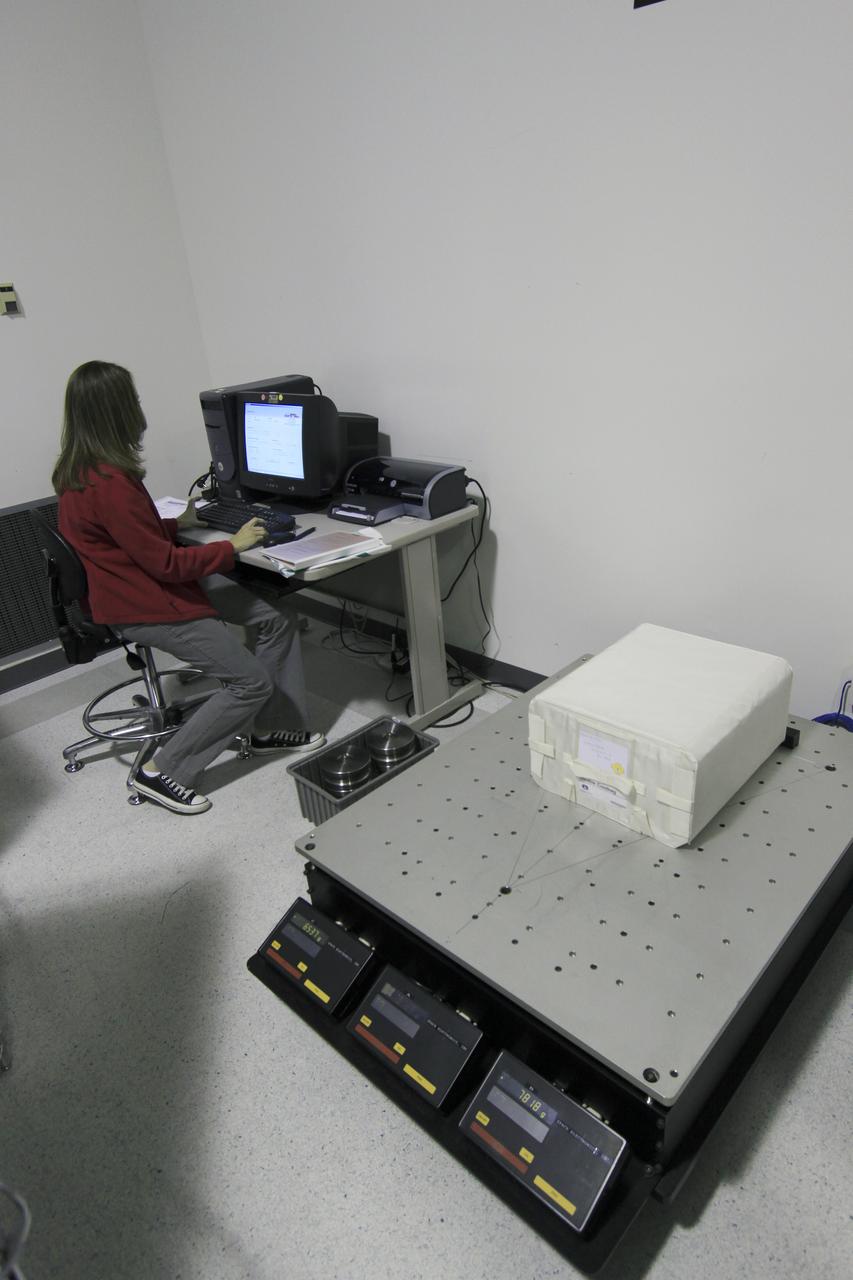

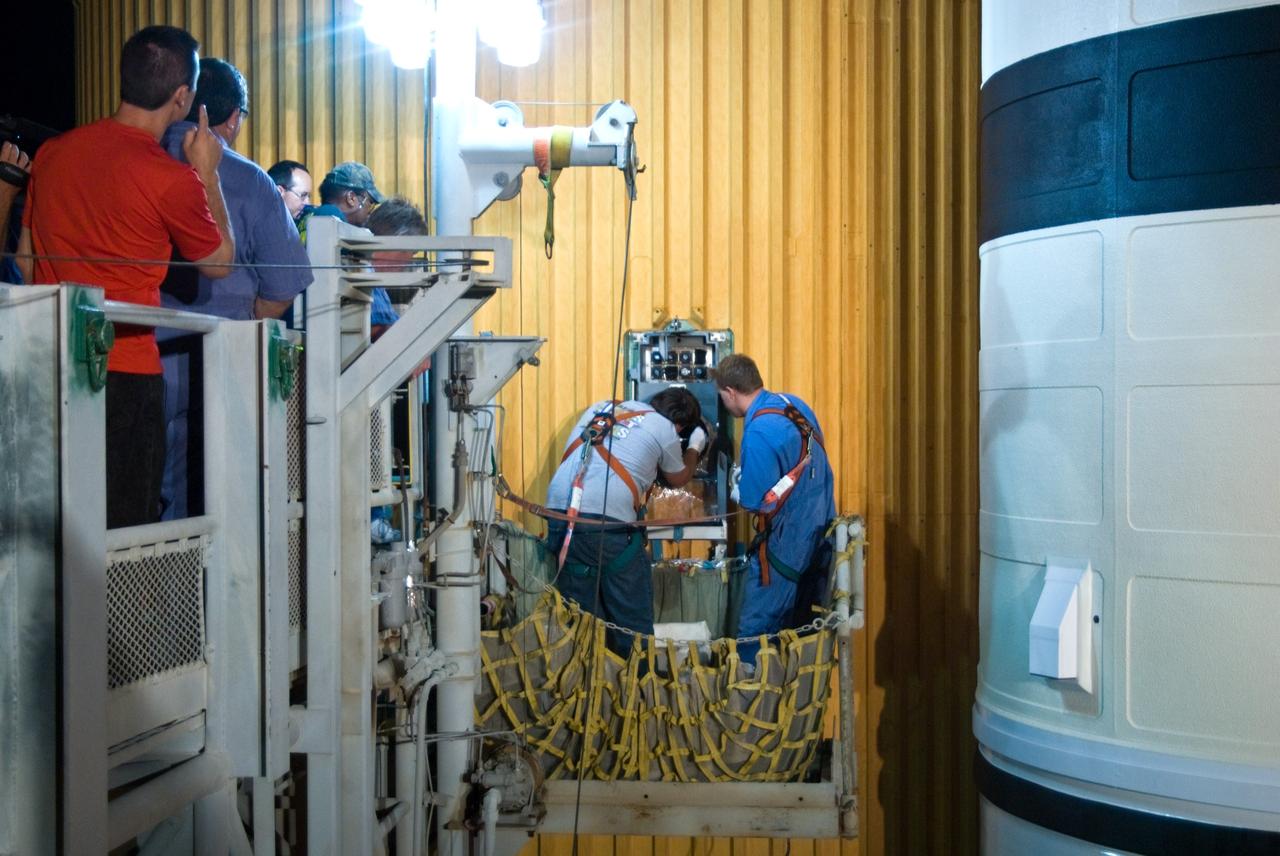
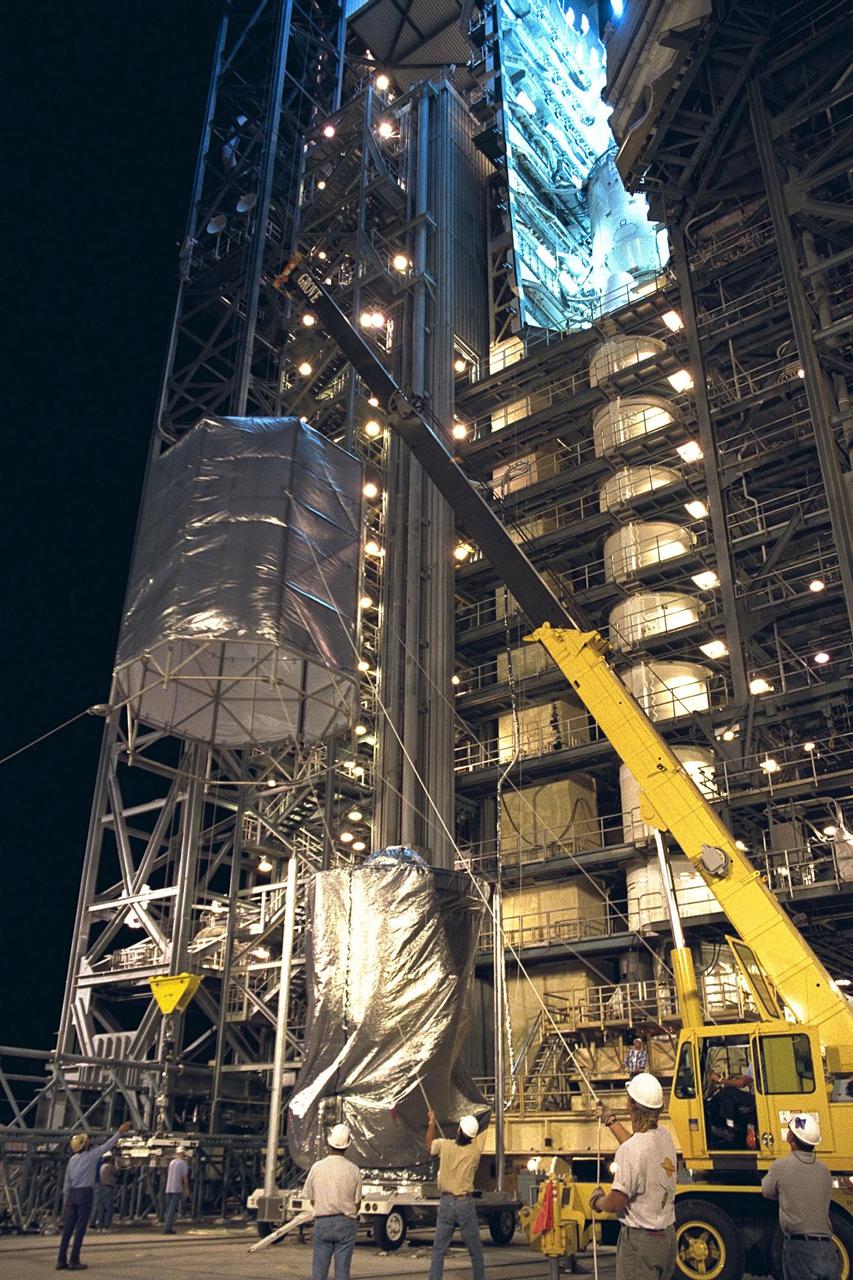
COTS-2 Cold Storage Nanorack Experiment Packaging for Dragon Capsule take from SSPF to Pad 40
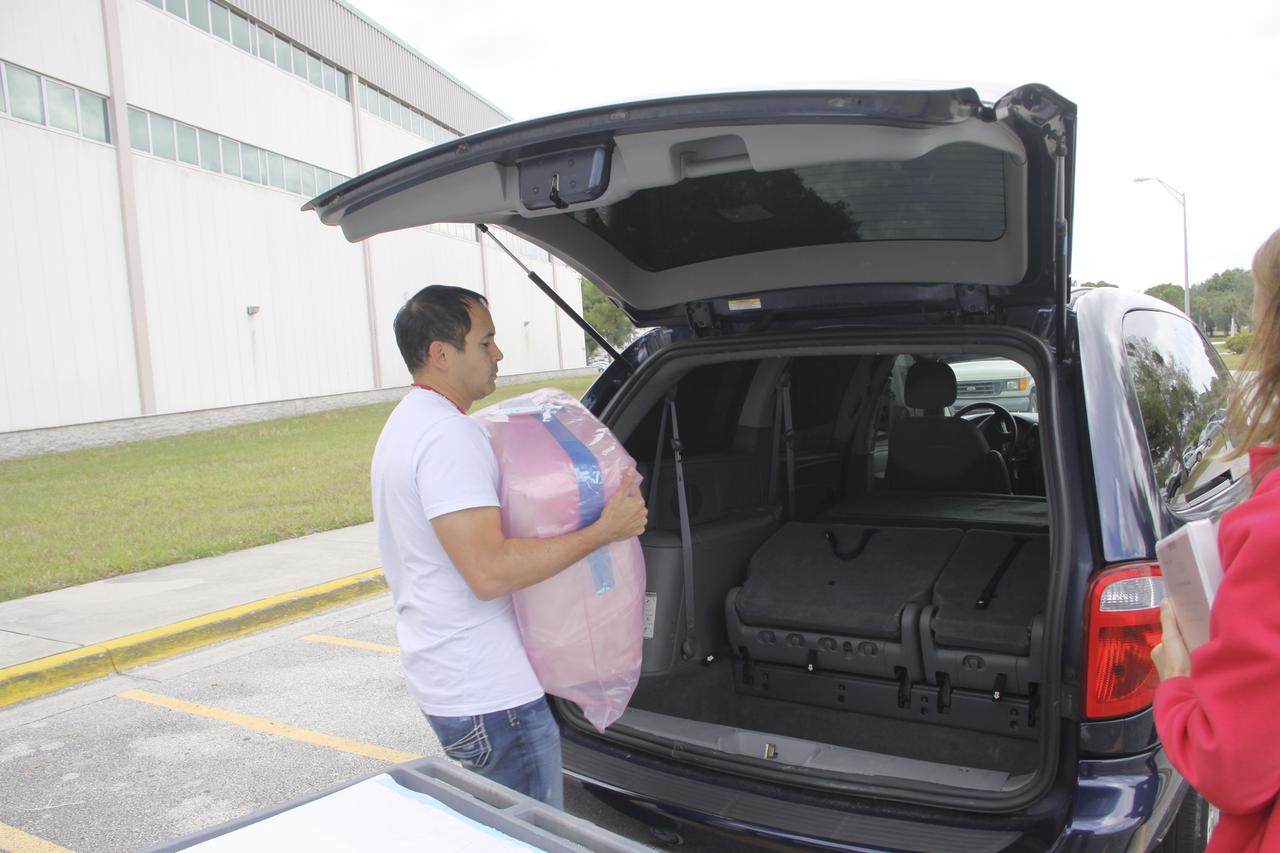

COTS-2 Cold Storage Nanorack Experiment Packaging for Dragon Capsule take from SSPF to Pad 40

COTS-2 Cold Storage Nanorack Experiment Packaging for Dragon Capsule take from SSPF to Pad 40

COTS-2 Cold Storage Nanorack Experiment Packaging for Dragon Capsule take from SSPF to Pad 40
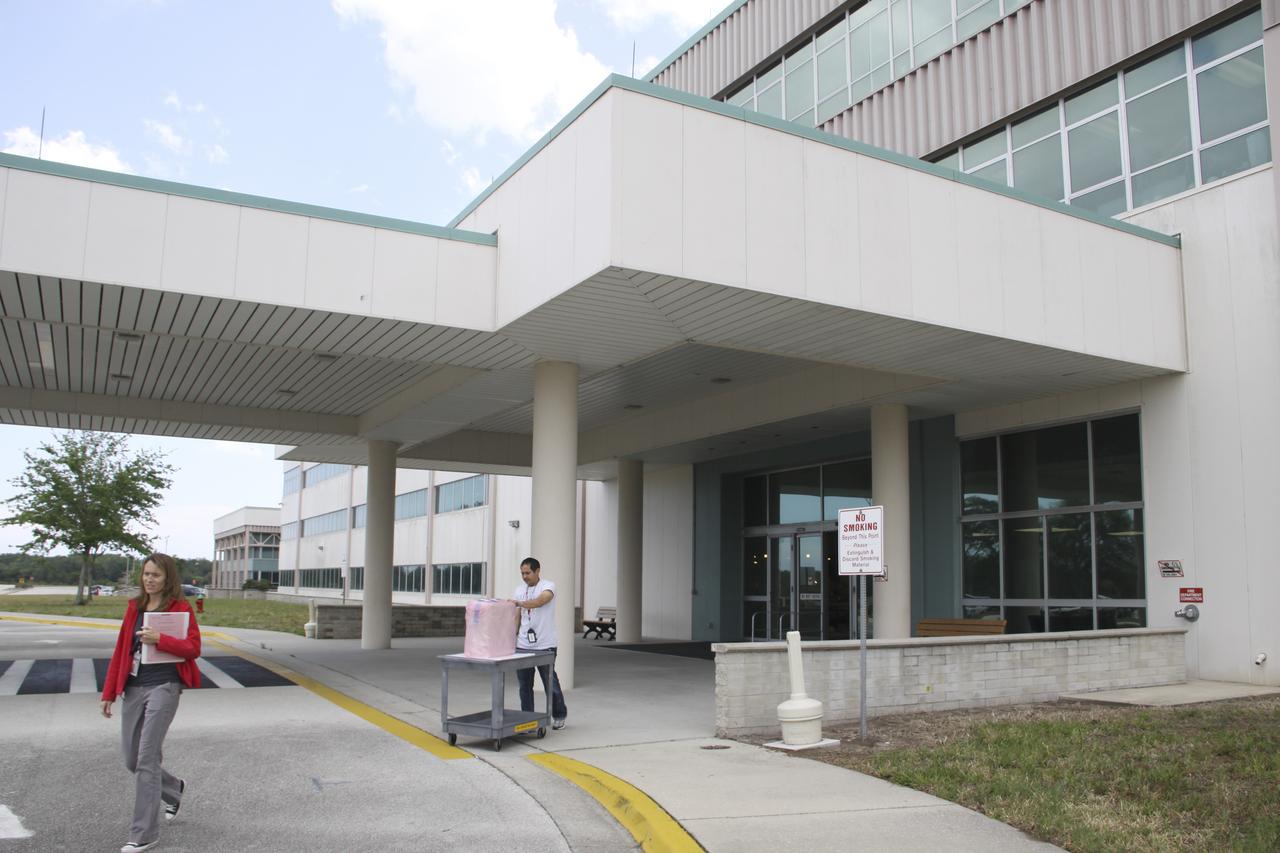

COTS-2 Cold Storage Nanorack Experiment Packaging for Dragon Capsule take from SSPF to Pad 40
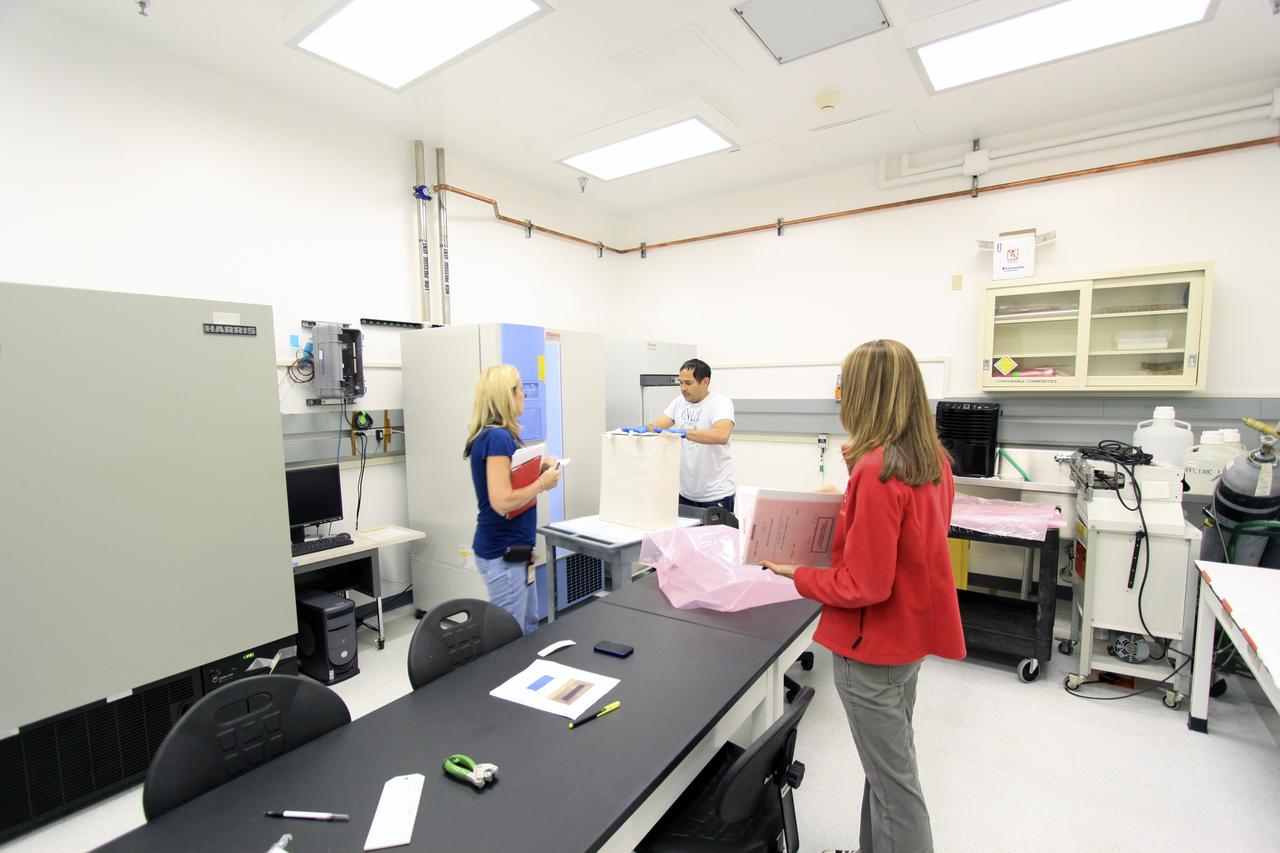

COTS-2 Cold Storage Nanorack Experiment Packaging for Dragon Capsule take from SSPF to Pad 40
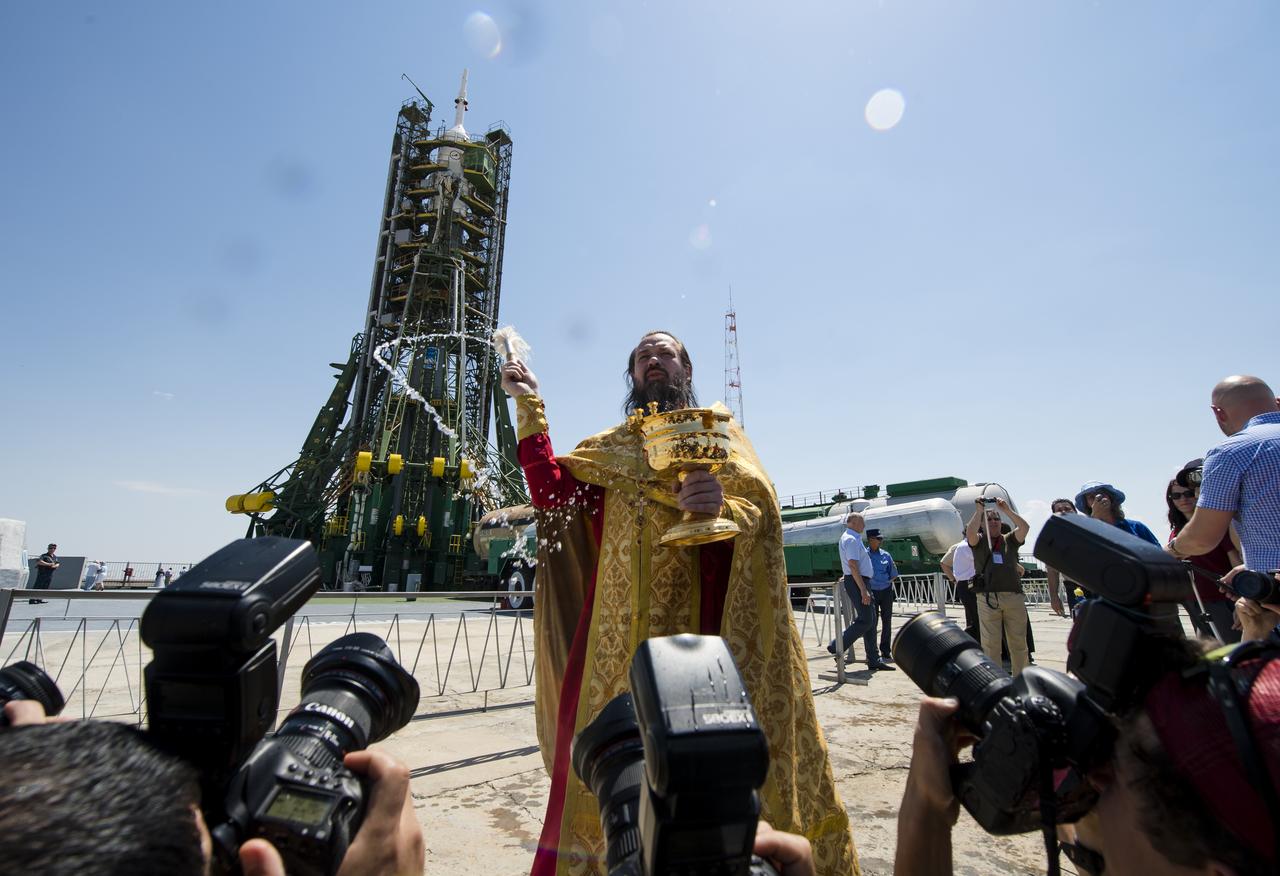

An Orthodox priest blesses members of the media at the Baikonur Cosmodrome launch pad on Tuesday, May 27, 2014 in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
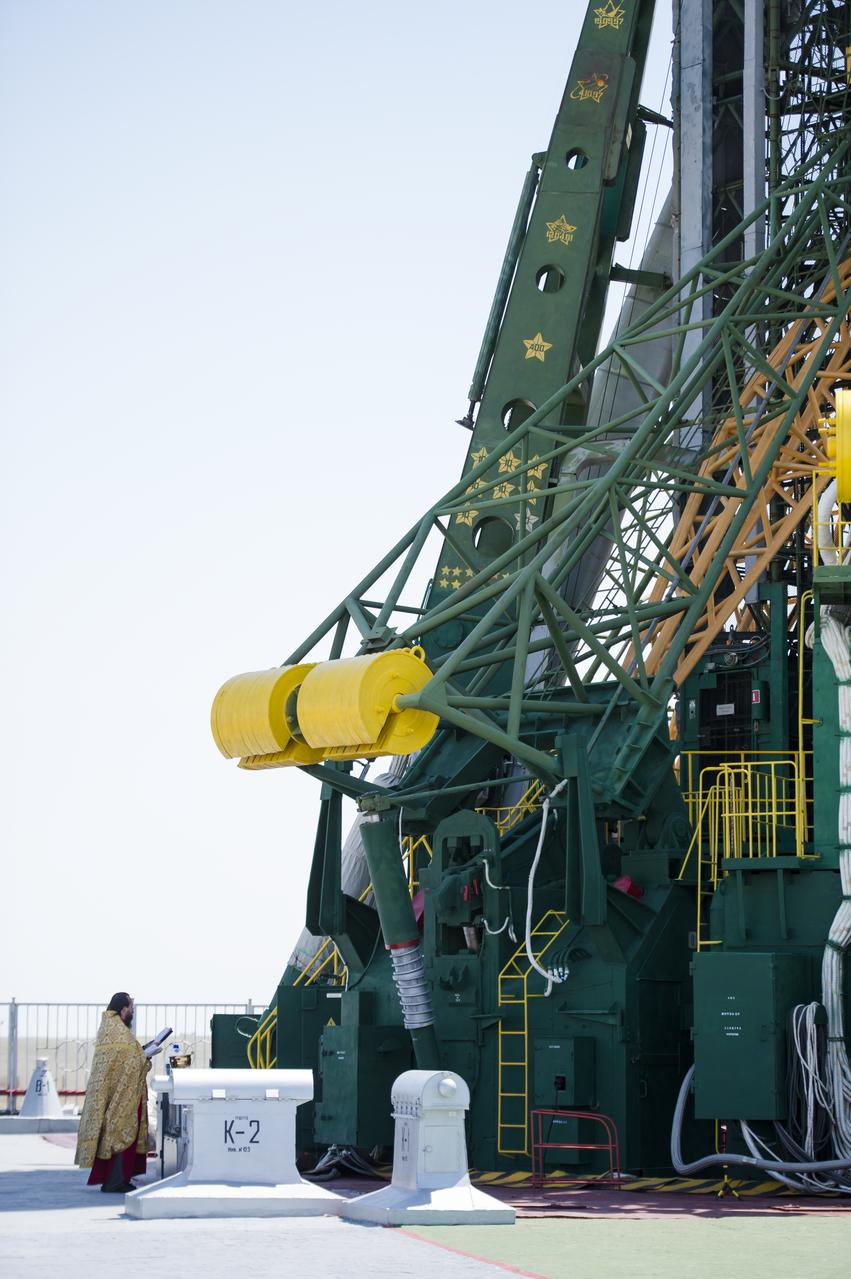

An Orthodox priest blesses the Soyuz rocket at the Baikonur Cosmodrome launch pad on Tuesday, May 27, 2014 in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
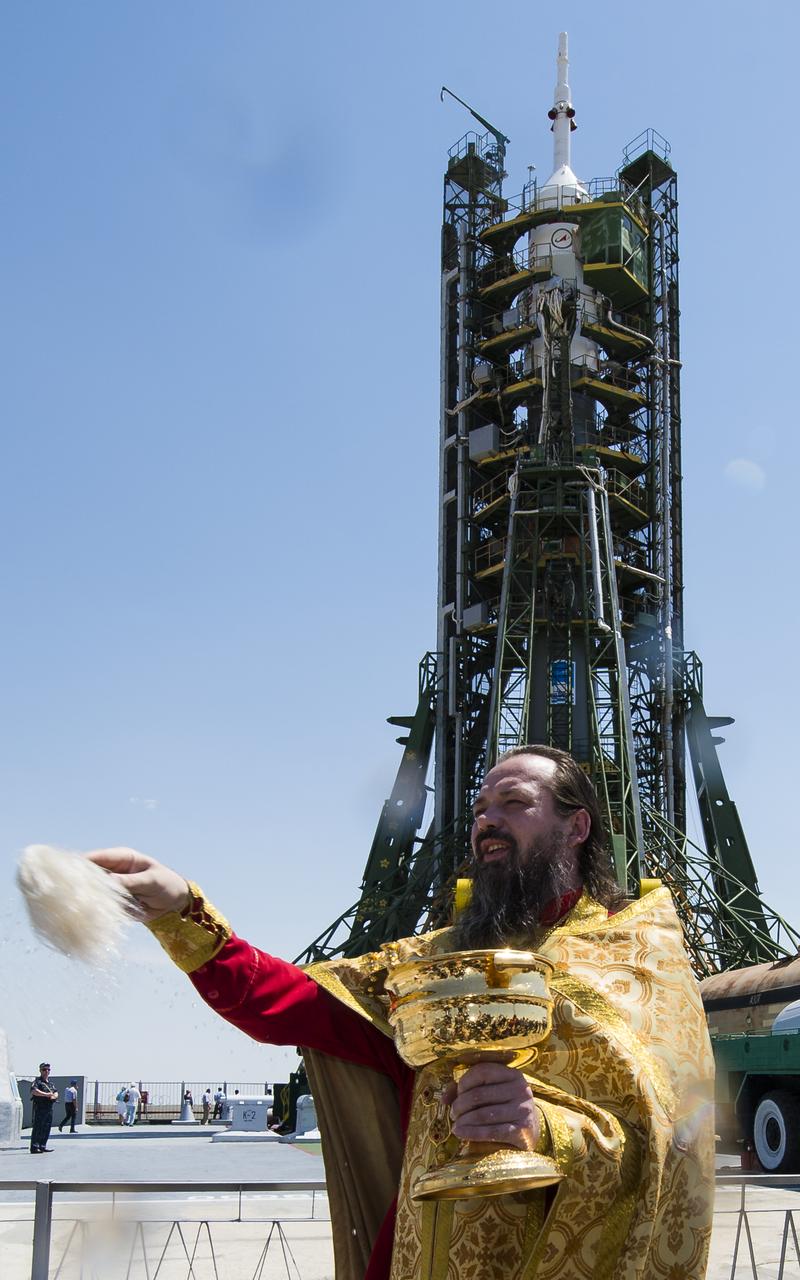

An Orthodox priest blesses members of the media at the Baikonur Cosmodrome launch pad on Tuesday, May 27, 2014 in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
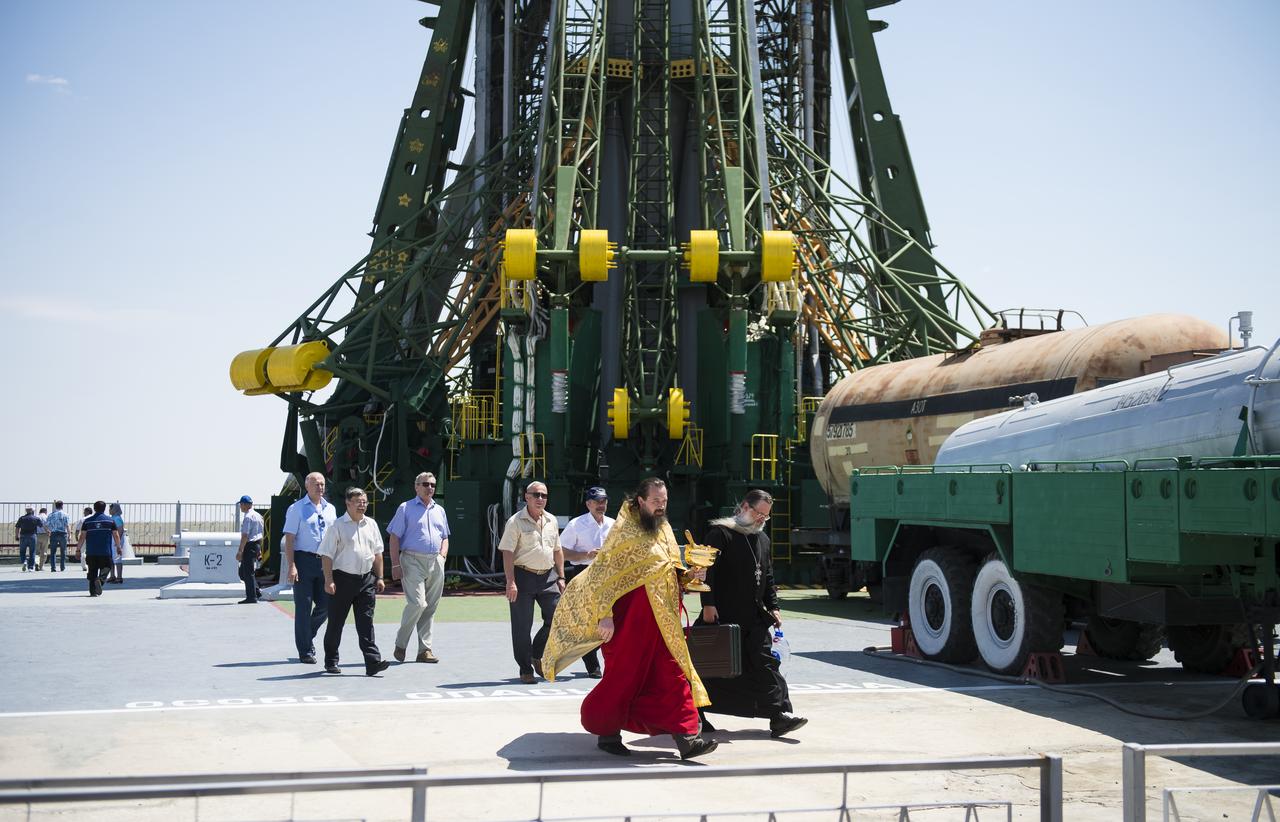

An Orthodox priest is seen after blessing the Soyuz rocket at the Baikonur Cosmodrome launch pad on Tuesday, May 27, 2014 in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
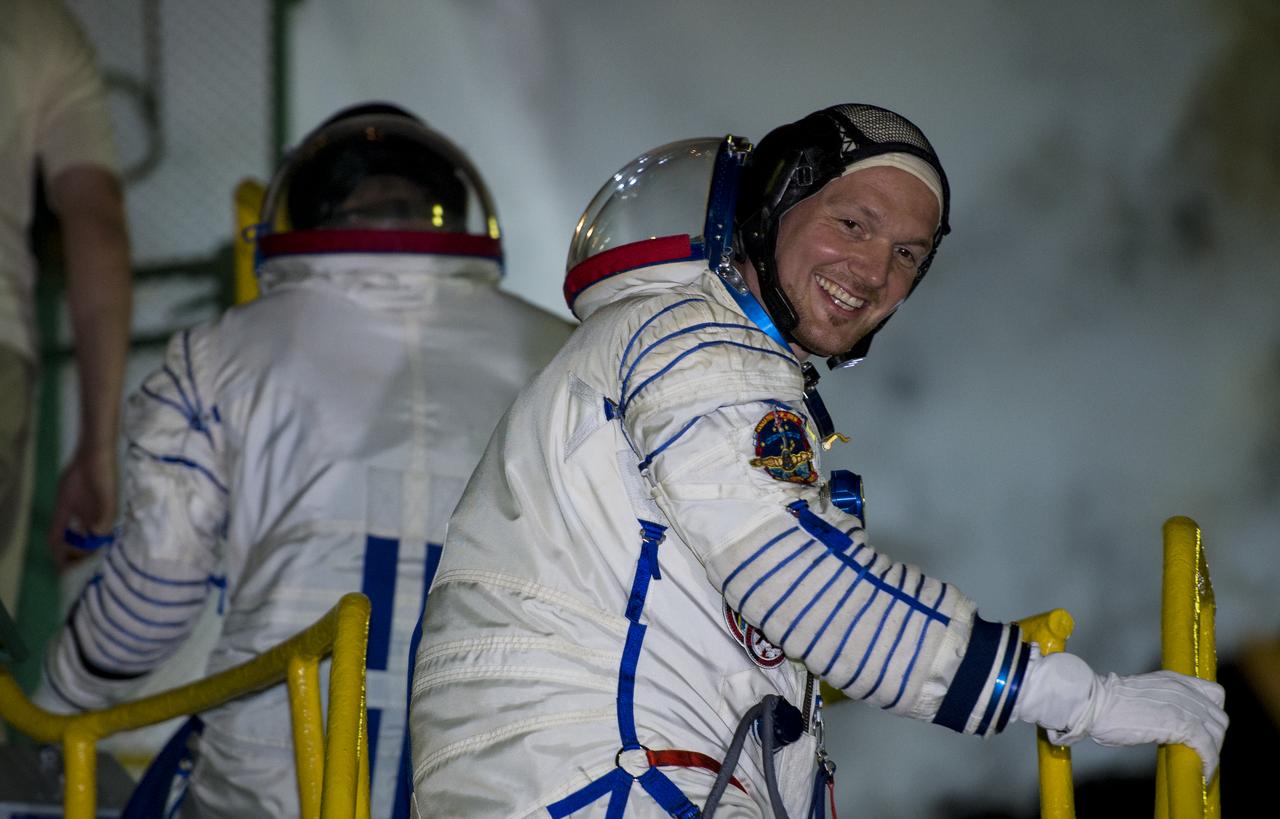

Expedition 40 Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency, ESA, is seen as he prepares to board the Soyuz TMA-13M spacecraft after waving farewell to those gathered on the pad on Wednesday, May 28, 2014 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Suraev, Gerst, and Wiseman will spend the next six months aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
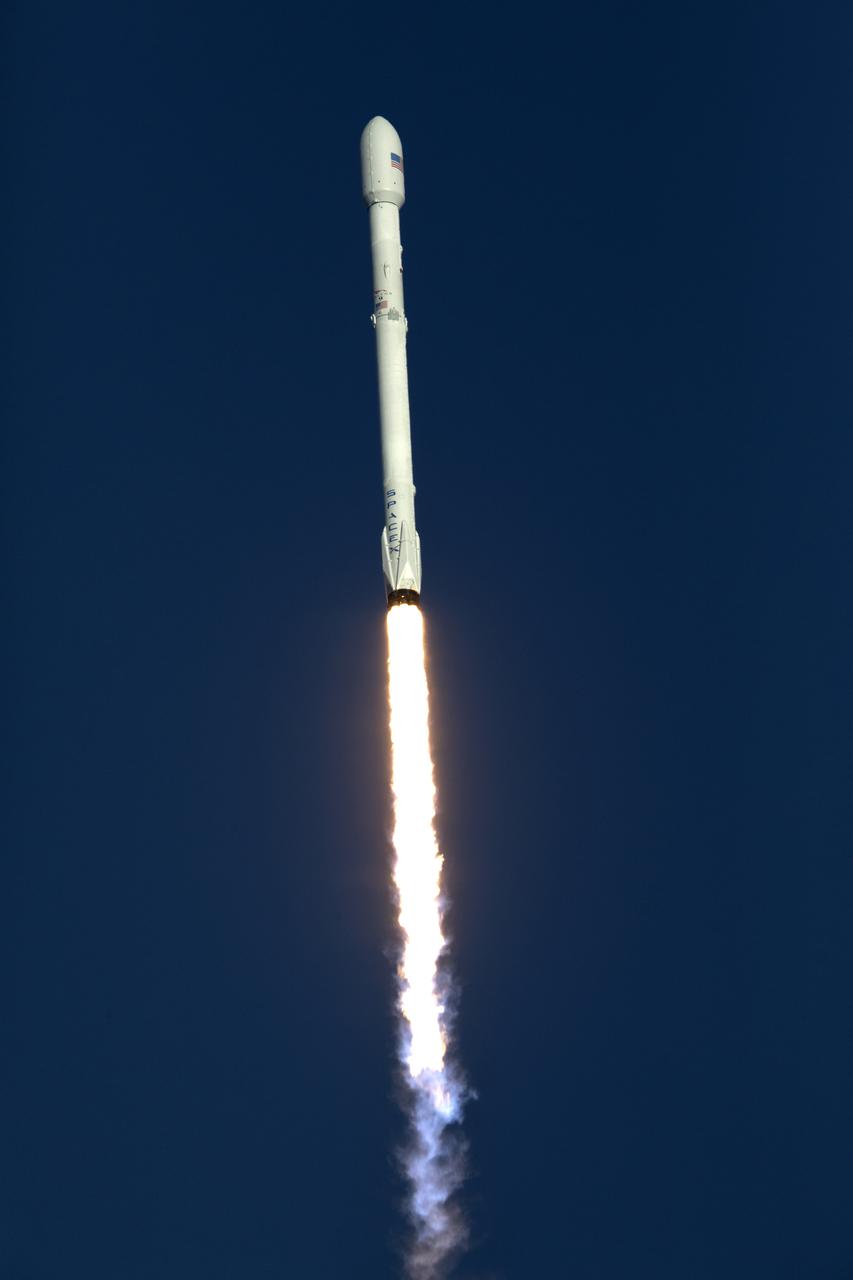

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
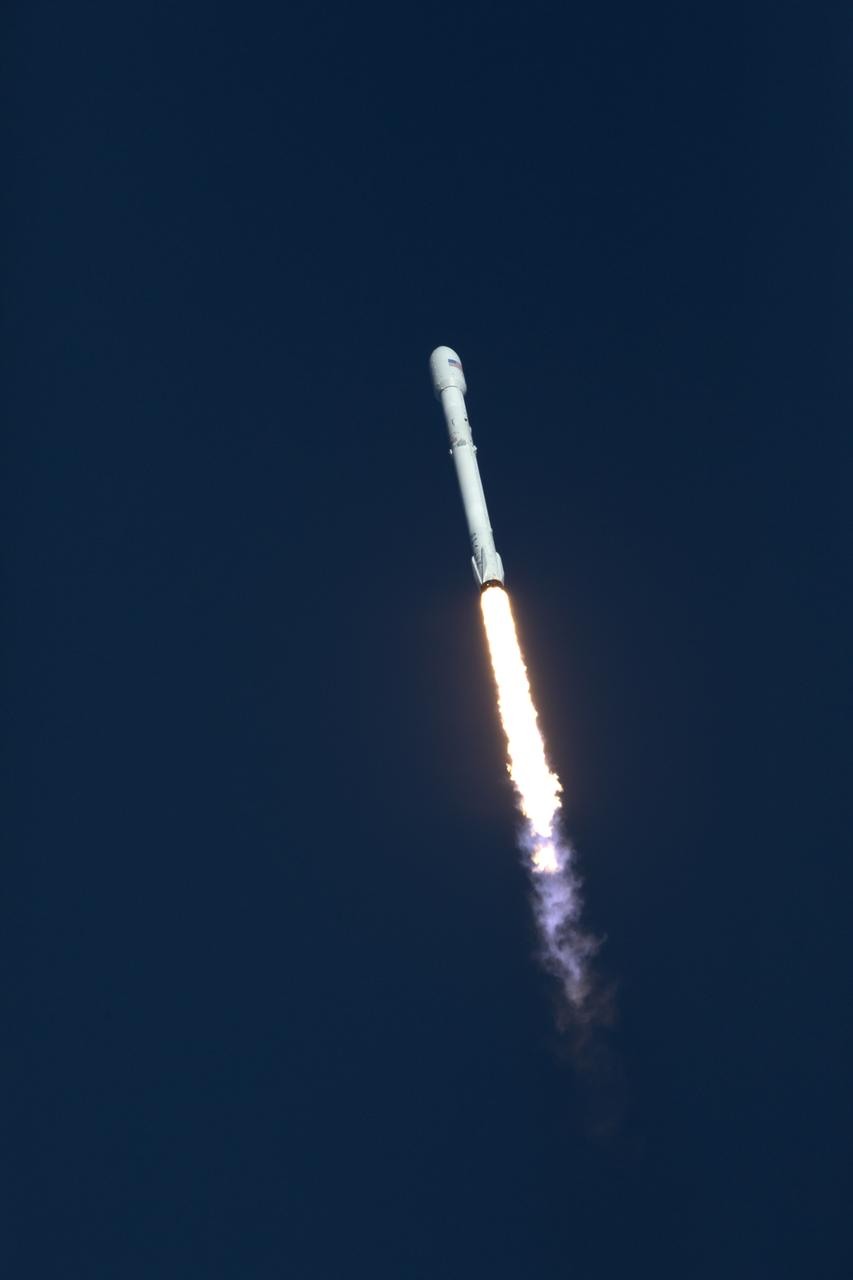

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
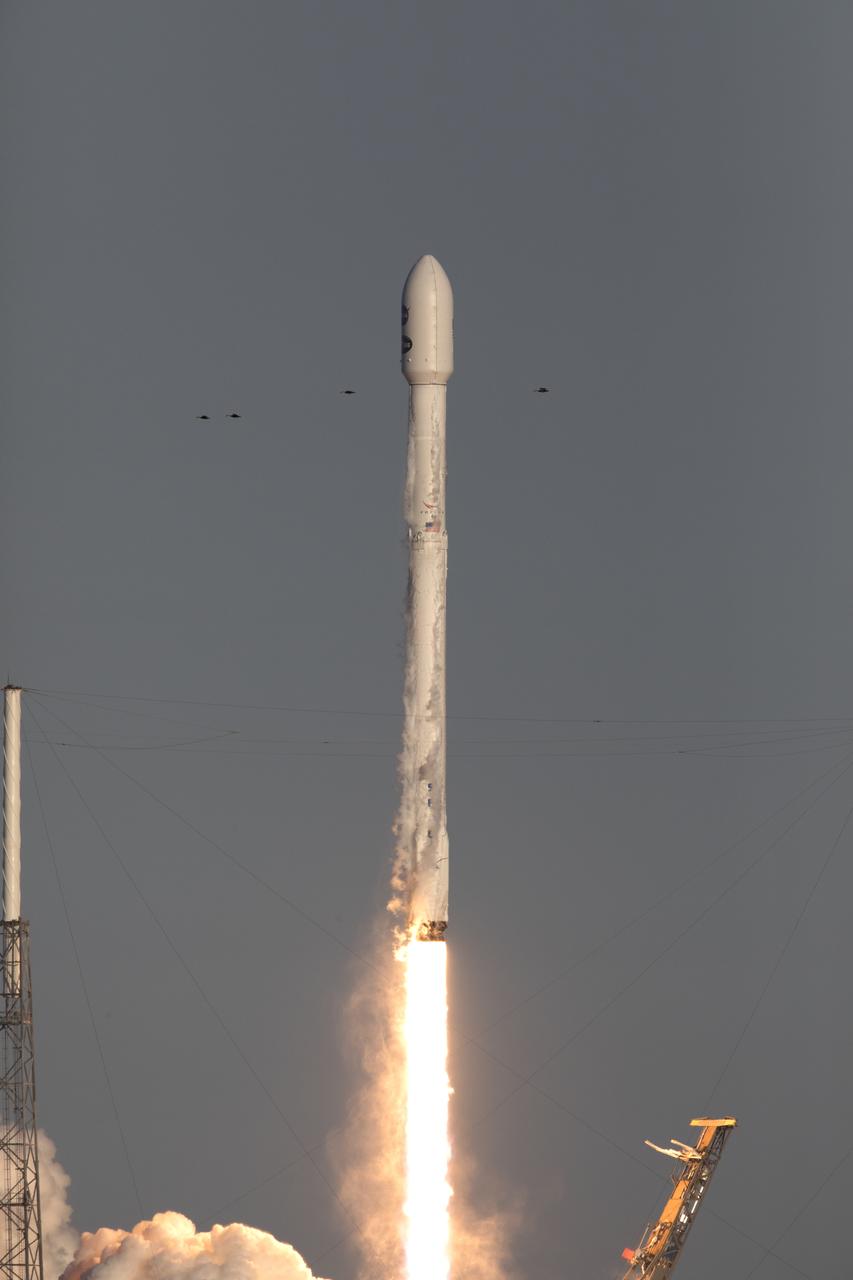

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
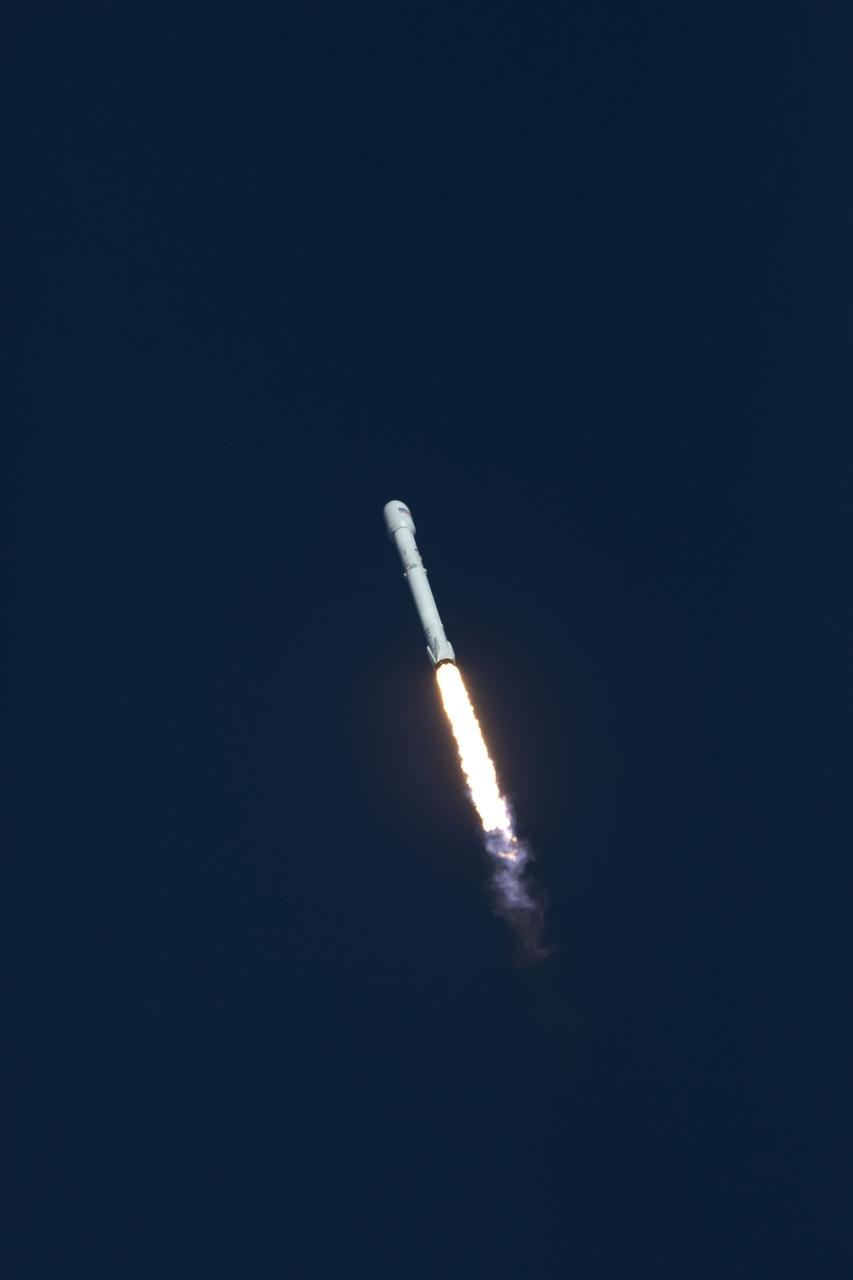

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
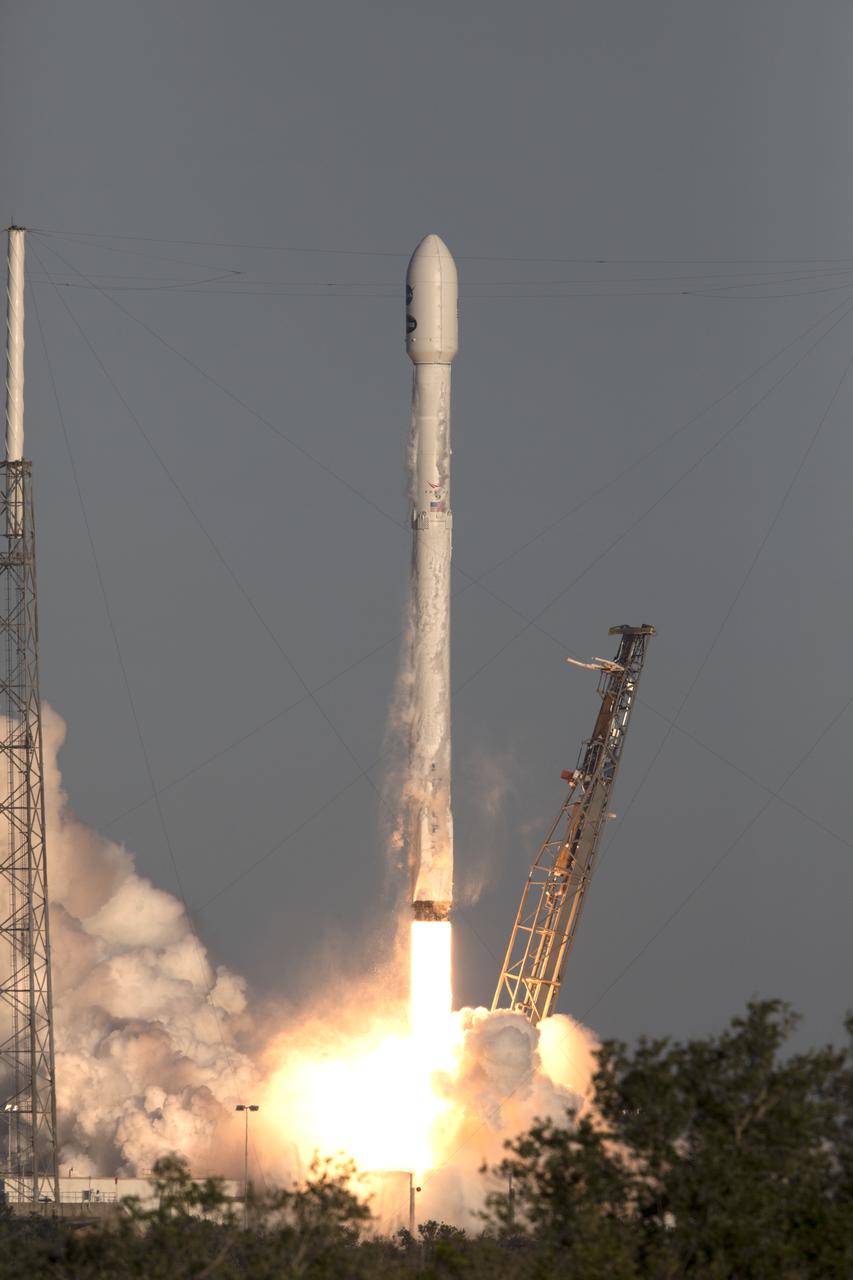

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
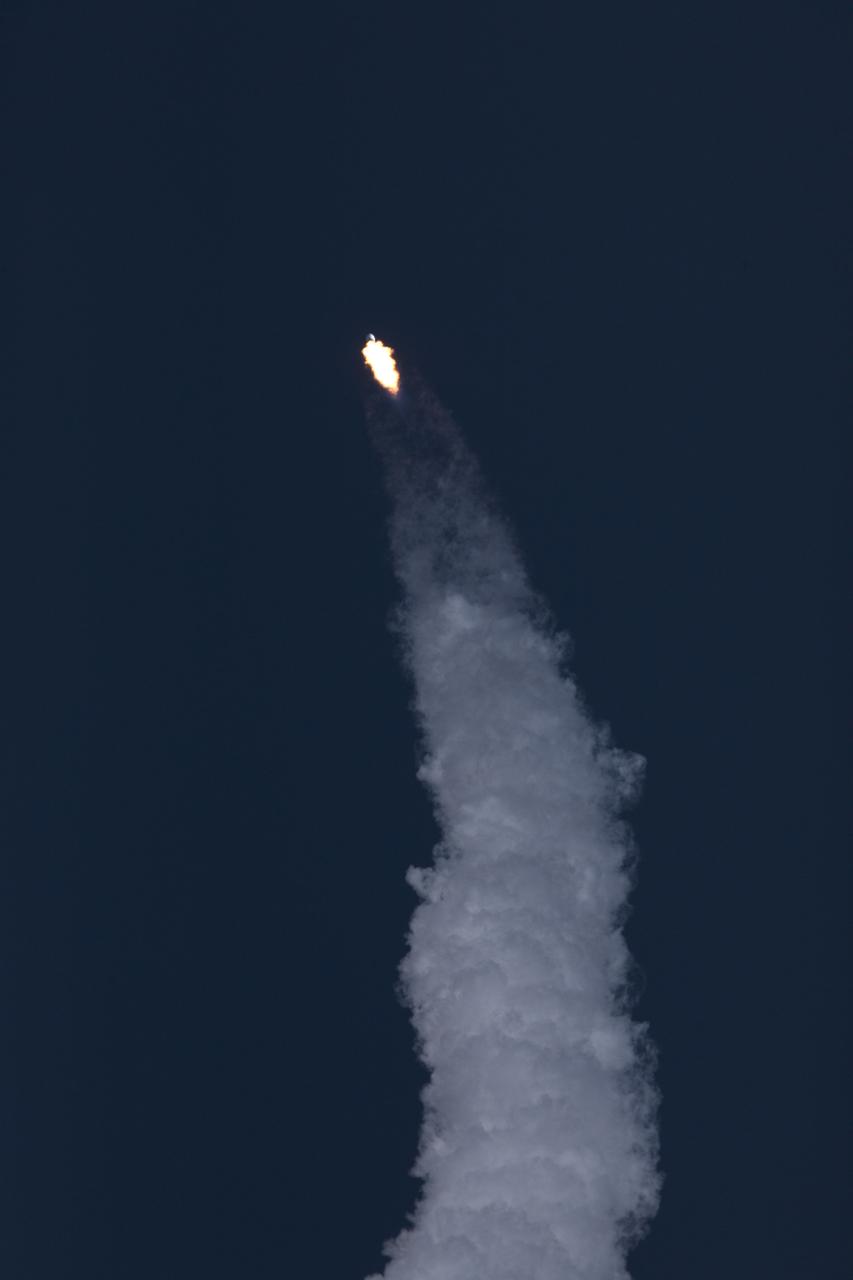

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
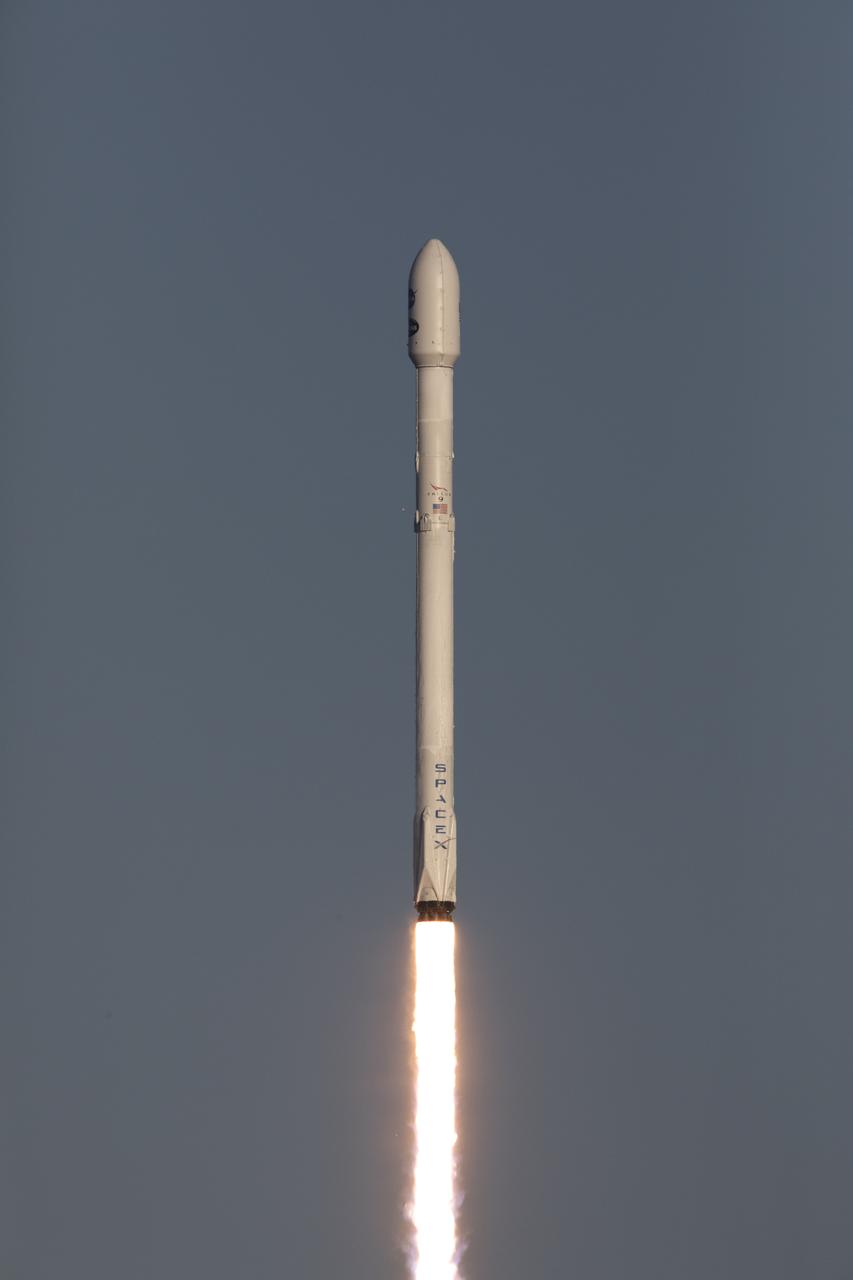

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Liftoff was at 6:51 p.m. EDT. TESS will search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets.
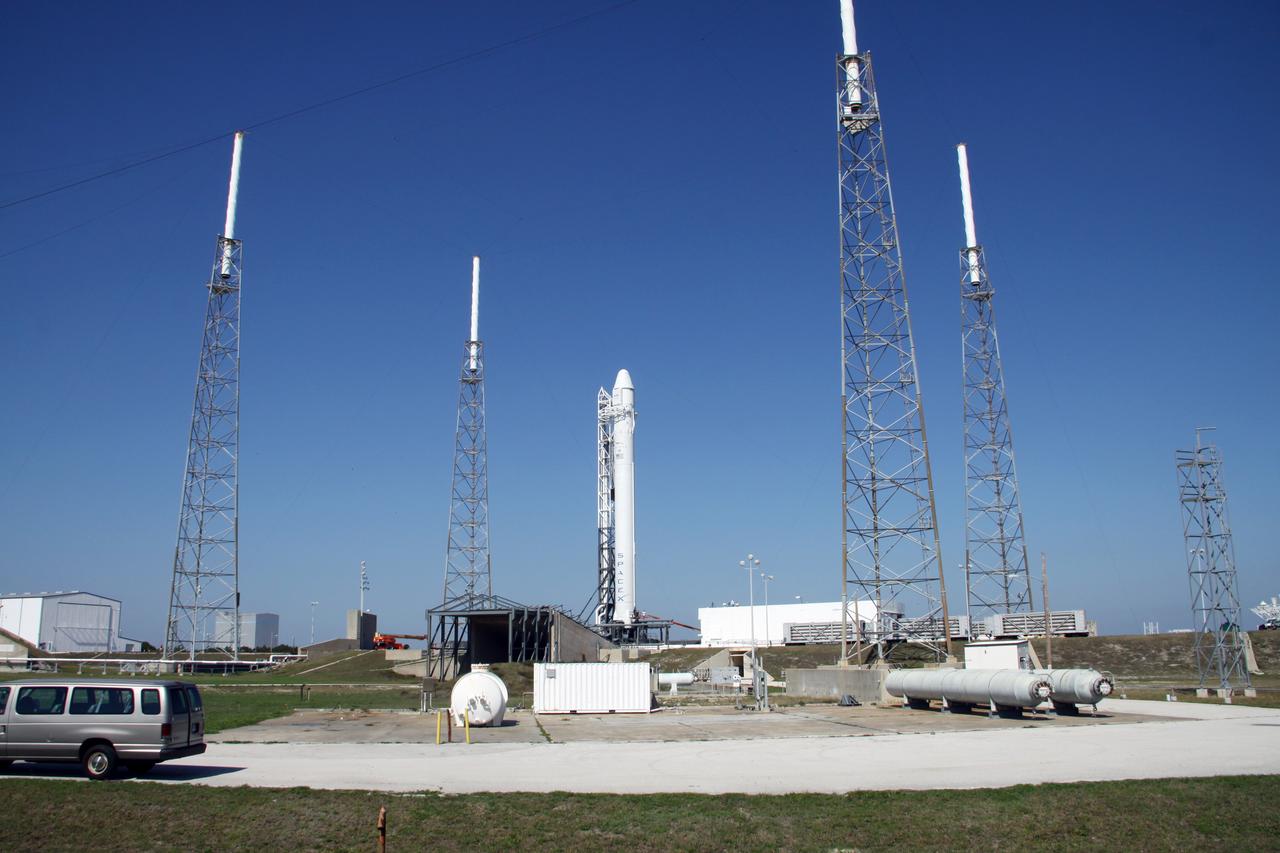

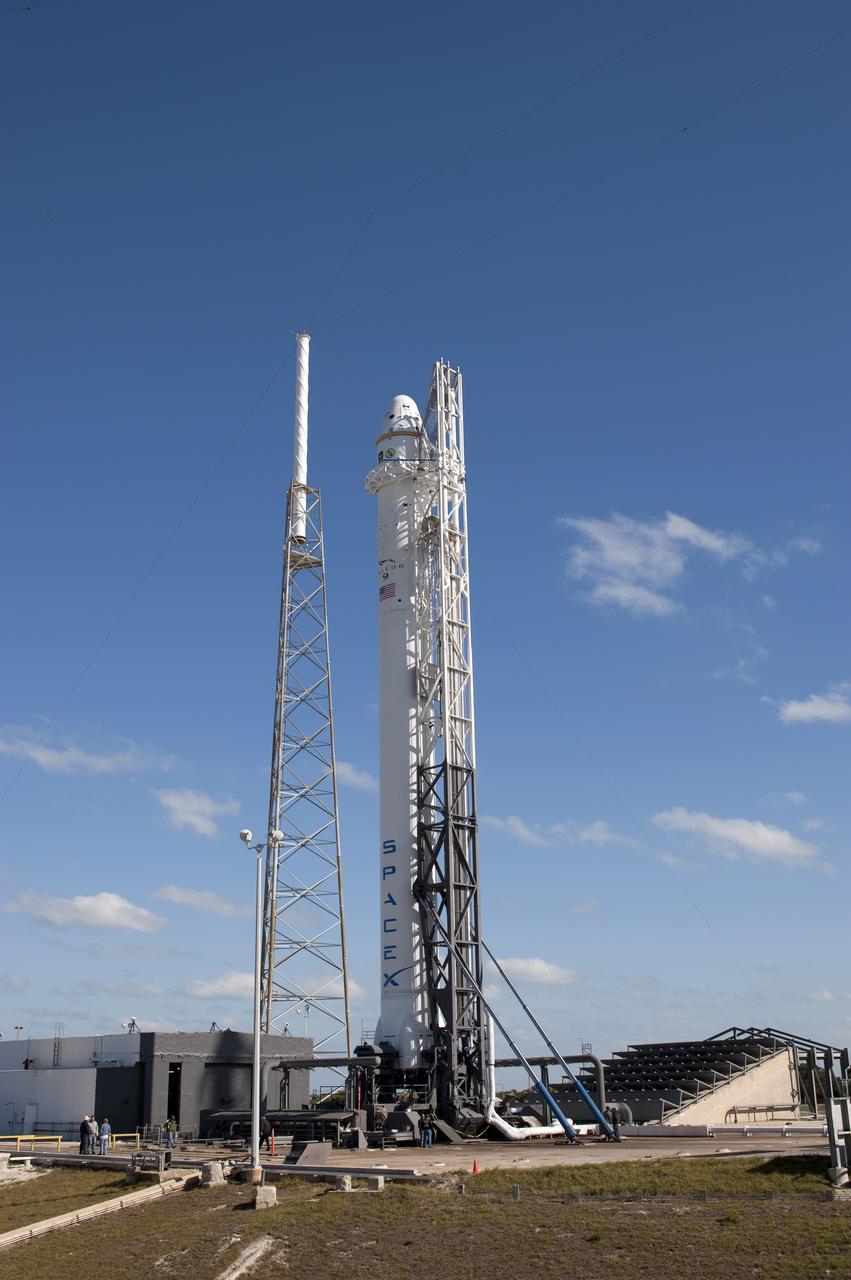
SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 on Pad 40 during Remote Camera Set-up
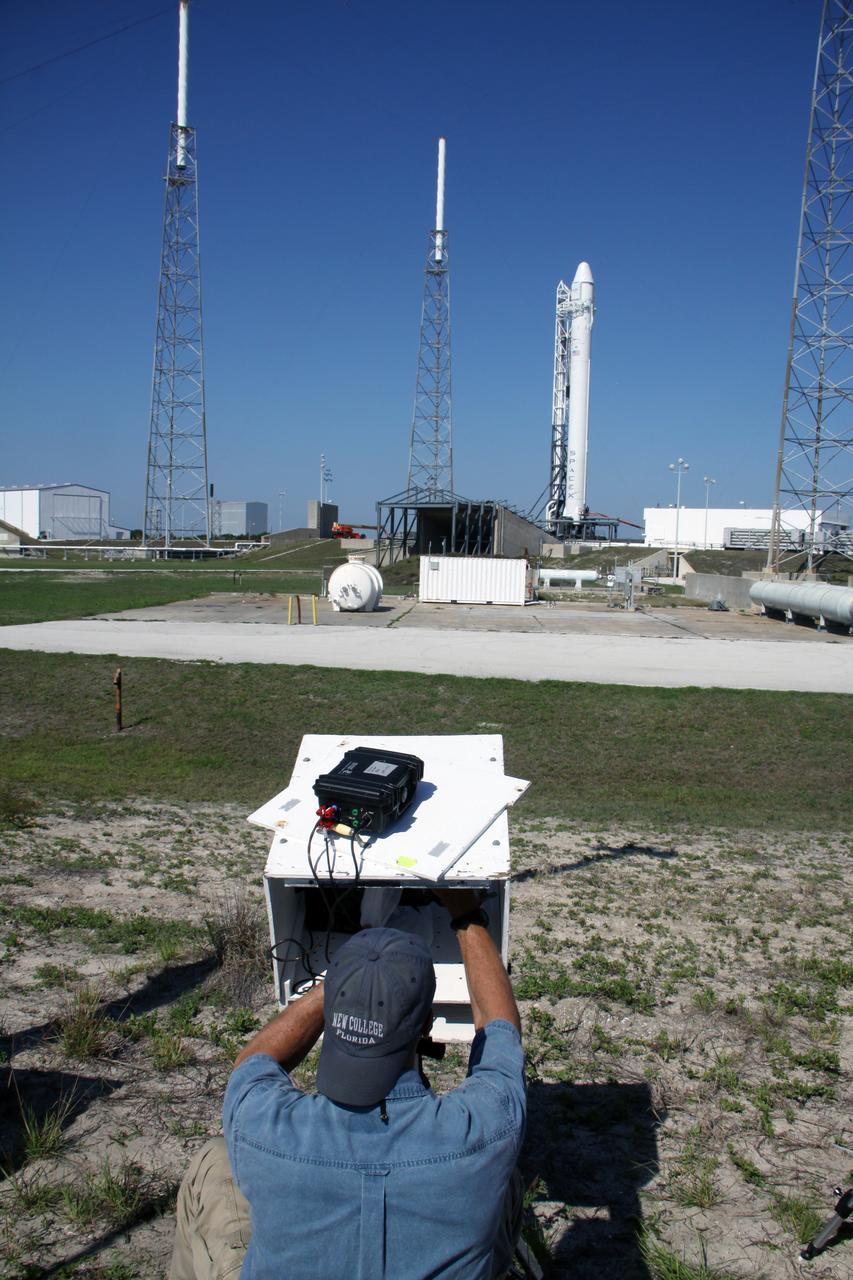

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 on Pad 40 during Remote Camera Set-up
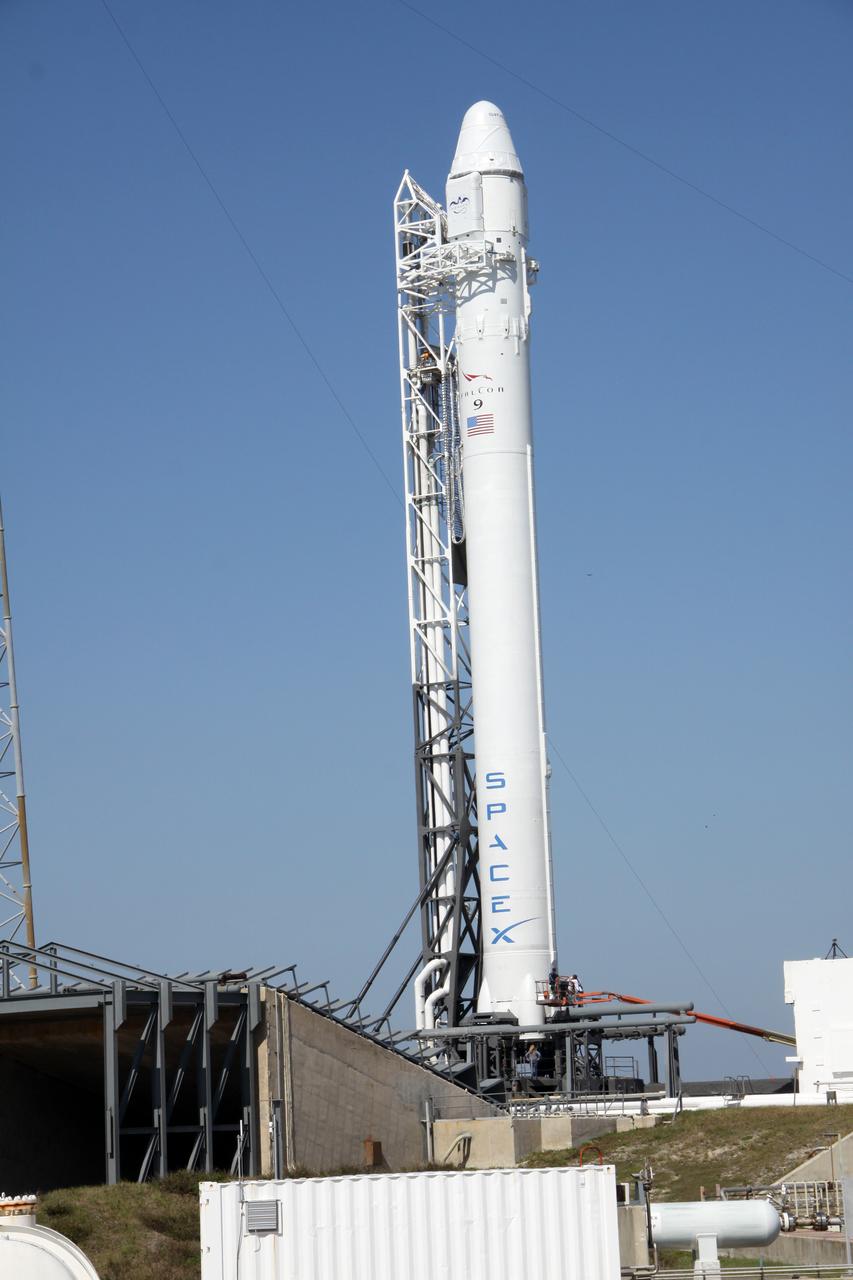

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 on Pad 40 during Remote Camera Set-up

A Titan IVB core vehicle and its twin Solid Rocket Motor Upgrades (SRMUs) depart from the Solid Rocket Motor Assembly and Readiness Facility (SMARF), Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), en route to Launch Complex 40. At the pad, the Centaur upper stage will be added and, eventually, the prime payload, the Cassini spacecraft. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings and moon, Titan. Launch of the Cassini mission to Saturn is scheduled for Oct. 6 from Pad 40, CCAS
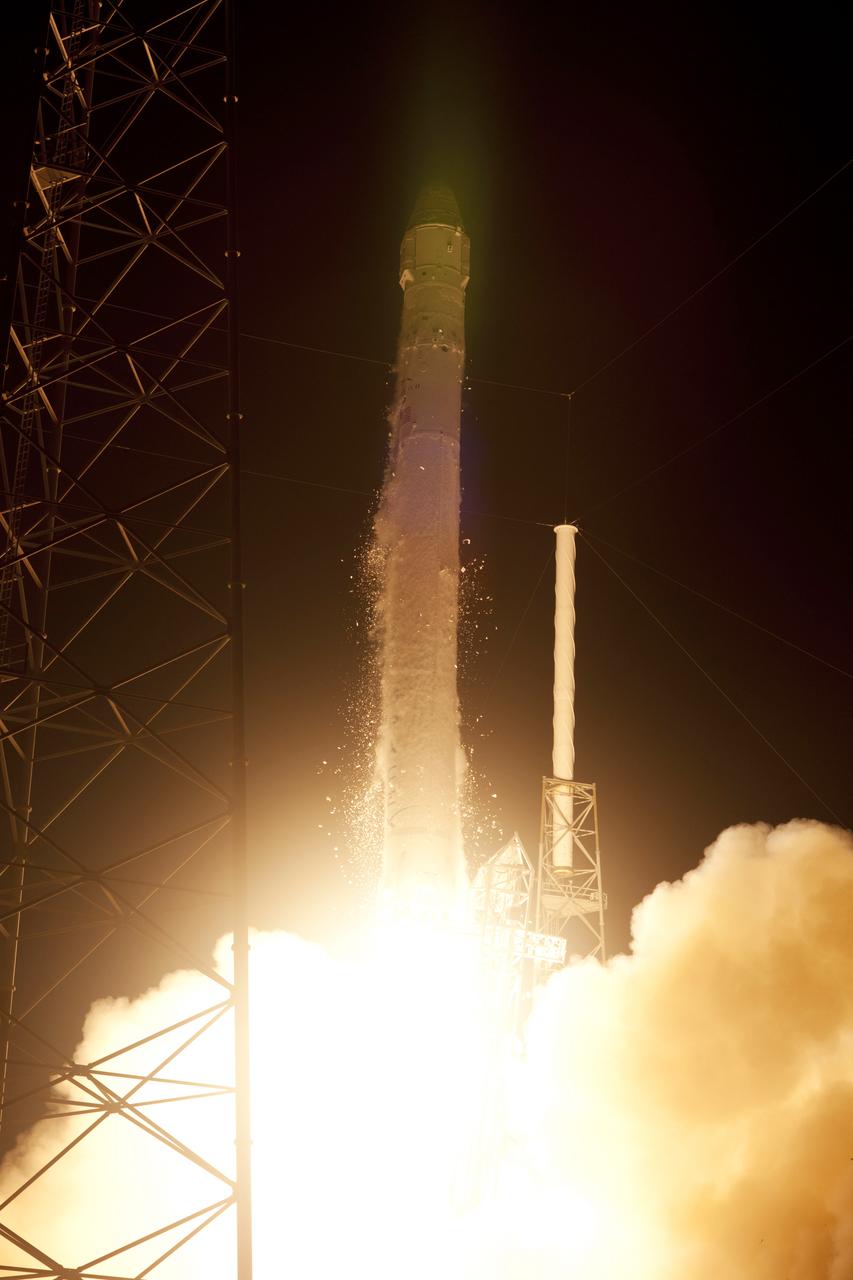

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch, DD24-203
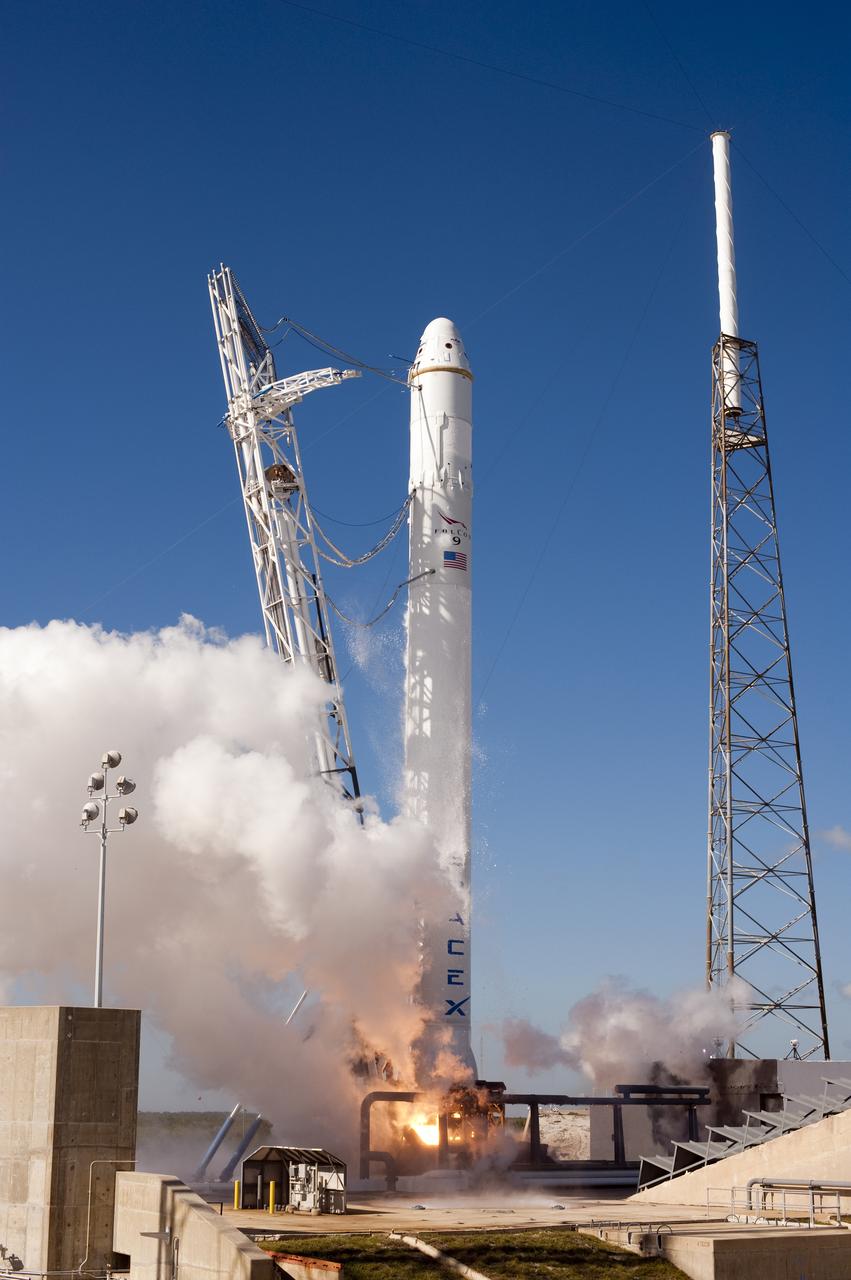

SPACE X FALCON 9 COTS-1 TEST FIRE - DAY 1
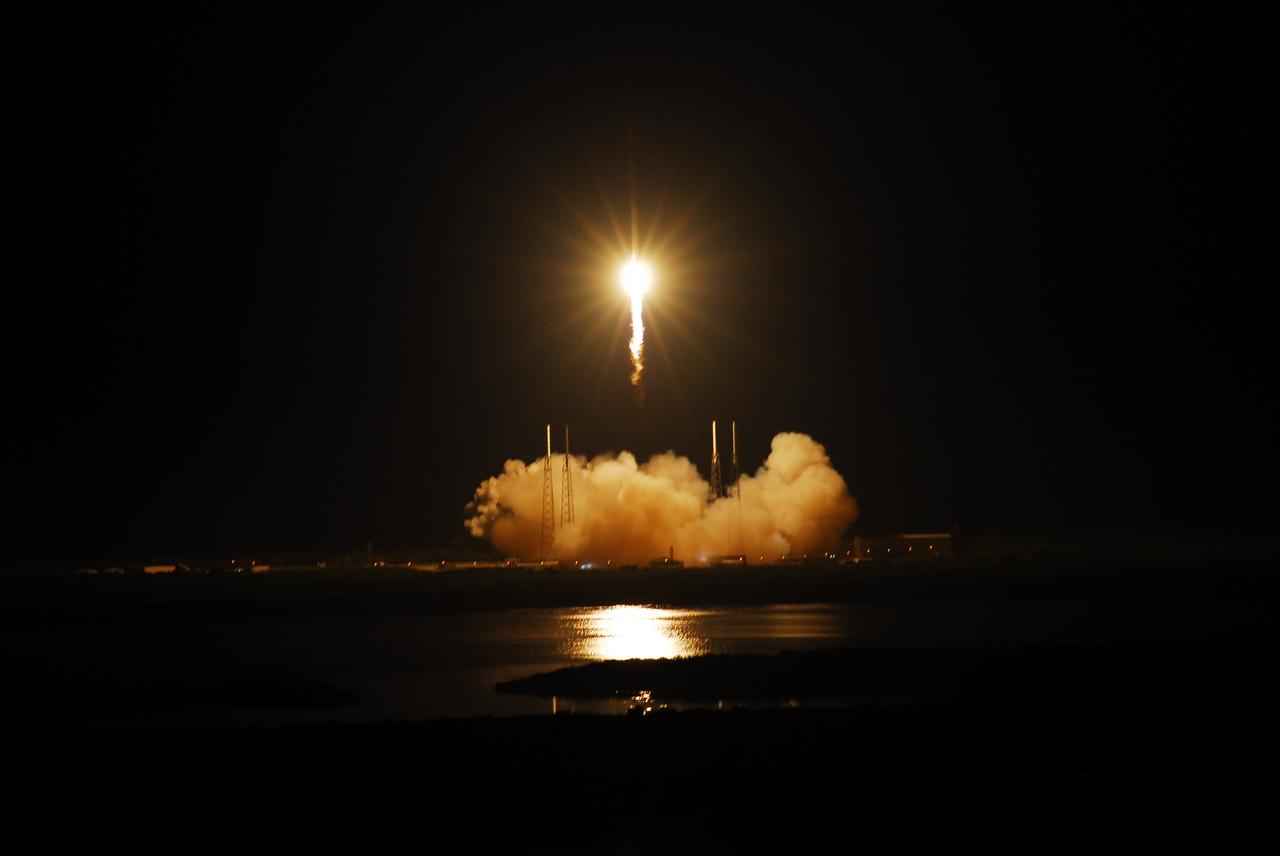

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch

SPACE X FALCON 9 COTS-1 TEST FIRE - DAY 1
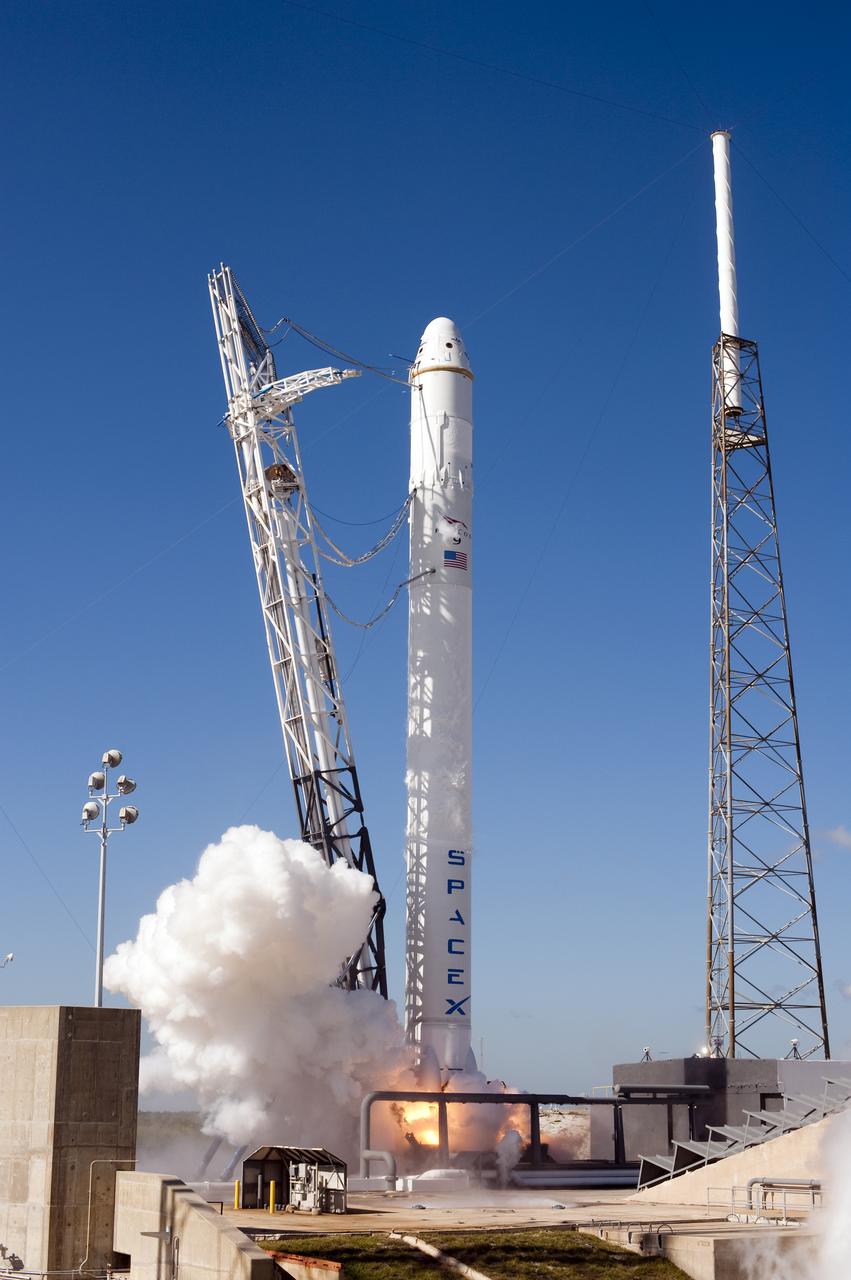

SPACE X FALCON 9 COTS-1 TEST FIRE - DAY 1
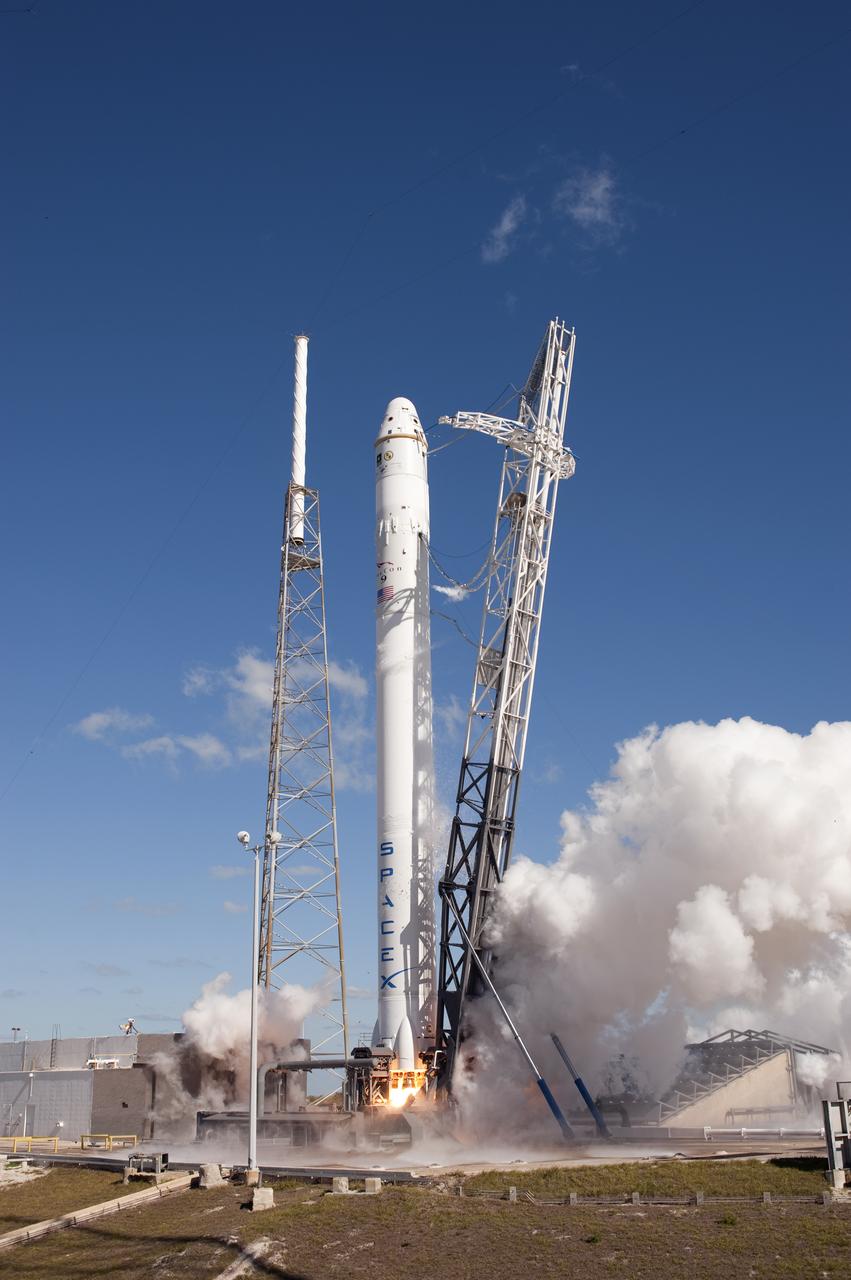

SPACE X FALCON 9 COTS-1 TEST FIRE - DAY 1
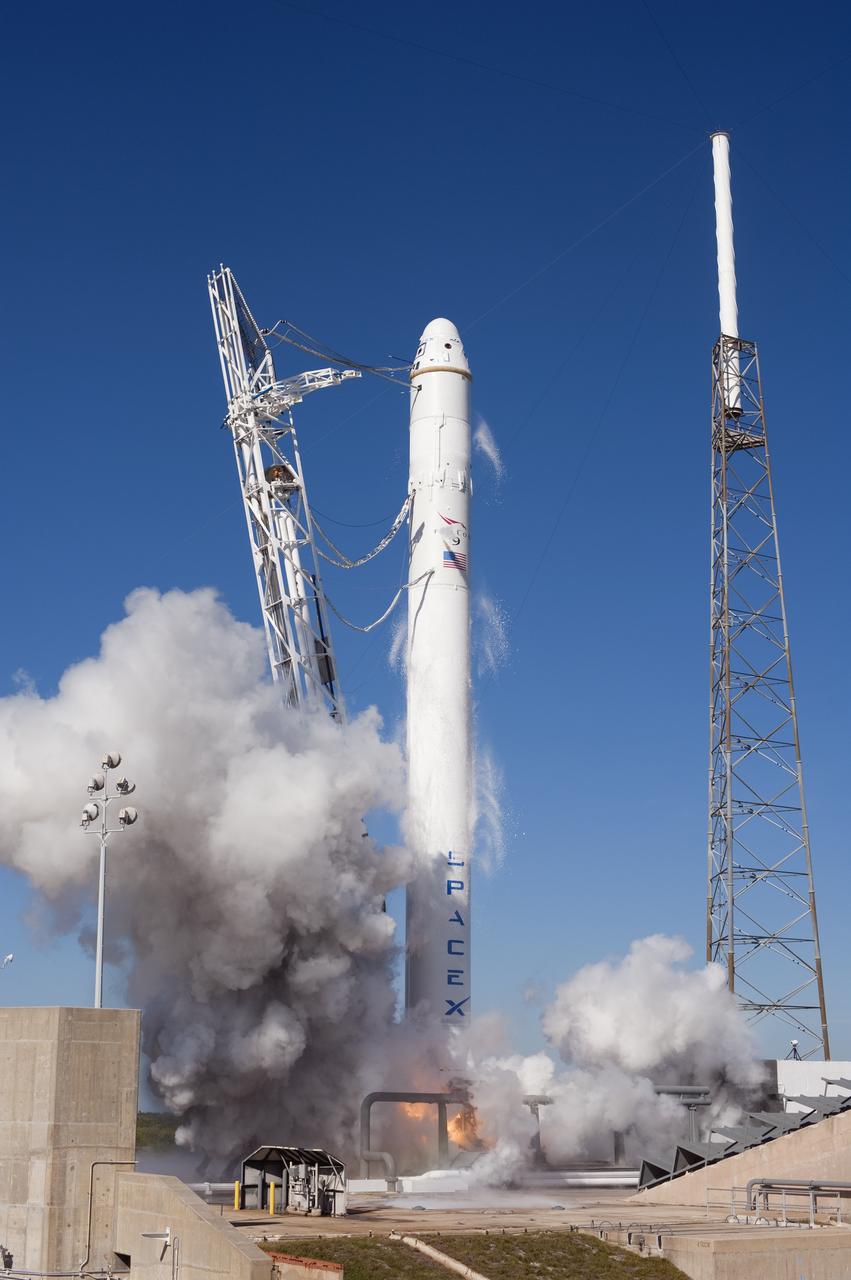

SPACE X FALCON 9 COTS-1 TEST FIRE - DAY 2
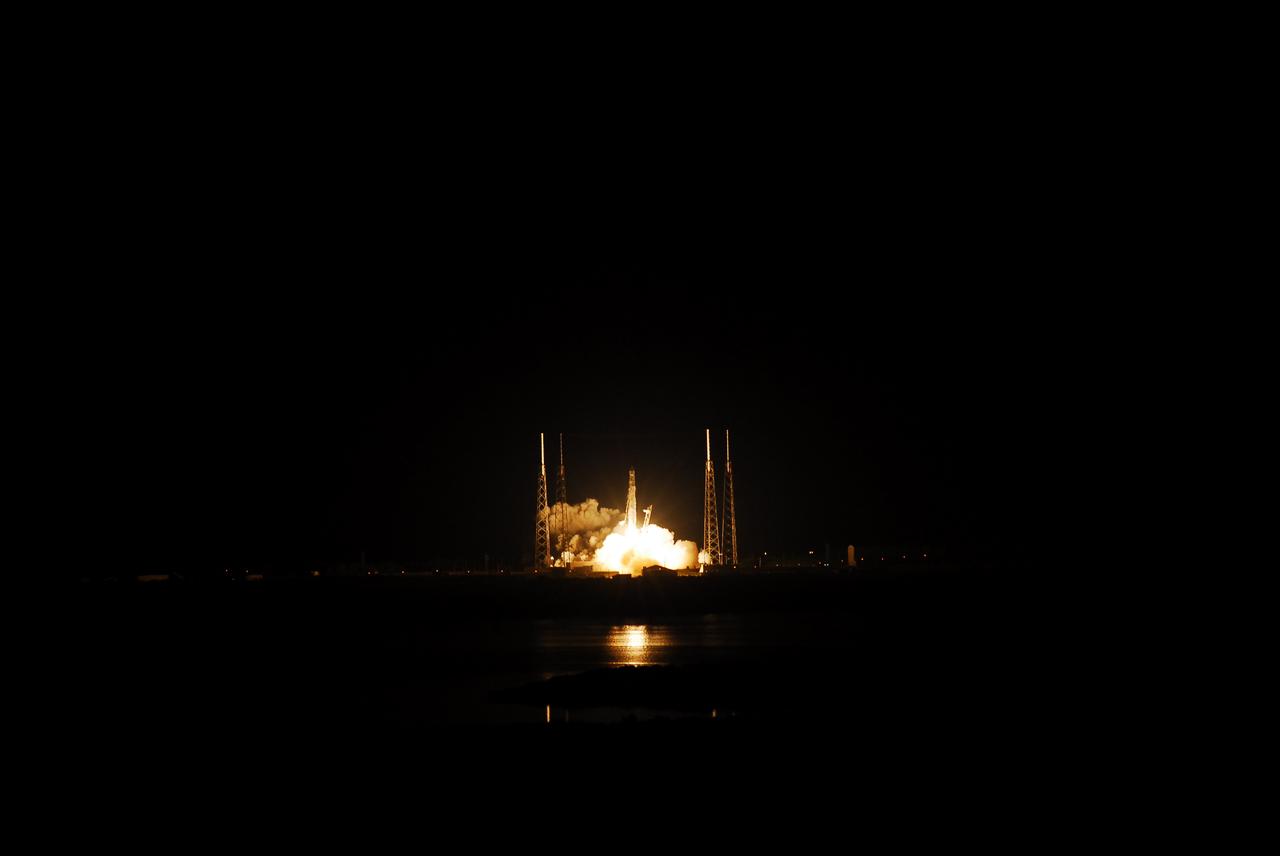

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch
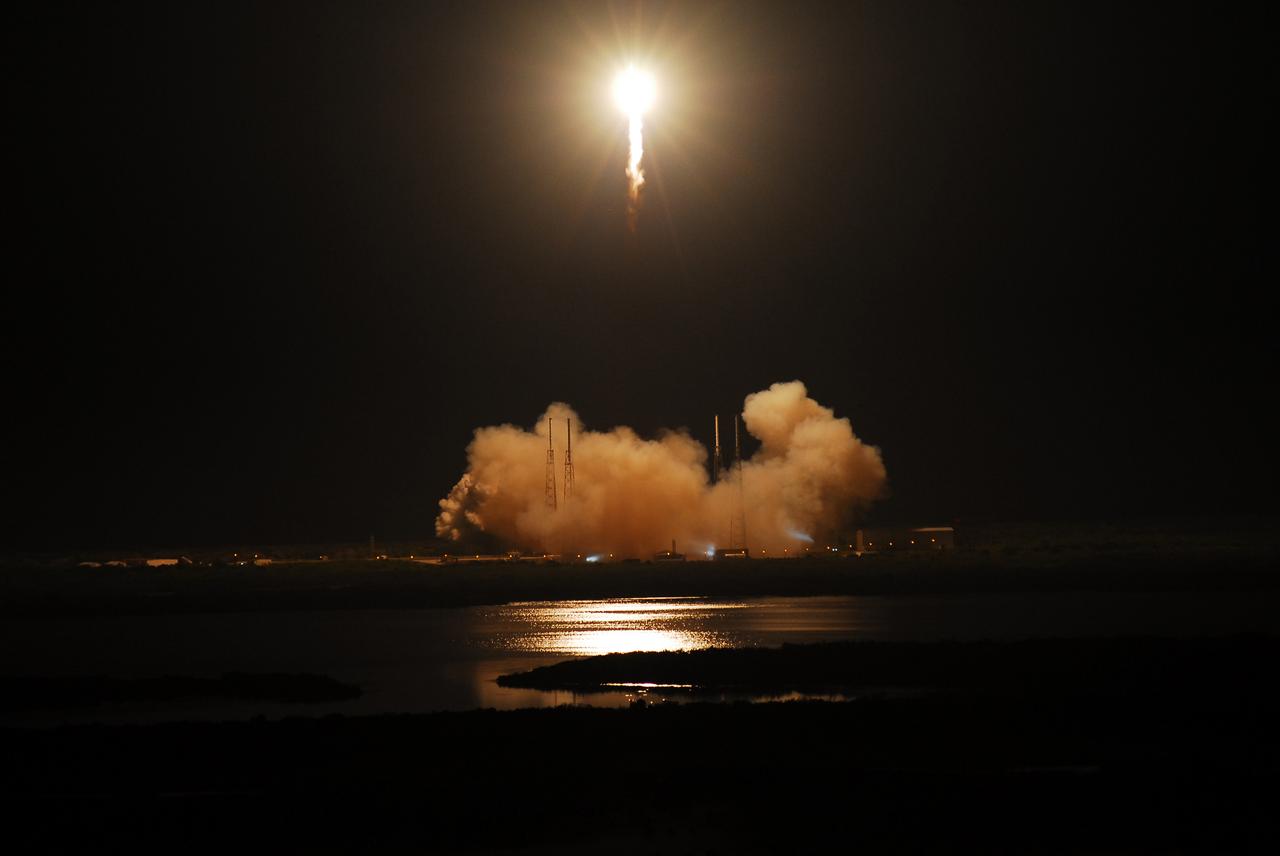

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch
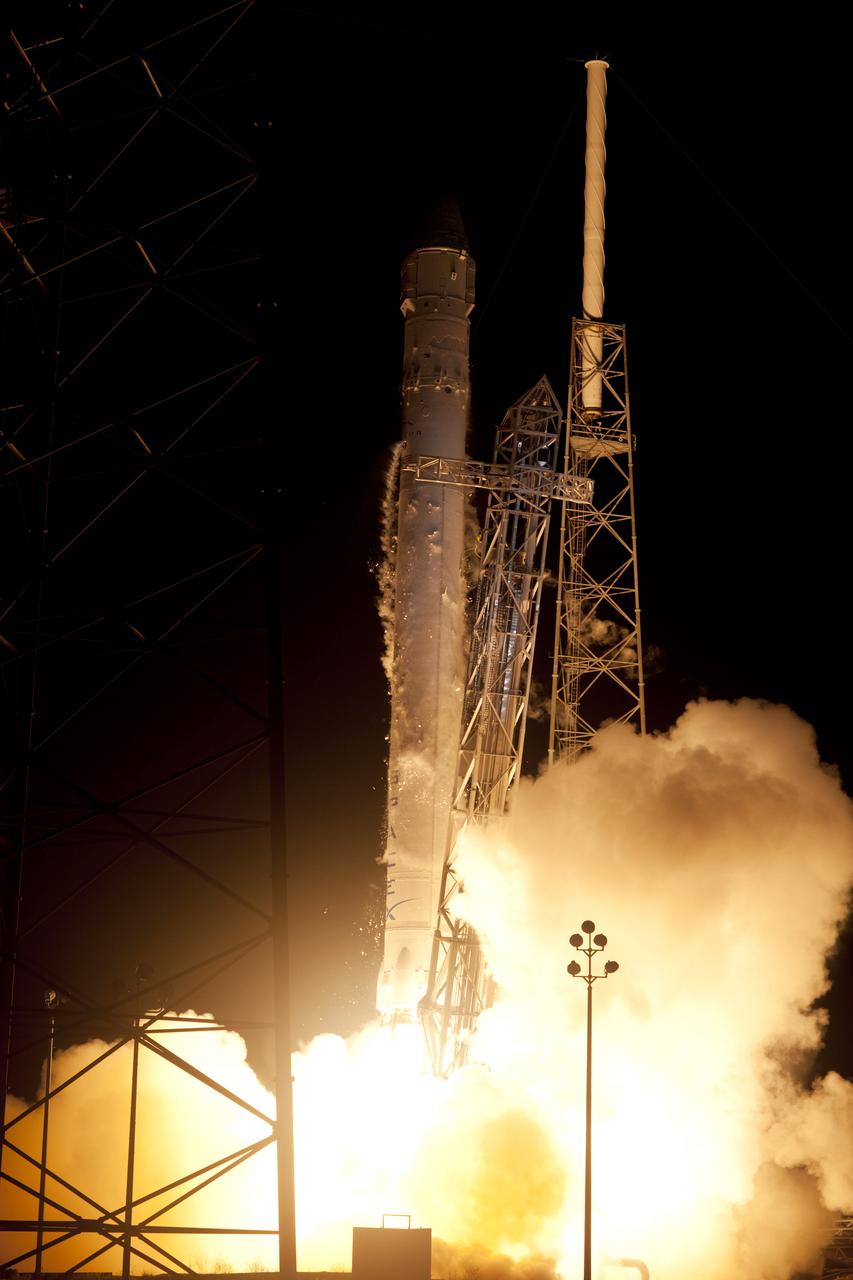

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch, DD24-203
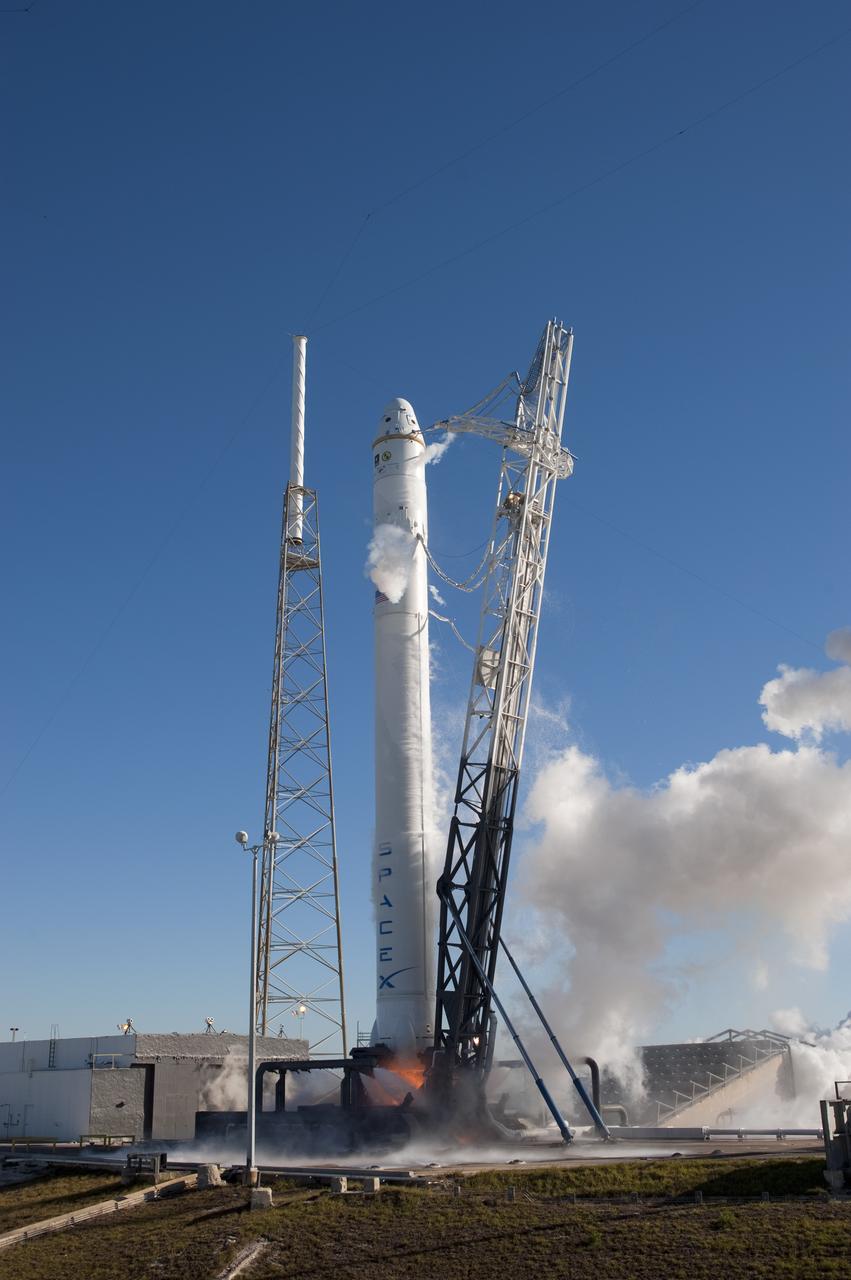

SPACE X FALCON 9 COTS-1 TEST FIRE - DAY 2
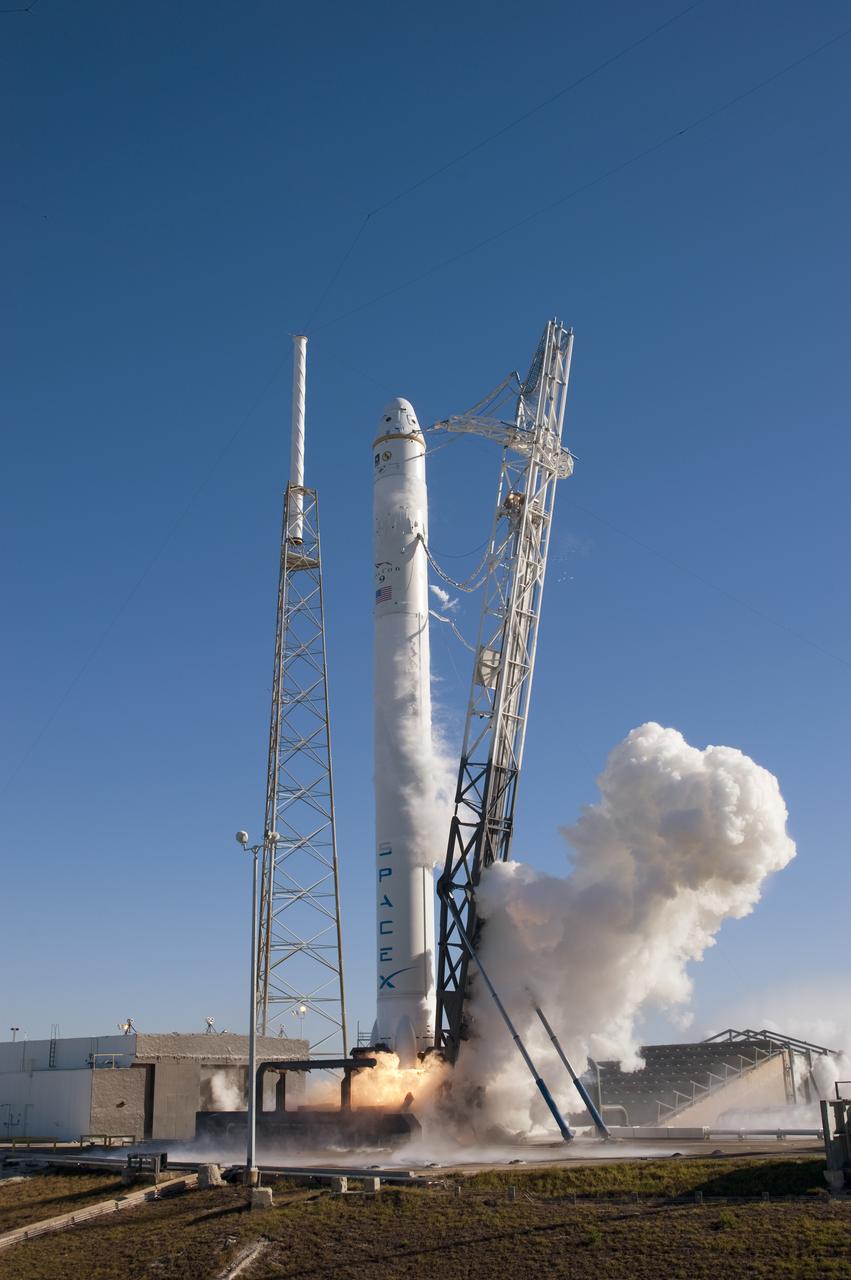

SPACE X FALCON 9 COTS-1 TEST FIRE - DAY 2
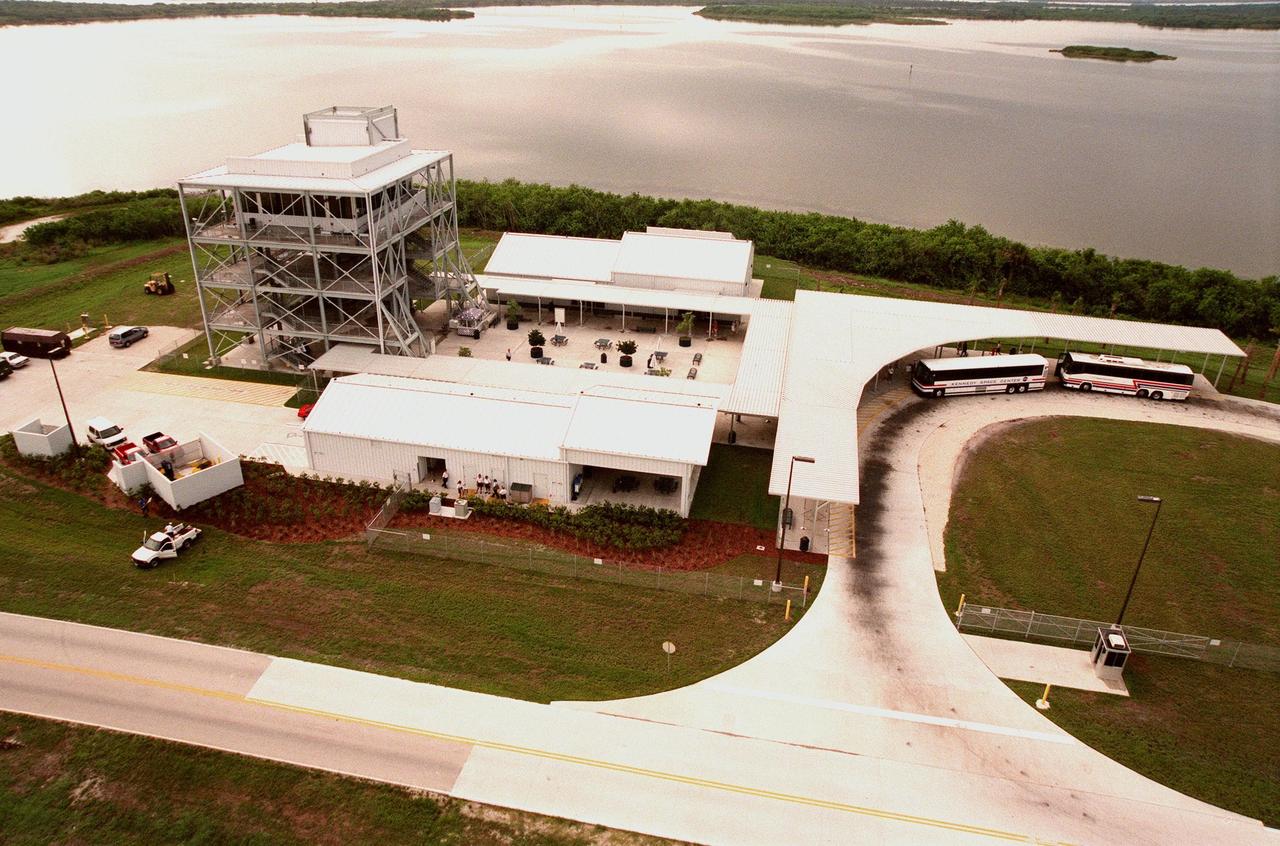

Tour buses unload passengers at a new stop on the KSC tour that allows visitors to view Pad LC-39B. The tour road runs parallel to the crawlerway (just out of sight) that is used to transport the Space Shuttle vehicles to the pad. The length of the crawlerway from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Pad B is 6,828 meters (22,440 ft); its width overall is 40 meters (130 ft); each lane is 12 meters (40ft) with a 15-meter (50ft) median. This view looks south
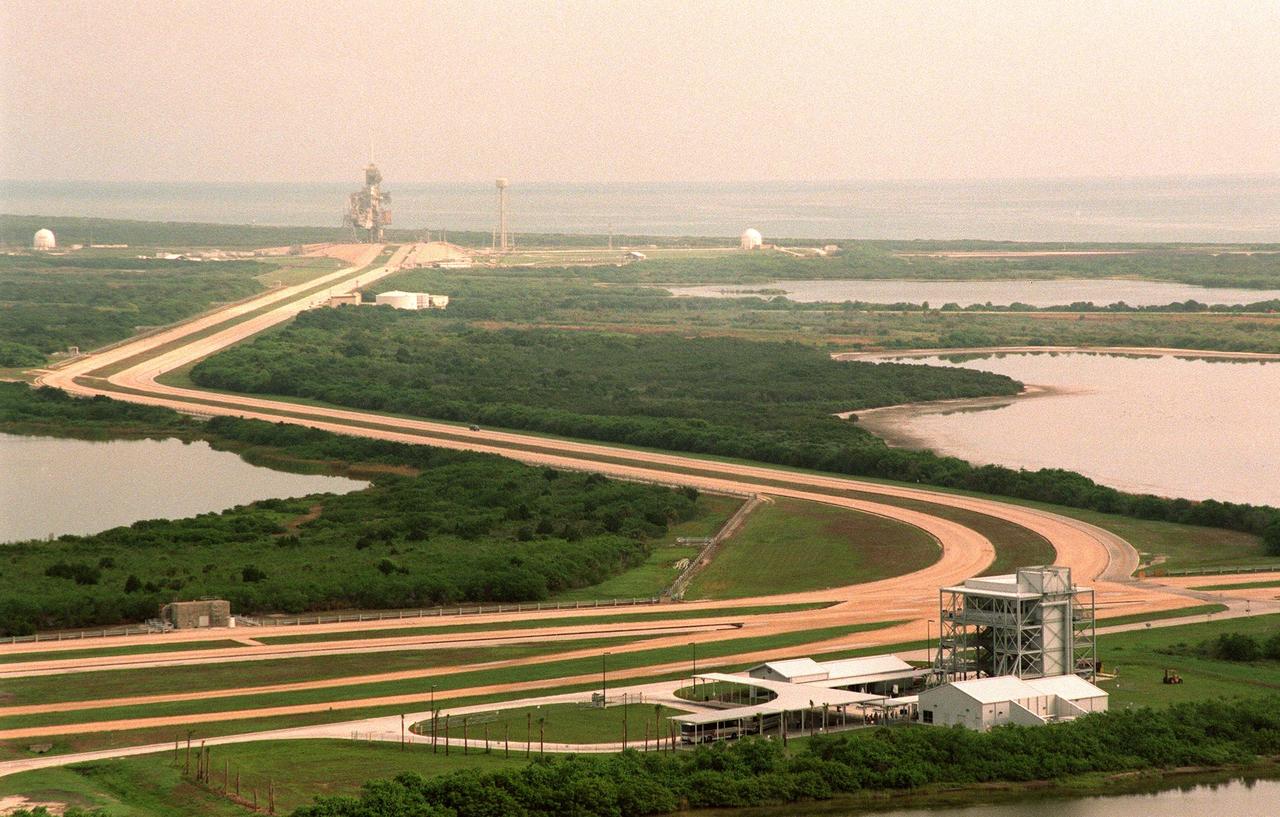

