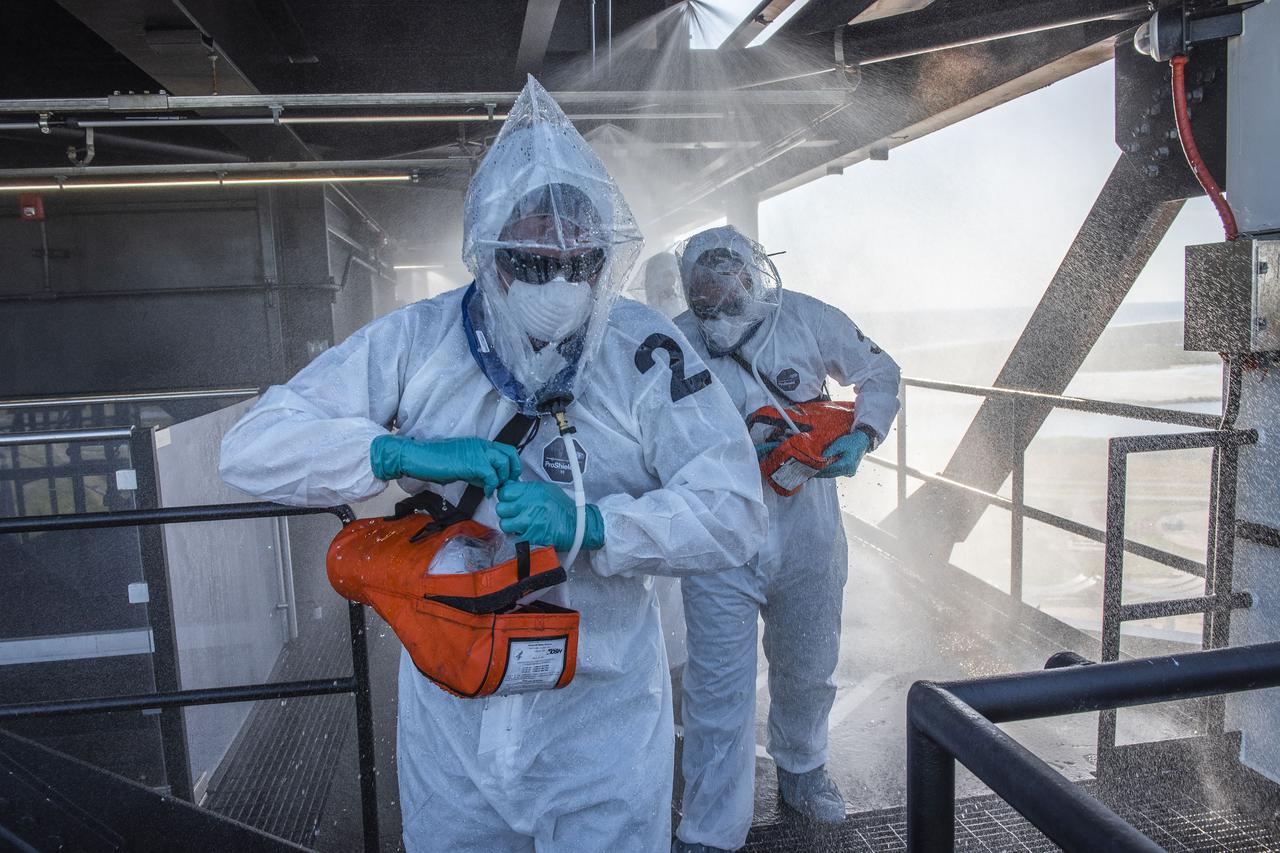

On Friday, April 3, 2020, NASA and SpaceX completed an end-to-end demonstration of the teams’ ability to safely evacuate crew members from the Fixed Service Structure during an emergency situation at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
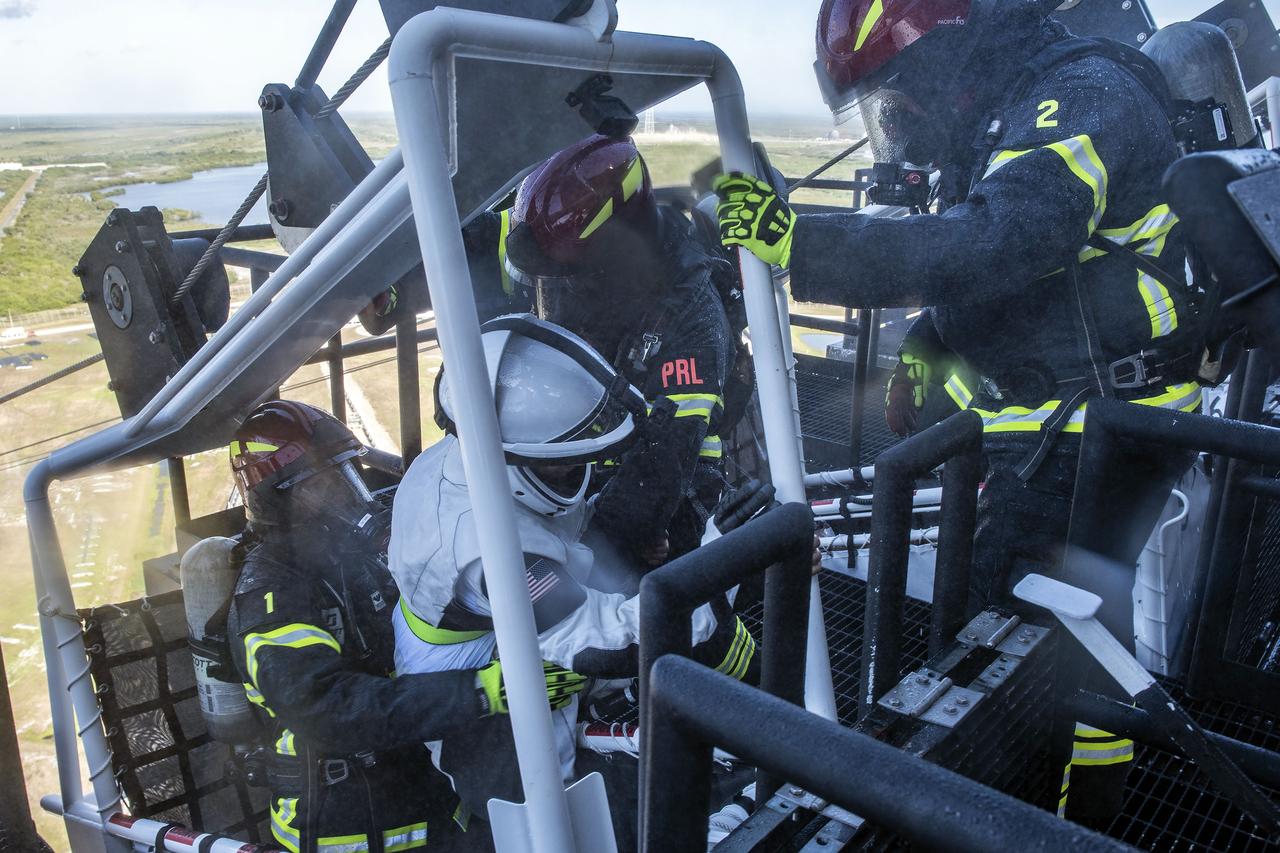

On Friday, April 3, 2020, NASA and SpaceX completed an end-to-end demonstration of the teams’ ability to safely evacuate crew members from the Fixed Service Structure during an emergency situation at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
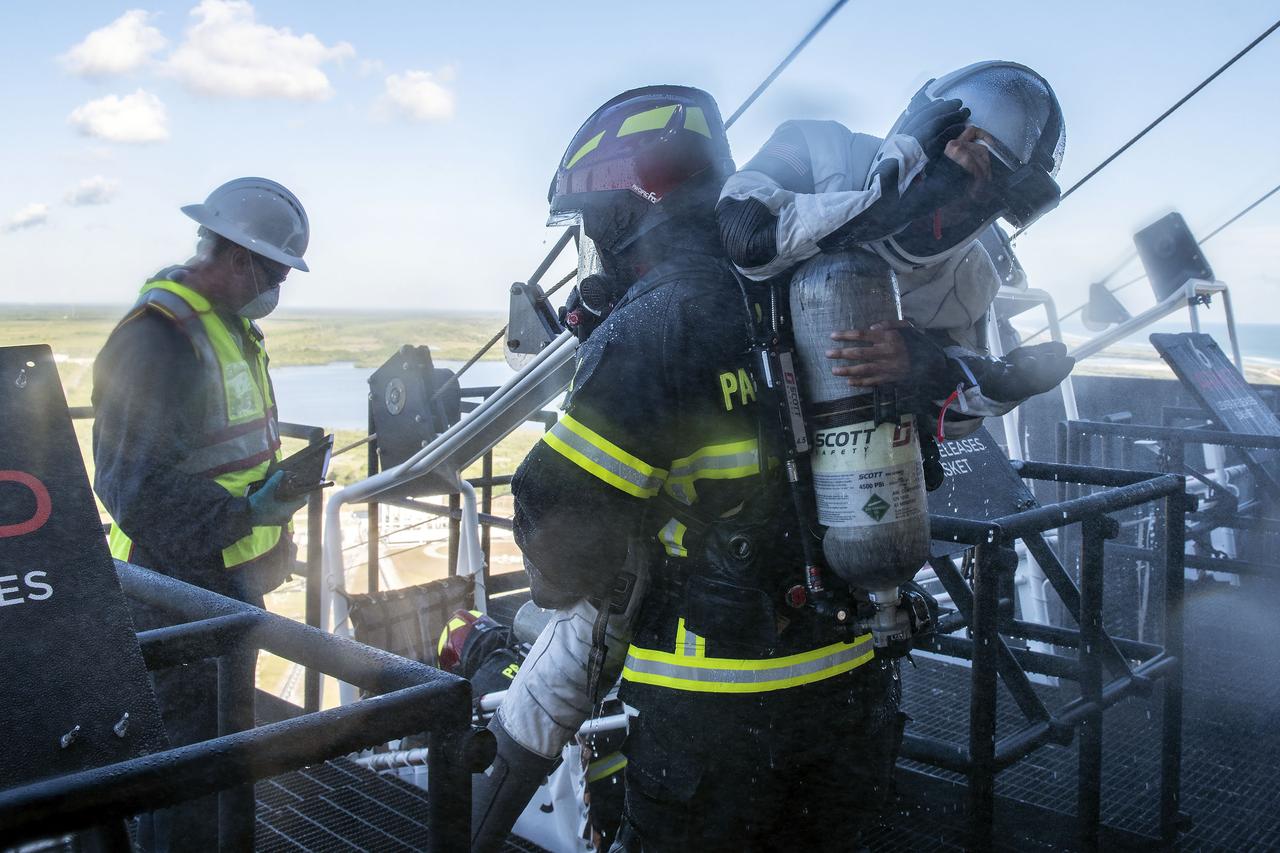

On Friday, April 3, 2020, NASA and SpaceX completed an end-to-end demonstration of the teams’ ability to safely evacuate crew members from the Fixed Service Structure during an emergency situation at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

On Friday, April 3, 2020, NASA and SpaceX completed an end-to-end demonstration of the teams’ ability to safely evacuate crew members from the Fixed Service Structure during an emergency situation at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
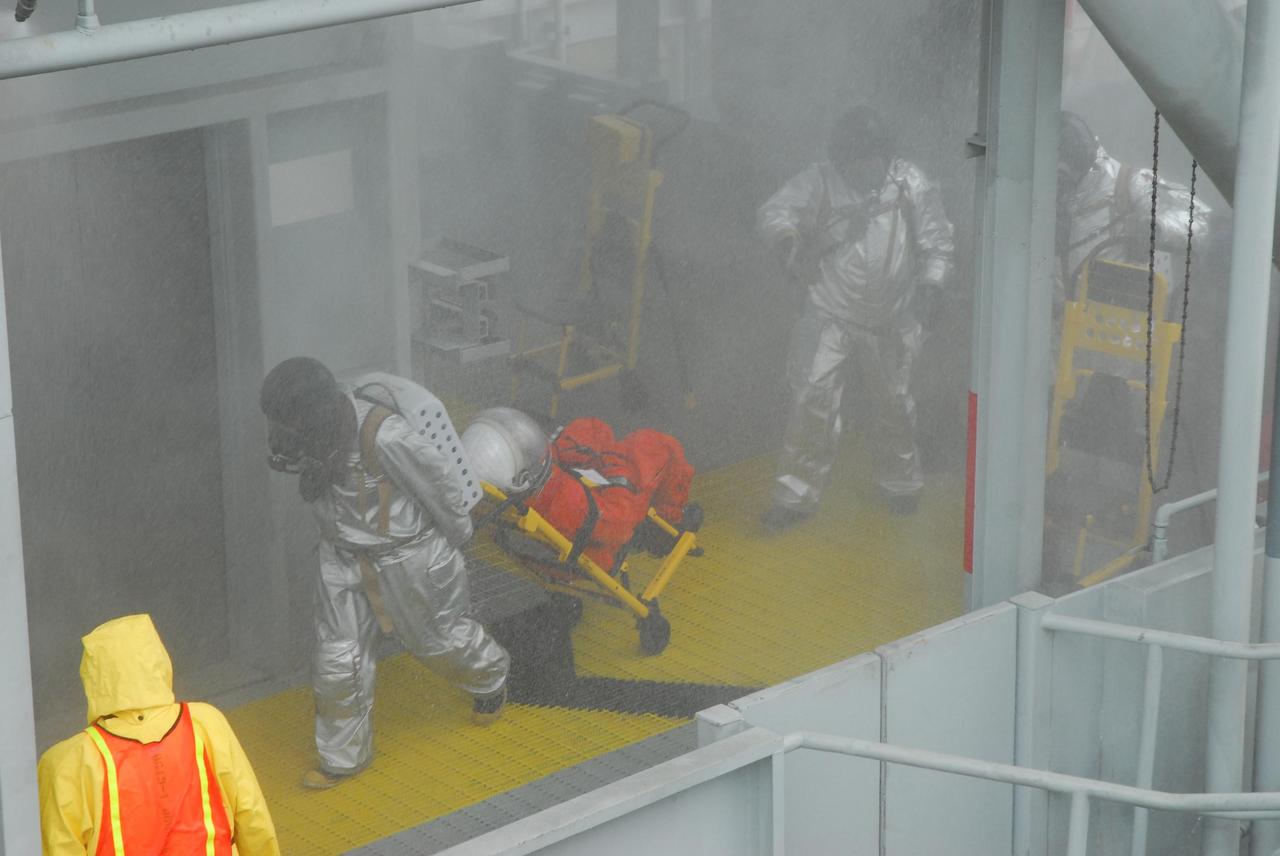

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a simulated rescue mission on Launch Pad 39A, known as Mode 2, KSC workers dressed in astronauts' launch-and-entry suits are helped by the fire rescue team to the slidewire baskets on the 195-foot level. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
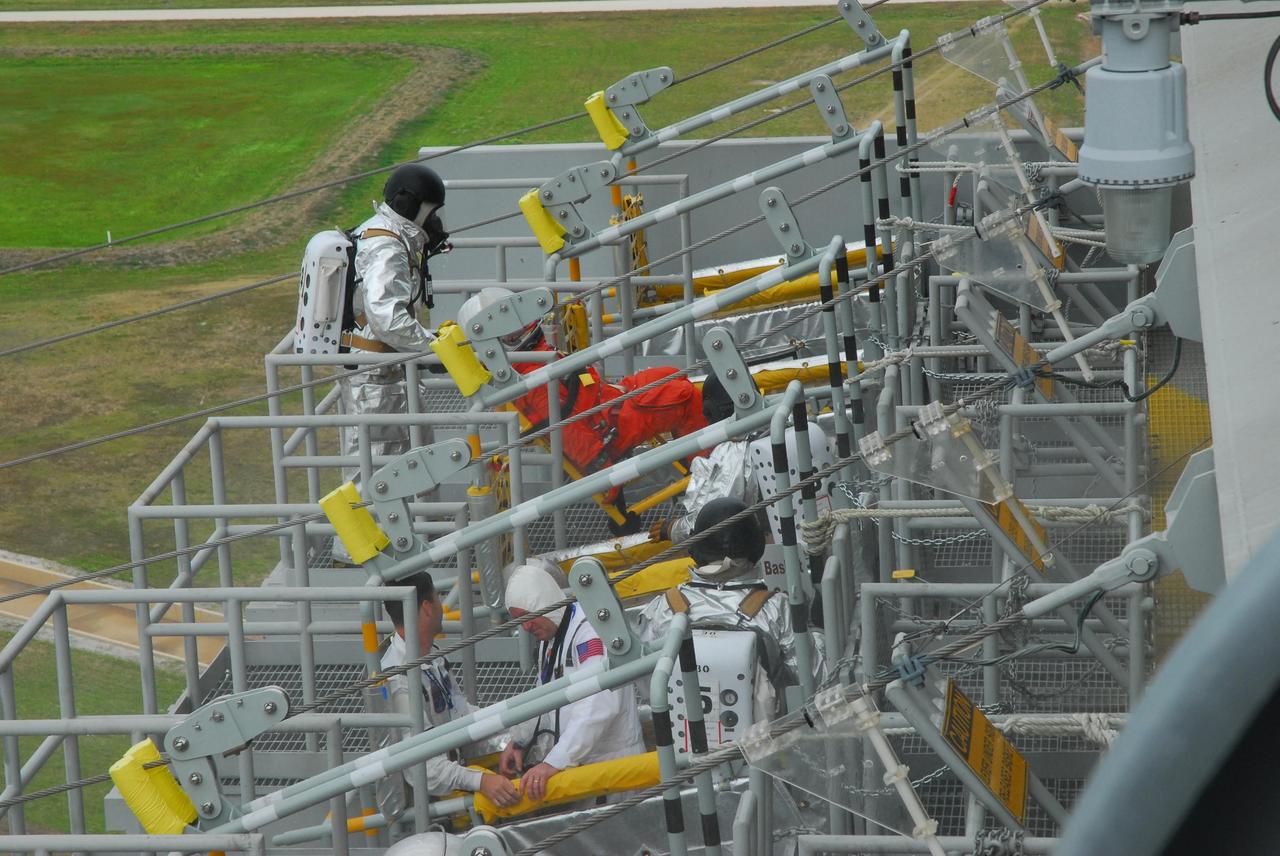

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a simulated rescue mission on Launch Pad 39A, known as Mode 2, KSC workers dressed in astronauts' launch-and-entry suits are climbing into the slidewire baskets. A fire rescue team is simulating extracting the crew from the orbiter and helping them to the baskets.The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a simulated rescue mission on Launch Pad 39A, known as Mode 2, KSC workers dressed in astronauts' launch-and-entry suits climb into the slidewire baskets. A fire rescue team is simulating extracting the crew from the orbiter and helping them to the baskets. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a simulated rescue mission on Launch Pad 39A, known as Mode 2, KSC workers dressed in astronauts' launch-and-entry suits climb into the slidewire baskets, helped by a fire rescue team. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
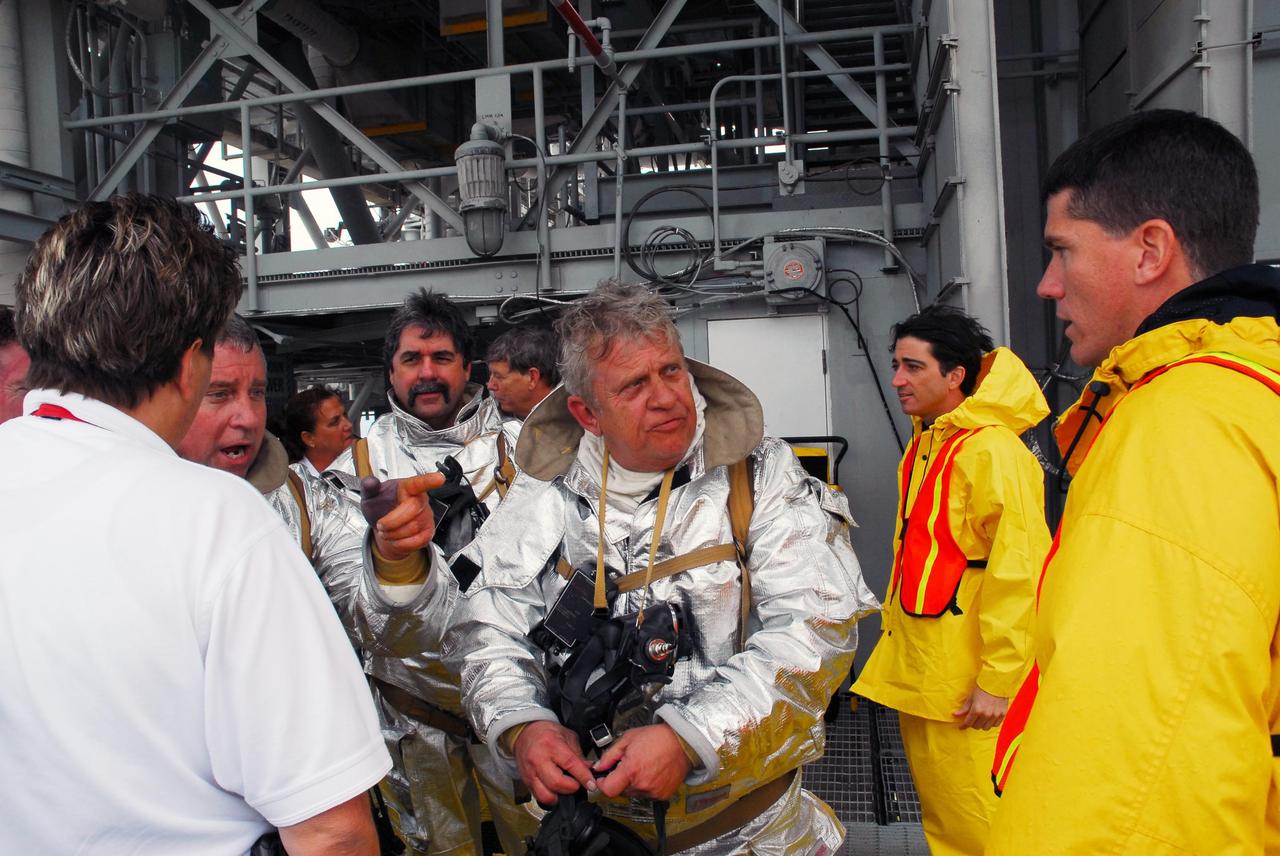

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After a simulated rescue mission on Launch Pad 39A, the fire rescue team compares notes about the activity. KSC workers dressed in official launch-and-entry suits portrayed astronauts. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
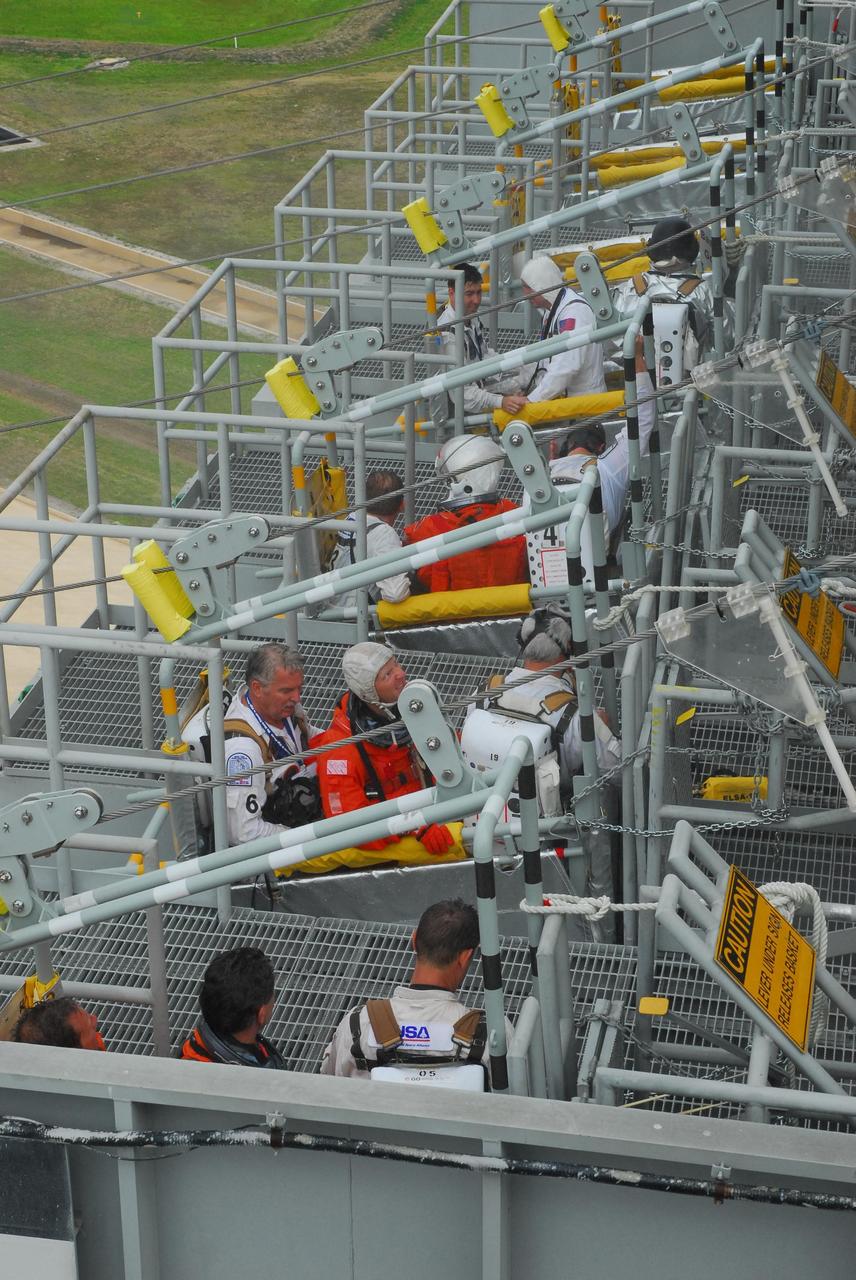

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a simulated rescue mission on Launch Pad 39A, known as Mode 2, KSC workers dressed in astronauts' launch-and-entry suits are climbing into the slidewire baskets. A fire rescue team is simulating extracting the crew from the orbiter and helping them to the baskets.The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
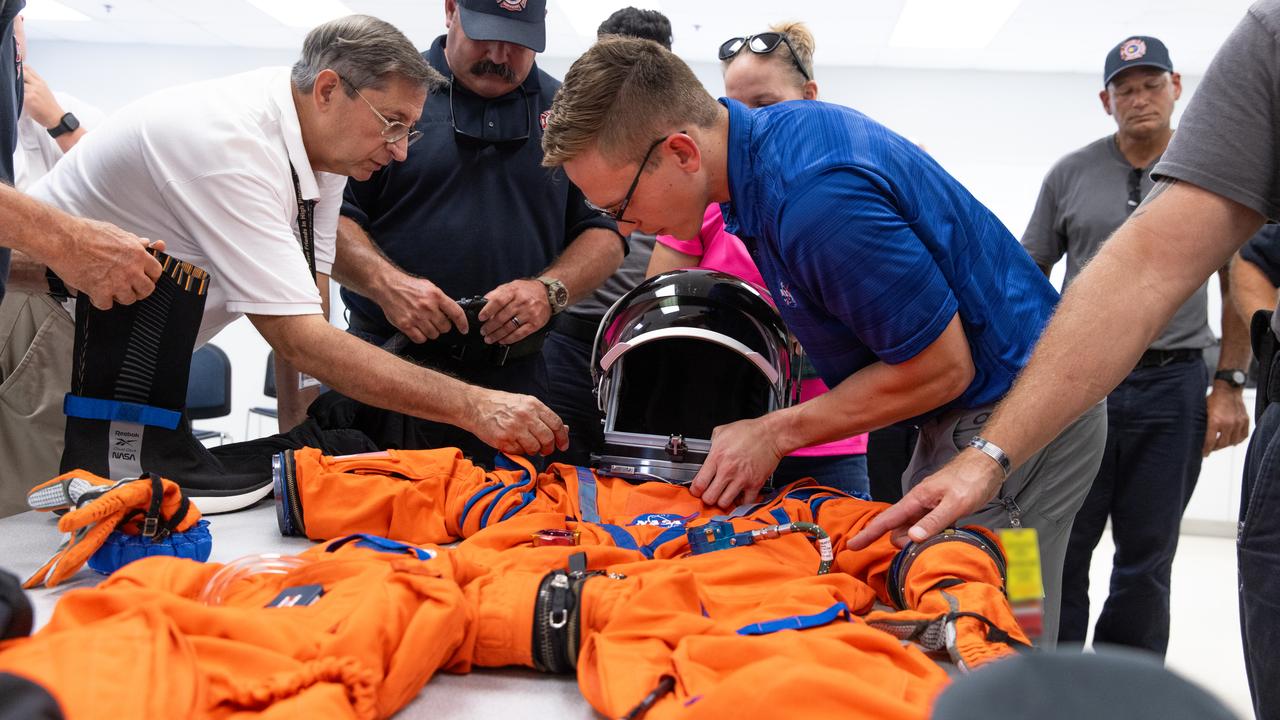

NASA’s pad rescue team learn about the Orion Crew Survival Suit ahead of the Artemis II emergency egress demonstration, which is one of the integrated system verification and validation tests taking place at Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 8, 2024. In the event of an emergency during launch countdown, the pad rescue team is there to help personnel leave the launch pad if needed.

NASA’s pad rescue team learn about the Orion Crew Survival Suit ahead of the Artemis II emergency egress demonstration, which is one of the integrated system verification and validation tests taking place at Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 8, 2024. In the event of an emergency during launch countdown, the pad rescue team is there to help personnel leave the launch pad if needed.
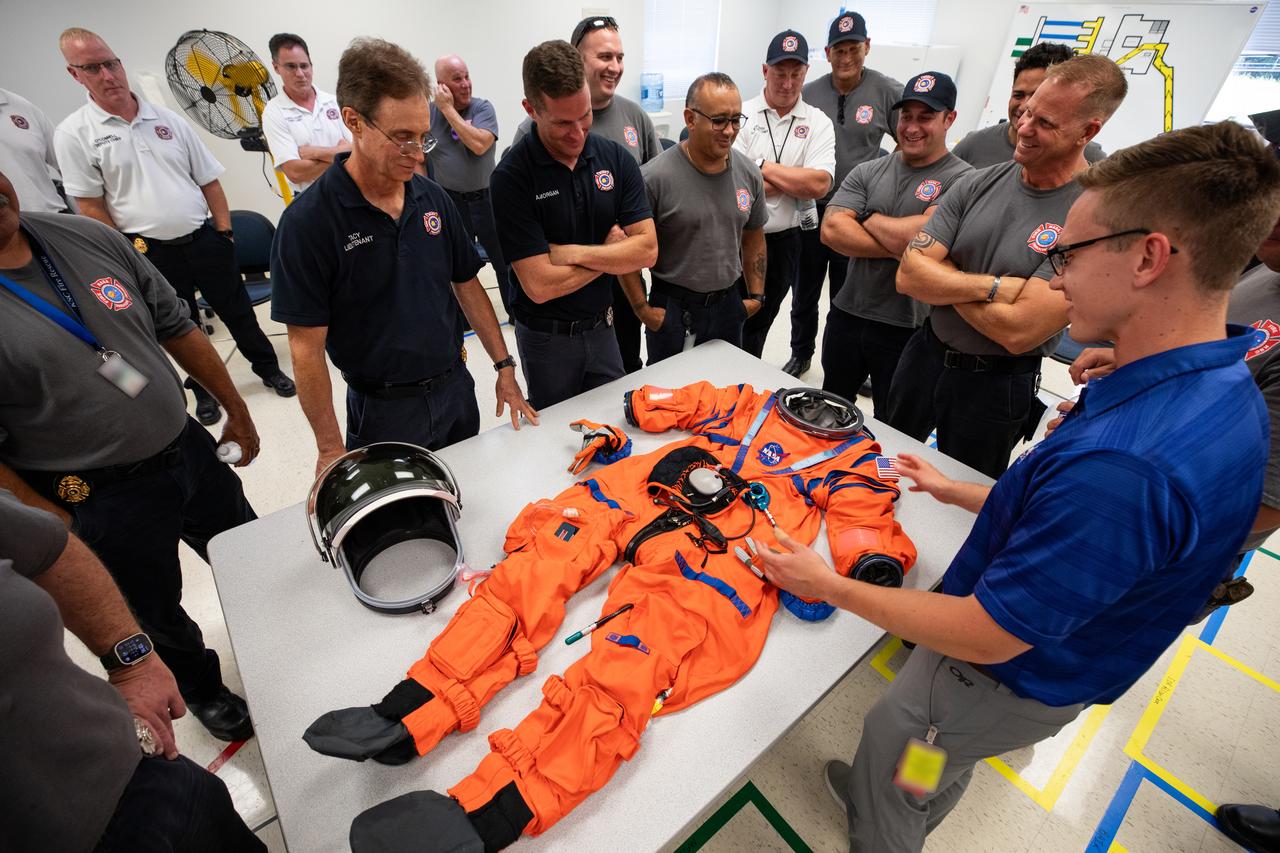

NASA’s pad rescue team learn about the Orion Crew Survival Suit ahead of the Artemis II emergency egress demonstration, which is one of the integrated system verification and validation tests taking place at Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 8, 2024. In the event of an emergency during launch countdown, the pad rescue team is there to help personnel leave the launch pad if needed.
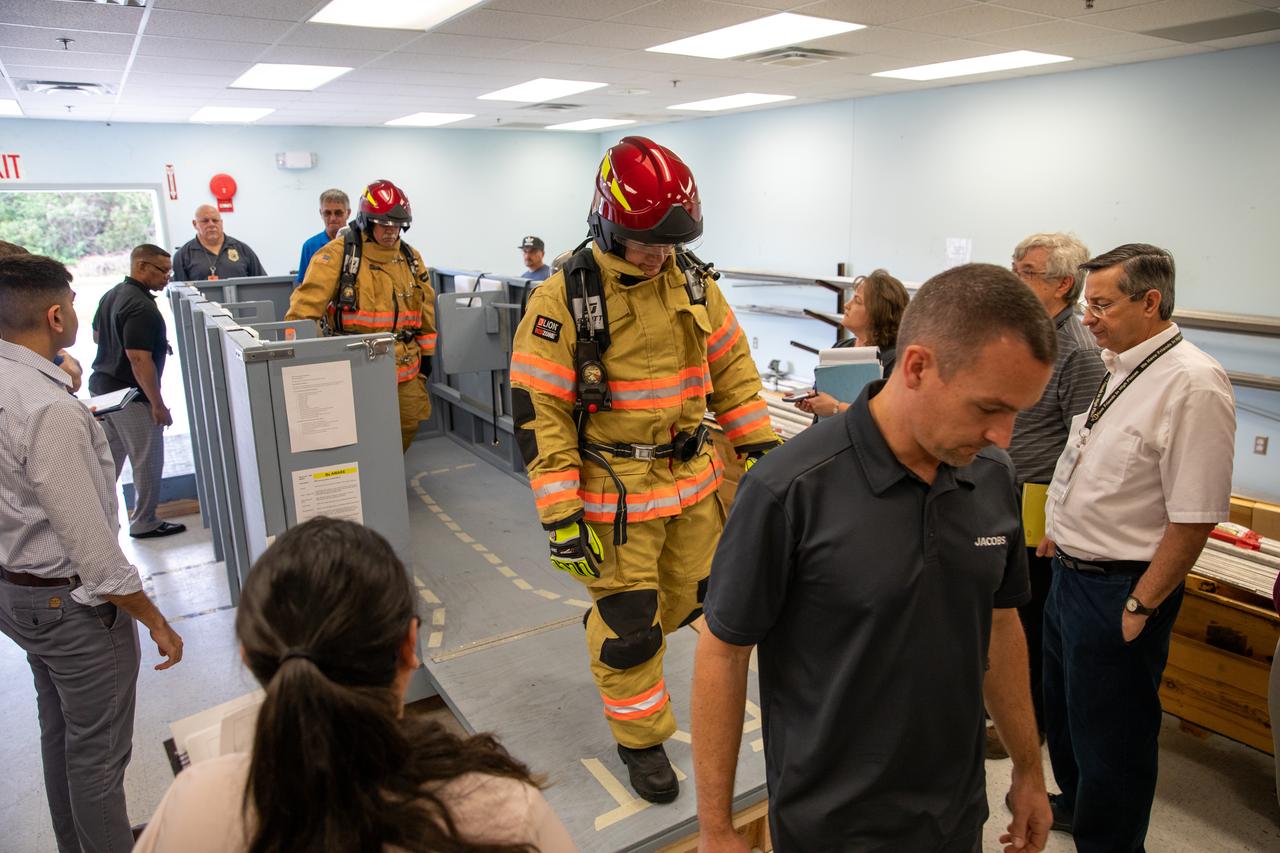

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Fire Rescue team walk through a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket on Feb. 19, 2020. Kennedy’s prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presented the mock-up to NASA, fire rescue personnel and other stakeholders at the Florida spaceport. The basket would be utilized at Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, a fire rescue team conducted a series of trial scenarios and addressed items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more.
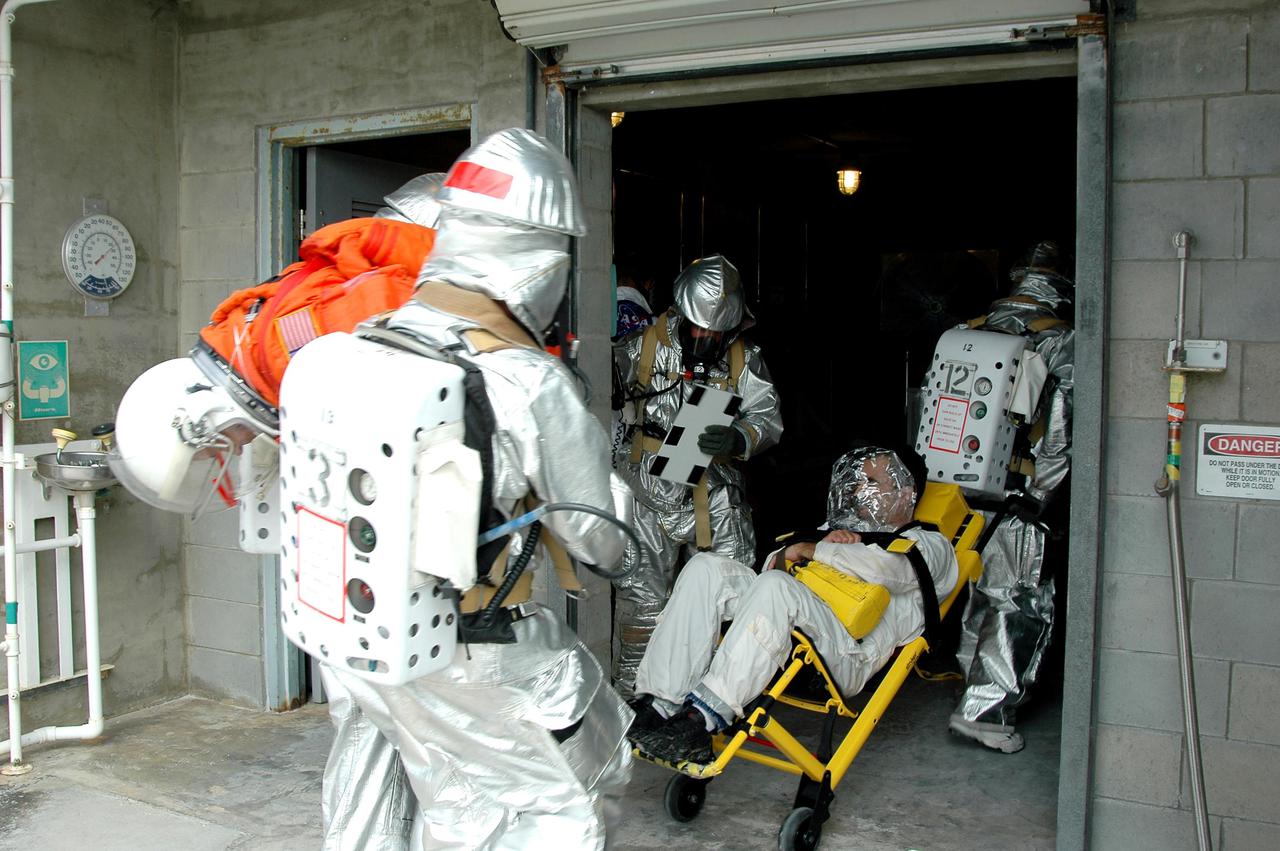

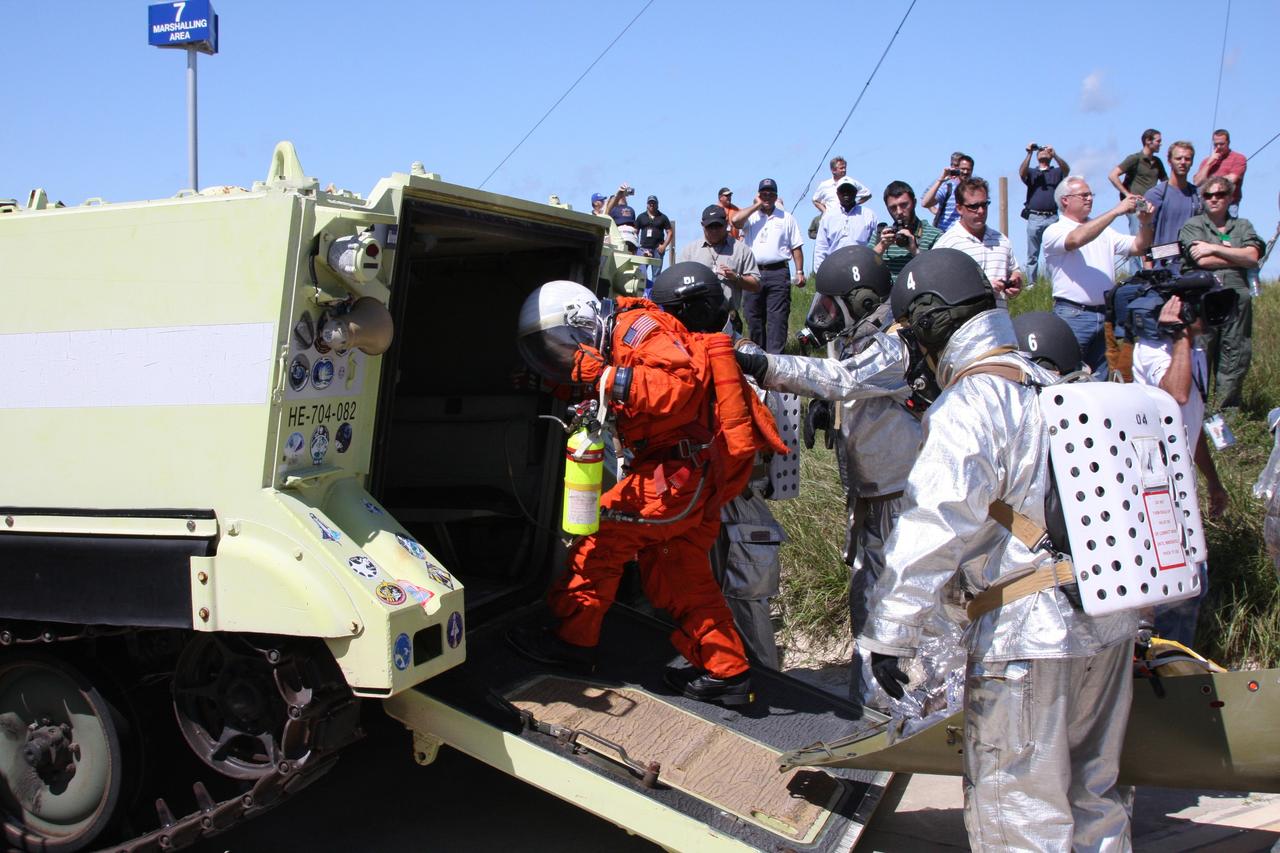
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During a simulated launch countdown_emergency simulation on Launch Pad 39A, the rescue team takes “injured” astronaut-suited workers into the pad bunker. The four-hour exercise simulated normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. It tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
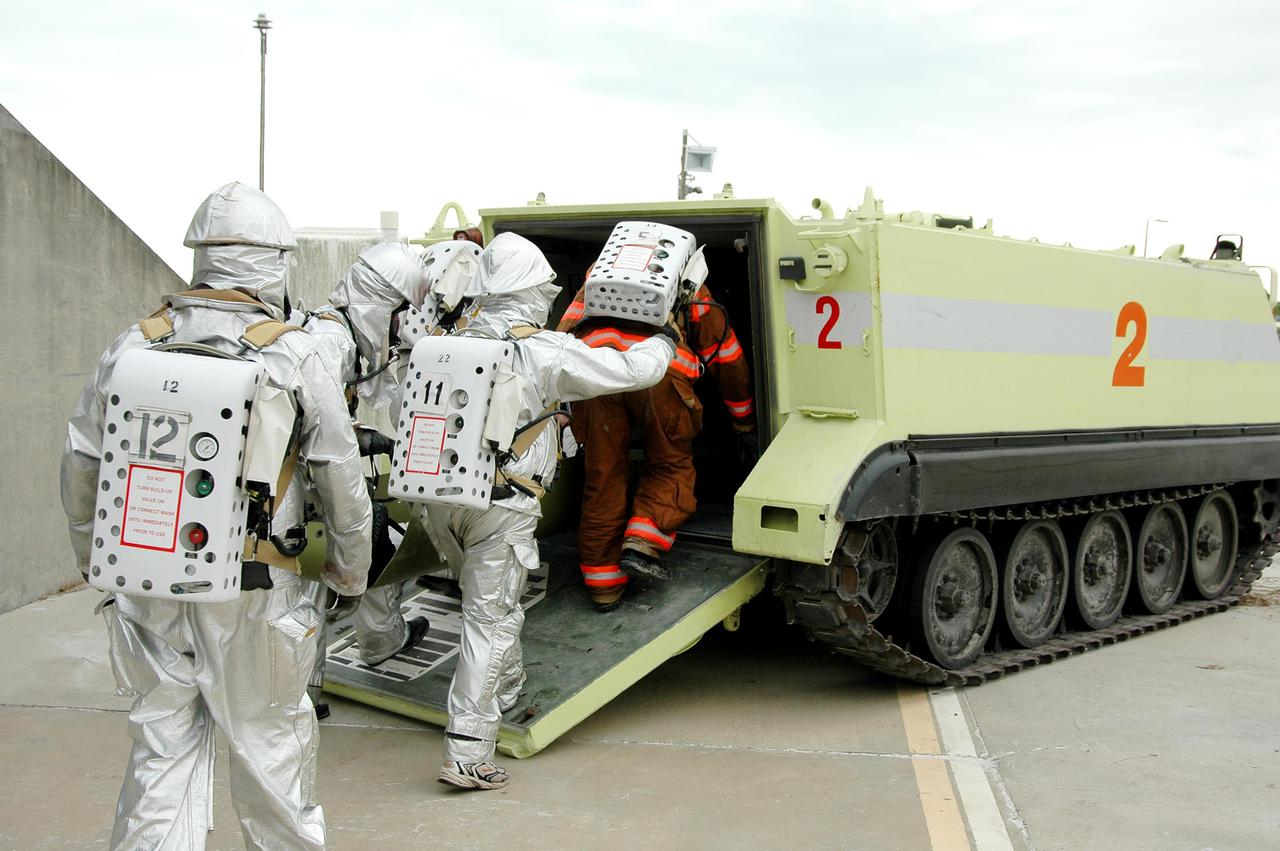

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During a simulated launch countdown_emergency simulation on Launch Pad 39A, the rescue team helps astronaut-suited workers climb into an M-113 armored personnel carrier for transport away from the pad. The four-hour exercise simulated normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. It tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
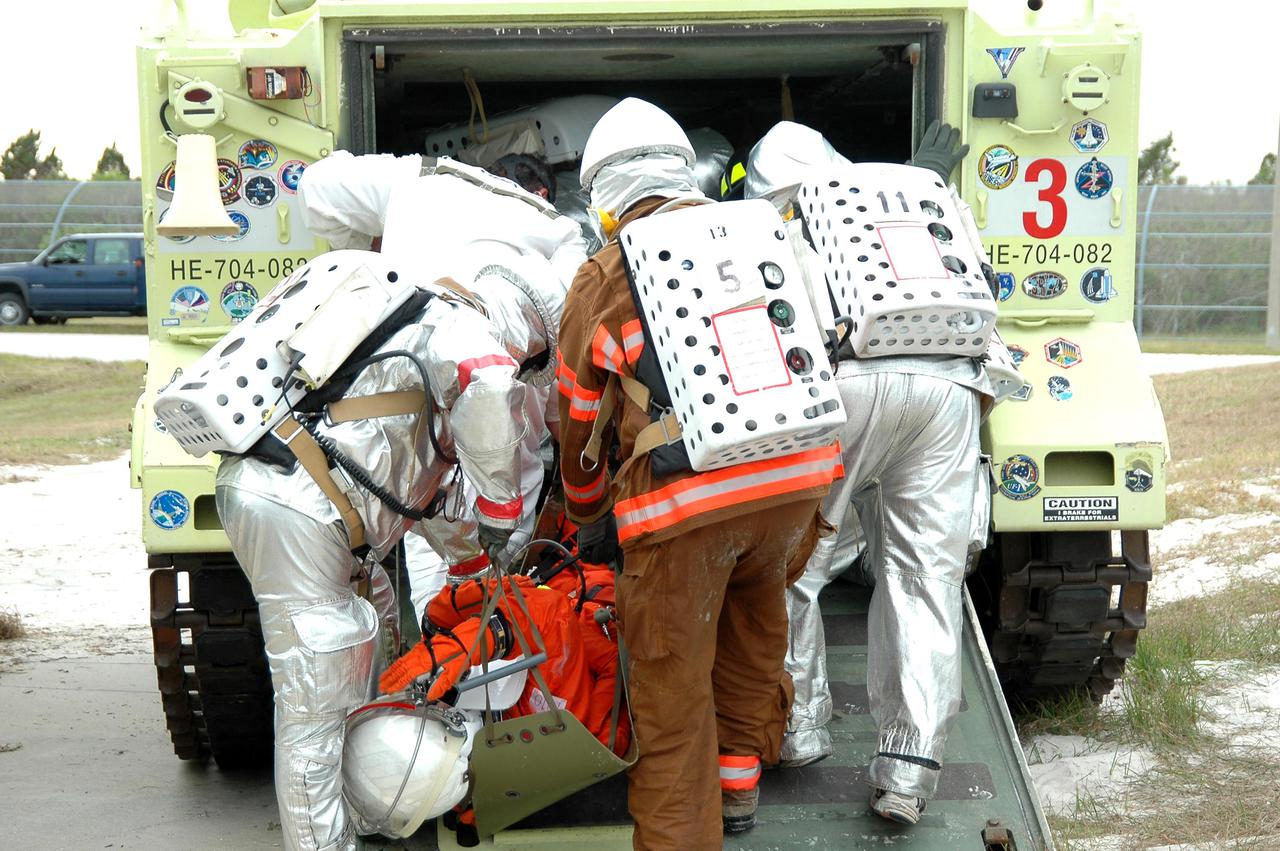

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During a simulated launch countdown_emergency simulation on Launch Pad 39A, the rescue team carries “injured” astronaut-suited workers into an M-113 armored personnel carrier for transport away from the pad. The four-hour exercise simulated normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. It tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
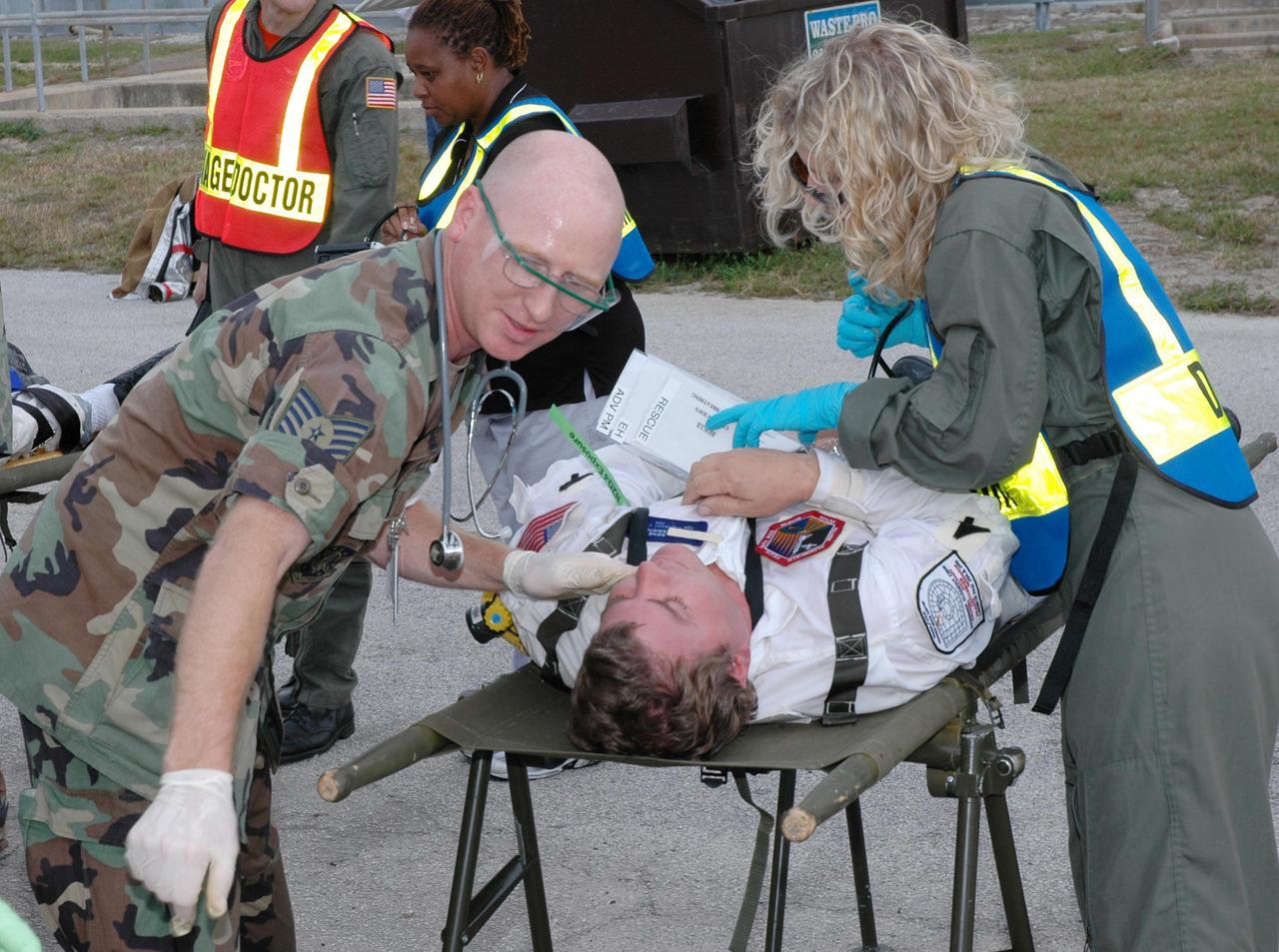
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During a simulated launch countdown_emergency simulation on Launch Pad 39A, the rescue team performs triage on “injured” astronaut-suited workers. Pad team members participated in the four-hour exercise simulating normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. The simulation tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
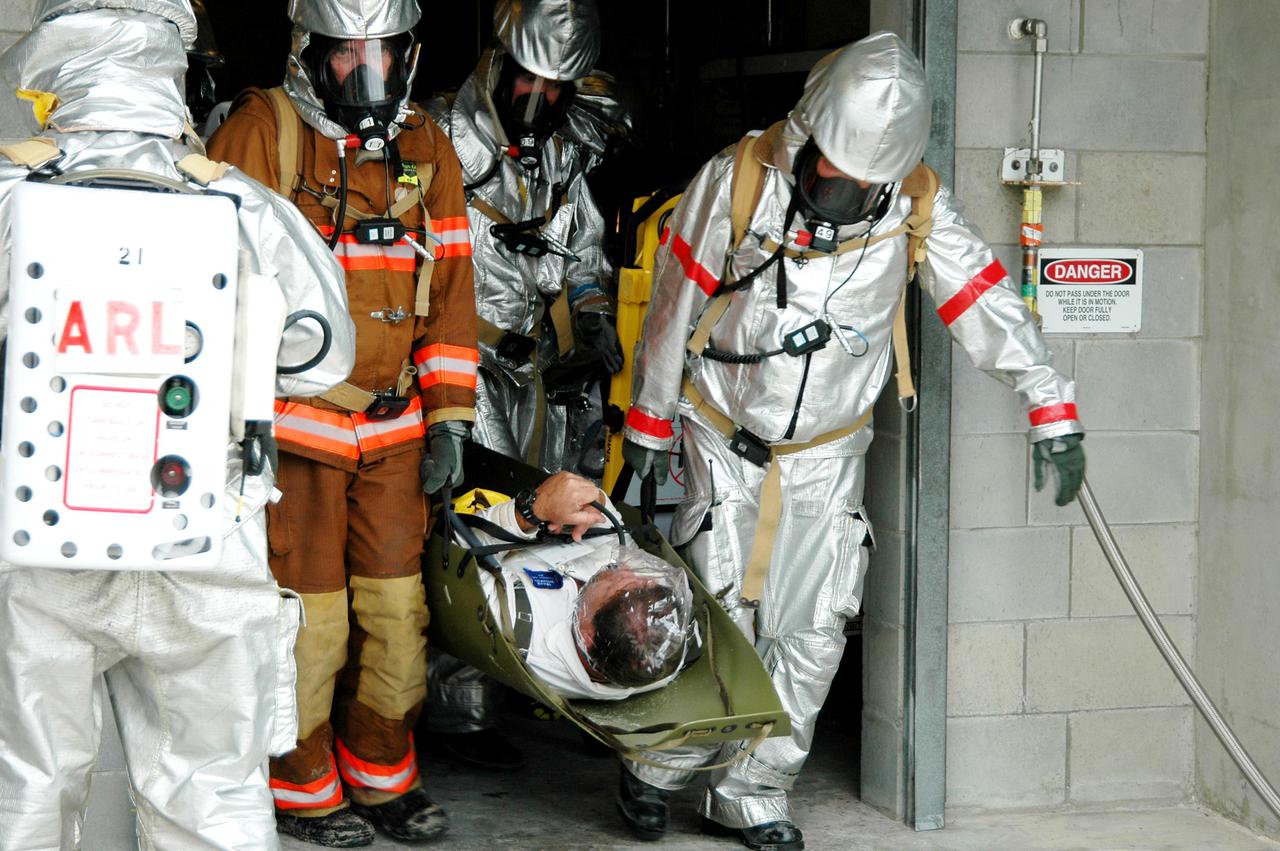

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During a simulated launch countdown_emergency simulation on Launch Pad 39A, the rescue team carries “injured” astronaut-suited workers out of the pad bunker. The four-hour exercise simulated normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. It tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
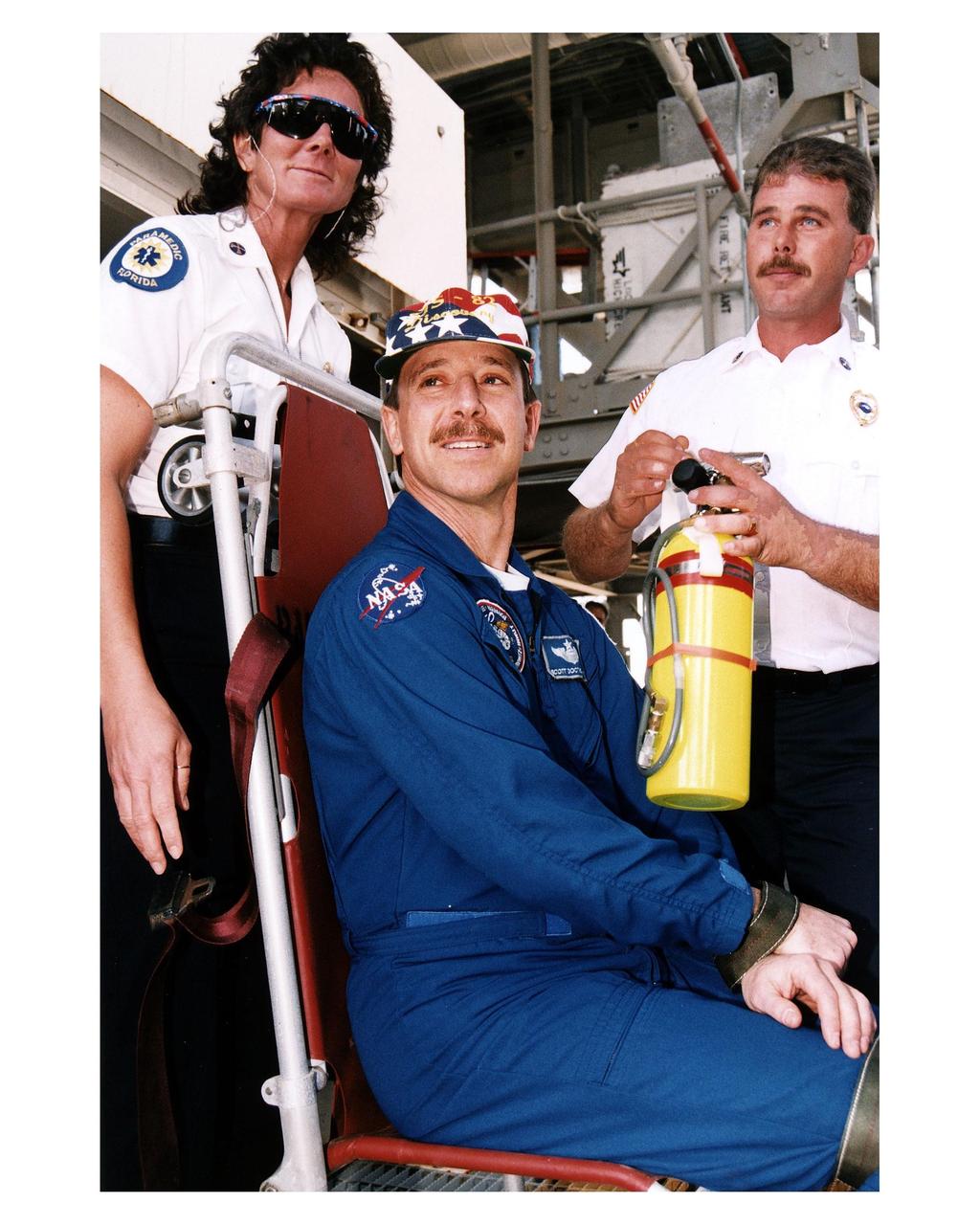

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-82 Pilot Scott J. "Doc" Horowitz, seated, poses as an immobilized person while pad rescue leaders Kathy Weaver and Steve Kelly of KSC Fire Rescue Services demonstrate the use of flight crew rescue equipment. The demonstration is part of crew training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities at Launch Pad 39A. The seven-member STS-82 crew will conduct the second Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission. Liftoff of the 10-day flight is scheduled Feb. 11
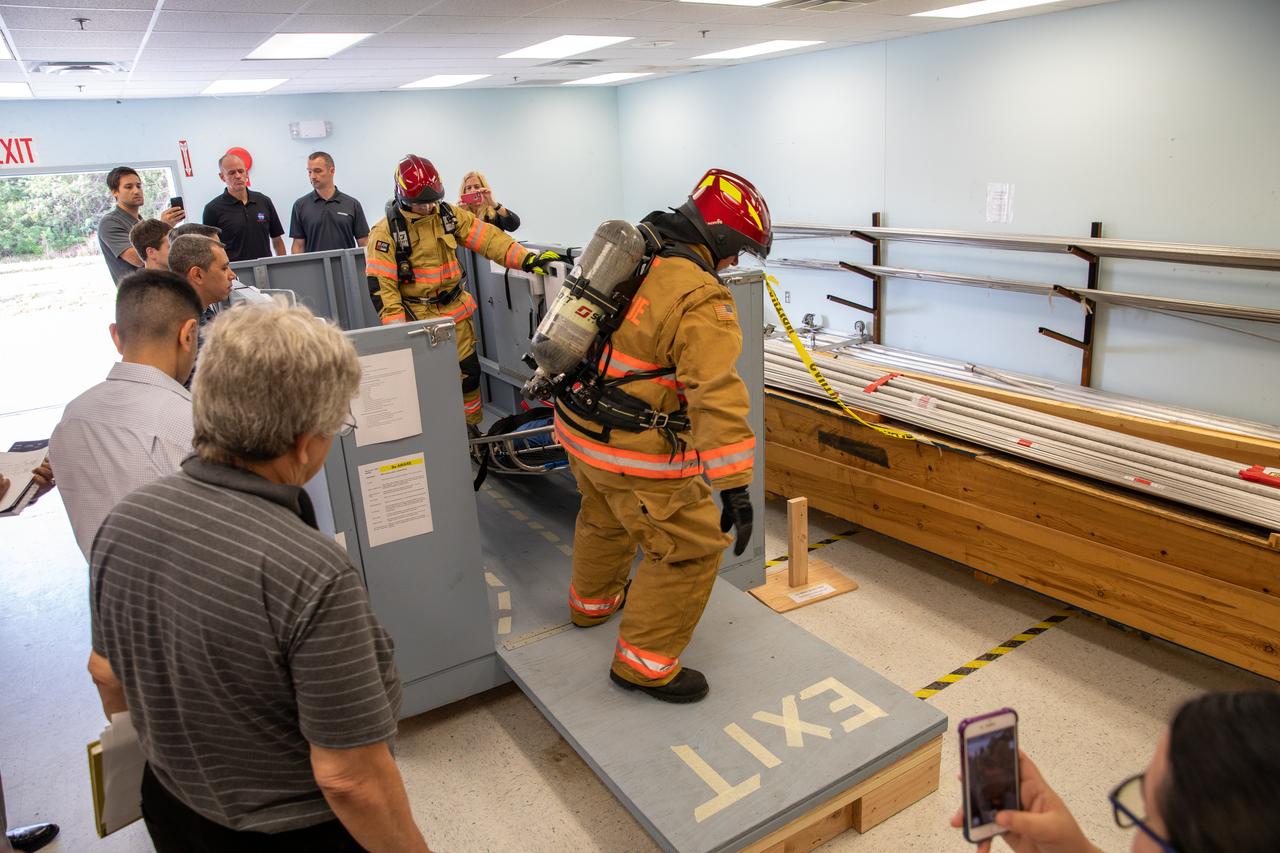

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Fire Rescue team conduct a series of trial scenarios in a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket on Feb. 19, 2020. Kennedy’s prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presented the mock-up to NASA, Kennedy Fire Rescue personnel and other stakeholders at the Florida spaceport. The basket would be utilized at Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more were addressed. Engineers will take what they learned during this presentation and discussion to advance the design of the pad egress system.
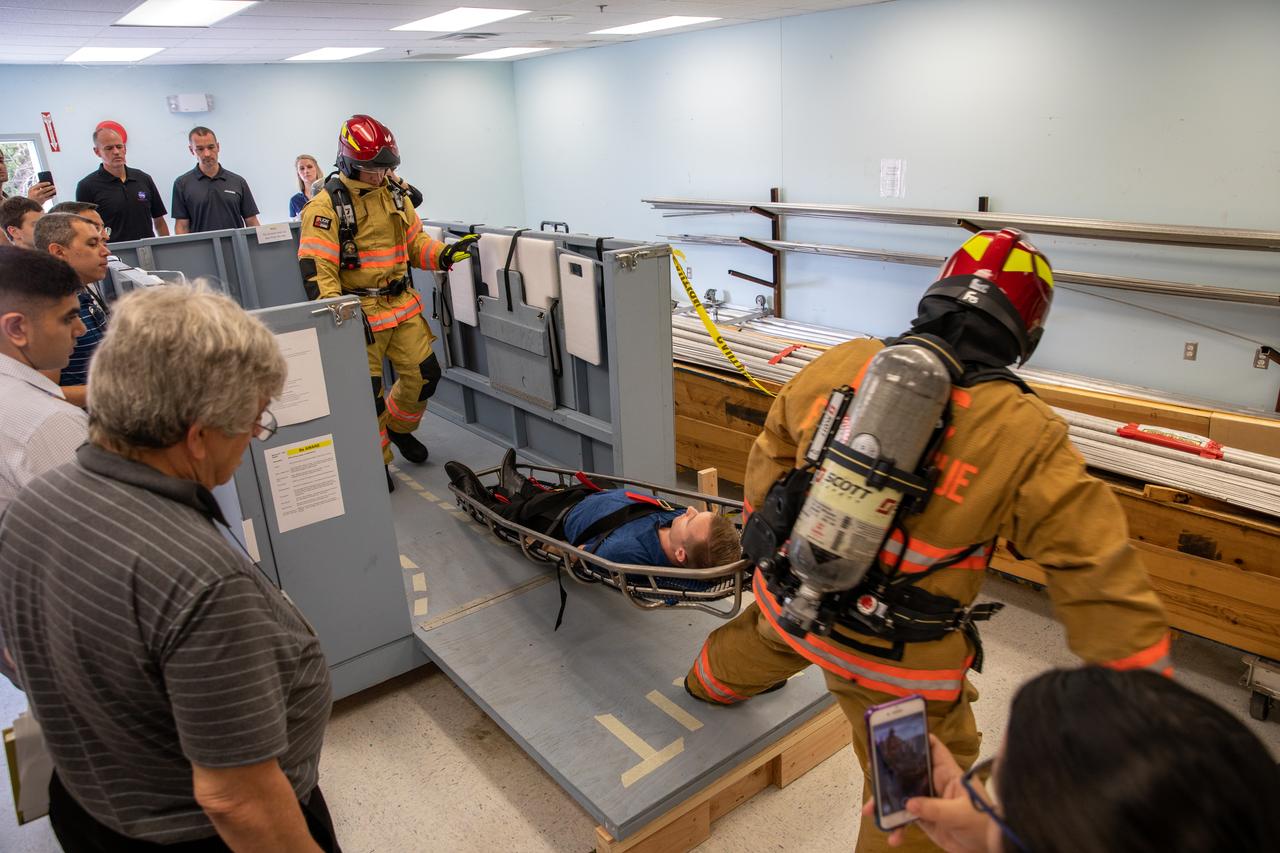

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Fire Rescue team conduct a series of trial scenarios in a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket on Feb. 19, 2020. Kennedy’s prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presented the mock-up to NASA, Kennedy Fire Rescue personnel and other stakeholders at the Florida spaceport. The basket would be utilized at Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more were addressed. Engineers will take what they learned during this presentation and discussion to advance the design of the pad egress system.
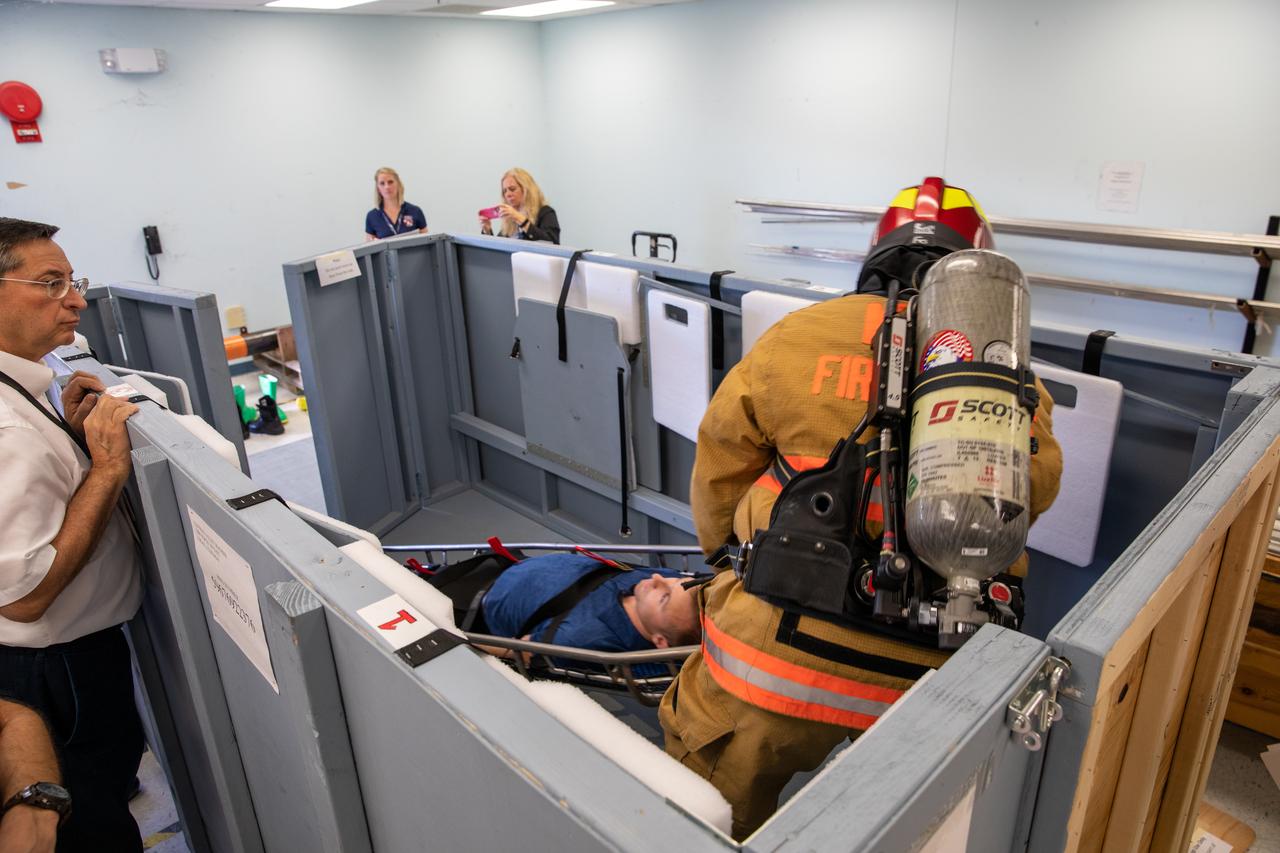

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Fire Rescue team participate in a series of trial scenarios in a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket on Feb. 19, 2020. Kennedy’s prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presented the mock-up to NASA, Kennedy Fire Rescue personnel and other stakeholders at the Florida spaceport. The basket would be utilized at Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more were addressed. Engineers will take what they learned during this presentation and discussion to advance the design of the pad egress system.
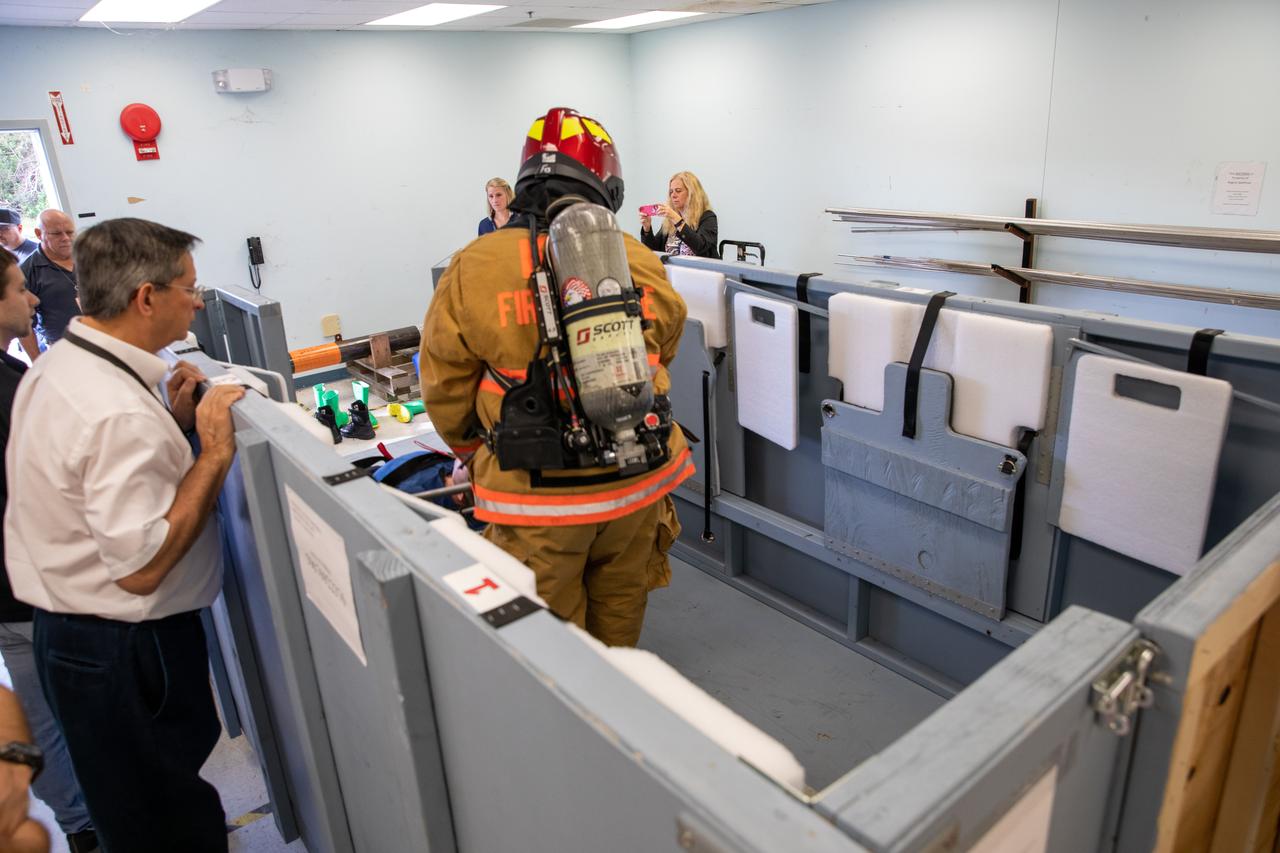

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Fire Rescue team conduct a series of trial scenarios in a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket on Feb. 19, 2020. Kennedy’s prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presented the mock-up to NASA, Kennedy Fire Rescue personnel and other stakeholders at the Florida spaceport. The basket would be utilized at Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more were addressed. Engineers will take what they learned during this presentation and discussion to advance the design of the pad egress system.
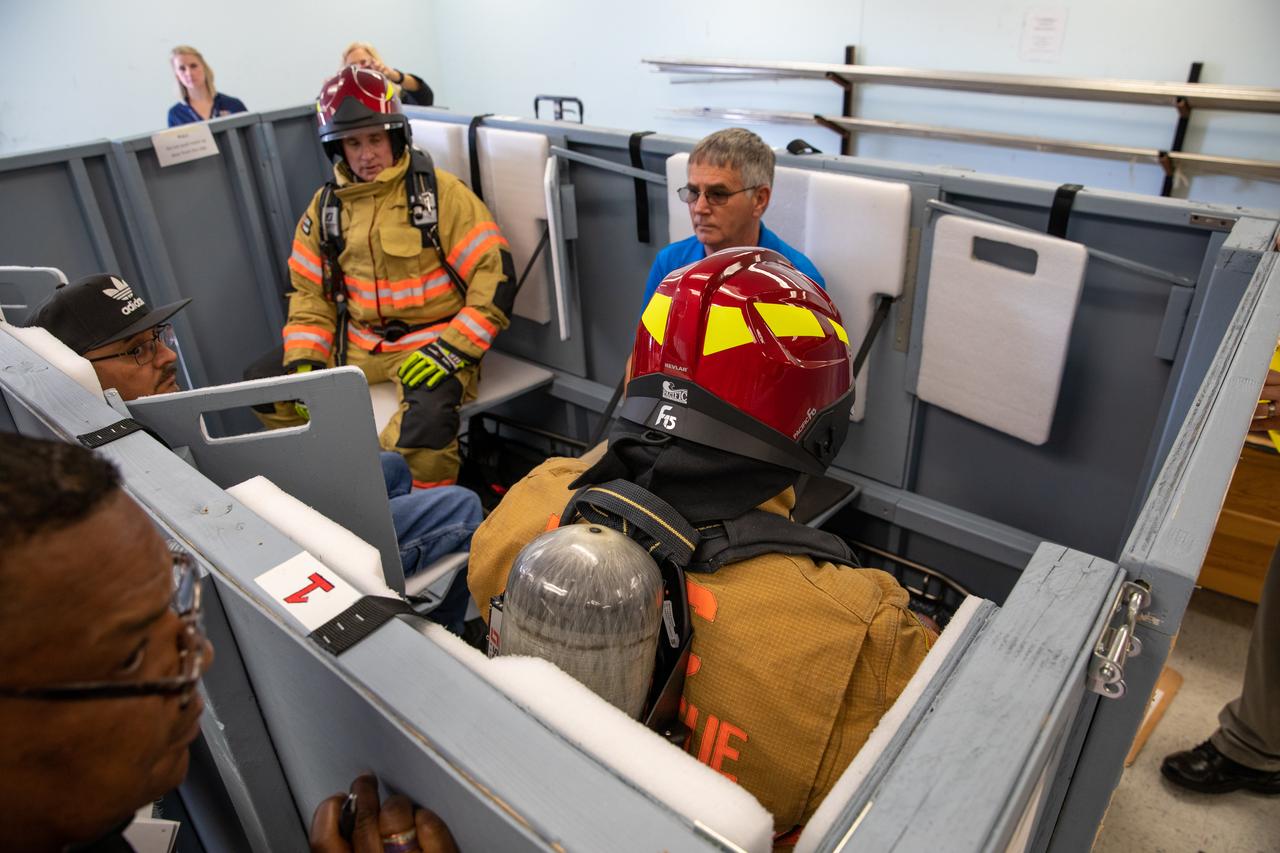

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Fire Rescue team conduct a series of trial scenarios in a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket on Feb. 19, 2020. Kennedy’s prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presented the mock-up to NASA, Kennedy Fire Rescue personnel and other stakeholders at the Florida spaceport. The basket would be utilized at Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more were addressed. Engineers will take what they learned during this presentation and discussion to advance the design of the pad egress system.
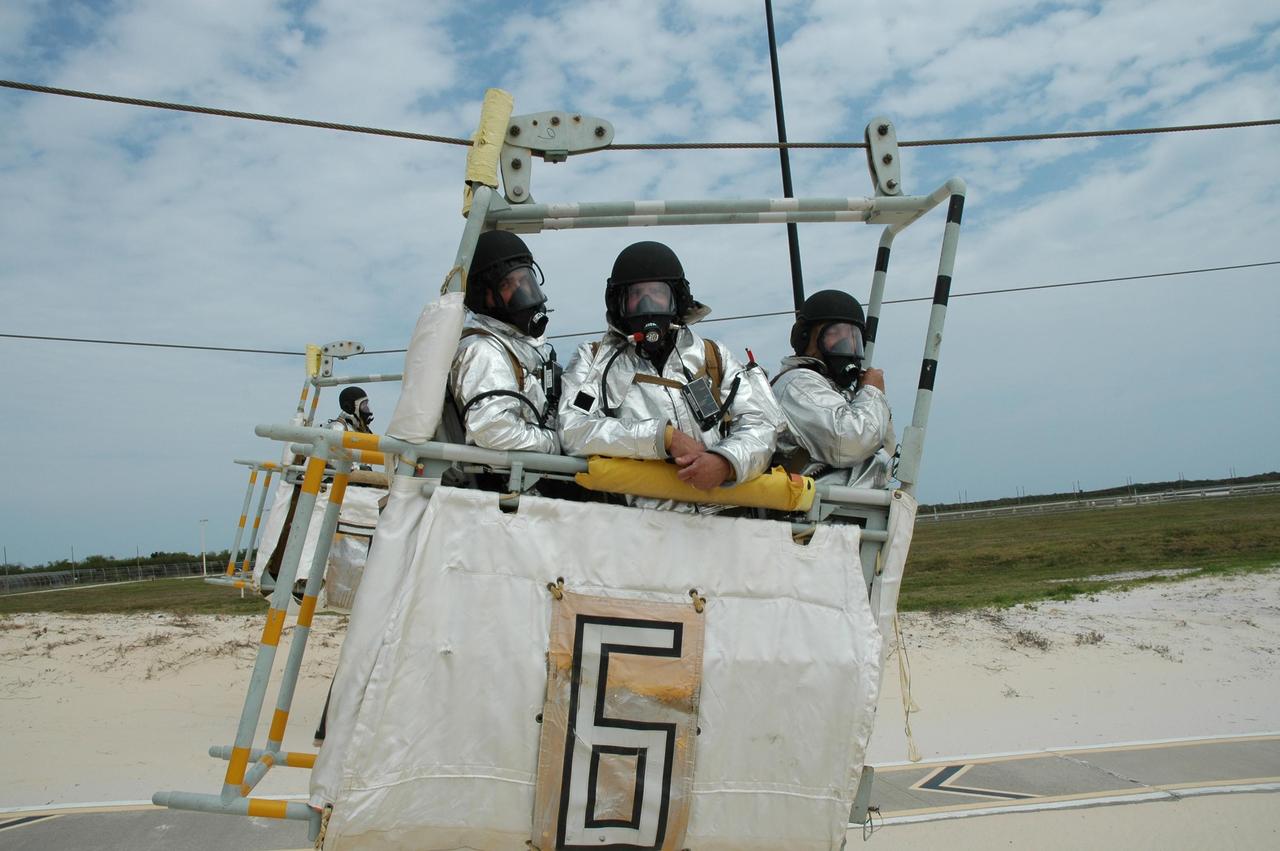

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, part of the KSC fire rescue team in a slidewire basket arrive at the landing site. The emergency exercise began at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
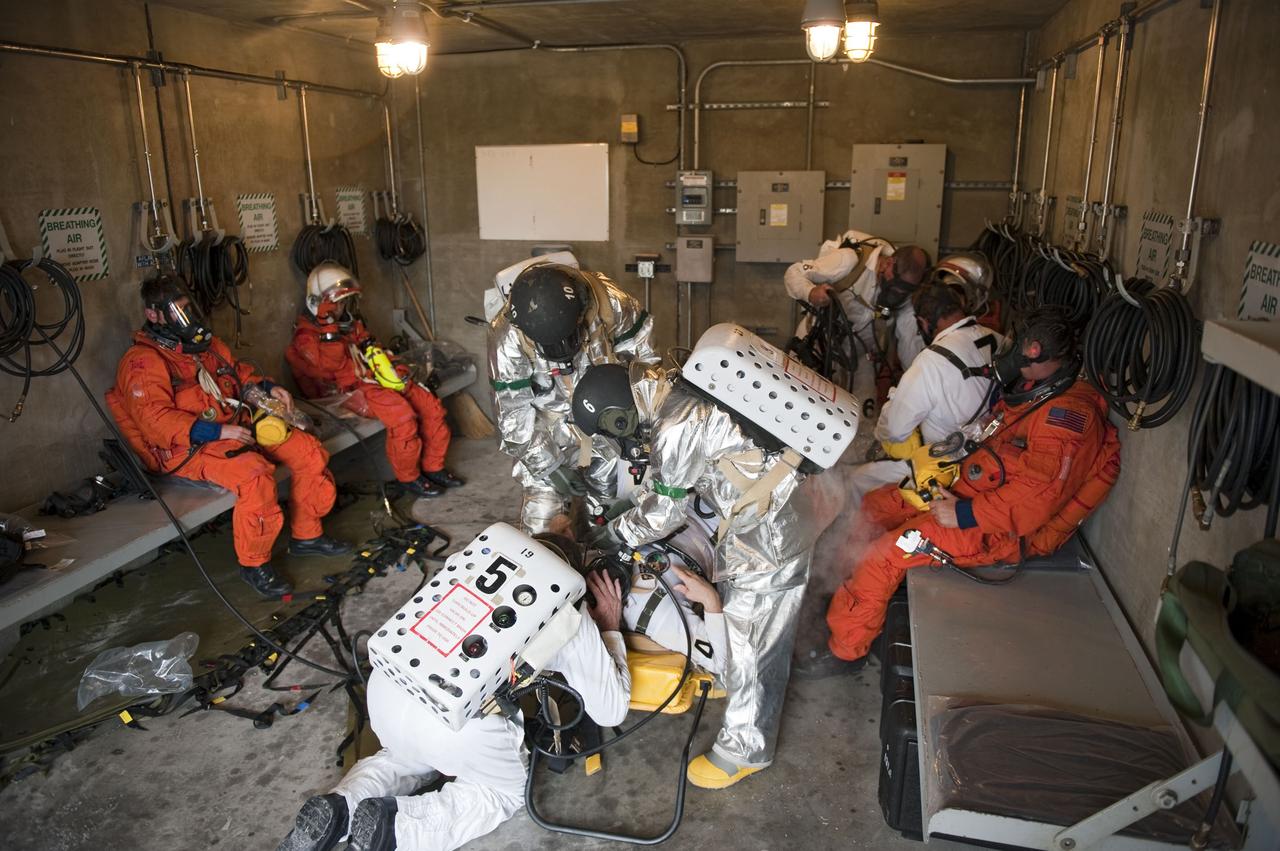

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An emergency exit, or Mode II/IV, exercise is under way in a bunker of Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The exercise involves NASA fire rescue personnel, volunteers portraying astronauts with simulated injuries, helicopters and personnel from the Air Force’s 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams at three Central Florida hospitals. The drill allows teams to practice an emergency response at the launch pad, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, part of the KSC fire rescue team helps an "injured" member of the closeout crew. The emergency exercise began at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Launch Pad 39A, a rescue force climbs into slidewire baskets on the Fixed Service Structure during an emergency egress scenario. The four-hour exercise simulated normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. It tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
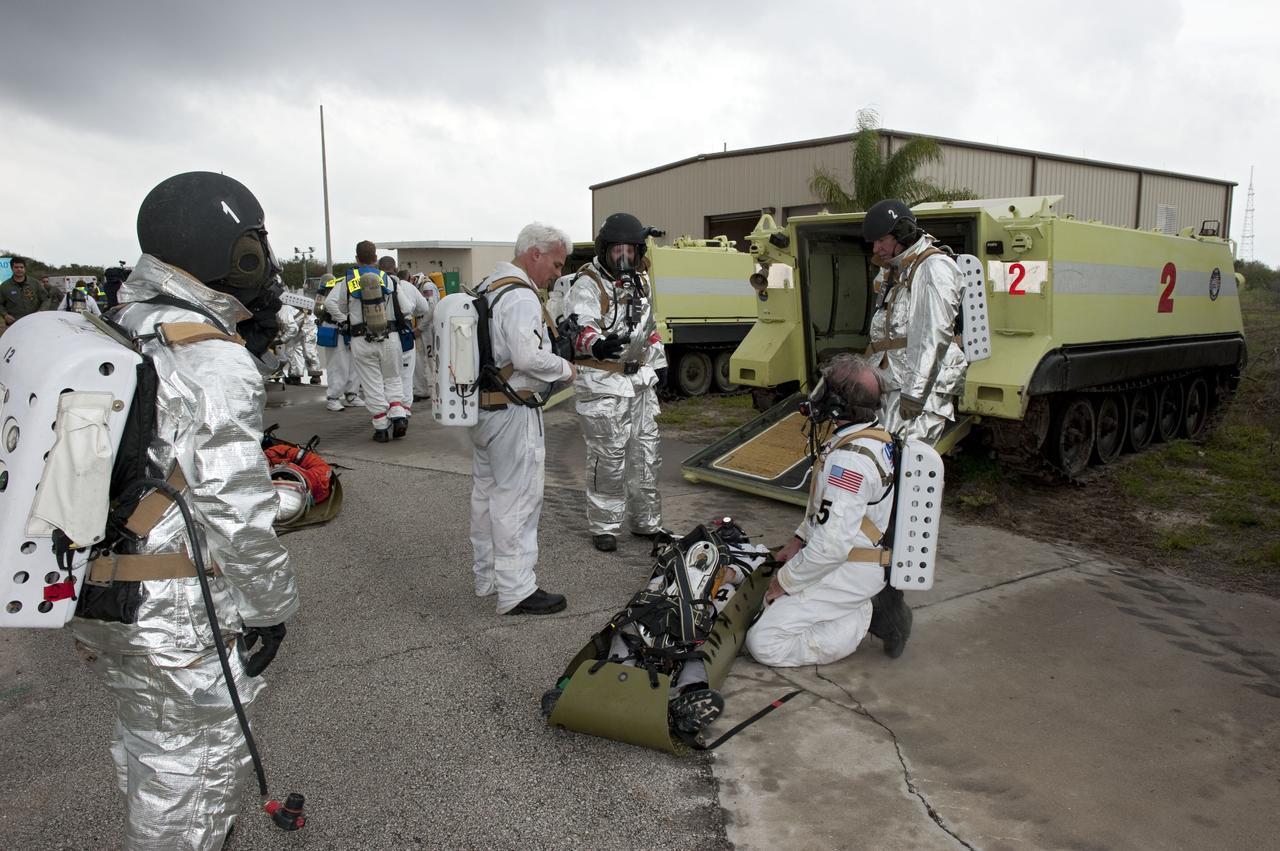

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An emergency exit, or Mode II/IV, exercise is under way near Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The exercise involves NASA fire rescue personnel, volunteers portraying astronauts with simulated injuries, helicopters and personnel from the Air Force’s 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams at three Central Florida hospitals. The drill allows teams to practice an emergency response at the launch pad, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

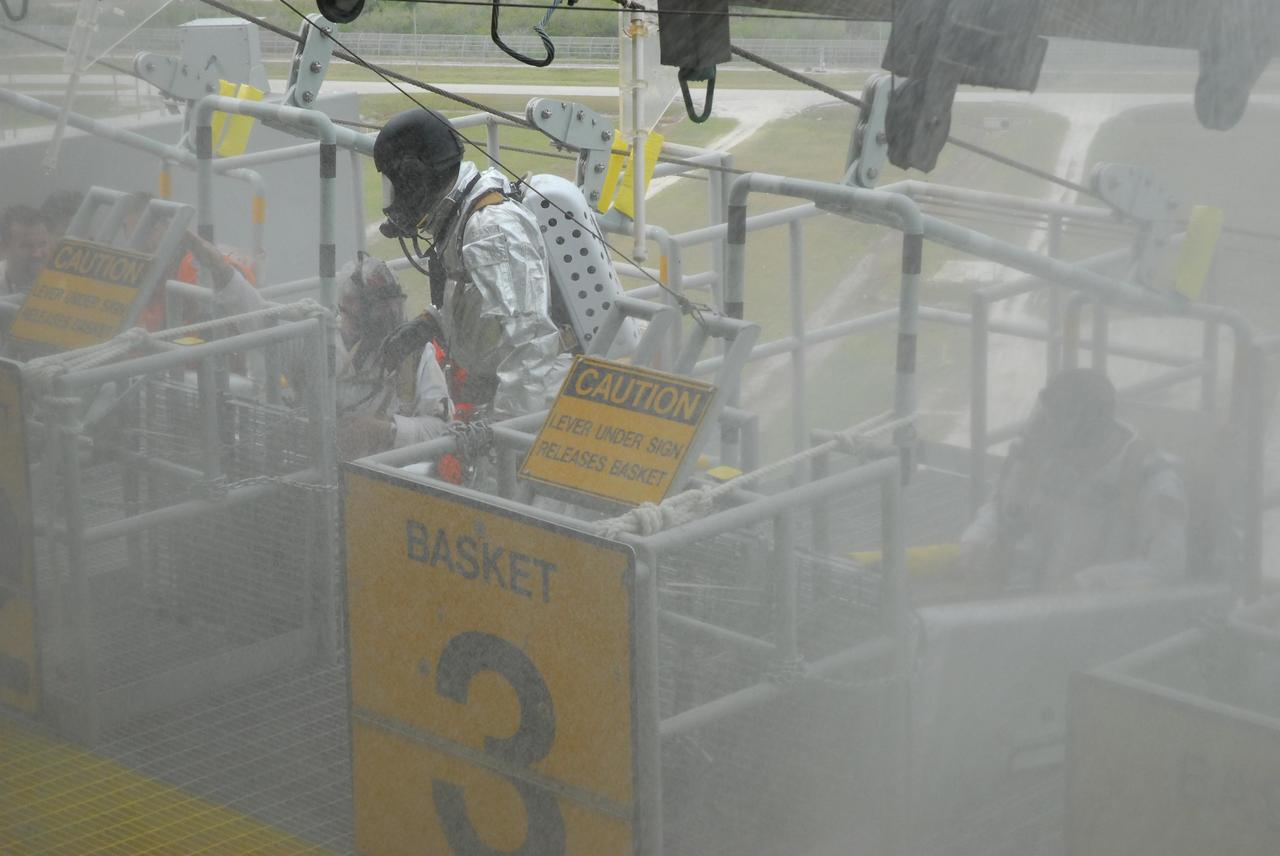
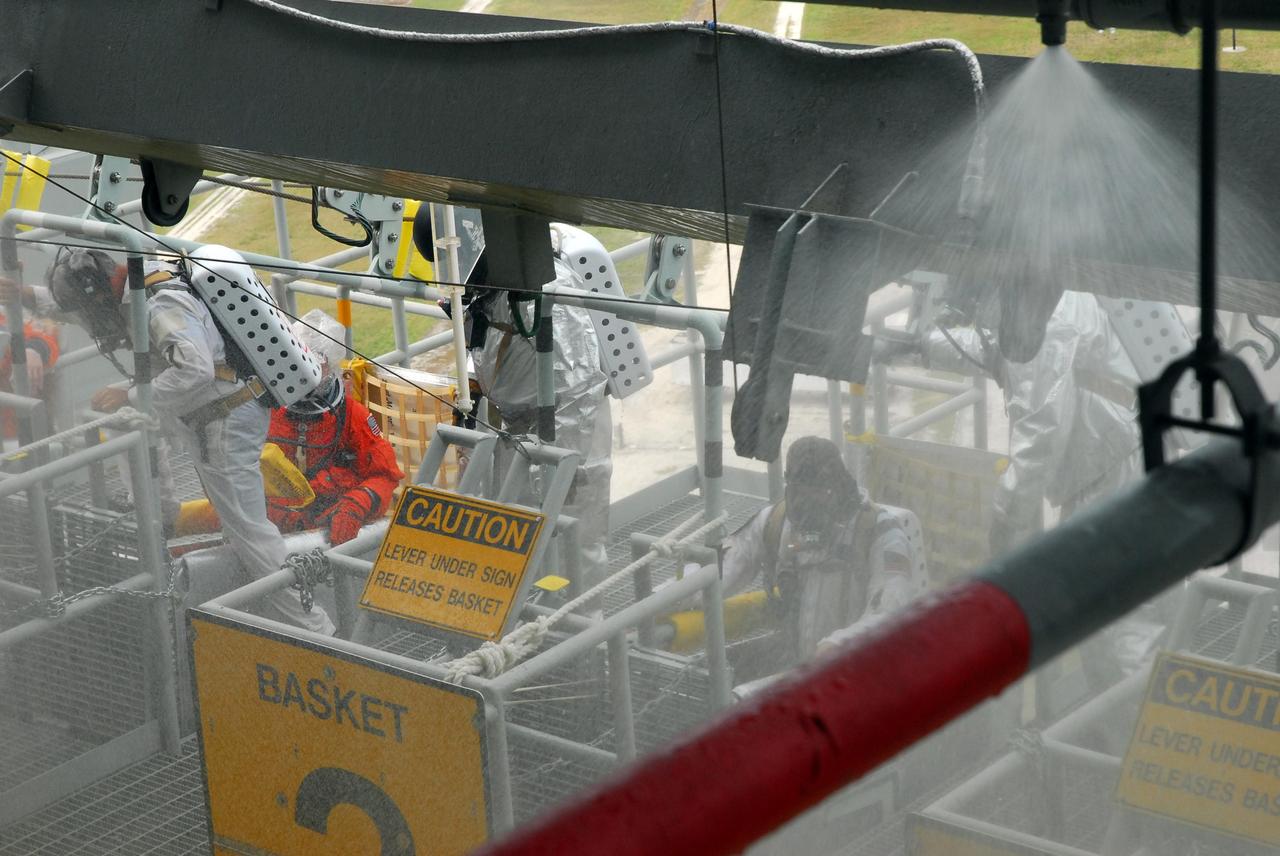
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, KSC rescue team members help "injured" astronauts, portrayed by KSC personnel, out of the slidewire baskets. The emergency exercise began at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
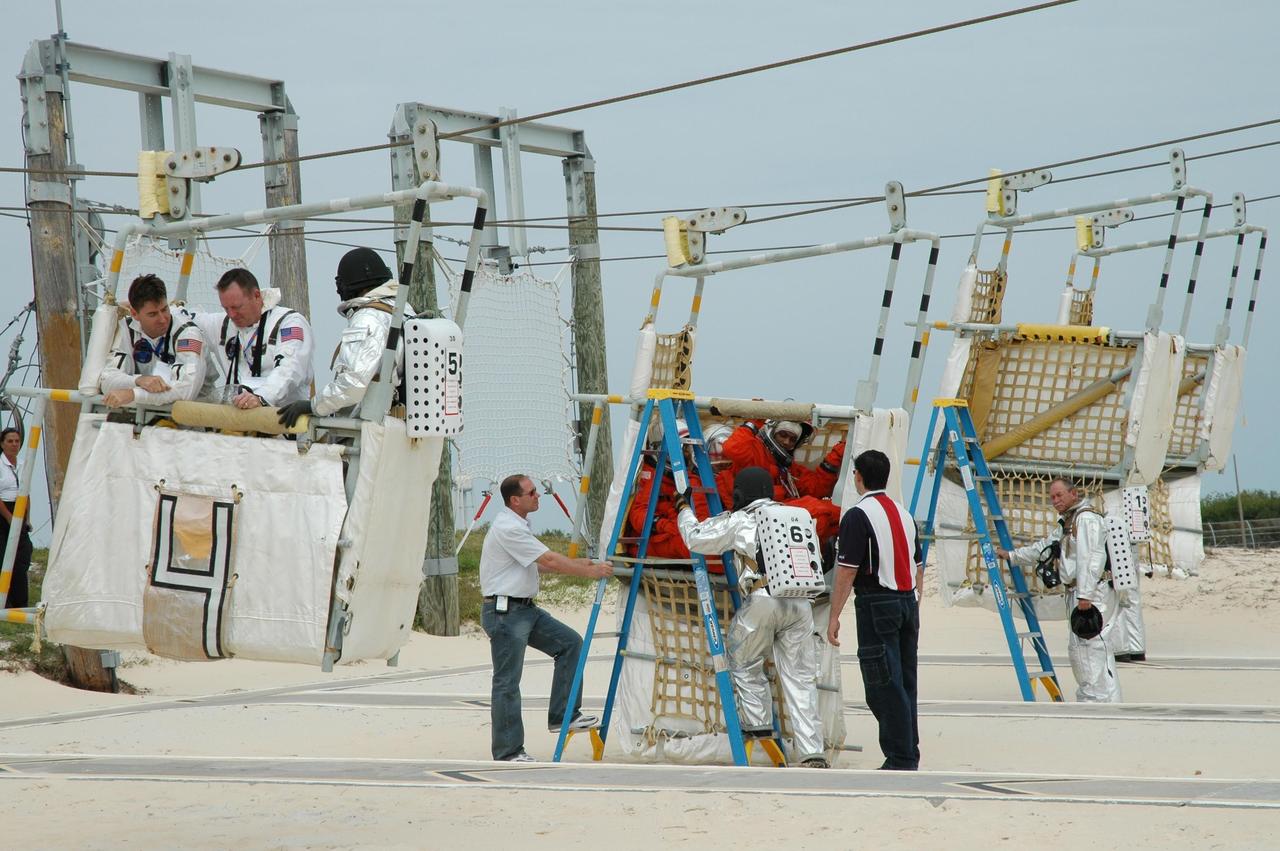

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, KSC personnel dressed in astronauts' launch-and-entry suits are helped by the fire rescue team at the slidewire basket landing site. The emergency exercise began at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
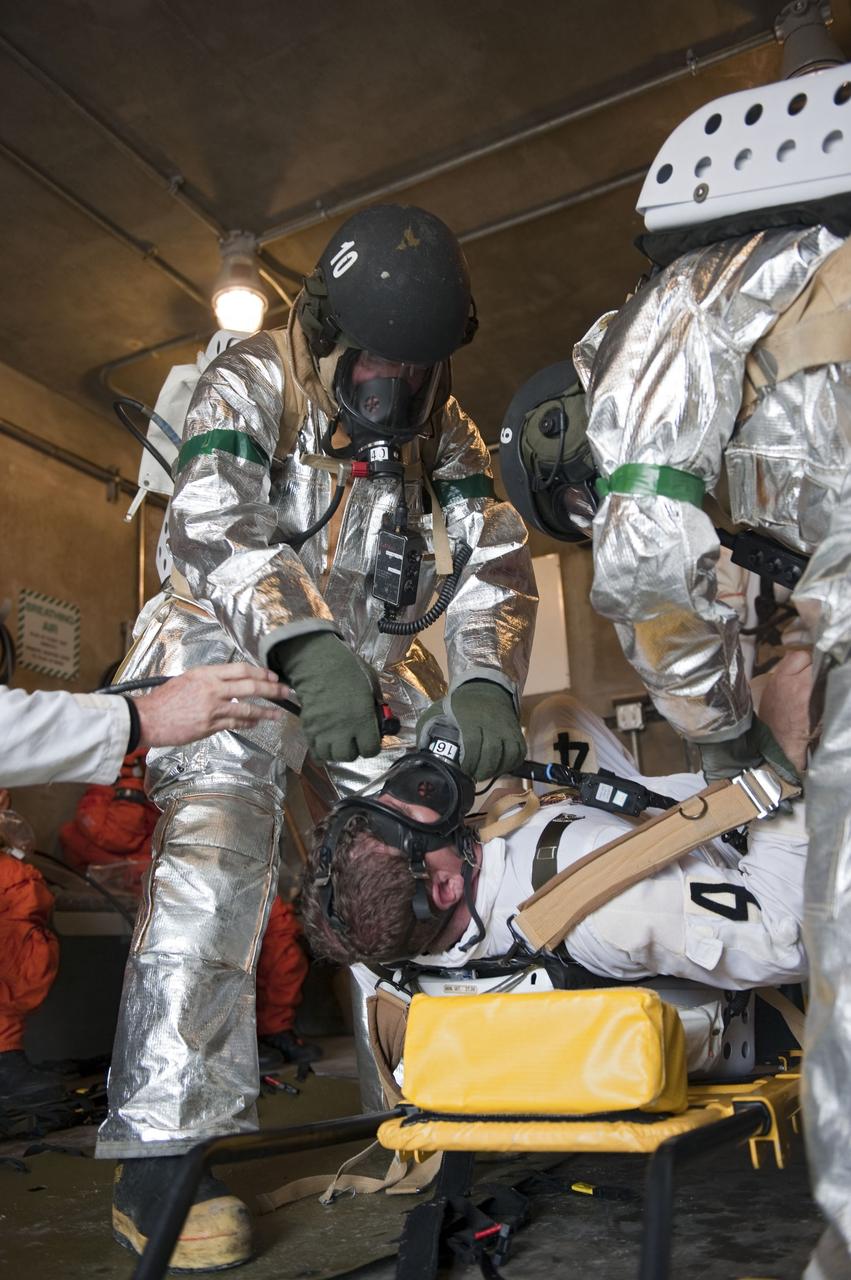

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An emergency exit, or Mode II/IV, exercise is under way in a bunker of Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The exercise involves NASA fire rescue personnel, volunteers portraying astronauts with simulated injuries, helicopters and personnel from the Air Force’s 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams at three Central Florida hospitals. The drill allows teams to practice an emergency response at the launch pad, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An emergency exit, or Mode II/IV, exercise is under way near Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The exercise involves NASA fire rescue personnel, volunteers portraying astronauts with simulated injuries, helicopters and personnel from the Air Force’s 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams at three Central Florida hospitals. The drill allows teams to practice an emergency response at the launch pad, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
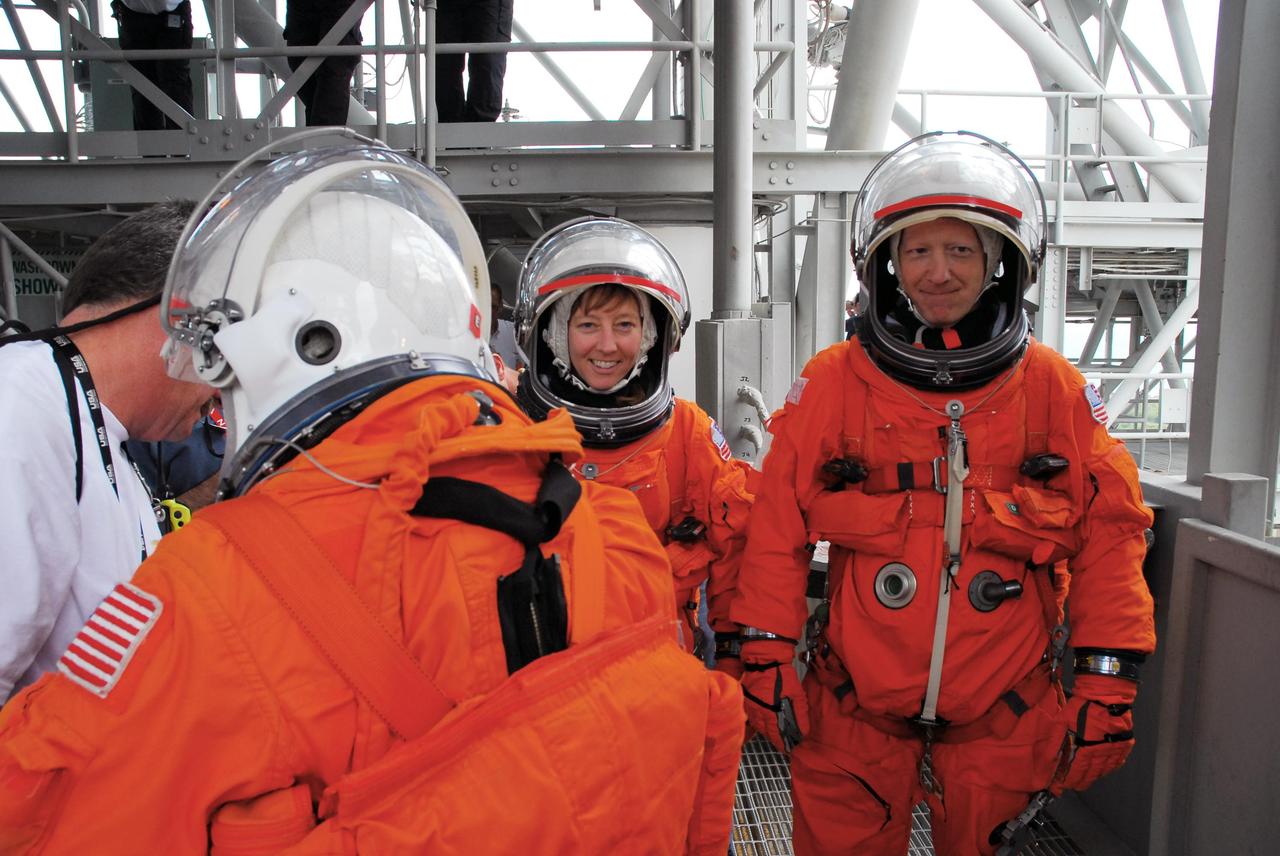

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a simulated rescue mission on Launch Pad 39A, known as Mode 2, KSC personnel dressed in astronauts' launch-and-entry suits move from the white room on the 195-foot level toward the slidewire baskets. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
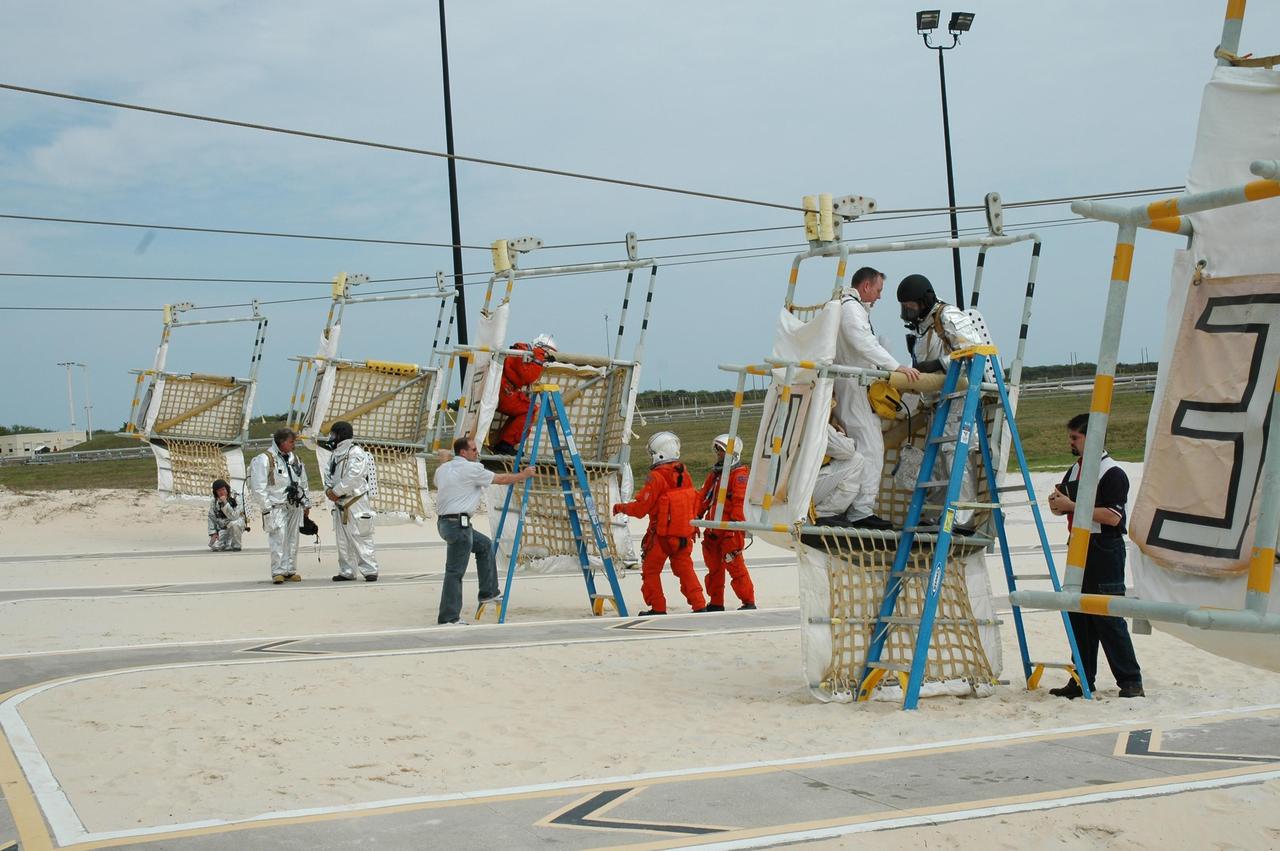

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, KSC personnel dressed in astronauts' launch-and-entry suits are helped by the fire rescue team at the slidewire basket landing site. The emergency exercise began at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
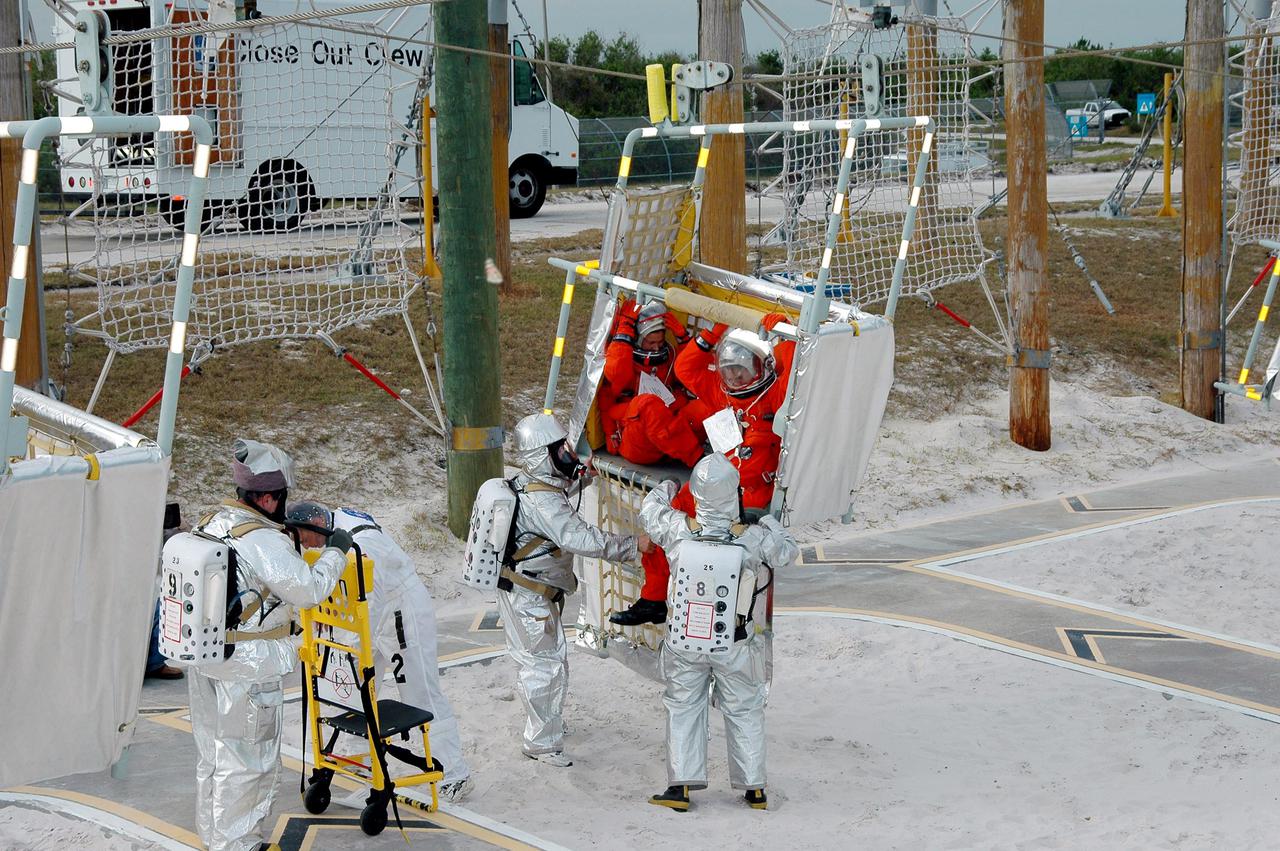

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Launch Pad 39A, rescue team members and astronaut-suited workers exit a slidewire basket during an emergency egress scenario. The four-hour exercise simulated normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. It tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An emergency exit, or Mode II/IV, exercise is under way near Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The exercise involves NASA fire rescue personnel, volunteers portraying astronauts with simulated injuries, helicopters and personnel from the Air Force’s 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams at three Central Florida hospitals. The drill allows teams to practice an emergency response at the launch pad, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, KSC rescue team members help "injured" astronauts, portrayed by KSC personnel, out of the slidewire baskets. The emergency exercise began at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
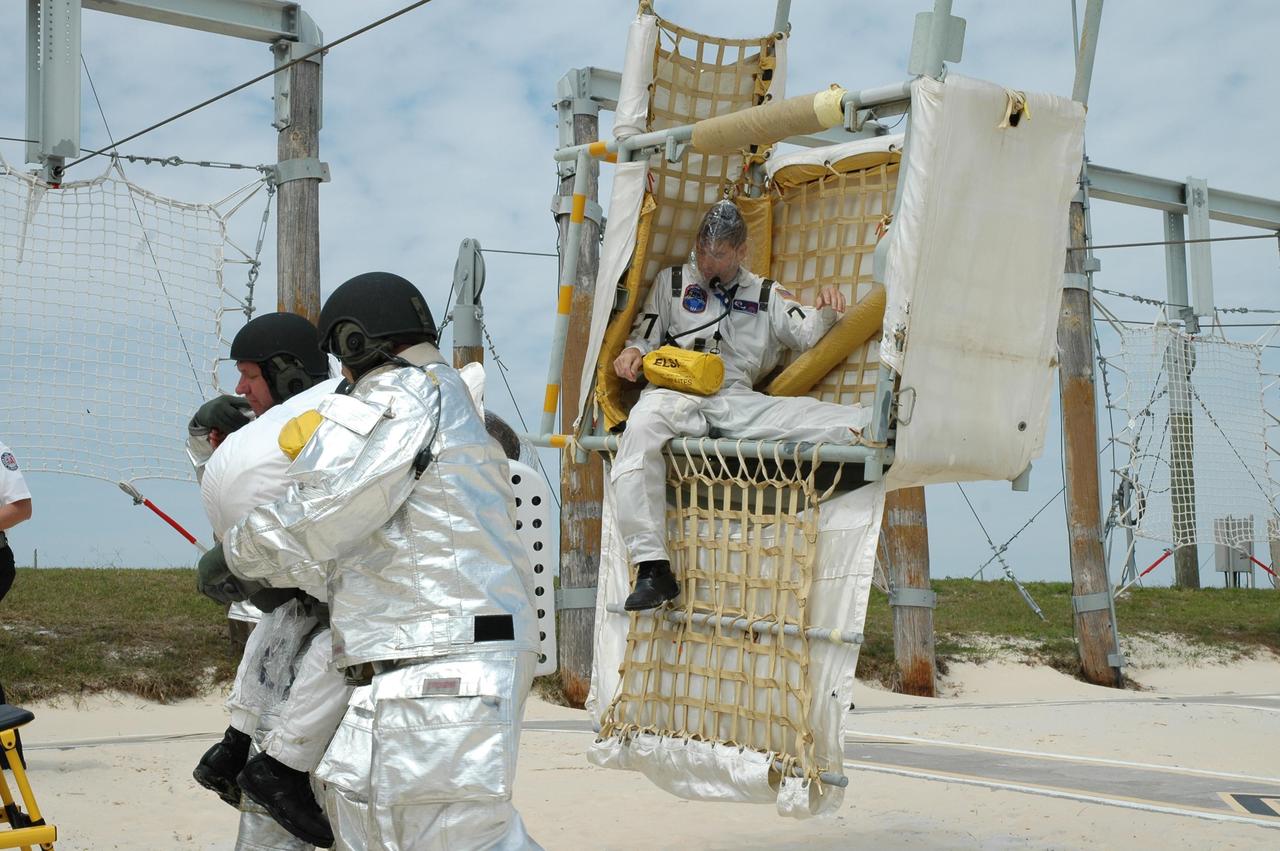

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, part of the KSC fire rescue team helps "injured" members of the closeout crew out of the slidewire baskets. The emergency exercise began at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An emergency exit, or Mode II/IV, exercise is under way near Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The exercise involves NASA fire rescue personnel, volunteers portraying astronauts with simulated injuries, helicopters and personnel from the Air Force’s 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams at three Central Florida hospitals. The drill allows teams to practice an emergency response at the launch pad, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

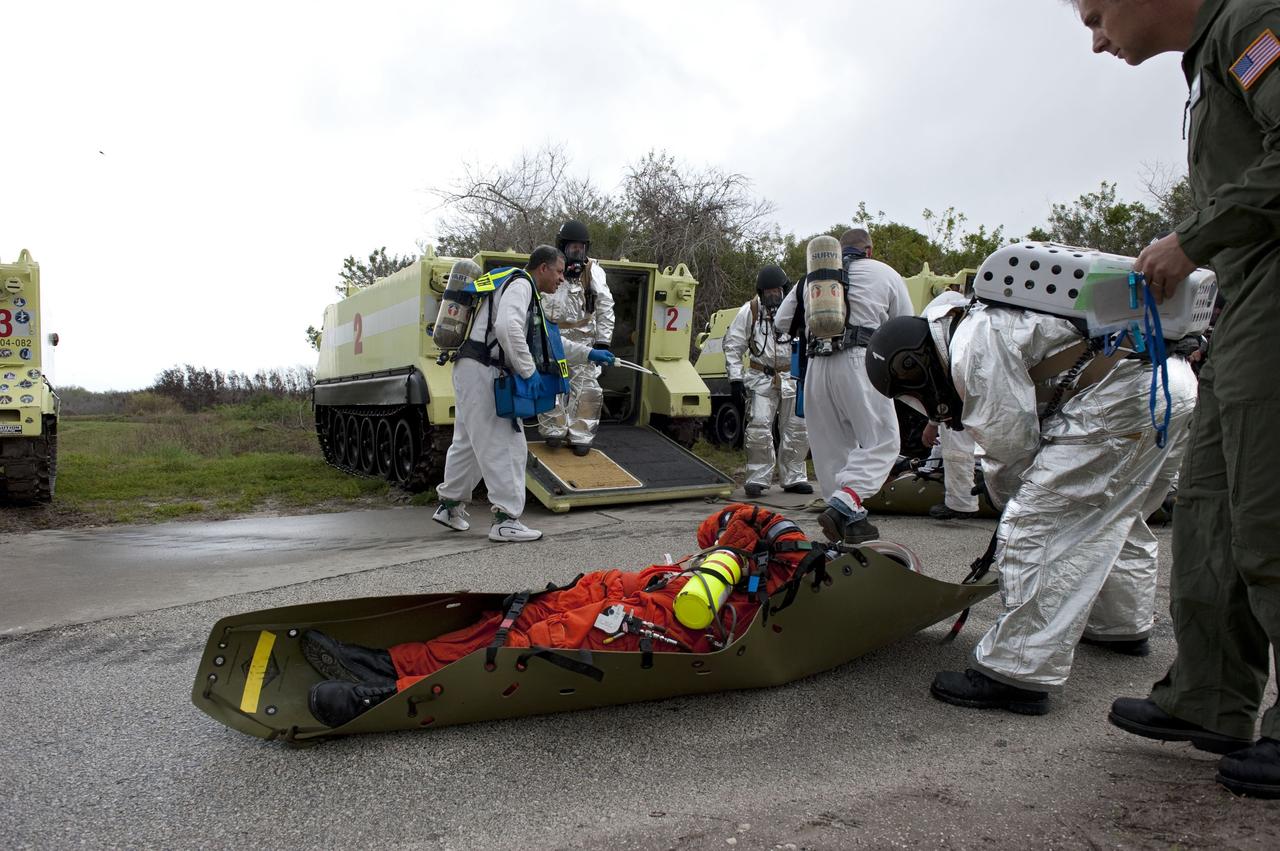
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Launch Pad 39-A, a rescue force helps co-workers as part of an emergency egress scenario. The four-hour exercise simulated normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. It tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
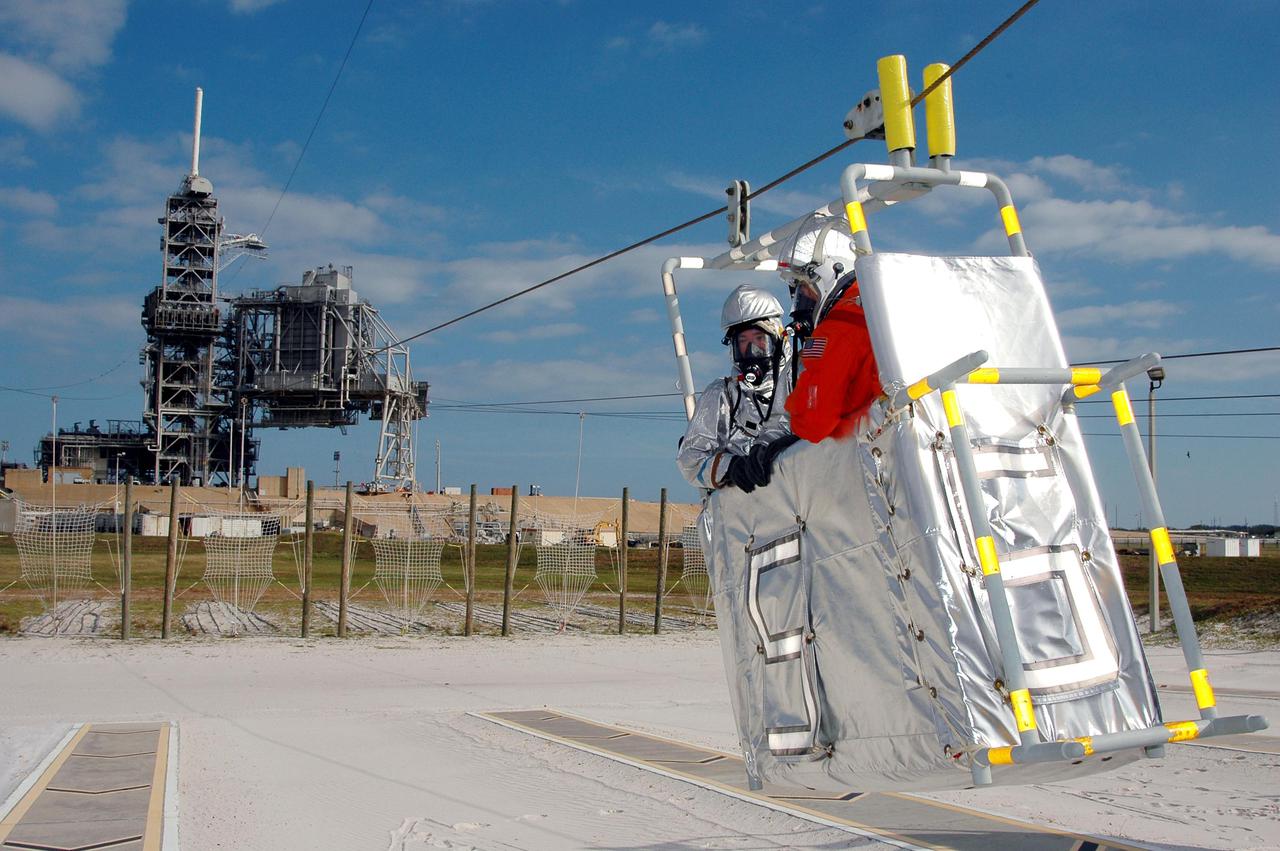

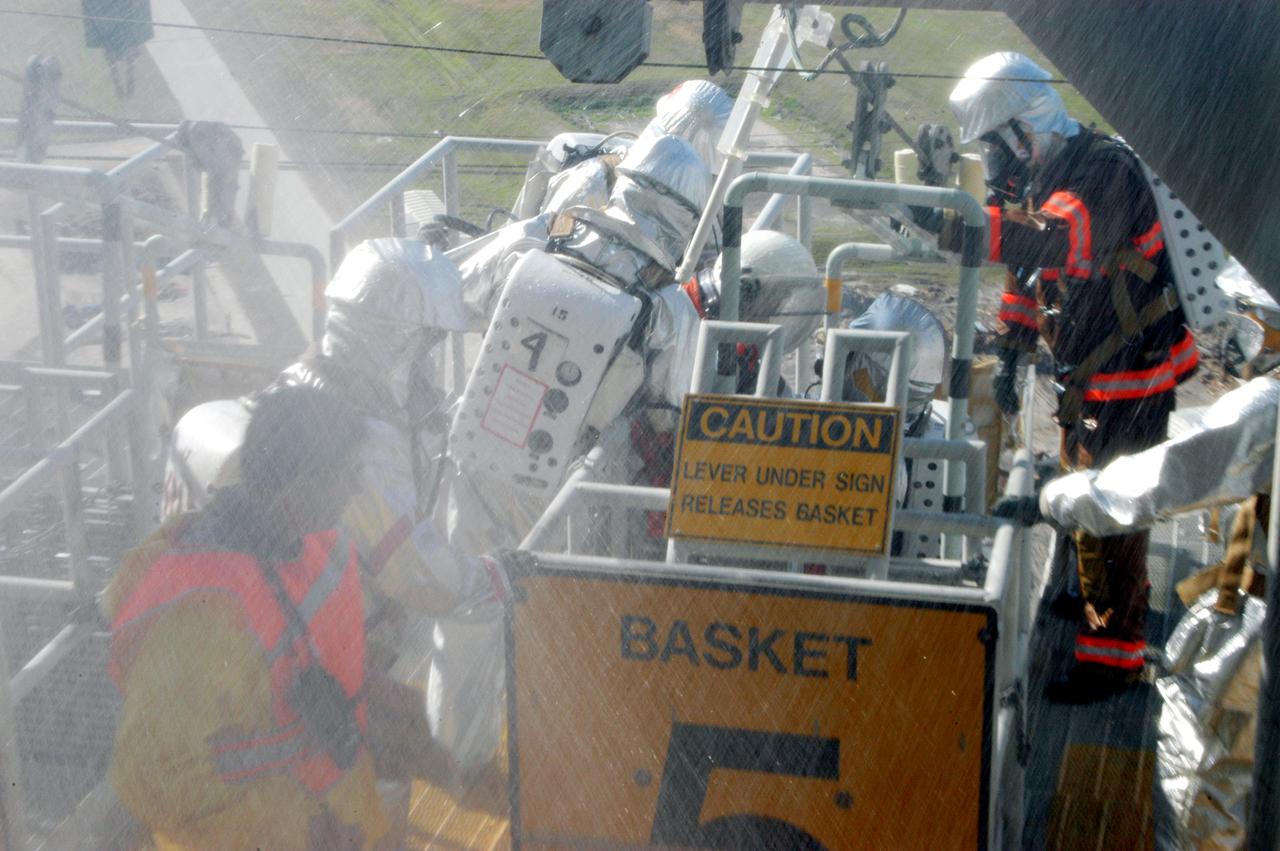
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Launch Pad 39A, a rescue team member and astronaut-suited worker approach landing in a slidewire basket reaching from the Fixed Service Structure in the background during an emergency egress scenario. The four-hour exercise simulated normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. It tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
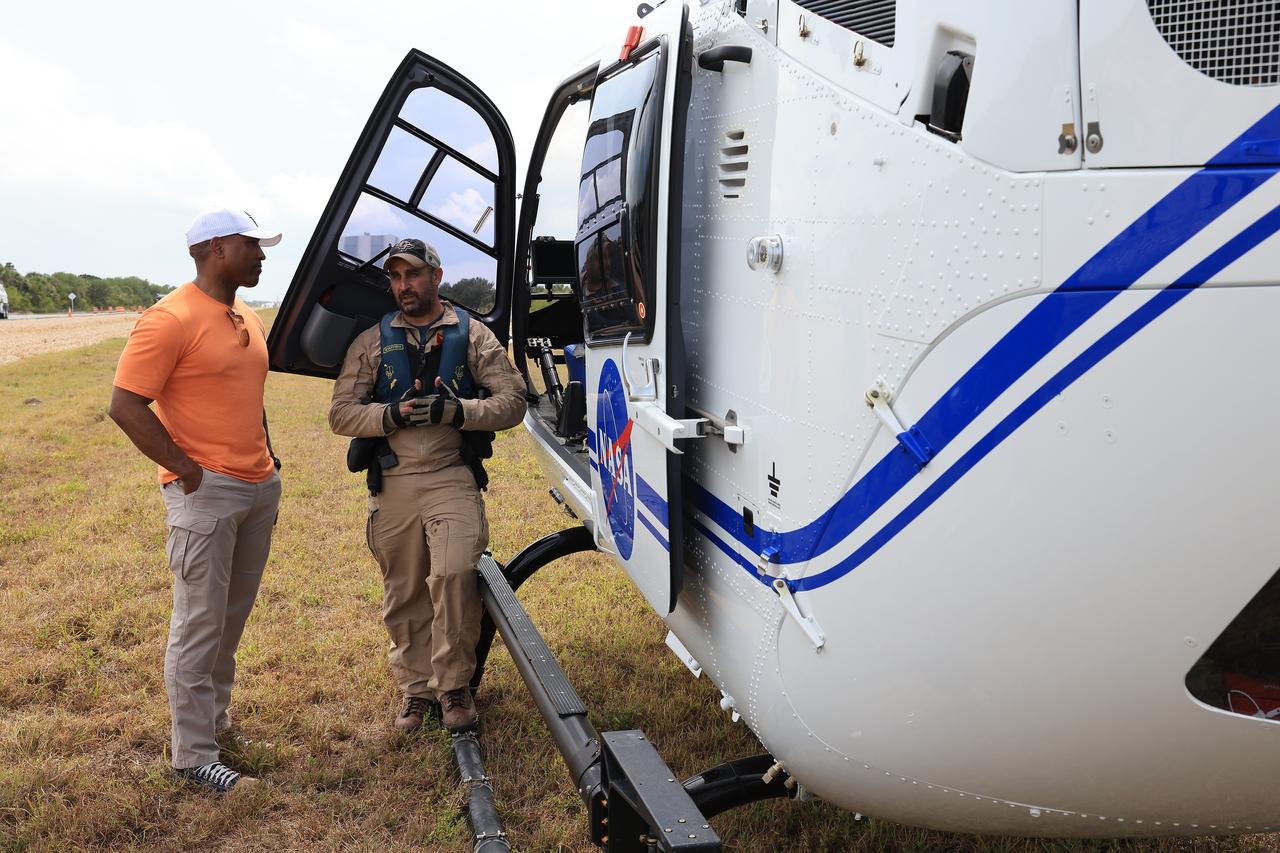

NASA astronaut Victor Glover (left) participates in emergency egress training with medical and fire-rescue personnel and teams near Launch Complex 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 6, 2025. During the training, Glover and fellow Artemis II crew members and backup members, along with members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced procedures in the event of an emergency at the launch pad.
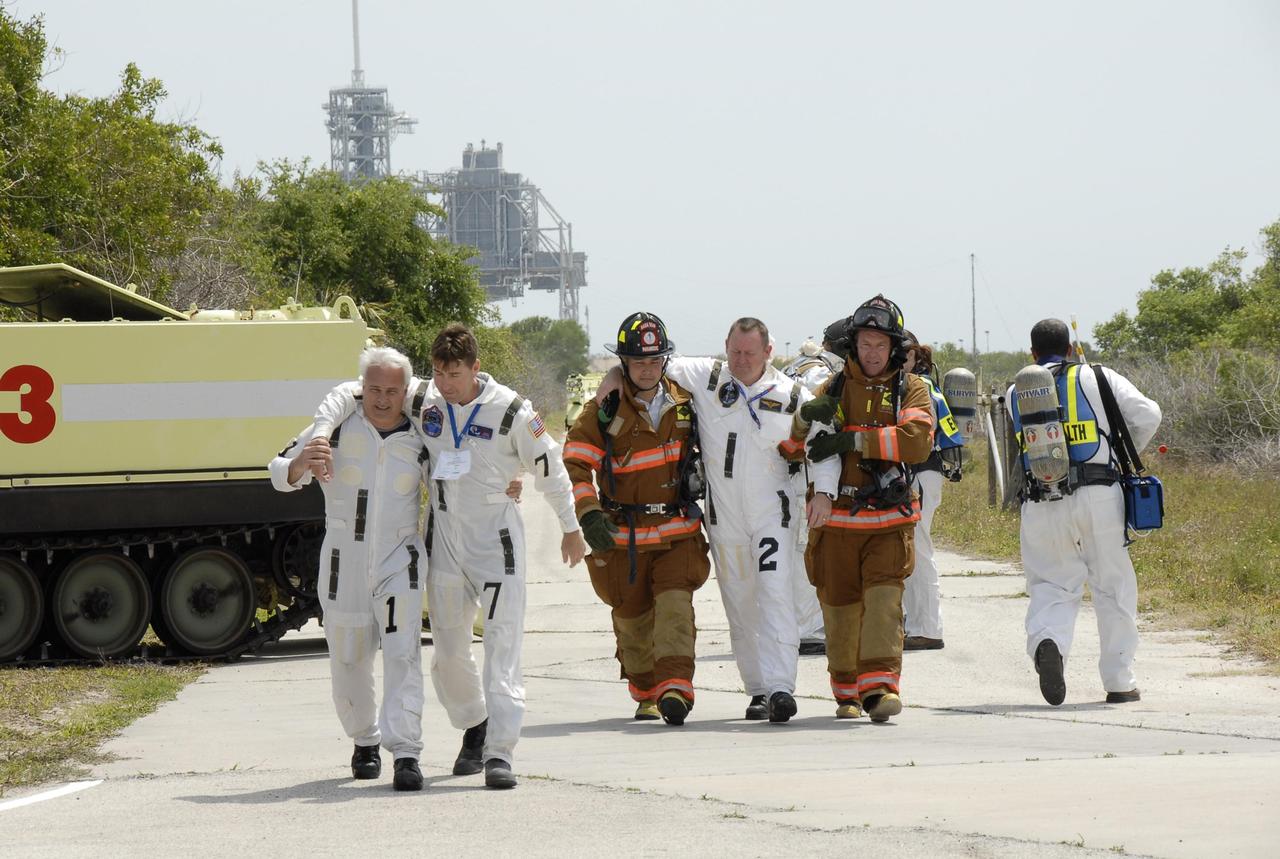

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, rescue workers help KSC personnel feigning injuries to a triage area set up at Helipad 8, located near the fire station between Launch Pads 39A and 39B. The emergency exercise began on Launch Pad 39A. The participants were helped off the pad and taken to the triage site. The "injured" workers will be airlifted to participating area hospitals. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
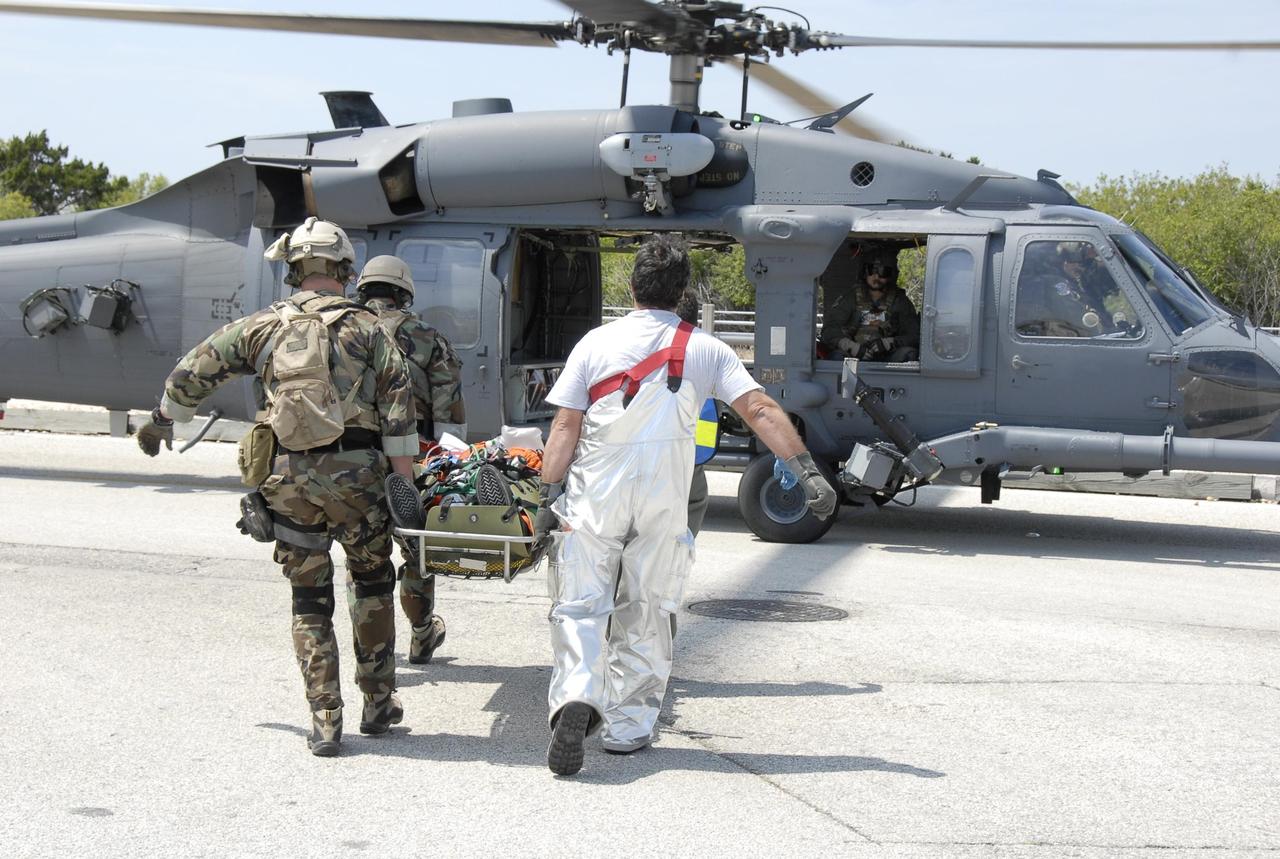

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, the KSC rescue team carries an "injured" astronaut toward one of five helicopters participating in the exercise. The triage area was set up at Helipad 8, located near the fire station between Launch Pads 39A and 39B. The emergency exercise began on Launch Pad 39A. The participants were helped off the pad and taken to the triage site. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
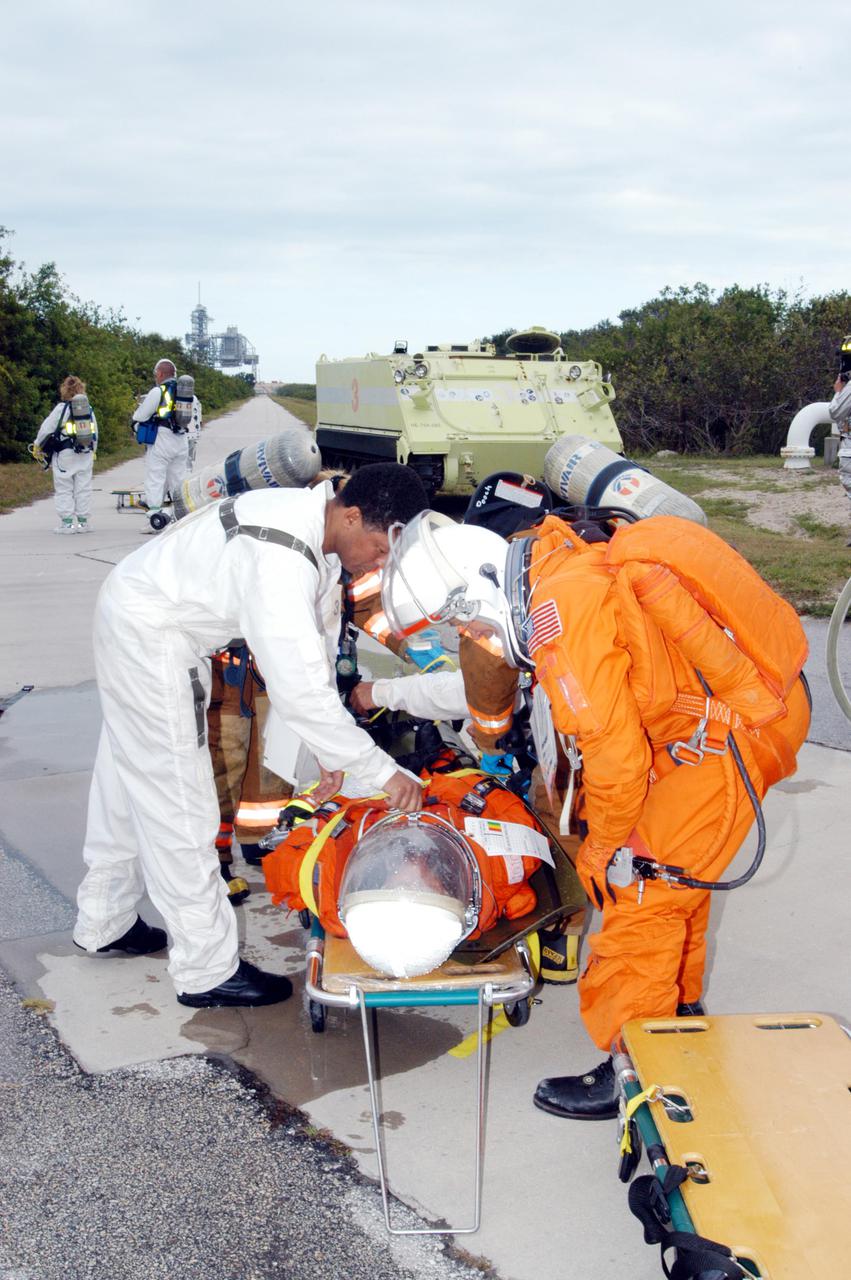

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During a simulated launch countdown_emergency simulation on Launch Pad 39A, the rescue team moves “injured” astronaut-suited workers out of the M-113 armored personnel carriers that transported them away from the pad (seen in the distance). Pad team members participated in the four-hour exercise simulating normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. The simulation tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
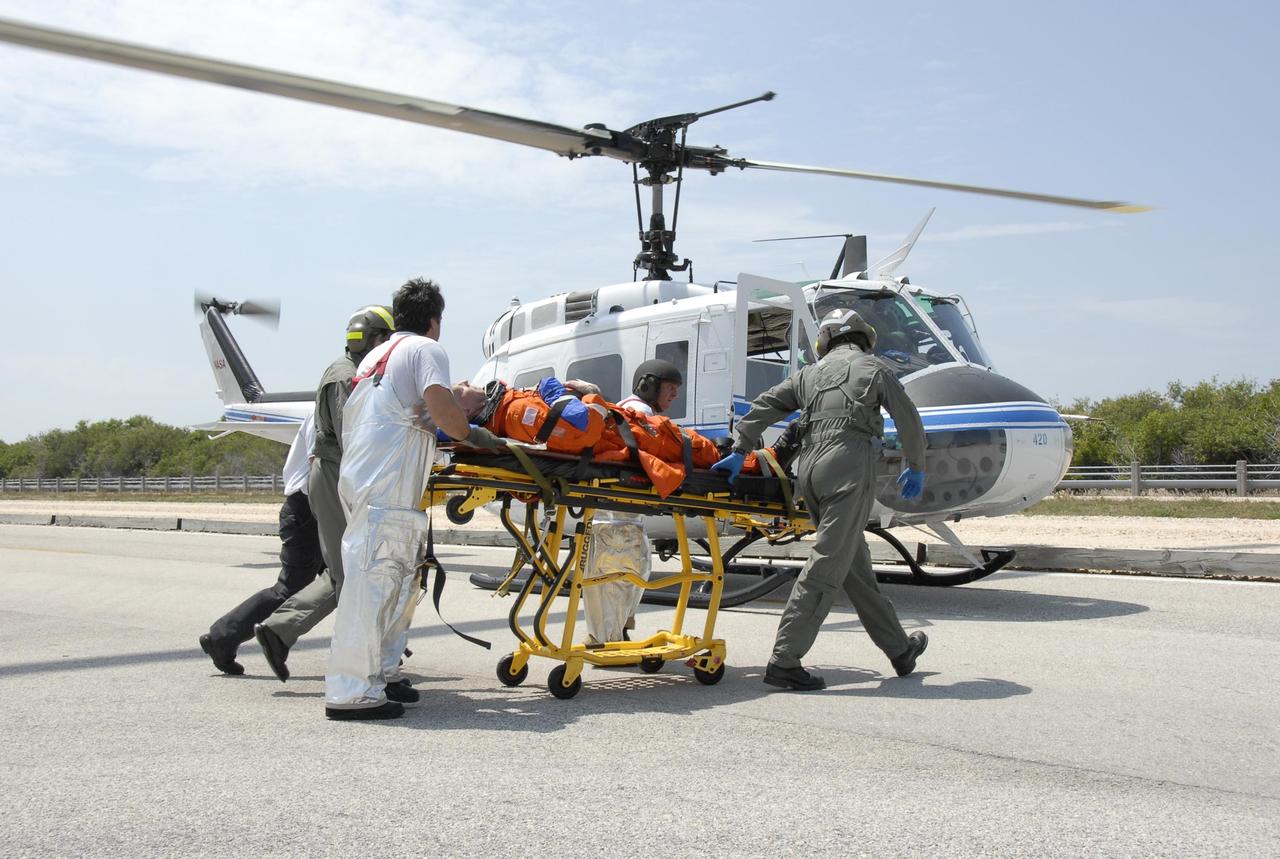
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, the KSC rescue team moves an "injured" astronaut toward a NASA helicopter, one of five participating in the exercise. The triage area was set up at Helipad 8, located near the fire station between Launch Pads 39A and 39B. The emergency exercise began on Launch Pad 39A. The participants were helped off the pad and taken to the triage site. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
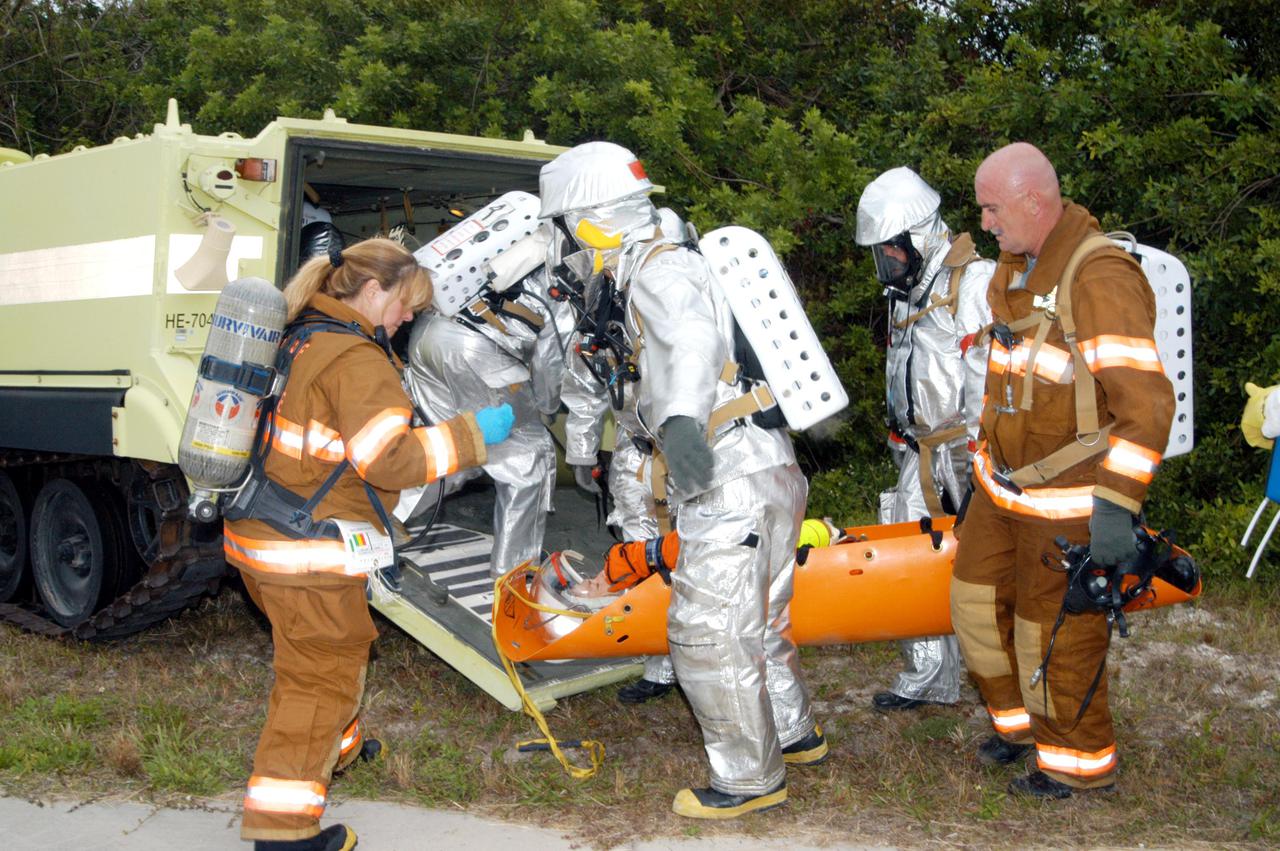

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During a simulated launch countdown_emergency simulation on Launch Pad 39A, the rescue team moves “injured” astronaut-suited workers out of the M-113 armored personnel carriers that transported them away from the pad (seen in the distance). Pad team members participated in the four-hour exercise simulating normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. The simulation tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
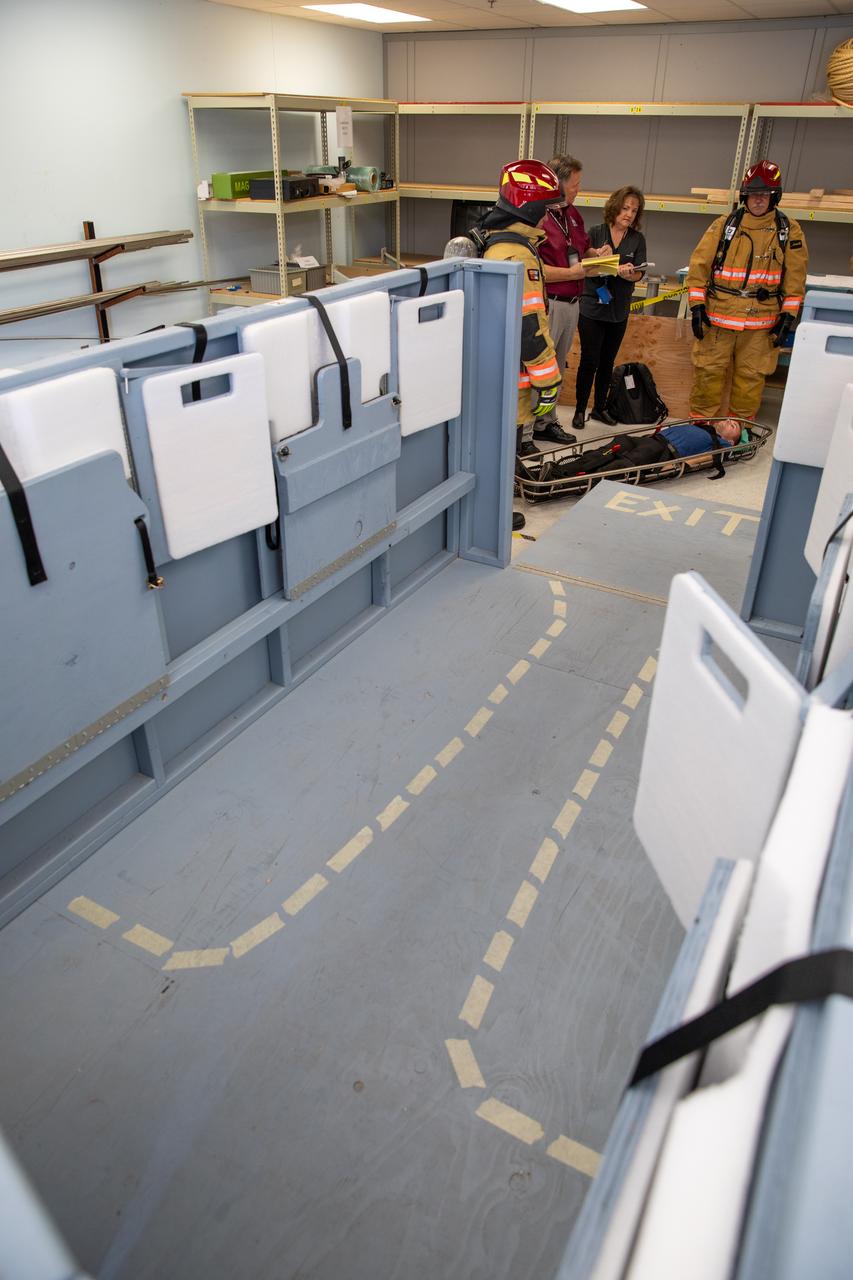

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presents a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket to NASA, Kennedy Fire Rescue personnel and other stakeholders on Feb. 19, 2020. The basket would be utilized at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, a fire rescue team walked through a series of trial scenarios and addressed items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more.
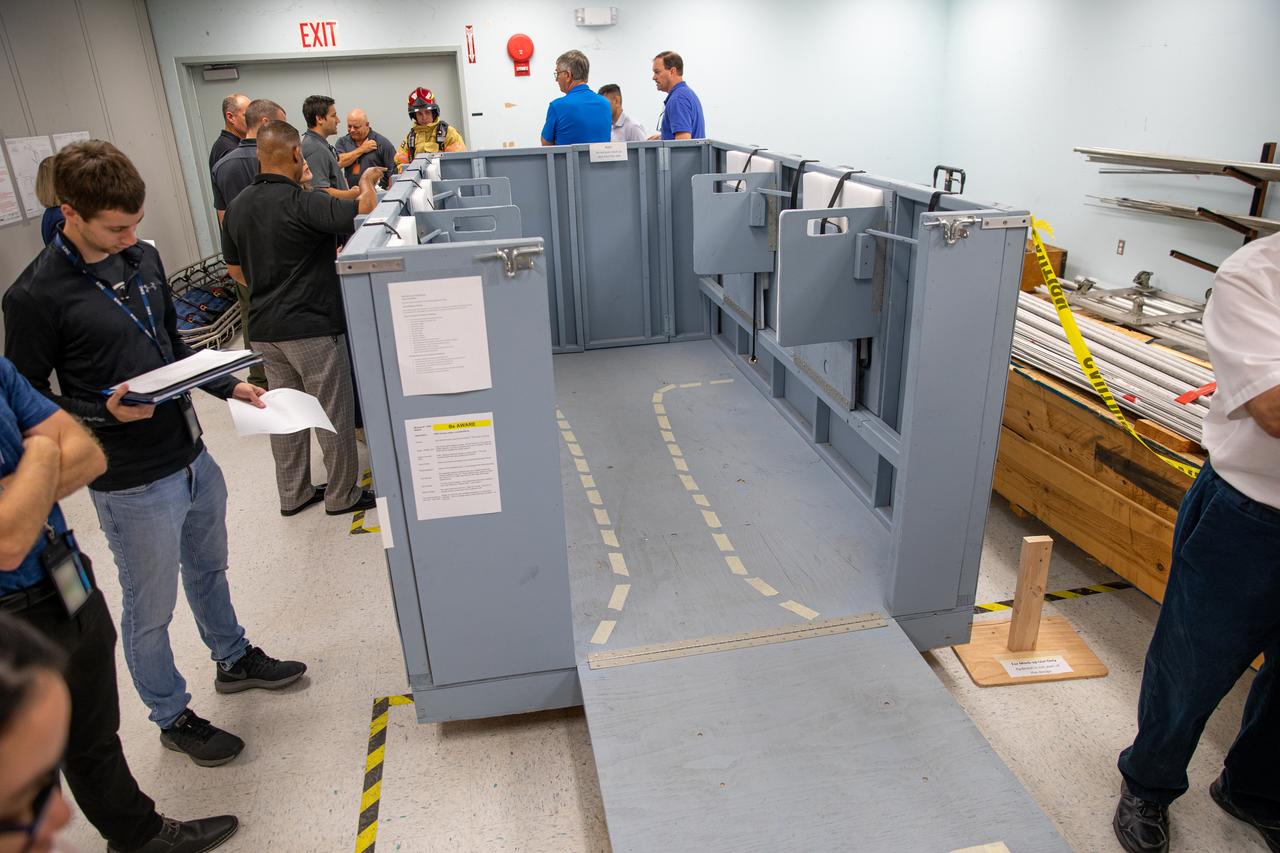

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presents a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket to NASA, Kennedy Fire Rescue personnel and other stakeholders on Feb. 19, 2020. The basket would be utilized at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, a fire rescue team walked through a series of trial scenarios and addressed items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more.
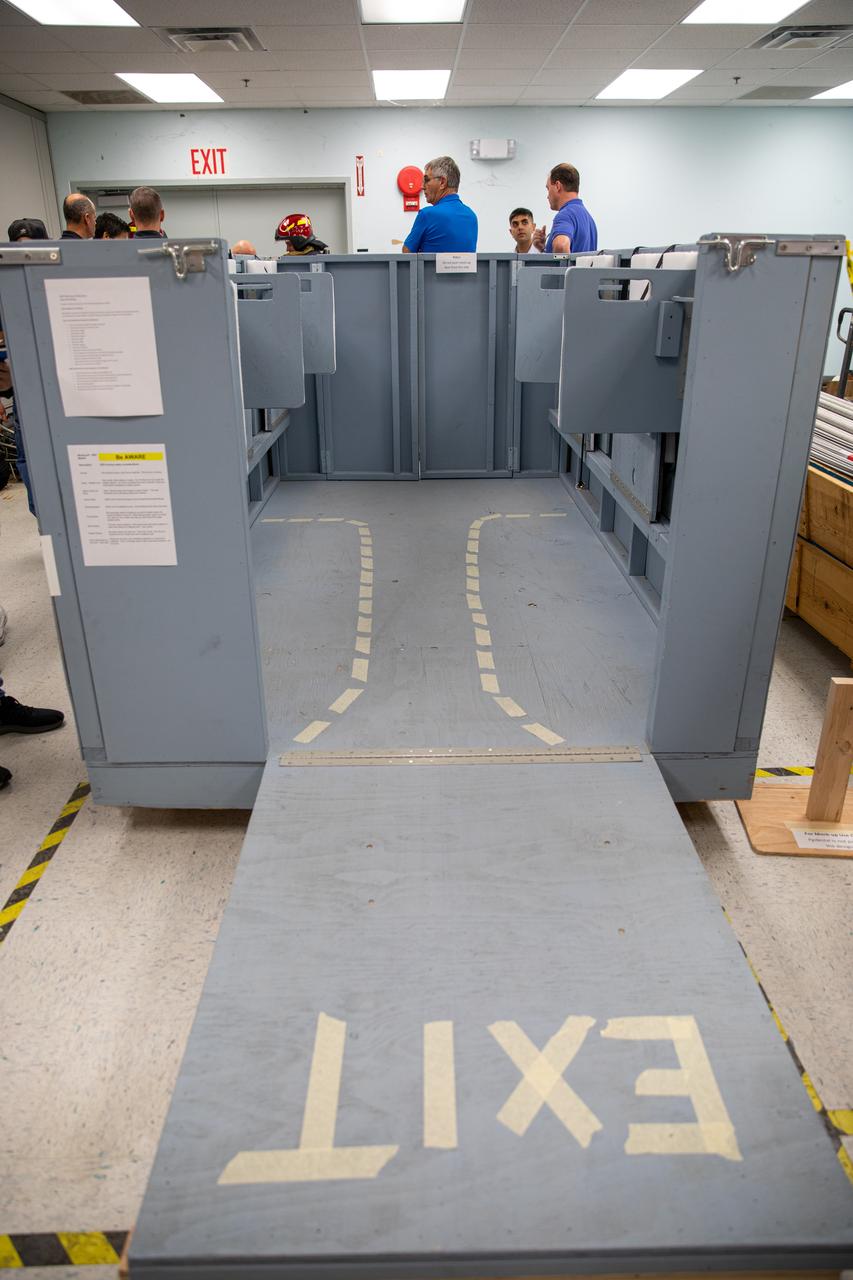

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presents a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket to NASA, Kennedy Fire Rescue personnel and other stakeholders on Feb. 19, 2020. The basket would be utilized at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, a fire rescue team walked through a series of trial scenarios and addressed items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more.
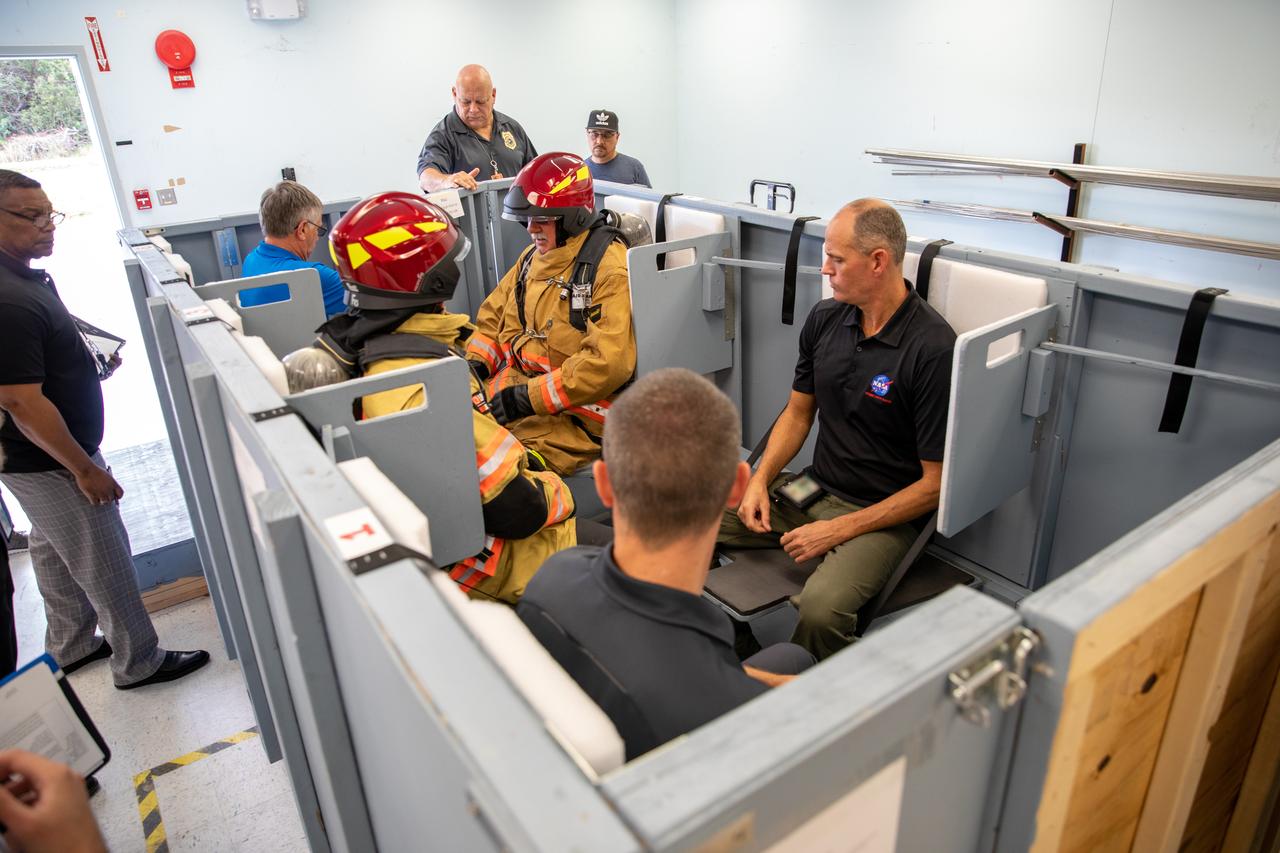

On Feb. 19, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prime contractor Reynolds, Smith and Hill presents a mock-up of a launch pad escape basket to NASA, Kennedy Fire Rescue personnel and other stakeholders. The basket would be utilized at Launch Pad 39B in the unlikely event of an emergency at the pad requiring evacuation during crewed missions under the Artemis Program. The actual egress basket will be designed larger than ones used during the shuttle era in order to accommodate fire rescue crew, astronauts and closeout crew. During the presentation, a fire rescue team walked through a series of trial scenarios and addressed items such as basket release location, seat depth to accommodate firefighters in full gear, sequence of loading and more.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Launch Pad 39A slidewire basket landing site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Mode II-IV exercise is underway, involving NASA fire rescue personnel, volunteers portraying astronauts with simulated injuries, helicopters and personnel from the Air Force’s 920th Rescue Wing and medical trauma teams at three central Florida hospitals. Here, participants move into an M-113 armored personnel vehicle for transport from the pad. The drill allows teams to practice an emergency response at Pad 39A, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. The Space Shuttle Program and U.S. Air Force are conducting the emergency simulation. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
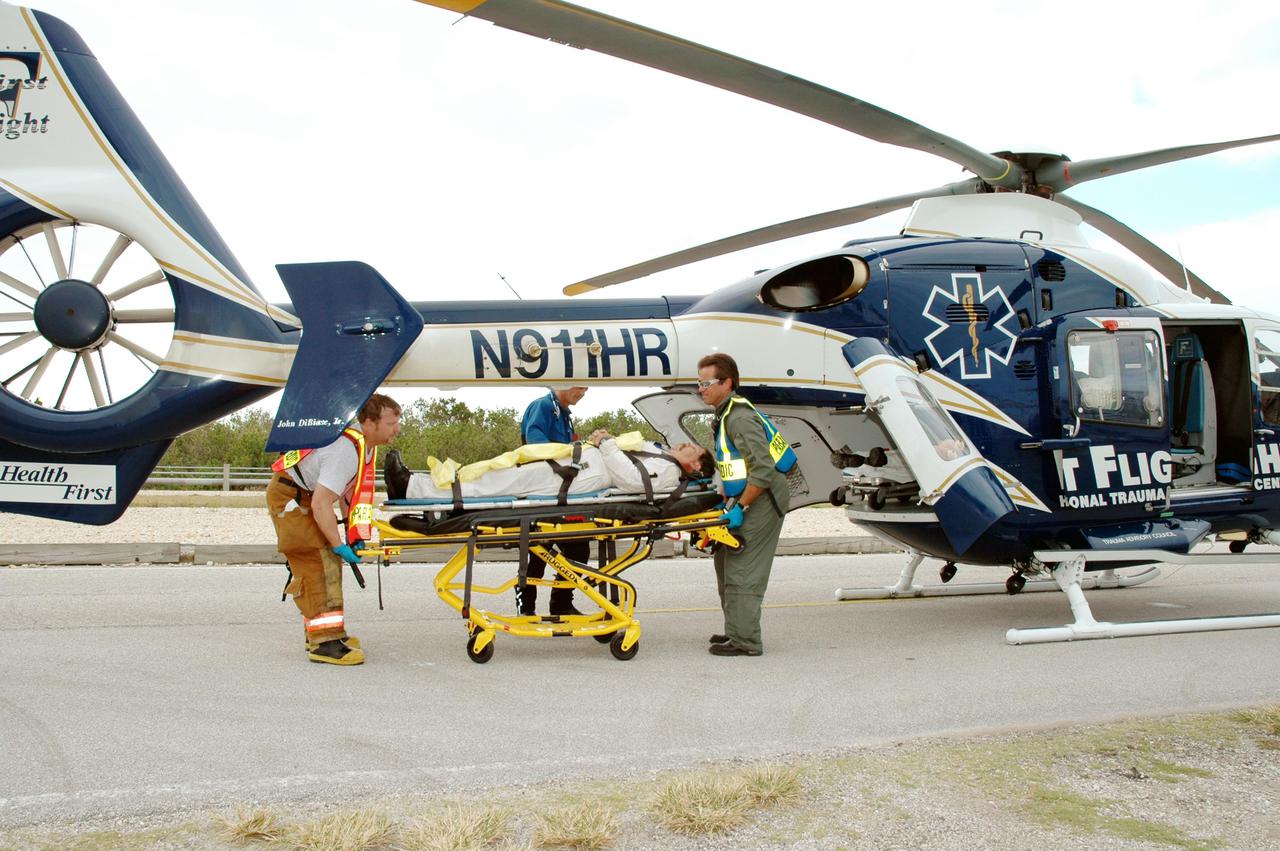

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During a simulated launch countdown_emergency simulation on Launch Pad 39A, astronaut-suited workers are placed in a medical-rescue helicopter for transport to a hospital participating in the simulation. Pad team members took part in the four-hour exercise simulating normal launch countdown operations, with the added challenge of a fictitious event causing an evacuation of the vehicle and launch pad. The simulation tested the team’s rescue approaches on the Fixed Service Structure, slidewire basket evacuation, triage care and transportation of injured personnel to hospitals, as well as communications and coordination.
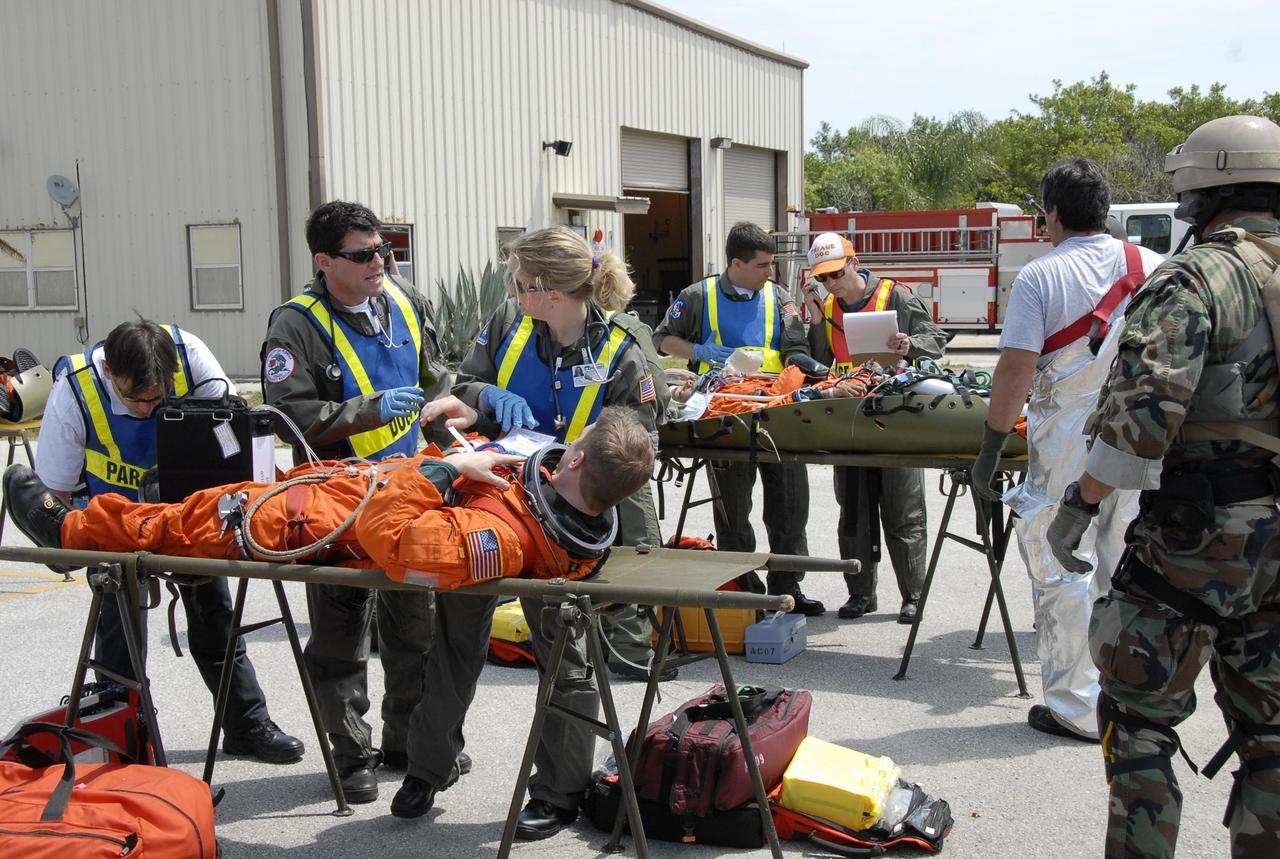

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During the second stage of a simulated emergency, known as Mode 4, a triage area set up at Helipad 8, located near the fire station between Launch Pads 39A and 39B, is busy as rescue workers monitor the "injured." KSC personnel portrayed the astronauts. The participants were helped off the pad and taken to the triage site. The "injured" worker may be airlifted to participating area hospitals. The KSC rescue teams are practicing emergency procedures in the unlikely scenario of a mishap on the pad during a launch sequence. The exercises are standard training procedures to assess and prepare emergency personnel, procedures and hardware. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After space shuttle Endeavour's rollout to Launch pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida this morning, two different shuttles are poised on two different launch pads. Shuttle Atlantis (right) already was on Launch Pad 39A. With the space shuttle fleet set for retirement in 2010, this is expected to be the final time two shuttles will be on launch pads at the same time. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during Atlantis' upcoming mission to upgrade NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Atlantis is targeted to launch May 12. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-127 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
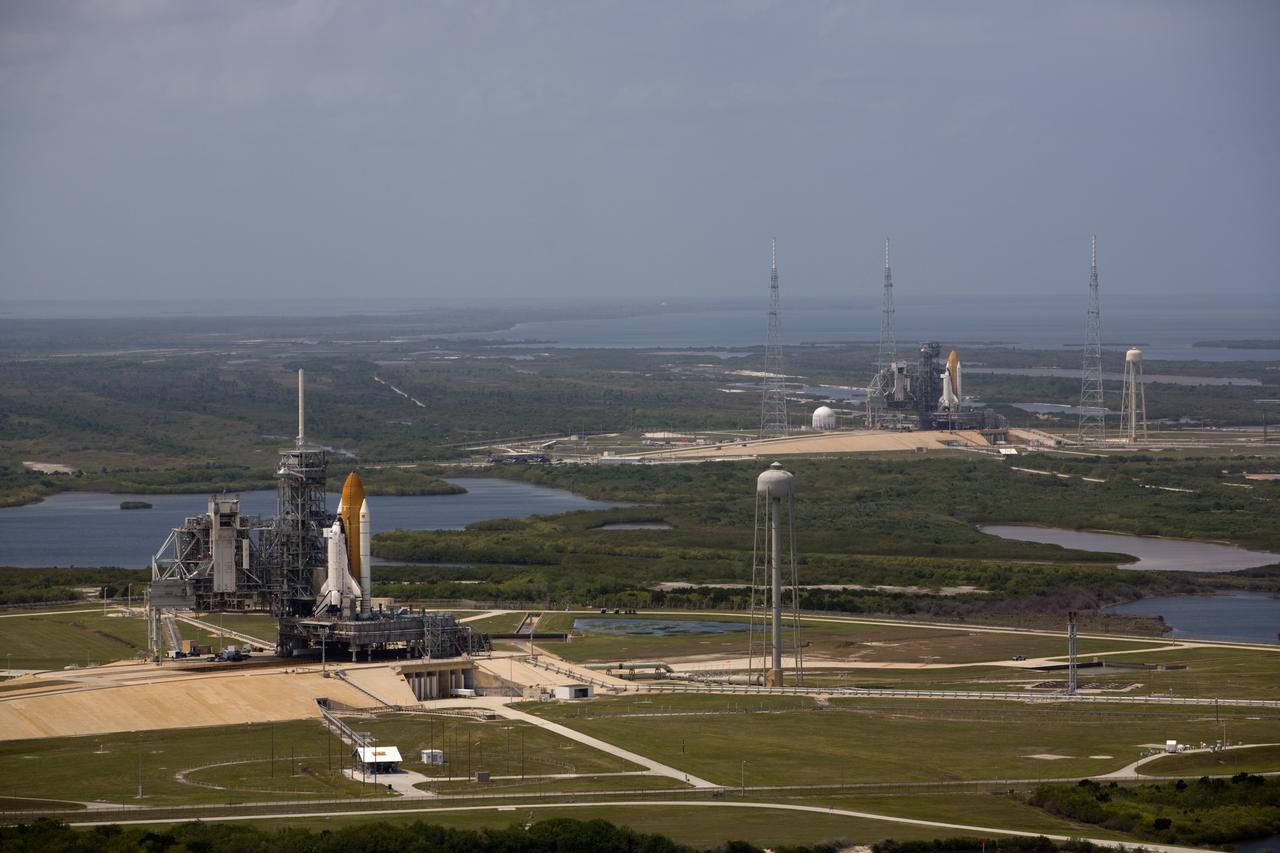

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After space shuttle Endeavour's rollout to Launch pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida this morning, two different shuttles are poised on two different launch pads. Shuttle Atlantis (left) already was on Launch Pad 39A. With the space shuttle fleet set for retirement in 2010, this is expected to be the final time two shuttles will be on launch pads at the same time. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during Atlantis' upcoming mission to upgrade NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Atlantis is targeted to launch May 12. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-127 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
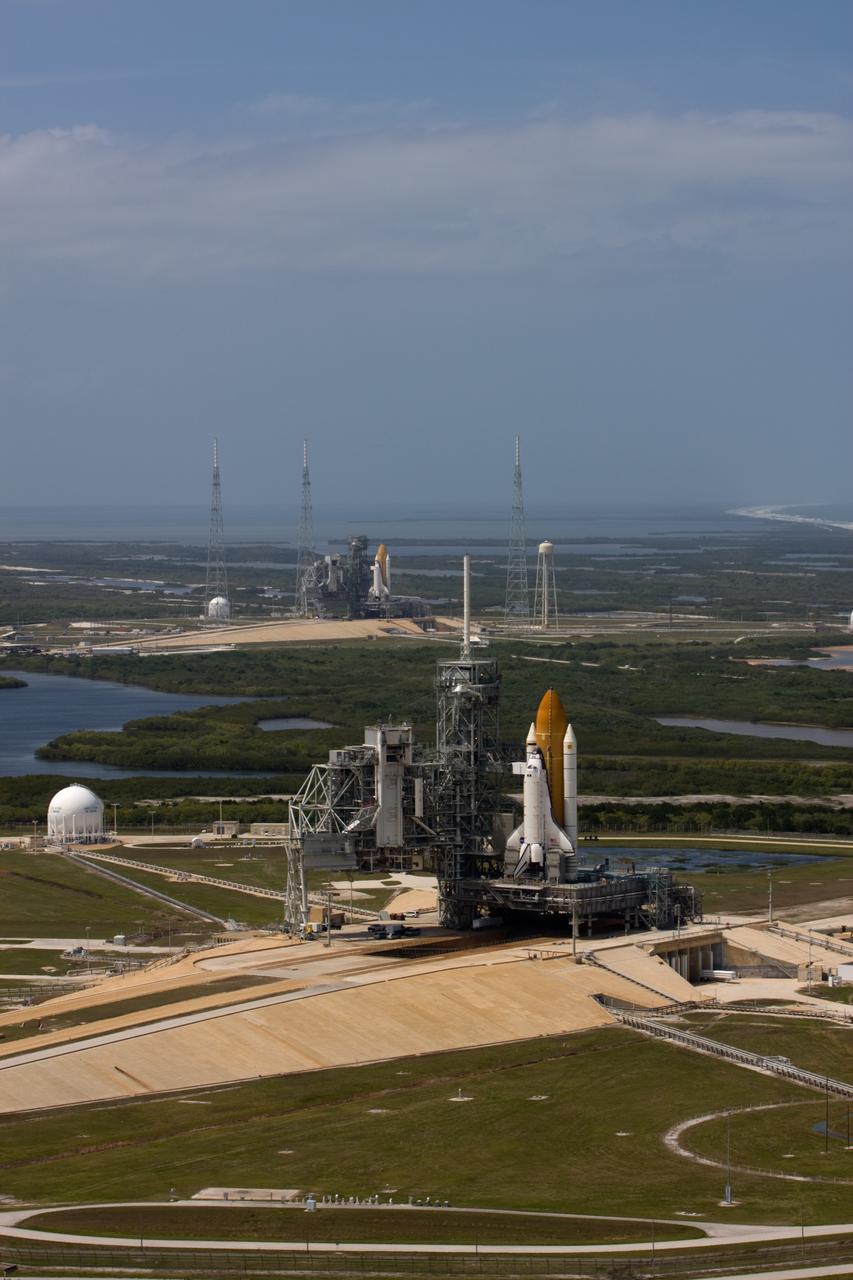

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After space shuttle Endeavour's rollout to Launch pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida this morning, two different shuttles are poised on two different launch pads. Shuttle Atlantis (foreground) already was on Launch Pad 39A. With the space shuttle fleet set for retirement in 2010, this is expected to be the final time two shuttles will be on launch pads at the same time. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during Atlantis' upcoming mission to upgrade NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Atlantis is targeted to launch May 12. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-127 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
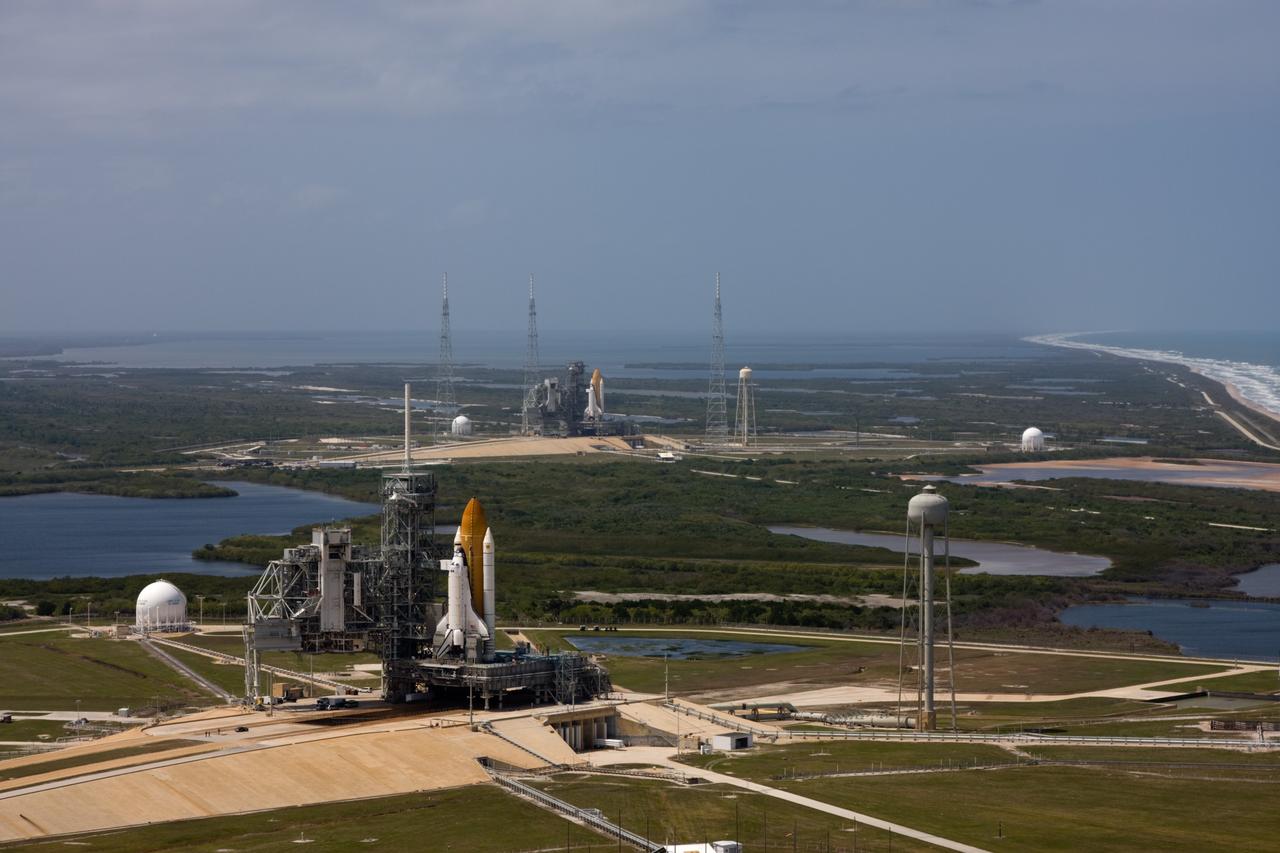

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After space shuttle Endeavour's rollout to Launch pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida this morning, two different shuttles are poised on two different launch pads. Shuttle Atlantis (foreground) already was on Launch Pad 39A. With the space shuttle fleet set for retirement in 2010, this is expected to be the final time two shuttles will be on launch pads at the same time. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during Atlantis' upcoming mission to upgrade NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Atlantis is targeted to launch May 12. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-127 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After space shuttle Endeavour's rollout to Launch pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida this morning, two different shuttles are poised on two different launch pads. Shuttle Atlantis (left) already was on Launch Pad 39A. With the space shuttle fleet set for retirement in 2010, this is expected to be the final time two shuttles will be on launch pads at the same time. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during Atlantis' upcoming mission to upgrade NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Atlantis is targeted to launch May 12. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-127 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After space shuttle Endeavour's rollout to Launch pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida this morning, two different shuttles are poised on two different launch pads. Shuttle Atlantis (left) already was on Launch Pad 39A. With the space shuttle fleet set for retirement in 2010, this is expected to be the final time two shuttles will be on launch pads at the same time. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during Atlantis' upcoming mission to upgrade NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Atlantis is targeted to launch May 12. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-127 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
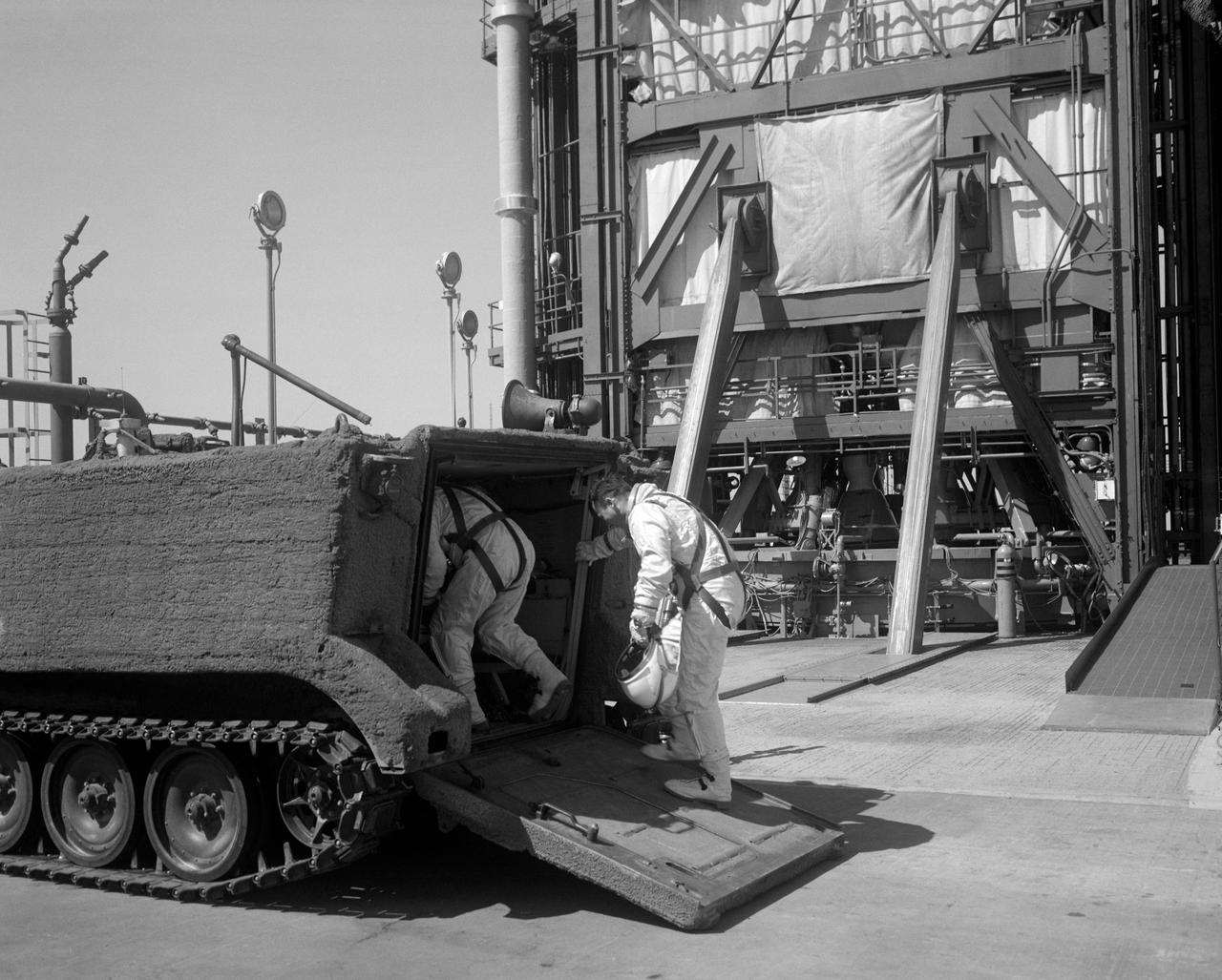

S65-20637 (1965) --- Astronauts John W. Young, pilot, and Virgil I. Grissom, command pilot, for the Gemini-Titan 3 flight, are shown entering launch pad abort rescue vehicle during training exercise.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
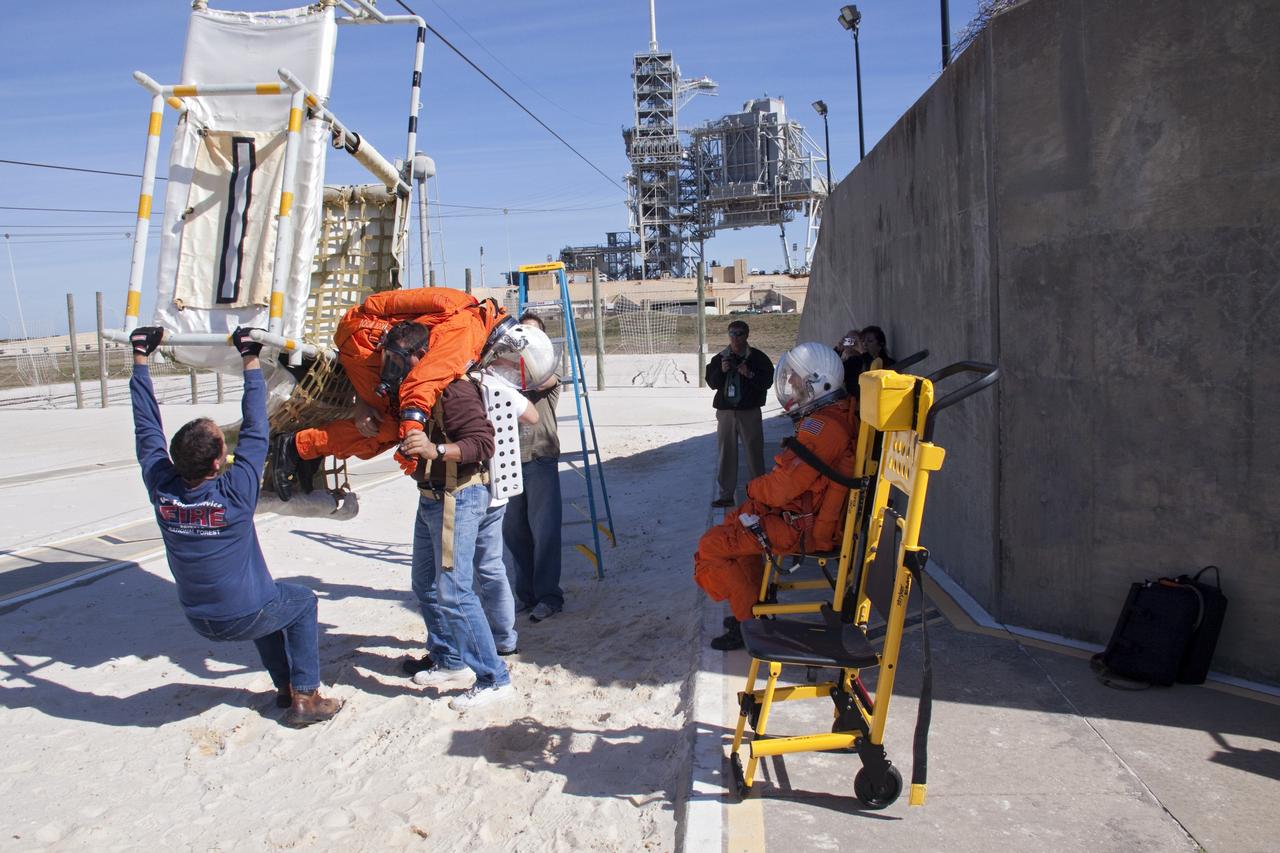

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise in the bunkers behind the slidewire basket landing site. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
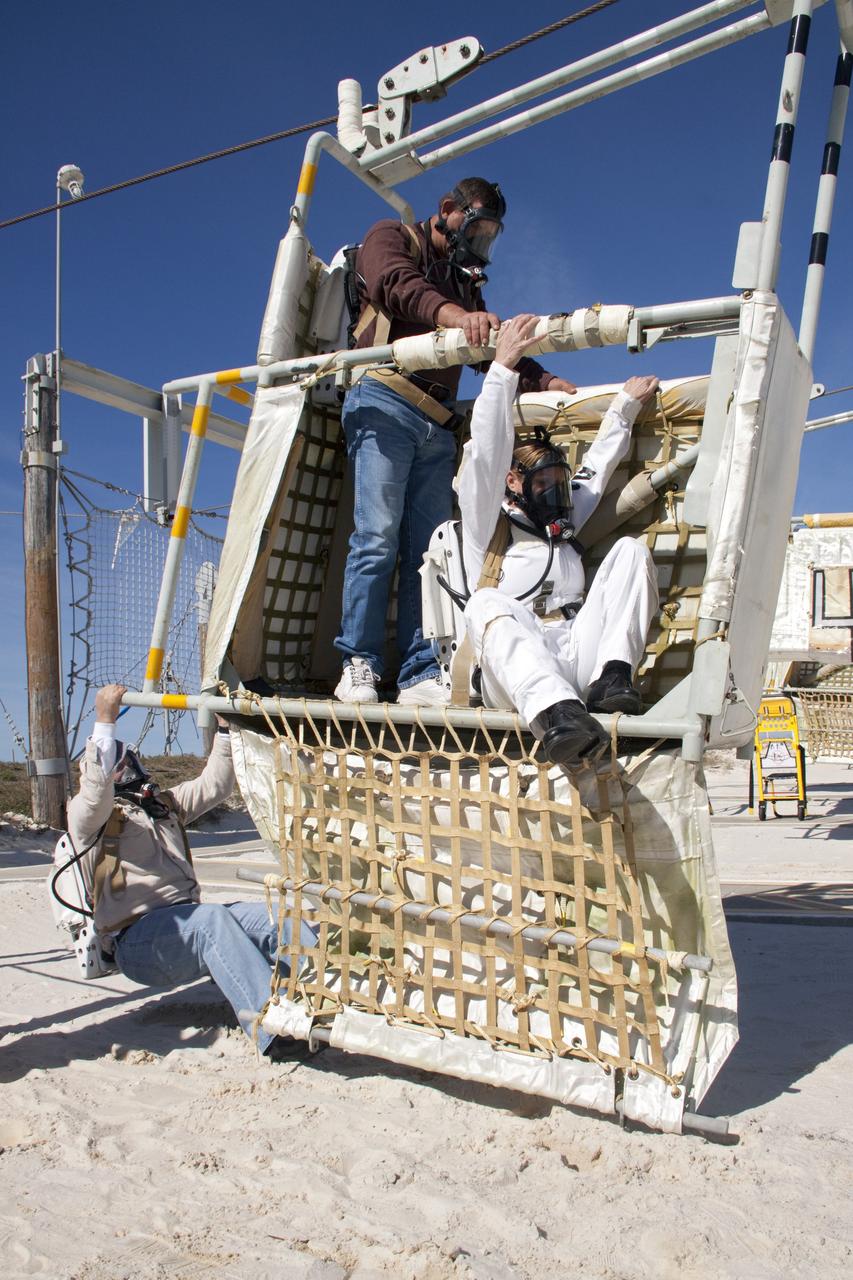

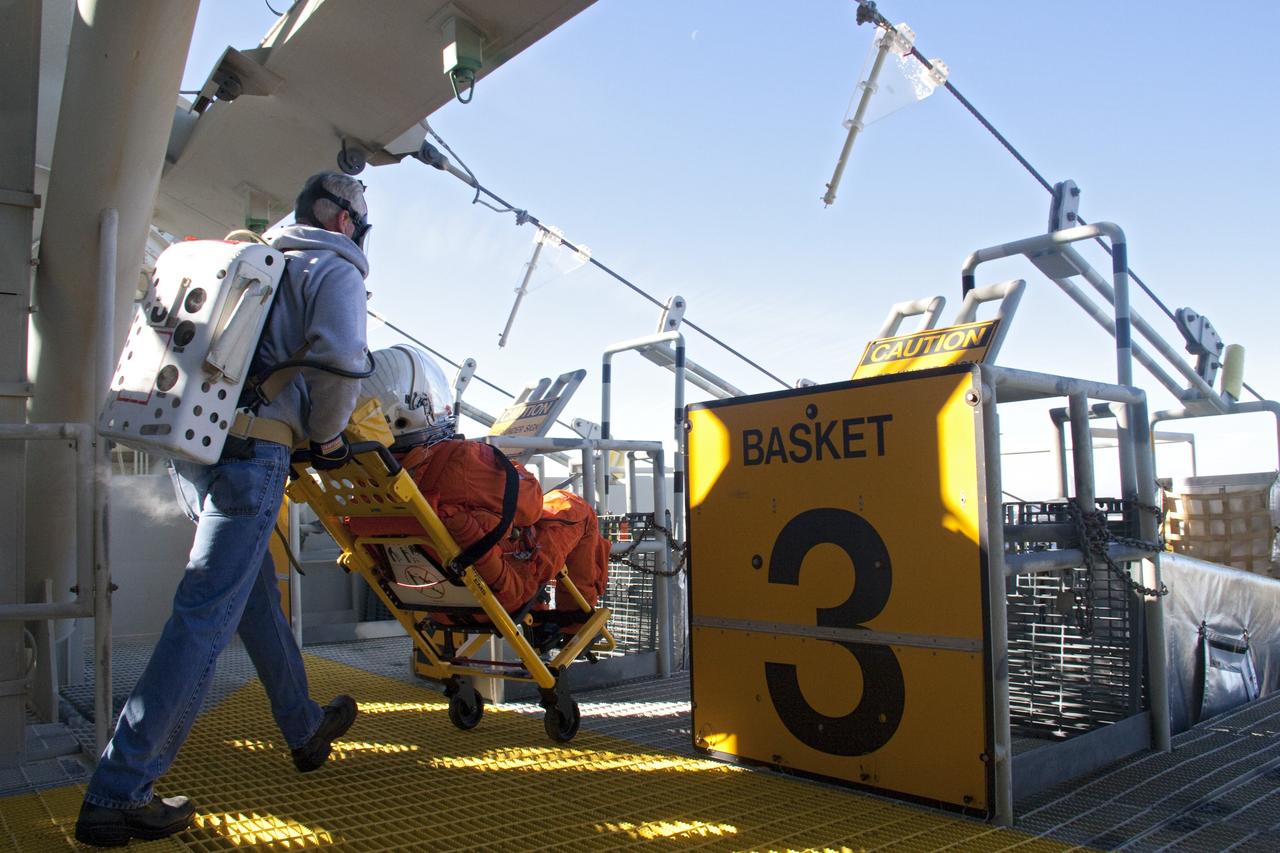
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at the slidewire basket landing site. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
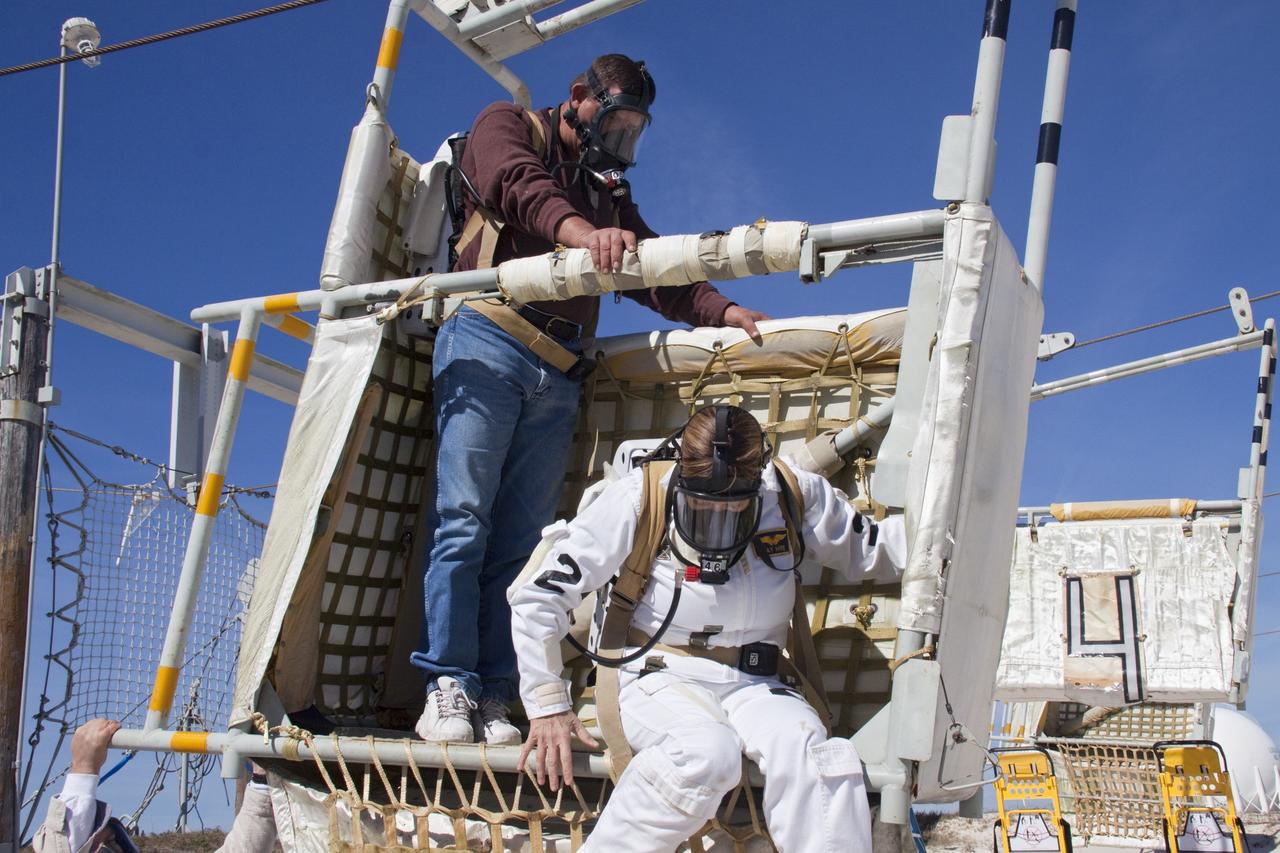

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at the slidewire basket landing site. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
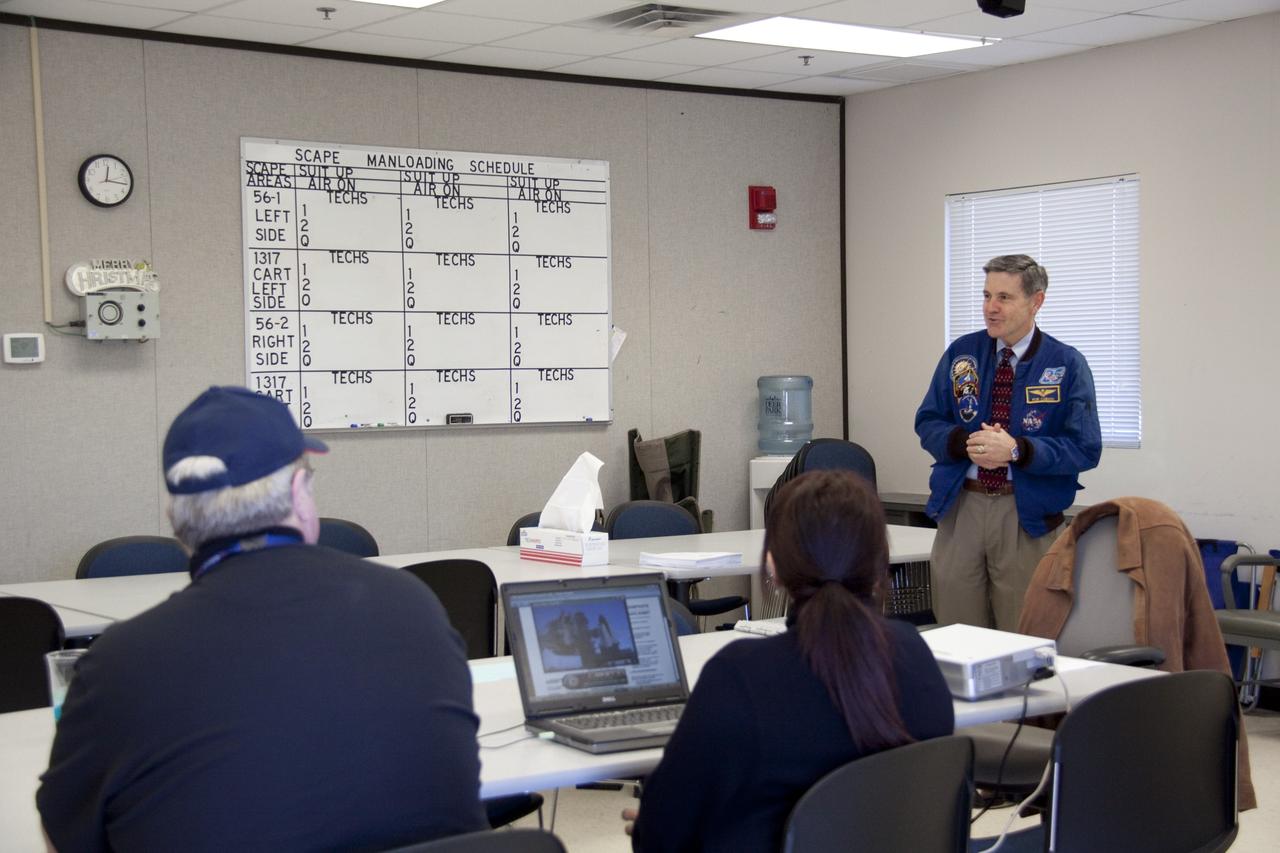

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Bob Cabana speaks to members of an emergency escape training class. The training is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in a training exercise that allows teams to practice emergency response procedures at Launch Pad 39A, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, helicopters and personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

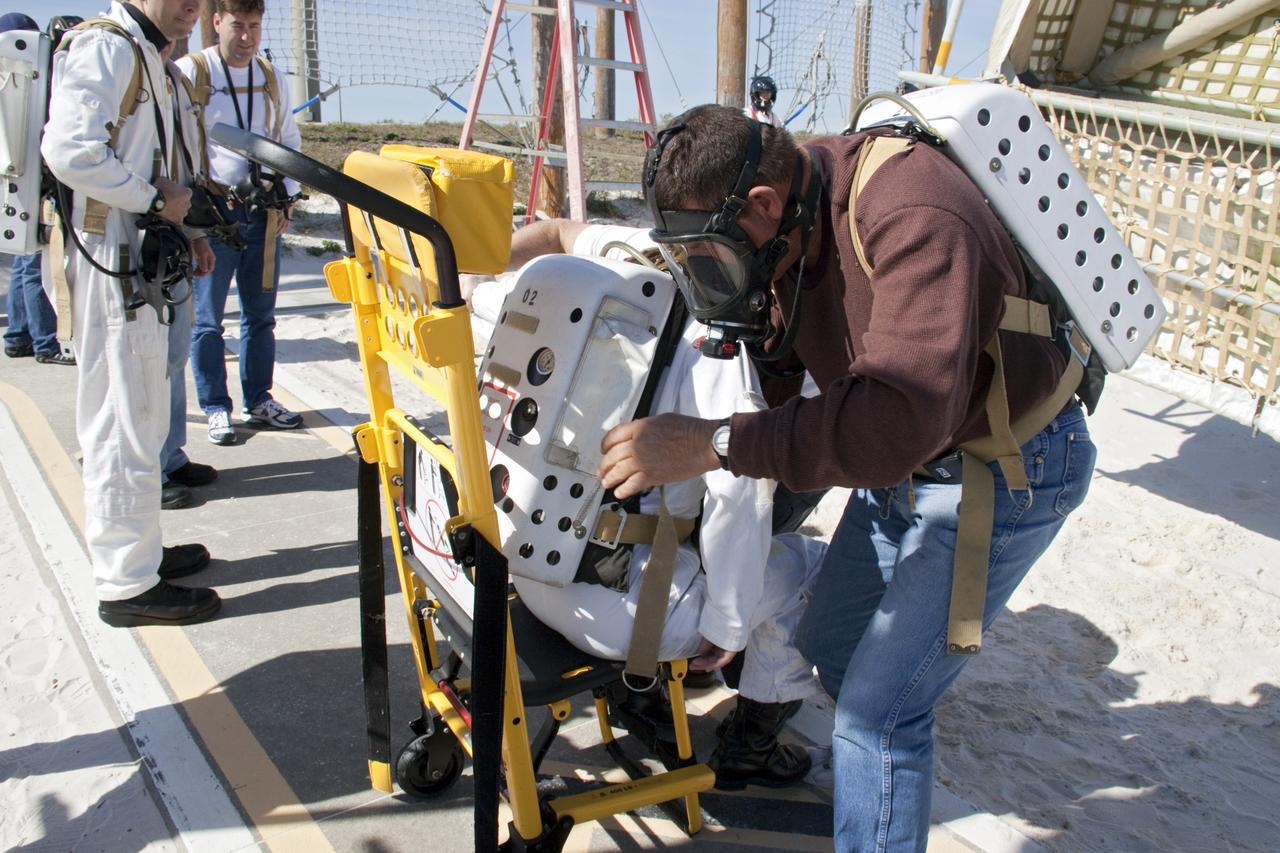
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise in the bunkers behind the slidewire basket landing site. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
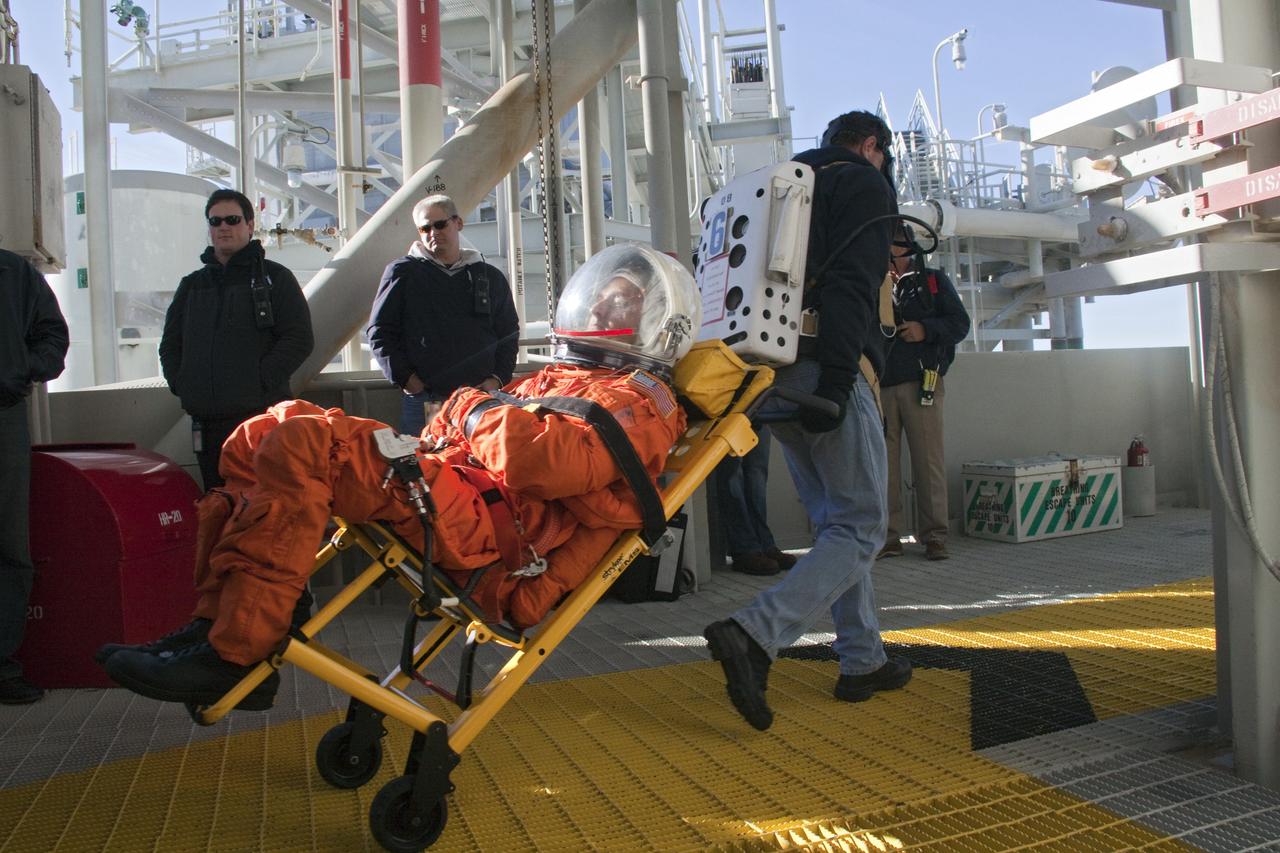
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

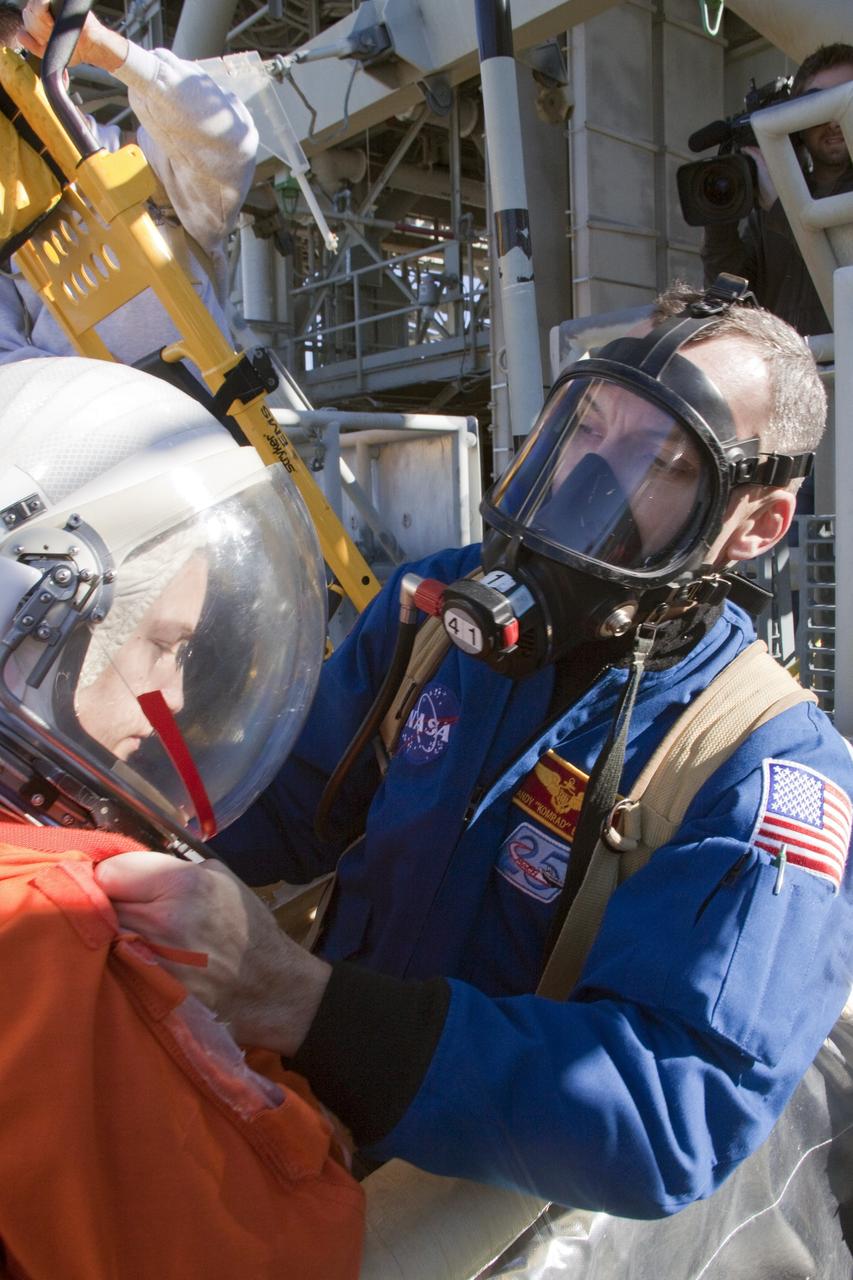
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at the slidewire basket landing site. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
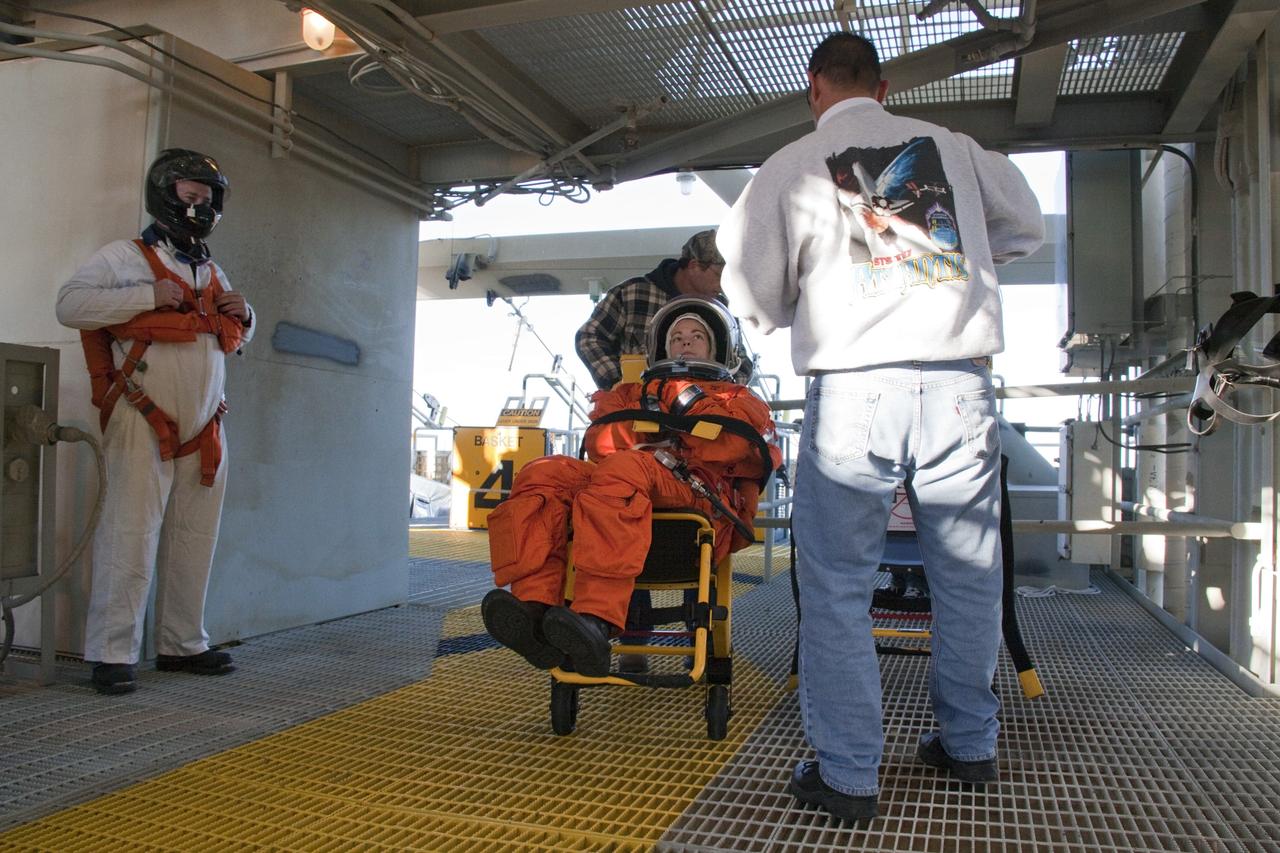
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

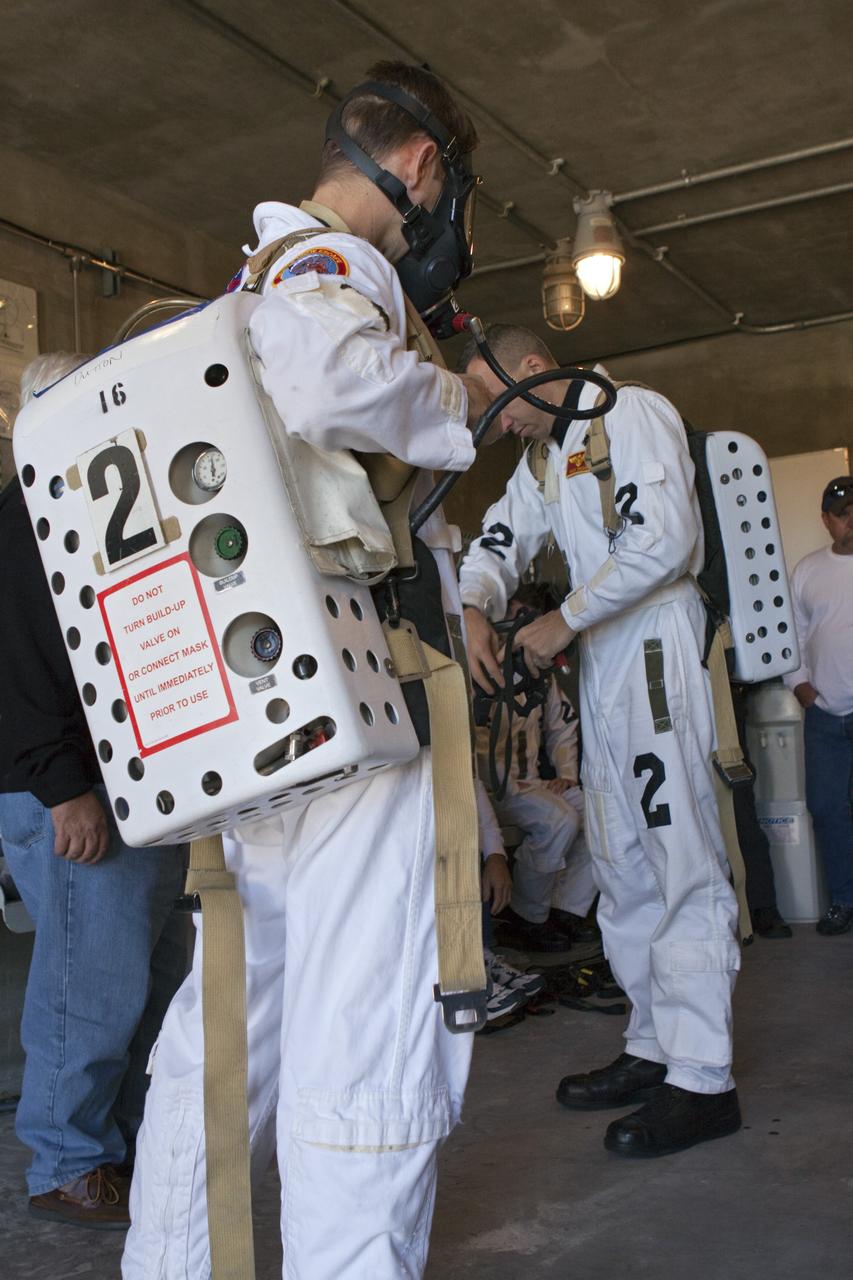
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

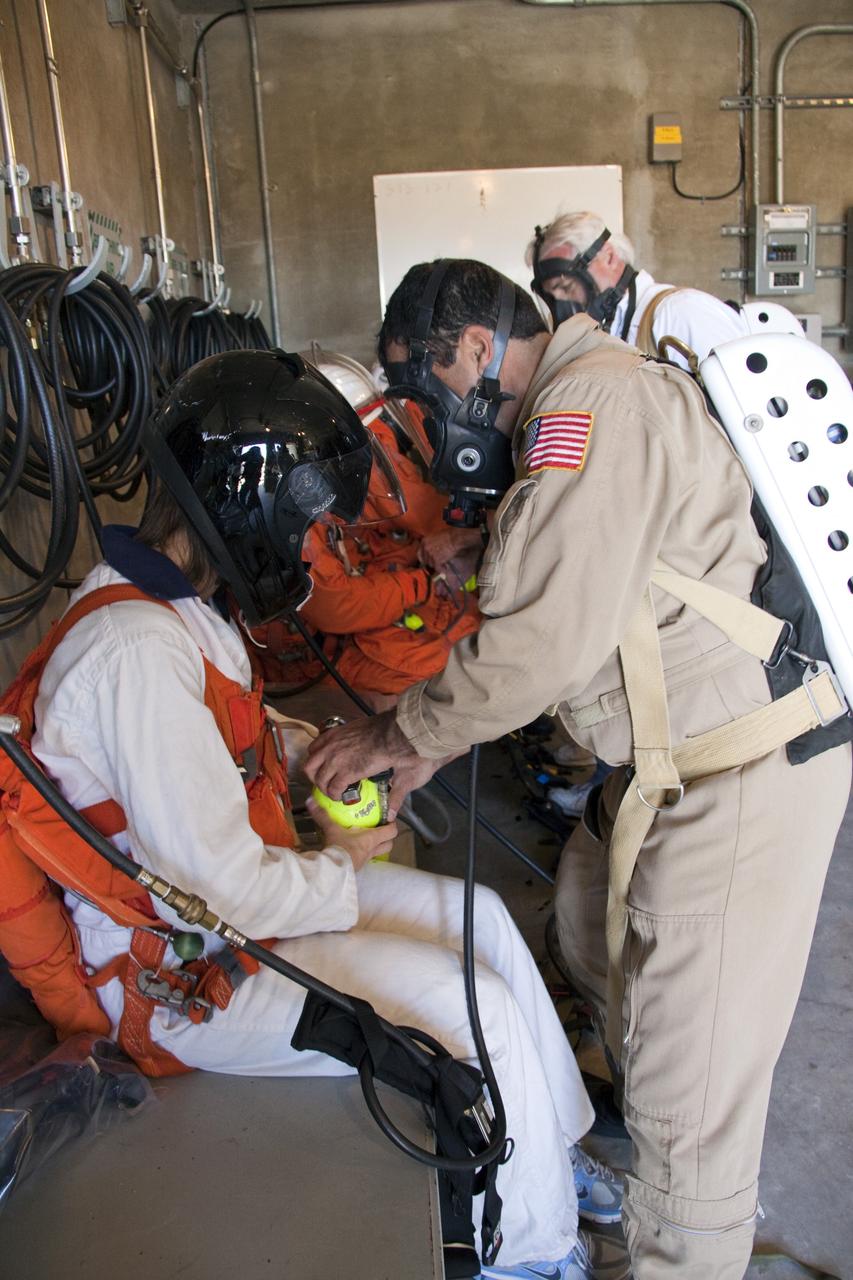
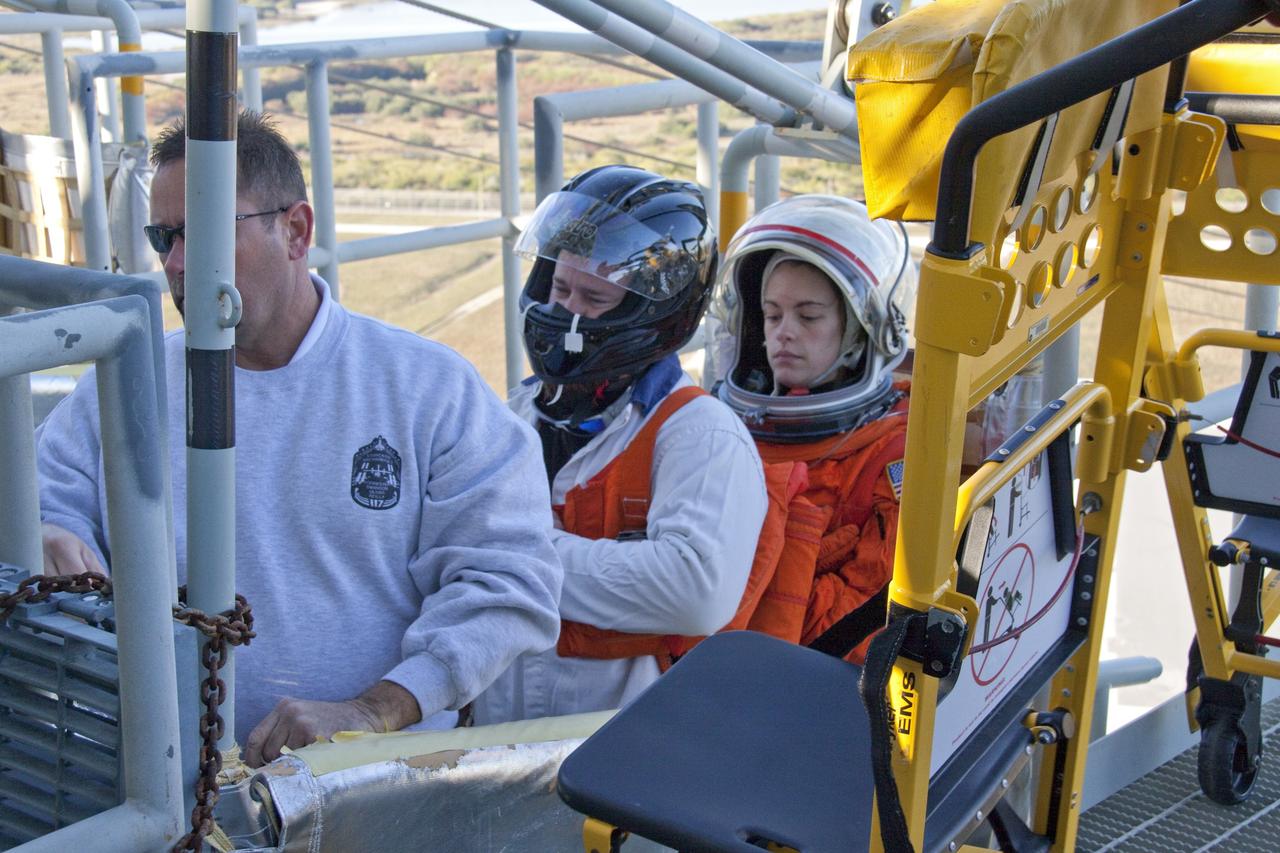
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team suit up in the bunkers below Launch Pad 39A prior to the start of a simulated evacuation exercise. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
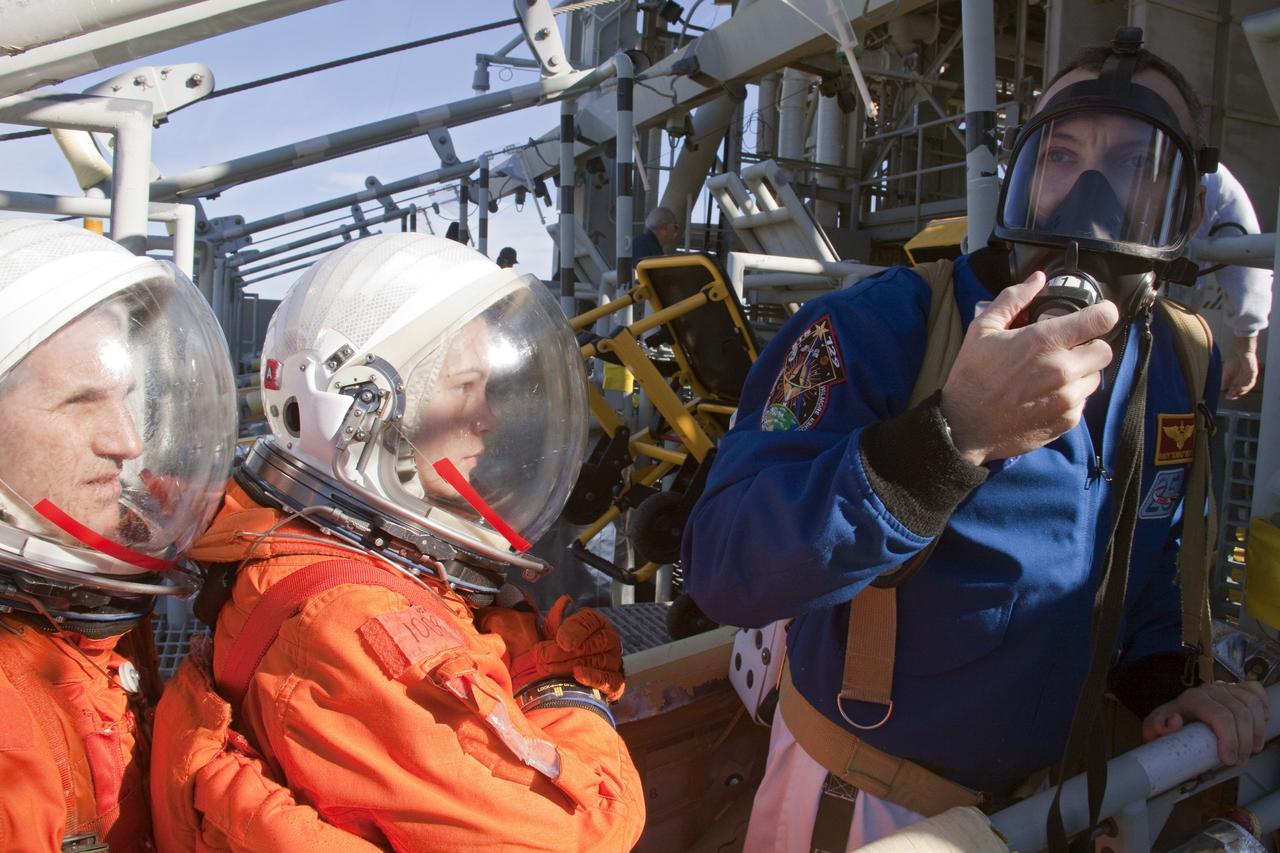

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
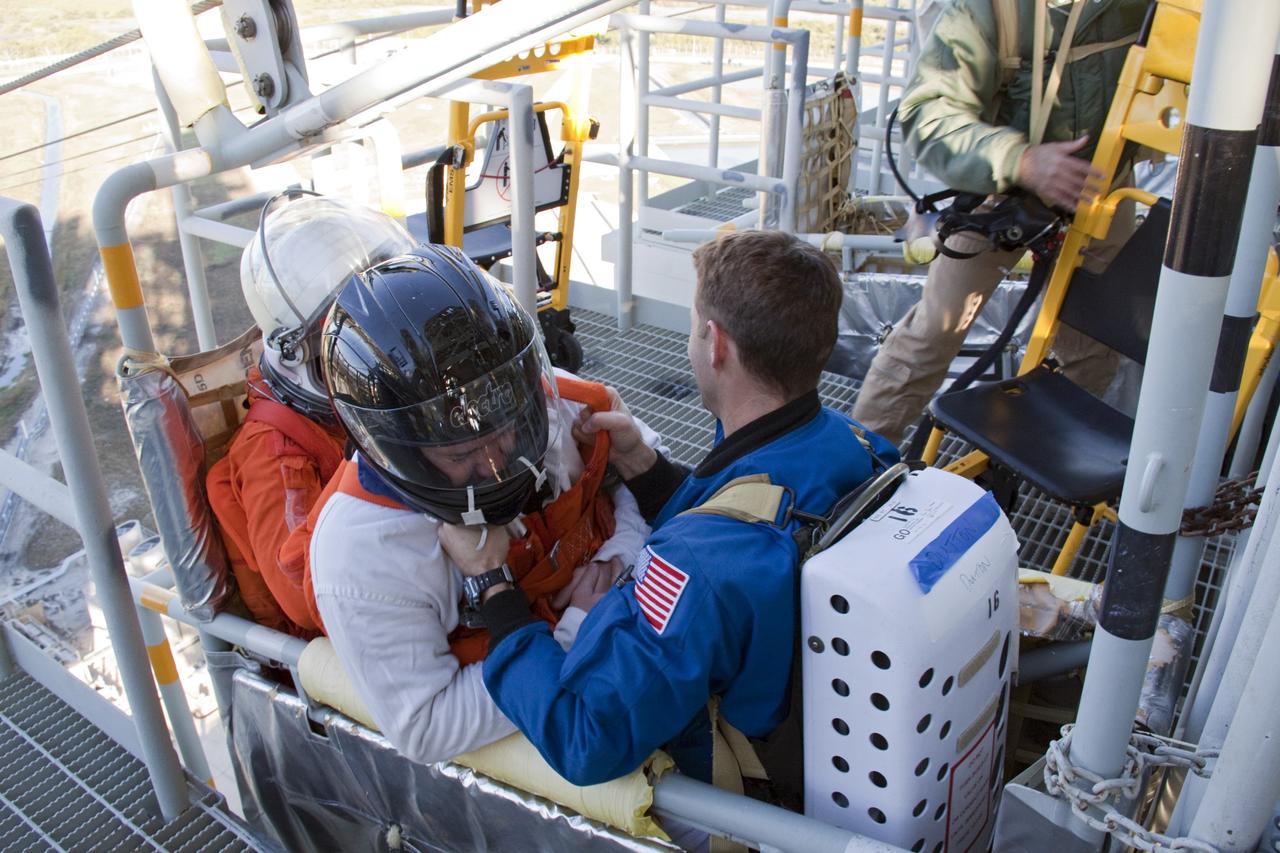

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
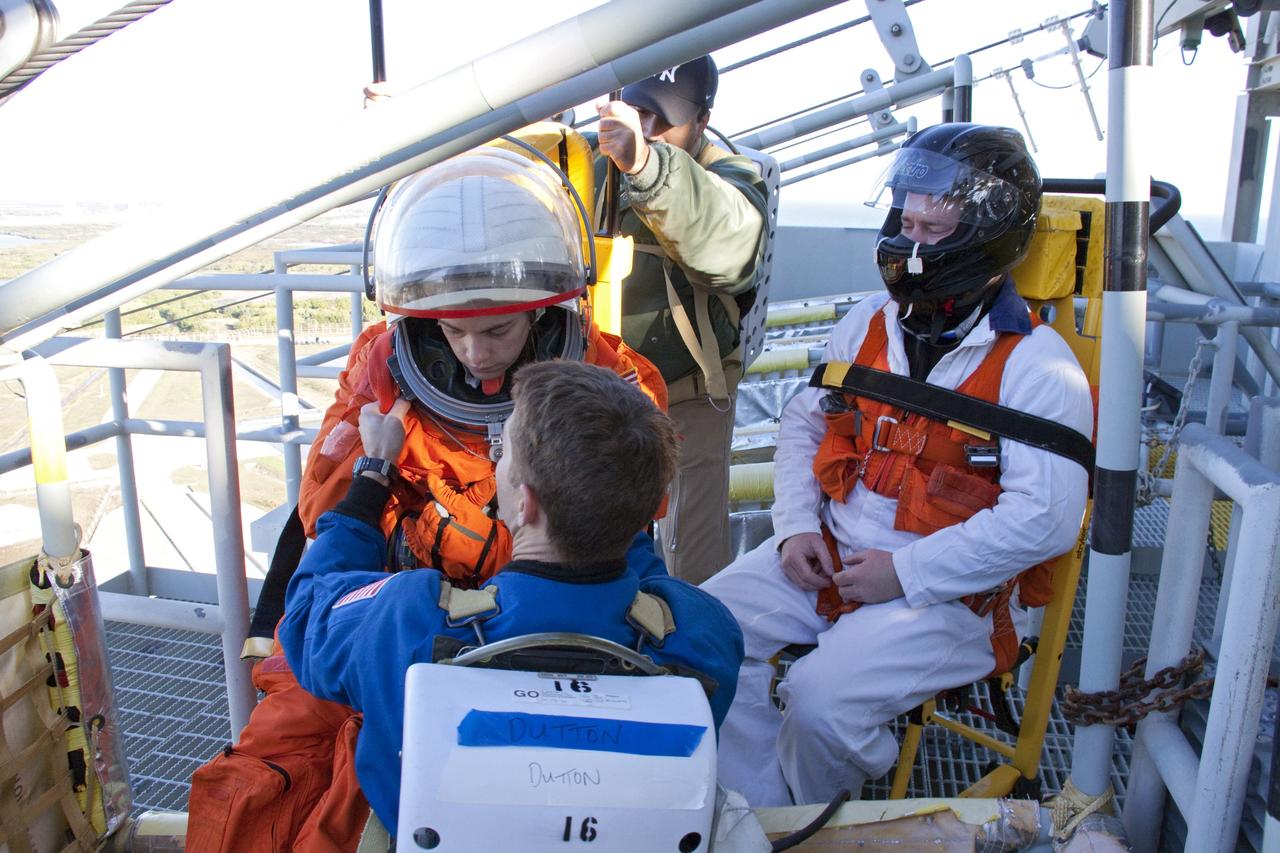

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
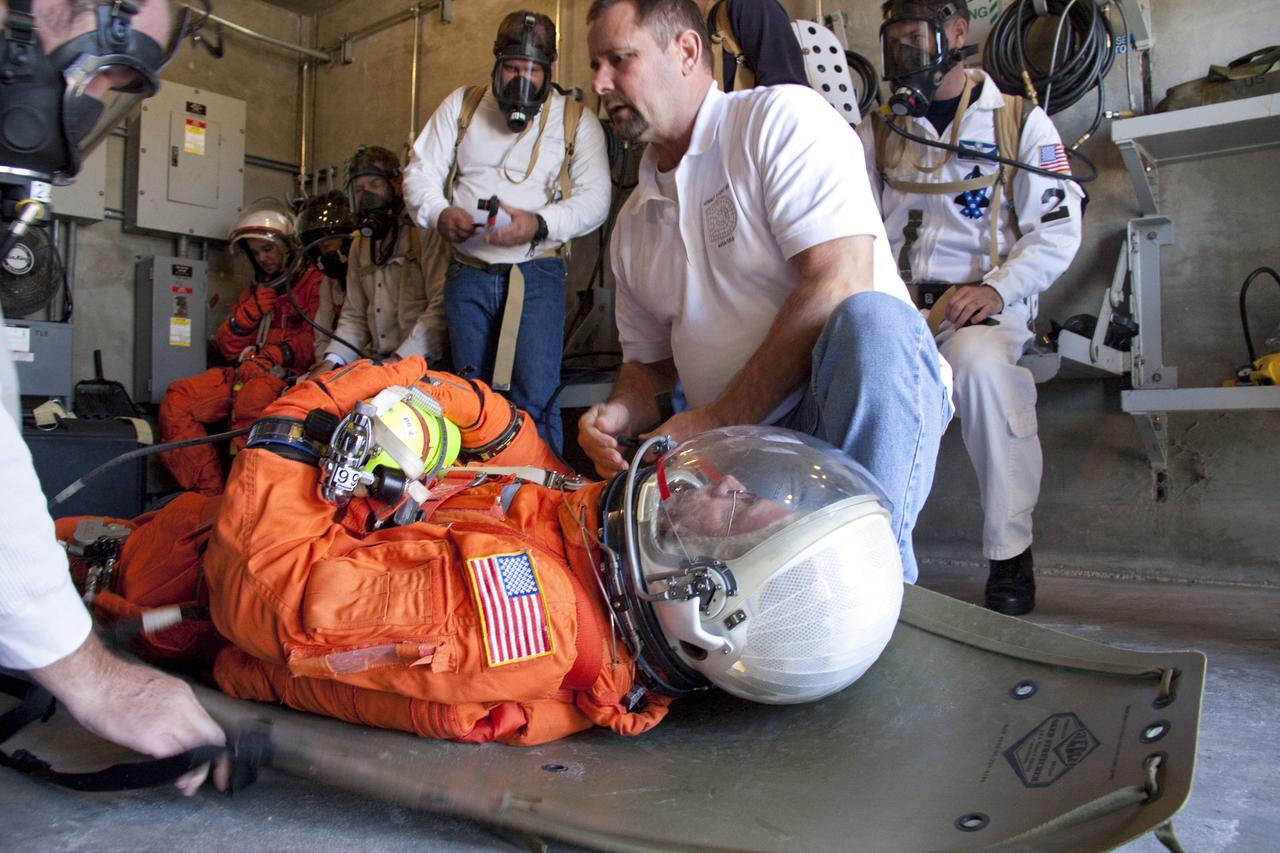

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise in the bunkers behind the slidewire basket landing site. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
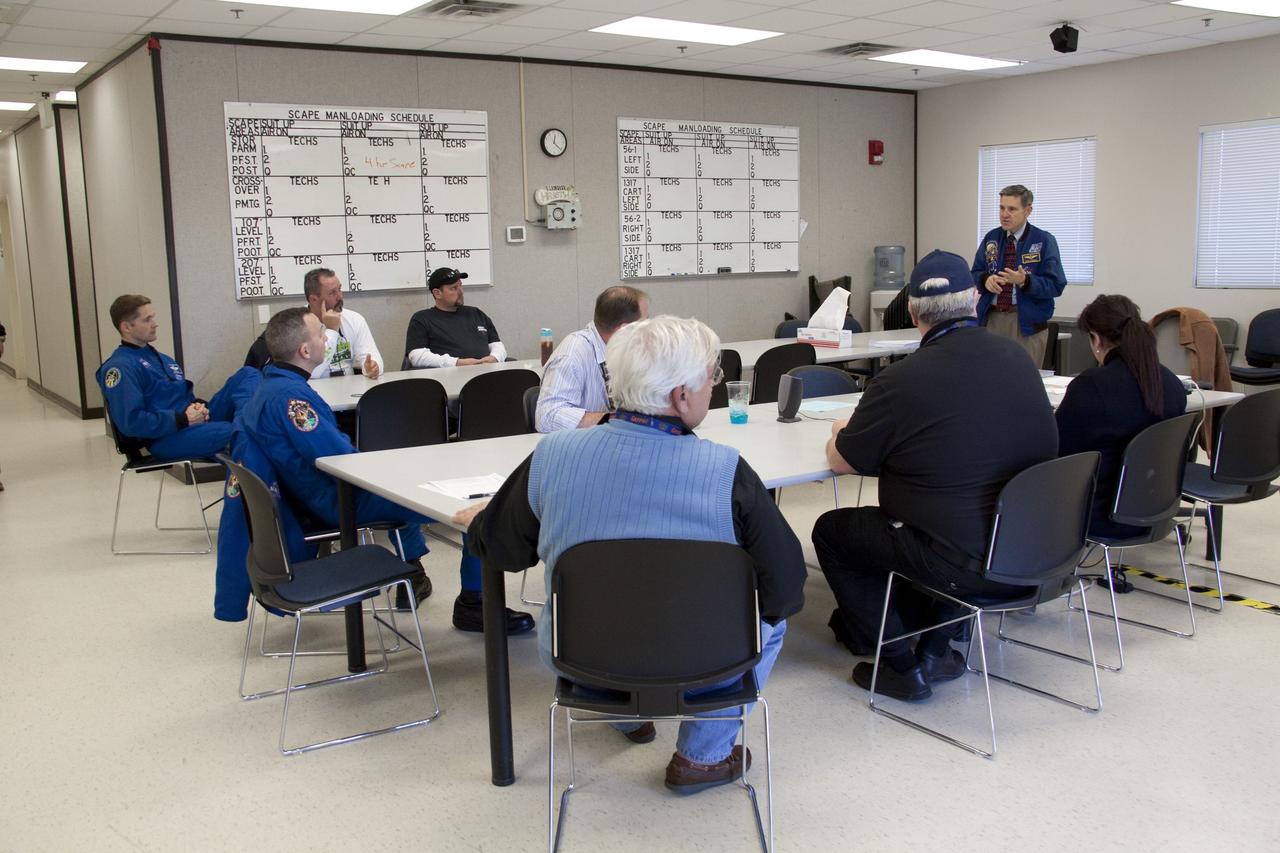

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Bob Cabana speaks to members of an emergency escape training class. The training is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in a training exercise that allows teams to practice emergency response procedures at Launch Pad 39A, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, helicopters and personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
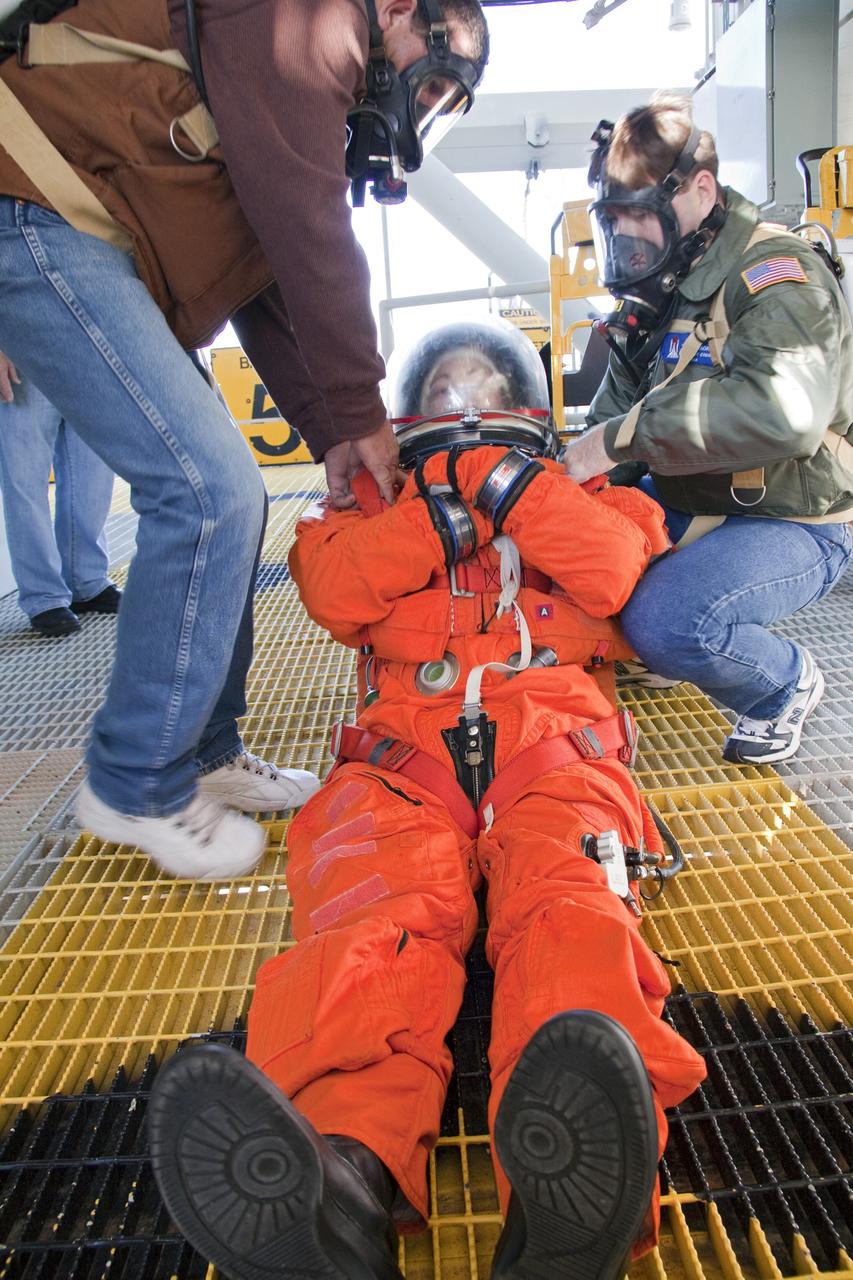

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
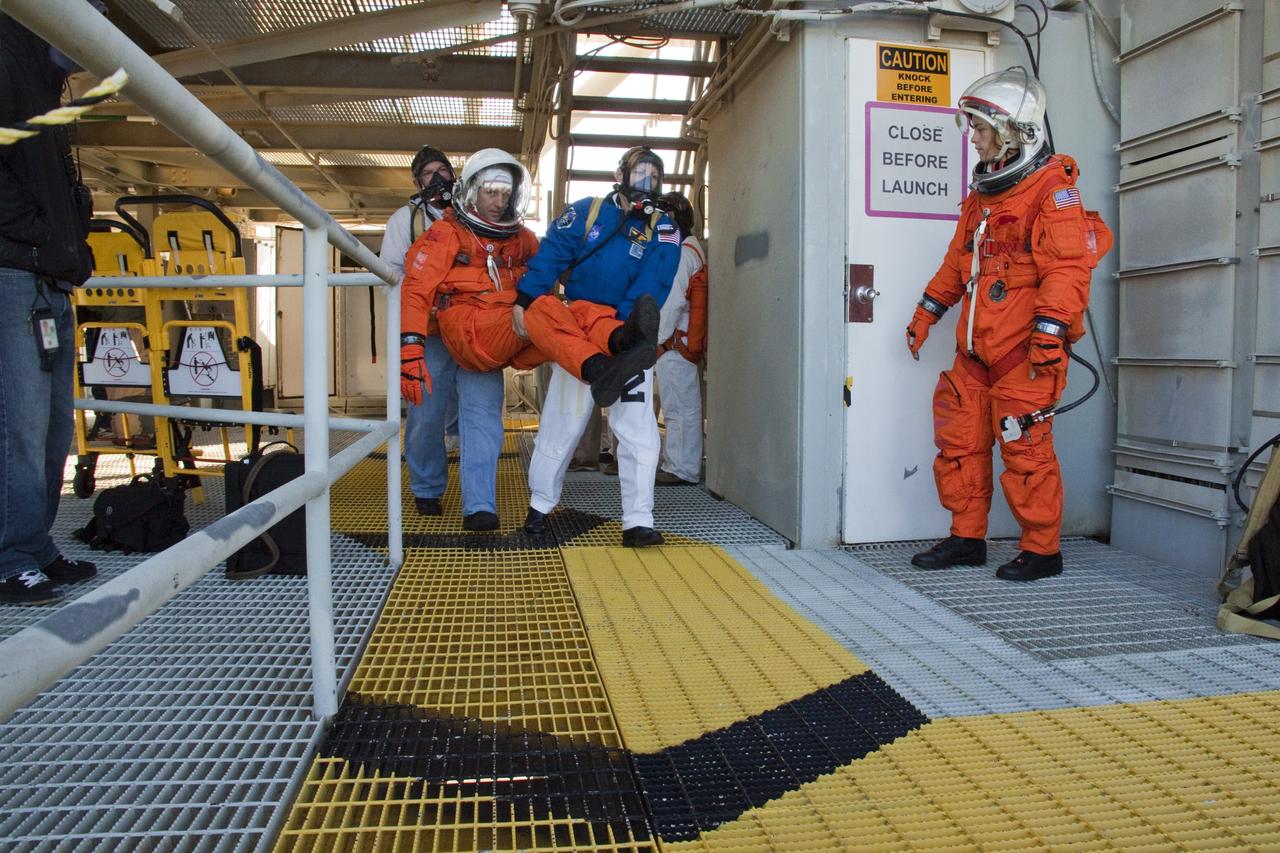

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at Launch Pad 39A. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
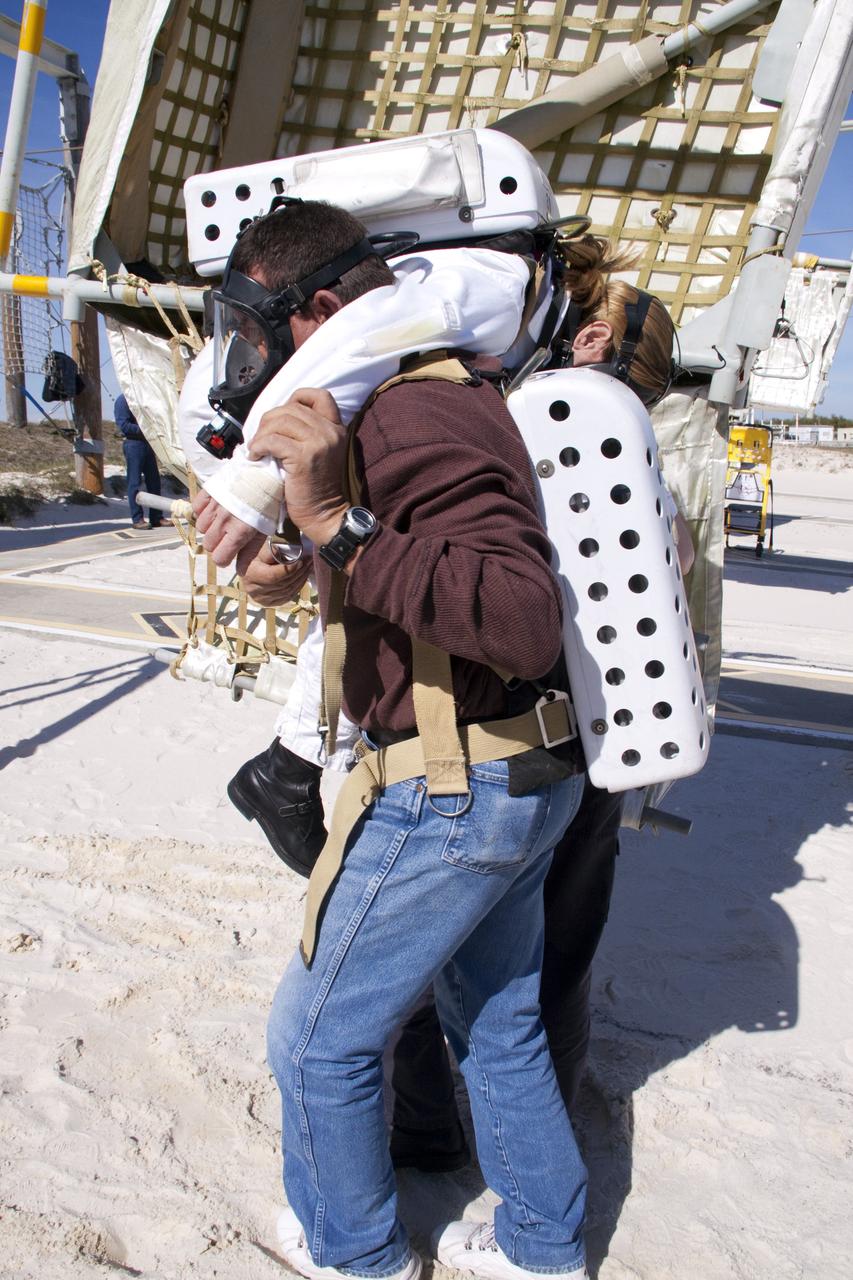

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team perform a simulated evacuation exercise at the slidewire basket landing site. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
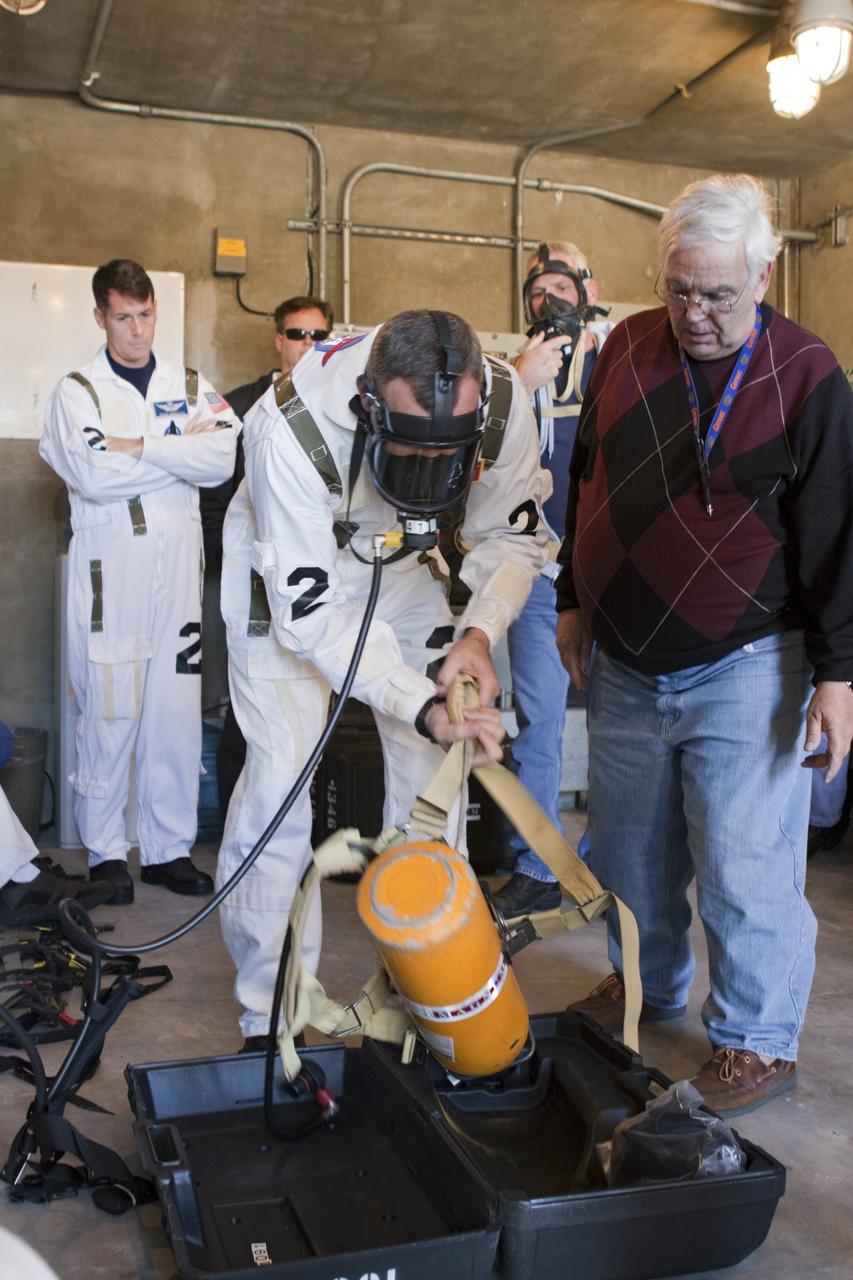

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of an emergency escape training team suit up in the bunkers below Launch Pad 39A prior to the start of a simulated evacuation exercise. For several days, volunteers portraying astronauts, take part in training exercises which allow teams to practice emergency response procedures, including helicopter evacuation to local hospitals. Training normally involves NASA fire rescue personnel, personnel from the Air Force's 920th Rescue Wing, and medical trauma teams from central Florida hospitals, and is required every 18 months to certify Fire Rescue and Closeout Crew personnel. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
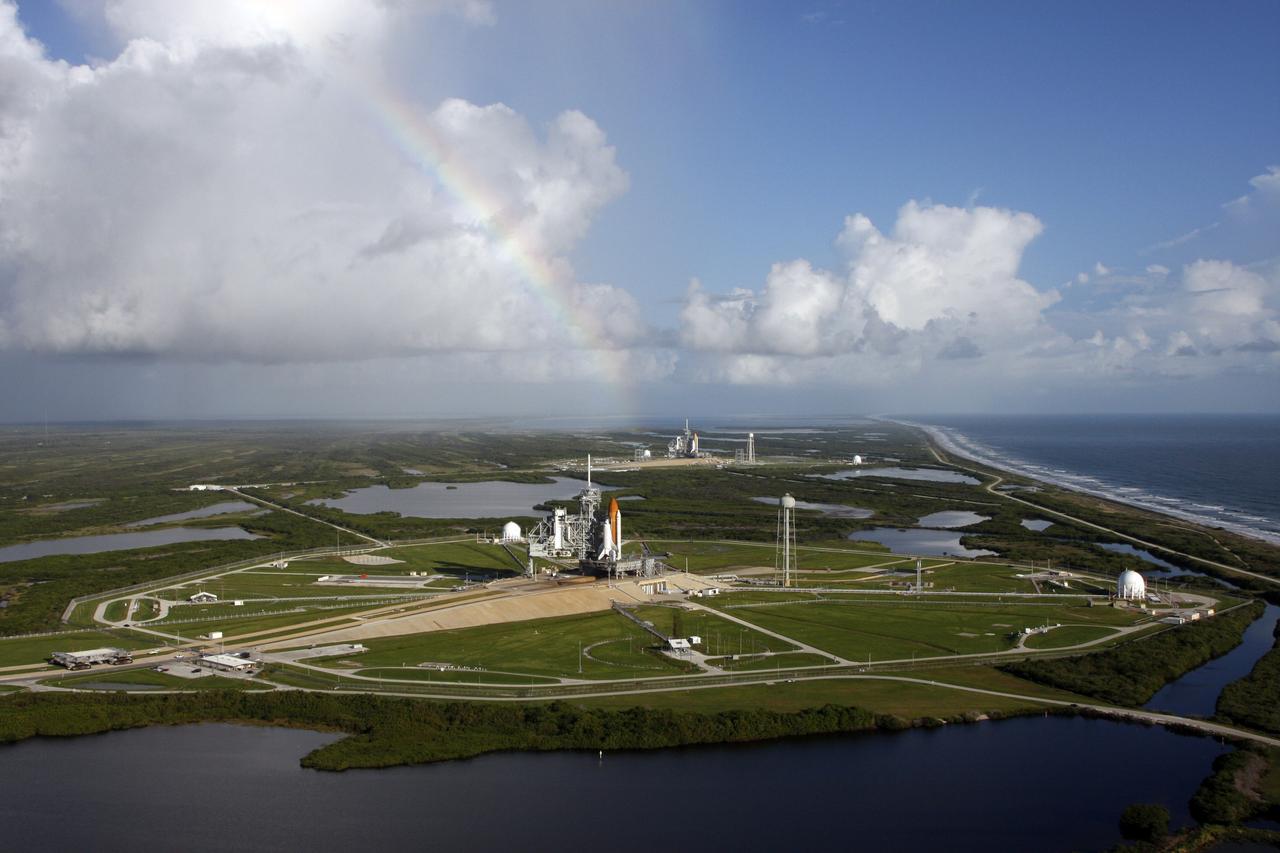

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With a rainbow serving as a backdrop in the sky, space shuttle Atlantis (foreground) sits on Launch Pad A and Endeavour on Launch Pad B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At the left of each shuttle are the open rotating service structures with the payload changeout rooms revealed. The rotating service structures provide protection for weather and access to the shuttle. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis’ upcoming mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With a rainbow serving as a backdrop in the sky, space shuttle Atlantis (foreground) sits on Launch Pad A and Endeavour on Launch Pad B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At the left of each shuttle are the open rotating service structures with the payload changeout rooms revealed. The rotating service structures provide protection for weather and access to the shuttle. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis’ upcoming mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - After rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour is secure on the launch pad. Workers on the pad connect lines on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour completed the 4.2-mile rollout at 6:59 a.m. EDT. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis' upcoming mission to repair NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
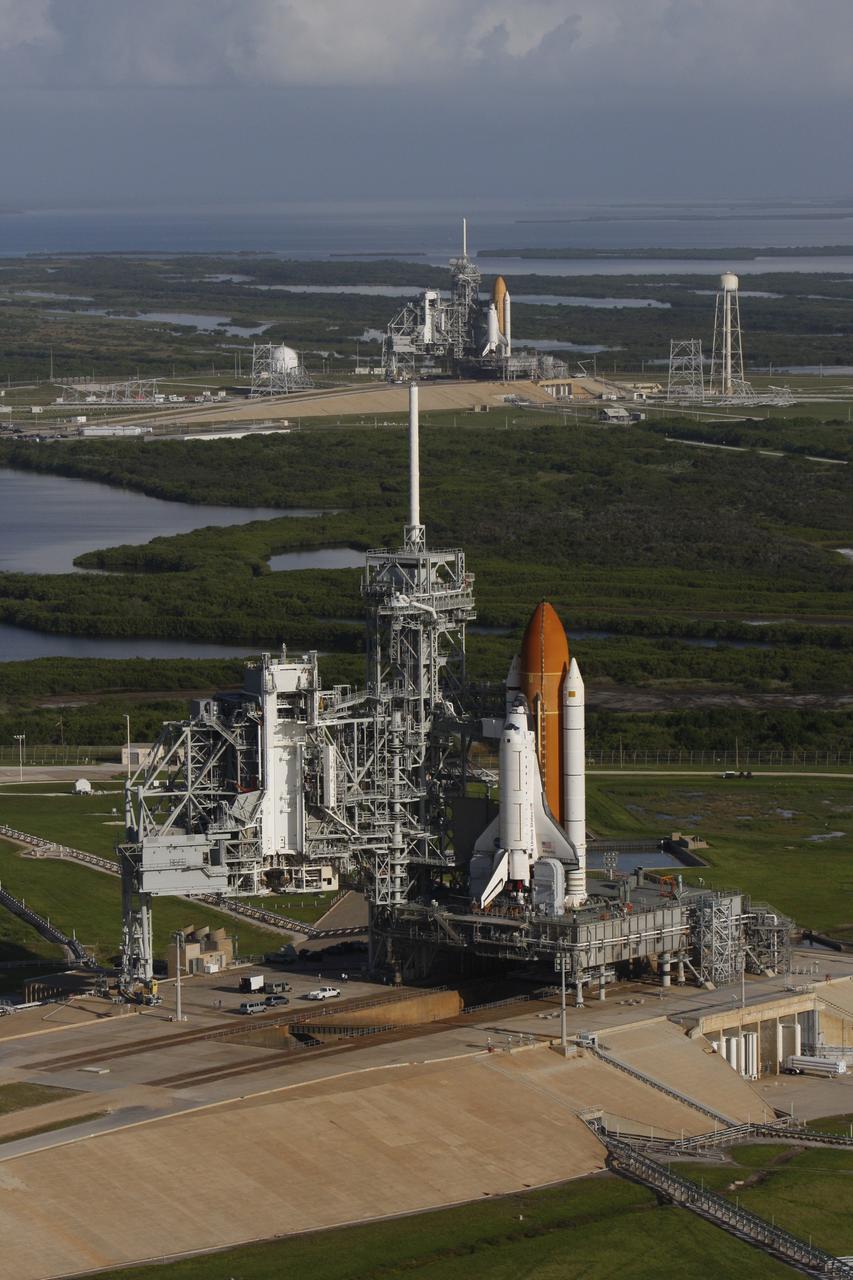

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis (foreground) sits on Launch Pad A and Endeavour on Launch Pad B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At the left of each shuttle are the open rotating service structures with the payload changeout rooms revealed. The rotating service structures provide protection for weather and access to the shuttle. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis’ upcoming mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Clouds serve as a backdrop to frame space shuttle Atlantis (foreground) on Launch Pad A and Endeavour on Launch Pad B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At the left of each shuttle are the open rotating service structures with the payload changeout rooms revealed. The rotating service structures provide protection for weather and access to the shuttle. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis’ upcoming mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - After rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour is being secured on the launch pad. First motion was at 11:15 p.m. Sept. 18. Endeavour completed the 4.2-mile journey to Launch Pad 39B on Sept. 19 at 6:59 a.m. EDT. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis' upcoming mission to repair NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - After rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour is being secured on the launch pad. First motion was at 11:15 p.m. Sept. 18. Endeavour completed the 4.2-mile journey to Launch Pad 39B on Sept. 19 at 6:59 a.m. EDT. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis' upcoming mission to repair NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - After rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour is being secured on the launch pad. First motion was at 11:15 p.m. Sept. 18. Endeavour completed the 4.2-mile journey to Launch Pad 39B on Sept. 19 at 6:59 a.m. EDT. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis' upcoming mission to repair NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
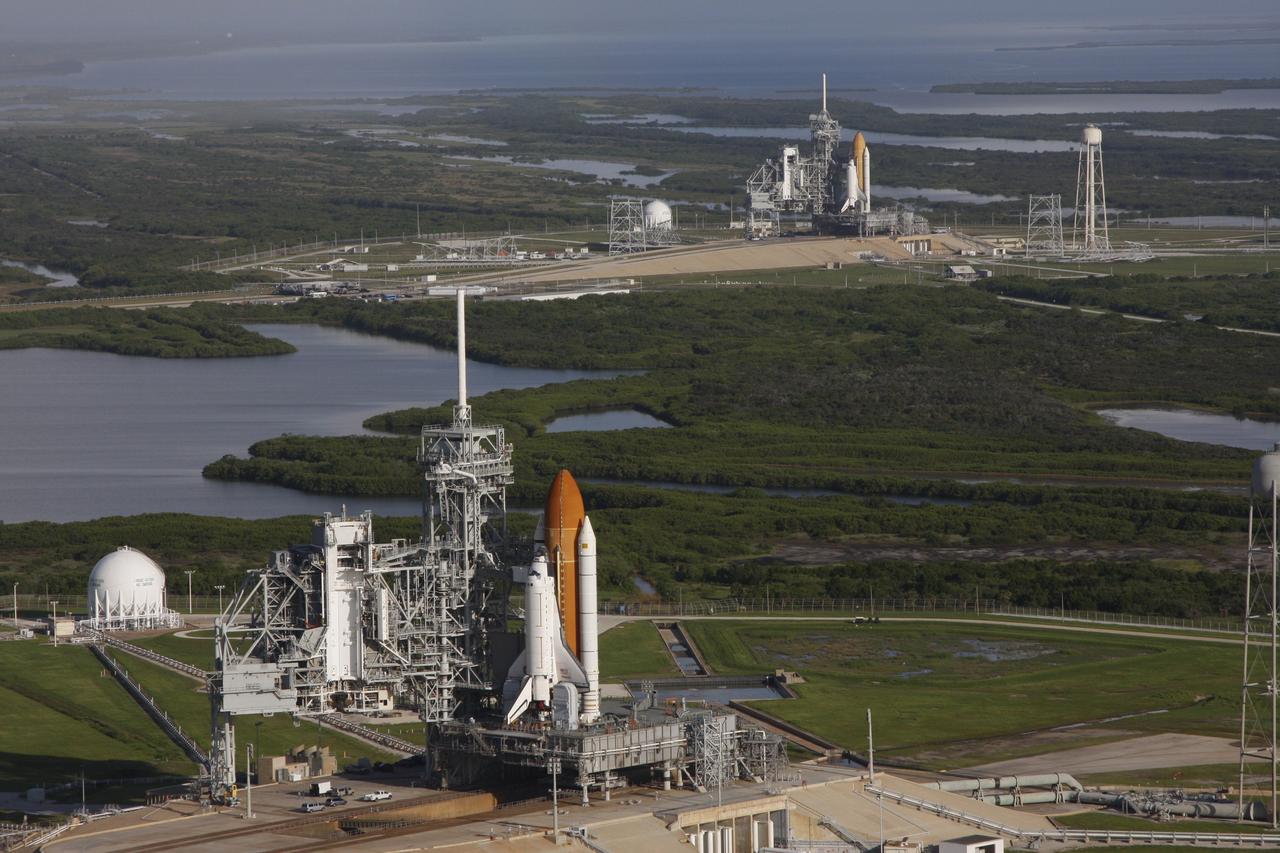

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis (foreground) sits on Launch Pad A and Endeavour on Launch Pad B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At the left of each shuttle are the open rotating service structures with the payload changeout rooms revealed. The rotating service structures provide protection for weather and access to the shuttle. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis’ upcoming mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
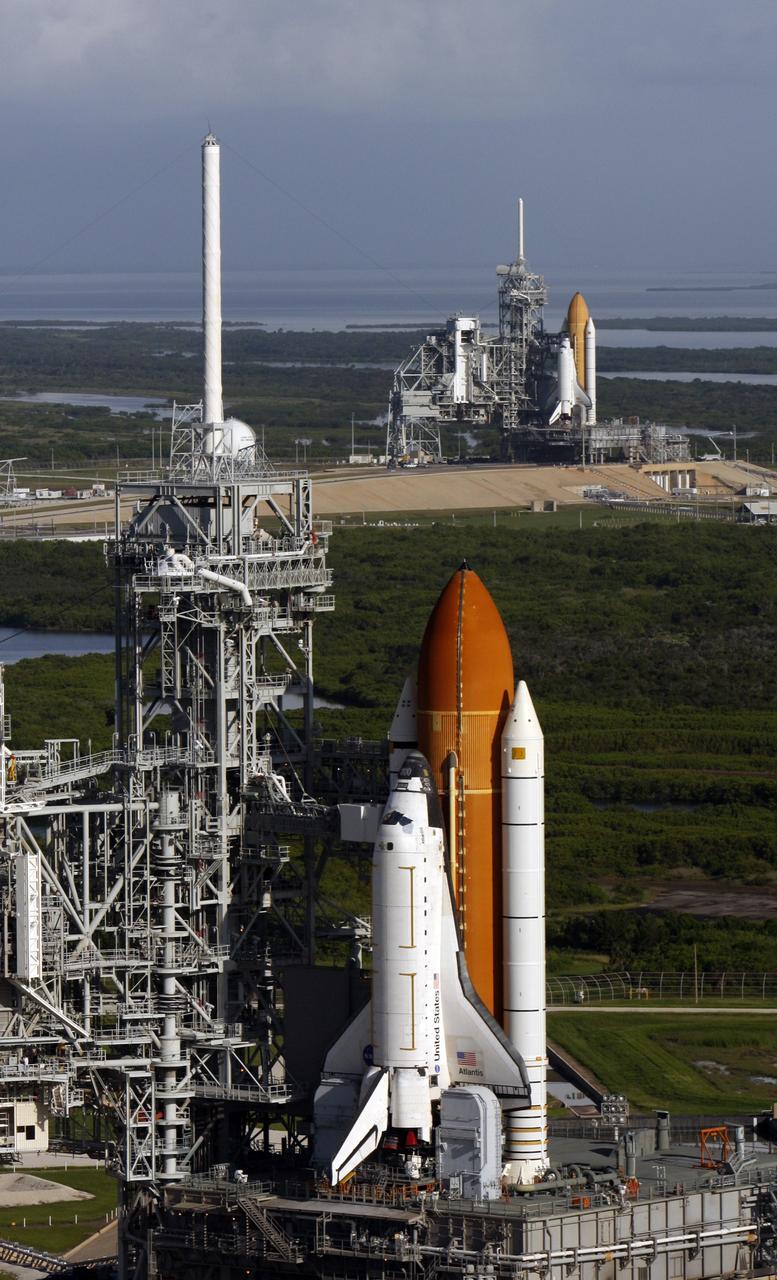

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis (foreground) sits on Launch Pad A and Endeavour on Launch Pad B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At the left of each shuttle are the open rotating service structures with the payload changeout rooms revealed. The rotating service structures provide protection for weather and access to the shuttle. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis’ upcoming mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The lighted crawler-transporter and mobile launcher platform reveal space shuttle Endeavour on top as it rolls out to the launch pad. First motion was at 11:15 p.m. Sept. 18. Endeavour completed the 4.2-mile journey to Launch Pad 39B on Sept. 19 at 6:59 a.m. EDT. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis' upcoming mission to repair NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis (foreground) sits on Launch Pad A and Endeavour on Launch Pad B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At the left of each shuttle are the open rotating service structures with the payload changeout rooms revealed. The rotating service structures provide protection for weather and access to the shuttle. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis’ upcoming mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
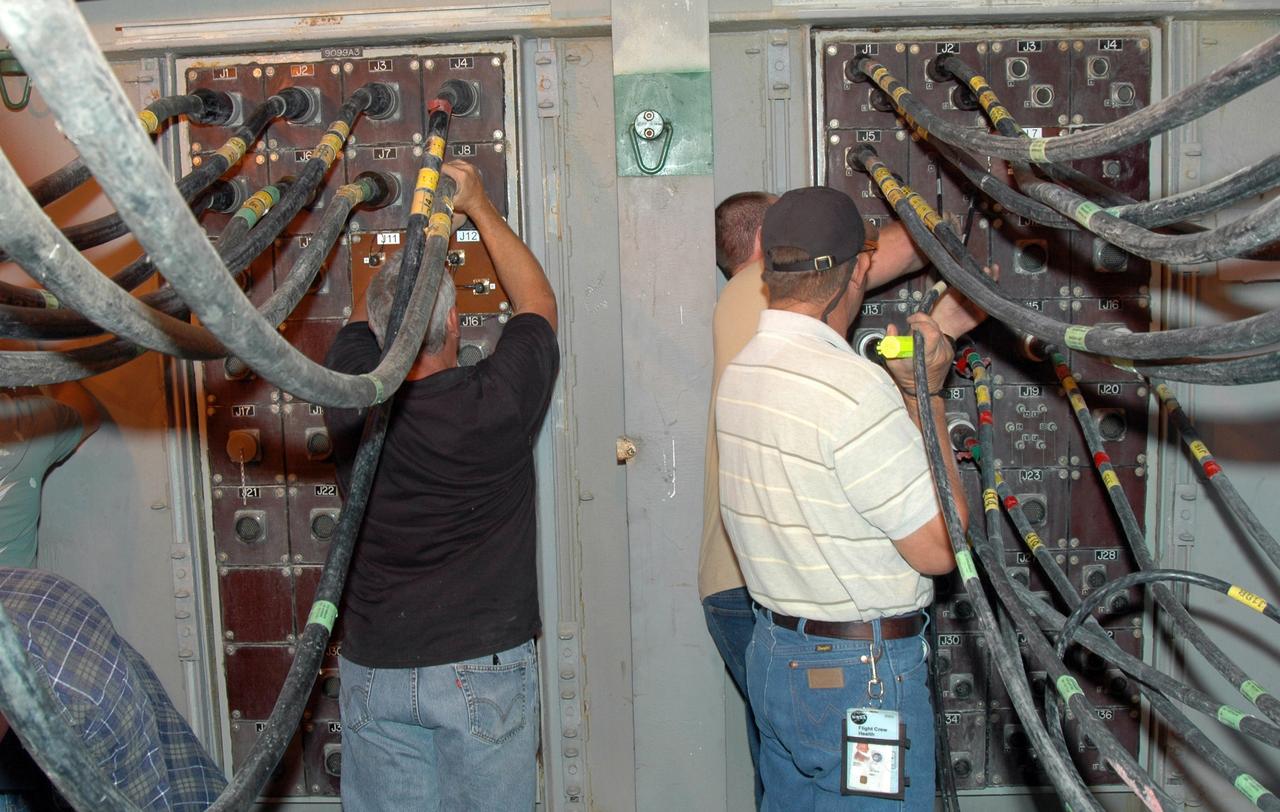

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - After rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Endeavour is secure on the launch pad. Workers on the pad connect lines on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour completed the 4.2-mile rollout at 6:59 a.m. EDT. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis' upcoming mission to repair NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
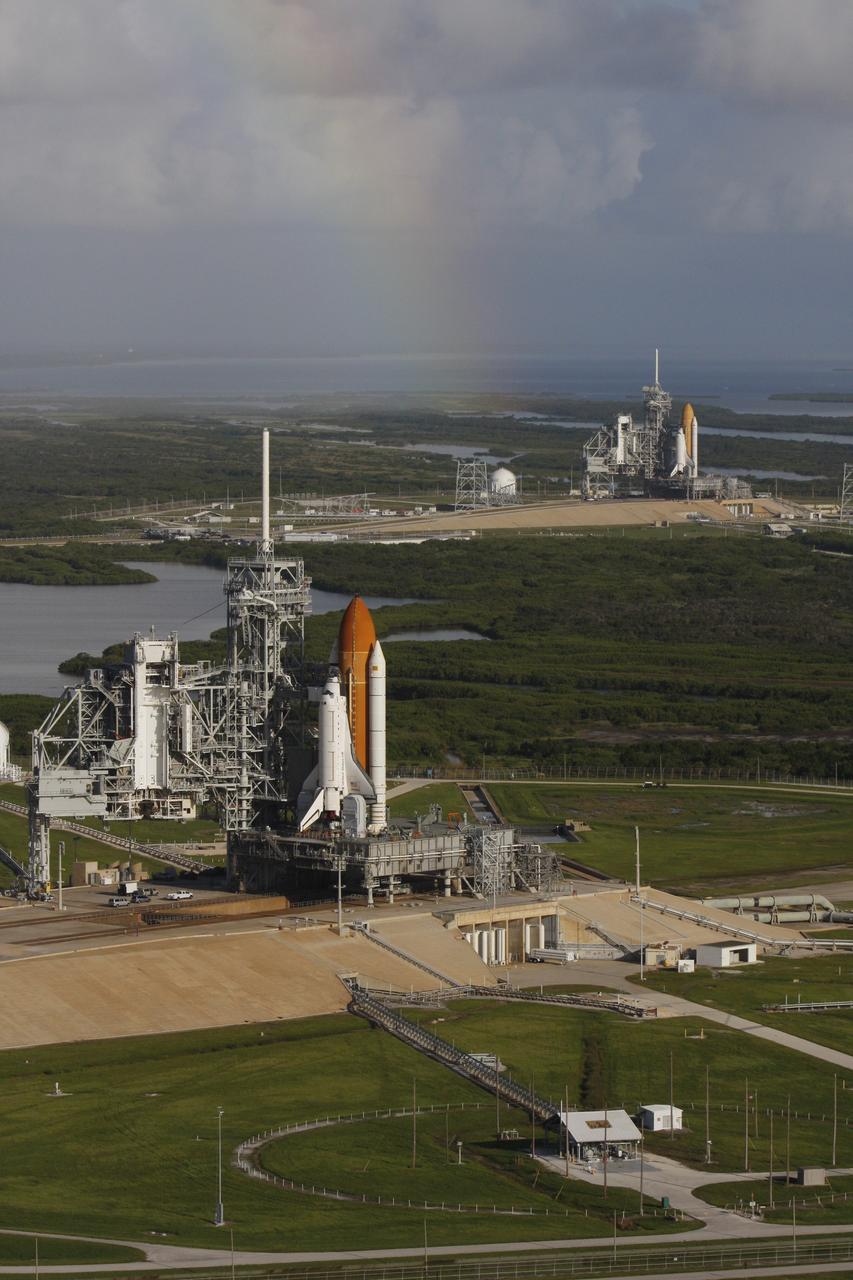

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With a rainbow serving as a backdrop in the sky, space shuttle Atlantis (foreground) sits on Launch Pad A and Endeavour on Launch Pad B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At the left of each shuttle are the open rotating service structures with the payload changeout rooms revealed. The rotating service structures provide protection for weather and access to the shuttle. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis’ upcoming mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
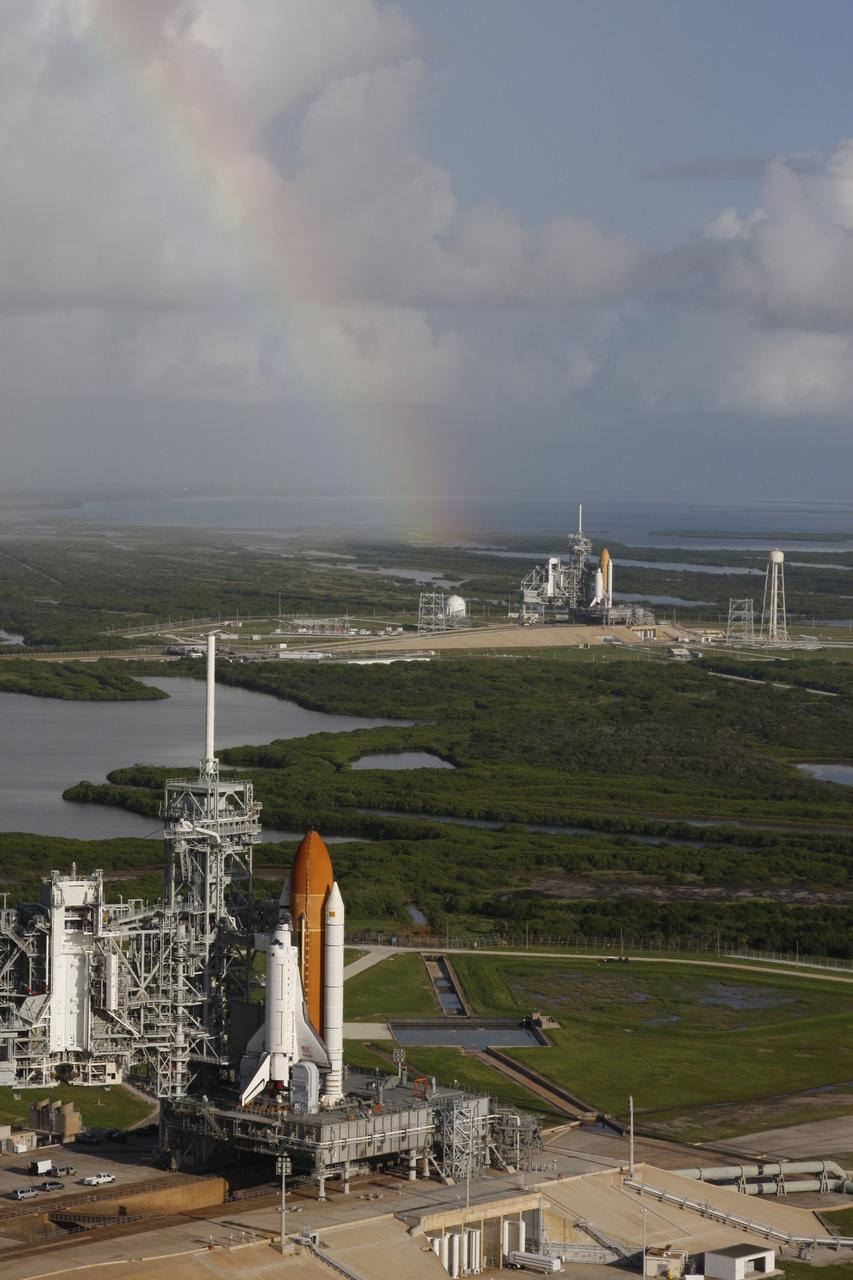

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With a rainbow beginning to appear in the sky, space shuttle Atlantis (foreground) sits on Launch Pad A and Endeavour on Launch Pad B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At the left of each shuttle are the open rotating service structures with the payload changeout rooms revealed. The rotating service structures provide protection for weather and access to the shuttle. For the first time since July 2001, two shuttles are on the launch pads at the same time at the center. Endeavour will stand by at pad B in the unlikely event that a rescue mission is necessary during space shuttle Atlantis’ upcoming mission to repair NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, targeted to launch Oct. 10. After Endeavour is cleared from its duty as a rescue spacecraft, it will be moved to Launch Pad 39A for its STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. That flight is targeted for launch Nov. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder