
A researcher from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepares pepper seeds for planting inside science carriers on April 8, 2021, inside the Space Life Sciences Lab for the Plant Habitat-04 (PH-04) experiment. The seeds will fly to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 22nd Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-22) mission. When the experiment starts, astronauts will grow the pepper seeds in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) growth chamber, which will monitor the experiment with more than 180 sensors. The astronauts will observe plant growth for about four months and conduct two harvests to study whether microgravity affects growth, flavor, or texture. Since peppers take longer to germinate, grow, and develop than previous crops grown in space, the PH-04 experiment also will test the durability and reliability of the various systems within the APH.

Inside the Space Life Sciences Lab at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, researchers plant pepper seeds in a science carrier on April 8, 2021, in preparation for the Plant Habitat-04 (PH-04) experiment. The seeds will fly to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 22nd Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-22) mission. When the experiment starts, astronauts will grow the pepper seeds in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) growth chamber, which will monitor the experiment with more than 180 sensors. The astronauts will observe plant growth for about four months and conduct two harvests to study whether microgravity affects growth, flavor, or texture. Since peppers take longer to germinate, grow, and develop than previous crops grown in space, the PH-04 experiment also will test the durability and reliability of the various systems within the APH.

Inside the Space Life Sciences Lab at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a researcher plants pepper seeds in science carriers on April 8, 2021, in preparation for the Plant Habitat-04 (PH-04) experiment. The seeds will fly to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 22nd Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-22) mission. When the experiment starts, astronauts will grow the pepper seeds in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) growth chamber, which will monitor the experiment with more than 180 sensors. The astronauts will observe plant growth for about four months and conduct two harvests to study whether microgravity affects growth, flavor, or texture. Since peppers take longer to germinate, grow, and develop than previous crops grown in space, the PH-04 experiment also will test the durability and reliability of the various systems within the APH.

A researcher from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepares pepper seeds for planting inside science carriers on April 8, 2021, inside the Space Life Sciences Lab for the Plant Habitat-04 (PH-04) experiment. The seeds will fly to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 22nd Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-22) mission. When the experiment starts, astronauts will grow the pepper seeds in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) growth chamber, which will monitor the experiment with more than 180 sensors. The astronauts will observe plant growth for about four months and conduct two harvests to study whether microgravity affects growth, flavor, or texture. Since peppers take longer to germinate, grow, and develop than previous crops grown in space, the PH-04 experiment also will test the durability and reliability of the various systems within the APH.

A researcher from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepares pepper seeds for planting inside science carriers on April 8, 2021, inside the Space Life Sciences Lab for the Plant Habitat-04 (PH-04) experiment. The seeds will fly to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 22nd Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-22) mission. When the experiment starts, astronauts will grow the pepper seeds in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) growth chamber, which will monitor the experiment with more than 180 sensors. The astronauts will observe plant growth for about four months and conduct two harvests to study whether microgravity affects growth, flavor, or texture. Since peppers take longer to germinate, grow, and develop than previous crops grown in space, the PH-04 experiment also will test the durability and reliability of the various systems within the APH.

A close-up photo of a pepper seed prepared by researchers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is shown before it’s planted inside a science carrier on April 8, 2021, inside the Space Life Sciences Lab for the Plant Habitat-04 (PH-04) experiment. The seeds will fly to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 22nd Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-22) mission. When the experiment starts, astronauts will grow the pepper seeds in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) growth chamber, which will monitor the experiment with more than 180 sensors. The astronauts will observe plant growth for about four months and conduct two harvests to study whether microgravity affects growth, flavor, or texture. Since peppers take longer to germinate, grow, and develop than previous crops grown in space, the PH-04 experiment also will test the durability and reliability of the various systems within the APH.
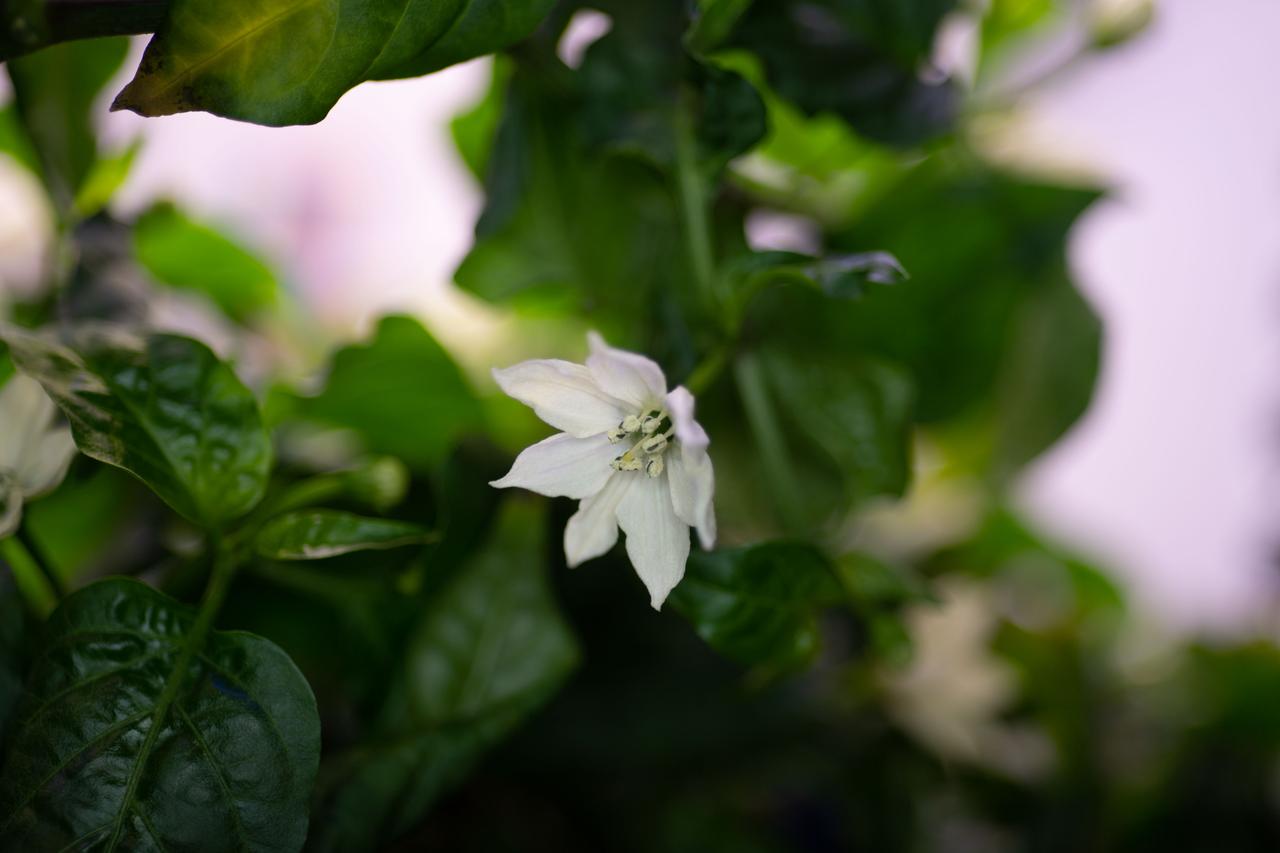

Hatch Green Chile plants are pictured growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Microgravity Growth of New Mexico Hatch Green Chile as a Technical Display of Advanced Plant Habitat’s Capabilities (Plant Habitat-04) demonstrates using the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) by growing peppers in space for the first time.
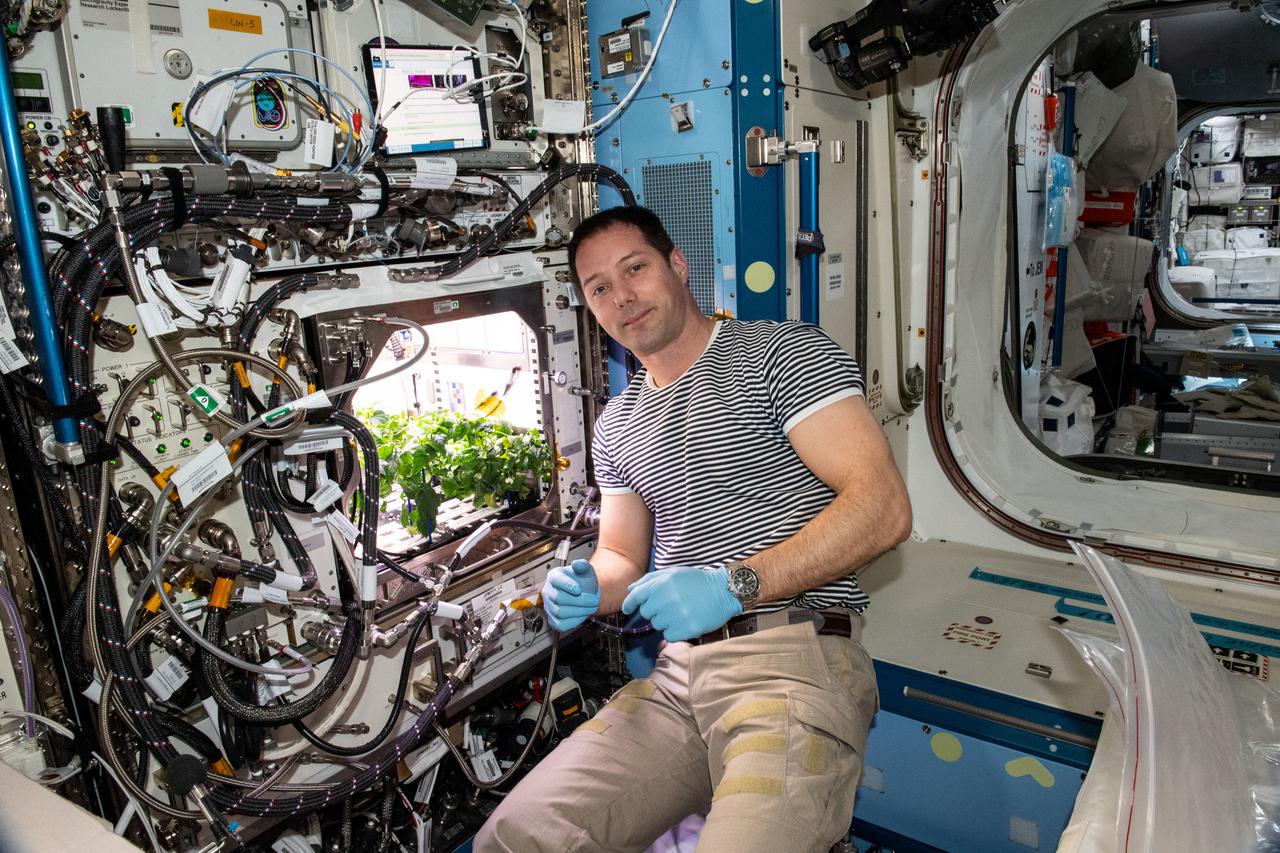

iss065e398621 (Sept. 20, 2021) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Thomas Pesquet cleans up debris in the International Space Station’s Plant Habitat which is growing Hatch Green chiles for the Plant Habitat-04 space crop experiment.

iss065e398600 (Sept. 20, 2021) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Thomas Pesquet cleans up debris in the International Space Station’s Plant Habitat which is growing Hatch Green chiles for the Plant Habitat-04 space crop experiment.
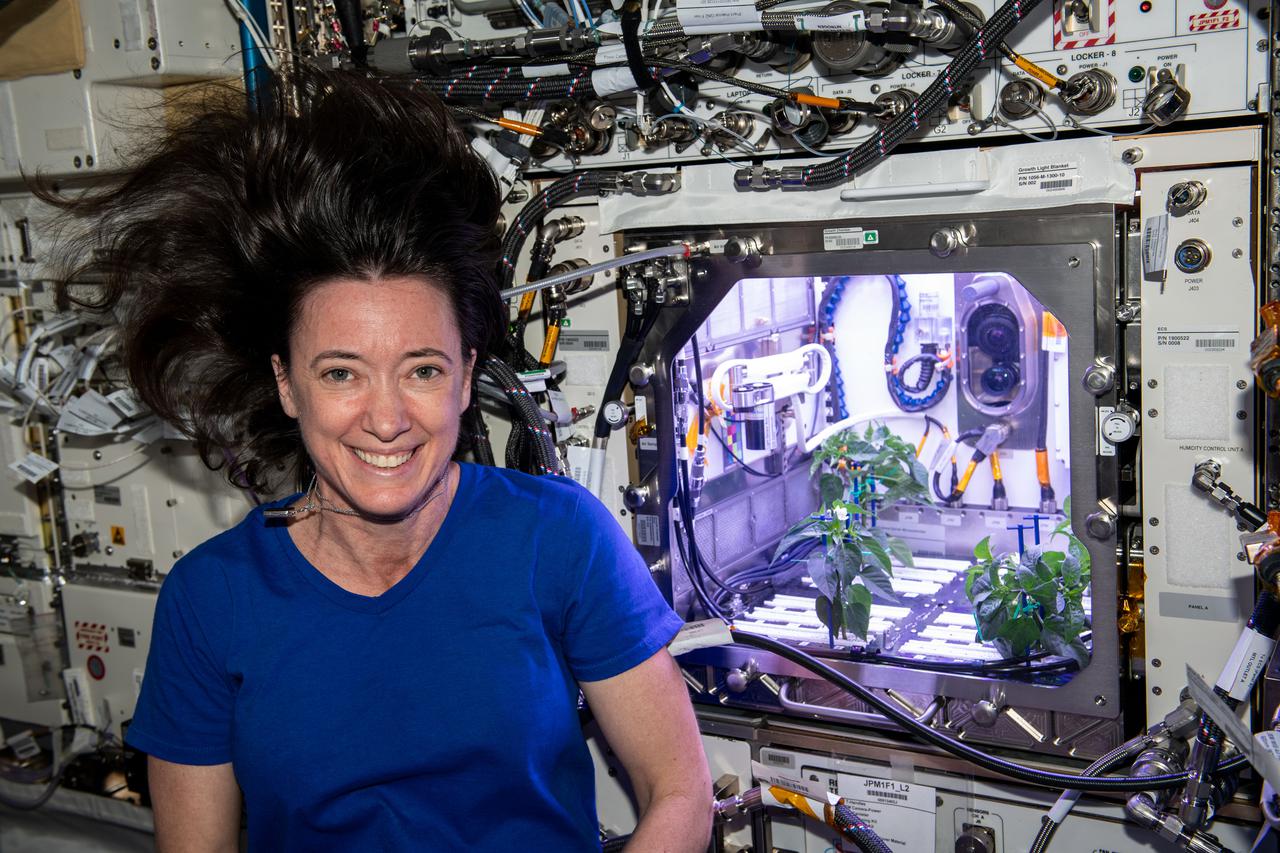

