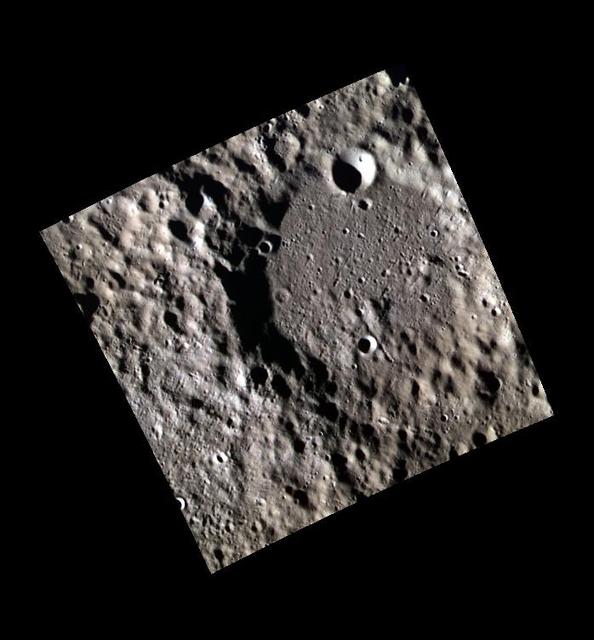

Mercury, a Planetary Punching Bag
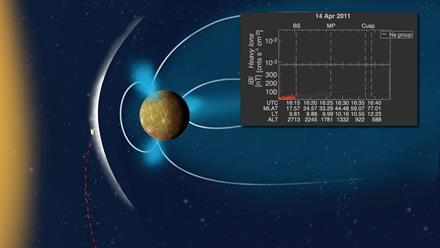
The Distribution of Planetary Ions near Mercury

Near-Earth objects (NEOs) are asteroids and comets that orbit the Sun like the planets with orbits that come within 30 million miles of Earth’s orbit. NASA established the Planetary Defense Coordination Office (PDCO) to manage the agency’s ongoing efforts in Planetary Defense, which is the “applied planetary science” to address the NEO impact hazard. One key element of the PDCO is NASA’s NEO Observations program, which is composed of projects to find, track, and characterize NEOs. Here’s what we’ve found so far. This page is updated monthly with the most up-to-date numbers.

Lindley Johnson, NASA’s Planetary Defense Officer and Program Executive of the Planetary Defense Coordination Office (PDCO), is seen in the audience at the sixth International Academy of Astronautics Planetary Defense Conference, Monday, April 29, 2019 at The Hotel at the University of Maryland in College Park Maryland. The conference brings together experts from around the world to present the latest research on Near-Earth Objects and will highlight the development of the first-ever mission to demonstrate an asteroid defection technique for planetary defense, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART). Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
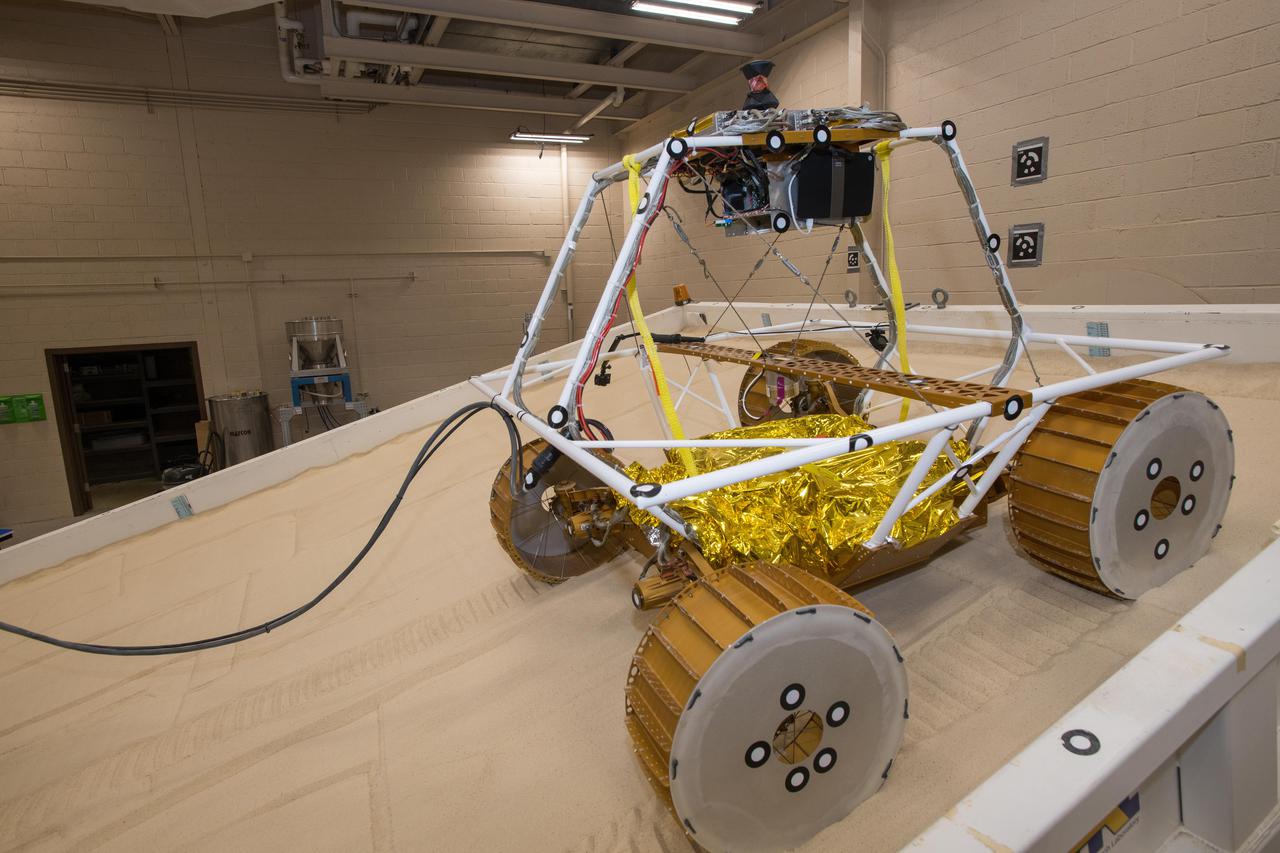
Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
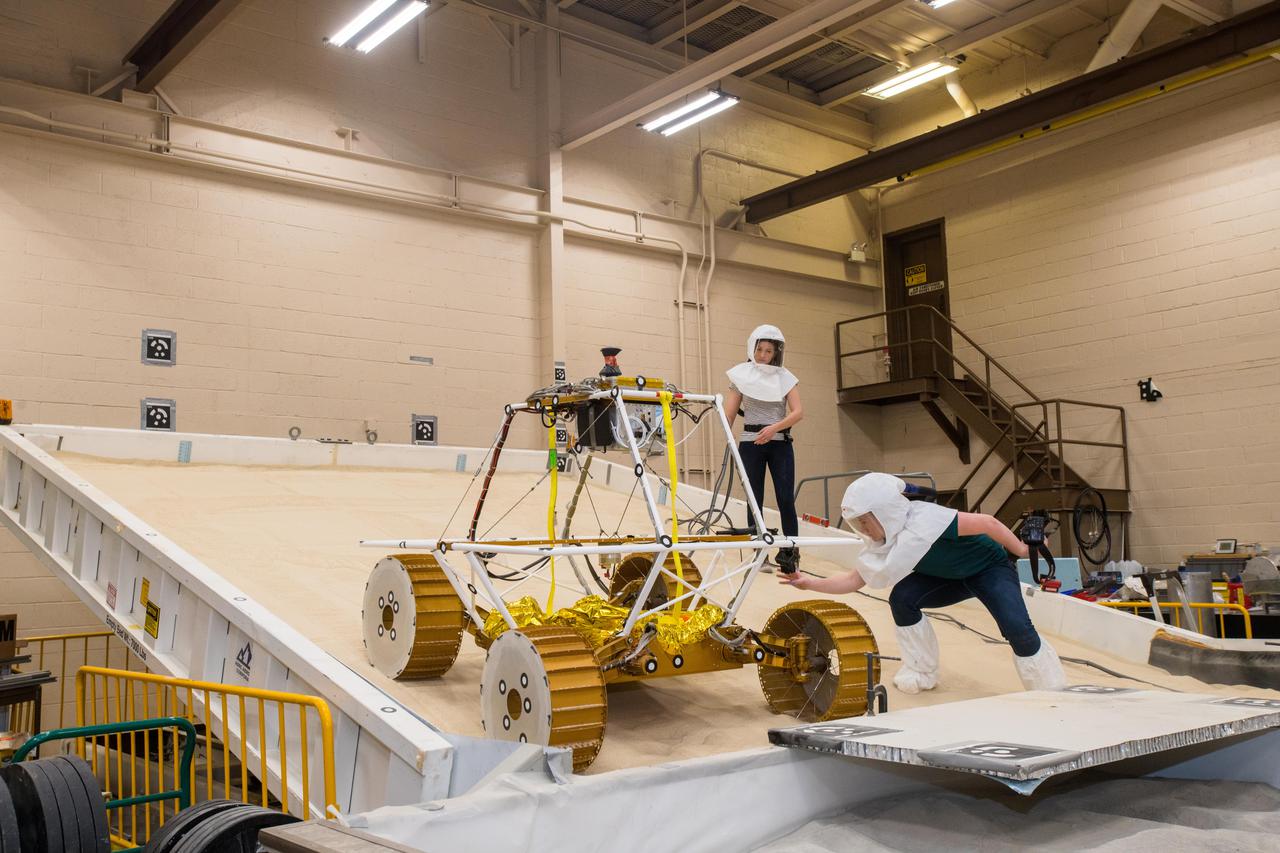

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
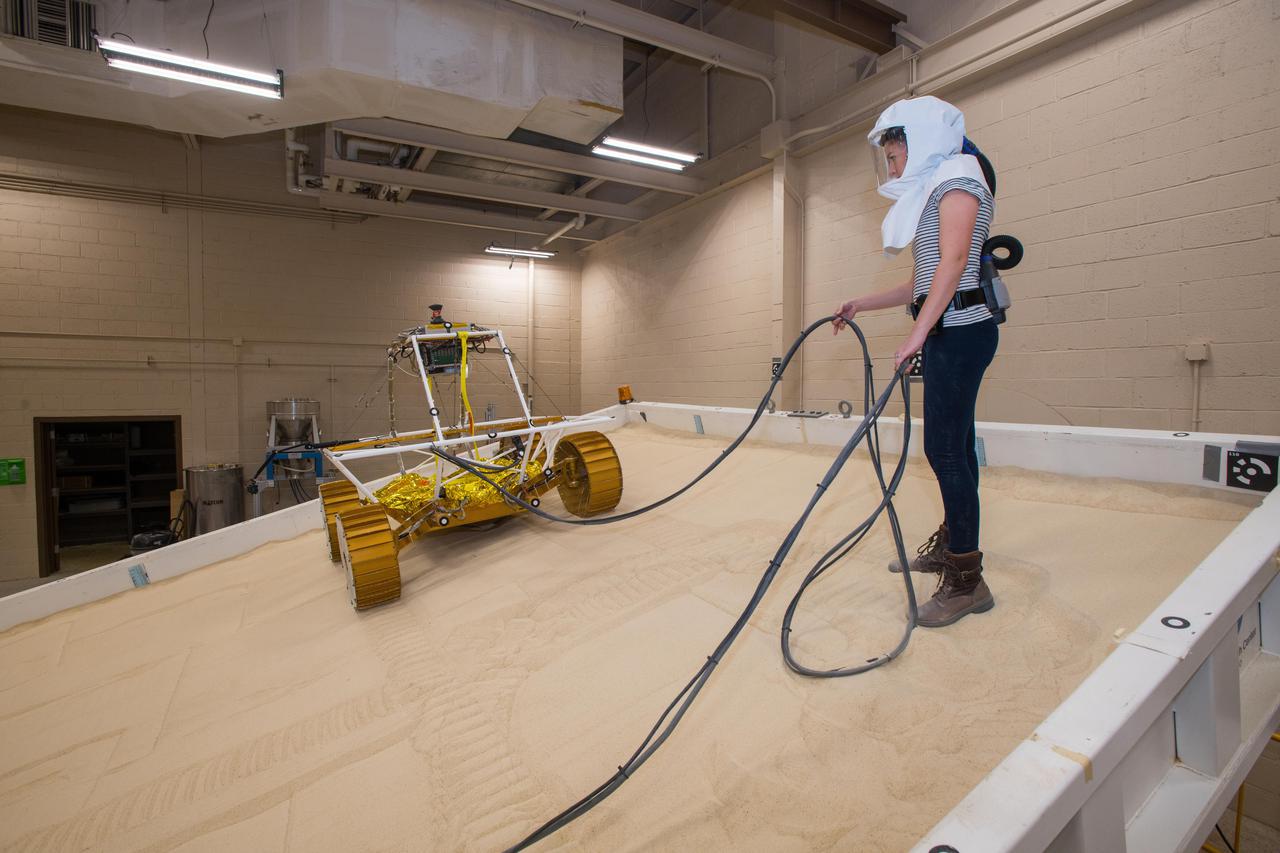

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
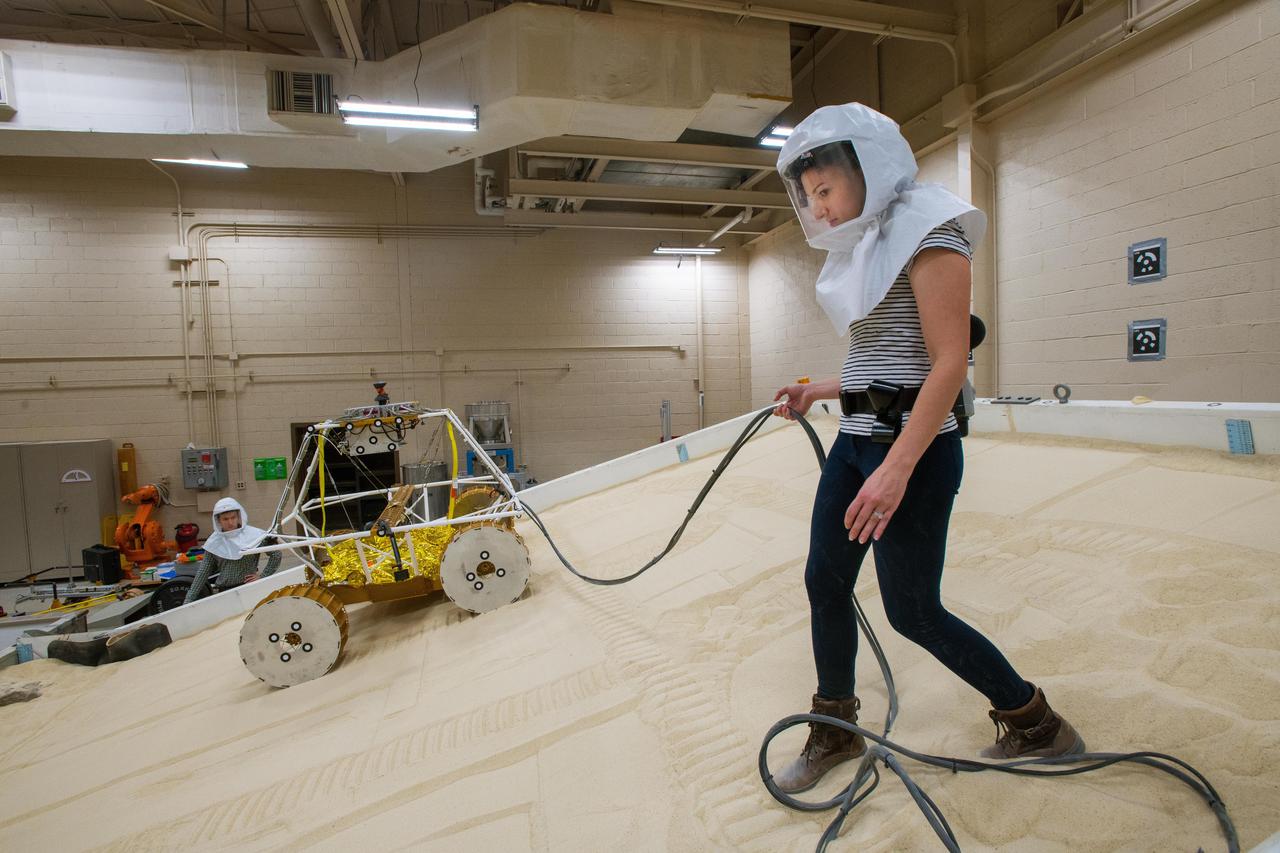

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
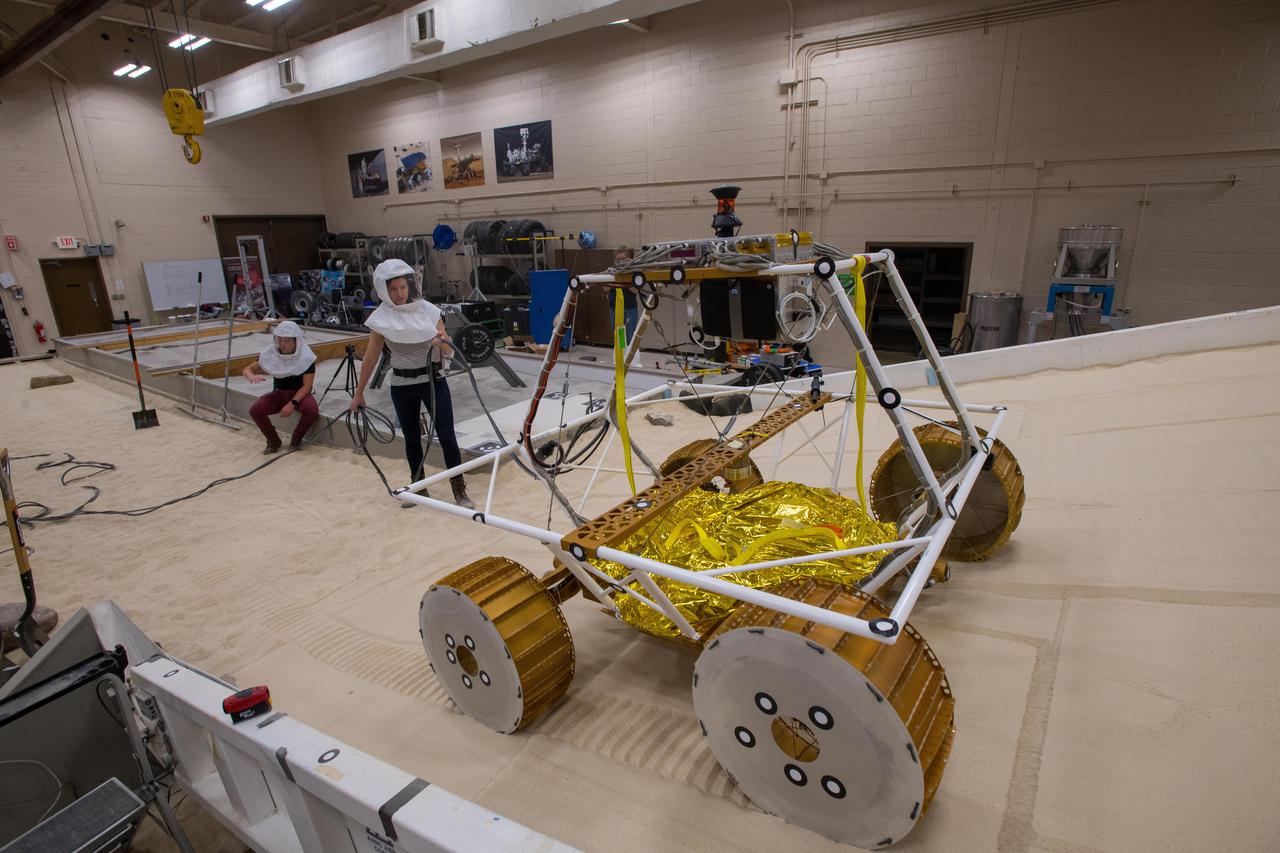

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
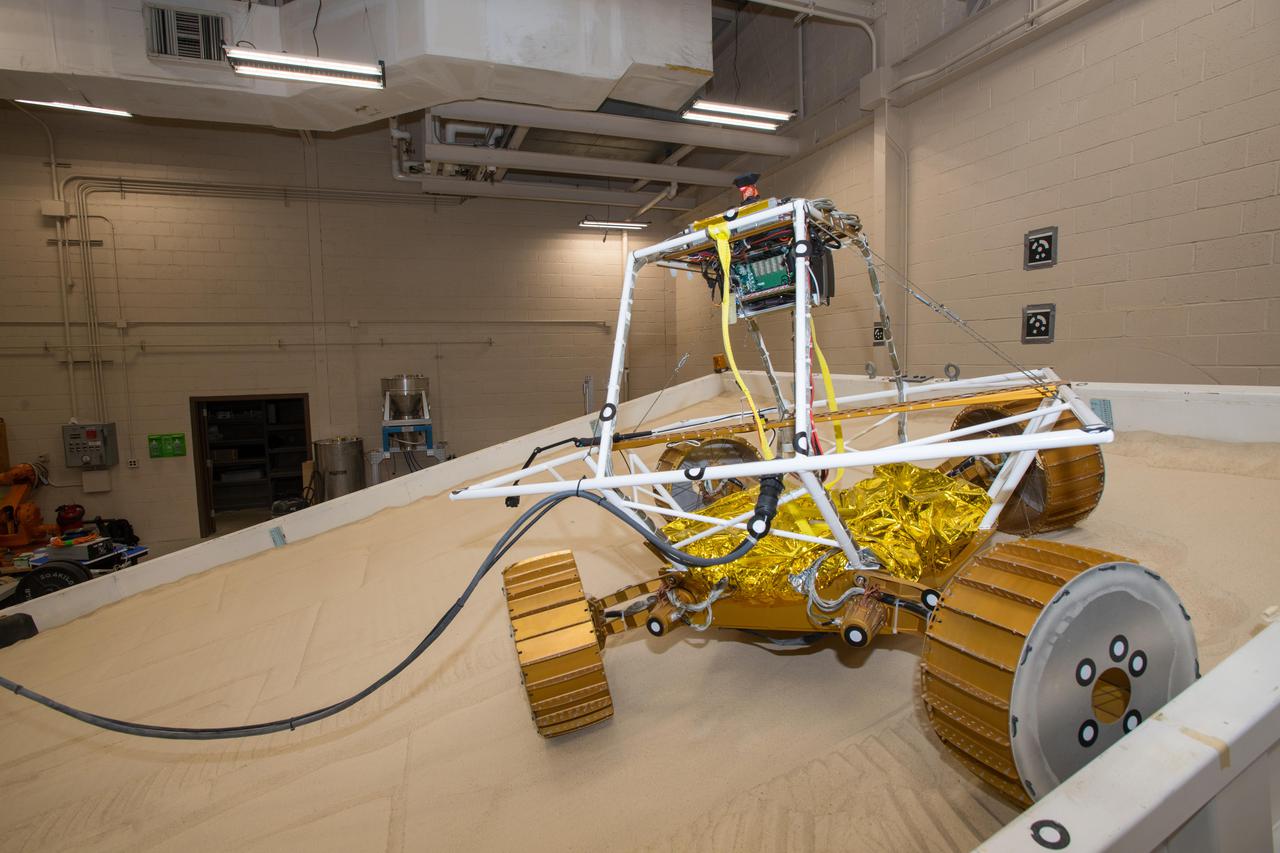

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
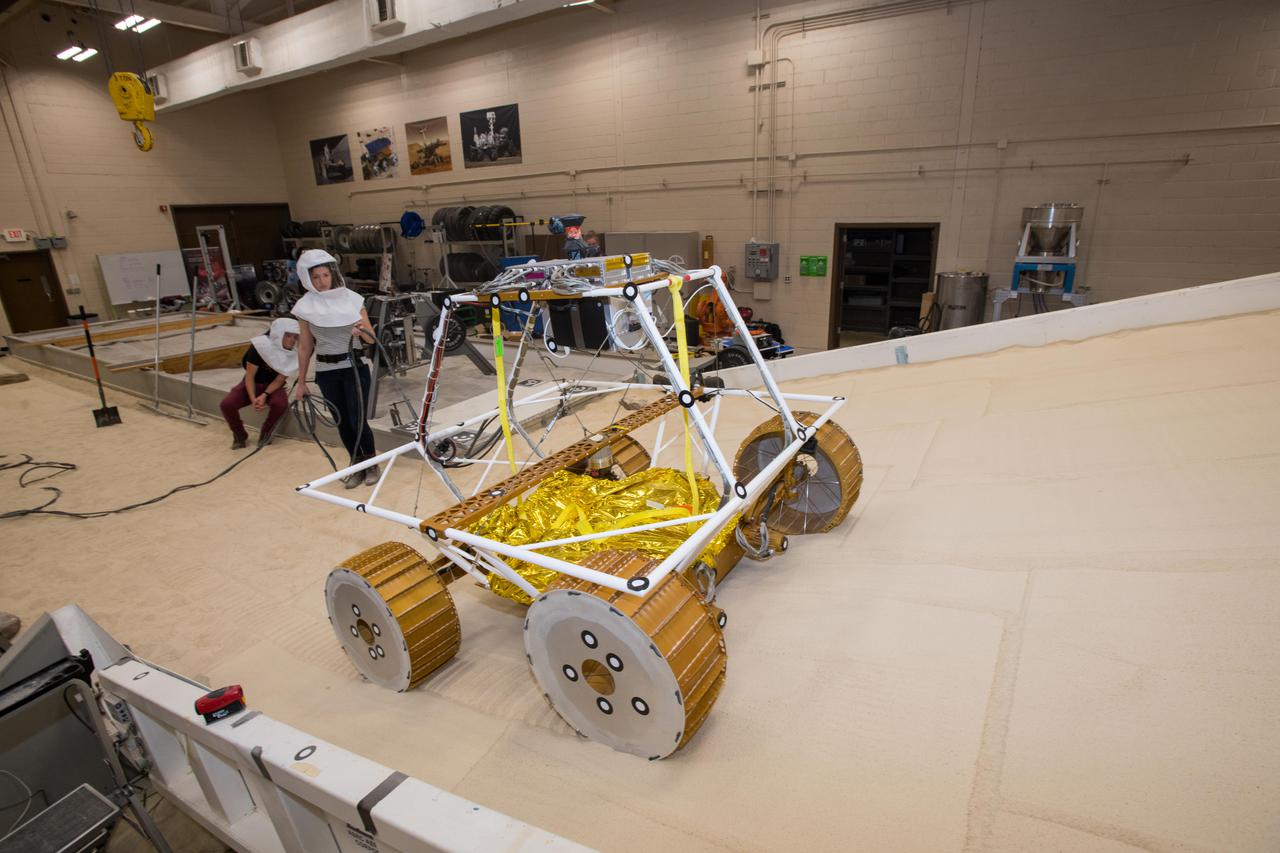
Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
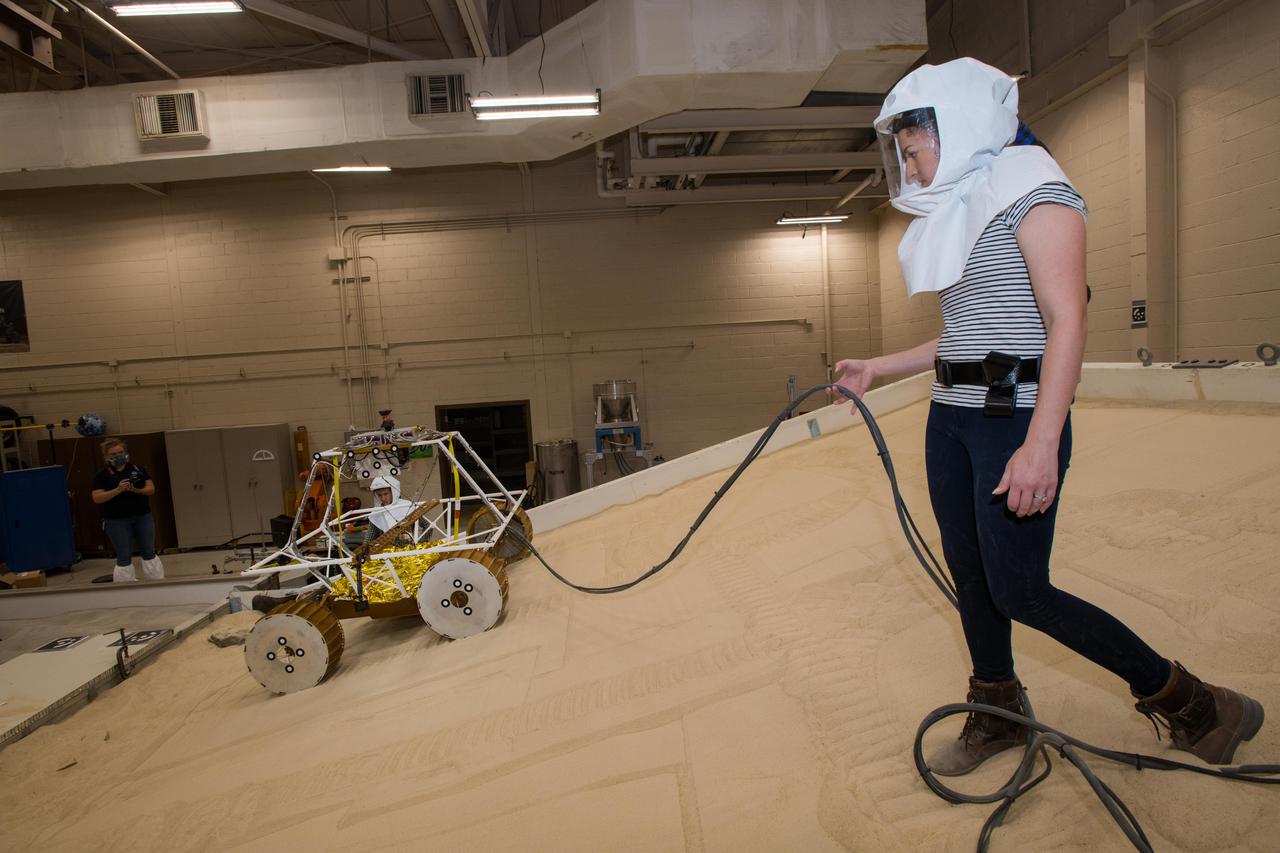

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
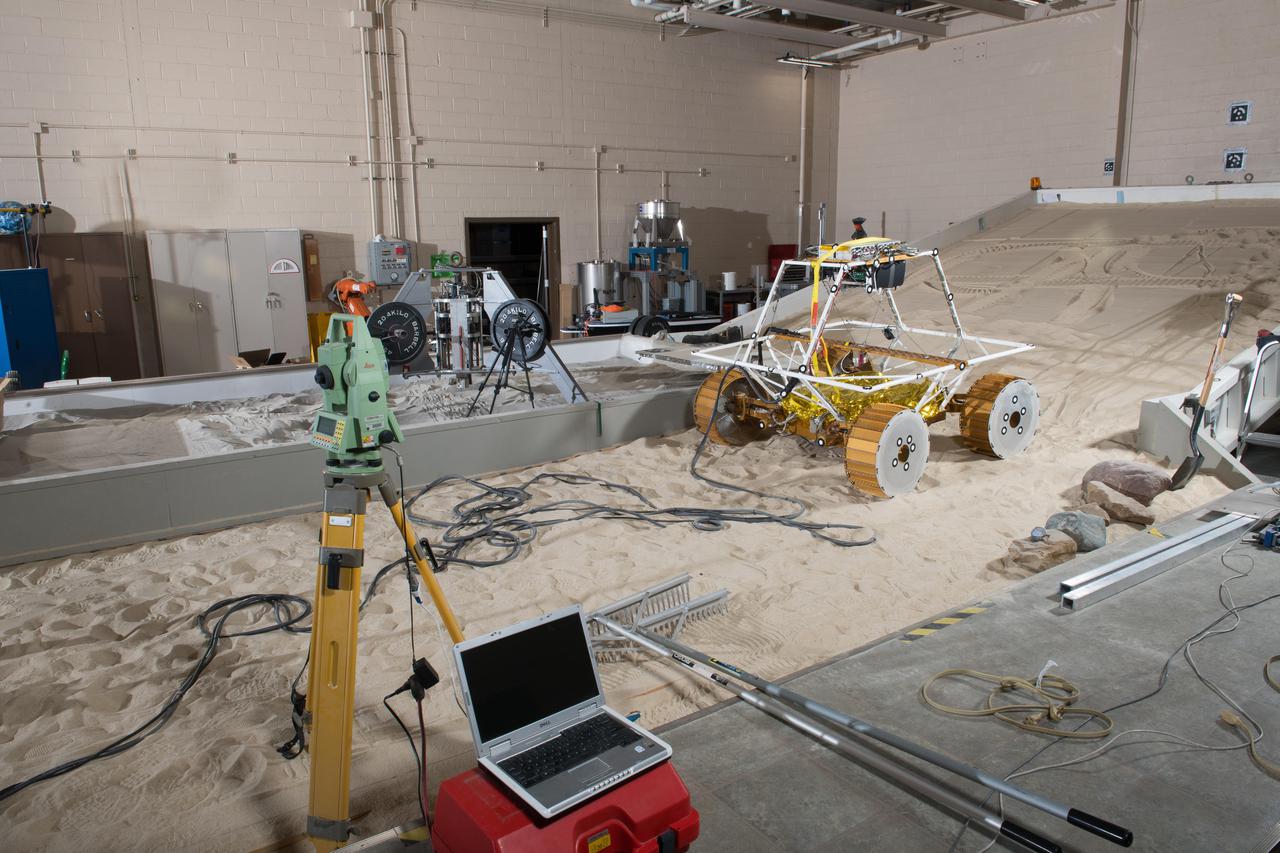

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
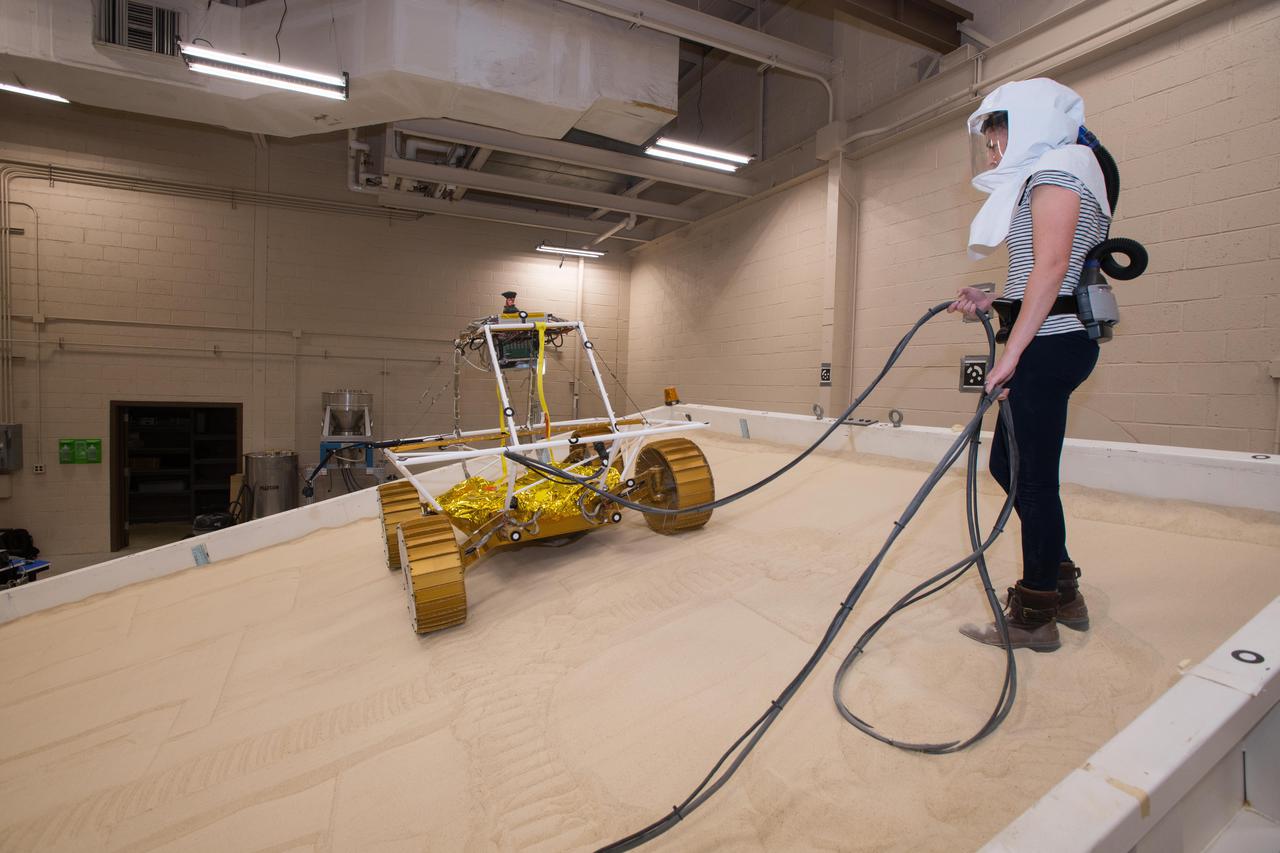

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
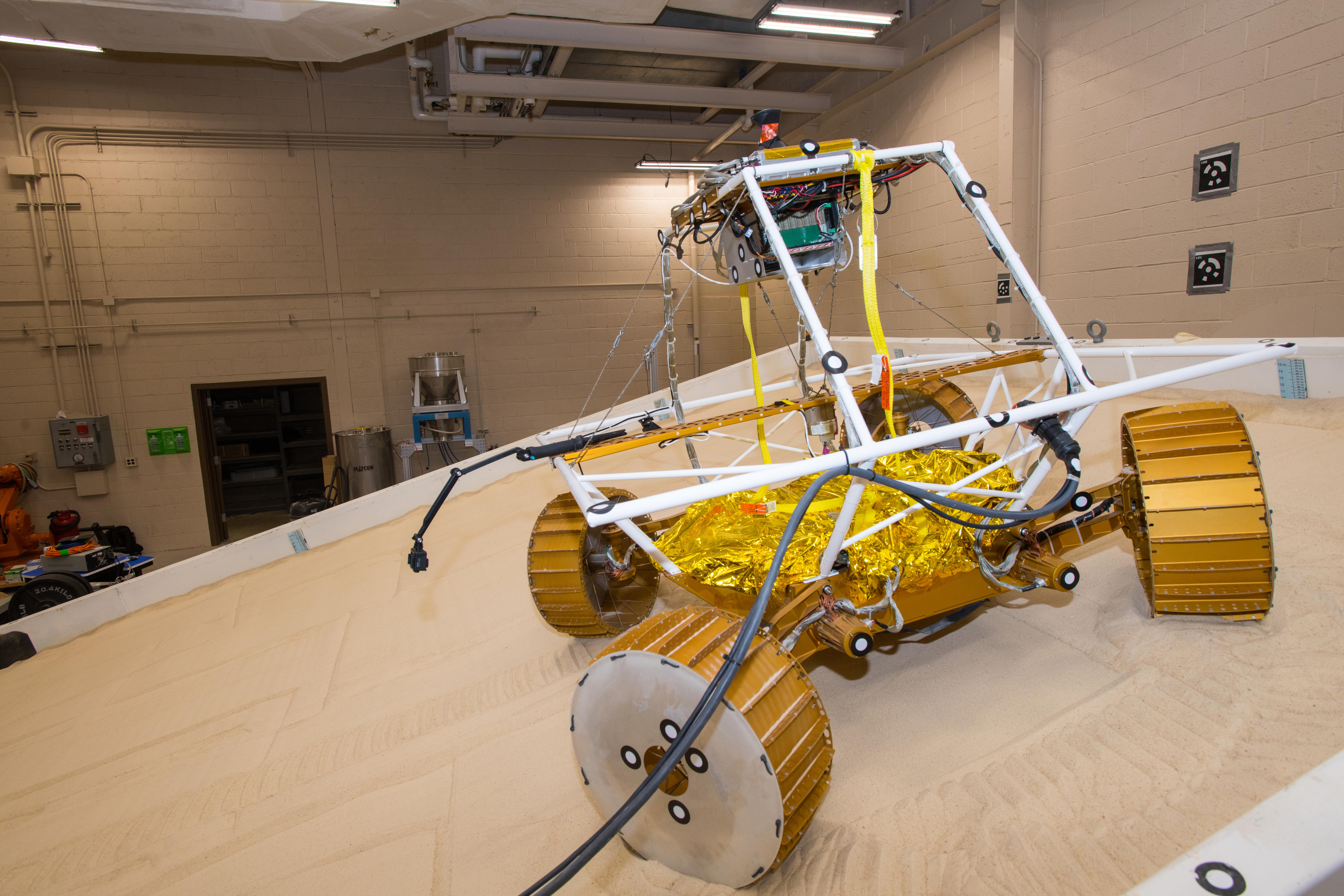
Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
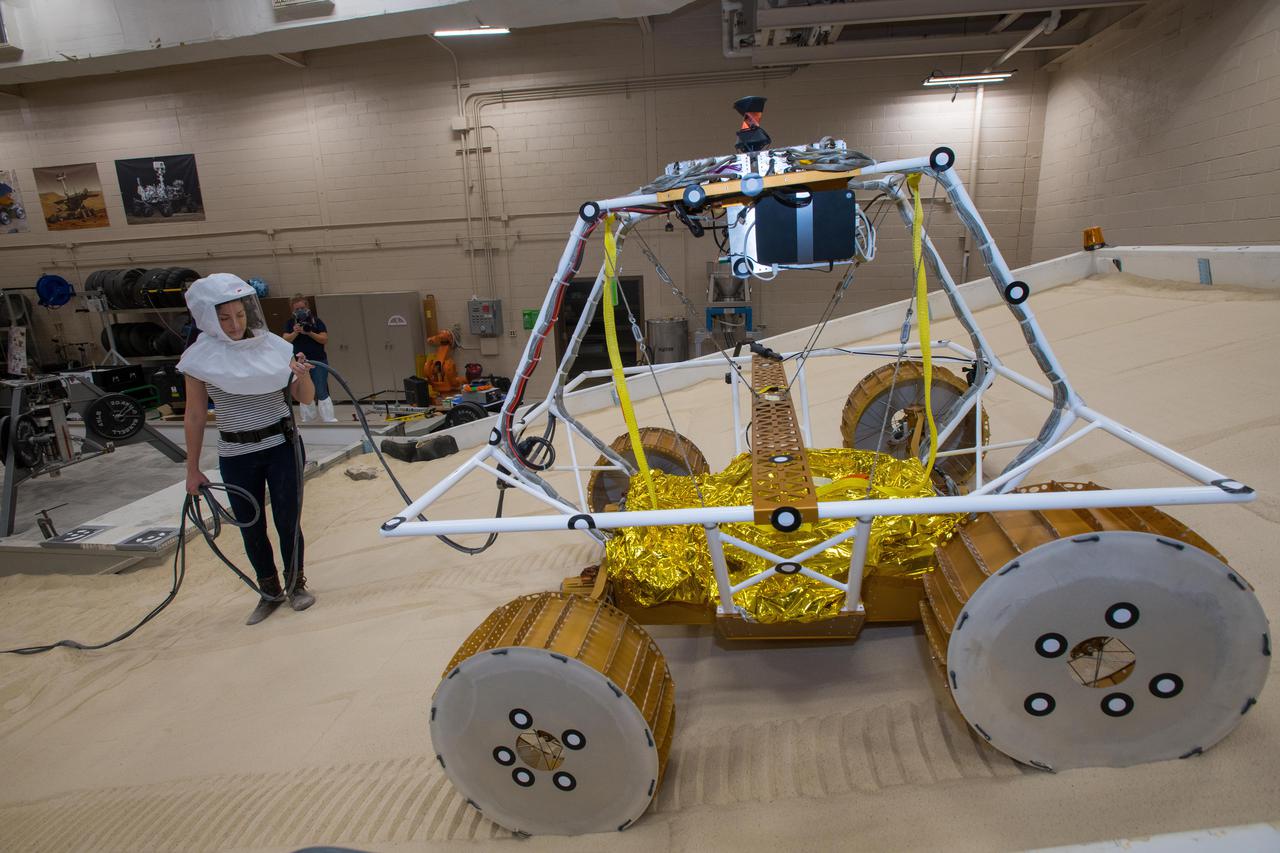

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
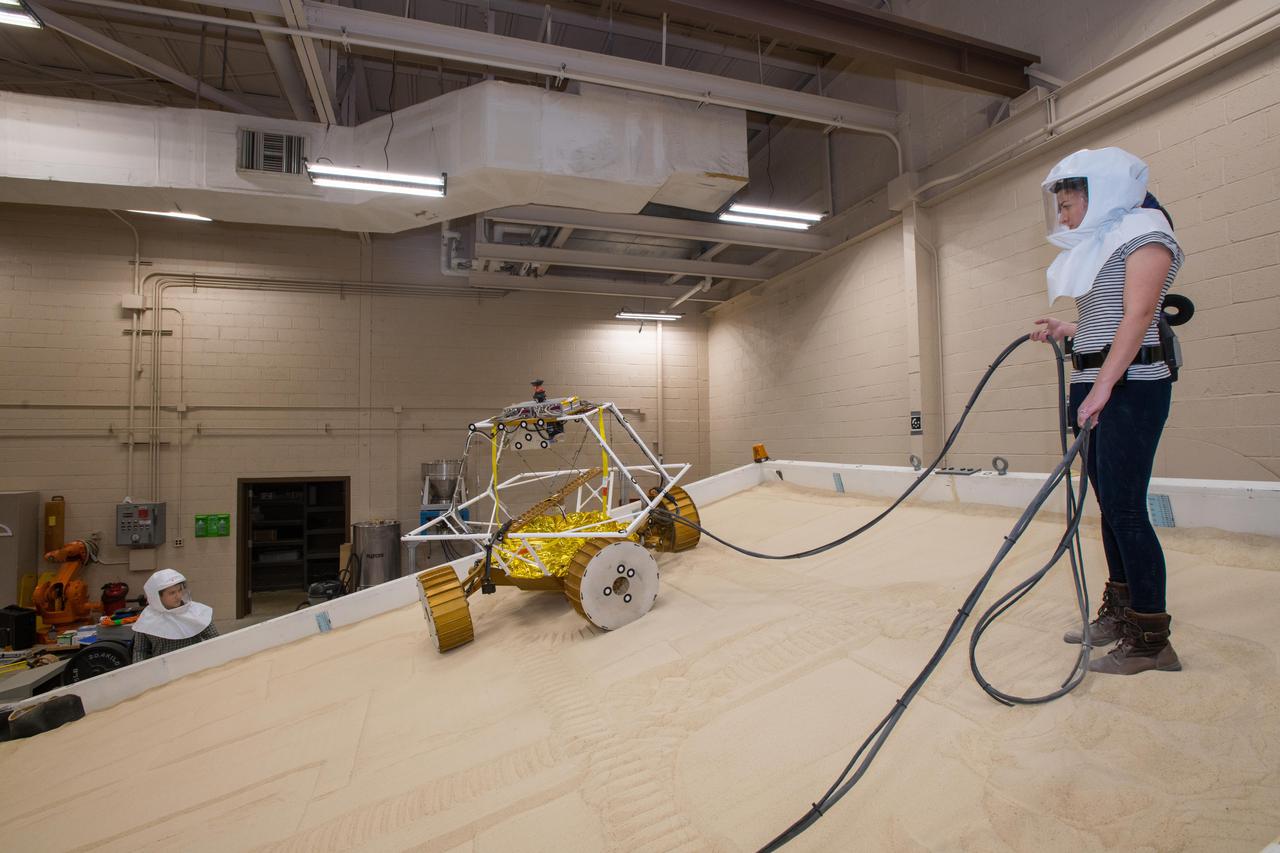

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
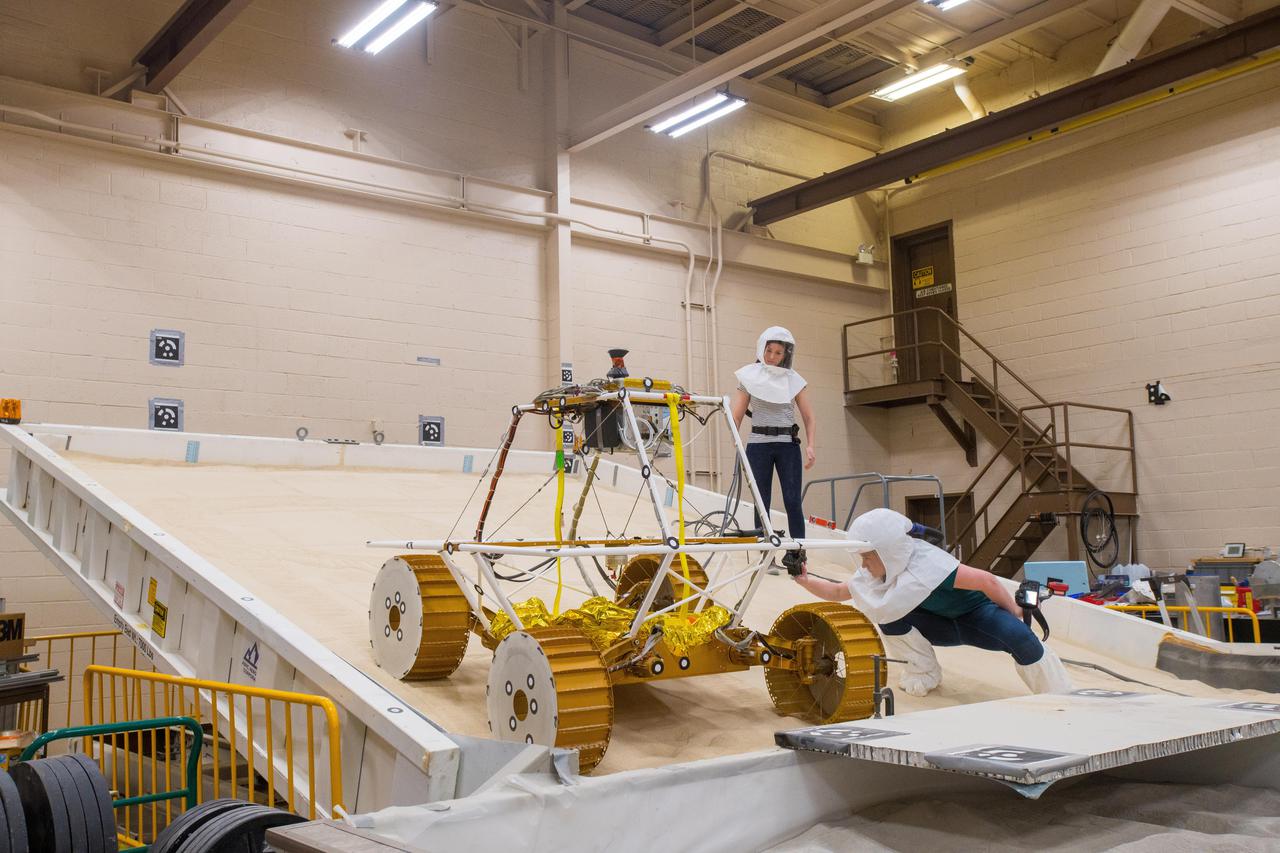

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
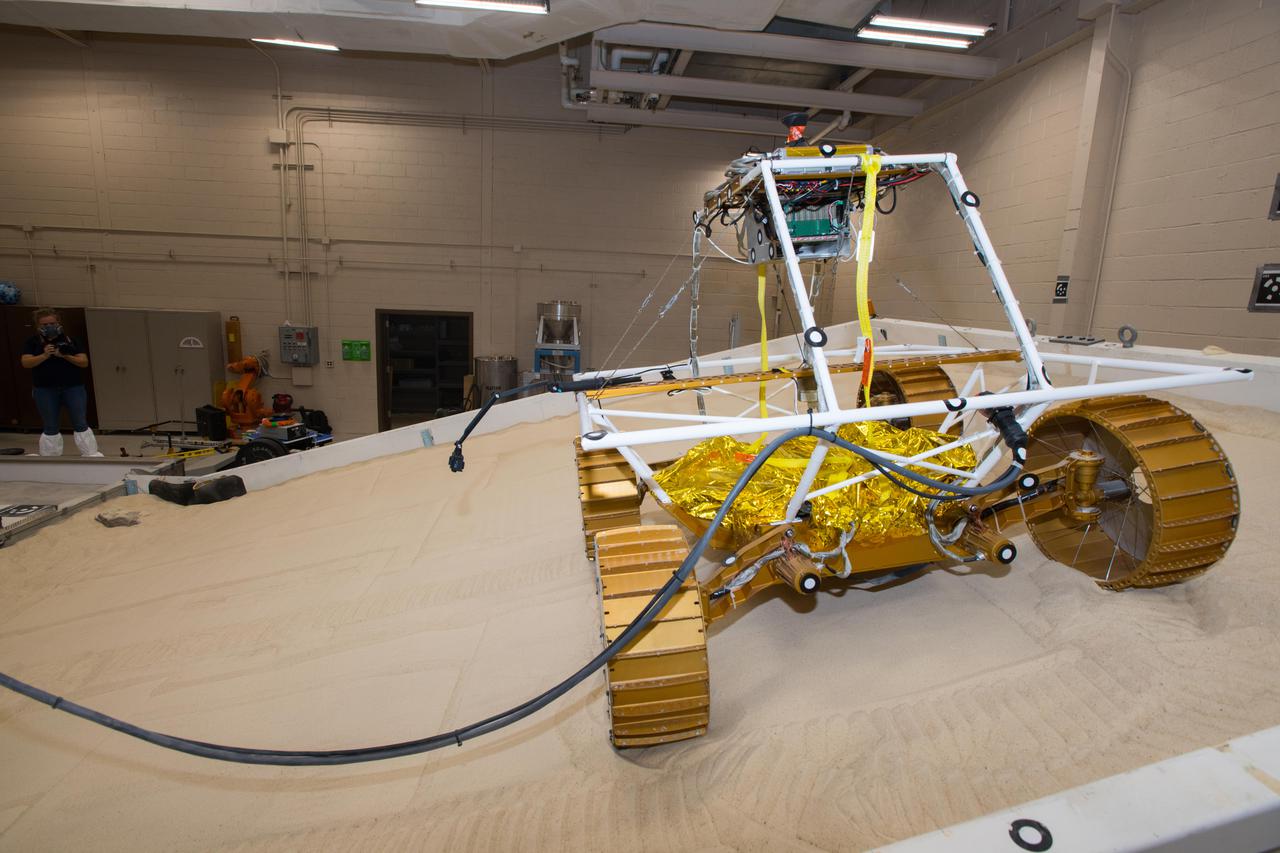
Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
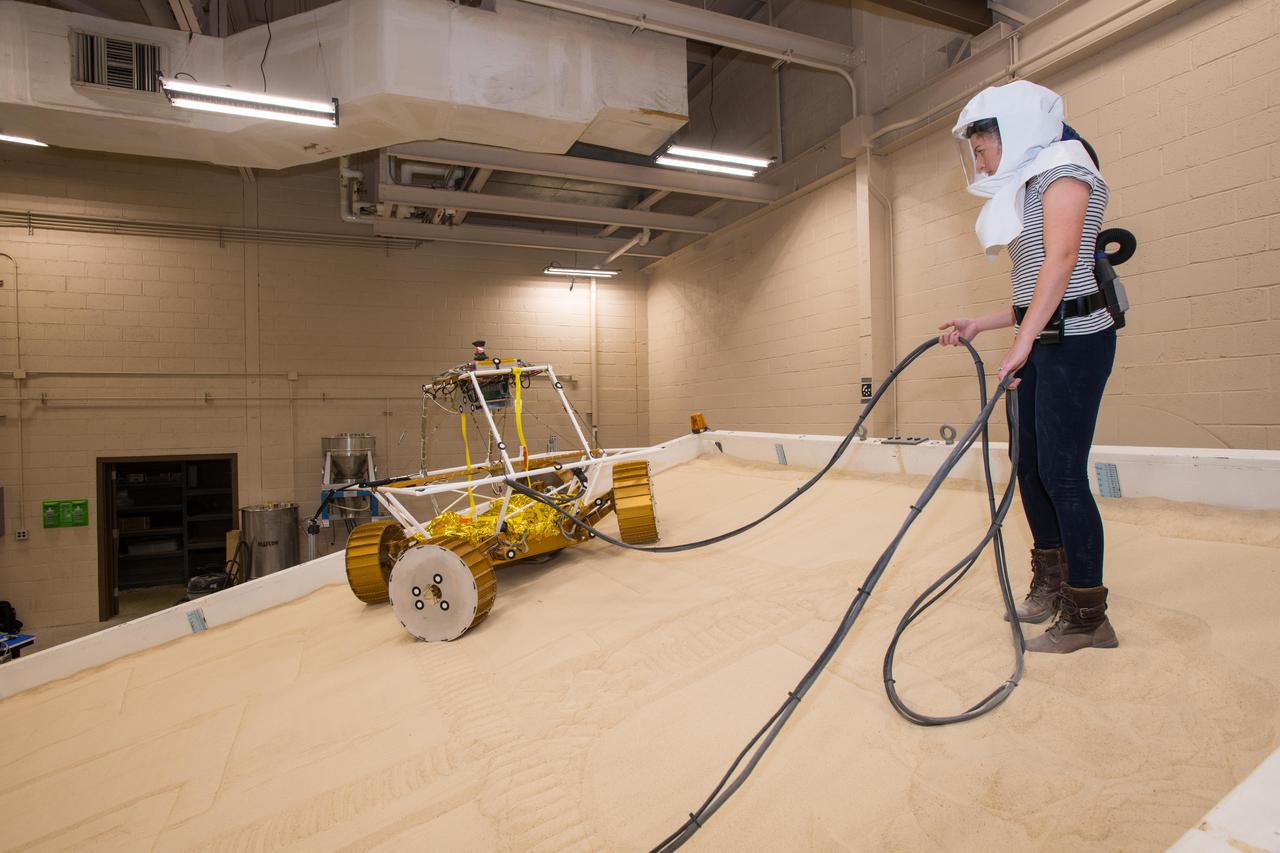

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing

This planetary nebula's simple, graceful appearance is thought to be due to perspective: our view from Earth looking straight into what is actually a barrel-shaped cloud of gas shrugged off by a dying central star. Hot blue gas near the energizing central star gives way to progressively cooler green and yellow gas at greater distances with the coolest red gas along the outer boundary. Credit: NASA/Hubble Heritage Team ---- The Ring Nebula's distinctive shape makes it a popular illustration for astronomy books. But new observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope of the glowing gas shroud around an old, dying, sun-like star reveal a new twist. "The nebula is not like a bagel, but rather, it's like a jelly doughnut, because it's filled with material in the middle," said C. Robert O'Dell of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. He leads a research team that used Hubble and several ground-based telescopes to obtain the best view yet of the iconic nebula. The images show a more complex structure than astronomers once thought and have allowed them to construct the most precise 3-D model of the nebula. "With Hubble's detail, we see a completely different shape than what's been thought about historically for this classic nebula," O'Dell said. "The new Hubble observations show the nebula in much clearer detail, and we see things are not as simple as we previously thought." The Ring Nebula is about 2,000 light-years from Earth and measures roughly 1 light-year across. Located in the constellation Lyra, the nebula is a popular target for amateur astronomers. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14VAOMk" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14VAOMk</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
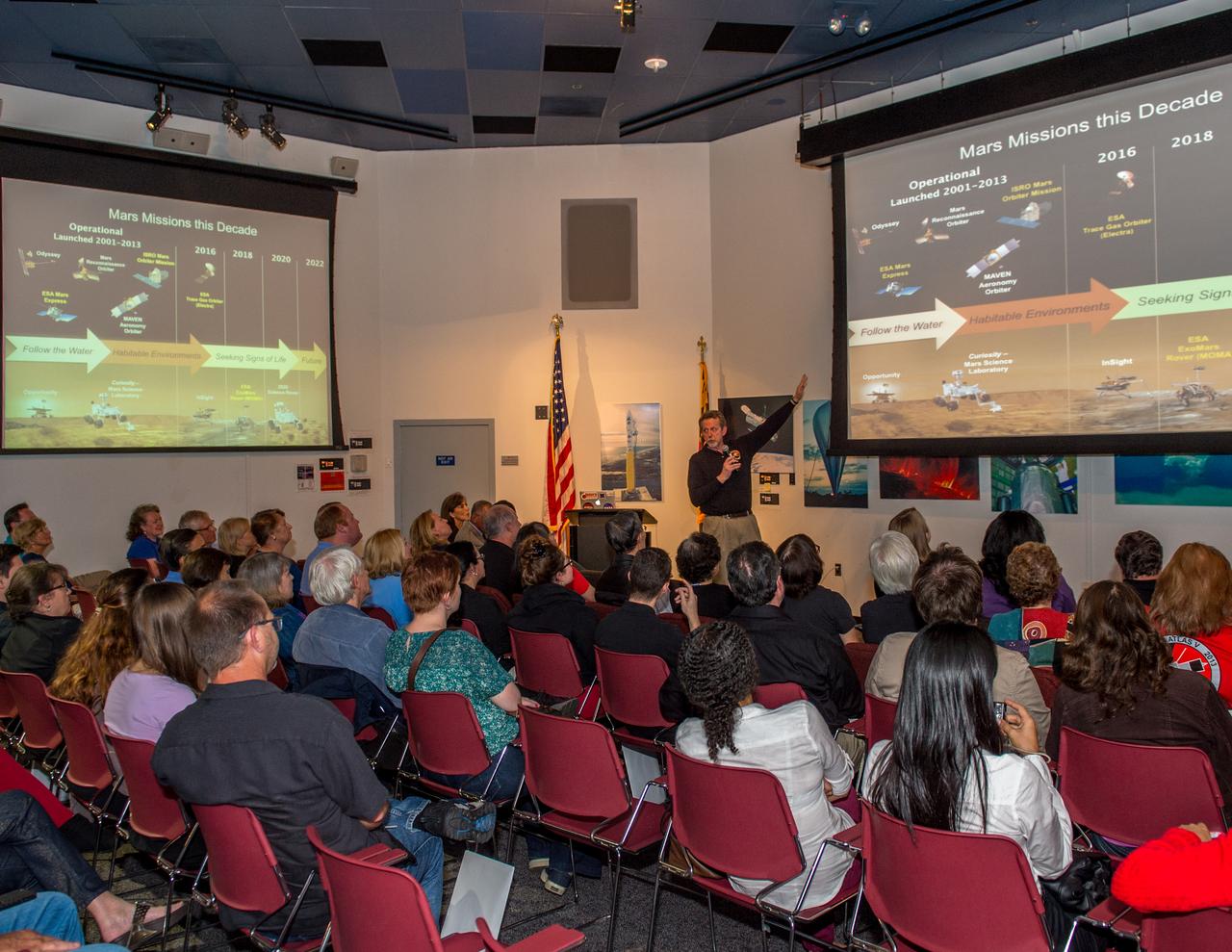

James Green , NASA PLanetary Science Division Director at the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission (MAVEN) ORBIT INSERTION event
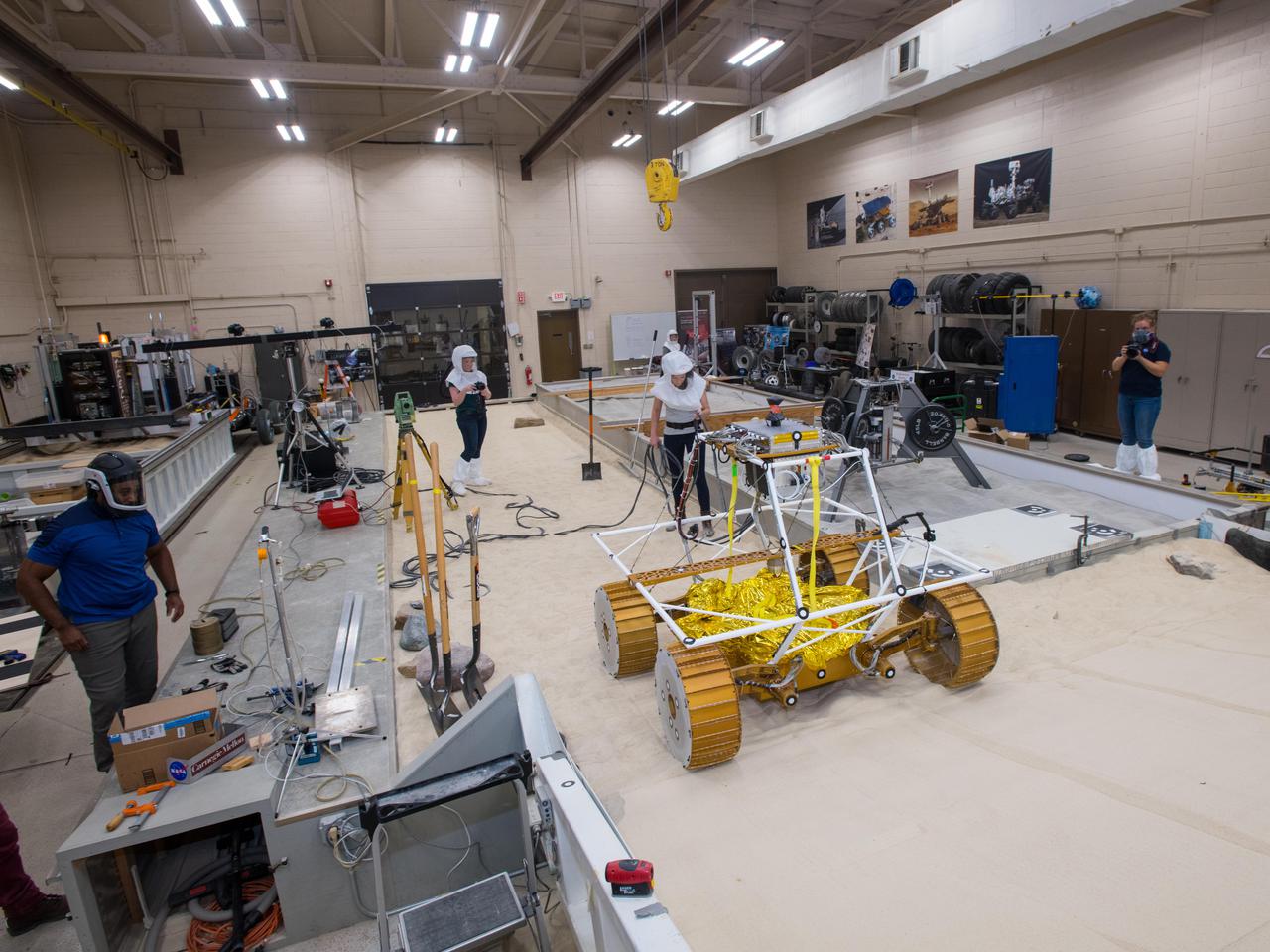

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
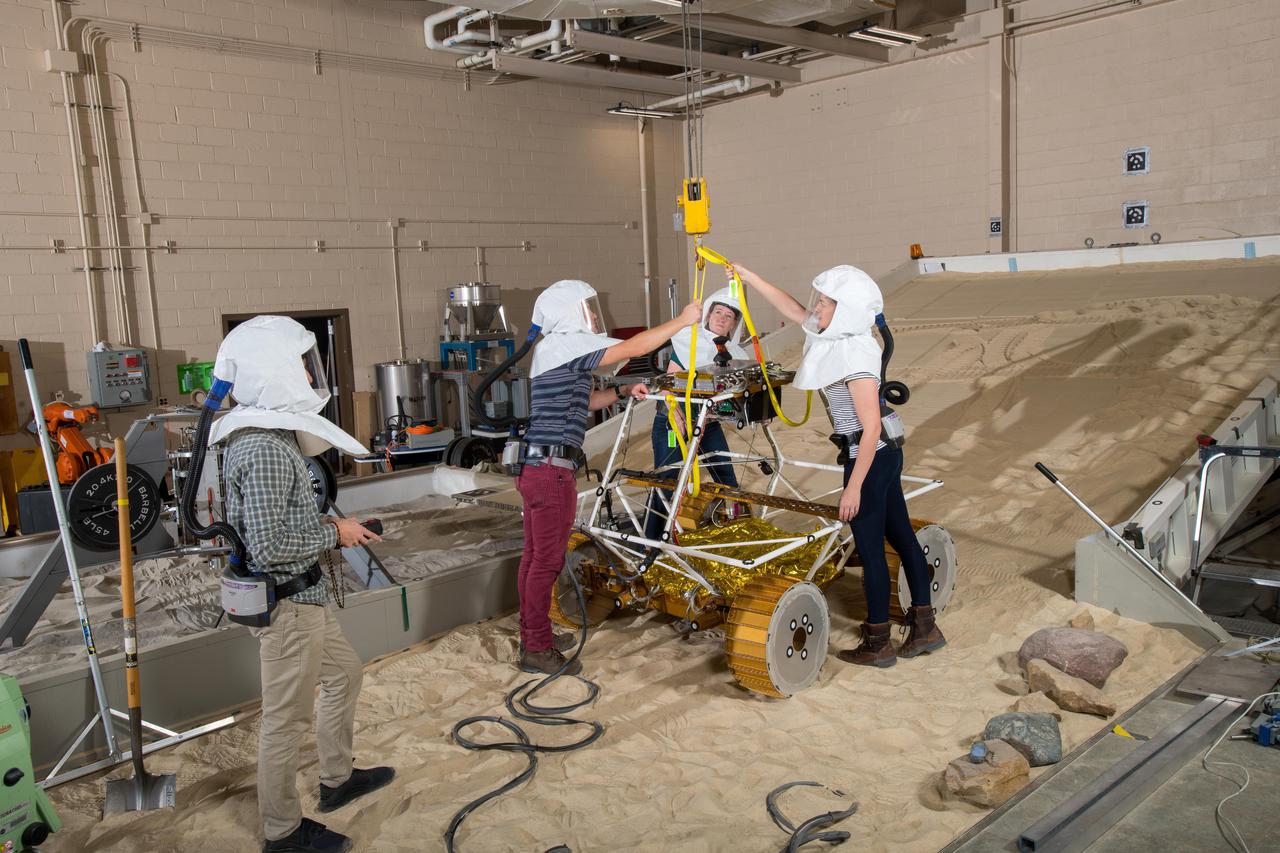

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
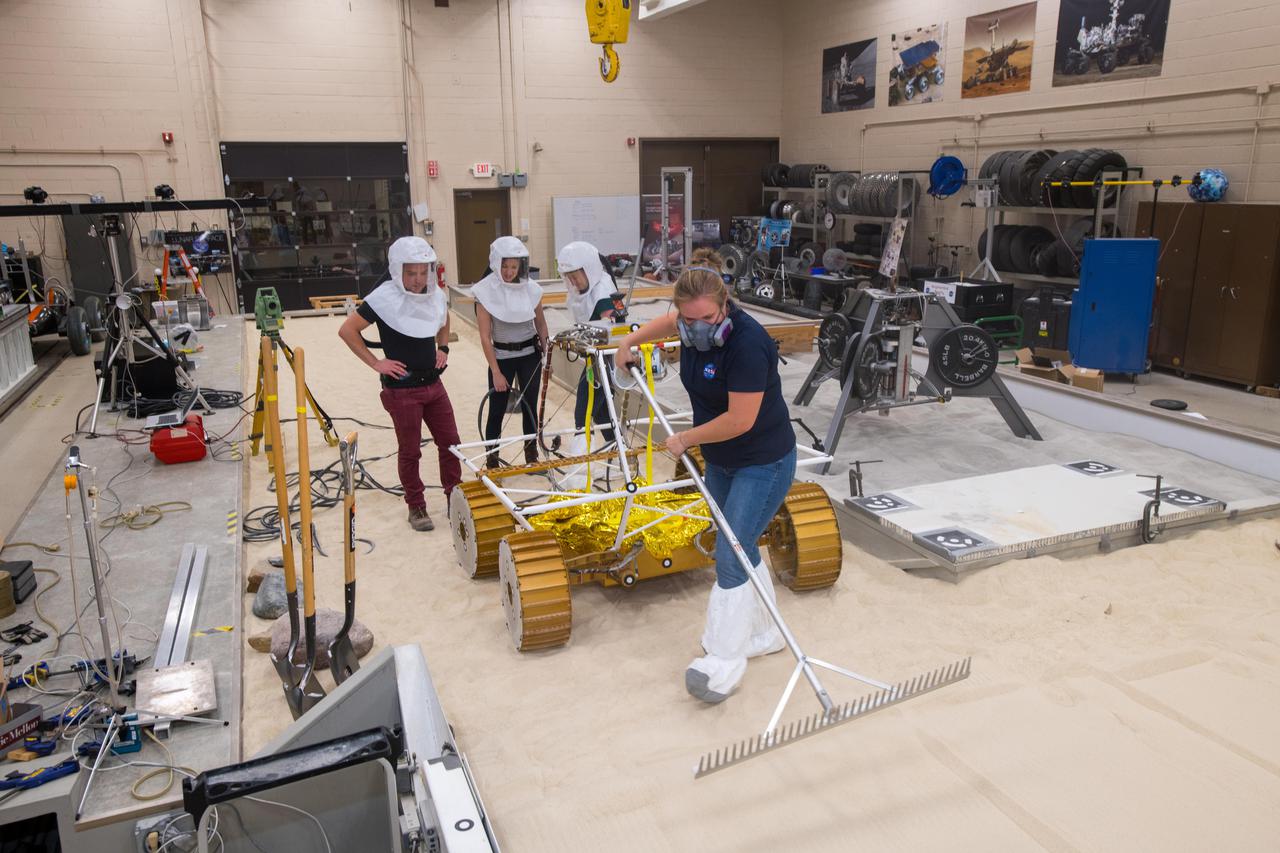

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
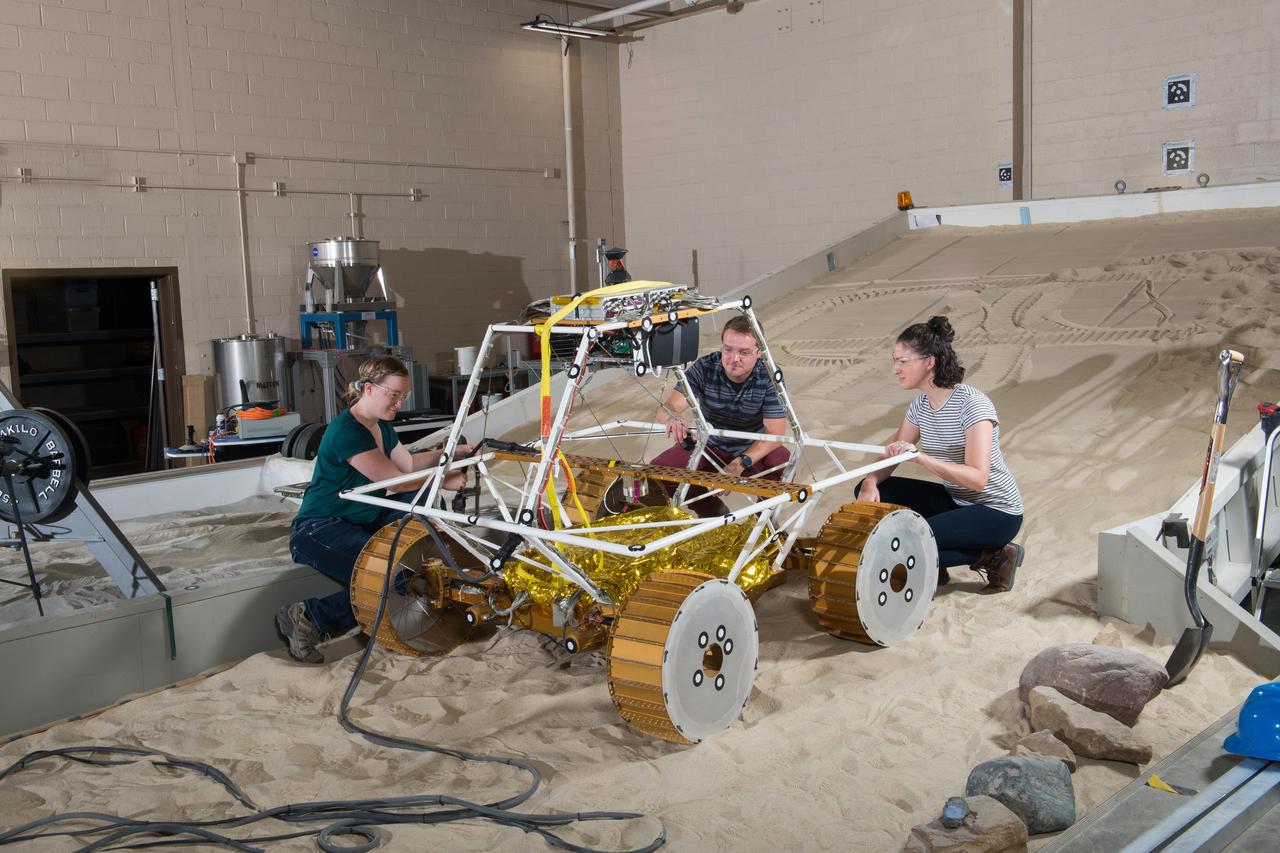

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
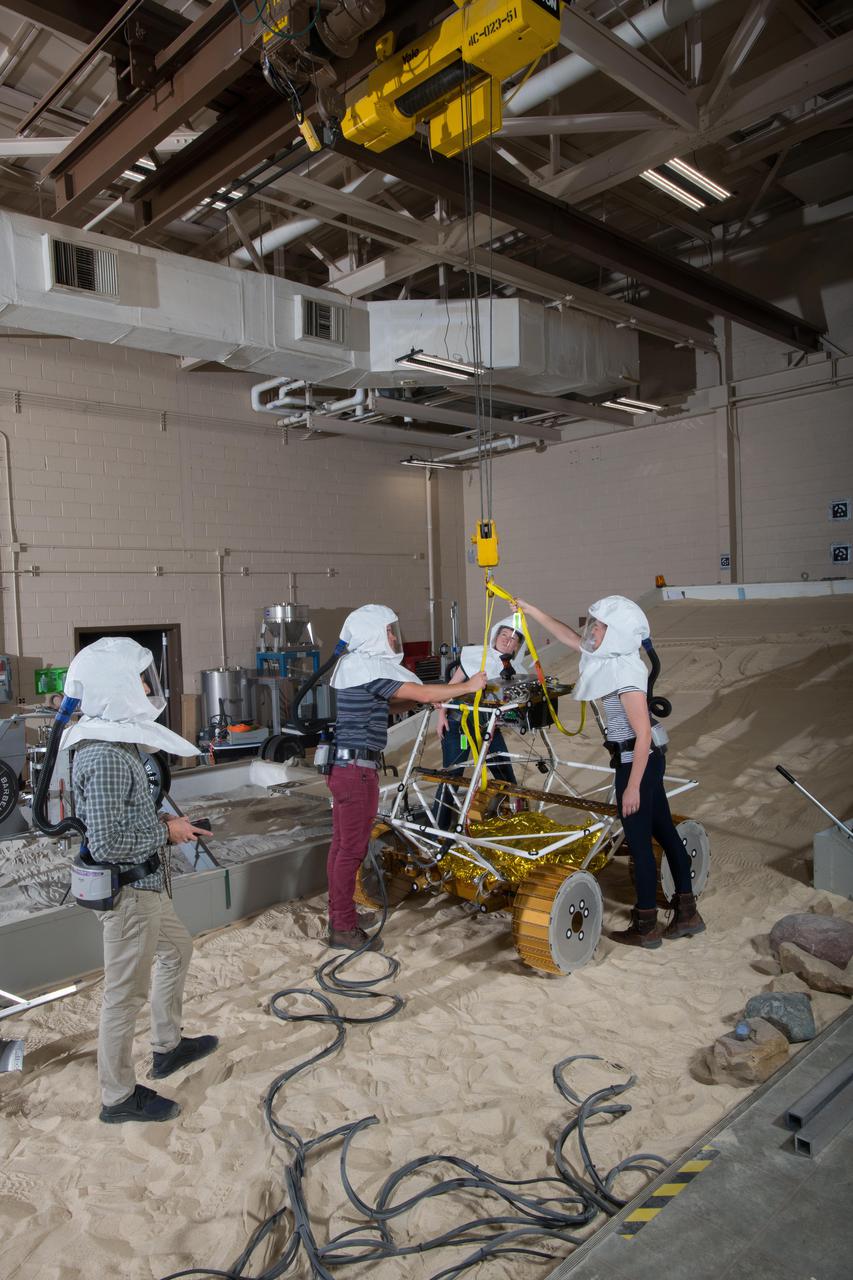

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
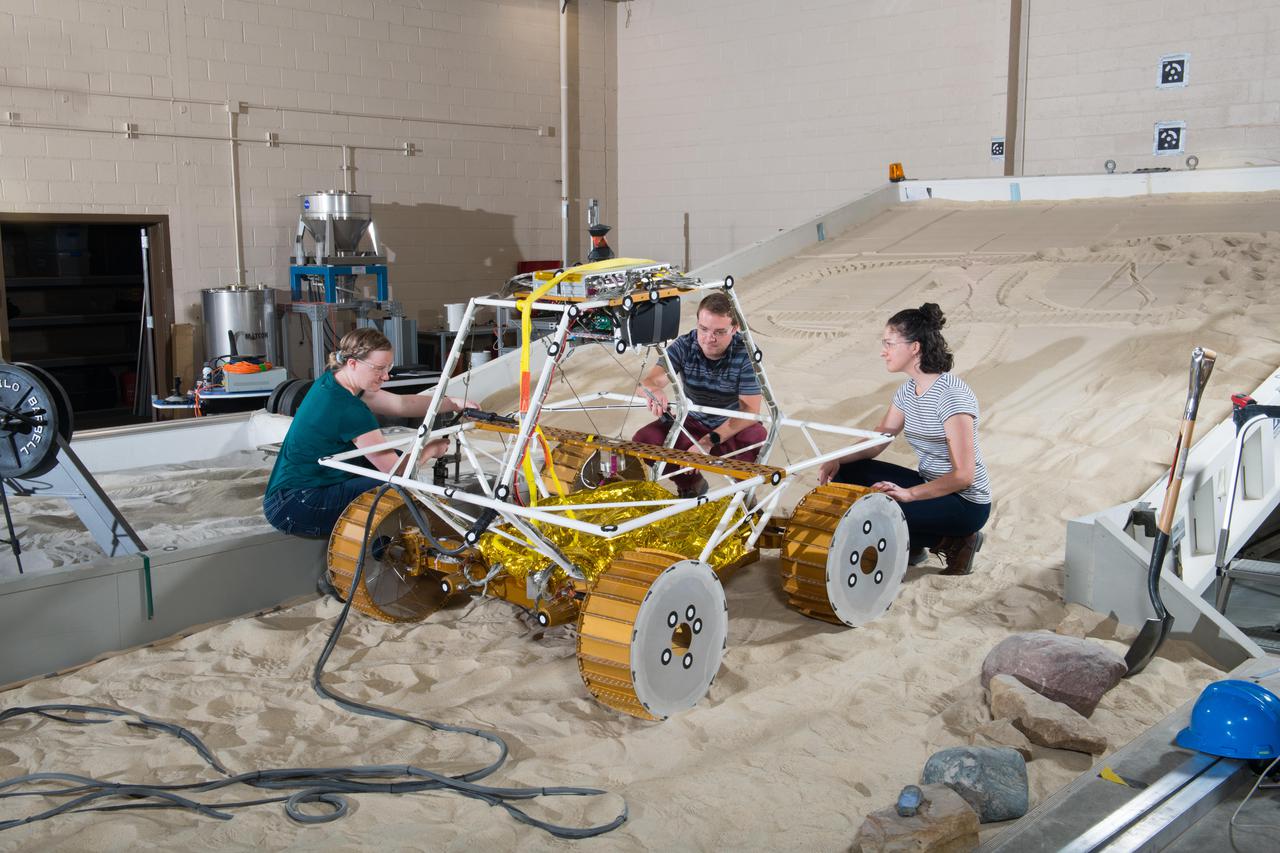

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
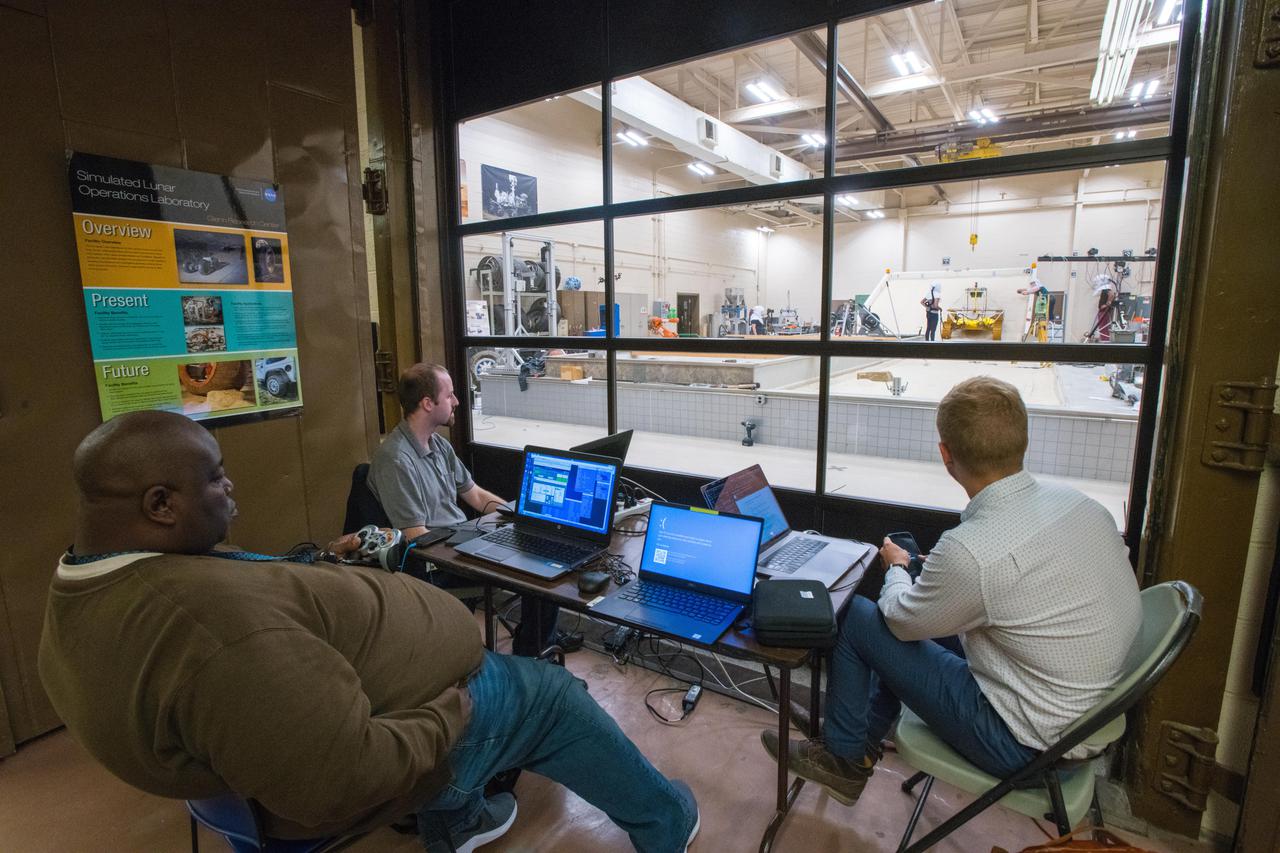

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
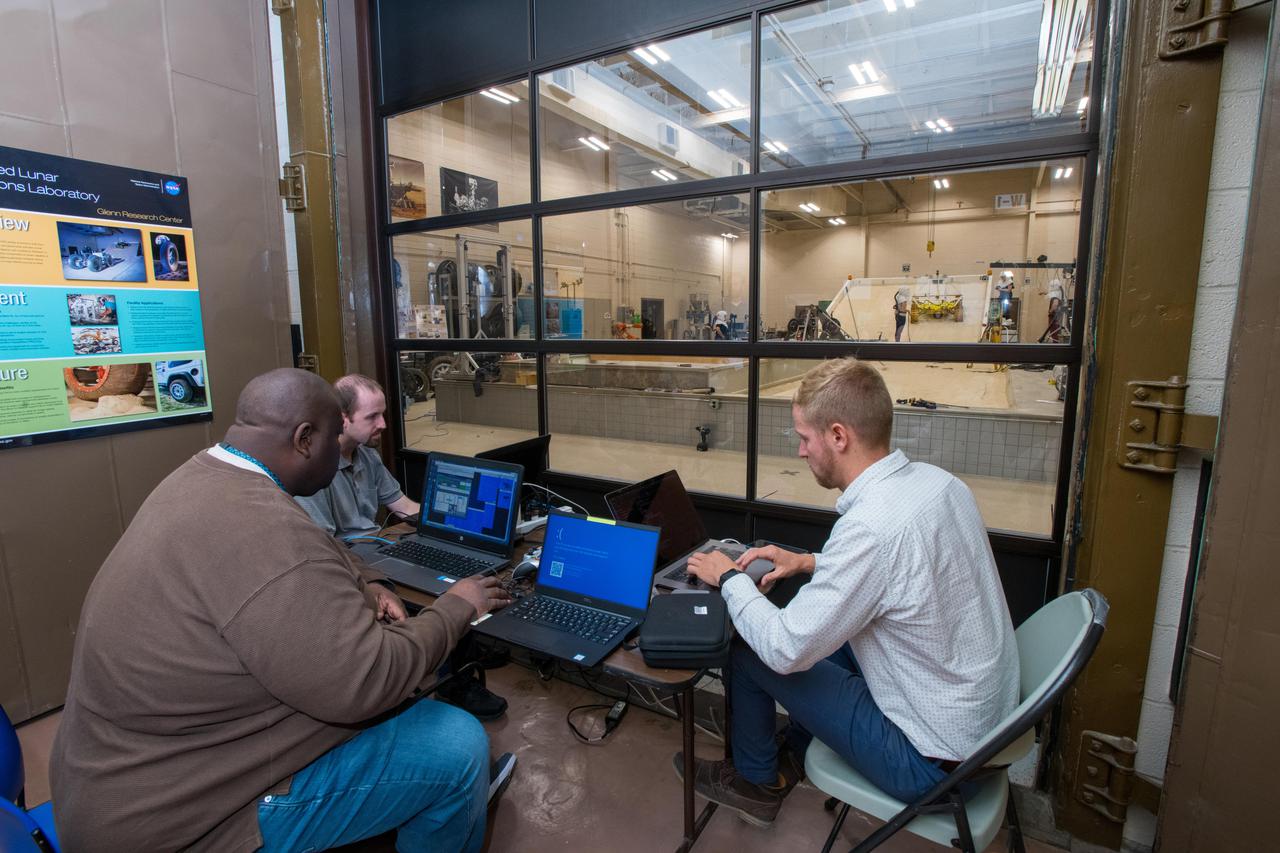

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
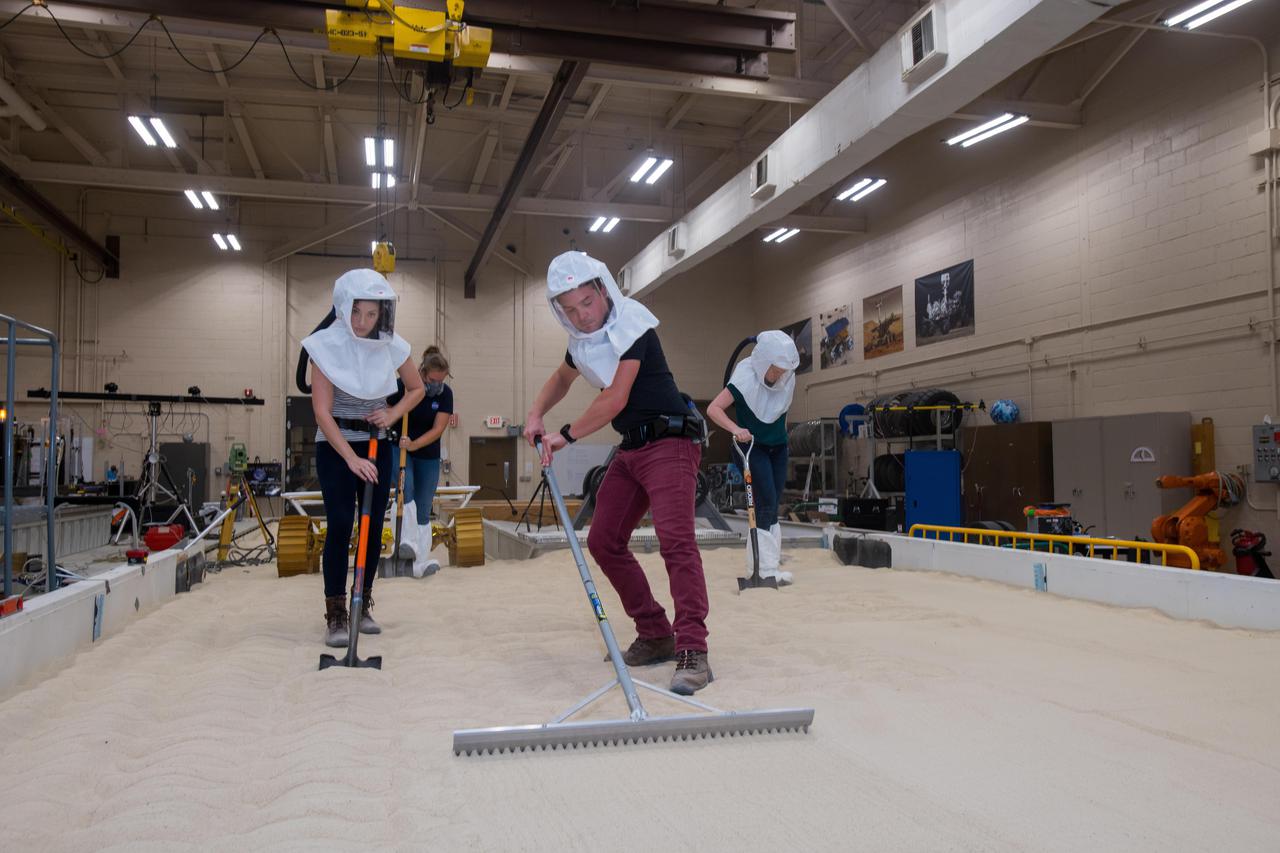

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
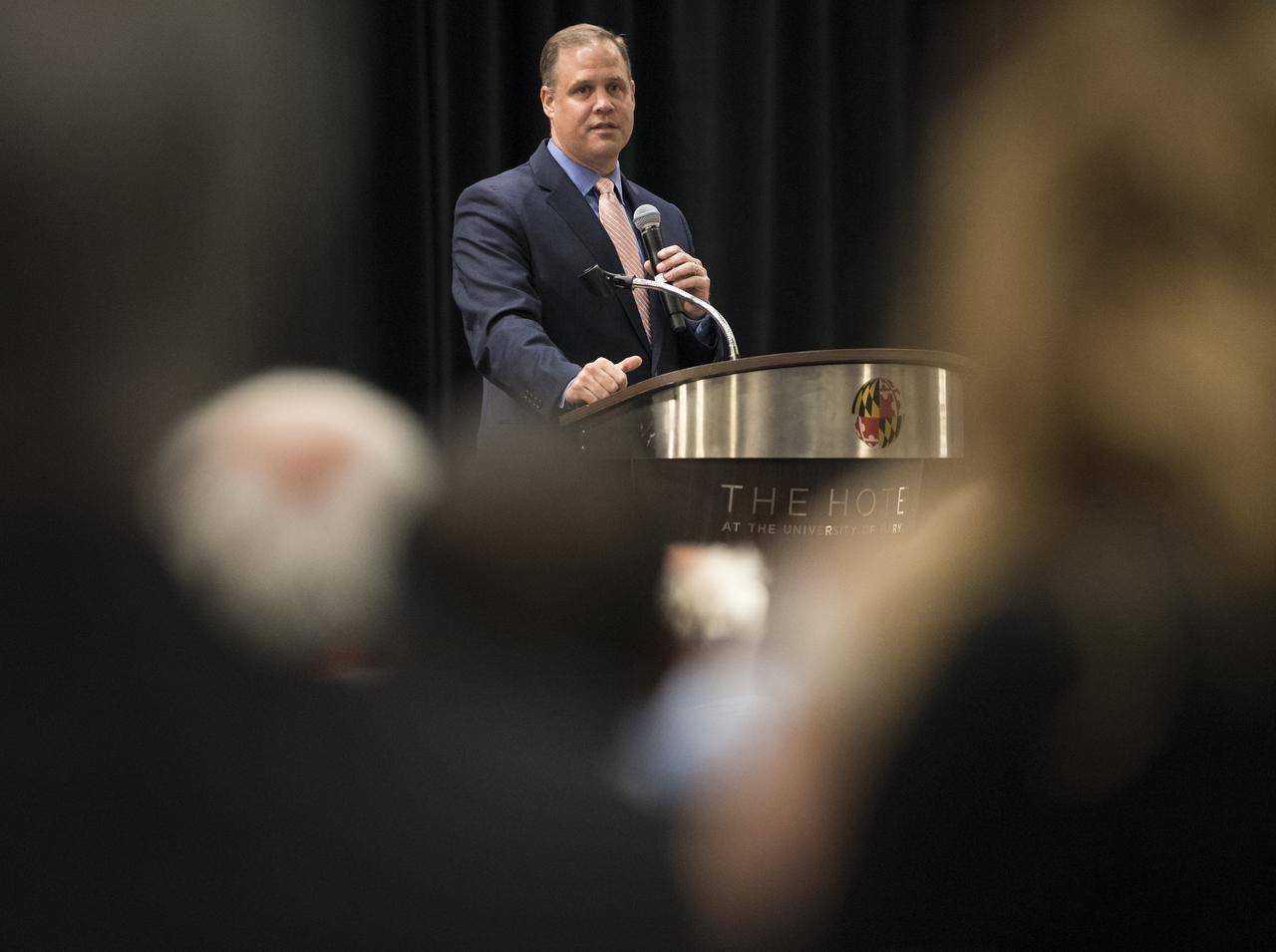

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine delivers a keynote speech at the sixth International Academy of Astronautics Planetary Defense Conference, Monday, April 29, 2019 at The Hotel at the University of Maryland in College Park Maryland. The conference brings together experts from around the world to present the latest research on Near-Earth Objects and will highlight the development of the first-ever mission to demonstrate an asteroid defection technique for planetary defense, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART). Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
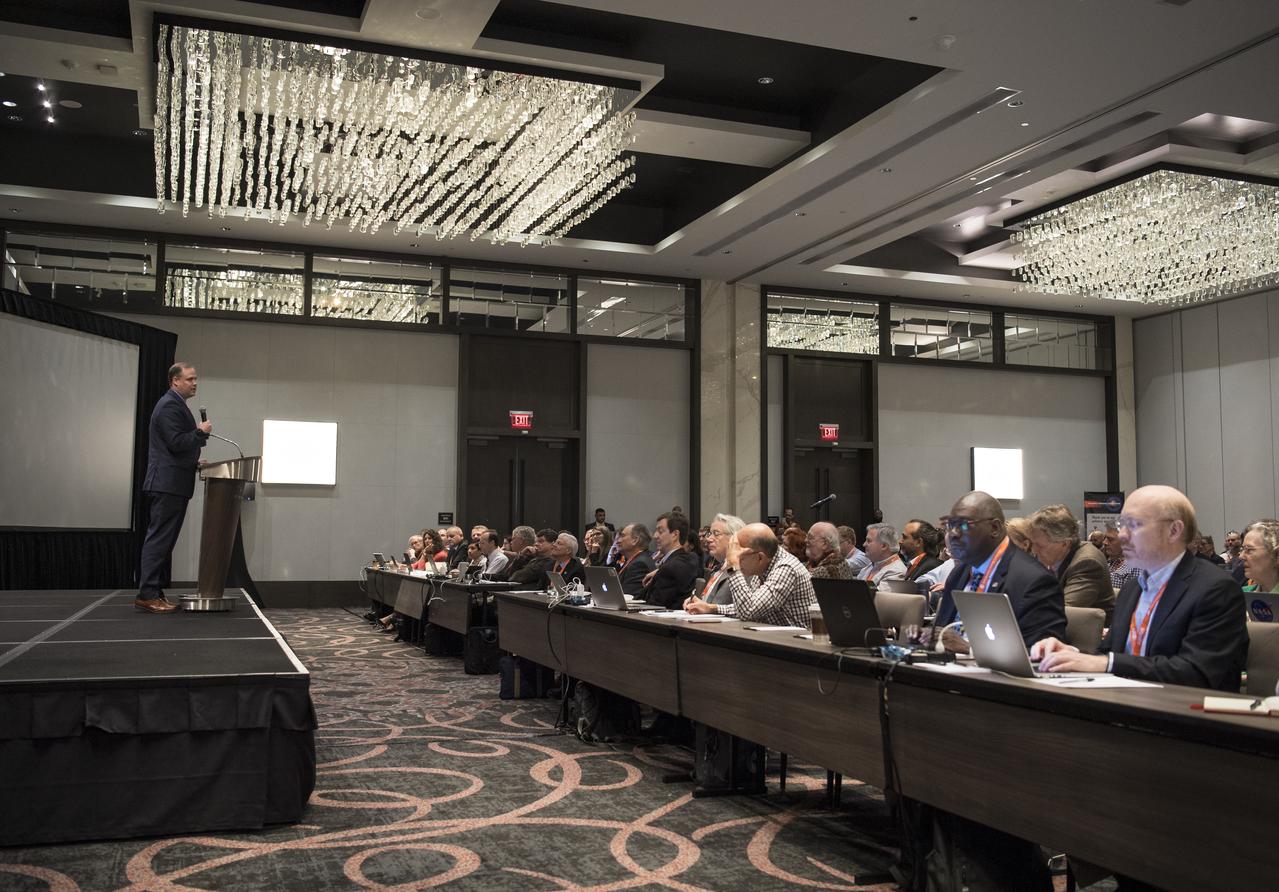

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine delivers a keynote speech at the sixth International Academy of Astronautics Planetary Defense Conference, Monday, April 29, 2019 at The Hotel at the University of Maryland in College Park Maryland. The conference brings together experts from around the world to present the latest research on Near-Earth Objects and will highlight the development of the first-ever mission to demonstrate an asteroid defection technique for planetary defense, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART). Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
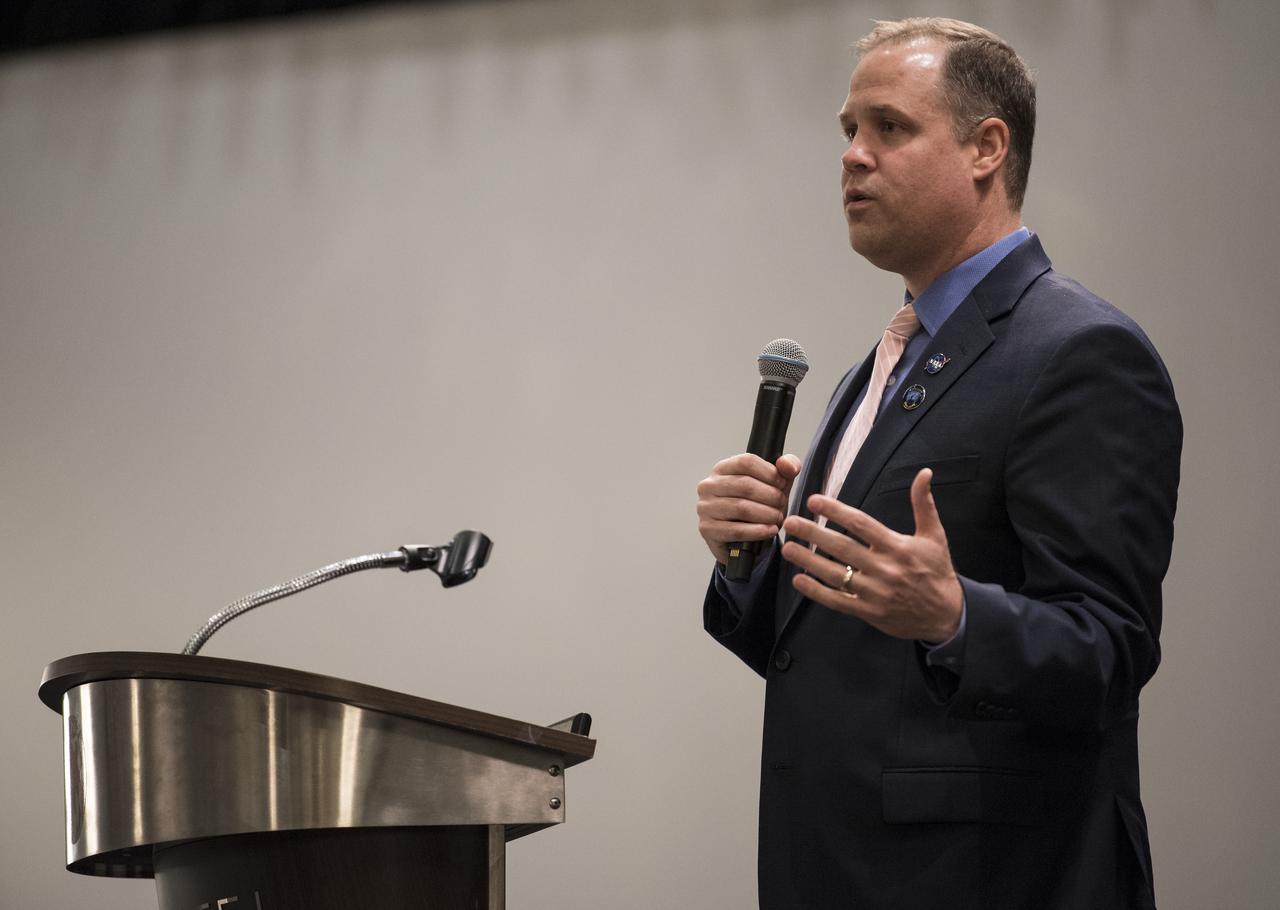

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine delivers a keynote speech at the sixth International Academy of Astronautics Planetary Defense Conference, Monday, April 29, 2019 at The Hotel at the University of Maryland in College Park Maryland. The conference brings together experts from around the world to present the latest research on Near-Earth Objects and will highlight the development of the first-ever mission to demonstrate an asteroid defection technique for planetary defense, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART). Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
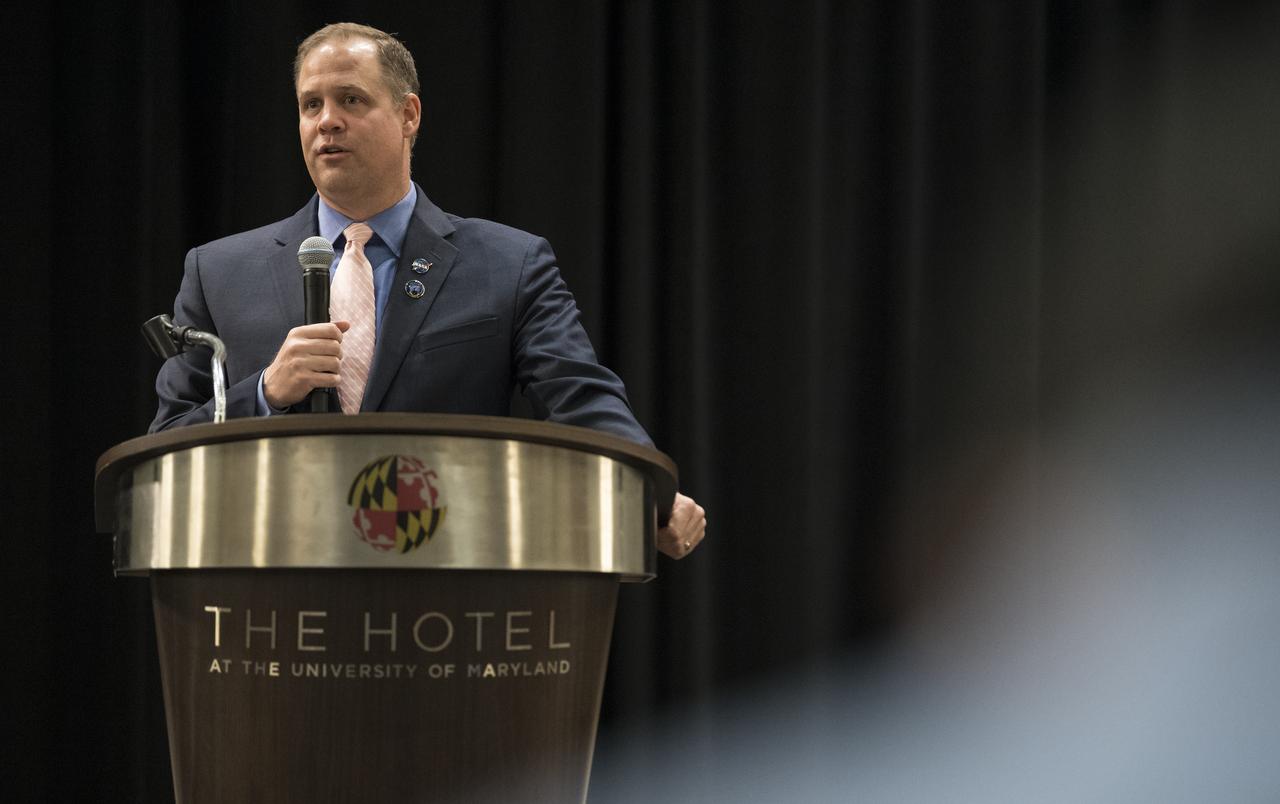

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine delivers a keynote speech at the sixth International Academy of Astronautics Planetary Defense Conference, Monday, April 29, 2019 at The Hotel at the University of Maryland in College Park Maryland. The conference brings together experts from around the world to present the latest research on Near-Earth Objects and will highlight the development of the first-ever mission to demonstrate an asteroid defection technique for planetary defense, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART). Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
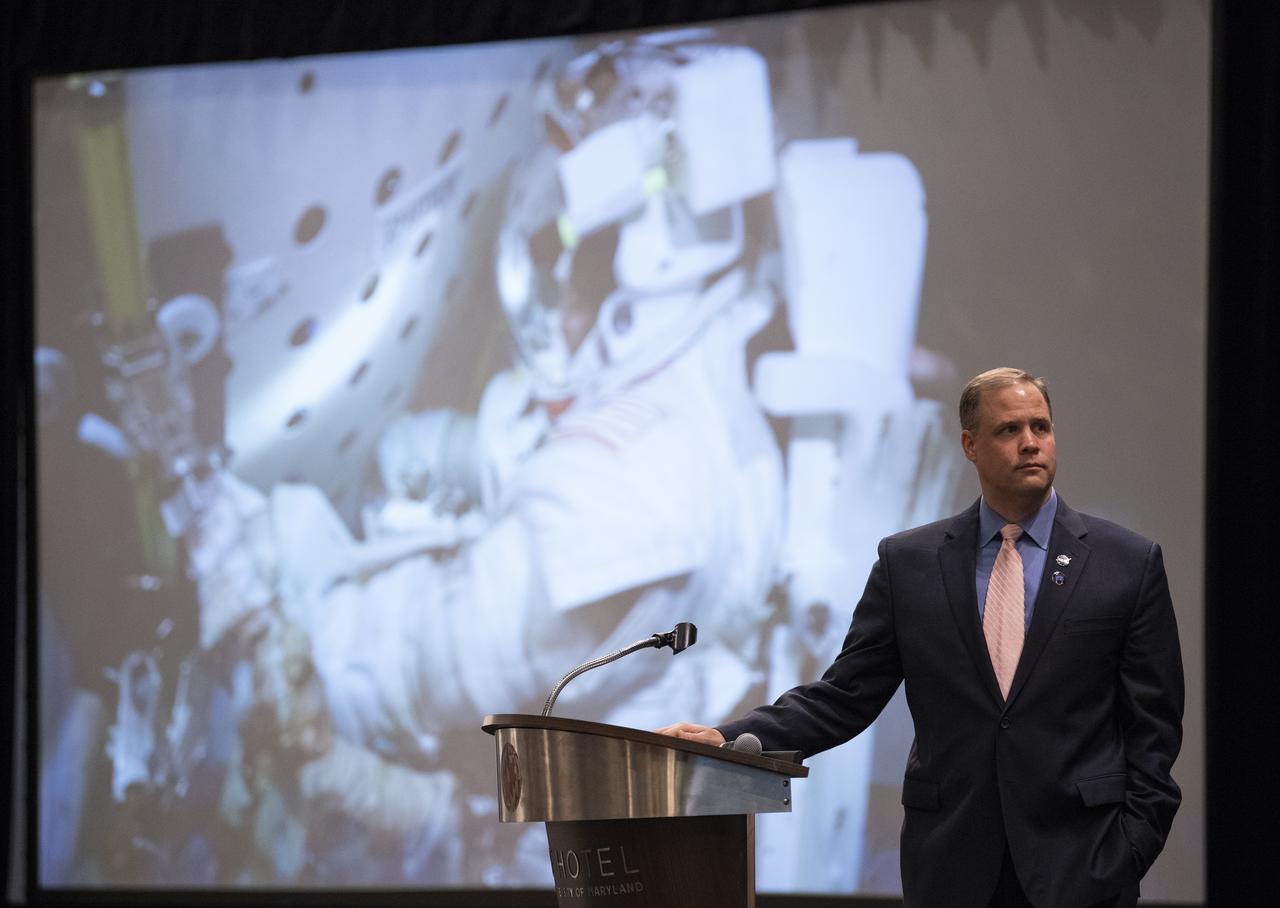

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine watches a short video as part of his keynote speech at the sixth International Academy of Astronautics Planetary Defense Conference, Monday, April 29, 2019 at The Hotel at the University of Maryland in College Park Maryland. The conference brings together experts from around the world to present the latest research on Near-Earth Objects and will highlight the development of the first-ever mission to demonstrate an asteroid defection technique for planetary defense, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART). Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
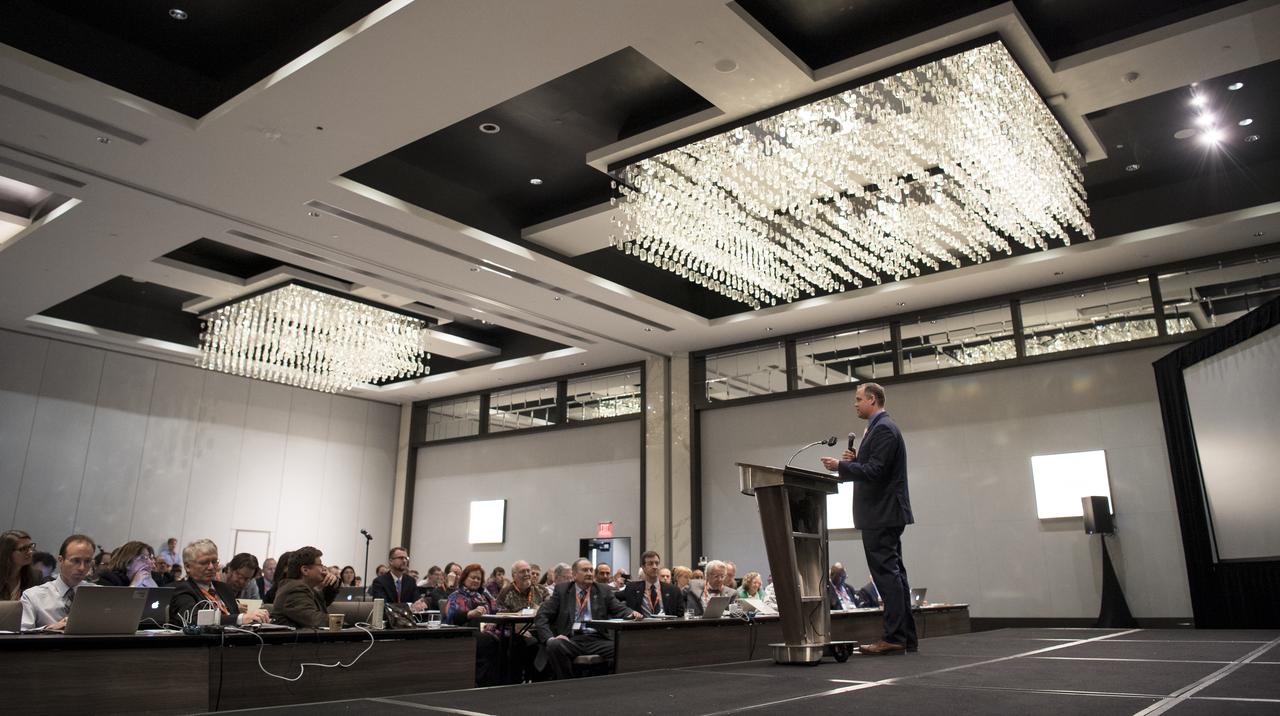

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine delivers a keynote speech at the sixth International Academy of Astronautics Planetary Defense Conference, Monday, April 29, 2019 at The Hotel at the University of Maryland in College Park Maryland. The conference brings together experts from around the world to present the latest research on Near-Earth Objects and will highlight the development of the first-ever mission to demonstrate an asteroid defection technique for planetary defense, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART). Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

