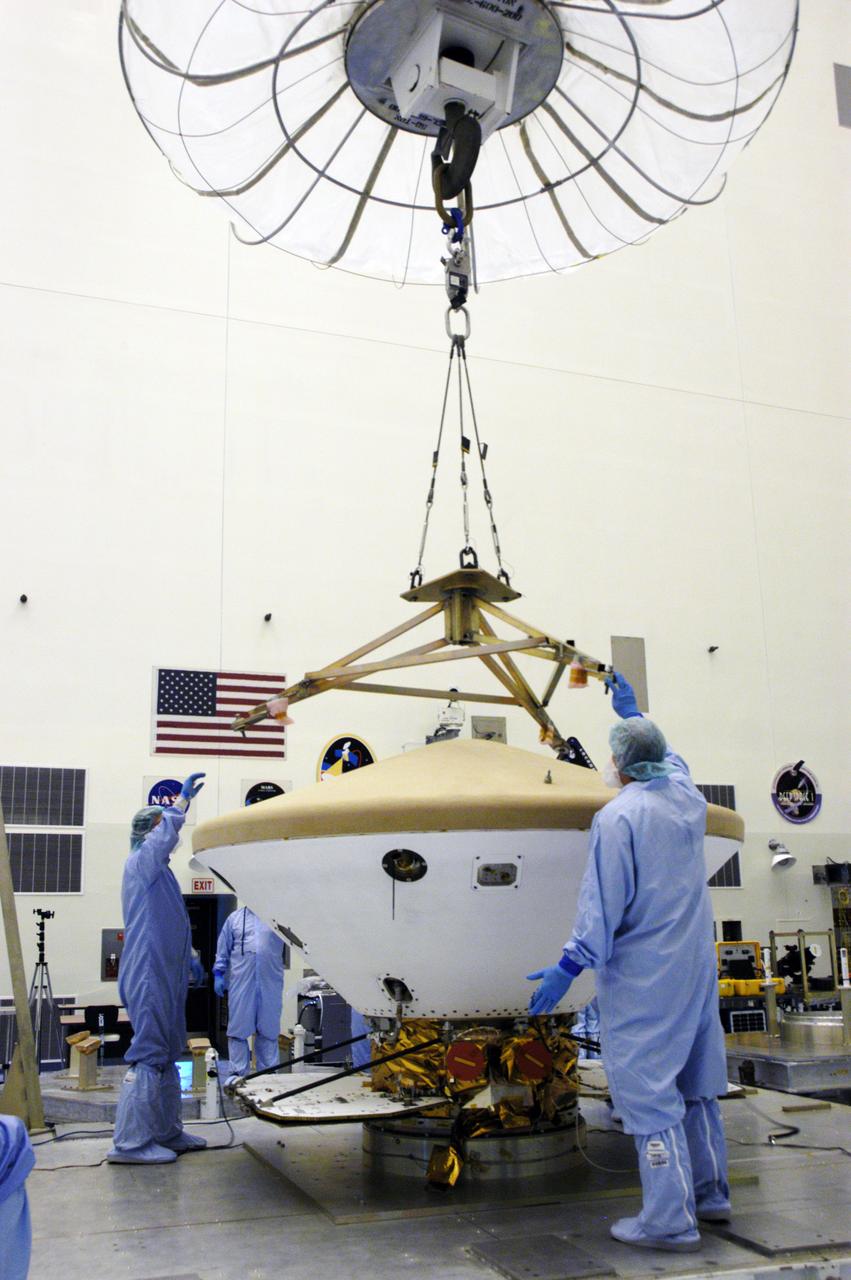

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, technicians lower a crane over the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The crane will be used to remove the heat shield from around the Phoenix. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
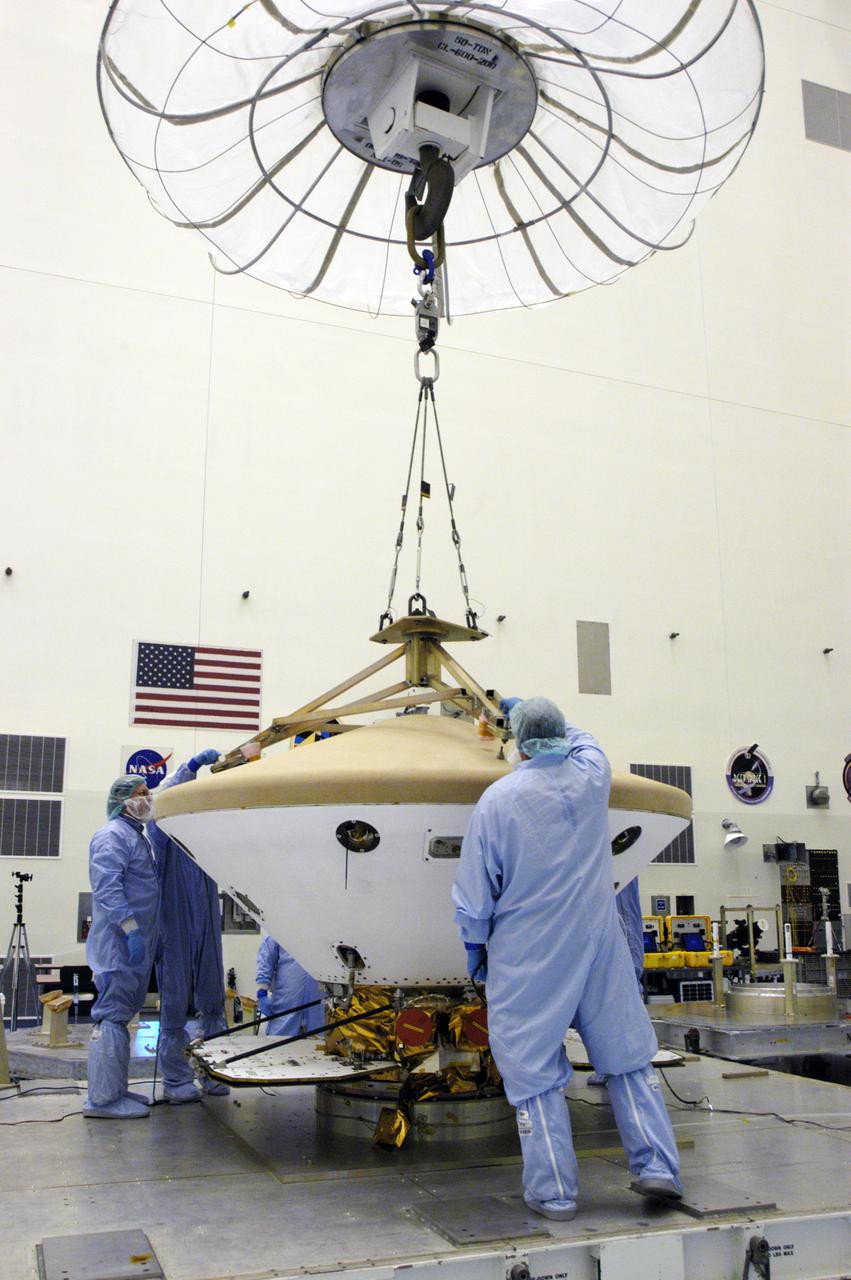

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, technicians attach a crane to the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The crane will be used to remove the heat shield from around the Phoenix. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
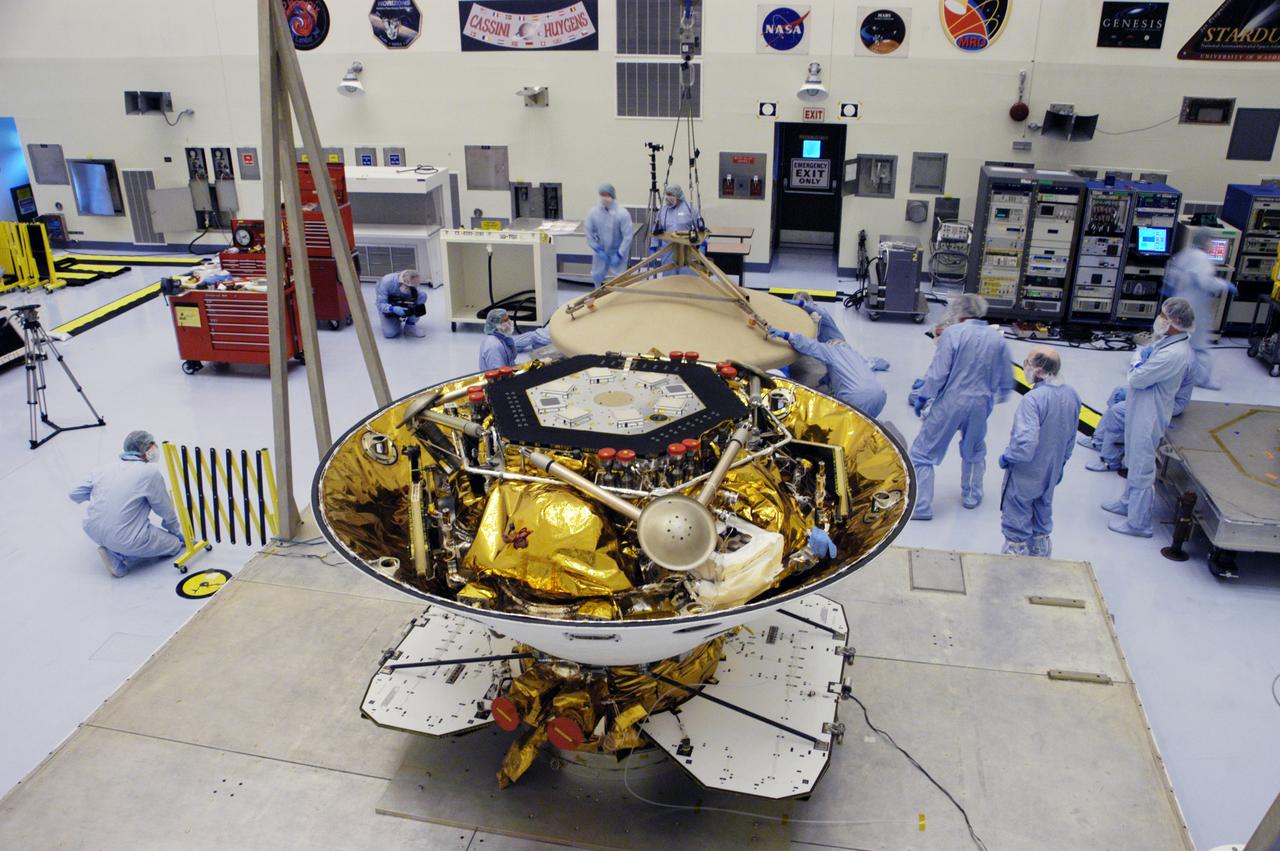

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the Phoenix Mars Lander (foreground) can be seen inside the backshell. In the background, workers are helping place the heat shield, just removed from the Phoenix, onto a platform. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
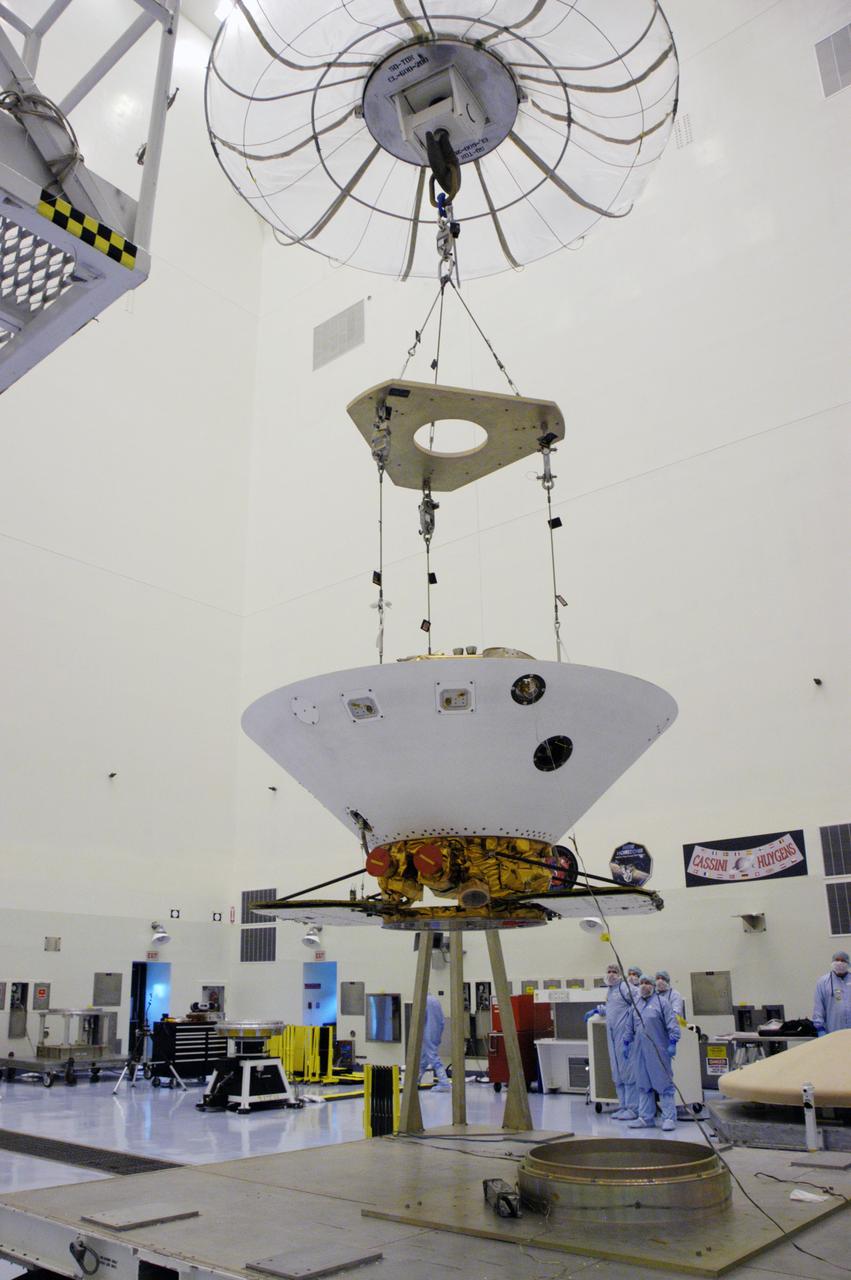

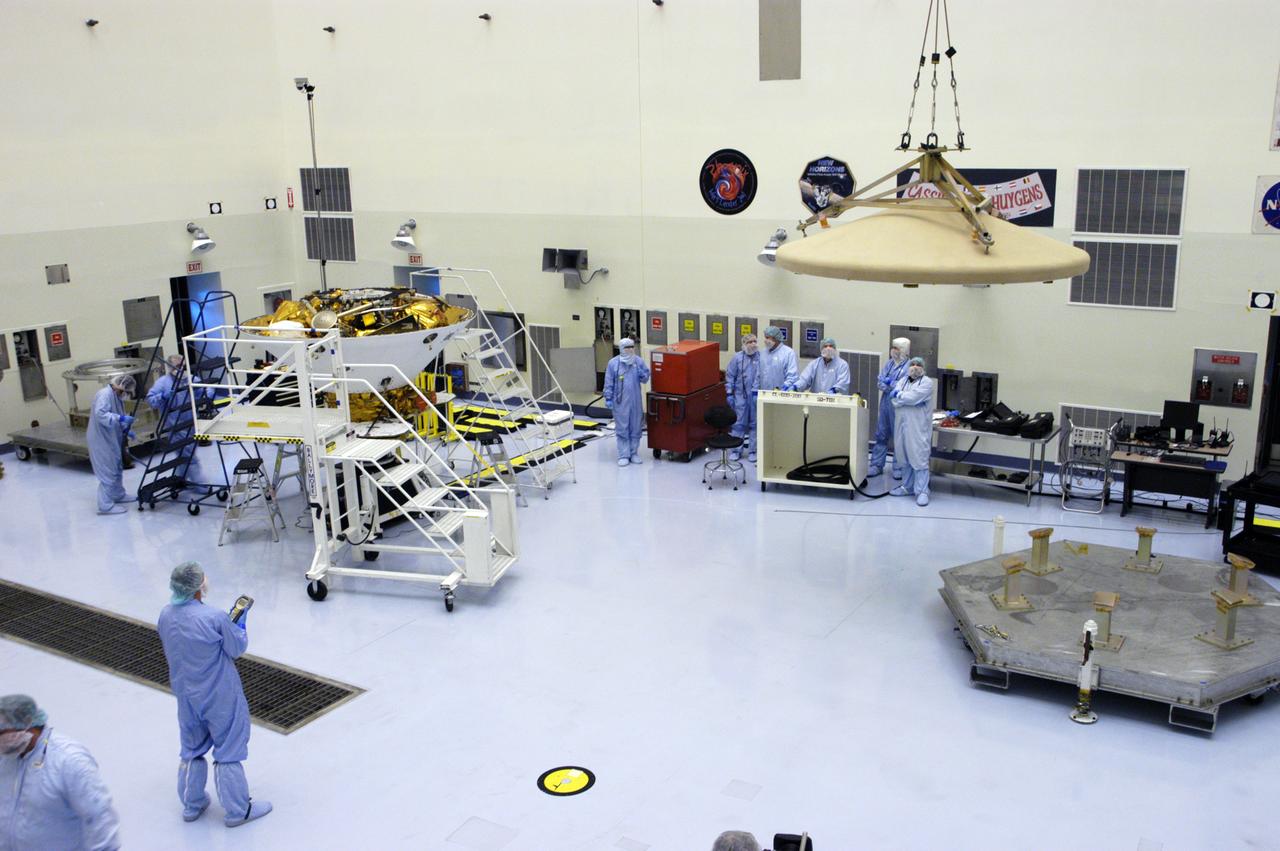
An overhead crane lifts the backshell with the Phoenix Mars Lander inside off its work stand in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The spacecraft is being moved to a spin table (back left) for spin testing. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
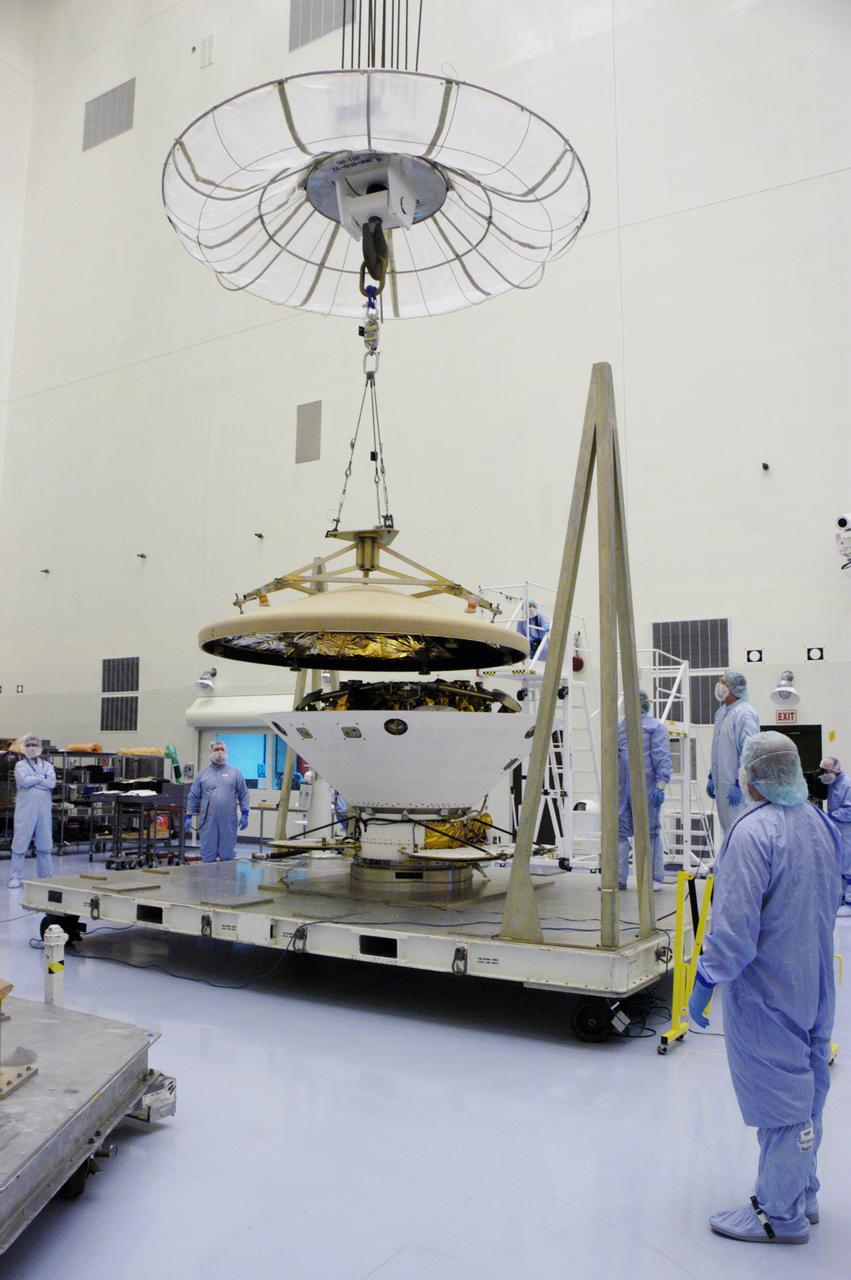

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the heat shield from the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
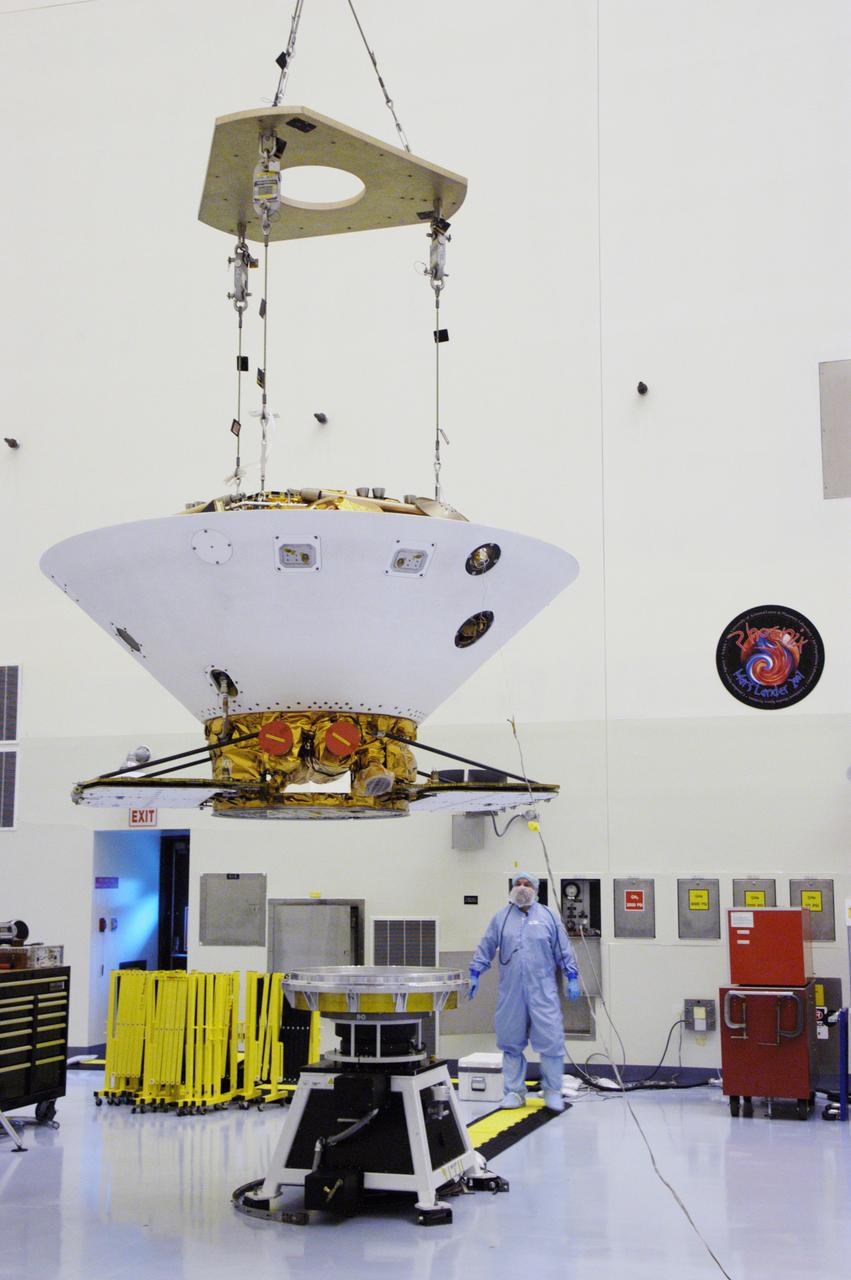

