
In this photograph the SATCOM KU-2 satellite attached to a Payload Assist Module-D (PAM-D) is being released from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis during STS-61B, the 23rd Shuttle Mission. The PAM-D is an upper stage system used to deploy payloads to a required orbit unattainable by the spacecraft. SATCOM KU-2 is an RCA communication satellite and was launched on November 26, 1985.

This image of the free-flying SATCOM KU-2 satellite, still attached to a Payload Assist Module-D (PAM-D), was photographed during STS-61B, the 23rd Space Shuttle mission. The SATCOM KU-2 is an RCA communication satellite and was launched on November 26, 1985, aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis. The PAM-D is an upper stage system used to deploy payloads to a required orbit unattainable by the launch vehicle.

The Space Shuttle Challenger, making its fourth space flight, highlights the 41B insignia. The reusable vehicle is flanked in the oval by an illustration of a Payload Assist Module-D solid rocket motor (PAM-D) for assisted satellite deployment; an astronaut making the first non-tethered extravehicular activity (EVA); and eleven stars.

41D-37-050 (1 Sept 1984) --- Telstar, the third of three satellites to be placed into space via the Earth-orbiting Discovery, departs from the cargo bay of the manned vehicle during 41-D's third day in space. The scene was photographed at 9:35 a.m. (CDT), Sept. 1, 1984, with a 70mm handheld hasselblad camera aimed through the windows on the flight deck. Heavy clouds cover much of the water and land mass of Earth in the background.
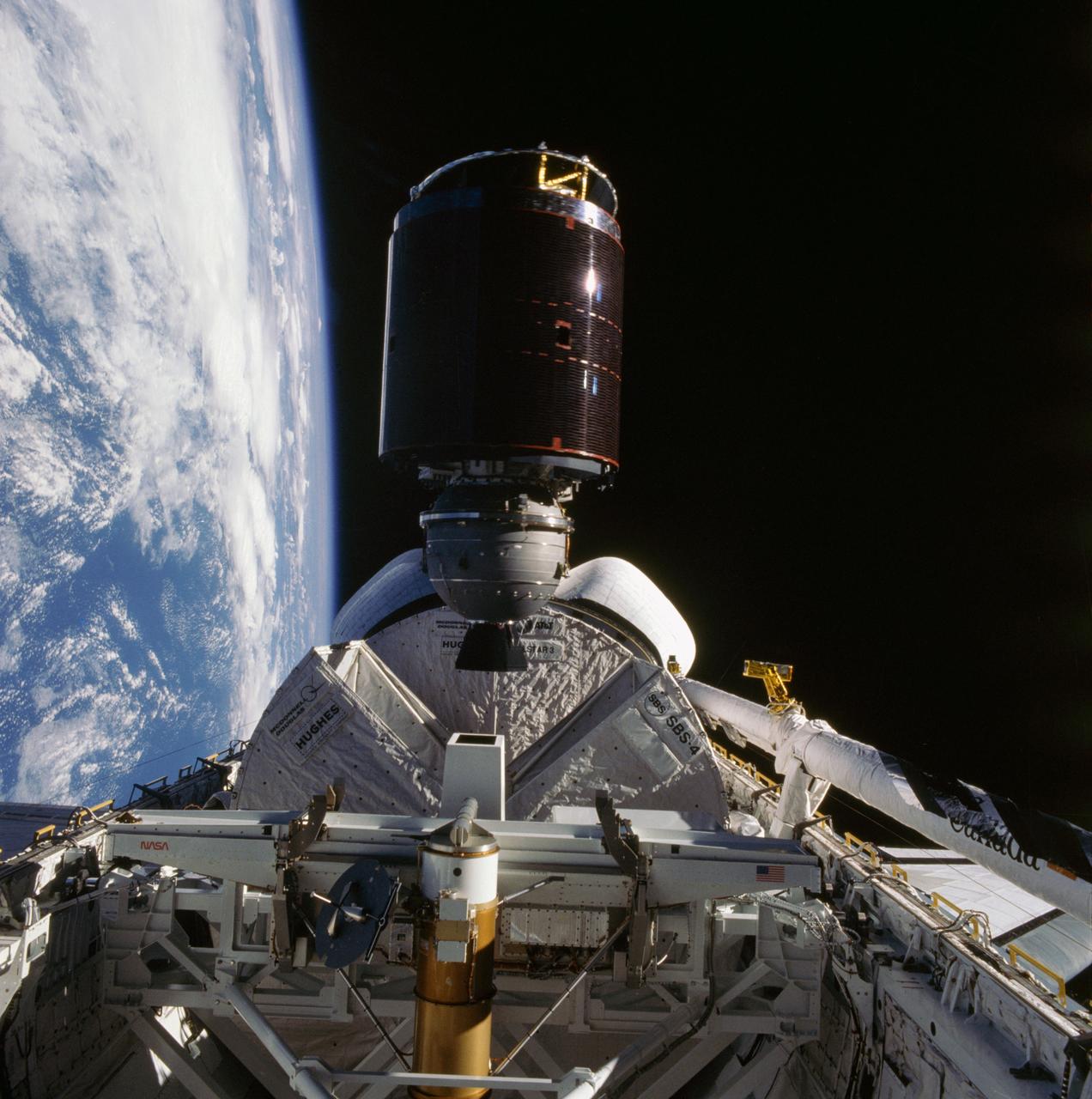

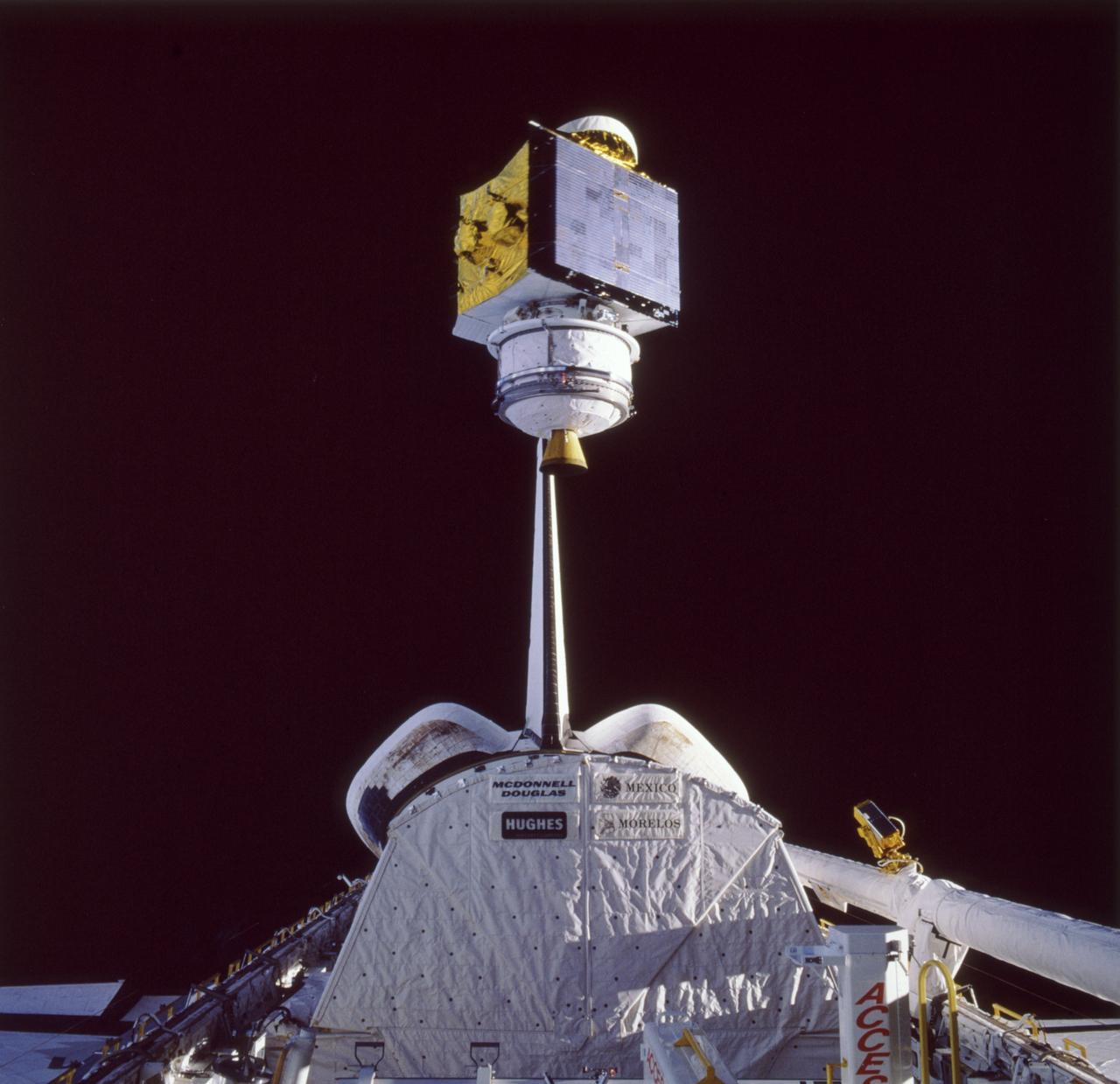
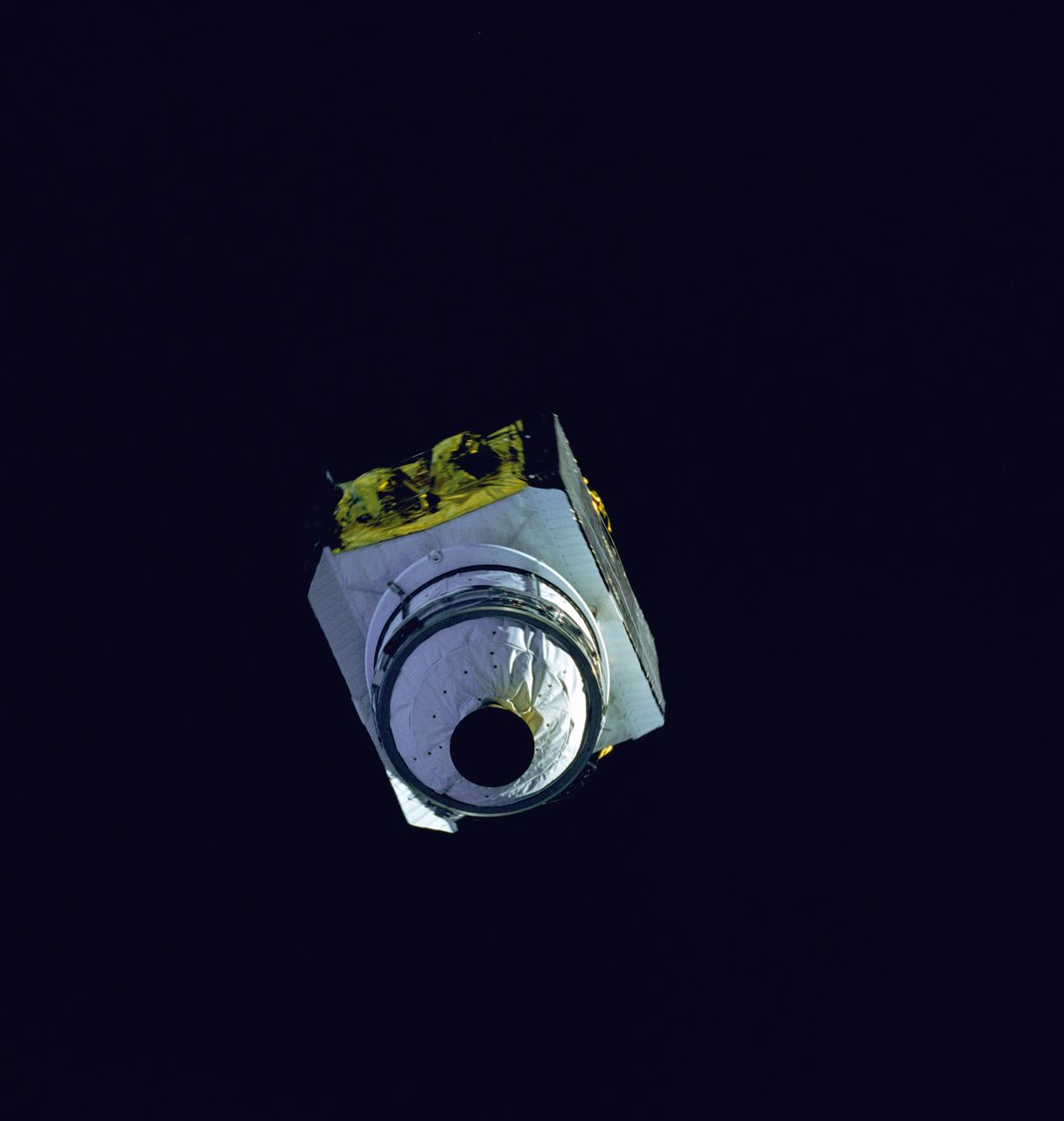
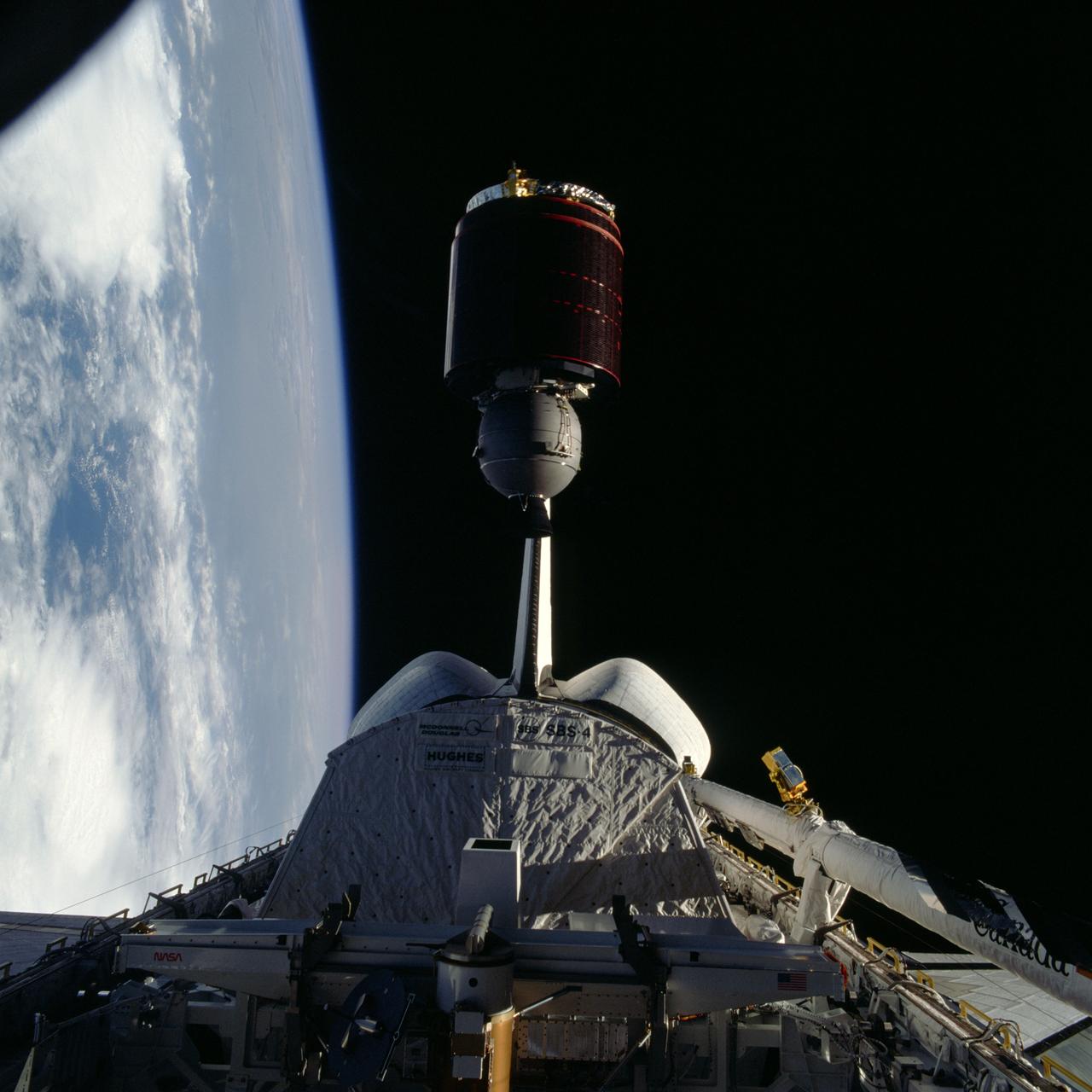
41D-36-034 (30 Aug 1984) --- Less than nine hours after the first launch of the Discovery, its astronaut crewmembers photographed deployment of the SBS-4 communications satellite. The cylindrical spacecraft spins and rises from its cradle-like protective shield to begin life in space. A number of maneuvers will place it in its desired orbit. A 70mm camera, aimed through the spacecraft’s aft flight deck windows, was used to expose the frame.
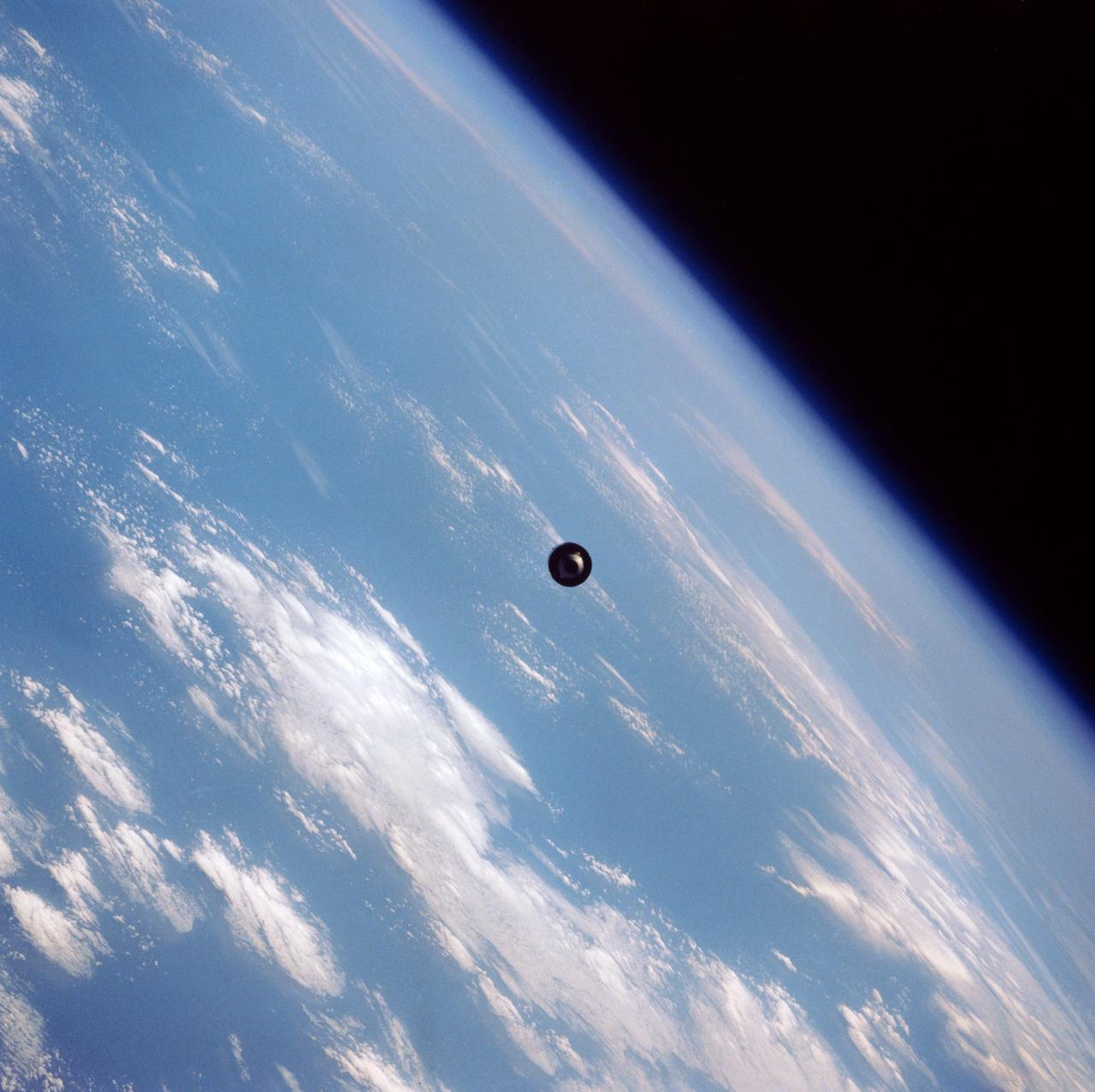

41D-39-068 (1 Sept 1984) --- Quickly moving away from the Space Shuttle Discovery is the Telstar 3 communications satellite, deployed September 1, 1984. The 41-D crew successfully completed three satellite placements, of which this was the last. Telstar was the second 41-D deployed satellite to be equipped with a payload assist module (PAM-D). The frame was exposed with a 70mm camera.
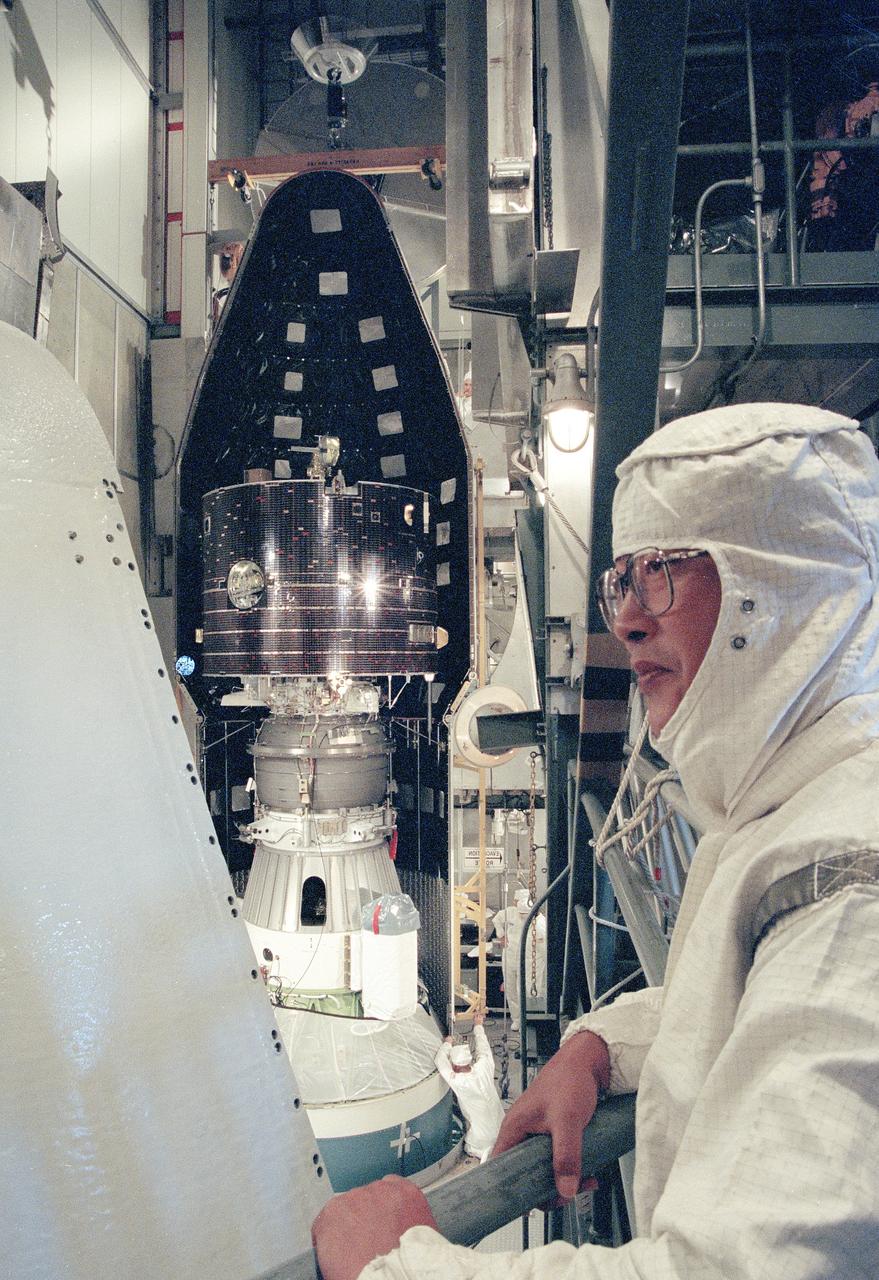
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 17, Pad A, technicians encapsulate the Geotail spacecraft upper and attached Payload Assist Module-D upper stage lower in the protective payload fairing. Geotail and secondary payload Diffuse Ultraviolet Experiment DUVE are scheduled for launch about the Delta II rocket on July 24. The GEOTAIL mission is a collaborative project undertaken by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science ISAS, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency JAXA and NASA. Photo Credit: NASA
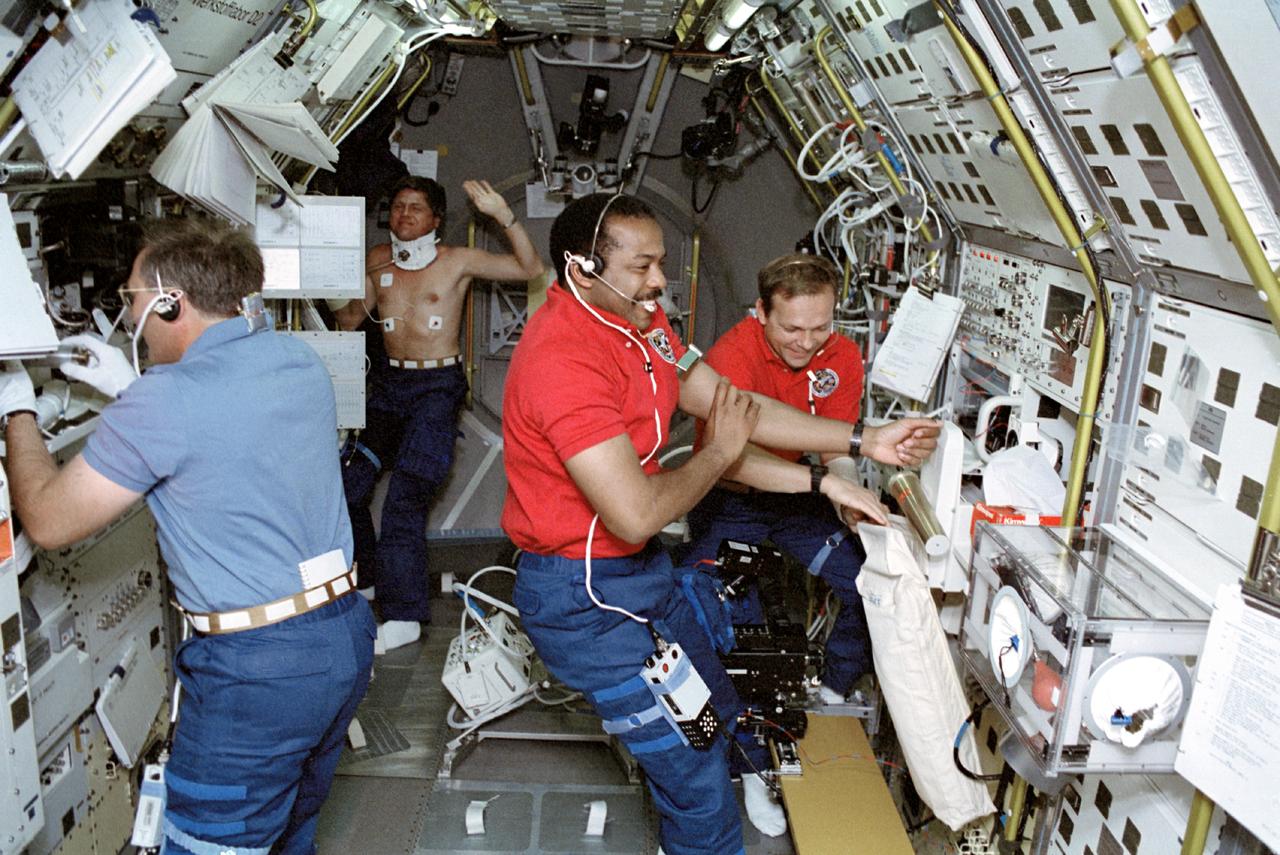

STS055-22-004 (26 April-6 May 1993) --- Four of the seven crew members who spent 10 days aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia are pictured during a brief shift overlap period in the Spacelab D-2 Science Module. Left to right are Jerry L. Ross, Ulrich Walter, Bernard A. Harris, Jr. and Hans Schlegel. Ross, STS-55 payload commander, is changing a sample in a materials processing furnace; Walter, a German payload specialist is in the midst of a baroreflex test and fellow payload specialist Schlegel assists mission specialist and physician Harris with a physiological test at the "Anthrorack".

Workers at Launch Complex 17 Pad A, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) encapsulate the Geomagnetic Tail (GEOTAIL) spacecraft (upper) and attached payload Assist Module-D upper stage (lower) in the protective payload fairing. GEOTAIL project was designed to study the effects of Earth's magnetic field. The solar wind draws the Earth's magnetic field into a long tail on the night side of the Earth and stores energy in the stretched field lines of the magnetotail. During active periods, the tail couples with the near-Earth magnetosphere, sometimes releasing energy stored in the tail and activating auroras in the polar ionosphere. GEOTAIL measures the flow of energy and its transformation in the magnetotail and will help clarify the mechanisms that control the imput, transport, storage, release, and conversion of mass, momentum, and energy in the magnetotail.