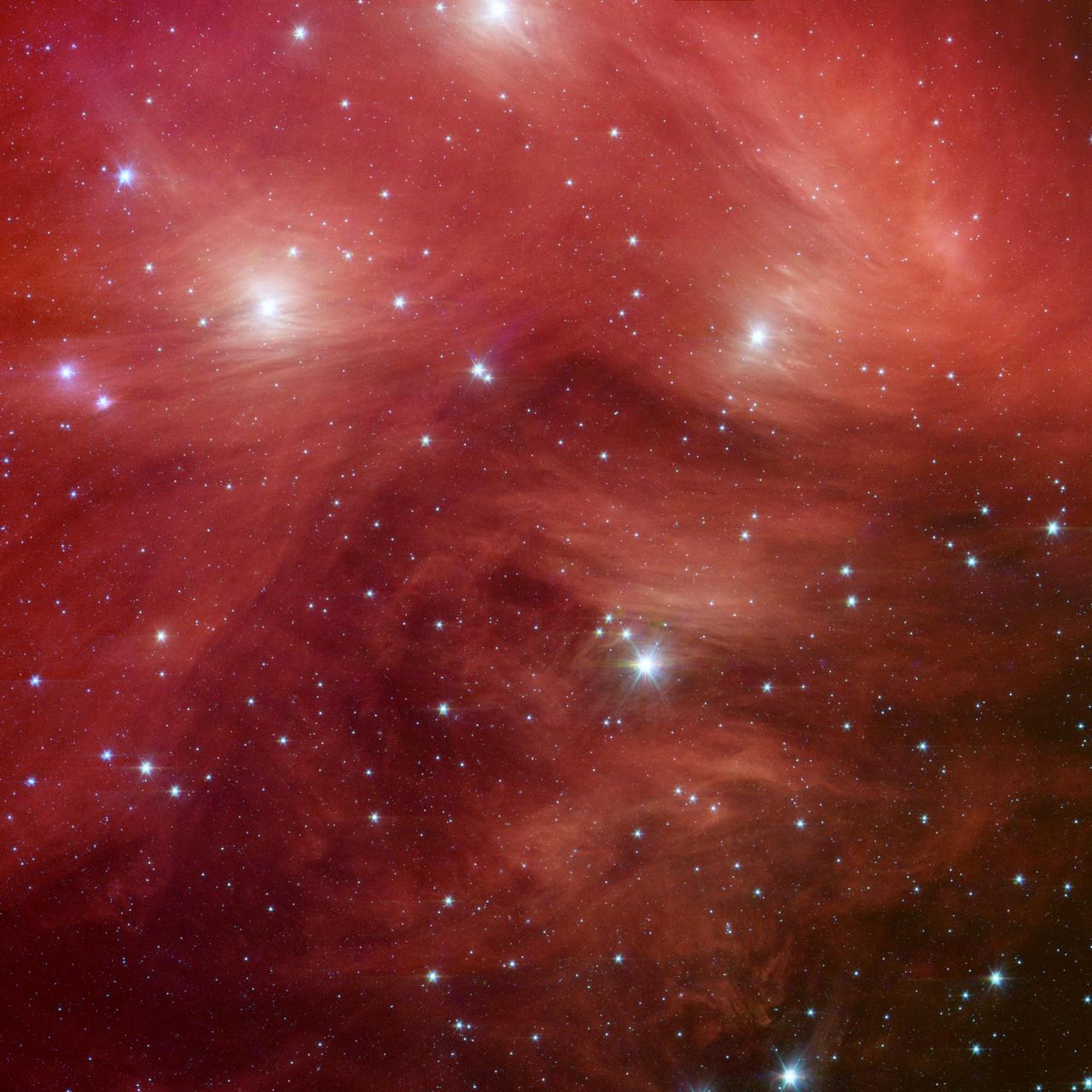

The Seven Sisters, also known as the Pleiades star cluster, seem to float on a bed of feathers in a new infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. Clouds of dust sweep around the stars, swaddling them in a cushiony veil.
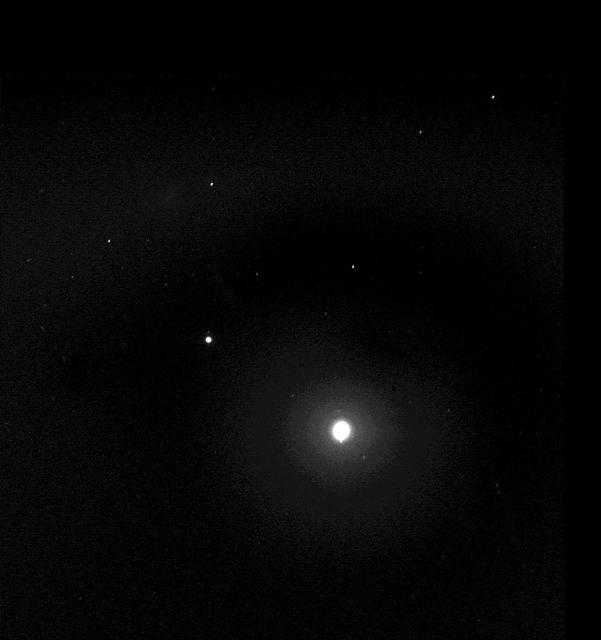
Two Moons and the Pleiades from Mars

Two Moons and the Pleiades from Mars
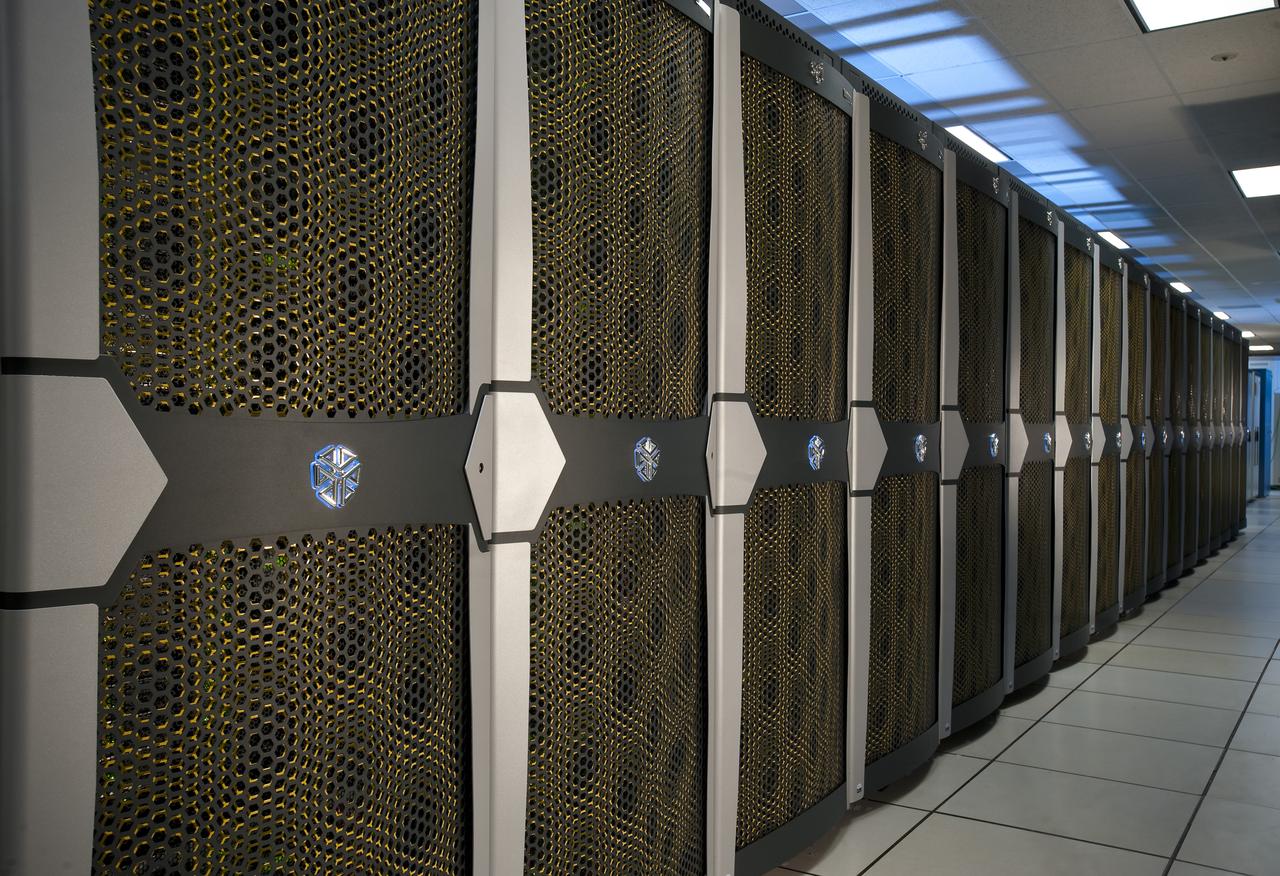

N-258 NAS Supercomputer Pleiades
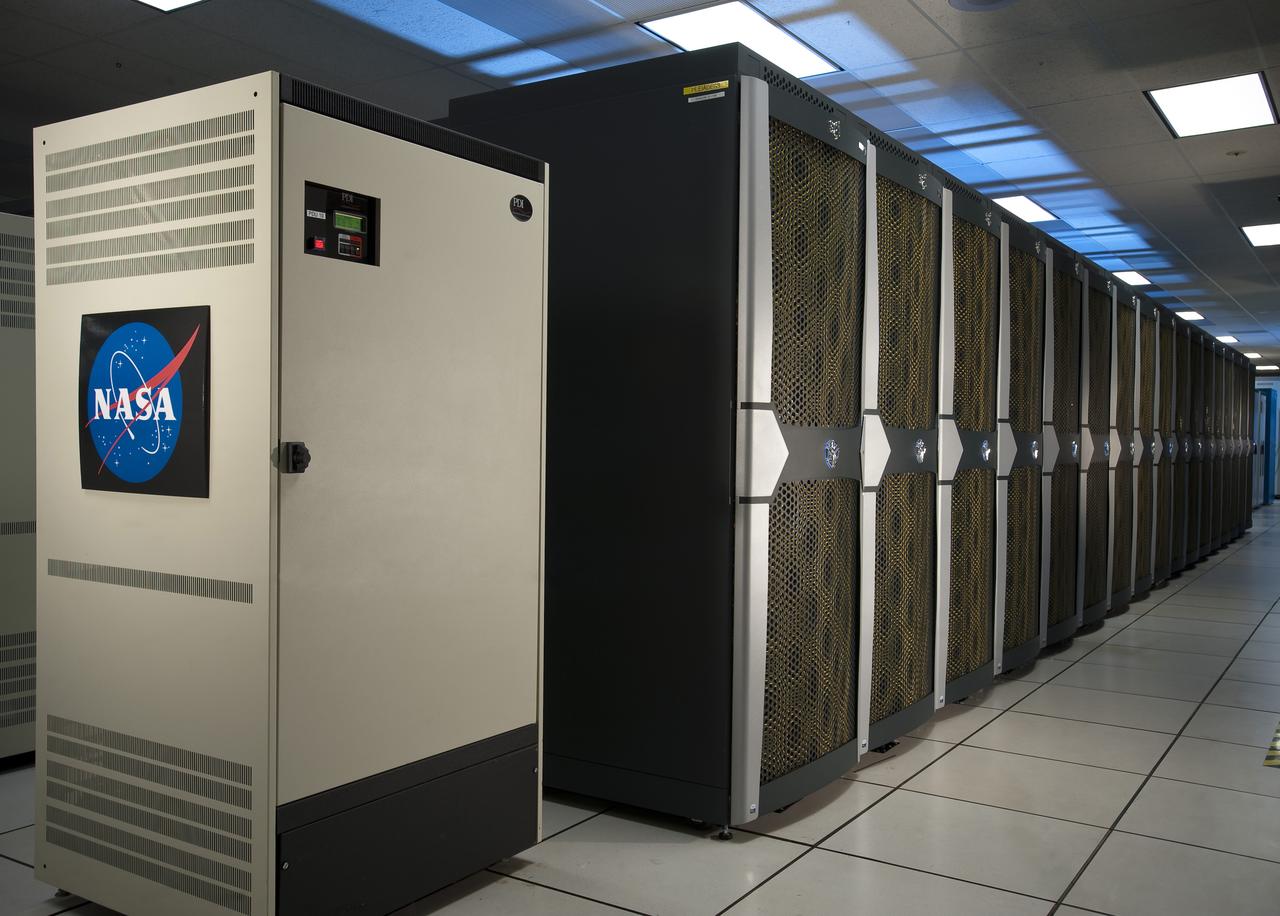

N-258 NAS Supercomputer Pleiades
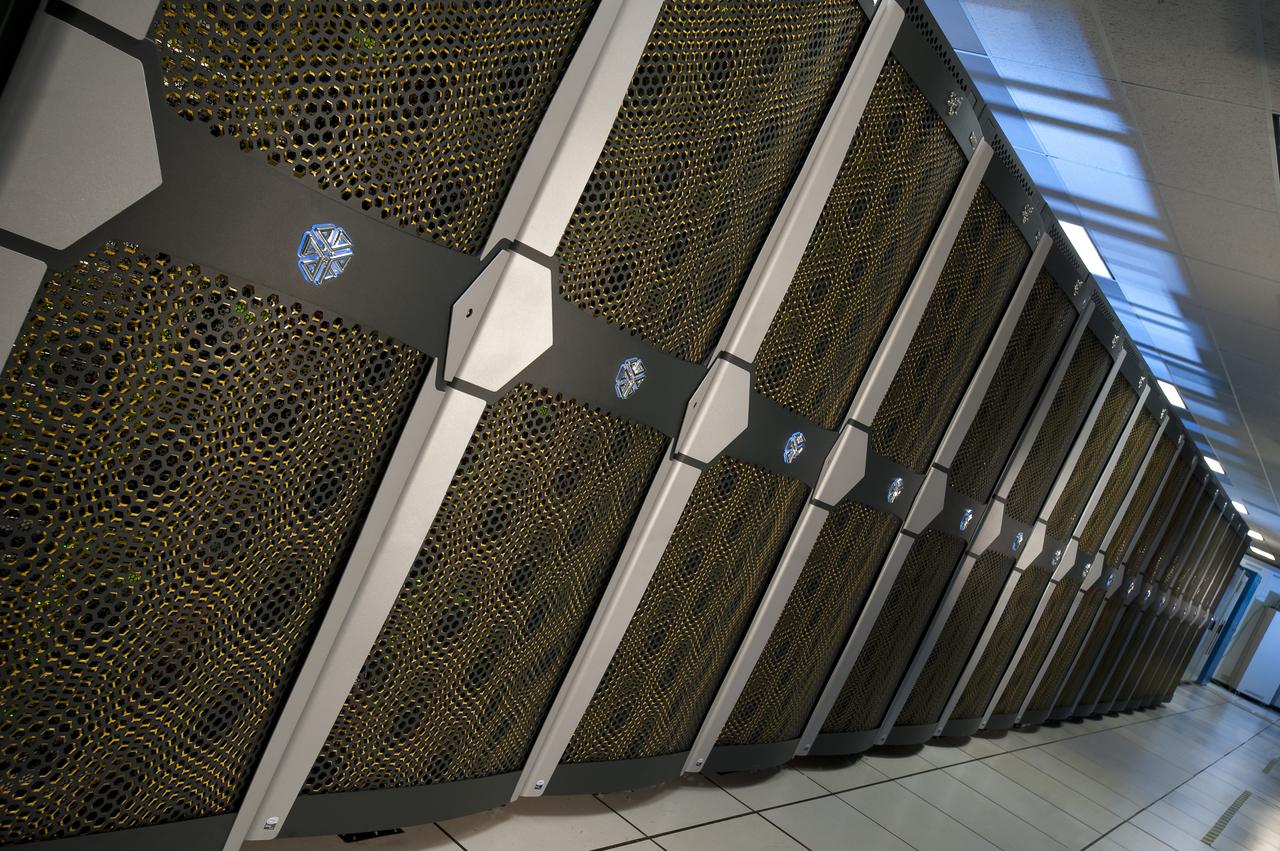

N-258 NAS Supercomputer Pleiades

N-258 NAS Supercomputer Pleiades

N-258 NAS Supercomputer Pleiades

N-258 NAS Supercomputer Pleiades

N-258 NAS Supercomputer Pleiades

N-258 NAS Supercomputer Pleiades
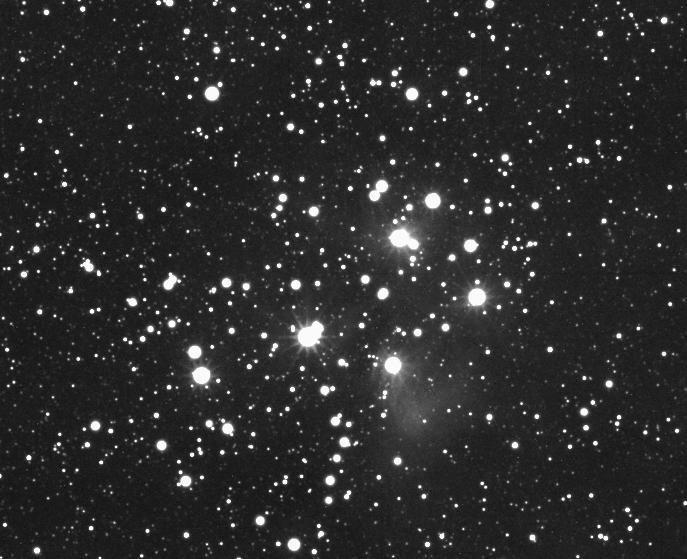

The stars of the Pleiades cluster, also known by the names M45 and the
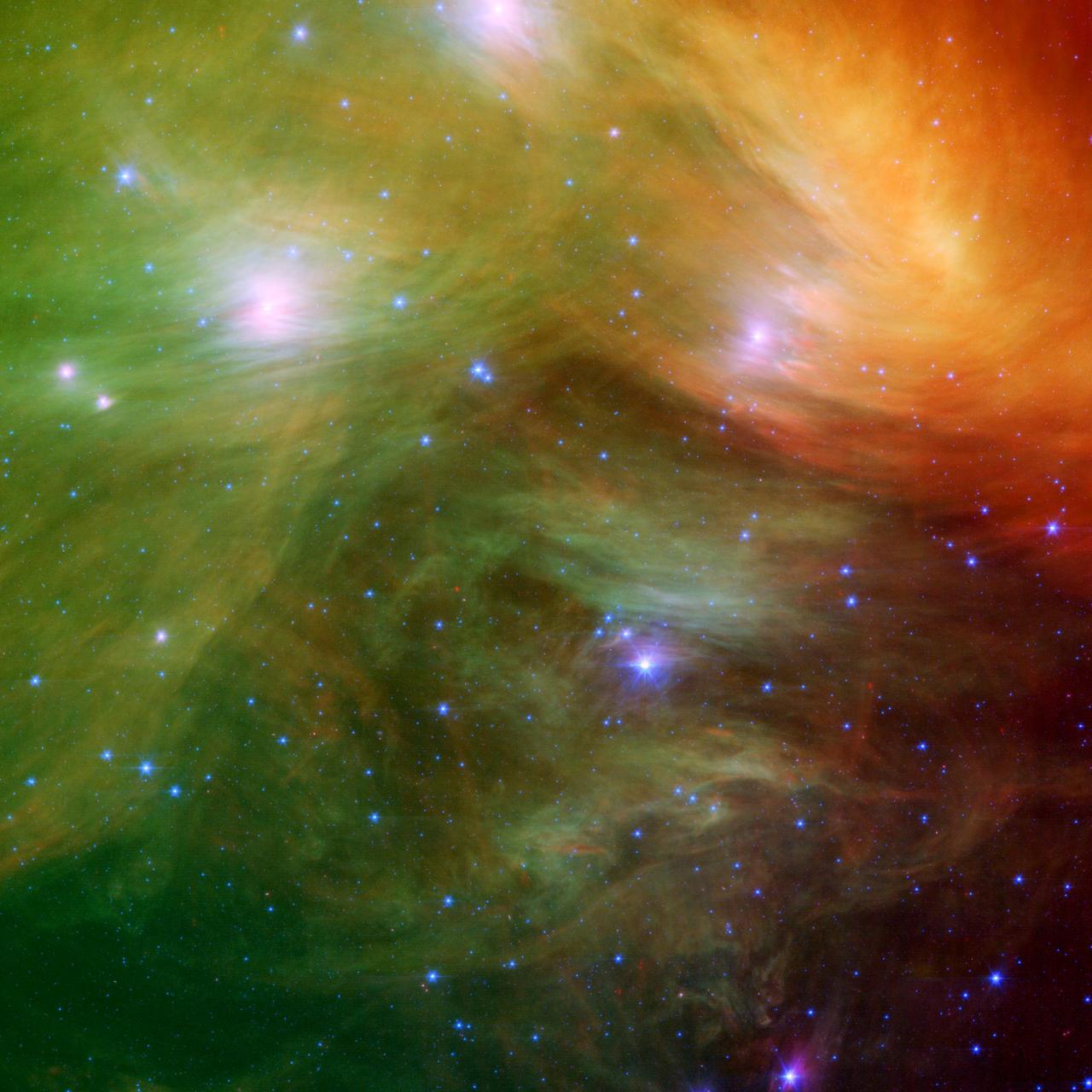

The Seven Sisters, also known as the Pleiades star cluster, seem to float on a bed of feathers in a new infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. Clouds of dust sweep around the stars, swaddling them in a cushiony veil.
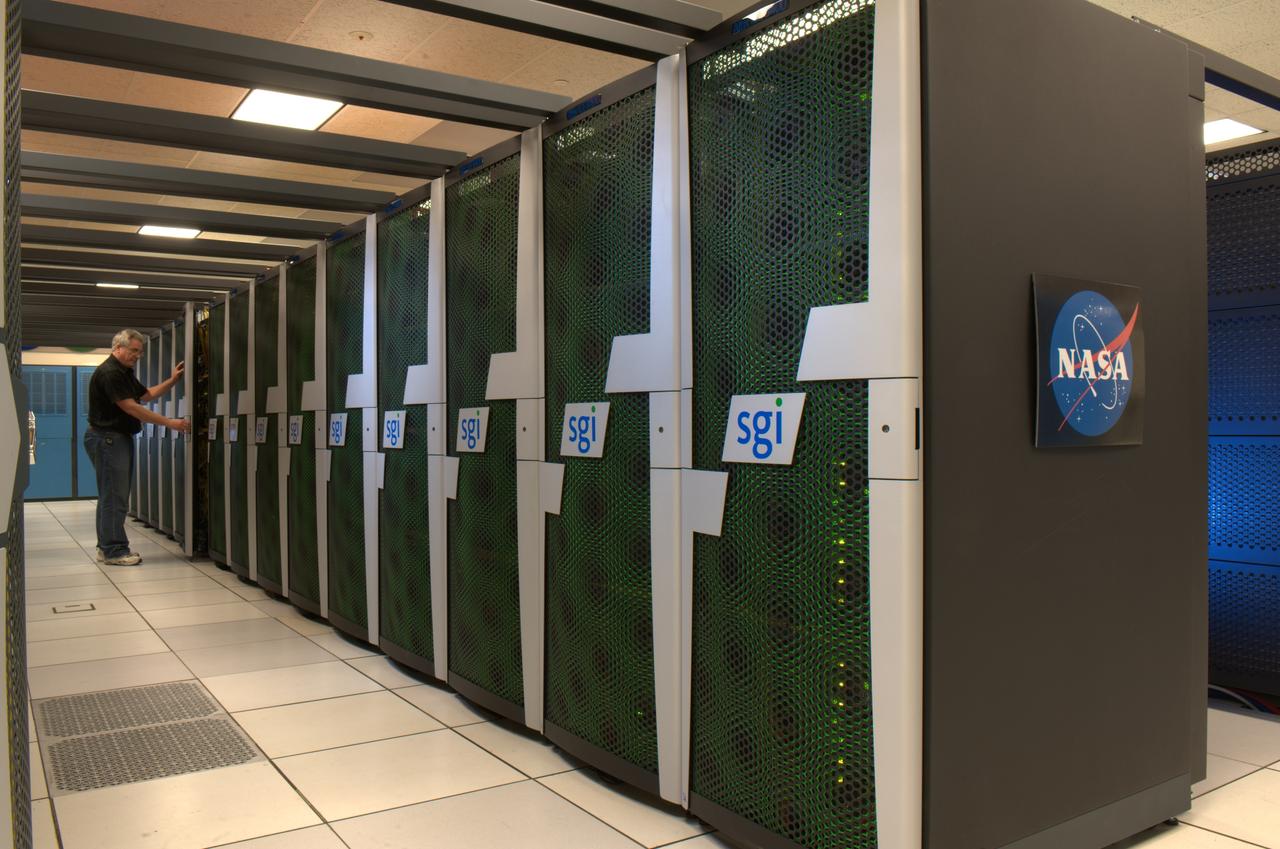

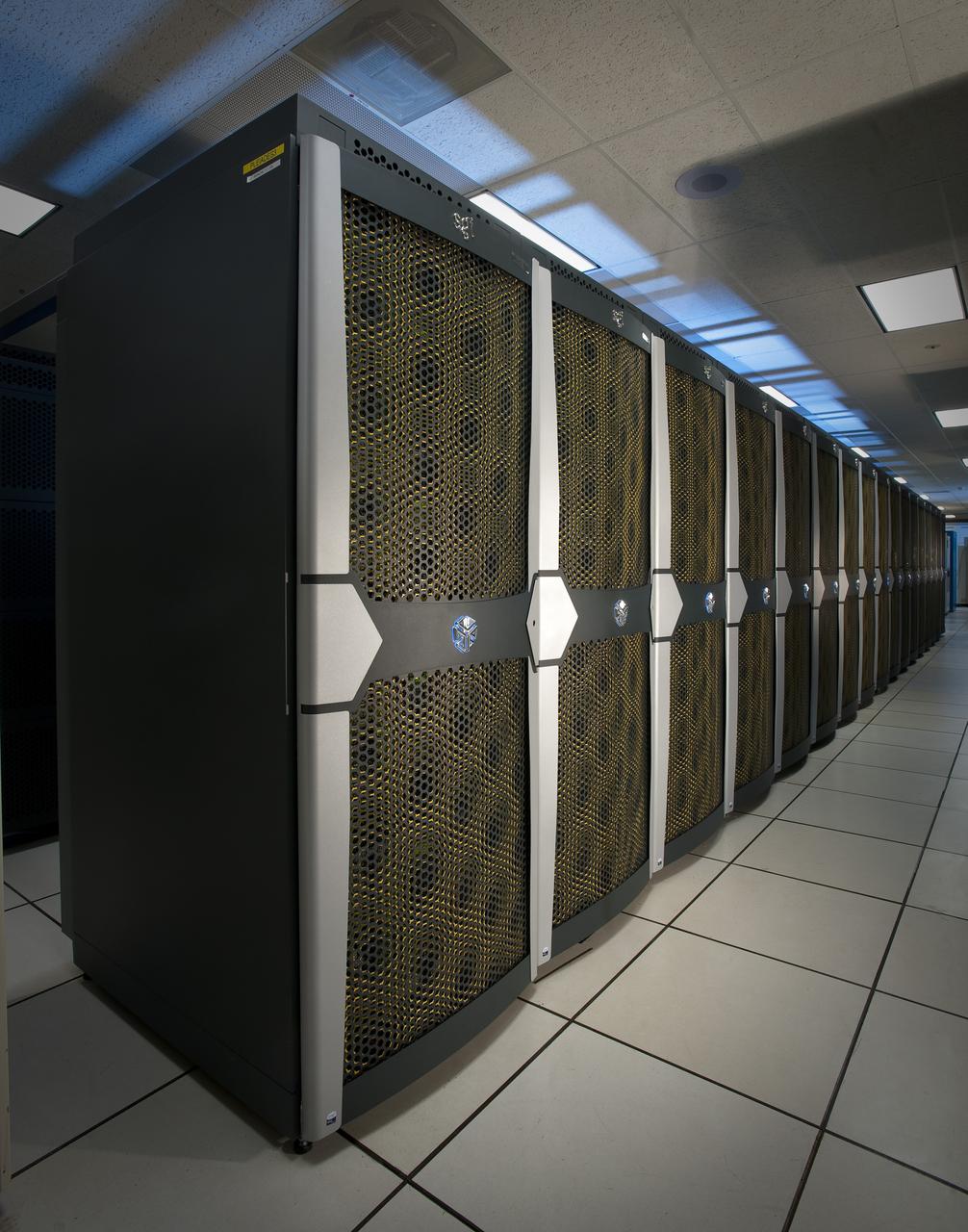
Pleiades, NASA's Supercomputing powerhouse, located at Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California doubles power, stays among world's fastest. Shown her with Chris Grimes.
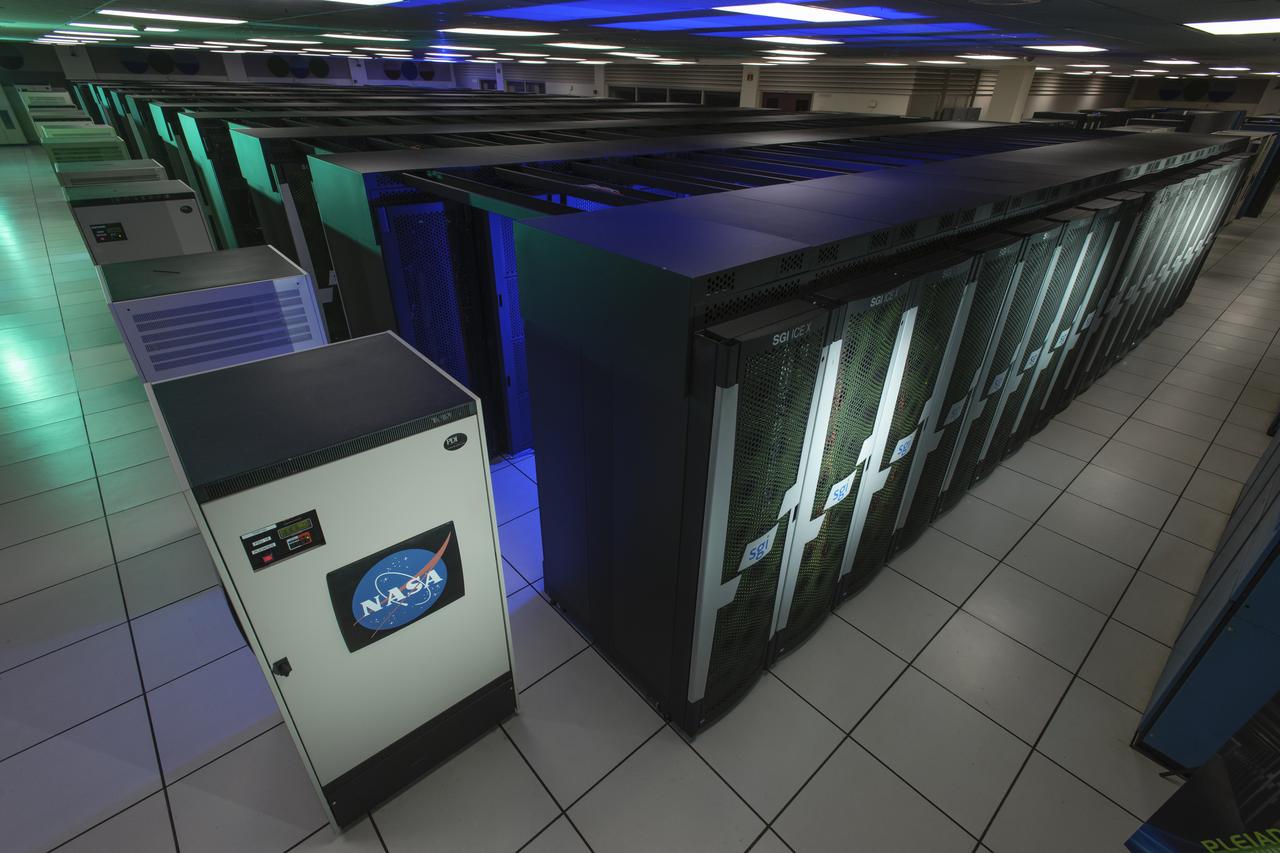

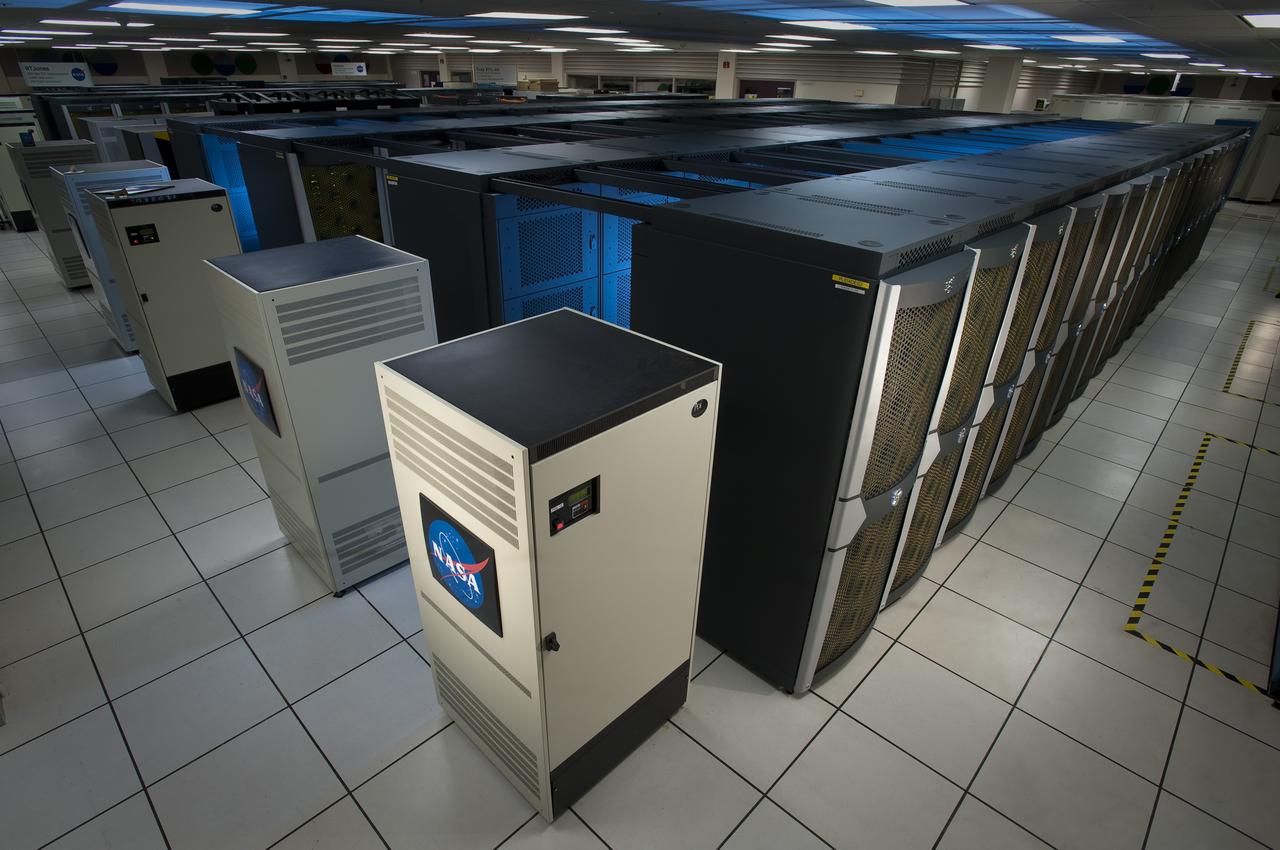
Supercomputer Pleiades as installed in the Spectra Logic room 131 of NASA Ames Numerical Aerodynamic Simulation (NAS) Facility N-258 located in Silicon Valley, CA.
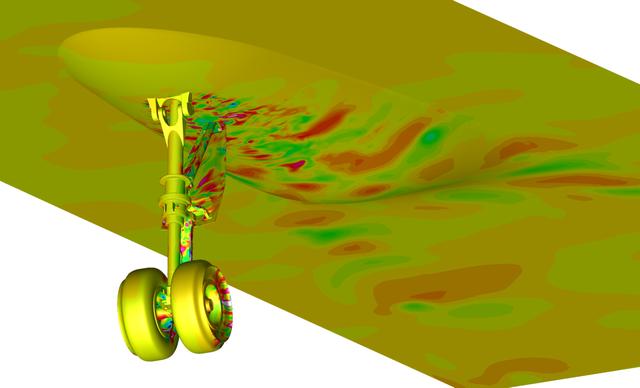
Snapshot from a simulation run on the Pleiades supercomputer. It depicts a fluctuating pressure field on aircraft nose landing gear and fuselage surfaces. The simulation helped scientists better understand the effects of landing gear and acoustic noise. The goal of the study was to improve the current understanding of aircraft nose landing gear noise, which will lead to quieter, more efficient airframe components for future aircraft designs. The visualization was produced with help from the NAS Data Analysis & Visualization group. Investigator: Mehdi Khorrami, NASA Langley Research Center.
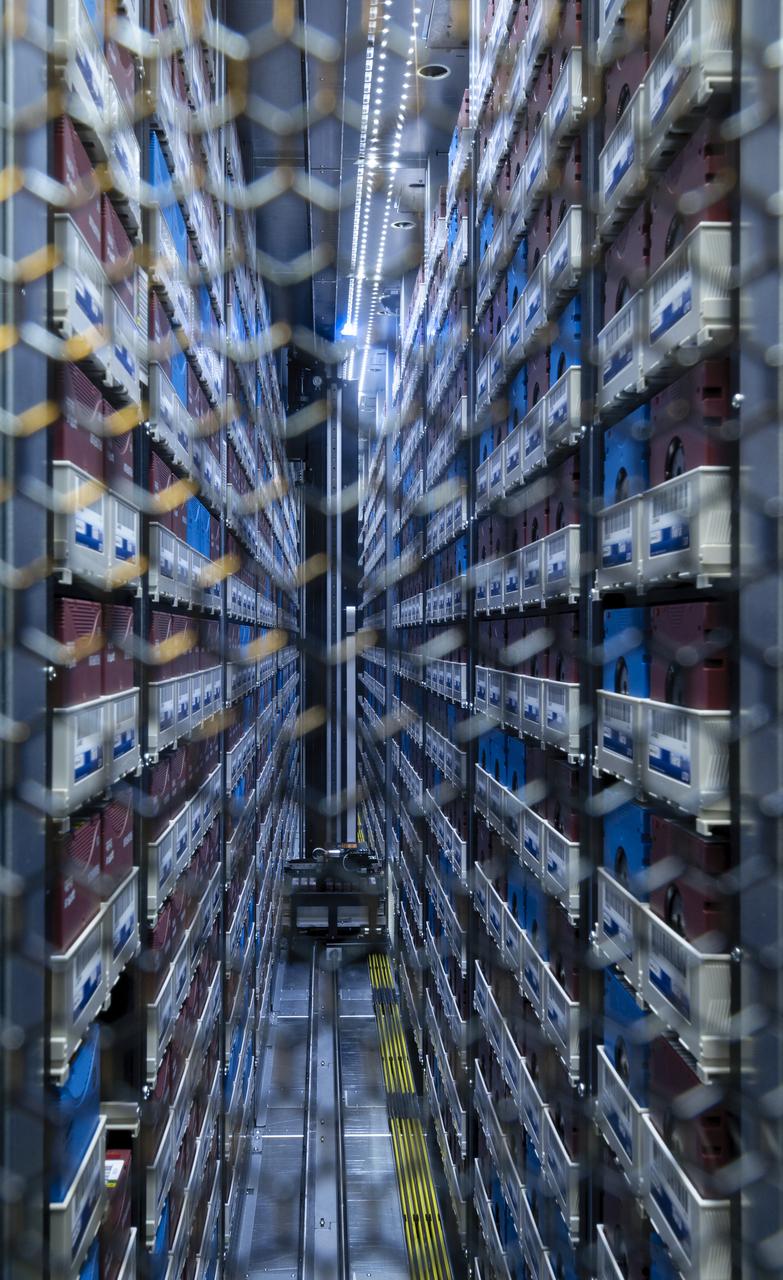

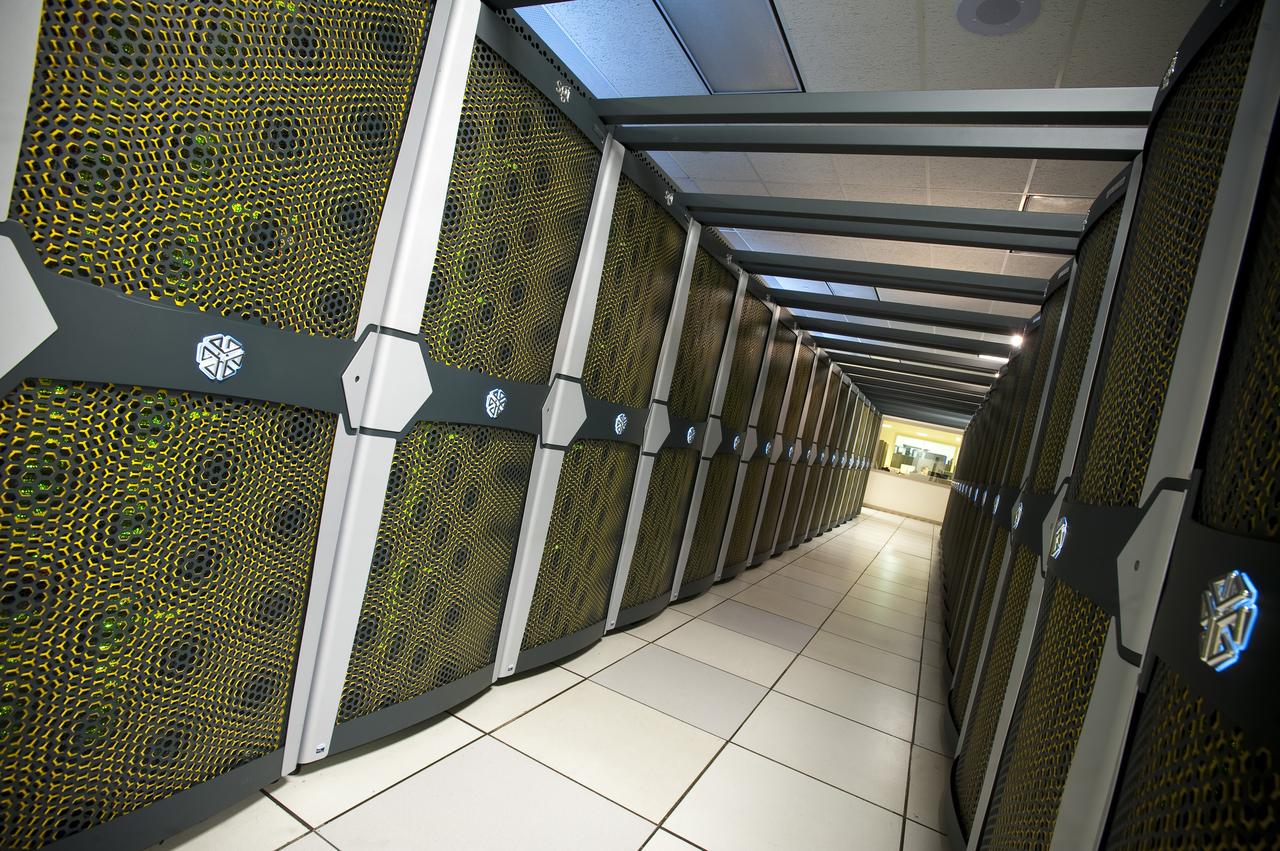
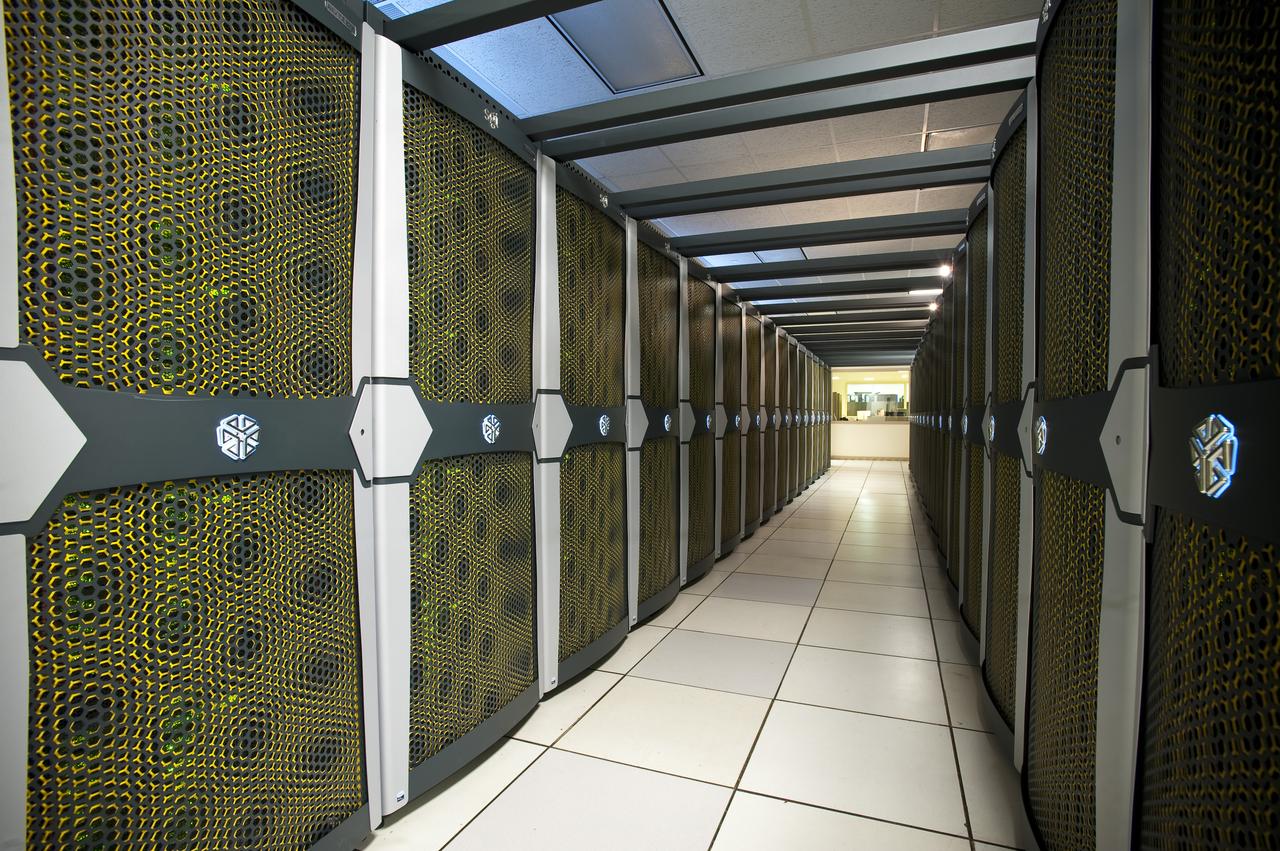
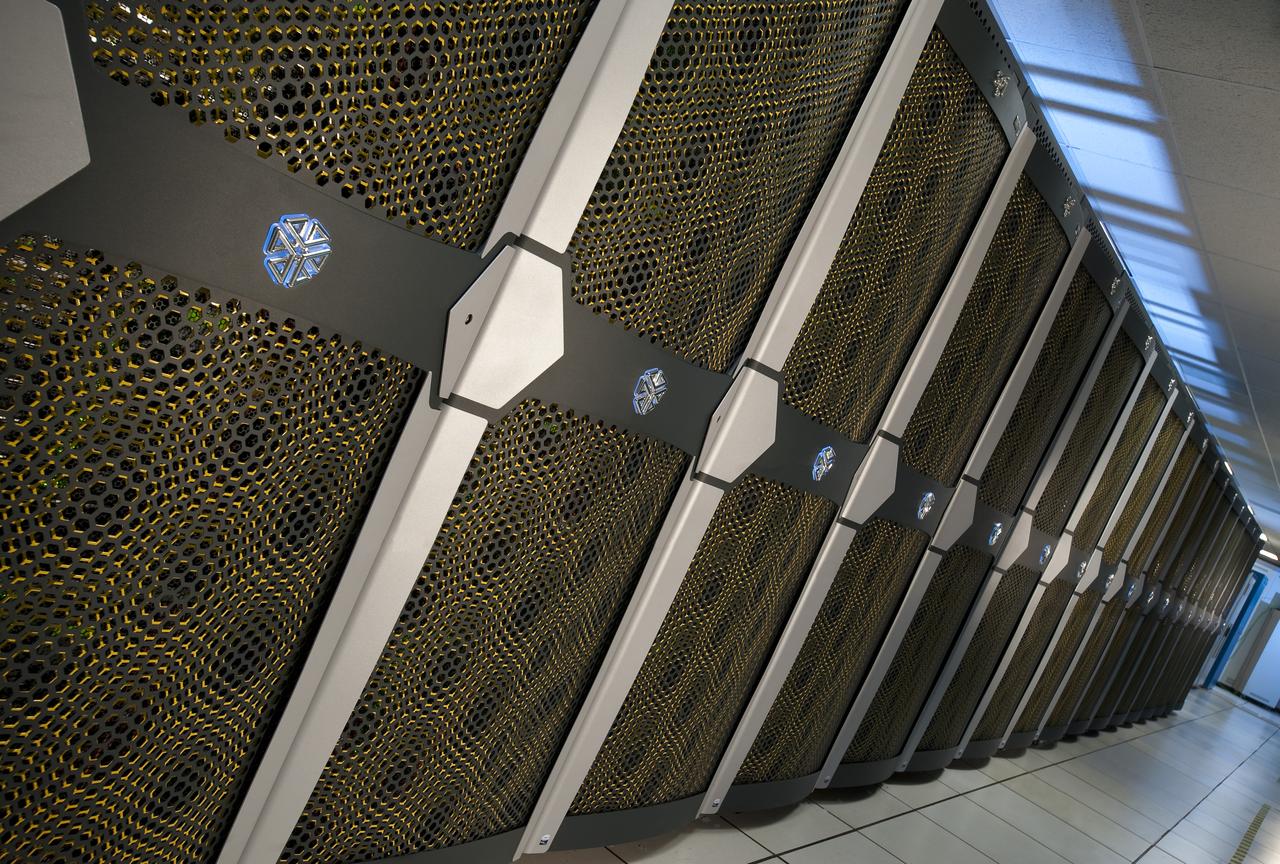
Interior view of the Supercomputer Pleiades as installed in the Spectra Logic room 131 of NASA Ames Numerical Aerodynamic Simulation (NAS) Facility N-258 located in Silicon Valley, CA.
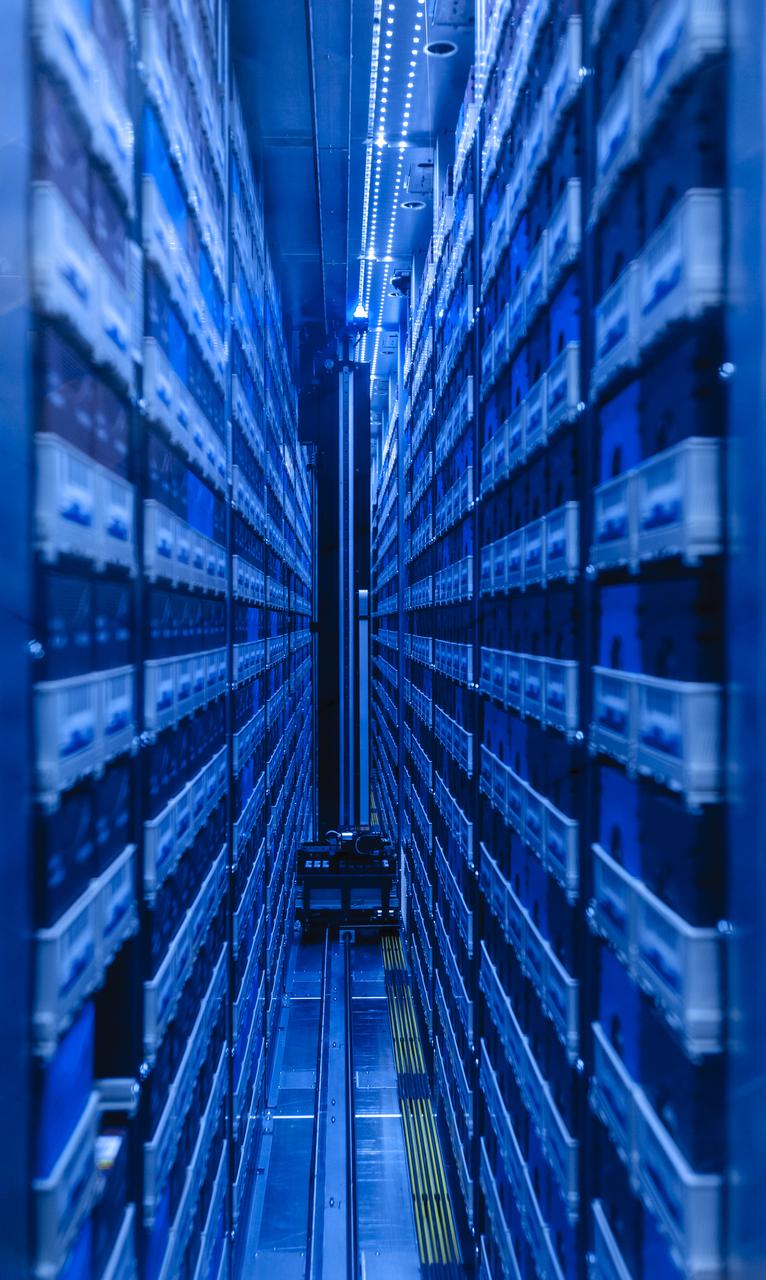

Interior view of the Supercomputer Pleiades as installed in the Spectra Logic room 131 of NASA Ames Numerical Aerodynamic Simulation (NAS) Facility N-258 located in Silicon Valley, CA.

Star clusters such as the Pleiades are often considered some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. This image of the star cluster NGC 2259 is from NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer.

This image is a tar cal frame collected about a month before NASA MESSENGER first flyby of Venus.

This image shows the famous Pleiades cluster of stars as seen through the eyes of NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer; they are what astronomers call an open cluster of stars, loosely bound to each other to eventually go their separate ways.

This photo shows the zodiacal light as it appeared on March 1, 2021, in Skull Valley, Utah. The Pleiades star cluster is visible near the top of the light column. Mars is just below that. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24432

The Cassini spacecraft takes a break from the Saturn system to check out the Seven Sisters.
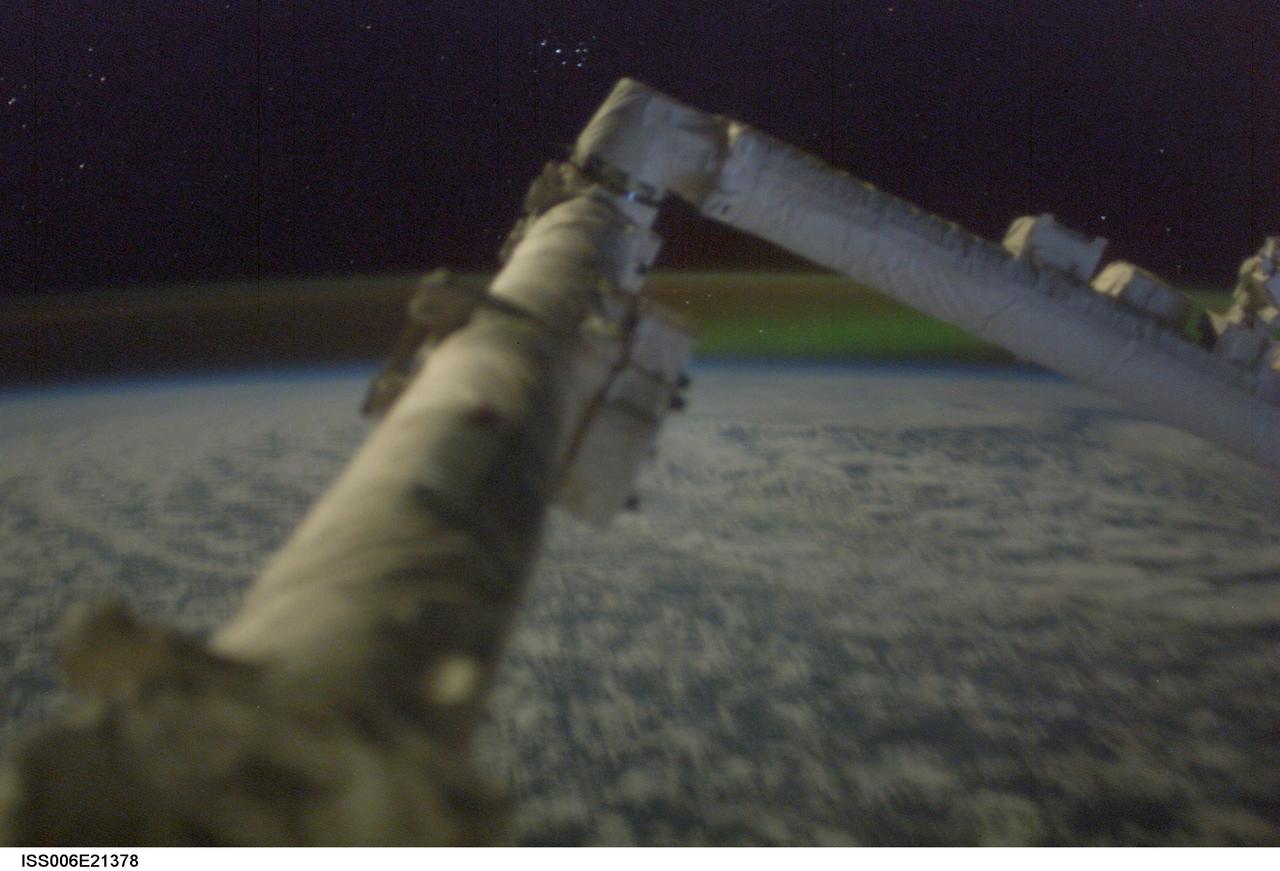

ISS006-E-21378 (18 January 2003) --- A portion of the Canadarm2, or Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS), was photographed by one of the Expedition 6 crewmembers onboard the International Space Station (ISS). Just above Canadarm2’s elbow are the Pleiades, also known as the Seven Sisters. These seven stars, arranged like a little dipper, are just the brightest members of a cluster of more than 3000 stars lying 400 light years from Earth. Between the robotic arm and the Pleiades is Earth itself. Below, the cloudy landscape is lit by a nearly-full Moon (out of frame). Above, the edge of Earth’s atmosphere is defined by a layer of glowing air—a brownish-yellow band of light stretching all the way across the image. And finally, just under Canadarm’s elbow, is a streak of green—the Aurora Borealis, also known as “northern lights”.
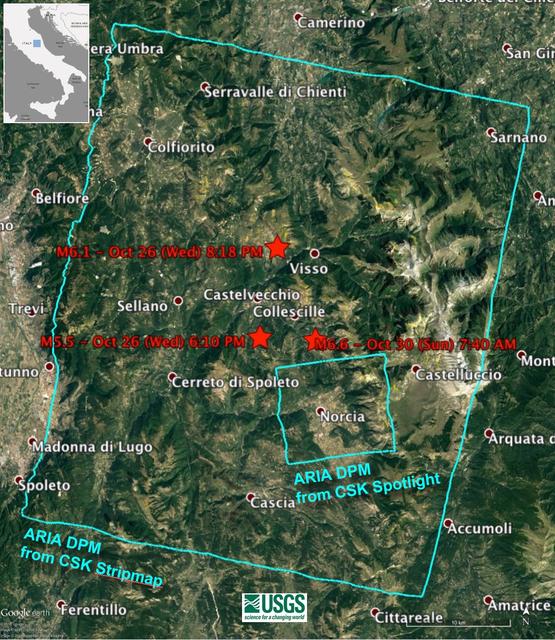
Damage Proxy Map (DPM) v0.5, derived from the Italian Space Agency's COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data acquired from an ascending orbit, covering an area of 6.2-by-6.2 miles (10-by-10 kilometers), centered at Norcia, Italy. Red pixels (pixel size about 16 feet, or 5 meters)represent areas of potential damage due to the Magnitude 6.6 Oct 30, 2016, Central Italy earthquakes, as well as ground surface change during the time period Oct. 30, 2016 -- Oct. 31, 2016. The color variation from yellow to red indicate increasingly more significant ground surface change. Preliminary validation was carried out by comparing with high-resolution pre- and post-event optical imagery acquired by DigitalGlobe's WorldView satellites, and a damage map produced by the European Commission Copernicus Emergency Management Service based upon visual inspection of high-resolution pre- (Orthophoto) and post-event (Pleiades-1) optical imagery. This DPM provides broad geographic coverage of the earthquake's impact in the region. Areas that fall in radar shadow and layover were masked out. The DPM should be used as guidance to identify damaged areas, and may be less reliable over vegetated areas. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA15374
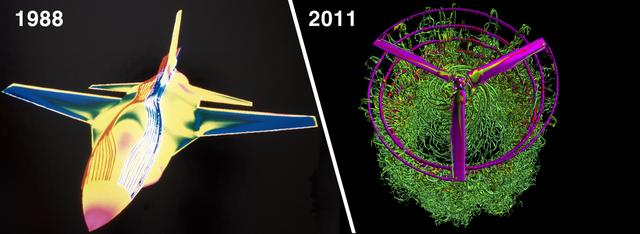
Then and Now: These images illustrate the dramatic improvement in NASA computing power over the last 23 years, and its effect on the number of grid points used for flow simulations. At left, an image from the first full-body Navier-Stokes simulation (1988) of an F-16 fighter jet showing pressure on the aircraft body, and fore-body streamlines at Mach 0.90. This steady-state solution took 25 hours using a single Cray X-MP processor to solve the 500,000 grid-point problem. Investigator: Neal Chaderjian, NASA Ames Research Center At right, a 2011 snapshot from a Navier-Stokes simulation of a V-22 Osprey rotorcraft in hover. The blade vortices interact with the smaller turbulent structures. This very detailed simulation used 660 million grid points, and ran on 1536 processors on the Pleiades supercomputer for 180 hours. Investigator: Neal Chaderjian, NASA Ames Research Center; Image: Tim Sandstrom, NASA Ames Research Center

This frame from a video depicts artist concepts of each of the seven planets orbiting TRAPPIST-1, an ultra-cool dwarf stars. Over 21 days, NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope measured the drop in light as each planet passed in front of the star. Spitzer was able to identify a total of seven rocky worlds, including three in the habitable zone where life is possible. The study established the planets' size, distance from their sun and, for some of them, their approximate mass and density. It also established that some, if not all, these planets are tidally locked, meaning one face of the planet permanently faces their sun. The planets appear in the order of innermost to outermost planets. These artist's concepts were designed as follows: TRAPPIST-1b, closest to the star, was modeled on Jupiter's moon Io, which has volcanic features due to strong gravitational tugs. TRAPPIST-1c is shown as a rocky, warm world with a small ice cap on the side that never faces the star. TRAPPSIT-1d is rocky and has water only in a thin band along the terminator, dividing the day side and night side. TRAPPIST-1e and TRAPPIST-1f are both shown covered in water, but with progressively larger ice caps on the night side. TRAPPIST-1g is portrayed with an atmosphere like Neptune's, although it is still a rocky world. The farthest planet, TRAPPIST-1h, is shown as covered in ice, similar to Jupiter's icy moon Europa. The background stars are what you would see if you were in the TRAPPIST-1 system. Orion passes behind the planets, recognizable but distorted from what we're familiar with, in addition to Taurus and Pleiades. A video is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21468
