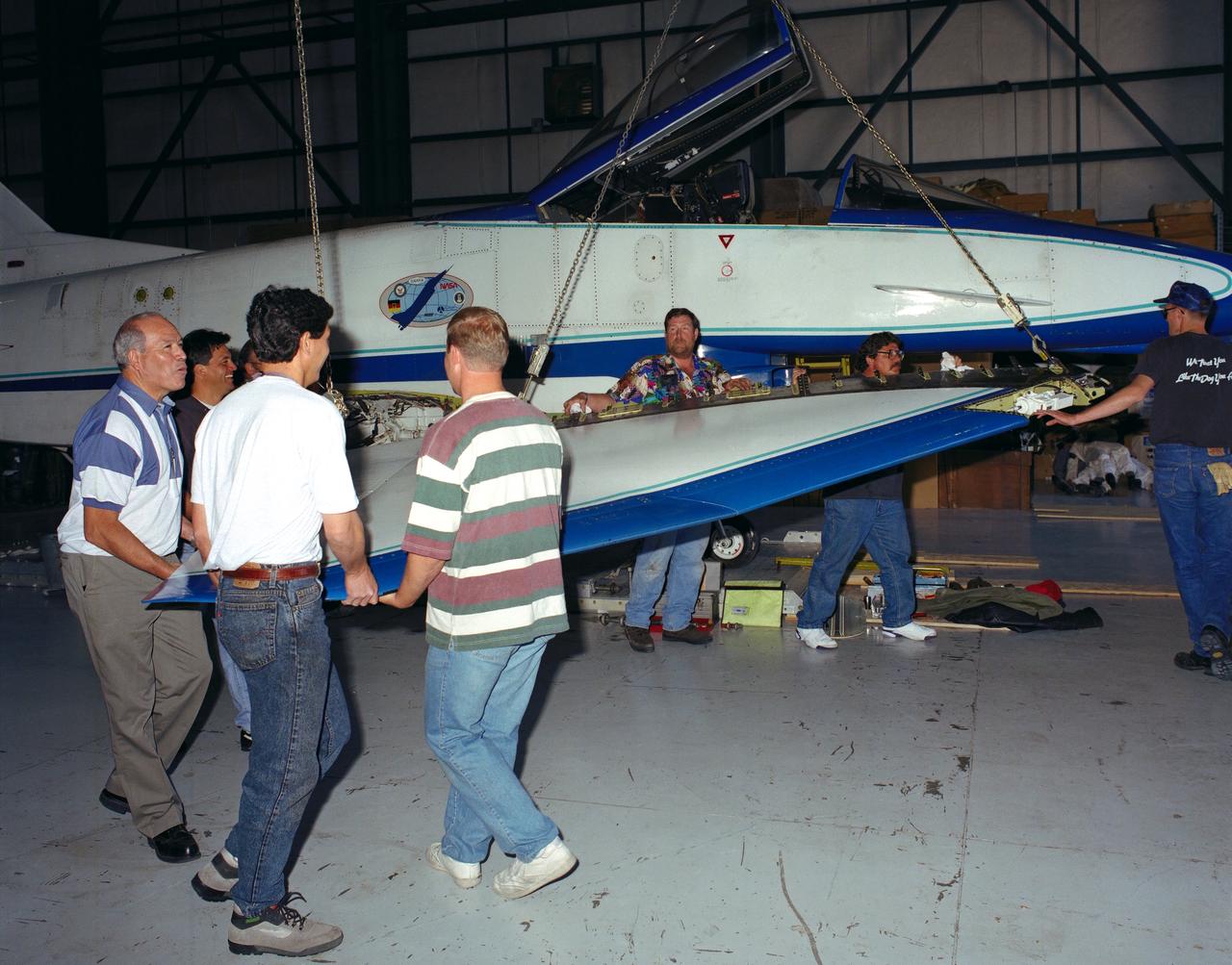

U.S. and German personnel of the X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator aircraft program removing the right wing of the aircraft, which was ferried from Edwards Air Force Base, California, to Europe on May 22, 1995 aboard an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport. The X-31, based at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center was ferried to Europe and flown in the Paris Air Show in June. The wing of the X-31 was removed on May 18, 1995, to allow the aircraft to fit inside the C-5 fuselage. Officials of the X-31 project used Manching, Germany, as a staging base to prepare the aircraft for the flight demonstration. At the air show, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack. The aircraft arrived back at Edwards in a Air Force Reserve C-5 on June 25, 1995 and off loaded at Dryden June 27. The X-31 aircraft was developed jointly by Rockwell International's North American Aircraft Division (now part of Boeing) and Daimler-Benz Aerospace (formerly Messerschmitt-Bolkow-Blohm), under sponsorship by the U.S. Department of Defense and the German Federal Ministry of Defense.
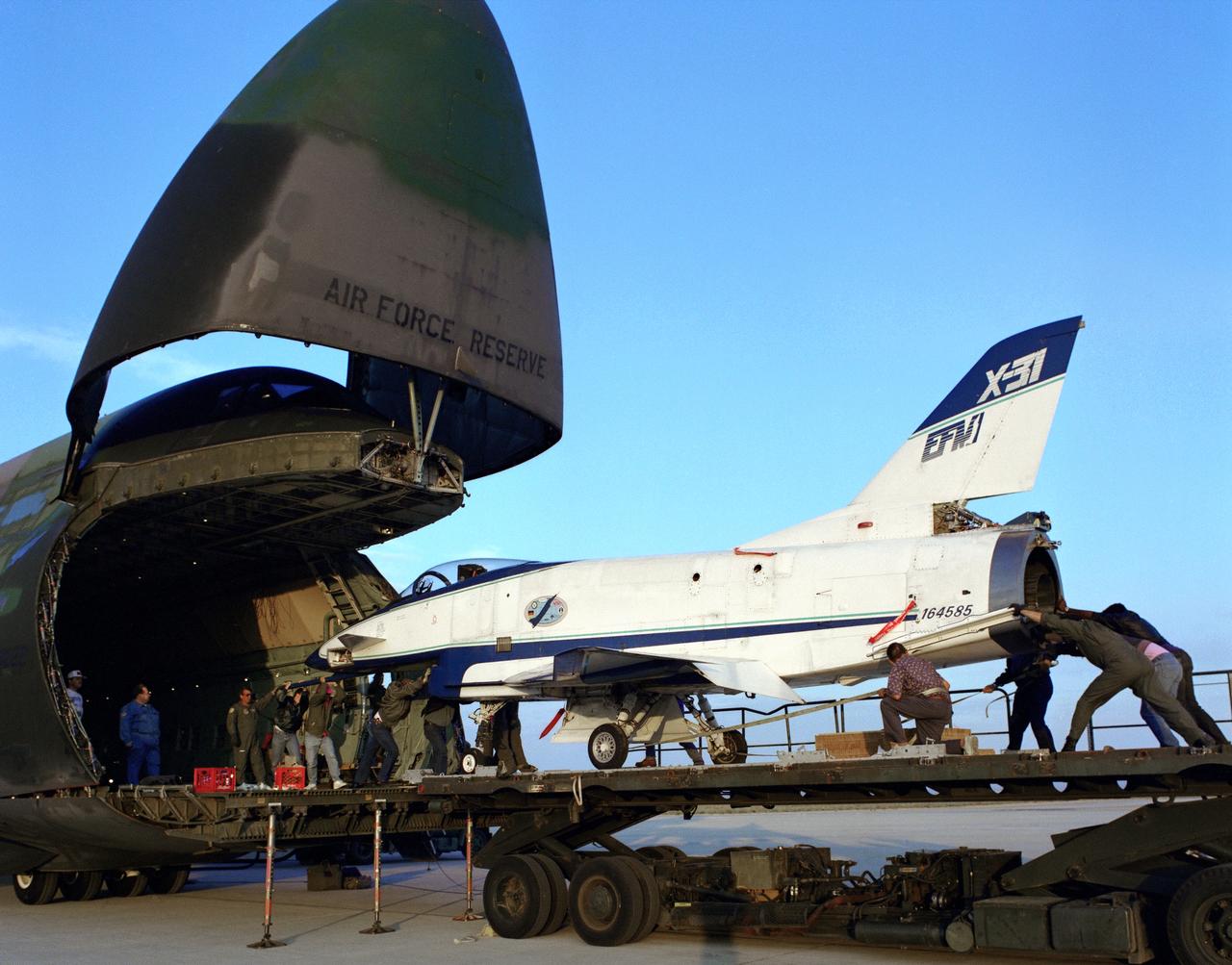

The X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator Aircraft, based at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, begins rolling aboard an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport which ferried it on May 22, 1995 to Europe where it was flown in the Paris Air Show in June 1995. To fit in the C-5 the right wing of the X-31 had to be removed. At the air show, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack.
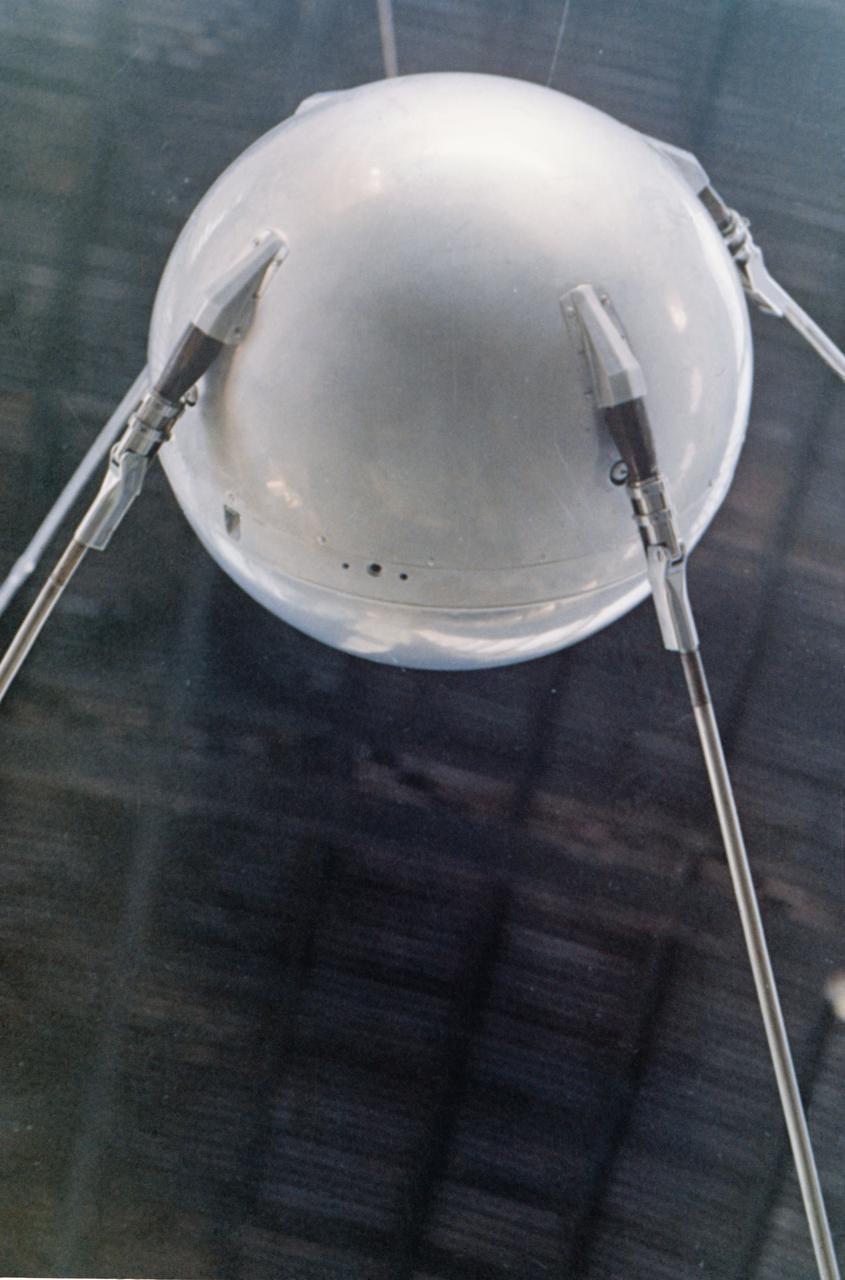
S76-22361 (June 1975) --- A close-up view of the full-scale mockup of the Sputnik 1 spacecraft on display at the Soviet Pavilion at the Paris Air Show, France. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
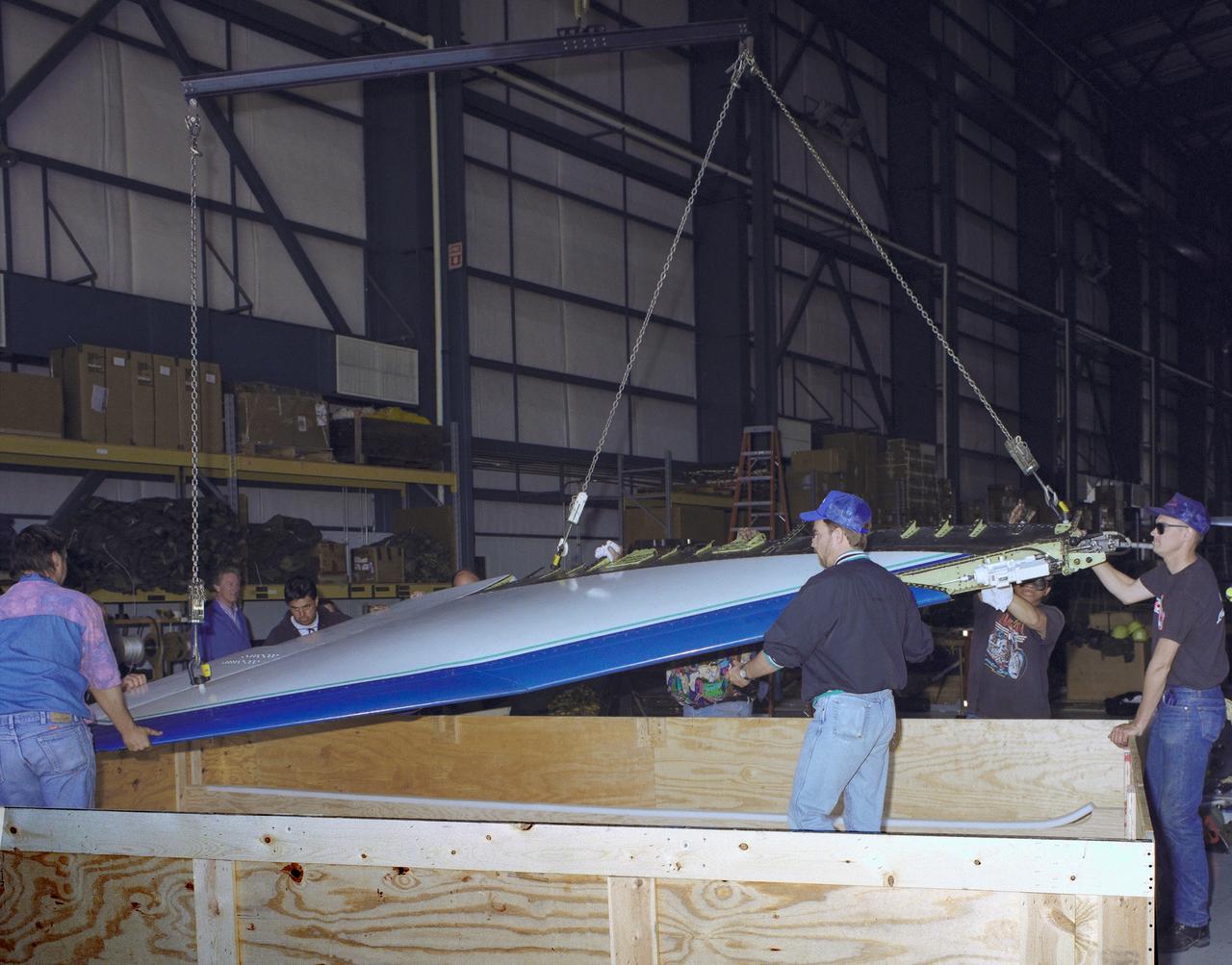

The right wing of the X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator Aircraft is seen here being put into a shipping container May 18, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, by U.S. and German members of the program. To fit inside an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport, which was used to ferry the X-31 to Europe on May 22, 1995, the right wing had to be removed. Manching, Germany, was used as a staging base to prepare the aircraft for participation in the Paris Air Show. At the air show on June 11 through the 18th, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack. The aircraft arrived back at Edwards in an Air Force Reserve C-5 on June 25, 1995, and off loaded at Dryden the 27th. The X-31 aircraft was developed jointly by Rockwell International's North American Aircraft Division (now part of Boeing) and Daimler-Benz Aerospace (formerly Messerschmitt-Bolkow-Blohm), under sponsorship by the U.S. Department of Defense and the German Federal Ministry of Defense.
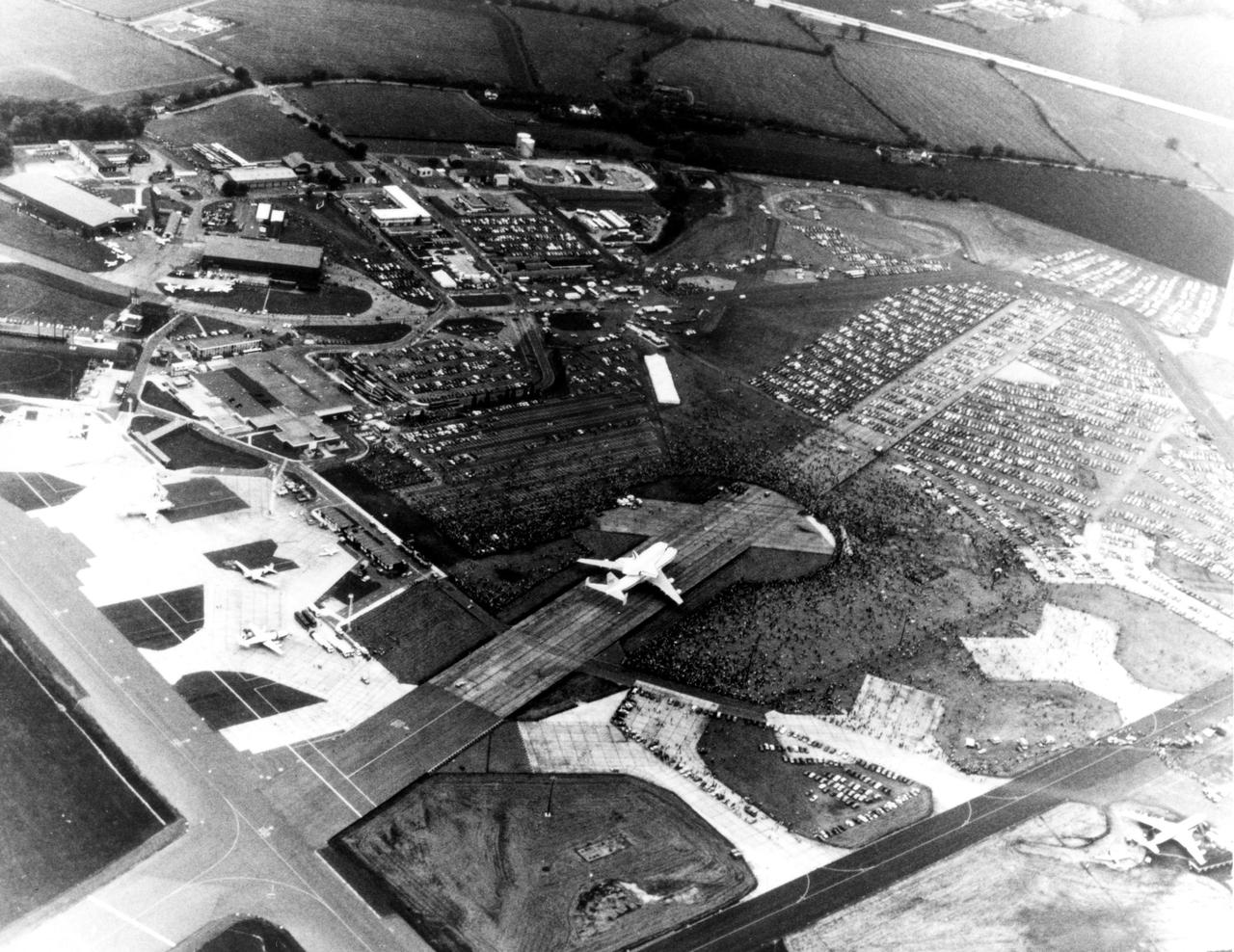

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Thousands of Britons surround the Space Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise at Stansted Airport, near London. The Enterprise atop its 747 carrier aircraft was viewed in London, Bonn-Cologne, West Germany, Rome and Ottawa, Canada, in addition to being shown at the Paris Air Show in June 1983.

The Space Shuttle Enterprise, the nation's prototype space shuttle orbiter, before departing NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, at 11:00 a.m., 16 May 1983, on the first leg of its trek to the Paris Air Show at Le Bourget Airport, Paris, France. Seen here atop the huge 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), the first stop for the Enterprise was Peterson AFB, Colorado Springs, Colorado. Piloting the 747 on the Europe trip were Joe Algranti, Johnson Space Center Chief Pilot, Astronaut Dick Scobee, and NASA Dryden Chief Pilot Tom McMurtry. Flight engineers for that portion of the flight were Dryden's Ray Young and Johnson Space Center's Skip Guidry. The Enterprise, named after the spacecraft of Star Trek fame, was originally carried and launched by the 747 during the Approach and Landing Tests (ALT) at Dryden Flight Research Center.

The Space Shuttle Enterprise, the nation's prototype space shuttle orbiter, departed NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, at 11:00 a.m., 16 May 1983, on the first leg of its trek to the Paris Air Show at Le Bourget Airport, Paris, France. Carried by the huge 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), the first stop for the Enterprise was Peterson AFB, Colorado Springs, Colorado. Piloting the 747 on the Europe trip were Joe Algranti, Johnson Space Center Chief Pilot, Astronaut Dick Scobee, and NASA Dryden Chief Pilot Tom McMurtry. Flight engineers for that portion of the flight were Dryden's Ray Young and Johnson Space Center's Skip Guidry. The Enterprise, named after the spacecraft of Star Trek fame, was originally carried and launched by the 747 during the Approach and Landing Tests (ALT) at Dryden Flight Research Center.
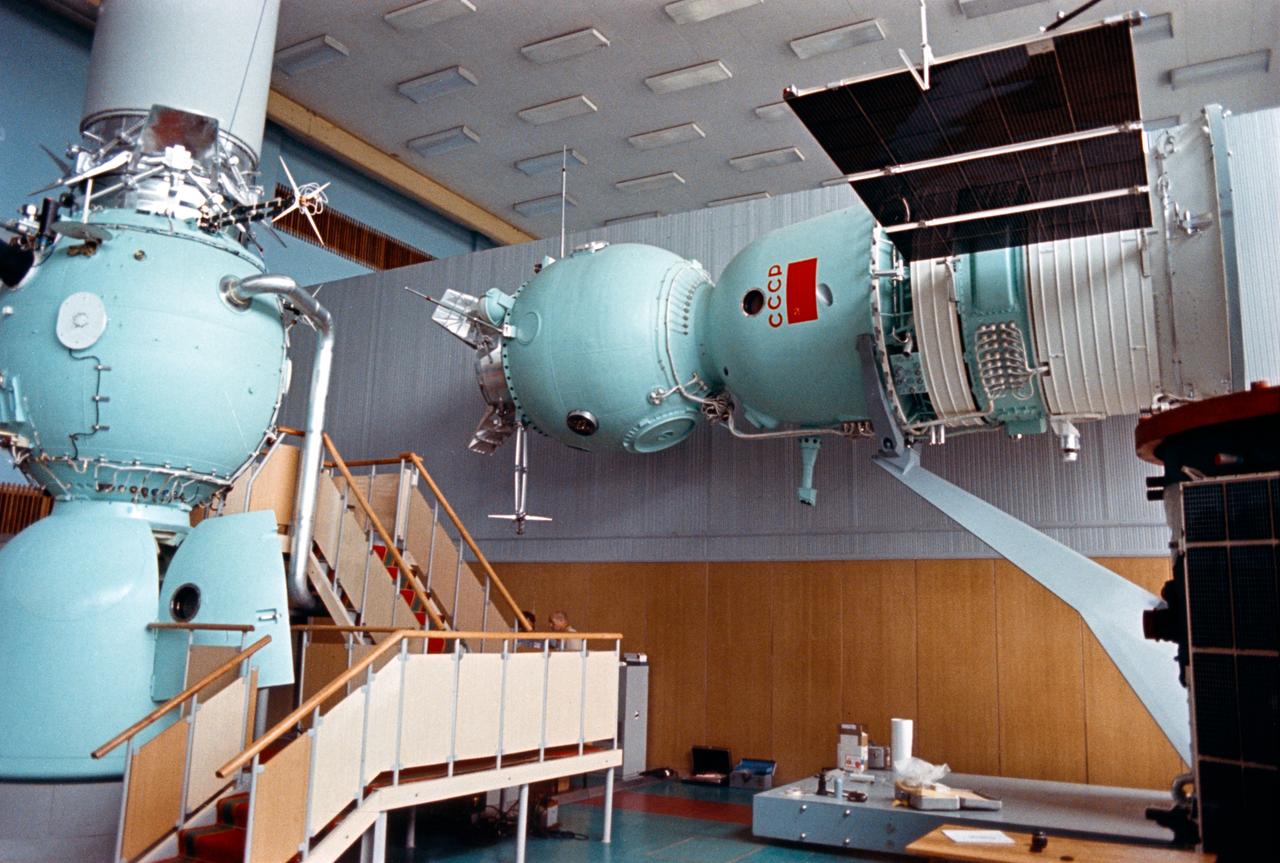
S74-24675 (June 1974) --- Two mock-ups of the USSR Soyuz spacecraft which are on display at the Cosmonaut Training Center (Star City) near Moscow. The Soyuz spacecraft mounted vertically on the left is a training mock-up. The Soyuz mounted horizontally on the right was exhibited at the Paris air show in May-June 1973 in a docked configuration with an Apollo spacecraft. The spherical-shaped section of the Soyuz is called the orbital module. The middle section with the lettering ?CCCP? (USSR) on it called the descent vehicle. Two solar panels extend out from the instrument-assembly module. The joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz docking mission in Earth orbit is scheduled for the summer of 1975. A docking module mock-up is atop the Soyuz training mock-up on the left.