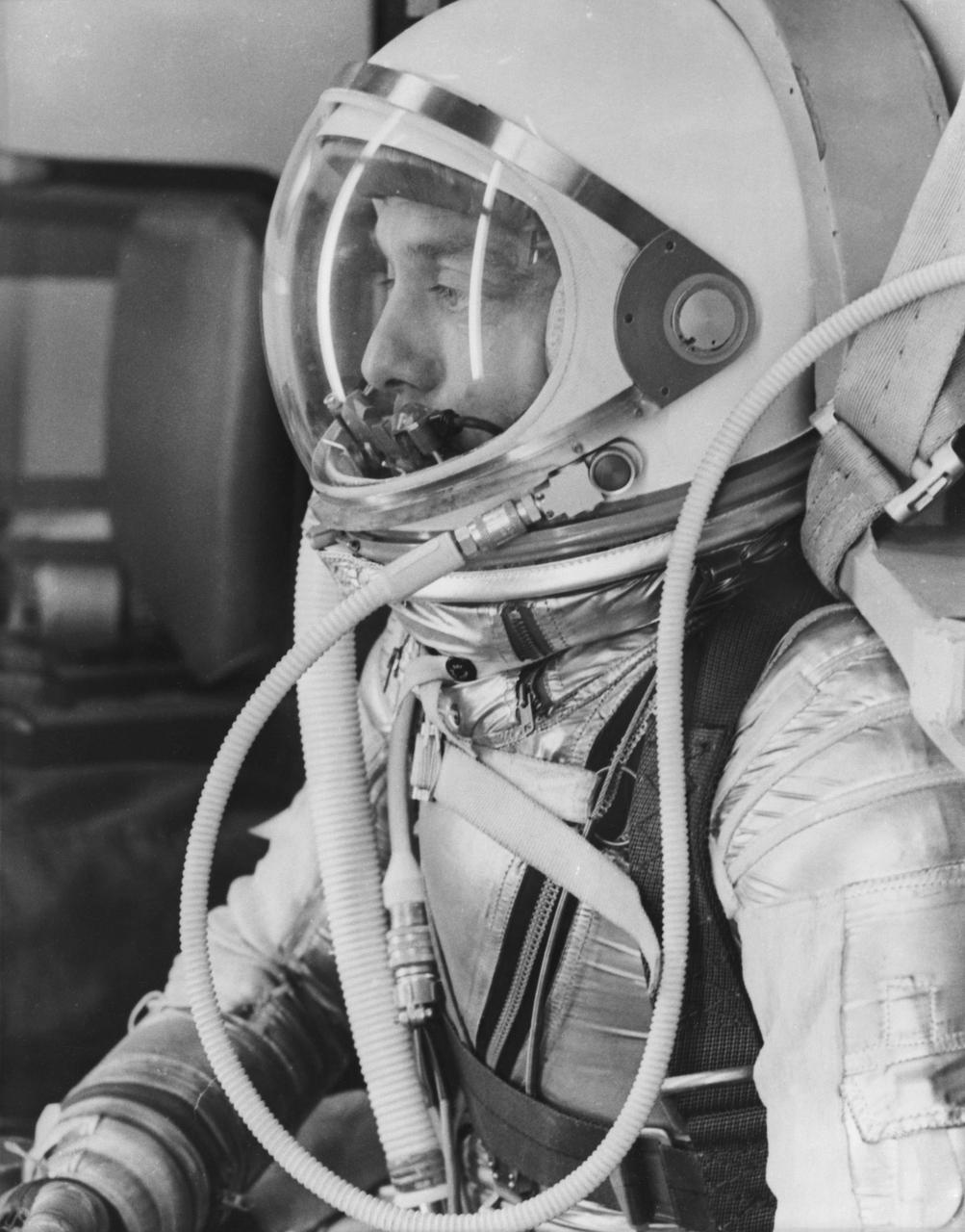

S61-02766 (5 May 1961) --- Side view of astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr. in his pressure suit, with helmet closed, for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) flight, the first American manned spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
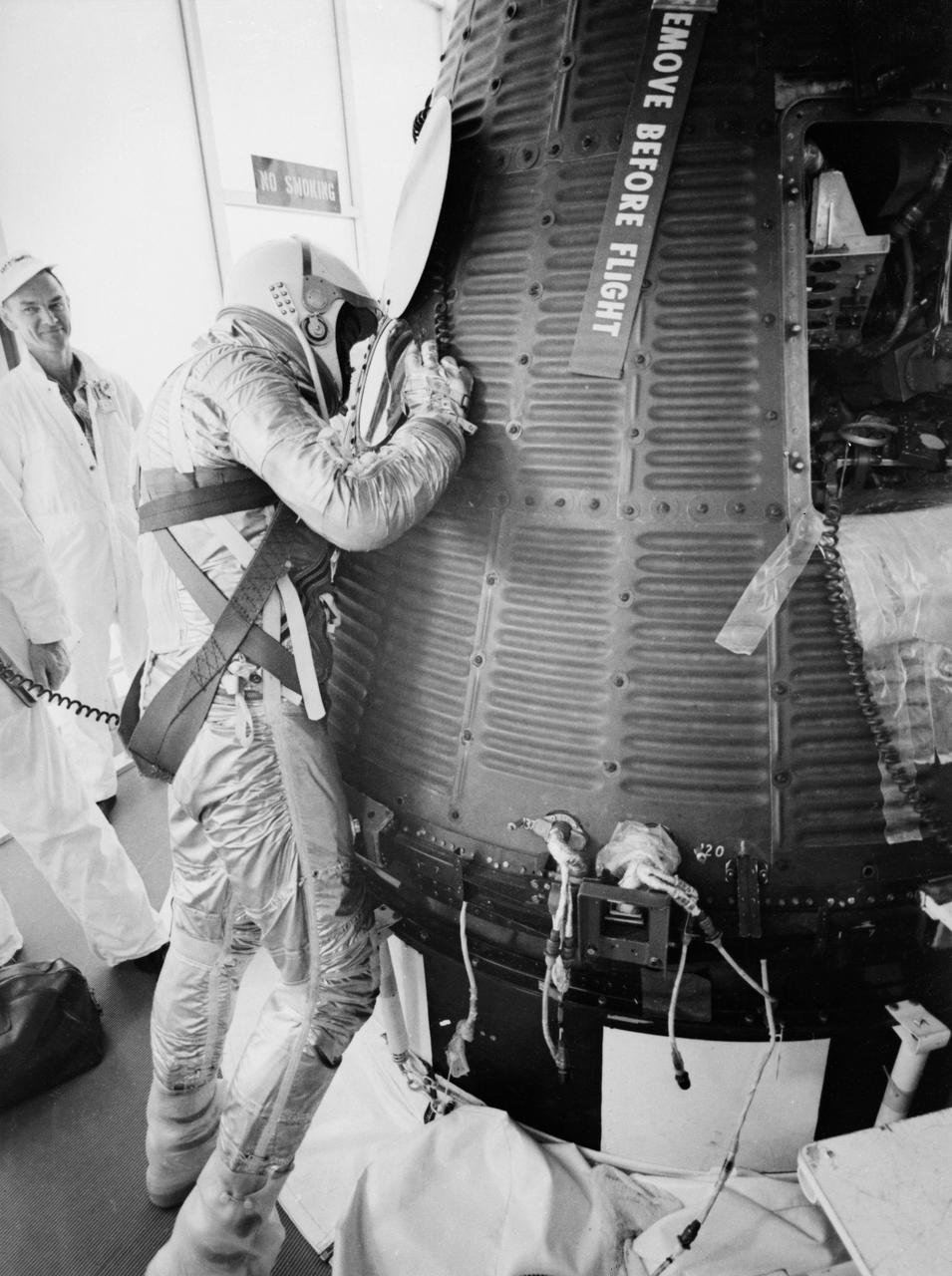

S61-02547 (5 May 1961) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., in his pressure suit and helmet, looks into the Freedom 7 capsule in preparation for ingress before the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) mission. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
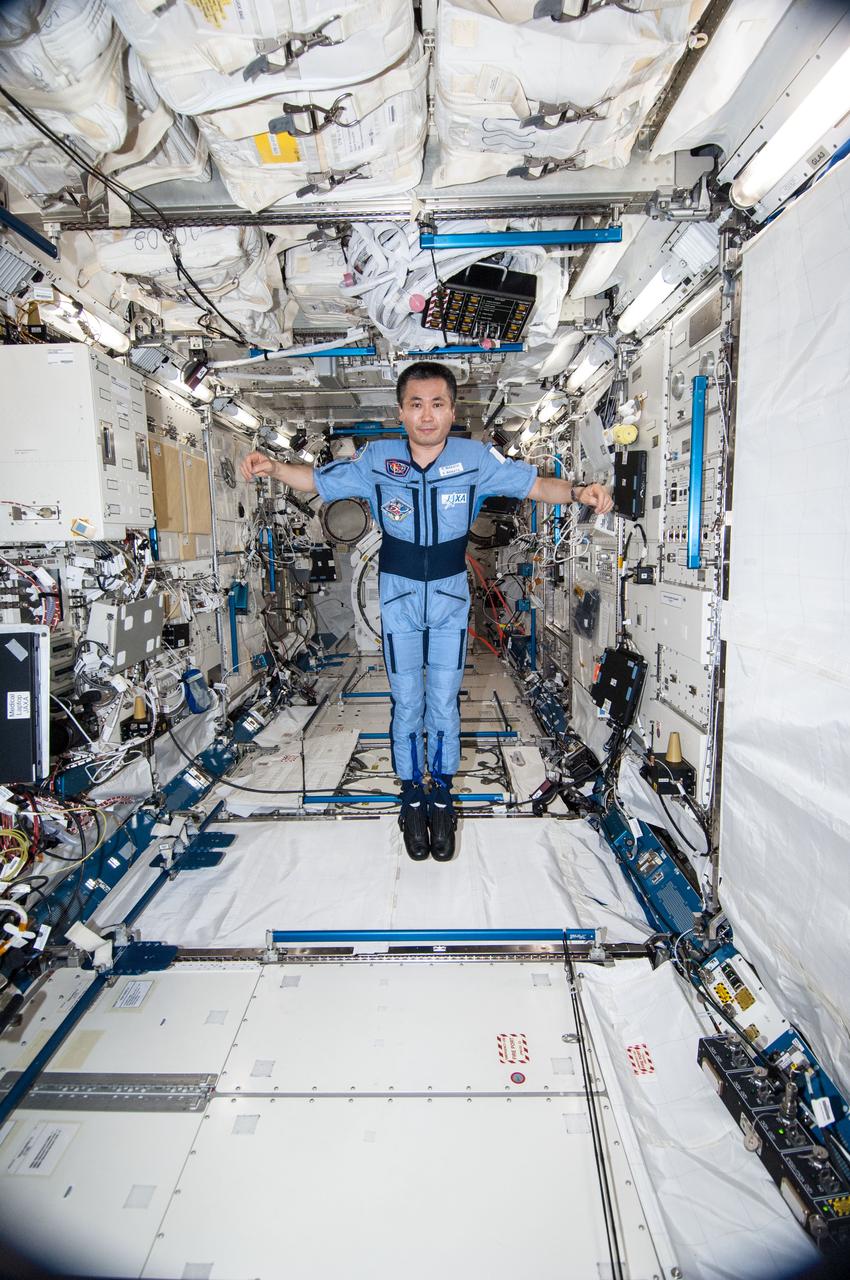

ISS038-E-035470 (24 Jan. 2014) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 38 flight engineer, is pictured wearing the Penguin-3 antigravity pressure/stress suit in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
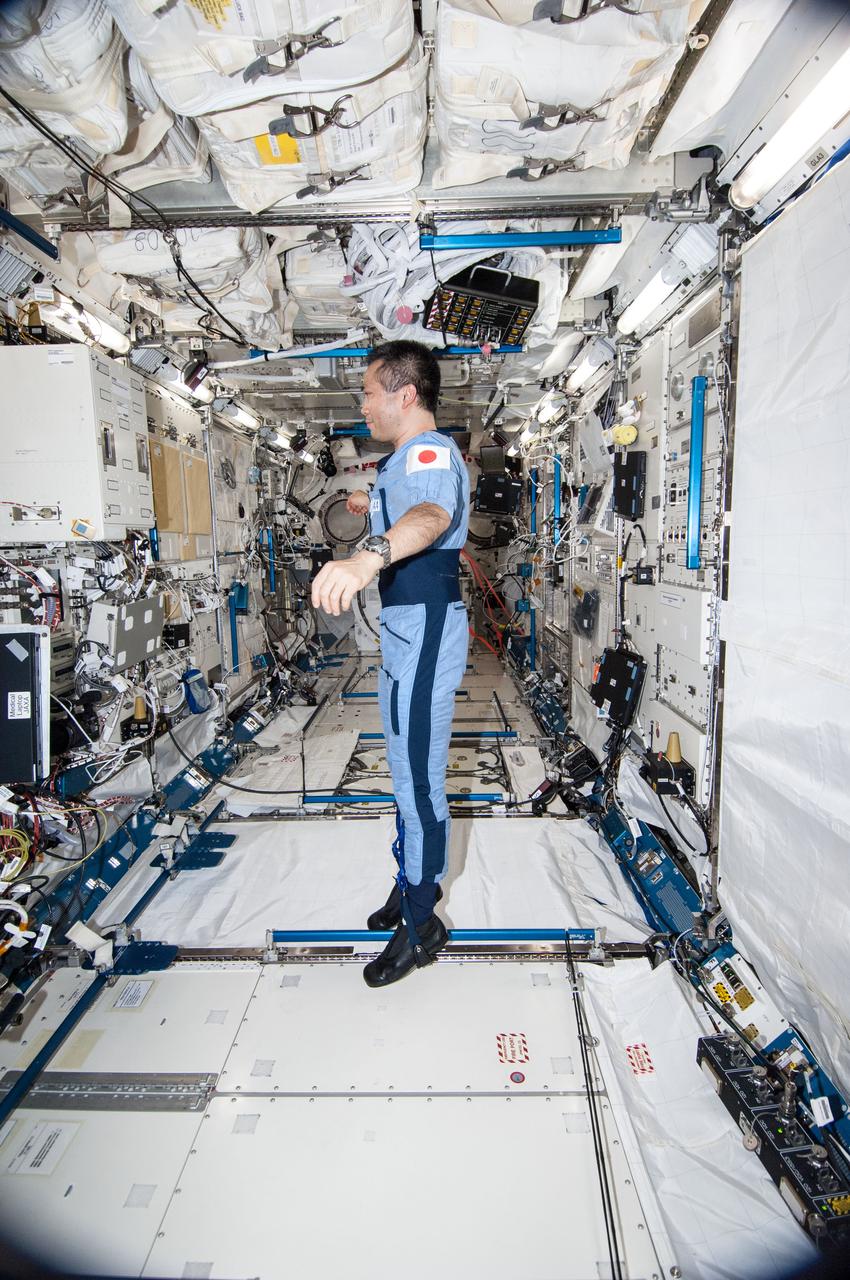

ISS038-E-035476 (24 Jan. 2014) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 38 flight engineer, is pictured wearing the Penguin-3 antigravity pressure/stress suit in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
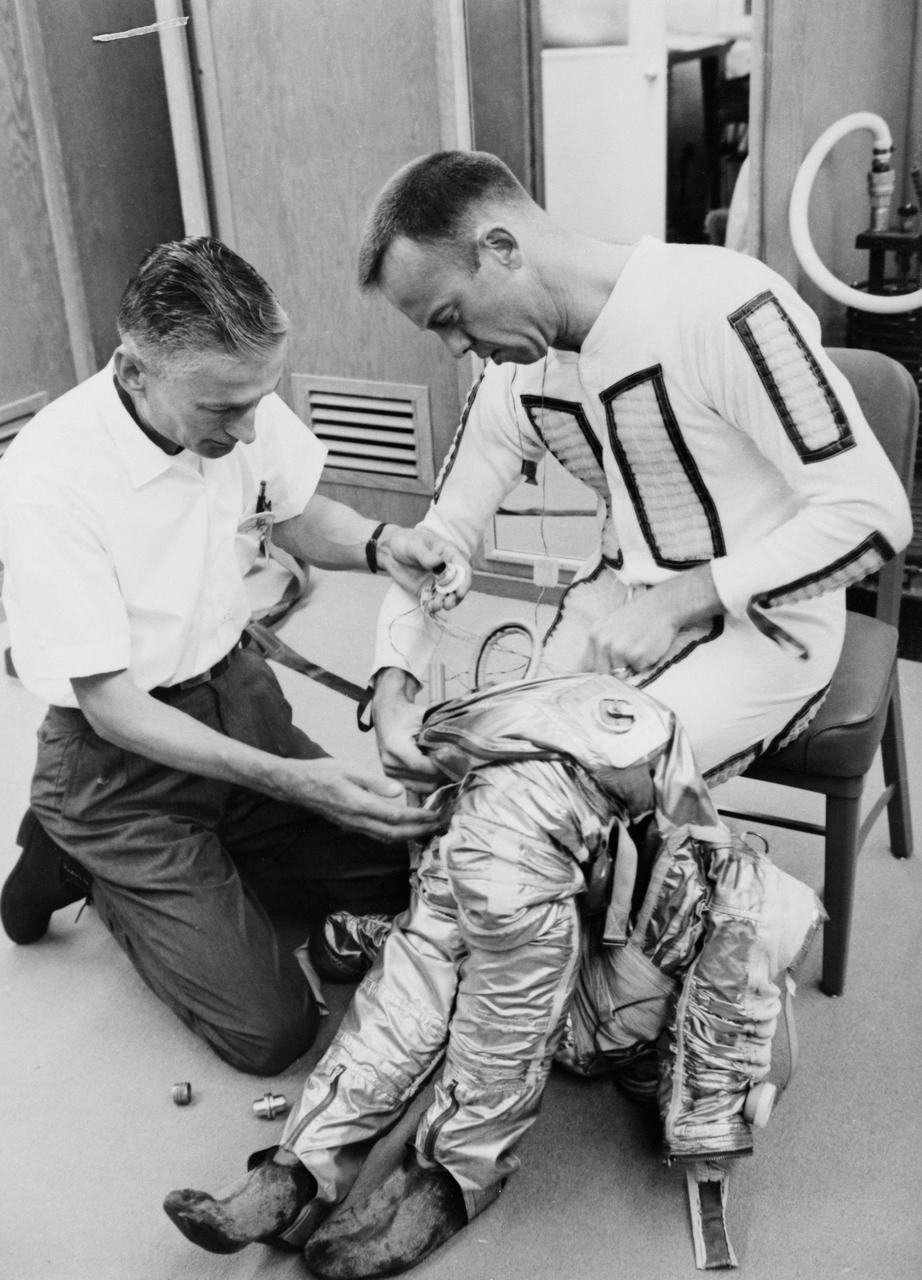
S61-02755 (5 May 1961) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr. is being helped into the lower half of his pressure suit for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) flight, the first American manned spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
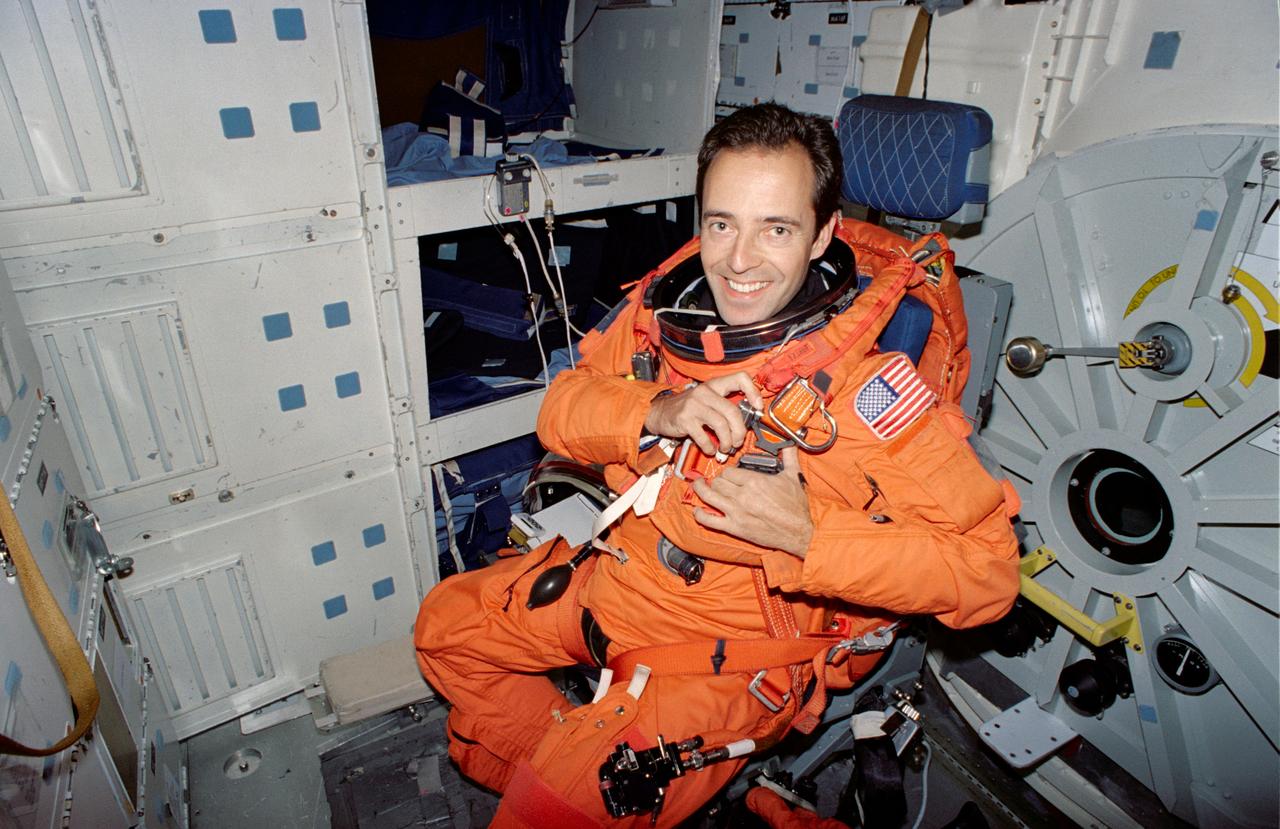

S94-40081 (23 June 1994) --- Wearing a training version of a partial pressure suit, Jean-Francois Clervoy, STS-66 international mission specialist, secures himself on a collapsible seat on the middeck of a Shuttle trainer during a rehearsal of procedures to be followed during launch and entry phases of his scheduled November flight. This rehearsal, held in the Crew Compartment Trainer (CCT) of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Shuttle Mockup and Integration Laboratory, was followed by a training session on emergency egress procedures. Clervoy, a European astronaut, will join five NASA astronauts for a week and a half aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis in Earth-orbit in support of the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3).
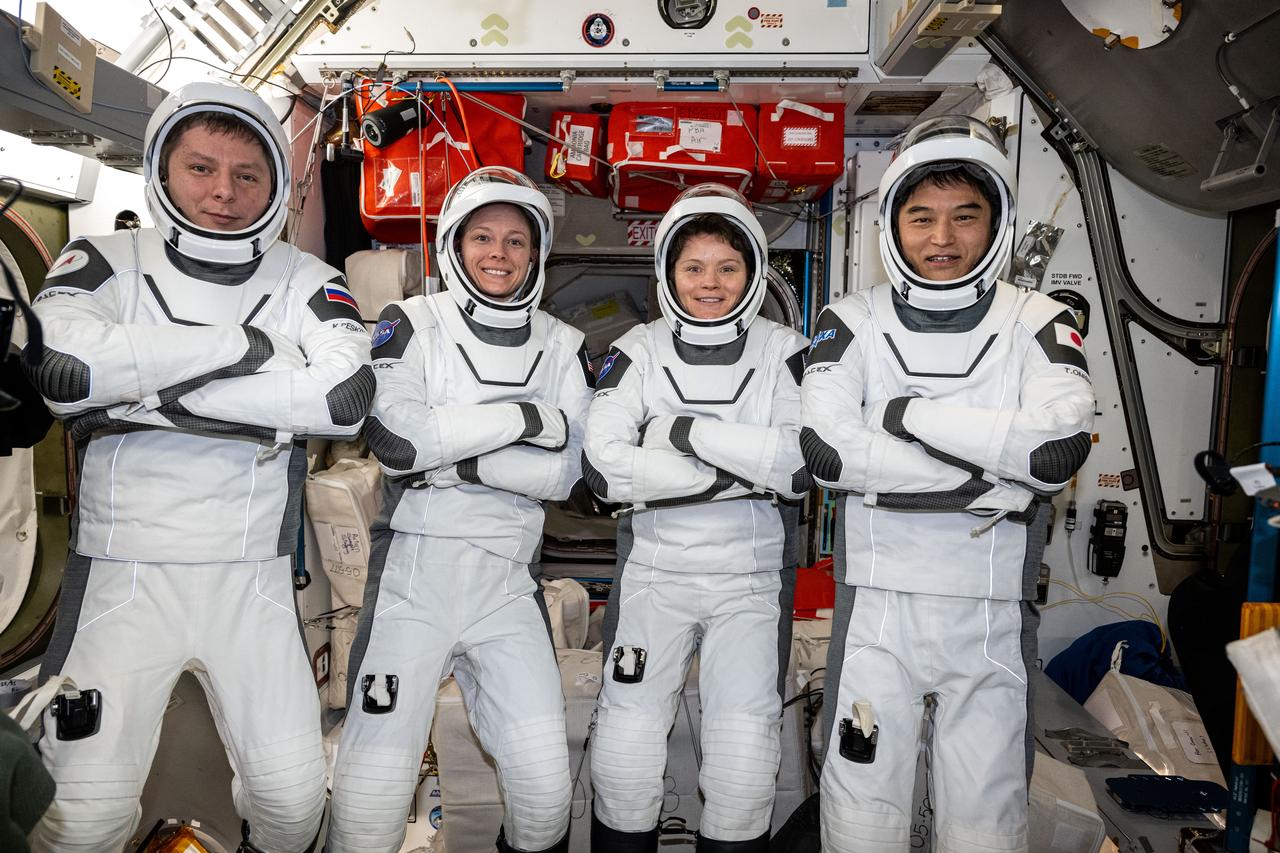

iss073e0414514 (July 29, 2025) --- The four members of NASA's SpaceX Crew-10 mission pose for a portrait in their Dragon pressure suits aboard the International Space Station's Harmony module. The Commercial Crew members were testing their suits' components and ensuring a proper fit before their departure on Aug. 8, 2025, aboard Dragon ending their five-month space research mission inside the orbital outpost. From left are, Roscosmos cosmonaut Kirill Peskov, NASA astronauts Nichole Ayers and Anne McClain, and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Takuya Onishi.
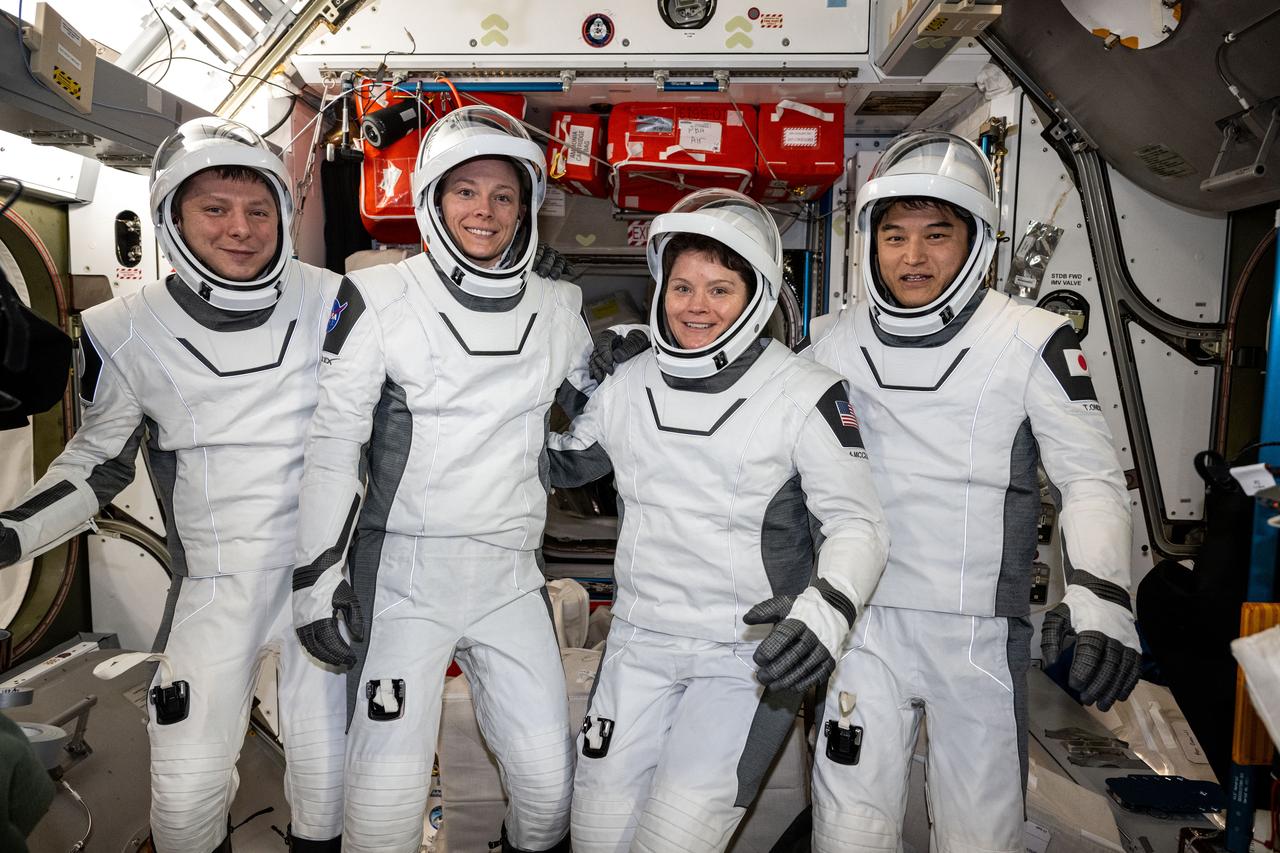

iss073e0414510 (July 29, 2025) --- The four members of NASA's SpaceX Crew-10 mission pose for a portrait in their Dragon pressure suits aboard the International Space Station's Harmony module. The Commercial Crew members were testing their suits' components and ensuring a proper fit before their departure on Aug. 8, 2025, aboard Dragon ending their five-month space research mission inside the orbital outpost. From left are, Roscosmos cosmonaut Kirill Peskov, NASA astronauts Nichole Ayers and Anne McClain, and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Takuya Onishi.
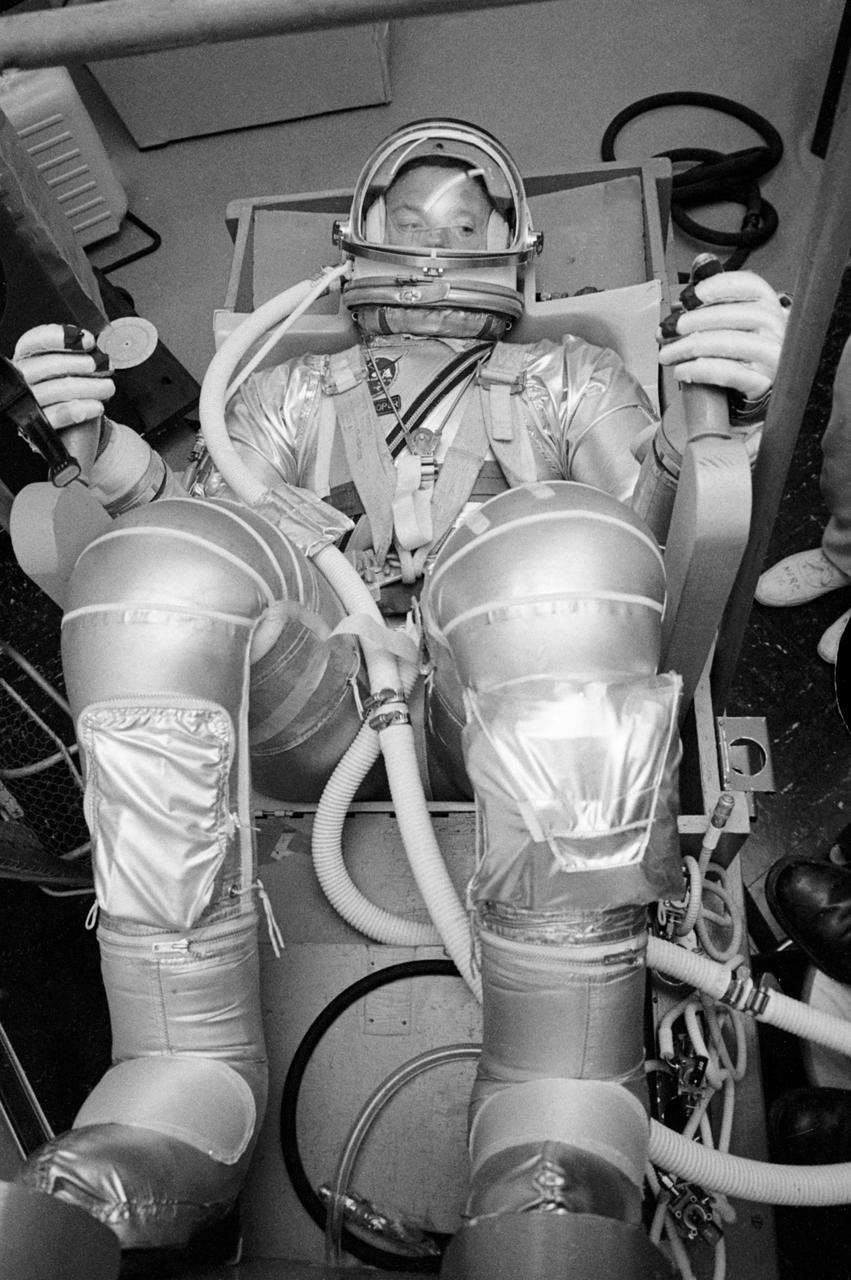

S63-03976 (1963) --- Astronaut L. Gordon Cooper Jr., prime pilot for the Mercury-Atlas 9 (MA-9) mission, undergoes suit pressurization tests. Photo credit: NASA

NASA Dryden life support technician Jim Sokolik assists pressure-suited pilot Dee Porter into the cockpit of NASA's ER-2 Earth resources aircraft.
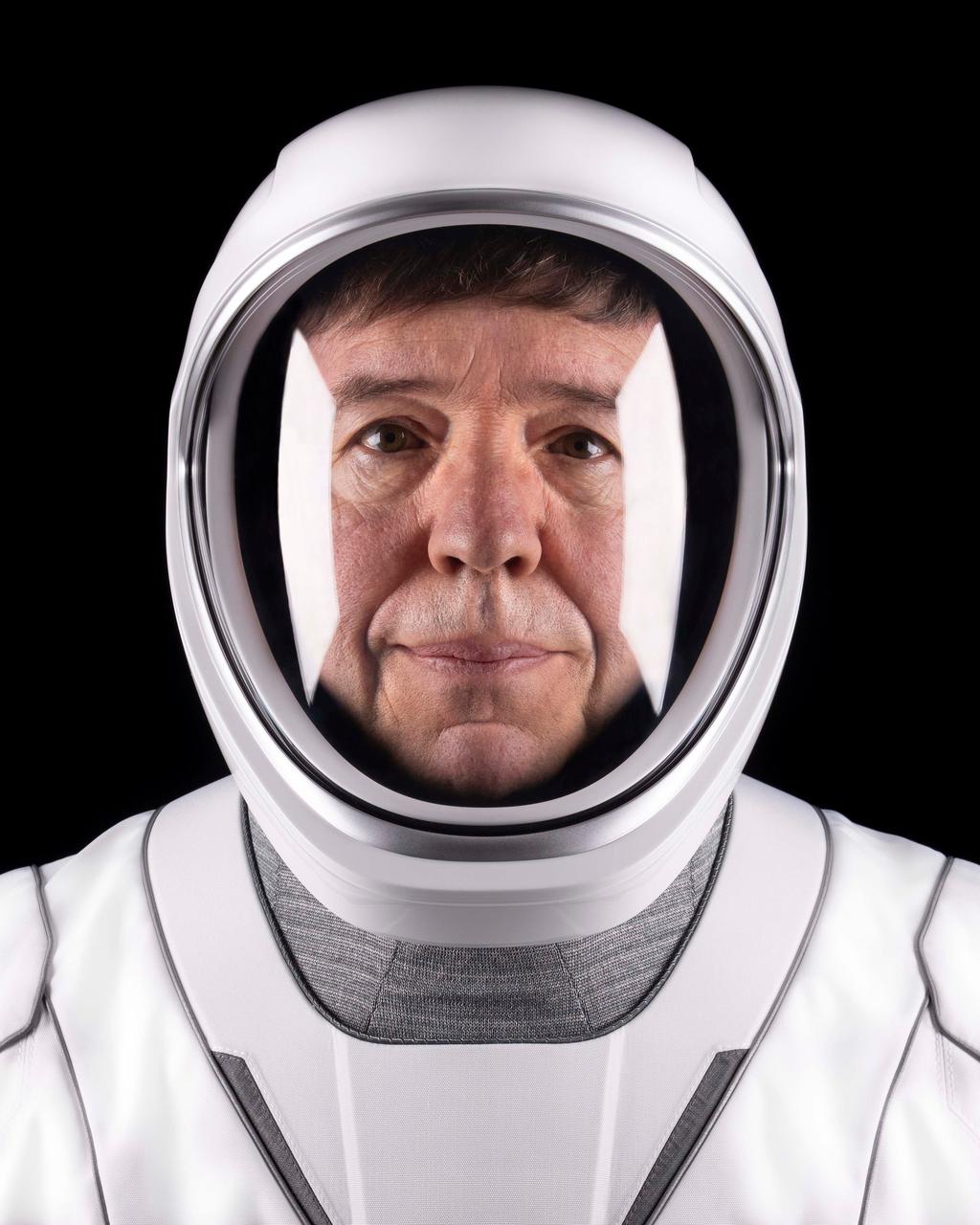

jsc2024e01170 (Dec. 3, 2023) --- SpaceX Crew-8 Pilot Michael Barratt of NASA's Commercial Crew Program poses for a portrait in his pressure suit at SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX
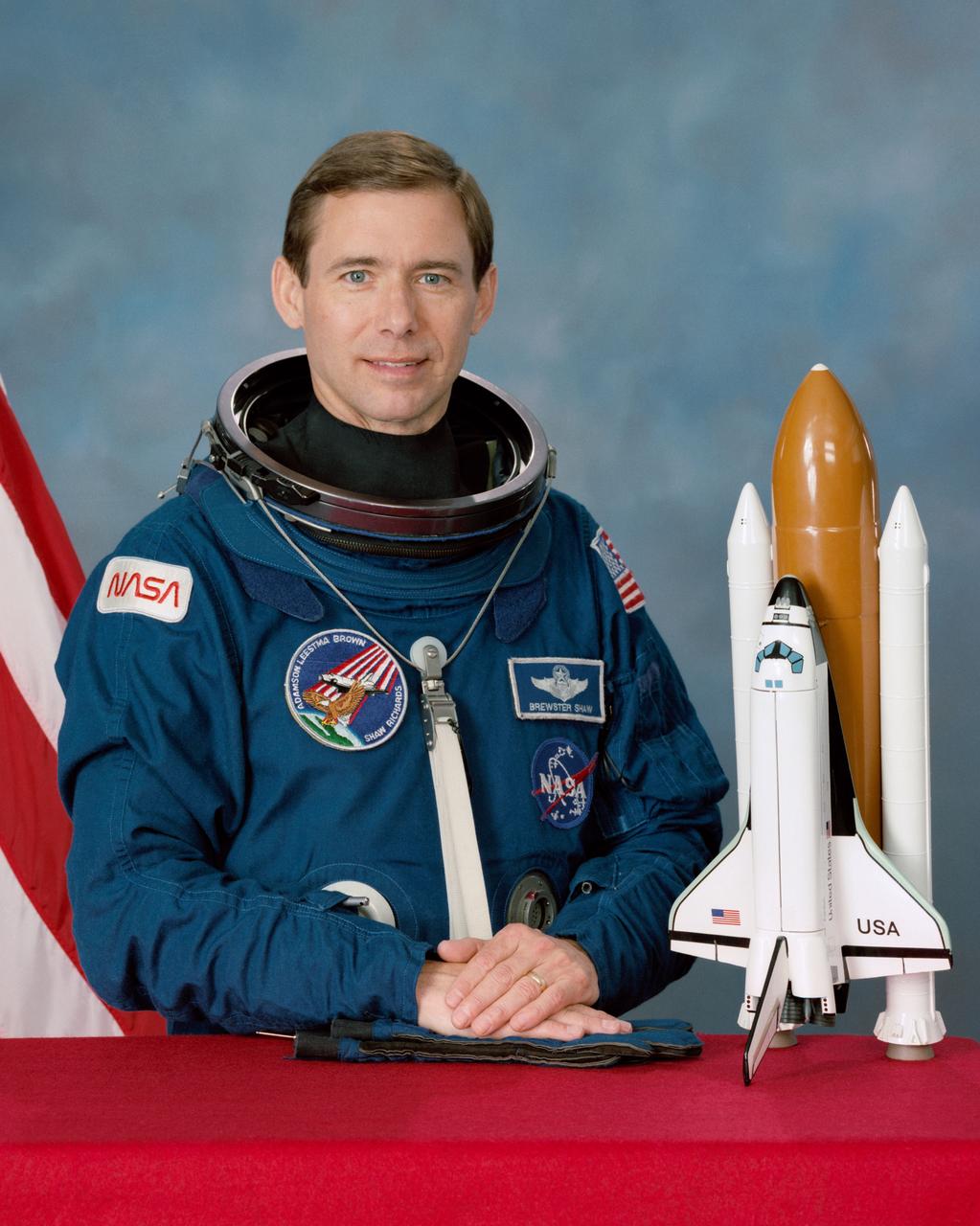

S89-29371 (19 March 1989) --- Astronaut Brewster H. Shaw, Jr.
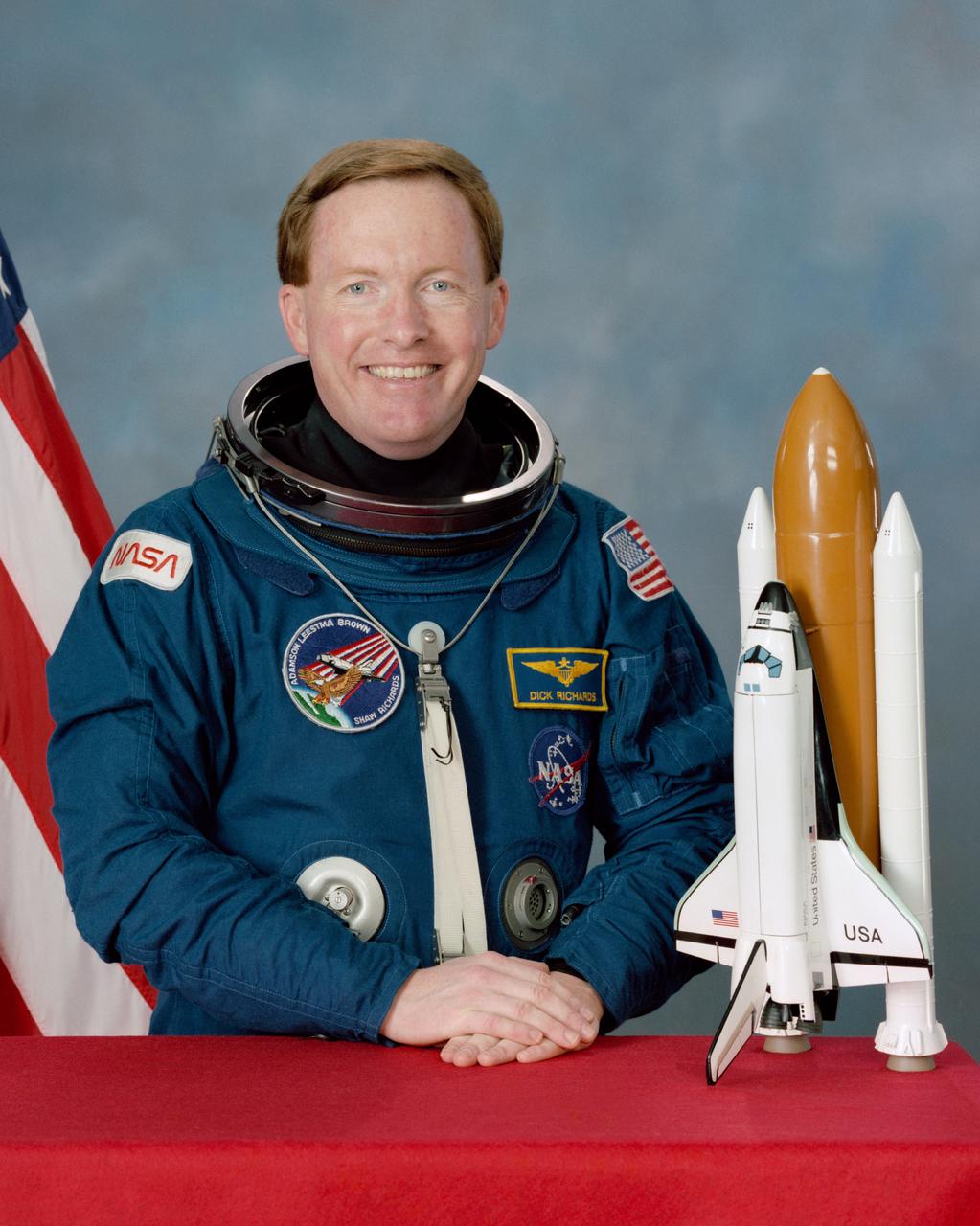

S89-29425 (20 March 1989) --- Astronaut Richard N. Richards.
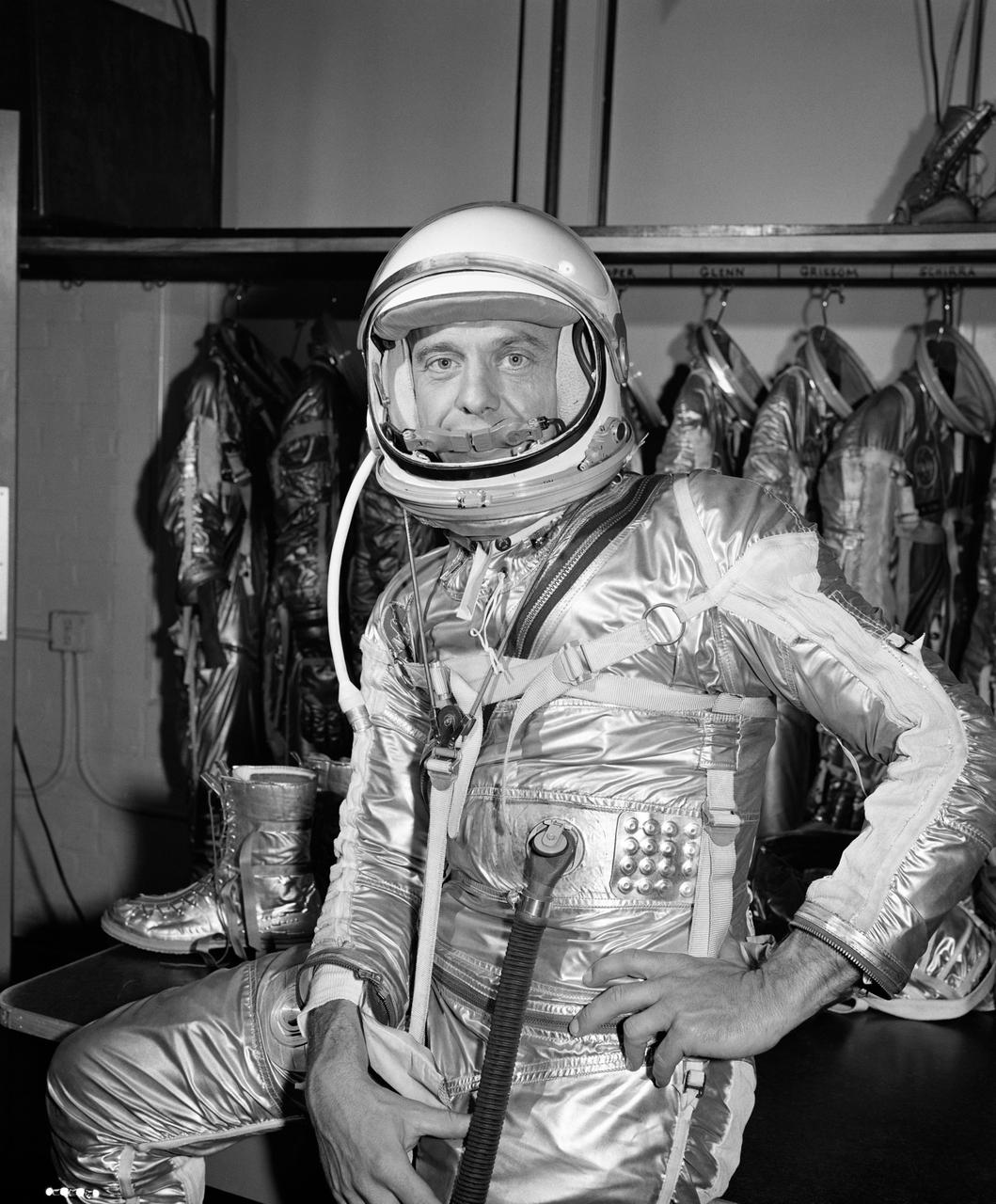

S61-00220 (20 April 1961) --- Close-up view of astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr. in his pressure suit, with helmet opened, for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) flight, the first American manned spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
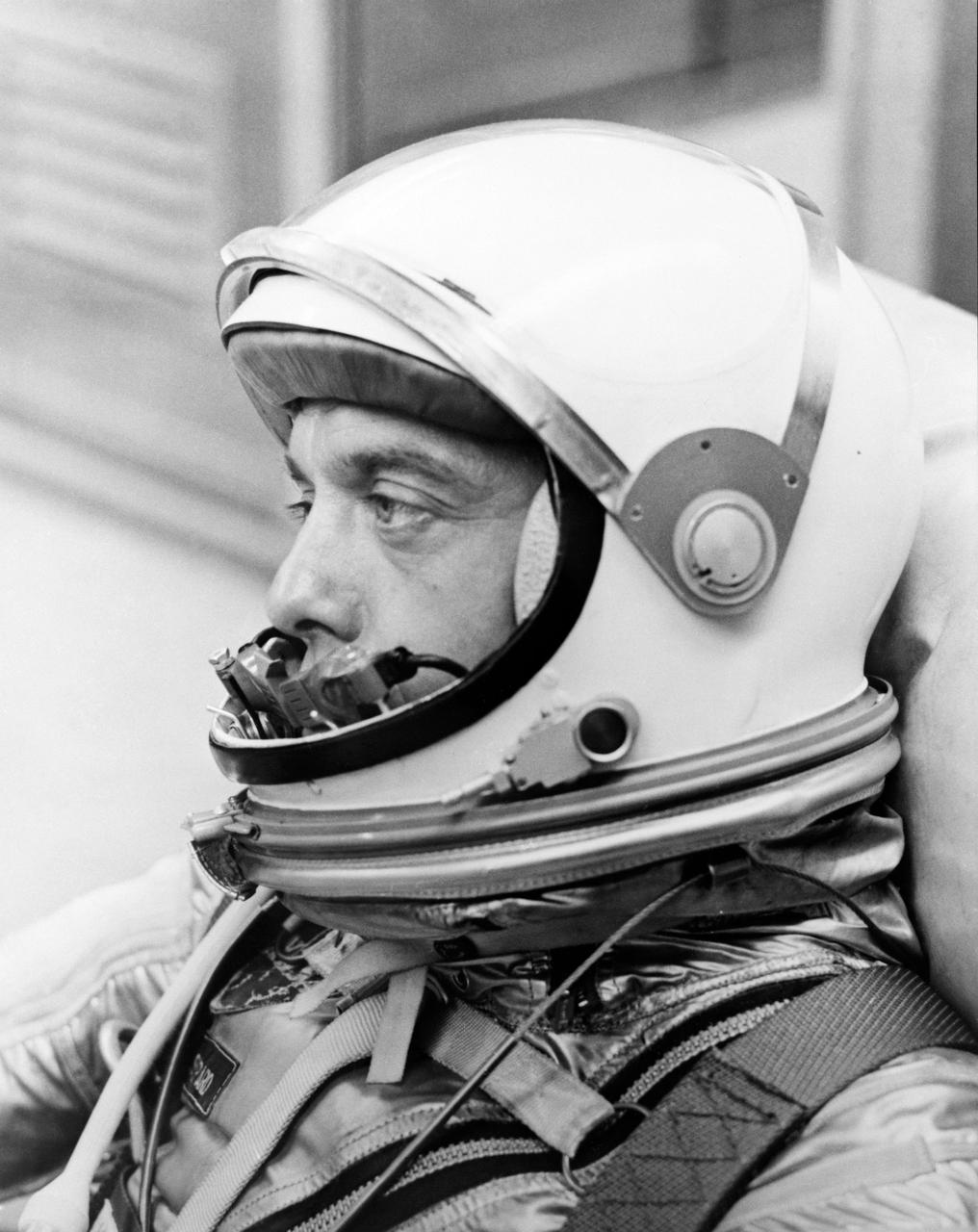

S61-02775 (5 May 1961) --- Close-up view of astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr. in his pressure suit, with helmet opened, for the Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) flight, the first American manned spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

jsc2025e015860 (March 7, 2025) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 Pilot Nichole Ayers poses for a portrait in her pressure suit at the SpaceX facility in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX
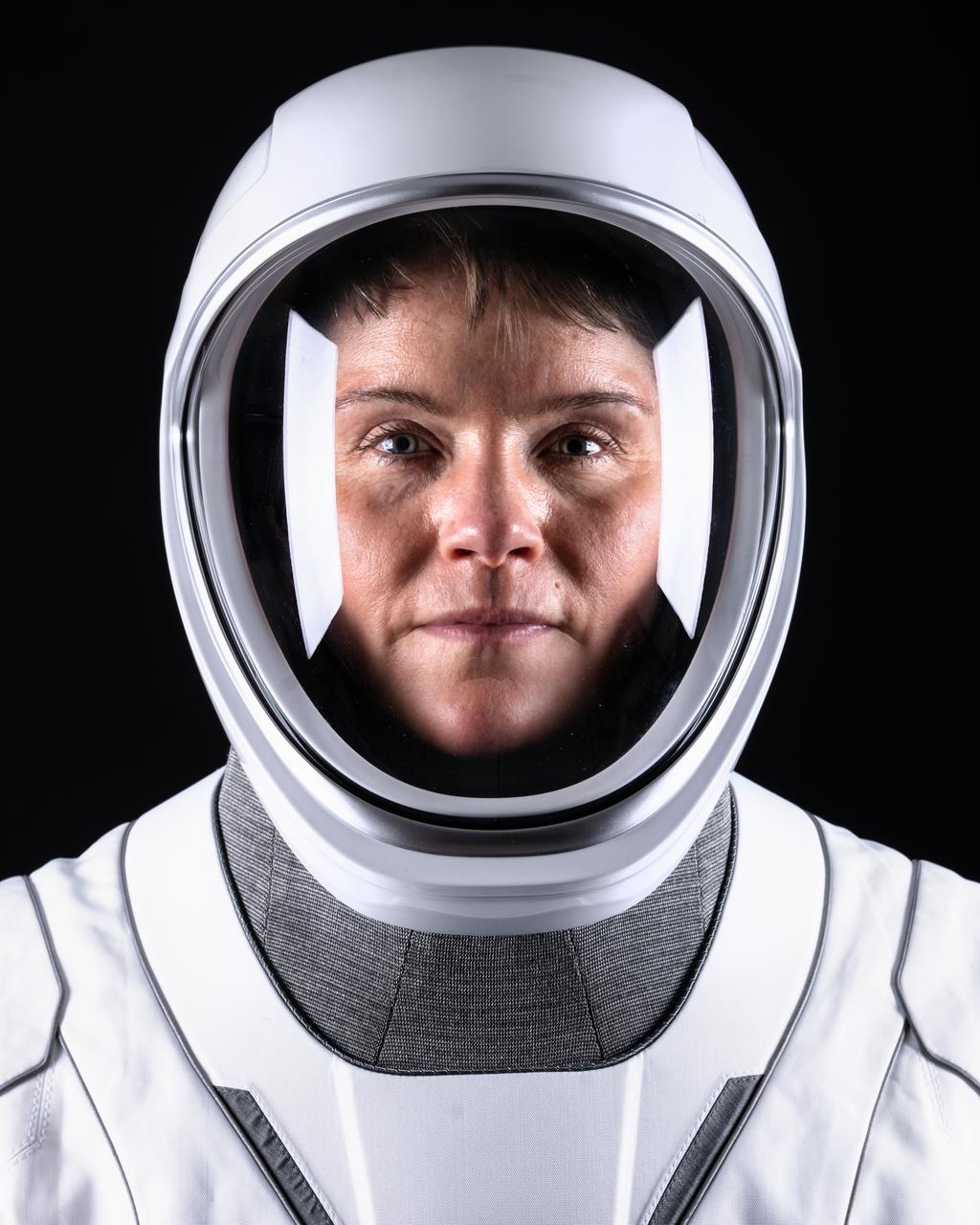

jsc2025e015859 (March 7, 2025) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 Commander Anne McClain poses for a portrait in her pressure suit at the SpaceX facility in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX
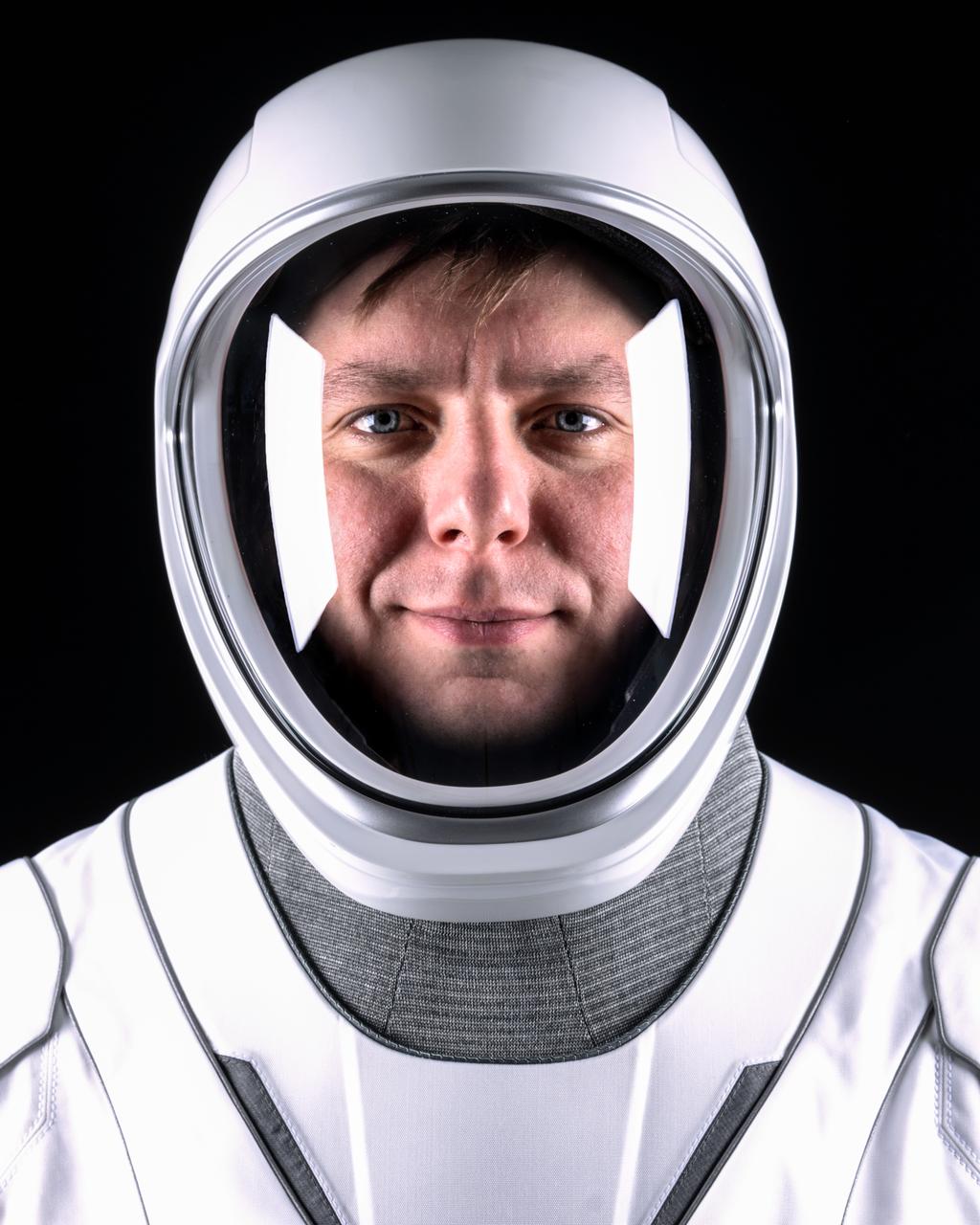

jsc2025e015861 (March 7, 2025) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 Mission Specialist Kirill Peskov poses for a portrait in his pressure suit at the SpaceX facility in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX
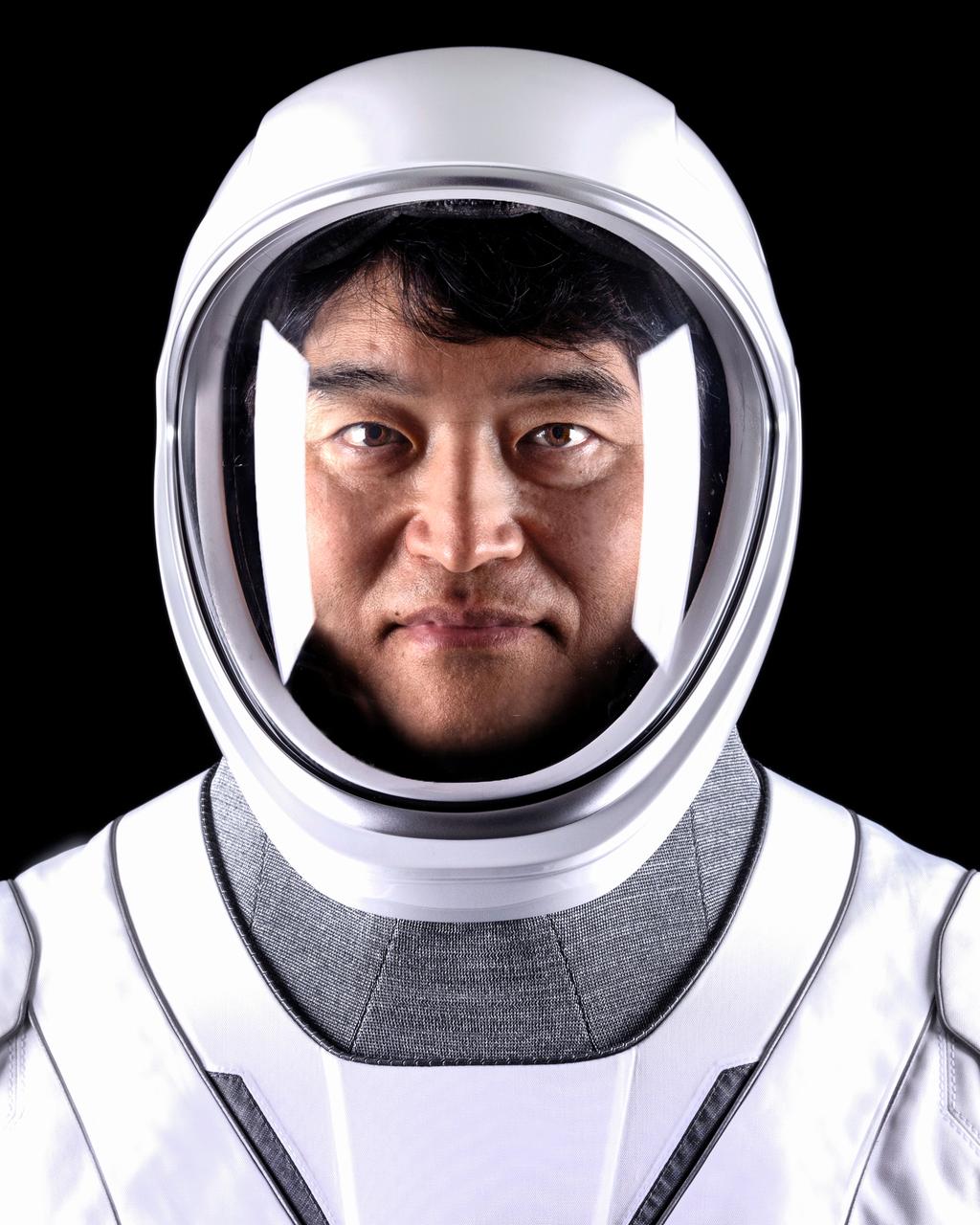

jsc2025e015862 (March 7, 2025) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 Mission Specialist Takuya Onishi poses for a portrait in his pressure suit at the SpaceX facility in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX
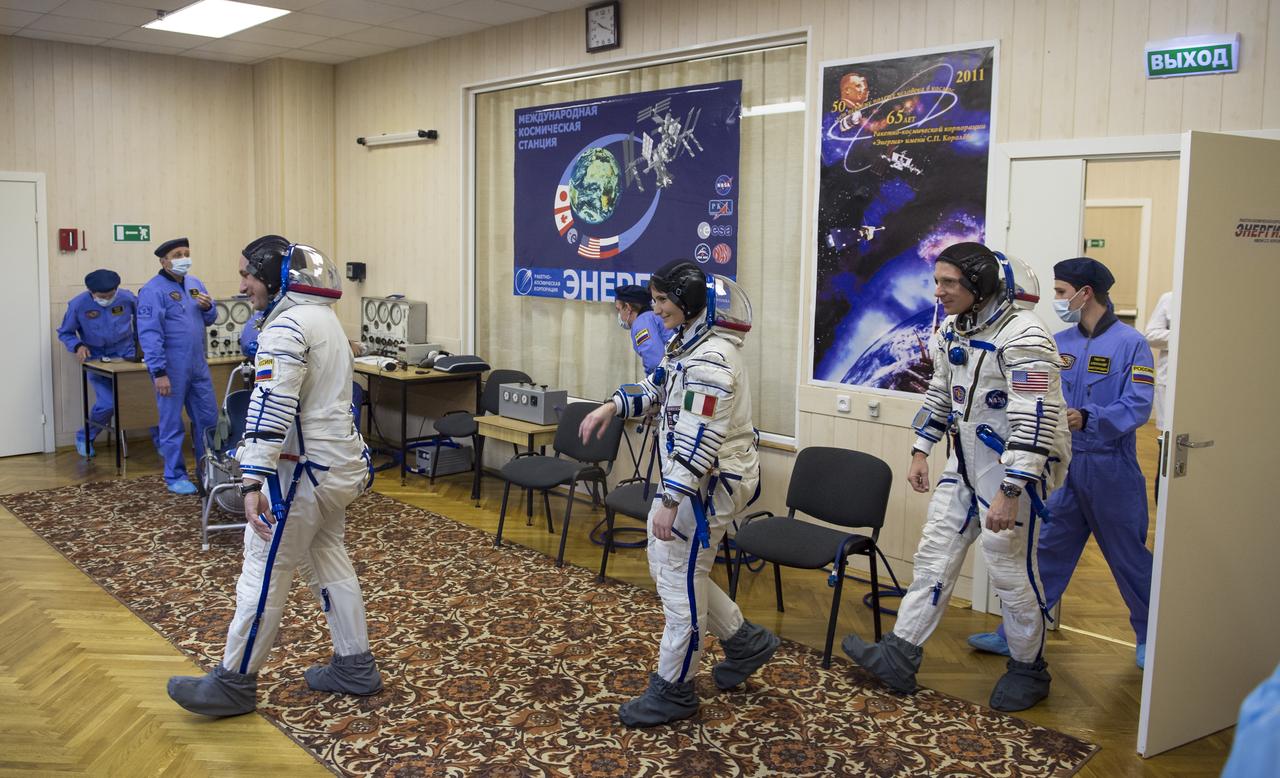

Expedition 42 crew members, Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), left, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA), center, and Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA, right, prepare for pressure checks of their Sokol suits in Building 254 following their suit up for launch, Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts, Shkaplerov, and Cristoforetti into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
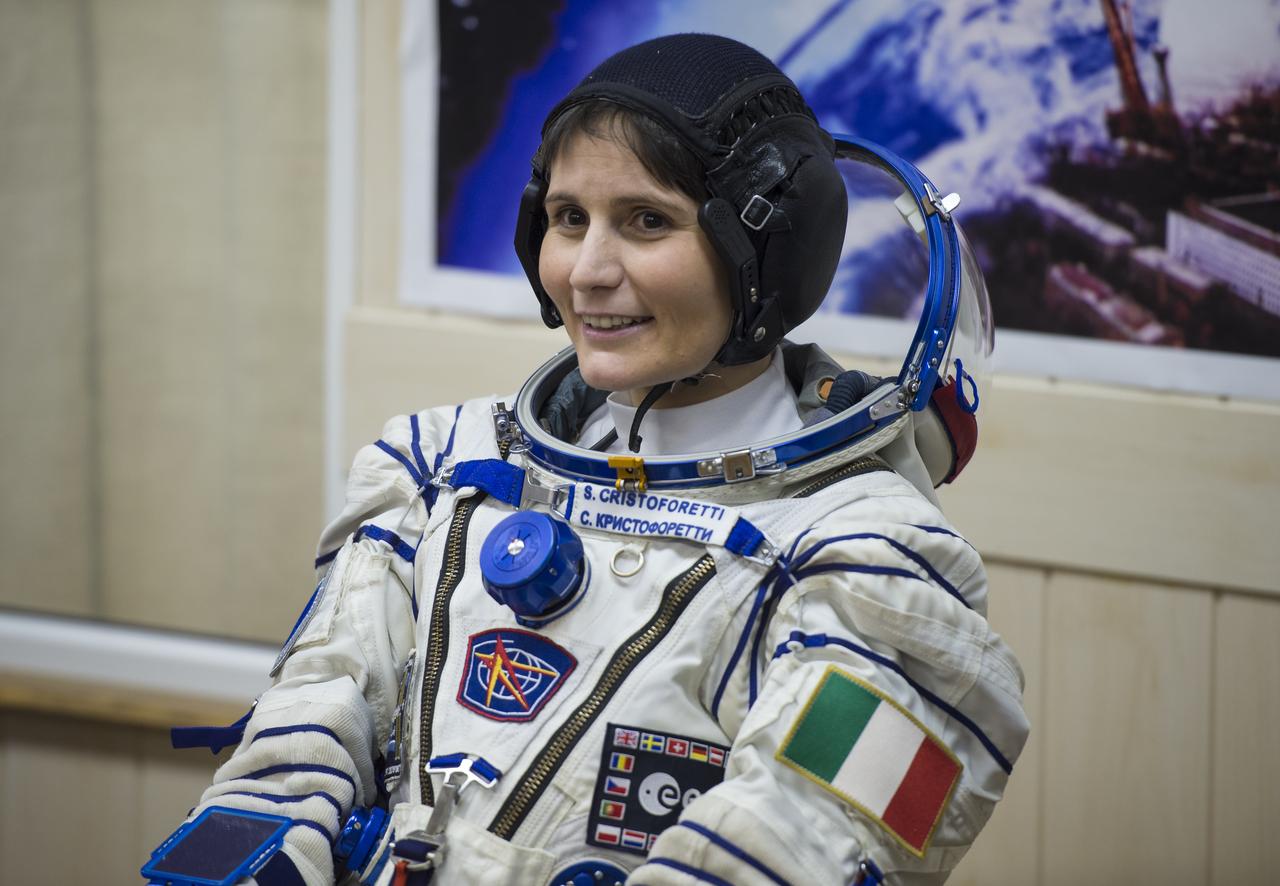

Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) waits for a pressure check of her Sokol suit in Building 254 following her suit up for launch, Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Cristoforetti and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA and Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
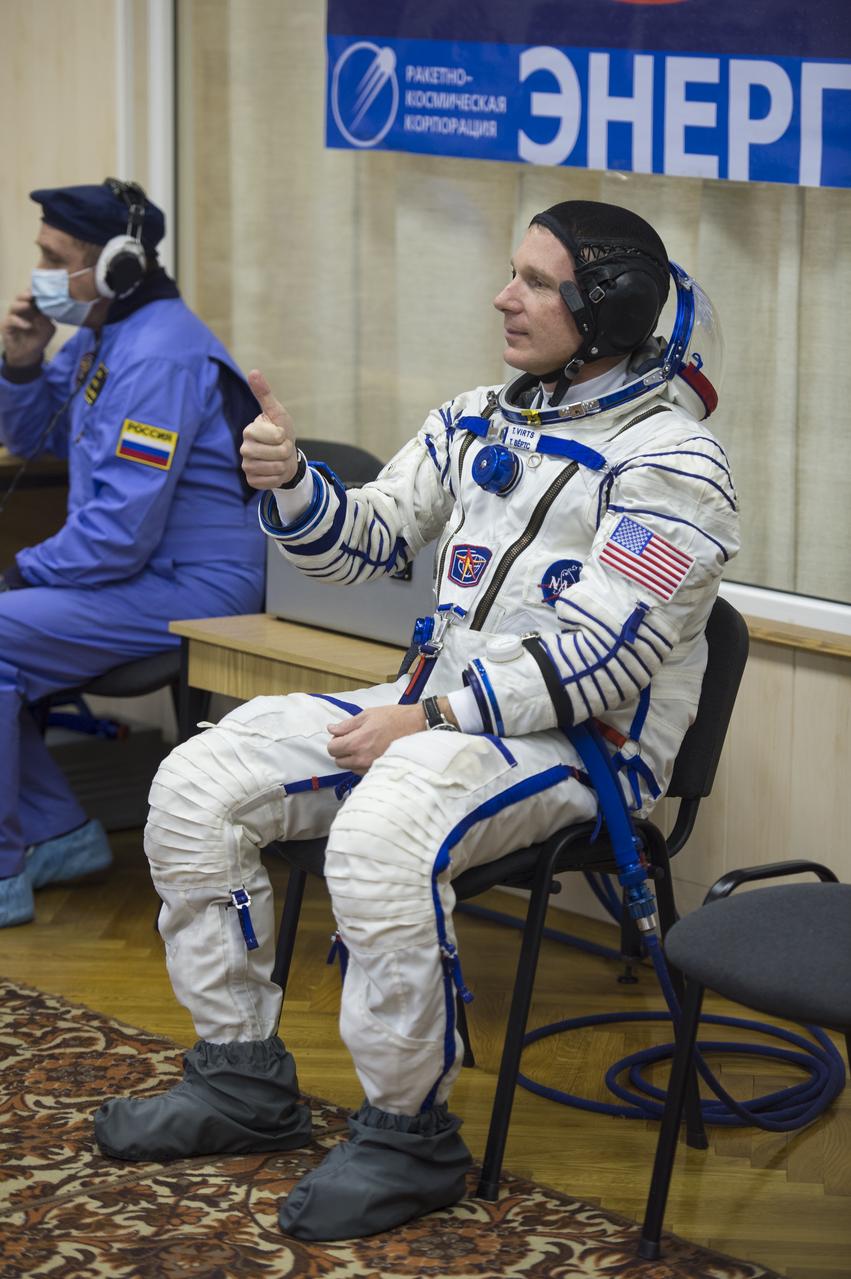

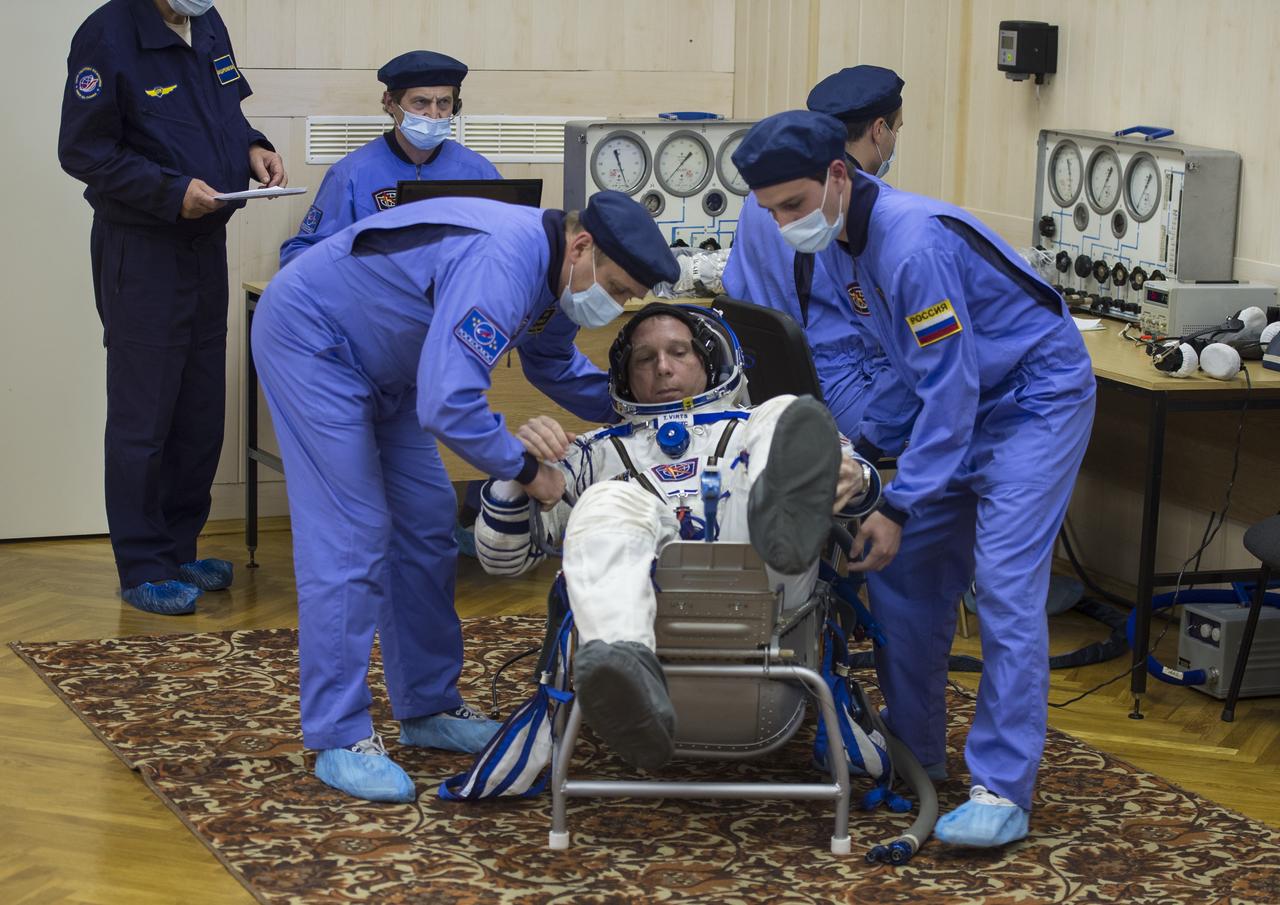
Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA gives a thumbs up while waiting for a pressure check of his Sokol suit in Building 254 following his suit up for launch, Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) and Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

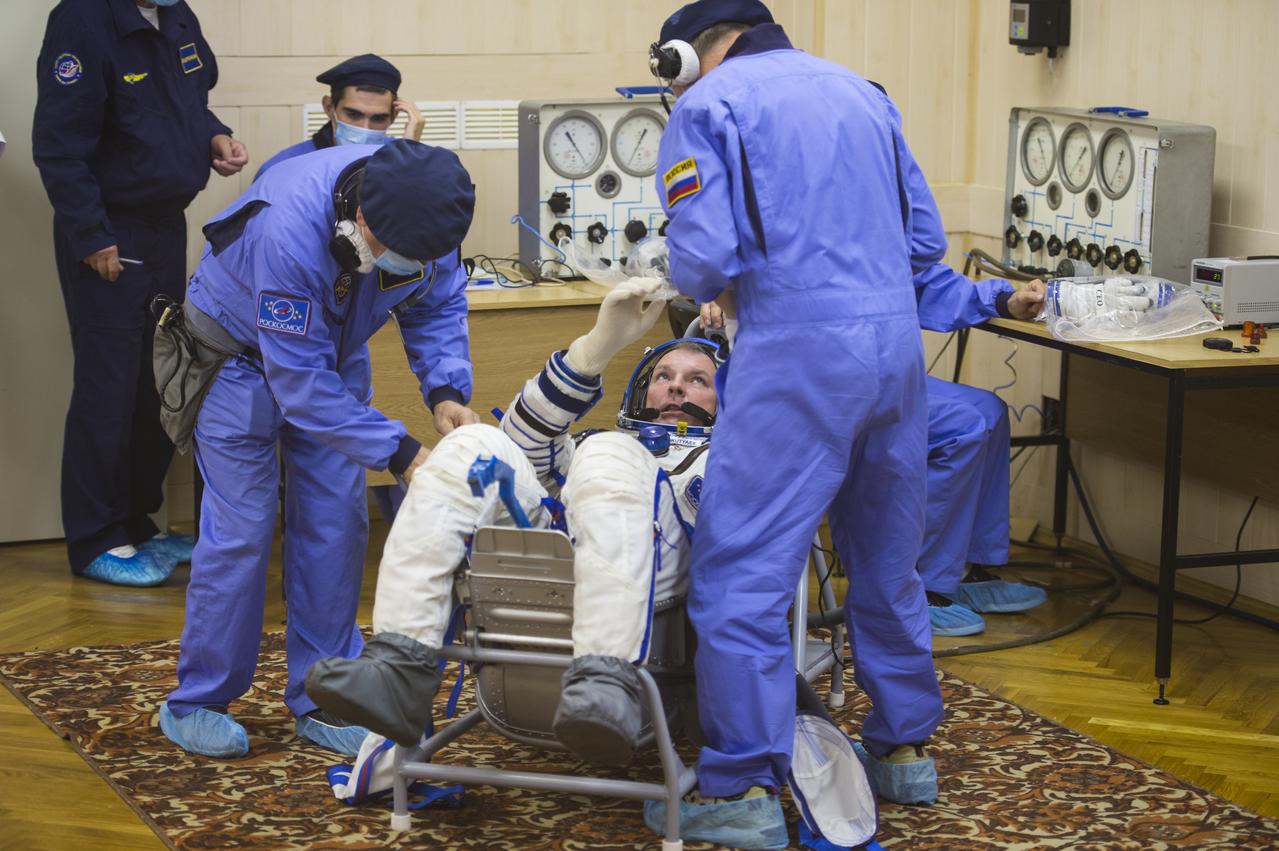
Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA, right, waits to have his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked while Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) has his suit checked on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Sept. 26 (Kazakhstan time) and will carry Samokutyaev, Wilmore, and Flight Engineer Elena Serova of Roscosmos into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
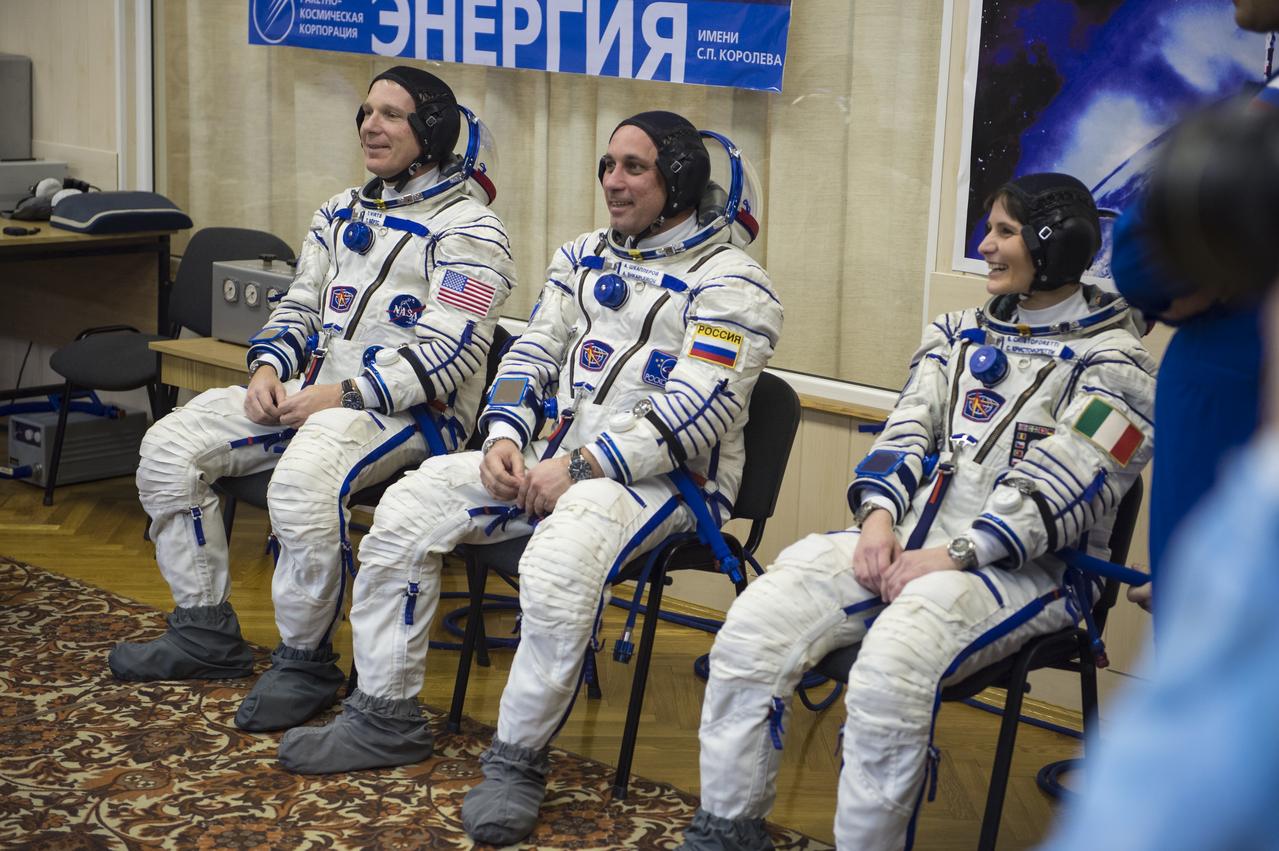

Expedition 42 crew members, Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA, left, Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), center, and Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA), right, prepare for pressure checks of their Sokol suits in Building 254 following their suit up for launch, Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts, Shkaplerov, and Cristoforetti into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
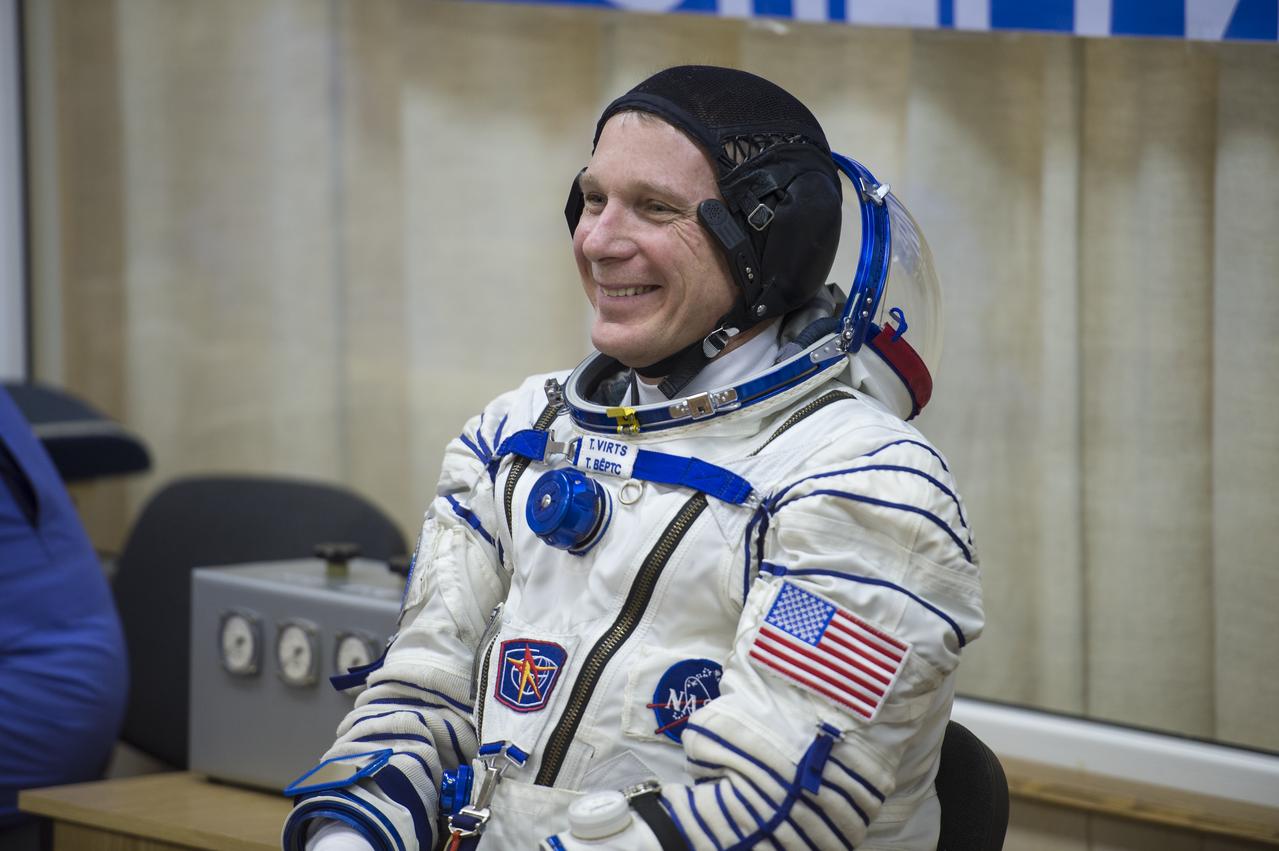

Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA waits for a pressure check of his Sokol suit in Building 254 following his suit up for launch, Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) and Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
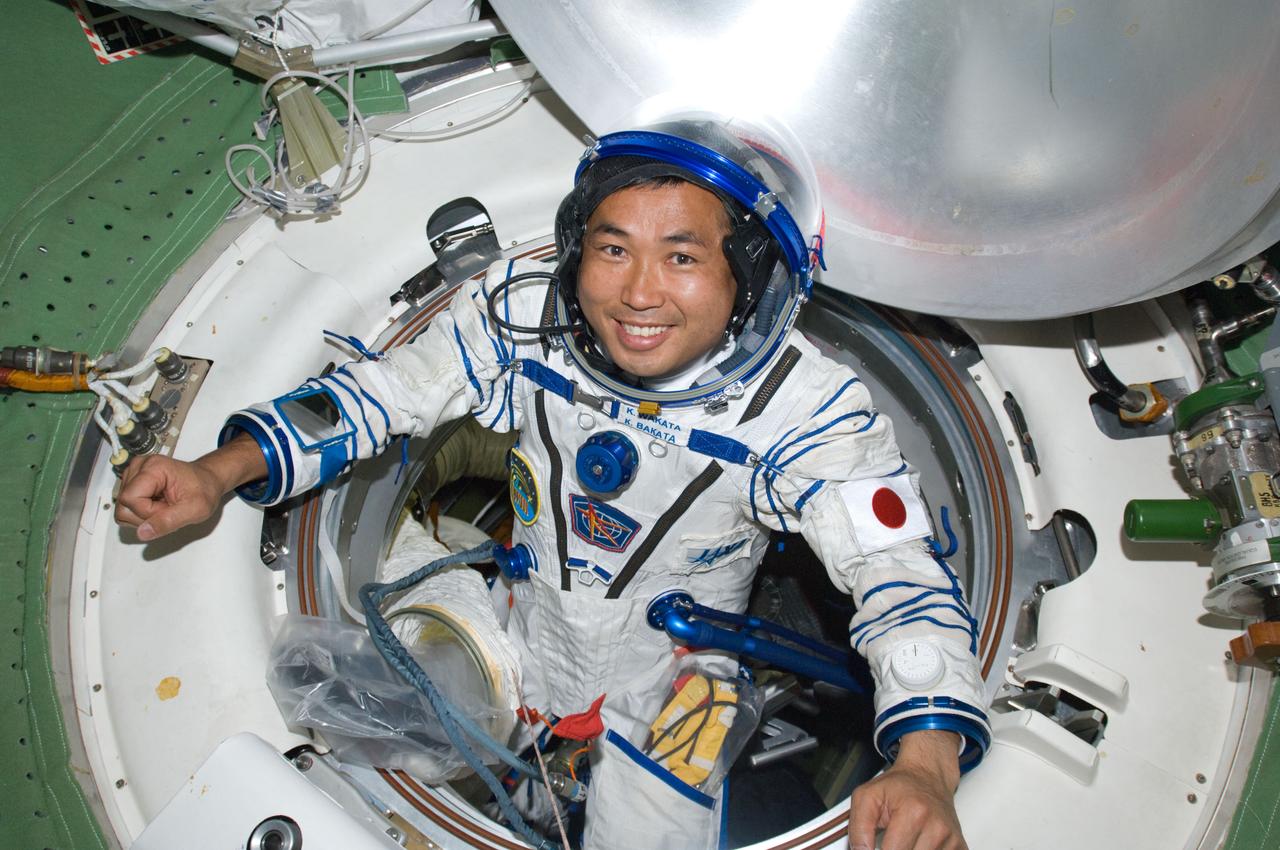

ISS018-E-040994 (18 March 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 18 flight engineer, attired in his Russian Sokol launch and entry suit, is pictured near a hatch on the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-119) remains docked with the station.
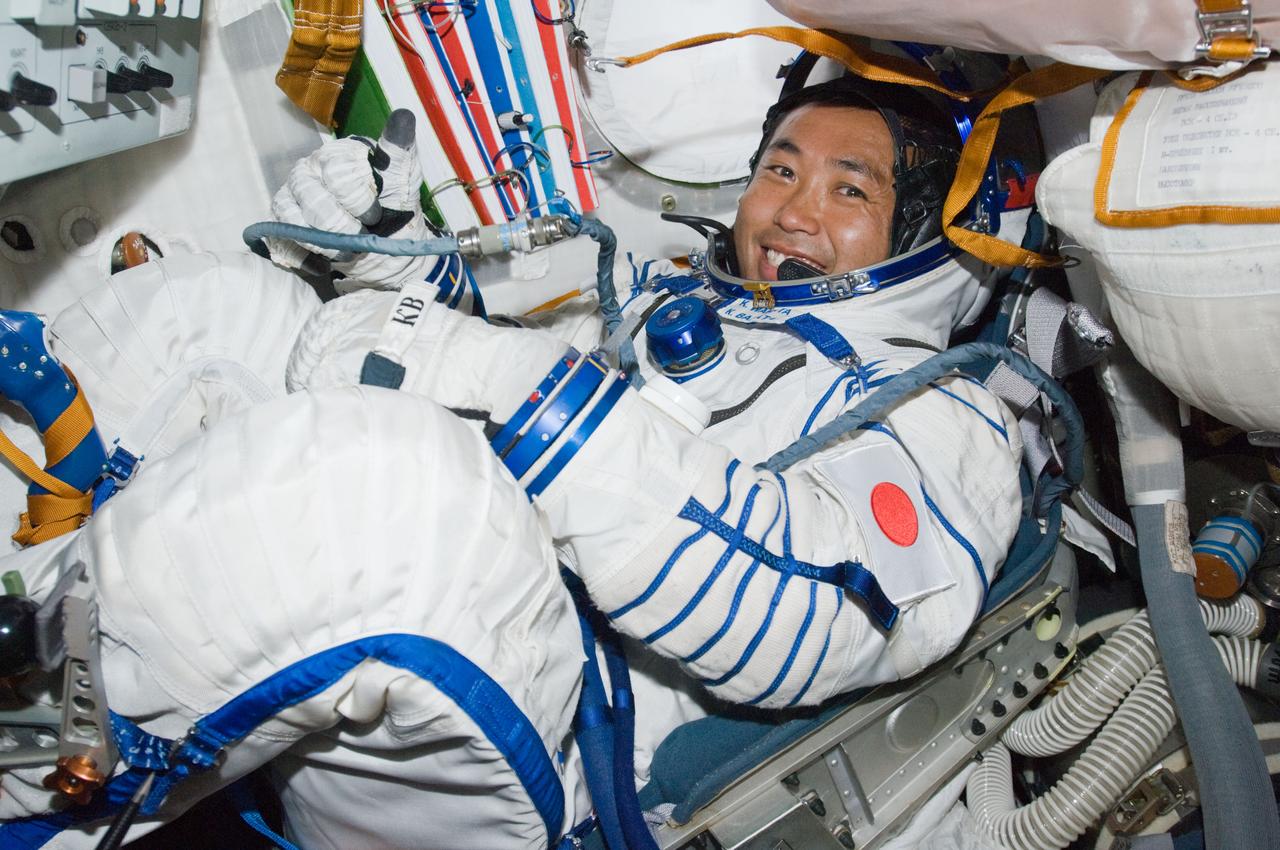

ISS018-E-040996 (18 March 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 18 flight engineer, attired in his Russian Sokol launch and entry suit, tries out his seat liner in the Soyuz TMA-13 spacecraft docked to the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-119) remains docked with the station.
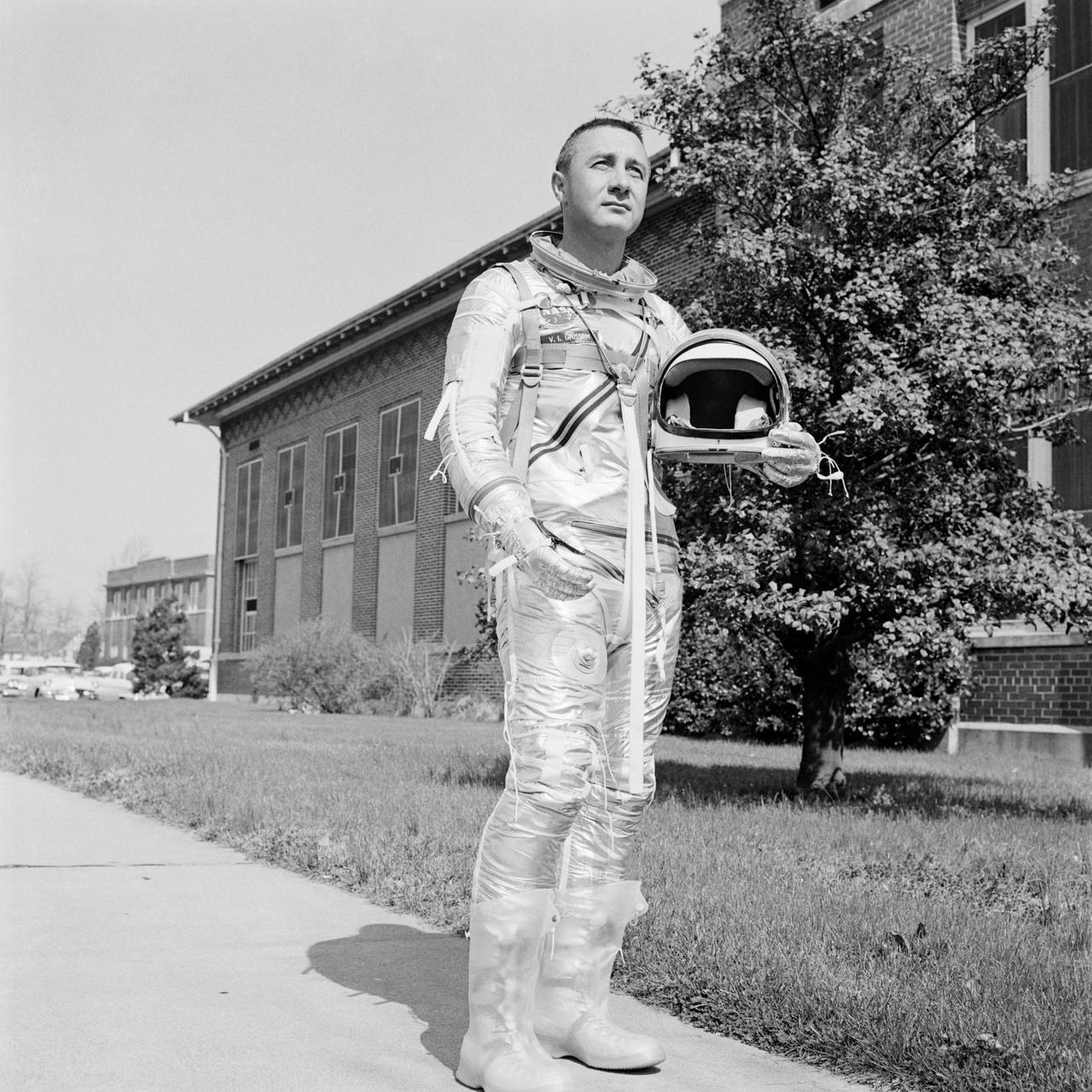

S61-01490 (4 April 1961) --- Astronaut Virgil Grissom photographed in the new Mercury spacesuit, holding his helmet. Photo credit: NASA
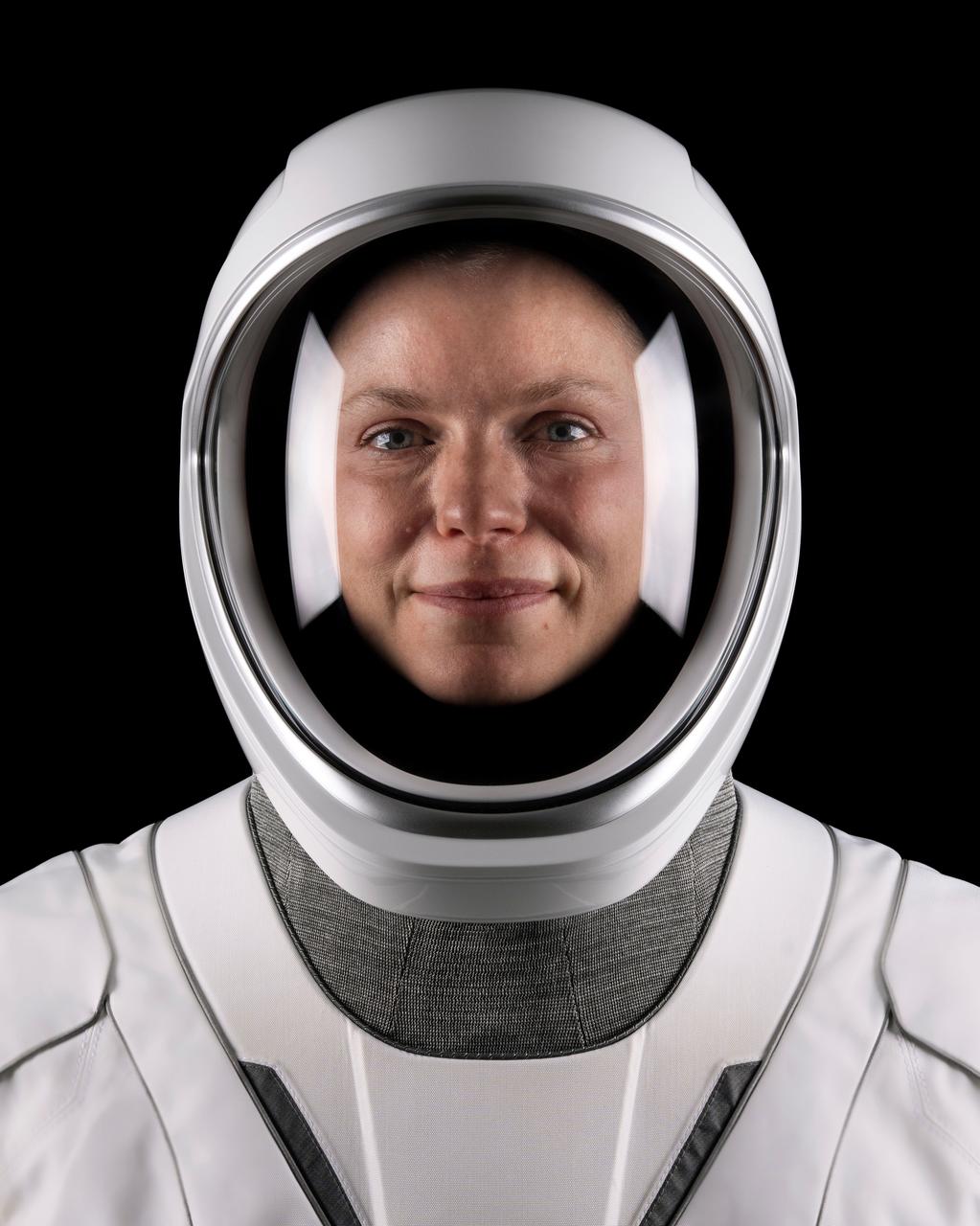

jsc2025e060299 (May 19, 2025) --- NASA astronaut Zena Cardman, commander of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-11 mission to the International Space Station, poses for a portrait in his pressure suit at SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX
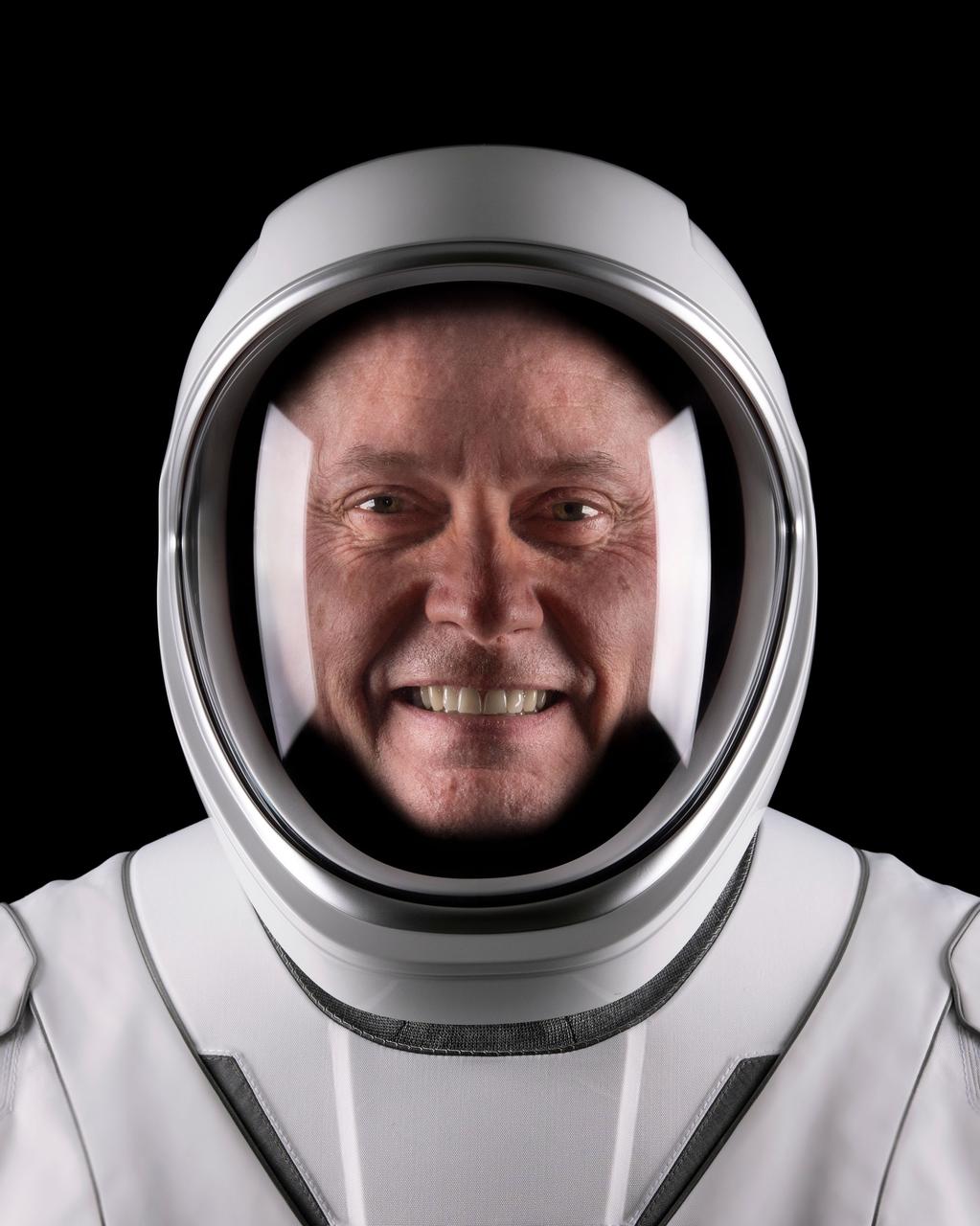

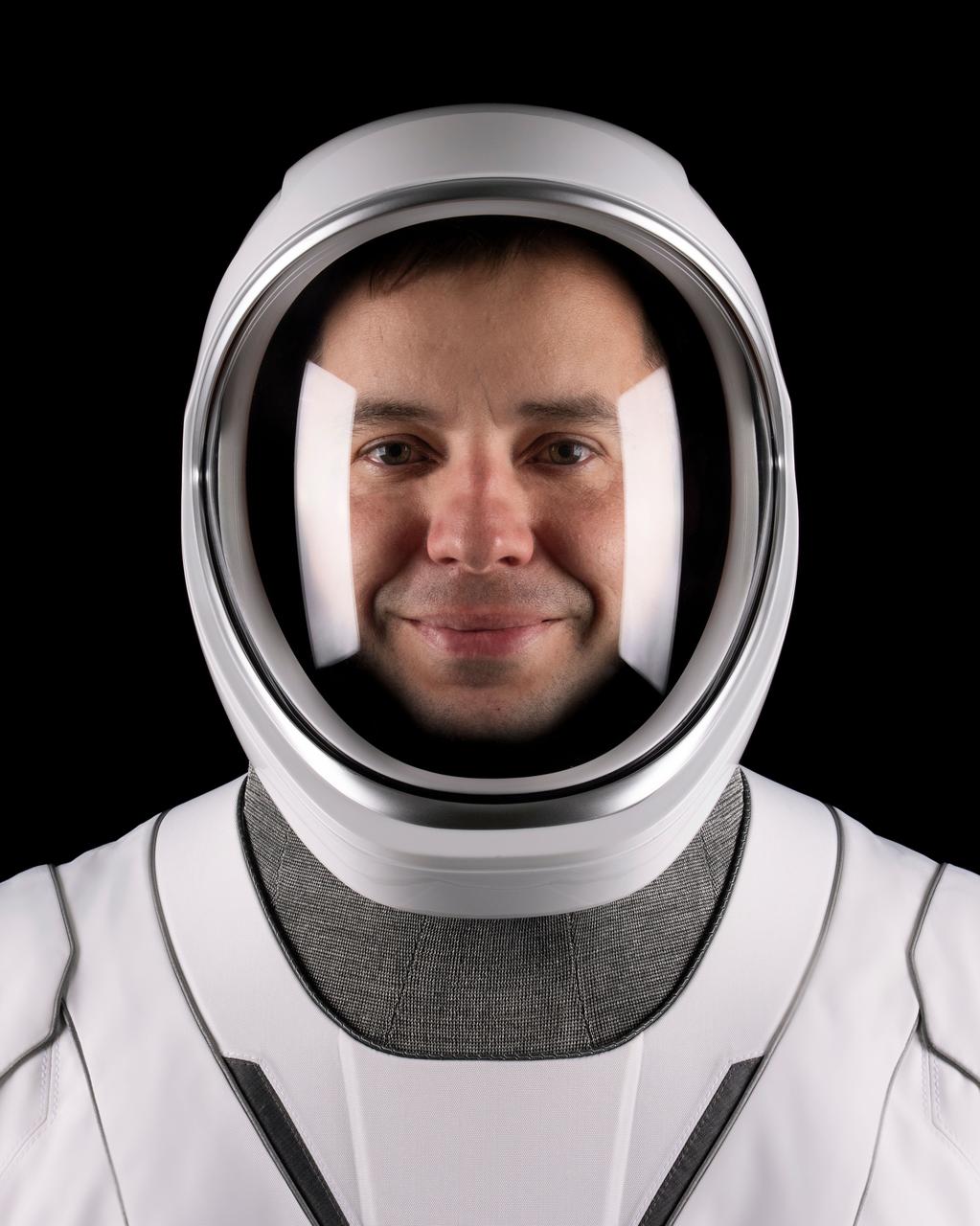
jsc2025e060301 (May 19, 2025) --- NASA astronaut Mike Fincke, pilot of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-11 mission to the International Space Station, poses for a portrait in his pressure suit at SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX

Astronaut John S. Bull wears the A6-L type Pressure Garment Assembly update to an A7-L configuration.
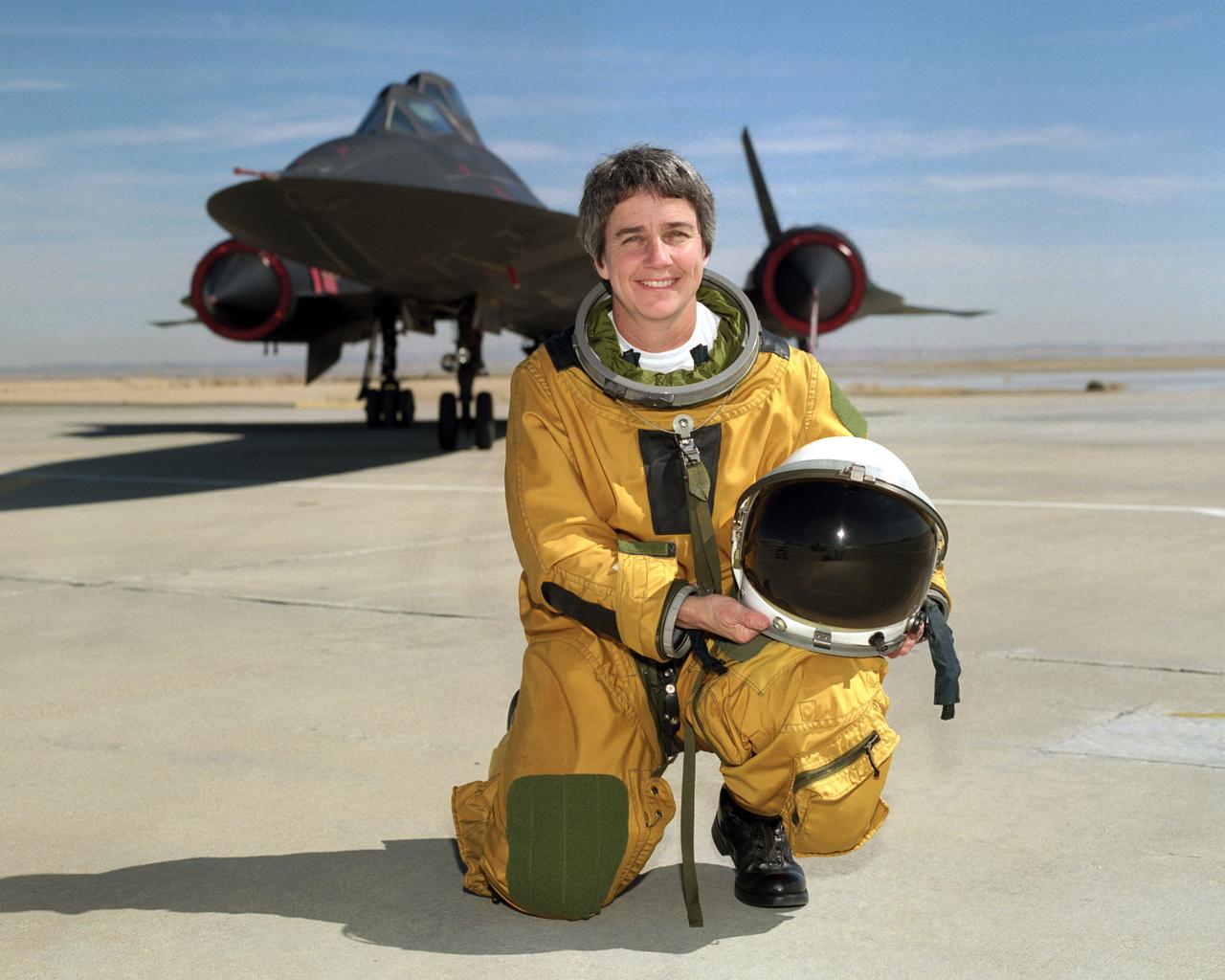