iss065e346115 (September 2, 2021) -- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur poses with the crop of chile peppers being grown as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation inside the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) aboard the International Space Station. This is the first time chile peppers are being grown aboard the orbiting laboratory, and are one of the most complex plant experiments on the station to date because of the long germination and growing times. The pepper seeds were activated on July 12. 2021 and will grow for about four months, during which time they will be harvested twice. Astronauts will sample some of the peppers and return the rest to Earth for scientific analysis.
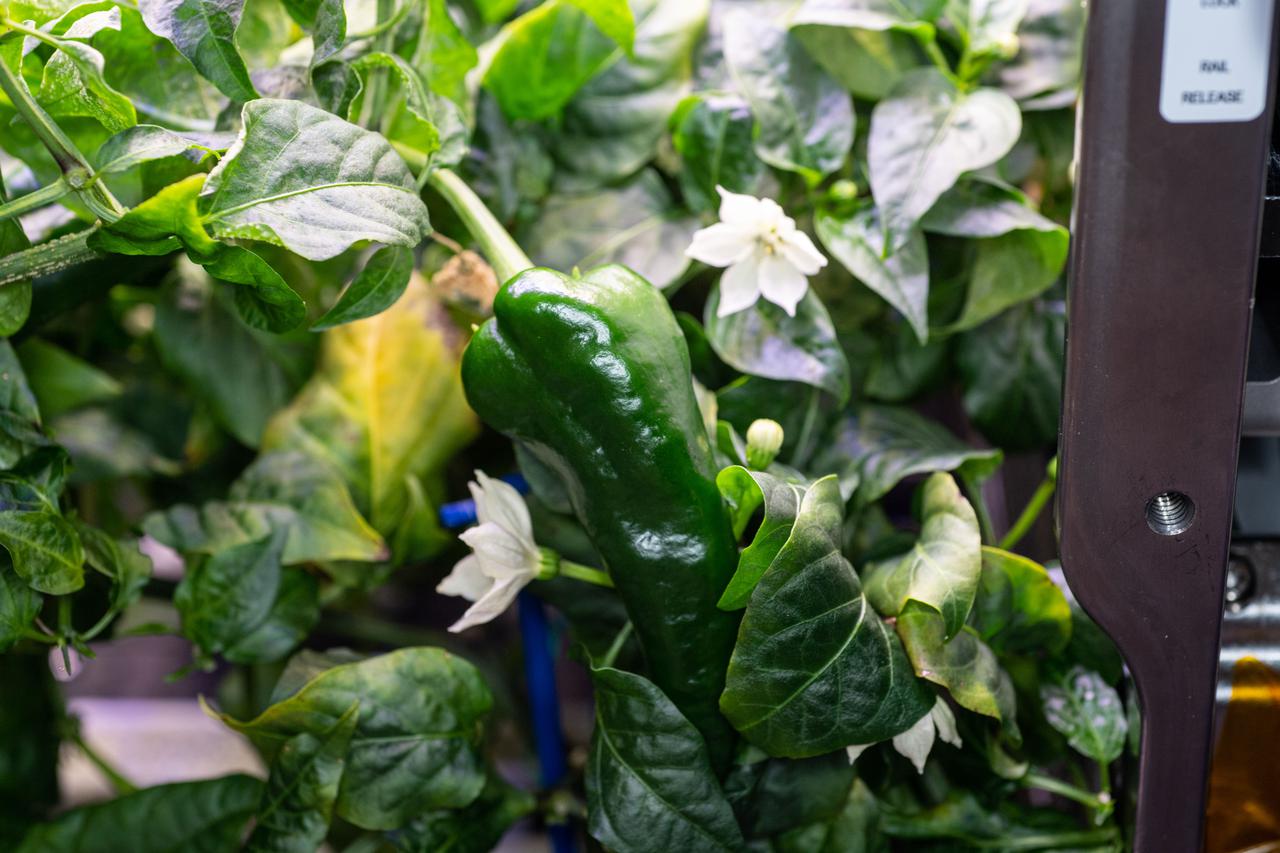

iss066e006170 (October 20, 2021) -- A view of a green chile pepper being grown as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation aboard the International Space Station. This is the first time chile peppers are being grown aboard the orbiting laboratory, and are one of the most complex plant experiments on the station to date because of the long germination and growing times. The pepper seeds were activated on July 12. 2021 and will grow for about four months, during which time they will be harvested twice. Astronauts will sample some of the peppers and return the rest to Earth for scientific analysis.

iss066e008110 (October 20, 2021) -- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei prepares to photograph chile peppers growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat as part of the Plant Habit-04 experiment being conducted aboard the International Space Station. The chile pepper seeds started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. They will be harvested twice, once in late October and again in late November. Astronauts will sanitize the peppers, eat part of their harvest, and return the rest to Earth for analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.
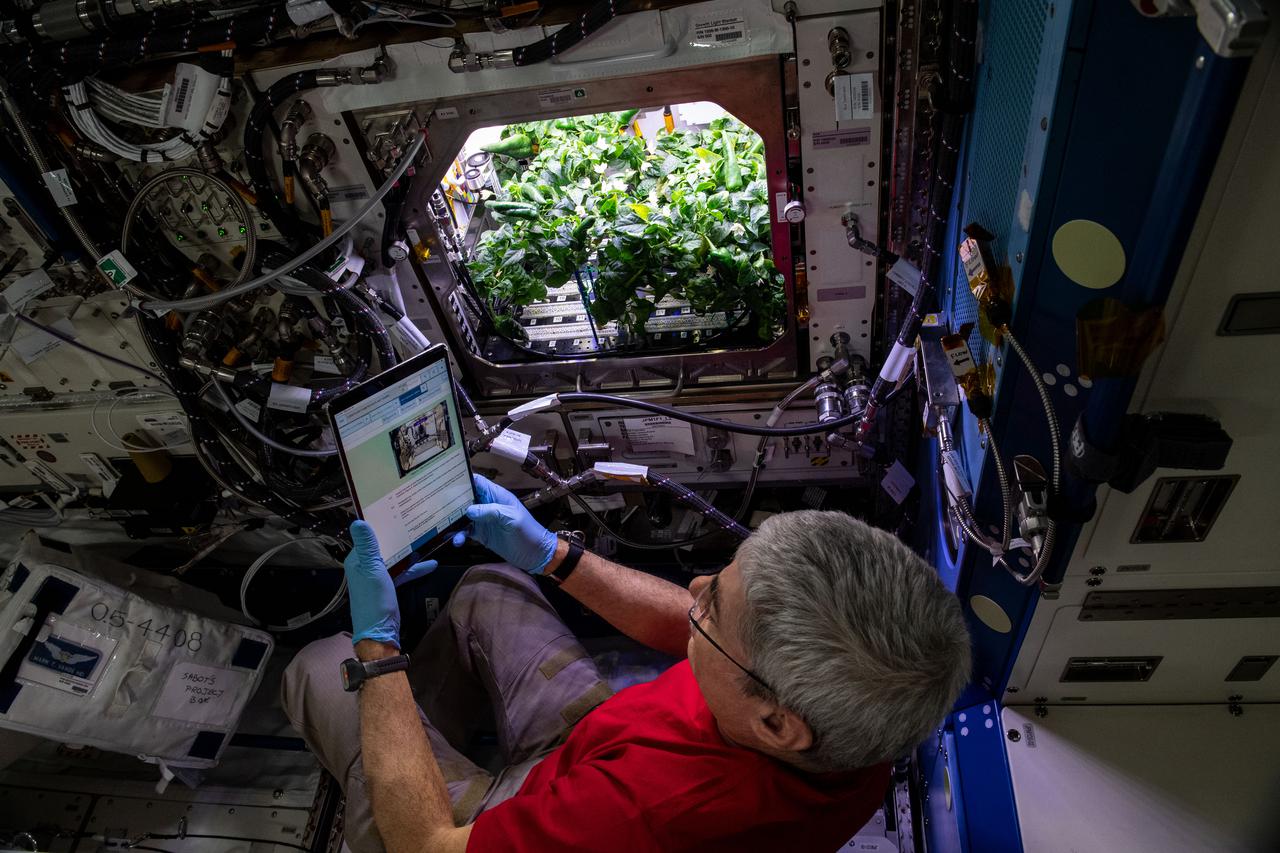

iss066e008125 (October 20, 2021) -- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei prepares for the routine debris removal procedure for chile peppers growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat as part of the Plant Habit-04 experiment being conducted aboard the International Space Station. The chile pepper seeds started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. They will be harvested twice, once in late October and again in late November. Astronauts will sanitize the peppers, eat part of their harvest, and return the rest to Earth for analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.
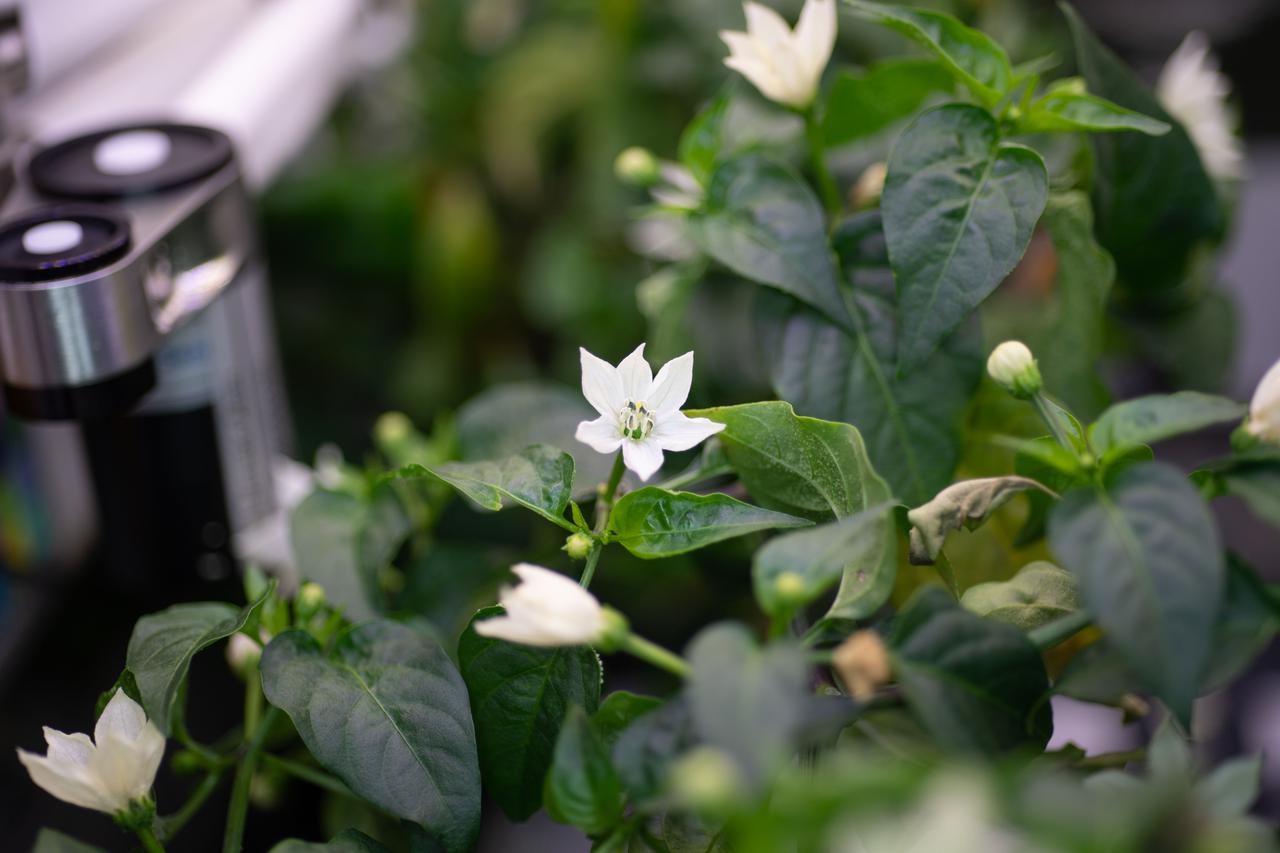

iss065e434036 (9/30/2021) --- Hatch Green Chile plants are pictured growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Microgravity Growth of New Mexico Hatch Green Chile as a Technical Display of Advanced Plant Habitat’s Capabilities (Plant Habitat-04) demonstrates using the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) by growing peppers in space for the first time.
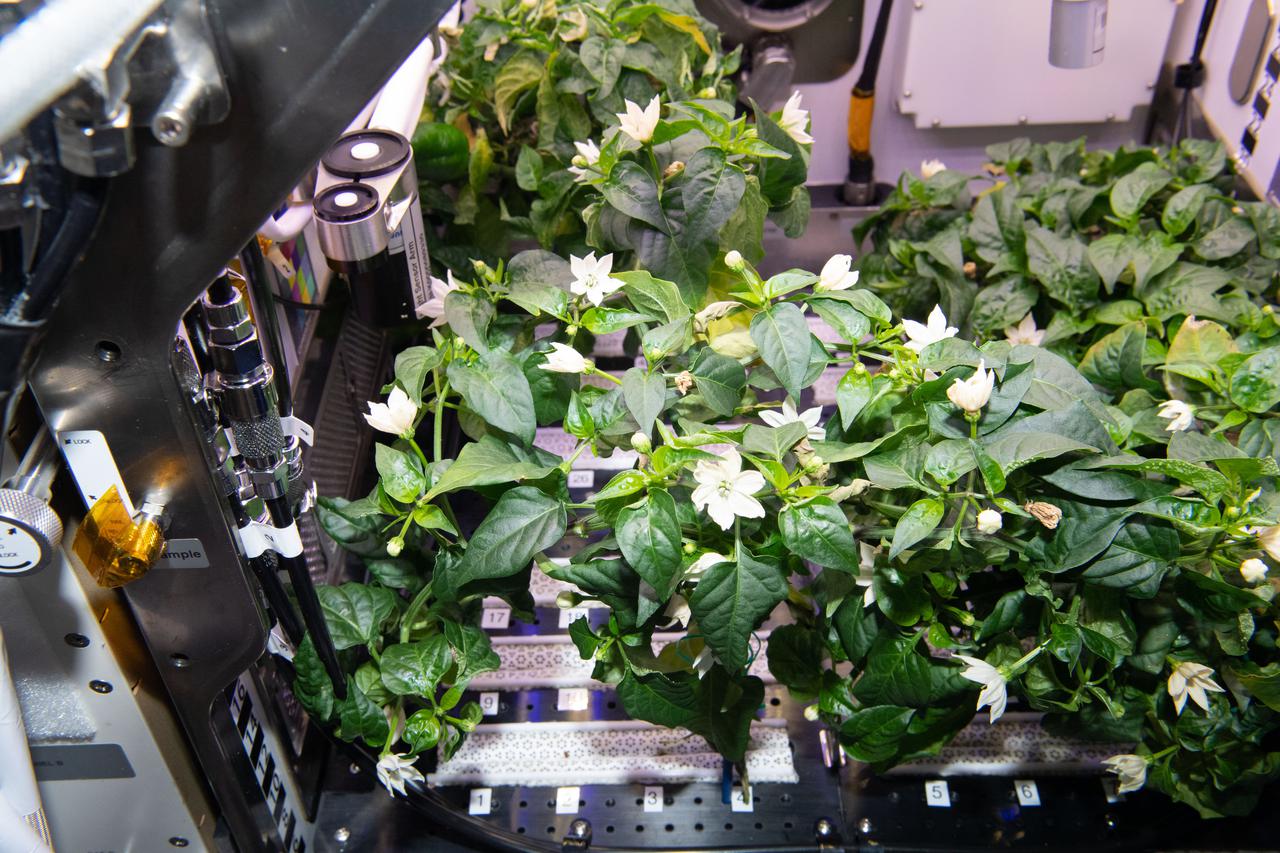

iss065e434054 (9/30/2021) --- Hatch Green Chile plants are pictured growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Microgravity Growth of New Mexico Hatch Green Chile as a Technical Display of Advanced Plant Habitat’s Capabilities (Plant Habitat-04) demonstrates using the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) by growing peppers in space for the first time.
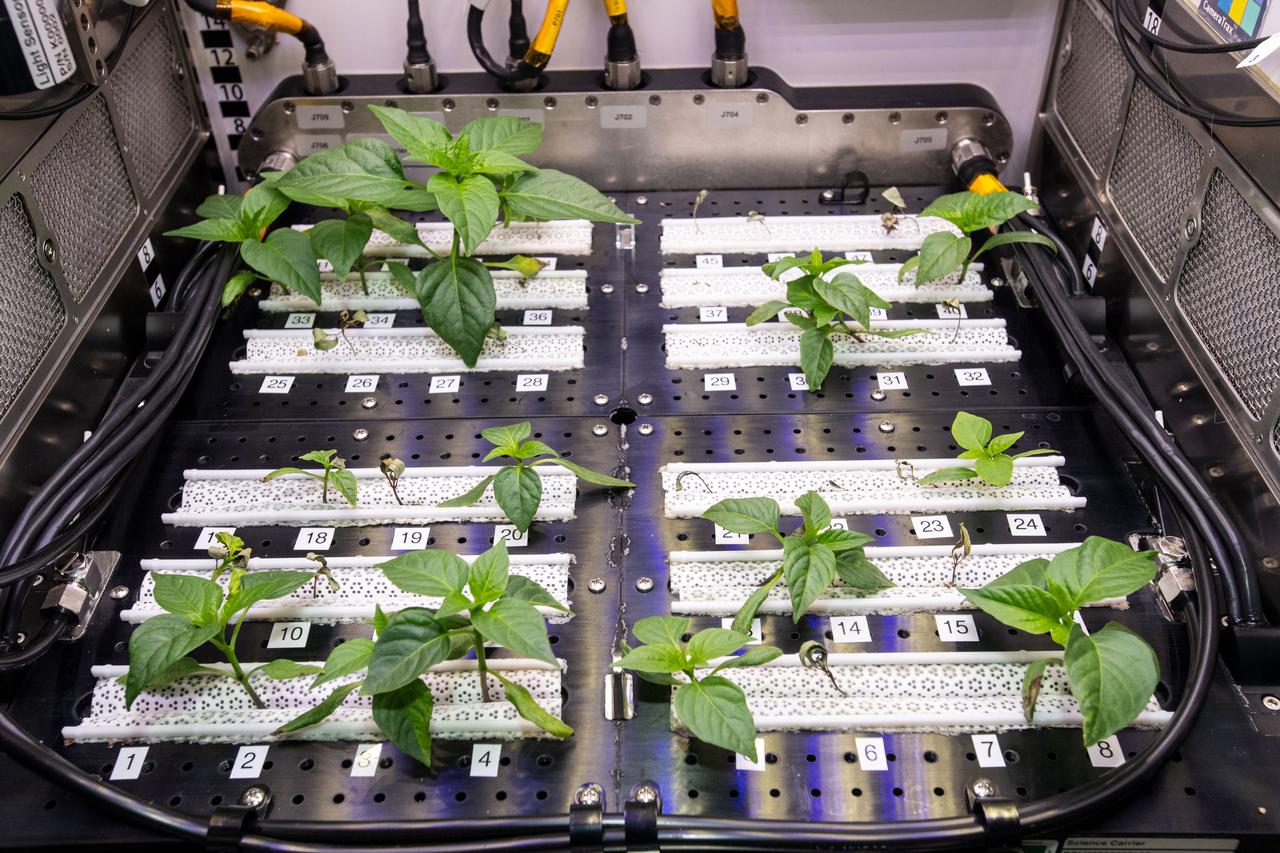

iss065e235366 (8/10/2021) --- Hatch Green Chile plants are pictured growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Microgravity Growth of New Mexico Hatch Green Chile as a Technical Display of Advanced Plant Habitat’s Capabilities (Plant Habitat-04) demonstrates using the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) by growing peppers in space for the first time.

iss065e235367 (8/10/2021) --- Hatch Green Chile plants are pictured growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Microgravity Growth of New Mexico Hatch Green Chile as a Technical Display of Advanced Plant Habitat’s Capabilities (Plant Habitat-04) demonstrates using the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) by growing peppers in space for the first time.
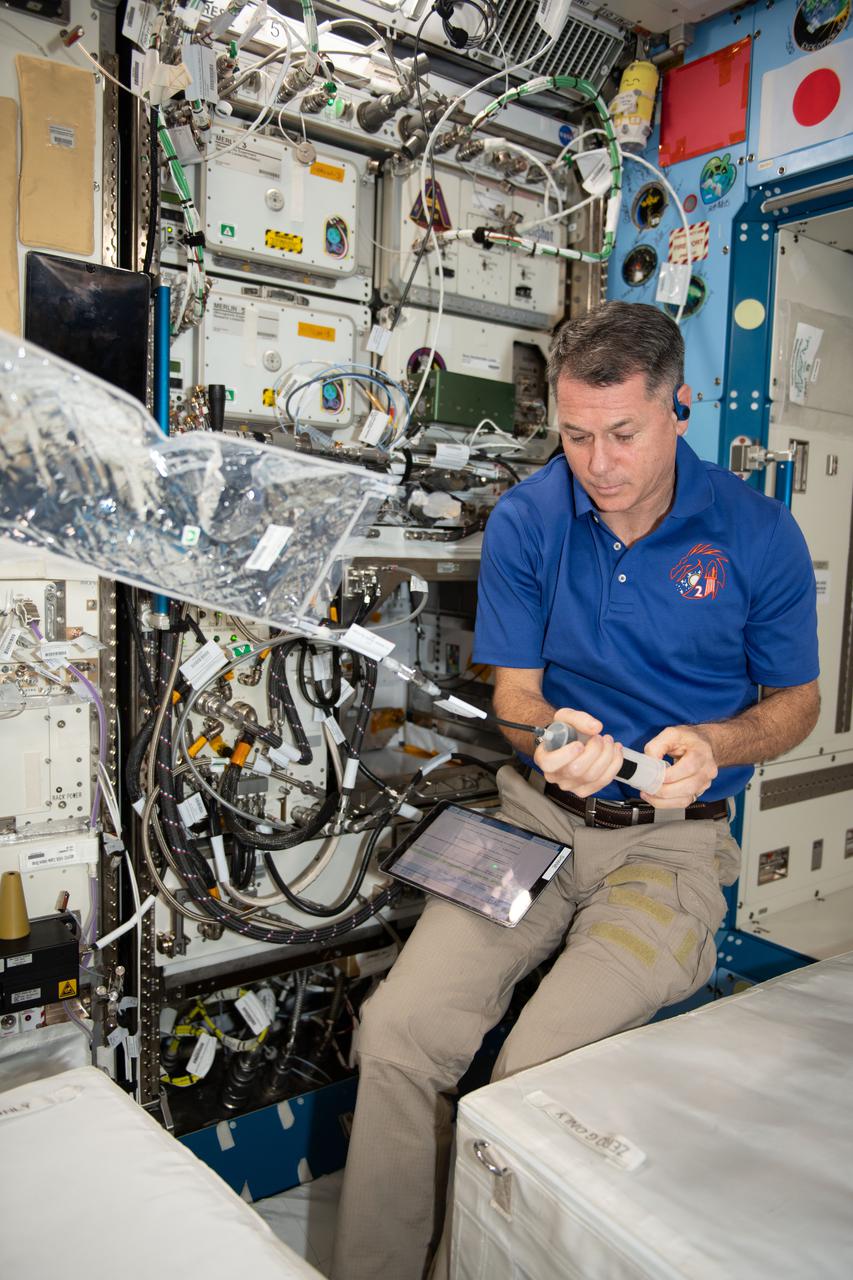

iss065e163206 (June 9, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough configures the Advanced Plant Habitat and fills it with water to support the Plant Habitat-04 space botany experiment. The study is demonstrating growing peppers, which are an excellent source of vitamin C, in space for the first time.
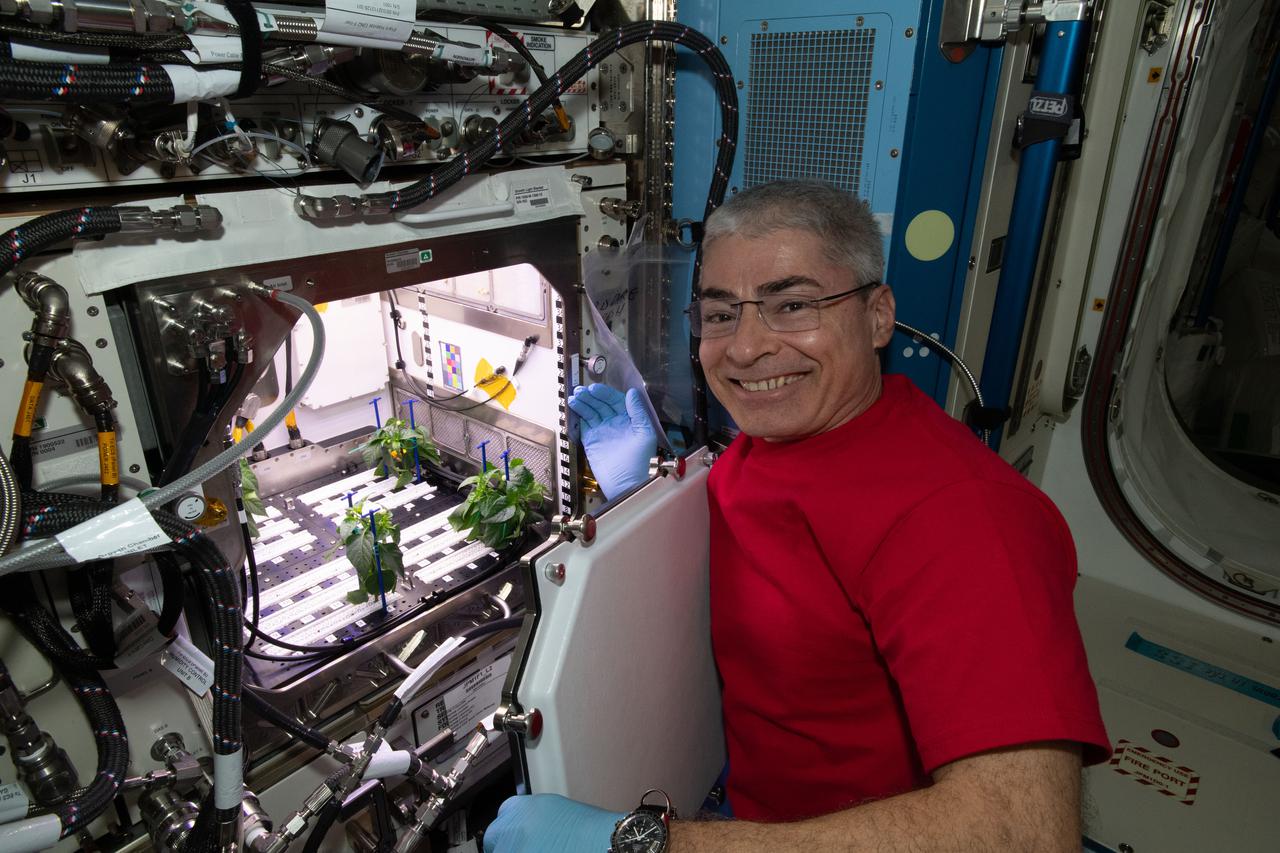

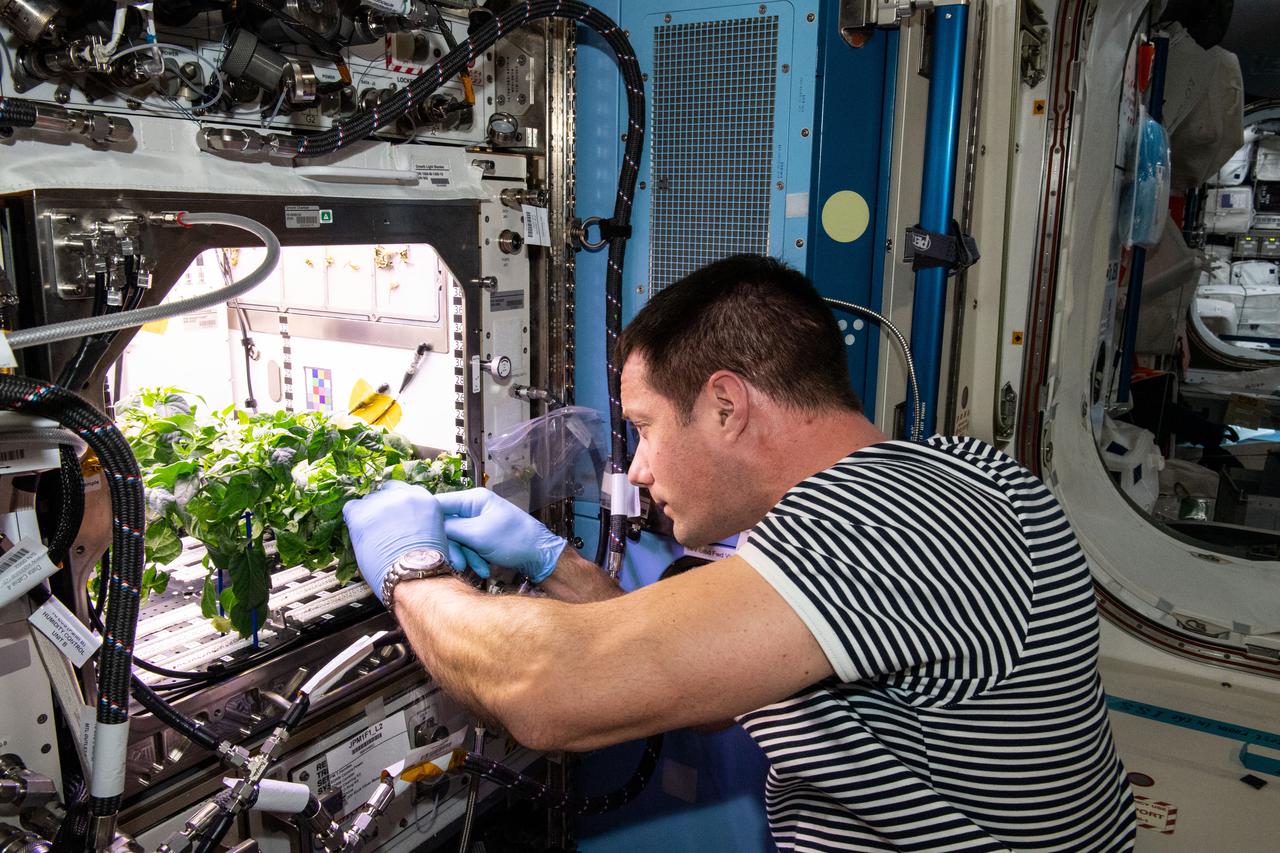
iss065e335291 (Aug. 31, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei cleans up debris in the International Space Station’s Plant Habitat, which is growing Hatch Green chiles for the Plant Habitat-04 space crop experiment.
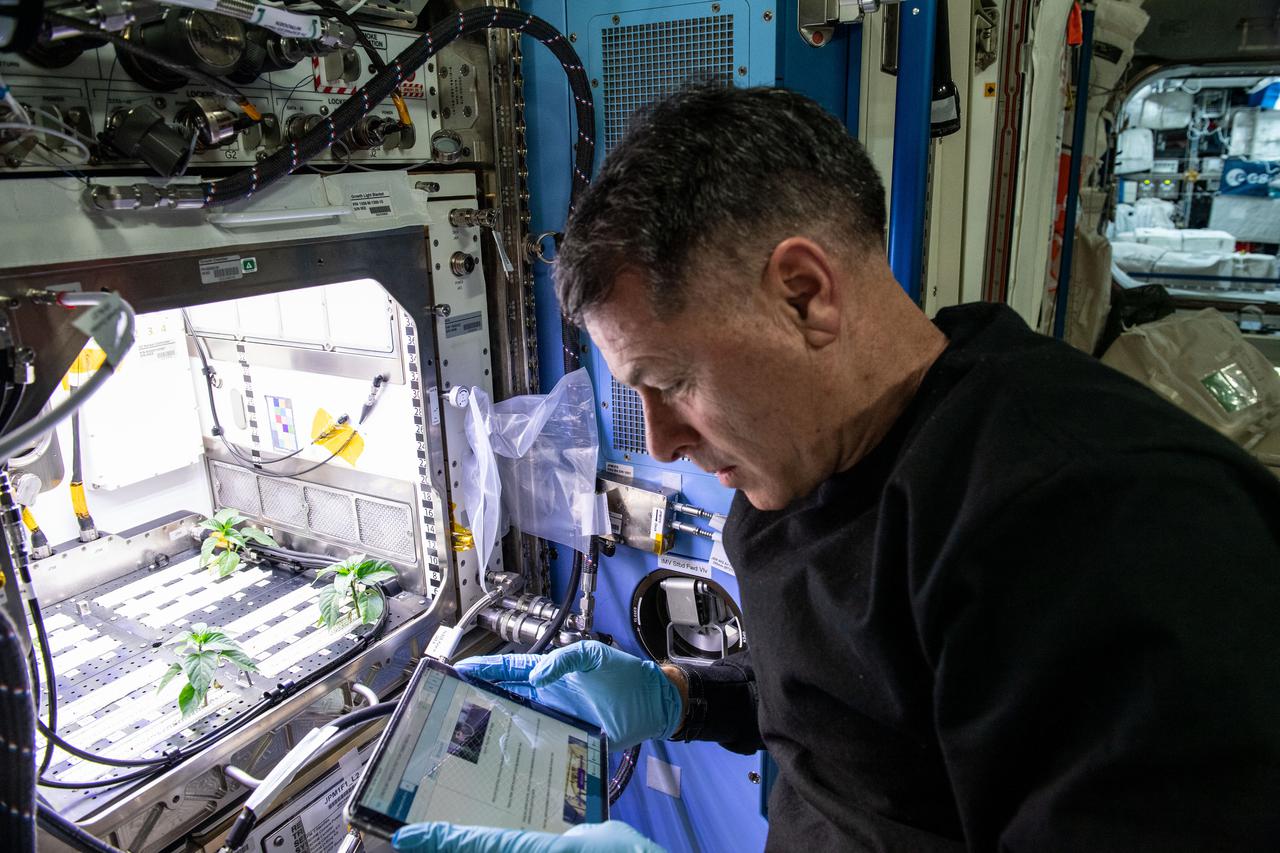

iss065e277585 (Aug. 20, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough cleans up debris around the Kibo laboratory module's Plant Habitat Facility that is growing Hatch chiles for the Plant Habitat-04 experiment.
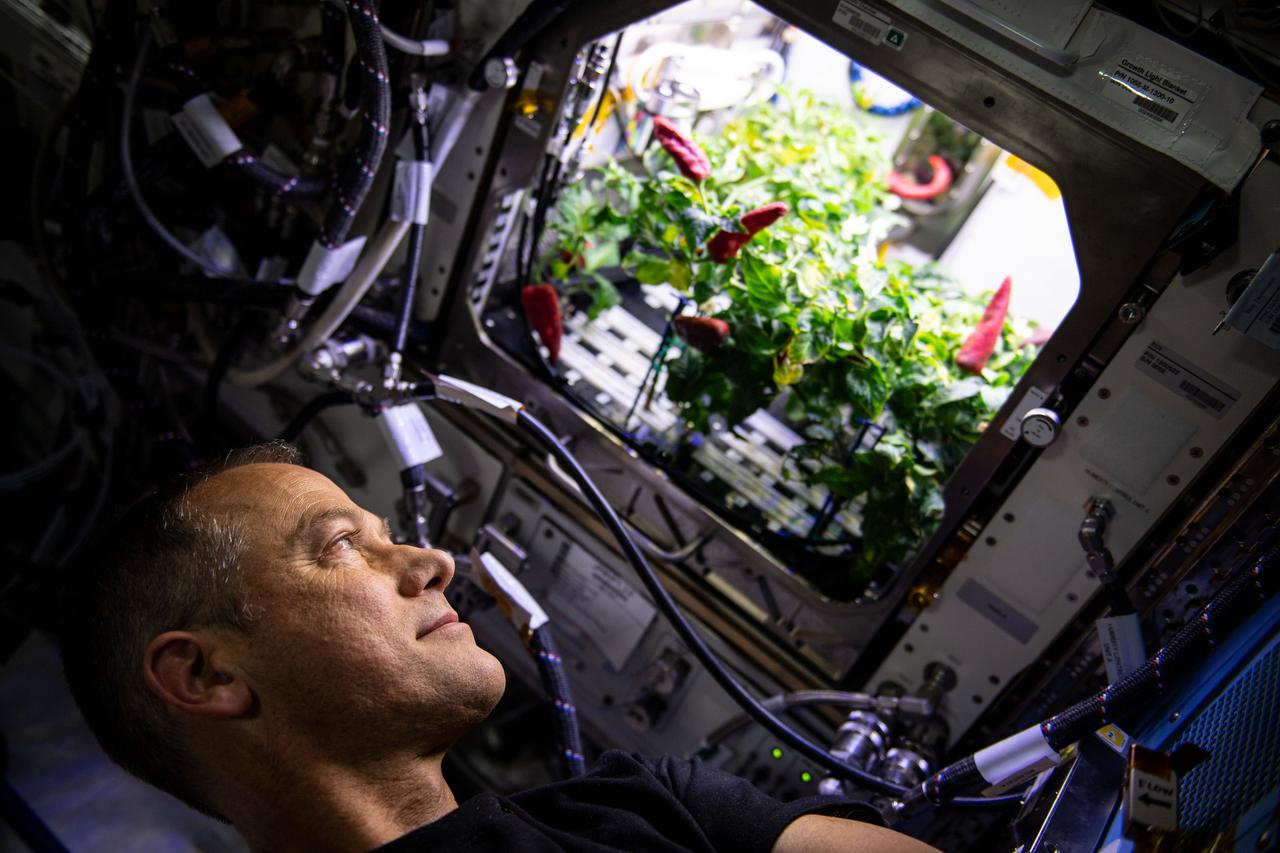

iss066e084306 (Nov. 26, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Thomas Marshburn checks out chile peppers growing inside the International Space Station's Advanced Plant Habitat before they were harvested for the Plant Habitat-04 space botany experiment.
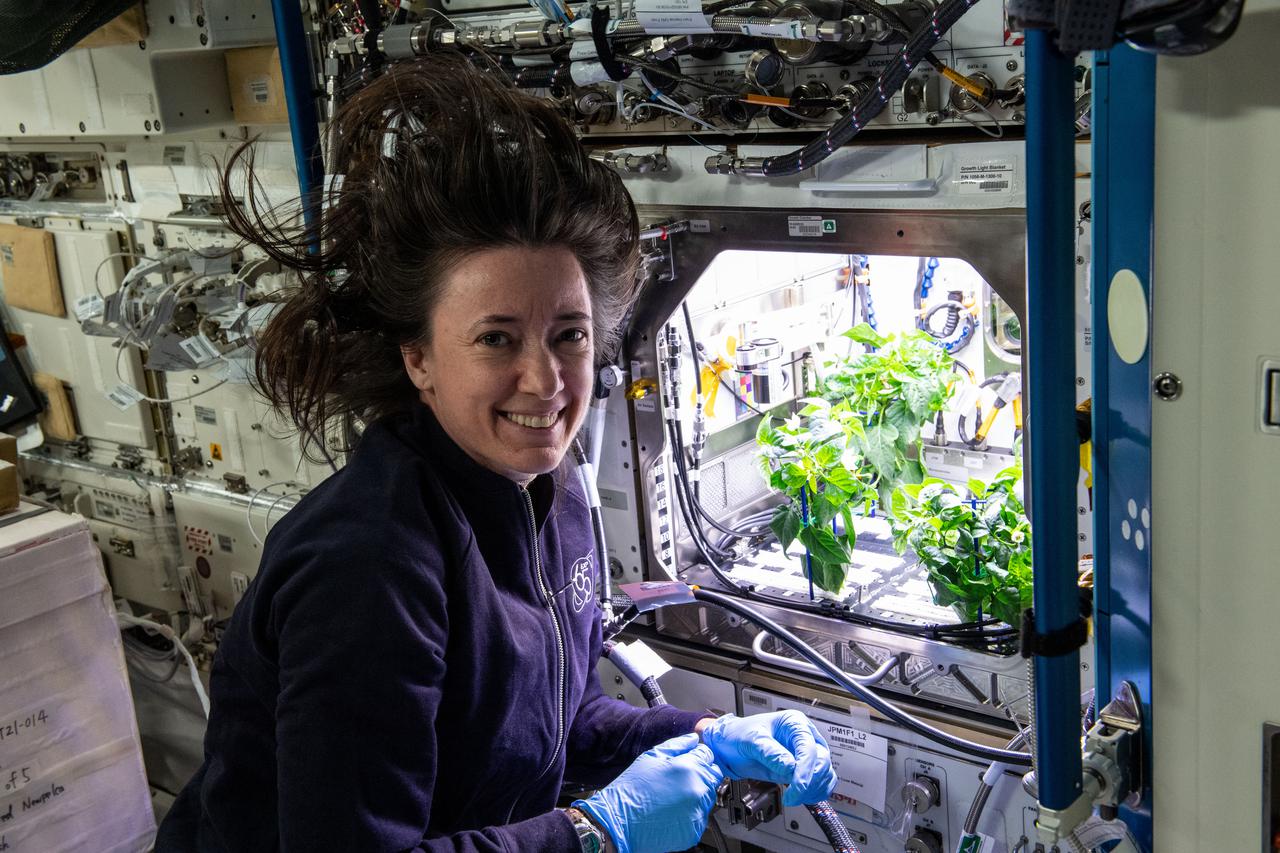

iss065e370568 (Sept. 10, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur cleans up debris in the International Space Station’s Plant Habitat, which is growing Hatch Green chiles for the Plant Habitat-04 space crop experiment.
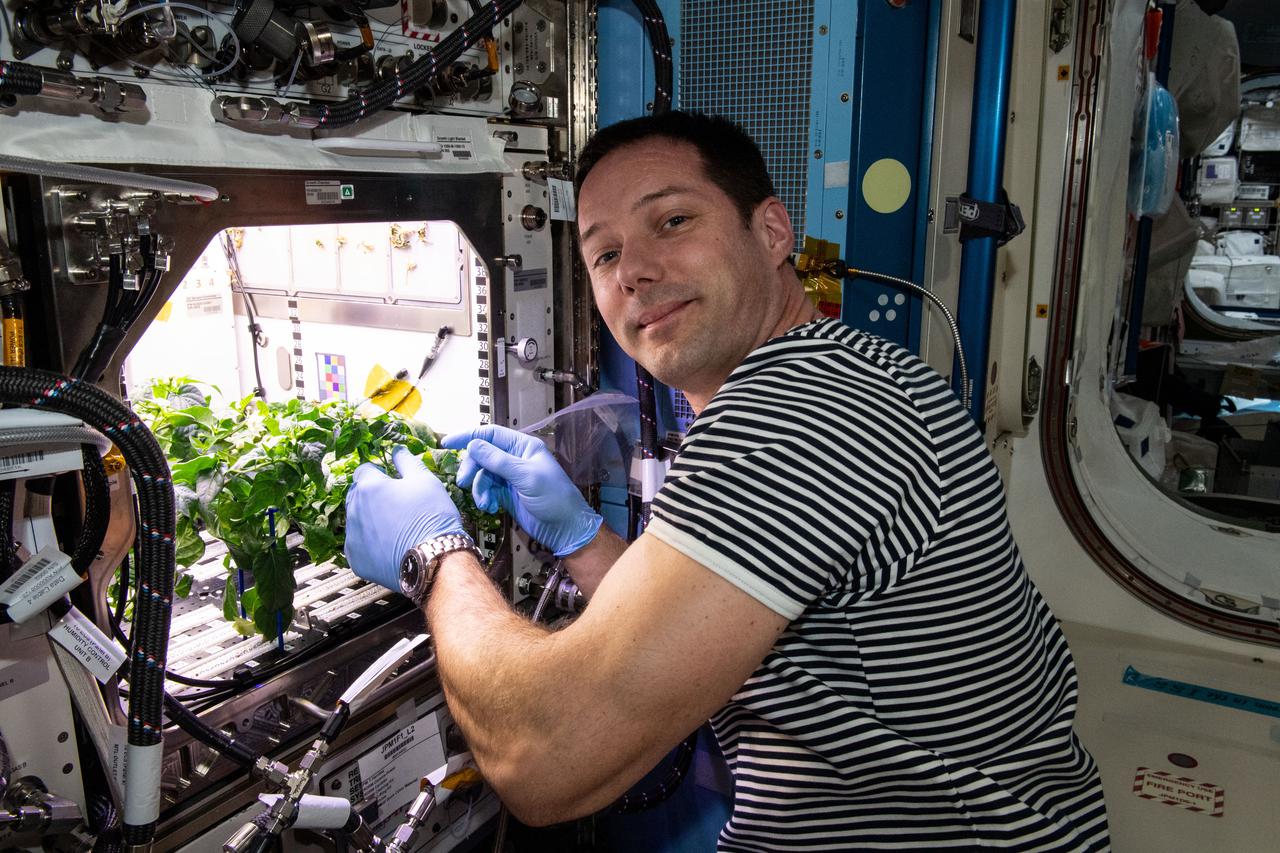

iss065e398603 (9/30/2021) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet cleans up debris in the International Space Station’s Plant Habitat, which is growing Hatch Green chiles for the Plant Habitat-04 space crop experiment.
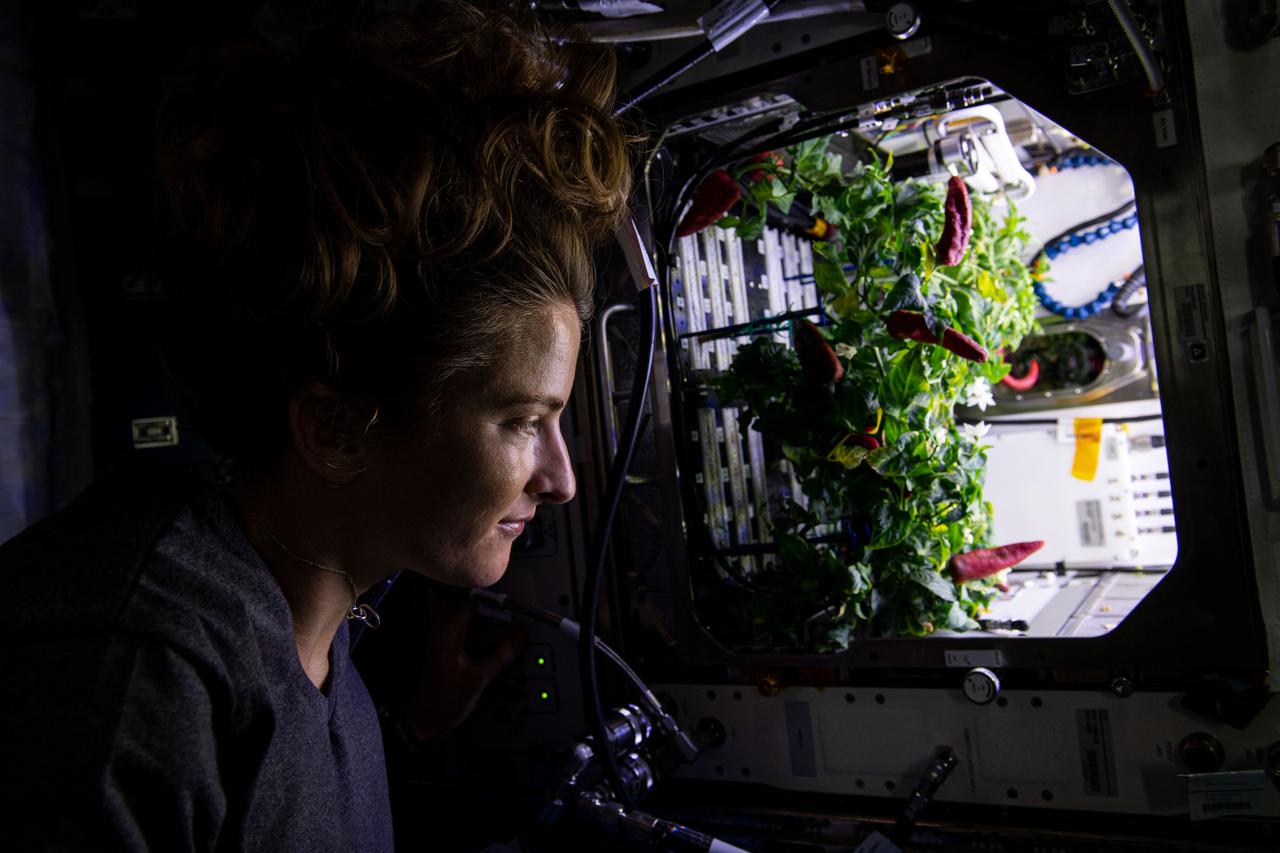

