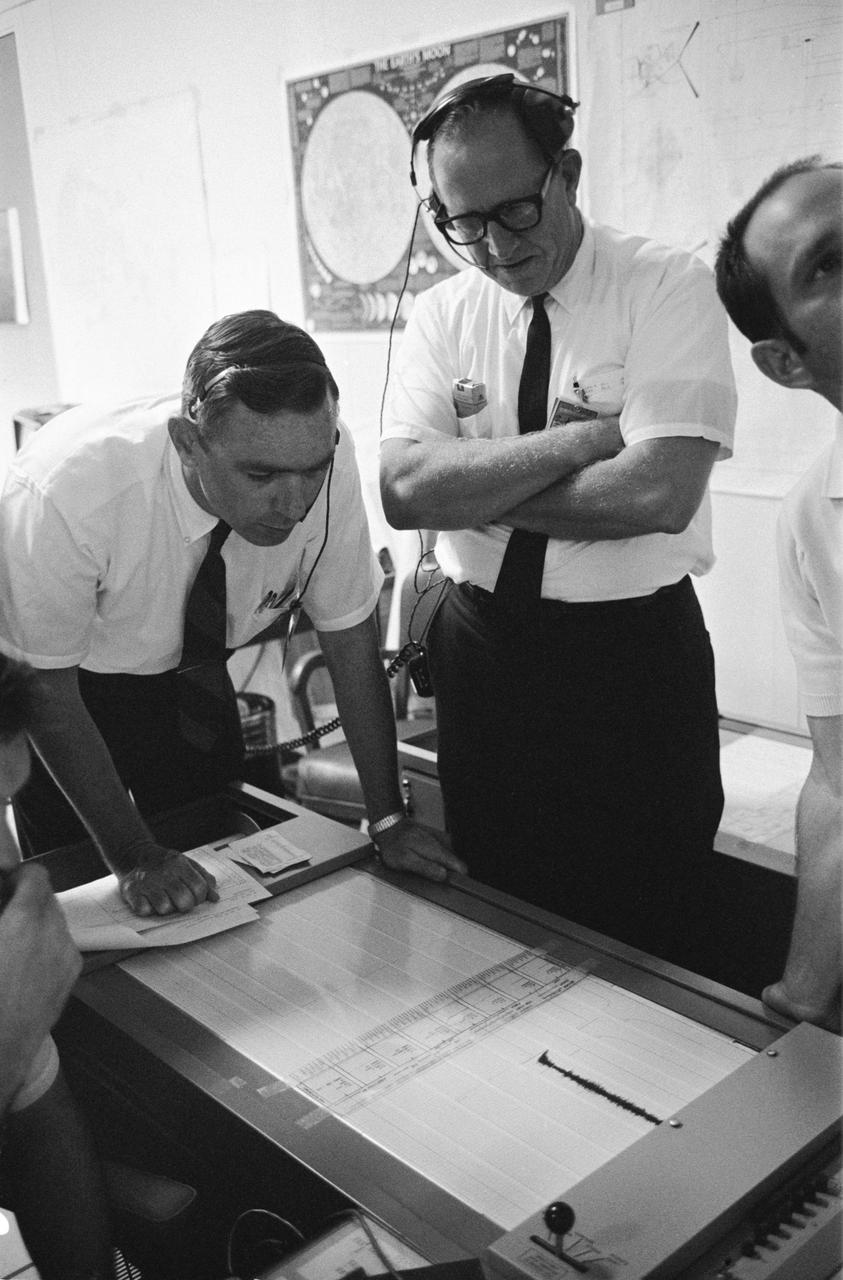

S69-39587 (20 July 1969) --- Dr. Garry Latham (left) with the Lamont Geological Observatory, studies seismometer tracings in the Mission Control Center's (MCC) ALSEP control room. The electronic data was coming from the Passive Seismic Experiments Package (PSEP) which the Apollo 11 astronauts had just deployed on the surface of the moon. Dr. Lamont is the principal investigator for the PSEP, a component of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP). PSEP uses three long-period seismometers and one short-period vertical seismometer for measuring meteoroid impacts and moonquakes. Such data will be useful in determining the interior structure of the moon; for example, does the moon have a core and mantle like Earth? Here, the flapping of the PSEP's solar panels is picked up and registered as a tracing. The PSEP was sensitive enough to pick up the footsteps of astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., as they walked on the moon.
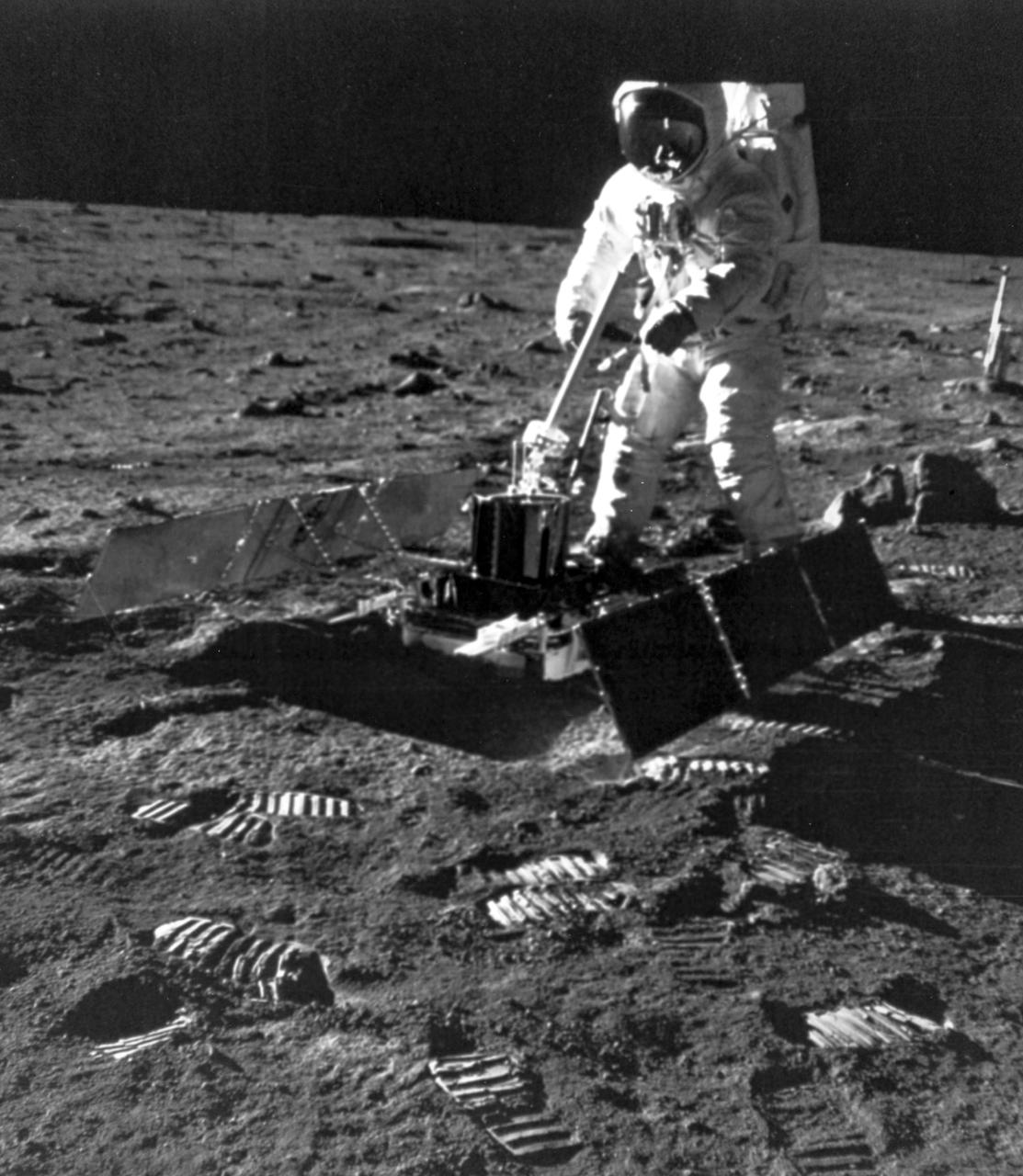
The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon, while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon in the Sea of Tranquility. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew set up experiments, collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth, planted the U.S Flag, and left a message for all mankind. In this photograph, Aldrin is deploying the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP).
The first manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon, while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon in the Sea of Tranquility. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew set up experiments, collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth, planted the U.S Flag, and left a message for all mankind. In this photograph, Aldrin is deploying the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP).
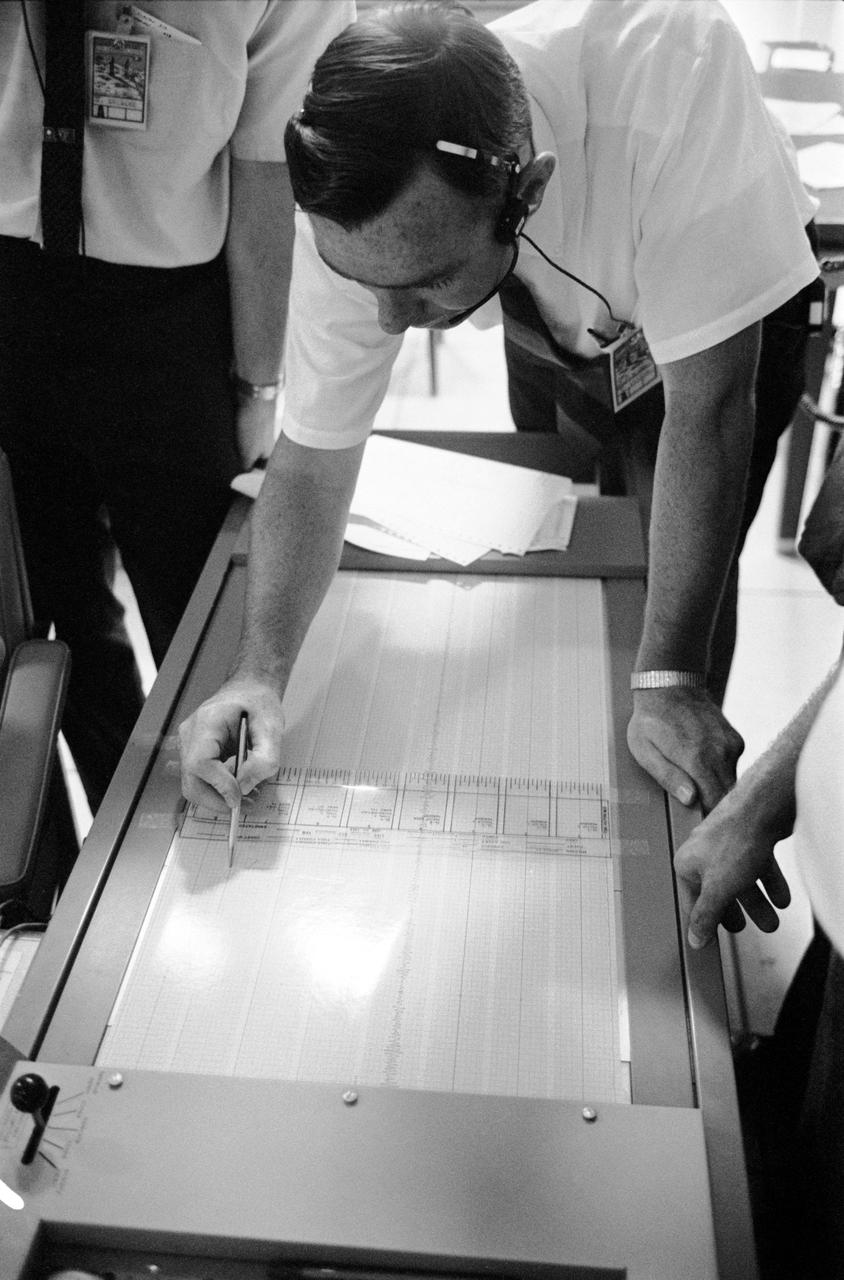

S69-39588 (20 July 1969) --- Dr. Garry Latham, with the Lamont Geological Observatory, studies seismometer tracings in the Mission Control Center?s ASEP control room. The electronic data was coming from the Passive Seismic Experiments Package which the Apollo 11 astronauts had just deployed on the surface of the moon. Dr. Lamont is the principal investigator for the PSEP, a component of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP). PSEP uses three long-period seismometers and one short-period vertical seismometer for measuring meteoroid impacts and moonquakes. Such data will be useful in determining the interior structure of the moon; for example, does the moon have a core and mantle like Earth? Here, the center trace shows evidence of activity on the moon. The PSEP was sensitive enough to pick up the footsteps of astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. as they walked on the moon.
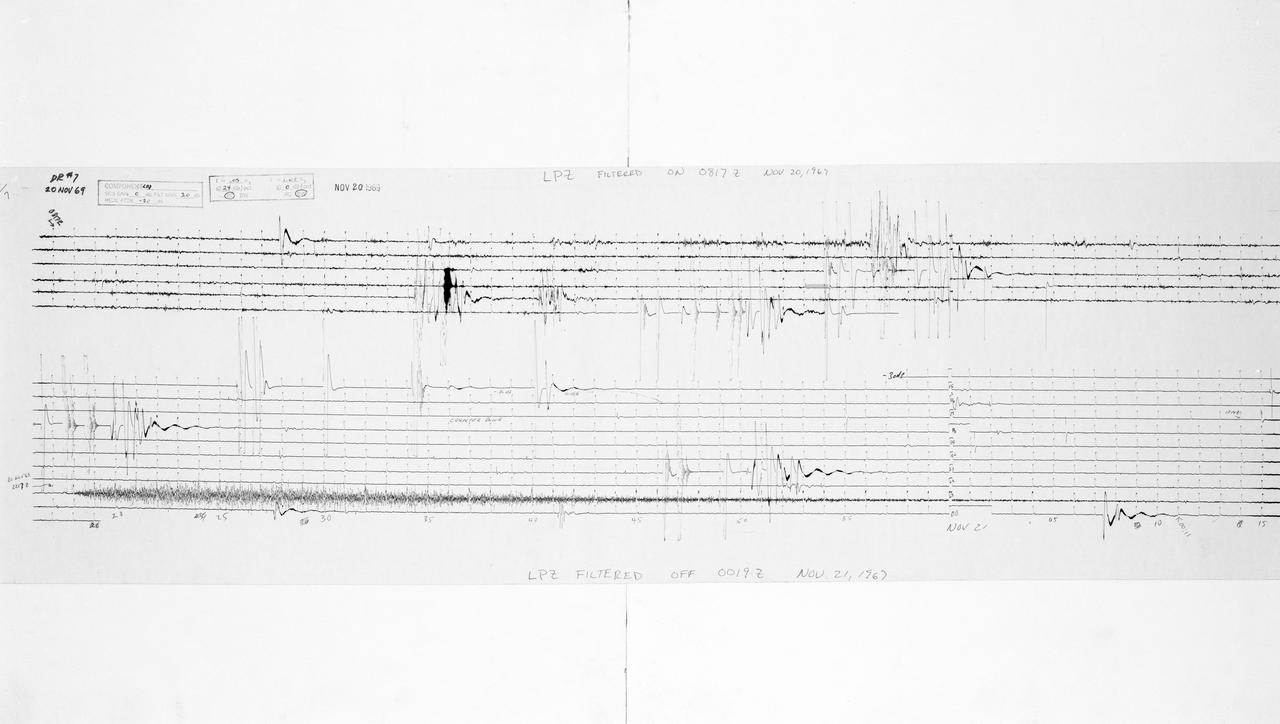
S69-59547 (20 Nov. 1969) --- The seismometer reading from the impact made by the Lunar Module ascent stage when it struck the lunar surface. The impact was registered by the Passive Seismic Experiment Package which was deployed on the moon by the Apollo 12 astronauts. PSEP, which is a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package, will detect surface tilt produced by tidal deformations, moonquakes, and meteorite impacts. The LM's ascent stage was jettisoned and sent journeying toward impact on the moon after astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean returned to lunar orbit and rejoined astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. in the Command and Service Modules. Information from the PSEP is transmitted to Earth through the ALSEP's central station and monitored by equipment at the Manned Spacecraft Center.

Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, moves toward a position to deploy two components of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP) on the surface of the Moon during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity. The Passive Seismic Experiments Package (PSEP) is in his left hand; and in his right hand is the Laser Ranging Retro-Reflector (LR3). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera.
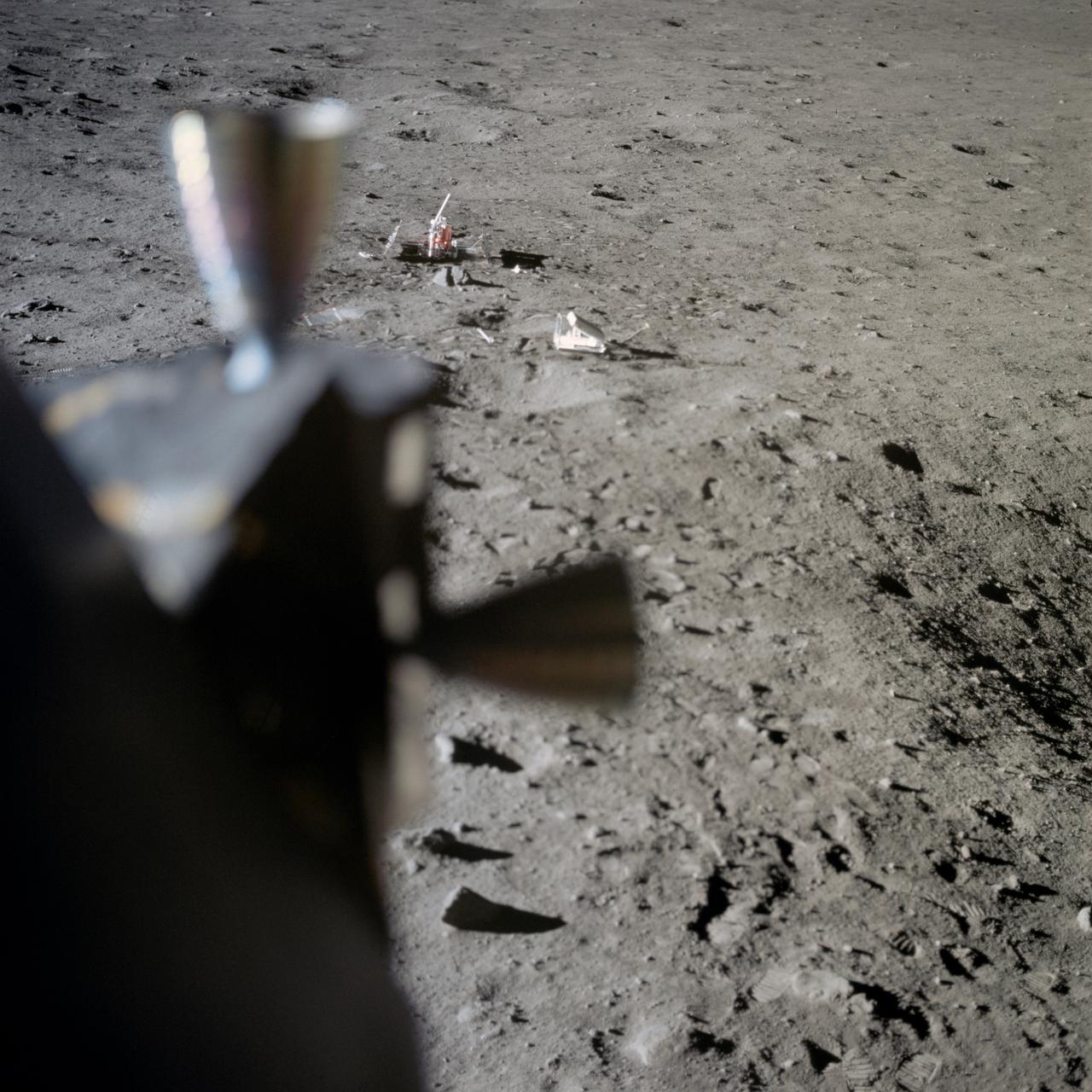

AS11-37-5551 (20 July 1969) --- Two components of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP) are seen deployed on the lunar surface in this view photographed from inside the Lunar Module (LM). In the far background is the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP); and to the right and closer to the camera is the Laser Ranging Retro-Reflector (LR-3). The footprints of Apollo 11 astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. are very distinct in the lunar soil.

AS11-40-5948 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. He has just deployed the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP). This is a good view of the deployed equipment. In the foreground is the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP); beyond it is the Laser Ranging Retro-Reflector (LR-3); in the center background is the United States flag; in the left background is the black and white lunar surface television camera; in the far right background is the Lunar Module (LM). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
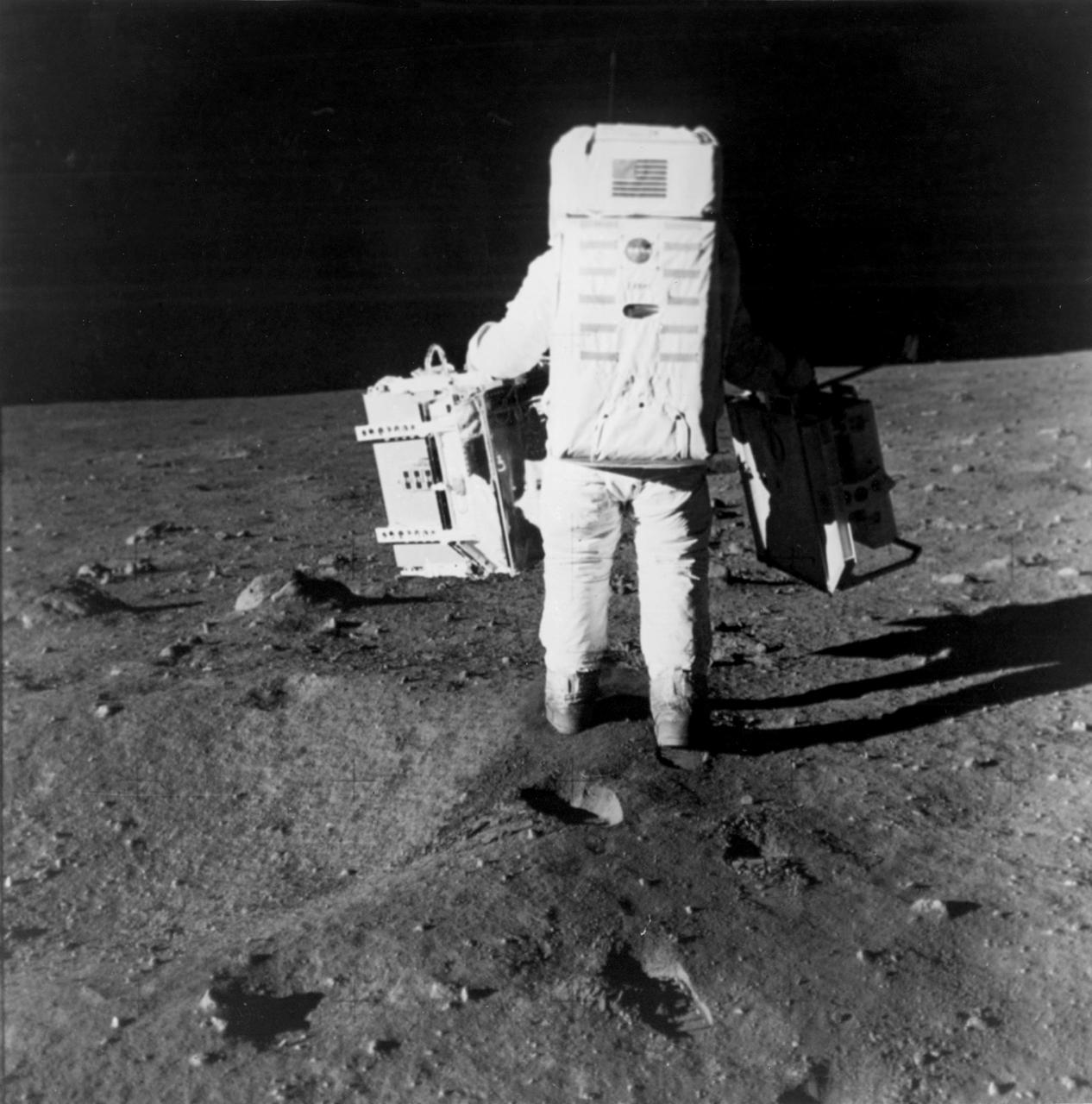

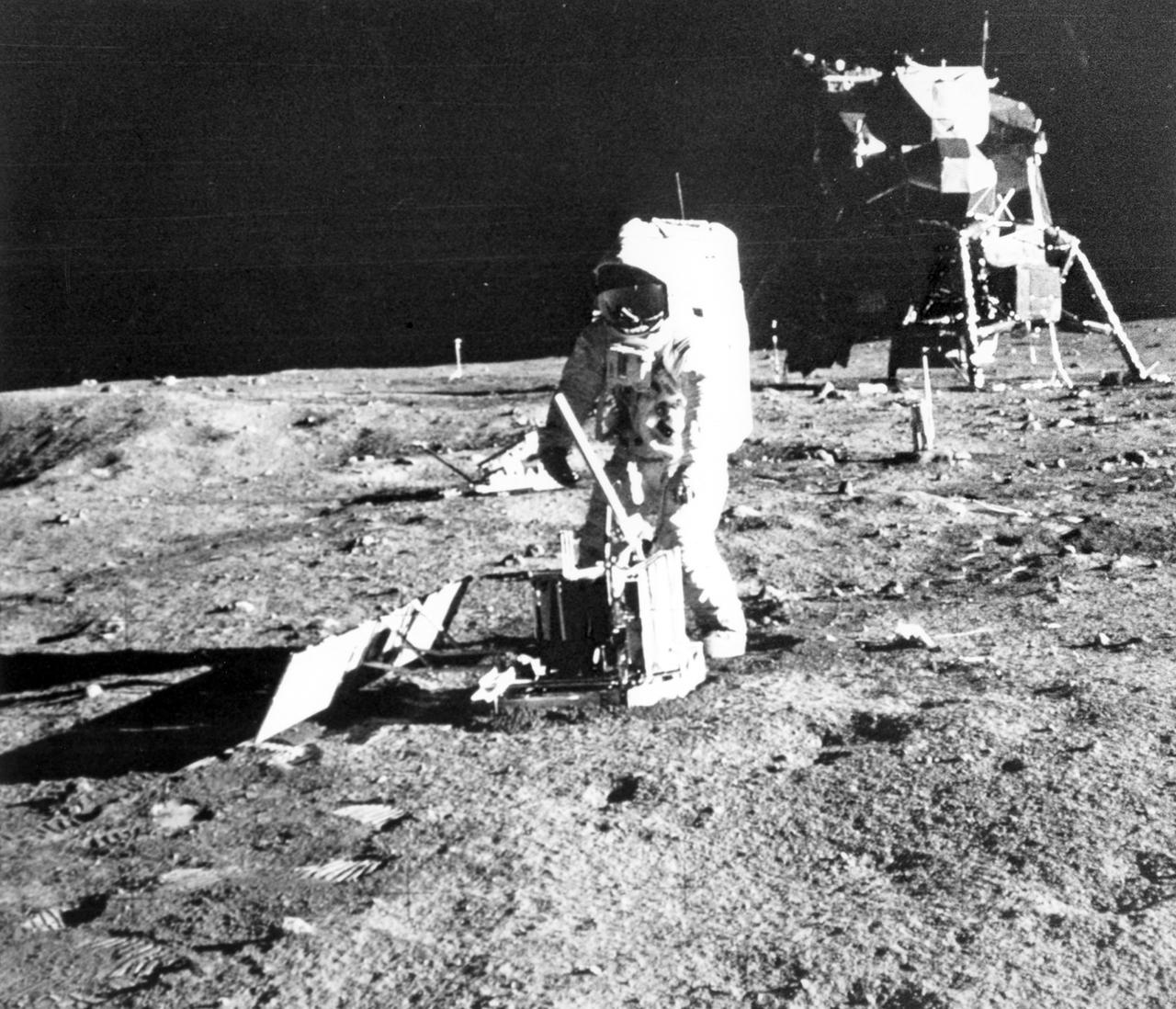
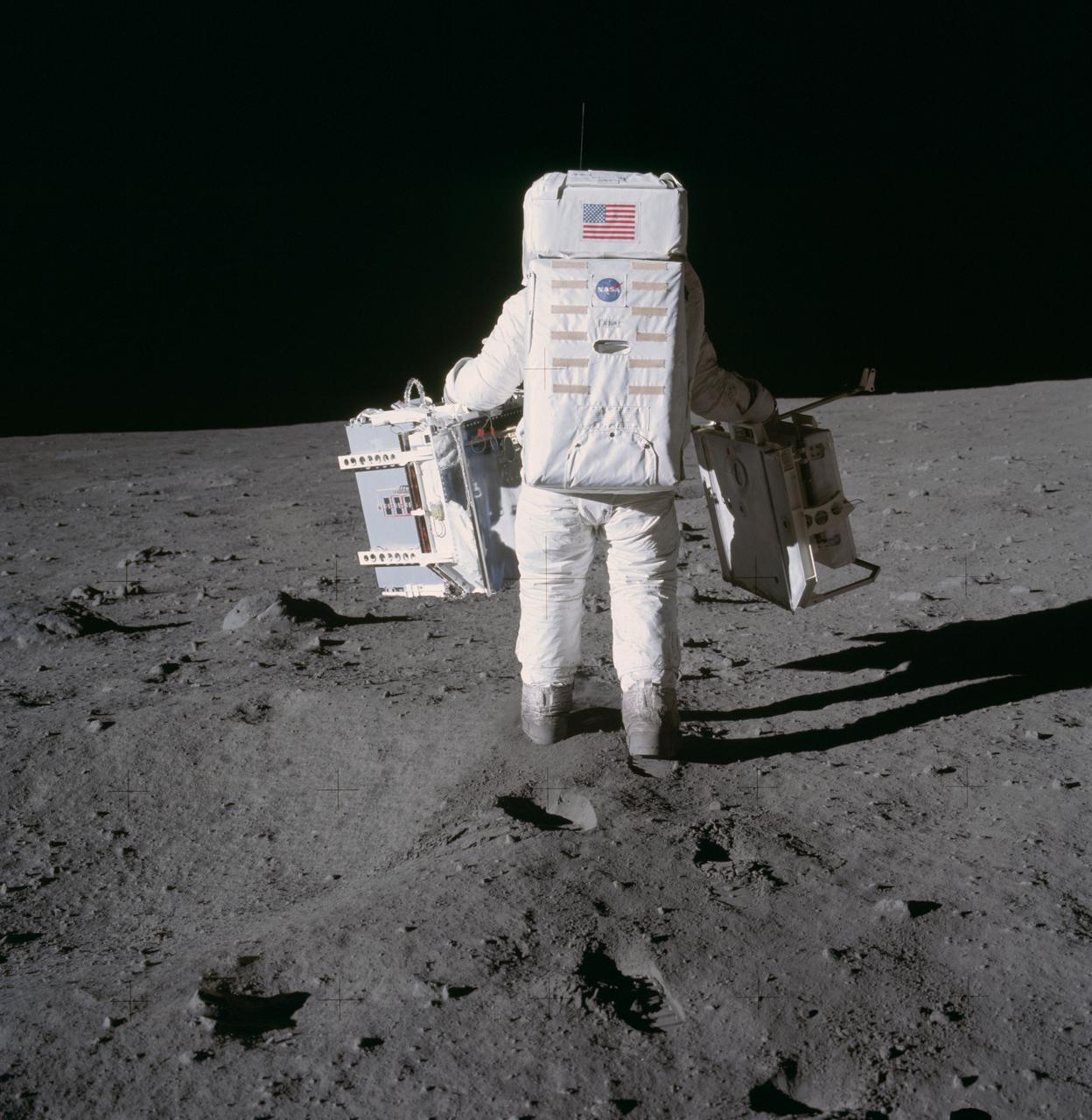
The first manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon, while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon in the Sea of Tranquility. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew set up experiments, collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth, planted the U.S Flag, and left a message for all mankind. In this photograph, Aldrin walks past some rocks, easily carrying scientific equipment which would have been too heavy to carry on Earth. The two packages made up the Early Apollo Scientific Experiment Package (EASEP) on Apollo 11. On the left is the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP) and on the right is the Laser Ranging Retroreflector (LRR).
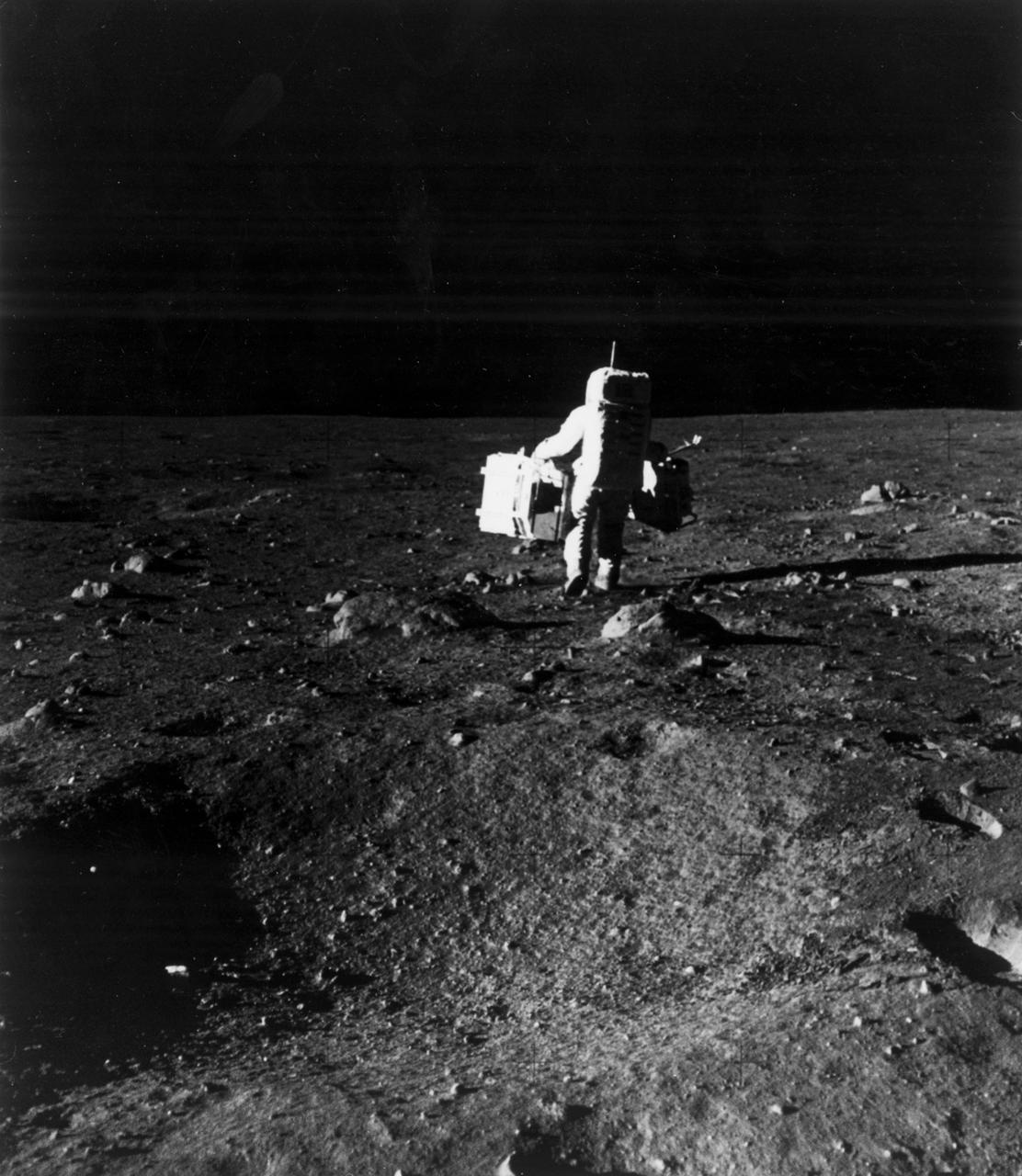

The first manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon, while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon in the Sea of Tranquility. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew set up experiments, collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth, planted the U.S. Flag, and left a message for all mankind. In this photograph, Aldrin walks past some rocks, easily carrying scientific equipment experiements, which would have been to heavy too carry on Earth. The two packages made up the Early Apollo Scientific Experiment Package (EASEP) on Apollo 11. On the left is the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP) and on the right is the Laser Ranging Retroreflector (LRRR).