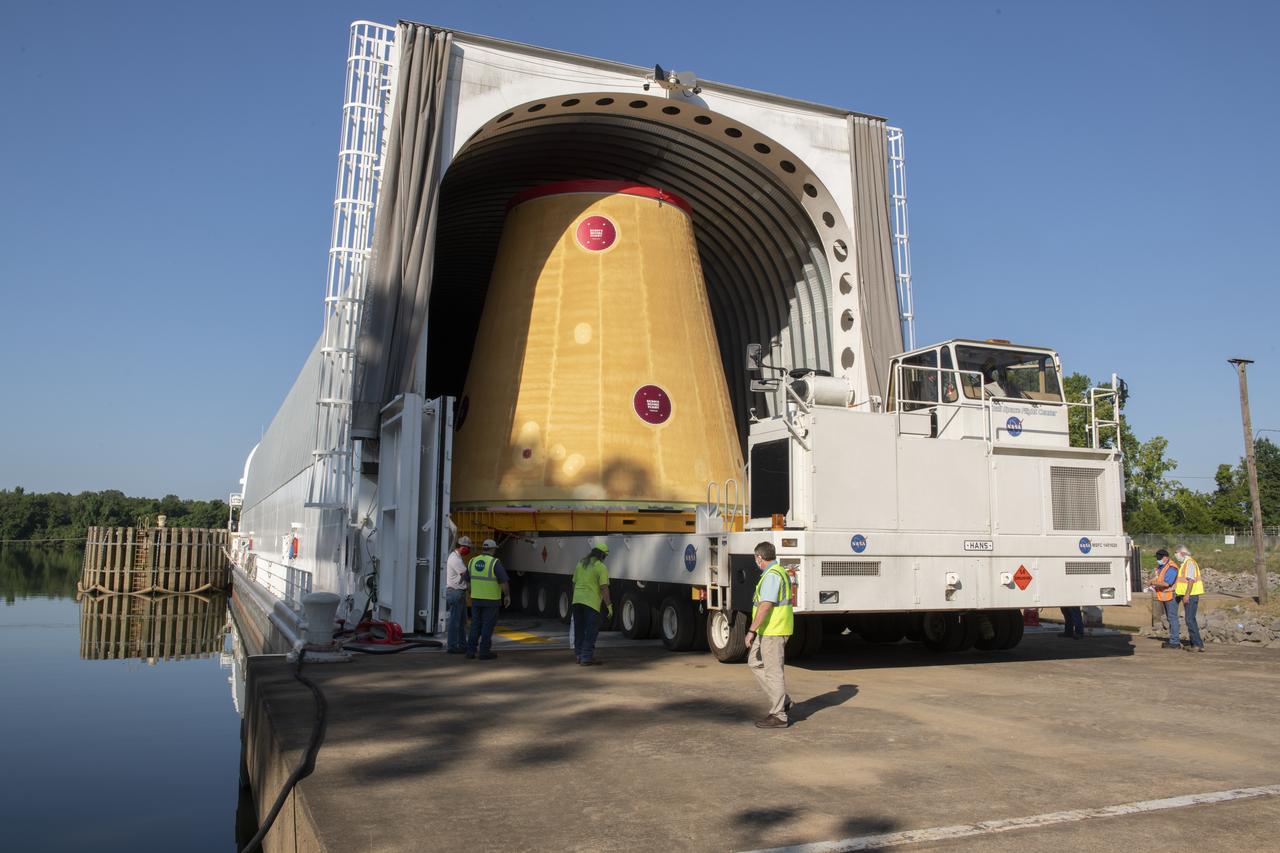

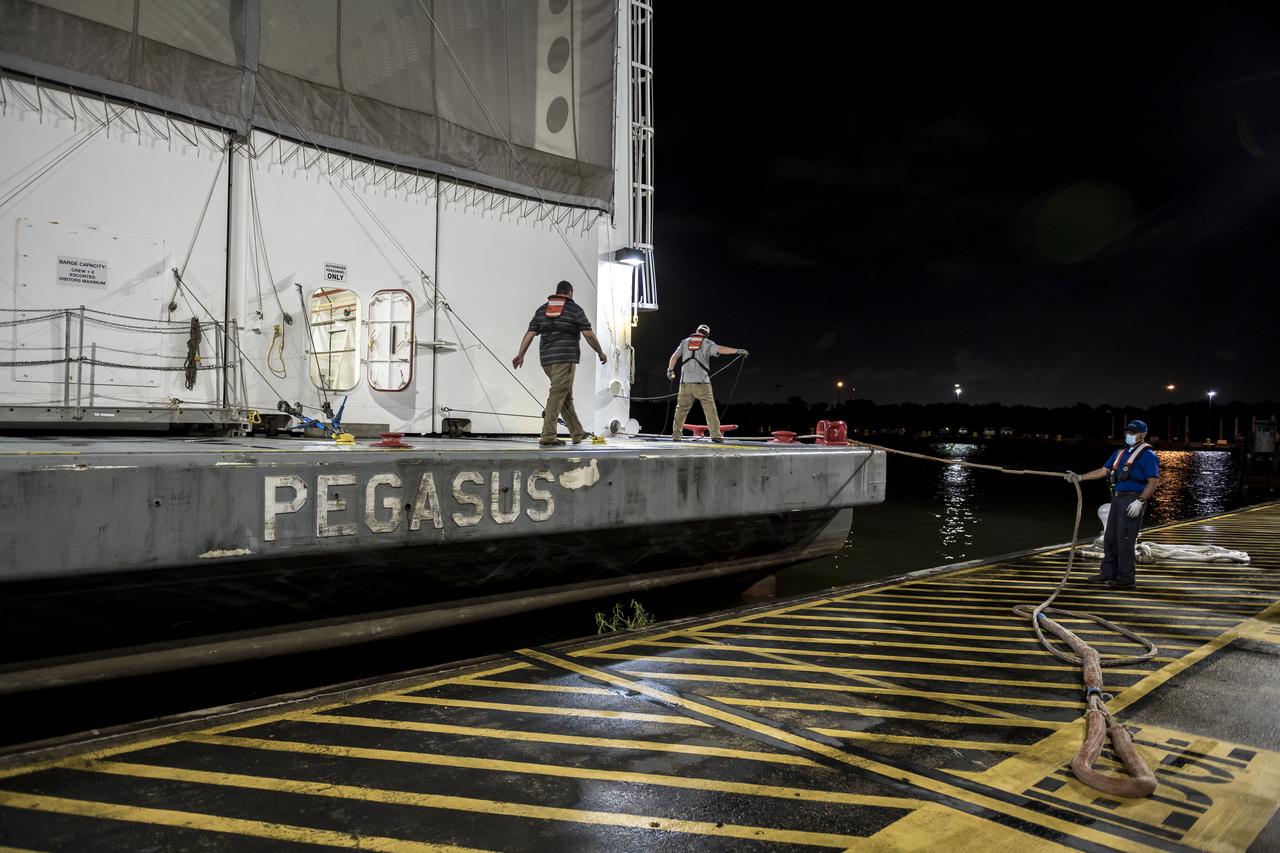
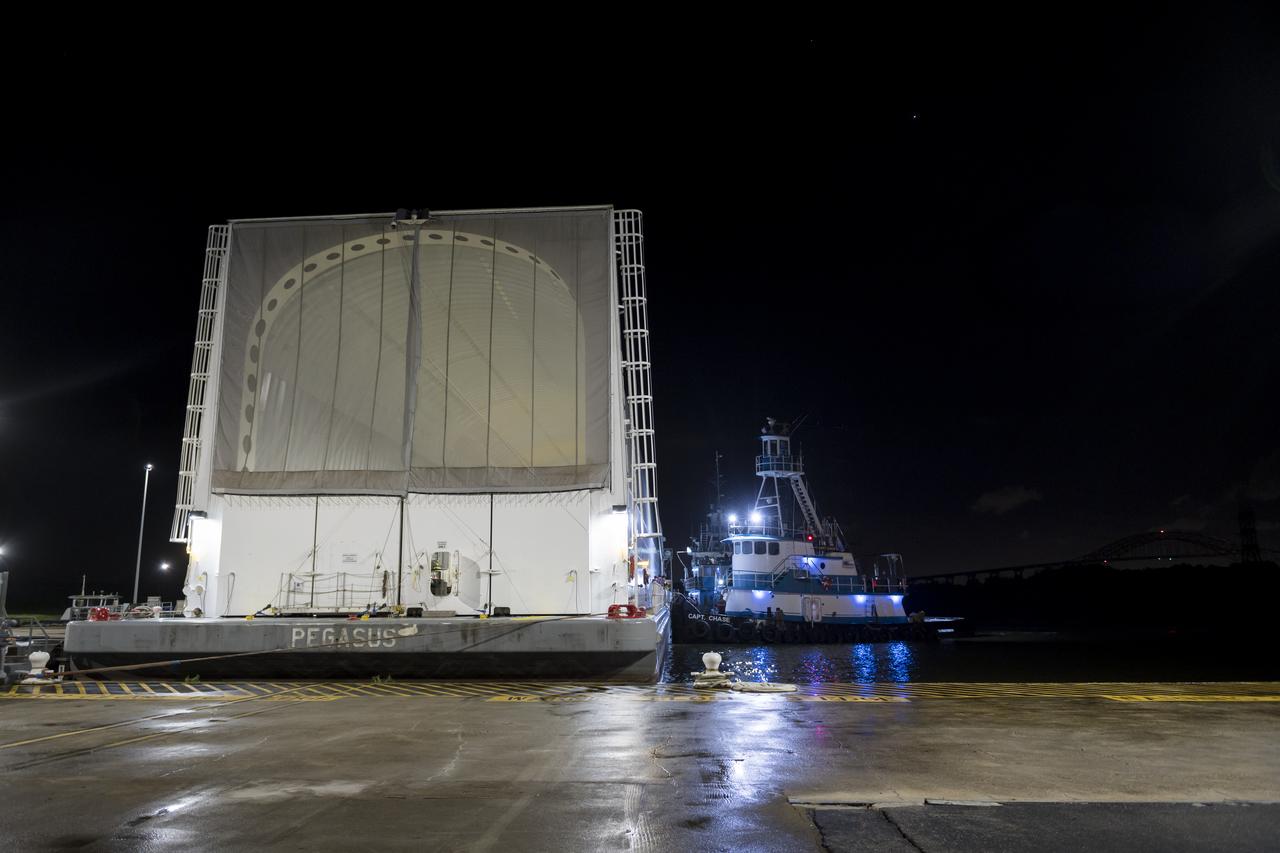
The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.

The move team loads the launch vehicle stage adapter, part of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, on NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 17. The launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage, is being shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for Artemis I launch preparations. This is the final piece of Artemis I SLS rocket hardware built at Marshall to be delivered to Kennedy. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for a new generation of deep space exploration.
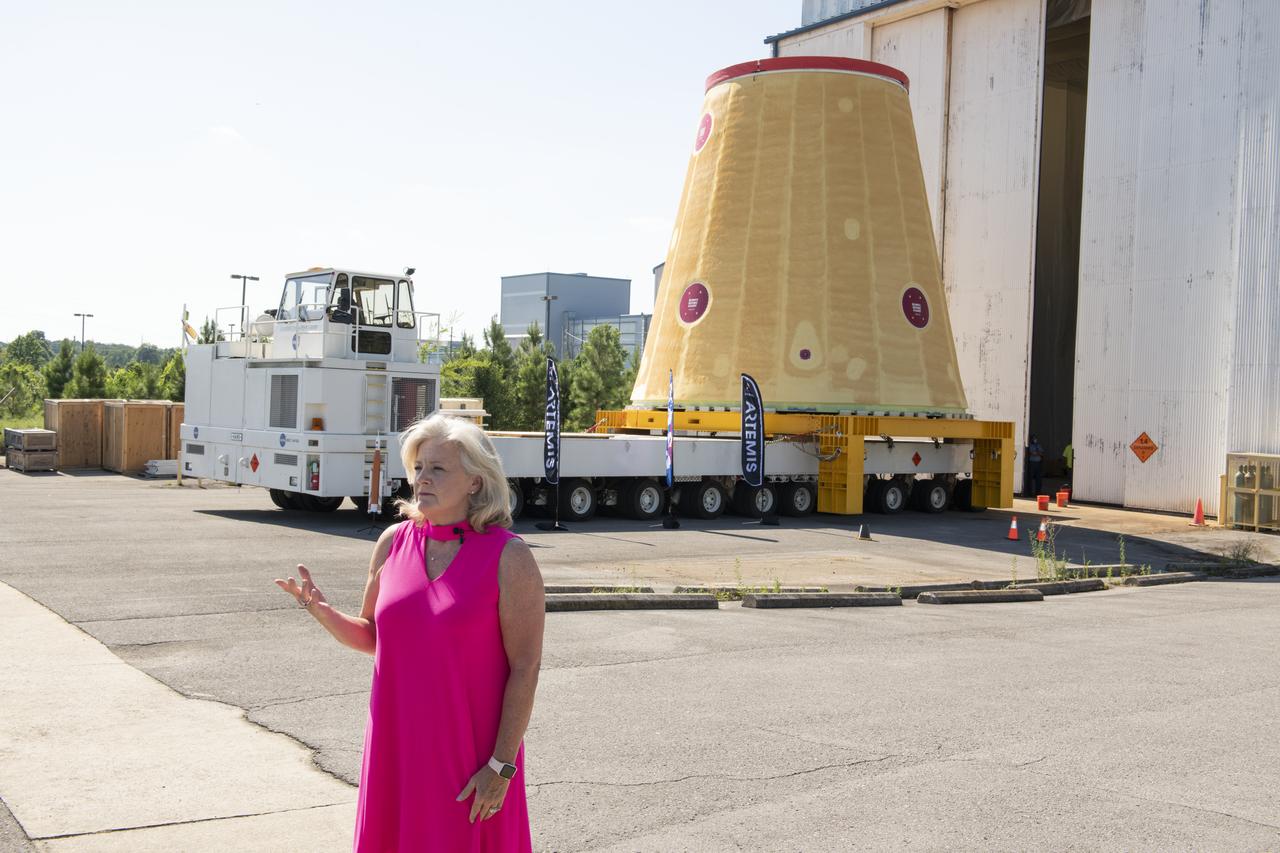

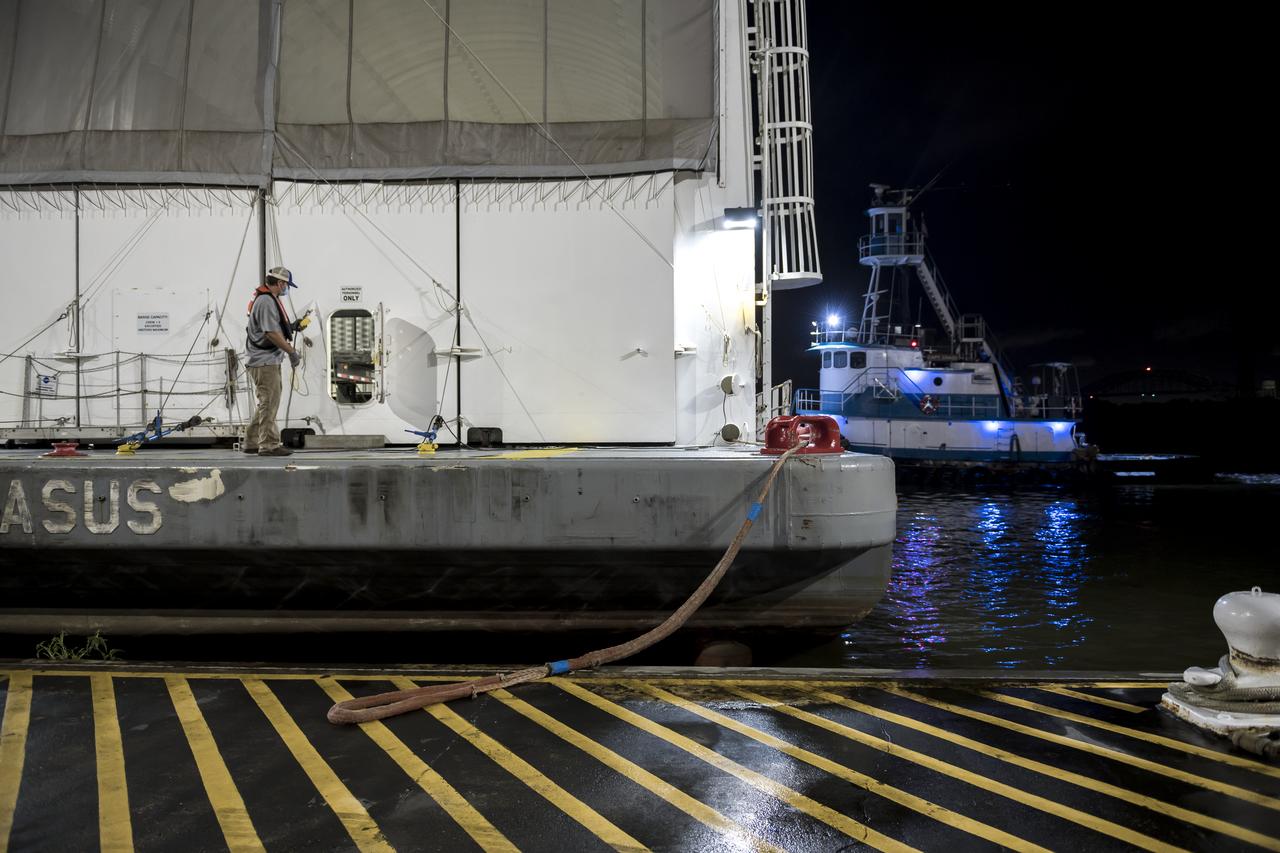
Jody Singer, director of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, joins local government officials and others as the Marshall move team prepares to transport the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Huntsville-based Teledyne Brown Engineering built the launch vehicle stage adapter at a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility at Marshall. Teledyne officials joined Singer to see the adapter one last time before it heads to the barge. This is the last piece of Marshall-built SLS rocket hardware set for delivery to Kennedy in preparation of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. A move team led by Marshall’s Center Operations will transport the adapter from the manufacturing facility to NASA’s Pegasus barge. The barge will take the adapter to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for assembly and launch. Other parts of the Artemis I SLS rocket that were manufactured in Alabama include the Orion stage adapter built by Marshall teams and the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, which was built by Boeing and United Launch Alliance in Decatur, Alabama and will provide the power to send Orion to the Moon.

Jody Singer, director of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, joins local government officials and others as the Marshall move team prepares to transport the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Huntsville-based Teledyne Brown Engineering built the launch vehicle stage adapter at a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility at Marshall. Teledyne officials joined Singer to see the adapter one last time before it heads to the barge. This is the last piece of Marshall-built SLS rocket hardware set for delivery to Kennedy in preparation of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. A move team led by Marshall’s Center Operations will transport the adapter from the manufacturing facility to NASA’s Pegasus barge. The barge will take the adapter to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for assembly and launch. Other parts of the Artemis I SLS rocket that were manufactured in Alabama include the Orion stage adapter built by Marshall teams and the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, which was built by Boeing and United Launch Alliance in Decatur, Alabama and will provide the power to send Orion to the Moon.

Jody Singer, director of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, joins local government officials and others as the Marshall move team prepares to transport the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Huntsville-based Teledyne Brown Engineering built the launch vehicle stage adapter at a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility at Marshall. Teledyne officials joined Singer to see the adapter one last time before it heads to the barge. This is the last piece of Marshall-built SLS rocket hardware set for delivery to Kennedy in preparation of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. A move team led by Marshall’s Center Operations will transport the adapter from the manufacturing facility to NASA’s Pegasus barge. The barge will take the adapter to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for assembly and launch. Other parts of the Artemis I SLS rocket that were manufactured in Alabama include the Orion stage adapter built by Marshall teams and the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, which was built by Boeing and United Launch Alliance in Decatur, Alabama and will provide the power to send Orion to the Moon.

Jody Singer, director of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, joins local government officials and others as the Marshall move team prepares to transport the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Huntsville-based Teledyne Brown Engineering built the launch vehicle stage adapter at a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility at Marshall. Teledyne officials joined Singer to see the adapter one last time before it heads to the barge. This is the last piece of Marshall-built SLS rocket hardware set for delivery to Kennedy in preparation of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. A move team led by Marshall’s Center Operations will transport the adapter from the manufacturing facility to NASA’s Pegasus barge. The barge will take the adapter to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for assembly and launch. Other parts of the Artemis I SLS rocket that were manufactured in Alabama include the Orion stage adapter built by Marshall teams and the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, which was built by Boeing and United Launch Alliance in Decatur, Alabama and will provide the power to send Orion to the Moon.

Jody Singer, director of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, joins local government officials and others as the Marshall move team prepares to transport the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Huntsville-based Teledyne Brown Engineering built the launch vehicle stage adapter at a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility at Marshall. Teledyne officials joined Singer to see the adapter one last time before it heads to the barge. This is the last piece of Marshall-built SLS rocket hardware set for delivery to Kennedy in preparation of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. A move team led by Marshall’s Center Operations will transport the adapter from the manufacturing facility to NASA’s Pegasus barge. The barge will take the adapter to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for assembly and launch. Other parts of the Artemis I SLS rocket that were manufactured in Alabama include the Orion stage adapter built by Marshall teams and the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, which was built by Boeing and United Launch Alliance in Decatur, Alabama and will provide the power to send Orion to the Moon.
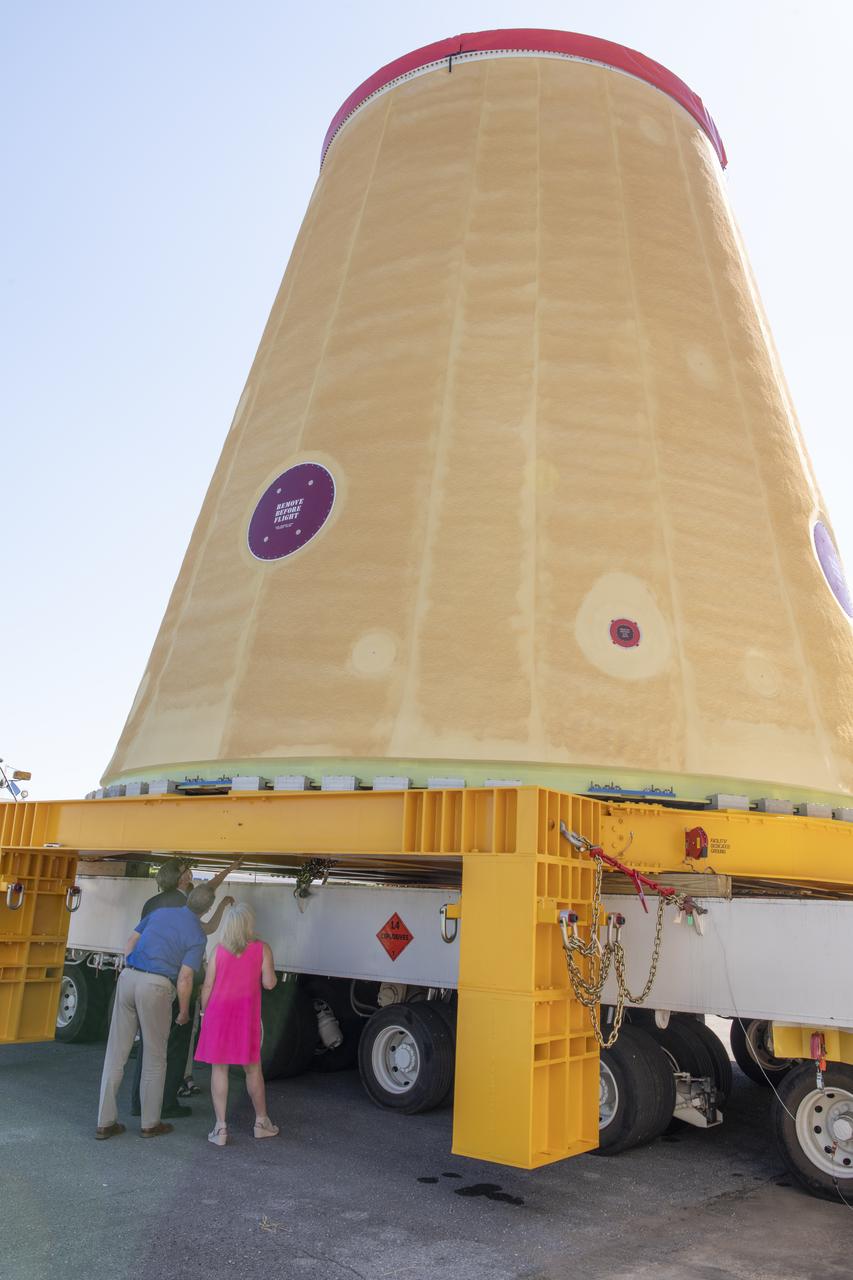

Jody Singer, director of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, joins local government officials and others as the Marshall move team prepares to transport the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Huntsville-based Teledyne Brown Engineering built the launch vehicle stage adapter at a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility at Marshall. Teledyne officials joined Singer to see the adapter one last time before it heads to the barge. This is the last piece of Marshall-built SLS rocket hardware set for delivery to Kennedy in preparation of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. A move team led by Marshall’s Center Operations will transport the adapter from the manufacturing facility to NASA’s Pegasus barge. The barge will take the adapter to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for assembly and launch. Other parts of the Artemis I SLS rocket that were manufactured in Alabama include the Orion stage adapter built by Marshall teams and the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, which was built by Boeing and United Launch Alliance in Decatur, Alabama and will provide the power to send Orion to the Moon.
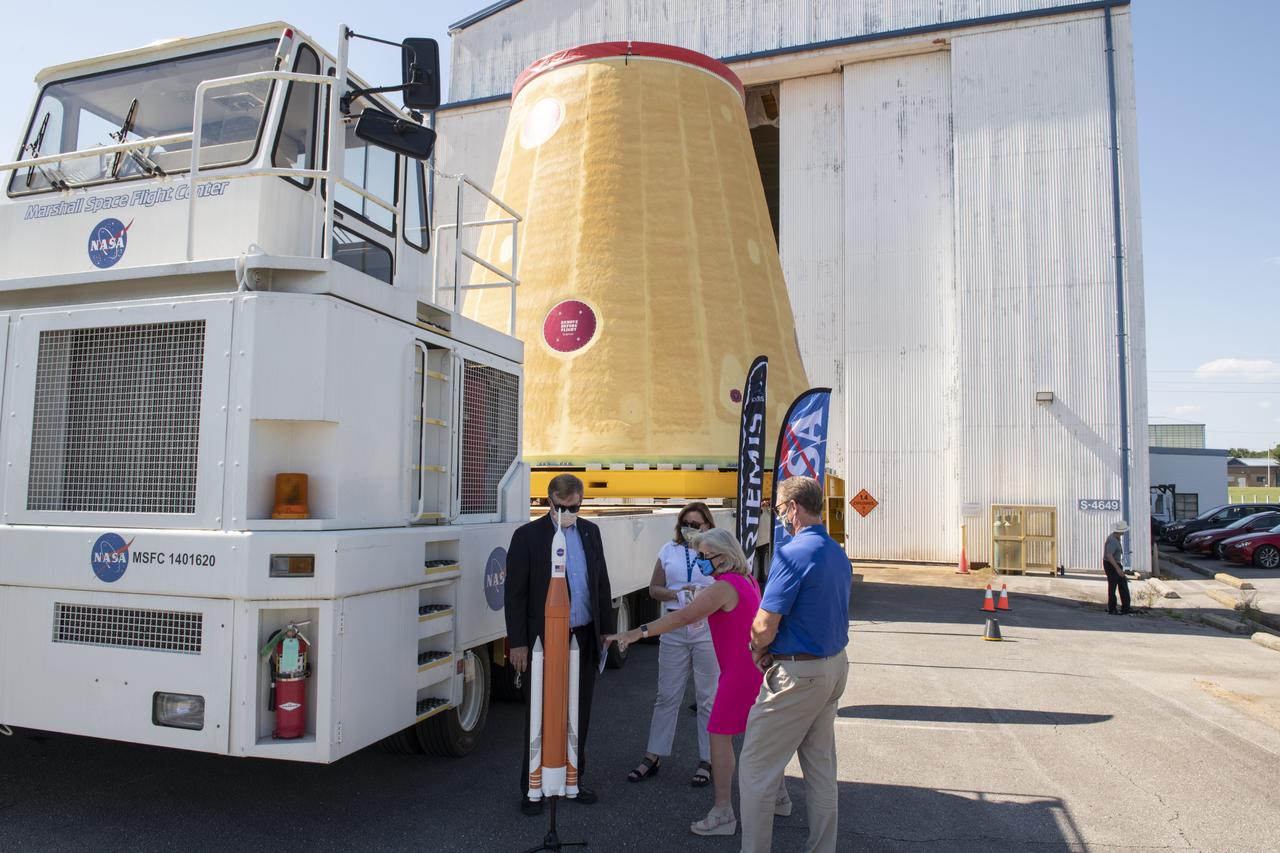

Jody Singer, director of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, joins local government officials and others as the Marshall move team prepares to transport the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Huntsville-based Teledyne Brown Engineering built the launch vehicle stage adapter at a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility at Marshall. Teledyne officials joined Singer to see the adapter one last time before it heads to the barge. This is the last piece of Marshall-built SLS rocket hardware set for delivery to Kennedy in preparation of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. A move team led by Marshall’s Center Operations will transport the adapter from the manufacturing facility to NASA’s Pegasus barge. The barge will take the adapter to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for assembly and launch. Other parts of the Artemis I SLS rocket that were manufactured in Alabama include the Orion stage adapter built by Marshall teams and the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, which was built by Boeing and United Launch Alliance in Decatur, Alabama and will provide the power to send Orion to the Moon.

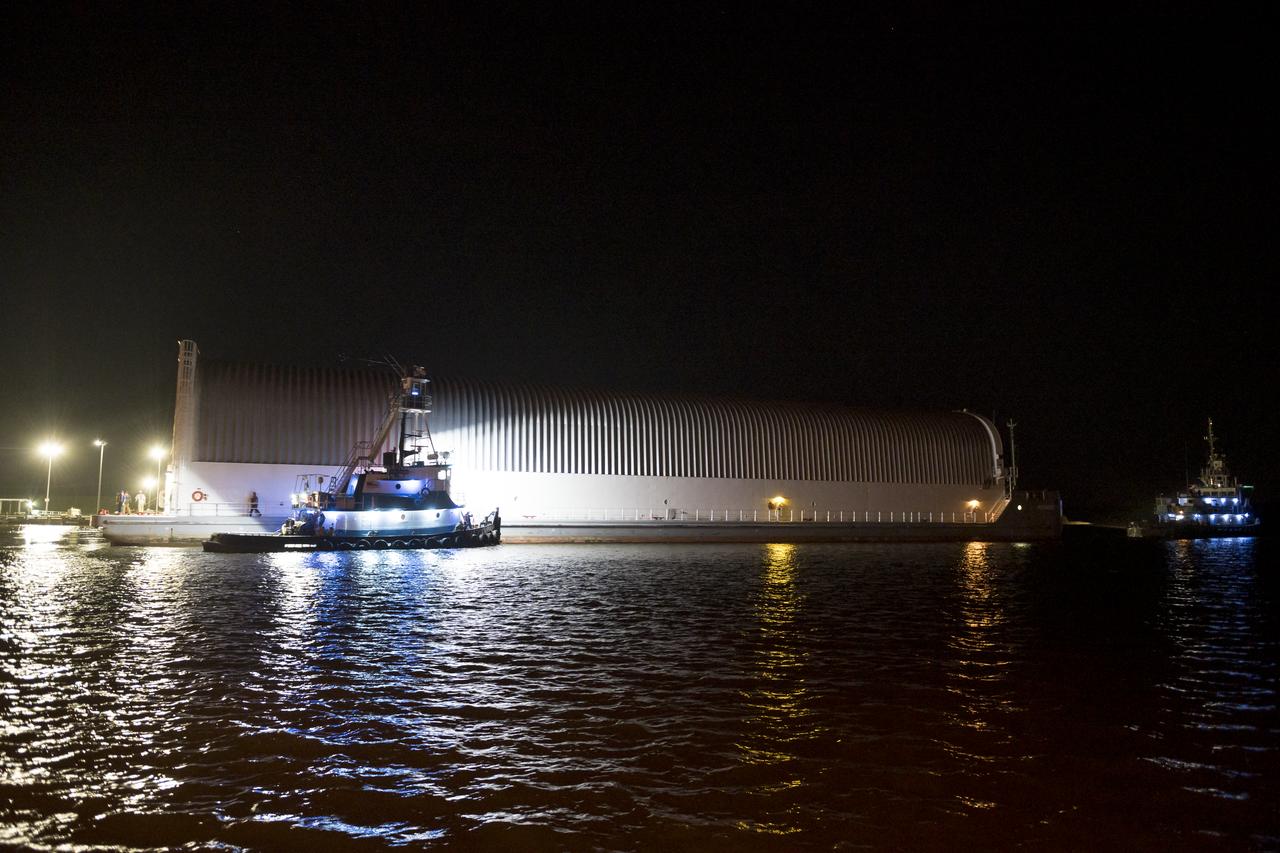
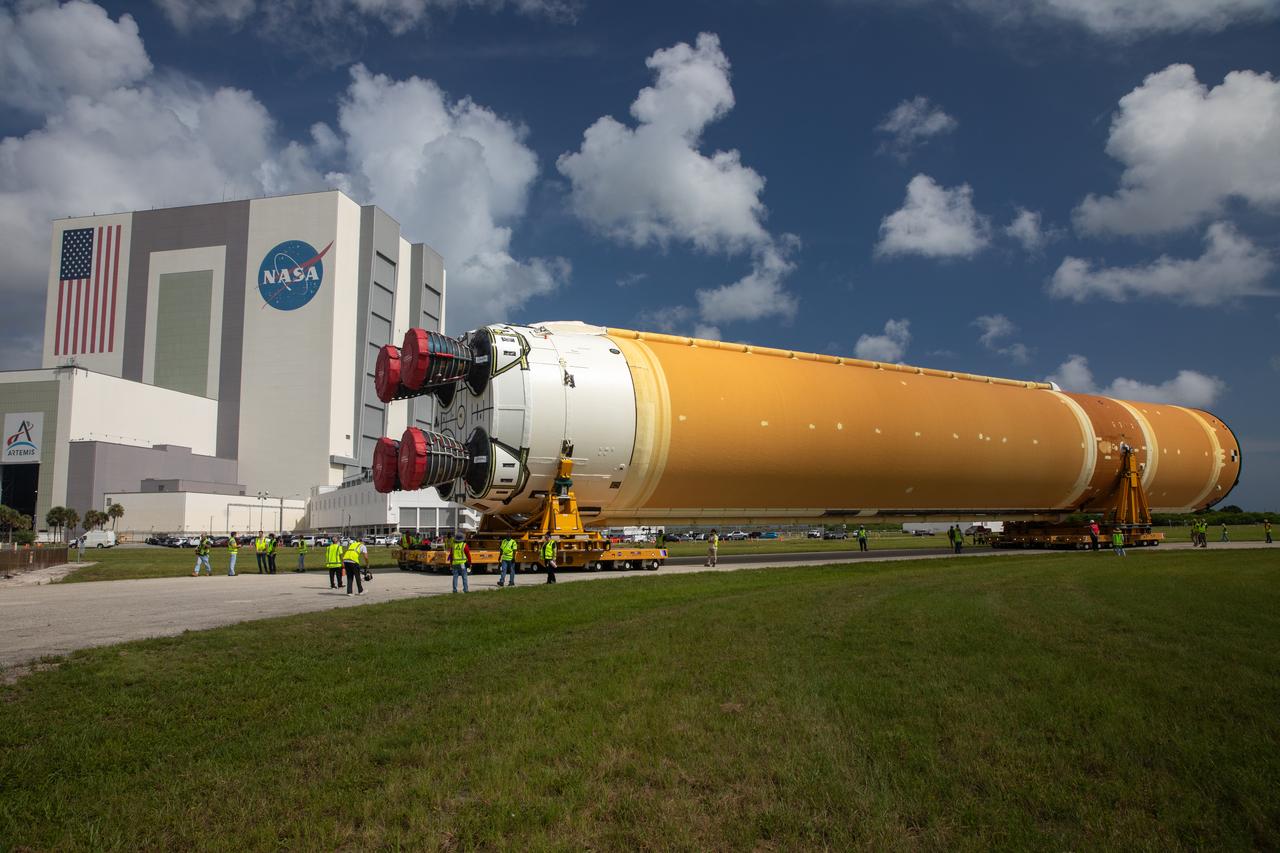
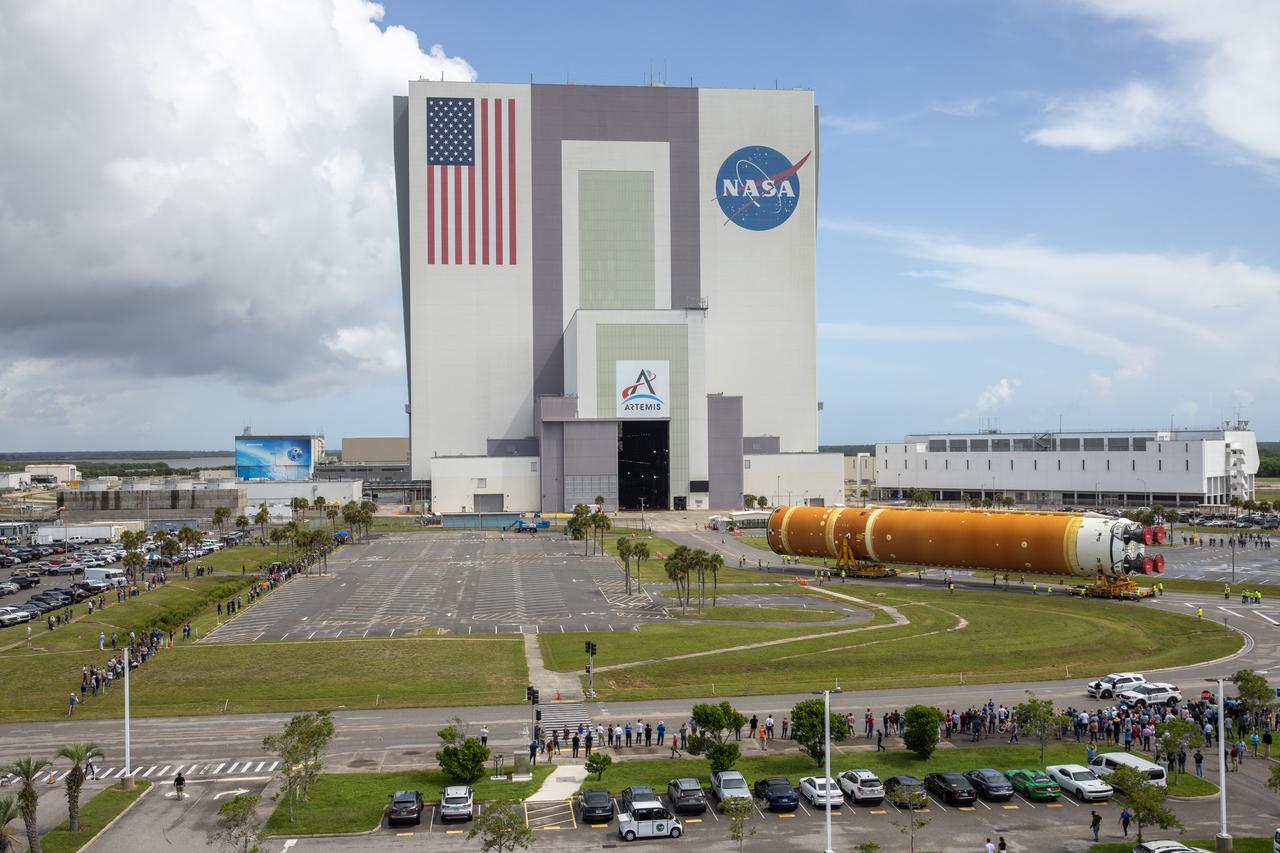
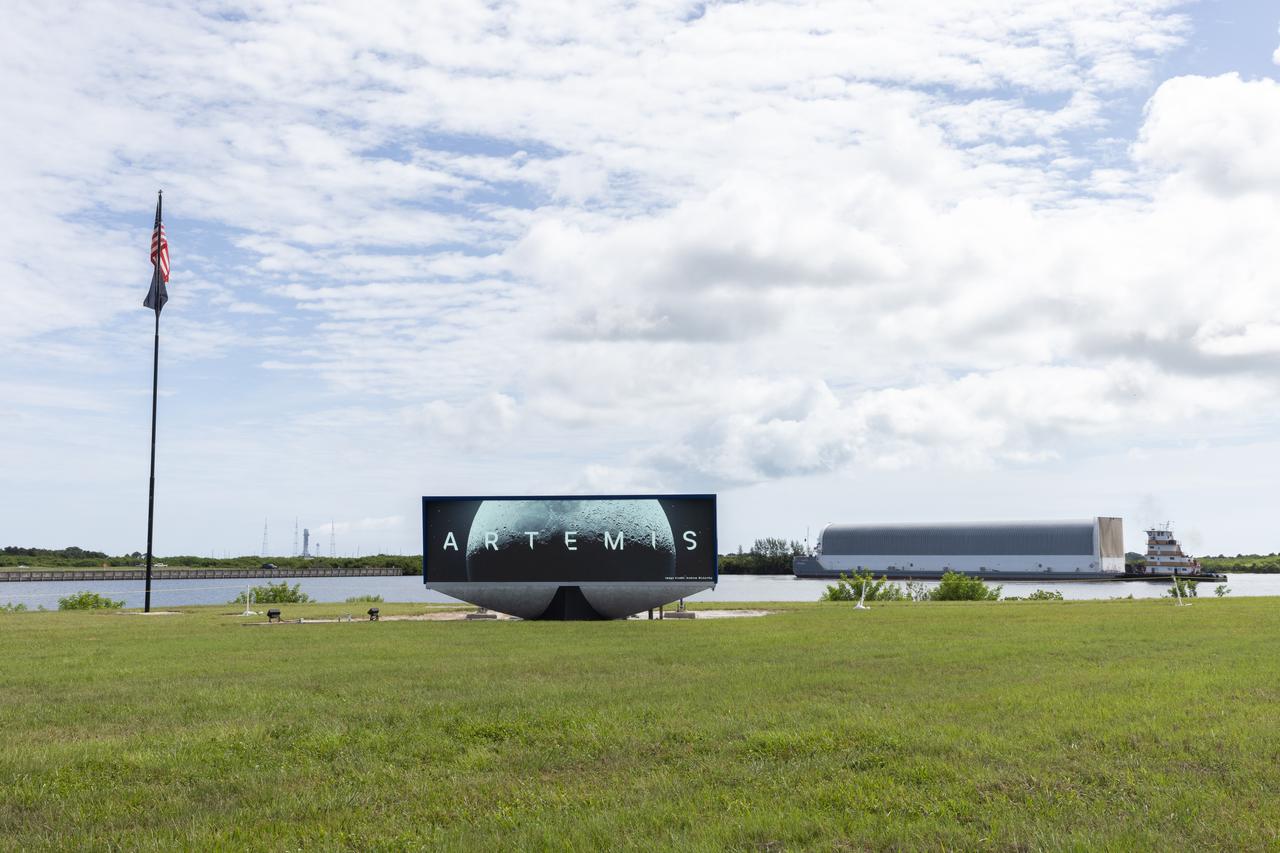
These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
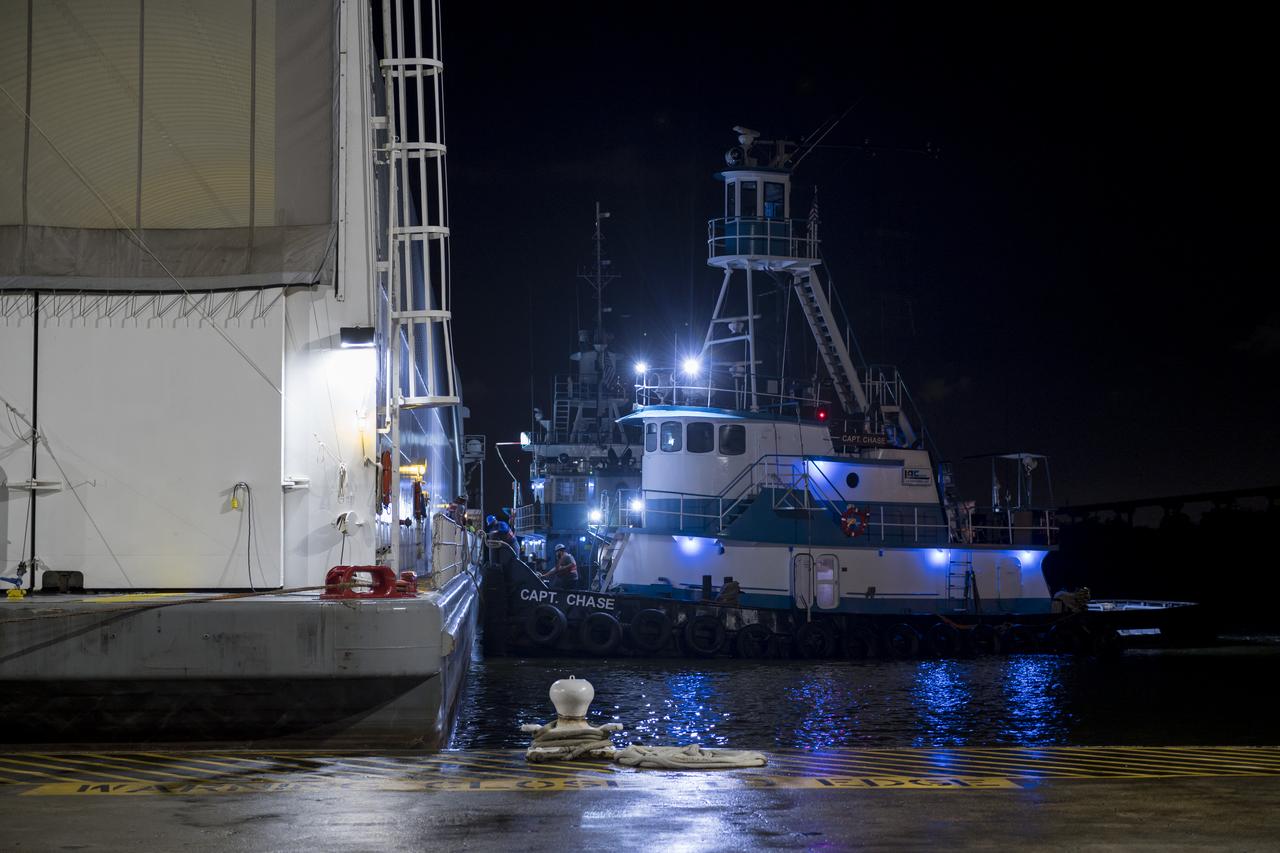

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
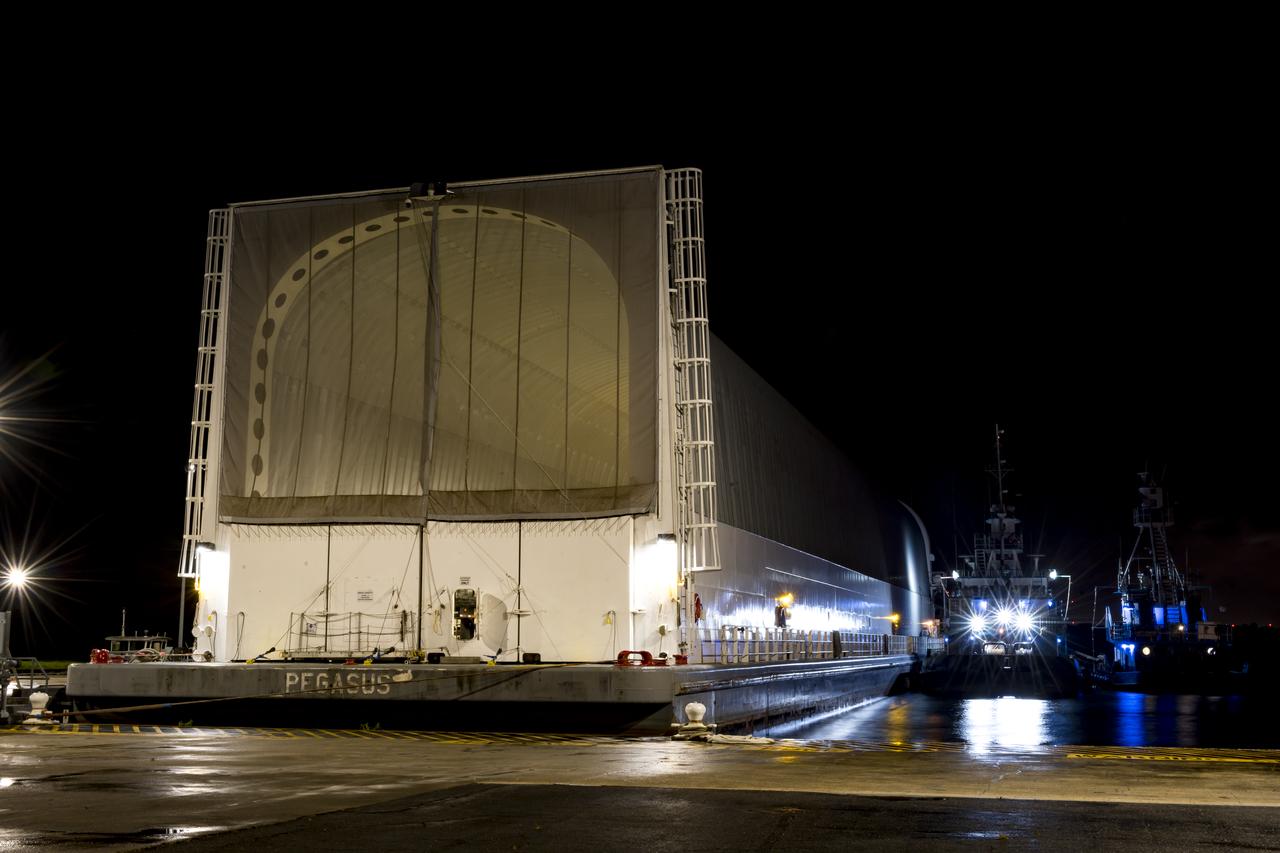

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
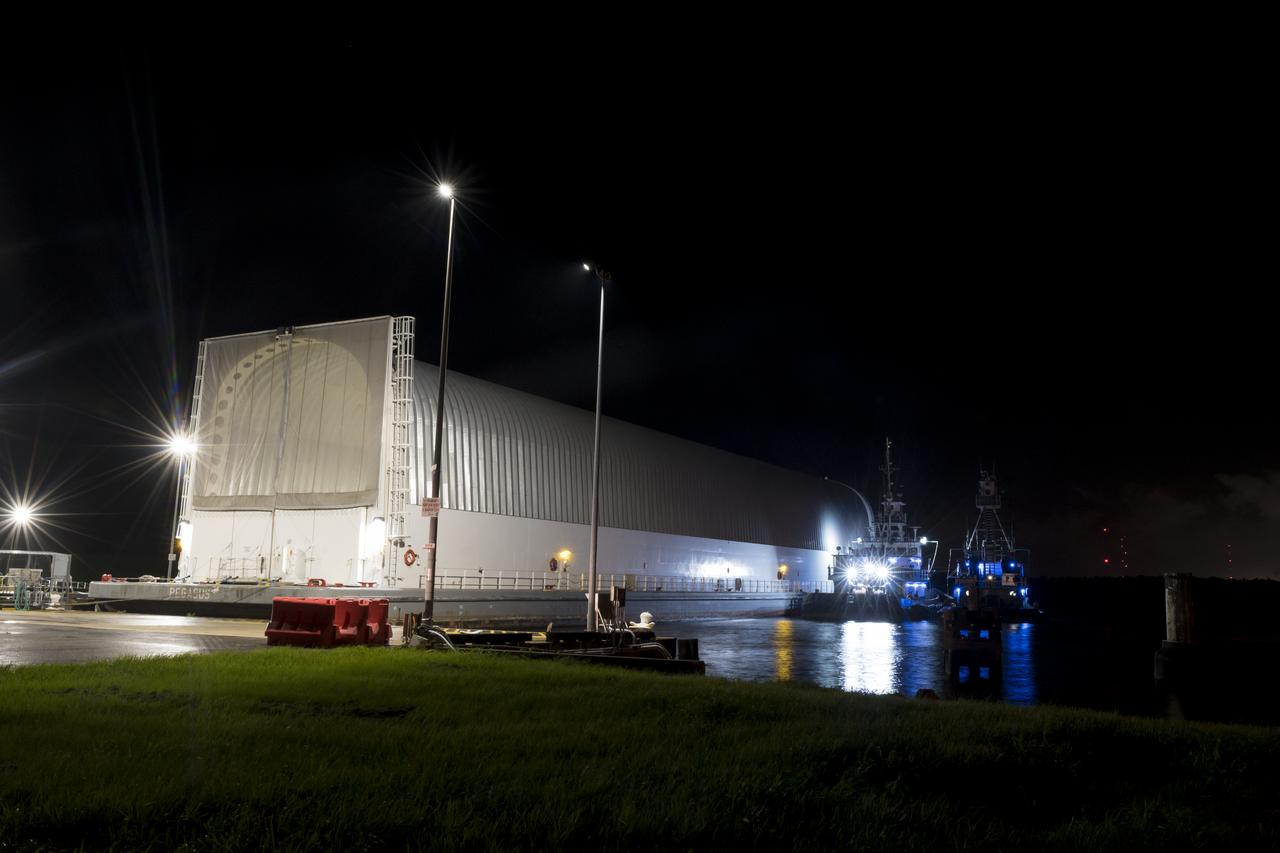

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
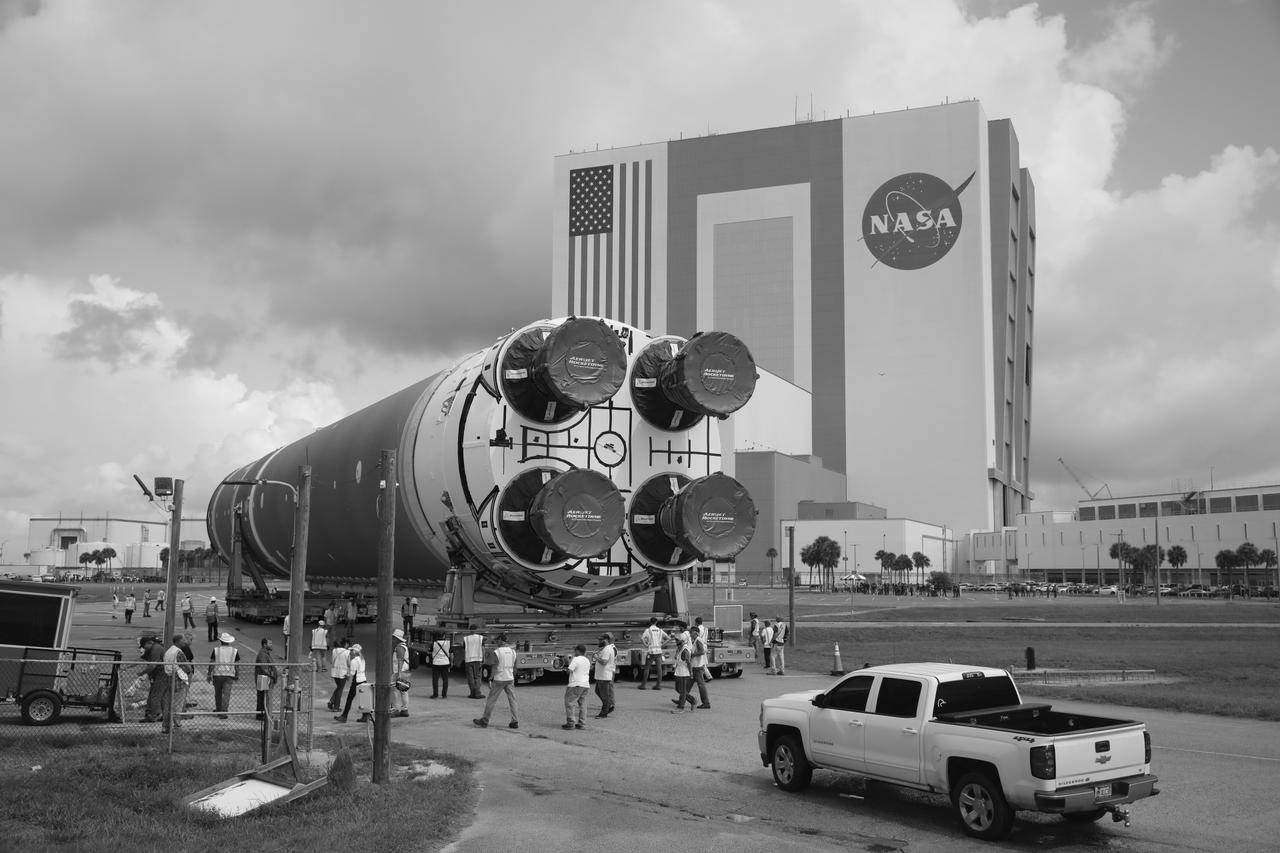

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
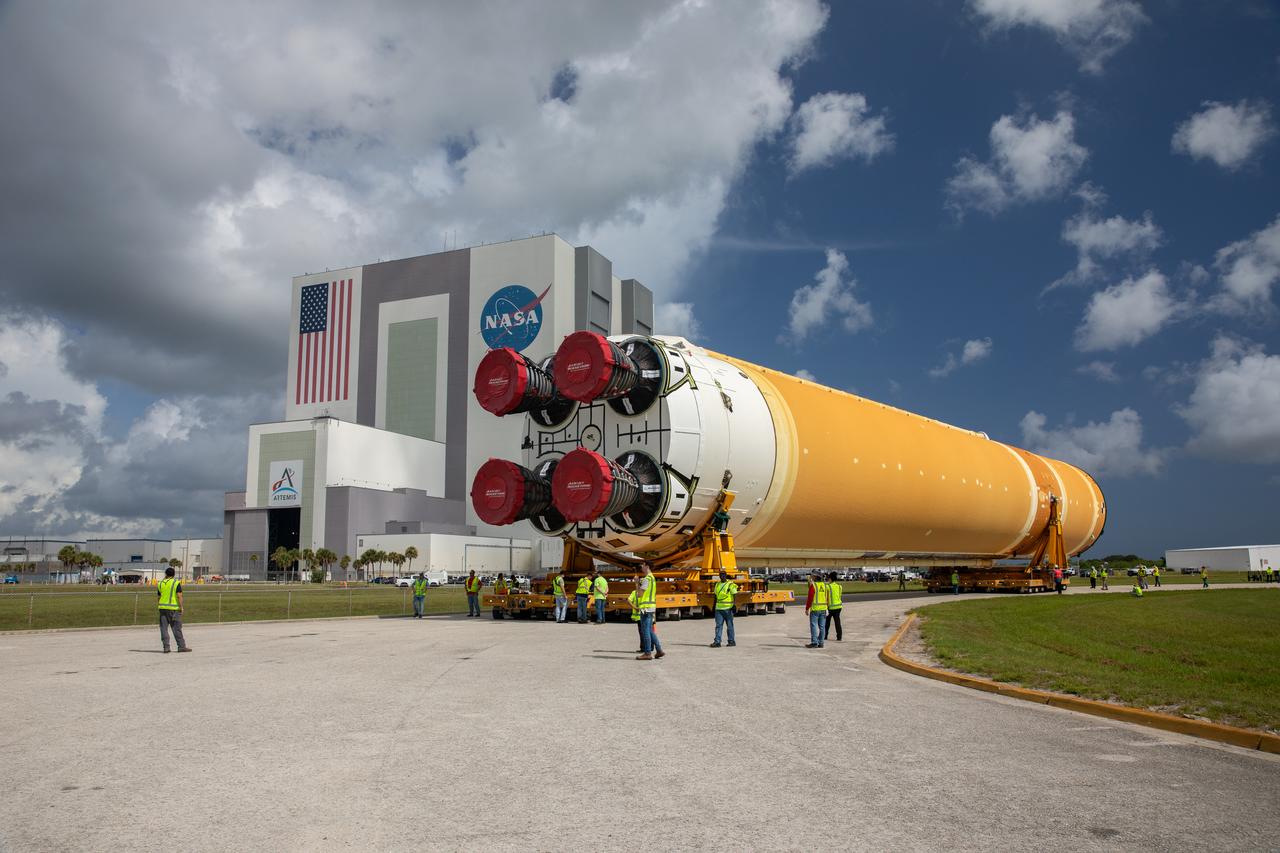

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
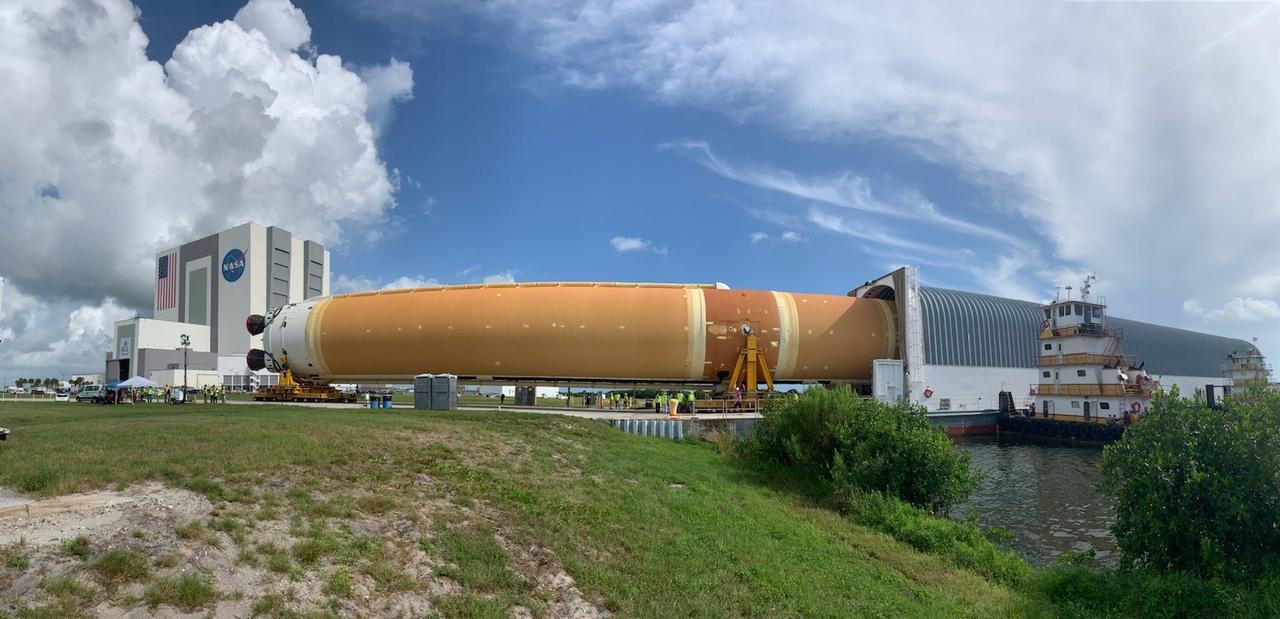

NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24, 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
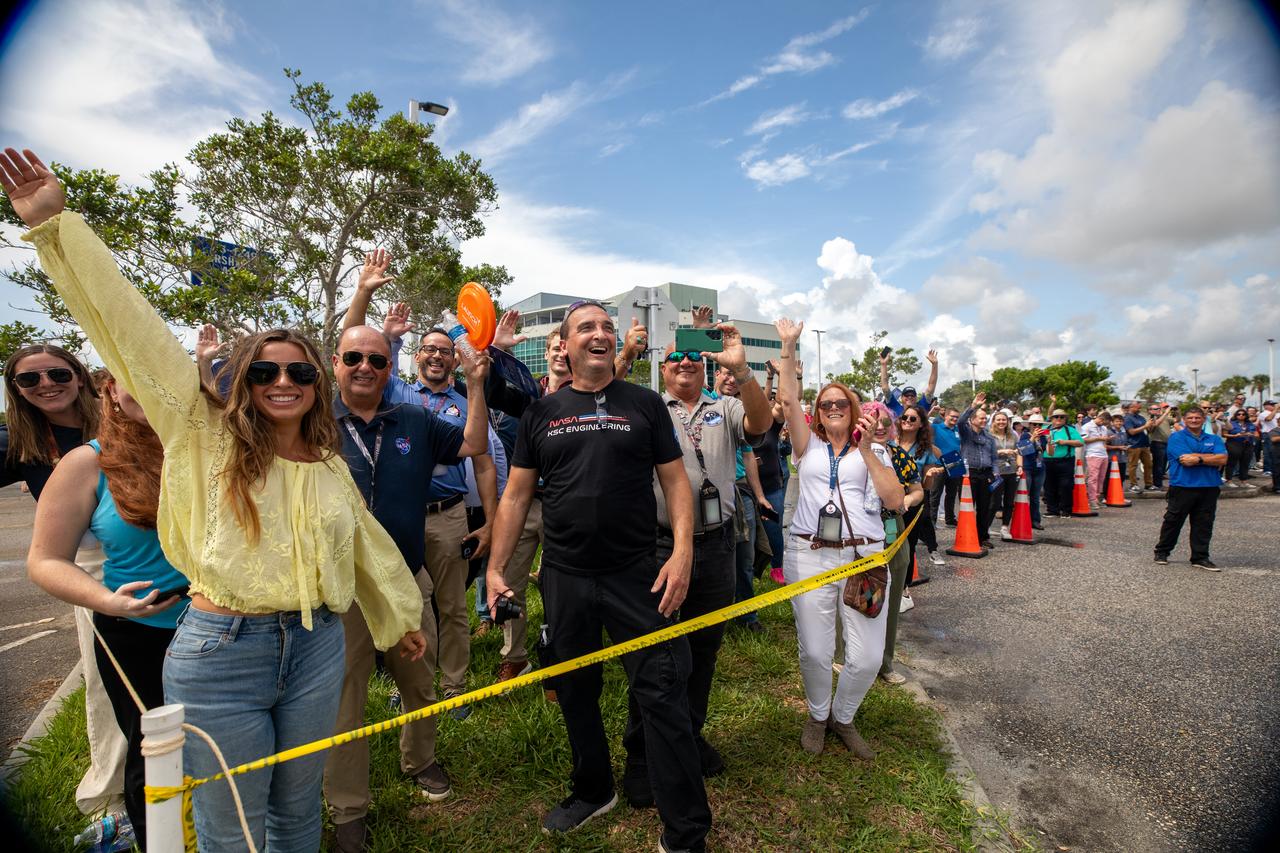

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
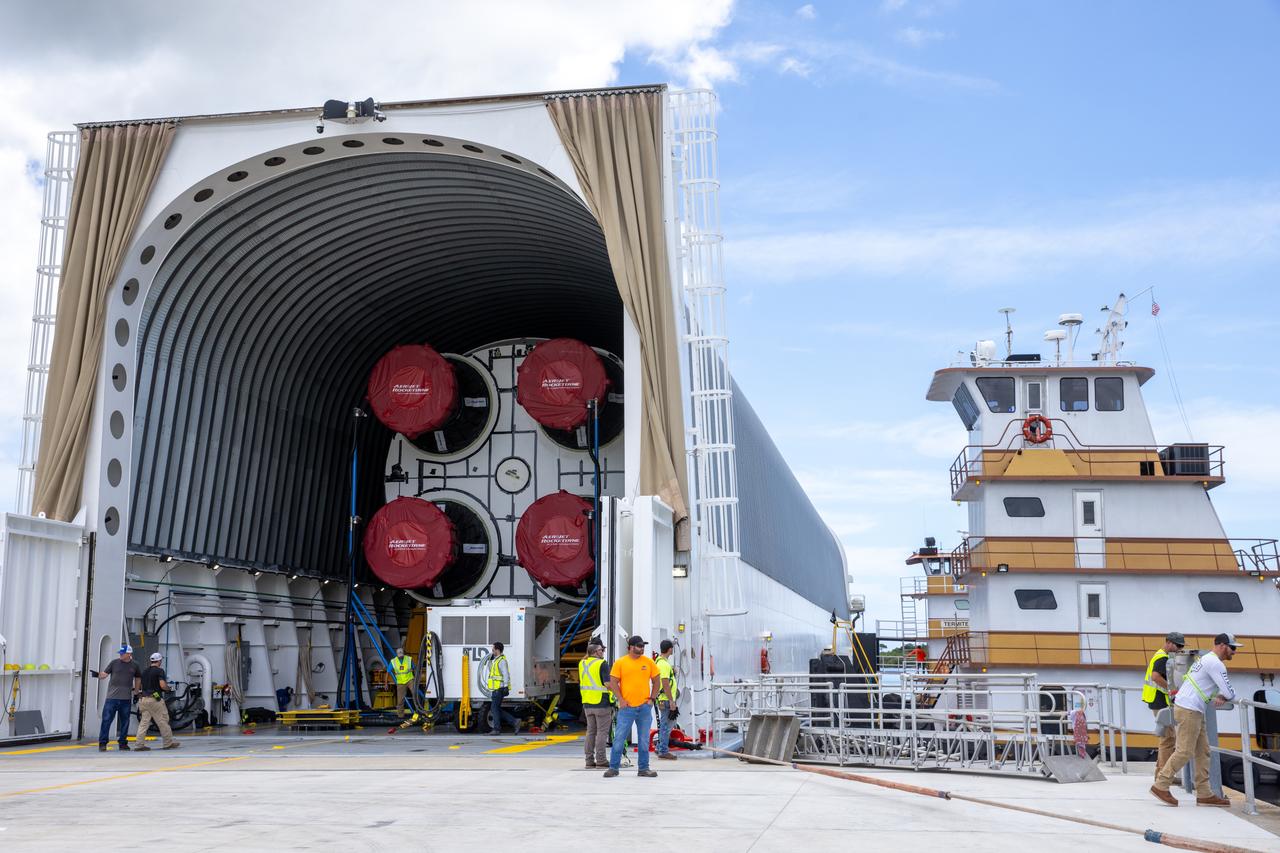

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.

NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
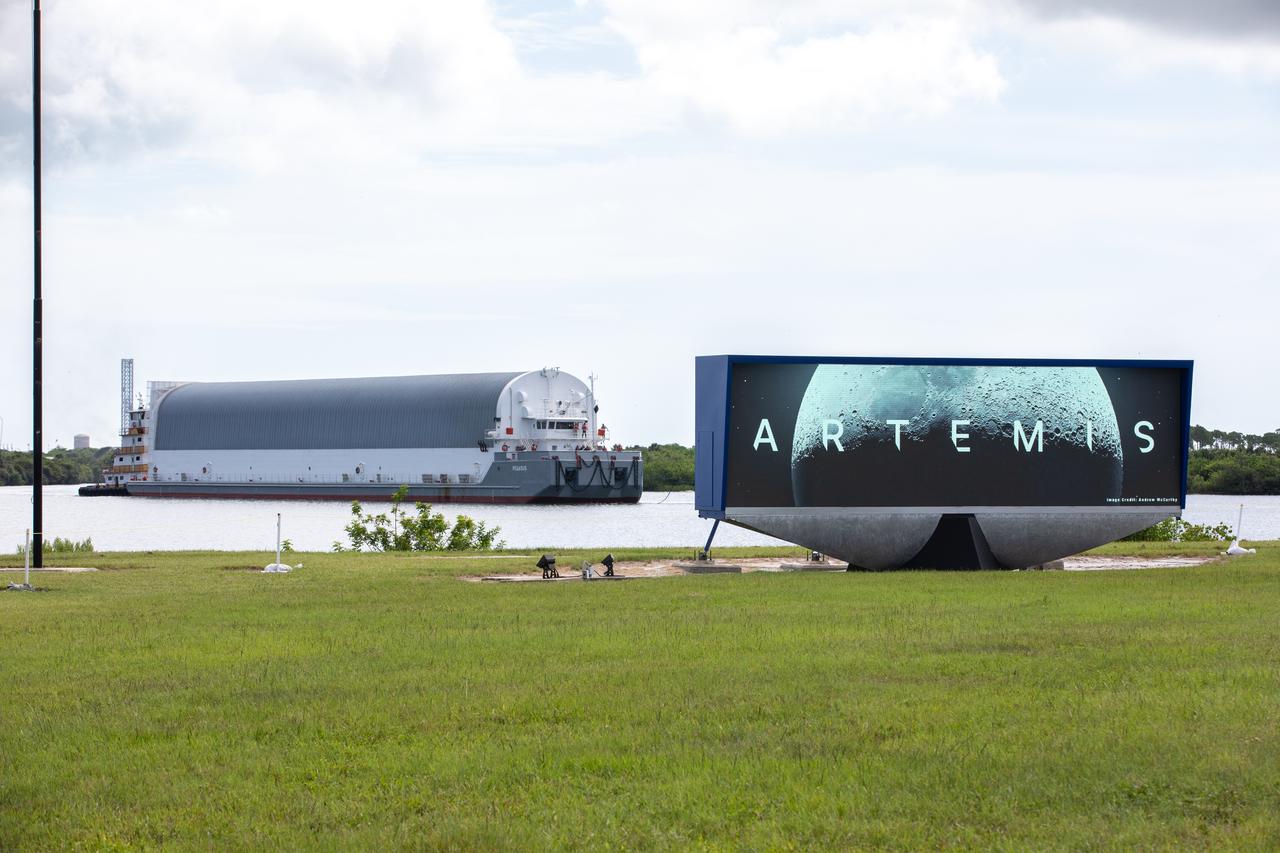
Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
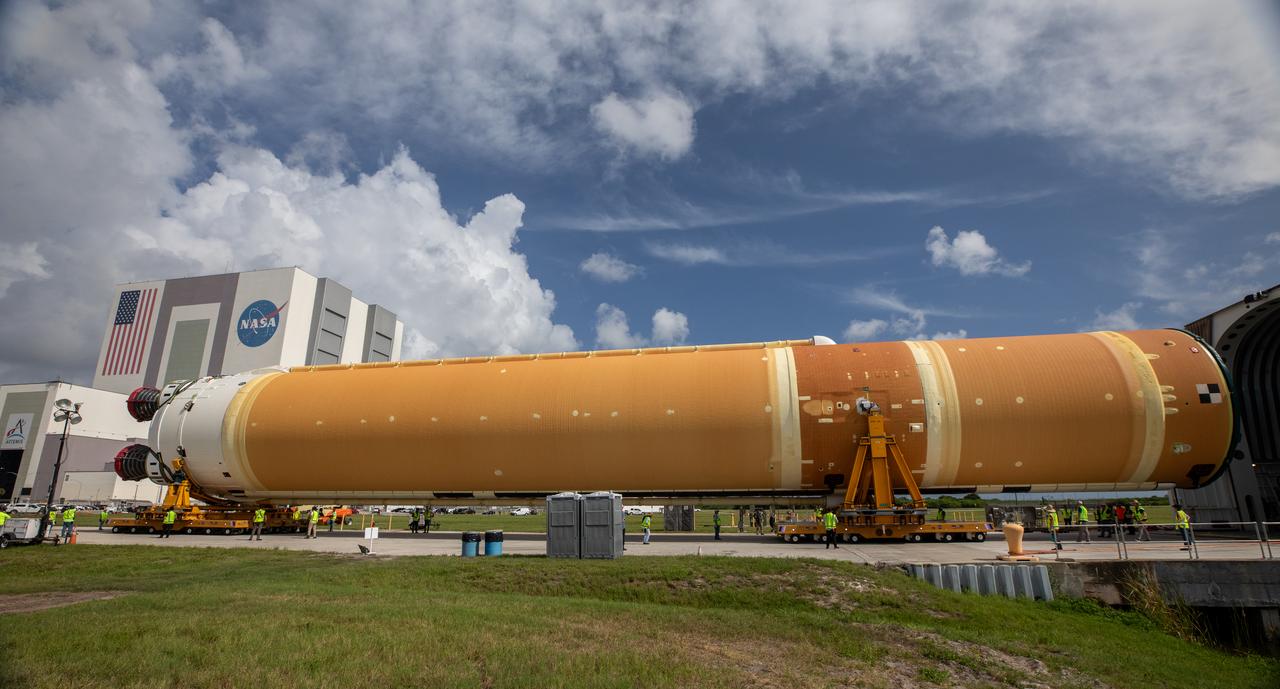

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
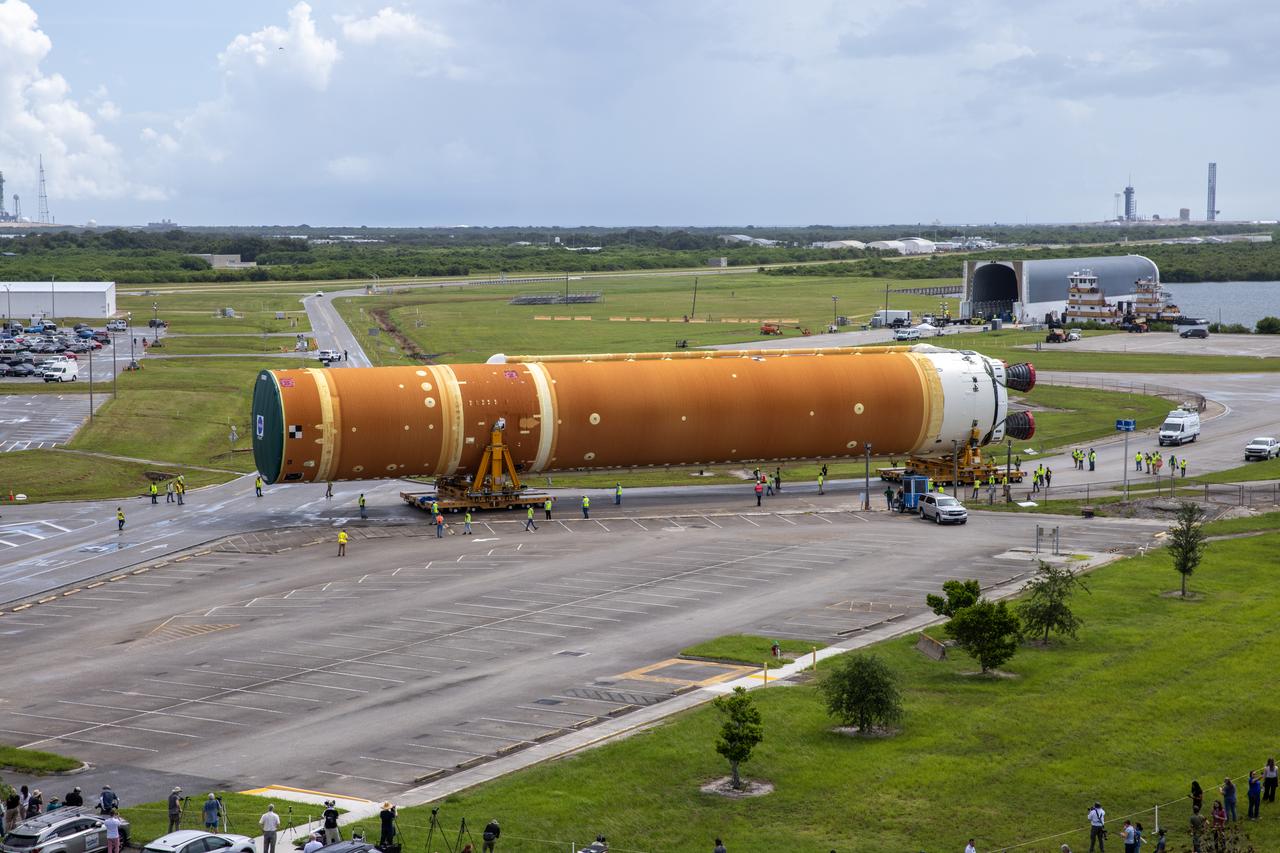

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
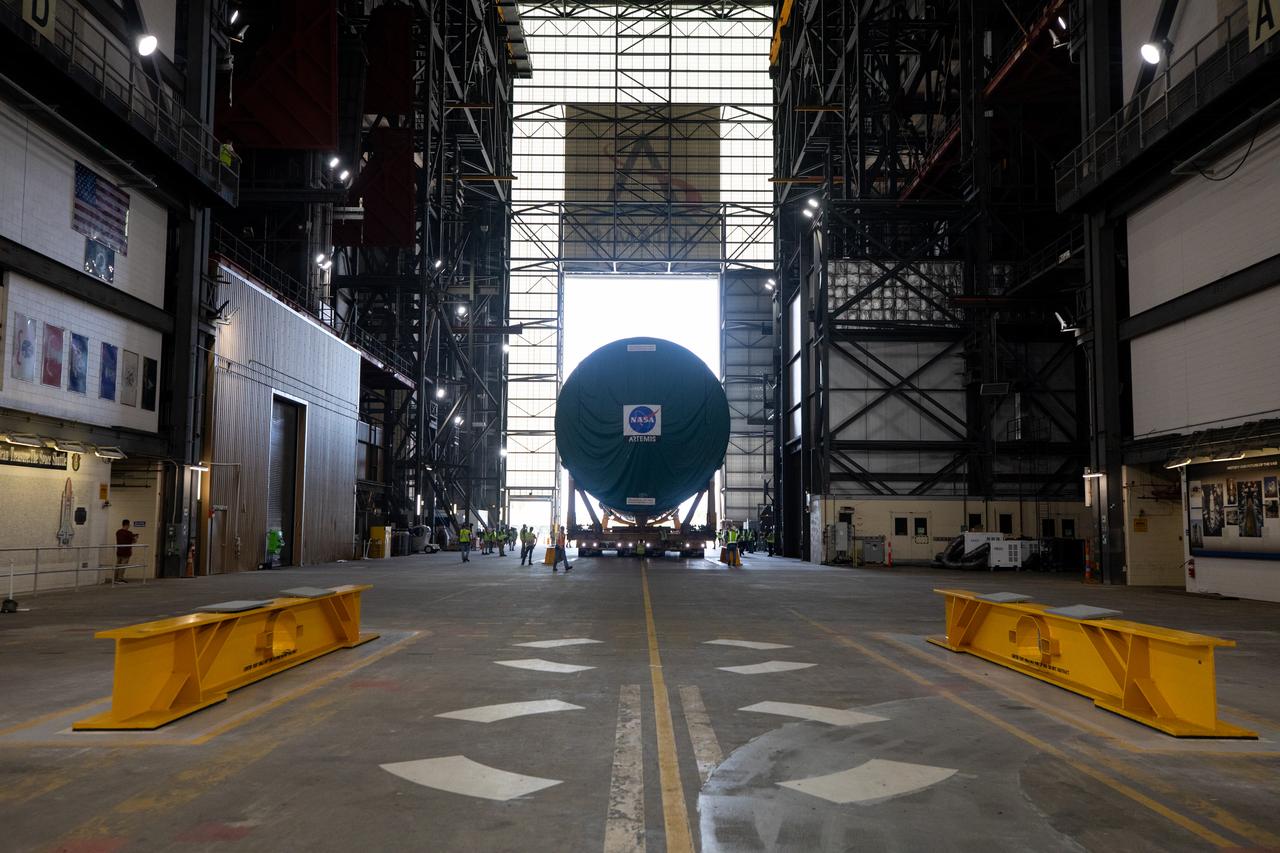

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage into the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. In the coming months, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
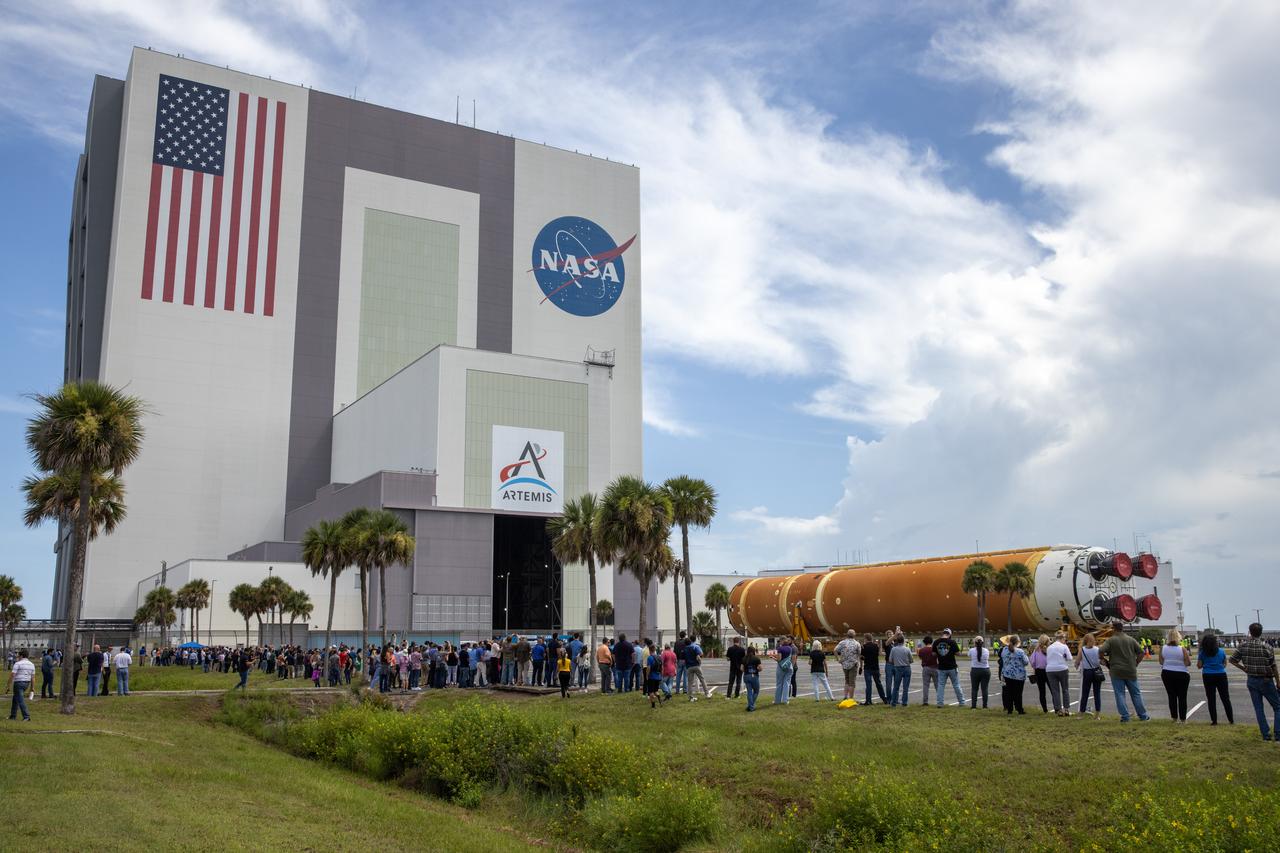

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
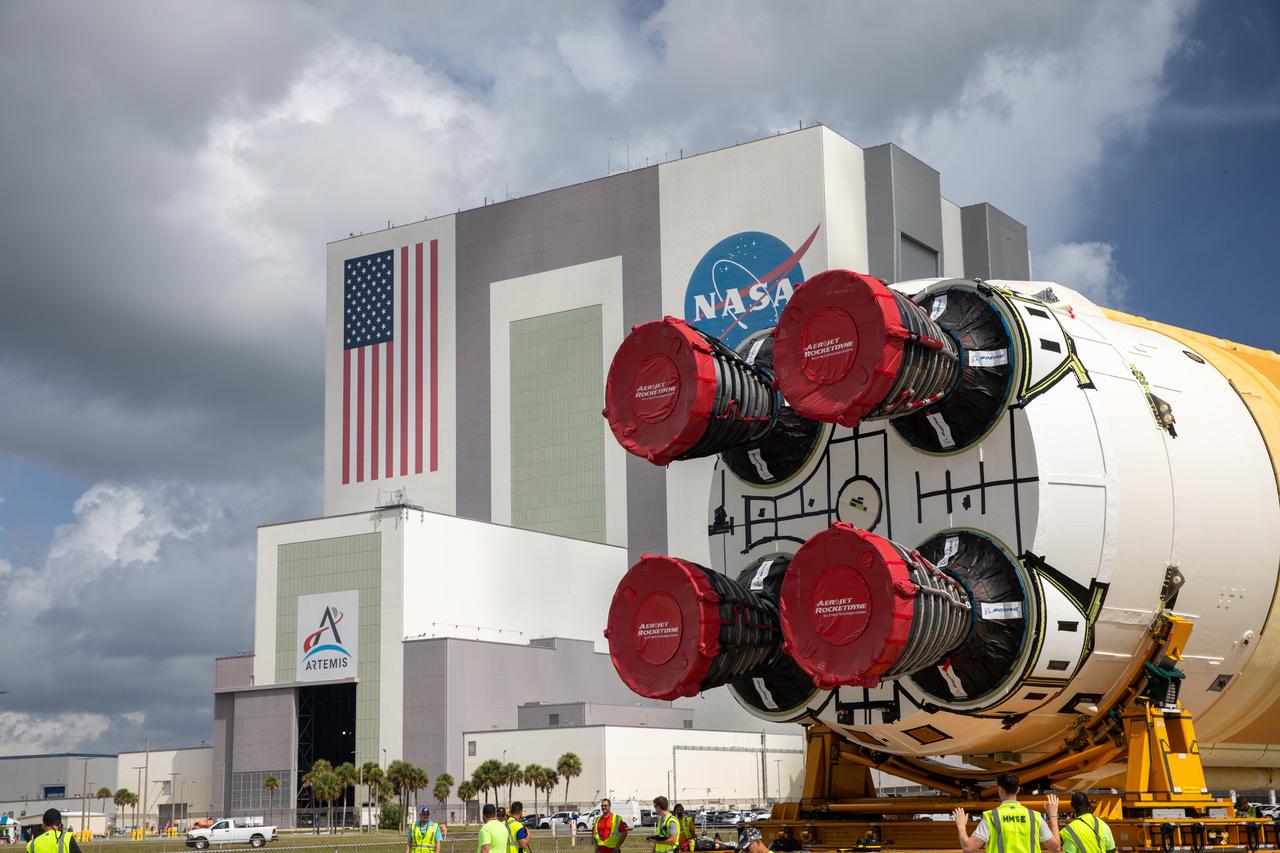
After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
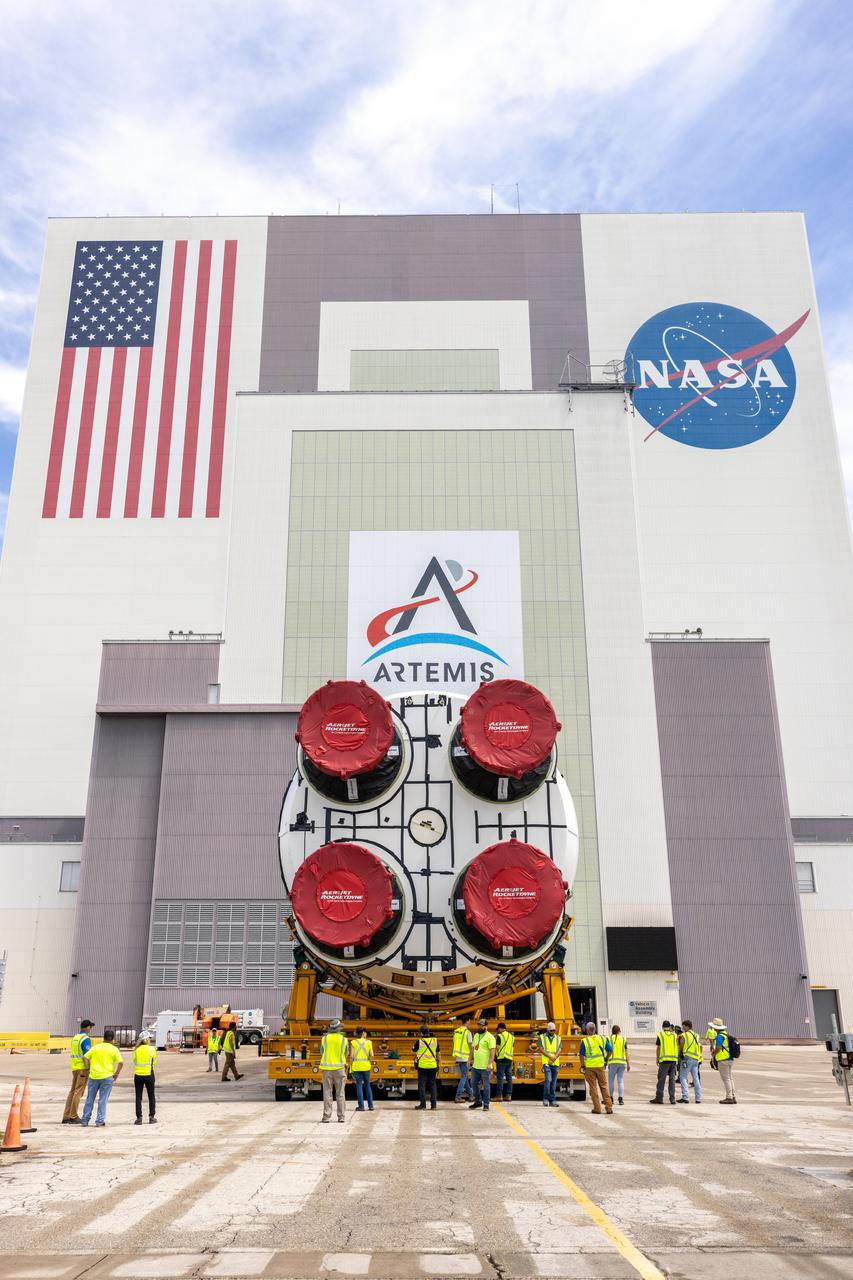

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
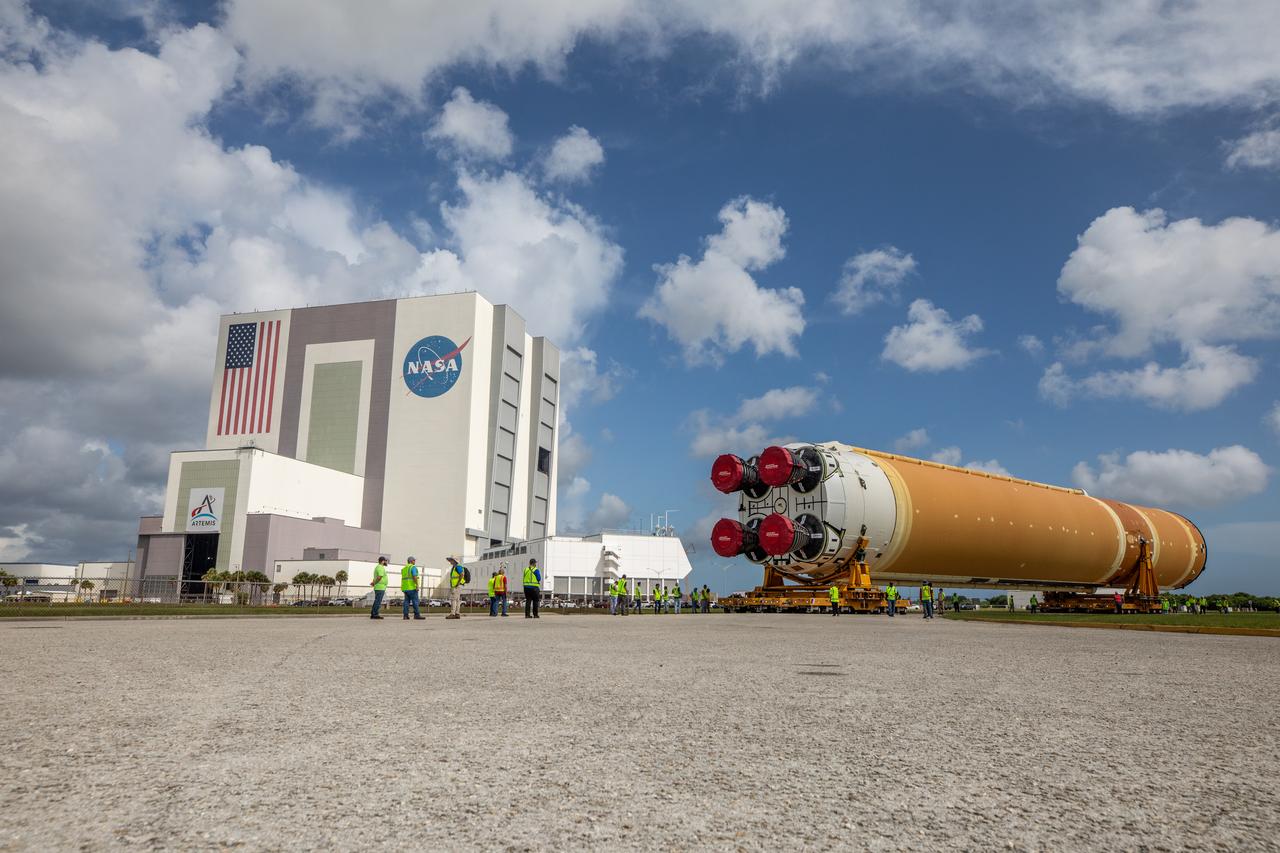

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
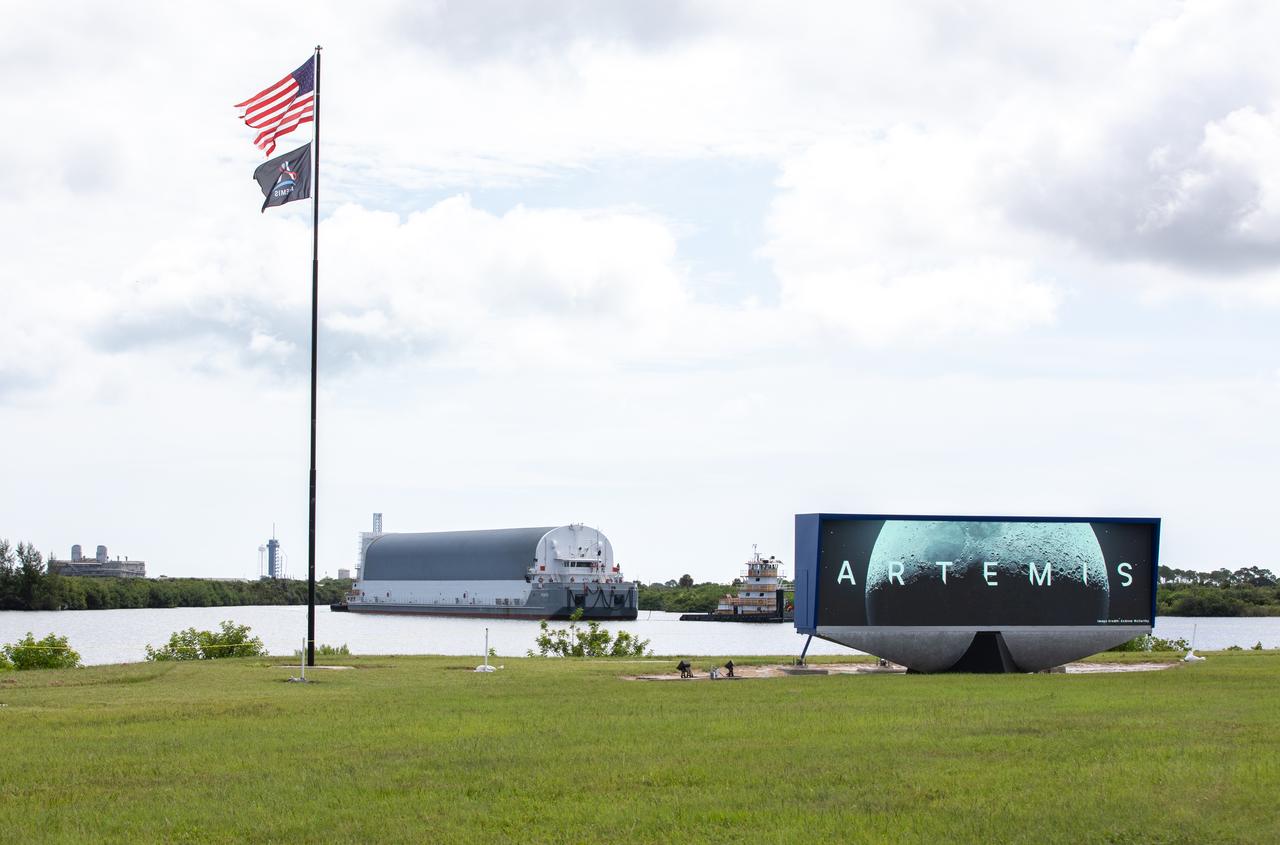

Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with NASA's Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
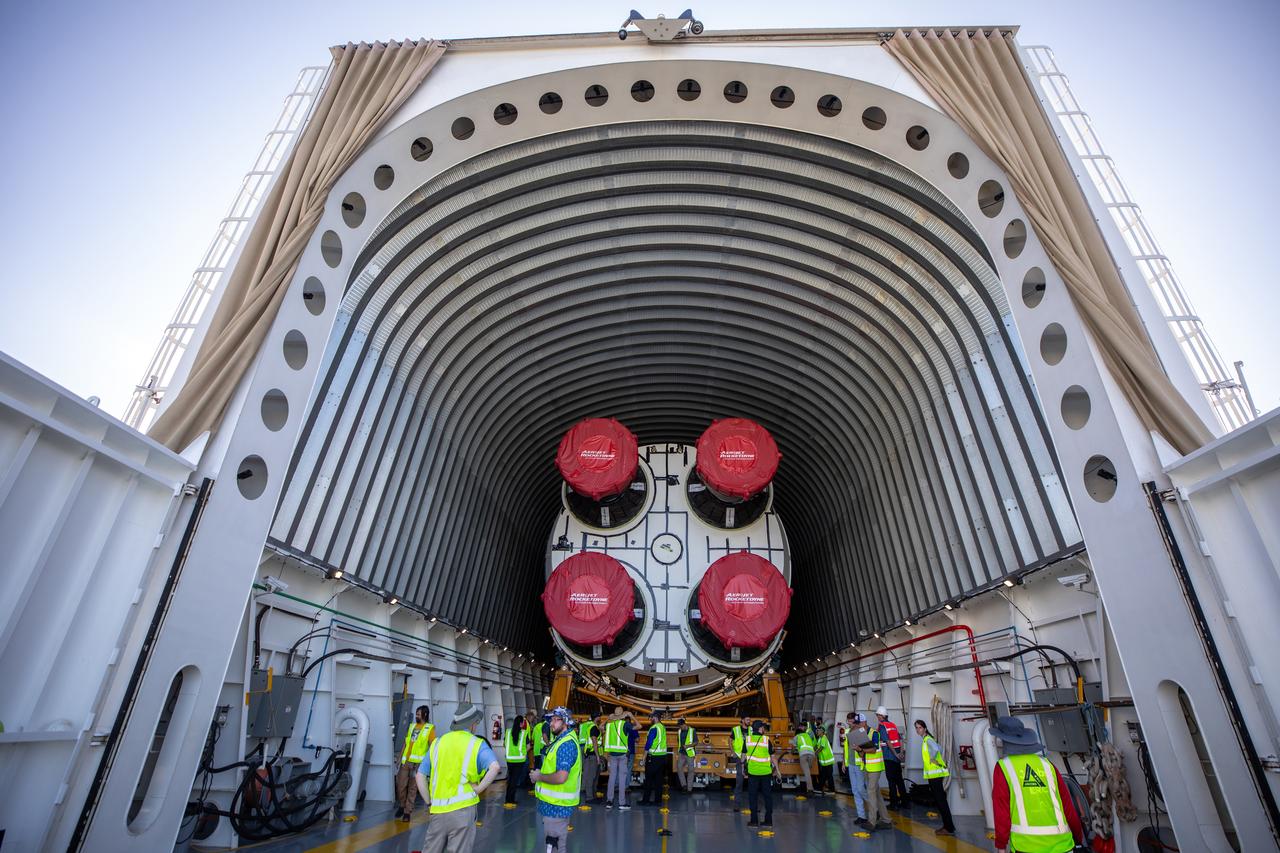

NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
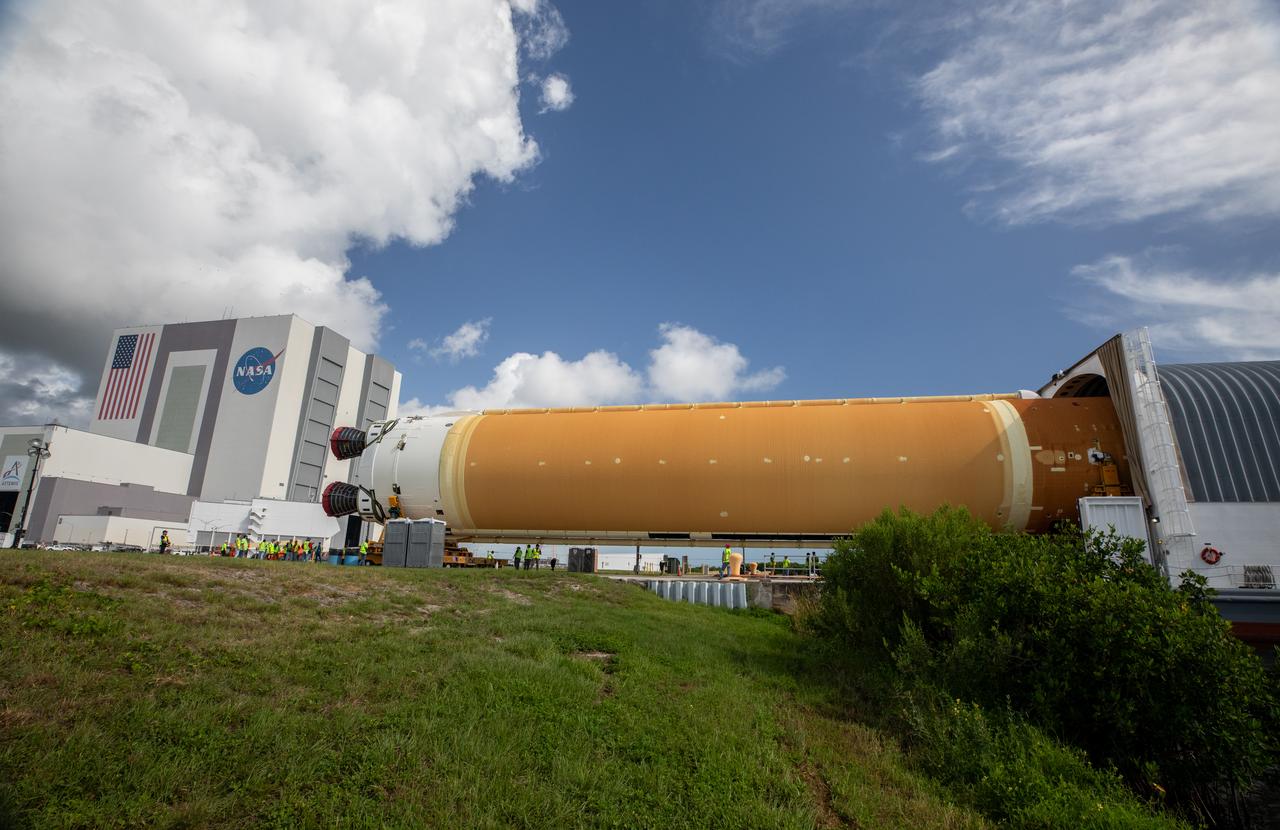

NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24, 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
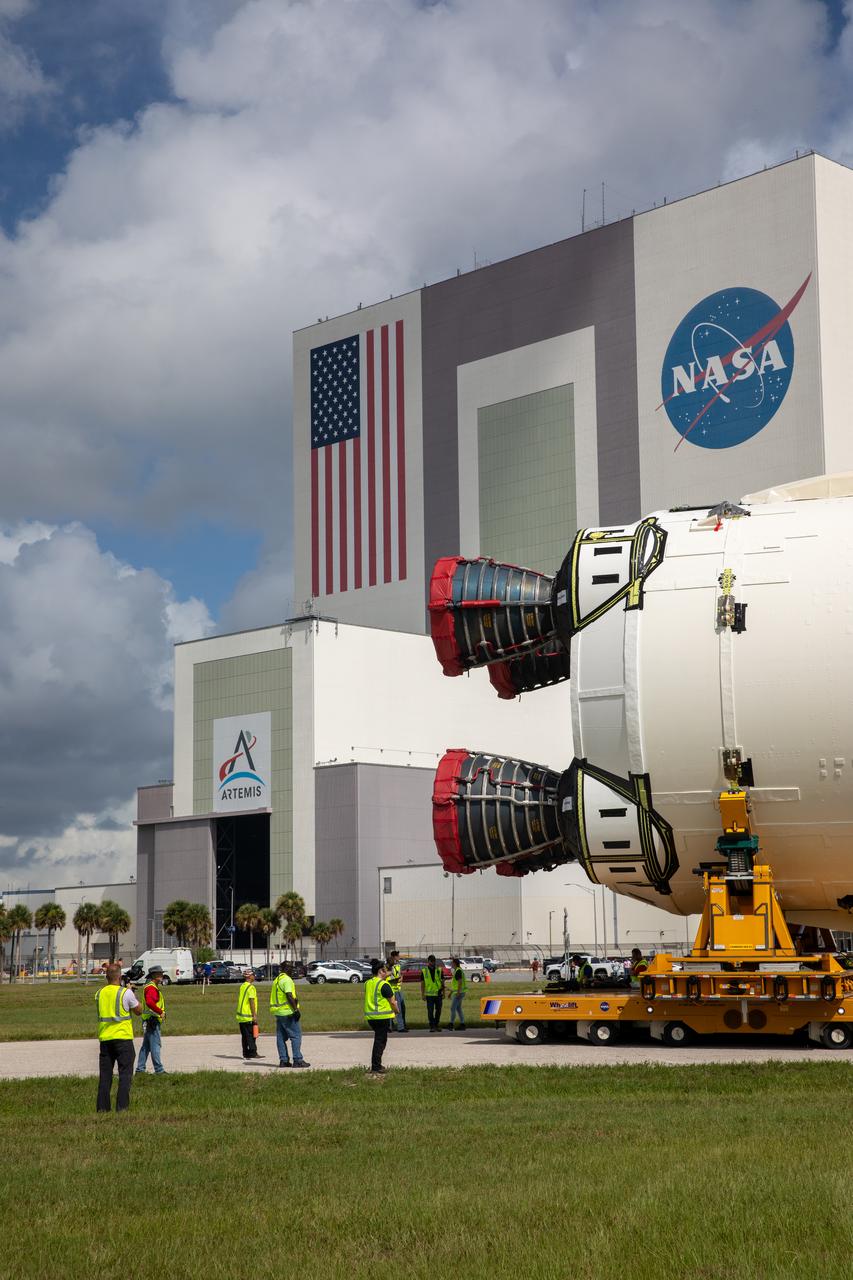

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
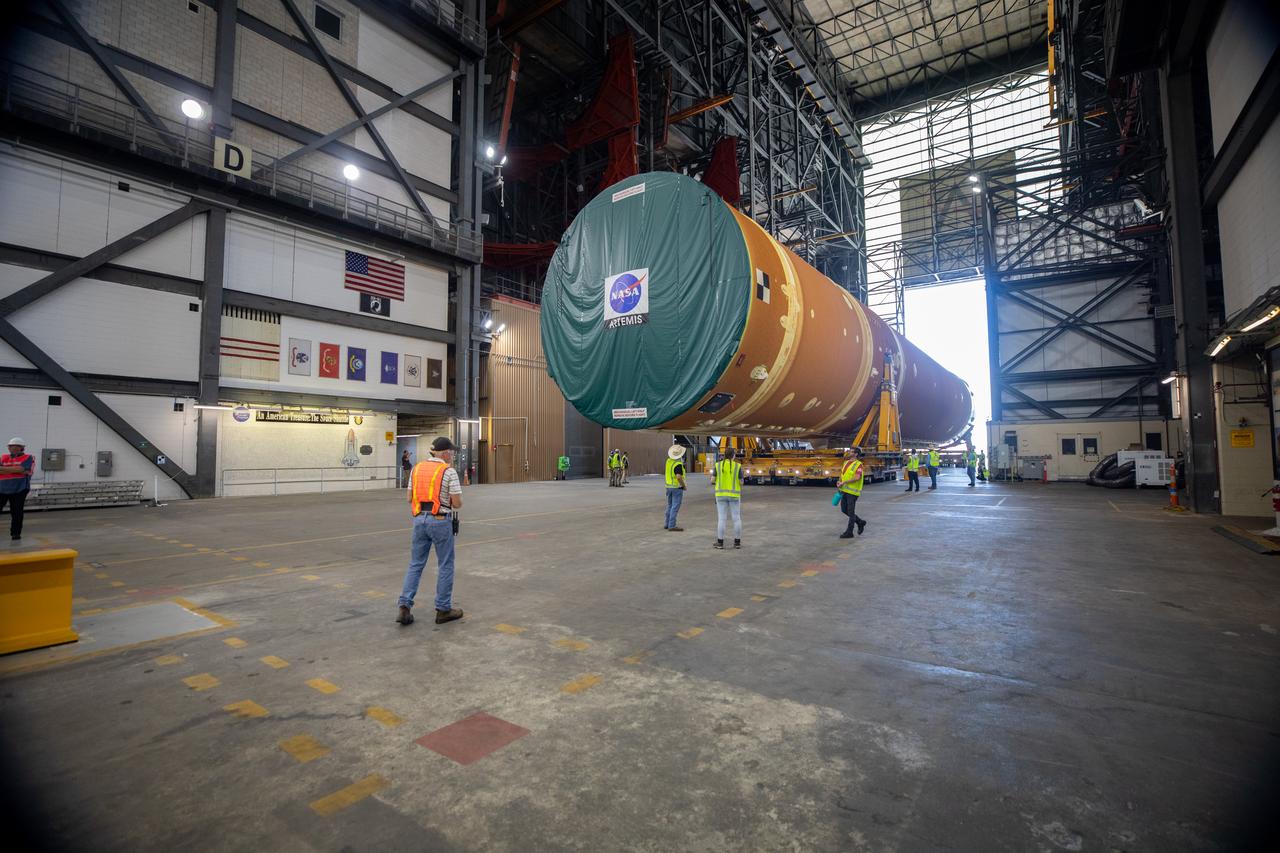

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage into the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. In the coming months, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
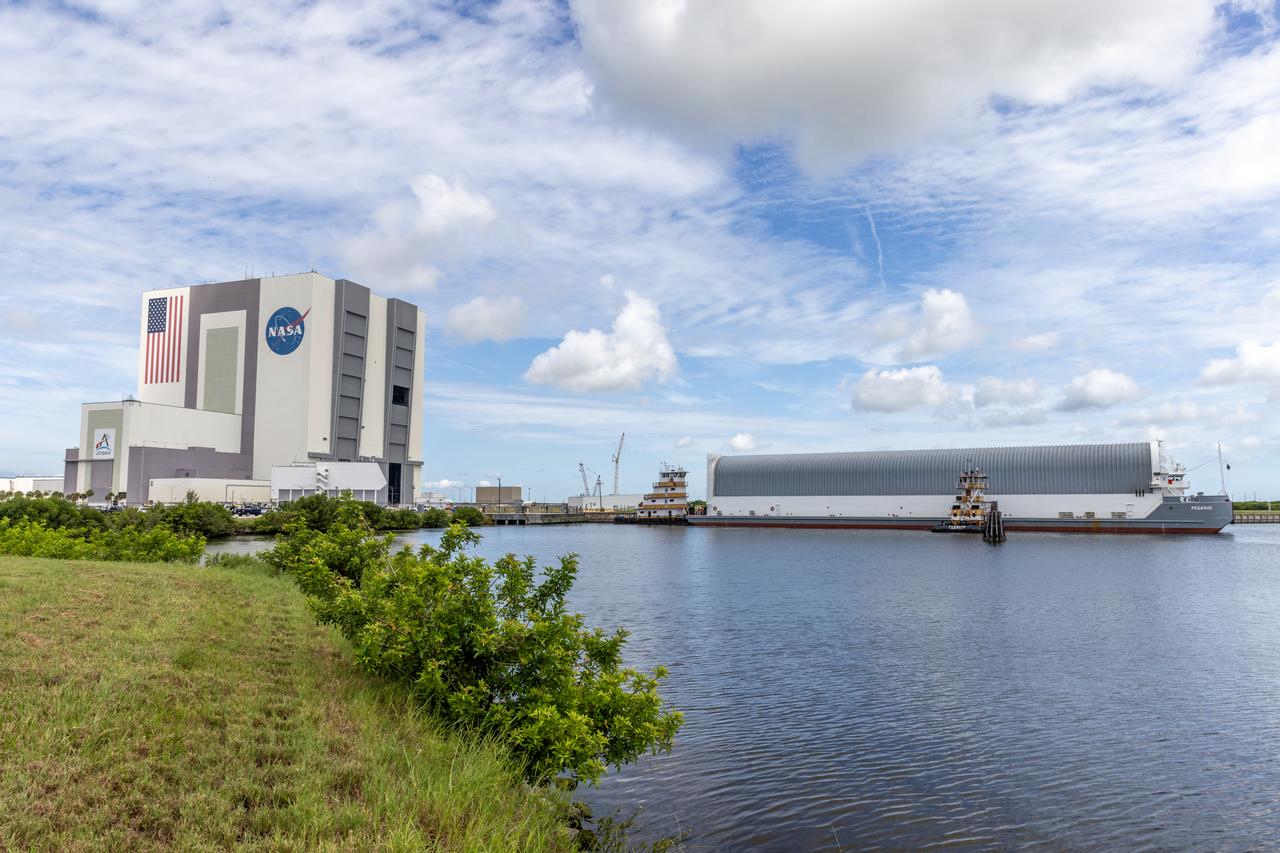

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
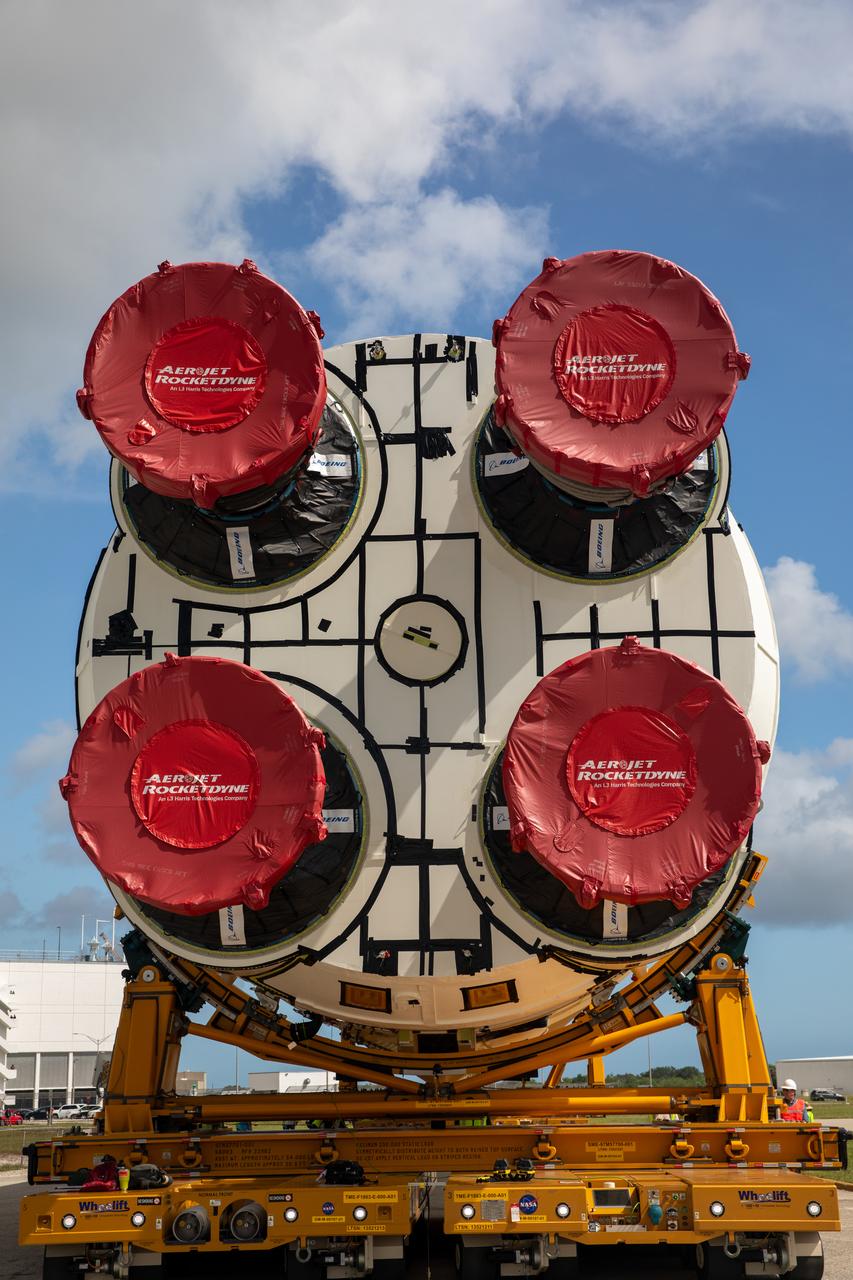

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
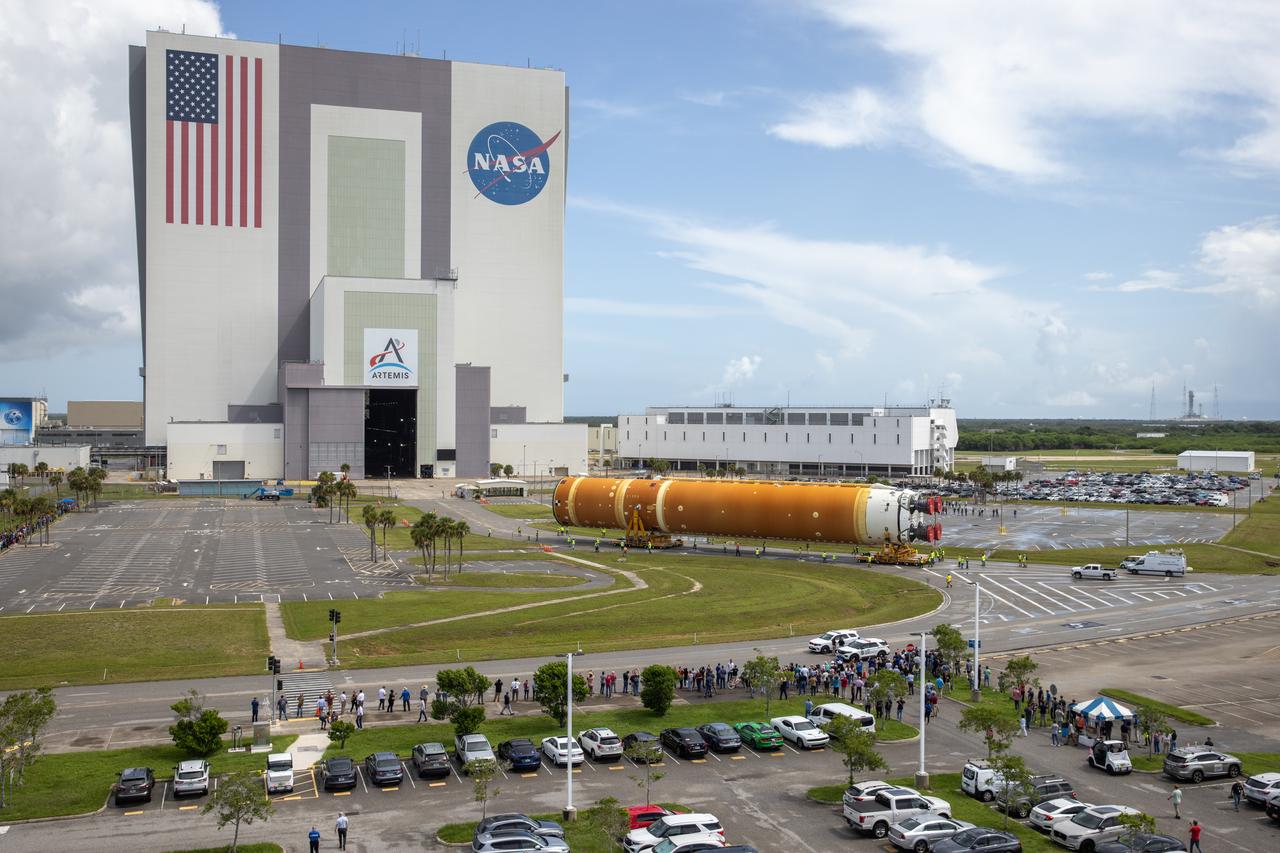

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
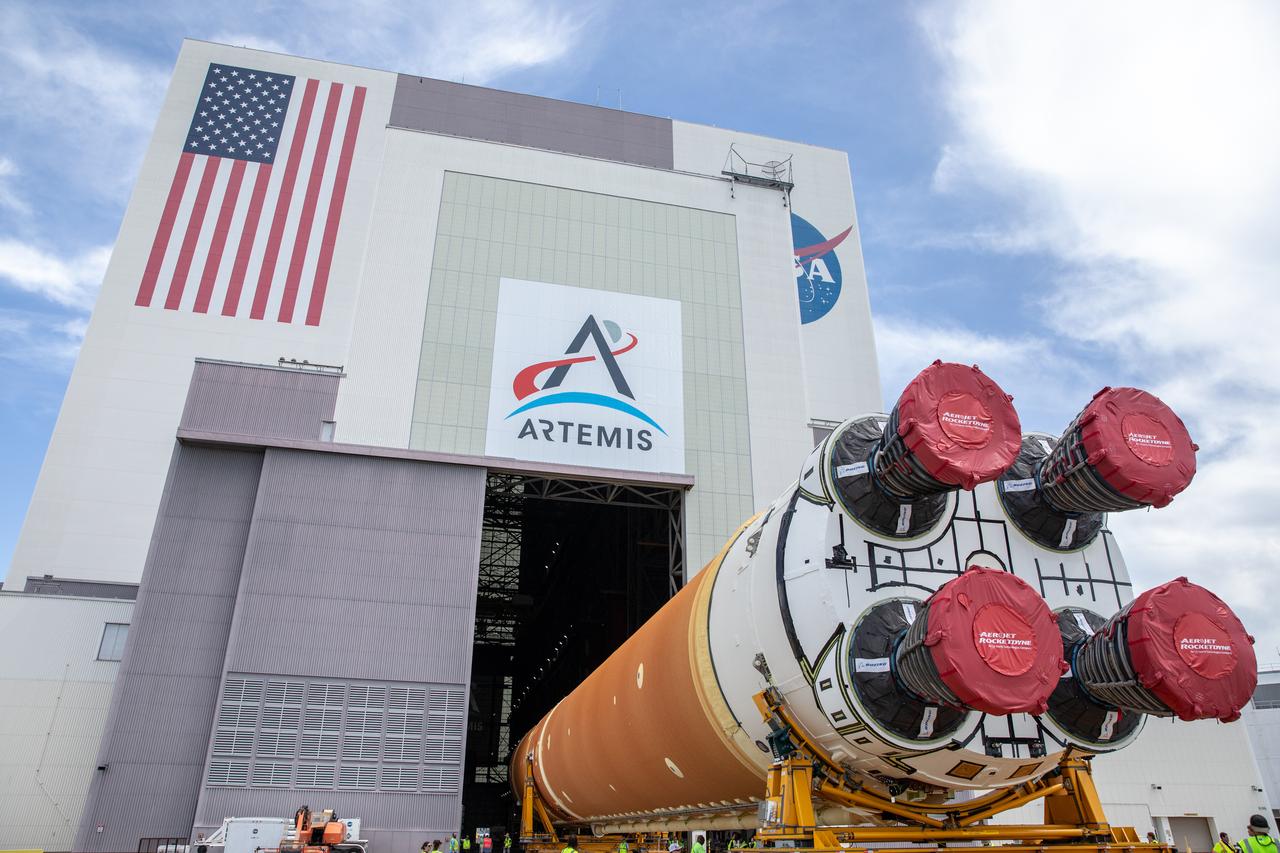
After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Tuesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
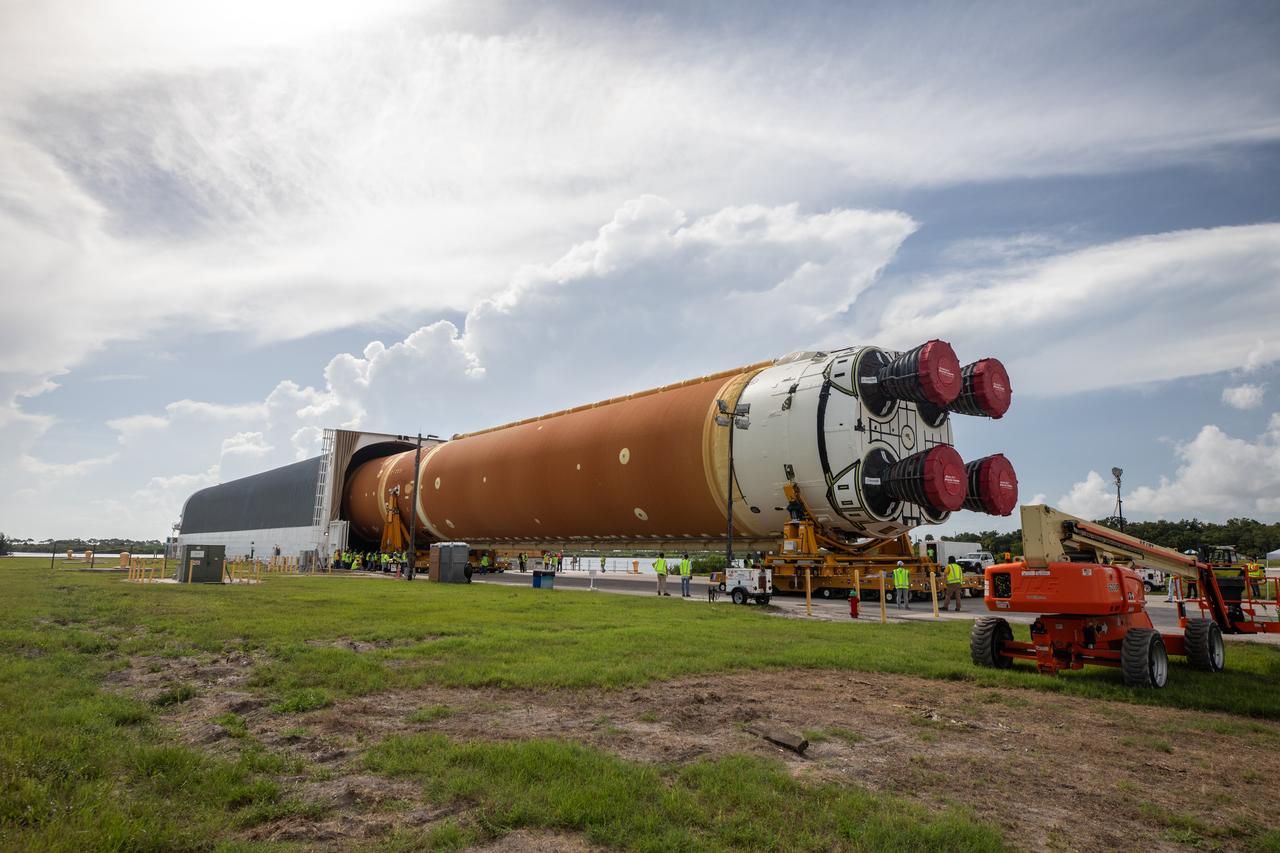

NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
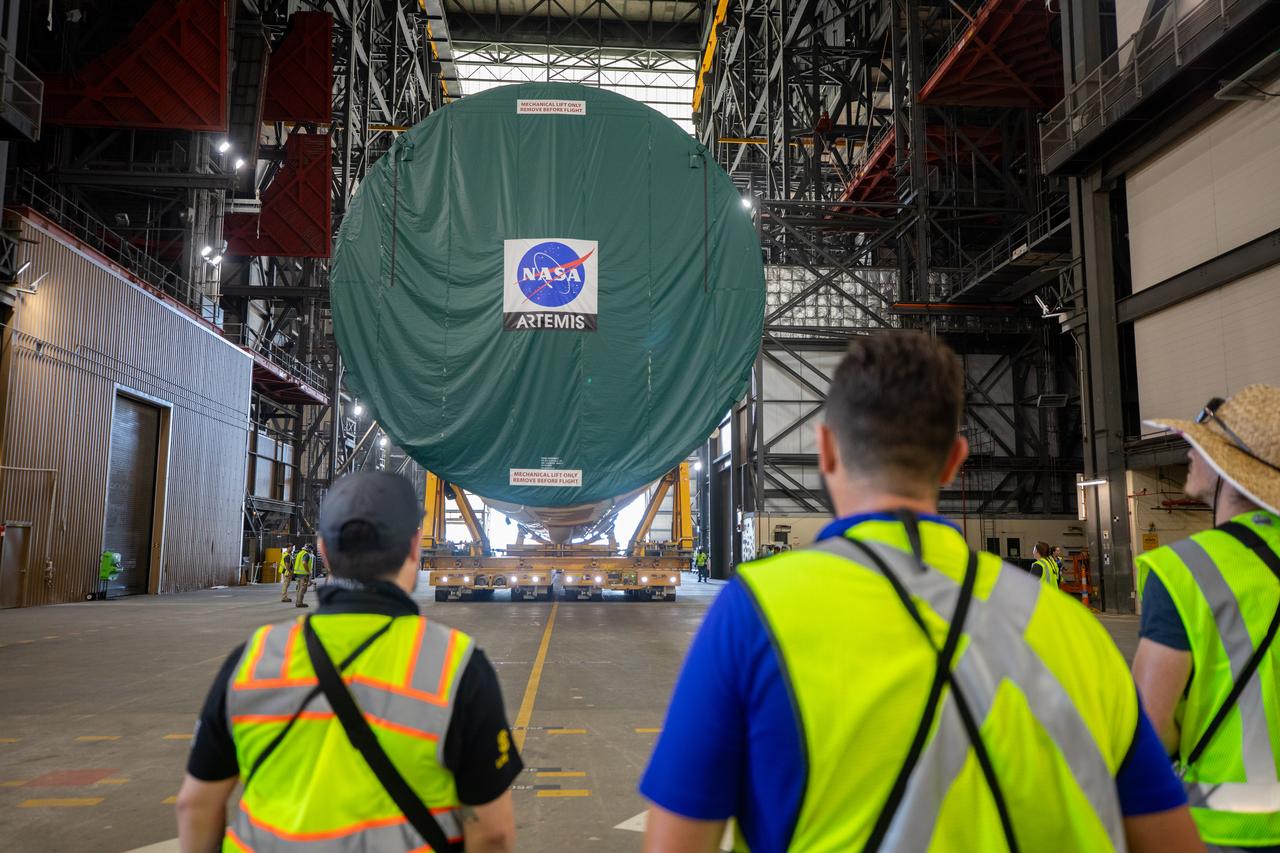

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage into the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. In the coming months, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
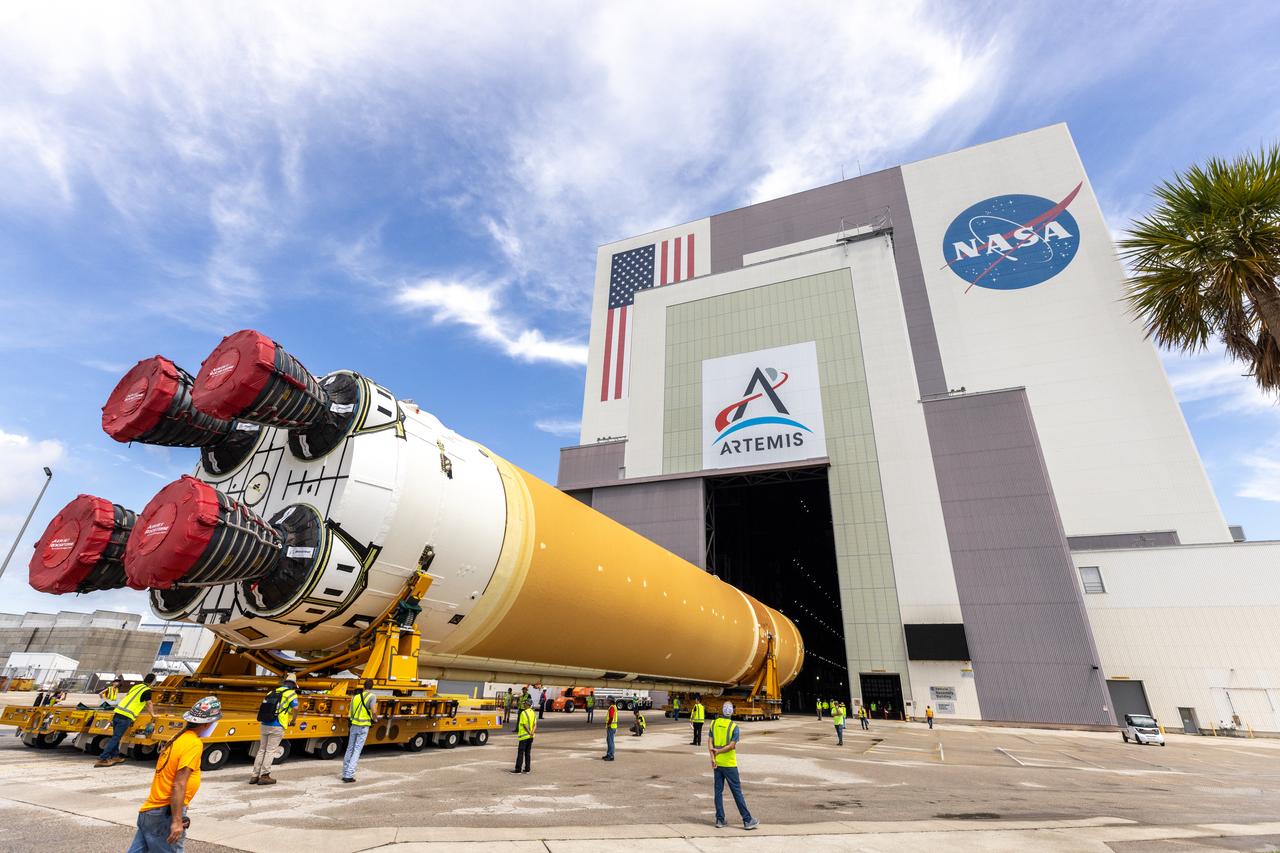

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
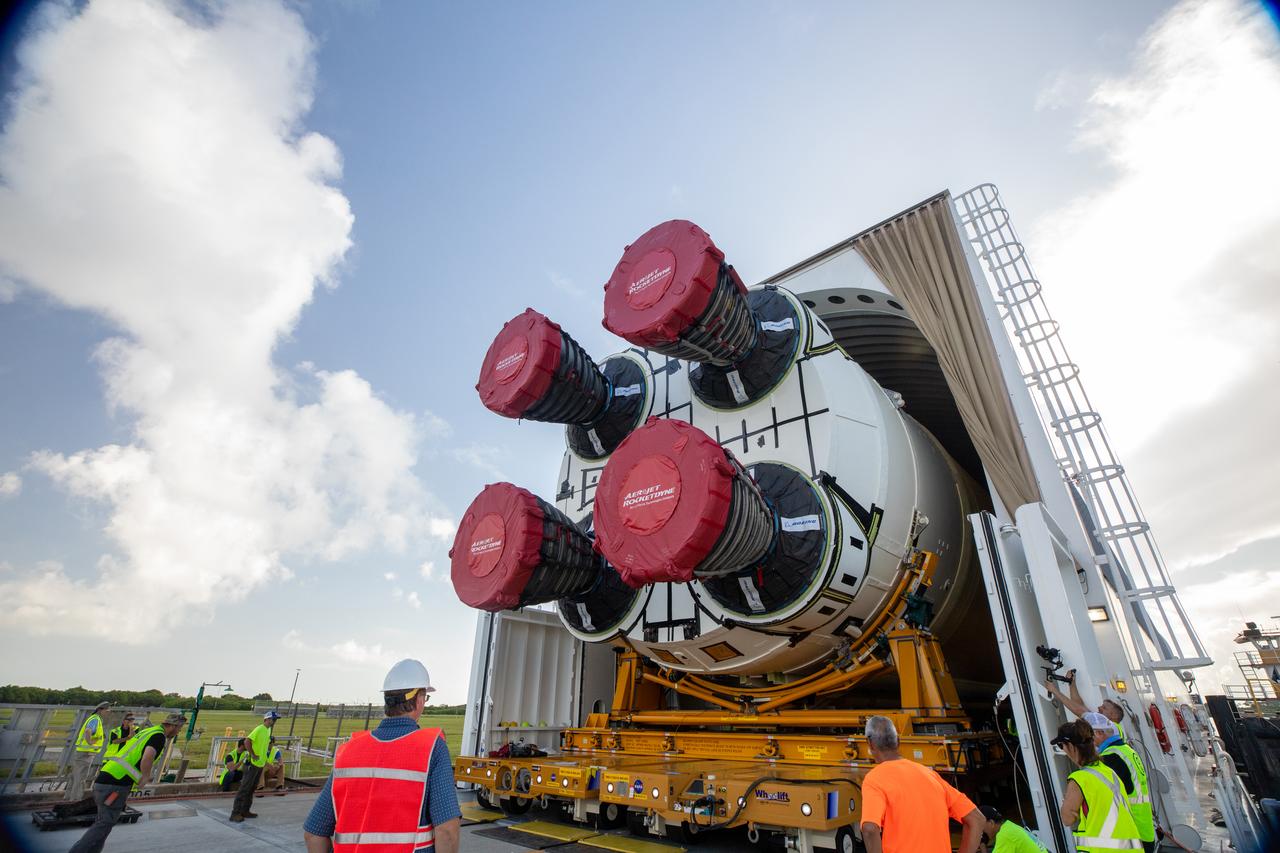

NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24, 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
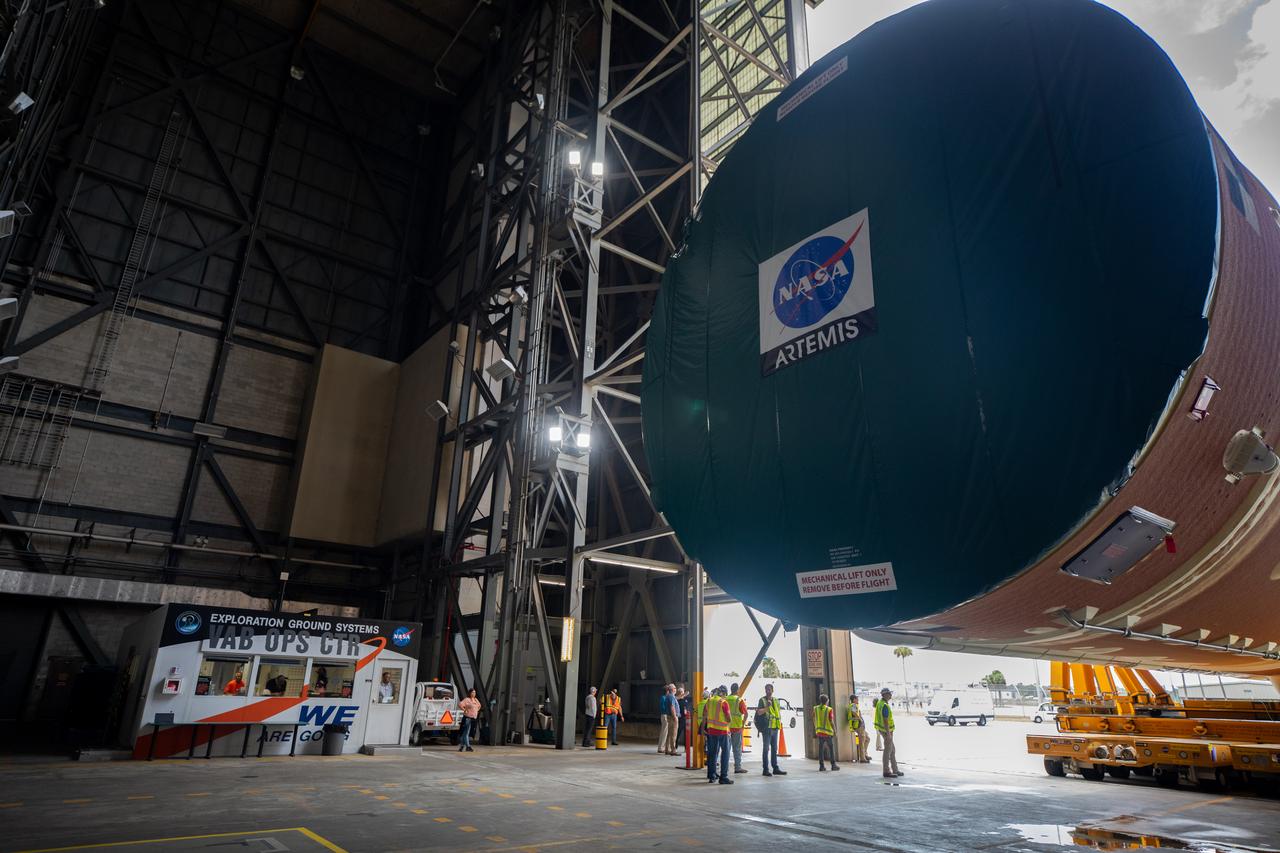

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage into the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. In the coming months, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
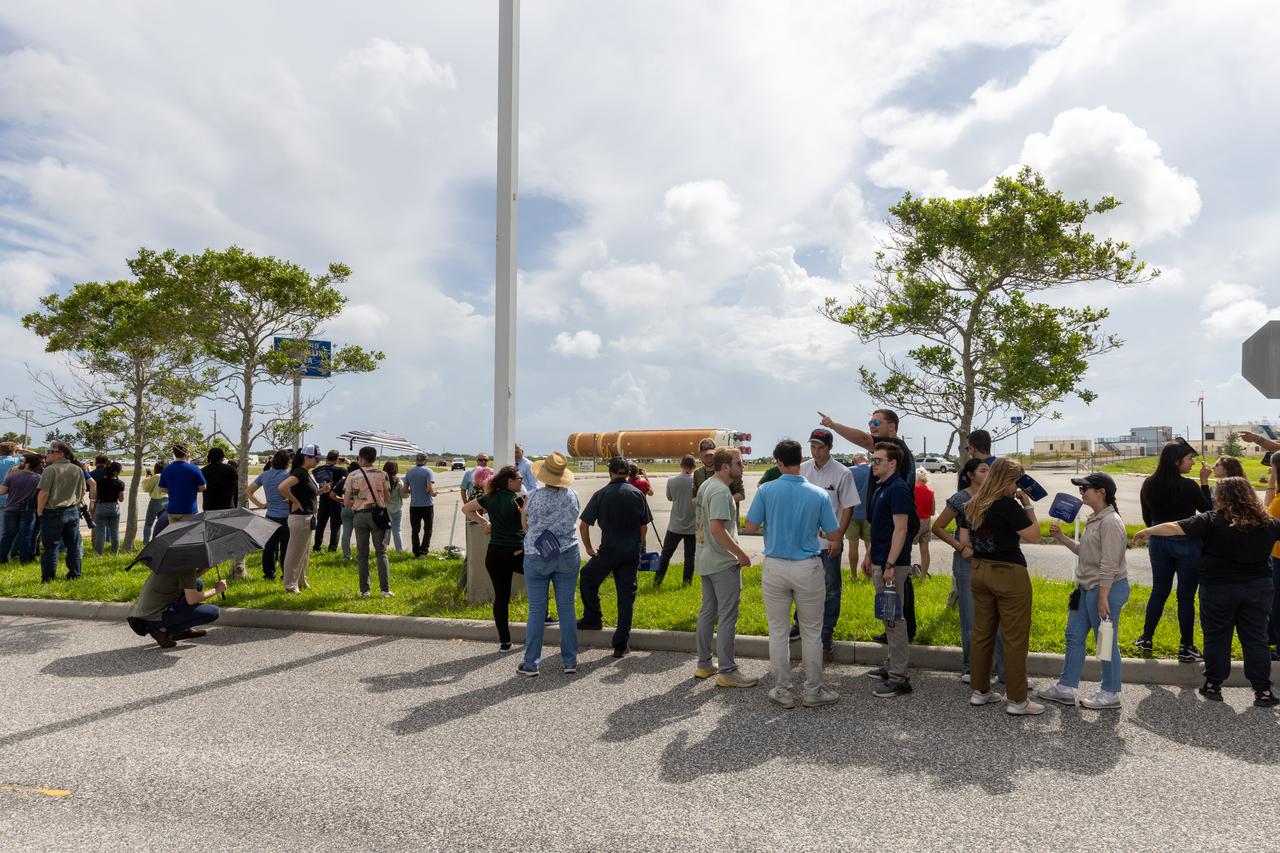

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
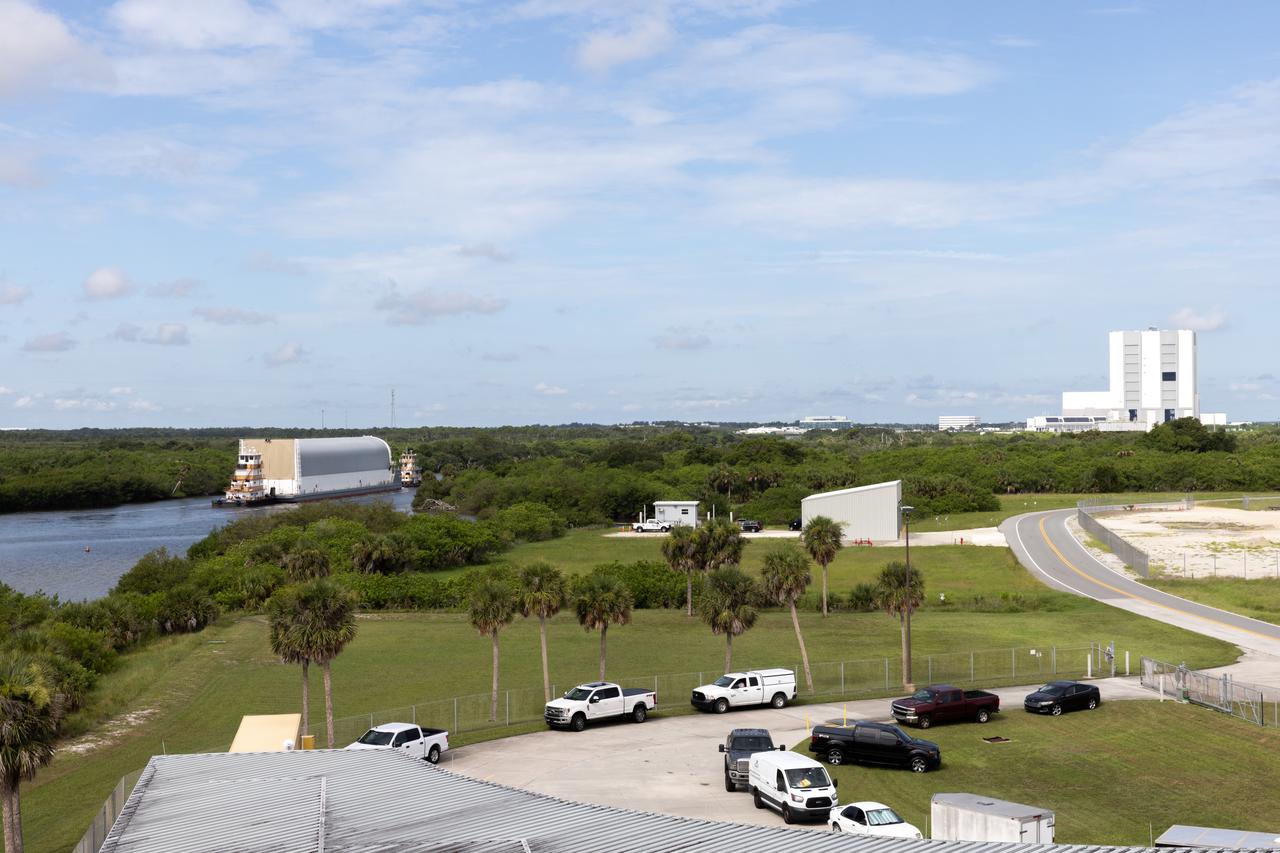

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
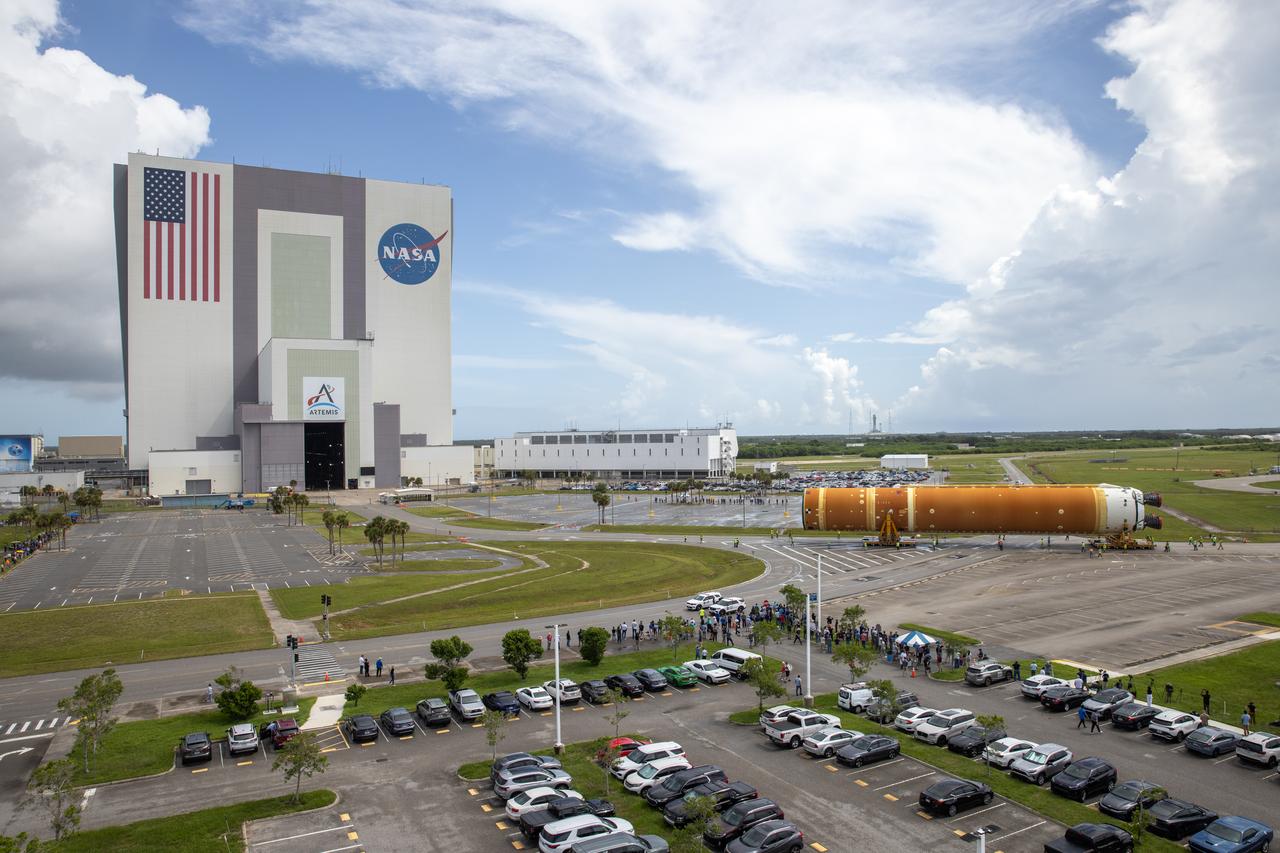

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
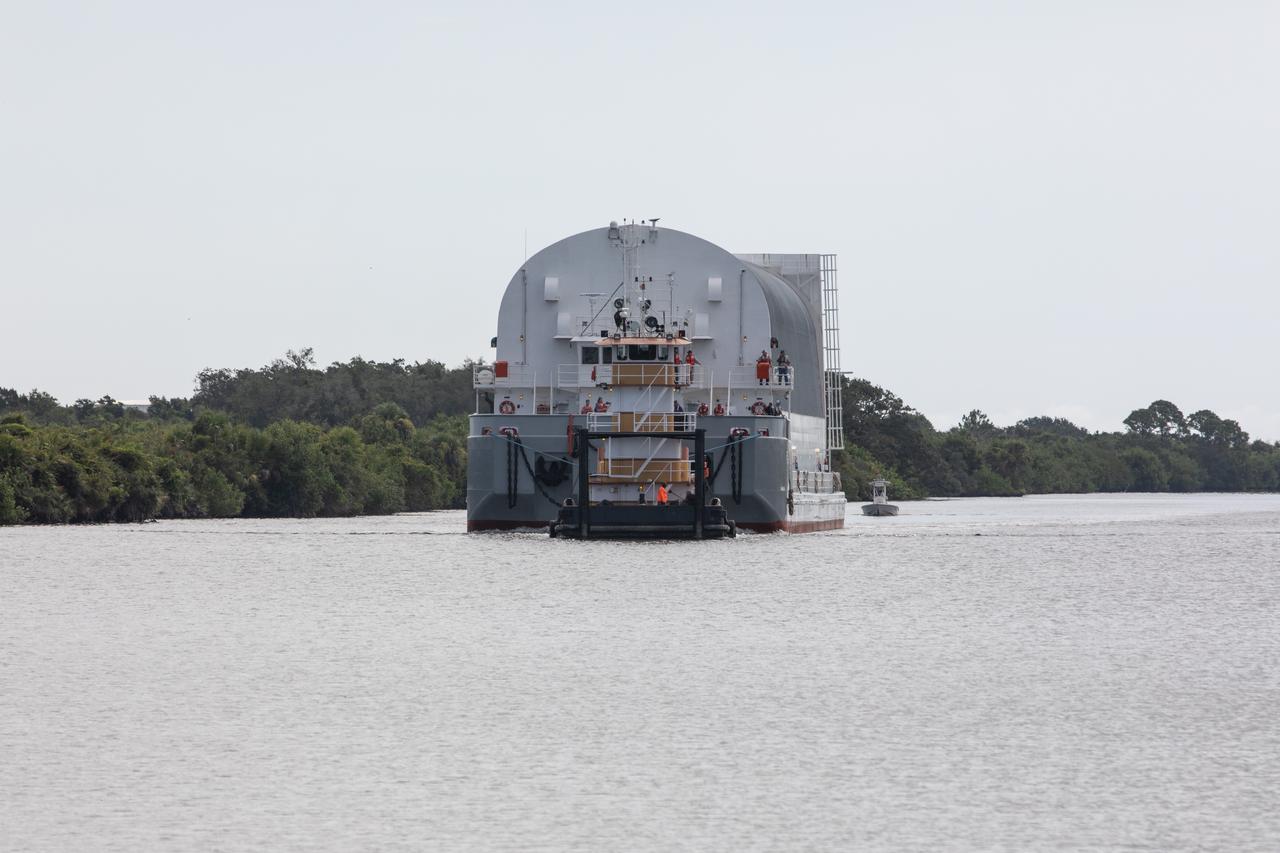

Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with NASA's Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
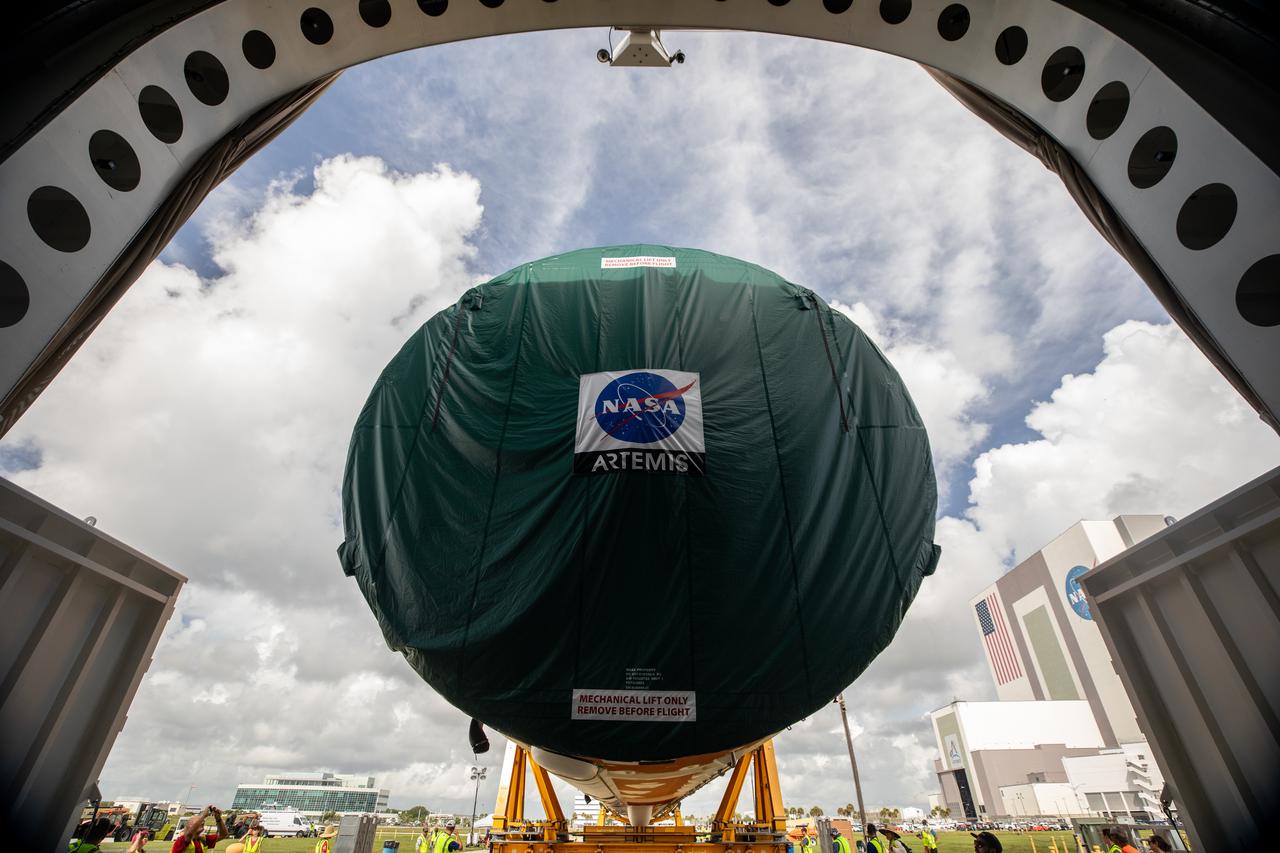

NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24, 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
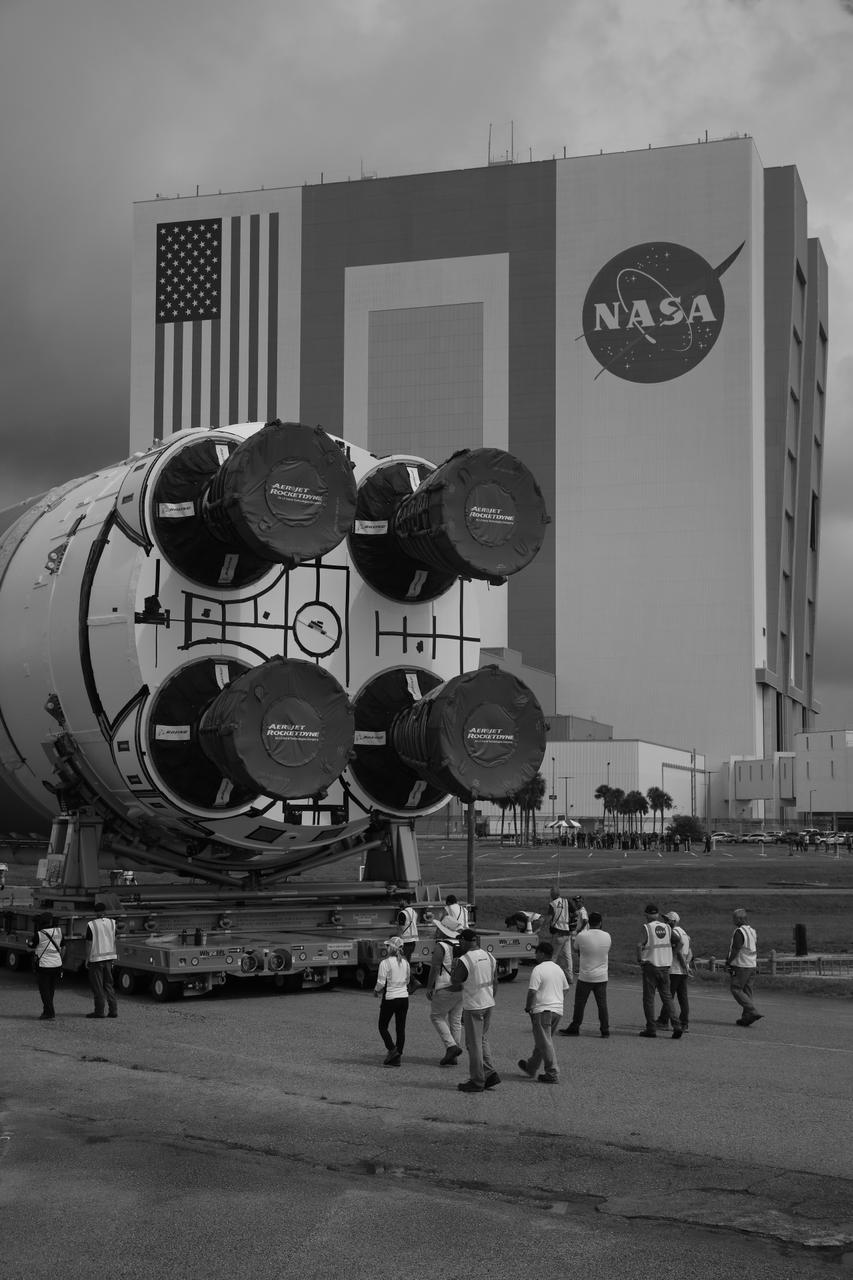

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
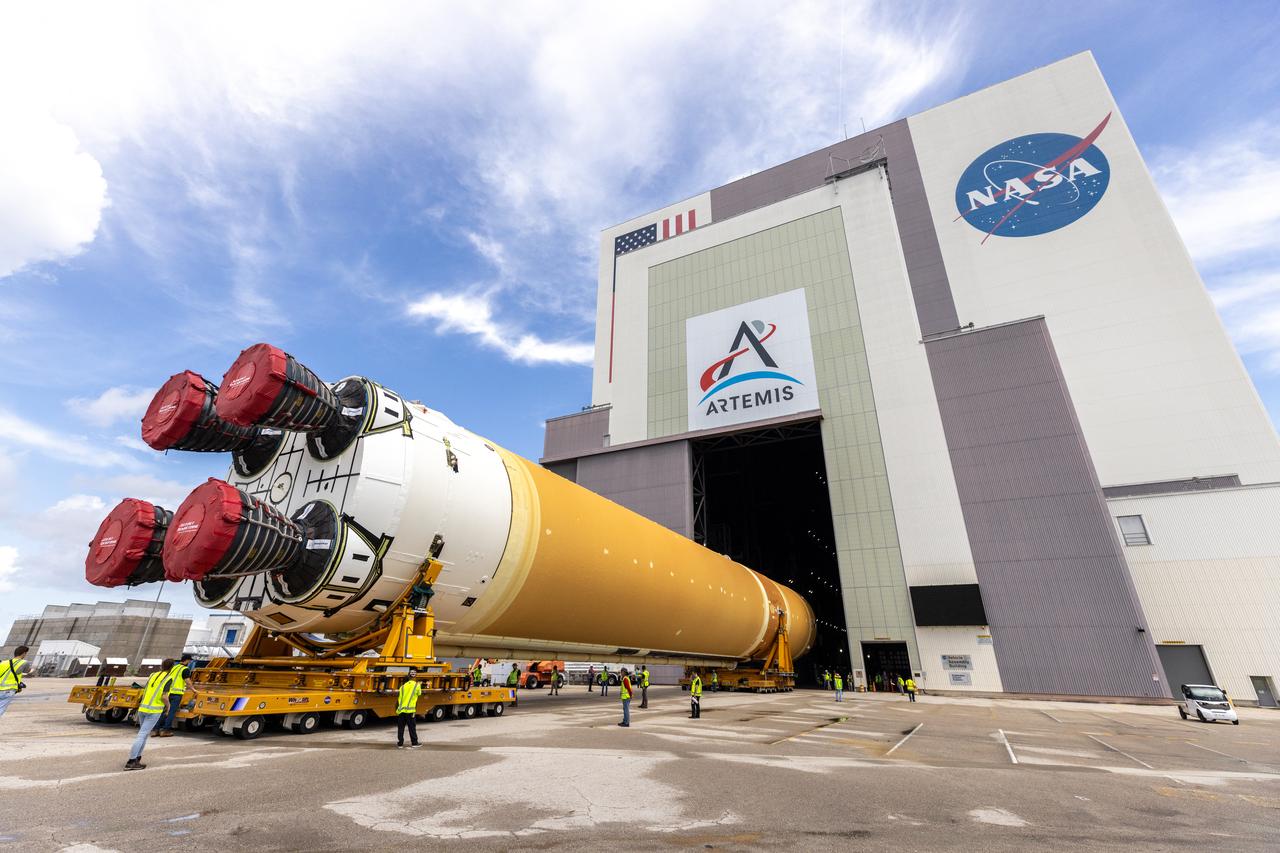

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
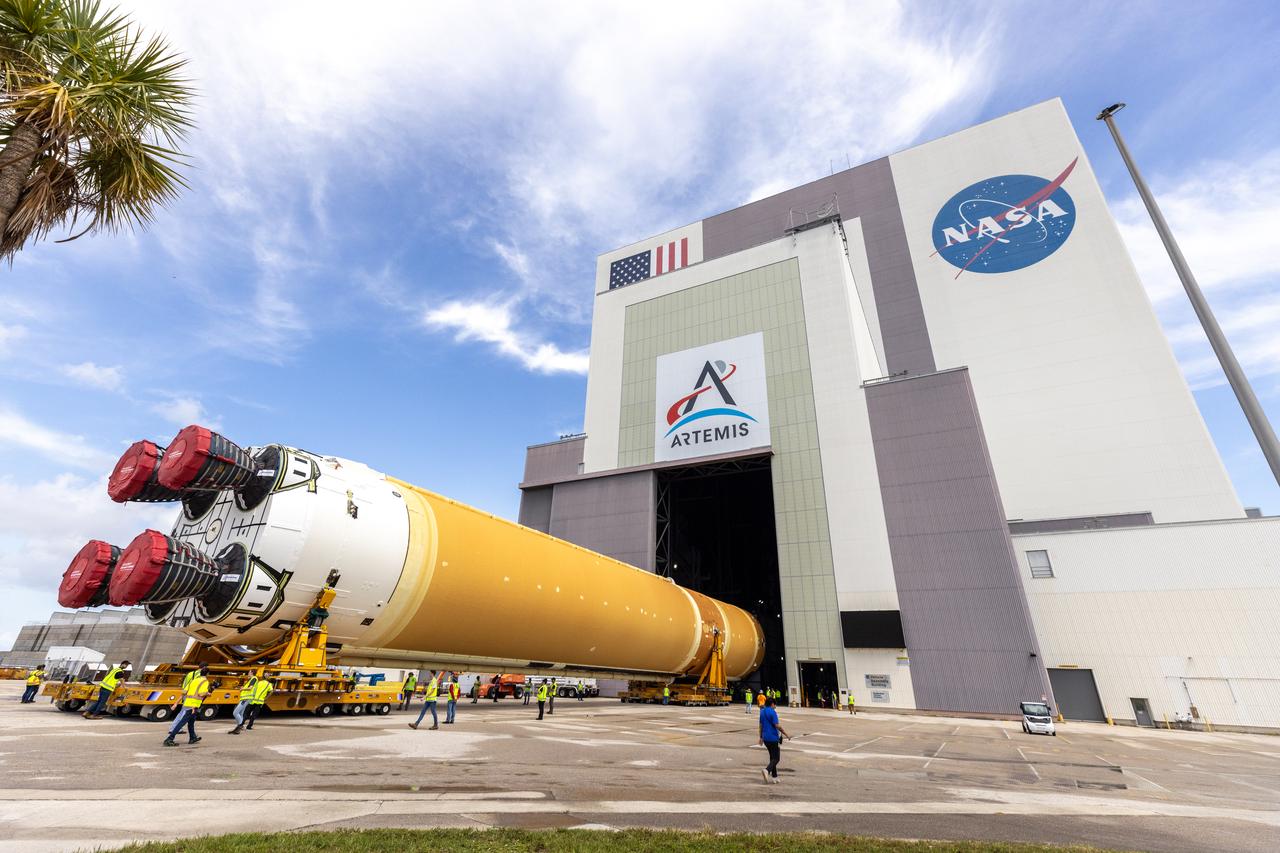

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
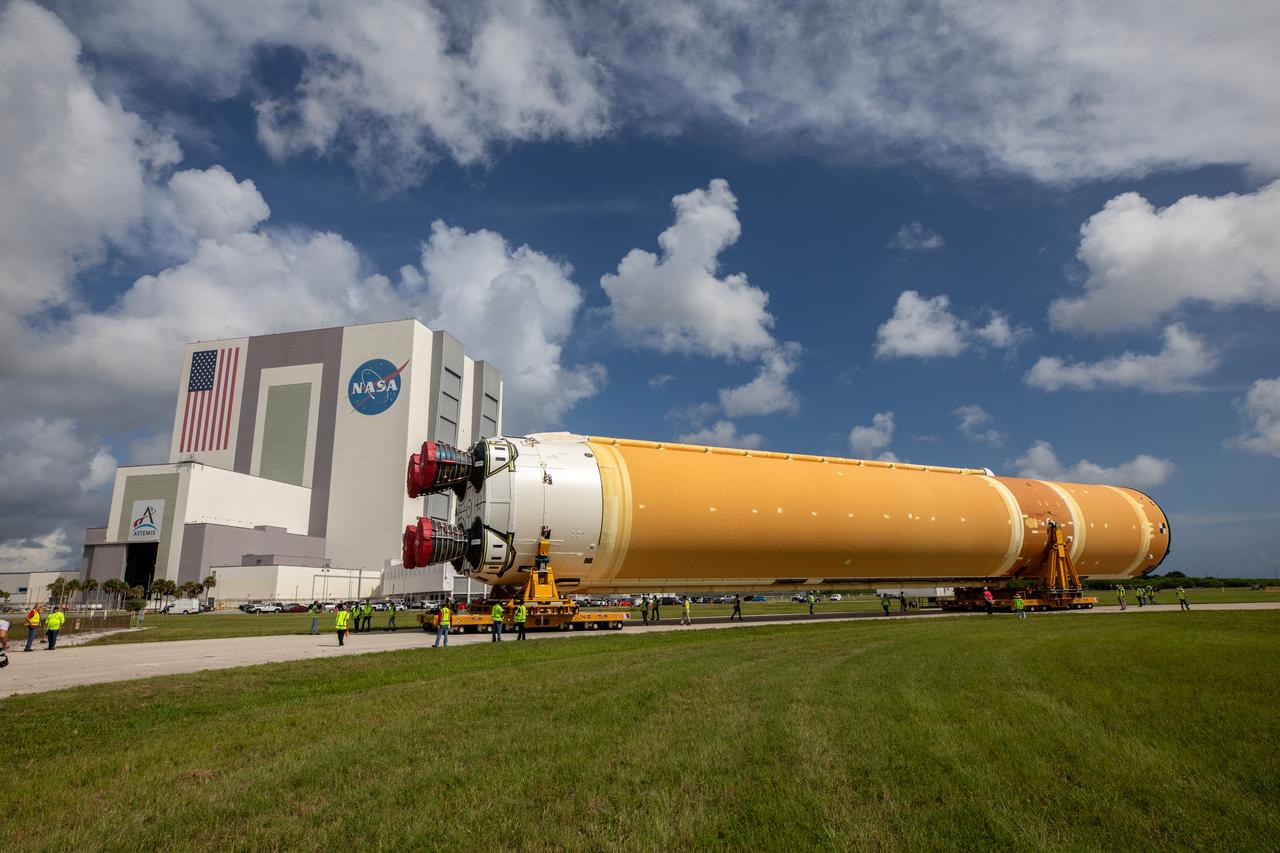

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
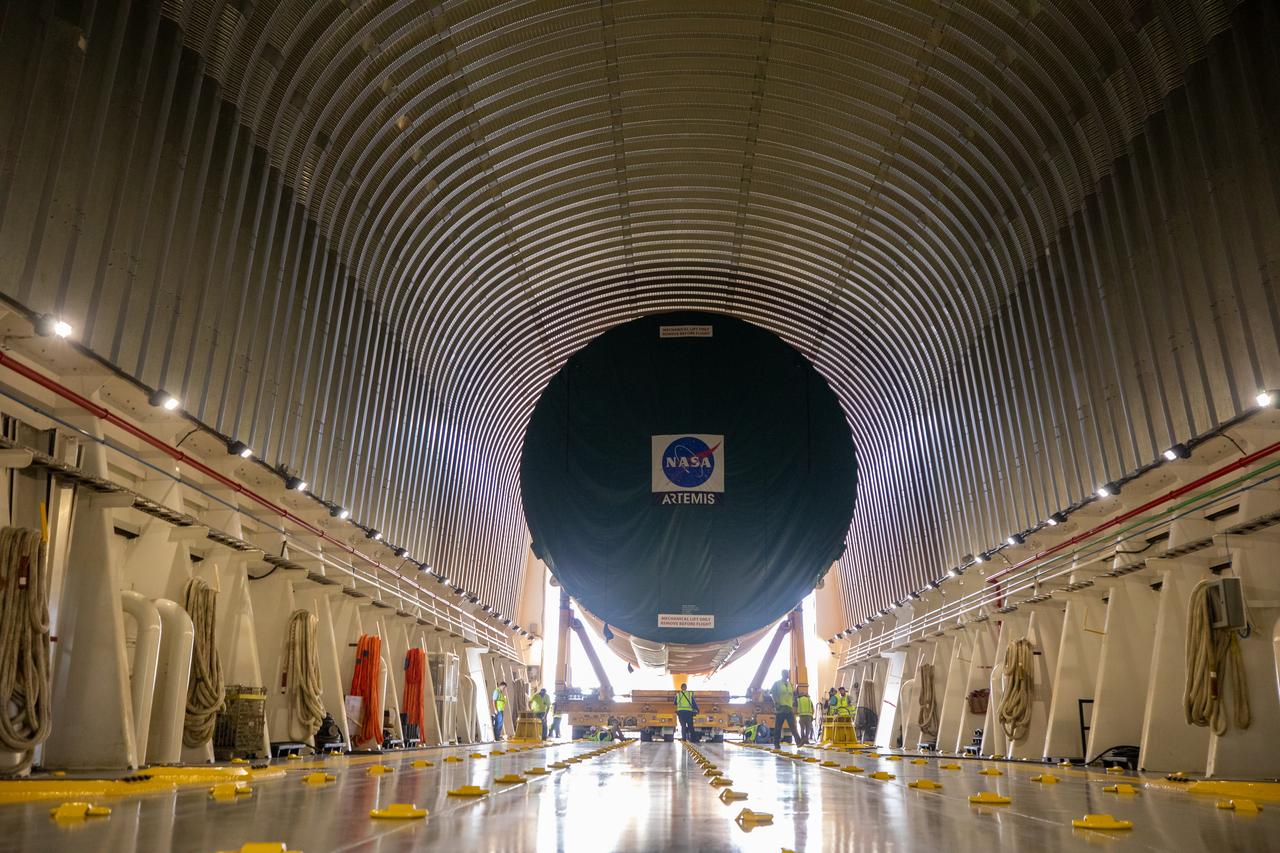

NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24, 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
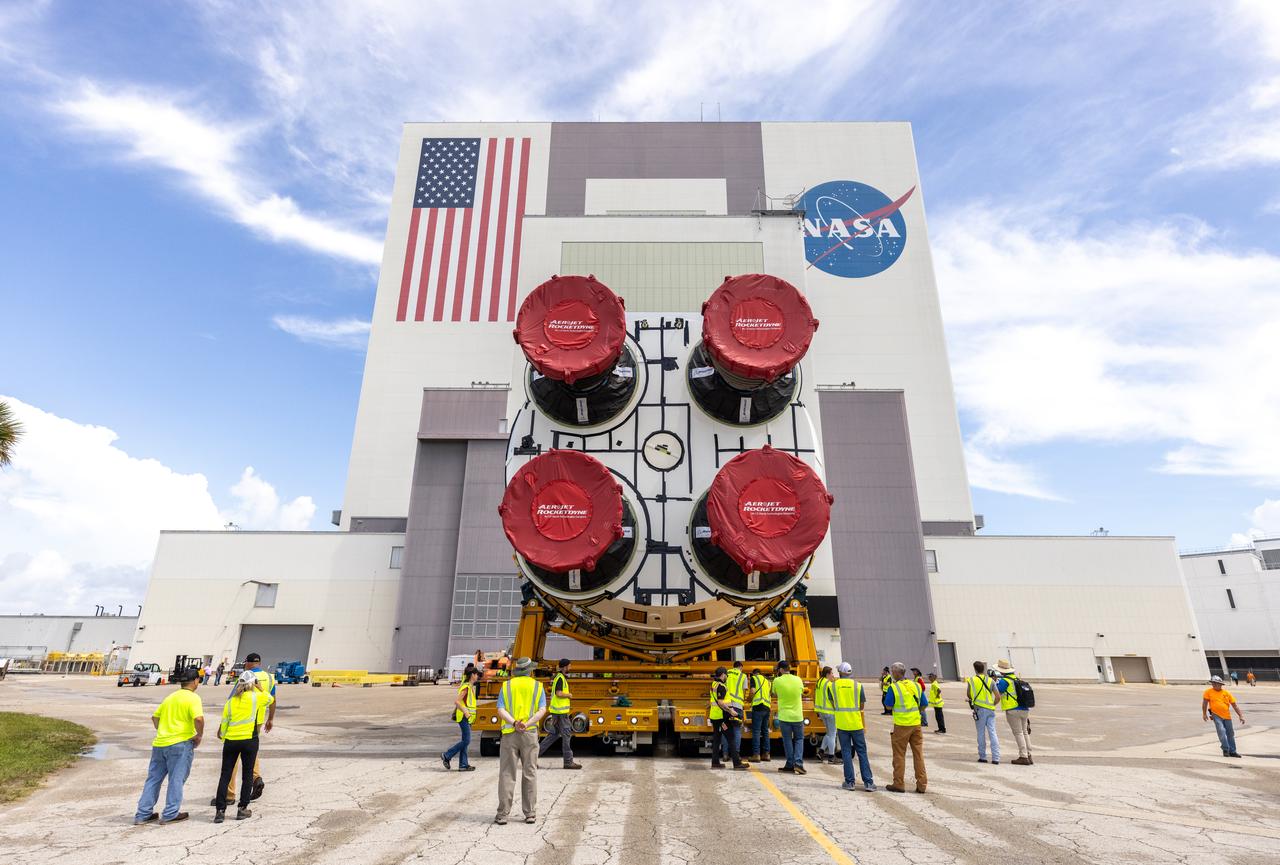

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
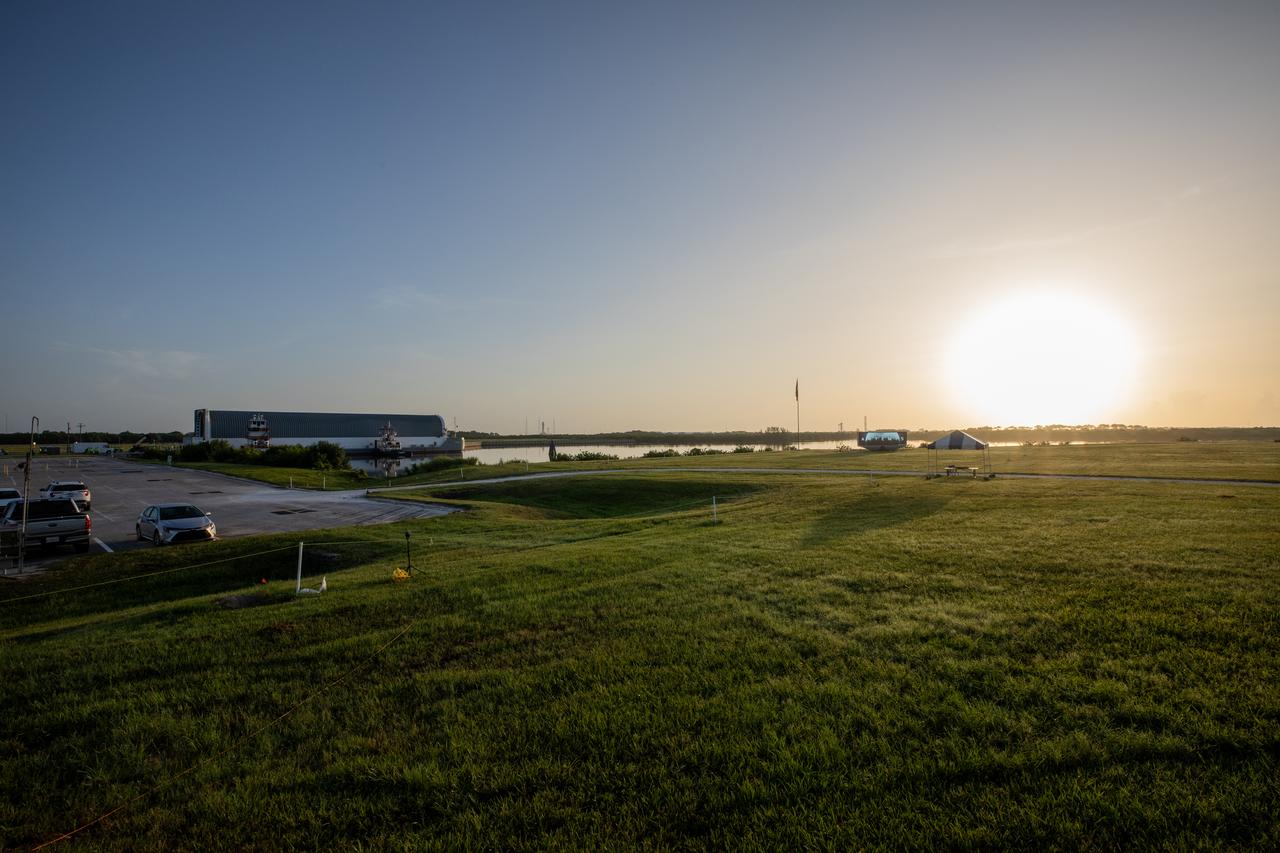

The sun rises over NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
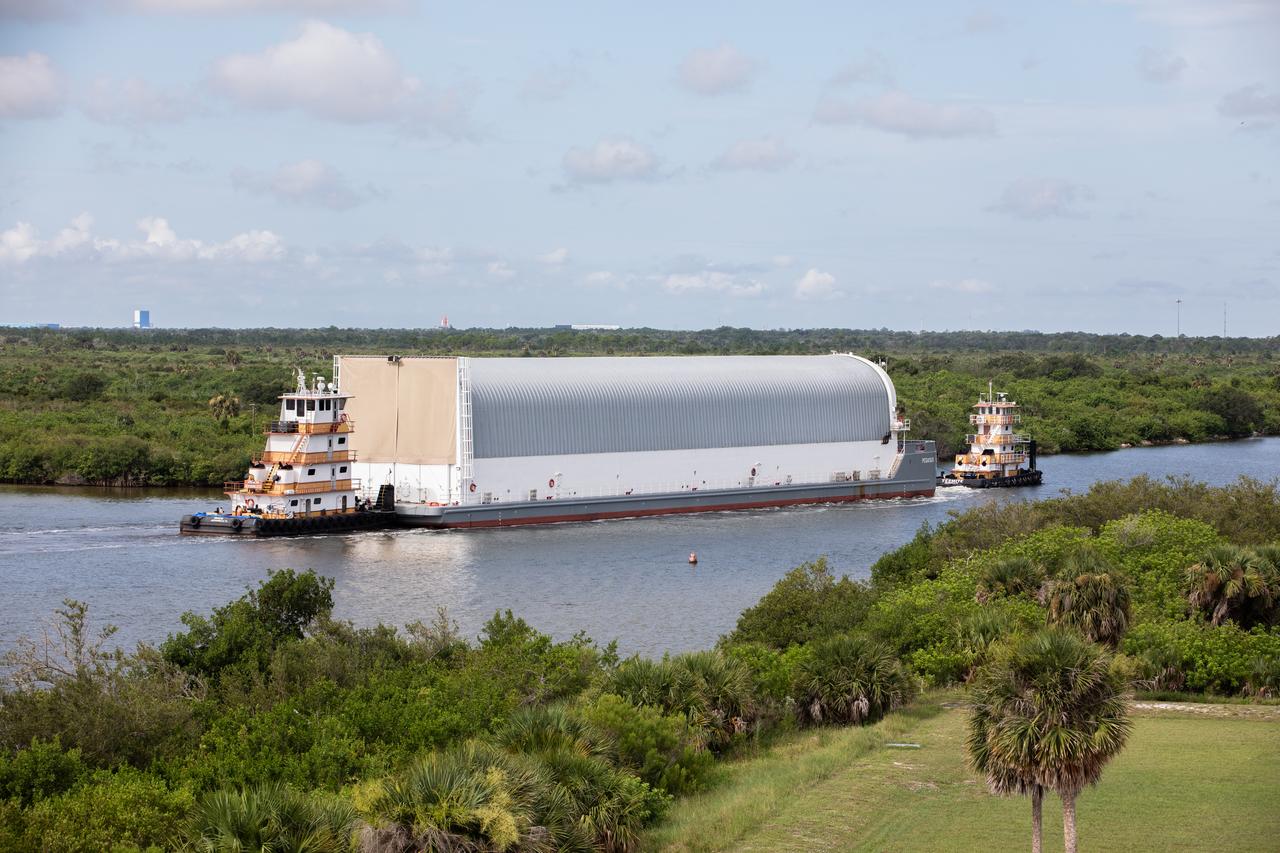

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
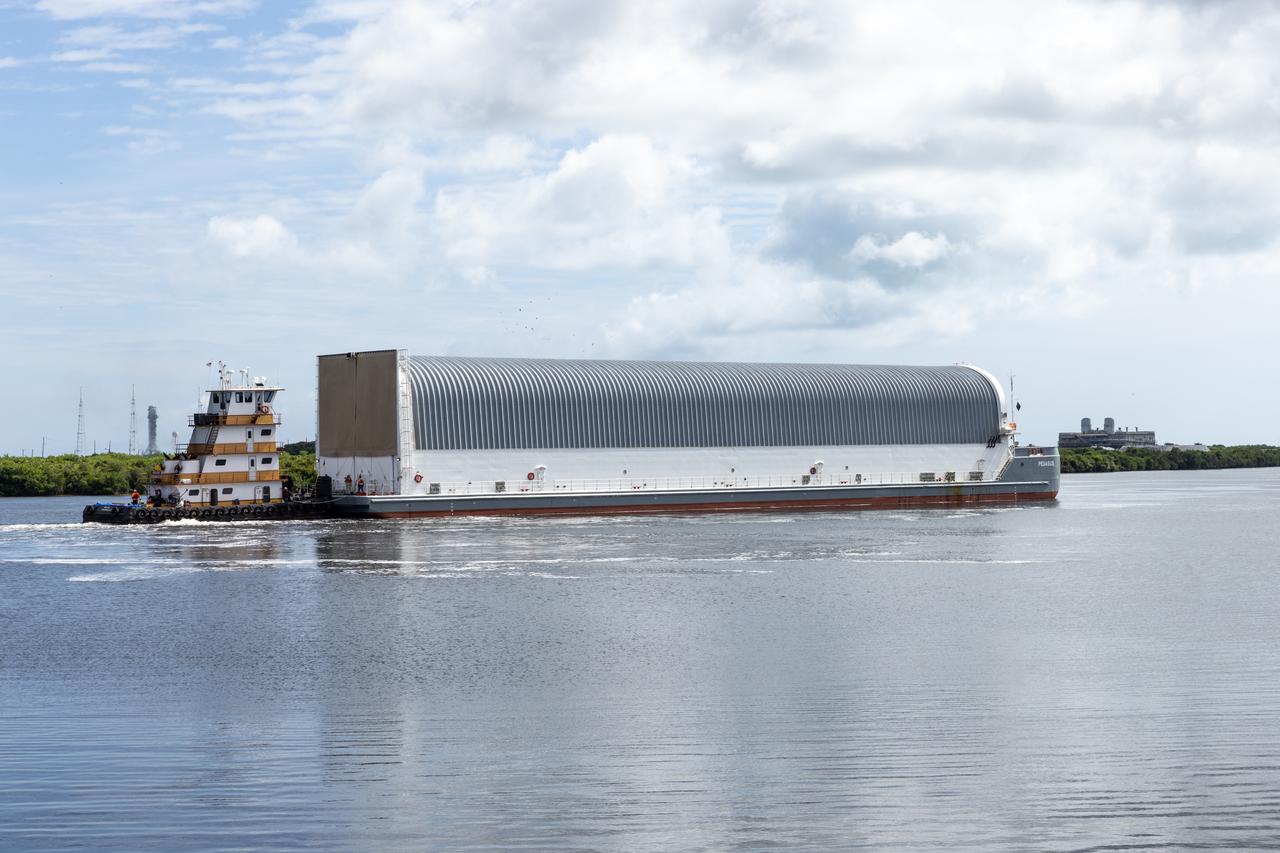

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
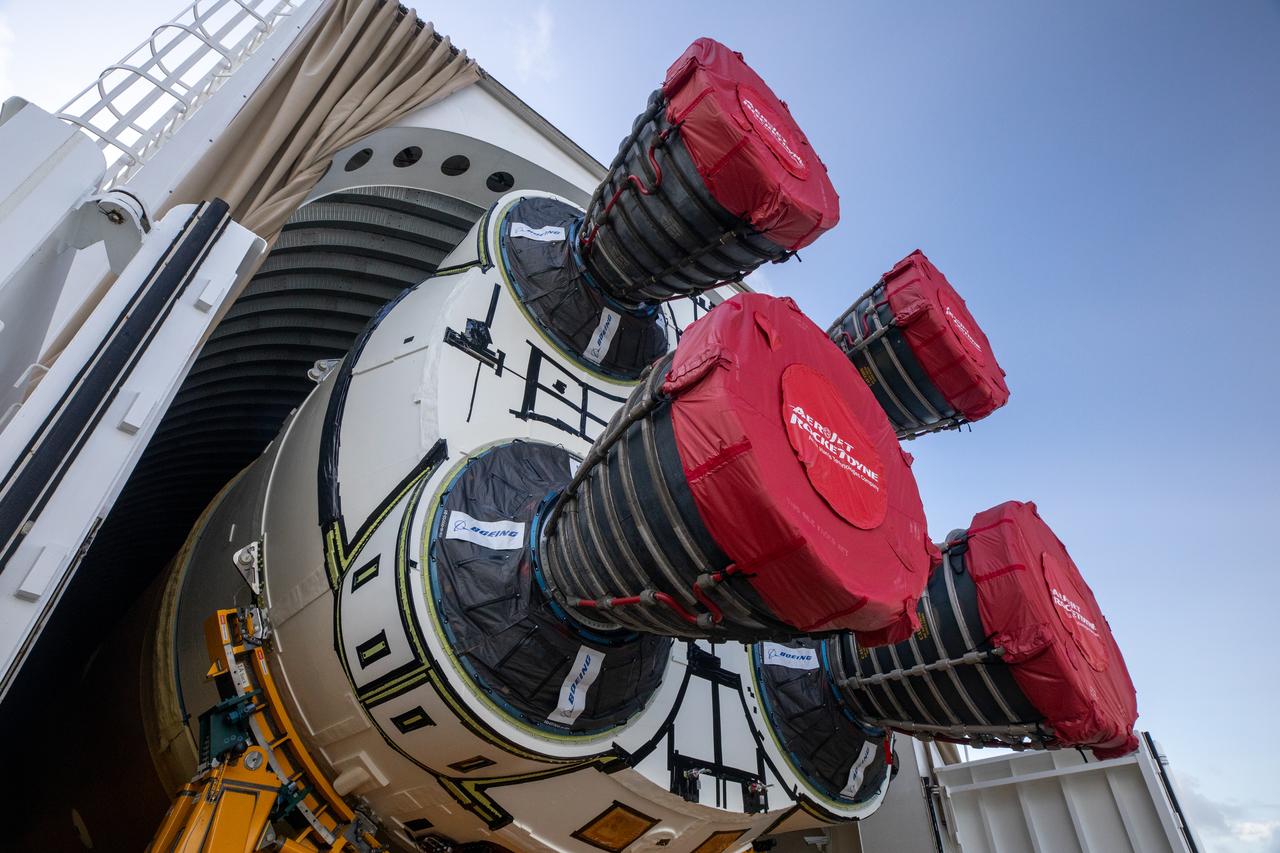
NASA’s massive 212-foot long SLS (Space Launch System) core stage is offloaded from the agency’s Pegasus Barge on Wednesday, July 24, 2024, after arriving at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will transfer the rocket stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
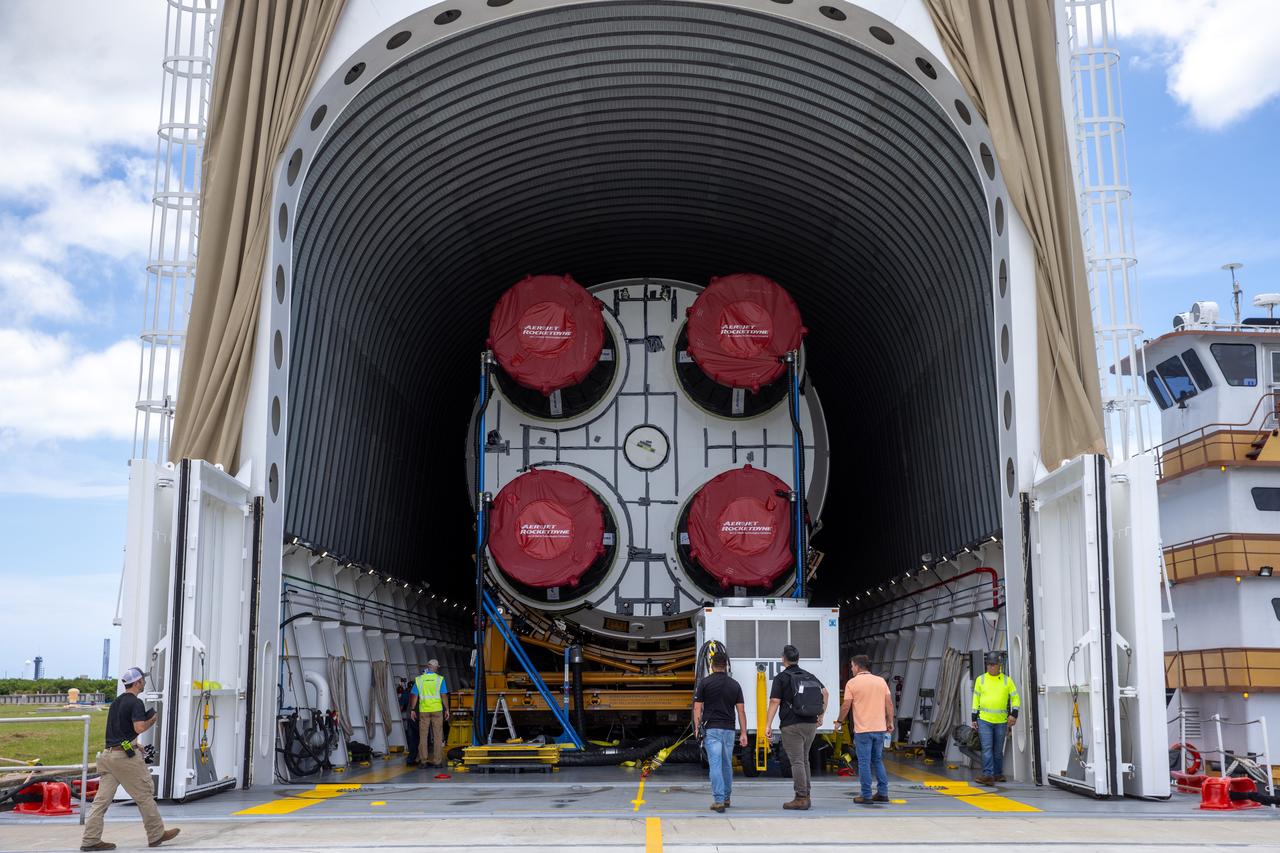

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
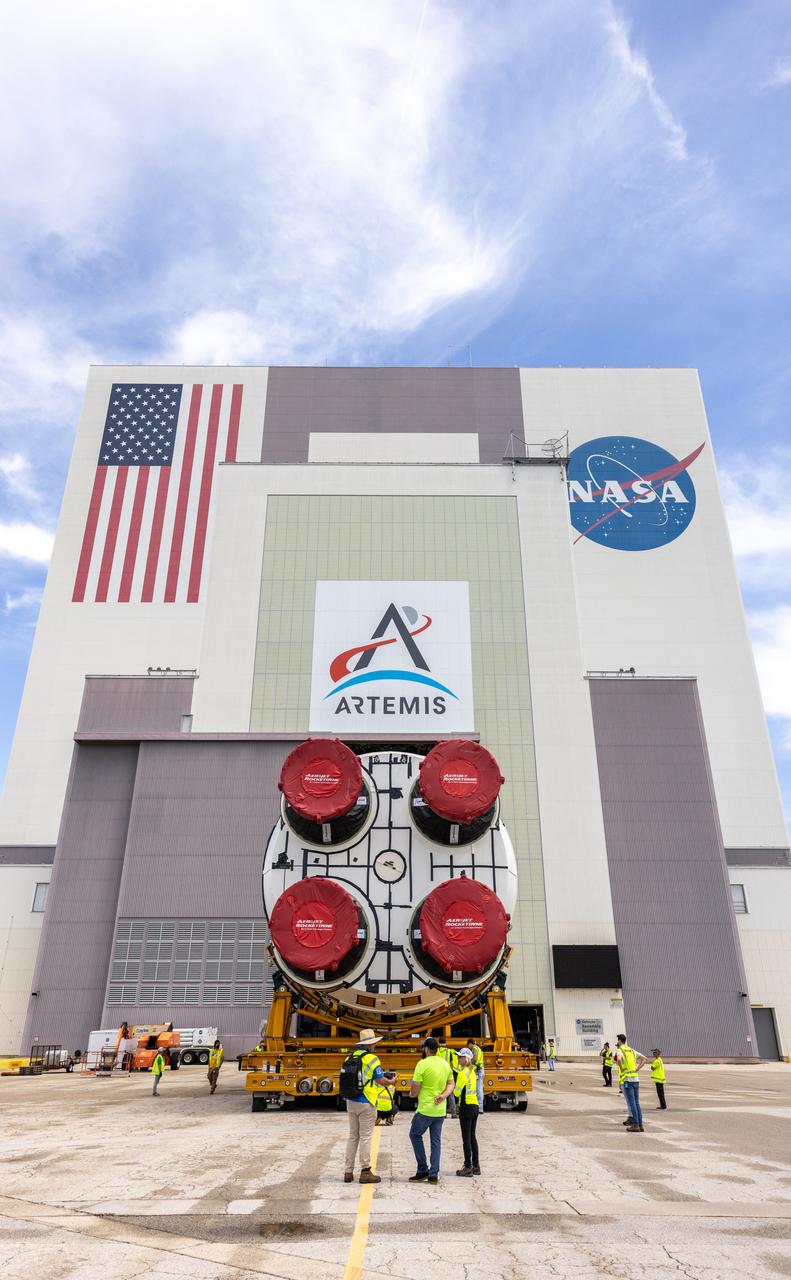

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
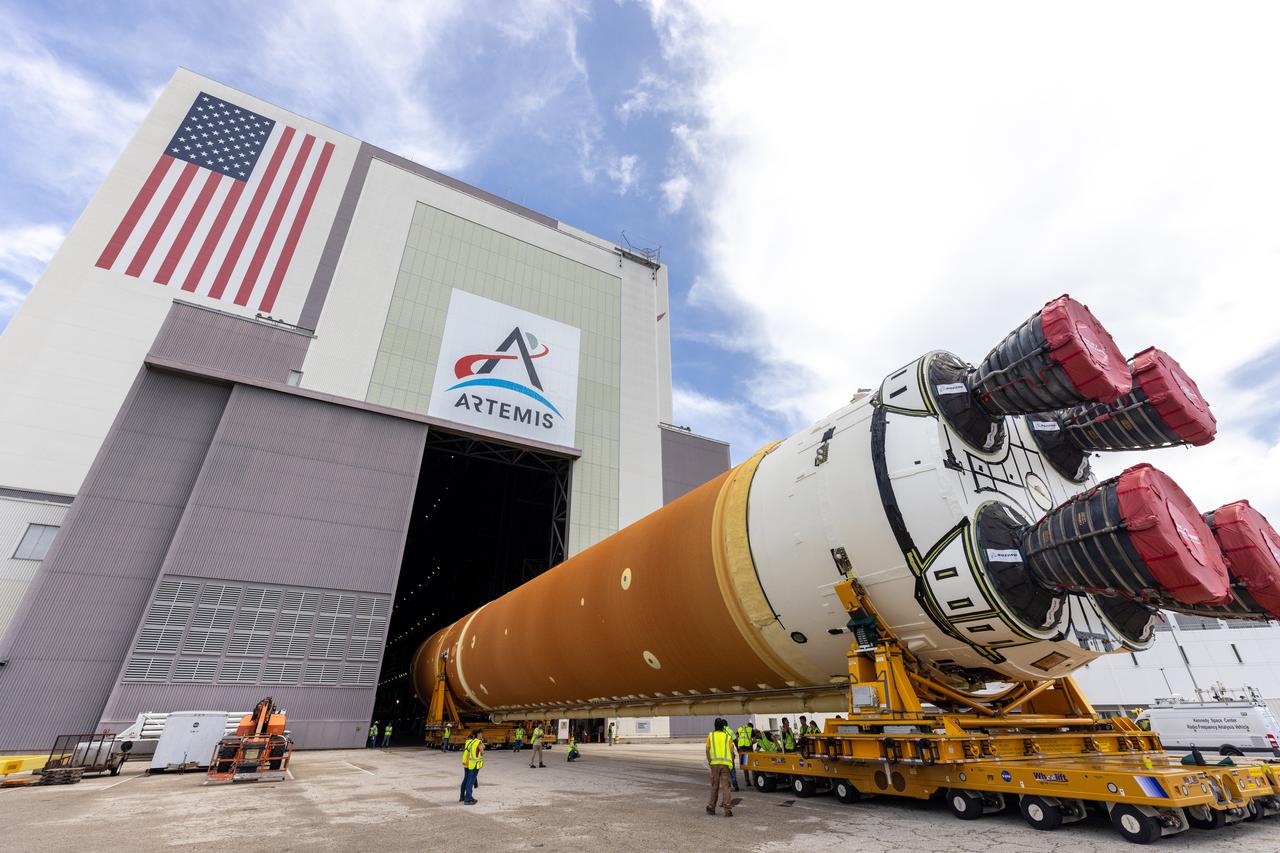

After completing its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge, teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
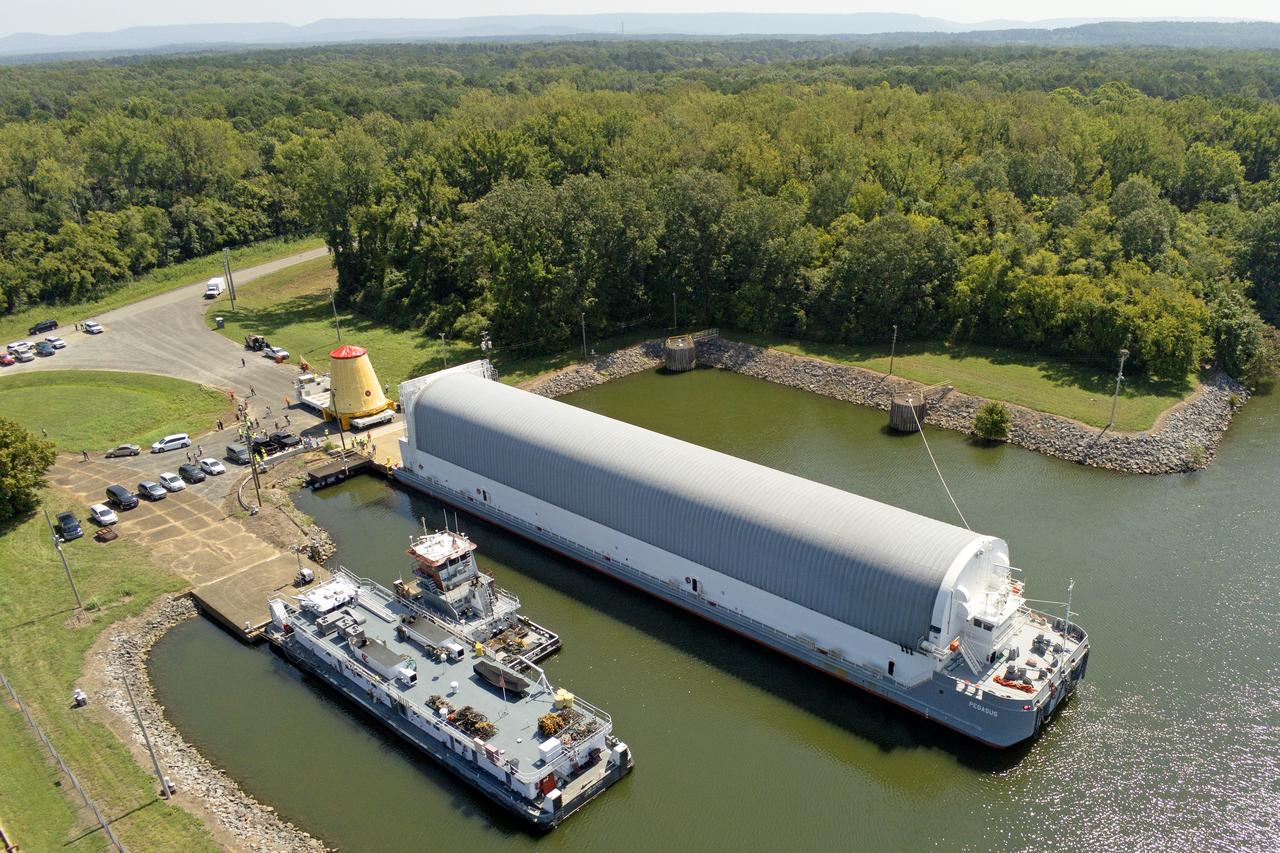

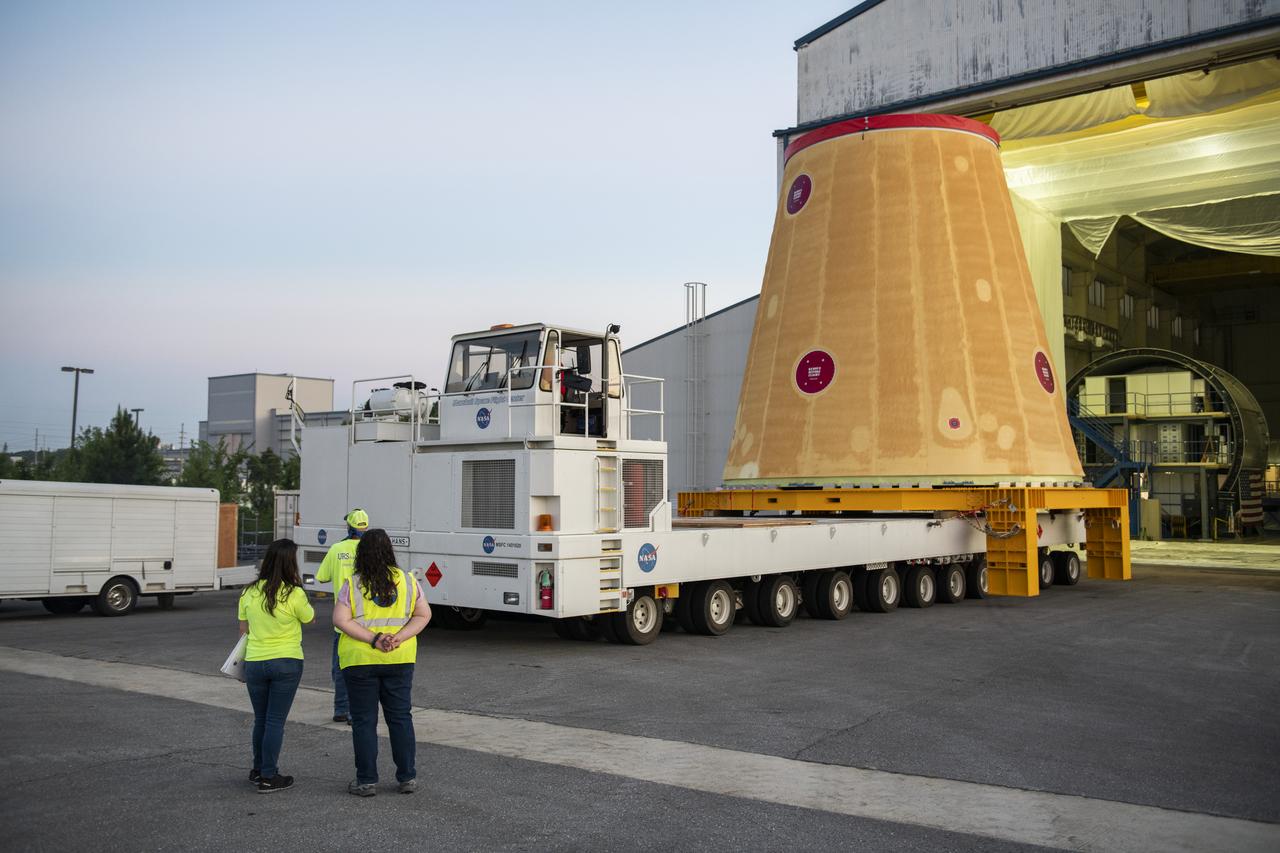
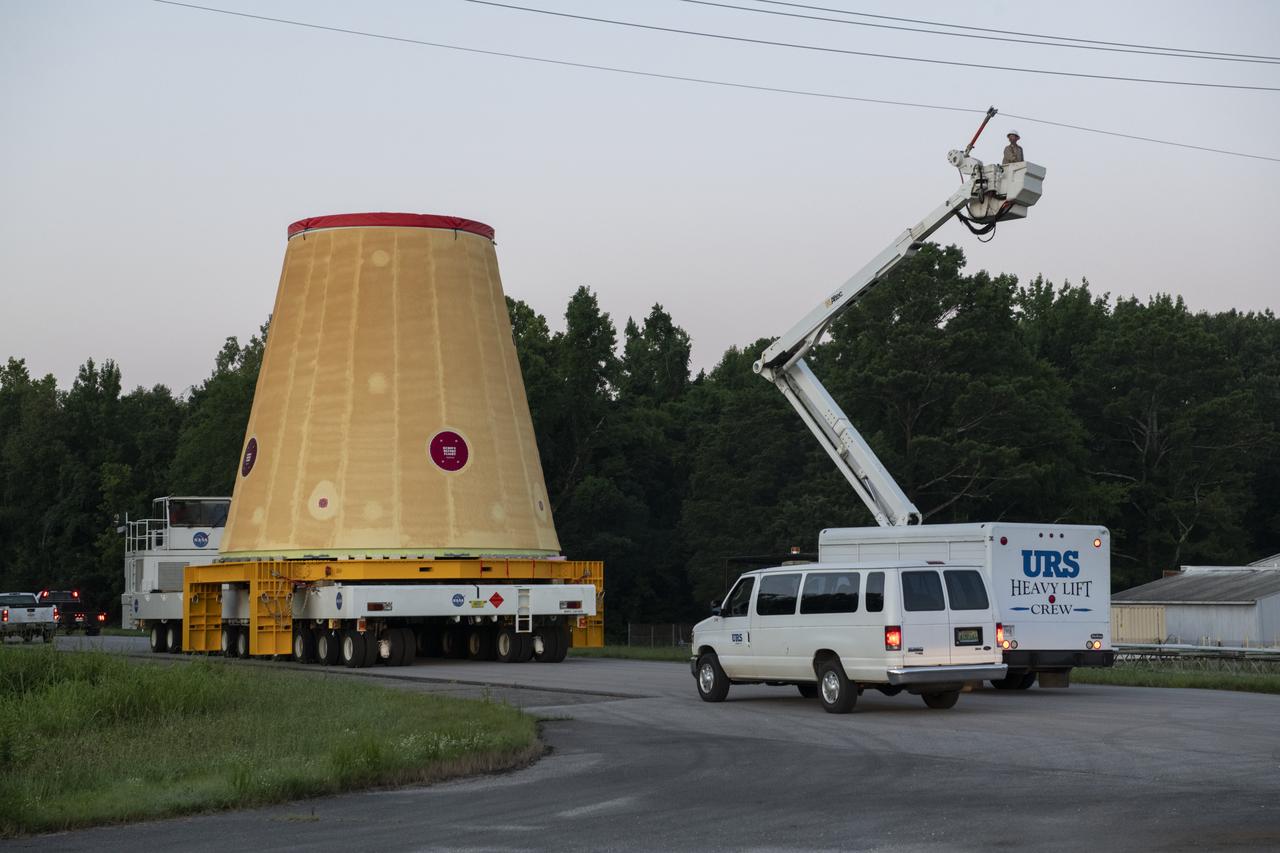
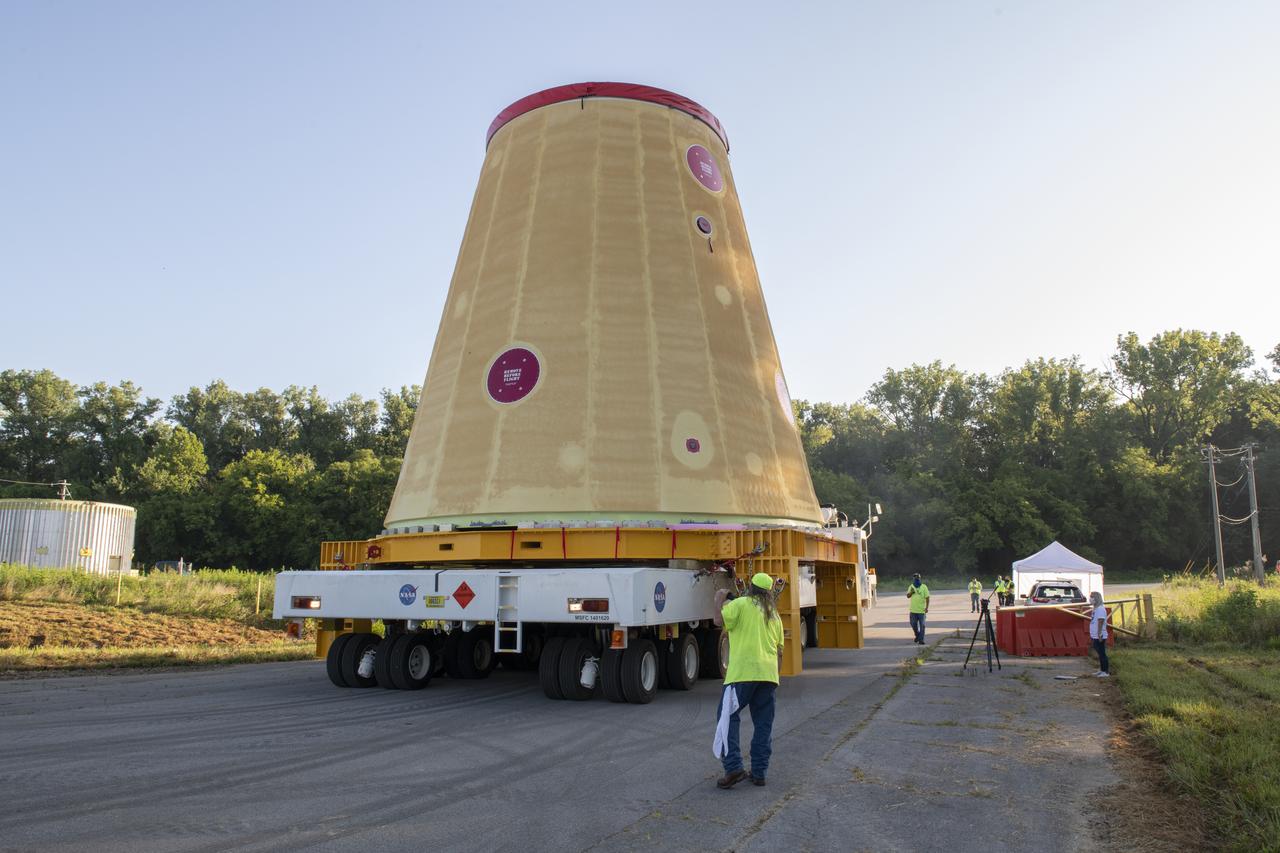
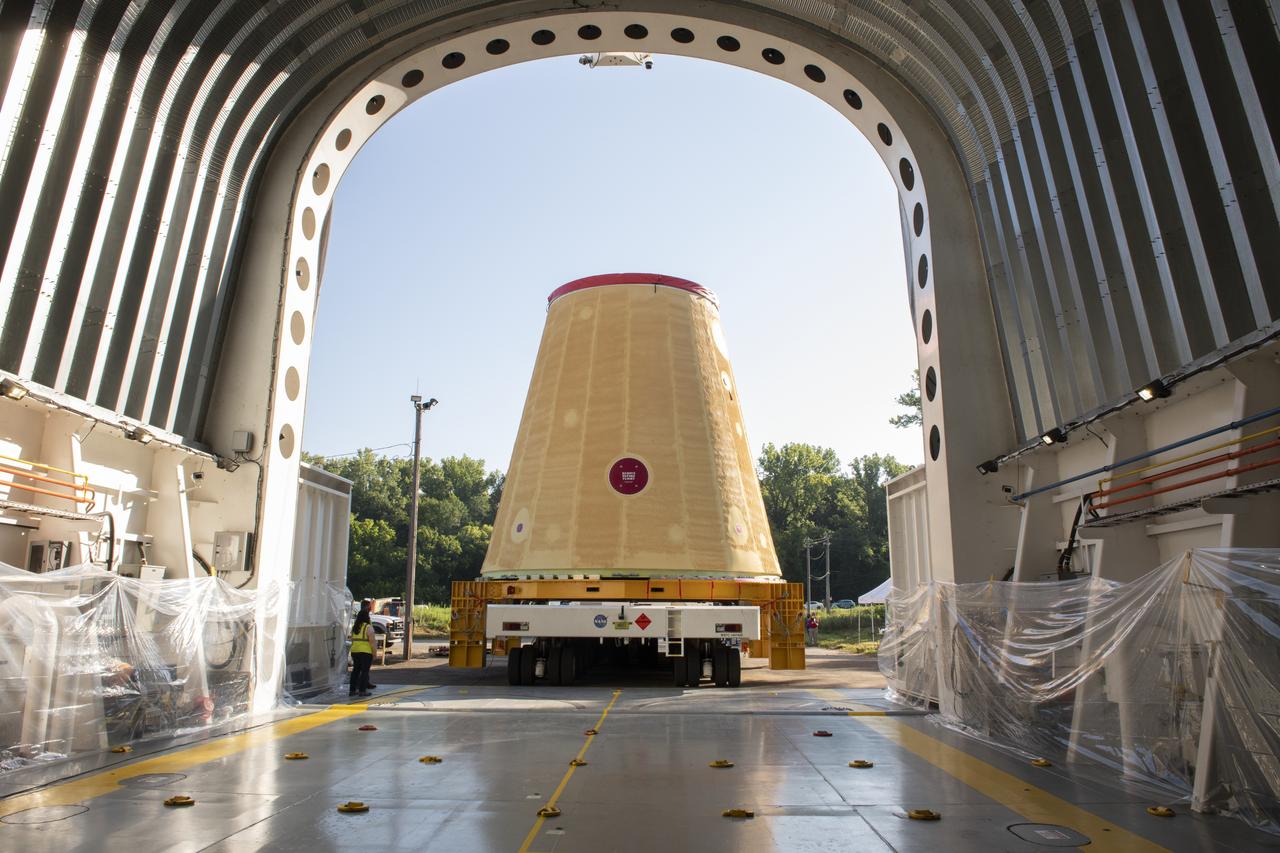
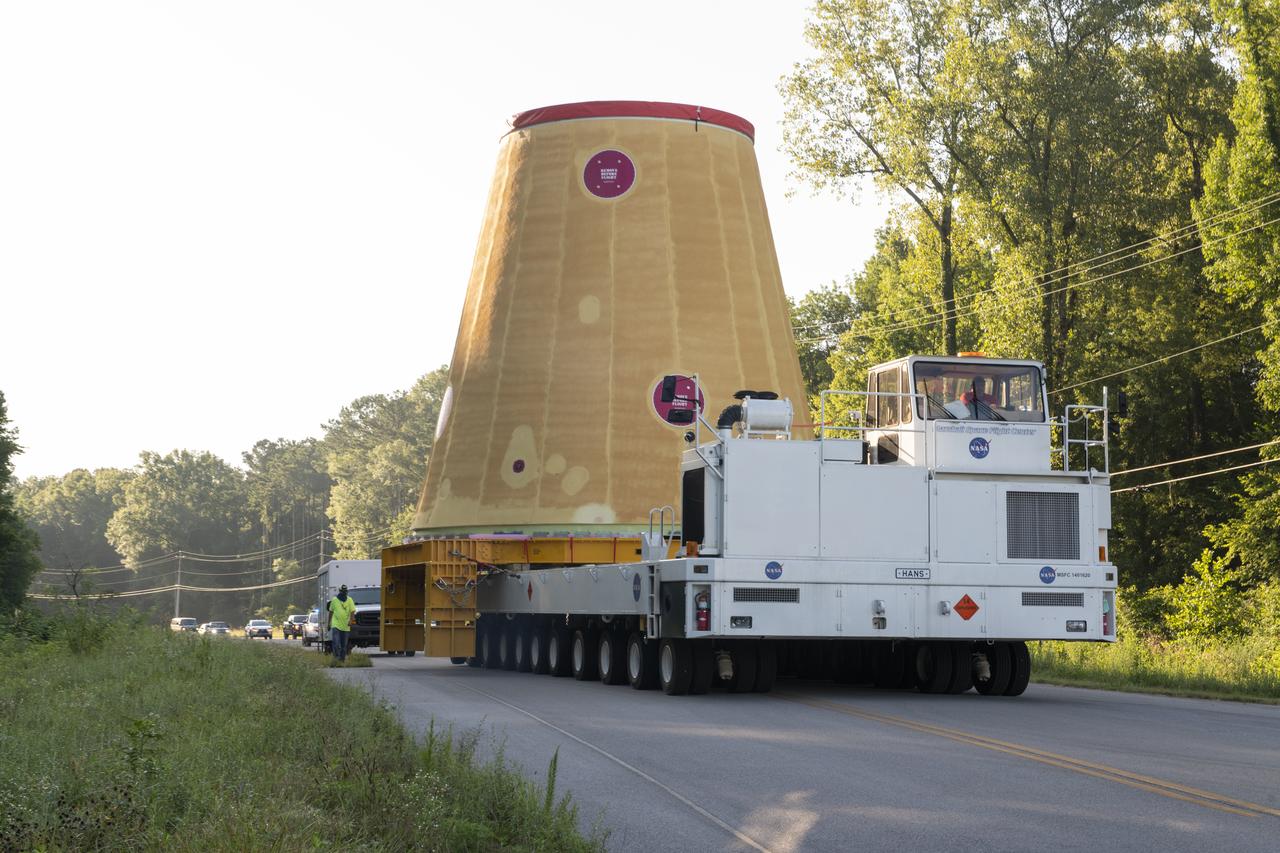
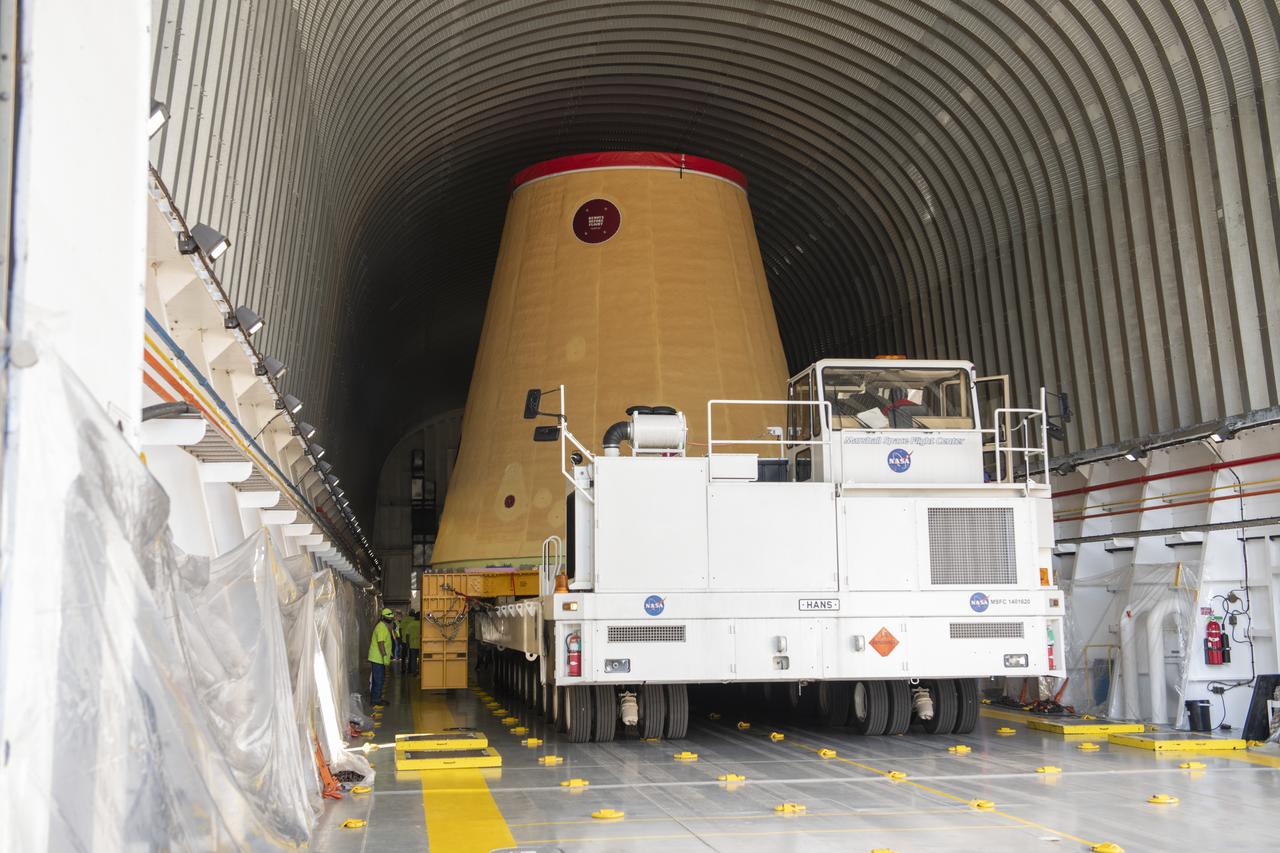
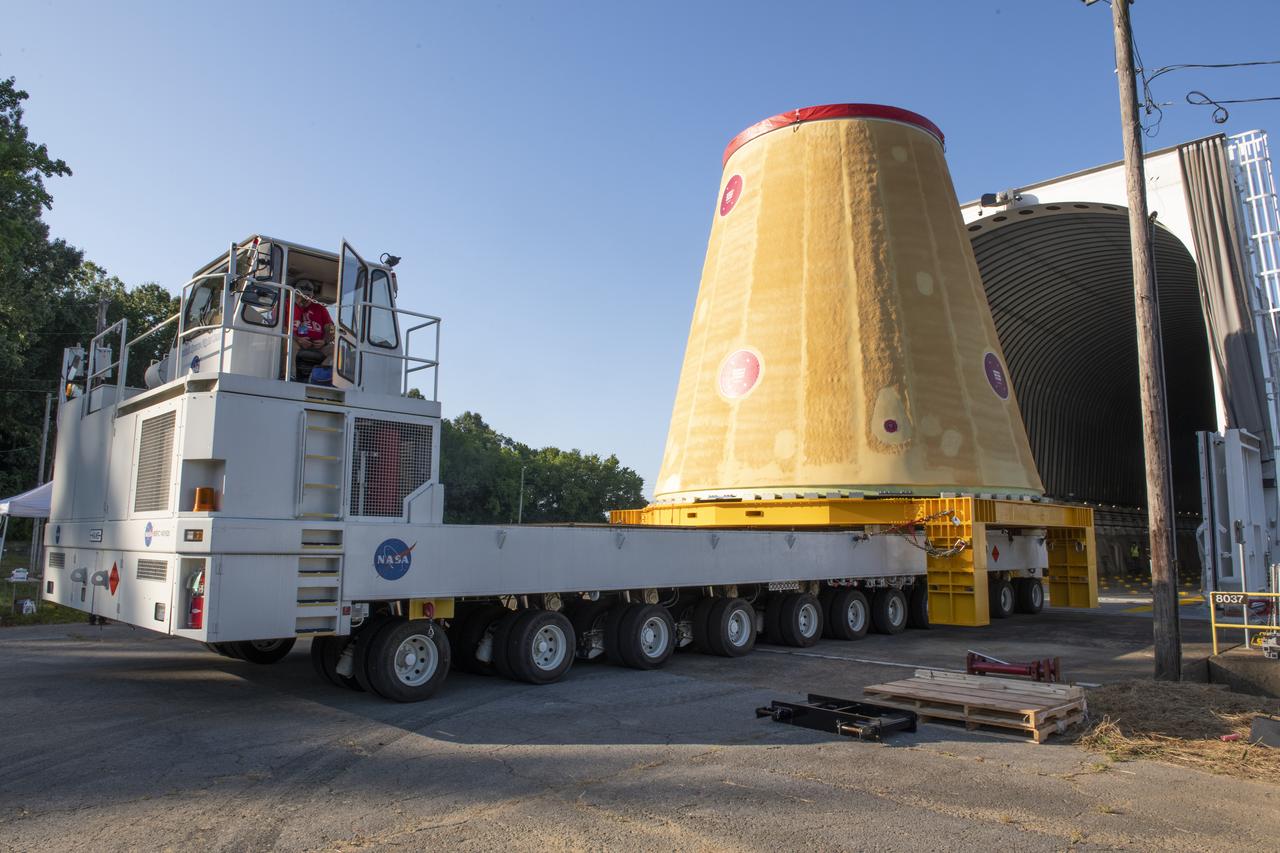
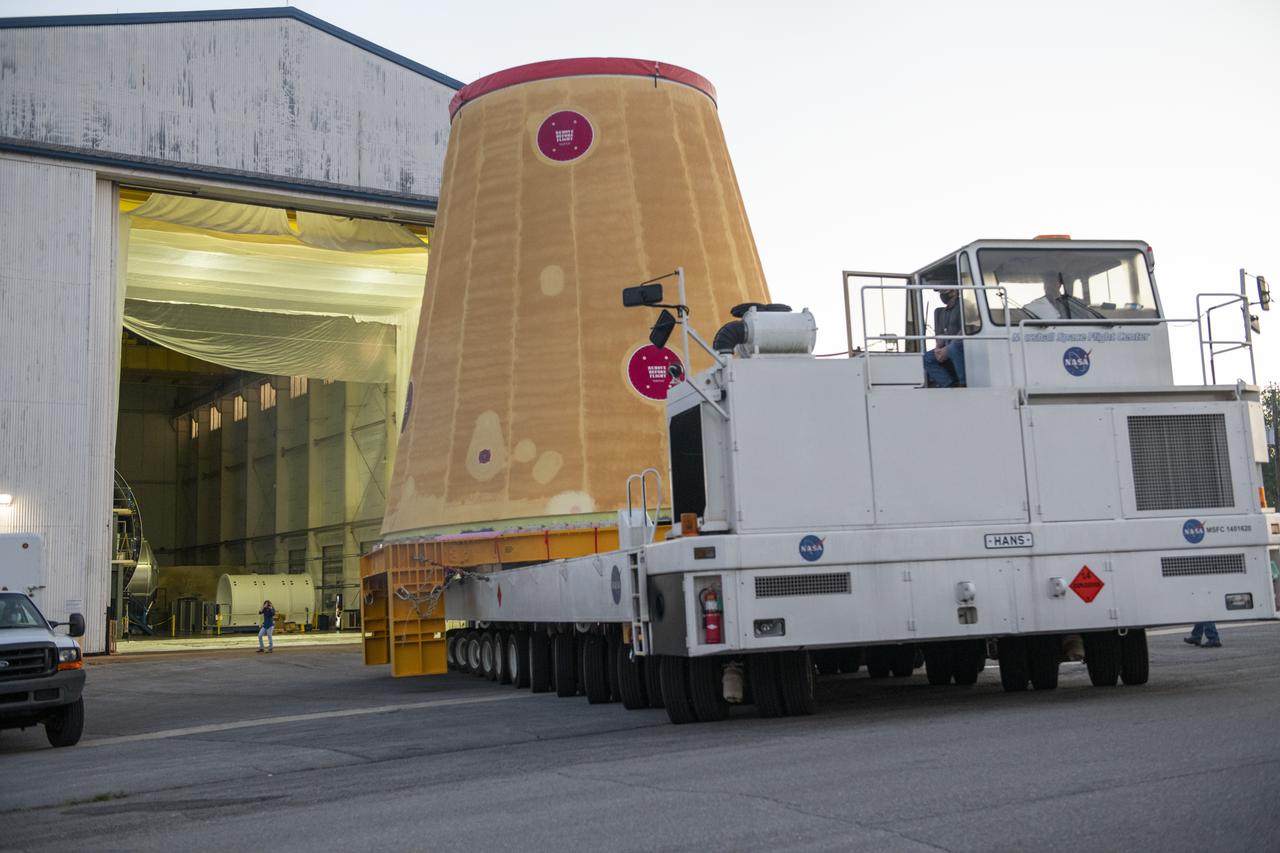
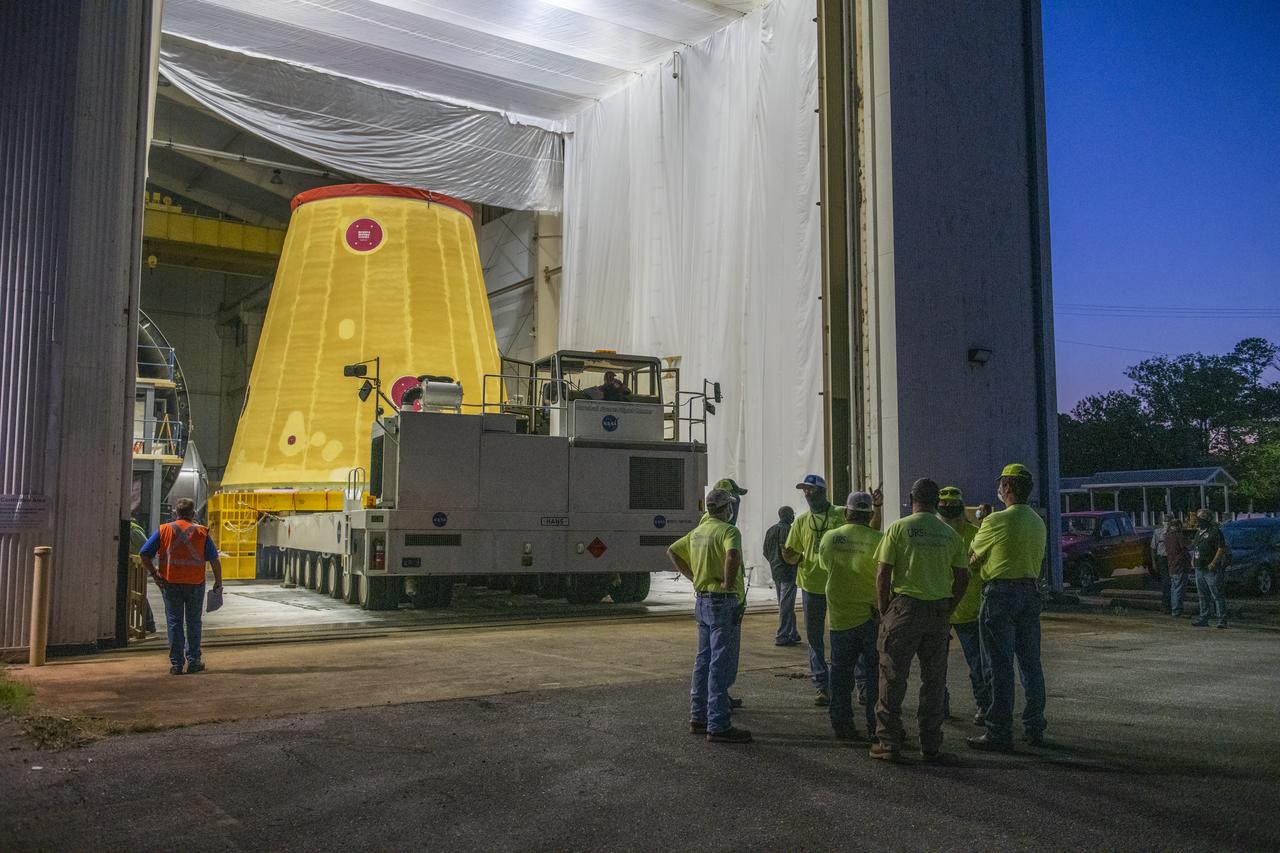
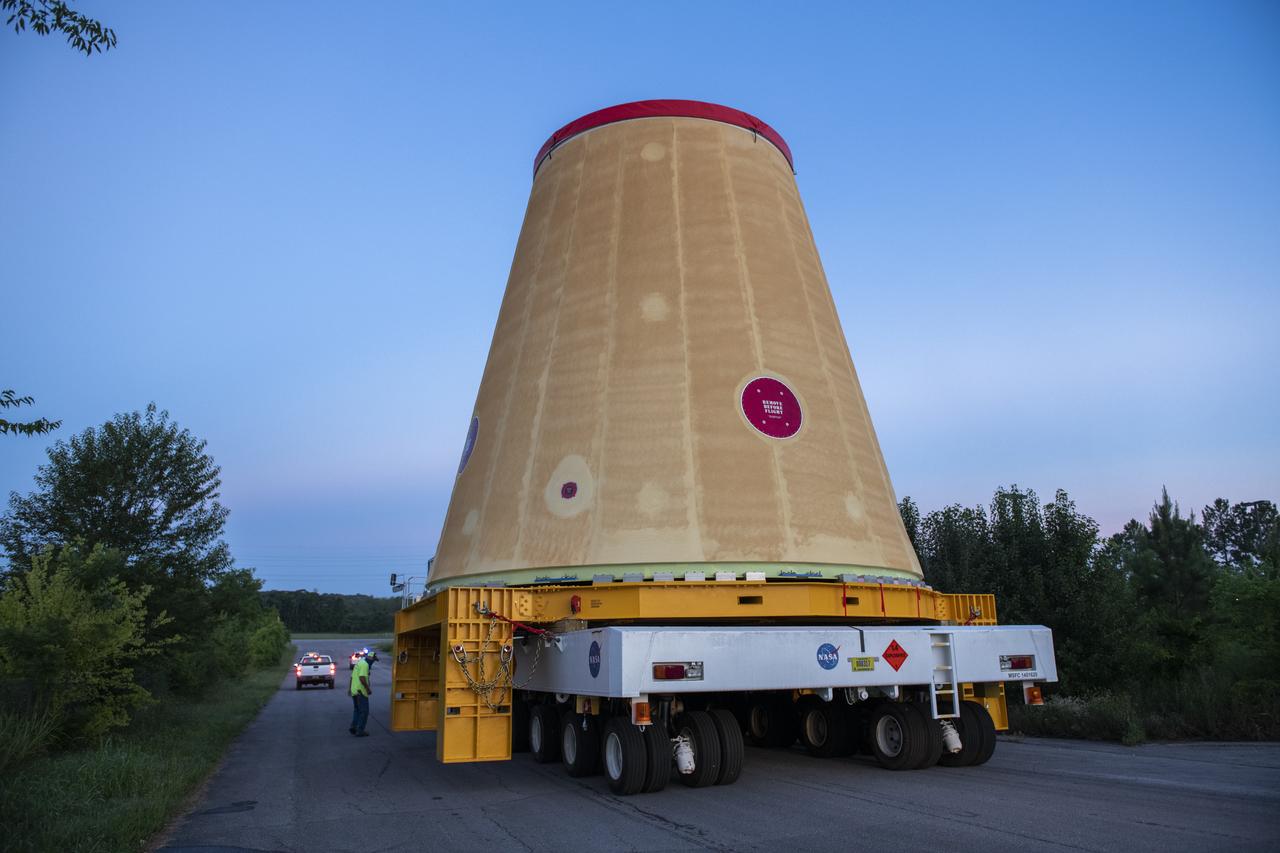
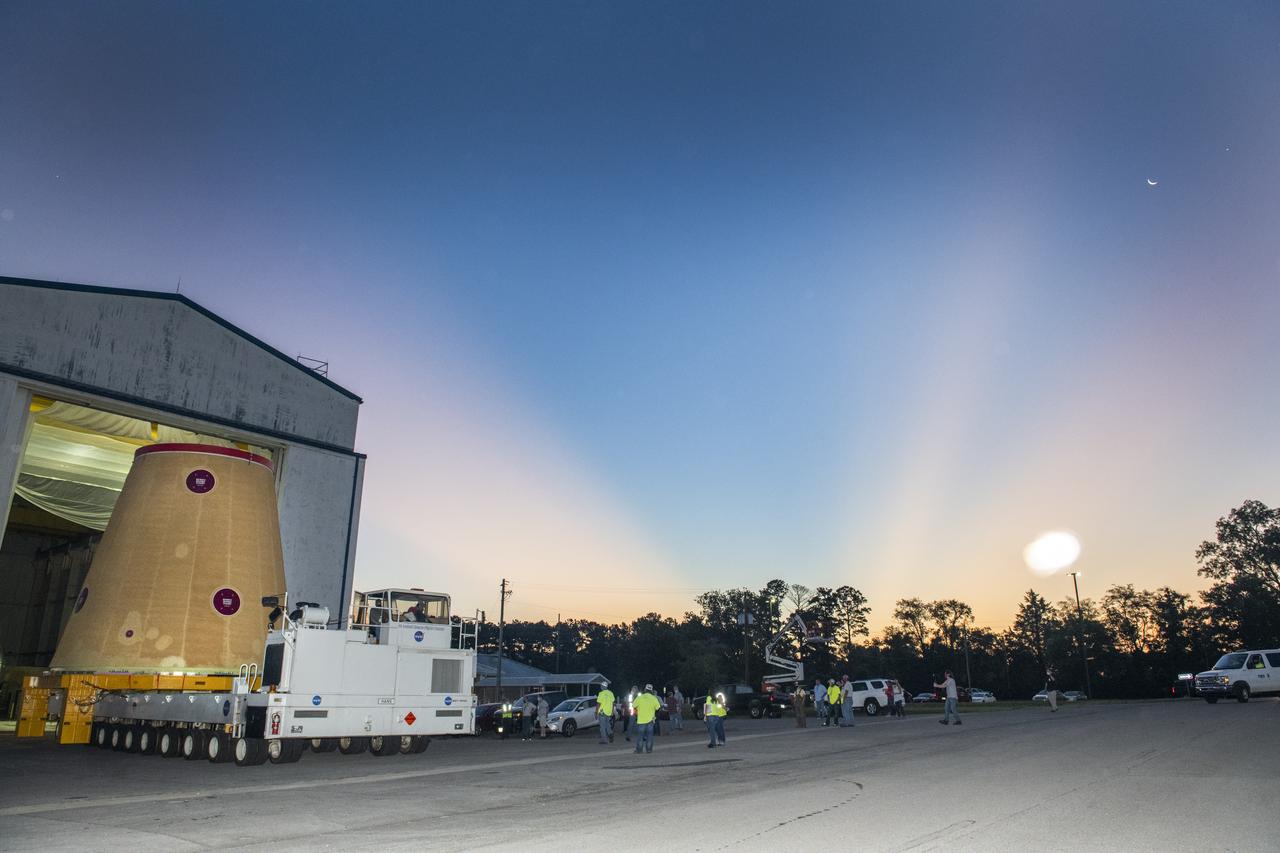
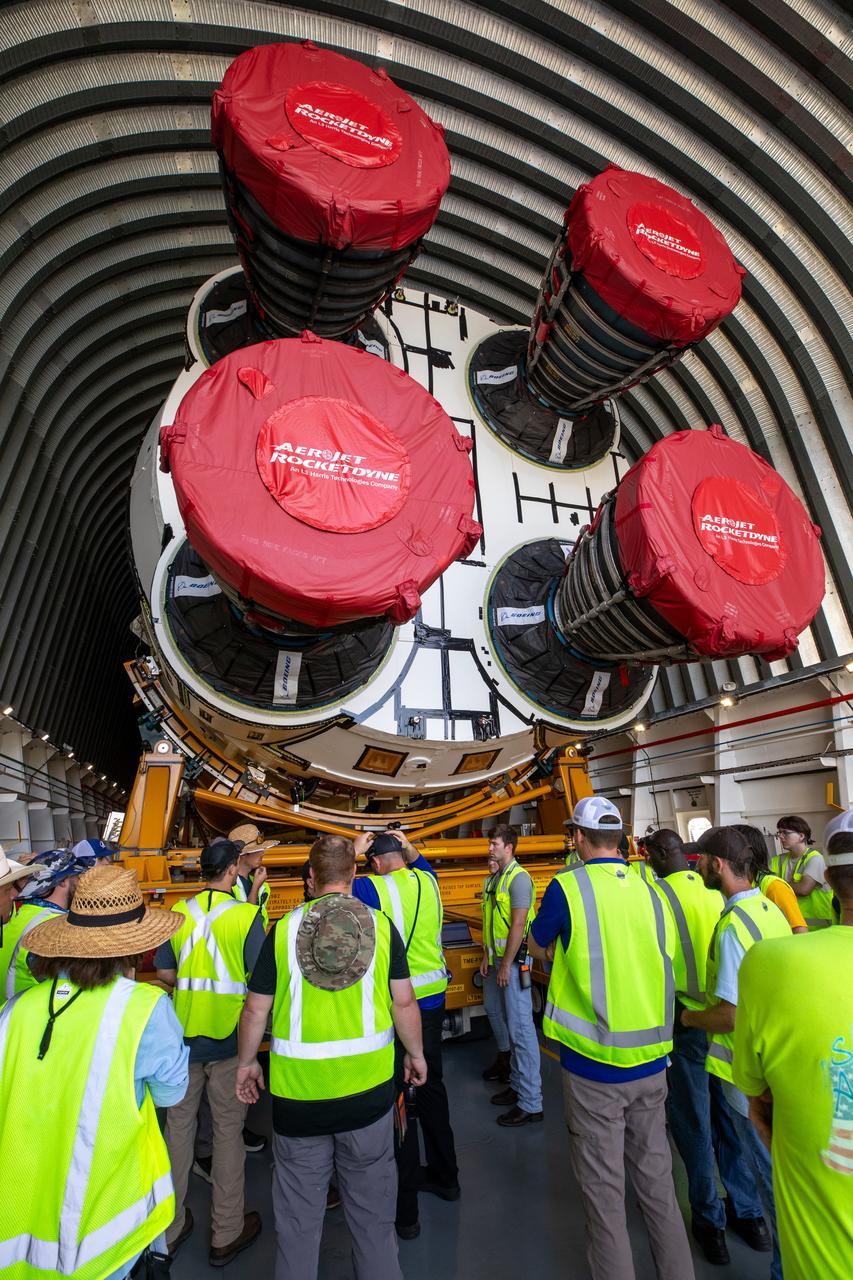
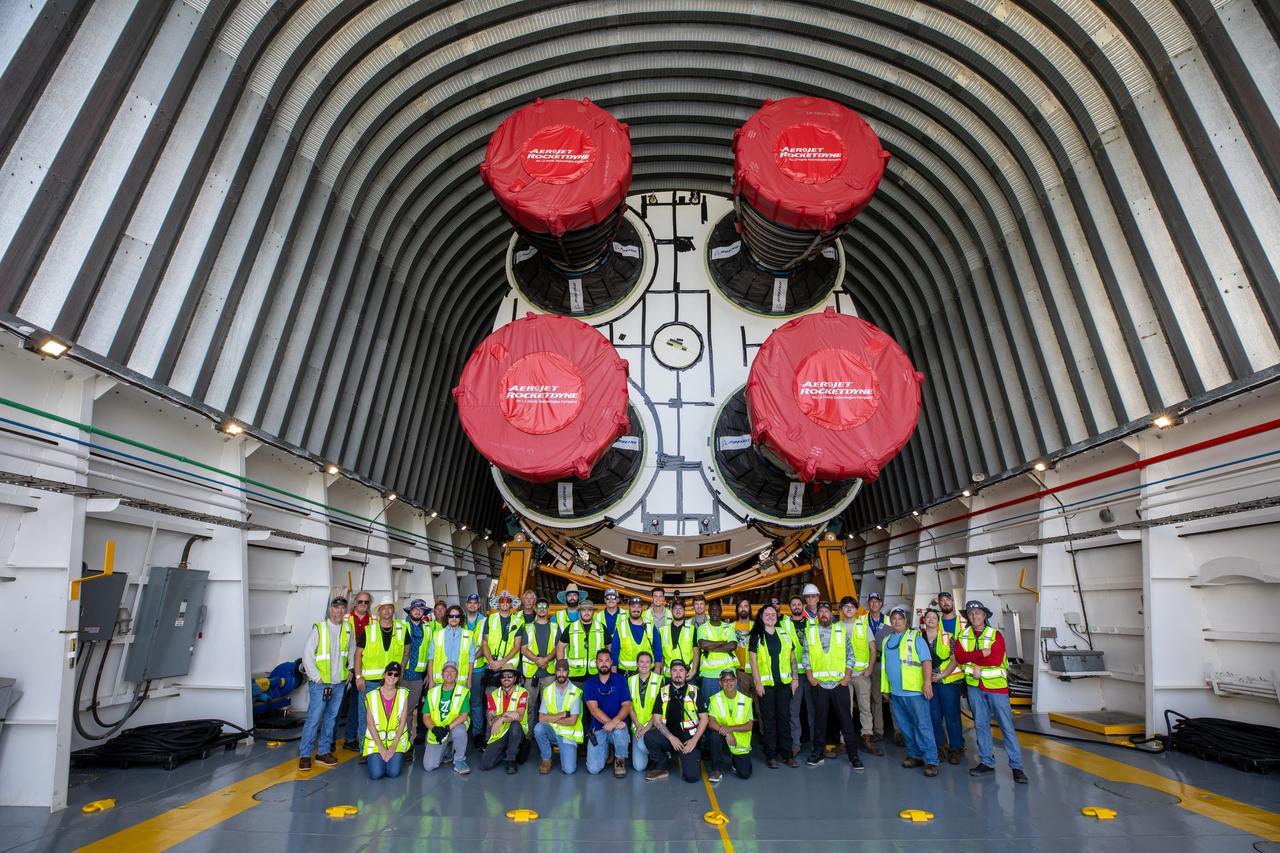
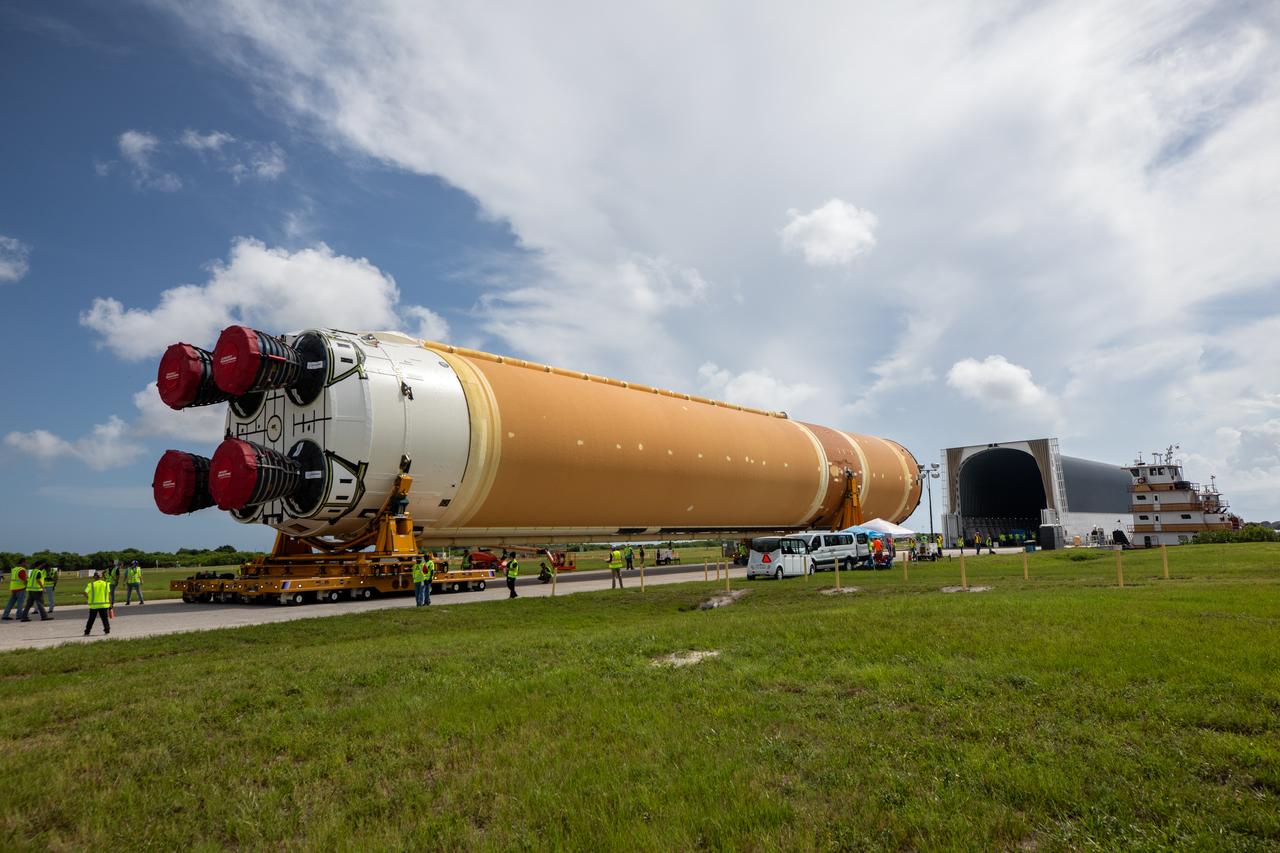
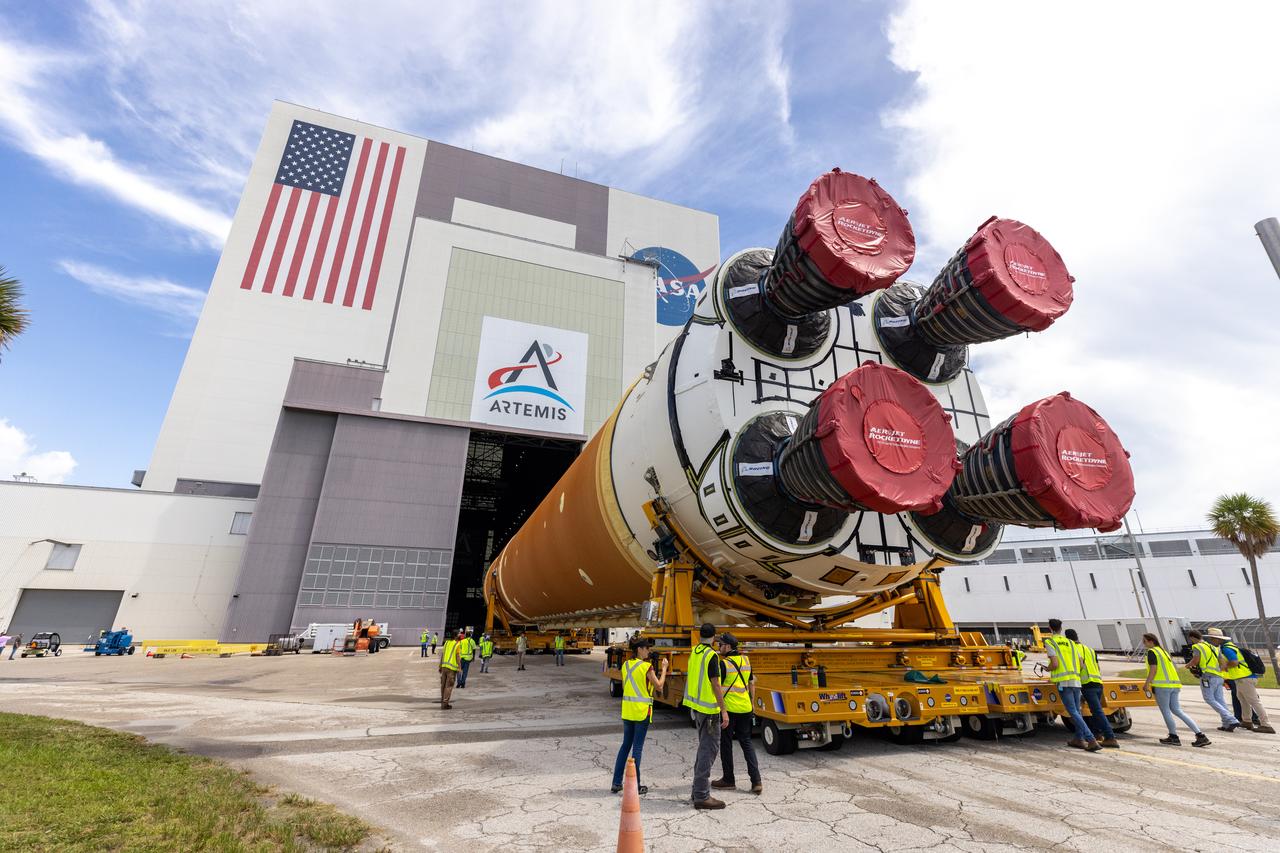
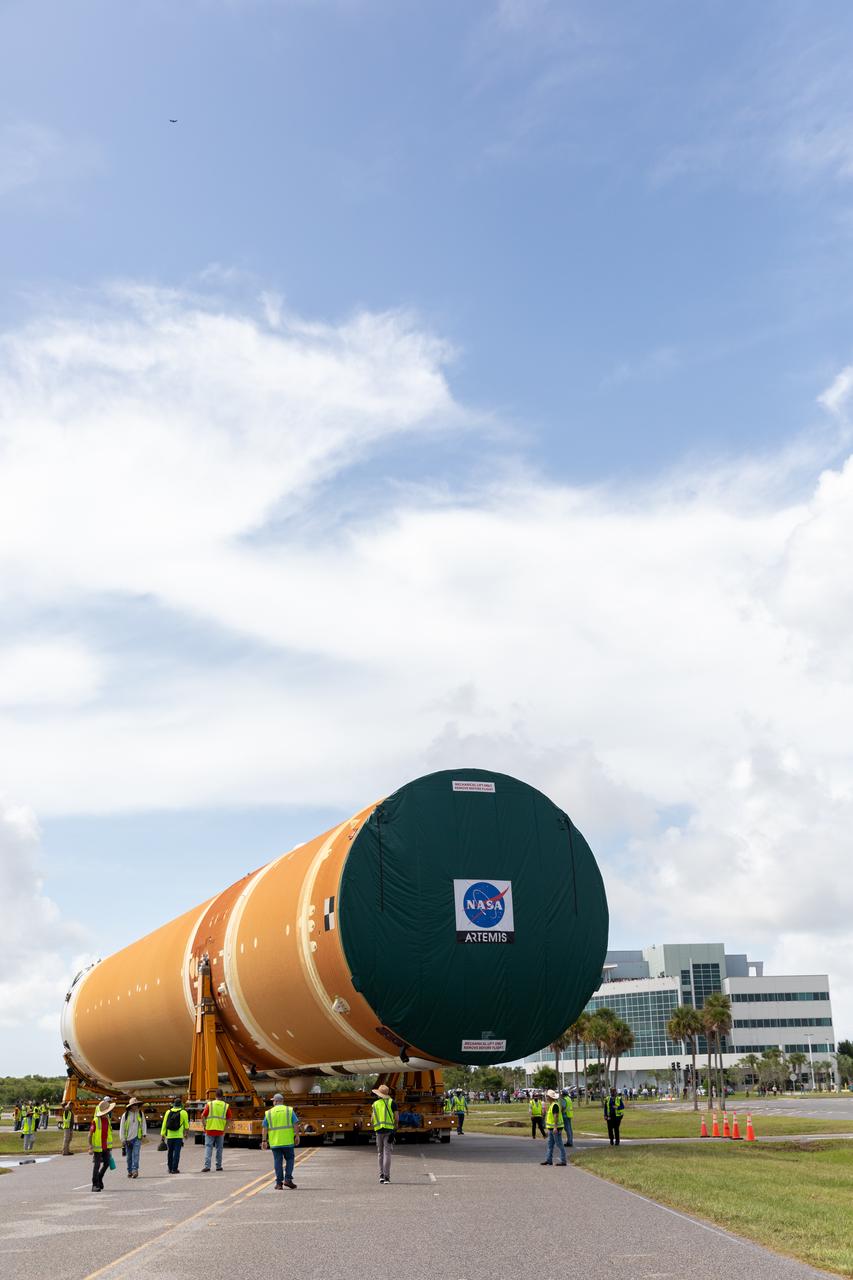
NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
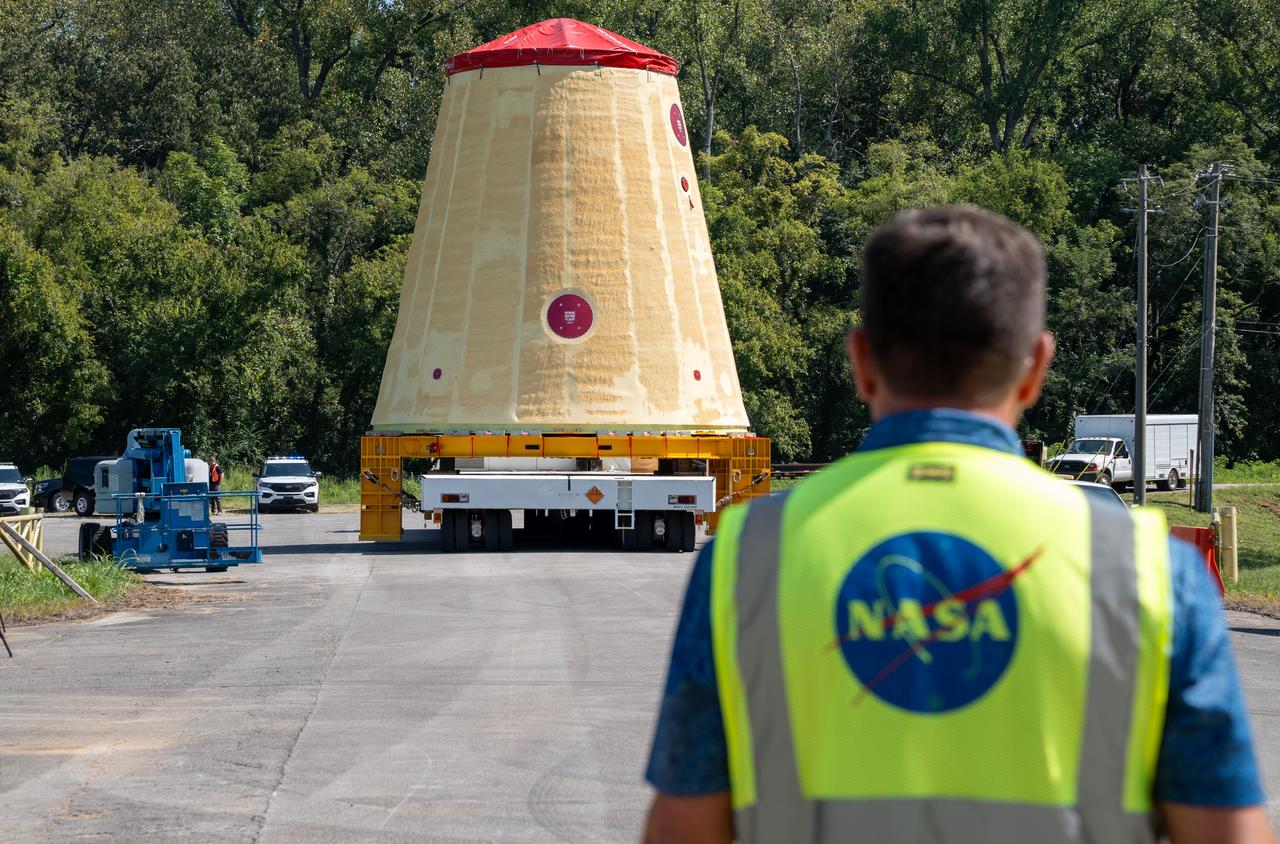

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
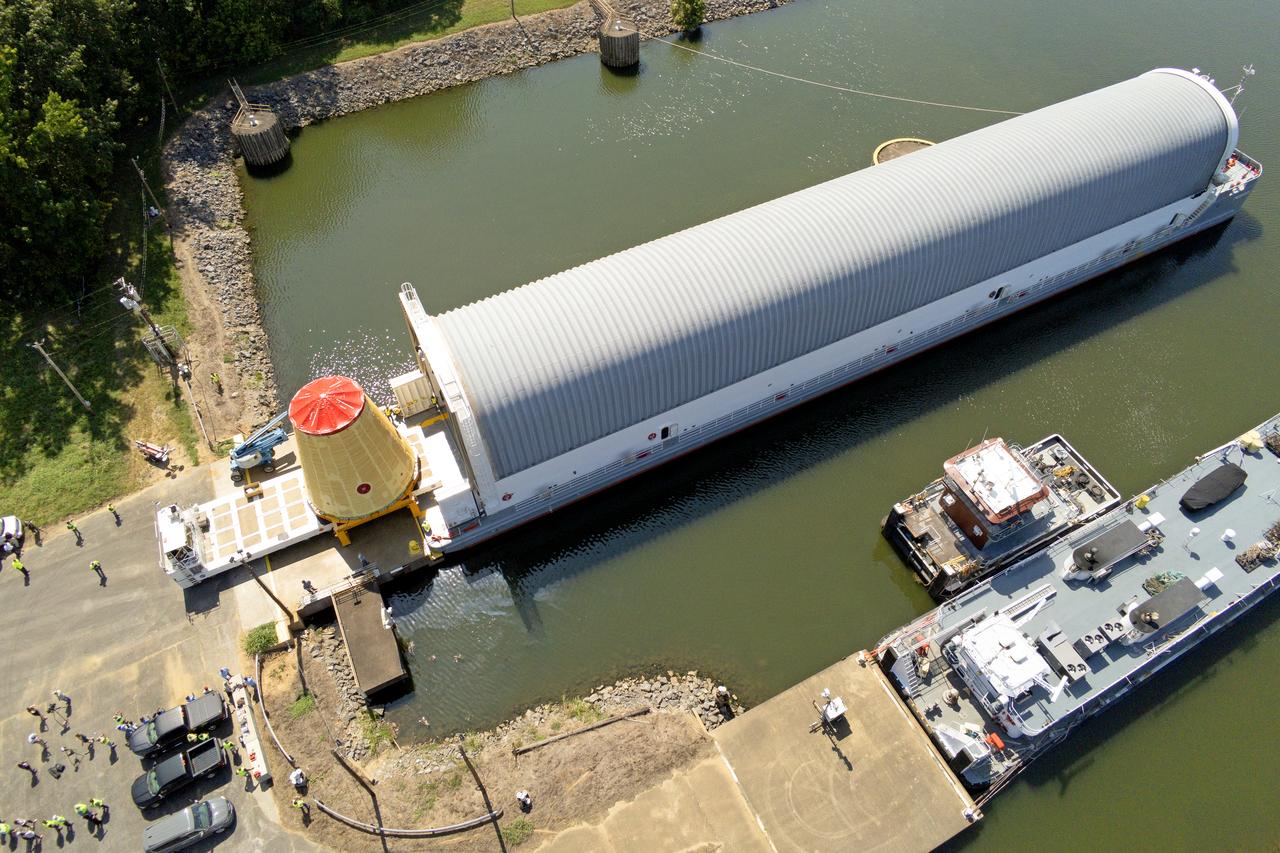

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
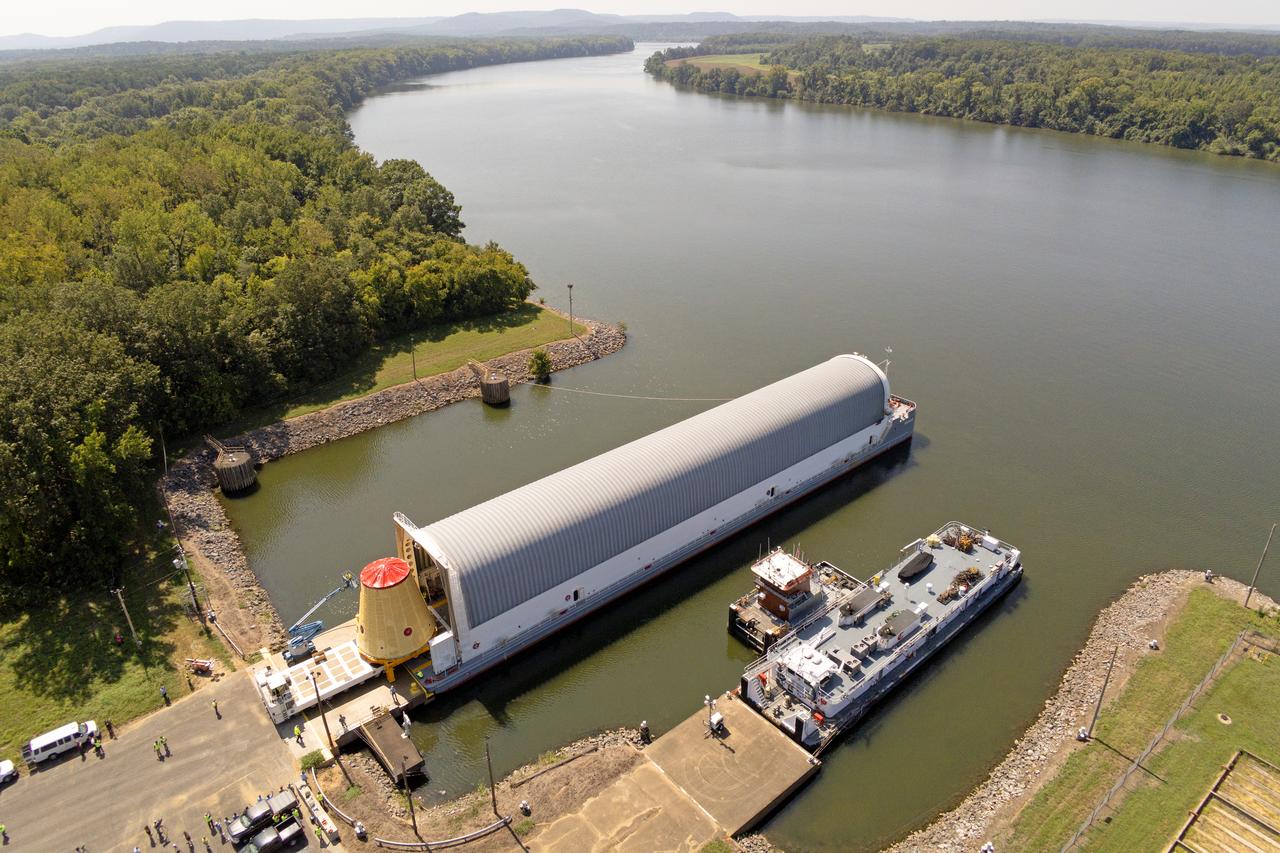

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
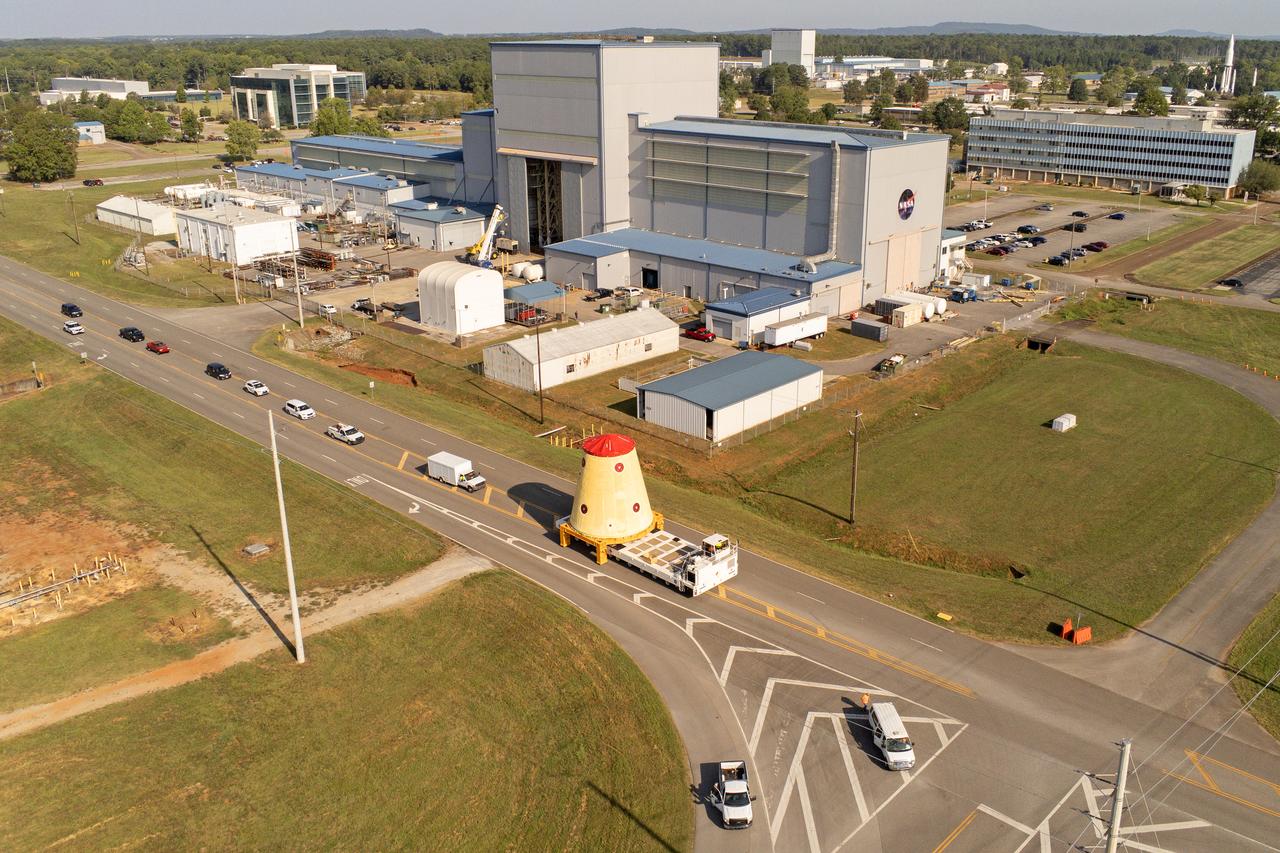

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
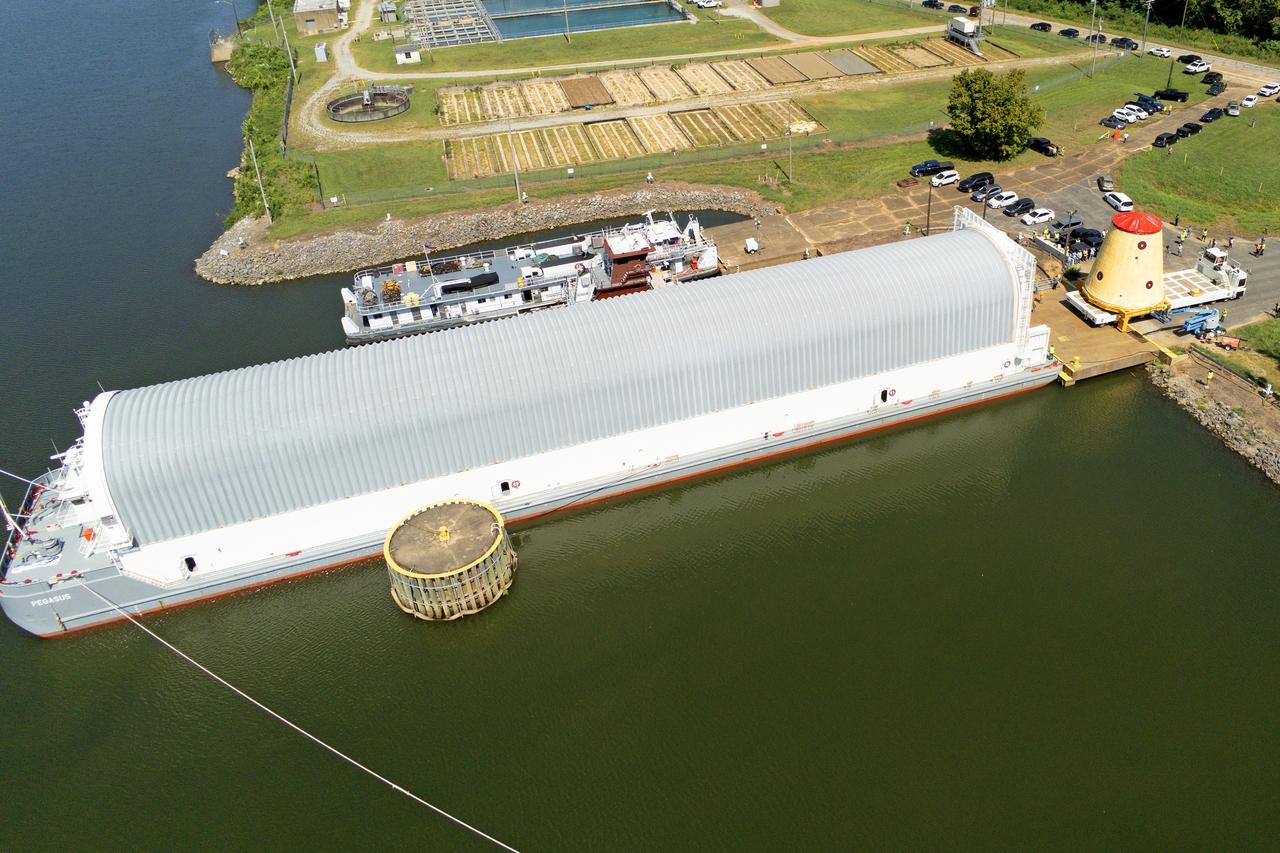

These images and videos show NASA rolling out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.