
Photo taken aboard a U.S. Air Force C-17 transport aircraft during a flight from Christchurch, New Zealand, to the U.S. Antarctic Program's McMurdo Station in Antarctica on Nov. 12, 2013. The C-17s that ferry people, equipment and supplies to Antarctica are operated by the U.S. Air Force's 62nd and 446th Airlift Wings based at Joint Base Lewis-McChord near Seattle, Wash. NASA's Operation IceBridge is an airborne science mission to study Earth's polar ice. In 2013, IceBridge is conducting its first field campaign directly from Antarctica. For more information about IceBridge, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/icebridge" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/icebridge</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Jefferson Beck <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
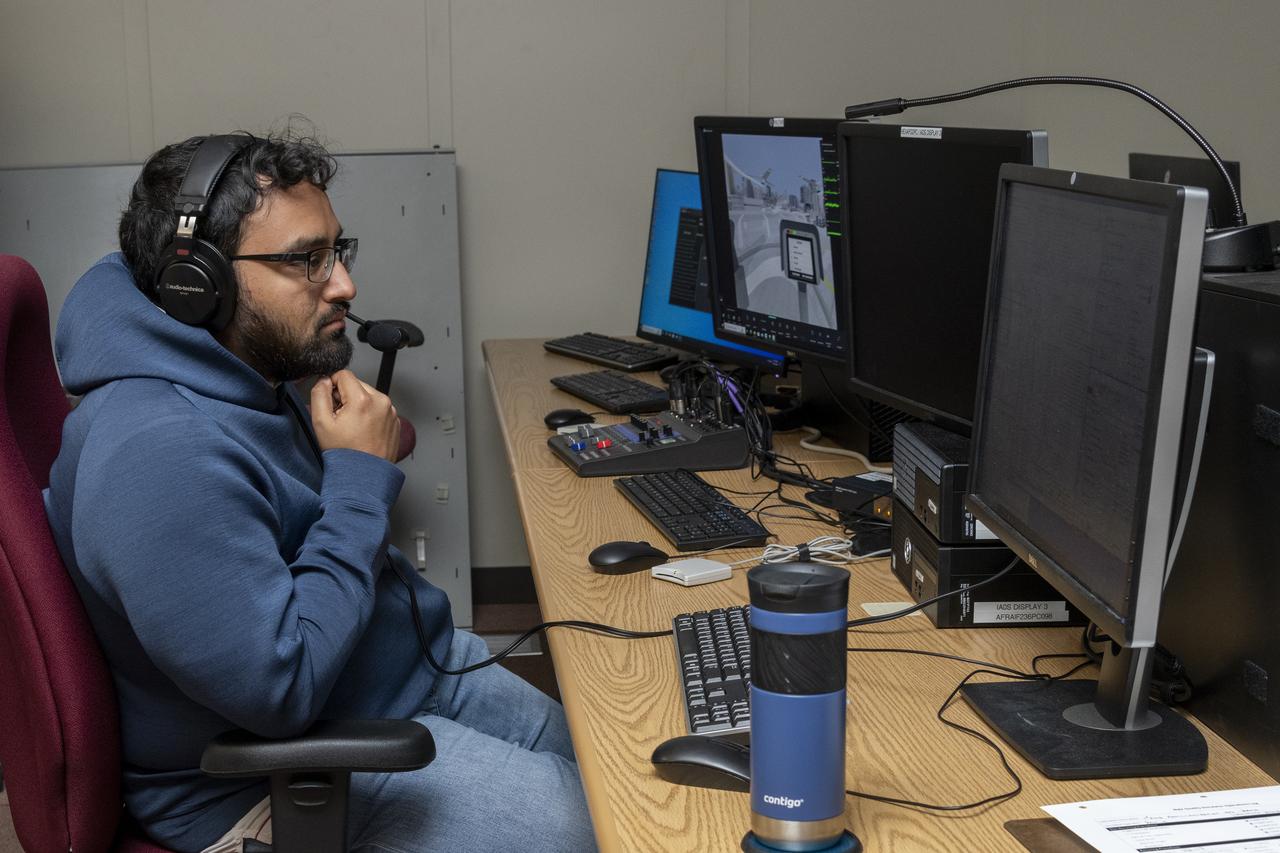

NASA researcher Saravanakumaar Ramia controls the air taxi passenger ride quality simulator by monitoring several computers in the Ride Quality Laboratory at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, during an experiment on Oct. 23, 2024. Studies continue in this lab to better understand passenger comfort for future air taxi rides.
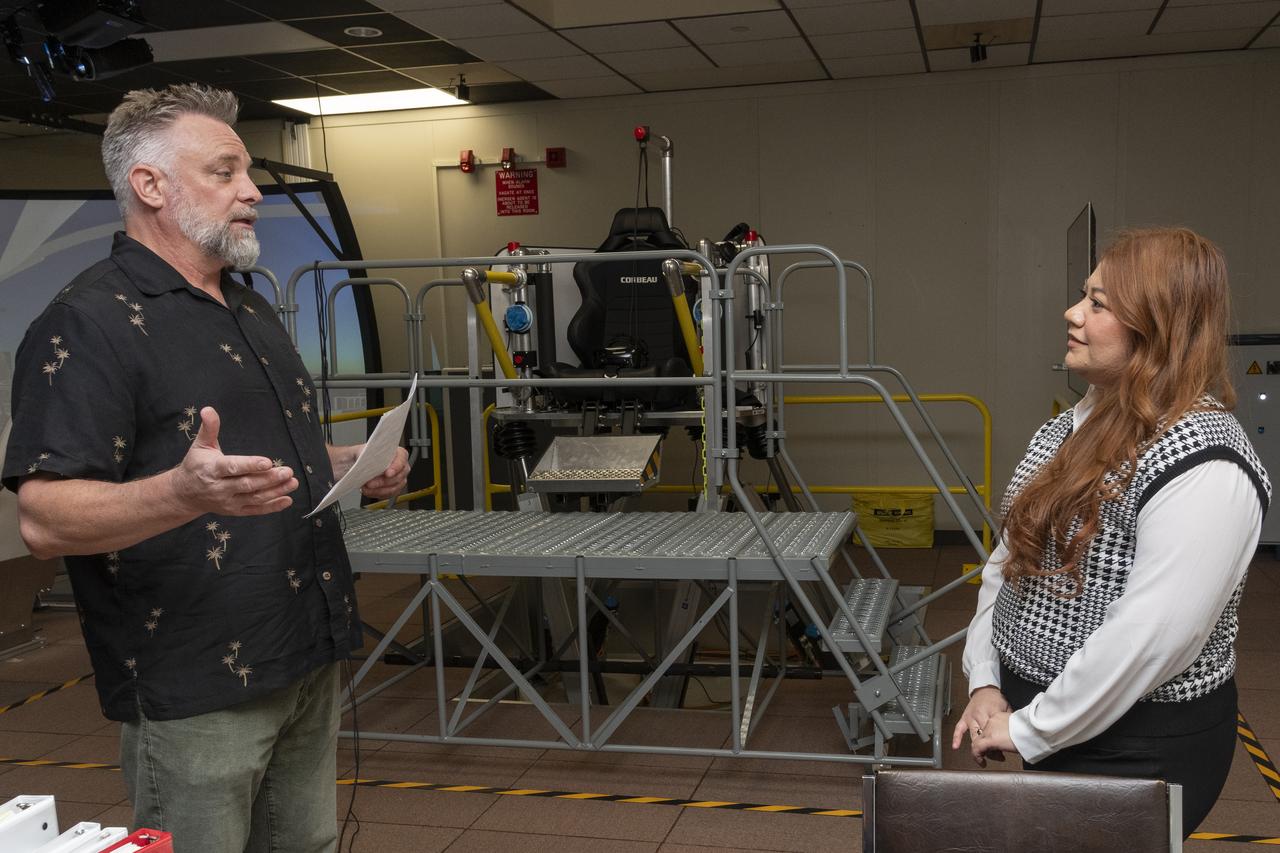

Curt Hanson, senior flight controls researcher for the Revolutionary Vertical Lift Technology project based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, explains the study about to begin to NASA employee and test subject Naomi Torres on Oct. 23, 2024. Behind them is the air taxi passenger ride quality simulator in NASA Armstrong’s Ride Quality Laboratory. Studies continue to better understand passenger comfort for future air taxi rides.
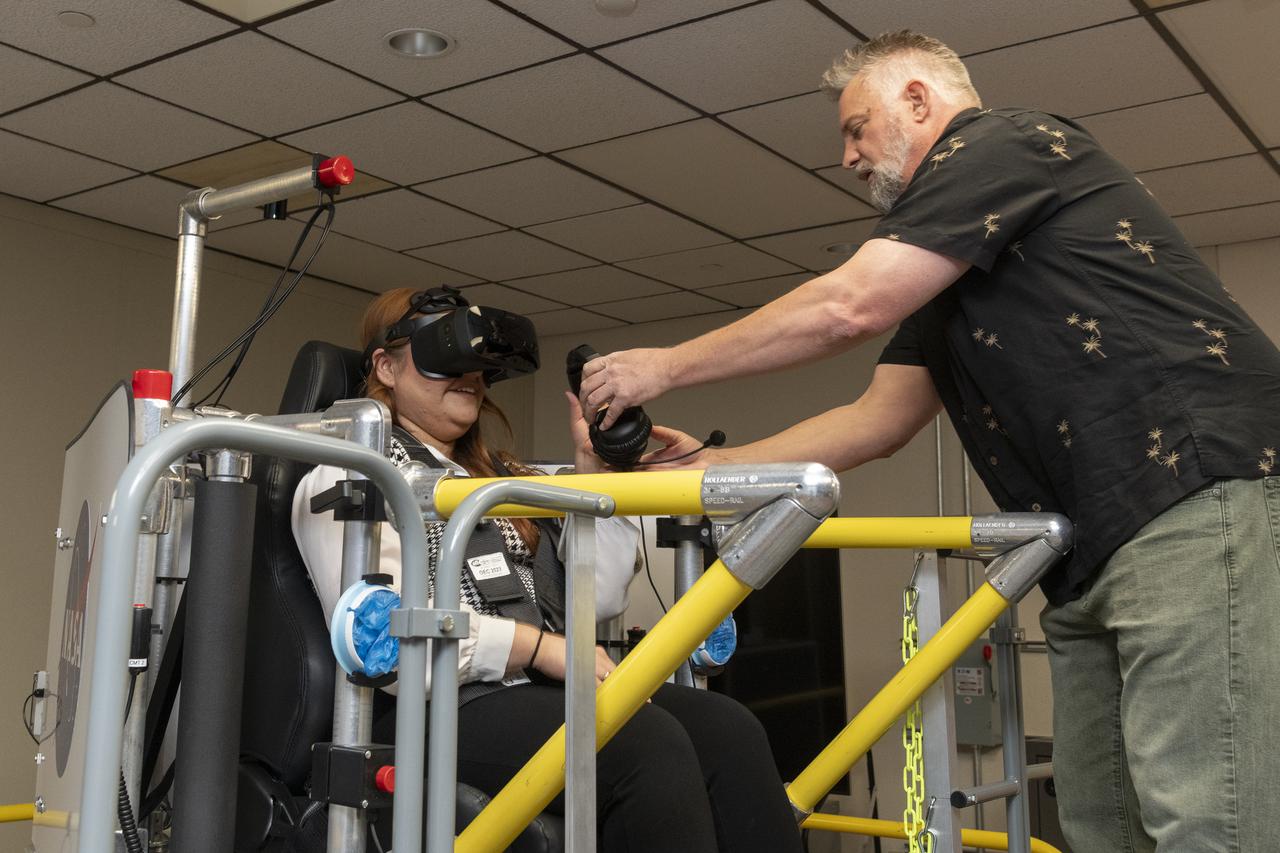

NASA employee Naomi Torres sits inside the air taxi passenger ride quality simulator at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as Curt Hanson, senior flight controls researcher for the Revolutionary Vertical Lift Technology project, sets up her equipment on Oct. 23, 2024. Studies continue in this lab to better understand passenger comfort for future air taxi rides.
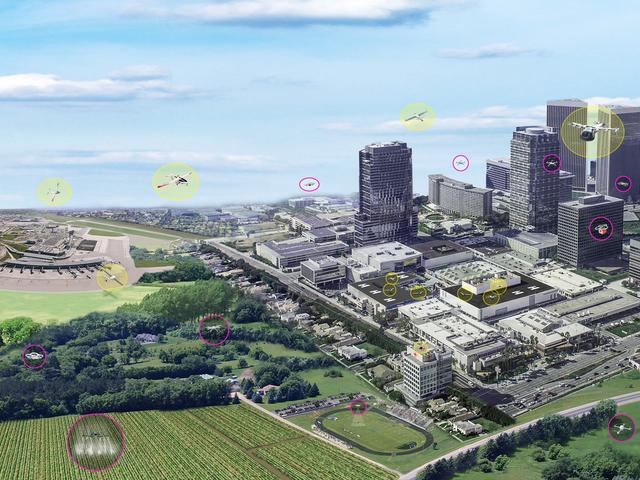
The concept of urban air mobility involves multiple aircraft safely operating within a city. (Yellow circles are vehicles with passengers; pink circles are vehicles without passengers.)
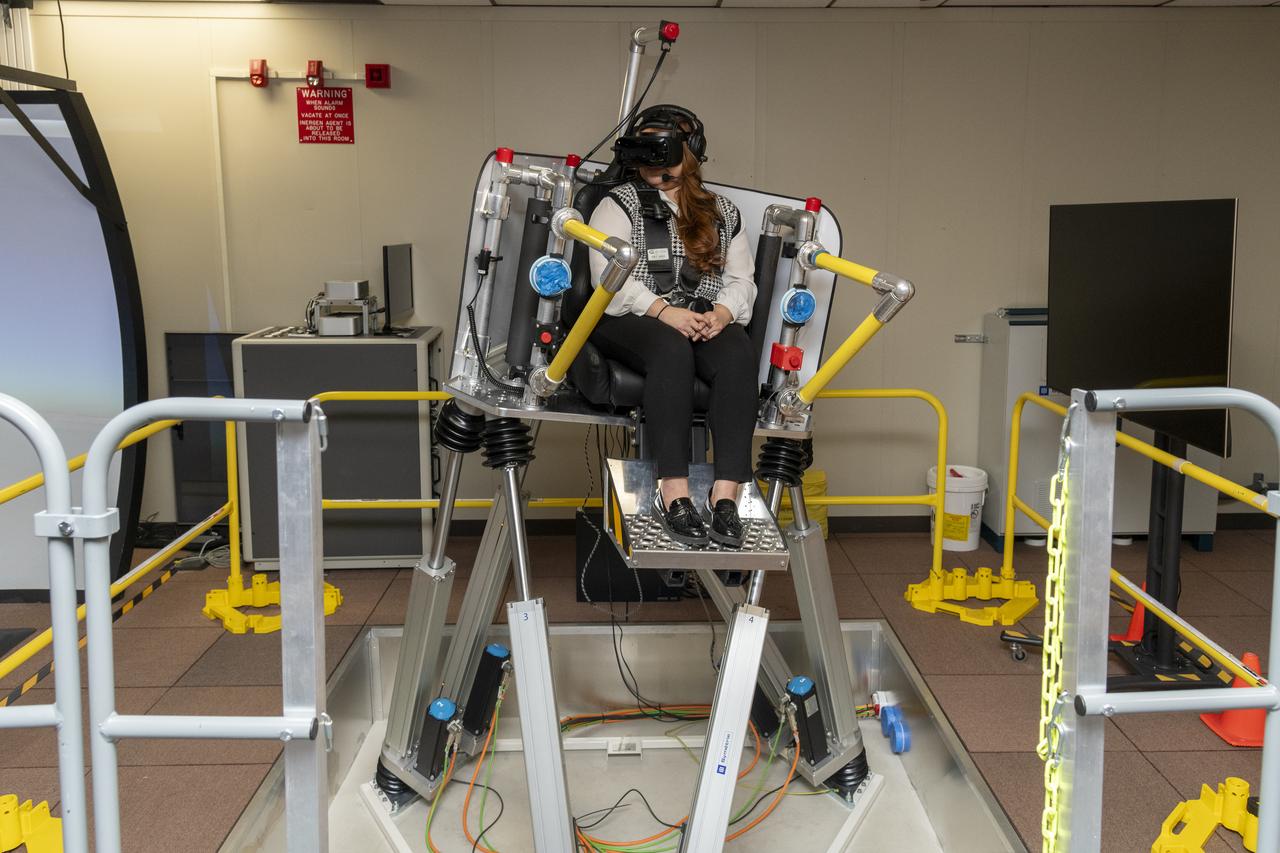

NASA employee Naomi Torres sits inside the air taxi passenger ride quality simulator at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, during a study on Oct. 23, 2024. Research continues to better understand how humans may interact with these new types of aircraft.

NASA employee Naomi Torres sits inside the air taxi passenger ride quality simulator at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as the simulator moves during a study on Oct. 23, 2024. Research continues to better understand how humans may interact with these new types of aircraft.
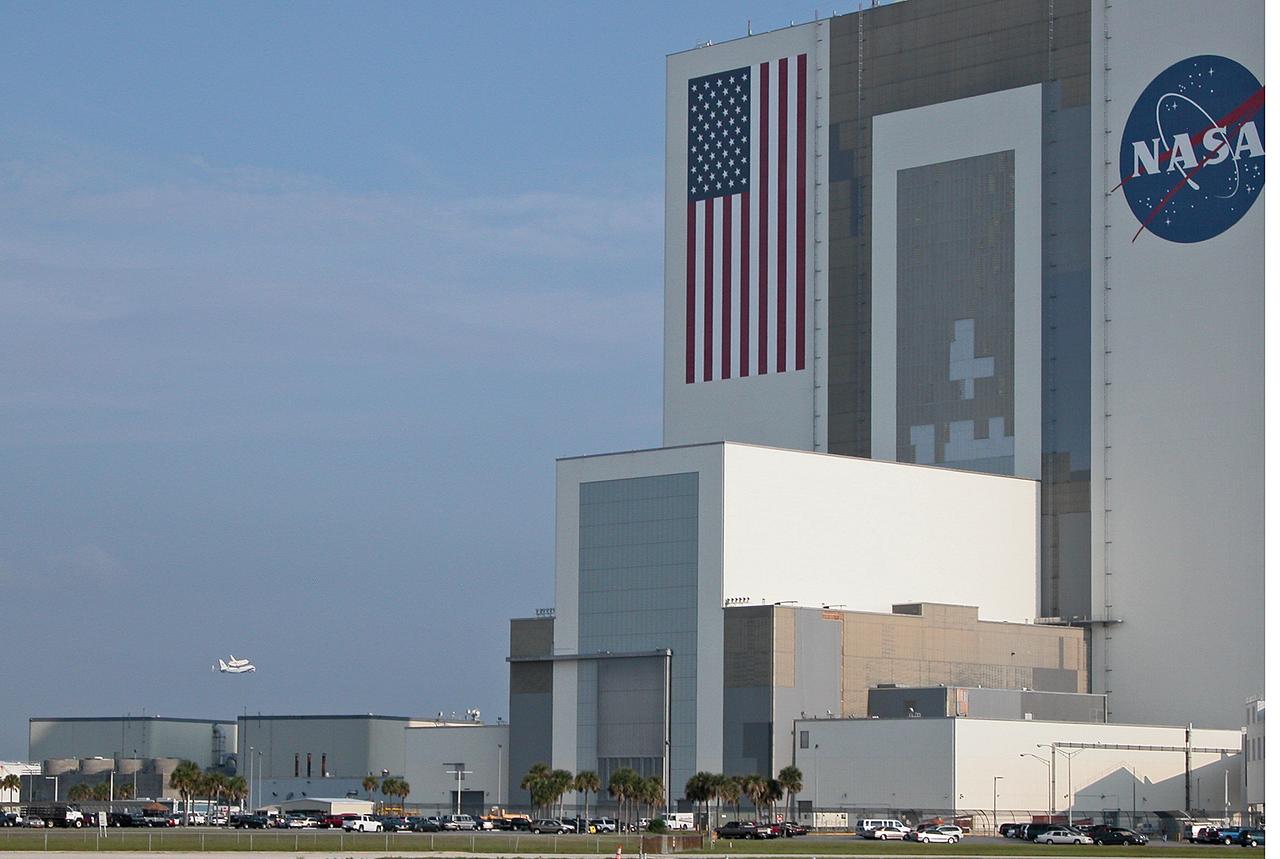
Through broken clouds, the shuttle carrier aircraft, or SCA, and its passenger Atlantis ease their way past the Vehicle Assembly Building, at right, for a landing at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, known as the SLF. The aircraft is a modified Boeing 747 jetliner. Atlantis landed at Edwards Air Force Base in California to end mission STS-117. The return to KSC began July 1 and took three days after stops across the country for fuel. The last stop was at Ft. Campbell in Kentucky. Weather conditions over the last leg postponed the return trip until July 3. Touchdown was at 8:27 a.m. EDT. Atlantis will be removed from the back of the SCA via the mate/demate device at the SLF. It will then be towed to the Orbiter Processing Facility to begin processing for its next launch, mission STS-122 in December.
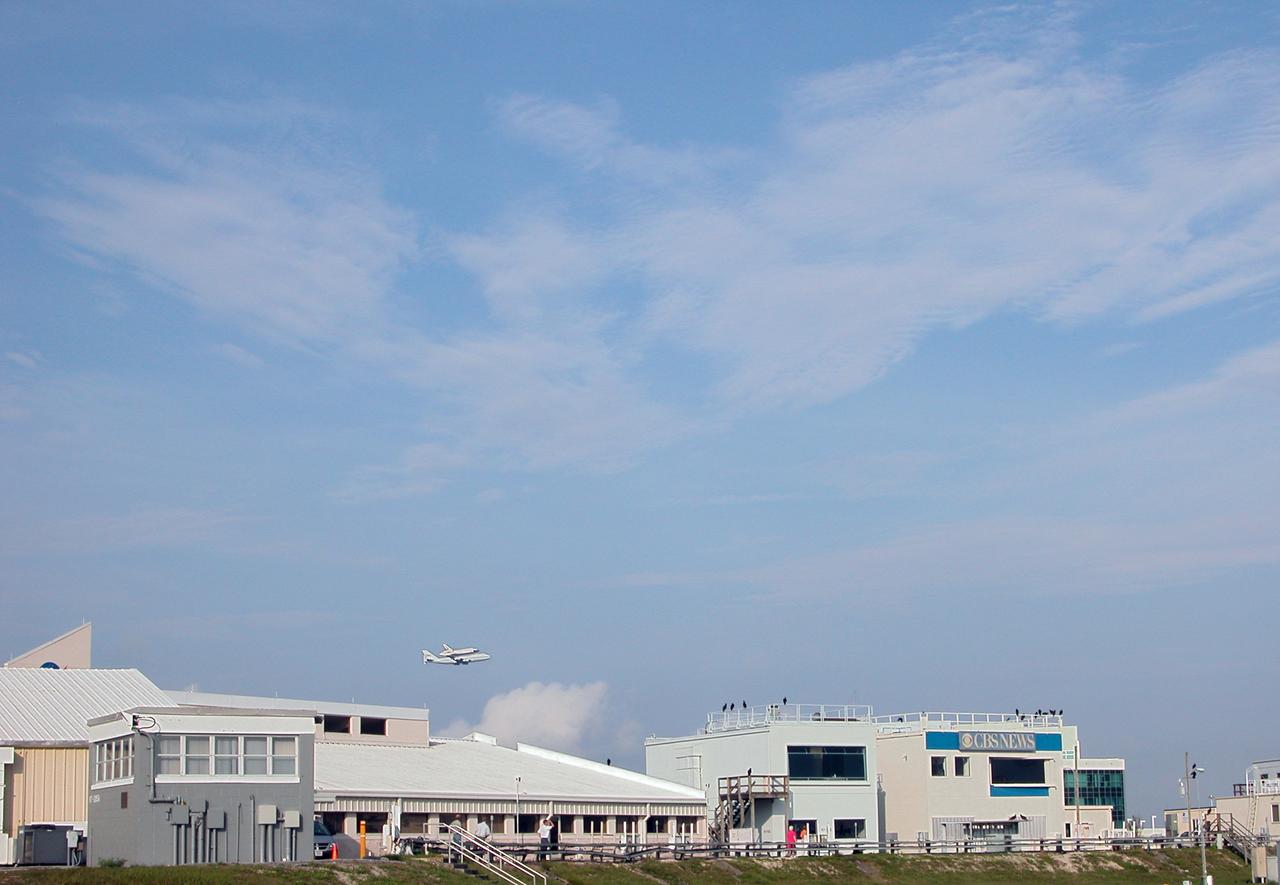

On a morning where broken clouds filled the sky of Central Florida, the shuttle carrier aircraft, or SCA, and its passenger Atlantis ease their way past the NASA News Center for a landing at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, known as the SLF. The aircraft is a modified Boeing 747 jetliner Atlantis landed at Edwards Air Force Base in California to end mission STS-117. The return to KSC began July 1 and took three days after stops across the country for fuel. The last stop was at Ft. Campbell in Kentucky. Weather conditions over the last leg postponed the return trip until July 3. Touchdown was at 8:27 a.m. EDT. Atlantis will be removed from the back of the SCA via the mate/demate device at the SLF. It will then be towed to the Orbiter Processing Facility to begin processing for its next launch, mission STS-122 in December.
Advanced Air Mobility will connect both urban dwellers and rural residents by adding a new way to travel by air. As shown in this concept art, passengers could travel from rural areas into the city quicker than by car to board a commercial airliner, access medical care or to purchase goods.
A ferry carrying more than 600 passengers sank in the Java Sea between the island of Java and Borneo just before midnight on December 29, 2006, during high winds and rough seas.

Artwork: N/A Flying Wing at Airport: approach on taxi way and at gate showing passenger loading concept
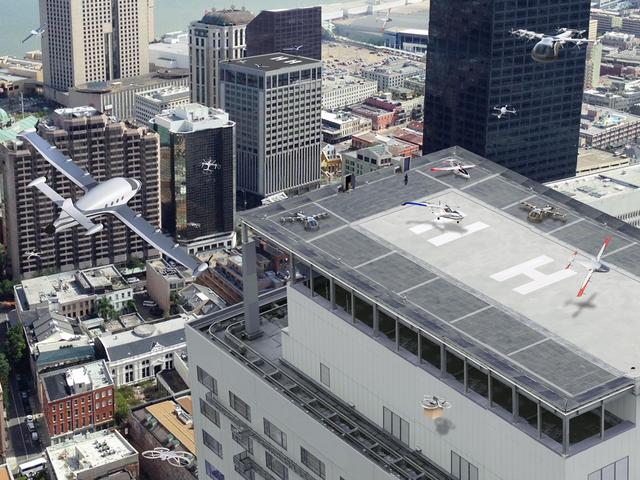

Urban air mobility means a safe and efficient system for vehicles, piloted or not, to move passengers and cargo within a city.
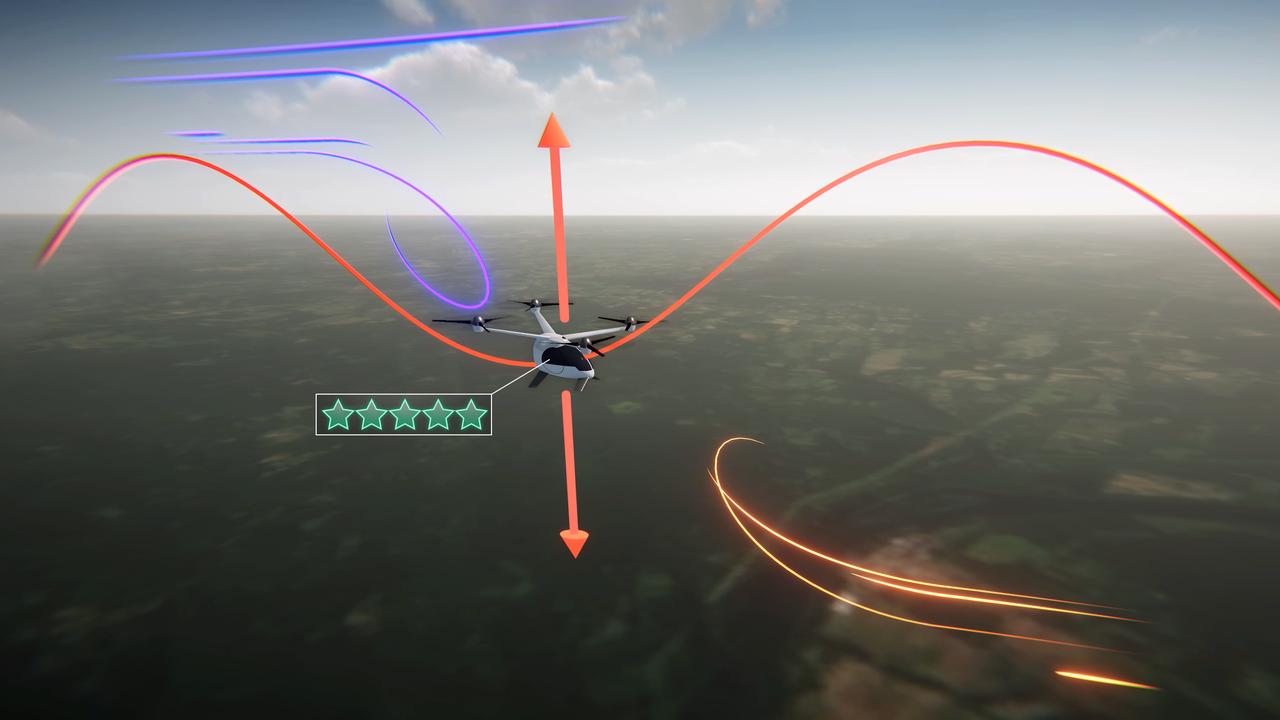
Electrical vertical takeoff and landing aircraft (eVTOLs), like the one shown in this concept art, could be a crucial part of the next generation of air transportation. In order to create a viable market, designers will have to create a comfortable passenger experience. NASA's Advanced Air Mobility mission is researching ride quality to better understand how these aircraft should be designed.

Artwork - Artist unknown High Speed Rotorcraft Concept Variable Diameter Civil Tilt-Rotor Artwork depicting vertiport (6-9 passenger)
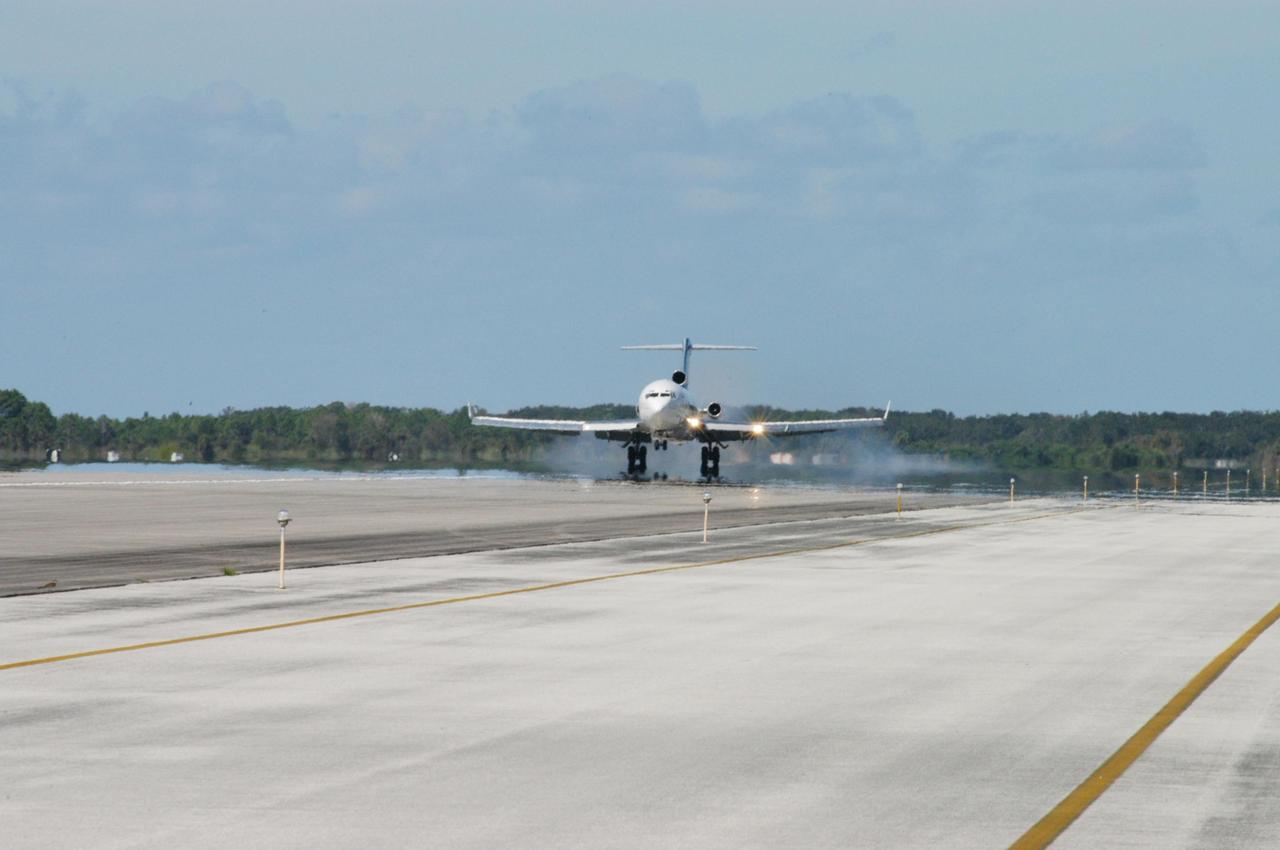

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., lands after taking a group of passengers for demonstration. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. This group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
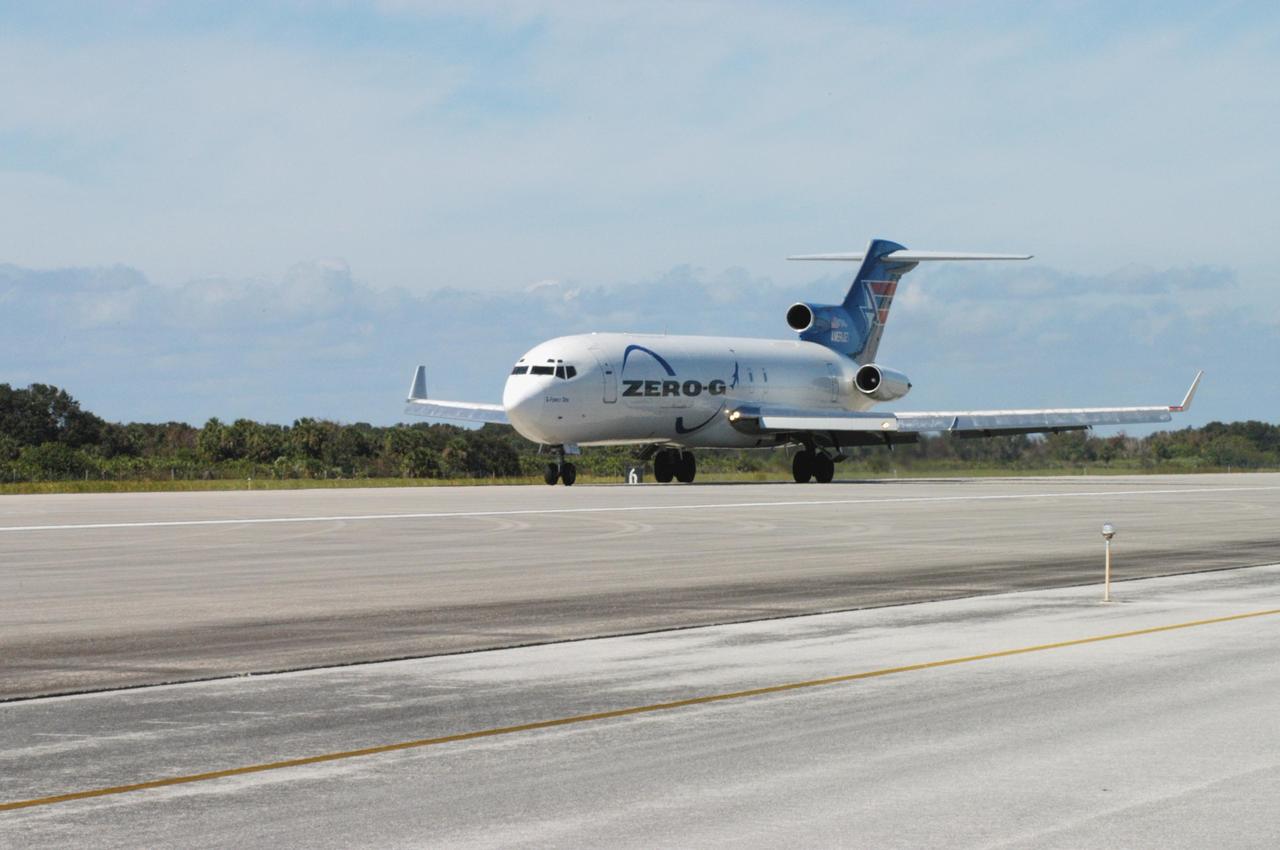

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., lands after taking a group of passengers for demonstration. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. This group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
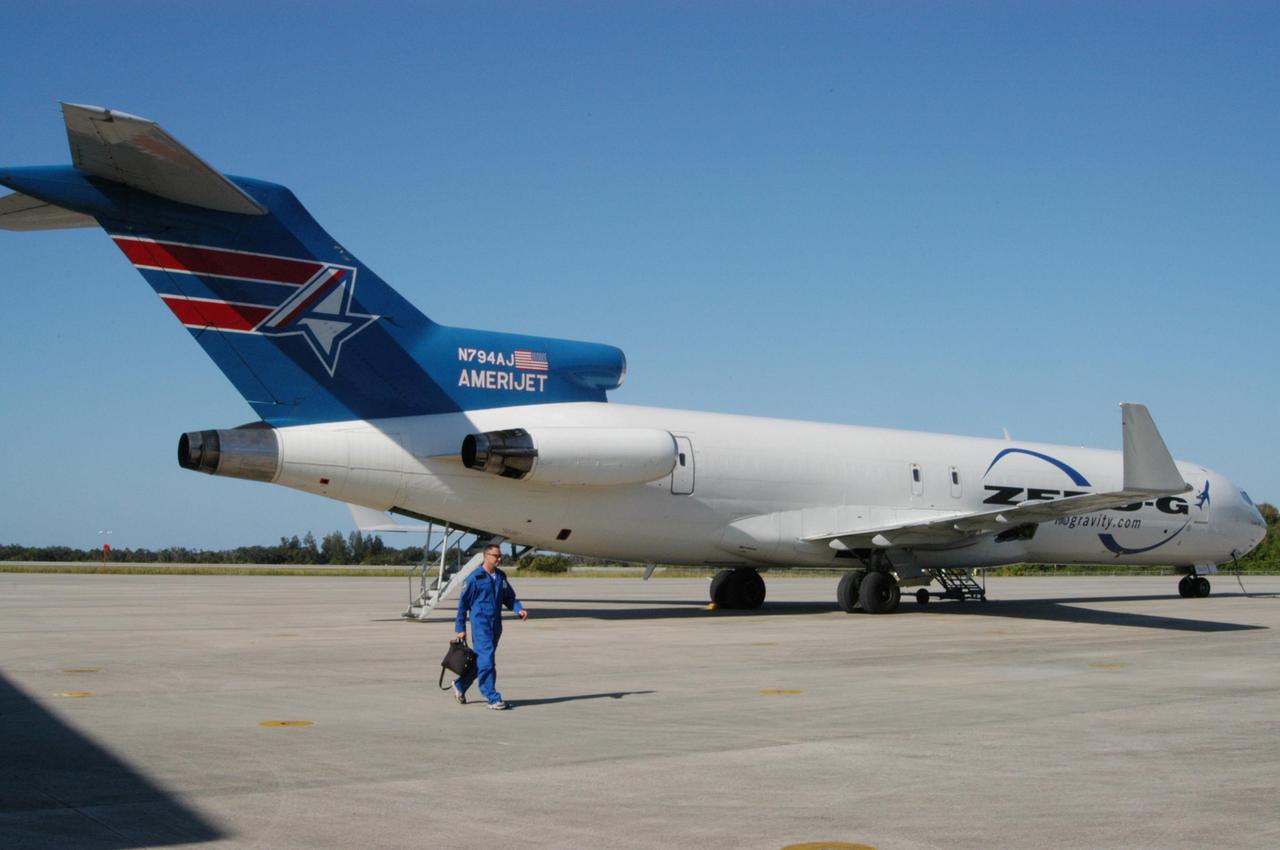

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., waits for its passengers. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. A group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.

Jules Verne published his first science fiction novel in 1865 called "From the Earth to the Moon." As shown here in an illustration, passengers in Verne's space ship enjoy their first taste of weightlessness.
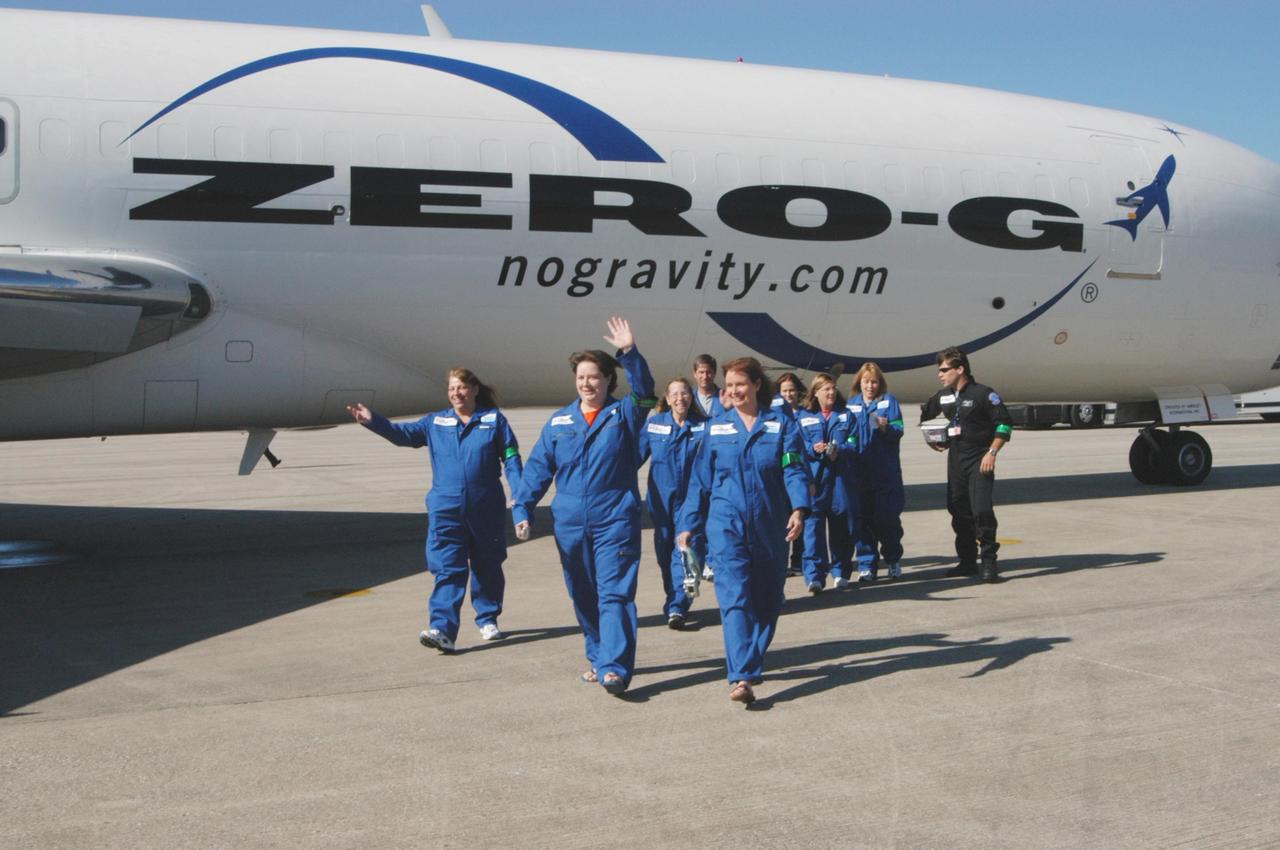

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first group of passengers to fly on the ZERO-G aircraft are eager to get started. The Boeing 727-200 aircraft is used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. The passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
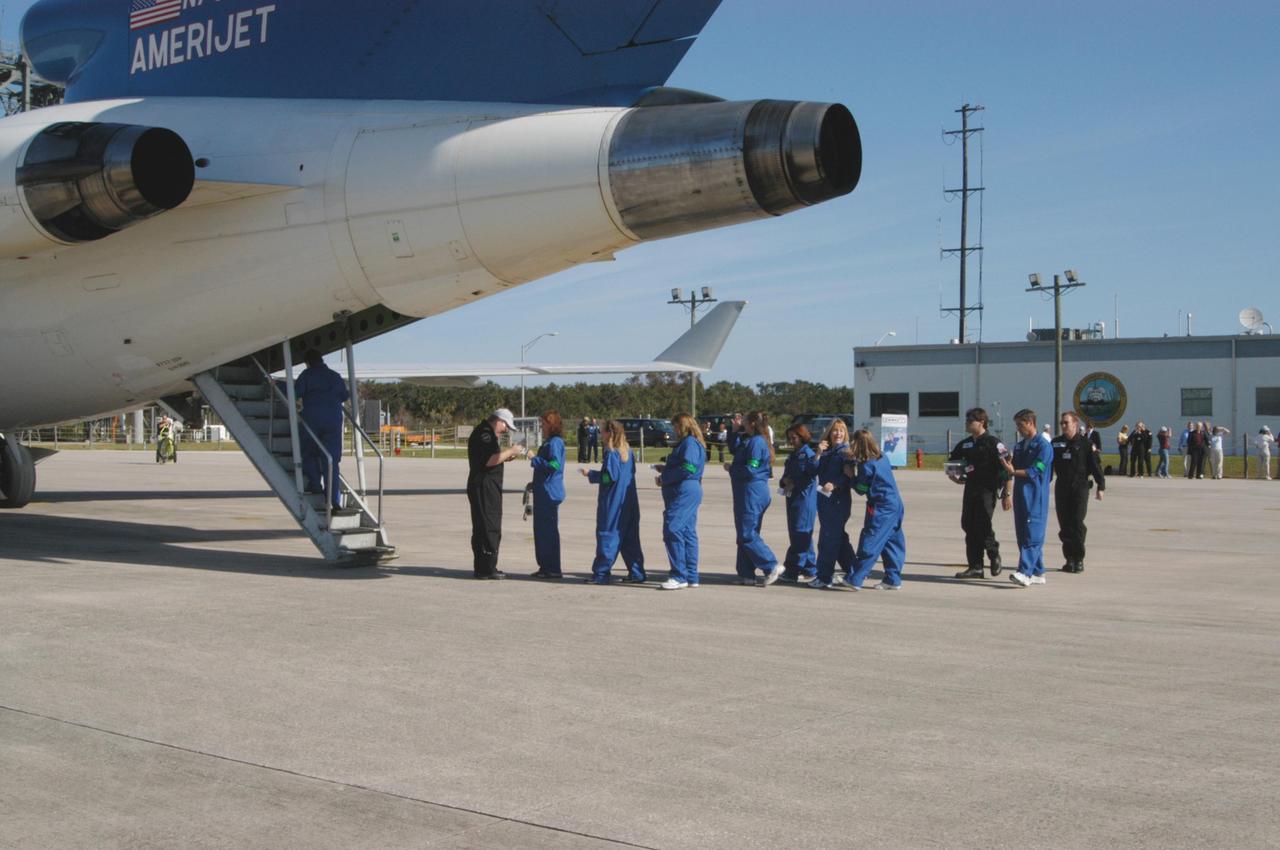

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first group of passengers to fly on the ZERO-G aircraft line up. The Boeing 727-200 aircraft is used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. The passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
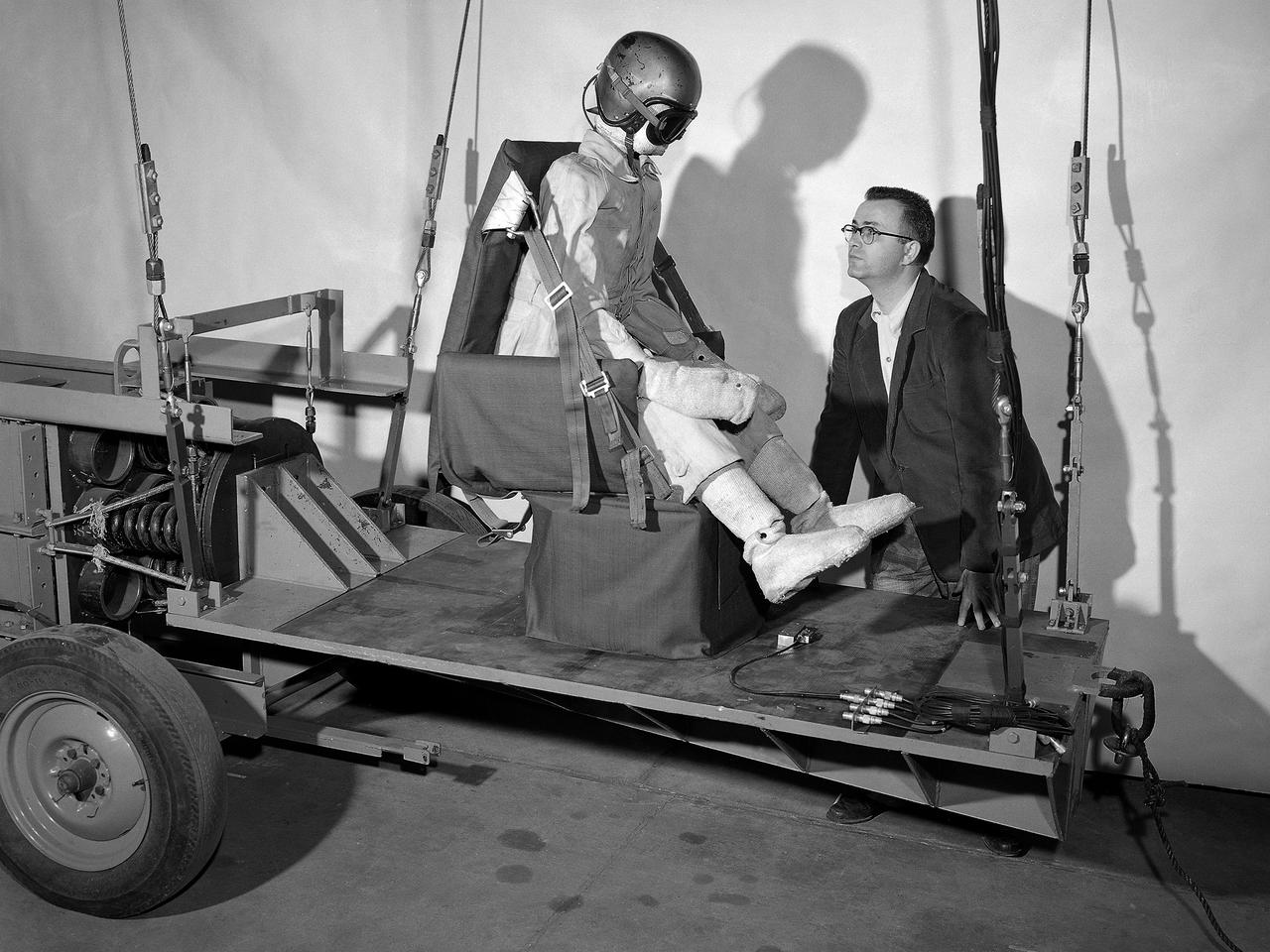

A researcher at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory prepares for a test of an NACA-designed aircraft seat. The laboratory had undertaken a multi-year investigation into the causes and prevention of fires on low altitude aircraft crashes. The program was expanded in the mid-1950s to include the study of impact on passengers, types of seat restraints, and seat design. The crash impact portion of the program began by purposely wrecking surplus Fairchild C-82 Packet and Piper Cub aircraft into barricades at the end of a test runway at the Ravenna Arsenal, located approximately 40 miles south of the Lewis lab in Cleveland. Instrumented dummies and cameras were installed in the pilot and passenger areas. After determining the different loads and their effects on the passengers, the NACA researchers began designing new types of seats and restraints. The result was an elastic seat that flexed upon impact, absorbing 75 percent of the loads before it slowly recoiled. This photograph shows the seats mounted on a pendulum with a large spring behind the platform to provide the jolt that mimicked the forces of a crash. The seat was constructed without any potentially damaging metal parts and included rubber-like material, an inflated back and arms, and a seat cushion. After the pendulum tests, the researchers compared the flexible seats to the rigid seats during a crash of a transport aircraft. They found the passengers in the rigid seats received 66 percent higher g-forces than the NACA-designed seats.
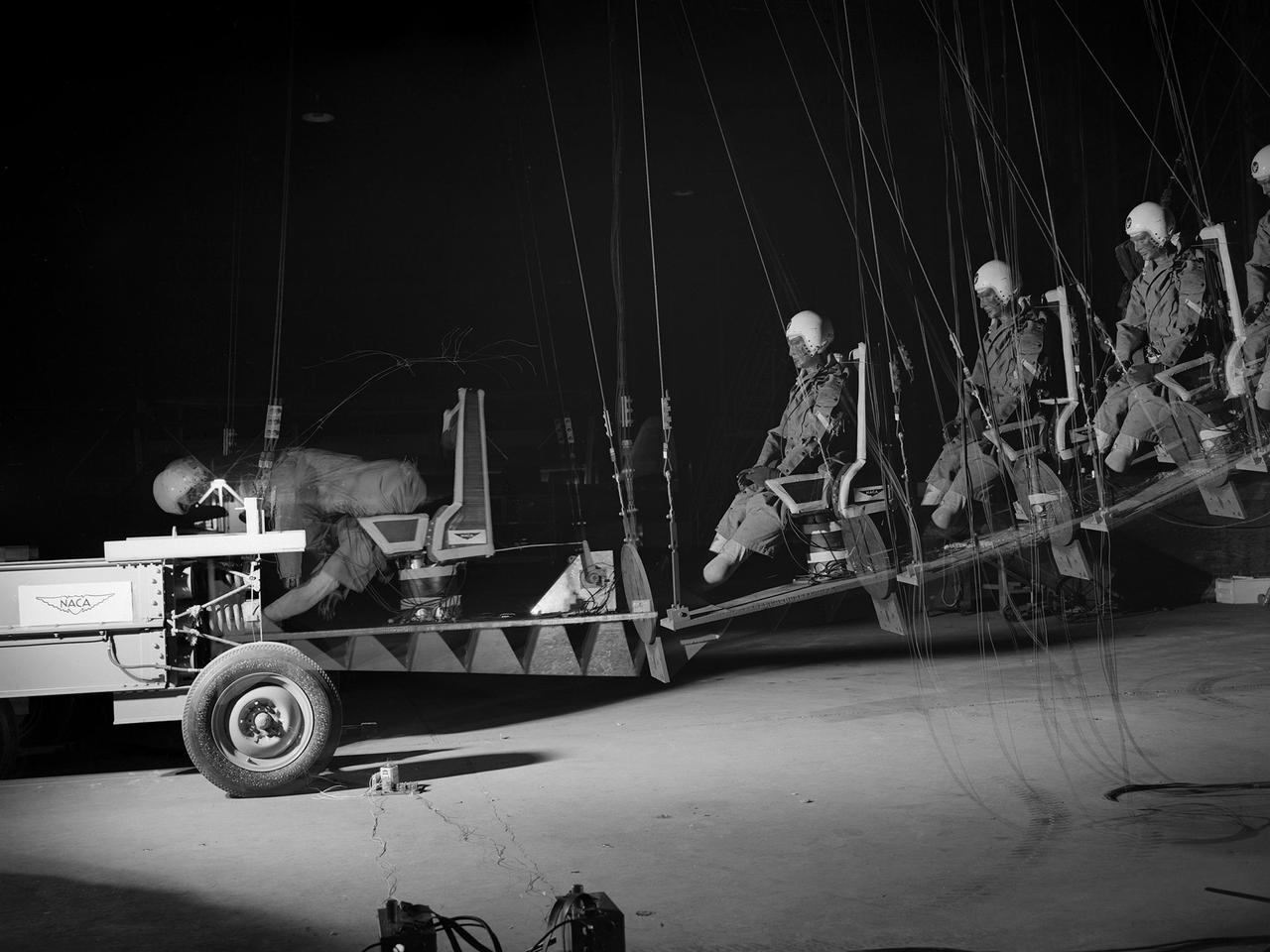

This time-lapse photograph shows the test of a pilot seat and restraint designed by researchers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The laboratory had undertaken a multi-year investigation into the causes and preventative measures for fires resulting from low altitude aircraft crashes. The program was expanded in the mid-1950s to include the study of crash impact on passengers, new types of types of seat restraints, and better seat designs. The impact program began by purposely wrecking surplus transport Fairchild C-82 Packet and Piper Cub aircraft into barricades at the end of a test runway. Instrumented dummies and cameras were installed in the pilot and passenger areas. After determining the different loads experienced during a crash and the effects on the passengers, the NACA researchers began designing new types of seats and restraints. The result was an elastic seat that flexed upon impact, absorbing 75 percent of the loads before it slowly recoiled. This photograph shows the seats mounted on a pendulum with a large spring behind the platform to provide the jolt that mimicked the forces of a crash. The seat was constructed without any potentially damaging metal parts and included rubber-like material, an inflated back and arms, and a seat cushion. After the pendulum tests, the researchers compared the flexible seats to the rigid seats during a crash of a transport aircraft. They found the passengers in the rigid seats received 66 percent higher g-forces than the NACA-designed seats.
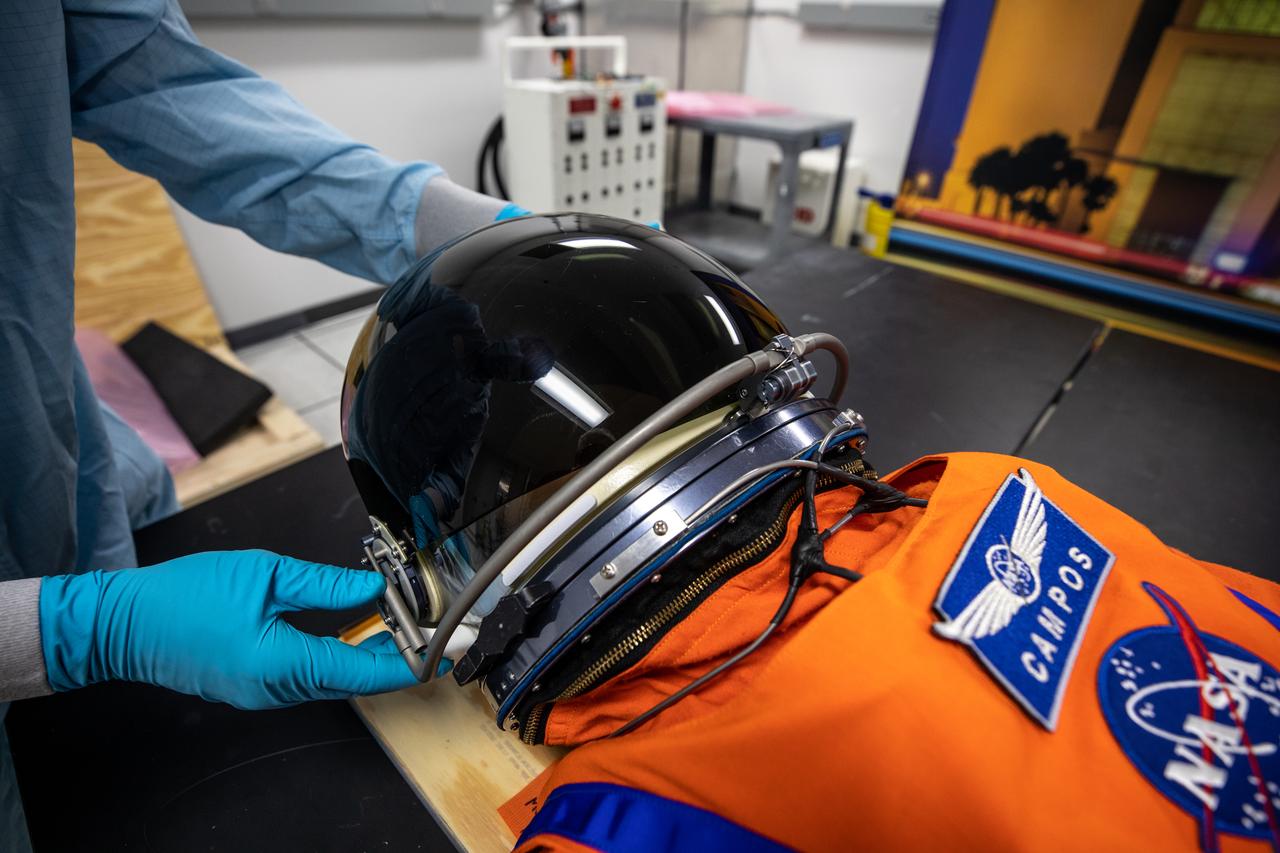

Teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Moonikin “Campos” will be installed into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, prior to installation into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

Teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Moonikin “Campos” will be installed into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, prior to installation into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

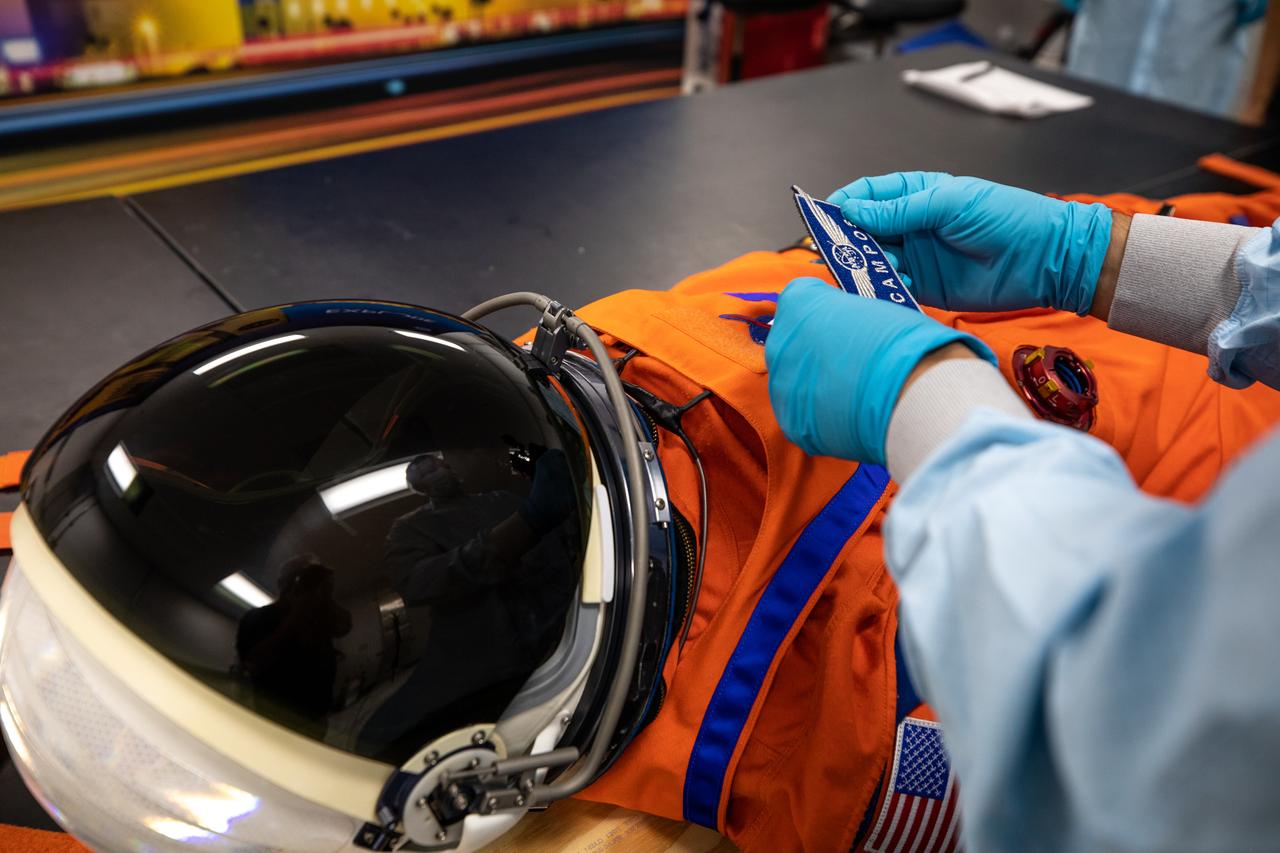
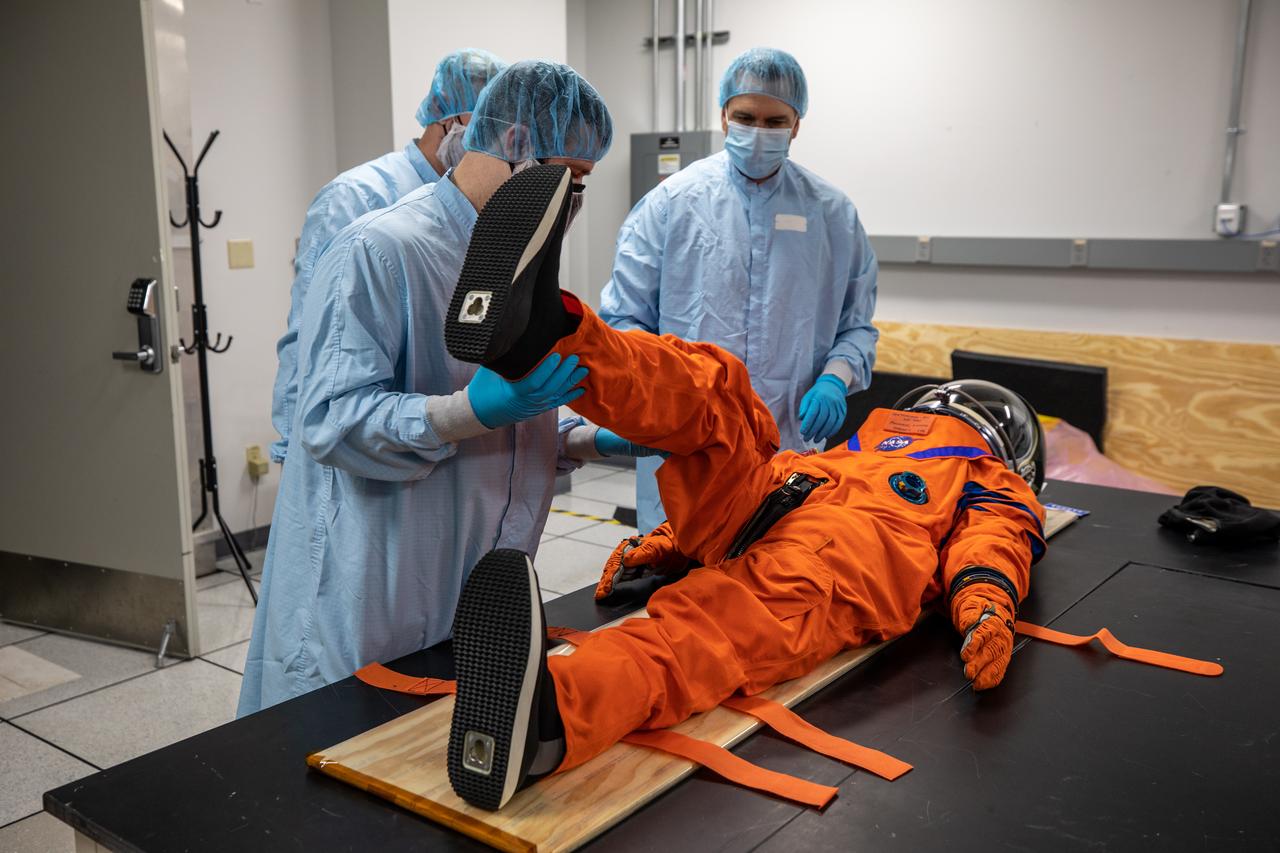
Teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Moonikin “Campos” will be installed into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
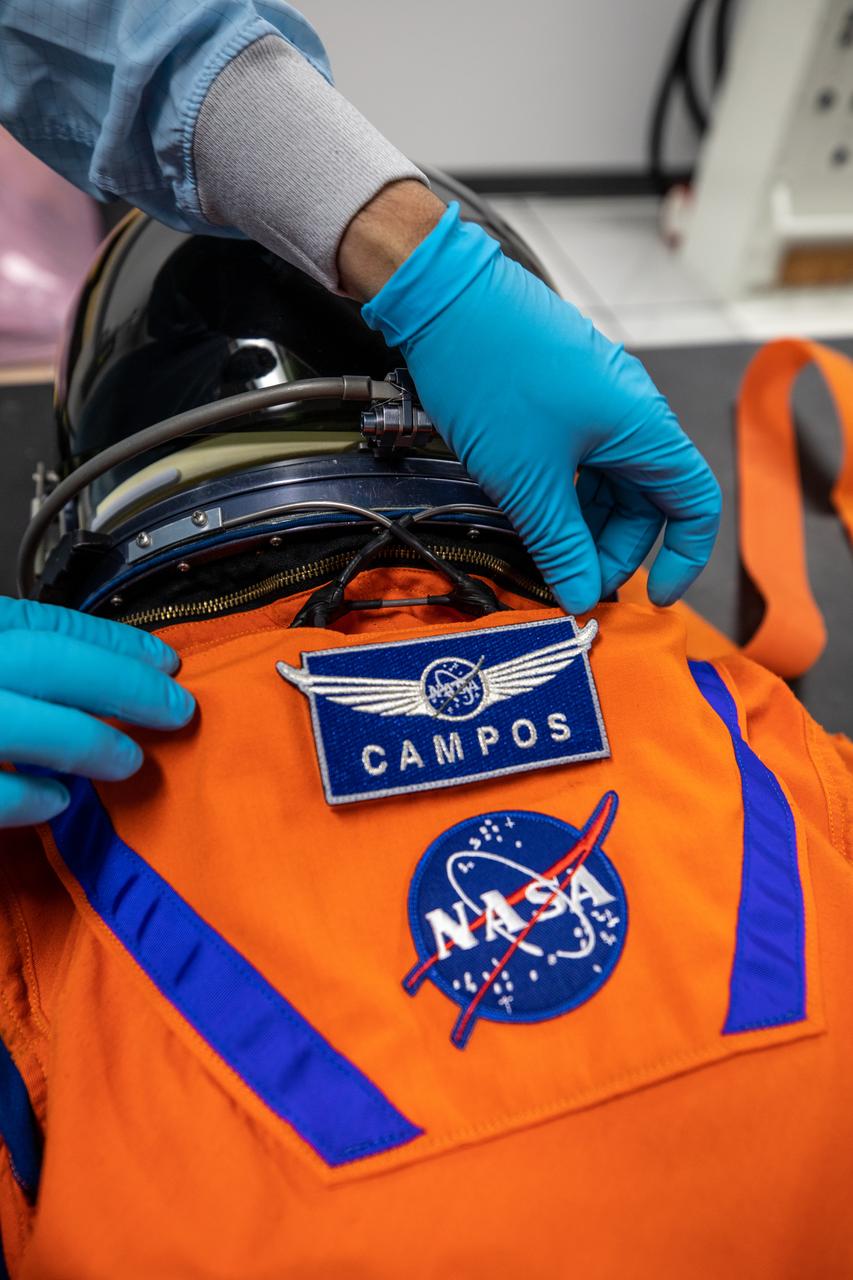

Teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Moonikin “Campos” will be installed into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
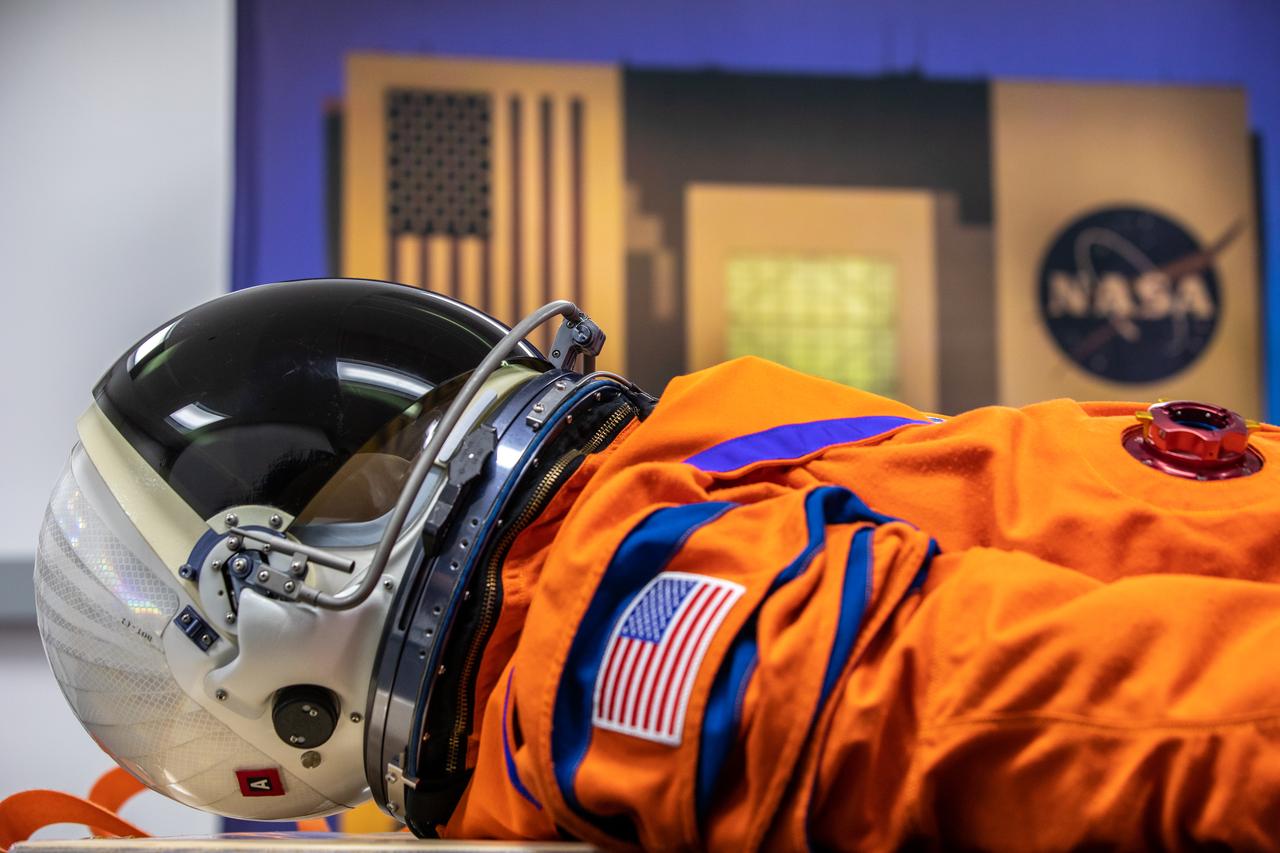

Teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Moonikin “Campos” will be installed into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
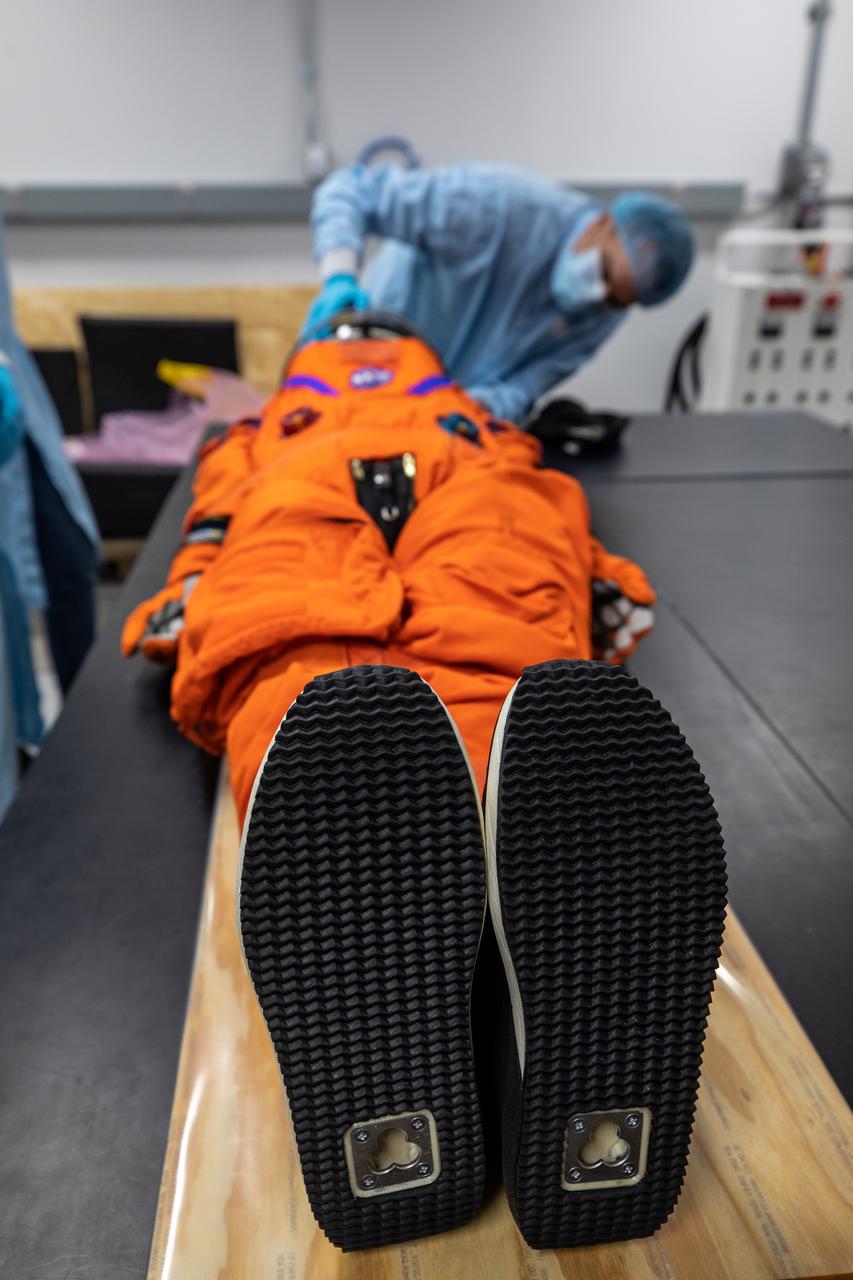

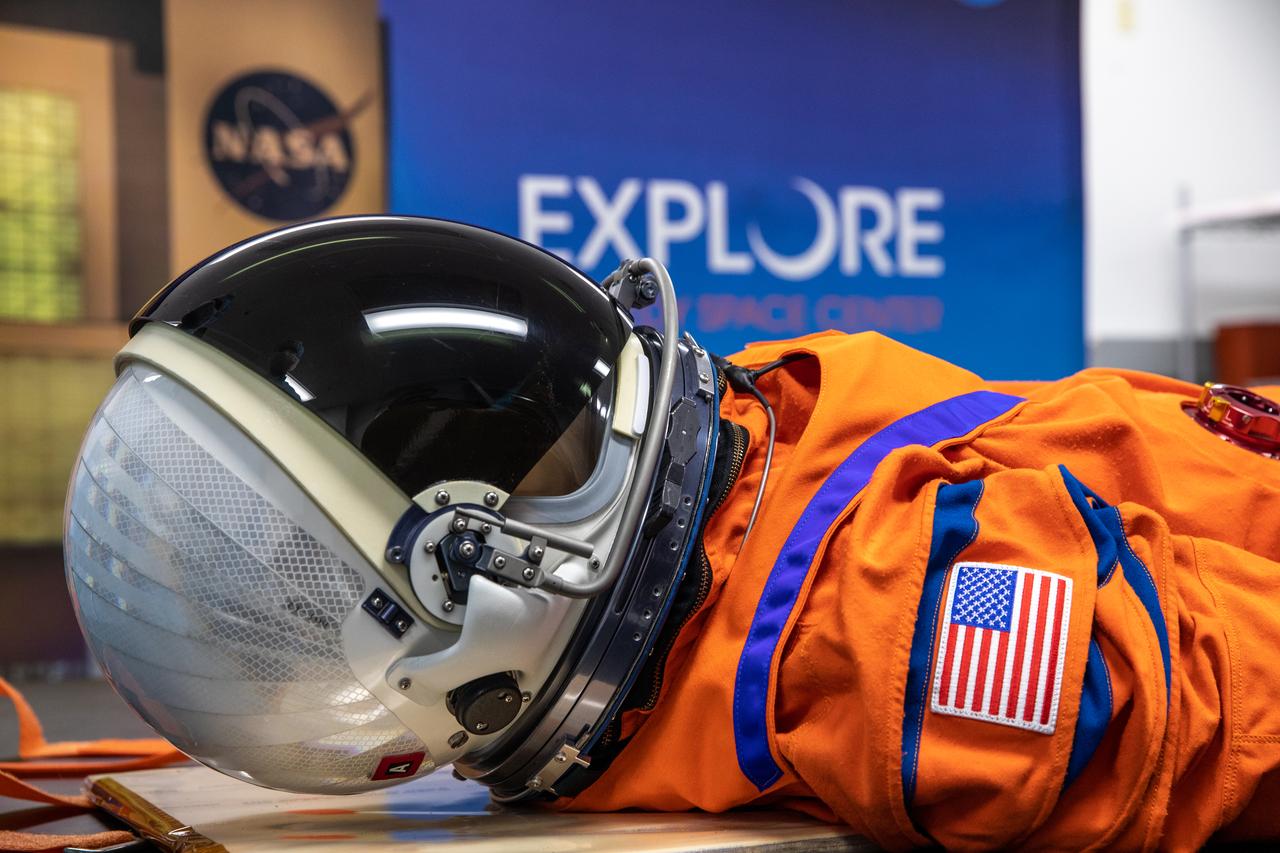
Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, prior to installation into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
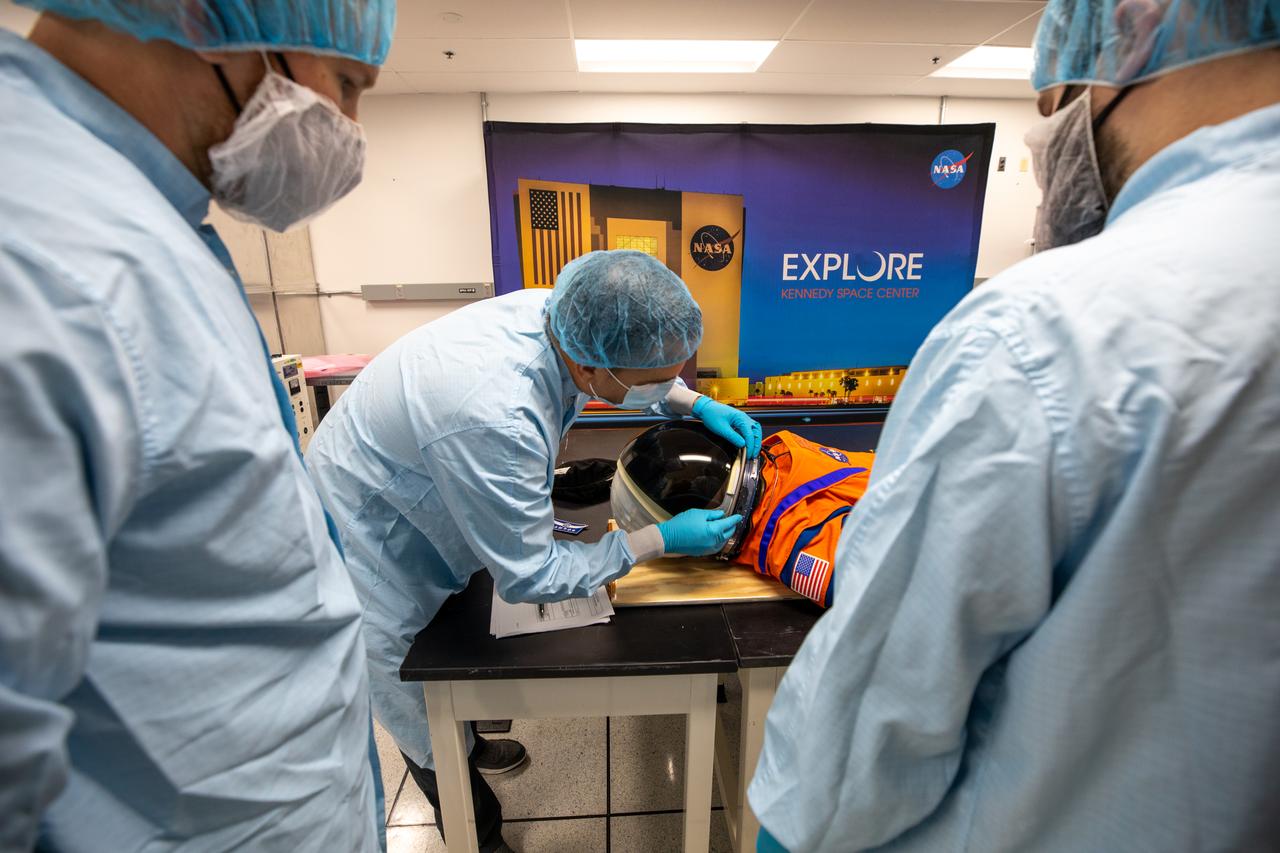

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, prior to installation into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
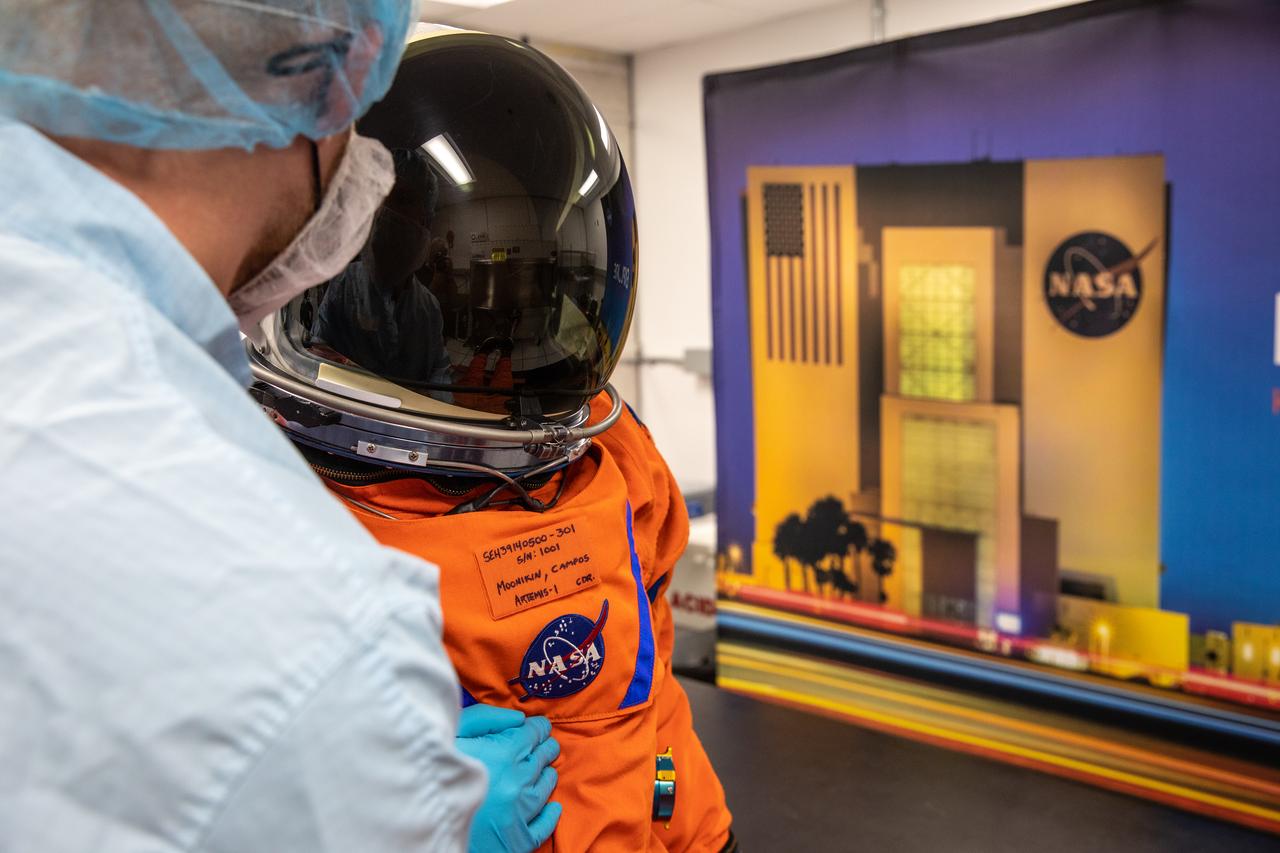

Teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Moonikin “Campos” will be installed into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
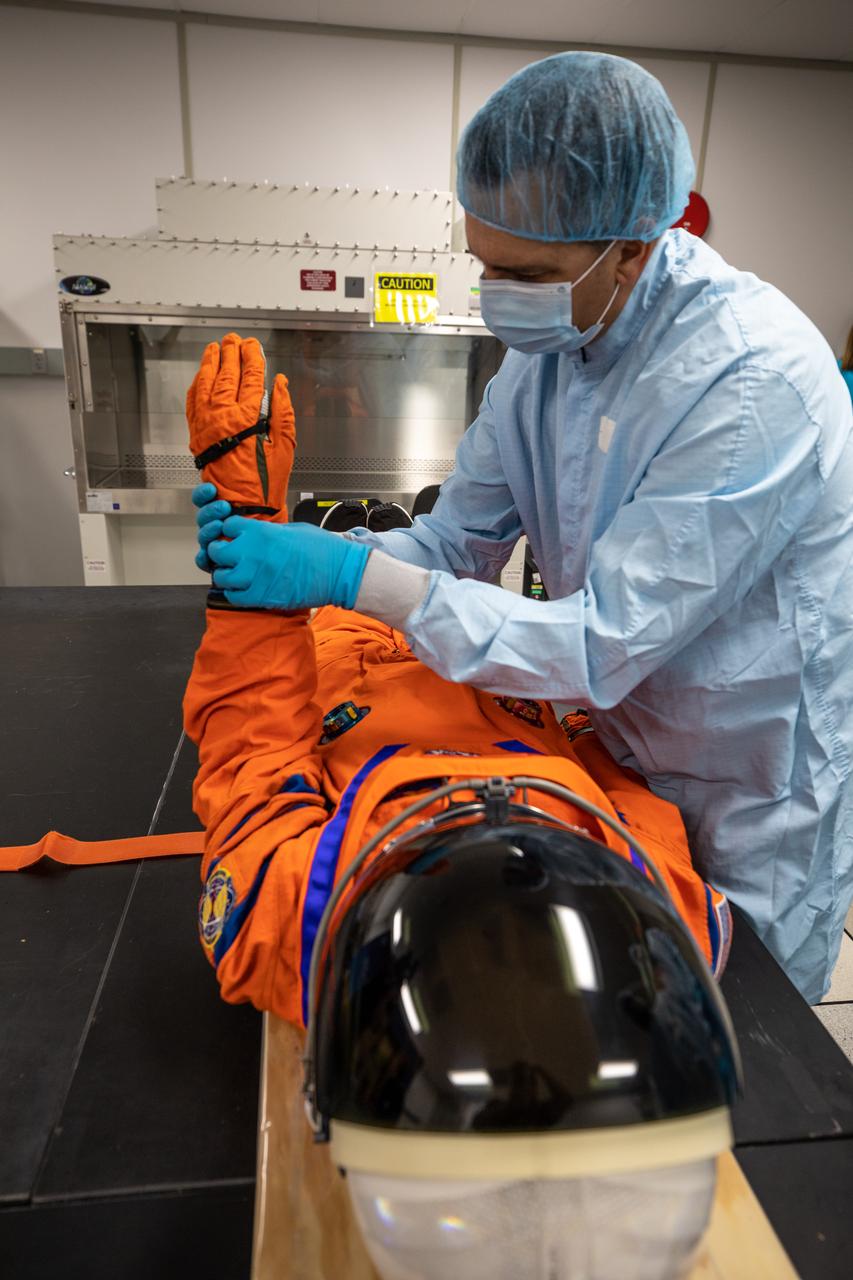

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, teams from Johnson Space Center, Exploration Ground Systems, and Jacobs TOSC conduct final inspections of Moonikin “Campos” on Nov. 9, 2021, prior to installation into the Orion crew module. Technicians checked connectivity and performed fit checks on his flight suit to ensure he is ready for flight aboard the Artemis flight test. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
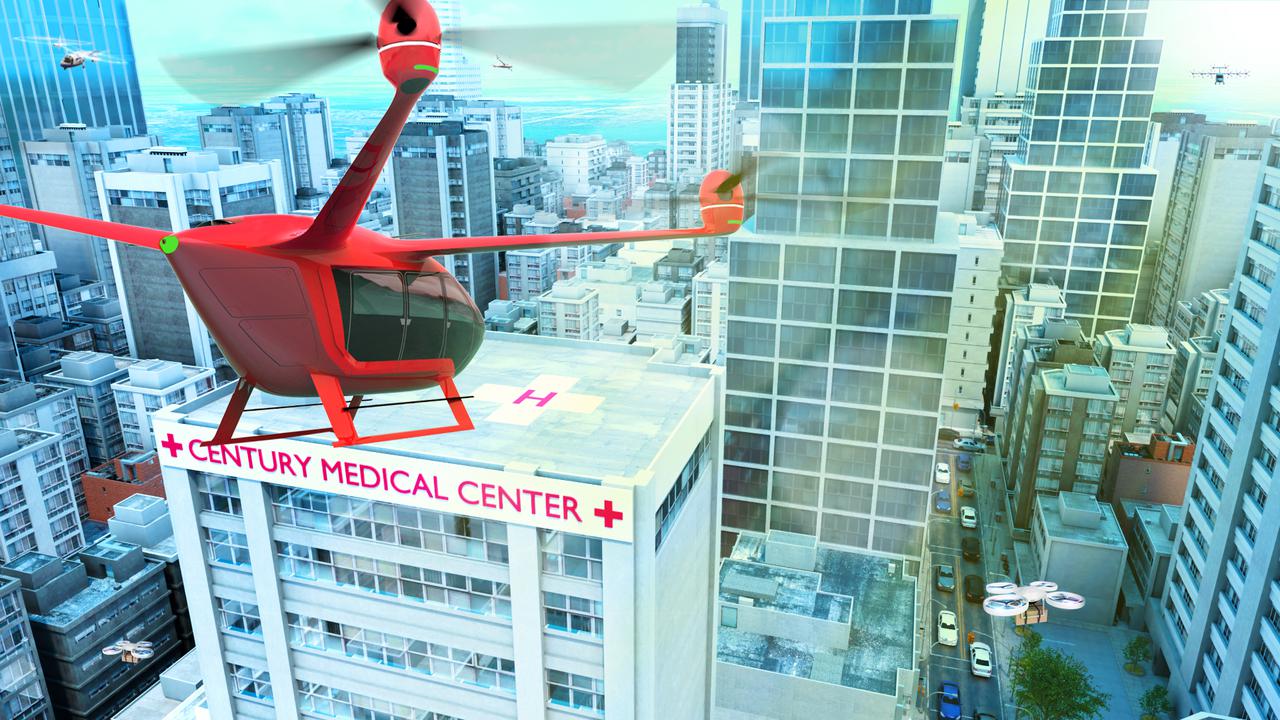

Several projects supporting NASA's Advanced Air Mobility or AAM mission are working on different research initiatives to help make AAM a reality. AAM could be used in healthcare operations in the form of air taxi ambulances or medical supply delivery in the future. This concept graphic shows how a future AAM vehicle could aid in healthcare by carrying passengers to a hospital.
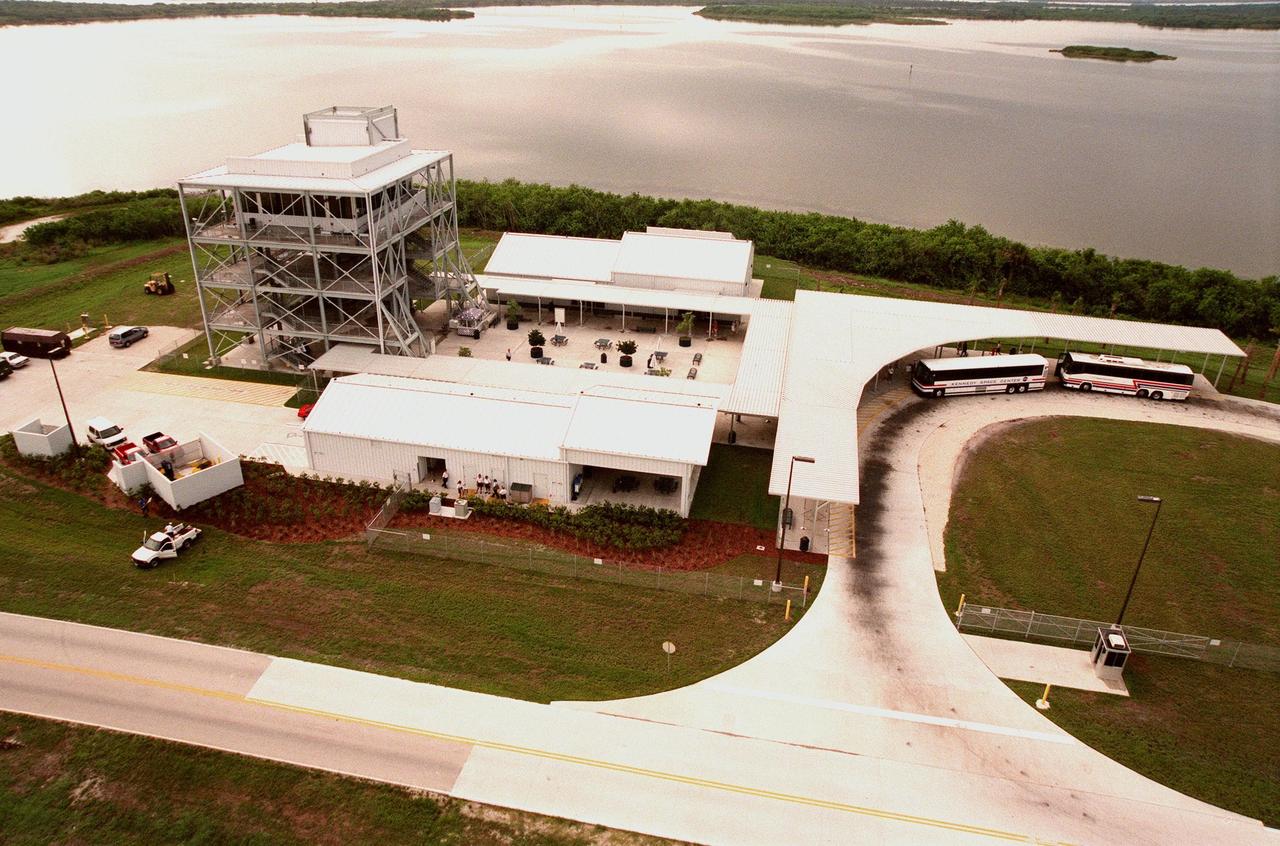

Tour buses unload passengers at a new stop on the KSC tour that allows visitors to view Pad LC-39B. The tour road runs parallel to the crawlerway (just out of sight) that is used to transport the Space Shuttle vehicles to the pad. The length of the crawlerway from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Pad B is 6,828 meters (22,440 ft); its width overall is 40 meters (130 ft); each lane is 12 meters (40ft) with a 15-meter (50ft) median. This view looks south
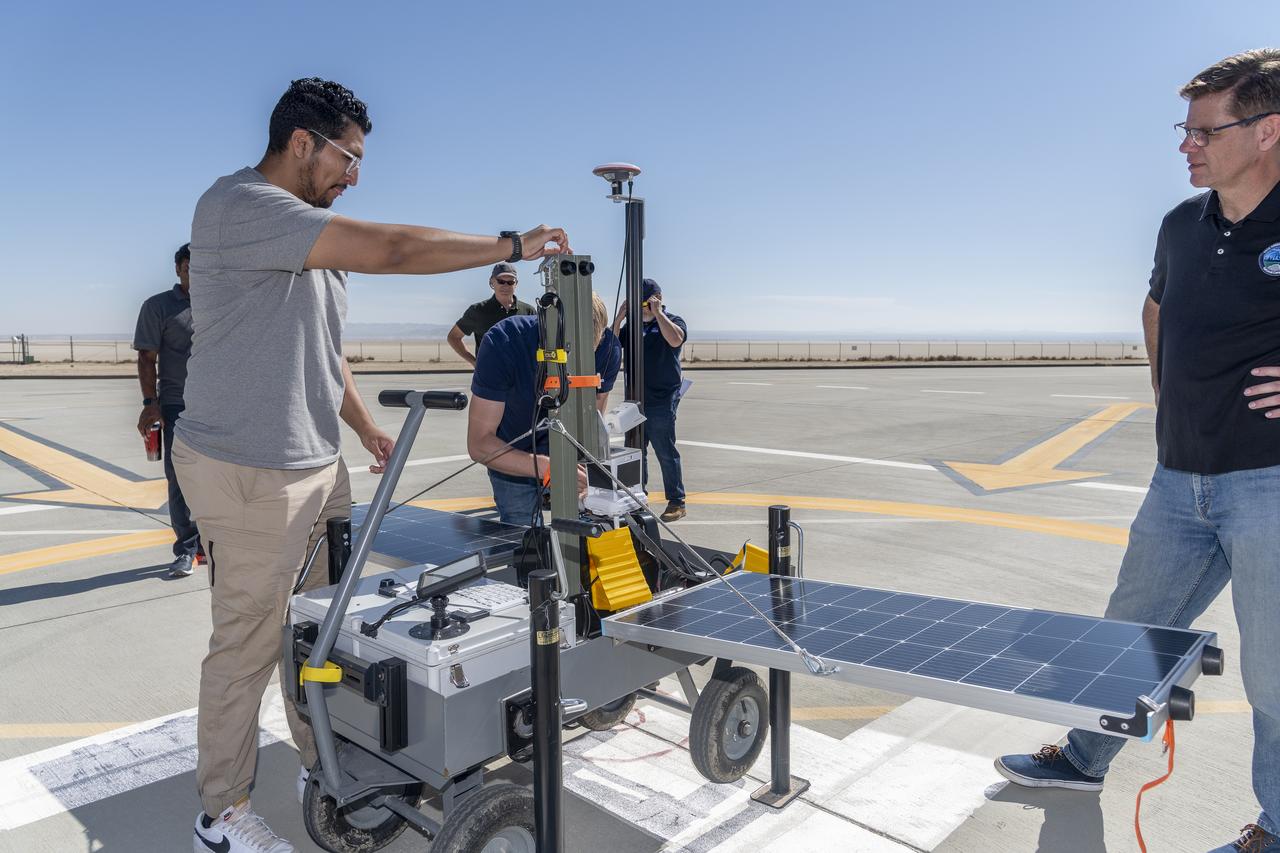

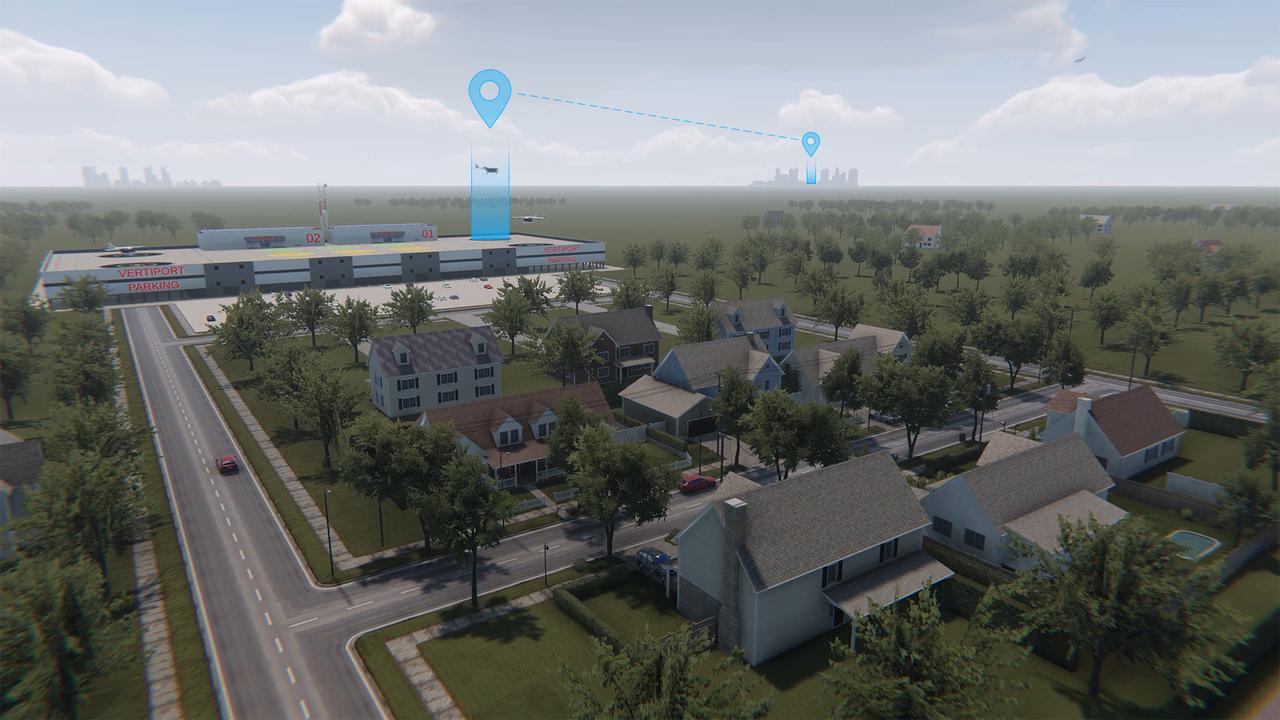
NASA operations engineer Daniel Velasquez, left, is reviewing the Mobile Vertipad Sensor Package system as part of the Air Mobility Pathways test project at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California on October 17, 2023. The portable system allows Advanced Air Mobility researchers to test and evaluate several factors involved in monitoring takeoff and landing conditions at vertipad sites. "Vertipads" or "vertiports" will be where future air taxis will land and take off to transport passengers.
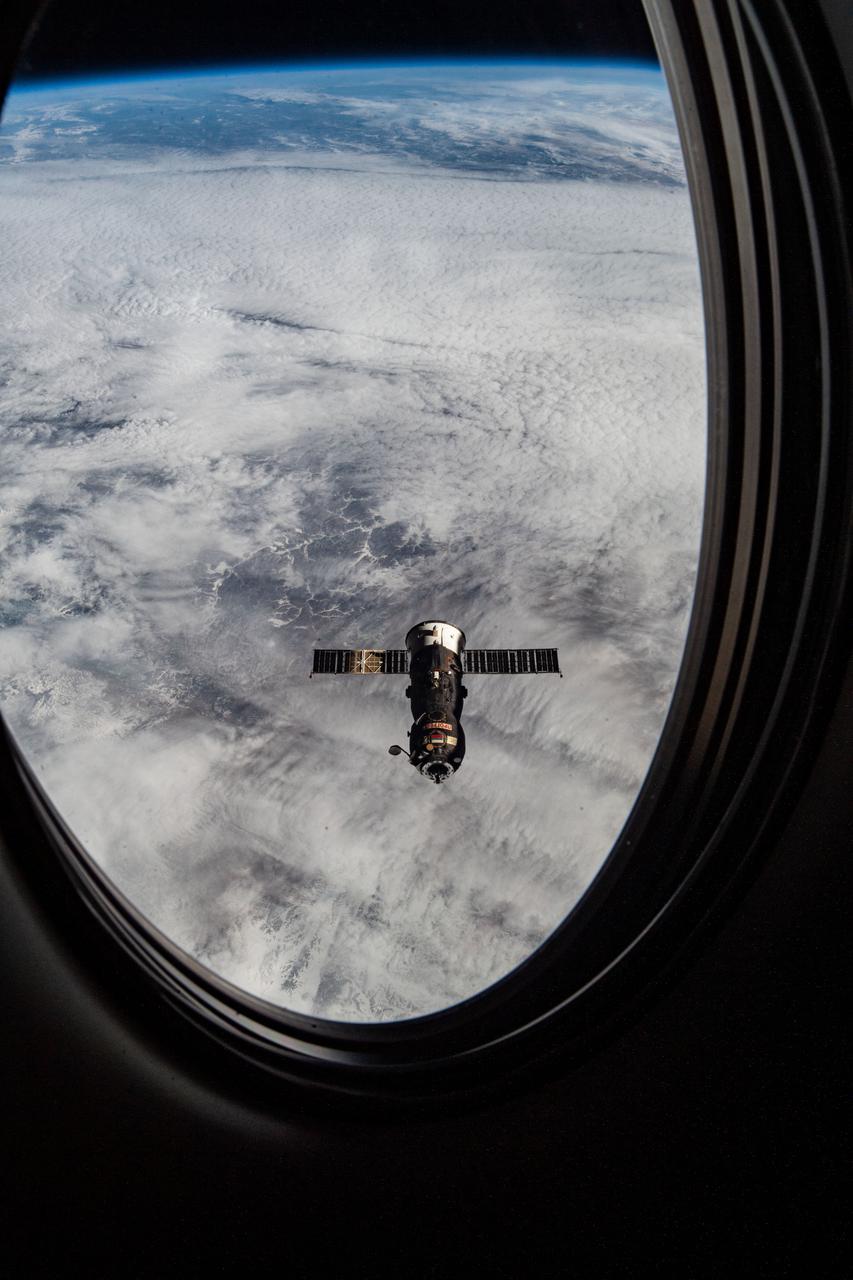

iss064e029934 (Feb. 9, 2021) --- This view of the departing ISS Progress 76 resupply ship looks out from a passenger window on the SpaceX Crew Dragon "Resilience." The Progress 76 had undocked moments earlier from the International Space Station's Pirs docking compartment. Both spacecraft were orbiting 264 miles above western Mongolia border when this photograph was taken.
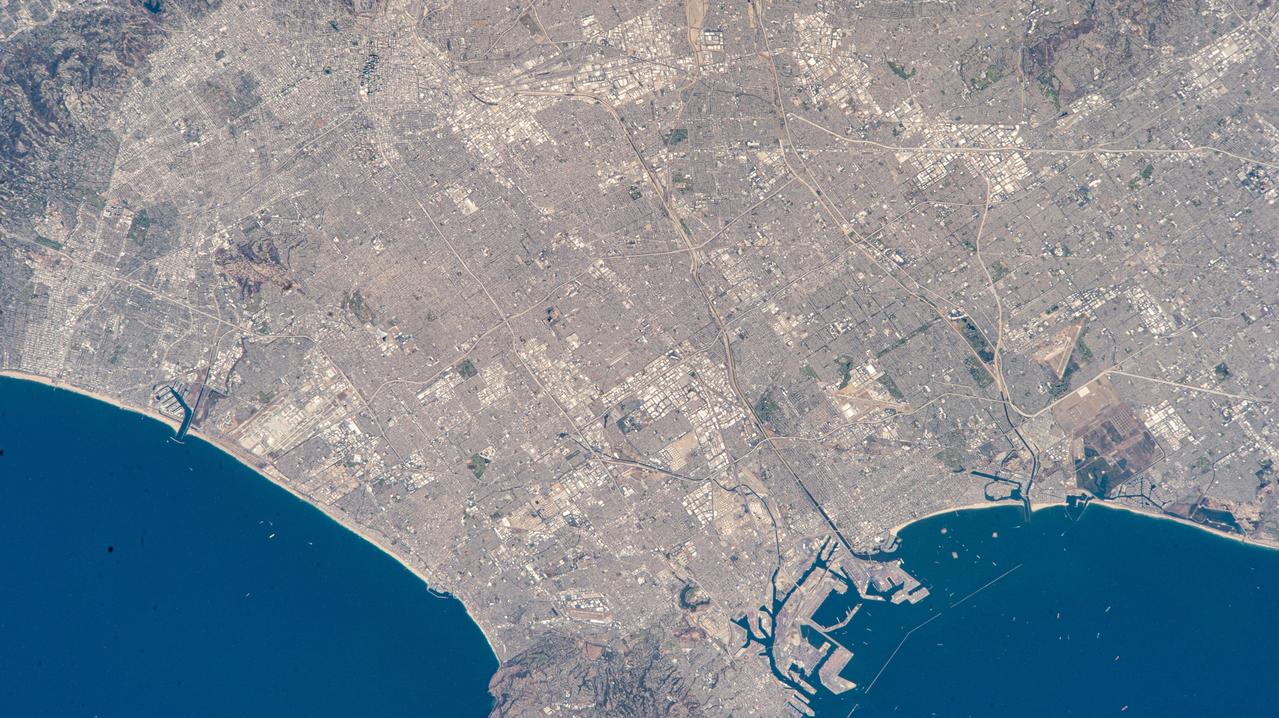

iss073e0513936 (Aug. 22, 2025) --- Los Angeles, California, surrounded by its suburbs including Santa Monica, Marina Del Rey, and Long Beach, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above the Golden State. Highlights include Terminal Island (bottom right), an artificial island used mainly for industrial and port-related activities. At left, near Marina Del Rey is Los Angeles International Airport (LAX) connecting over 80 million passengers annually to over 100 domestic and international destinations.
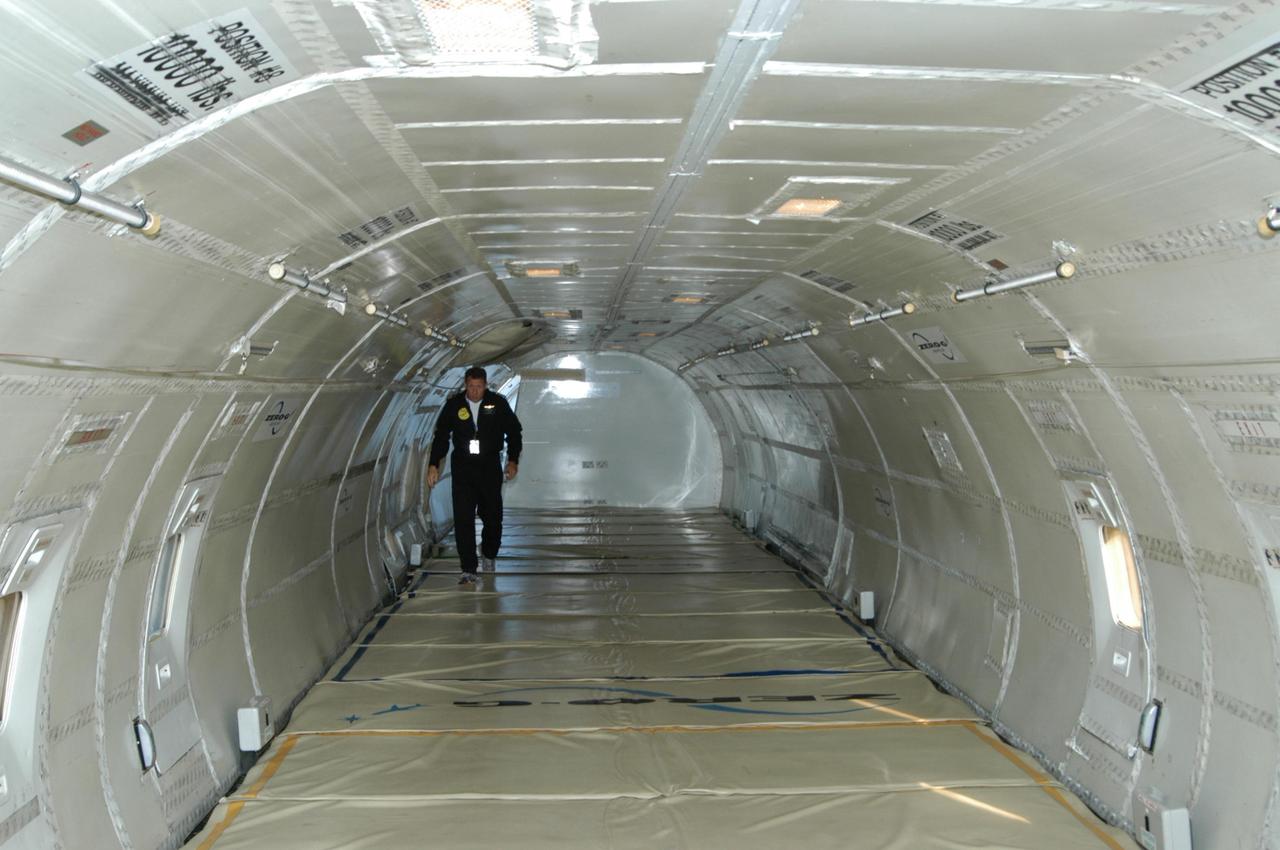

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A view inside the Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. A group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
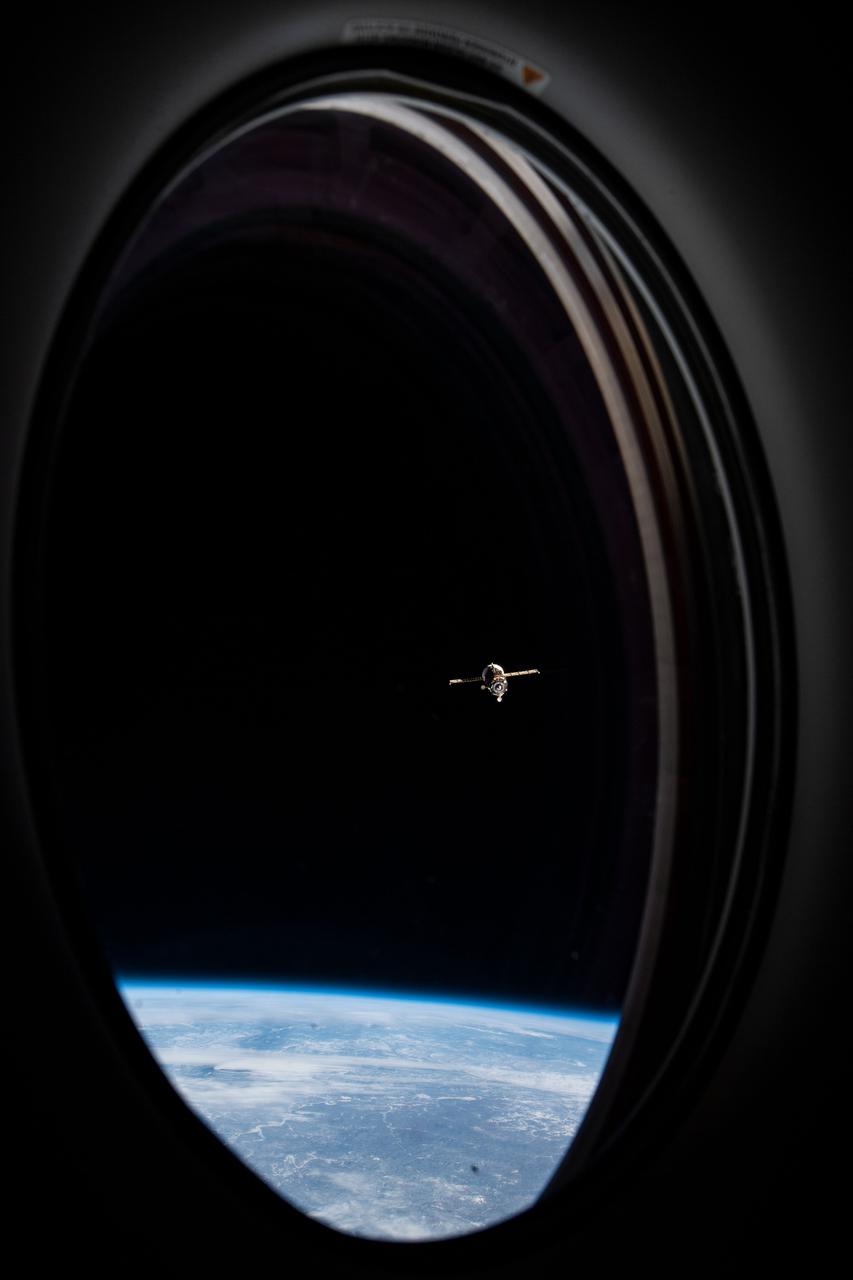

iss064e029985 (Feb. 9, 2021) --- This view of the departing ISS Progress 76 resupply ship looks out from a passenger window on the SpaceX Crew Dragon "Resilience." The Progress 76 had undocked moments earlier from the International Space Station's Pirs docking compartment. Both spacecraft were orbiting 264 miles above the Russia-Mongolia border when this photograph was taken.
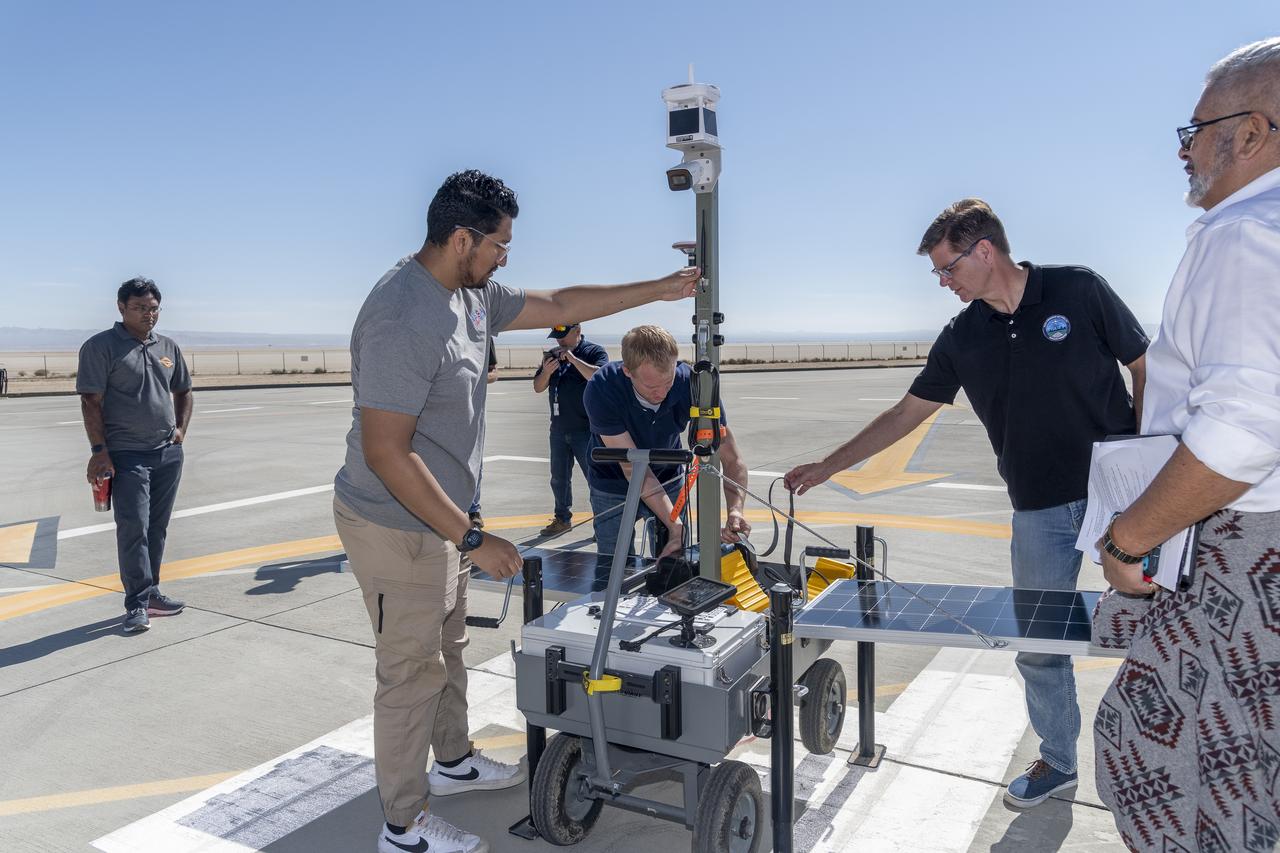

NASA operations engineer Daniel Velasquez, left, is reviewing the Mobile Vertipad Sensor Package system as part of the Air Mobility Pathways test project at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California on October 17, 2023. The portable system allows Advanced Air Mobility researchers to test and evaluate several factors involved in monitoring takeoff and landing conditions at vertipad sites. "Vertipads" or "vertiports" will be where future air taxis will land and take off to transport passengers.

iss073e0982081 (Oct. 25, 2025) --- Atlanta, Georgia—home to the world's busiest airport, Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport (center left), which handles over 107 million passengers annually—is pictured at approximately 2:20 a.m. local time from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above North America. Atlanta is also nicknamed the "City in a Forest," with approximately 48% of its area covered in trees.
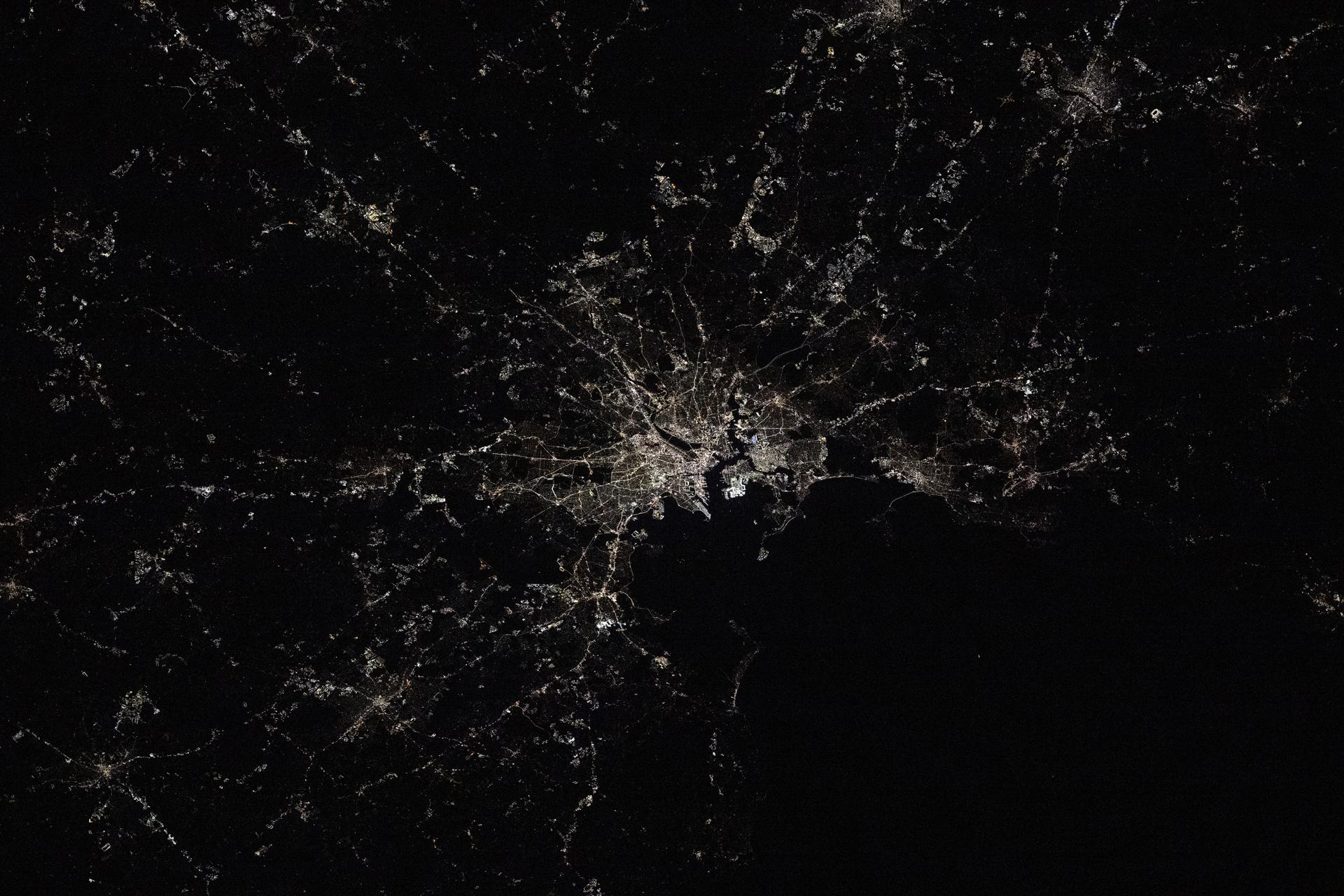

iss073e0982172 (Oct. 25, 2025) --- Boston, Massachusetts—home to America's first public park, public school, and subway system—is pictured at approximately 2:24 a.m. local time from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the northeastern United States. Located on Boston Harbor, Boston Logan International Airport (center) opened in 1923 and handled 43.5 million passengers and 568 million pounds of cargo in 2024.
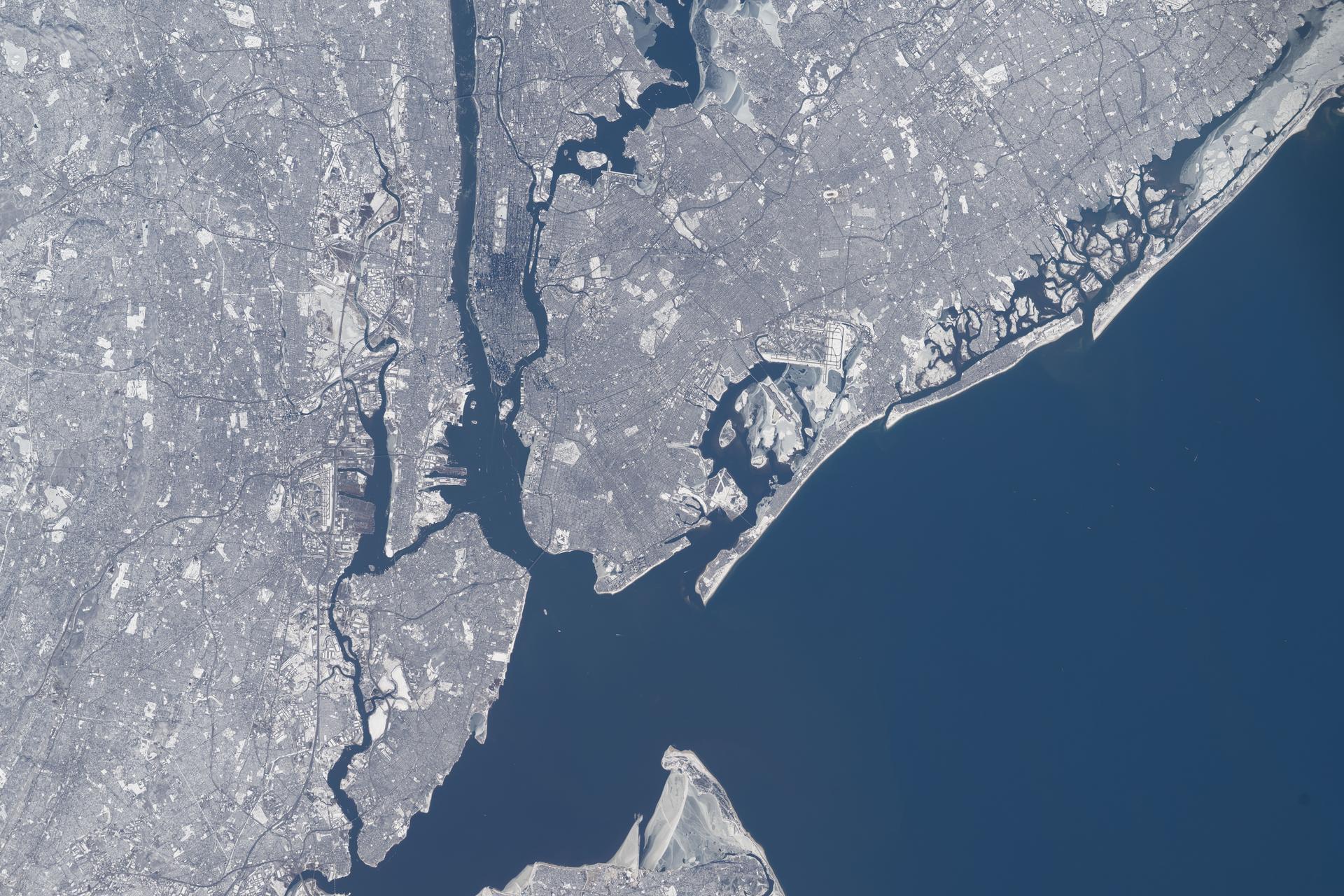

iss074e0315625 (Feb. 13, 2026) --- All five of New York City’s boroughs—Staten Island, Manhattan, Brooklyn, Queens, and the Bronx—are captured in this photograph of the wintry New York–Newark–Jersey City metropolitan area, which has a population of approximately 19.8 million. Near the center right is John F. Kennedy International Airport—America’s sixth-busiest airport, handling over 62 million passengers annually. Credit: NASA/Chris Williams
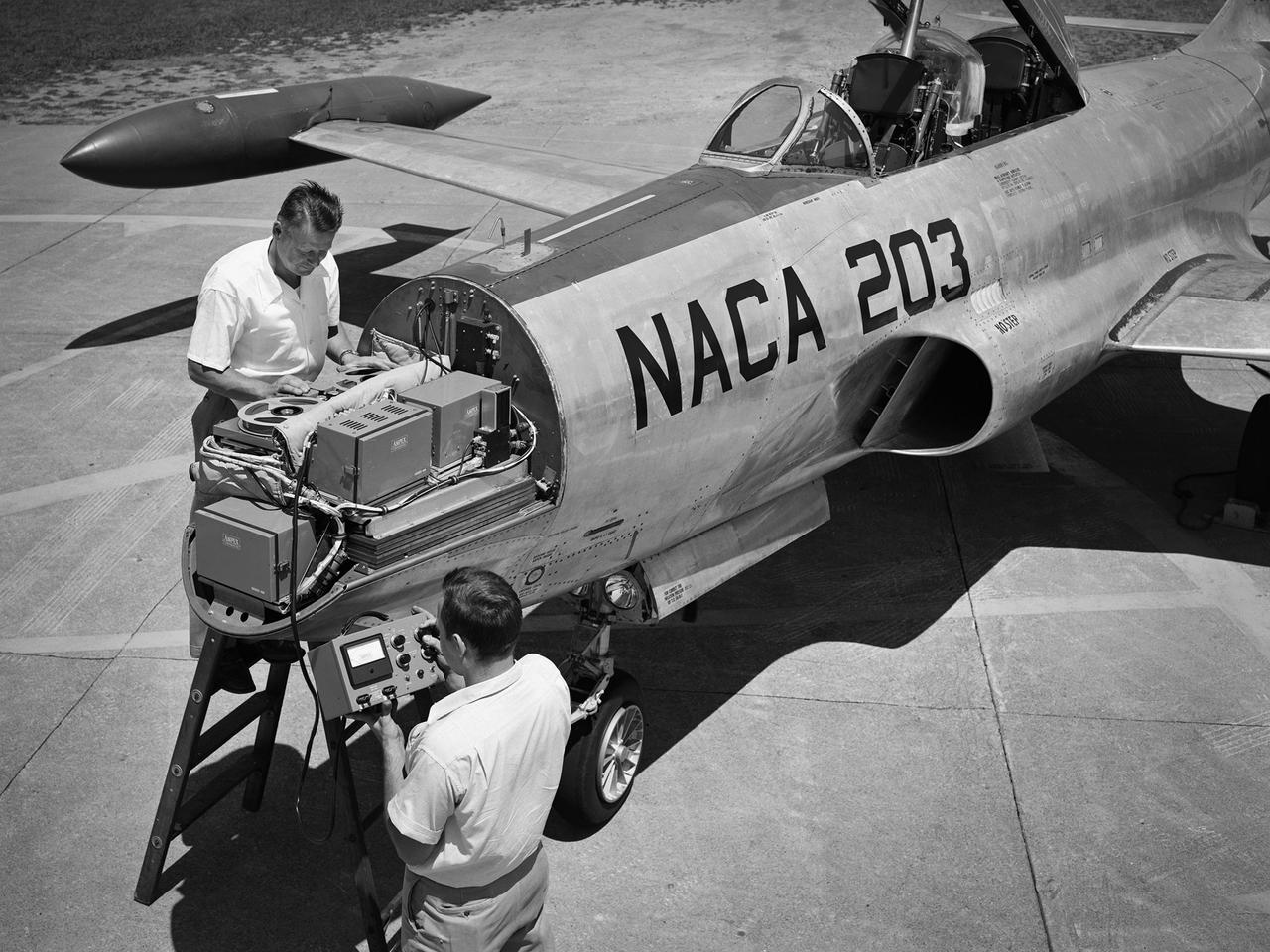

A Lockheed F-94B Starfire being equipped with an audio recording machine and sensors at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The NACA was investigating the acoustic effects caused by the engine’s nozzle and the air flowing along the fuselage. Airline manufacturers would soon be introducing jet engines on their passenger aircraft, and there was concern regarding the noise levels for both the passengers and public on the ground. NACA Lewis conducted a variety of noise reduction studies in its wind tunnels, laboratories, and on a F2H-2B Banshee aircraft. The F2H-2B Banshee’s initial test flights in 1955 and 1956 measured the noise emanating directly from airflow over the aircraft’s surfaces, particularly the wings. This problem was particularly pronounced at high subsonic speeds. The researchers found the majority of the noise occurred in the low and middle octaves. These investigations were enhanced with a series of flights using the F-94B Starfire. The missions measured wall-pressure, turbulence fluctuations, and mean velocity profiles. Mach 0.3 to 0.8 flights were flown at altitudes of 10,000, 20,000, and 30,000 feet with microphones mounted near the forward fuselage and on a wing. The results substantiated the wind tunnel findings. This photograph shows the tape recorder being installed in the F-94B’s nose.

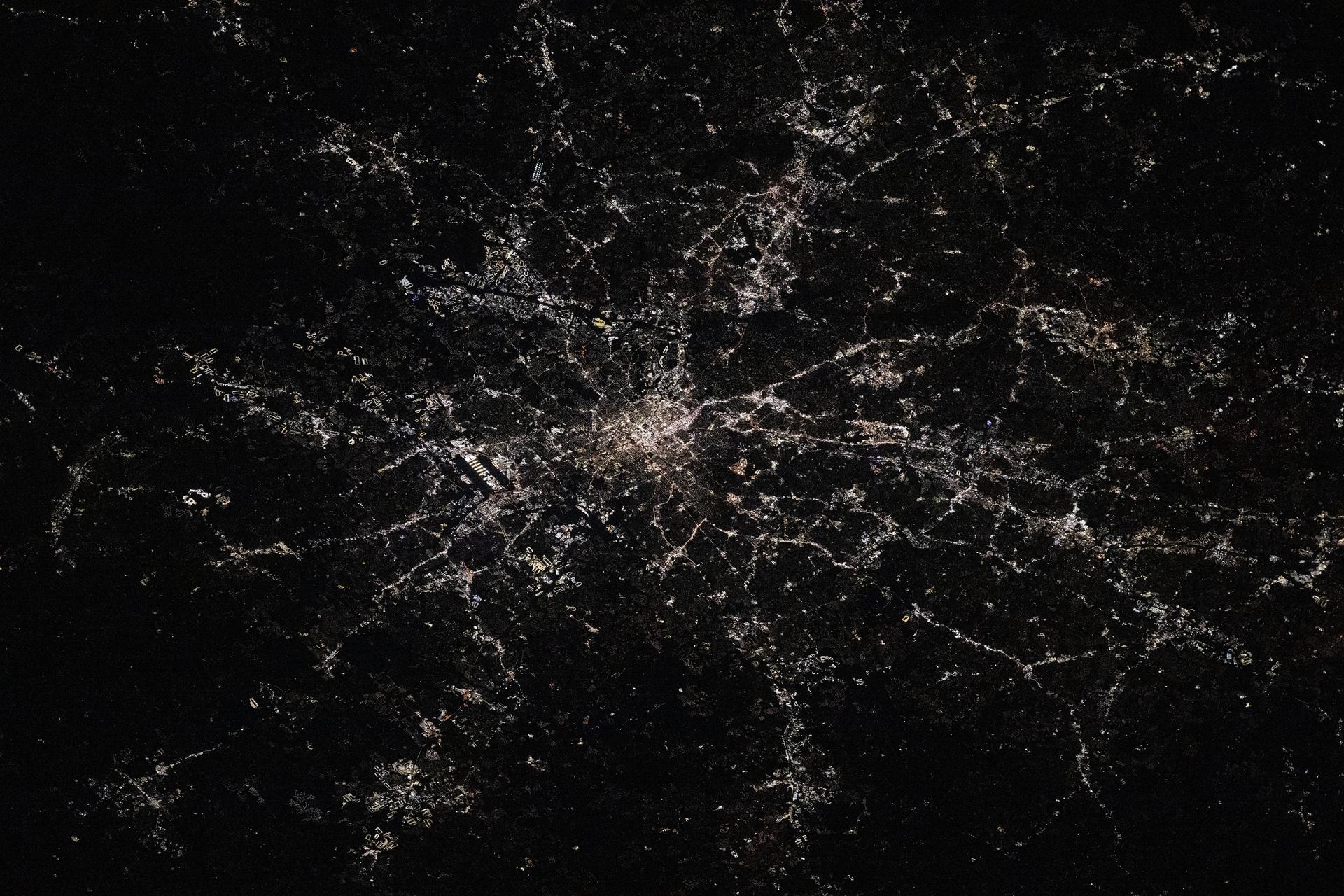
ISS013-E-18319 (12 May 2006) --- Munich International Airport, Germany is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. The Franz Joseph Strauss, or Munich, International Airport served 29 million passengers in 2005, making it the second-busiest airport (behind Frankfurt) in Germany. It is the busiest airport in Germany in terms of domestic passengers, serving over 9 million travelers during 2005. The airport serves the Bayern (Bavaria) region of southeastern Germany, and is a hub for the Lufthansa airline. Like other large international airports around the world, the facility occupies portions of multiple municipalities: Freising, Oberding, Hallbergmoos, and Marzling. The village of Franzheim was demolished, and its 500 residents relocated, during the airport construction. The airport is located 31 kilometers to the northeast of Munich; rather than being an extension of the metropolis, it is surrounded by agricultural fields and small towns. Expansion of the airport occurred in 2003 with the additional of Terminal 2, designed specifically to accommodate the needs of Lufthansa and its partner airlines. This view taken is sufficiently detailed to distinguish individual airplanes on the terminal apron as well as the dark gray-blue rooftop of Terminal 2. The white concrete airport runways are 4 kilometers in length. Surrounding agricultural fields in active use are a variety of shades of green, while the exposed soil of fallow fields are brown to tan.
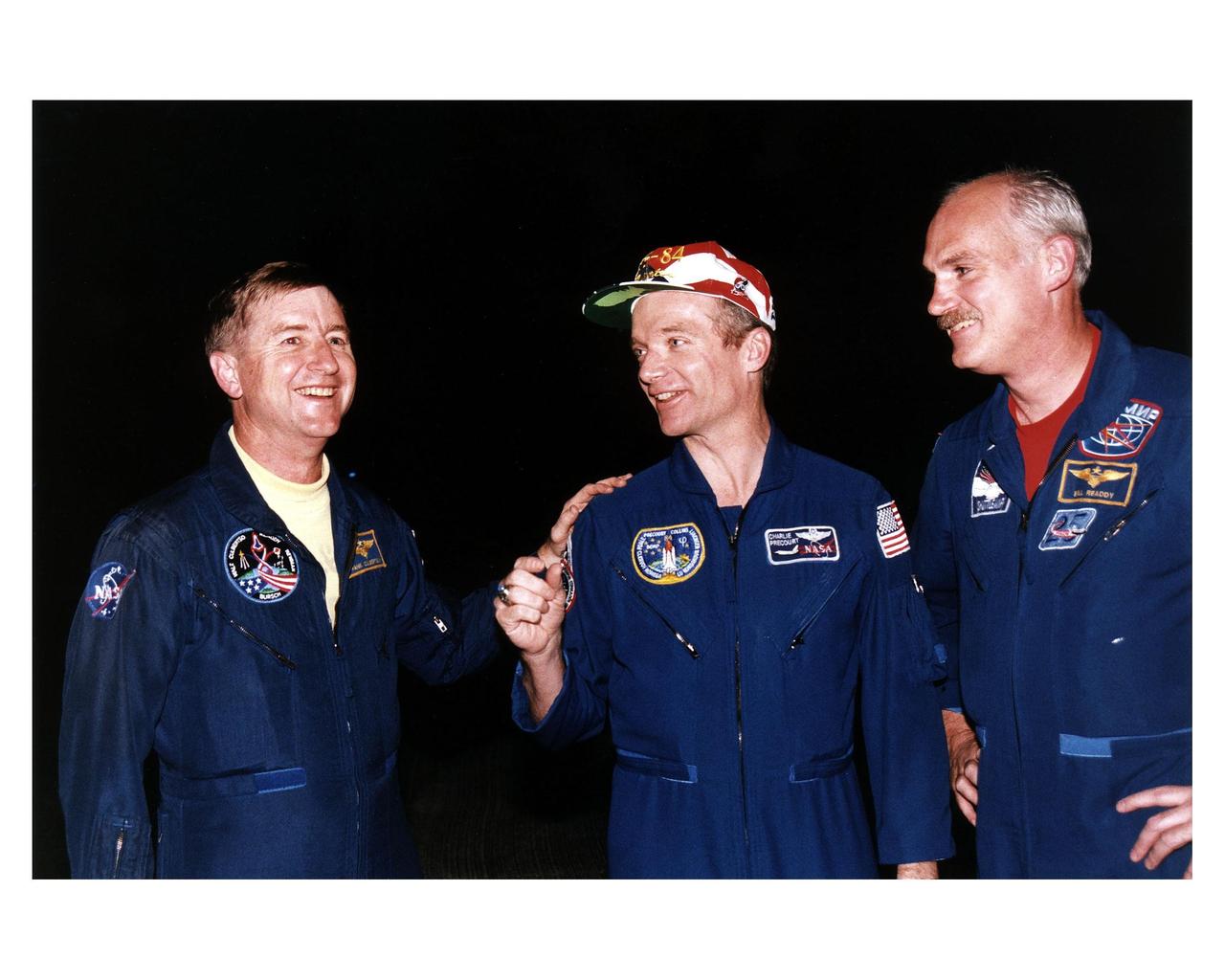

STS-84 Commander Charles J. Precourt talks with fellow astronauts Frank Culbertson, at left, and William F. Readdy after their arrival at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facilty. Culbertson, NASA director of the Phase One Program of the International Space Station, and Readdy, manager, program development, in the Space Shuttle Program Office at Johnson Space Center, were the pilots of T-38 jets which brought STS-84 crew members to KSC for the launch. Culbertson’s passenger was STS-84 Mission Specialist Carlos I. Noriega; Readdy’s passenger was Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale. Liftoff of Space Shuttle Mission STS-84 is scheduled May 15. STS-84 will be the sixth docking of the Space Shuttle with the Russian Space Station Mir. During the docking, Foale will transfer to the Russian space station to become a member of the Mir 23 crew, replacing U.S. astronaut Jerry M. Linenger, who will return to Earth on Atlantis. Foale is scheduled to remain on Mir about four months until his replacement arrives on STS-86 in September

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
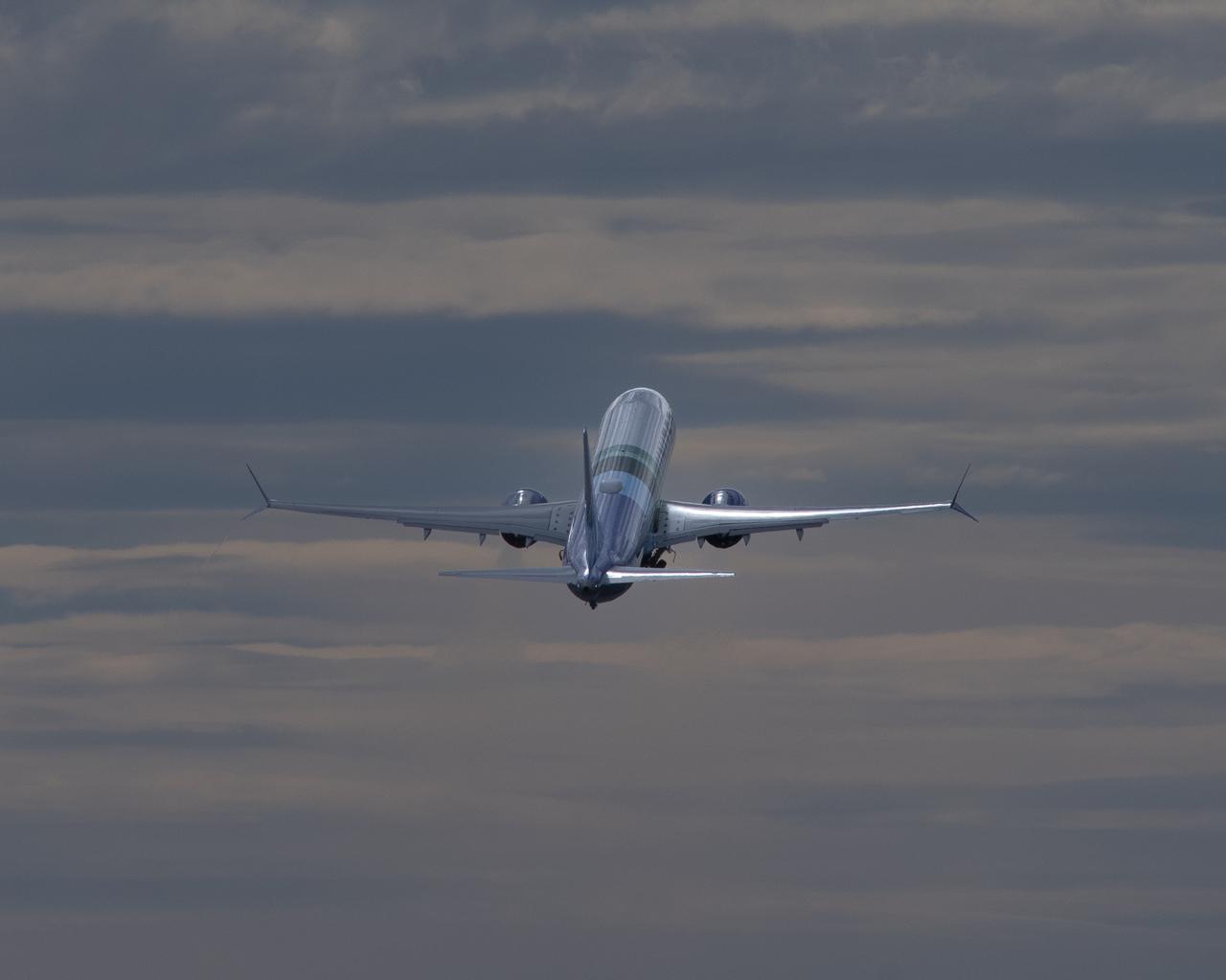

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
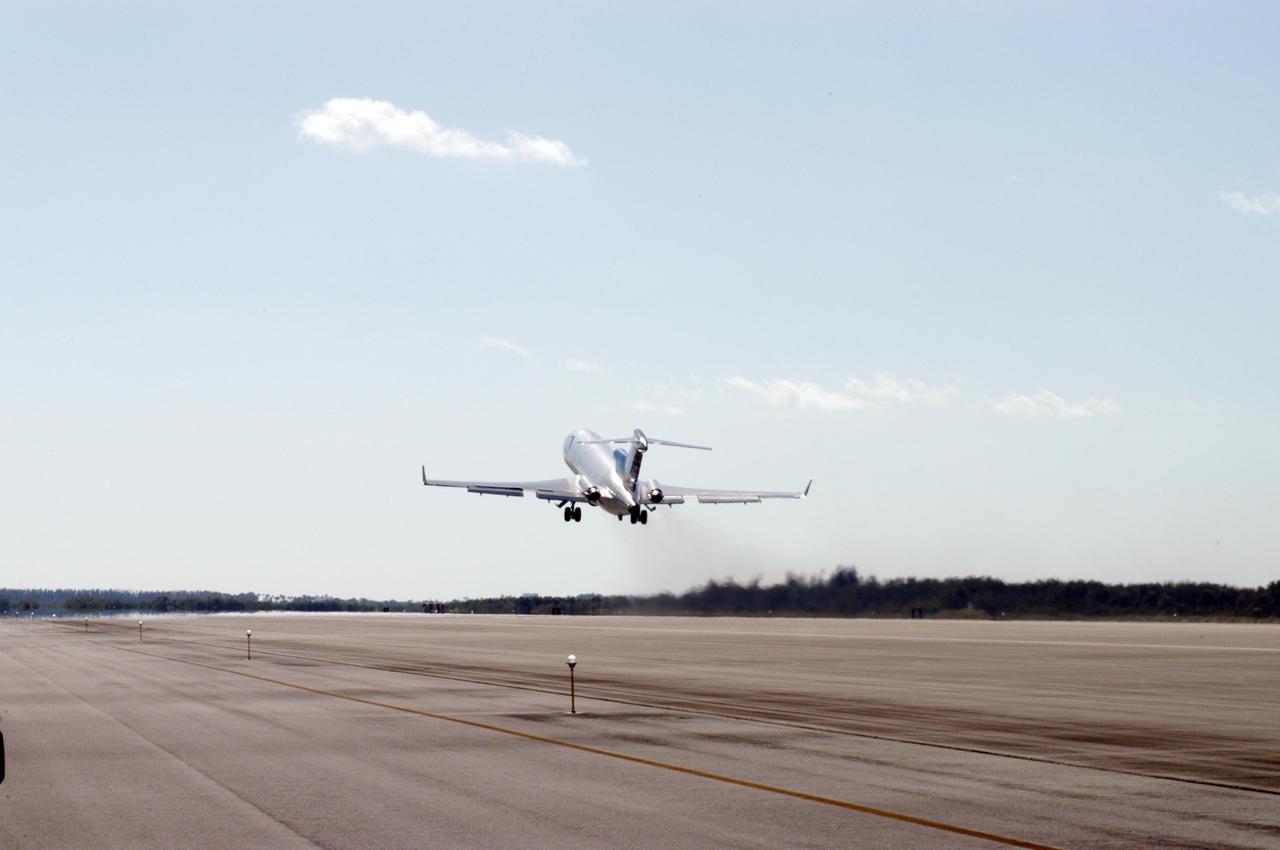

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., is airborne from Kennedy Space Center’s shuttle landing facility. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. The group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
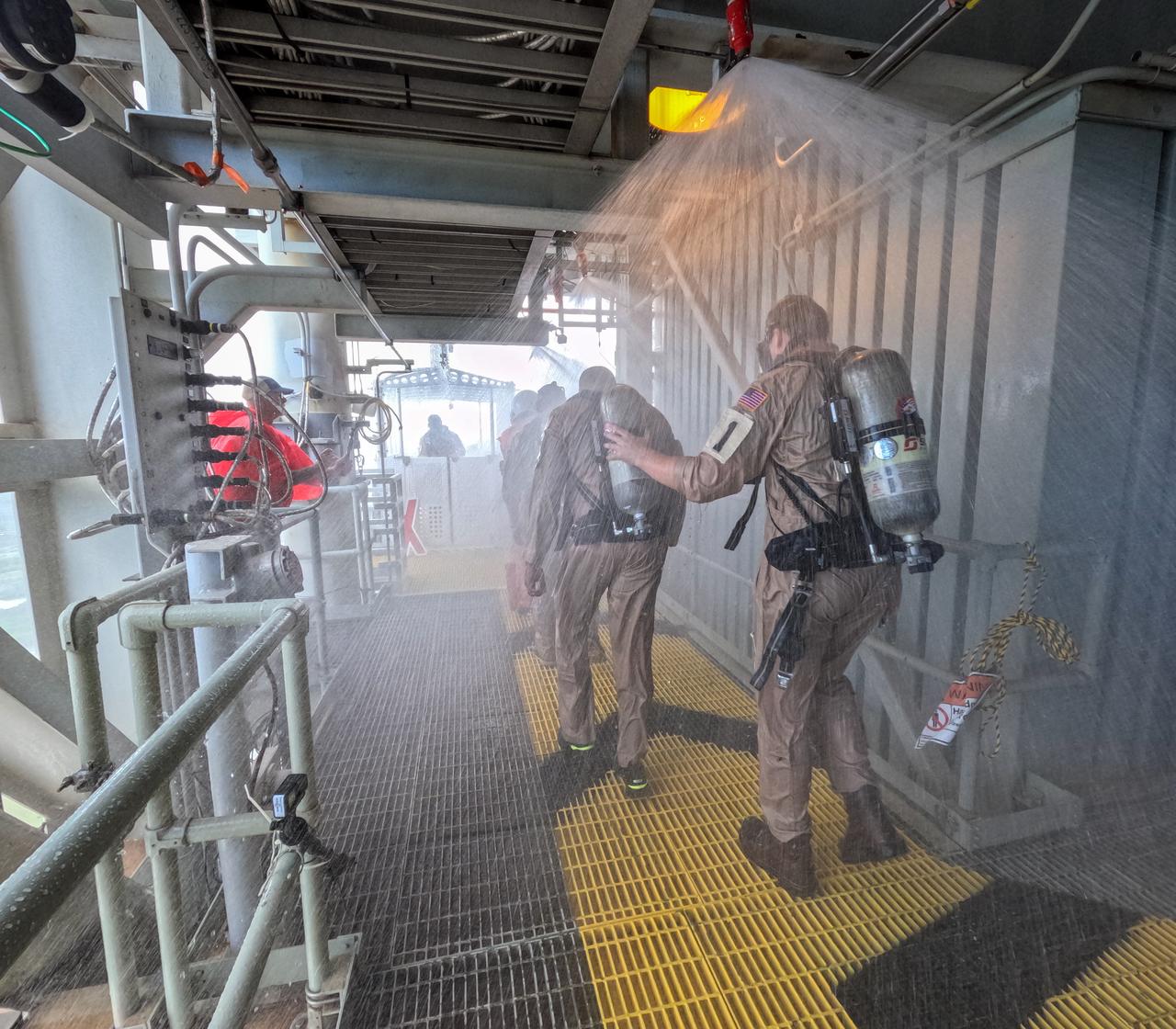

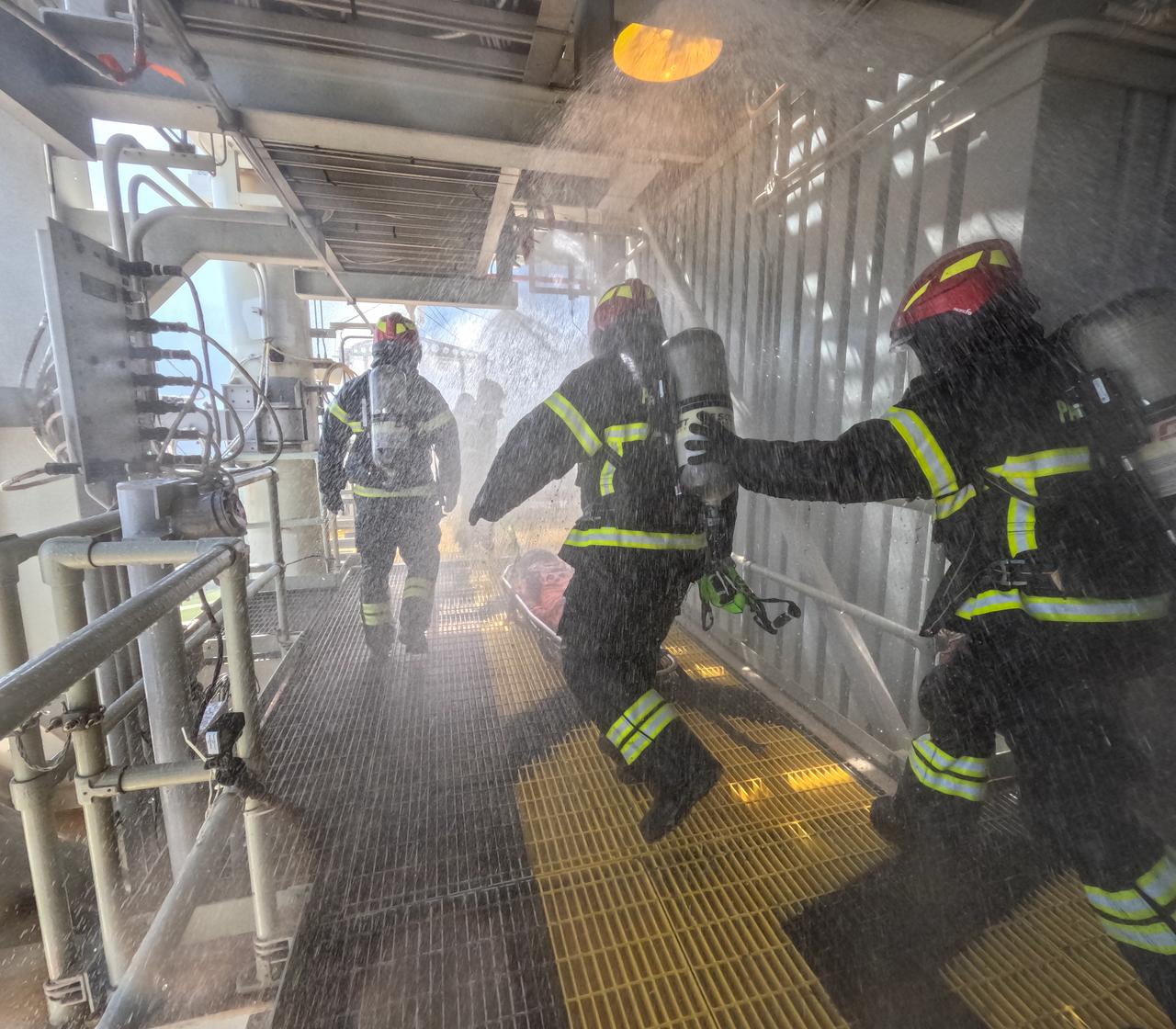
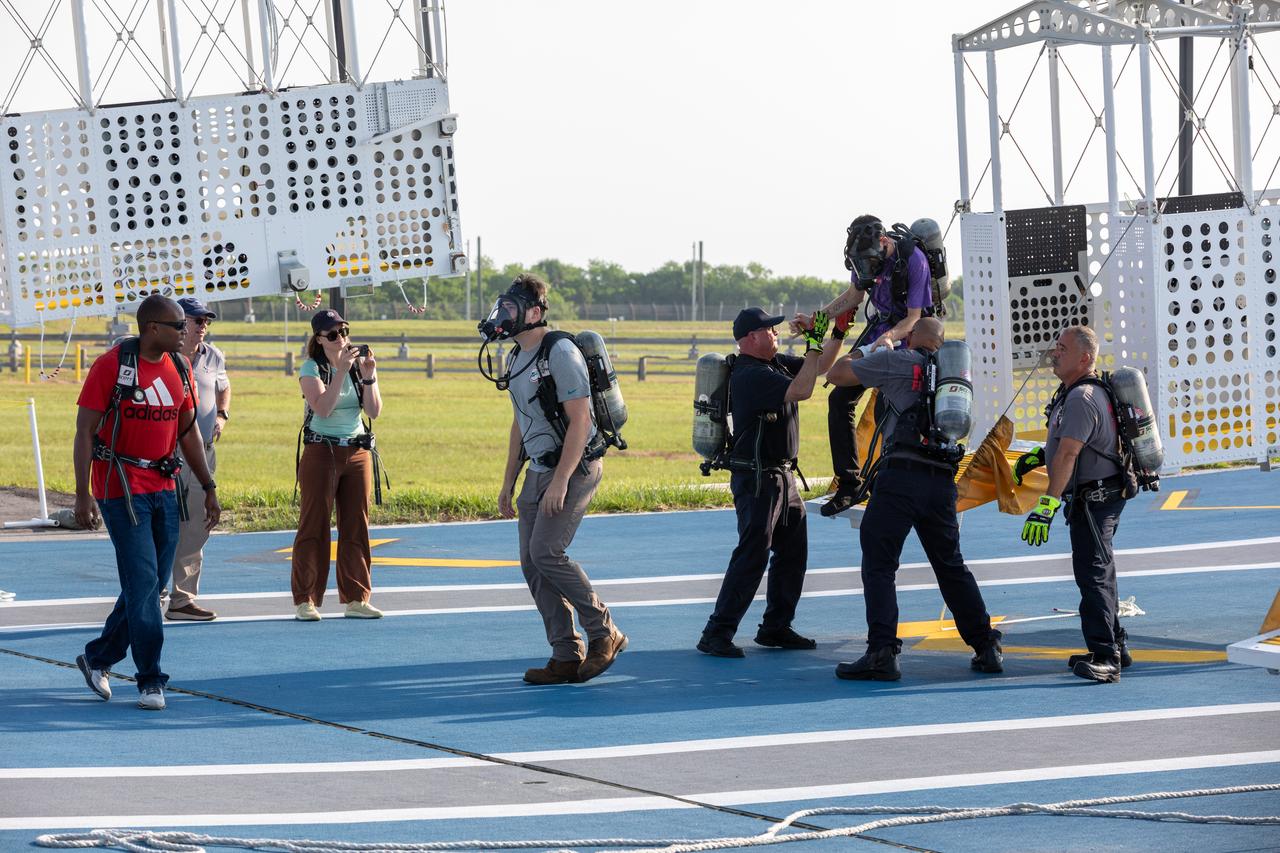
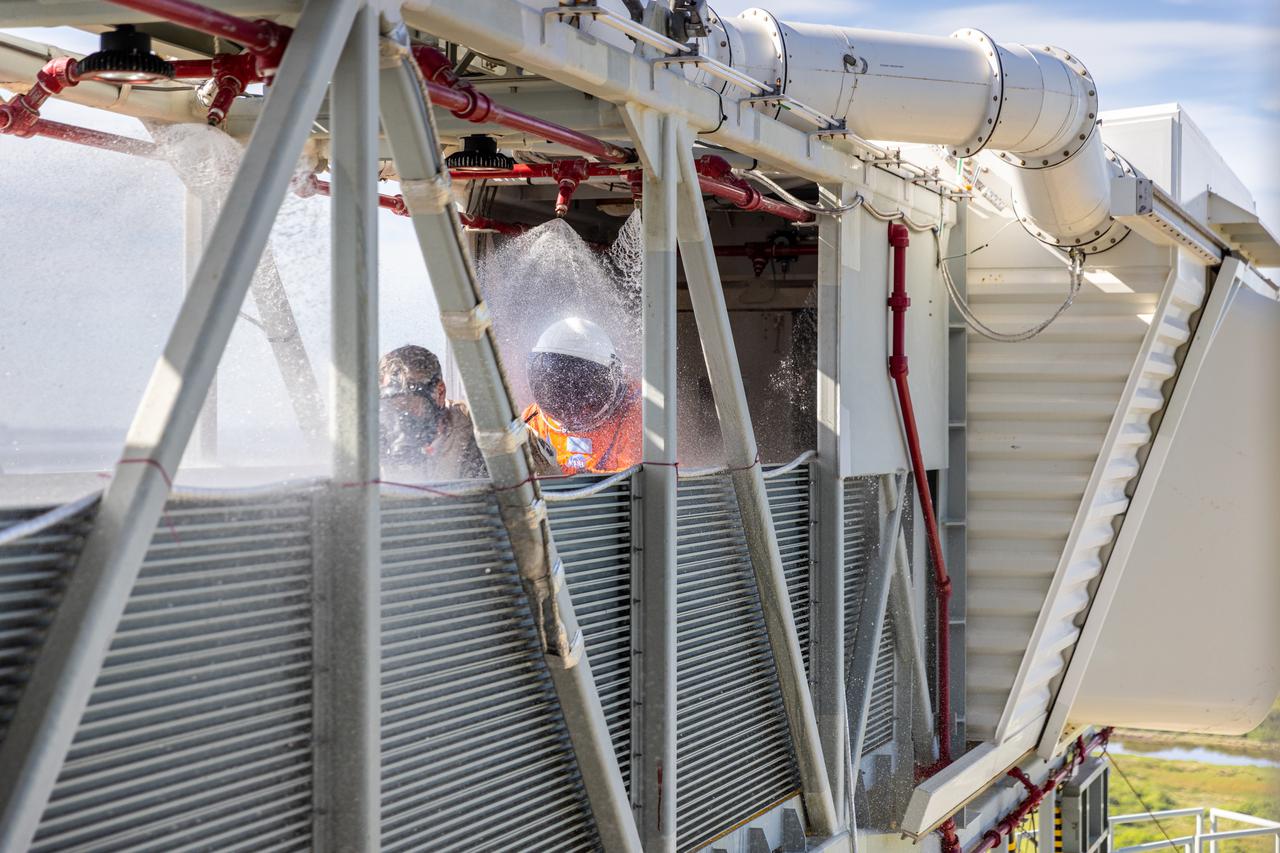
Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
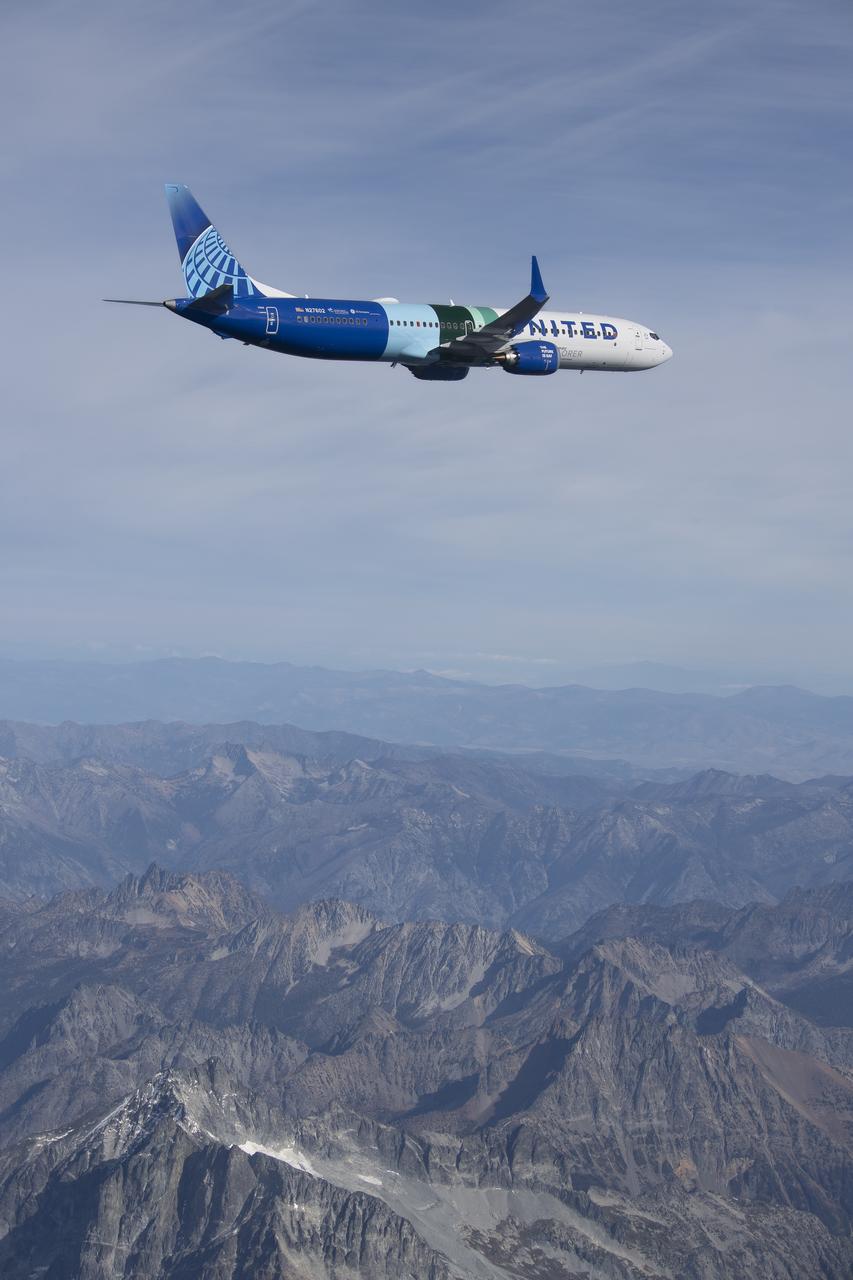

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
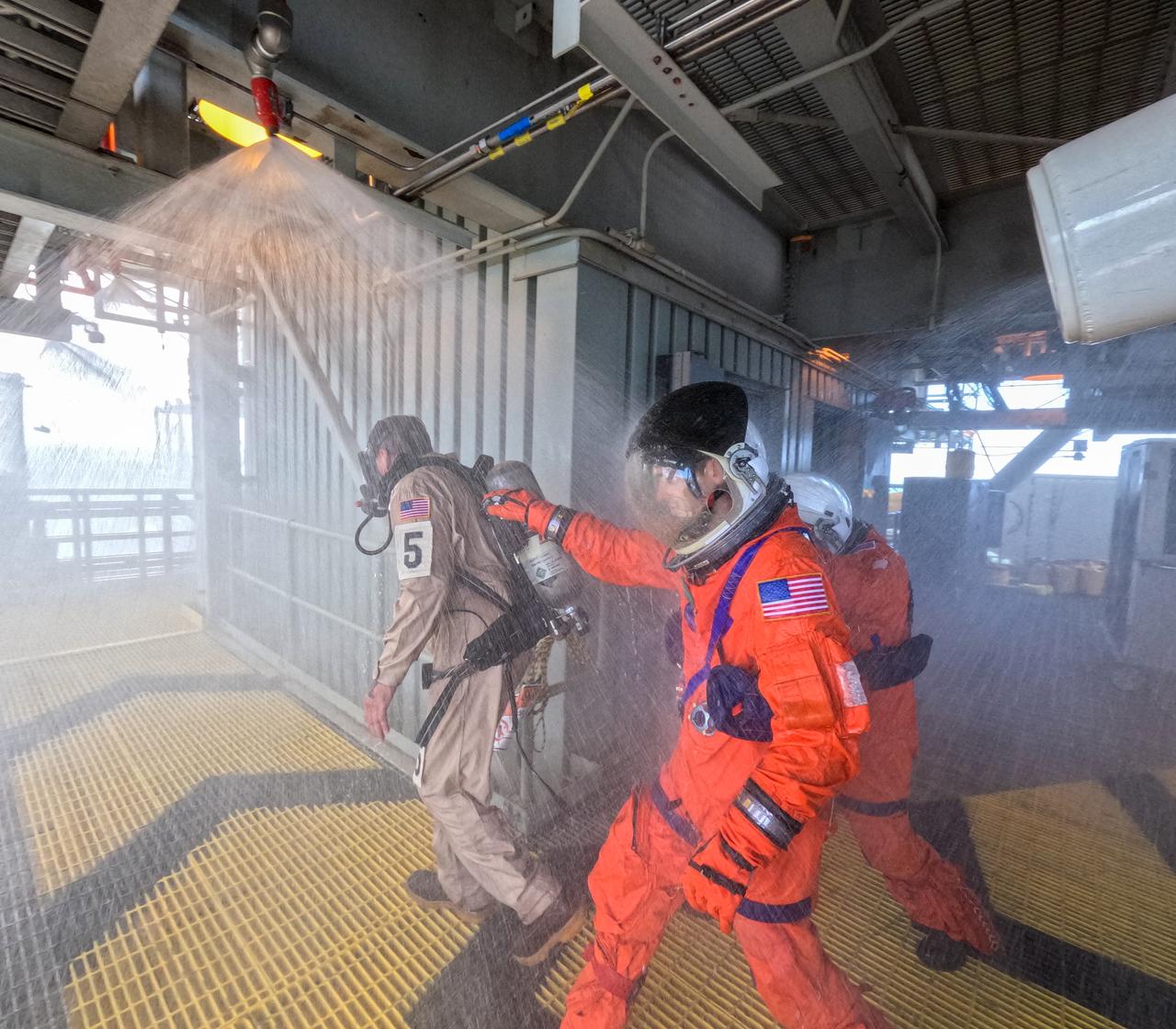

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
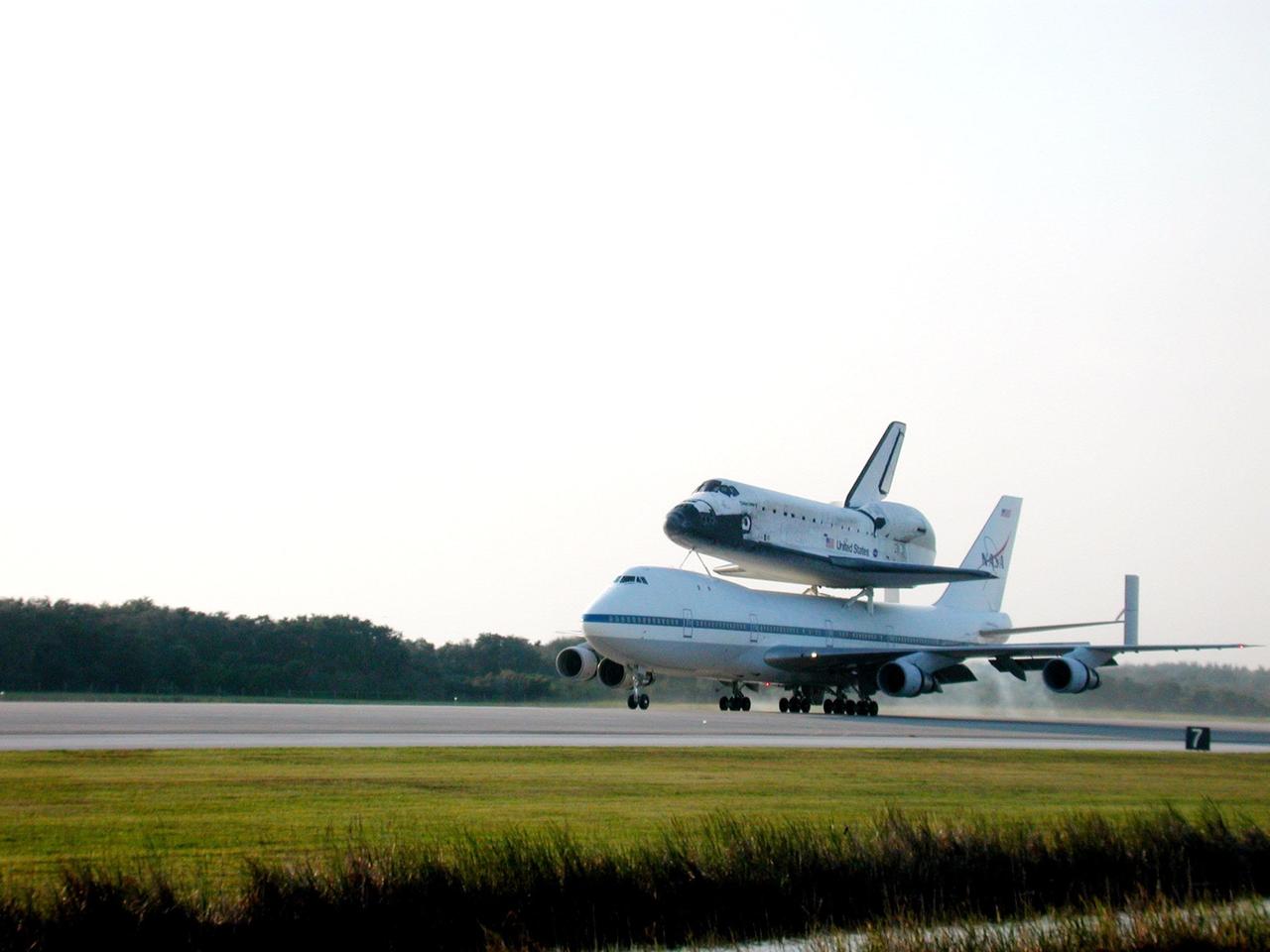

On a warm afternoon, the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), with its unique orbiter passenger attached to its back, rolls down the runway at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. The SCA is returning Discovery to KSC after the orbiter’s California landing more than a week ago at Edwards Air Force Base at the end of mission STS-92. Discovery will be demated from the SCA via the mate/demate device at the SLF and transported to the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1. There it will undergo preparations for its next launch, STS-102, scheduled for February 2001
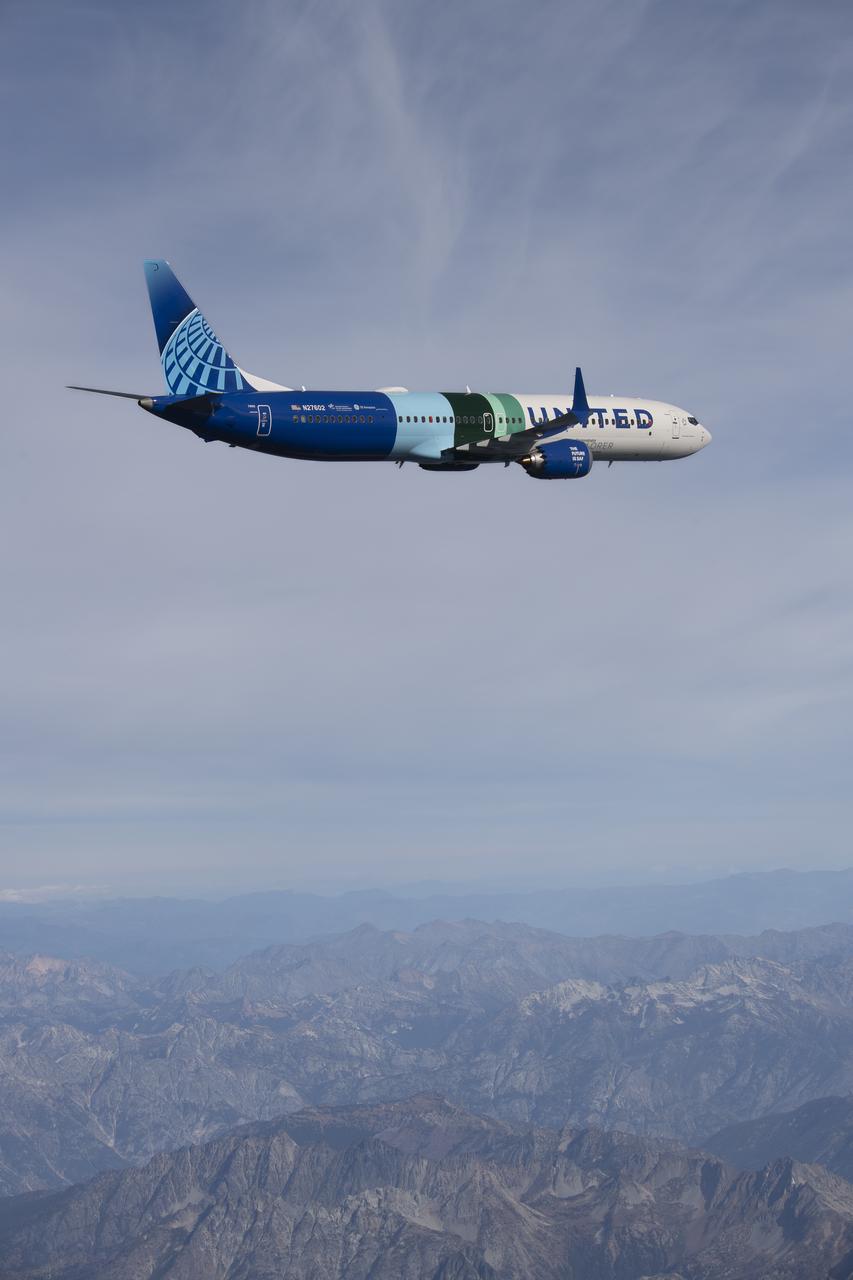

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
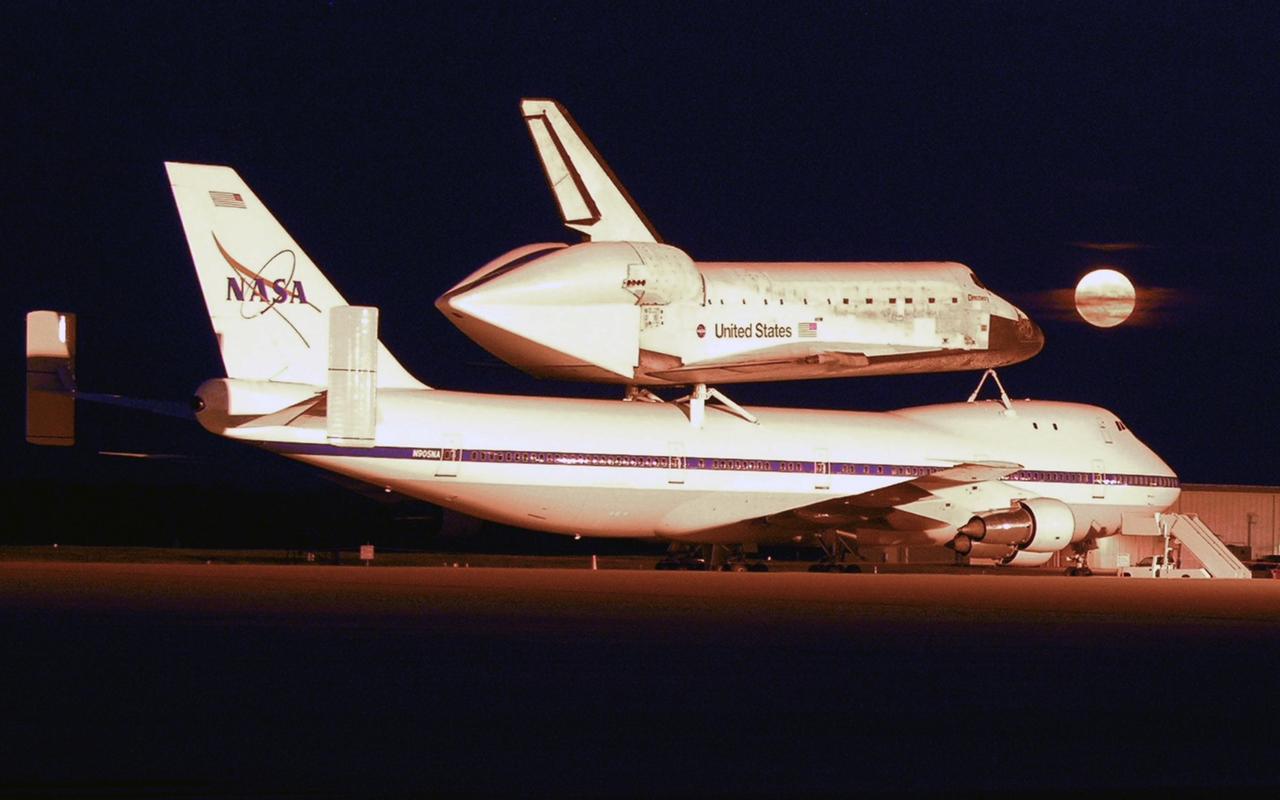

OFFUTT FIELD, NEB. -- The shuttle carrier aircraft, or SCA, and its piggyback passenger Atlantis are captured in the light of a full moon after landing at Offutt Field on the ferry flight from California to Florida. Atlantis landed at Edwards Air Force Base in California to end mission STS-117. Touchdown was at 8:27 a.m. EDT. The SCA is a modified Boeing 747 jetliner. The return to KSC began July 1 and took three days after stops across the country for fuel. The last stop was at Ft. Campbell in Kentucky. Weather conditions over the last leg postponed the return trip until July 3. Photo credit: NASA/Casey Wood
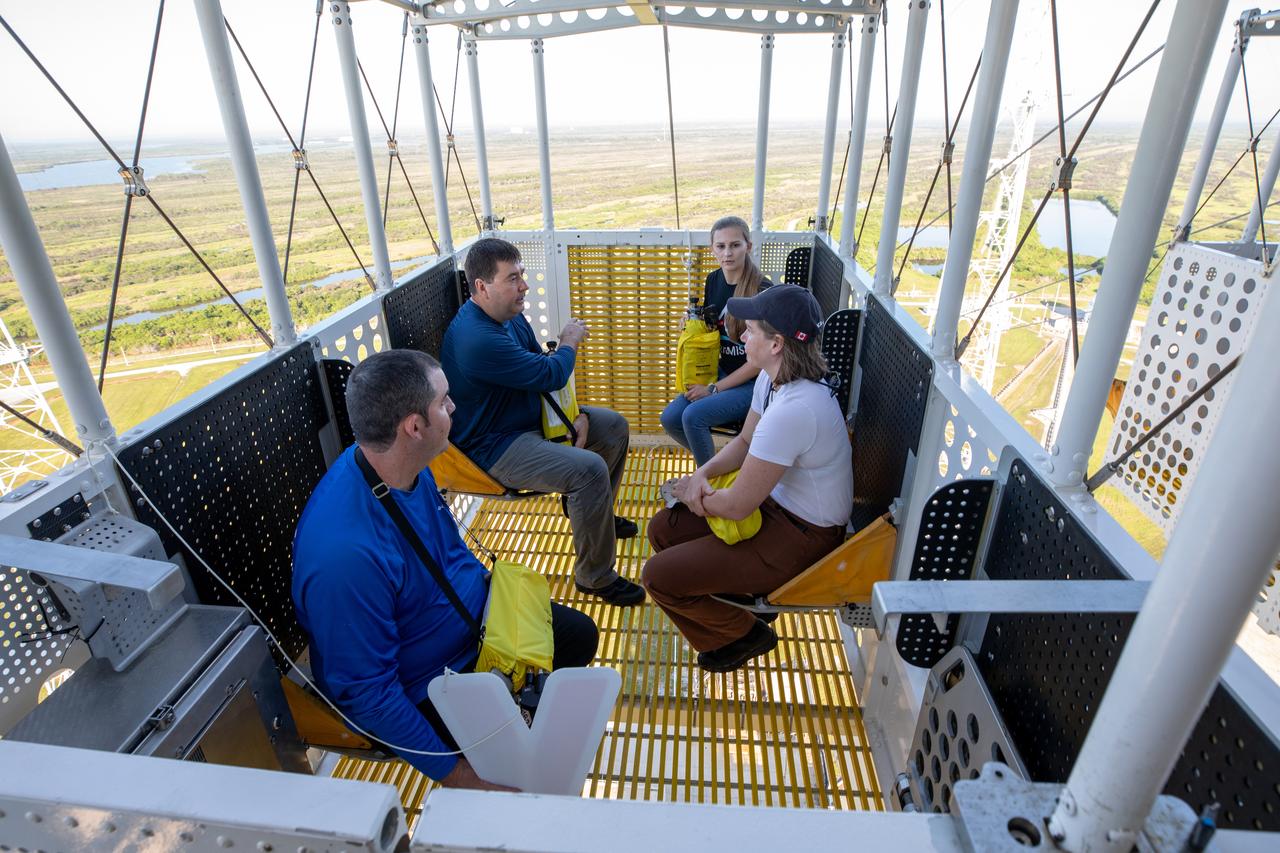

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
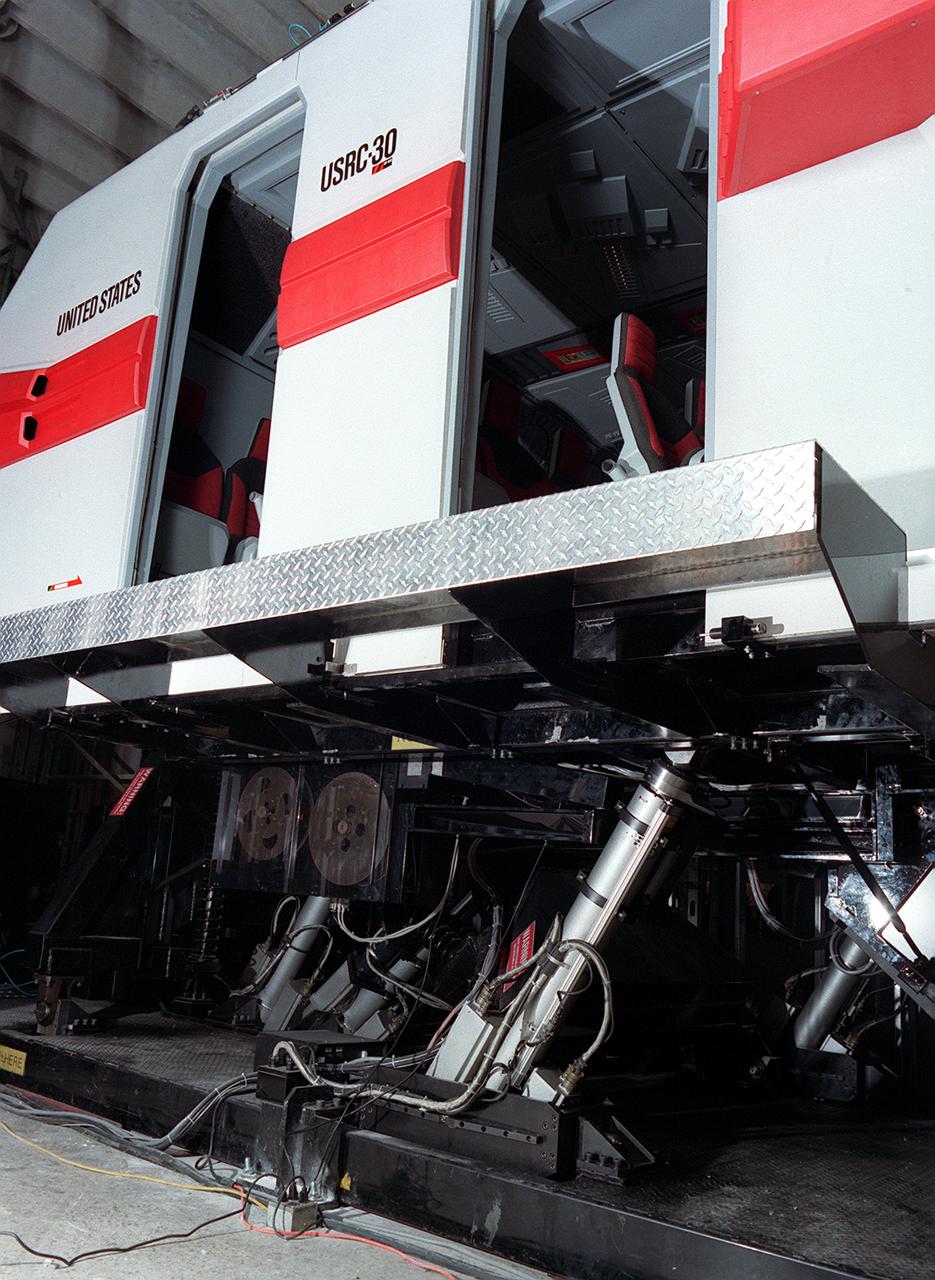

The development of the electric space actuator represents an unusual case of space technology transfer wherein the product was commercialized before it was used for the intended space purpose. MOOG, which supplies the thrust vector control hydraulic actuators for the Space Shuttle and brake actuators for the Space Orbiter, initiated development of electric actuators for aerospace and industrial use in the early 1980s. NASA used the technology to develop an electric replacement for the Space Shuttle main engine TVC actuator. An electric actuator is used to take passengers on a realistic flight to Jupiter at the US Space and Rocket Center, Huntsville, Alabama.
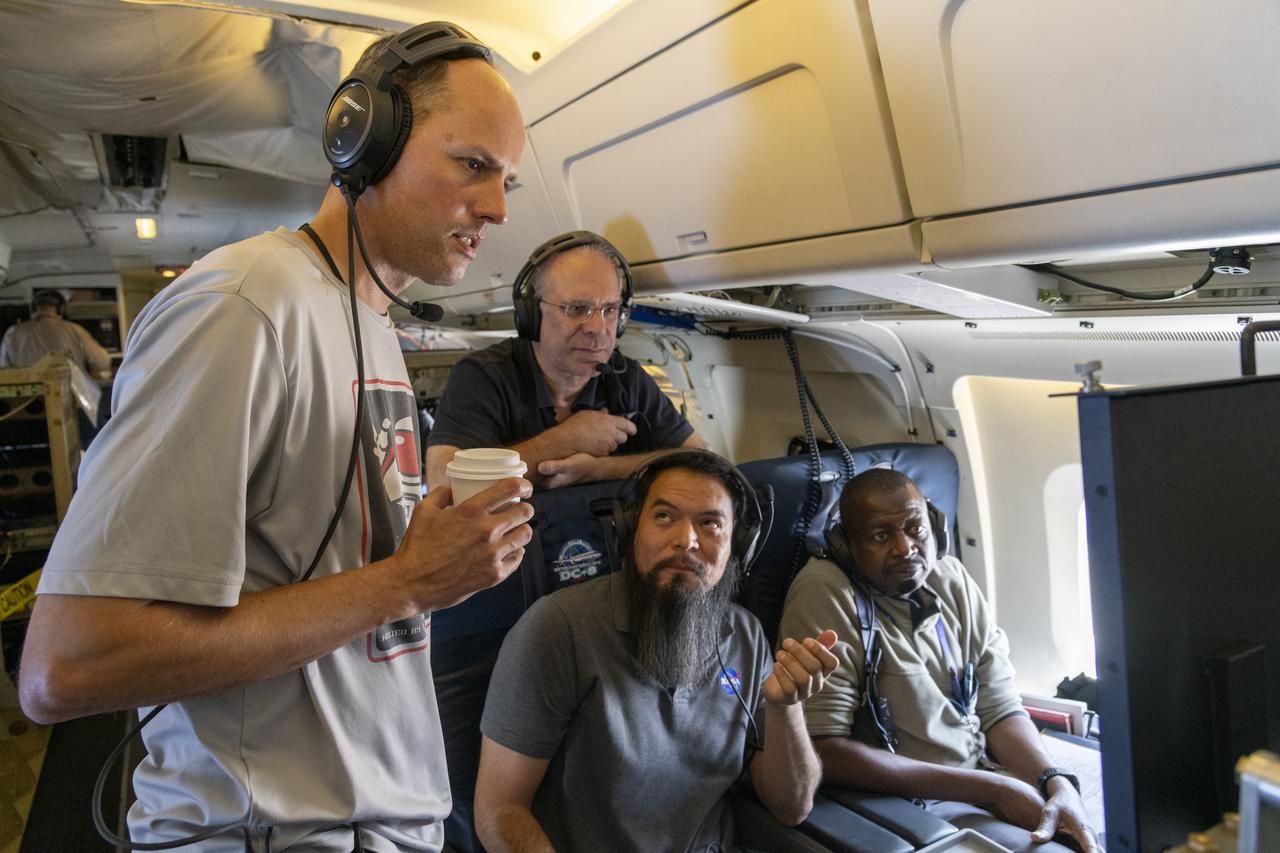

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
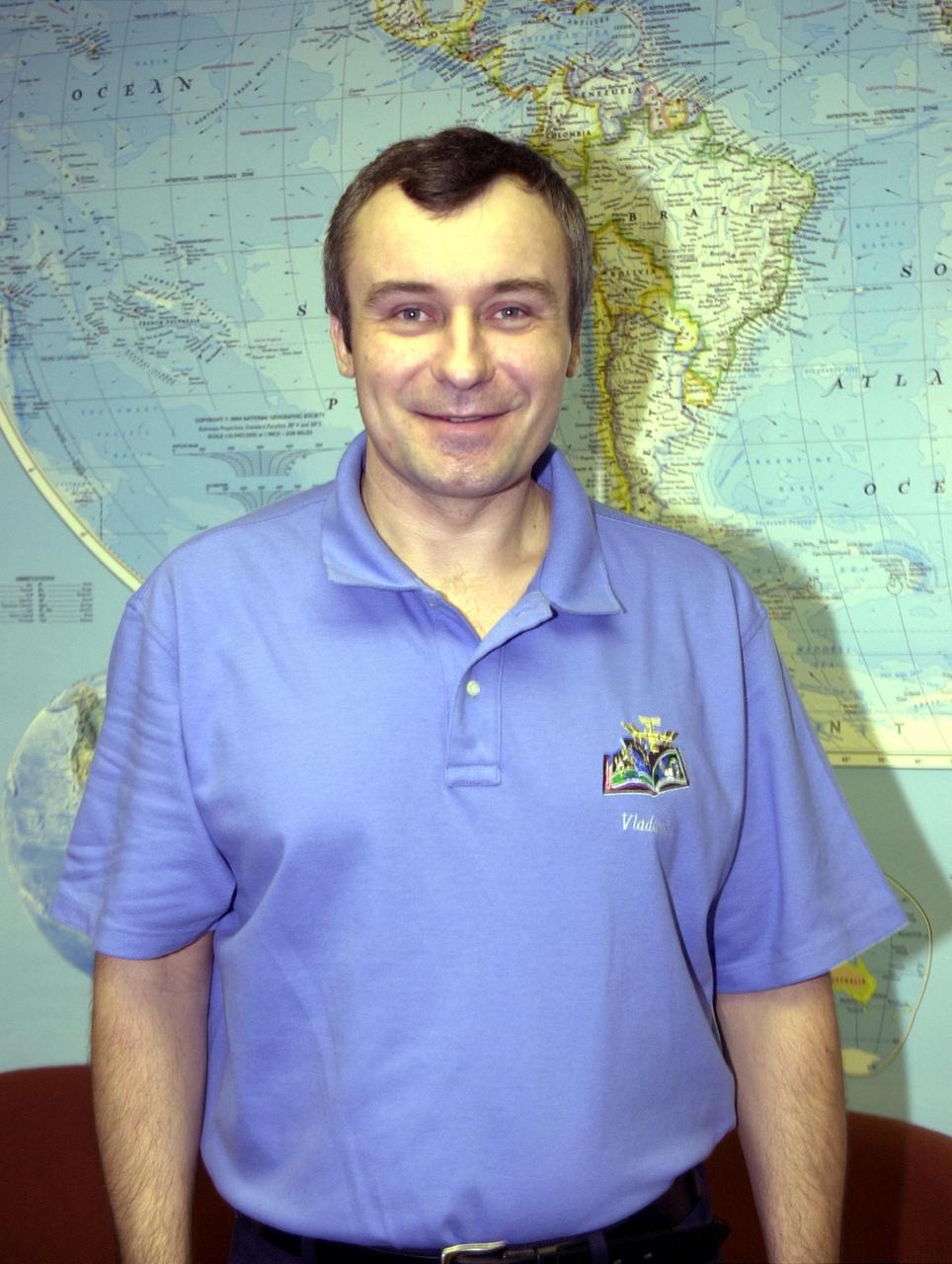

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Vladimir Dezhurov, a member of the Expedition 3 resident crew on the International Space Station, poses for a photo. He and the other crew members Mikhail Tyurin and Frank Culbertson, returned to Earth as passengers aboard the orbiter Endeavour, which landed at KSC at 12:55 p.m. EST (17:55 GMT) Dec. 17, 2001, after completing mission STS-108. The landing is the 57th at KSC in the history of the program STS-108 was the 12th mission to the Space Station. This mission was the 107th flight in the Shuttle program and the 17th flight for the orbiter
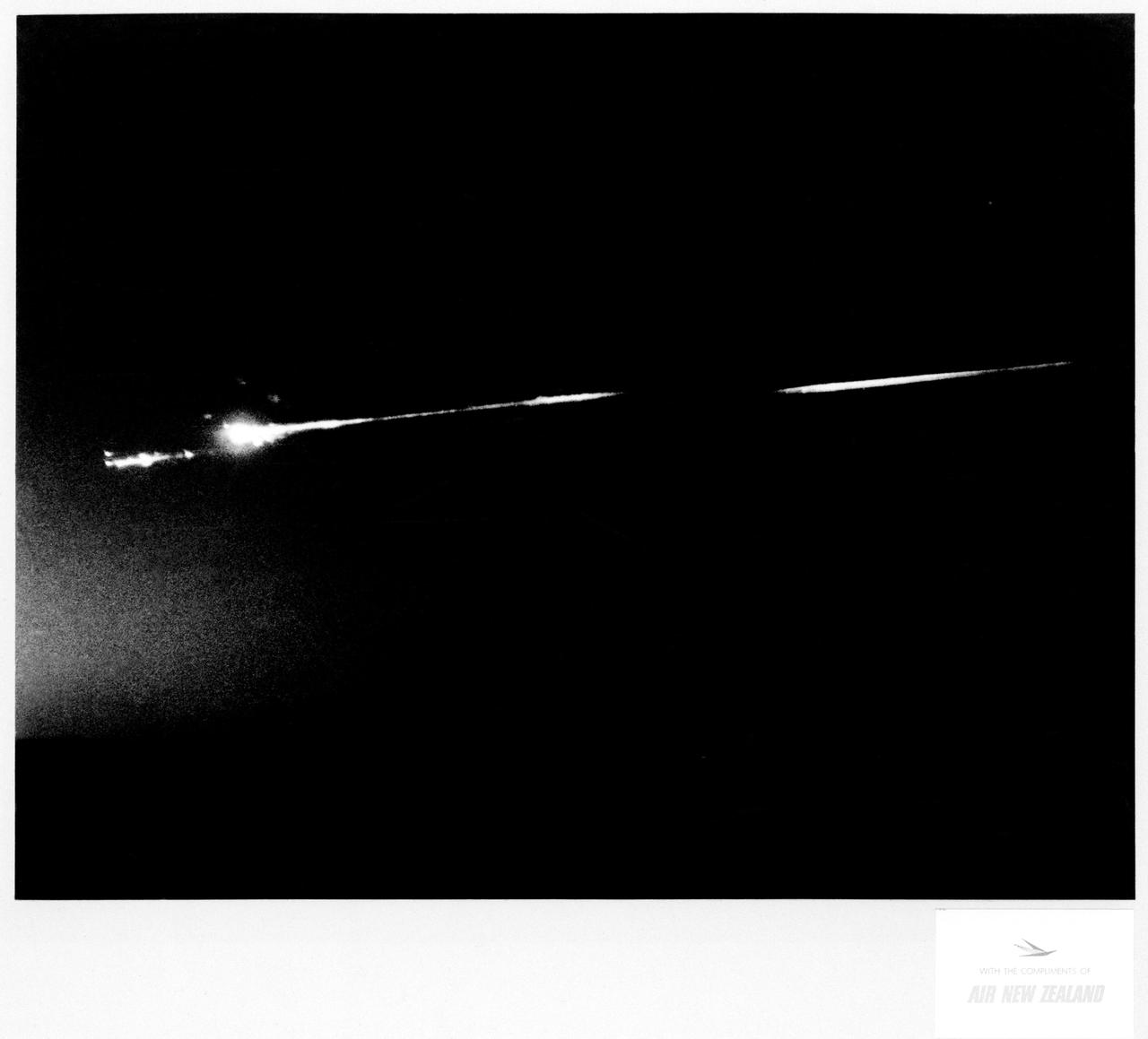

S70-17646 (18 April 1970) --- An unidentified airline passenger snapped these bright objects, believed to be the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) and Lunar Module (LM) as they entered Earth's atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean on April 18, 1970. The aircraft, an Air New Zealand DC-8 was midway between the Fiji Islands (Nandi Island to be specific) and Auckland, New Zealand, when the photograph was taken. The crew men of the problem plagued Apollo 13 mission jettisoned the LM and SM prior to entering Earth's atmosphere in the Apollo 13 Command Module (CM).
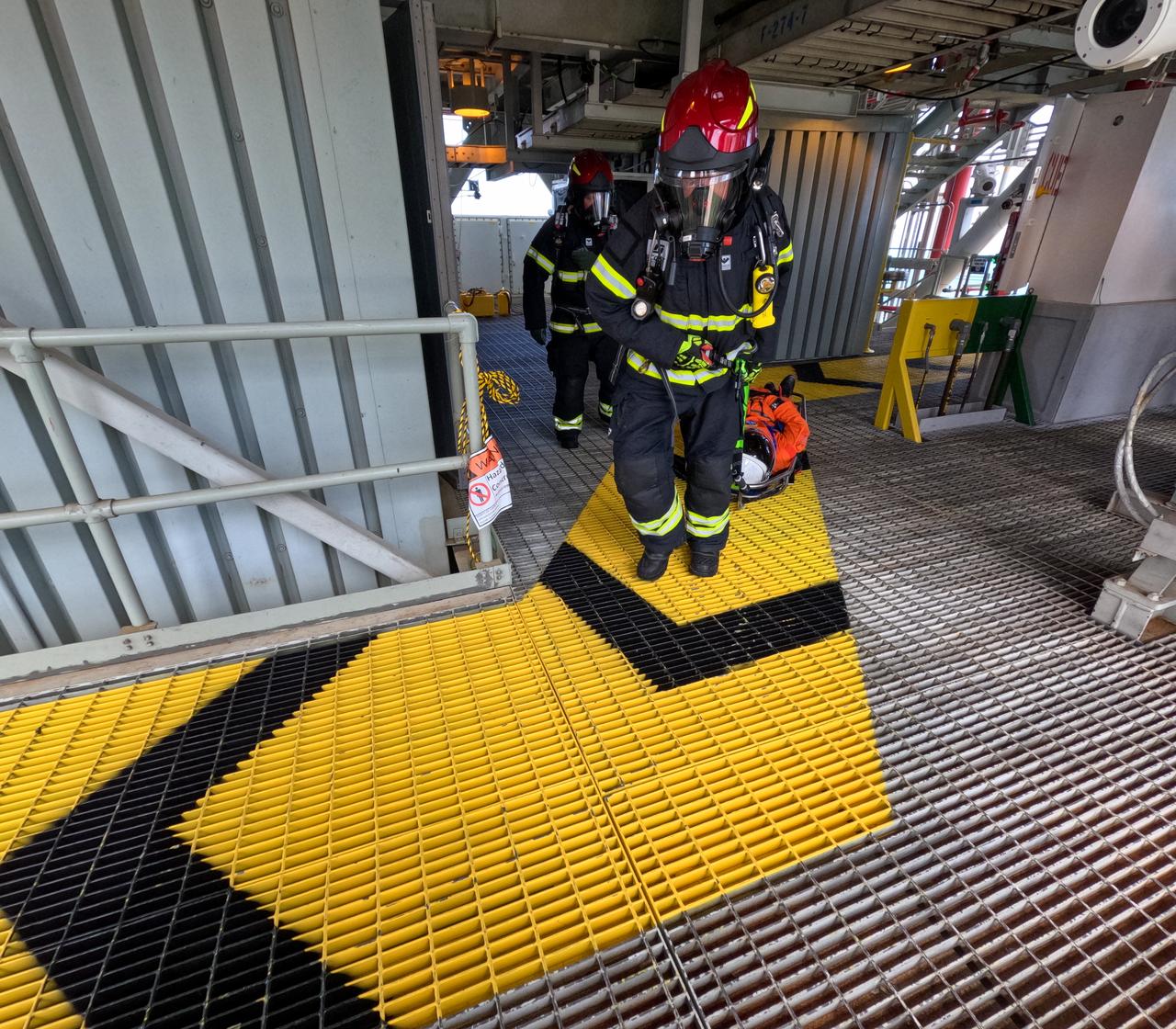

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
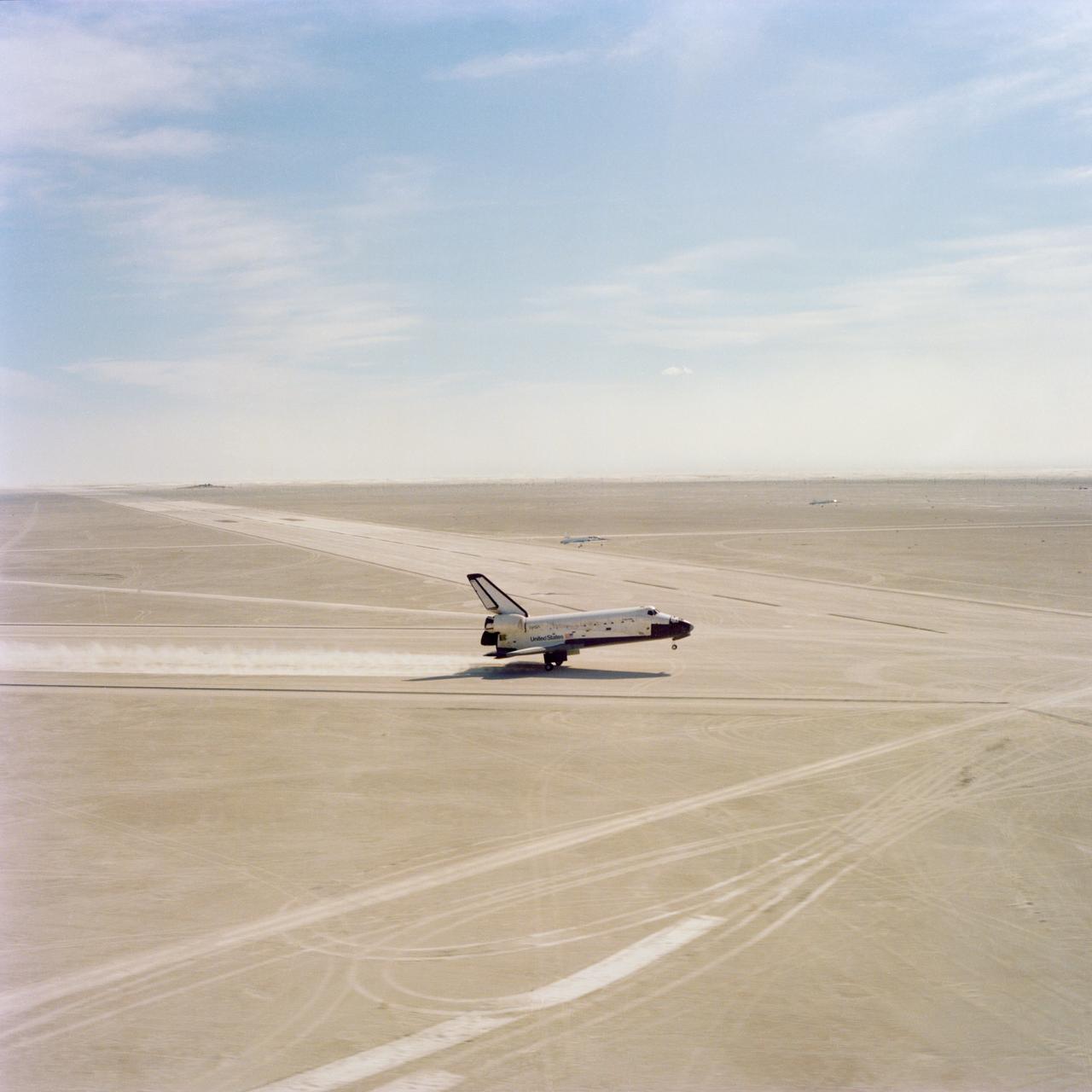

S82-28838 (30 March 1982) --- The space shuttle Columbia (STS-3) touches down on the Northrup Strip at White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico, marking the first time in its three-flight history that it has touched New Mexico soil. T-38 chase plane passenger, Mission Specialist-Astronaut Ronald E. McNair, who also shot some launch photography this flight, recorded a number of frames on 70mm film. Touchdown was shortly after 9 a.m. Mountain Standard Time, March 30, 1982. Photo credit: NASA
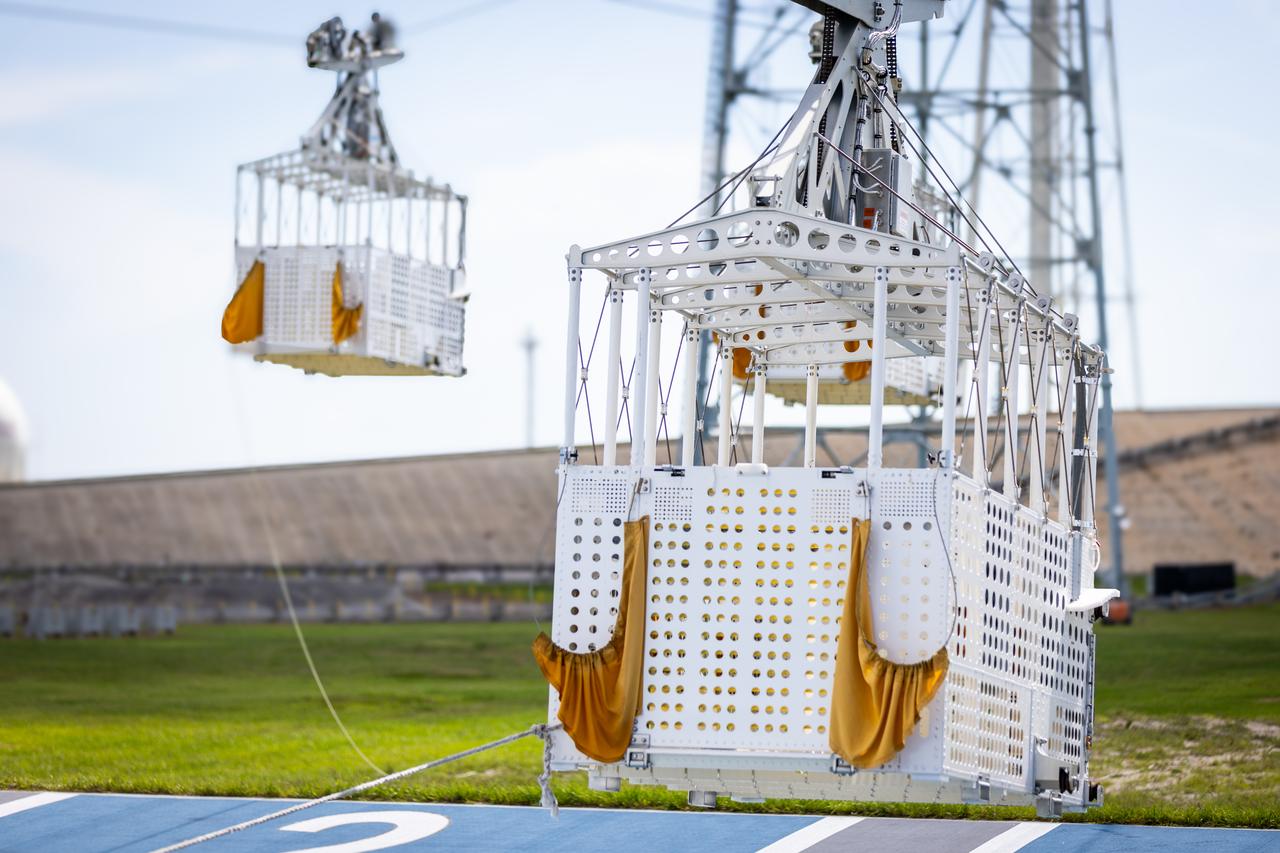

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
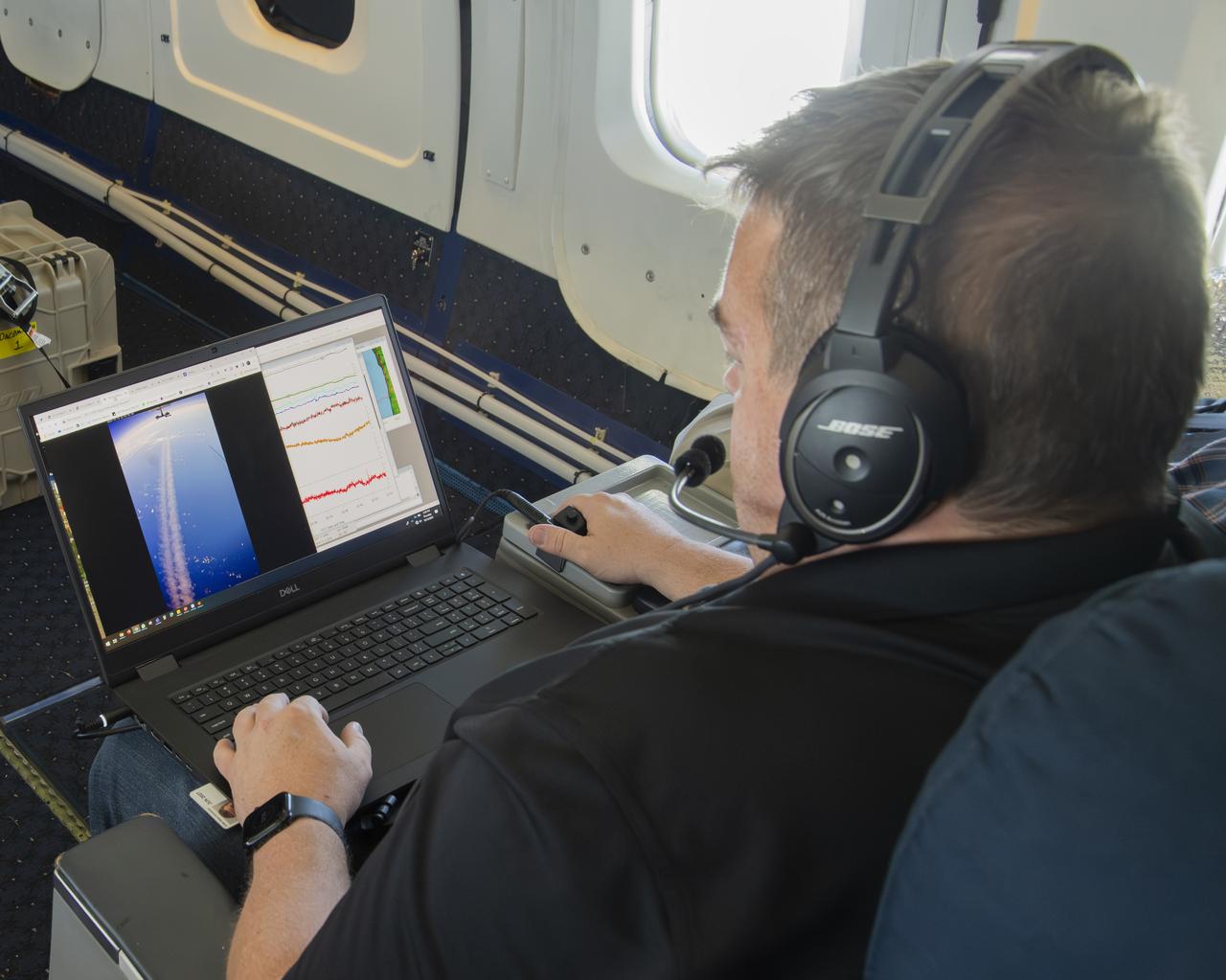

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Friday, Aug. 9, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
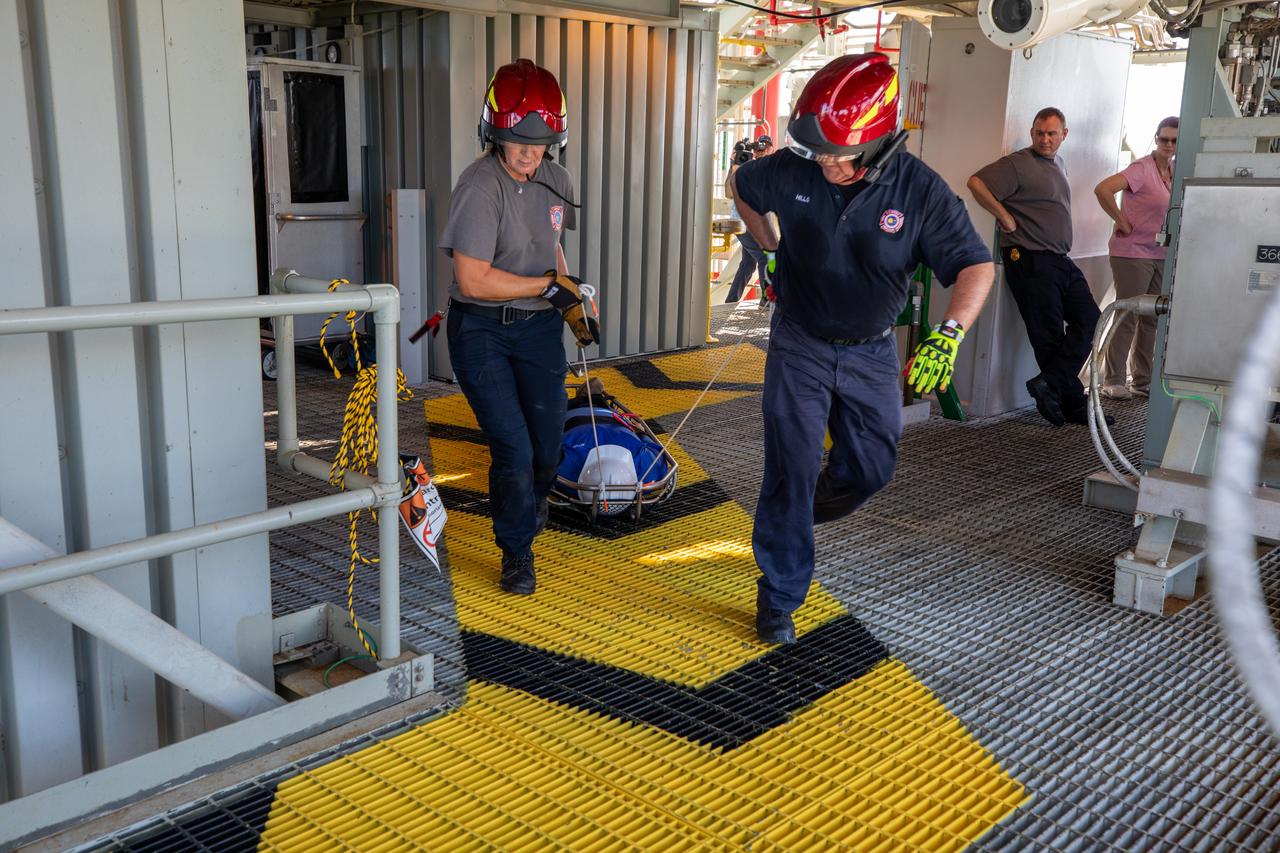

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
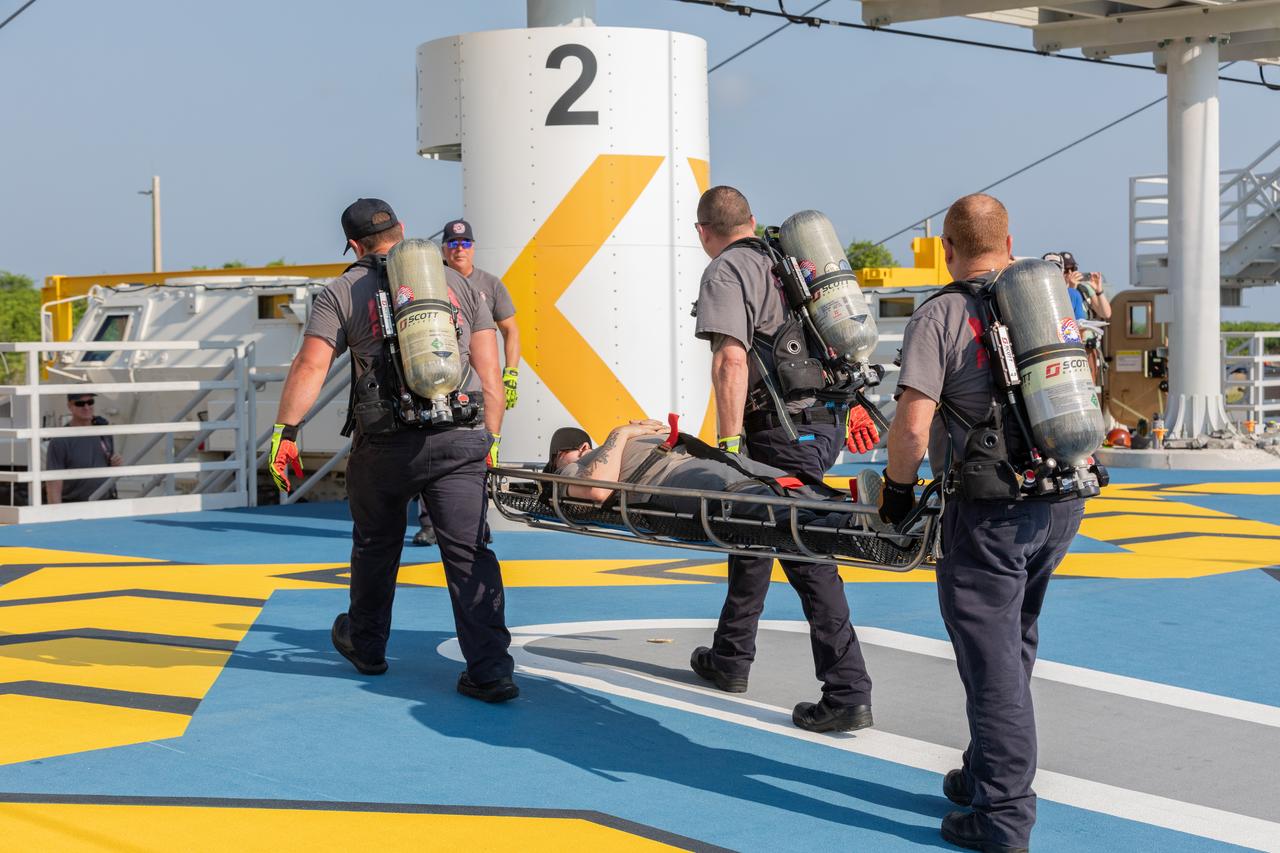

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Friday, Aug. 9, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
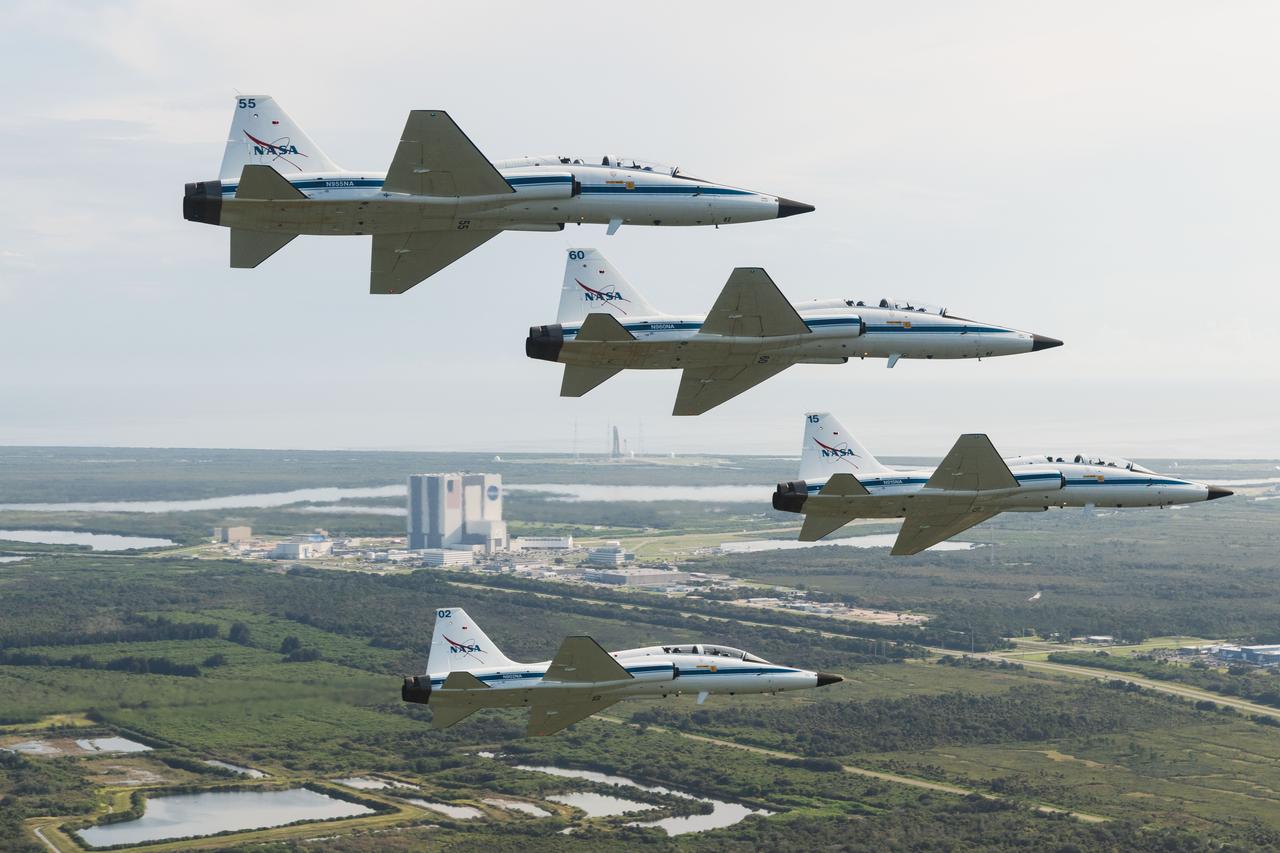

NASA's T-38 jets fly in formation above NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Several astronauts and astronaut candidates flew in to support the Artemis I launch and various pre-launch activities. Aircraft designations and passengers: NASA 901: Chris Condon / Astronaut Zena Cardman. 902: Astronaut Candidate Nicole Ayers / Astronaut Christina Koch. 903: Canadian Space Agency Astronaut Jeremy Hansen / Astronaut Drew Morgan. 904: Chief Astronaut Reid Wiseman / Astronaut Joe Acaba. 905 (Photo Chase): Astronaut Candidate Jack Hathaway / Josh Valcarcel Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
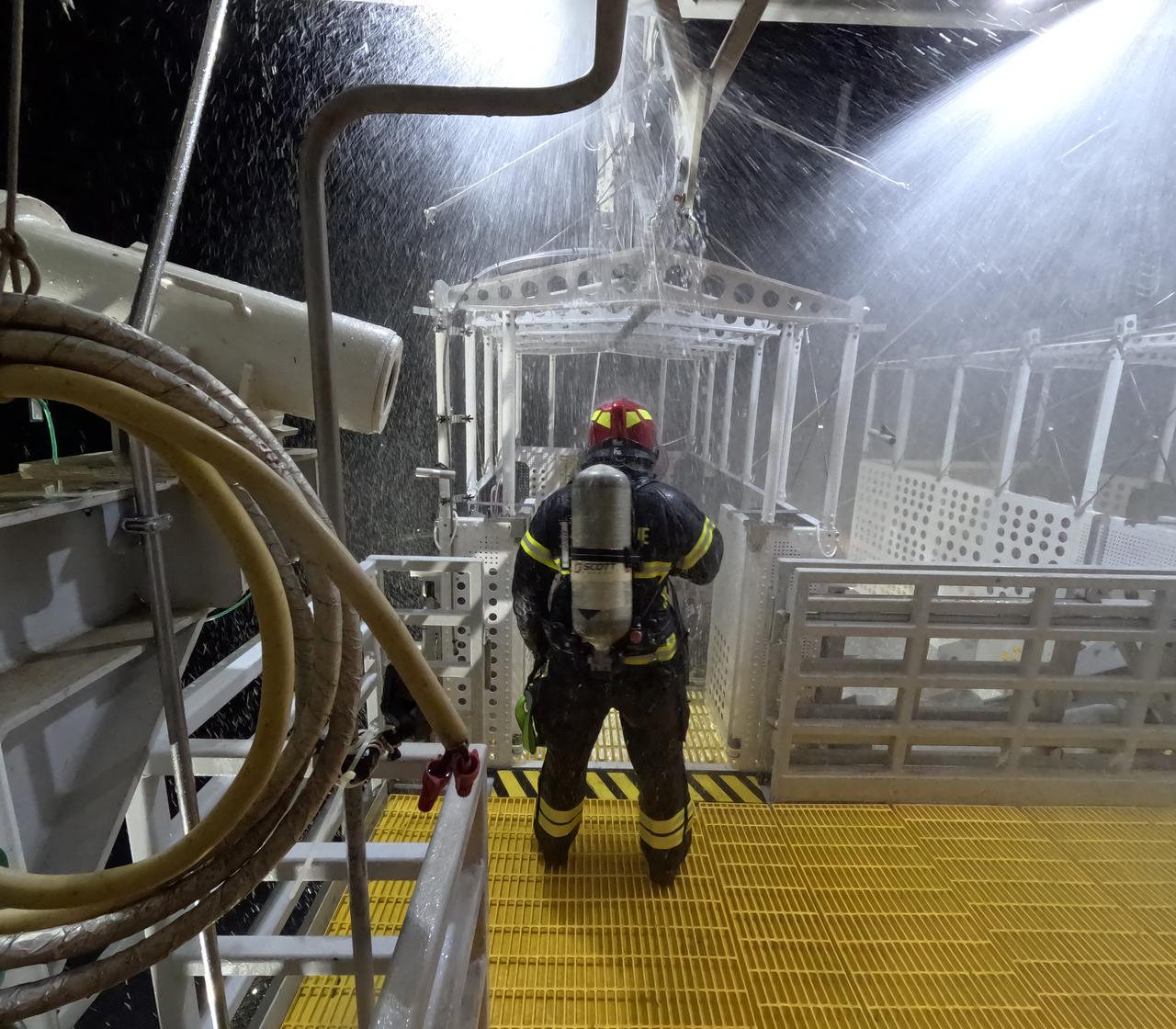

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Tuesday, Aug. 13, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program – who also suited up as astronauts – practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
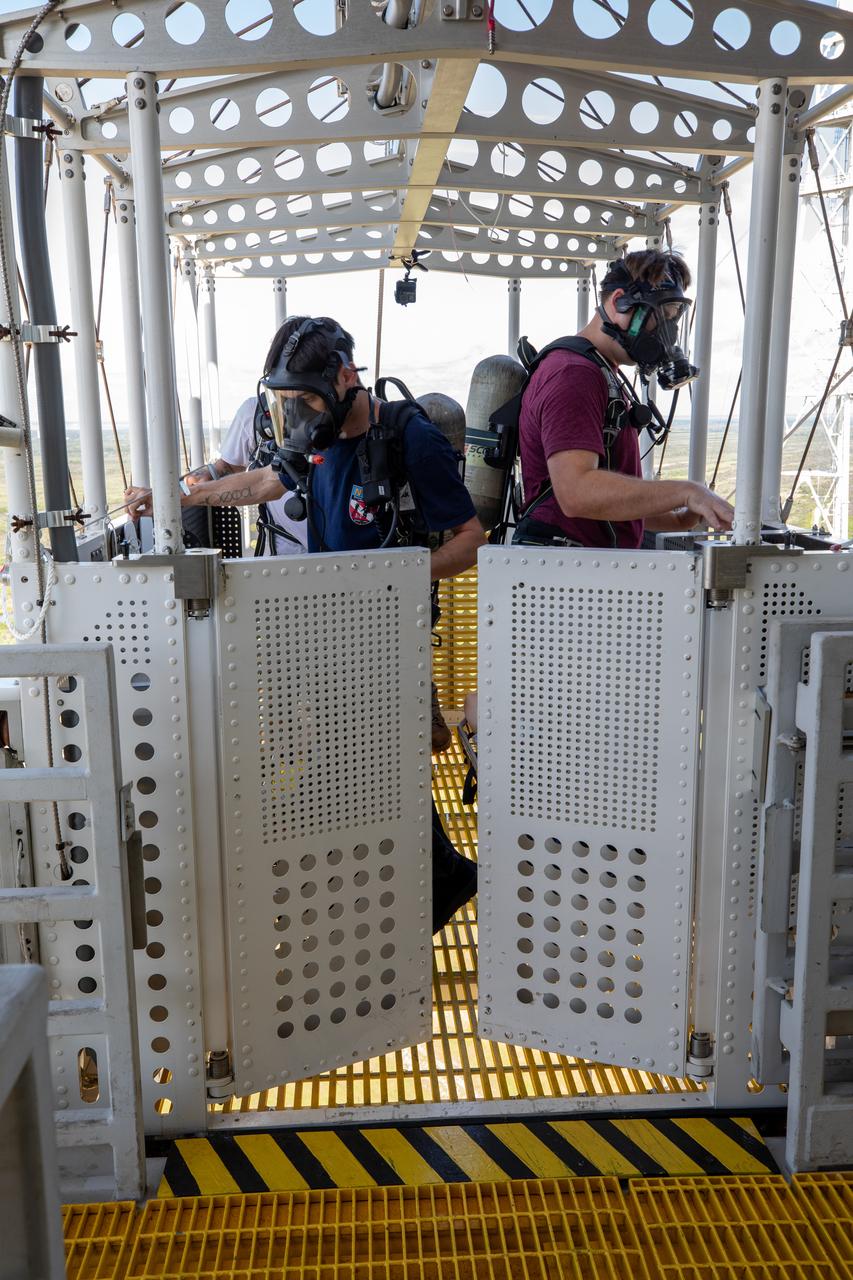

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Frank Culbertson, commander of the Expedition 3 resident crew on the International Space Station, poses for a photo. He and the other crew members Vladimir Dezhurov and Mikhail Dezhurov returned to Earth as passengers aboard the orbiter Endeavour, which landed at KSC at 12:55 p.m. EST (17:55 GMT) Dec. 17, 2001, after completing mission STS-108. The landing is the 57th at KSC in the history of the program STS-108 was the 12th mission to the Space Station. This mission was the 107th flight in the Shuttle program and the 17th flight for the orbiter
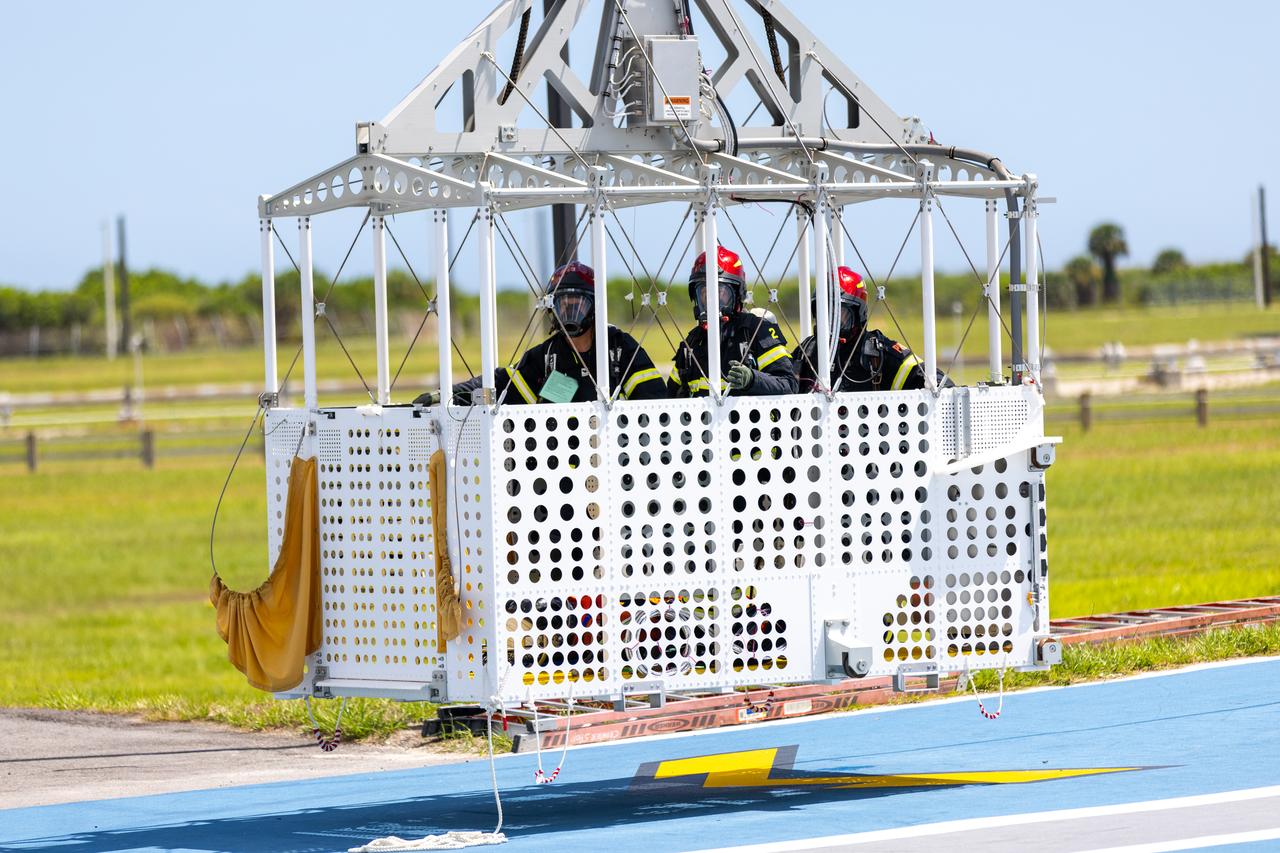

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
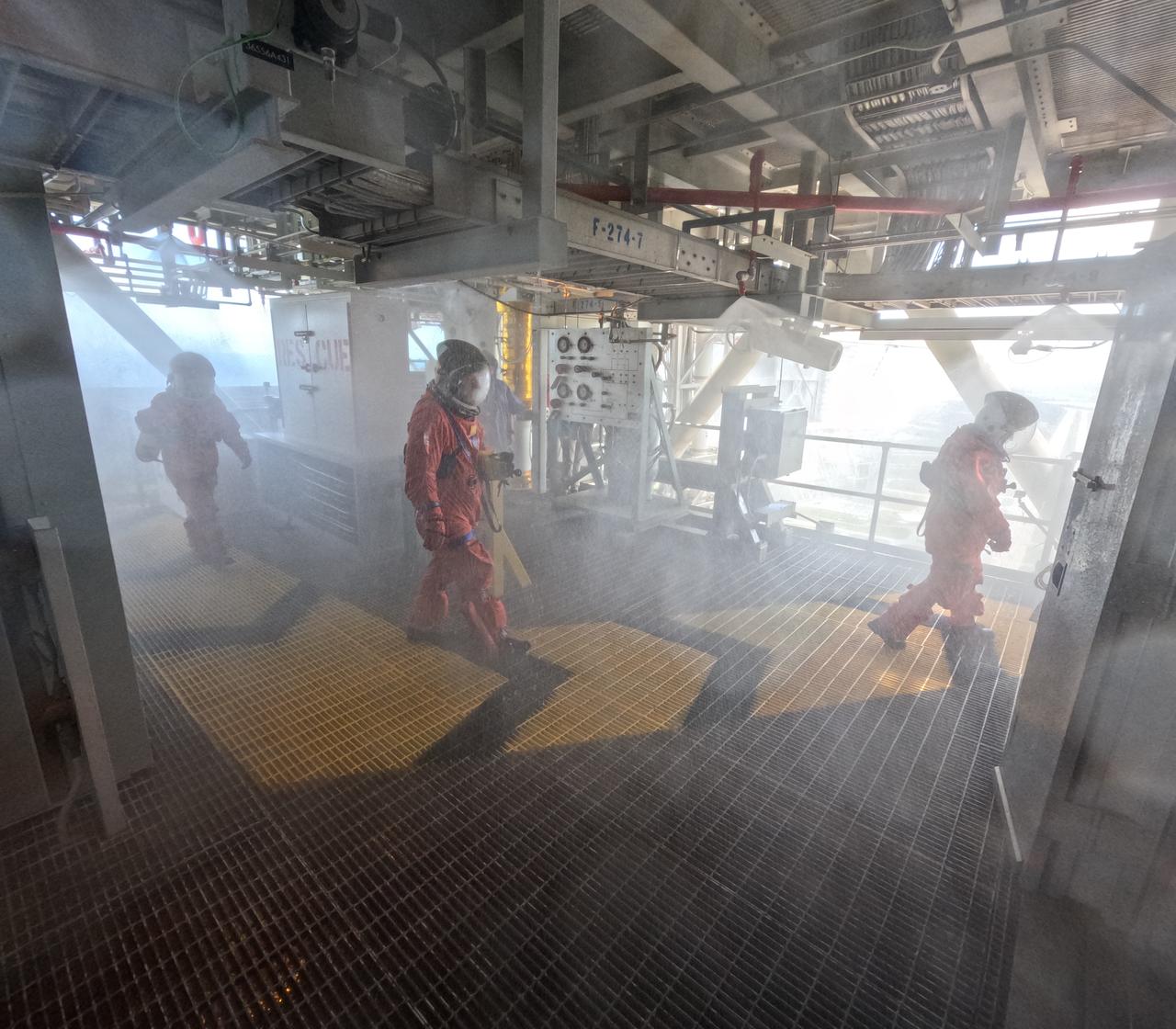

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
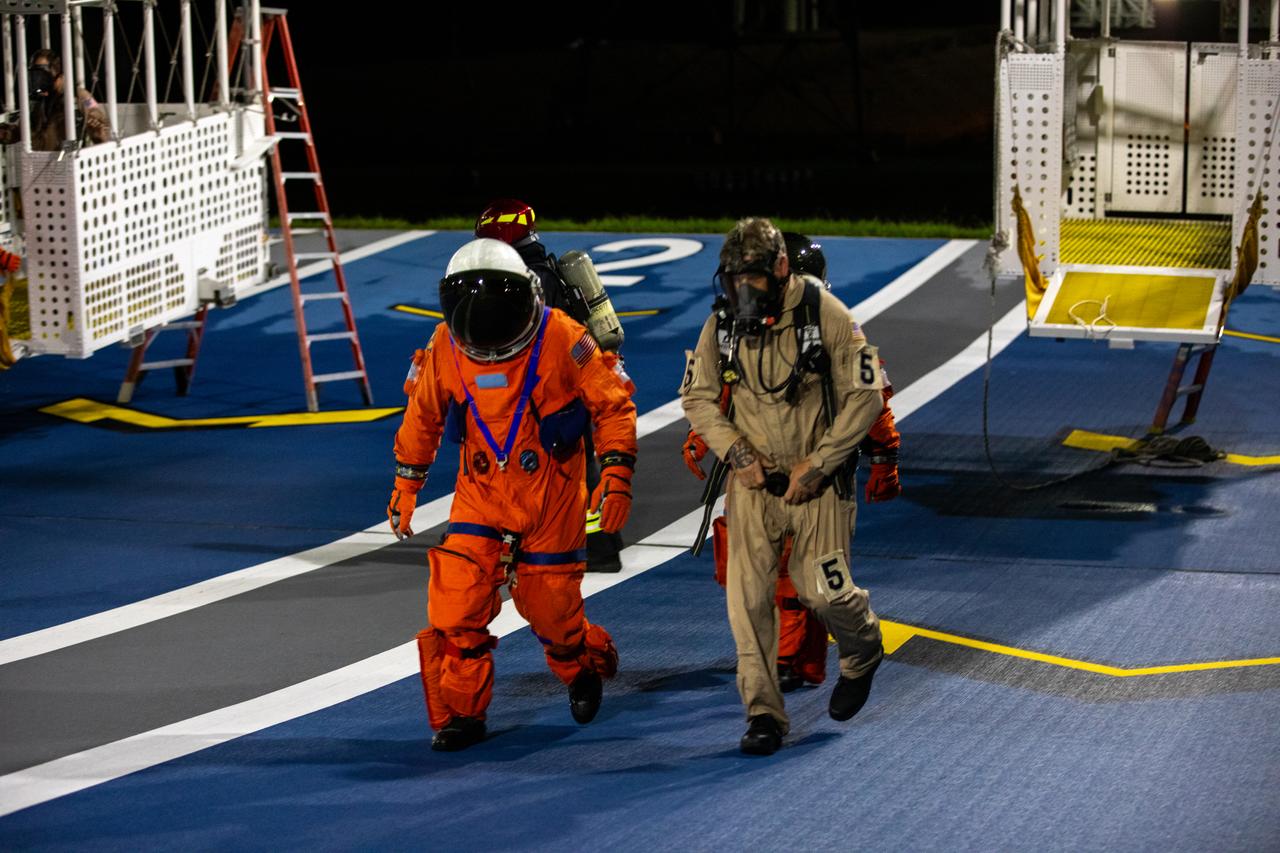

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Tuesday, Aug. 13, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
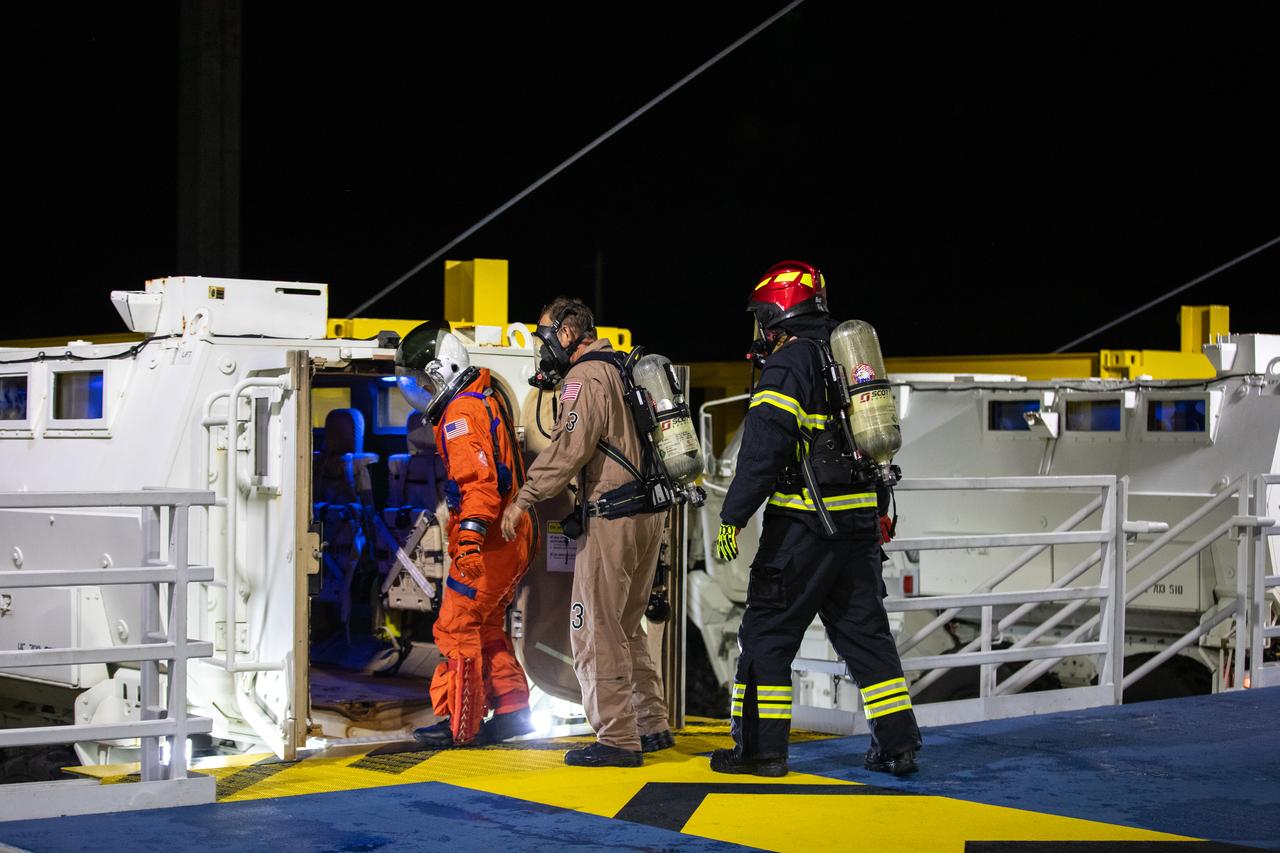

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Tuesday, Aug. 13, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
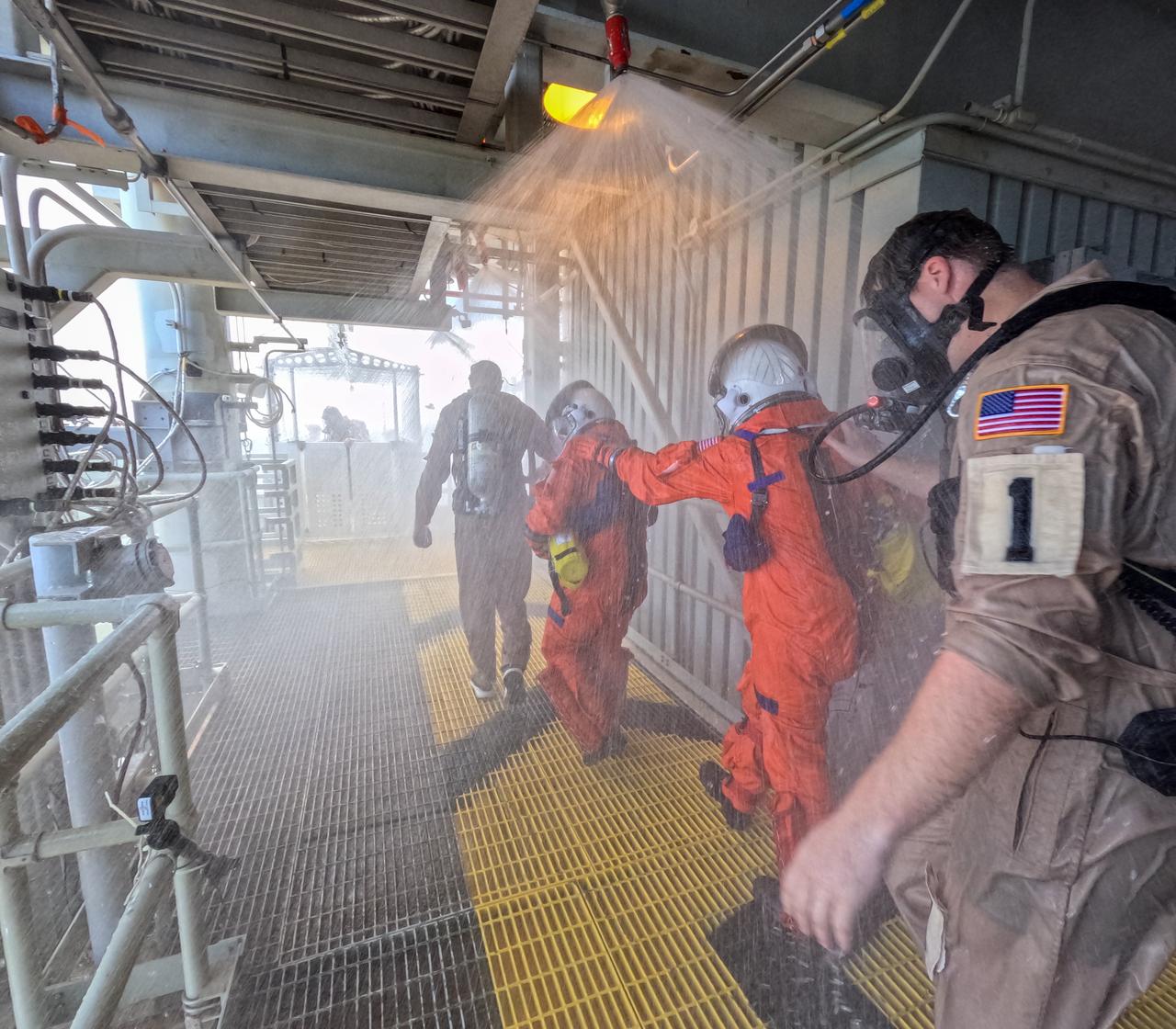

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
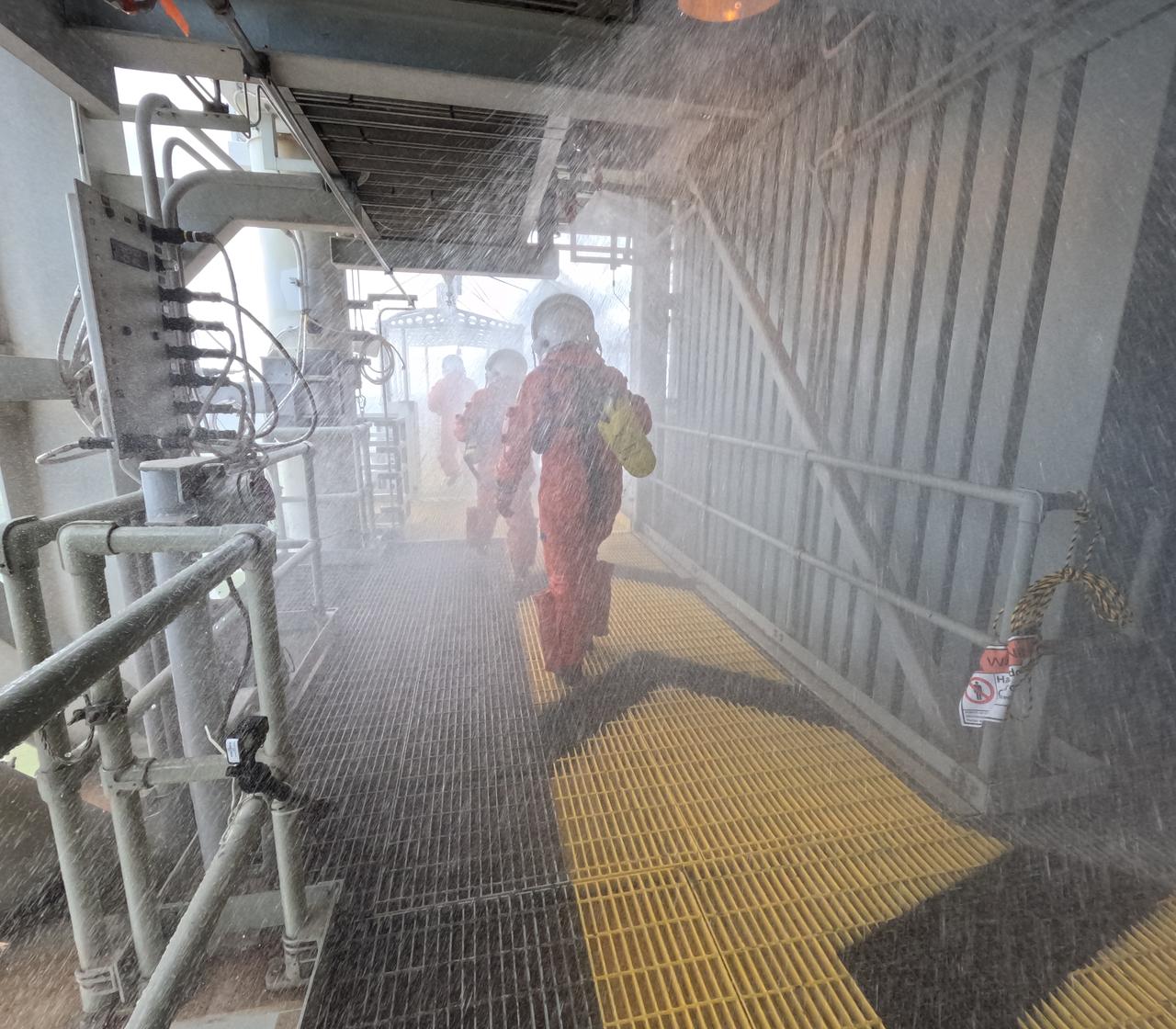

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

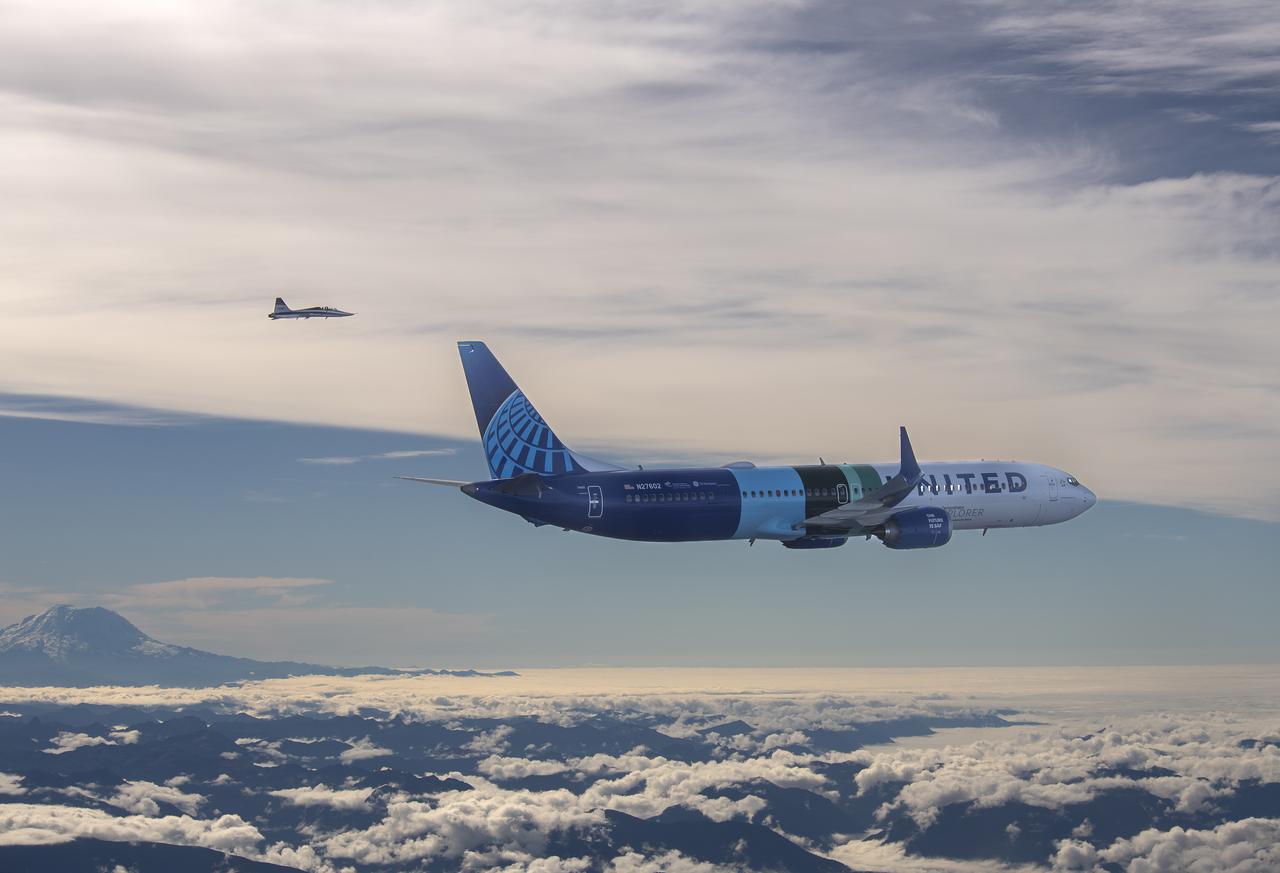
NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
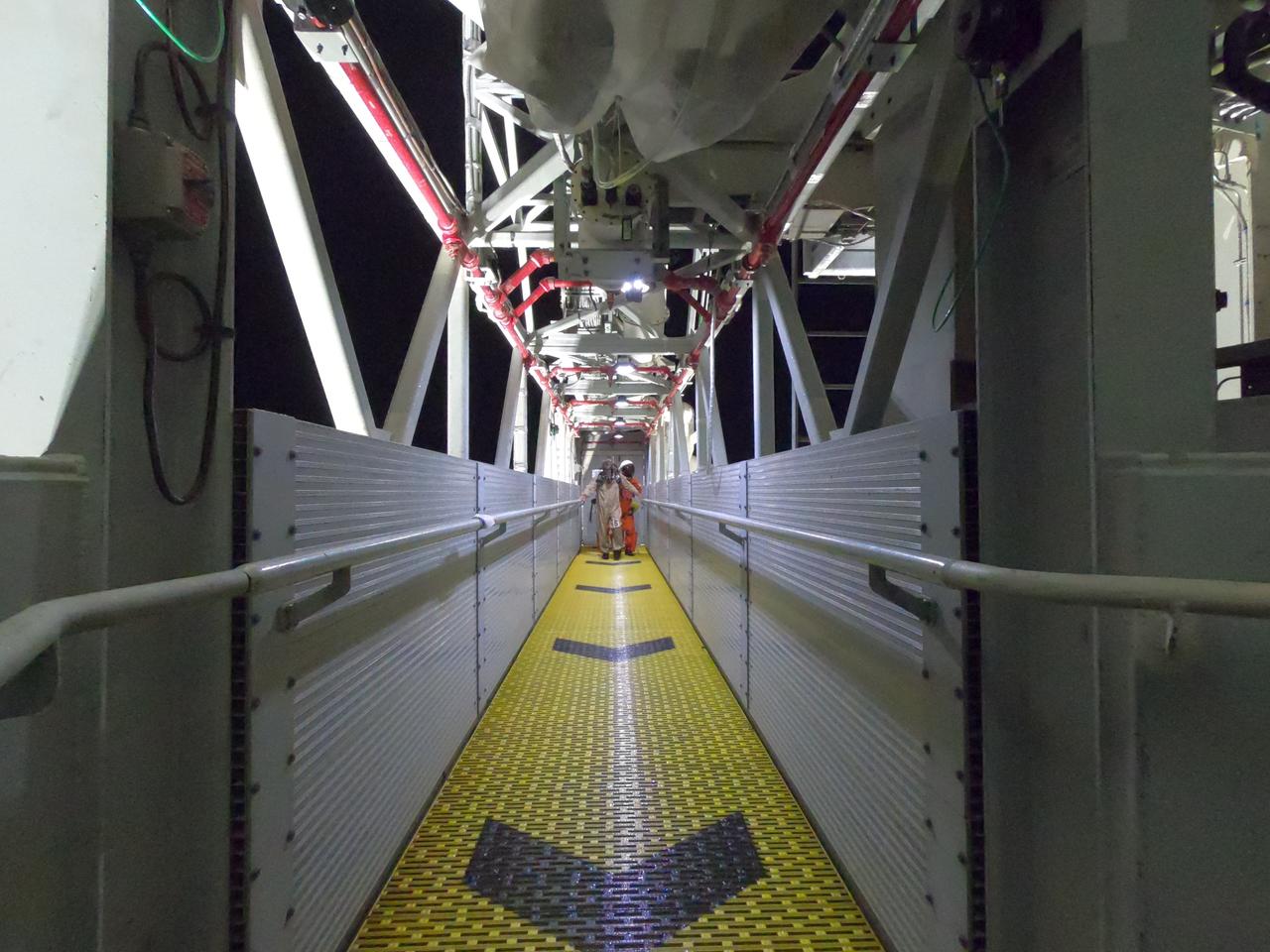

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Tuesday, Aug. 13, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program – who also suited up as astronauts – practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

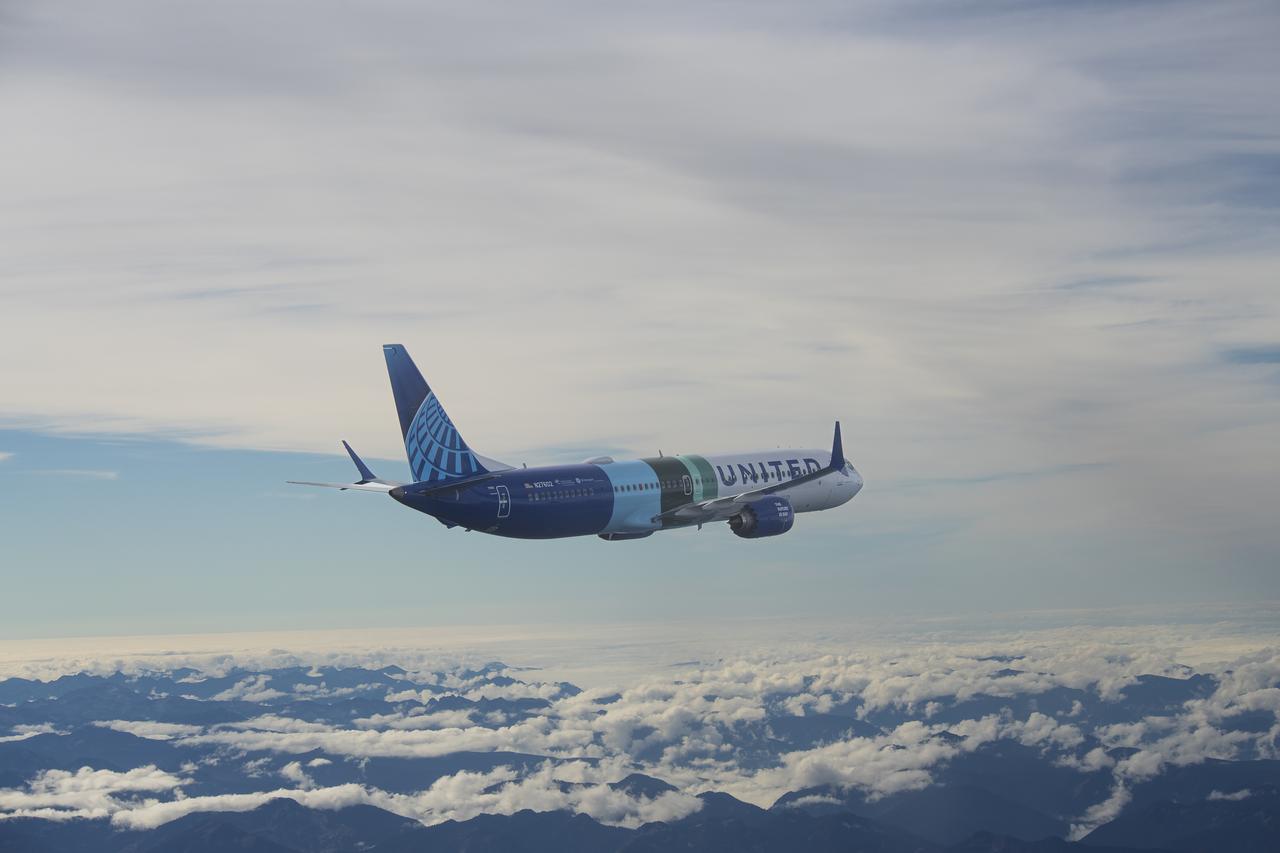
NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
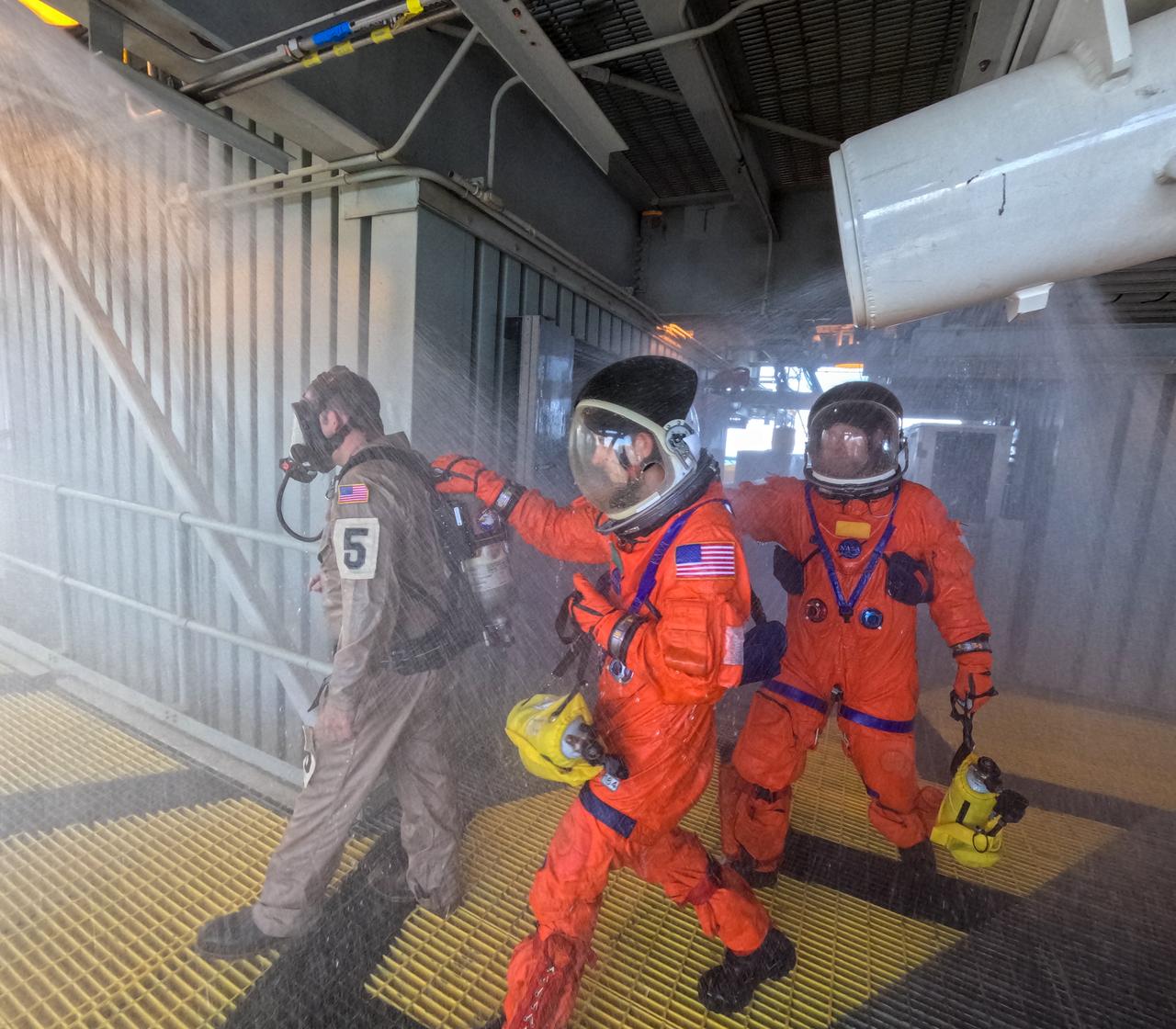

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
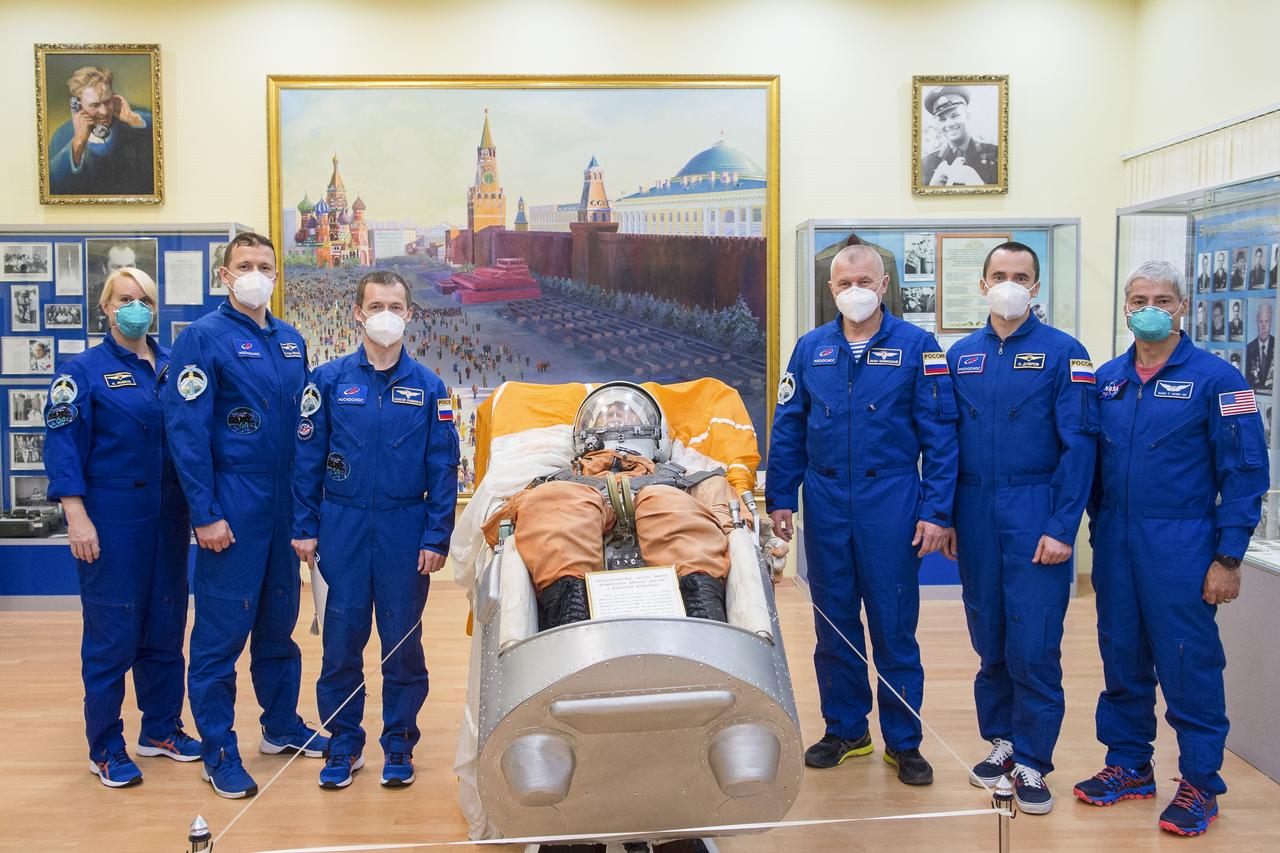

The Expedition 64 prime and backup crew members pose for a picture next to a replica of a Vostok seat and passenger at the Baikonur Cosmodrome Museum, Wednesday, Oct. 7, 2020, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. From left to right are the prime crew members Kate Rubins of NASA, Sergey Kud-Sverchkov of Roscosmos, and Sergey Ryzhikov of Roscosmos, and backup crew members Oleg Novitskiy of Roscosmos, Petr Dubrov of Roscosmos, and Mark Vande Hei of NASA. Rubins, Kud-Sverchkov, and Ryzhikov are scheduled to launch to the International Space Station aboard the Soyuz MS-17 spacecraft on October 14. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
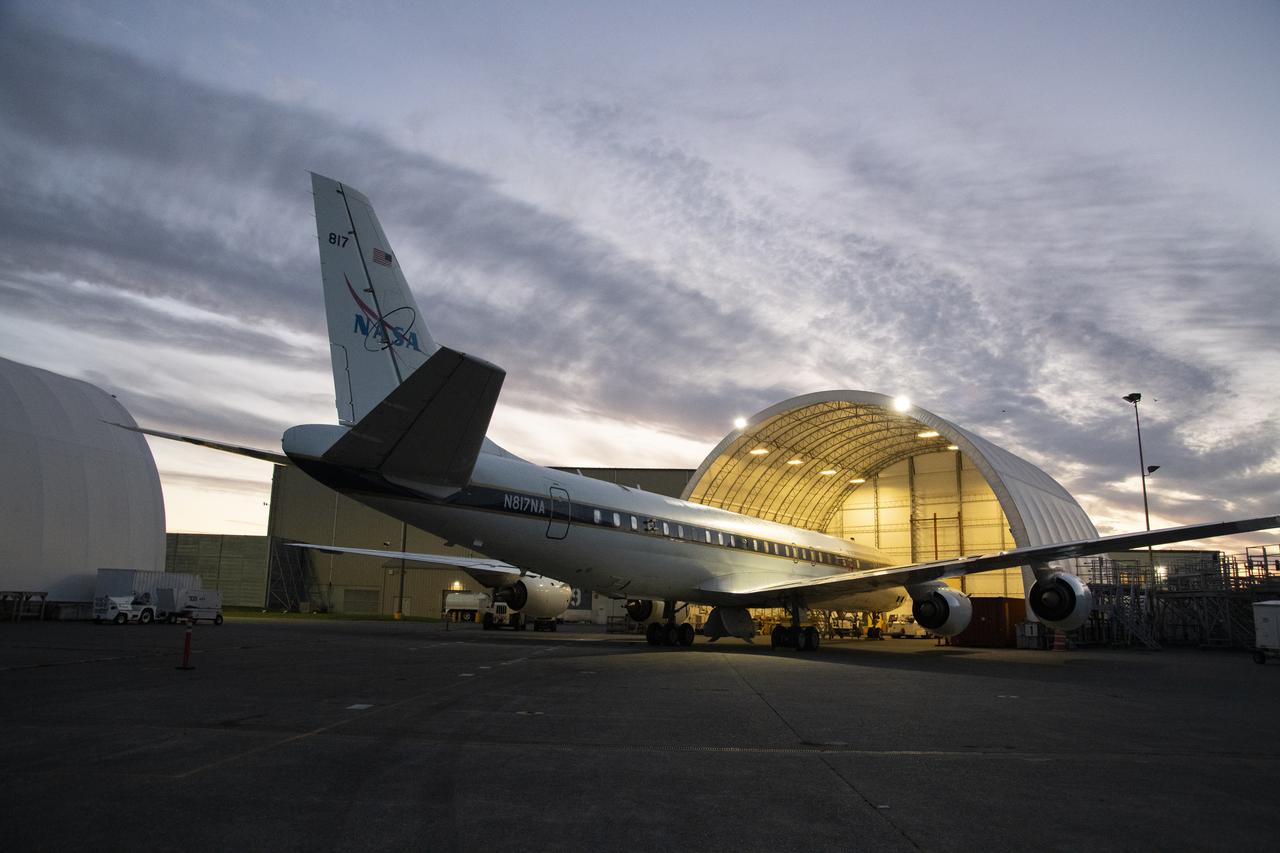

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
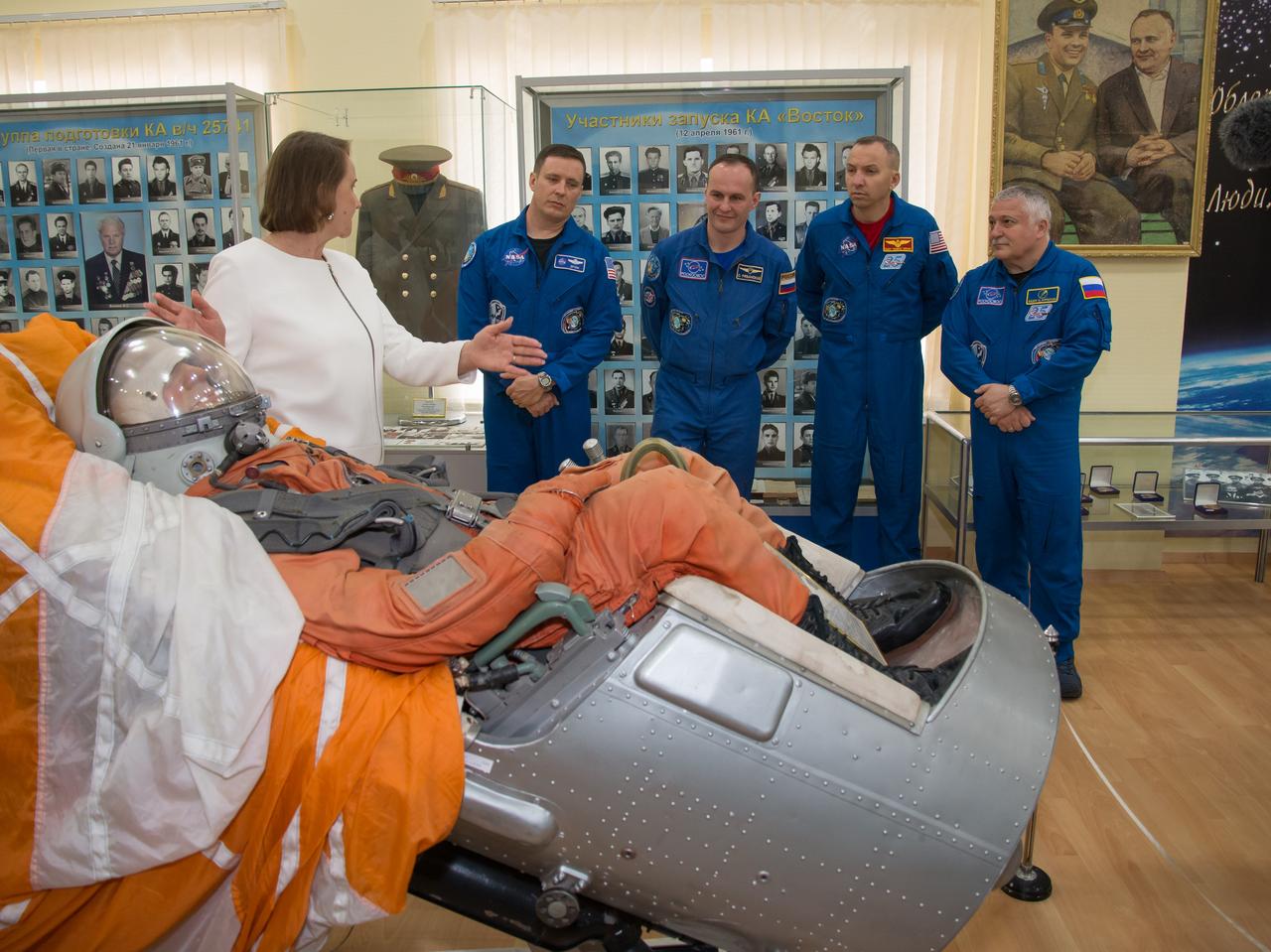

jsc2017e043851 (April 14, 2017) --- At the Baikonur Cosmodrome Museum in Kazakhstan, the Expedition 51 prime and backup crewmembers are shown a replica of a Soyuz seat and passenger April 14 during a traditional tour of the facility. From left to right are prime crewmember Jack Fischer of NASA, backup crewmember Sergey Ryazanskiy of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), backup crewmember Randy Bresnik of NASA and prime crewmember Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos. Fischer and Yurchikhin will launch April 20 on the Soyuz MS-04 spacecraft for a four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Credit: NASA/Victor Zelentsov
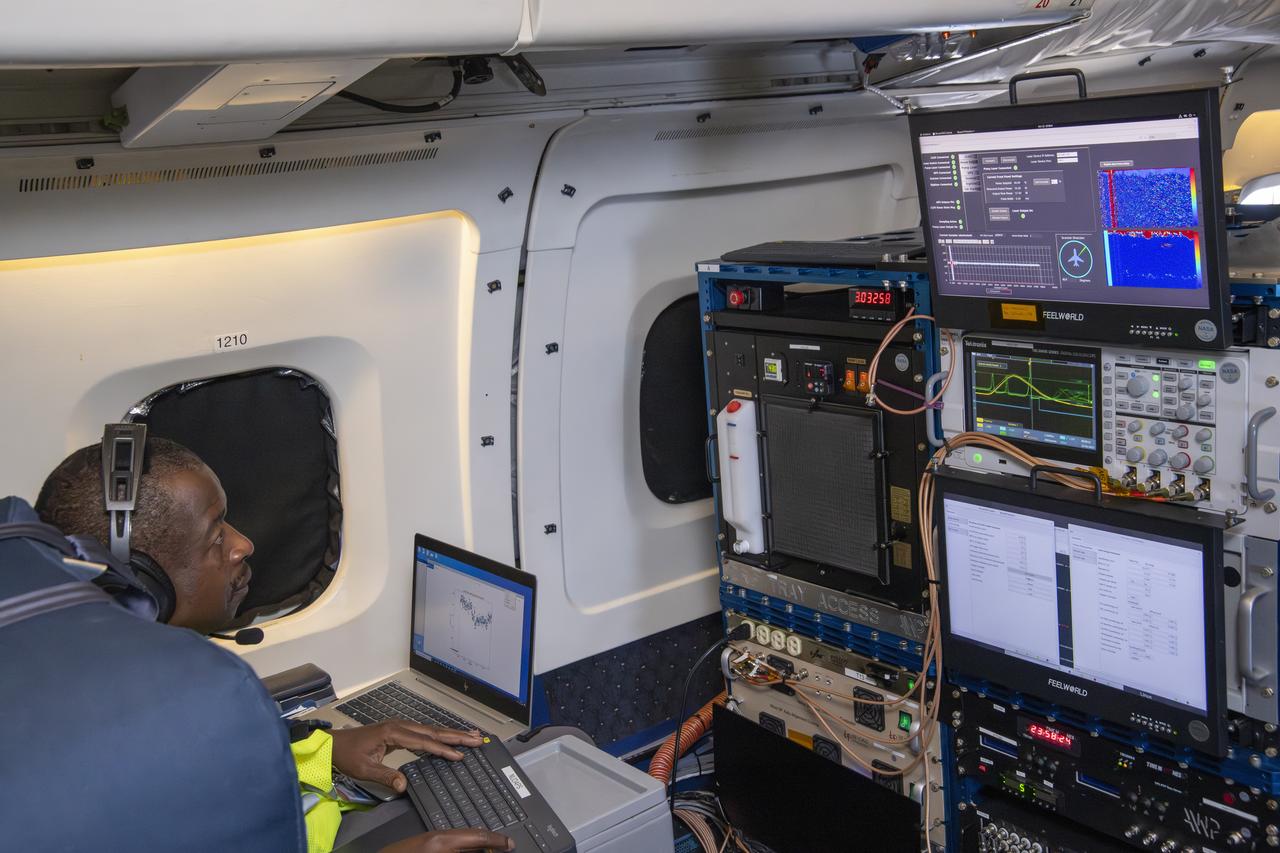

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
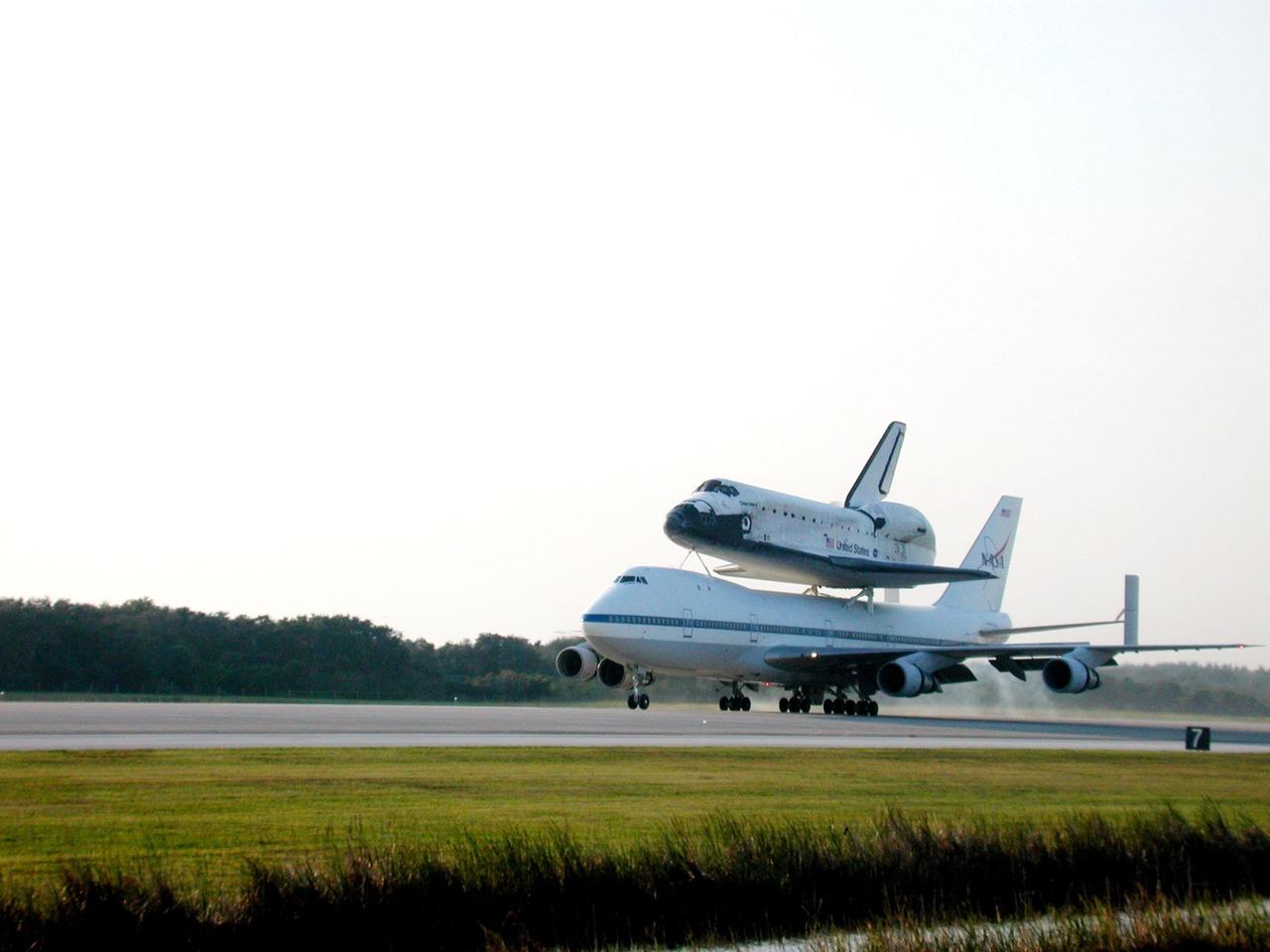

On a warm afternoon, the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), with its unique orbiter passenger attached to its back, rolls down the runway at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. The SCA is returning Discovery to KSC after the orbiter’s California landing more than a week ago at Edwards Air Force Base at the end of mission STS-92. Discovery will be demated from the SCA via the mate/demate device at the SLF and transported to the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1. There it will undergo preparations for its next launch, STS-102, scheduled for February 2001
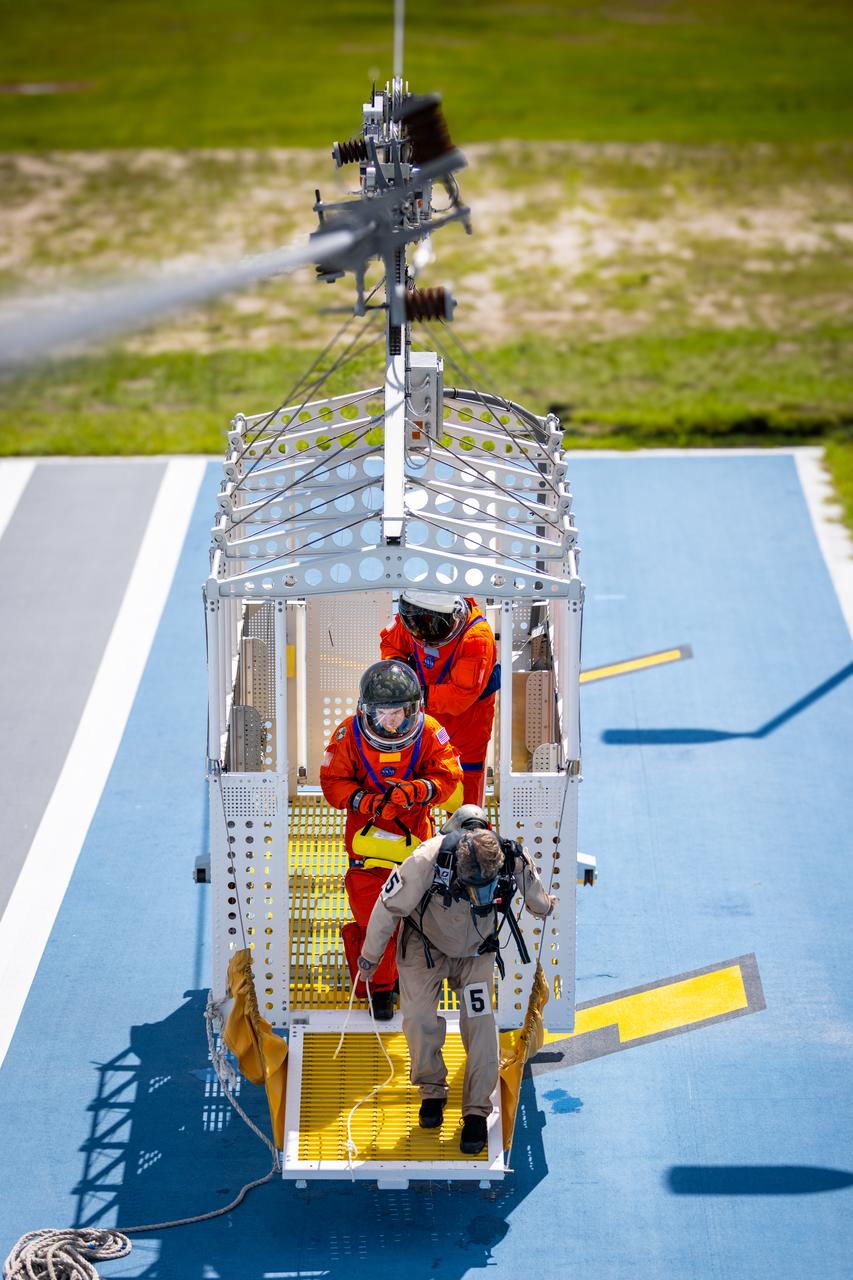

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
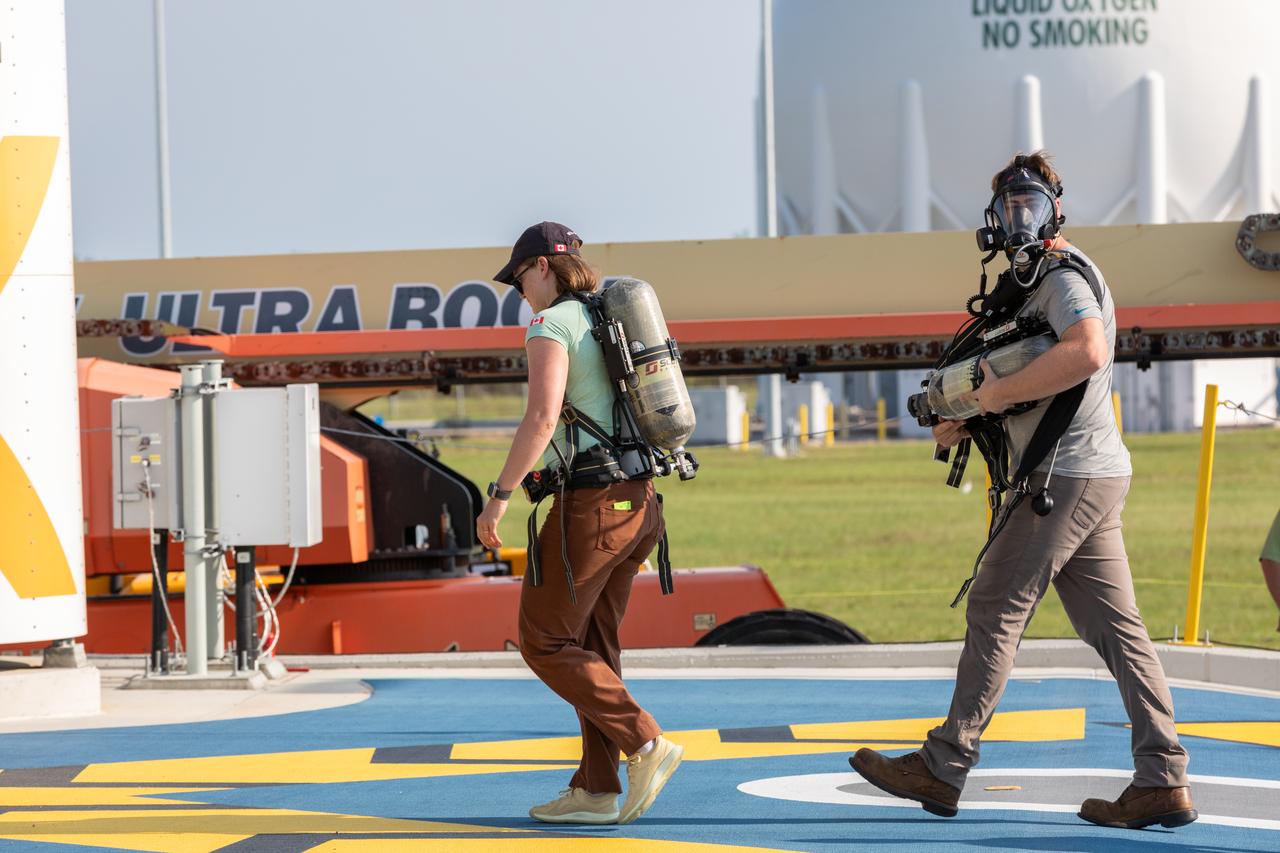

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Friday, Aug. 9, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
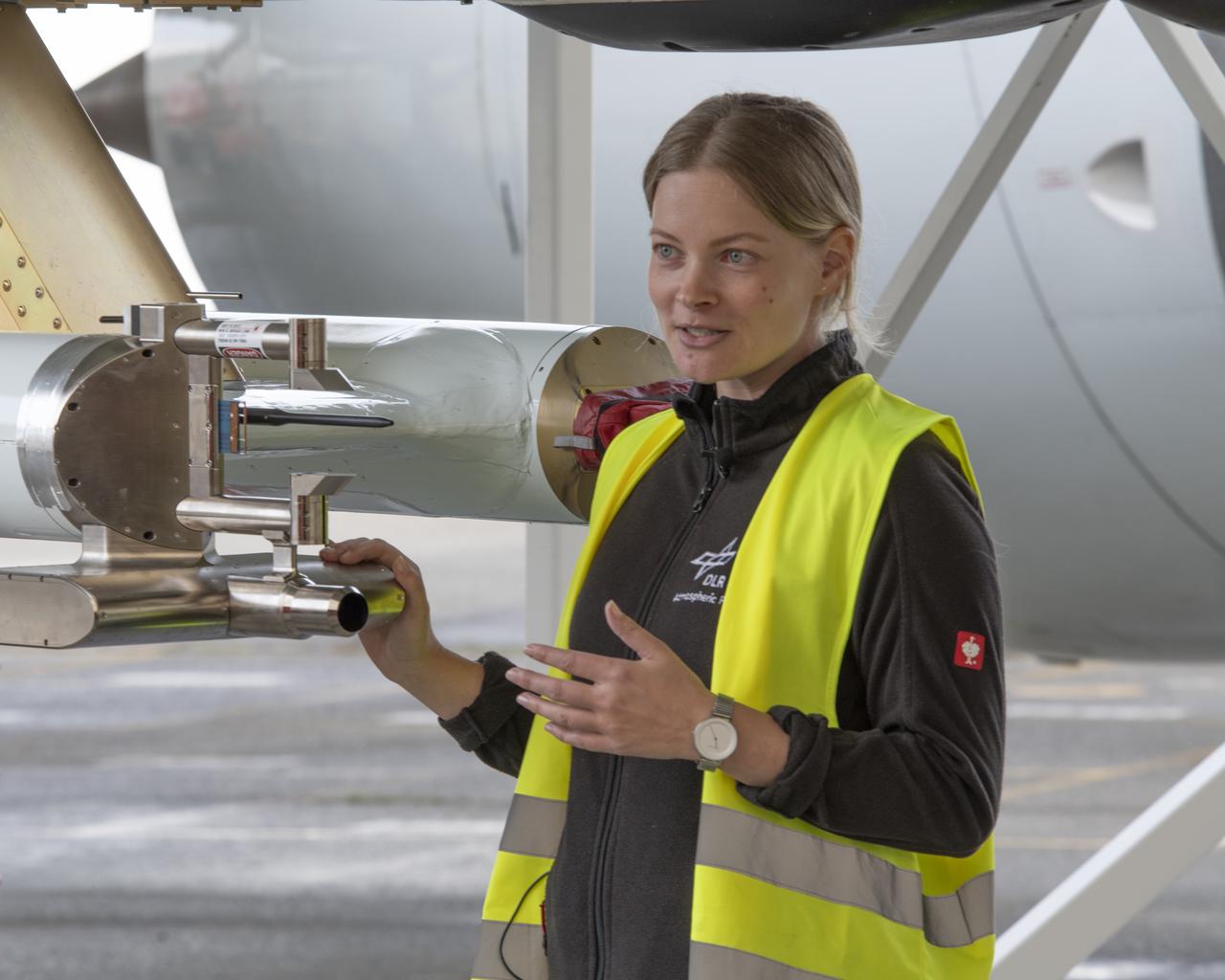

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
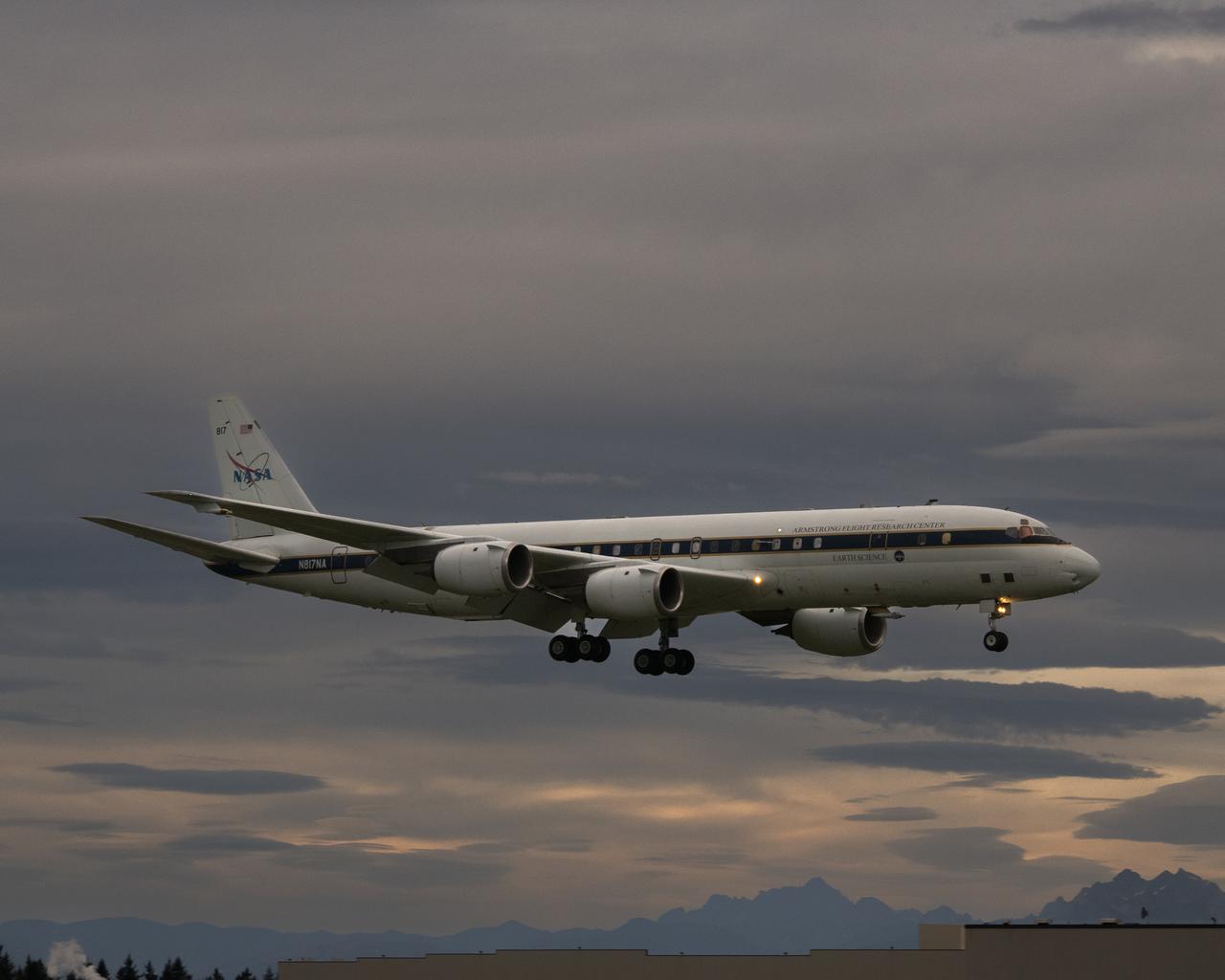

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
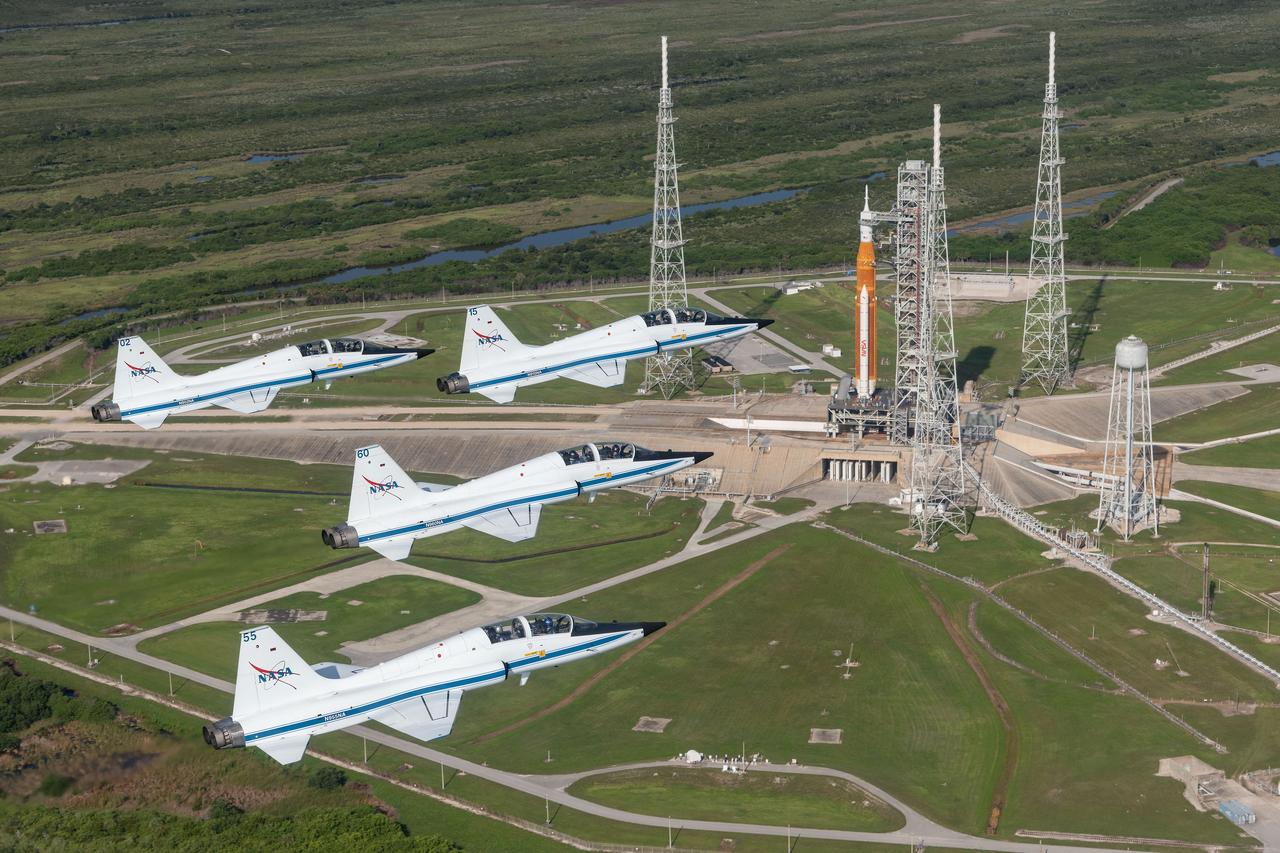

NASA's T-38 jets fly in formation above the Space Launch System rocket on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Aircraft designations and passengers: NASA 901: Chris Condon / Astronaut Zena Cardman. 902: Astronaut Candidate Nicole Ayers / Astronaut Christina Koch. 903: Canadian Space Agency Astronaut Jeremy Hansen / Astronaut Drew Morgan. 904: Chief Astronaut Reid Wiseman / Astronaut Joe Acaba. 905 (Photo Chase): Astronaut Candidate Jack Hathaway / Josh Valcarcel Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel