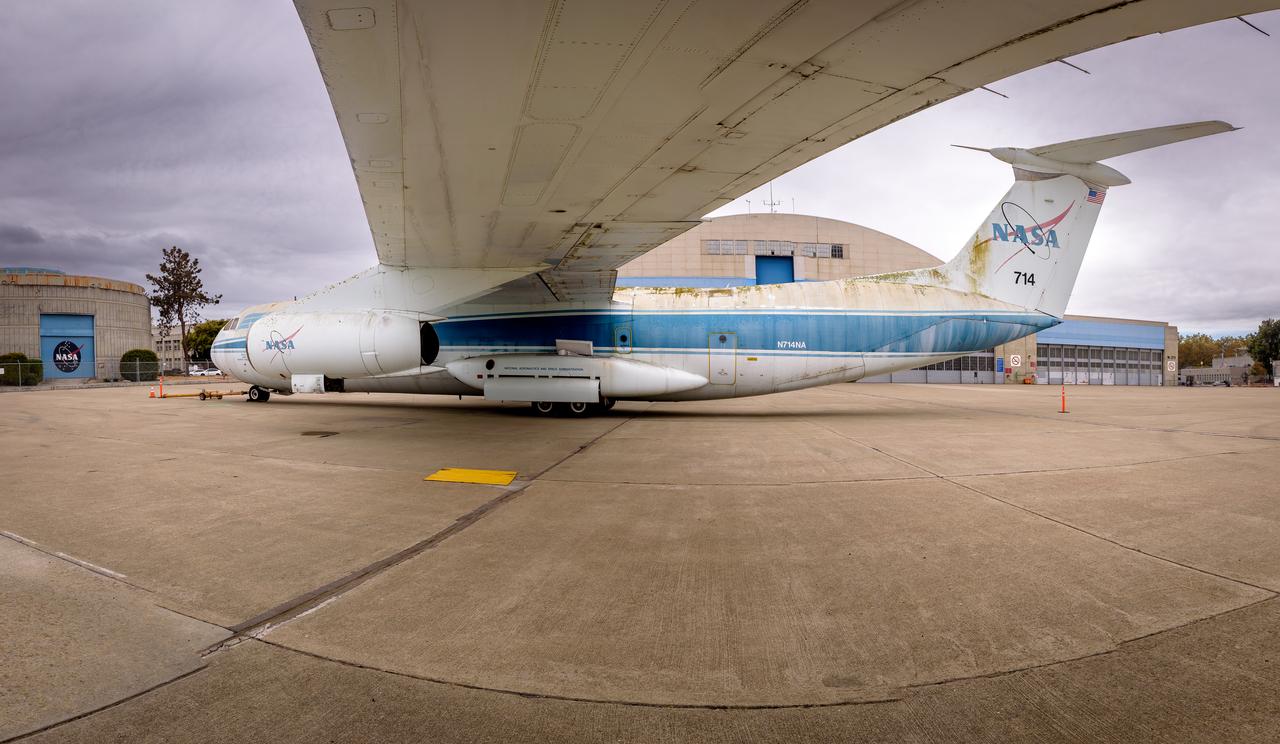

Photo composite (11 frames) of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), beneath the wing on the N211 apron at Moffett Field, California.
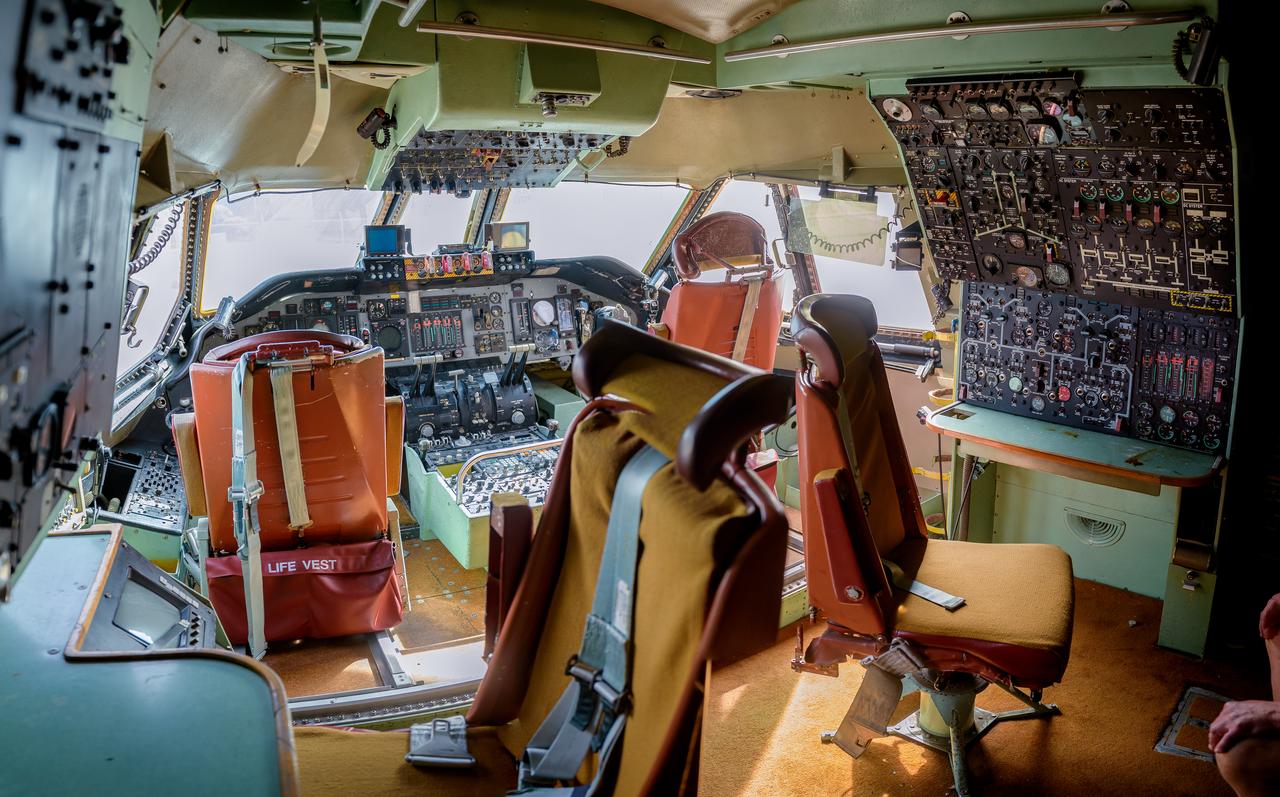

Photo composite (8 frames) of the flight deck of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), with stations for the flight engineer, co-pilot, pilot, and navigator, who typically only flew on long overseas flights.
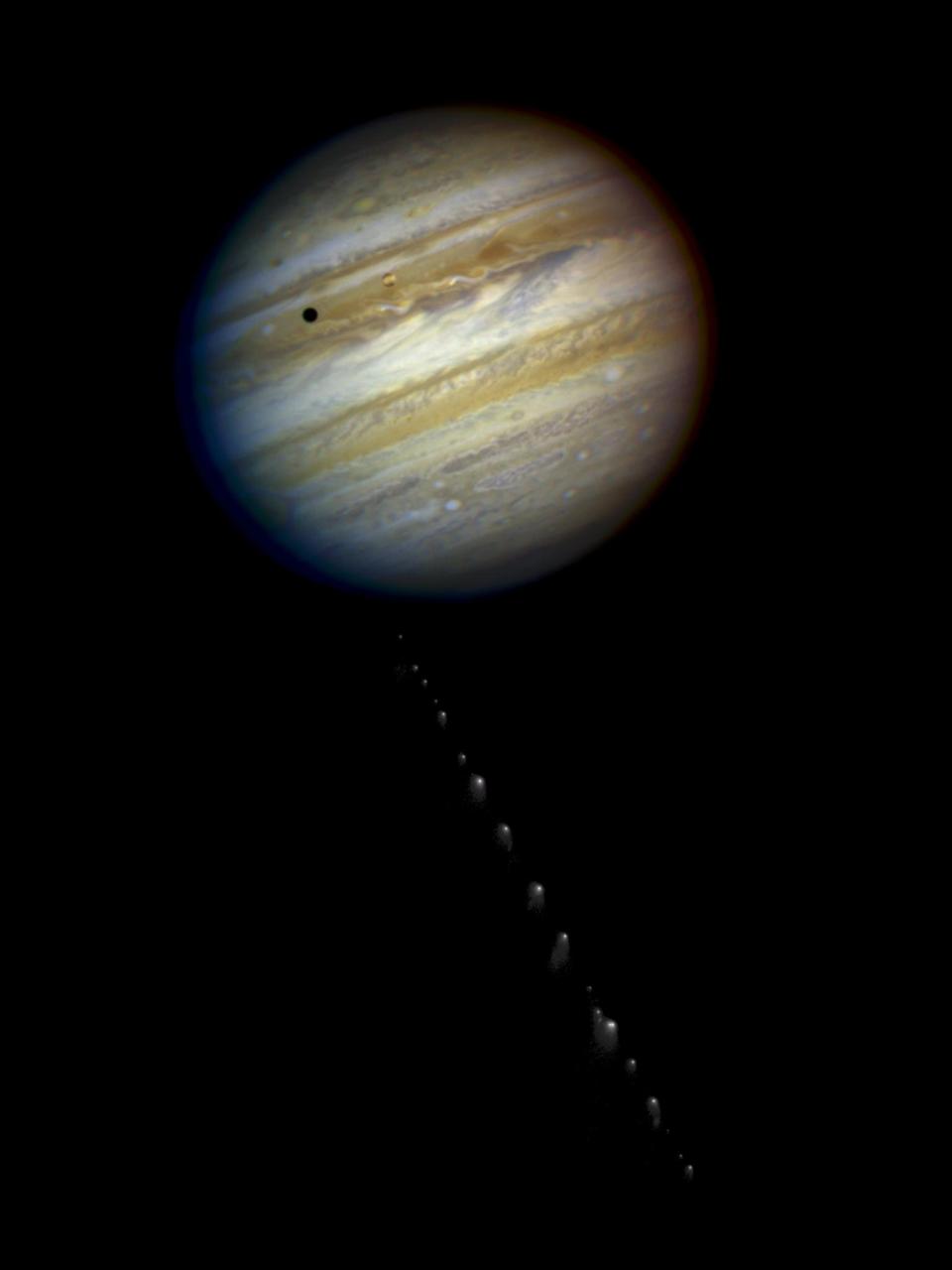

This is a composite photo, assembled from separate images of Jupiter and comet Shoemaker-Levy 9, as imaged by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope in 1994.

This photo composite shows an aerial view of FedEx Field in Landover, Md., home of the Washington Redskins, superimposed on Mars Victoria Crater to give a sense of the crater scale.

Variations in the appearance of the giant plume from the Tvashtar volcano on Jupiter moon Io are seen in this composite of the best photos taken by the New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager LORRI during its Jupiter flyby in late February.
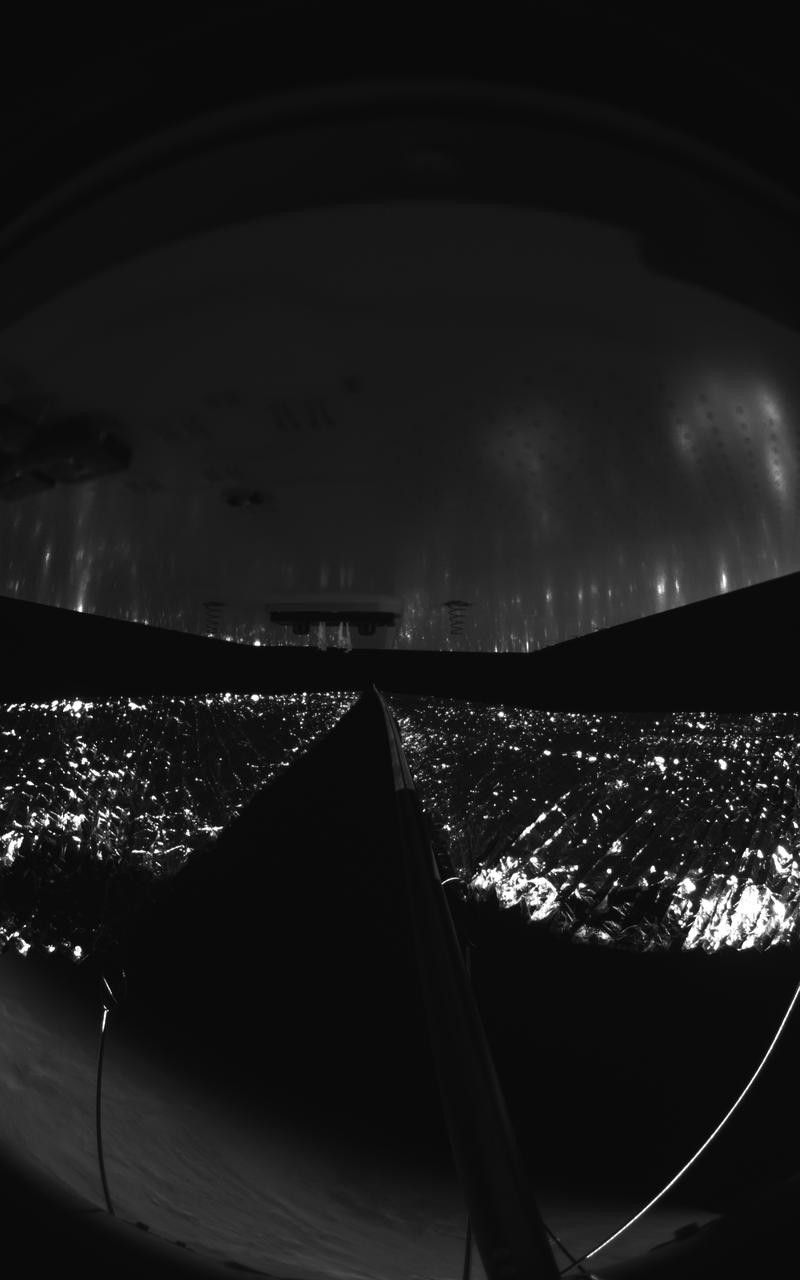

Four cameras aboard the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft show the four reflective sail quadrants supported by composite booms. The booms are mounted at right angles and the spacecraft’s solar panel is rectangular, but lines appear distorted because of the wide-angle camera field of view. View from a black-and-white wide-angle camera aboard the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System taken during sail unfurling in low Earth orbit. The spacecraft has four such cameras, centrally located aboard the spacecraft. Here, reflective sail quadrants supported by composite booms are seen when the booms are partially extended and the sail quadrants are not taut. At the top of the photo is the back surface of one of the spacecraft’s solar panels. On the lower left Earth’s limb is seen below.
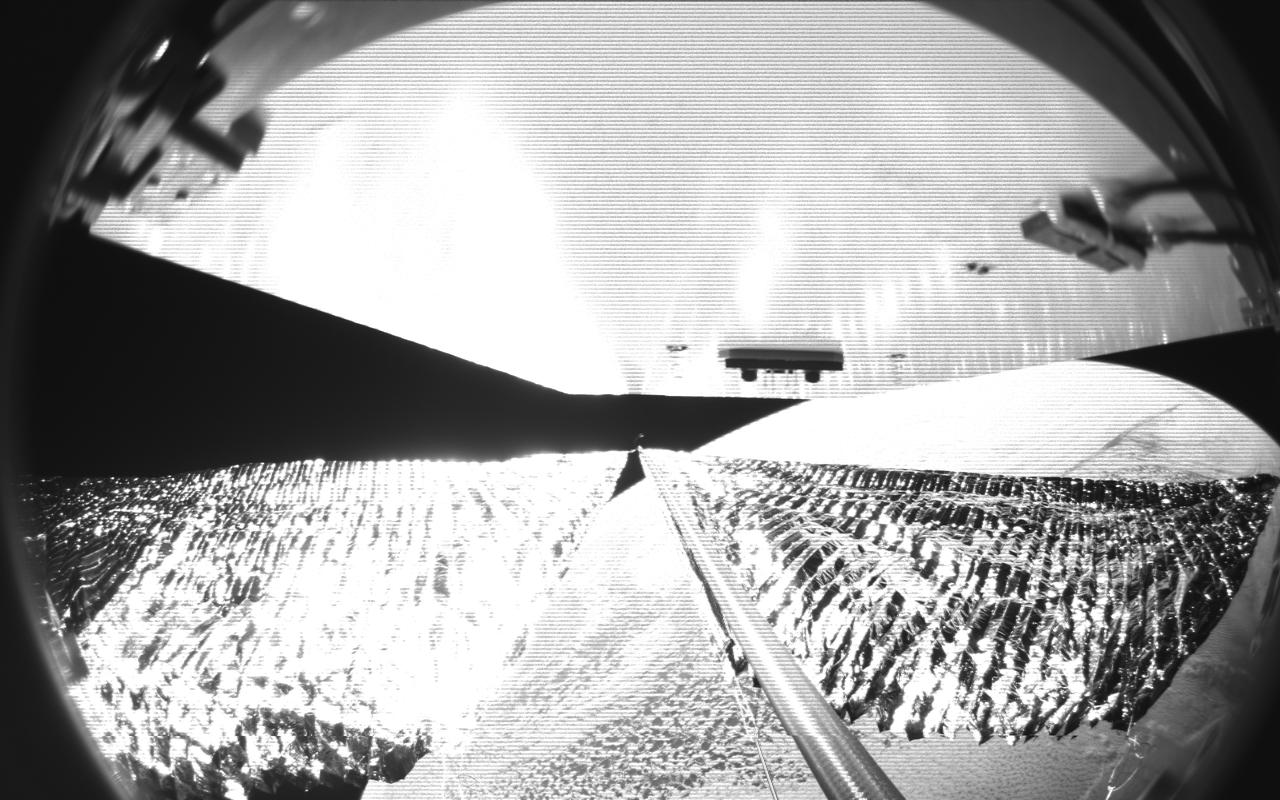

Four cameras aboard the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft show the four reflective sail quadrants supported by composite booms. The booms are mounted at right angles and the spacecraft’s solar panel is rectangular, but lines appear distorted because of the wide-angle camera field of view. View from a black-and-white wide-angle camera aboard the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System taken during sail unfurling in low Earth orbit. The spacecraft has four such cameras, centrally located aboard the spacecraft. Here, reflective sail quadrants supported by composite booms are seen when the booms are partially extended and the sail quadrants are not taut. At the top of the photo is the back surface of one of the spacecraft’s solar panels. On the lower right Earth is seen below.
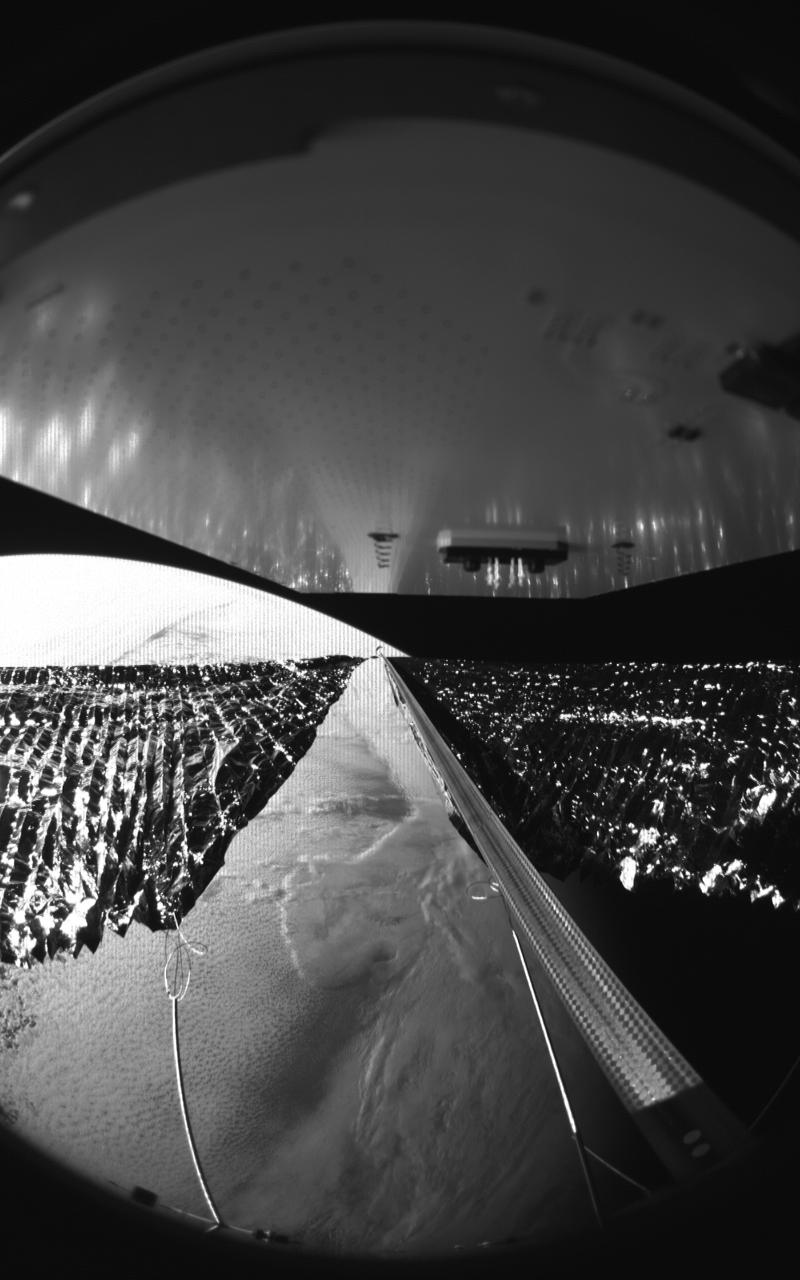

Four cameras aboard the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft show the four reflective sail quadrants supported by composite booms. The booms are mounted at right angles and the spacecraft’s solar panel is rectangular, but lines appear distorted because of the wide-angle camera field of view. View from a black-and-white wide-angle camera aboard the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System taken during sail unfurling in low Earth orbit. The spacecraft has four such cameras, centrally located aboard the spacecraft. Here, reflective sail quadrants supported by composite booms are seen when the booms are partially extended and the sail quadrants are not taut. At the top of the photo is the back surface of one of the spacecraft’s solar panels. On the lower left Earth is seen below.
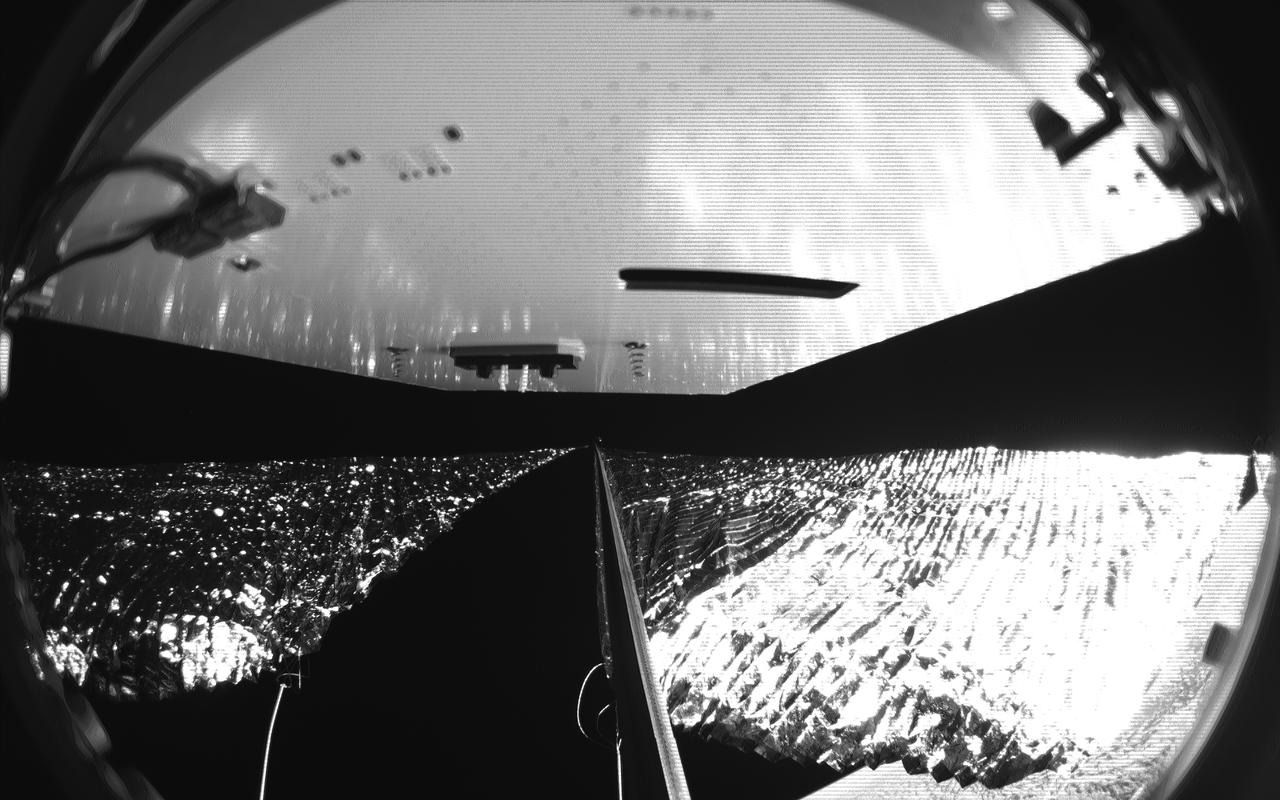

Four cameras aboard the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft show the four reflective sail quadrants supported by composite booms. The booms are mounted at right angles and the spacecraft’s solar panel is rectangular, but lines appear distorted because of the wide-angle camera field of view. View from a black-and-white wide-angle camera aboard the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System taken during sail unfurling in low Earth orbit. The spacecraft has four such cameras, centrally located aboard the spacecraft. Here, reflective sail quadrants supported by composite booms are seen when the booms are partially extended and the sail quadrants are not taut. At the top of the photo is the back surface of one of the spacecraft’s solar panels. On the lower right Earth is seen below.
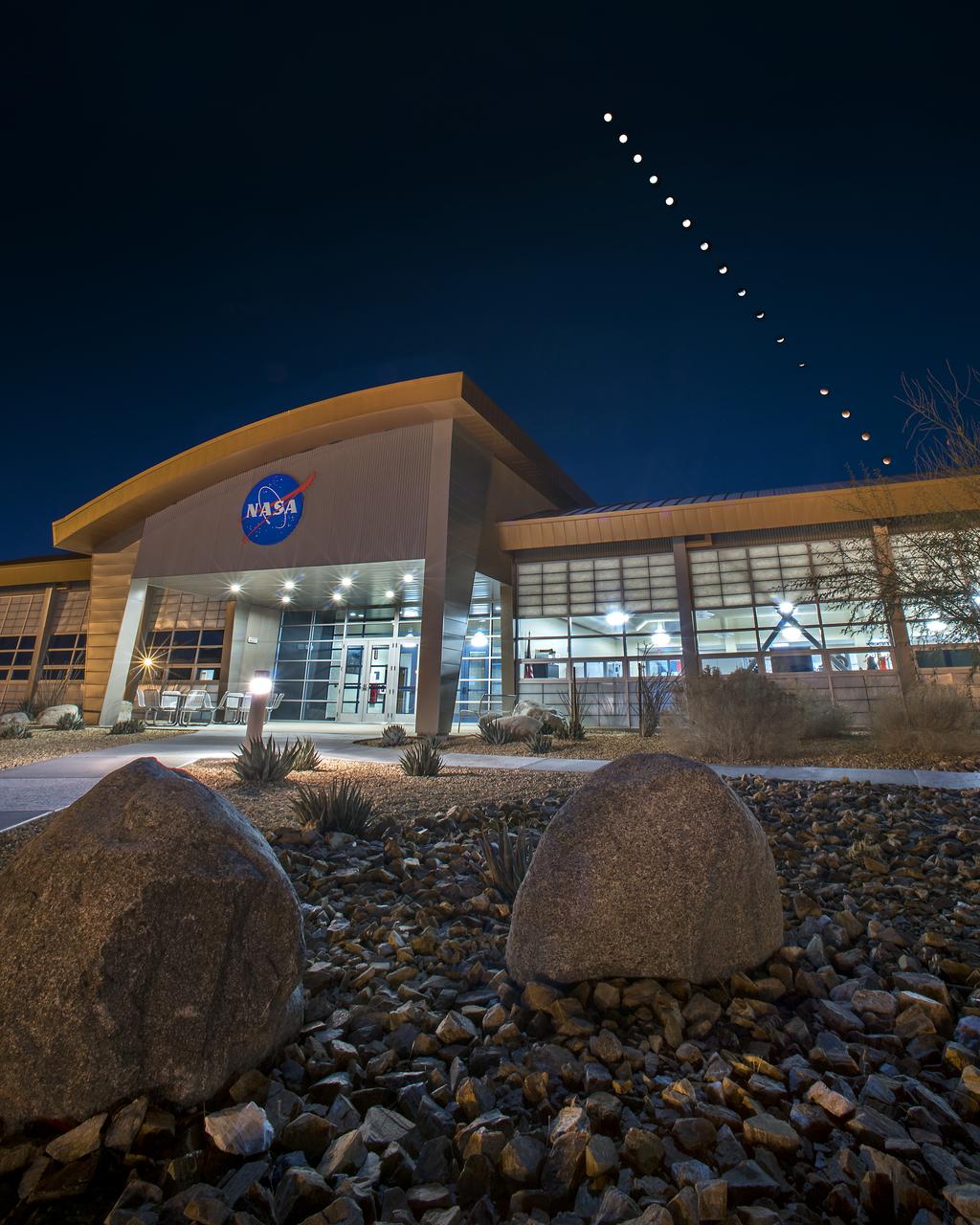

California’s NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center photographer Ken Ulbrich takes photos of Super Blue Blood Moon eclipse making a time-lapse composition of the event on January 31. The total lunar eclipse provided a rare opportunity to capture a supermoon, a blue moon and a lunar eclipse at the same time. A supermoon occurs when the Moon is closer to Earth in its orbit and appearing 14 percent brighter than usual. As the second full moon of the month, this moon is also commonly known as a blue moon, though it will not be blue in appearance. The super blue moon passed through Earth’s shadow and took on a reddish tint, known as a blood moon. This total lunar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth, and a full moon form a near-perfect lineup in space. The Moon passes directly behind the Earth into its umbra (shadow).

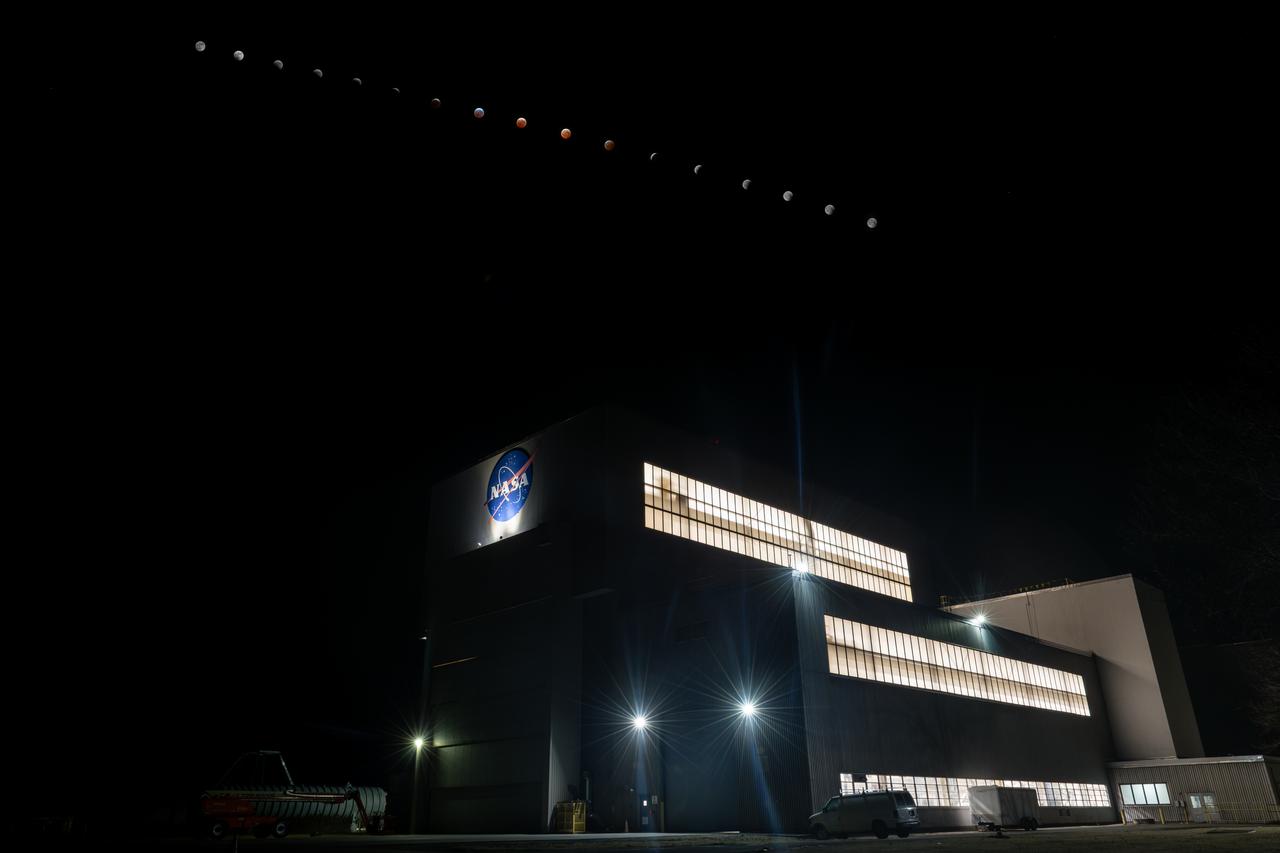
This composite made from ten images shows the progression of the Moon during a total lunar eclipse above the Vehicle Assembly Building, Nov. 8, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Visible trailing the Moon in this composite is Mars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
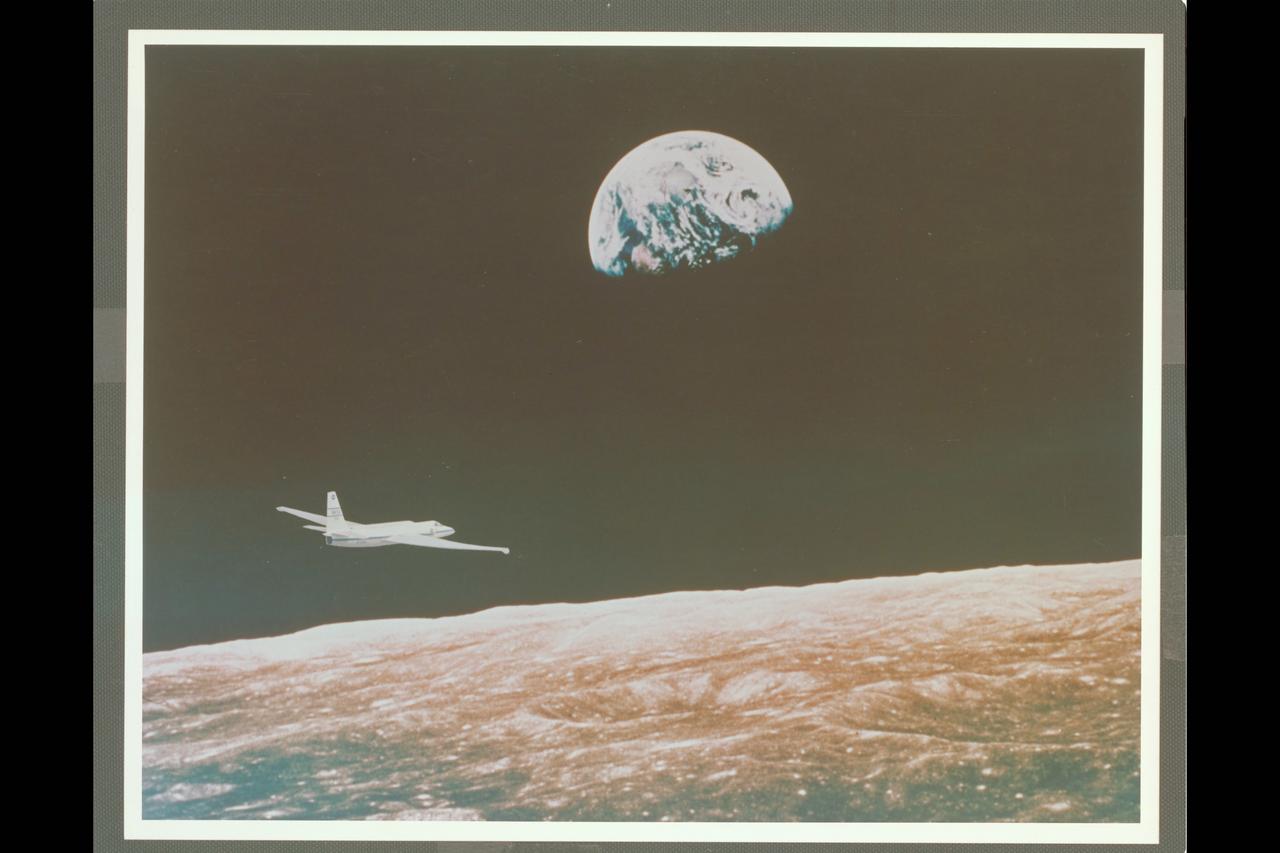

Composite Photo U-2 Aircraft in flight around the moon with the planet Earth in the background.

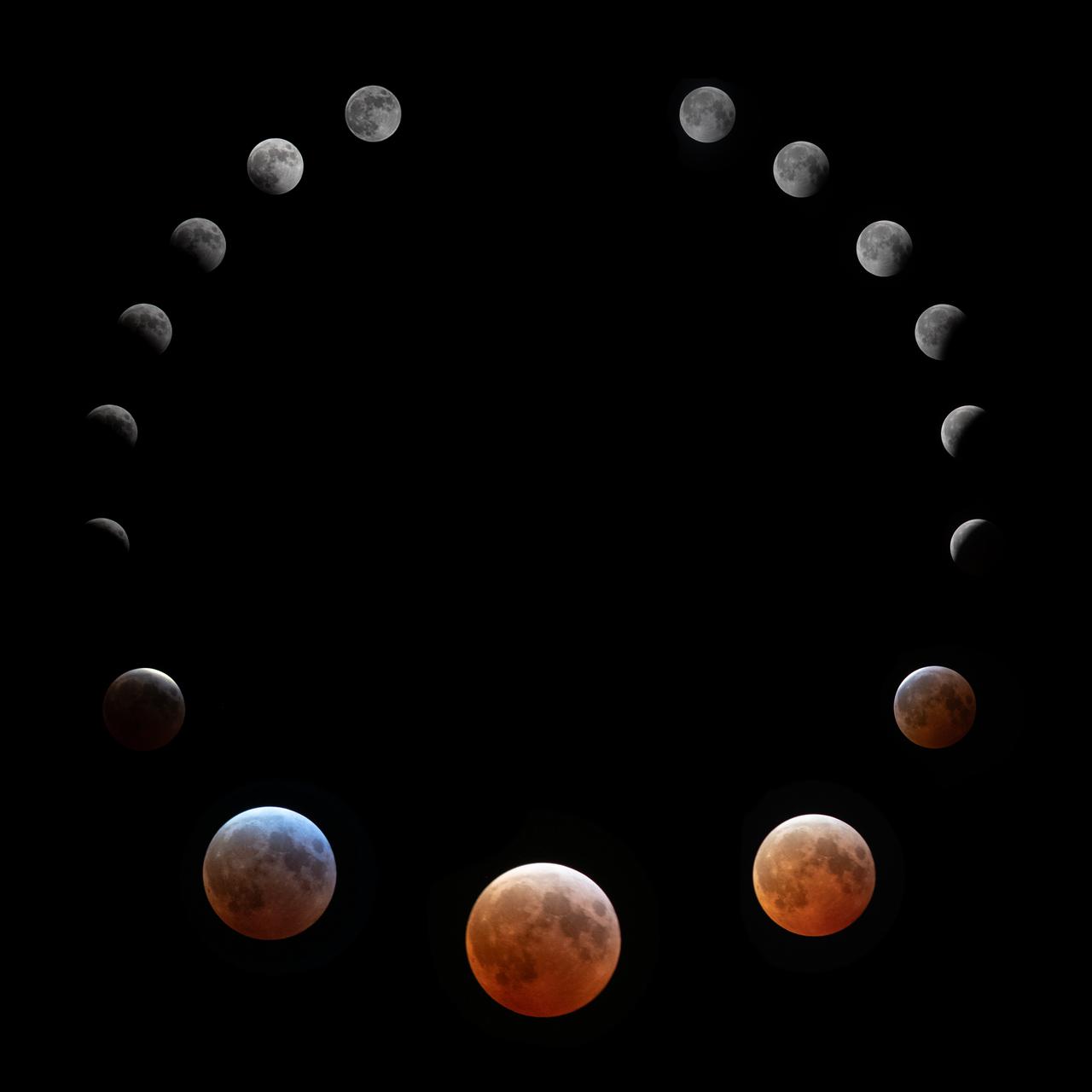
This composite photo made up of 11 images of shows the Blood Moon and the phases of the Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
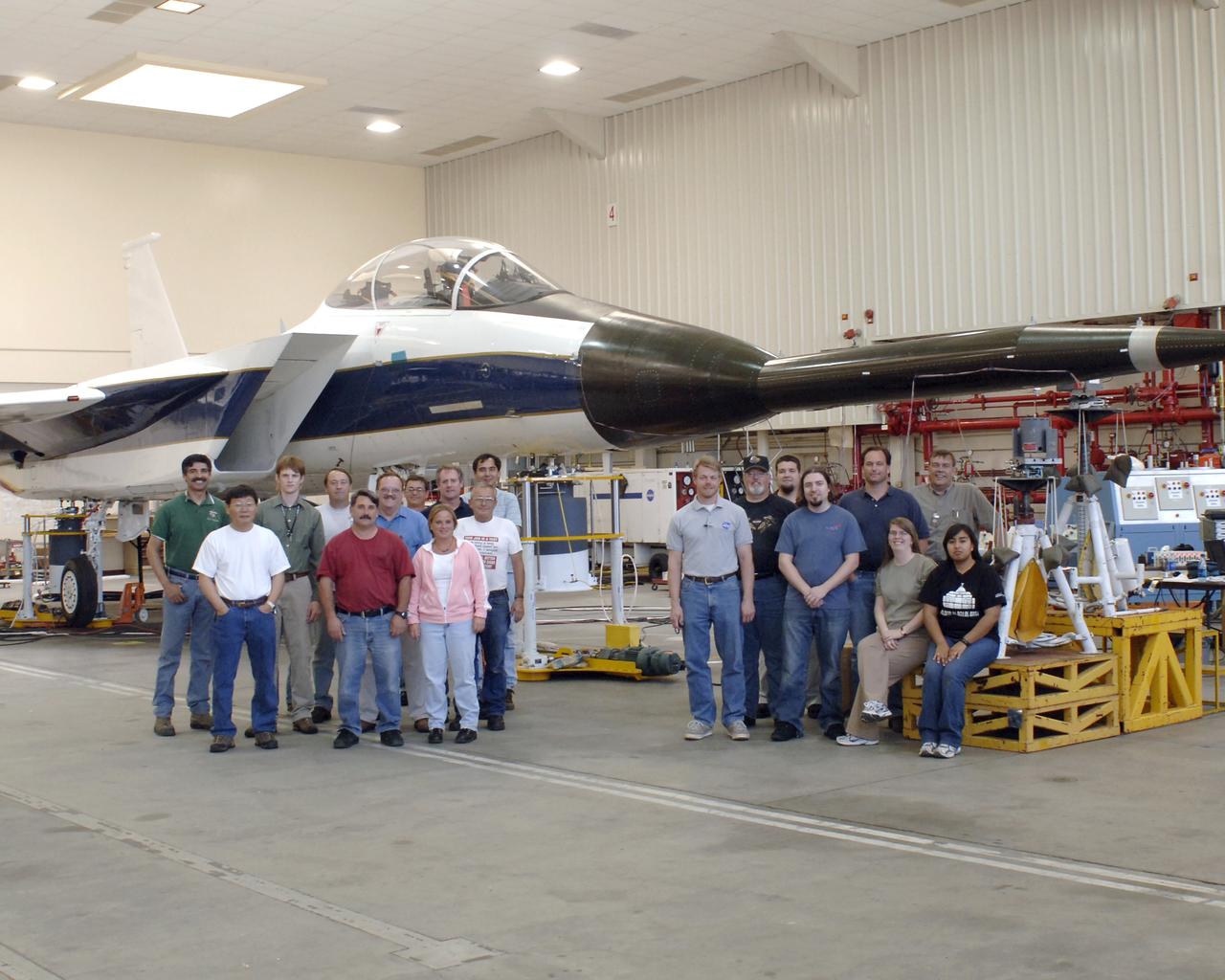

Some of the test team for the Gulfstream Quiet Spike project assembled for a group photo on May 3, 2006. The project seeks to verify the structural integrity of the multi-segmented, articulating spike attachment designed to reduce and control a sonic boom.
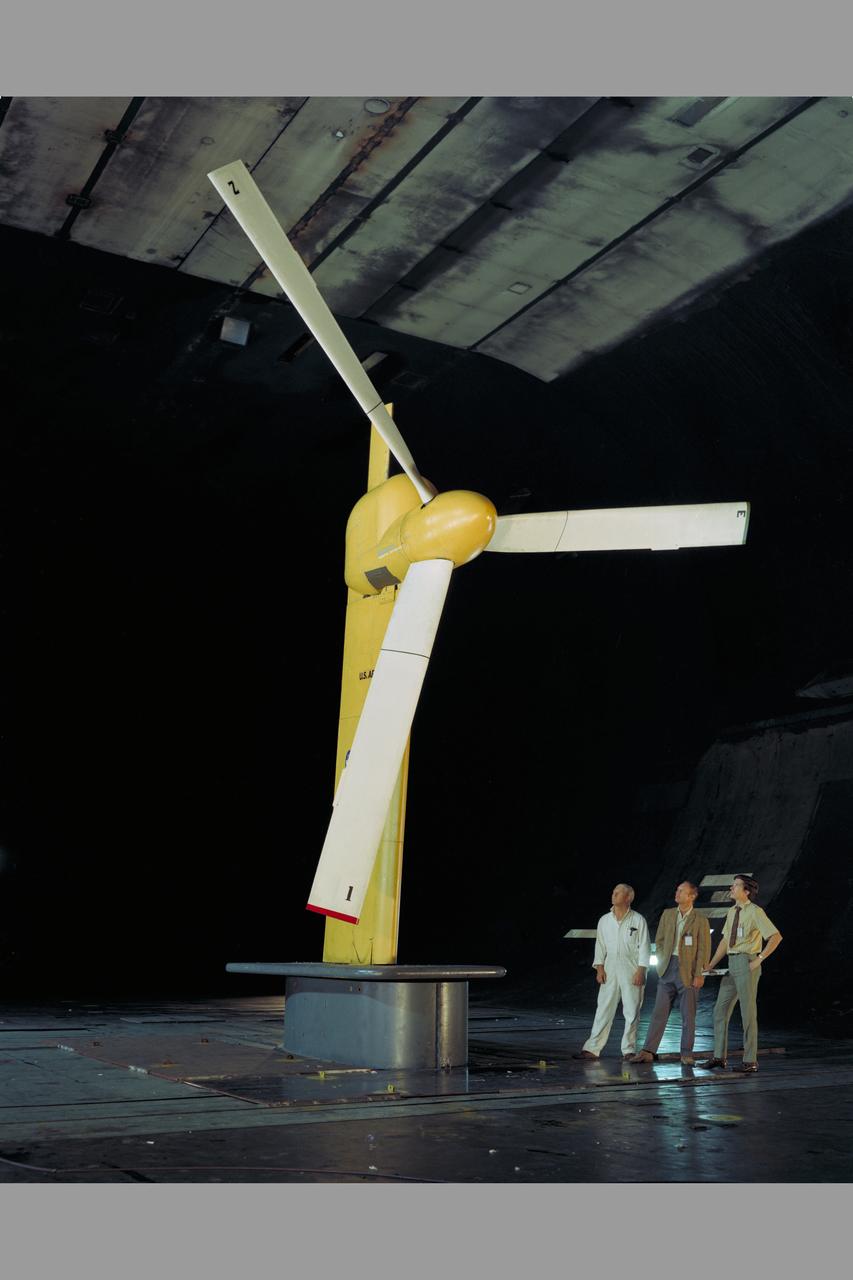

Rigid Tilt Rotor Research: Boeing 26-ft. diameter proprotor on semi-span wing in Ames Research Center 40x80ft w.t. (Photo by Ames photographer Lee Jones; composite of test results by Ames Graphics)
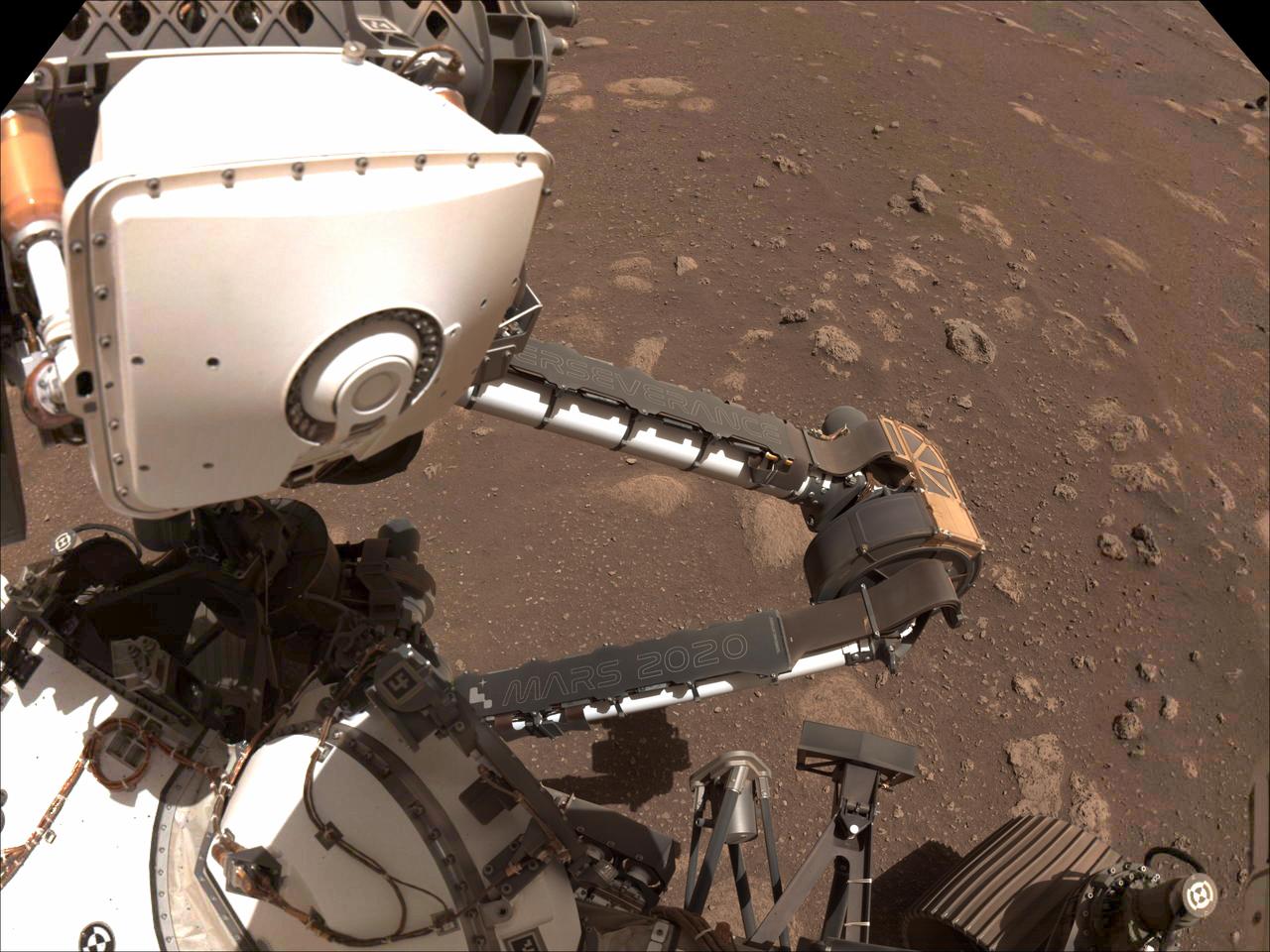

Two name plates mounted on the Mars Perseverance rover's robotic arm are visible in this composite image, made from photos taken by the rover's left Navcam on Sol 12 of its mission (March 2, 2021). The rover's name, "Perseverance," is inscribed on the plate attached to its forearm, and the mission name, "Mars 2020," is shown on its upper arm. Running vertically along the right side of the mission name plate is a string of 17 letters and numbers. These characters form a unique product identification number (PIN) similar to the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) on vehicles on Earth, but signifying that this is an off-road vehicle. Issued in part by the Society of Automotive Engineers, a PIN or VIN number provides a unique vehicle identifier, while encoding information about the vehicle's characteristics and manufacture. Perseverance's PIN can be decoded to reveal clues about its destination, mission objective and power source. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24467

A composite photo made from 18 images of the lunar eclipse above the Space Environments Complex at NASA’s Glenn Research Center at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, during the early hours of March 14, 2025. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)

A composite photo made from 17 images of the lunar eclipse. These photographs were taken at NASA’s Glenn Research Center at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, during the early hours of March 14, 2025. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
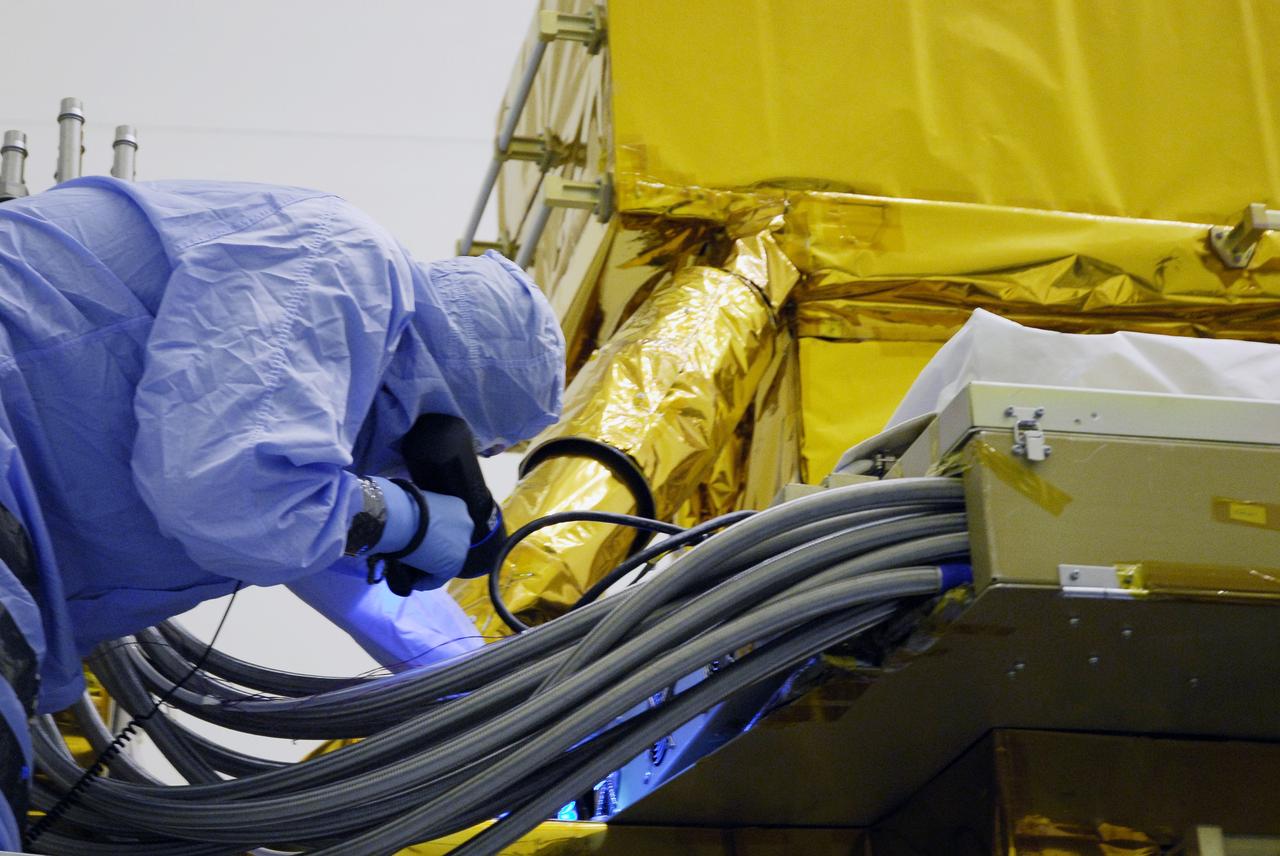

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician cleans contamination from the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
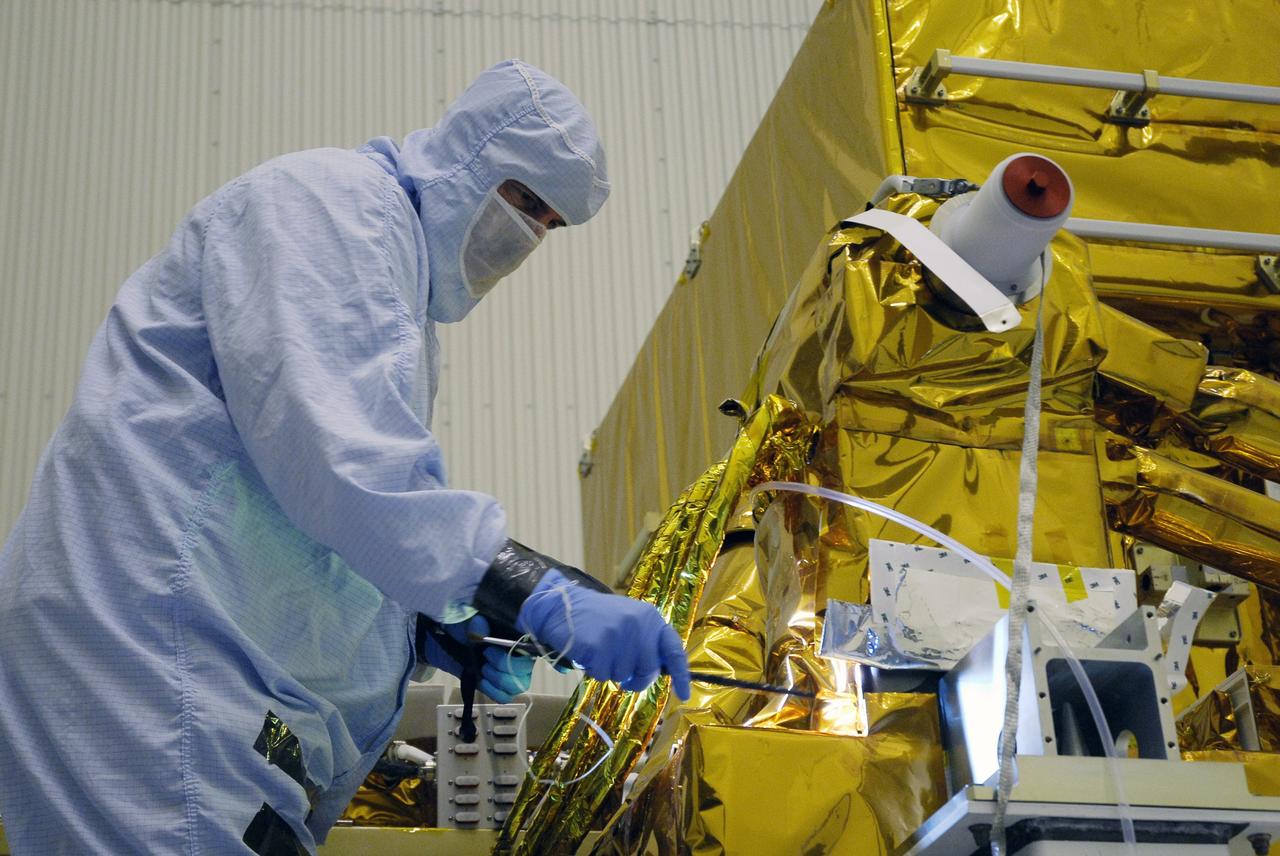

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician cleans contamination from the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
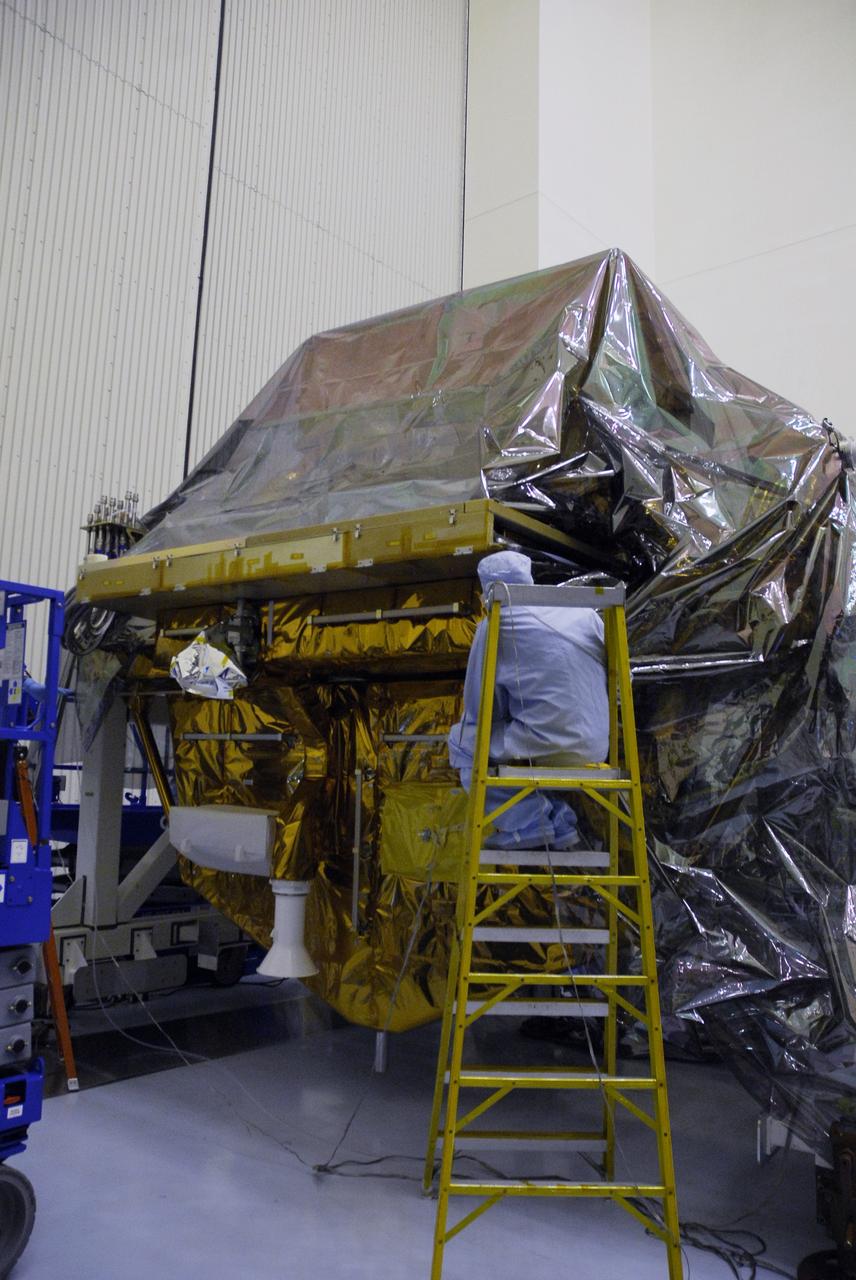

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the protective cover is being replaced on the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. The cover was removed to clean the carrier of contaminants found Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
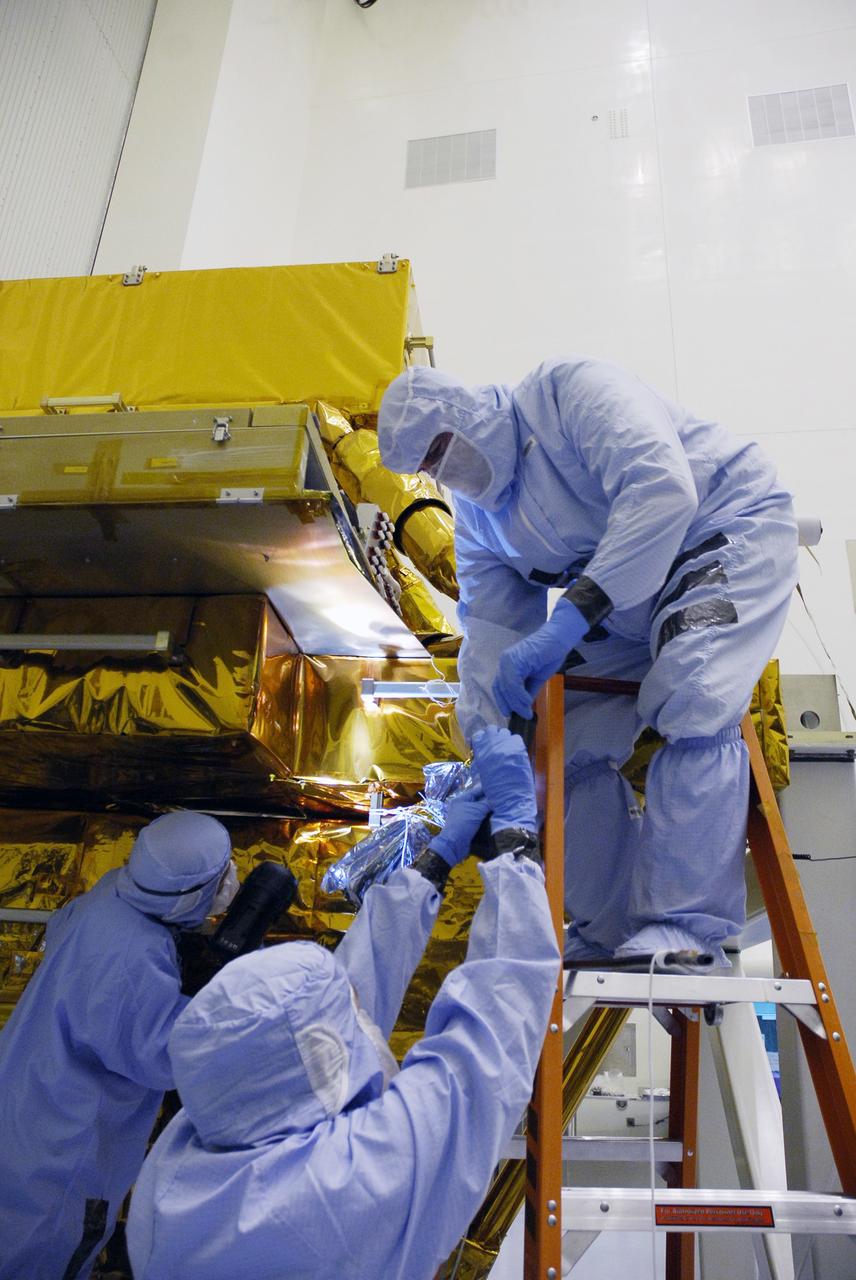

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians clean contamination from the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
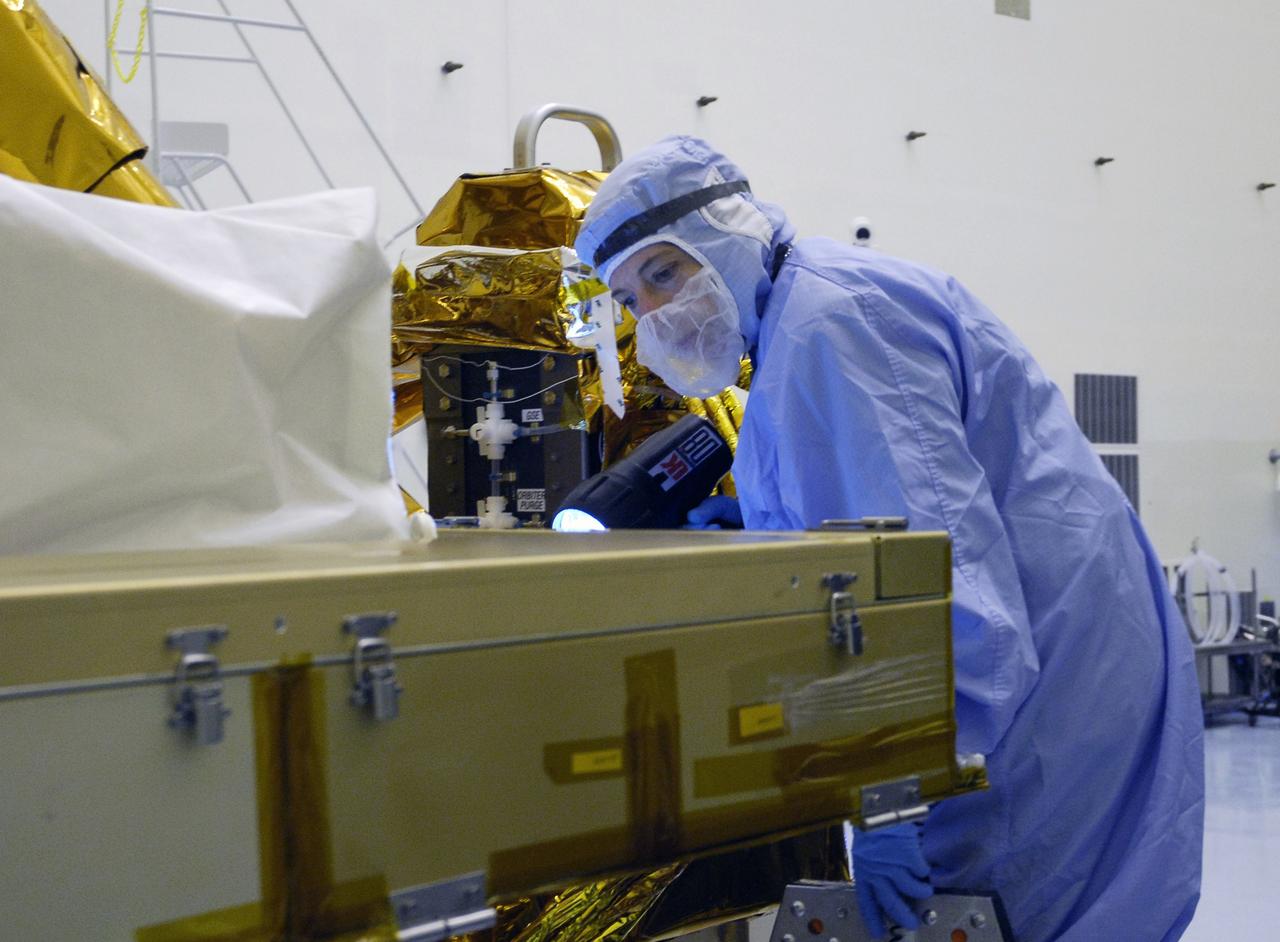

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician cleans contamination from the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System is seen orbiting Earth in this 13-second exposure photograph, Monday, Sept. 2, 2024, from Arlington, Virginia. The mission team confirmed the spacecraft’s unique composite boom system unfurled its reflective sail on Thursday, accomplishing a critical milestone in the agency’s demonstration of next-generation solar sail technology that will allow small spacecraft to “sail on sunlight.” Just as a sailboat is powered by wind in a sail, a spacecraft can use the pressure of sunlight on a solar sail for propulsion. This technology demonstration serves as a pathfinder for future missions powered by solar sail technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
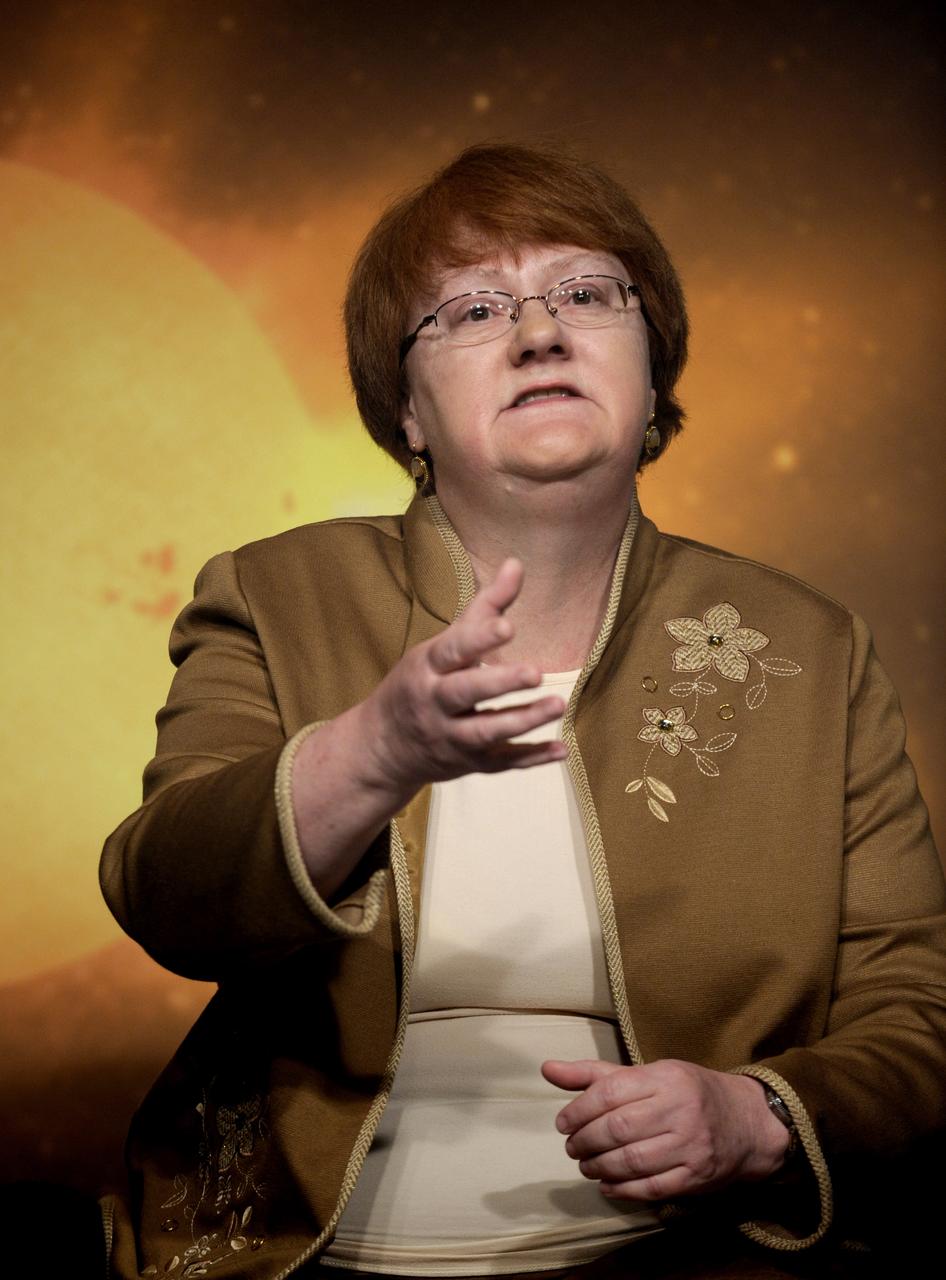

Toni Galvin, principal investigator, Plasma and Superthermal Ion Composition instrument at the University of New Hampshire makes a comment during a Science Update on the STEREO mission at NASA Headquarters in Washington, Tuesday, April 14, 2009. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Closeup of Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) experiment trays is documented during STS-32 retrieval activity and photo survey conducted by crewmembers onboard Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102. Partially visible is the Polymer Matrix Composite Materials Experiment. In the background is the surface of the Earth.

S74-23654 (22 June 1973) --- This mosaic of Baja and the Sea of Cortez in Mexico (28.0N, 112.0W) is a composite of six 70mm photos carefully pieced together to appear as one. Mosaics such as this one are useful to portray a large area in a single format instead of many photos covering only partial images. In this mosaic, almost the entire area of the Sea of Cortez, the adjacent Baja Peninsula and part of the Sonoran Desert of northwest Mexico can be seen. Photo credit: NASA

This composite image shows the weather situation over Europe at 12:00 UTC on 13 February 2014. The image is composed of infra-red imagery from the geostationary satellites of EUMETSAT and NOAA, overlaid on NASA's Blue Marble land imagery. Copyright: 2014 EUMETSAT, <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/eumetsat/12500210655">www.flickr.com/photos/eumetsat/12500210655</a>

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center documents the installation of a pallet support strut on the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center secure the Hubble vertical platform to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center install the pallet support struts on the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
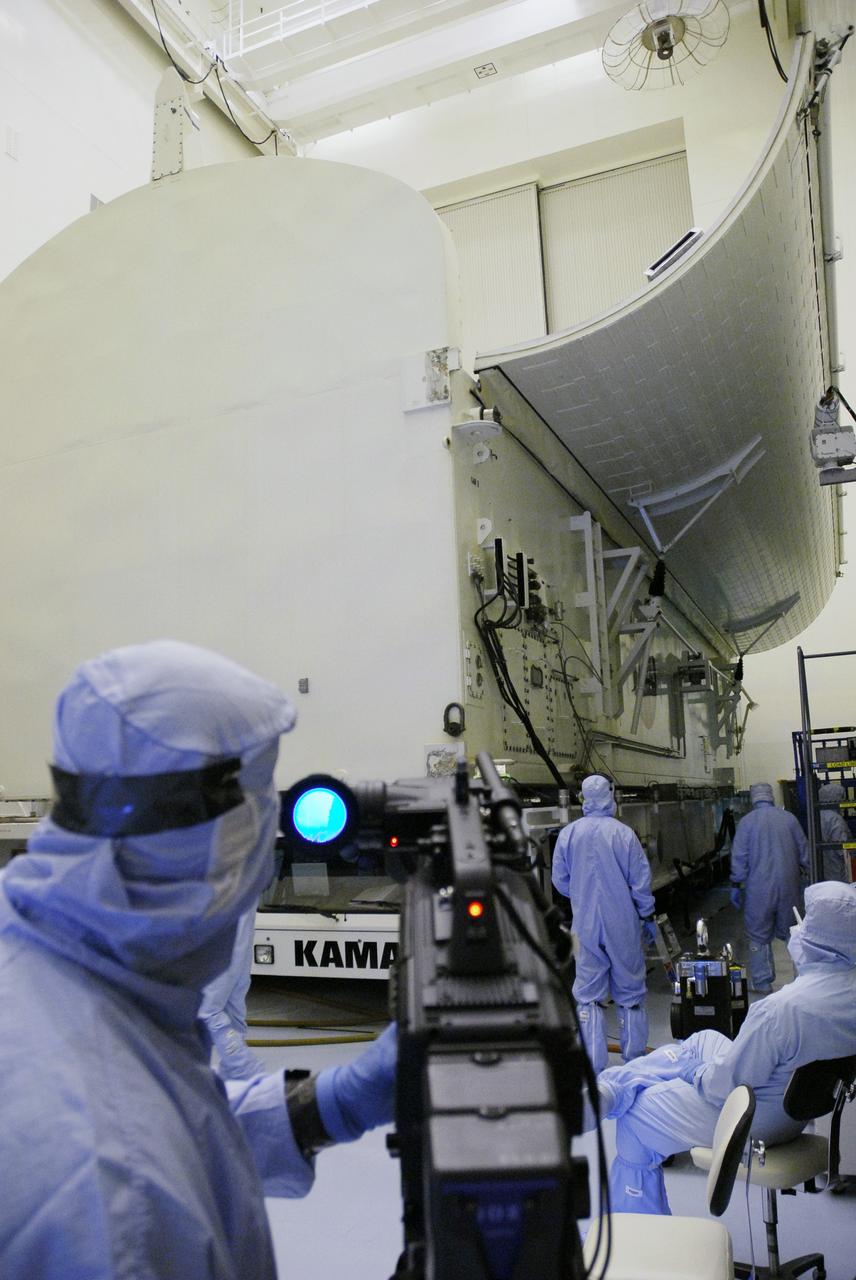

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister is moved on the floor for loading of the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A will be removed. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies for servicing of the Hubble Space Telescope on the STS-125 mission, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
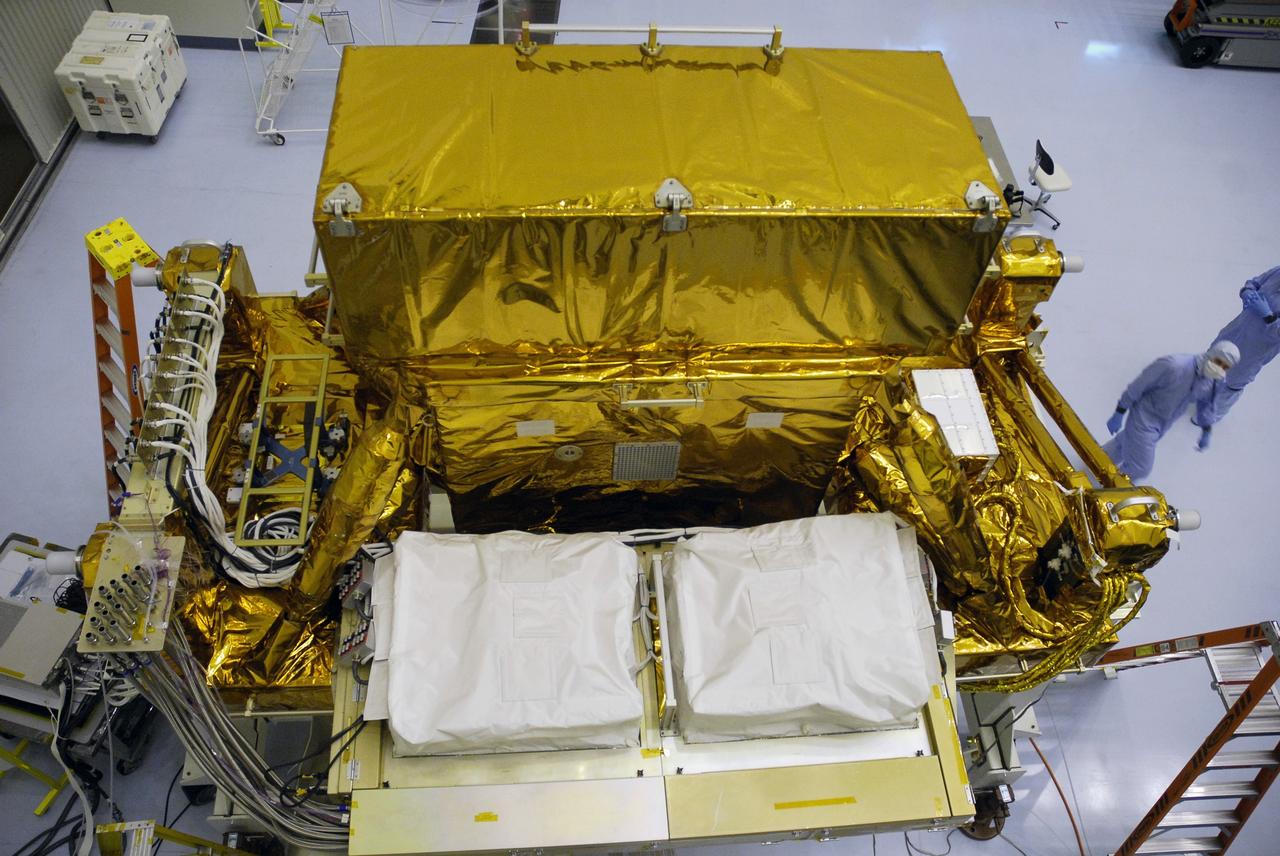

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is uncovered so that technicians can clean contaminants found earlier. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A will be removed. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
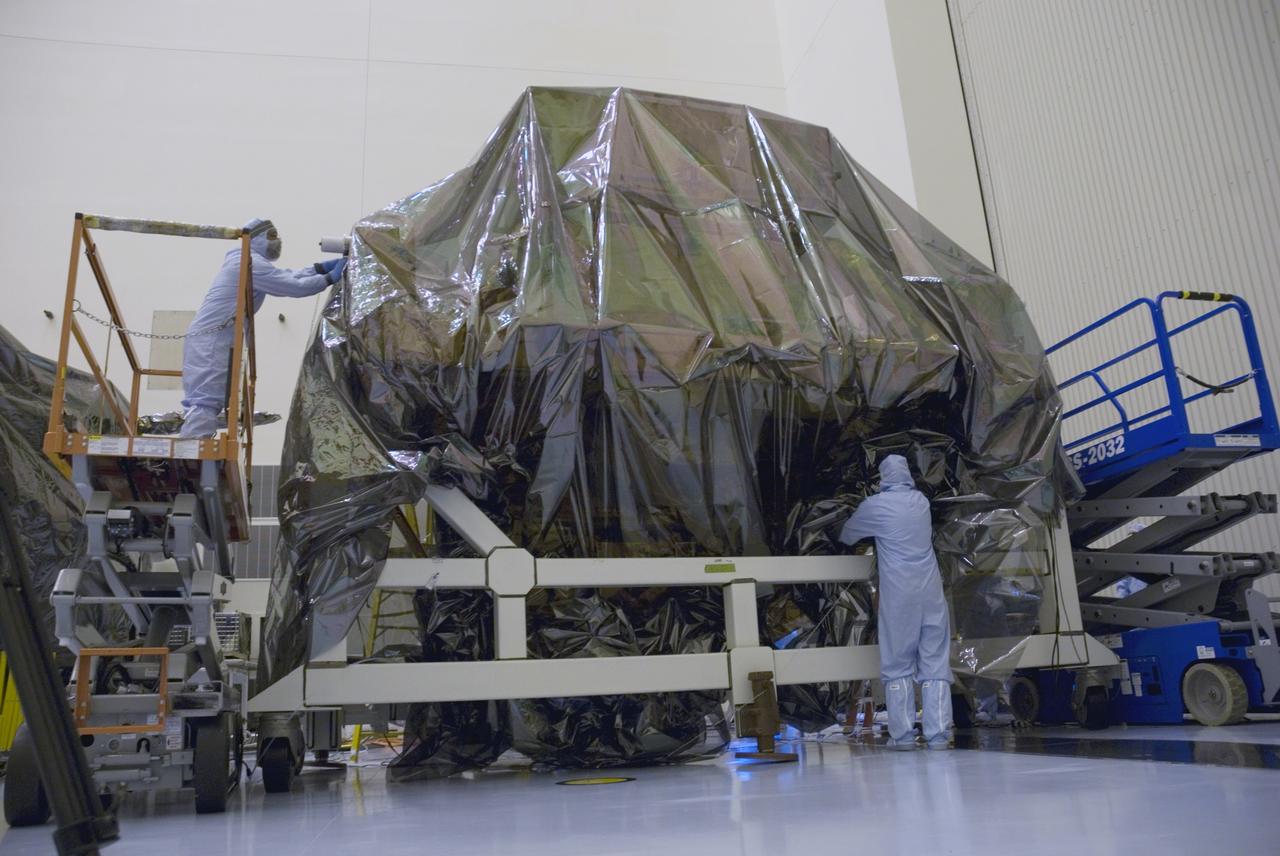

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians finish replacing the protective cover over the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. The cover was removed to clean the carrier of contaminants found Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
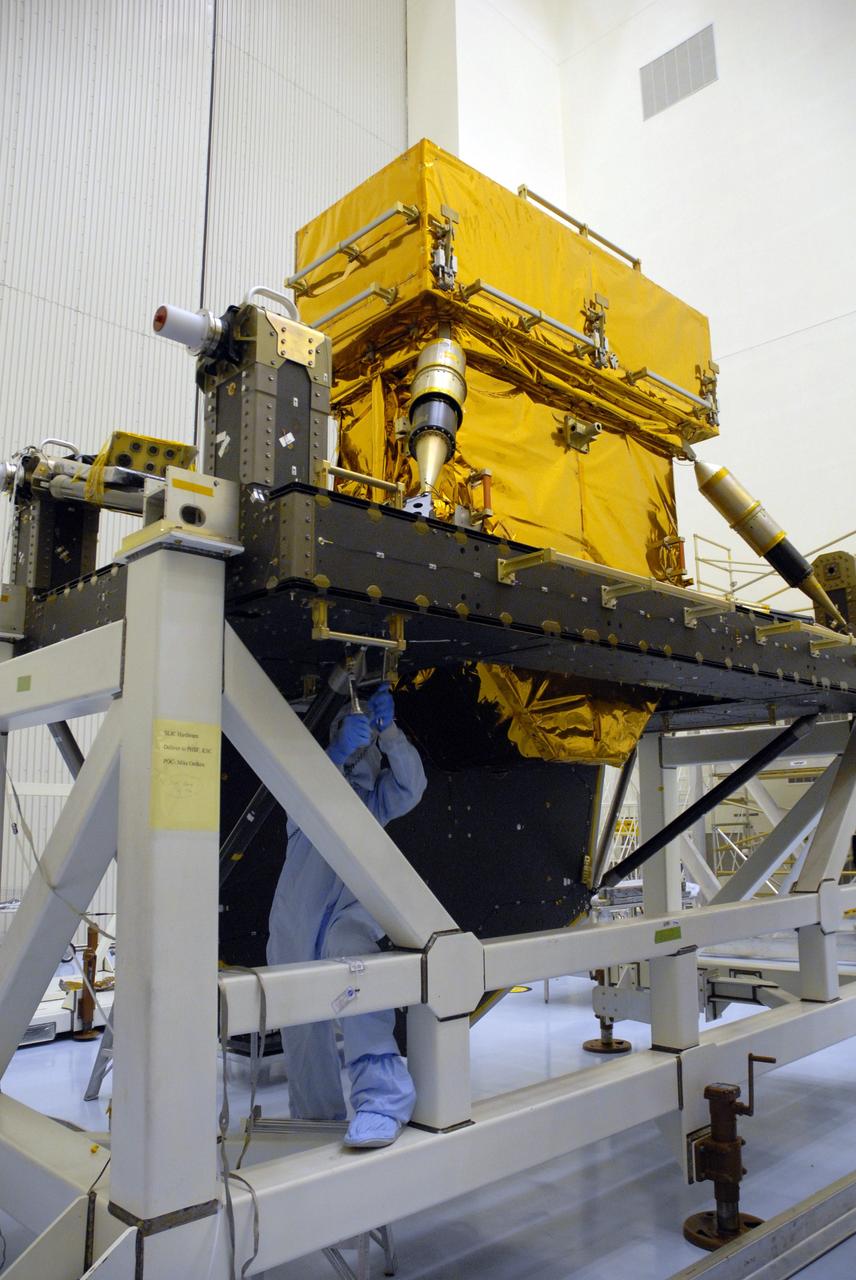

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center installs a pallet support strut on the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
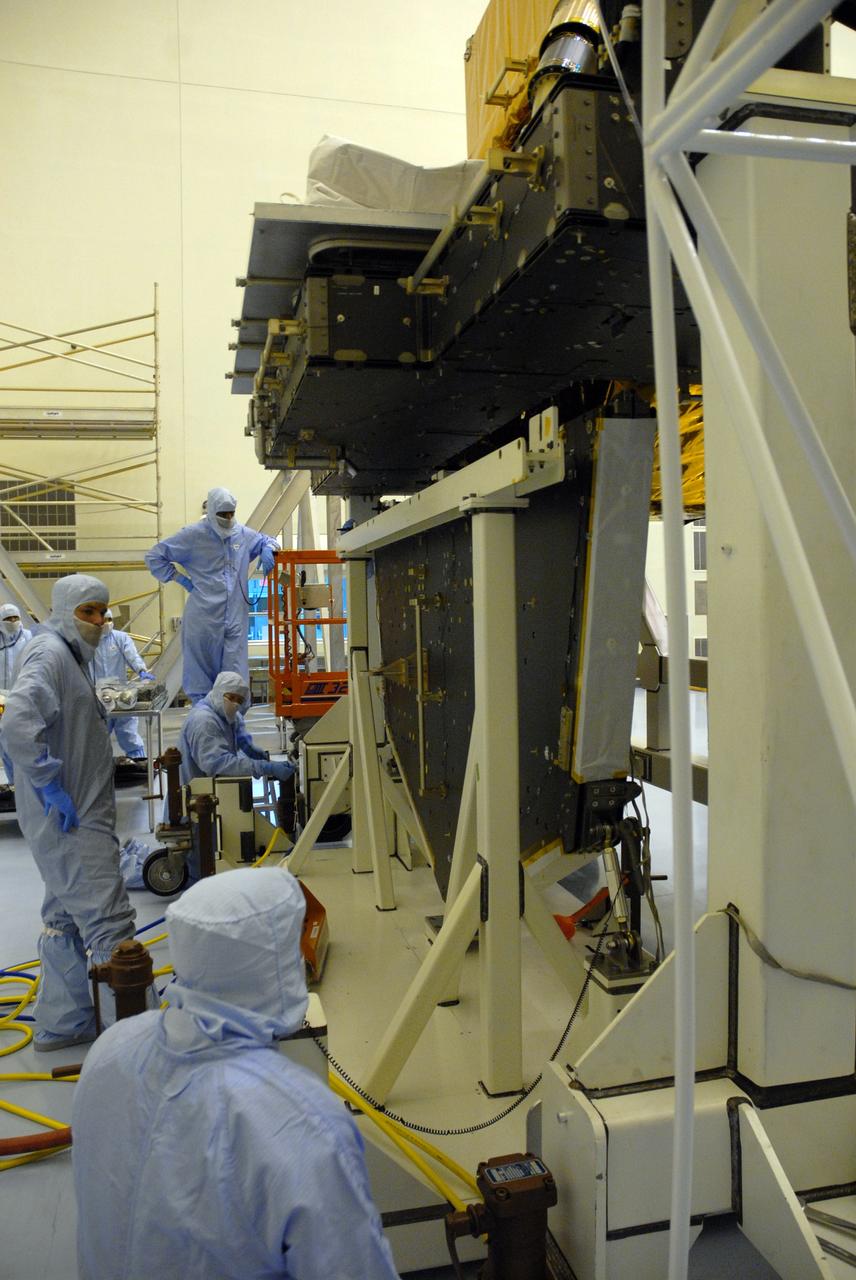

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center mate the Hubble vertical platform to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
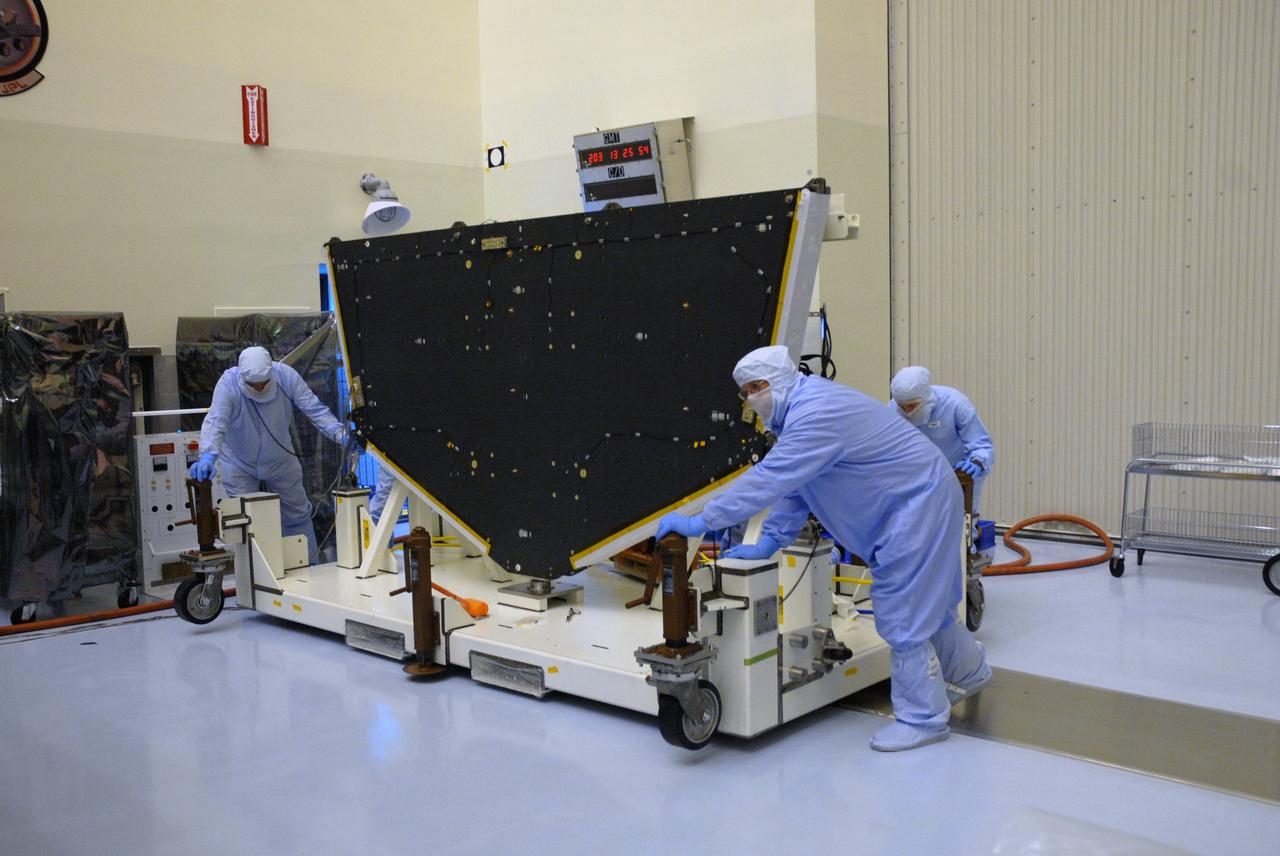

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center move the Hubble vertical platform toward the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope, to which it will be mated. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
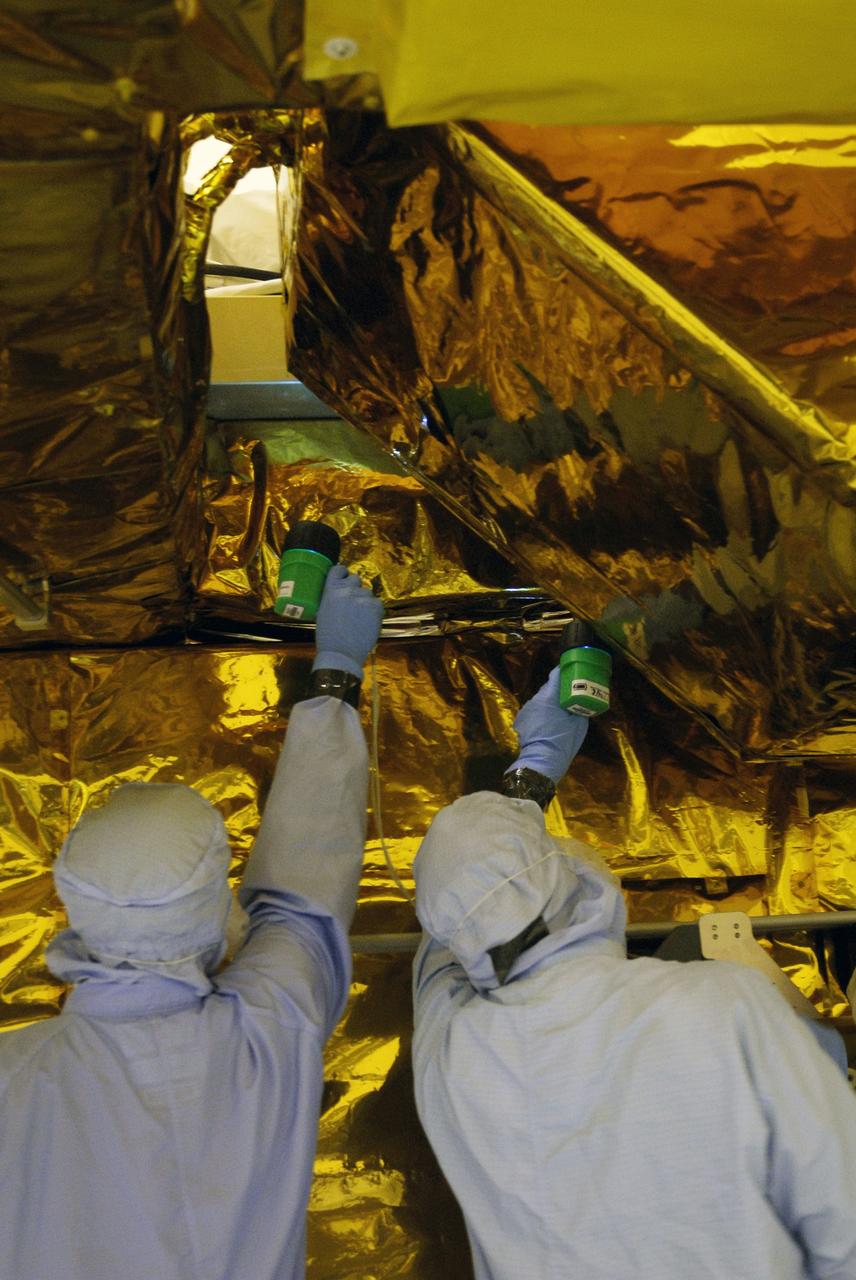