An overhead crane lowers the backshell with the Phoenix Mars Lander inside toward a spin table for spin testing in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
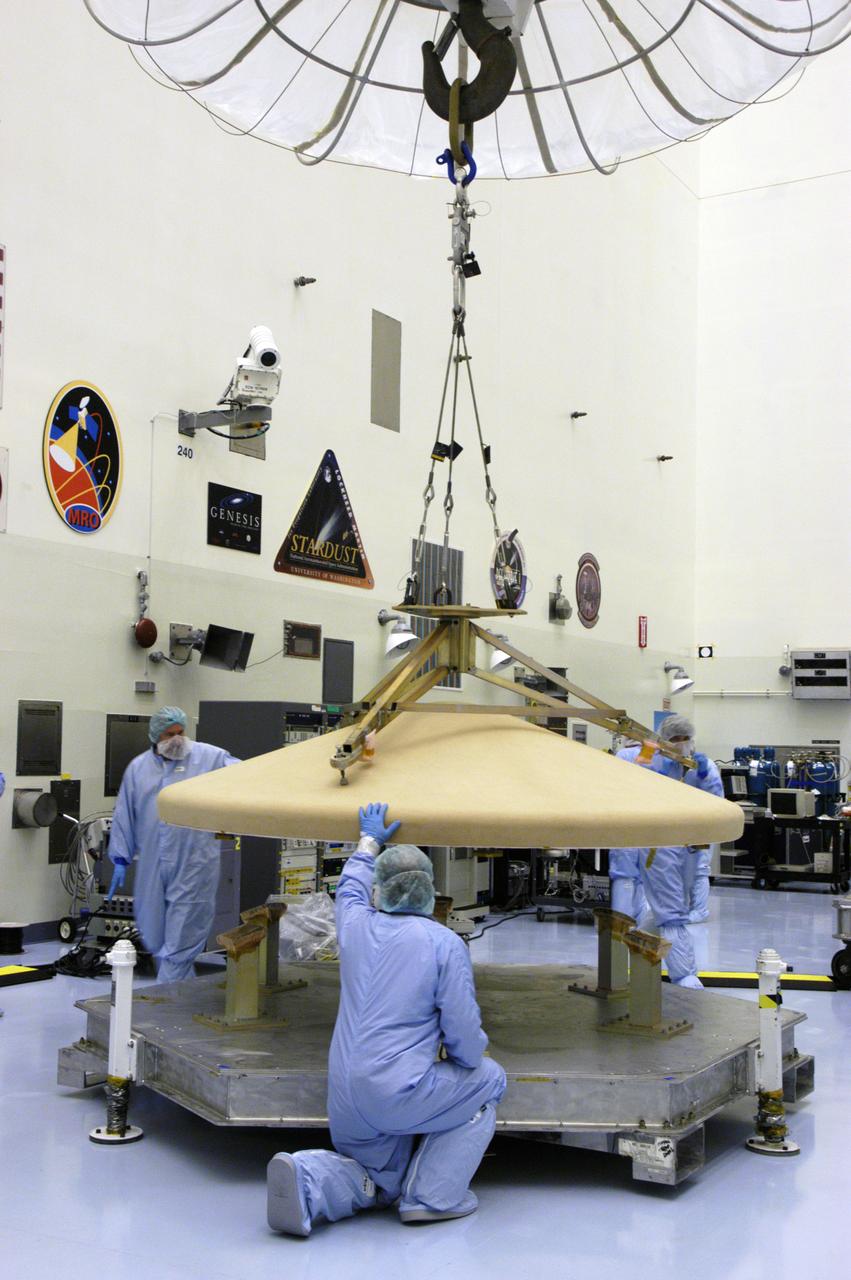

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, workers help guide the heat shield onto a platform. The heat shield was removed from the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft.. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
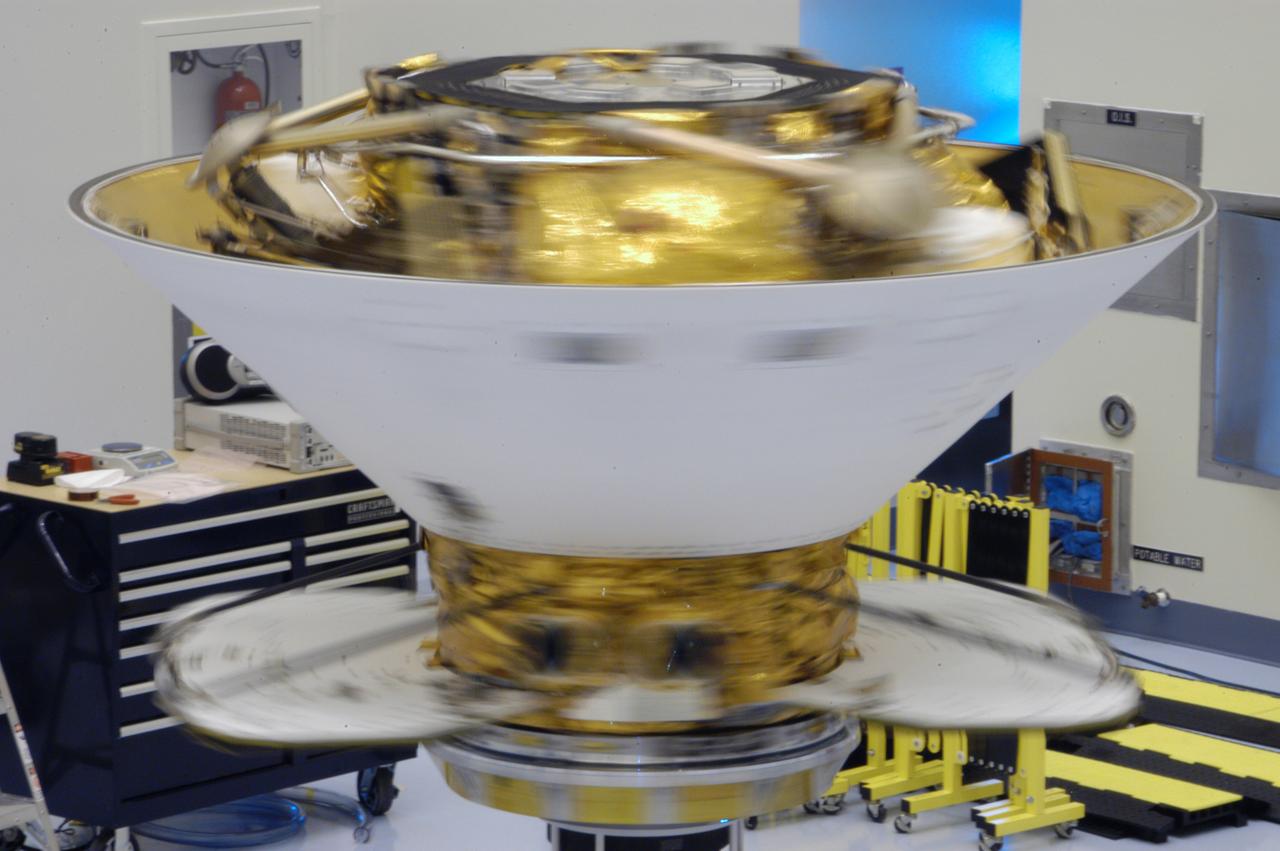

This closeup shows the spin test of the Phoenix Mars Lander in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
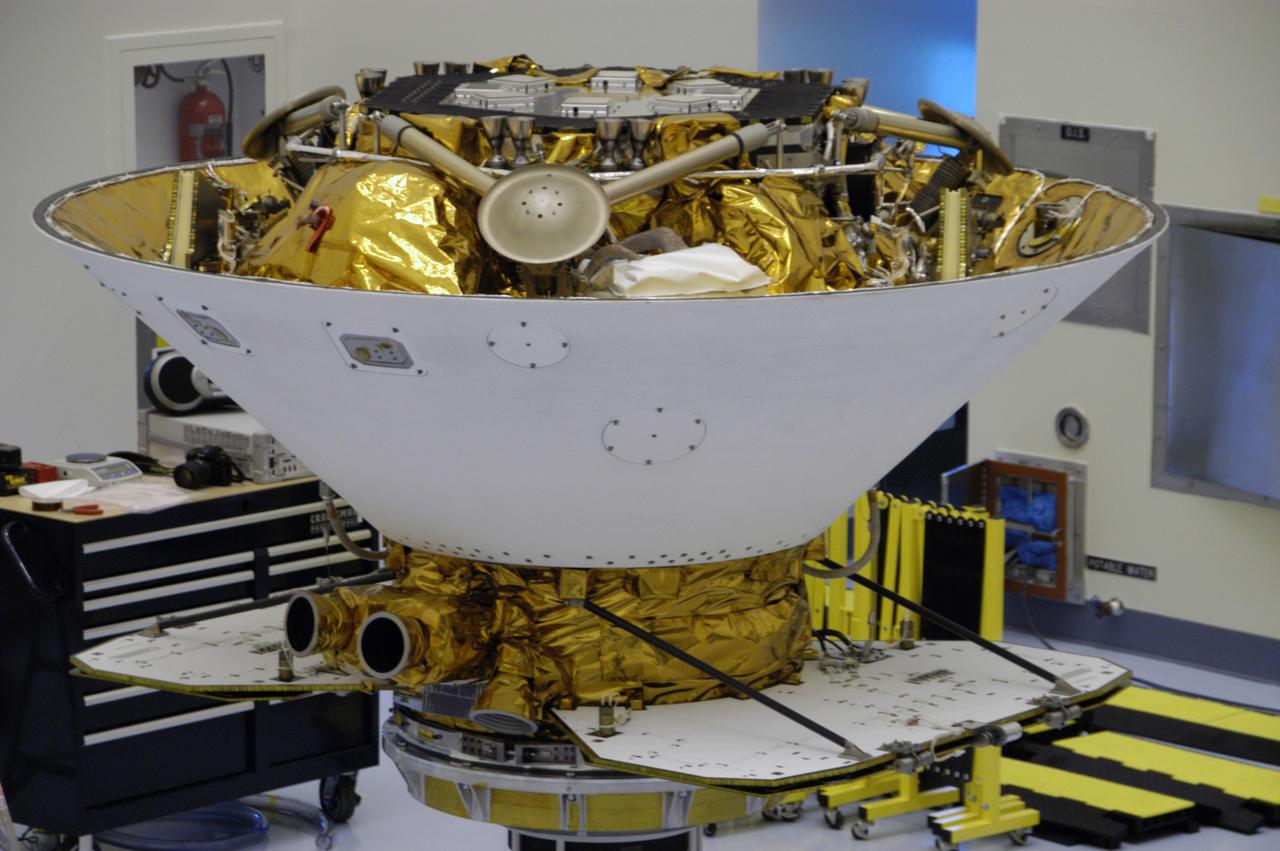

This closeup shows the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft nestled inside the backshell. The spacecraft is ready for spin testing on the spin table to which it is attached in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
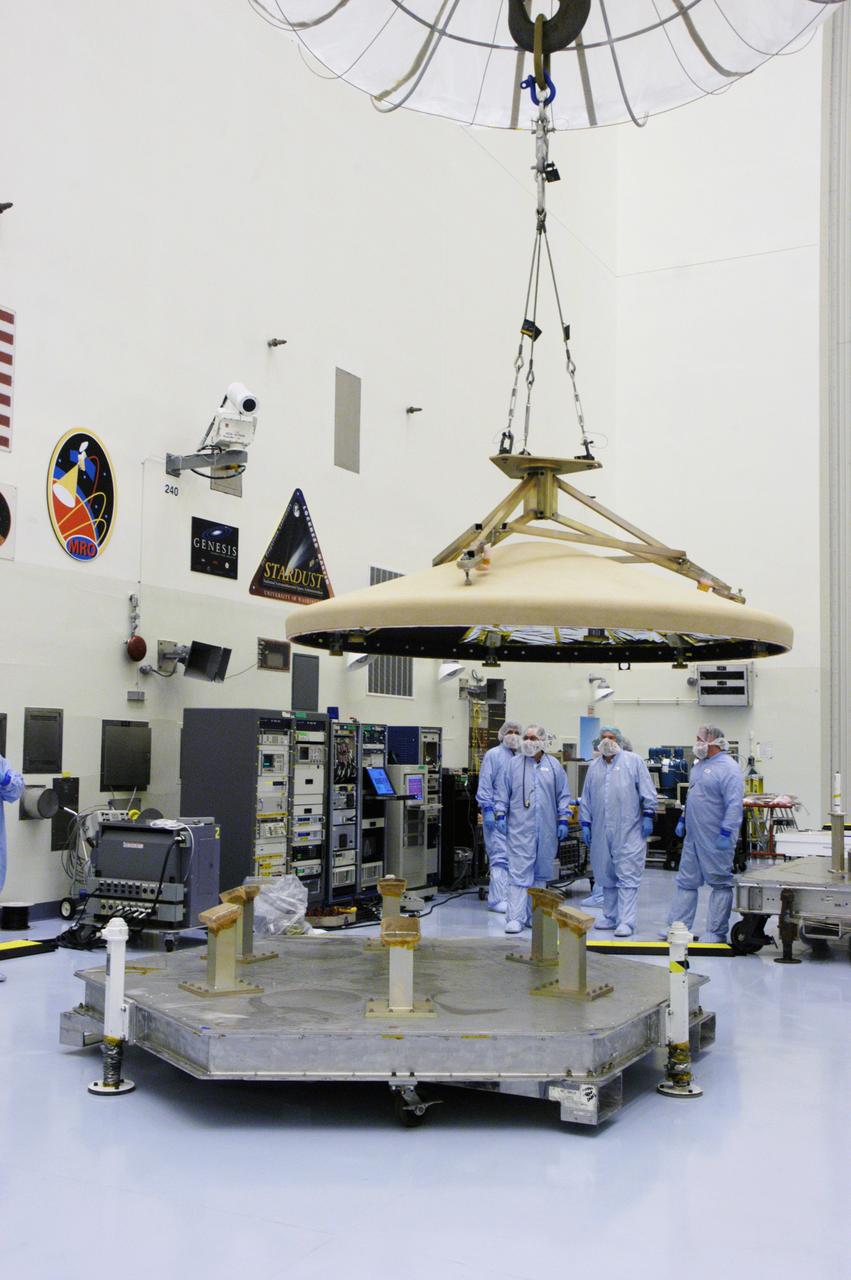

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, workers watch as an overhead crane lowers the heat shield toward a platform. The heat shield was removed from the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
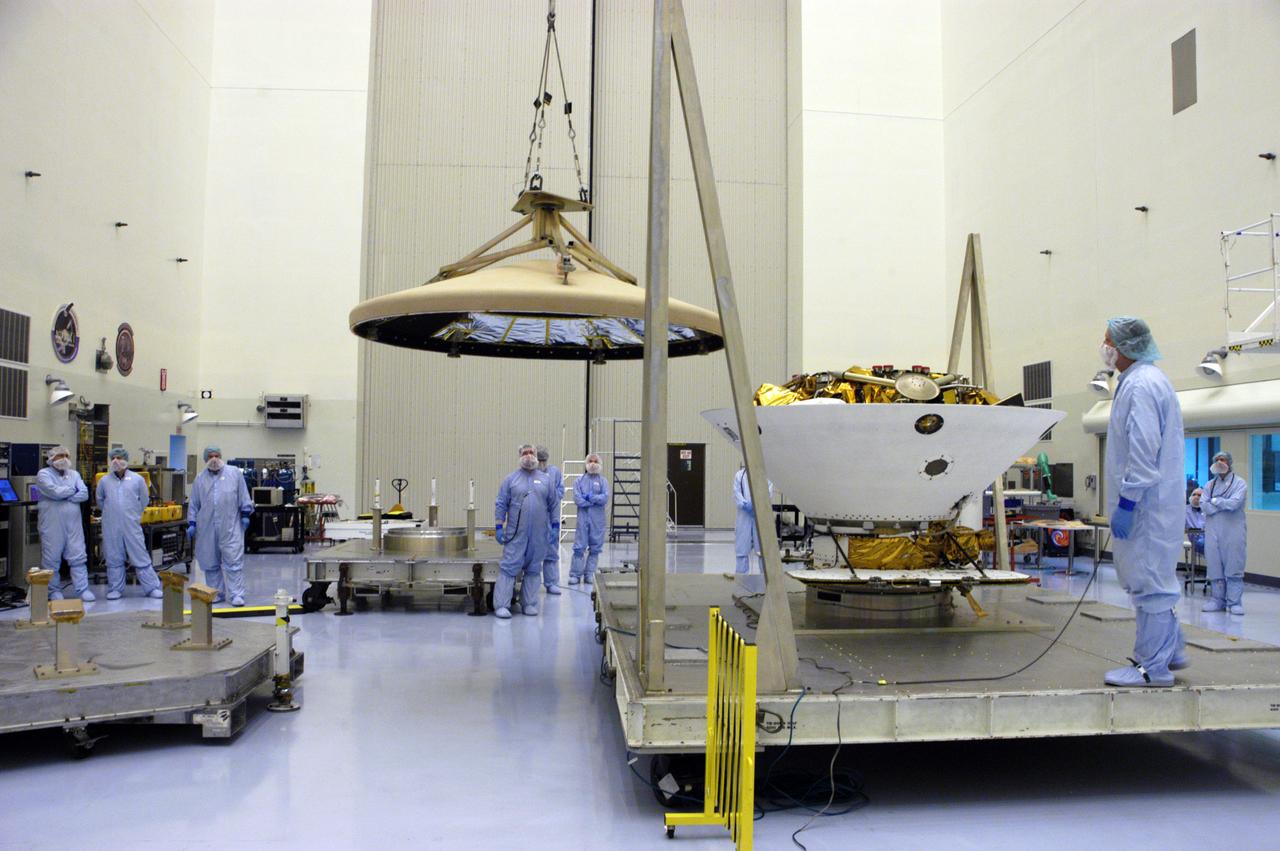

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, an overhead crane moves the heat shield toward a platform at left. The heat shield was removed from the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft at right. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
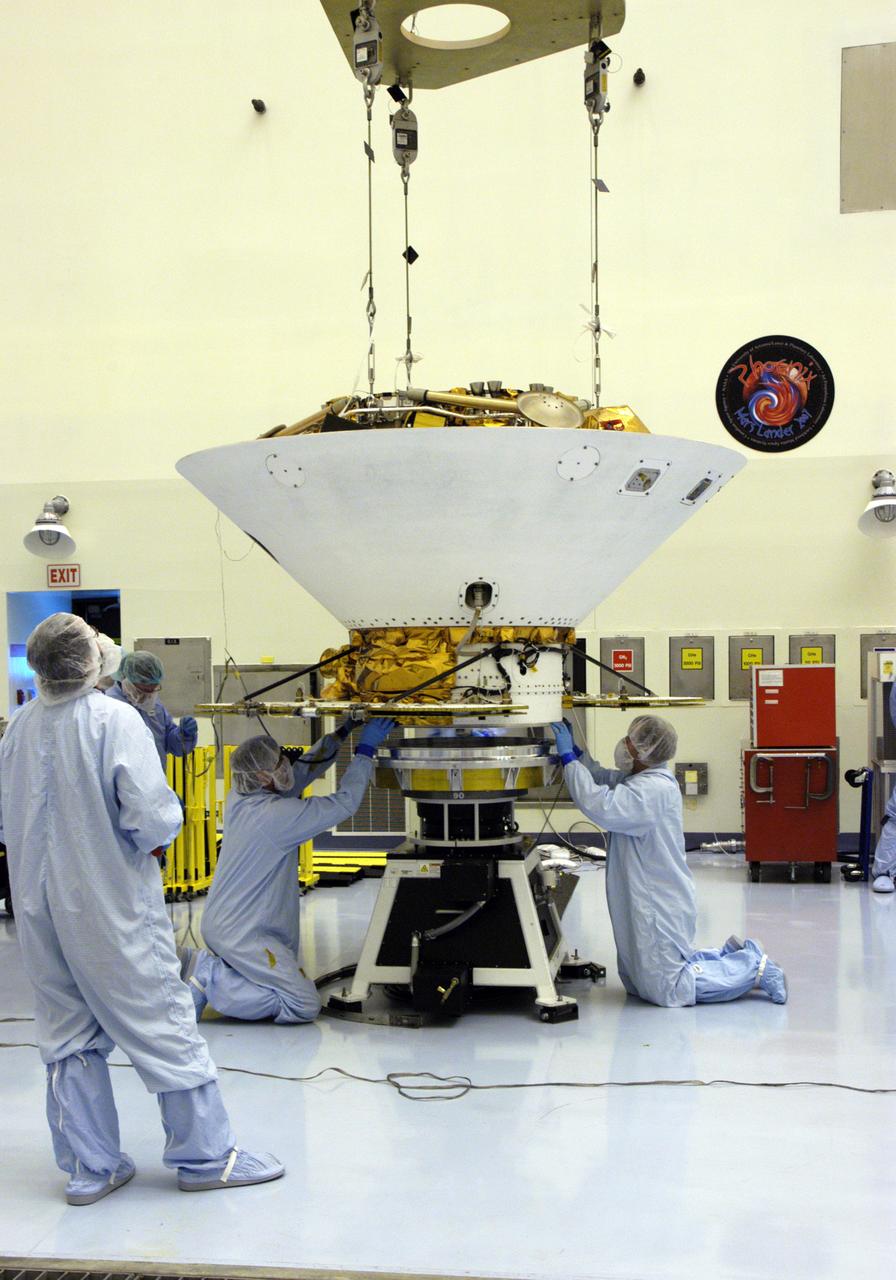

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, technicians secure the backshell with the Phoenix Mars Lander inside onto a spin table for spin testing. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
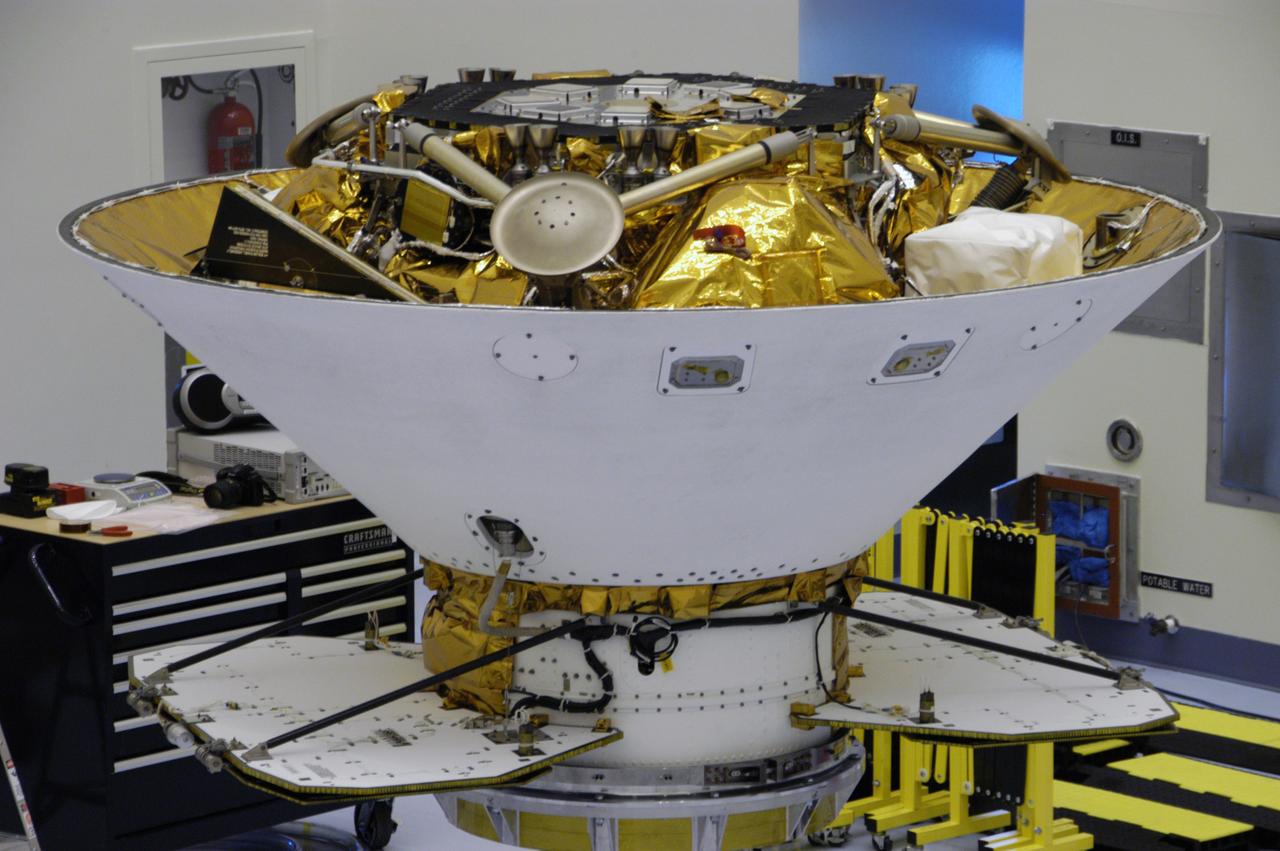

This closeup shows the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft nestled inside the backshell. The spacecraft will undergo spin testing on the spin table to which it is attached in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
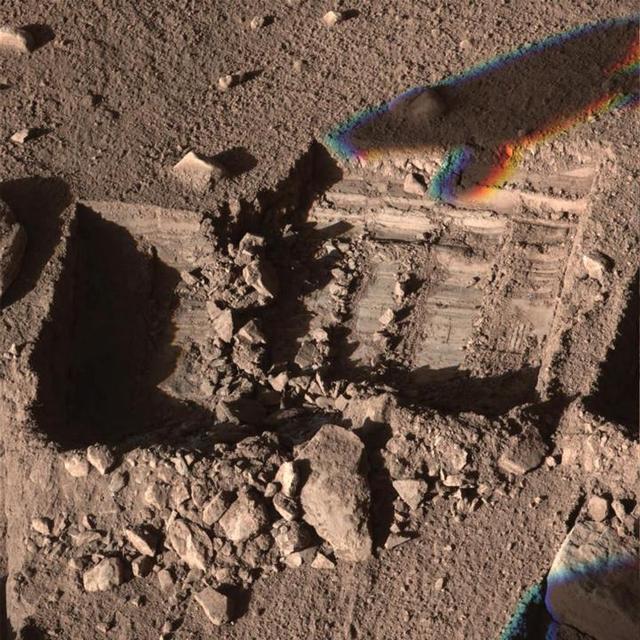

La Mancha Trench Dug by Phoenix Mars Lander
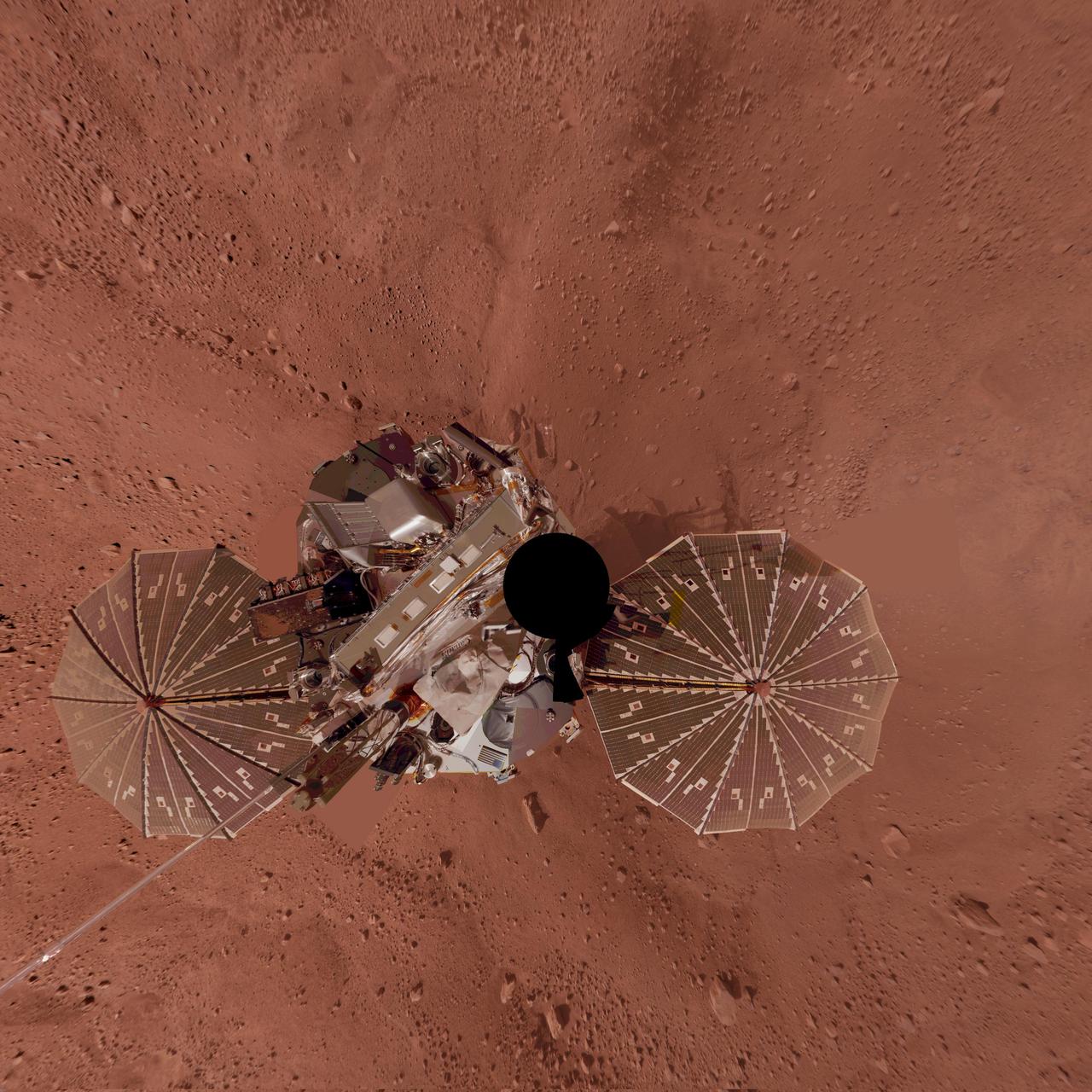

Phoenix Lander Self Portrait on Mars, Vertical Projection
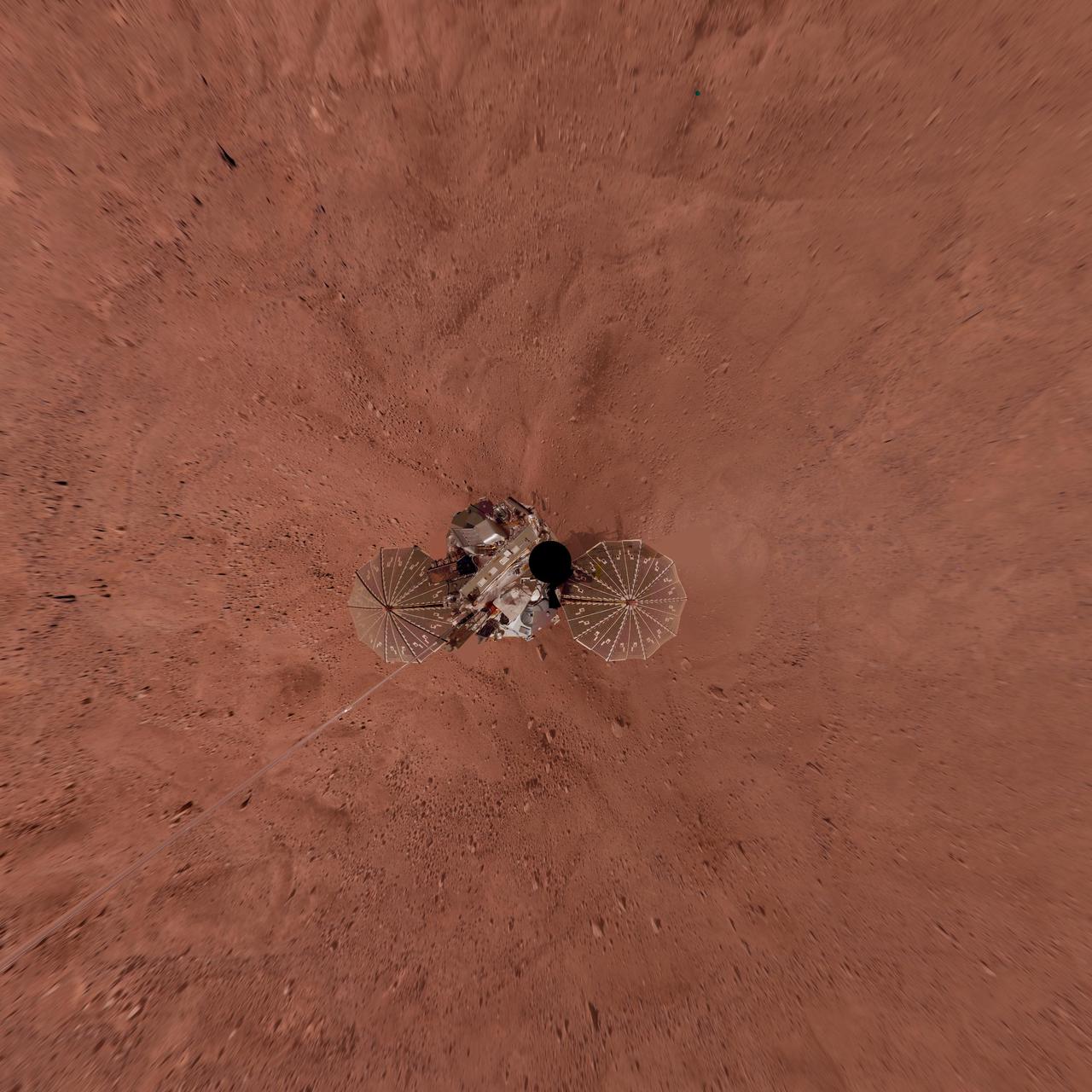

Phoenix Lander on Mars with Surrounding Terrain, Vertical Projection
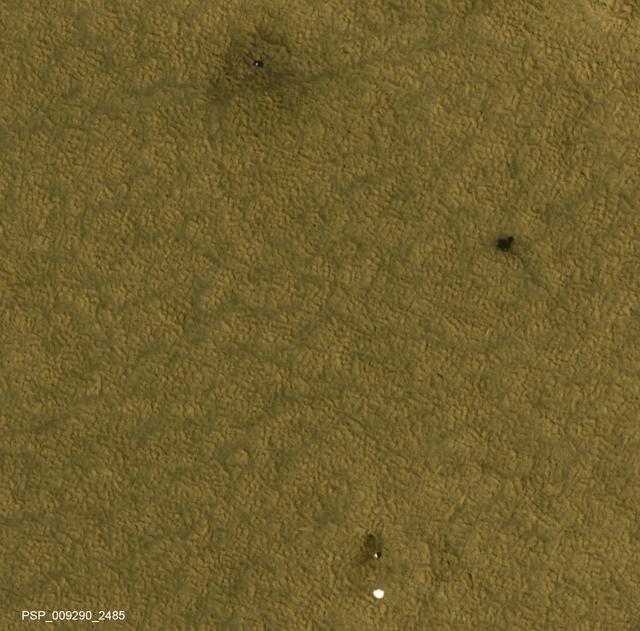
This is one of two images taken nearly a decade apart of NASA's Mars Phoenix Lander and related hardware around the mission's May 25, 2008, landing site on far-northern Mars. By late 2017, dust had obscured much of what was visible two months after the landing. Both images were taken by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The one with three patches of darker ground -- where landing events removed dust -- was taken on July 20, 2008. It is Fig. 1, an excerpt of HiRISE observation PSP_009290_2485. The one with a more even coating of pale dust throughout the area was taken on Dec. 21, 2017. It is Fig. 2, an excerpt of HiRISE observation ESP_053451_2485. Both cover an area roughly 300 meters wide at 68 degrees north latitude, 234 degrees east longitude, and the two are closely matched in viewing and illumination geometry, from about five Martian years apart in northern hemisphere summers. An animation comparing the two images shows a number of changes between mid-2008 and late 2017. The lander (top) appears darker, and is now covered by dust. The dark spot created by the heat shield impact (right) is brighter, again due to dust deposition. The back shell and parachute (bottom) shows a darker parachute and brighter area of impact disturbance, thanks again to deposits of dust. We also see that the parachute has shifted in the wind, moving to the east. In August 2008, Phoenix completed its three-month mission studying Martian ice, soil and atmosphere. The lander worked for two additional months before reduced sunlight caused energy to become insufficient to keep the lander functioning. The solar-powered robot was not designed to survive through the dark and cold conditions of a Martian arctic winter. An animation and both images are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22223

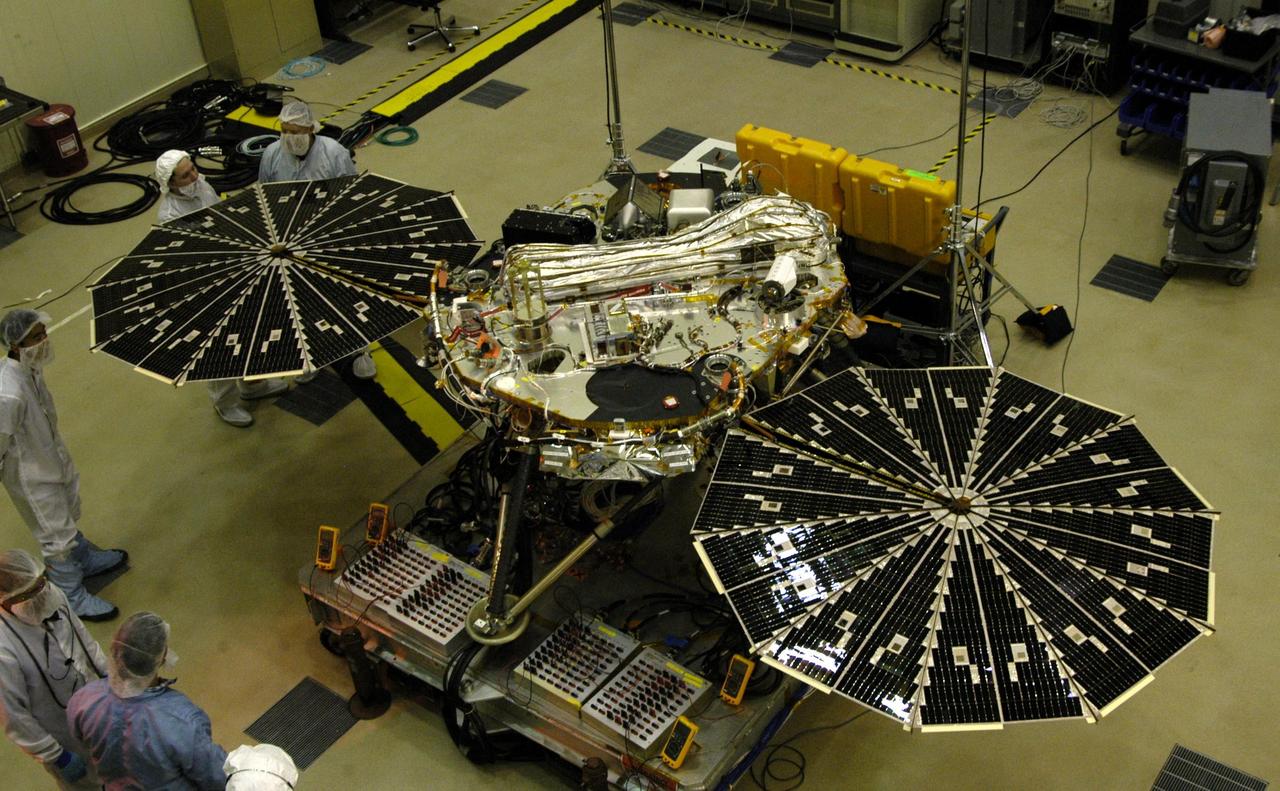
NASA next Mars-bound spacecraft, the Phoenix Mars Lander, partway through assembly and testing at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, in September 2006.

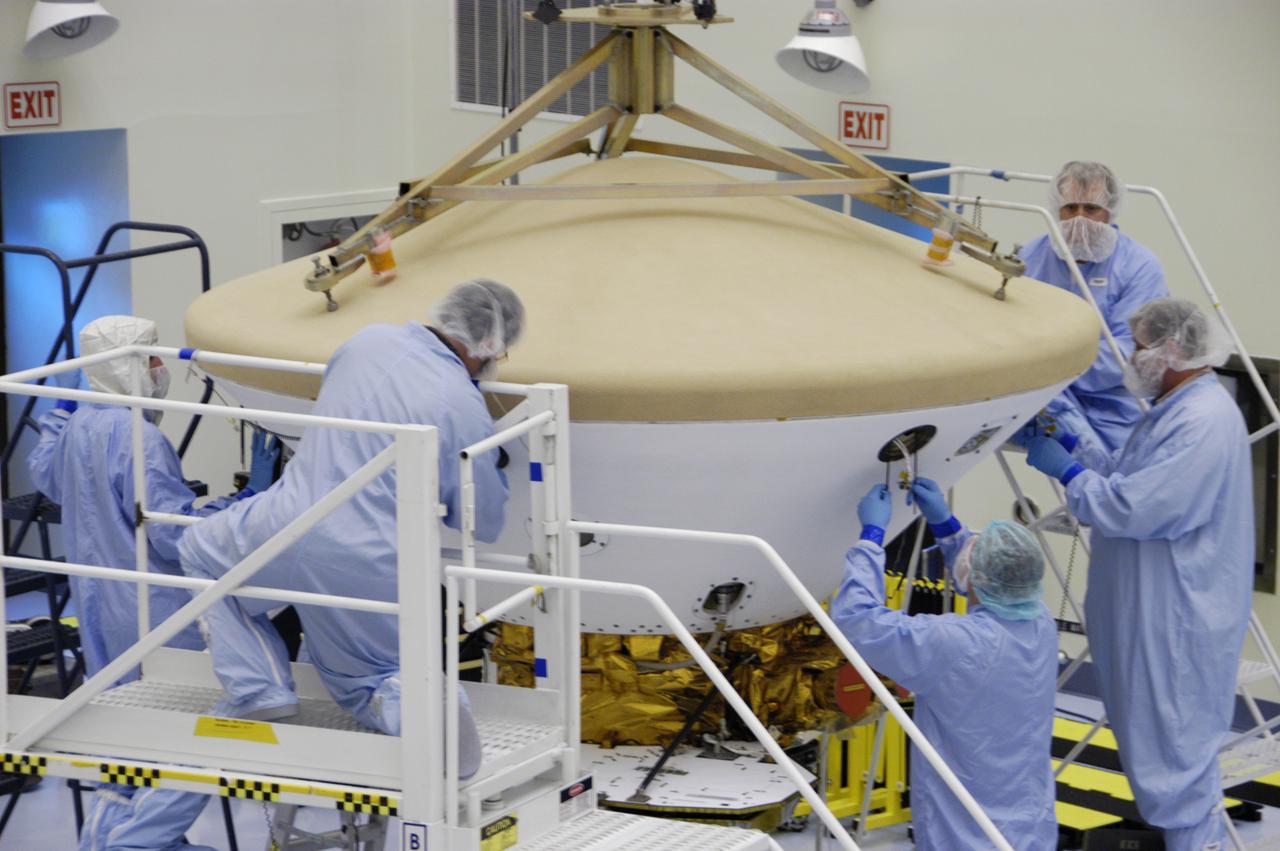
In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, technicians prepare to install the heat shield on the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA's Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the heat shield for the Phoenix Mars Lander is moved into position for installation on the spacecraft. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA's Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

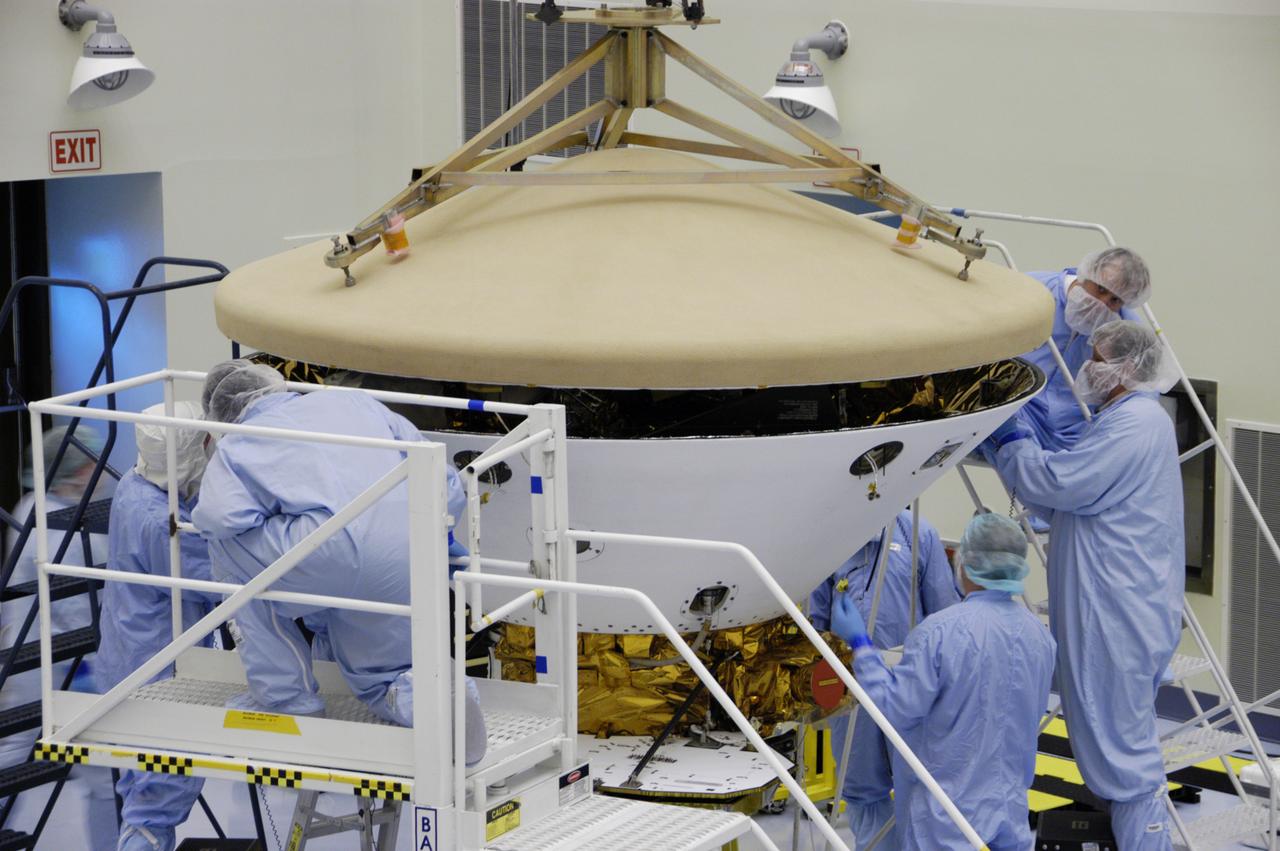
In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, technicians install the heat shield on the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA's Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
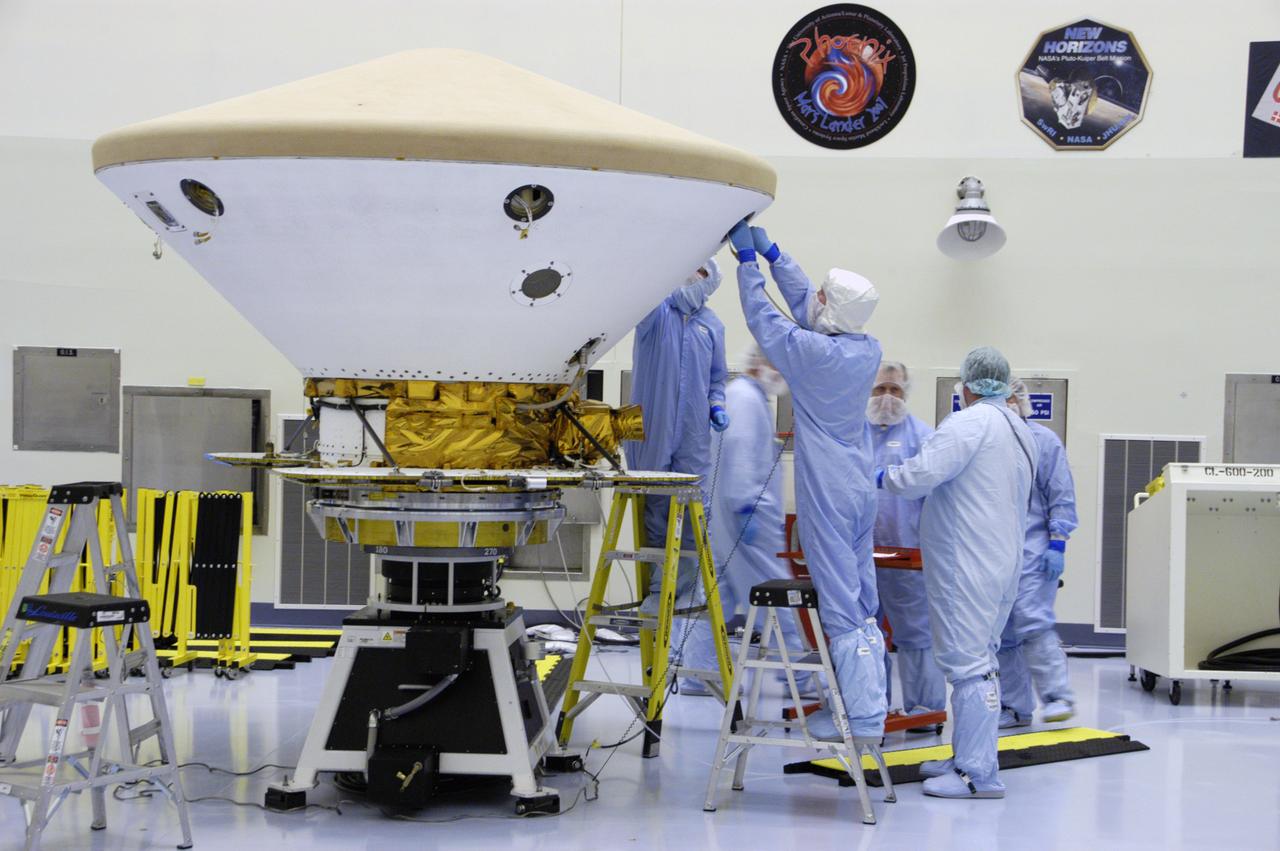

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, technicians complete the installation of the heat shield on the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA's Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
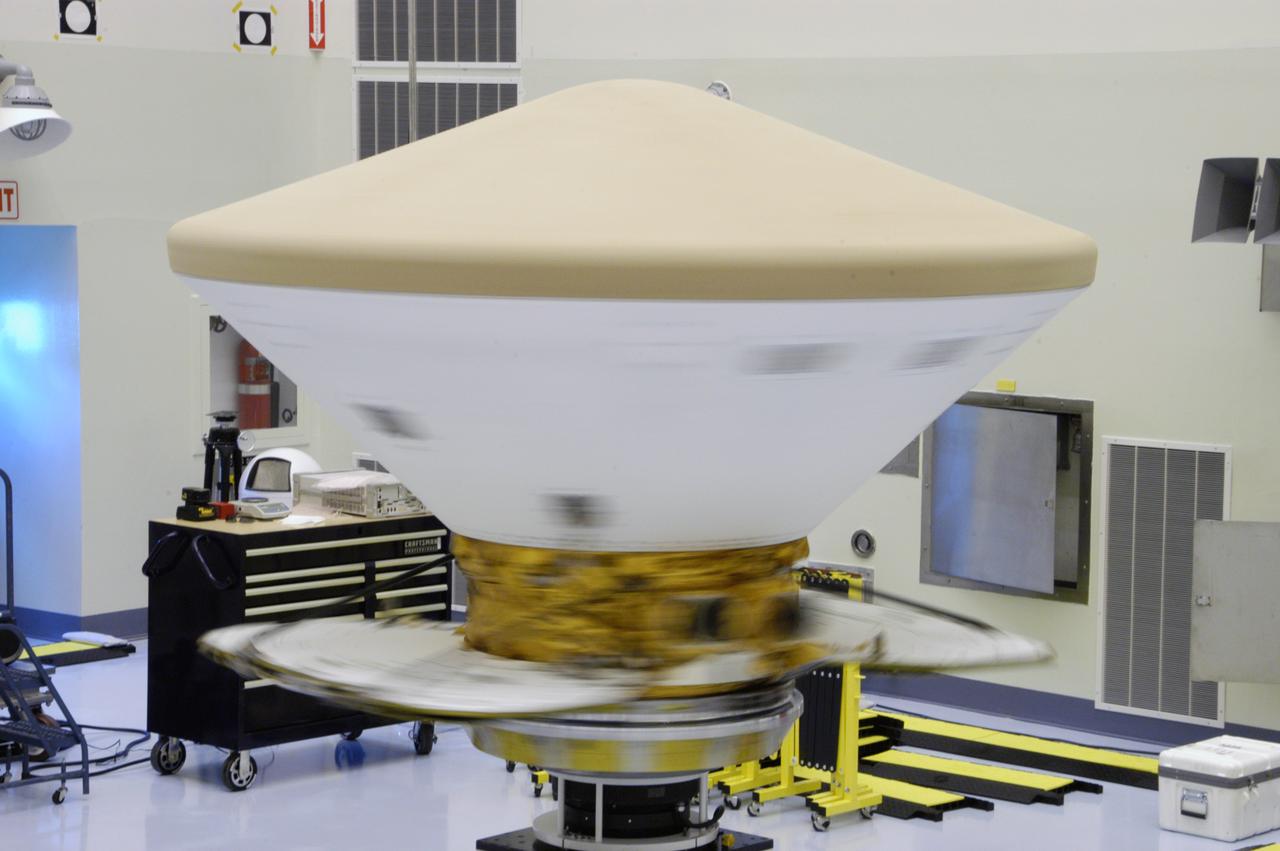

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft undergoes spin testing. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA's Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
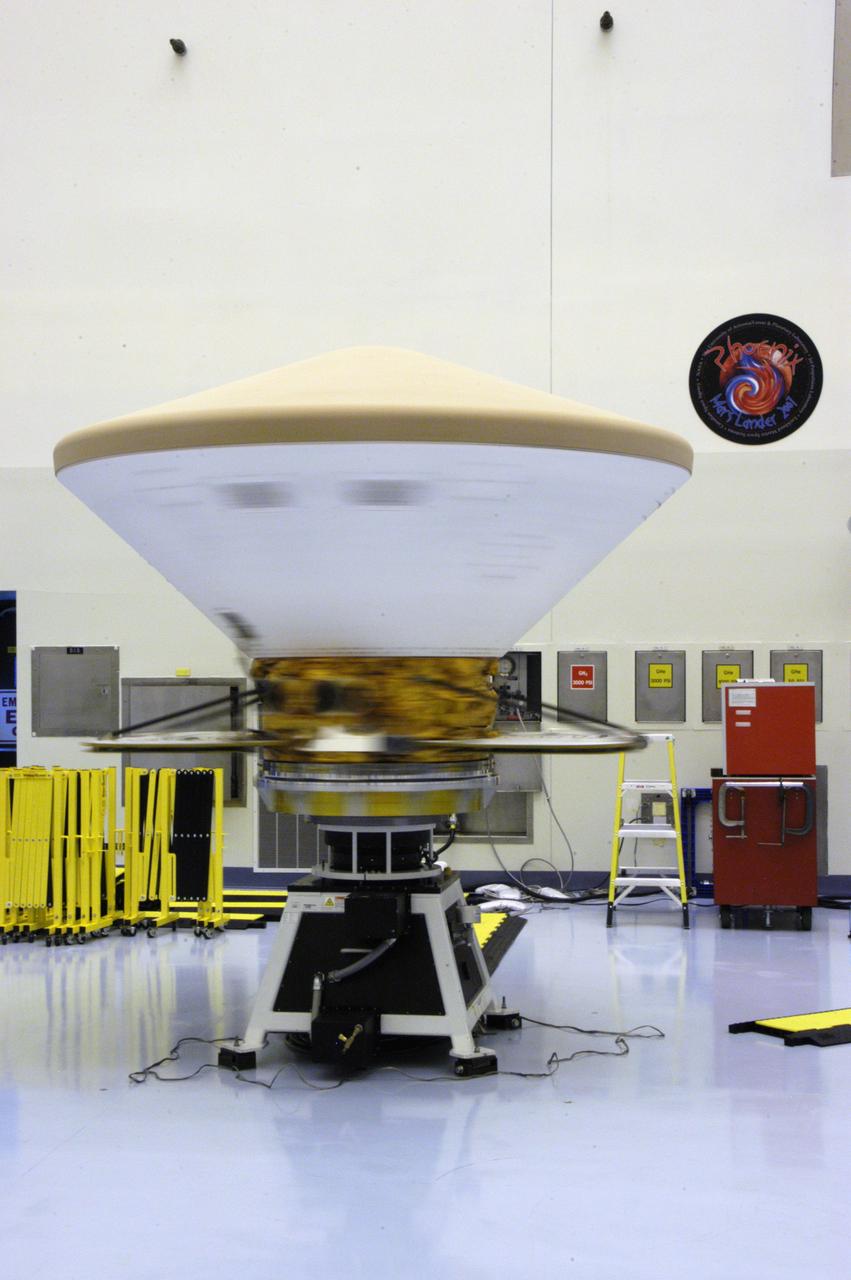

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft undergoes spin testing. The Phoenix mission is the first project in NASA's first openly competed program of Mars Scout missions. Phoenix will land in icy soils near the north polar permanent ice cap of Mars and explore the history of the water in these soils and any associated rocks, while monitoring polar climate. Landing is planned in May 2008 on arctic ground where a mission currently in orbit, Mars Odyssey, has detected high concentrations of ice just beneath the top layer of soil. It will serve as NASA's first exploration of a potential modern habitat on Mars and open the door to a renewed search for carbon-bearing compounds, last attempted with NASA's Viking missions in the 1970s. A stereo color camera and a weather station will study the surrounding environment while the other instruments check excavated soil samples for water, organic chemicals and conditions that could indicate whether the site was ever hospitable to life. Microscopes can reveal features as small as one one-thousandth the width of a human hair. Launch of Phoenix aboard a Delta II rocket is targeted for Aug. 3 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
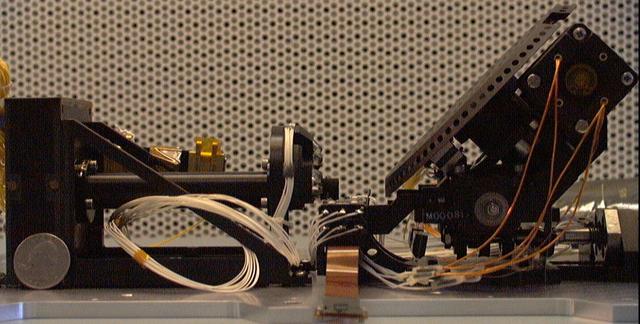
The science payload of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander includes a multi-tool instrument named the Microscopy, Electrochemistry, and Conductivity Analyzer MECA.
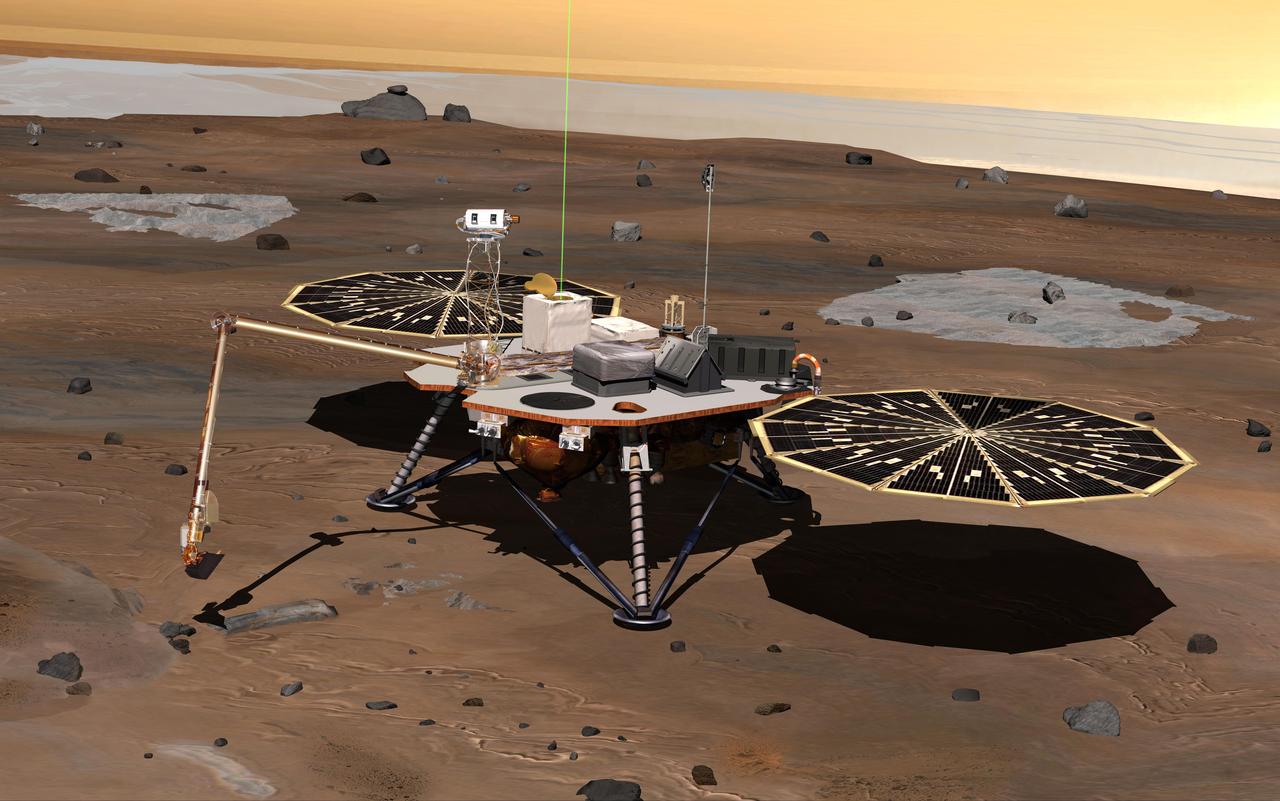

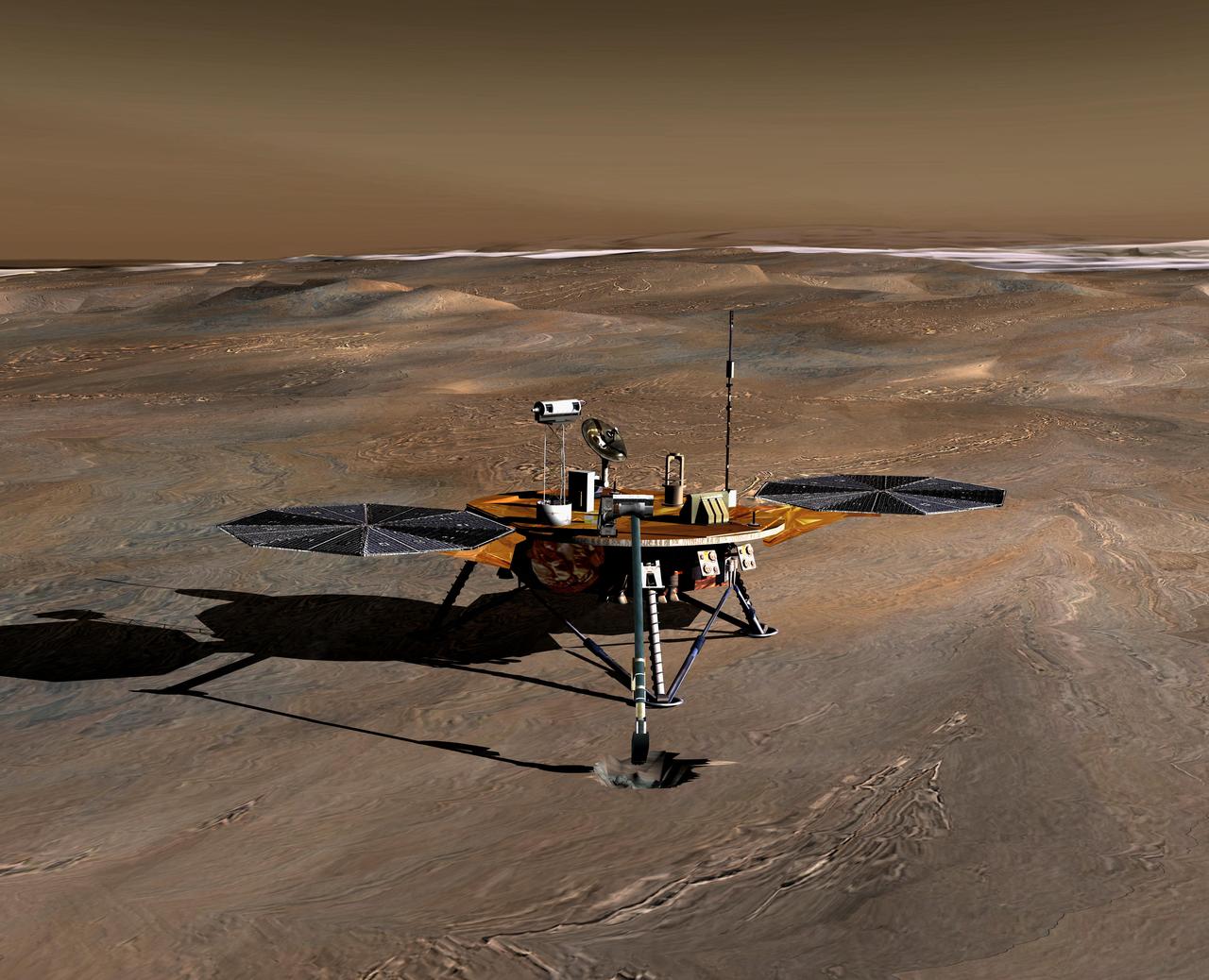
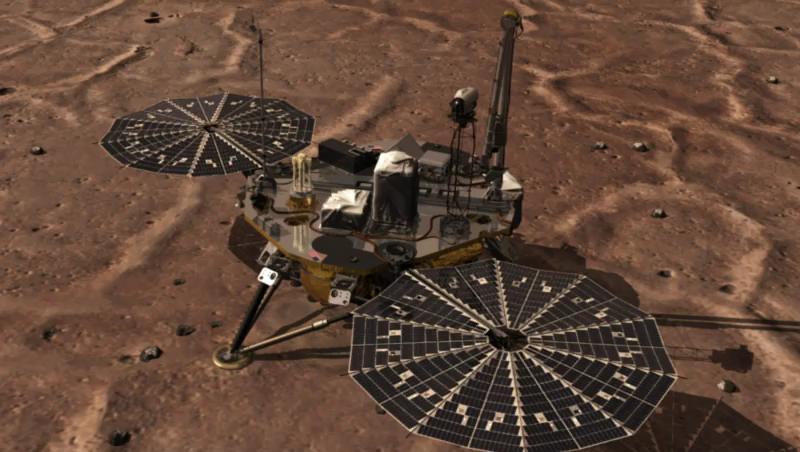
NASA Phoenix Mars Lander monitors the atmosphere overhead and reaches out to the soil below in this artist depiction of the spacecraft fully deployed on the surface of Mars.
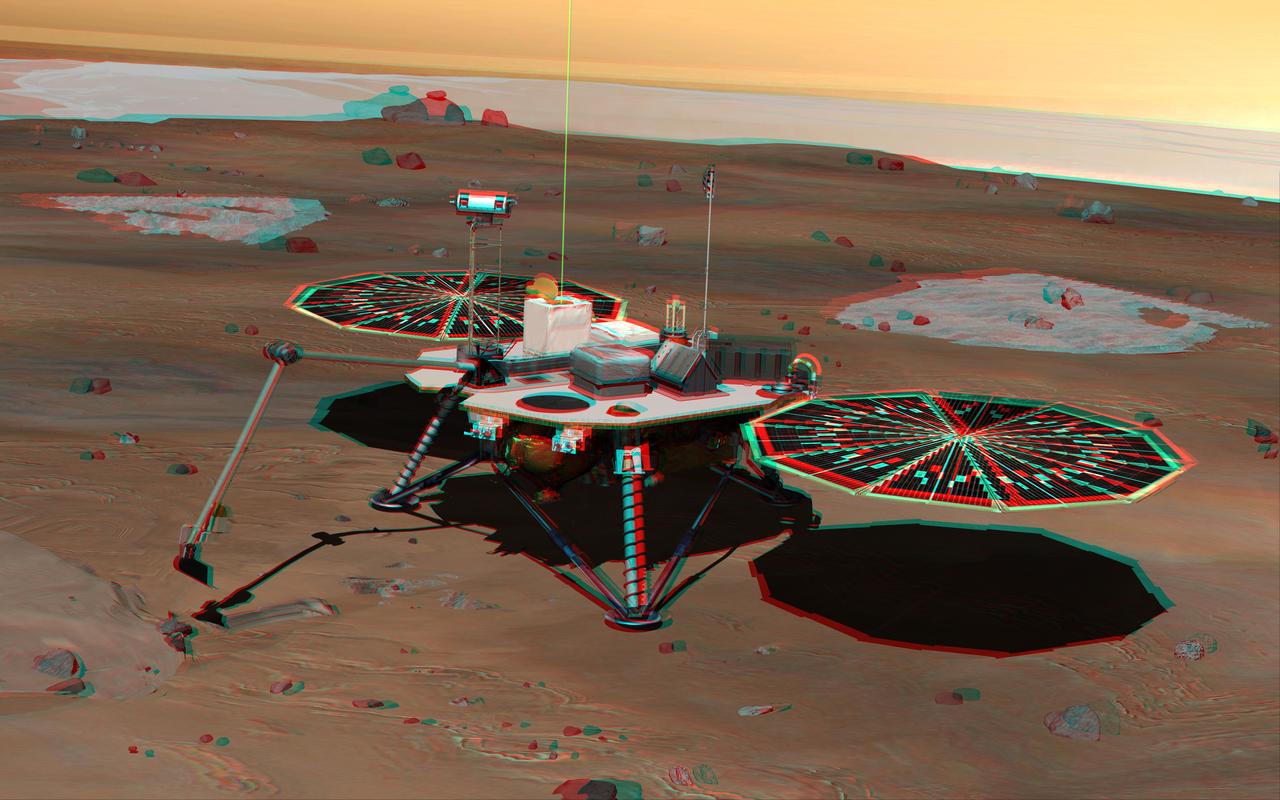

NASA Phoenix Mars Lander monitors the atmosphere overhead and reaches out to the soil below in this stereo illustration of the spacecraft fully deployed on the surface of Mars. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.

The targeted landing site for NASA Phoenix Mars Lander is at about 68 degrees north latitude, 233 degrees east longitude in the Martian arctic. The Phoenix lander, which landed May 25, 2008 ceased its operations about six months later.

NASA next Mars-bound spacecraft, the Phoenix Mars Lander, partway through assembly and testing at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, in September 2006.

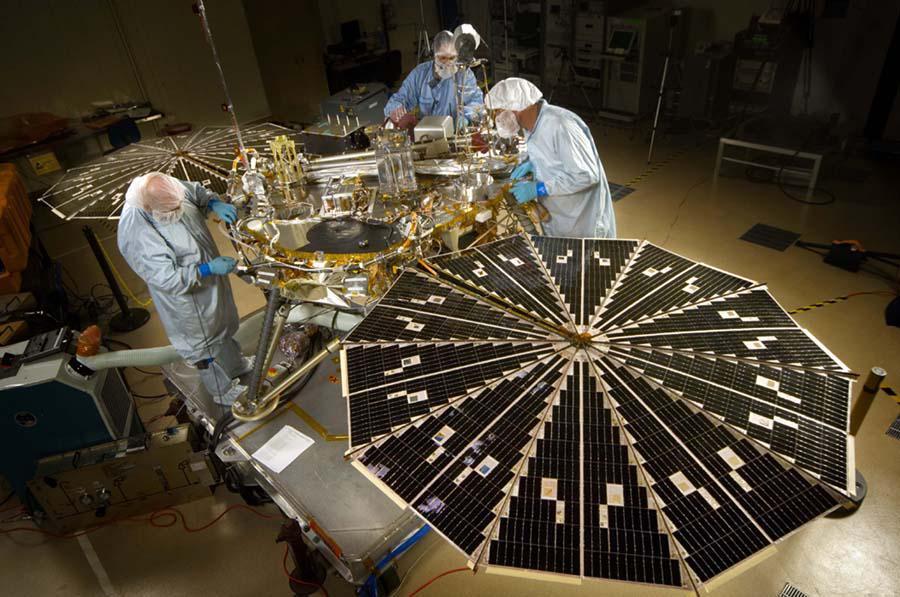
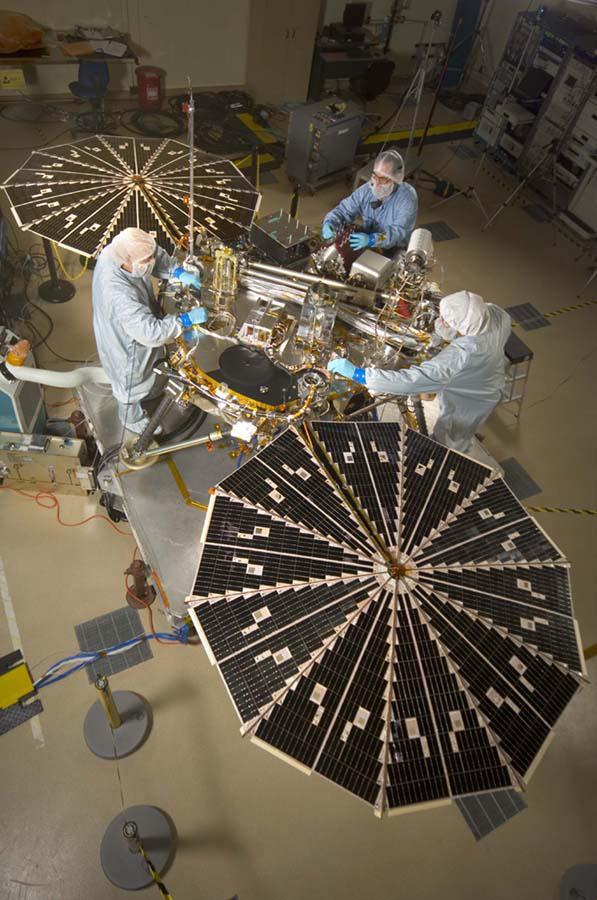
In this photograph of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander, the spacecraft specialists worked on the lander after its fan-like circular solar arrays had been spread open for testing.
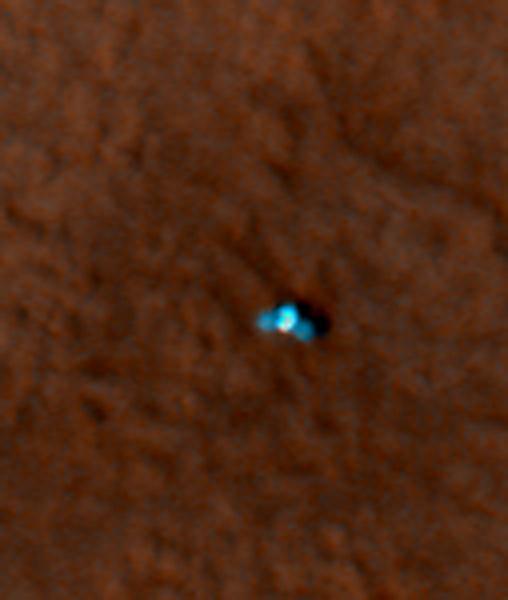
This is an enhanced-color image from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment HiRISE camera. It shows the NASA Mars Phoenix lander with its solar panels deployed on the Mars surface
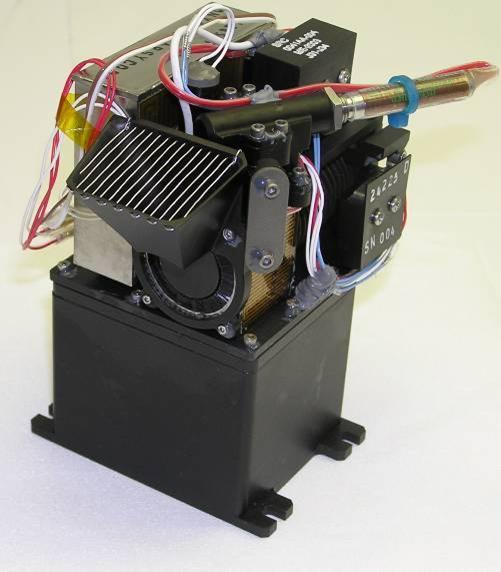

One part of the MECA instrument for NASA Phoenix Mars Lander is a pair of telescopes with a special wheel on the right in this photograph for presenting samples to be inspected with the microscopes.
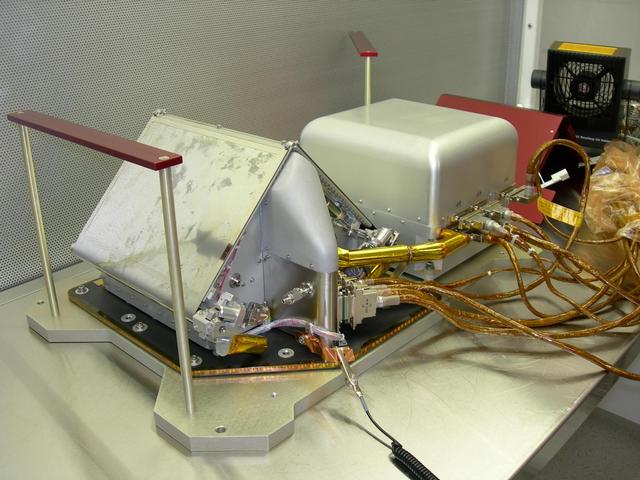
NASA Phoenix Mars Lander carried the Thermal and Evolved-Gas Analyzer t to heat and sniff samples of Martian soil and ice to analyze some ingredients.

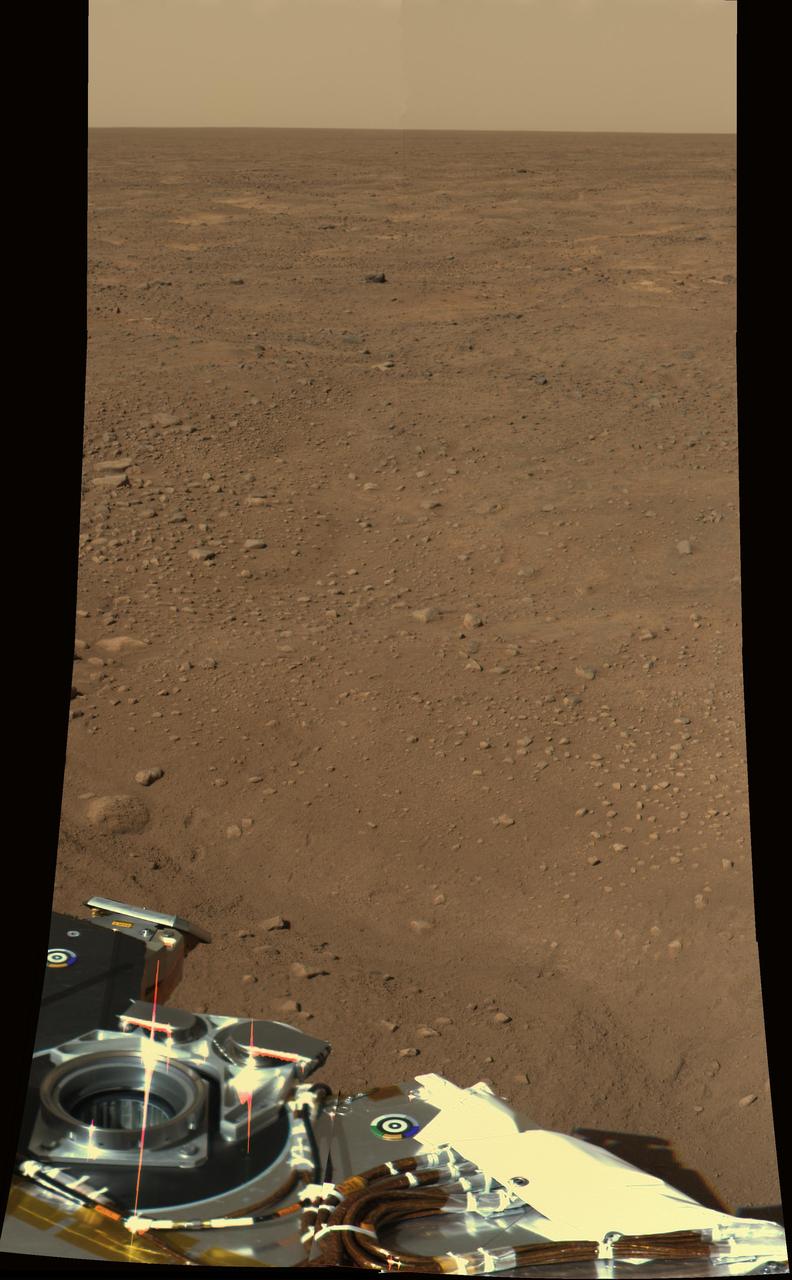
This view combines hundreds of images taken during the first several weeks after NASA Phoenix Mars Lander arrived on an arctic plain on Mars. The landing was on May 25, 2008.
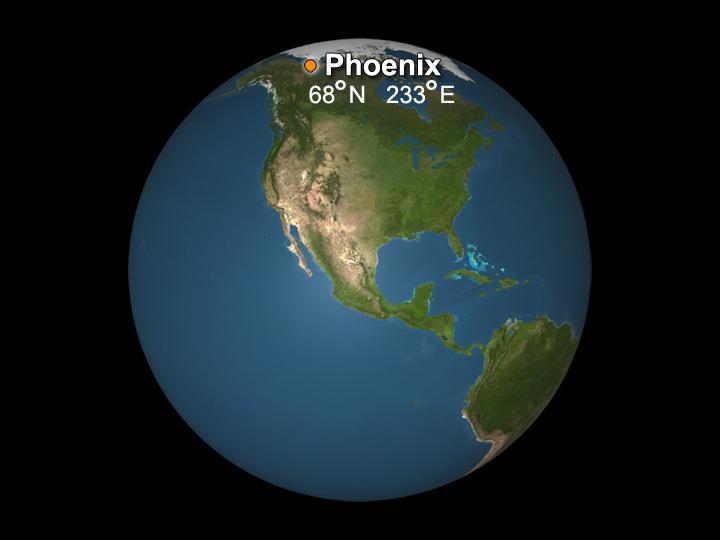
The targeted landing site for NASA Phoenix Mars Lander is at about 68 degrees north latitude, 233 degrees east longitude in the Martian arctic. The Phoenix lander, which landed May 25, 2008 ceased its operations about six months later.
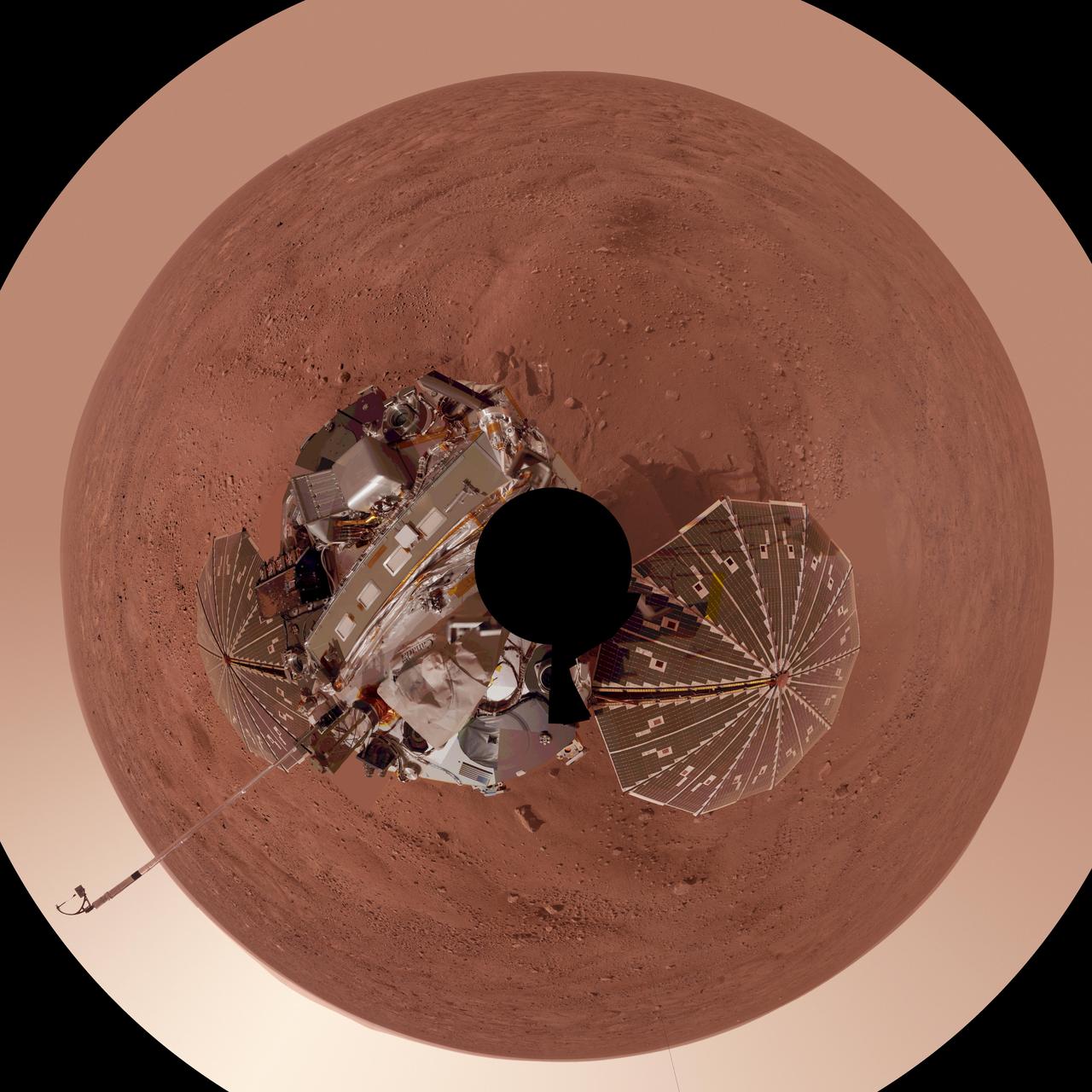
This view is a polar projection that combines more than 500 exposures taken by the Surface Stereo Imager camera on NASA Mars Phoenix Lander and projects them as if looking down from above.
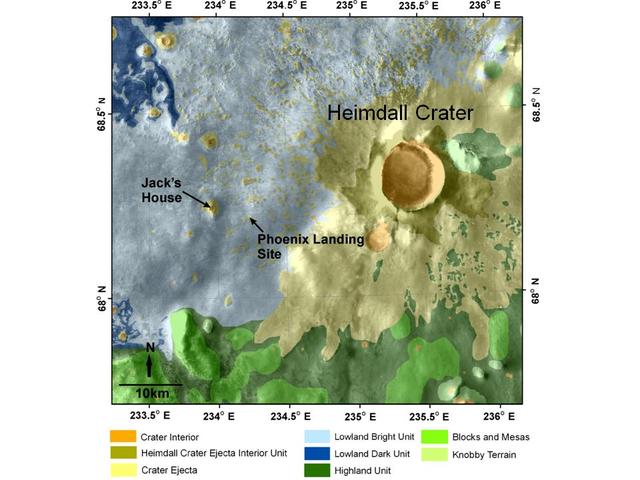
This map shows a color-coded interpretation of geomorphic units -- categories based on surface textures and contour -- in the region where NASA Phoenix Mars Lander has studied an arctic Martian plain.

This four-spike tool, called the thermal and electrical conductivity probe, is in the middle-right of this photo, mounted near the end of the arm near NASA Phoenix Mars Lander scoop upper left.

NASA Phoenix Mars Lander parachuted for nearly three minutes as it descended through the Martian atmosphere on May 25, 2008. Extensive preparations for that crucial period included this drop test near Boise, Idaho, in October 2006.

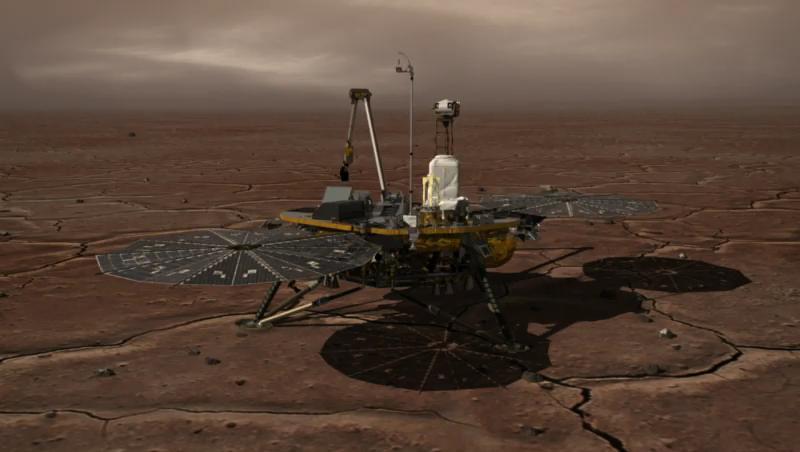
NASA Phoenix Mars Lander, landed on May 25, 2008, and explored the history of water and monitored polar climate on Mars until communications ended in November, 2008, about six months after landing, when its solar panels ceased operating in the winter.

Two images of the Phoenix Mars lander as captured by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter taken from Martian orbit in both 2008 and 2010.
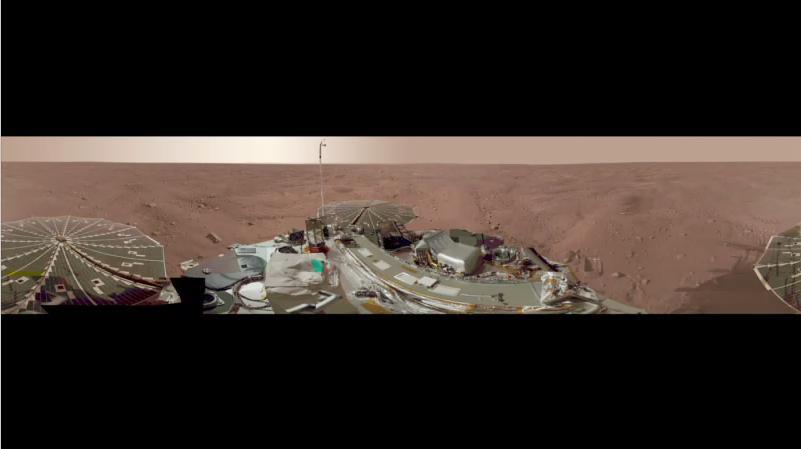

This view combines more than 500 images taken after NASA Phoenix Mars Lander arrived on an arctic plain at 68.22 degrees north latitude, 234.25 degrees east longitude on Mars.

NASA Phoenix Mars Lander will enter the Martian atmosphere at hypersonic speeds.

This image shows how NASA Phoenix Mars Lander stays in contact with Earth.

Images taken by NASA Phoenix Mars Lander Surface Stereo Imager, combined into a panoramic view looking north from the lander.

This artist conception shows NASA Phoenix Mars Lander during its more than 9-month journey to Mars.

This artist conception depicts NASA Phoenix Mars Lander a moment before its touchdown on the arctic plains of Mars.

NASA Phoenix Mars Lander will open its solar arrays 20 minutes after it touches down on the surface of Mars.
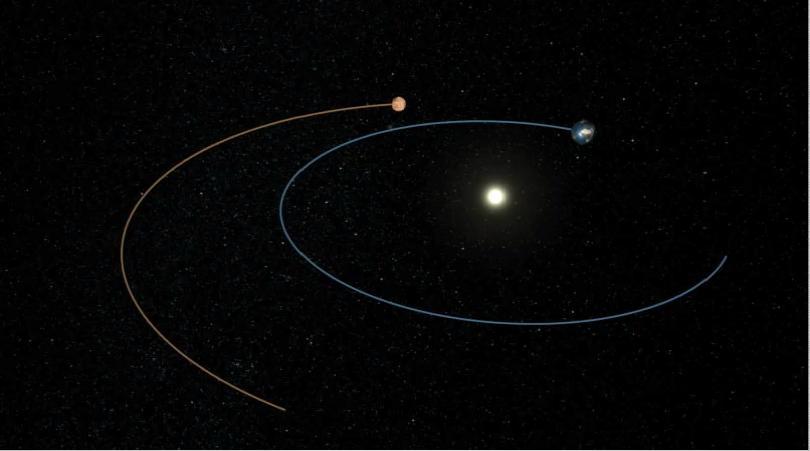
This artist animation shows the route NASA Phoenix Mars Lander took to get from Earth to Mars.
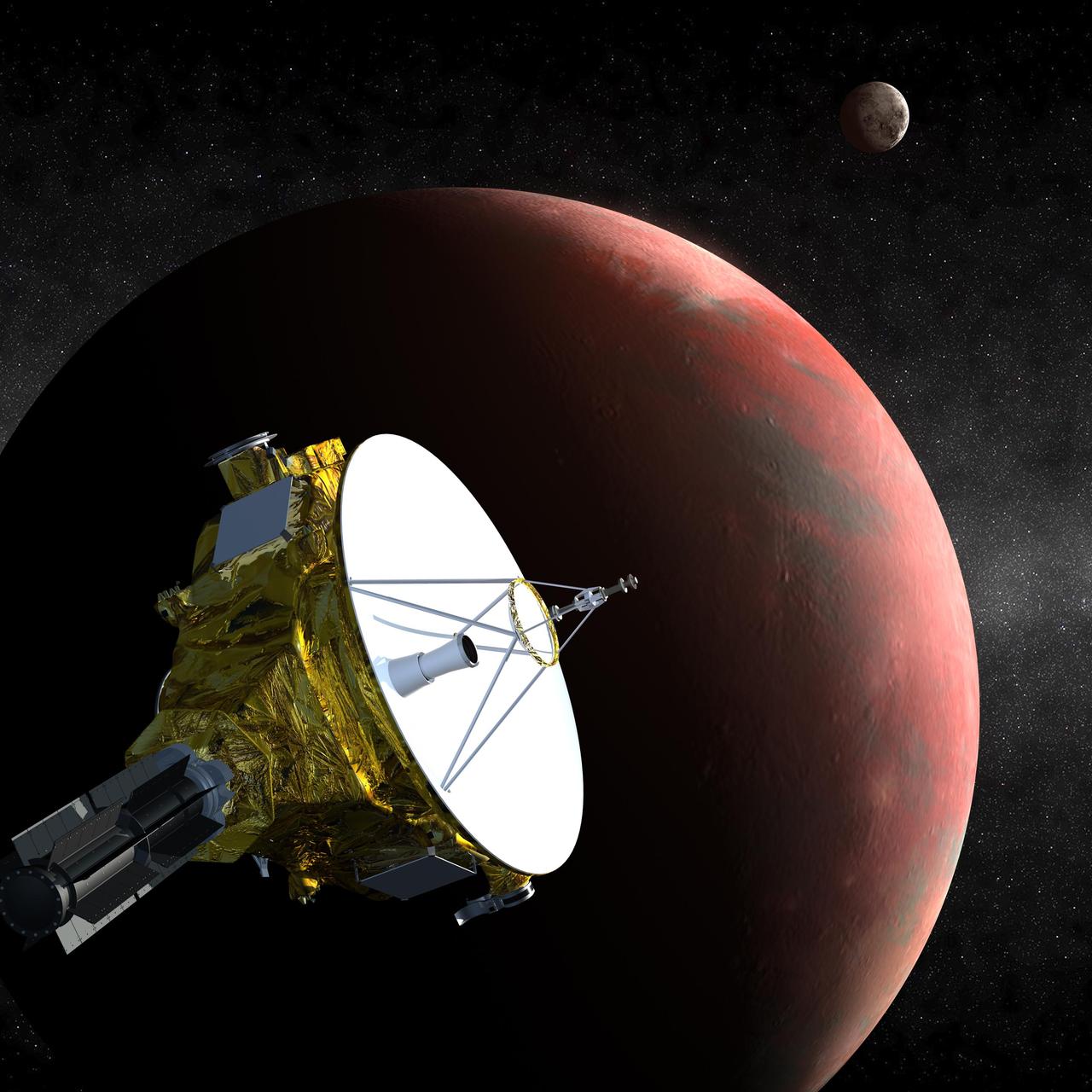
This artist conception shows NASA Phoenix Mars Lander during its more than 9-month journey to Mars.

This artist animation shows NASA Phoenix Mars Lander adjusting its course to Mars, an event called a trajectory correction maneuver.
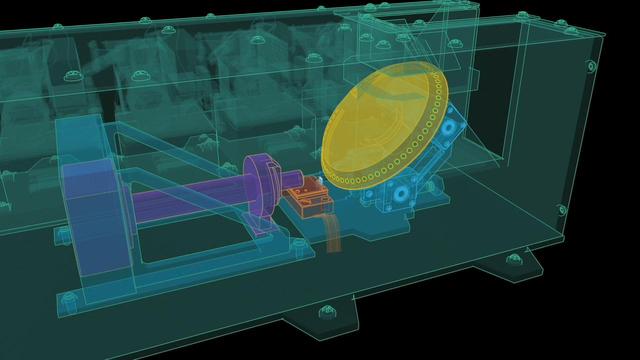
A scientific illustration of the operation of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander Atomic Force Microscope, or AFM. The AFM is part of Phoenix Microscopy, Electrochemistry, and Conductivity Analyzer, or MECA.

This from NASA Phoenix Mars Lander Stereo Surface Imager SSI camera shows Phoenix parachute, backshell, heatshield, and impact site.

This frame from an animation shows a zoom into the Mars Descent Imager MARDI instrument onboard NASA Phoenix Mars Lander. The Phoenix team will soon attempt to use a microphone on the MARDI instrument to capture sounds of Mars.

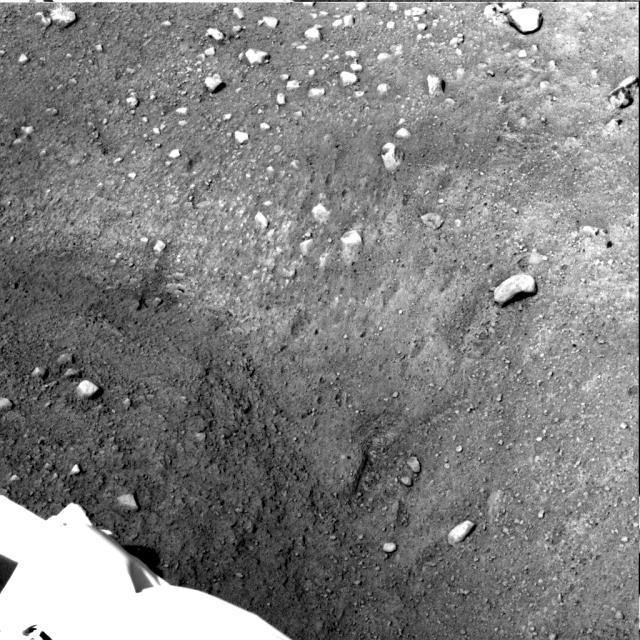
Several of the trenches dug by NASA Phoenix Mars Lander are displayed in this approximately true color mosaic of images from the lander Surface Stereo Imager camera.
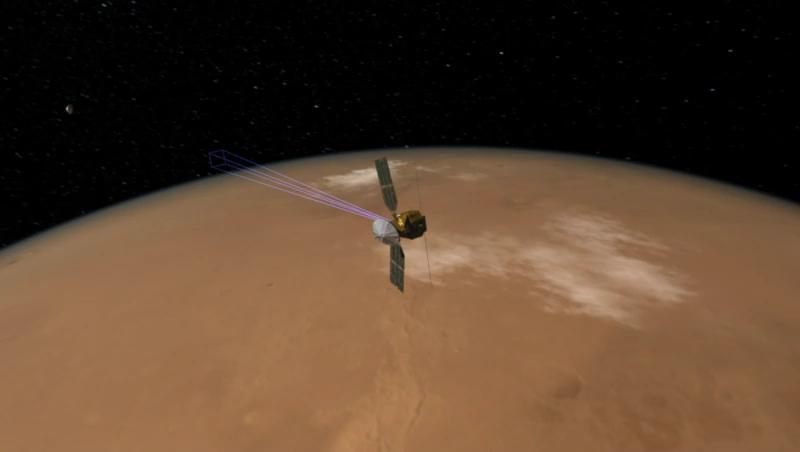

This image shows how NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter was able to snap a picture of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander as it parachuted down to the surface of Mars.
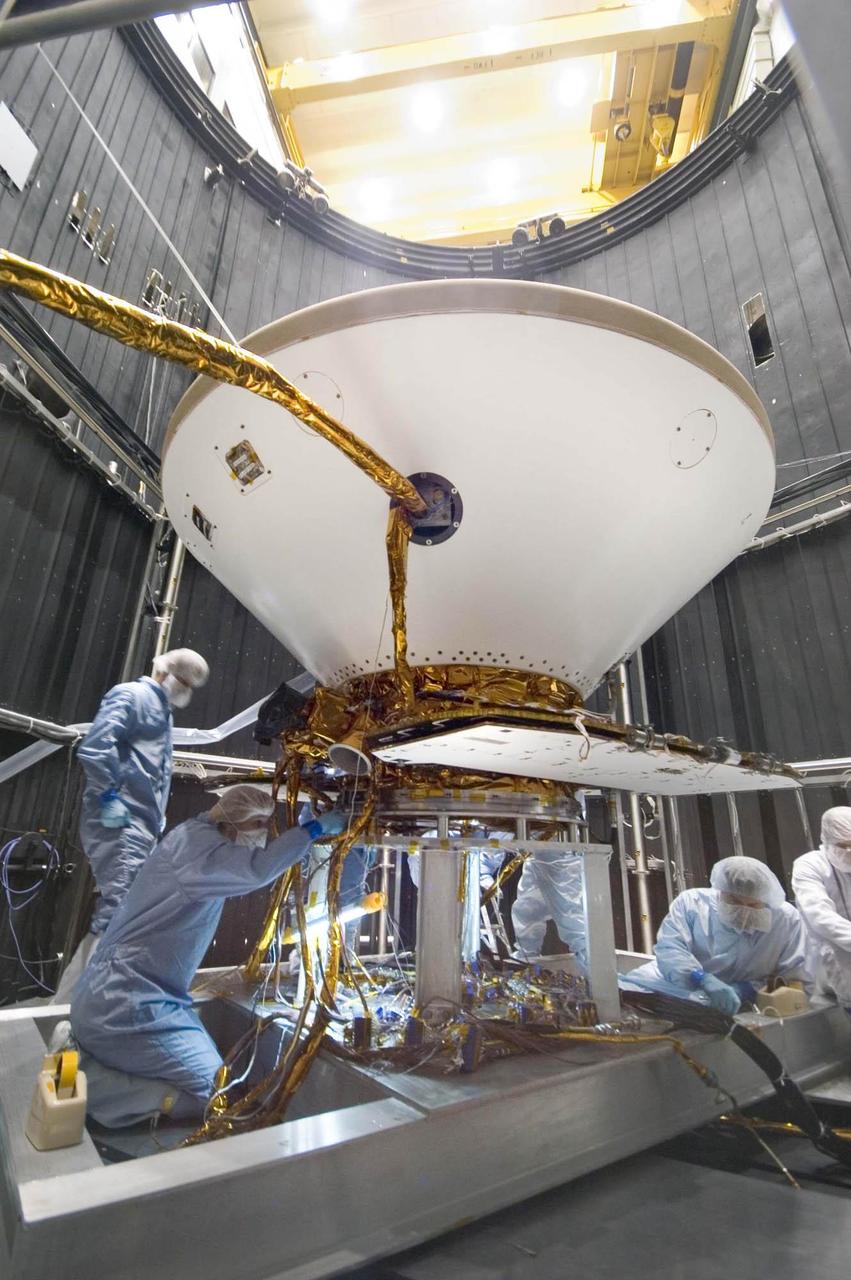

Inside a thermal vacuum at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, technicians prepared NASA Phoenix Mars Lander for environmental testing

This image is of the Canadian-built lidar in operation with the cover open was acquired at the NASA Mars Phoenix Lander landing site on Sol 3.

NASA Phoenix Mars Lander will be in free fall after it separates from its back shell and parachute, but not for long.
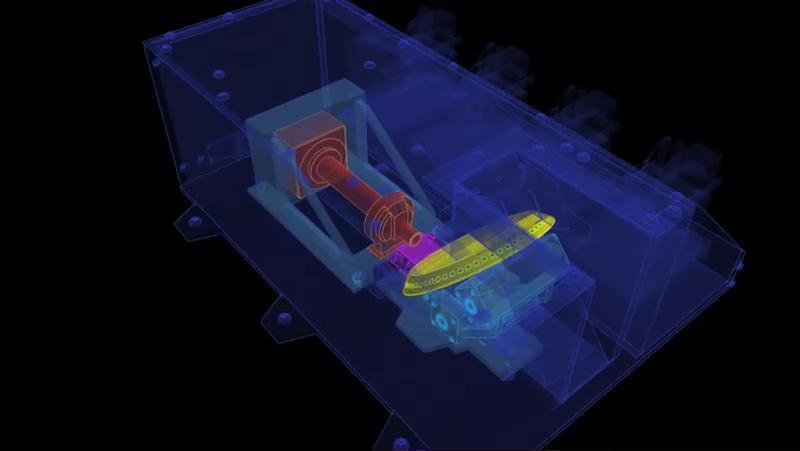
This image shows the workings of the microscope station of the Microscopy, Electrochemistry and Conductivity Analyzer MECA instrument suite of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander.

Lockheed Martin Space Systems technicians work on the science deck of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander
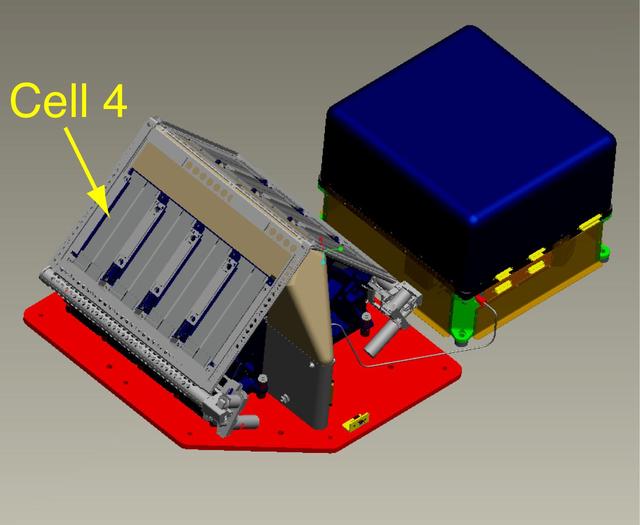
This is a computer-aided drawing of the Thermal and Evolved-Gas Analyzer, or TEGA, on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander.

This image of Snow Queen, was taken by the Robotic Arm Camera RAC aboard NASA Phoenix Mars Lander.
NASA Phoenix Mars Lander was lowered into a thermal vacuum chamber at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, in December 2006
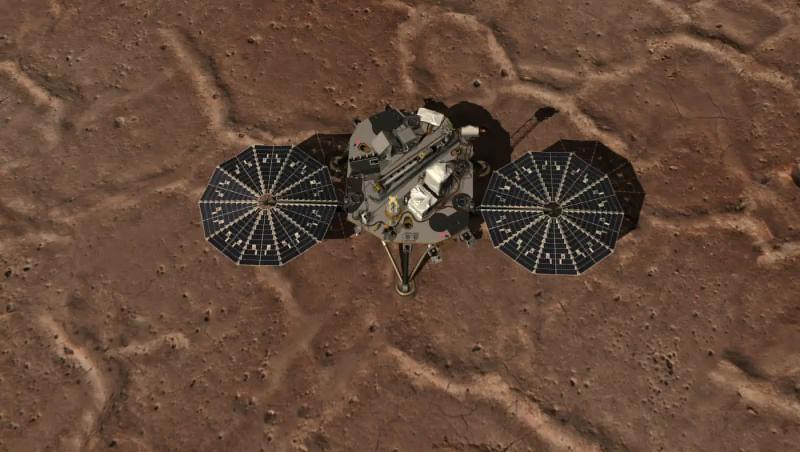

This image shows an overhead view of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander and the work area of the Robotic Arm.

This video shows the propulsion system on an engineering model of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander being successfully tested.

This is an image of a camera pushing through NASA Phoenix Mars Lander Stereo Surface Imager SSI.
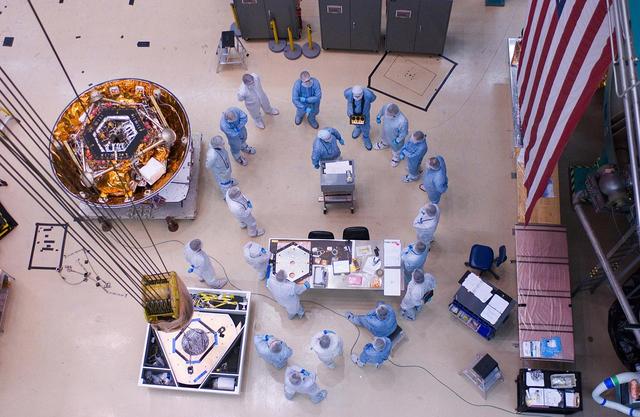

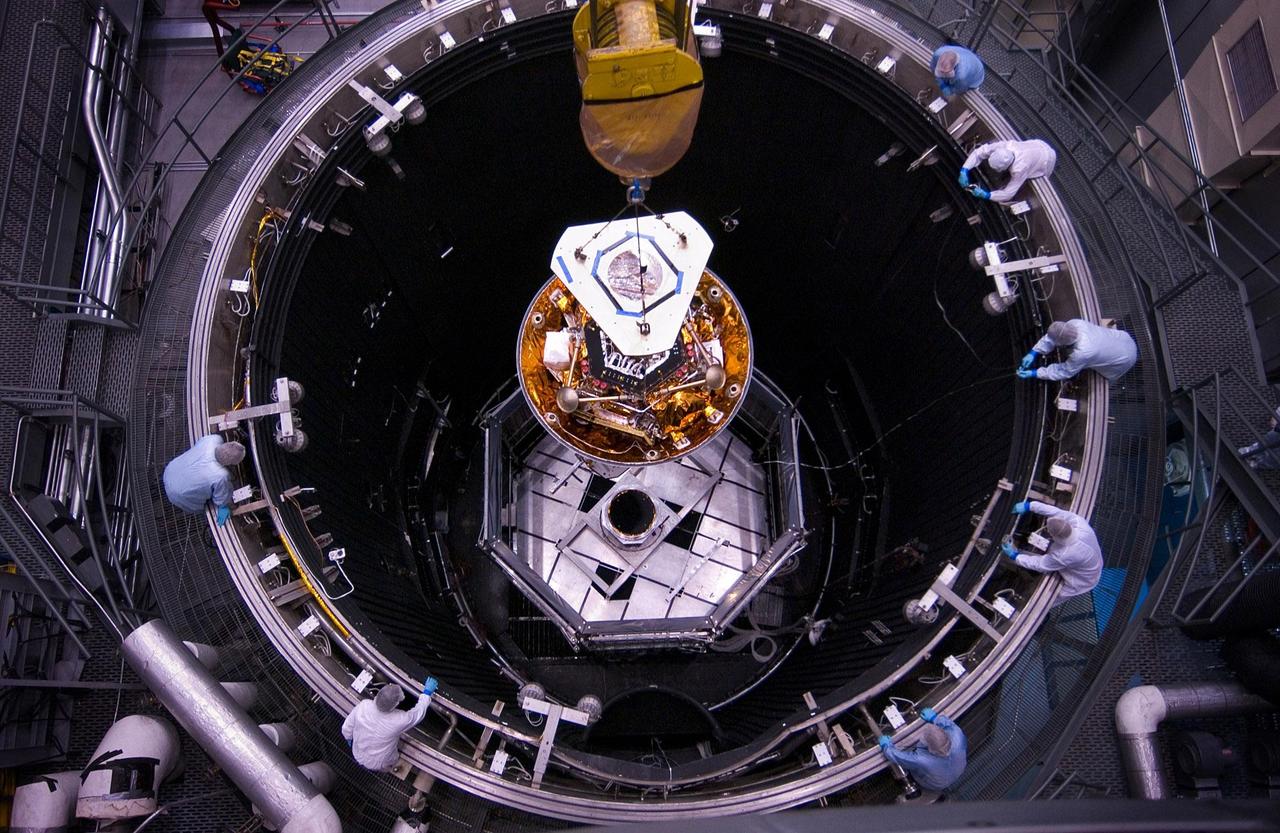
Spacecraft specialists huddle to discuss the critical lift of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander into a thermal vacuum chamber

This image shows the workspace reachable by the scoop on the robotic arm of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander, along with some measurements of rock sizes.
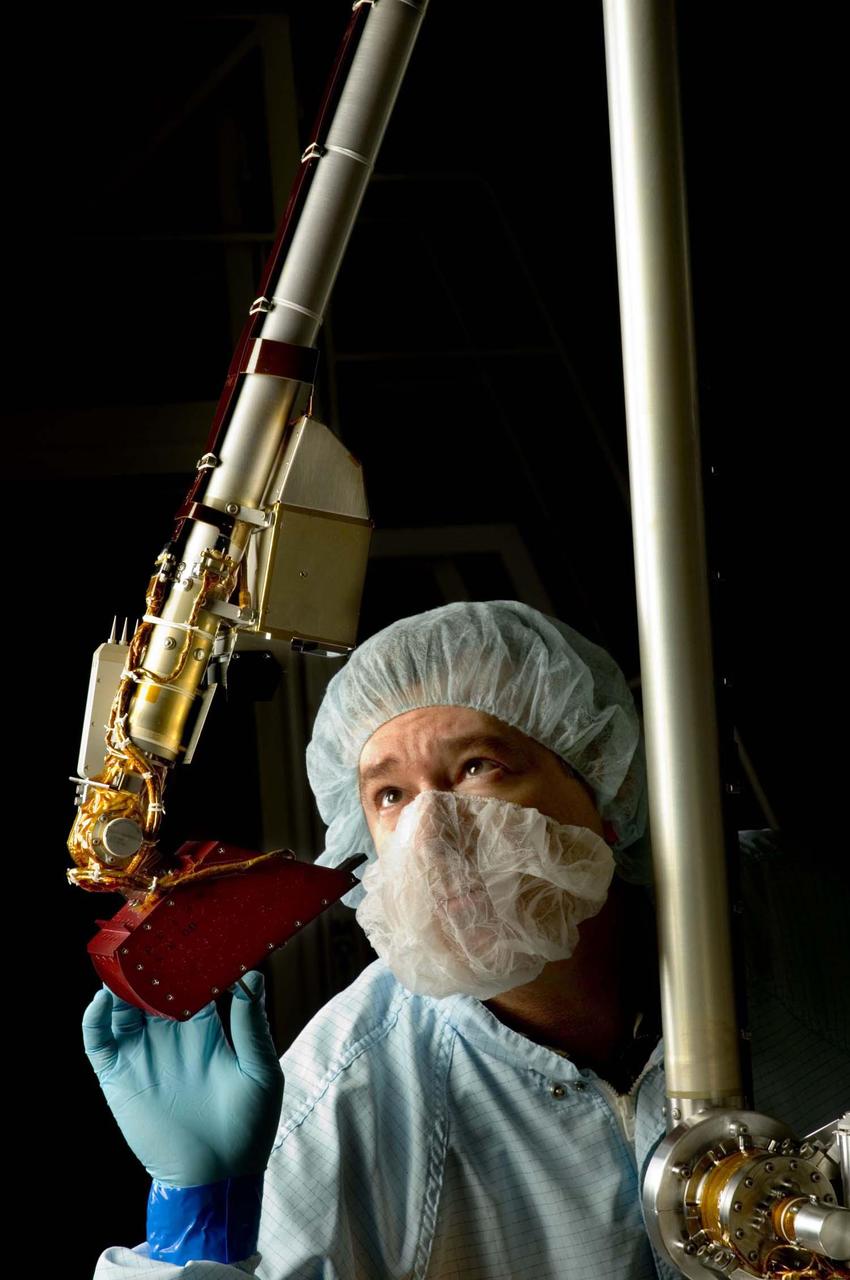
A spacecraft technician inspected the vital robotic arm of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander during the assembly phase of the mission
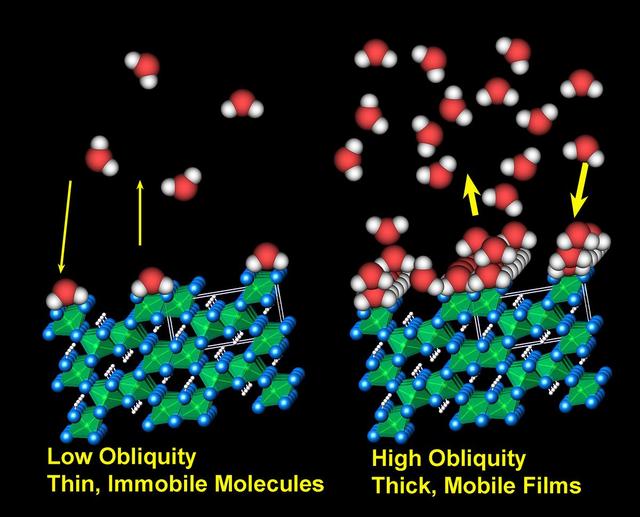
The Thermal and Electrical Conductivity Probe on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander detected small and variable amounts of water in the Martian soil.
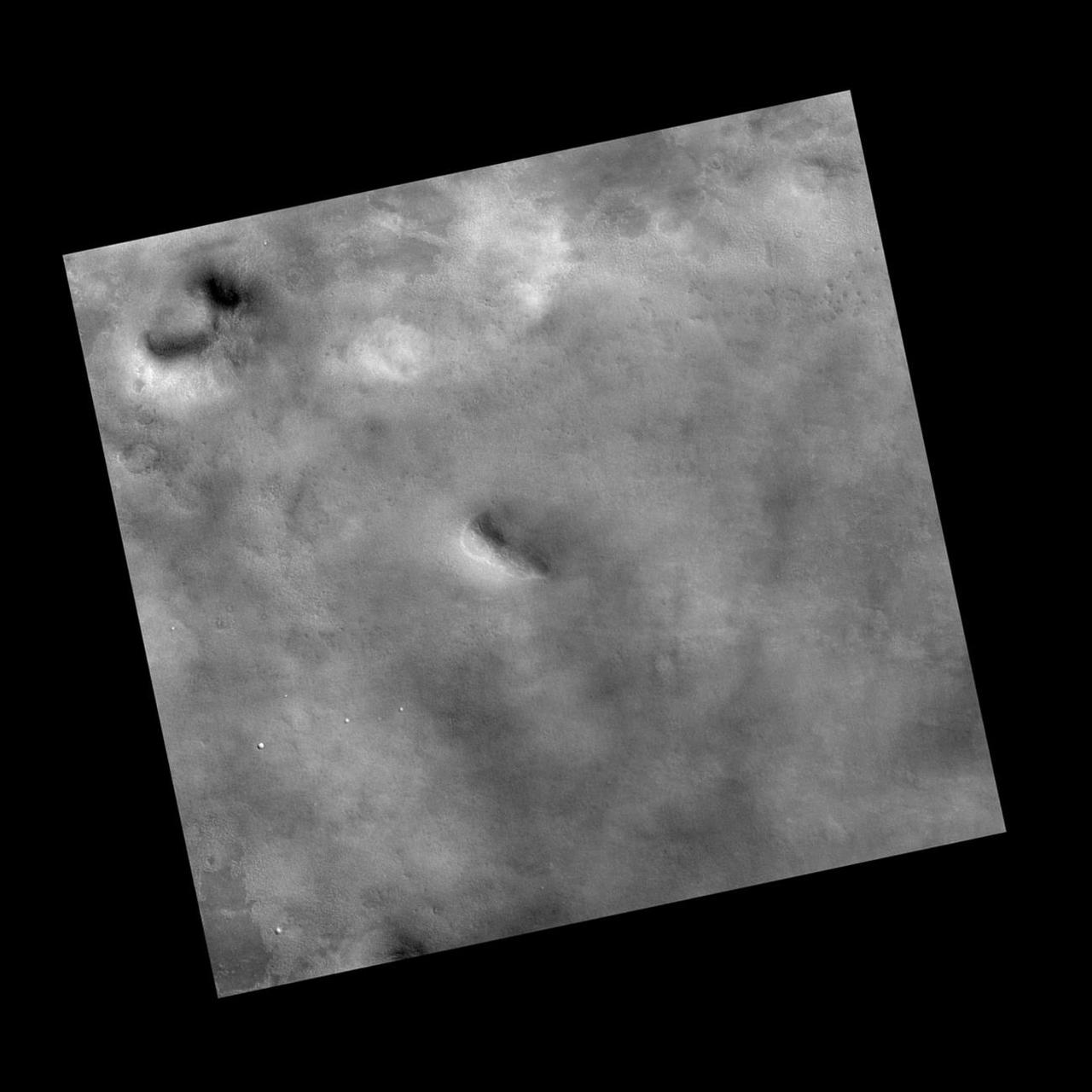
This view covers an area within the planned landing area for NASA Phoenix Mars Lander. It was taken by the Context Camera on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
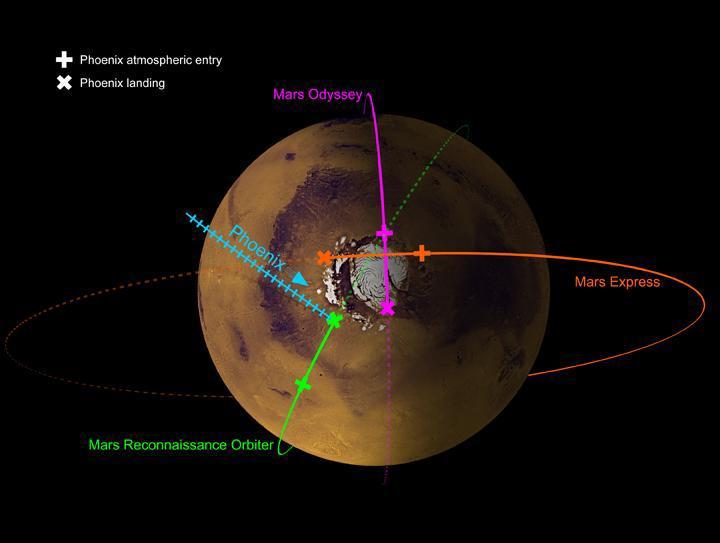
This image shows the paths of three spacecraft currently in orbit around Mars, as well as the path by which NASA Phoenix Mars Lander will approach and land on the planet.
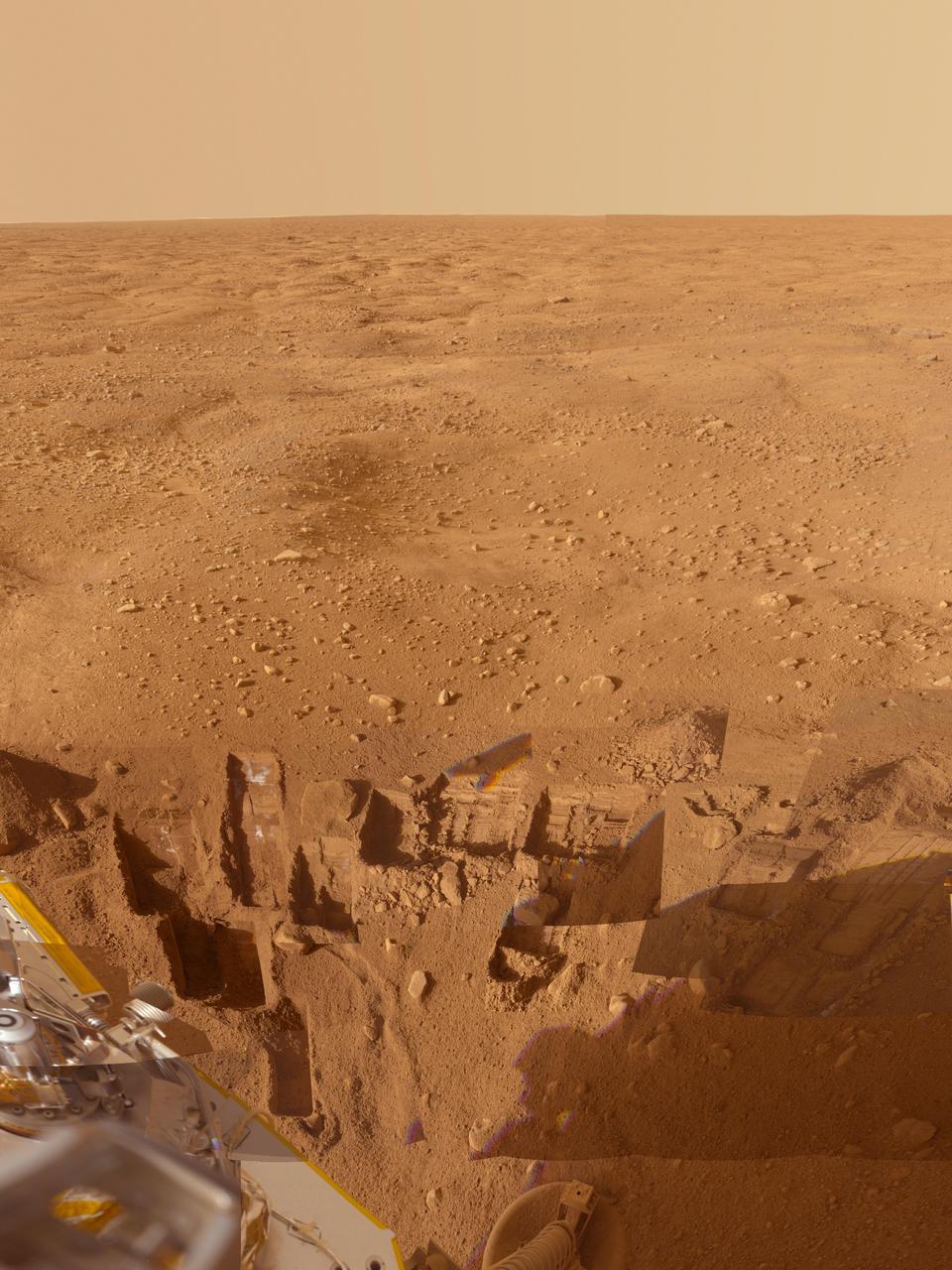

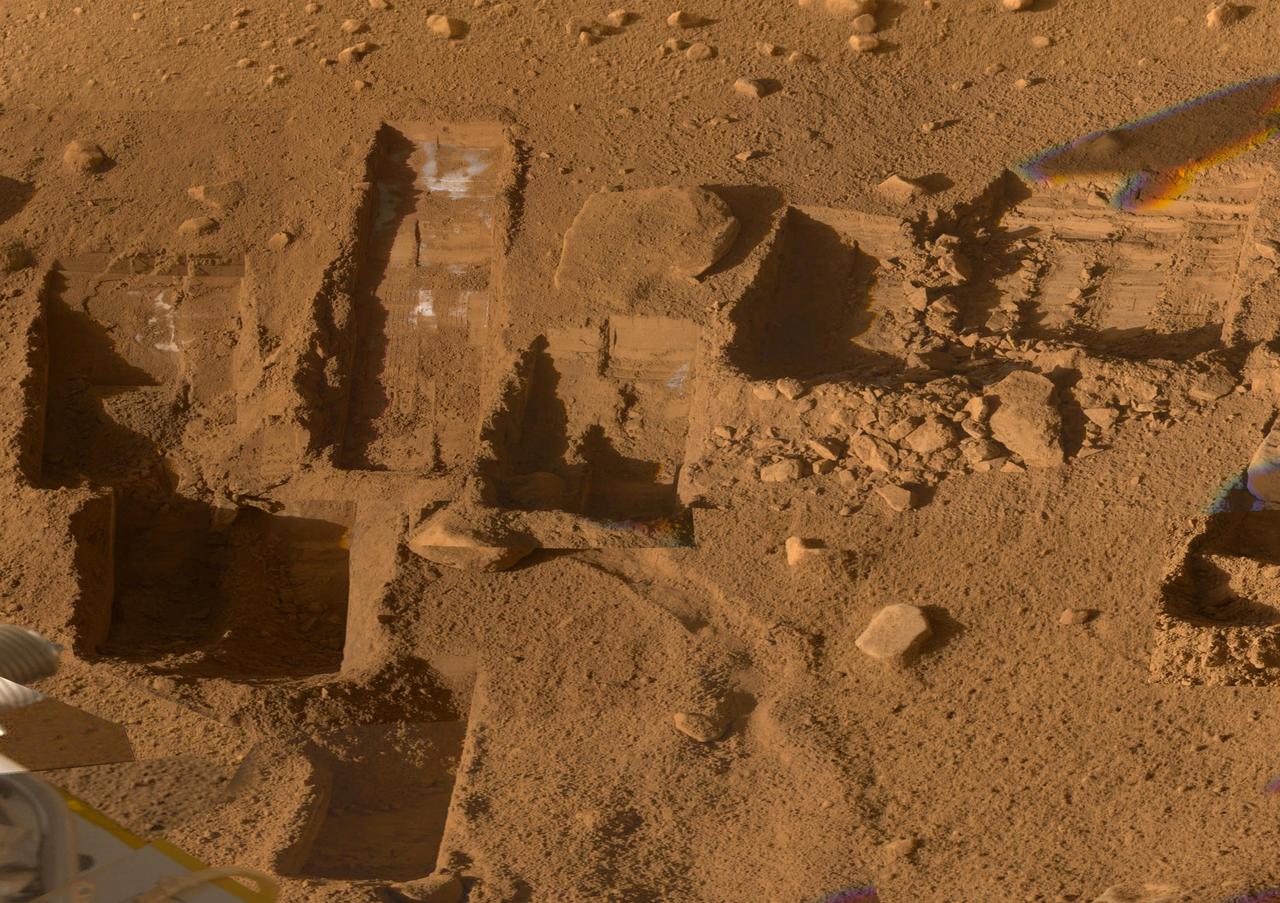
This mosaic of images from the Surface Stereo Imager camera on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander shows several trenches dug by Phoenix, plus a corner of the spacecraft deck and the Martian arctic plain stretching to the horizon.
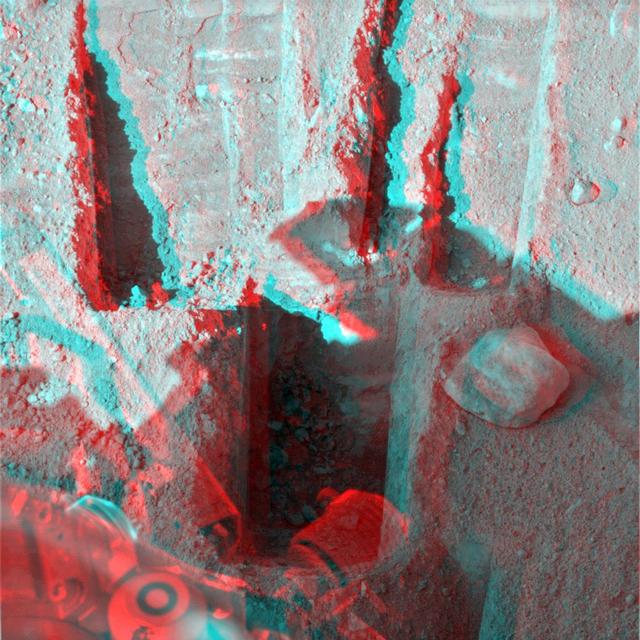
Digging by NASA Phoenix Mars Lander on Aug. 23, 2008, reached a depth about three times greater than in any trench Phoenix has excavated. 3D glasses are necessary.

A camera view zooms in from NASA Phoenix Mars Lander launch site all the way to Phoenix Microscopy and Electrochemistry and Conductivity Analyzer MECA aboard the spacecraft on the Martian surface.
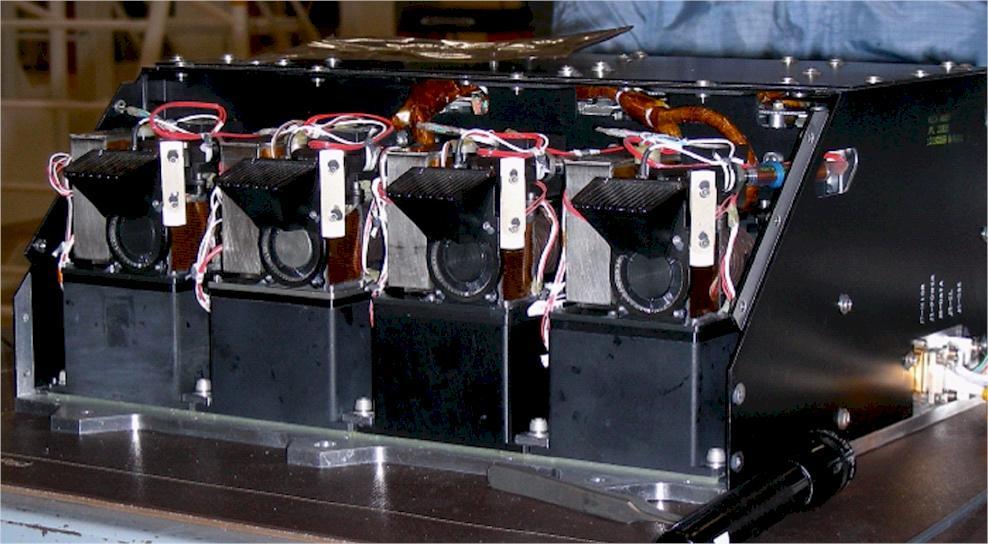

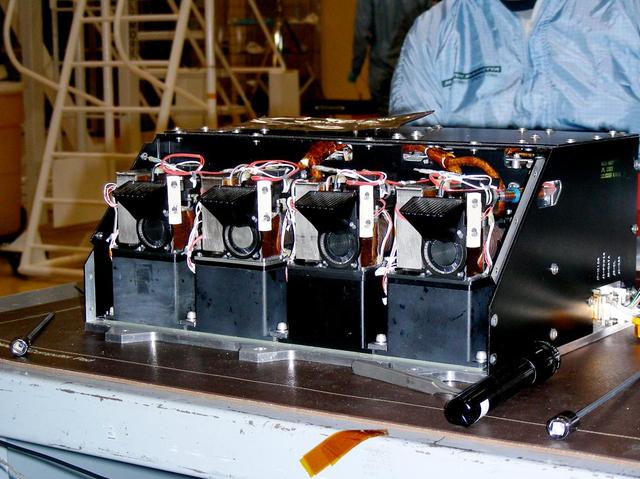
This image shows four Wet Chemistry Laboratory units, part of the Microscopy, Electrochemistry, and Conductivity Analyzer MECA instrument on board NASA Phoenix Mars Lander. This image was taken before Phoenix launch on August 4, 2007.
This image was taken by NASA Phoenix Mars Lander Stereo Surface Imager SSI on Sol 3. It illustrates the actions that Phoenix Robotic Arm took to deploy its wrist.
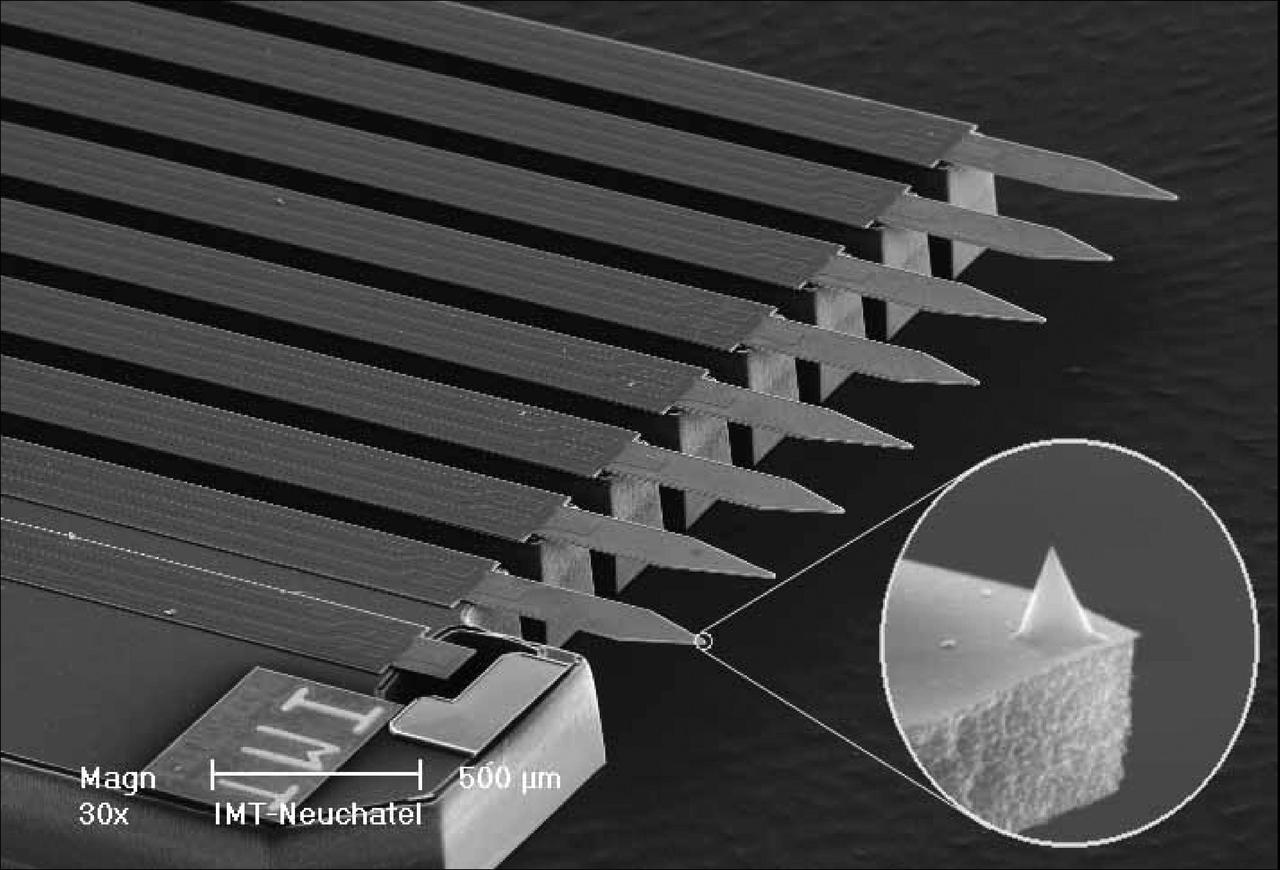
This image shows the eight sharp tips of the NASA Phoenix Mars Lander Atomic Force Microscope, or AFM. The AFM is part of Phoenix Microscopy, Electrochemistry, and Conductivity Analyzer, or MECA.
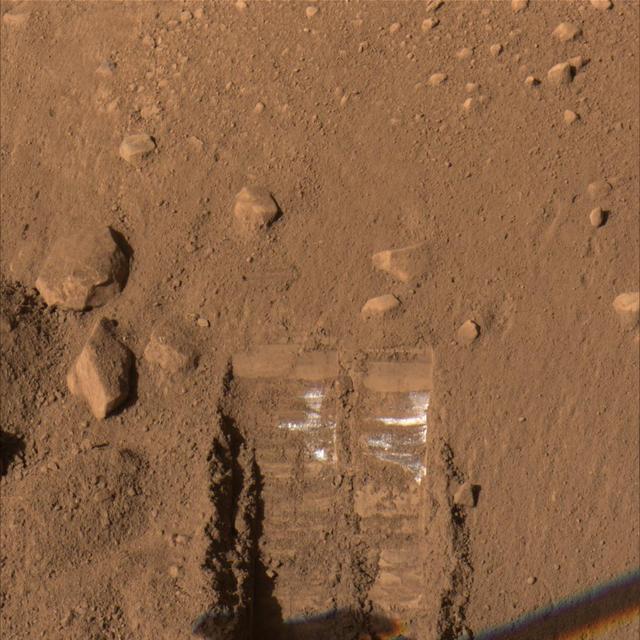

The Surface Stereo Imager on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander recorded this true-color image of the lander Robotic Arm enlarging and combining the two trenches informally named Dodo left and Goldilocks.

The Surface Stereo Imager on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander recorded this image of the lander Robotic Arm enlarging and combining the two trenches informally named Dodo left and Goldilocks.
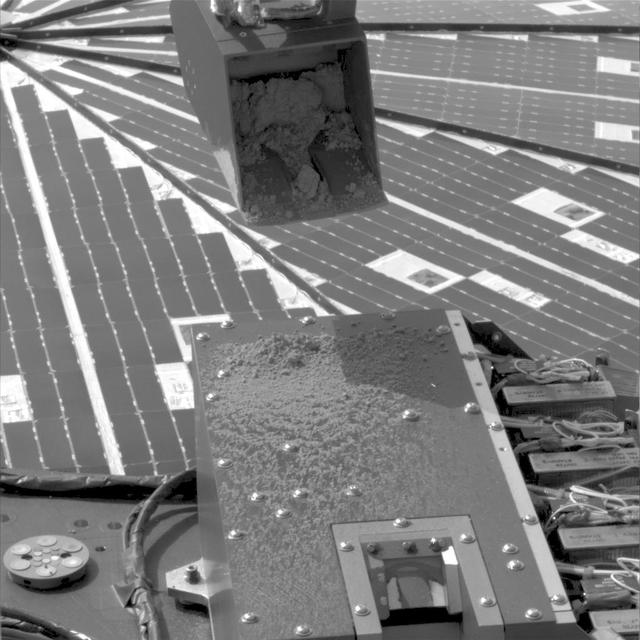

NASA Phoenix Mars Lander used its Robotic Arm during the mission 15th Martian day since landing June 9, 2008 to test a prinkle method for delivering small samples of soil to instruments on the lander deck.

The Surface Stereo Imager on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander caught this dust devil in action west of the lander on Sol 104, or the 104th Martian day of the mission, Sept. 9, 2008.

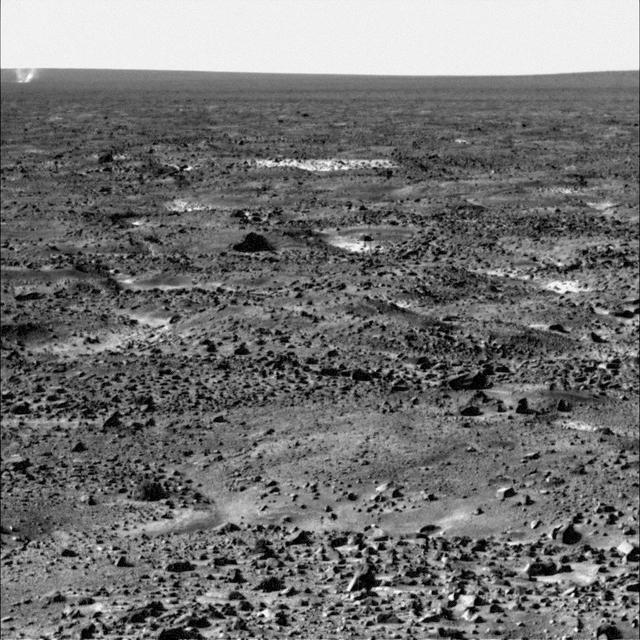
This approximate color view was obtained on sol 2 by the Surface Stereo Imager SSI on board NASA Mars Phoenix lander. The view is toward the northwest, showing polygonal terrain near the lander and out to the horizon.
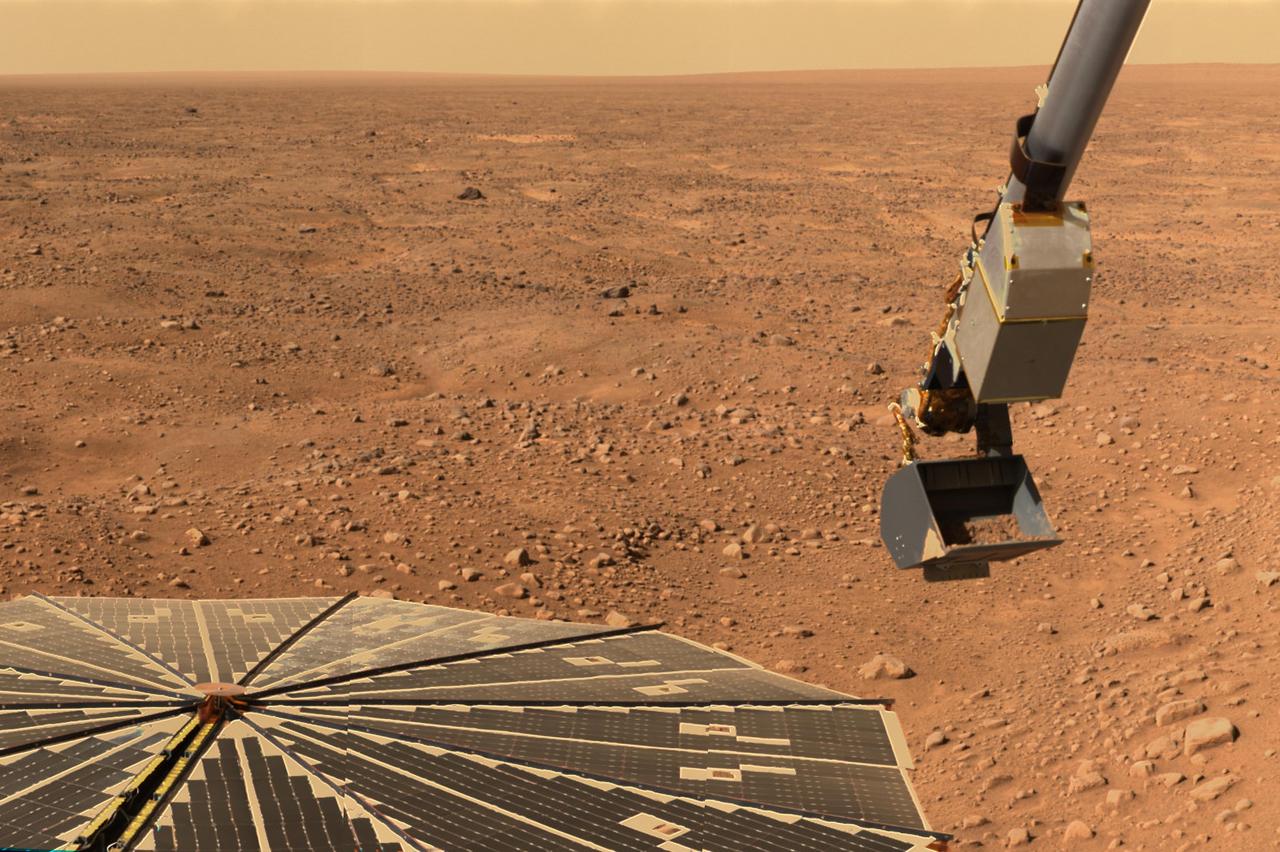
This panorama image of NASA’s Phoenix Mars Lander’s solar panel and the lander’s Robotic Arm with a sample in the scoop. The image was taken just before the sample was delivered to the Optical Microscope.

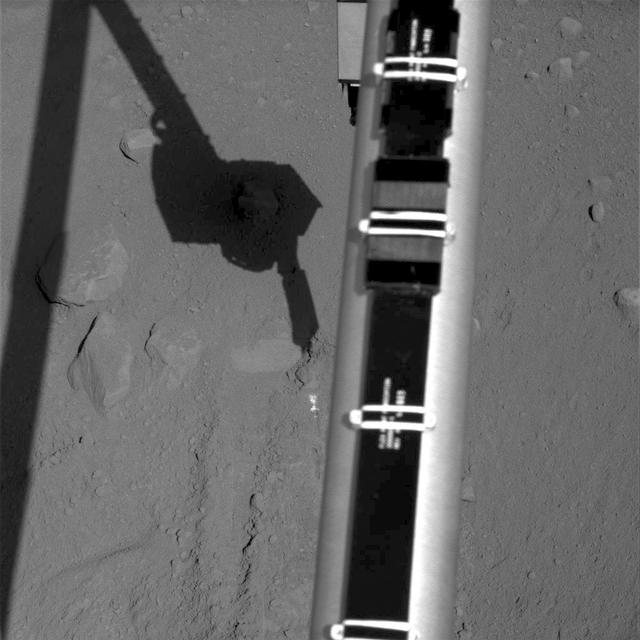
NASA Phoenix Mars Lander reaching with its Robotic Arm and taking a picture of the surface underneath the lander. The light feature in the middle of the image below the leg is informally called Holy Cow.
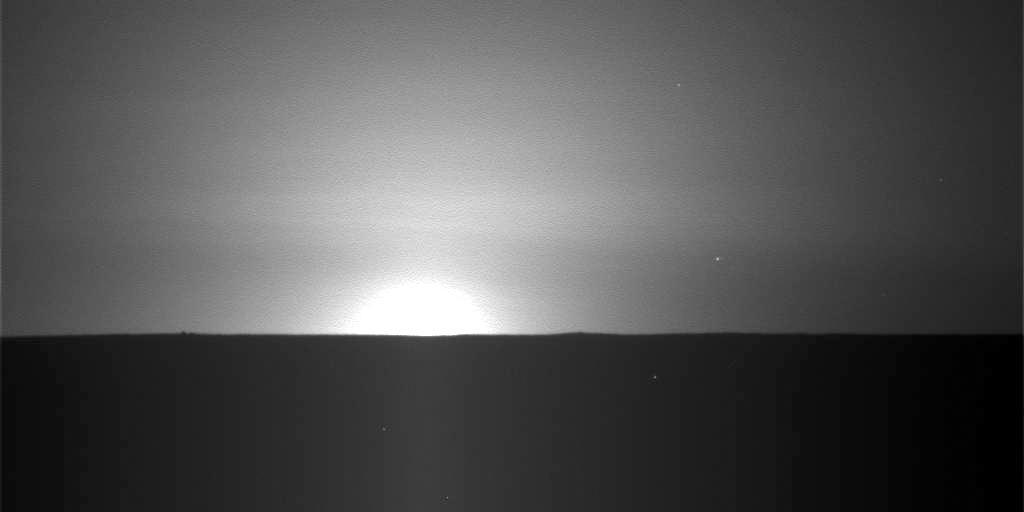

This frame from a sequence of nine images taken by the Surface Stereo Imager on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander shows the sun rising on the morning of the lander 101st Martian day after landing.
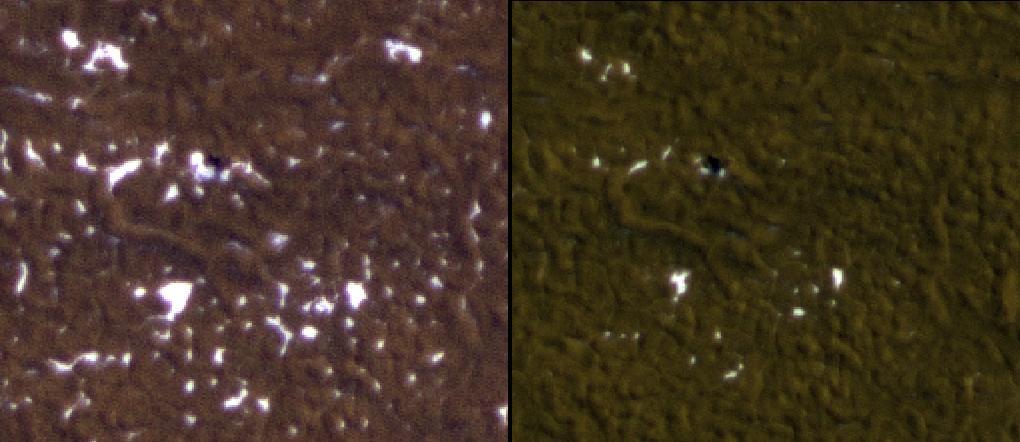
Stages in the seasonal disappearance of surface ice from the ground around the Phoenix Mars Lander are visible in these images taken by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Rover on 2-8-2010 and 2-25-2010, during springtime on northern Mars.
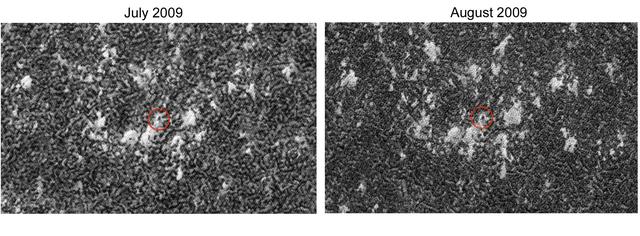
The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment camera on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured winter images of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander surrounded by dry-ice frost on Mars.
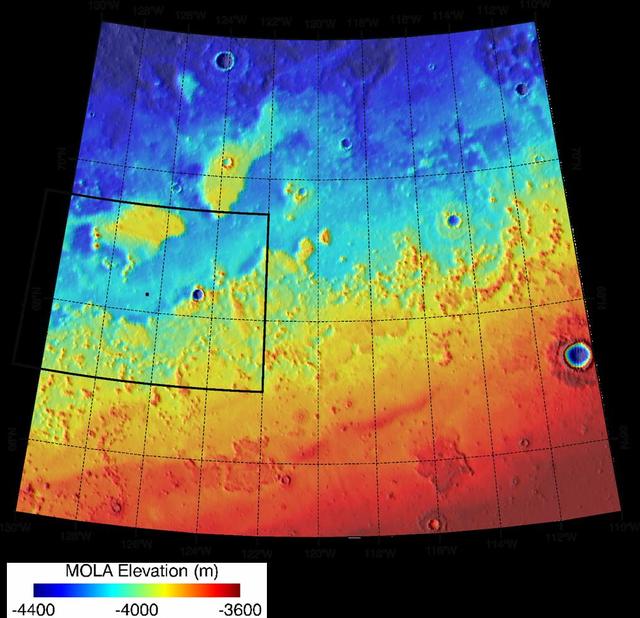
This area was designated Region D in the process of evaluating potential landing sites for NASA Phoenix Mars Lander. The topographical information is from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter on NASA Mars Global Surveyor orbiter.
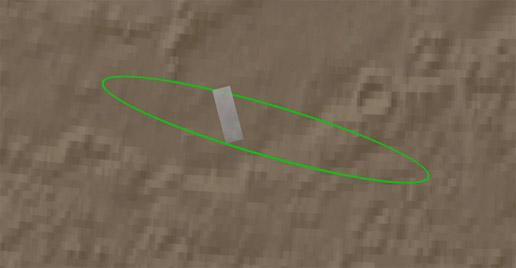
This animation zooms in on the area on Mars where NASA Phoenix Mars Lander will touchdown on May 25, 2008. The image was taken by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment HiRISE camera on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
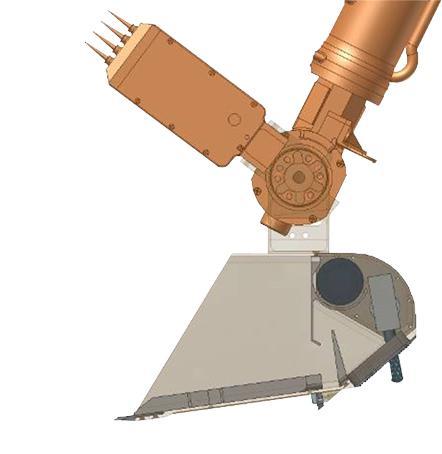
This illustration shows some of the components on and near the end of the robotic arm on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander. Primary and secondary blades on the scoop that aided in the collection of soil samples.
This image, taken Jan. 26, 2012, shows the back shell of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft after its second Martian arctic winter.
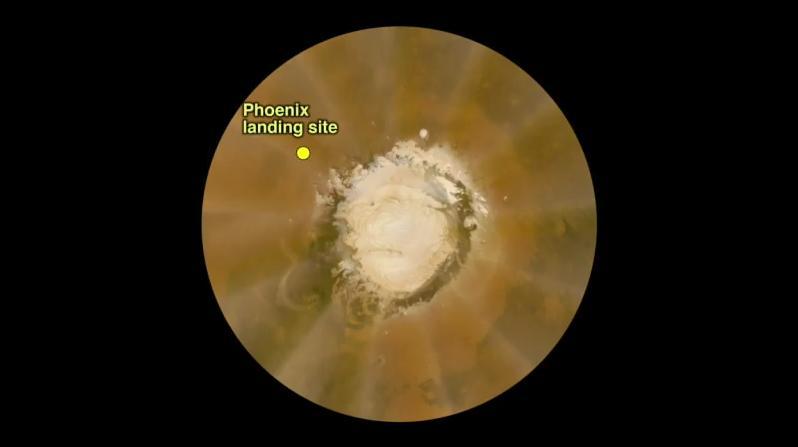
Scientists were anticipating clear skies when NASA Phoenix Mars Lander arrives on the north polar plains of the Red Planet Sunday, May 25, 2008.
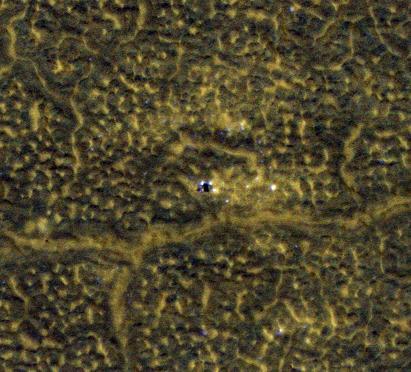
This image, taken Jan. 26, 2012, shows NASA no-longer-active Phoenix Mars Lander spacecraft after its second Martian arctic winter.

This image taken by the Stereo Surface Imager aboard NASA Phoenix Mars Lander focuses on items on the deck rather than the workspace or horizon on Sol 8.
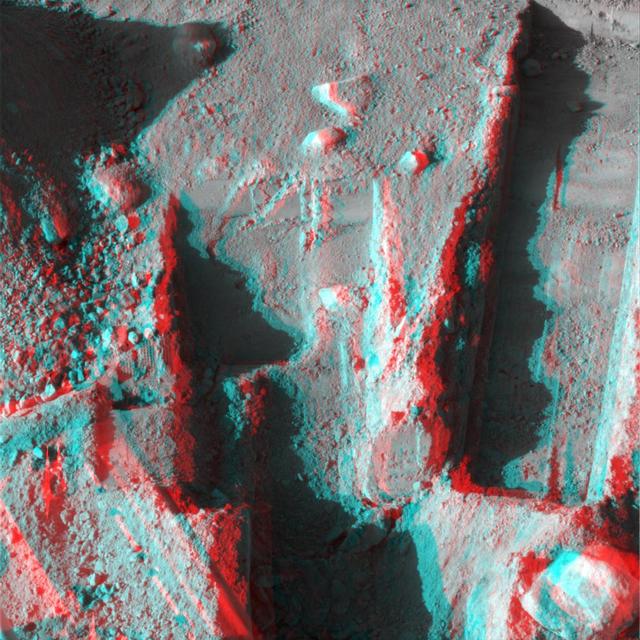
NASA Phoenix Mars Lander took this anaglyph on Oct. 21, 2008; the trench on the upper left is called Dodo-Goldilocks. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.

After NASA Phoenix Mars Lander enters the Martian atmosphere, and is traveling at about 1.7 times the speed of sound, it will deploy its parachute.
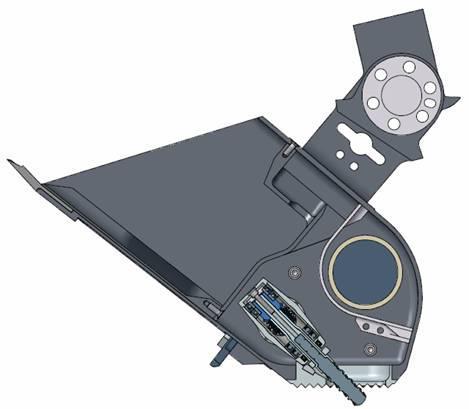
This drawing shows a side view of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander scoop with various tools for acquiring soil, icy soil and ice samples.

Seven minutes before NASA Phoenix Mars Lander enters the Martian atmosphere, it will jettison the cruise stage hardware that it relied on during the long flight from Earth.