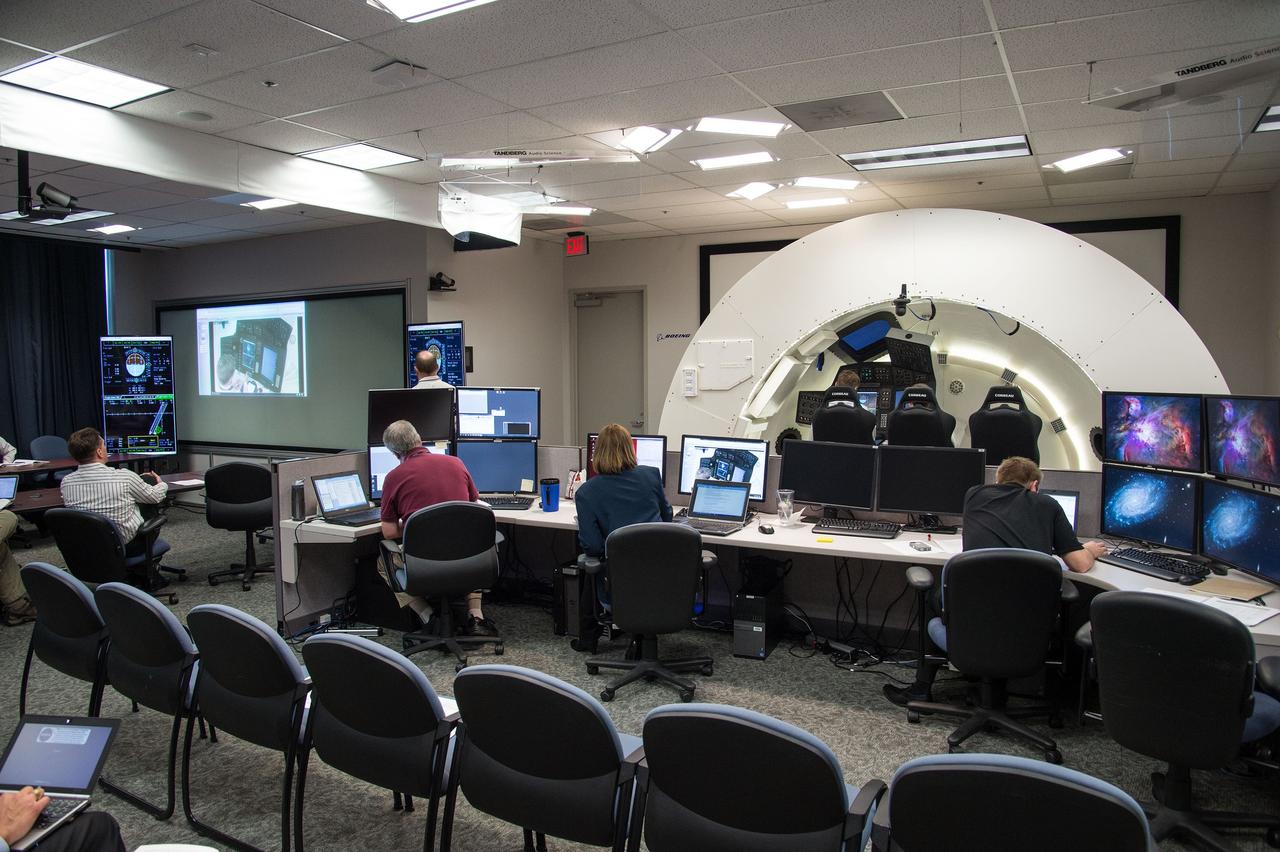
HOUSTON – Engineers for Boeing Space Exploration demonstrate that the CST-100 software allows a human pilot to take over control of the spacecraft from the computer during all phases of a mission following separation from the launch vehicle. The pilot-in-the-loop demonstration at the Houston Product Support Center is a milestone under Boeing's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with the agency and its Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Stafford
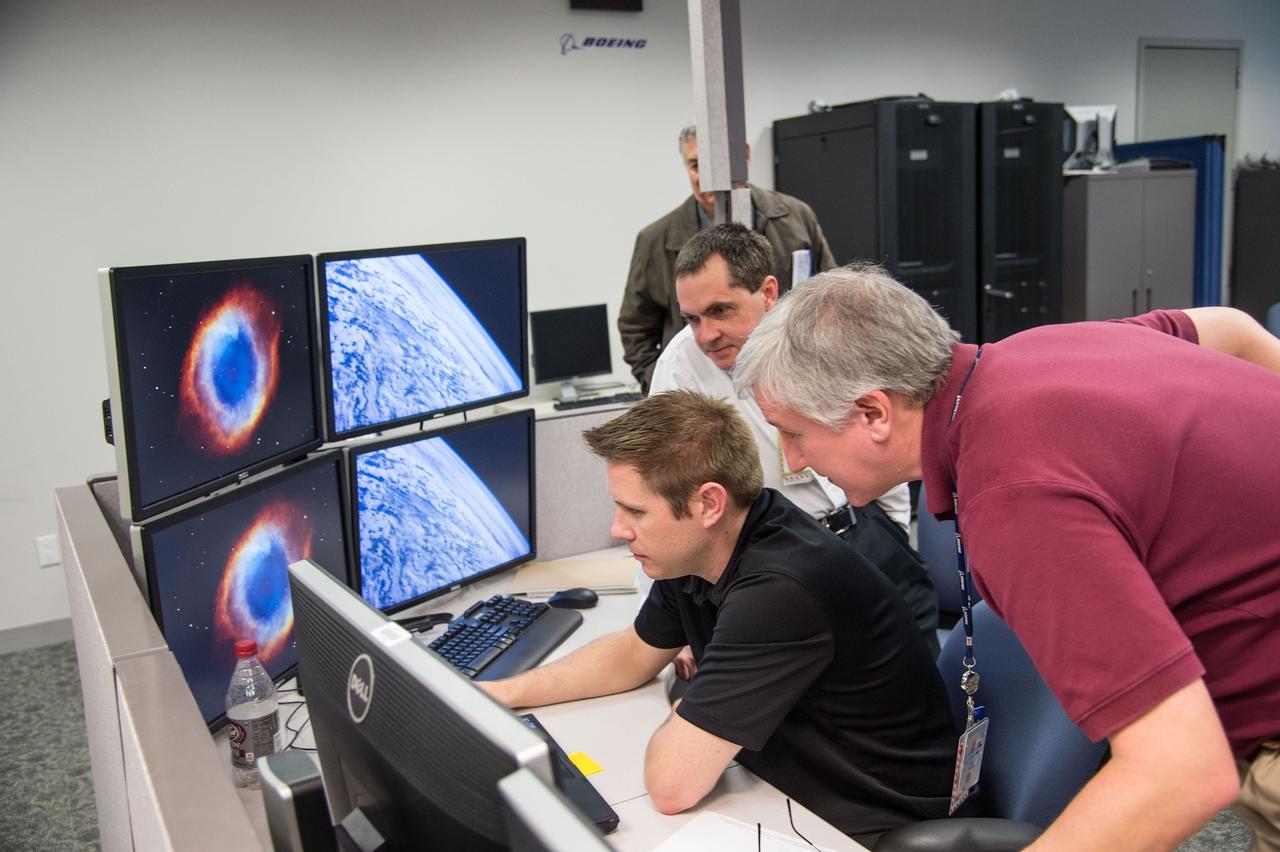

HOUSTON – Engineers for Boeing Space Exploration demonstrate that the CST-100 software allows a human pilot to take over control of the spacecraft from the computer during all phases of a mission following separation from the launch vehicle. The pilot-in-the-loop demonstration at the Houston Product Support Center is a milestone under Boeing's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with the agency and its Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Stafford
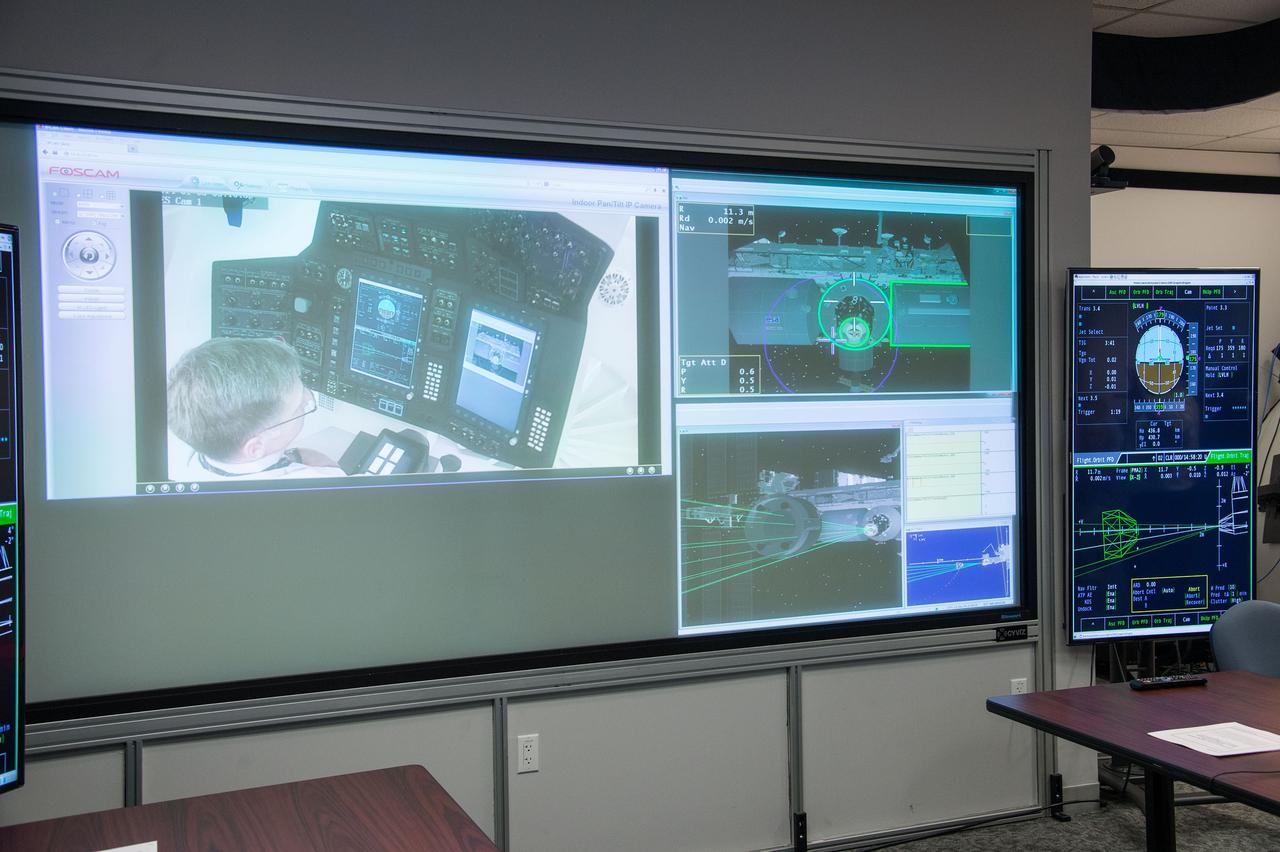

HOUSTON – Monitors show Chris Ferguson, a former space shuttle commander who is now director of Crew and Mission Operations for Boeing Space Exploration, at the controls in the inside the company's CST-100 spacecraft simulator. Boeing demonstrated that the CST-100 software allows a human pilot to take over control of the spacecraft from the computer during all phases of a mission following separation from the launch vehicle. The pilot-in-the-loop demonstration at the Houston Product Support Center is a milestone under Boeing's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with the agency and its Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Stafford
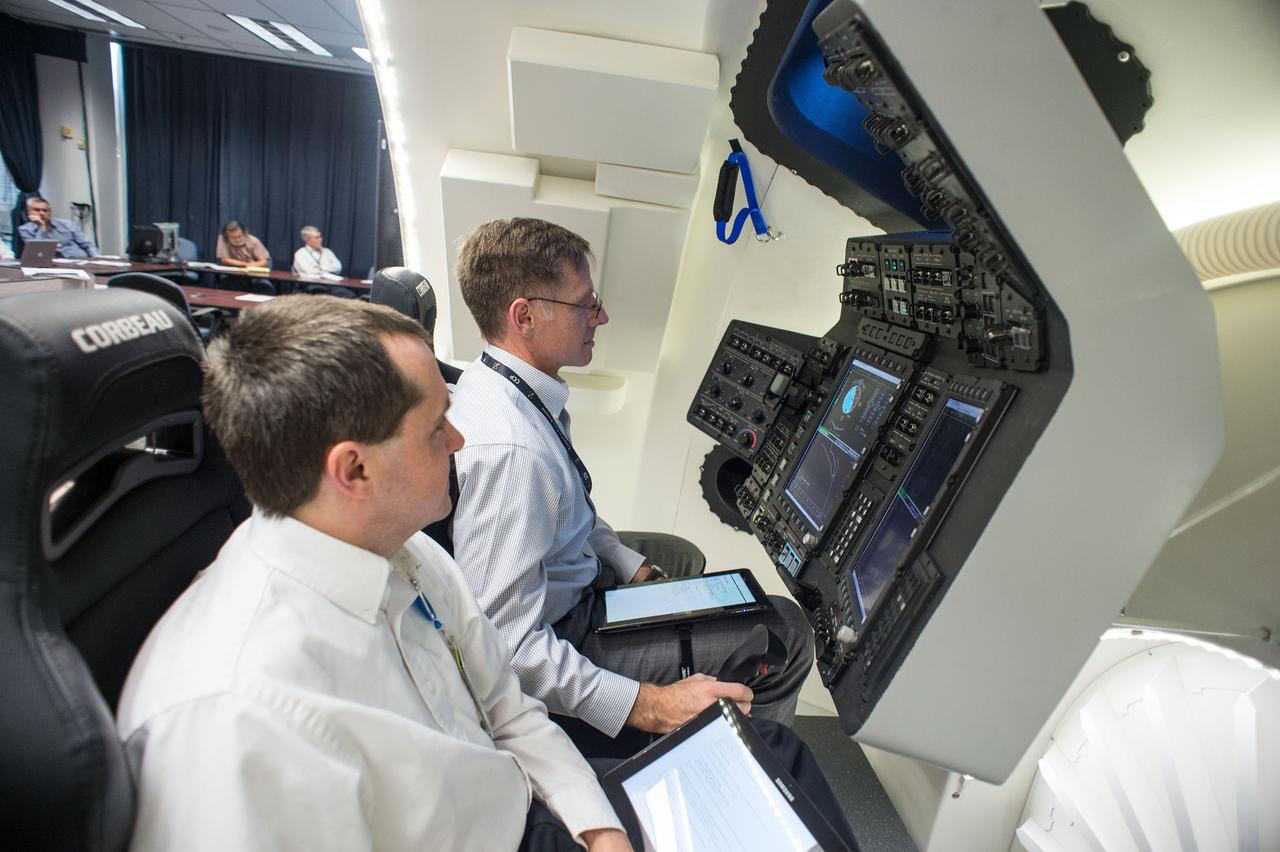

HOUSTON – Chris Ferguson, a former space shuttle commander who is now director of Crew and Mission Operations for Boeing Space Exploration, takes the controls inside the company's CST-100 spacecraft simulator. To Ferguson's right, an engineer observes the exercise. Boeing demonstrated that the CST-100's software allows a human pilot to take over control of the spacecraft from the computer during all phases of a mission following separation from the launch vehicle. The pilot-in-the-loop demonstration at the Houston Product Support Center is a milestone under Boeing's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with the agency and its Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Stafford
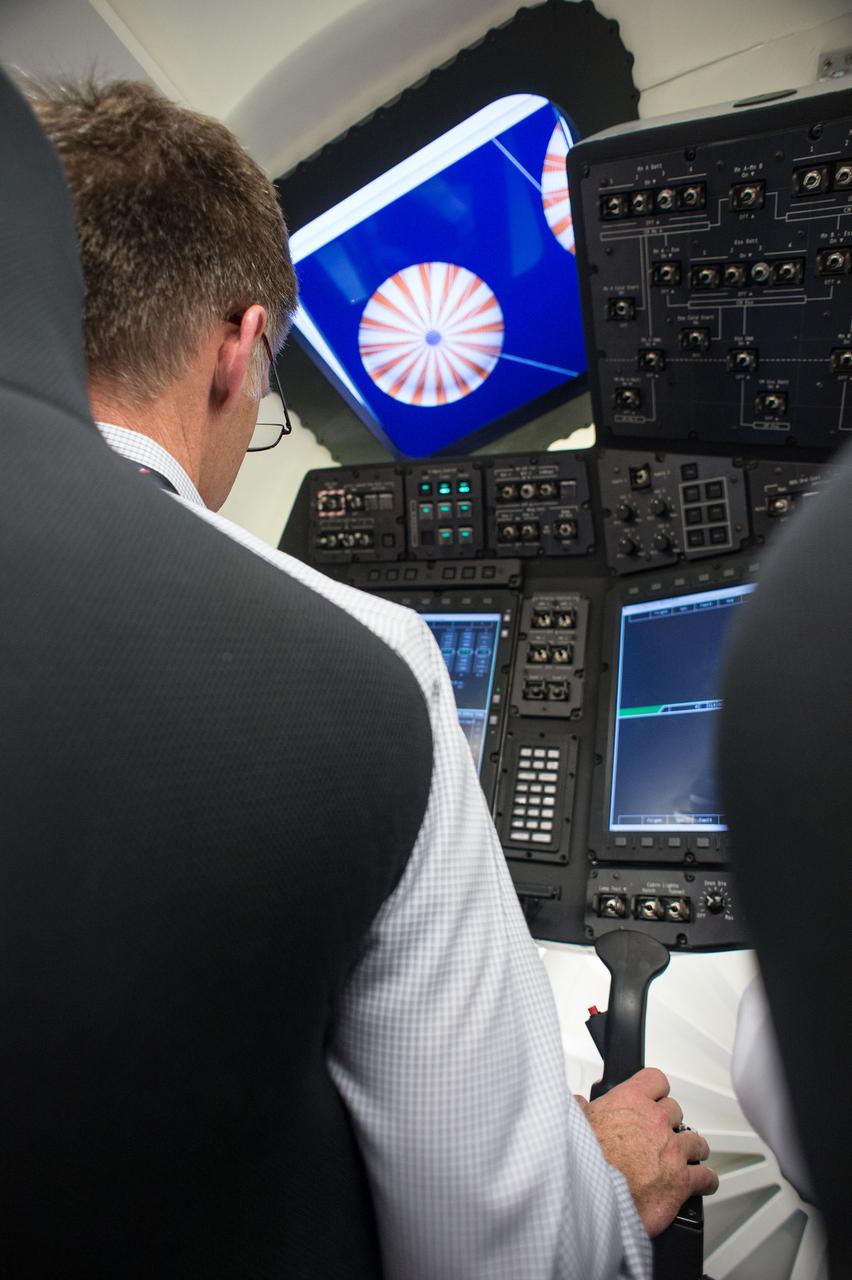

HOUSTON – Chris Ferguson, a former space shuttle commander who is now director of Crew and Mission Operations for Boeing Space Exploration, sits at the controls in the inside the company's CST-100 spacecraft simulator. Boeing demonstrated that the CST-100 software allows a human pilot to take over control of the spacecraft from the computer during all phases of a mission following separation from the launch vehicle. The pilot-in-the-loop demonstration at the Houston Product Support Center is a milestone under Boeing's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with the agency and its Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Stafford
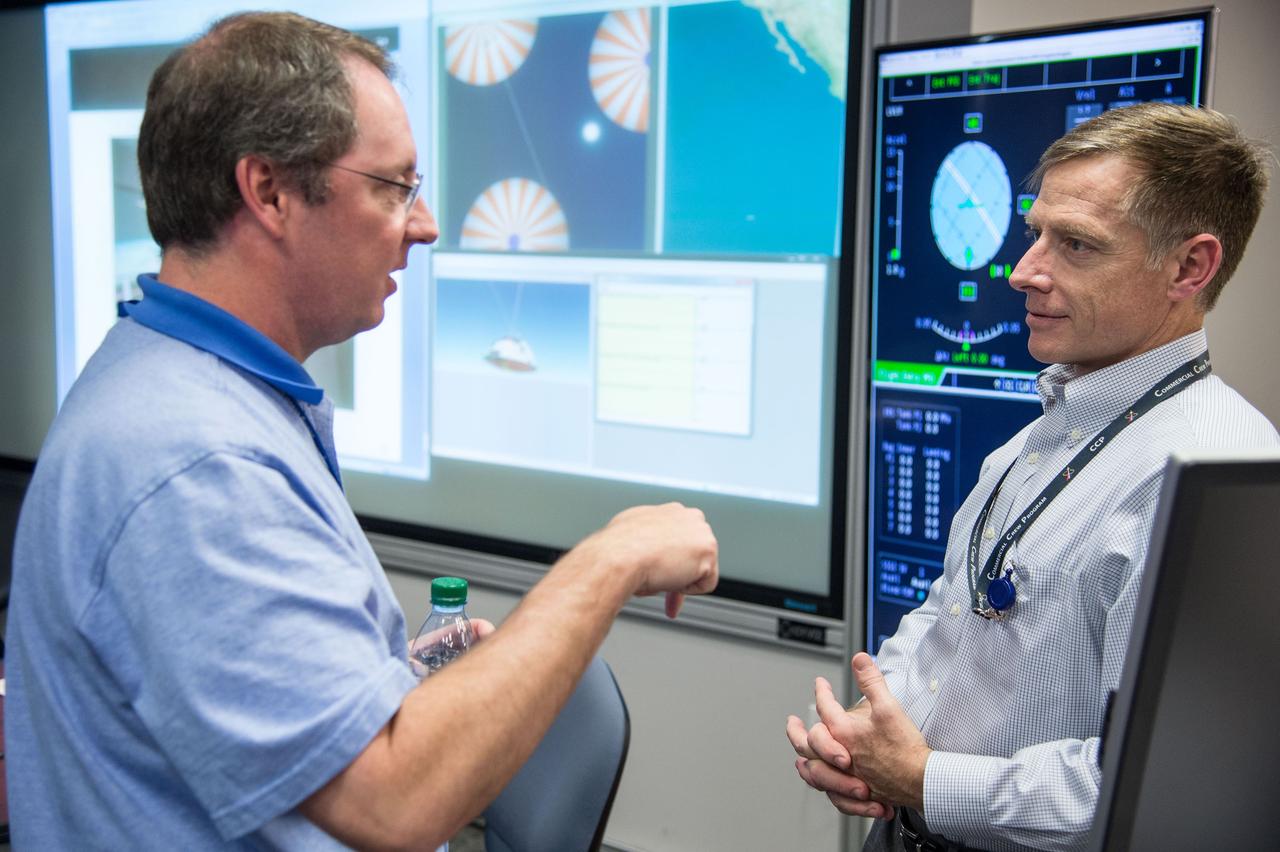

HOUSTON – Chris Ferguson, a former space shuttle commander who is now director of Crew and Mission Operations for Boeing Space Exploration, talks with an engineer following simulations that showed that the CST-100 software. Boeing demonstrated that the CST-100 software allows a human pilot to take over control of the spacecraft from the computer during all phases of a mission following separation from the launch vehicle. The pilot-in-the-loop demonstration at the Houston Product Support Center is a milestone under Boeing's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with the agency and its Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Stafford
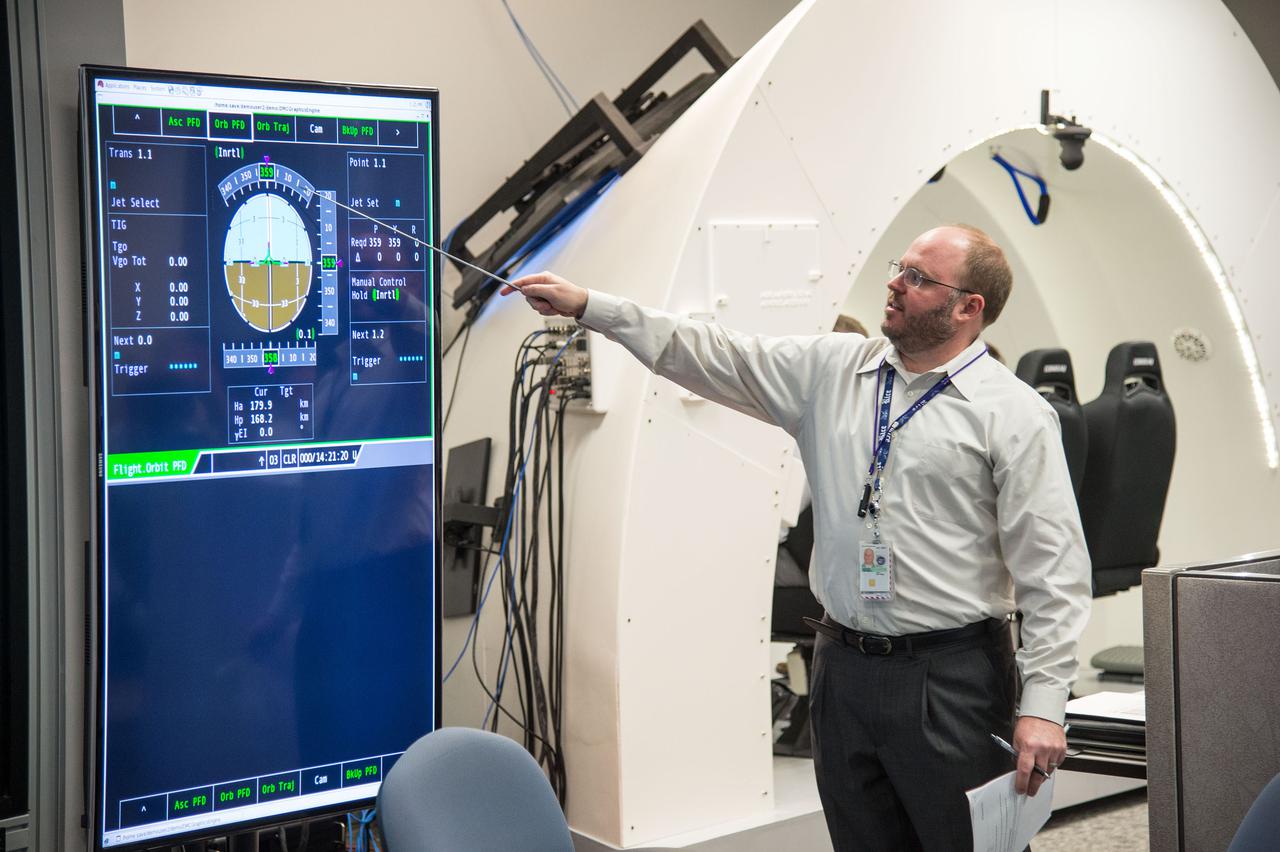

HOUSTON – An engineer with Boeing Space Exploration explains how to read the cockpit displays inside the company's CST-100 spacecraft simulator to NASA Commercial Crew Program engineers. Boeing demonstrated that the CST-100 software allows a human pilot to take over control of the spacecraft from the computer during all phases of a mission following separation from the launch vehicle. The pilot-in-the-loop demonstration at the Houston Product Support Center is a milestone under Boeing's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with the agency and its Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA_Bill Stafford
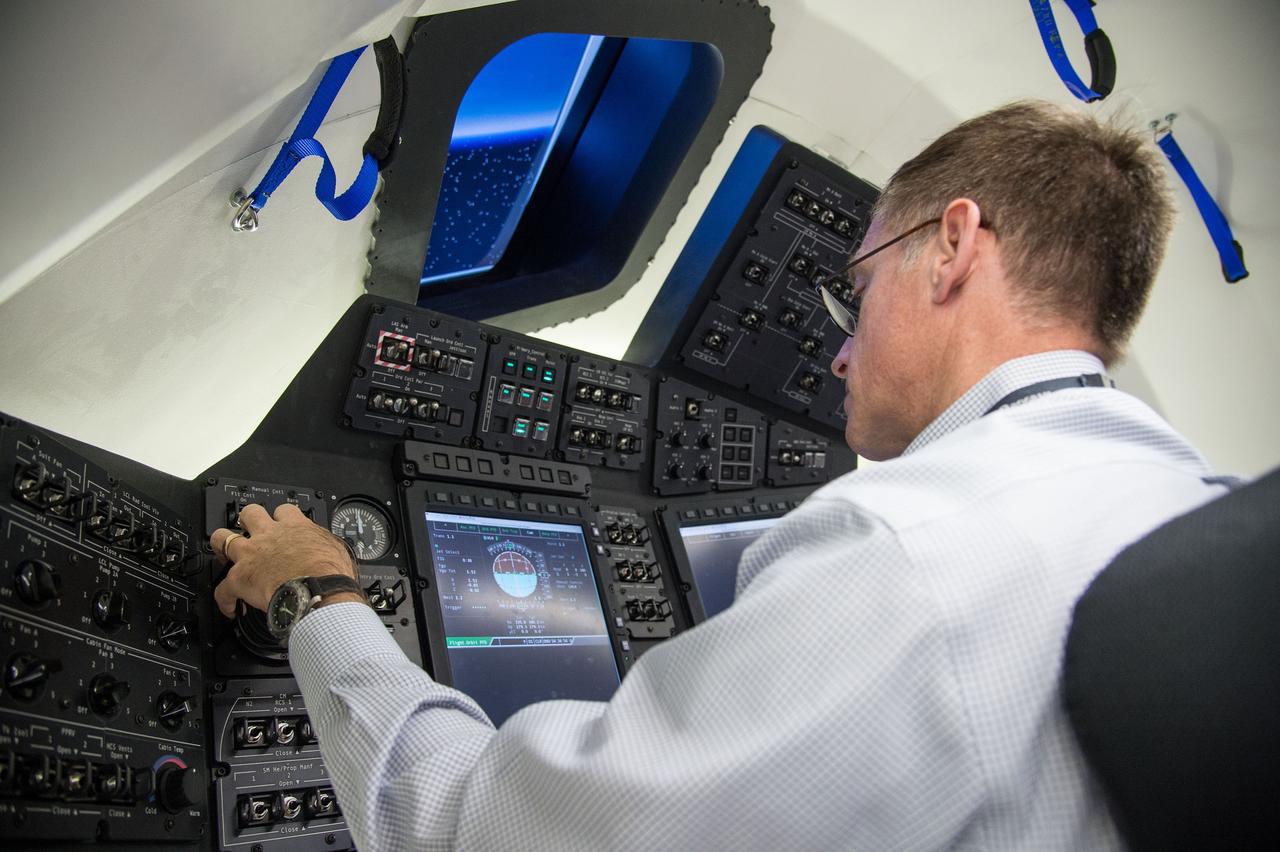

HOUSTON - Chris Ferguson, a former space shuttle commander who is now director of Crew and Mission Operations for Boeing Space Exploration, sits at the controls in the inside the company's CST-100 spacecraft simulator. Boeing demonstrated that the CST-100 software allows a human pilot to take over control of the spacecraft from the computer during all phases of a mission following separation from the launch vehicle. The pilot-in-the-loop demonstration at the Houston Product Support Center is a milestone under Boeing's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with the agency and its Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Stafford
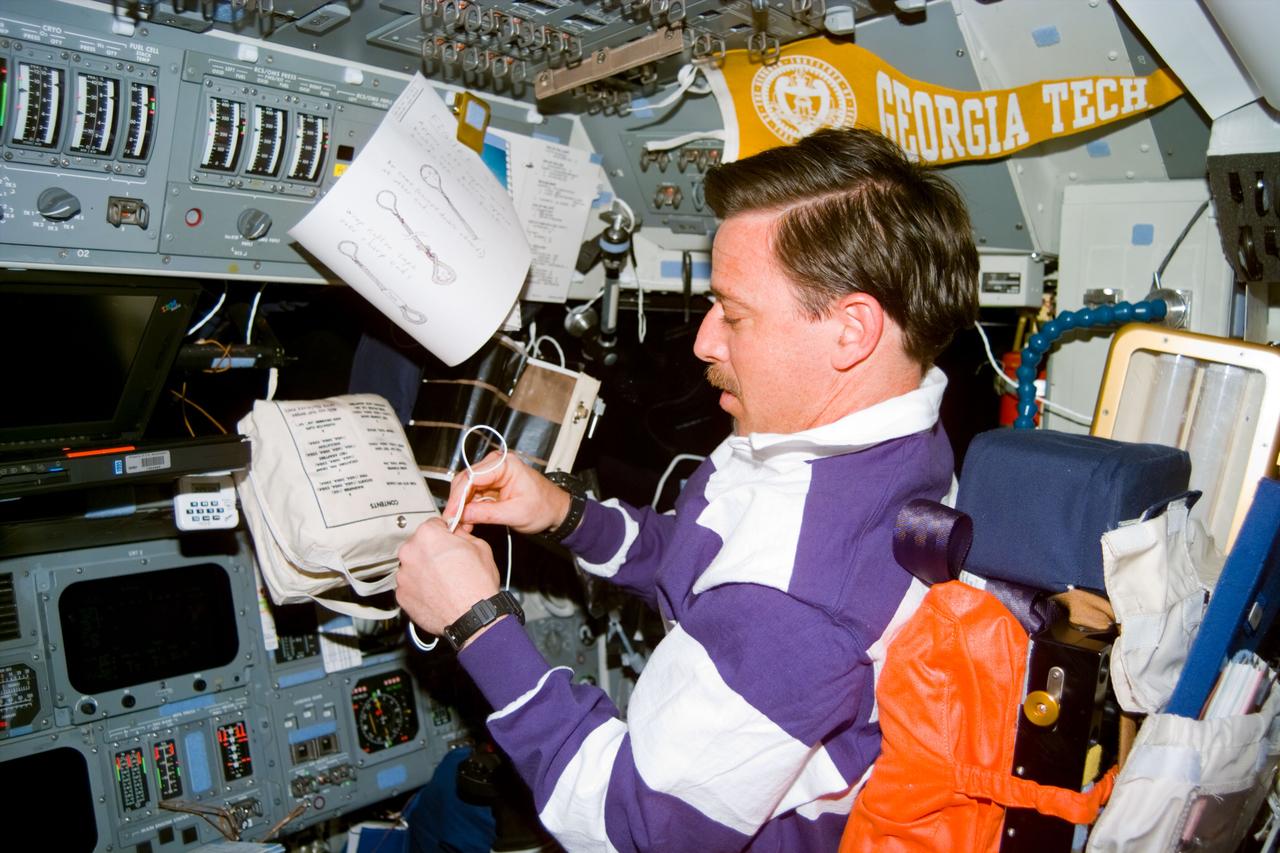

S82-E-5597 (17 Feb. 1997) --- Astronaut Scott J. Horowitz at pilot's station works with a hand-fashioned loop fastener device to be used in support of the additional STS-82 Extravehicular Activity (EVA) to service Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Note sketches overhead which were sent by ground controllers to guide the pilot's engineering of the task. This view was taken with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC).
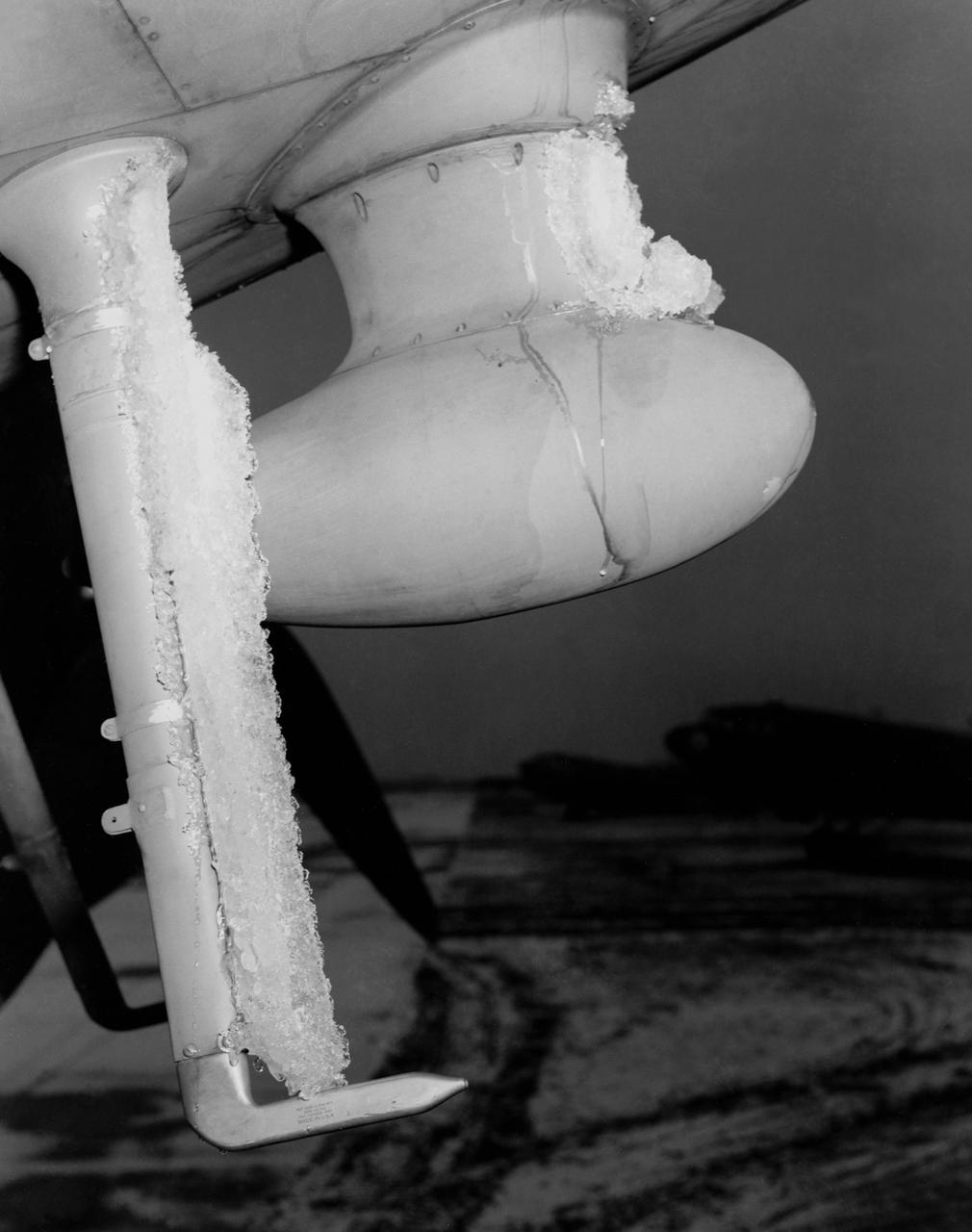

De-icing Research conducted at the NASA Ames Research Center. Icing flight test on C-46 airplane (flight 29 11:25am to 12:50 am) glaze ice on loop antenna co-pilots airspeed mast.
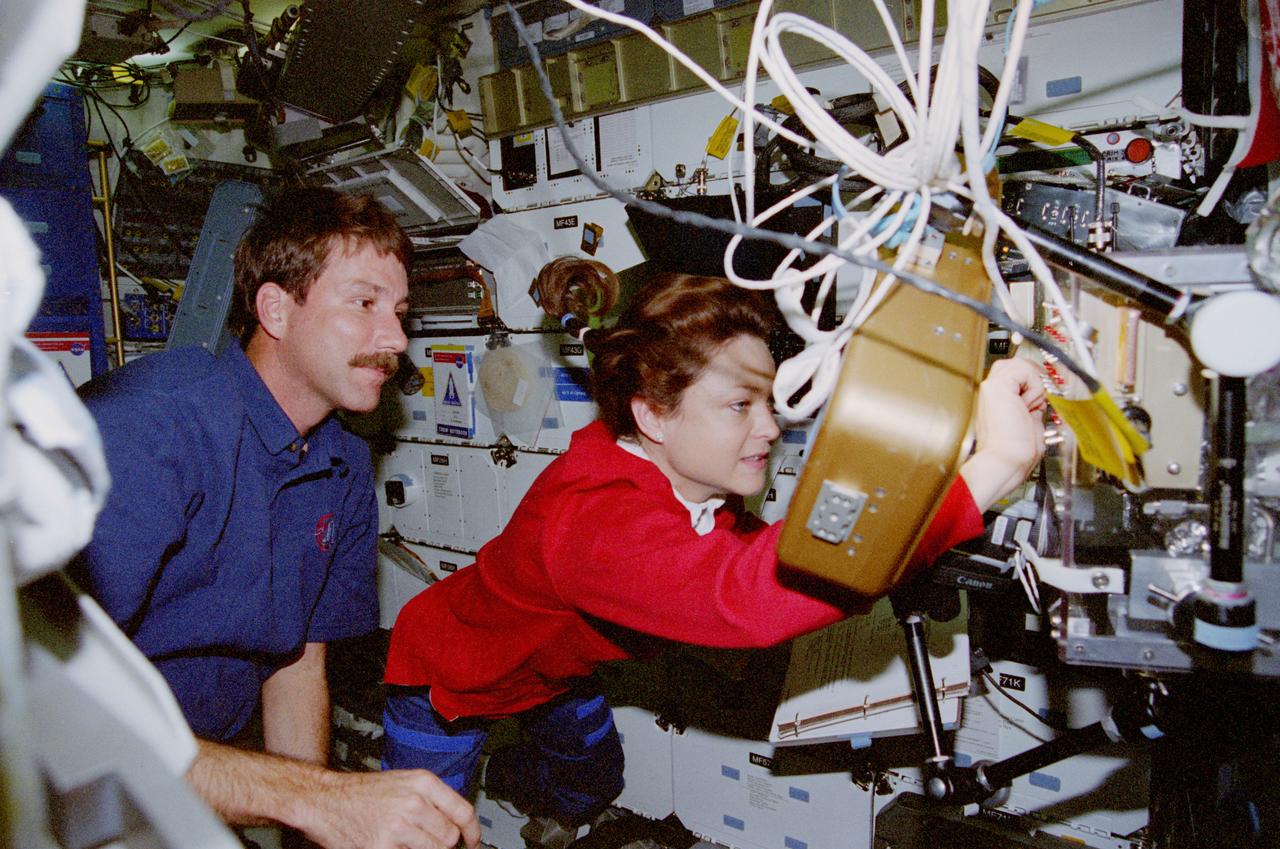

STS080-345-008 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Continuing with a heavy agenda of middeck science, astronaut Tamara E. Jernigan, STS-80 mission specialist, works with the Capillary Pumped Loop (CPL) experiment while astronaut Kent V. Rominger, pilot, offers a hand.
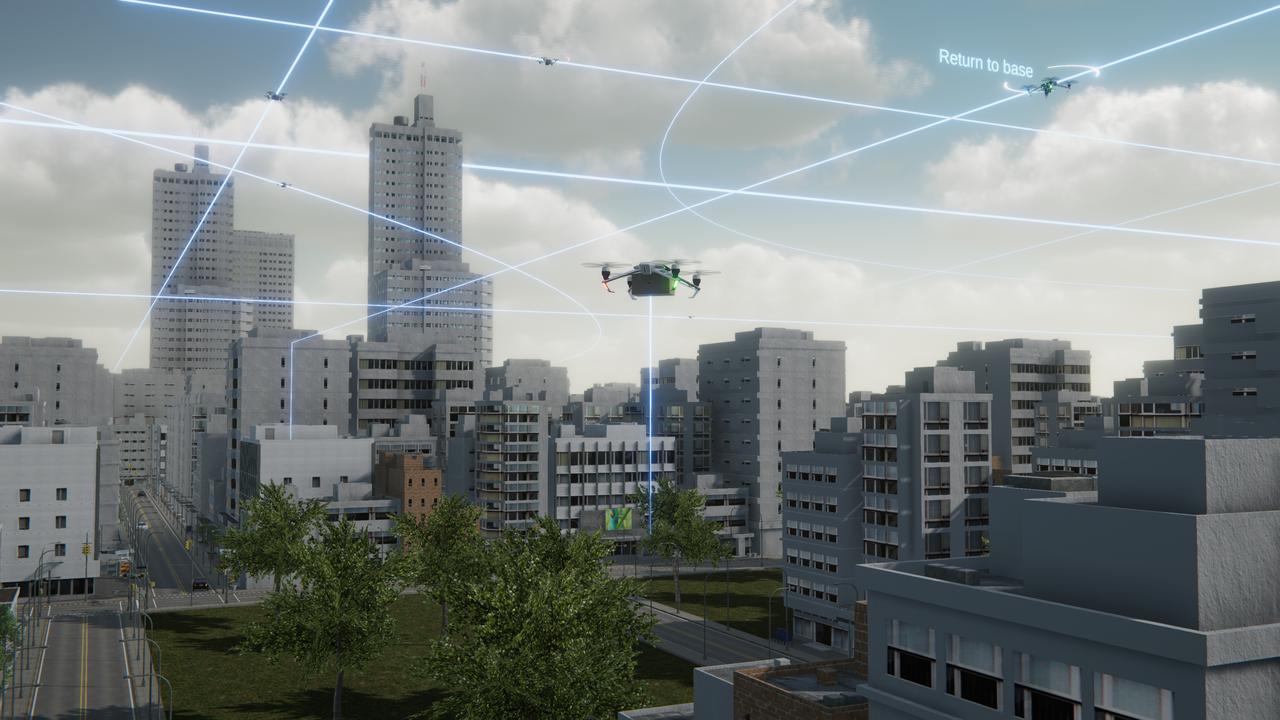

Several projects supporting NASA's Advanced Air Mobility or AAM mission are working on different elements to help make AAM a reality and one of these research areas is automation. This concept graphic shows how elements of automation could be integrated into a future airspace. Technology like this could enable vehicles to operate without a pilot, or if a pilot is in the loop, increase the safety.
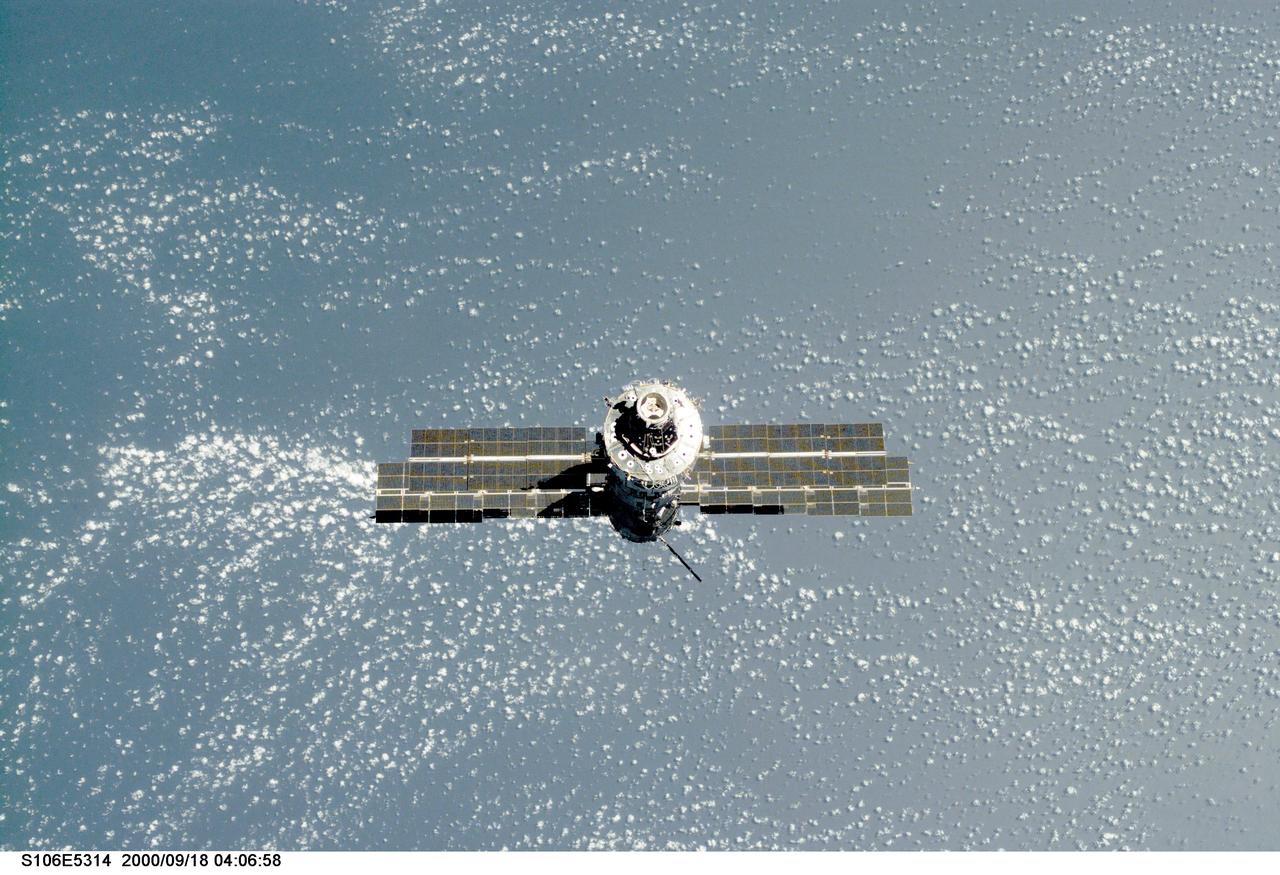

S106-E-5314 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against the blue and white Earth, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 (GMT) on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of the Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 GMT, September 18.
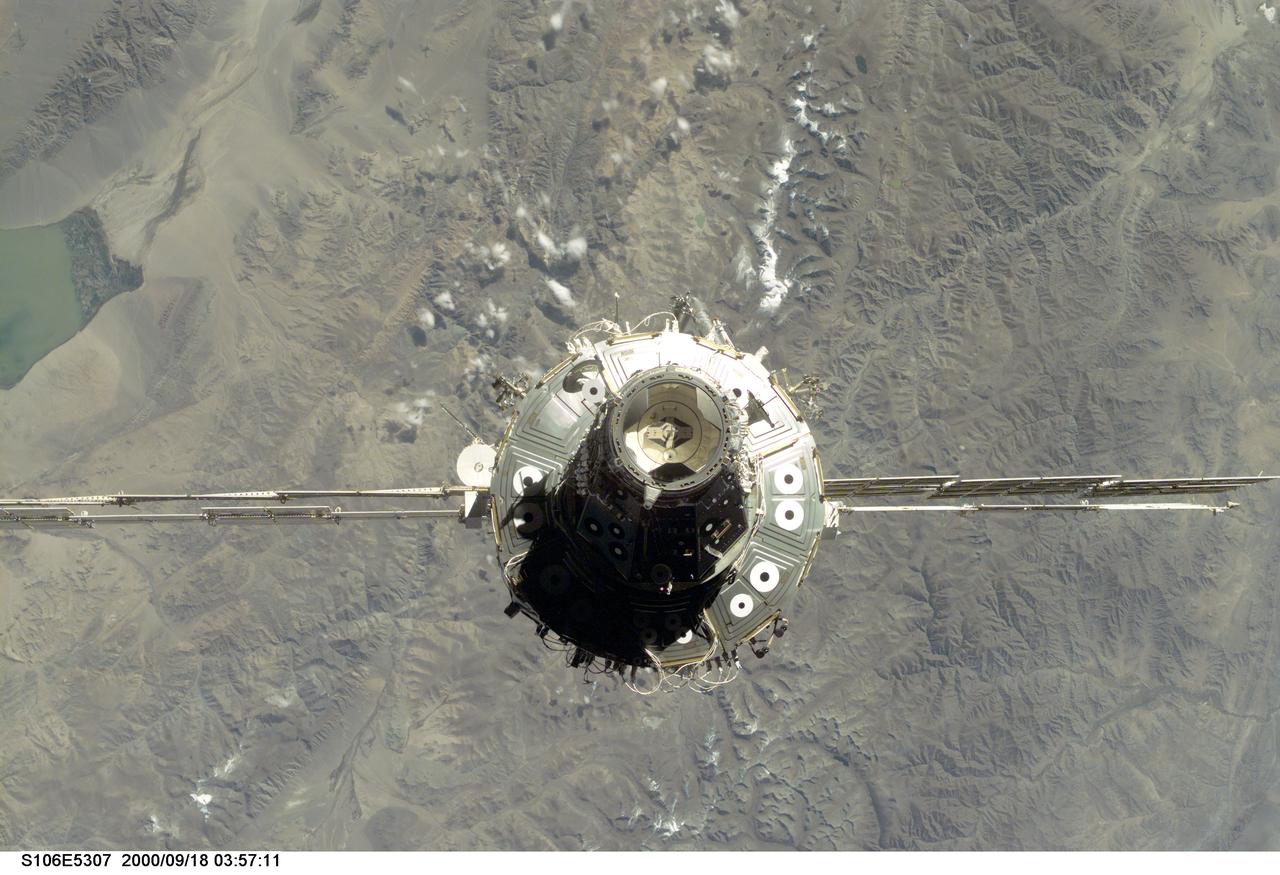

S106-E-5307 (18 September 2000) --- The International Space Station (ISS), with its U.S.-built Unity node facing the camera, is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 (GMT) on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 GMT, September 18.
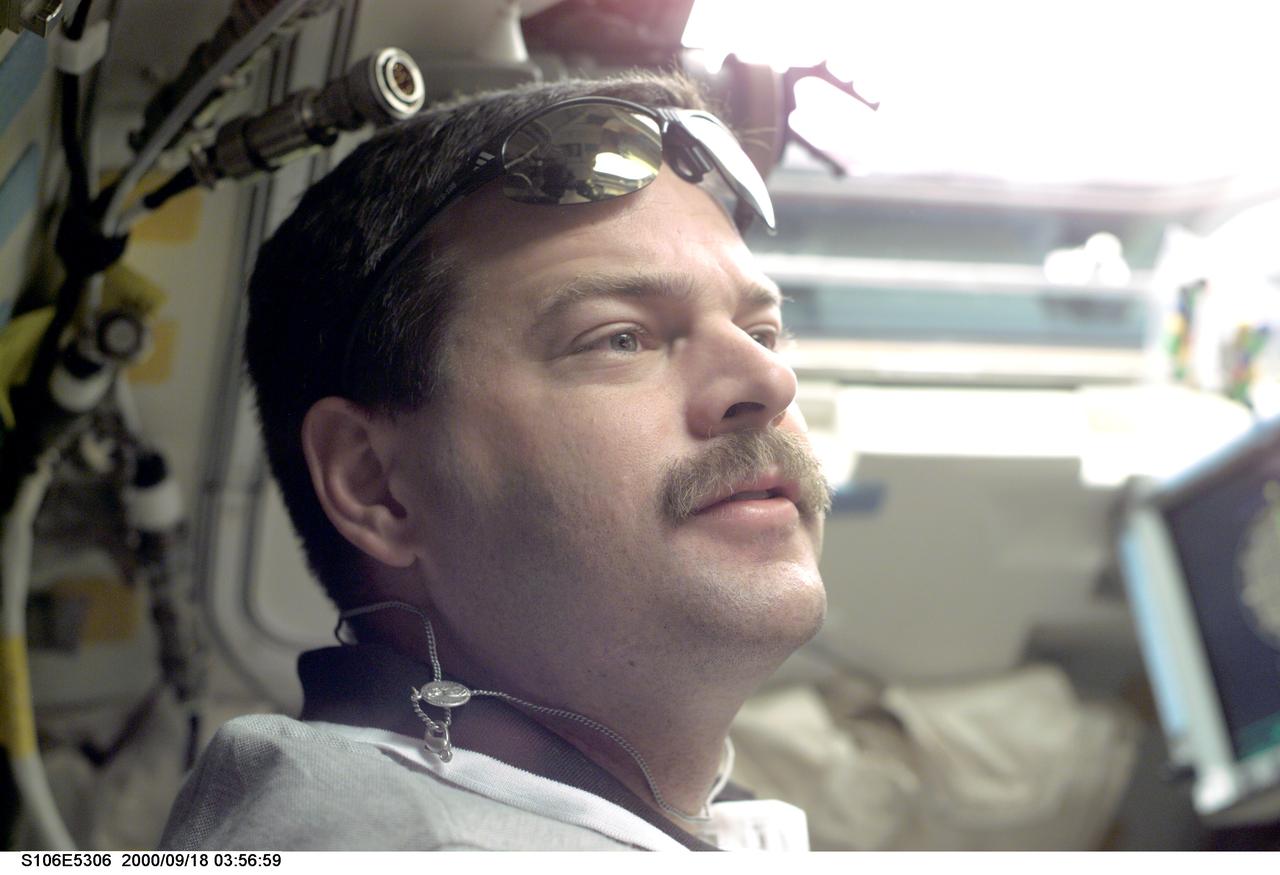
S106-E-5306 (18 September 2000) --- Astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, occupies the commander's station for some important maneuvers. Atlantis’ seven astronauts and cosmonauts successfully undocked from the International Space Station after accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew. Undocking occurred at 3:46 GMT, Sept. 18, over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, Altman performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 GMT, September 18.
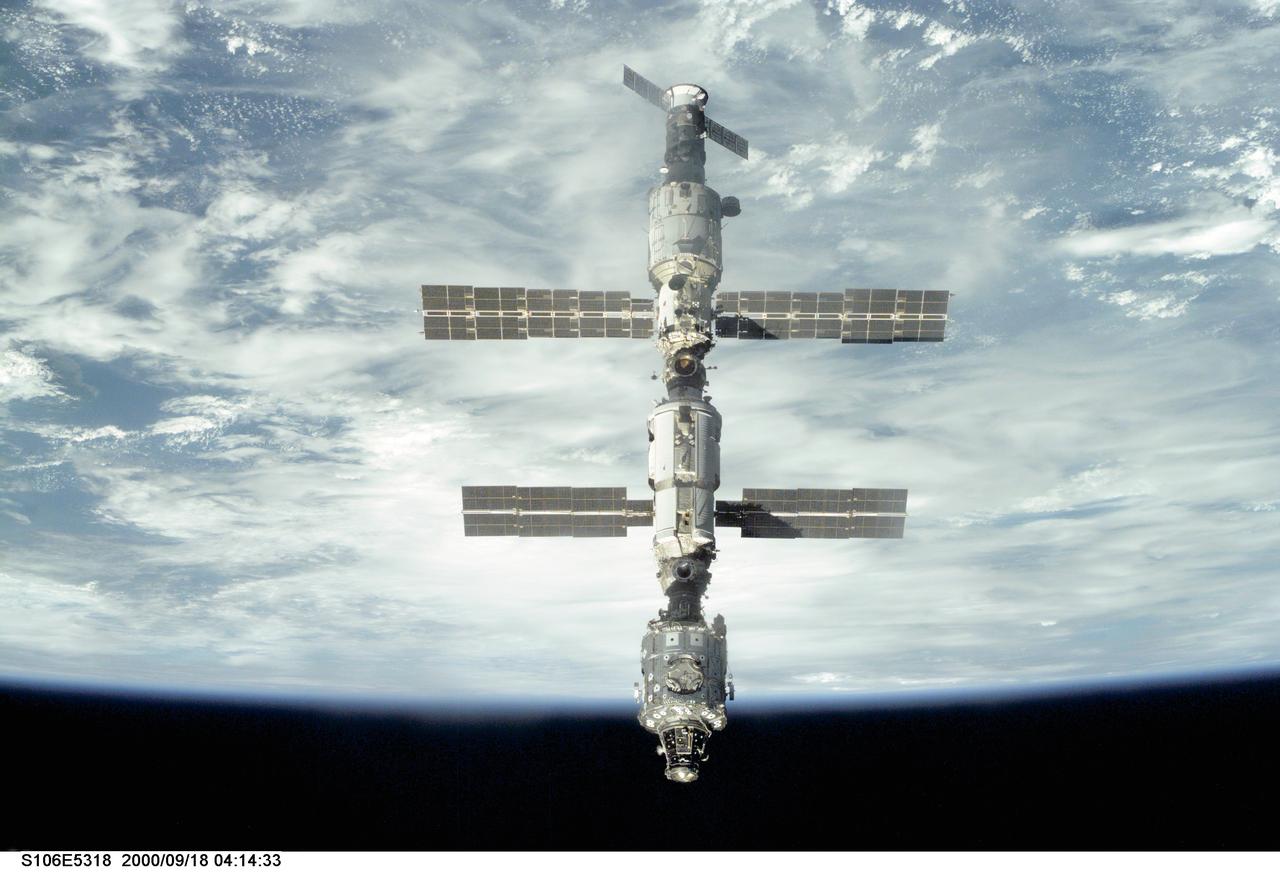

S106-E-5318 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against Earth's horizon, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 GMT on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 (GMT) September 18.
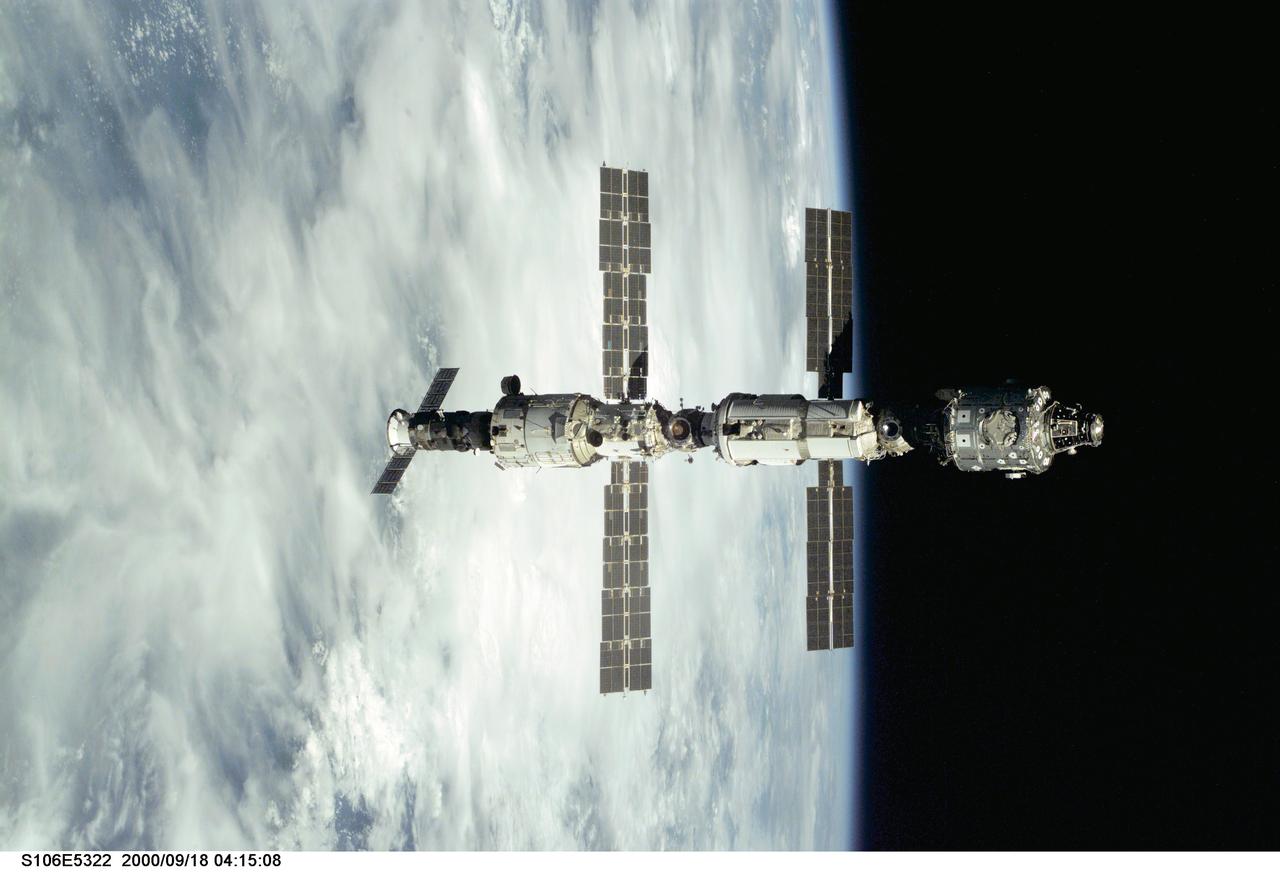

S106-E-5322 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against Earth's horizon, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 GMT on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 (GMT) September 18.
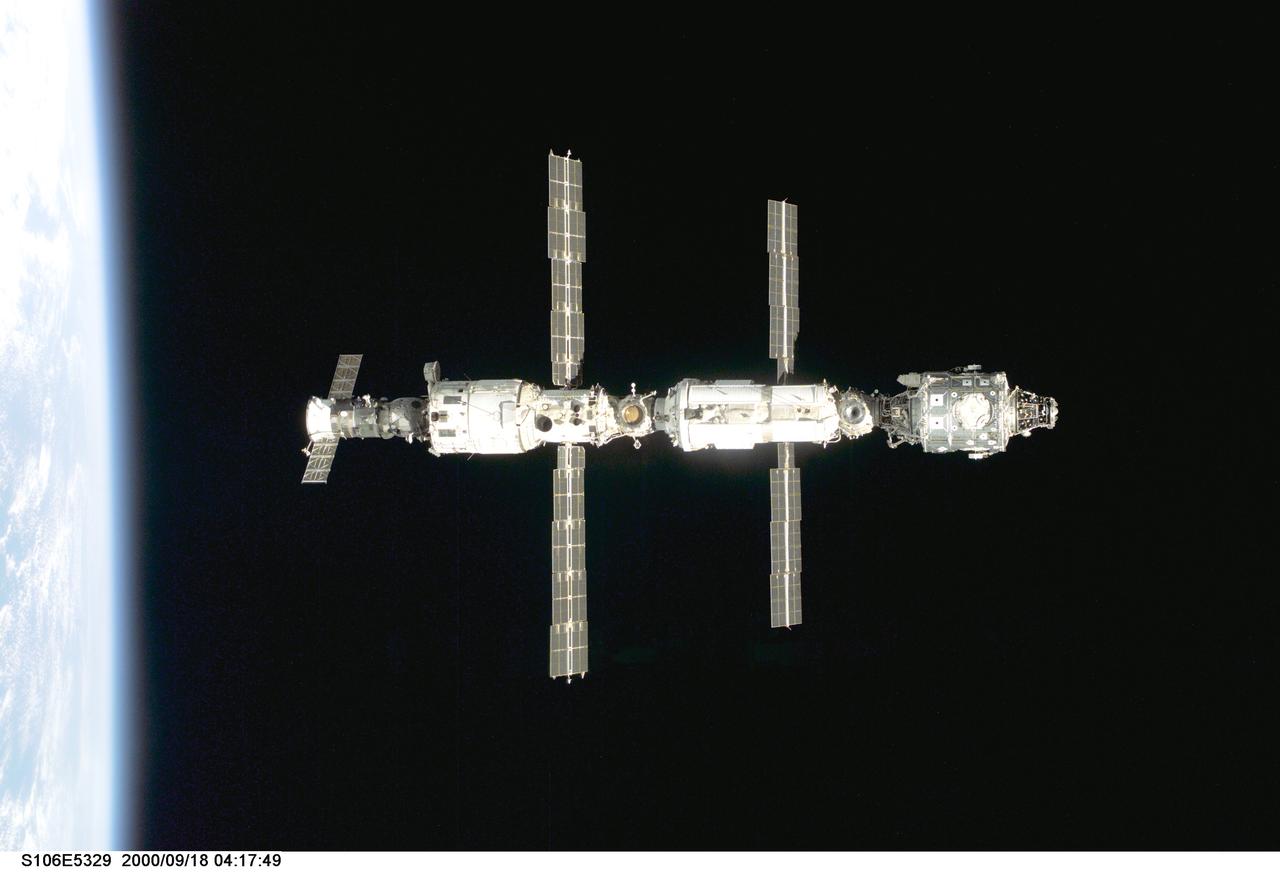

S106-E-5329 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against black space above Earth's horizon, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 GMT on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 (GMT) September 18.
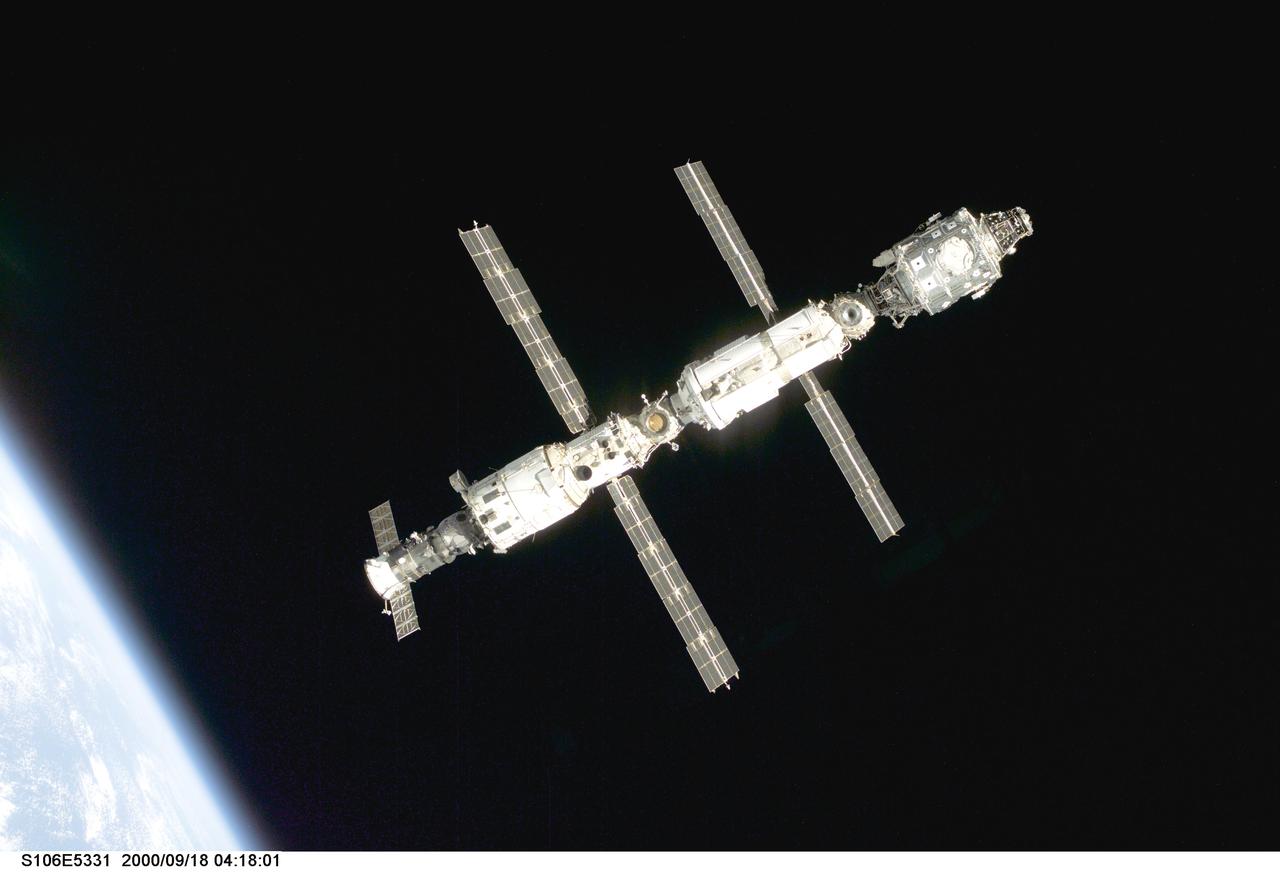

S106-E-5331 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against black space above Earth's horizon, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 GMT on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 (GMT) September 18.
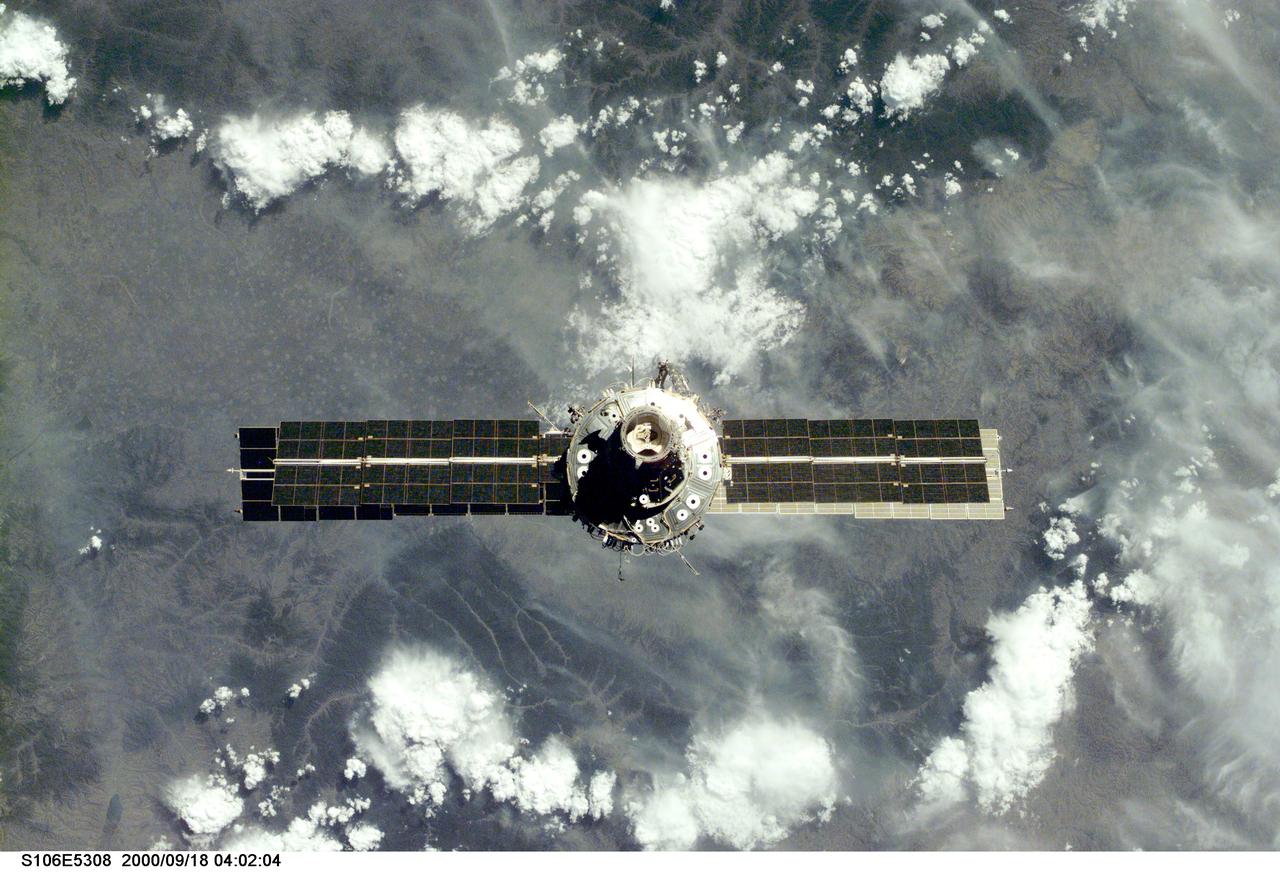

S106-E-5308 (18 September 2000) --- The International Space Station (ISS), with its U.S.-built Unity node facing the camera, is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 (GMT) on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 GMT, September 18.
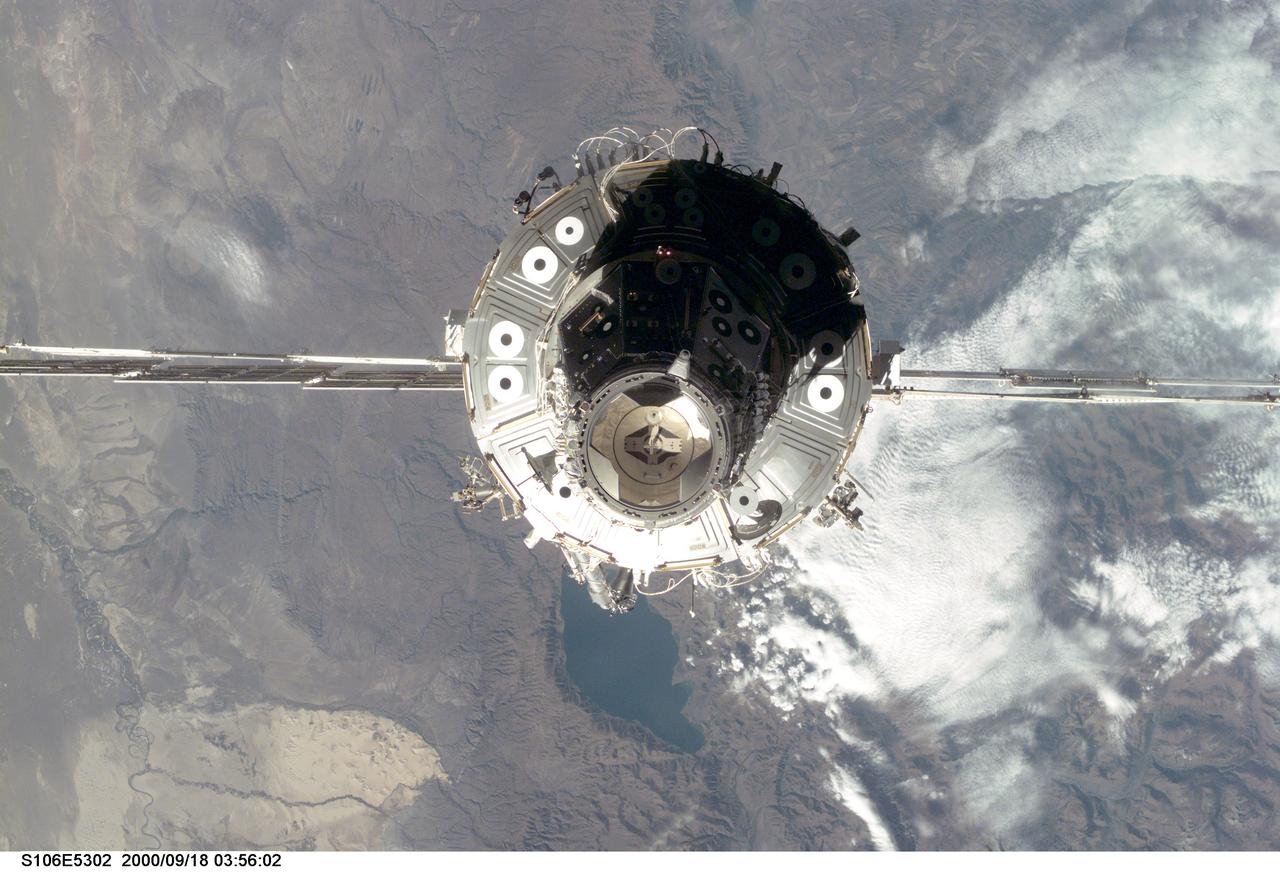

S106-E-5302 (18 September 2000) --- The International Space Station (ISS) is seen with the U.S.-built Unity node facing the camera, following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 (GMT) on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 GMT, September 18.
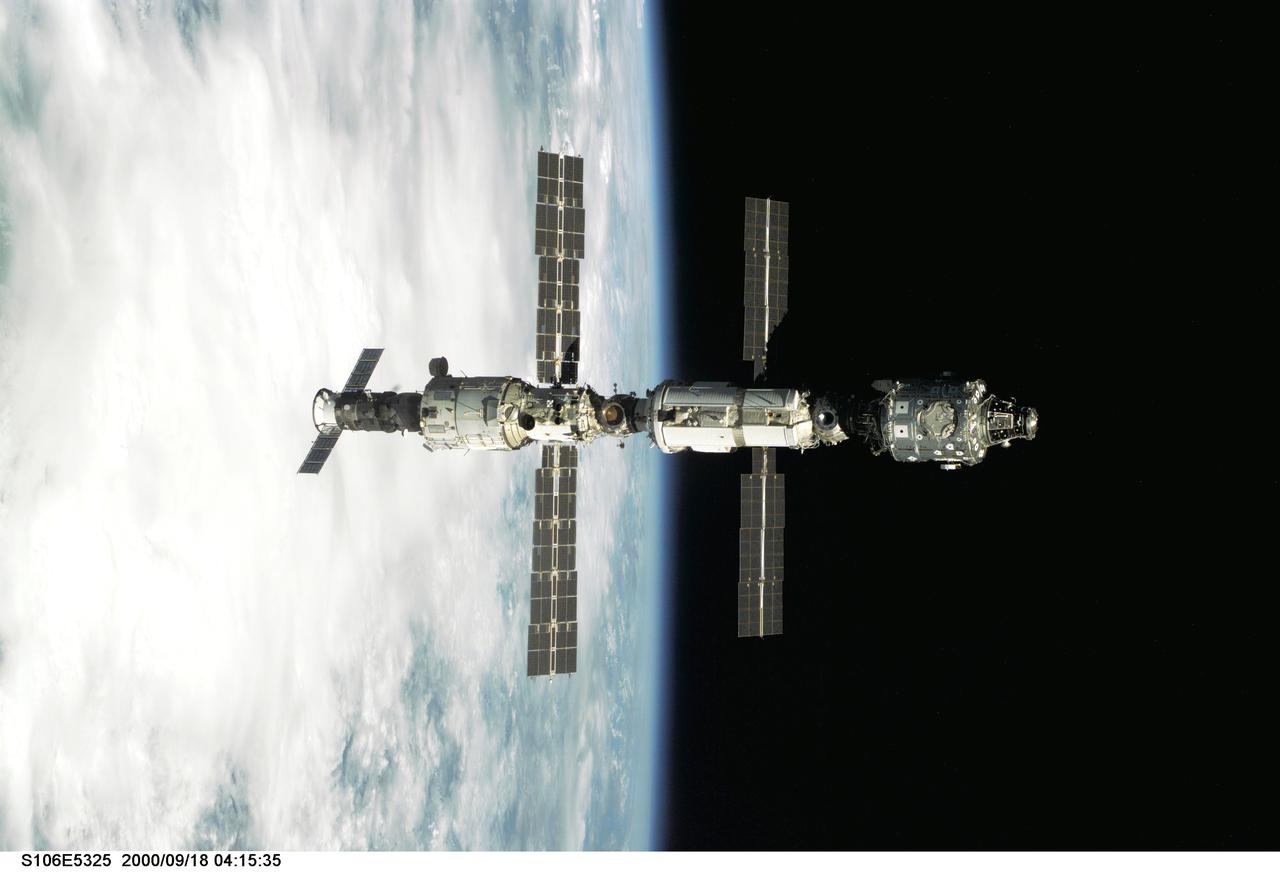

S106-E-5325 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against Earth's horizon, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 GMT on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 (GMT) September 18.
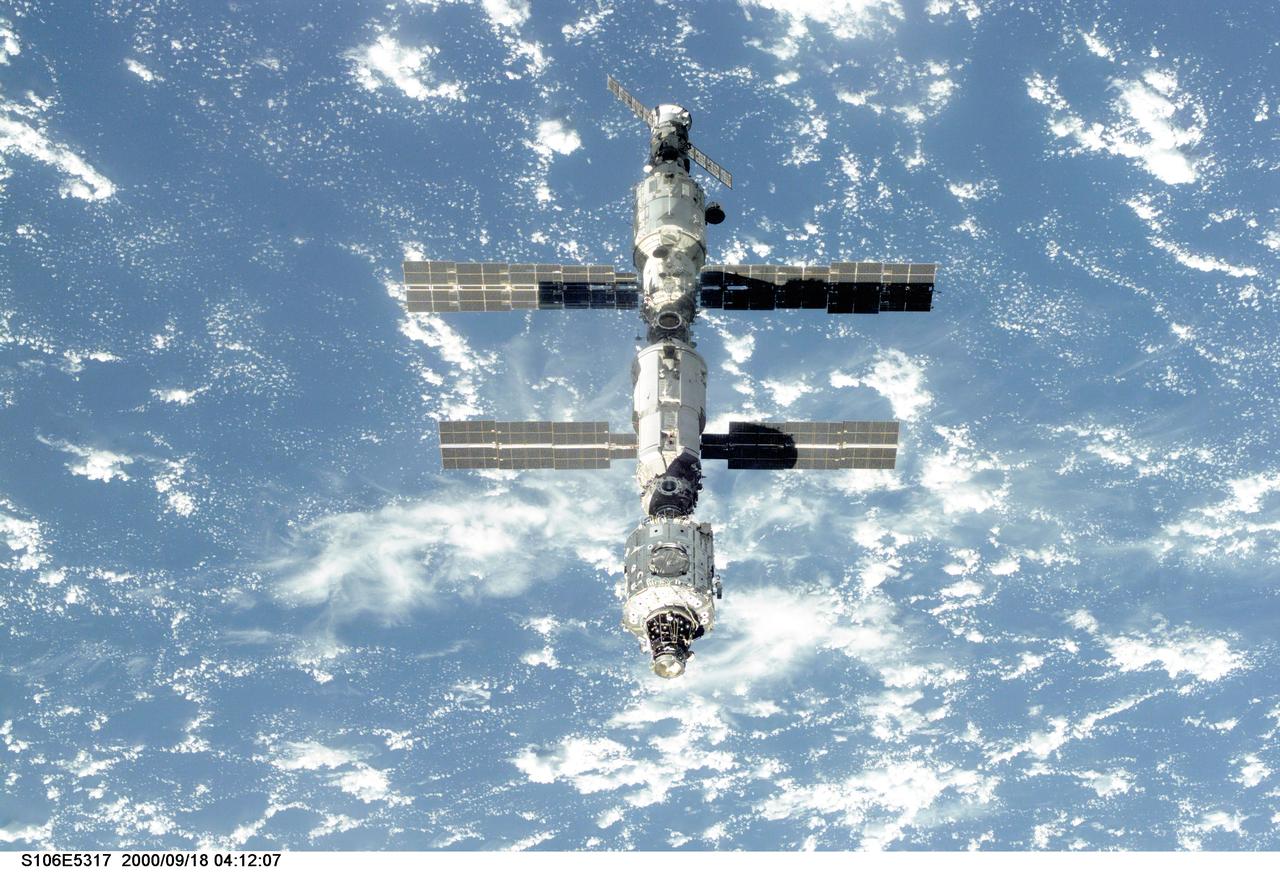

S106-E-5317 (18 September 2000) --- The International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 (GMT) on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 GMT, September 18.

S106-E-5299 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 (GMT) on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 GMT, September 18.
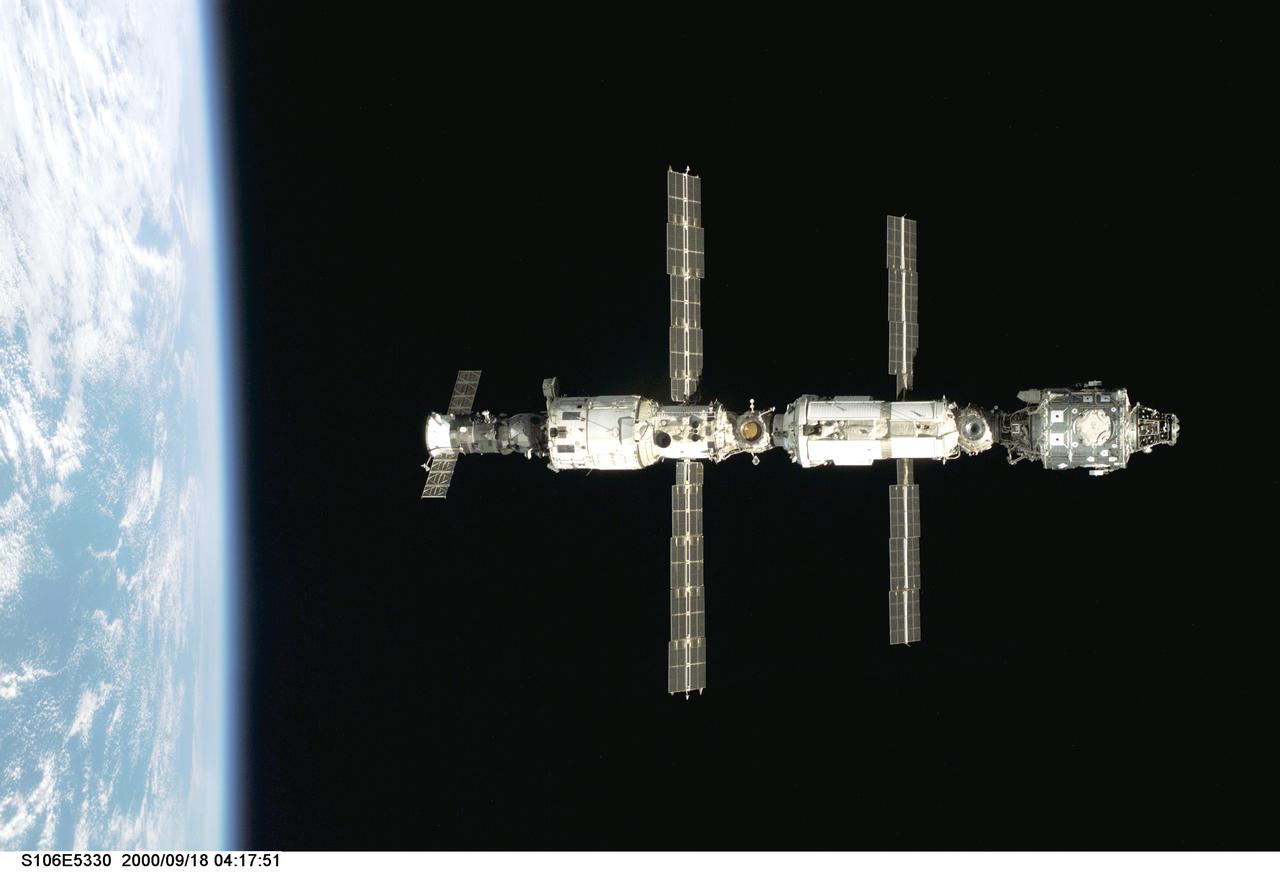

S106-E-5330 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against black space above Earth's horizon, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 GMT on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 (GMT) September 18.

S106-E-5319 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against Earth's horizon, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 GMT on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 (GMT) September 18.
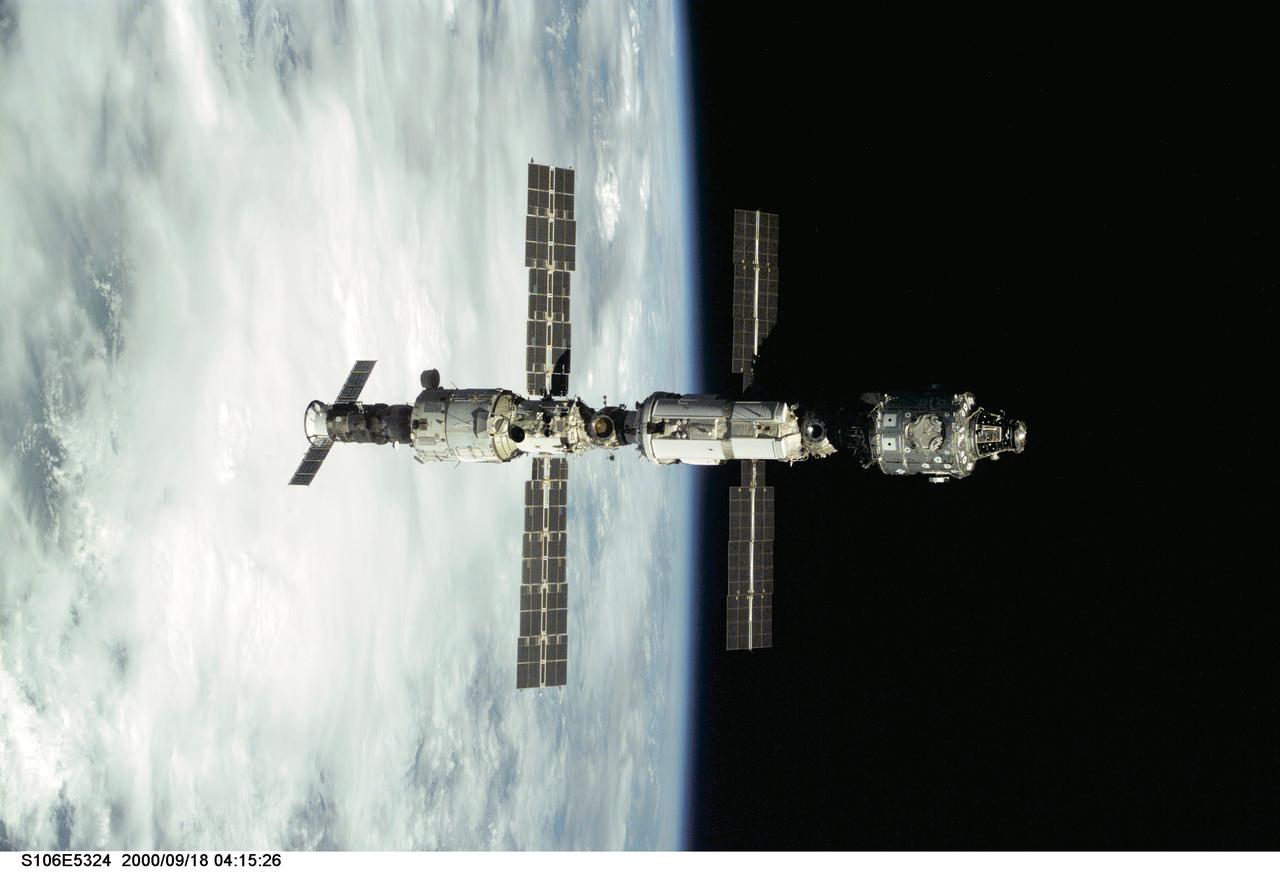

S106-E-5324 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against Earth's horizon, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 GMT on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 (GMT) September 18.
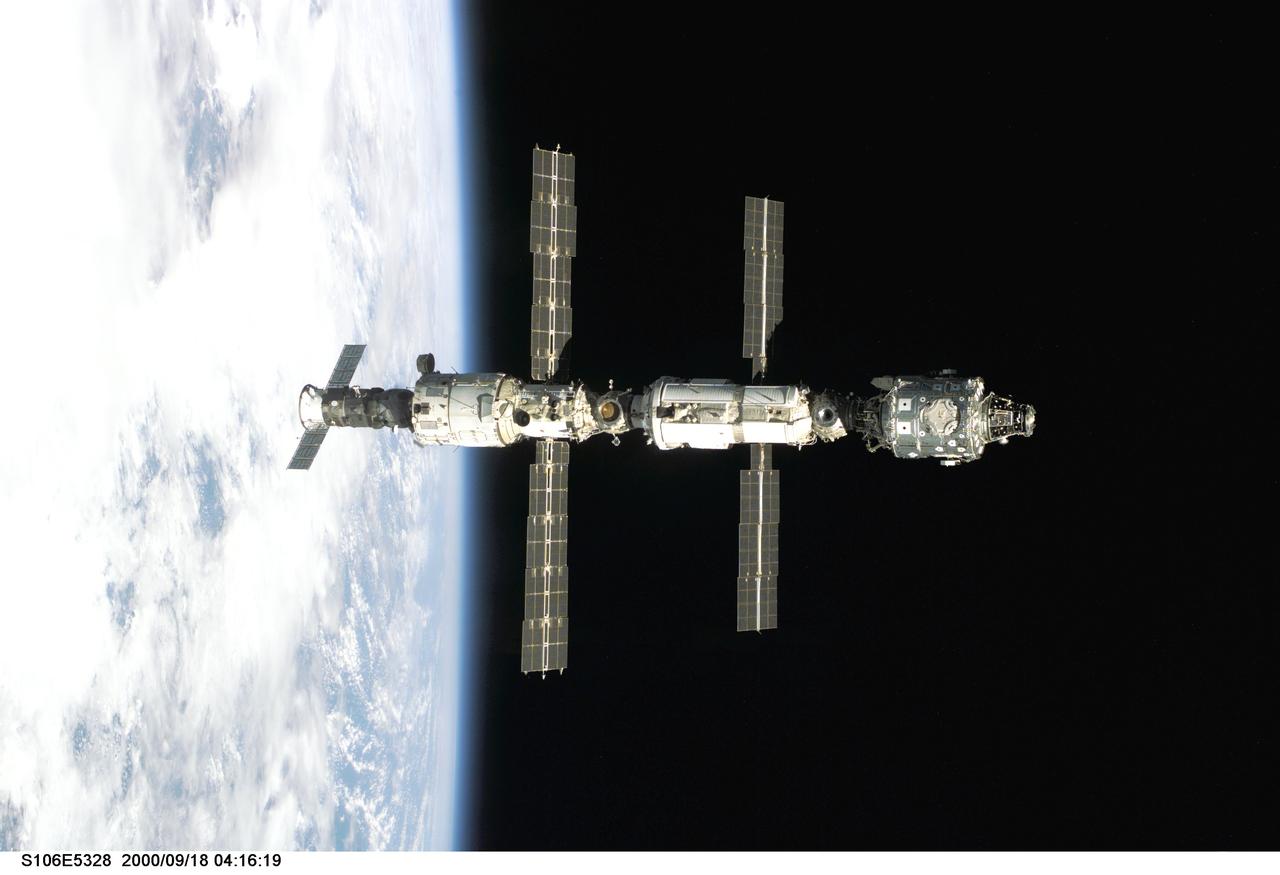

S106-E-5328 (18 September 2000) --- Backdropped against Earth's horizon, the International Space Station (ISS) is seen following its undocking with the Space Shuttle Atlantis. After accomplishing all mission objectives in outfitting the station for the first resident crew, the seven astronauts and cosmonauts undocked at 3:46 GMT on Sept. 18 over Russia near the northeastern portion of Ukraine. When Atlantis was at a safe distance from the station, about 450 feet, astronaut Scott D. Altman, pilot, performed a 90-minute, double-loop fly around to enable the crew to document the station’s exterior. He fired Atlantis’ jets one final time to separate from the station at 5:35 (GMT) September 18.