iss066e084293 (Nov. 26, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Kayla Barron checks out chile peppers growing inside the International Space Station's Advanced Plant Habitat before they were harvested for the Plant Habitat-04 space botany experiment.
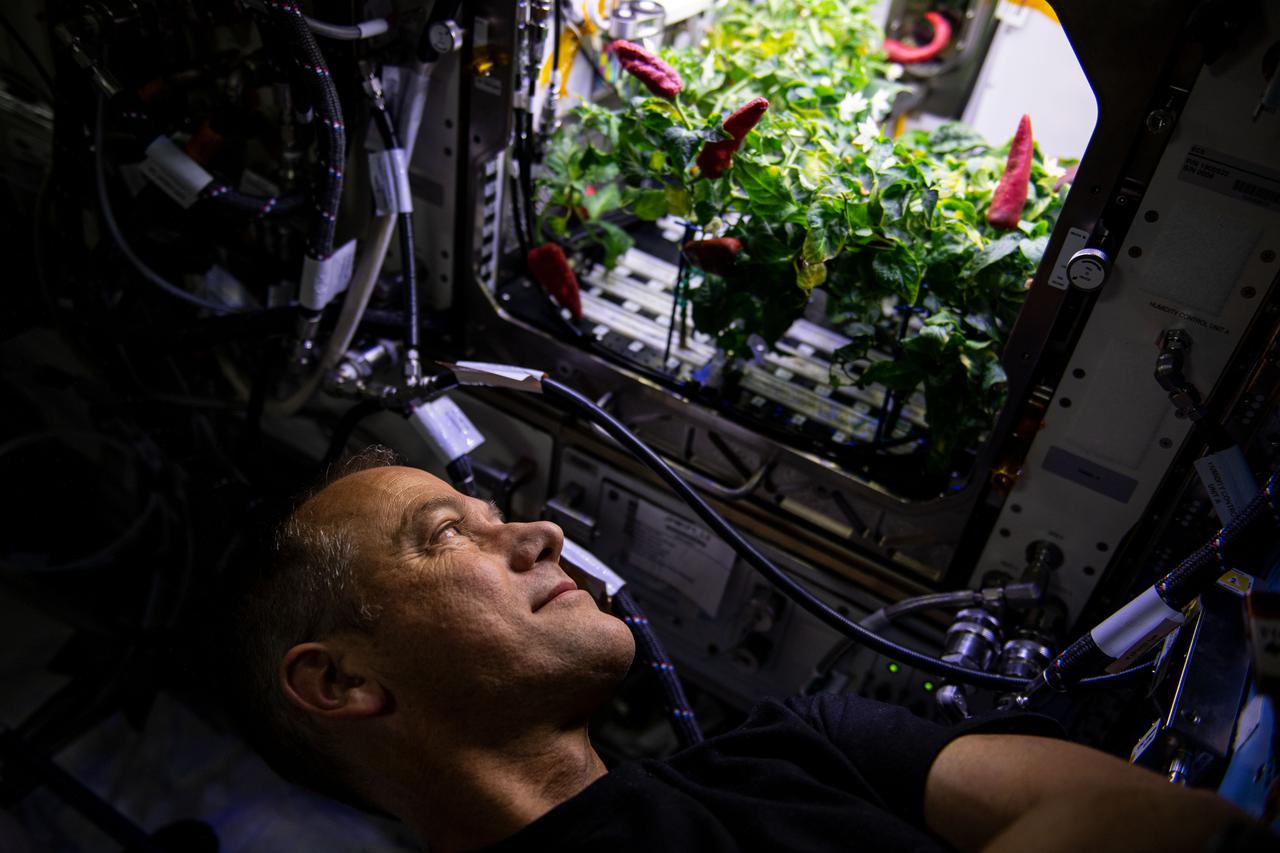

iss066e084304 (November 26, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Crew-3 member Tom Marshburn looks at chiles growing inside of the Advanced Plant Habitat. Crew-3 performed the second harvest of chiles aboard the International Space Station for the Plant Habitat-04 experiment. This plant experiment, one of the station’s most complex to date because of the long germination and growing times, will add to NASA’s knowledge of growing food crops for long-duration space missions.
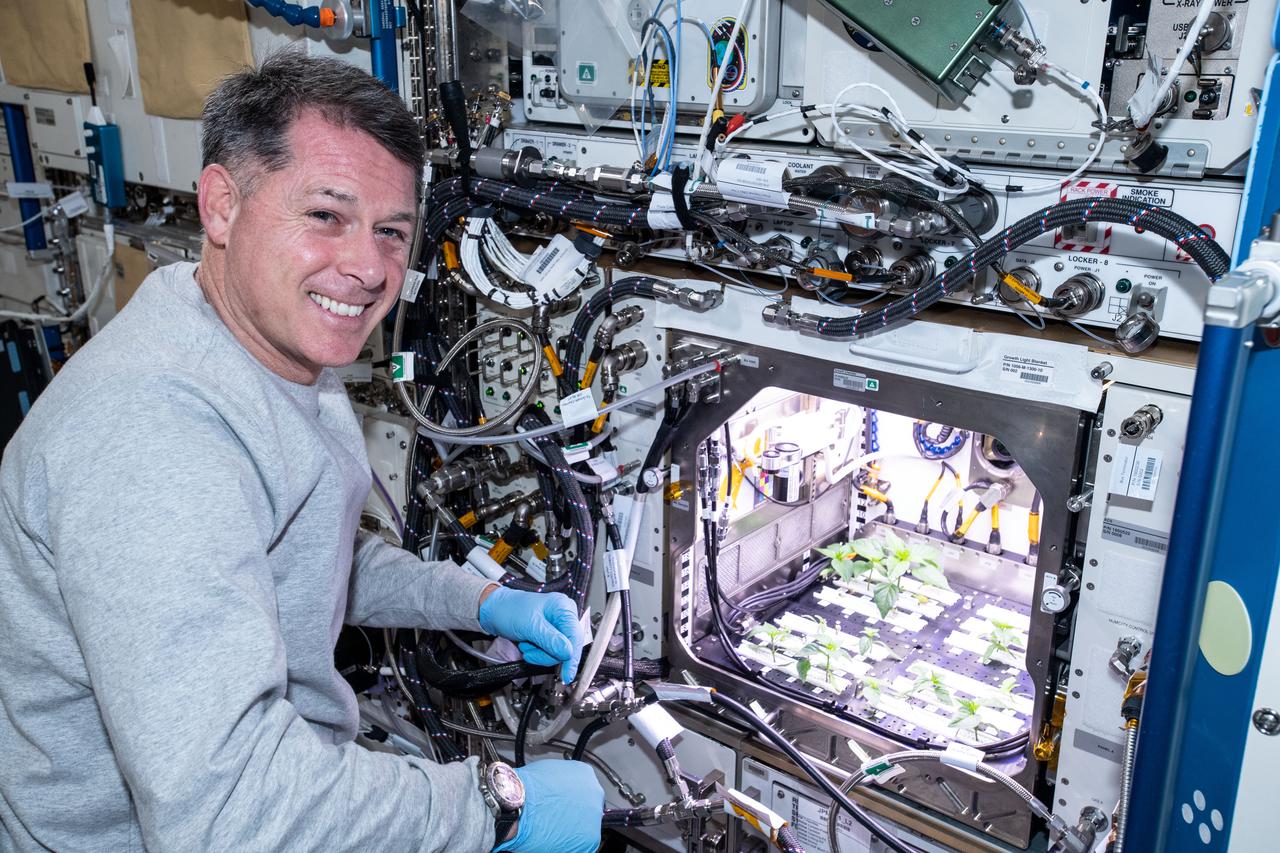

iss065e235375 (Aug. 10, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough checks Hatch chile plants growing for the Advanced Plant Habitat-04 space botany investigation taking place inside the Columbus laboratory module.
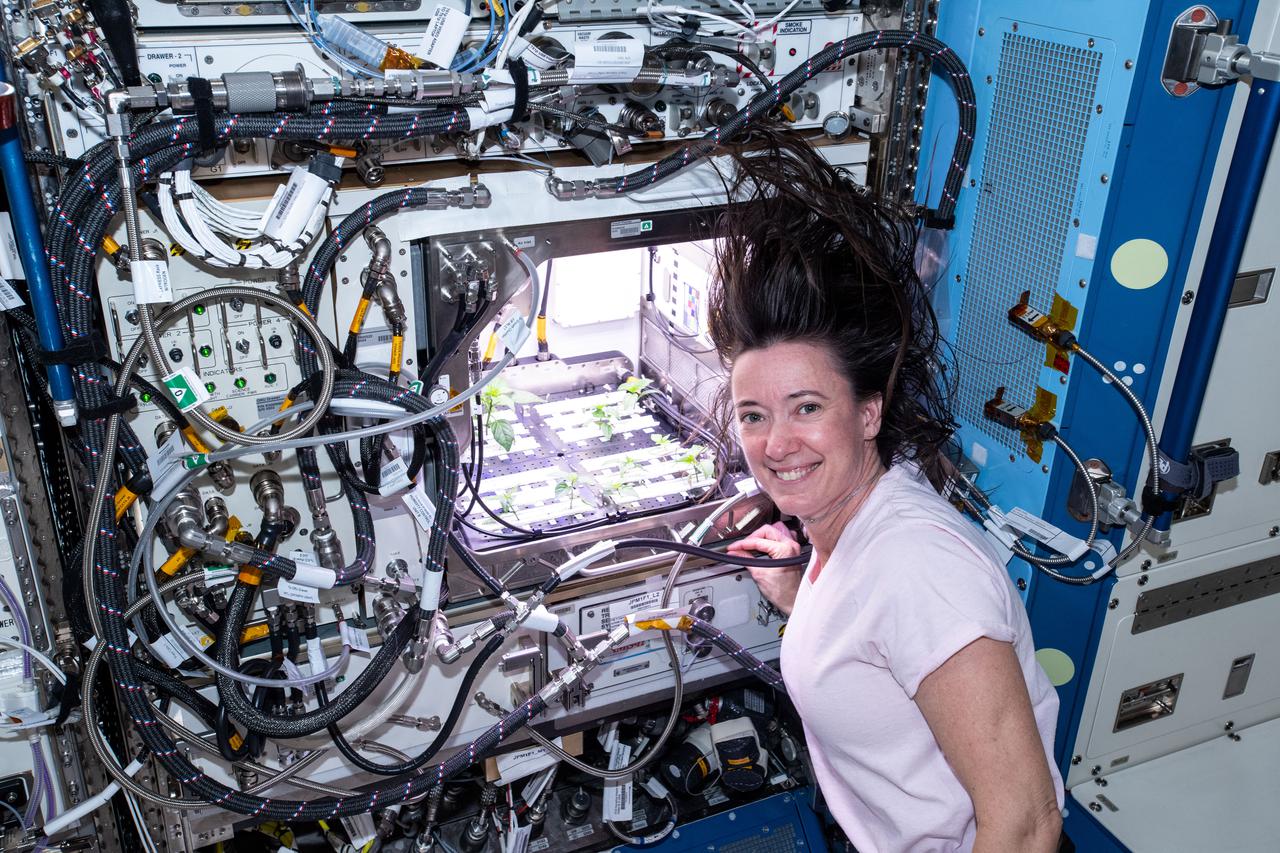

iss065e235377 (Aug. 10, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur checks Hatch chile plants growing for the Advanced Plant Habitat-04 space botany investigation taking place inside the Columbus laboratory module.
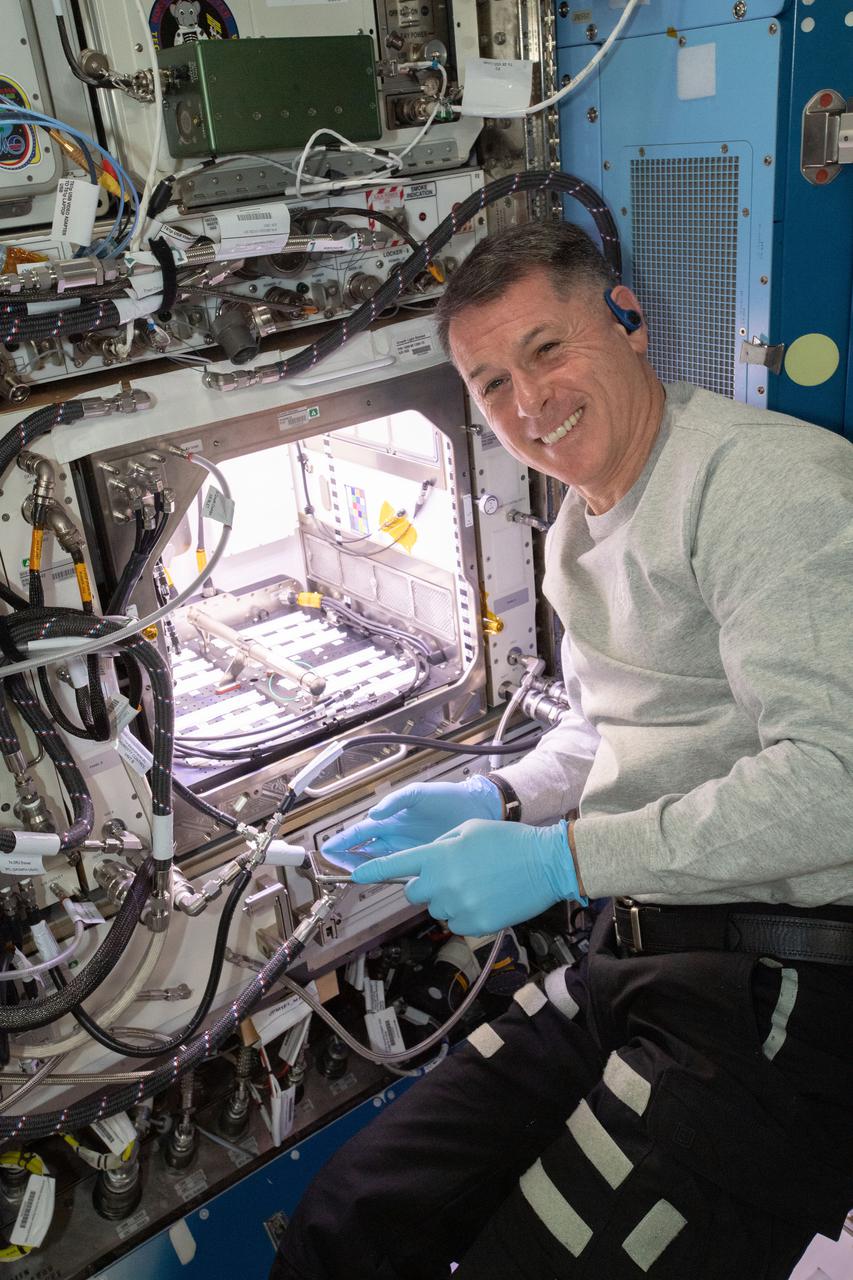

