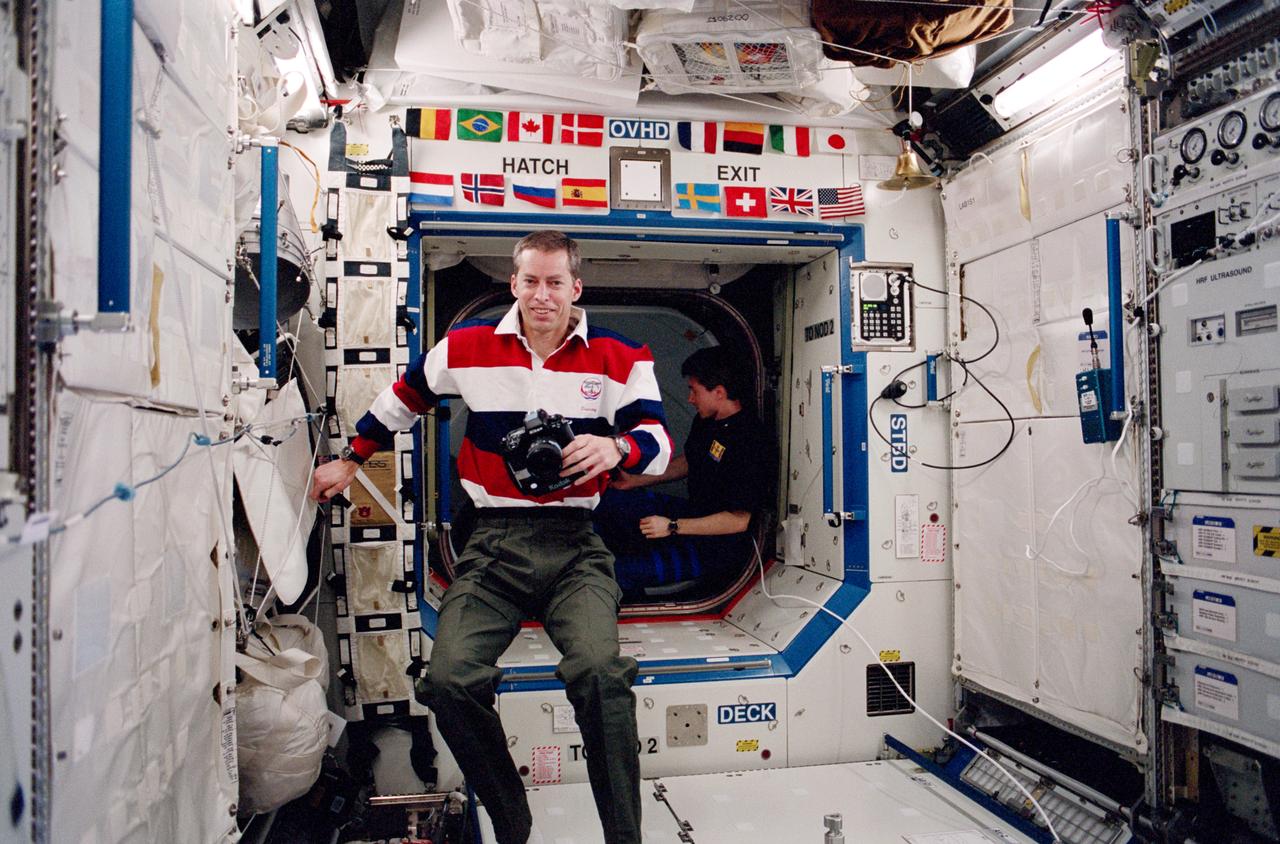

In this Space Shuttle STS-102 mission image, the Payload Equipment Restraint System H-Strap is shown at the left side of the U.S. Laboratory hatch and behind Astronaut James D. Weatherbee, mission specialist. PERS is an integrated modular system of components designed to assist the crew of the International Space Station (ISS) in restraining and carrying necessary payload equipment and tools in a microgravity environment. The Operations Development Group, Flight Projects Directorate at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), while providing operation support to the ISS Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF), recognized the need for an on-orbit restraint system to facilitate control of lose objects, payloads, and tools. The PERS is the offspring of that need and it helps the ISS crew manage tools and rack components that would otherwise float away in the near-zero gravity environment aboard the Space Station. The system combines Kevlar straps, mesh pockets, Velcro and a variety of cornecting devices into a portable, adjustable system. The system includes the Single Strap, the H-Strap, the Belly Pack, the Laptop Restraint Belt, and the Tool Page Case. The Single Strap and the H-Strap were flown on this mission. The PERS concept was developed by industrial design students at Auburn University and the MSFC Flight Projects Directorate.
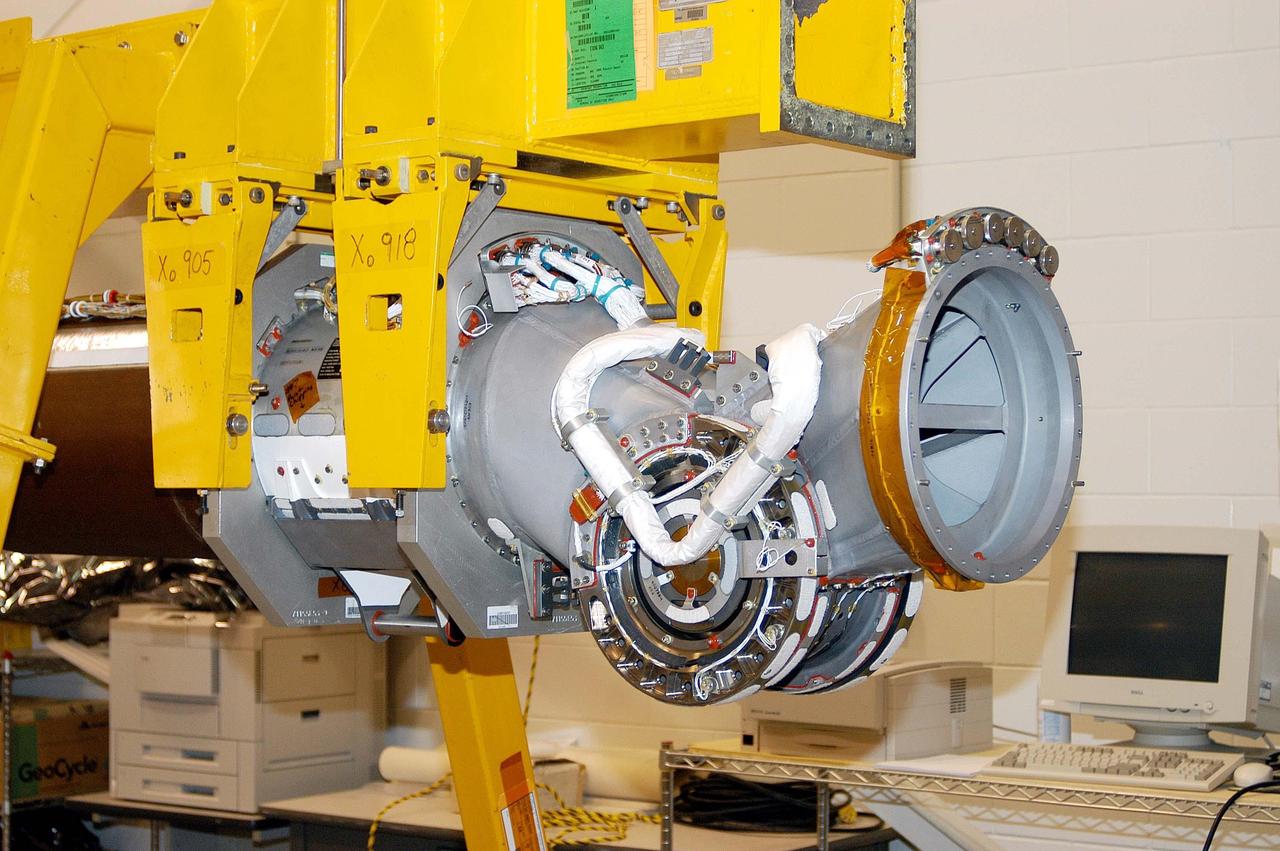
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Remote Manipulator System (RMS), also known as the Canadian robotic arm, for the orbiter Discovery has arrived at KSC’s Vehicle Assembly Building Lab. The part seen on the end is one of the joints that allow the basic structure of the arm to maneuver similar to a human arm. The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm is also serving as the base for the new Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), one of the safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the Shuttle with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of March 2005 on mission STS-114.
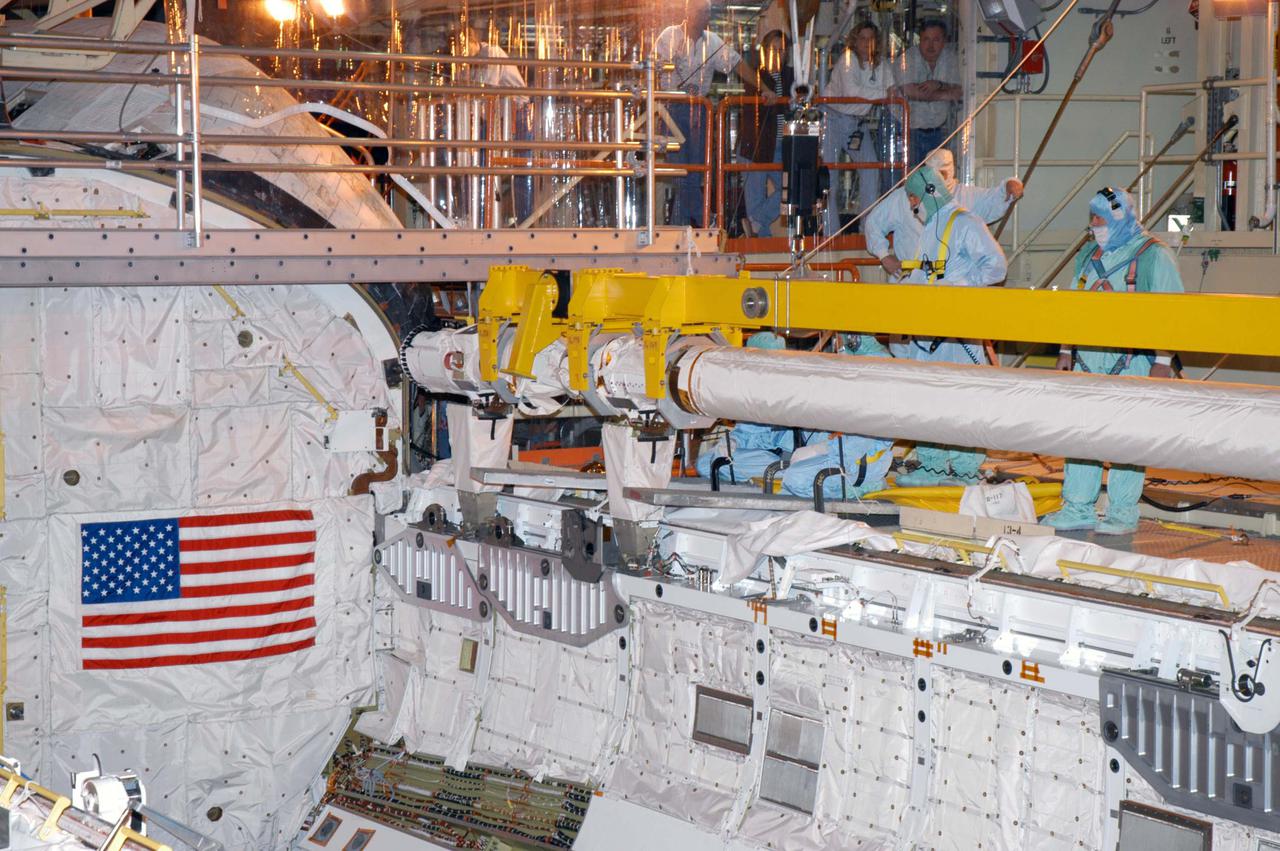
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), also known as the Canadian robotic arm, is being installed in Discovery’s payload bay. The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm is also serving as the base for the new Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), one of the safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the Shuttle with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of May 2005 on Return to Flight mission STS-114.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians in the Orbiter Processing Facility work to install the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), also known as the Canadian robotic arm, in Discovery’s payload bay. The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm is also serving as the base for the new Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), one of the safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the Shuttle with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of May 2005 on Return to Flight mission STS-114.
