
This planetary nebula's simple, graceful appearance is thought to be due to perspective: our view from Earth looking straight into what is actually a barrel-shaped cloud of gas shrugged off by a dying central star. Hot blue gas near the energizing central star gives way to progressively cooler green and yellow gas at greater distances with the coolest red gas along the outer boundary. Credit: NASA/Hubble Heritage Team ---- The Ring Nebula's distinctive shape makes it a popular illustration for astronomy books. But new observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope of the glowing gas shroud around an old, dying, sun-like star reveal a new twist. "The nebula is not like a bagel, but rather, it's like a jelly doughnut, because it's filled with material in the middle," said C. Robert O'Dell of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. He leads a research team that used Hubble and several ground-based telescopes to obtain the best view yet of the iconic nebula. The images show a more complex structure than astronomers once thought and have allowed them to construct the most precise 3-D model of the nebula. "With Hubble's detail, we see a completely different shape than what's been thought about historically for this classic nebula," O'Dell said. "The new Hubble observations show the nebula in much clearer detail, and we see things are not as simple as we previously thought." The Ring Nebula is about 2,000 light-years from Earth and measures roughly 1 light-year across. Located in the constellation Lyra, the nebula is a popular target for amateur astronomers. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14VAOMk" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14VAOMk</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This ultraviolet image from NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer is of the planetary nebula NGC 7293 also known as the Helix Nebula. It is the nearest example of what happens to a star, like our own Sun, as it approaches the end of its life when it runs out of fuel, expels gas outward and evolves into a much hotter, smaller and denser white dwarf star. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07902

This ultraviolet image from NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer shows NGC 3242, a planetary nebula frequently referred to as Jupiter Ghost. The small circular white and blue area at the center of the image is the well-known portion of the nebula.
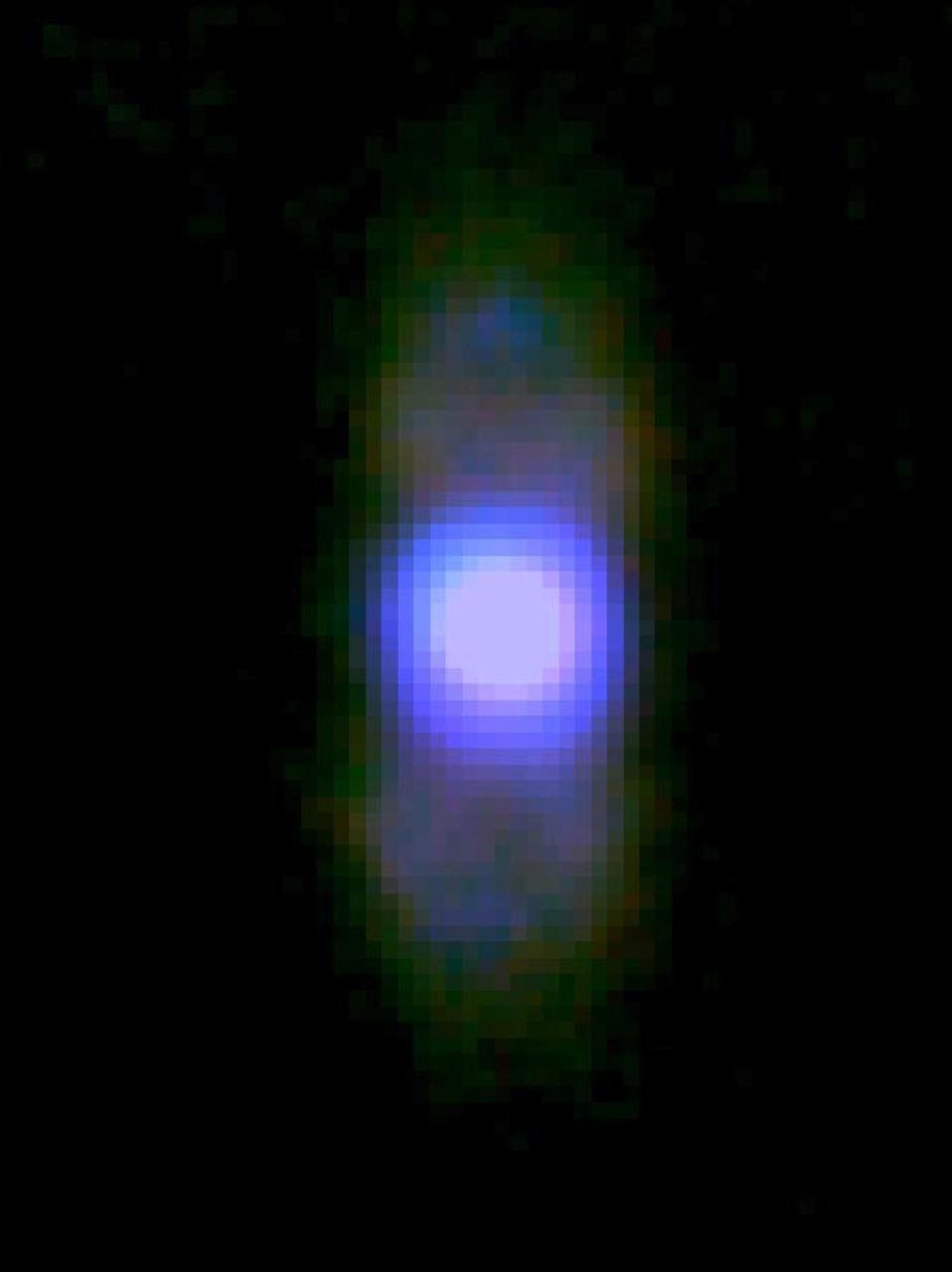

Researchers using NASA Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy SOFIA have captured infrared images of the last exhalations of a dying sun-like star. This image is of the planetary Nebula M2-9.

This trio of ghostly images from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows the disembodied remains of dying stars called planetary nebulas. Planetary nebulas are a late stage in a sun-like star life.

This Hubble telescope snapshot of MyCn18, a young planetary nebula, reveals that the object has an hourglass shape with an intricate pattern of etchings in its walls. A planetary nebula is the glowing relic of a dying, Sun-like star.
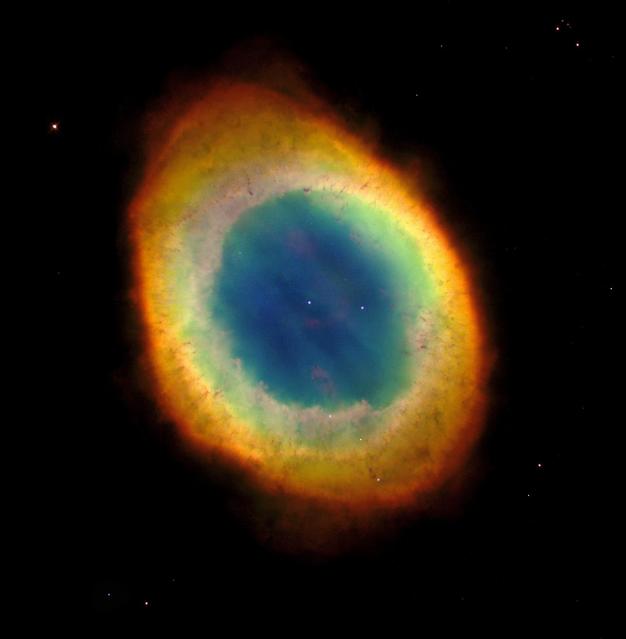
NASA Hubble Space Telescope captured this sharpest view yet of the most famous of all planetary nebulae: the Ring Nebula M57. The colors are approximately true colors.

This is a photograph of giant twisters and star wisps in the Lagoon Nebula. This superb Hubble Space Telescope (HST) image reveals a pair of one-half light-year long interstellar twisters, eerie furnels and twisted rope structures (upper left), in the heart of the Lagoon Nebula (Messier 8) that lies 5,000 light-years away in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. This image was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field/Planetary Camera 2 (WF/PC2).

This colorful bubble is a planetary nebula called NGC 6818, also known as the Little Gem Nebula. It is located in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer), roughly 6,000 light-years away from us. The rich glow of the cloud is just over half a light-year across — humongous compared to its tiny central star — but still a little gem on a cosmic scale. When stars like the sun enter "retirement," they shed their outer layers into space to create glowing clouds of gas called planetary nebulae. This ejection of mass is uneven, and planetary nebulae can have very complex shapes. NGC 6818 shows knotty filament-like structures and distinct layers of material, with a bright and enclosed central bubble surrounded by a larger, more diffuse cloud. Scientists believe that the stellar wind from the central star propels the outflowing material, sculpting the elongated shape of NGC 6818. As this fast wind smashes through the slower-moving cloud it creates particularly bright blowouts at the bubble’s outer layers. Hubble previously imaged this nebula back in 1997 with its Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, using a mix of filters that highlighted emission from ionized oxygen and hydrogen. This image, while from the same camera, uses different filters to reveal a different view of the nebula. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA Spitzer Space Telescope finds a delicate flower in the Ring Nebula, as shown in this image. The outer shell of this planetary nebula looks surprisingly similar to the delicate petals of a camellia blossom.

The Dumbbell nebula, also known as Messier 27, pumps out infrared light in this image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. Planetary nebulae are now known to be the remains of stars that once looked a lot like our sun.

This image of the Egg Nebula, also known as CRL-2688 and located roughly 3,000 light-years from us, was taken in red light with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WF/PC2) aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The image shows a pair of mysterious searchlight beams emerging from a hidden star, crisscrossed by numerous bright arcs. This image sheds new light on the poorly understood ejection of stellar matter that accompanies the slow death of Sun-like stars. The image is shown in false color.

An infrared photo of the Small Magellanic Cloud taken by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope is shown in this artist illustration; an example of a planetary nebula, and a magnified depiction of buckyballs.
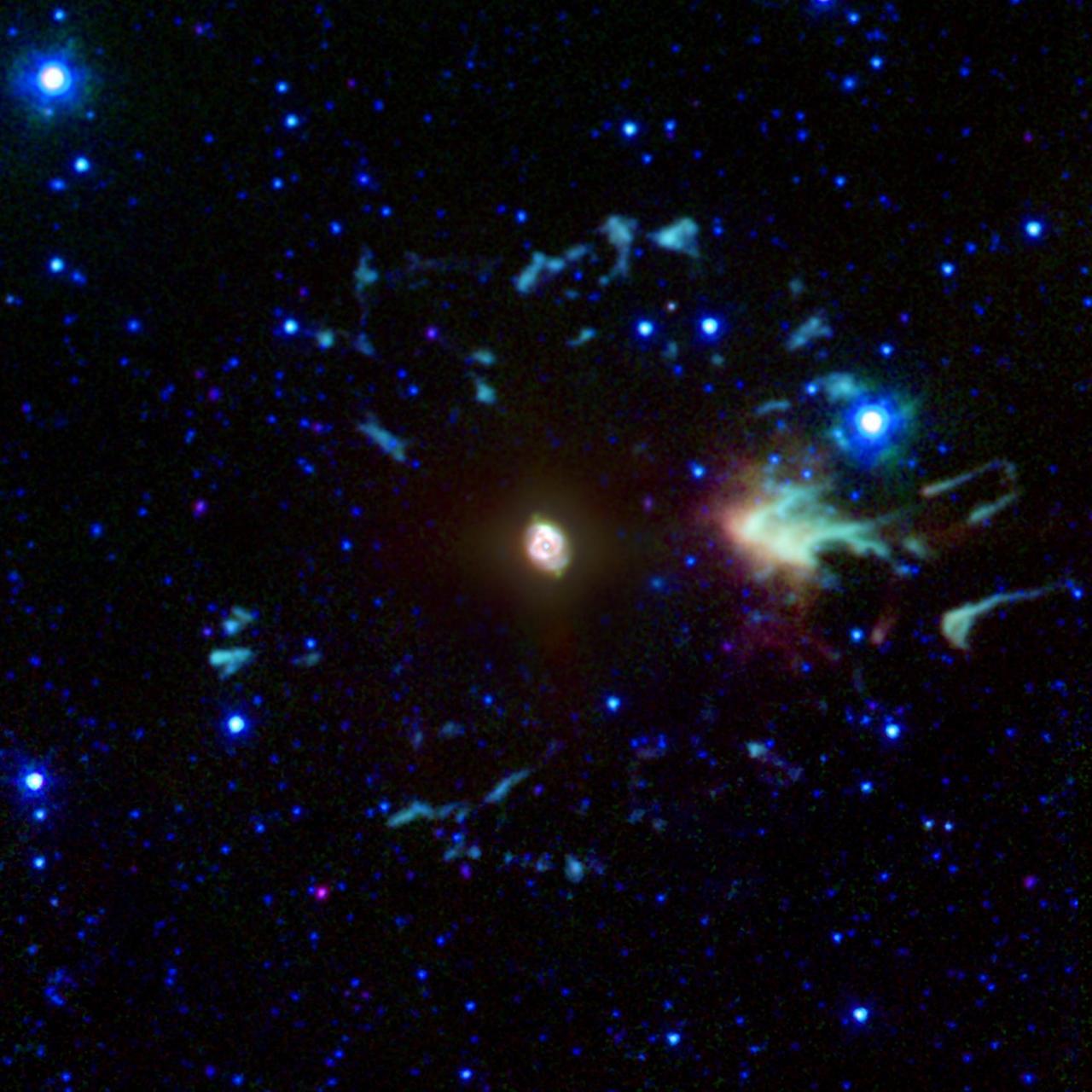

NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope captured the Cat’s Eye nebula, or NGC 6543, is a well-studied example of a planetary nebula. Such objects are the glowing remnants of dust and gas expelled from moderate-sized stars during their last stages of life.

NGC 7293, better known as the Helix nebula, displays its ultraviolet glow courtesy of NASA GALEX. The Helix is the nearest example of a planetary nebula, which is the eventual fate of a star, like our own Sun, as it approaches the end of its life.

Taken by the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), this image of MyCn18, a young planetary nebula located about 8,000 light-years away, reveals its true shape to be an hourglass with an intricate pattern of "etchings" in its walls. The arc-like etchings could be the remnants of discrete shells ejected from the star when it was younger, flow instabilities, or could result from the action of a narrow beam of matter impinging on the hourglass walls. According to one theory on the formation of planetary nebulae, the hourglass shape is produced by the expansion of a fast stellar wind within a slowly expanding cloud, which is denser near its equator than near its poles. Hubble has also revealed other features in MyCn18 which are completely new and unexpected. For example, there is a pair of intersecting elliptical rings in the central region which appear to be the rims of a smaller hourglass. This picture has been composed from three separate images taken in the light of ionized nitrogen (represented by red), hydrogen (green) and doubly-ionized oxygen (blue). The results are of great interest because they shed new light on the poorly understood ejection of stellar matter which accompanies the slow death of sun-like stars. An unseen companion star and accompanying gravitational effects may well be necessary in order to explain the structure of MyCn18. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST.

SCI2012_0003: SOFIA mid-infrared image of the planetary nebula Minkowski 2-9 (M2-9), also known as the Butterfly Nebula, compared with a visual-wavelength Hubble Space Telescope image at the same scale and orientation. The nebula is composed of two lobes of gas & dust expelled from a dying star with about the mass of our Sun that is seen at the center of the lobes. The HST image shows mostly ionized gas in the lobes whereas the SOFIA image shows mostly solid grains condensing in the gas. The SOFIA data were obtained during SOFIA's Early Science program in 2011 by a Guest Investigator team led by Michael Werner of Caltech/JPL using the FORCAST camera (P.I.Terry Herter, Cornell University). Credit: SOFIA image, RGB = 37, 24, 20 microns; NASA/DLR/USRA/DSI/FORCAST team/M. Werner et al./A. Helton, J. Rho; HST image: NASA/ESA/NSF/AURA/Hubble Heritage Team/STScI/B. Balick, V. Icke, G. Mellema

Astronomers using NASA Hubble Space Telescope stumbled upon a mysterious object that grudgingly yielded clues to its identity. The object is classified as a planetary nebula, the glowing remains of a dying, lightweight star.
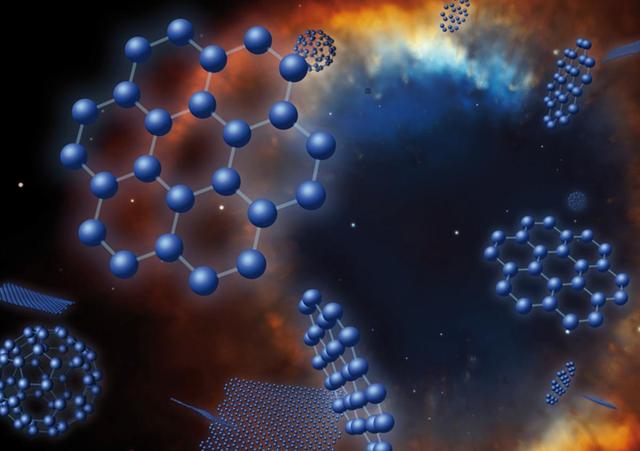
This is an artist concept, based on data from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, of graphene, buckyballs and C70 superimposed on an image of the Helix planetary nebula, a puffed-out cloud of material expelled by a dying star.

This composite picture is a seamless blend of ultra-sharp NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) images combined with the wide view of the Mosaic Camera on the National Science Foundation's 0.9-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory, part of the National Optical Astronomy Observatory, near Tucson, Ariz. Astronomers at the Space Telescope Science Institute assembled these images into a mosaic. The mosaic was then blended with a wider photograph taken by the Mosaic Camera. The image shows a fine web of filamentary "bicycle-spoke" features embedded in the colorful red and blue gas ring, which is one of the nearest planetary nebulae to Earth. Because the nebula is nearby, it appears as nearly one-half the diameter of the full Moon. This required HST astronomers to take several exposures with the Advanced Camera for Surveys to capture most of the Helix. HST views were then blended with a wider photo taken by the Mosaic Camera. The portrait offers a dizzying look down what is actually a trillion-mile-long tunnel of glowing gases. The fluorescing tube is pointed nearly directly at Earth, so it looks more like a bubble than a cylinder. A forest of thousands of comet-like filaments, embedded along the inner rim of the nebula, points back toward the central star, which is a small, super-hot white dwarf. The tentacles formed when a hot "stellar wind" of gas plowed into colder shells of dust and gas ejected previously by the doomed star. Ground-based telescopes have seen these comet-like filaments for decades, but never before in such detail. The filaments may actually lie in a disk encircling the hot star, like a collar. The radiant tie-die colors correspond to glowing oxygen (blue) and hydrogen and nitrogen (red). Valuable Hubble observing time became available during the November 2002 Leonid meteor storm. To protect the spacecraft, including HST's precise mirror, controllers turned the aft end into the direction of the meteor stream for about half a day. Fortunately, the Helix Nebula was almost exactly in the opposite direction of the meteor stream, so Hubble used nine orbits to photograph the nebula while it waited out the storm. To capture the sprawling nebula, Hubble had to take nine separate snapshots. Planetary nebulae like the Helix are sculpted late in a Sun-like star's life by a torrential gush of gases escaping from the dying star. They have nothing to do with planet formation, but got their name because they look like planetary disks when viewed through a small telescope. With higher magnification, the classic "donut-hole" in the middle of a planetary nebula can be resolved. Based on the nebula's distance of 650 light-years, its angular size corresponds to a huge ring with a diameter of nearly 3 light-years. That's approximately three-quarters of the distance between our Sun and the nearest star. The Helix Nebula is a popular target of amateur astronomers and can be seen with binoculars as a ghostly, greenish cloud in the constellation Aquarius. Larger amateur telescopes can resolve the ring-shaped nebula, but only the largest ground-based telescopes can resolve the radial streaks. After careful analysis, astronomers concluded the nebula really isn't a bubble, but is a cylinder that happens to be pointed toward Earth. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18164

The Twin Jet Nebula, or PN M2-9, is a striking example of a bipolar planetary nebula. Bipolar planetary nebulae are formed when the central object is not a single star, but a binary system, Studies have shown that the nebula’s size increases with time, and measurements of this rate of increase suggest that the stellar outburst that formed the lobes occurred just 1200 years ago.
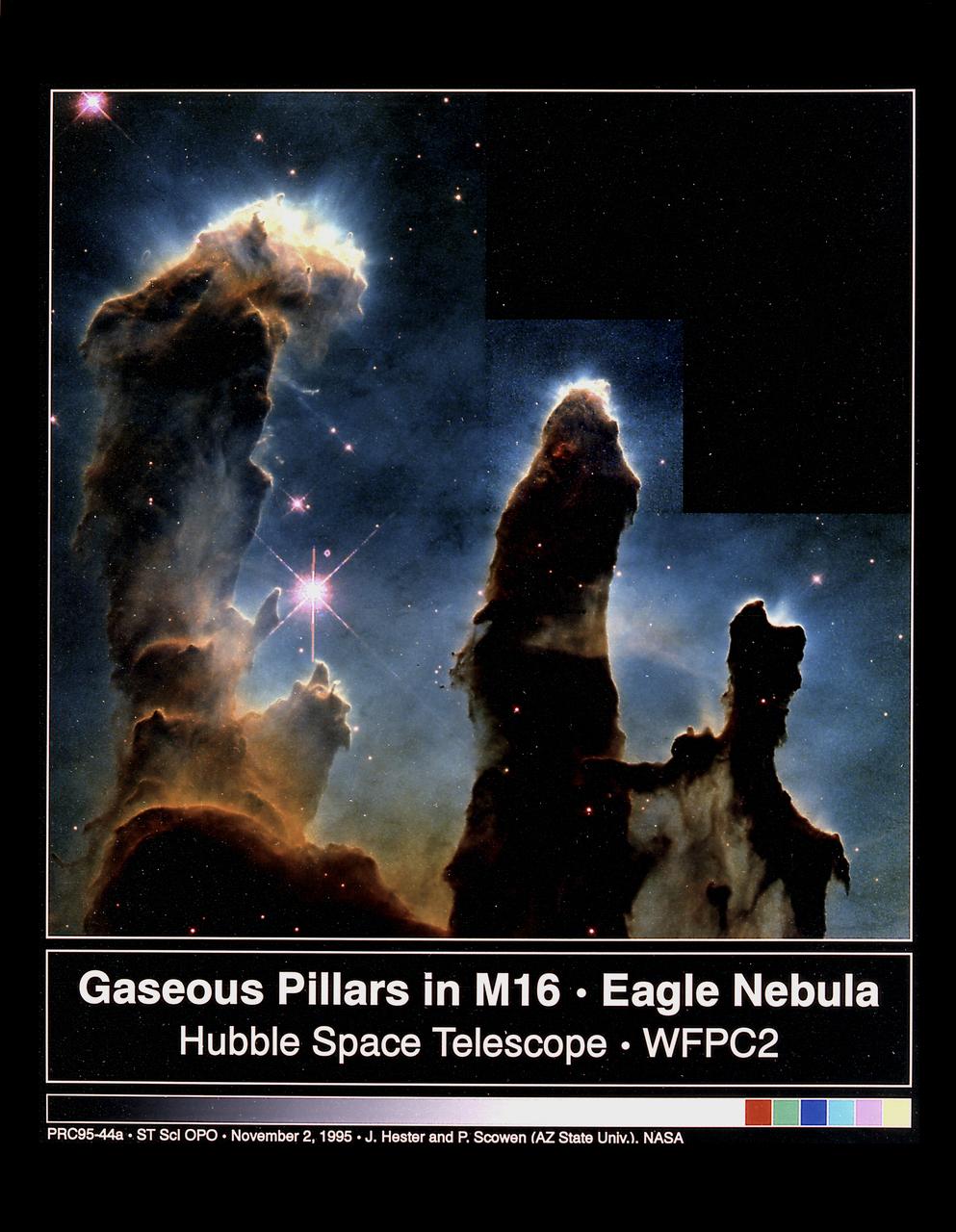
These eerie, dark, pillar-like structures are actually columns of cool interstellar hydrogen gas and dust that are also incubators for new stars. The pillars protrude from the interior wall of a dark molecular cloud like stalagmites from the floor of a cavern. They are part of the Eagle Nebula (also called M16), a nearby star-forming region 7,000 light-years away, in the constellation Serpens. The ultraviolet light from hot, massive, newborn stars is responsible for illuminating the convoluted surfaces of the columns and the ghostly streamers of gas boiling away from their surfaces, producing the dramatic visual effects that highlight the three-dimensional nature of the clouds. This image was taken on April 1, 1995 with the Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. The color image is constructed from three separate images taken in the light of emission from different types of atoms. Red shows emissions from singly-ionized sulfur atoms, green shows emissions from hydrogen, and blue shows light emitted by doubly-ionized oxygen atoms.
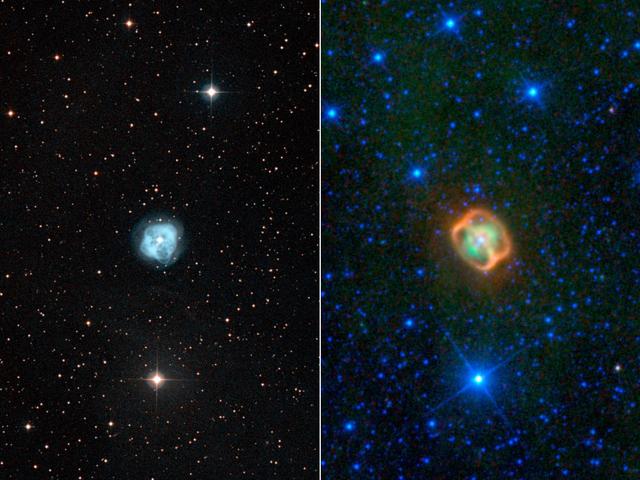

This image composite shows two views of a puffy, dying star, or planetary nebula, known as NGC 1514. At left is a view from a ground-based, visible-light telescope; the view on the right shows the object in infrared light from NASA WISE telescope.
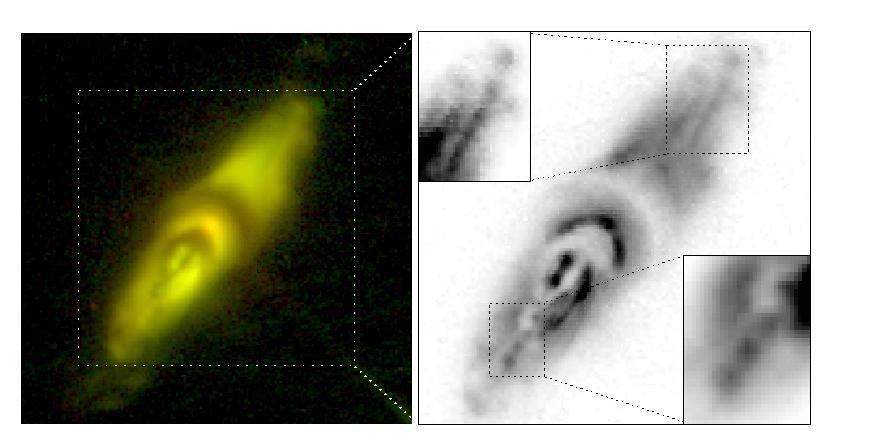
This image of a dying star, protoplanetary nebula IRAS22036+5306, containing strange, complex structures may help explain the death throes of stars and defy our current understanding of physics. Taken by NASA Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2.

This planetary nebula is called PK 329-02.2 and is located in the constellation of Norma in the southern sky. It is also sometimes referred to as Menzel 2, or Mz 2, named after the astronomer Donald Menzel who discovered the nebula in 1922. When stars that are around the mass of the Sun reach their final stages of life, they shed their outer layers into space, which appear as glowing clouds of gas called planetary nebulae. The ejection of mass in stellar burnout is irregular and not symmetrical, so that planetary nebulae can have very complex shapes. In the case of Menzel 2 the nebula forms a winding blue cloud that perfectly aligns with two stars at its centre. In 1999 astronomers discovered that the star at the upper right is in fact the central star of the nebula, and the star to the lower left is probably a true physical companion of the central star. For tens of thousands of years the stellar core will be cocooned in spectacular clouds of gas and then, over a period of a few thousand years, the gas will fade away into the depths of the Universe. The curving structure of Menzel 2 resembles a last goodbye before the star reaches its final stage of retirement as a white dwarf. A version of this image was entered into the Hubble's Hidden Treasures image processing competition by contestant Serge Meunier.

This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows a planetary nebula named NGC 6153, located about 4000 light-years away in the southern constellation of Scorpius (The Scorpion). The faint blue haze across the frame shows what remains of a star like the Sun after it has depleted most of its fuel. When this happens, the outer layers of the star are ejected, and get excited and ionised by the energetic ultraviolet light emitted by the bright hot core of the star, forming the nebula. NGC 6153 is a planetary nebula that is elliptical in shape, with an extremely rich network of loops and filaments, shown clearly in this Hubble image. However, this is not what makes this planetary nebula so interesting for astronomers. Measurements show that NGC 6153 contains large amounts of neon, argon, oxygen, carbon and chlorine — up to three times more than can be found in the Solar System. The nebula contains a whopping five times more nitrogen than the Sun! Although it may be that the star developed higher levels of these elements as it grew and evolved, it is more likely that the star originally formed from a cloud of material that already contained lots more of these elements. A version of this image was entered into the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures image processing competition by contestant Matej Novak. Links Matej Novak’s image on Flickr

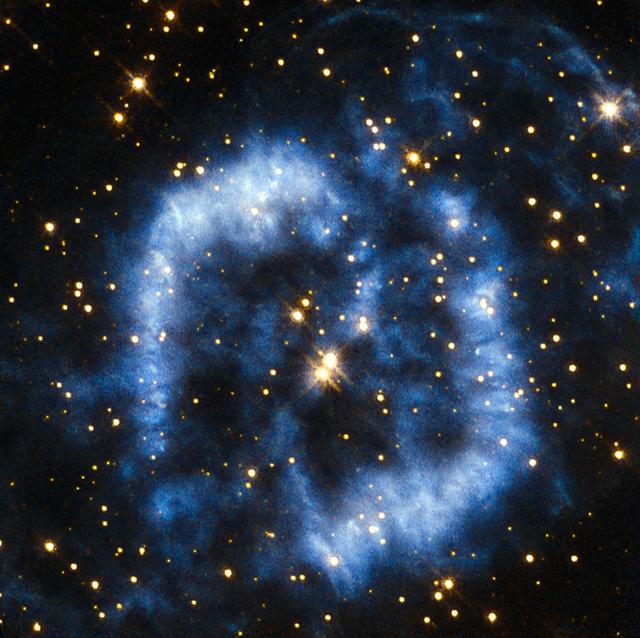
A dying star’s final moments are captured in this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. The death throes of this star may only last mere moments on a cosmological timescale, but this star’s demise is still quite lengthy by our standards, lasting tens of thousands of years! The star’s agony has culminated in a wonderful planetary nebula known as NGC 6565, a cloud of gas that was ejected from the star after strong stellar winds pushed the star’s outer layers away into space. Once enough material was ejected, the star’s luminous core was exposed and it began to produce ultraviolet radiation, exciting the surrounding gas to varying degrees and causing it to radiate in an attractive array of colours. These same colours can be seen in the famous and impressive Ring Nebula (heic1310), a prominent example of a nebula like this one. Planetary nebulae are illuminated for around 10 000 years before the central star begins to cool and shrink to become a white dwarf. When this happens, the star’s light drastically diminishes and ceases to excite the surrounding gas, so the nebula fades from view. A version of this image was entered into the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures basic image competition by contestant Matej Novak.

This colourful bubble is a planetary nebula called NGC 6818, also known as the Little Gem Nebula. It is located in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer), roughly 6000 light-years away from us. The rich glow of the cloud is just over half a light-year across — humongous compared to its tiny central star — but still a little gem on a cosmic scale. When stars like the Sun enter retirement, they shed their outer layers into space to create glowing clouds of gas called planetary nebulae. This ejection of mass is uneven, and planetary nebulae can have very complex shapes. NGC 6818 shows knotty filament-like structures and distinct layers of material, with a bright and enclosed central bubble surrounded by a larger, more diffuse cloud. Scientists believe that the stellar wind from the central star propels the outflowing material, sculpting the elongated shape of NGC 6818. As this fast wind smashes through the slower-moving cloud it creates particularly bright blowouts at the bubble’s outer layers. Hubble previously imaged this nebula back in 1997 with its Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, using a mix of filters that highlighted emission from ionised oxygen and hydrogen (opo9811h). This image, while from the same camera, uses different filters to reveal a different view of the nebula. A version of the image was submitted to the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures image processing competition by contestant Judy Schmidt.

This planetary nebula is called PK 329-02.2 and is located in the constellation of Norma in the southern sky. It is also sometimes referred to as Menzel 2, or Mz 2, named after the astronomer Donald Menzel who discovered the nebula in 1922. When stars that are around the mass of the sun reach their final stages of life, they shed their outer layers into space, which appear as glowing clouds of gas called planetary nebulae. The ejection of mass in stellar burnout is irregular and not symmetrical, so that planetary nebulae can have very complex shapes. In the case of Menzel 2 the nebula forms a winding blue cloud that perfectly aligns with two stars at its center. In 1999 astronomers discovered that the star at the upper right is in fact the central star of the nebula, and the star to the lower left is probably a true physical companion of the central star. For tens of thousands of years the stellar core will be cocooned in spectacular clouds of gas and then, over a period of a few thousand years, the gas will fade away into the depths of the universe. The curving structure of Menzel 2 resembles a last goodbye before the star reaches its final stage of retirement as a white dwarf. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Serge Meunier <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows a planetary nebula named NGC 6153, located about 4,000 light-years away in the southern constellation of Scorpius (The Scorpion). The faint blue haze across the frame shows what remains of a star like the sun after it has depleted most of its fuel. When this happens, the outer layers of the star are ejected, and get excited and ionized by the energetic ultraviolet light emitted by the bright hot core of the star, forming the nebula. NGC 6153 is a planetary nebula that is elliptical in shape, with an extremely rich network of loops and filaments, shown clearly in this Hubble image. However, this is not what makes this planetary nebula so interesting for astronomers. Measurements show that NGC 6153 contains large amounts of neon, argon, oxygen, carbon and chlorine — up to three times more than can be found in the solar system. The nebula contains a whopping five times more nitrogen than our sun! Although it may be that the star developed higher levels of these elements as it grew and evolved, it is more likely that the star originally formed from a cloud of material that already contained a lot more of these elements. Text credit: European Space Agency Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Matej Novak <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
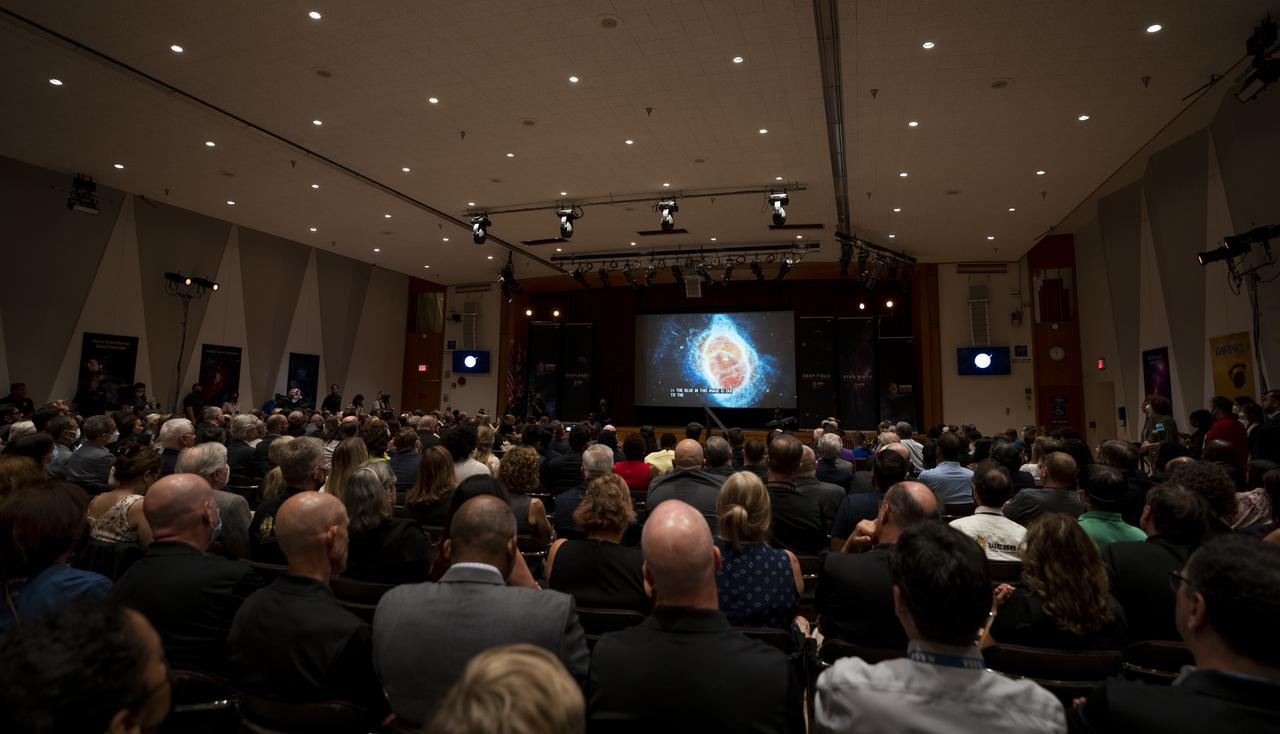

One of the images captured by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope of the planetary nebula cataloged as NGC 3132, and known informally as the Southern Ring Nebula, is seen on a screen as members of the media and guests watch the broadcast releasing the first full-color images from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, Tuesday, July 12, 2022, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The first full-color images and spectroscopic data from the James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership with ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), are a demonstration of the power of Webb as the telescope begins its science mission to unfold the infrared universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Taylor Mickal)

The Calabash Nebula, pictured here — which has the technical name OH 231.8+04.2 — is a spectacular example of the death of a low-mass star like the sun. This image taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows the star going through a rapid transformation from a red giant to a planetary nebula, during which it blows its outer layers of gas and dust out into the surrounding space. The recently ejected material is spat out in opposite directions with immense speed — the gas shown in yellow is moving close to one million kilometers per hour (621,371 miles per hour). Astronomers rarely capture a star in this phase of its evolution because it occurs within the blink of an eye — in astronomical terms. Over the next thousand years the nebula is expected to evolve into a fully-fledged planetary nebula. The nebula is also known as the Rotten Egg Nebula because it contains a lot of sulphur, an element that, when combined with other elements, smells like a rotten egg — but luckily, it resides over 5,000 light-years away in the constellation of Puppis. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Hubble’s Spirograph In this classic Hubble image from 2000, the planetary nebula IC 418 glows like a multifaceted jewel with enigmatic patterns. IC 418 lies about 2,000 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Lepus. A planetary nebula represents the final stage in the evolution of a star similar to our sun. The star at the center of IC 418 was a red giant a few thousand years ago, but then ejected its outer layers into space to form the nebula, which has now expanded to a diameter of about 0.1 light-year. The stellar remnant at the center is the hot core of the red giant, from which ultraviolet radiation floods out into the surrounding gas, causing it to fluoresce. Over the next several thousand years, the nebula will gradually disperse into space, and then the star will cool and fade away for billions of years as a white dwarf. Our own sun is expected to undergo a similar fate, but fortunately, this will not occur until some 5 billion years from now. The Hubble image of IC 418 is shown with colors added to represent the different camera filters used that isolate light from various chemical elements. Red shows emission from ionized nitrogen (the coolest gas in the nebula, located furthest from the hot nucleus), green shows emission from hydrogen and blue traces the emission from ionized oxygen (the hottest gas, closest to the central star). The remarkable textures seen in the nebula are newly revealed by the Hubble Space Telescope, and their origin is still uncertain. Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2roofKS" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2roofKS</a> Credit: NASA and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA); Acknowledgment: Dr. Raghvendra Sahai (JPL) and Dr. Arsen R. Hajian (USNO)

Some 5,000 light years (2,900 trillion miles) from Earth, in the constellation Puppis, is the 1.4 light years (more than 8 trillion miles) long Calabash Nebula, referred to as the Rotten Egg Nebula because of its sulfur content which would produce an awful odor if one could smell in space. This image of the nebula captured by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST) depicts violent gas collisions that produced supersonic shock fronts in a dying star. Stars, like our sun, will eventually die and expel most of their material outward into shells of gas and dust These shells eventually form some of the most beautiful objects in the universe, called planetary nebulae. The yellow in the image depicts the material ejected from the central star zooming away at speeds up to one and a half million kilometers per hour (one million miles per hour). Due to the high speeds of the gas, shock-fronts are formed on impact and heat the surrounding gas. Although computer calculations have predicted the existence and structure of such shocks for some time, previous observations have not been able to prove the theory.
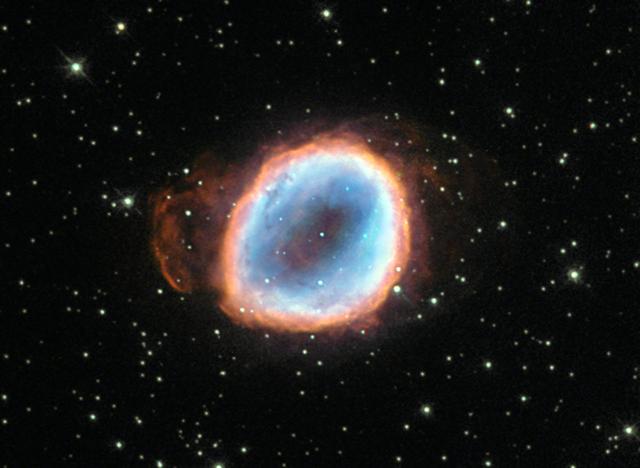

A dying star’s final moments are captured in this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. The death throes of this star may only last mere moments on a cosmological timescale, but this star’s demise is still quite lengthy by our standards, lasting tens of thousands of years! The star’s agony has culminated in a wonderful planetary nebula known as NGC 6565, a cloud of gas that was ejected from the star after strong stellar winds pushed the star’s outer layers away into space. Once enough material was ejected, the star’s luminous core was exposed, enabling its ultraviolet radiation to excite the surrounding gas to varying degrees and causing it to radiate in an attractive array of colors. These same colors can be seen in the famous and impressive Ring Nebula (heic1310), a prominent example of a nebula like this one. Planetary nebulae are illuminated for around 10,000 years before the central star begins to cool and shrink to become a white dwarf. When this happens, the star’s light drastically diminishes and ceases to excite the surrounding gas, so the nebula fades from view. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Matej Novak <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

What look like giant twisters are spotted by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). These images are, in actuality, pillars of gases that are in the process of the formation of a new star. These pillars can be billions of miles in length and may have been forming for millions of years. This one formation is located in the Lagoon Nebula and was captured by the Hubble's wide field planetary camera-2 (WFPC-2).
![Some of the most breathtaking views in the Universe are created by nebulae — hot, glowing clouds of gas. This new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows the centre of the Lagoon Nebula, an object with a deceptively tranquil name. The region is filled with intense winds from hot stars, churning funnels of gas, and energetic star formation, all embedded within an intricate haze of gas and pitch-dark dust. Nebulae are often named based on their key characteristics — particularly beautiful examples include the Ring Nebula (heic1310), the Horsehead Nebula (heic1307) and the Butterfly Nebula (heic0910). This new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows the centre of the Lagoon Nebula, otherwise known as Messier 8, in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer). The inspiration for this nebula’s name may not be immediately obvious — this is because the image captures only the very heart of the nebula. The Lagoon Nebula’s name becomes much clearer in a wider field view (opo0417i) when the broad, lagoon-shaped dust lane that crosses the glowing gas of the nebula can be made out. Another clear difference between this new image and others is that this image combines both infrared and optical light rather than being purely optical(heic1015). Infrared light cuts through thick, obscuring patches of dust and gas, revealing the more intricate structures underneath and producing a completely different landscape [1]. However, even in visible light, the tranquil name remains misleading as the region is packed full of violent phenomena. The bright star embedded in dark clouds at the centre of this image is known as Herschel 36. This star is responsible for sculpting the surrounding cloud, stripping away material and influencing its shape. Herschel 36 is the main source of ionising radiation [2] for this part of the Lagoon Nebula. This central part of the Lagoon Nebula contains two main structures of gas and dust connected by wispy twisters, visible in the middle third of this image (opo9638). These features are quite similar to their namesakes on Earth — they are thought to be wrapped up into their funnel-like shapes by temperature differences between the hot surface and cold interior of the clouds. The nebula is also actively forming new stars, and energetic winds from these newborns may contribute to creating the twisters. This image combines images taken using optical and infrared light gathered by Hubble’s Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. Credit: NASA, ESA, J. Trauger (Jet Propulson Laboratory) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/GSFC_20171208_Archive_e000671/GSFC_20171208_Archive_e000671~small.jpg)
Some of the most breathtaking views in the Universe are created by nebulae — hot, glowing clouds of gas. This new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows the centre of the Lagoon Nebula, an object with a deceptively tranquil name. The region is filled with intense winds from hot stars, churning funnels of gas, and energetic star formation, all embedded within an intricate haze of gas and pitch-dark dust. Nebulae are often named based on their key characteristics — particularly beautiful examples include the Ring Nebula (heic1310), the Horsehead Nebula (heic1307) and the Butterfly Nebula (heic0910). This new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows the centre of the Lagoon Nebula, otherwise known as Messier 8, in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer). The inspiration for this nebula’s name may not be immediately obvious — this is because the image captures only the very heart of the nebula. The Lagoon Nebula’s name becomes much clearer in a wider field view (opo0417i) when the broad, lagoon-shaped dust lane that crosses the glowing gas of the nebula can be made out. Another clear difference between this new image and others is that this image combines both infrared and optical light rather than being purely optical(heic1015). Infrared light cuts through thick, obscuring patches of dust and gas, revealing the more intricate structures underneath and producing a completely different landscape [1]. However, even in visible light, the tranquil name remains misleading as the region is packed full of violent phenomena. The bright star embedded in dark clouds at the centre of this image is known as Herschel 36. This star is responsible for sculpting the surrounding cloud, stripping away material and influencing its shape. Herschel 36 is the main source of ionising radiation [2] for this part of the Lagoon Nebula. This central part of the Lagoon Nebula contains two main structures of gas and dust connected by wispy twisters, visible in the middle third of this image (opo9638). These features are quite similar to their namesakes on Earth — they are thought to be wrapped up into their funnel-like shapes by temperature differences between the hot surface and cold interior of the clouds. The nebula is also actively forming new stars, and energetic winds from these newborns may contribute to creating the twisters. This image combines images taken using optical and infrared light gathered by Hubble’s Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. Credit: NASA, ESA, J. Trauger (Jet Propulson Laboratory) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

Release Date: May 3, 2004 A Dying Star Shrouded by a Blanket of Hailstones Forms the Bug Nebula (NGC 6302) The Bug Nebula, NGC 6302, is one of the brightest and most extreme planetary nebulae known. The fiery, dying star at its center is shrouded by a blanket of icy hailstones. This NASA Hubble Wide Field Plantery Camera 2 image shows impressive walls of compressed gas, laced with trailing strands and bubbling outflows. Object Names: NGC 6302, Bug Nebula Image Type: Astronomical Credit: NASA, ESA and A.Zijlstra (UMIST, Manchester, UK) To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/gallery/album/nebula/pr2004046a/" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/gallery/album/nebula/pr2004046a/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
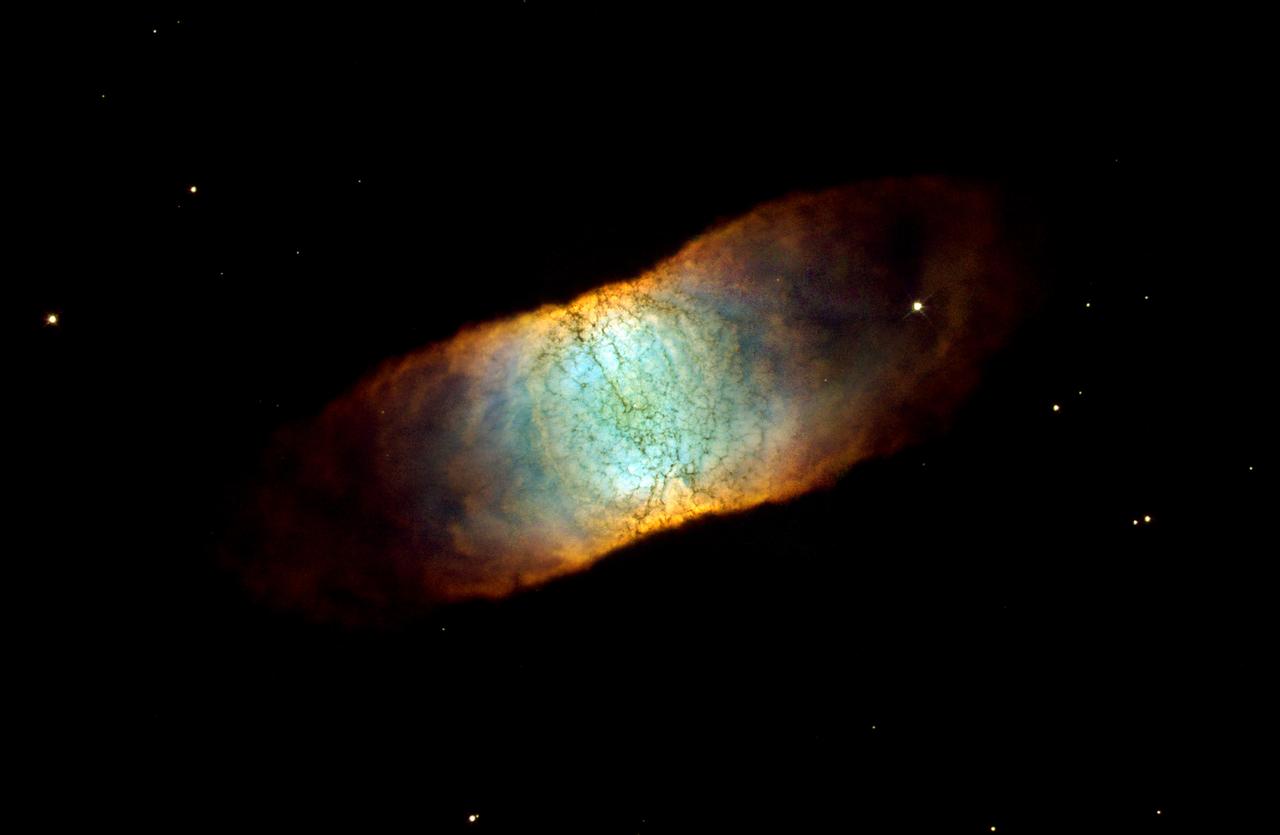

This Hubble Space Telescope image reveals a rainbow of colors in this dying star, called IC 446. Like many other so-called planetary nebulae, IC 4406 exhibits a high degree of symmetry. The nebula's left and right halves are nearly mirror images of the other. If we could fly around IC 446 in a spaceship, we would see that the gas and dust form a vast donut of material streaming outward from the dying star. We do not see the donut shape in this photograph because we are viewing IC 4406 from the Earth-orbiting HST. From this vantage point, we are seeing the side of the donut. This side view allows us to see the intricate tendrils of material that have been compared to the eye's retina. In fact, IC 4406 is dubbed the "Retina Nebula." The donut of material confines the intense radiation coming from the remnant of the dying star. Gas on the inside of the donut is ionized by light from the central star and glows. Light from oxygen atoms is rendered blue in this image; hydrogen is shown as green, and nitrogen as red. The range of color in the final image shows the differences in concentration of these three gases in the nebula. This image is a composite of data taken by HST's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 in June 2001 and in January 2002 by Bob O'Dell (Vanderbilt University) and collaborators, and in January by the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI). Filters used to create this color image show oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen gas glowing in this object.

NASA image release April 27, 2012 The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has been at the cutting edge of research into what happens to stars like our sun at the ends of their lives. One stage that stars pass through as they run out of nuclear fuel is called the preplanetary or protoplanetary nebula stage. This Hubble image of the Egg Nebula shows one of the best views to date of this brief but dramatic phase in a star’s life. The preplanetary nebula phase is a short period in the cycle of stellar evolution, and has nothing to do with planets. Over a few thousand years, the hot remains of the aging star in the center of the nebula heat it up, excite the gas, and make it glow as a subsequent planetary nebula. The short lifespan of preplanetary nebulae means there are relatively few of them in existence at any one time. Moreover, they are very dim, requiring powerful telescopes to be seen. This combination of rarity and faintness means they were only discovered comparatively recently. The Egg Nebula, the first to be discovered, was first spotted less than 40 years ago, and many aspects of this class of object remain shrouded in mystery. At the center of this image, and hidden in a thick cloud of dust, is the nebula’s central star. While we can’t see the star directly, four searchlight beams of light coming from it shine out through the nebula. It is thought that ring-shaped holes in the thick cocoon of dust, carved by jets coming from the star, let the beams of light emerge through the otherwise opaque cloud. The precise mechanism by which stellar jets produce these holes is not known for certain, but one possible explanation is that a binary star system, rather than a single star, exists at the center of the nebula. The onion-like layered structure of the more diffuse cloud surrounding the central cocoon is caused by periodic bursts of material being ejected from the dying star. The bursts typically occur every few hundred years. The distance to the Egg Nebula is only known very approximately, the best guess placing it at around 3,000 light-years from Earth. This in turn means that astronomers do not have any accurate figures for the size of the nebula (it may be larger and further away, or smaller but nearer). This image is produced from exposures in visible and infrared light from Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3. Credit: ESA/Hubble, NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This shot from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows a maelstrom of glowing gas and dark dust within one of the Milky Way’s satellite galaxies, the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). This stormy scene shows a stellar nursery known as N159, an HII region over 150 light-years across. N159 contains many hot young stars. These stars are emitting intense ultraviolet light, which causes nearby hydrogen gas to glow, and torrential stellar winds, which are carving out ridges, arcs, and filaments from the surrounding material. At the heart of this cosmic cloud lies the Papillon Nebula, a butterfly-shaped region of nebulosity. This small, dense object is classified as a High-Excitation Blob, and is thought to be tightly linked to the early stages of massive star formation. N159 is located over 160,000 light-years away. It resides just south of the Tarantula Nebula (heic1402), another massive star-forming complex within the LMC. This image comes from Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. The region was previously imaged by Hubble’s Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which also resolved the Papillon Nebula for the first time. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA
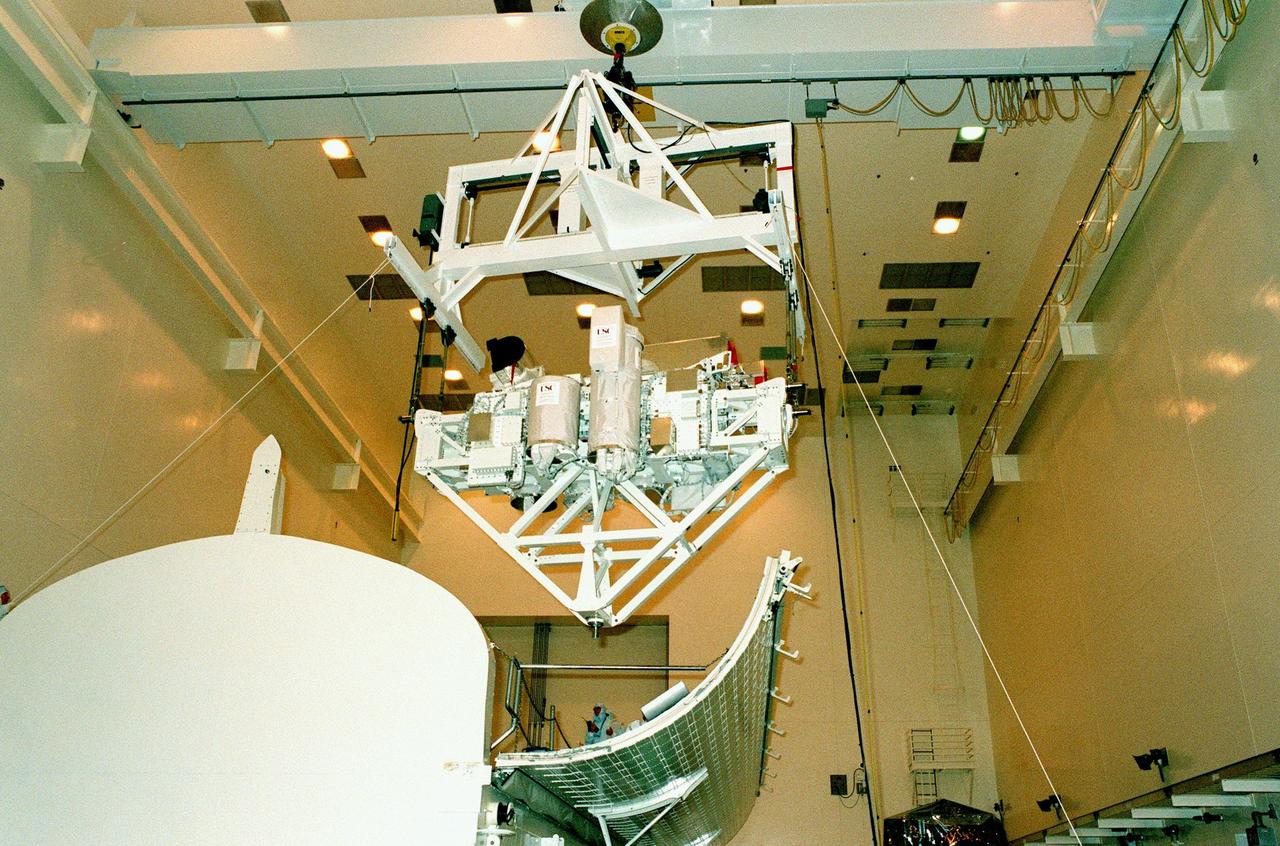
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-3), one of the payloads for the STS-95 mission, is suspended above its payload canister in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility. The mission is scheduled for liftoff on Space Shuttle Discovery on Oct. 29. IEH-3 comprises several experiments that will study the Jovian planetary system, hot stars, planetary and reflection nebulae, other stellar objects and their environments through remote observation of EUV/FUV emissions; study spacecraft interactions, Shuttle glow, thruster firings, and contamination; and measure the solar constant and identify variations in the value during a solar cycle. Other research payloads include the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, and the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
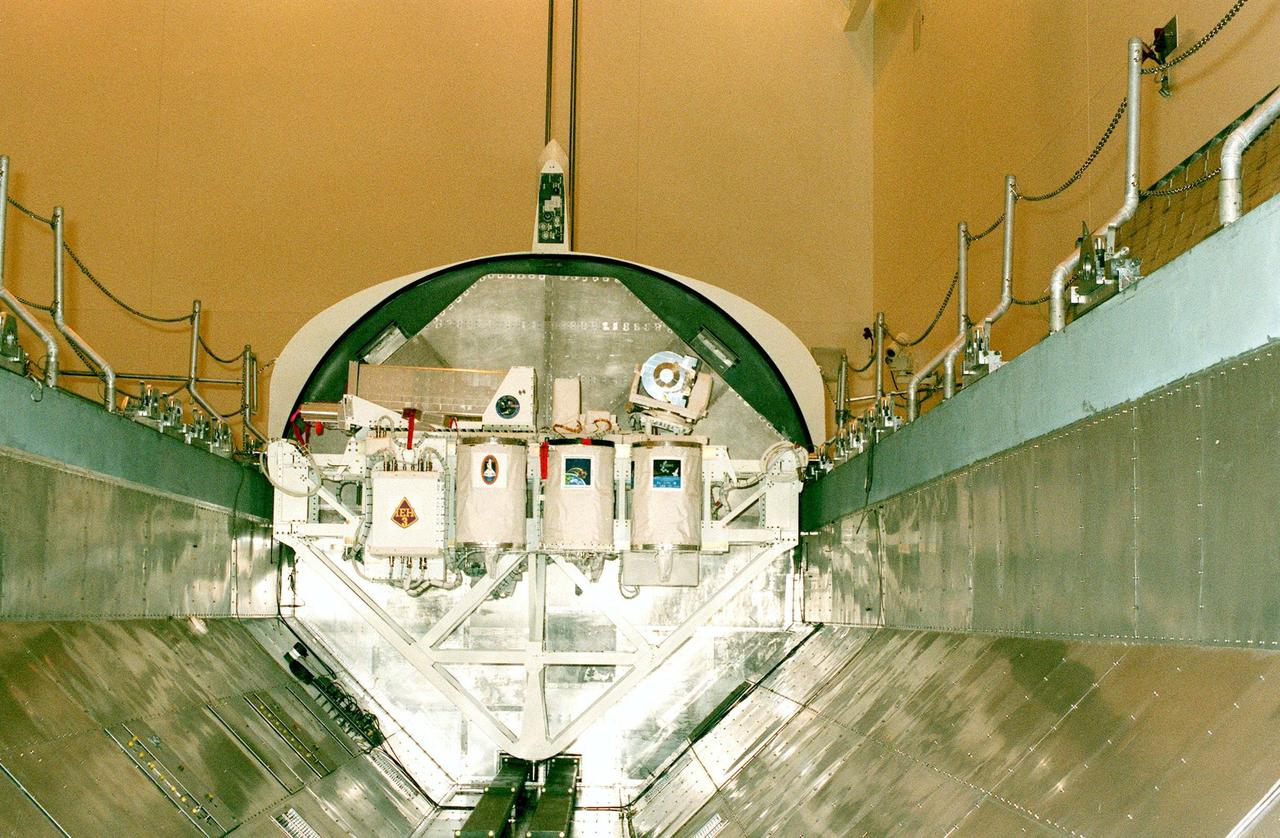

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-3), one of the payloads for the STS-95 mission, is moved to a payload canister in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility. The mission is scheduled for liftoff on Space Shuttle Discovery on Oct. 29. IEH-3 comprises several experiments that will study the Jovian planetary system, hot stars, planetary and reflection nebulae, other stellar objects and their environments through remote observation of EUV/FUV emissions; study spacecraft interactions, Shuttle glow, thruster firings, and contamination; and measure the solar constant and identify variations in the value during a solar cycle. Other research payloads include the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, and the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
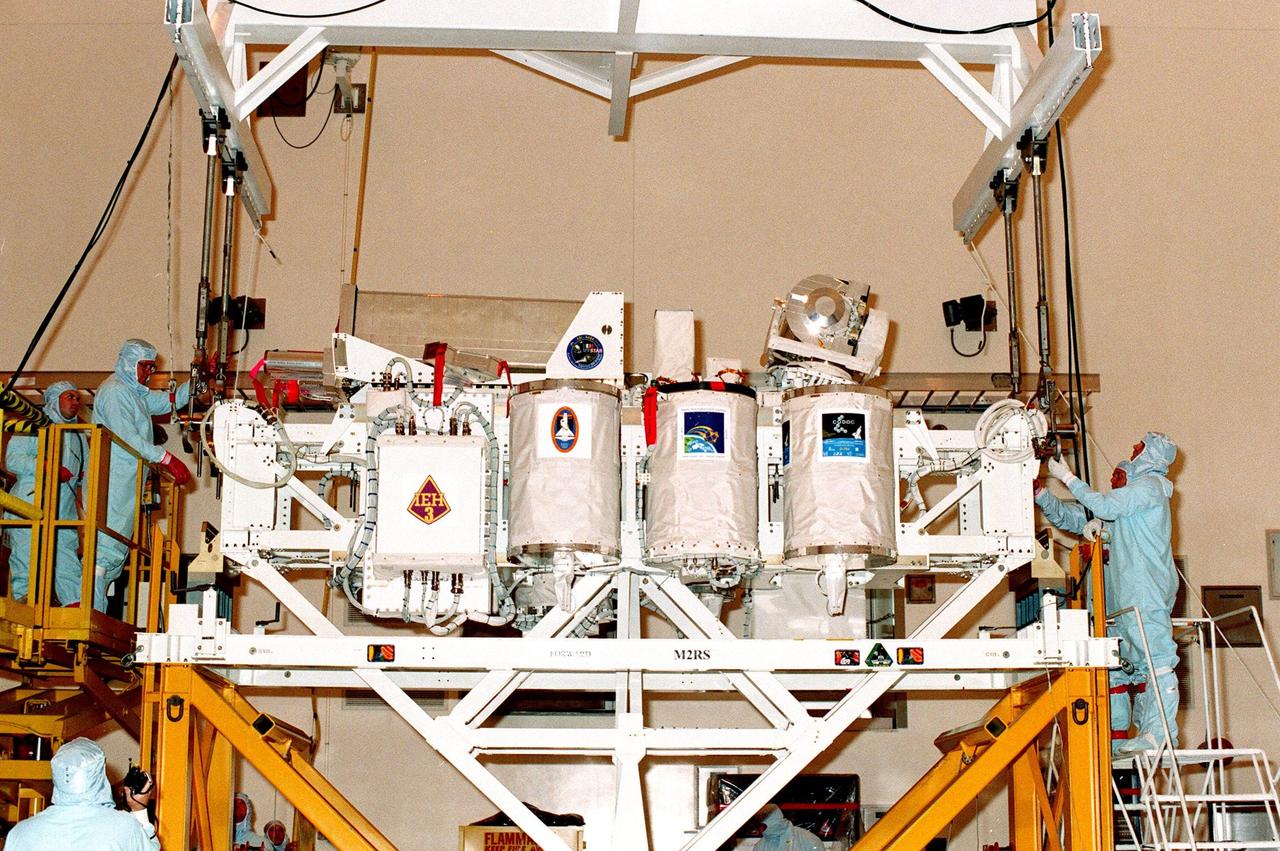
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-3), one of the payloads for the STS-95 mission, is prepared for its move to a payload canister in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility. The mission is scheduled for liftoff on Space Shuttle Discovery on Oct. 29. IEH-3 comprises several experiments that will study the Jovian planetary system, hot stars, planetary and reflection nebulae, other stellar objects and their environments through remote observation of EUV/FUV emissions; study spacecraft interactions, Shuttle glow, thruster firings, and contamination; and measure the solar constant and identify variations in the value during a solar cycle. Other research payloads include the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, and the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
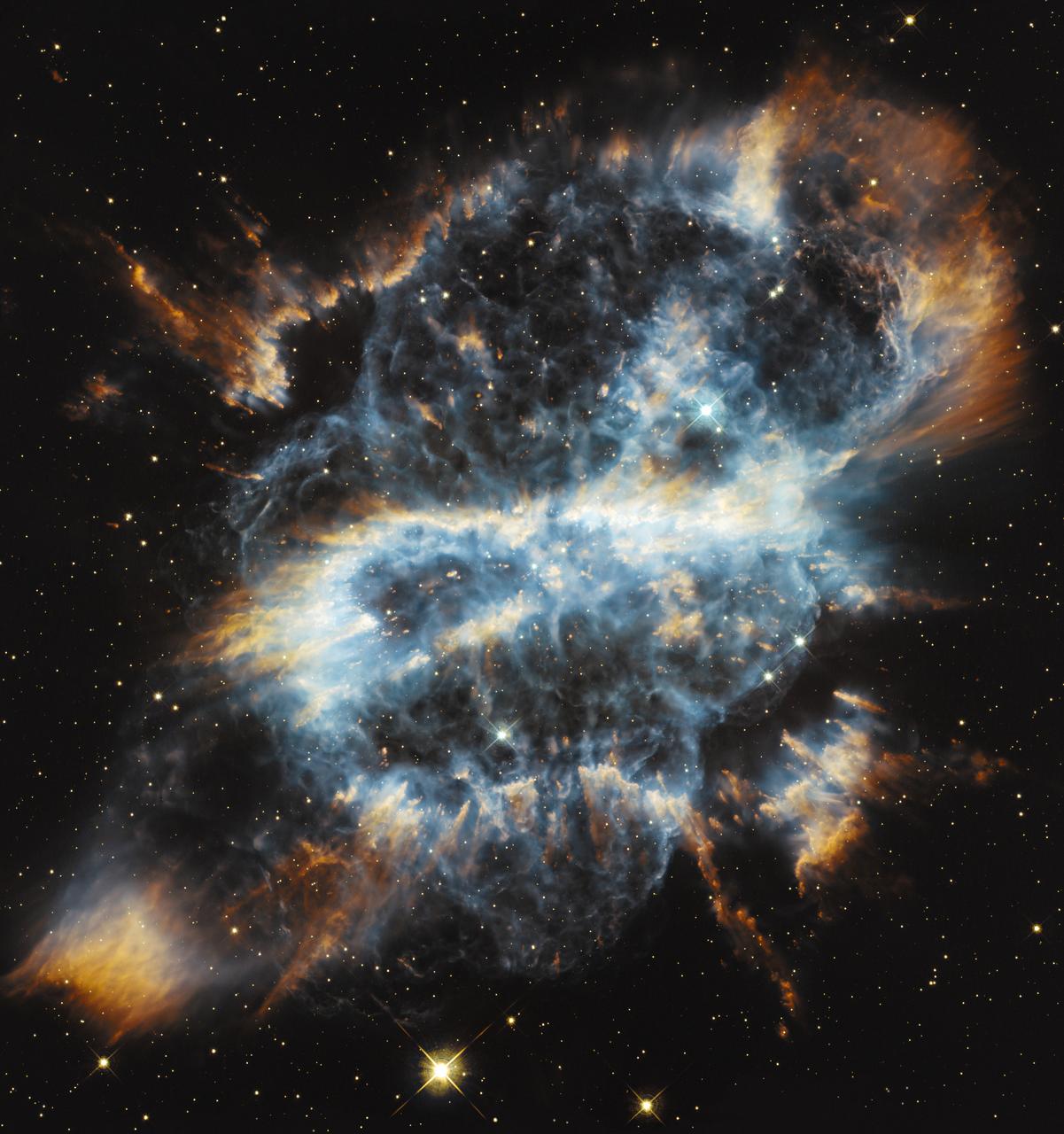

'Tis the season for holiday decorating and tree-trimming. Not to be left out, astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have photographed a festive-looking nearby planetary nebula called NGC 5189. The intricate structure of this bright gaseous nebula resembles a glass-blown holiday ornament with a glowing ribbon entwined. Planetary nebulae represent the final brief stage in the life of a medium-sized star like our sun. While consuming the last of the fuel in its core, the dying star expels a large portion of its outer envelope. This material then becomes heated by the radiation from the stellar remnant and radiates, producing glowing clouds of gas that can show complex structures, as the ejection of mass from the star is uneven in both time and direction. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/ngc5189.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/ngc5189.html</a> Credit: NASA, ESA, and G. Bacon (STScI) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
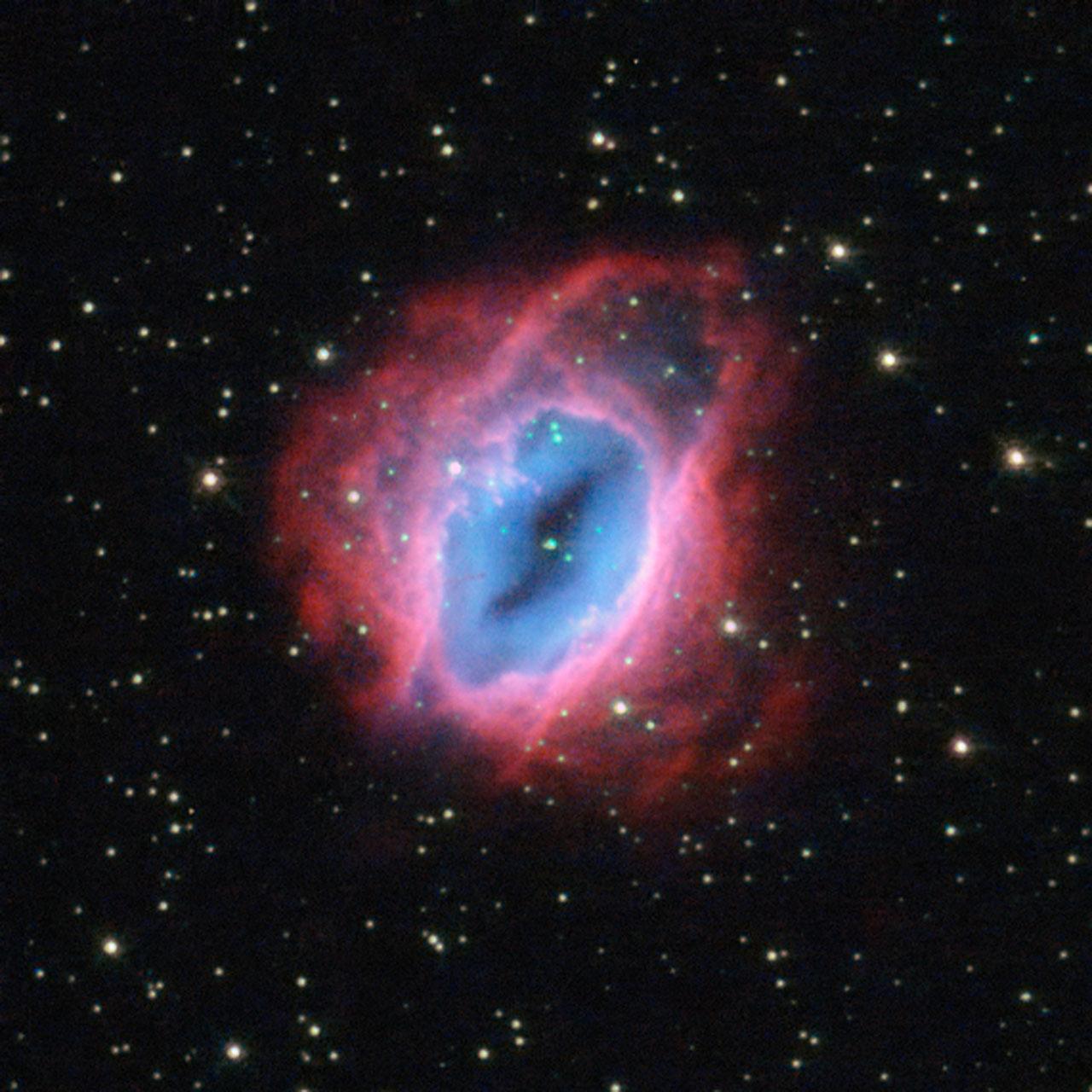

It may look like something from "The Lord of the Rings," but this fiery swirl is actually a planetary nebula known as ESO 456-67. Set against a backdrop of bright stars, the rust-colored object lies in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer), in the southern sky. In this image of ESO 456-67, it is possible to see the various layers of material expelled by the central star. Each appears in a different hue - red, orange, yellow, and green-tinted bands of gas are visible, with clear patches of space at the heart of the nebula. It is not fully understood how planetary nebulae form such a wide variety of shapes and structures; some appear to be spherical, some elliptical, others shoot material in waves from their polar regions, some look like hourglasses or figures of eight, and others resemble large, messy stellar explosions - to name but a few. Image Credit: ESA/Hubble and NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Image released 11 Aug 2011. The "Necklace Nebula" is located 15,000 light-years away in the constellation Sagitta (the Arrow). In this composite image, taken on July 2, 2011, Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 captured the glow of hydrogen (blue), oxygen (green), and nitrogen (red). The object, aptly named the Necklace Nebula, is a recently discovered planetary nebula, the glowing remains of an ordinary, Sun-like star. The nebula consists of a bright ring, measuring 12 trillion miles wide, dotted with dense, bright knots of gas that resemble diamonds in a necklace. <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/necklace-nebula.html" target="_blank" rel="nofollow"></a> <b>Credit:</b> NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This image, taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, shows the colorful "last hurrah" of a star like our sun. The star is ending its life by casting off its outer layers of gas, which formed a cocoon around the star's remaining core. Ultraviolet light from the dying star makes the material glow. The burned-out star, called a white dwarf, is the white dot in the center. Our sun will eventually burn out and shroud itself with stellar debris, but not for another 5 billion years. Our Milky Way Galaxy is littered with these stellar relics, called planetary nebulae. The objects have nothing to do with planets. Eighteenth- and nineteenth-century astronomers called them the name because through small telescopes they resembled the disks of the distant planets Uranus and Neptune. The planetary nebula in this image is called NGC 2440. The white dwarf at the center of NGC 2440 is one of the hottest known, with a surface temperature of more than 360,000 degrees Fahrenheit (200,000 degrees Celsius). The nebula's chaotic structure suggests that the star shed its mass episodically. During each outburst, the star expelled material in a different direction. This can be seen in the two bowtie-shaped lobes. The nebula also is rich in clouds of dust, some of which form long, dark streaks pointing away from the star. NGC 2440 lies about 4,000 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Puppis. The material expelled by the star glows with different colors depending on its composition, its density and how close it is to the hot central star. Blue samples helium; blue-green oxygen, and red nitrogen and hydrogen. Credit: NASA, ESA, and K. Noll (STScI), Acknowledgment: The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A panoramic view of a vast, sculpted area of gas and dust where thousands of stars are being born has been captured by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The image, taken by Hubble's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2, is online at http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2001/21/image/a/. The camera was designed and built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. The photo offers an unprecedented, detailed view of the entire inner region of the fertile, star-forming 30 Doradus Nebula. The mosaic picture shows that ultraviolet radiation and high-speed material unleashed by the stars in the cluster, called R136 (the large blue blob left of center), are weaving a tapestry of creation and destruction, triggering the collapse of looming gas and dust clouds and forming pillar-like structures that incubate newborn stars. The 30 Doradus Nebula is in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way located 170,000 light-years from Earth. Nebulas like 30 Doradus are signposts of recent star birth. High-energy ultraviolet radiation from young, hot, massive stars in R136 causes surrounding gaseous material to glow. Previous Hubble telescope observations showed that R136 contains several dozen of the most massive stars known, each about 100 times the mass of the Sun and about 10 times as hot. These stellar behemoths formed about 2 million years ago. The stars in R136 produce intense "stellar winds," streams of material traveling at several million miles an hour. These winds push the gas away from the cluster and compress the inner regions of the surrounding gas and dust clouds (seen in the image as the pinkish material). The intense pressure triggers the collapse of parts of the clouds, producing a new star formation around the central cluster. Most stars in the nursery are not visible because they are still encased in cocoons of gas and dust. This mosaic image of 30 Doradus consists of five overlapping pictures taken between January 1994 and September 2000 by the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. Several color filters enhance important details in the stars and the nebula. Blue corresponds to the hot stars. The greenish color denotes hot gas energized by the central cluster of stars. Pink depicts the glowing edges of the gas and dust clouds facing the cluster, which are being bombarded by winds and radiation. Reddish-brown represents the cooler surfaces of the clouds, which are not receiving direct radiation from the central cluster. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04200

The Cat's Eye Nebula, one of the first planetary nebulae discovered, also has one of the most complex forms known to this kind of nebula. Eleven rings, or shells, of gas make up the Cat's Eye. The full beauty of the Cat's Eye Nebula is revealed in this detailed view from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The image from Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) shows a bull's eye pattern of eleven or even more concentric rings, or shells, around the Cat's Eye. Each 'ring' is actually the edge of a spherical bubble seen projected onto the sky -- that's why it appears bright along its outer edge. Observations suggest the star ejected its mass in a series of pulses at 1,500-year intervals. These convulsions created dust shells, each of which contain as much mass as all of the planets in our solar system combined (still only one percent of the Sun's mass). These concentric shells make a layered, onion-skin structure around the dying star. The view from Hubble is like seeing an onion cut in half, where each skin layer is discernible. The bull's-eye patterns seen around planetary nebulae come as a surprise to astronomers because they had no expectation that episodes of mass loss at the end of stellar lives would repeat every 1,500 years. Several explanations have been proposed, including cycles of magnetic activity somewhat similar to our own Sun's sunspot cycle, the action of companion stars orbiting around the dying star, and stellar pulsations. Another school of thought is that the material is ejected smoothly from the star, and the rings are created later on due to formation of waves in the outflowing material. Credit: NASA, ESA, HEIC, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: R. Corradi (Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, Spain) and Z. Tsvetanov (NASA) The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute conducts Hubble science operations. Goddard is responsible for HST project management, including mission and science operations, servicing missions, and all associated development activities. To learn more about the Hubble Space Telescope go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
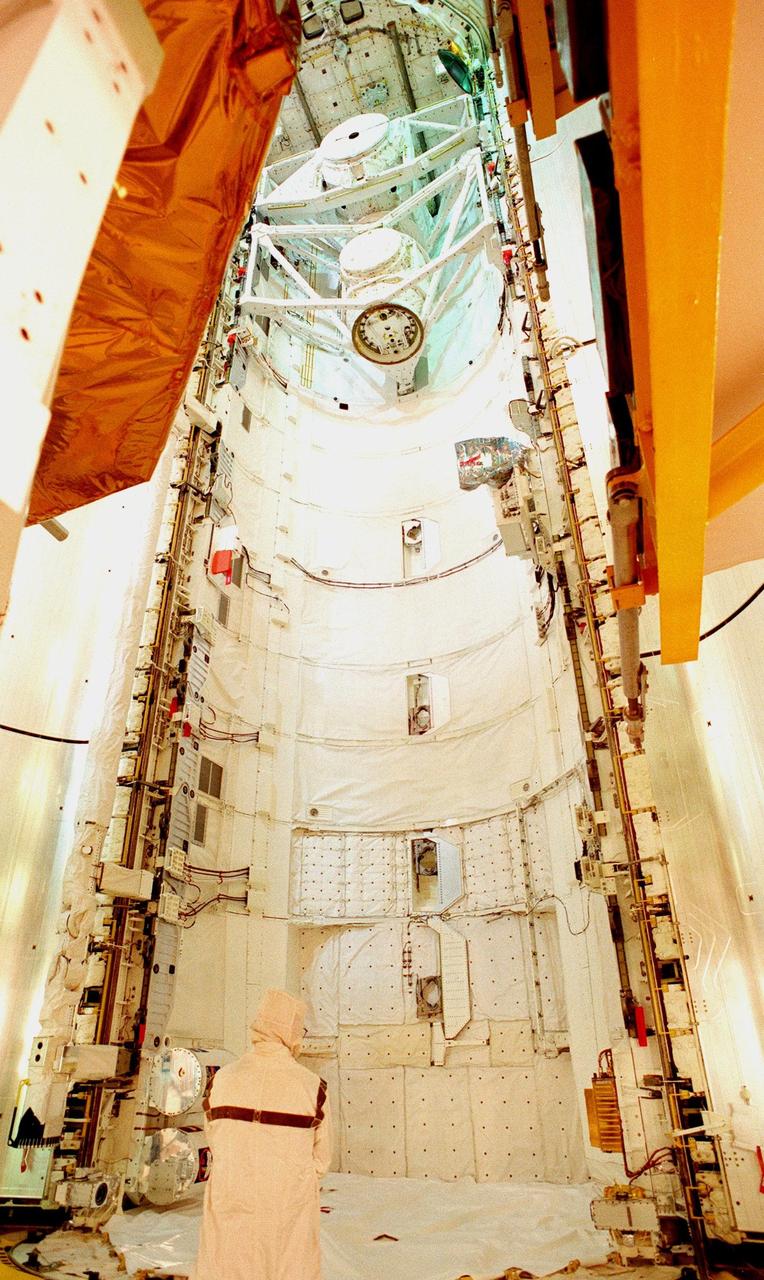
The open doors of the payload bay on Space Shuttle Discovery await the transfer of four of the payloads on mission STS-95: the SPACEHAB single module, Spartan, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbiting Systems Test Platform (HOST), and the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-3). At the top of bay are the airlock (used for depressurization and repressurization during extravehicular activity and transfer to Mir) and the tunnel adapter (enables the flight crew members to transfer from the pressurized middeck crew compartment to Spacelab's pressurized shirt-sleeve environment). SPACEHAB involves experiments on space flight and the aging process. Spartan is a solar physics spacecraft designed to perform remote sensing of the hot outer layers of the sun's atmosphere or corona. HOST carries four experiments to validate components planned for installation during the third Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission and to evaluate new technologies in an Earth-orbiting environment. IEH-3 comprises several experiments that will study the Jovian planetary system, hot stars, planetary and reflection nebulae, other stellar objects and their environments through remote observation of EUV/FUV emissions; study spacecraft interactions, Shuttle glow, thruster firings, and contamination; and measure the solar constant and identify variations in the value during a solar cycle. Discovery is scheduled to launch on Oct. 29, 1998

Huge waves are sculpted in this two-lobed nebula called the Red Spider Nebula, located some 3,000 light-years away in the constellation of Sagittarius. This warm planetary nebula harbors one of the hottest stars known and its powerful stellar winds generate waves 100 billion kilometers (62.4 billion miles) high. The waves are caused by supersonic shocks, formed when the local gas is compressed and heated in front of the rapidly expanding lobes. The atoms caught in the shock emit the spectacular radiation seen in this image. Image credit: ESA/Garrelt Mellema (Leiden University, the Netherlands) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
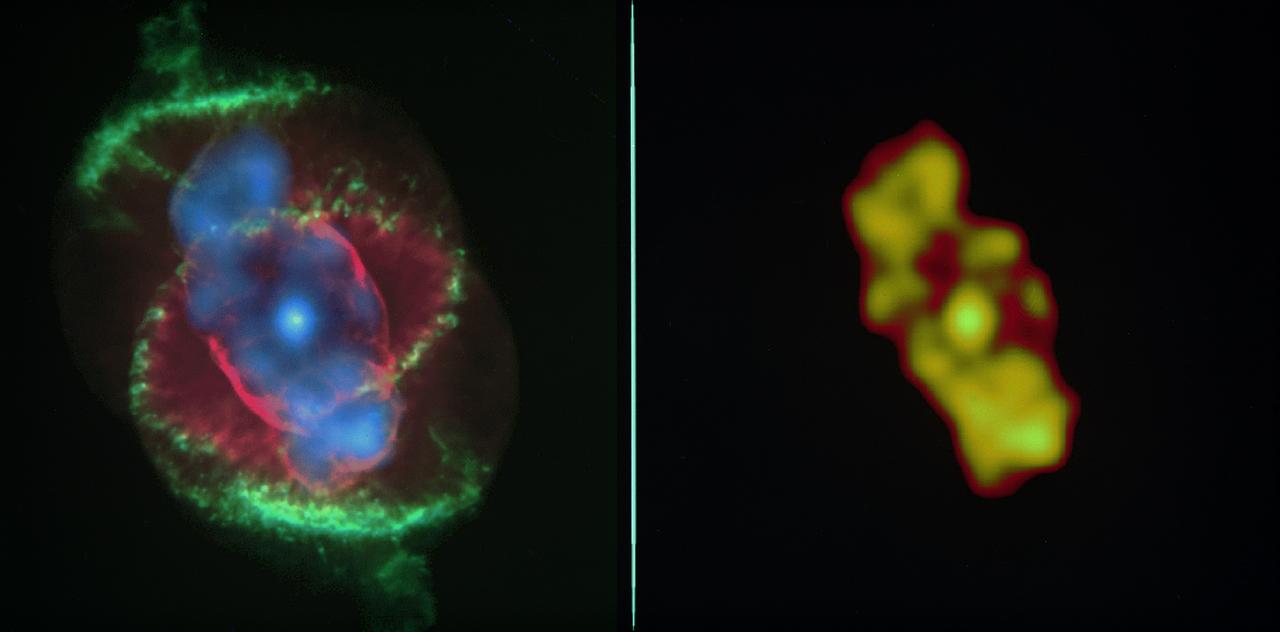
Left image: The x-ray data from the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) has revealed a bright central star surrounded by a cloud of multimillion-degree gas in the planetary nebula known as the Cat's Eye. This CXO image, where the intensity of the x-ray emission is correlated to the brightness of the orange coloring, captures the expulsion of material from a star that is expected to collapse into a white dwarf in a few million years. The intensity of x-rays from the central star was unexpected, and it is the first time astronomers have seen such x-ray emission from the central star of a planetary nebula. Right image: An image of Cat's Eye taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). By comparing the CXO data with that from the HST, researchers are able to see where the hotter, x-ray emitting gas appears in relation to the cooler material seen in optical wavelengths by the HST. The CXO team found that the chemical abundance in the region of hot gas (its x-ray intensity is shown in purple) was not like those in the wind from the central star and different from the outer cooler material (the red and green structures.) Although still incredibly energetic and hot enough to radiate x-rays, CXO shows the hot gas to be somewhat cooler than scientists would have expected for such a system. CXO image credit: (NASA/UIUC/Y. Chu et al.) HST image credit: (NASA/HST)

NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly known as the Space Infrared Telescope Facility, has captured in stunning detail the spidery filaments and newborn stars of theTarantula Nebula, a rich star-forming region also known as 30 Doradus. This cloud of glowing dust and gas is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, the nearest galaxy to our own Milky Way, and is visible primarily from the Southern Hemisphere. This image of an interstellar cauldron provides a snapshot of the complex physical processes and chemistry that govern the birth - and death - of stars. At the heart of the nebula is a compact cluster of stars, known as R136, which contains very massive and young stars. The brightest of these blue supergiant stars are up to 100 times more massive than the Sun, and are at least 100,000 times more luminous. These stars will live fast and die young, at least by astronomical standards, exhausting their nuclear fuel in a few million years. The Spitzer Space Telescope image was obtained with an infrared array camera that is sensitive to invisible infrared light at wavelengths that are about ten times longer than visible light. In this four-color composite, emission at 3.6 microns is depicted in blue, 4.5 microns in green, 5.8 microns in orange, and 8.0 microns in red. The image covers a region that is three-quarters the size of the full moon. The Spitzer observations penetrate the dust clouds throughout the Tarantula to reveal previously hidden sites of star formation. Within the luminescent nebula, many holes are also apparent. These voids are produced by highly energetic winds originating from the massive stars in the central star cluster. The structures at the edges of these voids are particularly interesting. Dense pillars of gas and dust, sculpted by the stellar radiation, denote the birthplace of future generations of stars. The Spitzer image provides information about the composition of the material at the edges of the voids. The surface layers closest to the massive stars are subject to the most intense stellar radiation. Here, the atoms are stripped of their electrons, and the green color of these regions is indicative of the radiation from this highly excited, or 'ionized,' material. The ubiquitous red filaments seen throughout the image reveal the presence of molecular material thought to be rich in hydrocarbons. The Tarantula Nebula is the nearest example of a 'starburst' phenomenon, in which intense episodes of star formation occur on massive scales. Most starbursts, however, are associated with dusty and distant galaxies. Spitzer infrared observations of the Tarantula provide astronomers with an unprecedented view of the lifecycle of massive stars and their vital role in regulating the birth of future stellar and planetary systems. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05062

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Payload Changeout Room (PCR) in the Rotating Service Structure (RSS) at Launch Pad 39-B, technicians in clean suits and tethers prepare to move the payloads for mission STS-95 through the open doors of the payload bay (right) of Space Shuttle Discovery. At the top of the RSS is the Spacehab module; below it are the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbiting Systems Test Platform (HOST), and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-3). The PCR is an environmentally controlled facility with seals around the mating surface that fit against the orbiter or payload canister and permit the payload bay or canister doors to be opened and cargo removed without exposing it to outside air and contaminants. Payloads are installed vertically in the orbiter using the extendable payload ground handling mechanism. Fixed and extendable work platforms provide work access in the PCR. The SPACEHAB single module involves experiments on space flight and the aging process. Spartan is a solar physics spacecraft designed to perform remote sensing of the hot outer layers of the sun's atmosphere or corona. HOST carries four experiments to validate components planned for installation during the third Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission and to evaluate new technologies in an Earth-orbiting environment. IEH-3 comprises several experiments that will study the Jovian planetary system, hot stars, planetary and reflection nebulae, other stellar objects and their environments through remote observation of EUV/FUV emissions; study spacecraft interactions, Shuttle glow, thruster firings, and contamination; and measure the solar constant and identify variations in the value during a solar cycle. Mission STS-95 is scheduled to launch Oct. 29, 1998

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER,FLA. -- Inside the Payload Changeout Room (PCR) in the Rotating Service Structure (RSS) at Launch Pad 39-B, technicians in clean suits and tethers prepare to move the payloads for mission STS-95 through the open doors of the payload bay (left) of Space Shuttle Discovery. At the top of the RSS is the Spacehab module; below it are the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbiting Systems Test Platform (HOST), and the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-3). The PCR is an environmentally controlled facility with seals around the mating surface that fit against the orbiter or payload canister and permit the payload bay or canister doors to be opened and cargo removed without exposing it to outside air and contaminants. Payloads are installed vertically in the orbiter using the extendable payload ground handling mechanism. Fixed and extendable work platforms provide work access in the PCR. The SPACEHAB single module involves experiments on space flight and the aging process. Spartan is a solar physics spacecraft designed to perform remote sensing of the hot outer layers of the sun's atmosphere or corona. HOST carries four experiments to validate components planned for installation during the third Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission and to evaluate new technologies in an Earth-orbiting environment. IEH-3 comprises several experiments that will study the Jovian planetary system, hot stars, planetary and reflection nebulae, other stellar objects and their environments through remote observation of EUV/FUV emissions; study spacecraft interactions, Shuttle glow, thruster firings, and contamination; and measure the solar constant and identify variations in the value during a solar cycle. Mission STS-95 is scheduled to launch Oct. 29, 1998

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Payload Changeout Room (PCR) in the Rotating Service Structure (RSS) at Launch Pad 39-B, technicians in clean suits move the payloads for mission STS-95 to the payload bay of Space Shuttle Discovery. At the top of the RSS is the Spacehab module; below it are the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbiting Systems Test Platform (HOST), and the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-3). The PCR is an environmentally controlled facility with seals around the mating surface that fit against the orbiter or payload canister and permit the payload bay or canister doors to be opened and cargo removed without exposing it to outside air and contaminants. Payloads are installed vertically in the orbiter using the extendable payload ground handling mechanism. Fixed and extendable work platforms provide work access in the PCR. The SPACEHAB single module involves experiments on space flight and the aging process. Spartan is a solar physics spacecraft designed to perform remote sensing of the hot outer layers of the sun's atmosphere or corona. HOST carries four experiments to validate components planned for installation during the third Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission and to evaluate new technologies in an Earth-orbiting environment. IEH-3 comprises several experiments that will study the Jovian planetary system, hot stars, planetary and reflection nebulae, other stellar objects and their environments through remote observation of EUV/FUV emissions; study spacecraft interactions, Shuttle glow, thruster firings, and contamination; and measure the solar constant and identify variations in the value during a solar cycle. Mission STS-95 is scheduled to launch Oct. 29, 1998
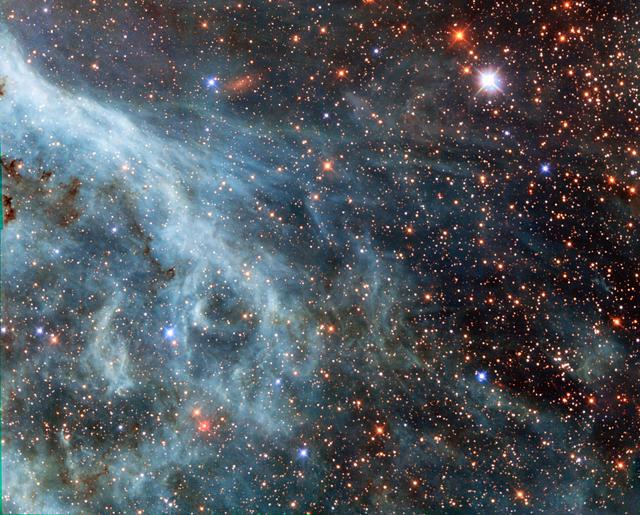

The brightly glowing plumes seen in this image are reminiscent of an underwater scene, with turquoise-tinted currents and nebulous strands reaching out into the surroundings. However, this is no ocean. This image actually shows part of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small nearby galaxy that orbits our galaxy, the Milky Way, and appears as a blurred blob in our skies. The NASA/European Space Agency (ESA) Hubble Space Telescope has peeked many times into this galaxy, releasing stunning images of the whirling clouds of gas and sparkling stars (opo9944a, heic1301, potw1408a). This image shows part of the Tarantula Nebula's outskirts. This famously beautiful nebula, located within the LMC, is a frequent target for Hubble (heic1206, heic1402). In most images of the LMC the color is completely different to that seen here. This is because, in this new image, a different set of filters was used. The customary R filter, which selects the red light, was replaced by a filter letting through the near-infrared light. In traditional images, the hydrogen gas appears pink because it shines most brightly in the red. Here however, other less prominent emission lines dominate in the blue and green filters. This data is part of the Archival Pure Parallel Project (APPP), a project that gathered together and processed over 1,000 images taken using Hubble’s Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, obtained in parallel with other Hubble instruments. Much of the data in the project could be used to study a wide range of astronomical topics, including gravitational lensing and cosmic shear, exploring distant star-forming galaxies, supplementing observations in other wavelength ranges with optical data, and examining star populations from stellar heavyweights all the way down to solar-mass stars. Image Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA: acknowledgement: Josh Barrington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This image depicts a vast canyon of dust and gas in the Orion Nebula from a 3-D computer model based on observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and created by science visualization specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md. A 3-D visualization of this model takes viewers on an amazing four-minute voyage through the 15-light-year-wide canyon. Credit: NASA, G. Bacon, L. Frattare, Z. Levay, and F. Summers (STScI/AURA) Go here to learn more about Hubble 3D: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premiere.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premier...</a> or <a href="http://www.imax.com/hubble/" rel="nofollow">www.imax.com/hubble/</a> Take an exhilarating ride through the Orion Nebula, a vast star-making factory 1,500 light-years away. Swoop through Orion's giant canyon of gas and dust. Fly past behemoth stars whose brilliant light illuminates and energizes the entire cloudy region. Zoom by dusty tadpole-shaped objects that are fledgling solar systems. This virtual space journey isn't the latest video game but one of several groundbreaking astronomy visualizations created by specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, the science operations center for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The cinematic space odysseys are part of the new Imax film "Hubble 3D," which opens today at select Imax theaters worldwide. The 43-minute movie chronicles the 20-year life of Hubble and includes highlights from the May 2009 servicing mission to the Earth-orbiting observatory, with footage taken by the astronauts. The giant-screen film showcases some of Hubble's breathtaking iconic pictures, such as the Eagle Nebula's "Pillars of Creation," as well as stunning views taken by the newly installed Wide Field Camera 3. While Hubble pictures of celestial objects are awe-inspiring, they are flat 2-D photographs. For this film, those 2-D images have been converted into 3-D environments, giving the audience the impression they are space travelers taking a tour of Hubble's most popular targets. "A large-format movie is a truly immersive experience," says Frank Summers, an STScI astronomer and science visualization specialist who led the team that developed the movie visualizations. The team labored for nine months, working on four visualization sequences that comprise about 12 minutes of the movie. "Seeing these Hubble images in 3-D, you feel like you are flying through space and not just looking at picture postcards," Summers continued. "The spacescapes are all based on Hubble images and data, though some artistic license is necessary to produce the full depth of field needed for 3-D." The most ambitious sequence is a four-minute voyage through the Orion Nebula's gas-and-dust canyon, about 15 light-years across. During the ride, viewers will see bright and dark, gaseous clouds; thousands of stars, including a grouping of bright, hefty stars called the Trapezium; and embryonic planetary systems. The tour ends with a detailed look at a young circumstellar disk, which is much like the structure from which our solar system formed 4.5 billion years ago. Based on a Hubble image of Orion released in 2006, the visualization was a collaborative effort between science visualization specialists at STScI, including Greg Bacon, who sculpted the Orion Nebula digital model, with input from STScI astronomer Massimo Roberto; the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; and the Spitzer Science Center at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. For some of the sequences, STScI imaging specialists developed new techniques for transforming the 2-D Hubble images into 3-D. STScI image processing specialists Lisa Frattare and Zolt Levay, for example, created methods of splitting a giant gaseous pillar in the Carina Nebula into multiple layers to produce a 3-D effect, giving the structure depth. The Carina Nebula is a nursery for baby stars. Frattare painstakingly removed the thousands of stars in the image so that Levay could separate the gaseous layers on the isolated Carina pillar. Frattare then replaced the stars into both foreground and background layers to complete the 3-D model. For added effect, the same separation was done for both visible and infrared Hubble images, allowing the film to cross-fade between wavelength views in 3-D. In another sequence viewers fly into a field of 170,000 stars in the giant star cluster Omega Centauri. STScI astronomer Jay Anderson used his stellar database to create a synthetic star field in 3-D that matches recent razor-sharp Hubble photos. The film's final four-minute sequence takes viewers on a voyage from our Milky Way Galaxy past many of Hubble's best galaxy shots and deep into space. Some 15,000 galaxies from Hubble's deepest surveys stretch billions of light-years across the universe in a 3-D sequence created by STScI astronomers and visualizers. The view dissolves into a cobweb that traces the universe's large-scale structure, the backbone from which galaxies were born. In addition to creating visualizations, STScI's education group also provided guidance on the "Hubble 3D" Educator Guide, which includes standards-based lesson plans and activities about Hubble and its mission. Students will use the guide before or after seeing the movie. "The guide will enhance the movie experience for students and extend the movie into classrooms," says Bonnie Eisenhamer, STScI's Hubble Formal Education manager. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) and is managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Greenbelt, Md. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. The institute is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., Washington, D.C.
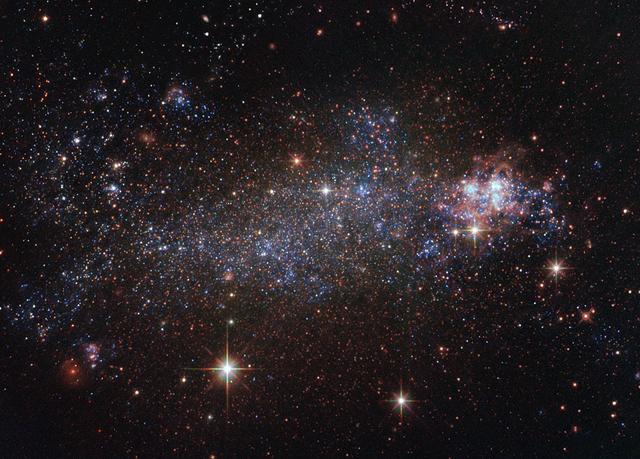

Most galaxies possess a majestic spiral or elliptical structure. About a quarter of galaxies, though, defy such conventional, rounded aesthetics, instead sporting a messy, indefinable shape. Known as irregular galaxies, this group includes NGC 5408, the galaxy that has been snapped here by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. English polymath John Herschel recorded the existence of NGC 5408 in June 1834. Astronomers had long mistaken NGC 5408 for a planetary nebula, an expelled cloud of material from an aging star. Instead, bucking labels, NGC 5408 turned out to be an entire galaxy, located about 16 million light-years from Earth in the constellation of Centaurus (The Centaur). In yet another sign of NGC 5408 breaking convention, the galaxy is associated with an object known as an ultraluminous X-ray source, dubbed NGC 5408 X-1, one of the best studied of its class. These rare objects beam out prodigious amounts of energetic X-rays. Astrophysicists believe these sources to be strong candidates for intermediate-mass black holes. This hypothetical type of black hole has significantly less mass than the supermassive black holes found in galactic centres, which can have billions of times the mass of the Sun, but have a good deal more mass than the black holes formed when giant stars collapse. A version of this image was entered into the Hubble's Hidden Treasures image processing competition by contestant Judy Schmidt.
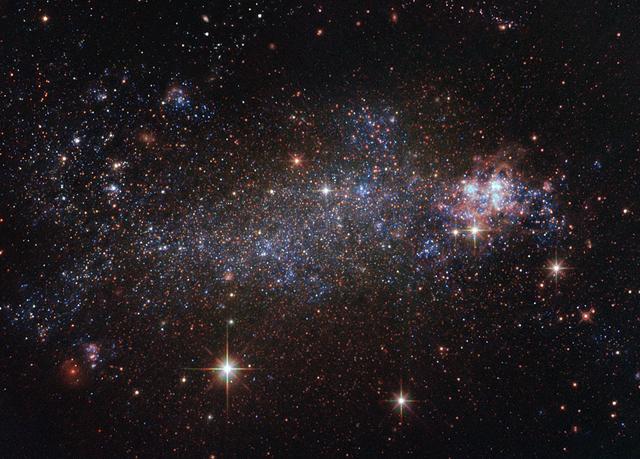

Most galaxies possess a majestic spiral or elliptical structure. About a quarter of galaxies, though, defy such conventional, rounded aesthetics, instead sporting a messy, indefinable shape. Known as irregular galaxies, this group includes NGC 5408, the galaxy that has been snapped here by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. John Herschel recorded the existence of NGC 5408 in June 1834. Astronomers had long mistaken NGC 5408 for a planetary nebula, an expelled cloud of material from an aging star. Instead, bucking labels, NGC 5408 turned out to be an entire galaxy, located about 16 million light-years from Earth in the constellation of Centaurus (The Centaur). In yet another sign of NGC 5408 breaking convention, the galaxy is associated with an object known as an ultraluminous X-ray source, dubbed NGC 5408 X-1, one of the best studied of its class. These rare objects beam out prodigious amounts of energetic X-rays. Astrophysicists believe these sources to be strong candidates for intermediate-mass black holes. This hypothetical type of black hole has significantly less mass than the supermassive black holes found in galactic centers, which can have billions of times the mass of the sun, but have a good deal more mass than the black holes formed when giant stars collapse. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>