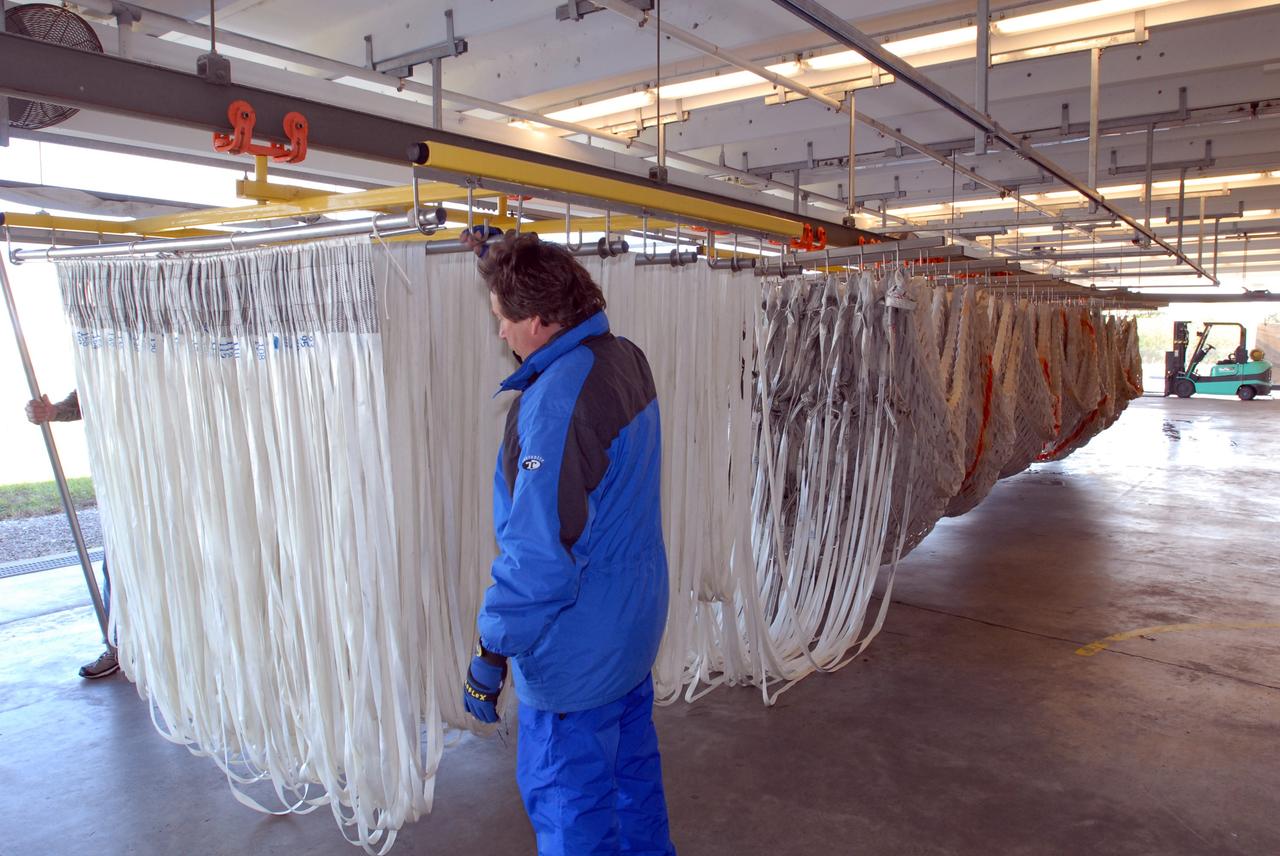

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker checks the parachute lines suspended from the monorail system. The parachutes were recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. The monorail will transport each parachute into a 30,000-gallon washer and a huge dryer heated with 140-degree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers begin hanging the parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission onto a monorail system. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. The monorail will transport each parachute into a 30,000-gallon washer and a huge dryer heated with 140-degree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
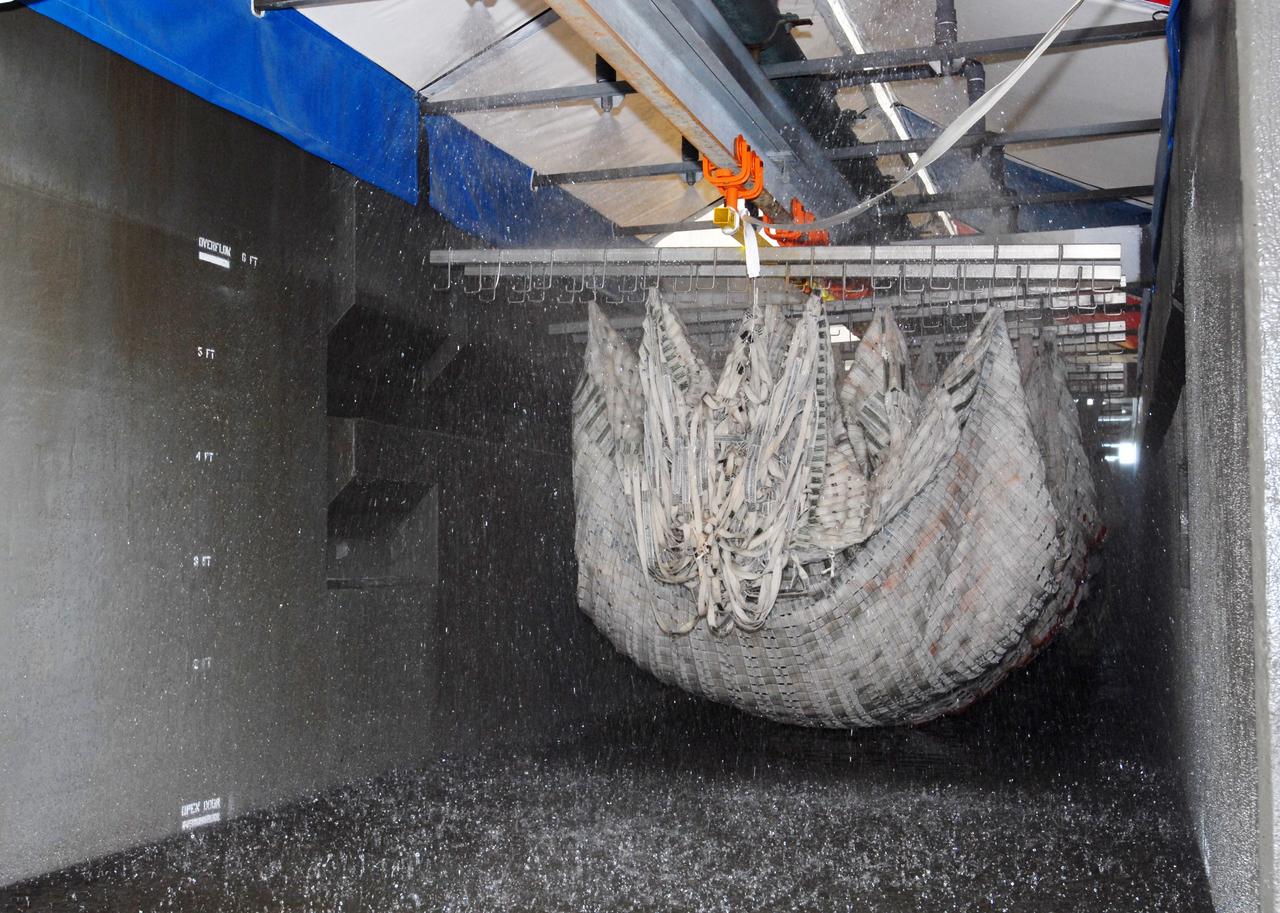

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission are moved through the 30,000-gallon washer. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. After washing, the monorail will move the parachutes into a huge dryer heated with 140-degree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
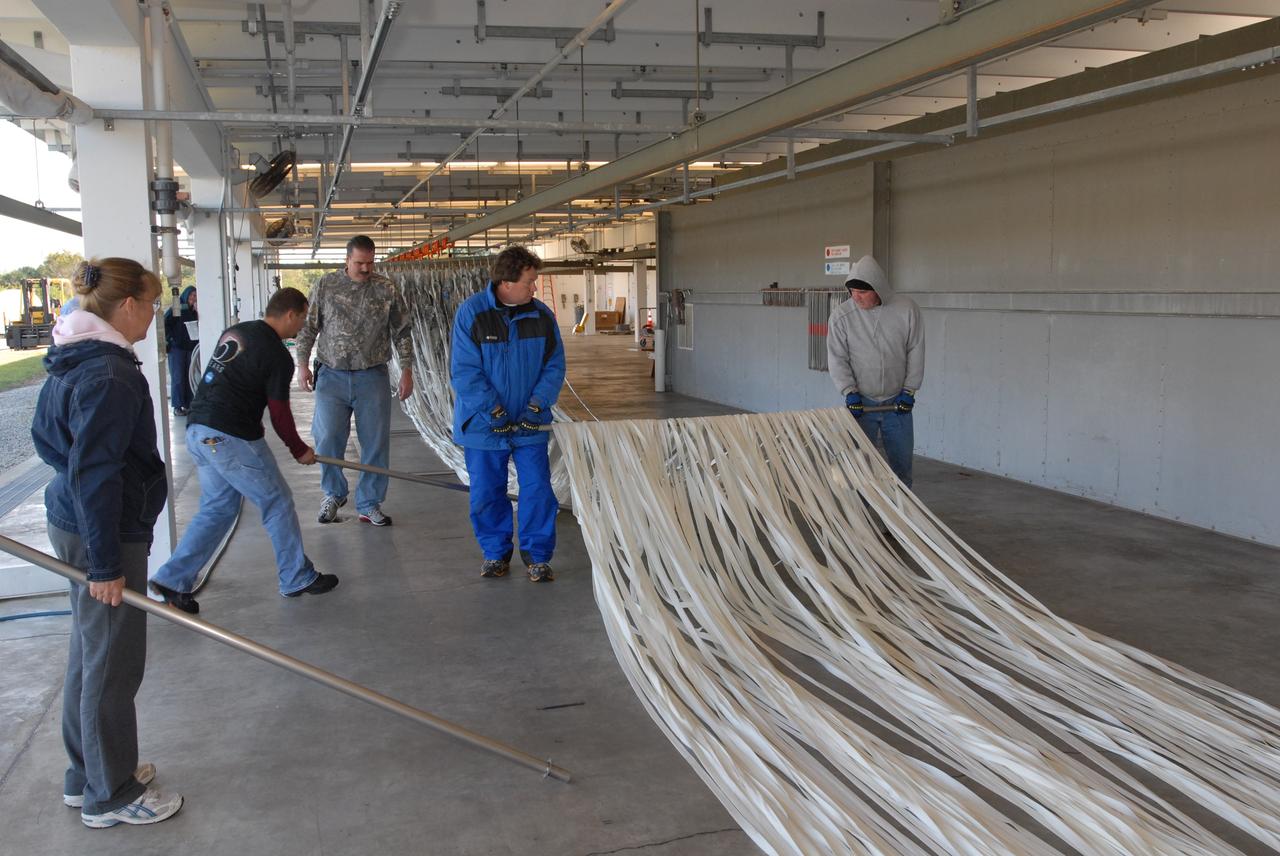

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers place rods under the lines of the parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission to hang them on a monorail system. Behind them, the parachutes are suspended from the monorail. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. The monorail will transport each parachute into a 30,000-gallon washer and a huge dryer heated with 140-degree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
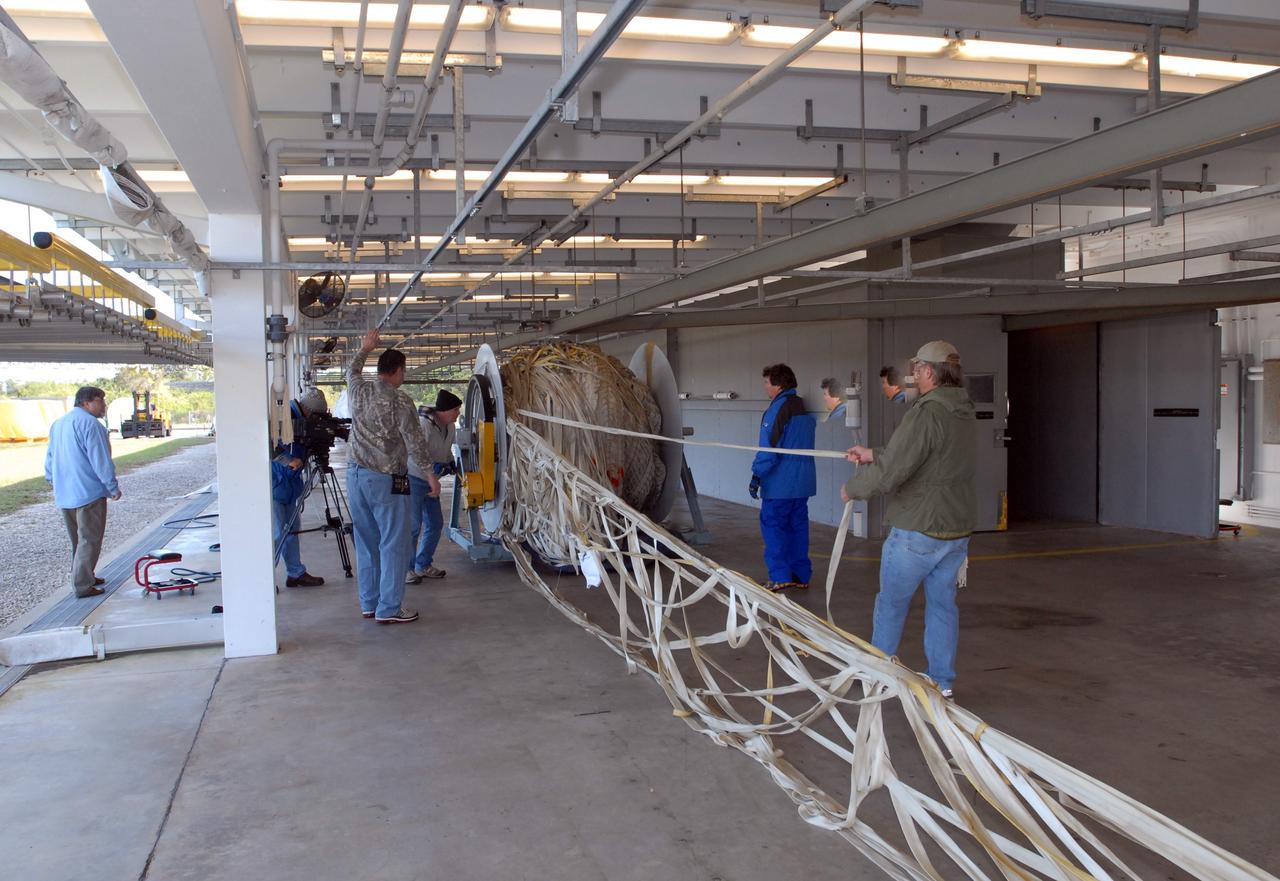

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, another parachute recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission is unwound from a large turnstile. After their recovery, the parachutes are untangled, hung on a monorail system and transported into a 30,000-gallon washer and a huge dryer heated with 140-degree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
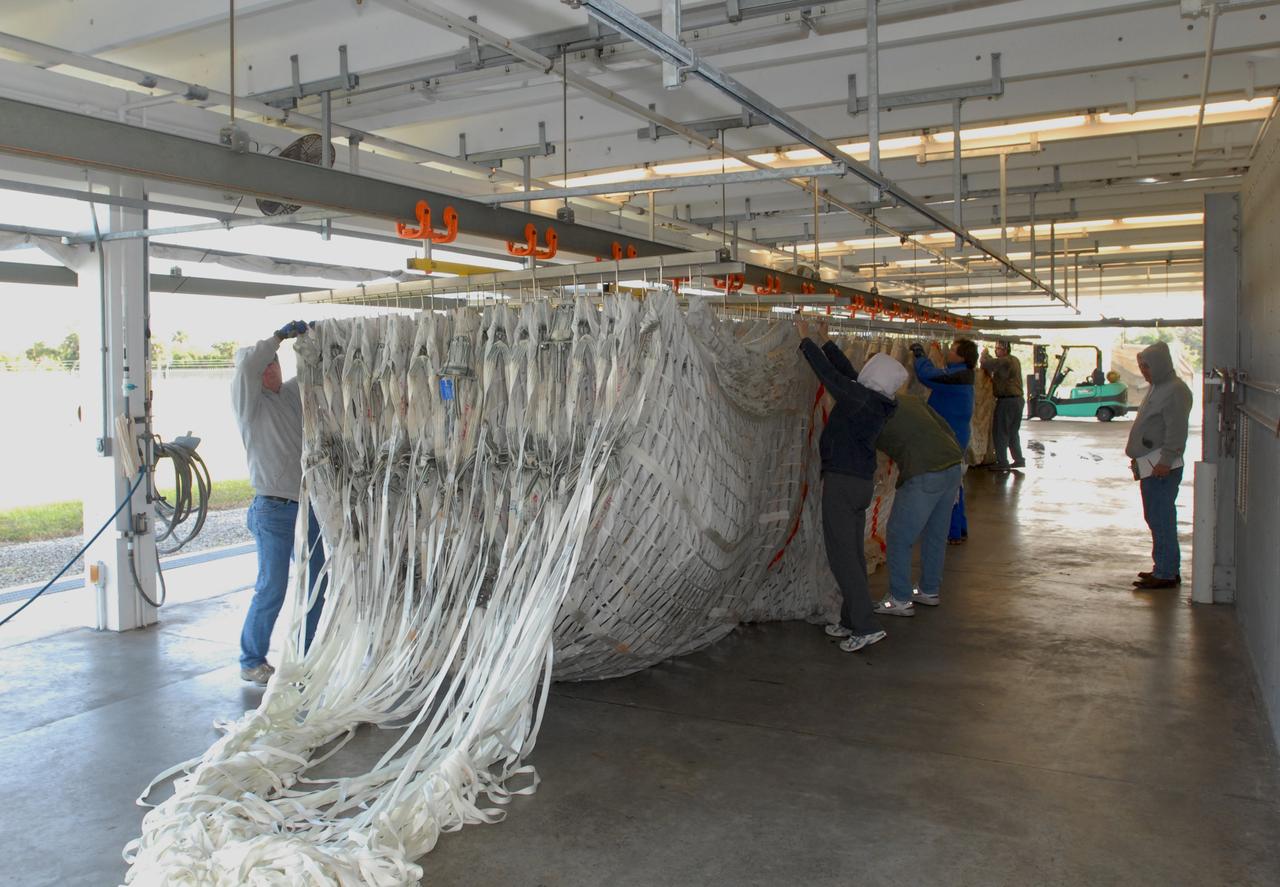

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers begin hanging the parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission onto a monorail system. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. The monorail will transport each parachute into a 30,000-gallon washer and a huge dryer heated with 140-degree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
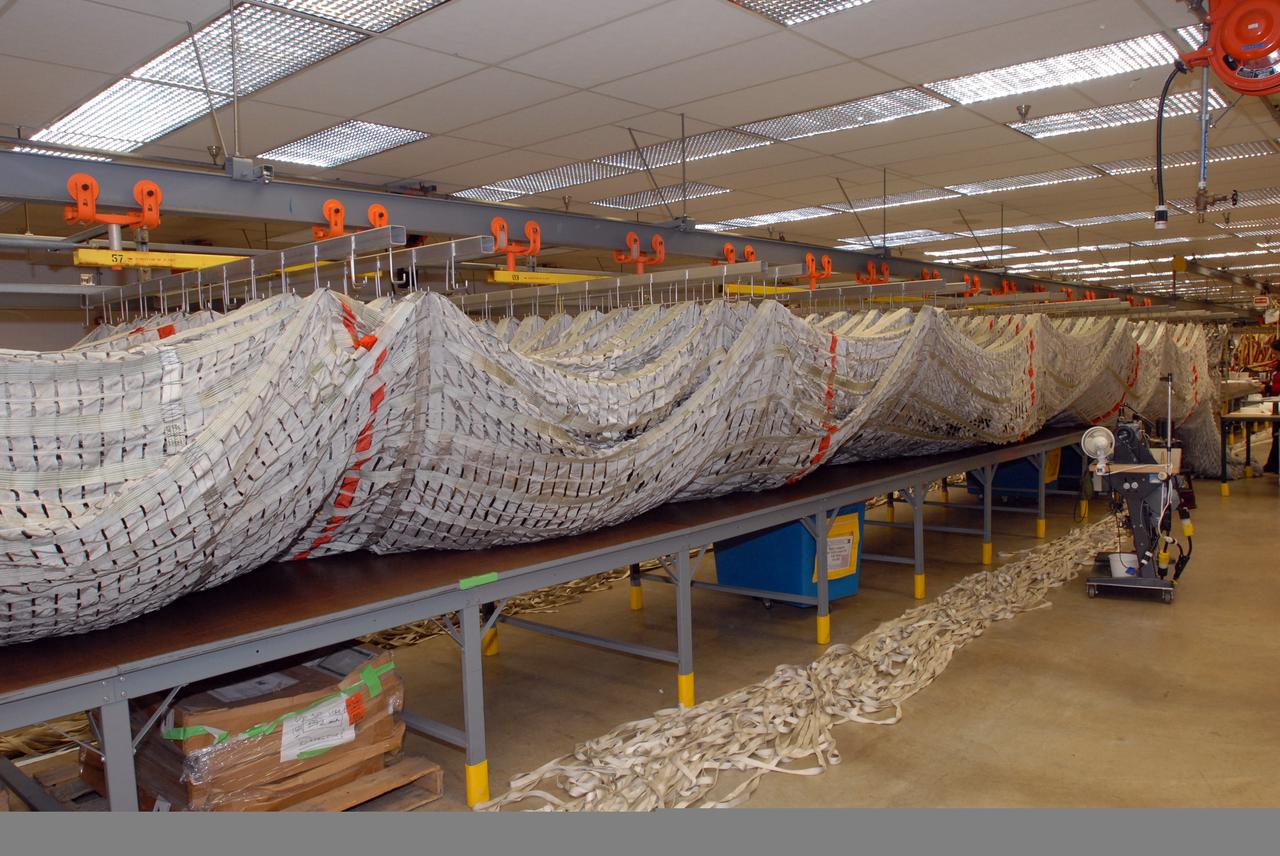

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission are suspended from a hanging monorail system at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. The monorail will transport each parachute into a 30,000-gallon washer and a huge dryer heated with 140-degree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker checks the parachute lines, recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission, as they move into the 30,000-gallon washer. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. After washing, the monorail will move the parachutes into a huge dryer heated with 140-degree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
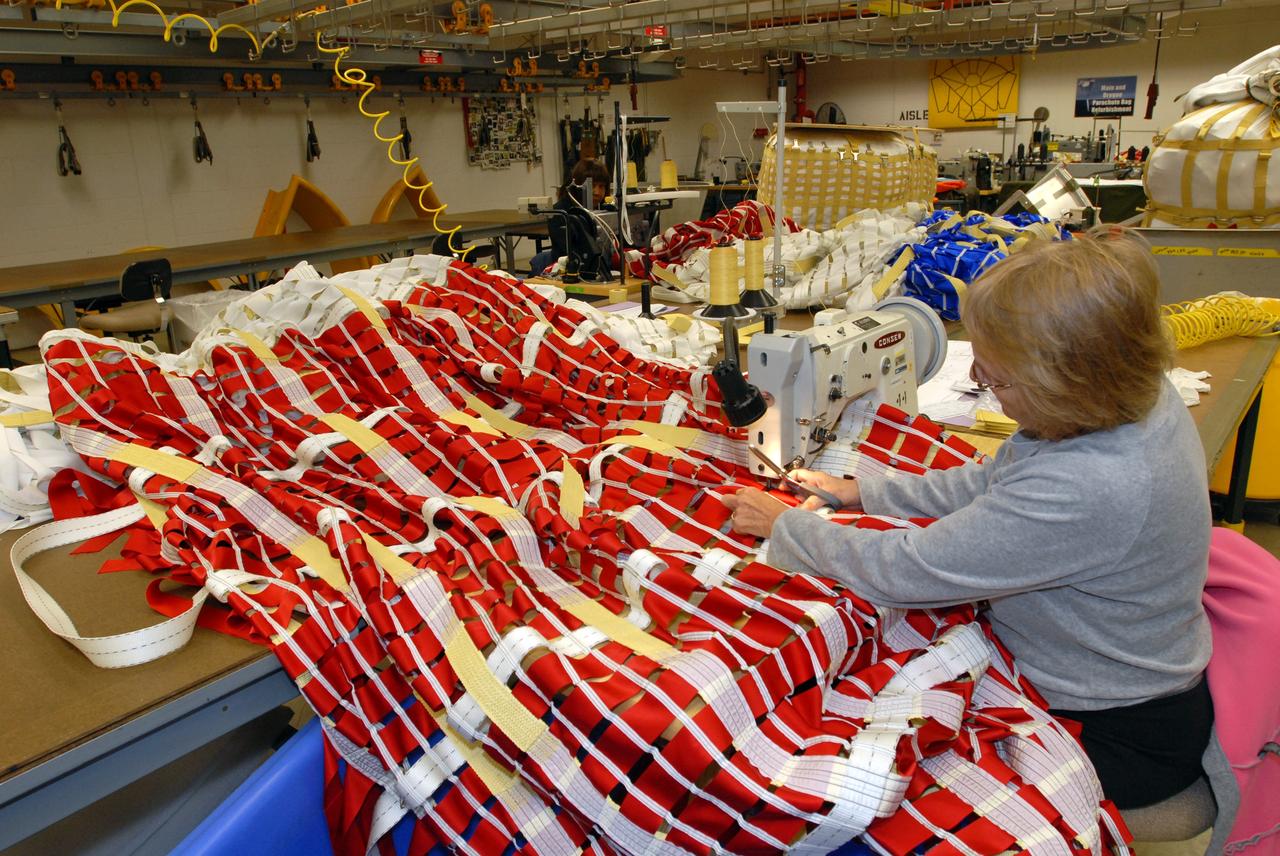

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers repair the parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission. Typically, each main canopy requires hundreds of repairs after each use. The smaller chutes and the parachute deployment bags they are packed in also require repairs. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
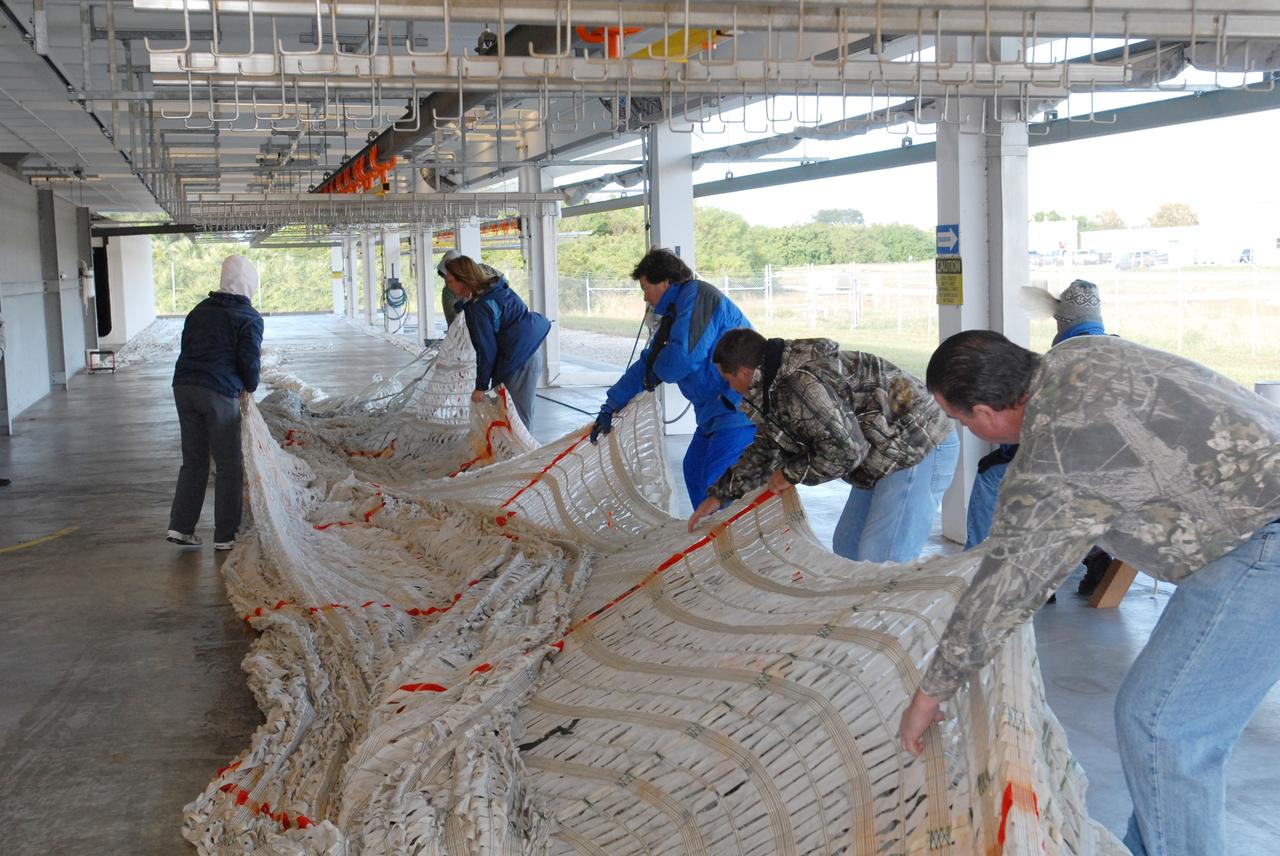

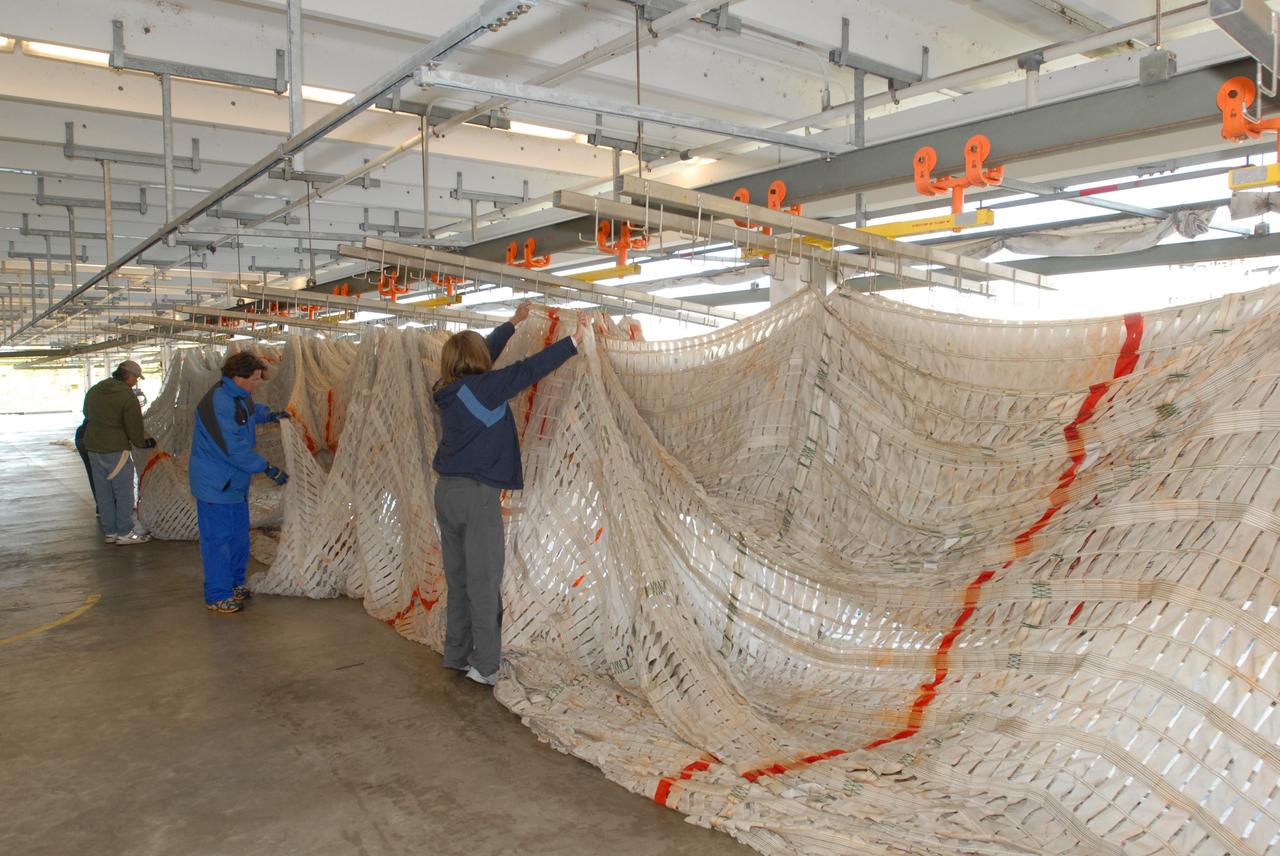
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers spread out the parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission to detangle them. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be carefully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
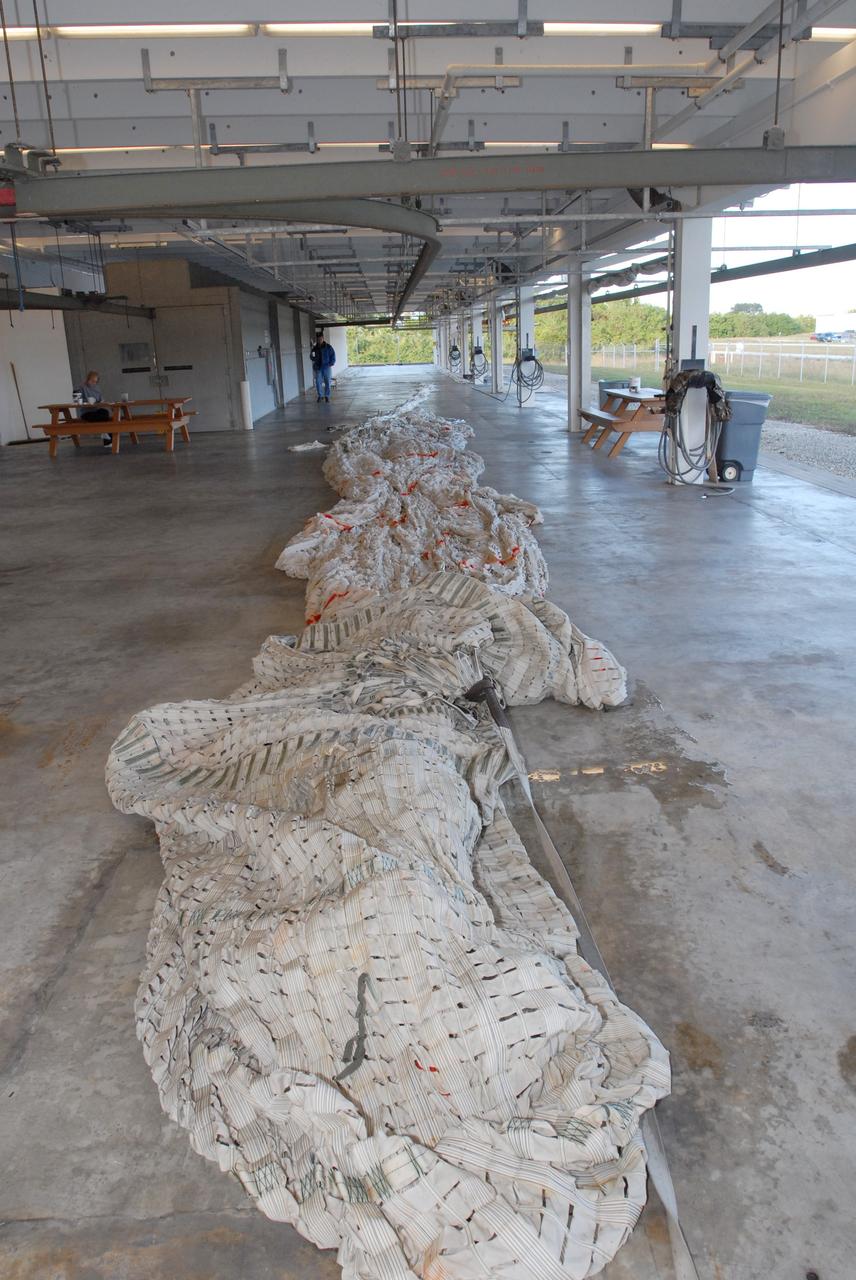