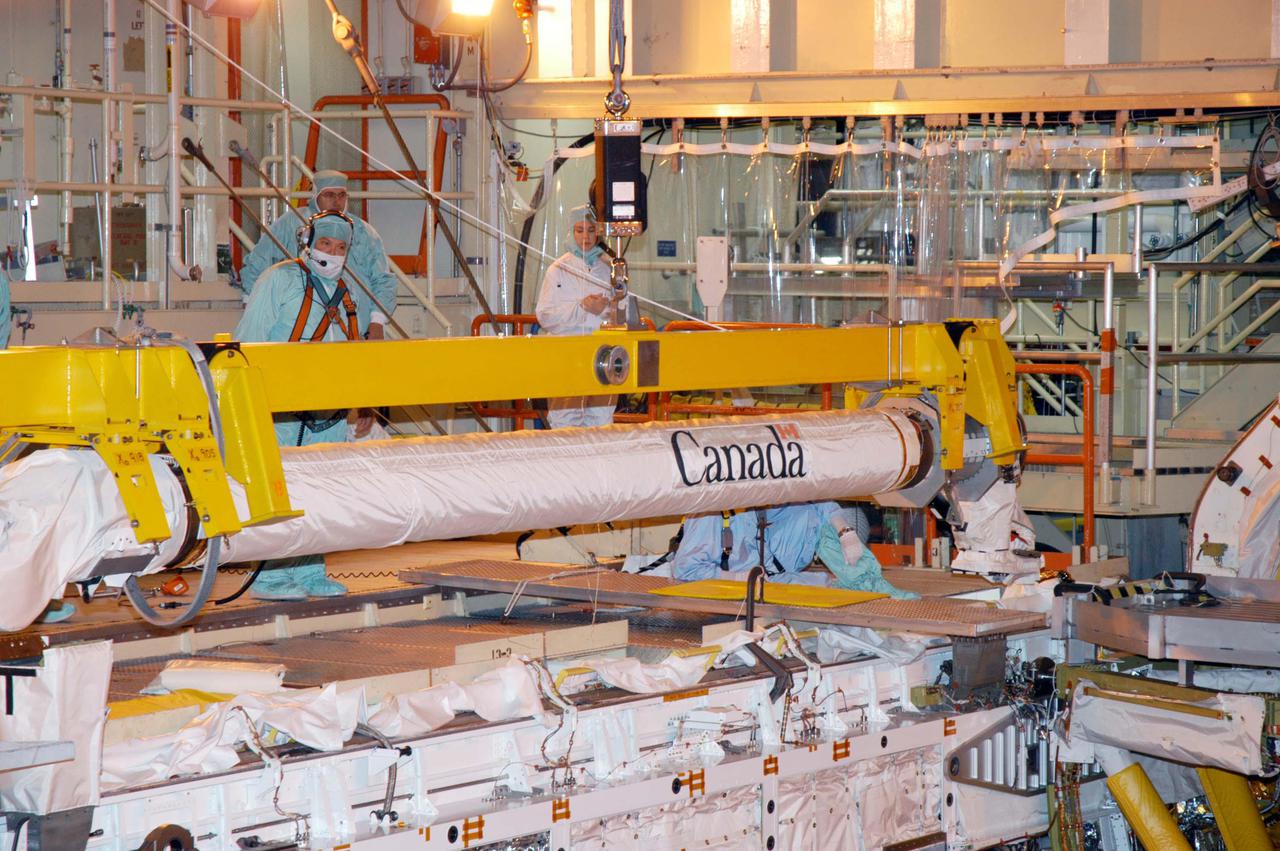

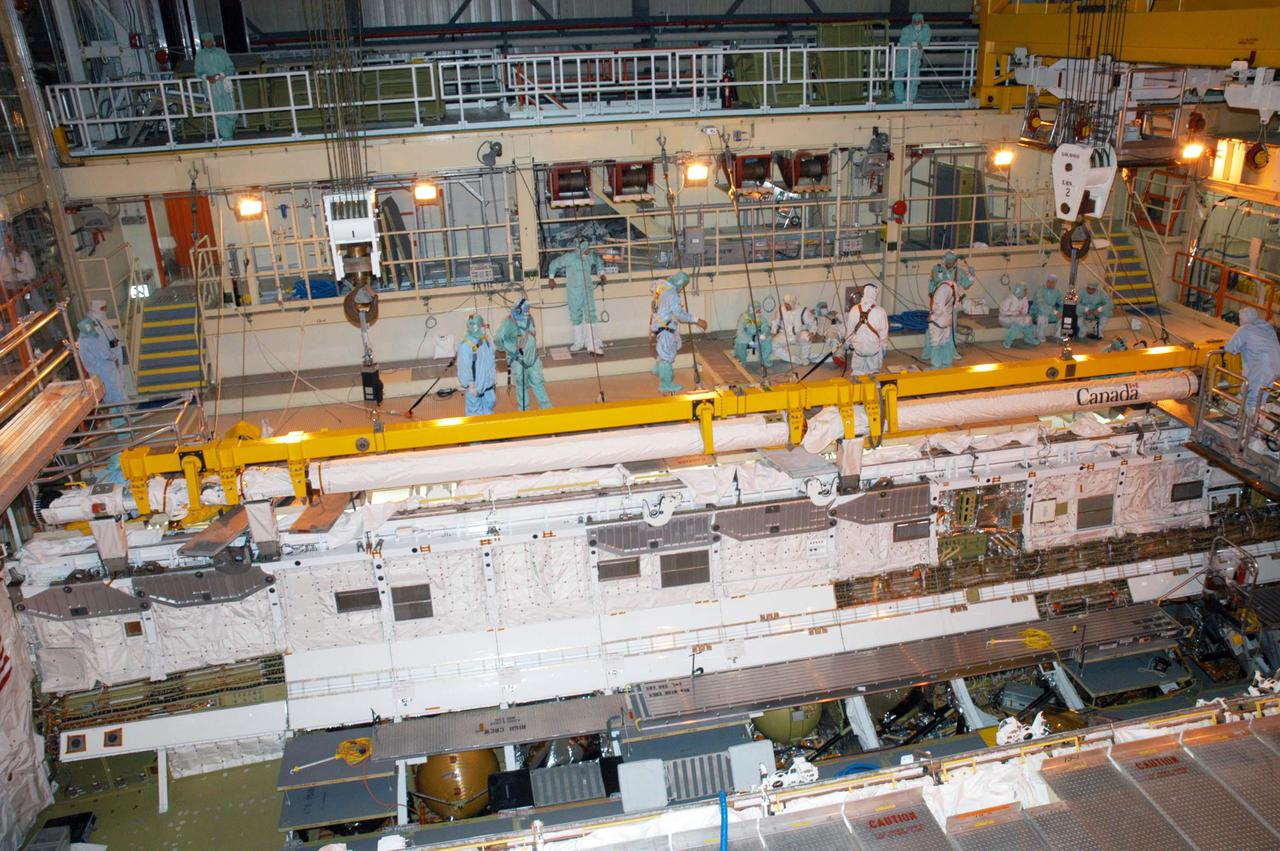
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), also known as the Canadian robotic arm, is lowered toward Discovery’s payload bay for installation. The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm is also serving as the base for the new Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), one of the safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the Shuttle with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of May 2005 on Return to Flight mission STS-114.
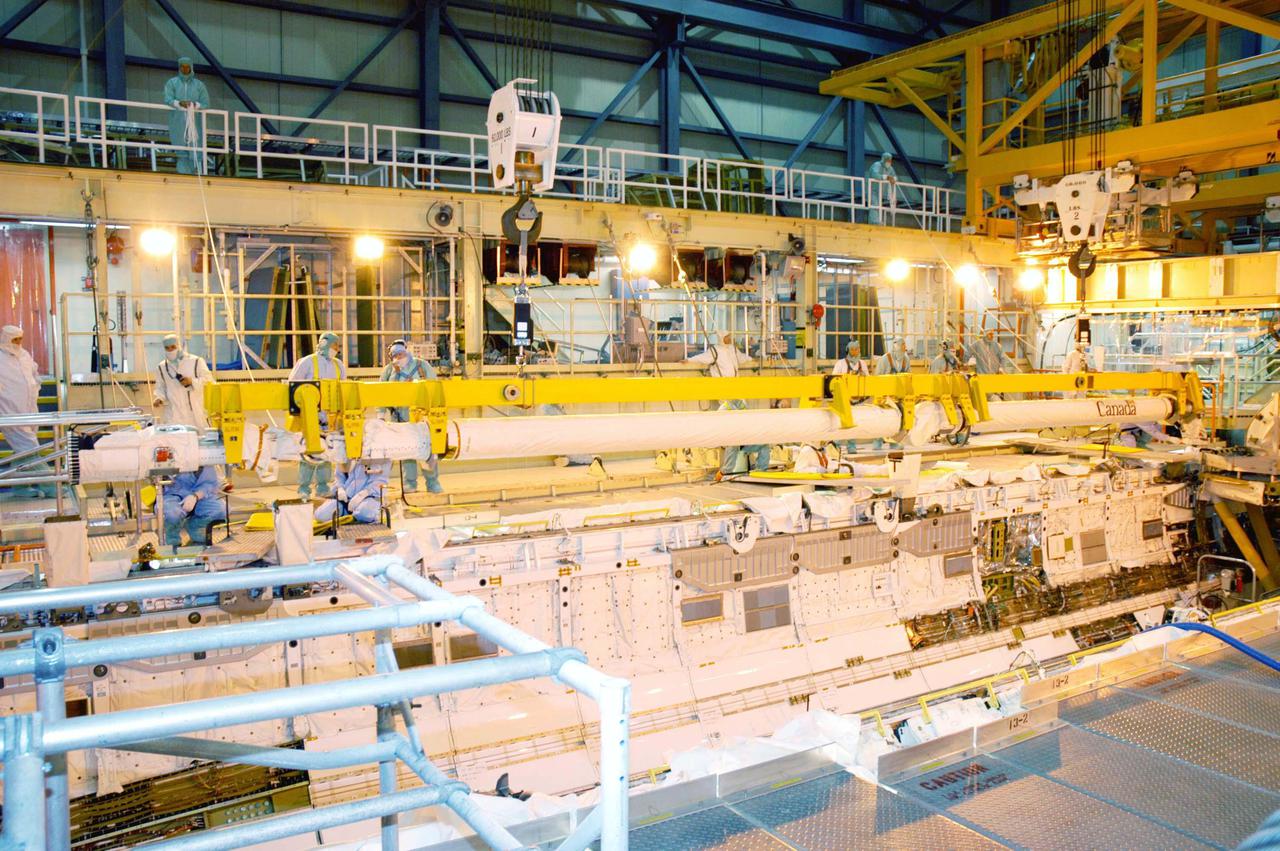

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), also known as the Canadian robotic arm, is moved toward Discovery’s payload bay for installation. The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm is also serving as the base for the new Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), one of the safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the Shuttle with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of May 2005 on Return to Flight mission STS-114.
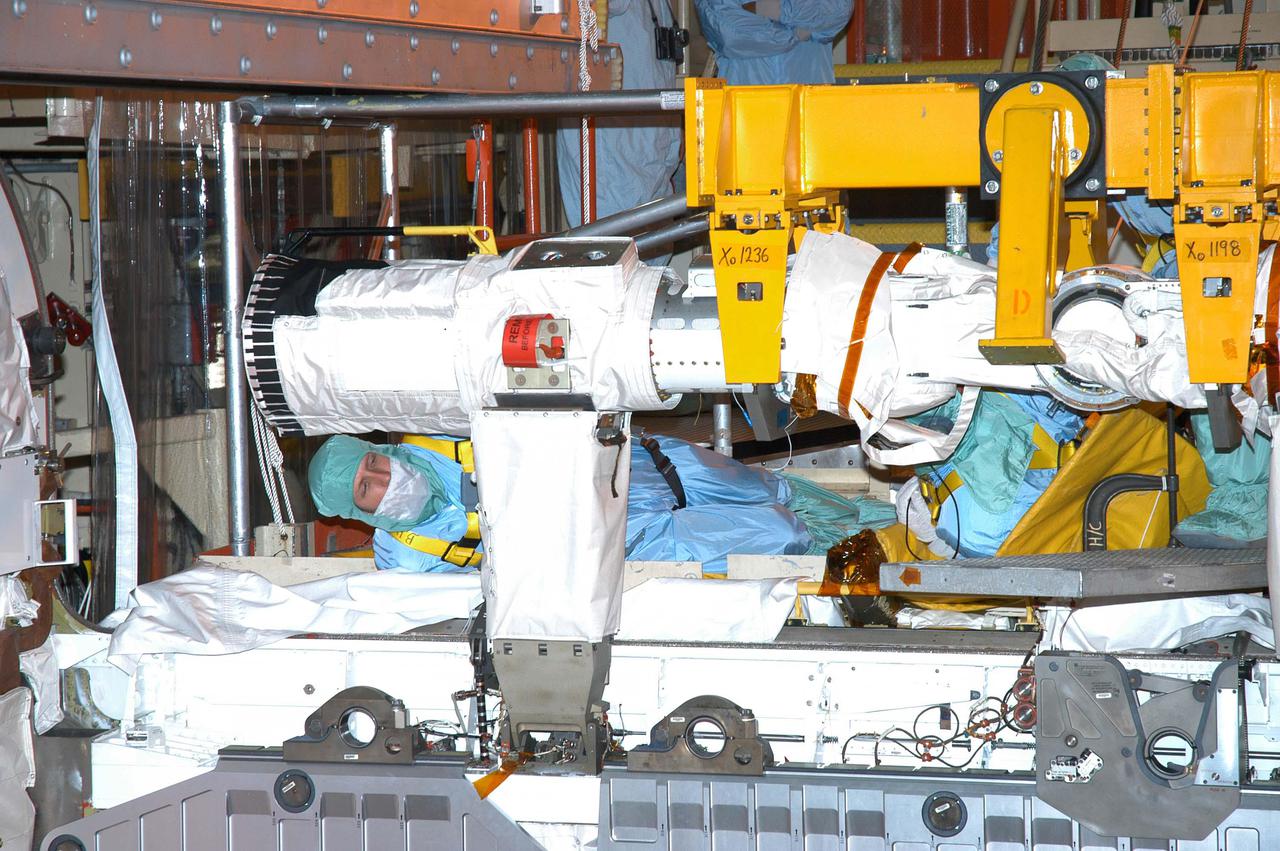

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians in the Orbiter Processing Facility work to install the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), also known as the Canadian robotic arm, in Discovery’s payload bay. The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm is also serving as the base for the new Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), one of the safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the Shuttle with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of May 2005 on Return to Flight mission STS-114.
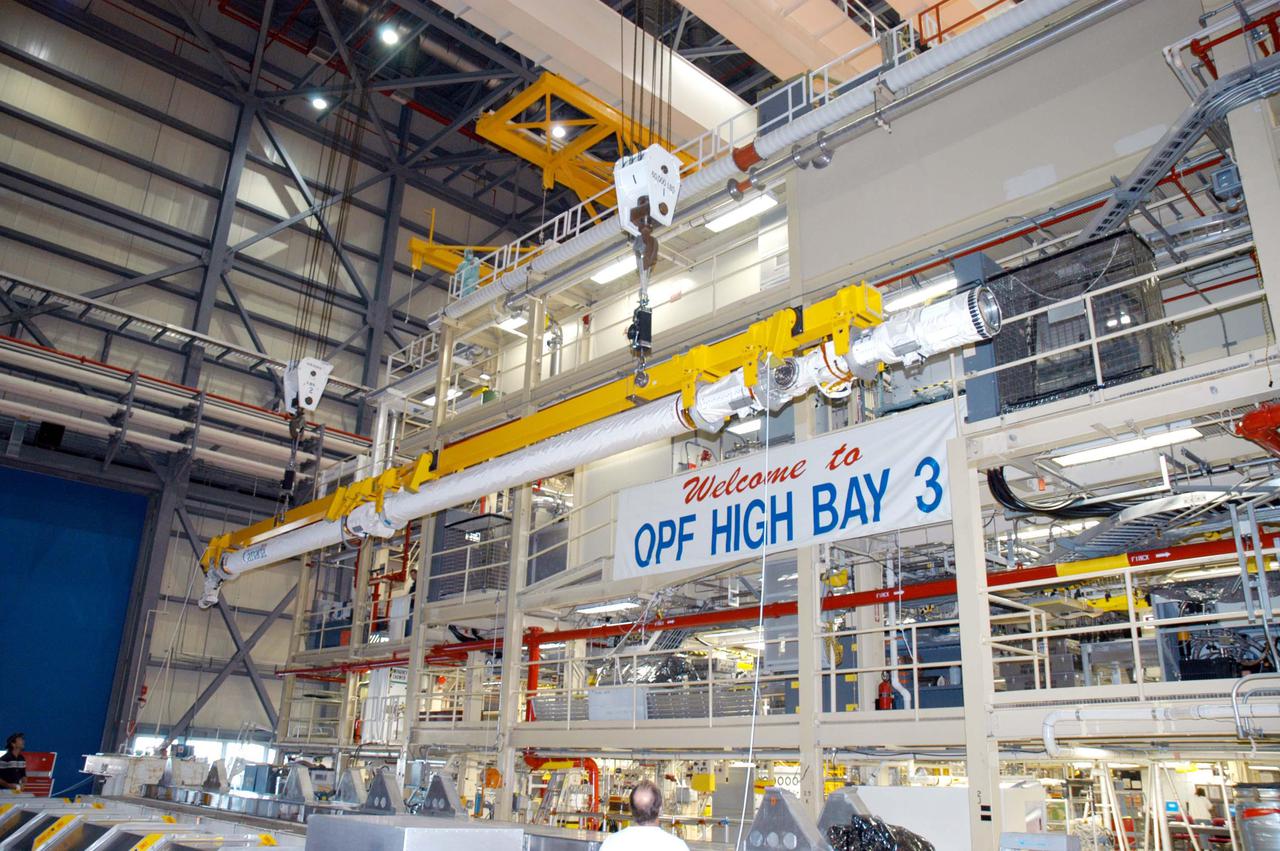

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Remote Manipulator System (RMS), also known as the Canadian robotic arm, is moved in the Orbiter Processing Facility for installation in Discovery’s payload bay. The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm is also serving as the base for the new Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), one of the safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the Shuttle with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of May 2005 on Return to Flight mission STS-114.
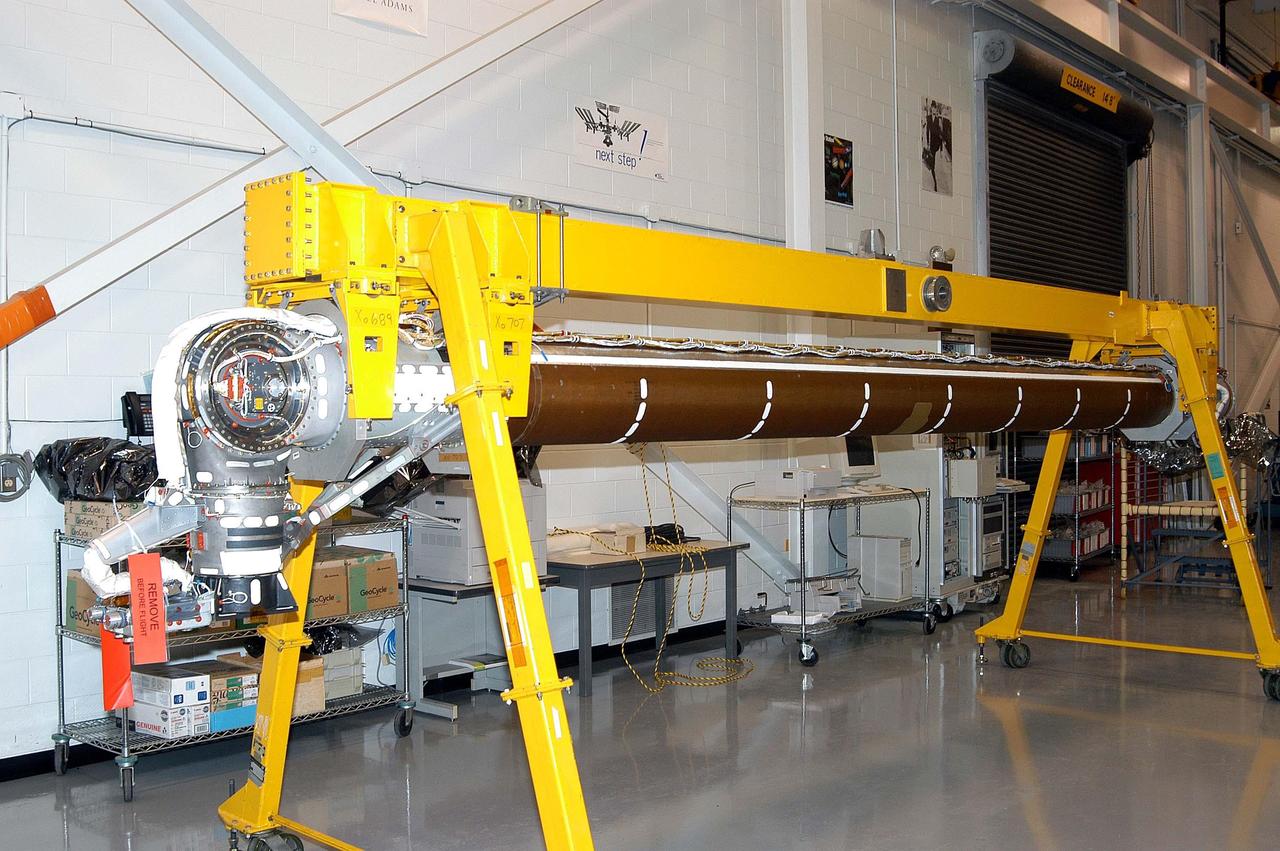

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Remote Manipulator System (RMS), also known as the Canadian robotic arm, for the orbiter Discovery has arrived at KSC’s Vehicle Assembly Building Lab. Seen on the left end is the shoulder pitch joint. The wrist and shoulder joints on the RMS allow the basic structure of the arm to maneuver similar to a human arm. The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm is also serving as the base for the new Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), one of the safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the Shuttle with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of March 2005 on mission STS-114.
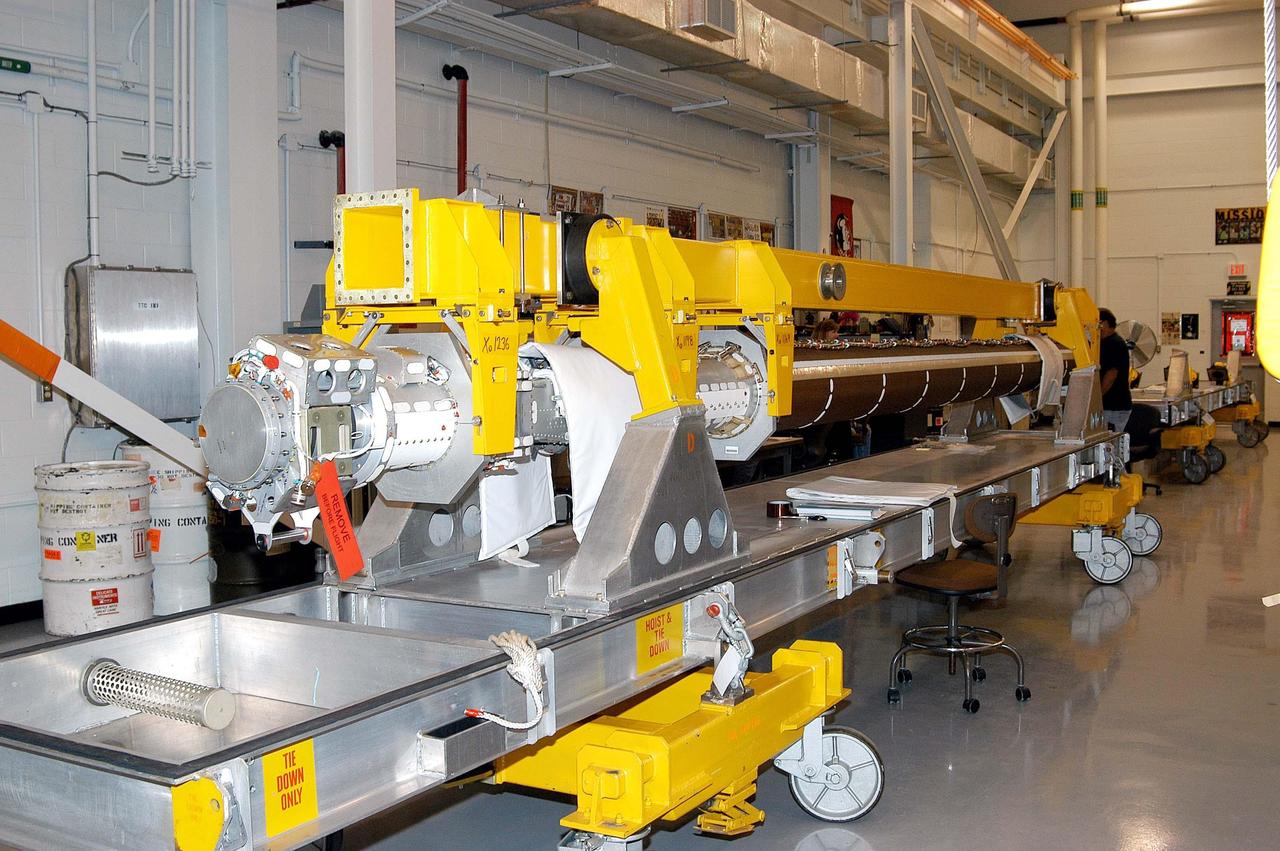

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Remote Manipulator System (RMS), also known as the Canadian robotic arm, for the orbiter Discovery has arrived at KSC’s Vehicle Assembly Building Lab. The RMS is used to deploy and retrieve payloads, provide a mobile extension ladder or foot restraints for crew members during extravehicular activities; and to aid the flight crew members in viewing surfaces of the orbiter or payloads through a television camera on the RMS. The arm is also serving as the base for the new Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), one of the safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the Shuttle with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of March 2005 on mission STS-114.
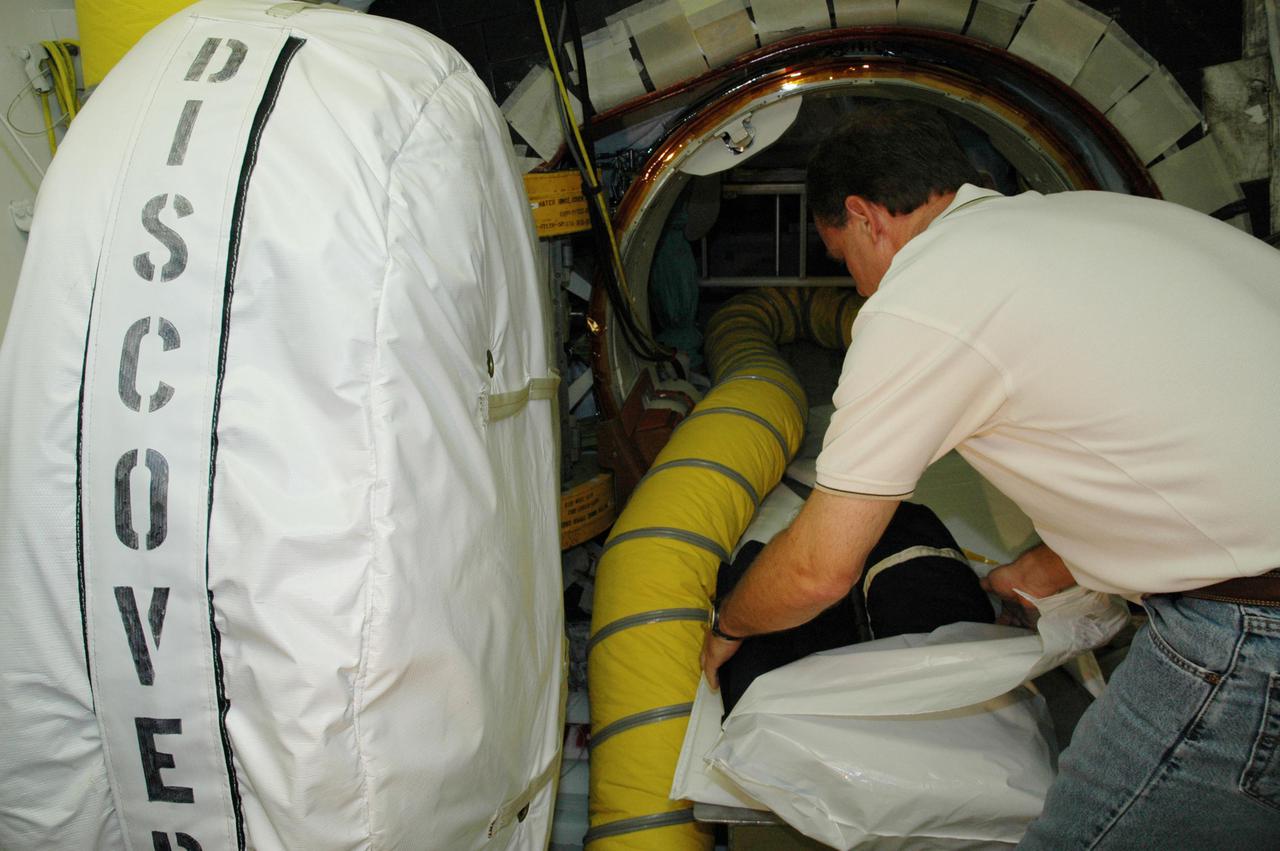

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Pad 39B, United Space Alliance Flight Crew Systems engineer John Biegert passes a sleep restraint to a technician inside Space Shuttle Discovery for installation, a final step in launch preparations. Launch of Discovery on its Return to Flight mission STS-114 is set for July 13, just days away. During its 12-day mission, Discovery’s seven-person crew will test new hardware and techniques to improve Shuttle safety, as well as deliver supplies to the International Space Station. Discovery’s payloads include the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC), and the External Stowage Platform-2 (ESP-2). Raffaello will deliver supplies to the International Space Station including food, clothing and research equipment. The LMC will carry a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope and a tile repair sample box. The ESP-2 is outfitted with replacement parts.
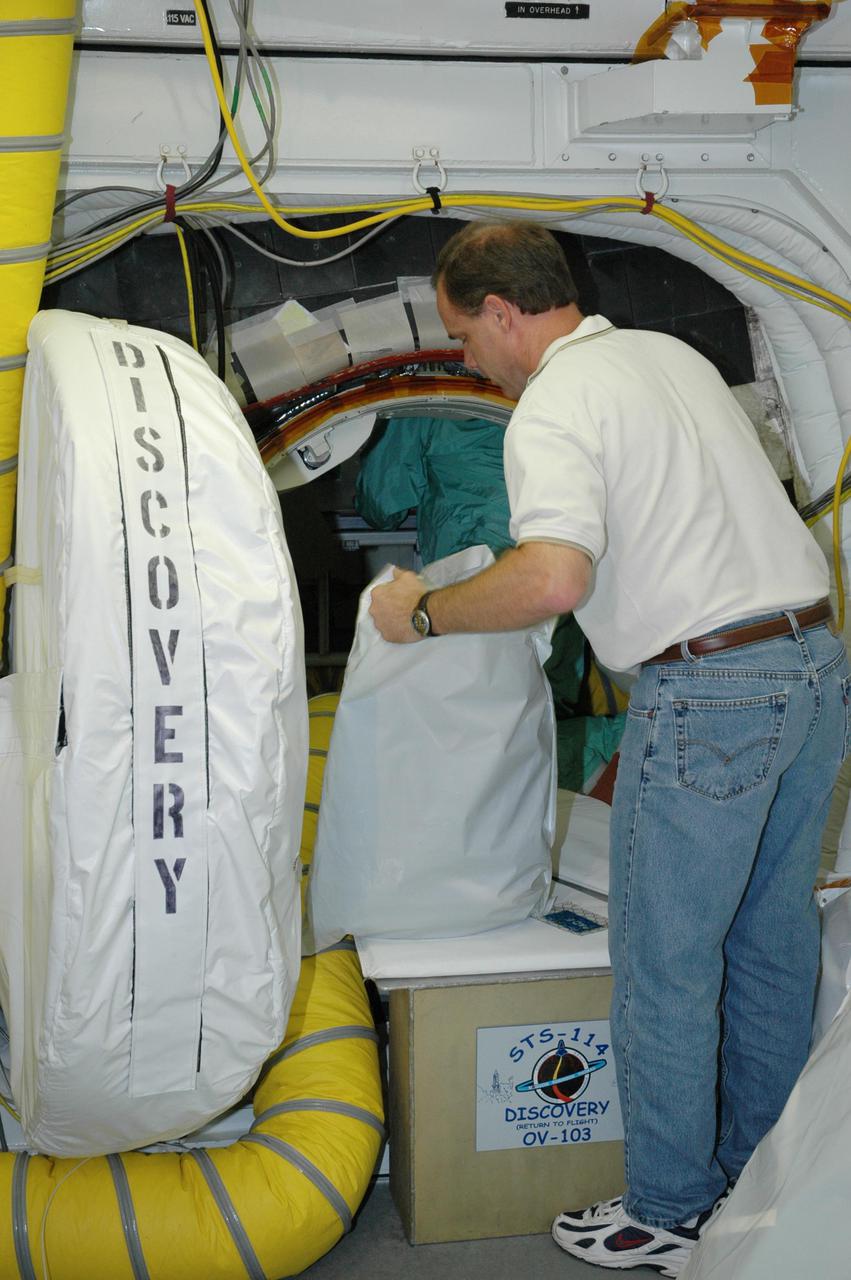

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Pad 39B, United Space Alliance Flight Crew Systems engineer John Biegert uncovers a sleep restraint to be installed inside Space Shuttle Discovery, a final step in launch preparations. Launch of Discovery on its Return to Flight mission STS-114 is set for July 13, just days away. During its 12-day mission, Discovery’s seven-person crew will test new hardware and techniques to improve Shuttle safety, as well as deliver supplies to the International Space Station. Discovery’s payloads include the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC), and the External Stowage Platform-2 (ESP-2). Raffaello will deliver supplies to the International Space Station including food, clothing and research equipment. The LMC will carry a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope and a tile repair sample box. The ESP-2 is outfitted with replacement parts.
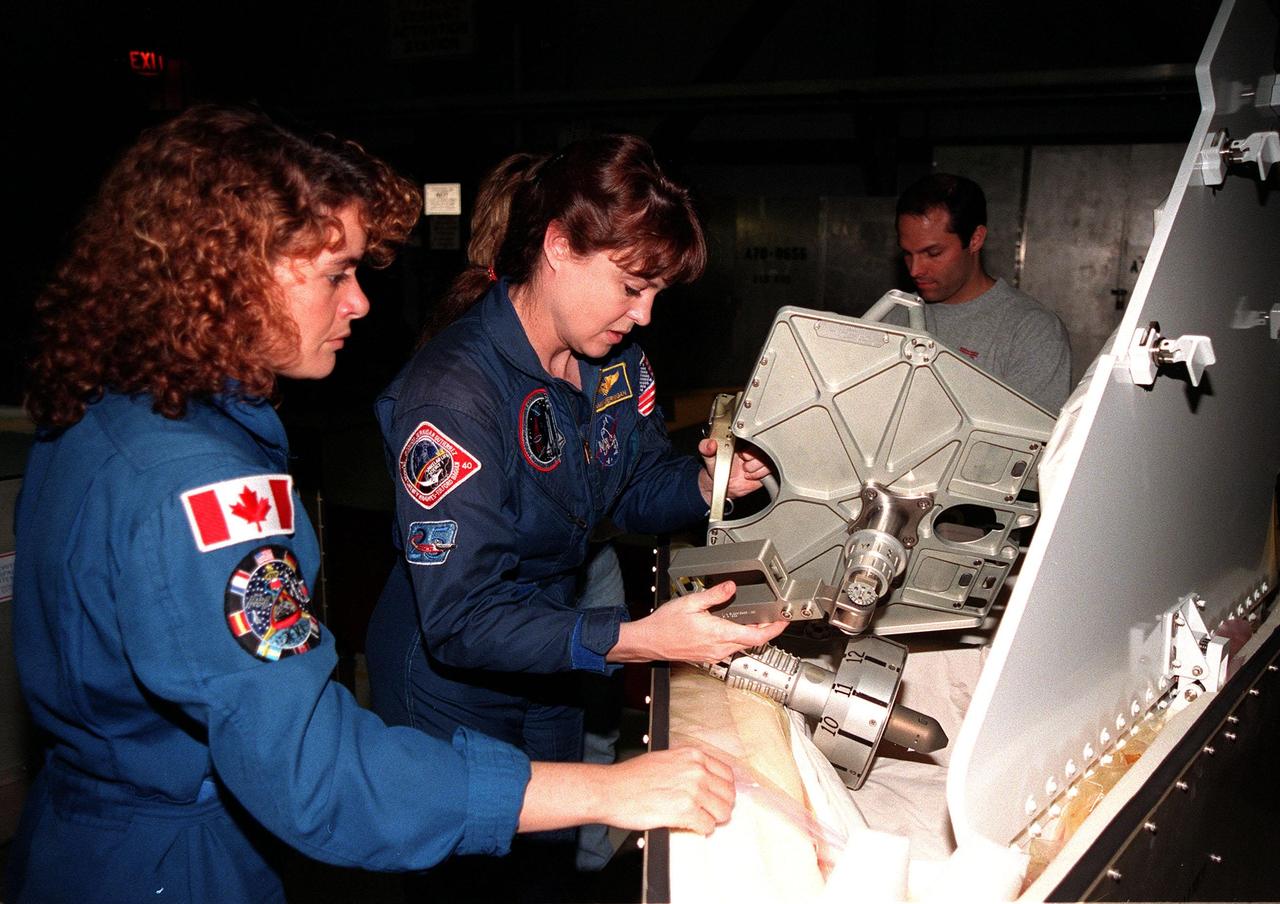

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-96 Mission Specialists (left) Julie Payette, with the Canadian Space Agency, and Tamara Jernigan, Ph.D., look over the foot restraint used during space walks. The STS-96 crew is at KSC to take part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test. The other crew members are Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Rick Douglas Husband, and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa (Ph.D), Daniel Barry (M.D., Ph.D.), and Valery Ivanovich Tokarev, who represents the Russian Space Agency. The primary payload of STS-96 is the SPACEHAB Double Module. In addition, the Space Shuttle will carry unpressurized cargo such as the external Russian cargo crane known as STRELA; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), which is a logistics items carrier; and an ORU Transfer Device (OTD), a U.S.-built crane that will be stowed on the station for use during future ISS assembly missions. These cargo items will be stowed on the International Cargo Carrier, fitted inside the payload bay behind the SPACEHAB module. STS-96 is targeted for launch on May 24 from Launch Pad 39B
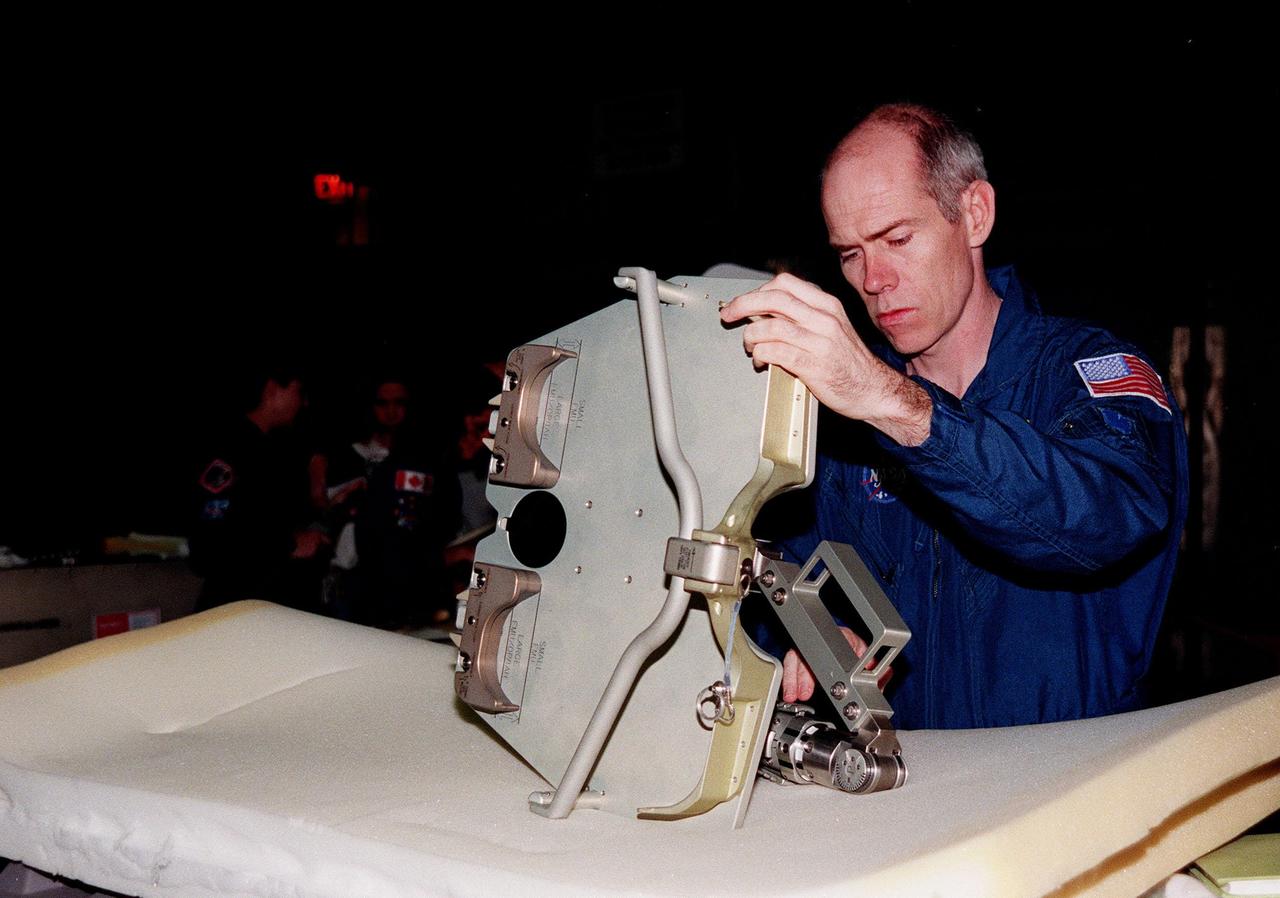

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-96 Mission Specialist Daniel Barry, M.D., Ph.D., looks at one of the foot restraints used for extravehicular activity, or space walks. The STS-96 crew is at KSC to take part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test. The other crew members are Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Rick Douglas Husband, and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa (Ph.D.), Tamara E. Jernigan (Ph.D.), Julie Payette and Valery Ivanovich Tokarev. Payette represents the Canadian Space Agency and Tokarev the Russian Space Agency. The primary payload of STS-96 is the SPACEHAB Double Module. In addition, the Space Shuttle will carry unpressurized cargo such as the external Russian cargo crane known as STRELA; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), which is a logistics items carrier; and an ORU Transfer Device (OTD), a U.S.-built crane that will be stowed on the station for use during future ISS assembly missions. These cargo items will be stowed on the International Cargo Carrier, fitted inside the payload bay behind the SPACEHAB module. STS-96 is targeted for launch on May 24 from Launch Pad 39B
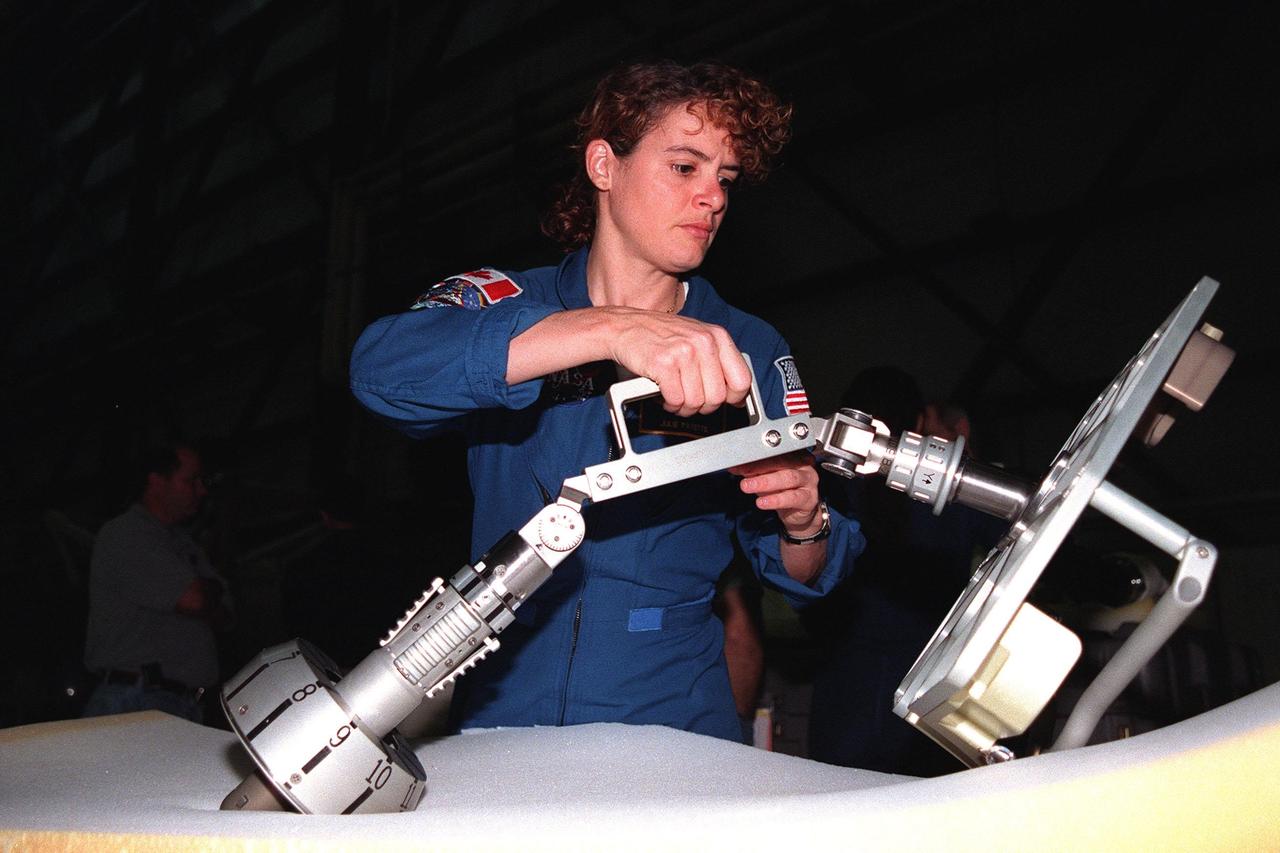

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-96 Mission Specialist Julie Payette, with the Canadian Space Agency, maneuvers a foot restraint used during space walks. The STS-96 crew is at KSC to take part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test. The other crew members are Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Rick Douglas Husband and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa (Ph.D.), Tamara E. Jernigan (Ph.D.), Daniel Barry (M.D., Ph.D.), and Valery Ivanovich Tokarev, who represents the Russian Space Agency. The primary payload of STS-96 is the SPACEHAB Double Module. In addition, the Space Shuttle will carry unpressurized cargo such as the external Russian cargo crane known as STRELA; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), which is a logistics items carrier; and an ORU Transfer Device (OTD), a U.S.-built crane that will be stowed on the station for use during future ISS assembly missions. These cargo items will be stowed on the International Cargo Carrier, fitted inside the payload bay behind the SPACEHAB module. STS-96 is targeted for launch on May 24 from Launch Pad 39B