
The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) flew in orbit inside the Spacelab science module for extended periods, providing scientists and researchers greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. This photograph shows Astronaut Larry De Lucas wearing a stocking plethysmograph during the mission. Muscle size in the legs changes with exposure to microgravity. A stocking plethysmograph, a device for measuring the volume of a limb, was used to help determine these changes. Several times over the course of the mission, an astronaut will put on the plethysmograph, pull the tapes tight and mark them. By comparing the marks, changes in muscle volume can be measured. The USML-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.
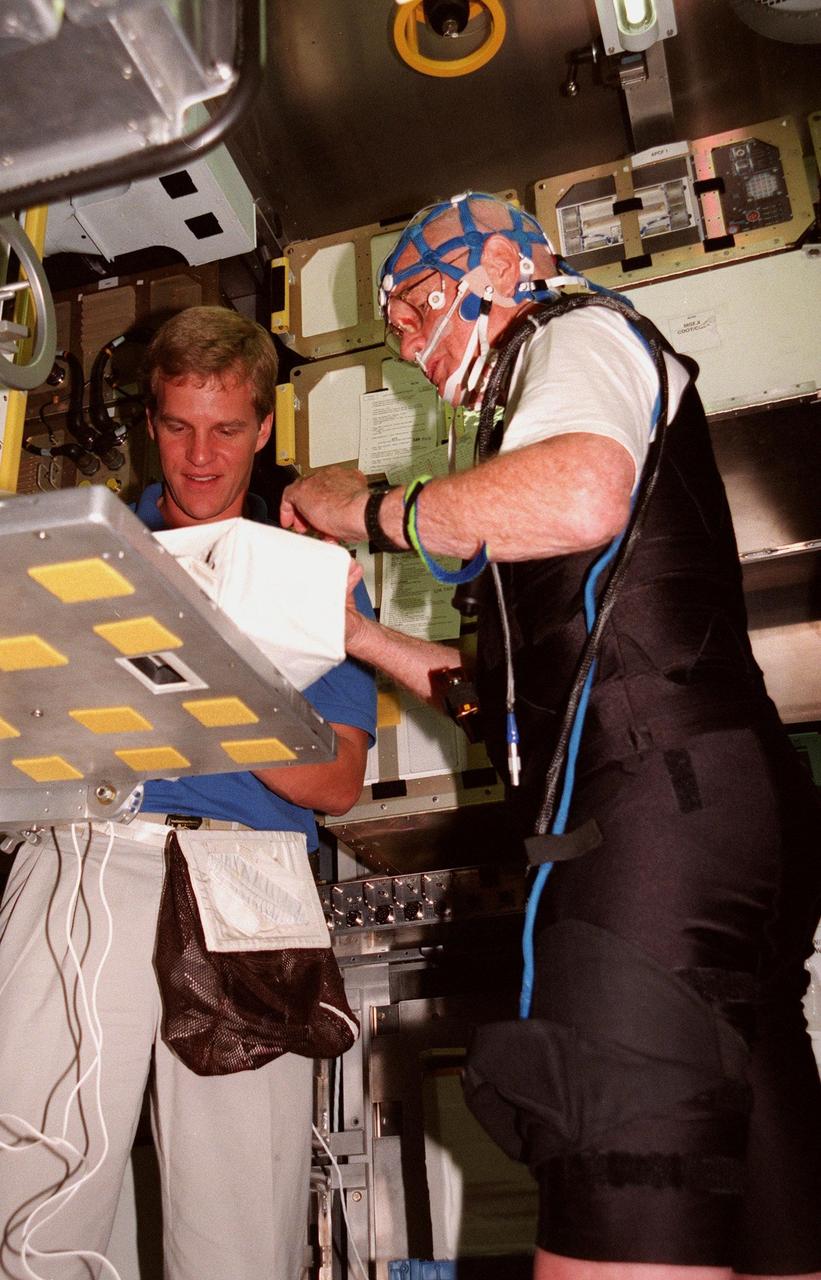

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the SPACEHAB training module, STS-95 Mission Specialist Scott Parazynski, M.D., helps adjust connections for the mesh cap and the Respiratory Inductance Plethysmograph (RIP) suit worn by Payload Specialist John Glenn, who is a senator from Ohio. The cap and suit, which Glenn will wear on the mission, are part of the equipment that will be used to seek to improve the quality of sleep for future astronauts. The STS-95 crew are participating in SPACEHAB familiarization at the SPACEHAB Payload Processing Facility, Cape Canaveral. The mission, scheduled to launch Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
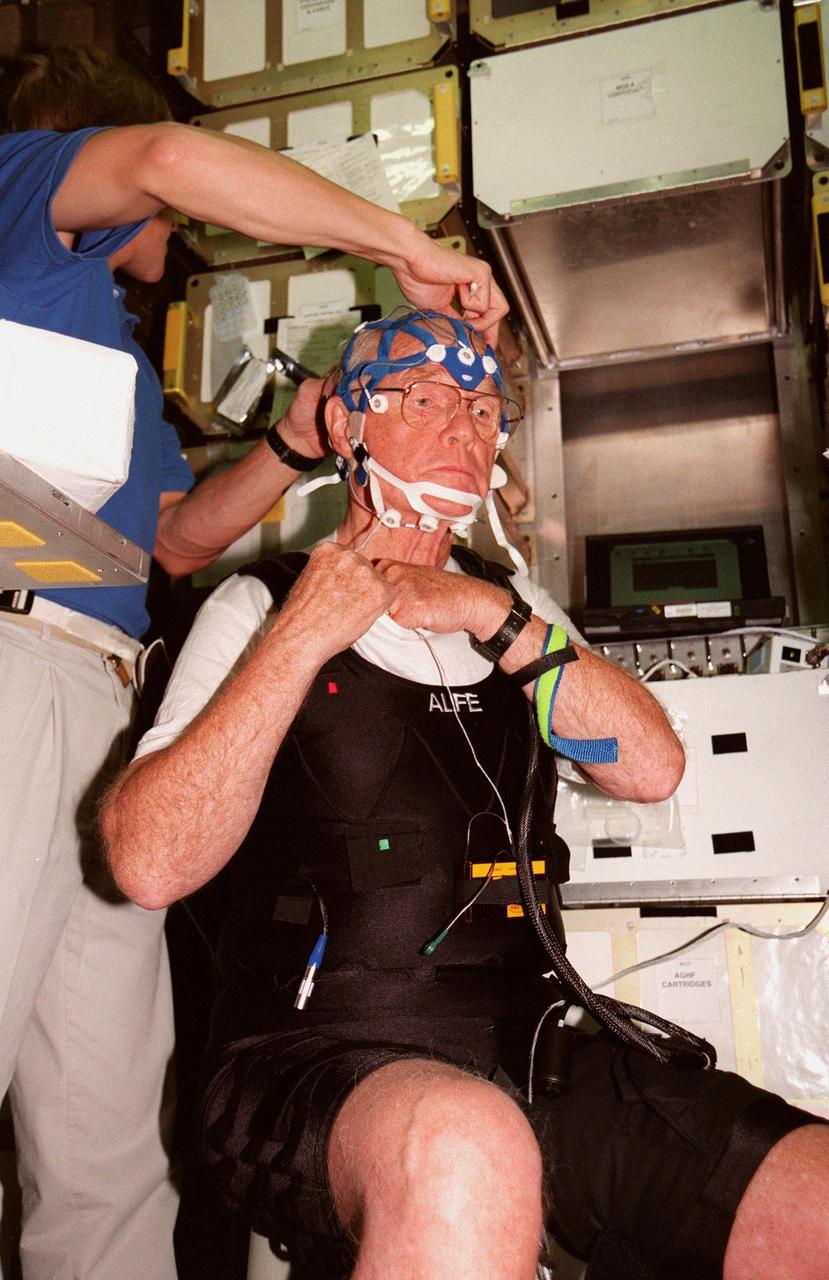
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the SPACEHAB training module, STS-95 Mission Specialist Scott Parazynski, M.D., helps with connections on the mesh cap worn by Payload Specialist John Glenn, who is a senator from Ohio. Glenn is also wearing the Respiratory Inductance Plethysmograph (RIP) suit he will wear on the mission to monitor respiration. The cap and suit are part of the equipment that will be used to seek to improve the quality of sleep for future astronauts. The STS-95 crew are participating in SPACEHAB familiarization at the SPACEHAB Payload Processing Facility, Cape Canaveral. The mission, scheduled to launch Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
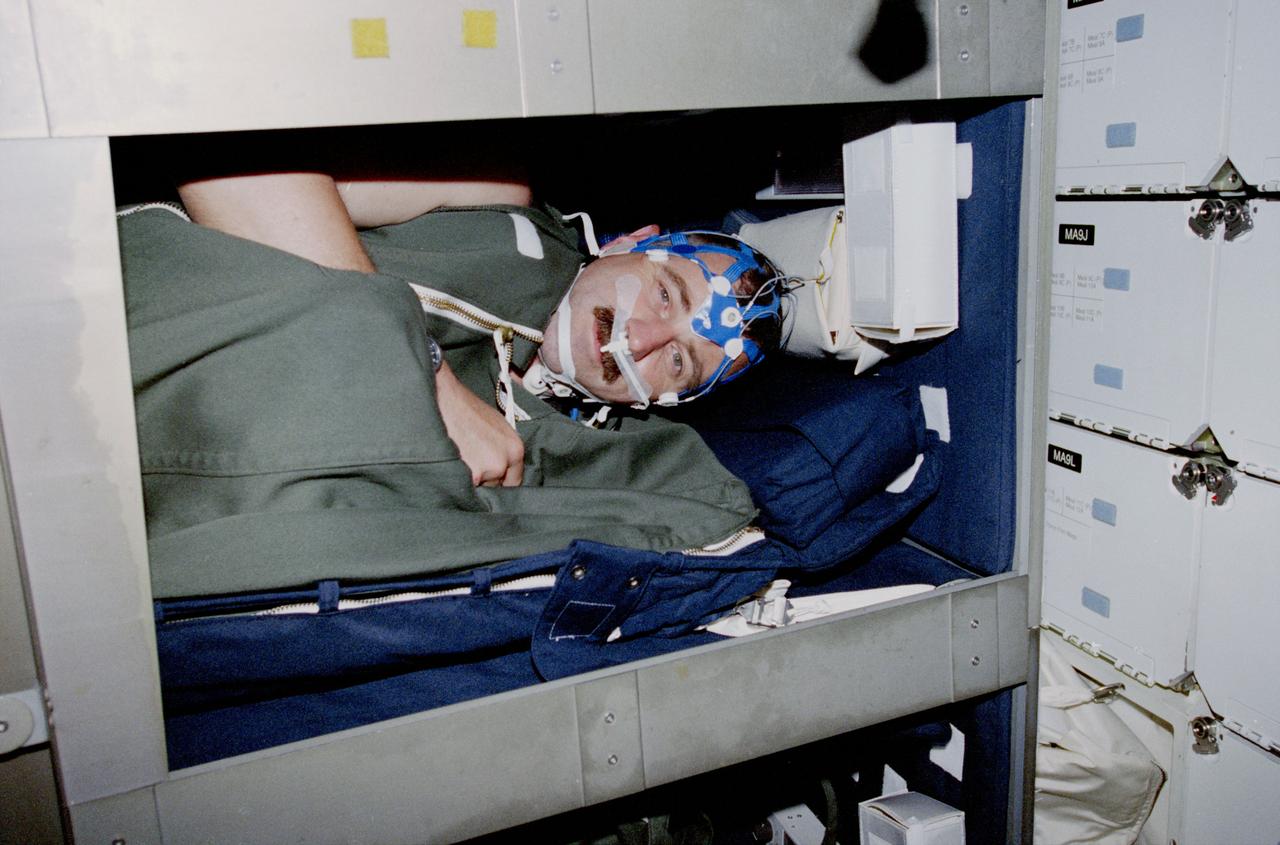
STS090-377-011 (17 APRIL-3 MAY 1998) --- Astronaut Dafydd R. (Dave) Williams, mission specialist representing the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), accomplishes more than one purpose when he sleeps in this bunk aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Conducting a Neurolab sleep experiment, Williams wears equipment which includes a sleep net (mesh cap that monitors and records brain waves); a Respiratory Inductance Plethysmograph (RIP) suit for monitoring respiration; and an activity monitor -- a device (out of view) worn on the wrist to detect and record body movement. Data on brain waves, eye movements, respiration, heart rate, and oxygen concentration are routed to a portable data recorder. The entire system has capabilities similar to a fully equipped sleep laboratory on Earth. The sleeping bag is conventional Shuttle ware and not part of the experiment.