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Parachutes recovered from sea after the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-126 mission are stretched out at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to detangle them. The parachutes are used to slow the descent of the solid rocket boosters that are jettisoned during liftoff. After the chutes are returned to the facility following launch, a hanging monorail system is used to transport each parachute into a 30,000-gallon washer and then into a huge dryer heated with 140-de¬gree air at 13,000 cubic feet per minute. One pilot, one drogue and three main canopies per booster slow the booster’s fall from about 360 mph to 50 mph. After the chutes are cleaned and repaired, they must be care¬fully packed into their bags so they will deploy correctly the next time they are used. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
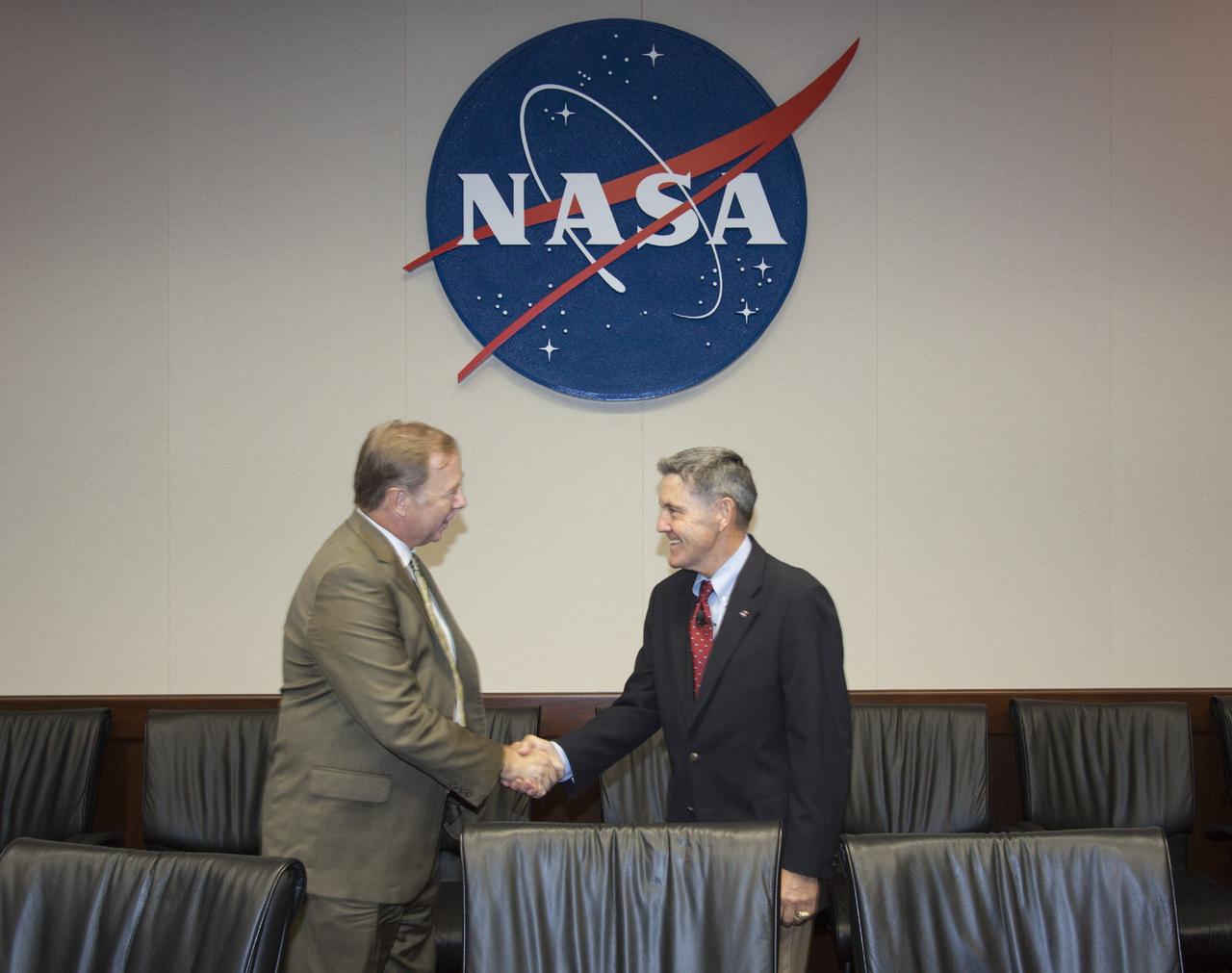

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Director Bob Cabana, at right, shakes hands with Larry Williams, president and CEO of Ballistic Recovery Systems Inc., or BRS Aerospace of Miami, Fla., after signing a new partnership agreement for use of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility, or PRF. Under a 10-year lease agreement, BRS Aerospace will operate and maintain the facility. The PRF previously was used during NASA’s Space Shuttle Program to manufacture and refurbish the solid rocket booster parachutes. Because of NASA’s transition from the shuttle to future commercial and government mission activities, the agreement allows NASA to preserve the unique facility capabilities for future spaceflight projects. Kennedy’s Center Planning and Development team and the Economic Development Commission of Florida’s Space Coast worked with BRS Aerospace to establish the agreement. For more information about BRS Aerospace, visit http://www.brsparachutes.com. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Director Bob Cabana, at right, shakes hands with Larry Williams, president and CEO of Ballistic Recovery Systems Inc., or BRS Aerospace of Miami, Fla., after signing a new partnership agreement for use of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility, or PRF. Under a 10-year lease agreement, BRS Aerospace will operate and maintain the facility. The PRF previously was used during NASA’s Space Shuttle Program to manufacture and refurbish the solid rocket booster parachutes. Because of NASA’s transition from the shuttle to future commercial and government mission activities, the agreement allows NASA to preserve the unique facility capabilities for future spaceflight projects. Kennedy’s Center Planning and Development team and the Economic Development Commission of Florida’s Space Coast worked with BRS Aerospace to establish the agreement. For more information about BRS Aerospace, visit http://www.brsparachutes.com. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility
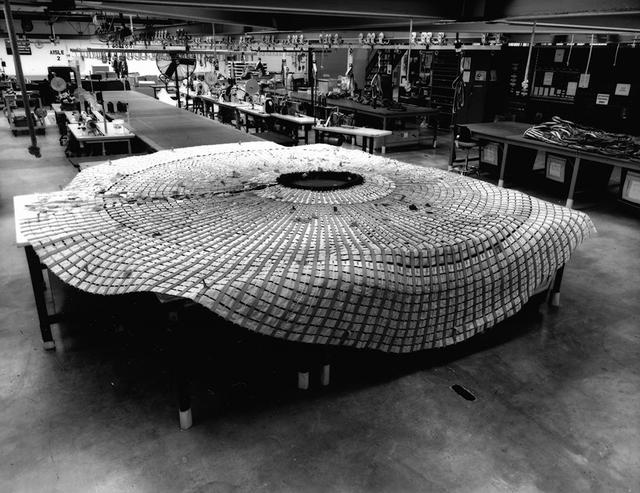

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility
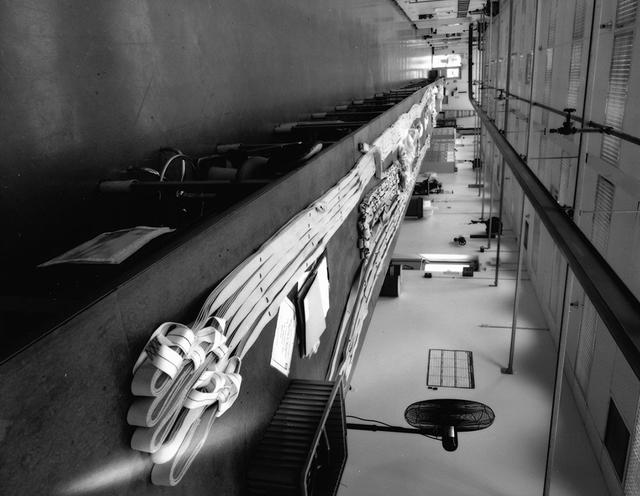

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility
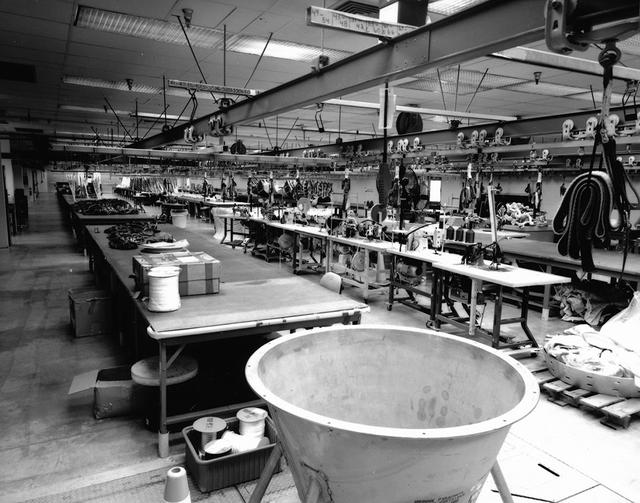

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility
Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility
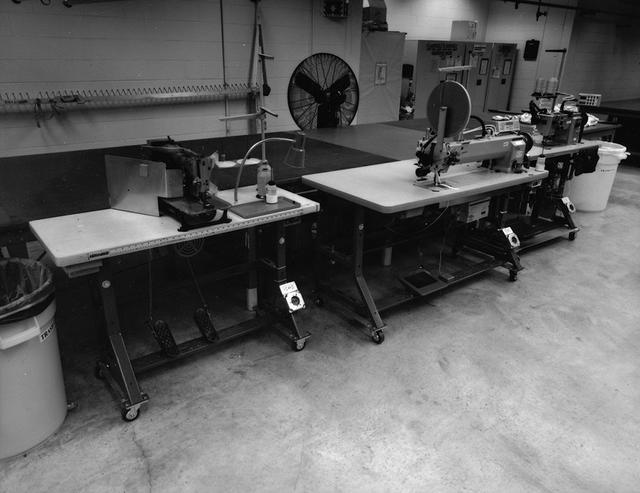

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility
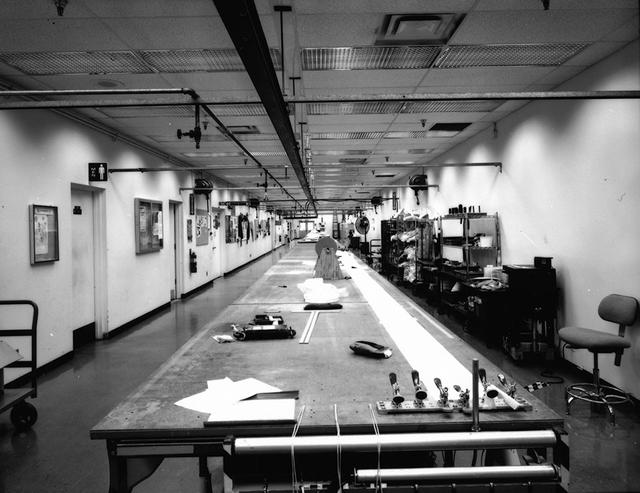

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility
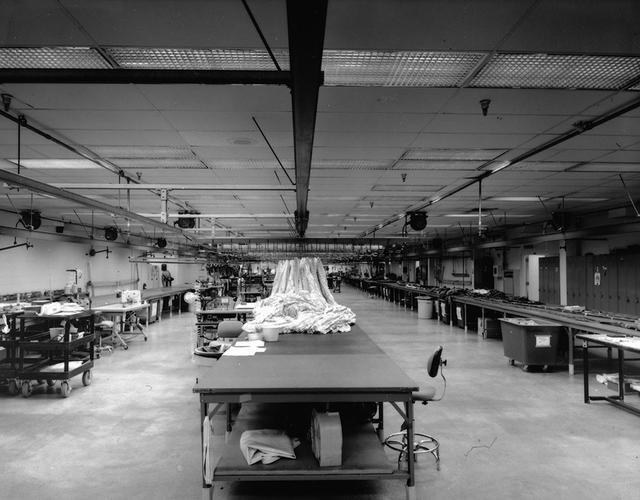

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility
Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Interior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility

Exterior view of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility
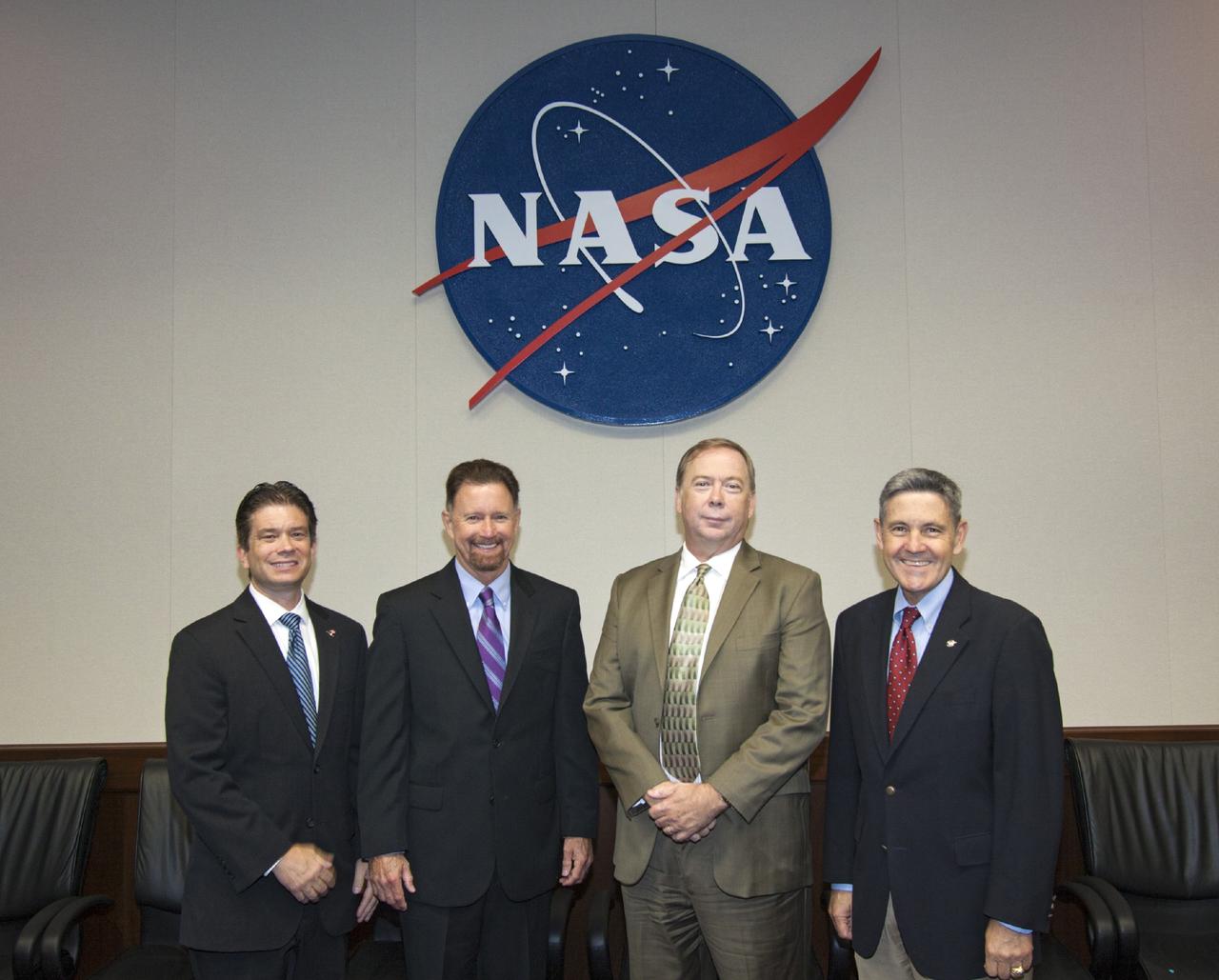

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida has signed a new partnership agreement with Ballistic Recovery Systems Inc., or BRS Aerospace of Miami, Fla., for use of the Parachute Refurbishment Facility, or PRF. From left, are Rob Salonen, director of Business Development with the Economic Development Commission, EDC, of Florida’s Space Coast Jim Barfield, EDC treasurer Larry Williams, president and CEO of BRS Aerospace and Center Director Bob Cabana. The PRF previously was used during NASA’s Space Shuttle Program to manufacture and refurbish the solid rocket booster parachutes. Because of NASA’s transition from the shuttle to future commercial and government mission activities, the agreement allows NASA to preserve the unique facility capabilities for future spaceflight projects. Kennedy’s Center Planning and Development team and the Economic Development Commission of Florida’s Space Coast worked with BRS Aerospace to establish the agreement. For more information about BRS Aerospace, visit http://www.brsparachutes.com. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann