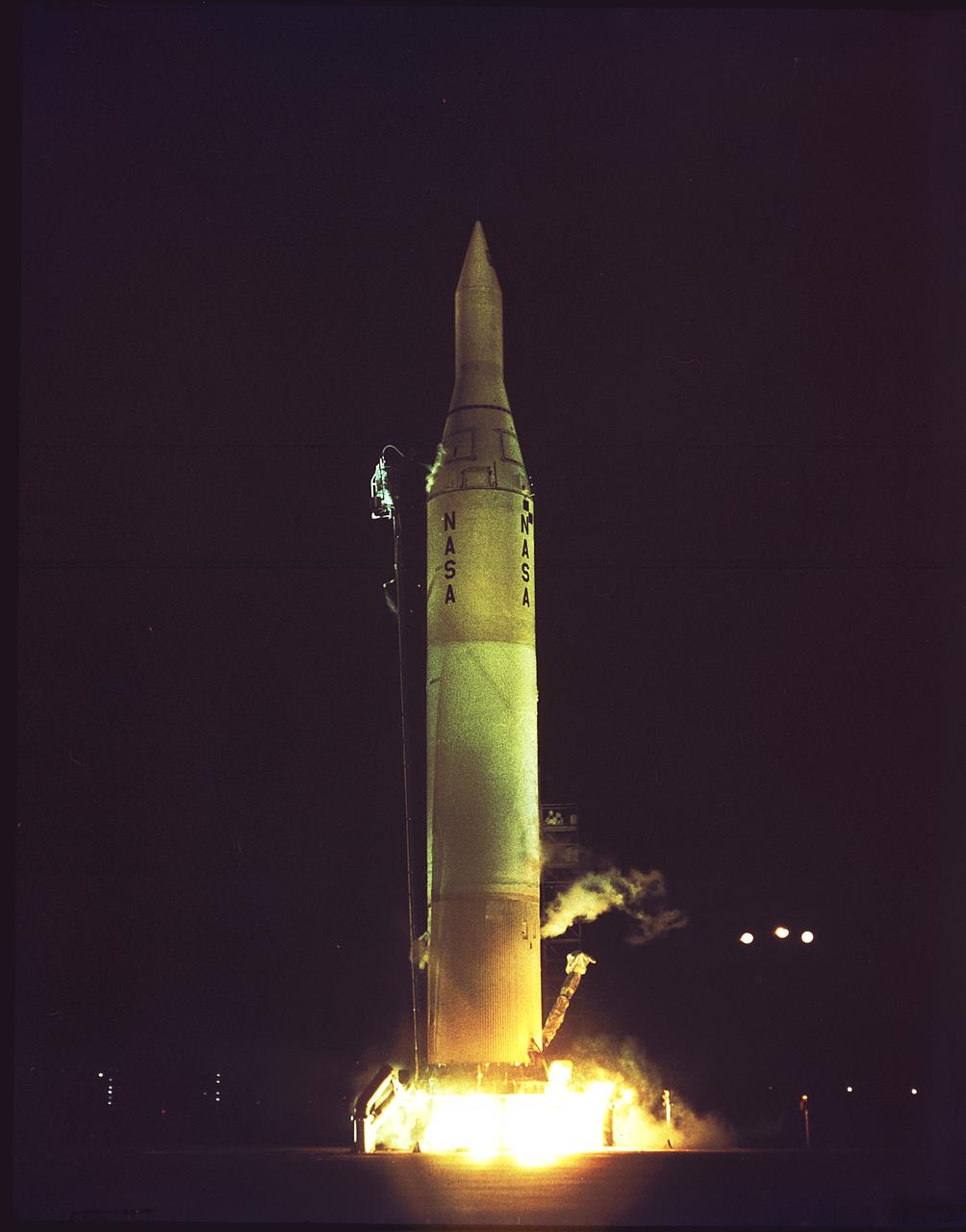

Wernher von Braun and his team were responsible for the Jupiter-C hardware. The family of launch vehicles developed by the team also came to include the Juno II, which was used to launch the Pioneer IV satellite on March 3, 1959. Pioneer IV passed within 37,000 miles of the Moon before going into solar orbit.
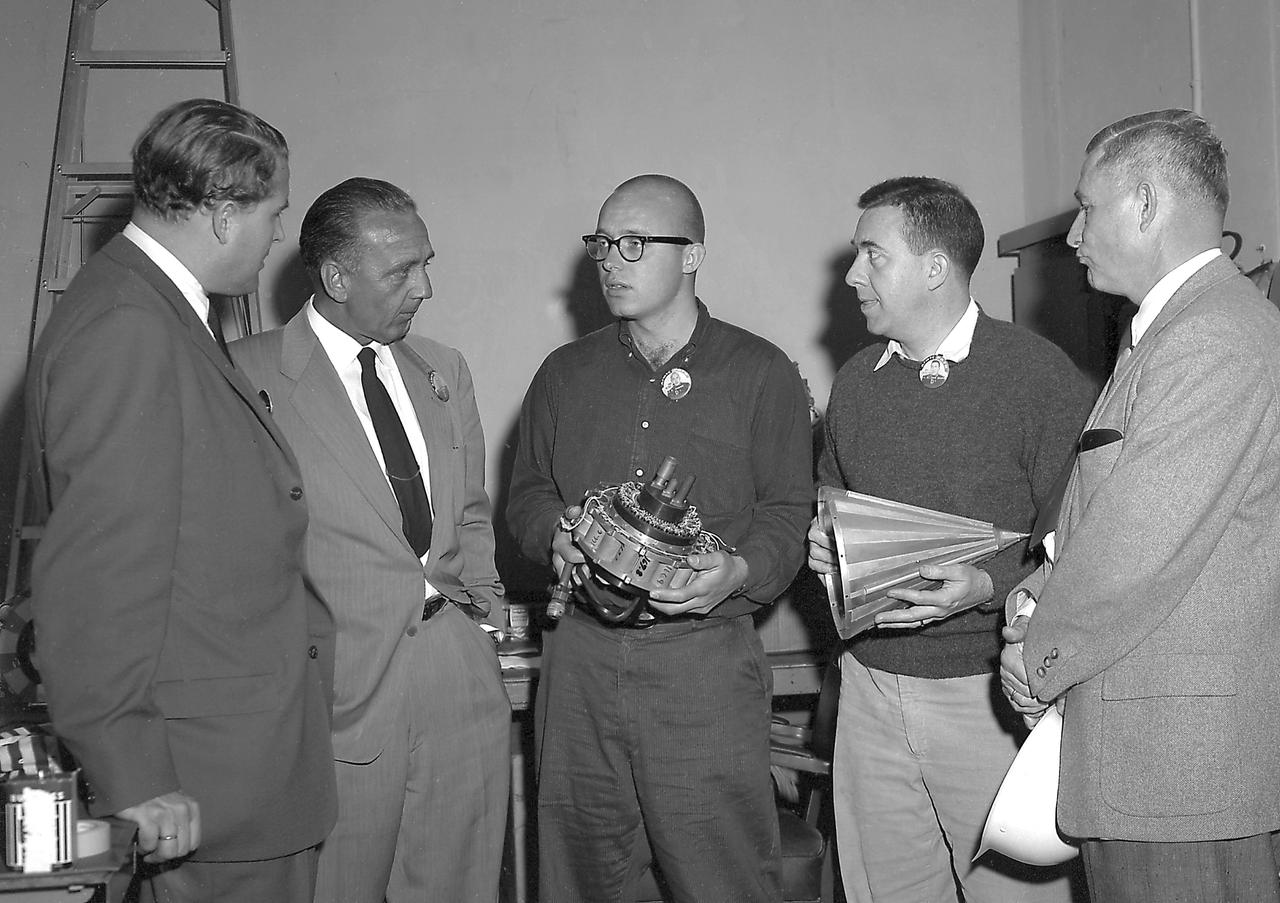

In this photo, Director of the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, Dr. Wernher von Braun, and Director of Missile Firing Division, Dr. Kurt Debus, are shown with unidentified individuals, discussing two components that would make up the Pioneer IV Lunar Probe. The mercury batteries (left) were used to power the radio transmitter, cosmic radiation counter and other instruments in Pioneer IV. The conical shroud placed over the instruments of Pioneer IV was plated with gold to improve conductivity. The metal surface also served as the anterna for the probe's instruments signaling back to the Earth receiving stations.
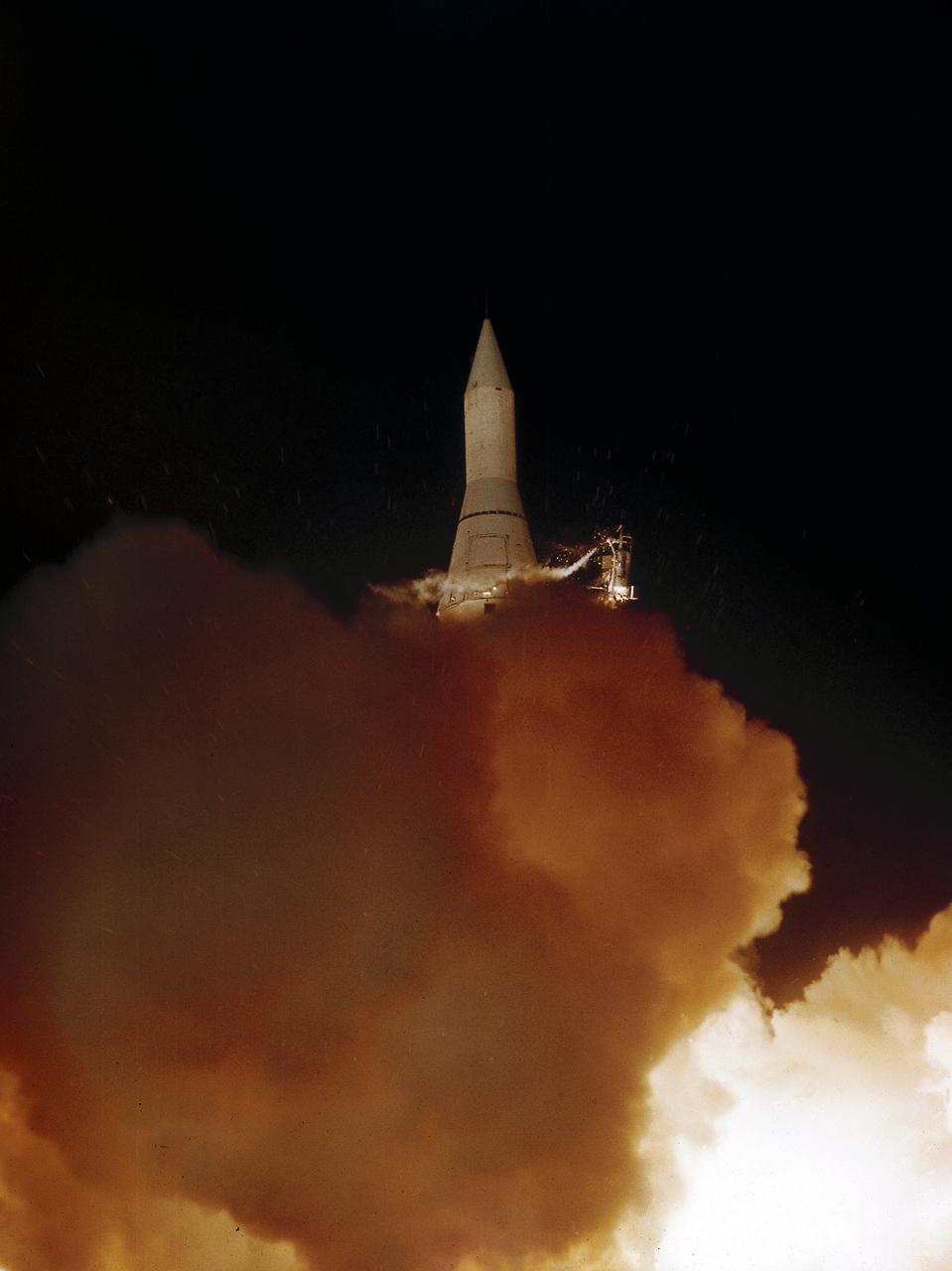

The launch of Juno II (AM-14), carrying the lunar and planetary exploration satellite in orbit, Pioneer IV, on March 3, 1959. the Pioneer IV probe was the first U.S. satellite to orbit the Sun.
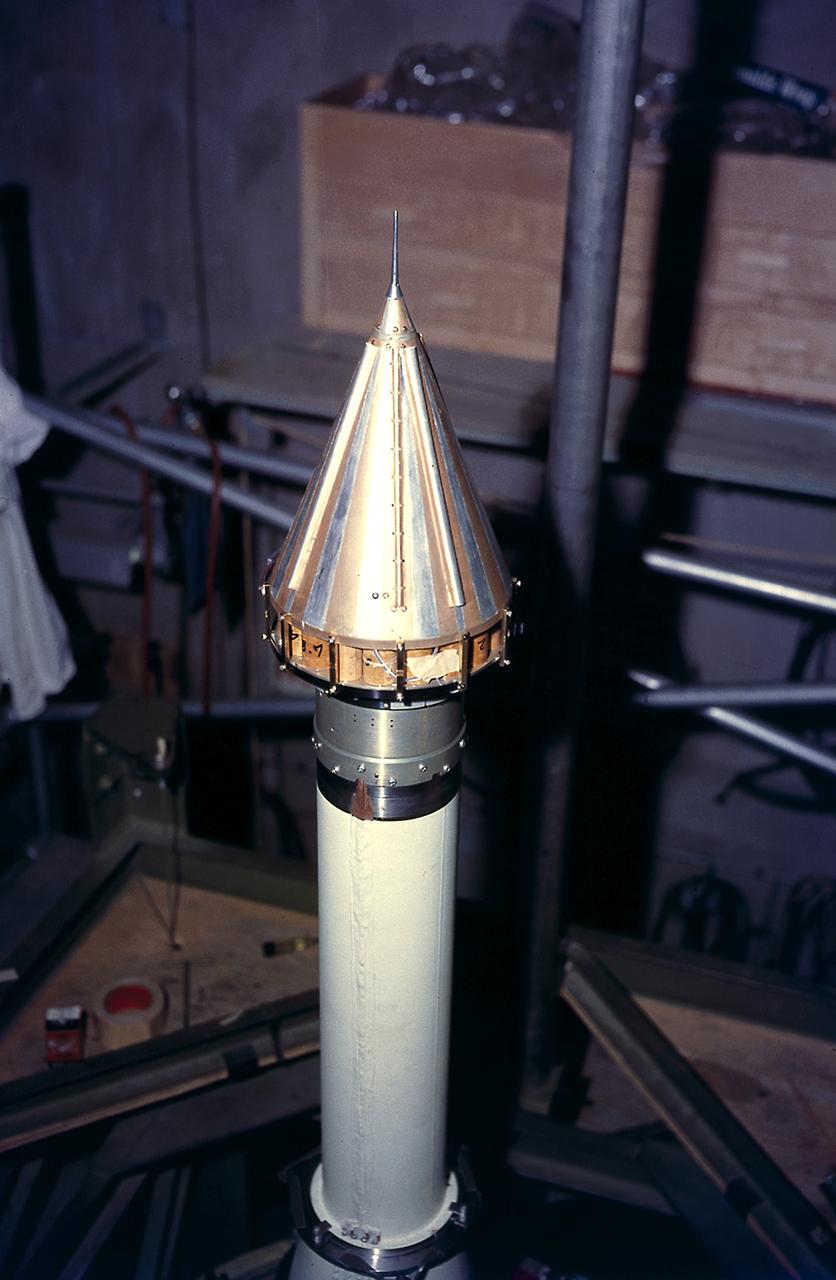
Installing Pioneer IV, payload for AM-14 (Juno II) onto the fourth stage on the cluster before a spin test, February 16, 1959. The Pioneer IV, lunar and planetary exploration satellite, was the first U.S. satellite to orbit the Sun.
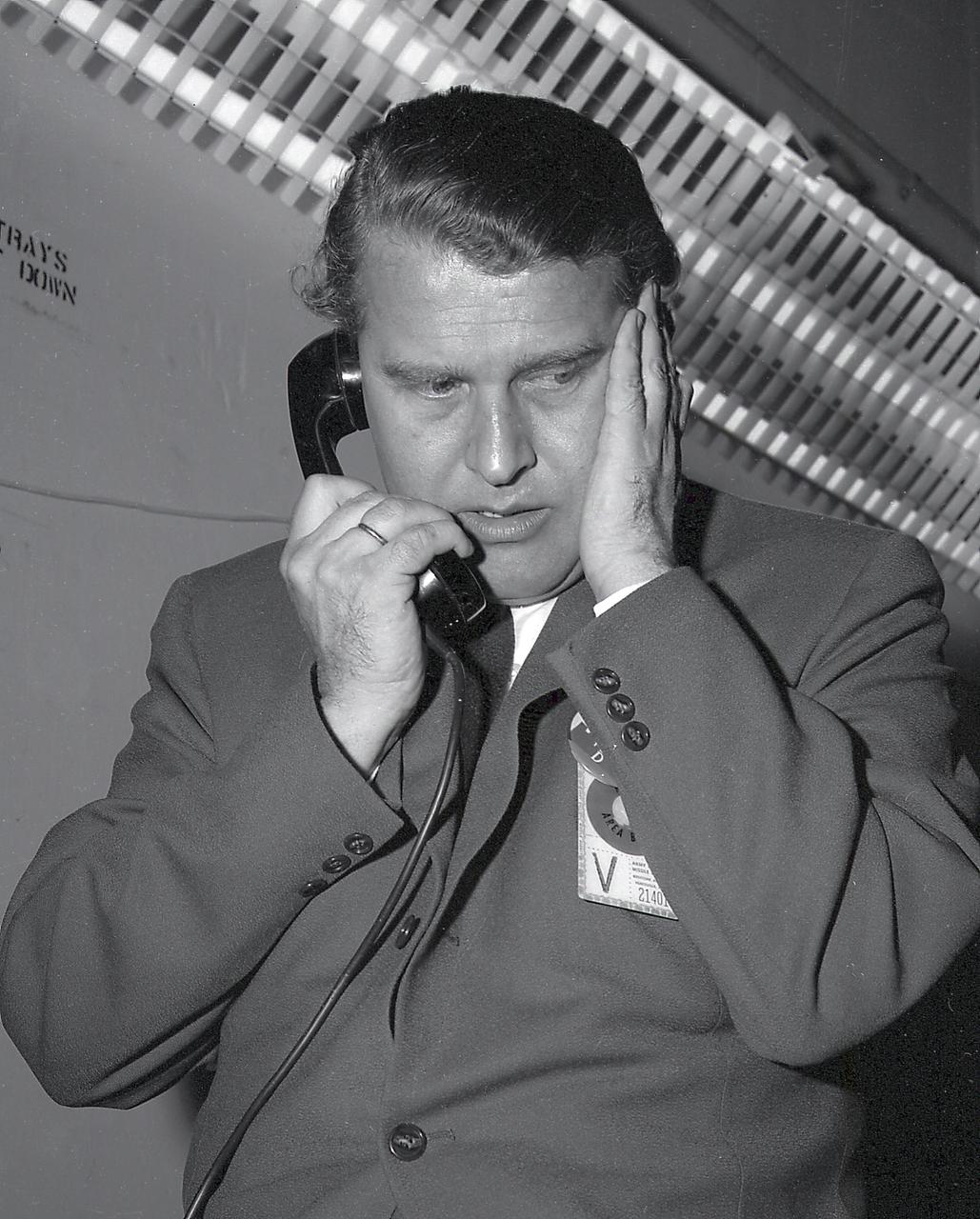

Dr. von Braun on the telephone prior to the launch of the Pioneer IV, March 1, 1959.
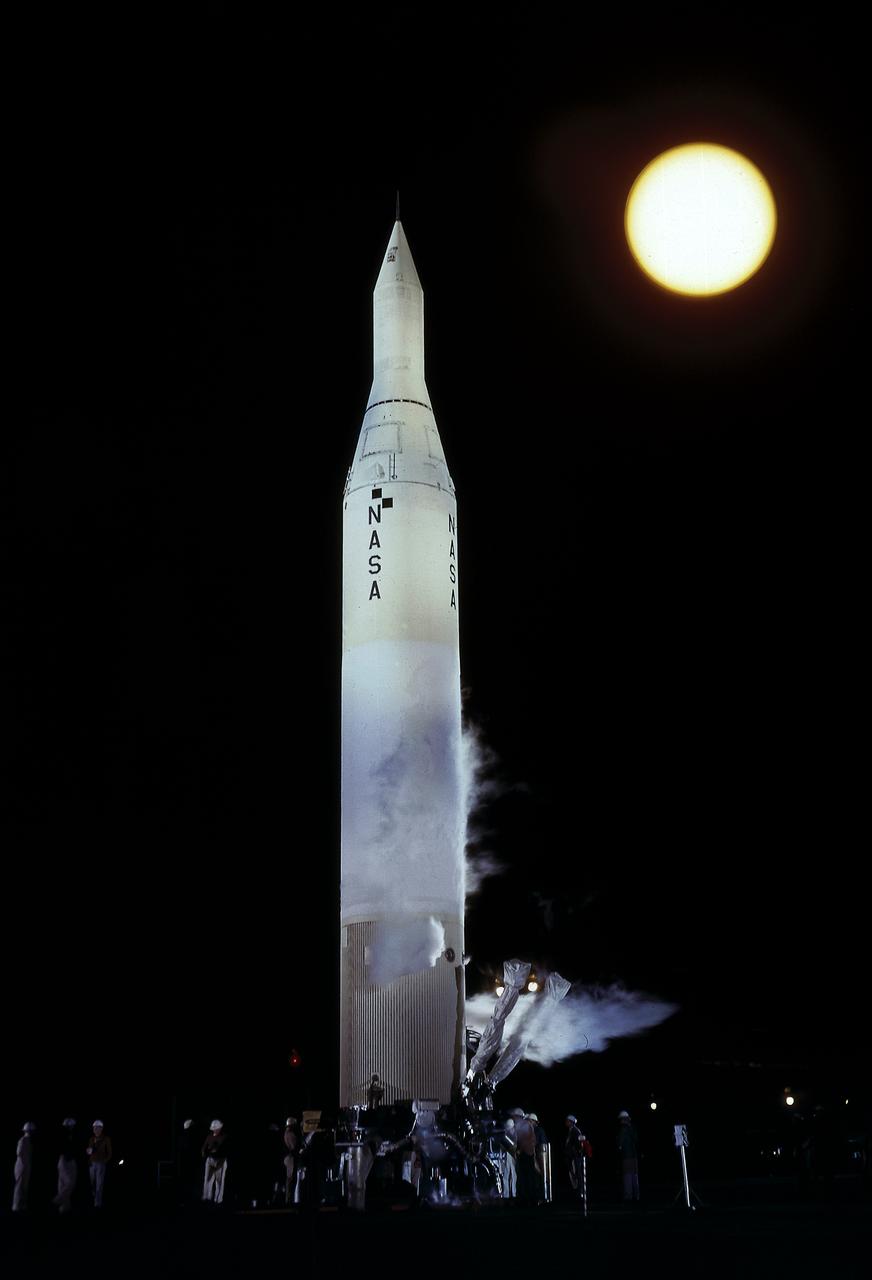

Juno II (AM-14) on the launch pad just prior to launch, March 3, 1959. The payload of AM-14 was Pioneer IV, America's first successful lunar mission. The Juno II was a modification of Jupiter ballistic missile
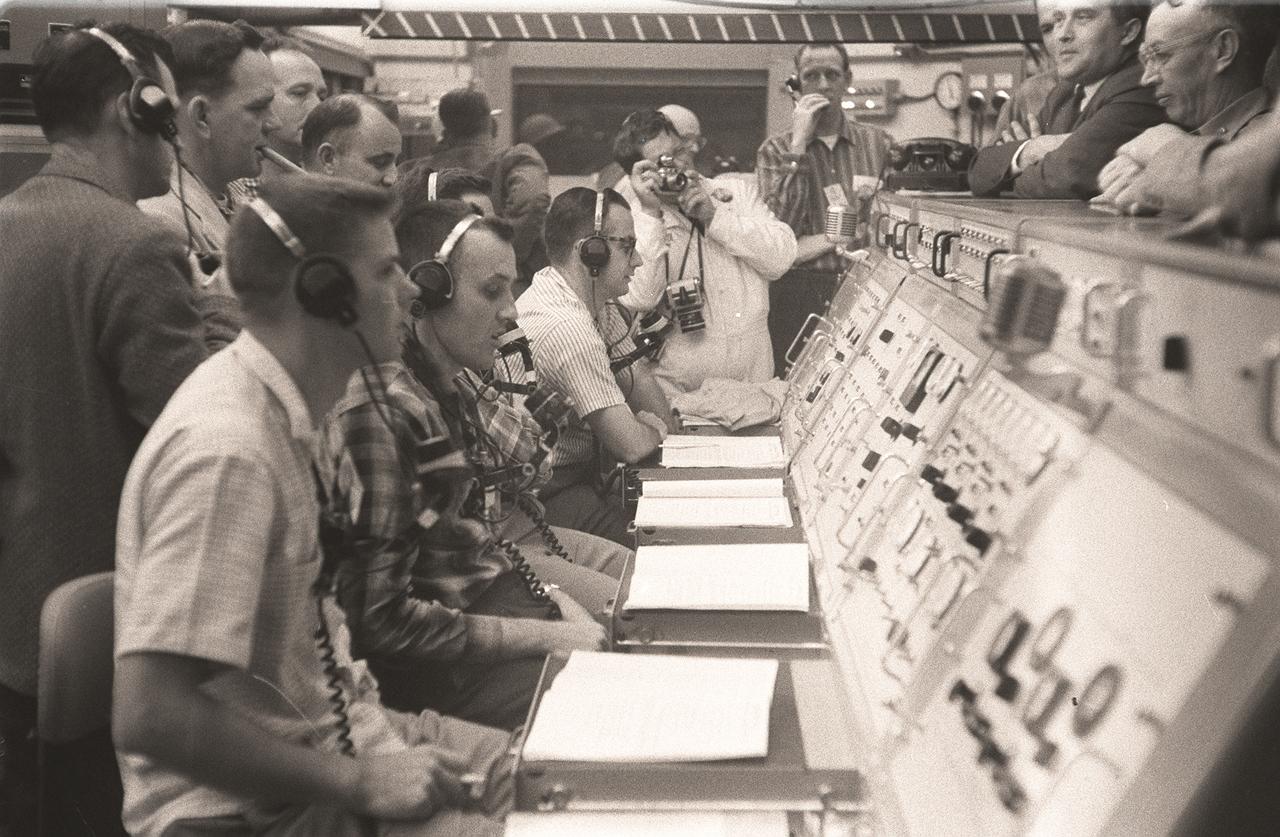

Dr. von Braun at the launch control room during the Pioneer IV launch, March 3, 1959.

Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director of the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, rides with his two daughters, Margrit and Iris, in a parade in downtown Huntsville, Alabama, March 4, 1959. Although the official occasion had been plarned a "Moon Day" weeks before, it was the successful launch of the sun probe Pioneer IV two days previously that increased the celebratory atmosphere.
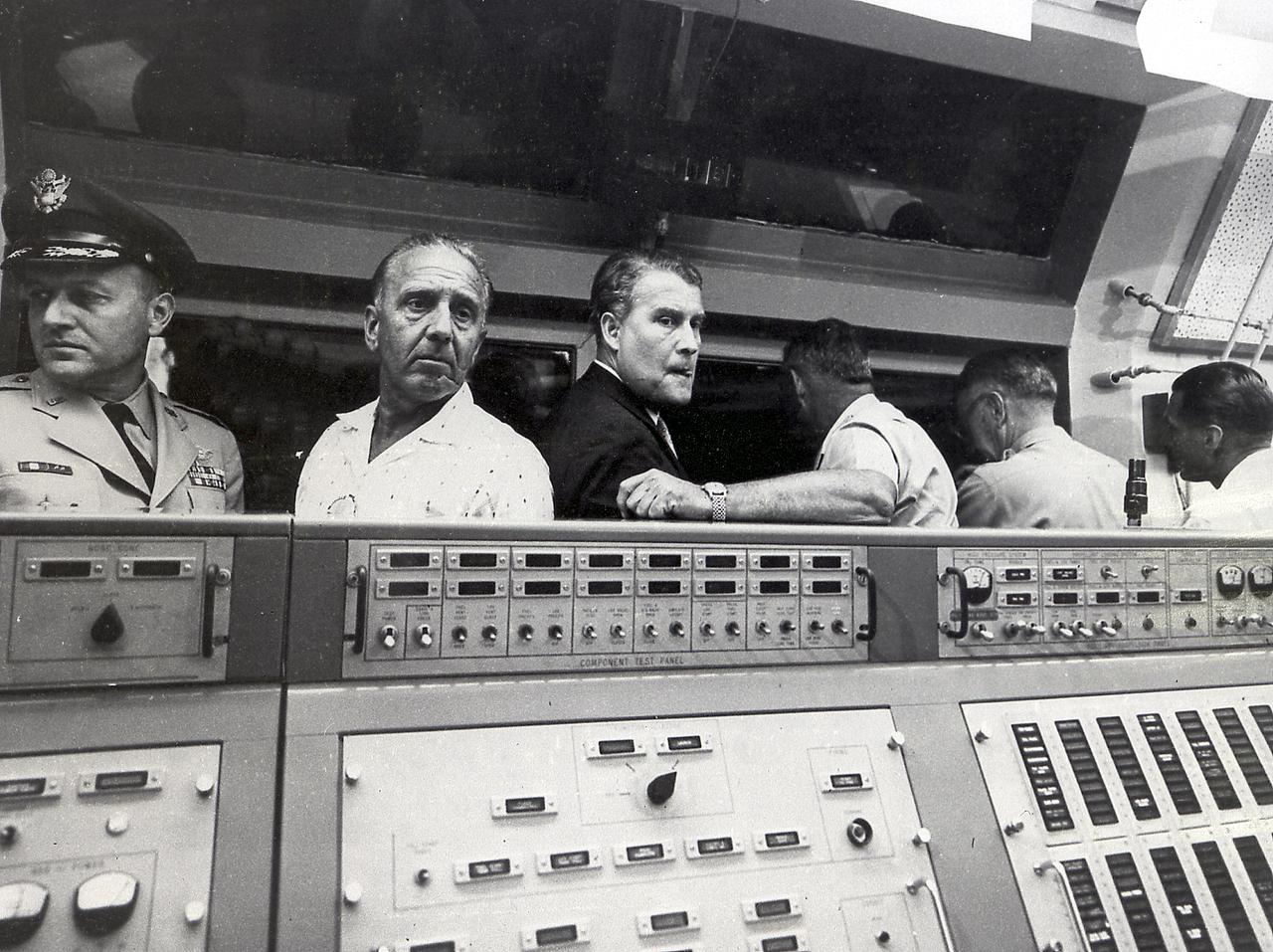

Dr. von Braun, Director of the Development Operations Divisons, and Dr. Debus, Director of the Missile Firing Laboratory; Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA), in the blockhouse during the launch of the Pioneer IV, March 3, 1959.
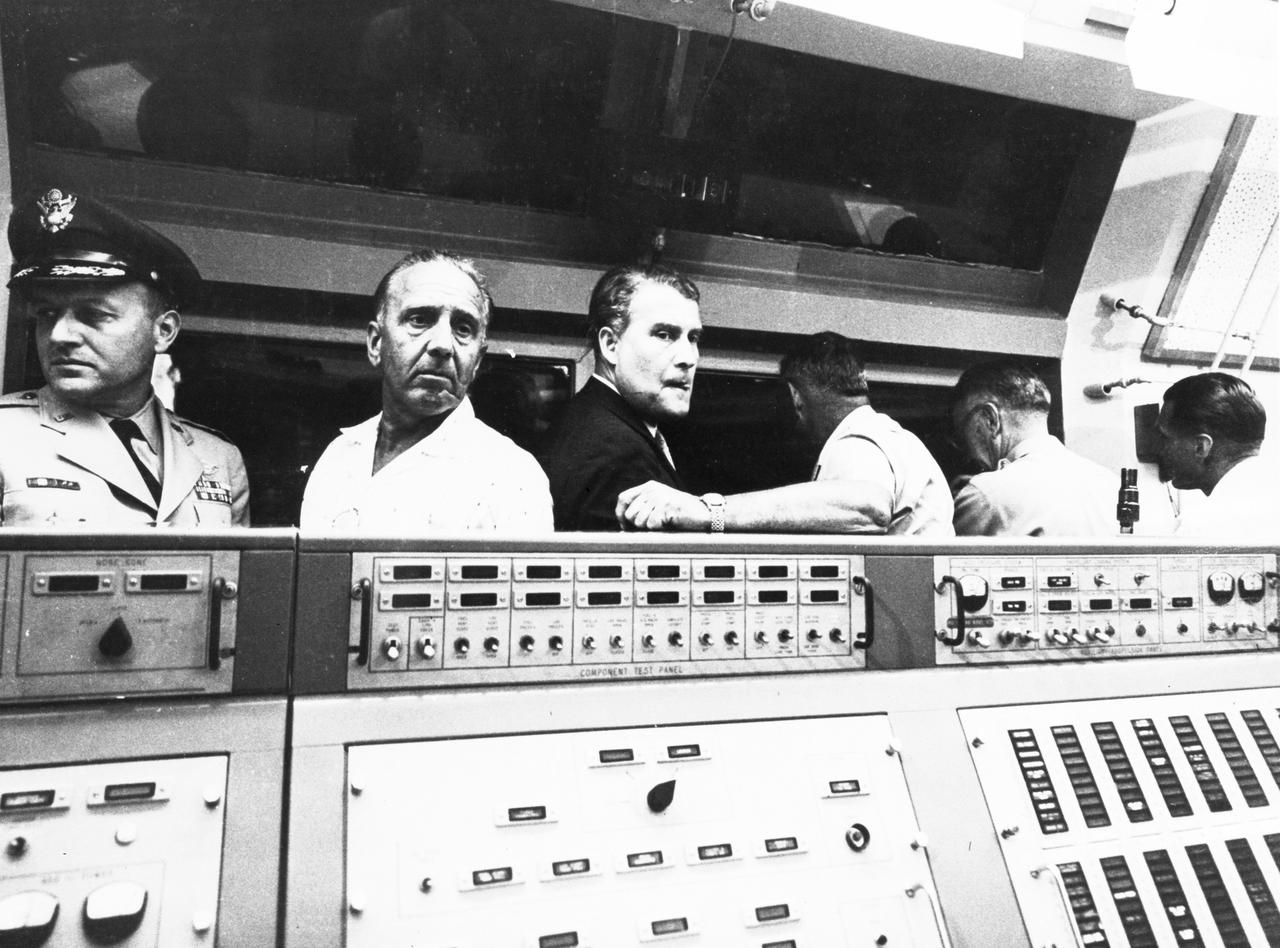

This photograph shows Dr. von Braun, second from the left, in the blockhouse at the Florida launch facilities on March 3, 1959. He and others gathered for the launch of the Pioneer IV satellite. On the left of Dr. von Braun is Kurt Debus, who managed the Florida launch facilities. To the right of Dr. von Braun is Army General John B. Medaris. Next to him is General John Barclay. At this time, Dr. von Braun and his associates were members of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency in Huntsville, Alabama.
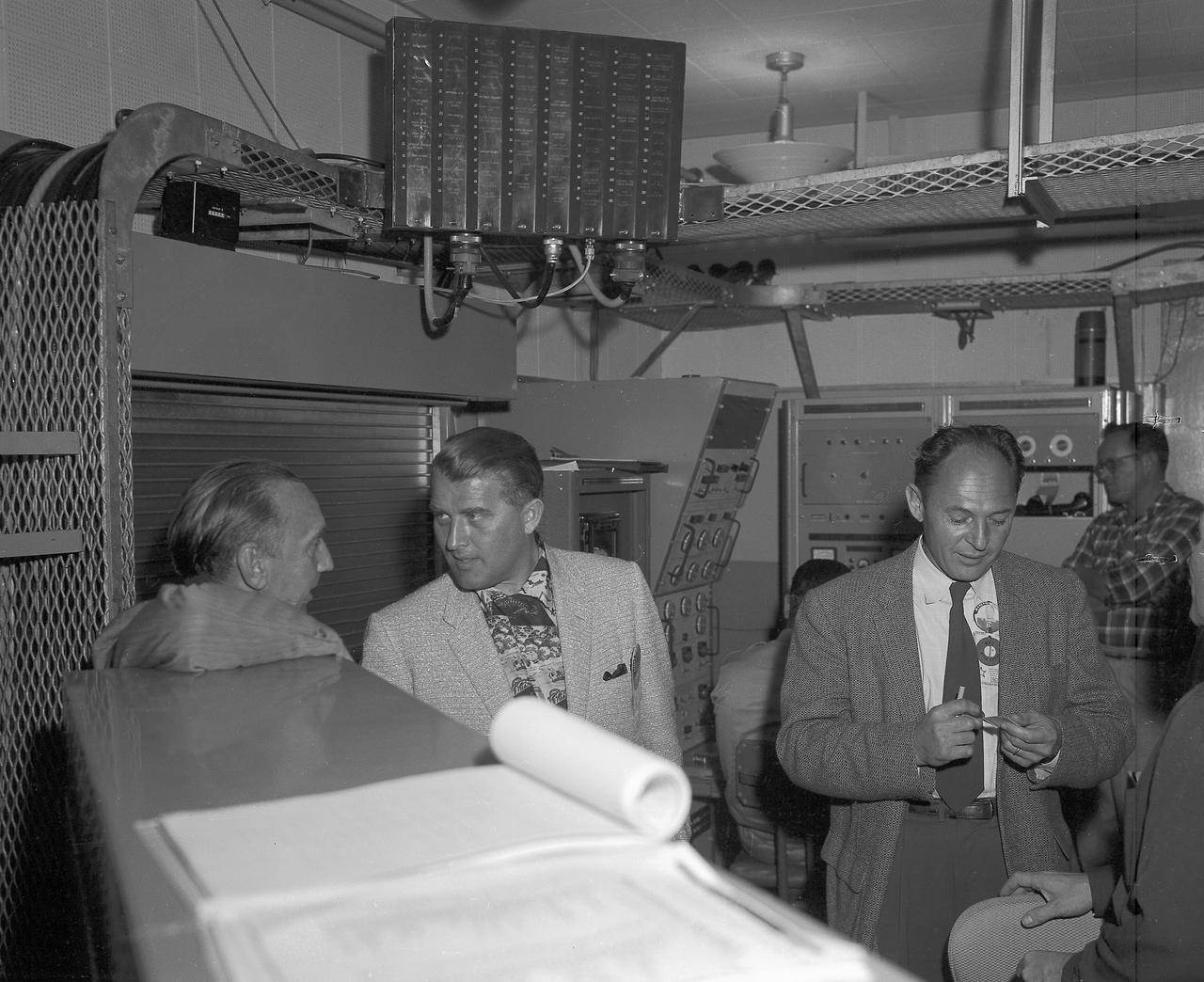

In this photo, (left to right) Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) Missile Firing Laboratory Chief Dr. Kurt Debus, Director of the ABMA Development Operations Division, Dr. von Braun and an unidentified individual in blockhouse during the CM-21 (Jupiter) firing. The Jupiter missile CM-21 became the first Chrysler production qualification missile to be fired and in March 1959 launched the Pioneer IV.
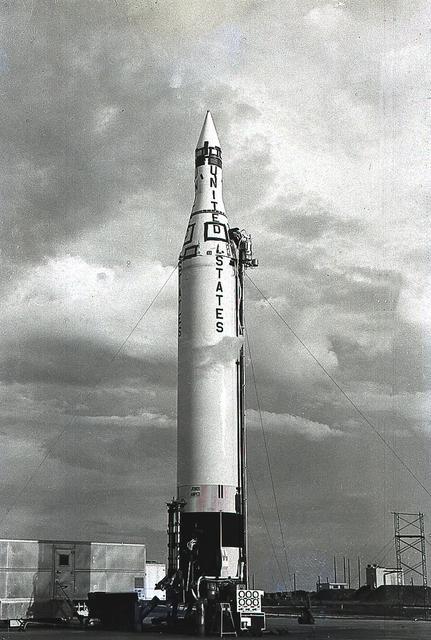
The Juno II launch vehicle, shown here, was a modified Jupiter Intermediate-Range Ballistic missionile, developed by Dr. Wernher von Braun and the rocket team at Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama. Between December 1958 and April 1961, the Juno II launched space probes Pioneer III and IV, as well as Explorer satellites VII, VIII and XI.
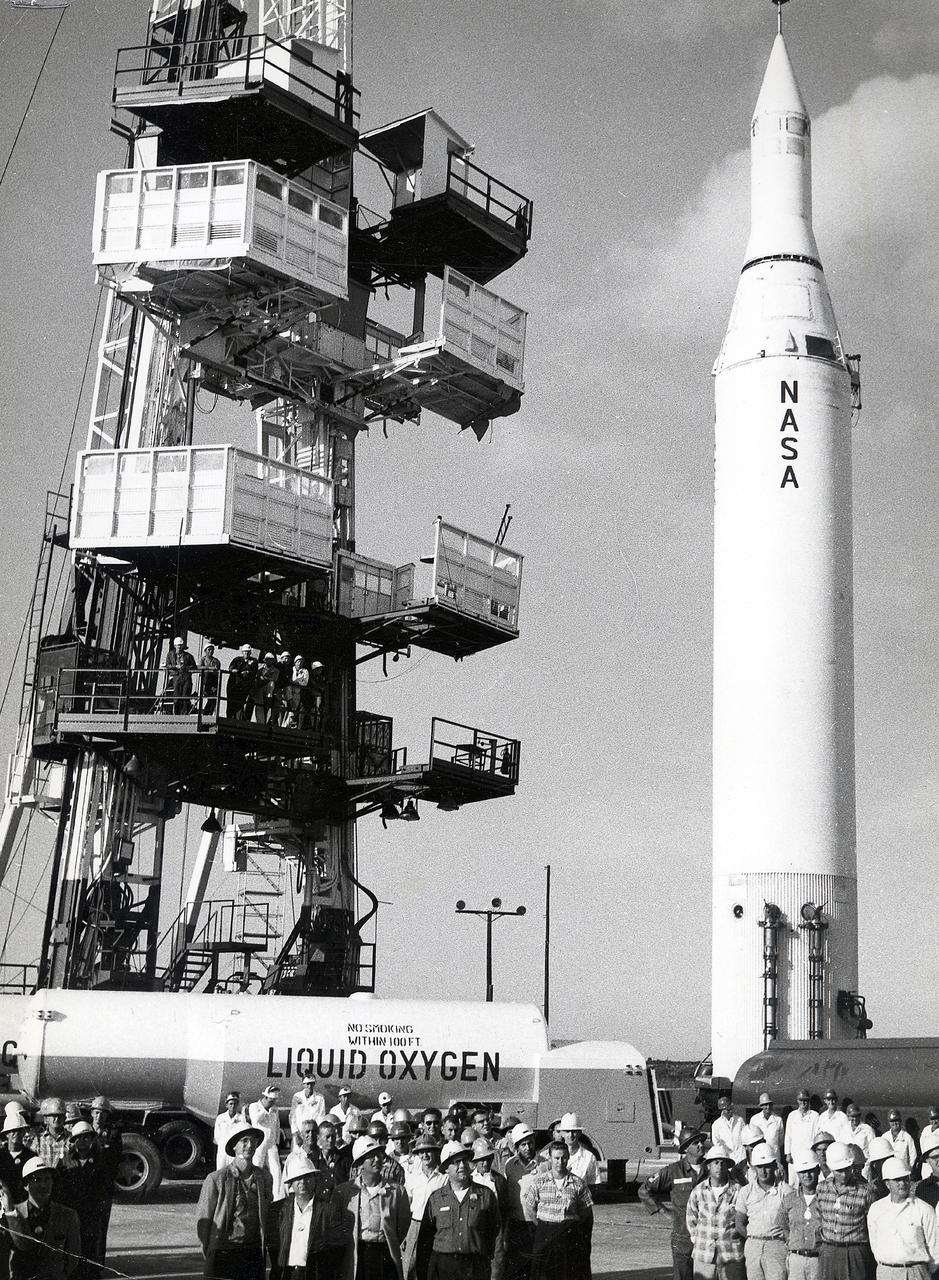

The modified Jupiter C (sometimes called Juno I), used to launch Explorer I, had minimum payload lifting capabilities. Explorer I weighed slightly less than 31 pounds. Juno II was part of America's effort to increase payload lifting capabilities. Among other achievements, the vehicle successfully launched a Pioneer IV satellite on March 3, 1959, and an Explorer VII satellite on October 13, 1959. Responsibility for Juno II passed from the Army to the Marshall Space Flight Center when the Center was activated on July 1, 1960. On November 3, 1960, a Juno II sent Explorer VIII into a 1,000-mile deep orbit within the ionosphere.
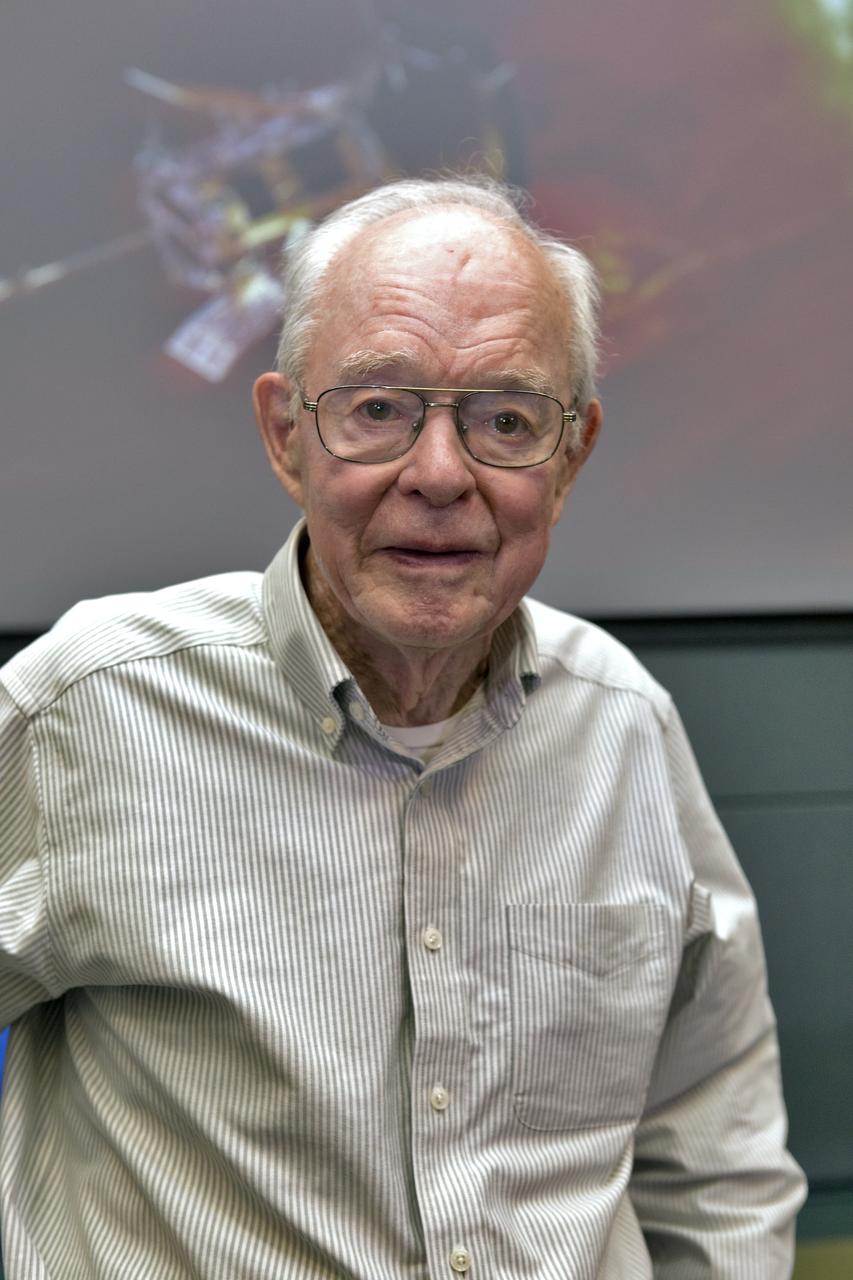

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Operations Support Building II, Dr. Eugene Parker, a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, speaks to members of news and social media in a prelaunch mission briefing about NASA's Parker Solar Probe on Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018. The spacecraft is designed to provide key observations on his groundbreaking theories about the Sun. This is the first NASA mission named for a living person. Lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket will take place from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Operations Support Building II, Dr. Eugene Parker, a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, speaks to members of news and social media in a prelaunch mission briefing about NASA's Parker Solar Probe on Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018. The spacecraft is designed to provide key observations on his groundbreaking theories about the Sun. This is the first NASA mission named for a living person. Lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket will take place from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

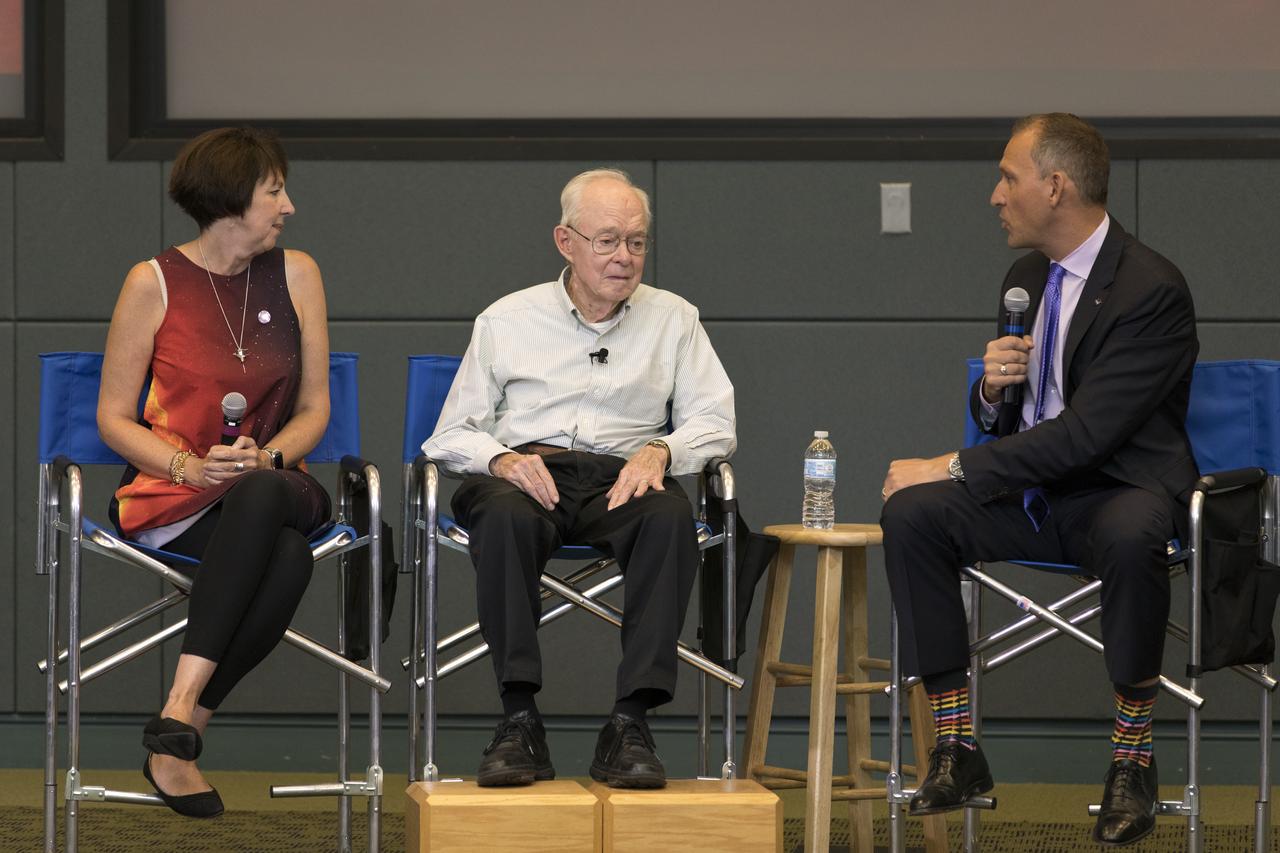
In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the news and social media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Briefing participants from left are: Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Dr. Eugene Parker, a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. This is the first NASA mission named for a living person. The Parker Solar Probe is designed to provide key observations on his groundbreaking theories about the Sun. Lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket will take place from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

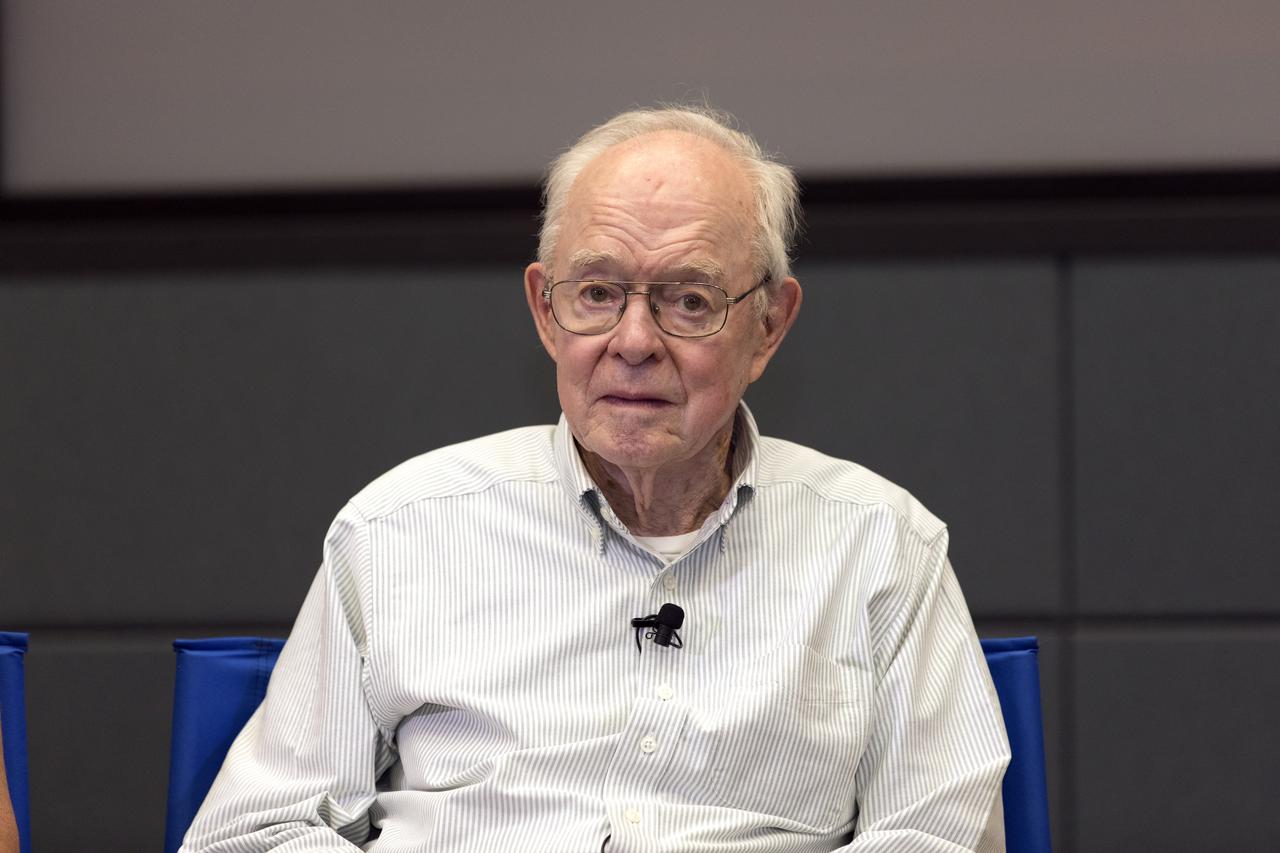
In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the news and social media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Briefing participants from left are: Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Dr. Eugene Parker, a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. This is the first NASA mission named for a living person. The Parker Solar Probe is designed to provide key observations on his groundbreaking theories about the Sun. Lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket will take place from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.