Marta Bohn-Meyer, Chief Engineer, NASA Dryden Flight Research Center
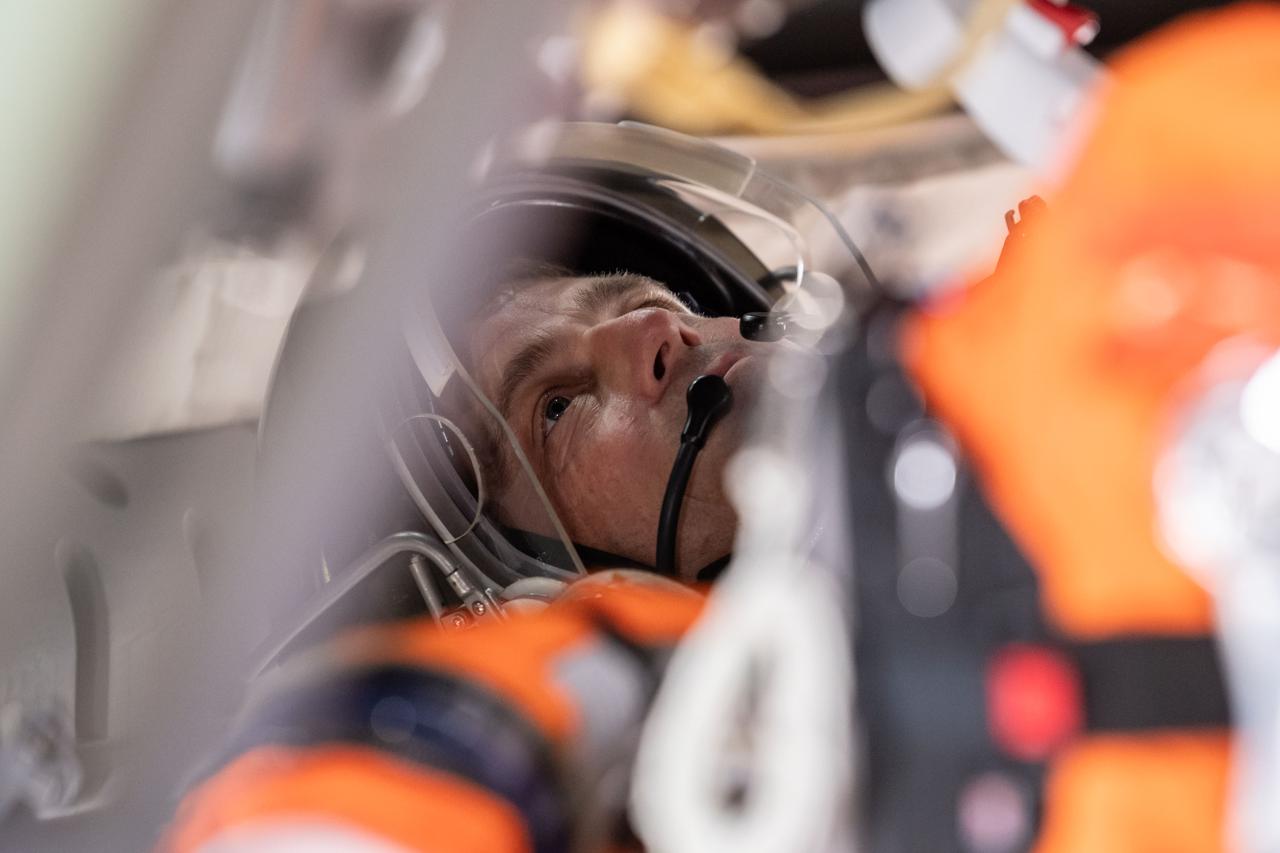

jsc2025e004079 (Jan. 30, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Artemis II commander Reid Wiseman during Post Insertion and Deorbit Preparation training at the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility in Houston, Texas. The crew practiced getting the Orion spacecraft configured once in orbit, how to make it habitable, and suited up in their entry pressure suits to prepare for their return from the Moon. Credit: NASA/Mark Sowa

jsc2025e060298 (May 19, 2025) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut Oleg Platonov, mission specialist of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-11 mission to the International Space Station, poses for a portrait in his pressure suit at SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX
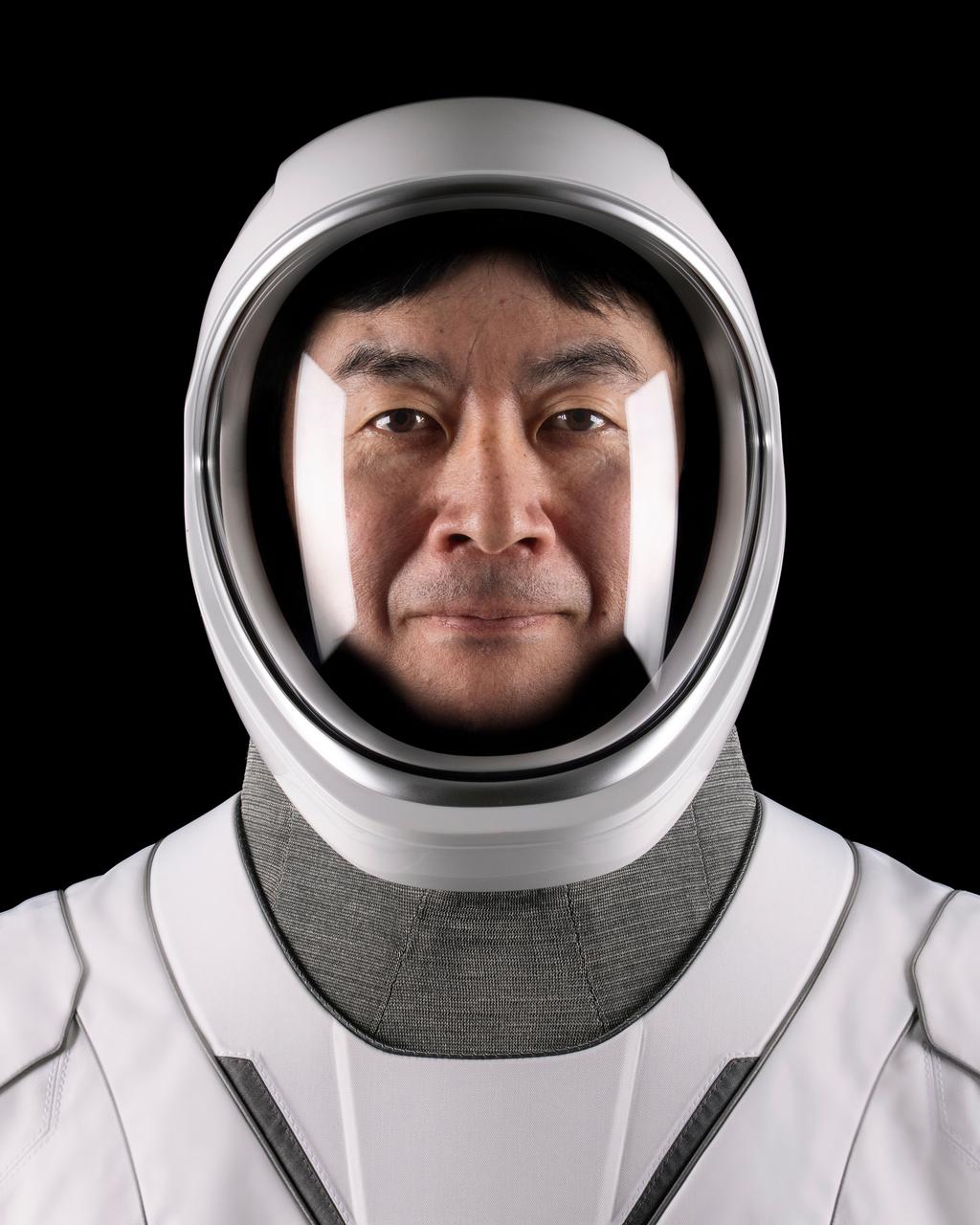

jsc2025e060300 (May 19, 2025) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Kimiya Yui, mission specialist of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-11 mission to the International Space Station, poses for a portrait in his pressure suit at SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California. Credit: SpaceX

Expedition 41 Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Sept. 26 (Kazakhstan time) and will carry Samokutyaev and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Elena Serova of Roscosmos and Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA, into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

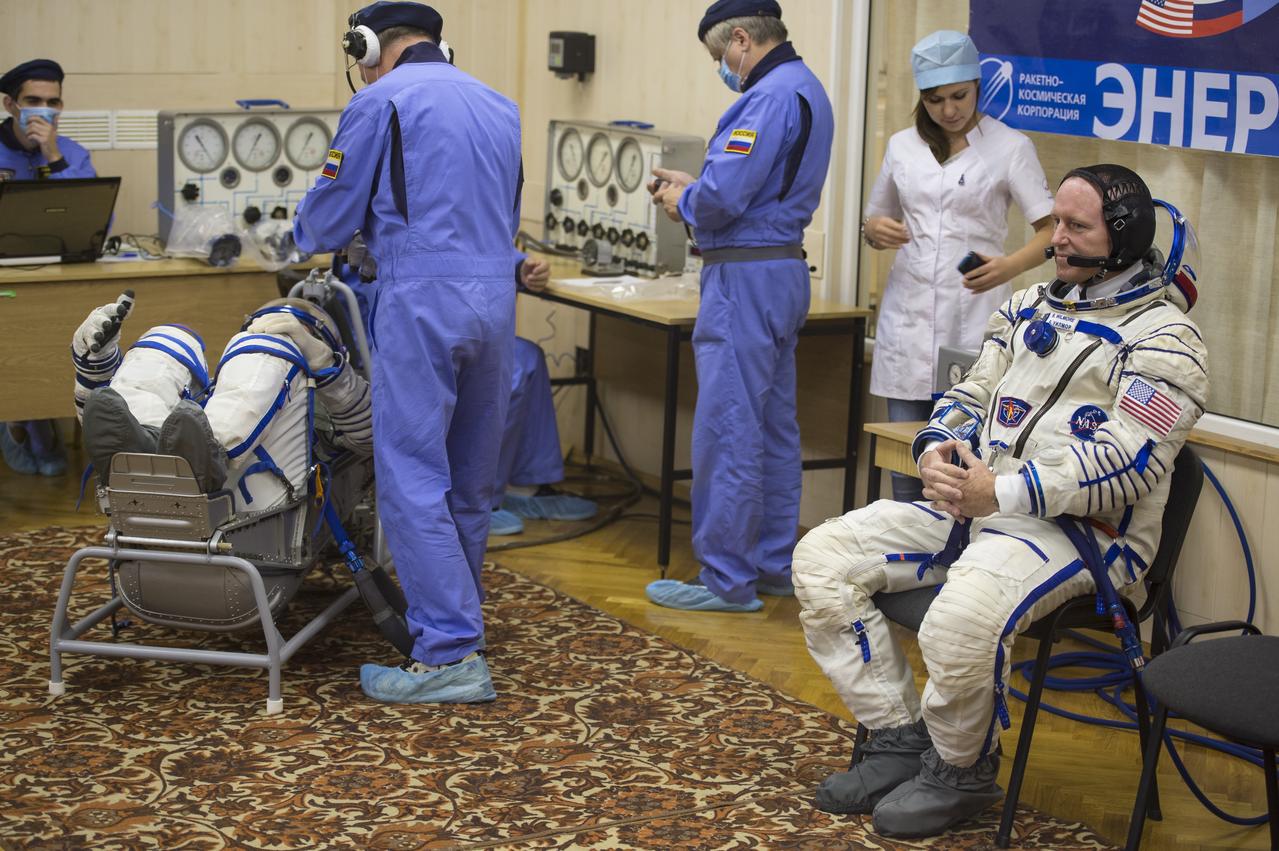
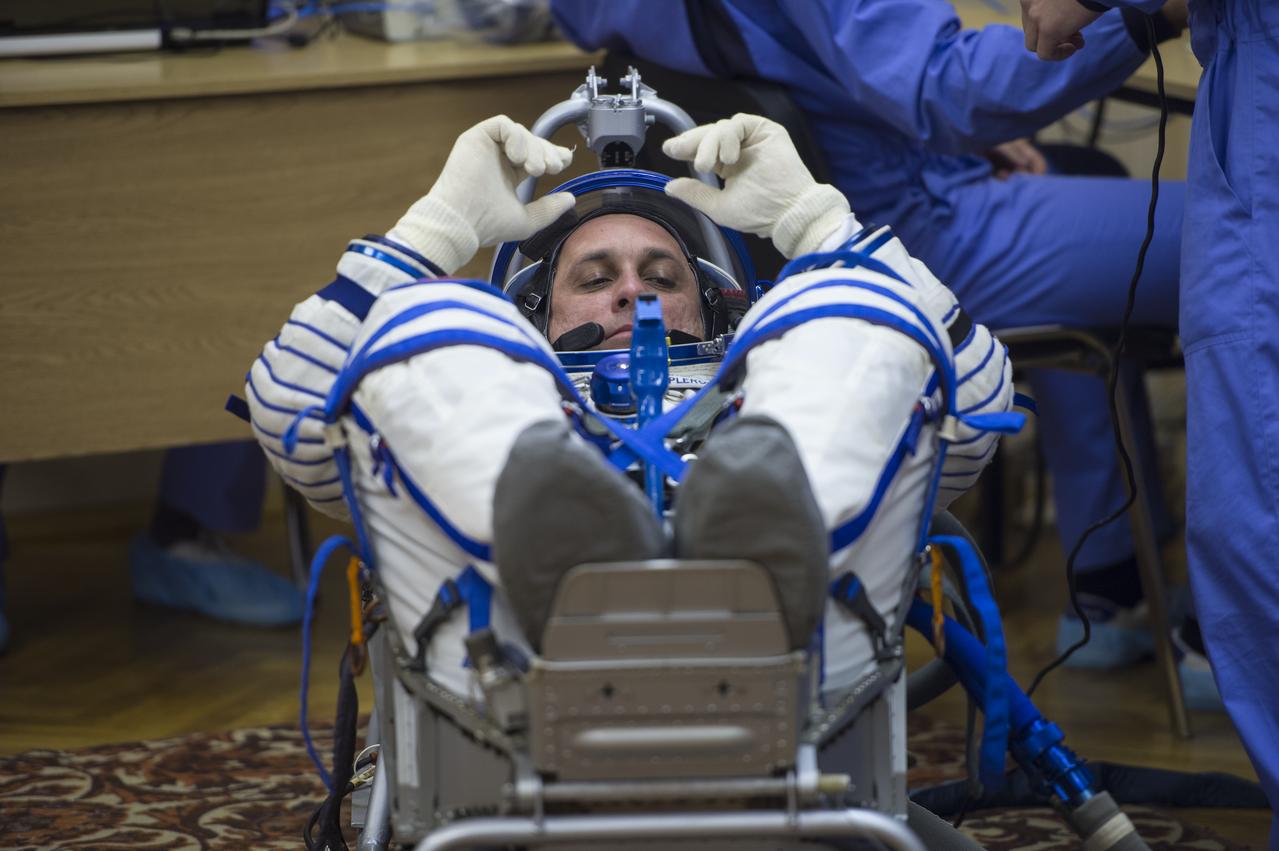
Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Terry Virts has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) and Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
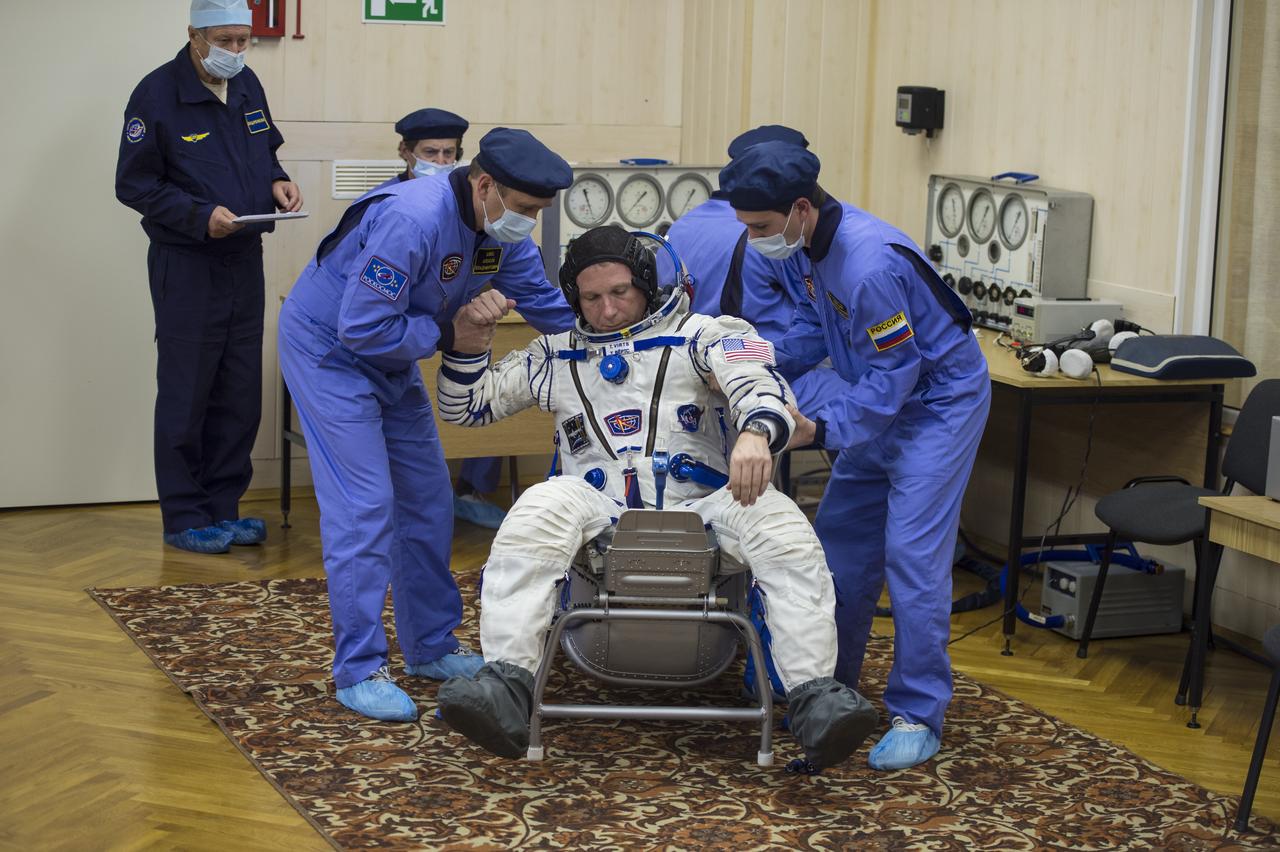

Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Terry Virts has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) and Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
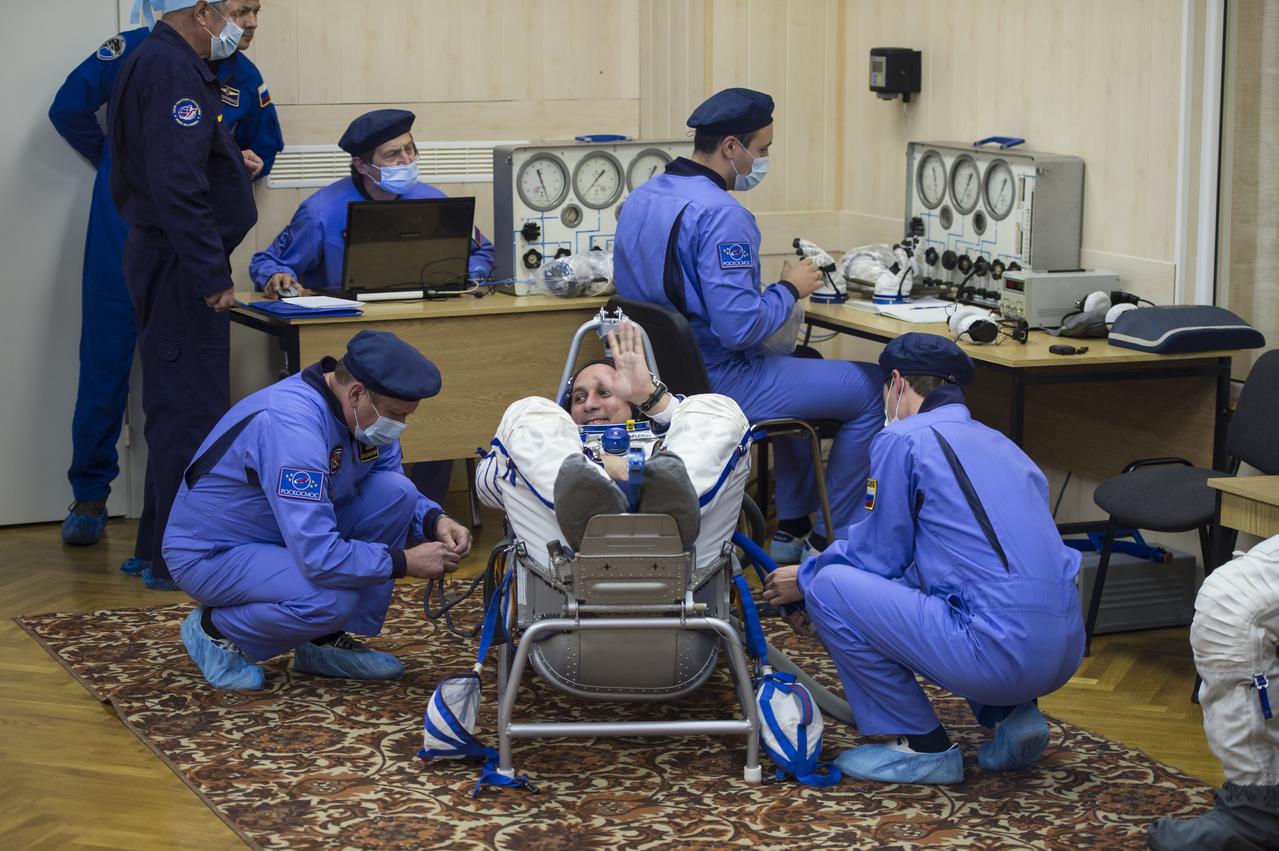

Expedition 42 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) waves to friends and family as he has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at Building 254 in the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Shkaplerov and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineers Terry Virts of NASA and Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
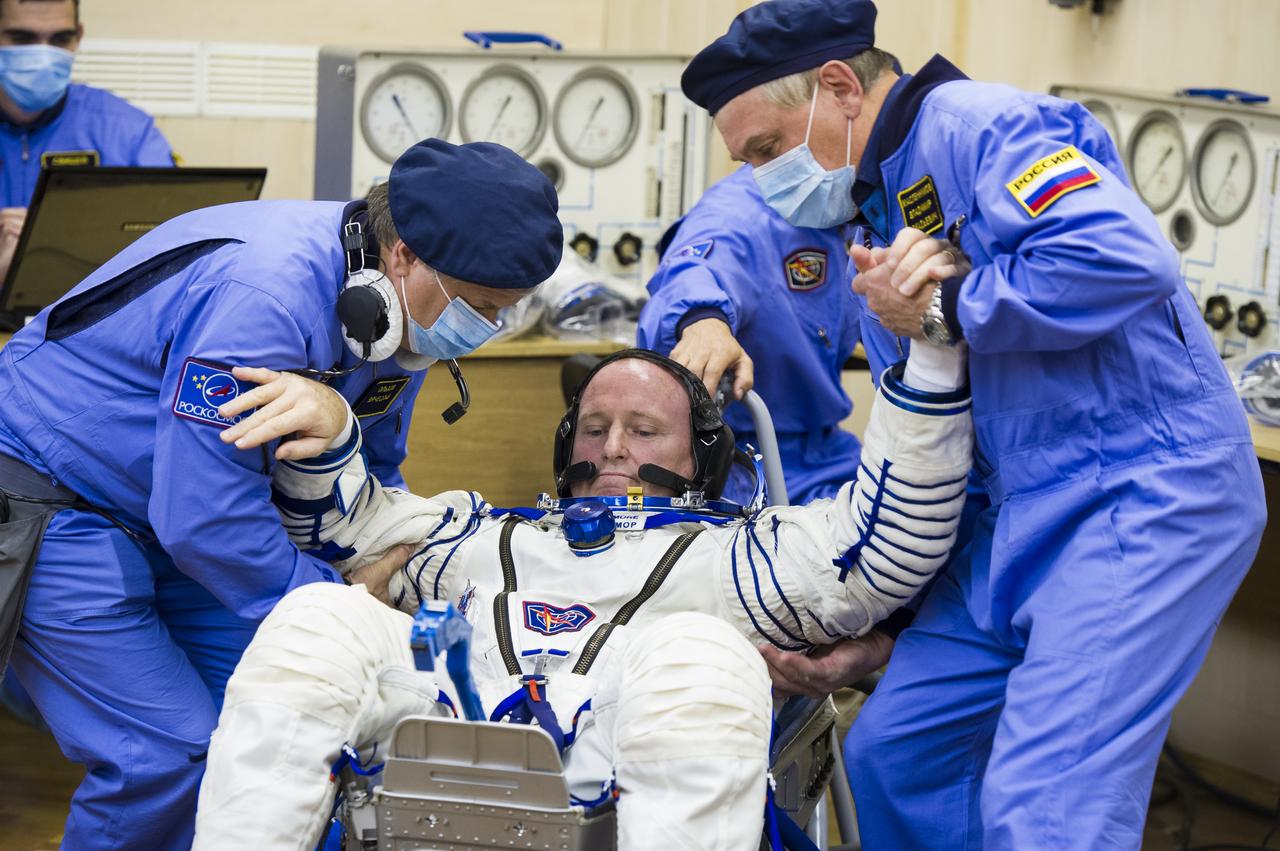

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA is helped up after having his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Sept. 26 (Kazakhstan time) and will carry Wilmore and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Elena Serova and Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)

Expedition 42 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at Building 254 in the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Shkaplerov and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineers Terry Virts of NASA and Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
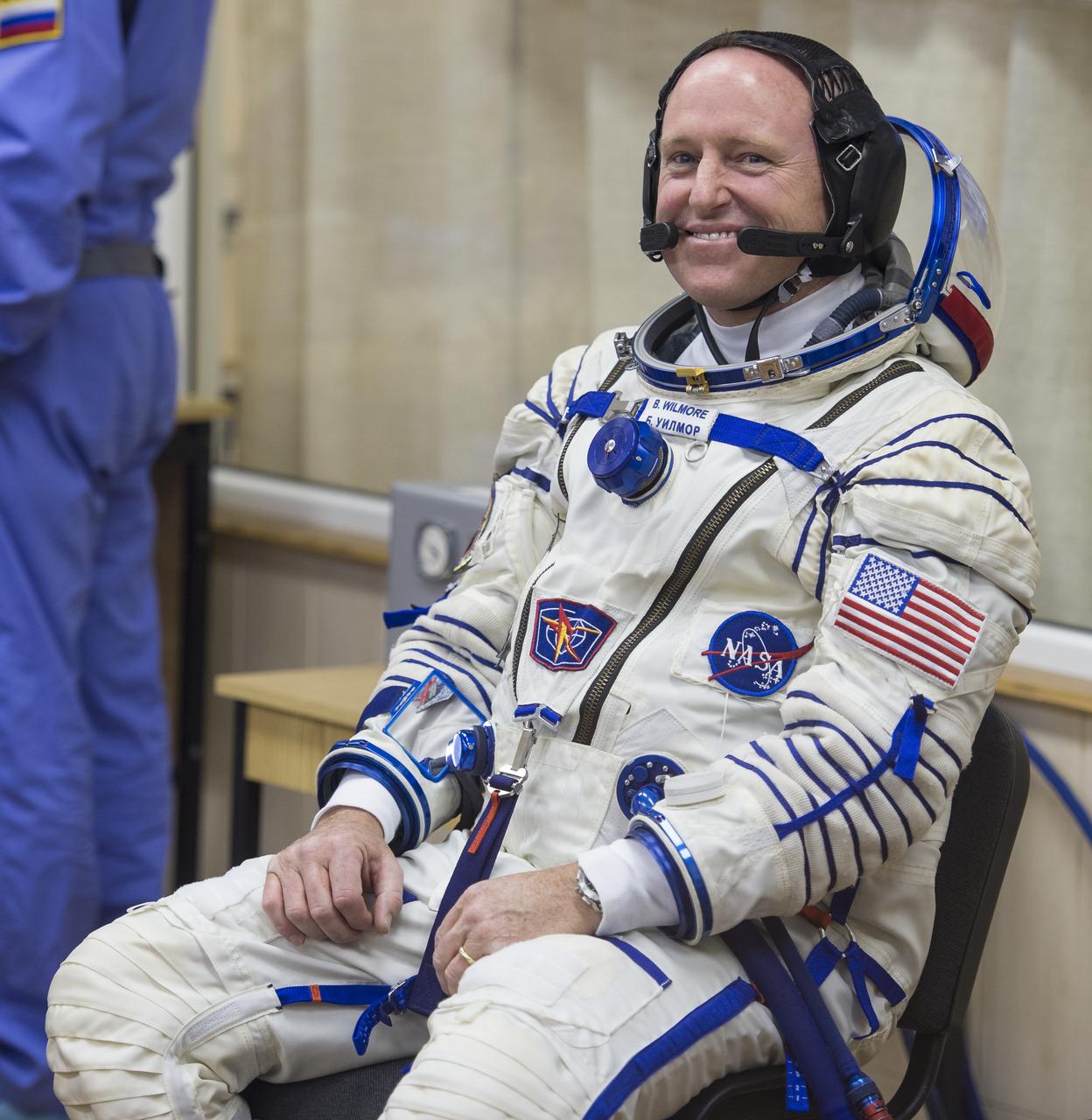

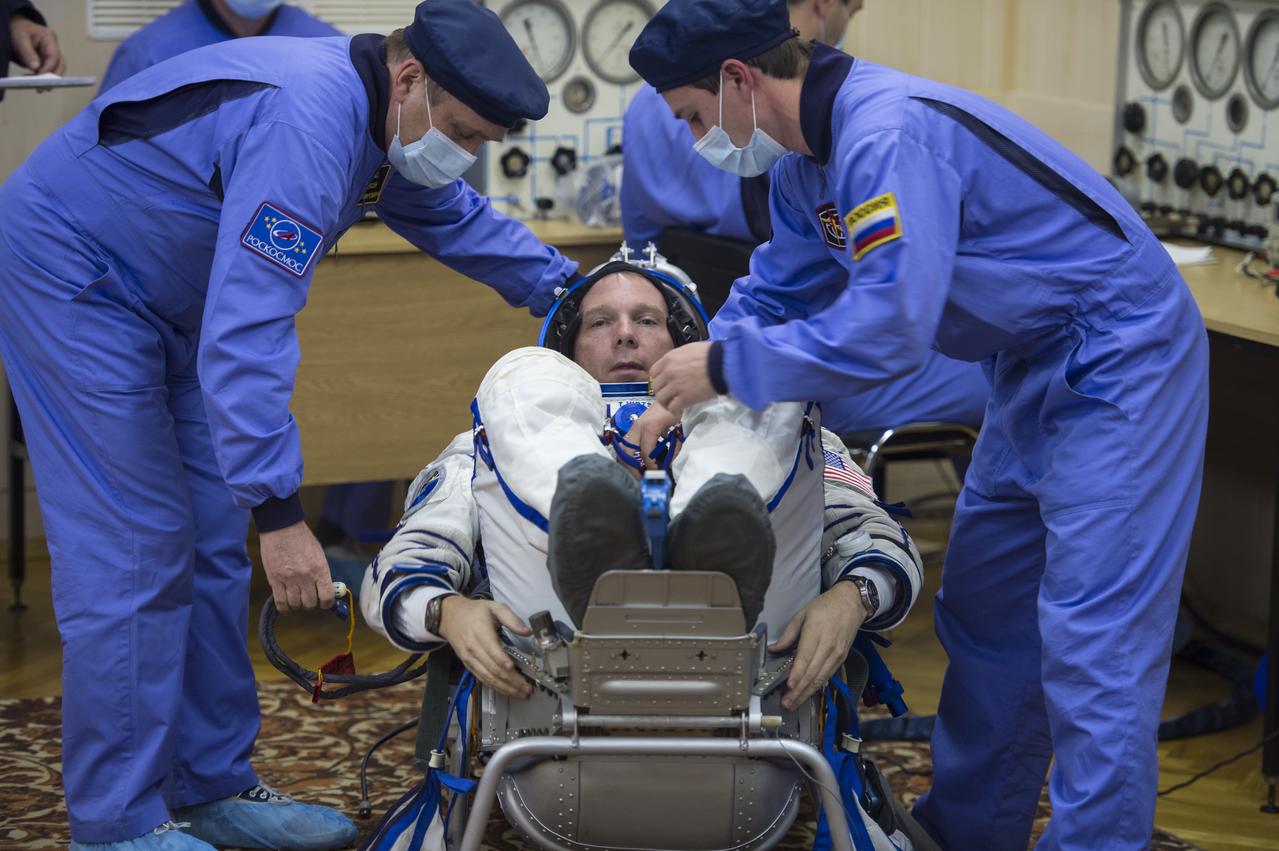
Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA waits to have his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Sept. 26 (Kazakhstan time) and will carry Wilmore and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Elena Serova and Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

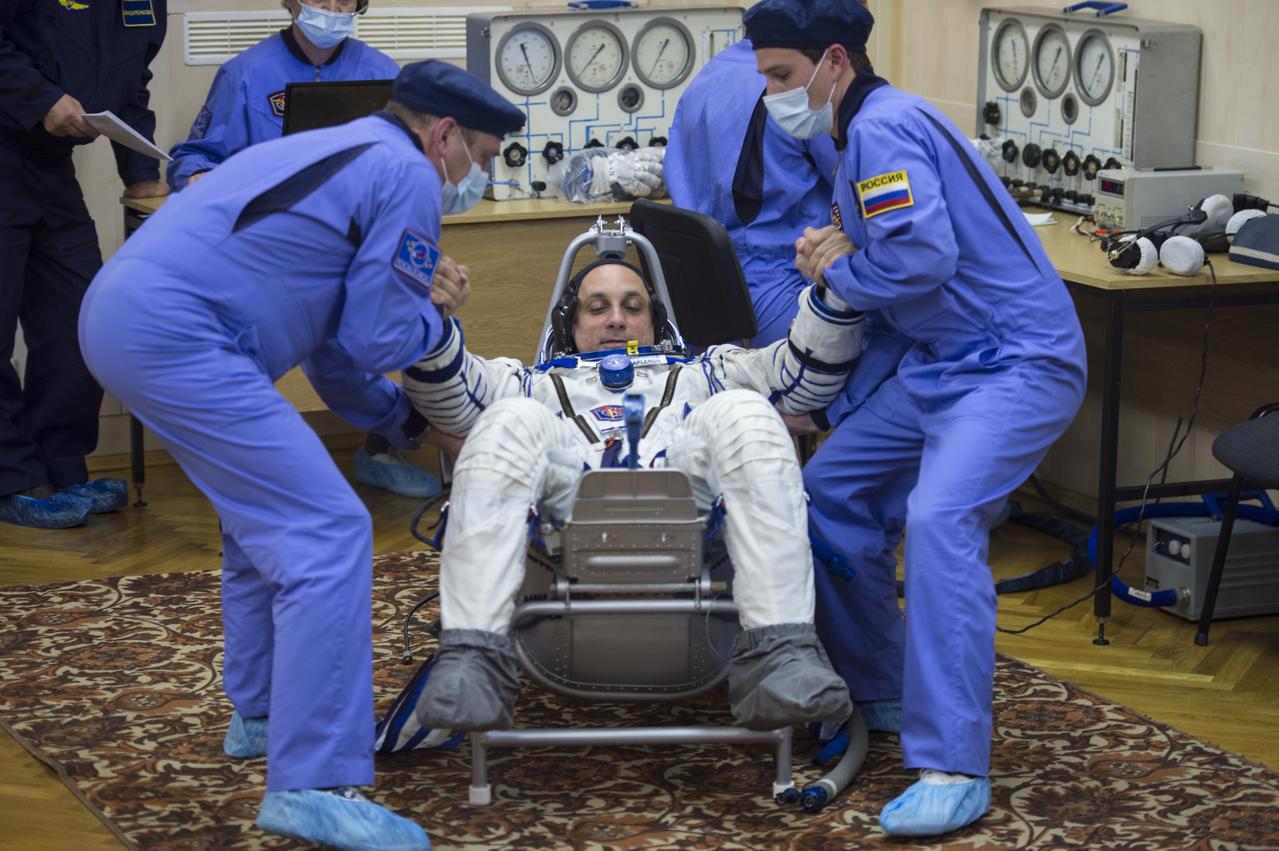
Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Terry Virts has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) and Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Sept. 26 (Kazakhstan time) and will carry Wilmore and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Elena Serova and Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)

Expedition 42 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) is helped up after having his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Shkaplerov and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineers Terry Virts of NASA and Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
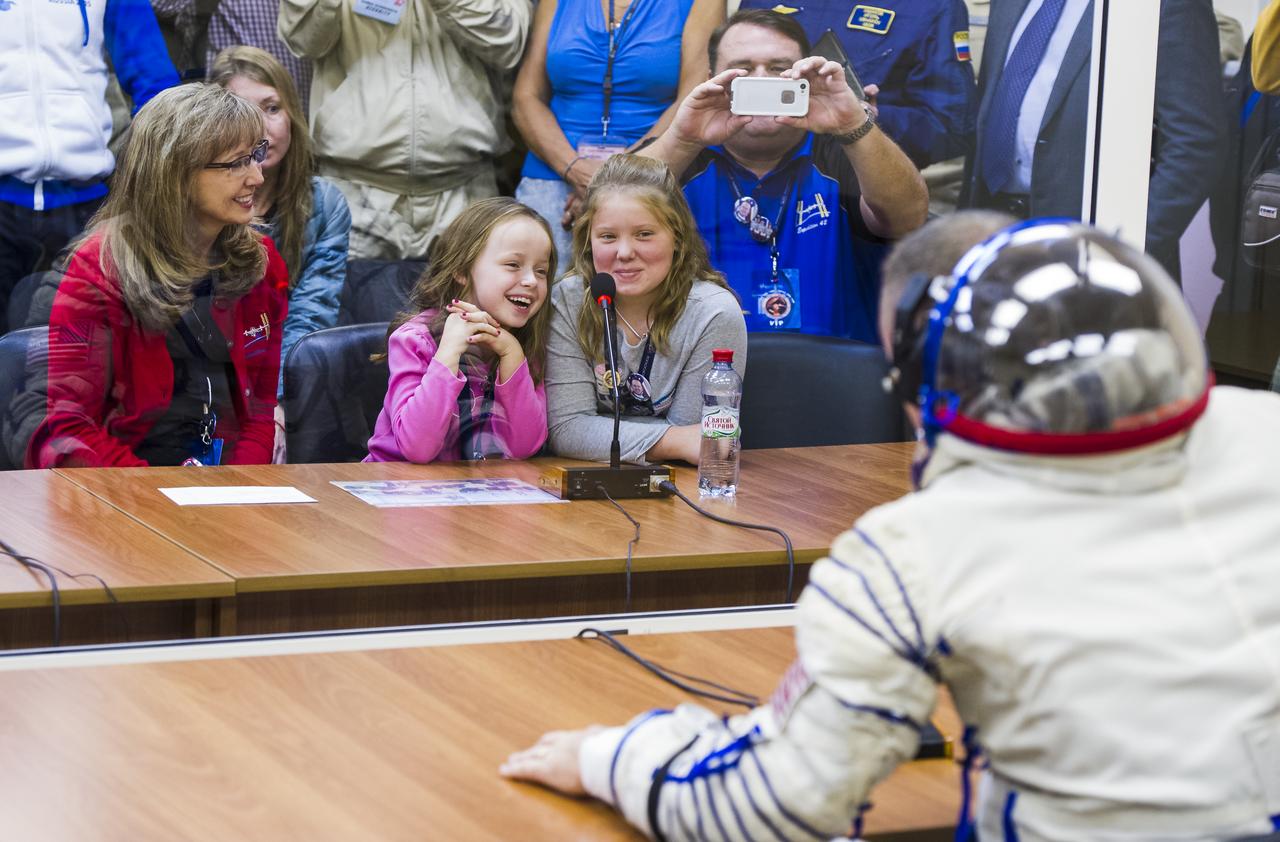

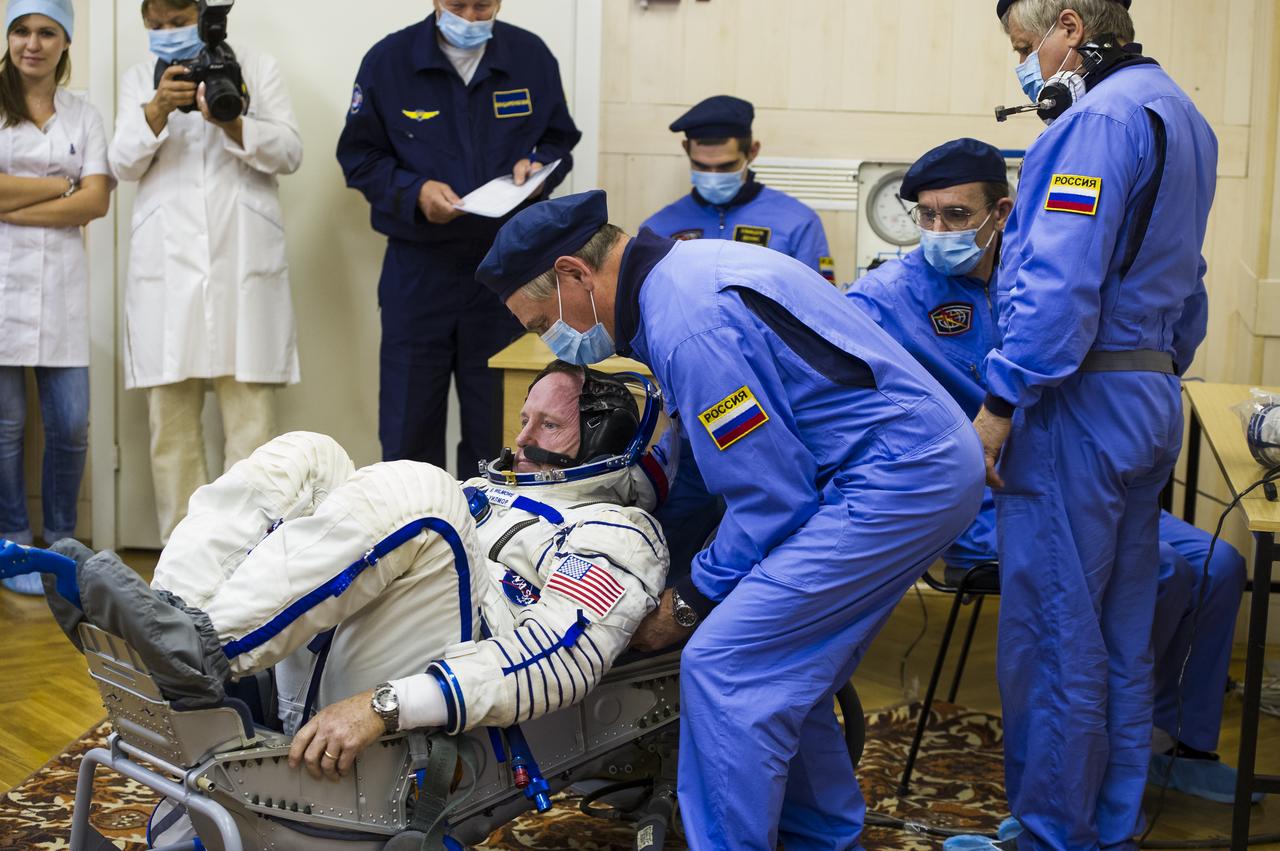
Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA speaks with his family after having his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch onboard the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The Soyuz spacecraft with Wilmore, Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), and Flight Engineer Elena Serova of Roscosmos is scheduled to launch at 2:25 a.m. Kazakhstan Time on Friday, Sept. 26. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
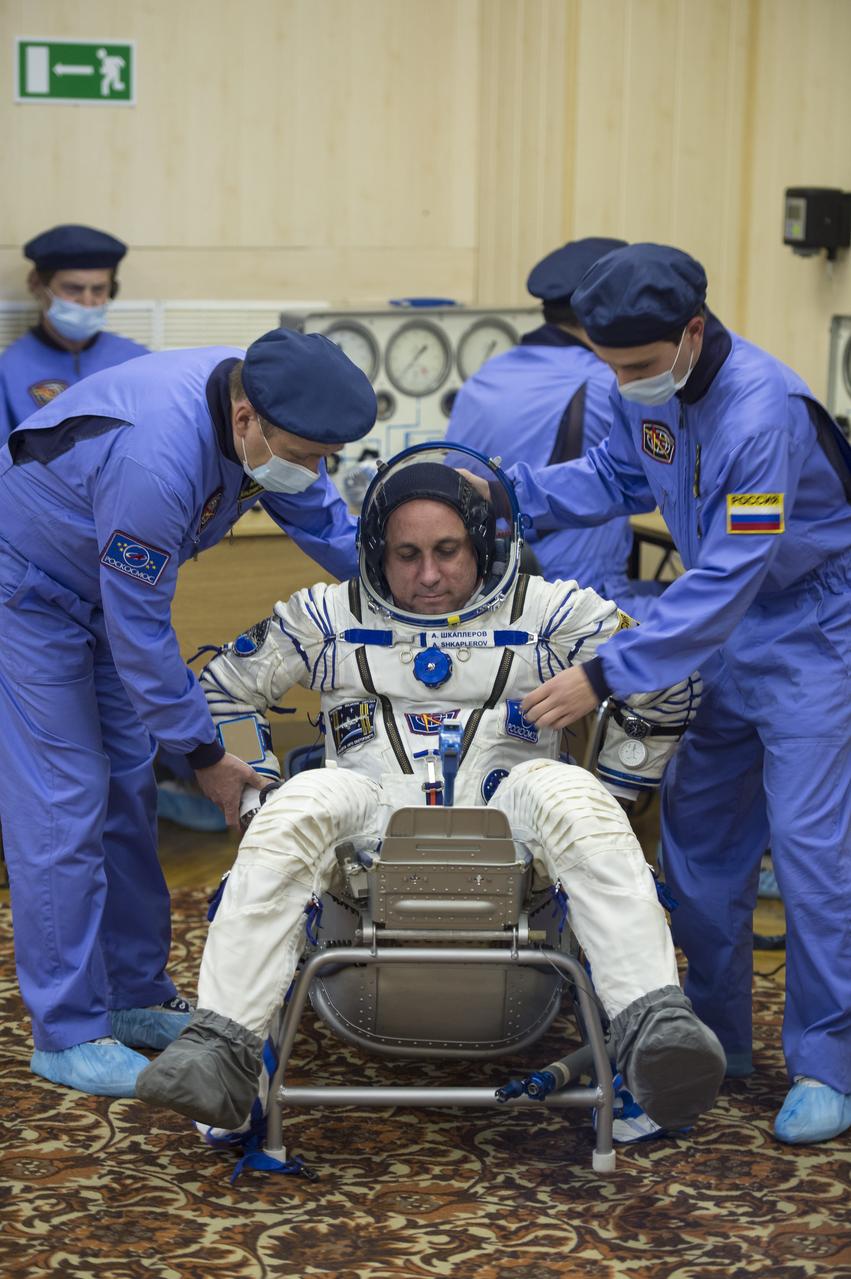

Expedition 42 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at Building 254 in the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Shkaplerov and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineers Terry Virts of NASA and Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
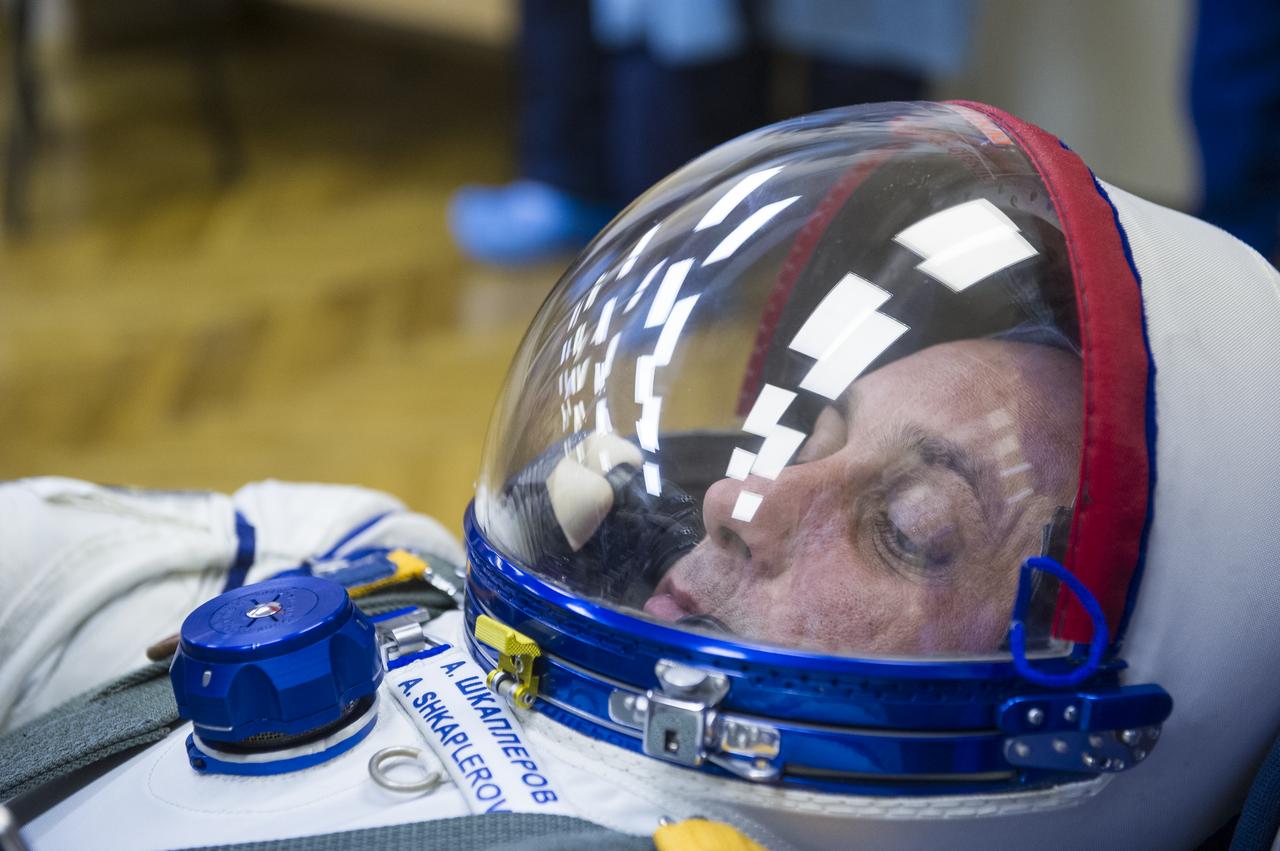

Expedition 42 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at Building 254 in the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Shkaplerov and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineers Terry Virts of NASA and Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
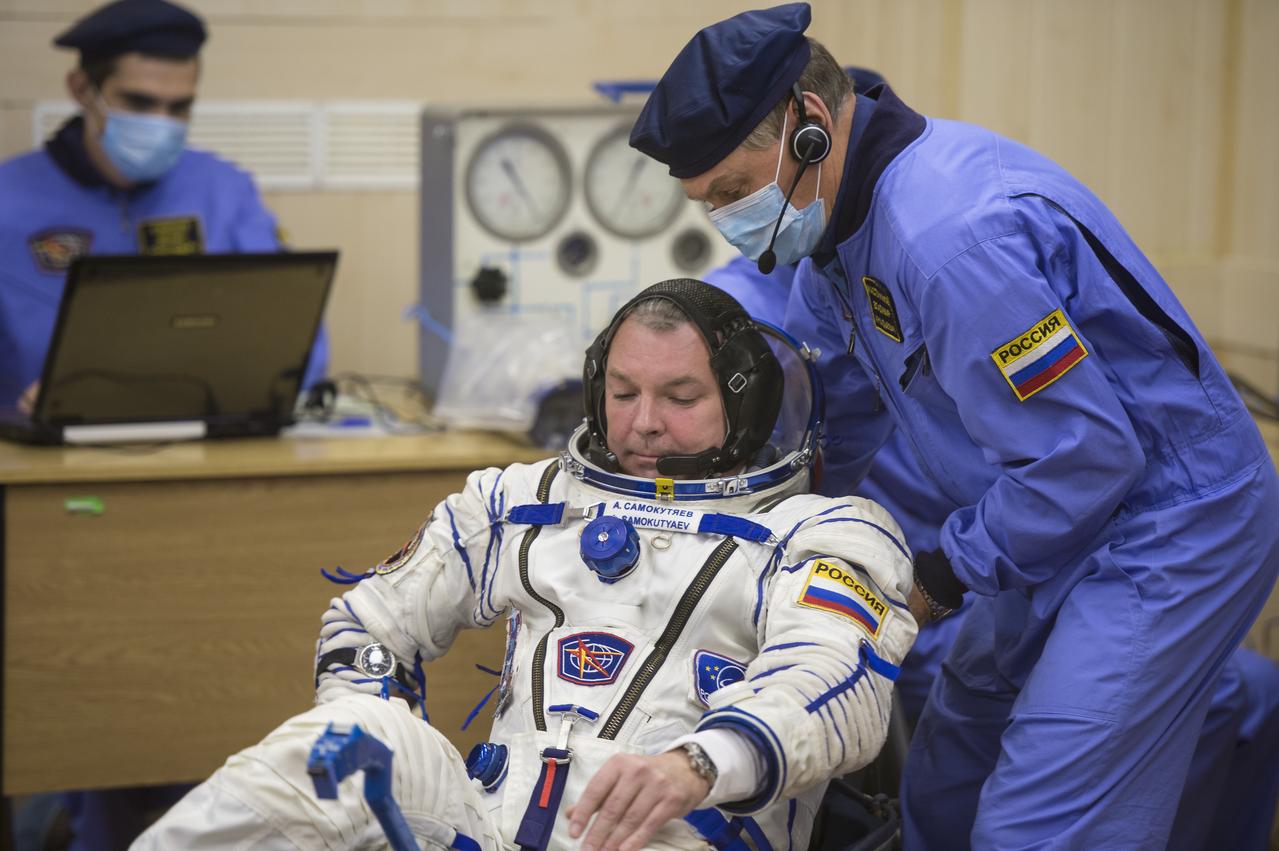

Expedition 41 Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) has his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for his launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Sept. 26 (Kazakhstan time) and will carry Samokutyaev and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Elena Serova of Roscosmos and Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA, into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
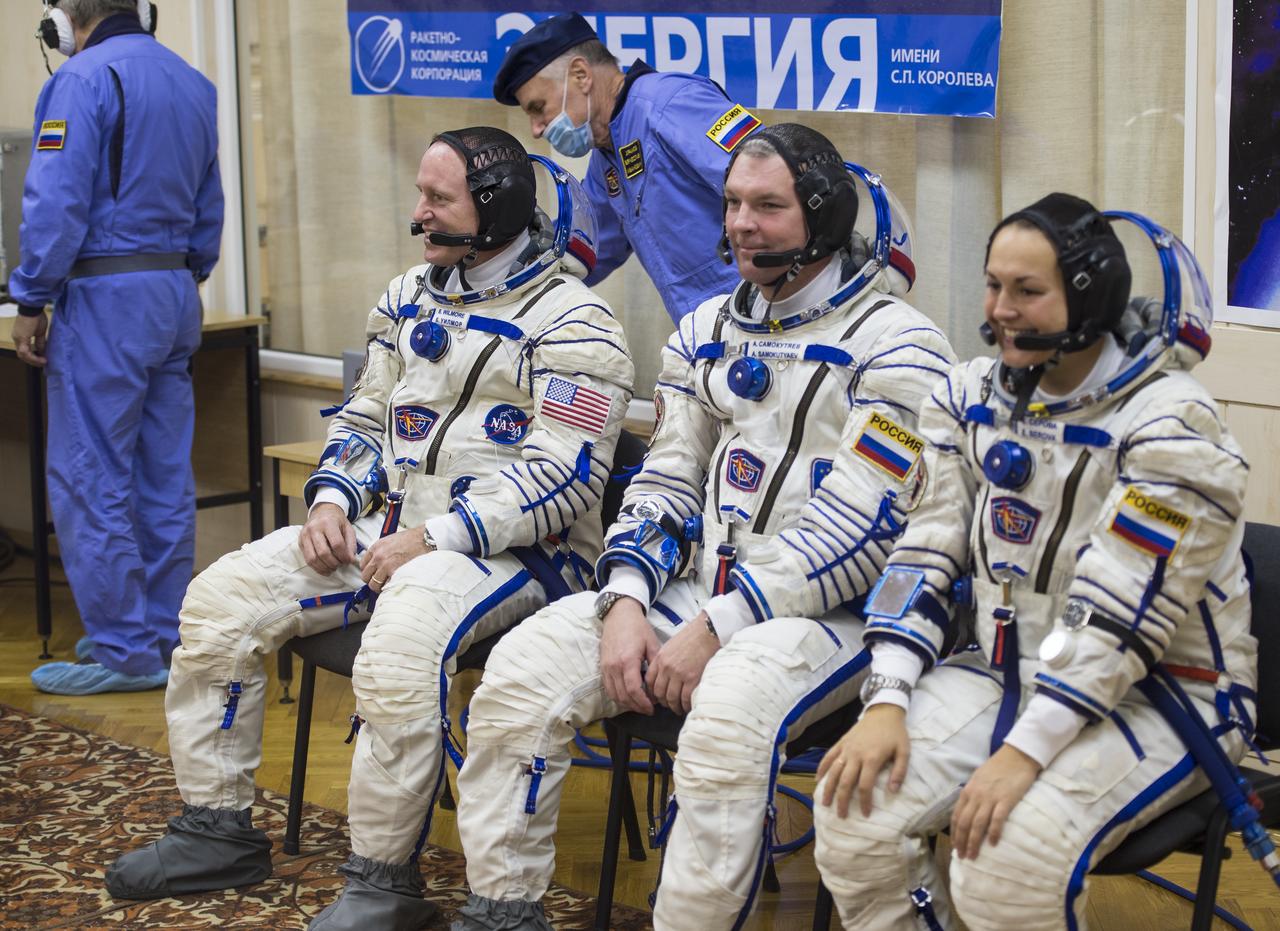

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA, left, Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), and Flight Engineer Elena Serova of Roscosmos are seen while they wait to have their Russian Sokol suits pressure checked in preparation for their launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014, at the Baiknour Cosmodrome, in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Sept. 26 (Kazakhstan time) and will carry Wilmore, Samokutyaev, and Serova into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
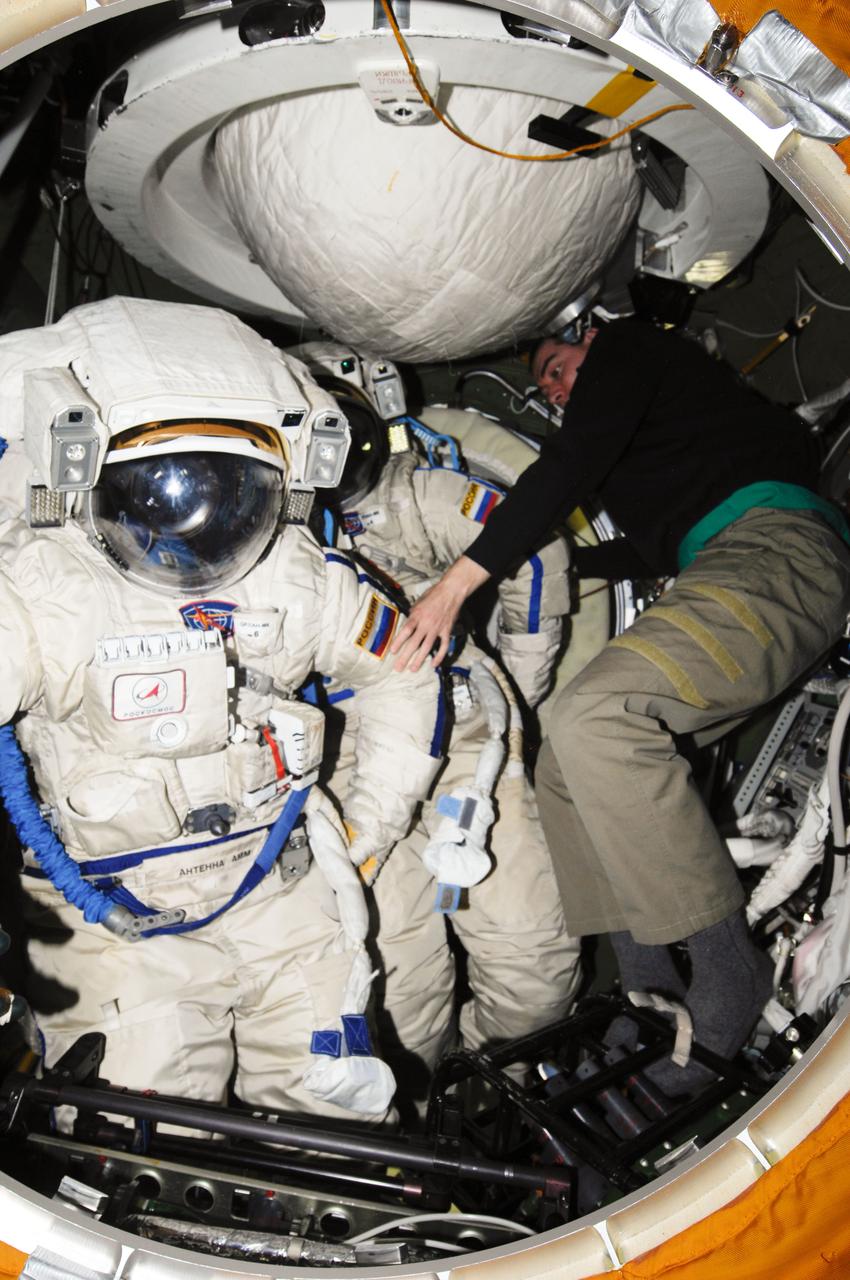

ISS028-E-019440 (29 July 2011) --- Russian cosmonaut Sergei Volkov, Expedition 28 flight engineer, works with Russian Orlan-MK spacesuits in the Pirs Docking Compartment of the International Space Station in preparation for a spacewalk scheduled for Aug. 3, 2011. During the six-hour excursion Volkov and Russian cosmonaut Alexander Samokutyaev (out of frame), flight engineer, will move a cargo boom from one airlock to another, install a prototype laser communications system and deploy an amateur radio micro-satellite.
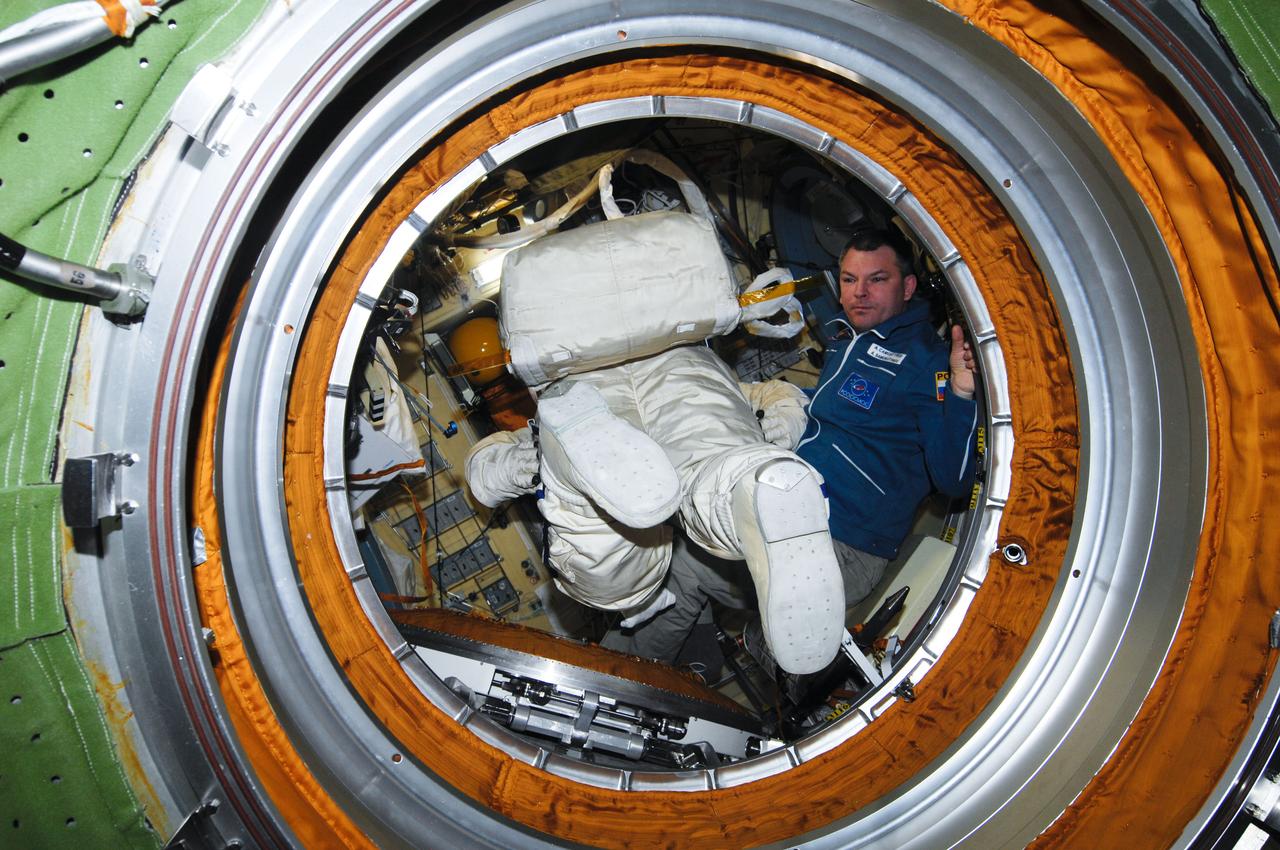

ISS028-E-019437 (29 July 2011) --- Russian cosmonaut Alexander Samokutyaev, Expedition 28 flight engineer, works with Russian Orlan-MK spacesuits in the Pirs Docking Compartment of the International Space Station in preparation for a spacewalk scheduled for Aug. 3, 2011. During the six-hour excursion Samokutyaev and Russian cosmonaut Sergei Volkov (out of frame), flight engineer, will move a cargo boom from one airlock to another, install a prototype laser communications system and deploy an amateur radio micro-satellite.
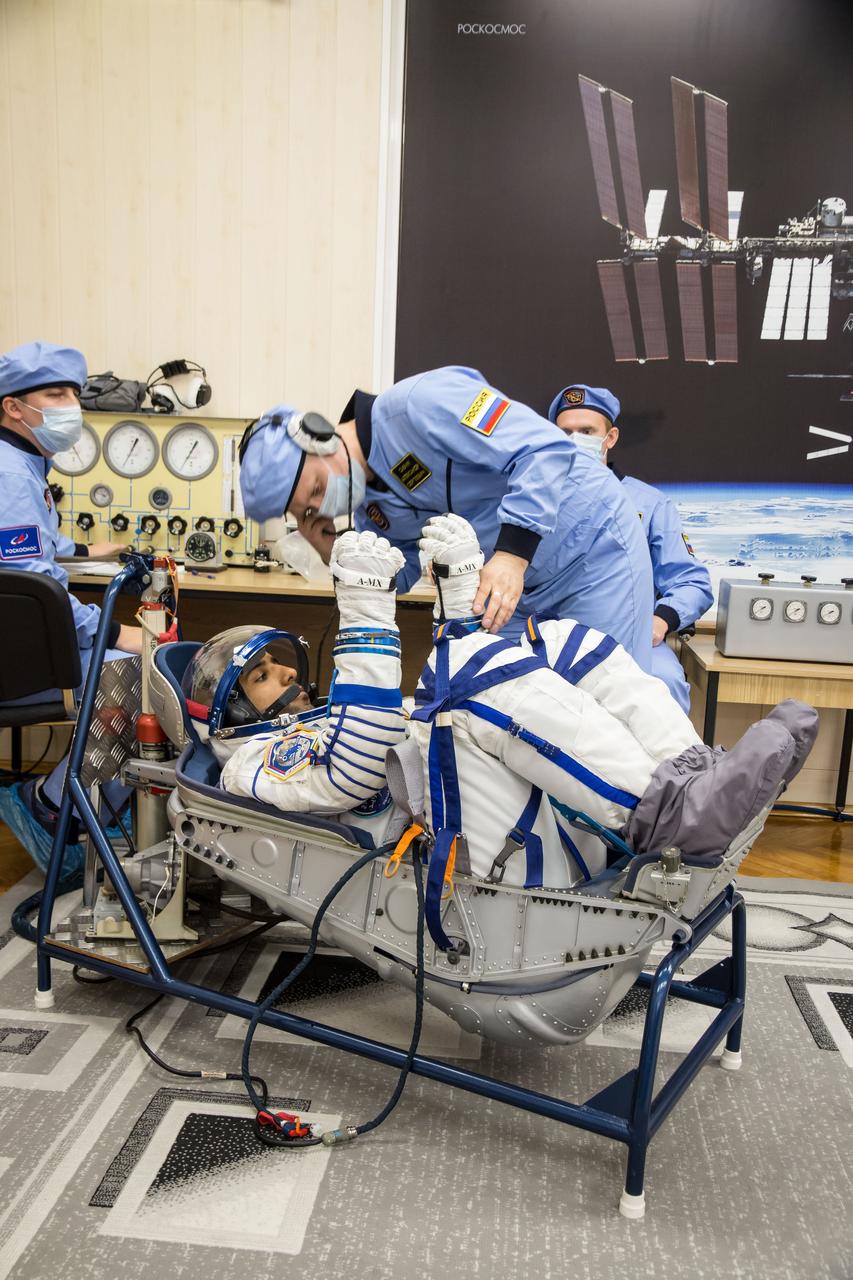

In the Integration Building at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, spaceflight participant Hazzaa Ali Almansoori of the United Arab Emirates undergoes a pressure and leak check of his Russian Sokol launch and entry suit Sept. 11 for a fit check aboard the Soyuz MS-15 spacecraft. Almansoori and Expedition 61 crewmembers Jessica Meir of NASA and Oleg Skripochka of Roscosmos will launch Sept. 25 on the Soyuz MS-15 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome for a mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Victor Zelentsov