(iss065e163671) July 12, 2021 --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough inserts a device called a science carrier into the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH), which contains 48 Hatch chile pepper seeds NASA started growing on July 12, 2021 as part of the Plant Habitat-04 experiment. Astronauts on station and a team of researchers at Kennedy will work together to monitor the peppers’ growth for about four months before harvesting them. This will be one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbital lab.
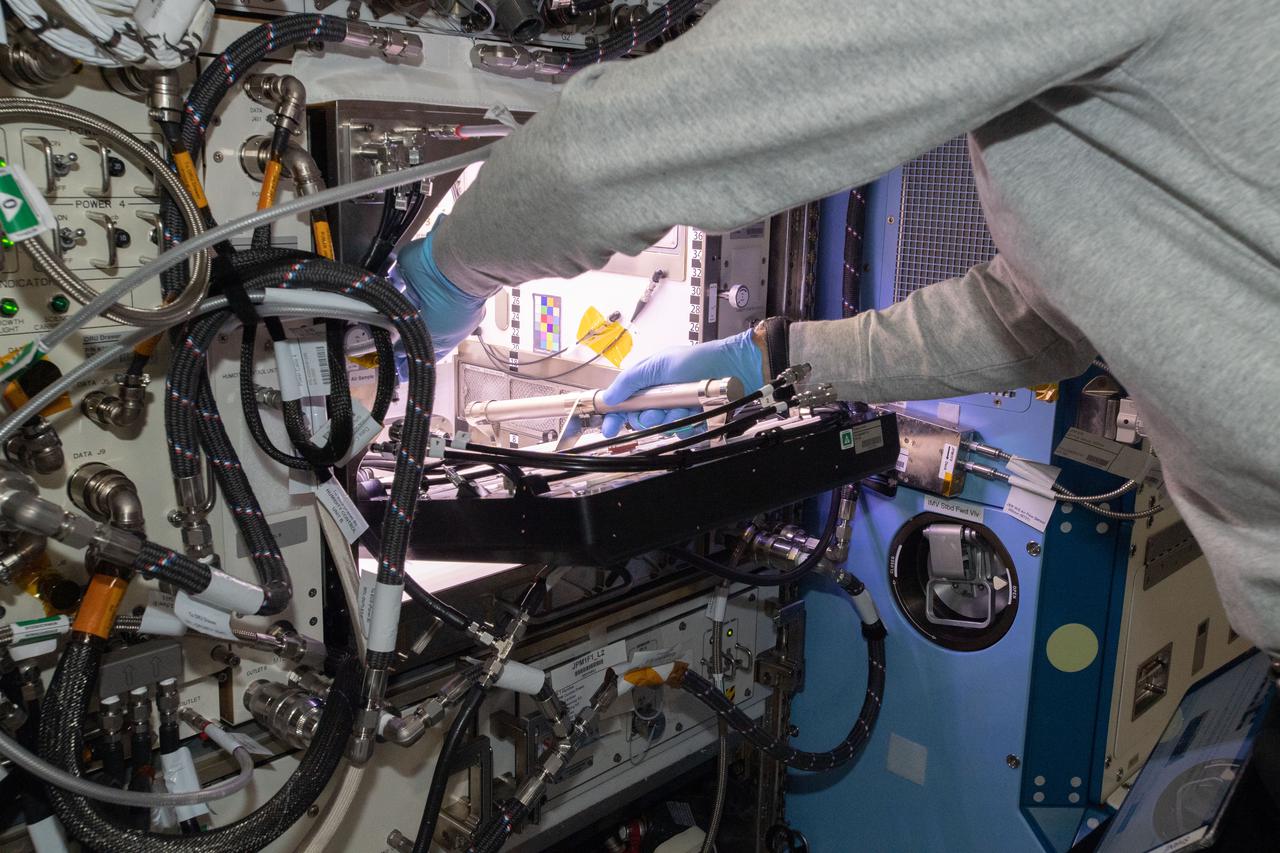

(iss065e163669) July 12, 2021 --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough inserts a device called a science carrier into the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH), which contains 48 Hatch chili pepper seeds NASA started growing on July 12, 2021 as part of the Plant Habitat-04 experiment. Astronauts on station and a team of researchers at Kennedy will work together to monitor the peppers’ growth for about four months before harvesting them. This will be one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbital lab.
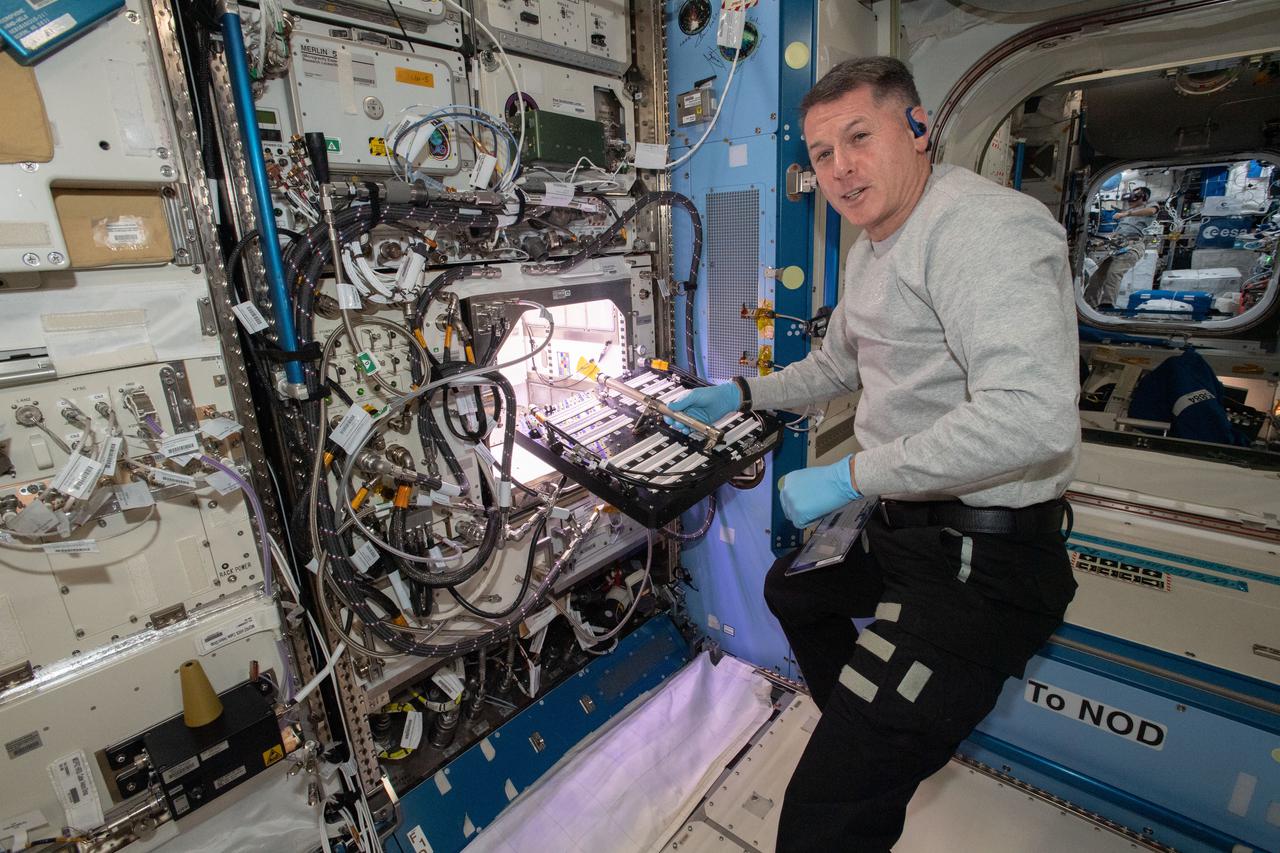

(iss065e163668) July 12, 2021 --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough inserts a device called a science carrier into the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH), which contains 48 Hatch chile pepper seeds NASA started growing on July 12, 2021 as part of the Plant Habitat-04 experiment. Astronauts on station and a team of researchers at Kennedy will work together to monitor the peppers’ growth for about four months before harvesting them. This will be one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbital lab.
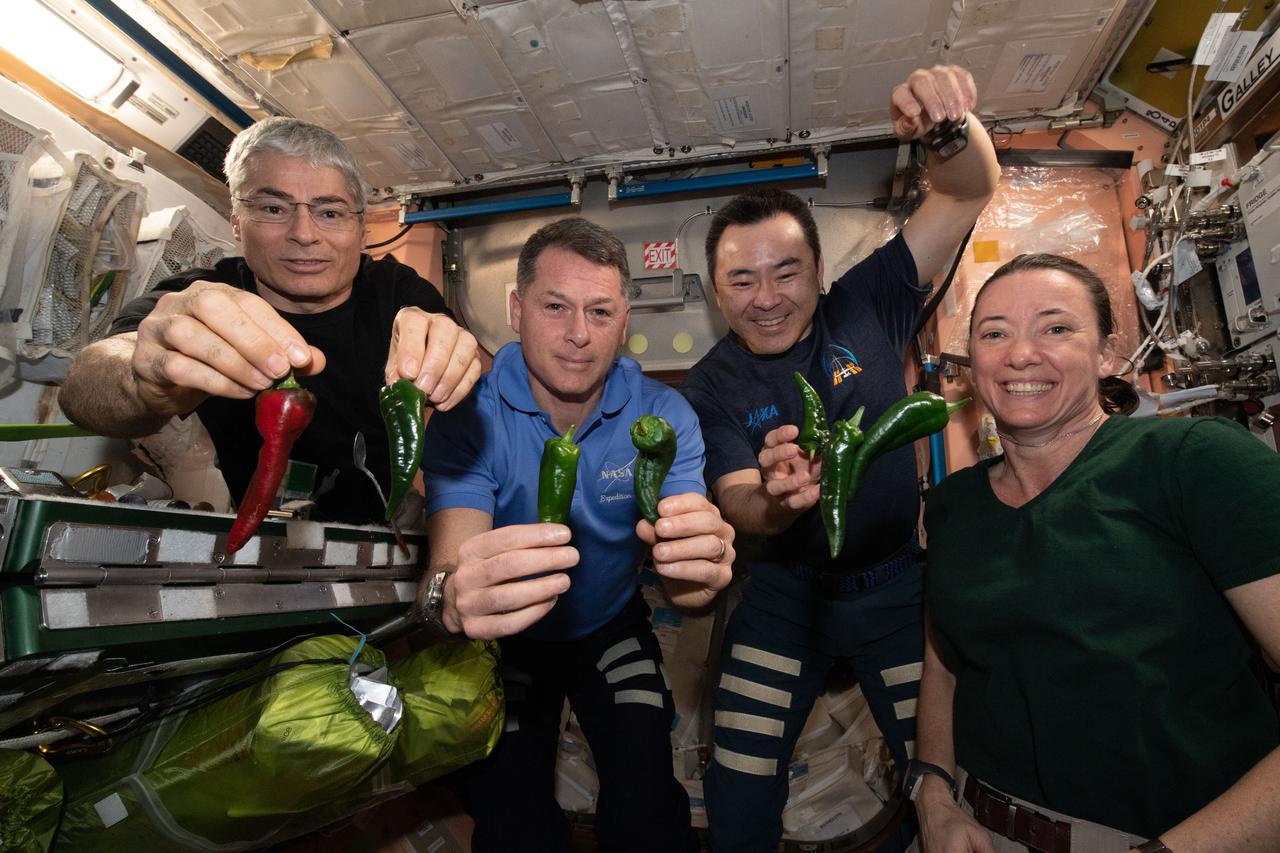

iss066e023255 (Oct. 29, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Flight Engineers (from left) Mark Vande Hei, Shane Kimbrough, Akihiko Hoshide and Megan McArthur, pose with chile peppers grown in space for the first time aboard the International Space Station for the Plant Habitat-04 investigation.
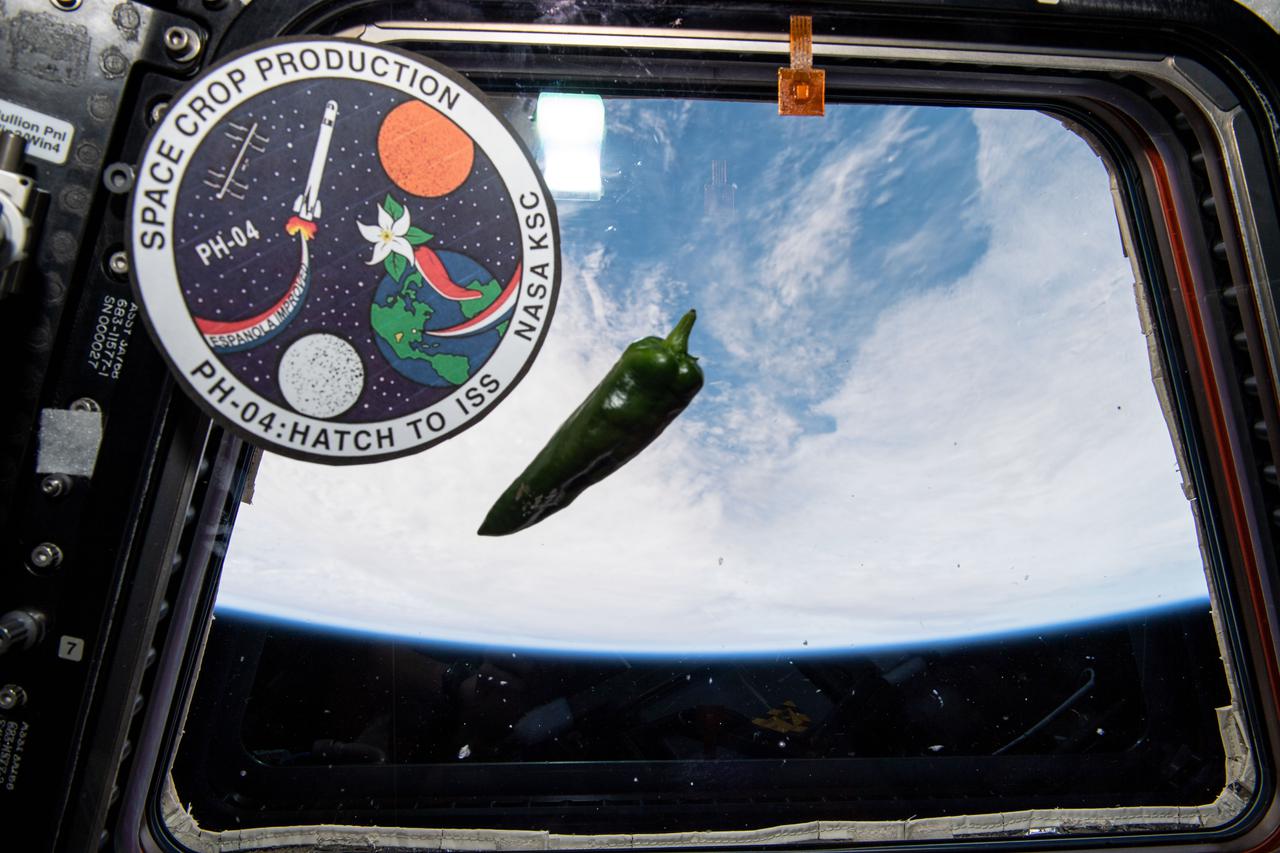

iss066e024210 (Oct. 31, 2021) --- A chile pepper is pictured suspended in weightlessness inside the International Space Station's "window to the world," the seven-windowed cupola. An insignia representing the Plant Habitat-04 investigation that successfully grew chile peppers in space for the first time is depicted next to the pepper.

iss066e023184 (October 29, 2021) -- An astronaut cuts slices of red chile pepper during a taste test of chile peppers grown as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation aboard the International Space Station. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers from the final harvest and their leaves will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.
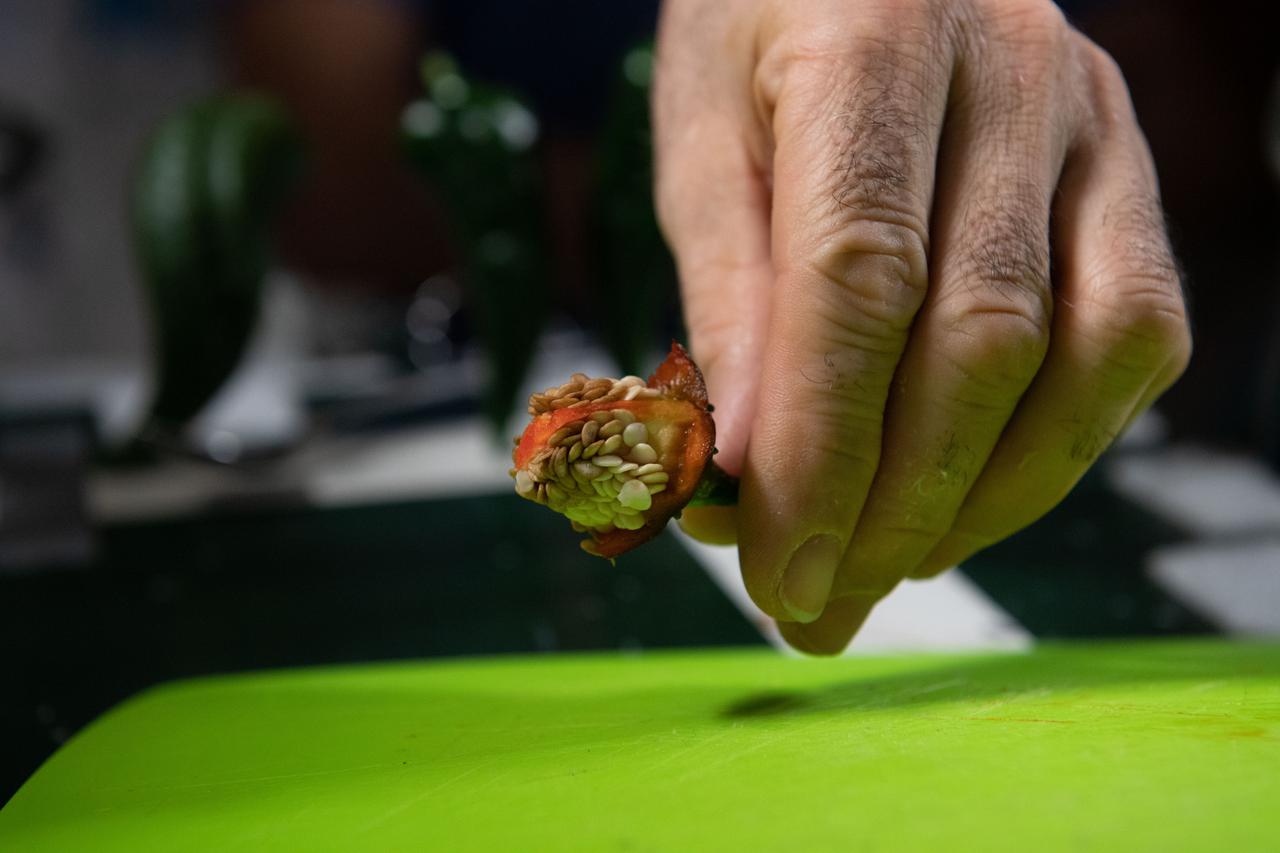

iss066e023185 (October 29, 2021) -- An astronaut cuts slices of red chile pepper during a taste test of chile peppers grown as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation aboard the International Space Station. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers from the final harvest and their leaves will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.
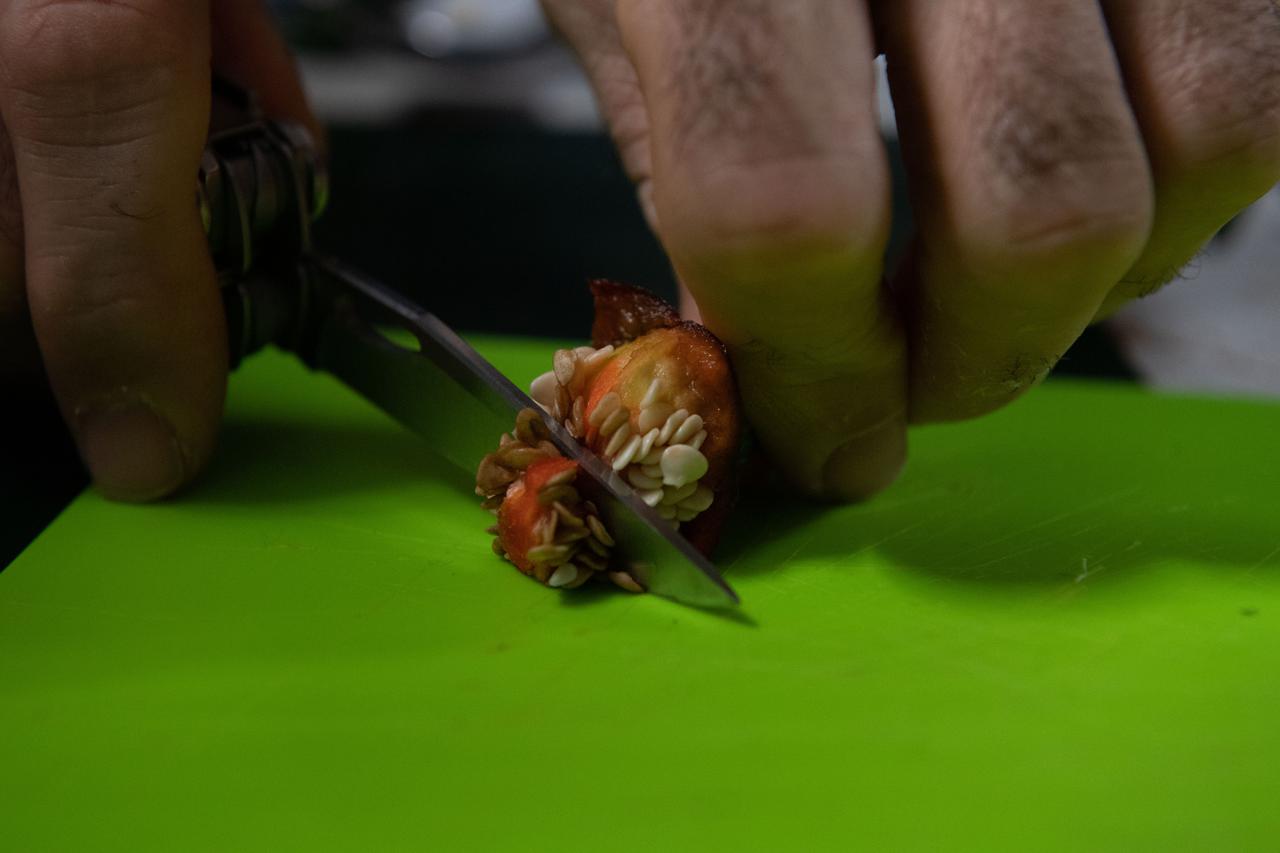

iss066e023187 (October 29, 2021) -- An astronaut cuts slices of red chile pepper during a taste test of chile peppers grown as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation aboard the International Space Station. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers from the final harvest and their leaves will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.
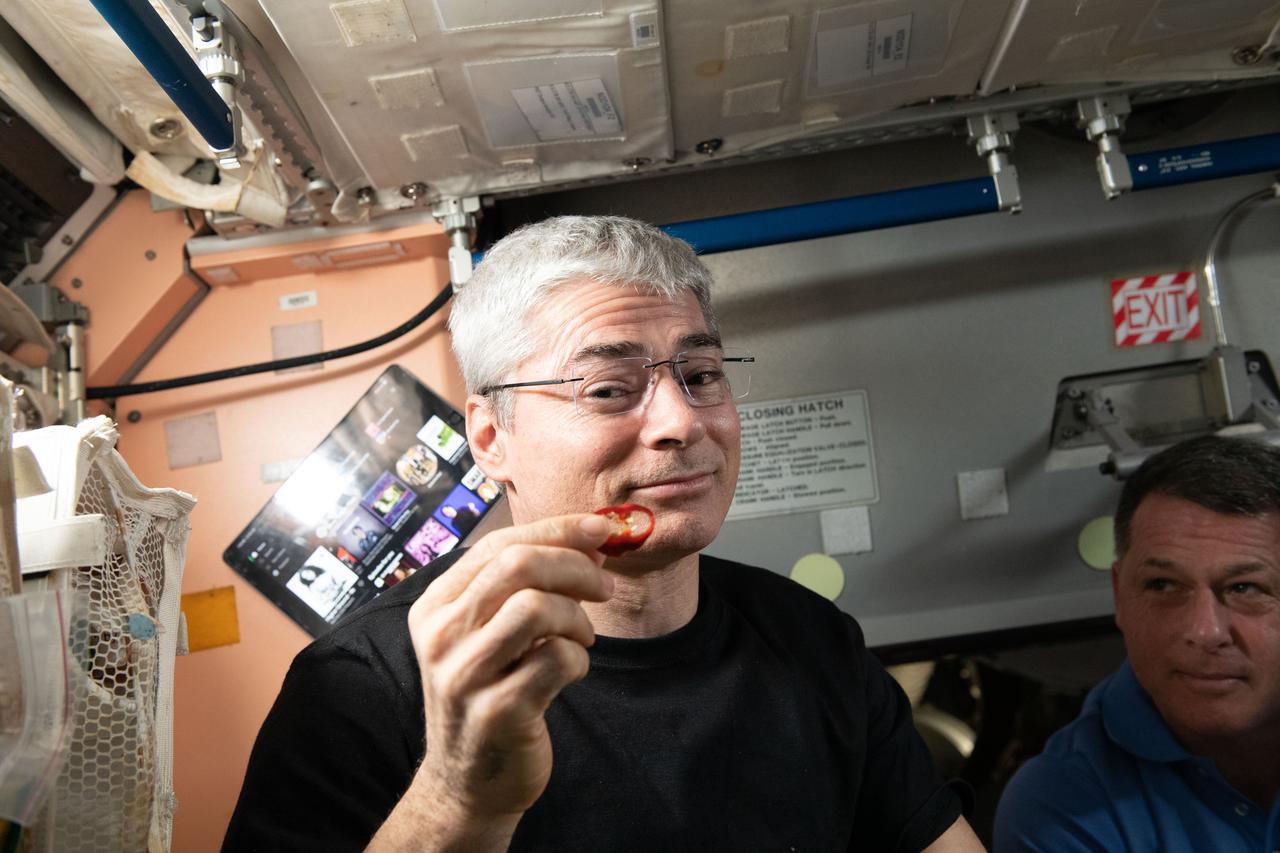
iss066e023179 (October 29, 2021) -- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei samples a red chile pepper grown as part of the Plant Habitat-04 experiment aboard the International Space Station. The chile pepper seeds started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers from the final harvest and their leaves will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.
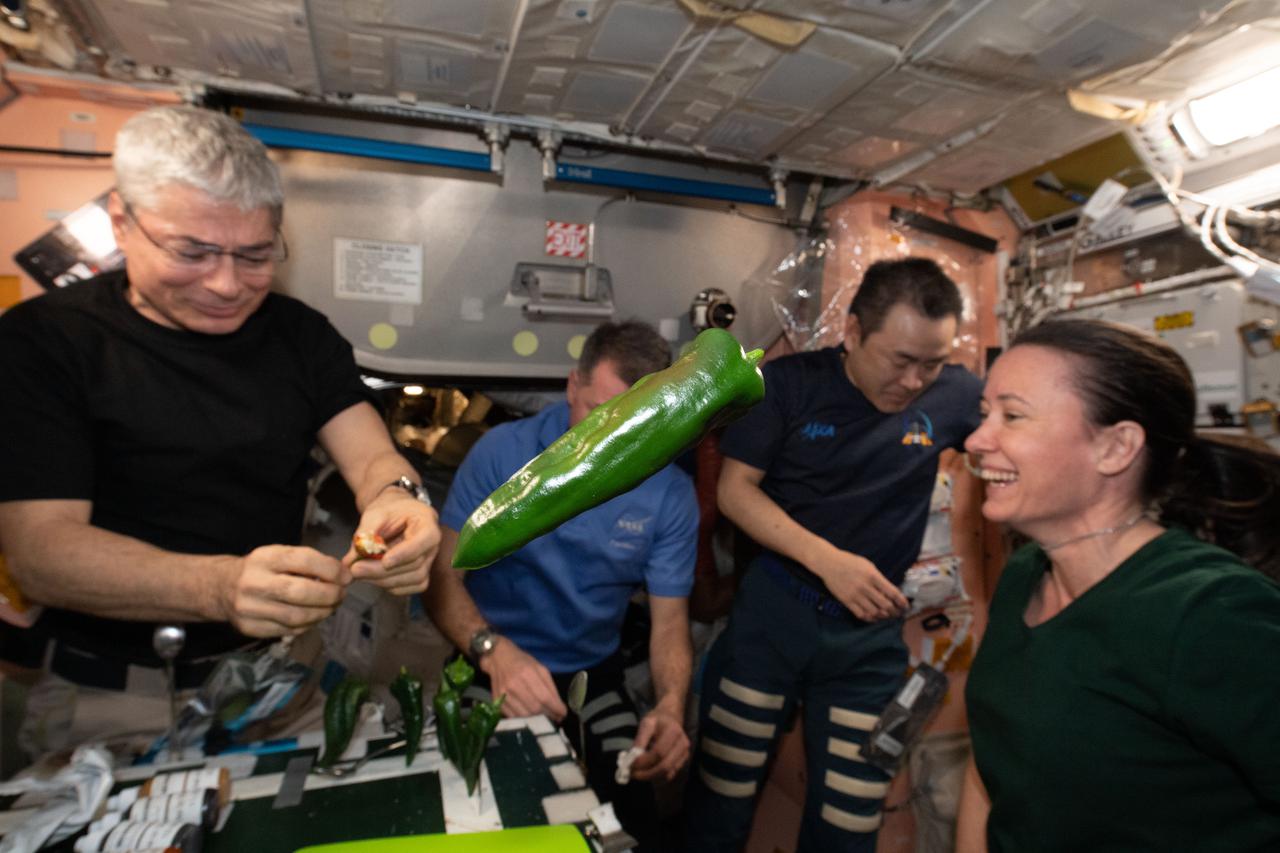

iss066e023272 (October 29, 2021) -- A green chile pepper is seen floating as Expedition 66 crew members conduct a taste test as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation aboard the International Space Station. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 flight engineer Mark Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers and their leaves from the final harvest will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.
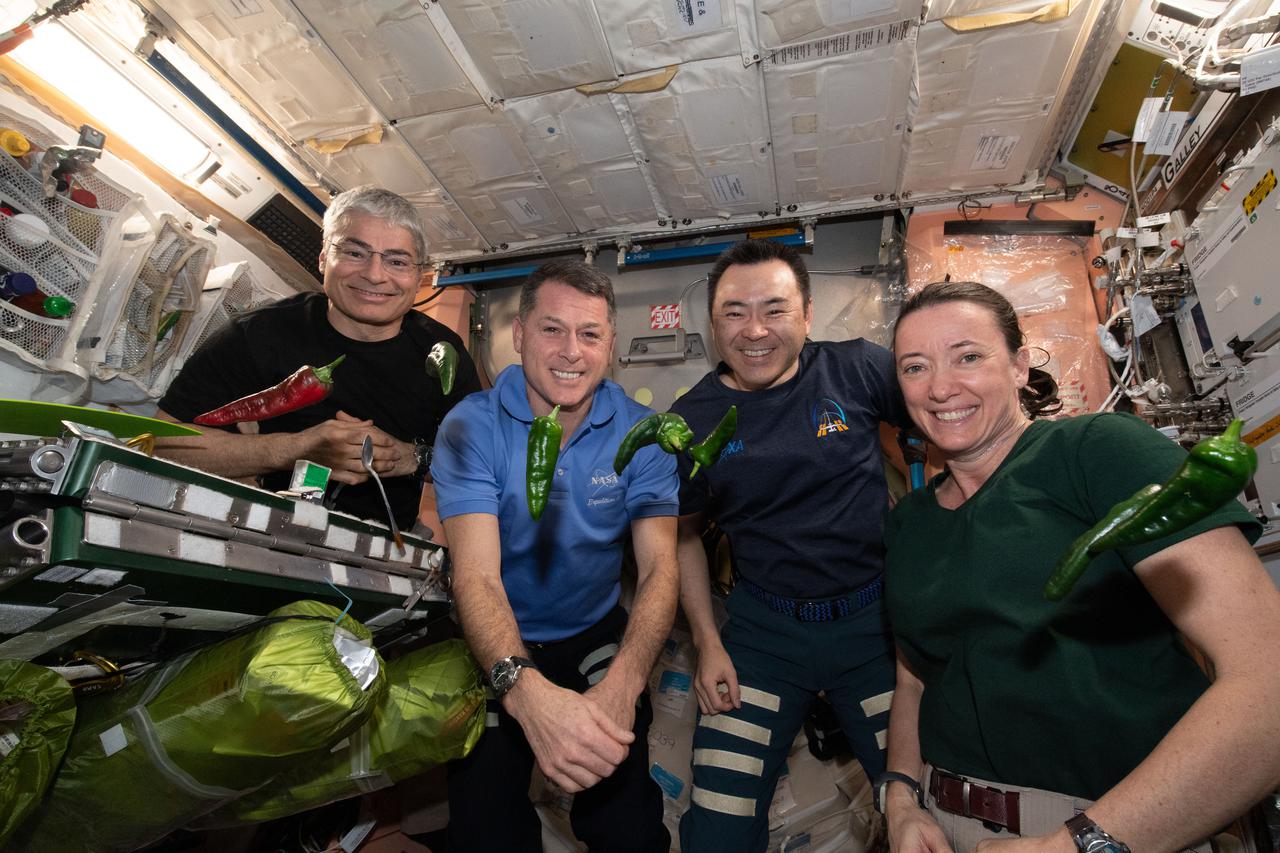

iss066e023260 (October 29, 2021) -- Expedition 66 astronauts are pictured with the first harvest of chile peppers grown aboard the International Space Station as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 flight engineer Mark Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers and their leaves from the final harvest will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration. Pictured, from left, are Expedition 66 flight engineers NASA astronauts Mark Vande Hei and Shane Kimbrough, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration) astronaut Aki Hoshide, and NASA astronaut Megan McArthur.
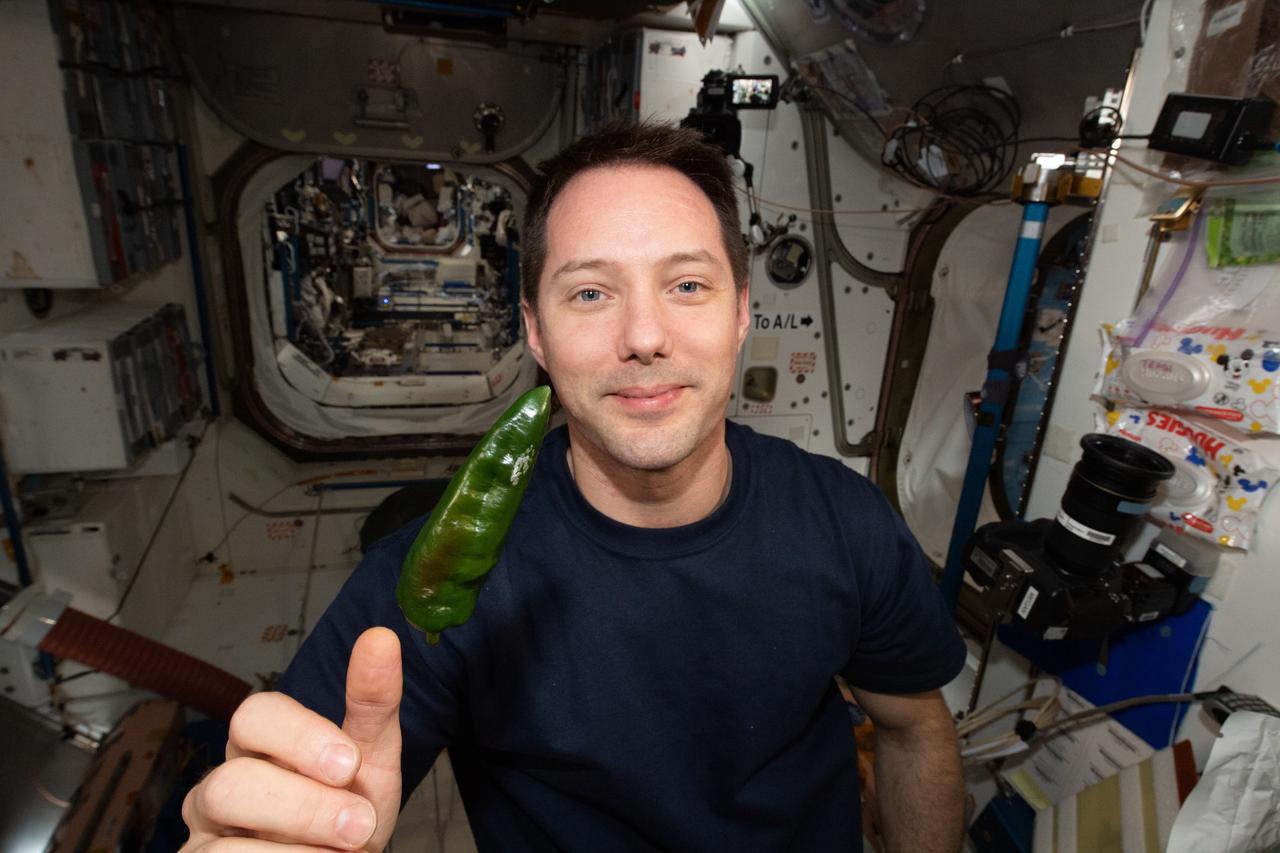

iss066e023273 (October 29, 2021) -- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 66 commander Thomas Pesquet is seen with a green chile pepper during a taste test as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation aboard the International Space Station. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 flight engineer Mark Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers and their leaves from the final harvest will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.
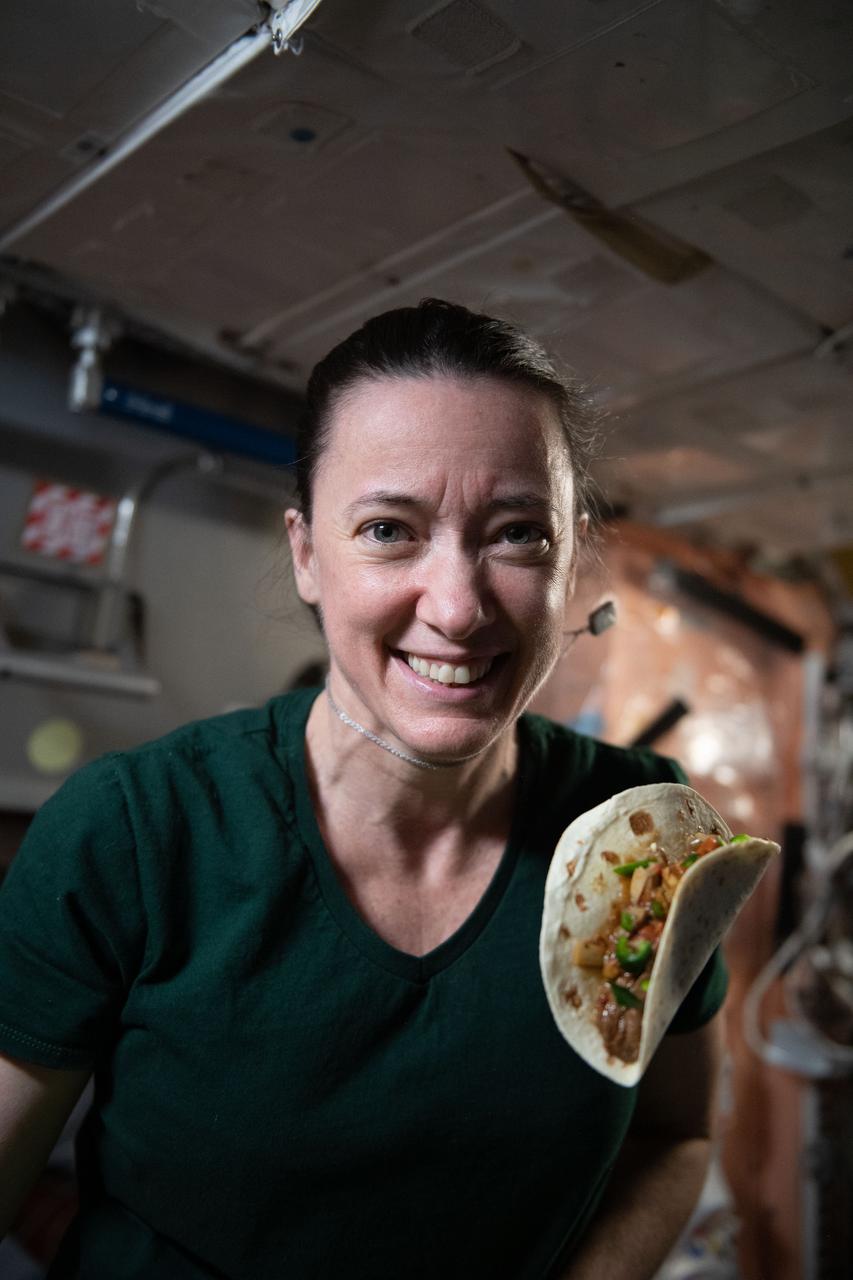

iss066e023198 (October 29, 2021) -- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 flight engineer Megan McArthur is seen with a taco made using fajita beef, rehydrated tomatoes and artichokes, and chile peppers. The chile peppers were grown as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation aboard the International Space Station. The crop started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 flight engineer Mark Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers and their leaves from the final harvest will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.
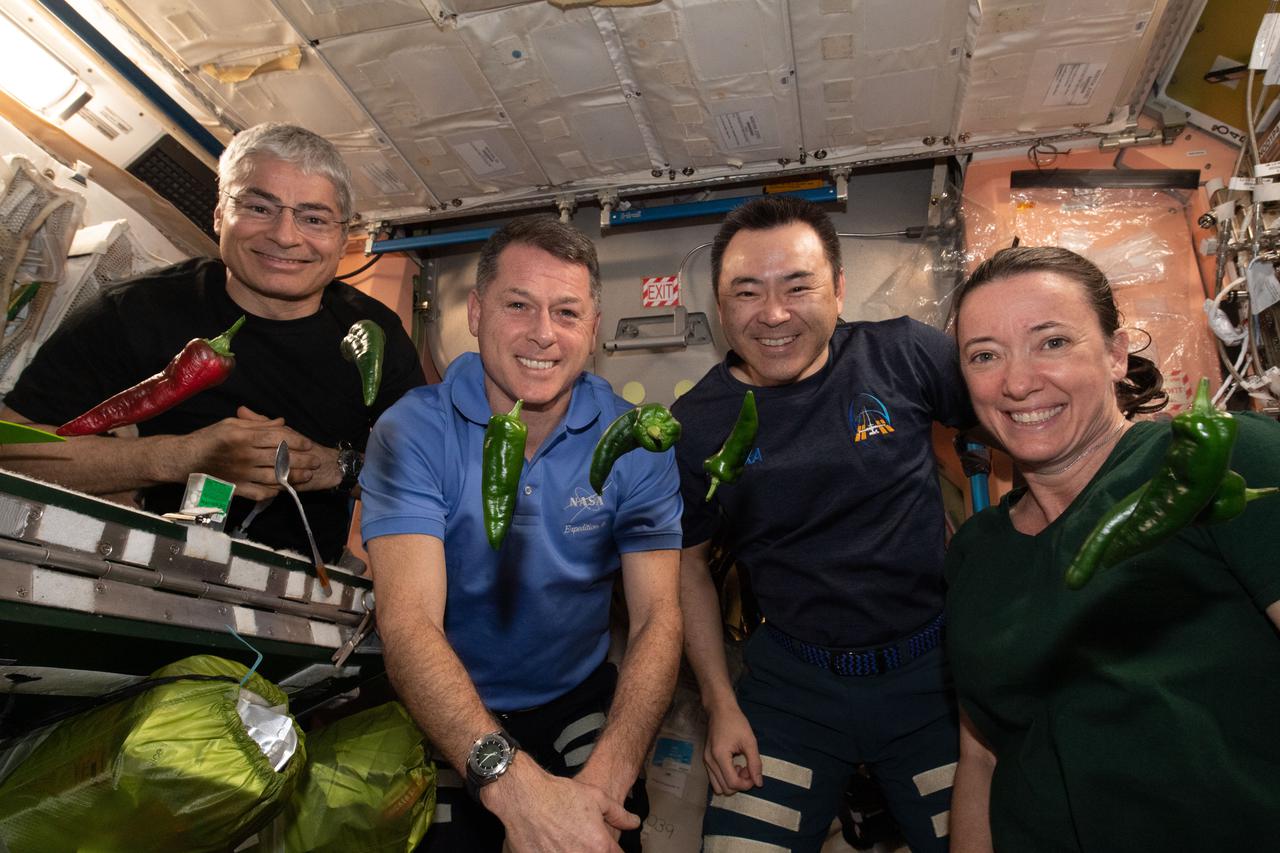

iss066e023259 (October 29, 2021) -- Expedition 66 astronauts are pictured with the first harvest of chile peppers grown aboard the International Space Station as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 flight engineer Mark Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers and their leaves from the final harvest will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration. Pictured, from left, are Expedition 66 flight engineers NASA astronauts Mark Vande Hei and Shane Kimbrough, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration) astronaut Aki Hoshide, and NASA astronaut Megan McArthur.
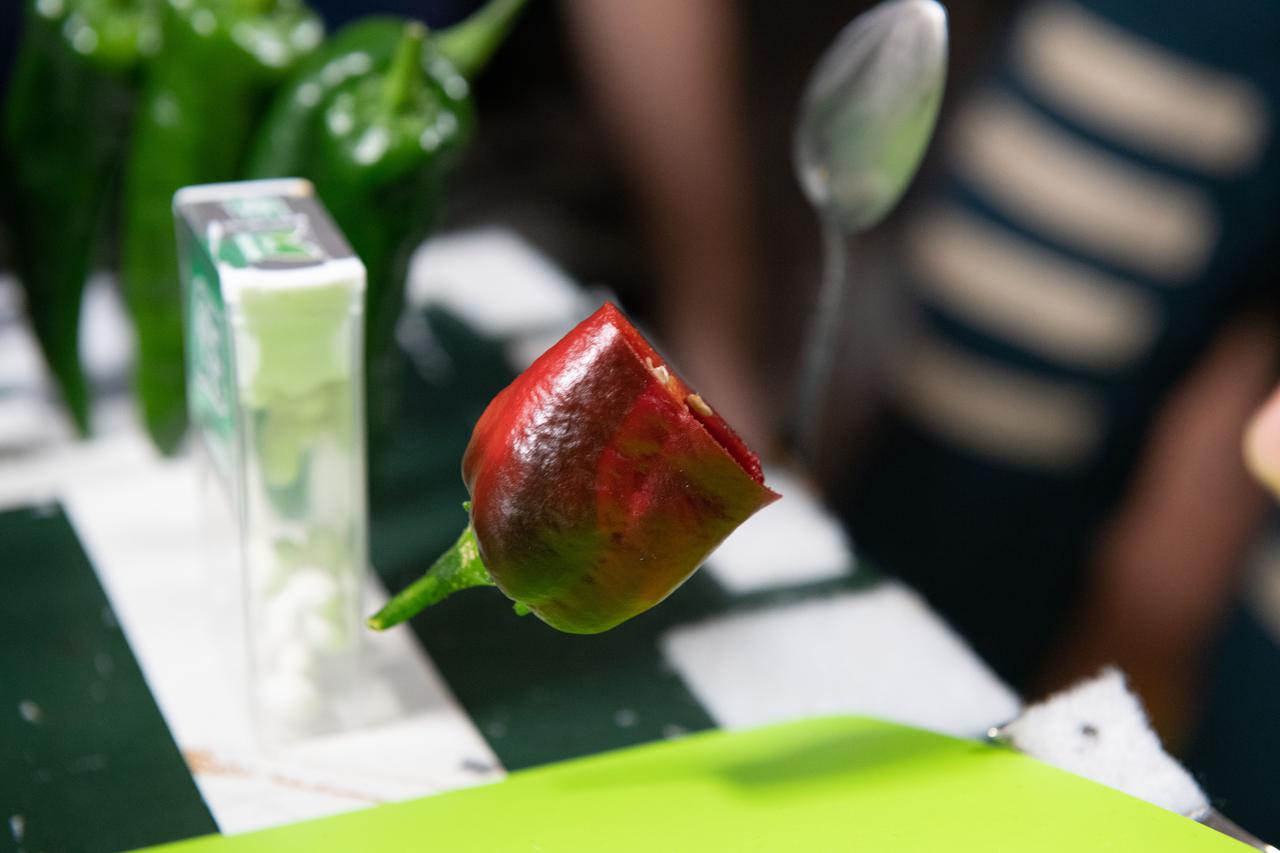

iss066e023165 (October 29, 2021) -- A red chile pepper is seen floating above a cutting board during the tasting of peppers grown as part of the Plant Habitat-04 investigation aboard the International Space Station. The chile peppers started growing on July 12, 2021, and represent one of the longest and most challenging plant experiments attempted aboard the orbiting laboratory. NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 flight engineer Mark Vande Hei conducted the first harvest of the pepper crop on October 29, 2021. Crew members sanitized the peppers and completed a scientific survey after their taste test. The Crew-3 astronauts will take over the crop when they arrive at the orbiting laboratory, and will conduct a final harvest of the peppers in late November. They will also sanitize and sample the crop, and complete surveys. Some peppers and their leaves from the final harvest will return to Earth for further analysis. What we learn will inform future crop growth and food supplementation activities for deep space exploration.