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians inspect areas of the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, for contamination. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A will be removed. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies for servicing of the Hubble Space Telescope on the STS-125 mission, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
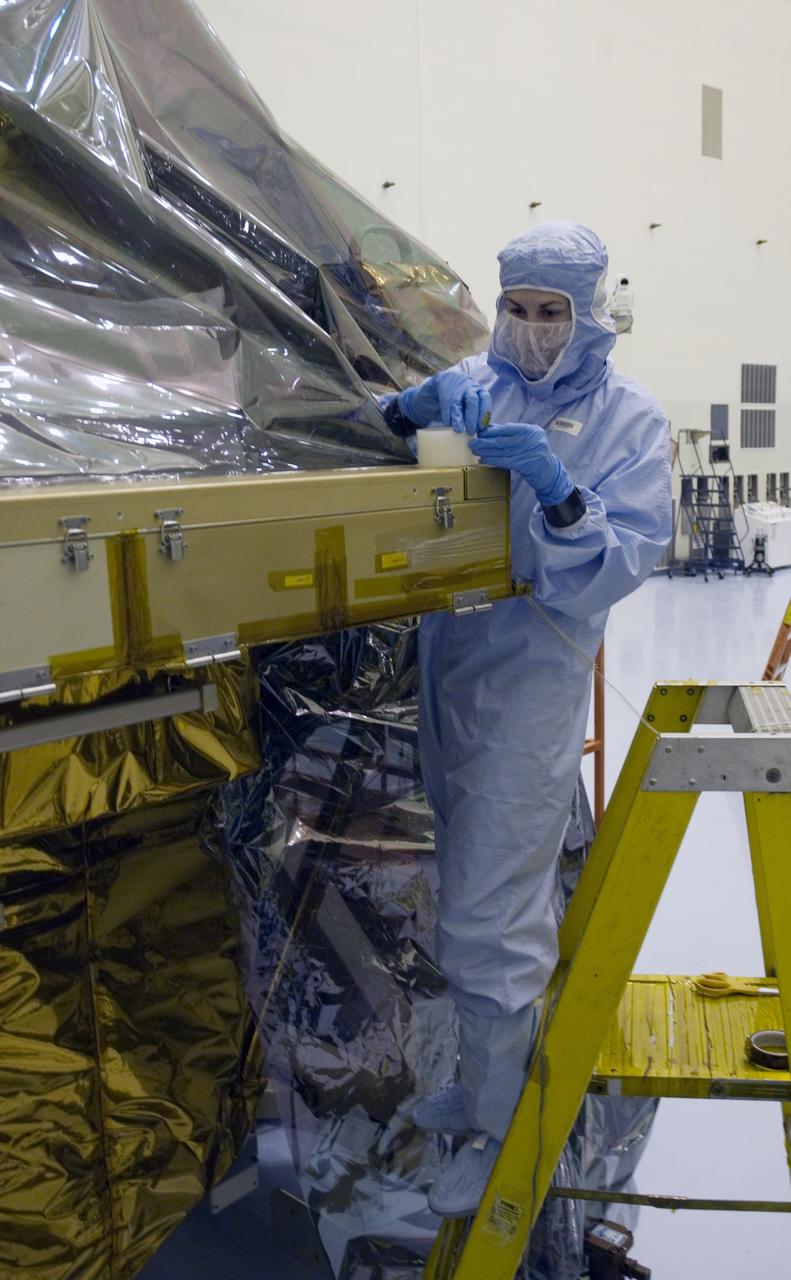

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician works to replace the protective cover on the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. The cover was removed to clean the carrier of contaminants found Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
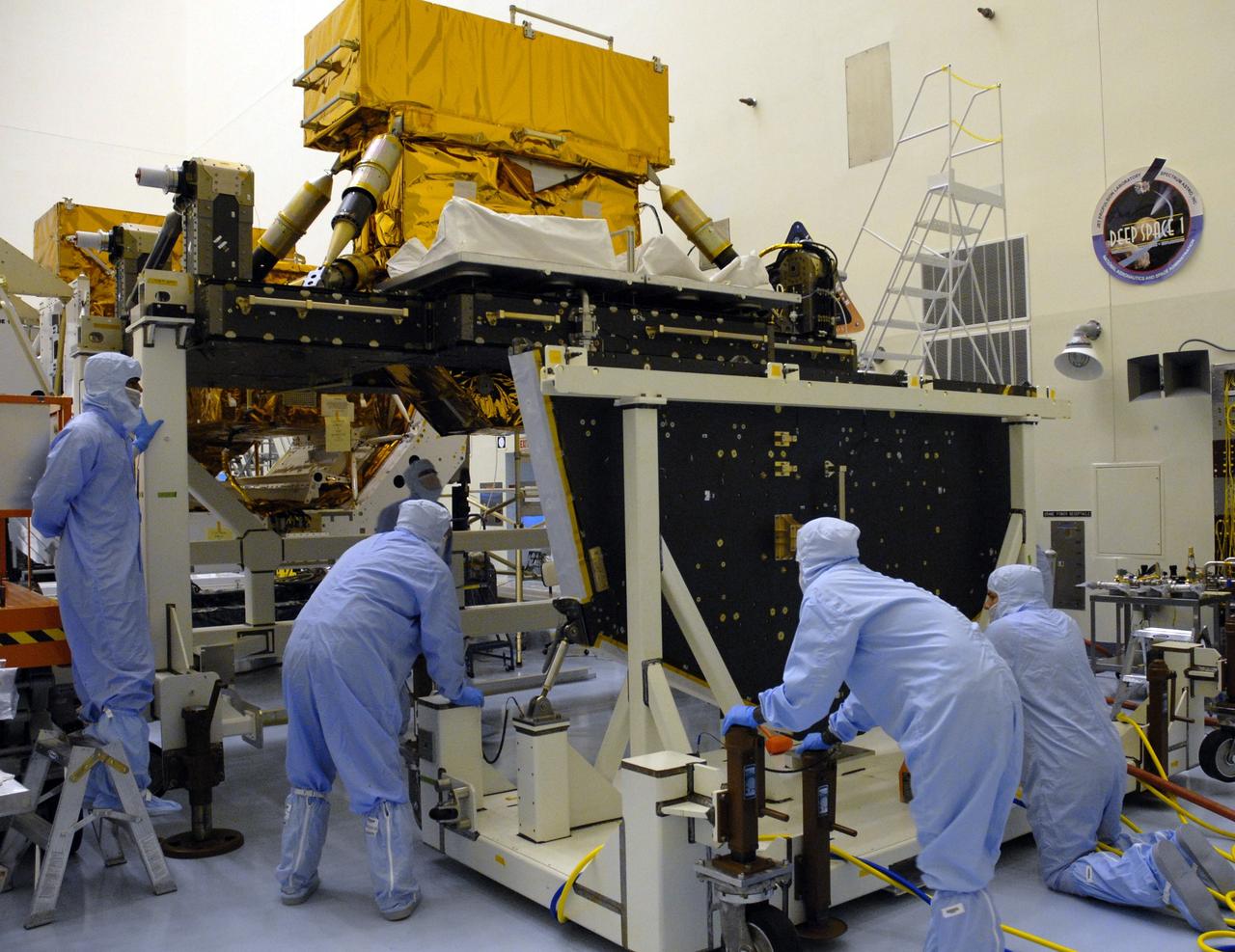

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center move the Hubble vertical platform toward the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope, to which it will be mated. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
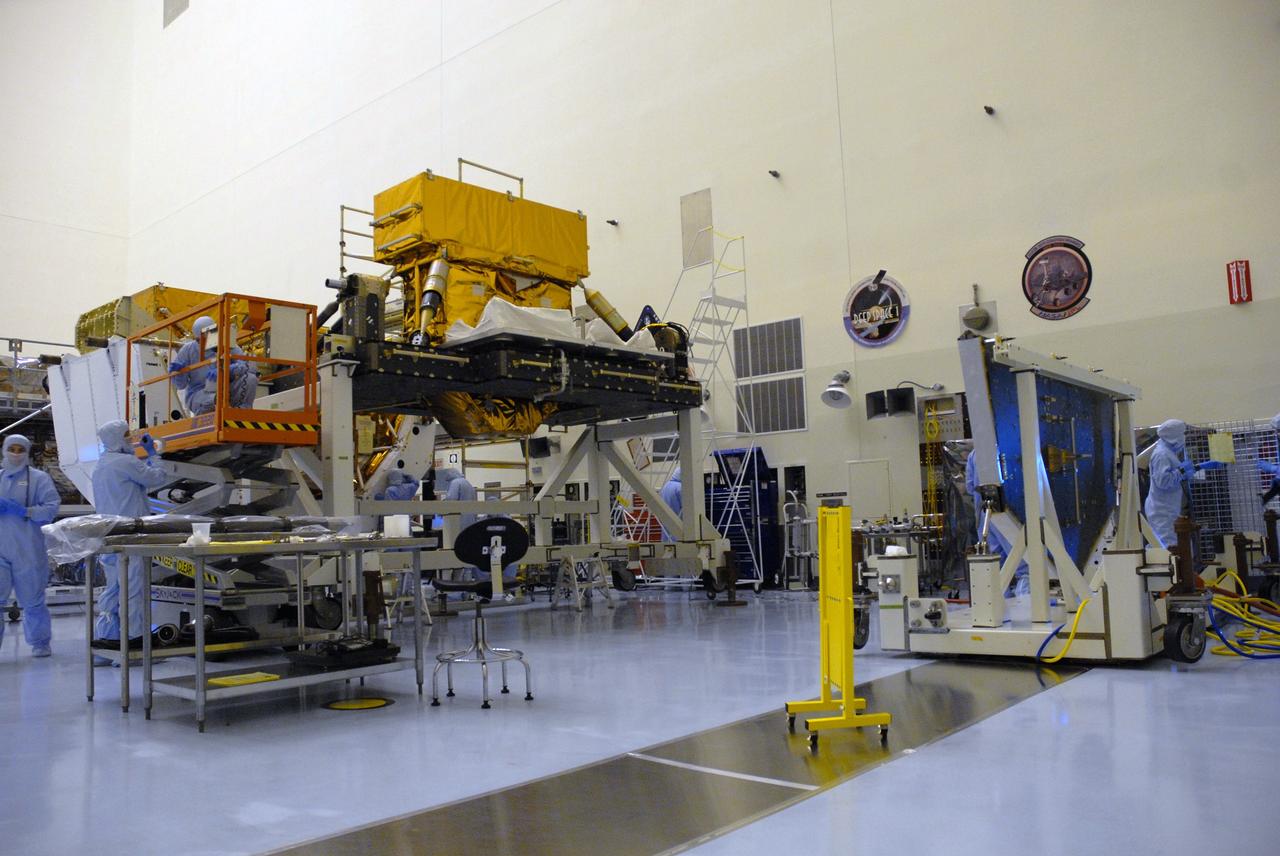

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope, elevated at left, is ready to be mated to the Hubble vertical platform, at right. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
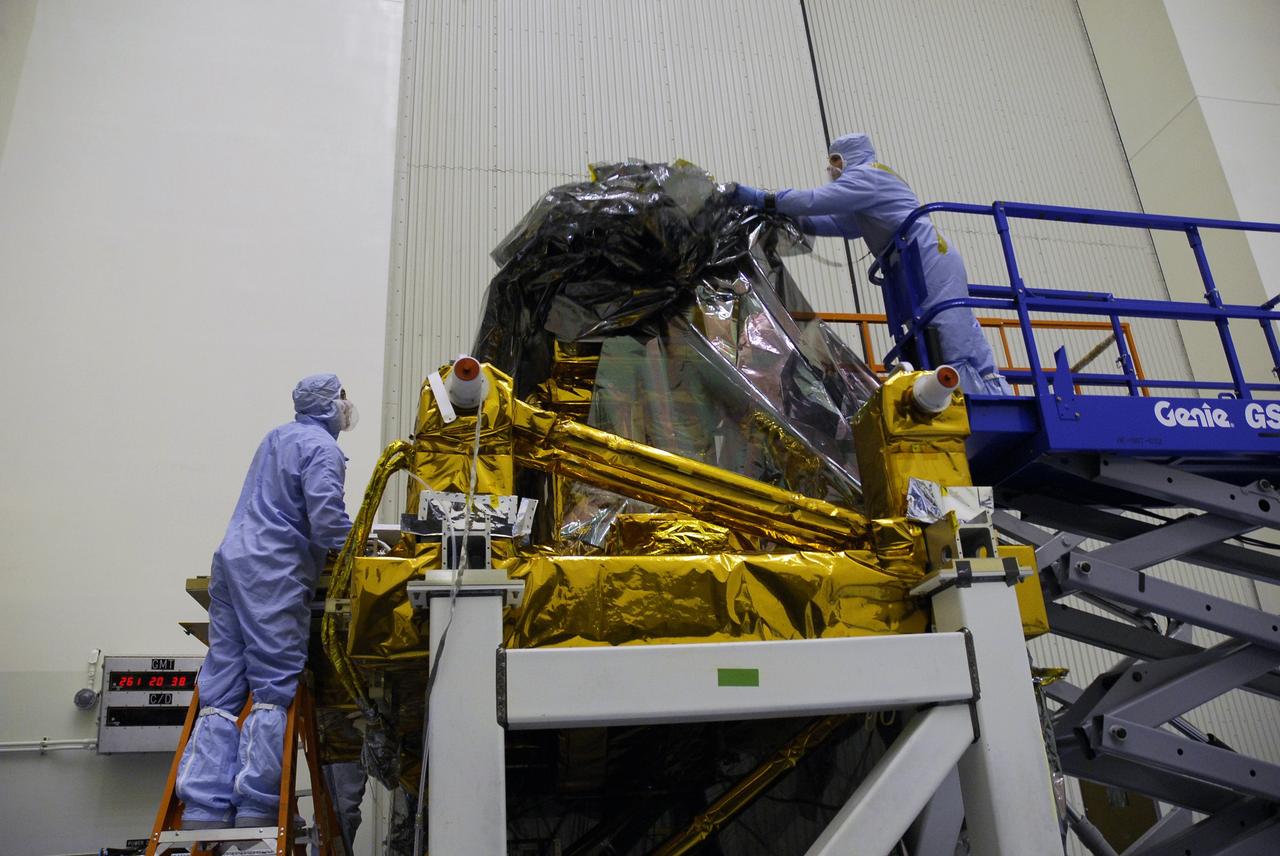

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician uncovers the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A will be removed. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies for servicing of the Hubble Space Telescope on the STS-125 mission, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center installs a pallet support strut on the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
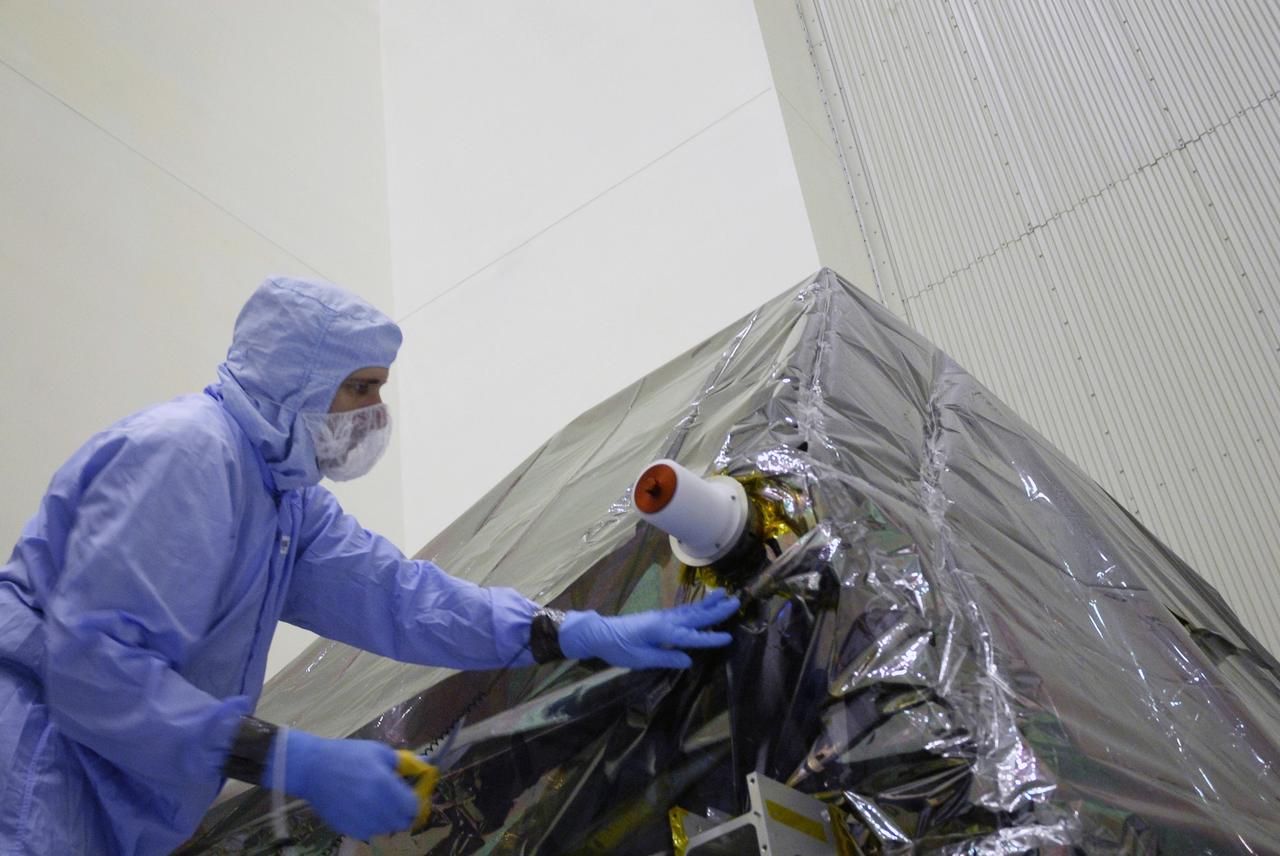

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician begins uncovering the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A will be removed. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies for servicing of the Hubble Space Telescope on the STS-125 mission, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
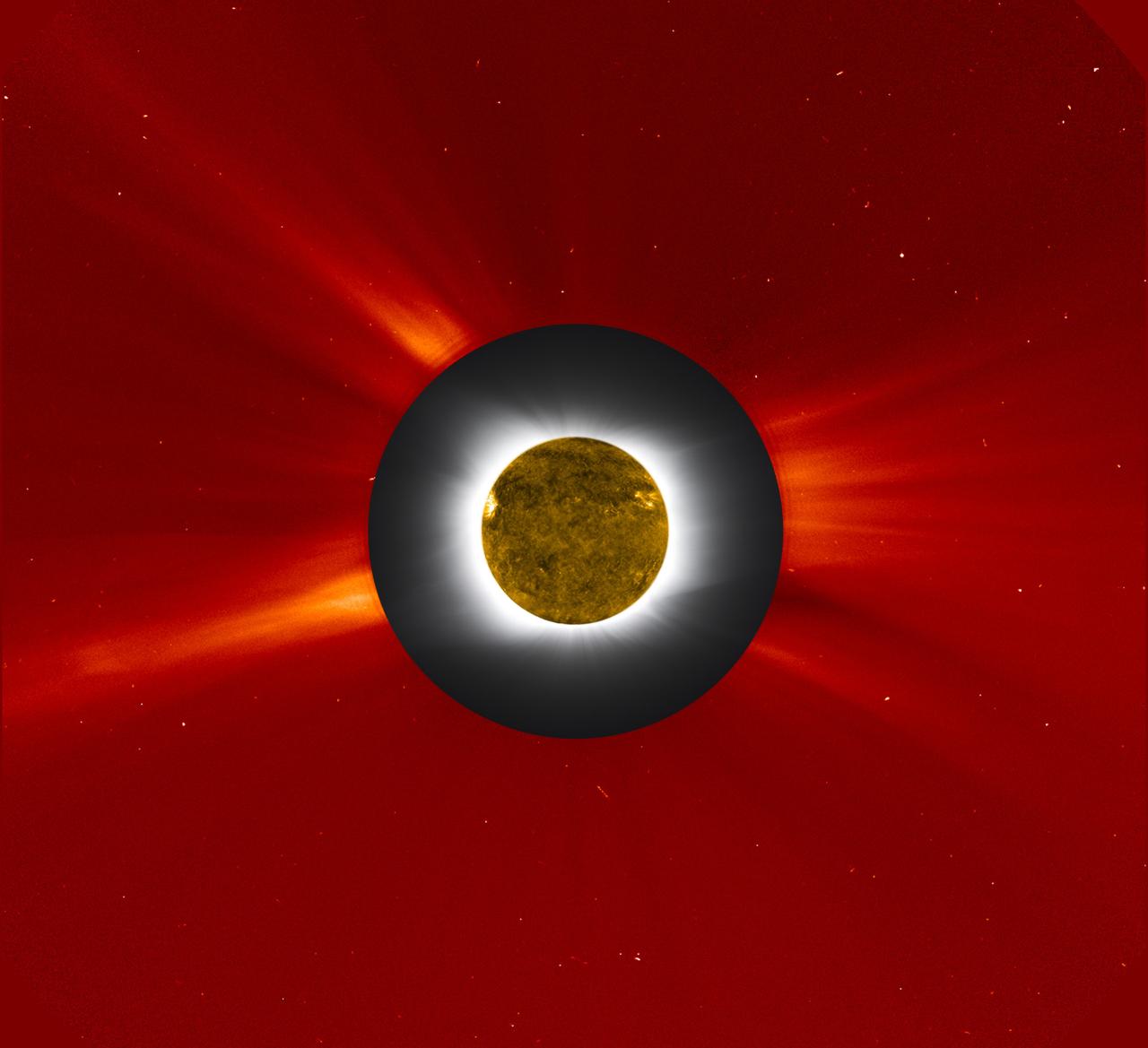

Eclipse 2010 Composite A solar eclipse photo (gray and white) from the Williams College Expedition to Easter Island in the South Pacific (July 11, 2010) was embedded with an image of the Sun’s outer corona taken by the Large Angle Spectrometric Coronagraph (LASCO) on the SOHO spacecraft and shown in red false color. LASCO uses a disk to blot out the bright sun and the inner corona so that the faint outer corona can be monitored and studied. Further, the dark silhouette of the moon was covered with an image of the Sun taken in extreme ultraviolet light at about the same time by the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly on Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). The composite brings out the correlation of structures in the inner and outer corona. Credits: Williams College Eclipse Expedition -- Jay M. Pasachoff, Muzhou Lu, and Craig Malamut; SOHO’s LASCO image courtesy of NASA/ESA; solar disk image from NASA’s SDO; compositing by Steele Hill, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians finish replacing the protective cover over the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. The cover was removed to clean the carrier of contaminants found Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians inspect areas of the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, for contamination. Contamination discovered Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A will be removed. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies for servicing of the Hubble Space Telescope on the STS-125 mission, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician works to replace the protective cover on the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC. The cover was removed to clean the carrier of contaminants found Sept. 17 during preparations to deliver NASA's Hubble Space Telescope servicing payload to Launch Pad 39A. Cleanliness is extremely important for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to Hubble, and the teams have insured that the SLIC is ready to fly. The SLIC, which holds battery module assemblies, is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The carrier is one of four being transferred to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the carriers will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
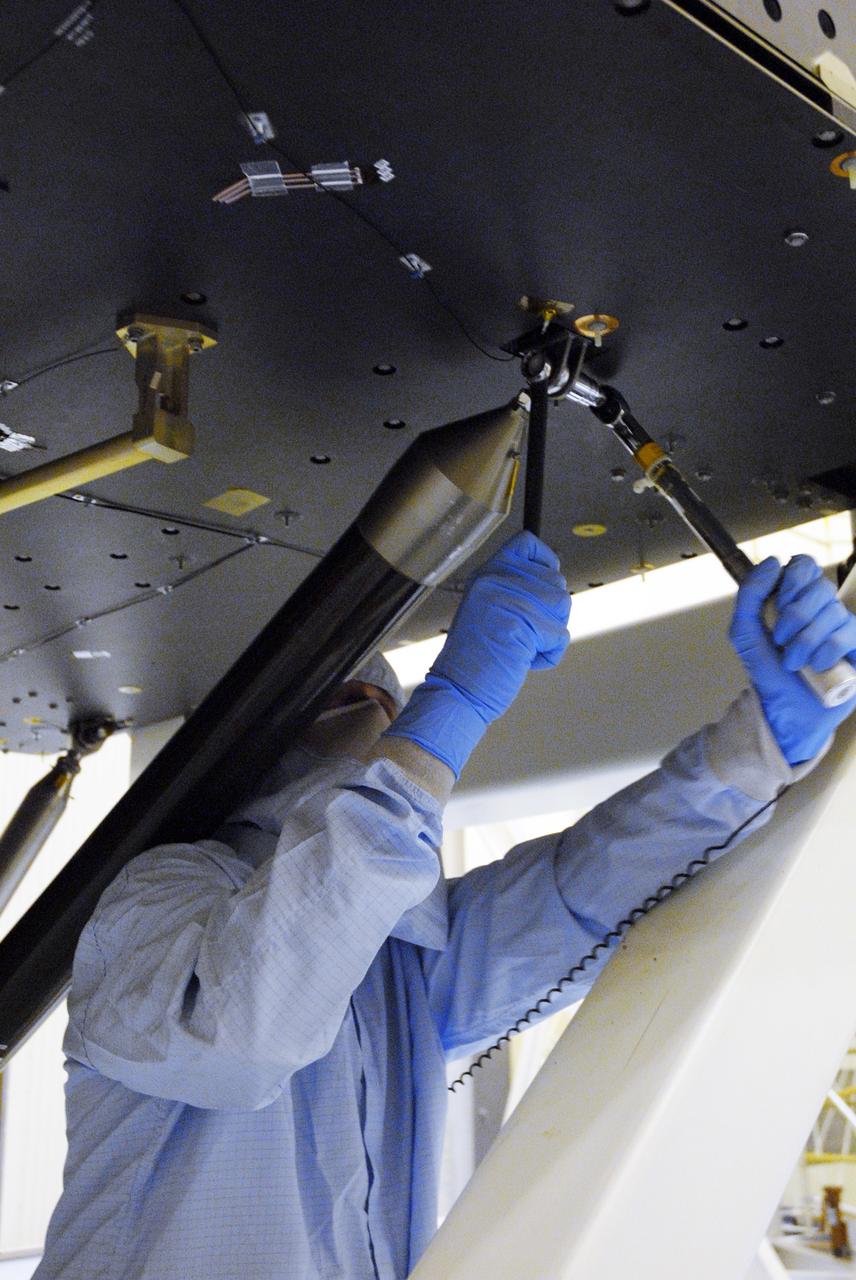

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center installs a pallet support strut on the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. SLIC is built with state-of-the-art, lightweight, composite materials - carbon fiber with a cyanate ester resin and a titanium metal matrix composite. These composites have greater strength-to-mass ratios than the metals typically used in spacecraft design. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in early August. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
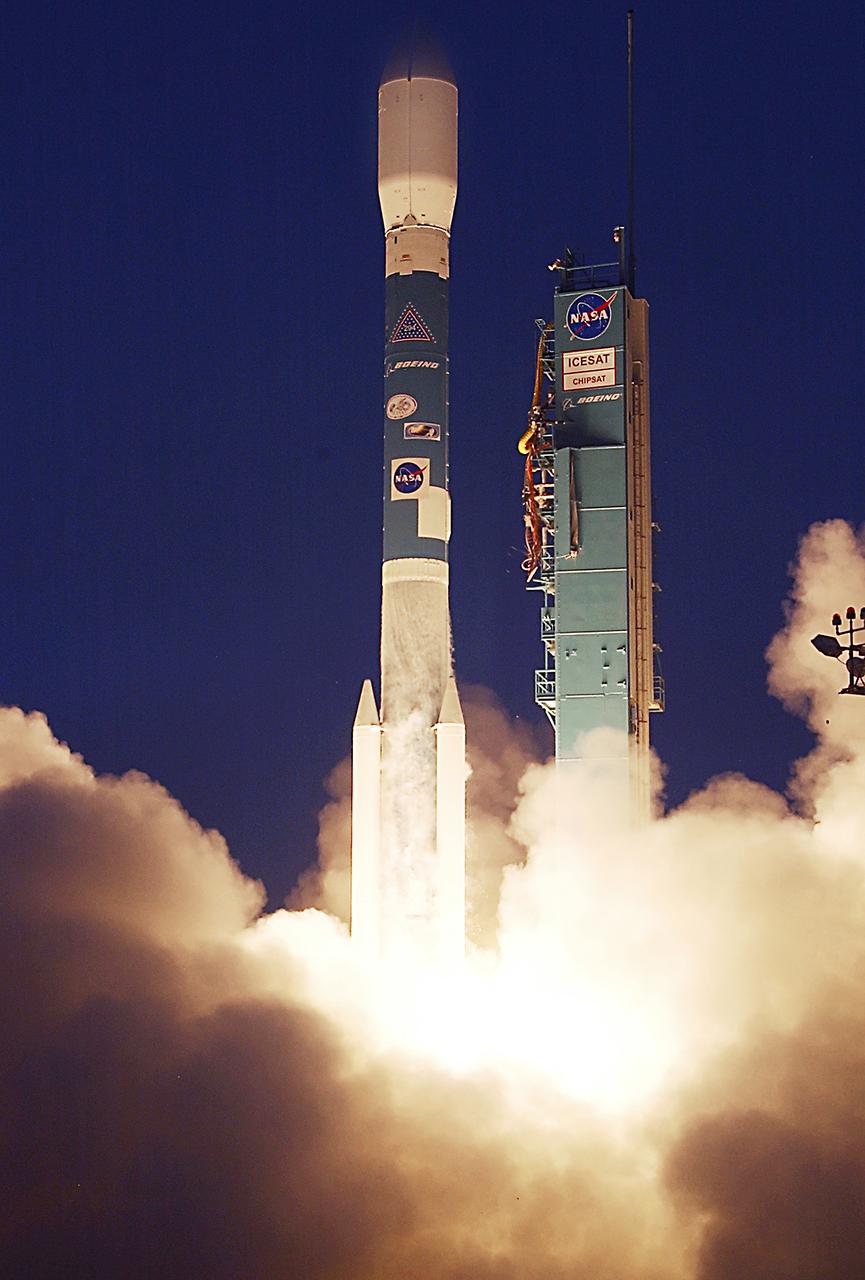

NASA's Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation satellite (ICESat) and Cosmic Hot Interstellar Spectrometer (CHIPS) satellite lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif at 4:45 p.m. PST aboard Boeing's Delta II rocket. ICESat will examine the role that ice plays in global climate change, while CHIPS will explore the composition of our galaxy. Photo Credit: "NASA/Bill Ingalls"

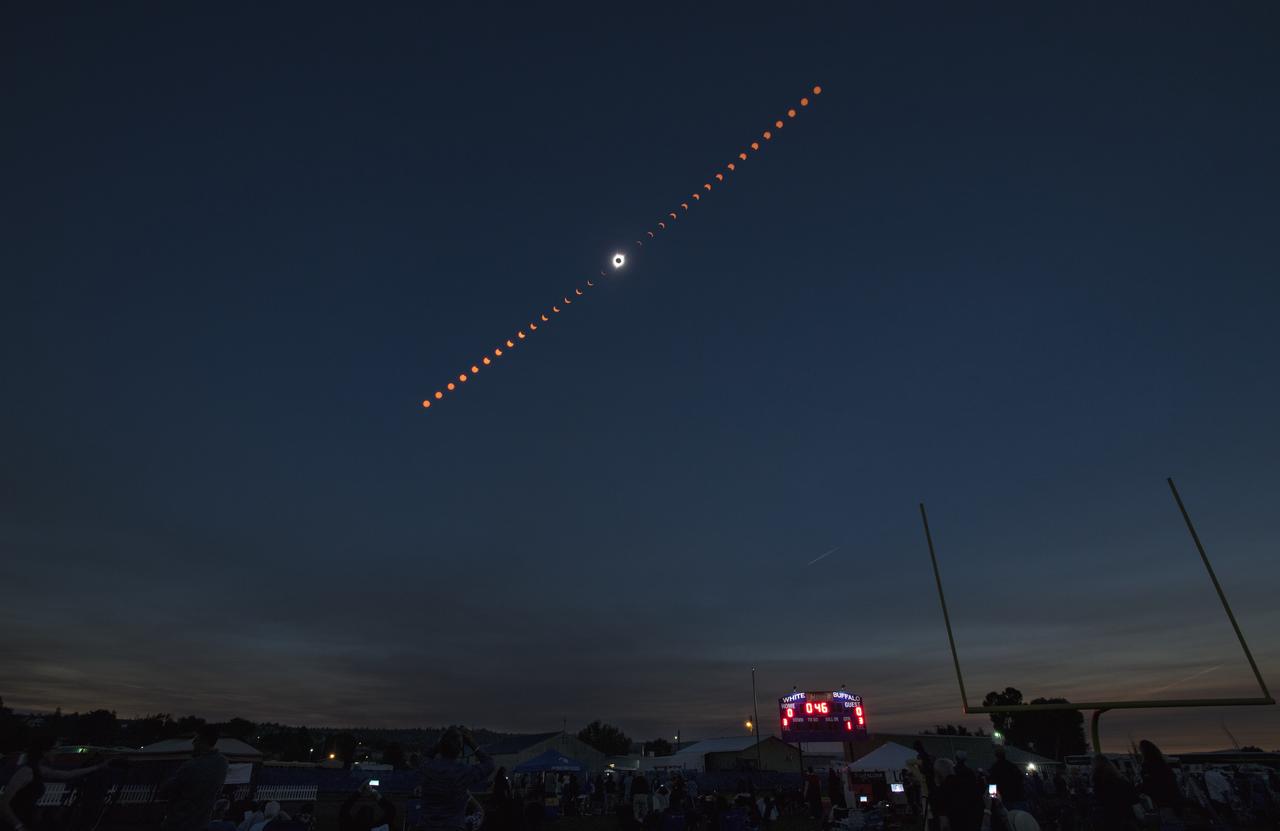
This composite image of multiple exposures shows the progression of a total solar eclipse in Dallas, Texas on Monday, April 8, 2024. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the North American continent from Mexico’s Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of Central America and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

This composite image of multiple exposures shows the progression of a total solar eclipse as seen from the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, Monday, April 8, 2024. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the North American continent from Mexico’s Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of Central America and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
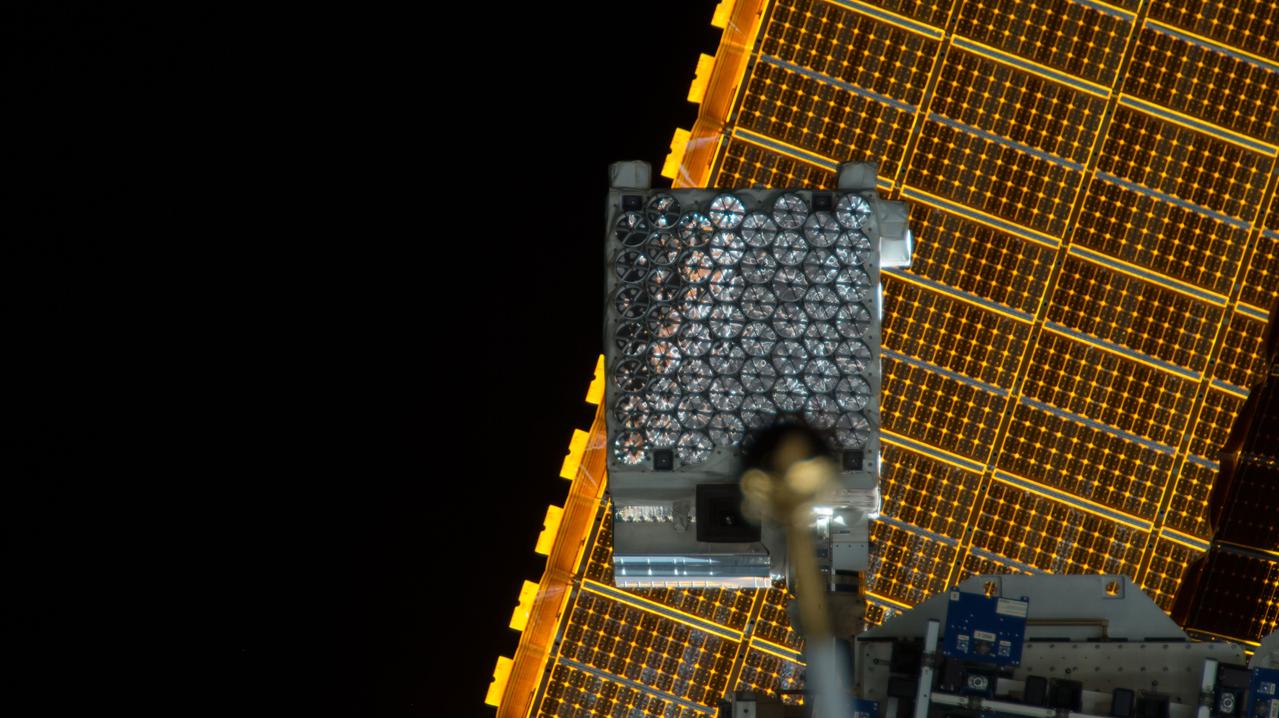
iss057e055460 (10/22/2018) --- View of the Neutron Star Interior Composition ExploreR (NICER) payload, attached to ExPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Logistics Carrier-2 (ELC-2) on the S3 Truss. Photo was taken by the ground-controlled External High Definition Camera 1 (EHDC1). NICER's primary mission to perform an in-depth study of neutron stars offers unrivaled astrophysics knowledge and can revolutionize the understanding of ultra-dense matter.
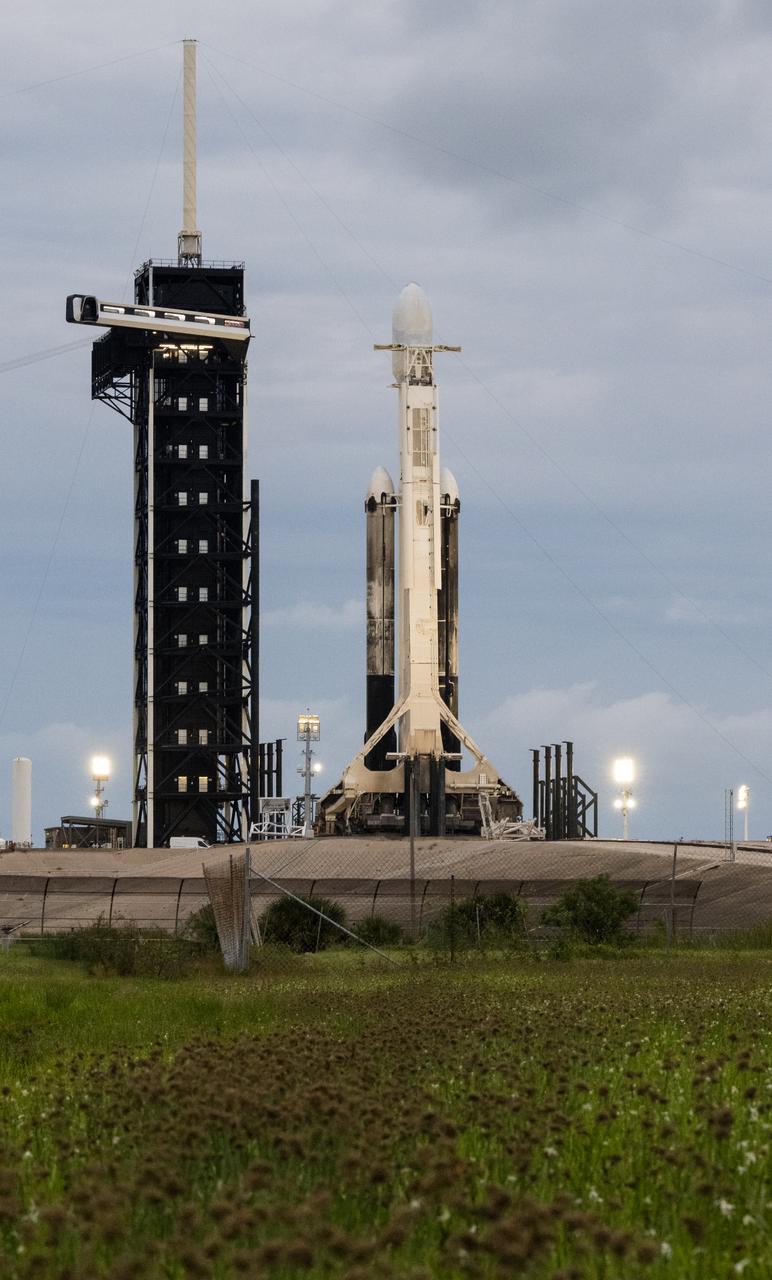

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is seen at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for the Psyche mission, Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

This composite image of nine pictures shows the progression of a partial solar eclipse near Banner, Wyoming on Monday, Aug. 21, 2017. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation satellite (ICESat) and Cosmic Hot Interstellar Spectrometer (CHIPS) satellite lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif at 4:45 p.m. PST aboard Boeing's Delta II rocket. ICESat will examine the role that ice plays in global climate change, while CHIPSat will explore the composition of our galaxy. [Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-03pd0060/KSC-03pd0060~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation satellite (ICESat) and Cosmic Hot Interstellar Spectrometer (CHIPS) satellite lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif at 4:45 p.m. PST aboard Boeing's Delta II rocket. ICESat will examine the role that ice plays in global climate change, while CHIPSat will explore the composition of our galaxy. [Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls]

The countdown clock is seen as preparations continue for the launch of a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
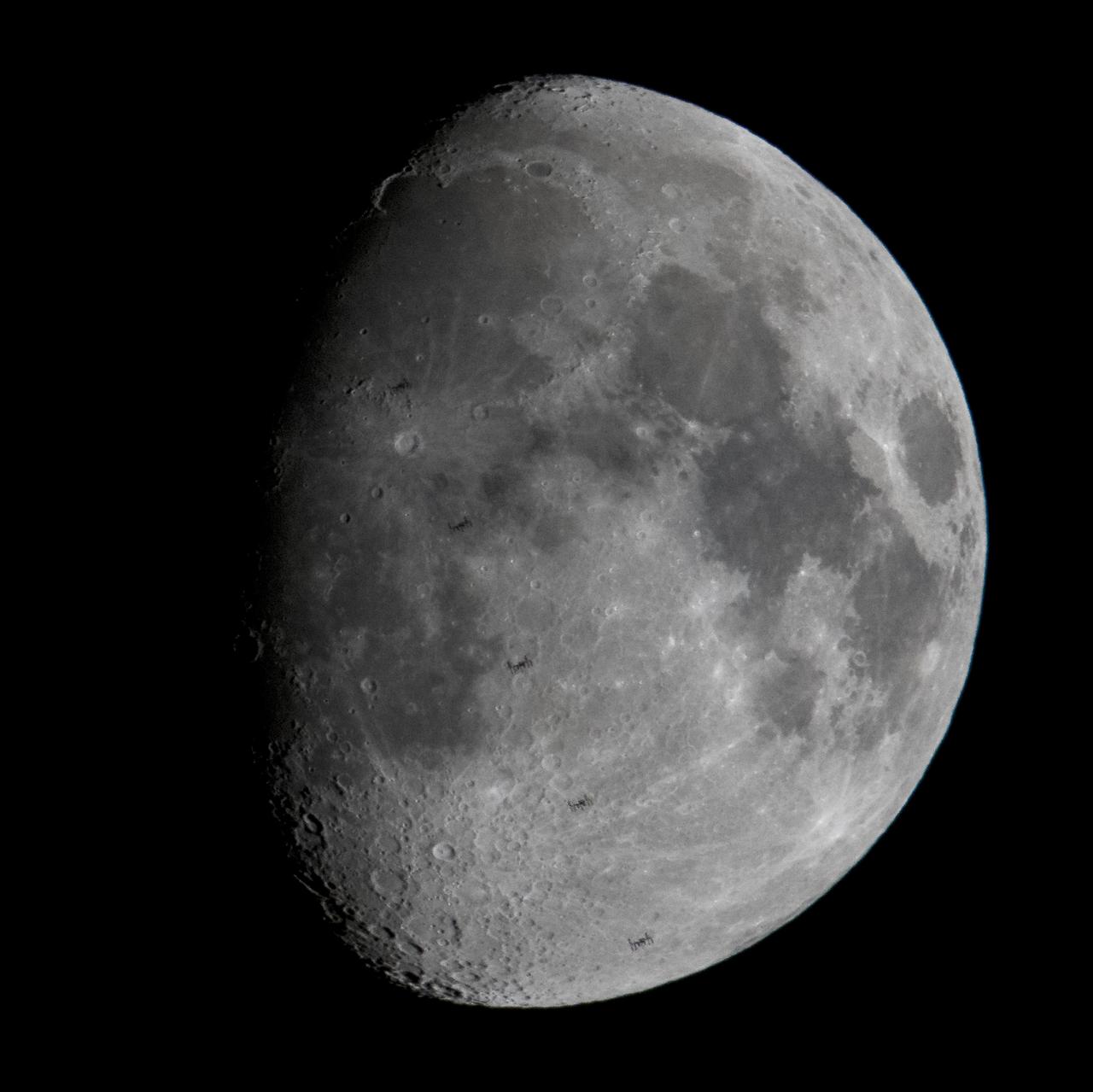

This composite image, made from five frames, shows the International Space Station, with a crew of six onboard, as it transits the Moon at roughly five miles per second, Saturday, March 16, 2019 from Chantilly, Va. Onboard are Expedition 59 Commander Oleg Kononenko and Alexey Ovchinin of Roscosmos, Anne McClain, Nick Hague, and Christina Koch of NASA, and David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

This composite image of thirteen photographs shows the progression of a total solar eclipse at Madras High School in Madras, Oregon on Monday, August 21, 2017. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
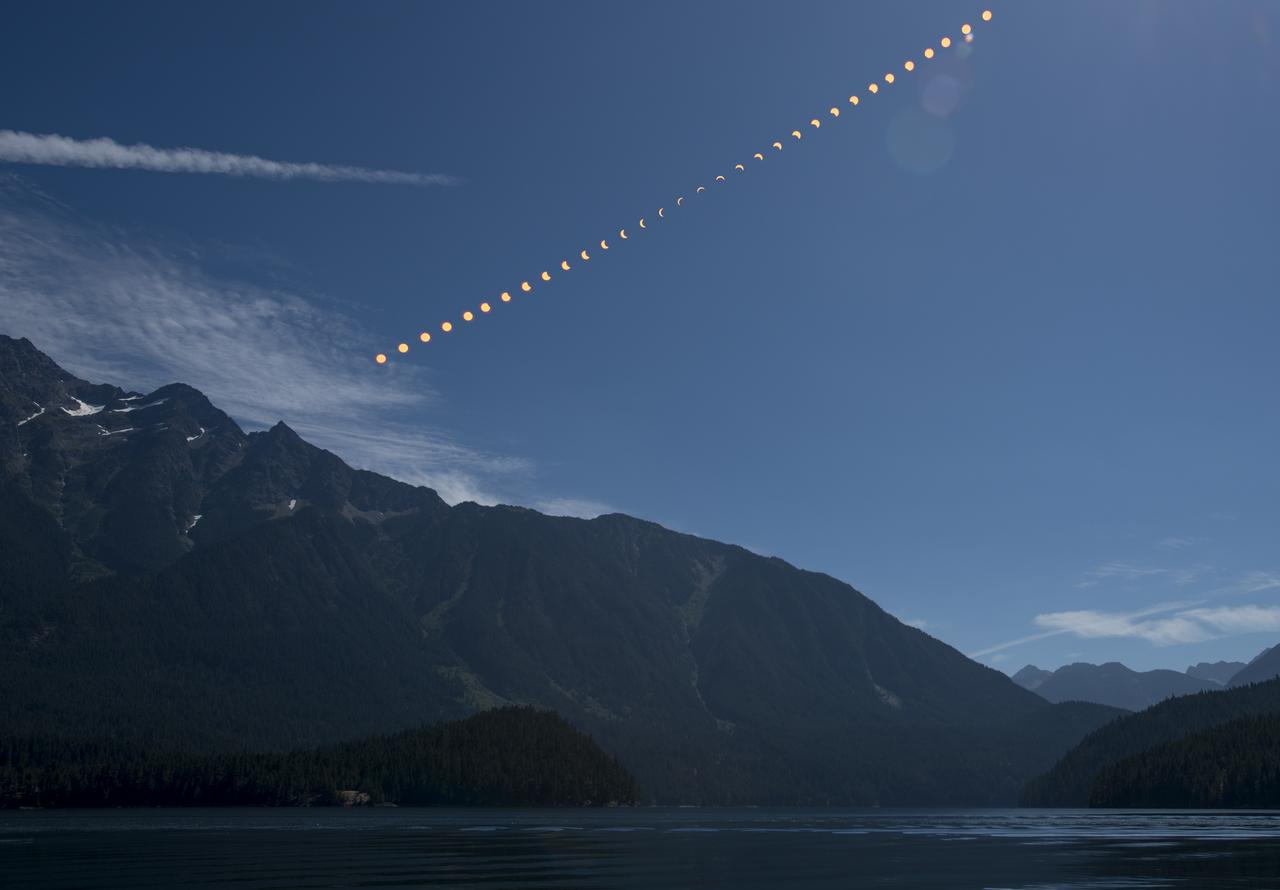

This composite image shows the progression of a partial solar eclipse over Ross Lake, in Northern Cascades National Park, Washington on Monday, Aug. 21, 2017. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
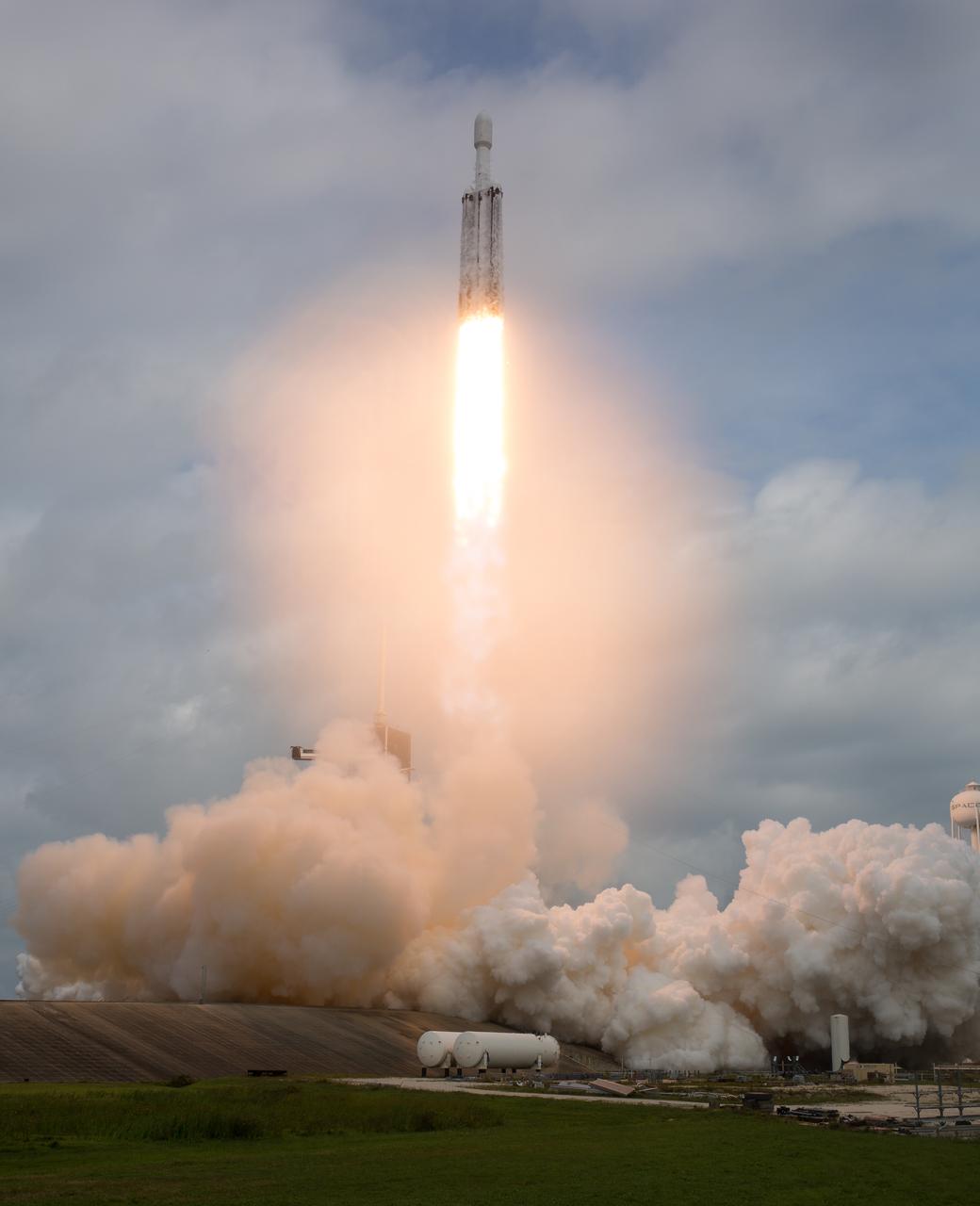

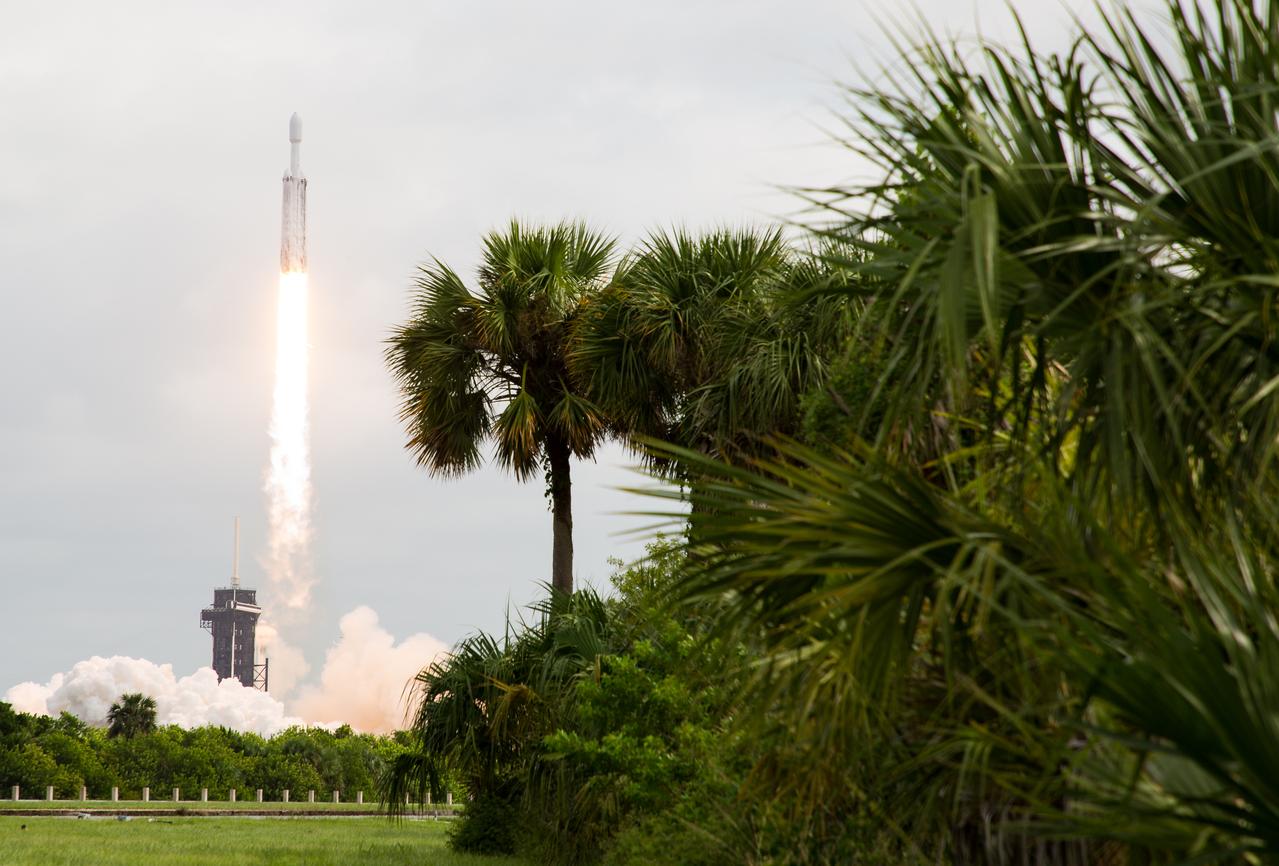
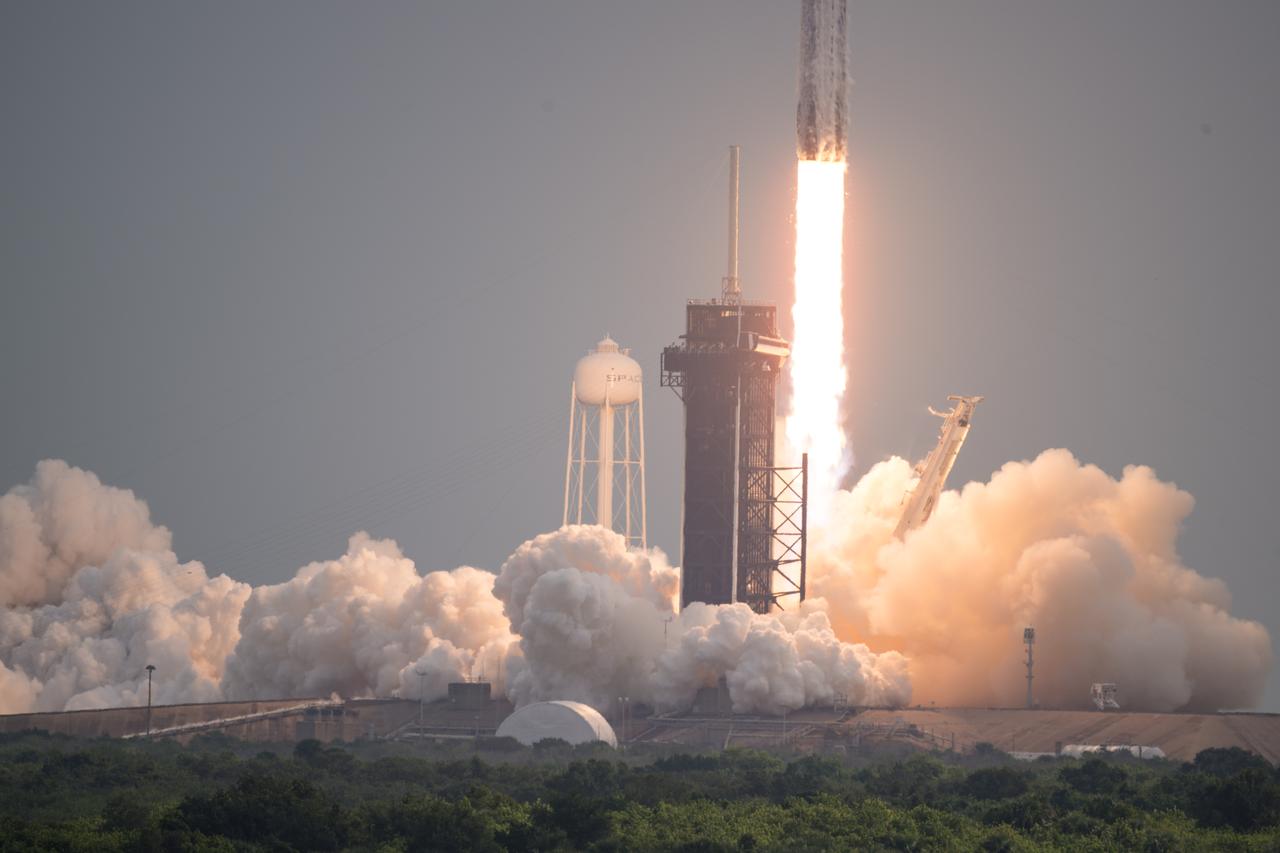
A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
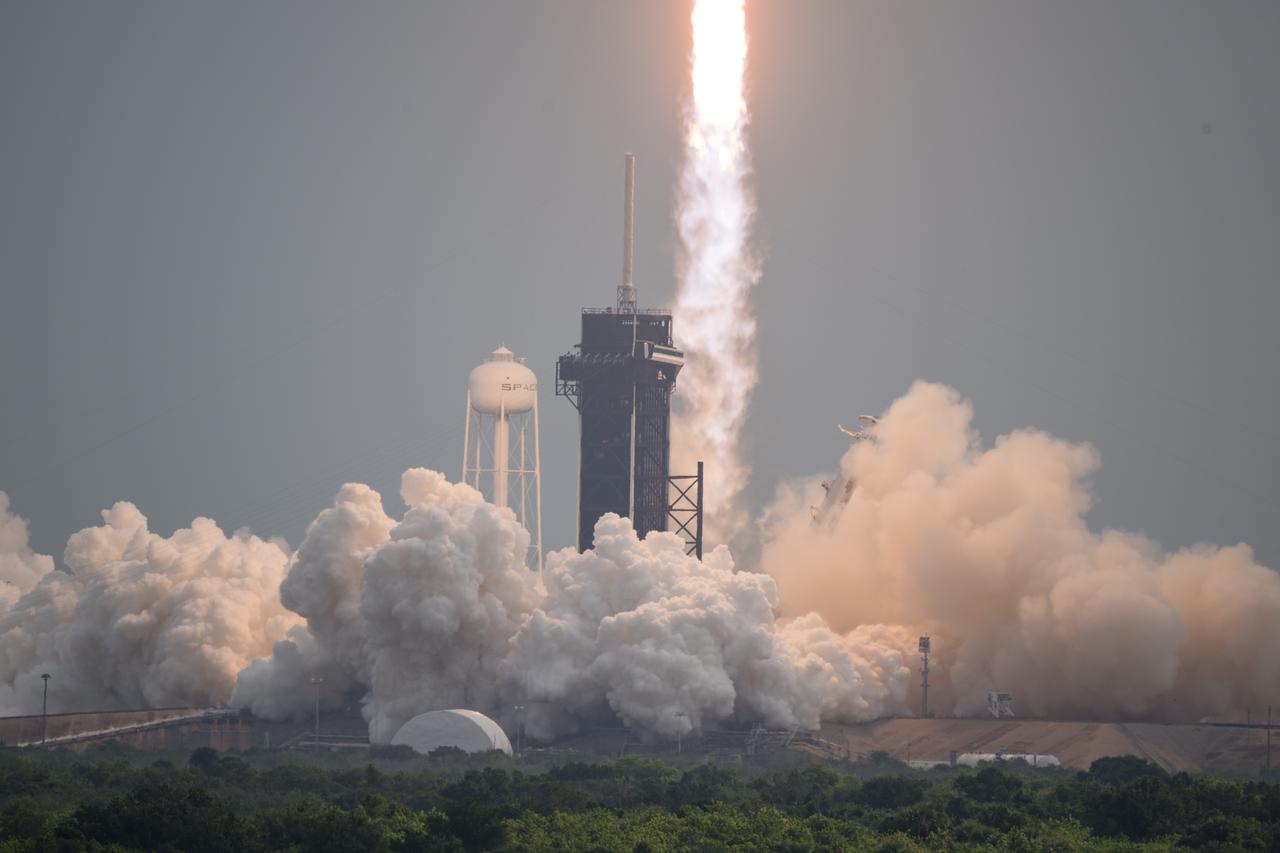

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
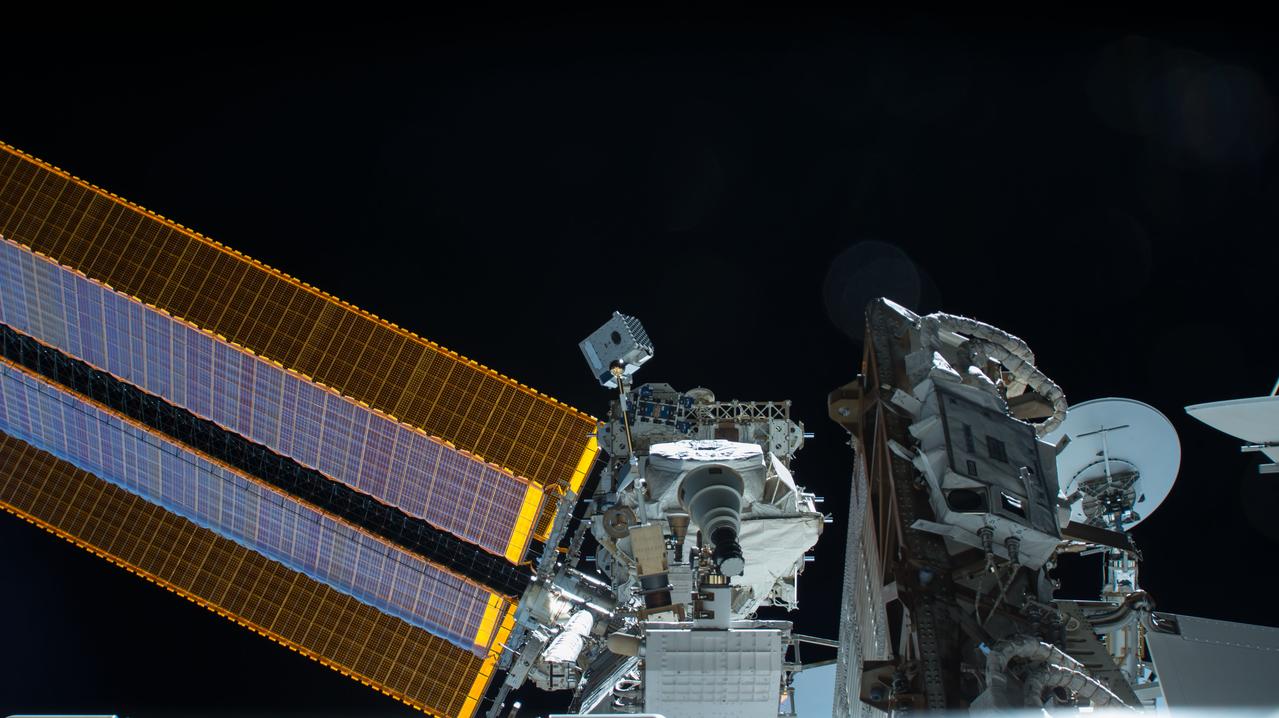

iss057e055440 (10/22/2018) --- View of the Neutron Star Interior Composition ExploreR (NICER) payload, attached to ExPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Logistics Carrier-2 (ELC-2) on the S3 Truss. Photo was taken by the ground-controlled External High Definition Camera 1 (EHDC1). NICER's primary mission to perform an in-depth study of neutron stars offers unrivaled astrophysics knowledge and can revolutionize the understanding of ultra-dense matter.
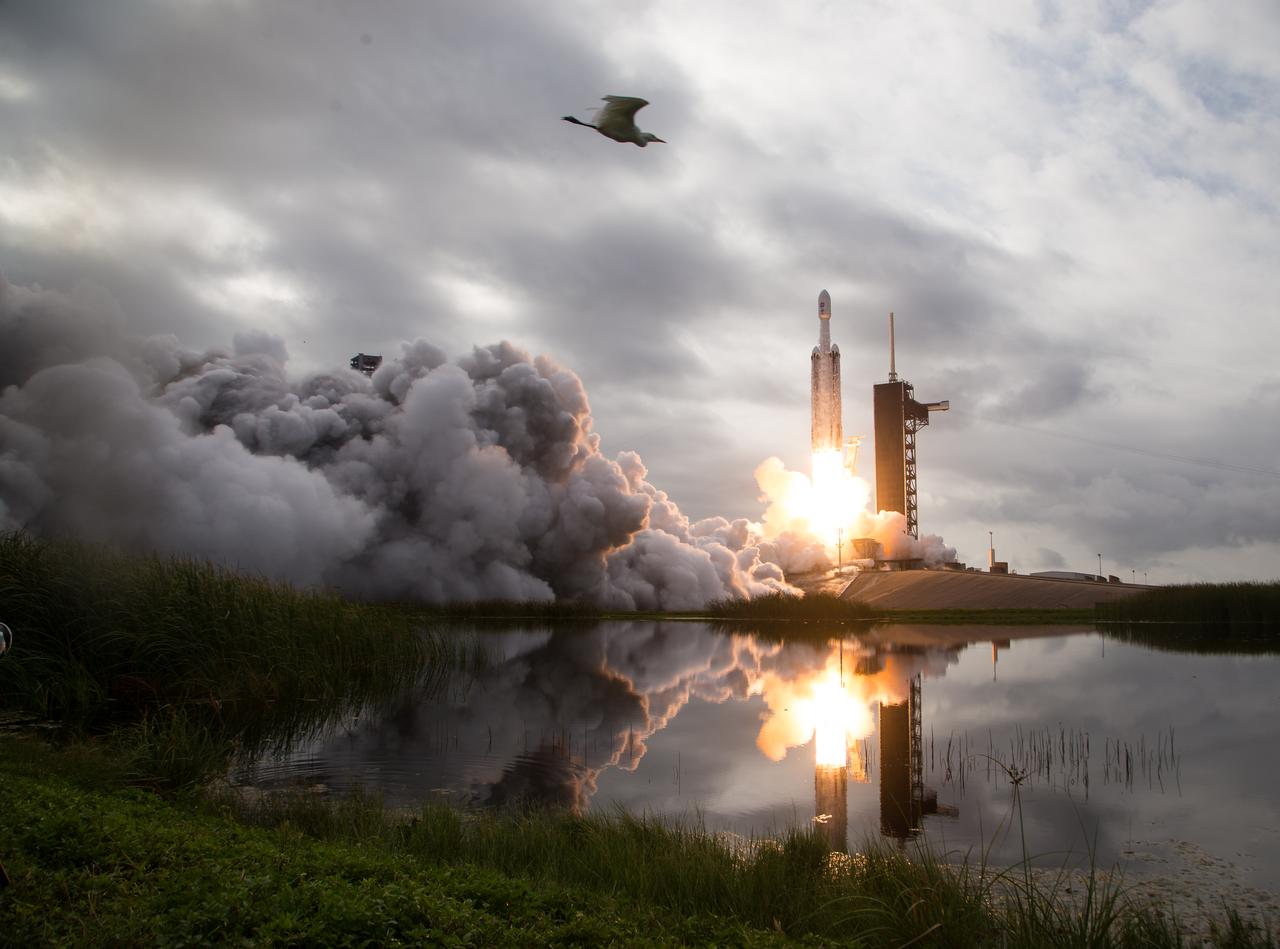

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is seen at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for the Psyche mission, Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
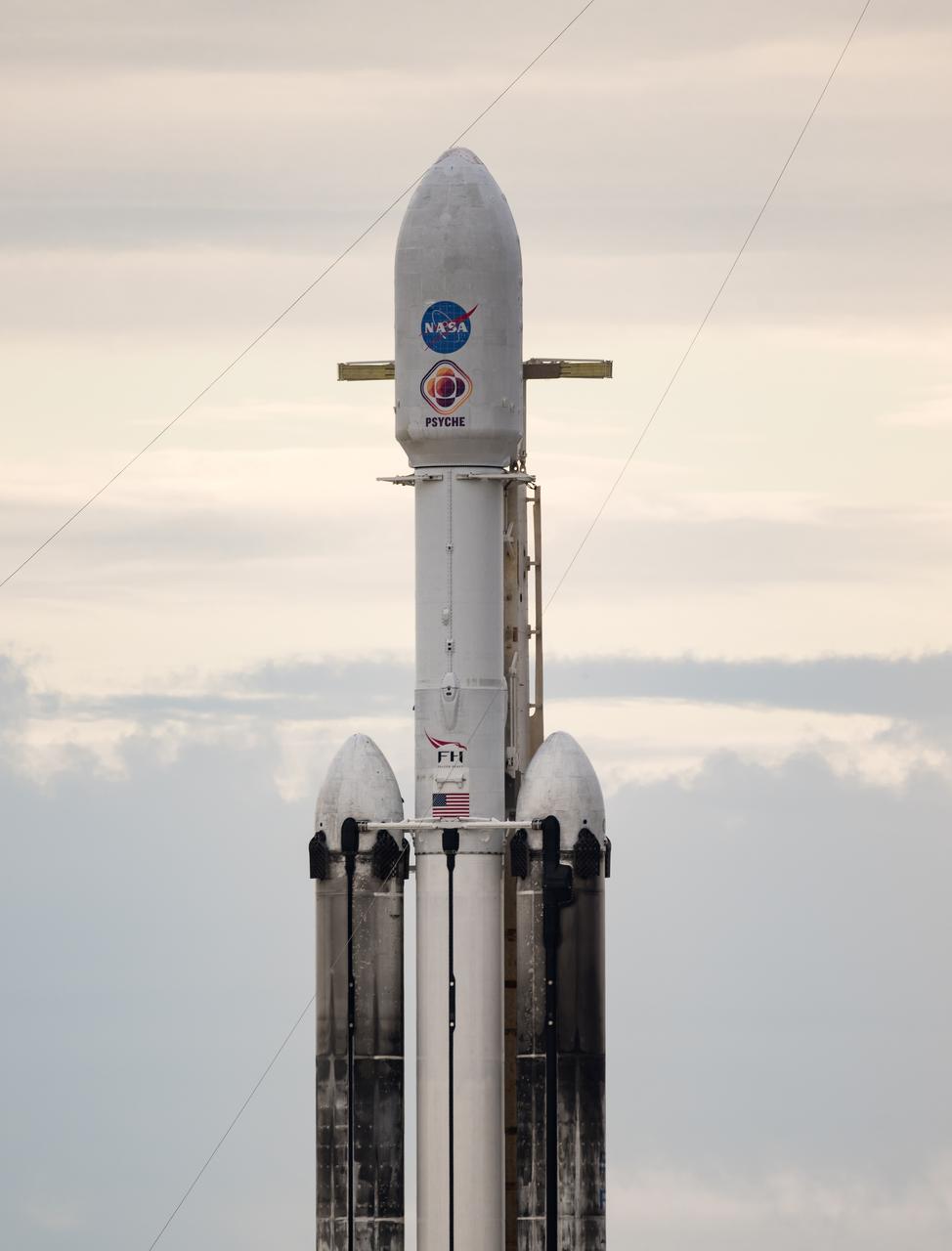

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is seen at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for the Psyche mission, Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
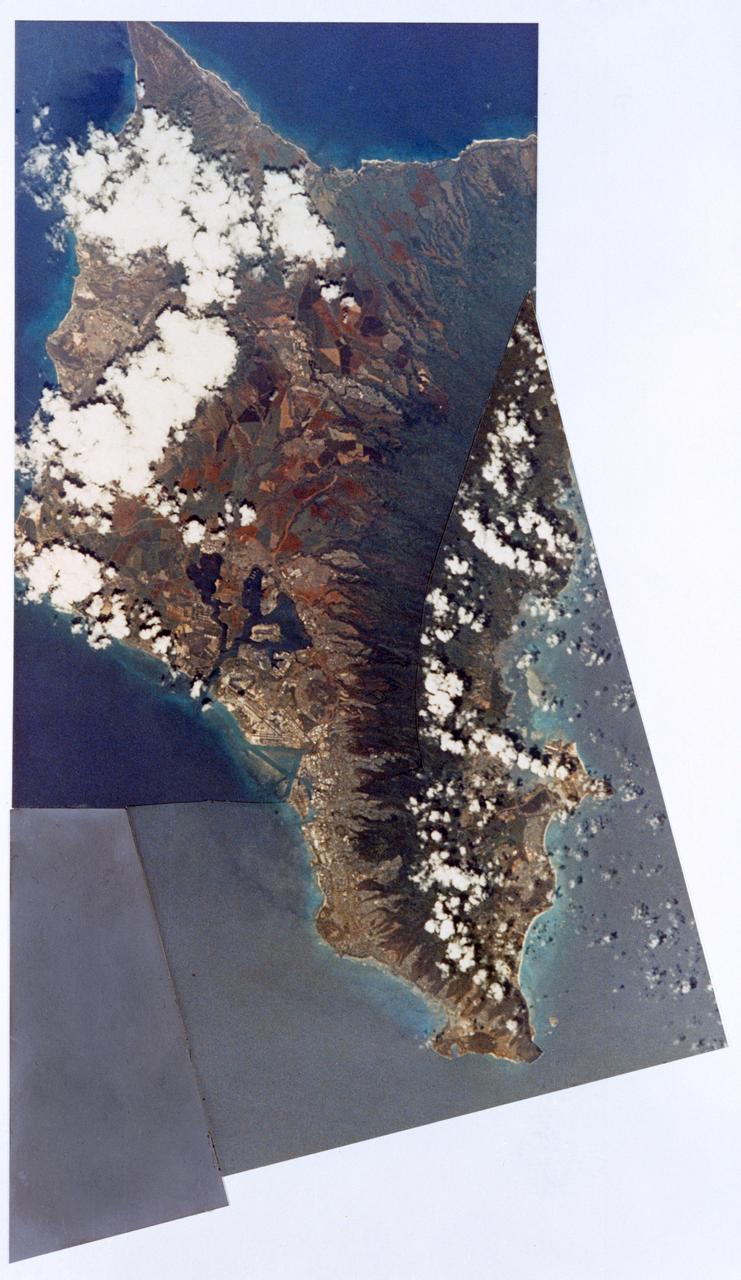

S73-34857 (July-September 1973) --- A composite of two photographs of the Island of Oahu, County of Honolulu, State of Hawaii, taken by one of the Skylab 3 crewmen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The two pictures (SL3-128-3009 and SL3-128-3010) were taken with a hand-held 35mm Nikon camera, a 55/300mm lens and so-368 medium-speed Ektacrome film. Pearl Harbor is clearly visible. The city of Honolulu is located next to the triangle-shaped seaplane runway. Photo credit: NASA
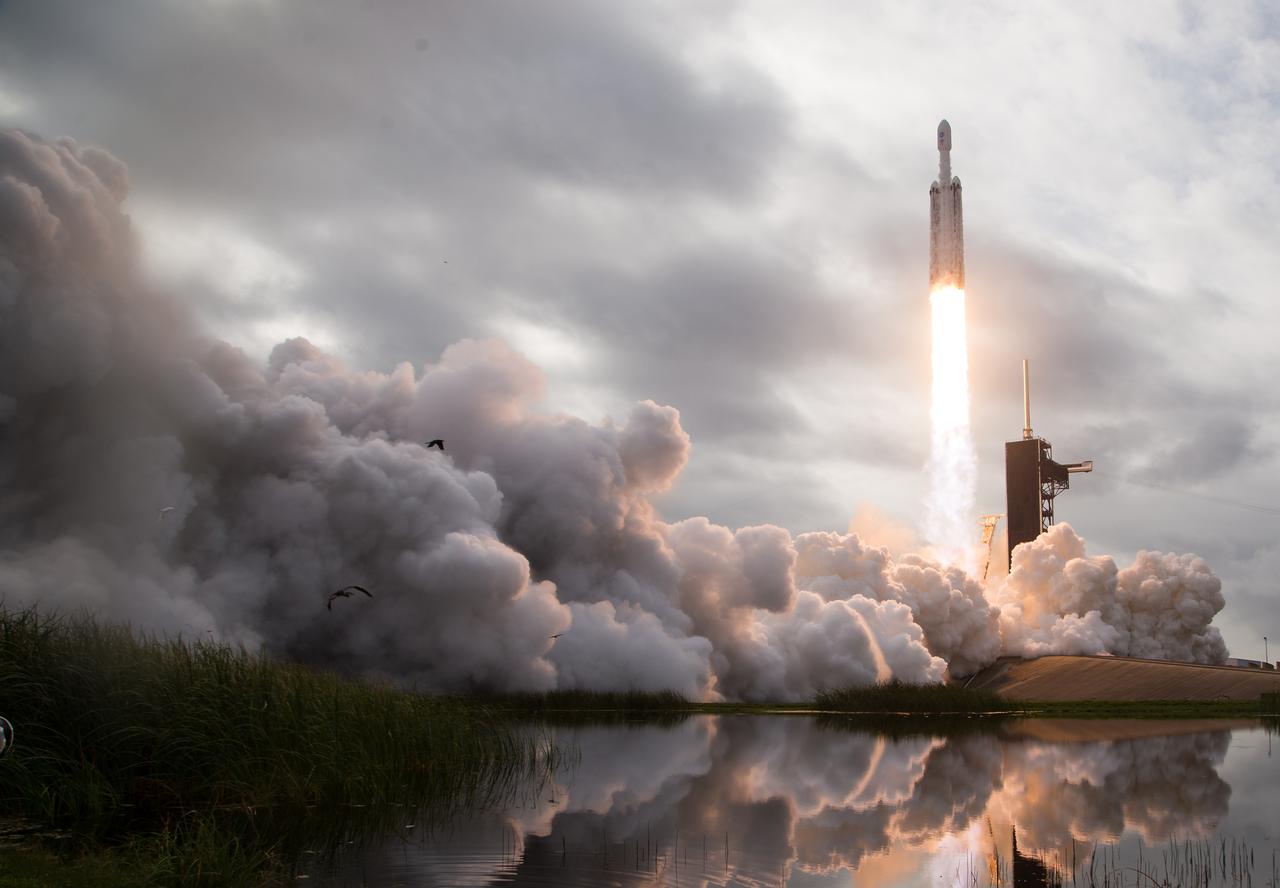

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
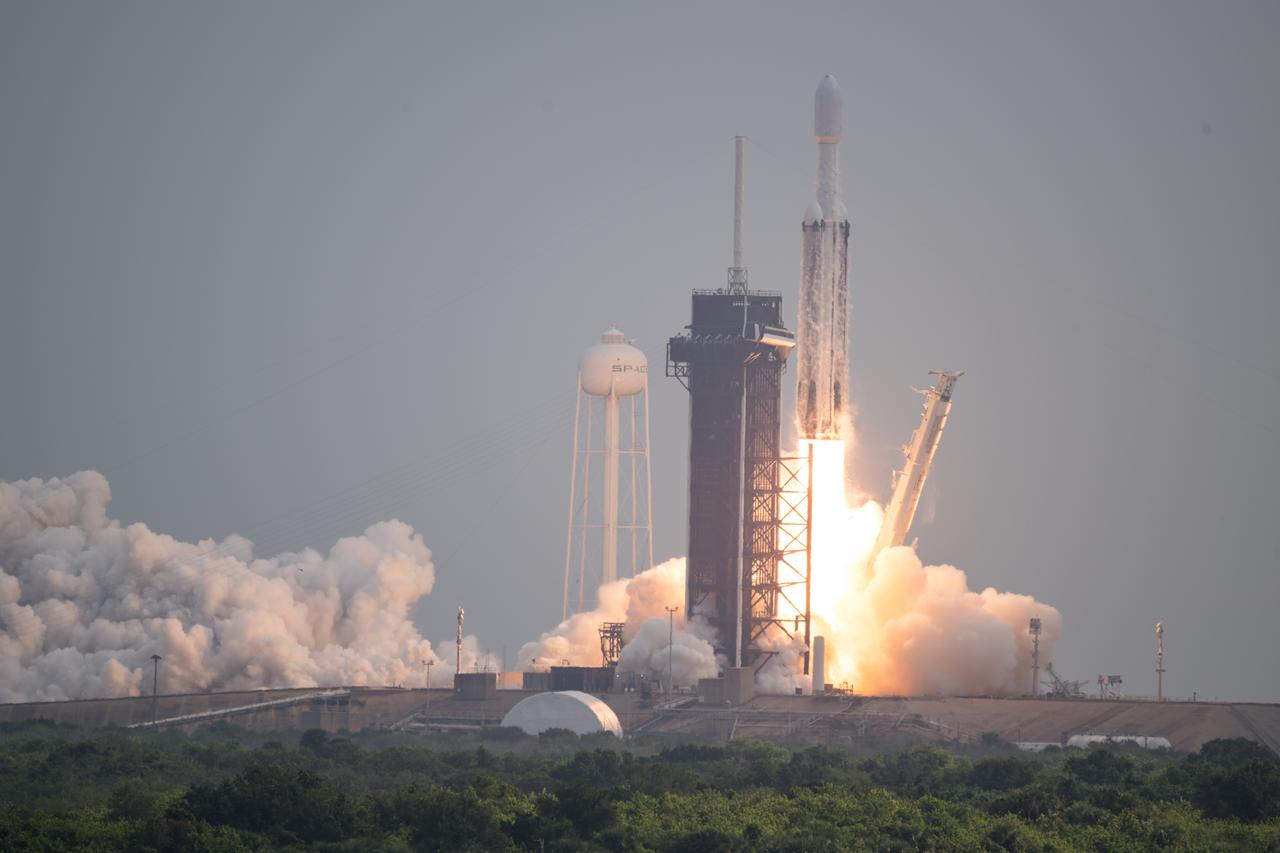

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
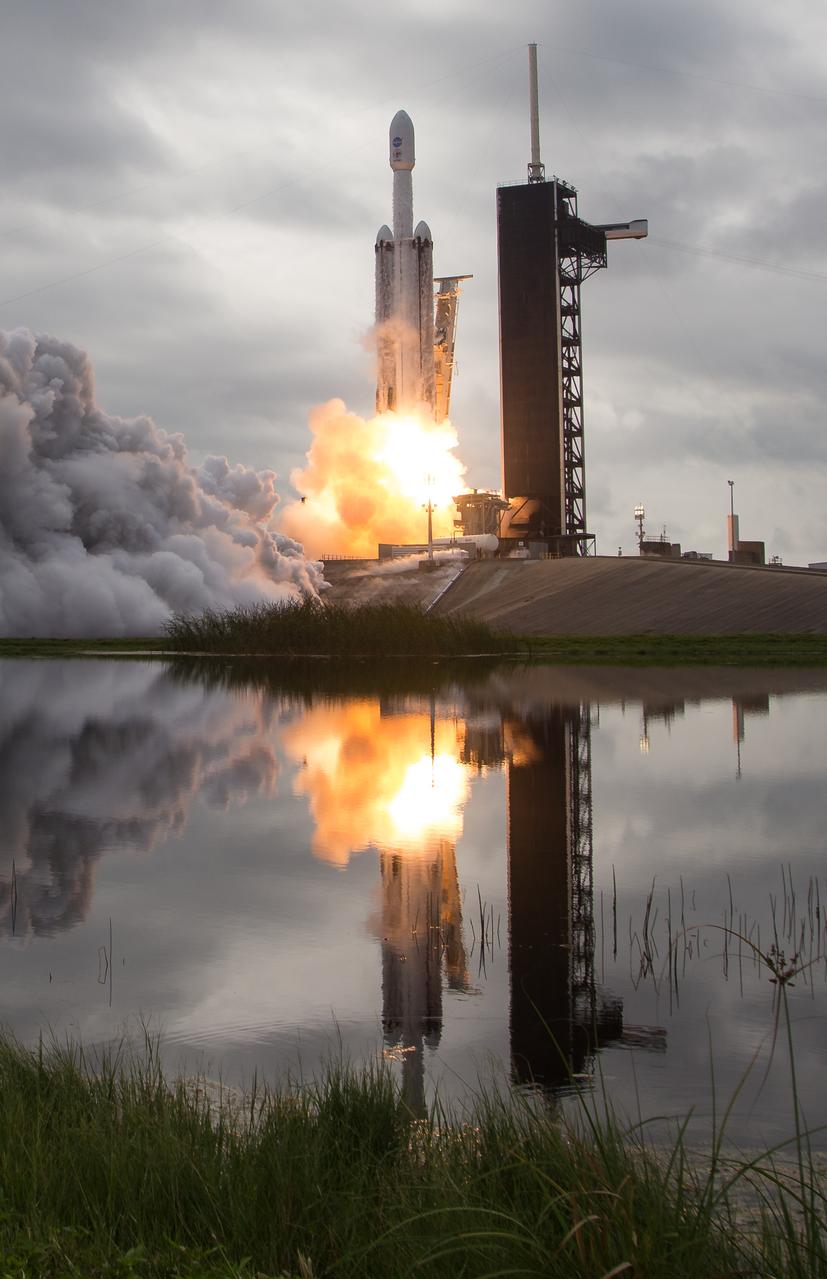

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
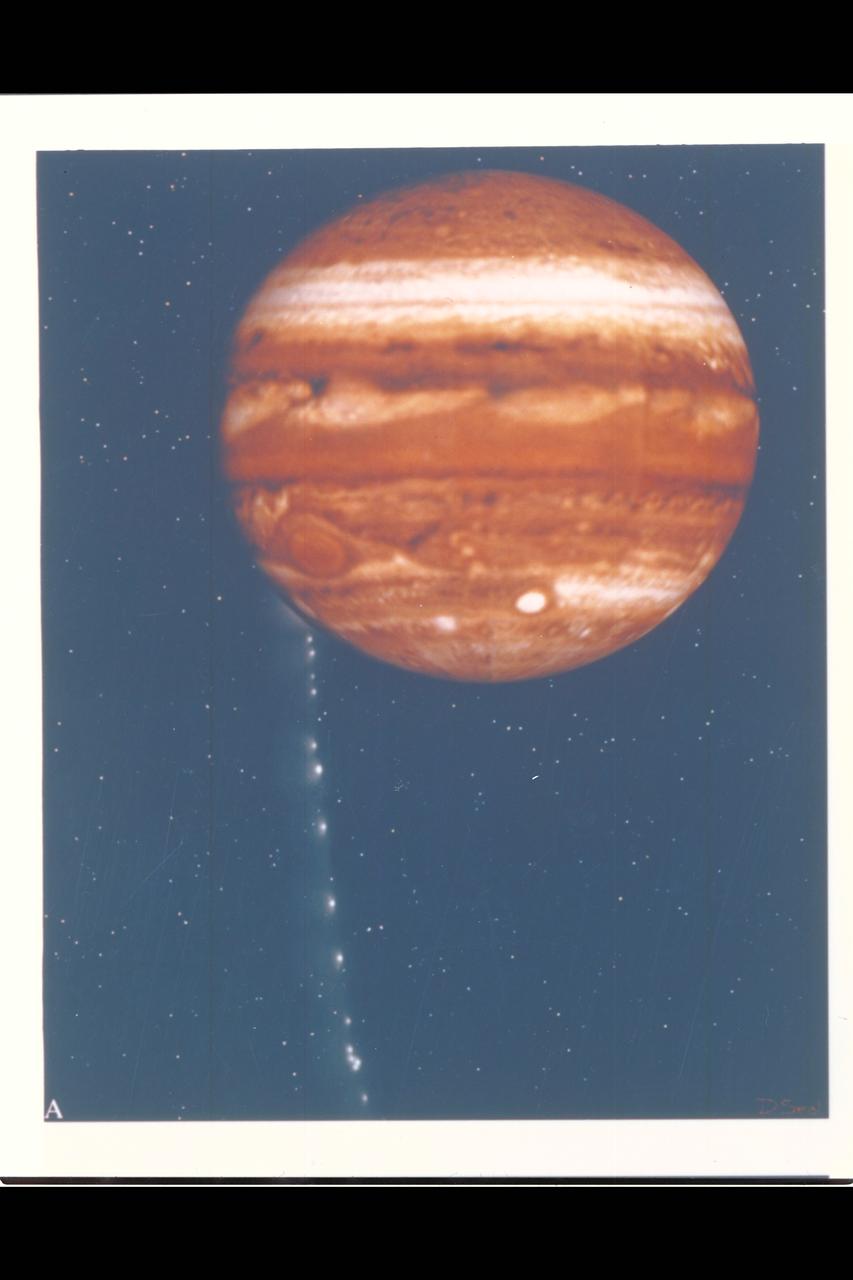

Photo Artwork composite by JPL This depiction of comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 impacting Jupiter is shown from several perspectives. IMAGE A is shown from the perspective of Earth based observers. For visual appeal, most of the large cometary fragments are shown close to one another in this image. At the time of Jupiter impact, the fragments will be separated from one another by serveral times the distances shown. This image was created by D.A. Seal of JPL's Mission Design Section using orbital computations provIded by P.W. Chodas and D.K. Yeomans of JPL's Navigation Section.
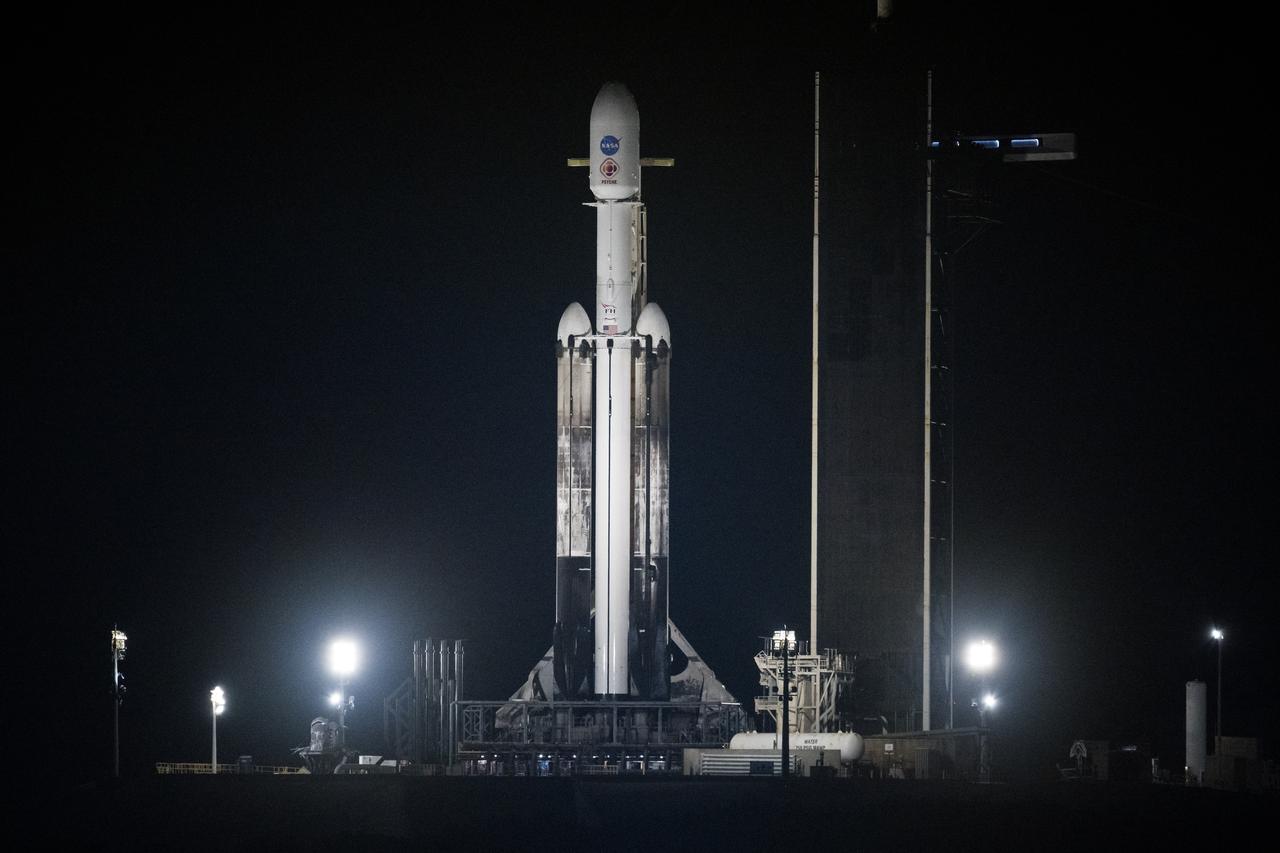

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is seen at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for the Psyche mission, Thursday, Oct. 12, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
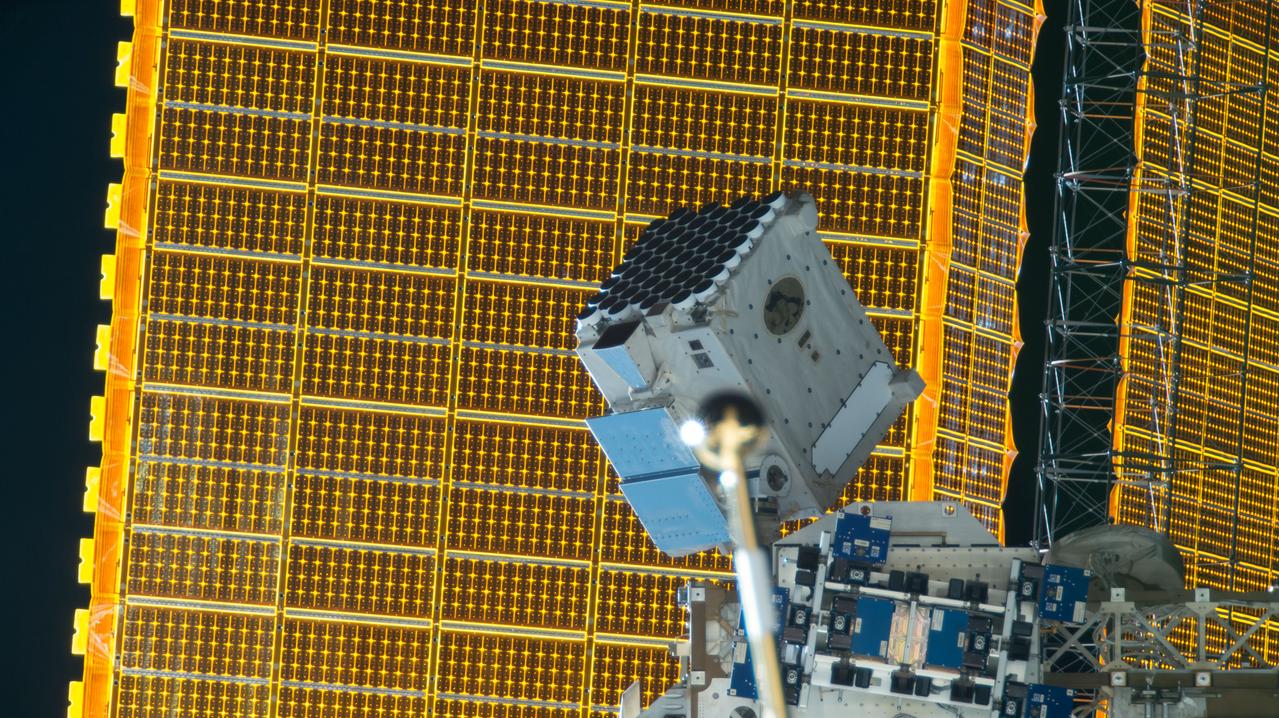
iss057e055490 (10/22/2018) --- View of the Neutron Star Interior Composition ExploreR (NICER) payload, attached to ExPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Logistics Carrier-2 (ELC-2) on the S3 Truss. Photo was taken by the ground-controlled External High Definition Camera 1 (EHDC1). NICER's primary mission to perform an in-depth study of neutron stars offers unrivaled astrophysics knowledge and can revolutionize the understanding of ultra-dense matter.
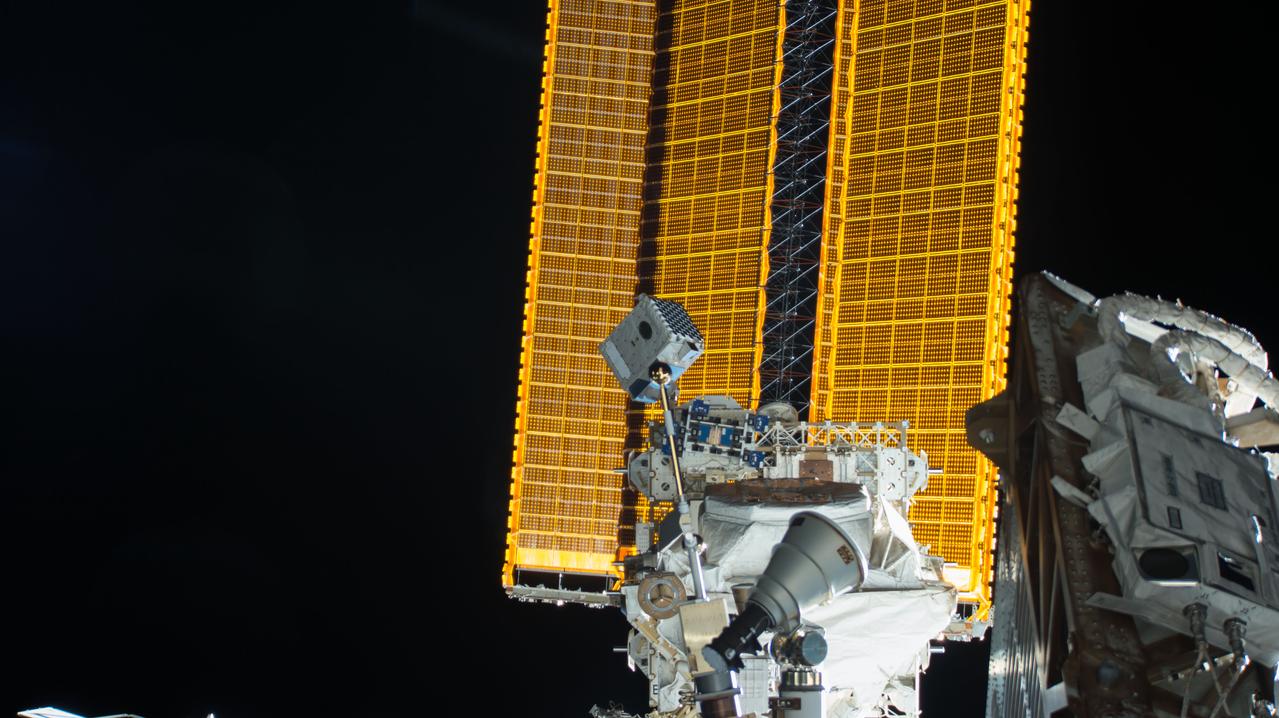

iss057e055482 (10/22/2018) --- View of the Neutron Star Interior Composition ExploreR (NICER) payload, attached to ExPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Logistics Carrier-2 (ELC-2) on the S3 Truss. Photo was taken by the ground-controlled External High Definition Camera 1 (EHDC1). NICER's primary mission to perform an in-depth study of neutron stars offers unrivaled astrophysics knowledge and can revolutionize the understanding of ultra-dense matter.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

This composite image shows the progression of a total solar eclipse over Madras, Oregon on Monday, Aug. 21, 2017. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
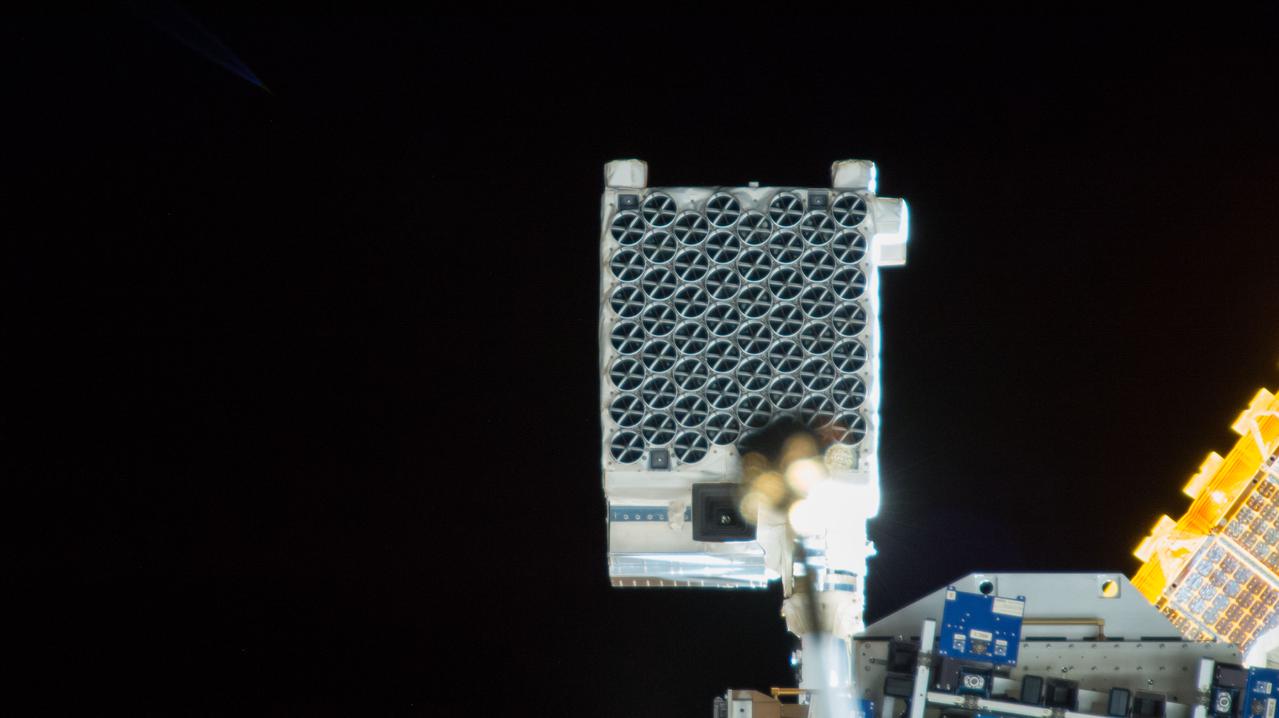
iss057e055482 (10/22/2018) --- View of the Neutron Star Interior Composition ExploreR (NICER) payload, attached to ExPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Logistics Carrier-2 (ELC-2) on the S3 Truss. Photo was taken by the ground-controlled External High Definition Camera 1 (EHDC1). NICER's primary mission to perform an in-depth study of neutron stars offers unrivaled astrophysics knowledge and can revolutionize the understanding of ultra-dense matter.
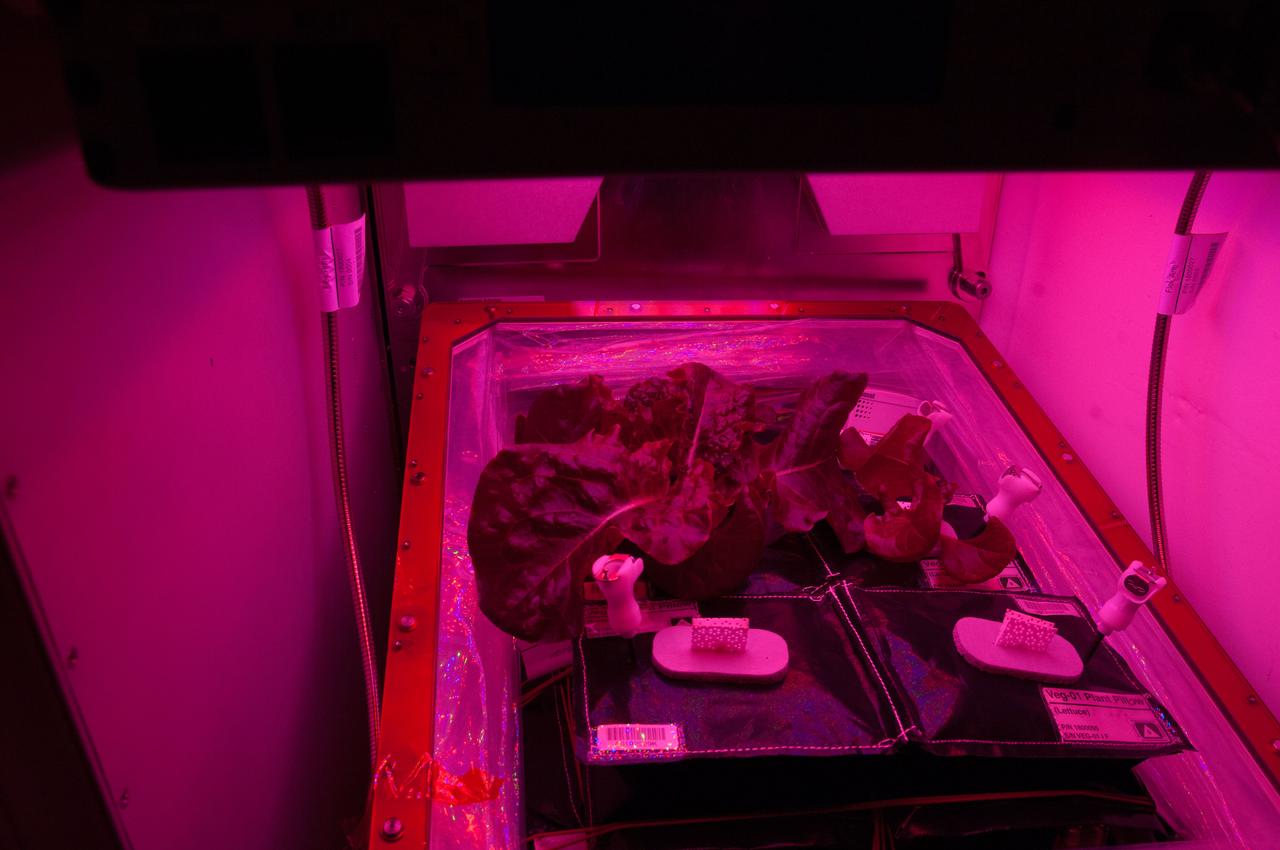

ISS040-E-007676 (5 June 2014) --- One of the Expedition 40 crew members on the International Space Station took a series of photos of the Vegetable Production System (Veggie) recently added to the orbital outpost. The experiment deals with the growth and development of ‘Outredgeous’ Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) seedlings in the spaceflight environment and the effects of the spaceflight environment on composition of microbial flora on the Veggie-grown plants and the Veggie facility. The purple light is the wavelength that is supposed to best promote photosynthesis and growth for the plants.
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation satellite (ICESat) and Cosmic Hot Interstellar Spectrometer (CHIPS) satellite lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif at 4:45 p.m. PST aboard Boeing's Delta II rocket. ICESat will examine the role that ice plays in global climate change, while CHIPSat will explore the composition of our galaxy. [Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-03pd0061/KSC-03pd0061~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation satellite (ICESat) and Cosmic Hot Interstellar Spectrometer (CHIPS) satellite lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif at 4:45 p.m. PST aboard Boeing's Delta II rocket. ICESat will examine the role that ice plays in global climate change, while CHIPSat will explore the composition of our galaxy. [Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls]
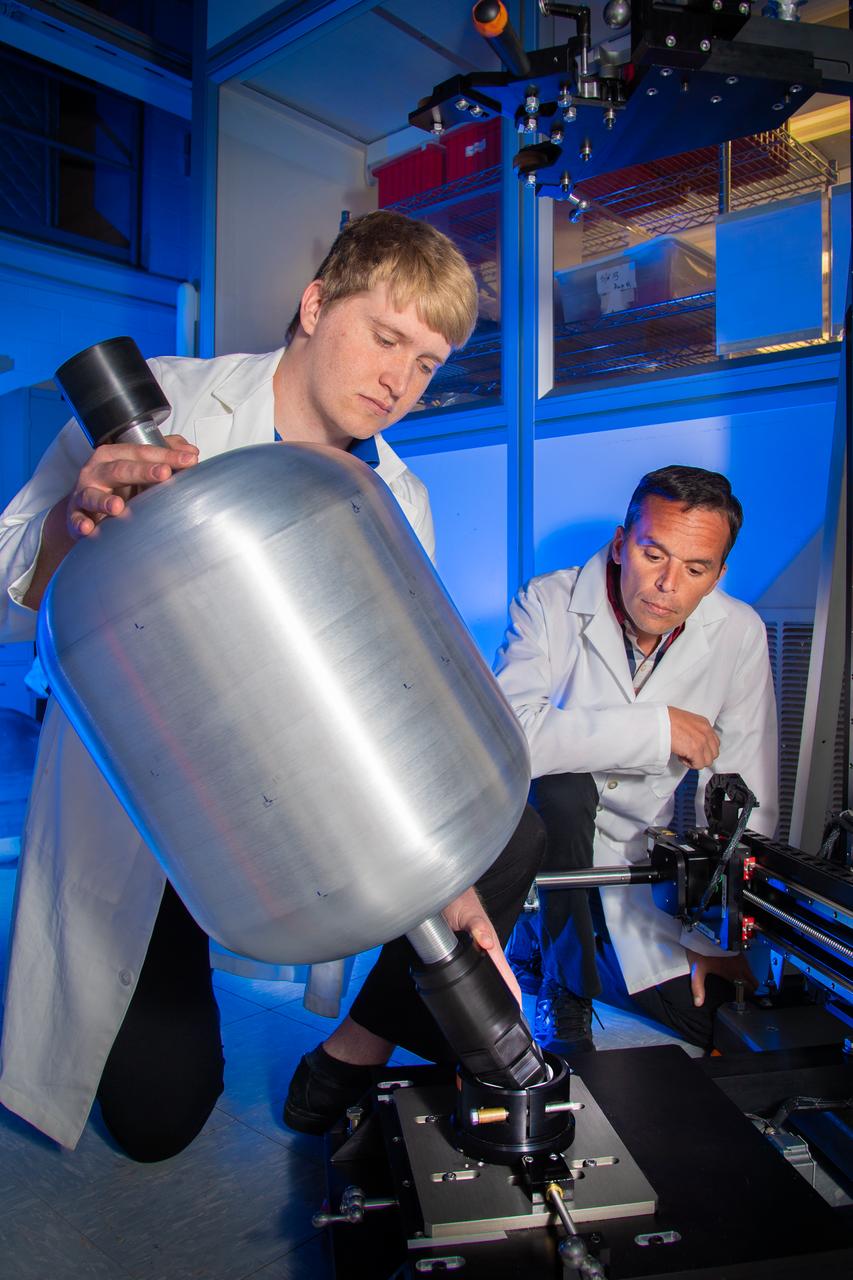

Engineers Ayrton Jordan (left) and Anthony Milana (right) at the NASA White Sands Test Facility (WSTF) in Las Cruces, N.M. install a metallic liner into the multipurpose pressure vessel scanner that could one day become part of a composite overwrapped pressure vessel. A slotted ball joint at the base of the rotary stage allows the tank to pivot resulting in helical scans that are more reliable when measuring interior and exterior 3D surface profiles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Reed P. Elliott)
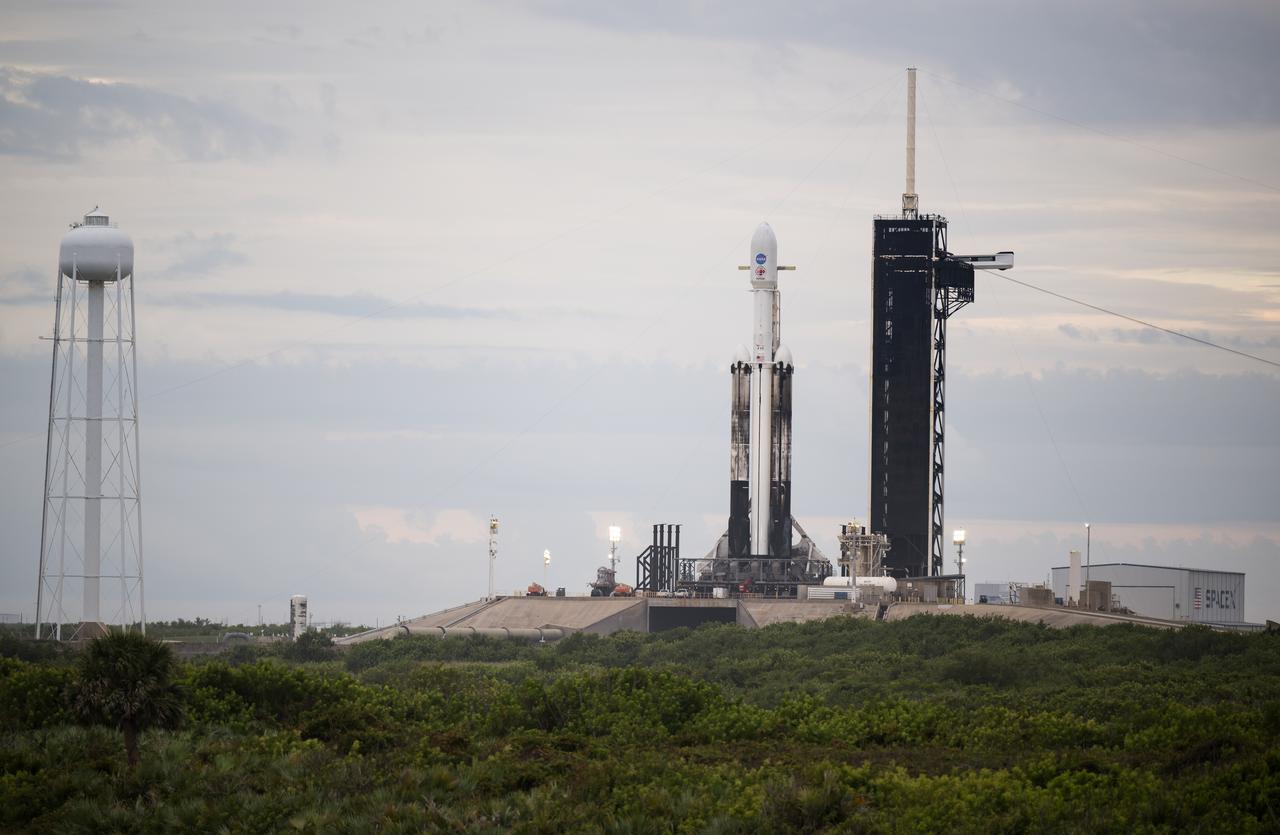

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is seen at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for the Psyche mission, Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
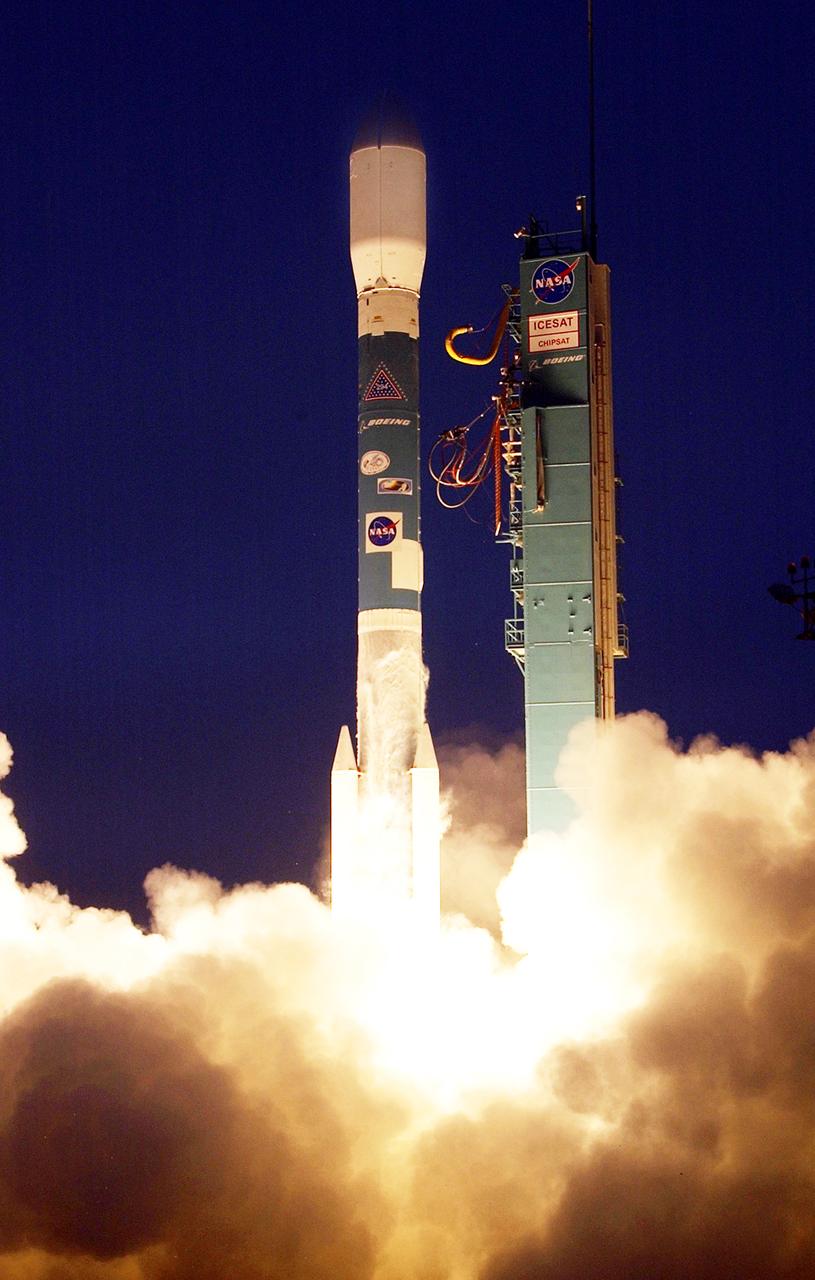

NASA's Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation satellite (ICESat) and Cosmic Hot Interstellar Spectrometer (CHIPS) satellite lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif at 4:45 p.m. PST aboard Boeing's Delta II rocket. ICESat will examine the role that ice plays in global climate change, while CHIPS will explore the composition of our galaxy. Photo Credit: "NASA/Bill Ingalls"
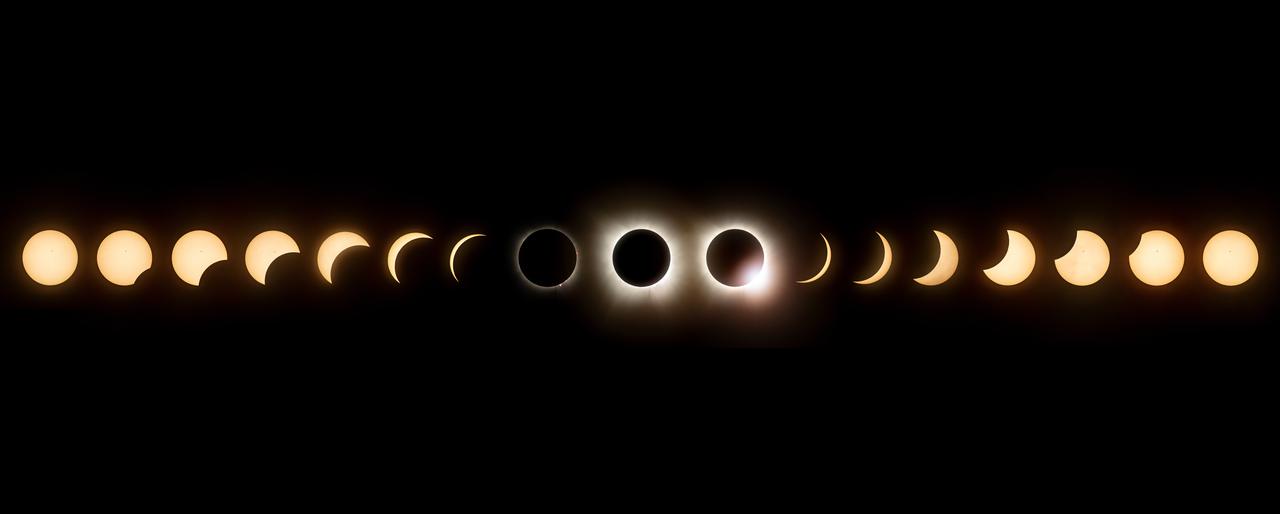

This composite image of seventeen images shows the progression of a total solar eclipse at the NASA's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio on Monday, April 8, 2024. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the North American continent from Mexico’s Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of Central America and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
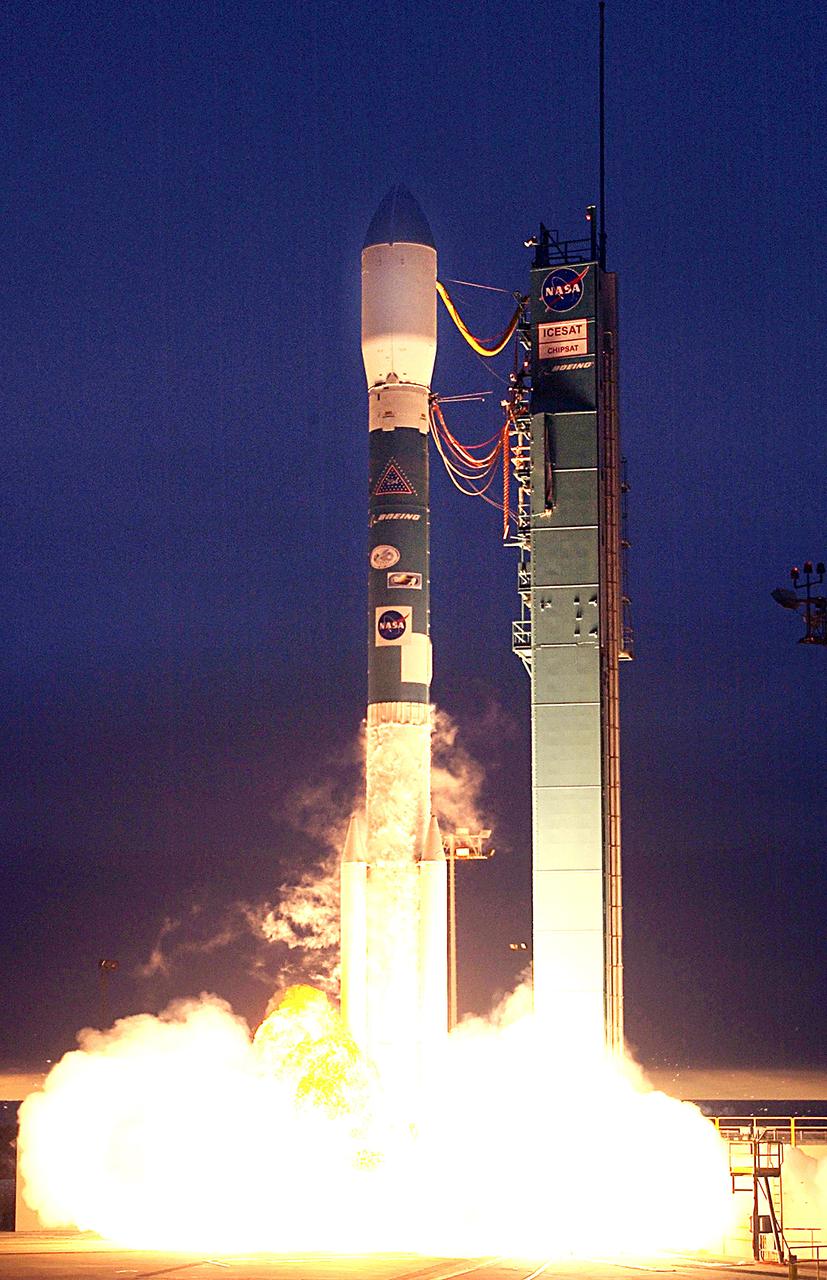

NASA's Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation satellite (ICESat) and Cosmic Hot Interstellar Spectrometer (CHIPS) satellite lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif at 4:45 p.m. PST aboard Boeing's Delta II rocket. ICESat will examine the role that ice plays in global climate change, while CHIPS will explore the composition of our galaxy. Photo Credit: "NASA/Bill Ingalls"
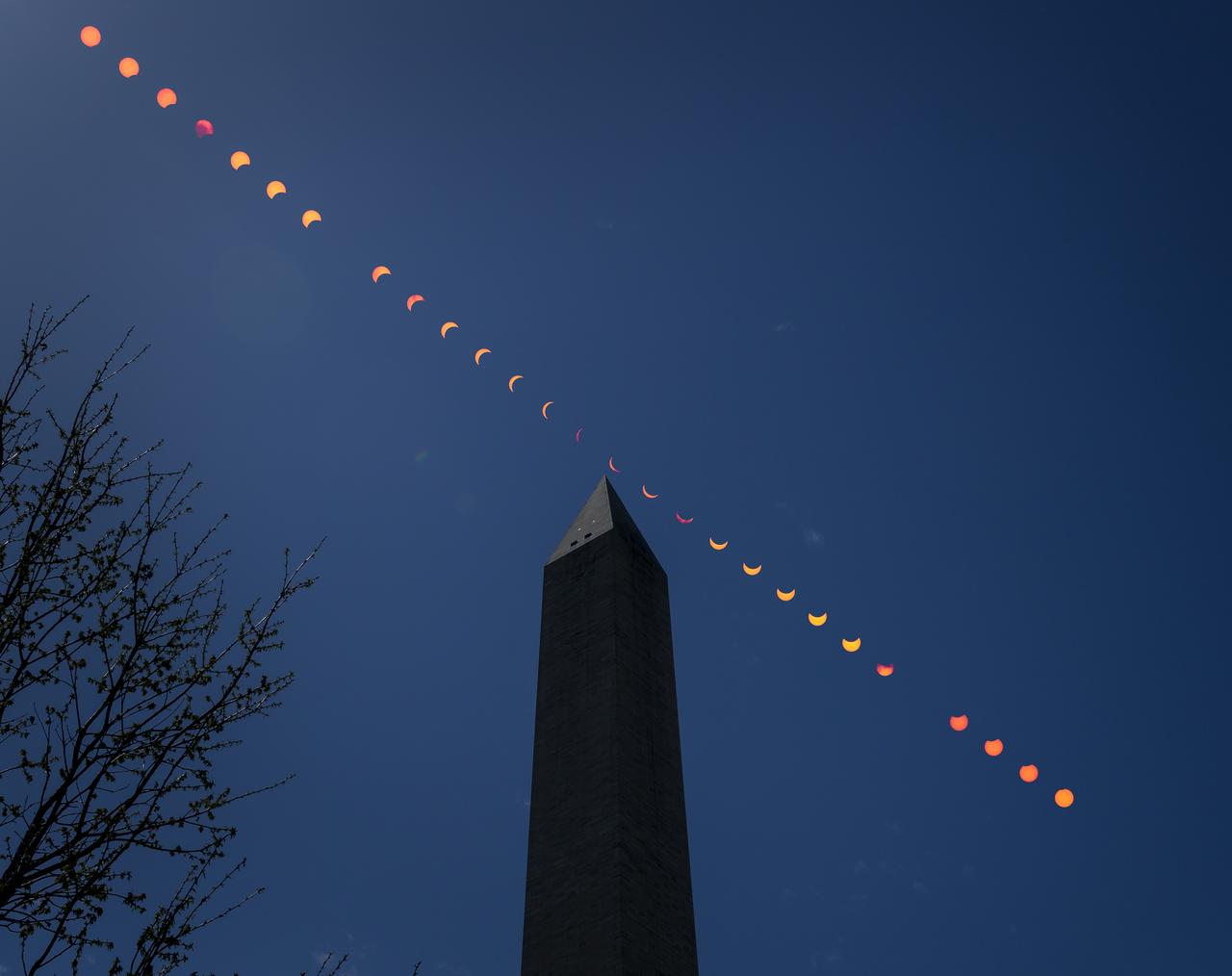

This composite image of multiple exposures shows the progression of a partial solar eclipse over the Washington Monument, Monday, April 8, 2024, in Washington. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the North American continent from Mexico’s Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of Central America and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
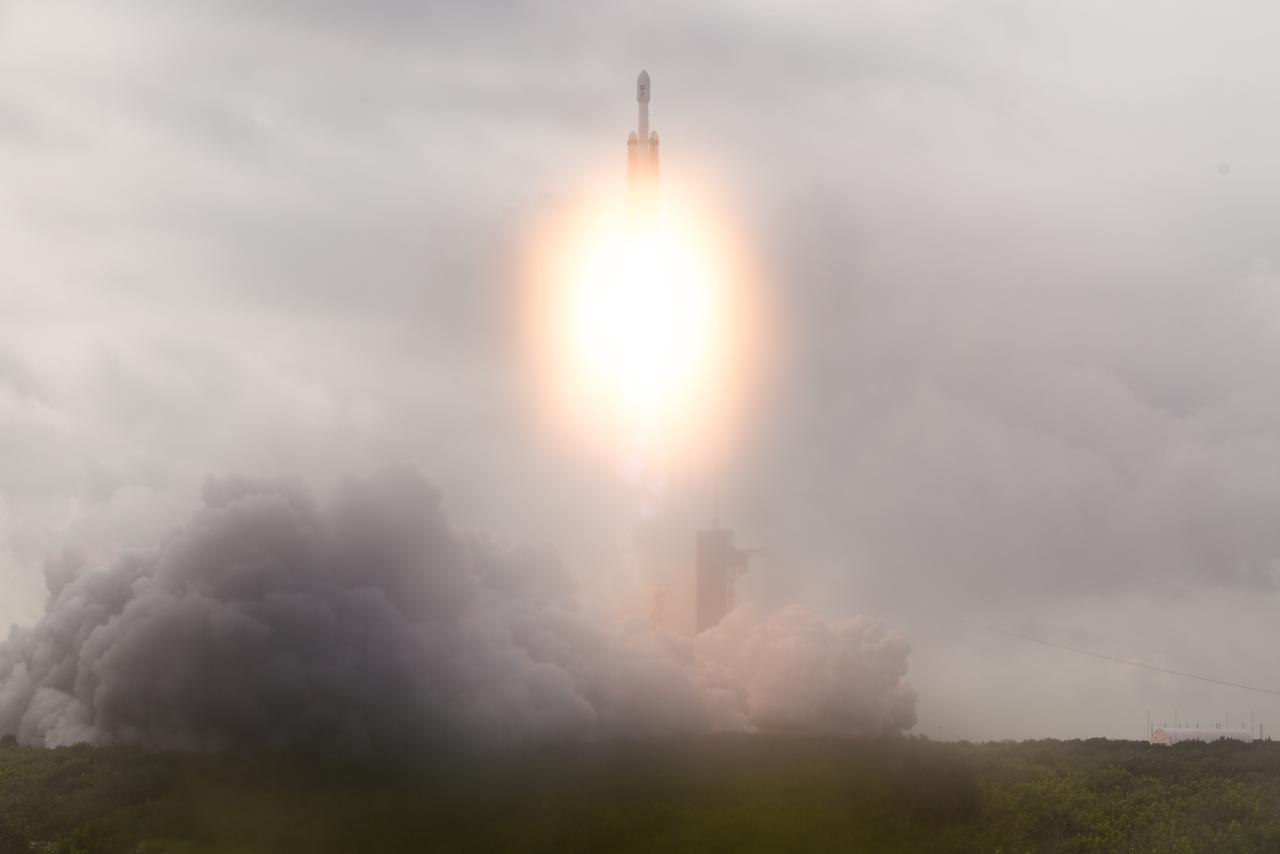

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

This composite image, made from six frames, shows the International Space Station, with a crew of five onboard, in silhouette as it transits the Sun at roughly five miles per second, Wednesday, June 24, 2020, from Fredericksburg, Va. Onboard are Expedition 63 NASA astronauts Chris Cassidy, Douglas Hurley, Robert Behnken, and Roscosmos cosmonauts Anatoly Ivanishin and Ivan Vagner. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
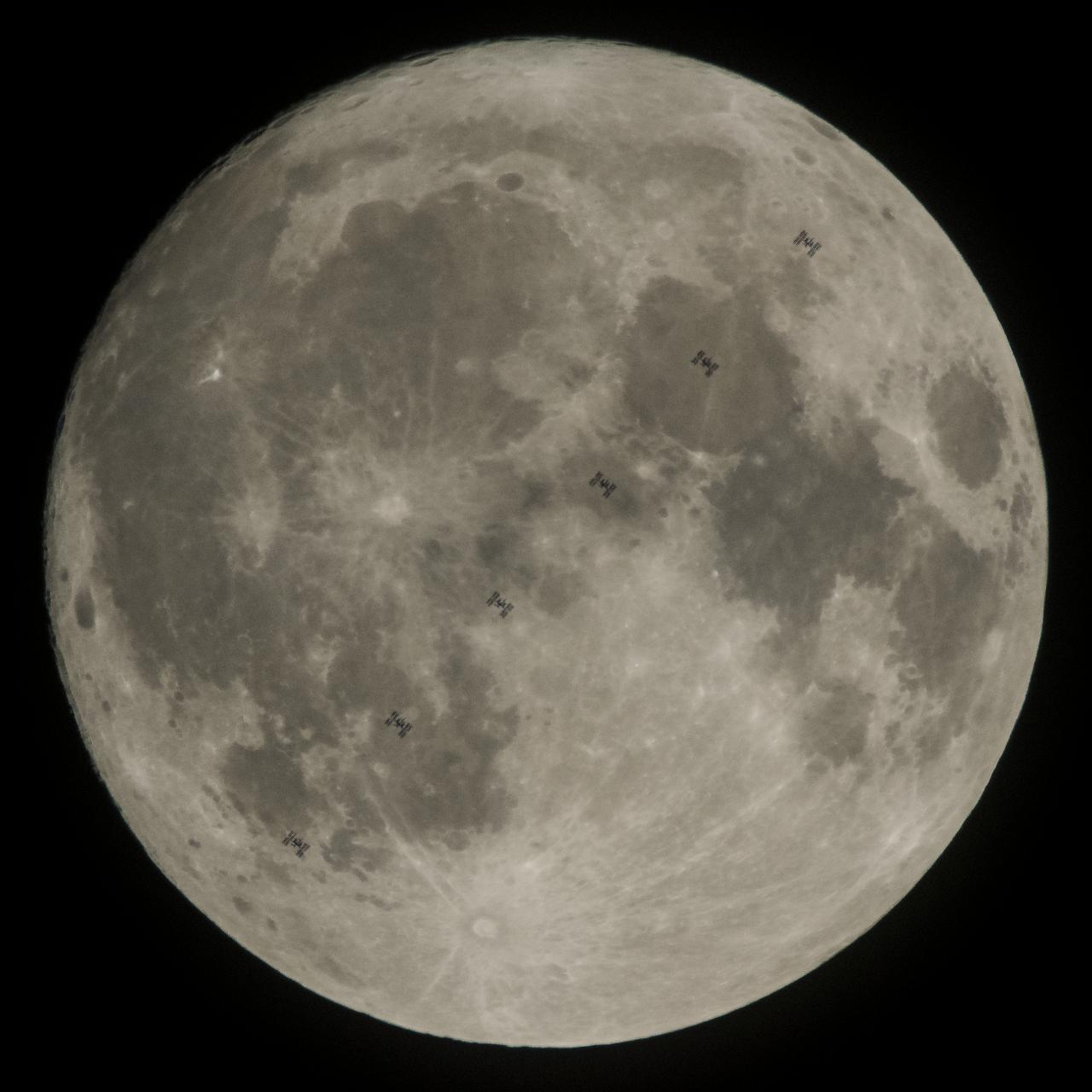

This composite image made from six frames shows the International Space Station, with a crew of six onboard, as it transits the Moon at roughly five miles per second, Saturday, Dec. 2, 2017, in Manchester Township, York County, Pennsylvania. Onboard are NASA astronauts Joe Acaba, Mark Vande Hei, and Randy Bresnik; Russian cosmonauts Alexander Misurkin and Sergey Ryanzansky; and ESA astronaut Paolo Nespoli. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
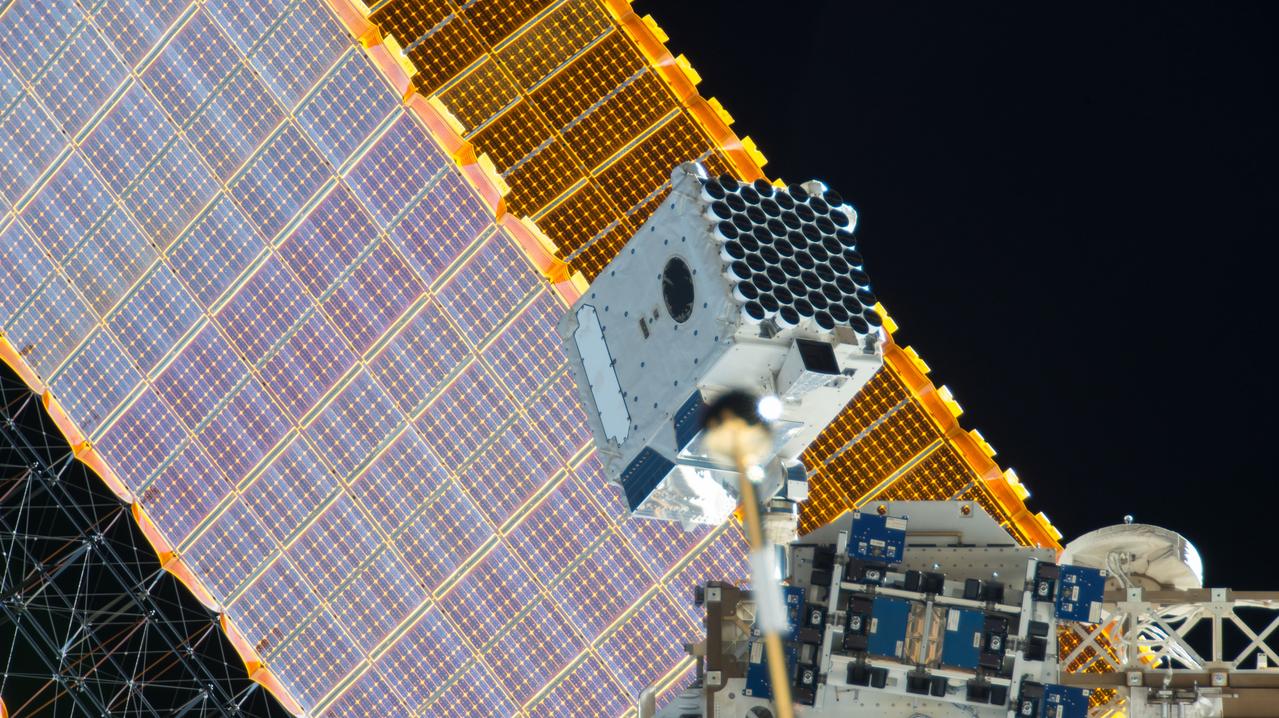
iss057e055500 (10/22/2018) --- View of the Neutron Star Interior Composition ExploreR (NICER) payload, attached to ExPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Logistics Carrier-2 (ELC-2) on the S3 Truss. Photo was taken by the ground-controlled External High Definition Camera 1 (EHDC1). NICER's primary mission to perform an in-depth study of neutron stars offers unrivaled astrophysics knowledge and can revolutionize the understanding of ultra-dense matter.

This composite image of multiple exposures shows the progression of a total solar eclipse in Dallas, Texas on Monday, April 8, 2024. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the North American continent from Mexico’s Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of Central America and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
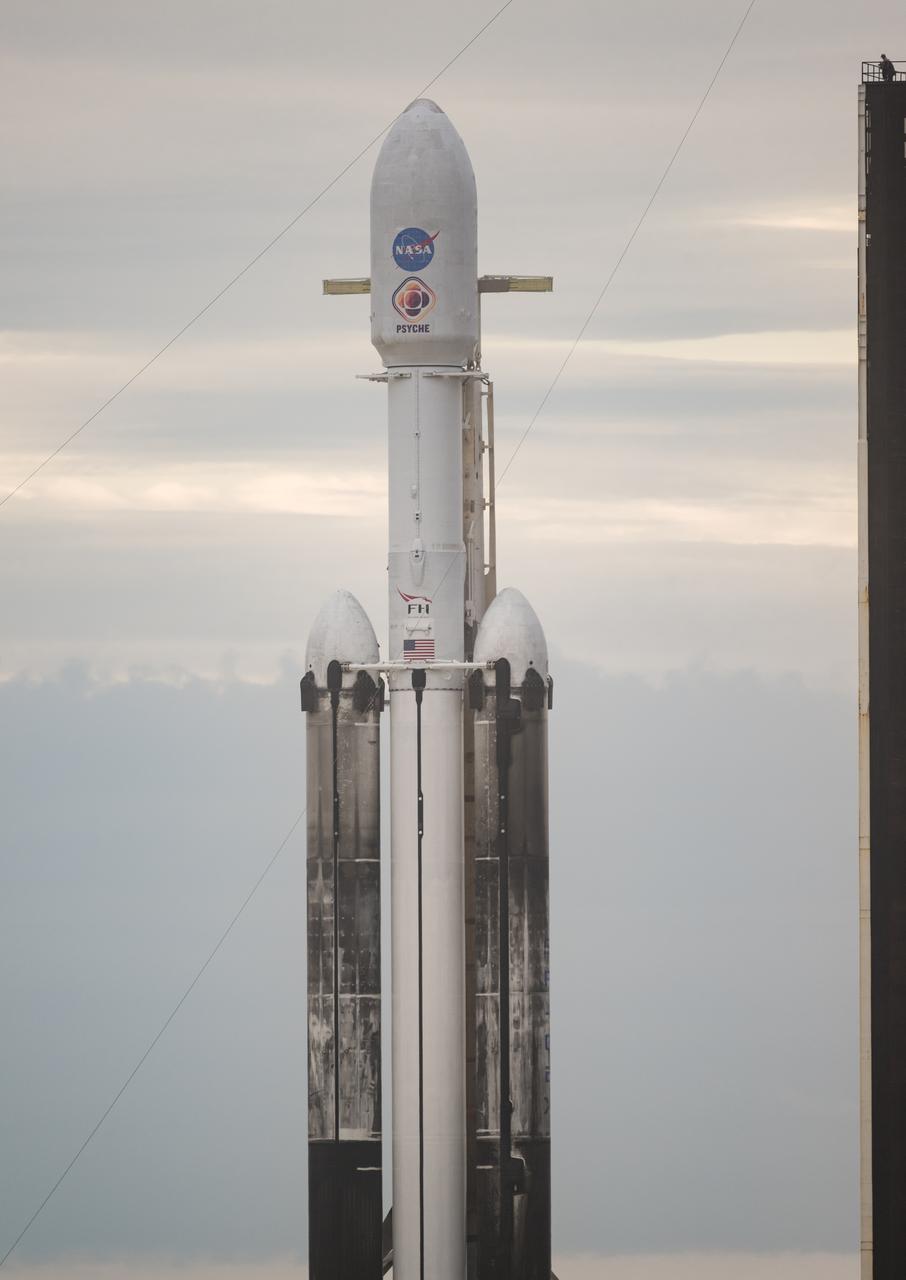

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is seen at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for the Psyche mission, Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
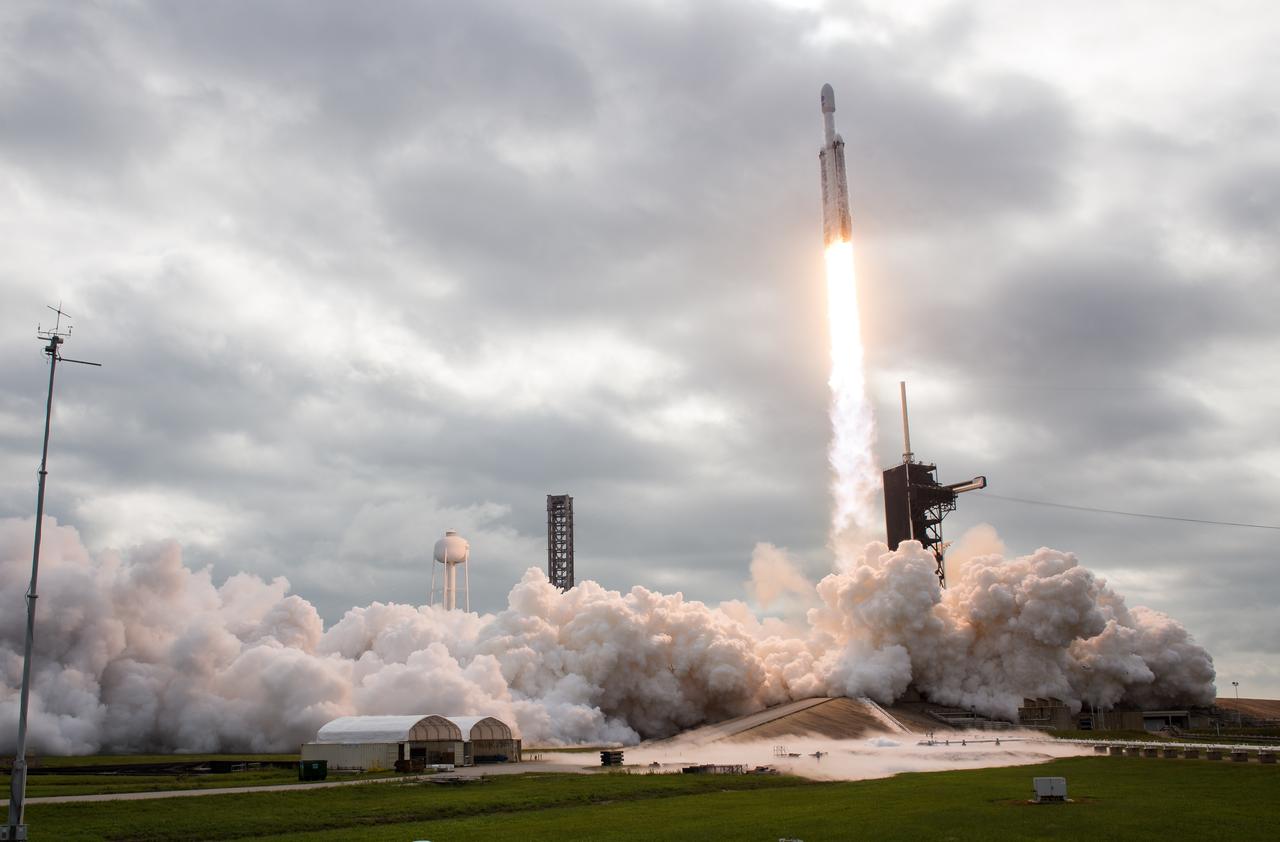

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is launched from Launch Complex 39A, Friday, Oct. 13, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

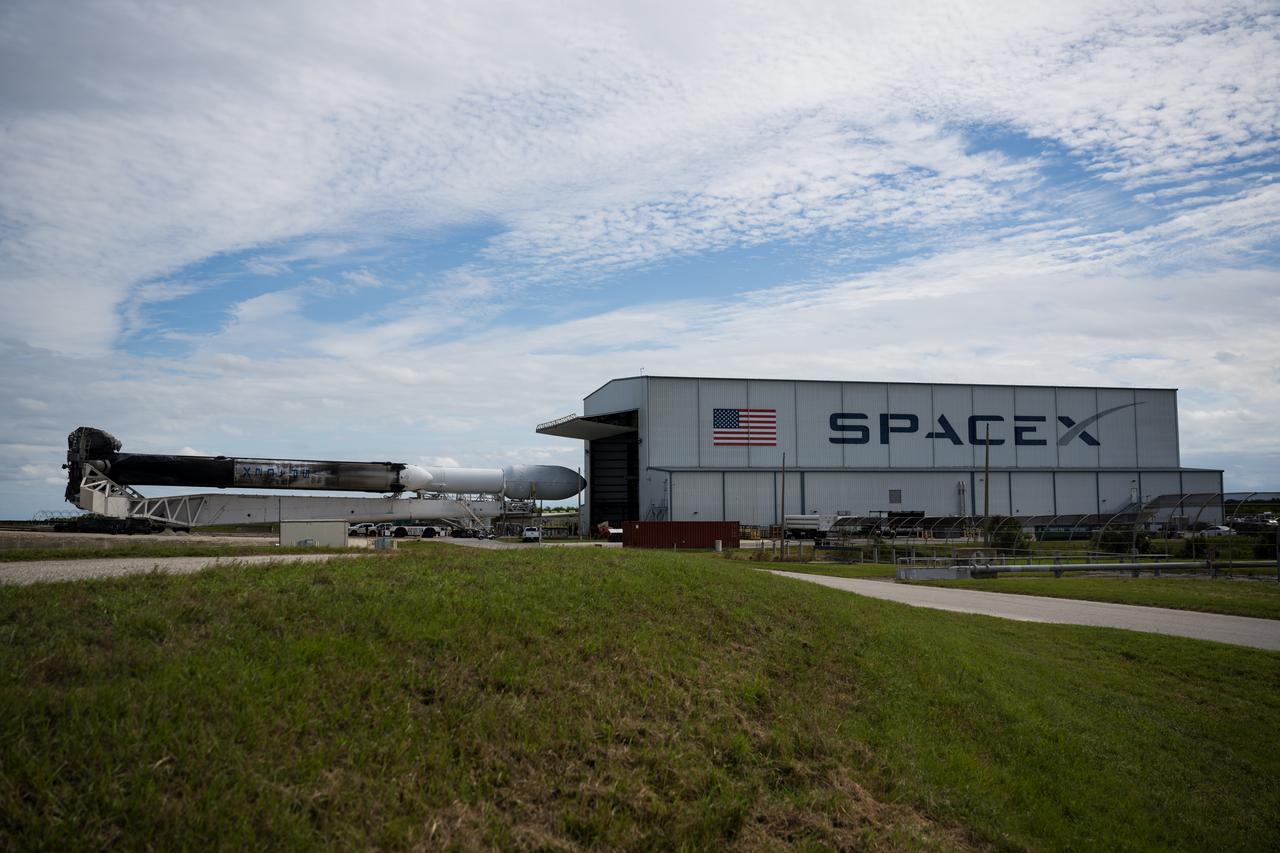
A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is seen at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for the Psyche mission, Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation satellite (ICESat) and Cosmic Hot Interstellar Spectrometer (CHIPS) satellite lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif at 4:45 p.m. PST aboard Boeing's Delta II rocket. ICESat will examine the role that ice plays in global climate change, while CHIPSat will explore the composition of our galaxy. [Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-03pd0059/KSC-03pd0059~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Ice, Cloud and Land Elevation satellite (ICESat) and Cosmic Hot Interstellar Spectrometer (CHIPS) satellite lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif at 4:45 p.m. PST aboard Boeing's Delta II rocket. ICESat will examine the role that ice plays in global climate change, while CHIPSat will explore the composition of our galaxy. [Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls]

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians are testing the range of motion on the high-gain antenna for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

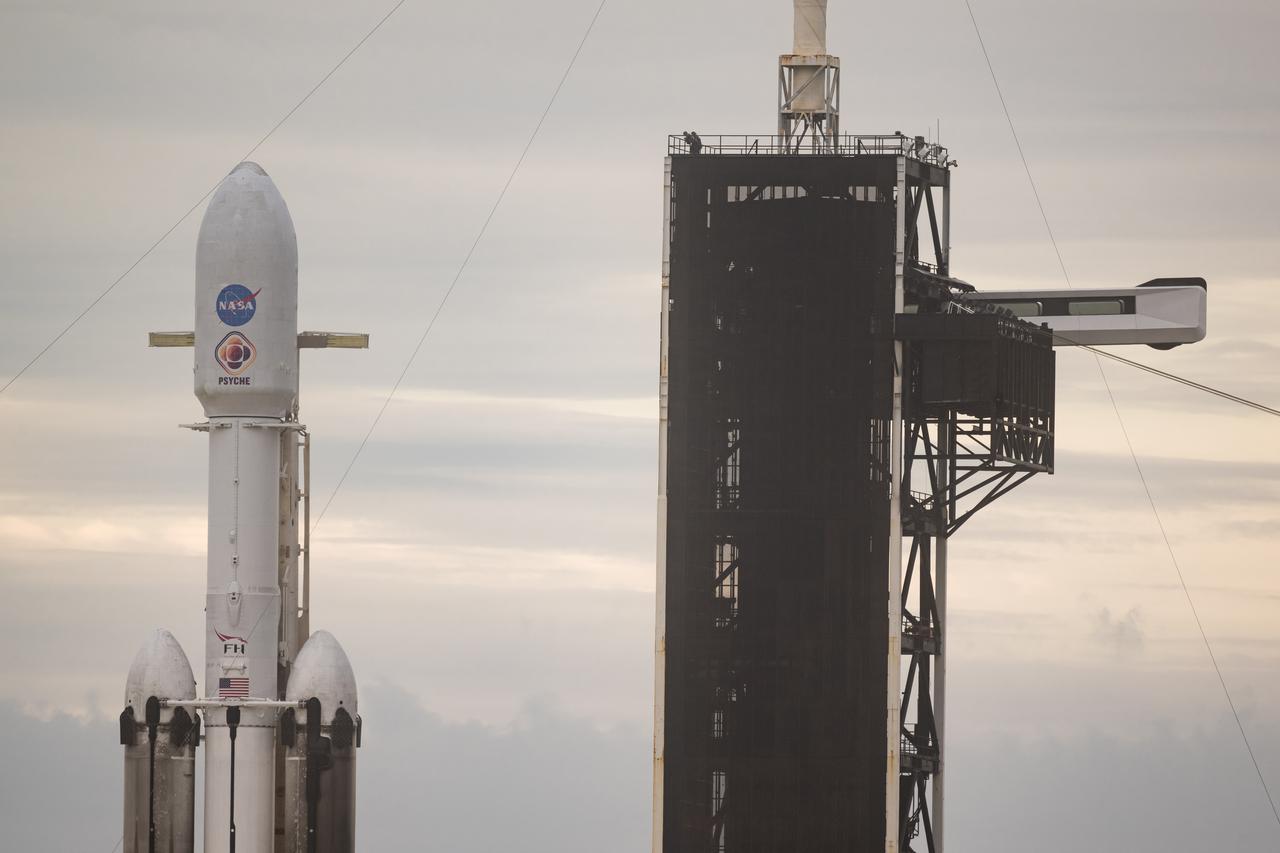
A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with the Psyche spacecraft onboard is seen as it is rolled out of the horizontal integration facility at Launch Complex 39A as preparations continue for the Psyche mission, Tuesday, Oct. 10, 2023, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Psyche spacecraft will travel to a metal-rich asteroid by the same name orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter to study it’s composition. The spacecraft also carries the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications technology demonstration, which will test laser communications beyond the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians secure NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's high-gain antenna into place for stowage. The antenna completed a range of motion test. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
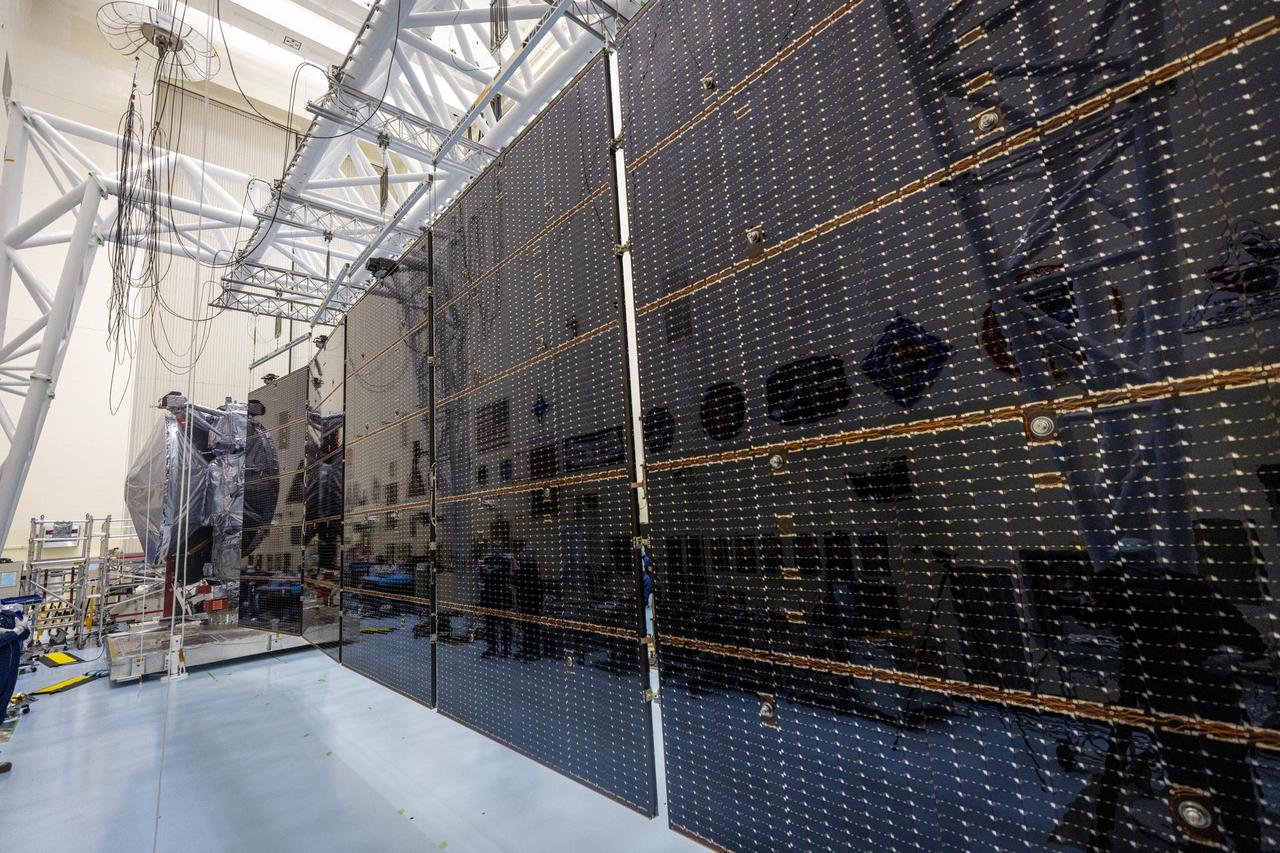

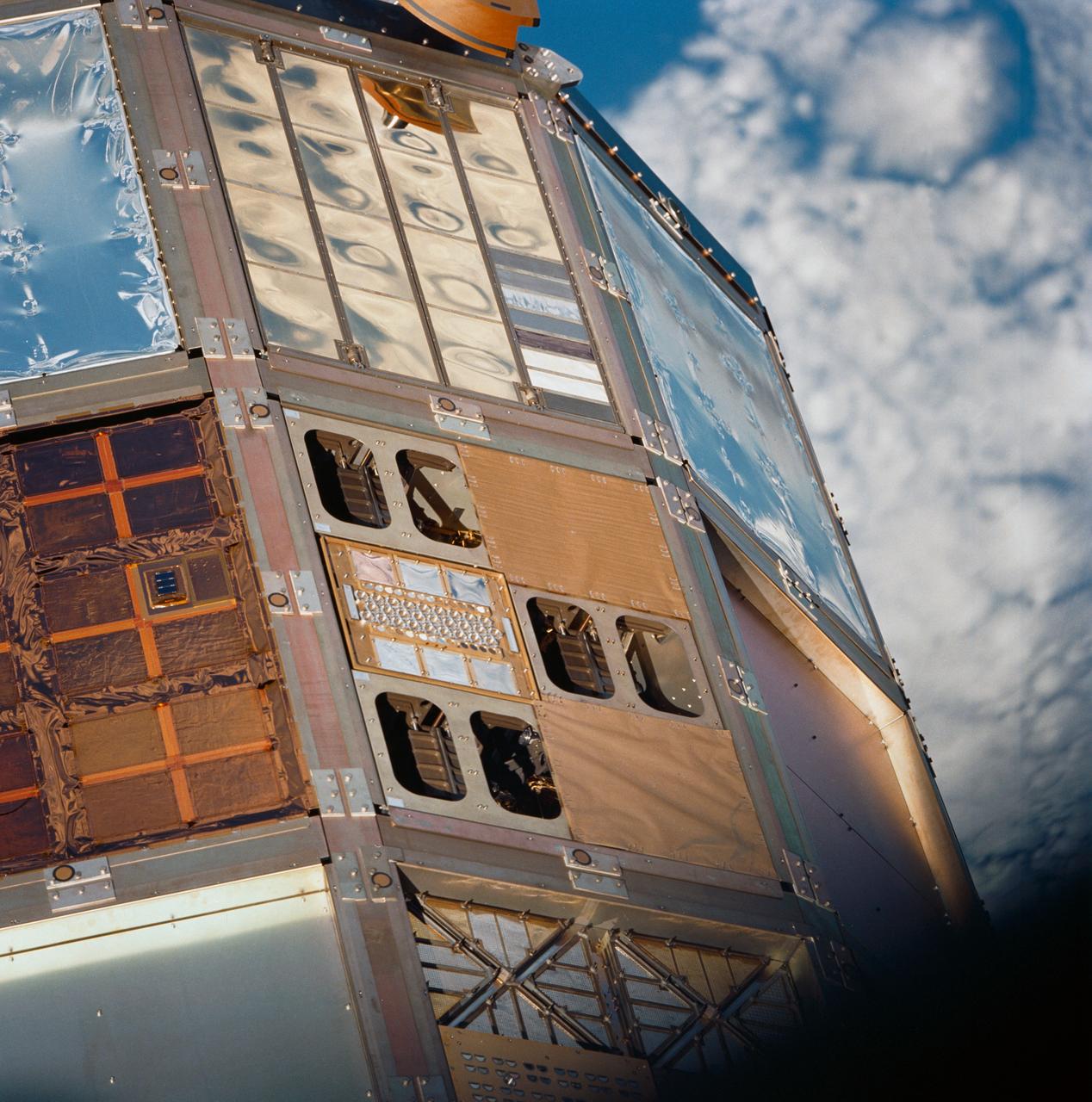
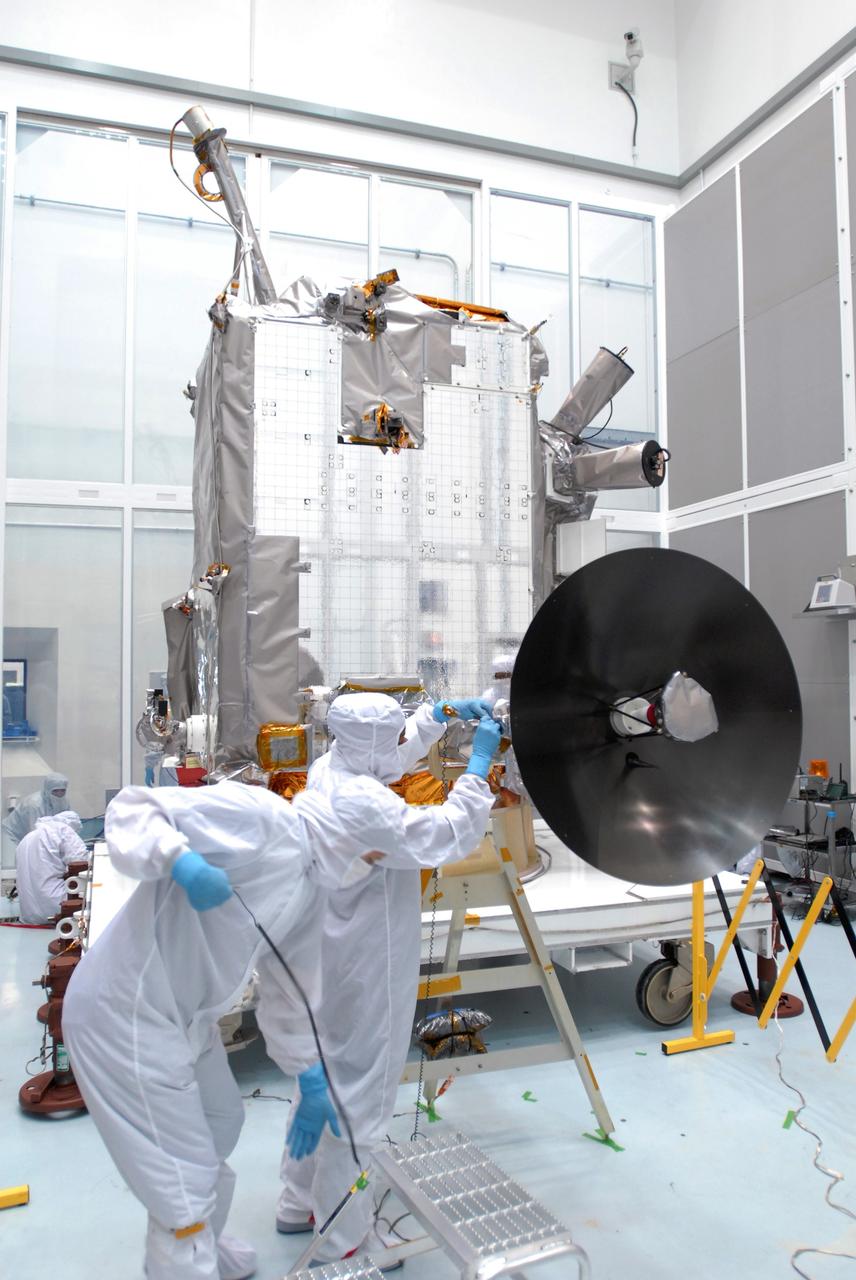
NASA's Europa Clipper is seen here on Aug. 21, 2024, in a clean room at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The photo was taken as engineers and technicians deployed and tested the spacecraft's giant solar arrays, each of which measures about 46.5 feet (14.2 meters) long and about 13.5 feet (4.1 meters) high. Europa Clipper's three main science objectives are to determine the thickness of the moon's icy shell and its interactions with the ocean below, to investigate its composition, and to characterize its geology. The mission's detailed exploration of Europa will help scientists better understand the astrobiological potential for habitable worlds beyond our planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26066