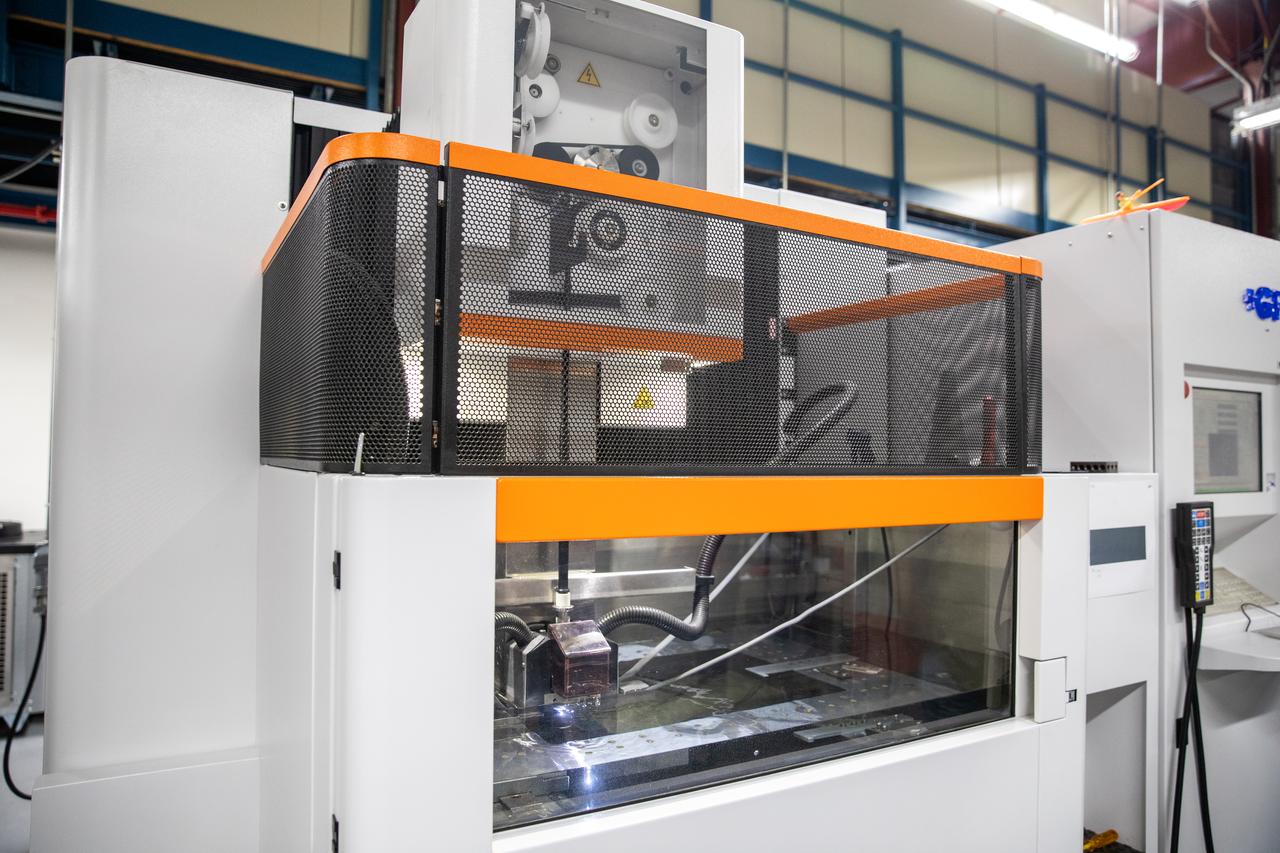

Testing of the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiment is underway inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a ten percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
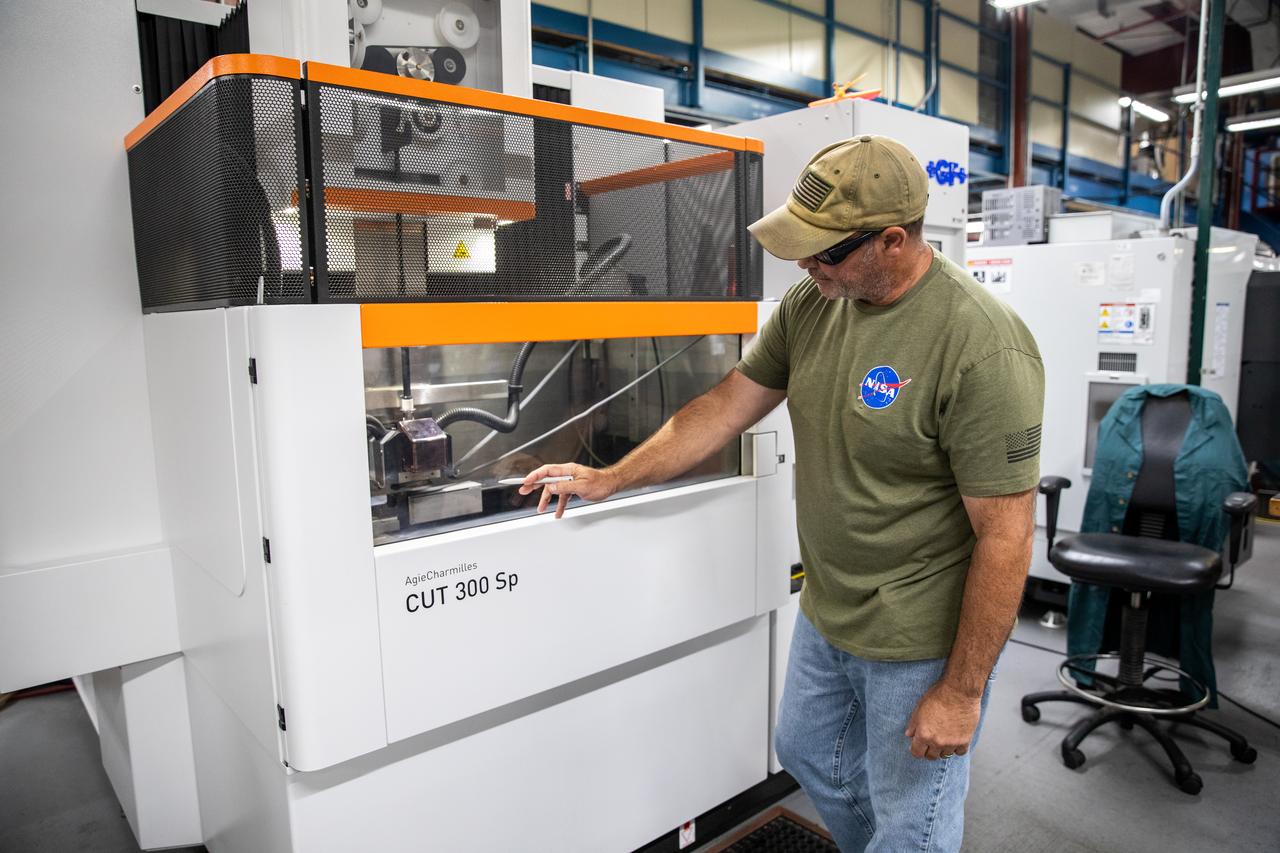

Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician with NASA, prepares the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) specimens for testing inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
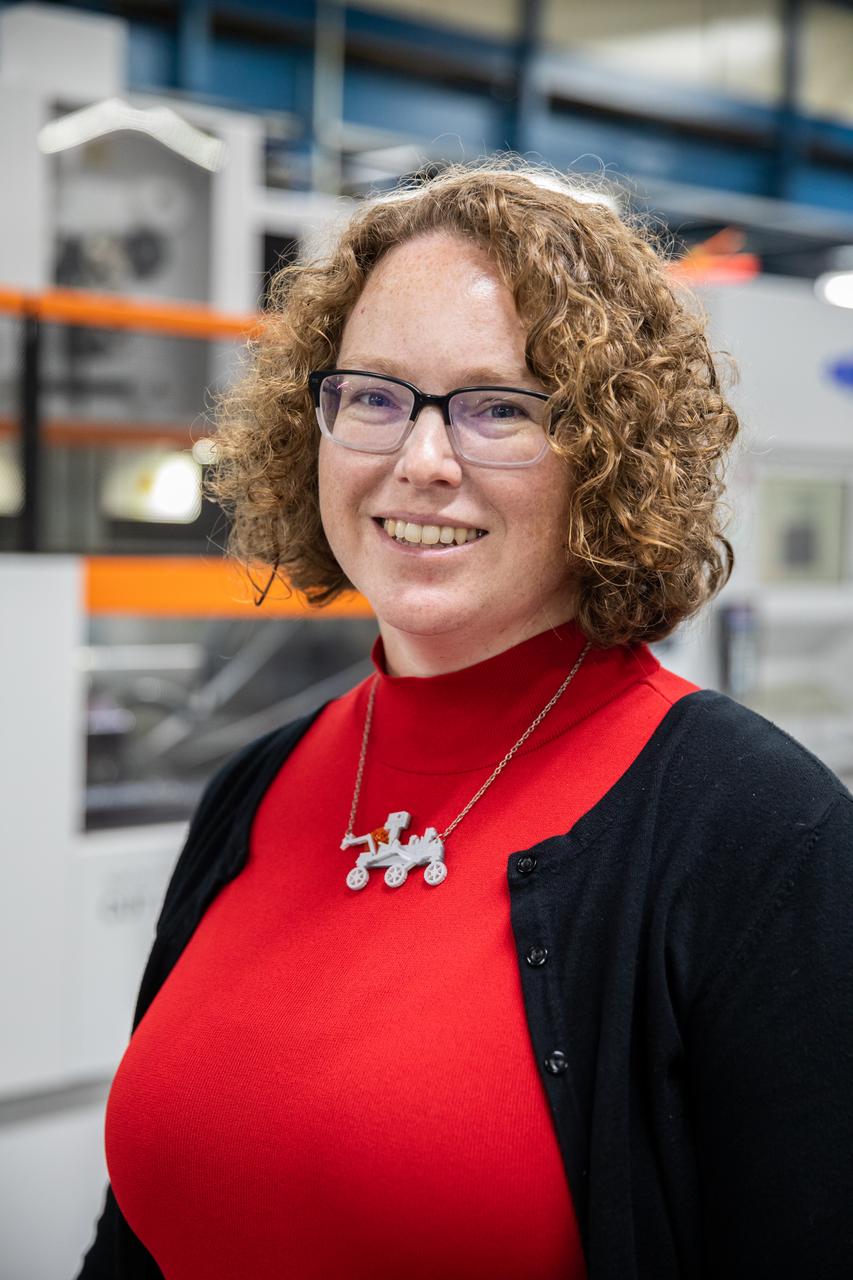

Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, is inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to begin testing on the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied to spacecraft and launch vehicles.
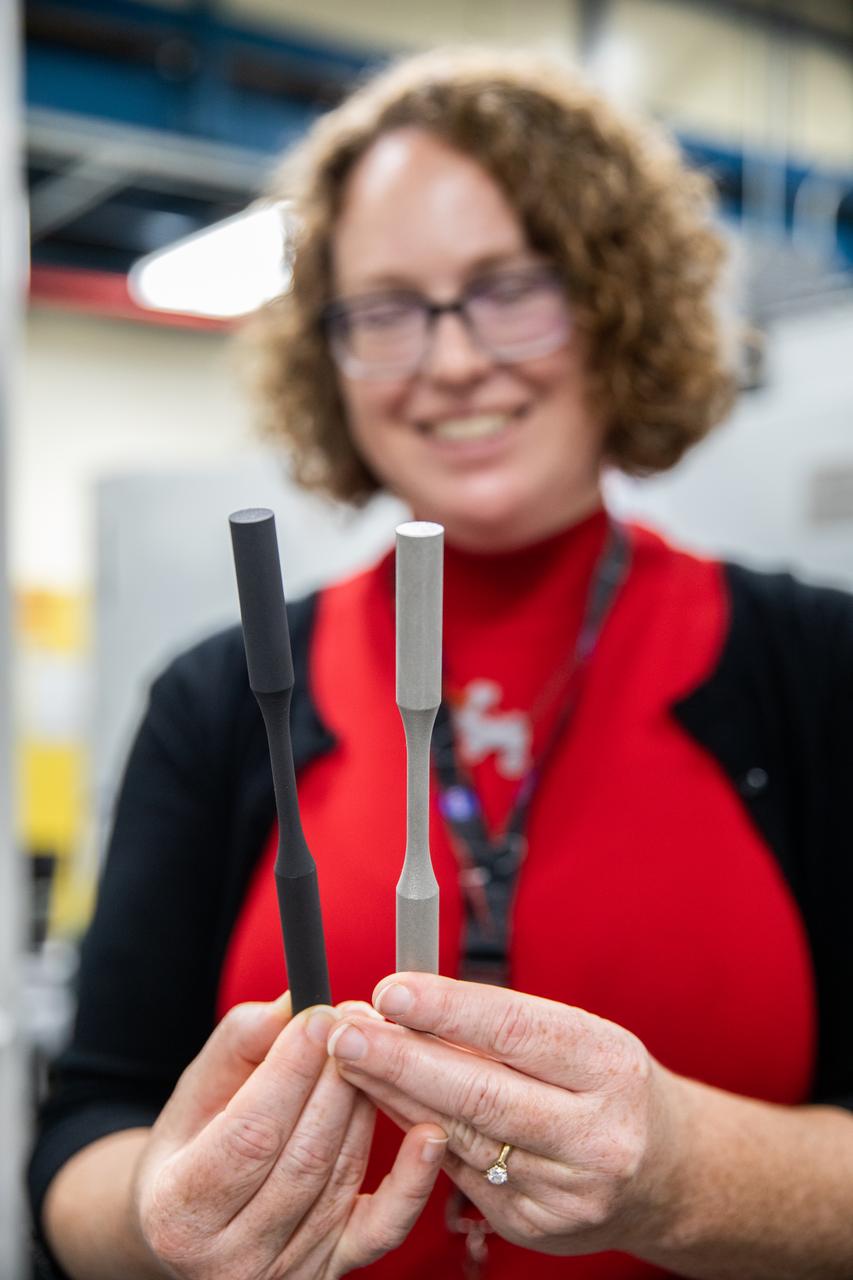

Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, displays two fatigue samples that will be tested in the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiments inside the Prototype Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied to spacecraft and launch vehicles.
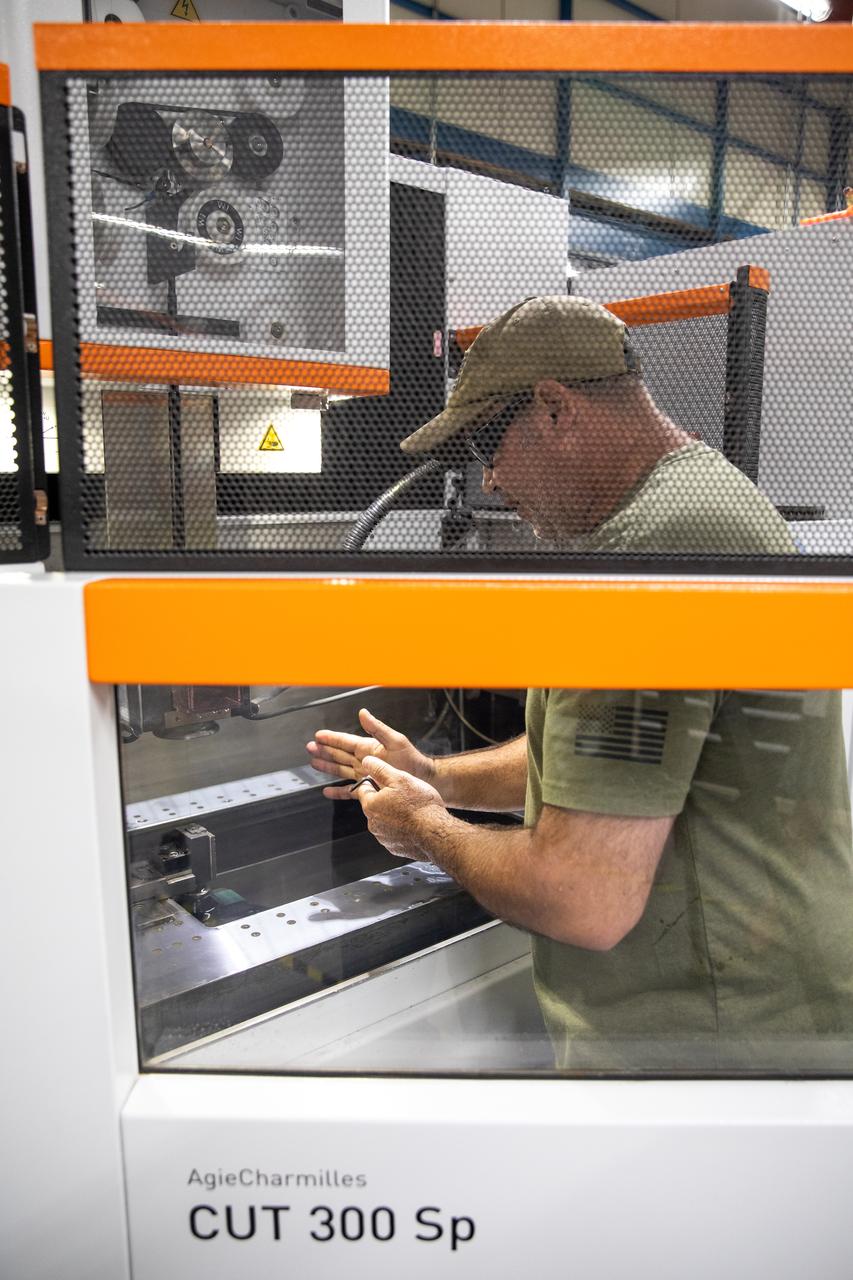

Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician with NASA, handles a sample that is being prepared for fatigue and corrosion testing for the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a ten percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
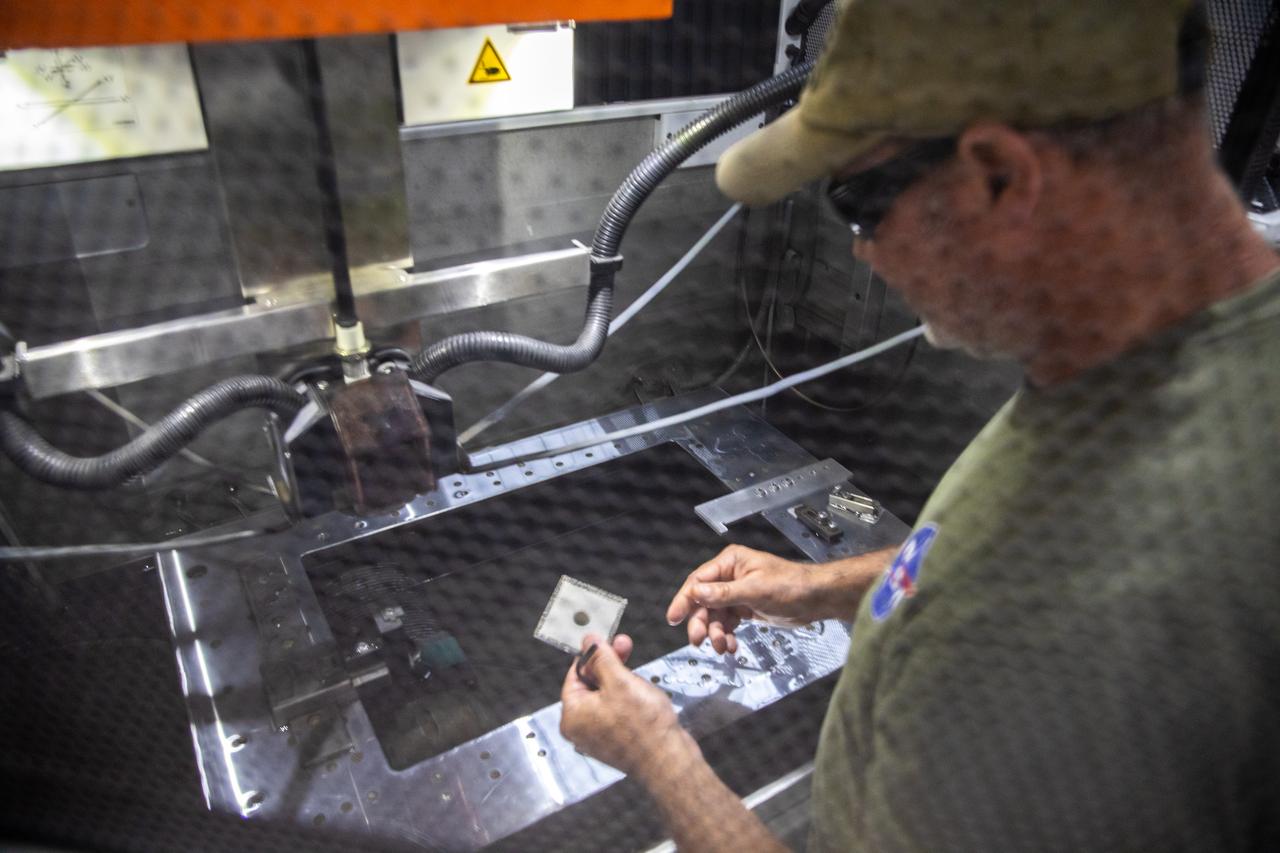

Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician with NASA, prepares a sample for testing for the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
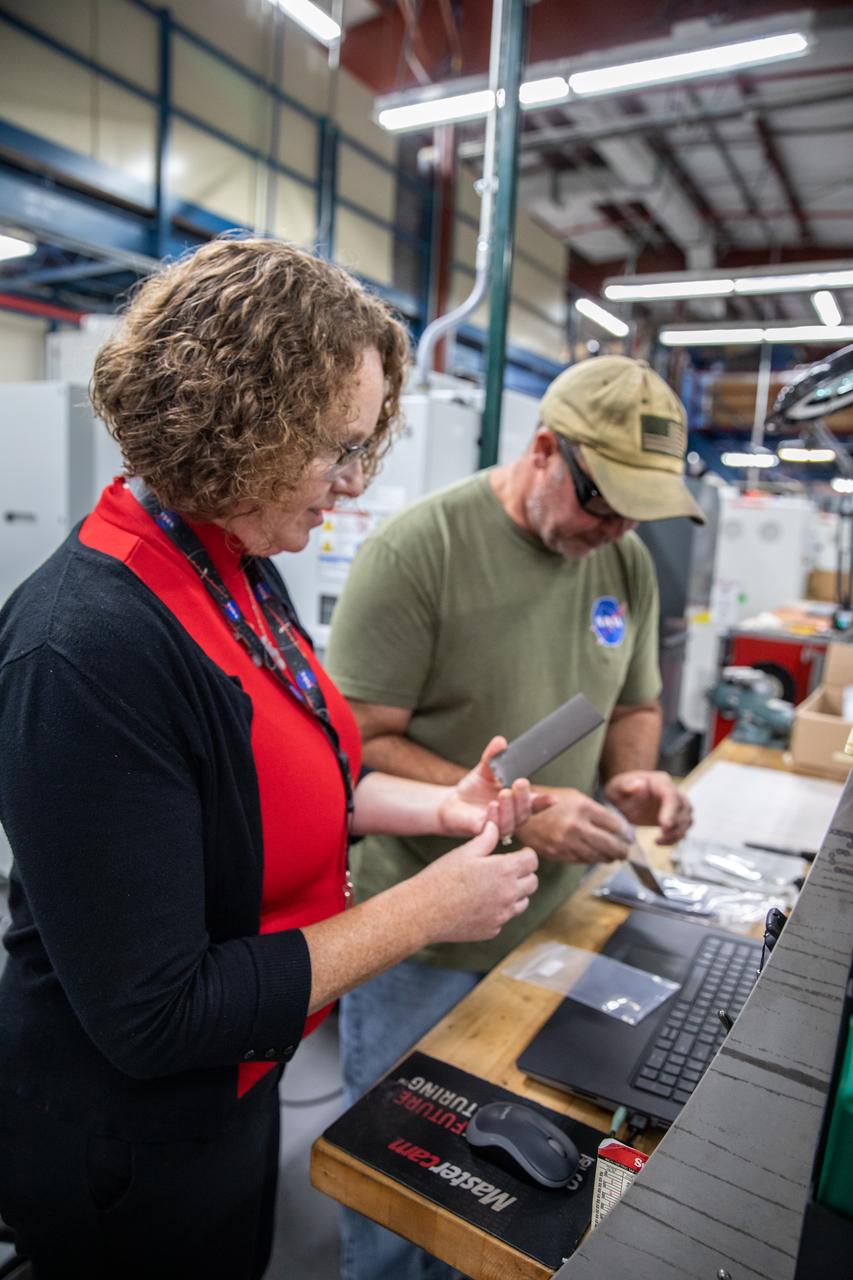

From left, Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, and Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician, inspect specimens prepared forthe Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiment inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied used on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
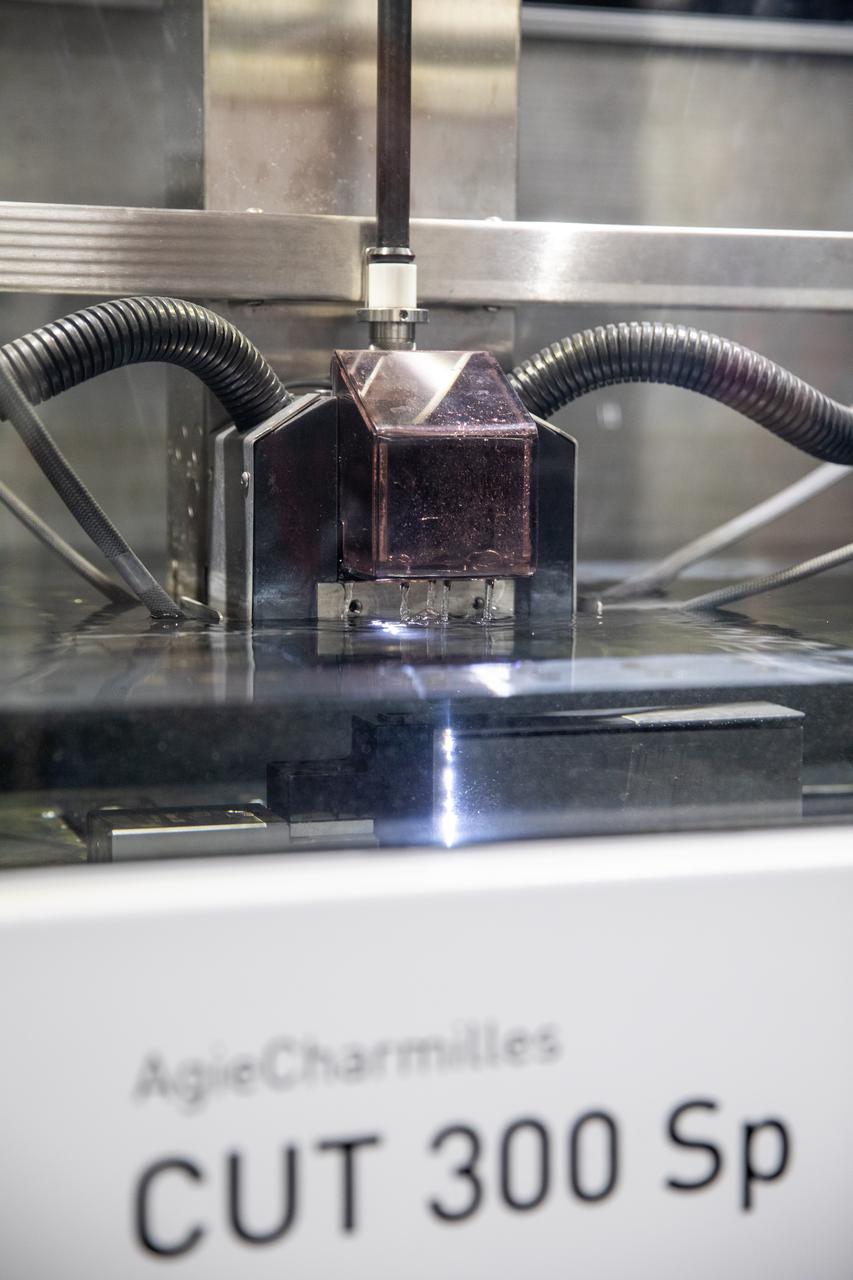
Testing of the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiment is underway inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.