Processes of Geology

Slope Processes

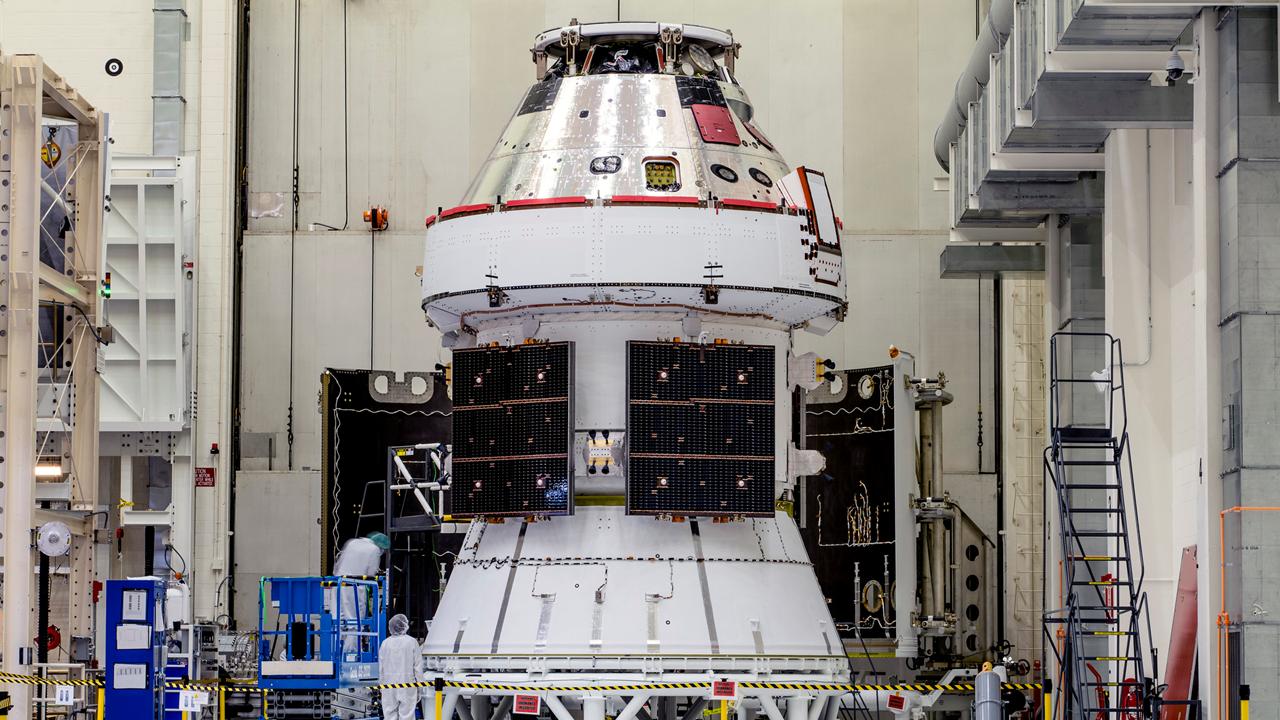
NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on May 8. The fluid transfer module will demonstrate innovative methods to store, transfer and freeze standard cryogenic fluid in space. RRM3 is scheduled to launch to the International Space Station later this year.
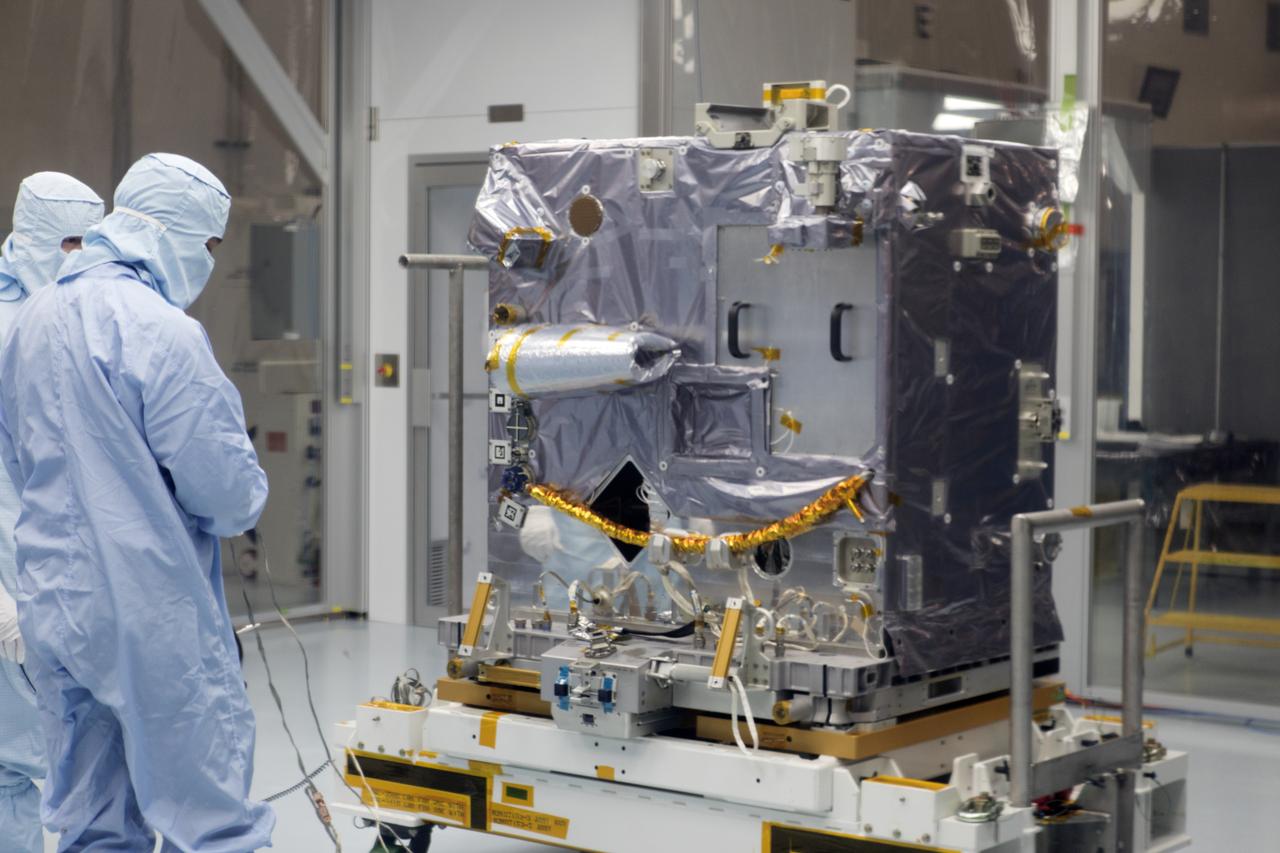

NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on May 8. The mission, which is scheduled to launch to the International Space Station later this year, will advance satellite servicing capabilities that will enable long duration, deep space exploration.
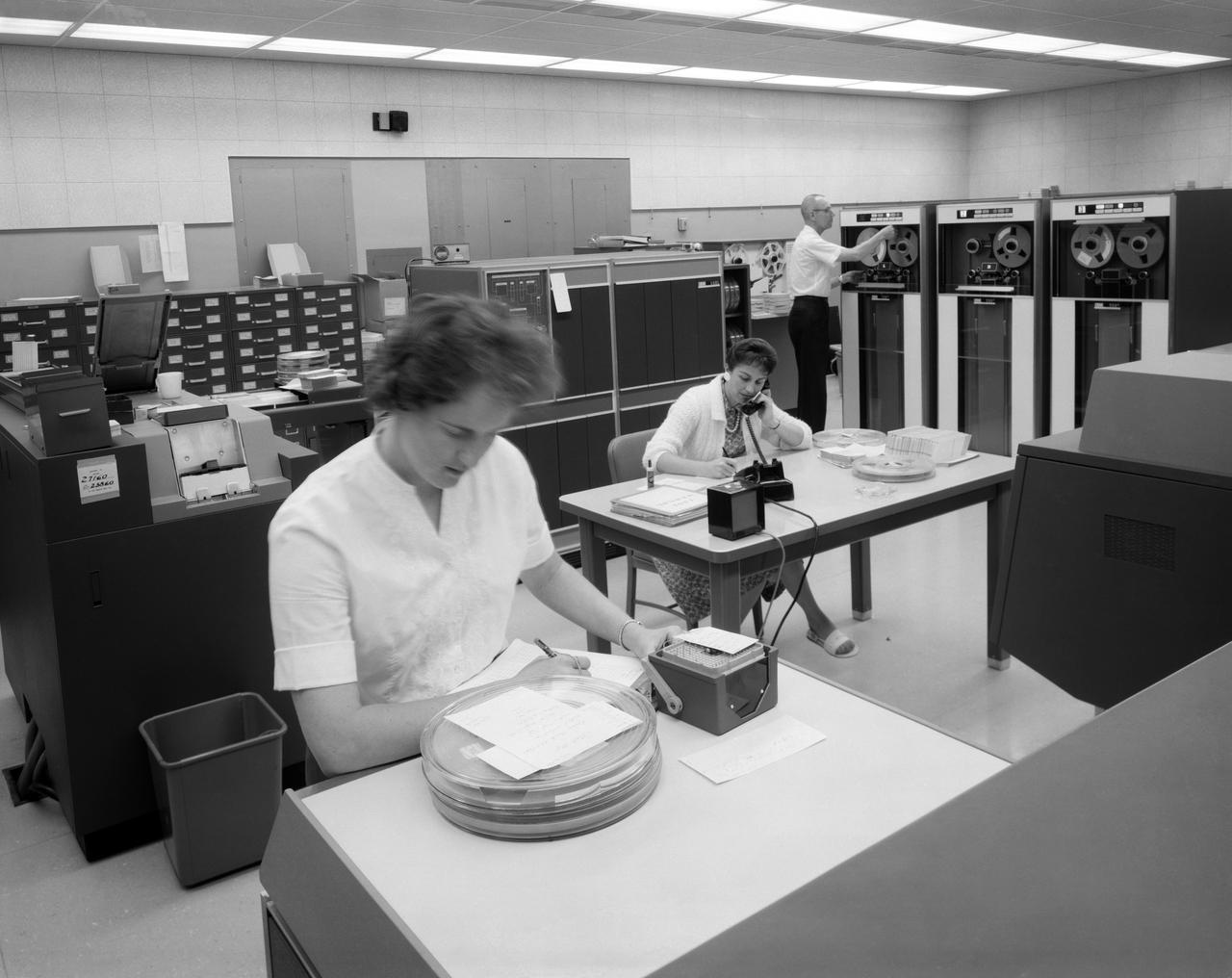

IBM 1401 Data Processing System, at NASA's Ames Research Center.
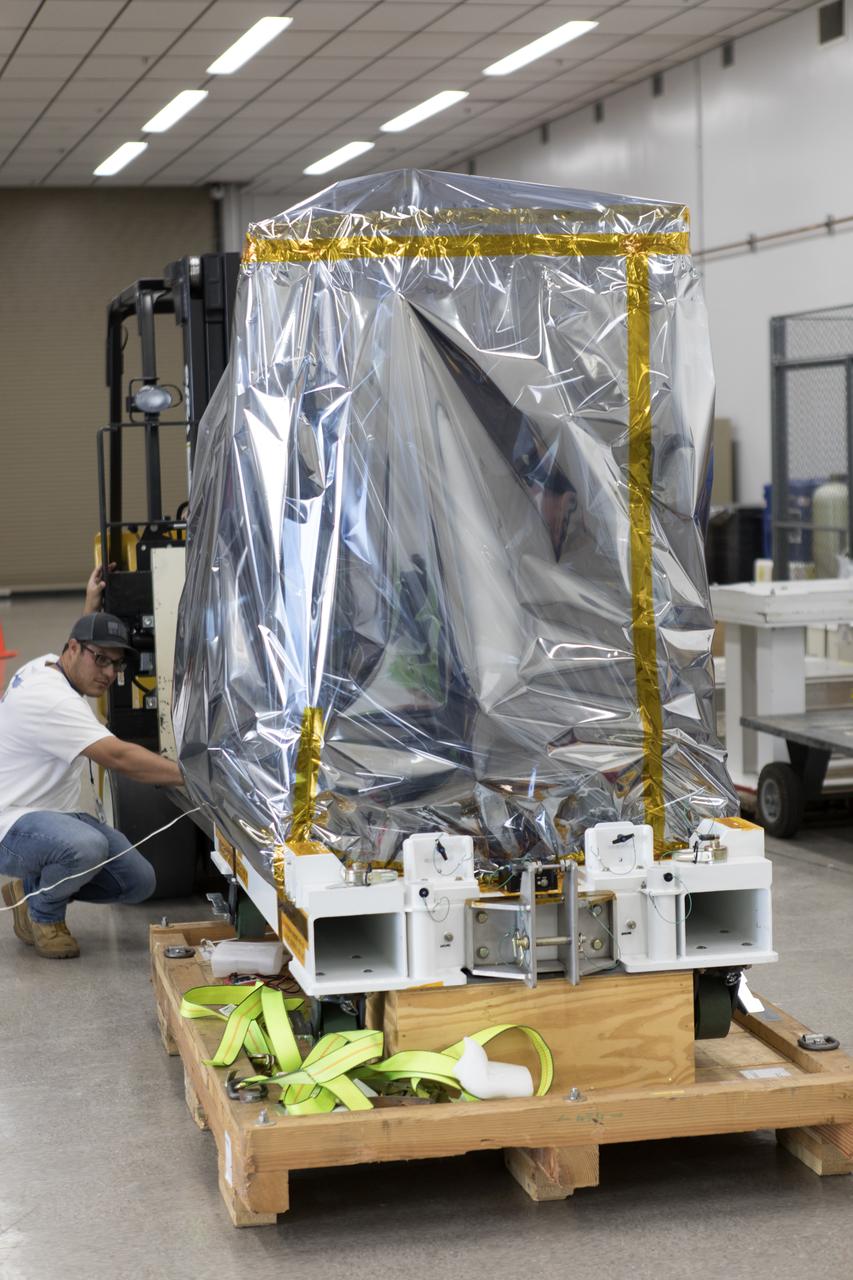

NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) builds on the first two phases of International Space Station (ISS) technology demonstrations that tested tools, technologies and techniques to refuel and repair satellites in orbit. RRM3, which arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on May 8, is planned to launch to the ISS later this year.
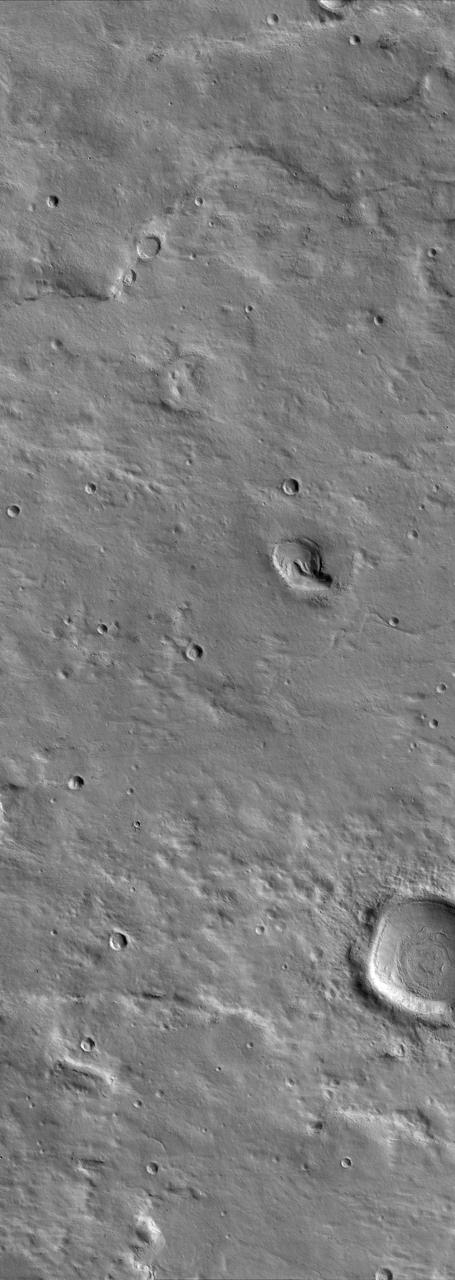

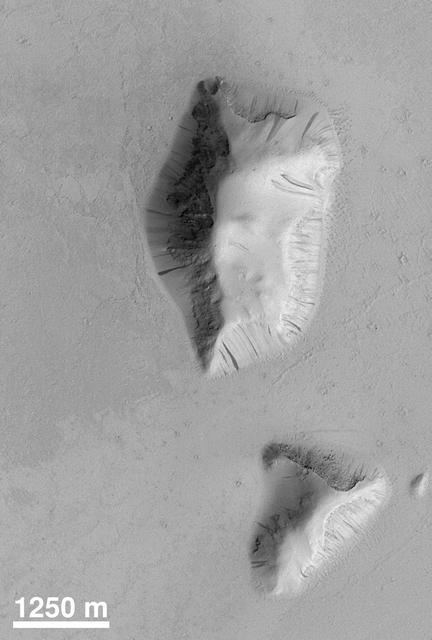
A Myriad of Geologic Processes in Terra Cimmeria

Eros Details Enhanced by Computer Processing
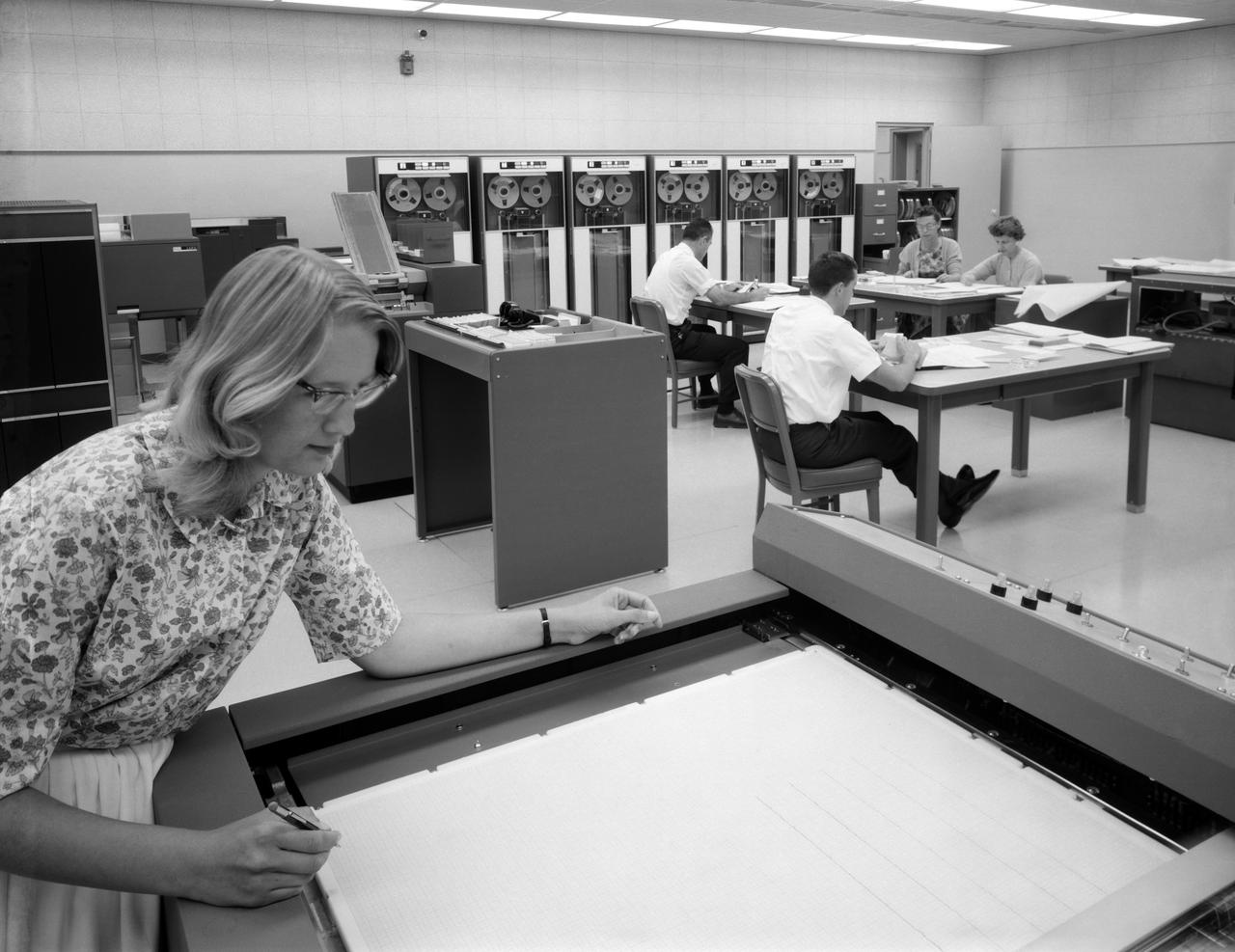

IBM 1401 Data Processing System at NASA Ames Research Center.
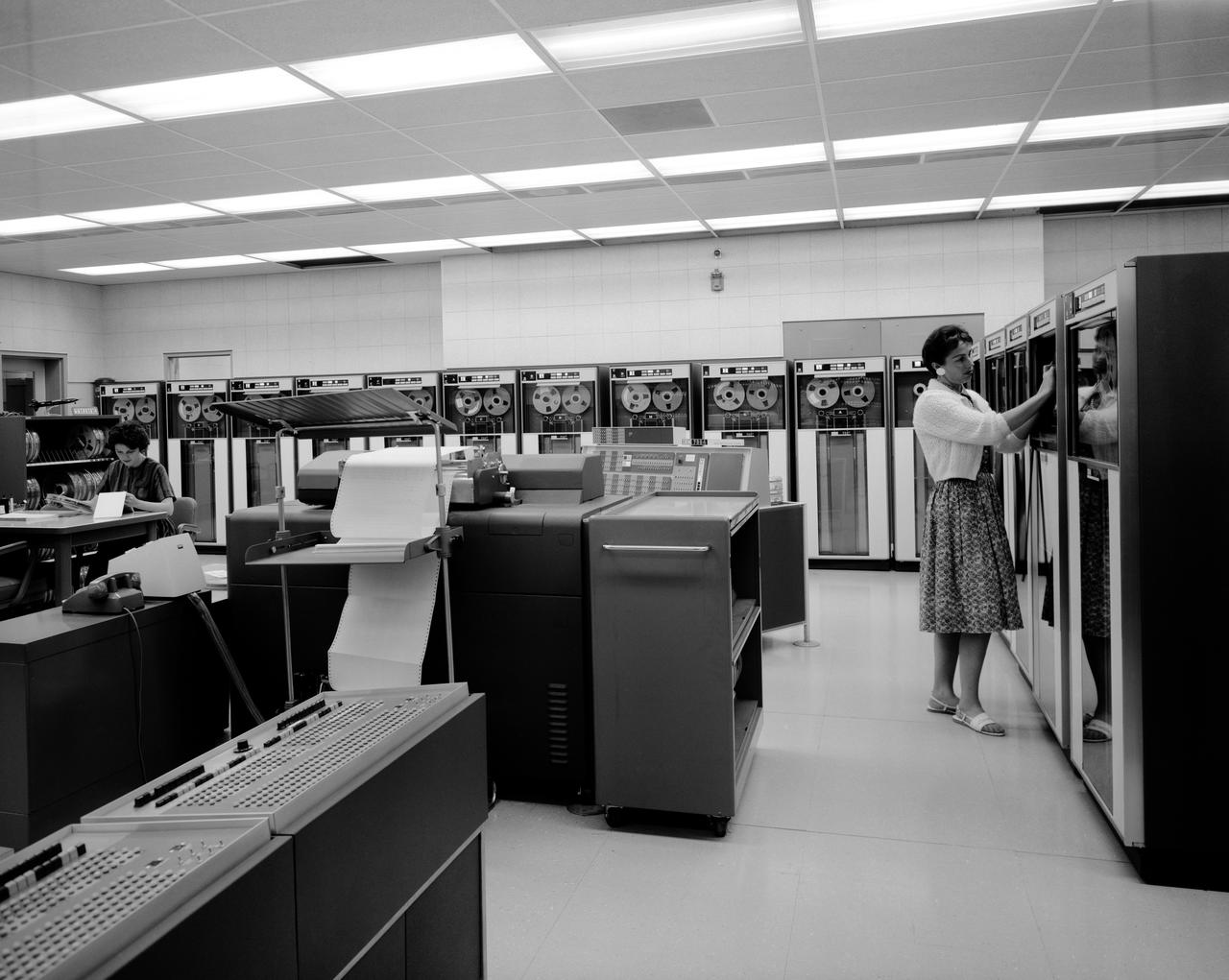

Equipment: Data Processing and Data Reduction at the NASA Ames Research Center, EMC. IBM 7090 Data Processing System.
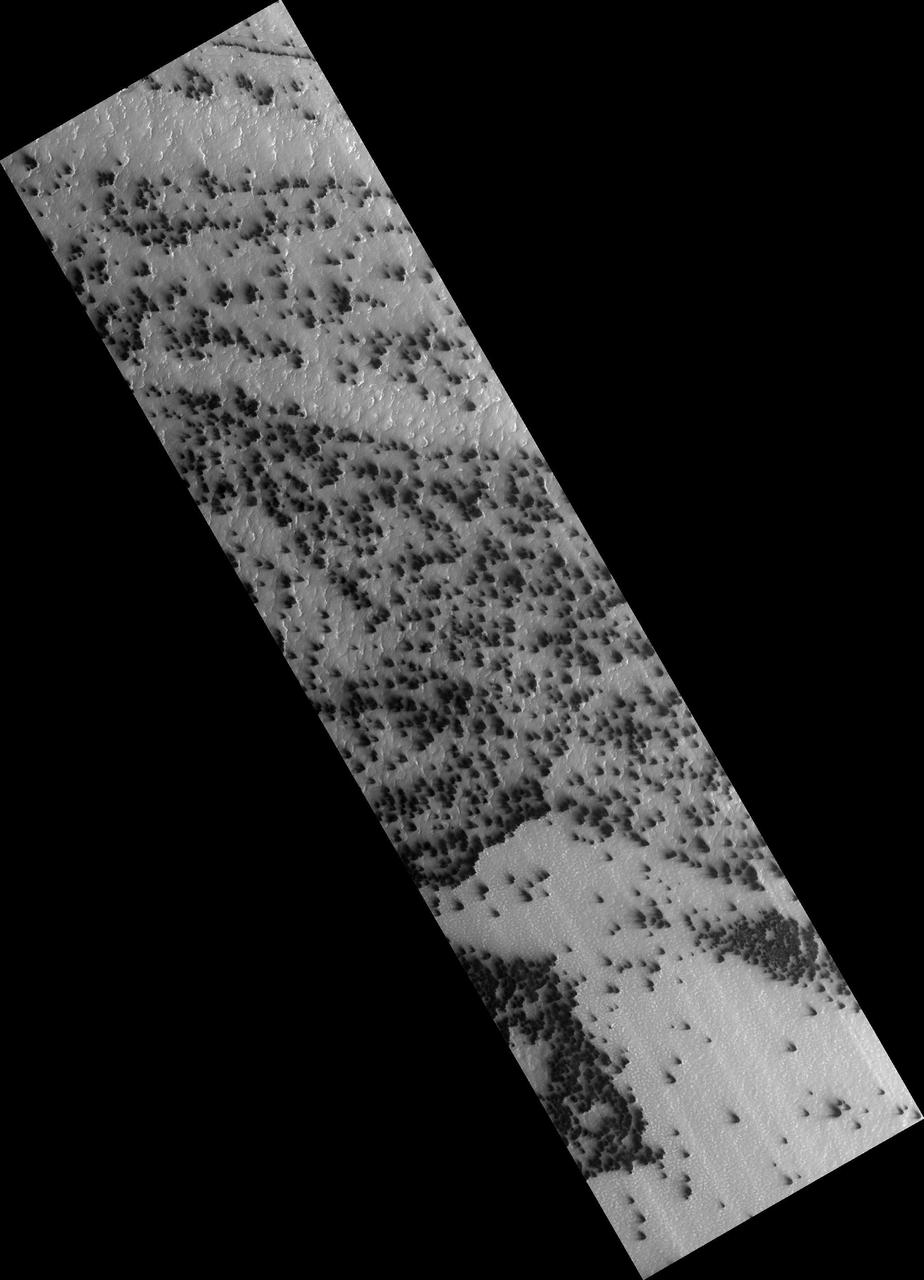

Active Processes: Bright Streaks and Dark Fans

The technology to replenish crucial satellite supplies in space currently does not exist. NASA is looking to help change that with Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3). The fluid transfer module arrived at Kennedy Space Center on May 8, and is planned to launch to the International Space Station later this year.
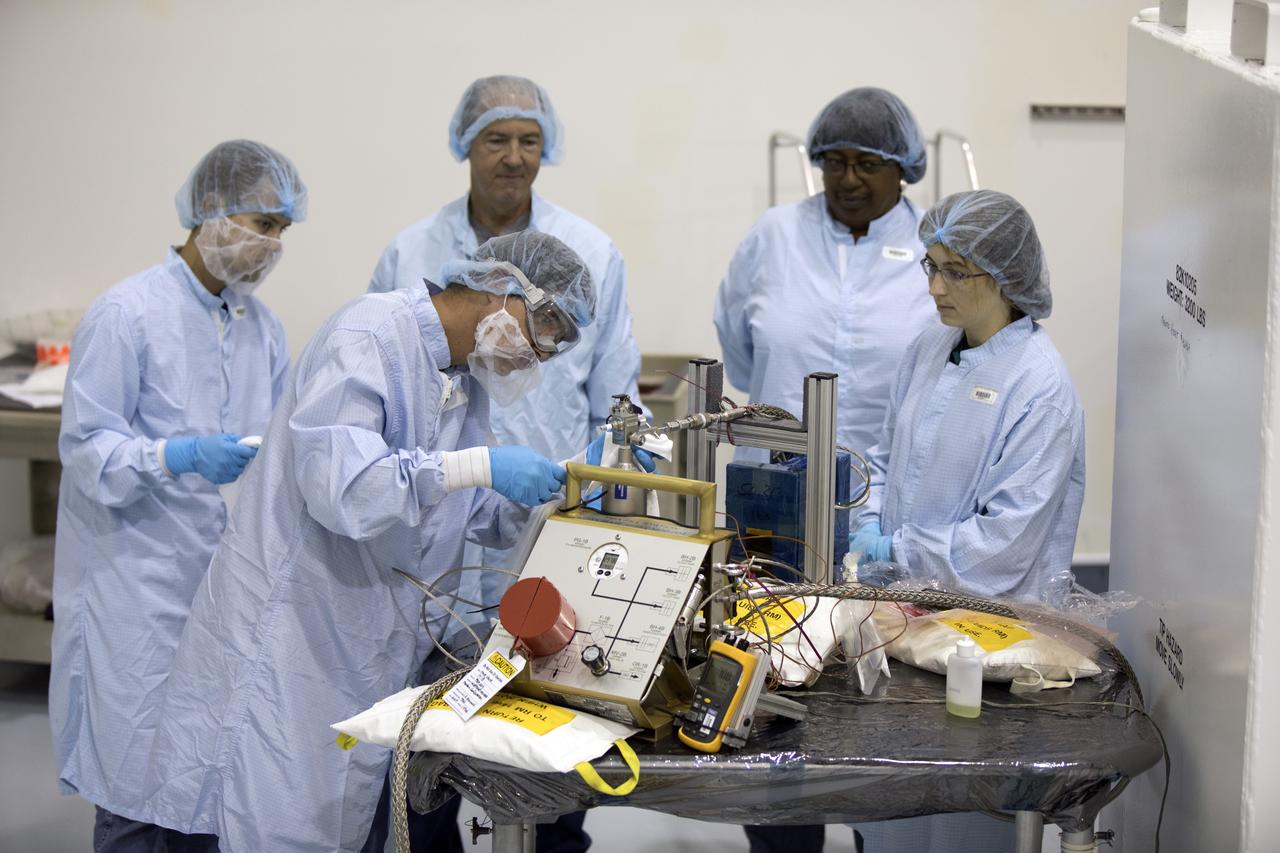

In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacobs Test and Operations Support Contract, or TOSC, technicians fill portable breathing apparatuses, or PBAS. The PBAs are to be use on board the International Space Staton to provide astronauts with breathable air in the event of a fire or other emergency situation.
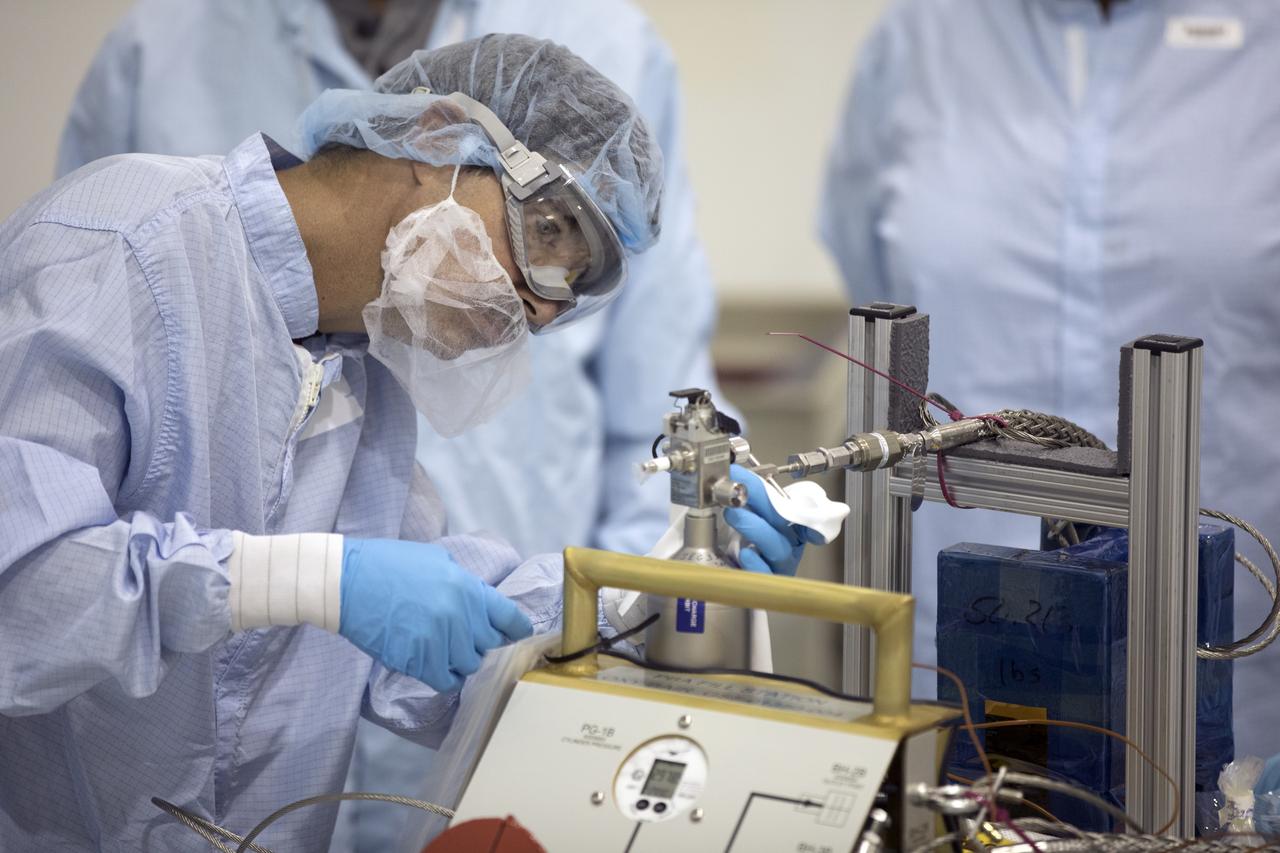

In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacobs Test and Operations Support Contract, or TOSC, technician Rod Ostgrard helps fill portable breathing apparatuses, or PBAS. The PBAs are to be use on board the International Space Staton to provide astronauts with breathable air in the event of a fire or other emergency situation.
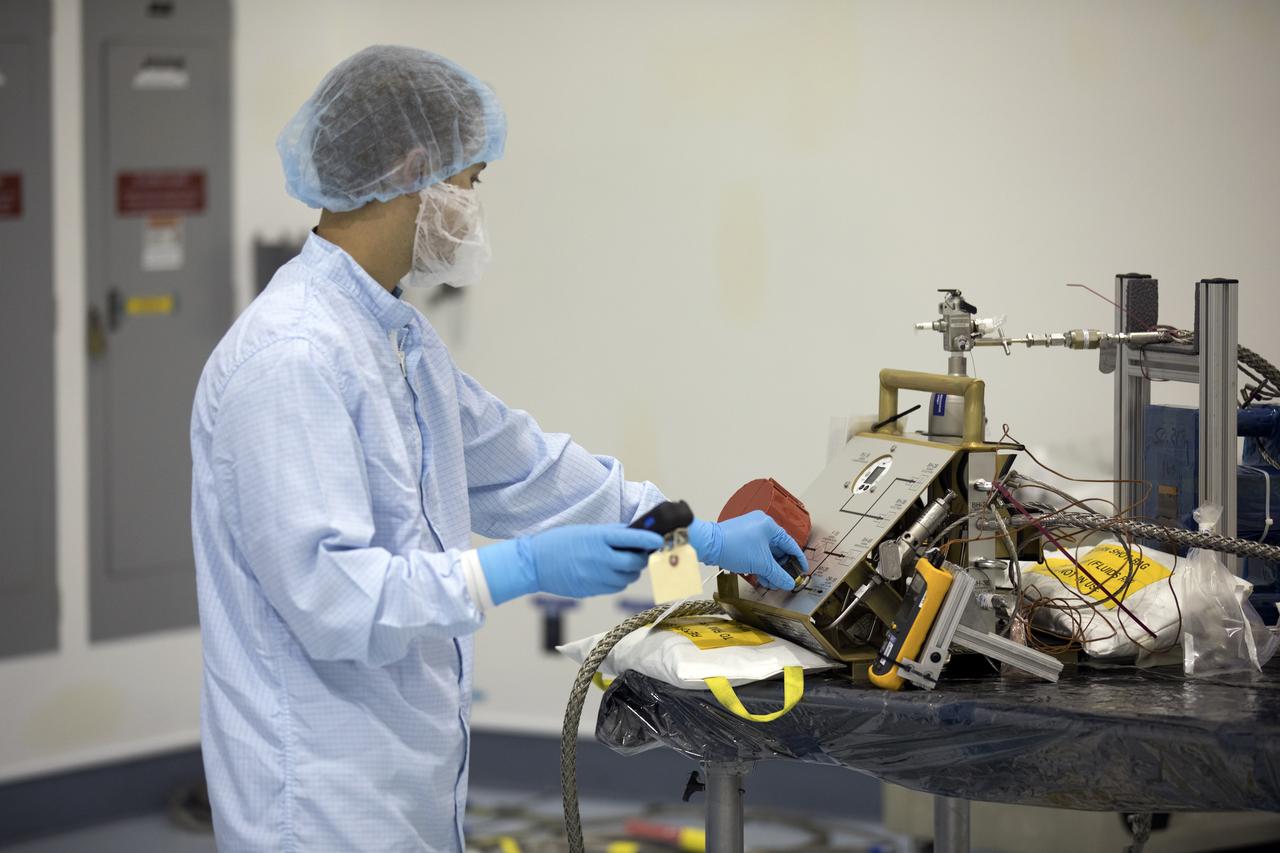

In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacobs Test and Operations Support Contract, or TOSC, technician John Thompson helps fill portable breathing apparatuses, or PBAS. The PBAs are to be use on board the International Space Staton to provide astronauts with breathable air in the event of a fire or other emergency situation.
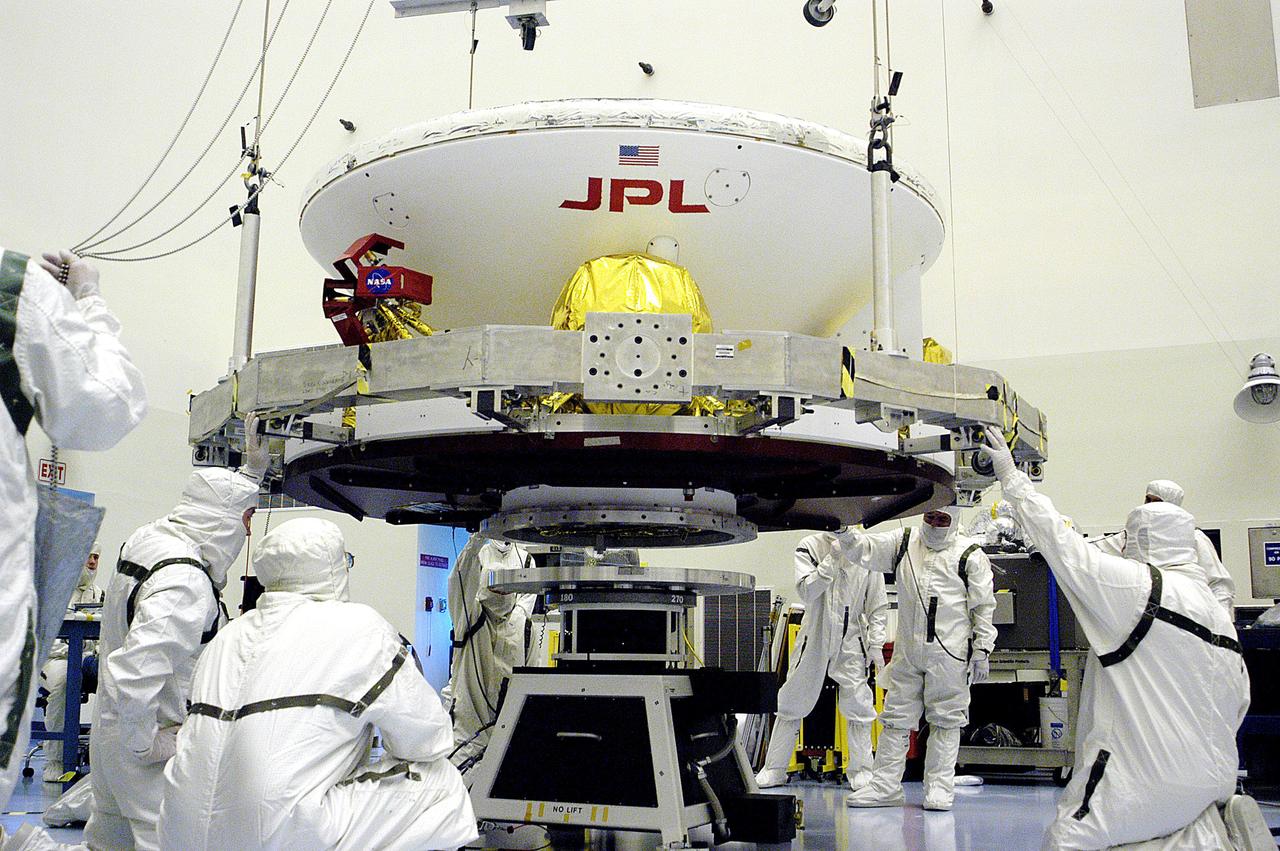

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, workers prepare to lift the Mars Exploration Rover-1 MER-B onto a spin table during preflight processing of the spacecraft.
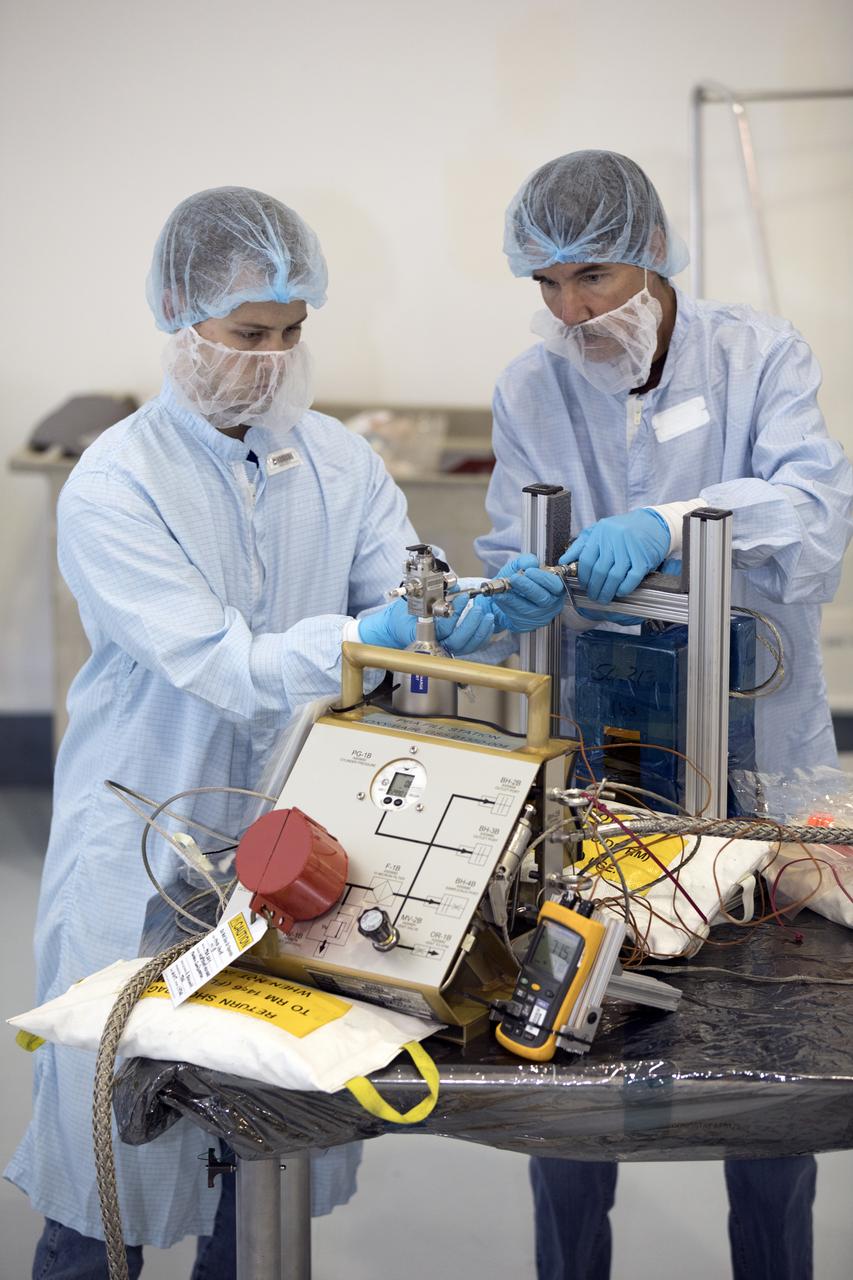

In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacobs Test and Operations Support Contract, or TOSC, technicians John Thompson, left and Rod Ostgrad, help fill portable breathing apparatuses, or PBAS. The PBAs are to be use on board the International Space Staton to provide astronauts with breathable air in the event of a fire or other emergency situation.
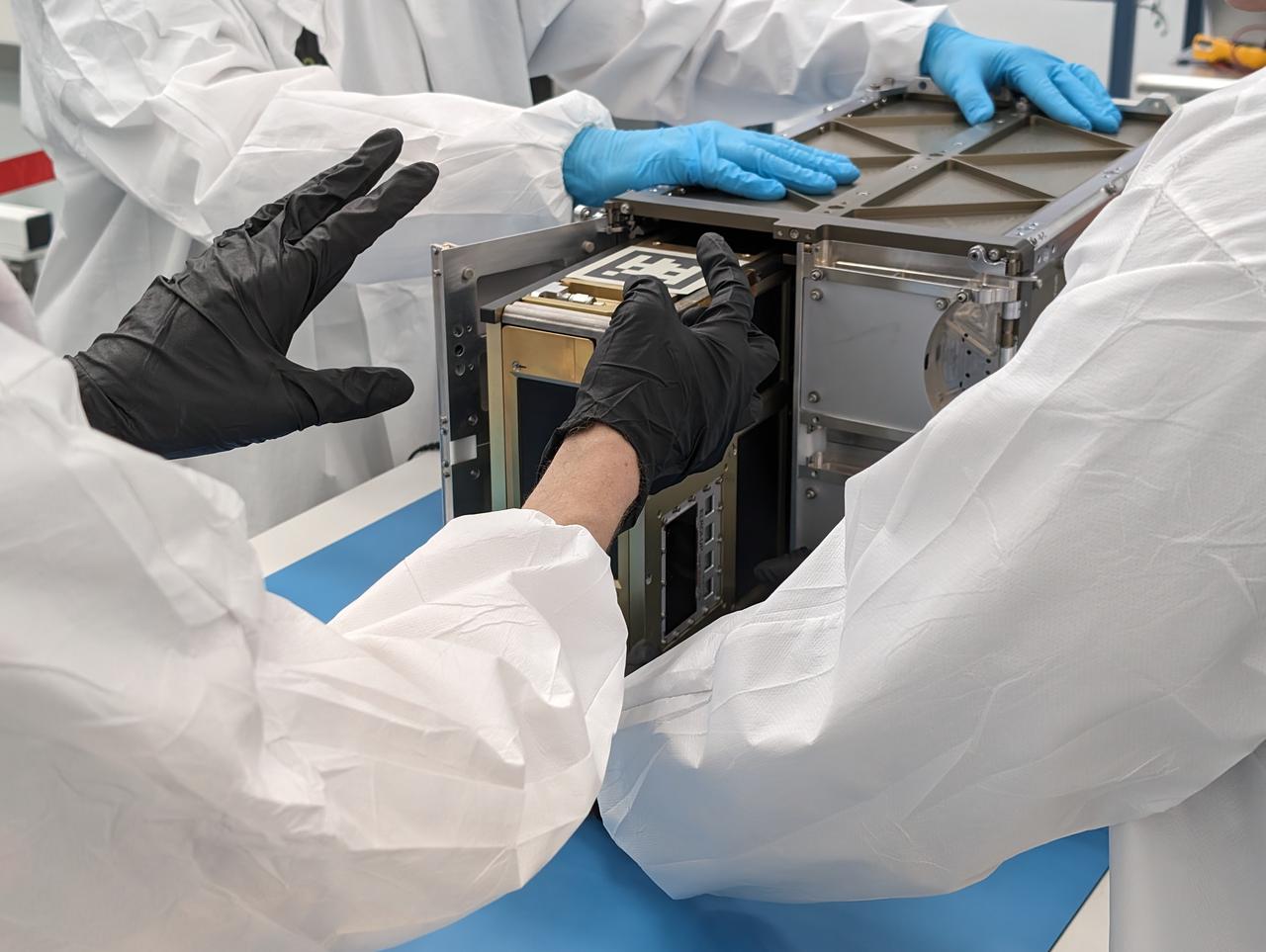

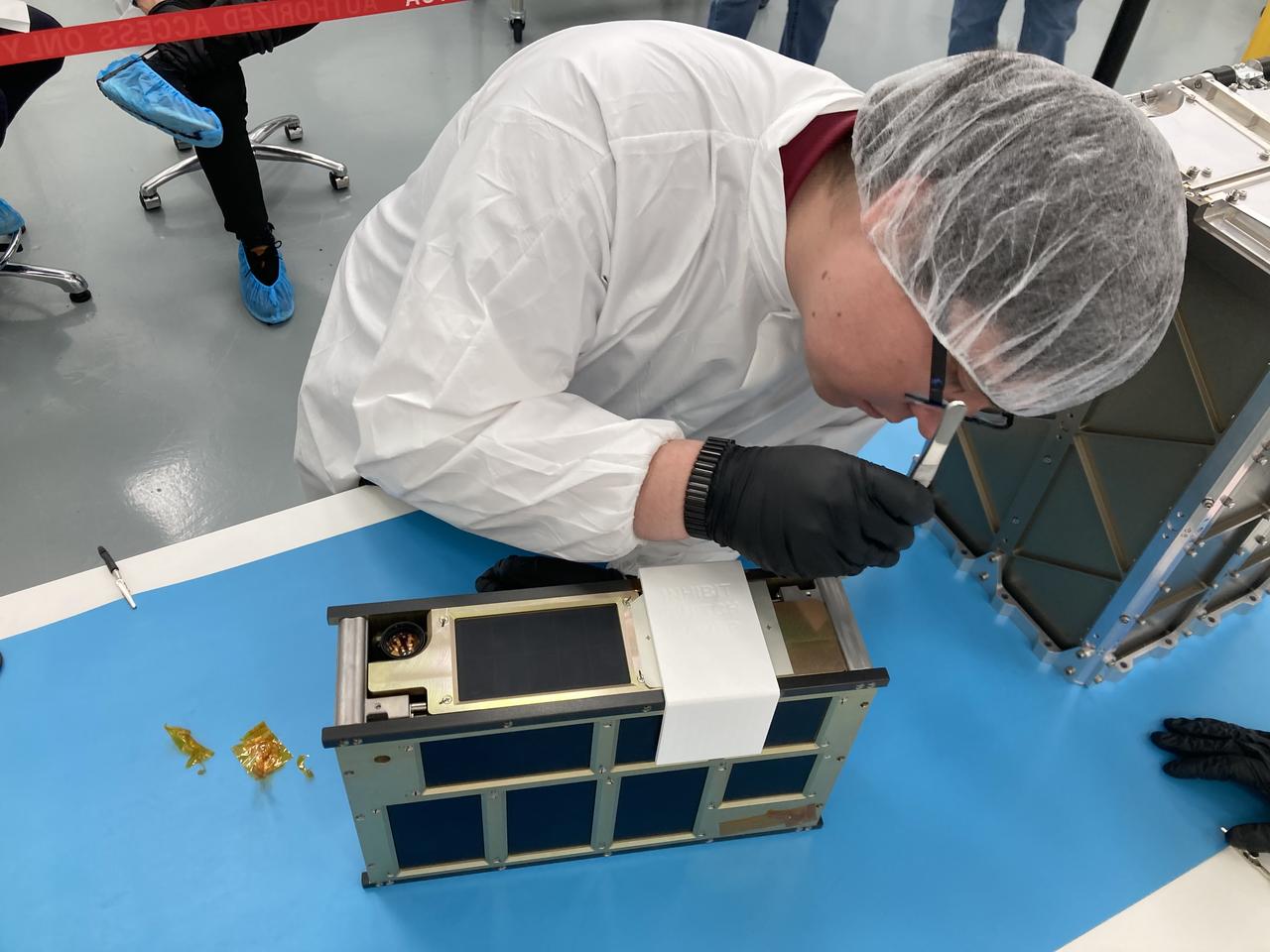
A NASA engineer installs the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) into the dispenser at Firefly Aerospace's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
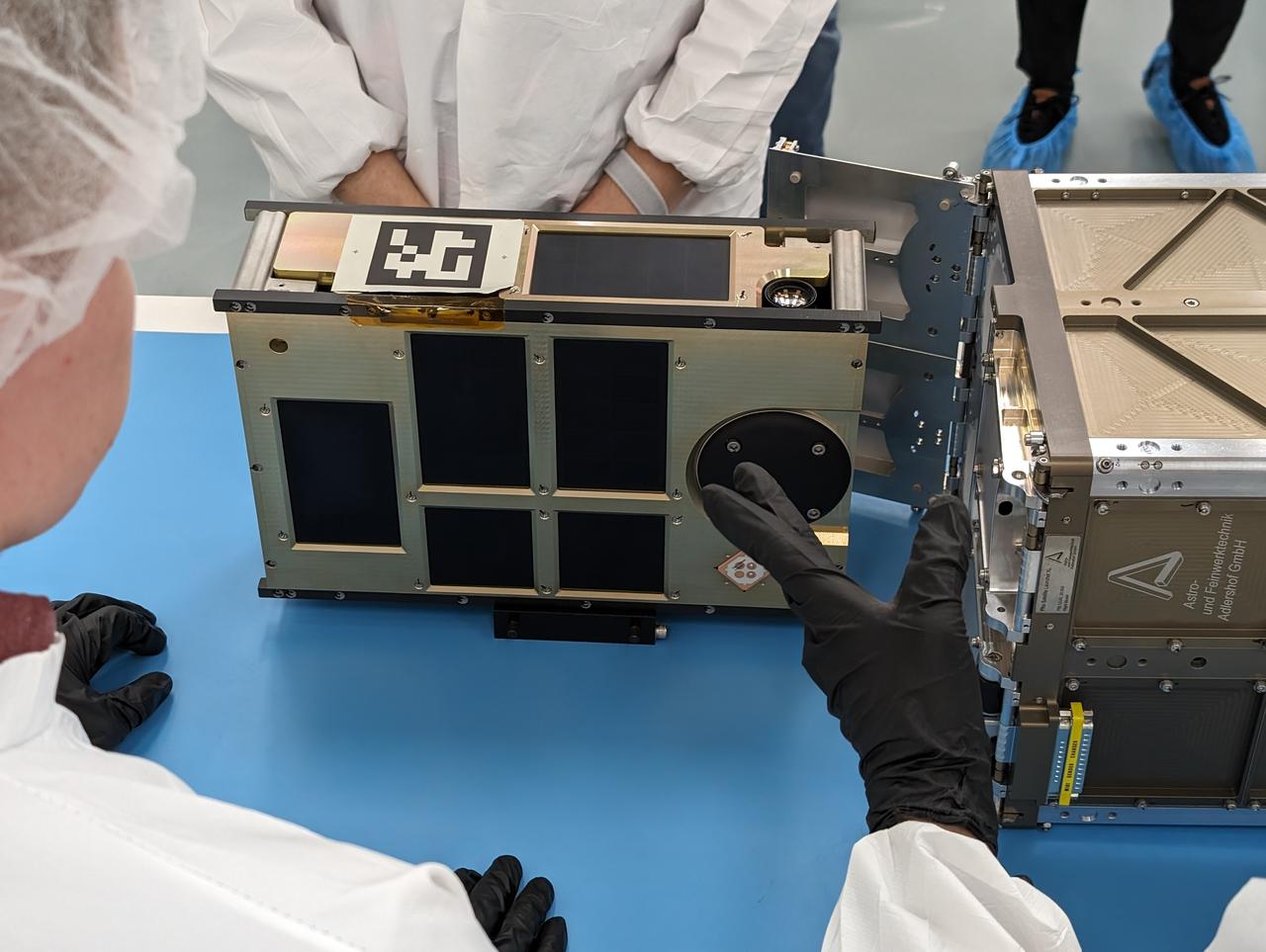

NASA and Firefly Aerospace engineers review the integration plan for the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
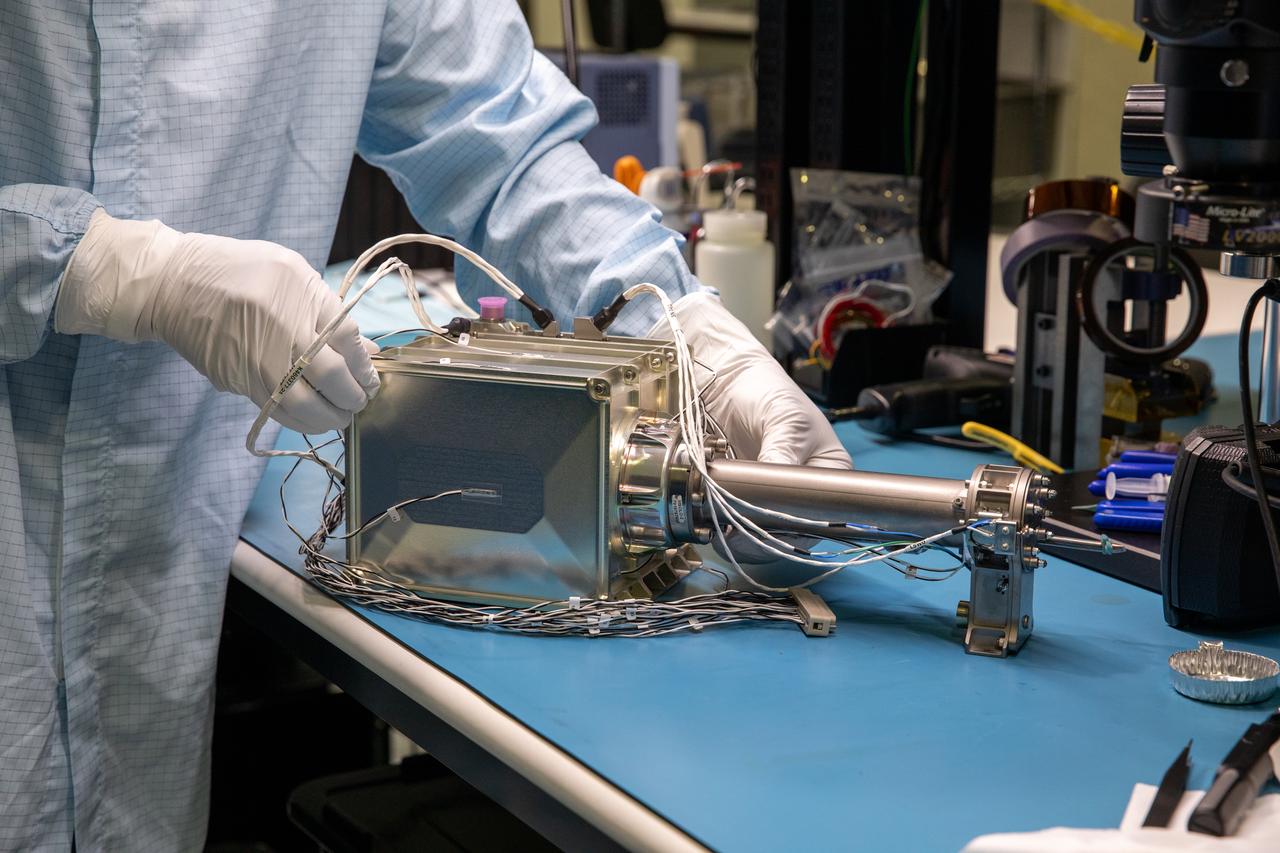

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
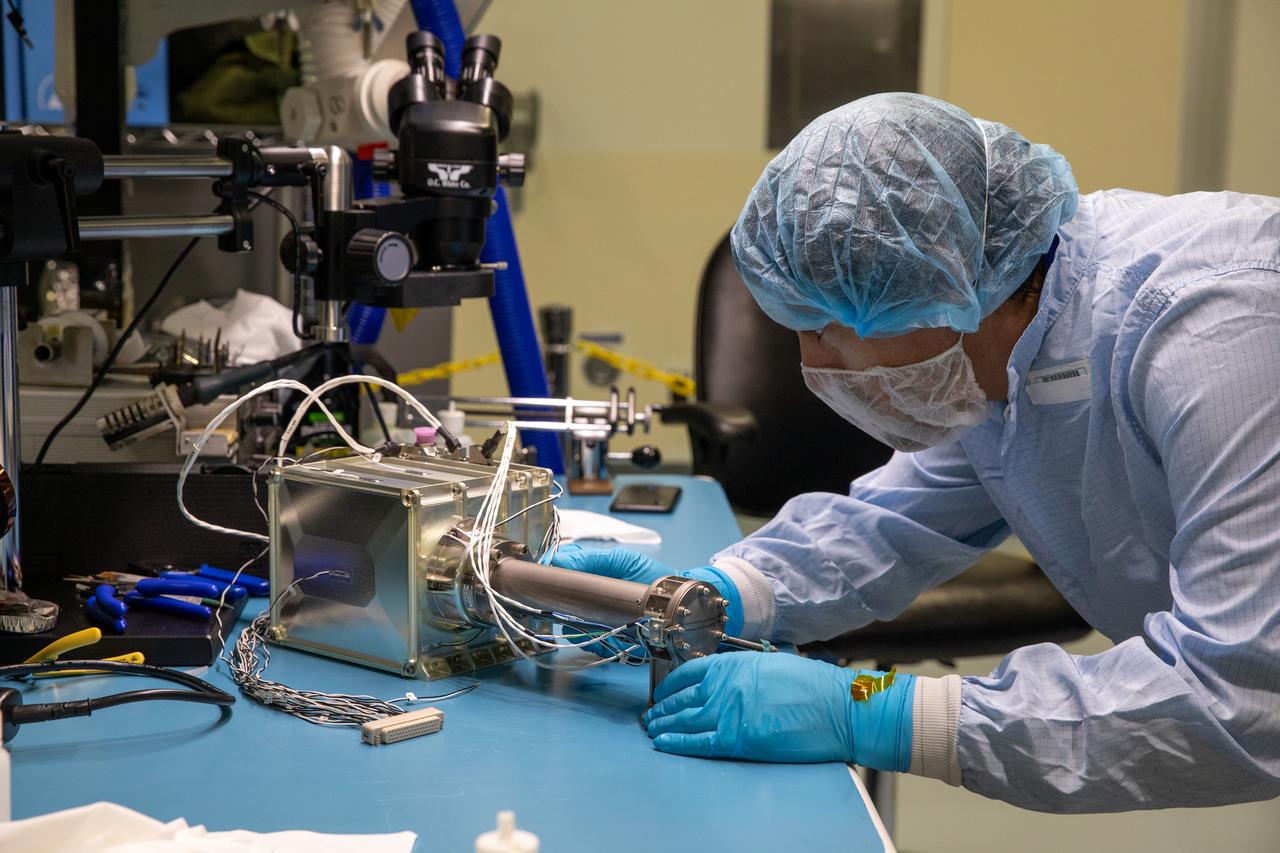

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
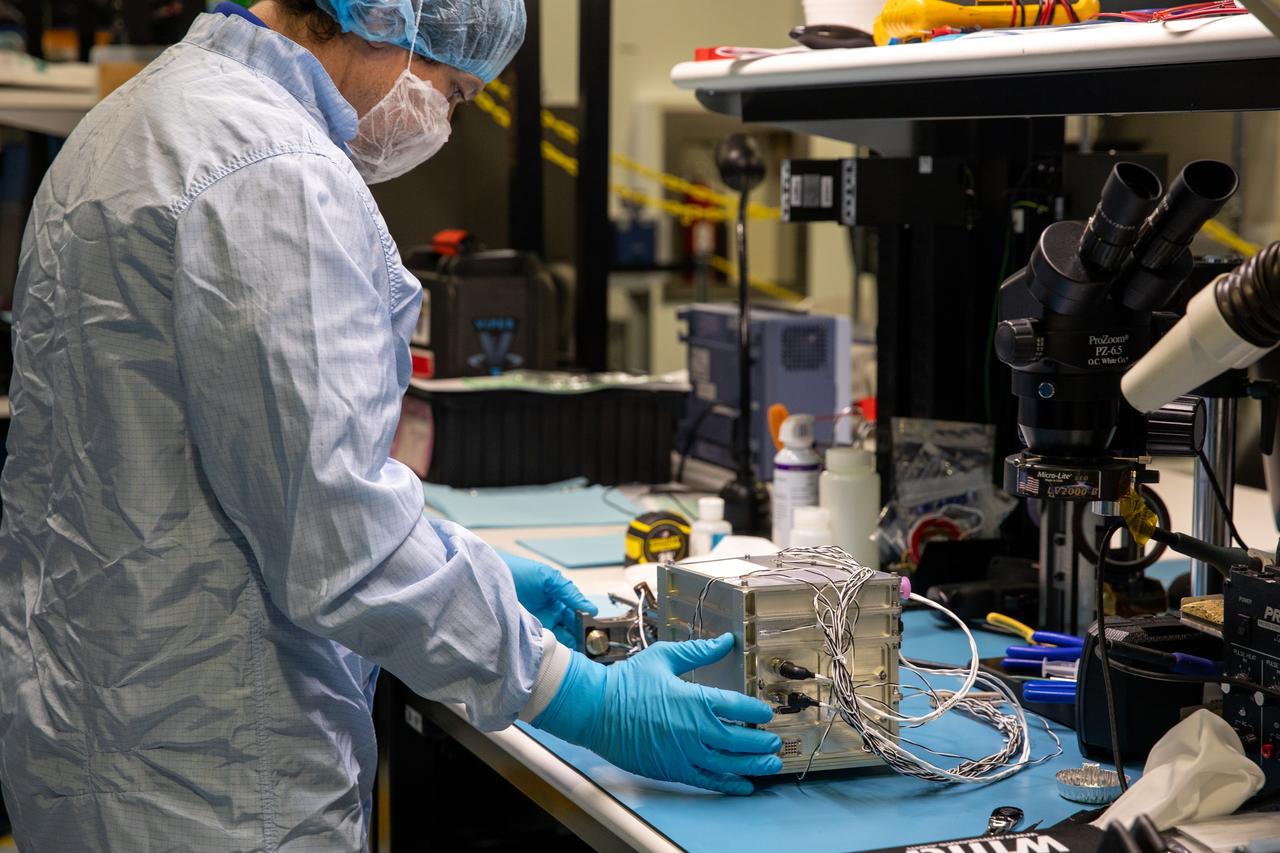

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
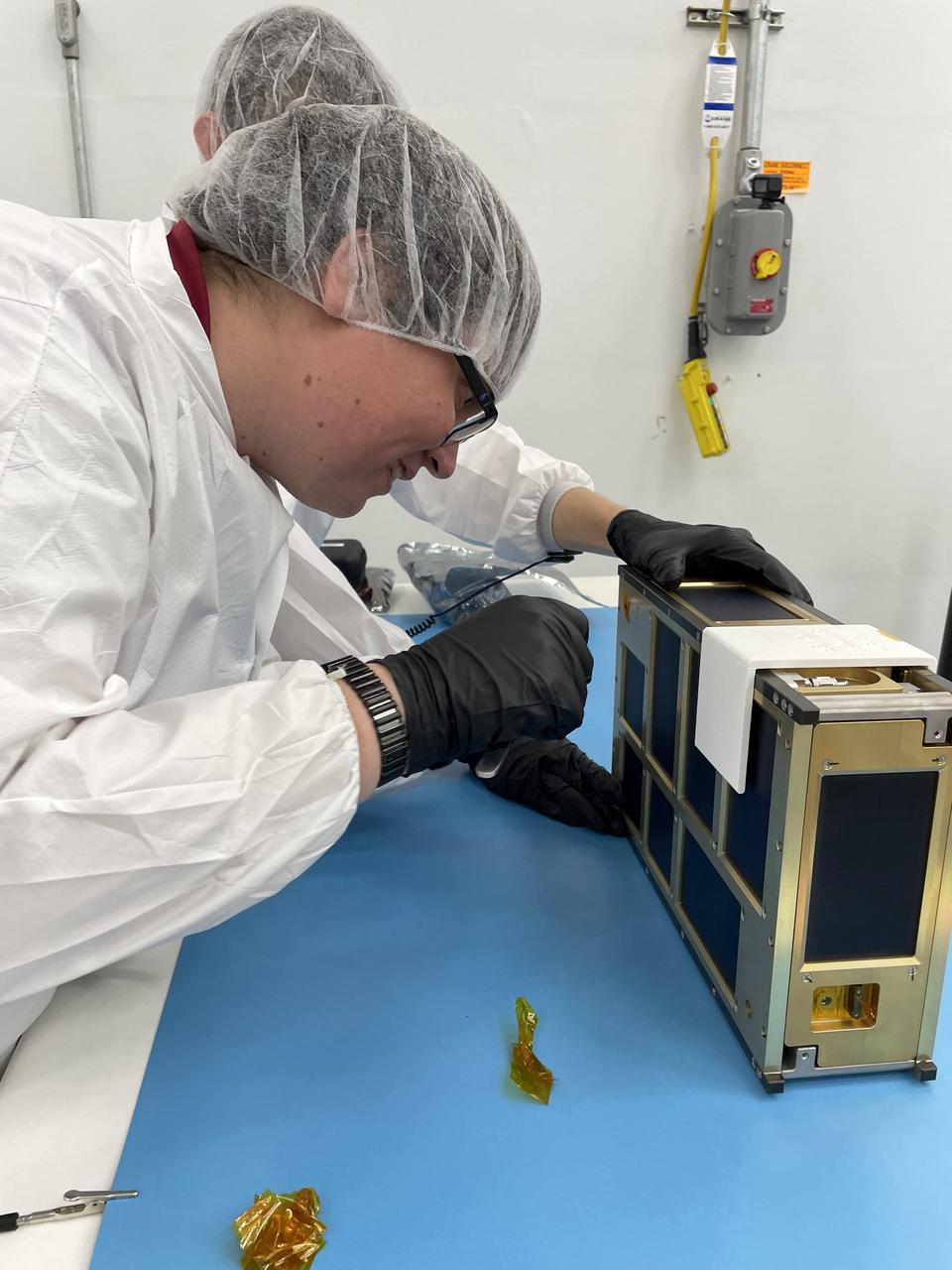

NASA engineer Jacob Nunez-Kearny removes the foreign object debris (FOD) cover from the propulsion system on the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract .
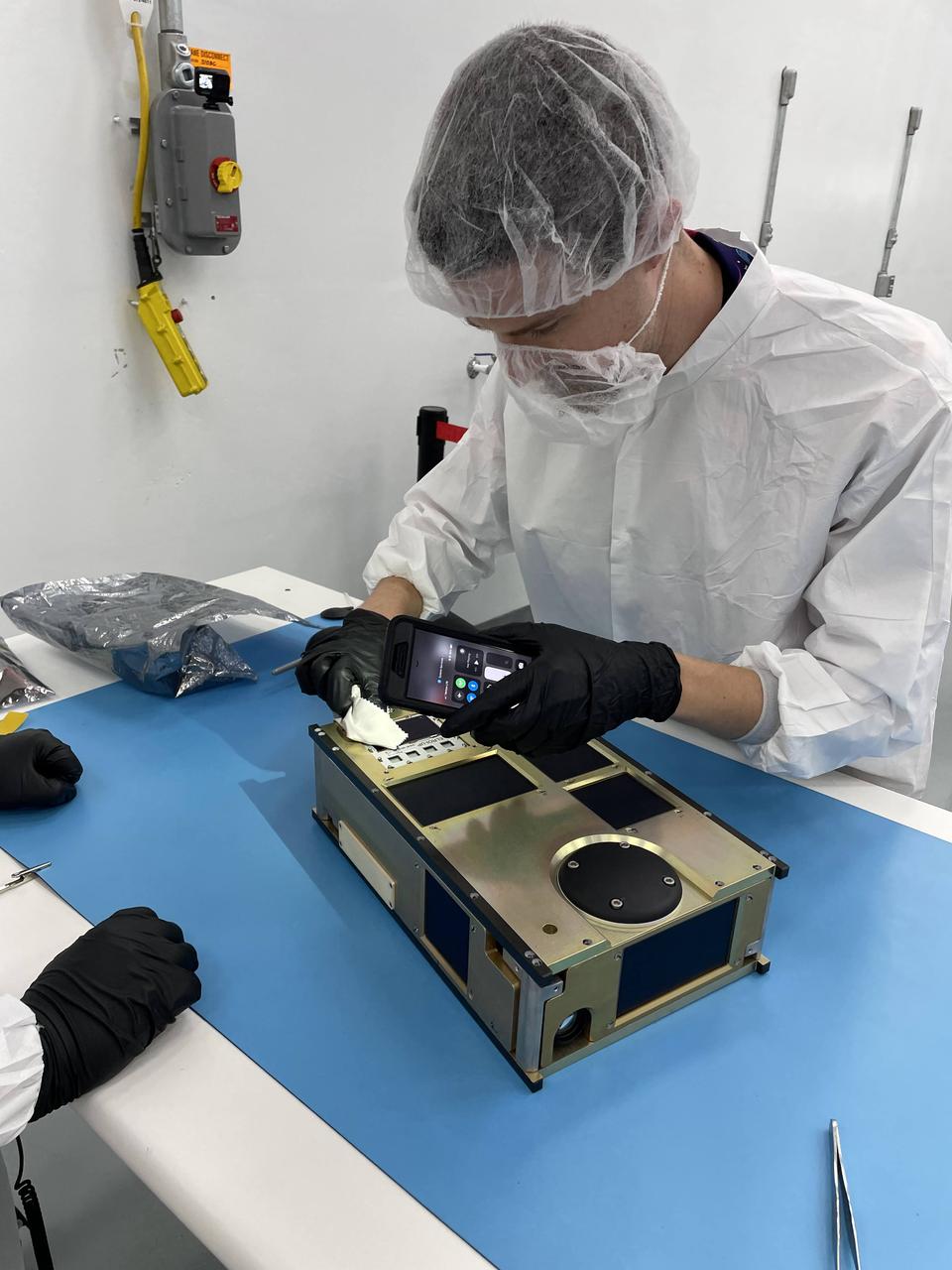

NASA engineer Sam Pedrotty performs final cleaning of Los Alamos National Laboratory’s (LANL’s) Extremely Low Resource Optical Identifier (ELROI) on the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

From left, Firefly mission manager Marcy Mabry observes NASA engineer James Berck install the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) into the dispenser at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

NASA engineer Jacob Nunez-Kearny removes foreign object debris (FOD) cover from the propulsion system on the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
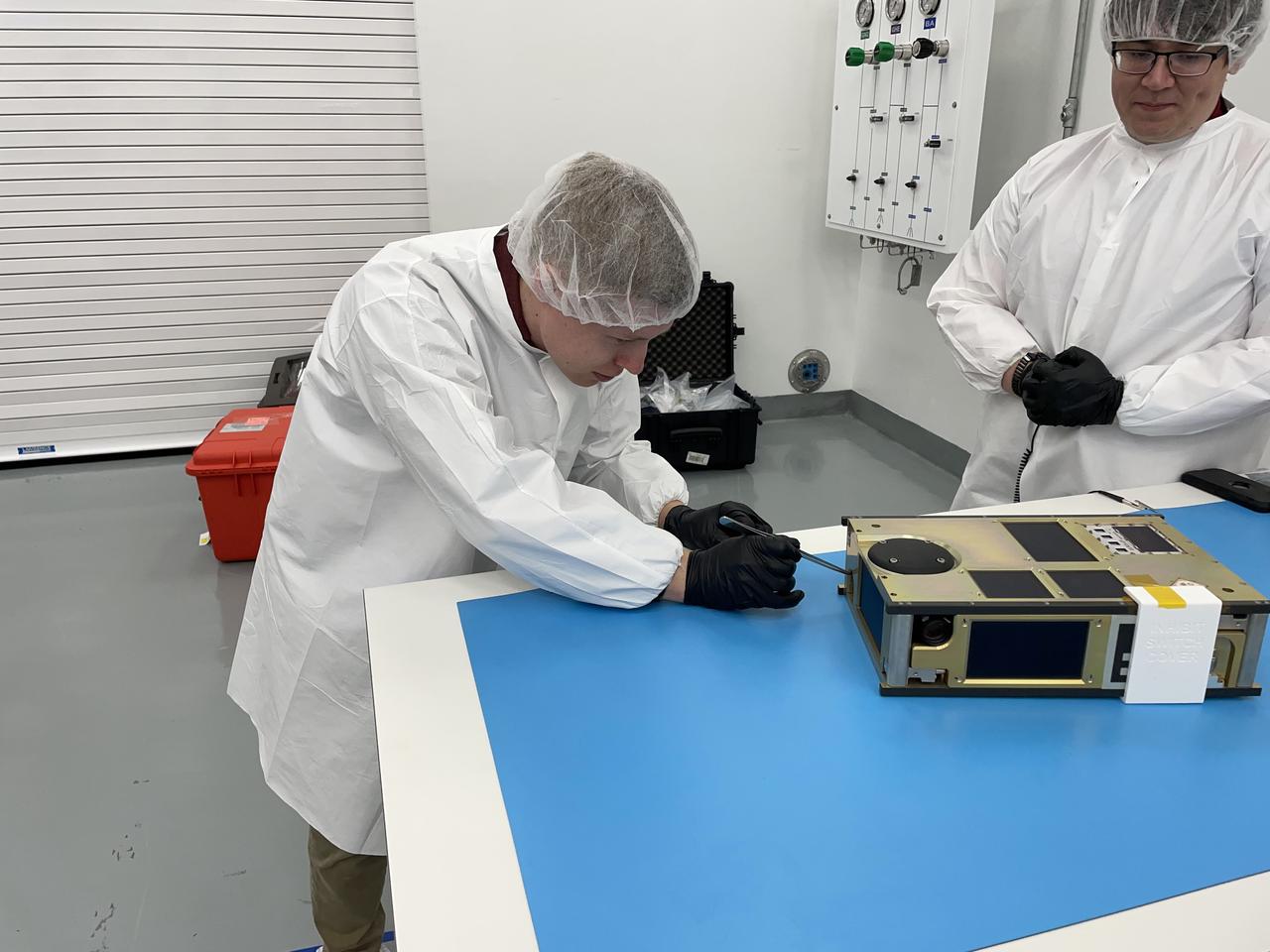

From left, NASA engineer James Berck removes the foreign object debris (FOD) cover from the relative navigation camera on the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) while NASA engineer Jacob Nunez-Kearny observes, at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

NASA engineers work on the Restore-L payload in the high bay inside the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on May 16, 2019. Restore-L, managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is an in-flight robotic satellite servicer spacecraft. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The SSPF was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
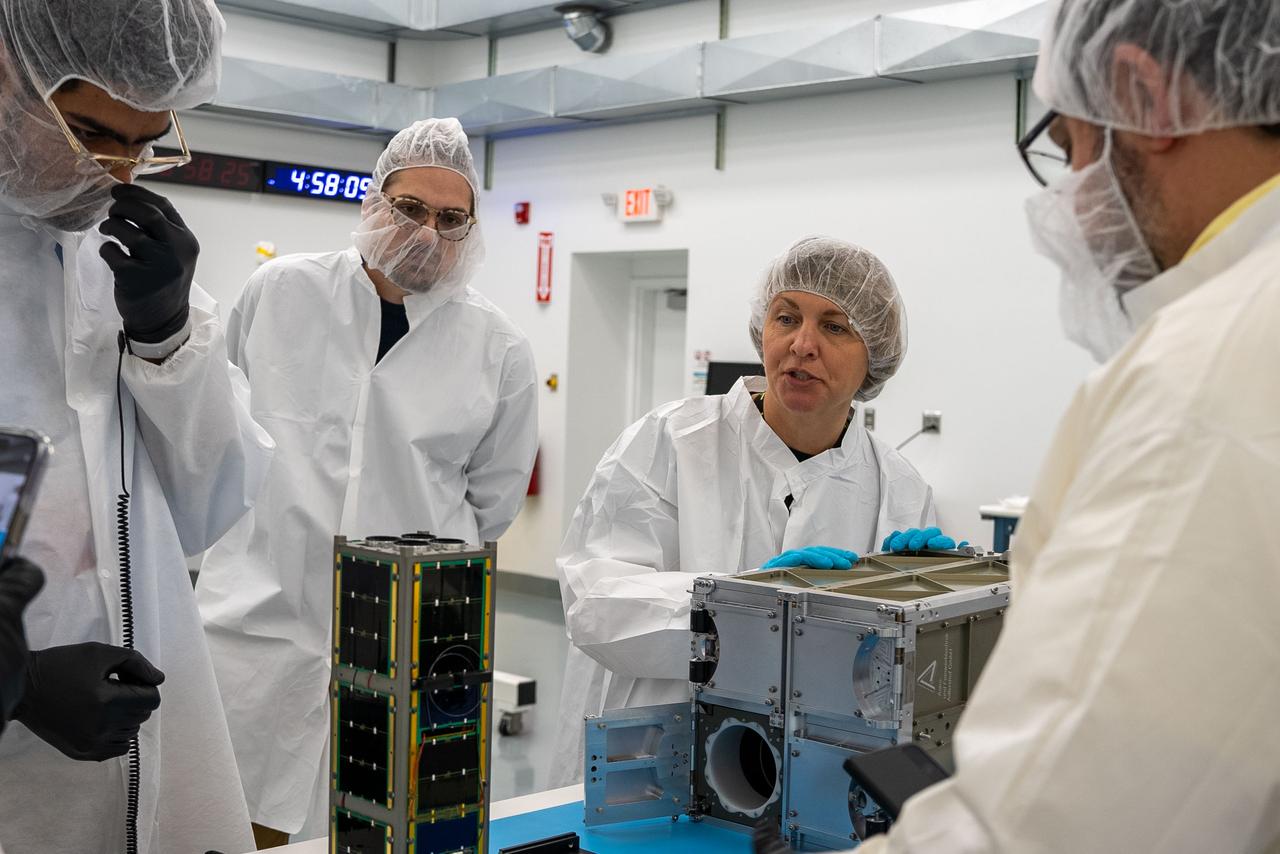

Technicians from the University of Maine prepare CubeSat MESAT-1 for integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Monday, April 22, 2024. MESAT-1, along with seven other payloads, will be integrated into a Firefly Aerospace Alpha rocket for NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
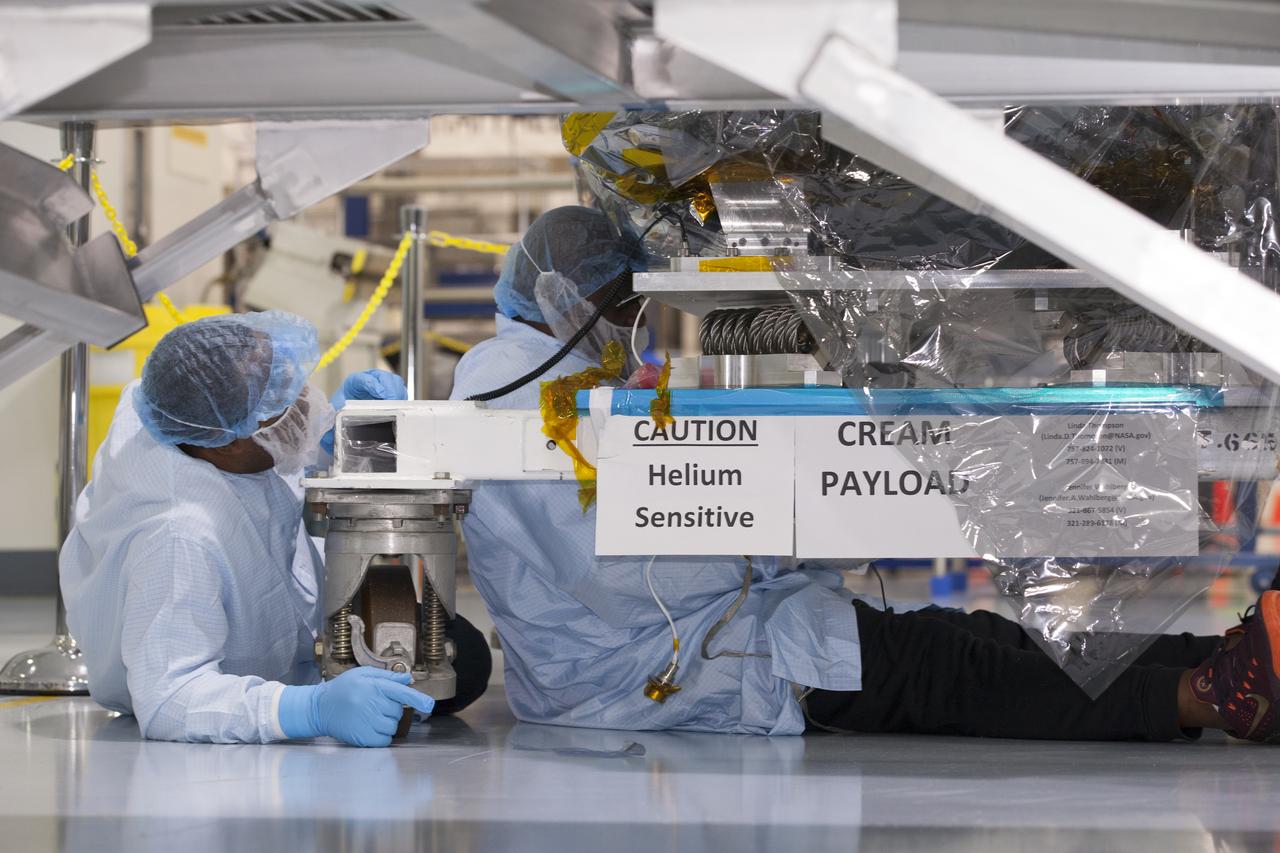

In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians and engineers remove a protective cover on the Cosmic-Ray Energetics and Mass investigation, or CREAM, instrument. It is designed to measure the charges of cosmic rays to better understand what gives them such incredible energies, and how that effects the composition of the universe. The instrument will be launched to the space station on the SpaceX CRS-12 commercial resupply mission in August 2017.
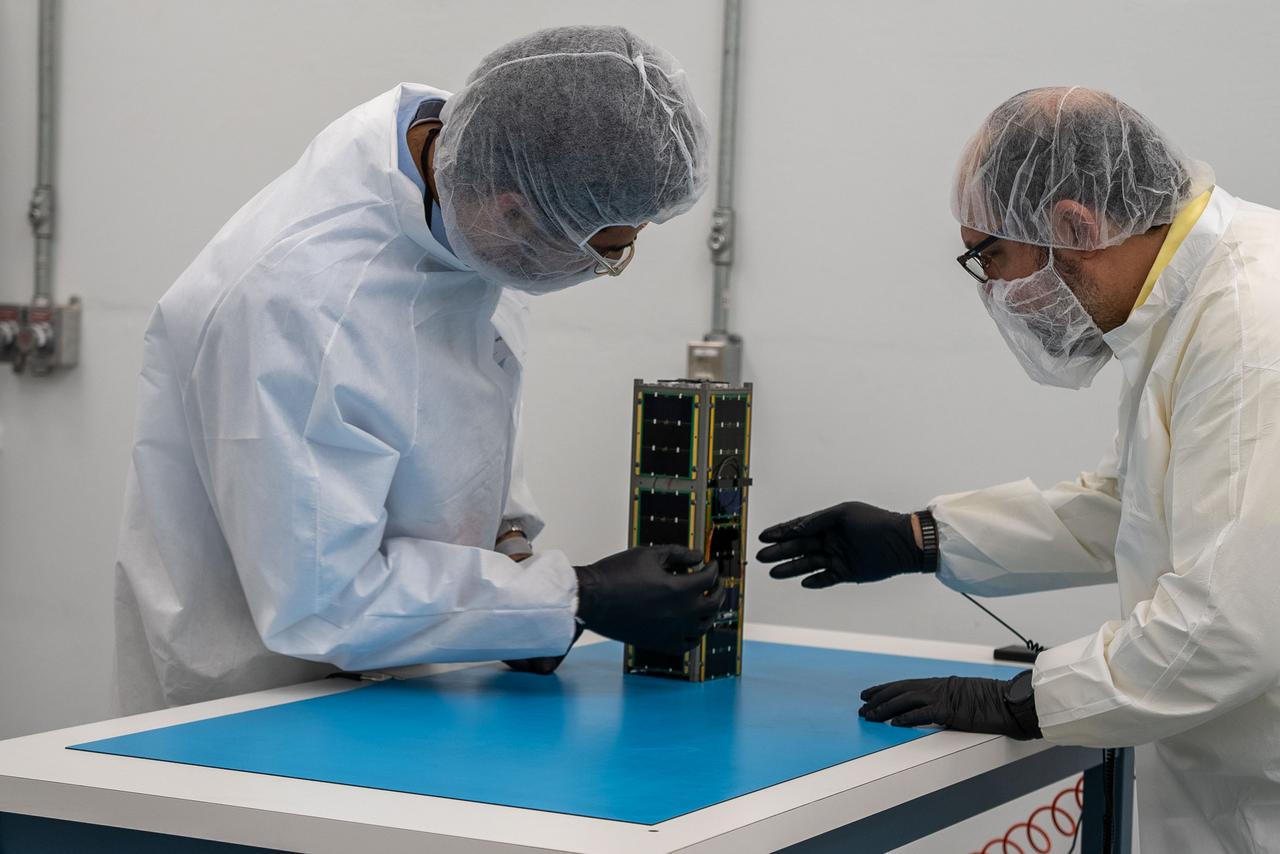

Technicians from the University of Maine prepare CubeSat MESAT-1 for integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Monday, April 22, 2024. MESAT-1, along with seven other payloads, will be integrated into a Firefly Aerospace Alpha rocket for NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
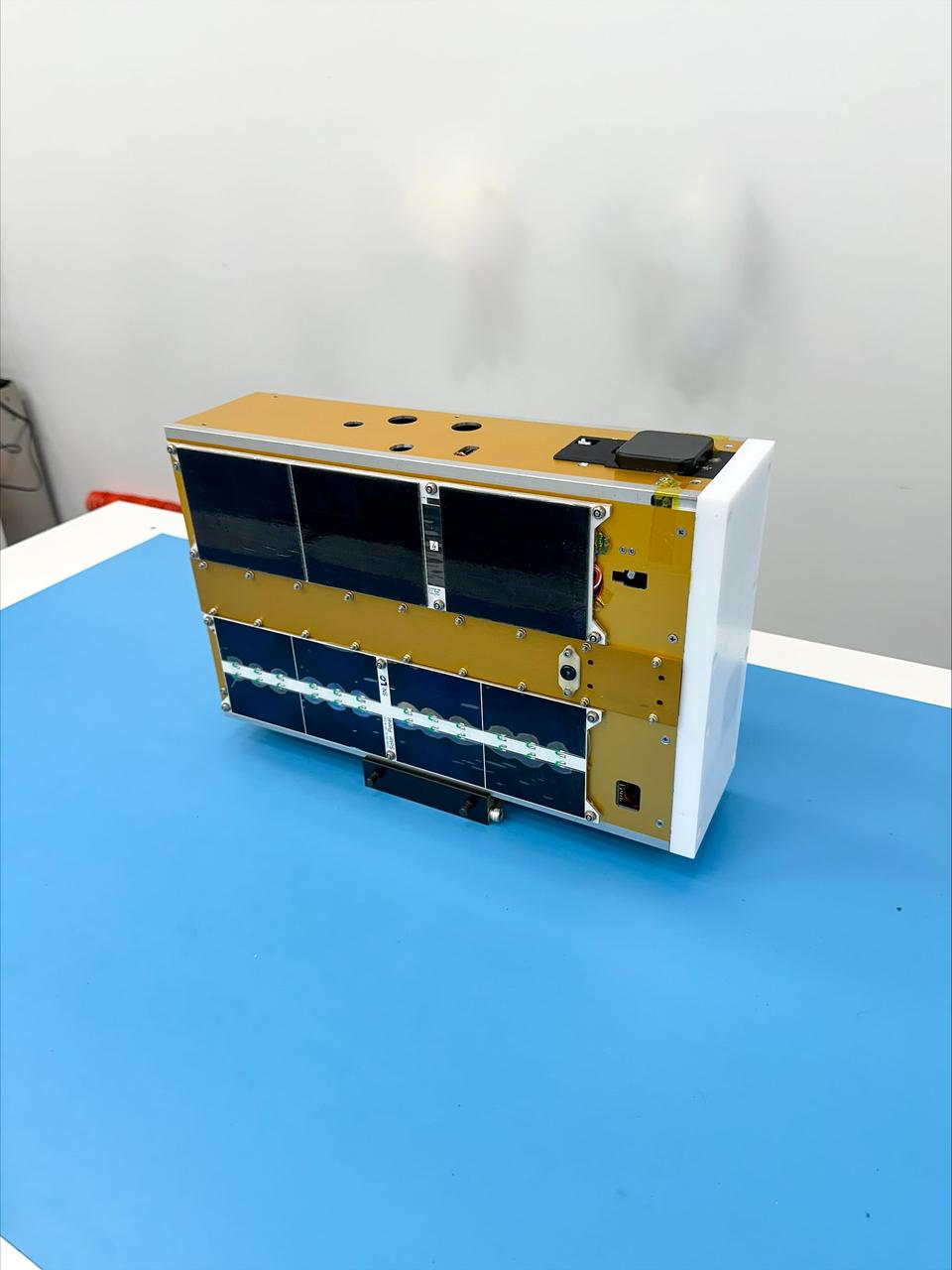

NASA’s TechEdSat-11 (TES-11) CubeSat awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Saturday, June 8, 2024. Serenity, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
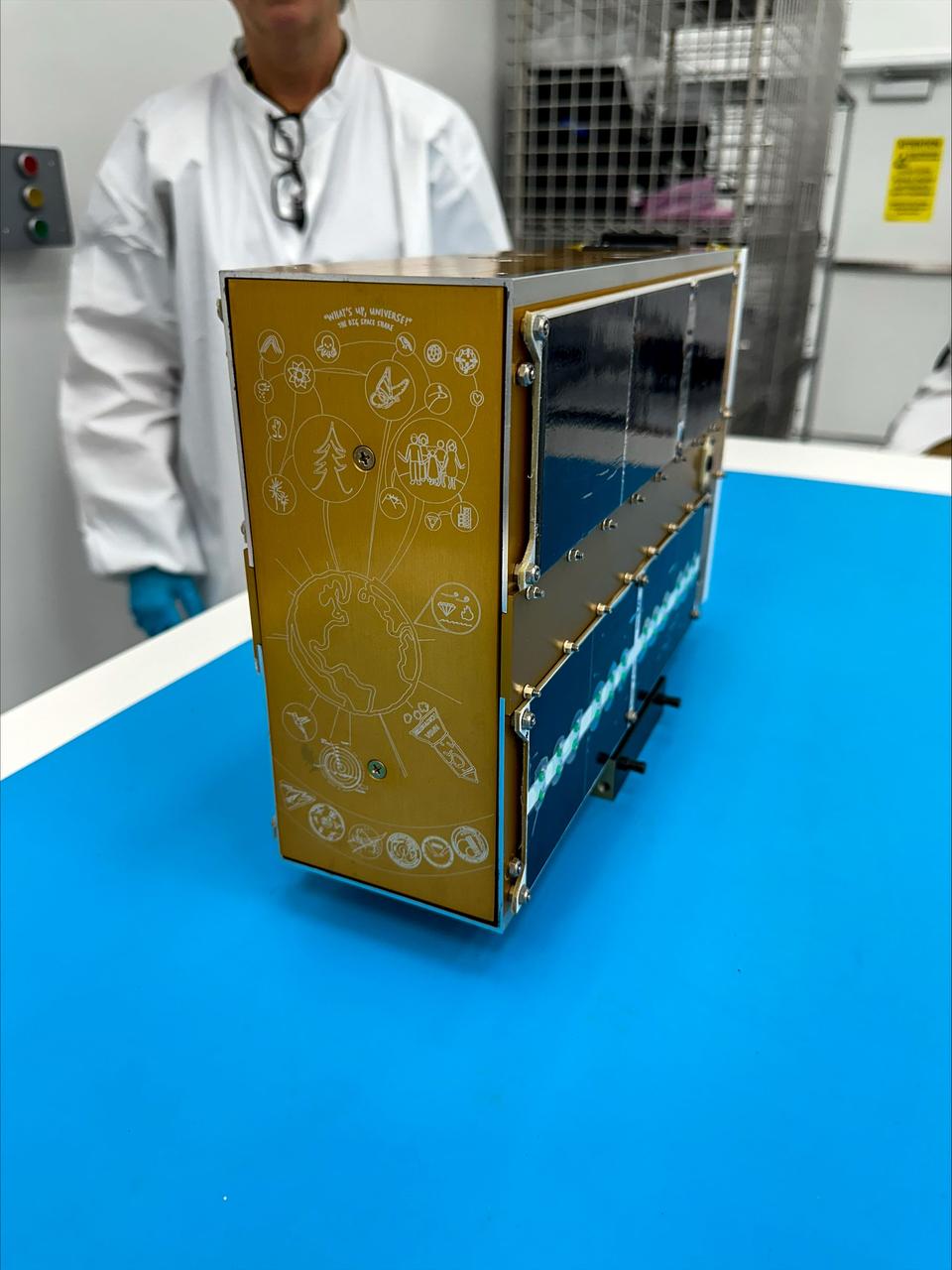

NASA’s TechEdSat-11 (TES-11) CubeSat awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Saturday, June 8, 2024. Serenity, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
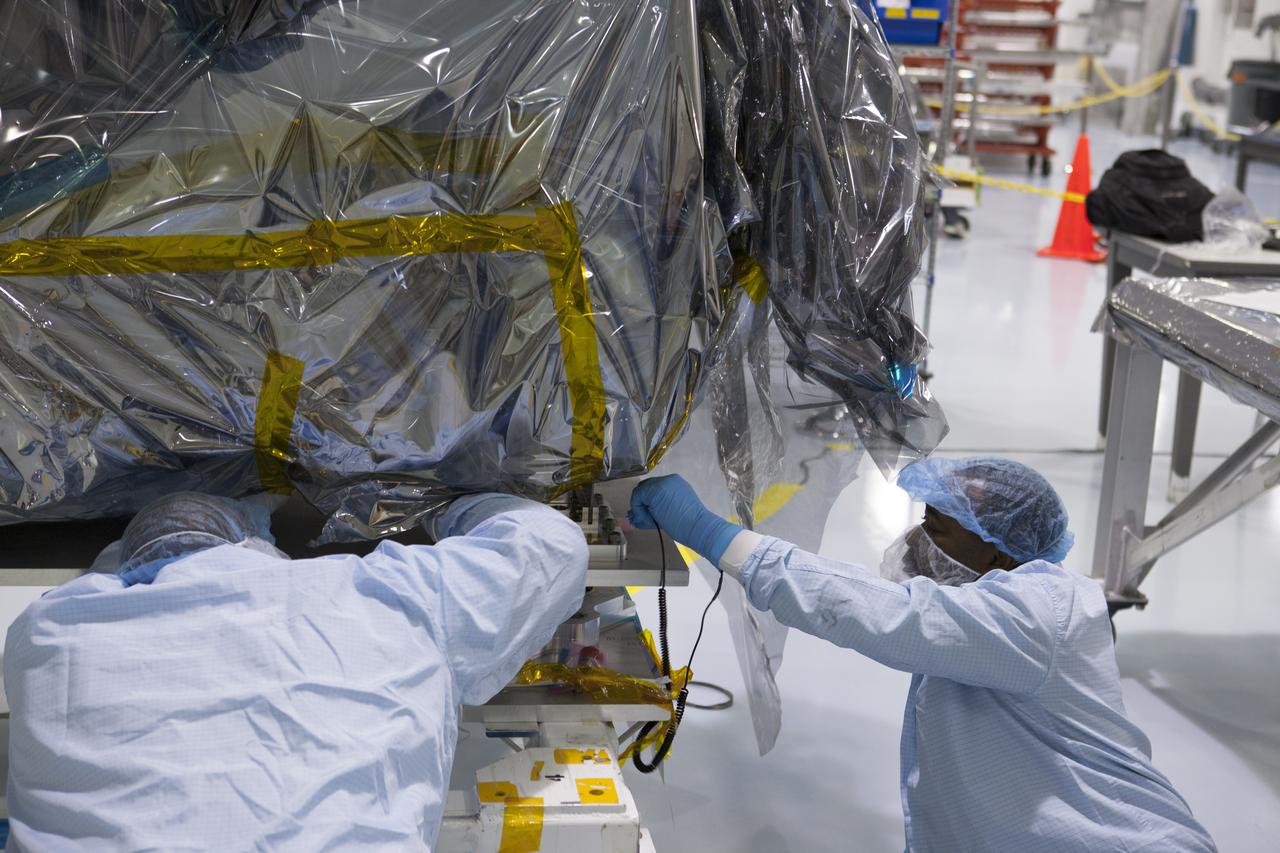

In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians and engineers remove a protective cover on the Cosmic-Ray Energetics and Mass investigation, or CREAM, instrument. It is designed to measure the charges of cosmic rays to better understand what gives them such incredible energies, and how that effects the composition of the universe. The instrument will be launched to the space station on the SpaceX CRS-12 commercial resupply mission in August 2017.
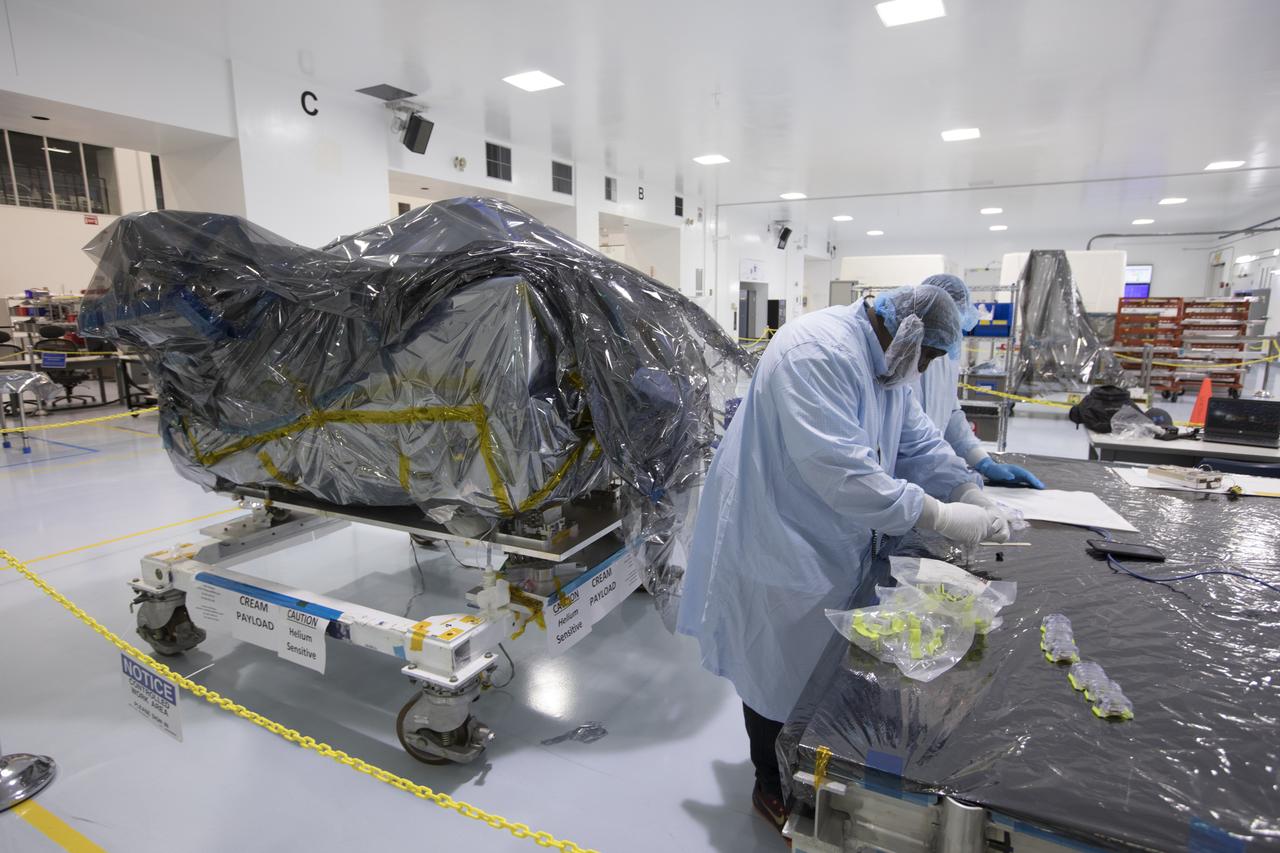

In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians and engineers inspect components for the Cosmic-Ray Energetics and Mass investigation, or CREAM, instrument. It is designed to measure the charges of cosmic rays to better understand what gives them such incredible energies, and how that effects the composition of the universe. The instrument will be launched to the space station on the SpaceX CRS-12 commercial resupply mission in August 2017.
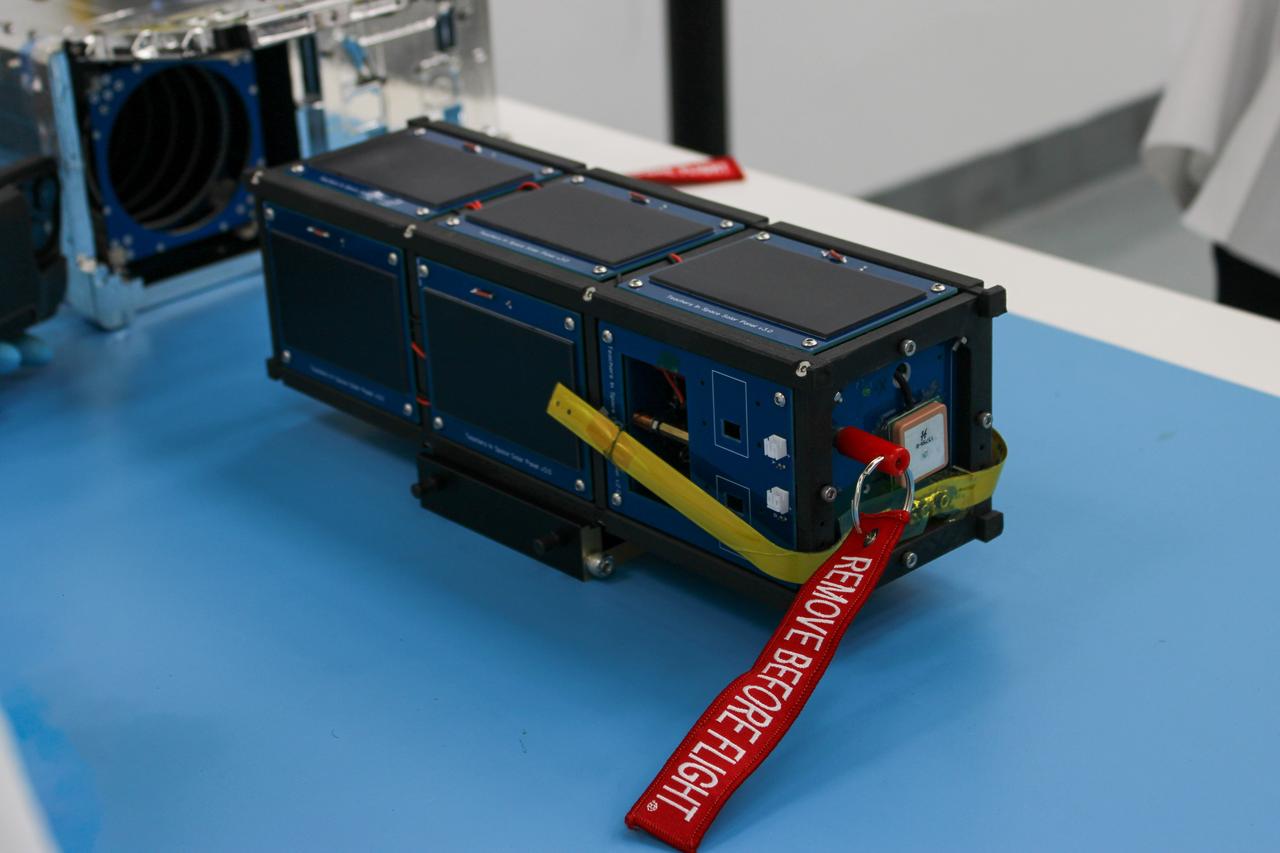
Serenity, a 3U CubeSat, awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Friday, June 7, 2024. Serenity, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
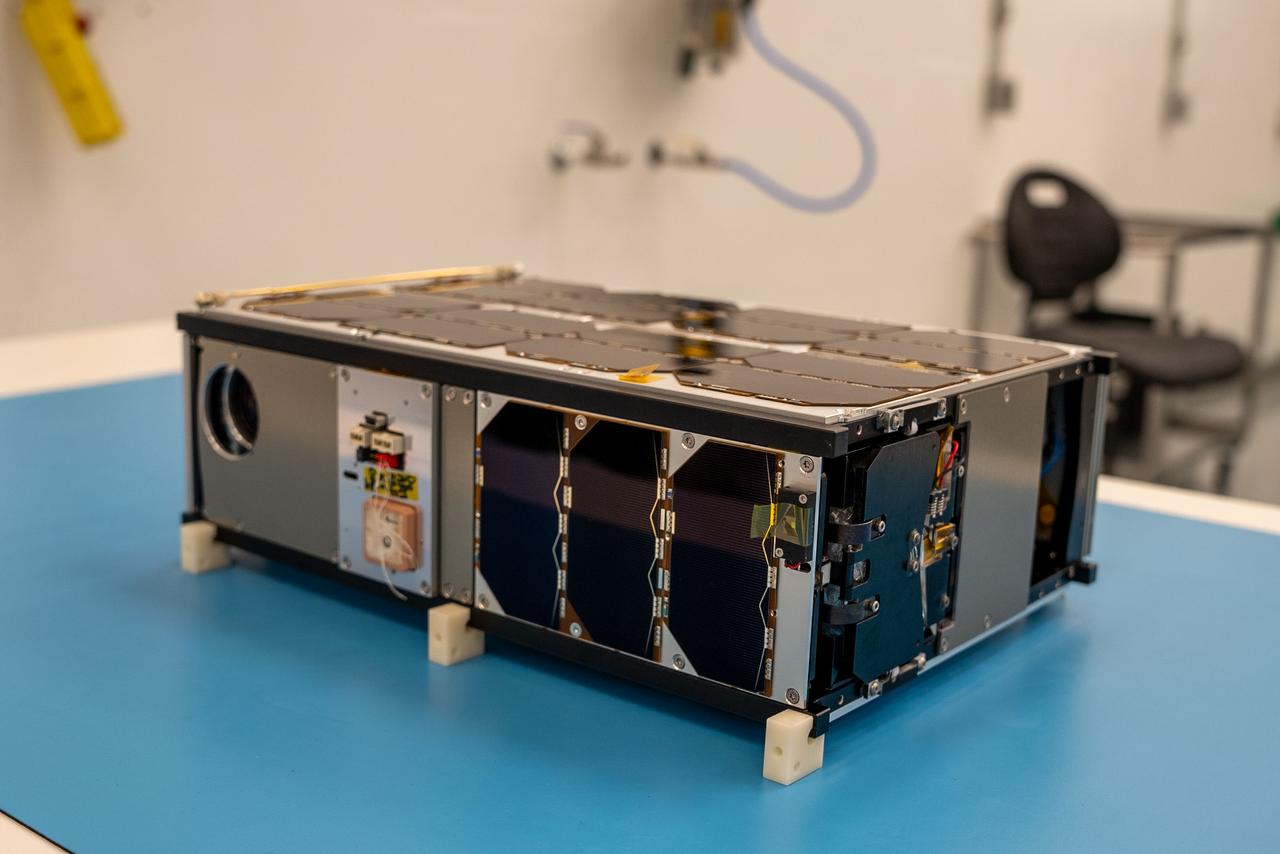
A CubeSat named CatSat from the University of Arizona awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Thursday, April 25, 2024. CatSat, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician remove a protective cover on the Cosmic-Ray Energetics and Mass investigation, or CREAM, instrument. It is designed to measure the charges of cosmic rays to better understand what gives them such incredible energies, and how that effects the composition of the universe. The instrument will be launched to the space station on the SpaceX CRS-12 commercial resupply mission in August 2017.
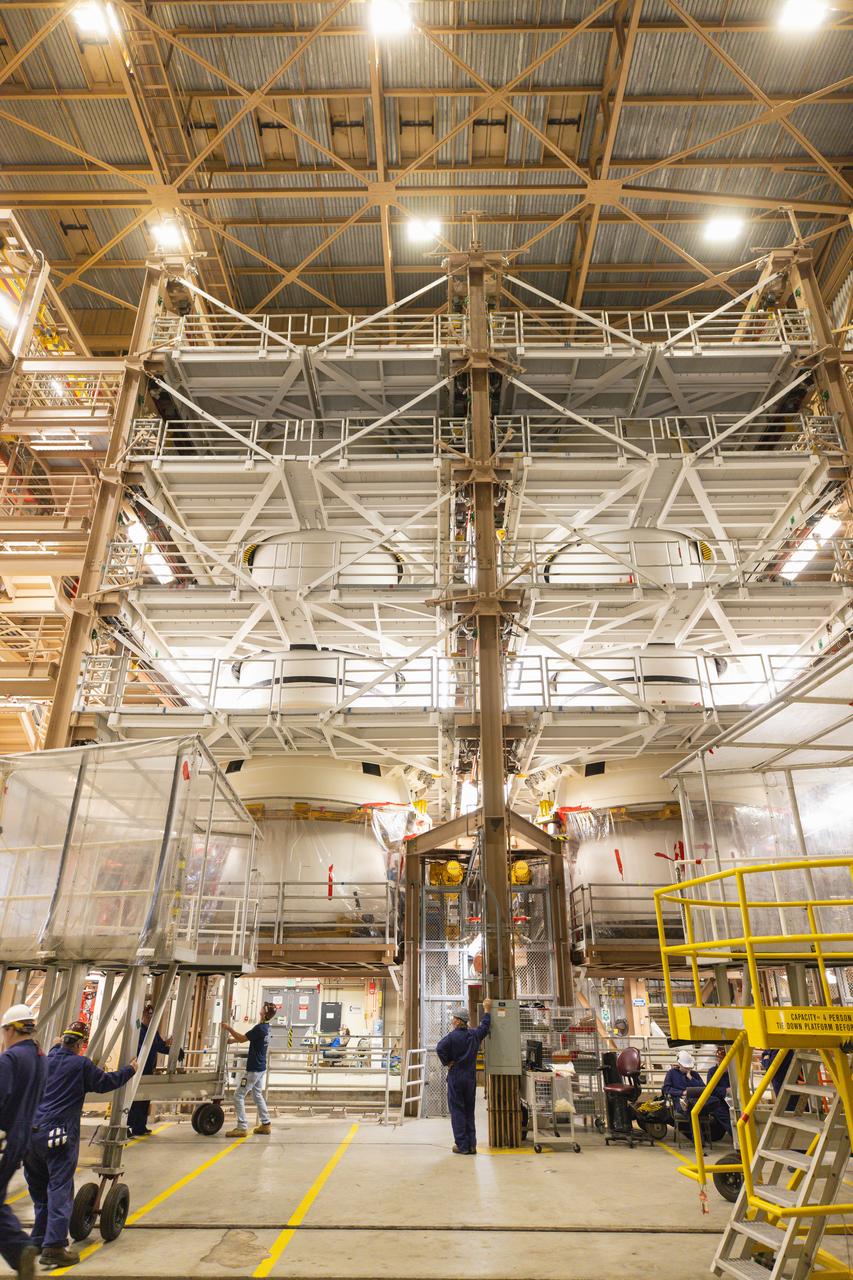

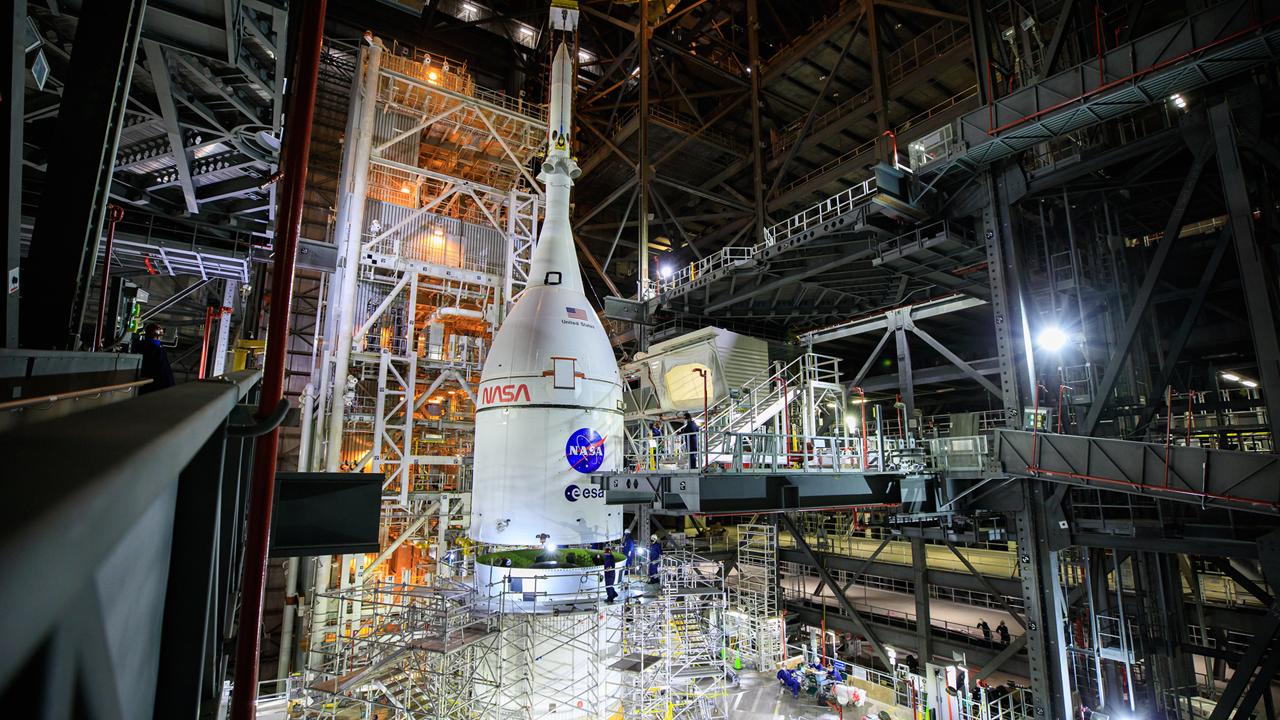
Technicians with Exploration Ground Systems perform inspections of the Northrop Grumman-manufactured two aft exit cones on Wednesday, Dec. 13, 2023, inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida before mating processes begin for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The aft exit cones are attached to the bottom piece of the two boosters, (seen here in these photos), which is called the aft segment, and the exit cones act like a battery pack to provide added thrust for the boosters while protecting the aft skirts from thermal environment during launch of the agency’s first crewed mission under Artemis that will test all of the Orion spacecraft systems.
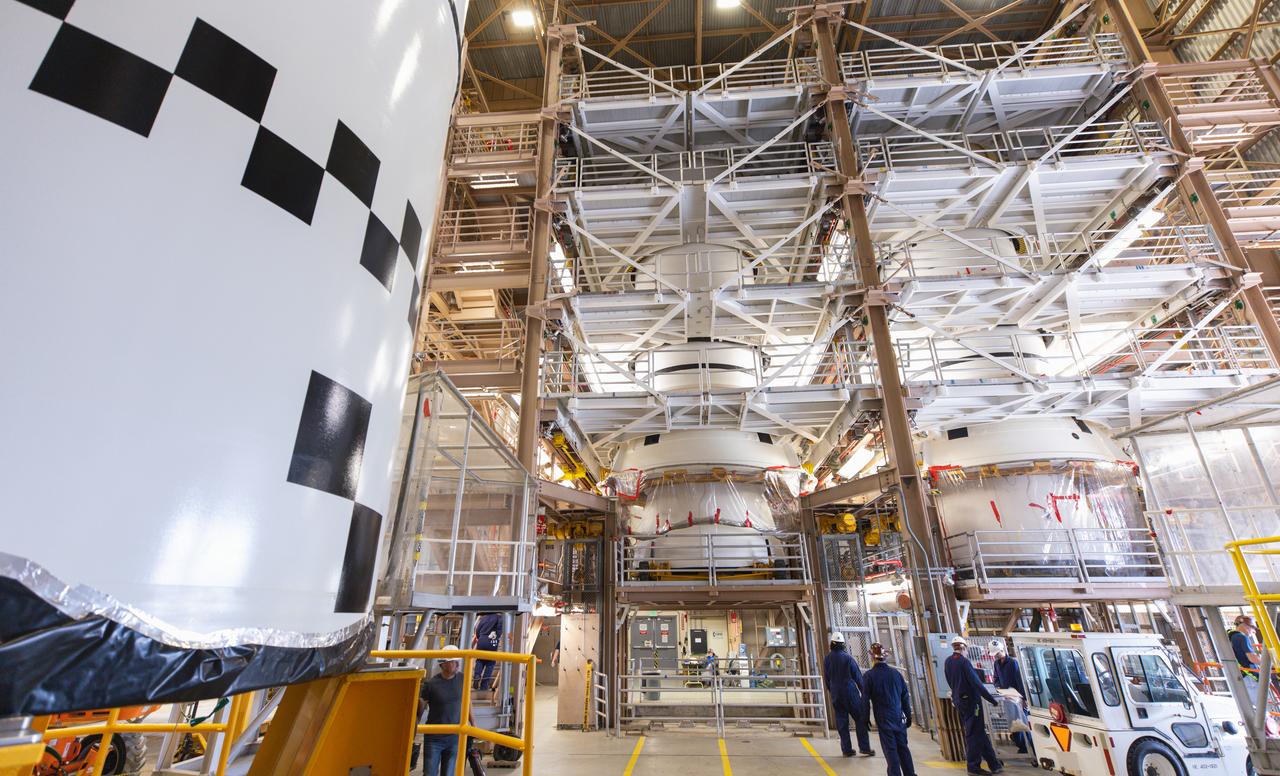

Technicians with Exploration Ground Systems perform inspections of the Northrop Grumman-manufactured two aft exit cones on Wednesday, Dec. 13, 2023, inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida before mating processes begin for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The aft exit cones are attached to the bottom piece of the two boosters, (seen here in these photos), which is called the aft segment, and the exit cones act like a battery pack to provide added thrust for the boosters while protecting the aft skirts from thermal environment during launch of the agency’s first crewed mission under Artemis that will test all of the Orion spacecraft systems.

Technicians with Exploration Ground Systems perform inspections of the Northrop Grumman-manufactured two aft exit cones on Wednesday, Dec. 13, 2023, inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida before mating processes begin for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The aft exit cones are attached to the bottom piece of the two boosters, (seen here in these photos), which is called the aft segment, and the exit cones act like a battery pack to provide added thrust for the boosters while protecting the aft skirts from thermal environment during launch of the agency’s first crewed mission under Artemis that will test all of the Orion spacecraft systems.
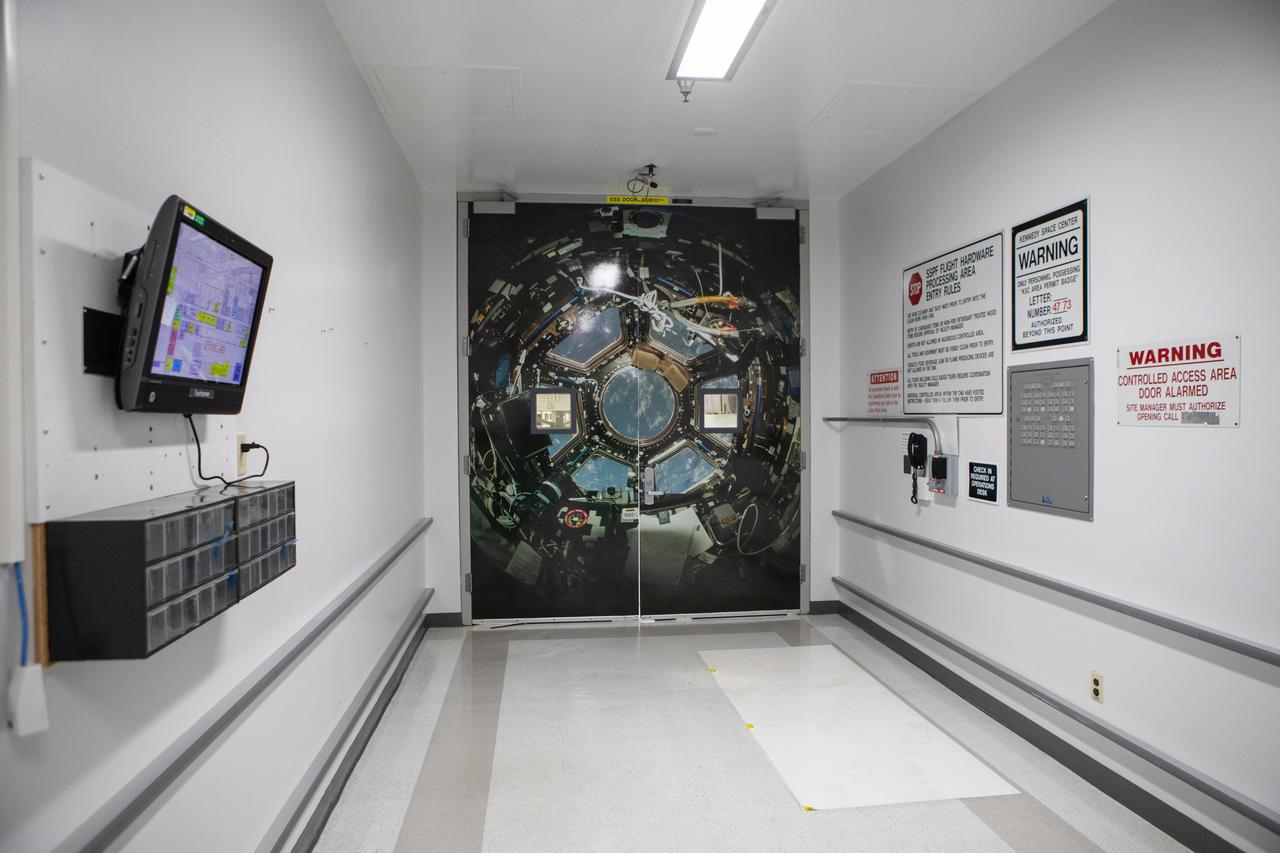

Artwork simulating a view inside the International Space Station marks the entranceway to the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on May 16, 2019. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
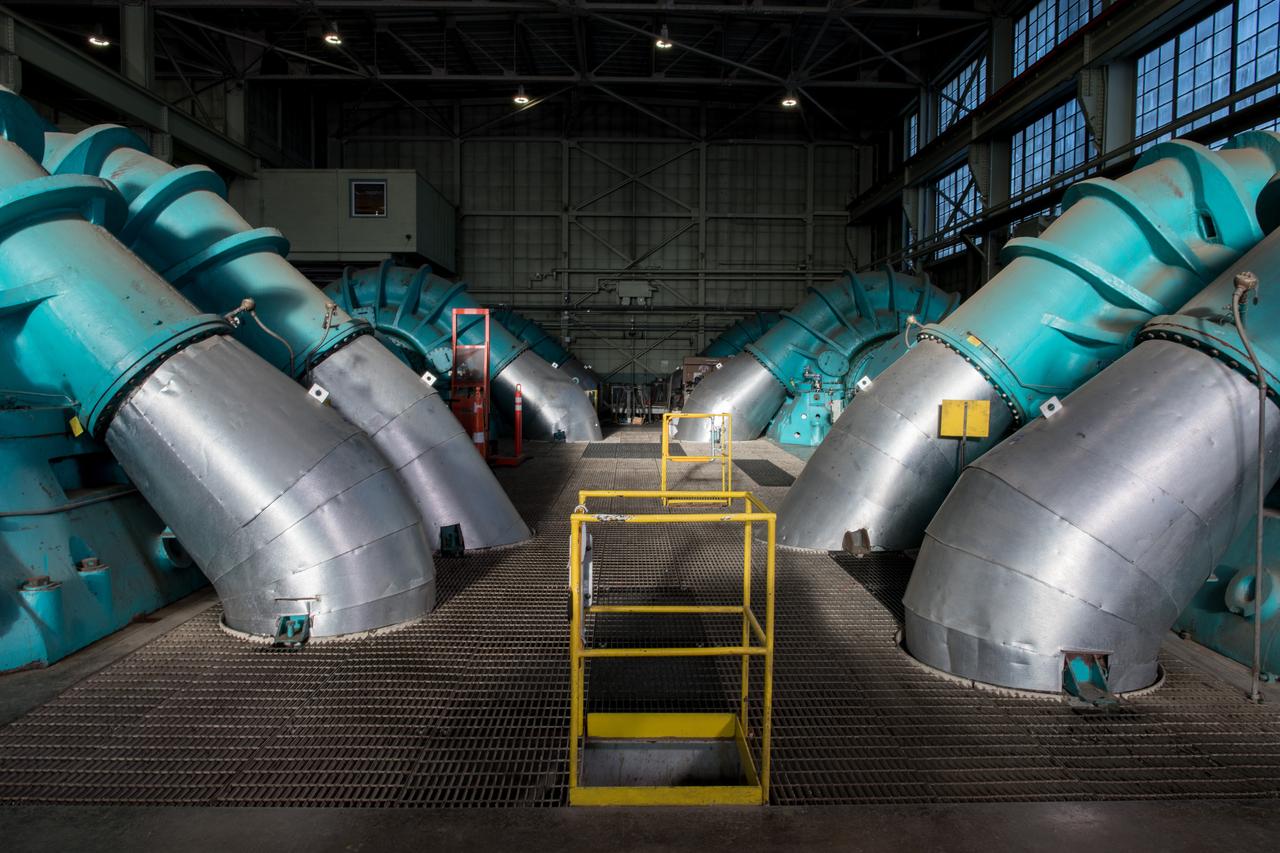

The Central Processing System at Glenn Research Center controls operations in the wind tunnels, propulsion systems lab, engine components research lab, and compressor, turbine and combustor test cells. Documentation photos of the facility were taken on December 19, 2023. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)

Arabidopsis thaliana plants are seen inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 prior to harvest of half the plants. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, harvests half the Arabidopsis thaliana plants inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.
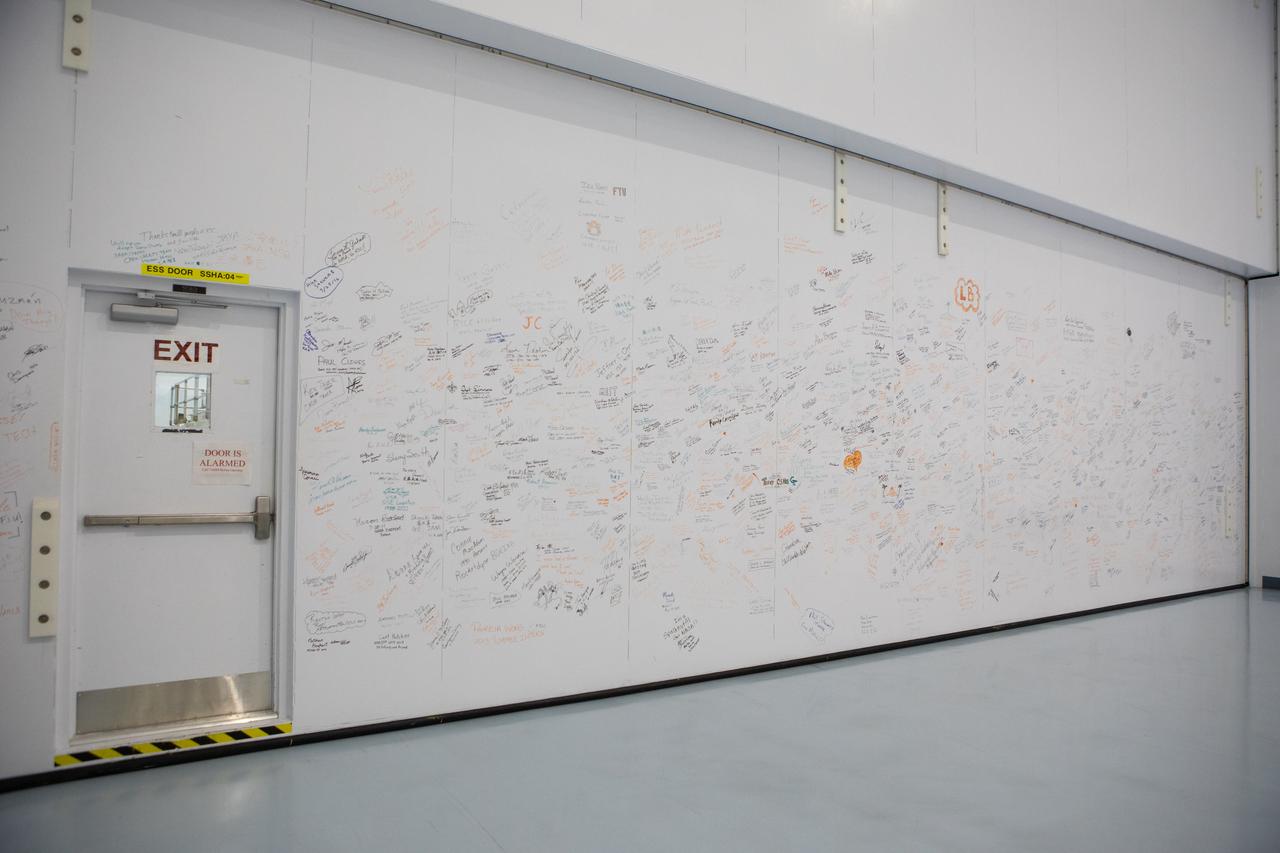

A photograph taken on May 16, 2019, shows a wall inside the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, containing signatures of many of those who worked on the International Space Station Program. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the space station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
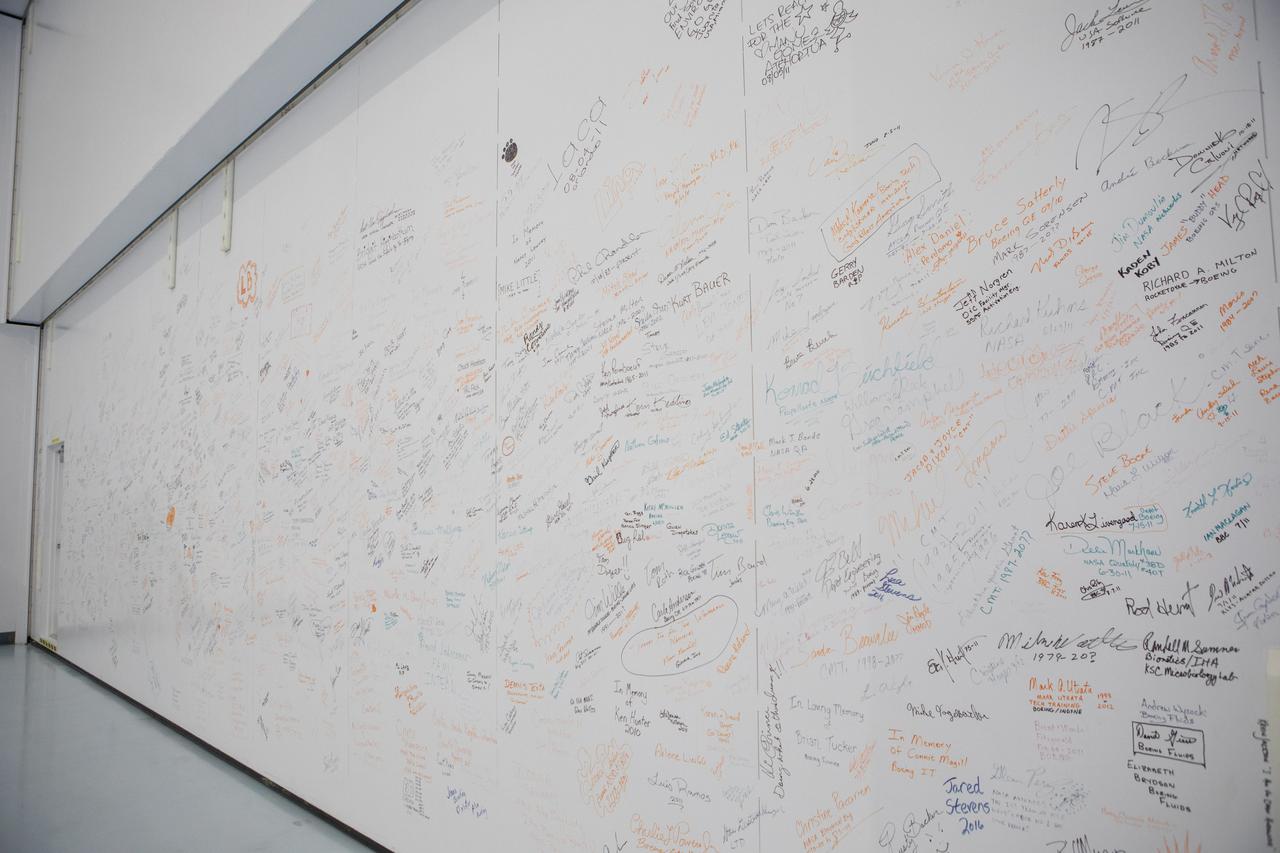

A photograph taken on May 16, 2019, shows a wall inside the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, containing signatures of many of those who worked on the International Space Station Program. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the space station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
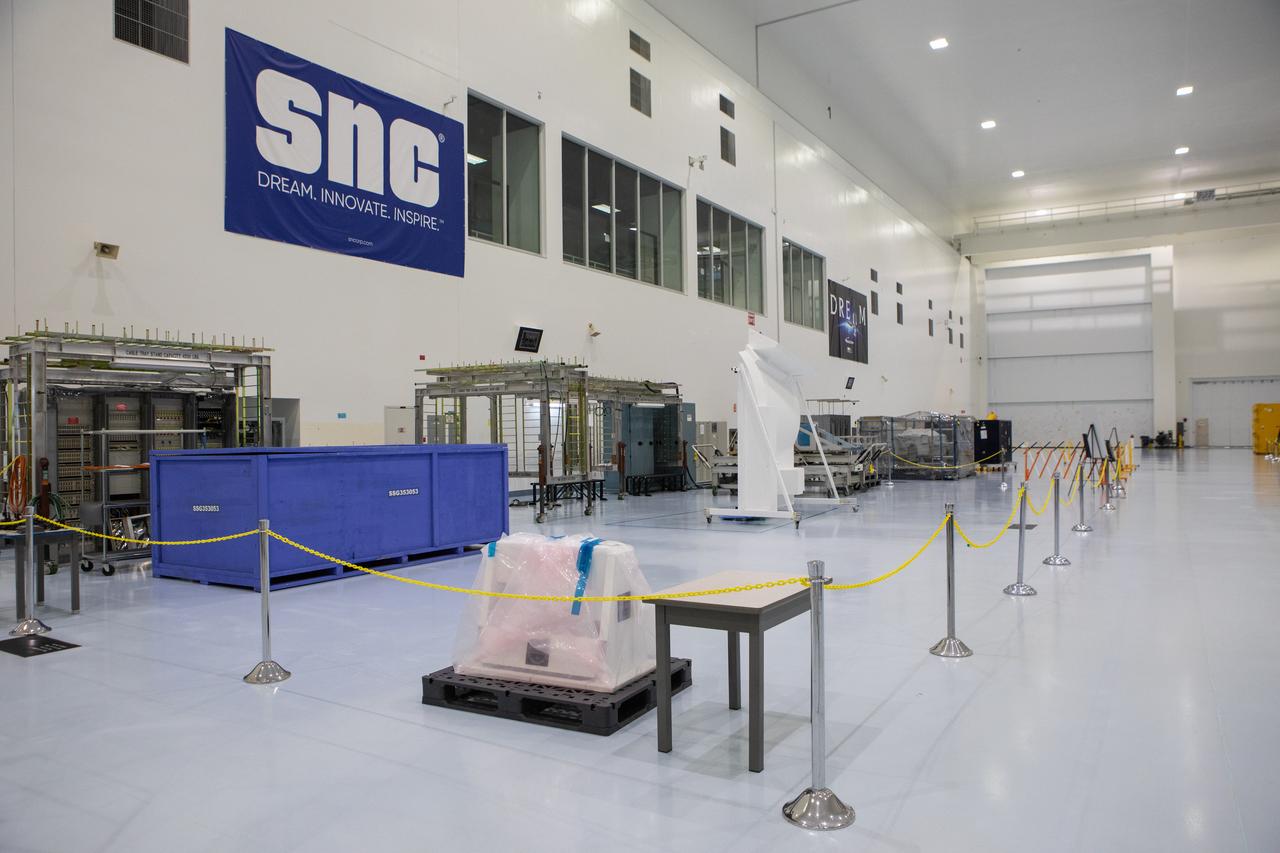

In view in this photograph, taken on May 16, 2019, is the area where the Sierra Nevada Corporation will process its Dream Chaser spacecraft in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
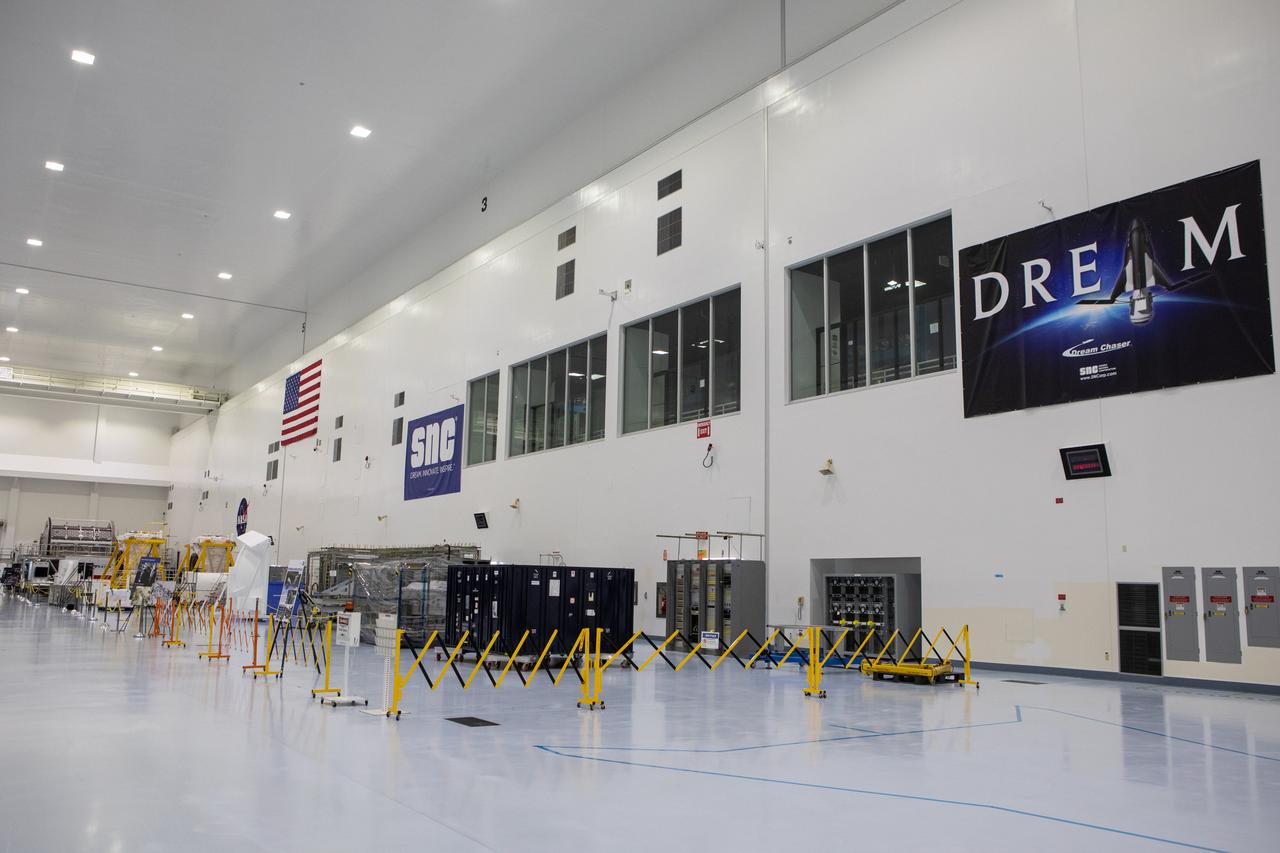

In view in this photograph, taken on May 16, 2019, is the area where the Sierra Nevada Corporation will process its Dream Chaser spacecraft in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.

In view in this photograph, taken on May 16, 2019, is the area where the Sierra Nevada Corporation will process its Dream Chaser spacecraft in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
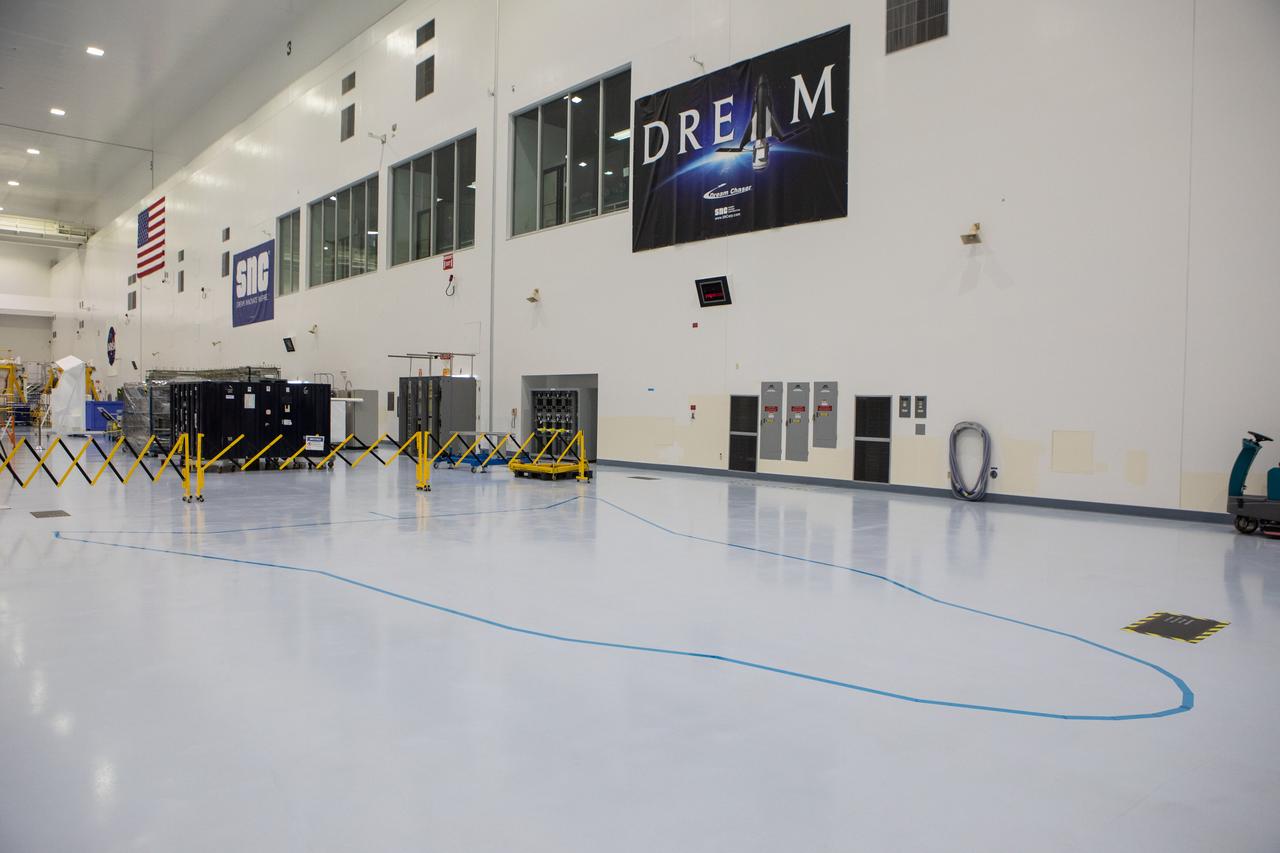

In view in this photograph, taken on May 16, 2019, is the area where the Sierra Nevada Corporation will process its Dream Chaser spacecraft in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
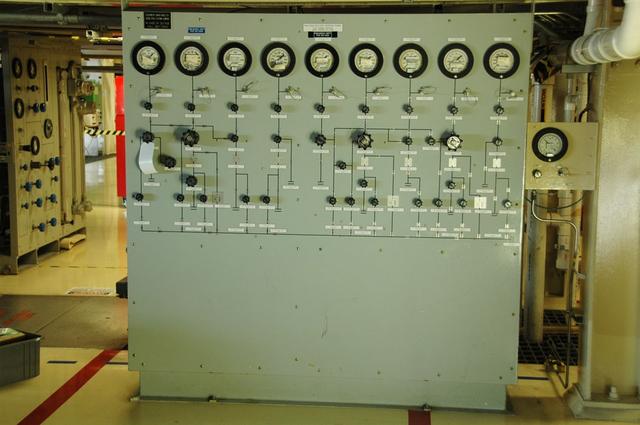

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
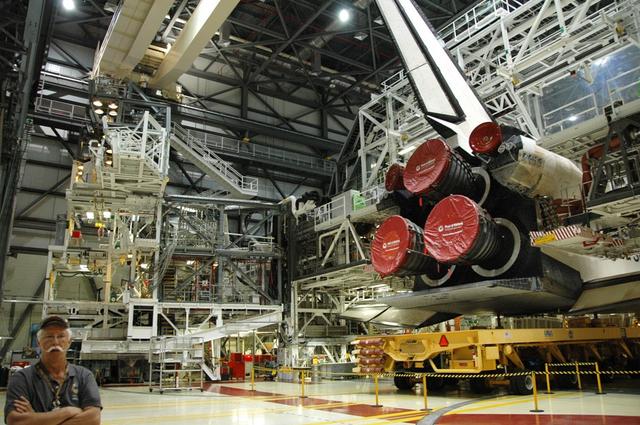

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Exterior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Exterior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
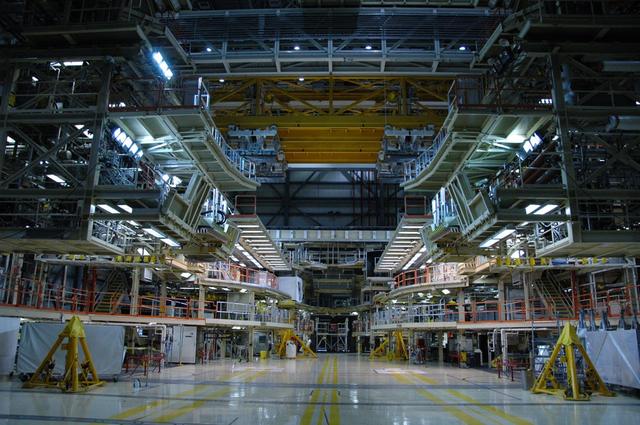

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
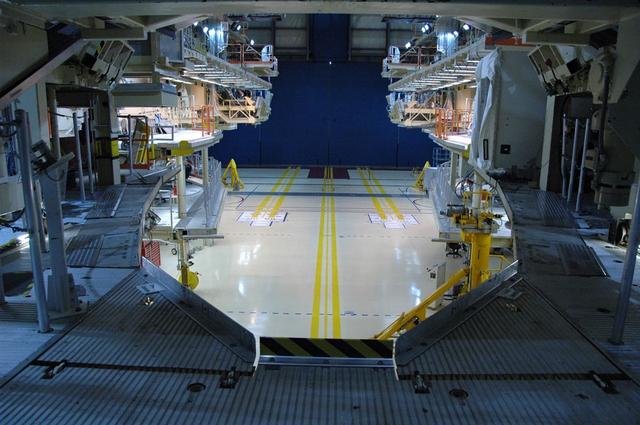

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
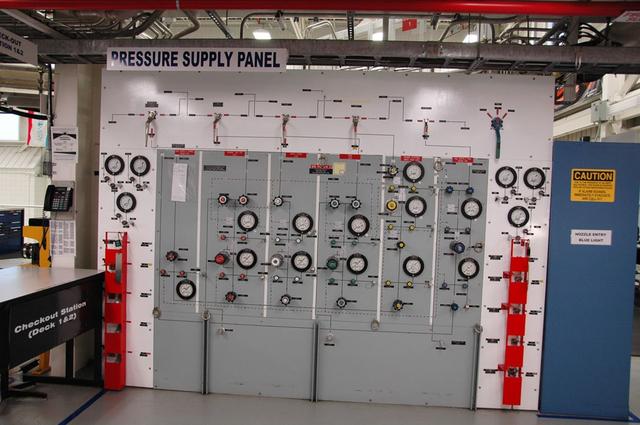

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
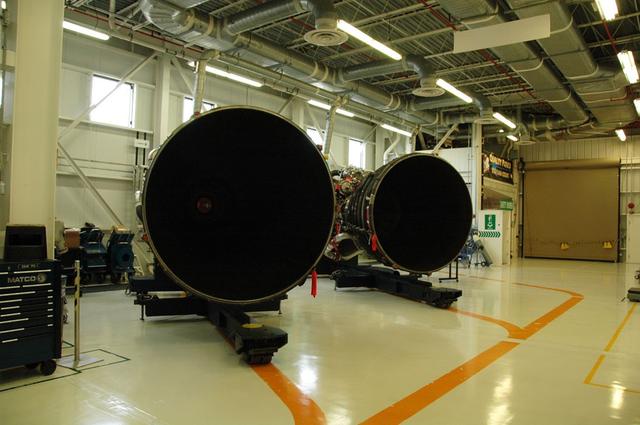

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Exterior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
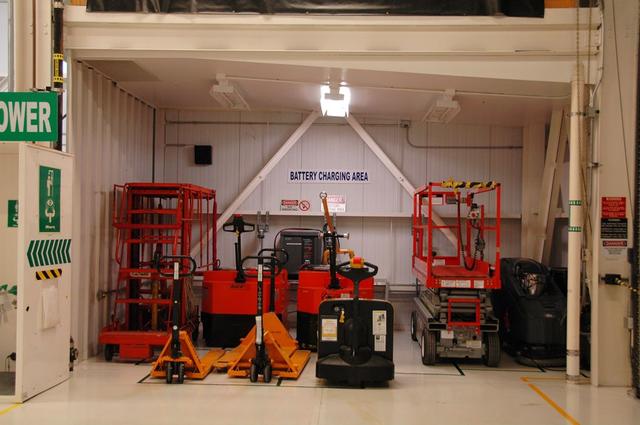

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
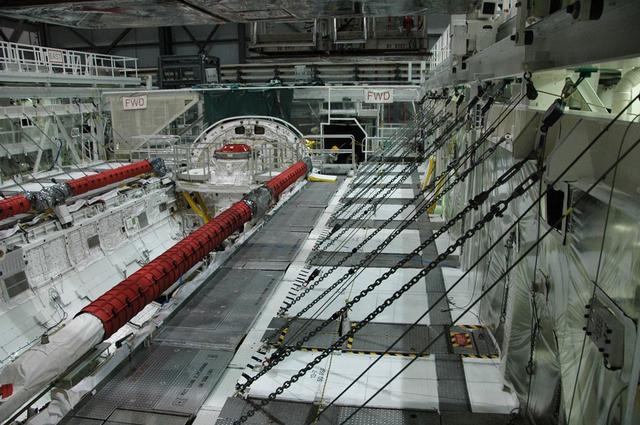

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

