
NASA’s Beaming Energy for Air Mobility team successfully completed a first-of-its-kind power beaming test at NASA Glenn on June 4, 2025. Later this year, the tested transmitter will be used in a demonstration to wirelessly transmit power using microwaves to a custom power receiver — a step toward gap-filling technology that could one day deliver power on the surface of the Moon or Mars. Seth Waldstein, Seth Schisler and Bryan Schoenholz are in the control room reviewing the results.
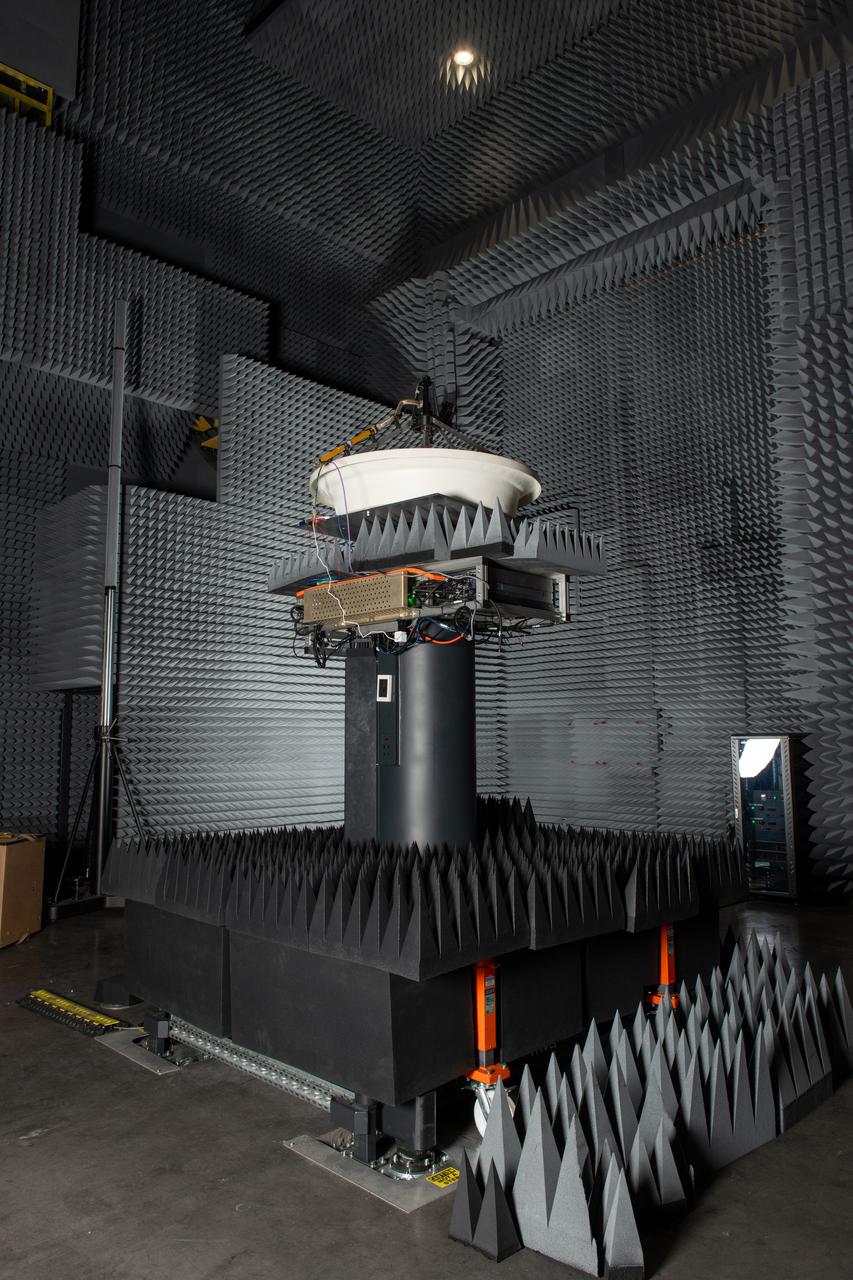

NASA’s Beaming Energy for Air Mobility team successfully completed a first-of-its-kind power beaming test at NASA Glenn on June 4, 2025. Later this year, the tested transmitter will be used in a demonstration to wirelessly transmit power using microwaves to a custom power receiver — a step toward gap-filling technology that could one day deliver power on the surface of the Moon or Mars.
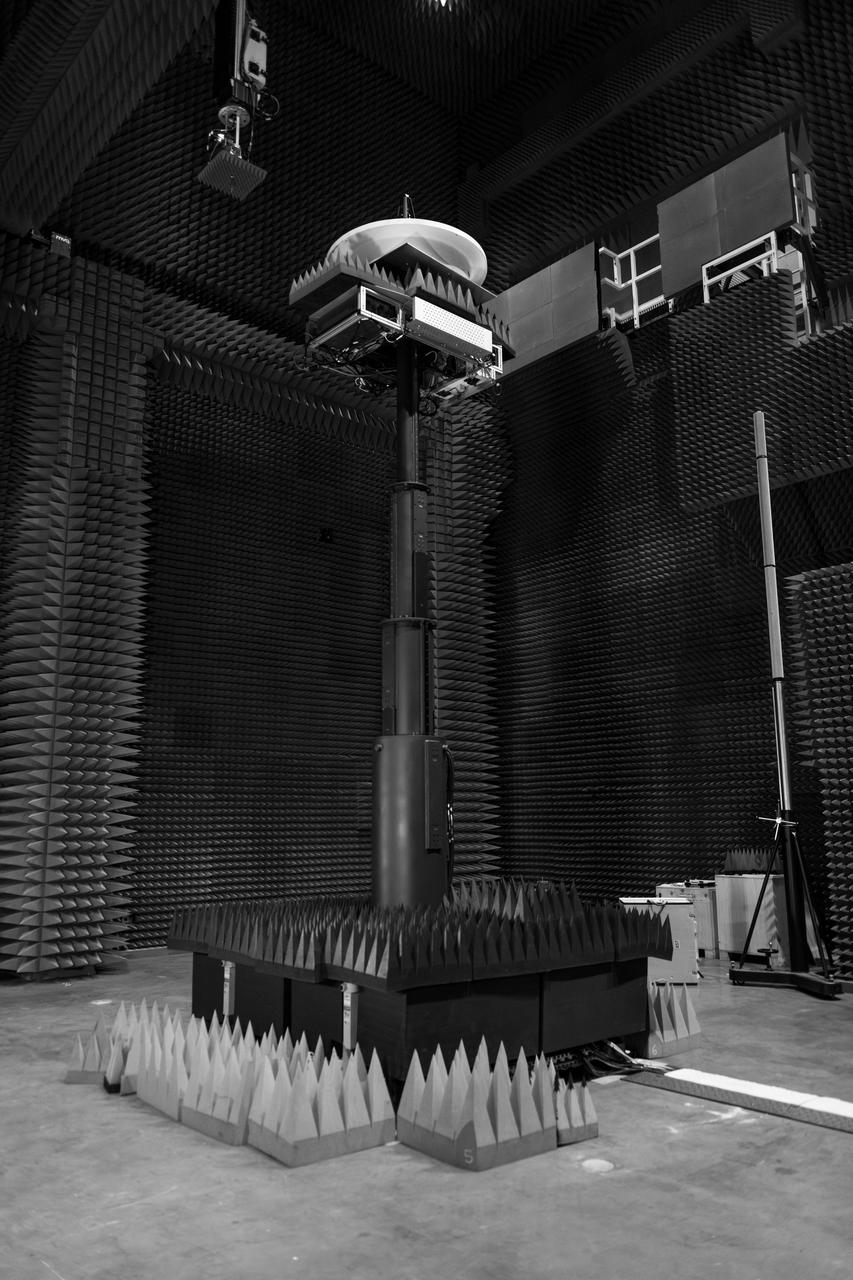

NASA’s Beaming Energy for Air Mobility team successfully completed a first-of-its-kind power beaming test at NASA Glenn on June 4, 2025. Later this year, the tested transmitter will be used in a demonstration to wirelessly transmit power using microwaves to a custom power receiver — a step toward gap-filling technology that could one day deliver power on the surface of the Moon or Mars.
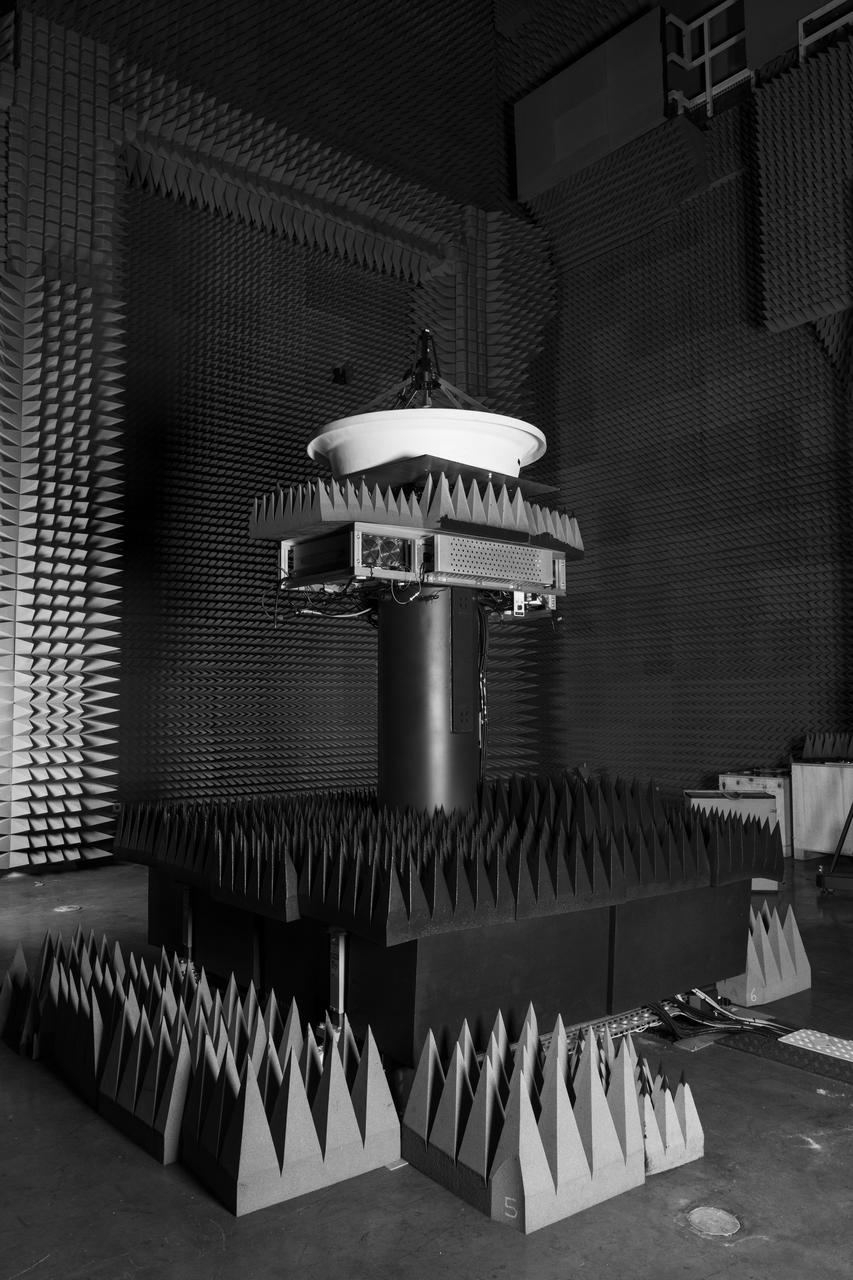

NASA’s Beaming Energy for Air Mobility team successfully completed a first-of-its-kind power beaming test at NASA Glenn on June 4, 2025. Later this year, the tested transmitter will be used in a demonstration to wirelessly transmit power using microwaves to a custom power receiver — a step toward gap-filling technology that could one day deliver power on the surface of the Moon or Mars.
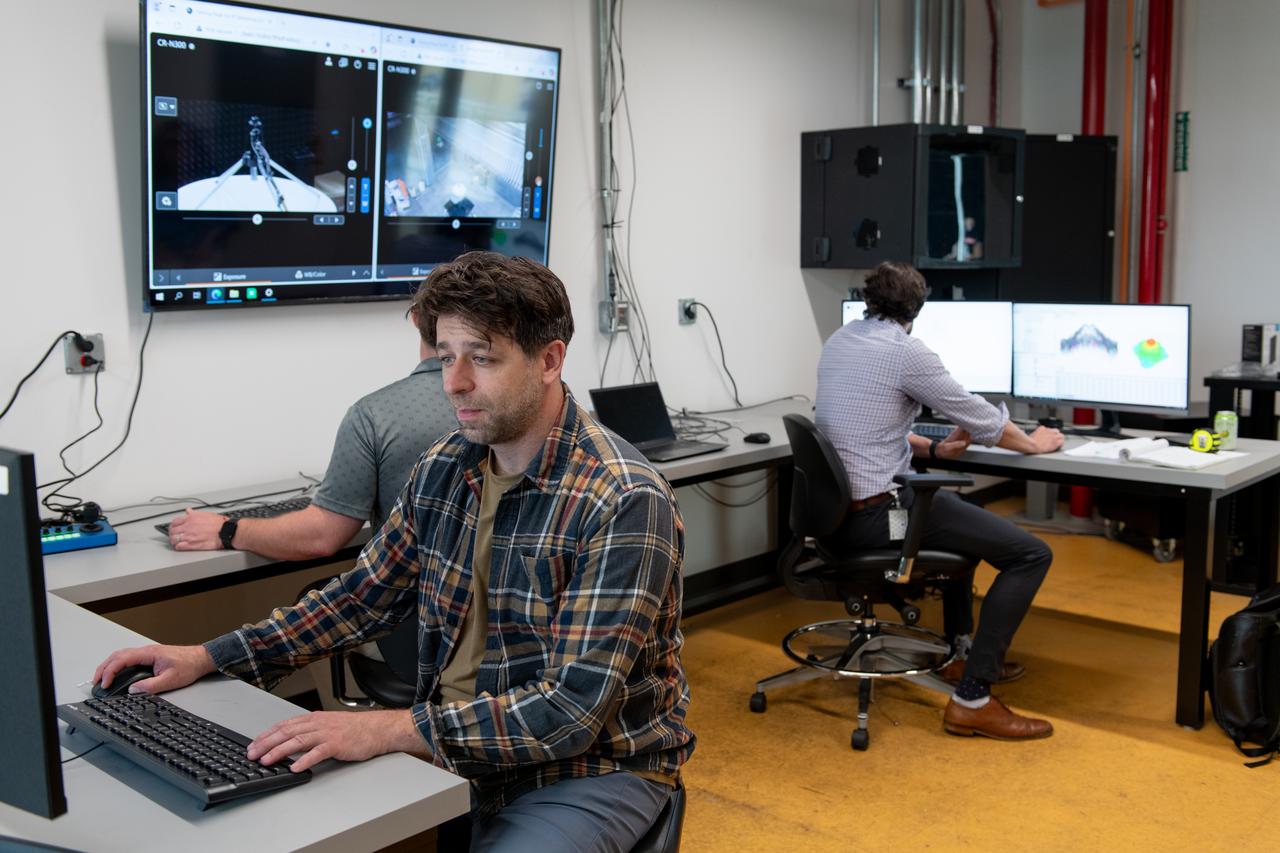

NASA’s Beaming Energy for Air Mobility team successfully completed a first-of-its-kind power beaming test at NASA Glenn. Later this year, the tested transmitter will be used in a demonstration to wirelessly transmit power using microwaves to a custom power receiver — a step toward gap-filling technology that could one day deliver power on the surface of the Moon or Mars. Seth Waldstein, Seth Schisler and Bryan Schoenholz are in the control room reviewing the data.
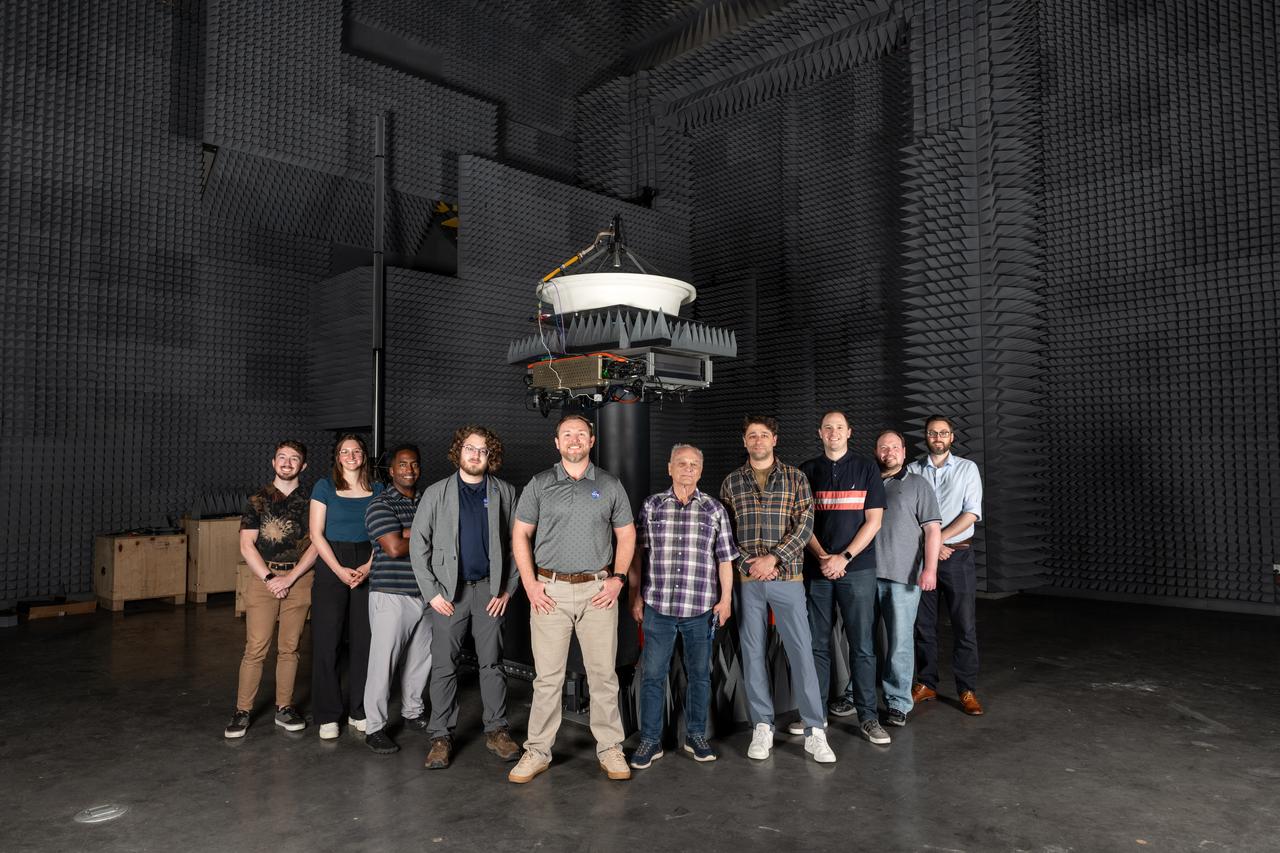

NASA’s Beaming Energy for Air Mobility team successfully completed a first-of-its-kind power beaming test at NASA Glenn on June 4, 2025. Later this year, the tested transmitter will be used in a demonstration to wirelessly transmit power using microwaves to a custom power receiver — a step toward gap-filling technology that could one day deliver power on the surface of the Moon or Mars. Pictured from left to right are Hayden Klopp, Rebecca Buehrle, Kerry Johnson, Avery Brock, Seth Schisler, Vladimir Volman, Seth Waldstein, David Rinehart, Rocco Viggiano, and Donald Dornbusch.
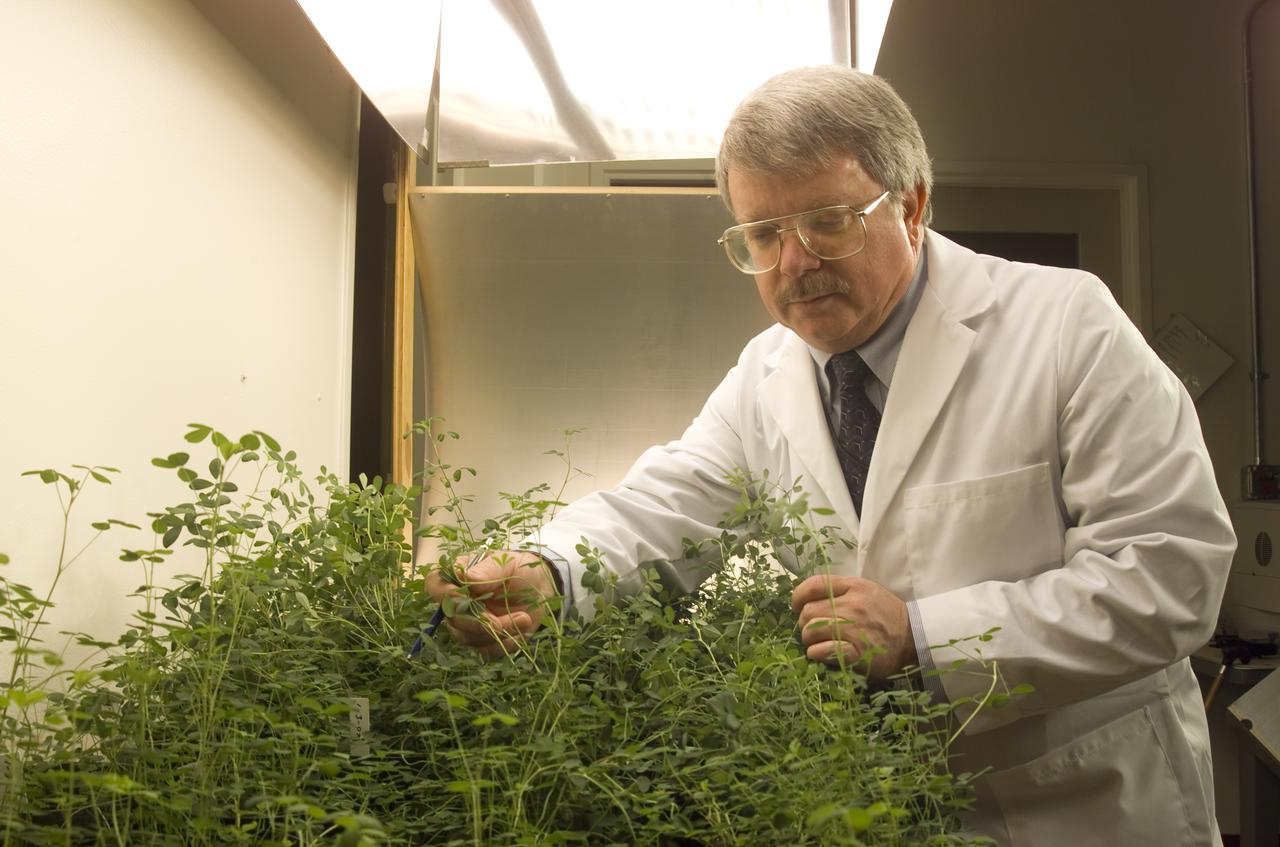

Microvave effects on plant growth (alfalfa), shown here is Dr. Jay Skiles of NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. NASA scientists are about to test that hypothesis by evaluating the effects of continuously beaming weak microwaves on alfalfa plants during laboratory tests. Microwaves derived from solar power and transmitted by orbiting satellites to electric power stations on Earth may someday enable U.S. energy self-sufficiency, but is this method safe for local plant life?
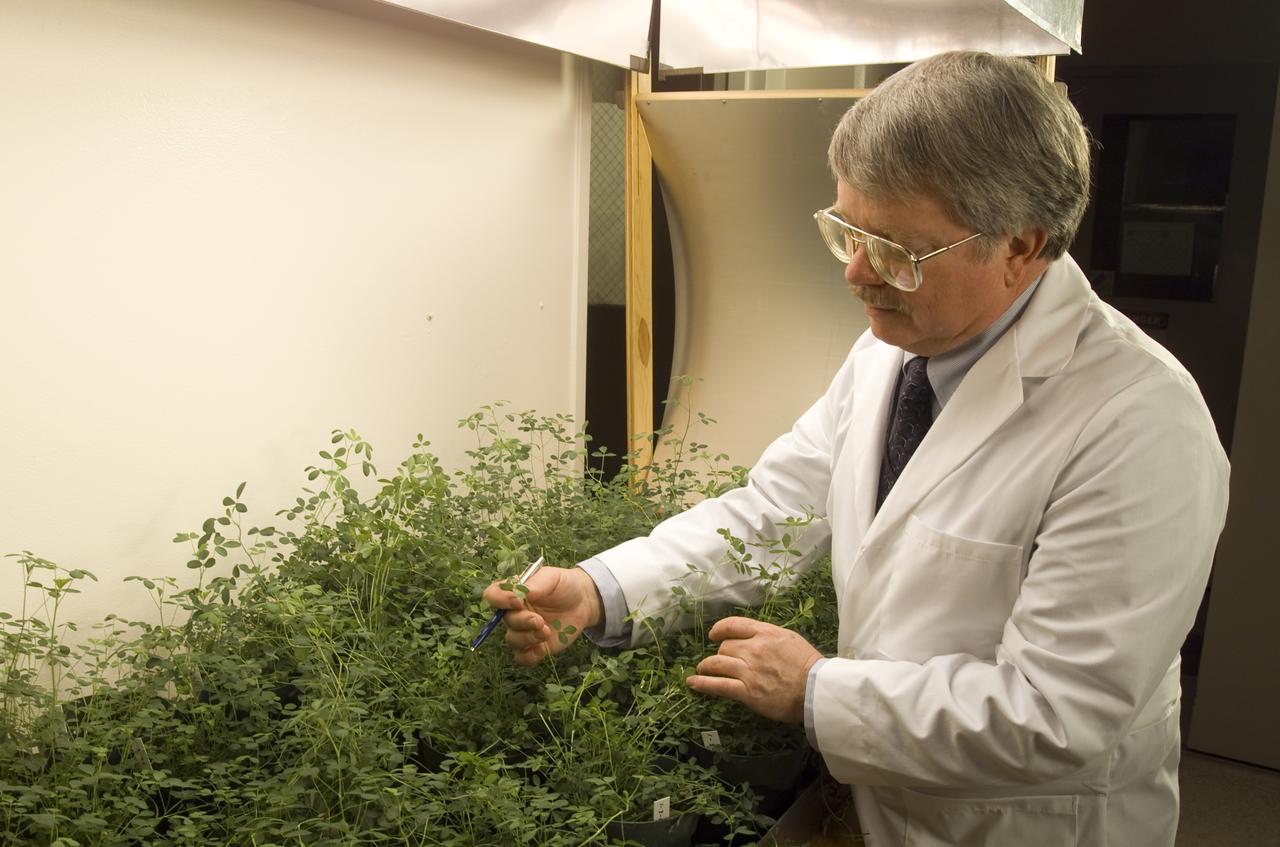

Microvave effects on plant growth (alfalfa), shown here is Dr. Jay Skiles of NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. NASA scientists are about to test that hypothesis by evaluating the effects of continuously beaming weak microwaves on alfalfa plants during laboratory tests. Microwaves derived from solar power and transmitted by orbiting satellites to electric power stations on Earth may someday enable U.S. energy self-sufficiency, but is this method safe for local plant life?
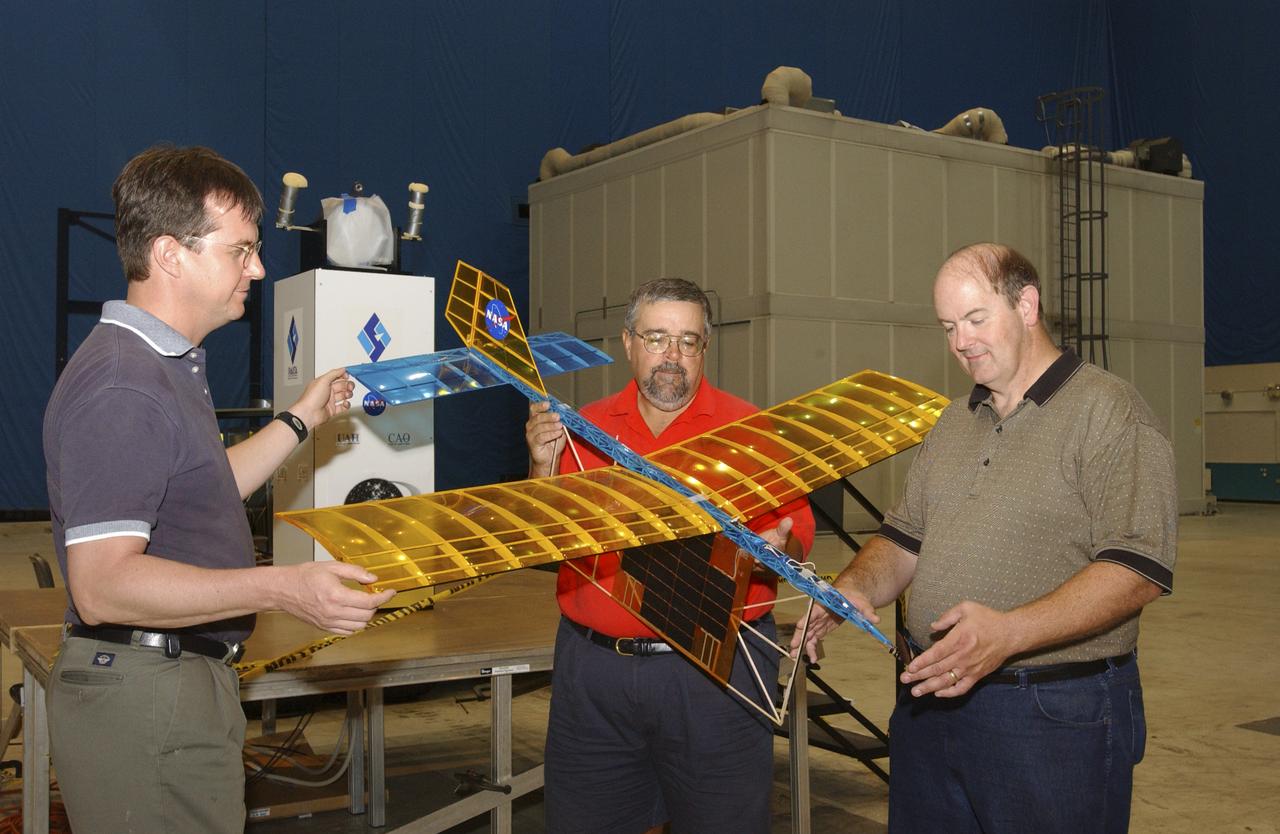

A team of NASA researchers from Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and Dryden Flight Research center have proven that beamed light can be used to power an aircraft, a first-in-the-world accomplishment to the best of their knowledge. Using an experimental custom built radio-controlled model aircraft, the team has demonstrated a system that beams enough light energy from the ground to power the propeller of an aircraft and sustain it in flight. Special photovoltaic arrays on the plane, similar to solar cells, receive the light energy and convert it to electric current to drive the propeller motor. In a series of indoor flights this week at MSFC, a lightweight custom built laser beam was aimed at the airplane `s solar panels. The laser tracks the plane, maintaining power on its cells until the end of the flight when the laser is turned off and the airplane glides to a landing. The laser source demonstration represents the capability to beam more power to a plane so that it can reach higher altitudes and have a greater flight range without having to carry fuel or batteries, enabling an indefinite flight time. The demonstration was a collaborative effort between the Dryden Center at Edward's, California, where the aircraft was designed and built, and MSFC, where integration and testing of the laser and photovoltaic cells was done. Laser power beaming is a promising technology for consideration in new aircraft design and operation, and supports NASA's goals in the development of revolutionary aerospace technologies. Photographed with their invention are (from left to right): David Bushman and Tony Frackowiak, both of Dryden; and MSFC's Robert Burdine.

jsc2025e076915 (September 25, 2025) -- This is the ENPULSION Nano Lark thruster, a unit that contains its own power, propellant, and ion beam systems. While this thruster is not tested on station, the MICATOS investigation observes how molten indium behaves in microgravity, which could improve future thrusters of this type and refine methods for in-space soldering. Image courtesy of Enpulsion.
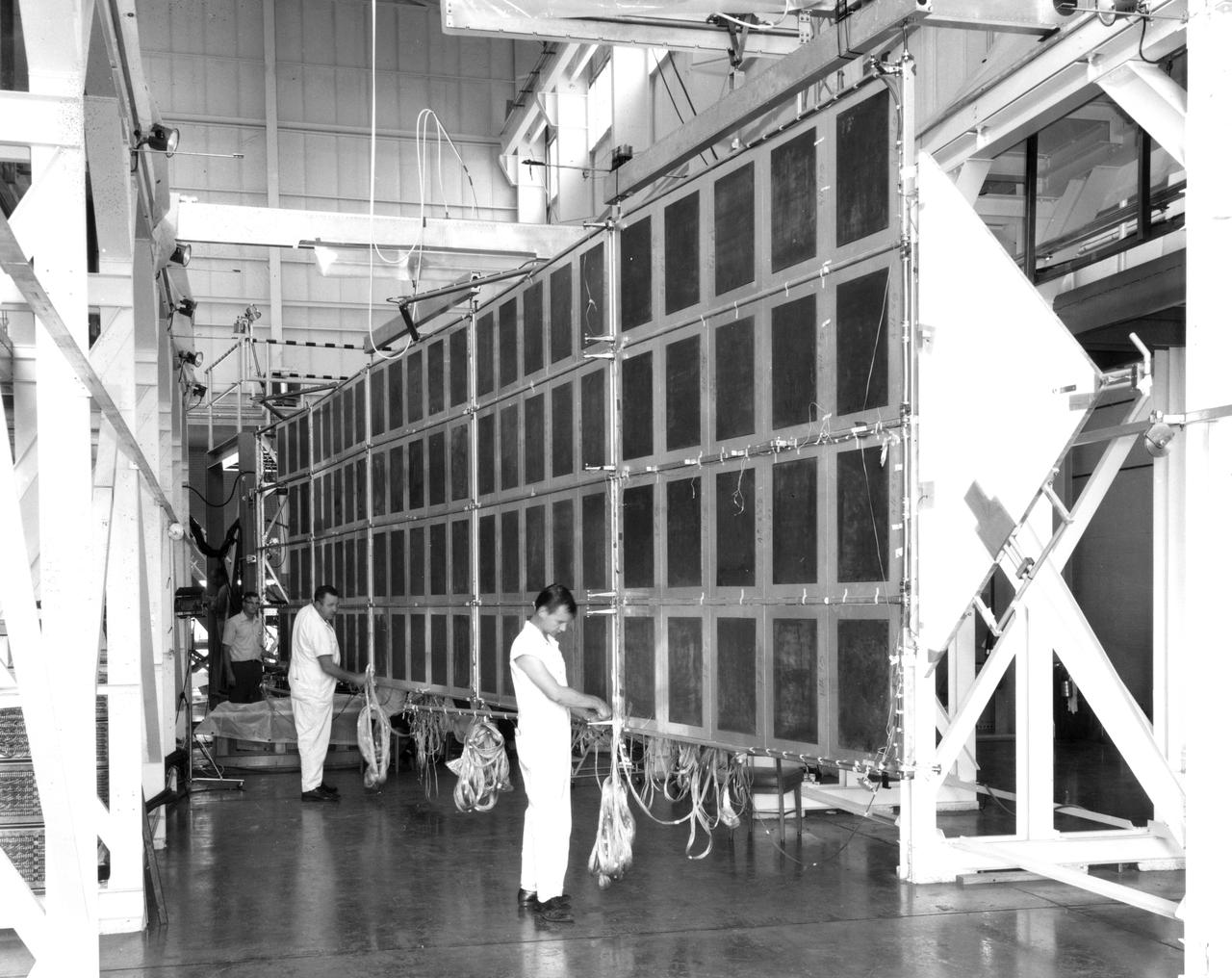

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center check the wiring on a mechanical test article of the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) solar array. Four such arrays were joined in a cross to provide electric power for the ATM in Earth orbit. The deployment mechanism for extending the wing to the fully open position had just been tested when this photograph was taken. The array was suspended from beams riding on air bearings to closely simulate the weightless conditions under which it would be deployed in space. The wings are folded against the sides of the ATM for launch and are deployed by a scissors mechanism in Earth’s orbit.
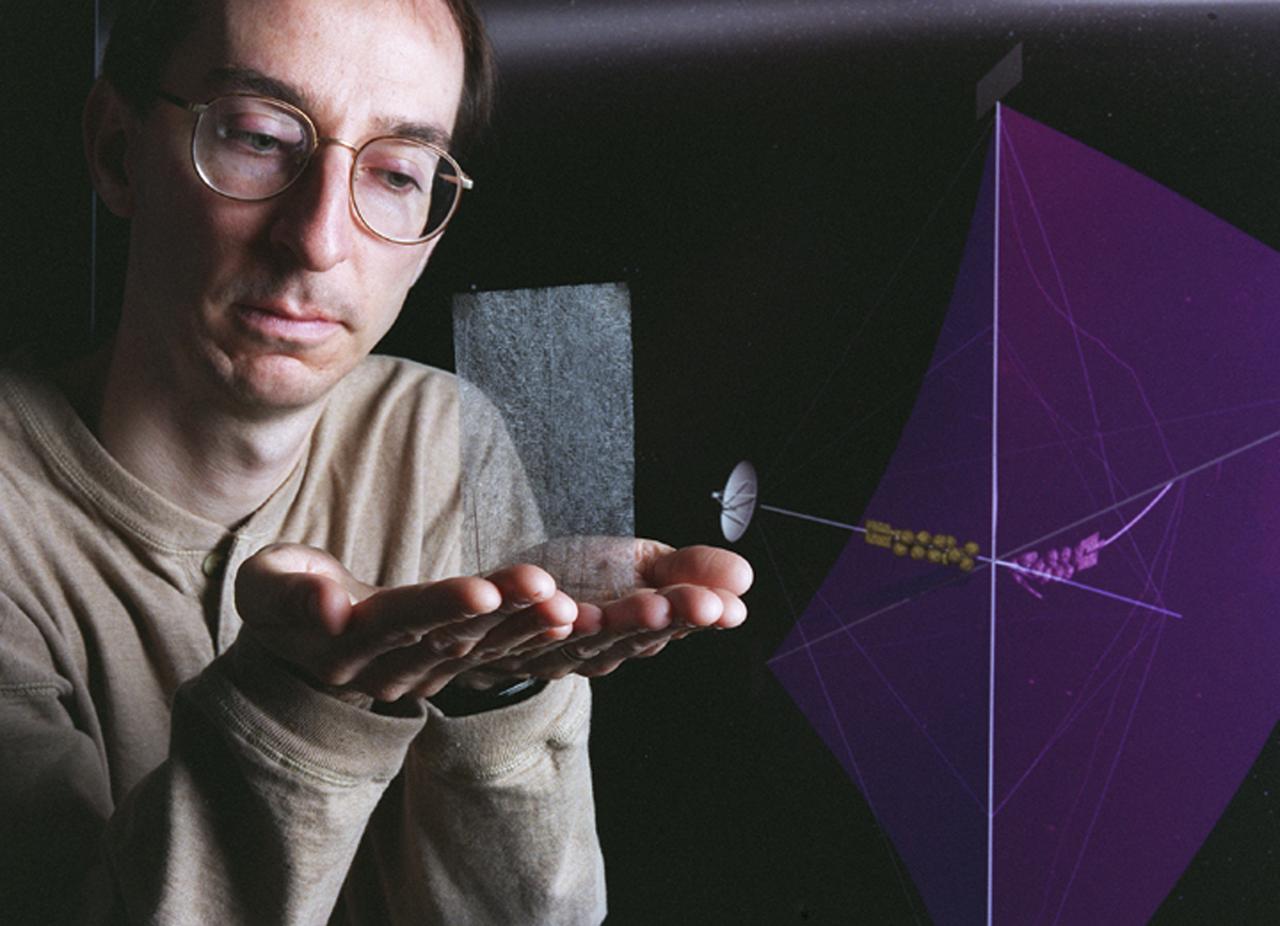

Engineers at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Interstellar Propulsion Research department are proposing different solutions to combustion propellants for future space travel. One alternative being tested is the solar sail. The idea is, once deployed, the sail will allow solar winds to propel a spacecraft away from Earth and towards its destination. This would allow a spacecraft to travel indefinitely without the need to refuel during its ong journey. Thin reflective sails could be propelled through space by sunlight, microwave beams, or laser beams, just as the wind pushes sailboats on Earth. The sail will be the largest spacecraft ever built, sparning 440 yards, twice the diameter of the Louisiana Super Dome. Construction materials are being tested in a simulated space environment, where they are exposed to harsh conditions to test their performance and durability in extremely hot and cold temperatures. A leading candidate for the construction material is a carbon fiber material whose density is less than 1/10 ounce per square yard, the equivalent of flattening one raisin to the point that it covers a square yard. In space, the material would unfurl like a fan when it is deployed from an expendable rocket. This photo shows Les Johnson, manager of MSFC's Interstellar Propulsion Research Center holding the rigid, lightweight carbon fiber. An artist's concept of the sail is on the right. Mankind's first venture outside of our solar system is proposed for launch in a 2010 timeframe. An interstellar probe, powered by the fastest spacecraft ever flown, will zoom toward the stars at 58 miles per second. It will cover the distance from New York to Los Angeles in less than a minute and will travel over 23 billion miles beyond the edge of the solar system.
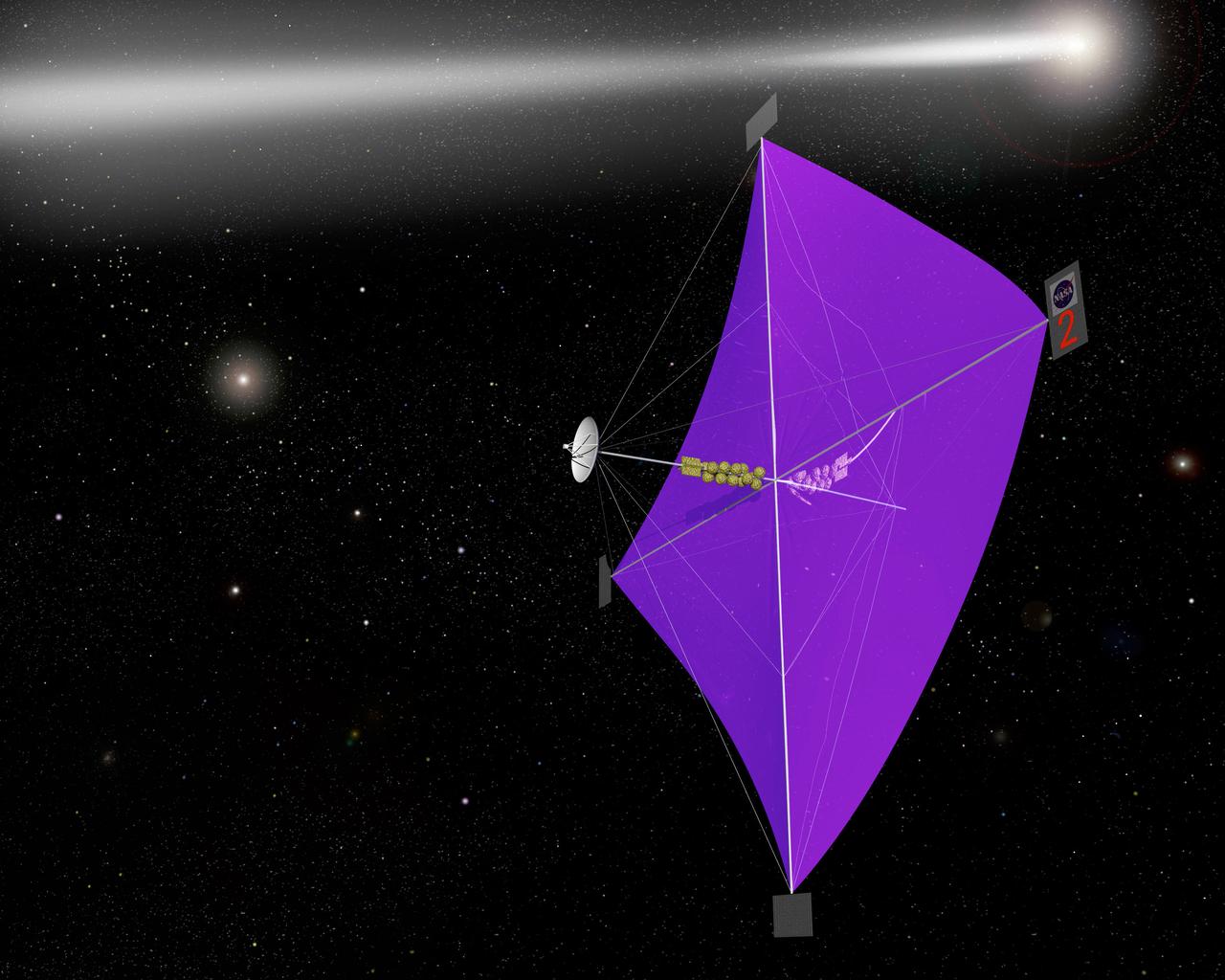
Engineers at Marshall Space Flight Center's Interstellar Propulsion Research department are proposing different solutions to combustion propellants for future space travel. Pictured here is one alternative, the solar sail, depicted through an artist's concept. The idea is, once deployed, the sail will allow solar winds to propel a spacecraft away from Earth and towards its destination. This would allow a spacecraft to travel indefinitely without the need to refuel during its prolong journey. Thin reflective sails could be propelled through space by sunlight, microwave beams, or laser beams, just as the wind pushes sailboats on Earth. The sail will be the largest spacecraft ever built, sparning 440 yards, twice the diameter of the Louisiana Super Dome. Construction materials are being tested in a simulated space environment, where they are exposed to harsh conditions to test their performance and durability in extremely hot and cold temperatures. A leading candidate for the construction material is a carbon fiber material whose density is less than 1/10 ounce per square yard, the equivalent of flattening one raisin to the point that it covers a square yard. In space, the material would unfurl like a fan when it is deployed from an expendable rocket. Mankind's first venture outside of our solar system is proposed for launch in a 2010 timeframe. An interstellar probe, powered by the fastest spacecraft ever flown, will zoom toward the stars at 58 miles per second. It will cover the distance from New York to Los Angeles in less than a minute and will travel over 23 billion miles beyond the edge of the solar system.
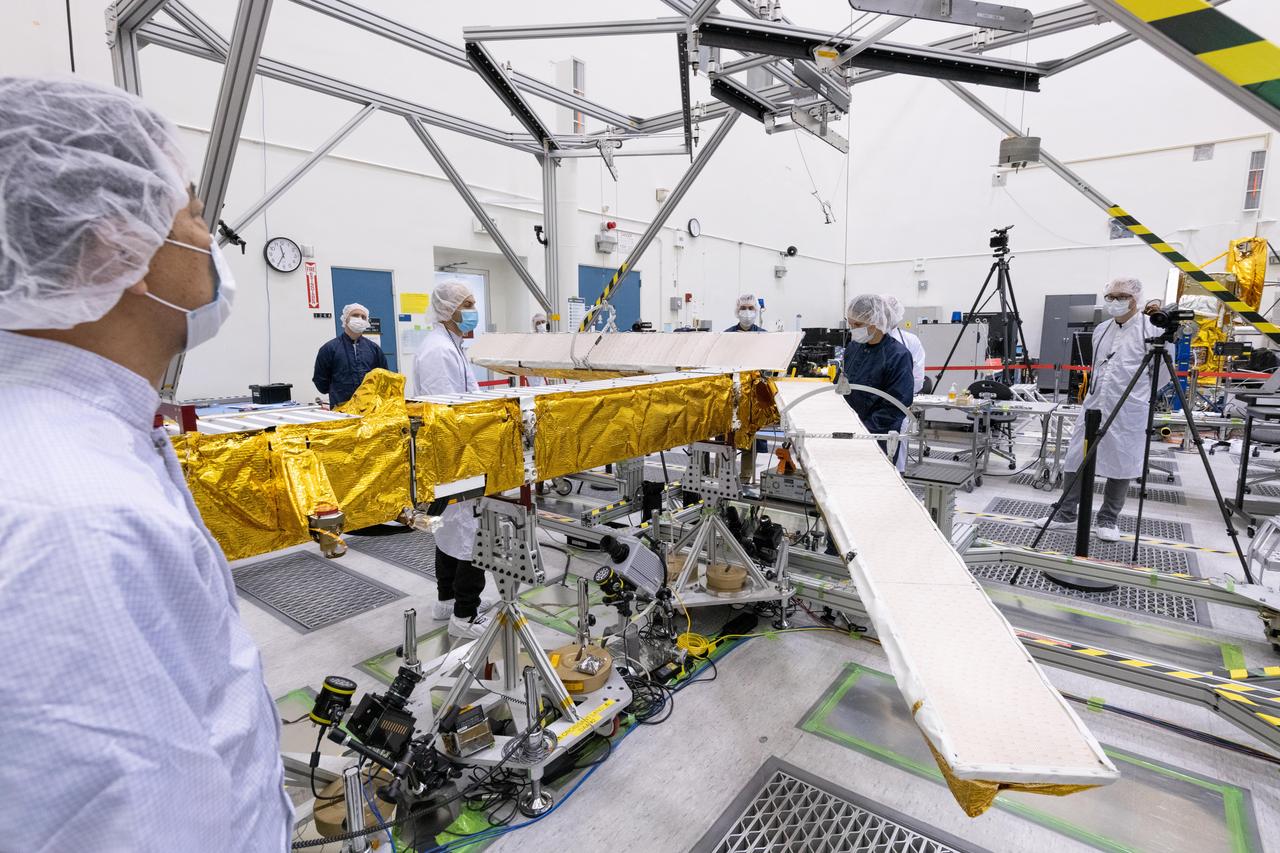

Members of the international Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission test one of the antennas for the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES) – with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the UK Space Agency. KaRIn is the scientific heart of the SWOT satellite, which will survey the water on more than 90% of Earth's surface, measuring the height of water in lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. To do that, KaRIn will transmit radar pulses to Earth's surface and use its two antennas to triangulate the return signals that bounce back. Mounted at the ends of a boom 33 feet (10 meters) long, the antennas will collect data along a swath 30 miles (50 kilometers) wide on either side of the satellite. KaRIn will operate in two modes: A lower-resolution mode over the ocean will involve significant onboard processing of the data to reduce the volume of information sent during downlinks to Earth; a higher-resolution mode will be used mainly over land. Scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Dec. 15, 2022, SWOT is being jointly developed by NASA and CNES, with contributions from the CSA and the UK Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, leads the U.S. component of the project. For the flight system payload, NASA is providing the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument, a GPS science receiver, a laser retroreflector, a two-beam microwave radiometer, and NASA instrument operations. CNES is providing the Doppler Orbitography and Radioposition Integrated by Satellite (DORIS) system, the dual frequency Poseidon altimeter (developed by Thales Alenia Space), the KaRIn radio-frequency subsystem (together with Thales Alenia Space and with support from the UK Space Agency), the satellite platform, and ground control segment. CSA is providing the KaRIn high-power transmitter assembly. NASA is providing the launch vehicle and associated launch services. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25594
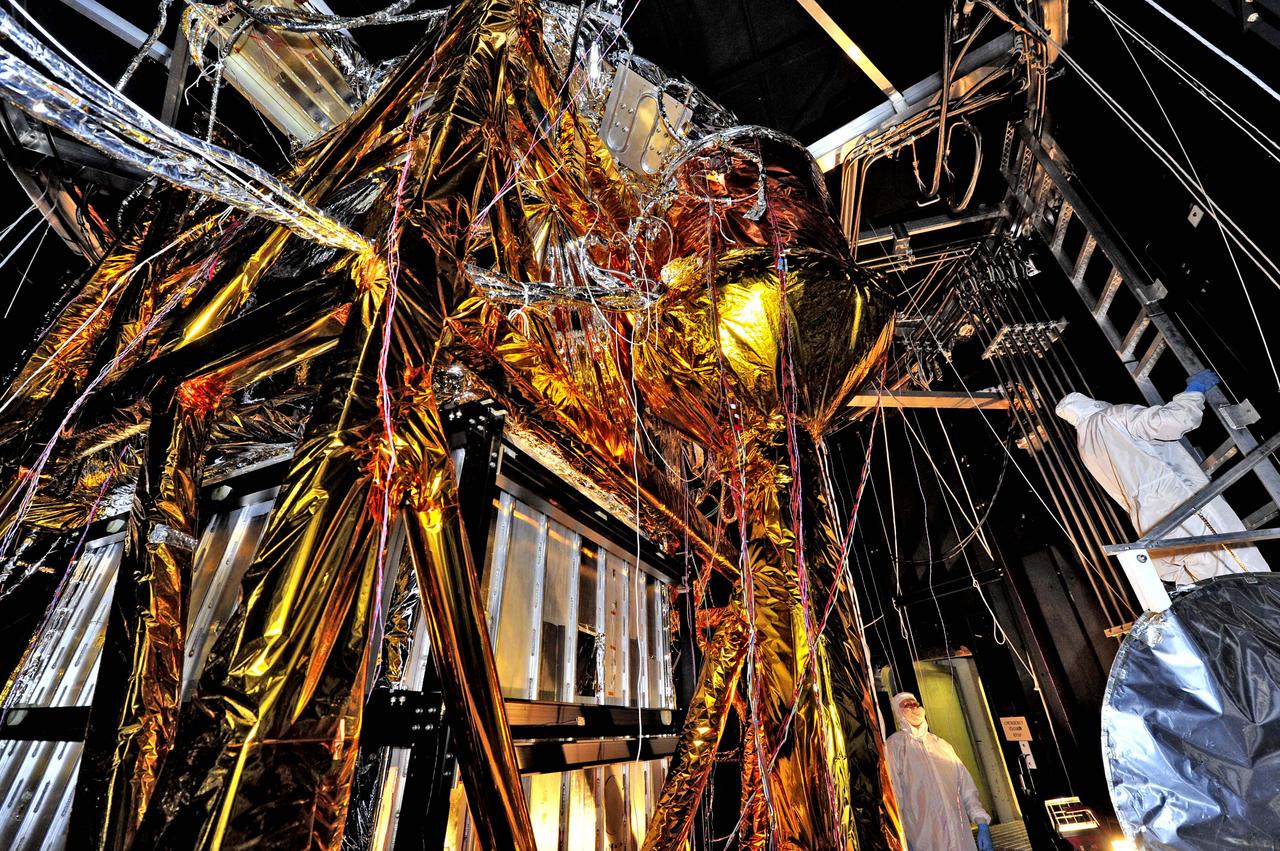

NASA image release August 23, 2012 What looks like a giant golden spider weaving a web of cables and cords, is actually ground support equipment, including the Optical Telescope Simulator (OSIM), for the James Webb Space Telescope. OSIM's job is to generate a beam of light just like the one that the real telescope optics will feed into the actual flight instruments. Because the real flight instruments will be used to test the real flight telescope, their alignment and performance first have to be verified by using the OSIM. Engineers are thoroughly checking out OSIM now in preparation for using it to test the flight science instruments later. This photo was taken from inside a large thermal-vacuum chamber called the Space Environment Simulator (SES), at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Engineers have blanketed the structure of the OSIM with special insulating material to help control its temperature while it goes into the deep freeze testing that mimics the chill of space that Webb will ultimately experience in its operational orbit over 1 million miles from Earth. The golden-colored thermal blankets are made of aluminized kapton, a polymer film that remains stable over a wide range of temperatures. The structure that looks like a silver and black cube underneath the "spider" is a set of cold panels that surround OSIM's optics. During testing, OSIM's temperature will drop to 100 Kelvin (-280 F or -173 C) as liquid nitrogen flows through tubes welded to the chamber walls and through tubes along the silver panels surrounding OSIM's optics. These cold panels will keep the OSIM optics very cold, but the parts covered by the aluminized kapton blankets will stay warm. "Some blankets have silver facing out and gold facing in, or inverted, or silver on both sides, etc.," says Erin Wilson, a Goddard engineer. "Depending on which side of the blanket your hardware is looking at, the blankets can help it get colder or stay warmer, in an environmental test." Another reason for thermal blankets is to shield the cold OSIM optics from unwanted stray infrared light. When the OSIM is pointing its calibrated light beam at Webb's science instruments, engineers don't want any stray infrared light, such as "warm photons" from warm structures, leaking into the instruments' field of view. Too much of this stray light would raise the background too much for the instruments to "see" light from the OSIM—it would be like trying to photograph a lightning bug flying in front of car headlights. To get OSIM's optics cold, the inside of the chamber has to get cold, and to do that, all the air has to be pumped out to create a vacuum. Then liquid nitrogen has to be run though the plumbing along the inner walls of the chamber. Wilson notes that's why the blankets have to have vents in them: "That way, the air between all the layers can be evacuated as the chamber pressure drops, otherwise the blankets could pop," says Wilson. The most powerful space telescope ever built, Webb is the successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Webb's four instruments will reveal how the universe evolved from the Big Bang to the formation of our solar system. Webb is a joint project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>