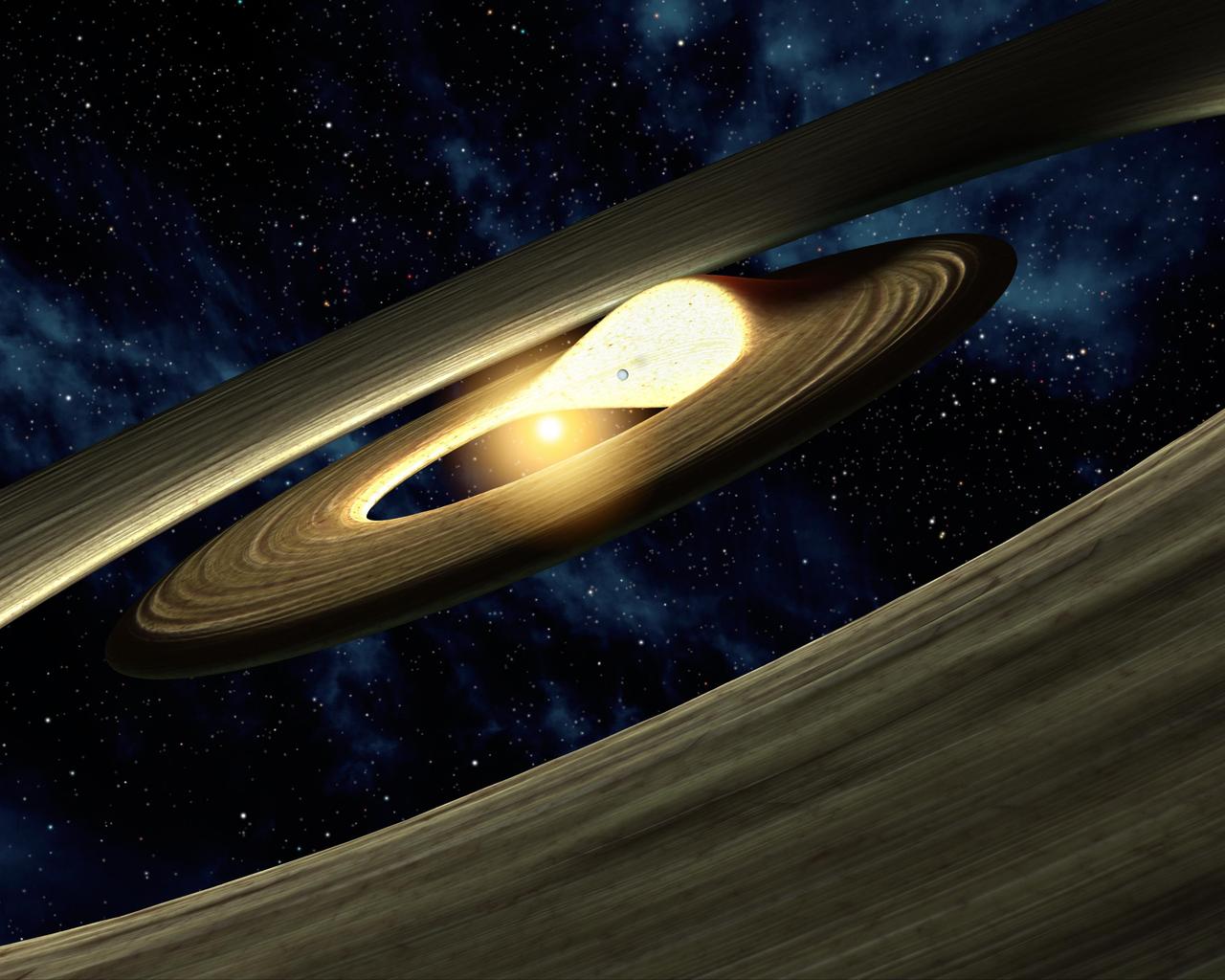
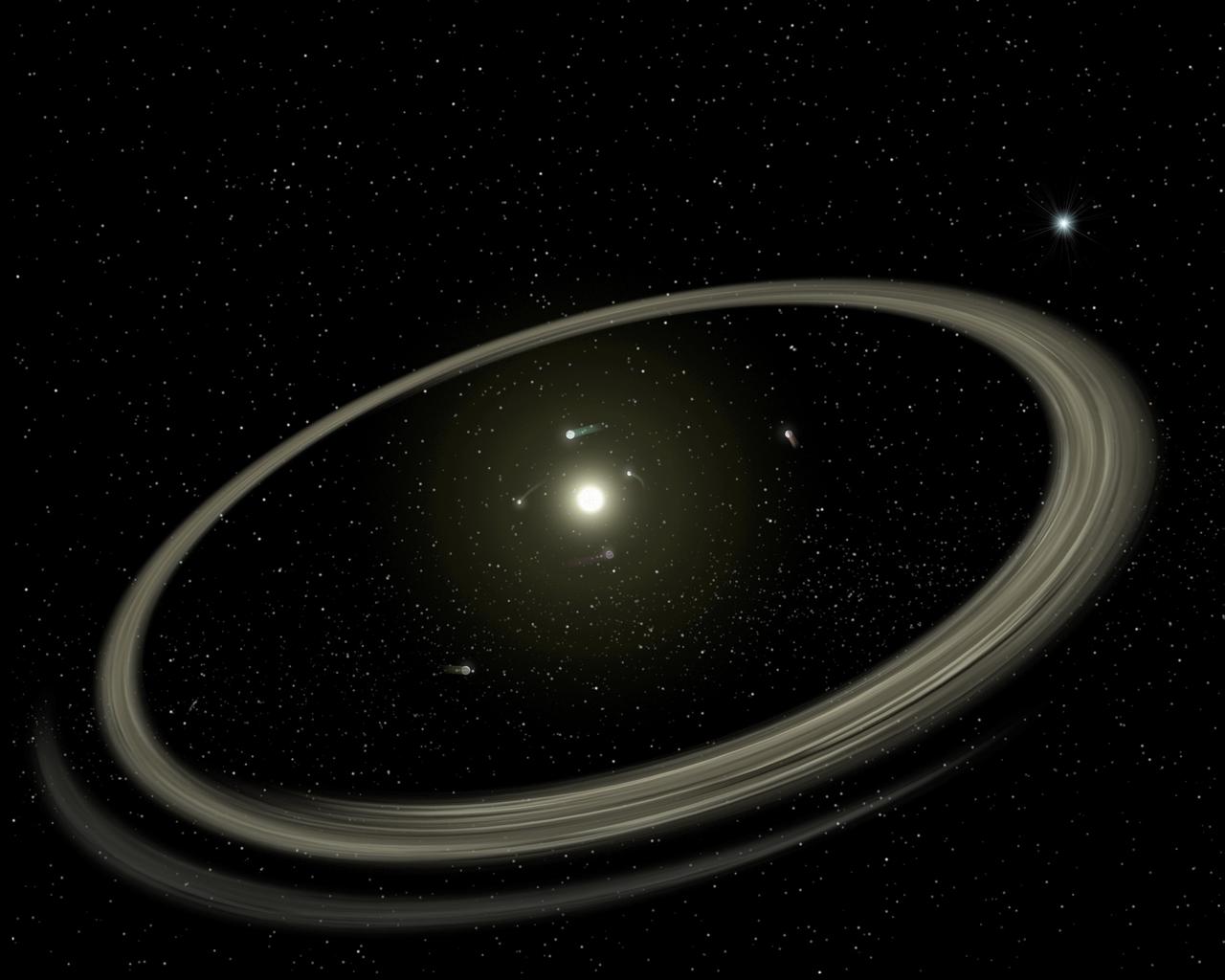
This artist conception compares the KOI-961 planetary system to Jupiter and the largest four of its many moons. The KOI-961 planetary system hosts the three smallest planets known to orbit a star beyond our sun.
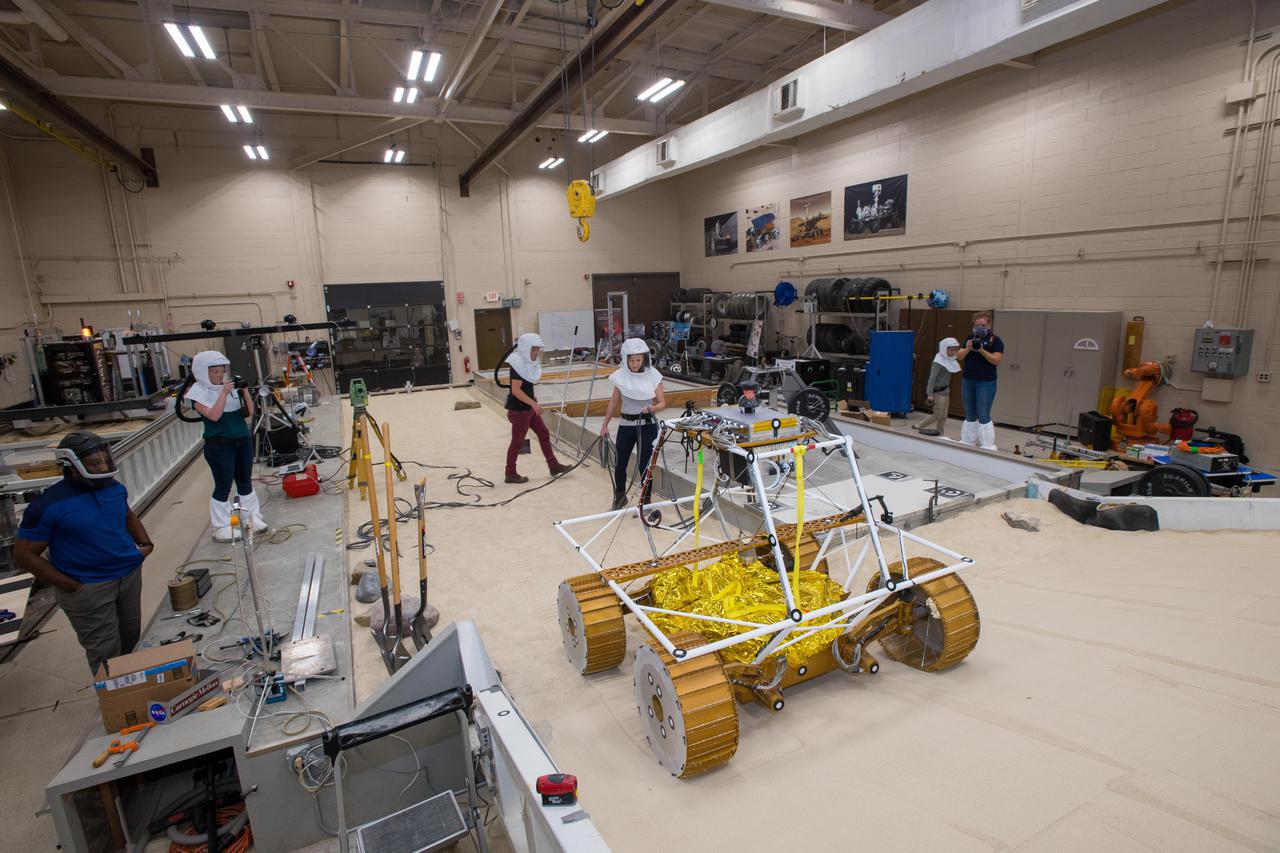

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
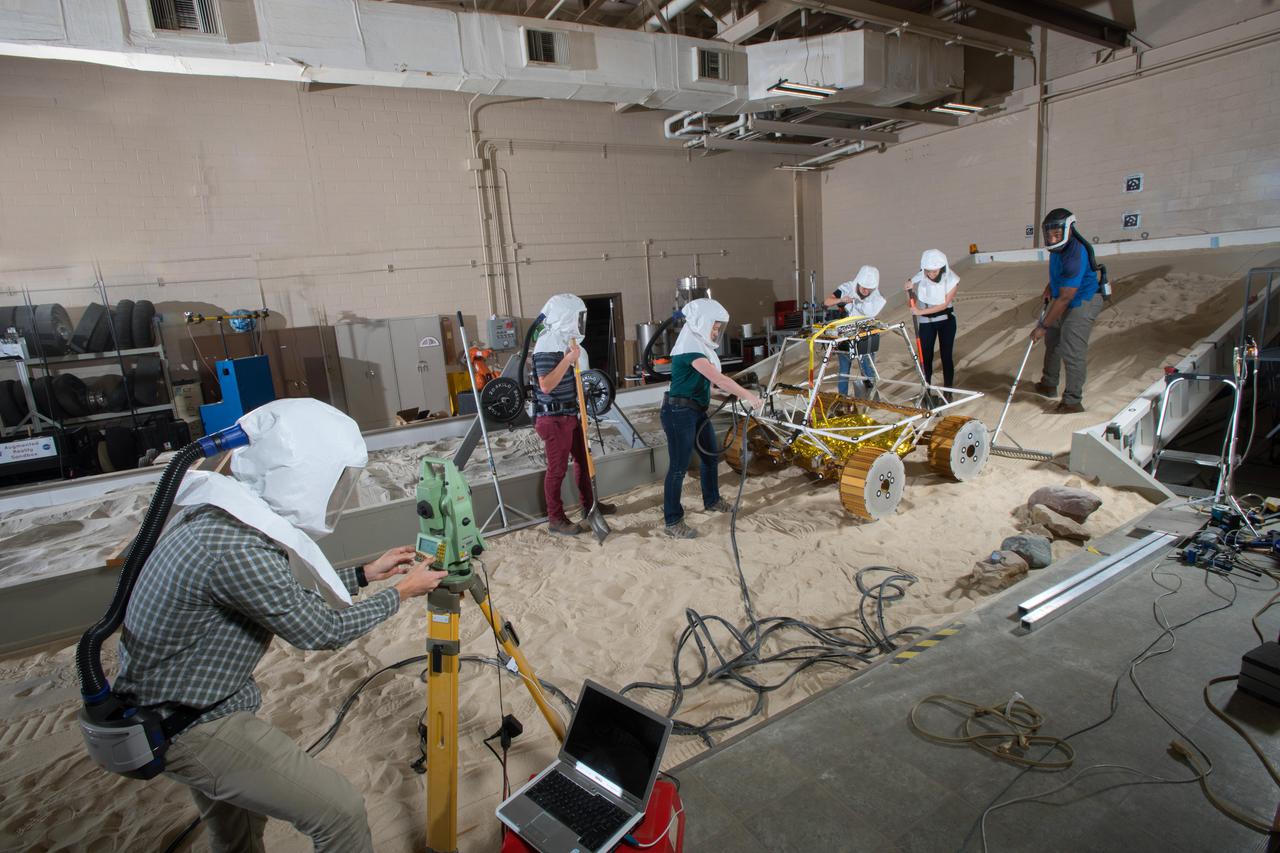

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing

Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing
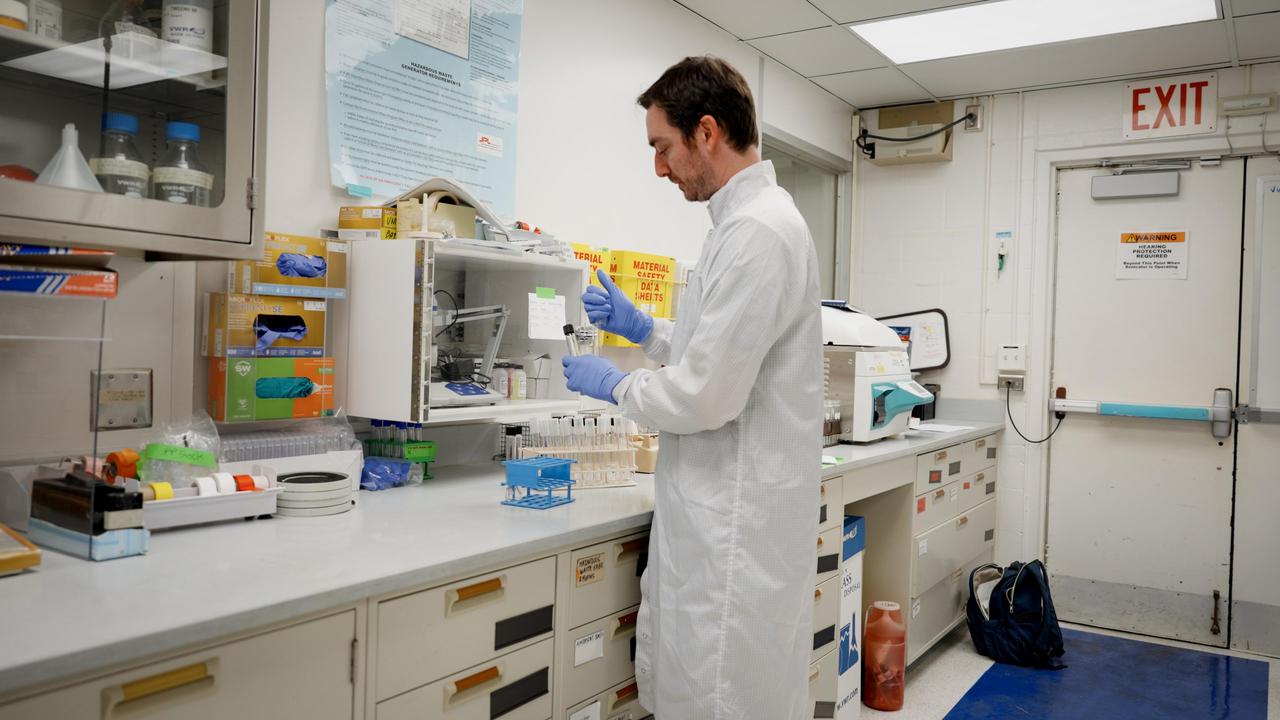

A planetary protection engineer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory prepares samples for analysis on March 20, 2024. The samples, swabbed from the surfaces of the agency's Europa Clipper spacecraft during its construction, were collected to help monitor the mission's adherence to strict standards for biological cleanliness. Created in keeping with the international 1967 Outer Space Treaty, the mission's planetary protection protocols are designed to minimize the chance that microbes brought from Earth could compromise future scientific investigations at its target destination: Jupiter's icy moon Europa. Europa Clipper's three main science objectives are to determine the thickness of the moon's icy shell and its interactions with the ocean below, to investigate its composition, and to characterize its geology. The mission's detailed exploration of Europa will help scientists better understand the astrobiological potential for habitable worlds beyond our planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26441
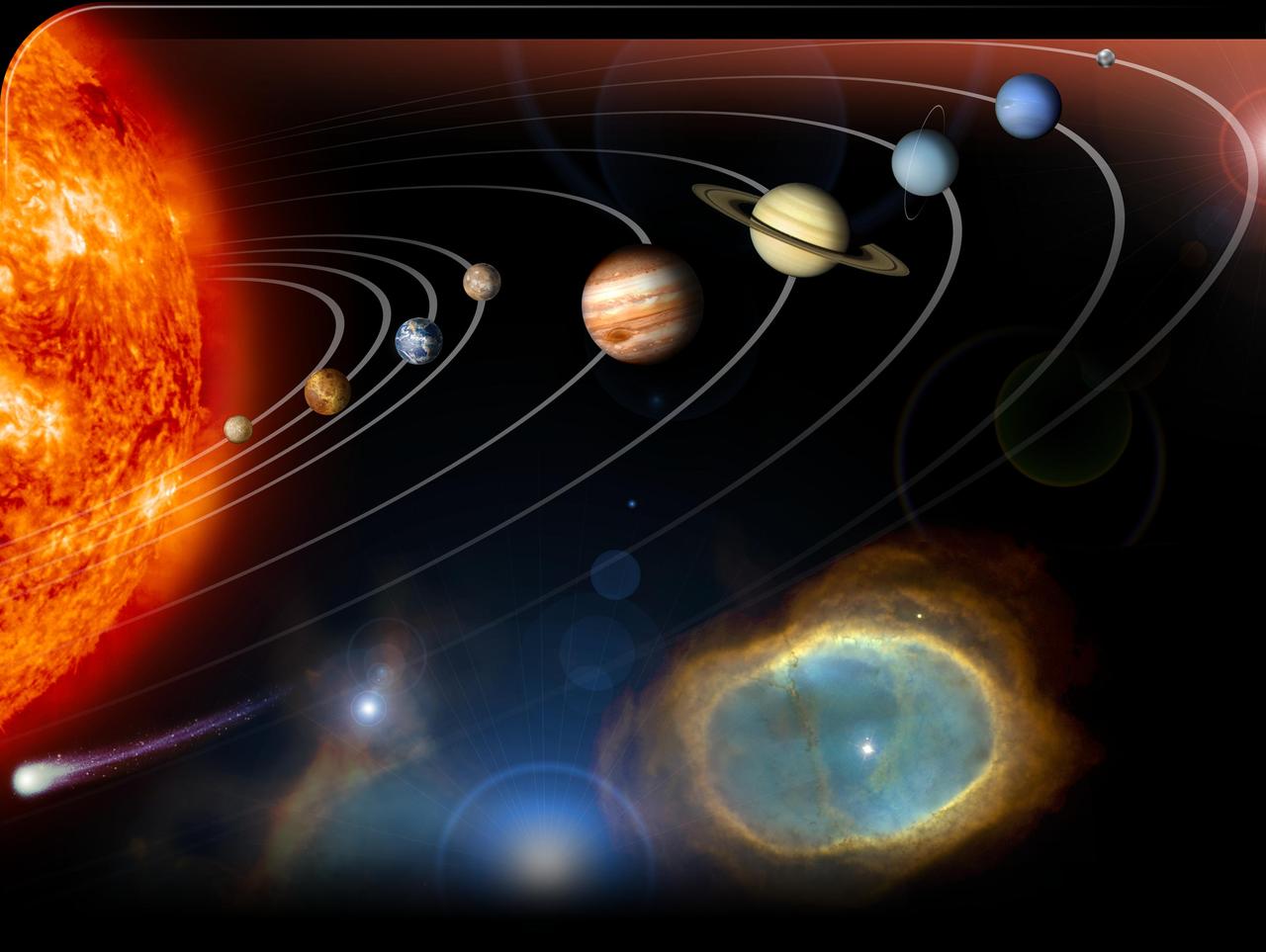
This image is an unannotated version of NASA Planetary Photojournal Home Page graphic. This digital collage contains a highly stylized rendition of our solar system and points beyond.
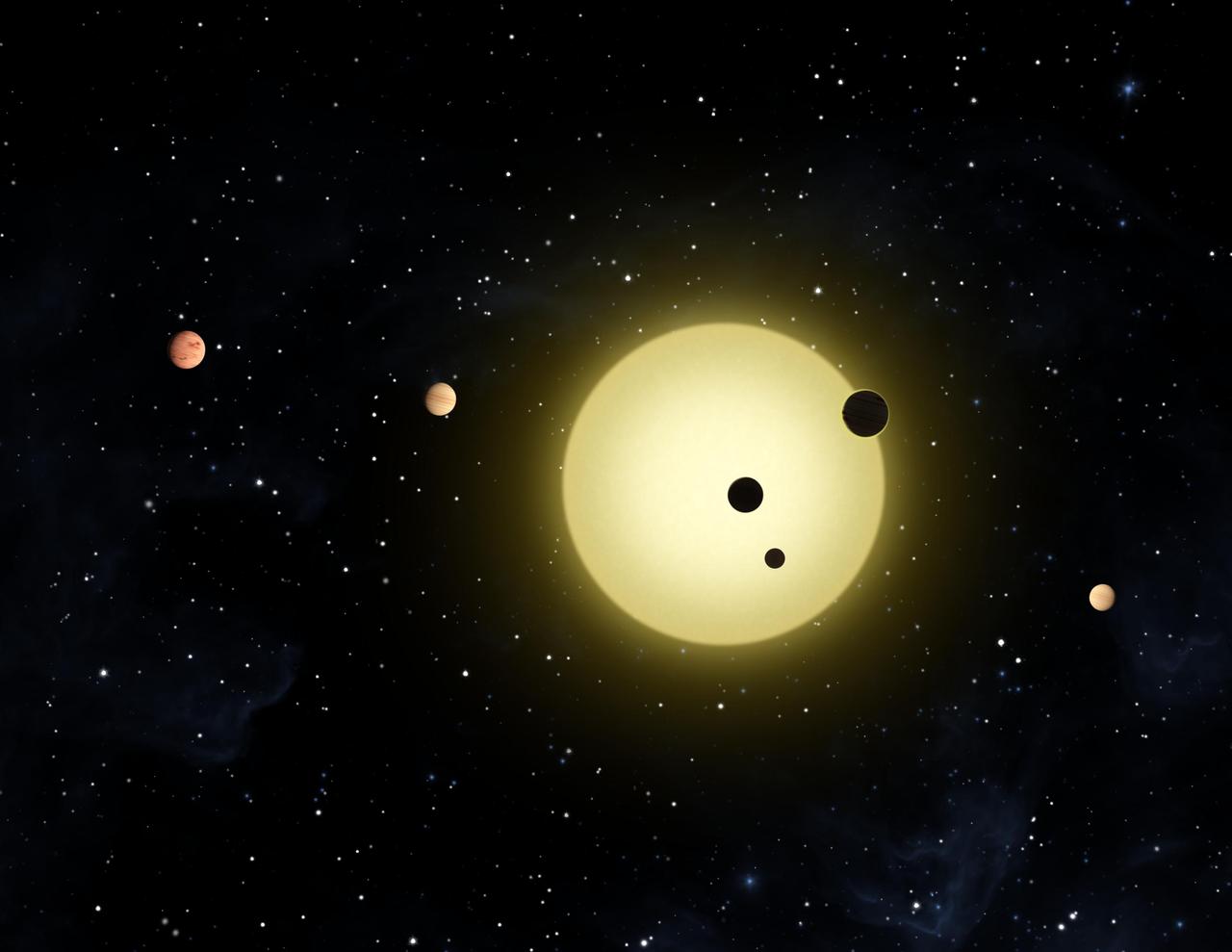

This artist concept shows Kepler-11 -- the most tightly packed planetary system yet discovered.
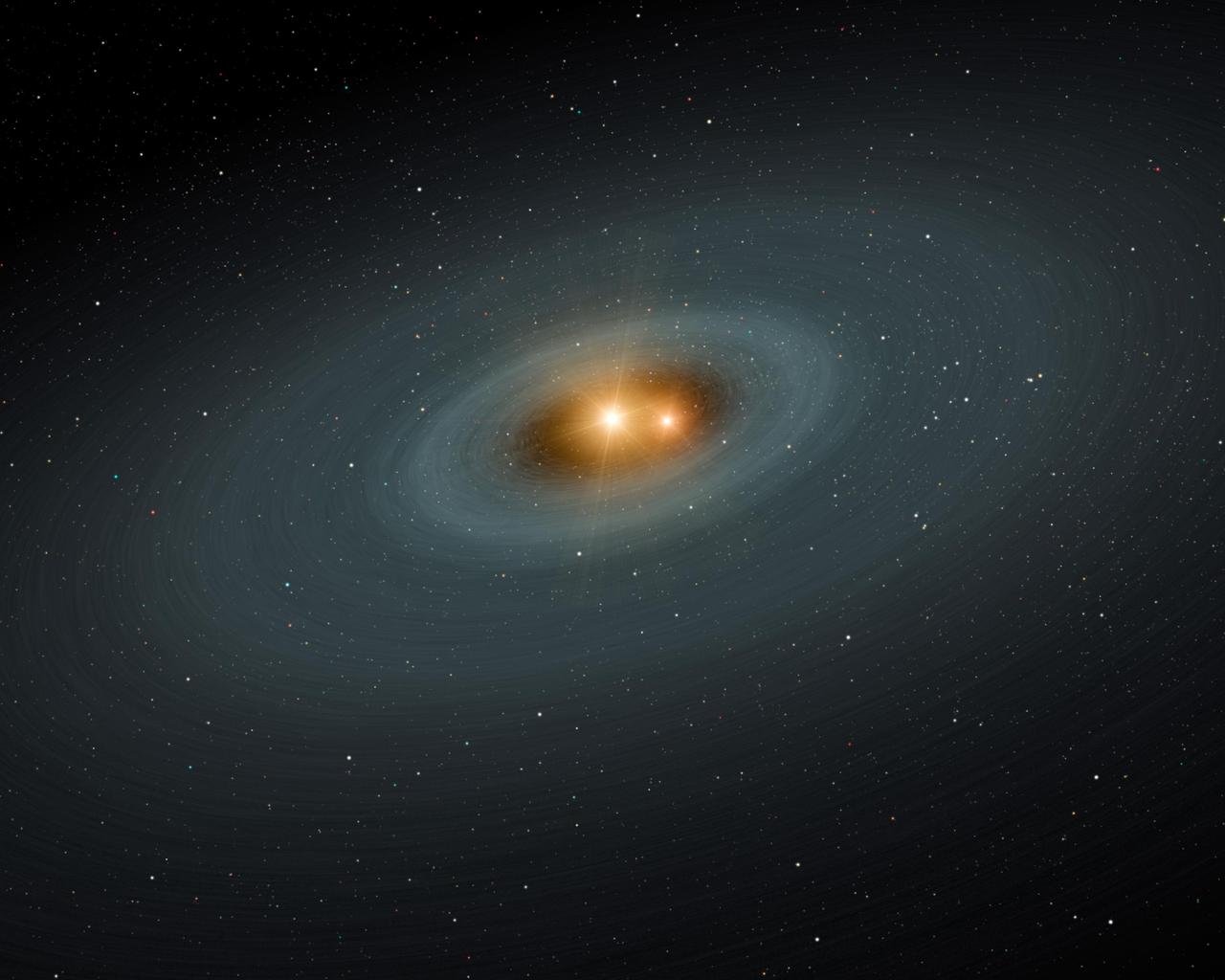

This artist concept illustrates a tight pair of stars and a surrounding disk of dust, most likely the shattered remains of planetary smashups. Using NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, the scientists found dusty evidence for such collisions.
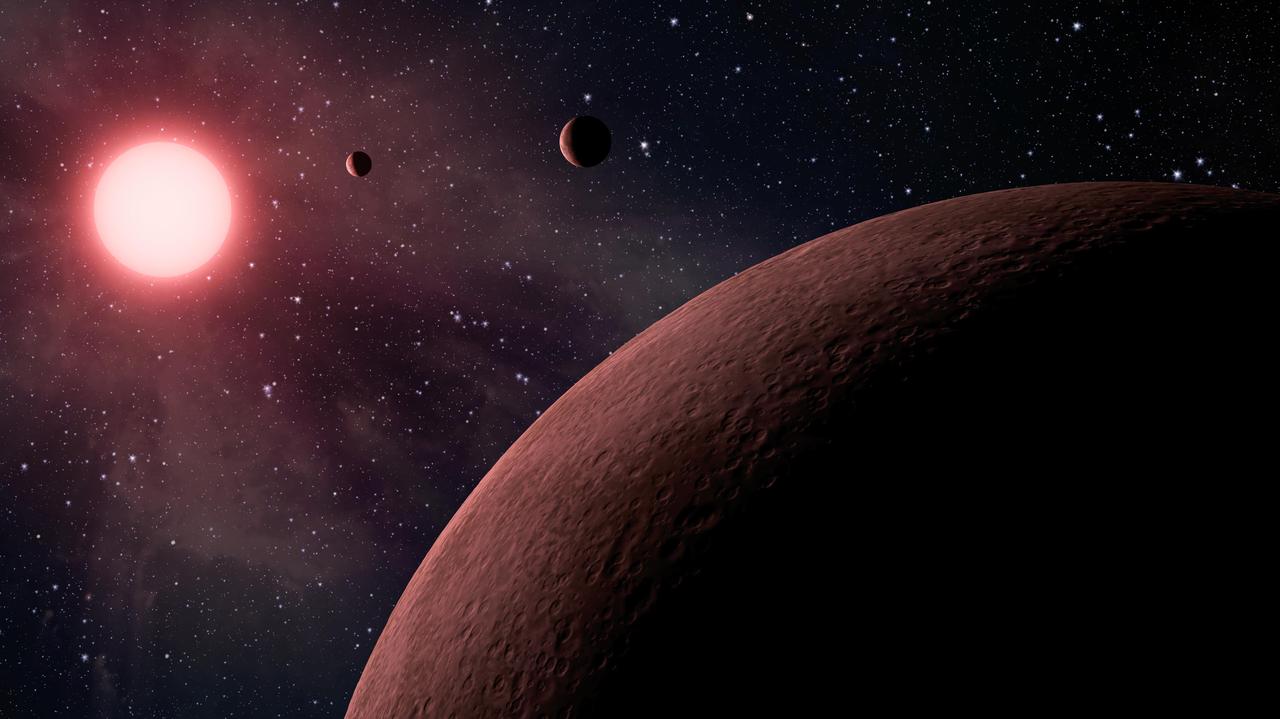

This artist concept, based on data from NASA Kepler mission and ground-based telescopes, depicts an itsy bitsy planetary system -- so compact, in fact, that it more like Jupiter and its moons than a star and its planets.
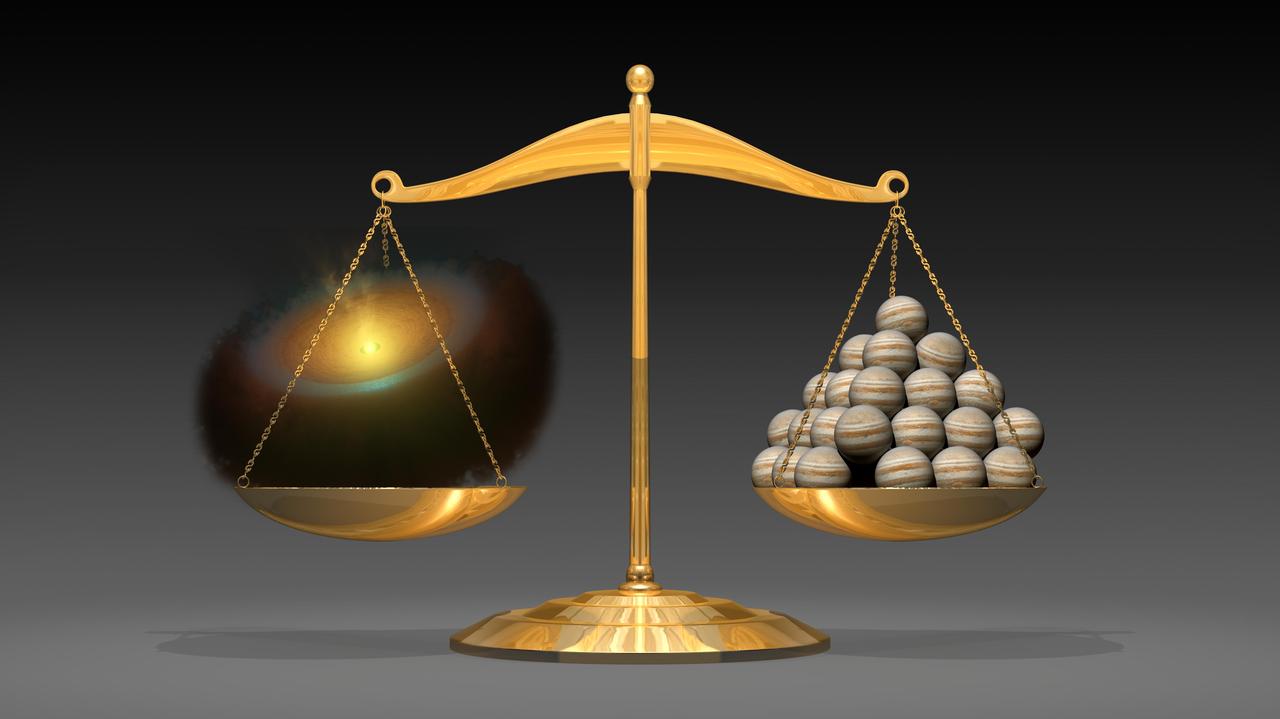

This artist illustration shows a planetary disk left that weighs the equivalent of 50 Jupiter-mass planets. It demonstrates a first-of-its-kind feat from astronomers using the Herschel space observatory.

This artist conception shows a lump of material in a swirling, planet- forming disk. Astronomers using NASA Spitzer Space Telescope found evidence that either another star or a planet could be pushing planetary material together, as illustrated here.

Lori Glaze, acting director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division, right, visited NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center March 7 to see firsthand the work done by center scientists. Glaze, along with Marshall planetary scientists Renee Weber, left, and Debra Needham, center, and intern James Mavo, second from right, toured multiple facilities at Marshall – including the Deep Space Habitat facility – to discuss how Marshall is working to support astronauts on long-duration missions.
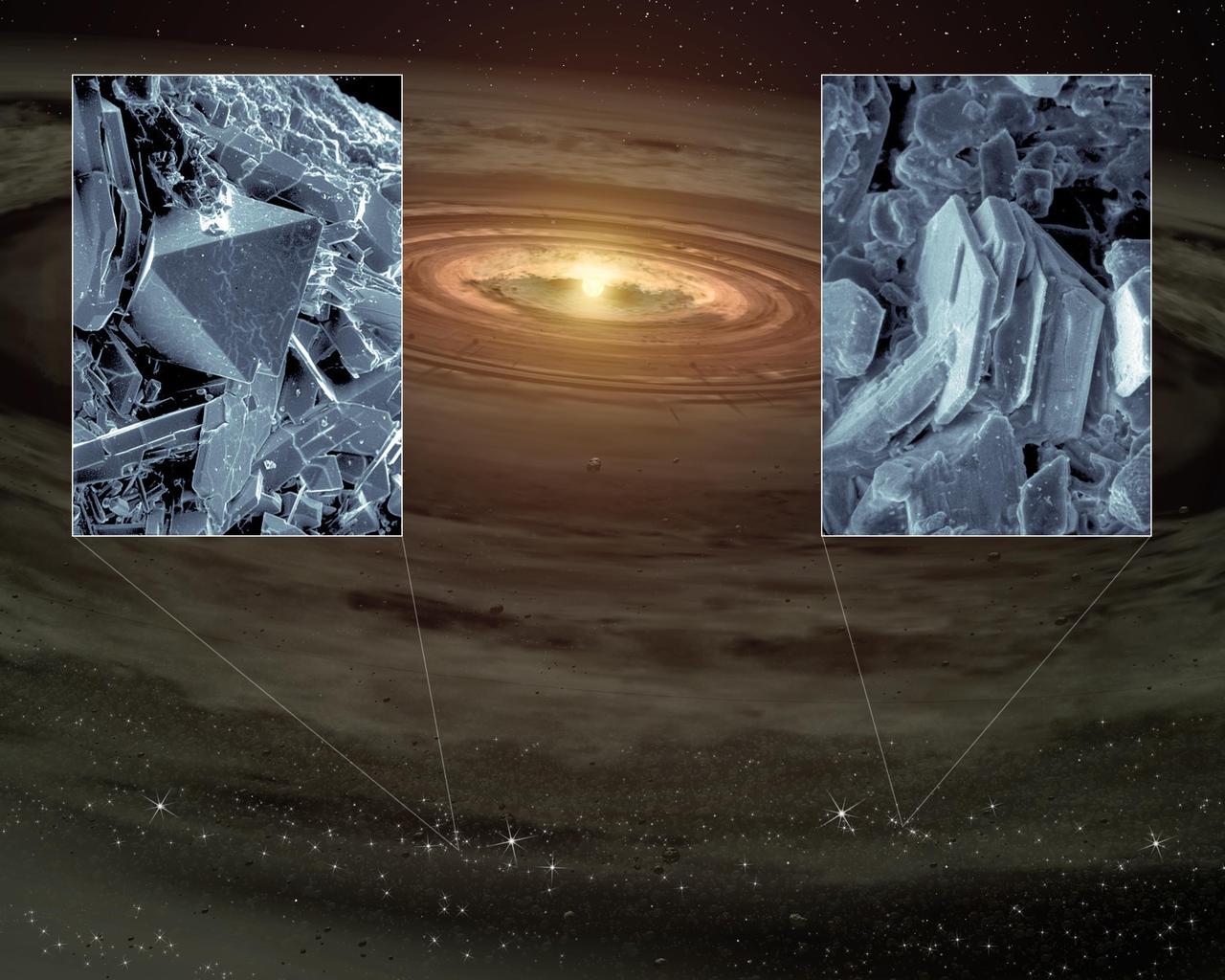

NASA Spitzer Space Telescope has, for the first time, detected tiny quartz-like crystals sprinkled in young planetary systems. The crystals, which are types of silica minerals called cristobalite and tridymite.

This ultraviolet image from NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer shows NGC 3242, a planetary nebula frequently referred to as Jupiter Ghost. The small circular white and blue area at the center of the image is the well-known portion of the nebula.
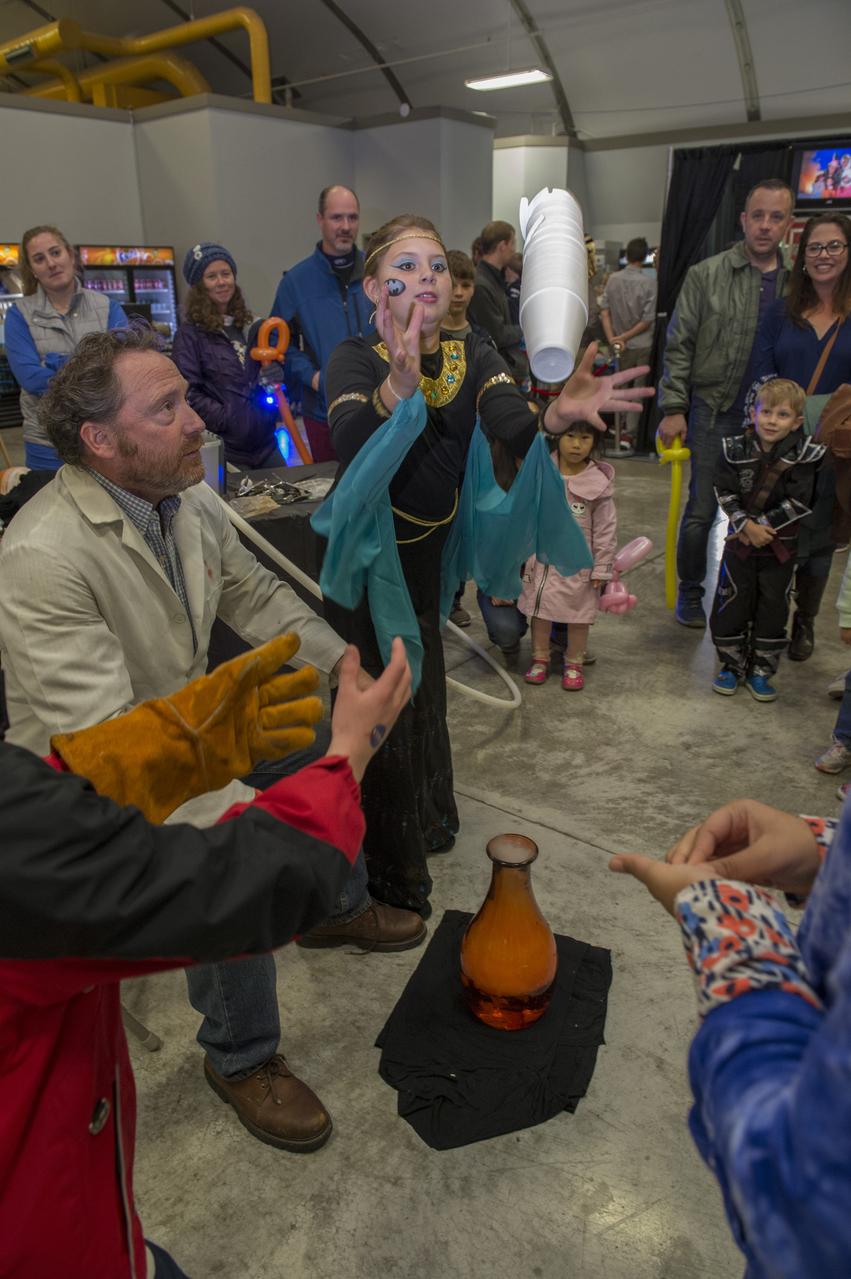

A volunteer assists an eager participant at International Observe the Moon Night Oct. 28 at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center. The event, hosted by the Planetary Missions Program at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, encourages observation and appreciation of the Moon and its connection to NASA planetary science and exploration, as well as our cultural and personal connections to it. Children attending the event had the opportunity to participate in planetary, science-based, hands-on activities
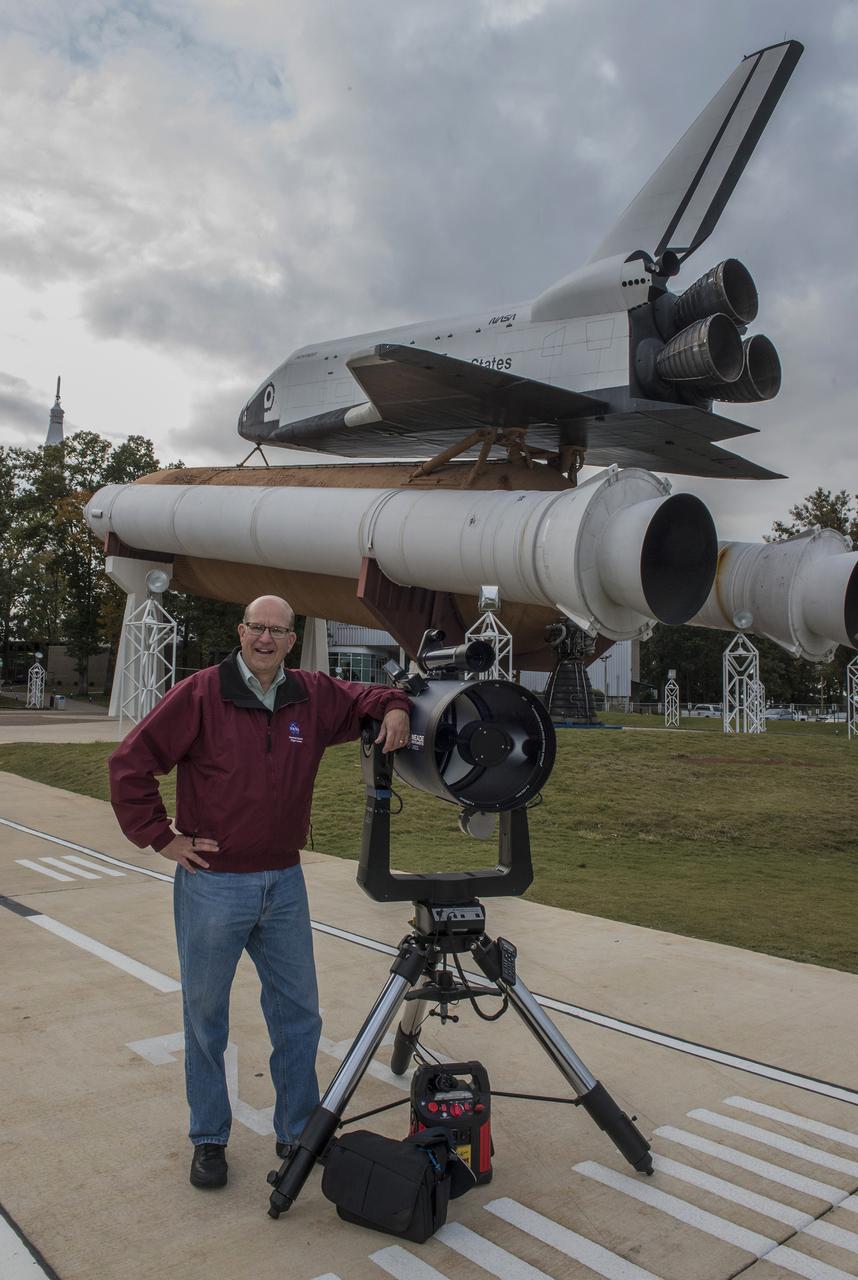

Volunteer Billy Hix with his telescope at International Observe the Moon Night. The event, hosted by the Planetary Missions Program at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, encourages observation and appreciation of the Moon and its connection to NASA planetary science and exploration, as well as our cultural and personal connections to it. Children attending the event had the opportunity to participate in planetary, science-based, hands-on activities
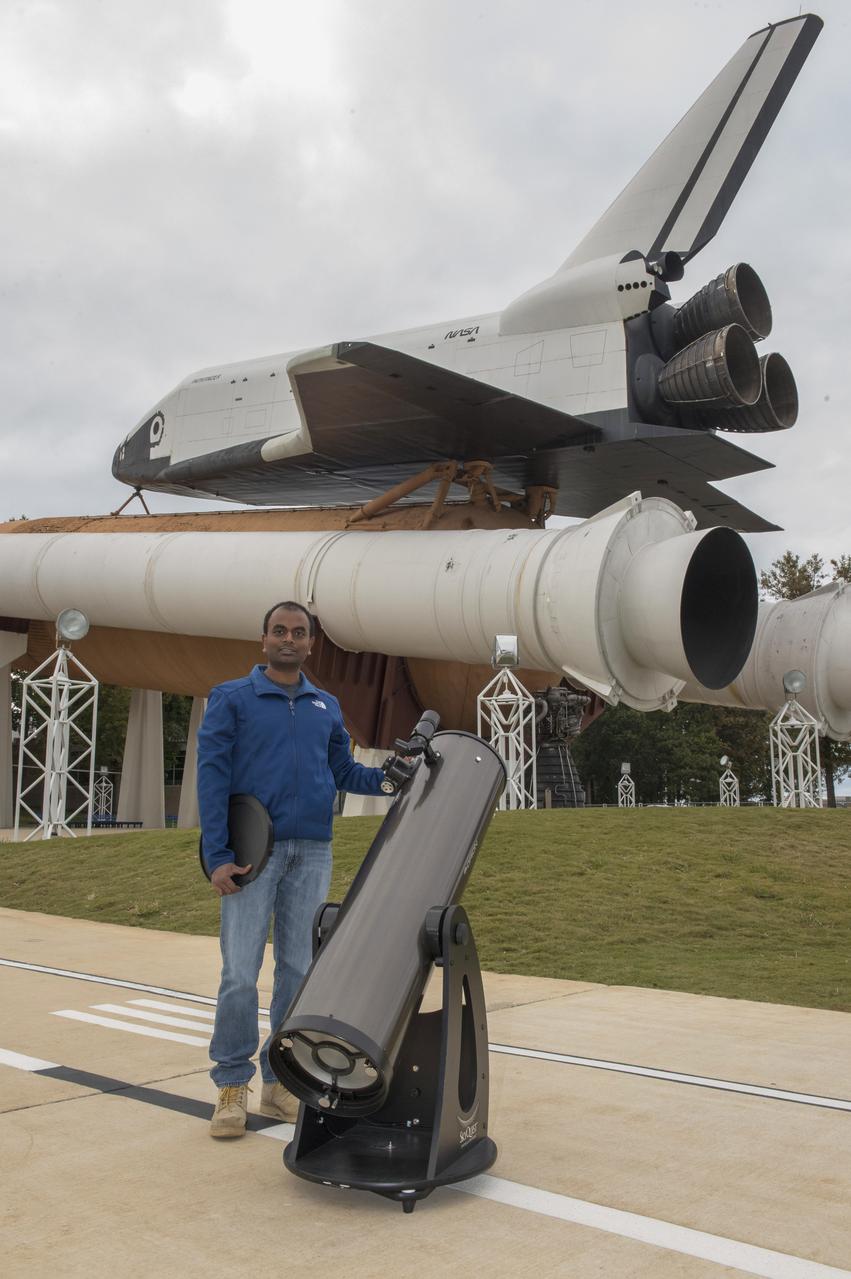

Marshall engineer Naveen Vetcha with his telescope. The event, hosted by the Planetary Missions Program at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, encourages observation and appreciation of the Moon and its connection to NASA planetary science and exploration, as well as our cultural and personal connections to it. Children attending the event had the opportunity to participate in planetary, science-based, hands-on activities

This artist concept illustrates how planetary systems arise out of massive collisions between rocky bodies. NASA Spitzer Space Telescope show that these catastrophes continue to occur around stars even after they have developed full-sized planets.
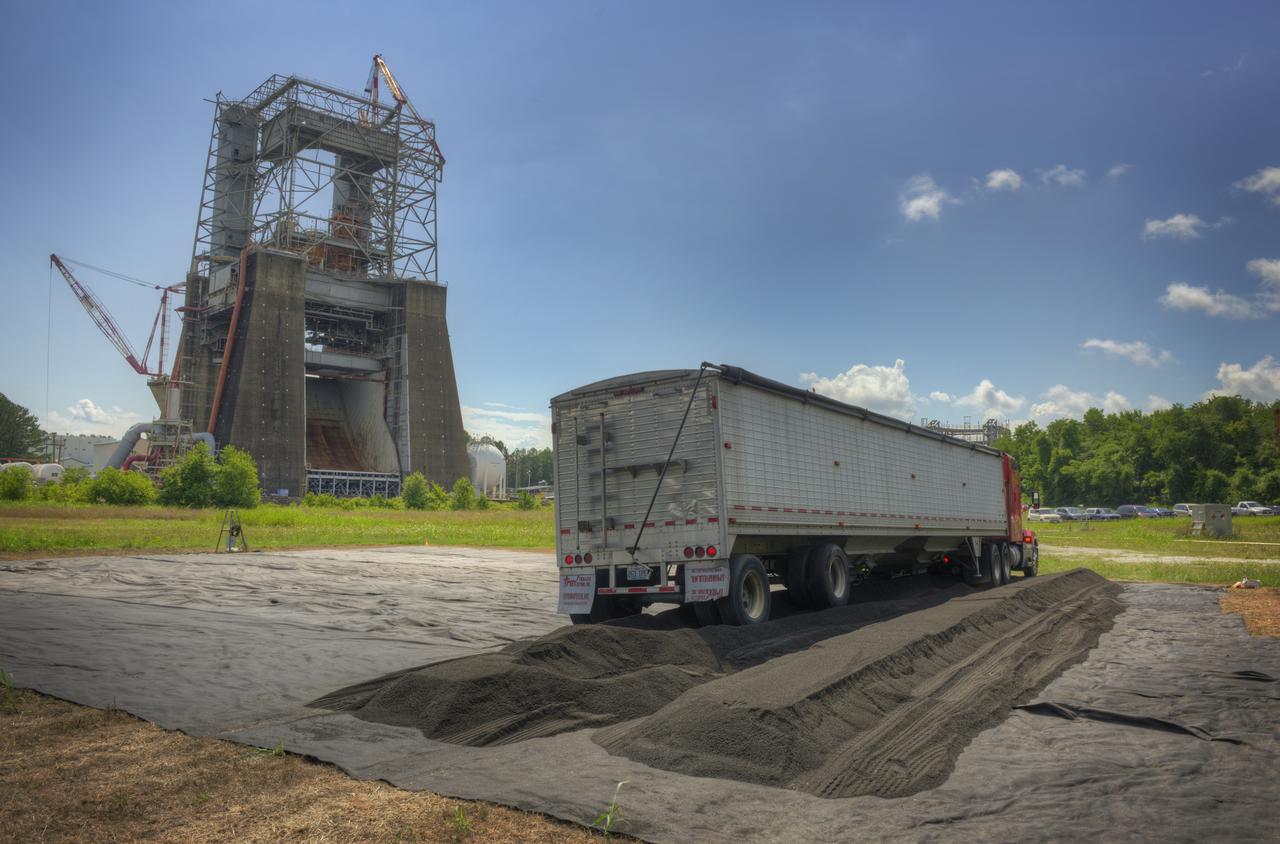

SOIL UNLOAD FOR THE SIMULATED PLANETARY BODY FIELD IN THE WEST TEST AREA. AREA TO BE USED FOR TESTING OF THE MIGHTY EAGLE LANDER
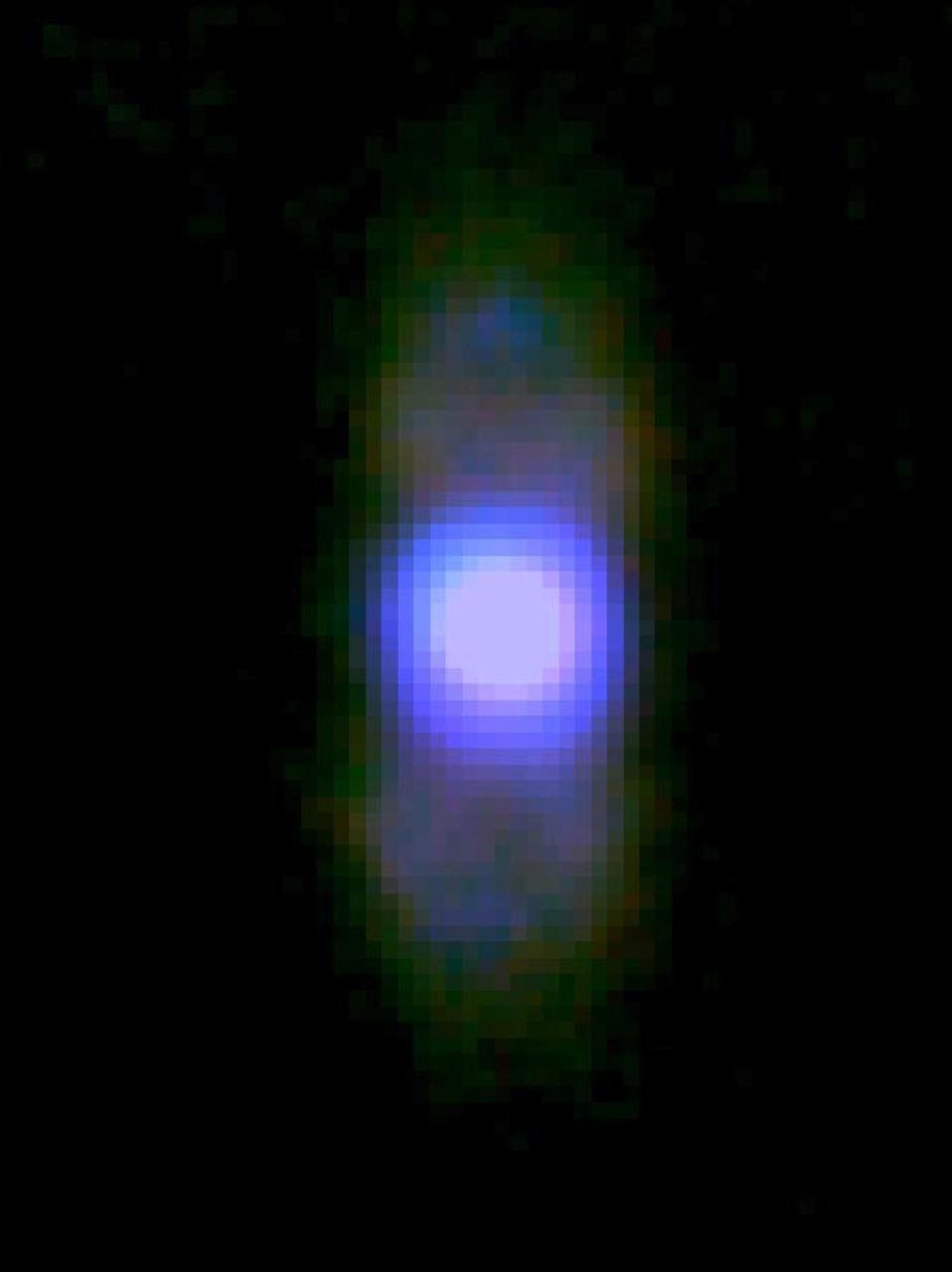

Researchers using NASA Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy SOFIA have captured infrared images of the last exhalations of a dying sun-like star. This image is of the planetary Nebula M2-9.
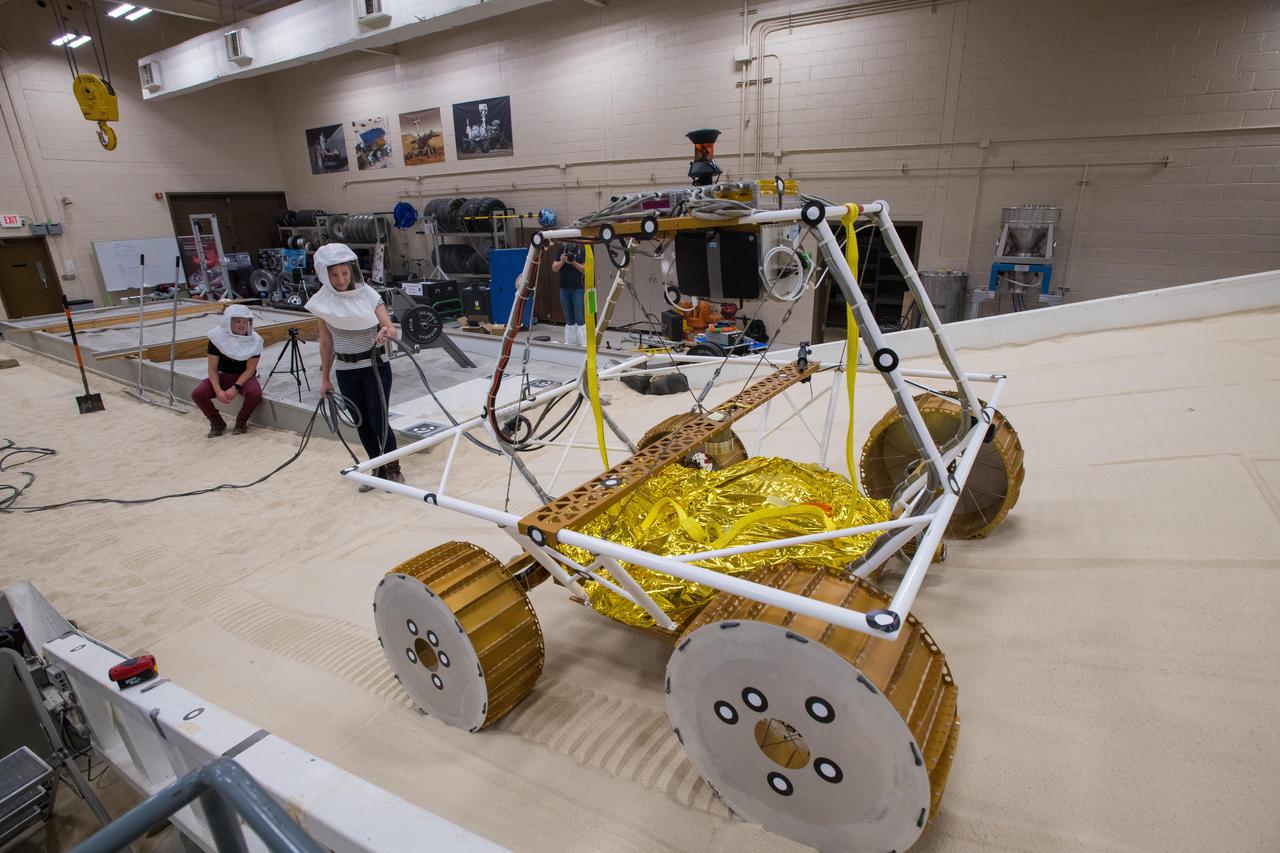
Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing An engineering model of the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER, is tested in the Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. About the size of a golf cart, VIPER is a mobile robot that will roam around the Moon’s South Pole looking for water ice in the region and for the first time ever, actually sample the water ice at the same pole where the first woman and next man will land in 2024 under the Artemis program. The large, adjustable soil bin contains lunar simulant and allows engineers to mimic the Moon’s terrain. Engineers from NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, where the rover was designed and built, joined the Glenn team to complete the tests. Test data will be used to evaluate the traction of the vehicle and wheels, determine the power requirements for a variety of maneuvers and compare methods of traversing steep slopes. Respirators are worn by researchers to protect against the airborne silica that is present during testing. VIPER is a collaboration within and beyond the agency. NASA's Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley is managing the project, leading the mission’s science, systems engineering, real-time rover surface operations and software. The rover’s instruments are provided by Ames, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida and commercial partner, Honeybee Robotics in California. The spacecraft, lander and launch vehicle that will deliver VIPER to the surface of the Moon will be provided through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services program, delivering science and technology payloads to and near the Moon.
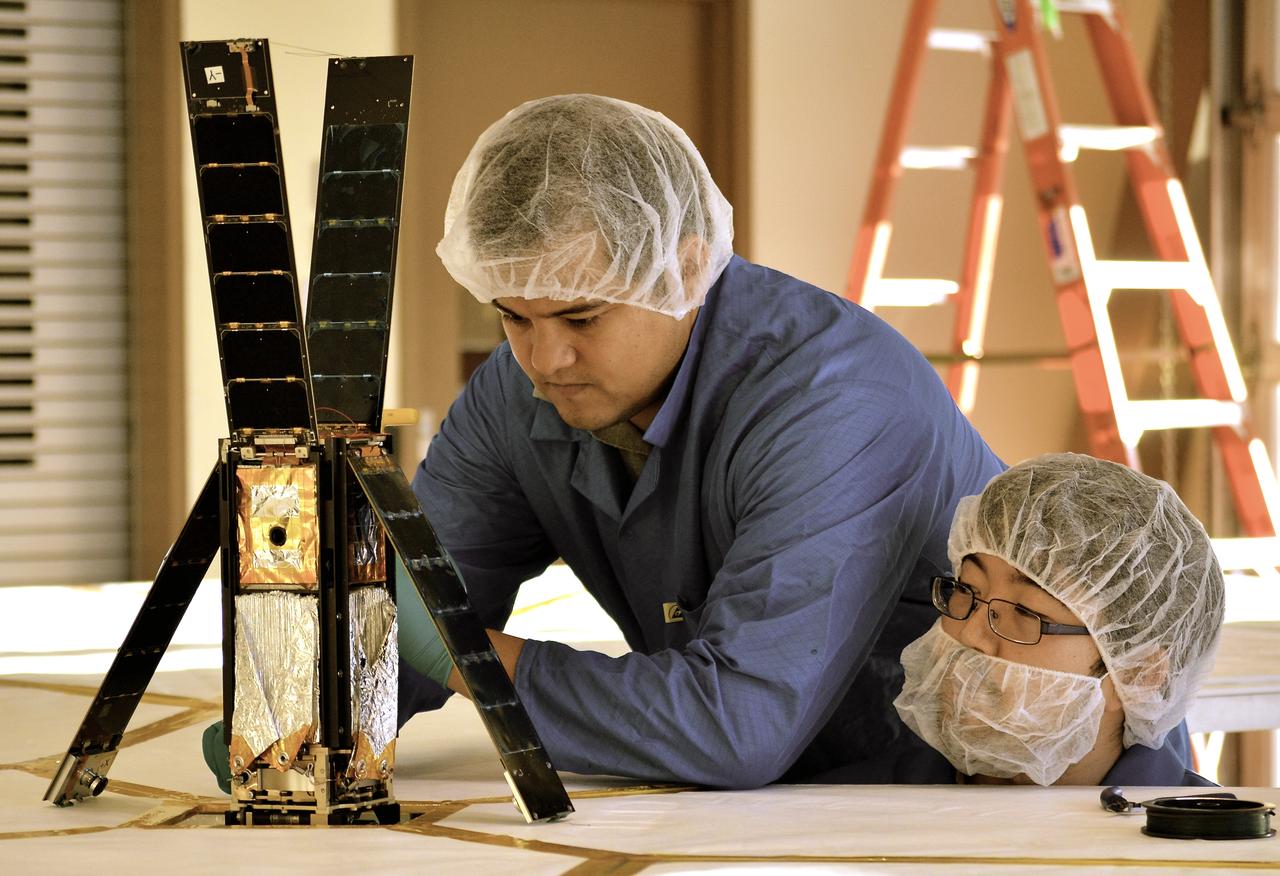

Students Alex Diaz and Riki Munakata of California Polytechnic State University testing the LightSail CubeSat. LightSail is a citizen-funded technology demonstration mission sponsored by the Planetary Society using solar propulsion for CubeSats. The spacecraft is designed to “sail” on the energy of solar photons striking the thin, reflective sail material. The first LightSail mission is designed to test the spacecraft’s critical systems, including the sequence to autonomously deploy a Mylar solar sail with an area of 32 square meters (344 square feet). The Planetary Society is planning a second, full solar sailing demonstration flight for 2016. Light is made of packets of energy called photons. While photons have no mass, they have energy and momentum. Solar sails use this momentum as a method of propulsion, creating flight by light. LightSail’s solar sail is packaged into a three-unit CubeSat about the size of a loaf of bread. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the ELaNa XI mission as an auxiliary payload aboard the U.S. Air Force X-37B space plane mission on May 20, 2015.

This ultraviolet image from NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer is of the planetary nebula NGC 7293 also known as the Helix Nebula. It is the nearest example of what happens to a star, like our own Sun, as it approaches the end of its life when it runs out of fuel, expels gas outward and evolves into a much hotter, smaller and denser white dwarf star. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07902
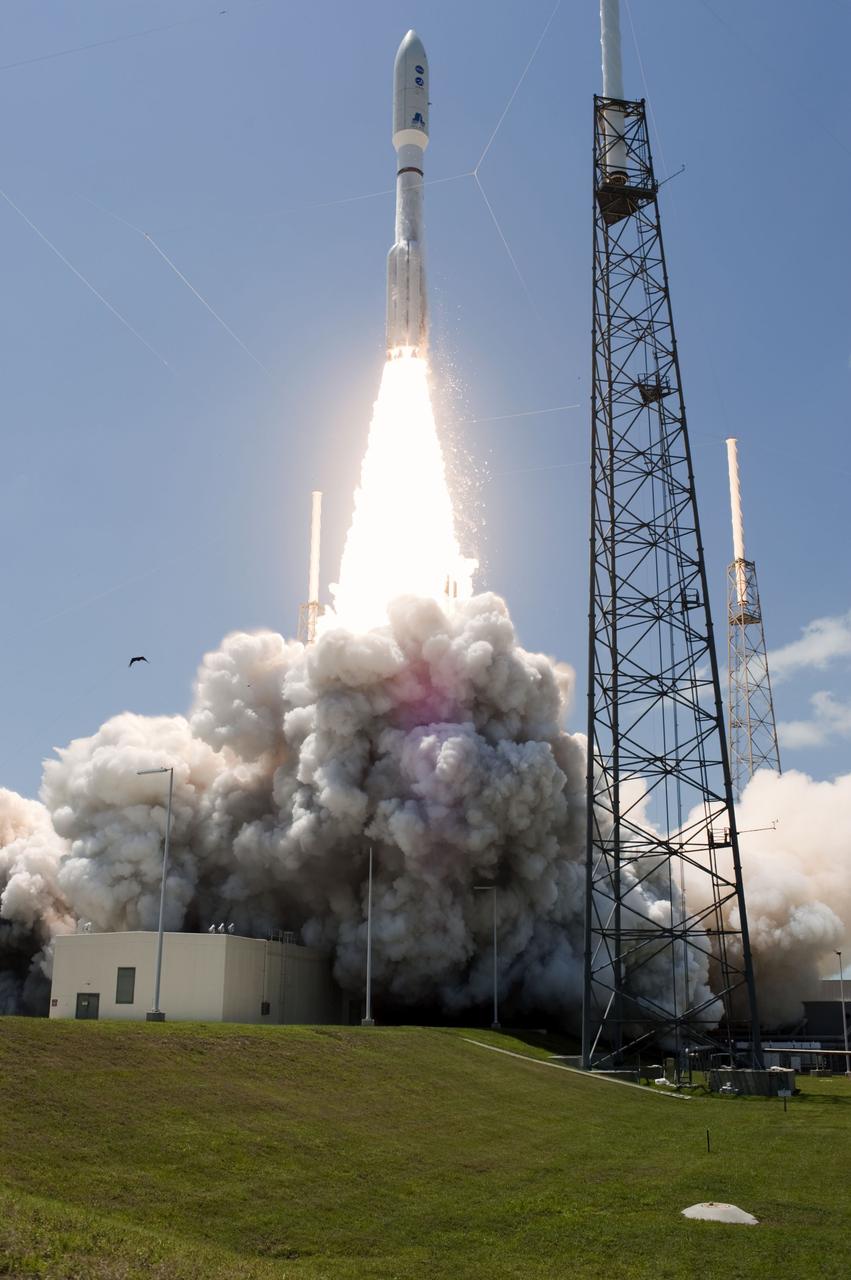

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tim Powers
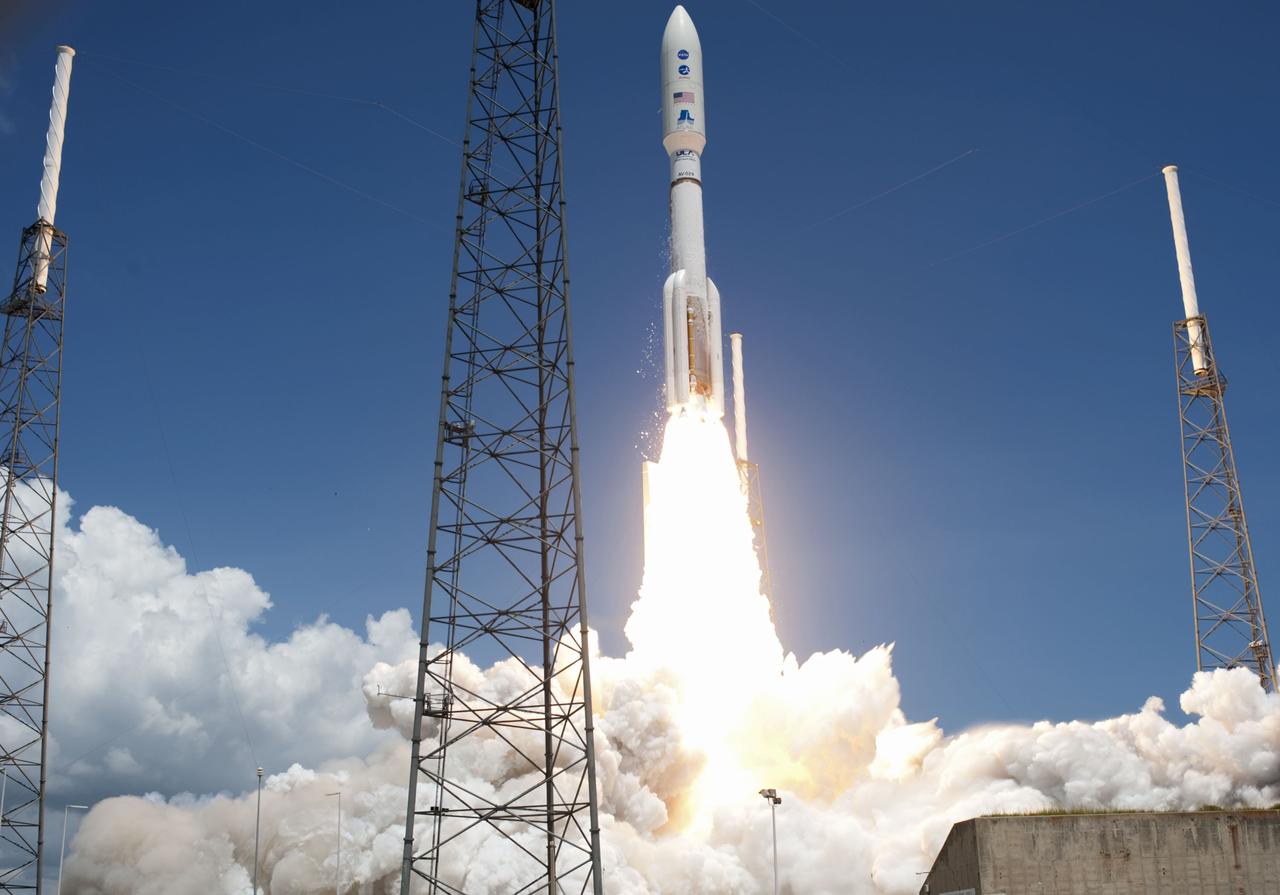

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Fire lights up a crystal-clear blue sky on Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida as a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lofts NASA's Juno planetary probe into space. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight
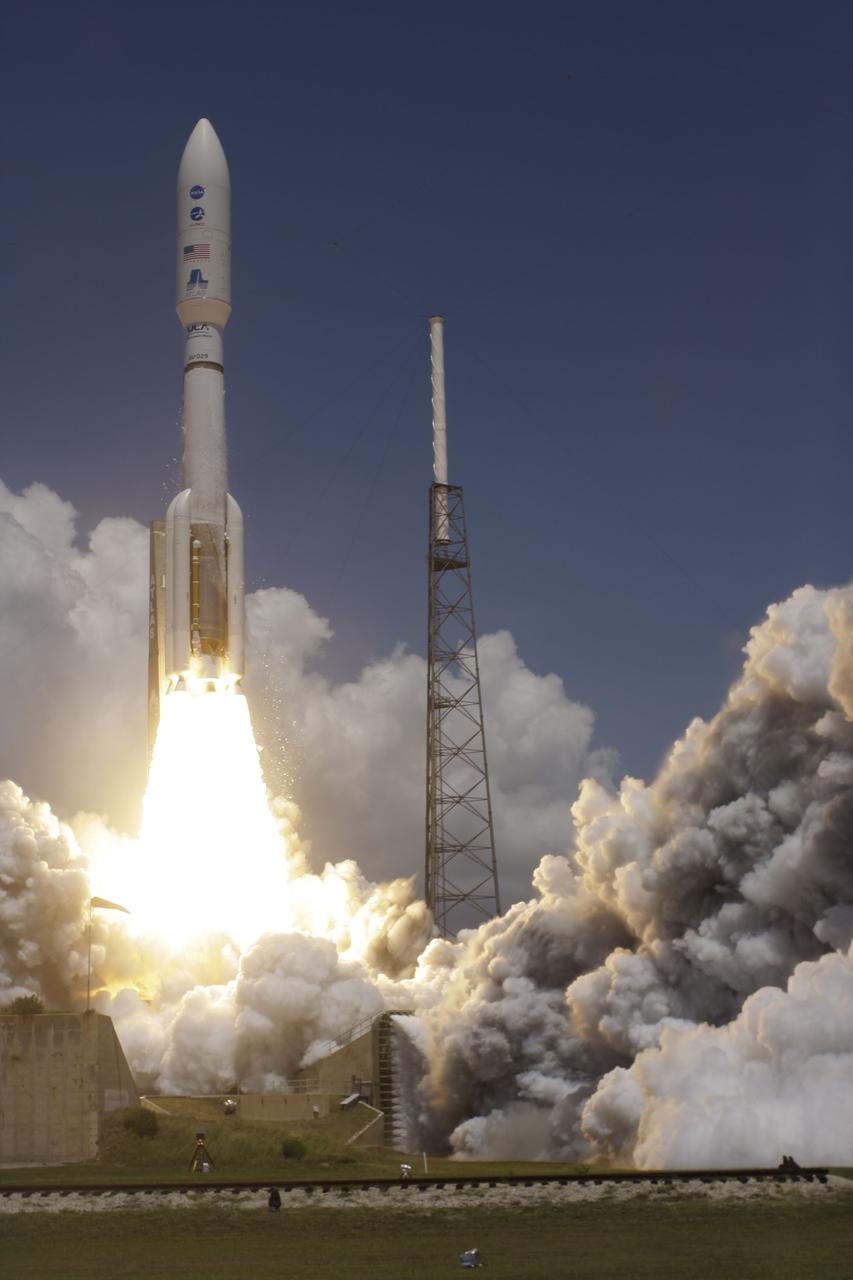

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: Courtesy Scott Andrews
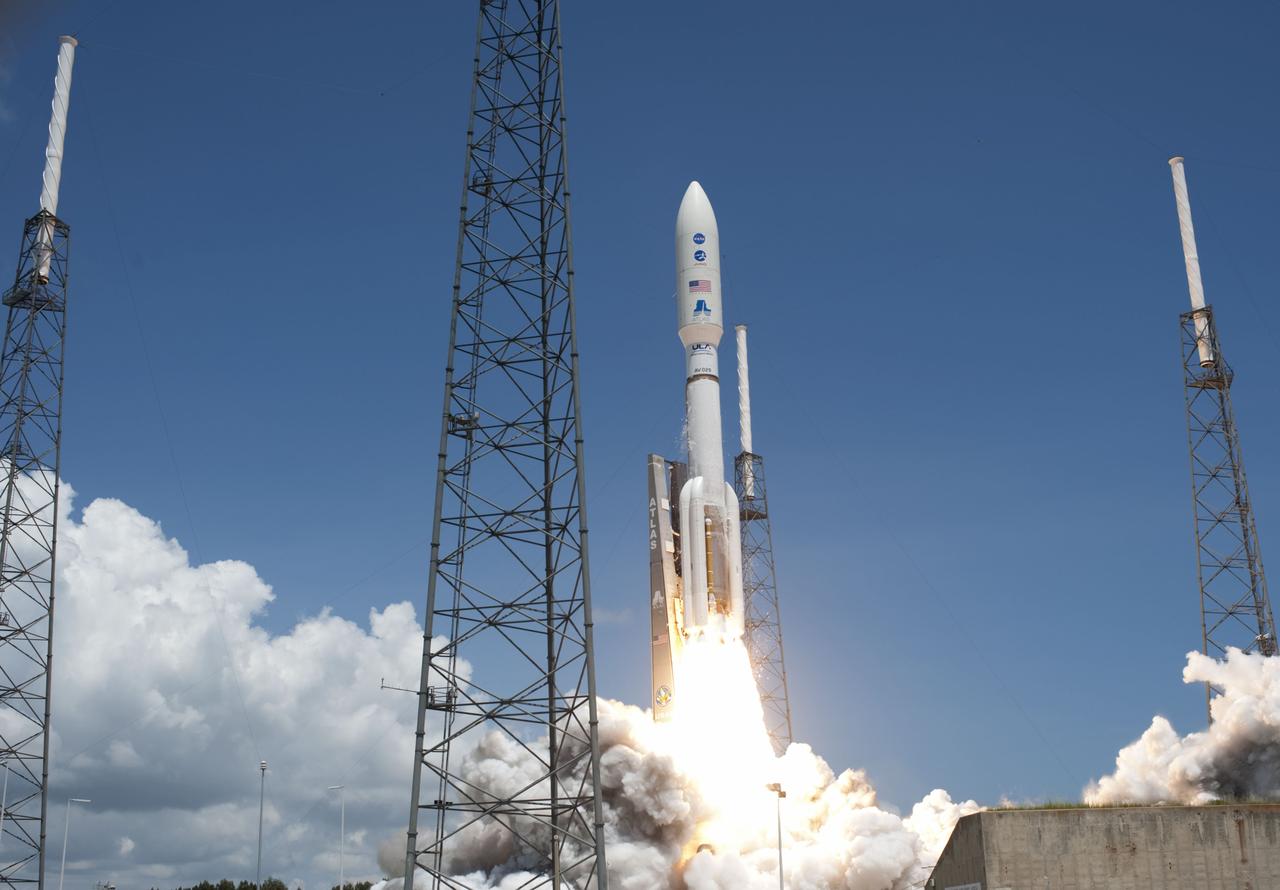

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Fire lights up a crystal-clear blue sky on Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida as a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lofts NASA's Juno planetary probe into space. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight
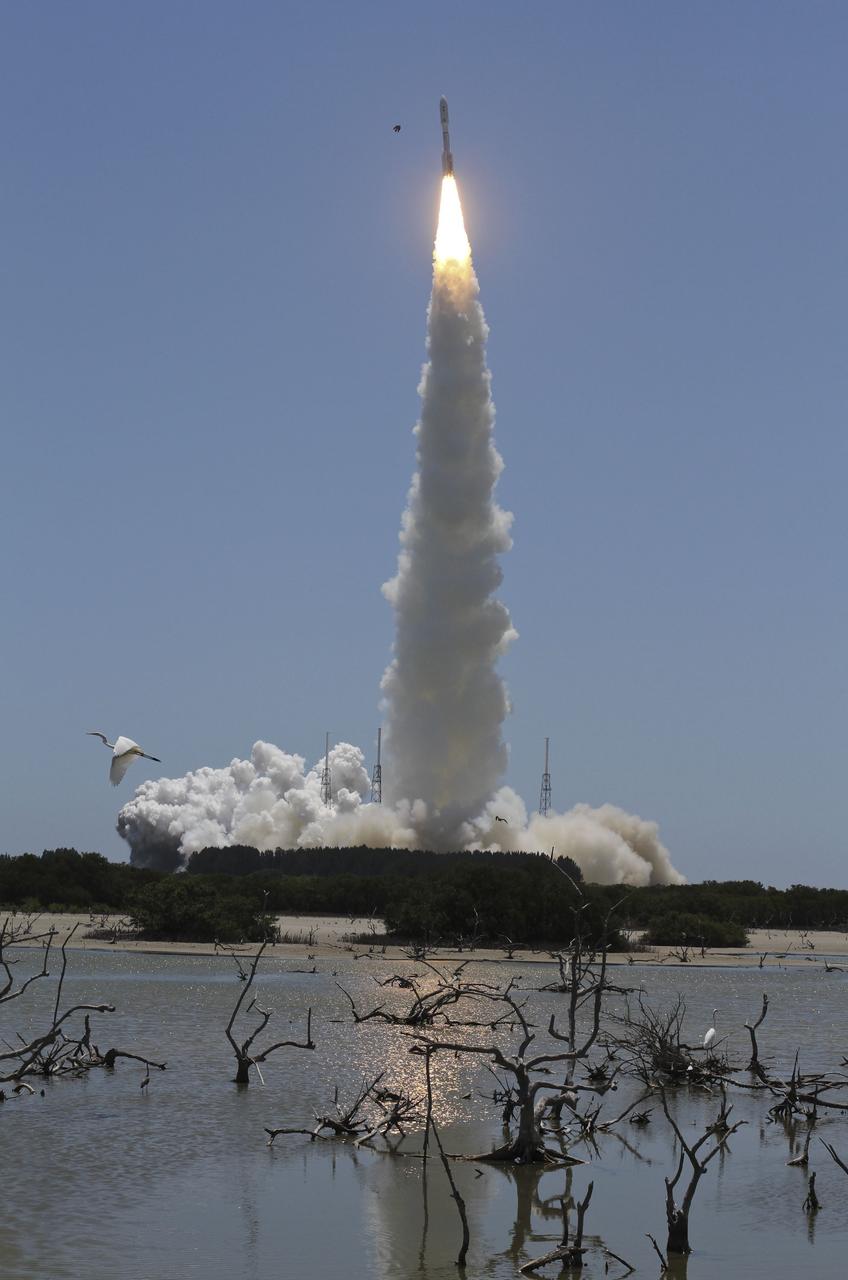

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Reflected in water surrounding Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, fire lights up a crystal-clear blue sky as a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lofts NASA's Juno planetary probe into space. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: Courtesy Scott Andrews
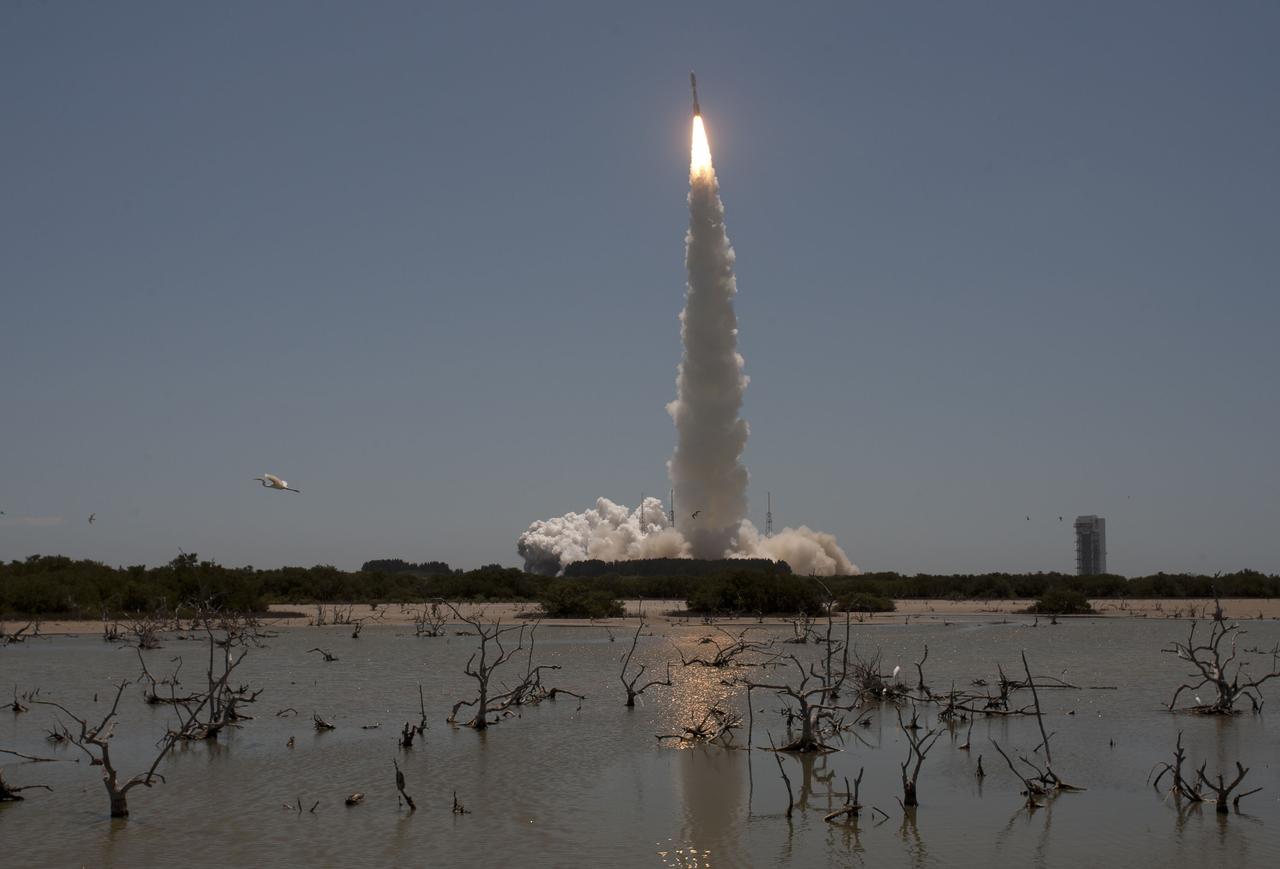

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Reflected in water surrounding Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, fire lights up the sky as a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lofts NASA's Juno planetary probe into space. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: Courtesy Scott Andrews
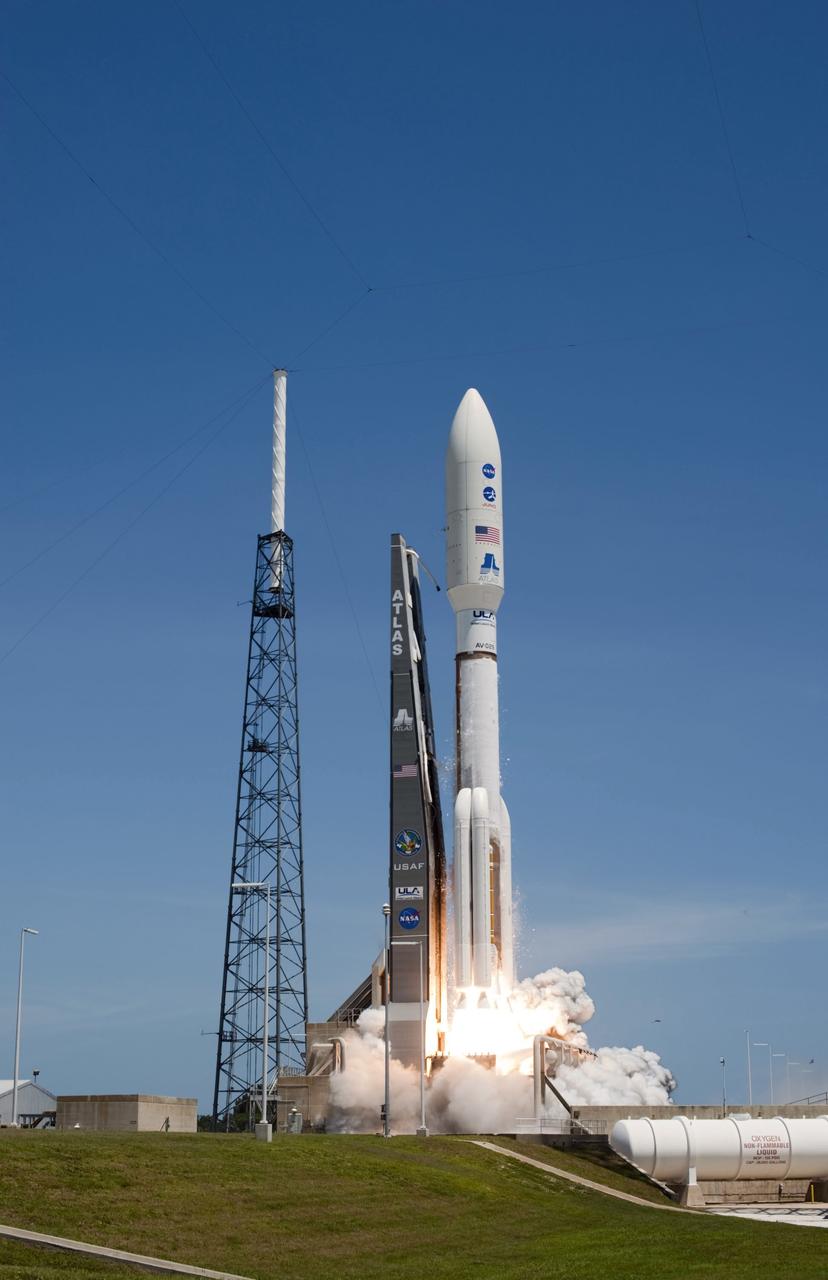

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight
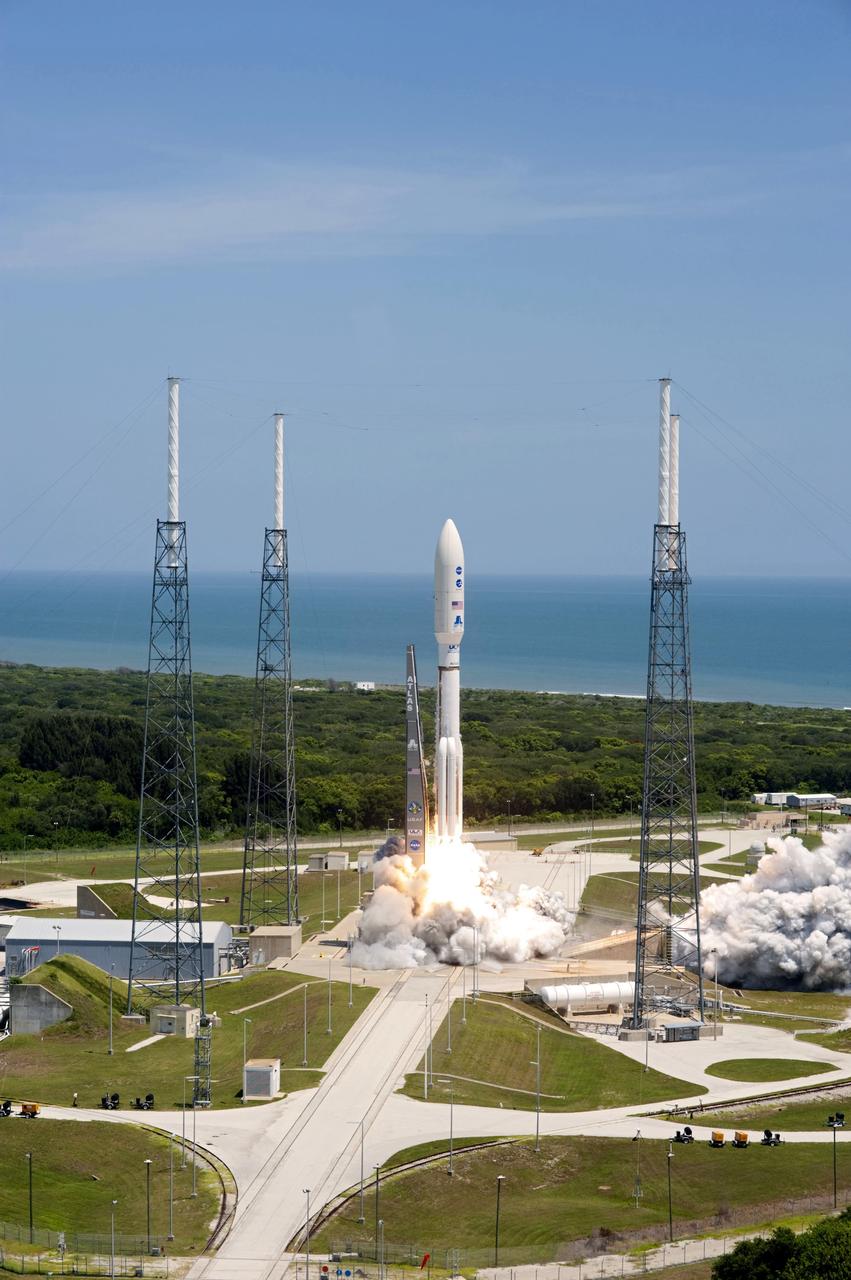

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tim Powers

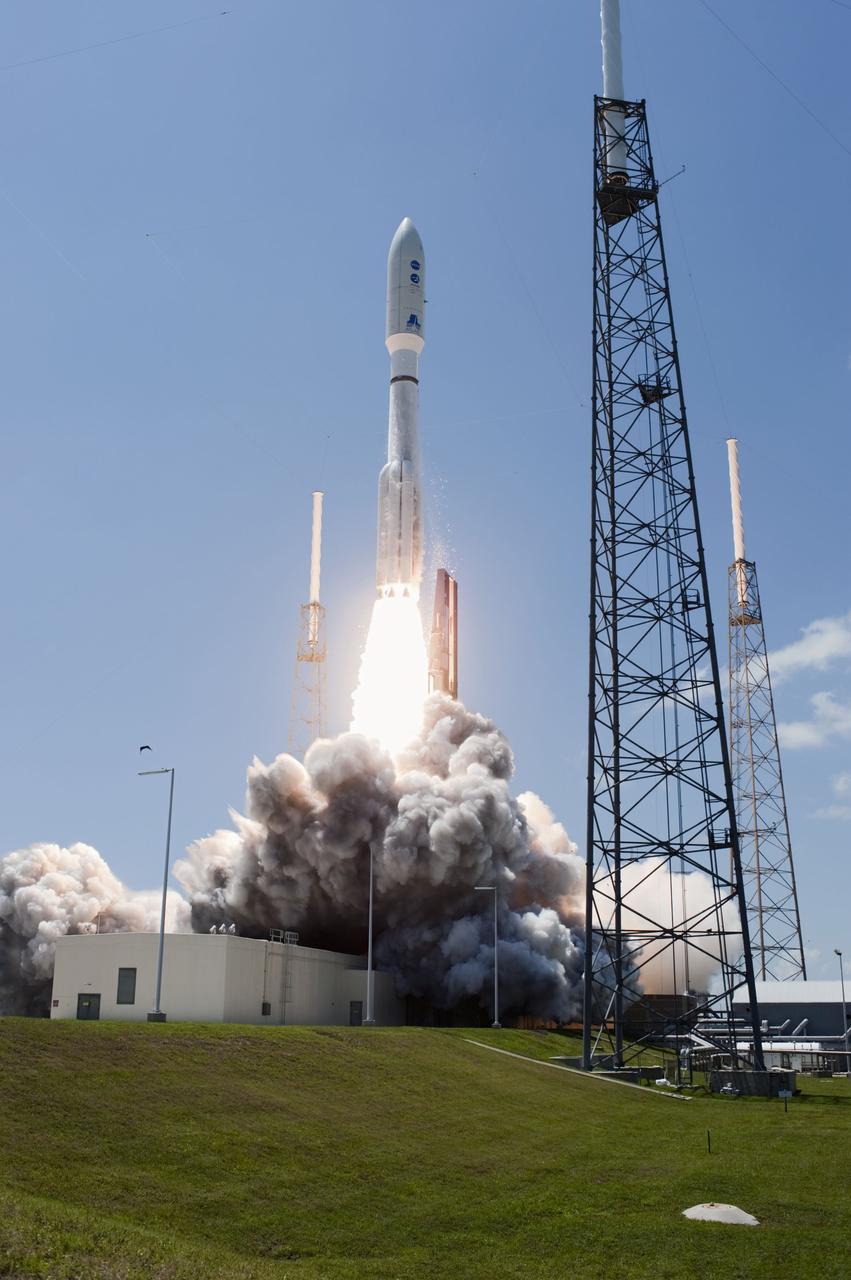
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, is moments away from liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tim Powers
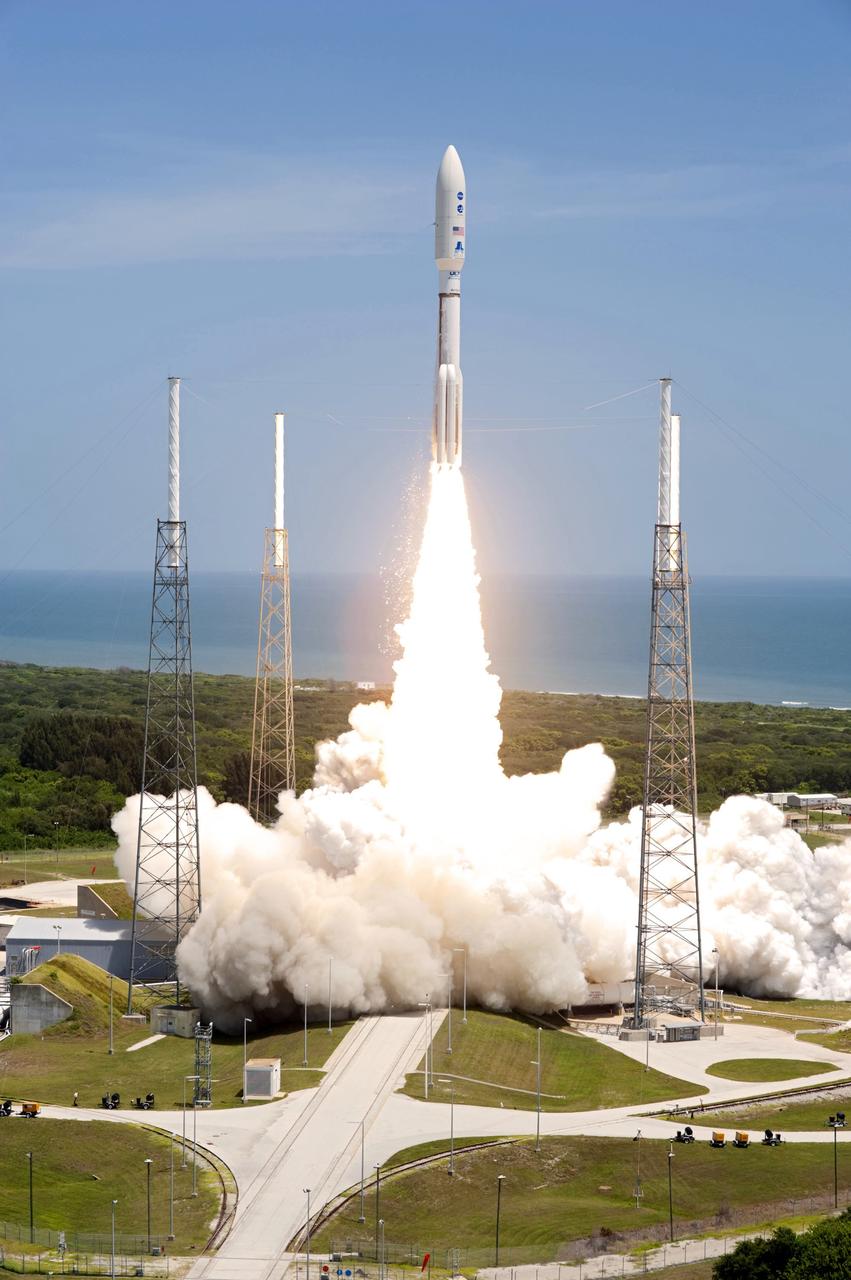

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tim Powers

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tim Powers
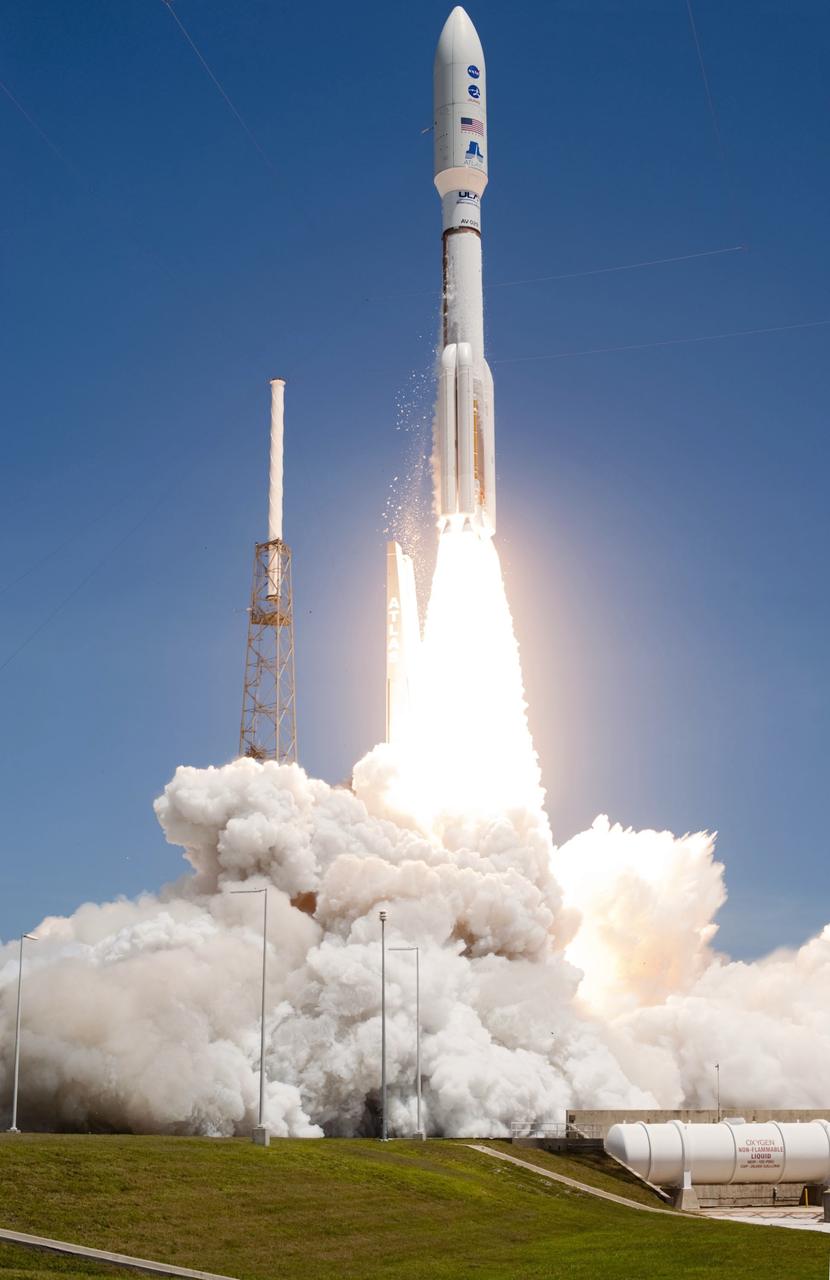

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight
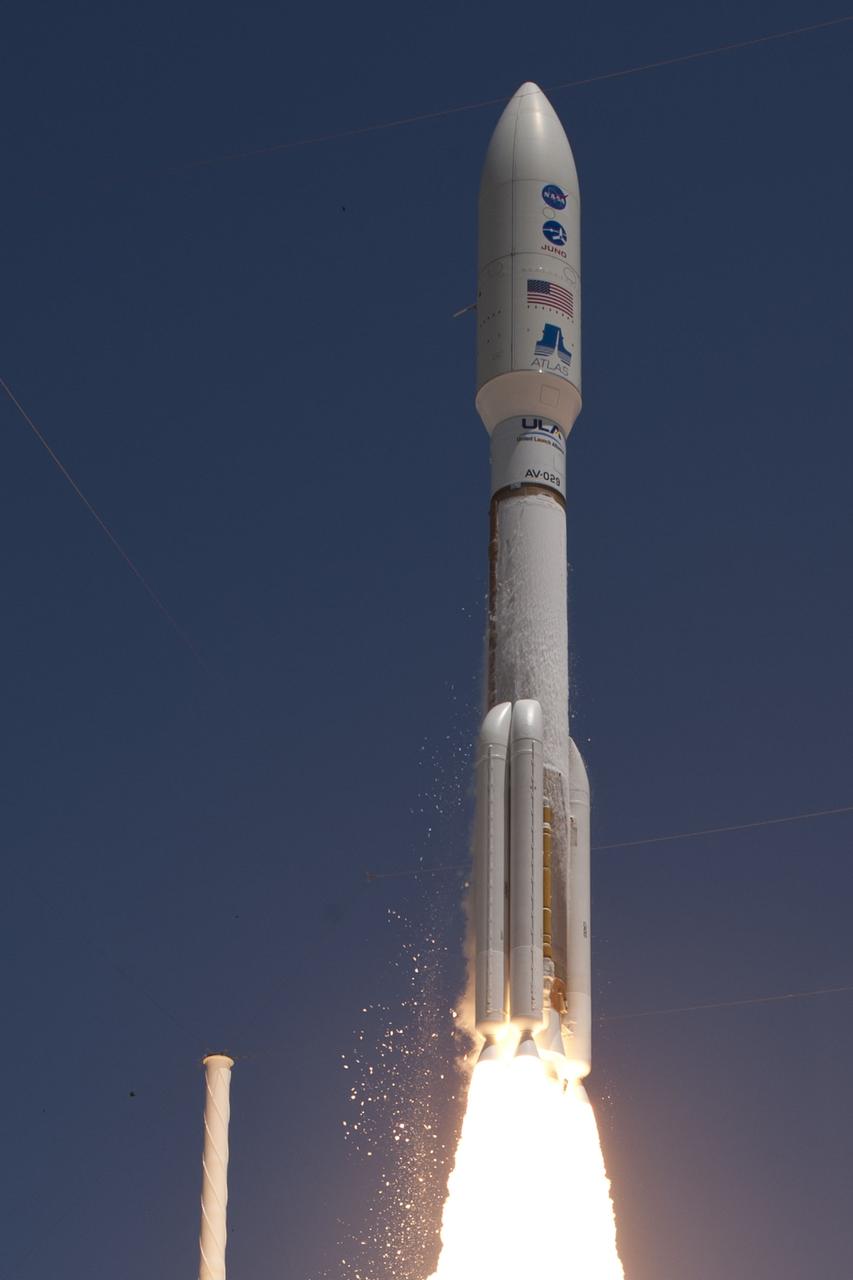

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Fire lights up a crystal-clear blue sky on Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida as a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lofts NASA's Juno planetary probe into space. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: Courtesy Scott Andrews
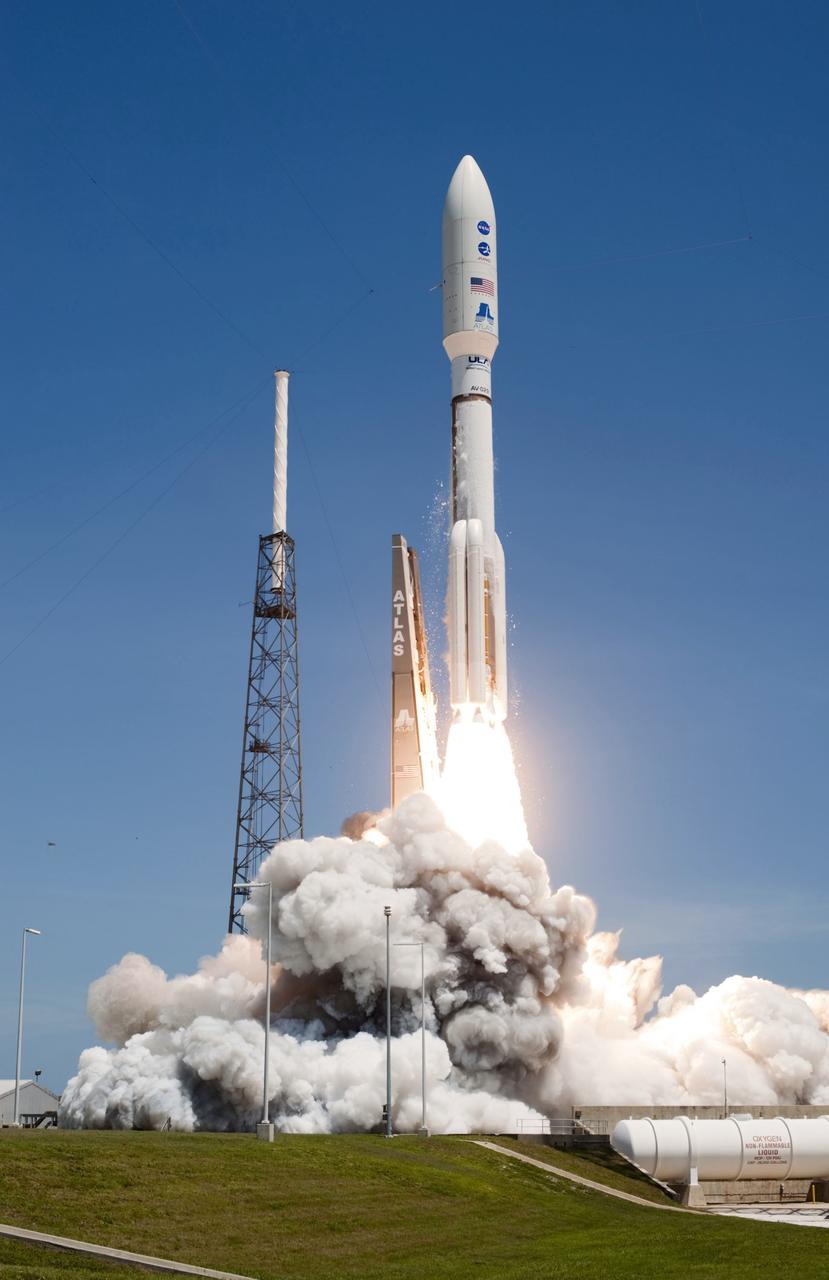

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight
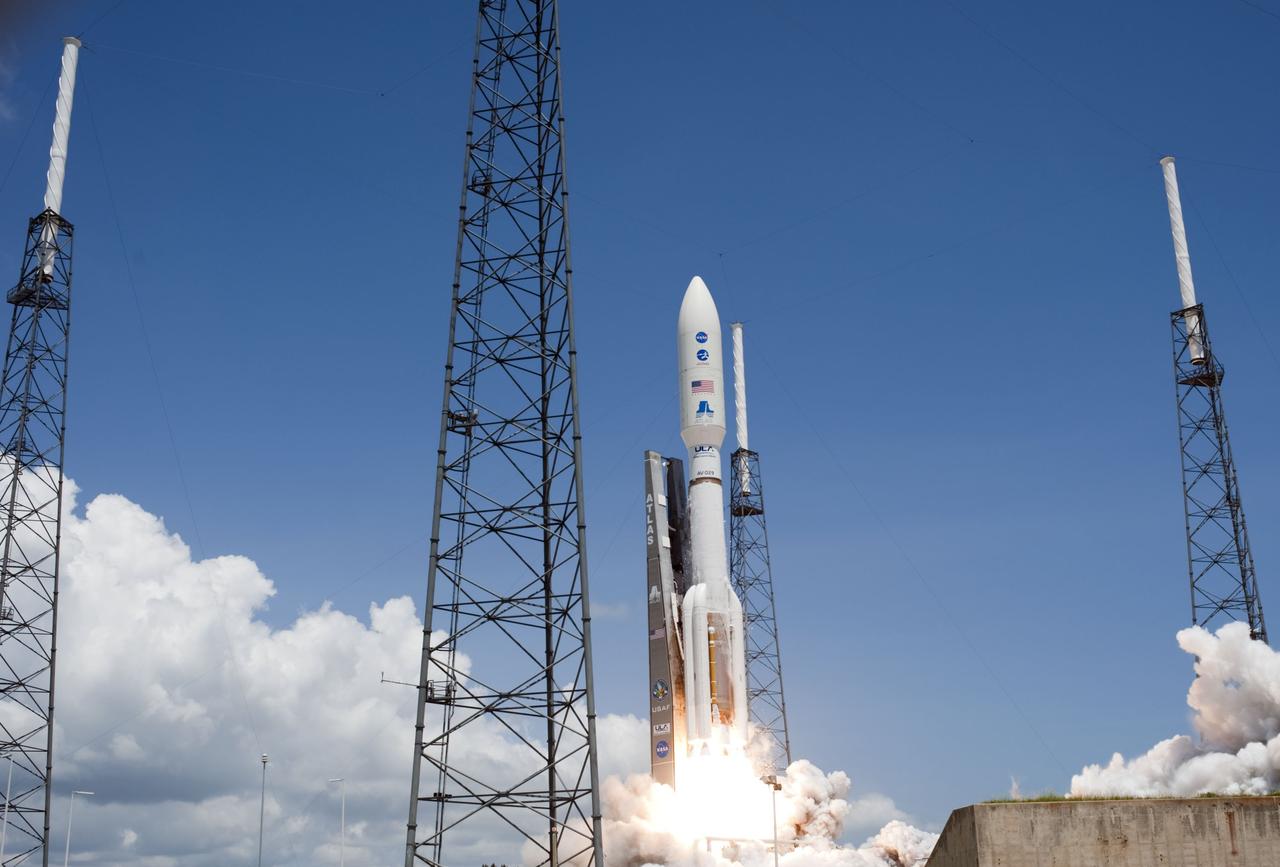

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Fire lights up a crystal-clear blue sky on Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida as a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lofts NASA's Juno planetary probe into space. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight
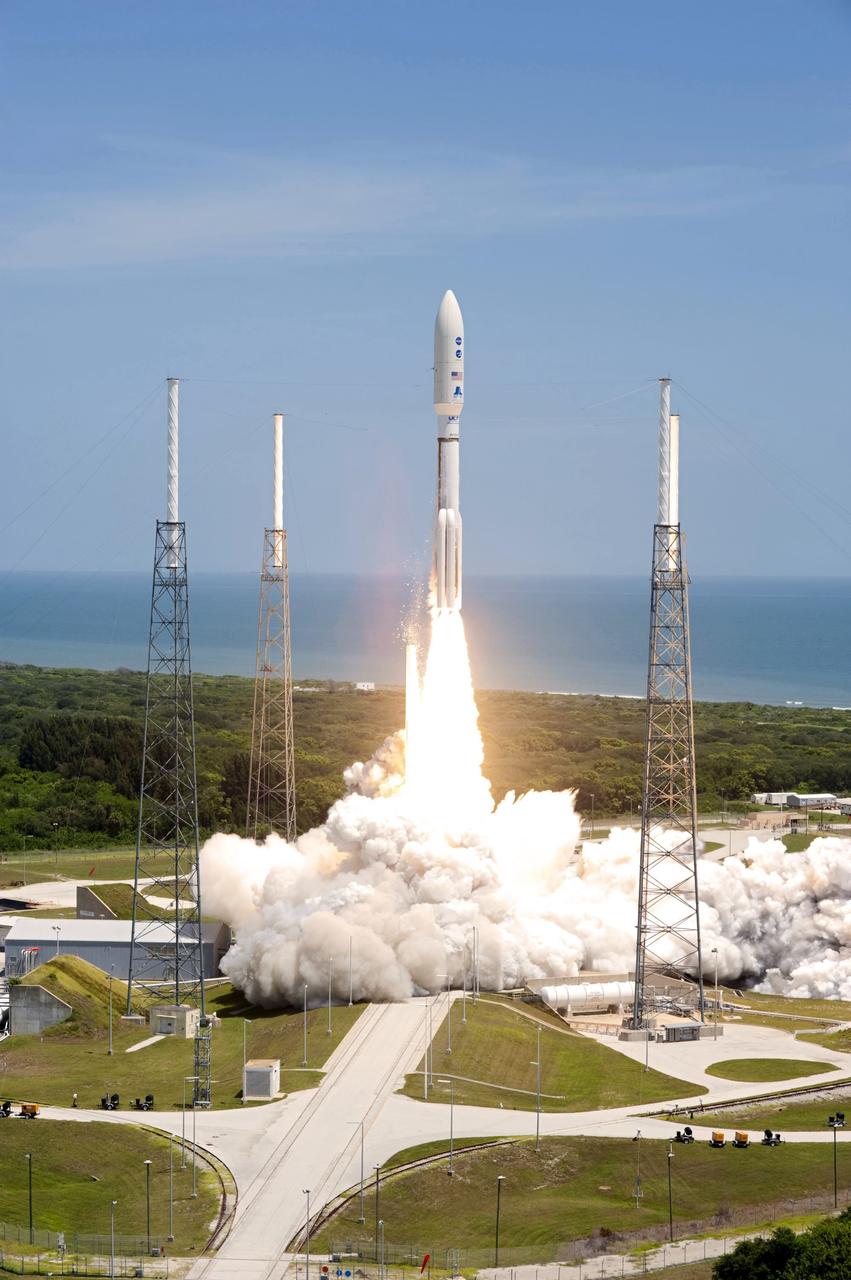

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tim Powers
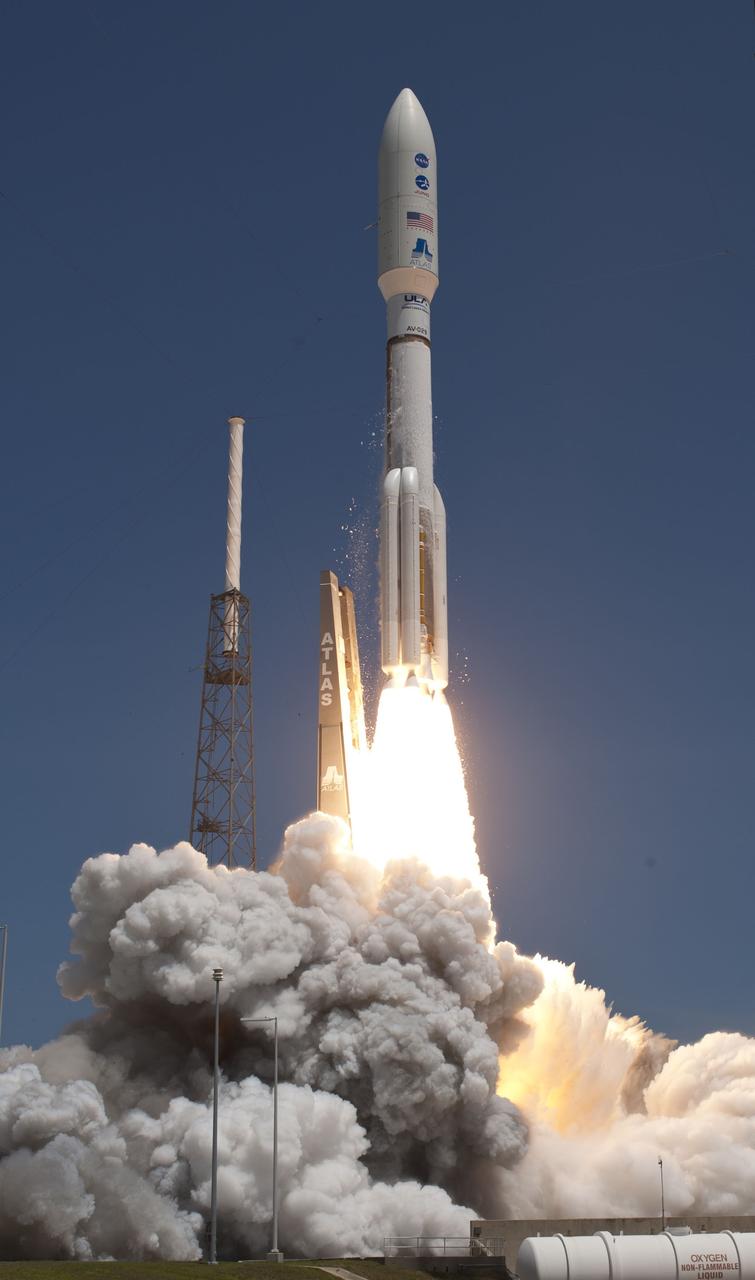

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: Courtesy Scott Andrews
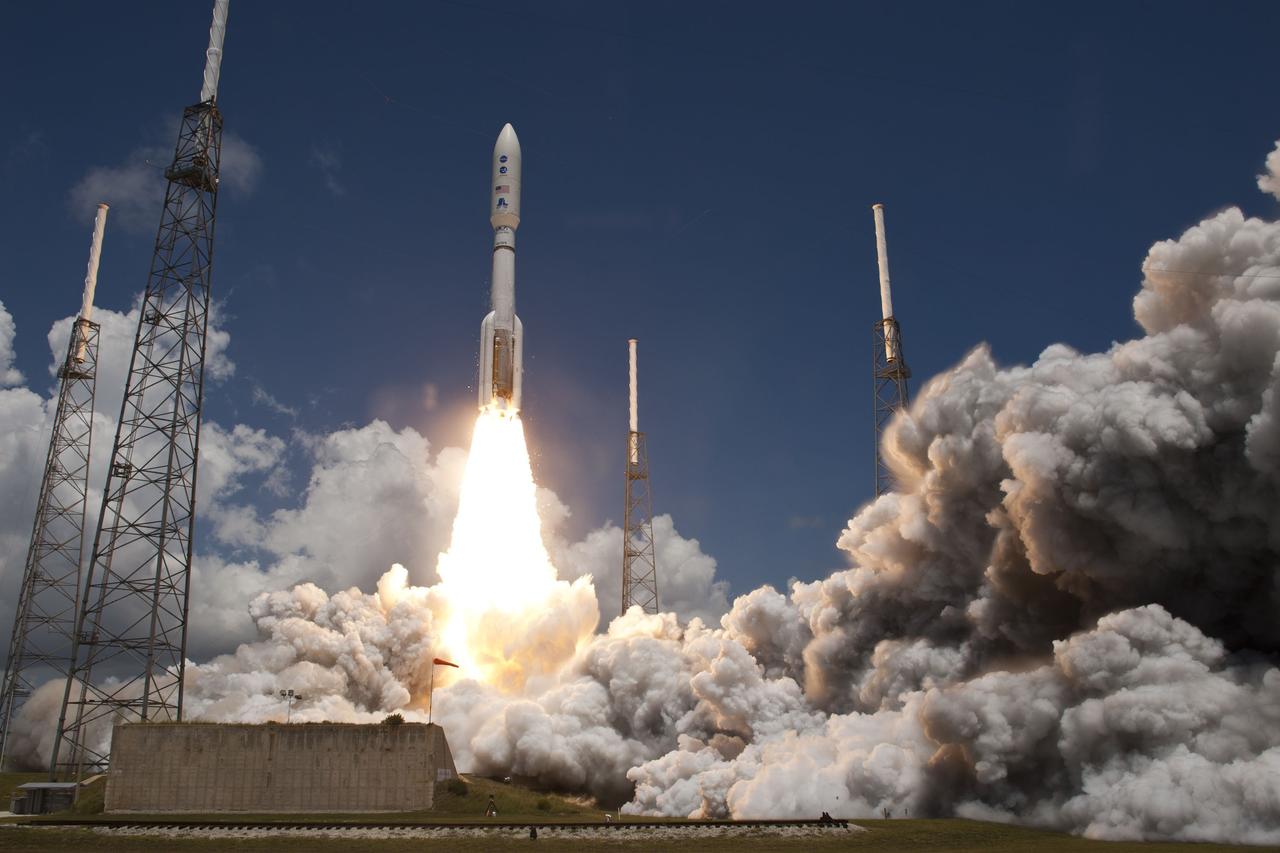

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: Courtesy Scott Andrews
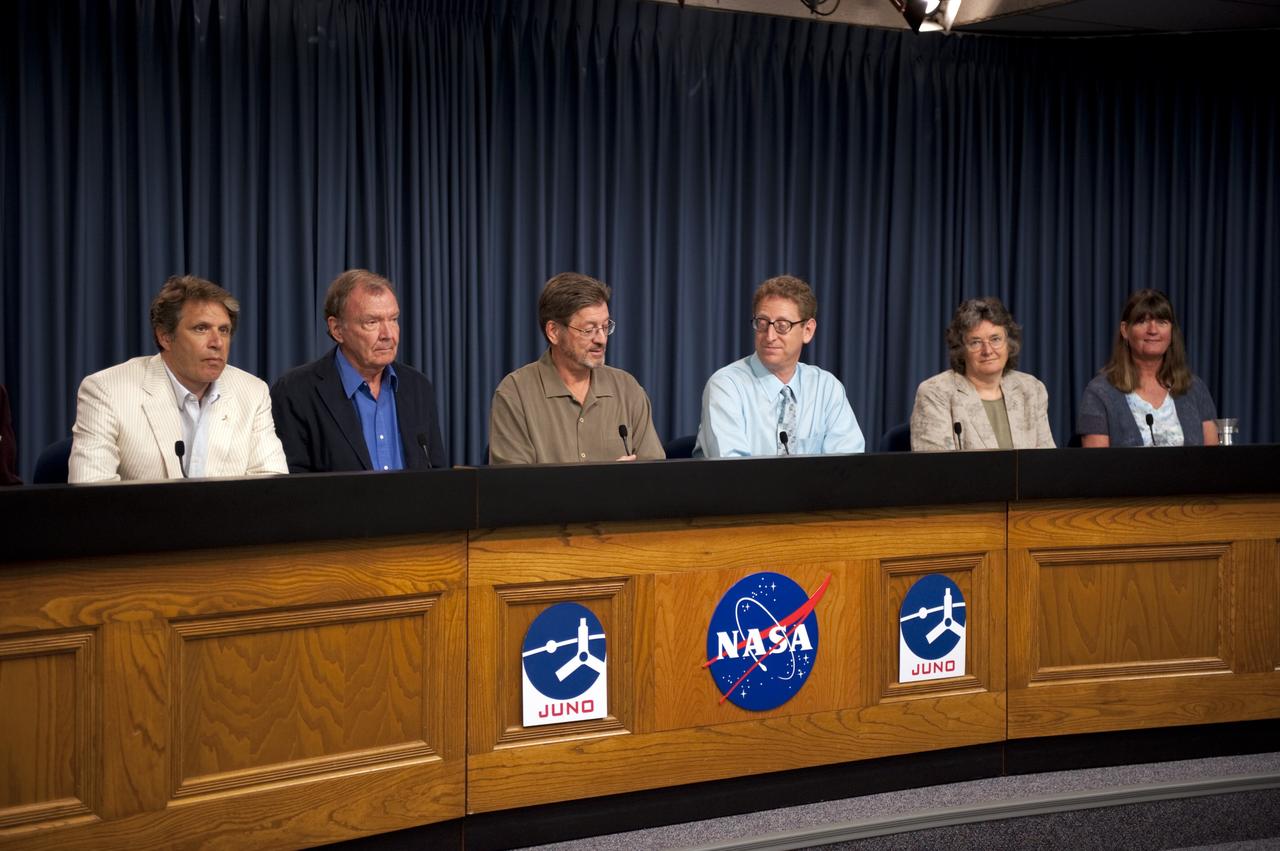

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Juno mission science briefing is held in the NASA Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio; Toby Owen, Juno co-investigator, University of Hawaii; Jack Connerney, Juno MAG Instrument Lead, Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.; Steve Levin, Juno project scientist, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.; Fran Bagenai, Juno co-investigator, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colo.; and Candy Hansen, Juno co-investigator, Planetary Science Institute, Tucson, Ariz. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
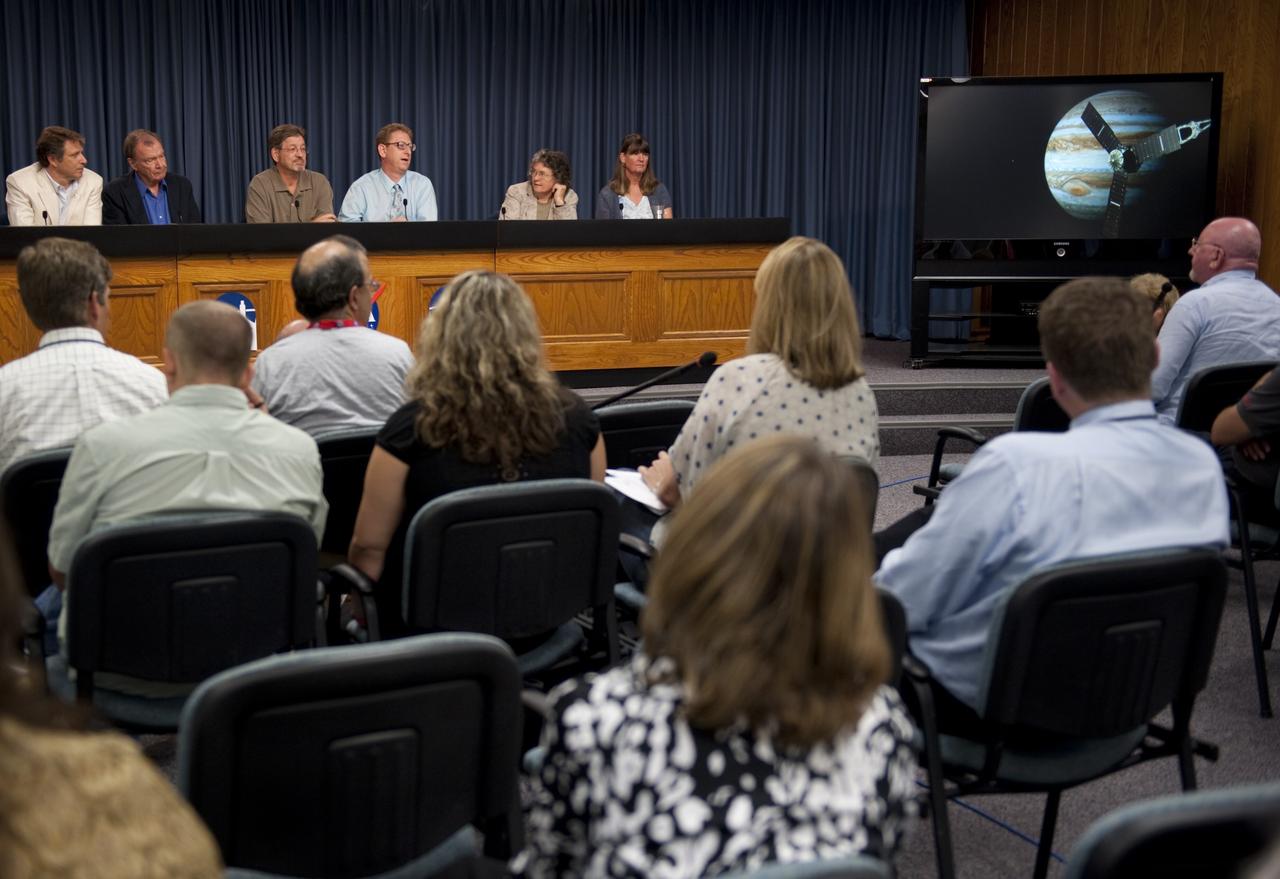

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media representatives question the participants of a Juno mission science briefing in the NASA Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio; Toby Owen, Juno co-investigator, University of Hawaii; Jack Connerney, Juno MAG Instrument Lead, Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.; Steve Levin, Juno project scientist, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.; Fran Bagenai, Juno co-investigator, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colo.; and Candy Hansen, Juno co-investigator, Planetary Science Institute, Tucson, Ariz. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
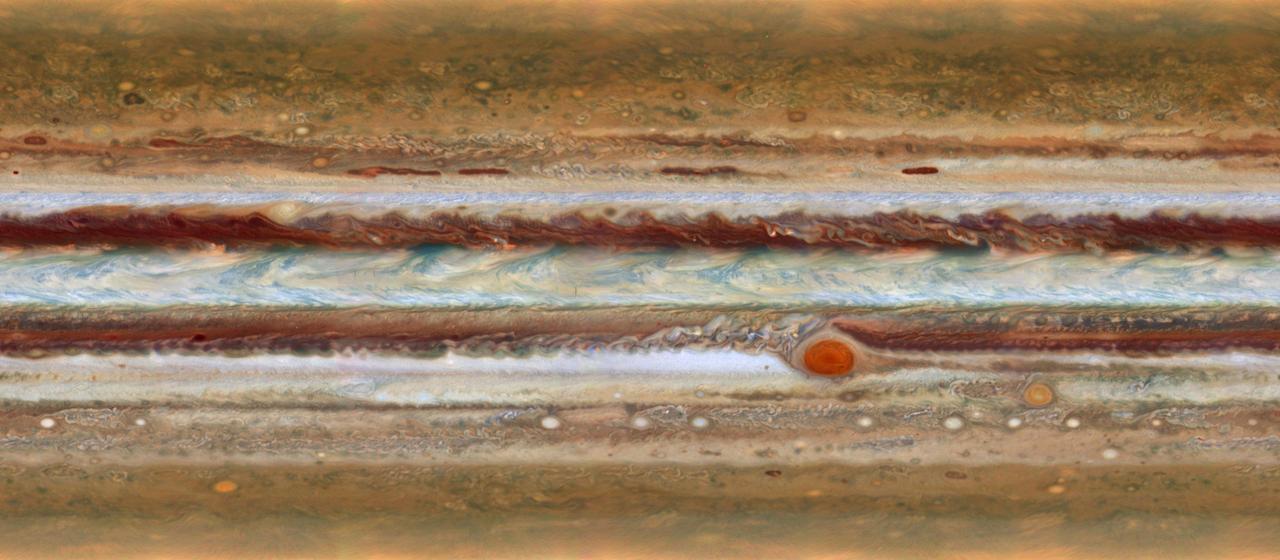

New imagery from the Hubble Space Telescope is revealing details never before seen on Jupiter. Hubble’s new Jupiter maps were used to create this Ultra HD animation. These new maps and spinning globes of Jupiter were made from observations performed with NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. They are the first products to come from a program to study the solar system’s outer planets – Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune and, later, Saturn – each year using Hubble. The observations are designed to capture a broad range of features, including winds, clouds, storms and atmospheric chemistry. These annual studies will help current and future scientists see how these giant worlds change over time. Scientists at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and the University of California at Berkeley produced two global maps of Jupiter from the observations, which were made using Hubble’s high-performance Wide Field Camera 3. The two maps represent nearly back-to-back rotations of the planet, making it possible to determine the speeds of Jupiter’s winds. Already, the images have revealed a rare wave just north of the planet’s equator and a unique filament-like feature in the core of the Great Red Spot that had not been seen previously. In addition, the new images confirm that the Great Red Spot continues to shrink and become more circular, as it has been doing for years. The long axis of this characteristic storm is about 150 miles (240 kilometers) shorter now than it was in 2014. Recently, the storm had been shrinking at a faster-than-usual rate, but the latest change is consistent with the long-term trend. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/press-release/goddard/hubble-s-planetary-portrait-captures-new-changes-in-jupiter-s-great-red-spot" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/press-release/goddard/hubble-s-planetary-por...</a> Credits: NASA/ESA/Goddard/UCBerkeley/JPL-Caltech/STScI <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
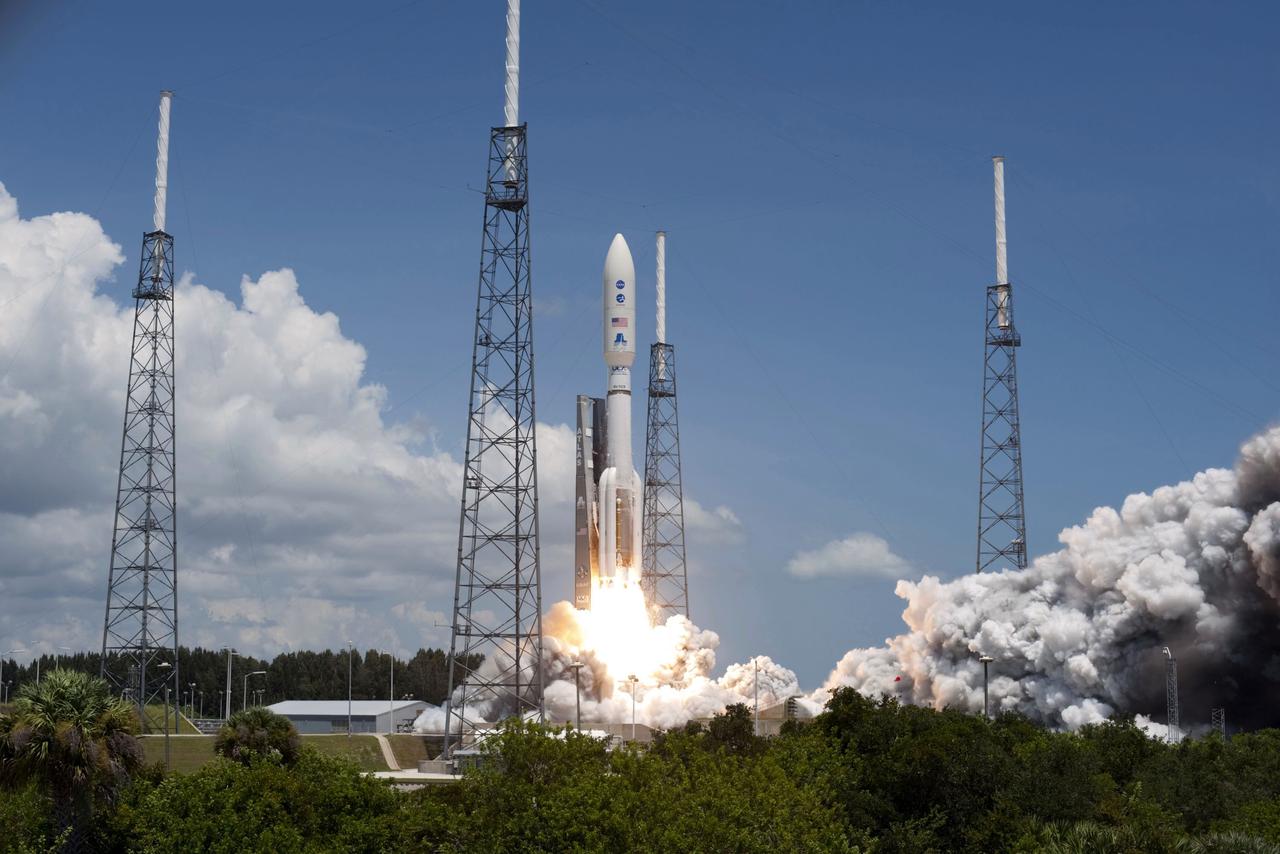

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 and its four lightning protection system towers on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 and its four lightning protection system towers on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight
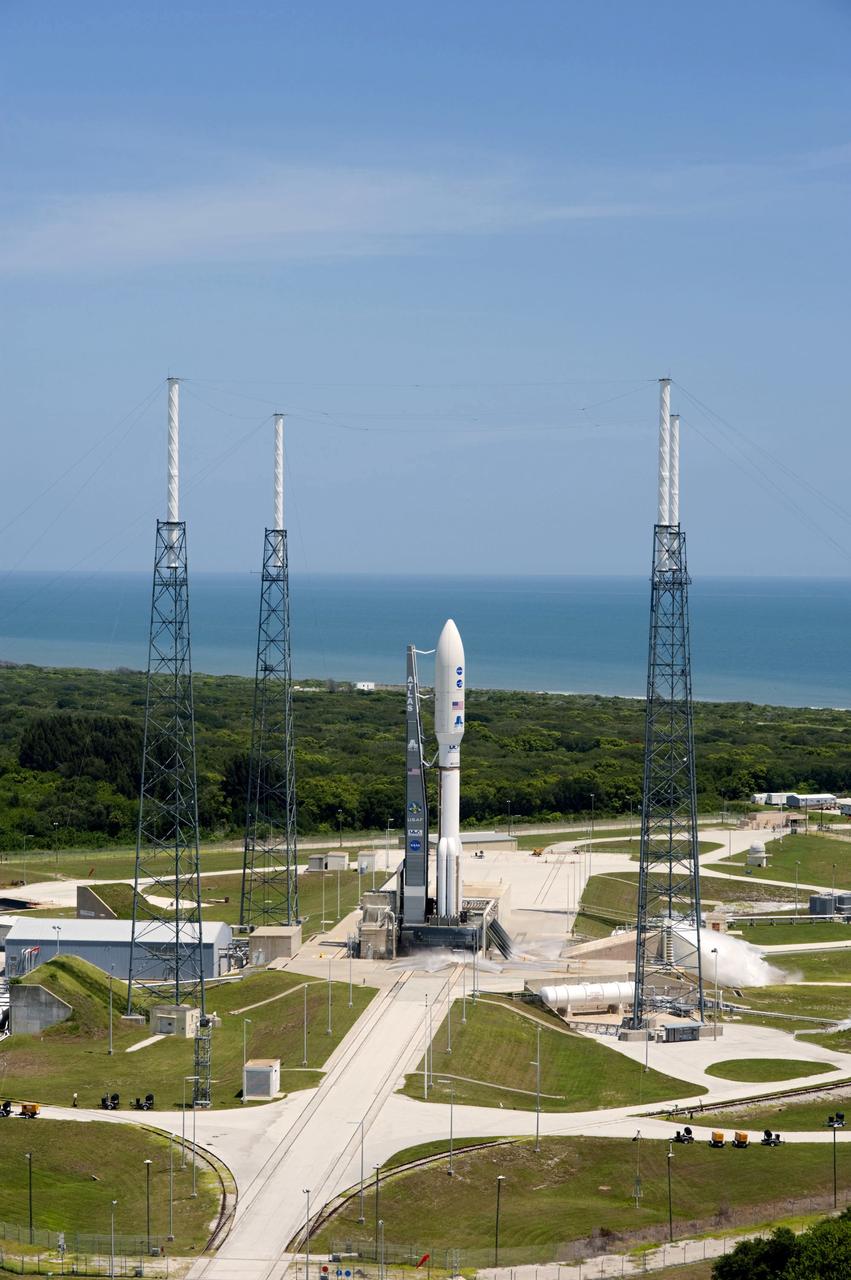

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Backdropped by the Atlantic Ocean and surrounded by its four-tower lightning protection system, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, is seconds away from liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. On the right, water is seen dumping into a flame trench to suppress vibrations at launch. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tim Powers

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, is moments away from liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 and its four lightning protection system towers on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight
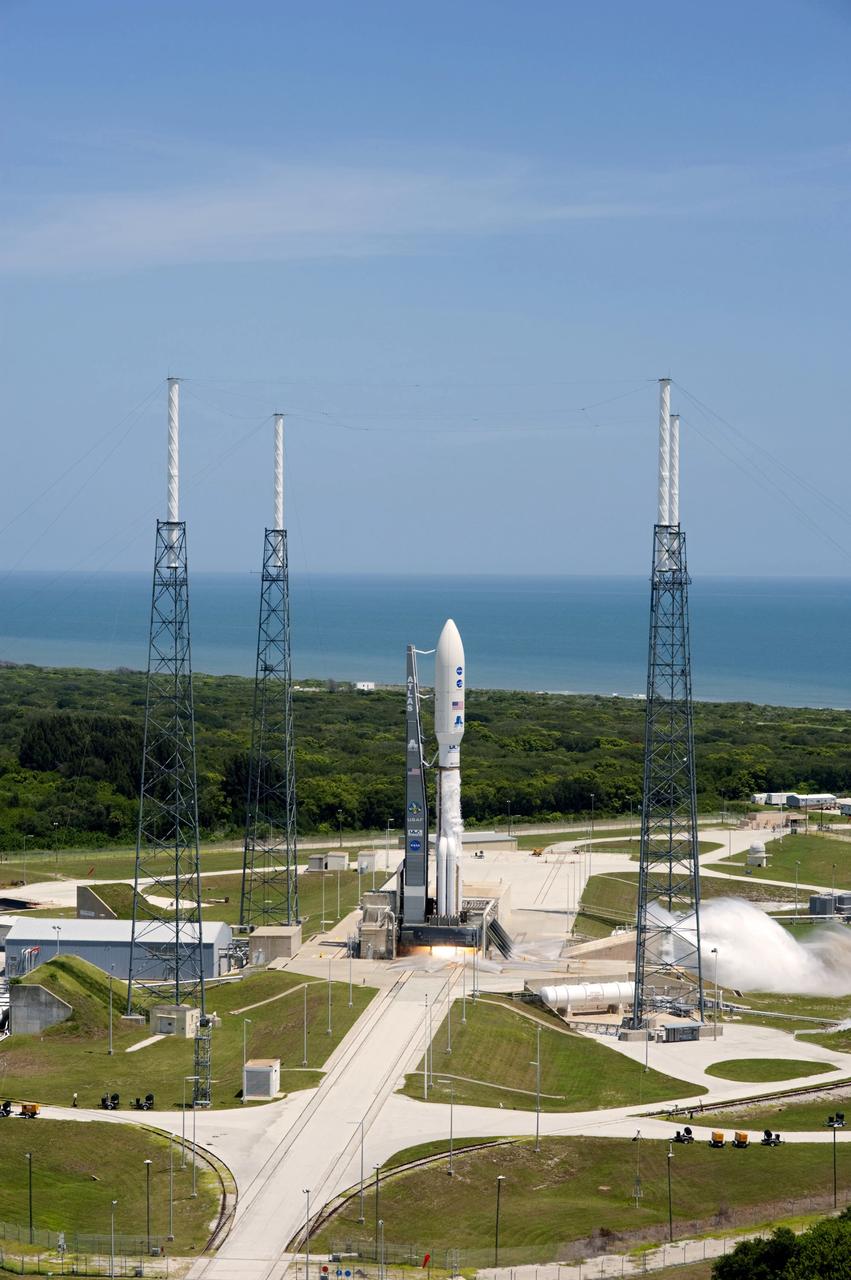

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Backdropped by the Atlantic Ocean and surrounded by its four-tower lightning protection system, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, is seconds away from liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. On the right, water is seen dumping into a flame trench to suppress vibrations at launch. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tim Powers
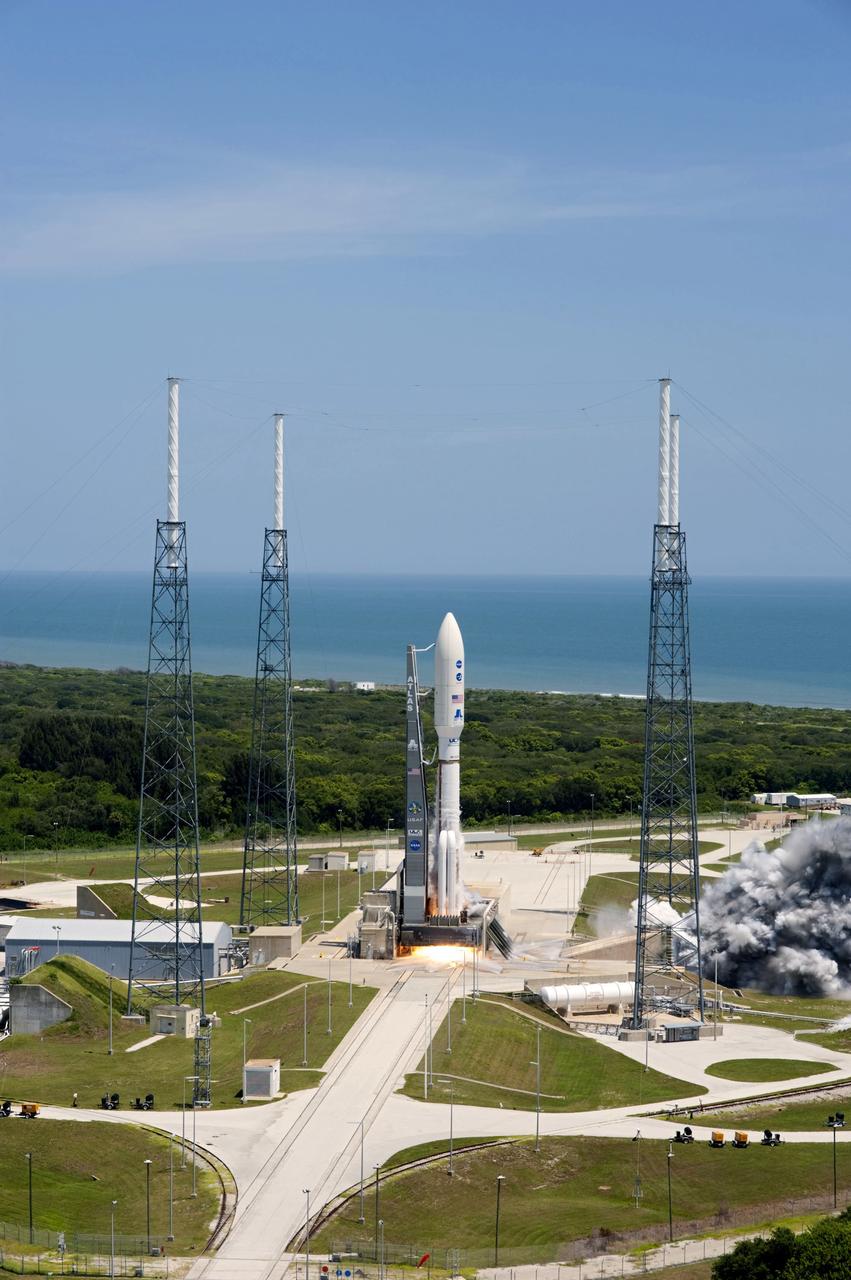

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Backdropped by the Atlantic Ocean and surrounded by its four-tower lightning protection system, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, is seconds away from liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tim Powers
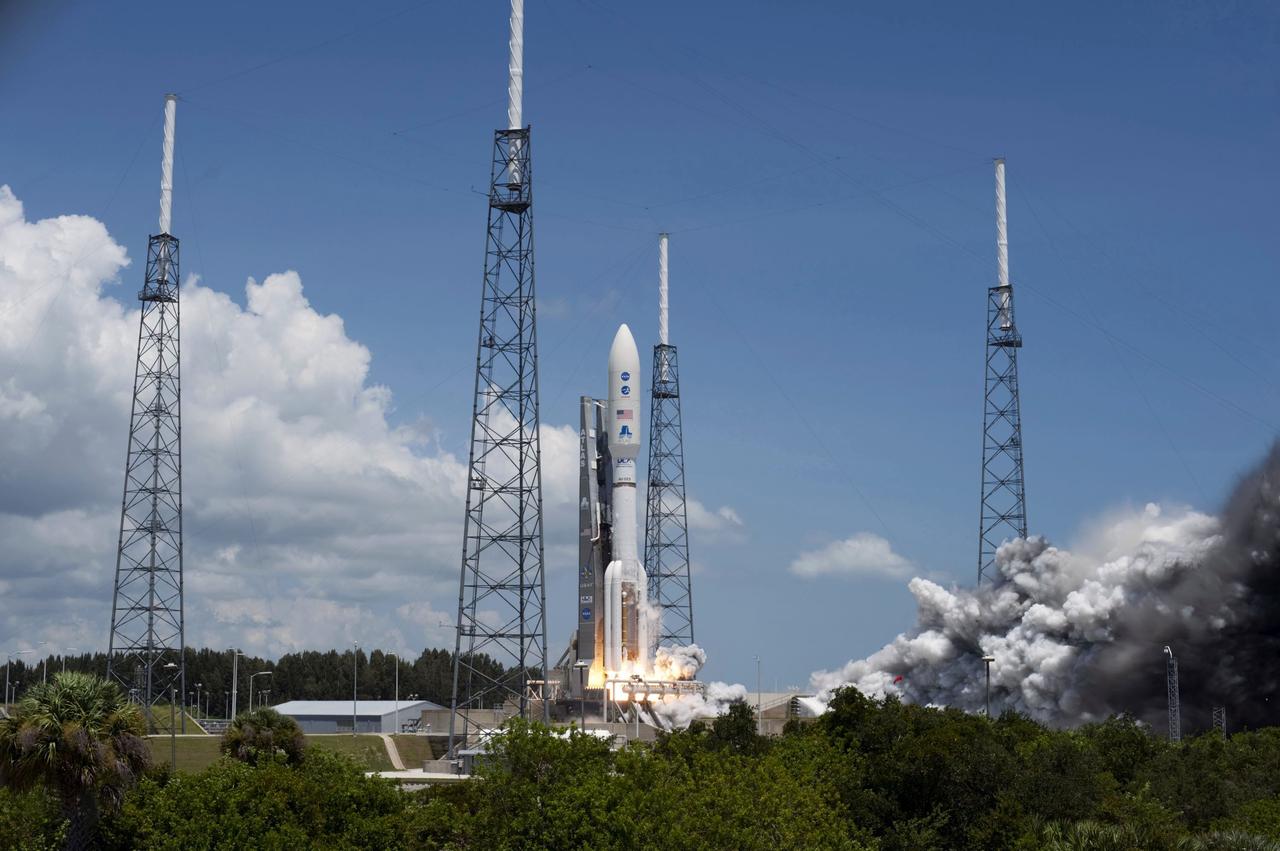

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising from fire and smoke, NASA's Juno planetary probe, enclosed in its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Leaving from Space Launch Complex 41 and its four lightning protection system towers on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the spacecraft will embark on a five-year journey to Jupiter. Liftoff was at 12:25 p.m. EDT Aug. 5. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Don Kight
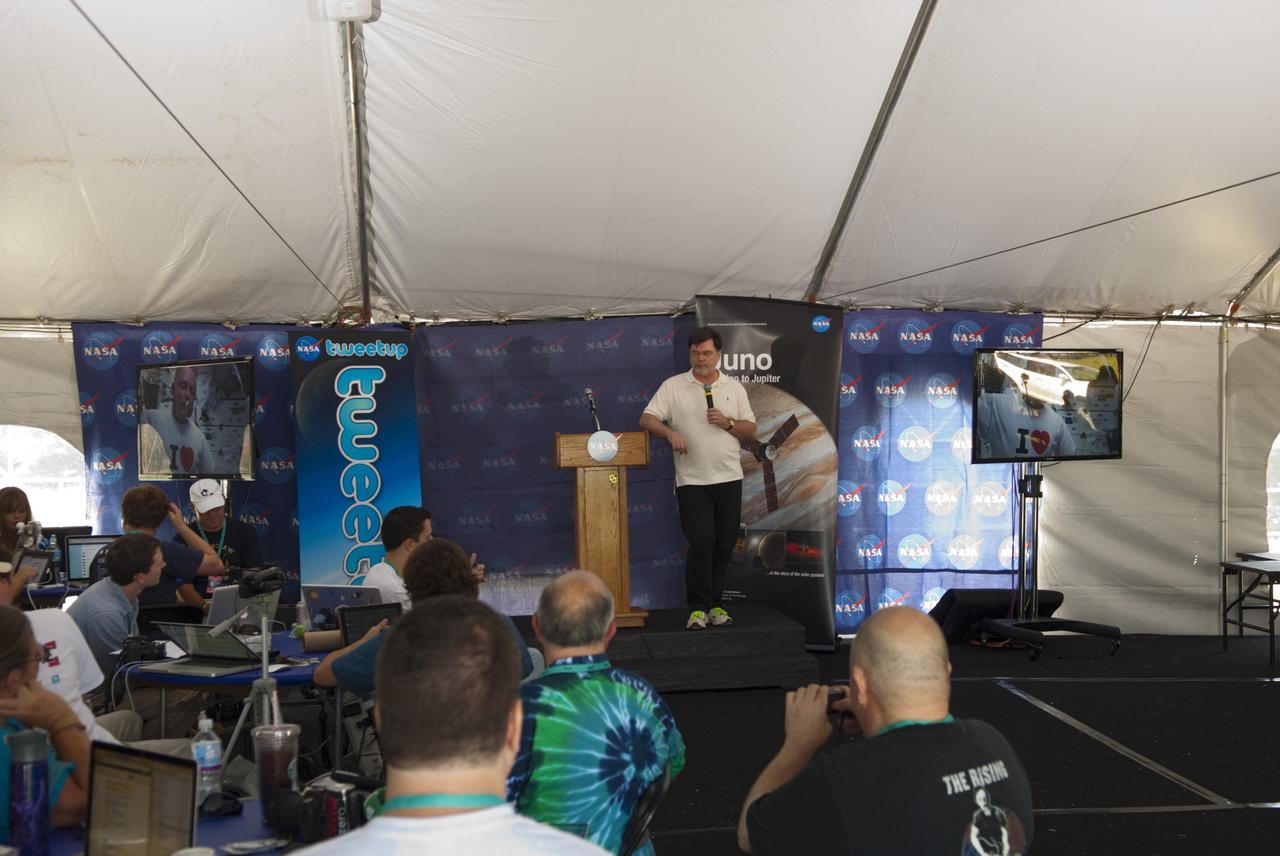

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jim Adams, NASA deputy director of Planetary Science, speaks to about 150 followers of the agency’s Twitter account during Juno Tweetup activities inside a tent at the Press Site. The tweeters are at the center for two days of prelaunch activities. Juno is NASA’s mission to Jupiter to study the giant planet and improve our understanding of the planet’s formation and evolution. The tweeters will share their experiences with followers through the social networking site Twitter. Attendees represent 28 states, the District of Columbia and five other countries: Canada, Finland, Norway, Spain and the United Kingdom. This is the first time NASA has invited Twitter followers to experience the launch of a planetary spacecraft. The Juno spacecraft is scheduled to launch on an Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, Aug. 5, at 11:34 a.m. EDT. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: Jim Grossmann
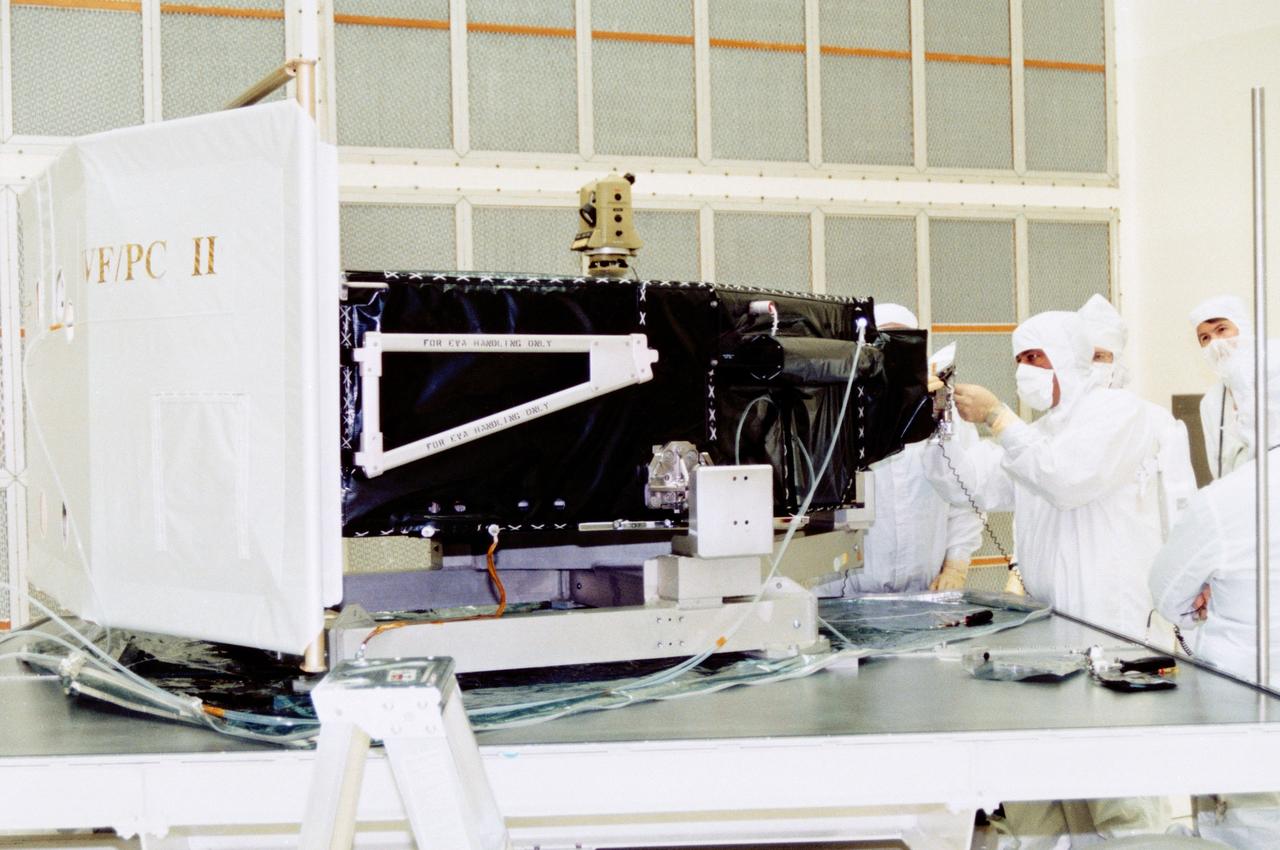

Workers in bldg AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, install a mirror on the Wide Field/Planetary Camera II as part of the preparations for launch later this year on the first servicing mission of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
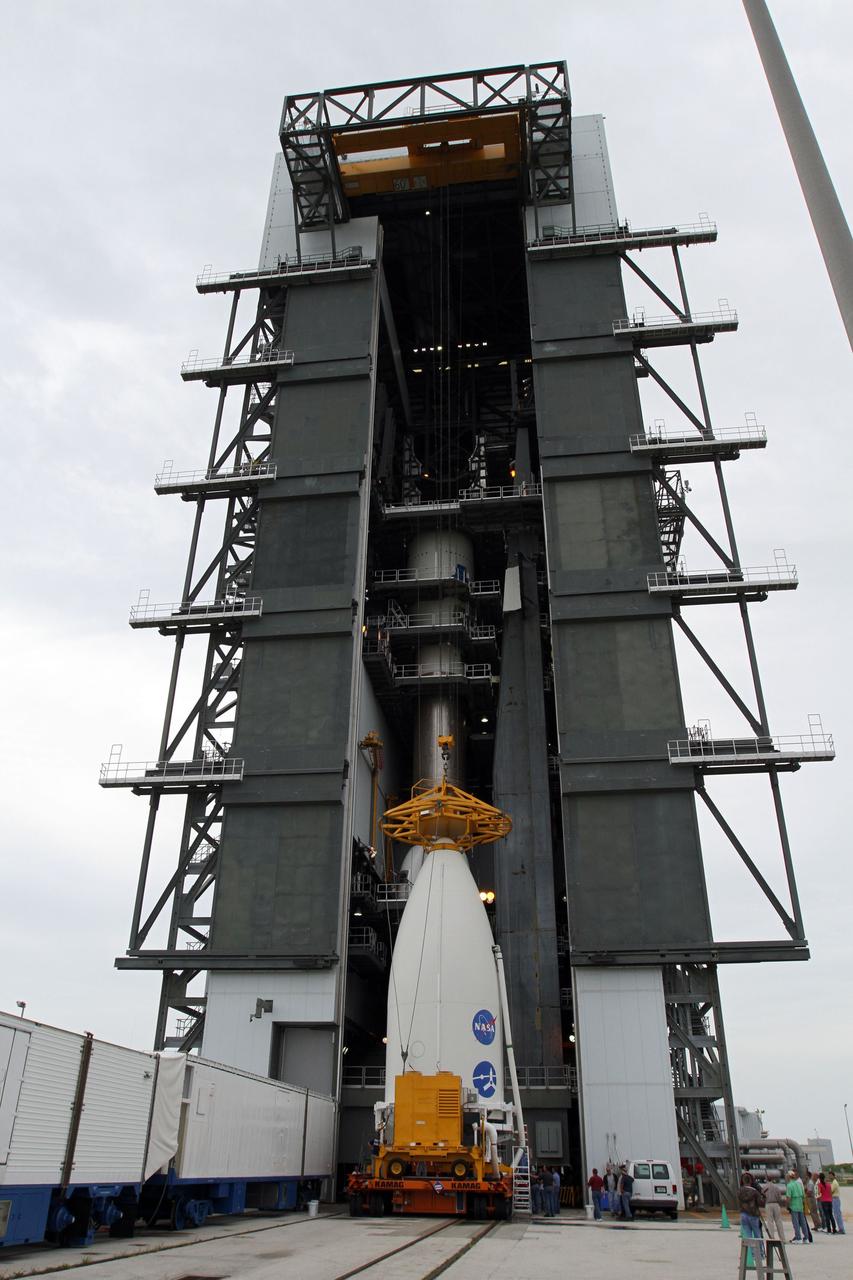

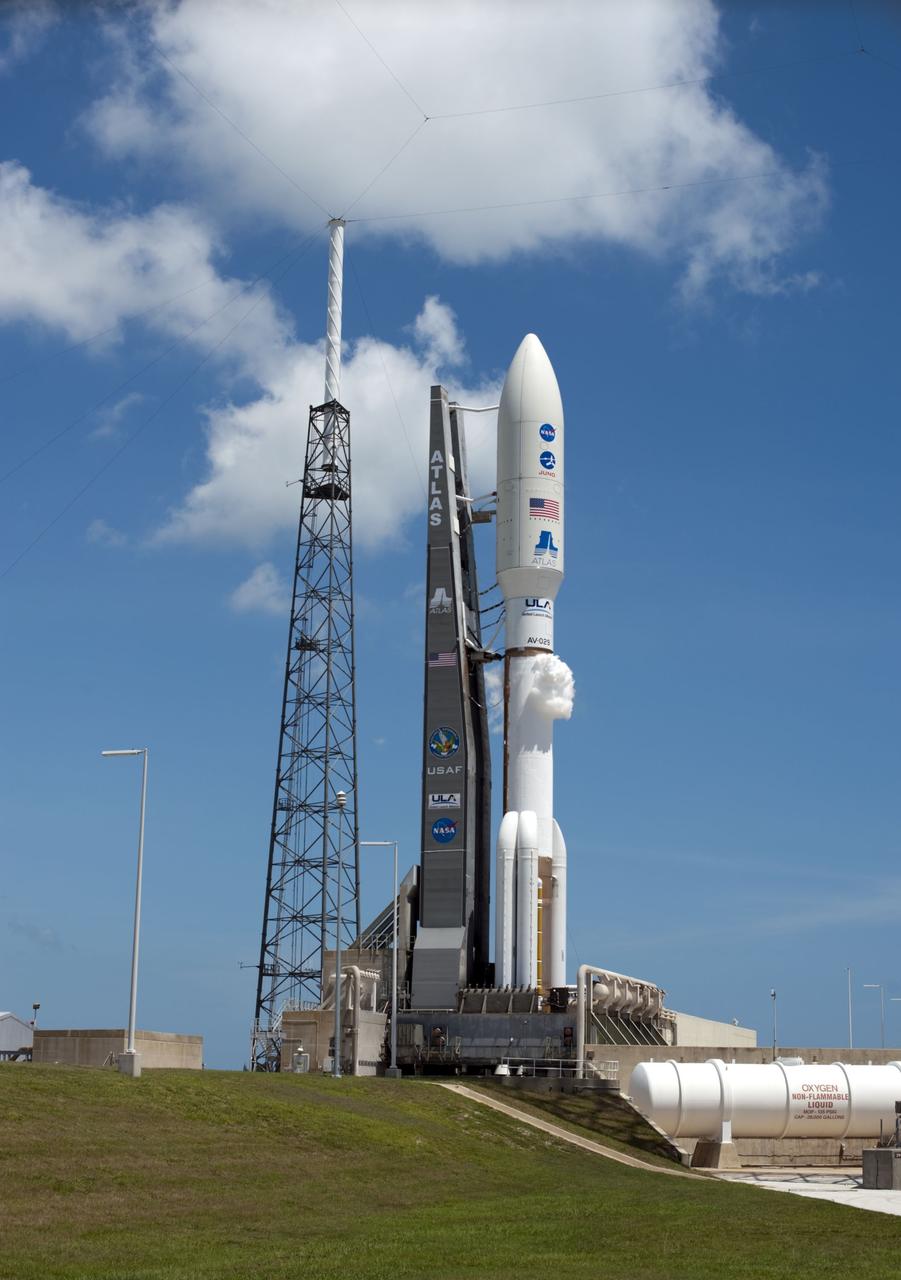
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Space Launch Complex 41, a crane is attached to the nose of the Atlas payload fairing enclosing the Juno spacecraft in preparation for its lift to the top of the Atlas rocket stacked in the Vertical Integration Facility. The spacecraft was prepared for launch in the Astrotech Space Operations' payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent and will be jettisoned once the spacecraft is outside the Earth's atmosphere. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
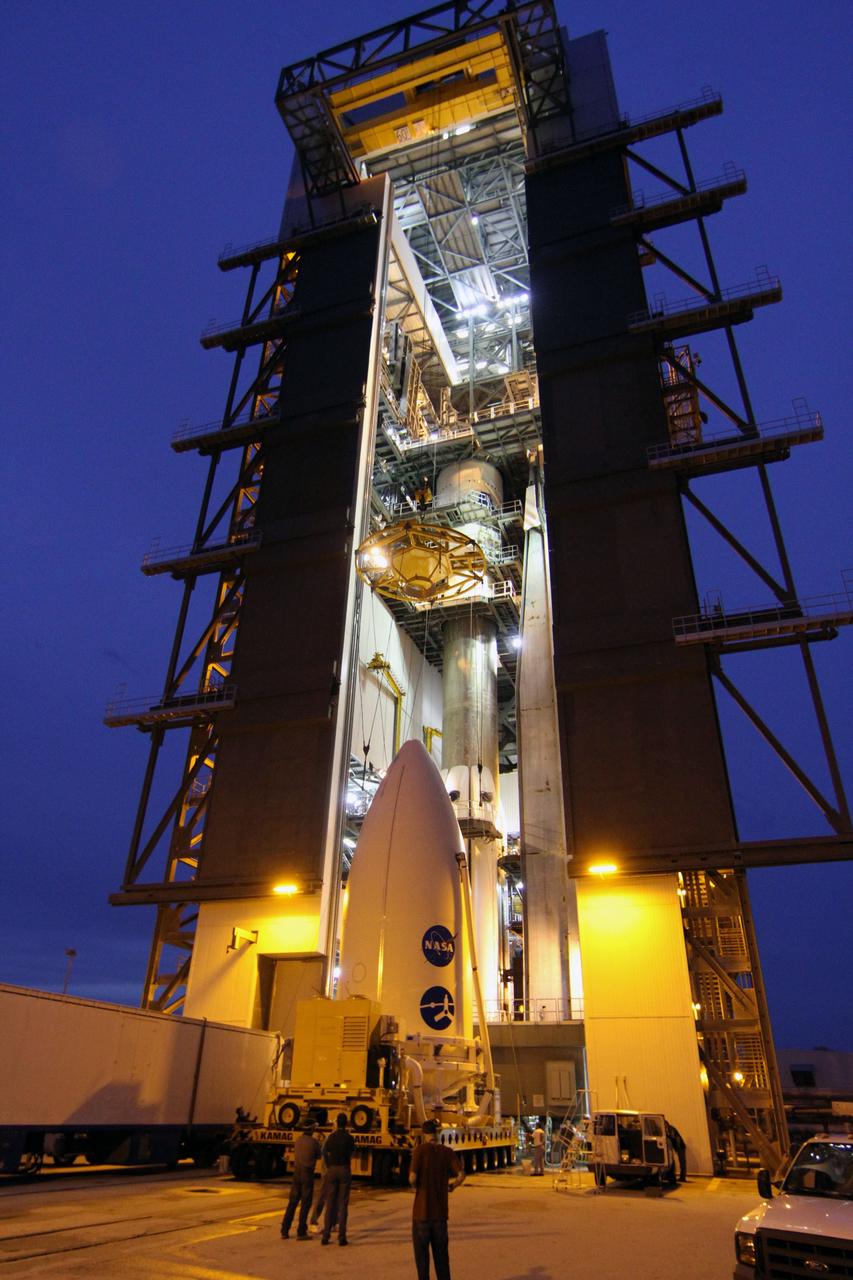

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Space Launch Complex 41, technicians monitor a crane as it is lowered toward the Juno spacecraft, enclosed in an Atlas payload fairing, for its lift to the top of the Atlas rocket stacked in the Vertical Integration Facility. The spacecraft was prepared for launch in the Astrotech Space Operations' payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent and will be jettisoned once the spacecraft is outside the Earth's atmosphere. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
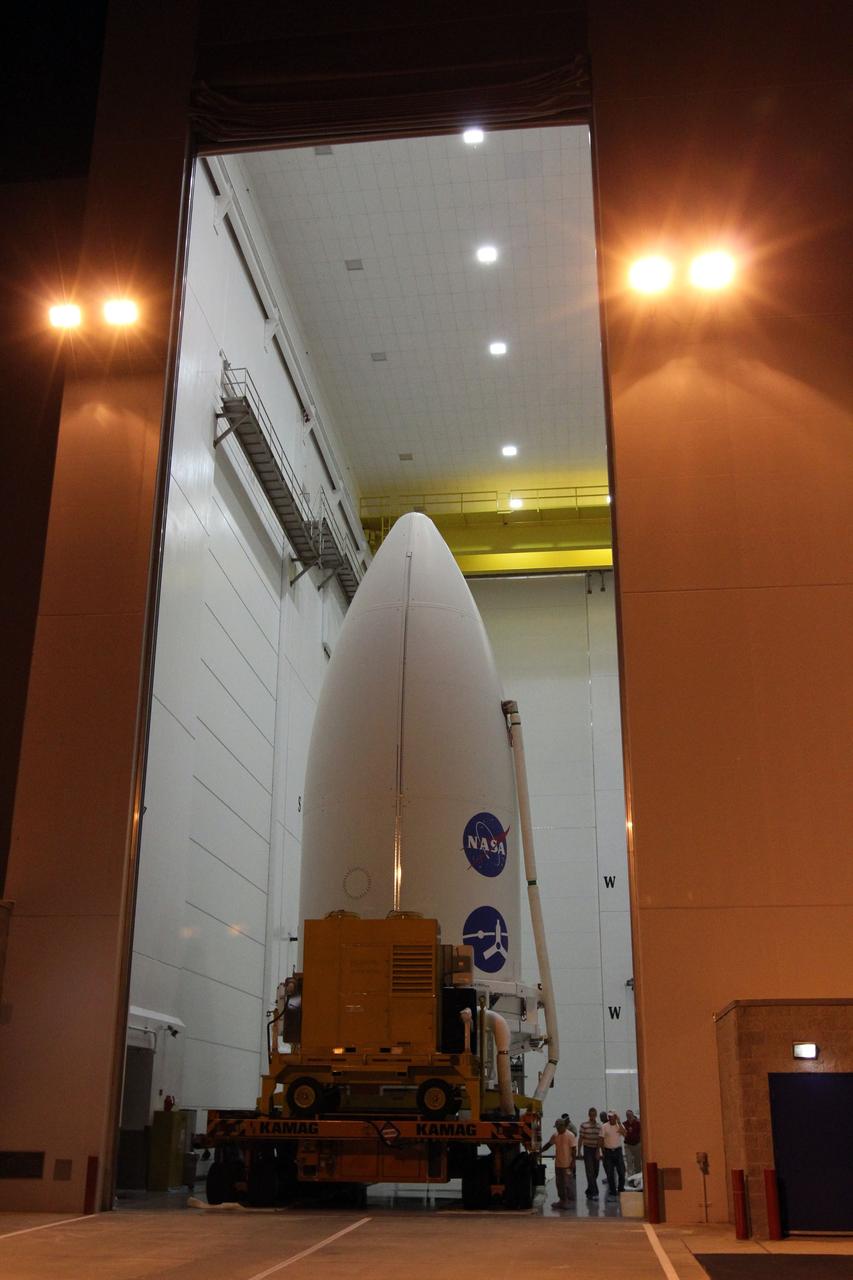

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Astrotech Space Operations' payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., preparations are under way to transport the Juno spacecraft, enclosed in an Atlas payload fairing, to Space Launch Complex 41. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent and will be jettisoned once the spacecraft is outside the Earth's atmosphere. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
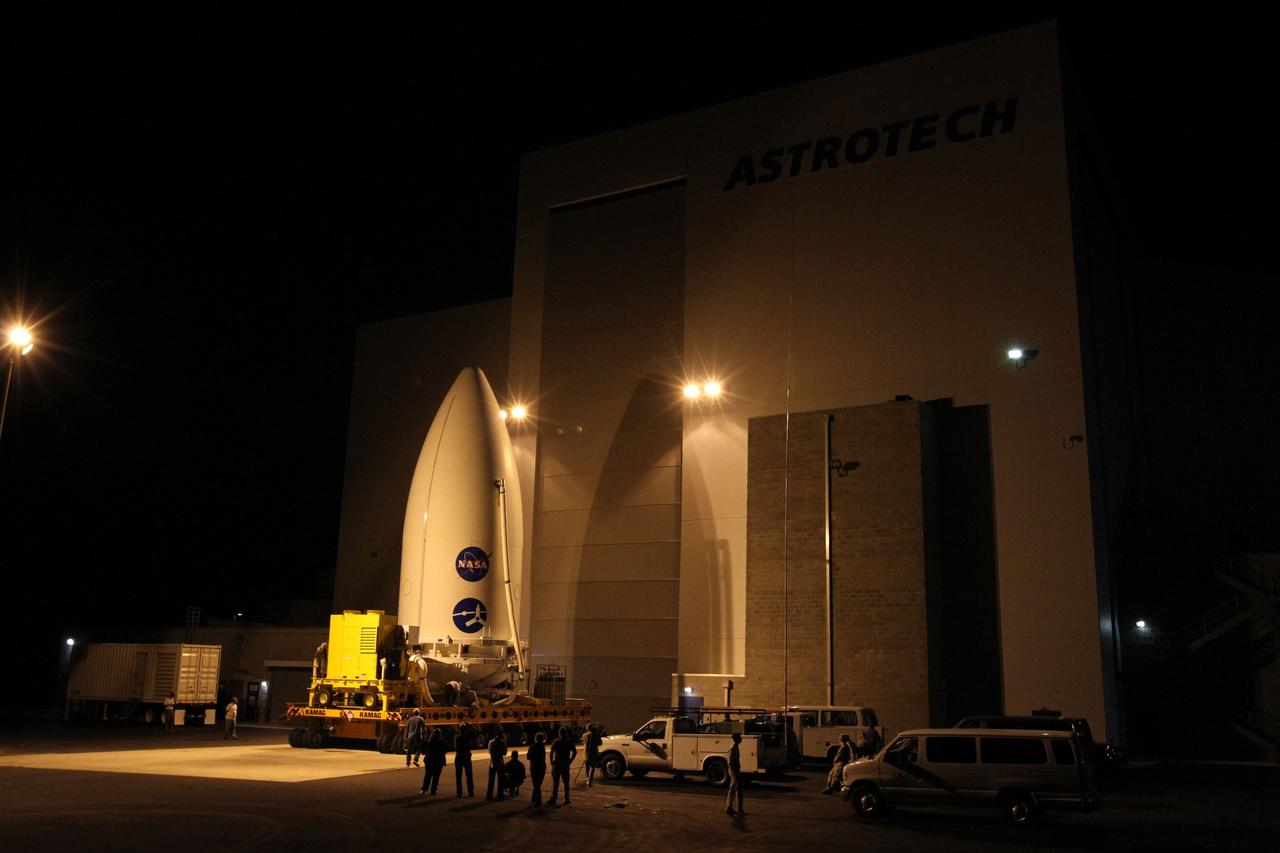

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Juno spacecraft, enclosed in an Atlas payload fairing, begins its trip from the Astrotech Space Operations' payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., to Space Launch Complex 41. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent and will be jettisoned once the spacecraft is outside the Earth's atmosphere. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
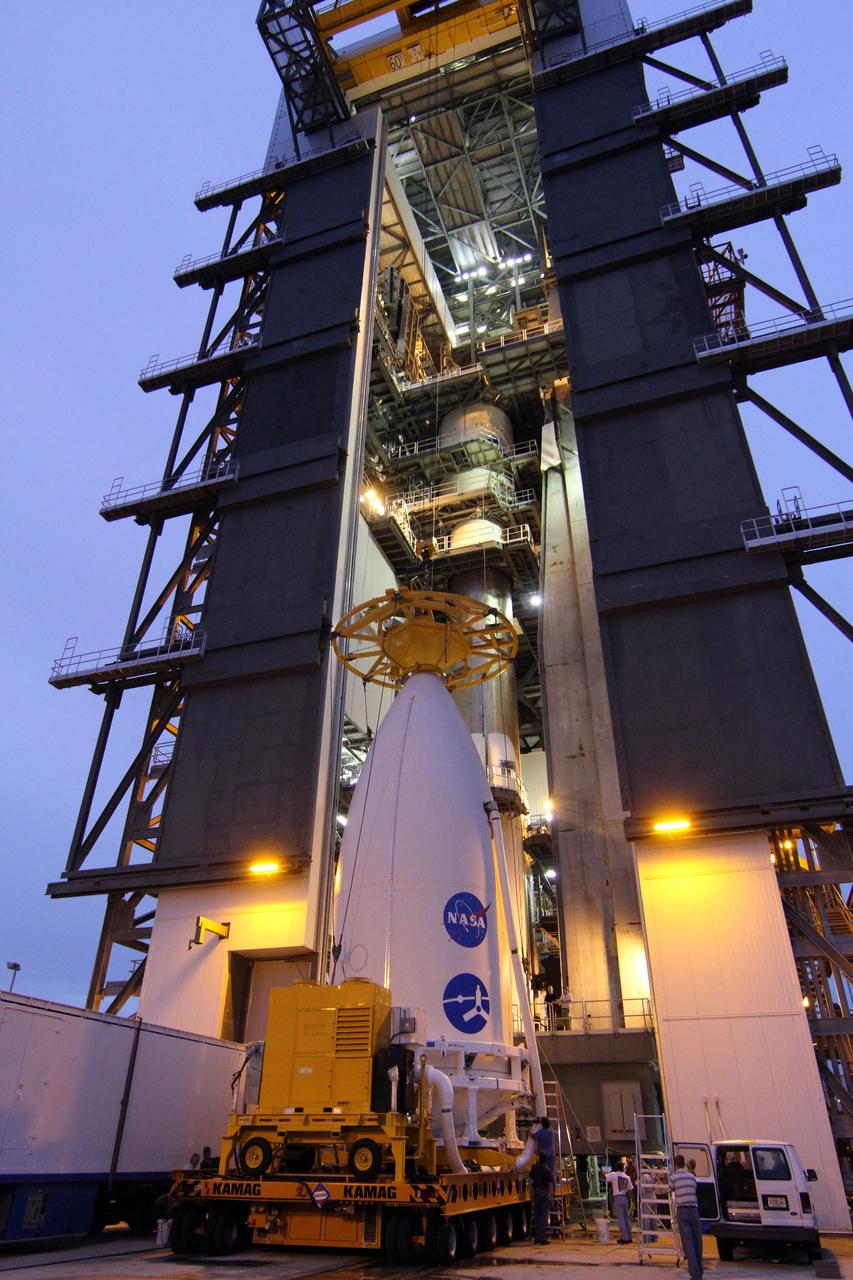

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Space Launch Complex 41, a crane is lowered over the nose of the Atlas payload fairing enclosing the Juno spacecraft in preparation for its lift to the top of the Atlas rocket stacked in the Vertical Integration Facility. The spacecraft was prepared for launch in the Astrotech Space Operations' payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent and will be jettisoned once the spacecraft is outside the Earth's atmosphere. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
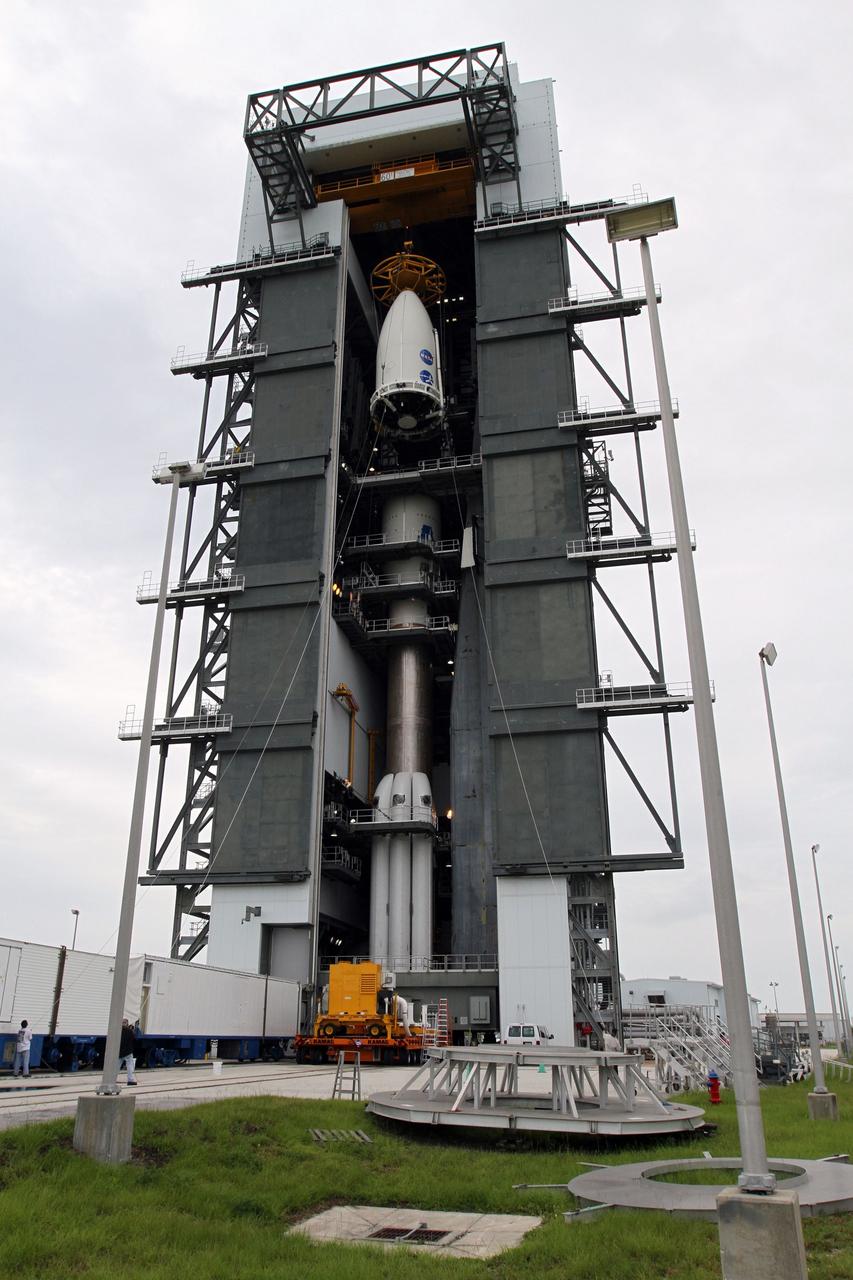

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Space Launch Complex 41, the Atlas rocket stacked inside the Vertical Integration Facility stands ready to receive the Juno spacecraft, enclosed in an Atlas payload fairing. The spacecraft was prepared for launch in the Astrotech Space Operations' payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent and will be jettisoned once the spacecraft is outside the Earth's atmosphere. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
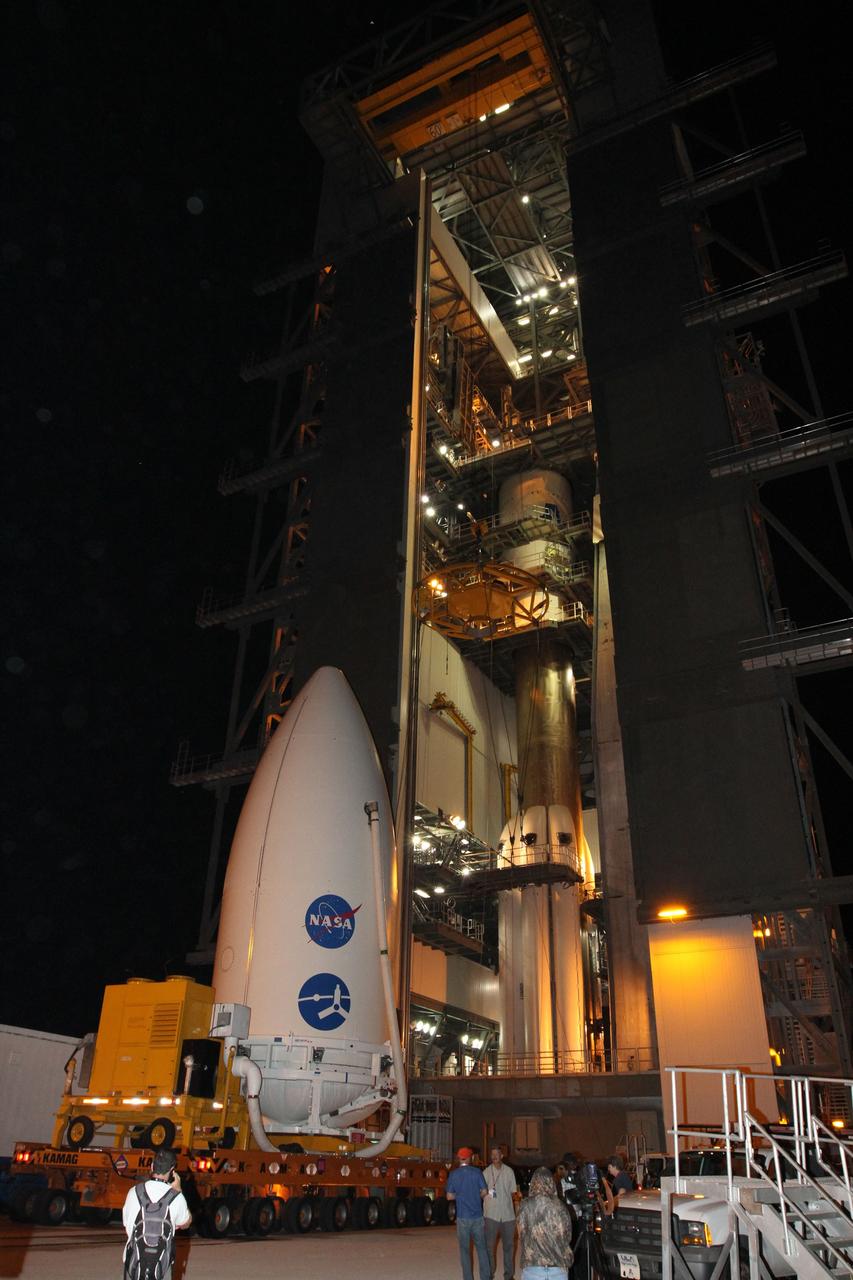

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Juno spacecraft, enclosed in an Atlas payload fairing, arrives at Space Launch Complex 41. The spacecraft was prepared for launch in the Astrotech Space Operations' payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent and will be jettisoned once the spacecraft is outside the Earth's atmosphere. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Space Launch Complex 41, a crane hoists the Atlas payload fairing enclosing the Juno spacecraft off its transporter for its lift to the top of the Atlas rocket stacked in the Vertical Integration Facility. The spacecraft was prepared for launch in the Astrotech Space Operations' payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The fairing will protect the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent and will be jettisoned once the spacecraft is outside the Earth's atmosphere. Juno is scheduled to launch Aug. 5 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston