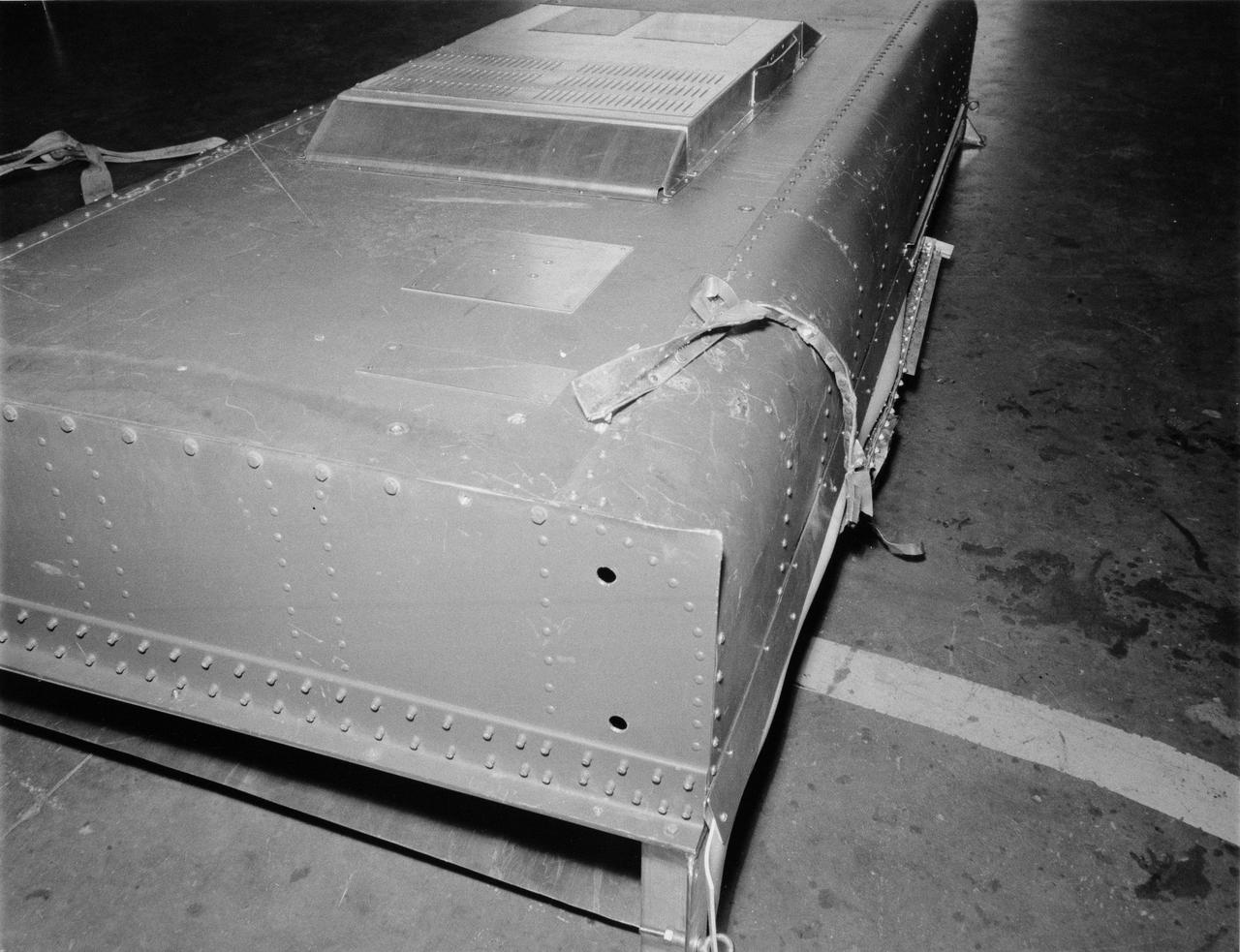

S73-27406 (5 June 1973) --- This structure duplicates the current problem with solar array wing number one on Skylab. The wing is being held against the side of the Orbital Workshop by what appears to be a strip of metal from the Meteoroid shield. Photo credit: NASA
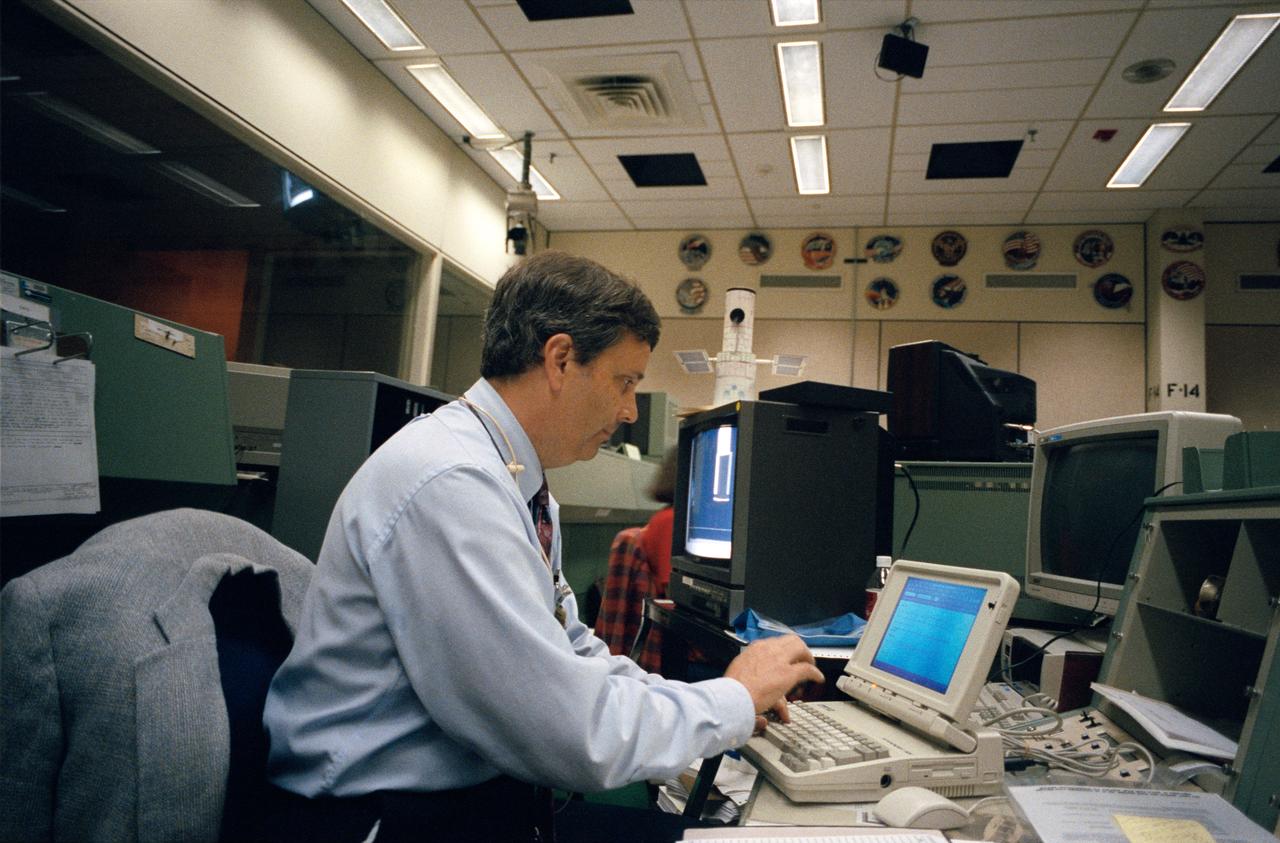

Flight Director Robert E. Castle Jr. works out a problem during joint integrated simulations for the STS-61 mission. Astronauts assigned to extravehicular activity (EVA) tasks with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) were simultaneously rehearsing in a neutral buoyancy tank at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Alabama.
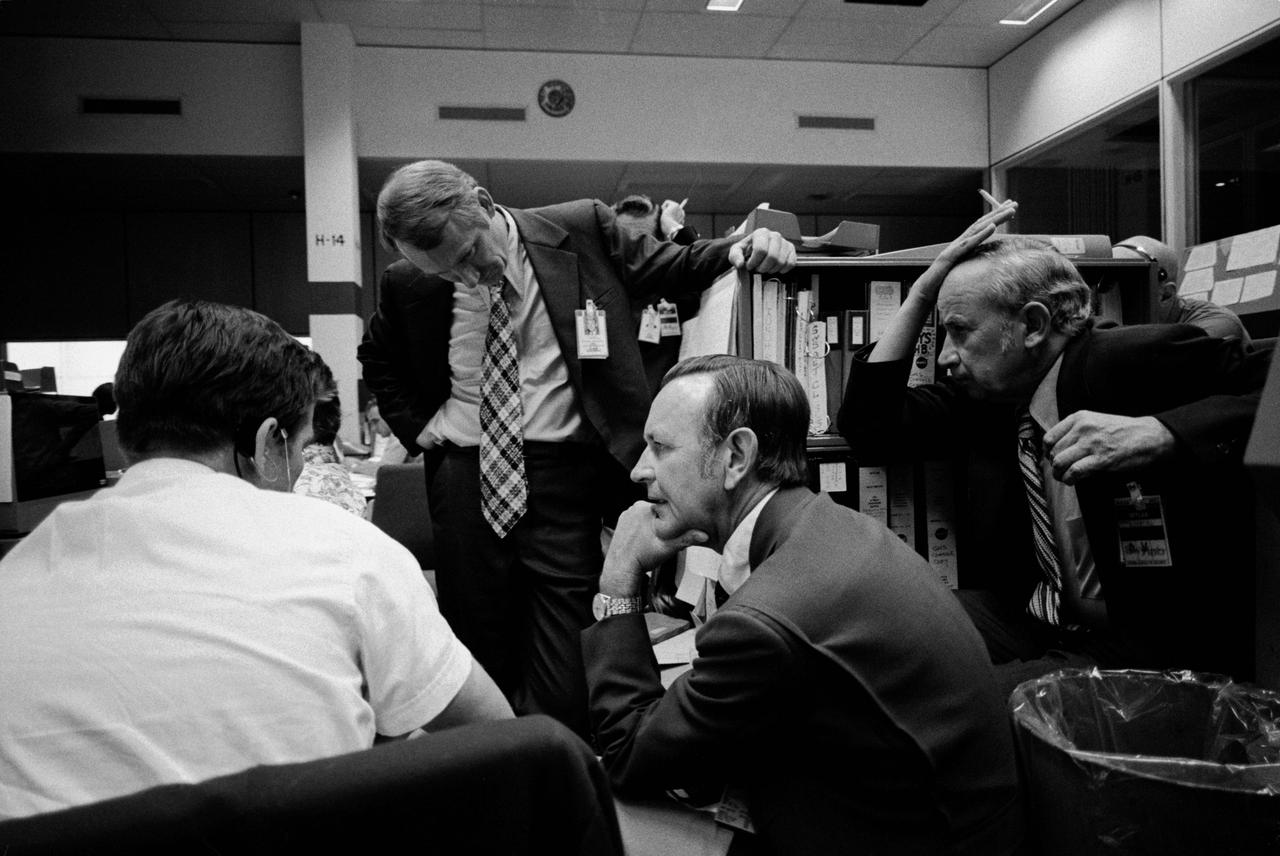

S73-31875 (2 Aug. 1973) --- After learning of a problem in the Command/Service Module which was used to transport the Skylab 3 crew to the orbiting Skylab space station cluster, NASA officials held various meetings to discuss the problem. Here, four men monitor the current status of the problem in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) of the Mission Control Center (MCC) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). From the left are Gary E. Coen, Guidance and Navigation System flight controller; Howard W. Tindall Jr., Director of Flight Operations at JSC; Dr. Christopher C. Kraft Jr., JSC Director; and Sigurd A. Sjoberg, JSC Deputy Director. Photo credit: NASA
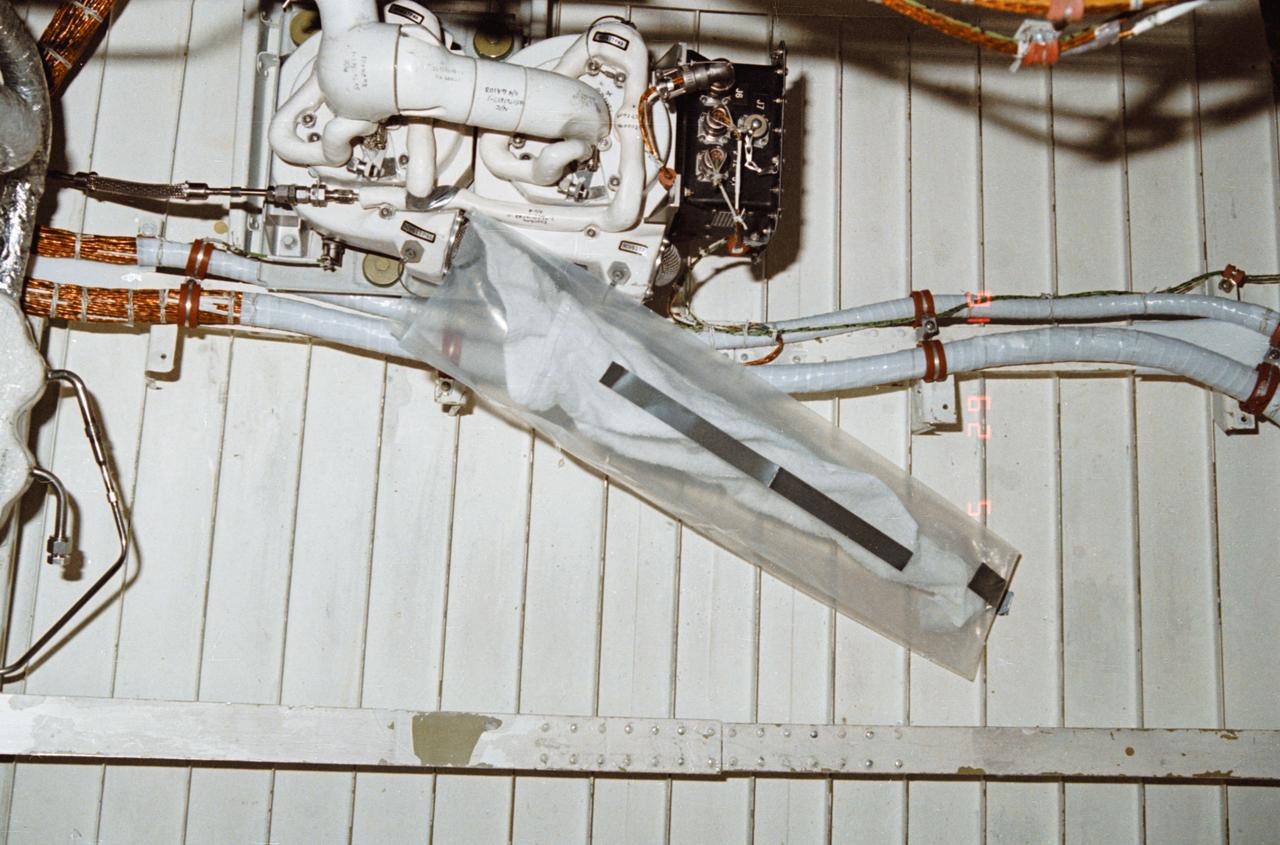
During STS-32, onboard Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, a leakage problem at environmental control and life support system (ECLSS) air revitalization system (ARS) humidity separator A below the middeck is solved with a plastic bag and a towel. The towel inserted inside a plastic bag absorbed the water that had collected at the separator inlet.
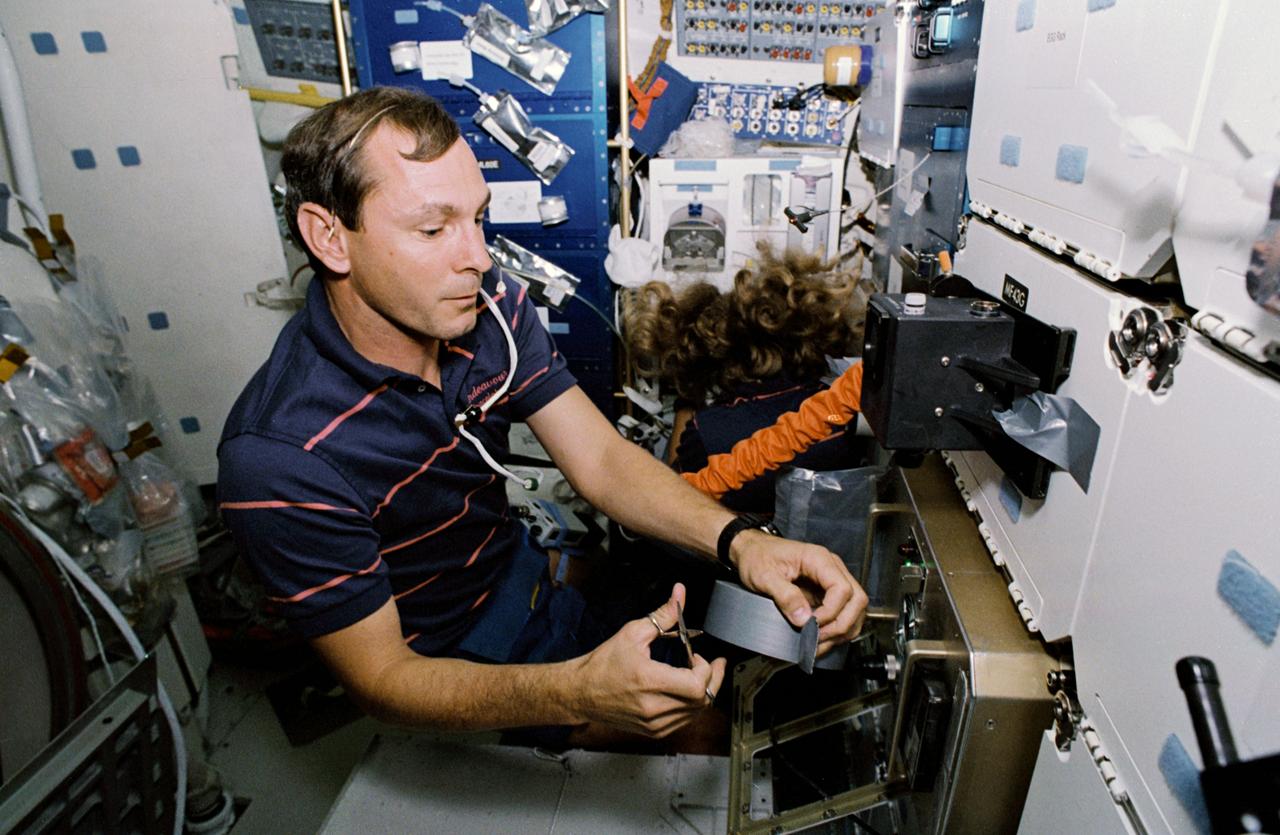

STS047-35-022 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr., pilot, and N. Jan Davis, mission specialist, team up to cure a high humidity problem in the hornet experiment in the Spacelab-J Science Module of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Via a jury-rigged hose hook-up, the two were able to blow air from a spacesuit fan into the experiment, thus eliminating condensation that obscured the viewing of the Israeli hornet experiment. The experiment examined the effects of microgravity on the orientation, reproductive capability and social activity of 180 female Oriental Hornets.
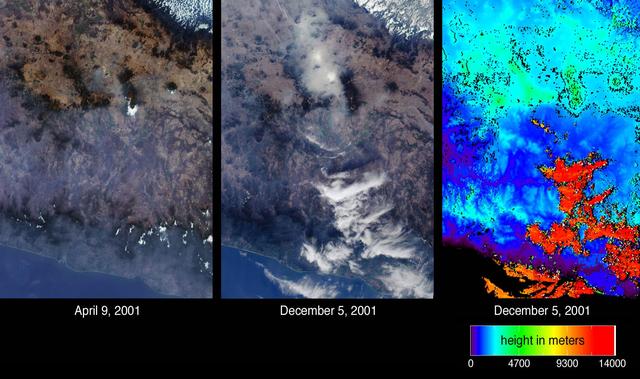
Mexico City has one of the world most serious air pollution problems. These images from NASA Terra satellite were captured on April 9 and December 5, 2001.
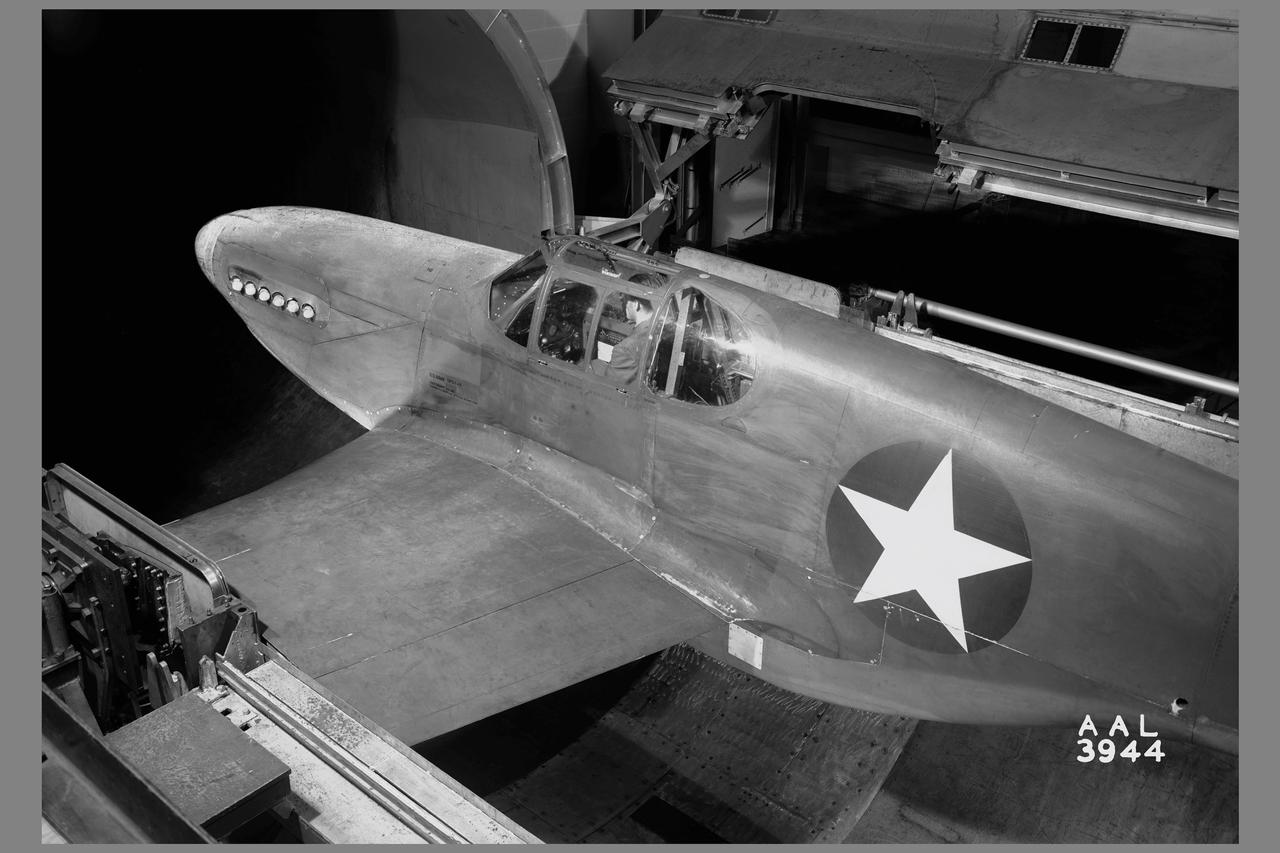

3/4 rear view of a XP-51B airplane mounted in the 16ft w.t. (Ames contribution to the solution of the duct-rumble problem)
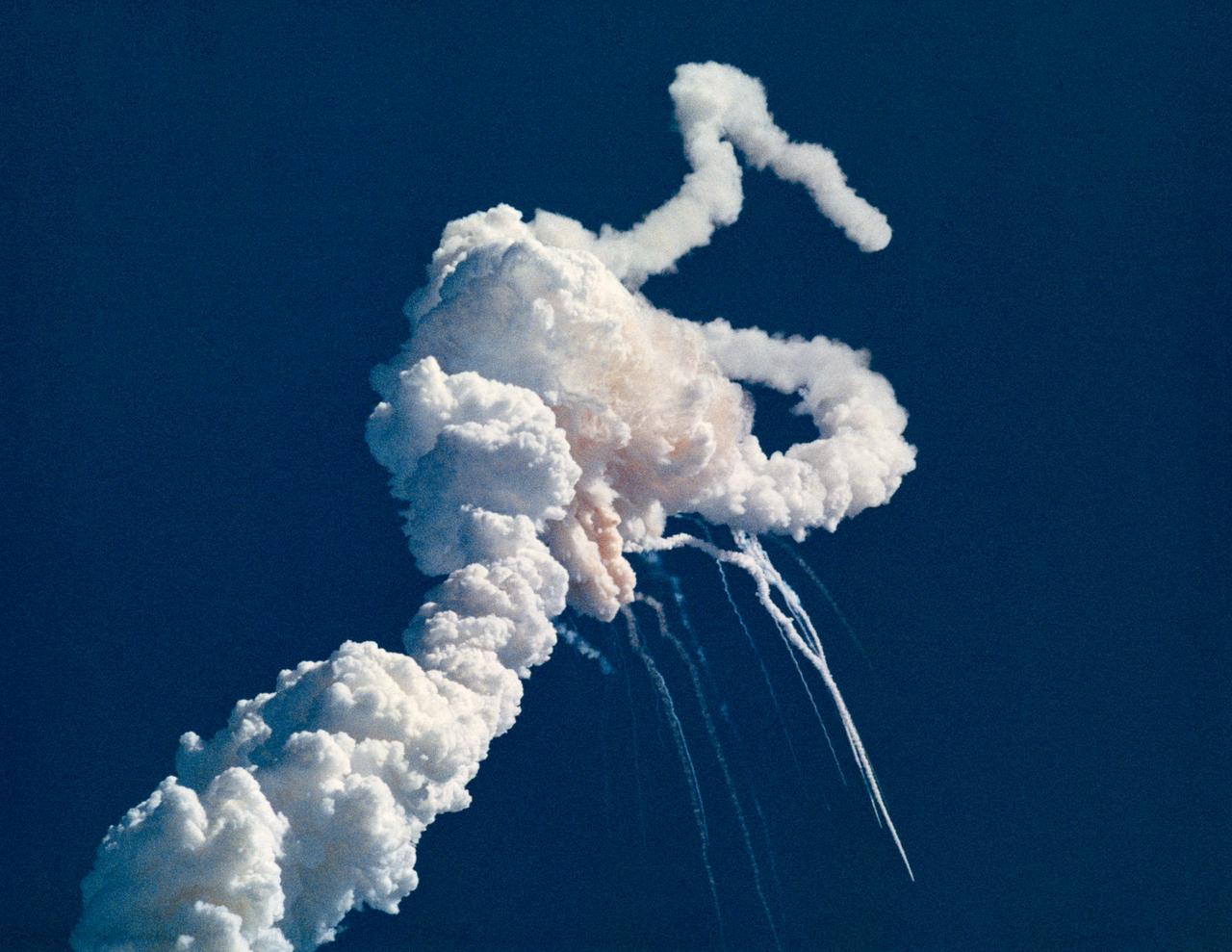

S86-38989 (28 Jan. 1986) --- Main engine exhaust, solid rocket booster plume and an expanding ball of gas from the external tank is visible seconds after the space shuttle Challenger accident on Jan. 28, 1986. (NOTE: The 51-L crew members lost their lives in the space shuttle Challenger accident moments after launch on Jan. 28, 1986 from the Kennedy Space Center.) Photo credit: NASA
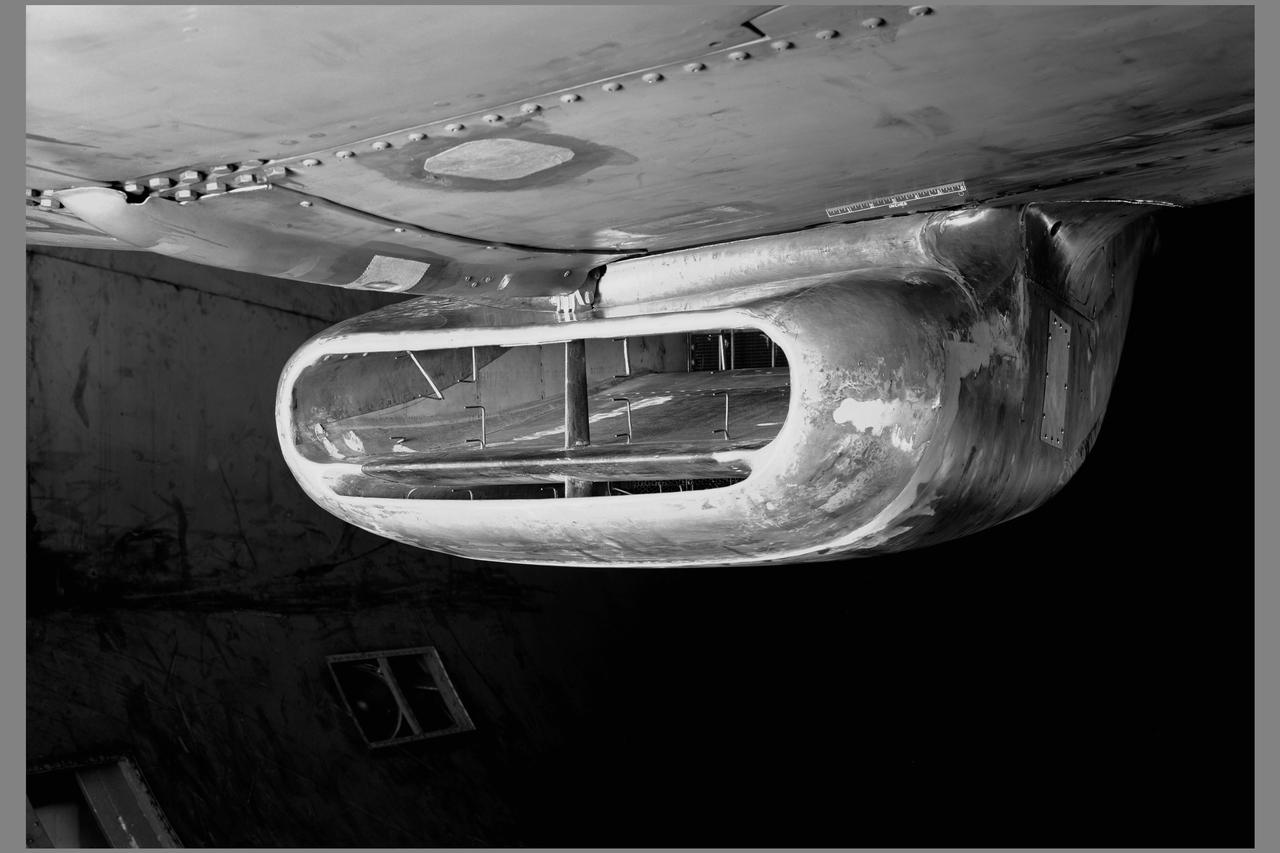

3/4 front view of modified production scoop on XP-51B airplane mounted in the 16ft w.t. (Ames contribution to the solution of the duct-rumble problem)
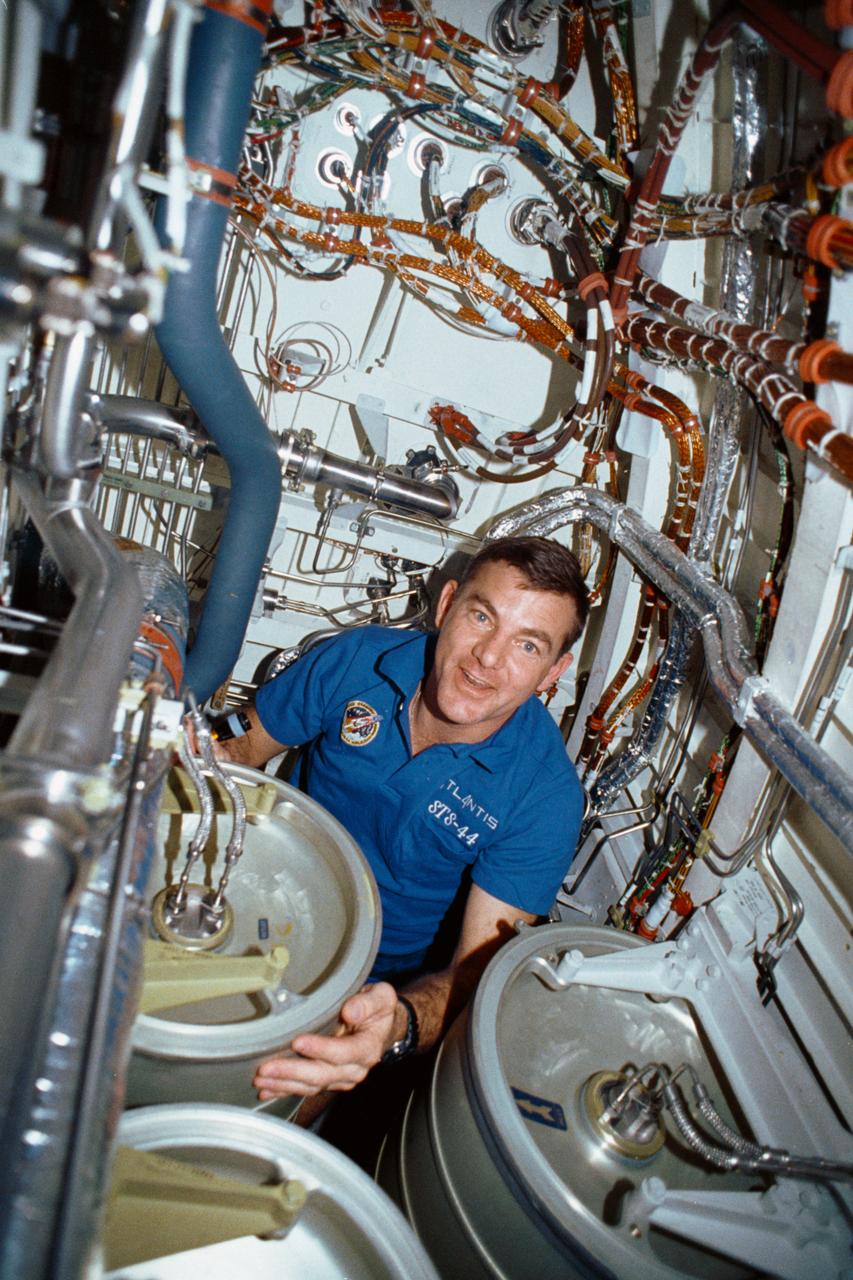

STS-44 Mission Specialist (MS) James S. Voss works under the middeck subfloor of Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, to repair humidity separator leakage problems. Voss is surrounded by several water tanks and a maze of shuttle wiring and plumbing. Voss earned the nickname of "Bilge Man" because of his time spent on the lower deck tending to the leakage problem. This is the first photo released of a crewmember in this area of the shuttle.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Viewed from outside the Vehicle Assembly Building, the stack of external tank and solid rocket boosters on Columbia can be seen sitting atop the Mobile Launcher Platform. The Shuttle never left the VAB due to a steering problem on the crawler-transporter under the MLP. The problem was a faulty bearing in the steering linkage of Power Truck Drive D, which was detected before the C-T left the VAB. Rollout has been rescheduled for Jan. 24
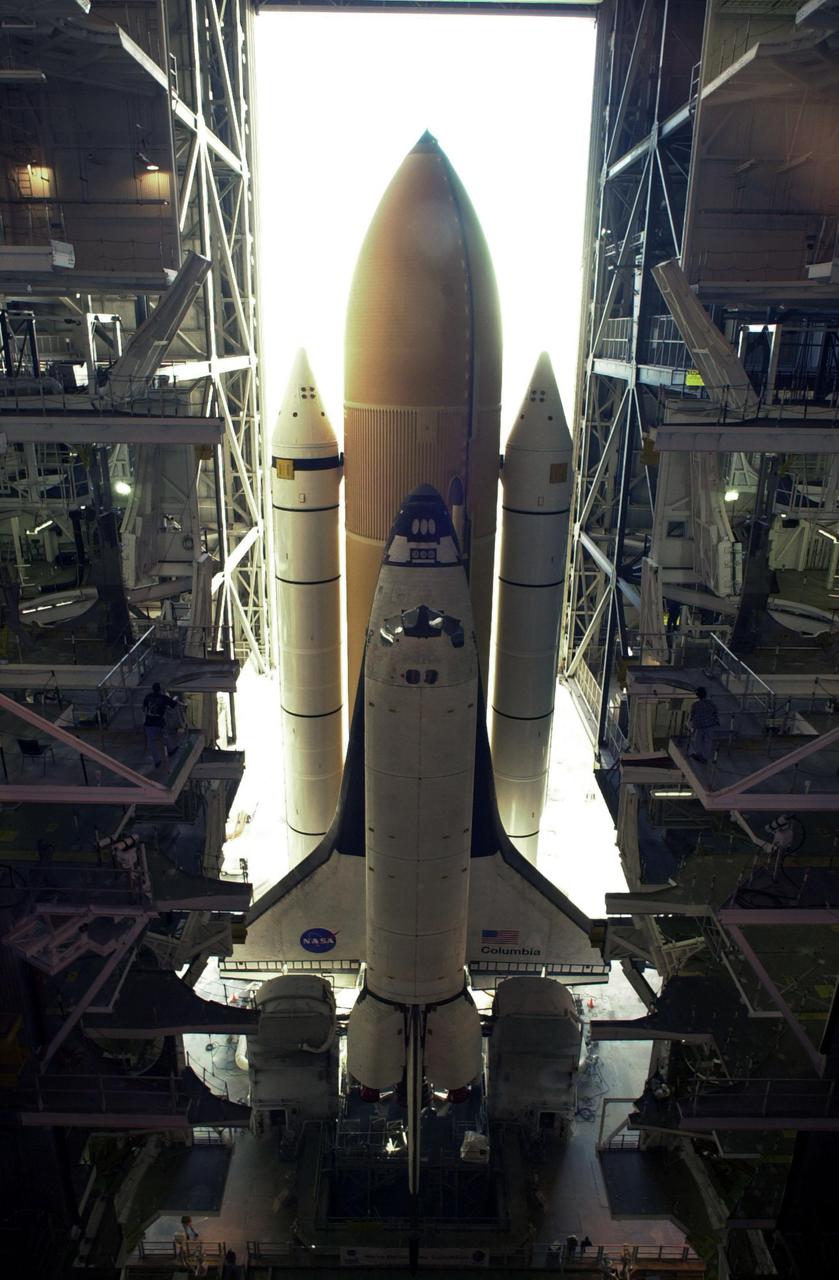

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Columbia sits atop its Mobile Launcher Platform in the open doorway of the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Shuttle never left the VAB due to a steering problem on the crawler-transporter under the MLP. The problem was a faulty bearing in the steering linkage of Power Truck Drive D, which was detected before the C-T left the VAB. Rollout has been rescheduled for Jan. 24
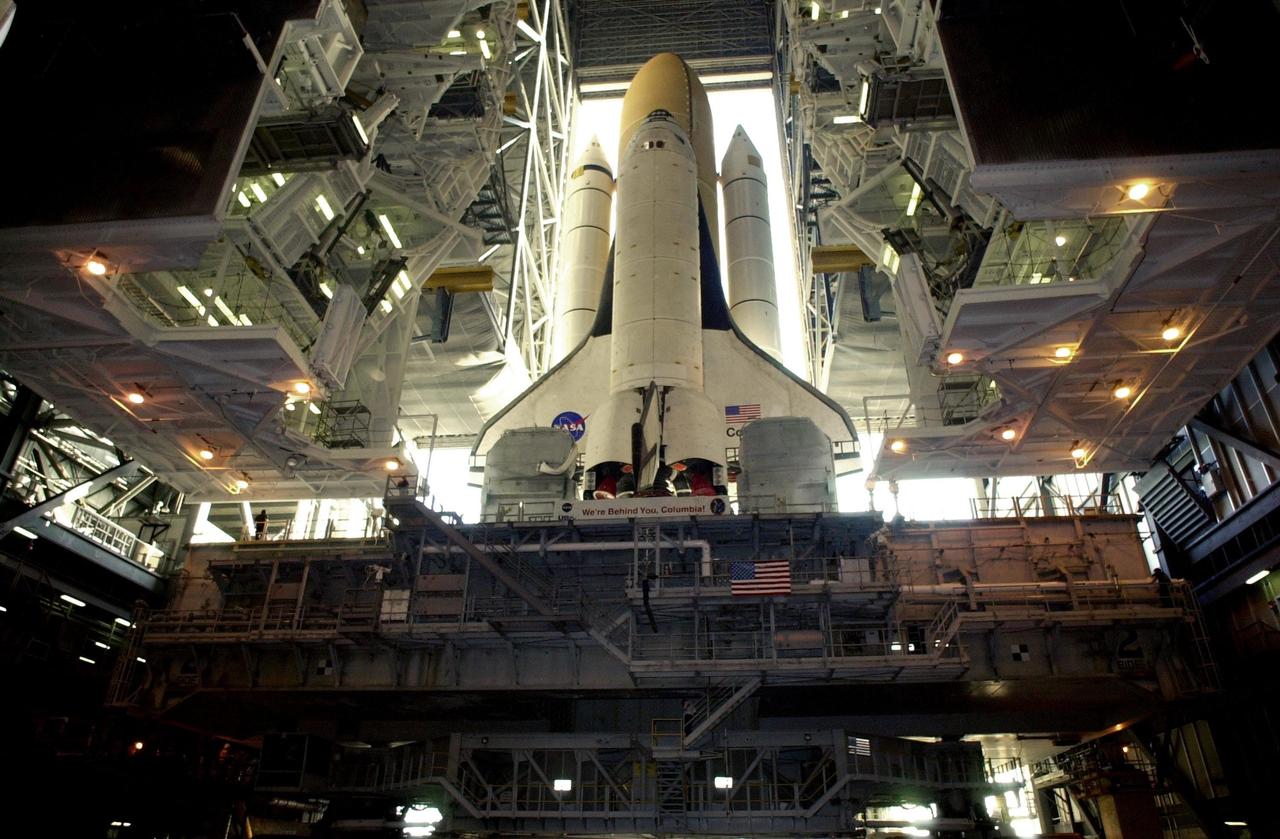

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Columbia sits atop its Mobile Launcher Platform in the open doorway of the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Shuttle never left the VAB due to a steering problem on the crawler-transporter under the MLP. The problem was a faulty bearing in the steering linkage of Power Truck Drive D, which was detected before the C-T left the VAB. Rollout has been rescheduled for Jan. 24
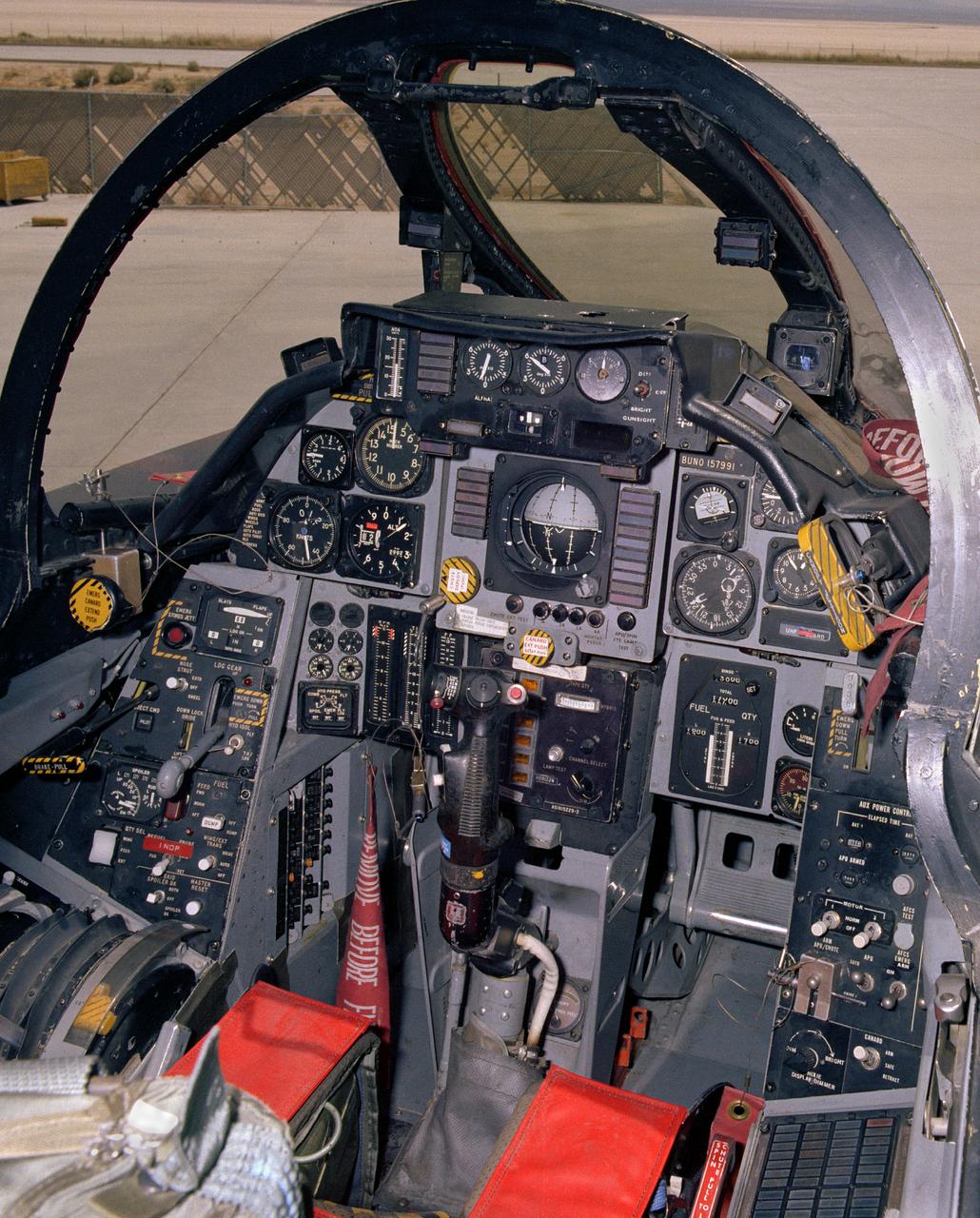

View of the cockpit of NASA's F-14, tail number 991. This aircraft was the first of a series of post-Vietnam fighters, followed by the F-15, F-16, and F-18. They were designed for maneuverability in air-to-air combat. The F-14s had a spin problem that posed problems for its ability to engage successfully in a dogfight, since it tended to depart from controlled flight at the high angles of attack that frequently occur in close-in engagements.

S73-26127 (1973) --- An artist's concept of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit illustrating the deployment of the twin pole thermal shield to shade the Orbital Workshop (OWS) from the sun. This is one of the sunshade possibilities considered to solve the problem of the overheated OWS. Here the two Skylab 2 astronauts have completely deployed the sunshade. Note the evidence of another Skylab problem - the solar panels on the OWS are not deployed as required. Photo credit: NASA
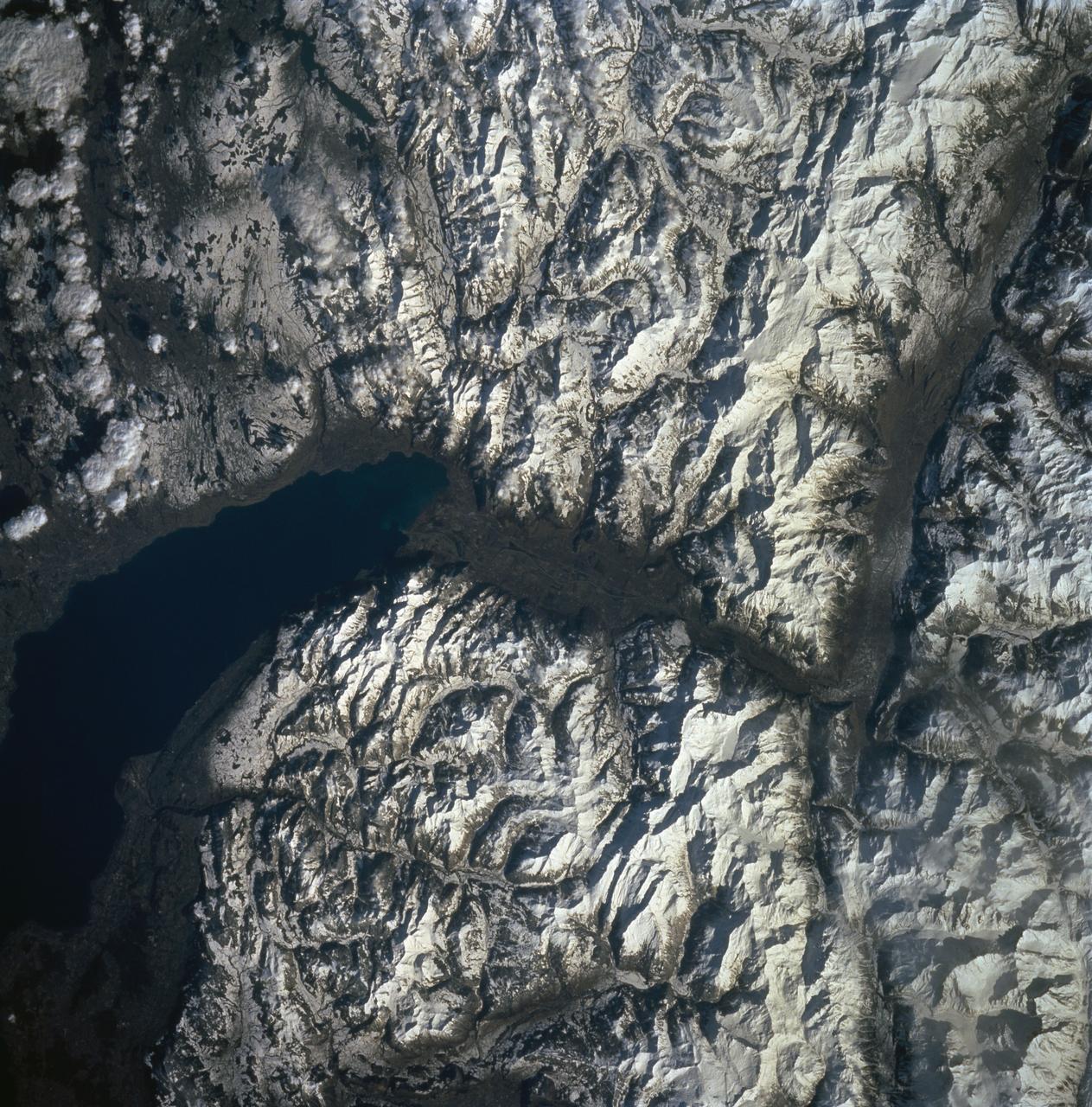

STS060-90-007 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- Parts of the Swiss Cantons of Vaud and Valois and the French province of Chablais are shown. These mountains were created in the last great mountain-building episode in Europe around 50 million years ago. They have been reshaped by glaciers during the Pleistocene. The glaciers created the wide valley of the Rhone River by scouring a pre-existing stream. The fertile Swiss Plateau runs northwest from the shore of Lake Geneva and is visible in the upper right. The Franco-Swiss border is located in the center of the lake and follows a mountain divide east of the Rhone Valley. According to NASA geologists eutrofication is a problem in Lake Geneva. In 1971 a Swiss Commission was formed to try to slow the problem. Strong discharge laws were enacted, but they are hard to enforce due to the multi-national and multi-organizational parties contributing to the problem.
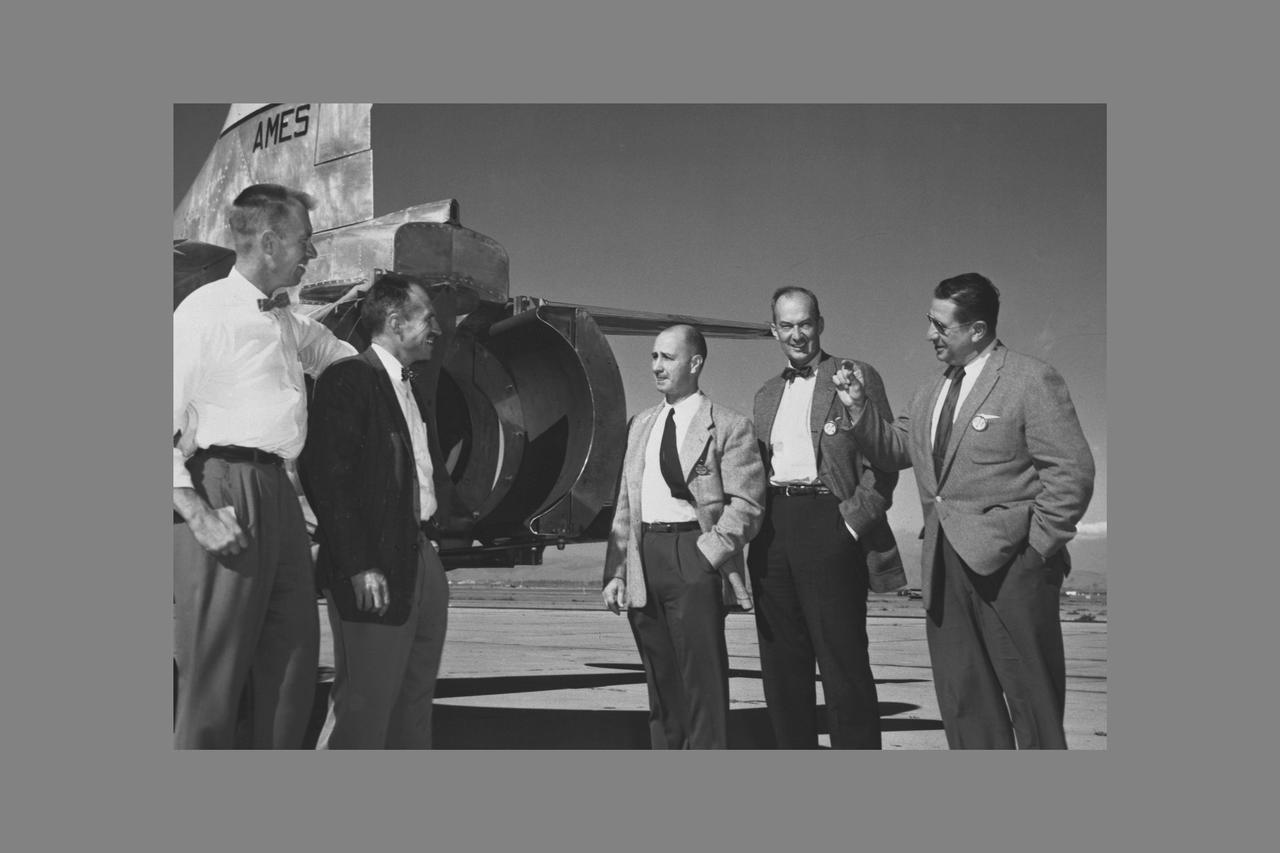

NACA AMES ENGINEERS: Seth B. ANDERSON AND NACA AMES PILOT Gorge E. COOPER WITH W.E. RHOADES, ROBERT McIVER, MICHAEL CASSENLY OF UNITED AIRLINES. Visit Ames to dicuss Thrust Reverser Problems.
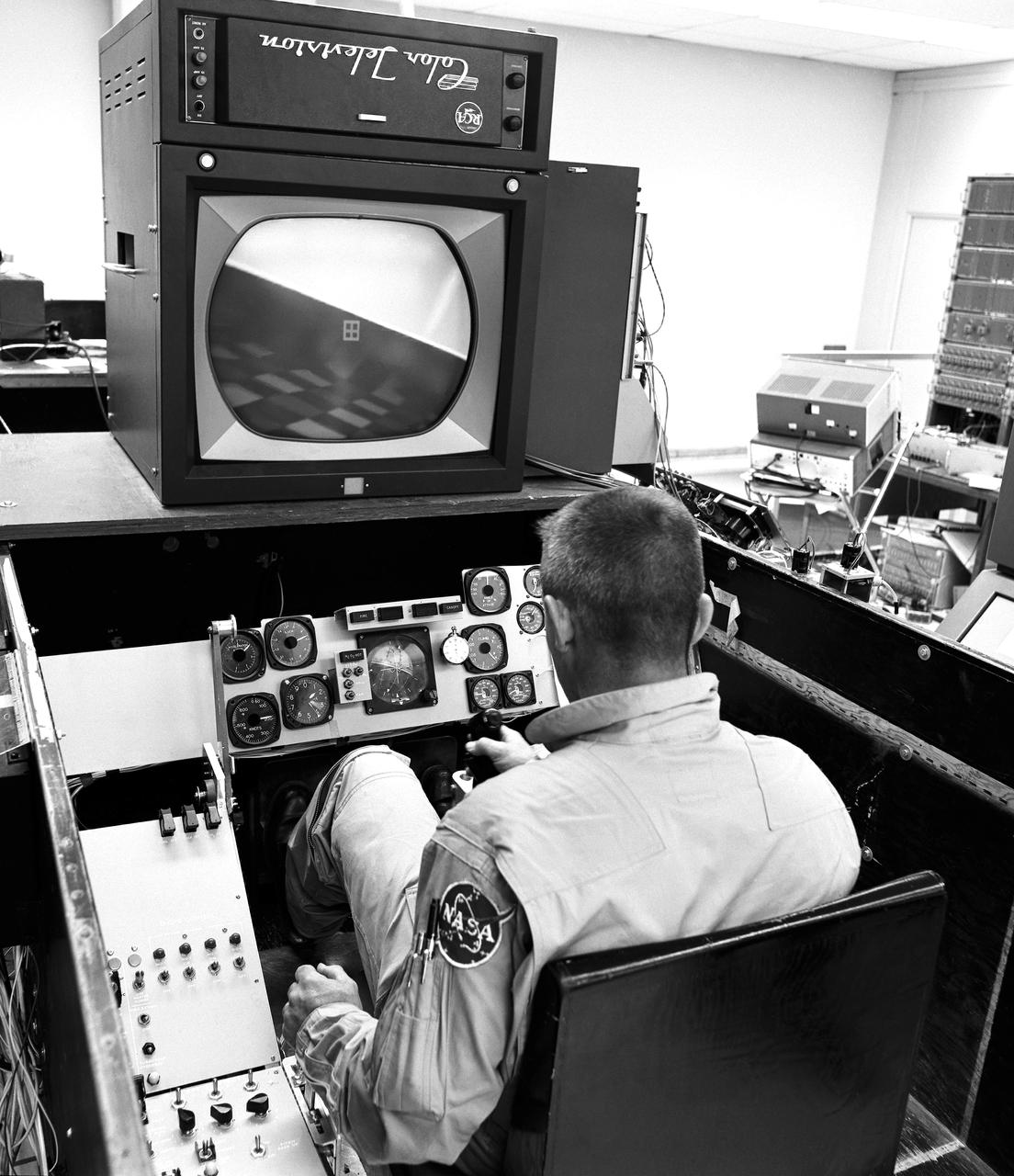

As shown in this photo of the HL-10 flight simulator, the lifting-body pilots and engineers made use of early simulators for both training and the determination of a given vehicle's handling at various speeds, attitudes, and altitudes. This provided warning of possible problems.
Close-up from stand, 0 degrees nose flap deflection. Supersonic Transport model - landing & take-off problems, extended wing tips. 40x80ft w.t.
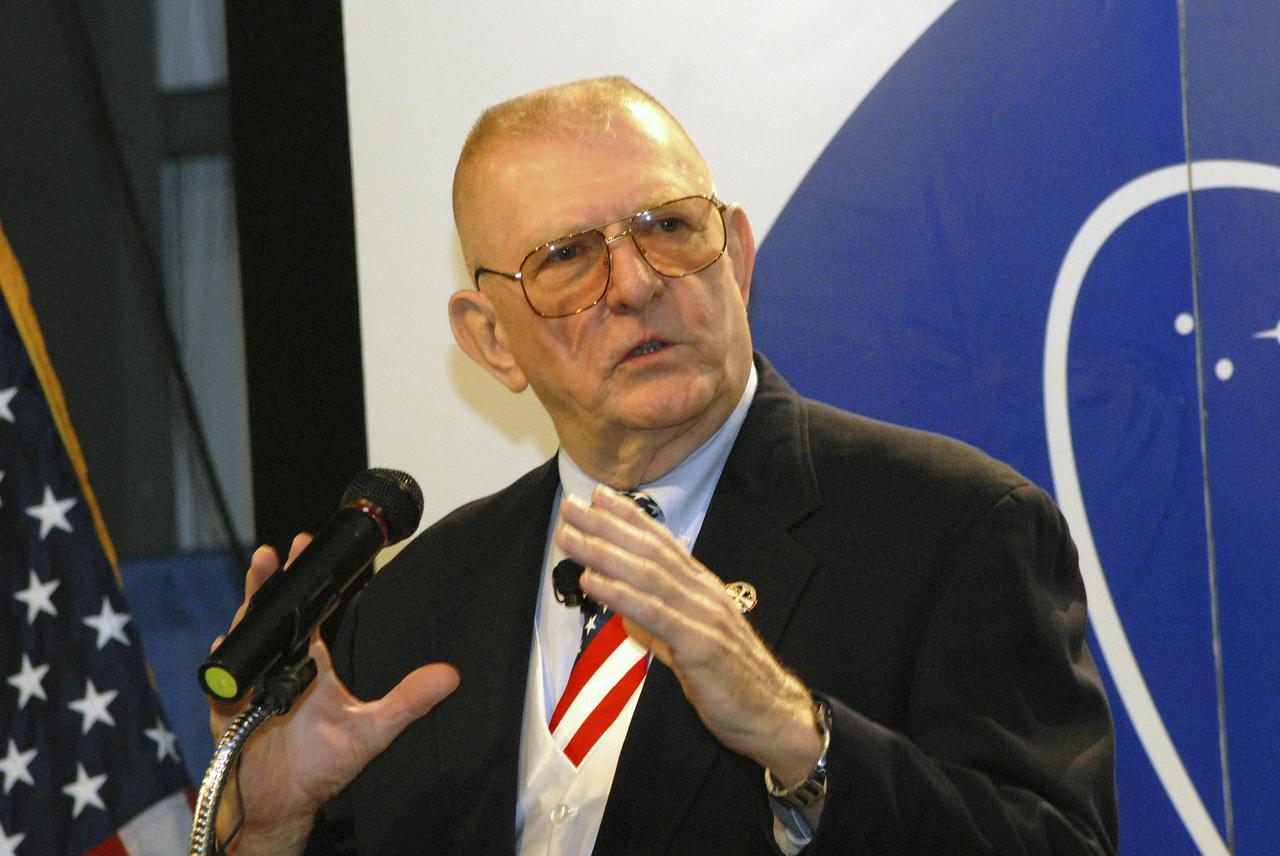

On October 19, 2006, former NASA director of Mission Operations Gene Kranz was a keynote speaker at the Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC’s) 2006 Annual Safety Day program. The best selling author of “Failure Is Not An Option” and past Apollo flight director was featured during a morning session called “Coffee and Kranz”. Marshall employees hung on his every word as he told the fascinating story of Apollo 13. Kranz was the acting flight director during the Apollo 13 mission, a mission that seemed doomed to fail due to an onboard explosion. Kranz and his flight control team worked around the clock relentlessly, solving problem after problem, until the crew was returned safely to Earth.
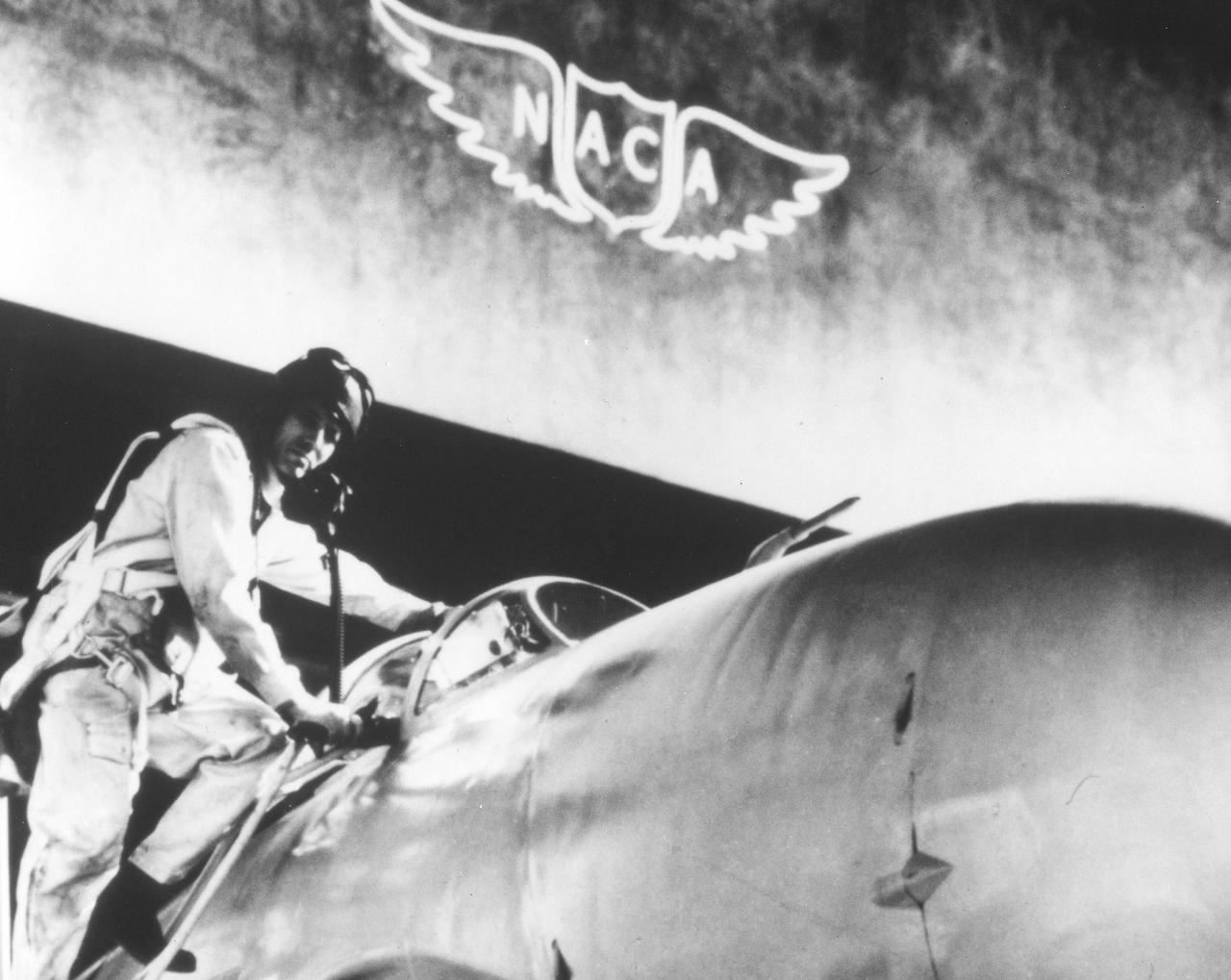

The Marshall Space Flight Center was activated on July 1, 1960 as a part of NASA, which had been established on October 1, 1958 by Congressional passage of the National Aeronautics and Space Act. The nucleus of NASA was the Advisory Committee for Aeronautics later named the National Advisory Committee for Aeronauts (NACA). The NACA was founded in 1915 to study the problems of flight and to recommend practical solutions to basic aircraft design and construction problems. NACA's wind turnels and other research facilities made NACA technical reports the basis for aviation progress for more than 40 years.
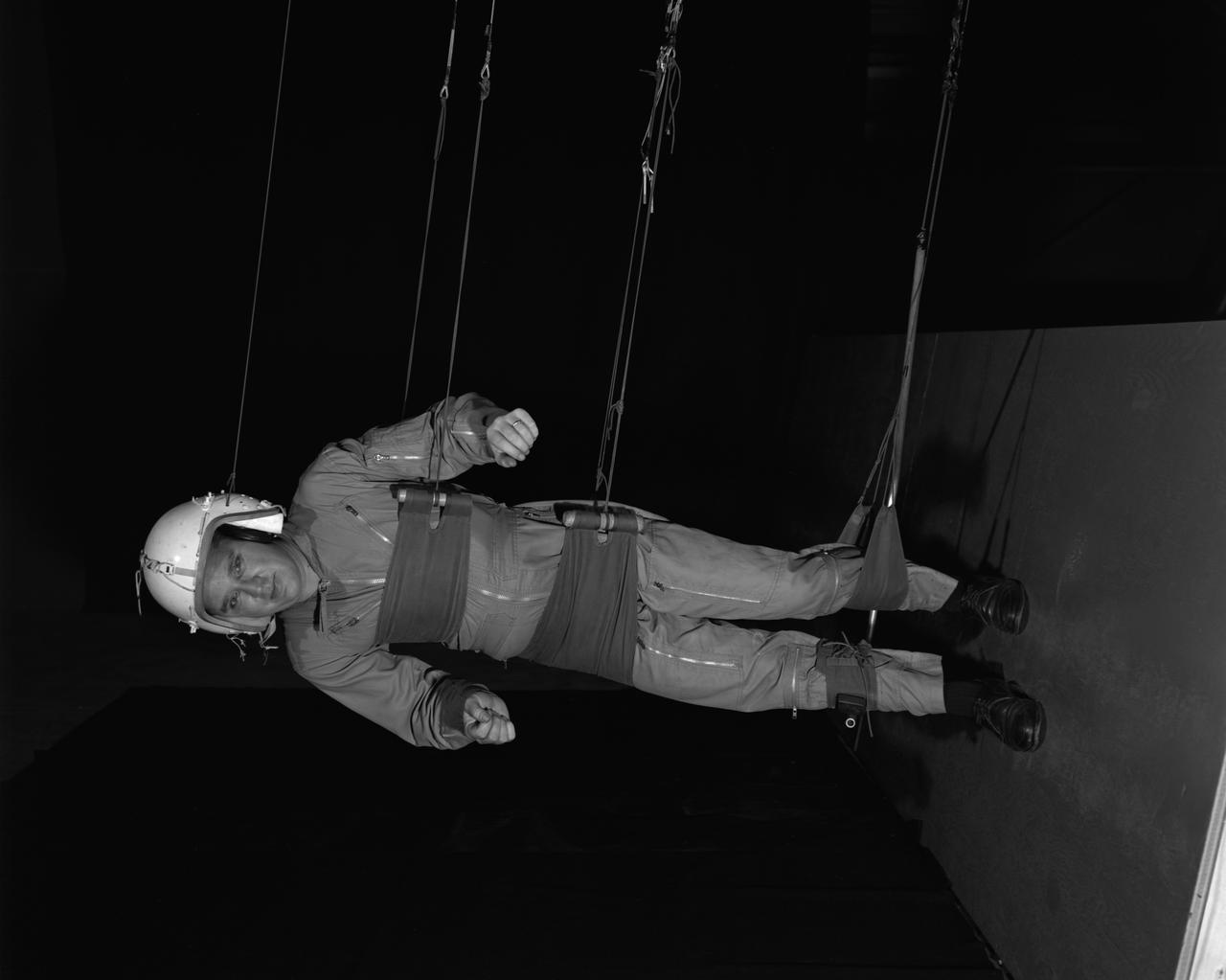

Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located in the hangar at Langley Research Center. The initial version of this simulator was located inside the hangar. Later a larger version would be located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil wrote in his paper Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research, When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject' s weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, p. 377 A.W. Vigil, Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research, Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.

Astronaut Roger Chaffee on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil, described the simulator as follows: "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
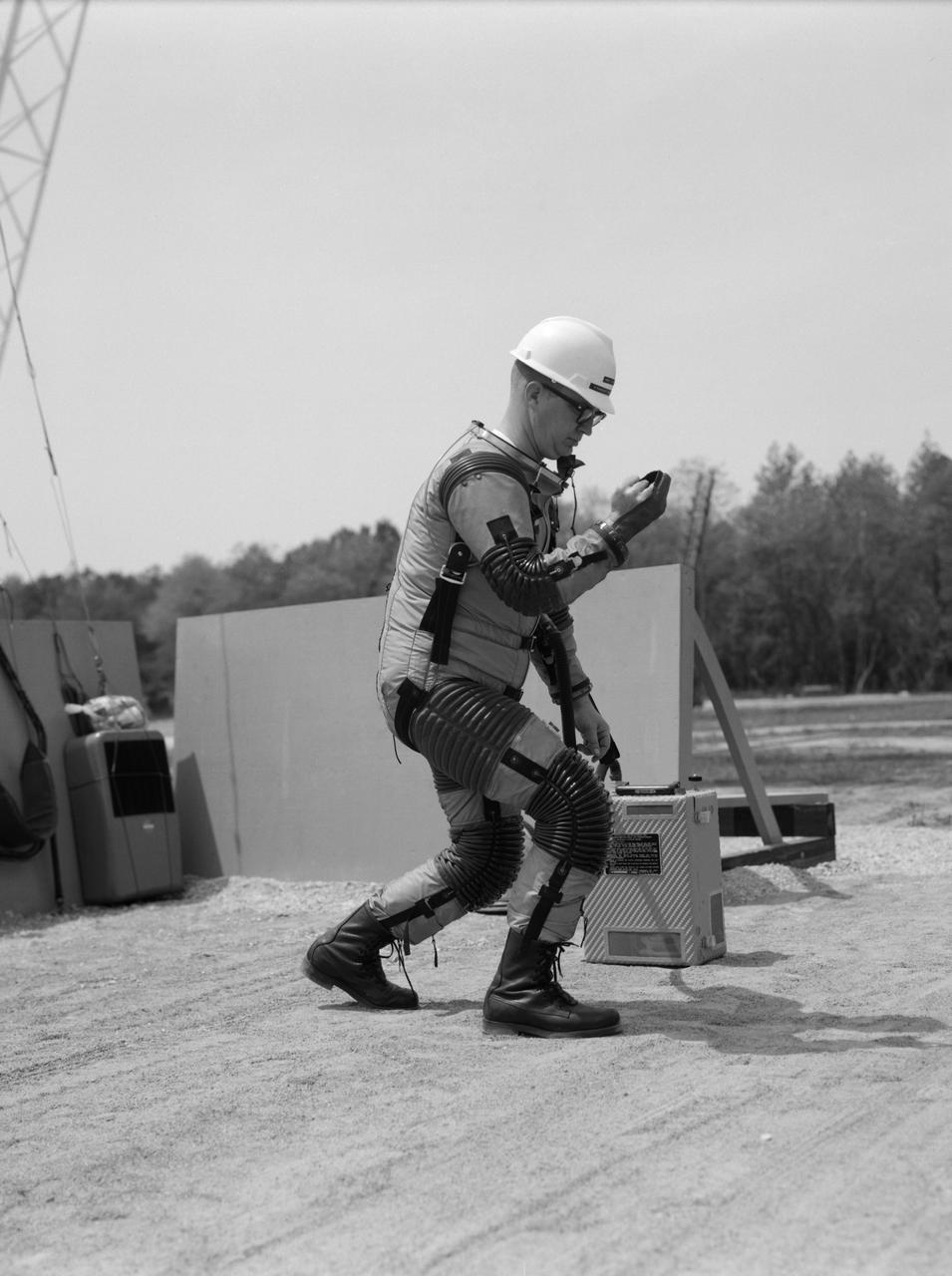

Special "space" suit for the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
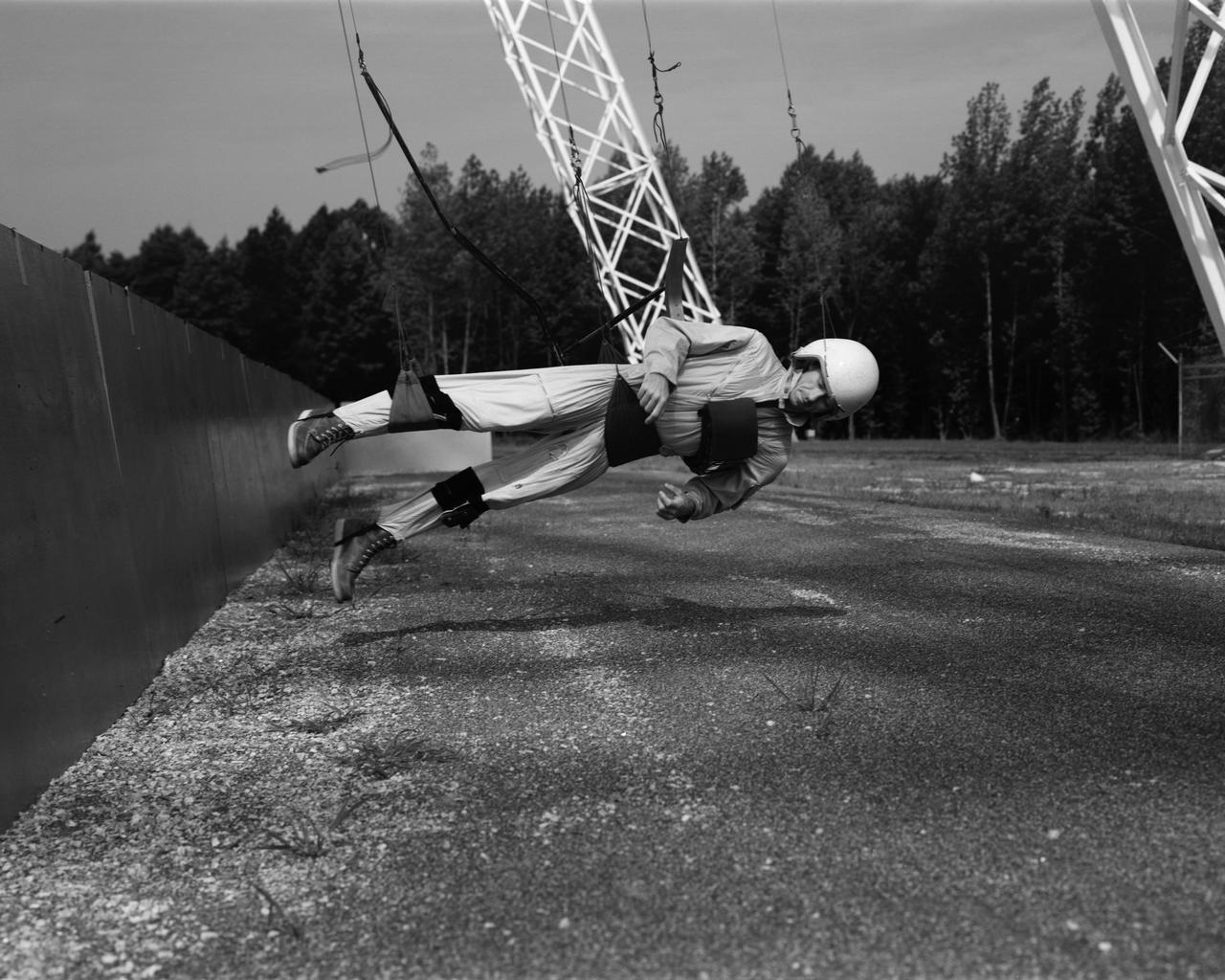

Astronaut Walt Cunningham on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
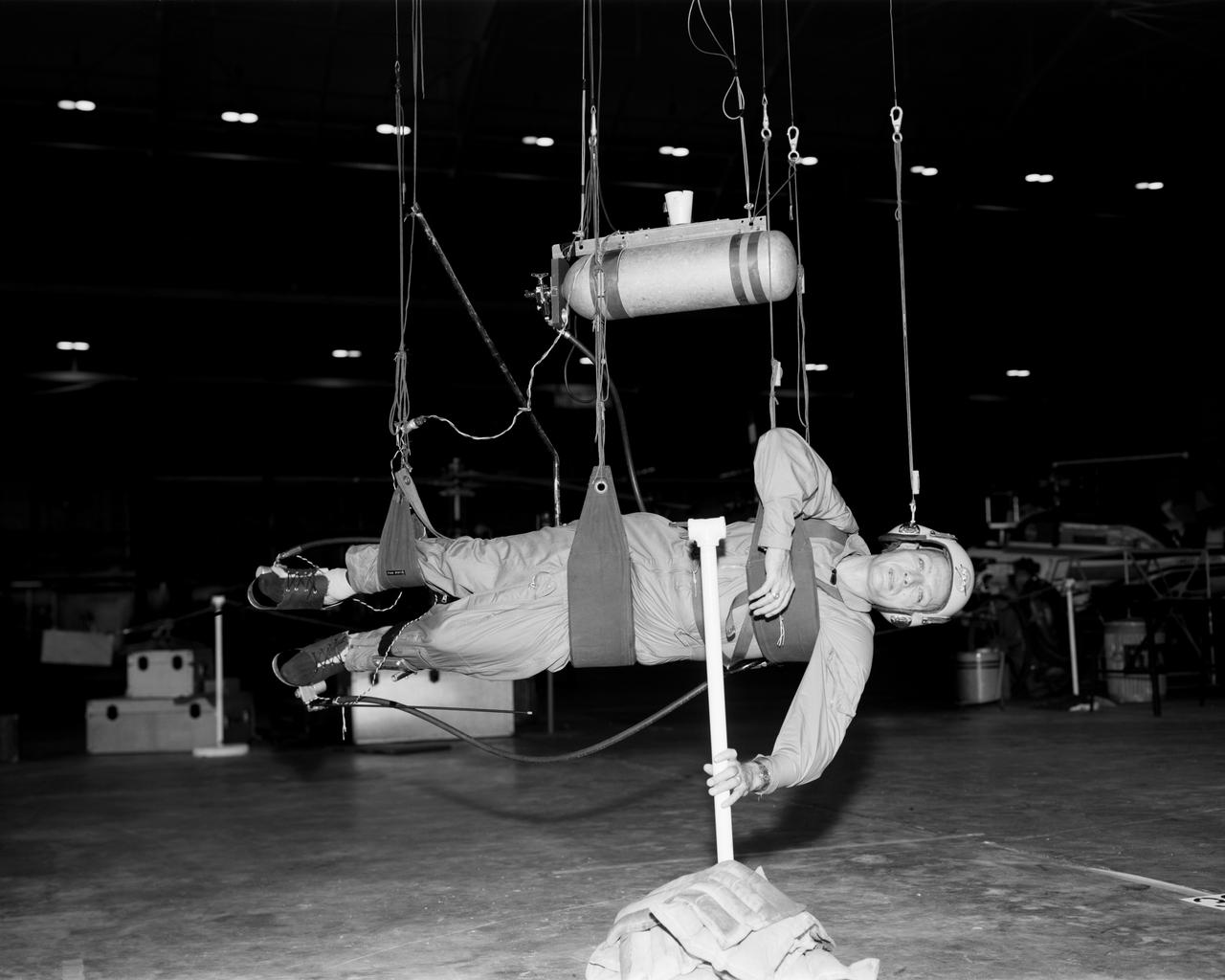

Cable system which supports the test subject on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator as follows: "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995); A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
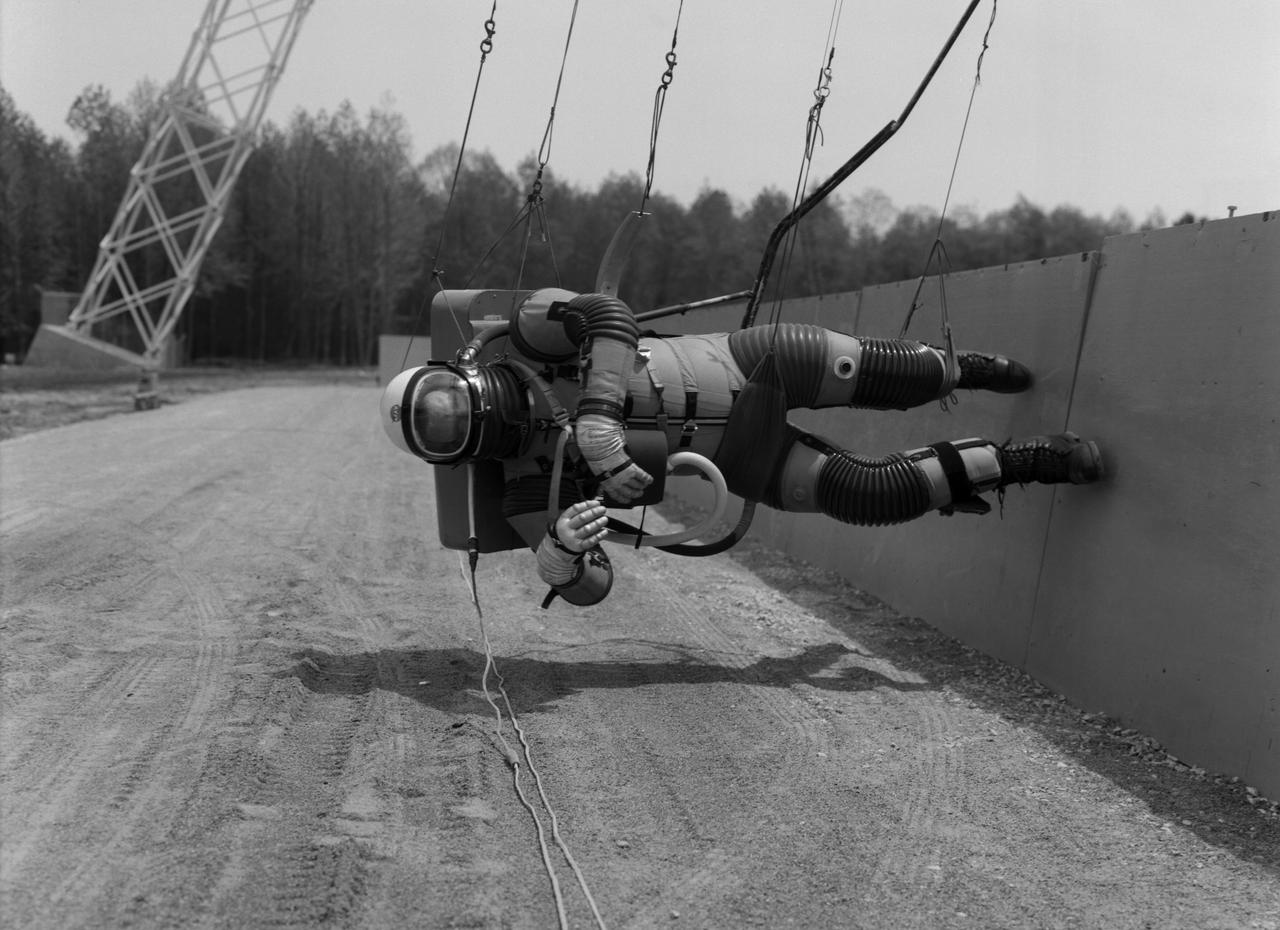

Test subject wearing the pressurized "space" suit for the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
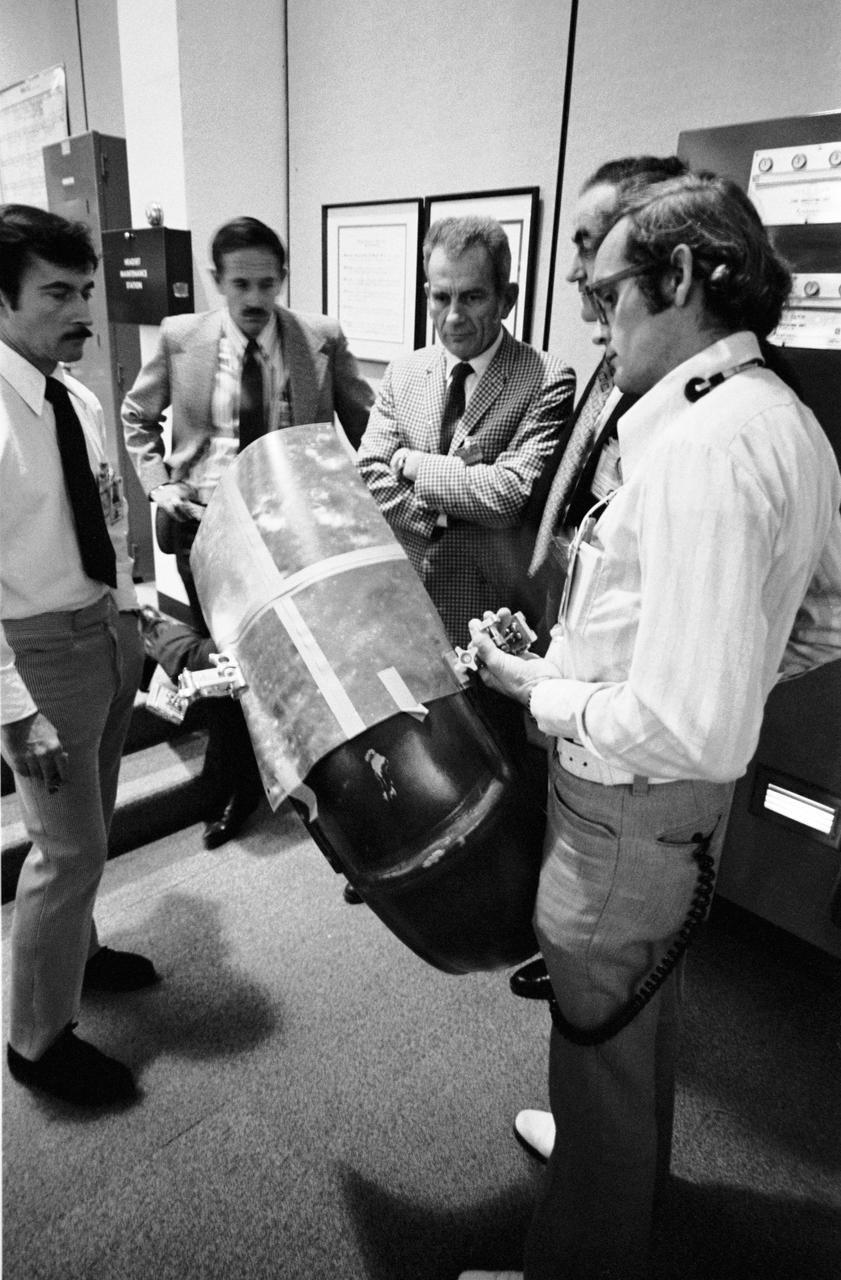

S72-55170 (11 Dec. 1972) --- These five men in the Mission Control Center ponder the solution to the problem of the damage to the right rear fender of the Apollo 17 Lunar Roving Vehicle at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. During the first lunar surface extravehicular activity a hammer got underneath the fender and a part of it was knocked off. Astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt were reporting a problem with lunar dust because of the damaged fender. They sought some way to repair the broken fender. Clockwise are astronauts John W. Young and Charles M. Duke Jr., two Apollo 17 CAPCOM; Donald K. Slayton, director of flight crew operations at MSC; Dr. Roco A. Petrone, Apollo program director, Office of Manned Space Flight, NASA HQ; and Ronald V. Blevins, an EVA-1 flight controller with General Electric. They are looking over a makeshift repair arrangement which uses lunar maps and clamps from the optical alignment telescope lamp, a repair suggestion made by astronaut Young. The suggestion was relayed to Cernan and Schmitt and the repair made at the beginning of EVA-2. The problem was solved satisfactorily.
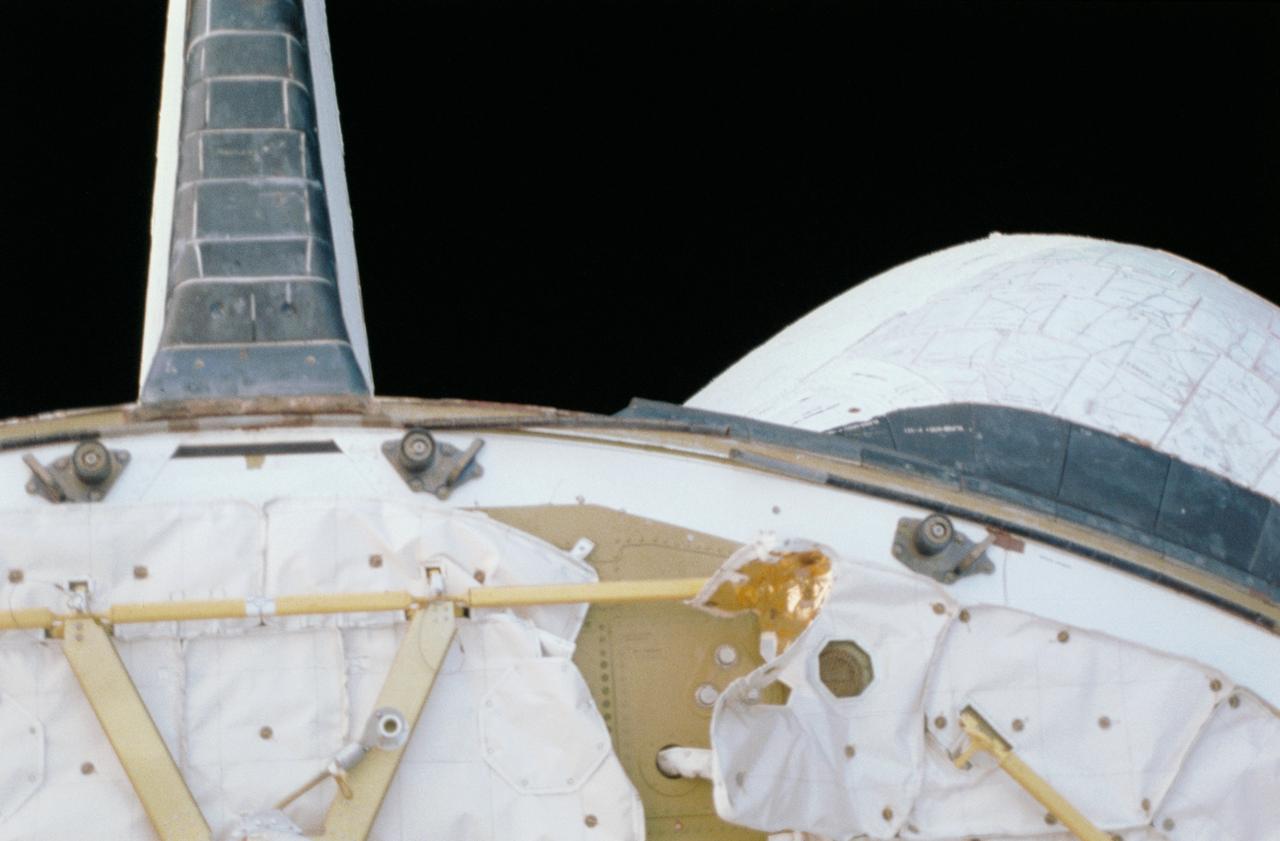

STS040-031-030 (5-14 June 1991) --- Early on the first day of STS-40, the crew noticed that some of the thermal material on the aft firewall had loosened. They shot this 35mm frame of the area, which proved to pose no problems for the flight.
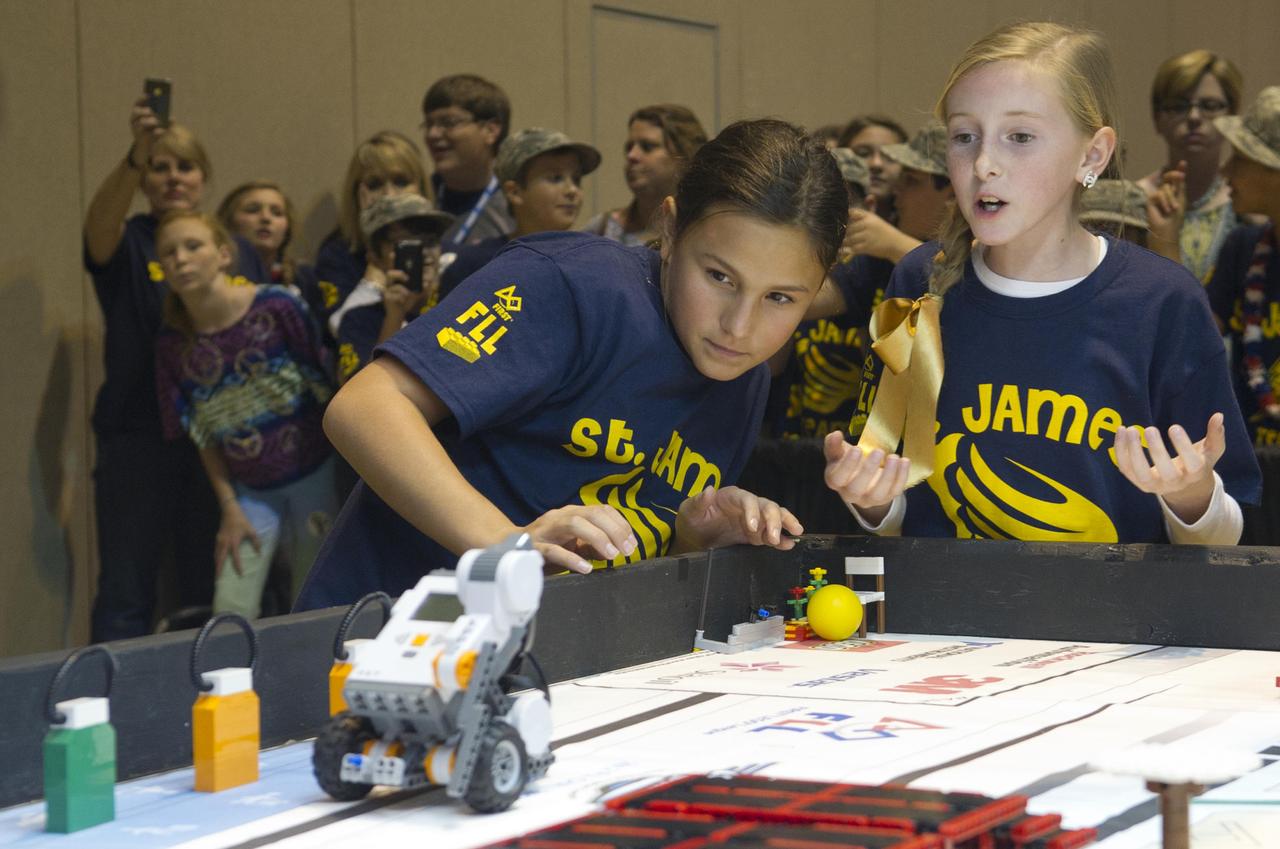

Two students anxiously watch their robot during the 2012 FIRST LEGO League Mississippi Championship Tournament in Hattiesburg, Miss., on Dec. 1. In addition to competing with robots, students presented research on this year's 'Senior Solutions' theme, which focused on addressing problems faced by senior adults.
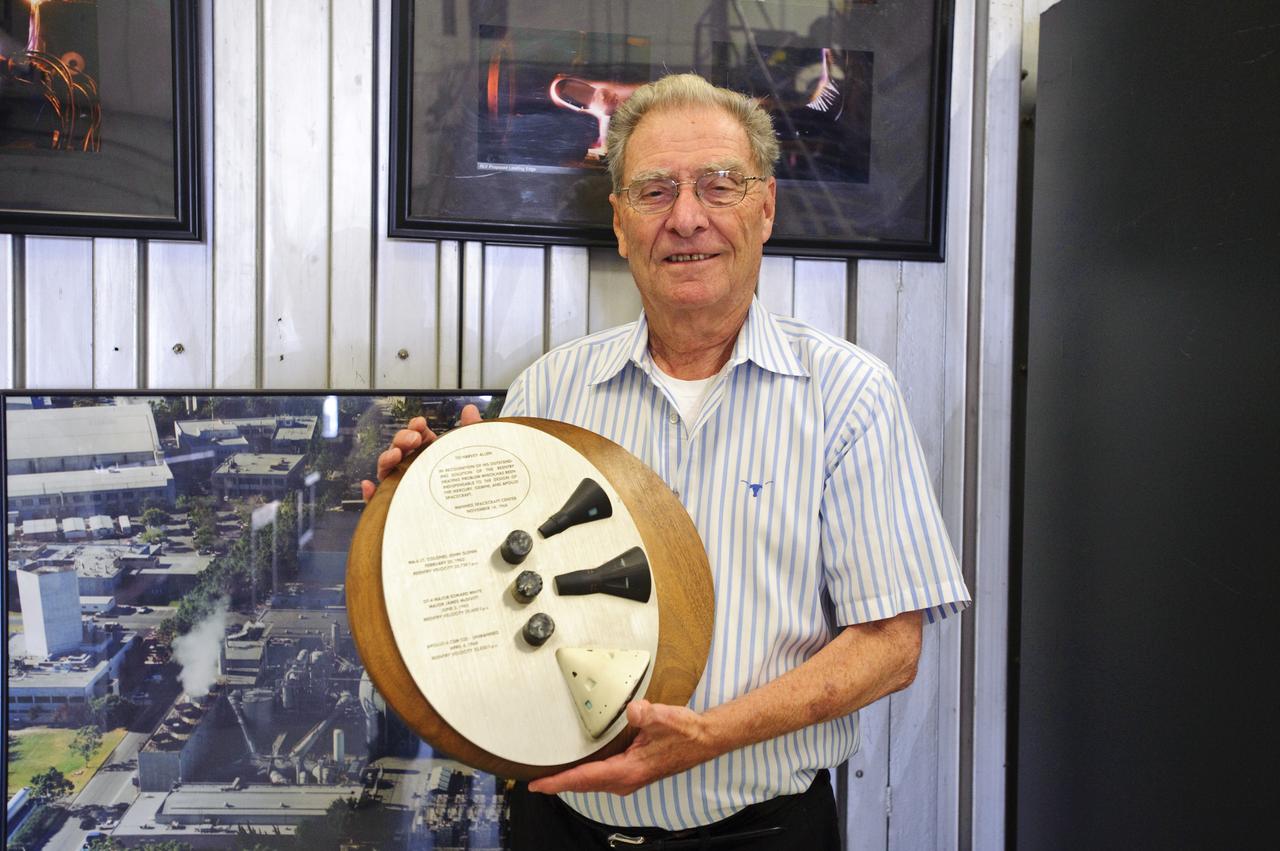

John W. 'Jack Boyd holds a plaque presented to Harvey Allen in recognition of his outstanding solution of the reentry heating problem which has been indispensable to the design of the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo spacecraft (Manned Spacecraft Center, November 14, 1968) Plaque contains samples of tested materials and models of spacecraft.
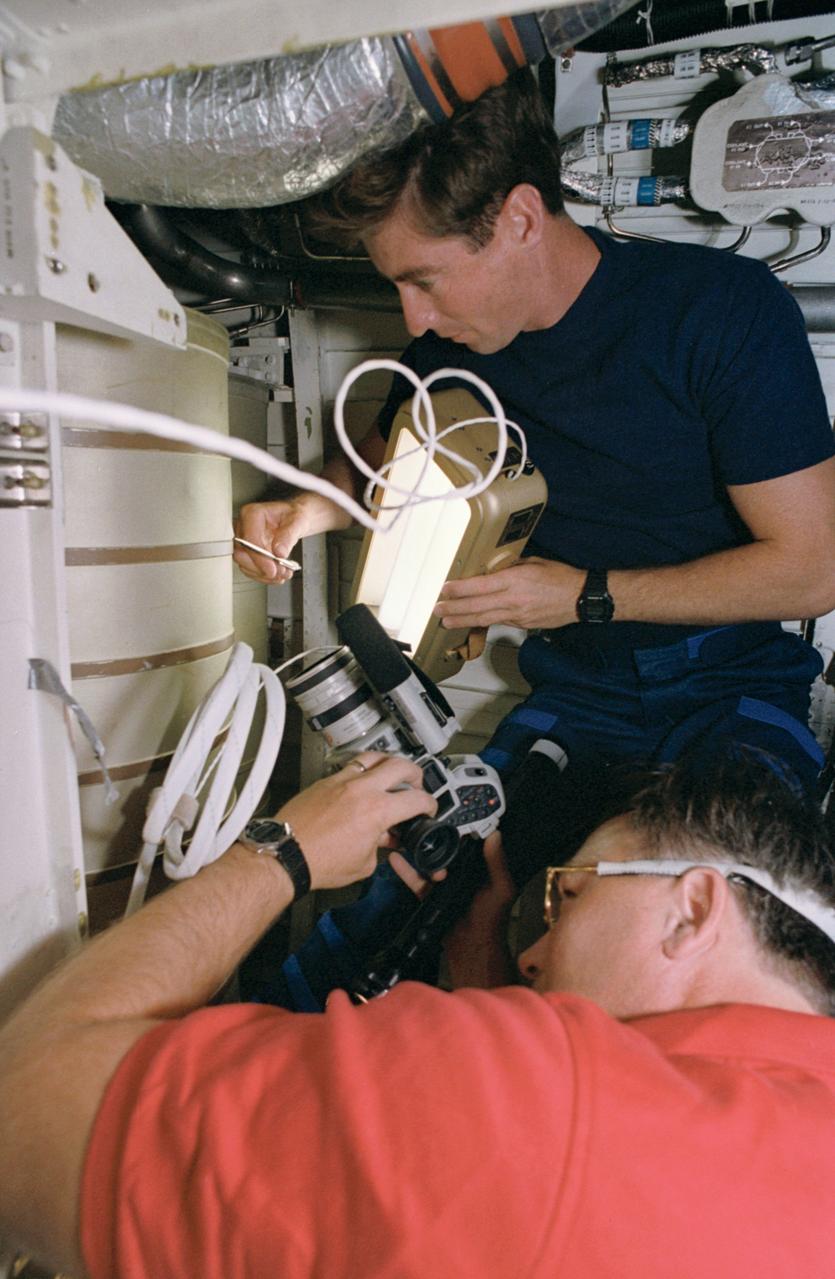

STS055-39-036 (26 April-6 May 1993) --- Astronaut Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, pilot, uses a spotlight and pen to point out a possible problem area on a waste water tank in the bilge area below Columbia's middeck. Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, payload commander, records the activity with a camera.
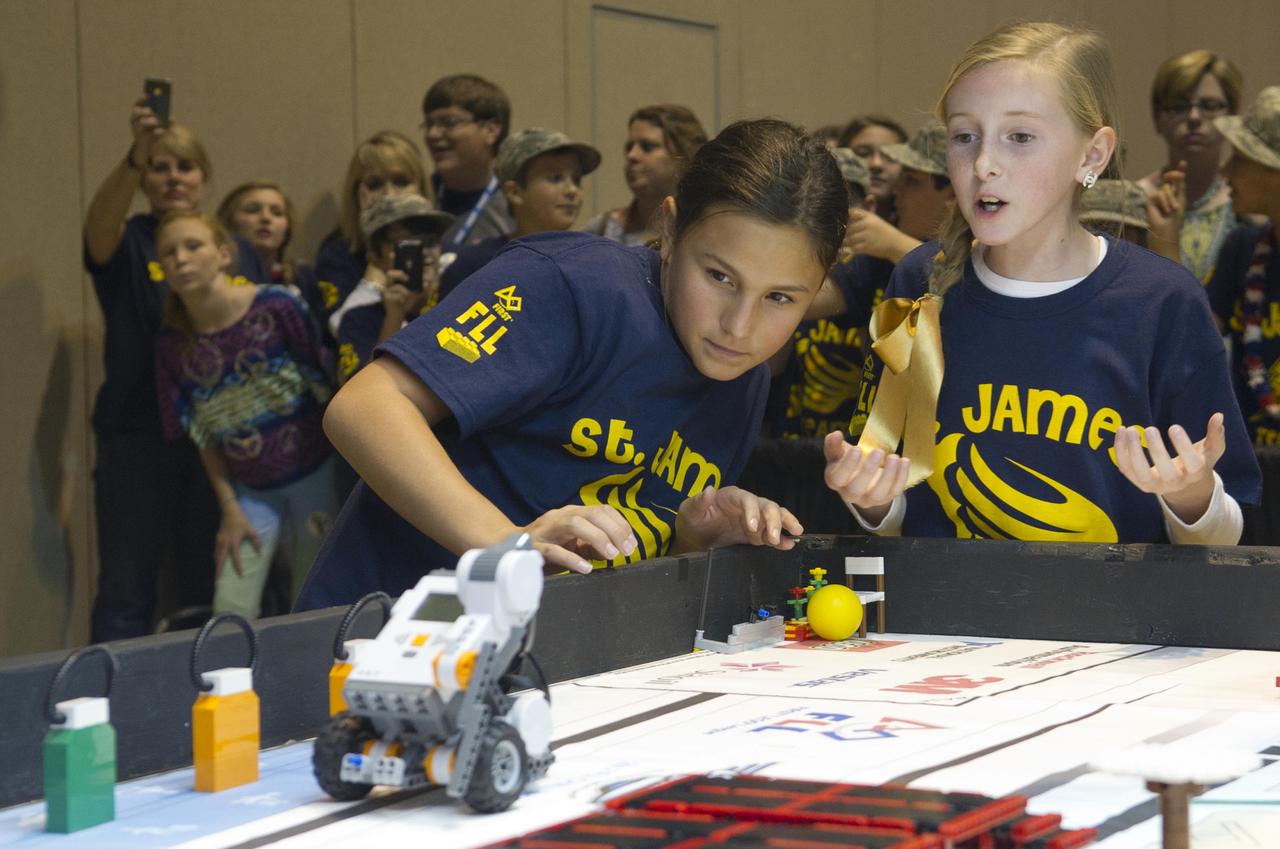

Two students anxiously watch their robot during the 2012 FIRST LEGO League Mississippi Championship Tournament in Hattiesburg, Miss., on Dec. 1. In addition to competing with robots, students presented research on this year's 'Senior Solutions' theme, which focused on addressing problems faced by senior adults.
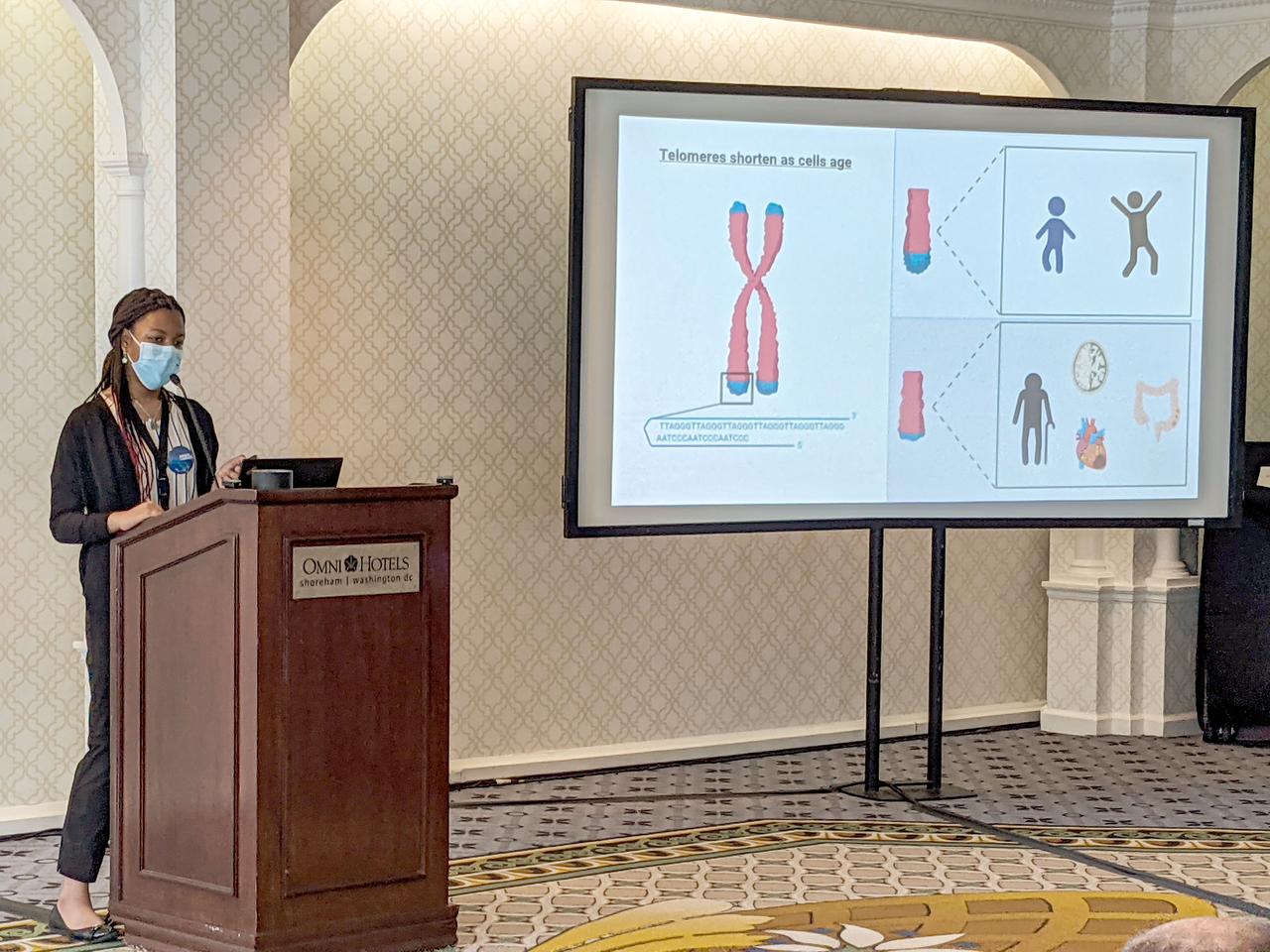

jsc2023e031078 (7/27/2022) --- Pristine Onuoha, Genes in Space-10 winner, presents her idea to contest judges. The Genes in Space program allows for 10 student projects to be selected for spaceflight analysis, which gives students a chance to attempt to solve real-world problems. Image courtesy of Genes in Space.
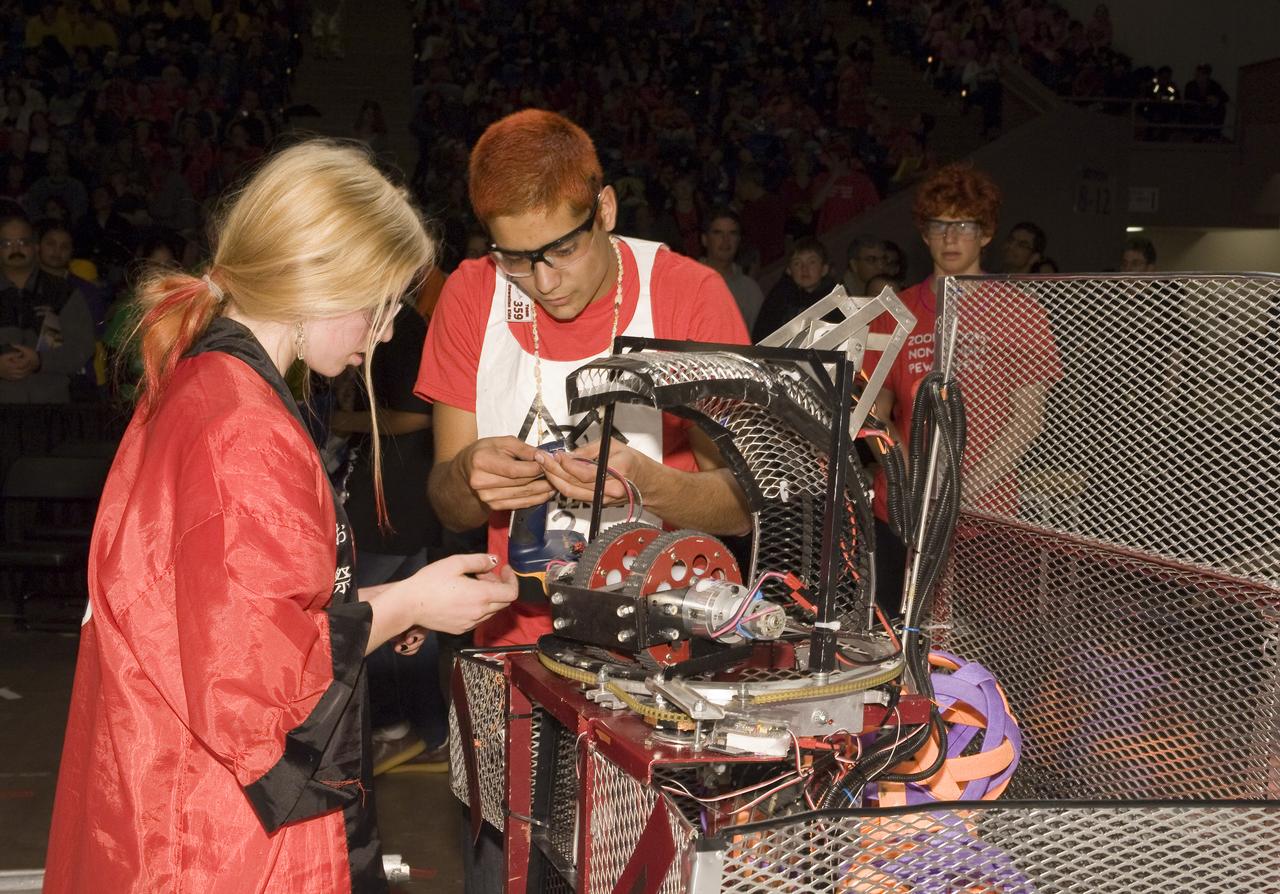

FIRST Robotics Competition 'Lunacy' hosted by NASA at San Jose State University Event Center. For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology let the games begin. Ragin' C-Biscuits of San Ramon Valley High team #1280 and the Hawaiian Kids team #359 look over a problem bot.
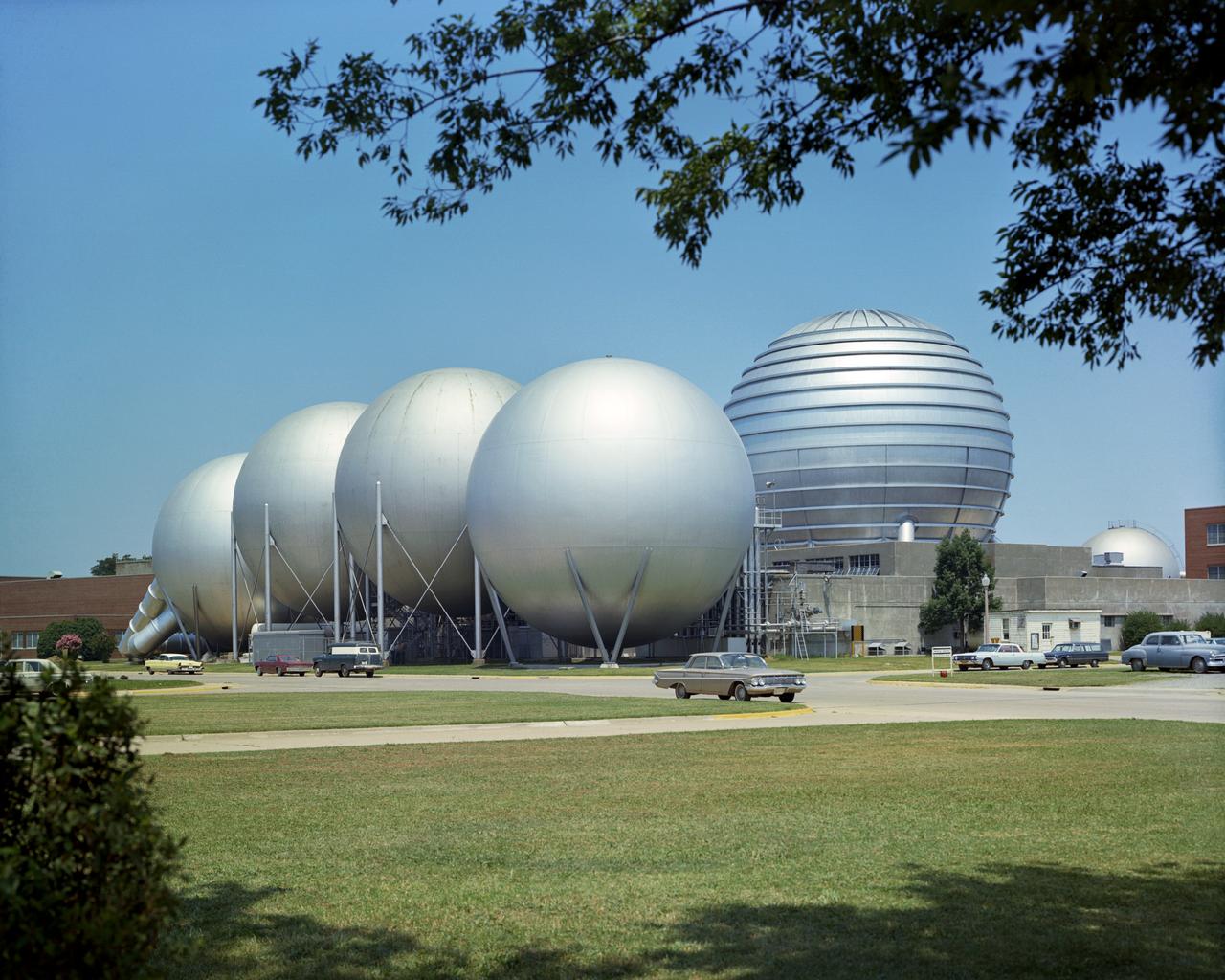

L65-5505 In the Gas Dynamics Laboratory, completed in 1951, researchers explored basic aerodynamic, heating and fluid-mechanical problems in the speed range from Mach 1.5 to Mach 8.0. Photograph published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen. Page 348.
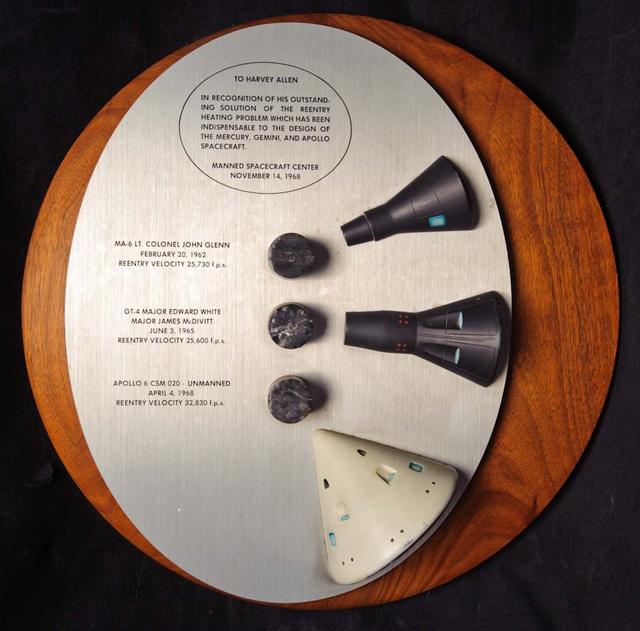

A plaque presented to Harvey Allen in recognition of his outstanding solution of the reentry heating problem which has been indispensable to the design of the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo spacecraft (Manned Spacecraft Center, November 14, 1968) Plaque contains samples of tested materials and models of spacecraft.
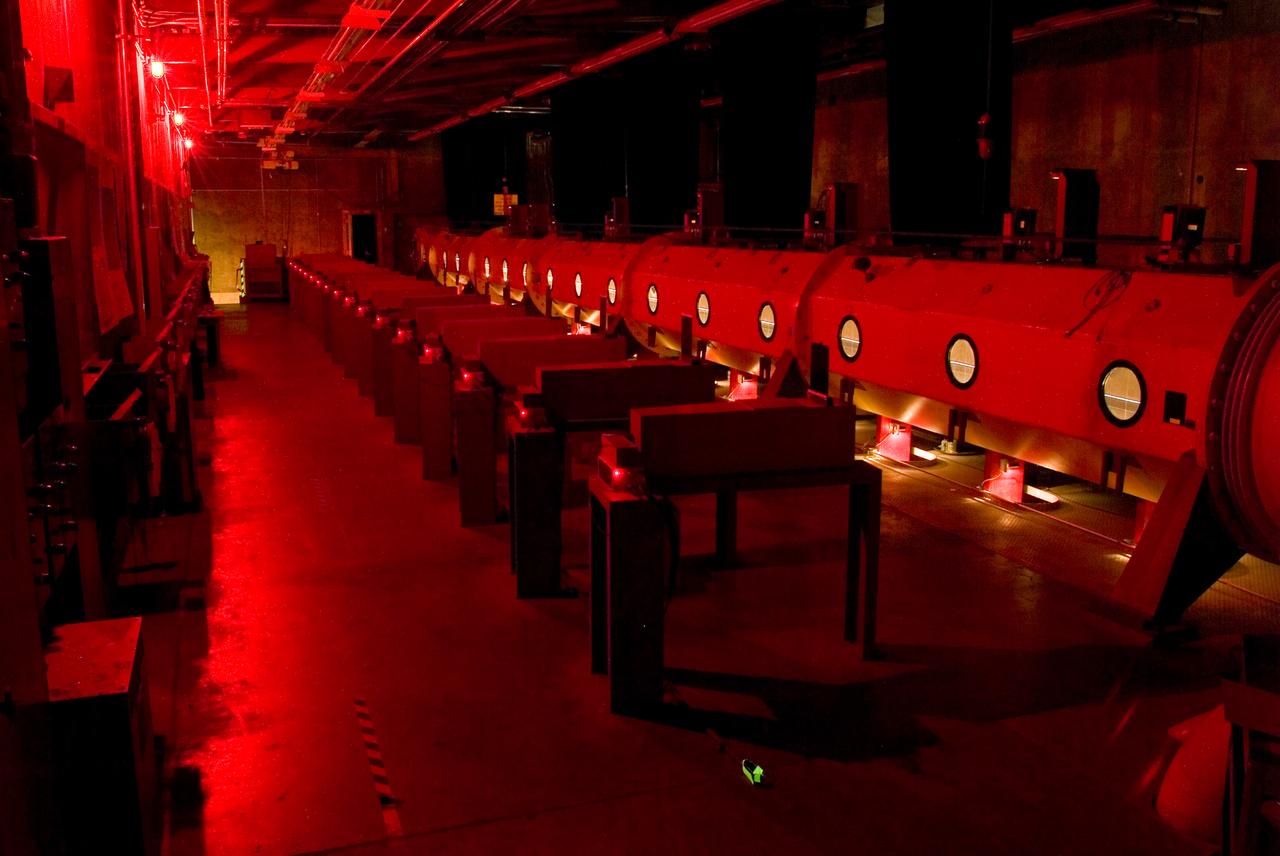

Ames Hypersonic Free Flight Aerodynamic Facility is used for research on gas dynamic problems of atmospheric entry. High relative speeds are achieved by launching models (in sabots if necessary) from high-speed guns into a countercurrent hypersonic air stream (14,000 ft/sec) driven by combustion-powered shock tube.
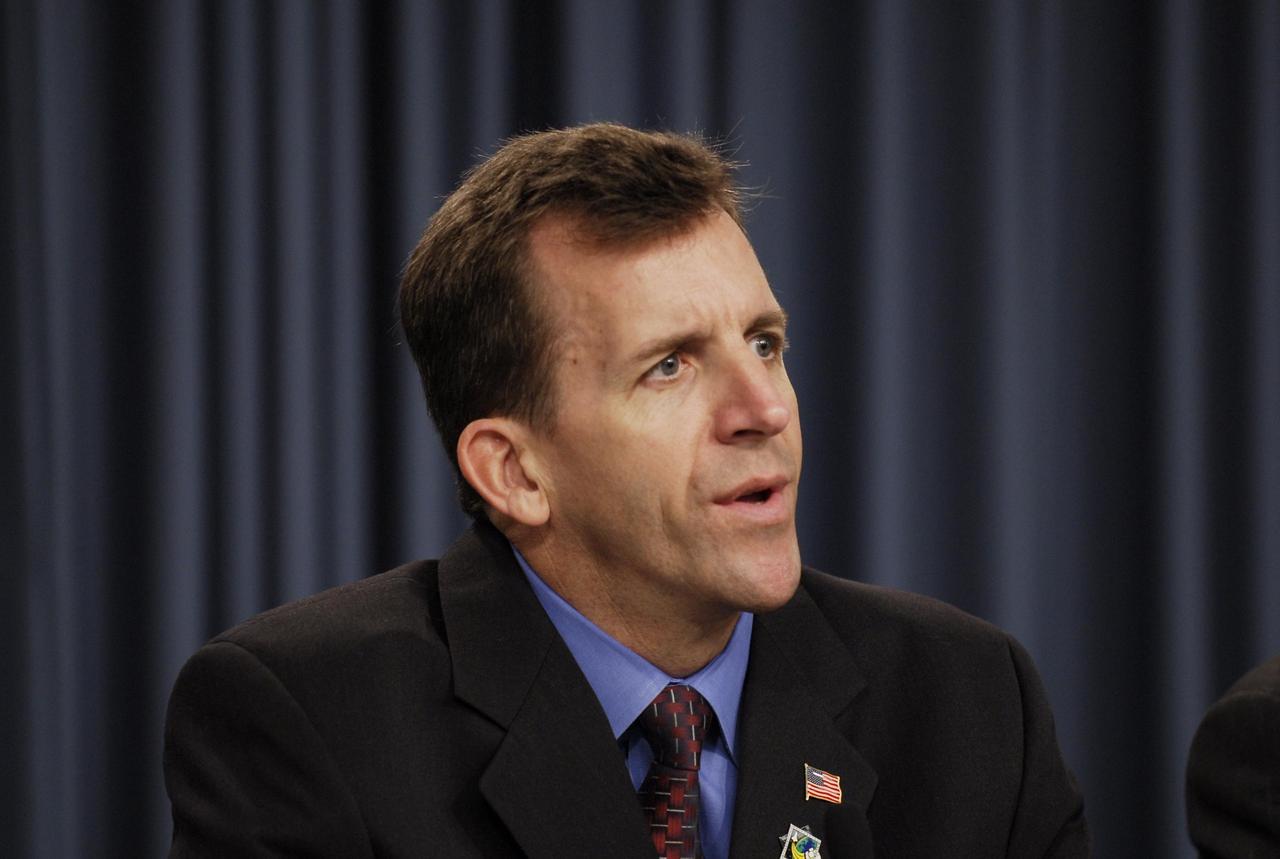

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- LeRoy Cain, the Mission Management Team chairman, participates in a news briefing following the conclusion of a team meeting. The meeting followed the morning's launch scrub caused by problems experienced with the space shuttle Atlantis STS-122 external tank's engine cutoff sensor system during tanking for the second launch attempt. An announcement was made during the briefing that the STS-122 launch is postponed to no earlier than Jan. 2, 2008, to give the team time to resolve the system's problems. Atlantis will carry the Columbus Laboratory, the European Space Agency's largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station. It will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. Permanently attached to the Harmony node of the space station, the laboratory will carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as perform a number of technological applications. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
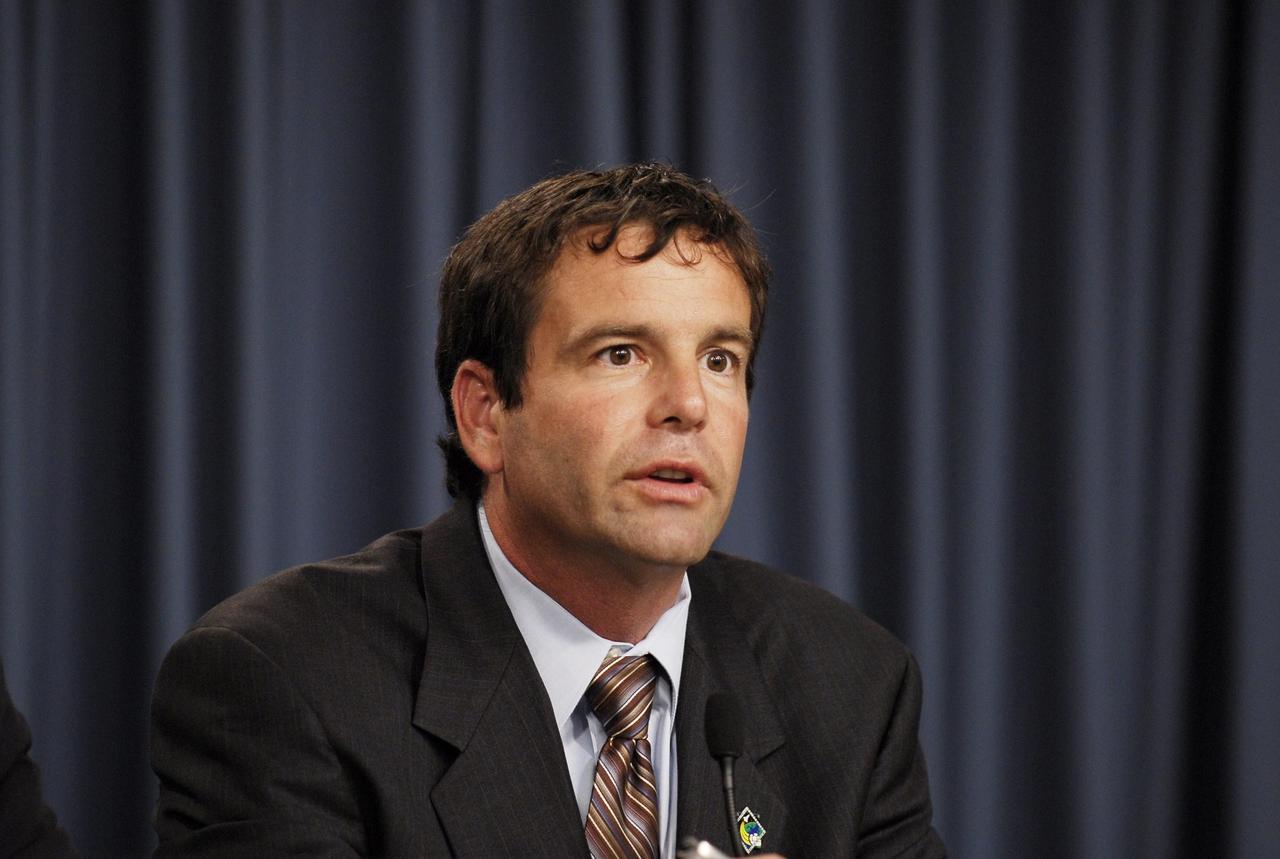

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Doug Lyons, STS-122 launch director, participates in a news briefing following the conclusion of a Mission Management Team, or MMT, meeting. The meeting followed the morning's launch scrub of the space shuttle Atlantis STS-122 mission caused by problems experienced with the external tank's engine cutoff sensor system during tanking for the second launch attempt. An announcement was made during the briefing that the STS-122 launch is postponed to no earlier than Jan. 2, 2008, to give the team time to resolve the system's problems. Atlantis will carry the Columbus Laboratory, the European Space Agency's largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station. It will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. Permanently attached to the Harmony node of the space station, the laboratory will carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as perform a number of technological applications. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Bill Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for Space Operations, participates in a news briefing following the conclusion of a Mission Management Team, or MMT, meeting. The meeting followed the morning's launch scrub of the space shuttle Atlantis STS-122 mission caused by problems experienced with the external tank's engine cutoff sensor system during tanking for the second launch attempt. An announcement was made during the briefing that the STS-122 launch is postponed to no earlier than Jan. 2, 2008, to give the team time to resolve the system's problems. Atlantis will carry the Columbus Laboratory, the European Space Agency's largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station. It will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. Permanently attached to the Harmony node of the space station, the laboratory will carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as perform a number of technological applications. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
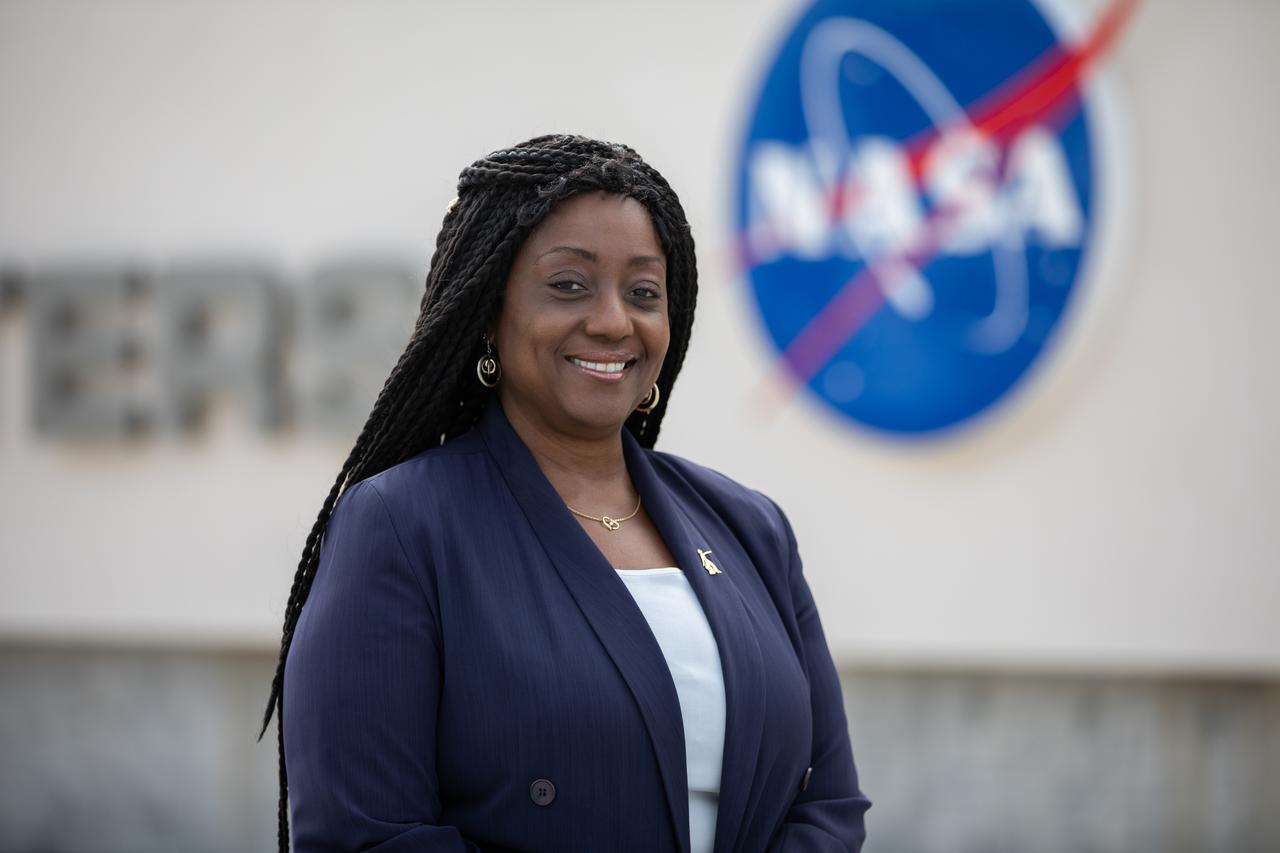

"I’ve worked in many different roles and what drives my passion is learning things that I don’t know. It is a part of my thirst for knowledge and knowing how things work. The harder the problem for me the better. When I first joined NASA as a full time employee, my supervisor would give me an assignment, and I would get it done quickly and come back to his desk and ask, ‘What do you have for me now?’ At one point, after about two months of working for him, he looked at me and kind of sighed. I said, ‘Okay, okay. If you don’t have anything for me right now, is it okay if I see if any of the other supervisors in the building need any help with anything?’ He agreed, and so I approached the other supervisors. "Now, here’s the interesting thing. I was a young Black female in an engineering role that was pretty much dominated by white males at the time, so it was not a norm for there to be females in the building – much less black females. I came to understand later that there was some skepticism on their part that I could do design engineering. I didn’t know that some of them, not all of them, were throwing things at me to show me I wasn’t qualified. But I would tackle their problems the same way I do anything else: if I don’t know it, I’ll go find it. I’ll research. I’ll dig. I’ll look for people that might have some experience that I don’t have and ask them. So, every hard problem that they threw at me, I solved. Eventually, my supervisor told me he didn't know what he was getting into when he agreed to let me go to the other supervisors because now, they were coming to him with their hardest problems, asking, 'Hey, can Barbara help with this?' So, I started to broaden my experience base right away." — Barbara Brown, Director of Exploration Research and Technology Programs, Kennedy Space Center Interviewer: NASA / Tahira Allen
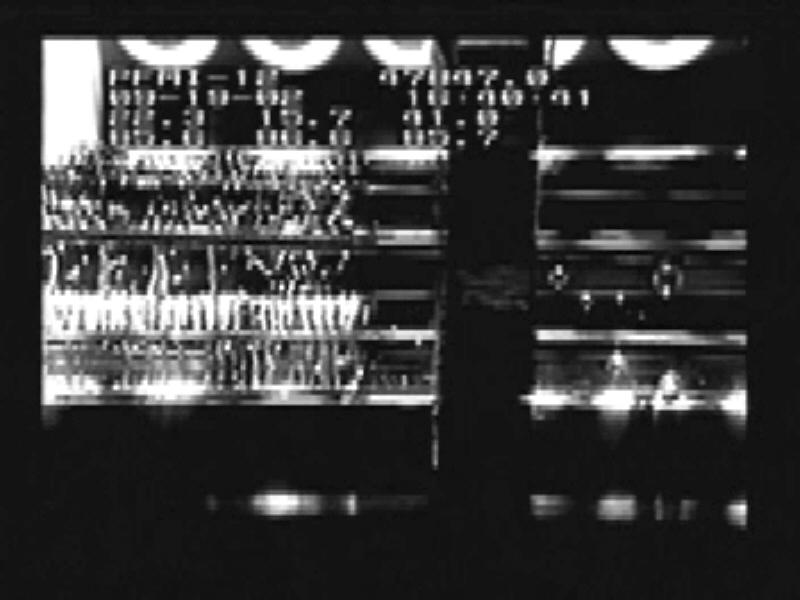

Video images sent to the ground allow scientists to watch the behavior of the bubbles as they control the melting and freezing of the material during the Pore Formation and Mobility Investigation (PFMI) in the Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. While the investigation studies the way that metals behave at the microscopic scale on Earth -- and how voids form -- the experiment uses a transparent material called succinonitrile that behaves like a metal to study this problem. The bubbles do not float to the top of the material in microgravity, so they can study their interactions.
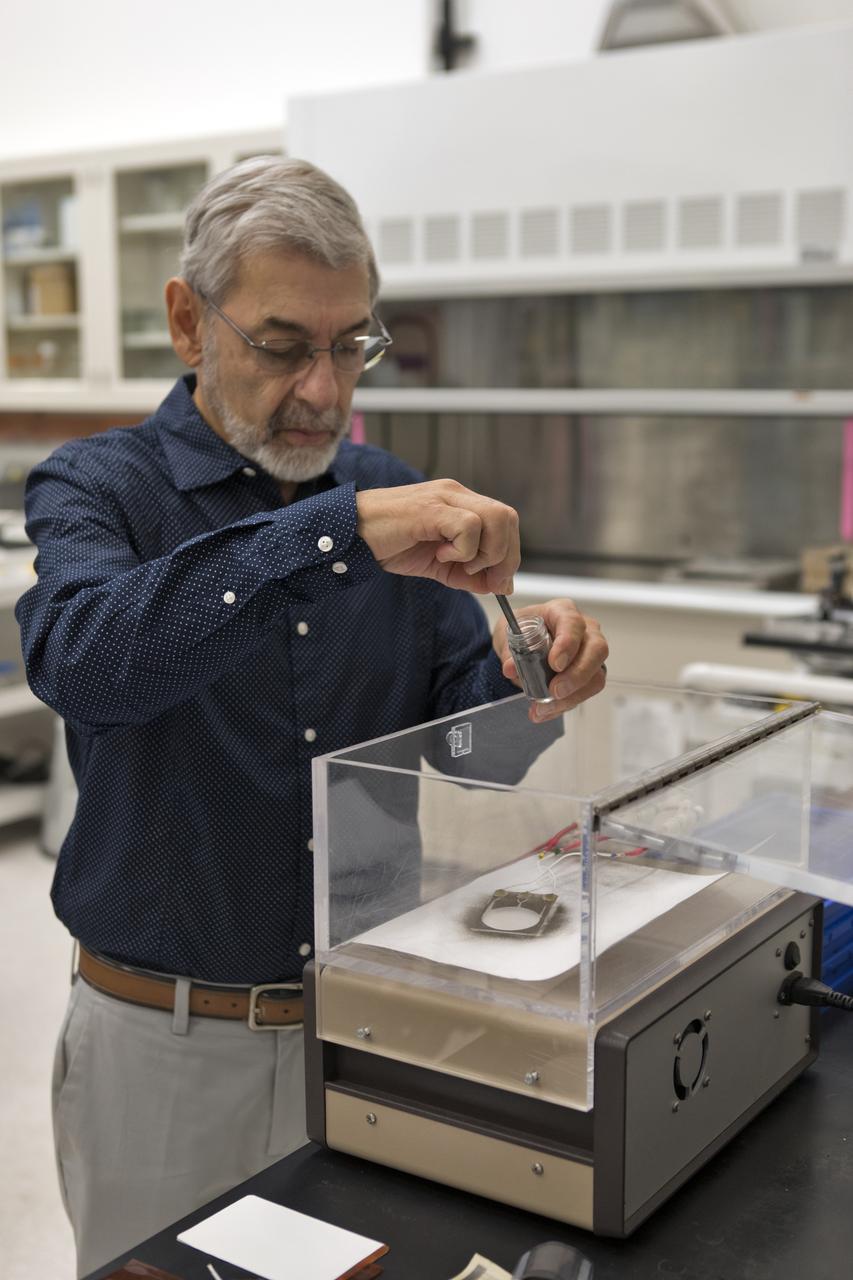

Dr. Carlos Calle, lead scientist in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares an Electrostatic Dust Shield for testing on Thursday, July 19, 2018. Scientists are developing the Electrostatic Dust Shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, astronauts' space suits and helmet visors of astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.
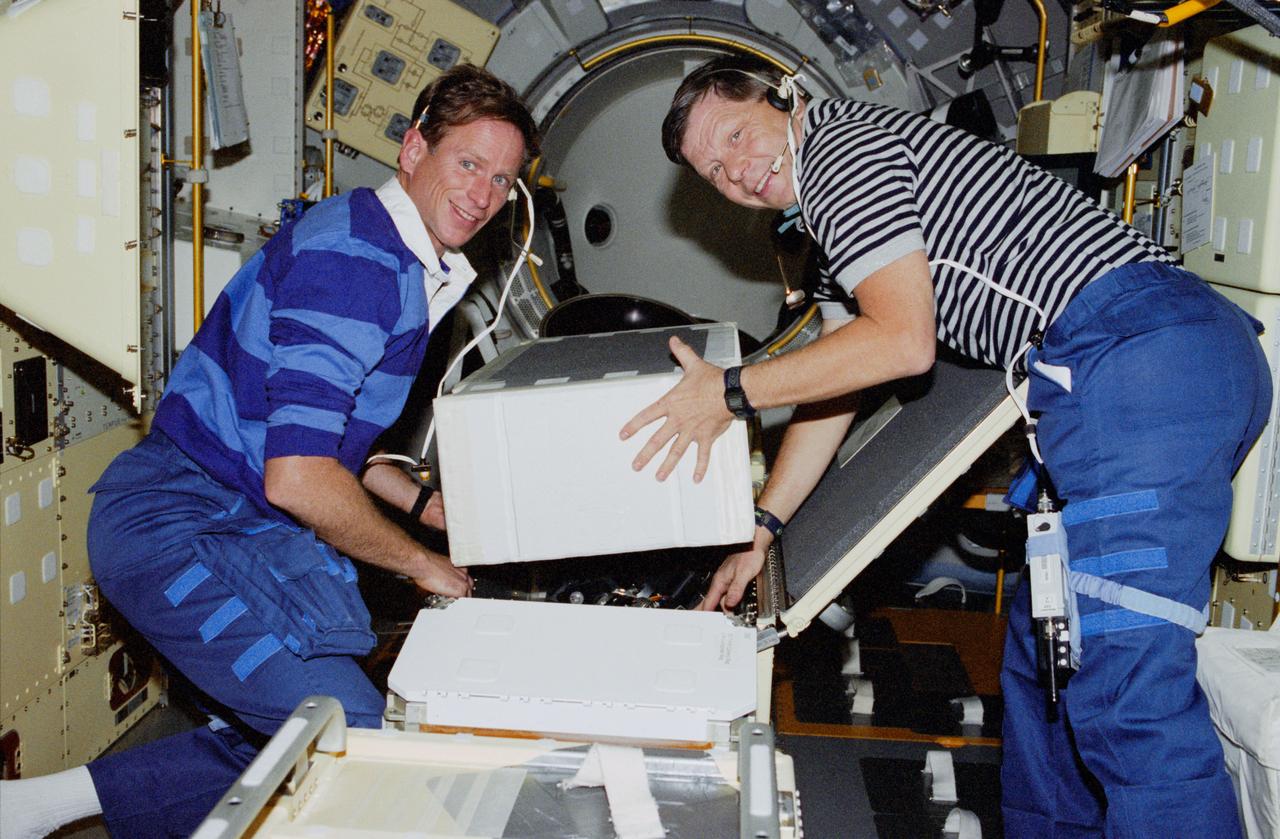

STS083-308-021 (4-8 April 1997) --- Payload specialist Roger K. Crouch and astronaut Michael L. Gernhardt, mission specialist, load boxes as they prepare to deactivate the Spacelab Science Module. Crouch and Gernhardt, along with five other NASA astronauts and a second payload specialist supporting the Microgravity Sciences Laboratory (MSL-1) mission, were less than a fourth of the way through a scheduled 16-day flight when a power problem cut short their planned stay.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Banks of lights dry tiles on orbiter Atlantis in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused the moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing
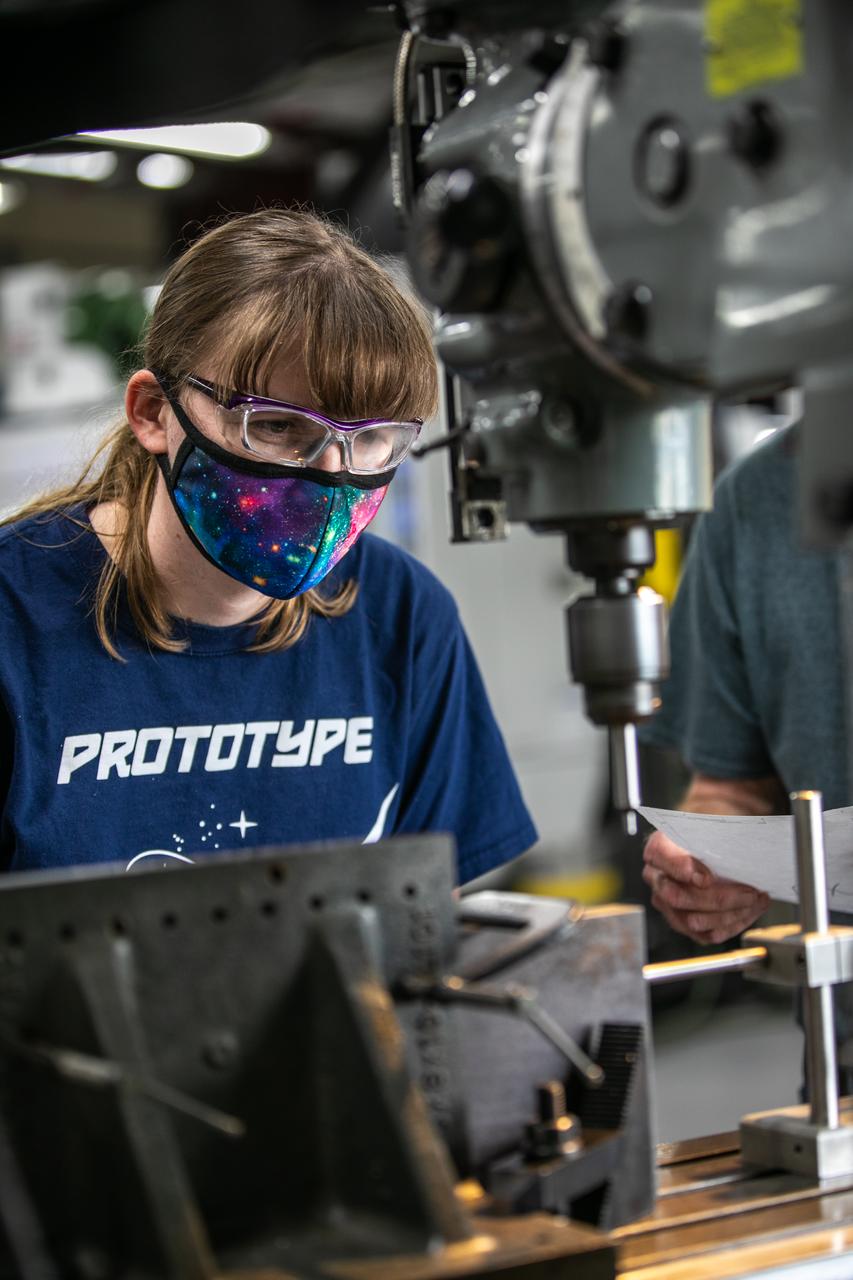

Katie Mortensen, a mechanical engineering technician, machines test article materials inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. The prototype laboratory designs, fabricates, and tests prototypes, test articles and test support equipment. It has a long history of providing fast solutions to complex operations problems. The lab’s teams of engineers use specialized equipment to produce exacting, one-of-a-kind items made from a range of materials depending on the design. The lab supports projects at Kennedy and at the agency level.
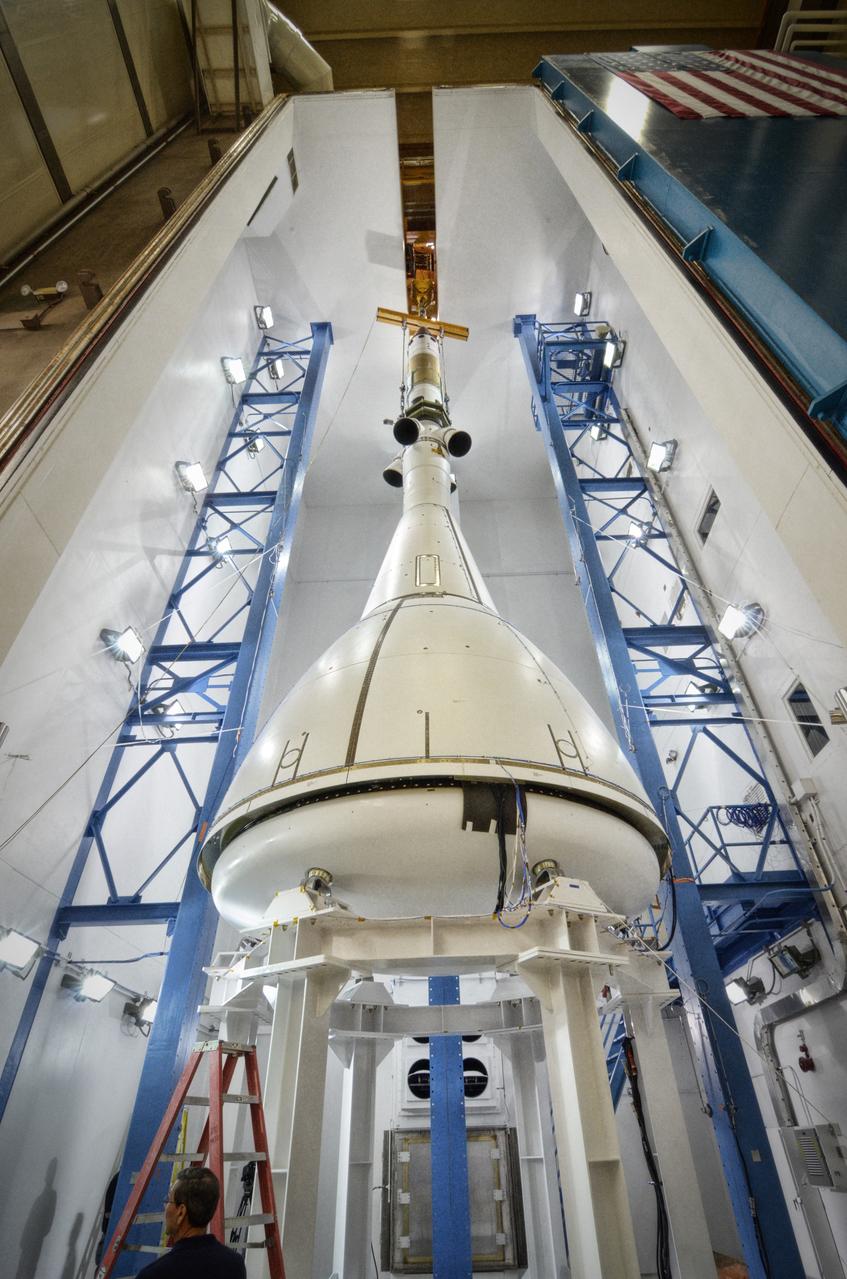

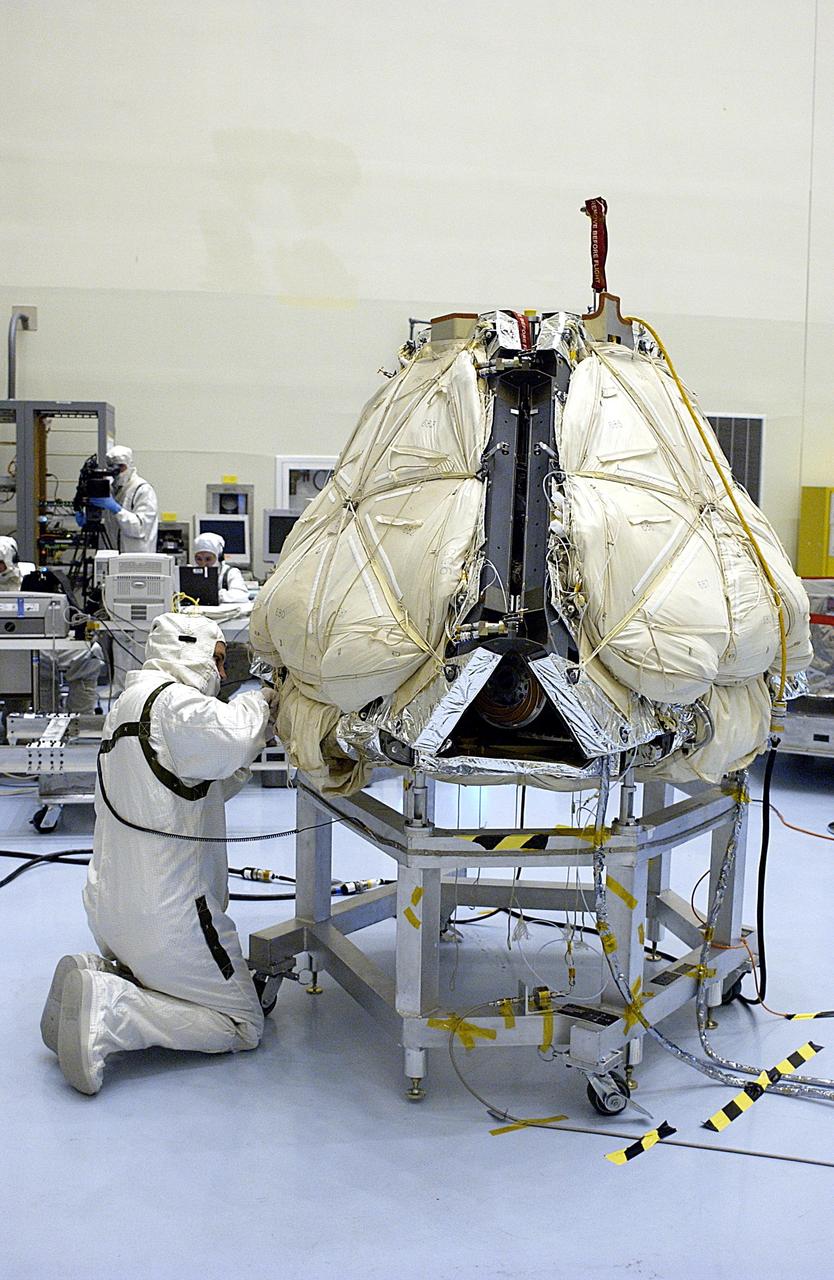
The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
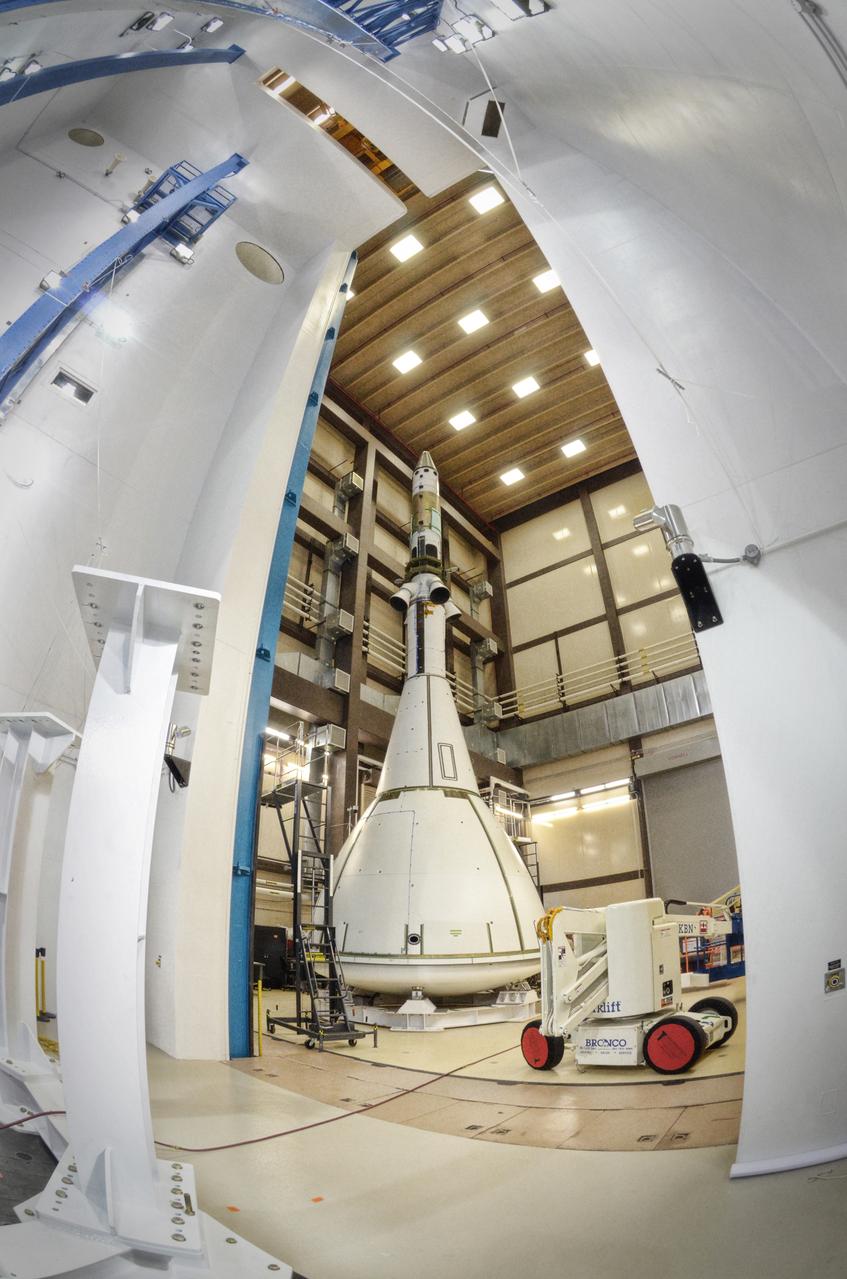

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
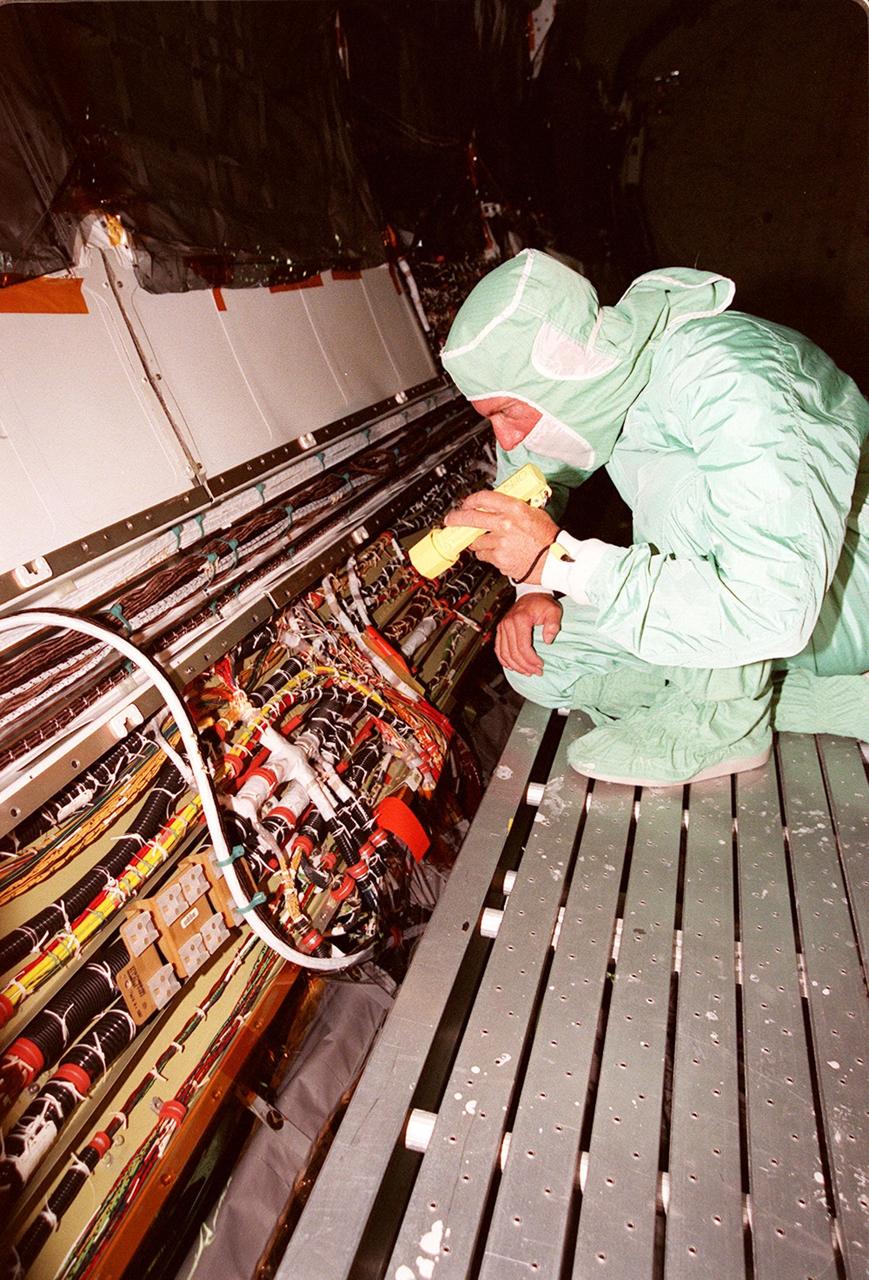

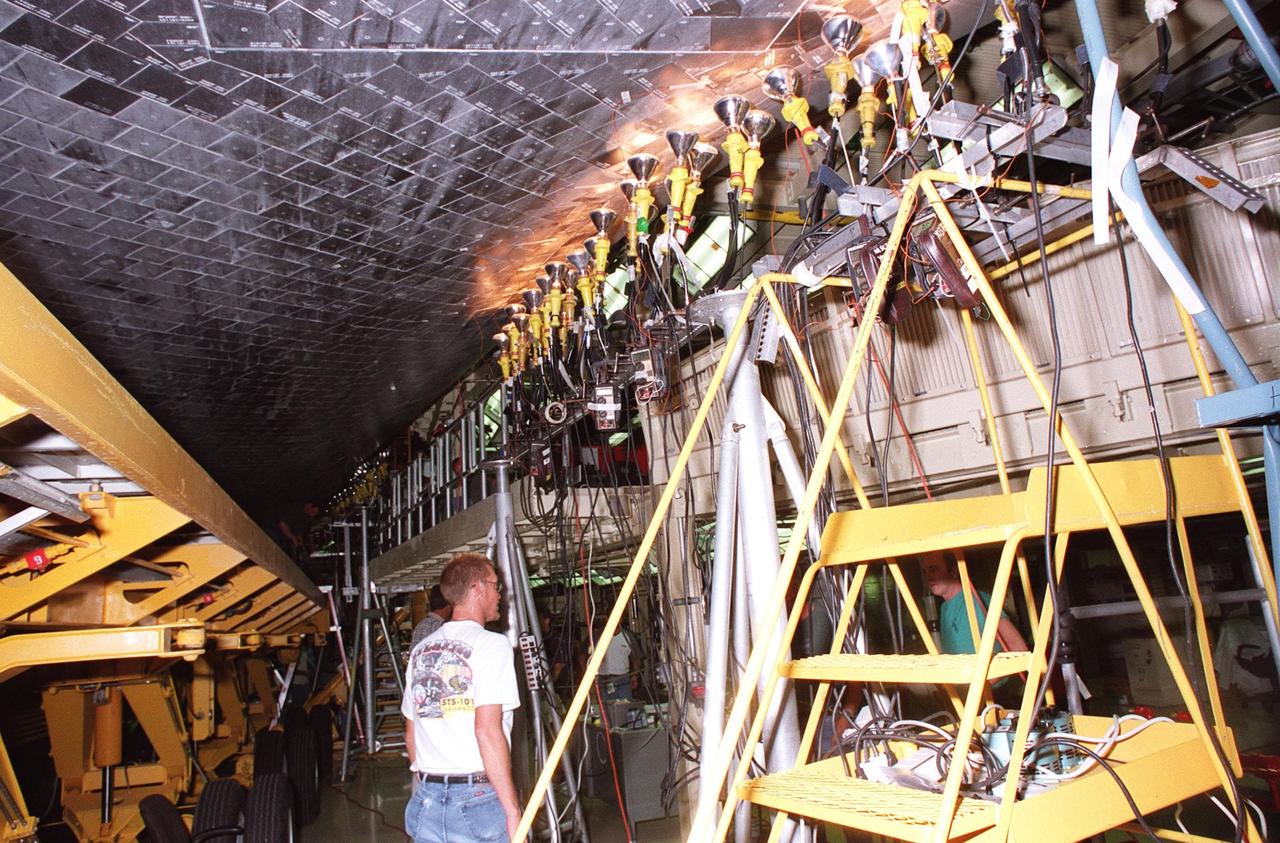
A short during liftoff of Space Shuttle Columbia in July was traced to a wire in the payload bay with damaged insulation. As a result of that problem, NASA decided to inspect much of the wiring in all four Space Shuttles and make repairs as required. Here a technician is examining the wires onboard orbiter Endeavour. The next Shuttle mission, STS-103, the Third Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, is currently scheduled for launch no earlier than Nov. 19, 1999
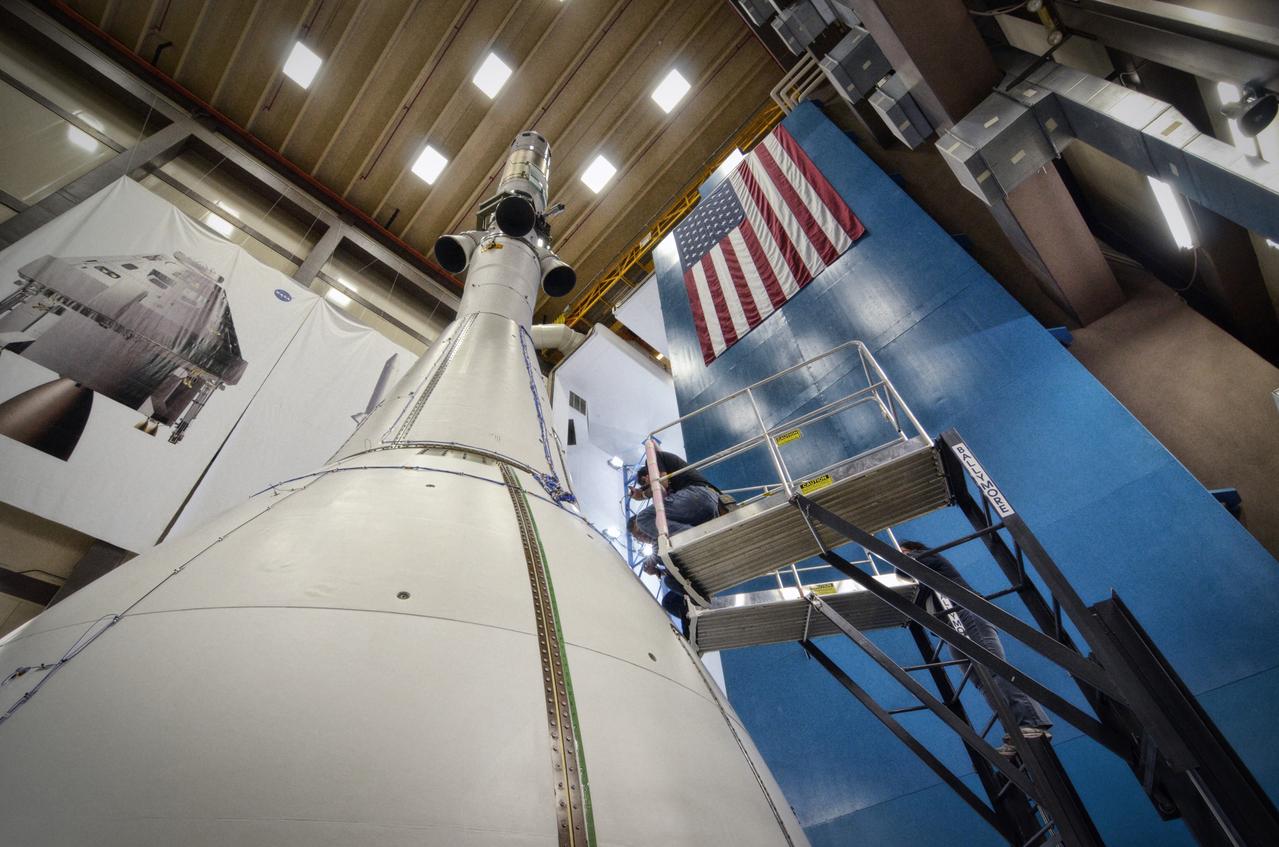

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 14, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
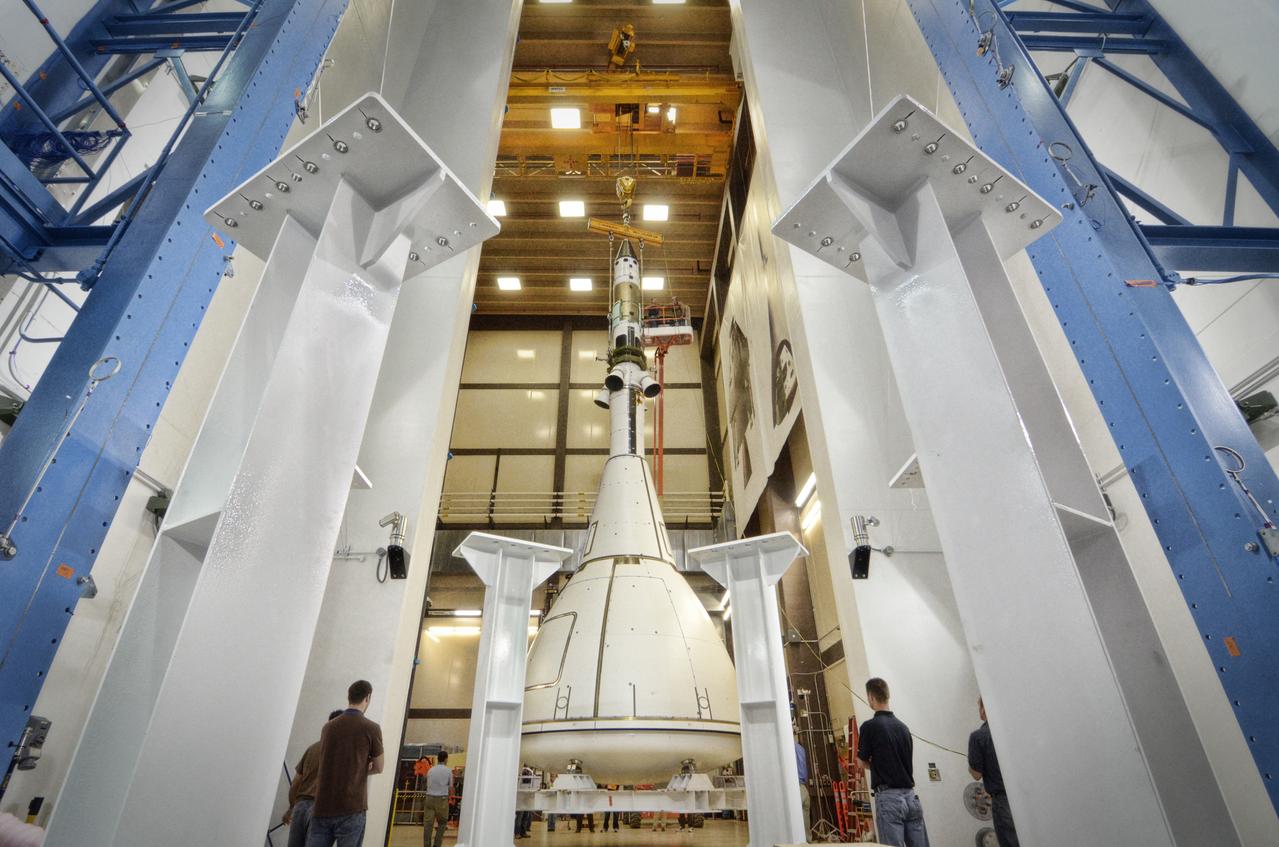

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
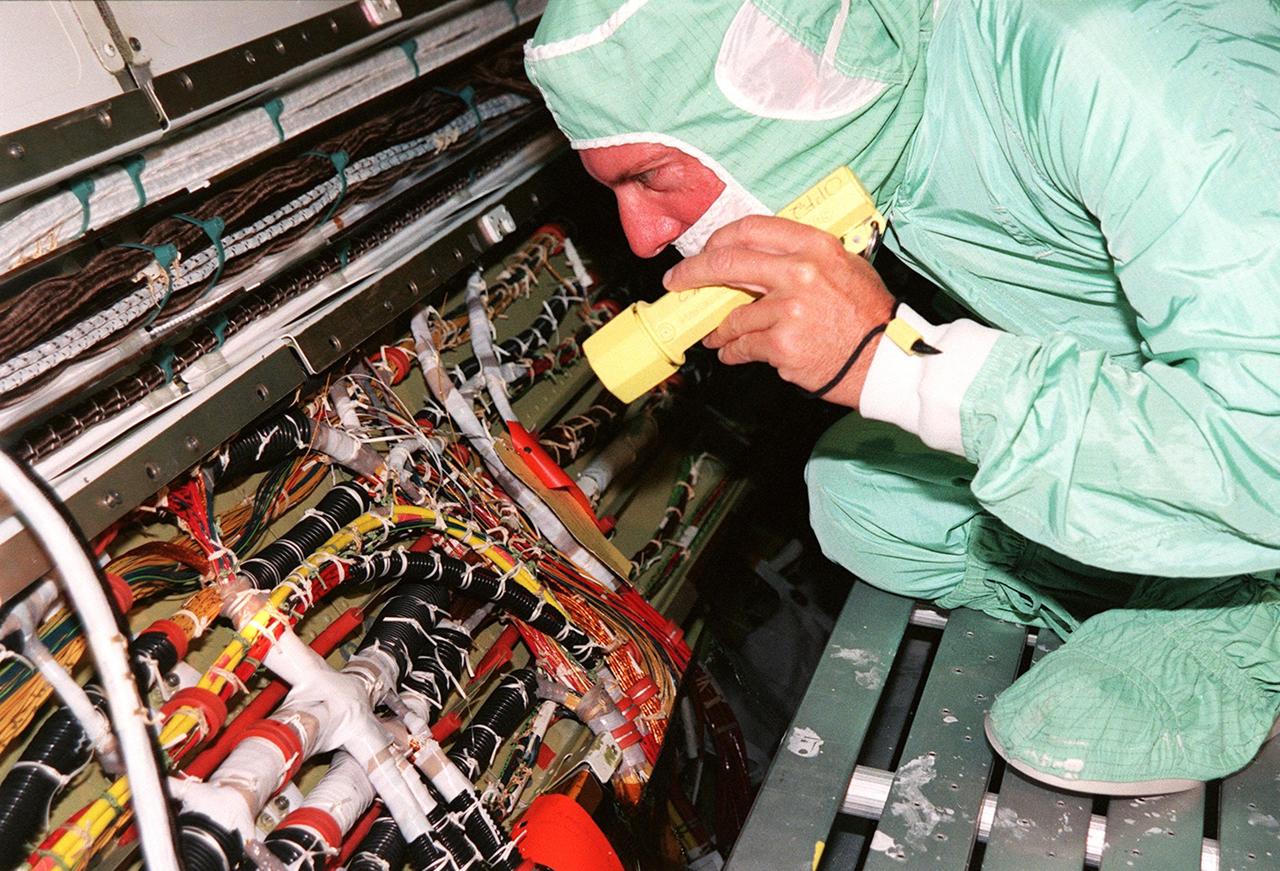

A short during liftoff of Space Shuttle Columbia in July was traced to a wire in the payload bay with damaged insulation. As a result of that problem, NASA decided to inspect much of the wiring in all four Space Shuttles and make repairs as required. Here a technician is examining the wires onboard orbiter Endeavour. The next Shuttle mission, STS-103, the Third Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, is currently scheduled for launch no earlier than Nov. 19, 1999
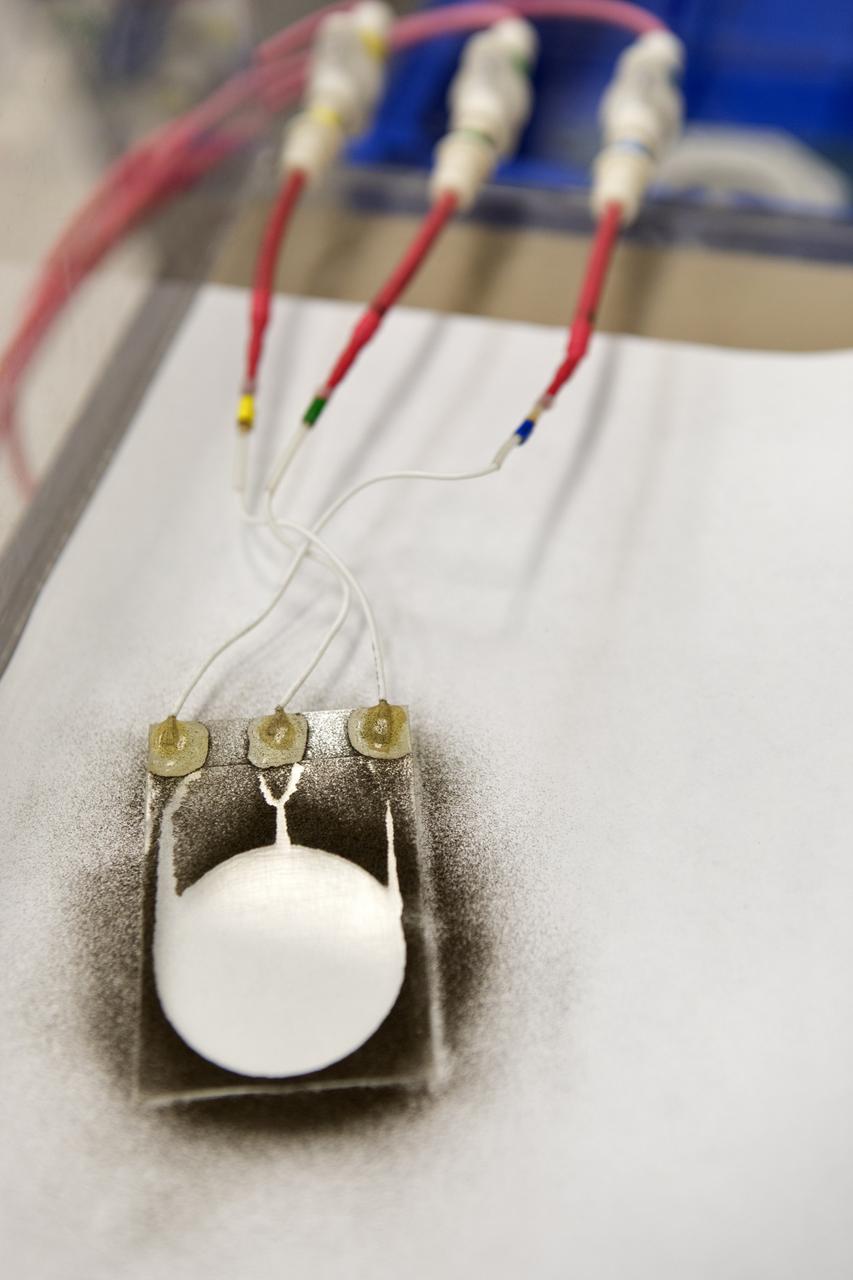
In the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, July 19, 2018, an experiment is underway in which an Electrostatic Dust Shield was been covered with dust similar to that which may be encountered by astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. When activated, the device shook off the dust. Scientists are developing the dust shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, astronauts' space suits and helmet visors. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.
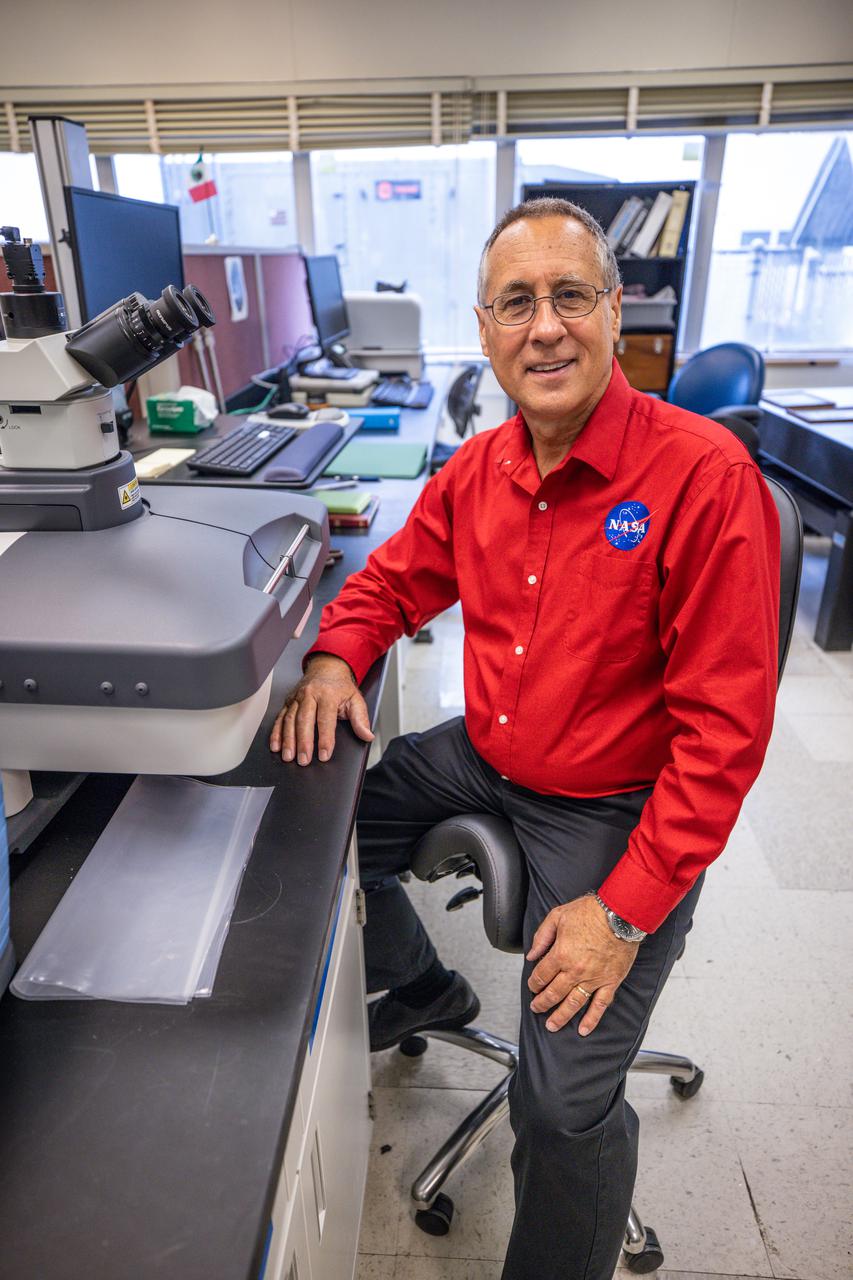

Lead chemist Philip Howard poses for a photo inside NASA Engineering’s Analytical Laboratories at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 7, 2021. One of seven branches in the NASA Laboratories, Development, and Testing Division, the Analytical Laboratories branch provides microscopic imagery and analysis through the use of a wide variety of microscopic techniques to identify contaminants and other urgent problems associated with aerospace flight hardware, ground support equipment, and related facilities.
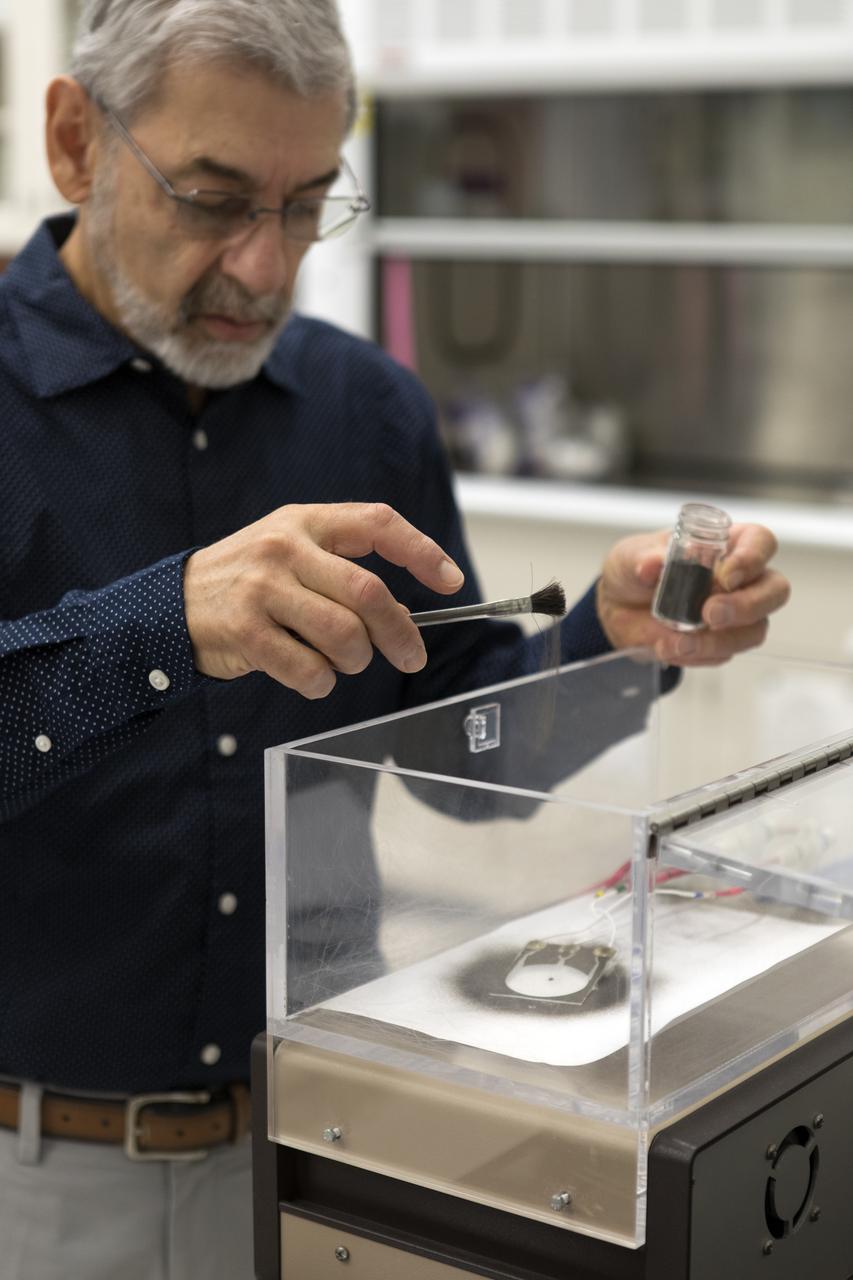

Dr. Carlos Calle, lead scientist in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares an Electrostatic Dust Shield for testing on Thursday, July 19, 2018. Scientists are developing the Electrostatic Dust Shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, astronauts' space suits and helmet visors of astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.
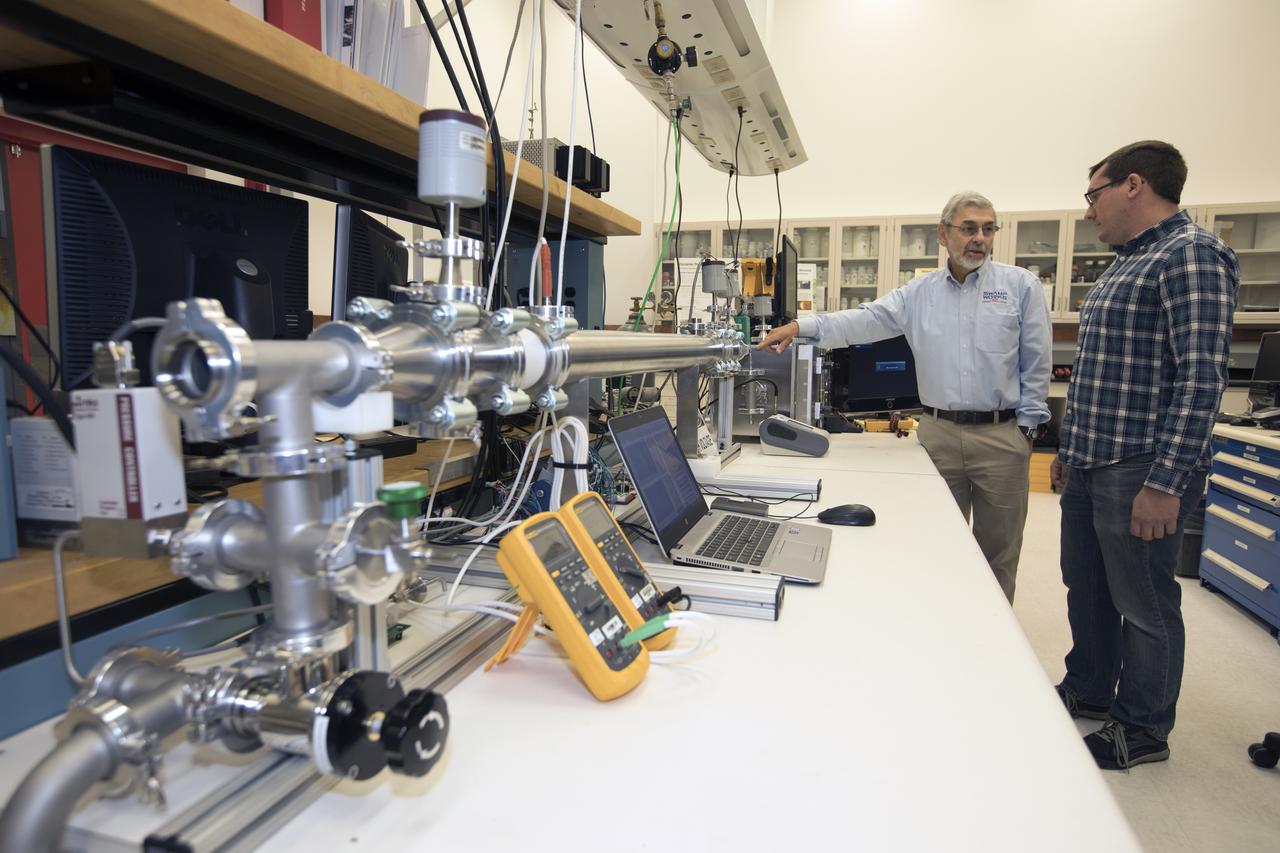
Dr. Carlos Calle, lead scientist in the Kennedy Space Center's Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory, left, and Jay Phillips, a research physicist, are modifying an electrostatic precipitator to help remove dust from a simulated Martian atmosphere. NASA's Journey to Mars requires cutting-edge technologies to solve the problems explorers will face on the Red Planet. Scientists are developing some of the needed solutions by adapting a device to remove the ever-present dust from valuable elements in the Martian atmosphere. Those commodities include oxygen, water and methane.
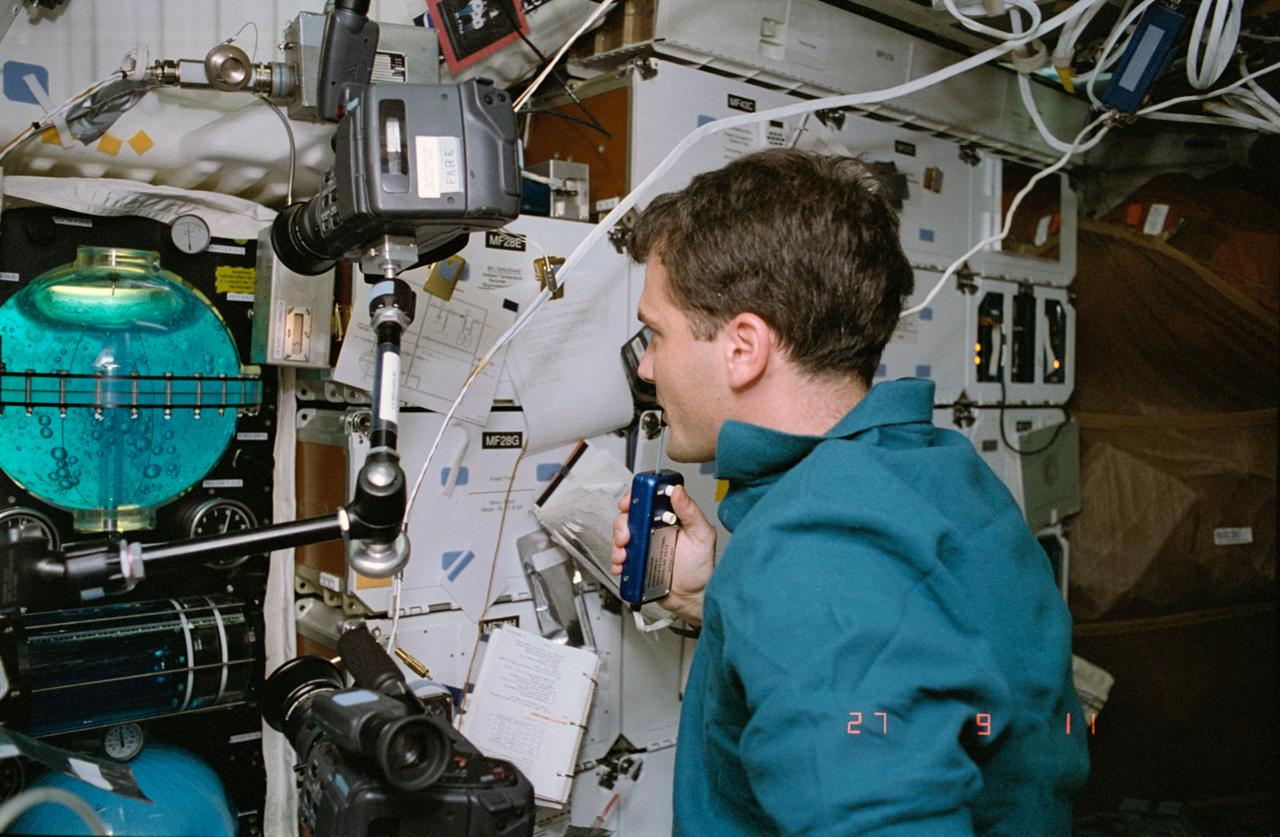

STS057-39-021 (21 June-1 July 1993) --- Astronaut Peter J. K. (Jeff) Wisoff, mission specialist, monitors the Fluid Acquisition and Resupply Experiment (FARE II), housed in four middeck lockers onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The successor to FARE I (STS 53, 1992), FARE II was designed to demonstrate the effectiveness of a device to alleviate the problems associated with vapor-free liquid transfer.

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Banks of lights dry tiles on orbiter Atlantis in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused the moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing
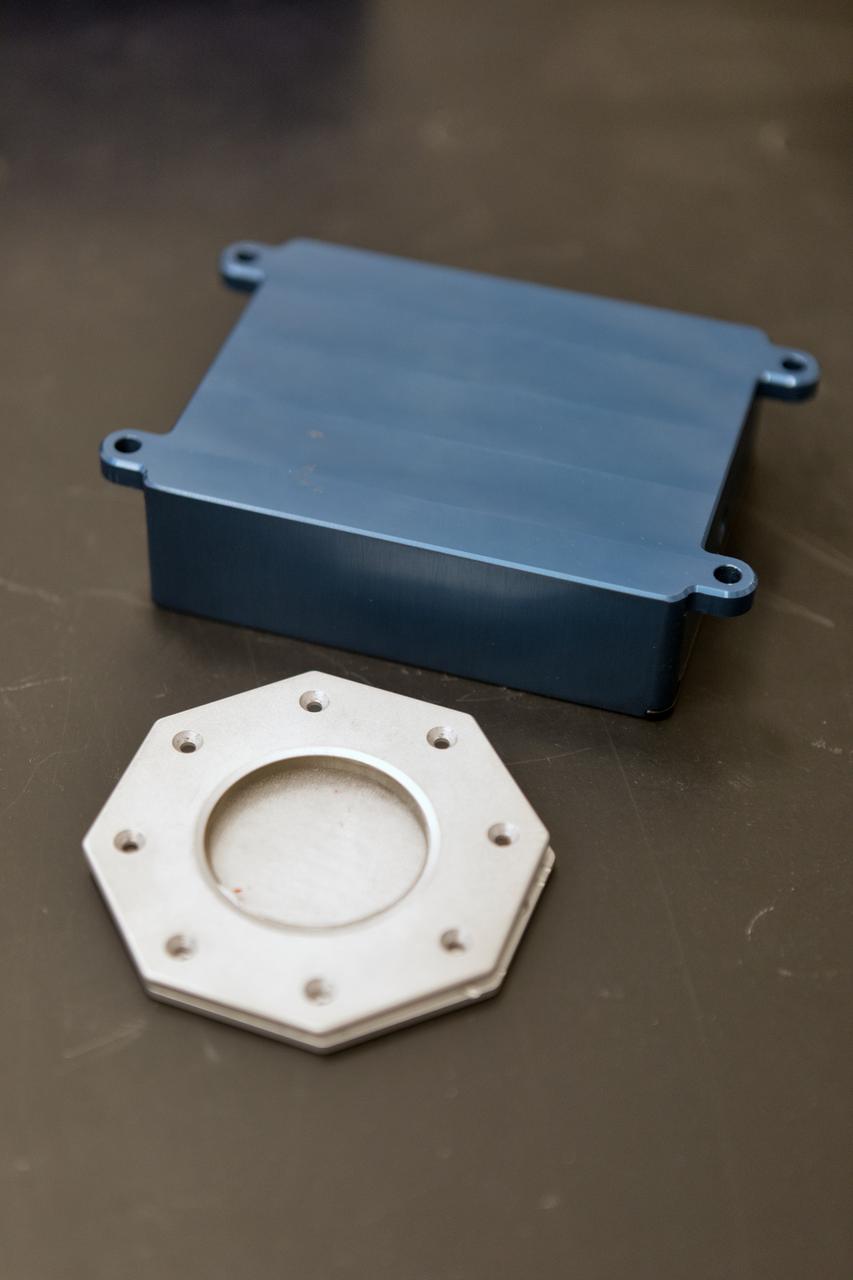

In the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, scientists are developing the Electrostatic Dust Shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, astronauts' space suits and helmet visors of astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. The hardware in display on Thursday, July 19, 2018, is slated for testing the Electrostatic Dust Shield aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.
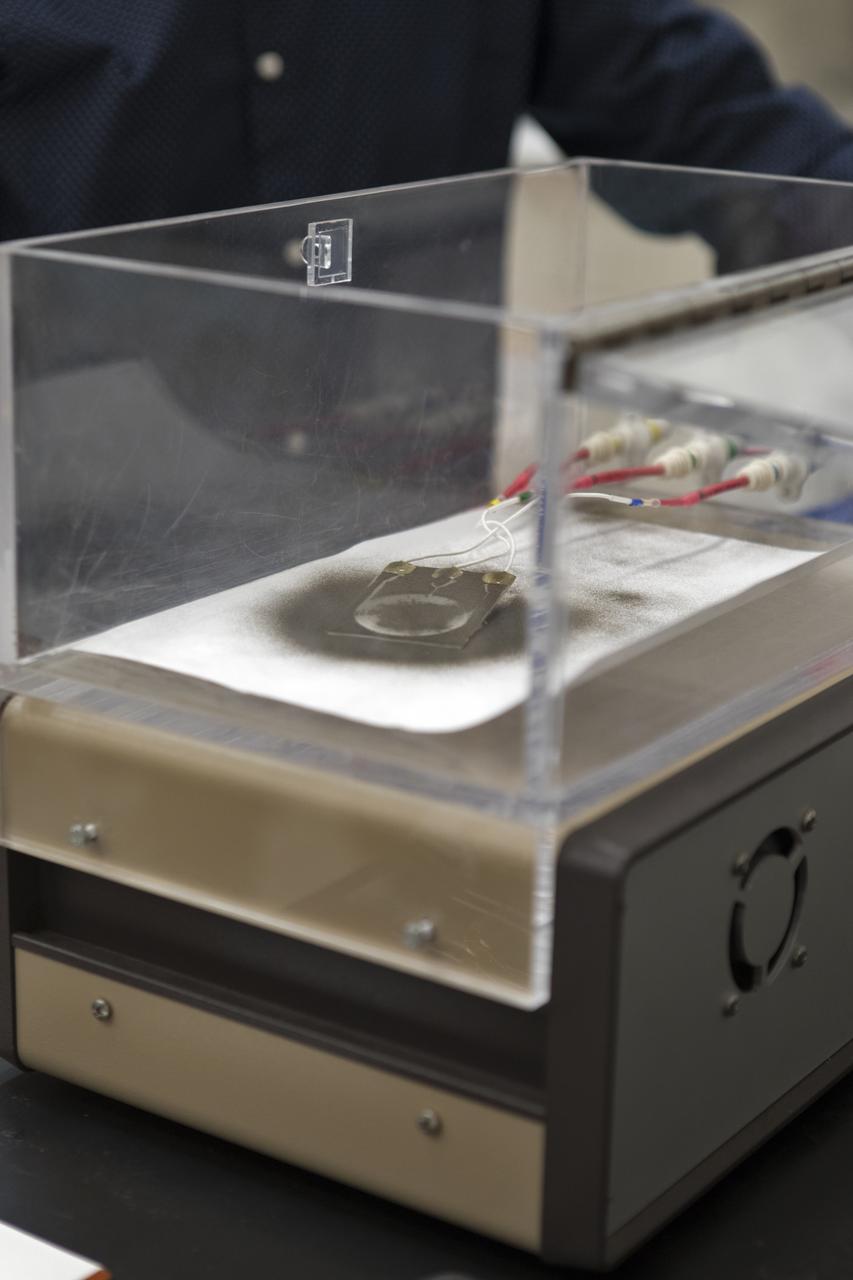
In the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, July 19, 2018, an experiment is underway in which an Electrostatic Dust Shield was been covered with dust similar to that which may be encountered by astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. When activated, the device shook off the dust. Scientists are developing the dust shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, astronauts' space suits and helmet visors. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
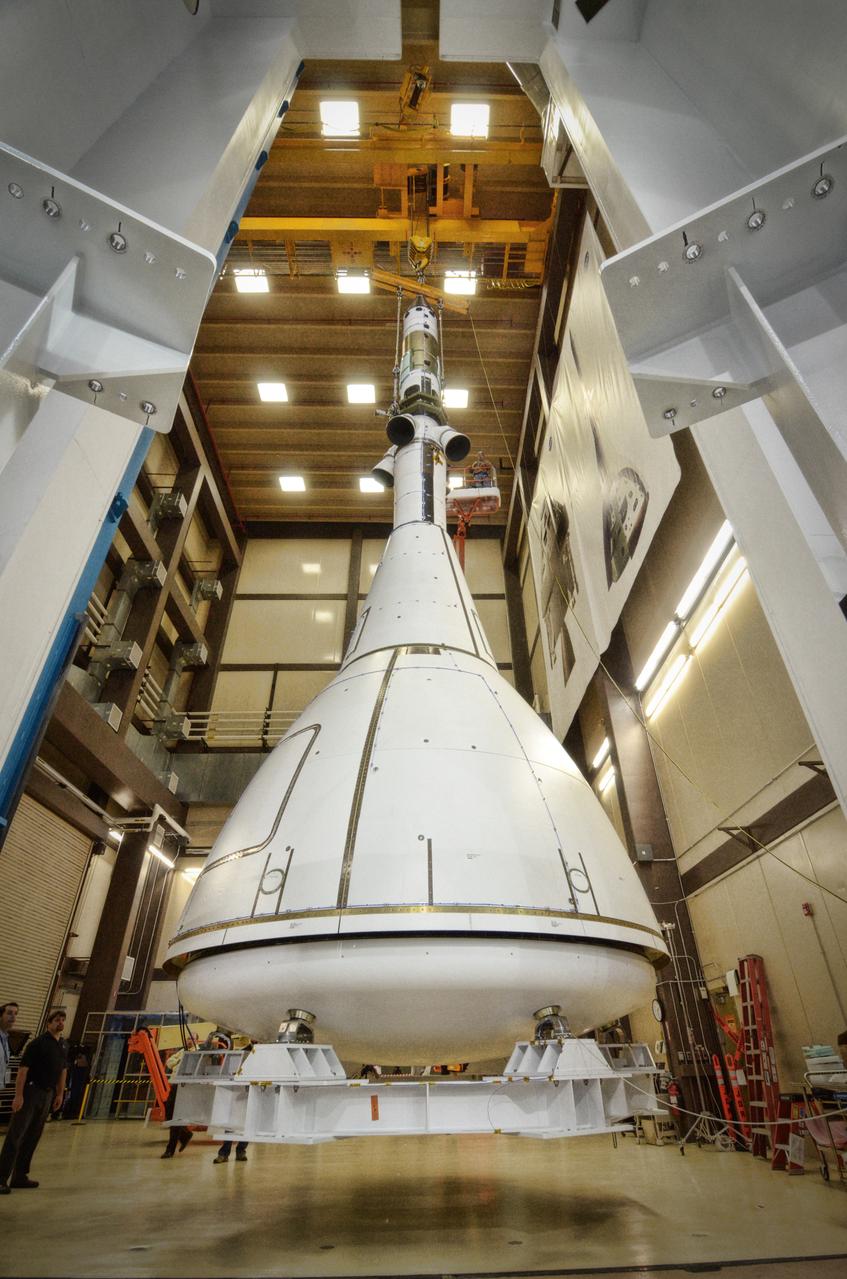

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
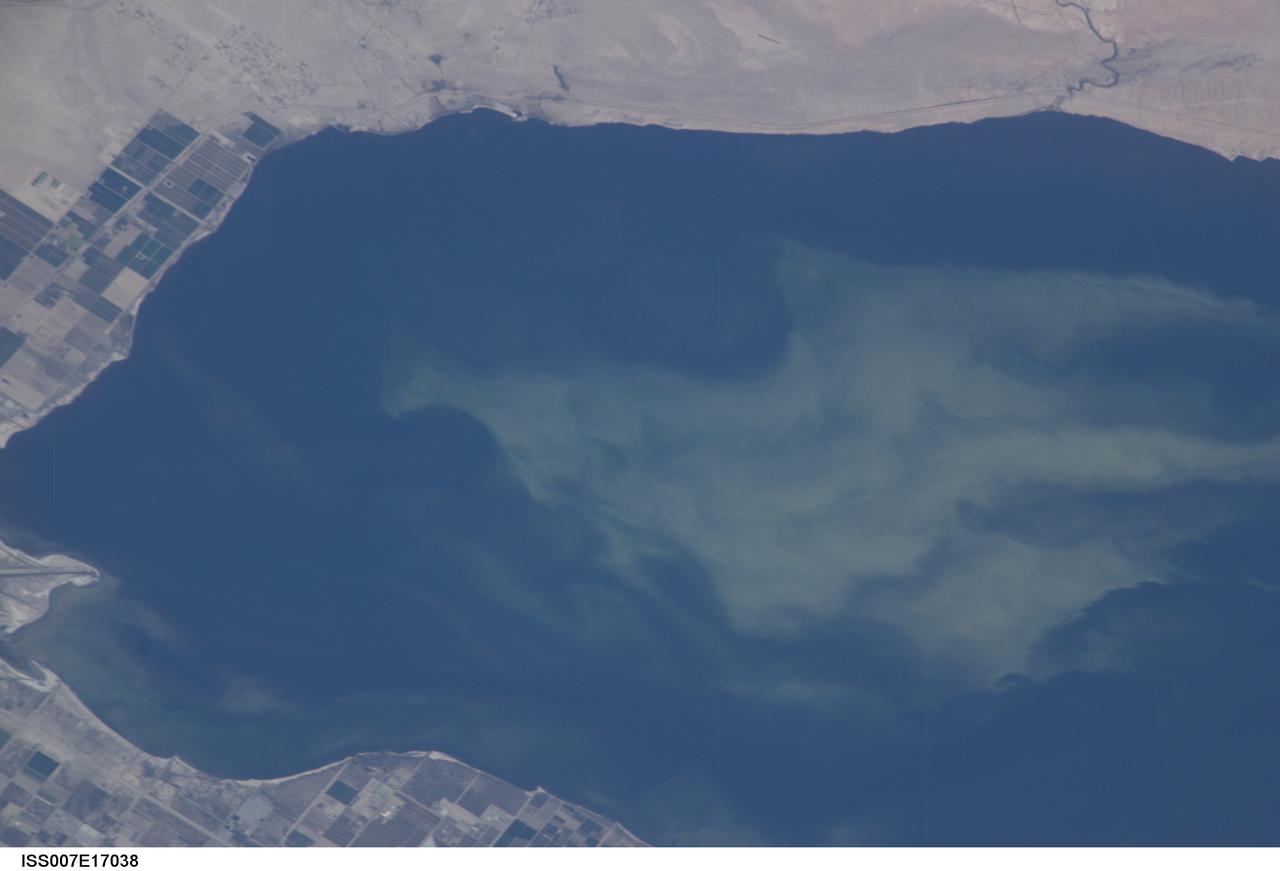

ISS007-E-17038 (11 October 2003) --- This view featuring a close-up of the Salton Sea was taken by an Expedition 7 crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The image provides detail of the structure of the algal bloom. These blooms continue to be a problem for the Salton Sea. They are caused by high concentrations of nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorous, which drain into the basin from the agricultural run-off. As the algae die and decompose, oxygen levels in the sea drop, causing fish kills and hazardous condition for other wildlife.
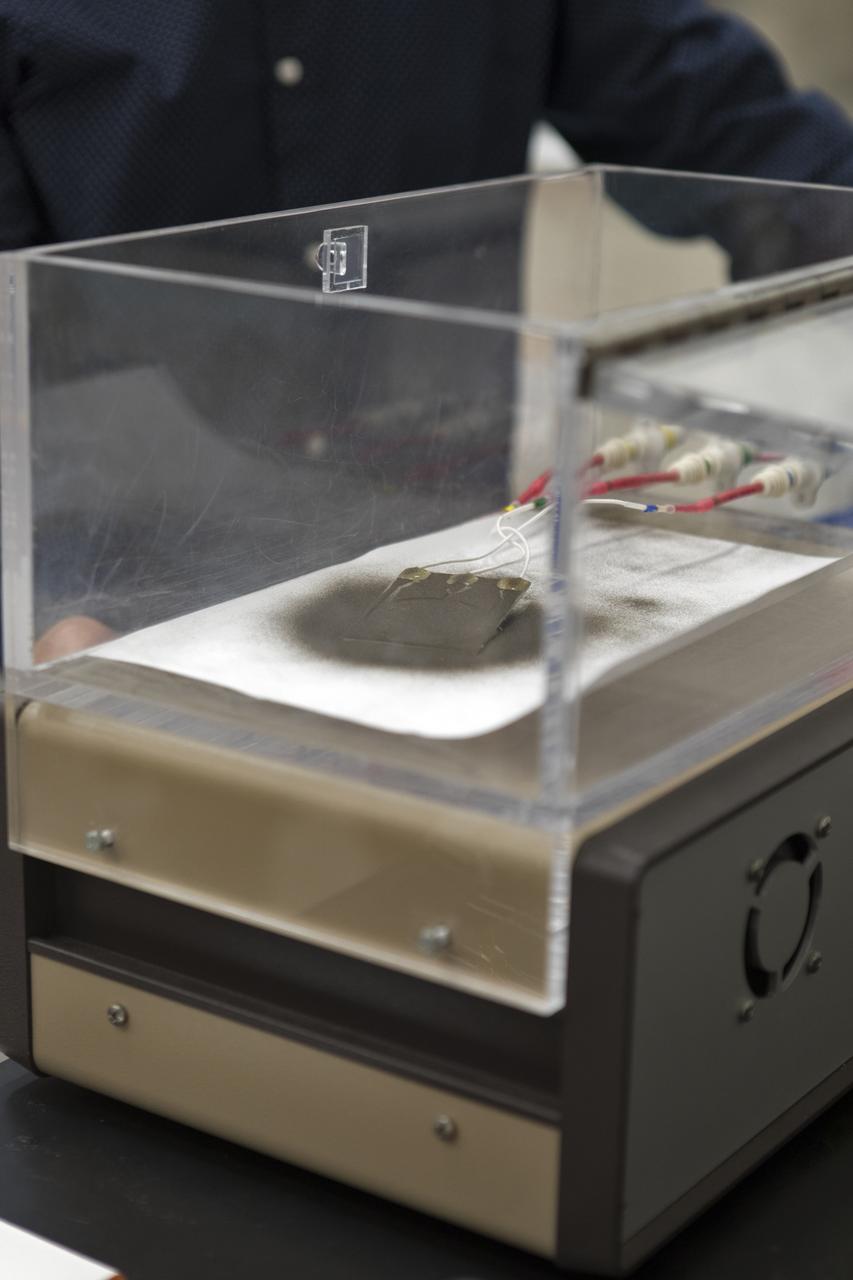

In the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, July 19, 2018, an experiment is underway in which an Electrostatic Dust Shield was been covered with dust similar to that which may be encountered by astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. When activated, the device shook off the dust. Scientists are developing the dust shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, astronauts' space suits and helmet visors. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
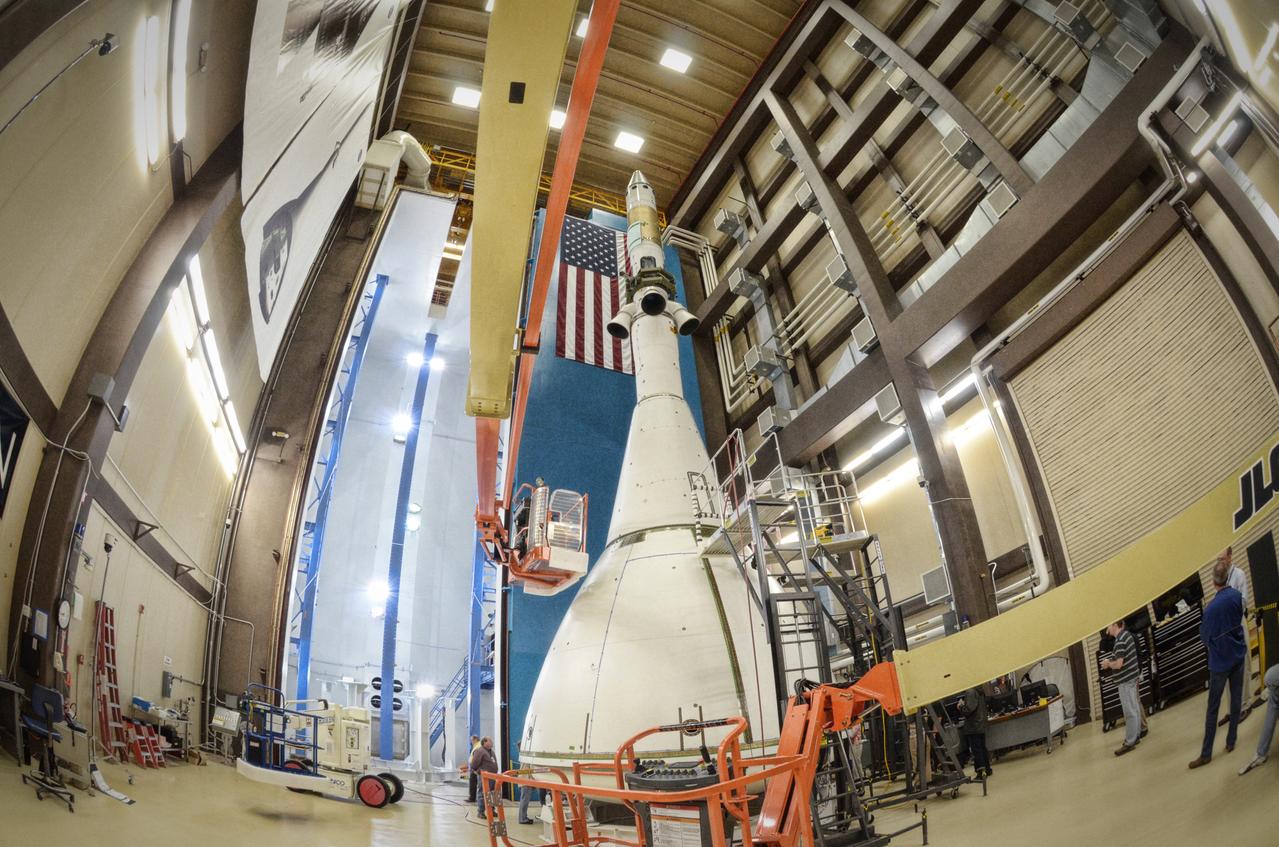

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
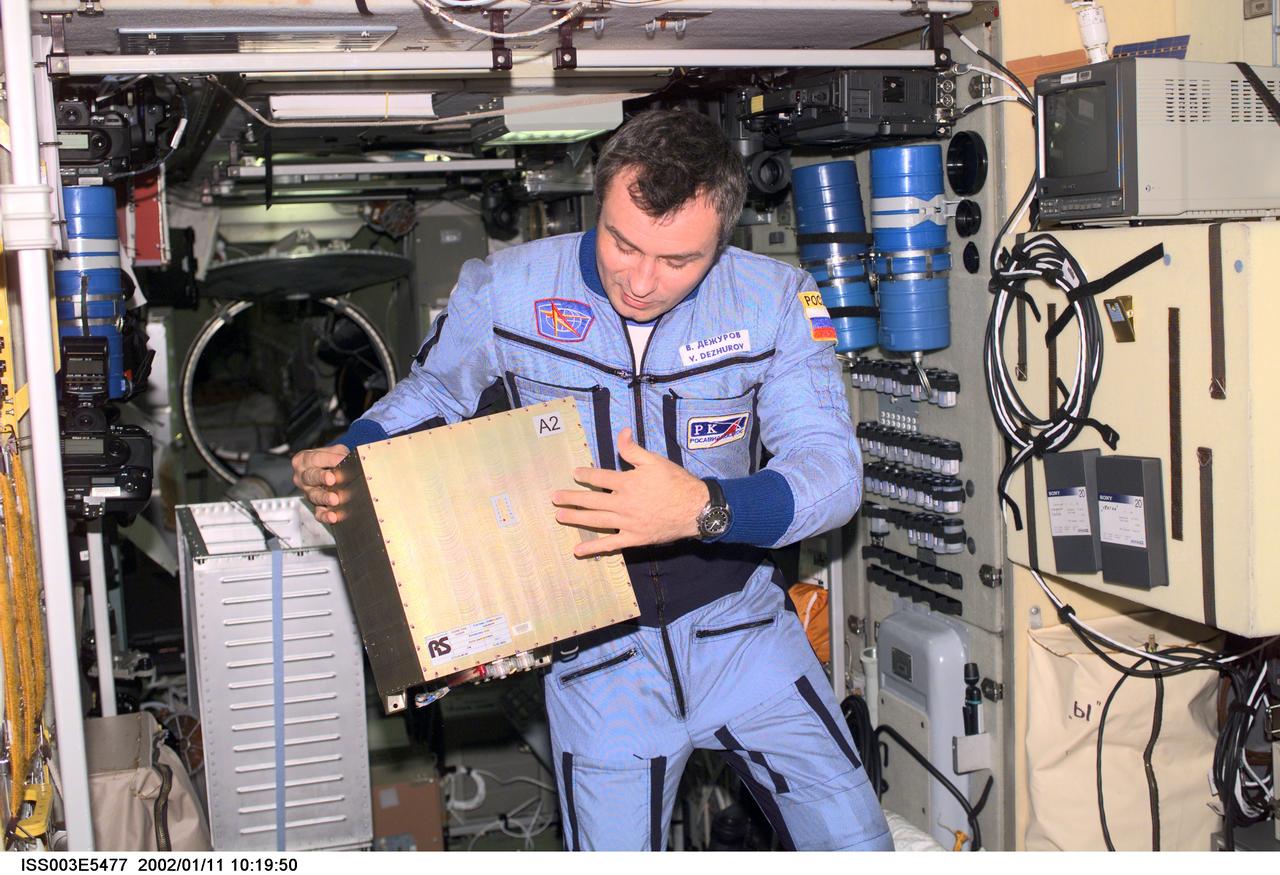

ISS003-E-5477 (August 2001) --- Cosmonaut Vladimir Dezhurov of Rosaviakosmos, Expedition Three flight engineer, holds a Global Time System (GTS) electronics unit in the Zvezda Service Module. Please note: The date identifiers on some frames are not accurate due to a technical problem with one of the Expedition Three cameras. When a specific date is given in the text or description portion, it is correct.
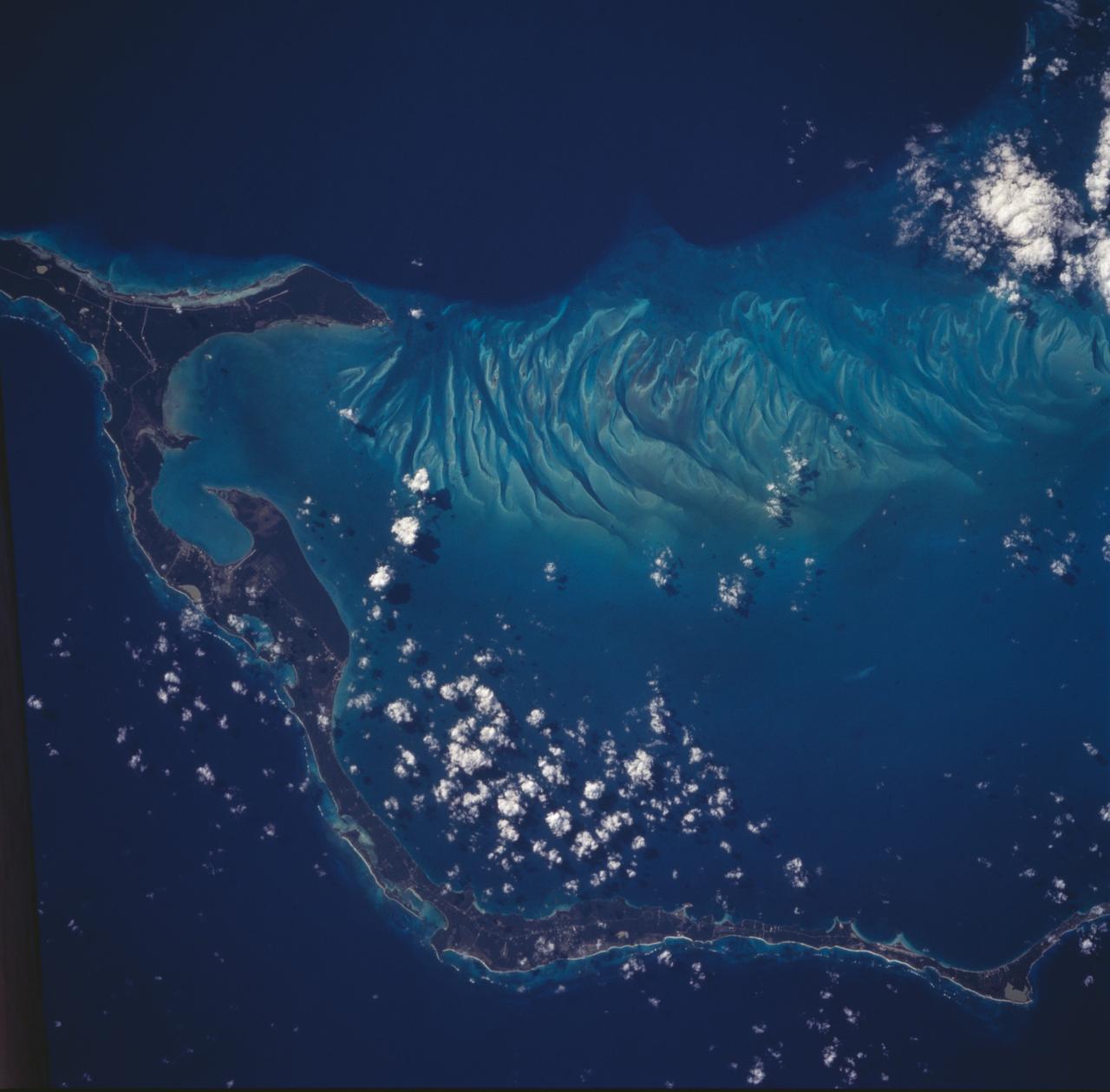

The striking views provided by the Bahama Islands lend insights into the important problems of limestone (CaCO3) production and transport. This photograph includes the southern part of Eleuthera Island in the northern Bahamas. The hook-shaped island encloses a relatively shallow platform (light blue) which is surrounded by deep water (dark blue). The feathery pattern along the western edge of Eleuthera's platform are sand bars and sand channels created by tidal currents sweeping on and off the platform. The channels serve to funnel large amounts of CaCO3 off the platform and into the deeper water.

Jay Phillips, a research physicist in the Kennedy Space Center's Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory, left, and Dr. Carlos Calle, lead scientist in the lab, are modifying an electrostatic precipitator to help remove dust from simulated Martian atmosphere. NASA's Journey to Mars requires cutting-edge technologies to solve the problems explorers will face on the Red Planet. Scientists are developing some of the needed solutions by adapting a device to remove the ever-present dust from valuable elements in the Martian atmosphere. Those commodities include oxygen, water and methane.
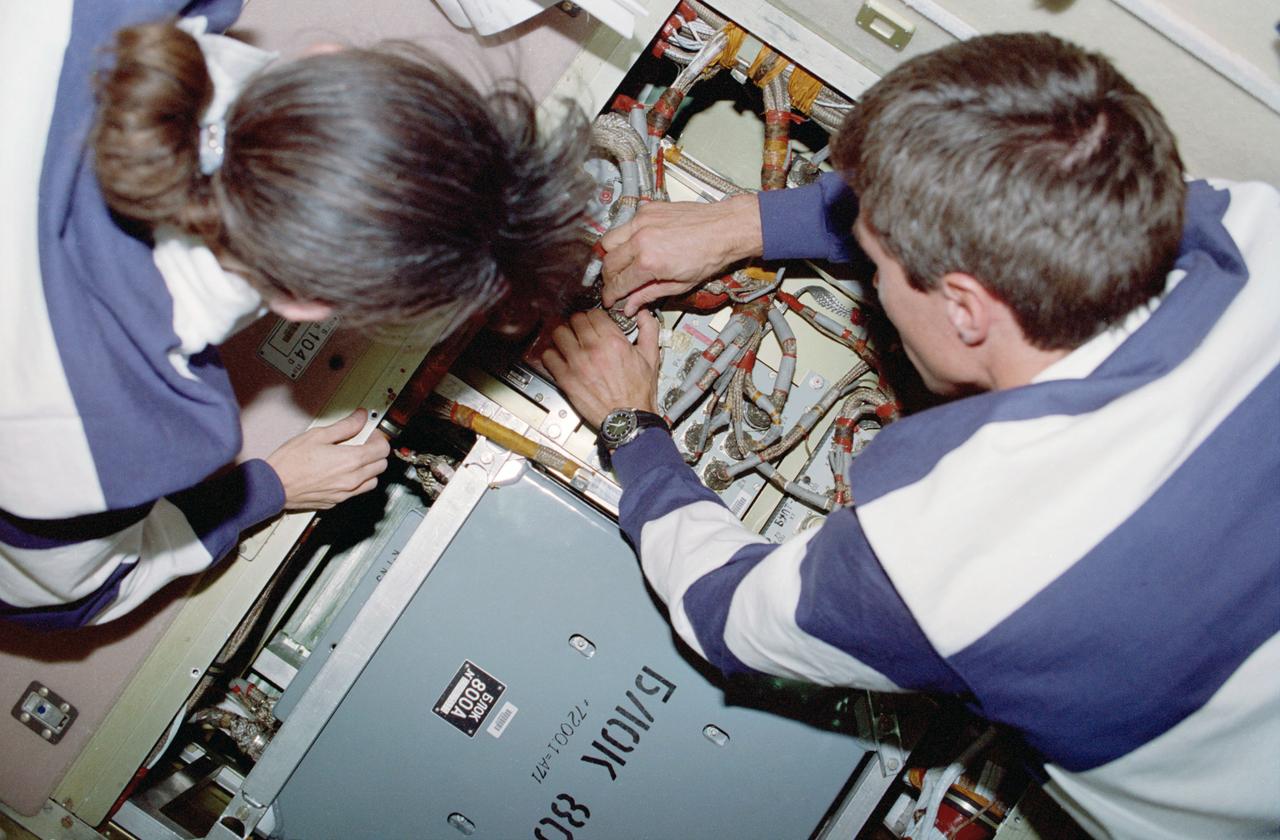

STS088-334-029 (4-15 Dec. 1998) --- Astronaut Nancy J. Currie, mission specialist, and cosmonaut Sergei K. Krikalev, mission specialist representing the Russian Space Agency (RSA), perform an in-flight maintenance on a battery charging unit on the Russian-built FGB Module (Zarya). One of Zarya's six batteries had experienced a problem discharging stored energy in its automatic configuration. Krikalev had swapped out an identical component during two previous flights on the Russia?s Mir Space Station.
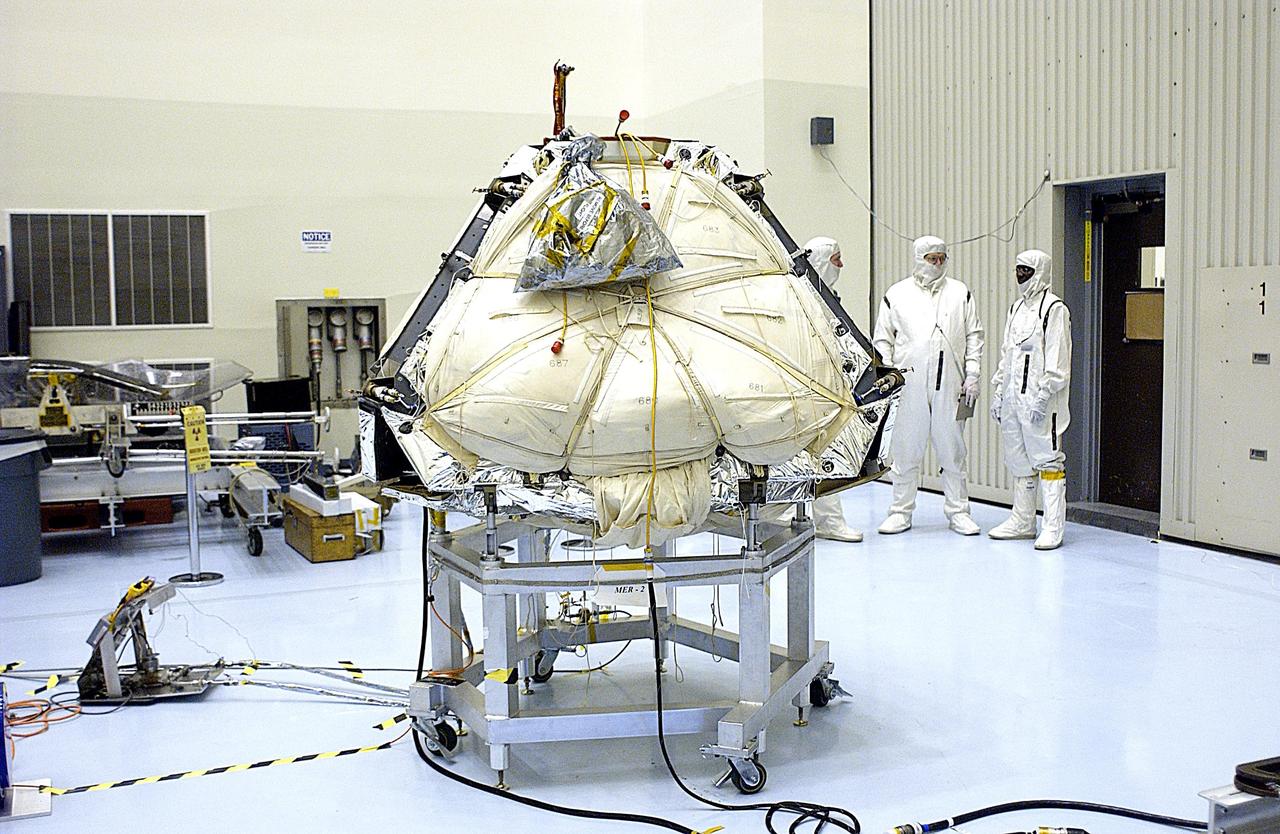

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, preparations are under way to reopen the lander petals of the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) to allow technicians access to one of the spacecraft's circuit boards. A concern arose during prelaunch testing regarding how the spacecraft interprets signals sent from its main computer to peripherals in the cruise stage, lander and small deep space transponder. The MER Mission consists of two identical rovers set to launch in June 2003. The problem will be fixed on both rovers.
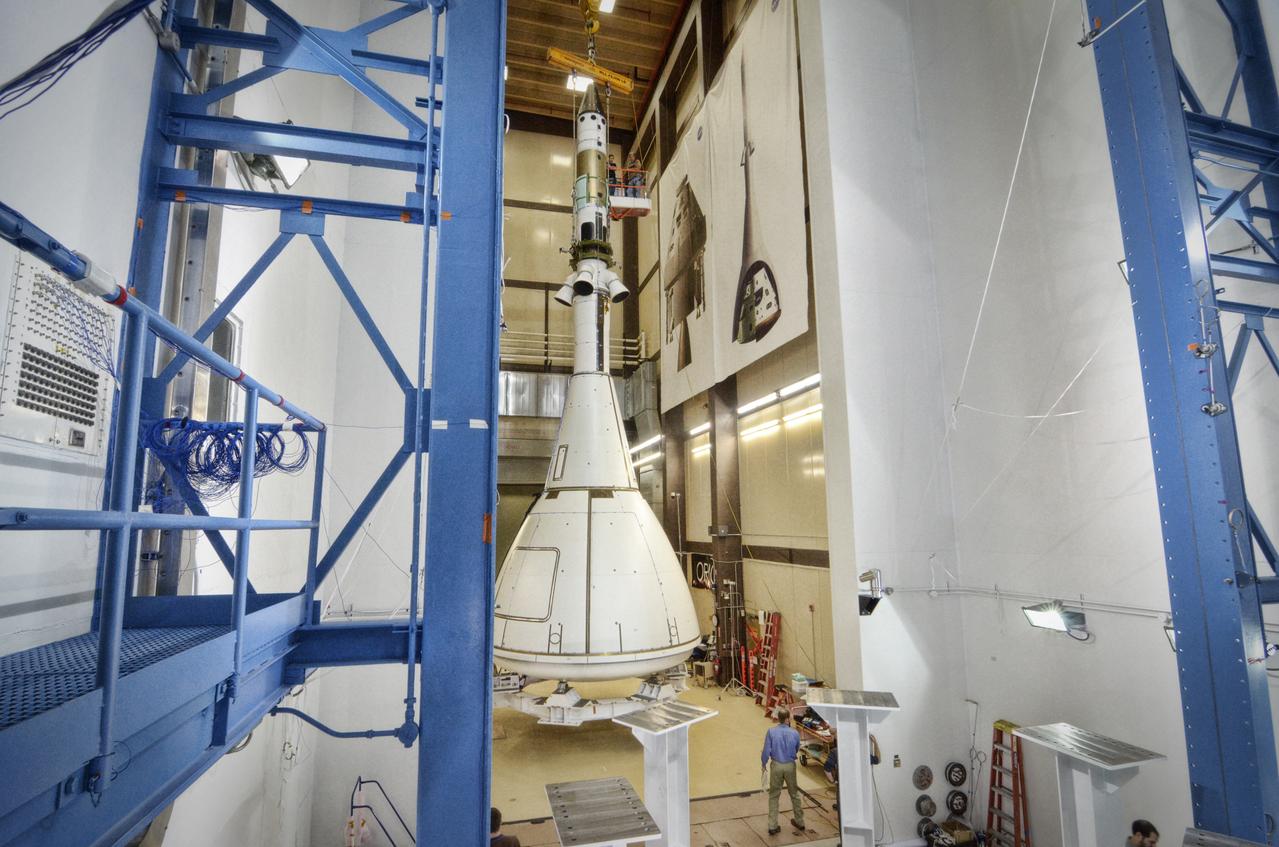

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
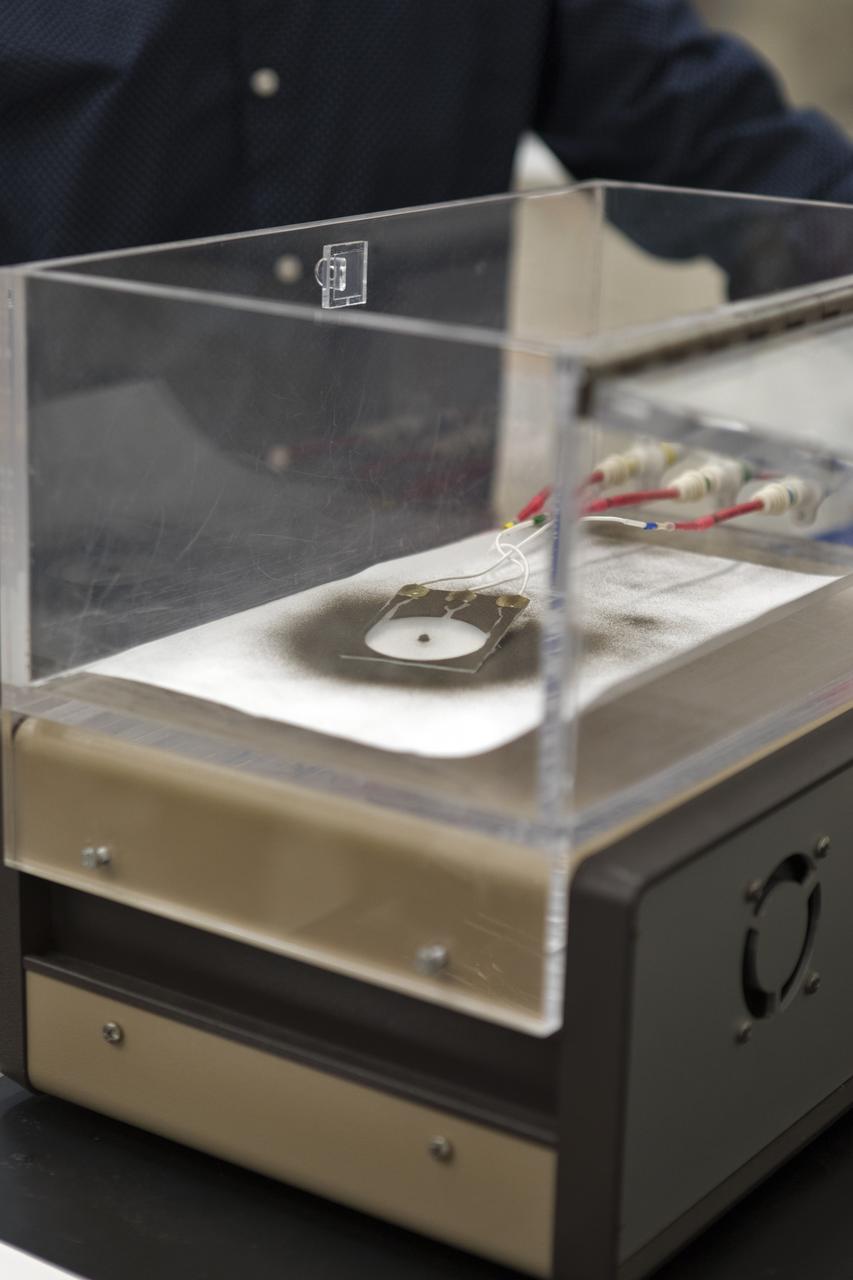

In the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, July 19, 2018, an experiment is underway in which an Electrostatic Dust Shield was been covered with dust similar to that which may be encountered by astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. After activation, the device shakes off the dust. Scientists are developing the dust shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, astronauts' space suits and helmet visors. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.
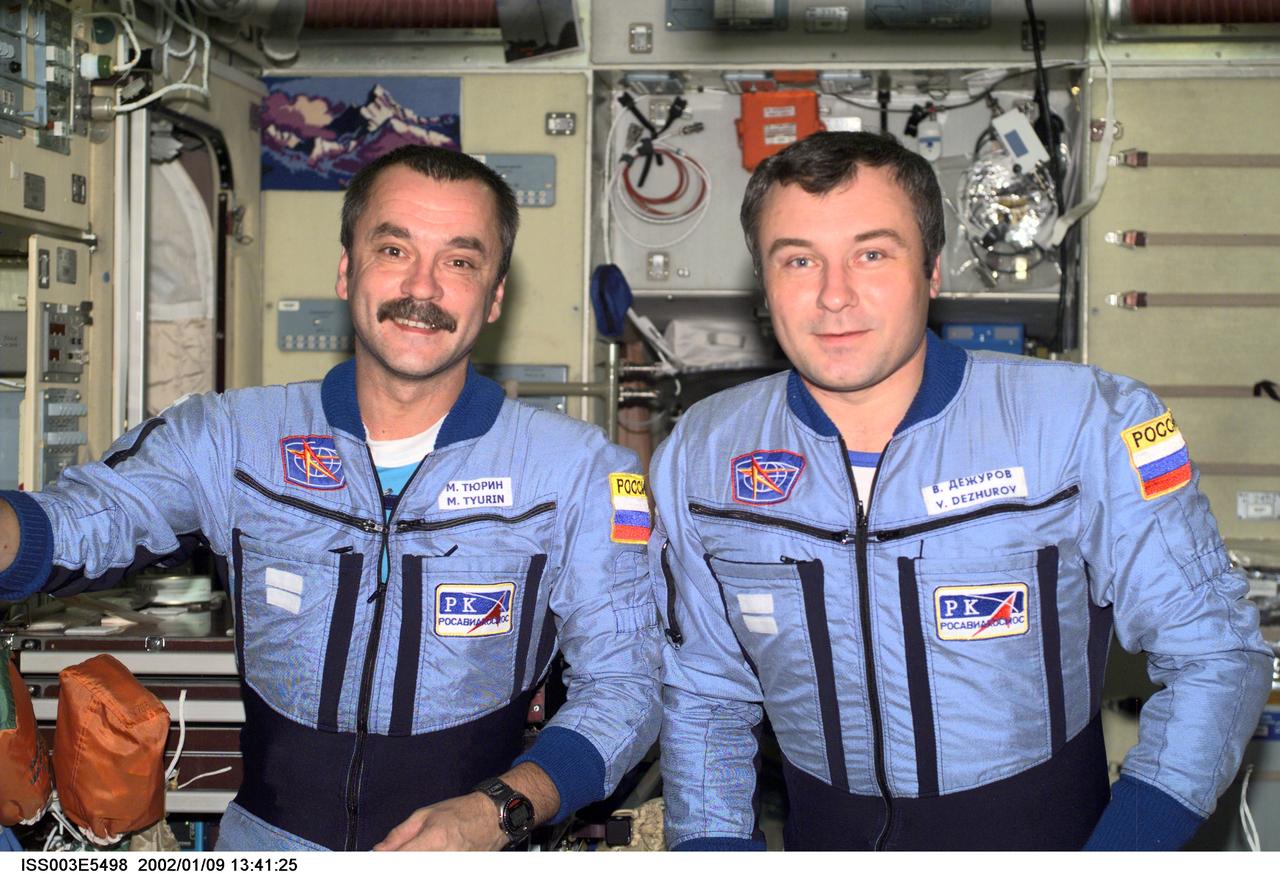

ISS003-E-5498 (August 2001) --- Cosmonauts Mikhail Tyurin (left) and Vladimir Dezhurov, Expedition Three flight engineers, pose for a photograph in the Zvezda Service Module. Tyurin and Dezhurov represent Rosaviakosmos. Please note: The date identifiers on some frames are not accurate due to a technical problem with one of the Expedition Three cameras. When a specific date is given in the text or description portion, it is correct.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a worker points to some of the tiles on orbiter Atlantis that are being dried by clusters of 200-300 watt heat lamps. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused a moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing. Engineers are evaluating the current procedures to assure the tiles are in a safe and flight-ready condition
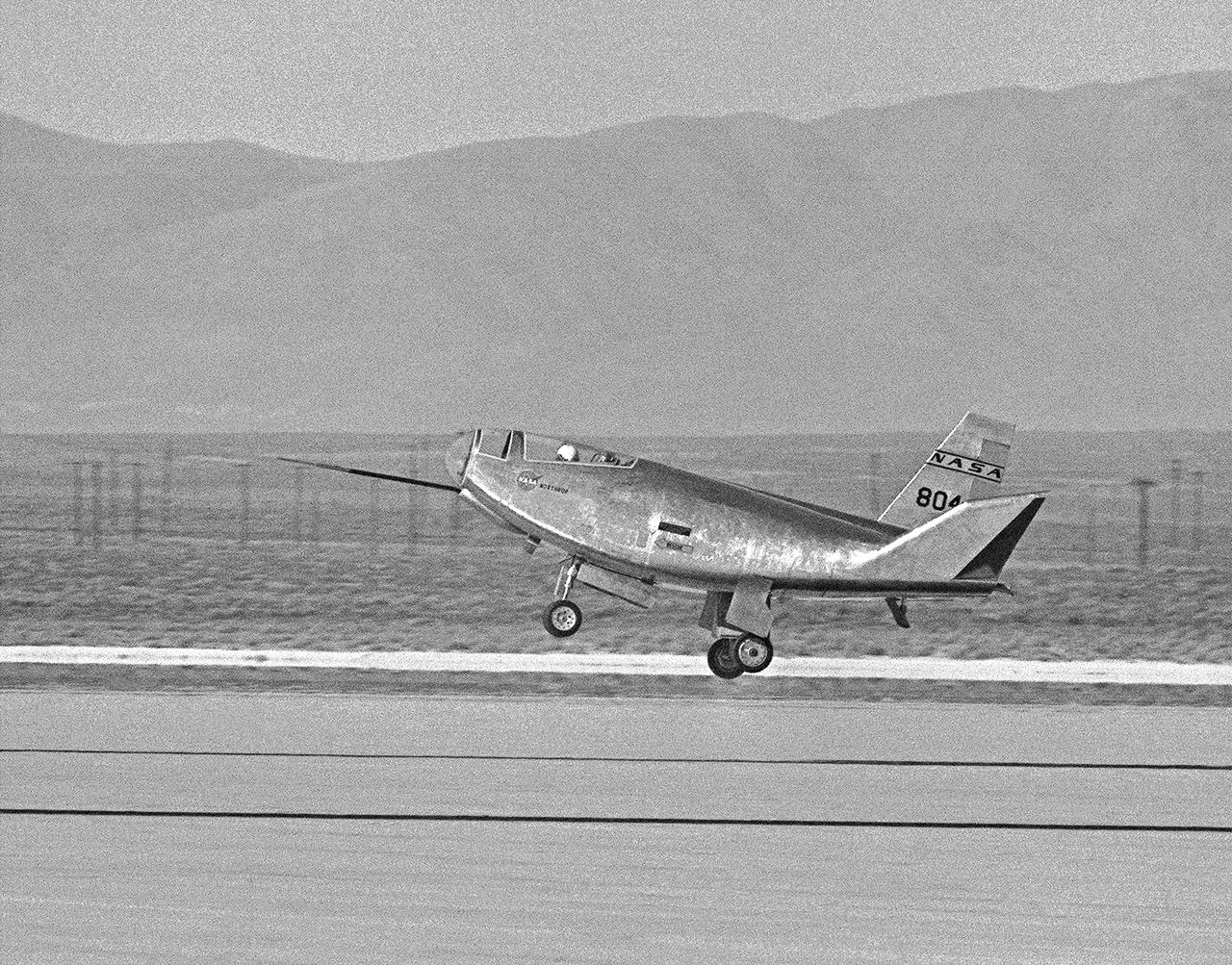

The HL-10 Lifting Body completes its first research flight with a landing on Rogers Dry Lake. Due to control problems, pilot Bruce Peterson had to land at a higher speed than originally planned in order to keep the vehicle under control. The actual touchdown speed was about 280 knots. This was 30 knots above the speed called for in the flight plan. The HL-10's first flight had lasted 3 minutes and 9 seconds.
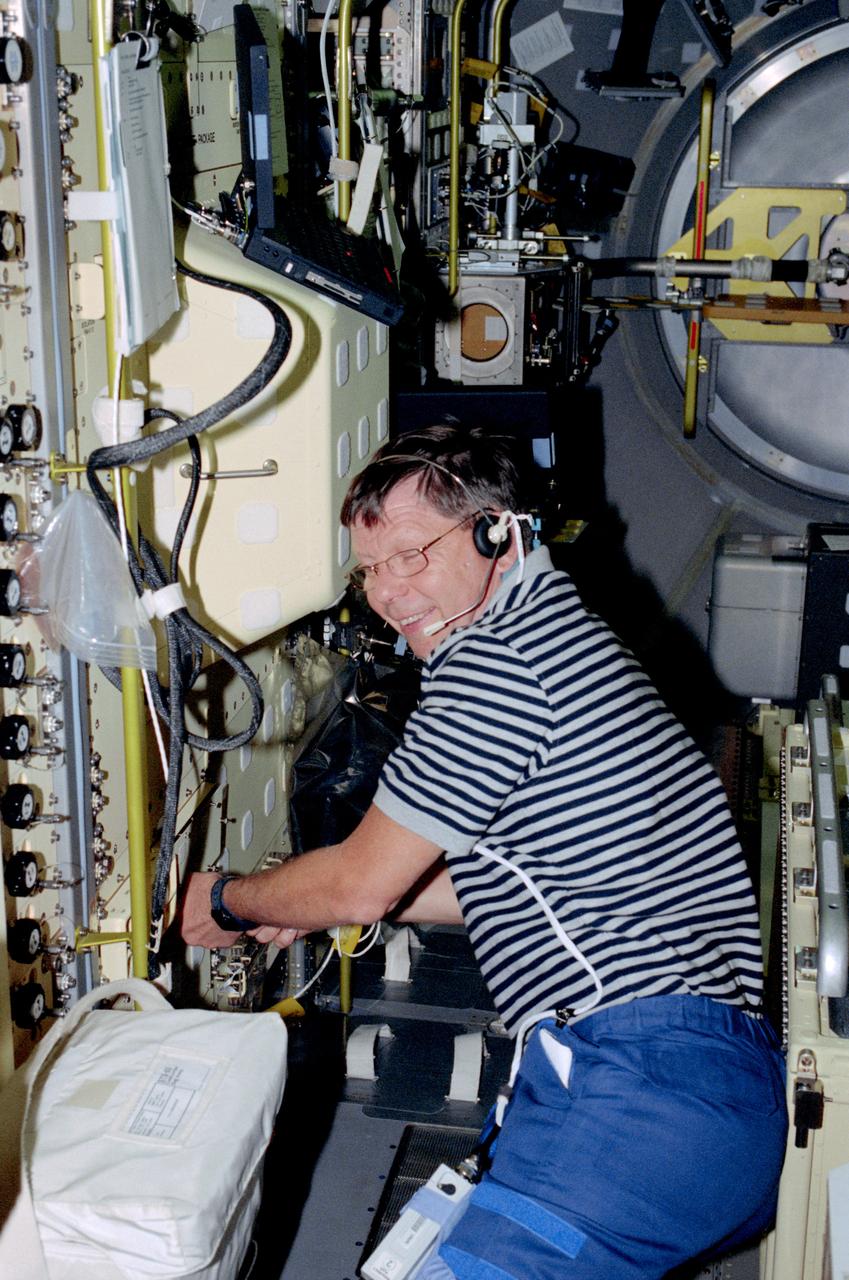

STS083-308-025 (4-8 April 1997) --- Payload specialist Roger K. Crouch, talks to ground controllers while working at Combustion Module-1 in the Spacelab Science Module. Crouch, along with five other NASA astronauts and a second payload specialist supporting the Microgravity Sciences Laboratory (MSL-1) mission were less than a fourth of the way through a scheduled 16-day flight when a power problem cut short their planned stay.
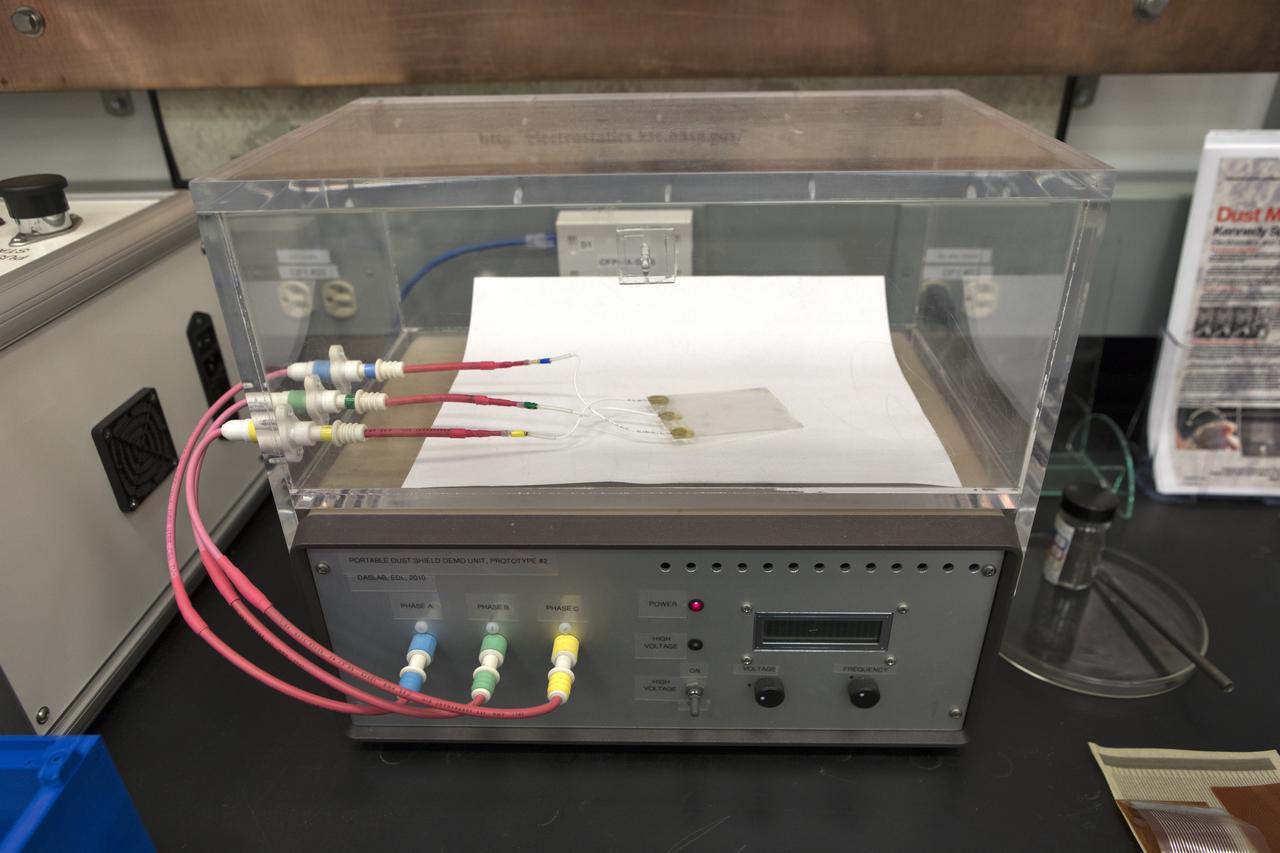
In the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an Electrostatic Dust Shield is prepared for testing on Thursday, July 19, 2018. Scientists are developing the Electrostatic Dust Shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, space suits and helmet visors of astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.
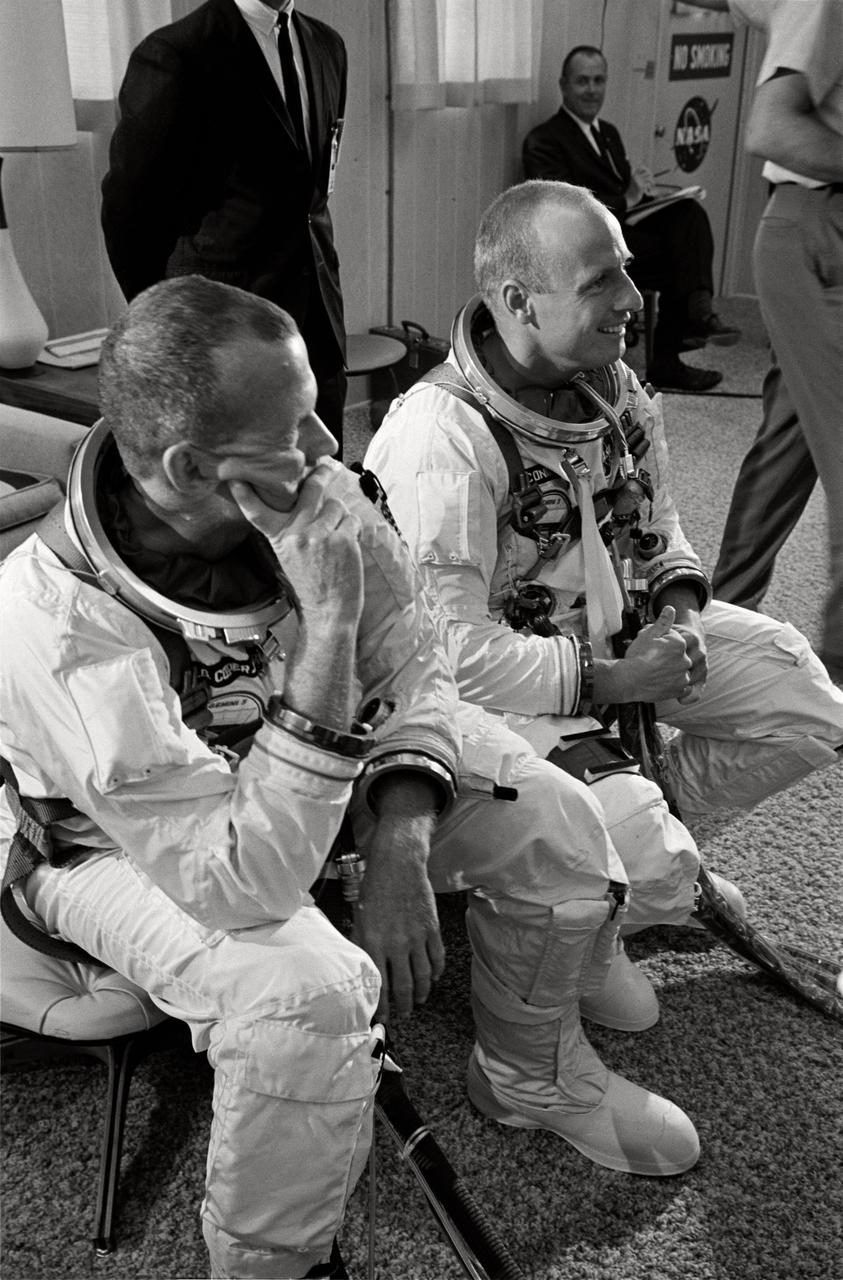

S65-46367 (19 Aug. 1965) --- Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. (right) and L. Gordon Cooper Jr. are pictured during suiting up operations before Gemini-5 spaceflight. Editor's note: The scheduled Aug. 19 launch was postponed due to weather conditions and problems with loading cryogenic fuel for the fuel cell. The launch occurred on Aug. 21, 1965.
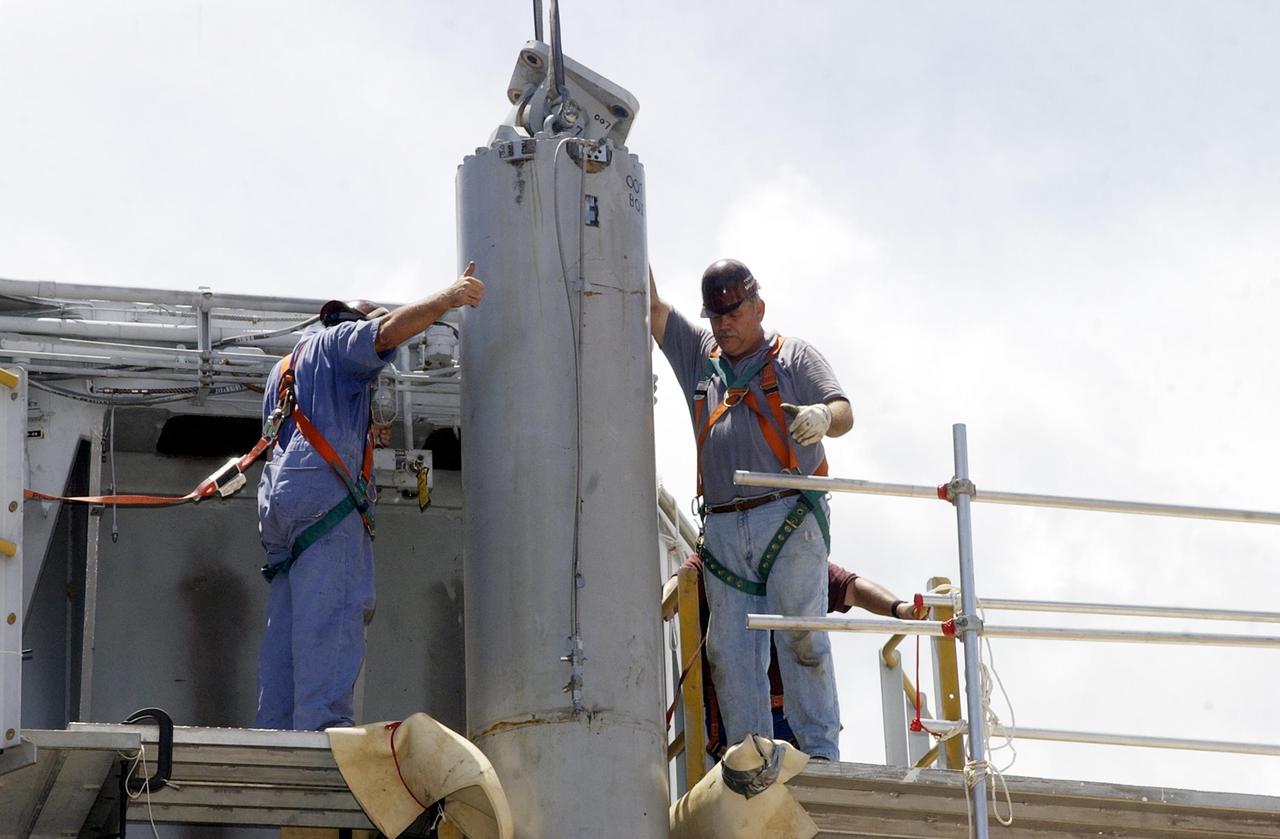

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians give the signal for a crane to begin lifting a jacking, equalization and leveling (JEL) cylinder and bearing on Crawler-Transporter No. 2. During routine maintenance inspections last week, technicians removed two of the 16 JEL cylinders on the crawler to gain access to the bearings and found three of the four bearings cracked. Further eddy current inspections indicated that cracks are present on 15 of the bearings. There are 16 cylinders and 32 bearings per crawler. Engineers are evaluating the situation to determine the cause of the cracks and an appropriate solution to the problem.
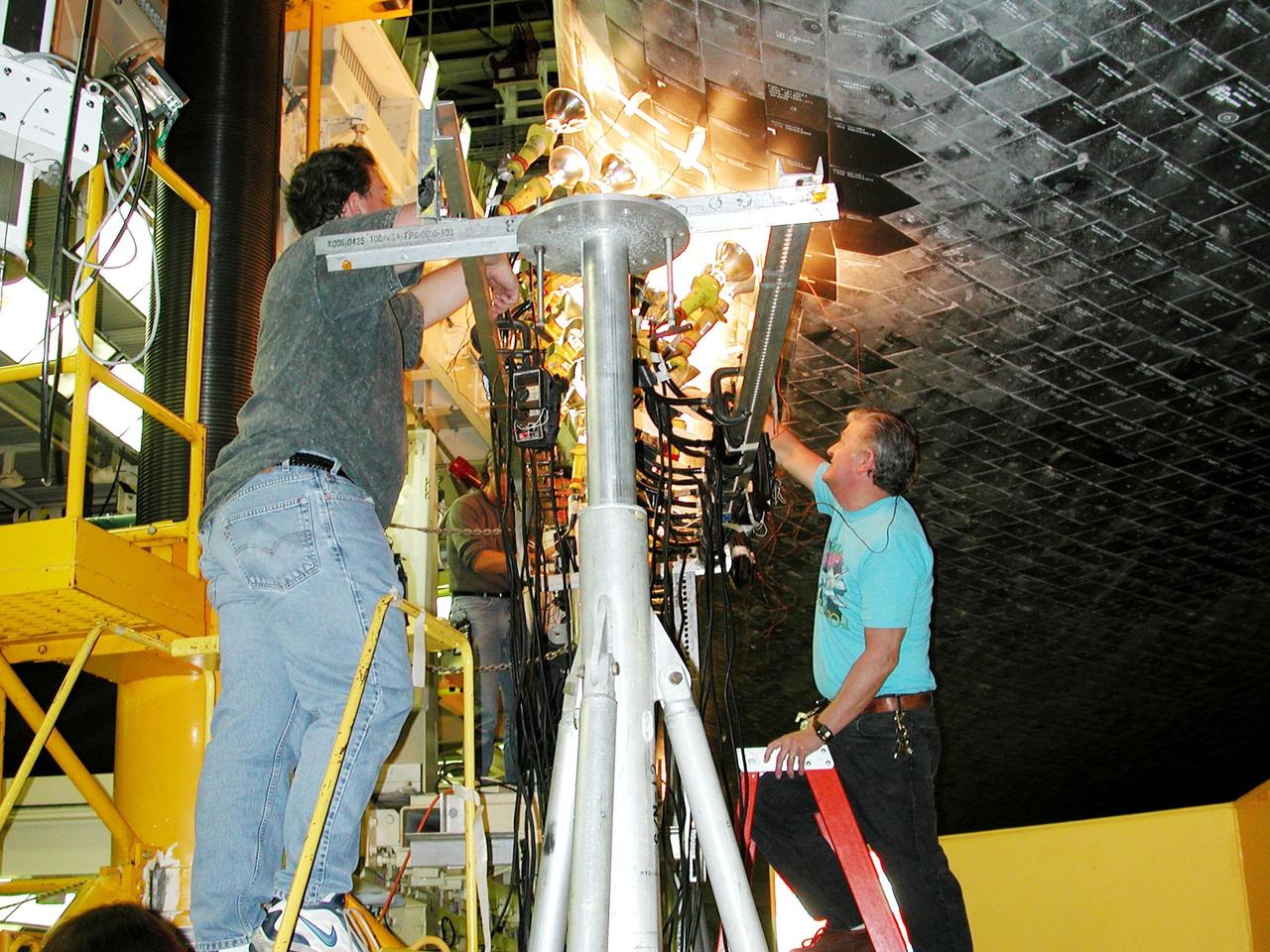

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Banks of lights dry tiles on orbiter Atlantis in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused the moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing
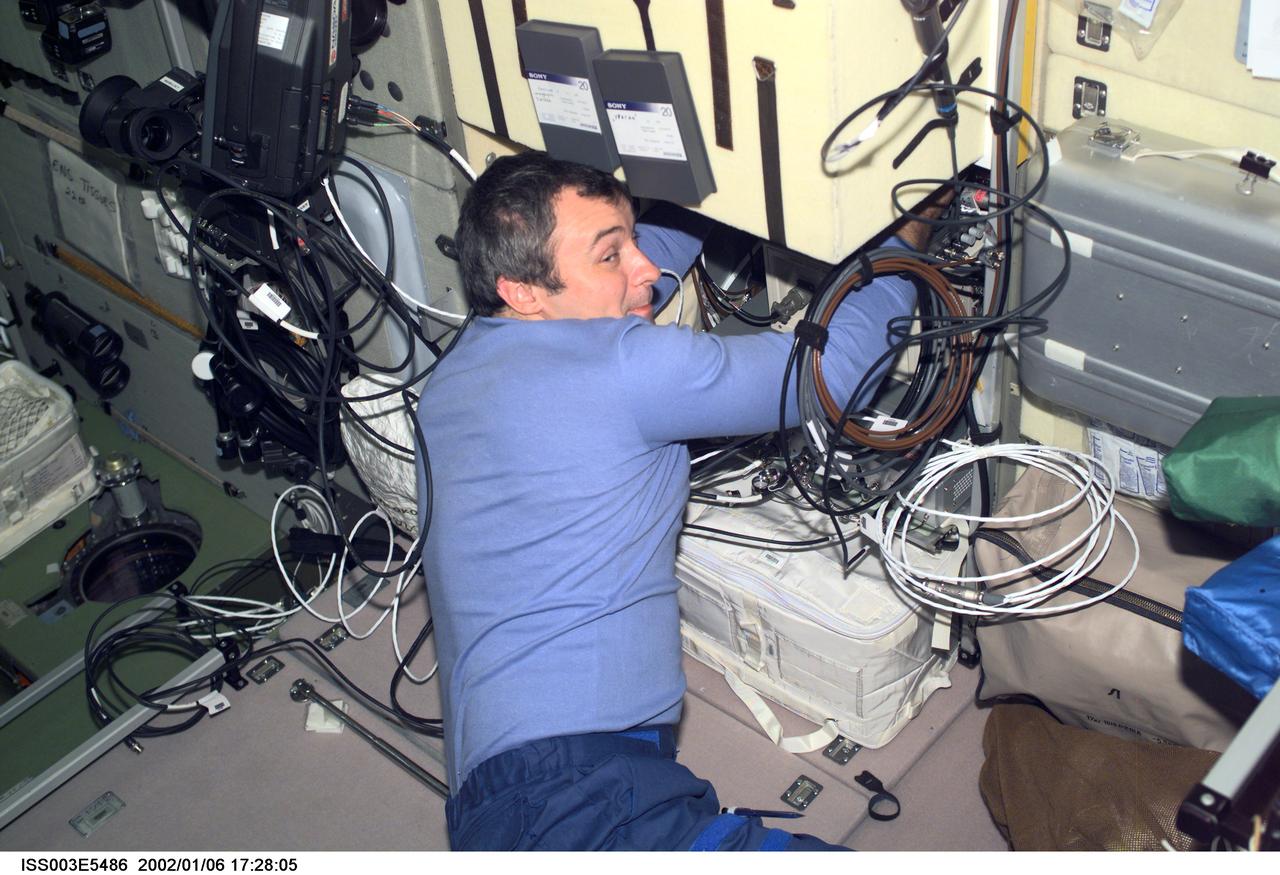

ISS003-E-5486 (August 2001) --- Cosmonaut Vladimir Dezhurov of Rosaviakosmos, Expedition Three flight engineer, works on electronic equipment behind a panel in the Zvezda Service Module. Please note: The date identifiers on some frames are not accurate due to a technical problem with one of the Expedition Three cameras. When a specific date is given in the text or description portion, it is correct.
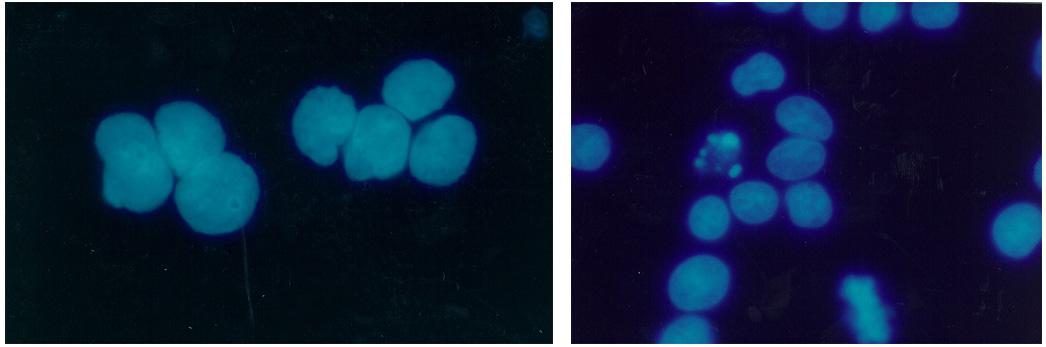
Biomedical research offers hope for a variety of medical problems, from diabetes to the replacement of damaged bone and tissues. Bioreactors, which are used to grow cells and tissue cultures, play a major role in such research and production efforts. The objective of the research was to define a way to differentiate between effects due to microgravity and those due to possible stress from non-optimal spaceflight conditions.

The X-38 prototypes are intended to perfect a "crew lifeboat" for the International Space Station. The X-38 vehicle 131R demonstrates a huge 7,500 square-foot parafoil that will that will enable the Crew Return Vehicle (CRV) to land on the length of a football field after returning from space. The CRV is intended to serve as an emergency transport to carry a crew to safety in the event of problems with the International Space Station.
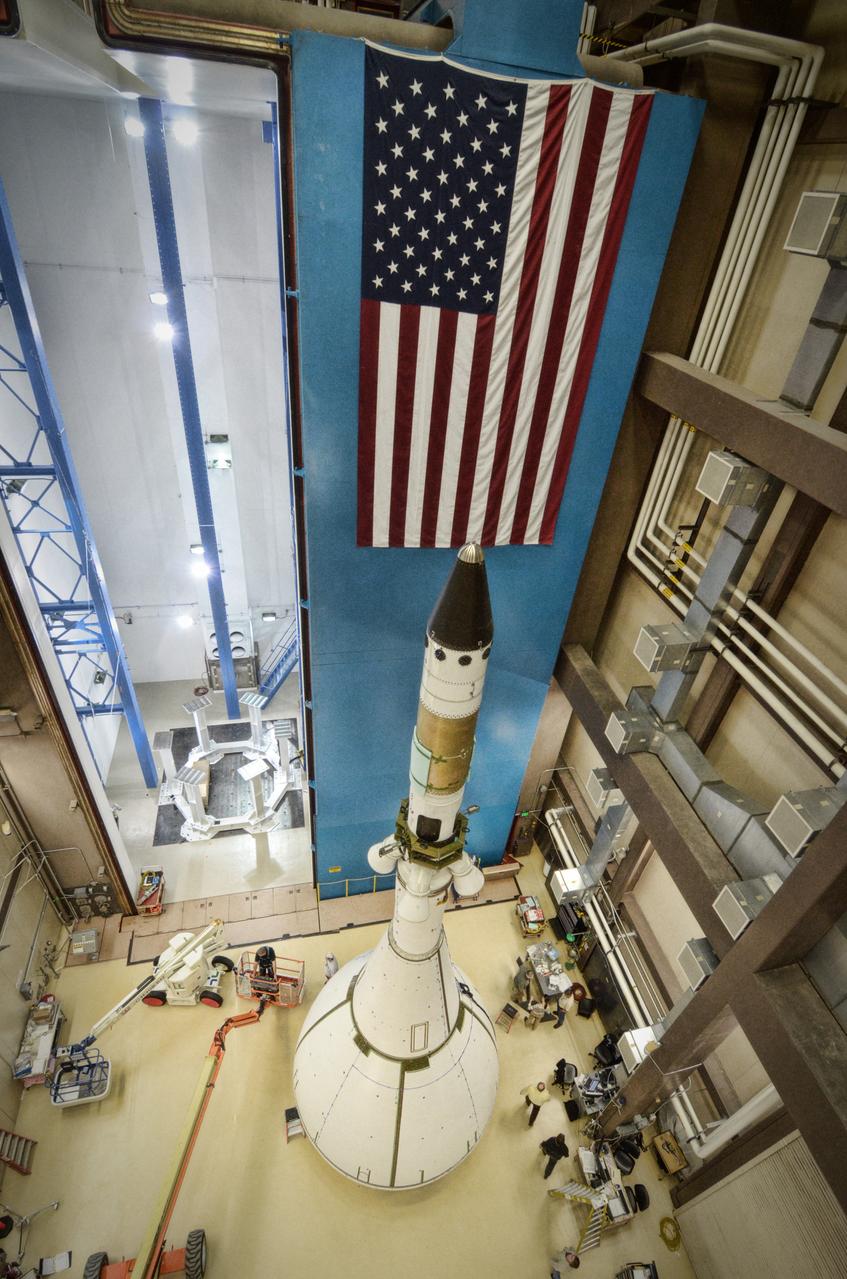

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
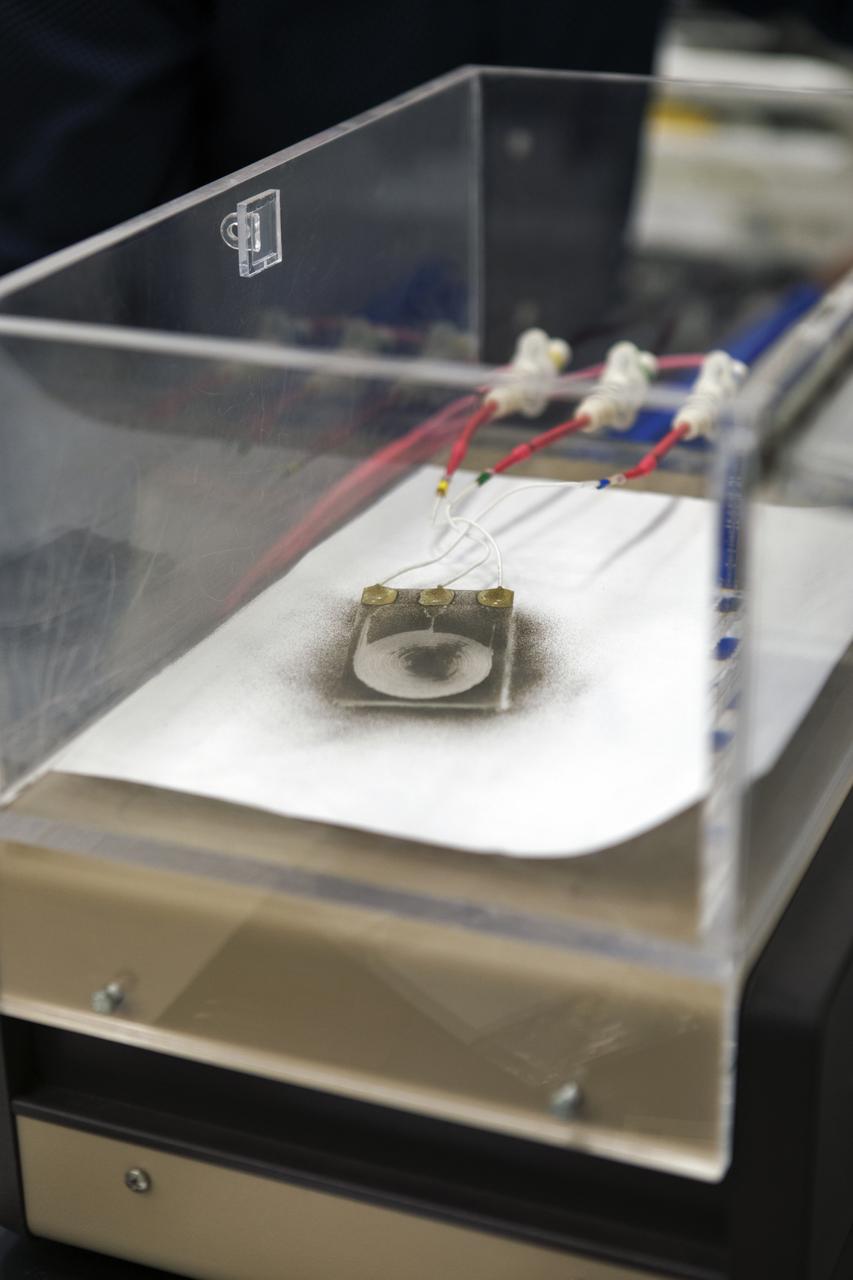
In the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, July 19, 2018, an experiment is underway in which an Electrostatic Dust Shield has been covered with dust similar to that which may be encountered by astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. When activated, the device shakes off the dust. Scientists are developing the dust shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, astronauts' space suits and helmet visors. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.
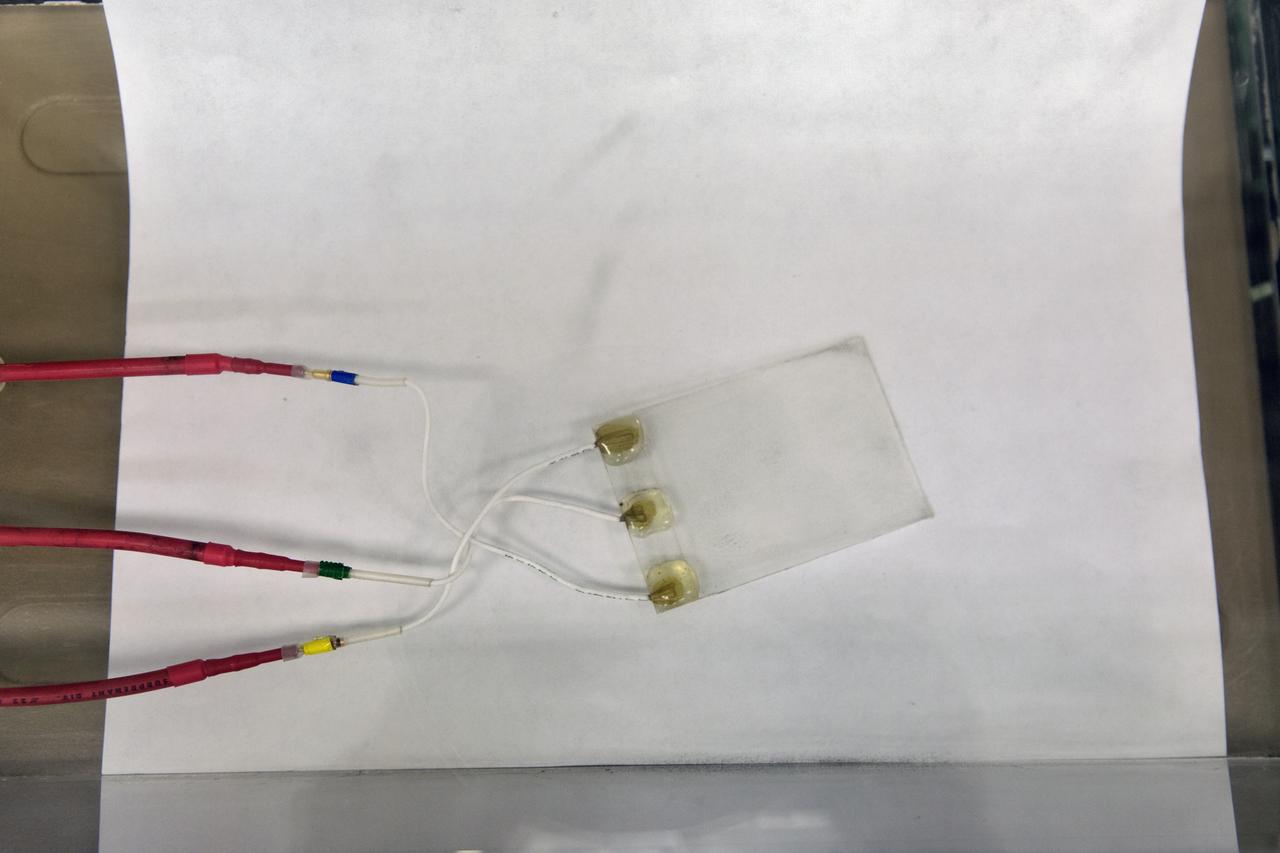
In the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an Electrostatic Dust Shield is prepared for testing on Thursday, July 19, 2018. Scientists are developing the Electrostatic Dust Shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, space suits and helmet visors of astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.
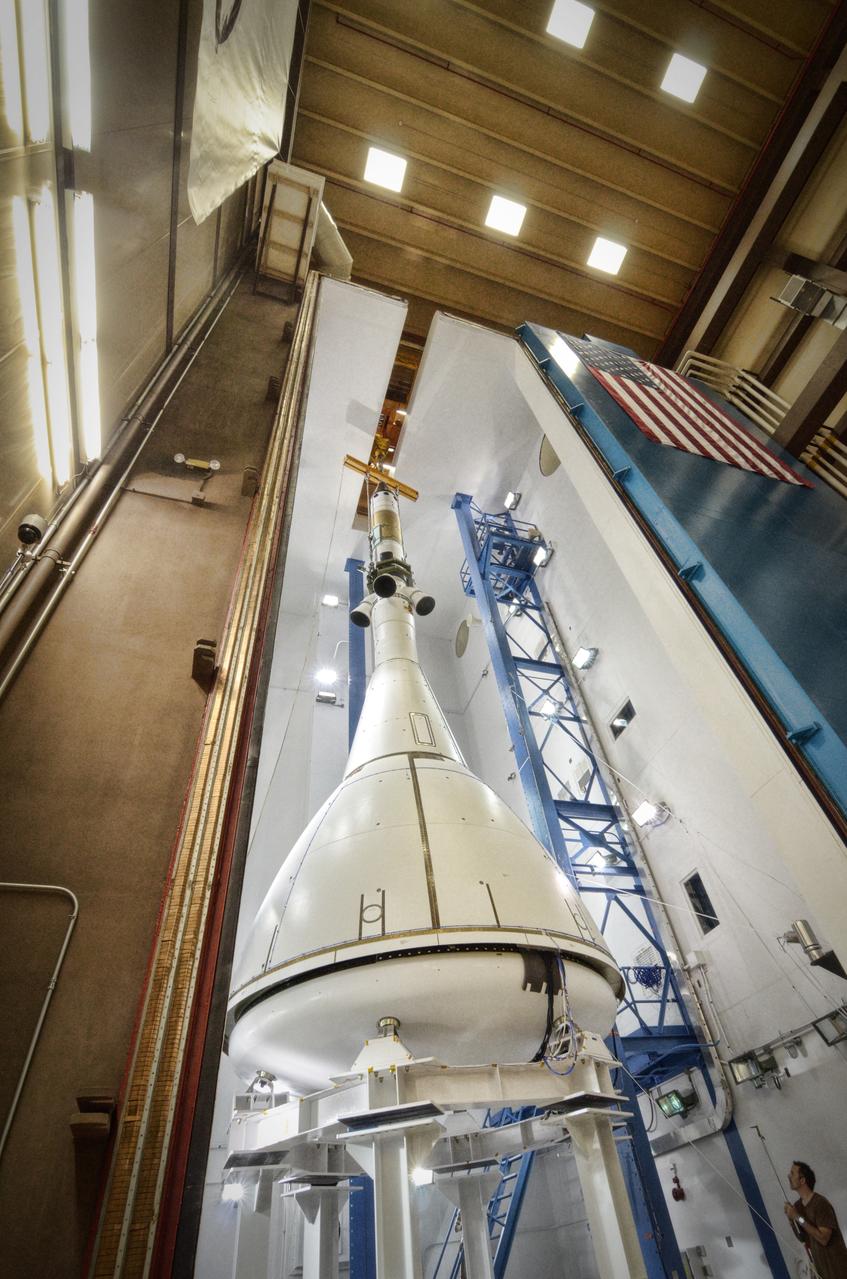

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, a technician prepares to reopen the lander petals of the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) to allow access to one of the spacecraft's circuit boards. A concern arose during prelaunch testing regarding how the spacecraft interprets signals sent from its main computer to peripherals in the cruise stage, lander and small deep space transponder. The MER Mission consists of two identical rovers set to launch in June 2003. The problem will be fixed on both rovers.

An image of the F-16XL #1 during its functional flight check of the Digital Flight Control System (DFCS) on December 16, 1997. The mission was flown by NASA research pilot Dana Purifoy, and lasted 1 hour and 25 minutes. The tests included pilot familiarly, functional check, and handling qualities evaluation maneuvers to a speed of Mach 0.6 and 300 knots. Purifoy completed all the briefed data points with no problems, and reported that the DFCS handled as well, if not better than the analog computer system that it replaced.

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 15, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
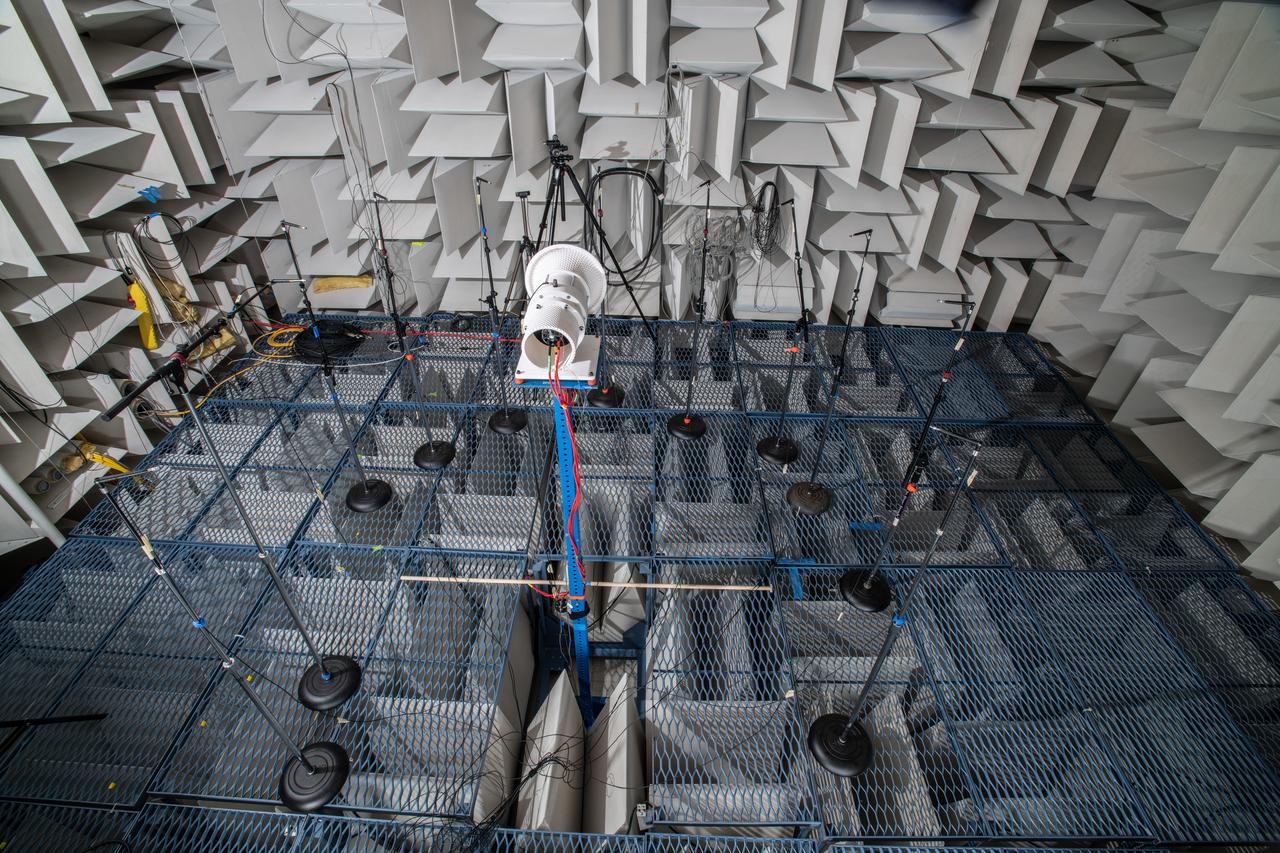

The Quiet Electric Engine V1 (QUEEN V1) experiment that was performed in the NASA GRC Acoustical Testing Laboratory (ATL). Equipment is installed in the anechoic chamber and in the adjacent control room. In response to the pervasive health and environmental problems associated with aviation noise and air pollution, NASA’s Quiet Electric Engine (QUEEN) team is working to increase the peace and quiet in the world by researching ways to make engines for large single-aisle aircraft safer, cleaner, and quieter.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a worker points to some of the tiles on orbiter Atlantis that are being dried by clusters of 200-300 watt heat lamps. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused a moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing. Engineers are evaluating the current procedures to assure the tiles are in a safe and flight-ready condition

The Orion ground test vehicle is prepared for the Launch Abort Vehicle Configuration Test at Lockheed Martin's facilities in Denver on Sept. 14, 2011. For this test, the vehicle was covered with fillets and ogive panels that resemble the vehicle's launch configuration. The spacecraft underwent testing at sound pressure levels that emulate those experienced at launch and in the event an abort is needed to carry the crew to safety away from a potential problem on the launch pad or during ascent. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.