This aerial view looking northeast shows a new stop (bottom) on the KSC bus tour that allow visitors to view Pad LC-39B (top). The tour stop is next to the crawlerway that is used to transport the Space Shuttle vehicles to the pad. The length of the crawlerway from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Pad B is 6,828 meters (22,440 ft); its width overall is 40 meters (130 ft); each lane is 12 meters (40ft) with a 15-meter (50ft) median.
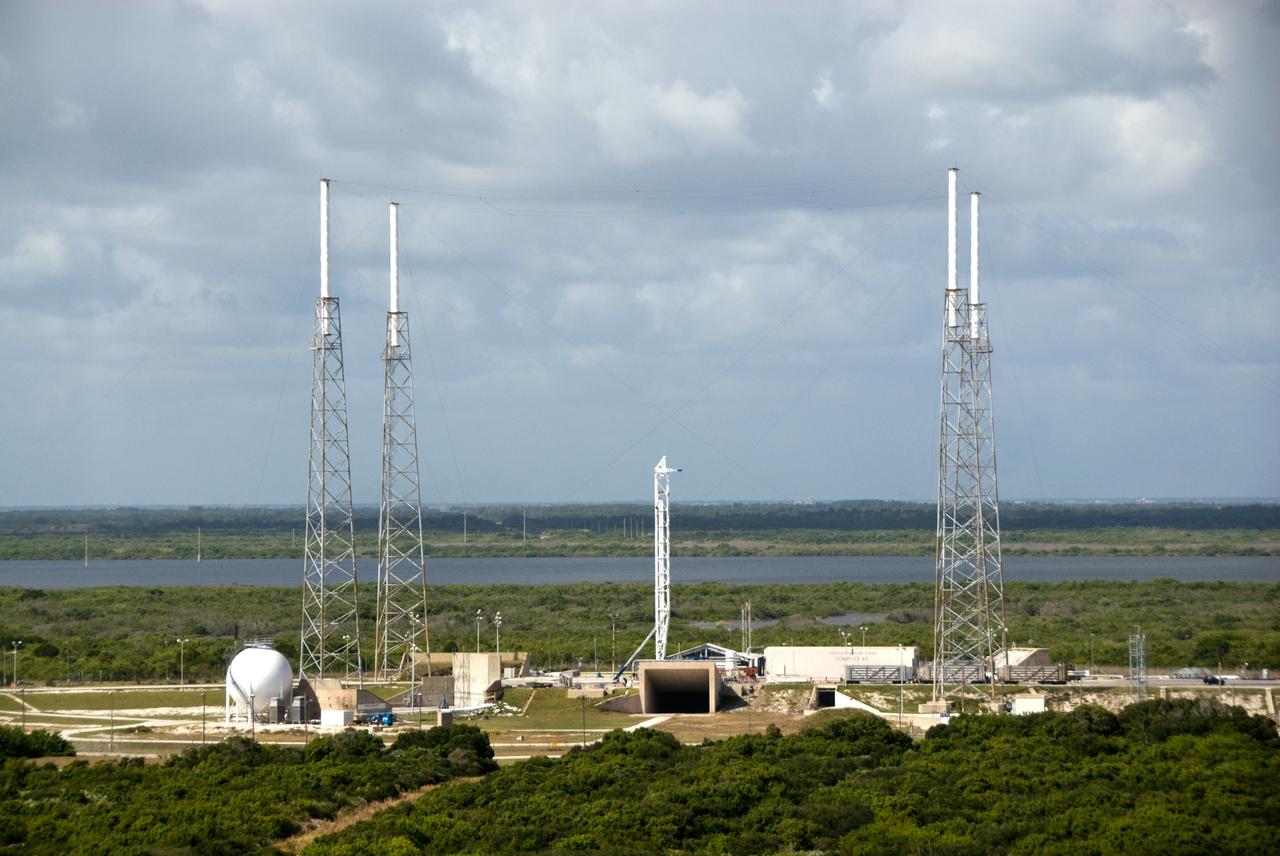

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The pad will be used to support the new Falcon rockets to be launched by Space Exploration Technologies, known as SpaceX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
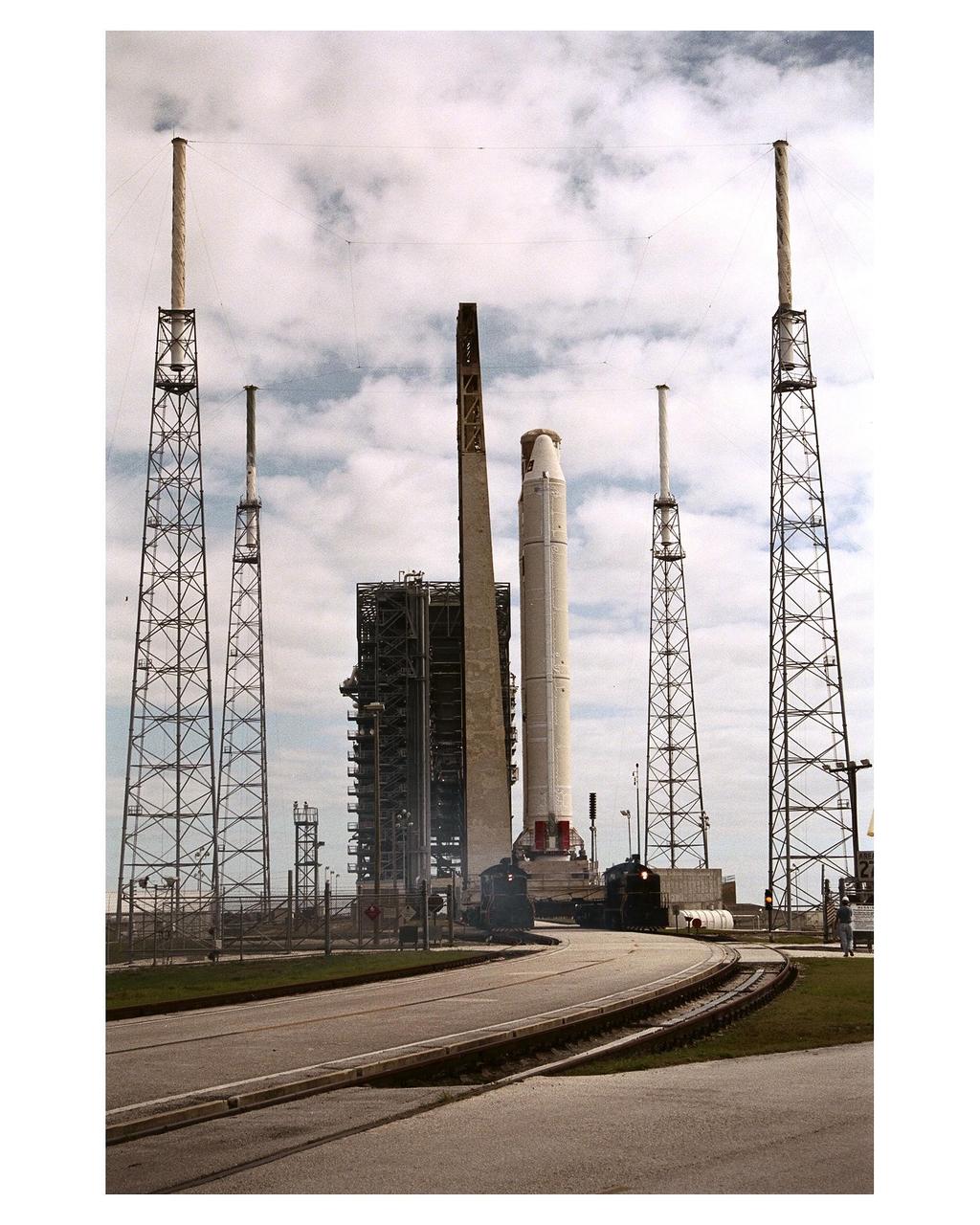

The Titan IVB core vehicle and its twin Solid Rocket Motor Upgrades (SRMUs) which will be used to propel the Cassini spacecraft to its final destination, Saturn, approaches the pad at Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station. At the pad, the Centaur upper stage will be added and, eventually, the prime payload, the Cassini spacecraft. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings and moon, Titan. Launch of the Cassini mission to Saturn is scheduled for Oct. 6
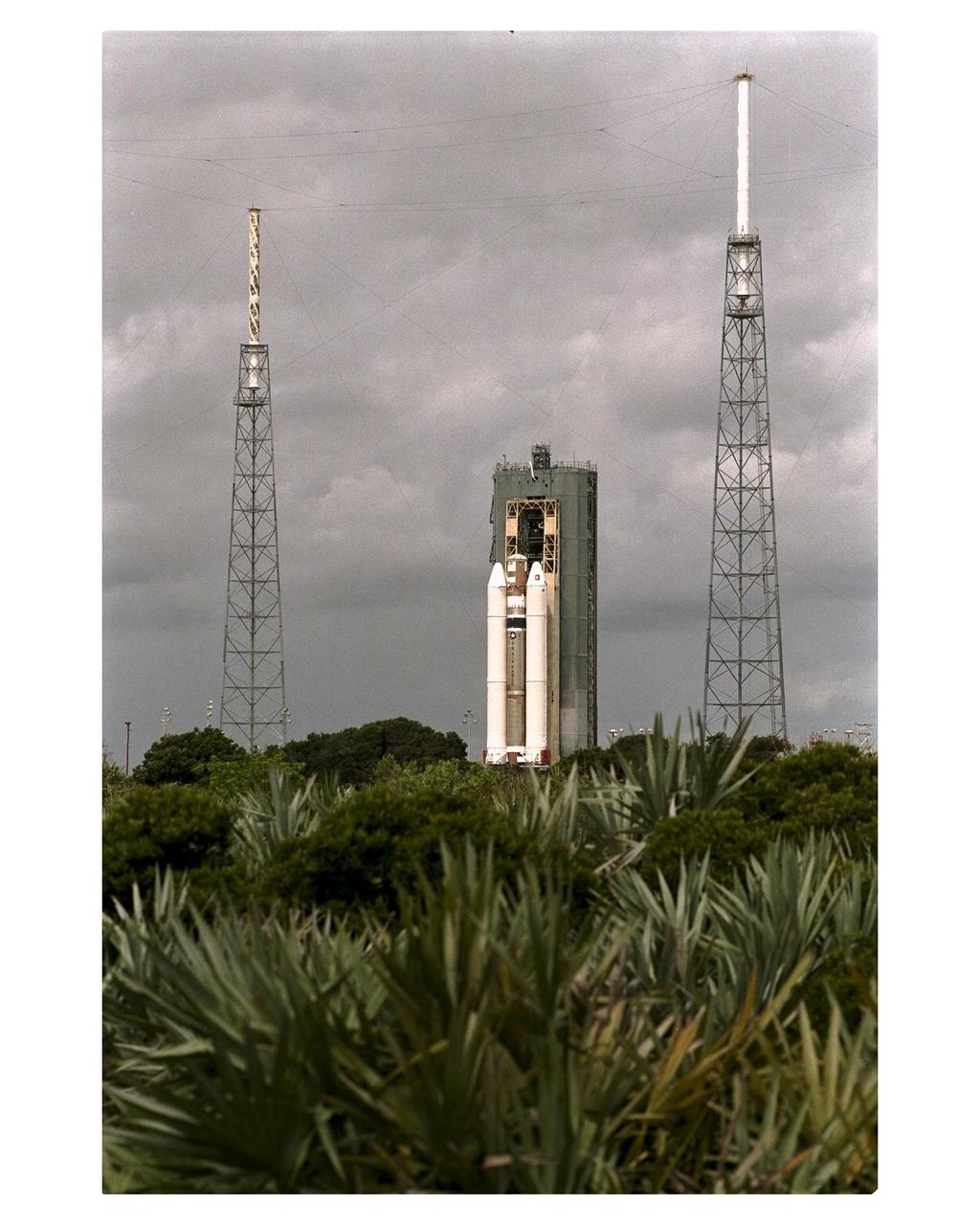

The Titan IVB core vehicle and its twin Solid Rocket Motor Upgrades (SRMUs) which will be used to propel the Cassini spacecraft to its final destination, Saturn, arrive at the pad at Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station. At the pad, the Centaur upper stage will be added and, eventually, the prime payload, the Cassini spacecraft. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings and moon, Titan. Launch of the Cassini mission to Saturn is scheduled for Oct. 6
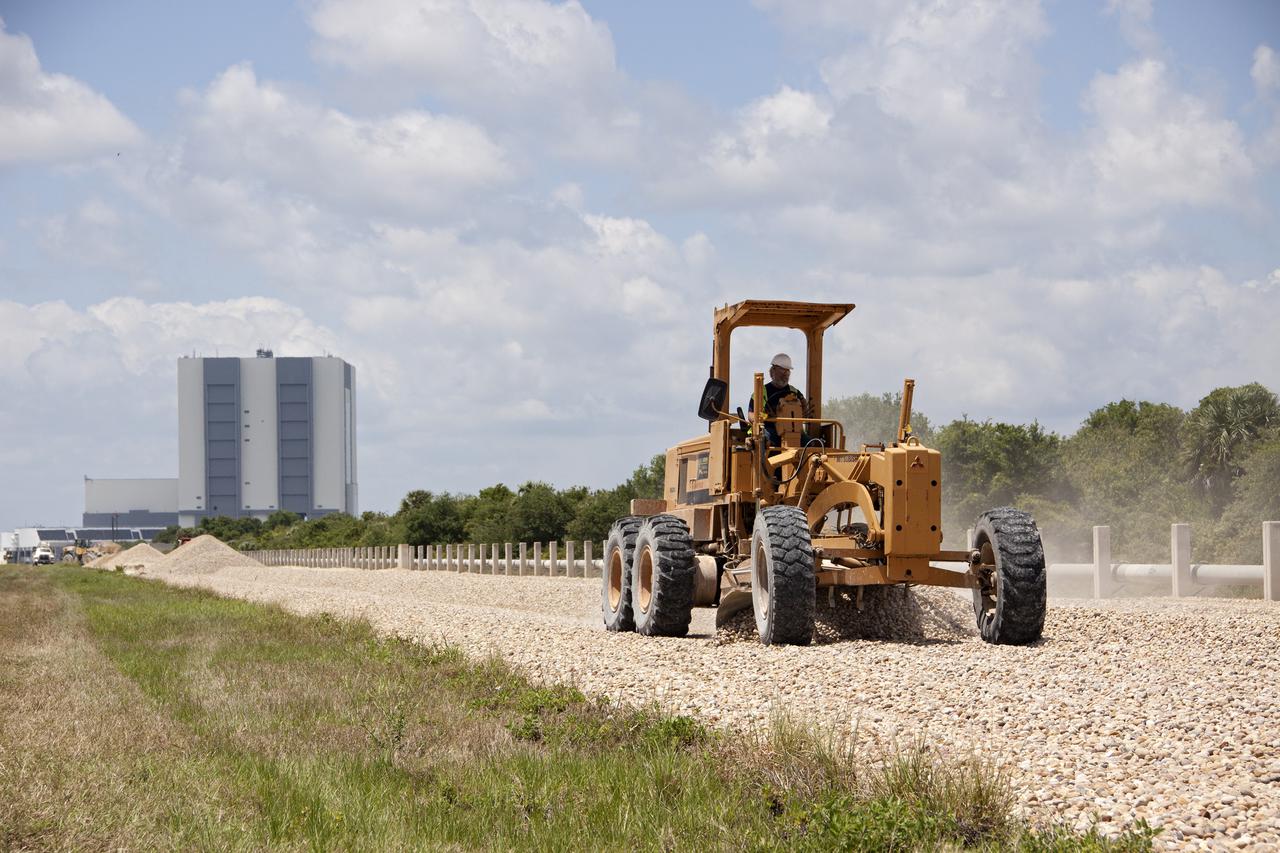

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a road-grader resurfaces a section of the crawlerway leading from the Vehicle Assembly Building VAB to the launch pads. The Ground Systems Development and Operations GSDO Program office at Kennedy is working to upgrade the two 40-foot-wide pathways the crawler-transporter will travel as it transports launch vehicles such as NASA's Space Launch System SLS rocket from the VAB to the launch pad. For more: http:__www.nasa.gov_exploration_systems_ground_crawlerway_upgrades.html Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossman
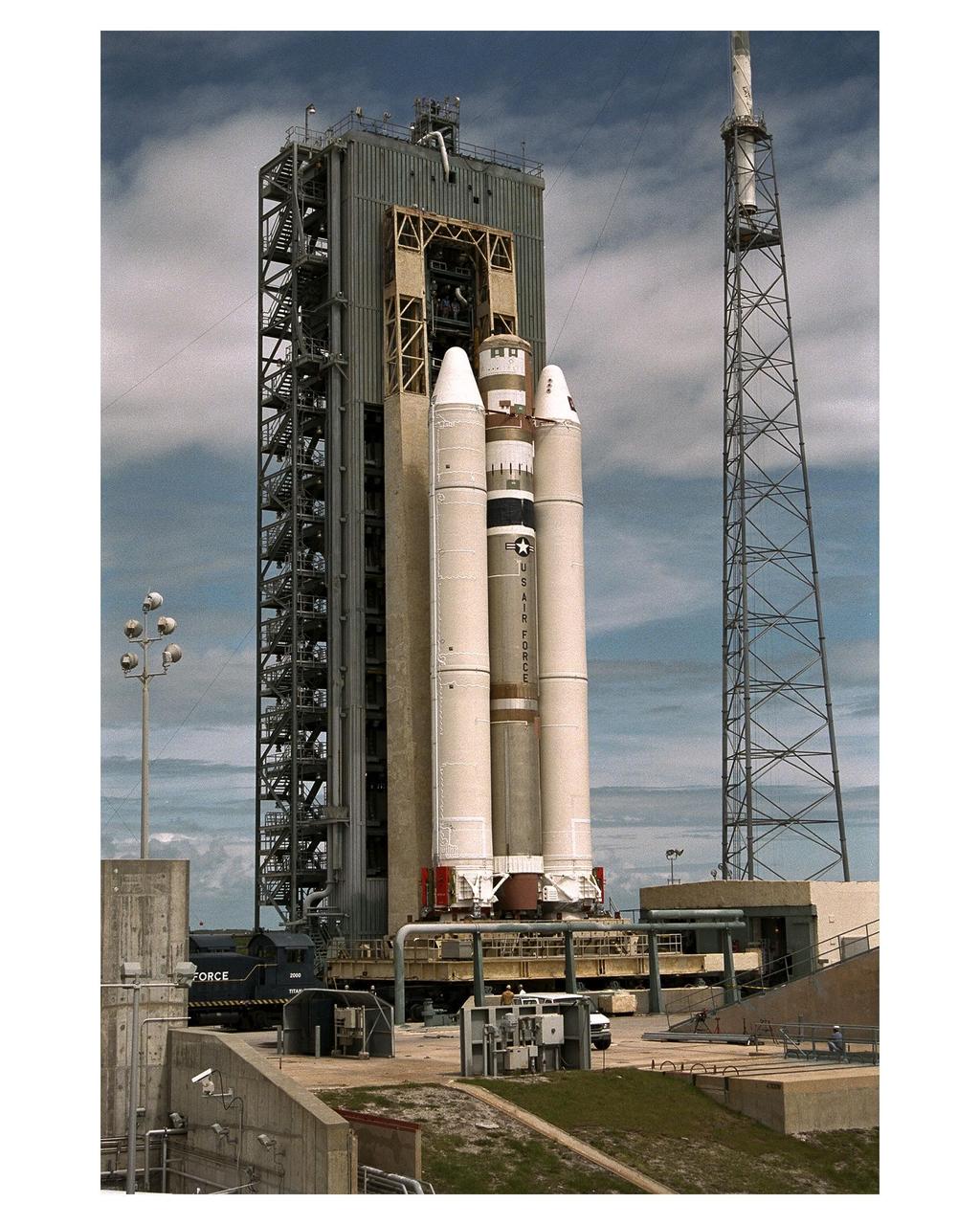

The Titan IVB core vehicle and its twin Solid Rocket Motor Upgrades (SRMUs) which will be used to propel the Cassini spacecraft to its final destination, Saturn, arrive at the pad at Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station. At the pad, the Centaur upper stage will be added and, eventually, the prime payload, the Cassini spacecraft. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings and moon, Titan. Launch of the Cassini mission to Saturn is scheduled for Oct. 6
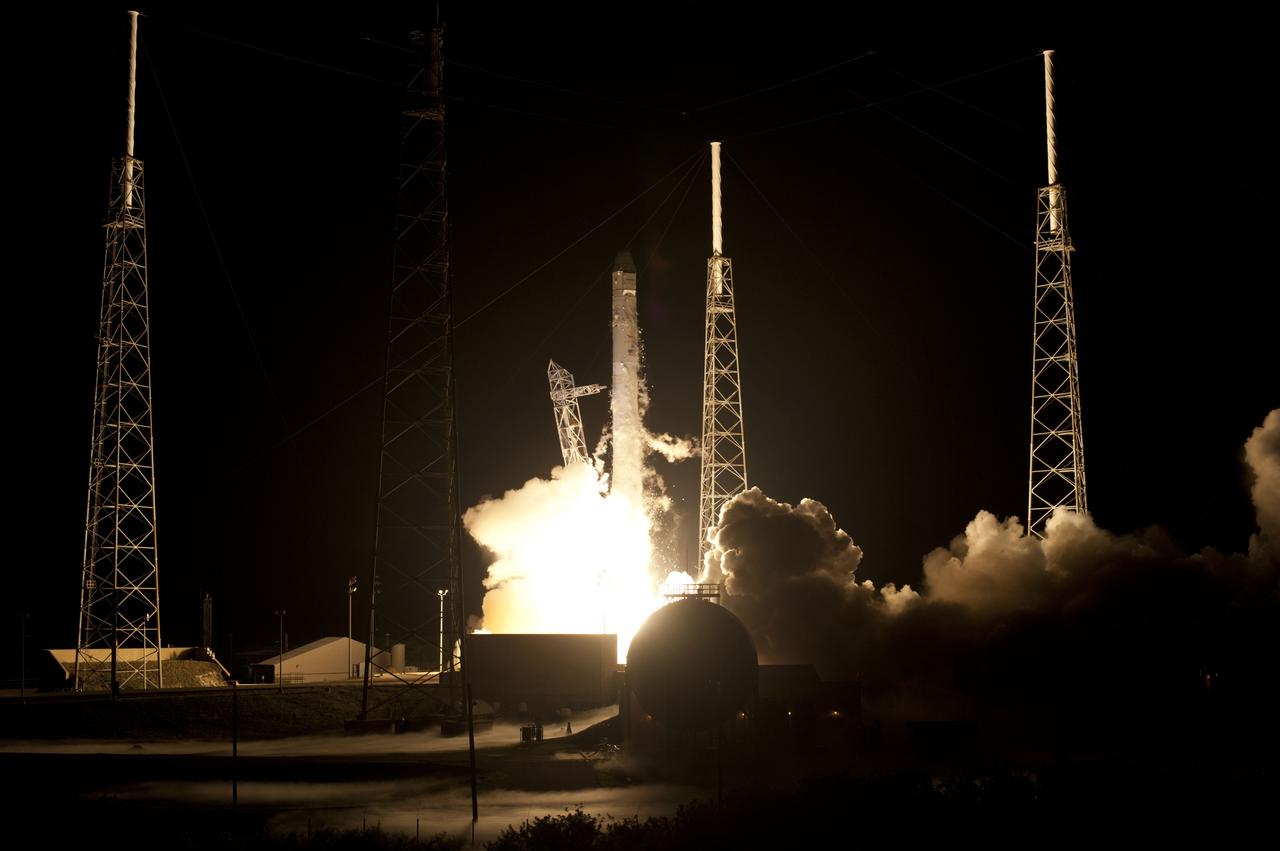

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch - DD028-203
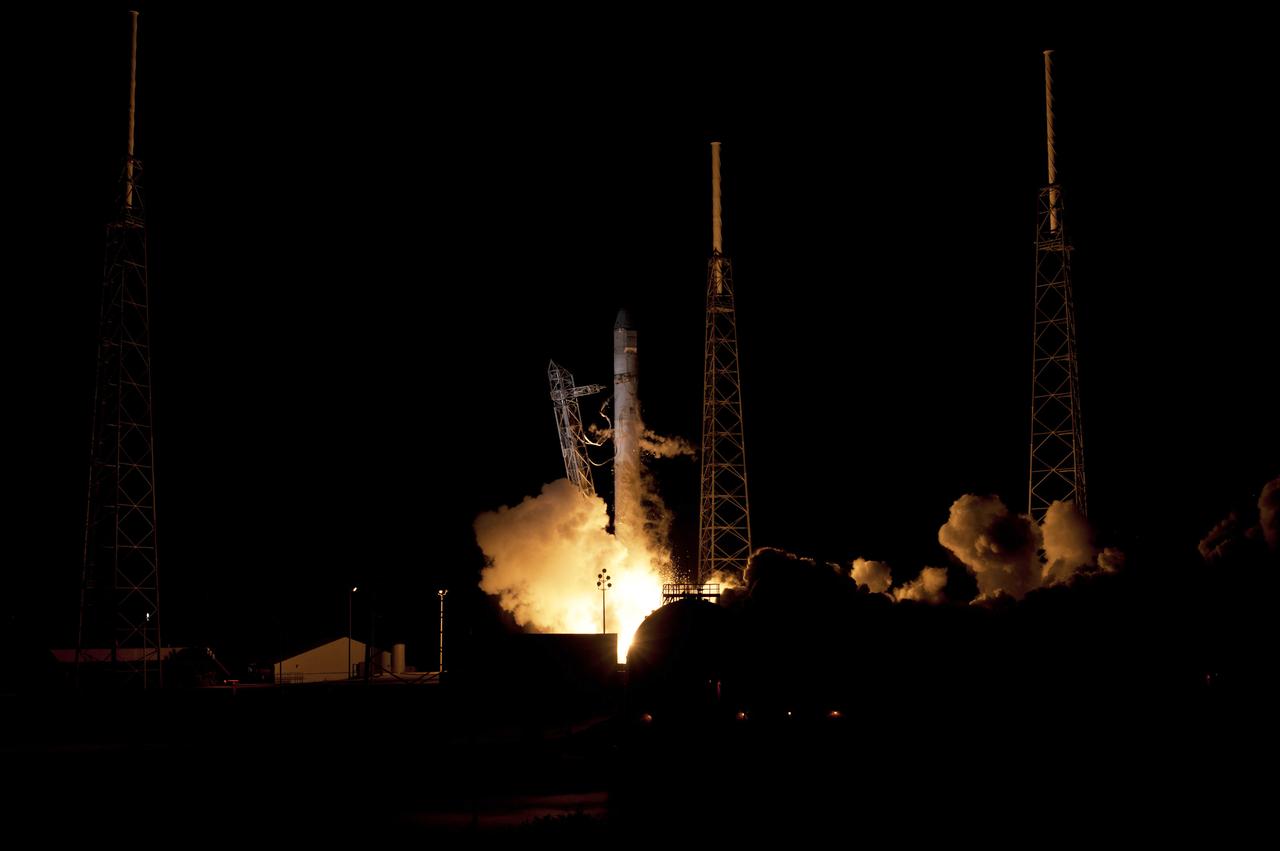

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch - DD028-203
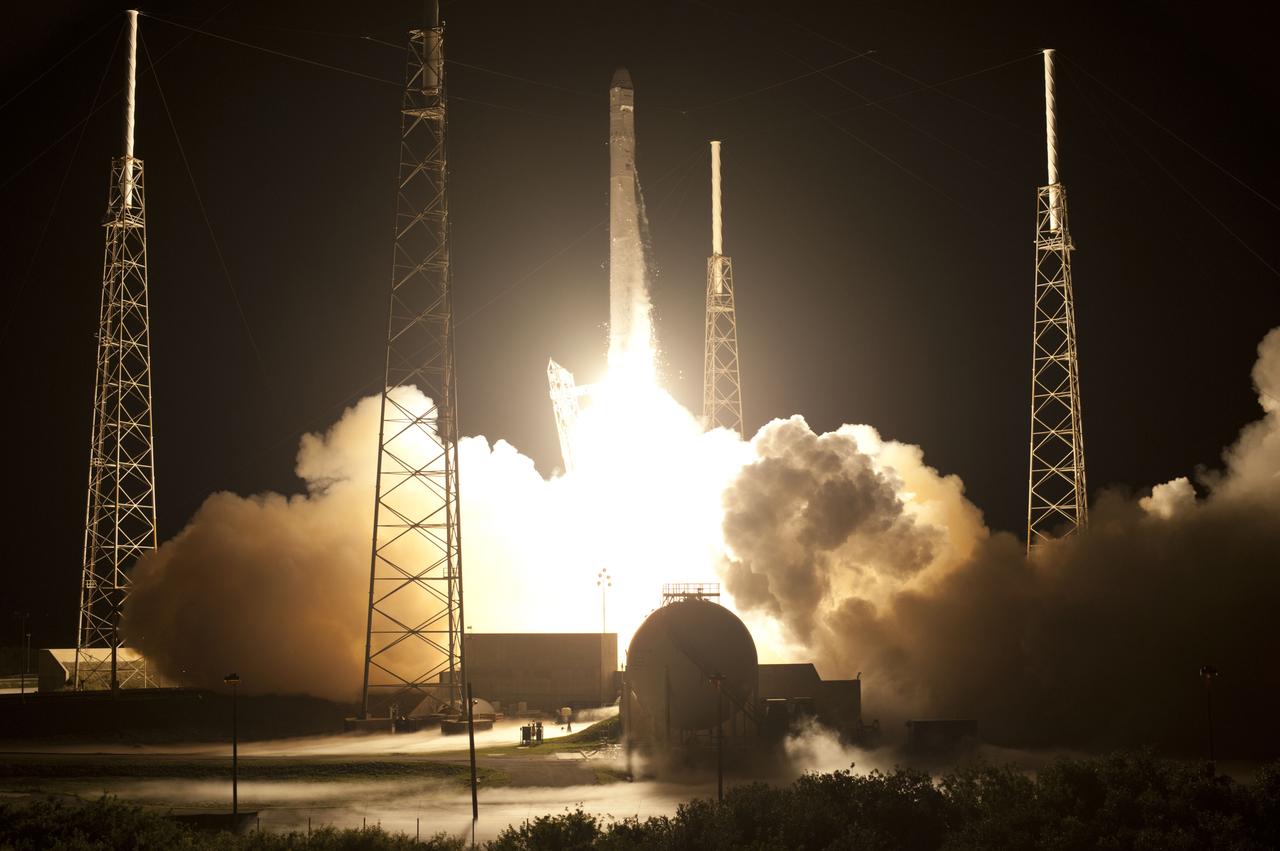

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch - DD028-203
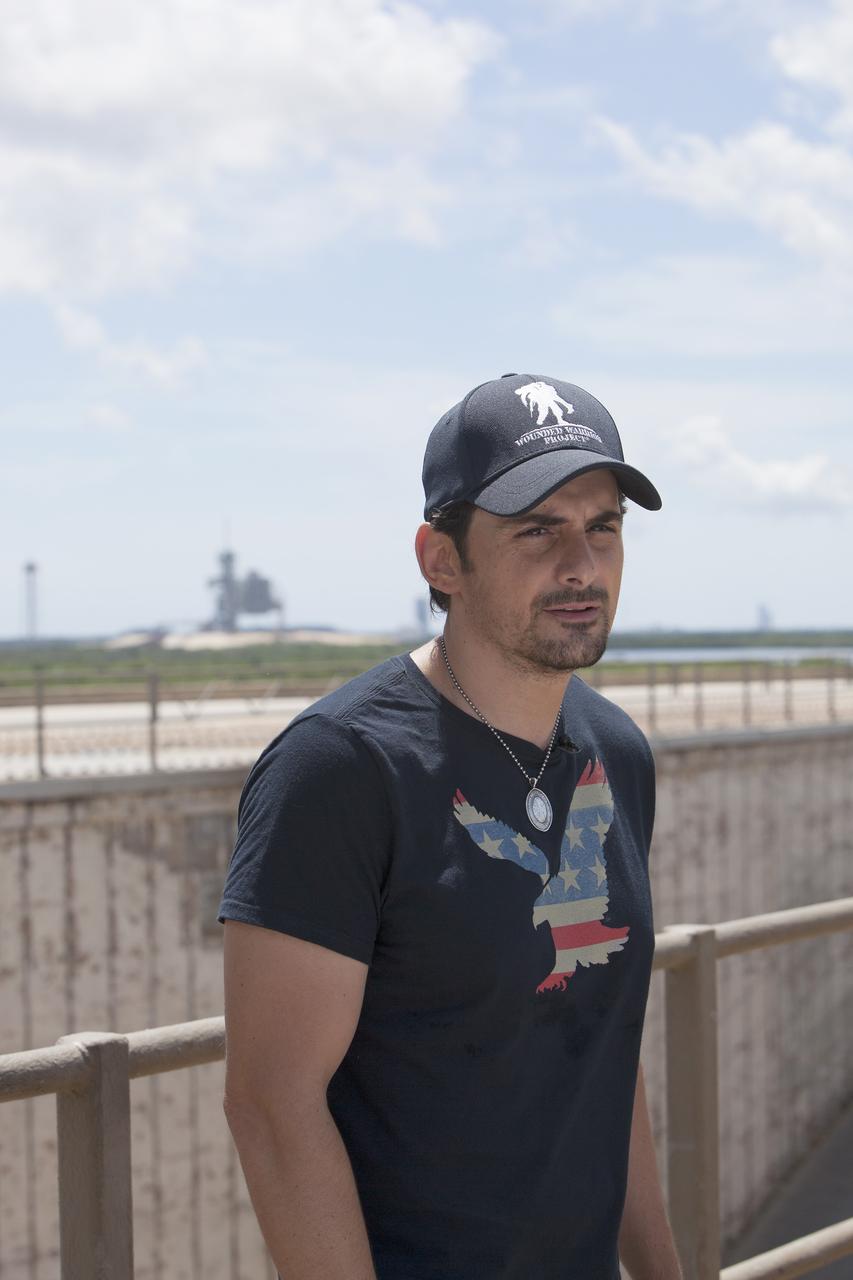

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Singer-songwriter Brad Paisley announces the release of a new song titled "American Flag on the Moon" from Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the background is Launch Pad 39A from which the Apollo moon landing missions were launched. Upon seeing Paisley's Twitter post that he was at NASA's Apollo launch pad leaking his new song, astronaut Reid Wiseman responded, "Hold on @BradPaisley, we don't usually like leaks at the launch pad." Wiseman is a member of the Expedition 40 crew currently in Earth orbit on the International Space Station. For more on Kennedy Space Center, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. To read more of Wiseman's Twitter posts from the station, go to https://twitter.com/astro_reid. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
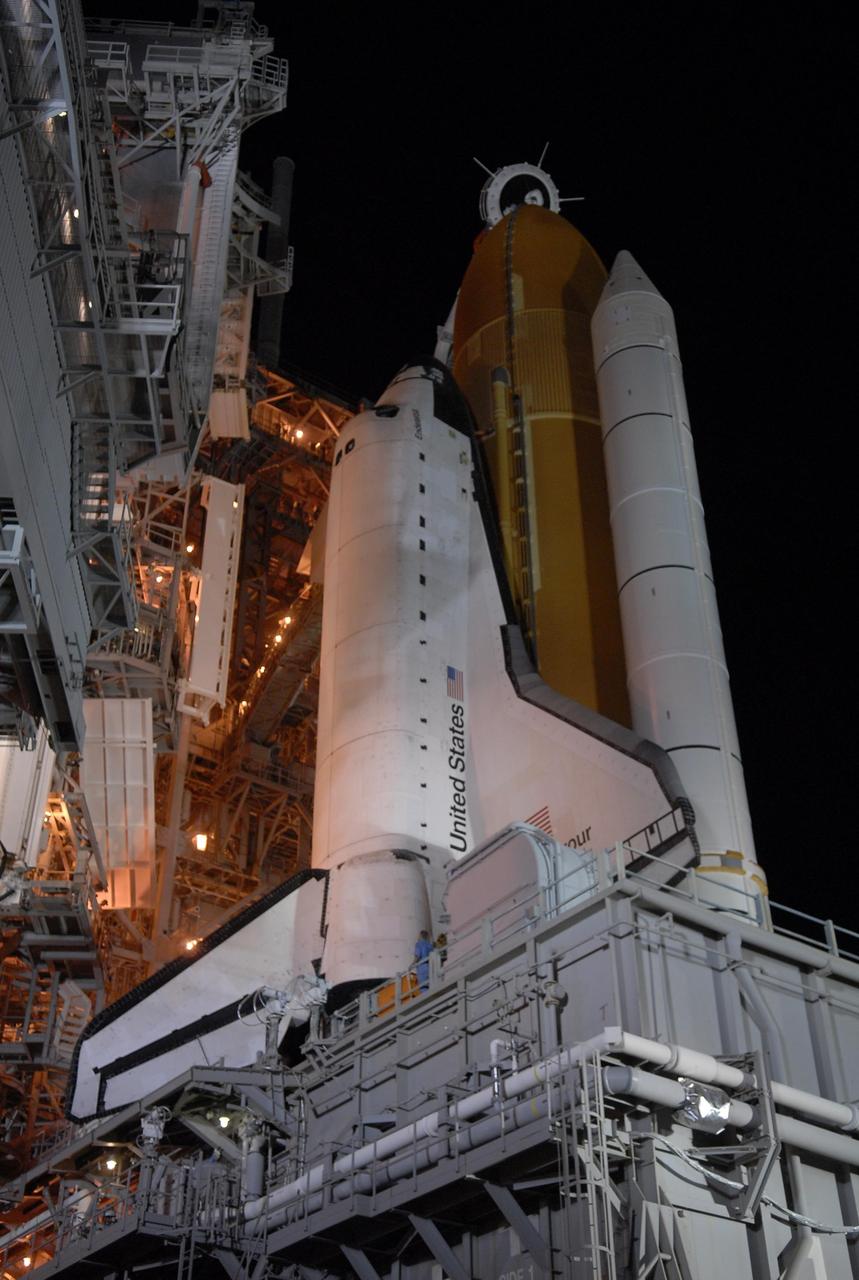

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Endeavour is revealed on Launch Pad 39A after rollback of the rotating service structure, or RSS, at left of the pad. Rollback started at 9 p.m. EDT Aug. 7 and was complete at 10:40 p.m. Beneath the shuttle is the mobile launcher platform. The RSS provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. Rollback of the pad's RSS is one of the milestones in preparation for the launch of mission STS-118 at 6:36 p.m. EDT on Aug. 8. Space Shuttle Endeavour's STS-118 mission is the 22nd shuttle flight to the International Space Station. It will continue space station construction by delivering a third starboard truss segment, S5, and other payloads such as the SPACEHAB module and the external stowage platform 3. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
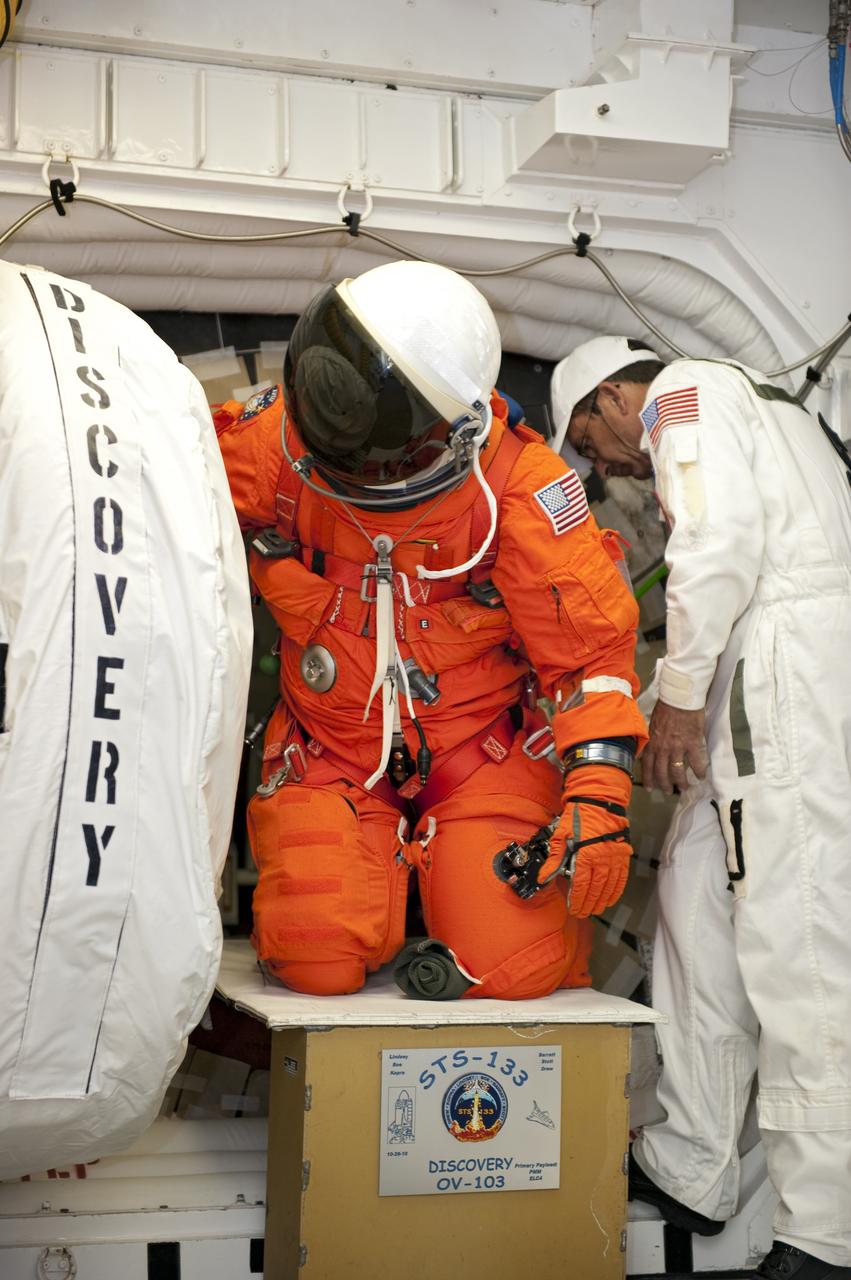

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a simulated pad emergency on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-133 Mission Specialist Michael Barratt exits space shuttle Discovery through the pad's White Room. Next, the crew members will hop into the slidewire basket that will take them to a safe bunker below the pad. The emergency training is part of a week-long Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 1 at 4:40 p.m. For more information on the STS-133 mission, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
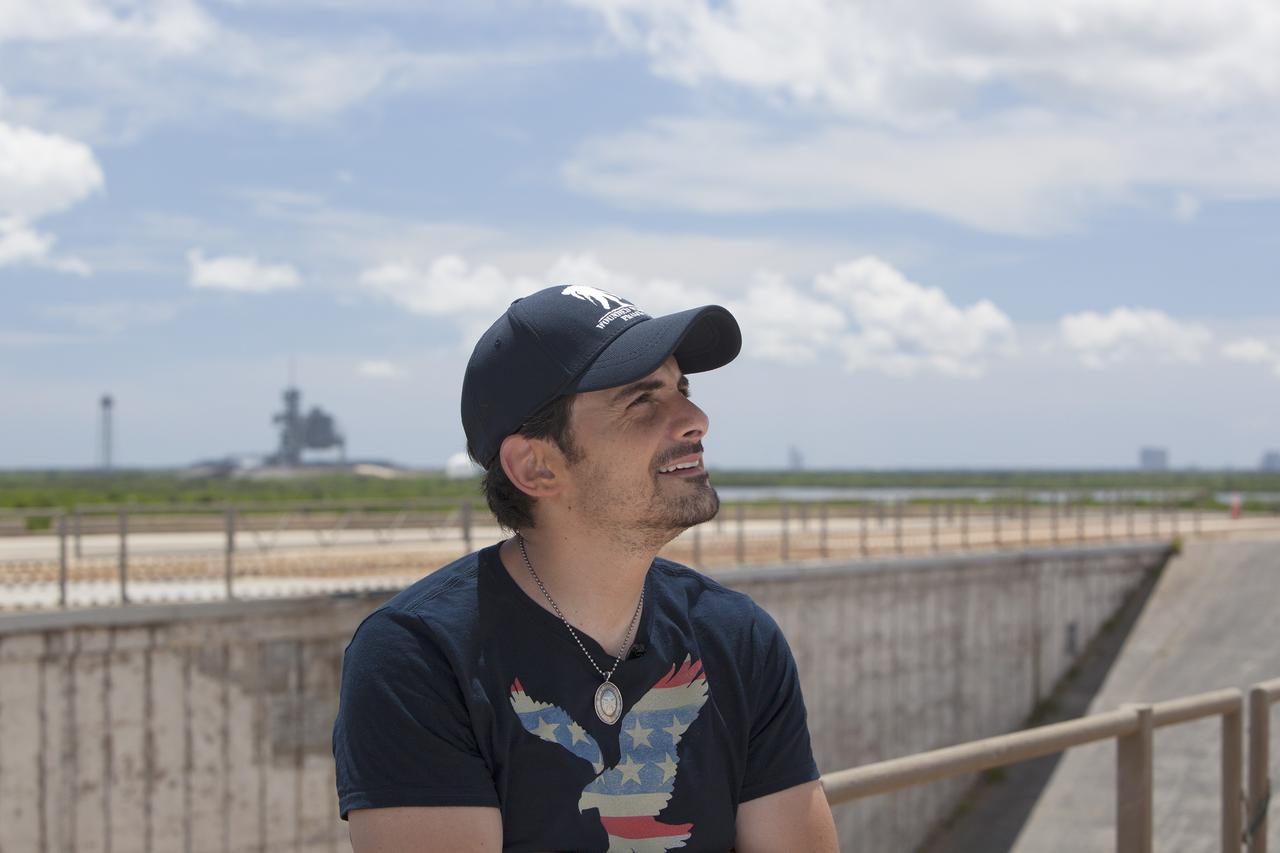

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Singer-songwriter Brad Paisley announces the release of a new song titled "American Flag on the Moon" from Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the background is Launch Pad 39A from which the Apollo moon landing missions were launched. Upon seeing Paisley's Twitter post that he was at NASA's Apollo launch pad leaking his new song, astronaut Reid Wiseman responded, "Hold on @BradPaisley, we don't usually like leaks at the launch pad." Wiseman is a member of the Expedition 40 crew currently in Earth orbit on the International Space Station. For more on Kennedy Space Center, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. To read more of Wiseman's Twitter posts from the station, go to https://twitter.com/astro_reid. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
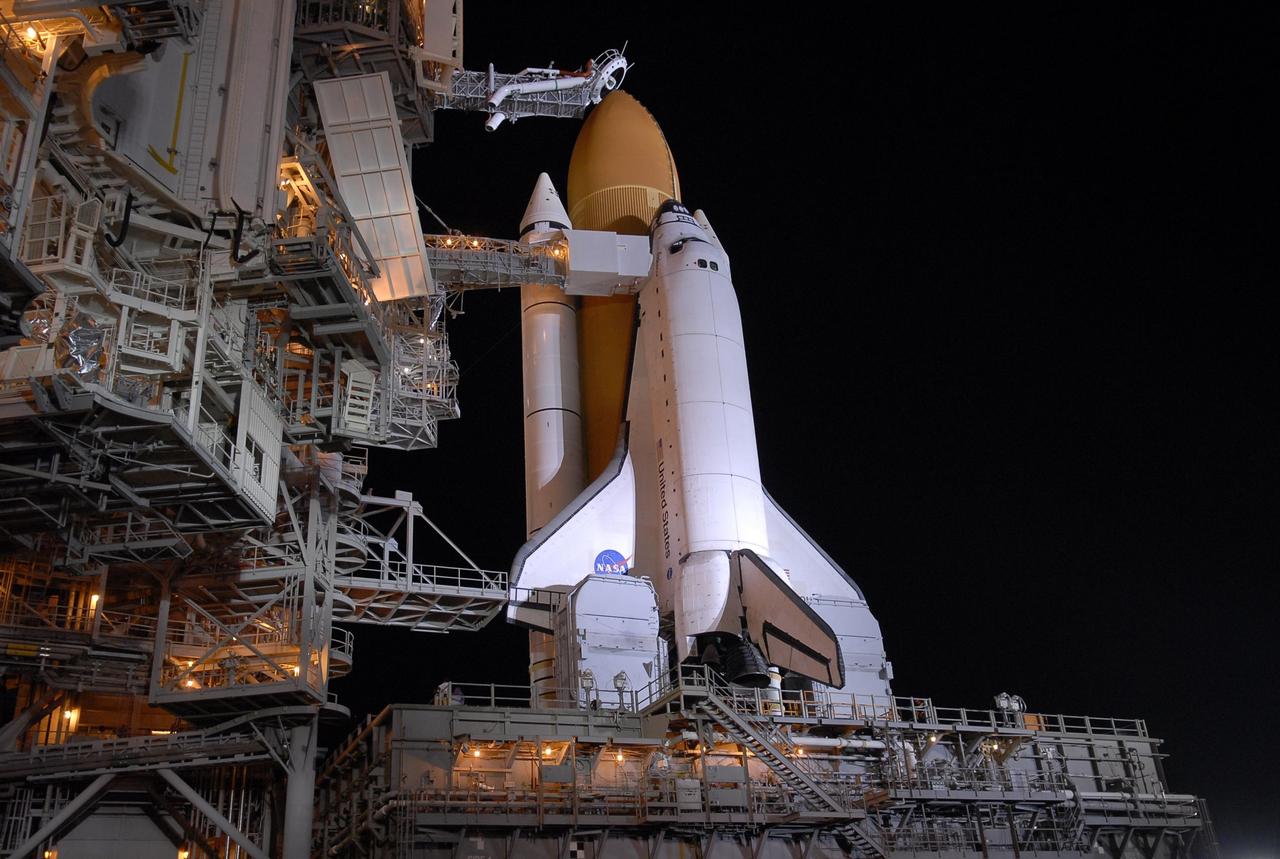

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Endeavour is revealed on Launch Pad 39A after rollback of the rotating service structure, or RSS, at left of the pad. Rollback started at 9 p.m. EDT Aug. 7 and was complete at 10:40 p.m. Beneath the shuttle is the mobile launcher platform which supports the shuttle until liftoff. The RSS provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. Rollback of the pad's RSS is one of the milestones in preparation for the launch of mission STS-118 at 6:36 p.m. EDT on Aug. 8. Space Shuttle Endeavour's STS-118 mission is the 22nd shuttle flight to the International Space Station. It will continue space station construction by delivering a third starboard truss segment, S5, and other payloads such as the SPACEHAB module and the external stowage platform 3. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
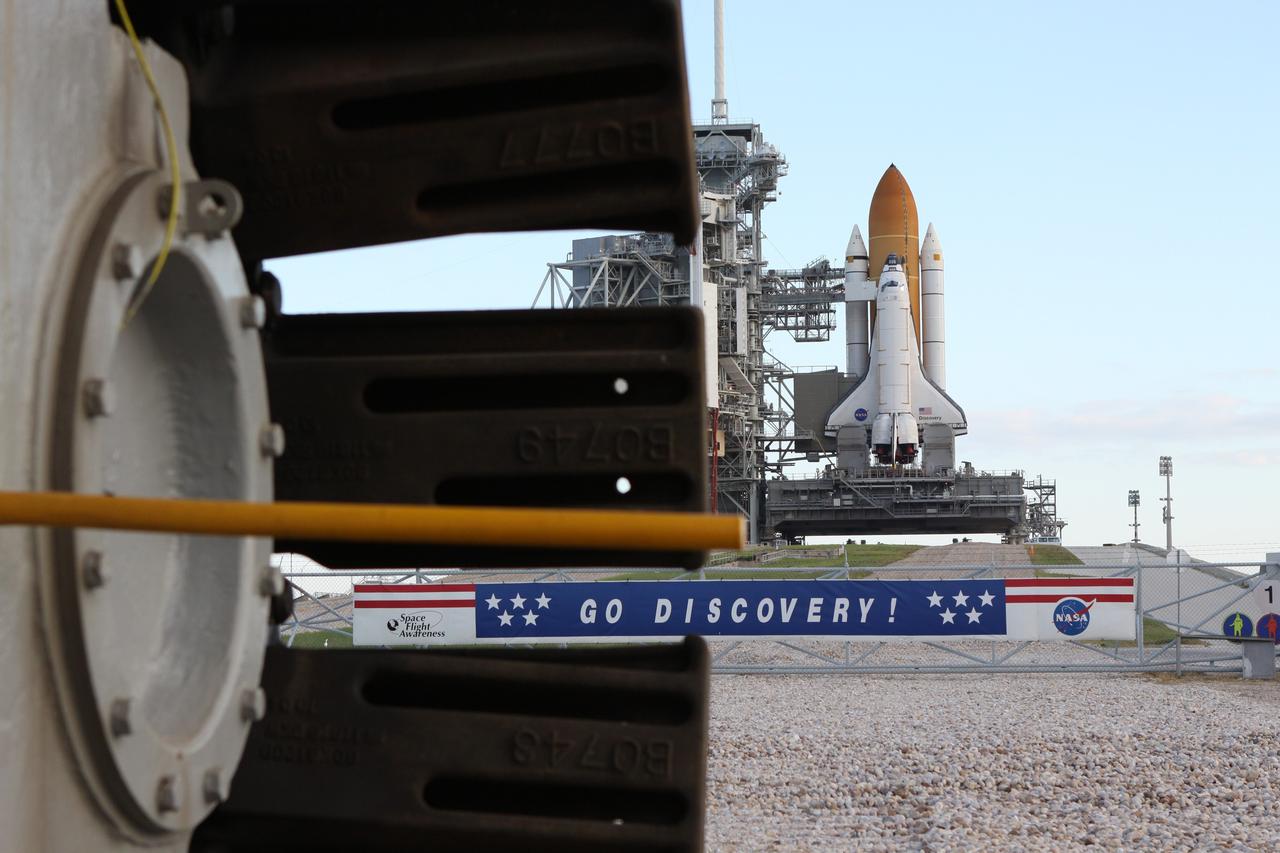

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the STS-133 payload canister now is in the rotating service structure on Launch Pad 39A. A sign hanging on the fence in front of the pad entrance supporting space shuttle Discovery is seen through the tred from a crawler-transporter. The payload then will be moved into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
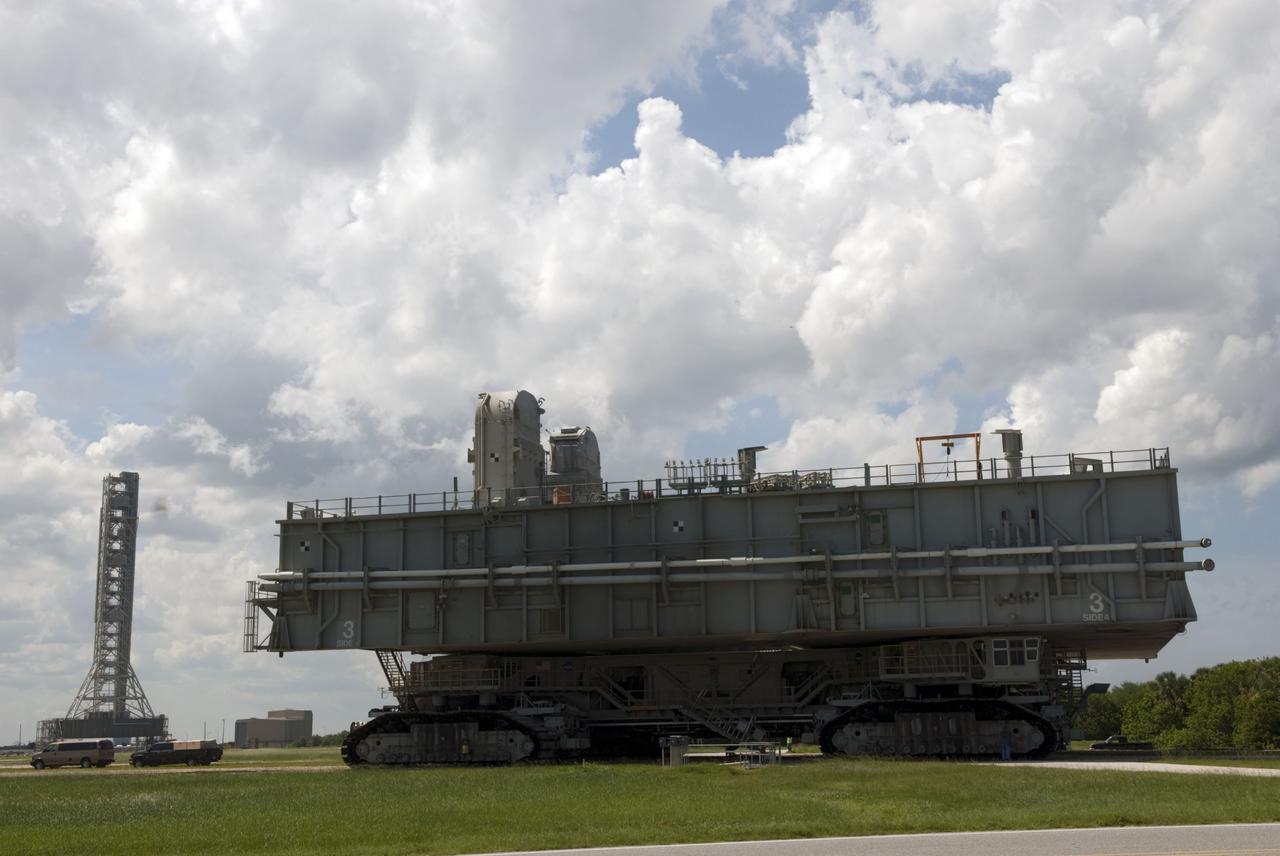

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mobile Launcher Platform-3 (MLP), which supported space shuttle Atlantis for its final flight to the International Space Station on the STS-135 mission, is making its last journey atop a massive crawler-transporter from Launch Pad 39A into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). For more than 40 years, the MLPs have traveled between the VAB to both launch pads at Launch Complex 39, and then returned to the VAB for future use. MLP-3 was first used to launch Columbia on the STS-32 mission on Jan. 9, 1990. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
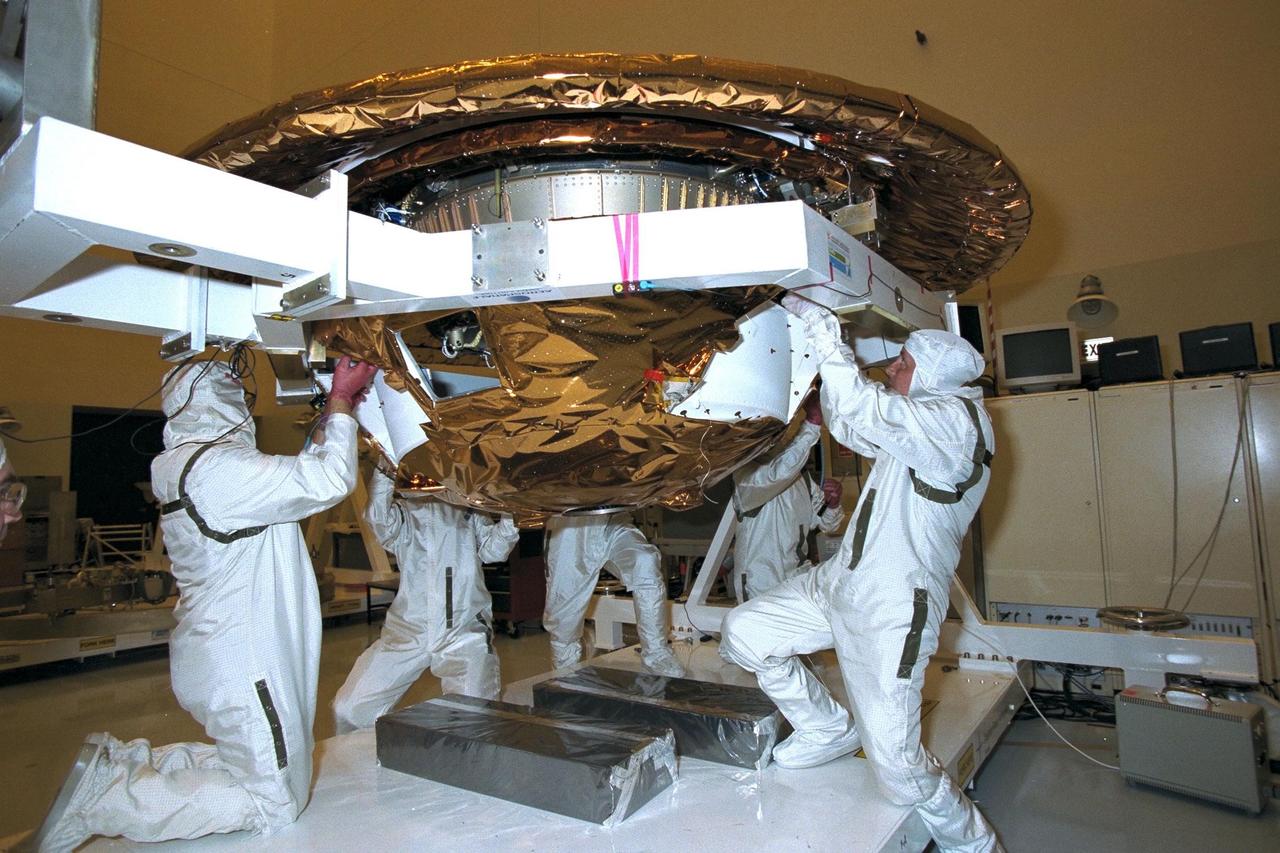

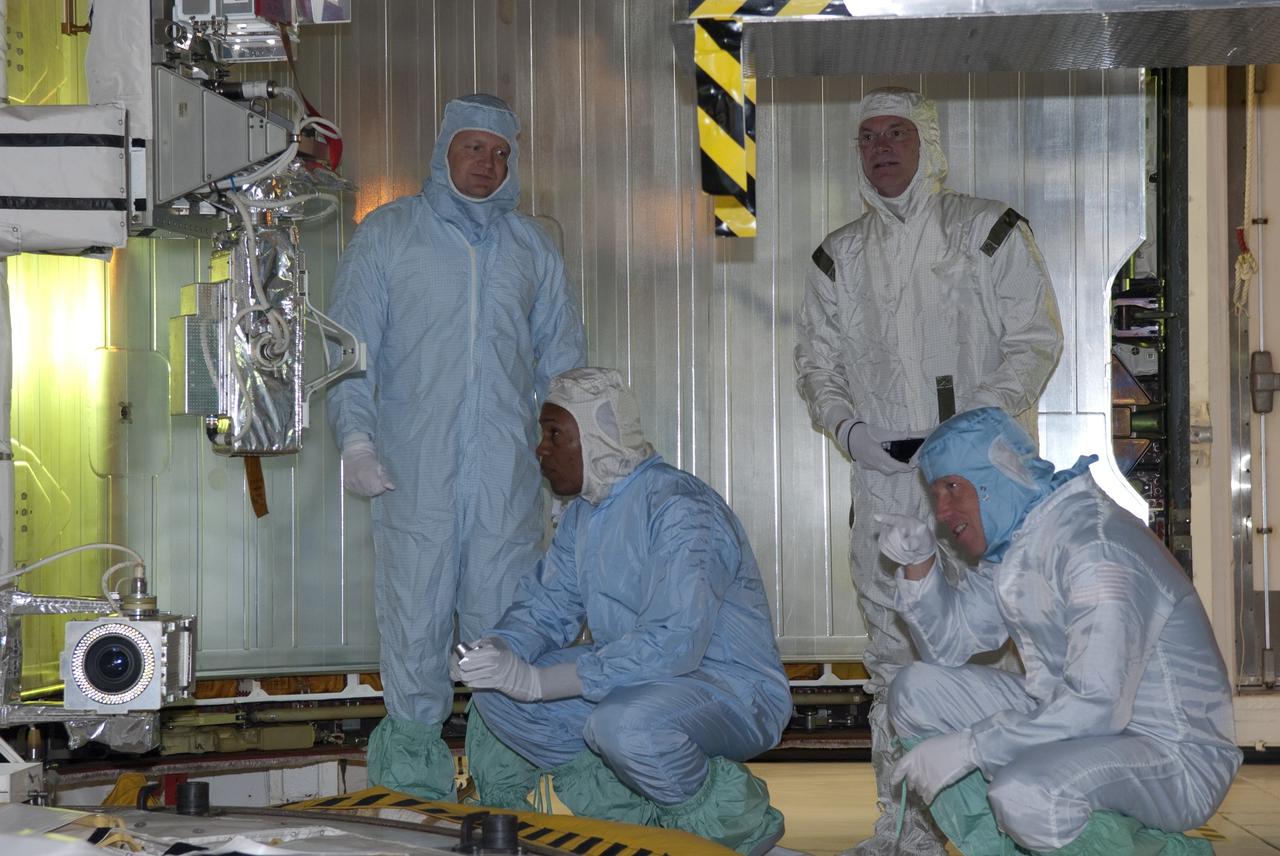
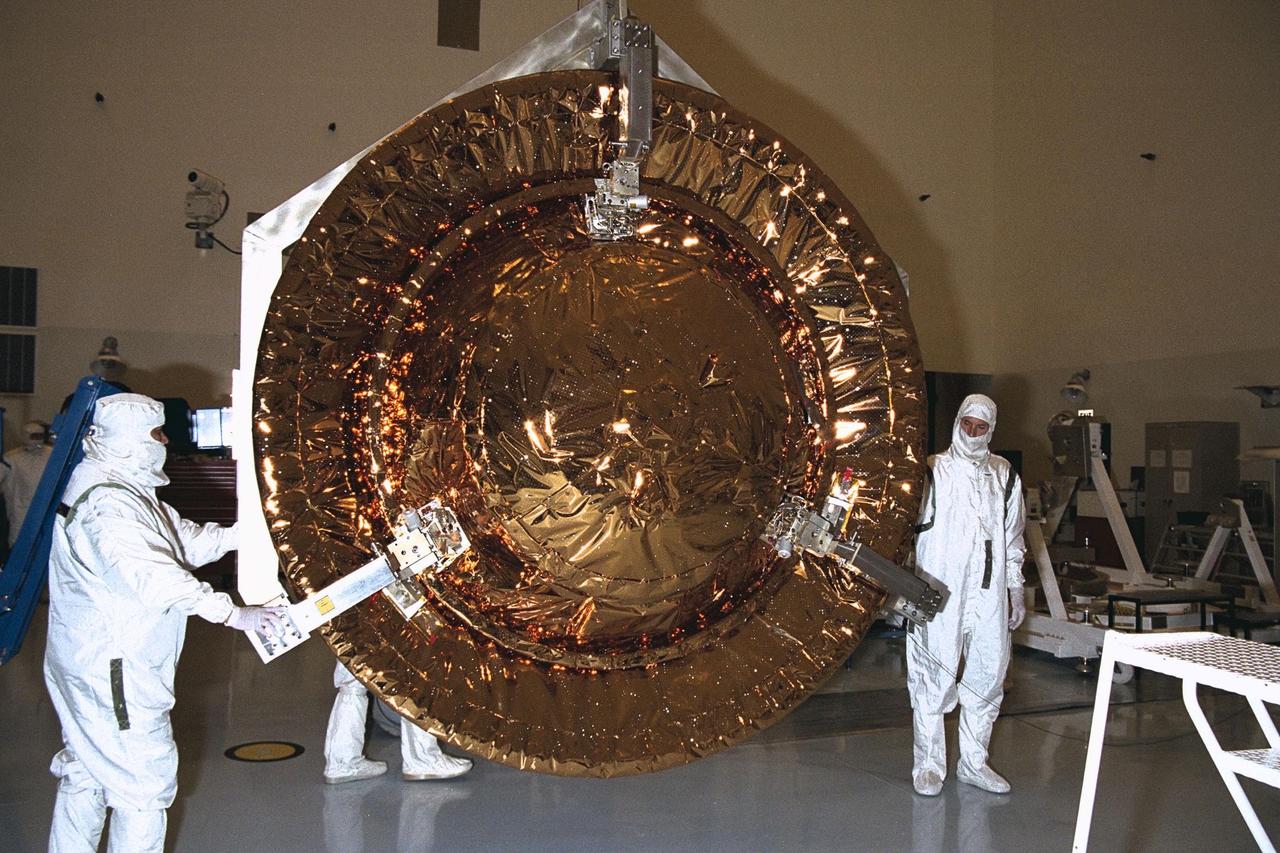
Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers place the back cover of the Huygens probe under its front heat shield in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers place the back cover of the Huygens probe under its front heat shield in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
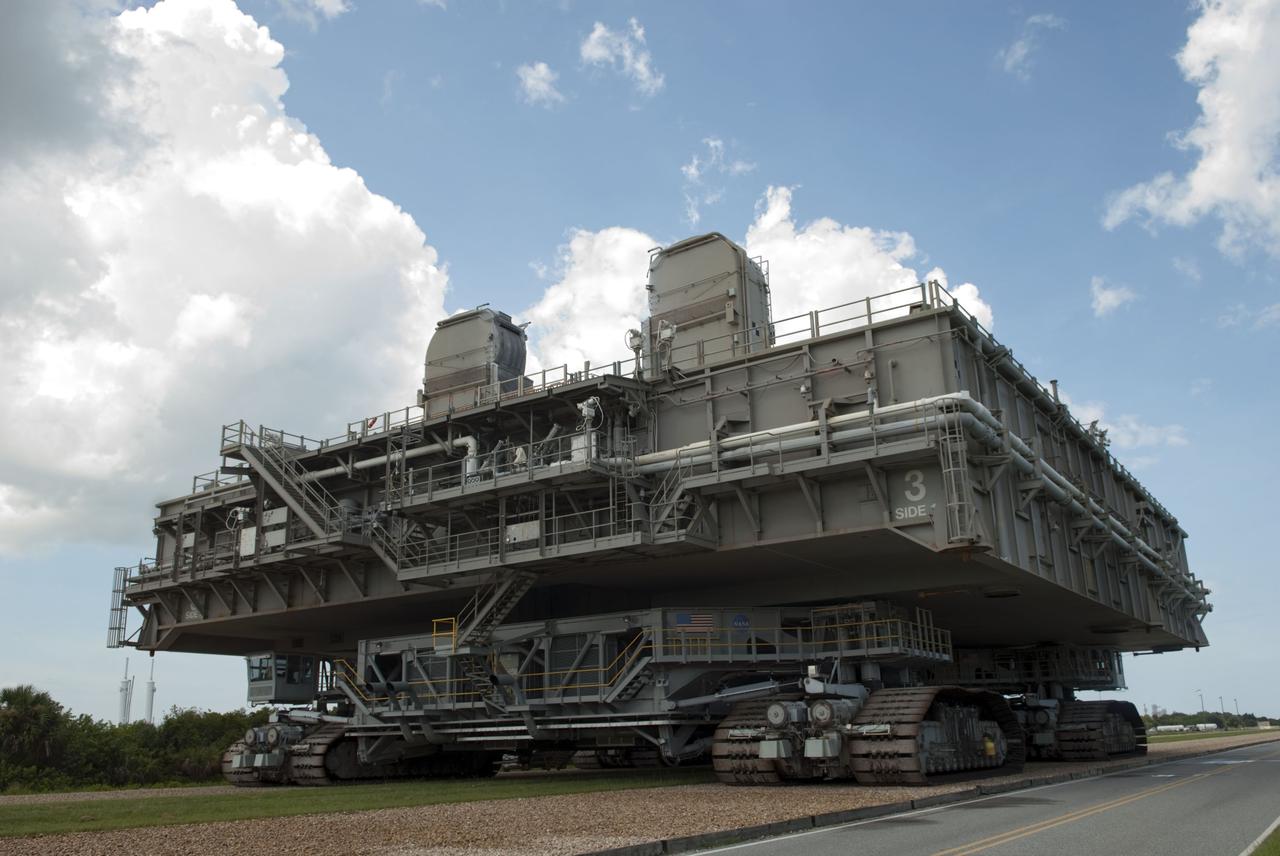

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mobile Launcher Platform-3 (MLP), which supported space shuttle Atlantis for its final flight to the International Space Station on the STS-135 mission, is making its last journey from Launch Pad 39A back to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) atop a massive crawler-transporter. For more than 40 years, the MLPs have traveled between the VAB to both launch pads at Launch Complex 39, and then returned to the VAB for future use. MLP-3 was first used to launch Columbia on the STS-32 mission on Jan. 9, 1990. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
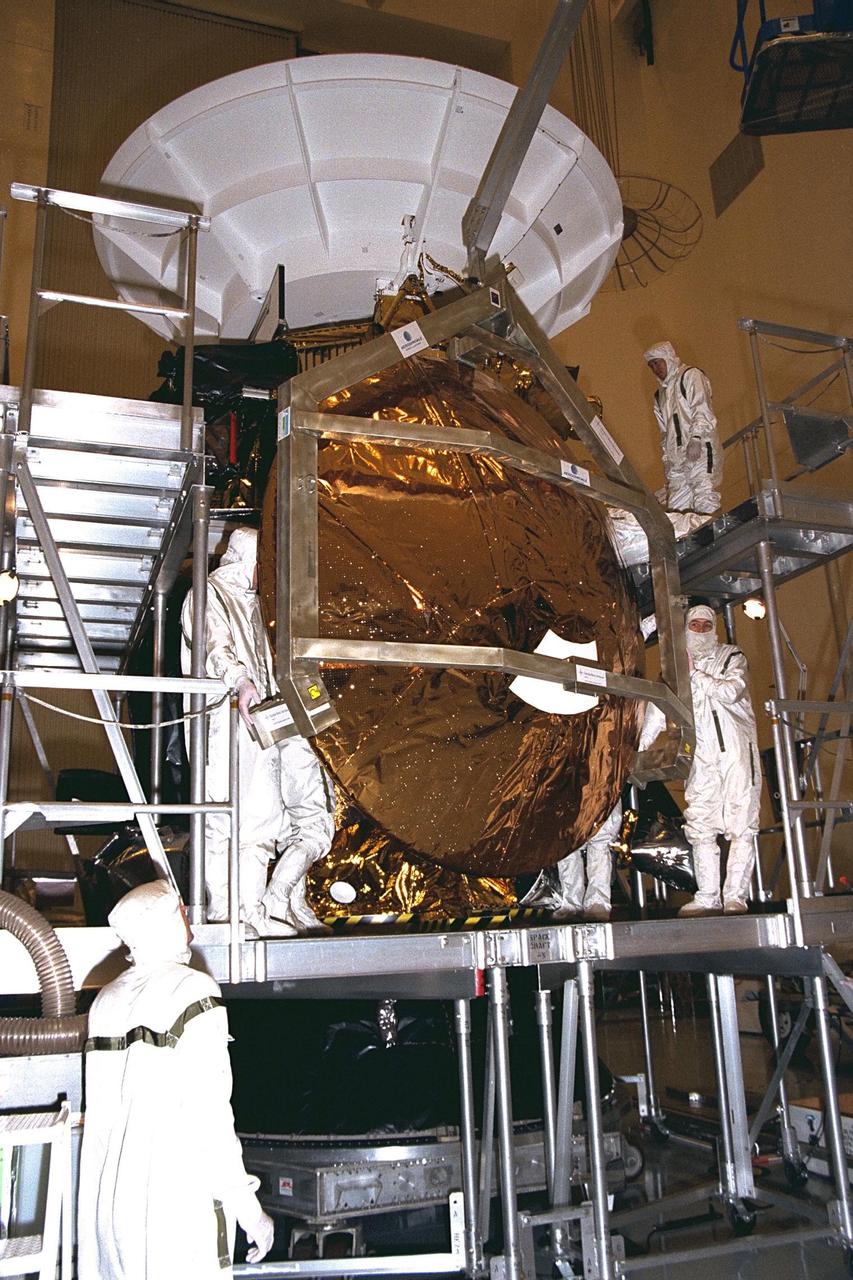

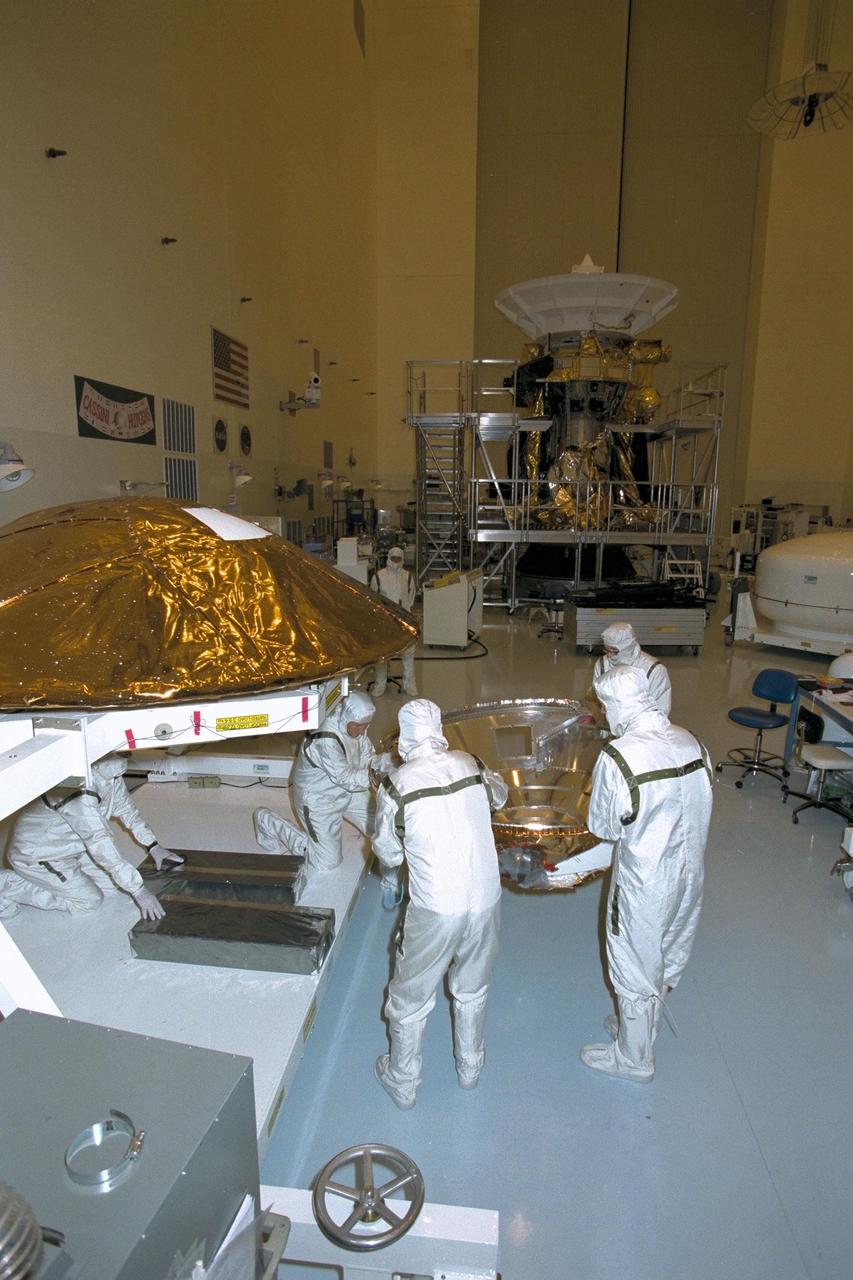
Workers remove the Huygens probe from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
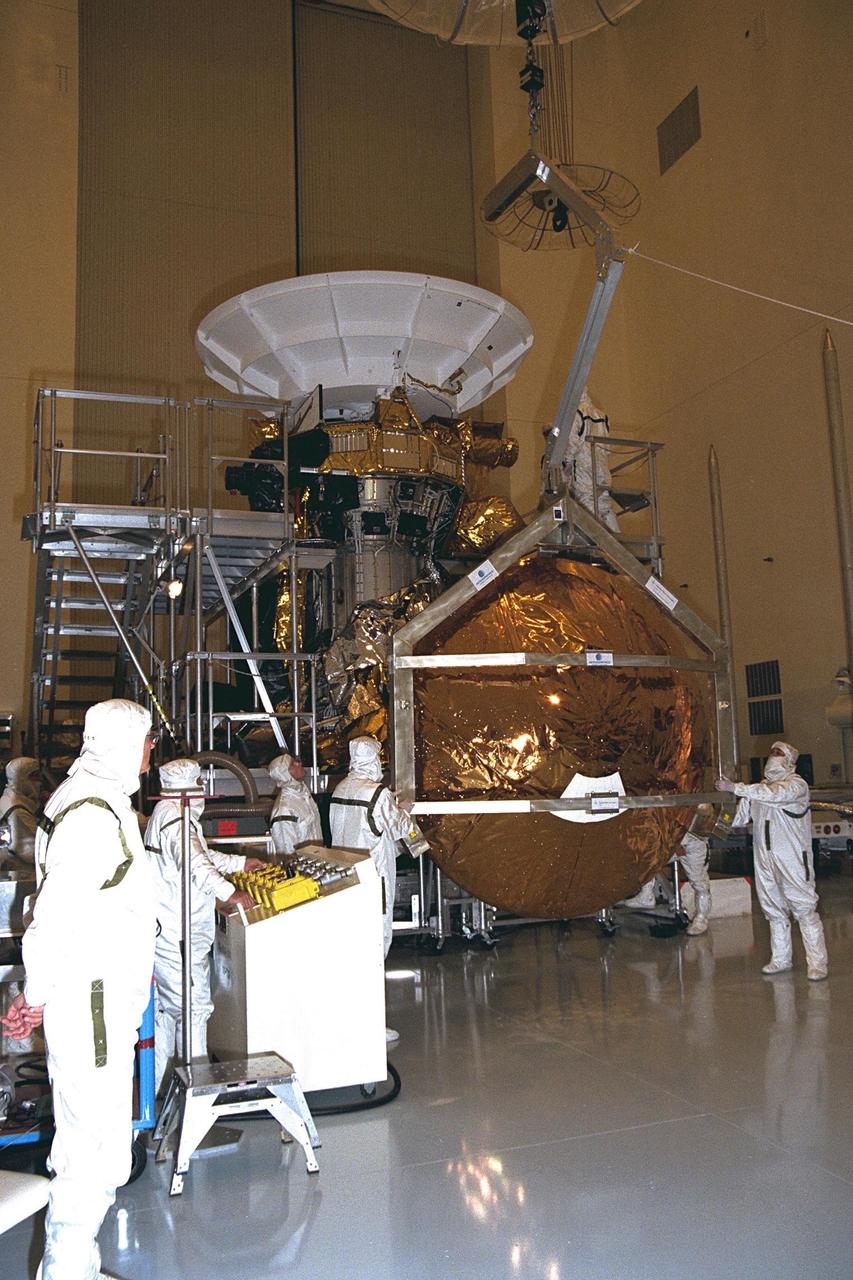

Workers remove the Huygens probe from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers at right repair the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate, or GUCP. A leak of hydrogen at the location during tanking June 12 for the STS-127 mission caused the mission to be scrubbed at 12:26 a.m. June 13. The GUCP is the overboard vent to the pad and the flare stack where the vented hydrogen is burned off. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on its STS-127 mission on June 17 at 5:40 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
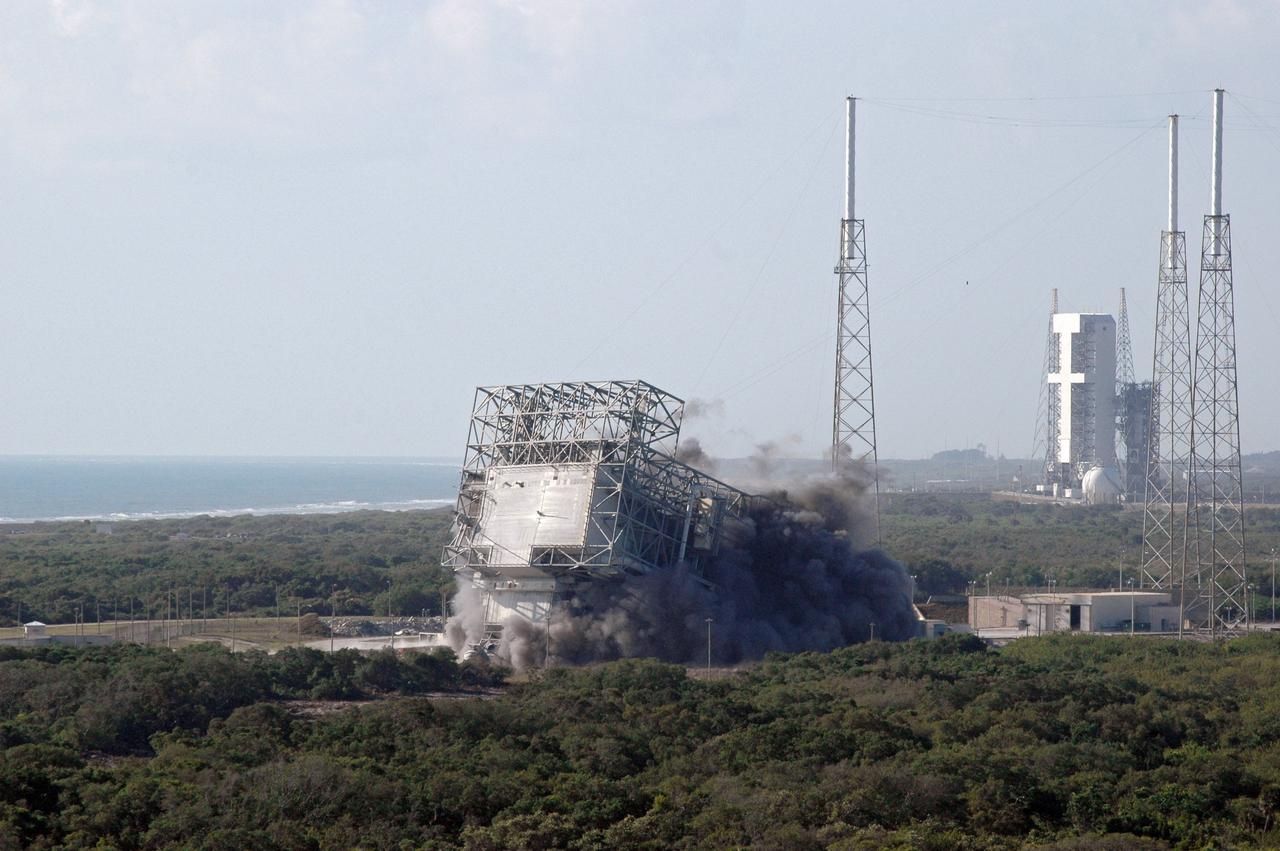

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The mobile service tower, or gantry, at Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station falls to the ground after the base was demolished. The tall lightning towers around it will remain. This mammoth structure, with its cavernous clean room, was used for the final spacecraft launch preparations for NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, currently orbiting Saturn. The launch occurred on Oct. 15, 1997, aboard an Air Force Titan IV-Centaur rocket. The facilities at the pad are being dismantled to make room for the construction of launch pad access and servicing facilities for the new Falcon rockets to be launched by Space Exploration Technologies, known as SpaceX. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers at right repair the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate, or GUCP. A leak of hydrogen at the location during tanking June 12 for the STS-127 mission caused the mission to be scrubbed at 12:26 a.m. June 13. The GUCP is the overboard vent to the pad and the flare stack where the vented hydrogen is burned off. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on its STS-127 mission on June 17 at 5:40 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
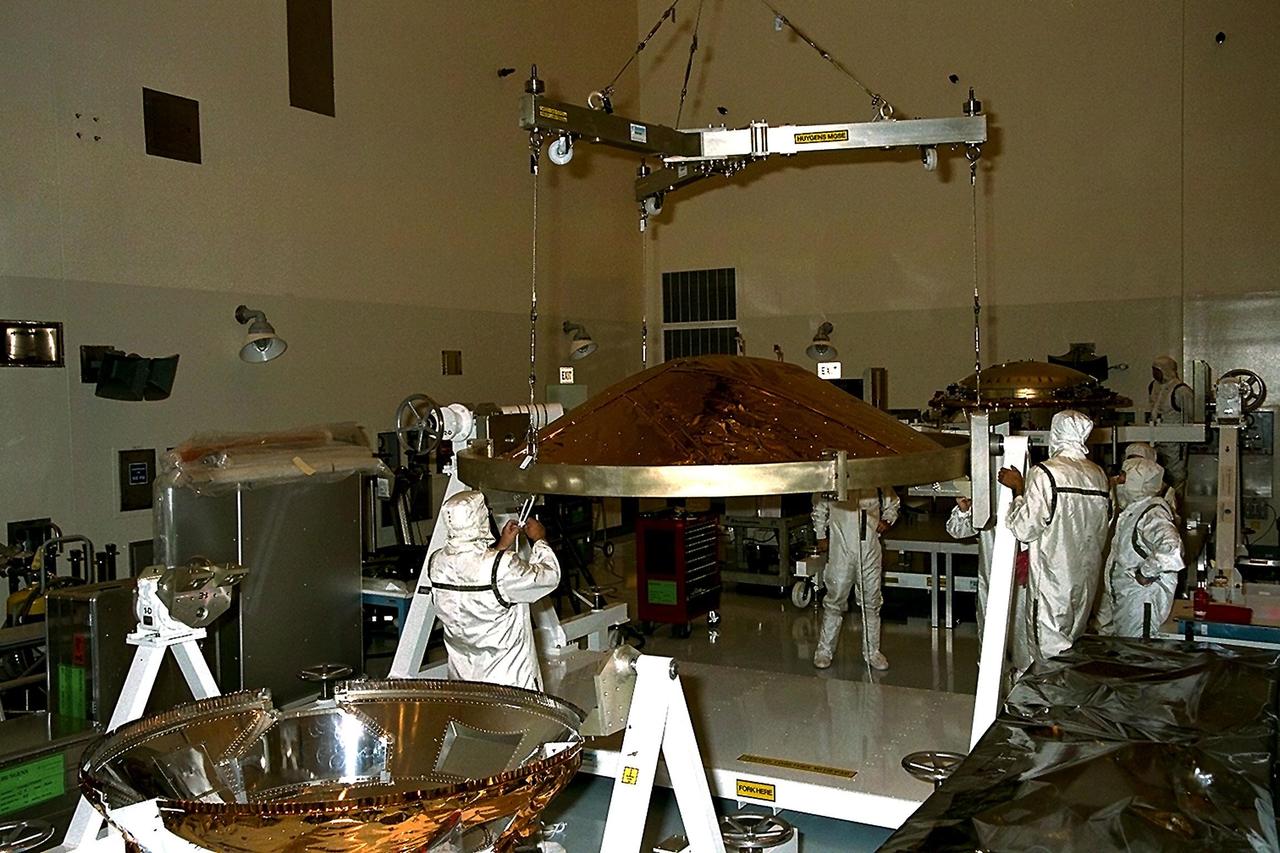

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers lift the front heat shield of the Huygens probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
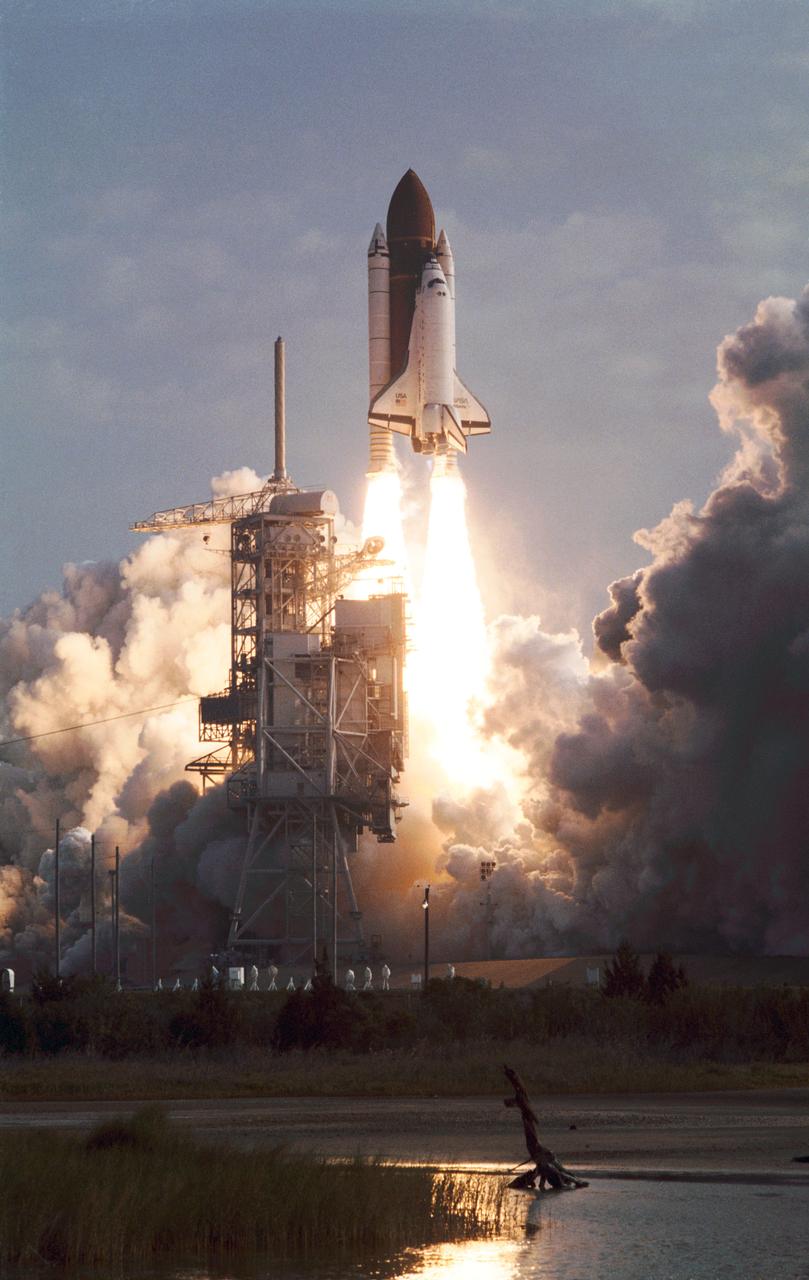

STS-45 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, lifts off from a Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad at 8:13:40:048 am (Eastern Standard Time (EST)). Exhaust billows out the solid rocket boosters (SRBs) as OV-104 atop its external tank (ET) soars above the mobile launcher platform and is nearly clear of the fixed service structure (FSS) tower. The diamond shock effect produced by the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) is visible. The glow of the SRB/SSME firings is reflected in a nearby waterway. An exhaust cloud covers the launch pad area.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-133 crew members check out their mission's payload while at Launch Pad 39A for the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). From left, are Pilot Eric Boe, and Mission Specialists Alvin Drew, and Tim Kopra. Standing behind Kopra in a white "bunny suit" is a pad technician. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
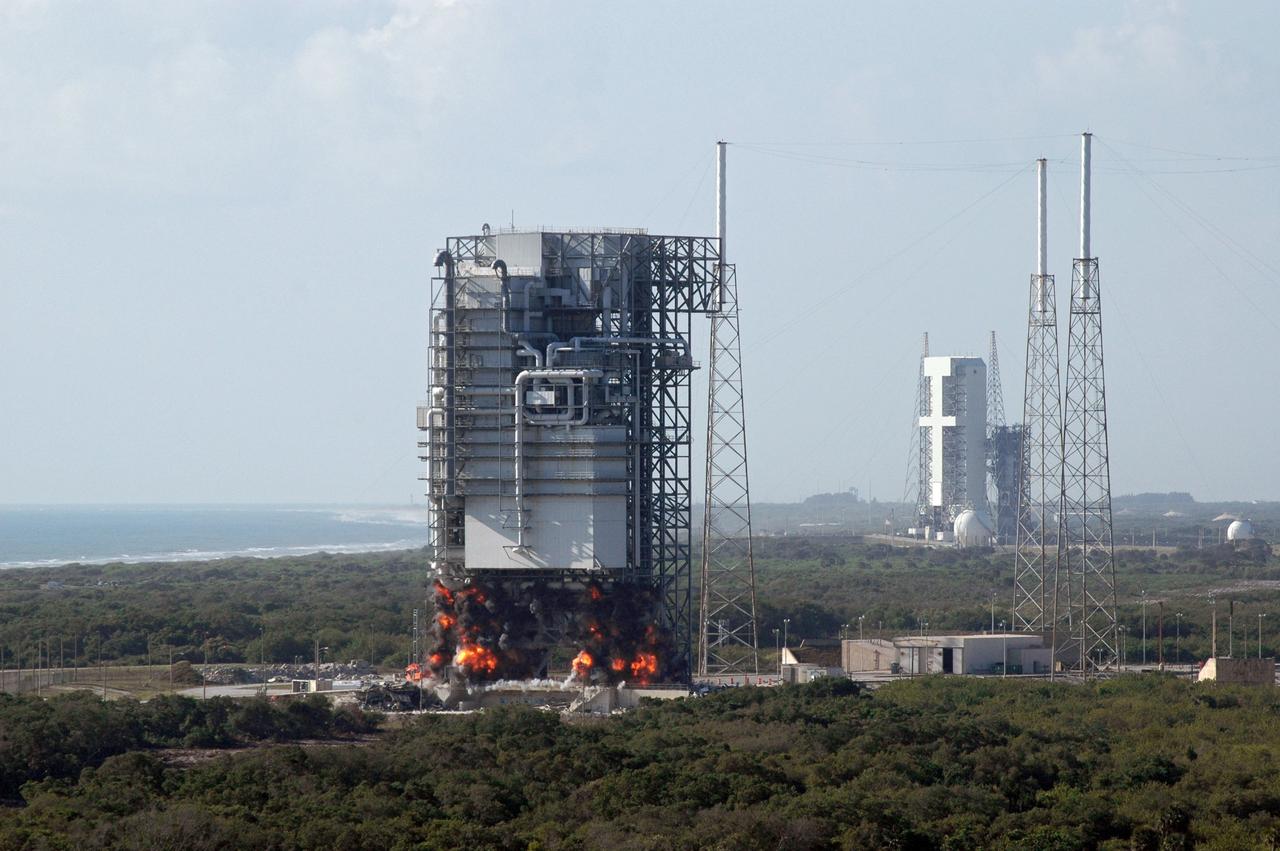

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Fire erupts beneath the mobile service tower, or gantry, at Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station signals the beginning of its demolition. The tall lightning towers around it will remain. This mammoth structure, with its cavernous clean room, was used for the final spacecraft launch preparations for NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, currently orbiting Saturn. The launch occurred on Oct. 15, 1997, aboard an Air Force Titan IV-Centaur rocket. The facilities at the pad are being dismantled to make room for the construction of launch pad access and servicing facilities for the new Falcon rockets to be launched by Space Exploration Technologies, known as SpaceX. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
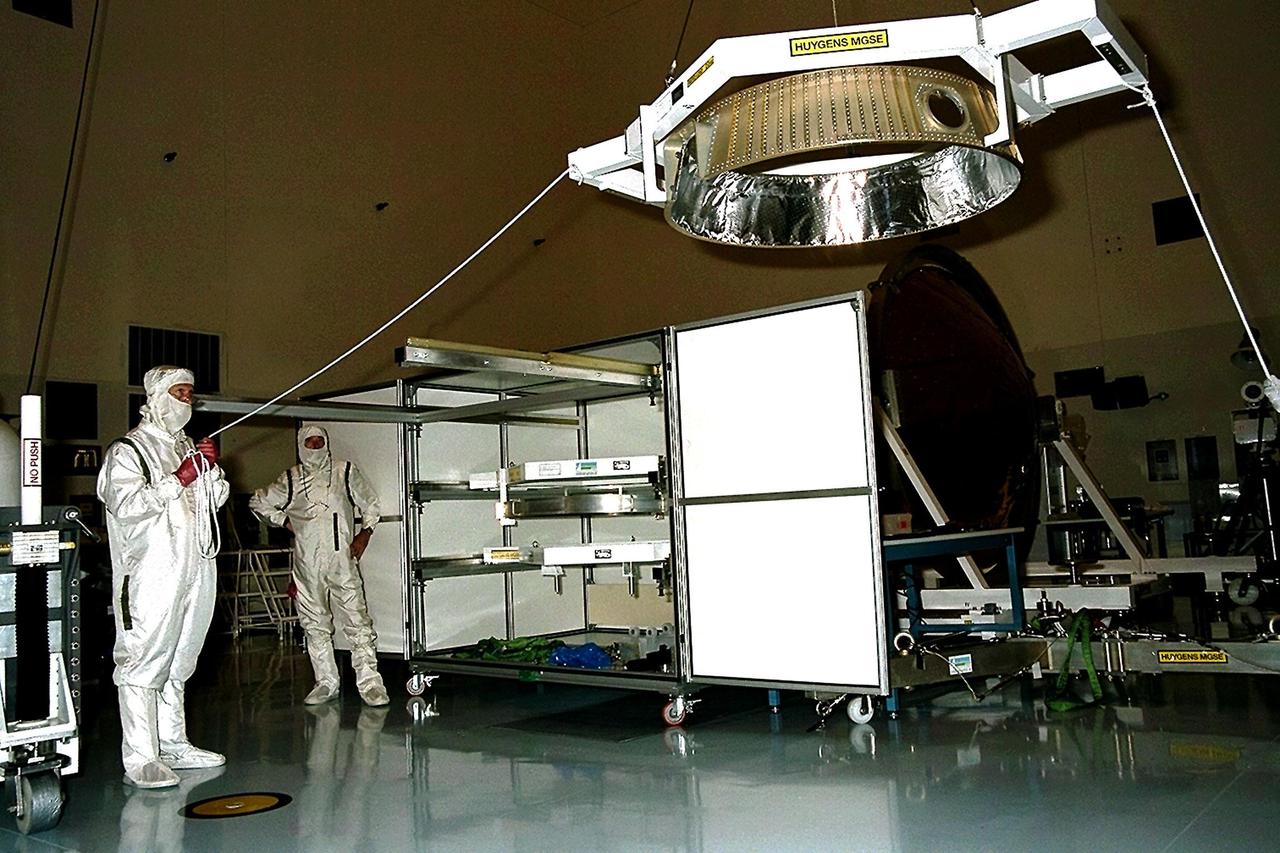

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers lift part of the Huygens probe aft cover assembly in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
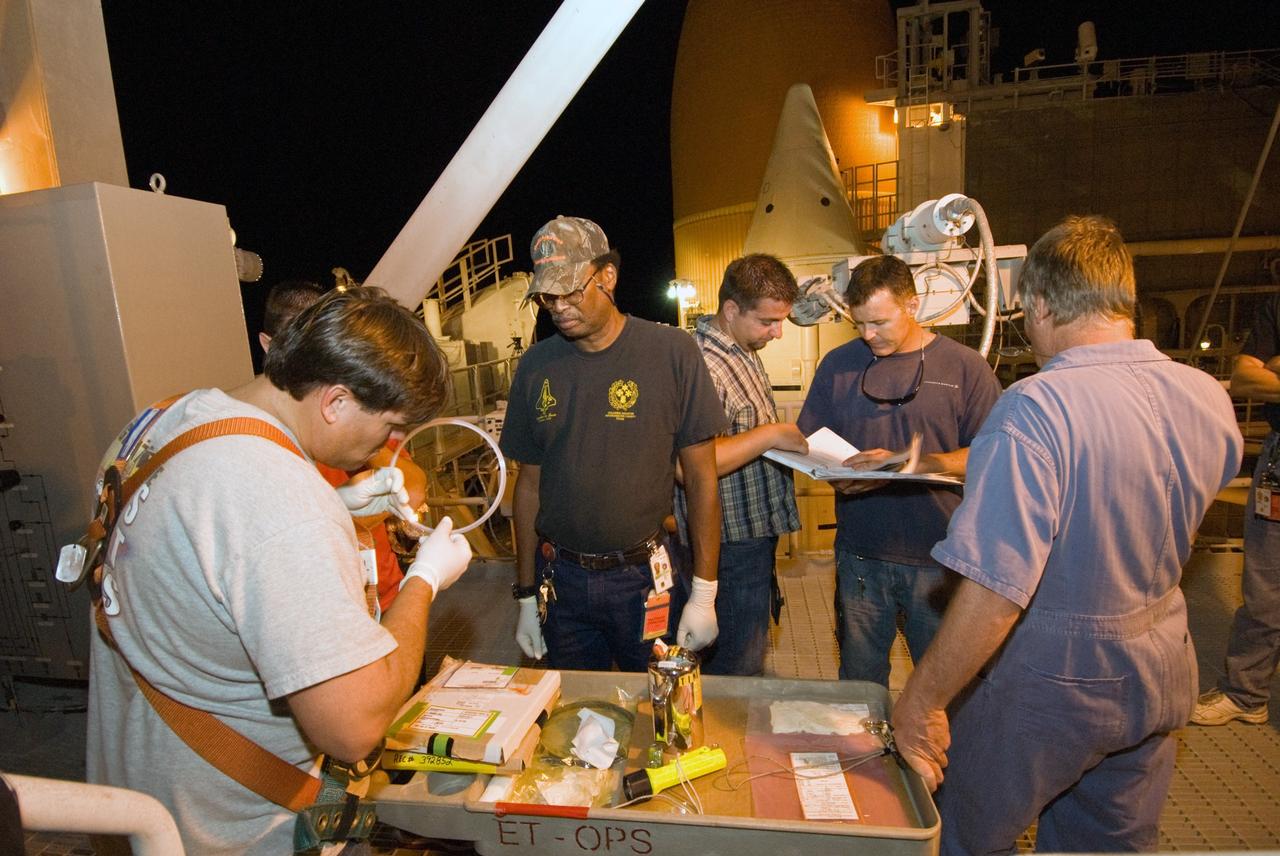

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker (left) checks a seal that may be used to repair the 7-inch quick disconnect from the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate, or GUCP. A leak of hydrogen at the location during tanking June 12 for the STS-127 mission caused the mission to be scrubbed at 12:26 a.m. June 13. The GUCP is the overboard vent to the pad and the flare stack where the vented hydrogen is burned off. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on its STS-127 mission on June 17 at 5:40 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
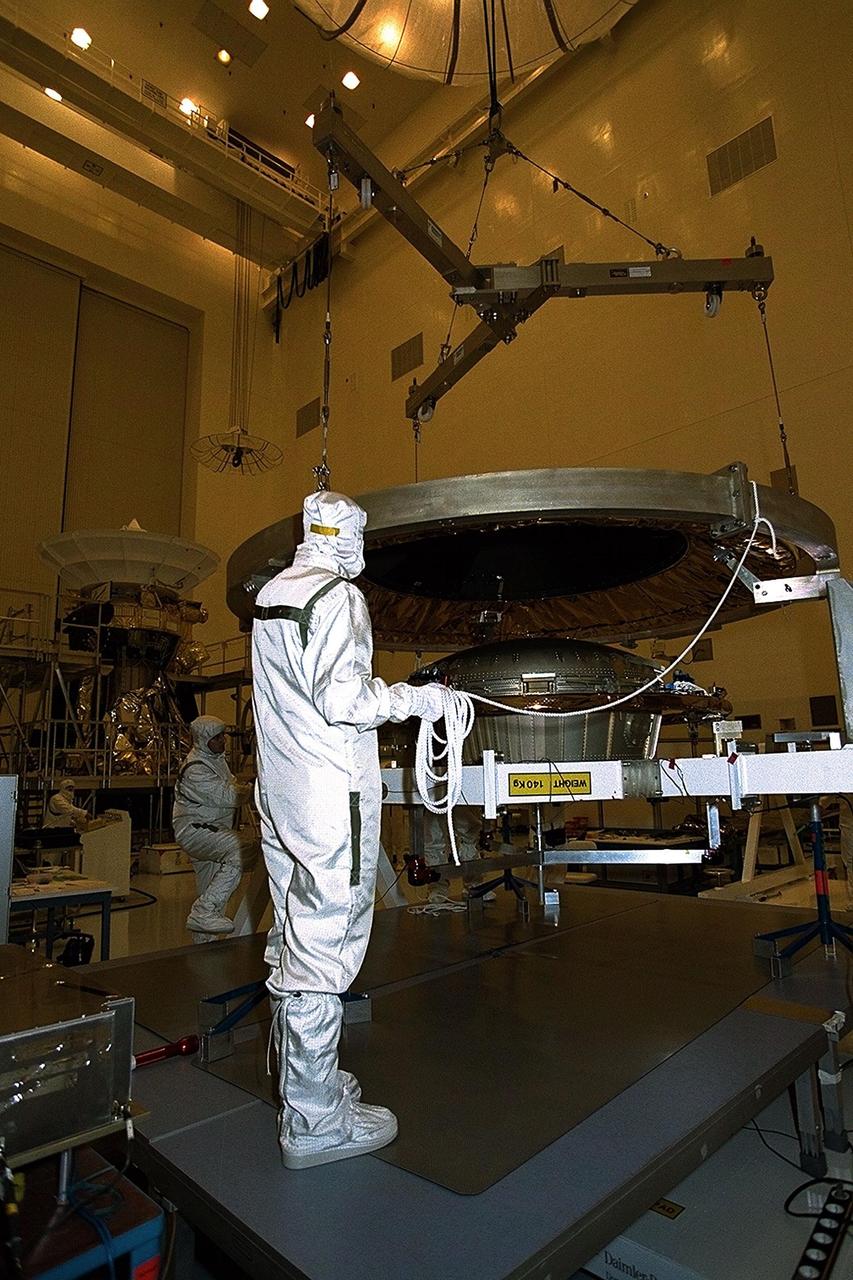

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers lift the heat shield of the Huygens probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
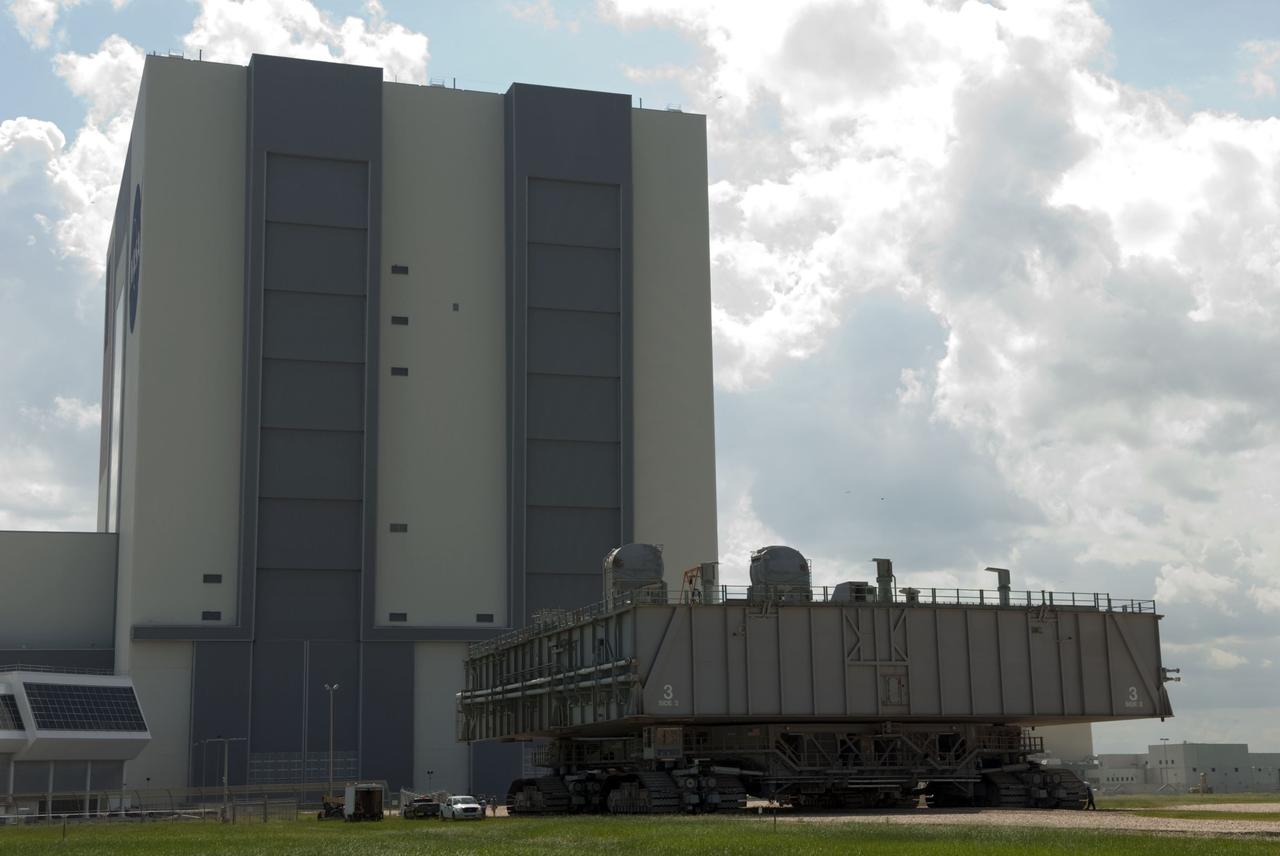

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mobile Launcher Platform-3 (MLP), which supported space shuttle Atlantis for its final flight to the International Space Station on the STS-135 mission, is making its last journey from Launch Pad 39A into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) atop a massive crawler-transporter. For more than 40 years, the MLPs have traveled between the VAB to both launch pads at Launch Complex 39, and then returned to the VAB for future use. MLP-3 was first used to launch Columbia on the STS-32 mission on Jan. 9, 1990. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

A crane lowers a protective transportation cover over the Cassini spacecraft, with its attached Huygens probe, at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station for the spacecraft’s return trip to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). Damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings, while the Huygens probe will explore the moon Titan
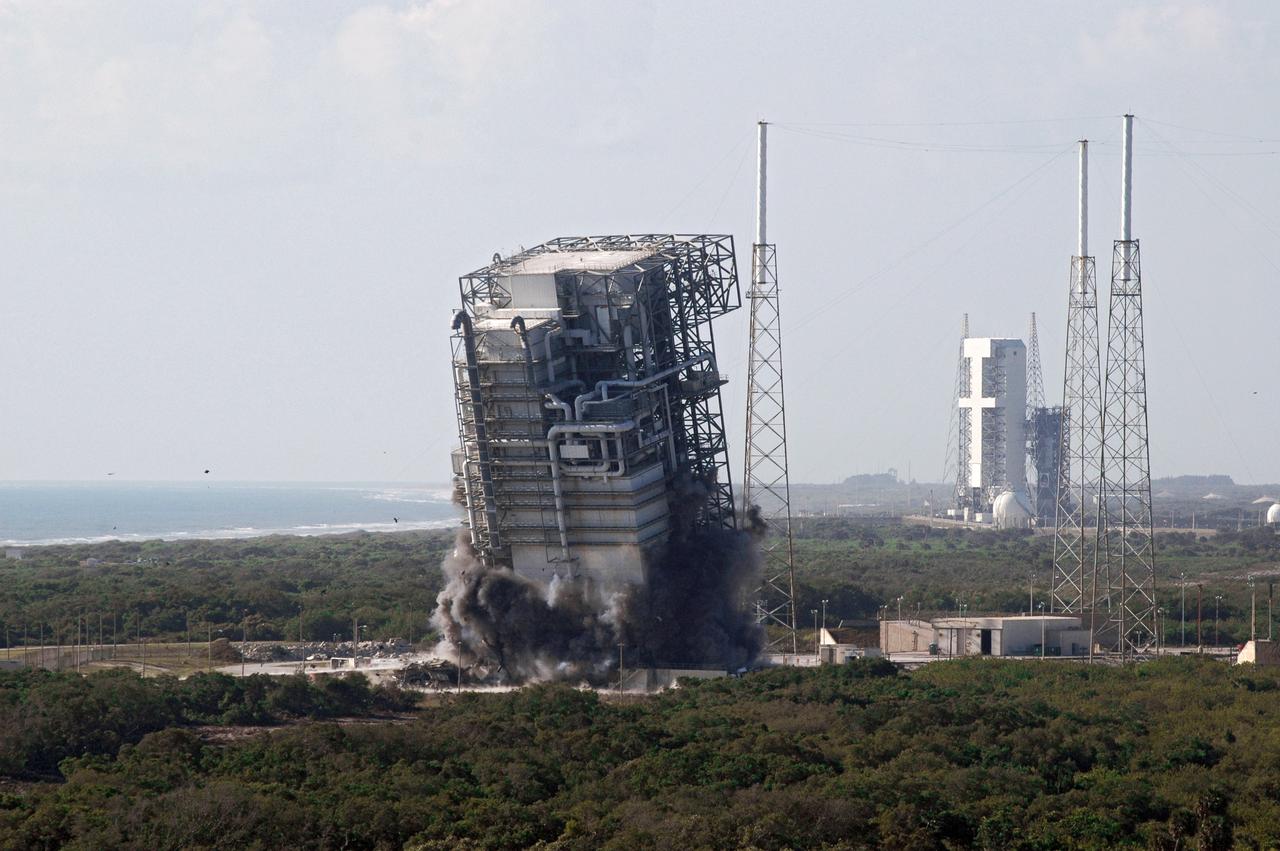

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The tilt of the mobile service tower, or gantry, at Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station signals the early stages of the tower’s implosion. The tall lightning towers around it will remain. This mammoth structure, with its cavernous clean room, was used for the final spacecraft launch preparations for NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, currently orbiting Saturn. The launch occurred on Oct. 15, 1997, aboard an Air Force Titan IV-Centaur rocket. The facilities at the pad are being dismantled to make room for the construction of launch pad access and servicing facilities for the new Falcon rockets to be launched by Space Exploration Technologies, known as SpaceX. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
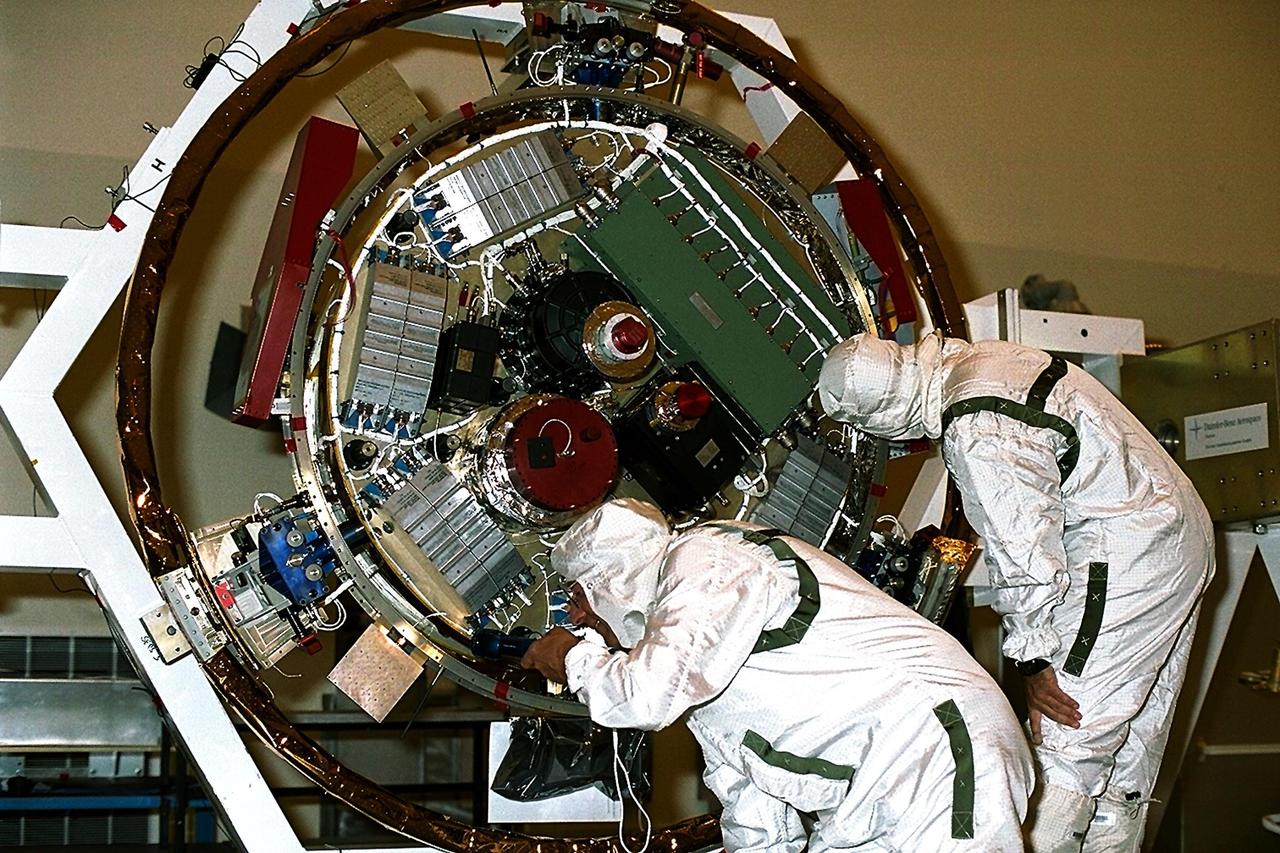
Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) workers examine the Huygens probe after removal from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
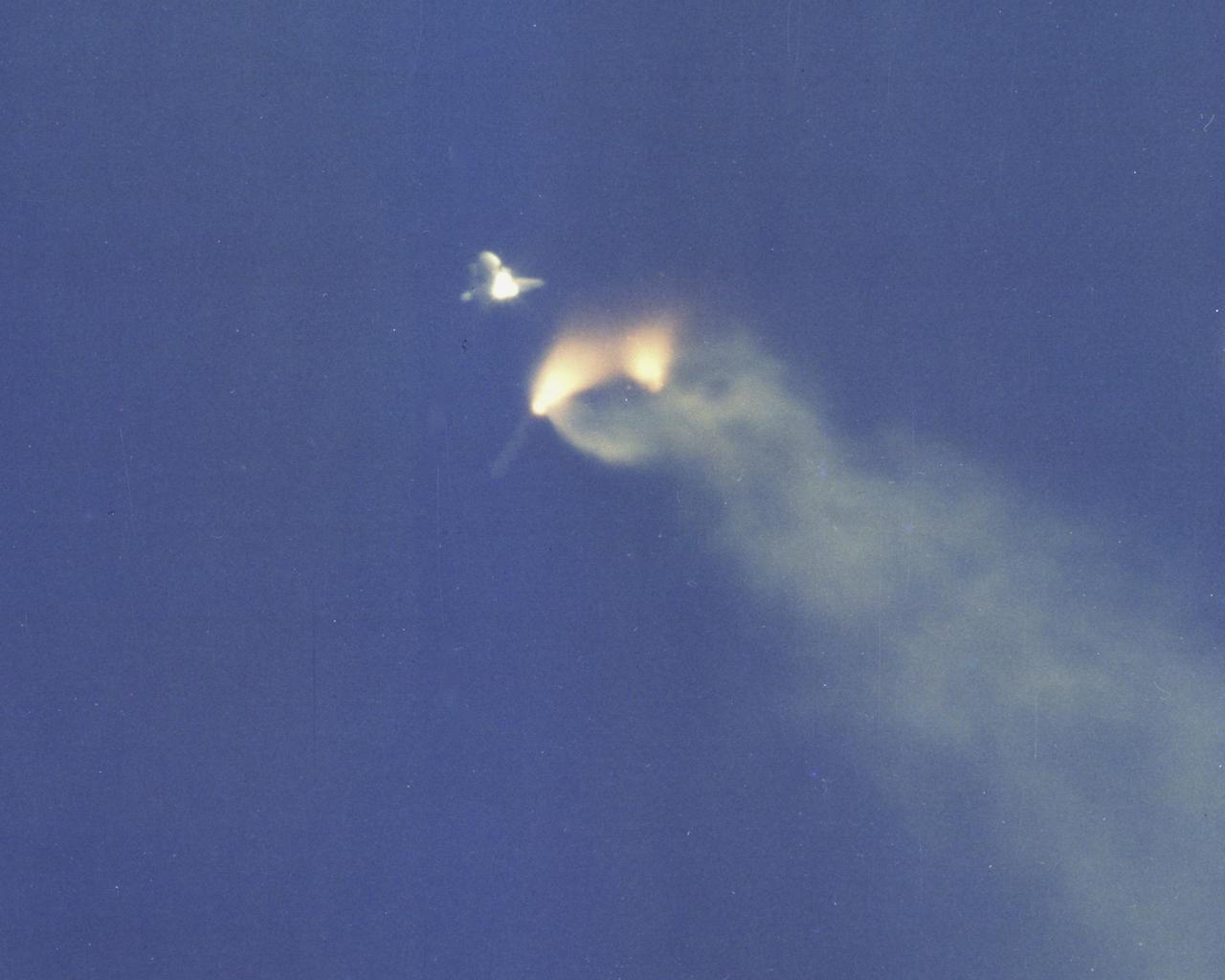

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Separation of the Space Shuttle’s solid rocket boosters (SRB’s) occurs at two minutes, 11 seconds after launch from Pad A, Launch Complex 39. This sequence, showing initiation of separations, and falling away of the two booster casings, still spewing sparks from their white-hot linings, was taken by a 70mm radar-tracked Photosonic motion picture camera with a 360-inch focal lens, from Universal Camera Site 10, located on KSC approximately eight miles north of the launch pad. The three frames were taken from a 1,000 foot run of EF film exposed at a rate of 40 frames per second.

The Cassini spacecraft, with its attached Huygens probe, is lowered from Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station for its return trip to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). Damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings, while the Huygens probe will explore the moon Titan
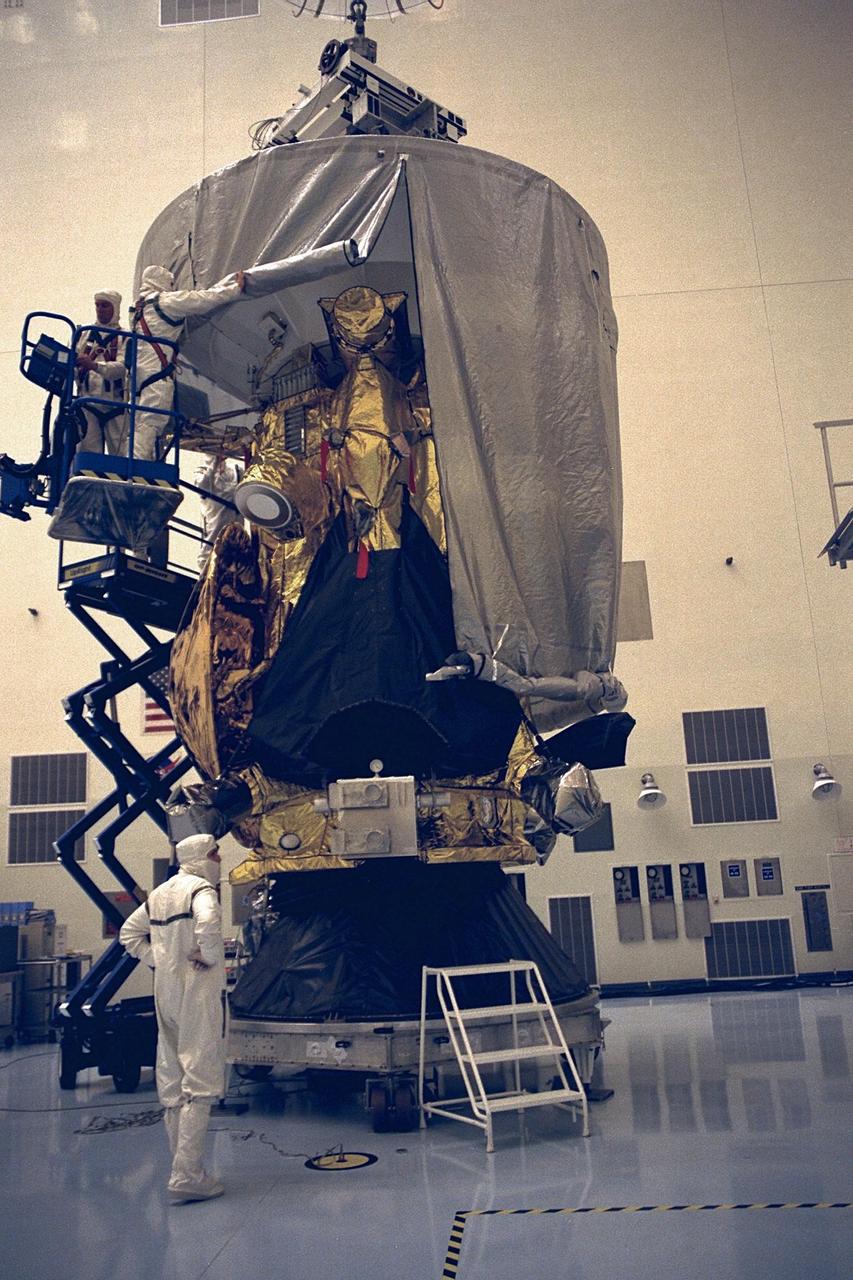

Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) begin to remove a protective cover from the Cassini spacecraft with its attached Huygens probe. Damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings, while the Huygens probe will explore the moon Titan
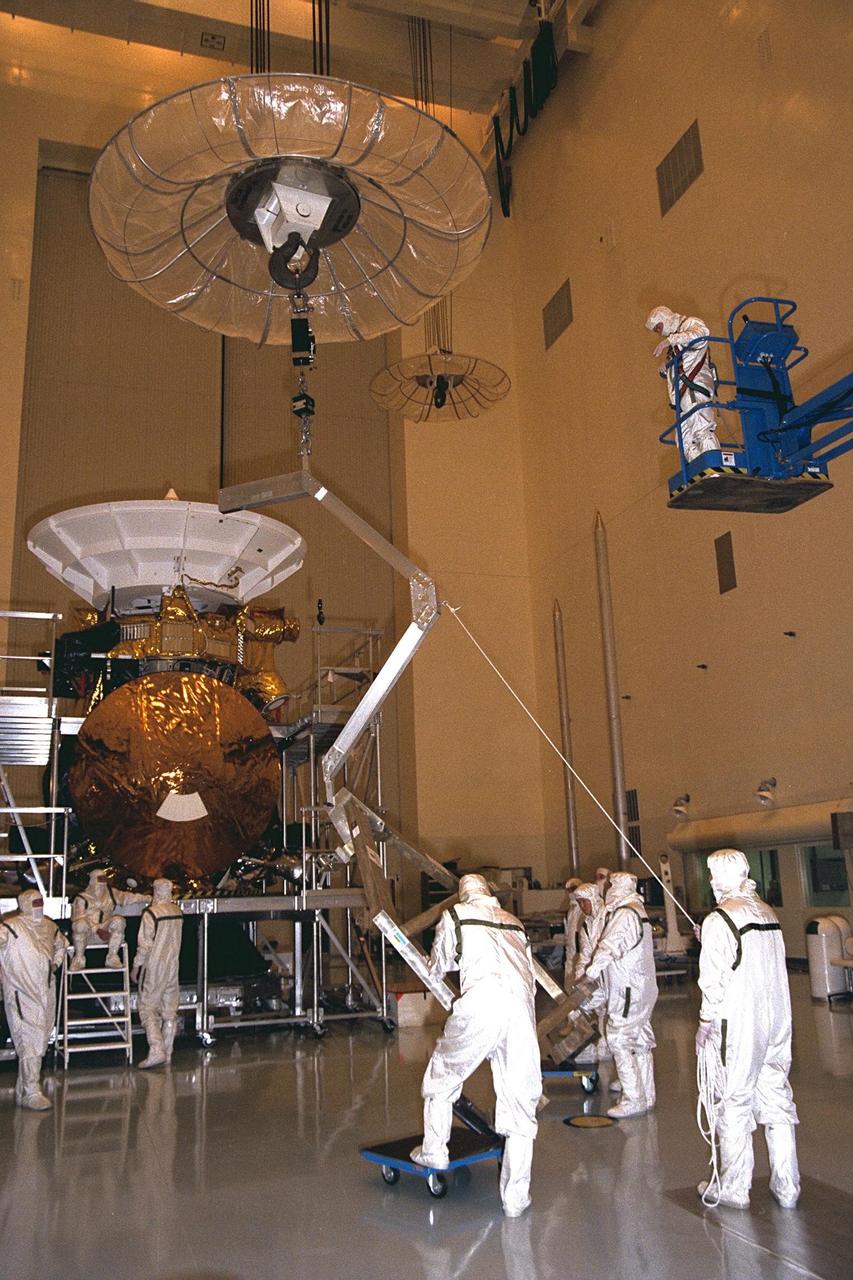

Workers remove the Huygens probe from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
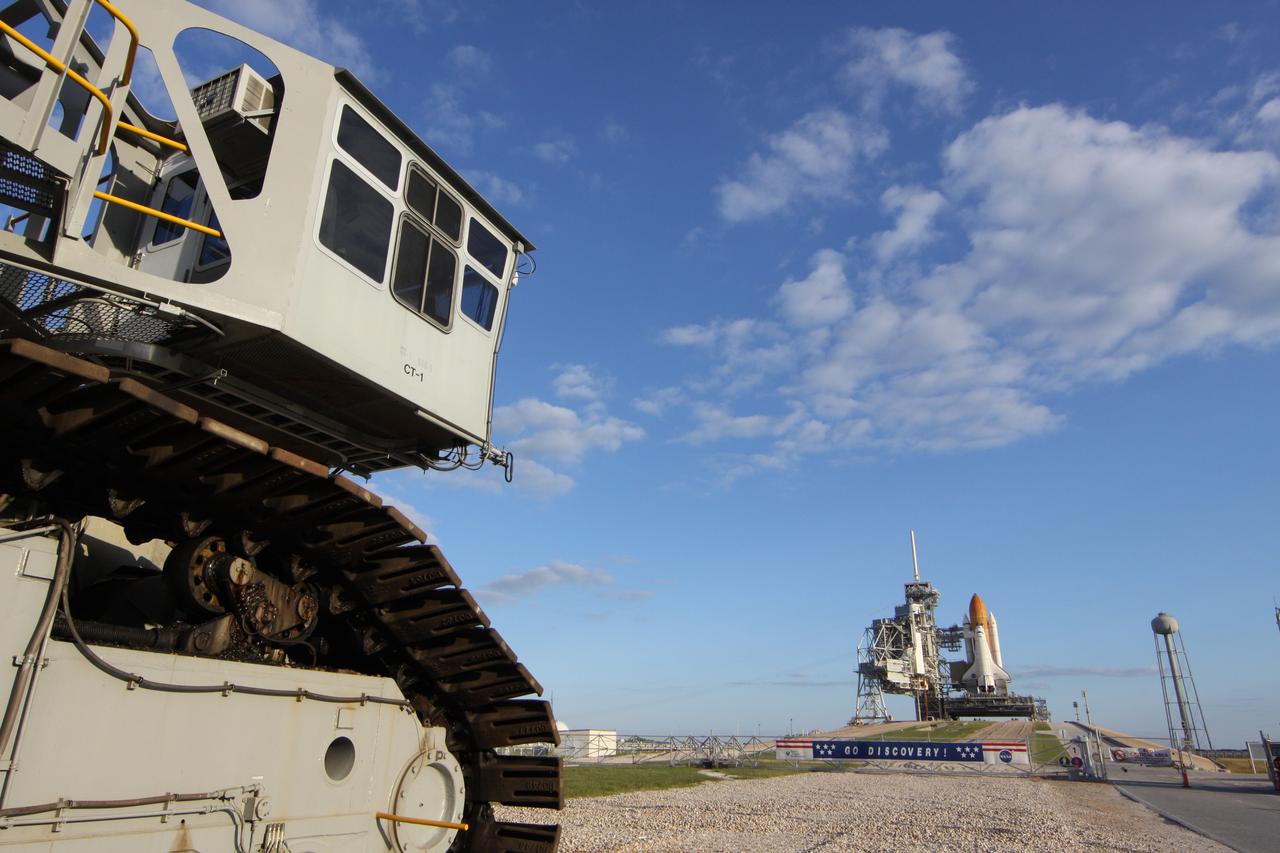

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the STS-133 payload canister now is in the rotating service structure on Launch Pad 39A. A crawler-transporter sits to the left of a sign hanging on the fence in front of the pad entrance supporting space shuttle Discovery. The payload then will be moved into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
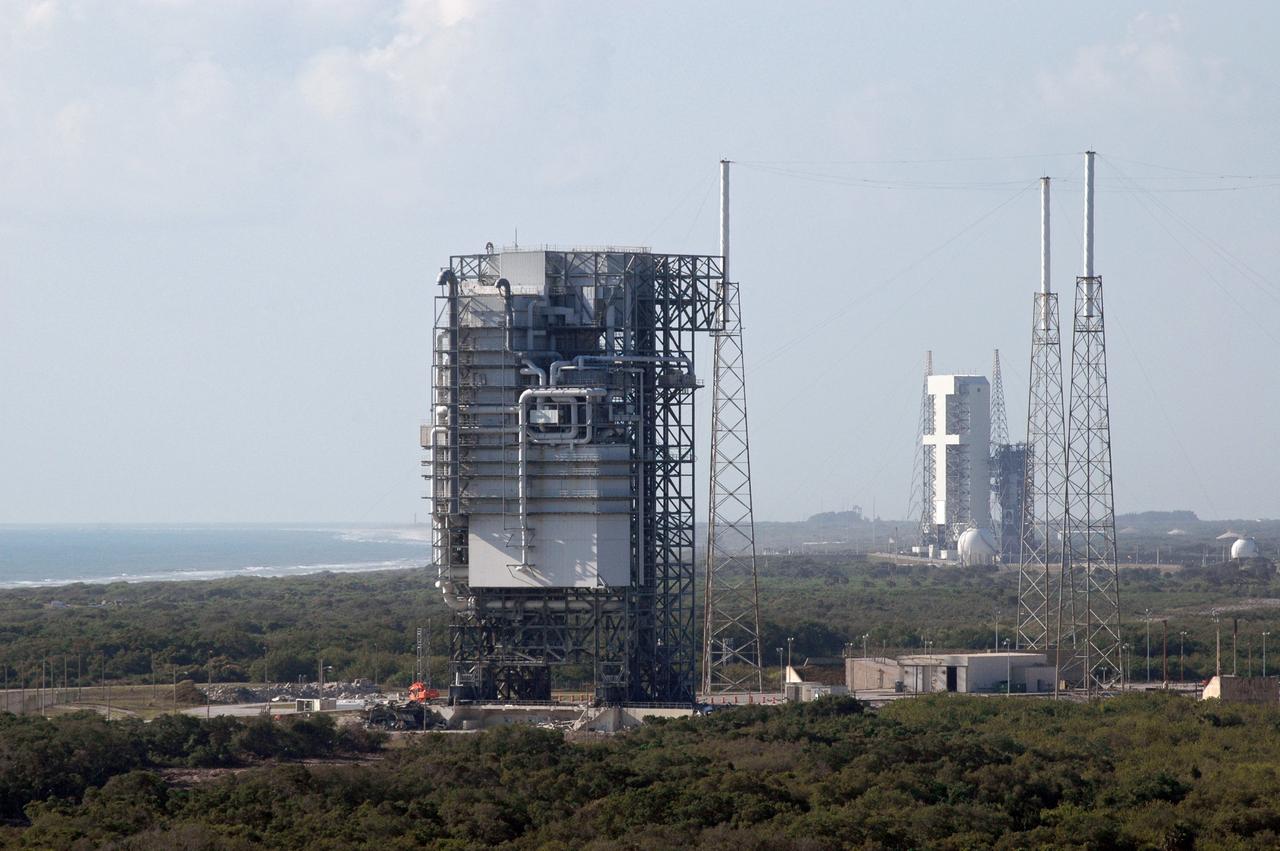

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The mobile service tower, or gantry, in the foreground at Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, is scheduled for demolition. The tall lightning towers around it will remain. This mammoth structure, with its cavernous clean room, was used for the final spacecraft launch preparations for NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, currently orbiting Saturn. The launch occurred on Oct. 15, 1997, aboard an Air Force Titan IV-Centaur rocket. The facilities at the pad are being dismantled to make room for the construction of launch pad access and servicing facilities for the new Falcon rockets to be launched by Space Exploration Technologies, known as SpaceX. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) finish the removal of a protective cover from the Cassini spacecraft with its attached Huygens probe. Damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings, while the Huygens probe will explore the moon Titan
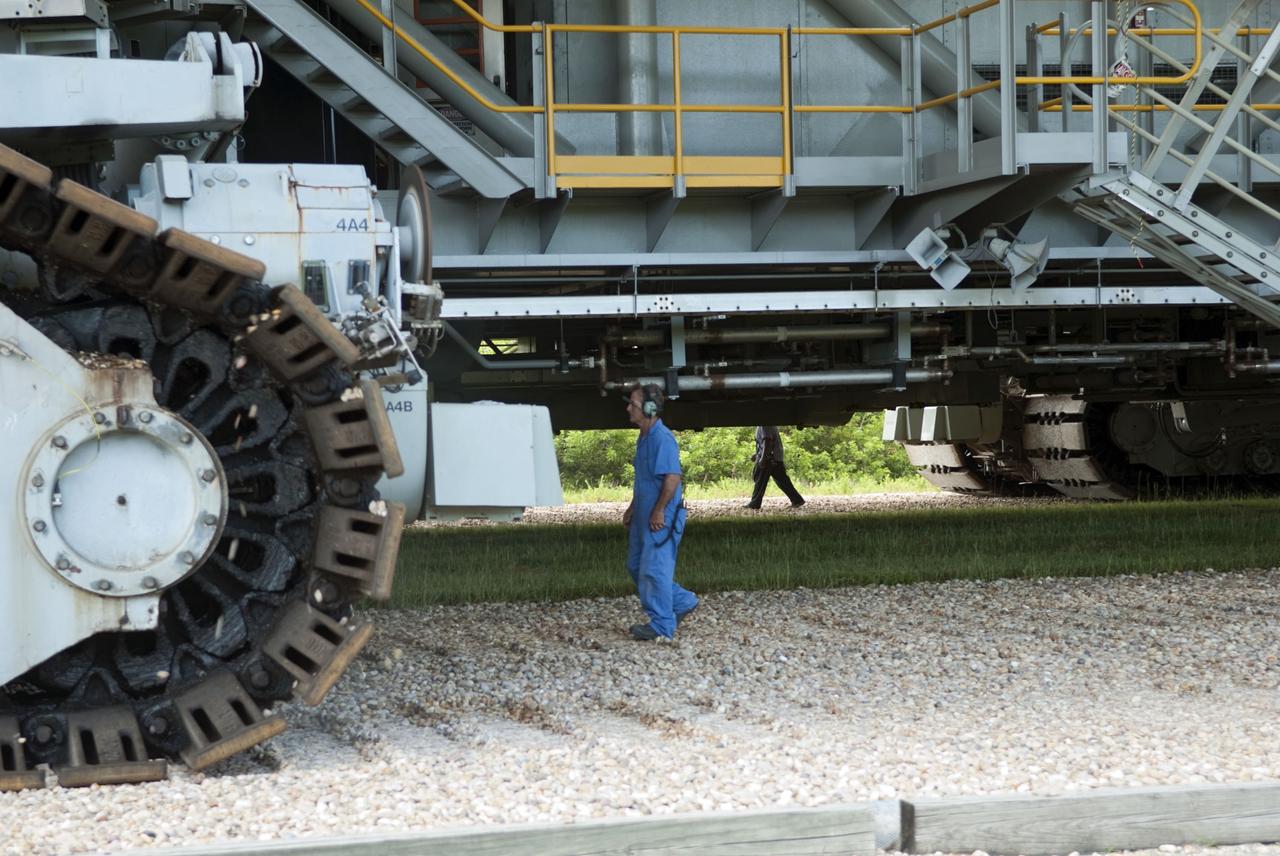

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers accompany Mobile Launcher Platform-3 (MLP), which supported space shuttle Atlantis for its final flight to the International Space Station on the STS-135 mission, while making its last journey from Launch Pad 39A back to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) atop a massive crawler-transporter. For more than 40 years, the MLPs have traveled between the VAB to both launch pads at Launch Complex 39, and then returned to the VAB for future use. MLP-3 was first used to launch Columbia on the STS-32 mission on Jan. 9, 1990. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers lift the heat shield of the Huygens probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
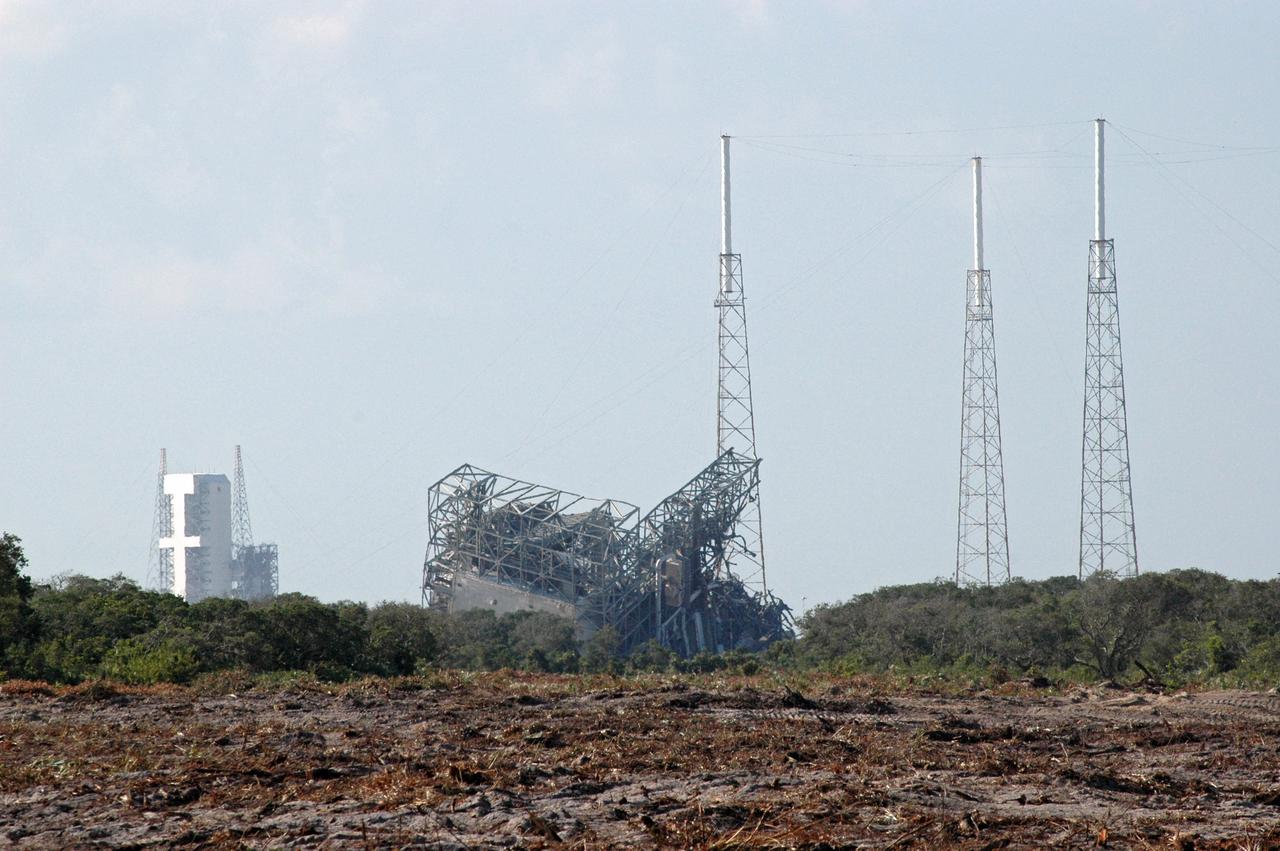

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The upper part of the mobile service tower, or gantry, at Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station lies on the ground after implosion. The tall lightning towers around it remain. This mammoth structure, with its cavernous clean room, was used for the final spacecraft launch preparations for NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, currently orbiting Saturn. The launch occurred on Oct. 15, 1997, aboard an Air Force Titan IV-Centaur rocket. The facilities at the pad are being dismantled to make room for the construction of launch pad access and servicing facilities for the new Falcon rockets to be launched by Space Exploration Technologies, known as SpaceX. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) workers remove the Huygens probe from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
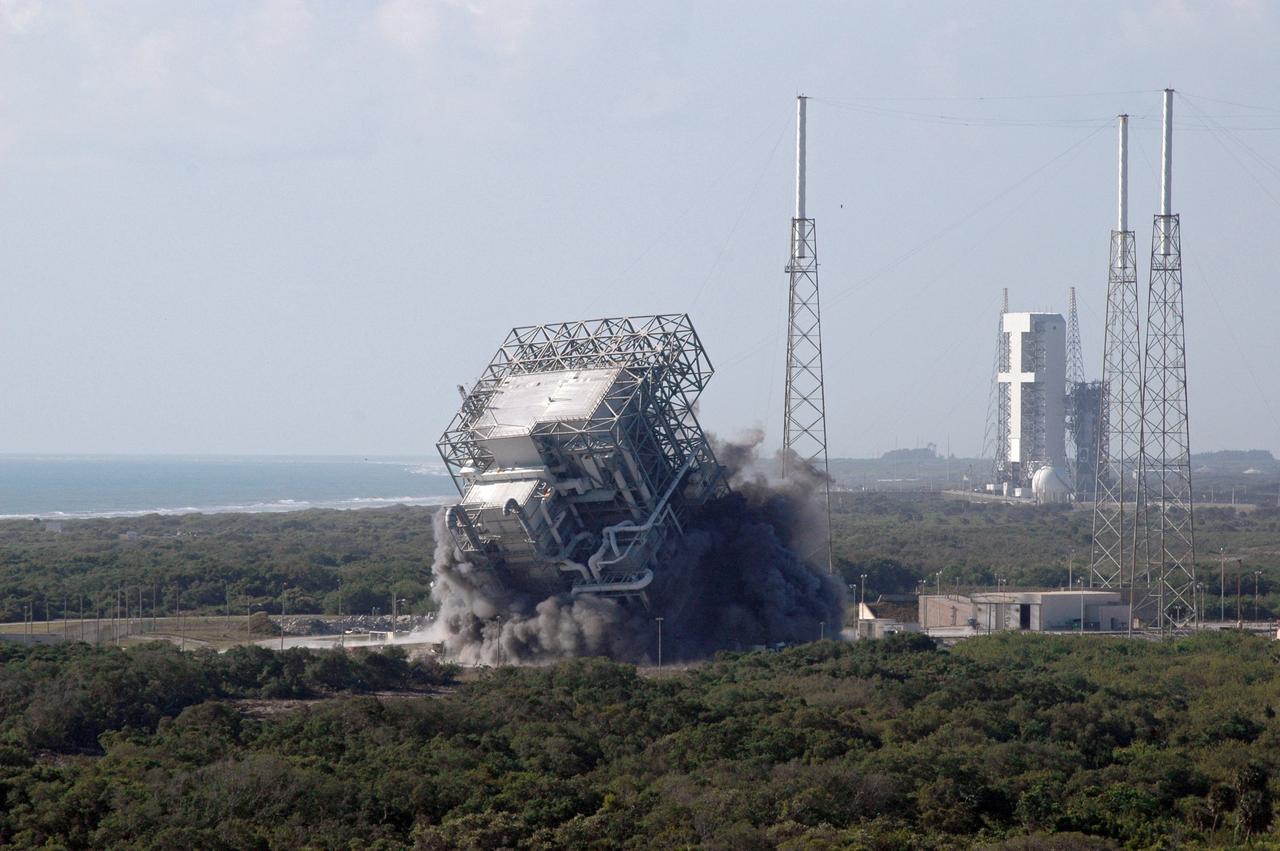

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The upper part of the mobile service tower, or gantry, at Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station falls to the ground after the base was demolished. The tall lightning towers around it will remain. This mammoth structure, with its cavernous clean room, was used for the final spacecraft launch preparations for NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, currently orbiting Saturn. The launch occurred on Oct. 15, 1997, aboard an Air Force Titan IV-Centaur rocket. The facilities at the pad are being dismantled to make room for the construction of launch pad access and servicing facilities for the new Falcon rockets to be launched by Space Exploration Technologies, known as SpaceX. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
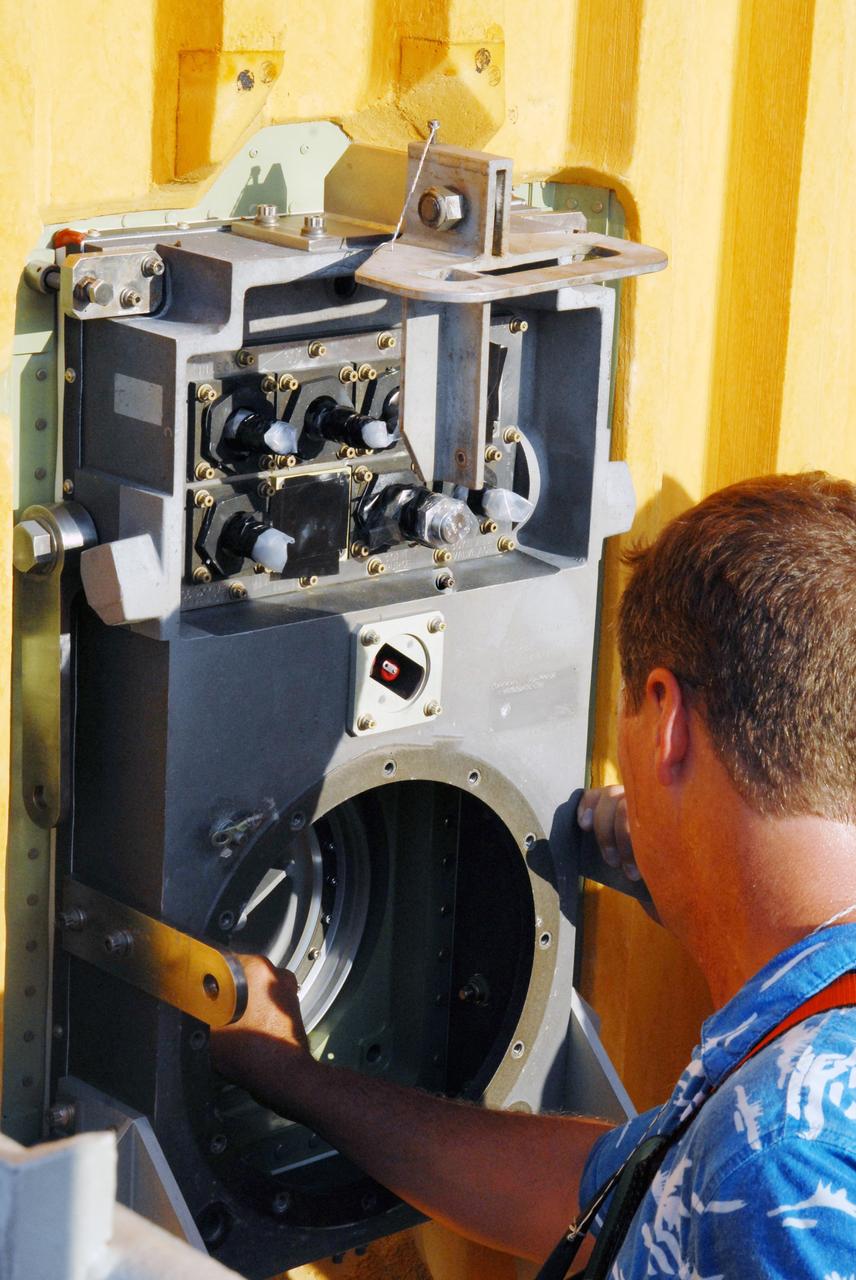

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker checks the area on the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate, or GUCP, where the 7-inch quick disconnect was removed. A leak of hydrogen at the location during tanking June 12 for the STS-127 mission caused the mission to be scrubbed at 12:26 a.m. June 13. The GUCP is the overboard vent to the pad and the flare stack where the vented hydrogen is burned off. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on its STS-127 mission on June 17 at 5:40 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
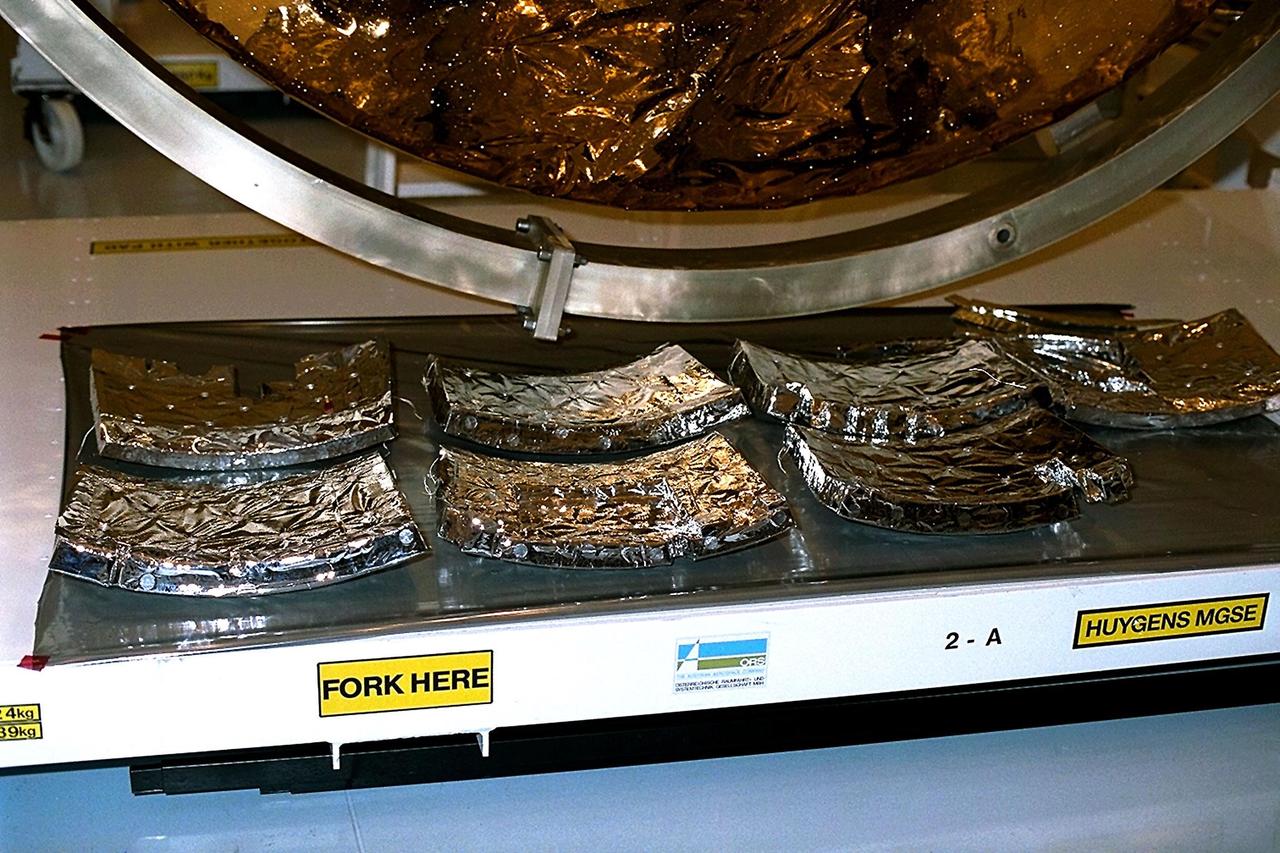

Pieces of the Huygens probe internal insulating foam await inspection after removal from the probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
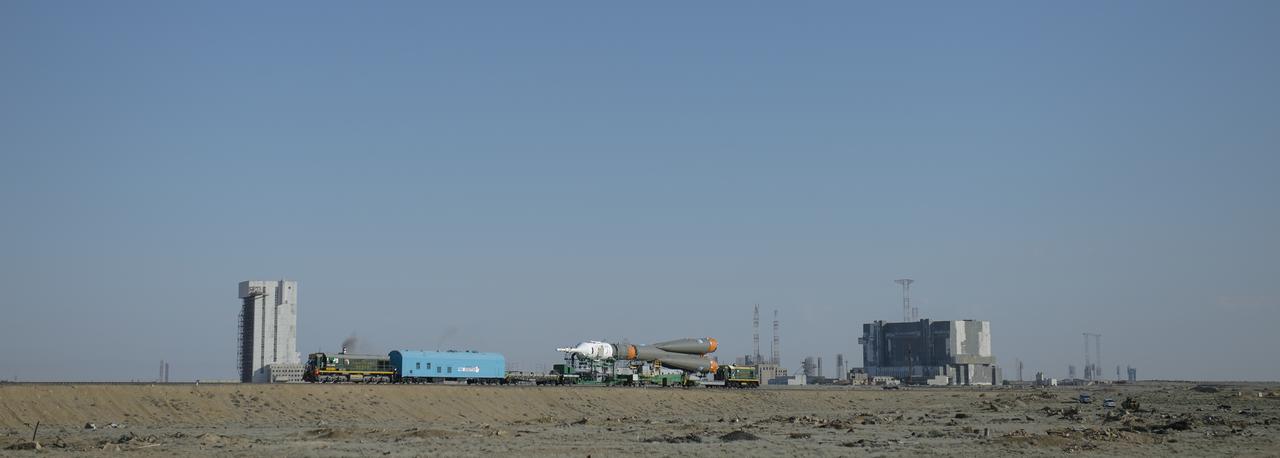

The Soyuz TMA-13M spacecraft is rolled out to the launch pad by train on Monday, May 26, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
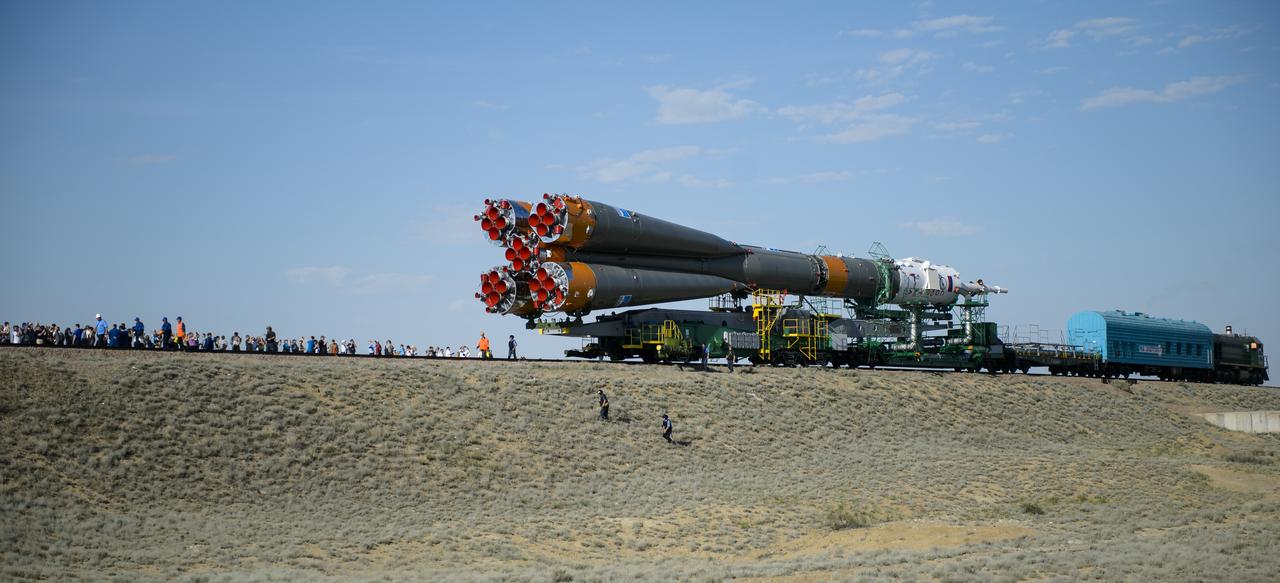

Guests and members of the media watch as the Soyuz TMA-13M spacecraft is rolled out to the launch pad by train on Monday, May 26, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
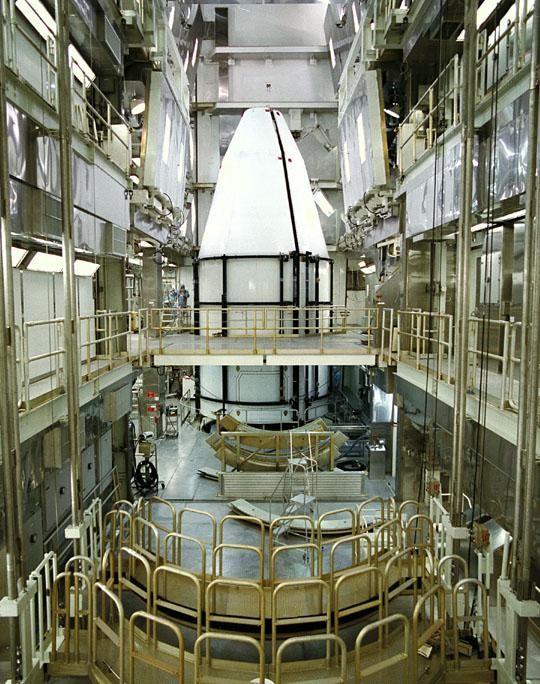

The Cassini spacecraft, protected by an environmentally controlled protective fairing, is sitting at Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station, awaiting its launch scheduled for mid-October atop a Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle. A four-year, close-up study of the Saturnian system, the Cassini mission will take seven years for the spacecraft to reach Saturn. Scientific instruments carried aboard the spacecraft will study Saturn’s atmosphere, magnetic field, rings, and several moons. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is managing the Cassini project
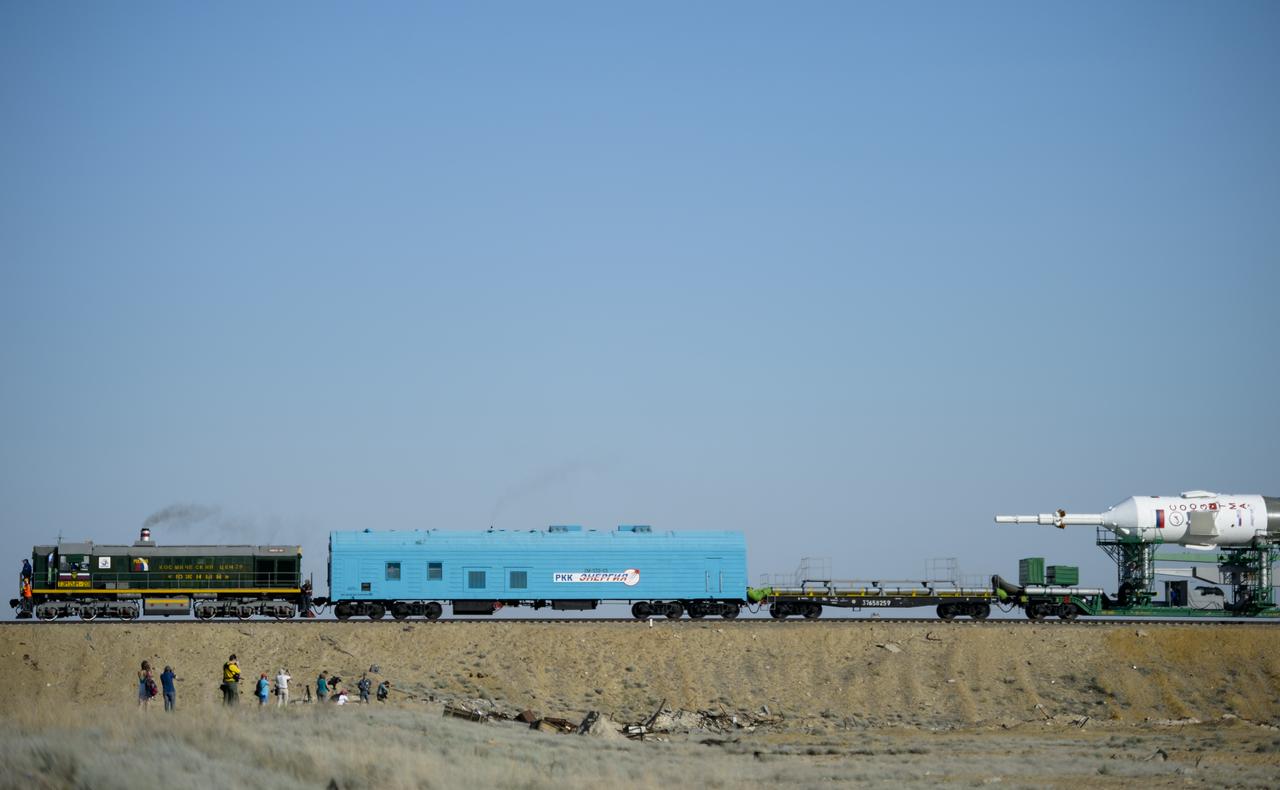

The Soyuz TMA-13M spacecraft is rolled out to the launch pad by train on Monday, May 26, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
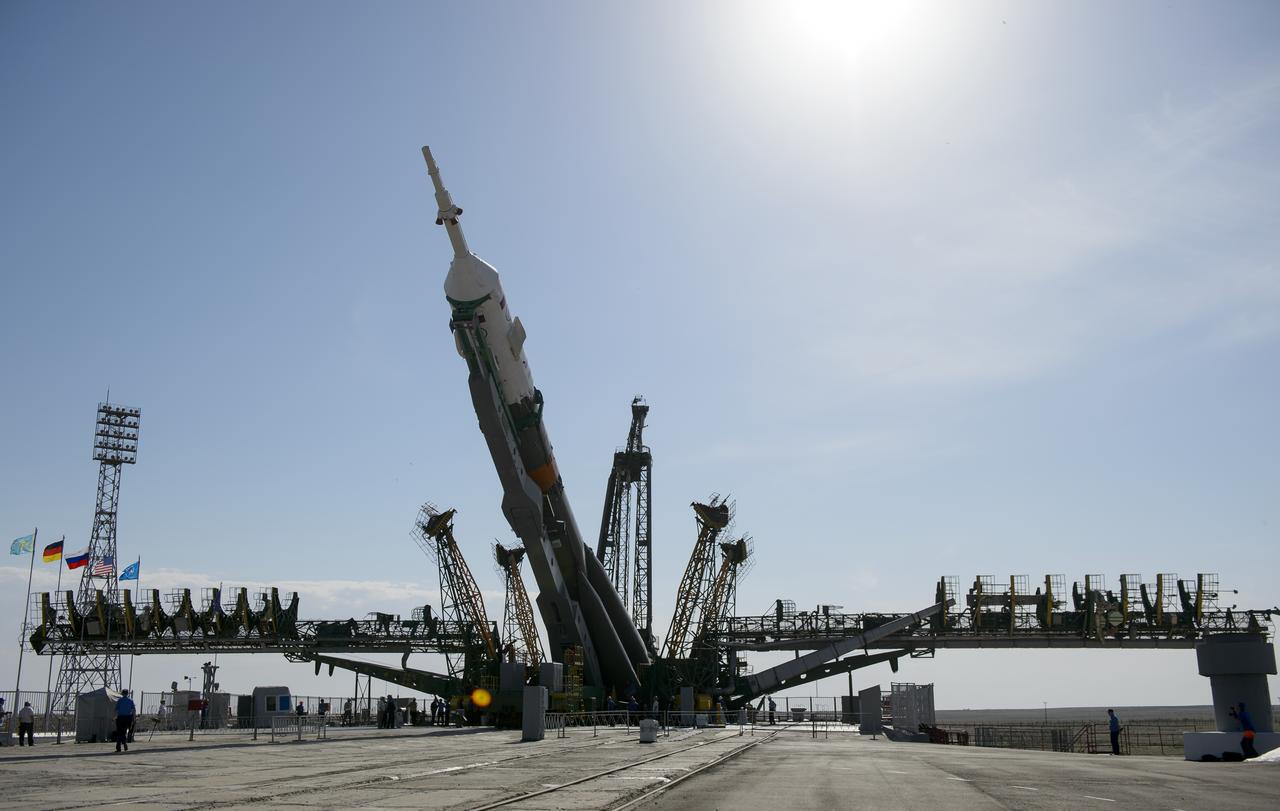

The Soyuz TMA-13M spacecraft is raised into a vertical position on the launch pad on Monday, May 26, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
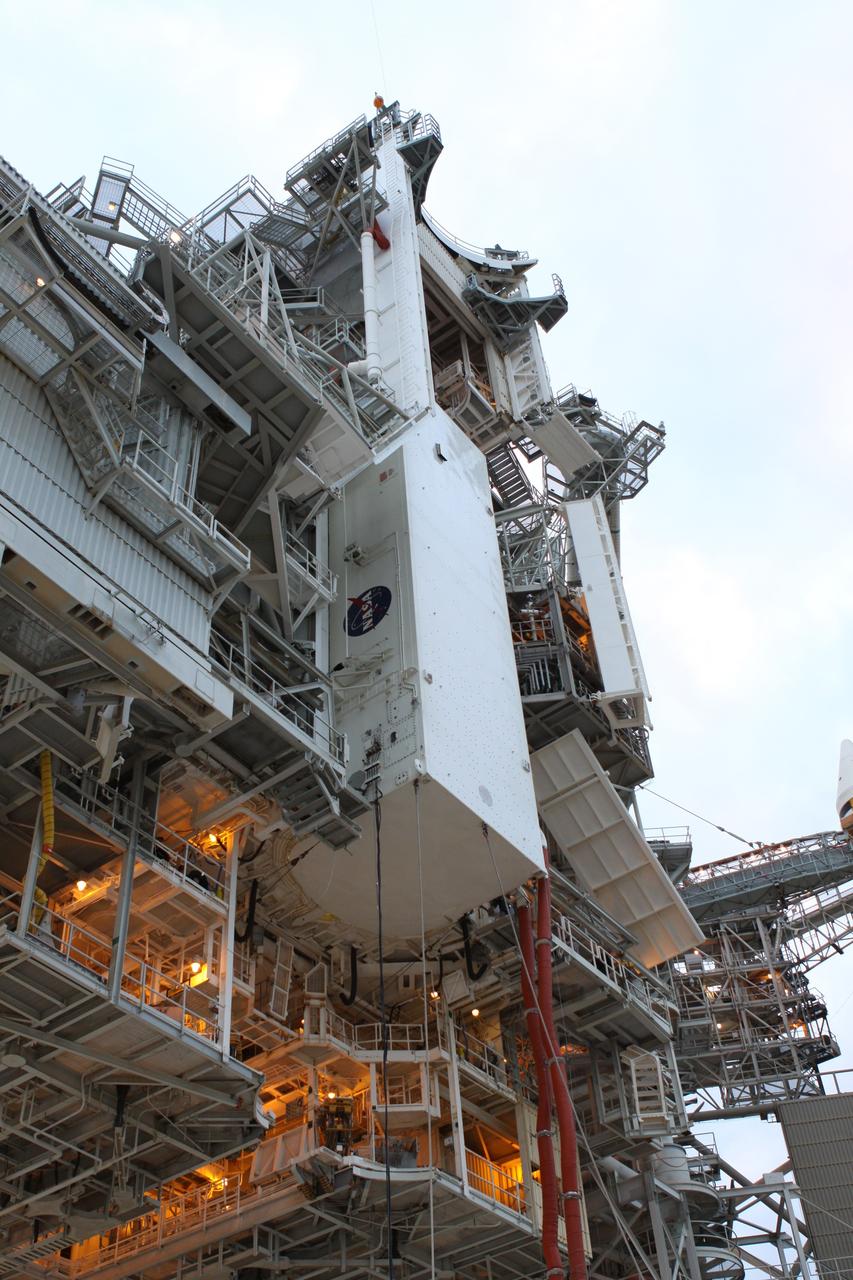

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the STS-133 payload canister now is in the rotating service structure on Launch Pad 39A. The payload then will be moved into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
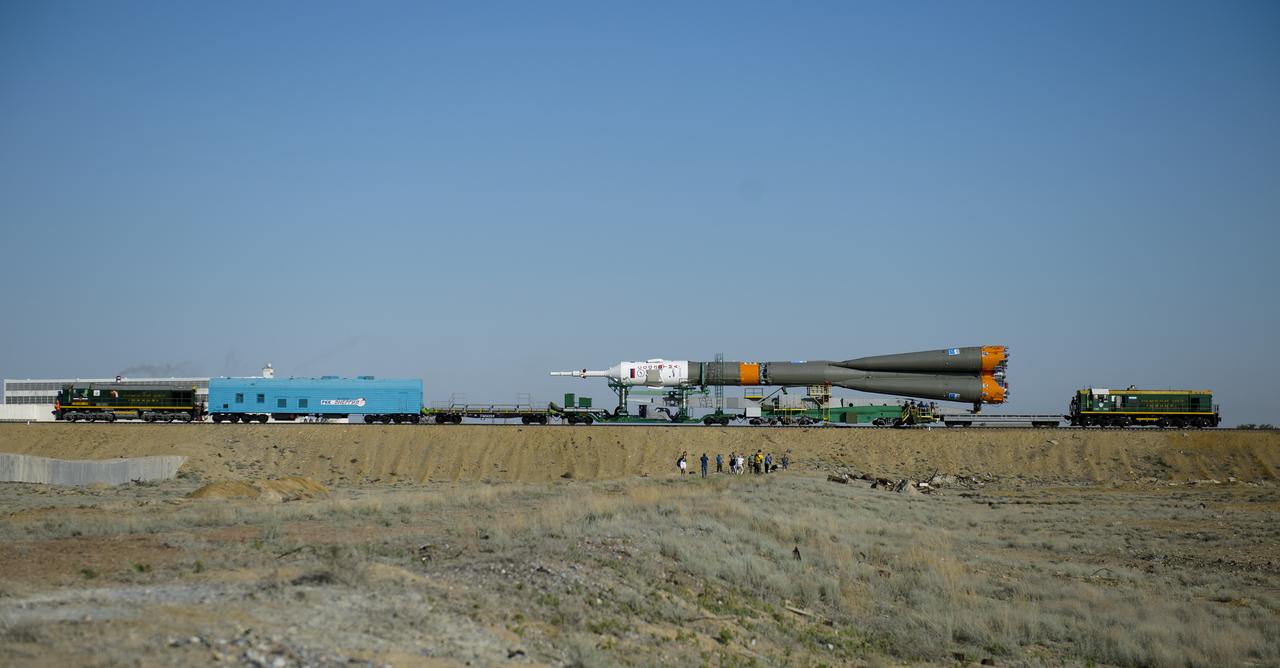

The Soyuz TMA-13M spacecraft is rolled out to the launch pad by train on Monday, May 26, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
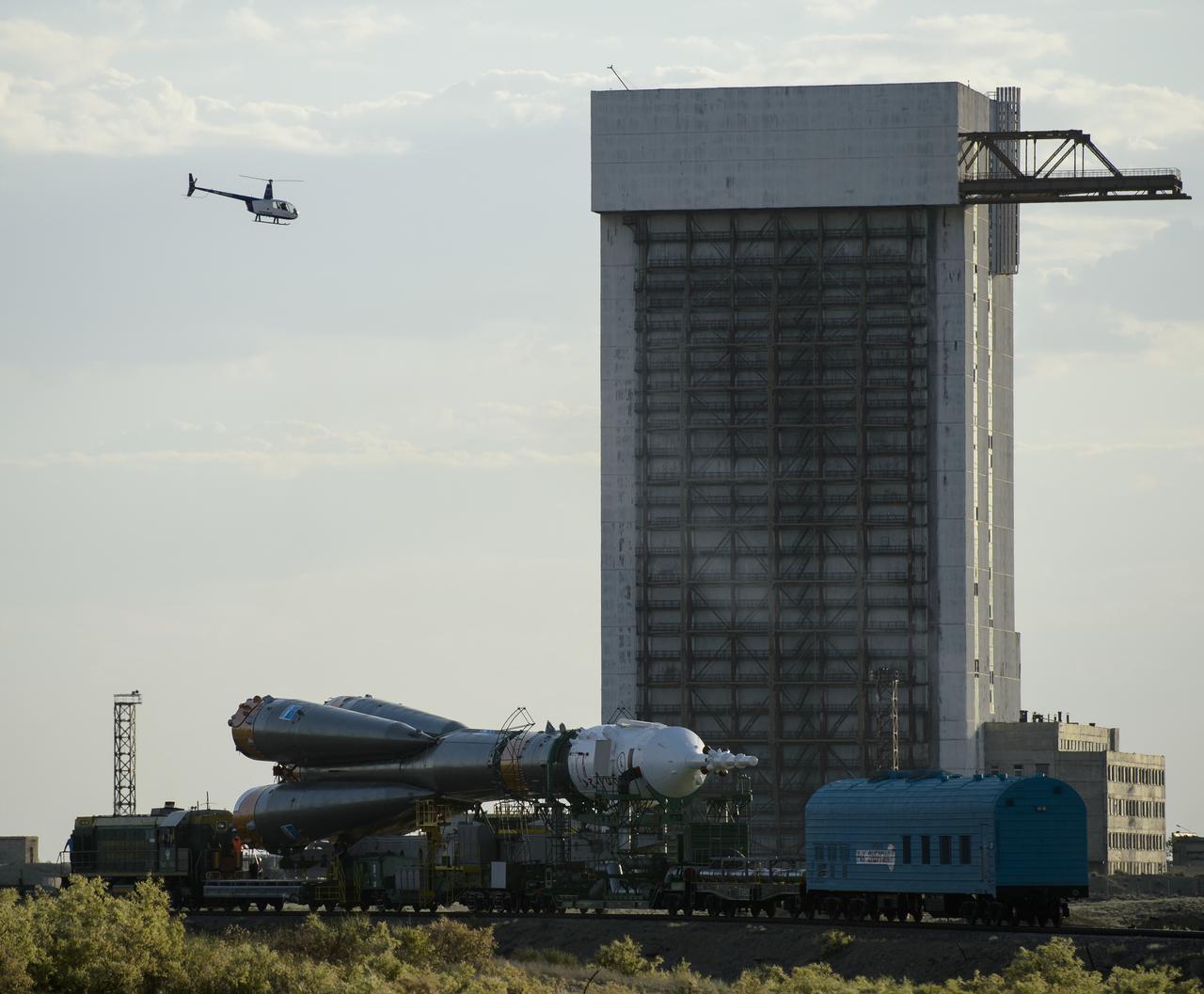

The Soyuz TMA-13M spacecraft is rolled out to the launch pad by train on Monday, May 26, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
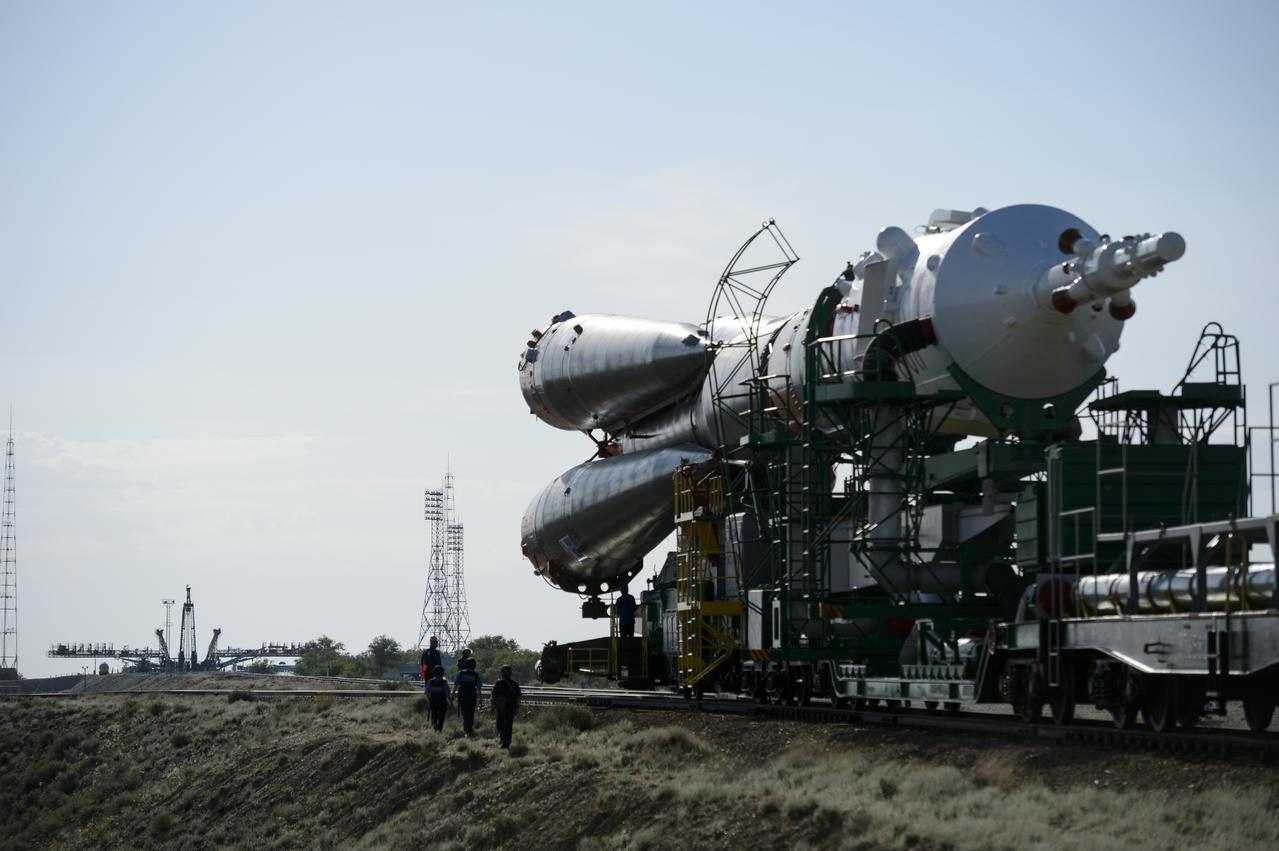

The Soyuz TMA-13M spacecraft is rolled out to the launch pad by train on Monday, May 26, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for May 29 and will send Expedition 40 Soyuz Commander Maxim Suraev, of the Russian Federal Space Agency, Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst, of the European Space Agency, ESA, and Flight Engineer Reid Wiseman of NASA on a five and a half month mission aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
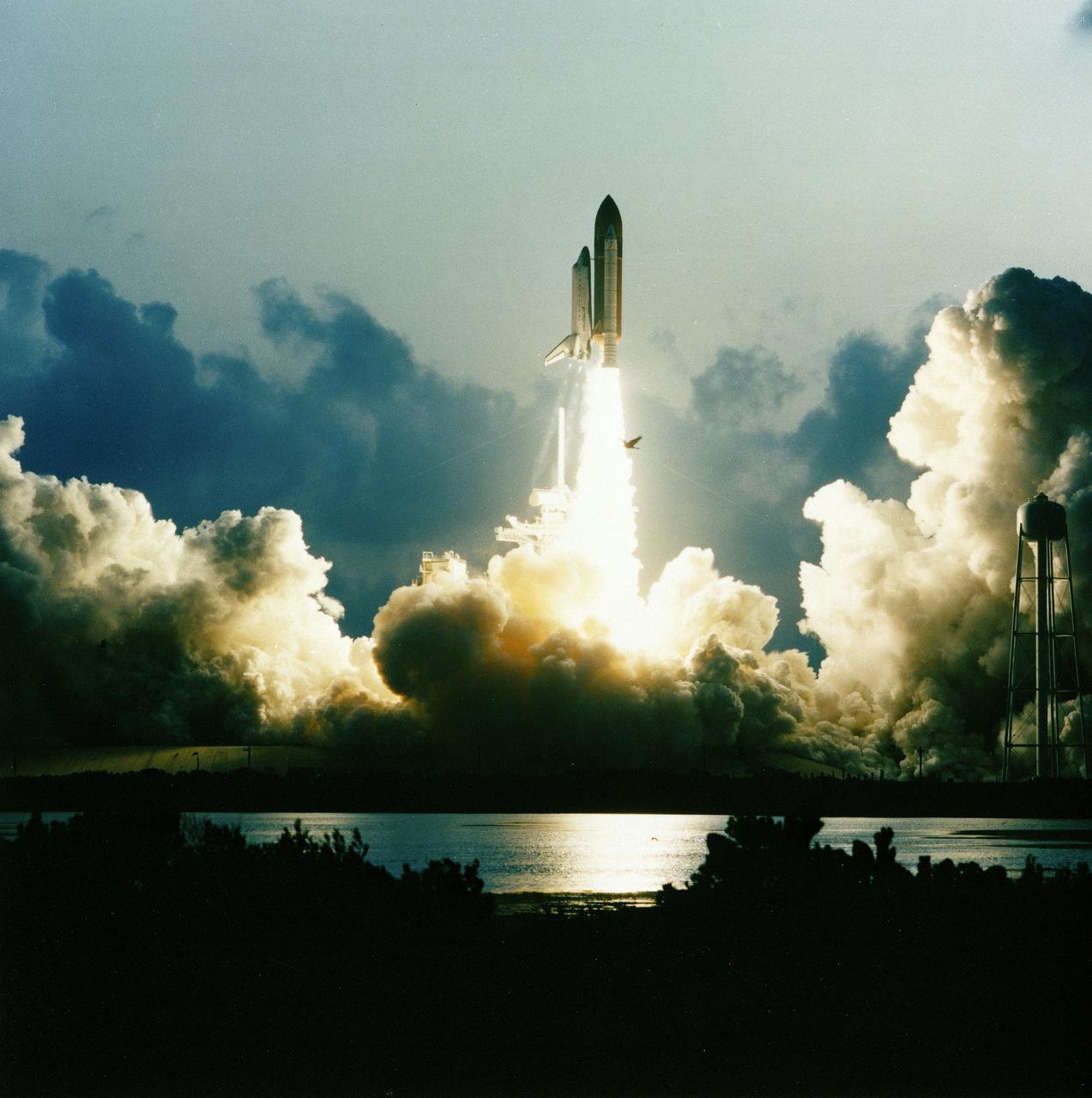

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990.
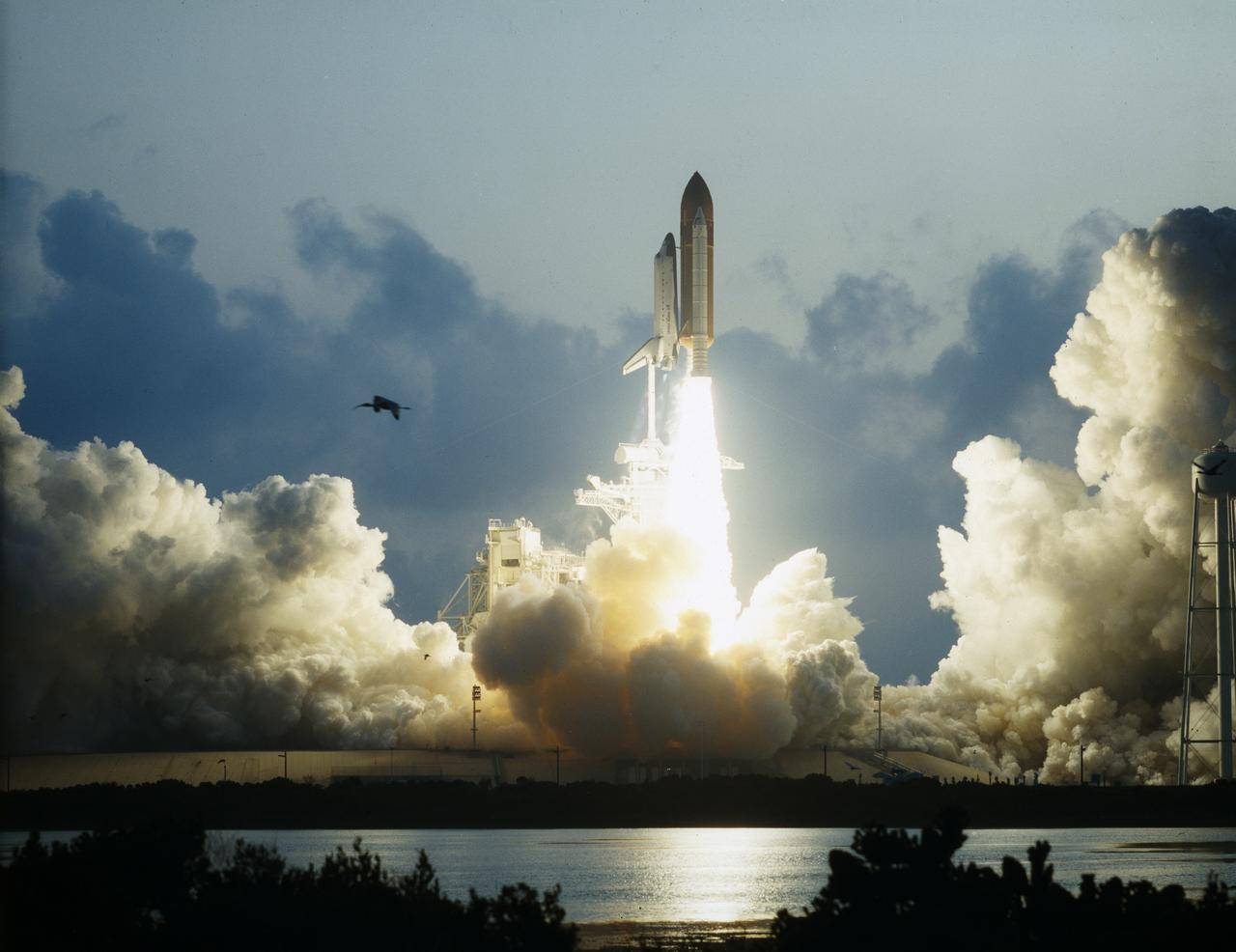

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990.
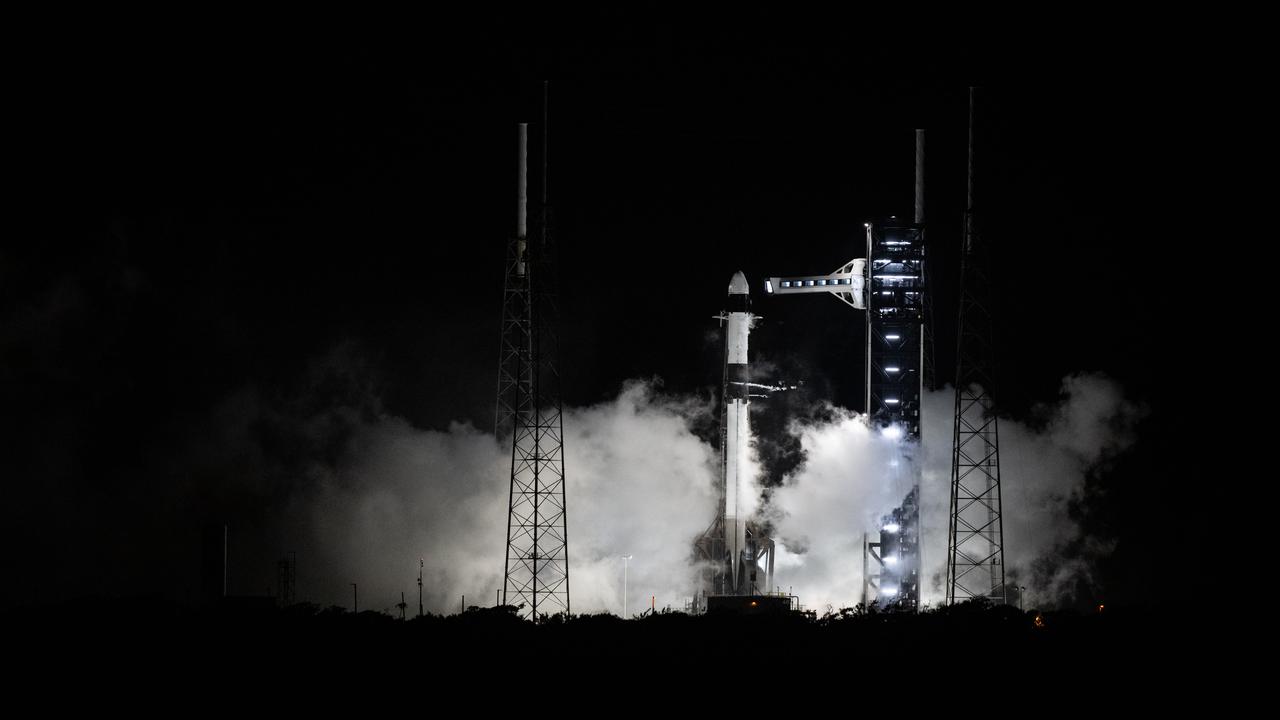

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the company's Dragon spacecraft onboard is seen on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 40 following a brief static fire test ahead of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission, Tuesday, Sept. 24, 2024, at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission is the ninth crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
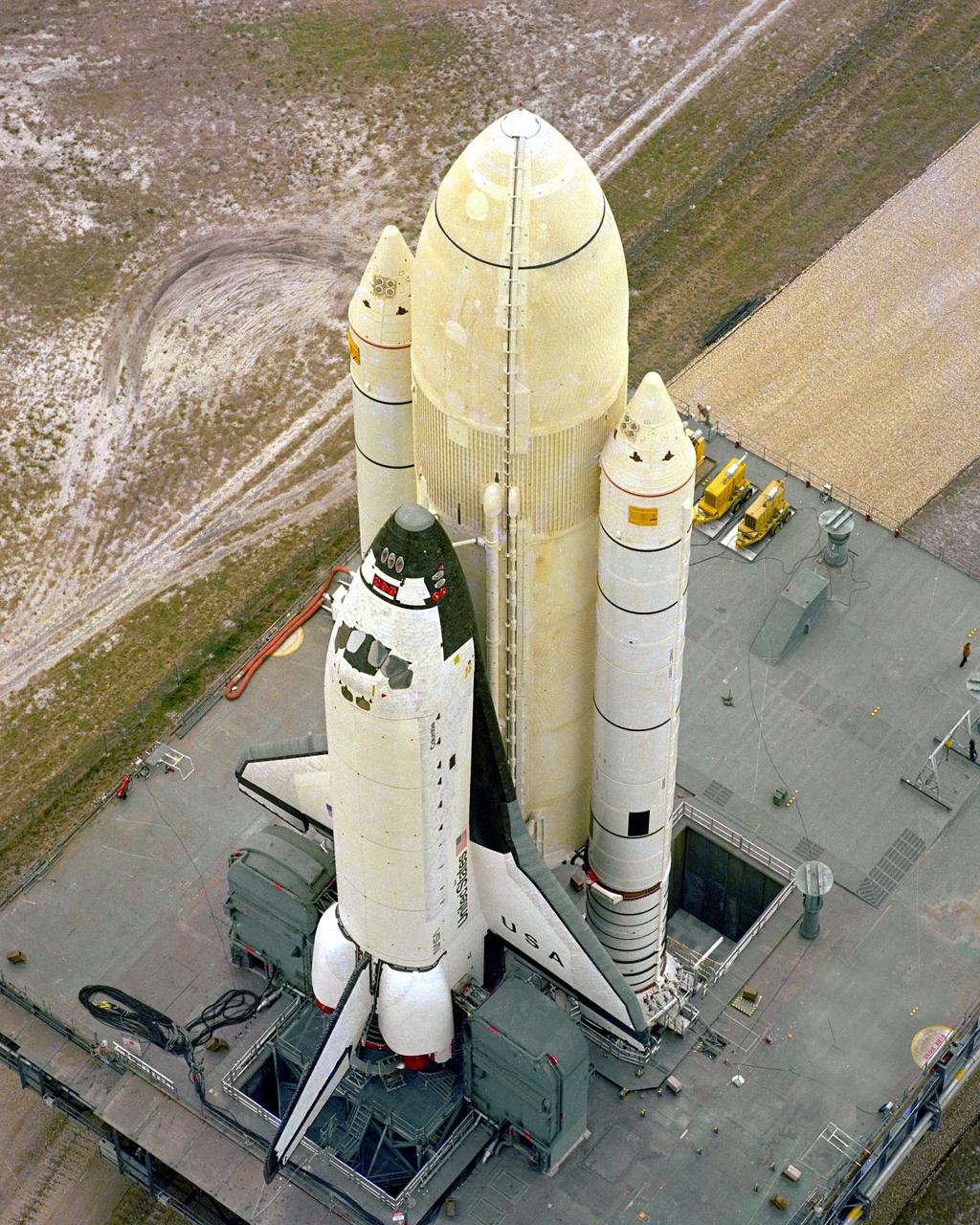

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This eagle's eye view of STS-1 shows the space vehicle for the first Space Shuttle mission shortly after it was moved out of the Vehicle Assembly Builidng at 8 a.m. today for the 3.5-mile journey to Complex 39's Pad A. The Shuttle rests atop the Mobile Launcher Platform from which launch is scheduled no earlier than March 1981. Thousands of visitors and hundreds of news media representatives viewed the beginning of the move under leaden skies and in unseasonably cold temperatures in the low 40s.
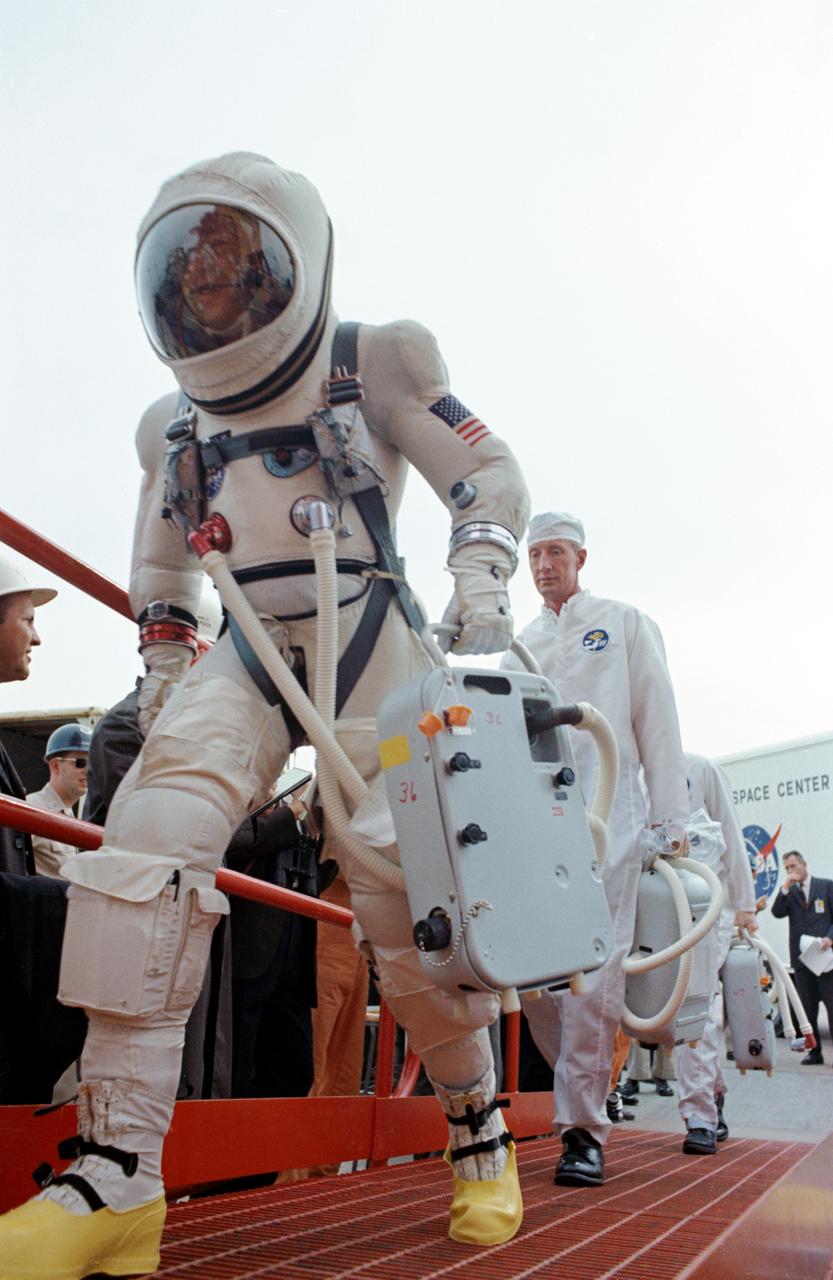

S65-61848 (4 Dec. 1965) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., pilot for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Gemini-7 spaceflight, walks to the elevator at Pad 19 one hour and 40 minutes before launch of the spacecraft. Moments later astronauts Lovell and Frank Borman, command pilot, rode the elevator to the White Room where they were inserted into the spacecraft to await the final moments of the countdown. Photo credit: NASA
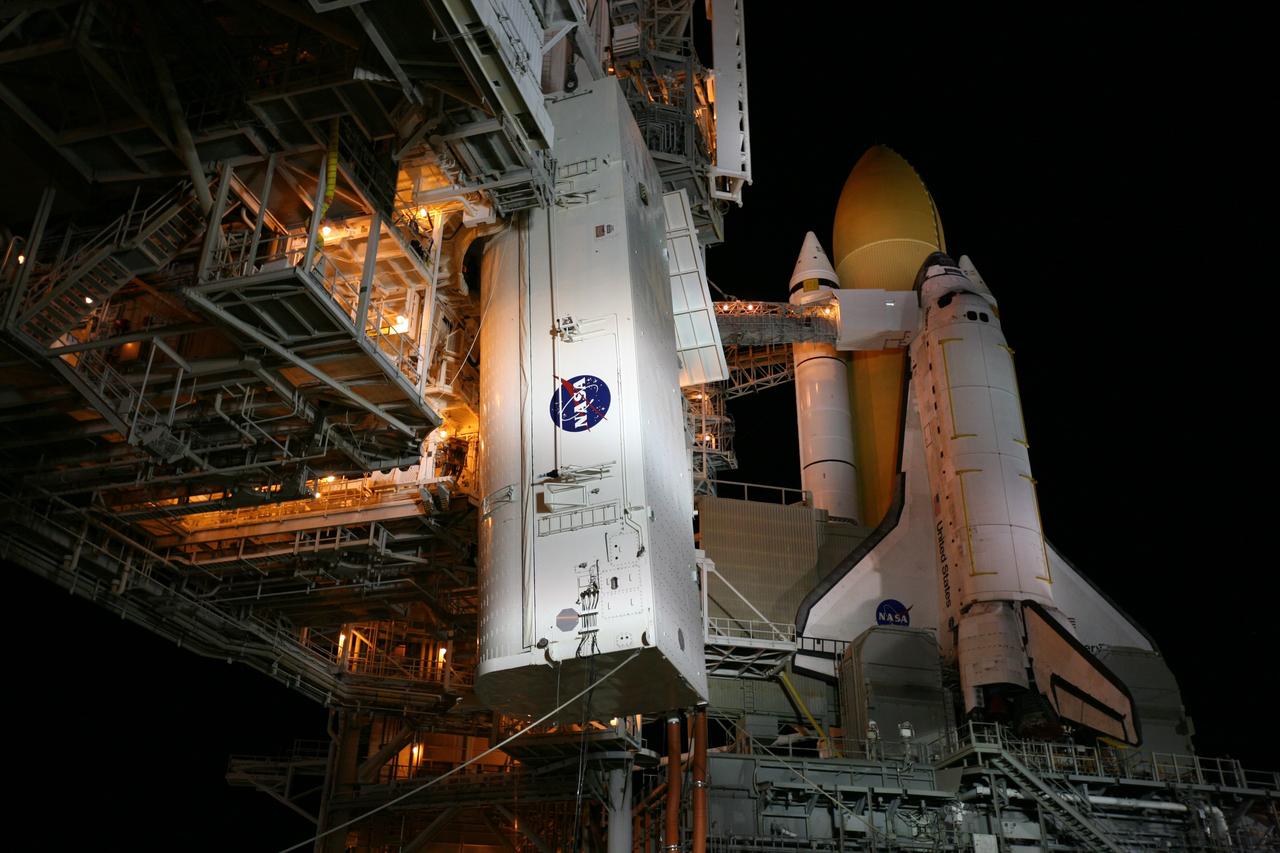

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the STS-133 payload canister is lifted into the rotating service structure on Launch Pad 39A. The payload then will be moved into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller