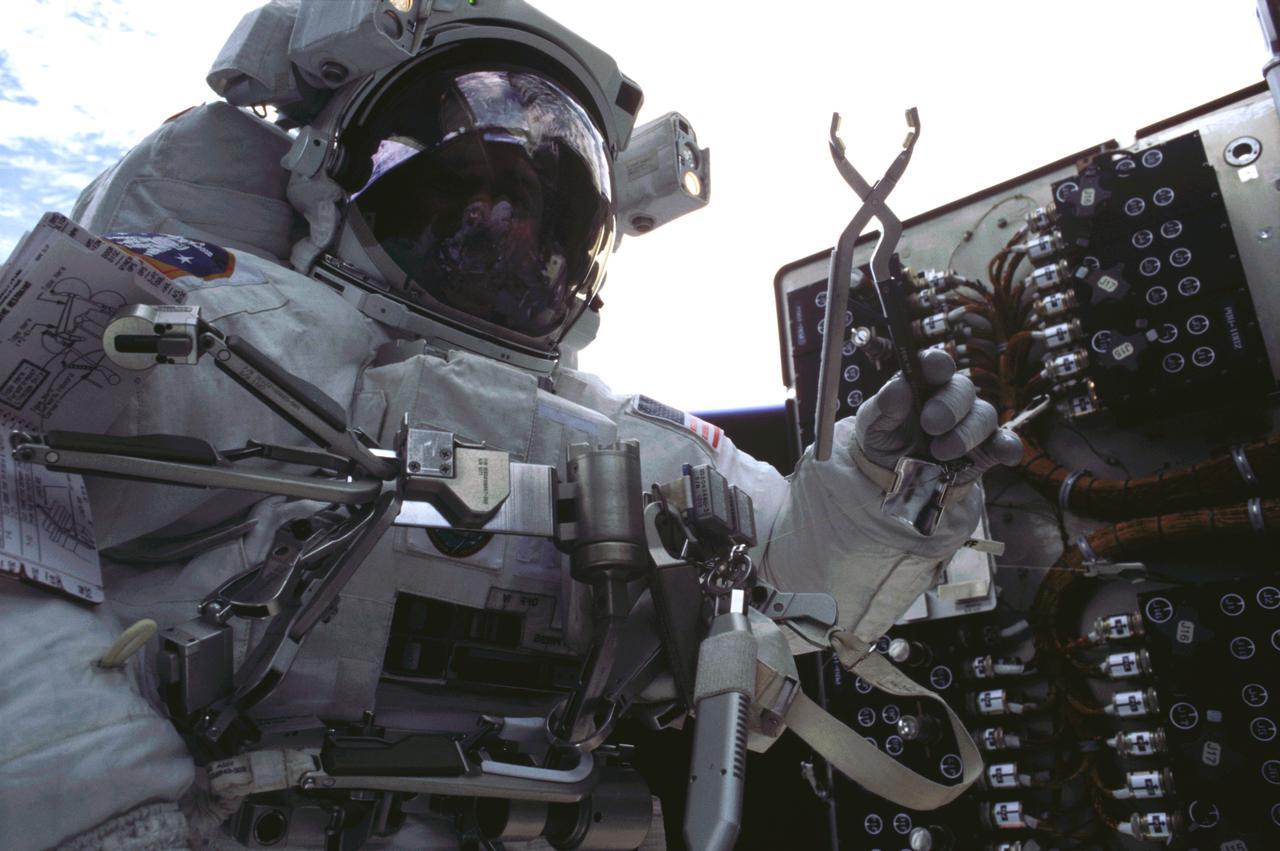

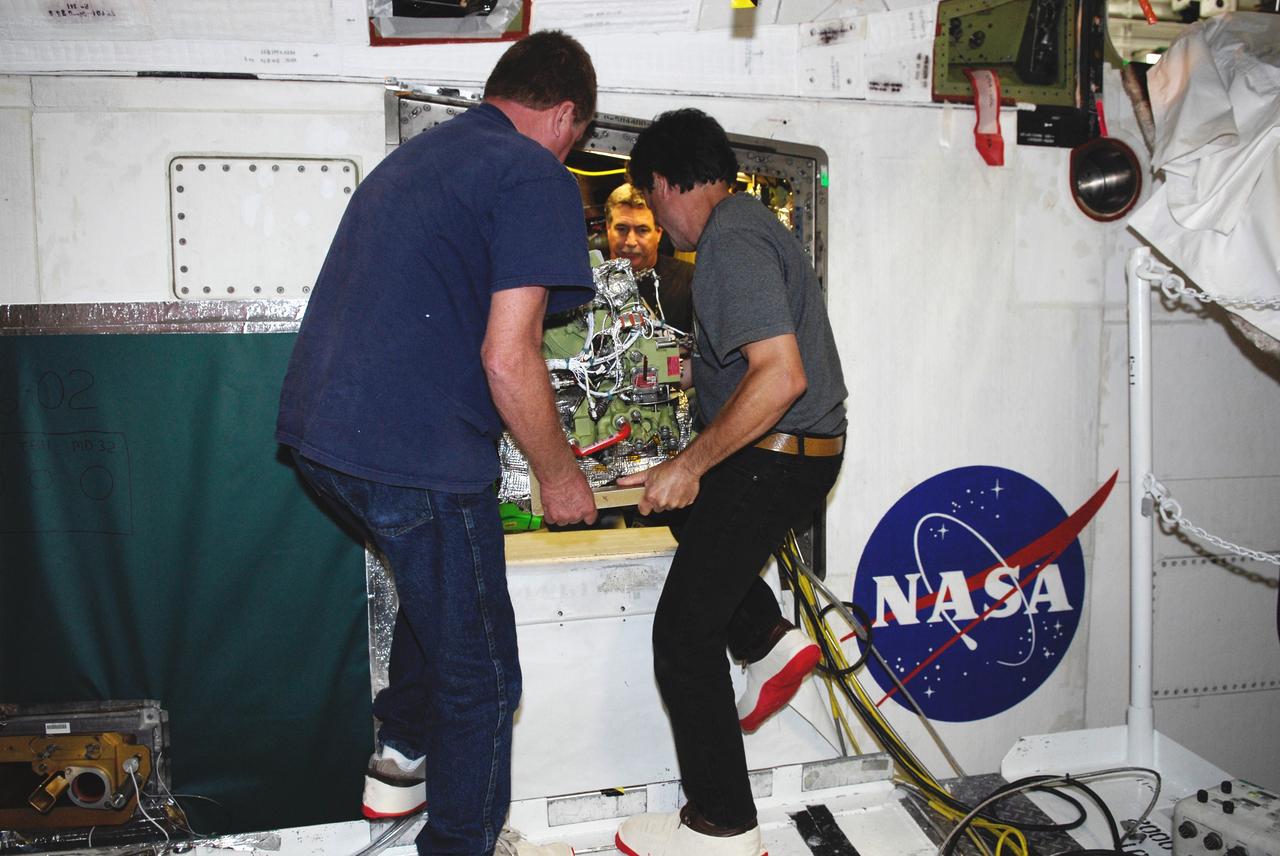
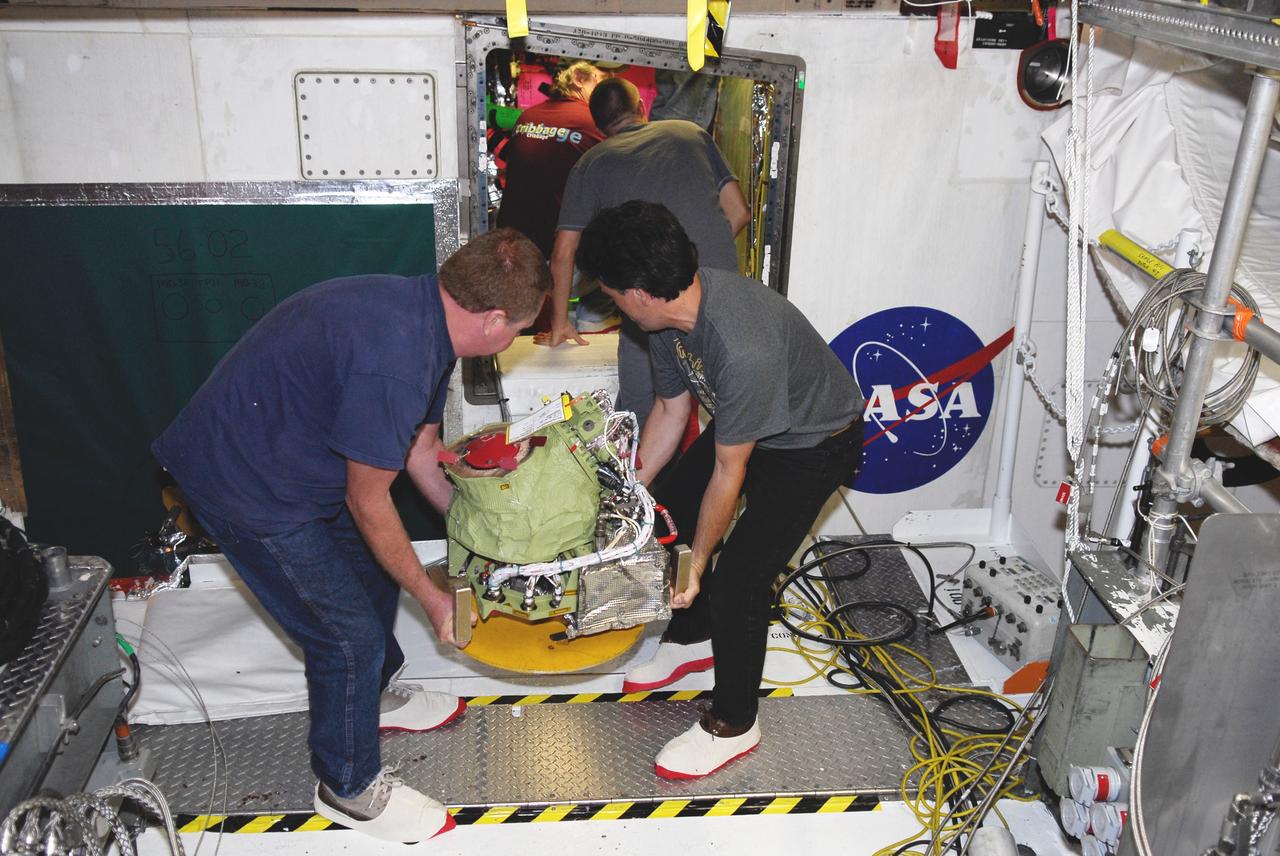
STS109-322-029 (6 March 2002) --- Astronaut John M. Grunsfeld, STS-109 payload commander, participates in the third of five space walks to perform work on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The third overall STS-109 extravehicular activity (EVA) marked the second of three for Grunsfeld, who was joined by astronaut Richard M. Linnehan on them all. On this particular walk, astronauts Grunsfeld and Linnehan turned off the telescope in order to replace its power control unit or PCU, the heart of the HST’s power system.
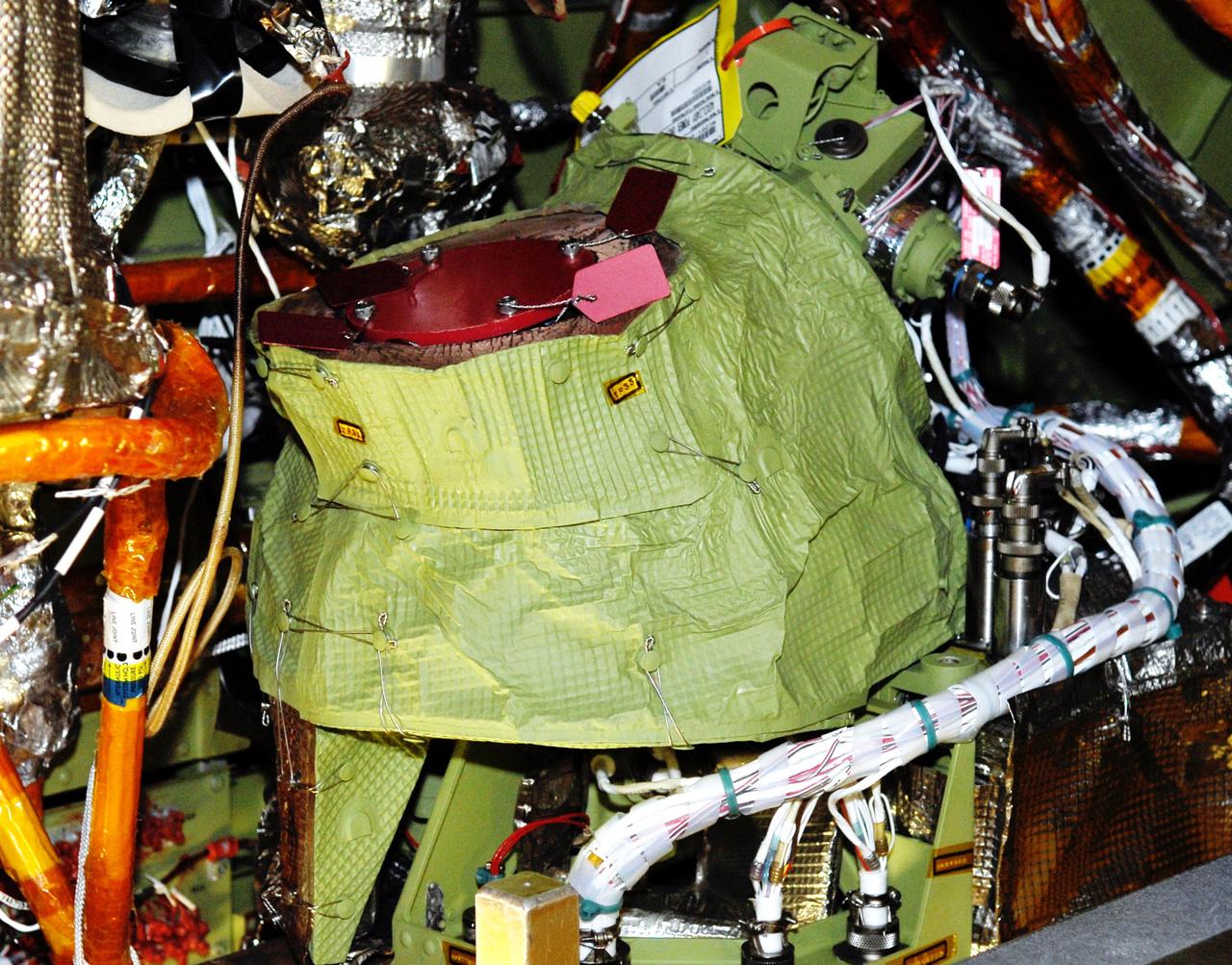
This is an onboard photo of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) power control unit (PCU), the heart of the HST's power system. STS-109 payload commander John M. Grunsfeld, joined by Astronaut Richard M. Lirnehan, turned off the telescope in order to replace its PCU while participating in the third of five spacewalks dedicated to servicing and upgrading the HST. Other upgrades performed were: replacement of the solar array panels; replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS); and installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS), which had been dormant since January 1999 when its original coolant ran out. The telescope was captured and secured on a work stand in Columbia's payload bay using Columbia's robotic arm, where crew members completed the system upgrades. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the responsibility for the design, development, and construction of the HST, which is the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. Launched March 1, 2002 the STS-109 HST servicing mission lasted 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes. It was the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program.
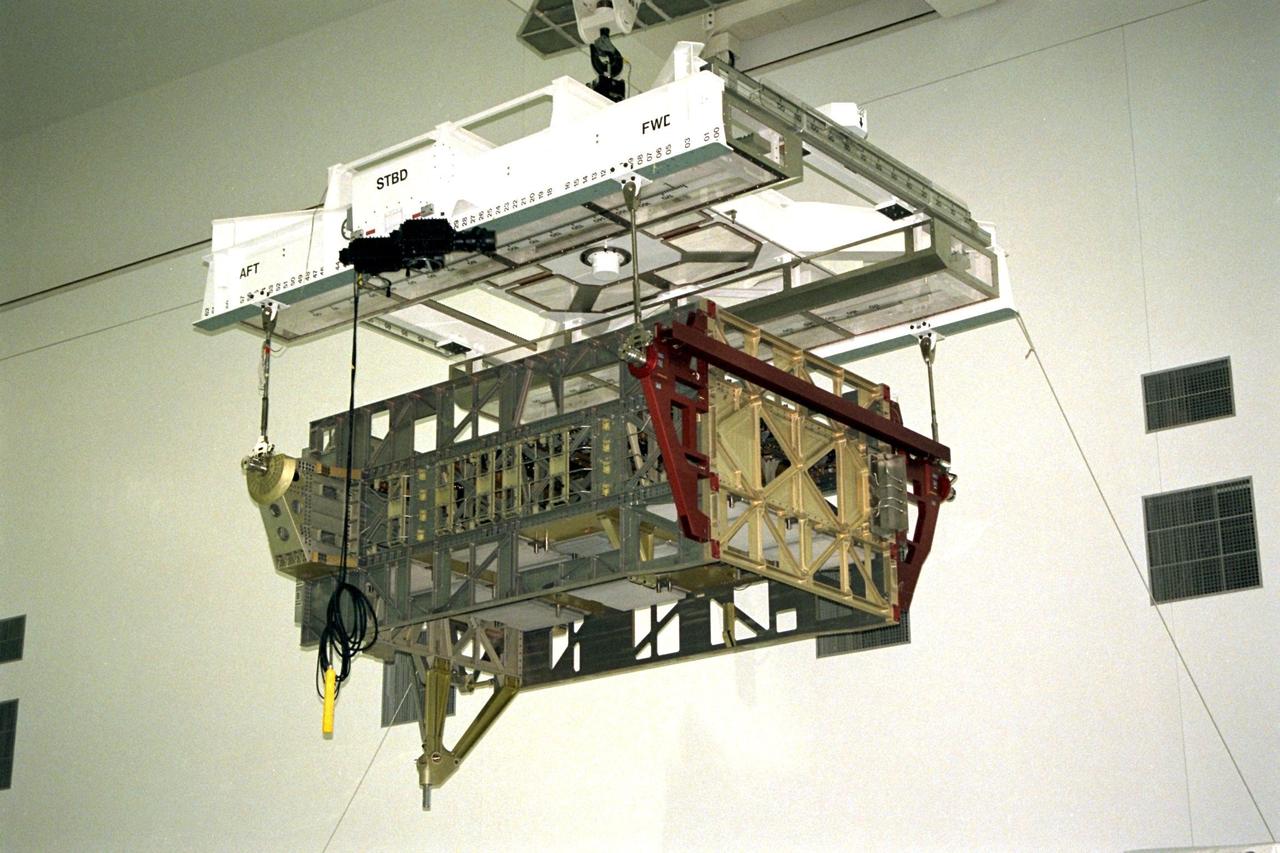

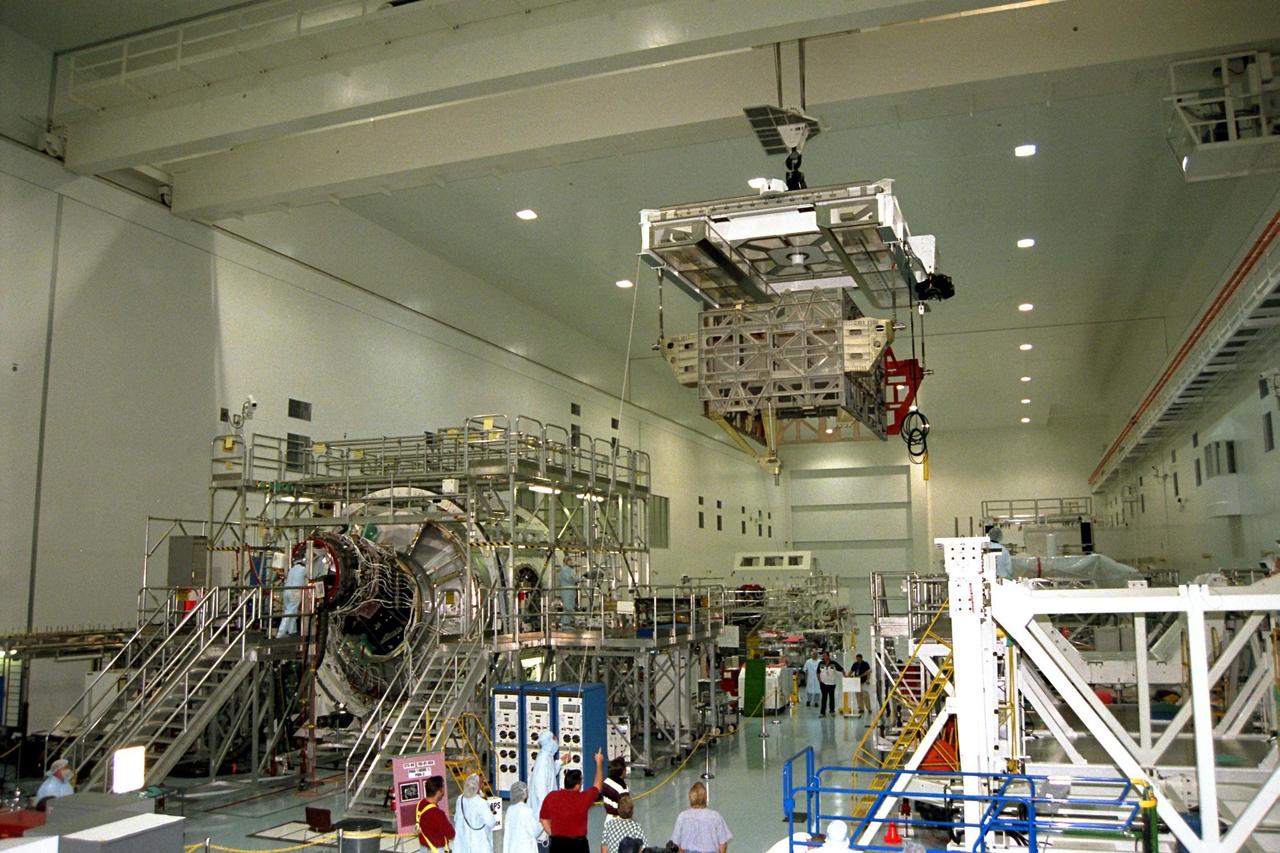
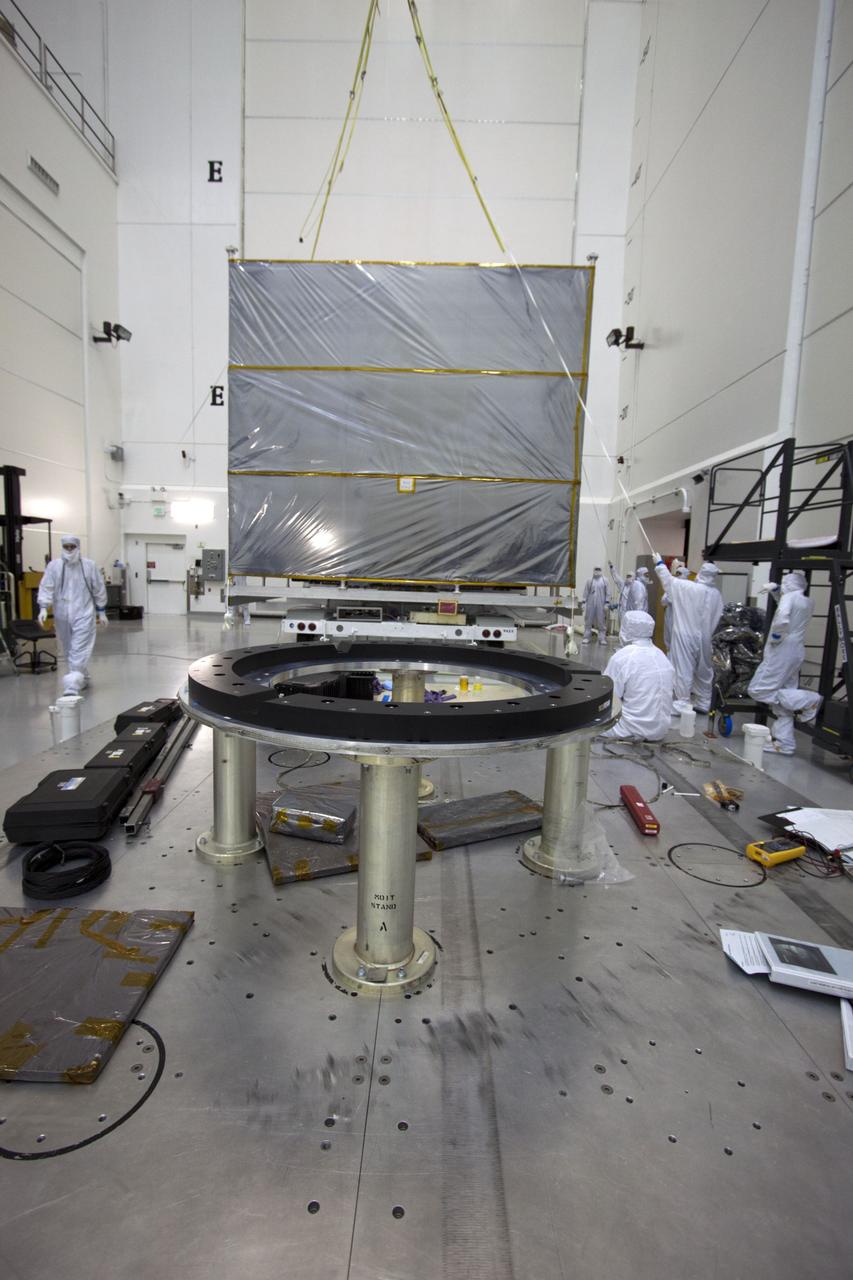
The Photovoltaic Module 1 Integrated Equipment Assembly (IEA) is moved through Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) toward the workstand where it will be processed for flight on STS-97, scheduled for launch in April 1999. The IEA is one of four integral units designed to generate, distribute, and store power for the International Space Station. It will carry solar arrays, power storage batteries, power control units, and a thermal control system. The 16-foot-long, 16,850-pound unit is now undergoing preflight preparations in the SSPF
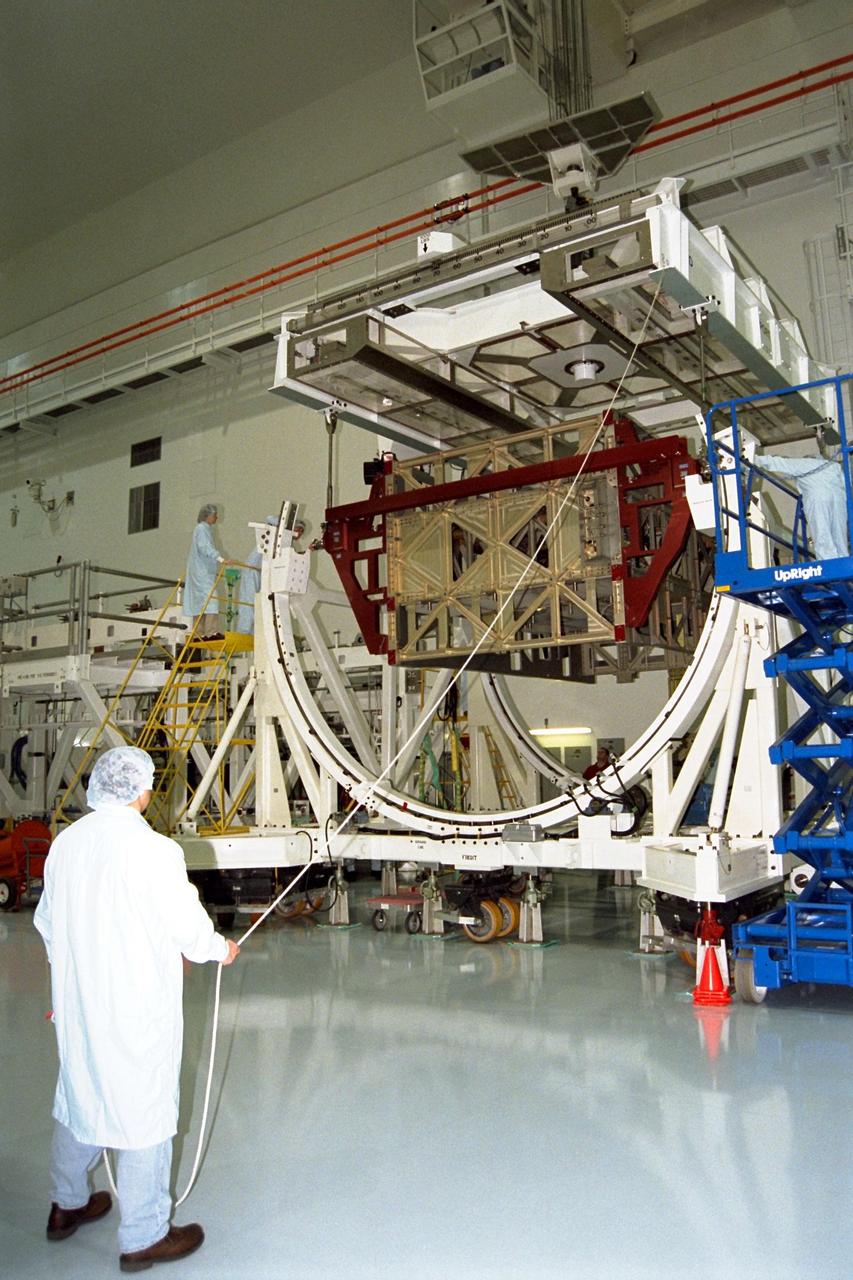

The Photovoltaic Module 1 Integrated Equipment Assembly (IEA) is lowered into its workstand at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF), where it will be processed for flight on STS-97, scheduled for launch in April 1999. The IEA is one of four integral units designed to generate, distribute, and store power for the International Space Station. It will carry solar arrays, power storage batteries, power control units, and a thermal control system. The 16-foot-long, 16,850-pound unit is now undergoing preflight preparations in the SSPF
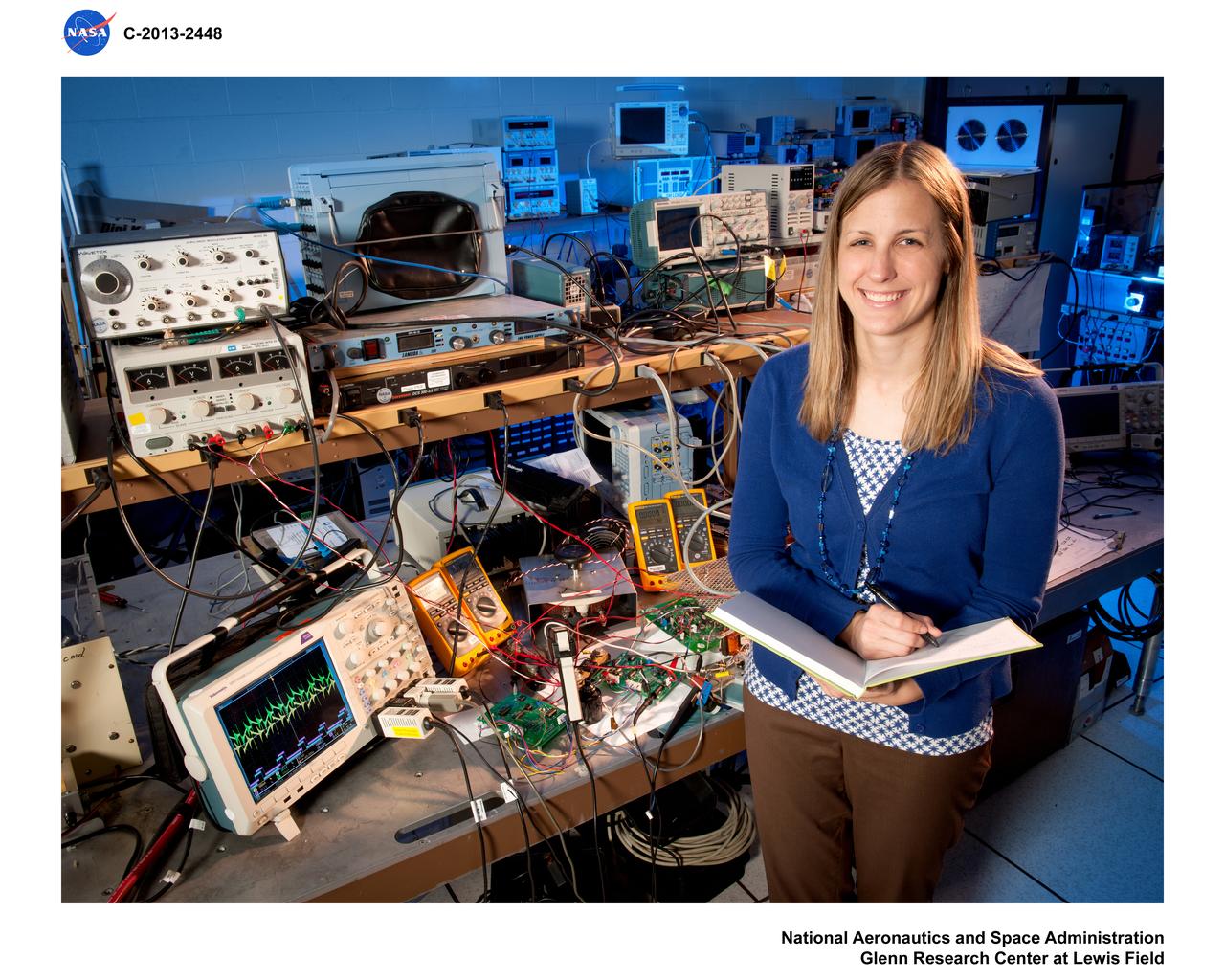
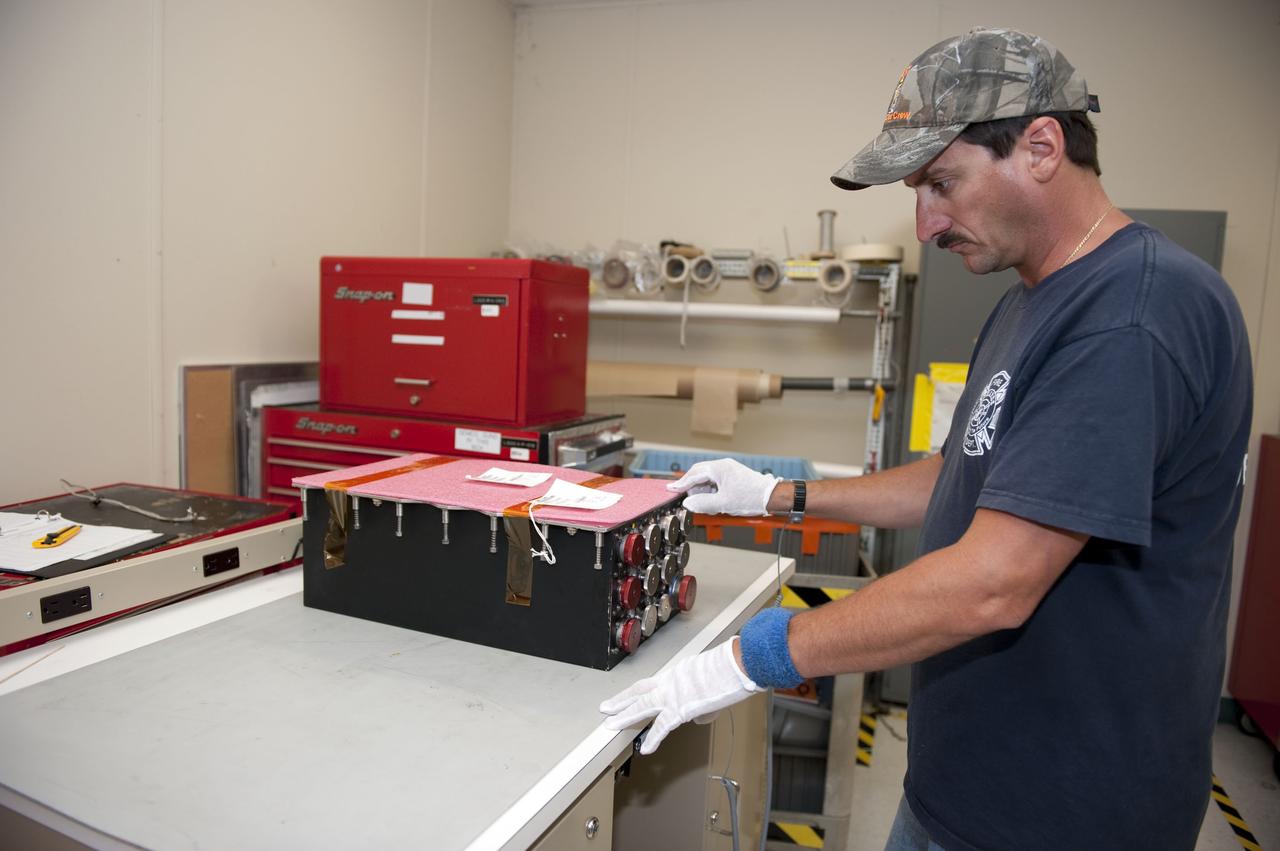
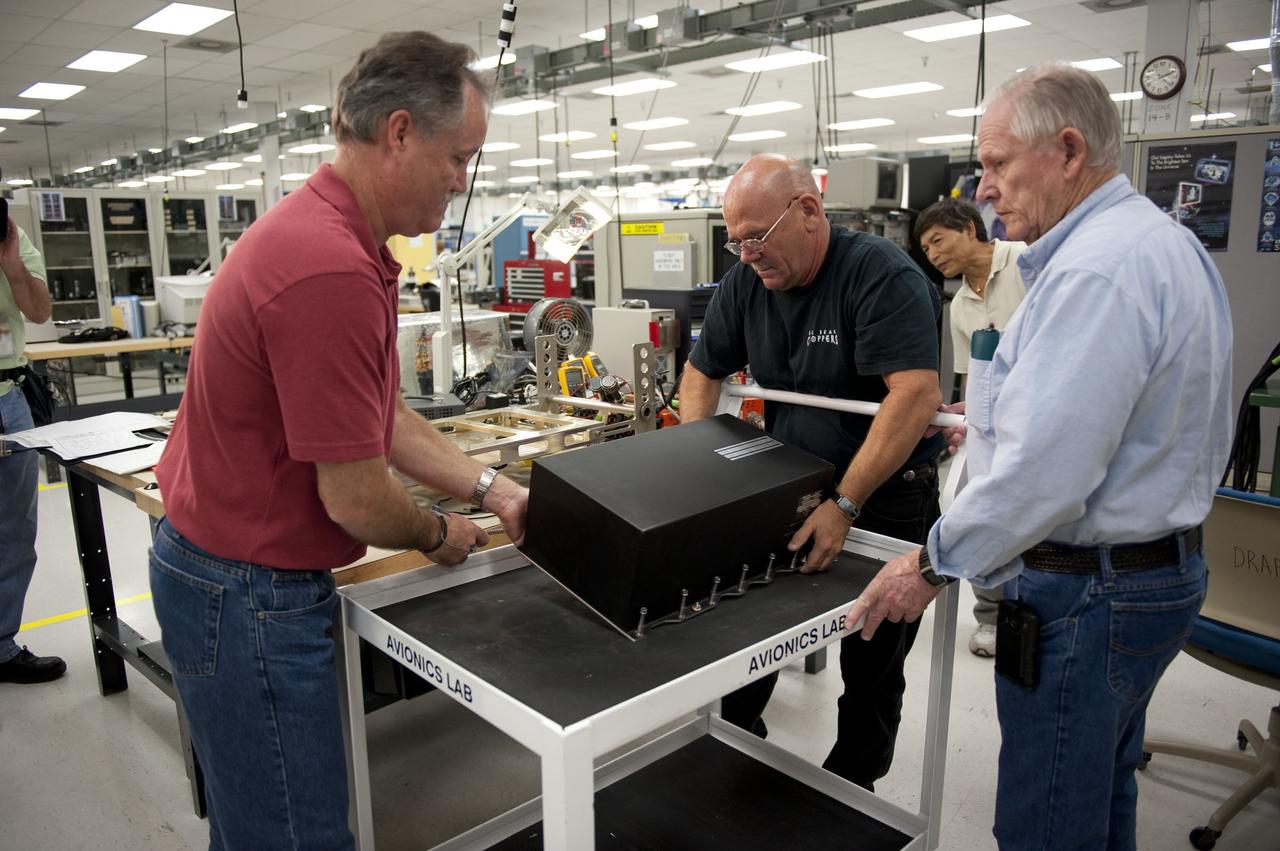
Environmental Portrait, Electrical Power Systems Employee, hardware for the High Power 300-Volt Power Processing Unit (PPU). The Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the Discharge Module Inverter and the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Controller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility bay No. 2, auxiliary power unit 3, or APU3, is in place on space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-126 mission. The auxiliary power unit is a hydrazine-fueled, turbine-driven power unit that generates mechanical shaft power to drive a hydraulic pump that produces pressure for the orbiter's hydraulic system. There are three separate APUs, three hydraulic pumps and three hydraulic systems, located in the aft fuselage of the orbiter. When the three auxiliary power units are started five minutes before lift-off, the hydraulic systems are used to position the three main engines for activation, control various propellant valves on the engines and position orbiter aerosurfaces. The auxiliary power units are not operated after the first orbital maneuvering system thrusting period because hydraulic power is no longer required. One power unit is operated briefly one day before deorbit to support checkout of the orbiter flight control system. One auxiliary power unit is restarted before the deorbit thrusting period. The two remaining units are started after the deorbit thrusting maneuver and operate continuously through entry, landing and landing rollout. On STS-126, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Auxiliary power unit 3, or APU3, is ready for installation in space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-126 mission. The auxiliary power unit is a hydrazine-fueled, turbine-driven power unit that generates mechanical shaft power to drive a hydraulic pump that produces pressure for the orbiter's hydraulic system. There are three separate APUs, three hydraulic pumps and three hydraulic systems, located in the aft fuselage of the orbiter. When the three auxiliary power units are started five minutes before lift-off, the hydraulic systems are used to position the three main engines for activation, control various propellant valves on the engines and position orbiter aerosurfaces. The auxiliary power units are not operated after the first orbital maneuvering system thrusting period because hydraulic power is no longer required. One power unit is operated briefly one day before deorbit to support checkout of the orbiter flight control system. One auxiliary power unit is restarted before the deorbit thrusting period. The two remaining units are started after the deorbit thrusting maneuver and operate continuously through entry, landing and landing rollout. On STS-126, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility bay No. 2, technicians begin installation of an auxiliary power unit 3, or APU3, in space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-126 mission. The auxiliary power unit is a hydrazine-fueled, turbine-driven power unit that generates mechanical shaft power to drive a hydraulic pump that produces pressure for the orbiter's hydraulic system. There are three separate APUs, three hydraulic pumps and three hydraulic systems, located in the aft fuselage of the orbiter. When the three auxiliary power units are started five minutes before lift-off, the hydraulic systems are used to position the three main engines for activation, control various propellant valves on the engines and position orbiter aerosurfaces. The auxiliary power units are not operated after the first orbital maneuvering system thrusting period because hydraulic power is no longer required. One power unit is operated briefly one day before deorbit to support checkout of the orbiter flight control system. One auxiliary power unit is restarted before the deorbit thrusting period. The two remaining units are started after the deorbit thrusting maneuver and operate continuously through entry, landing and landing rollout. On STS-126, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility bay No. 2, technicians begin installation of an auxiliary power unit 3, or APU3, in space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-126 mission. The auxiliary power unit is a hydrazine-fueled, turbine-driven power unit that generates mechanical shaft power to drive a hydraulic pump that produces pressure for the orbiter's hydraulic system. There are three separate APUs, three hydraulic pumps and three hydraulic systems, located in the aft fuselage of the orbiter. When the three auxiliary power units are started five minutes before lift-off, the hydraulic systems are used to position the three main engines for activation, control various propellant valves on the engines and position orbiter aerosurfaces. The auxiliary power units are not operated after the first orbital maneuvering system thrusting period because hydraulic power is no longer required. One power unit is operated briefly one day before deorbit to support checkout of the orbiter flight control system. One auxiliary power unit is restarted before the deorbit thrusting period. The two remaining units are started after the deorbit thrusting maneuver and operate continuously through entry, landing and landing rollout. On STS-126, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility bay No. 2, technicians install auxiliary power unit 3, or APU3, in space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-126 mission. The auxiliary power unit is a hydrazine-fueled, turbine-driven power unit that generates mechanical shaft power to drive a hydraulic pump that produces pressure for the orbiter's hydraulic system. There are three separate APUs, three hydraulic pumps and three hydraulic systems, located in the aft fuselage of the orbiter. When the three auxiliary power units are started five minutes before lift-off, the hydraulic systems are used to position the three main engines for activation, control various propellant valves on the engines and position orbiter aerosurfaces. The auxiliary power units are not operated after the first orbital maneuvering system thrusting period because hydraulic power is no longer required. One power unit is operated briefly one day before deorbit to support checkout of the orbiter flight control system. One auxiliary power unit is restarted before the deorbit thrusting period. The two remaining units are started after the deorbit thrusting maneuver and operate continuously through entry, landing and landing rollout. On STS-126, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
The Photovoltaic Module 1 Integrated Equipment Assembly (IEA) is moved past a Pressurized Mating Adapter in Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) toward the workstand where it will be processed for flight on STS-97, scheduled for launch in April 1999. The IEA is one of four integral units designed to generate, distribute, and store power for the International Space Station. It will carry solar arrays, power storage batteries, power control units, and a thermal control system. The 16-foot-long, 16,850-pound unit is now undergoing preflight preparations in the SSPF
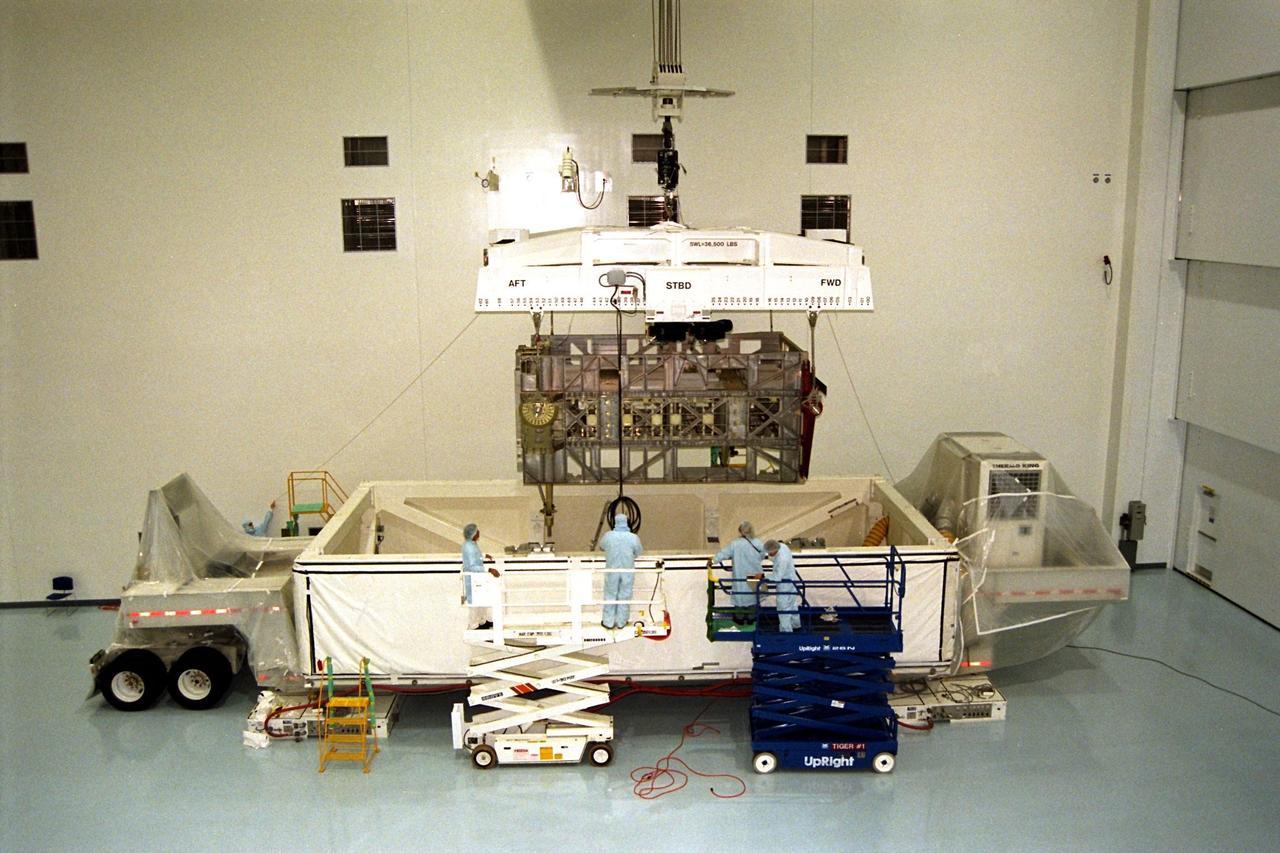
The Photovoltaic Module 1 Integrated Equipment Assembly (IEA) is lifted from its container in Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) before it is moved into its workstand, where it will be processed for flight on STS-97, scheduled for launch in April 1999. The IEA is one of four integral units designed to generate, distribute, and store power for the International Space Station. It will carry solar arrays, power storage batteries, power control units, and a thermal control system. The 16-foot-long, 16,850-pound unit is now undergoing preflight preparations in the SSPF

The Photovoltaic Module 1 Integrated Equipment Assembly (IEA) is moved past Node 1, seen at left, of the International Space Station (ISS) in Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The IEA will be processed at the SSPF for flight on STS-97, scheduled for launch in April 1999. The IEA is one of four integral units designed to generate, distribute, and store power for the ISS. It will carry solar arrays, power storage batteries, power control units, and a thermal control system. The 16-foot-long, 16,850-pound unit is now undergoing preflight preparations in the SSPF
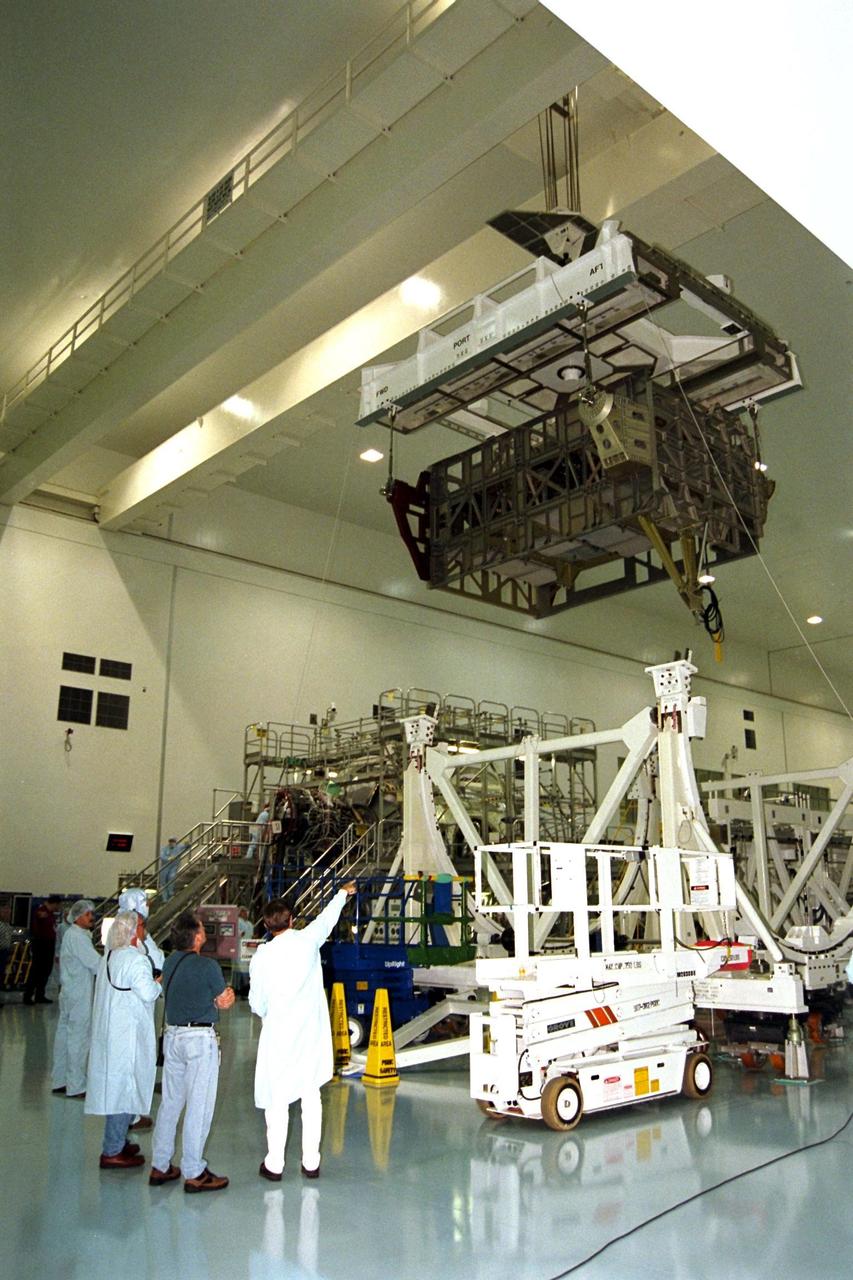

Workers in Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) observe the Photovoltaic Module 1 Integrated Equipment Assembly (IEA) as it moves past them on its way to its workstand, where it will be processed for flight on STS-97, scheduled for launch in April 1999. The IEA is one of four integral units designed to generate, distribute, and store power for the International Space Station. It will carry solar arrays, power storage batteries, power control units, and a thermal control system. The 16-foot-long, 16,850-pound unit is now undergoing preflight preparations in the SSPF

STS109-E-5660 (6 March 2002) --- Astronauts John M. Grunsfeld (top) and Richard M. Linnehan participate in a 6 hour, 48 minute space walk designed to install a new Power Control Unit (PCU) on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The two went on to replace the original unit launched with the telescope in April 1990. Grunsfeld is on the end of Columbia's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) robotic arm, controlled from inside the crew cabin by astronaut Nancy J. Currie. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
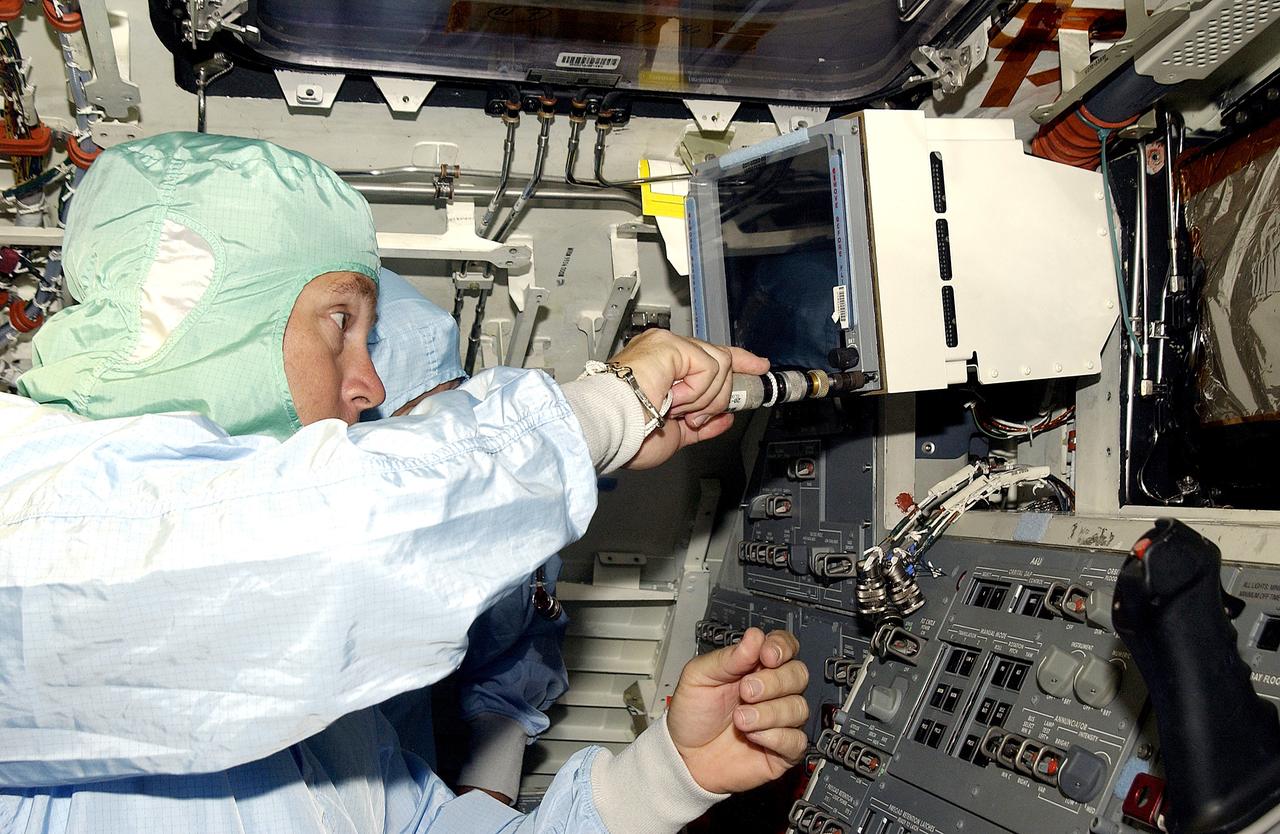

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A technician with United Space Alliance works inside orbiter Discovery before power-up of the vehicle in the Orbiter Processing Facility . Discovery has been undergoing Orbiter Major Modifications in the past year, ranging from wiring, control panels and black boxes to gaseous and fluid systems tubing and components. These systems were deserviced, disassembled, inspected, modified, reassembled, checked out and reserviced, as were most other systems onboard. The work includes the installation of the Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS) - a state-of-the-art “glass cockpit.”
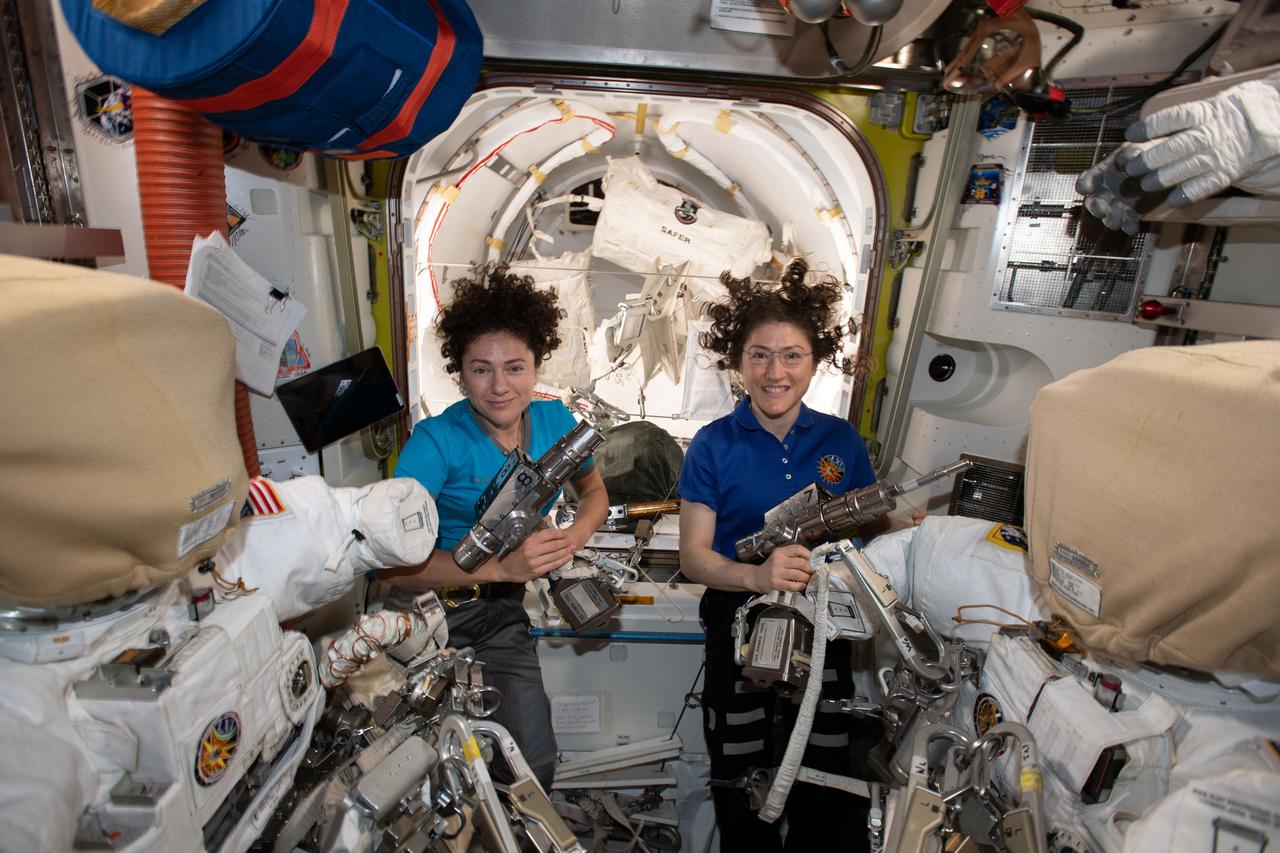

iss061e006498 (Oct. 15, 2019) --- NASA astronauts Jessica Meir (left) and Christina Koch are inside the Quest airlock preparing the U.S. spacesuits and tools they will use on their first spacewalk together. The Expedition 61 flight engineers are holding the pistol grip tools they will use to swap out a failed power controller, also known as a battery charge-discharge unit, that regulates the charge to batteries that collect and distribute power to the International Space Station.
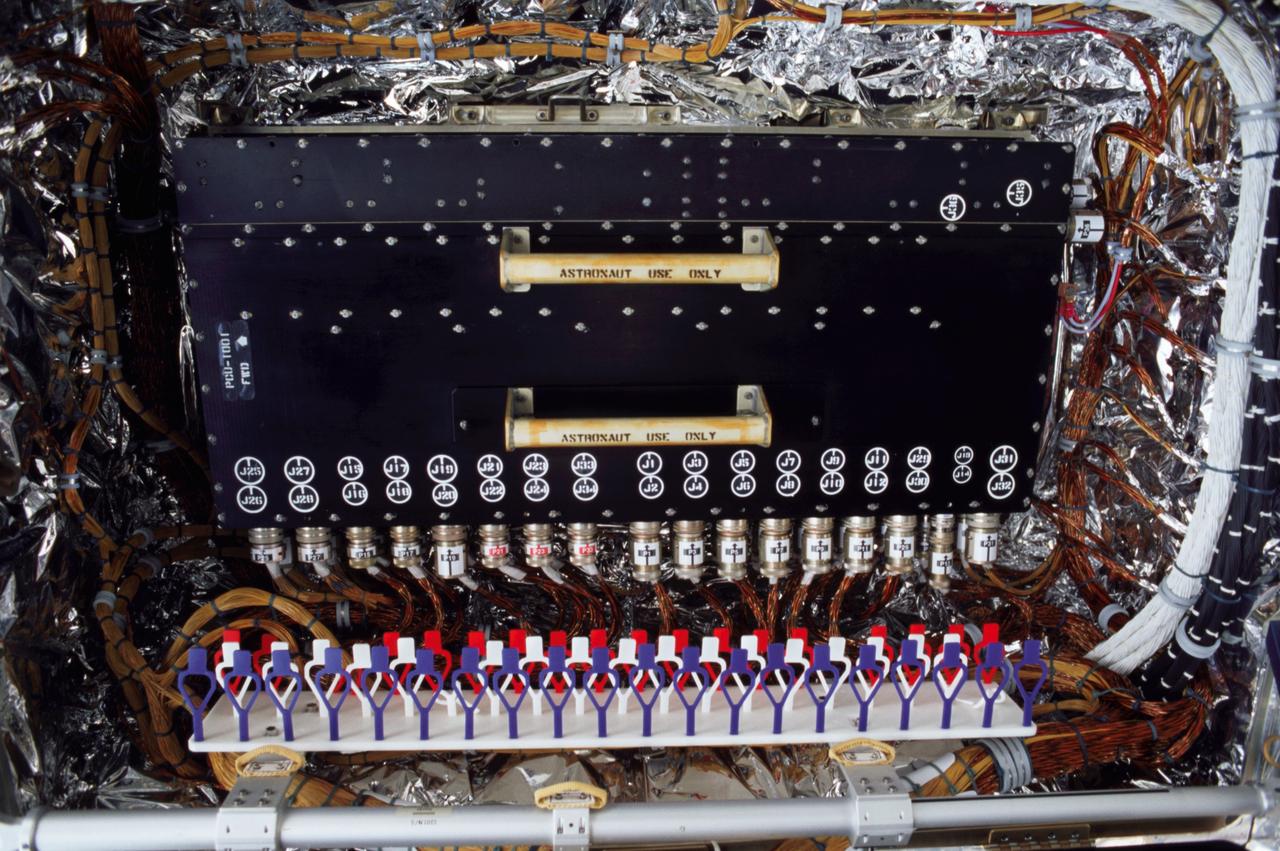
STS109-322-025 (1-12 March 2002) --- A close-up view of the power control unit or PCU, which is the heart of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) power system. Astronauts John M. Grunsfeld and Richard M. Linnehan, STS-109 payload commander and mission specialist, respectively, replaced the PCU on March 6, 2002, during the third space walk of the mission.
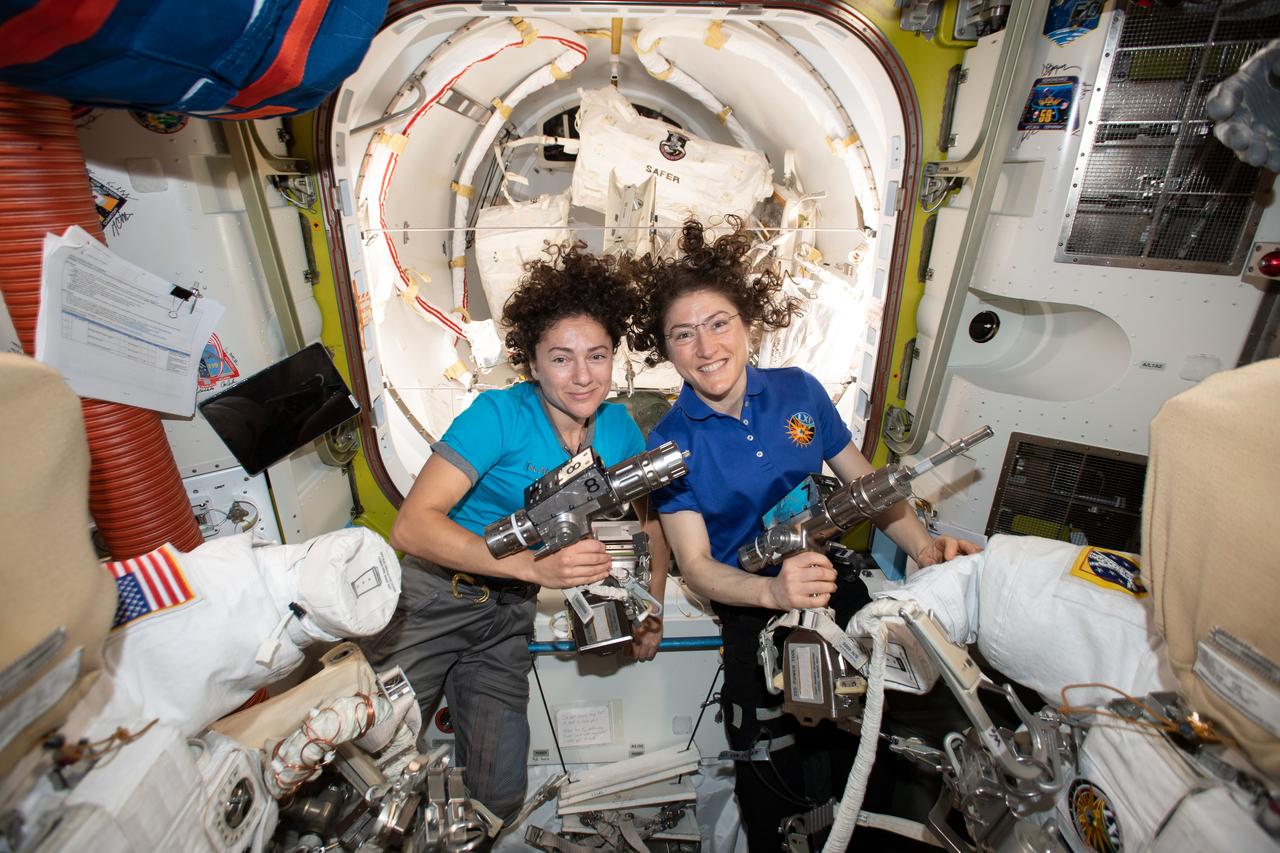

iss061e006501 (Oct. 15, 2019) --- NASA astronauts Jessica Meir (left) and Christina Koch are inside the Quest airlock preparing the U.S. spacesuits and tools they will use on their first spacewalk together. The Expedition 61 flight engineers are holding the pistol grip tools they will use to swap out a failed power controller, also known as a battery charge-discharge unit, that regulates the charge to batteries that collect and distribute power to the International Space Station.
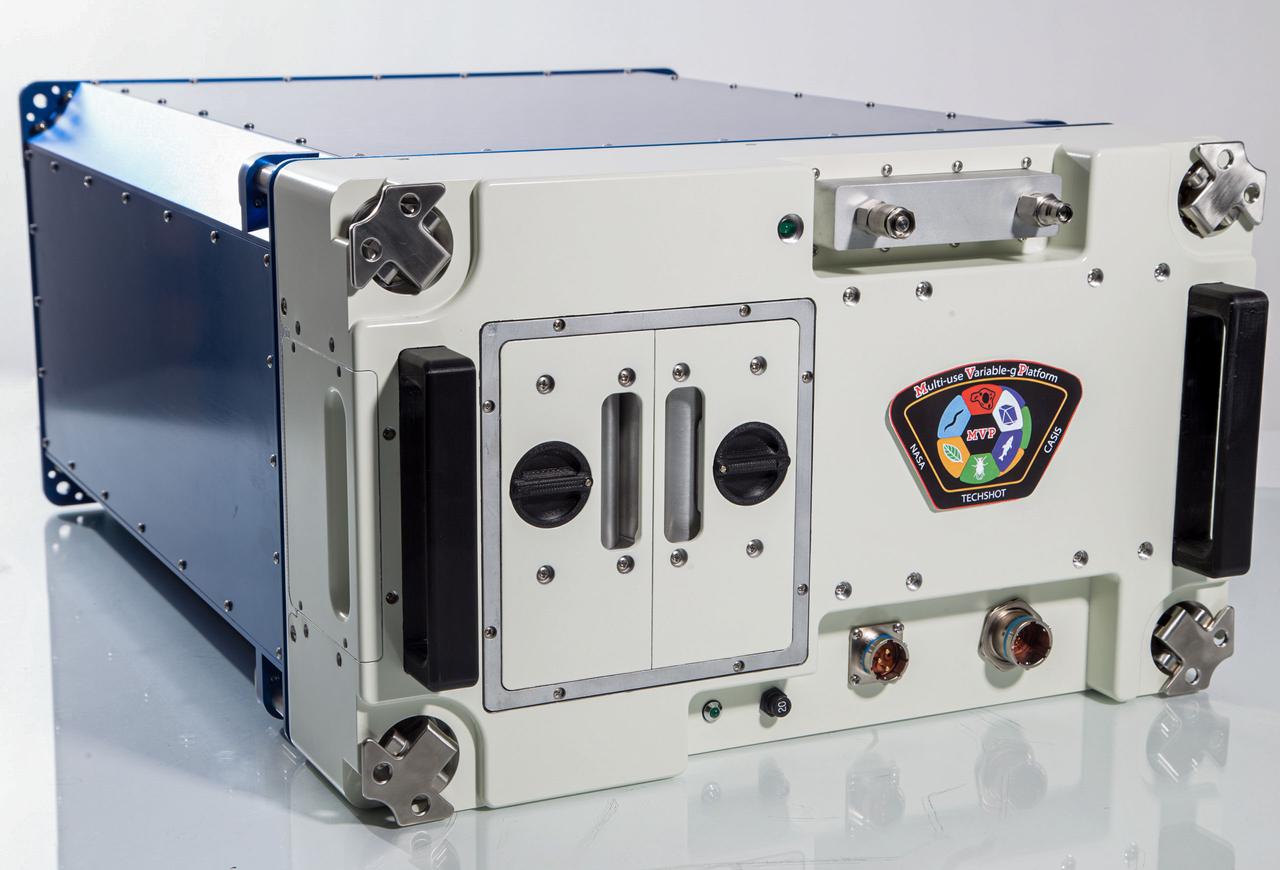

jsc2024e036958 (7/26/2016) --- The Multi-use Variable-g Platform (MVP) facility houses up to 12 modules of science. Pictured in this front view are two installed consumable modules that are used for minor environmental control, such as desiccation, CO2control, and ethylene scrubbing. Power and data connectors are also visible to provide the ground control team with health and status of the unit. Image courtesy of Grant Vellinger, Redwire.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, astronaut Tracy Caldwell (left) assists a technician check out the Pump Flow Control Subsystem (PFCS) before it is installed on the upper deck of the S6 Truss. The PFCS pumps and controls the liquid ammonia used to cool the various Orbital Replacement Units on the Integrated Equipment Assembly that make up the S6 Photo-Voltaic Power Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth starboard truss segment, the S6 Truss measures 112 feet long by 39 feet wide. The solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery to the ISS. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. When completed, the Station's electrical power system (EPS) will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays to convert sunlight to electricity. Delivery of the S6 Truss, the last power module truss segment, is targeted for mission STS-119.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, astronaut Tracy Caldwell (second from left) assists technicians lower the Pump Flow Control Subsystem (PFCS) into position onto the upper deck of the S6 Truss. The PFCS pumps and controls the liquid ammonia used to cool the various Orbital Replacement Units on the Integrated Equipment Assembly that make up the S6 Photo-Voltaic Power Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth starboard truss segment, the S6 Truss measures 112 feet long by 39 feet wide. Its solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery to the ISS. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. When completed, the Station's electrical power system (EPS) will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays to convert sunlight to electricity. Delivery of the S6 Truss, the last power module truss segment, is targeted for mission STS-119.
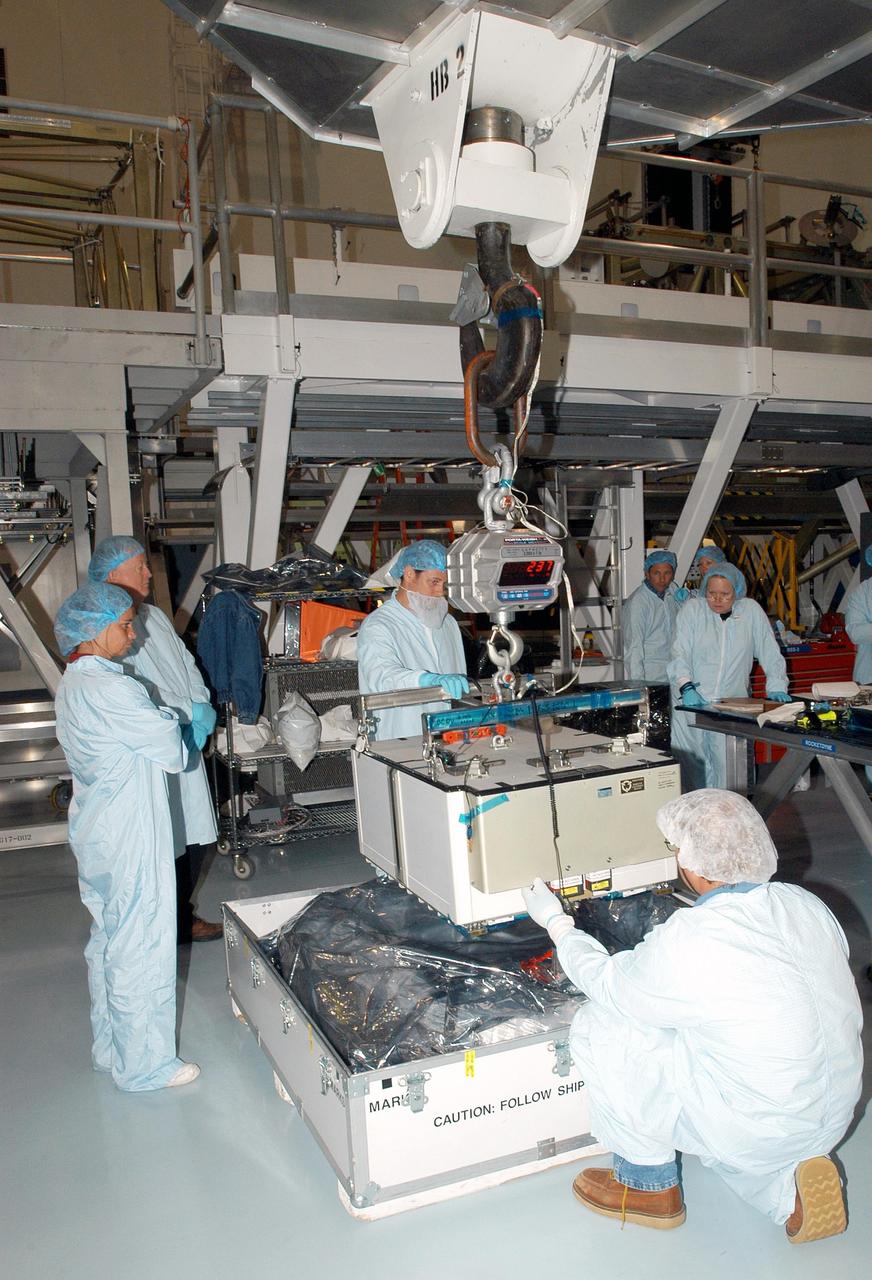

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians attach a crane to the Pump Flow Control Subsystem (PFCS) in the Space Station Processing Facility. The PFCS pumps and controls the liquid ammonia used to cool the various Orbital Replacement Units on the Integrated Equipment Assembly that make up the S6 Photo-Voltaic Power Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth starboard truss segment, the S6 Truss measures 112 feet long by 39 feet wide. Its solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery to the ISS. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. When completed, the Station's electrical power system (EPS) will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays to convert sunlight to electricity. Delivery of the S6 Truss, the last power module truss segment, is targeted for mission STS-119.
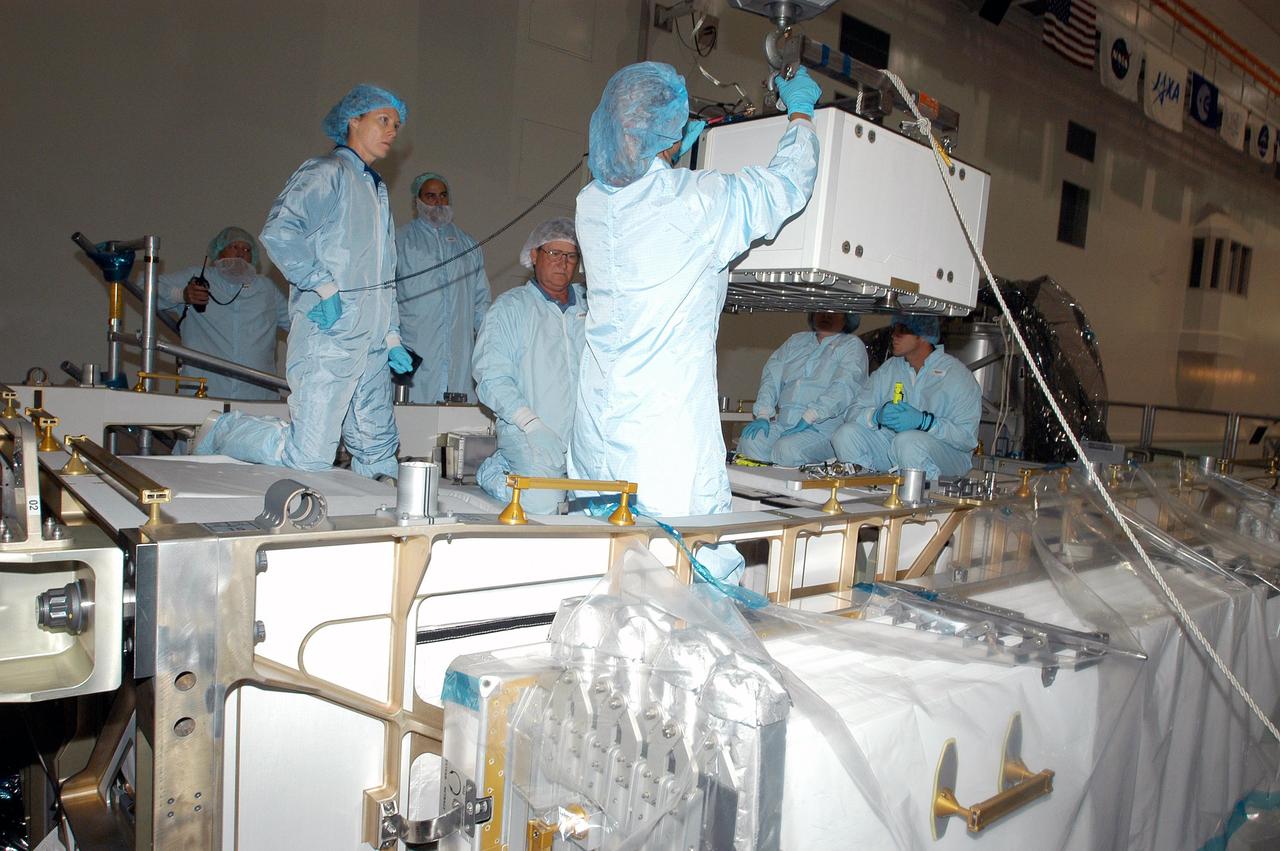

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, astronaut Tracy Caldwell (second from left) assists technicians position the Pump Flow Control Subsystem (PFCS) over the upper deck of the S6 Truss. The PFCS pumps and controls the liquid ammonia used to cool the various Orbital Replacement Units on the Integrated Equipment Assembly that make up the S6 Photo-Voltaic Power Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth starboard truss segment, the S6 Truss measures 112 feet long by 39 feet wide. Its solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery to the ISS. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. When completed, the Station's electrical power system (EPS) will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays to convert sunlight to electricity. Delivery of the S6 Truss, the last power module truss segment, is targeted for mission STS-119.
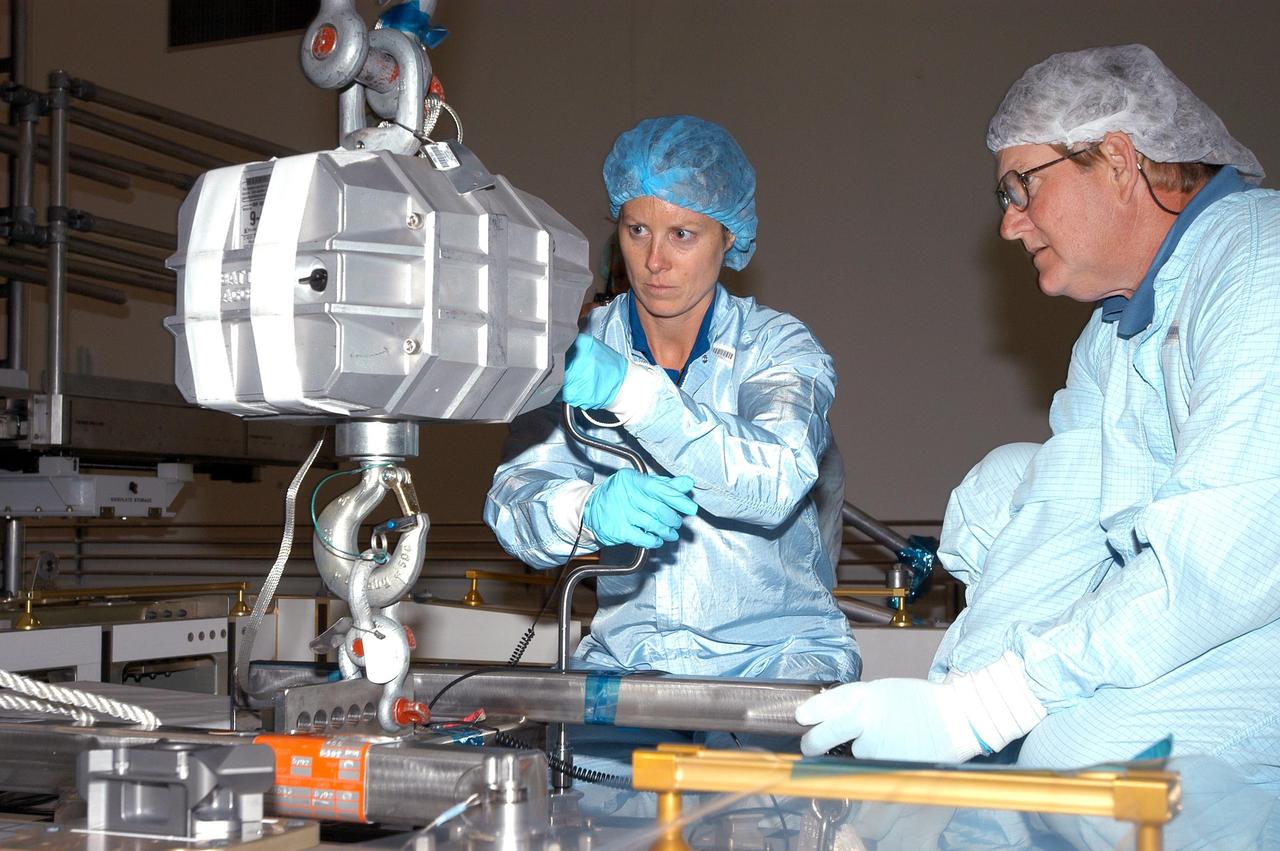

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, astronaut Tracy Caldwell (left) assists technicians install the Pump Flow Control Subsystem (PFCS) onto the upper deck of the S6 Truss. The PFCS pumps and controls the liquid ammonia used to cool the various Orbital Replacement Units on the Integrated Equipment Assembly that make up the S6 Photo-Voltaic Power Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth starboard truss segment, the S6 Truss measures 112 feet long by 39 feet wide. Its solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery to the ISS. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. When completed, the Station's electrical power system (EPS) will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays to convert sunlight to electricity. Delivery of the S6 Truss, the last power module truss segment, is targeted for mission STS-119.
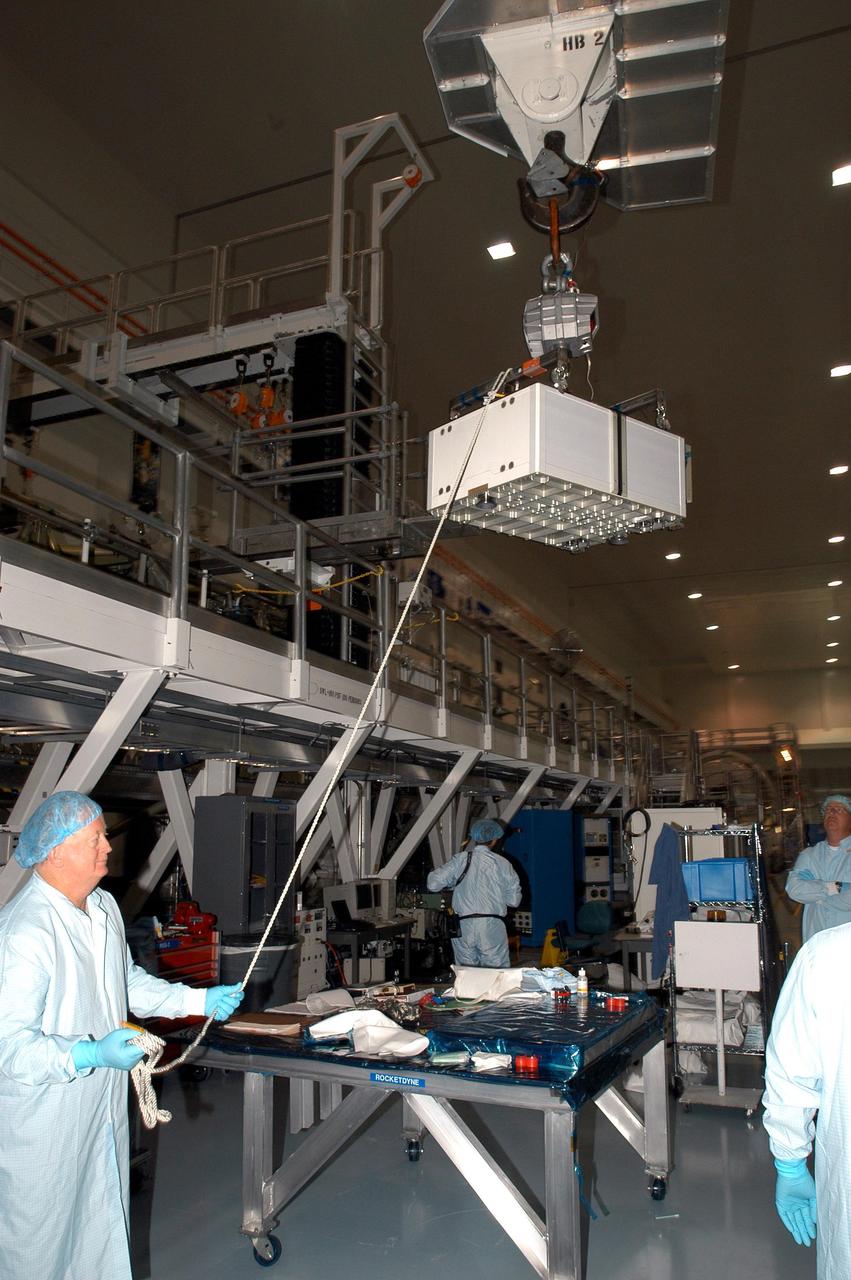

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, a technician steadies the Pump Flow Control Subsystem (PFCS) as it is lifted and moved toward the S6 Truss. The PFCS pumps and controls the liquid ammonia used to cool the various Orbital Replacement Units on the Integrated Equipment Assembly that make up the S6 Photo-Voltaic Power Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth starboard truss segment, the S6 Truss measures 112 feet long by 39 feet wide. Its solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery to the ISS. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. When completed, the Station's electrical power system (EPS) will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays to convert sunlight to electricity. Delivery of the S6 Truss, the last power module truss segment, is targeted for mission STS-119.
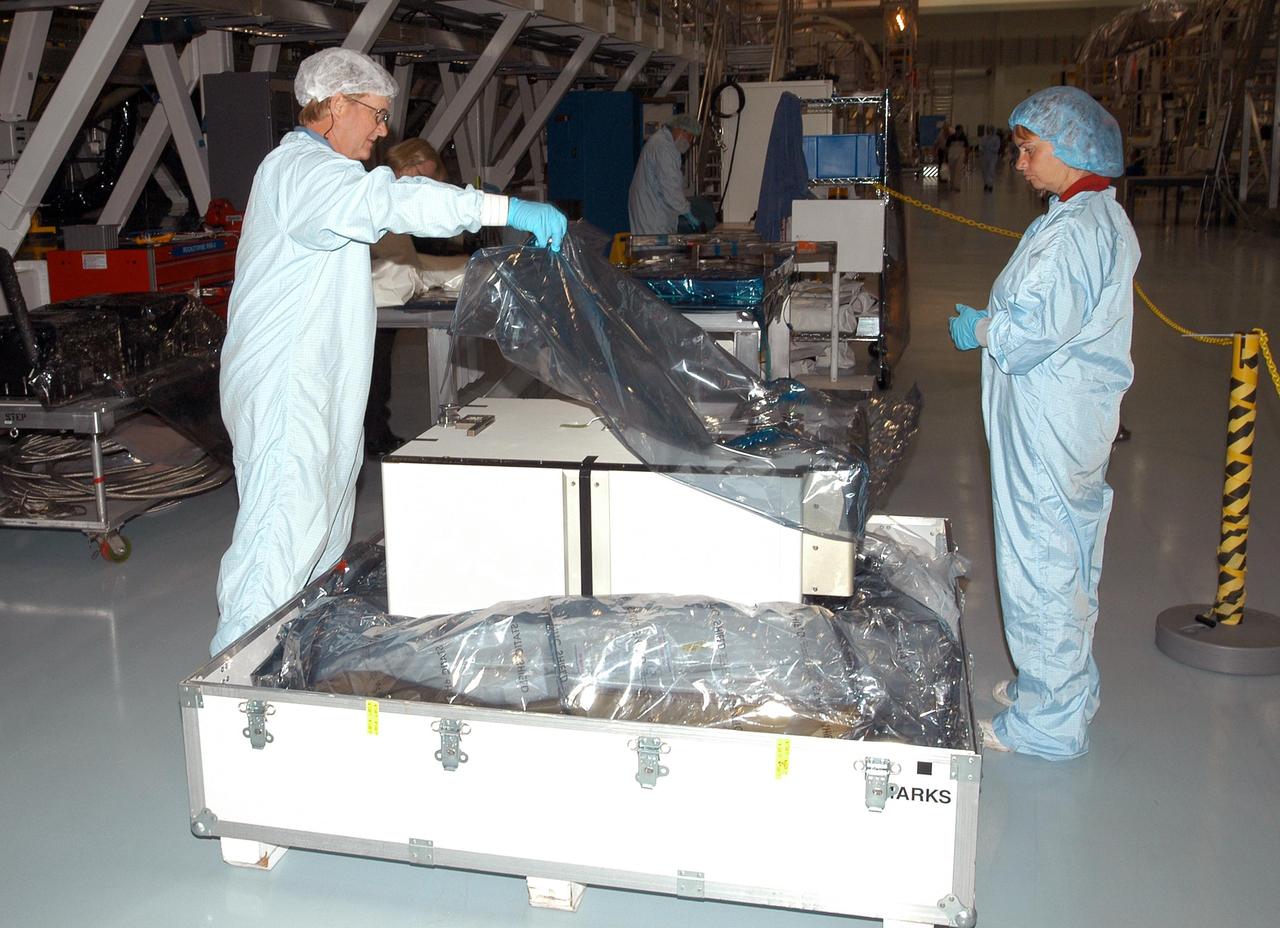

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Unpacking of the Pump Flow Control Subsystem (PFCS) begins in the Space Station Processing Facility. The PFCS pumps and controls the liquid ammonia used to cool the various Orbital Replacement Units on the Integrated Equipment Assembly that make up the S6 Photo-Voltaic Power Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth starboard truss segment, the S6 Truss measures 112 feet long by 39 feet wide. Its solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery to the ISS. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. When completed, the Station's electrical power system will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays to convert sunlight to electricity. Delivery of the S6 Truss, the last power module truss segment, is targeted for mission STS-119.
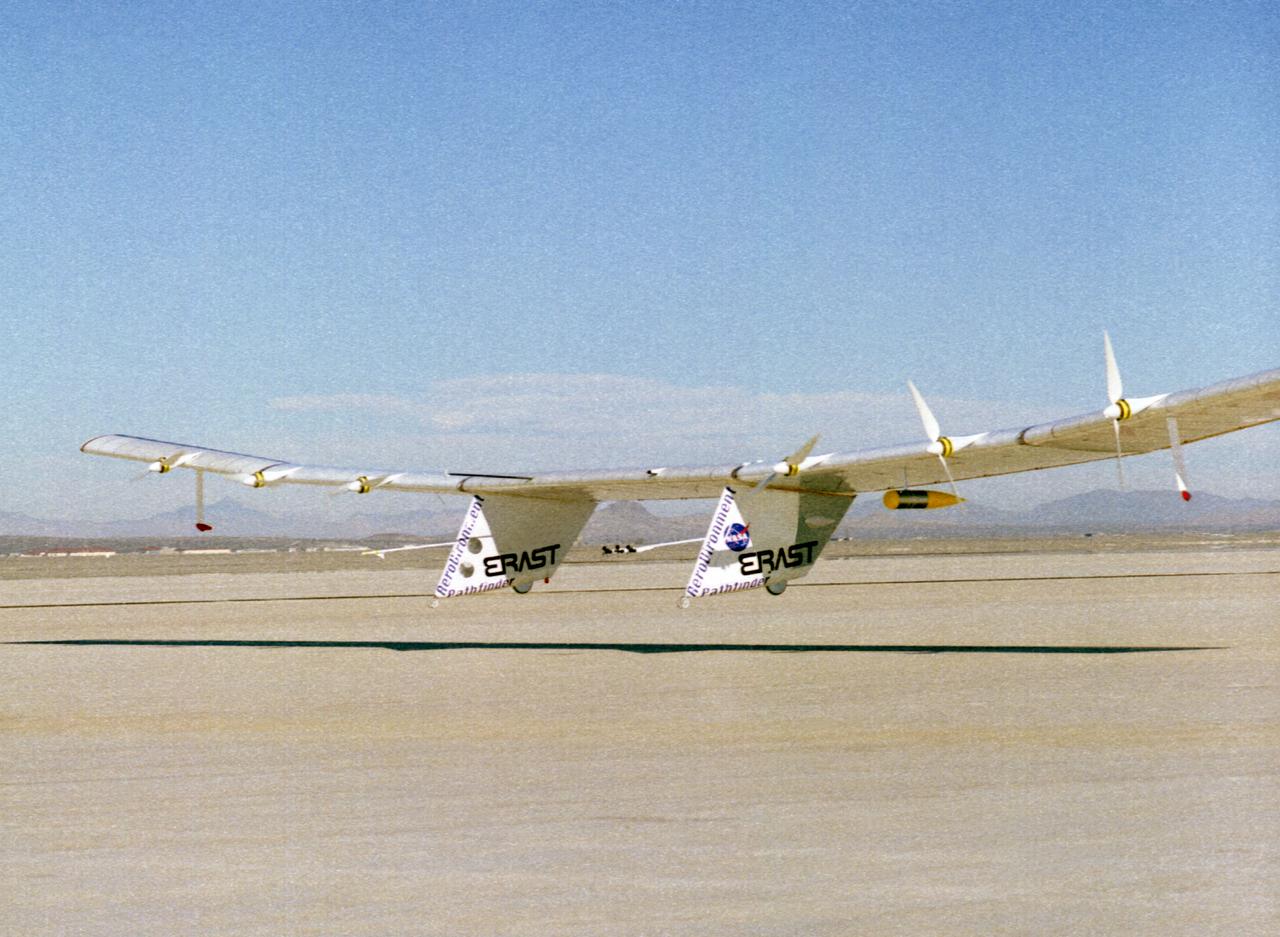

The Pathfinder solar-powered research aircraft settles in for landing on the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, after a successful test flight Nov. 19, 1996. The ultra-light craft flew a racetrack pattern at low altitudes over the flight test area for two hours while project engineers checked out various systems and sensors on the uninhabited aircraft. The Pathfinder was controlled by two pilots, one in a mobile control unit which followed the craft, the other in a stationary control station. Pathfinder, developed by AeroVironment, Inc., is one of several designs being evaluated under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
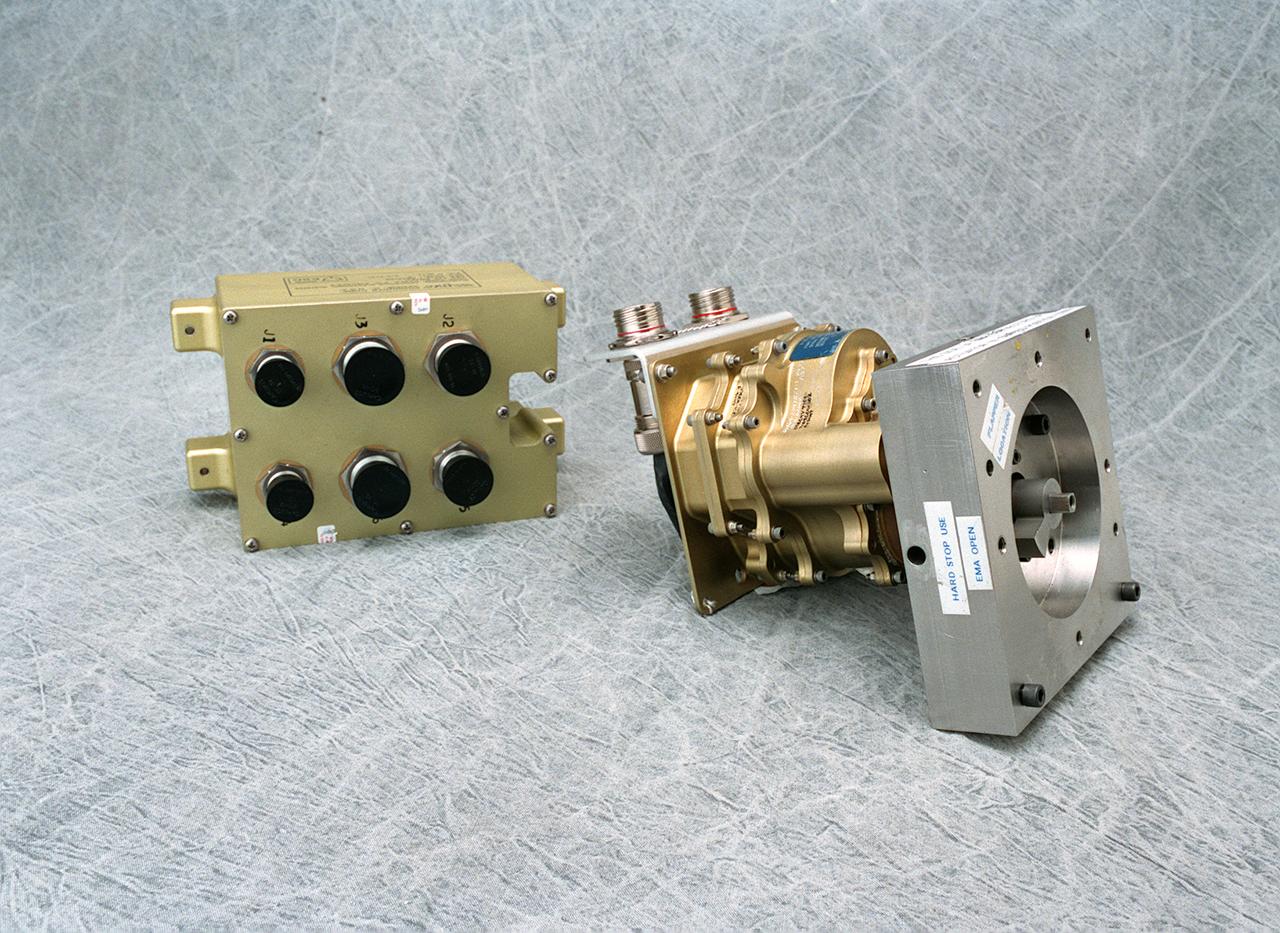
The electro-mechanical actuator, a new electronics technology, is an electronic system that provides the force needed to move valves that control the flow of propellant to the engine. It is proving to be advantageous for the main propulsion system plarned for a second generation reusable launch vehicle. Hydraulic actuators have been used successfully in rocket propulsion systems. However, they can leak when high pressure is exerted on such a fluid-filled hydraulic system. Also, hydraulic systems require significant maintenance and support equipment. The electro-mechanical actuator is proving to be low maintenance and the system weighs less than a hydraulic system. The electronic controller is a separate unit powering the actuator. Each actuator has its own control box. If a problem is detected, it can be replaced by simply removing one defective unit. The hydraulic systems must sustain significant hydraulic pressures in a rocket engine regardless of demand. The electro-mechanical actuator utilizes power only when needed. A goal of the Second Generation Reusable Launch Vehicle Program is to substantially improve safety and reliability while reducing the high cost of space travel. The electro-mechanical actuator was developed by the Propulsion Projects Office of the Second Generation Reusable Launch Vehicle Program at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
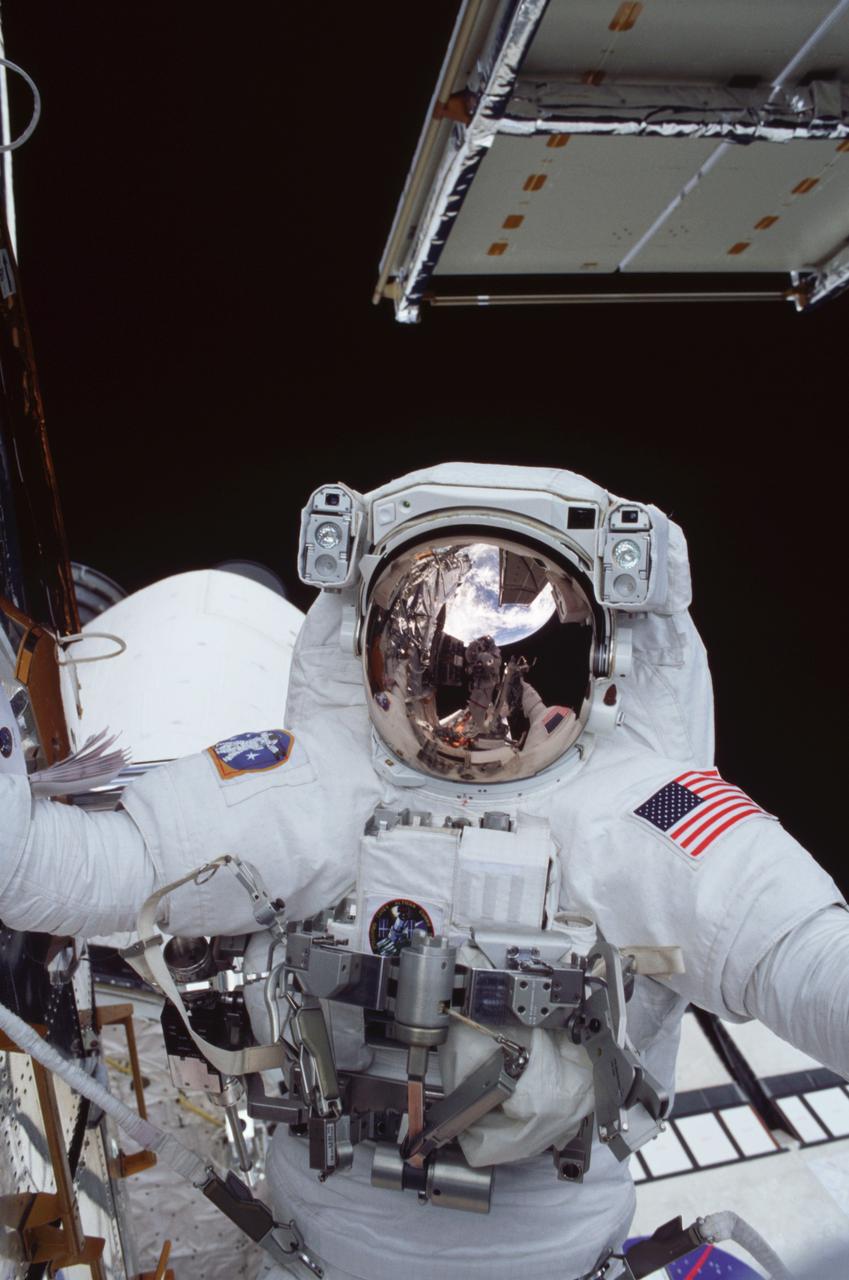

STS109-322-028 (6 March 2002) --- Astronaut Richard M. Linnehan, STS-109 mission specialist, participates in the third of five space walks to perform work on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Linnehan's sun shield reflects astronaut John M. Grunsfeld and the blue and white Earth's hemisphere as well as one of the telescope's new solar arrays. The third overall STS-109 extravehicular activity (EVA) marked the second of three for Linnehan and Grunsfeld, payload commander. On this particular walk, the two turned off the telescope in order to replace the power control unit or PCU--the heart of its power system. Grunsfeld took this photo with a 35mm camera.
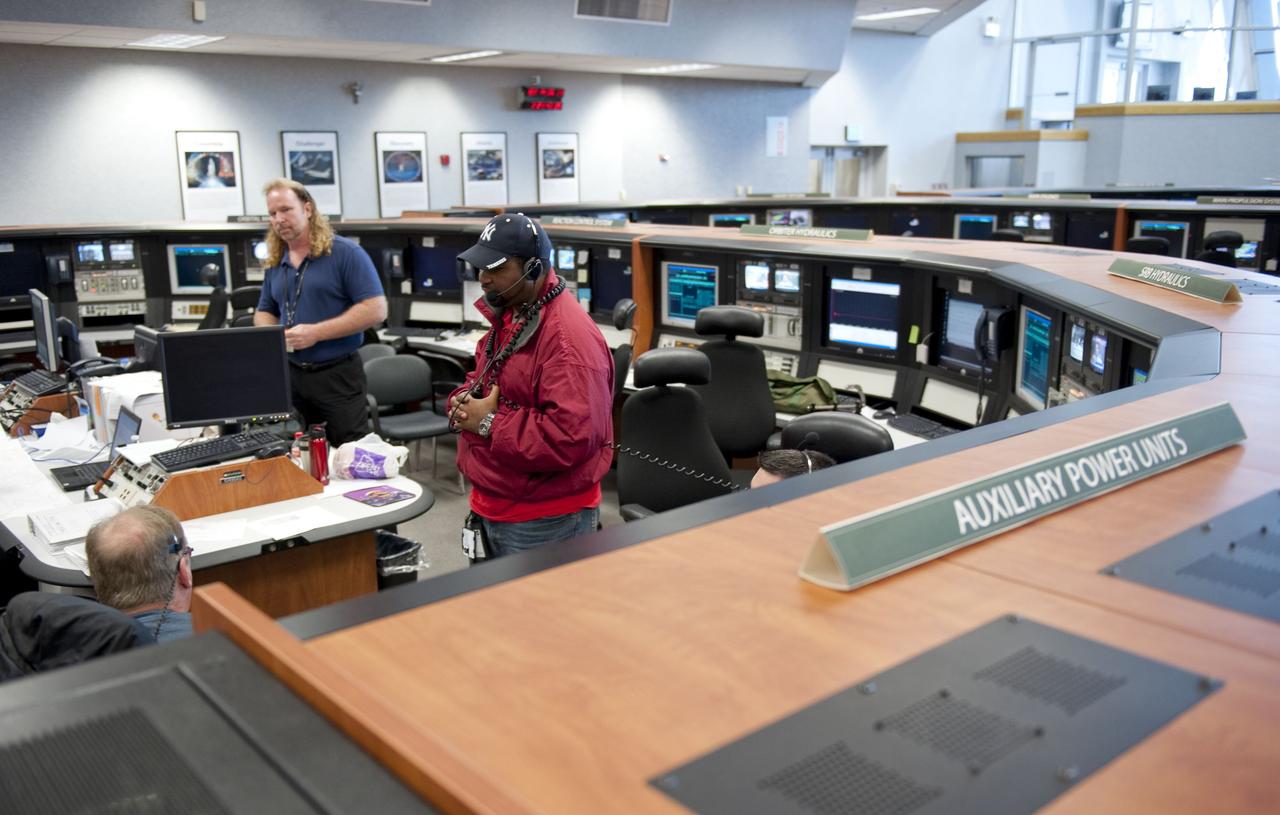

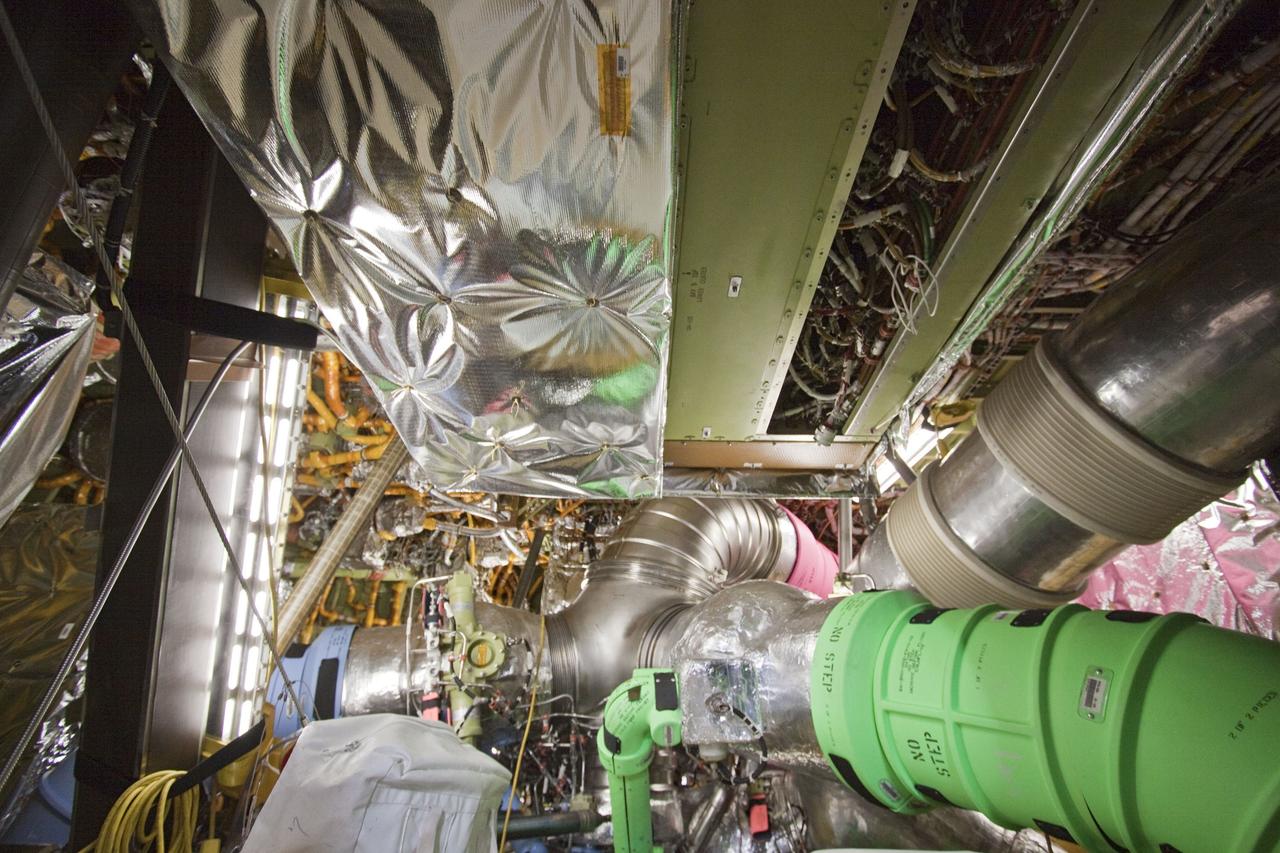
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Control Center, teams monitor the testing of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
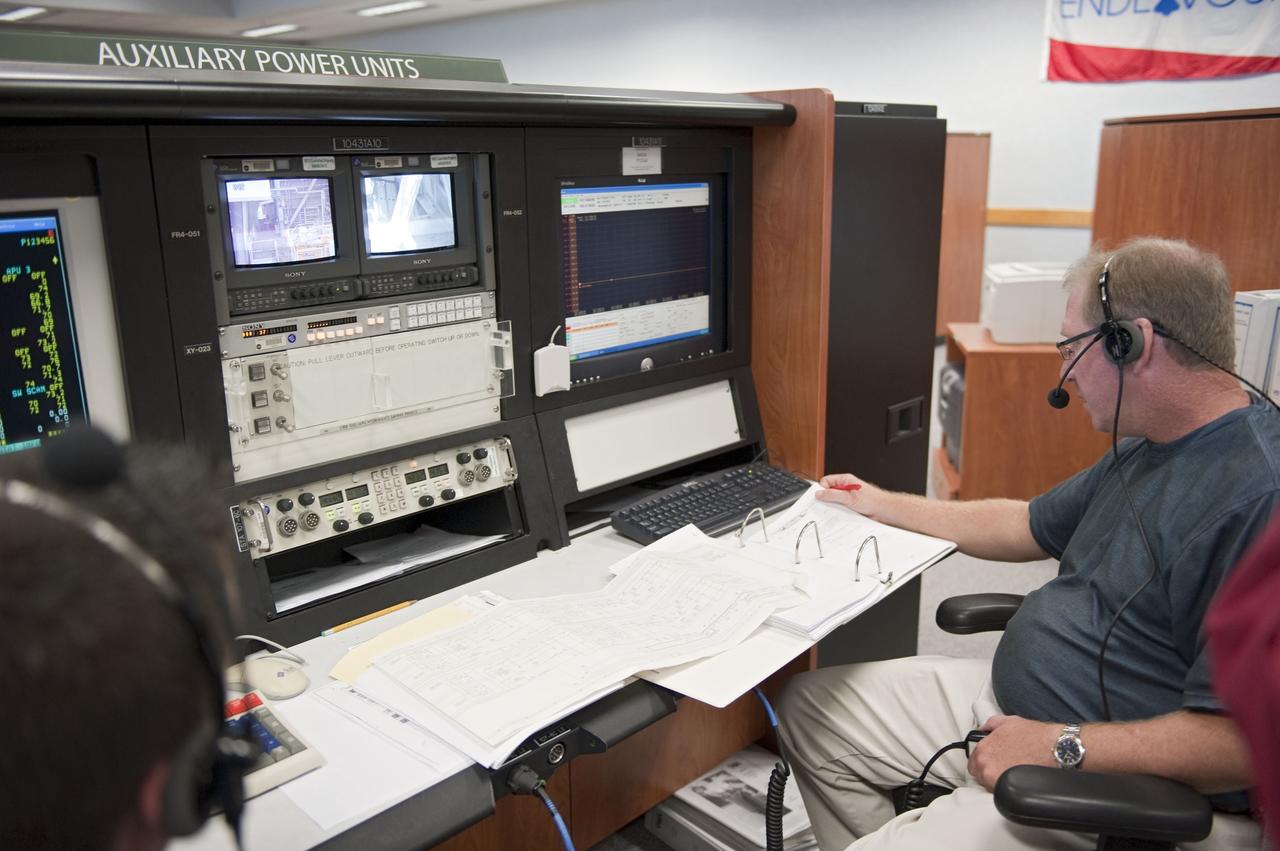

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Control Center, teams monitor the testing of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
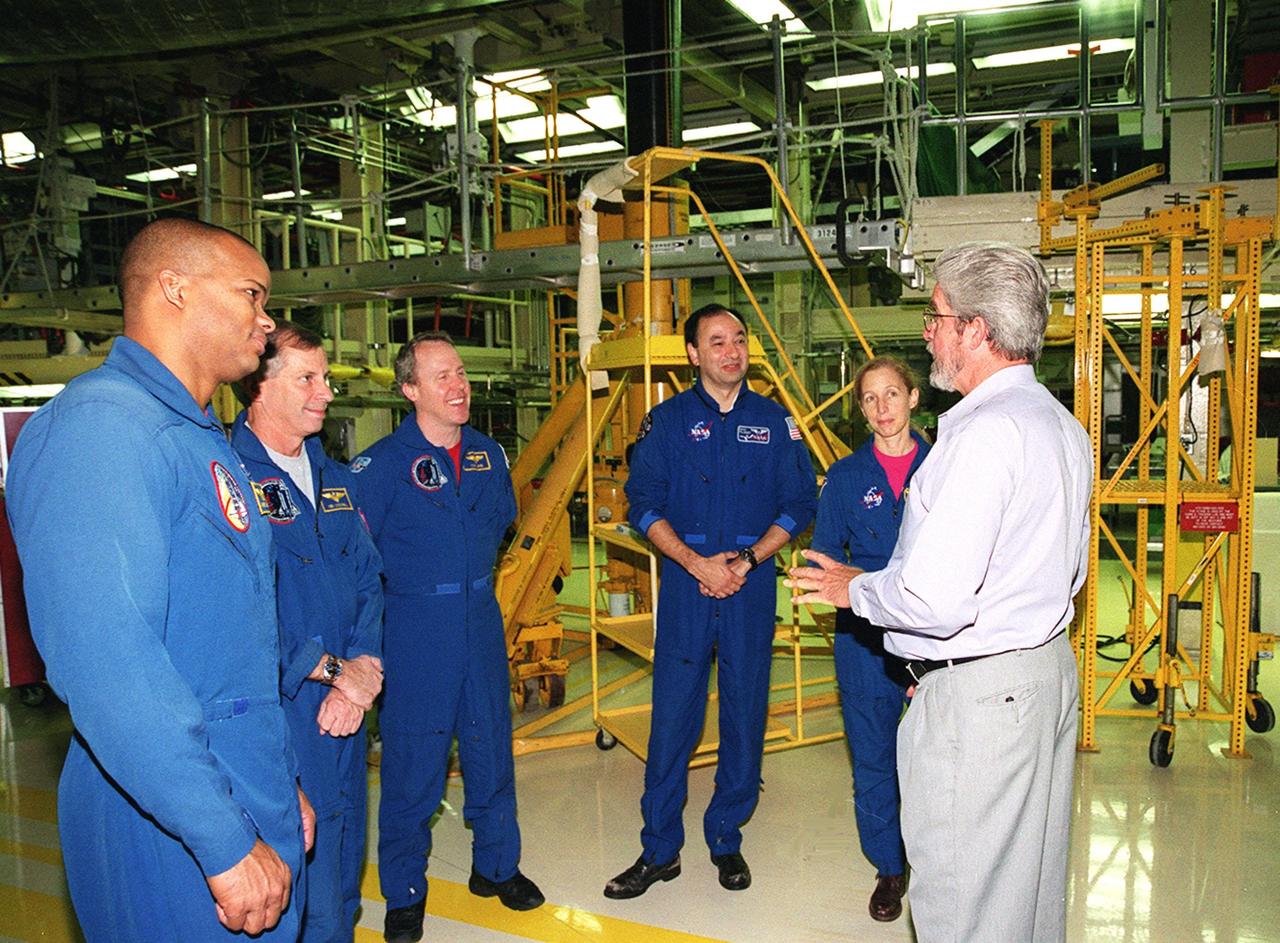

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, the STS-98 crew talks with United Space Alliance worker Larry Oshein (right). Standing left to right are Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam, Commander Ken Cockrell, Mission Specialist Tom Jones, and Mission Specialists Mark Polansky and Marsha Ivins. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Launch on mission STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001. It will be transporting the U.S. Lab, Destiny, to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated
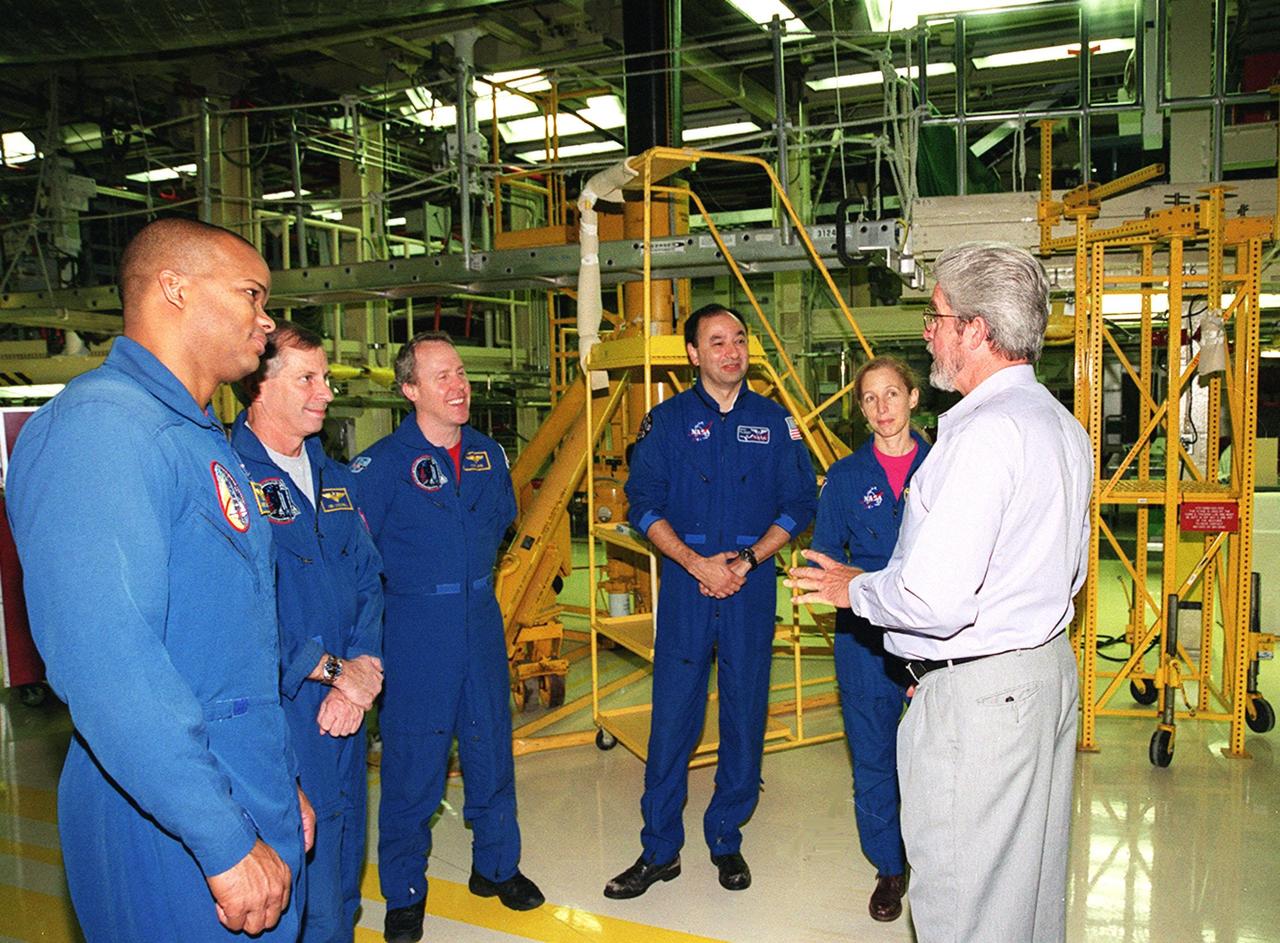

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, the STS-98 crew talks with United Space Alliance worker Larry Oshein (right). Standing left to right are Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam, Commander Ken Cockrell, Mission Specialist Tom Jones, and Mission Specialists Mark Polansky and Marsha Ivins. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Launch on mission STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001. It will be transporting the U.S. Lab, Destiny, to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated
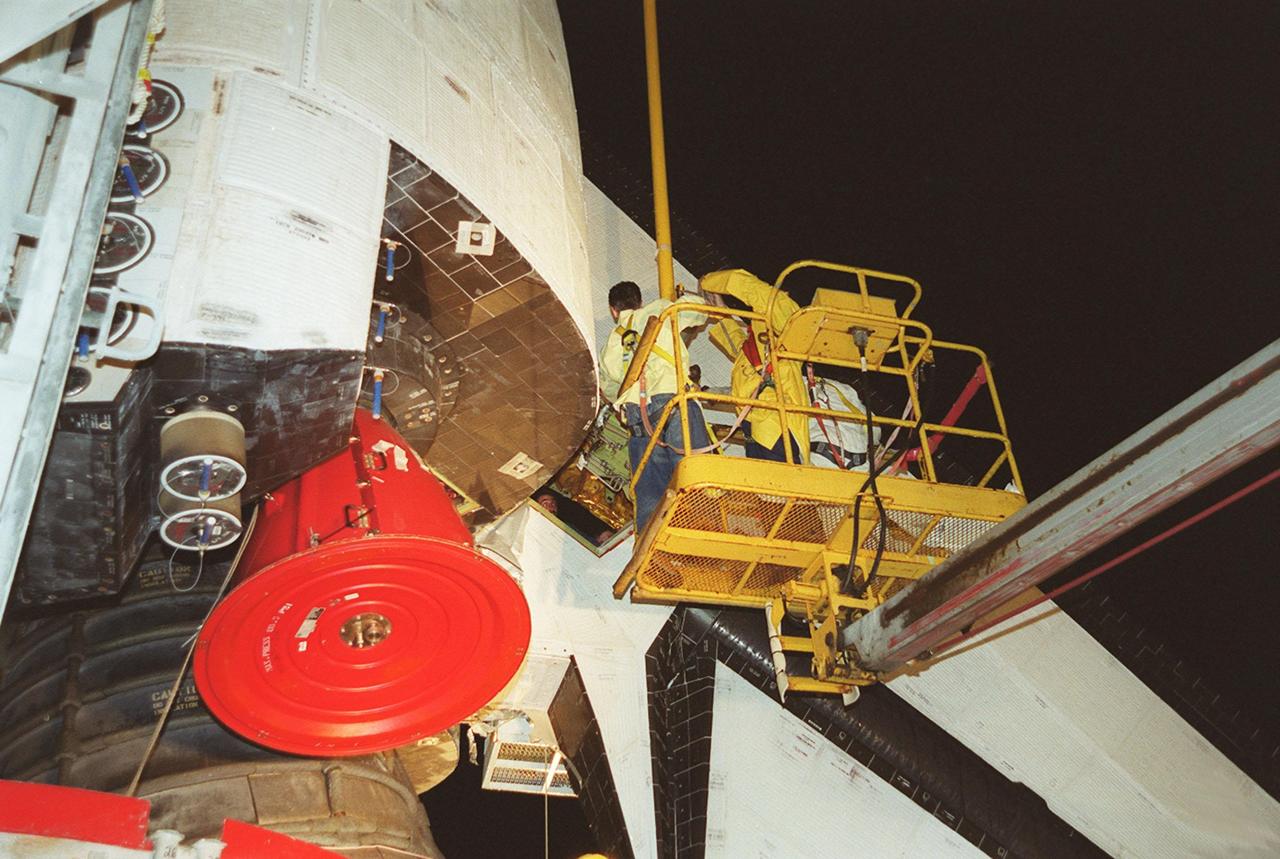

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers help guide the replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis into place. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
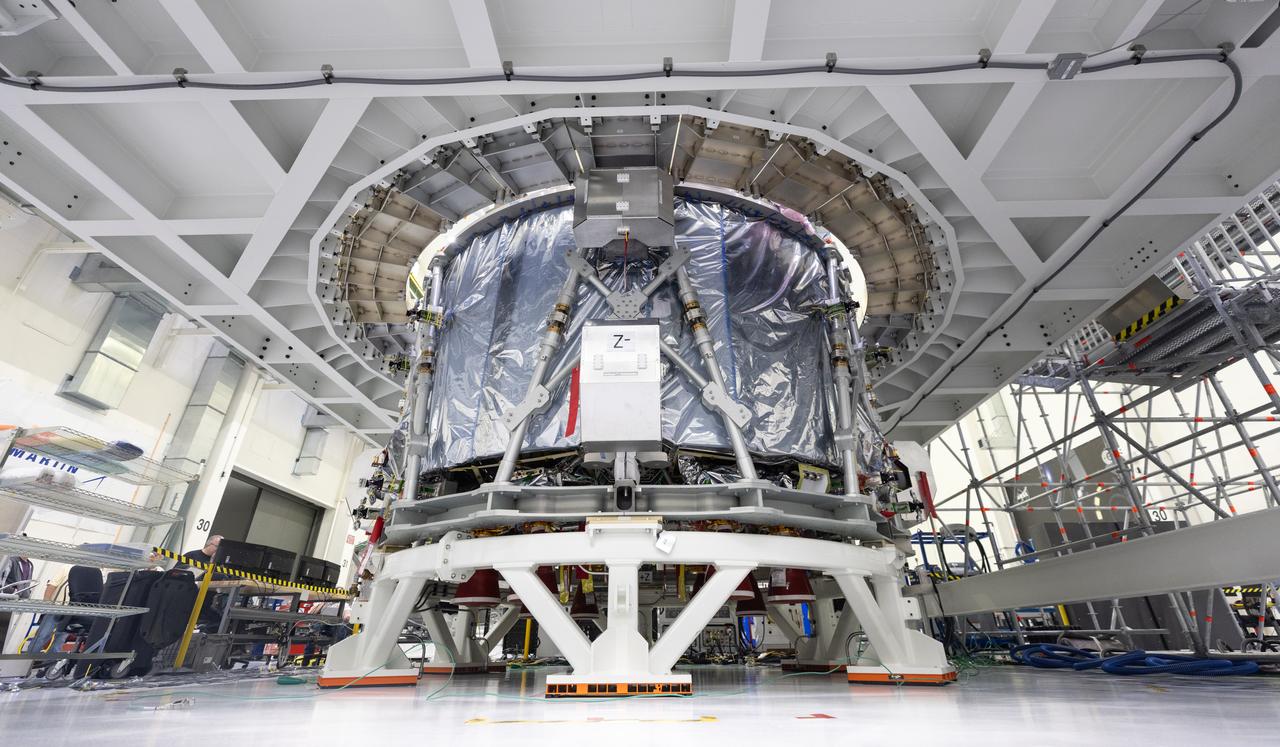

The transport carrier containing the European Service Module for NASA’s Artemis III mission arrives at the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Sept. 3, 2024. The European Service Module, which is assembled by Airbus in Bremen, Germany, from parts made in 10 European countries and the United States, acts as the driving force behind Orion for deep space exploration, providing essential propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power.
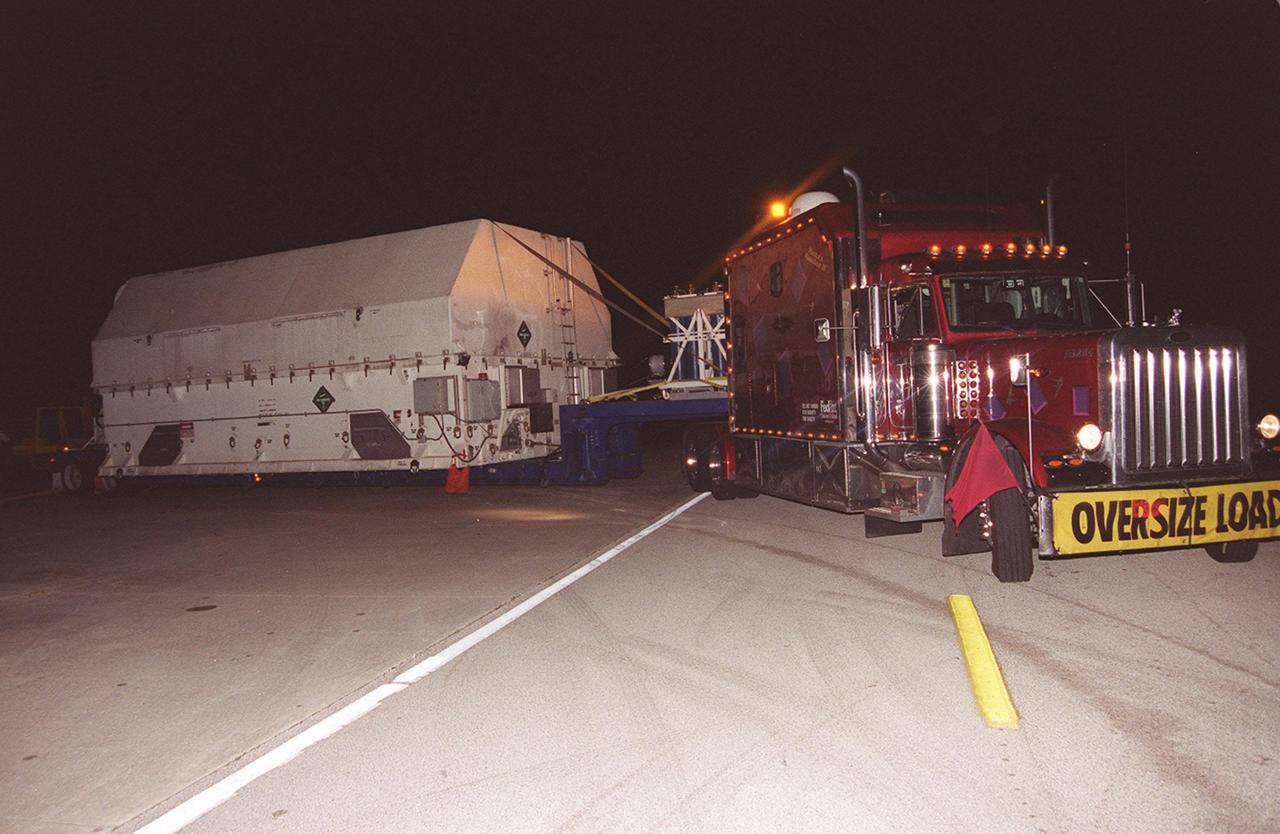

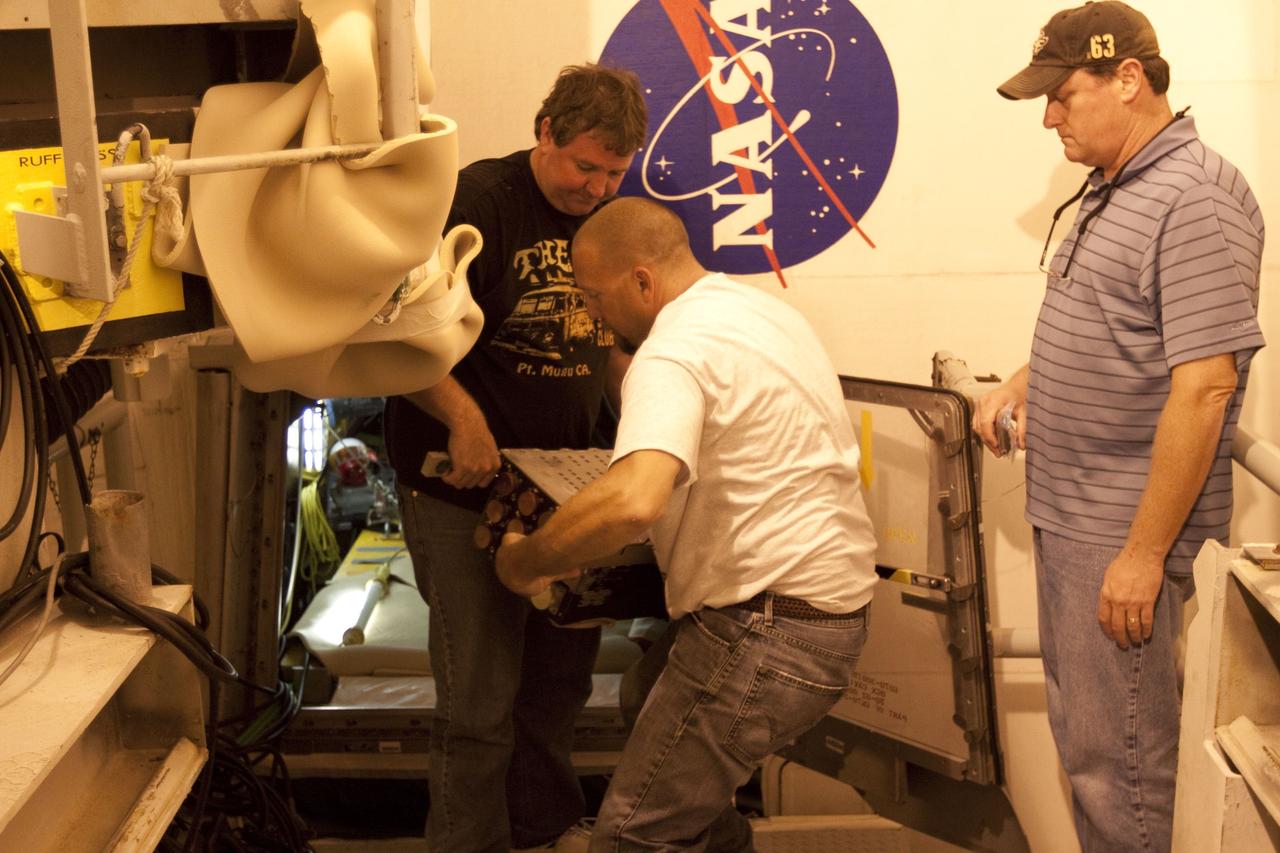
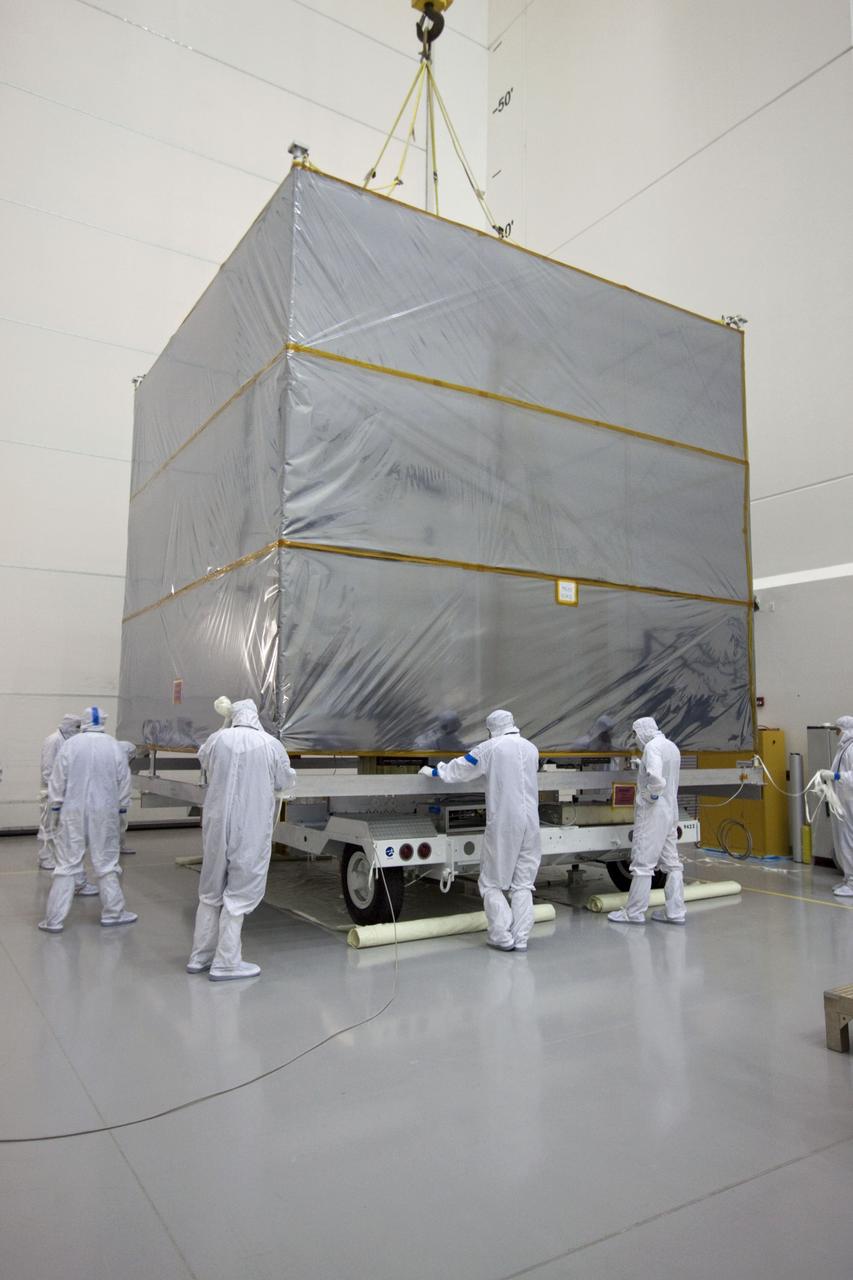
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- A large truck delivers part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, to KSC. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002

The transport carrier containing the European Service Module for NASA’s Artemis III mission arrives at the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Sept. 3, 2024. The European Service Module, which is assembled by Airbus in Bremen, Germany, from parts made in 10 European countries and the United States, acts as the driving force behind Orion for deep space exploration, providing essential propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power.
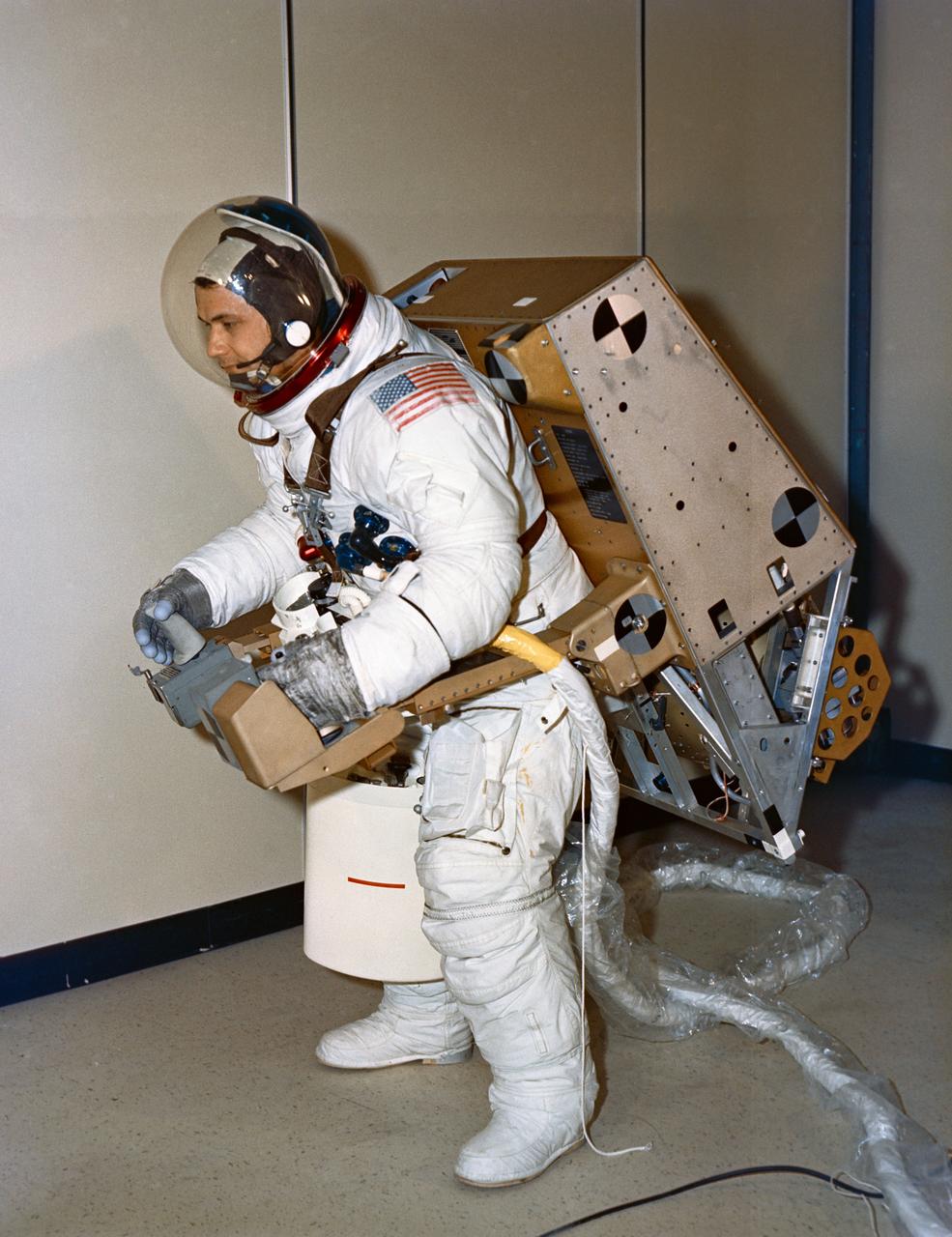

S72-30704 (1972) --- Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, backup pilot for Skylab 2, tests the balance and control of an astronaut maneuvering unit (AMU) test model at Martin Marietta Corporation's Denver division. The jet-powered backpack can fly for 30 minutes and can be worn over normal clothing or spacesuit. Photo credit: NASA
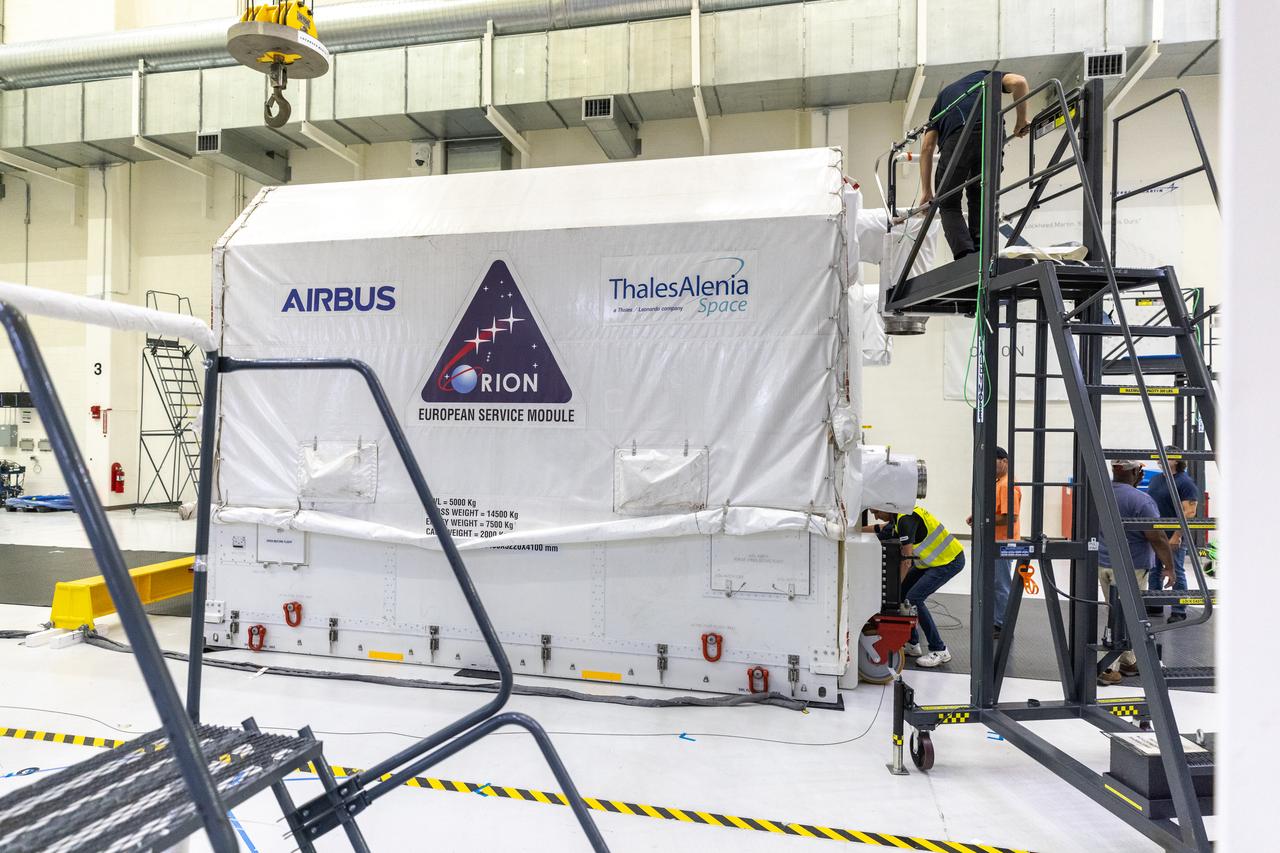

The transport carrier containing the European Service Module for NASA’s Artemis III mission arrives at the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Sept. 3, 2024. The European Service Module, which is assembled by Airbus in Bremen, Germany, from parts made in 10 European countries and the United States, acts as the driving force behind Orion for deep space exploration, providing essential propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power.
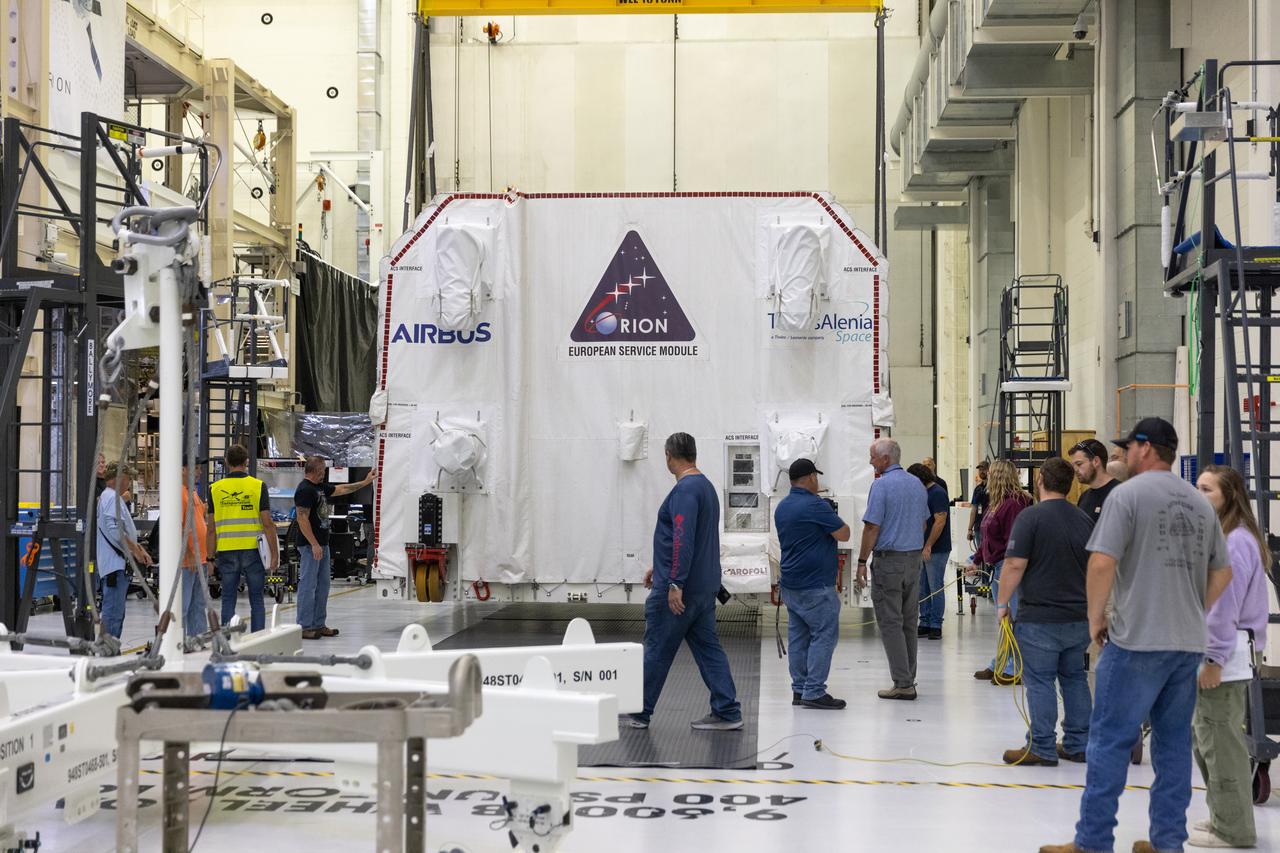

The transport carrier containing the European Service Module for NASA’s Artemis III mission arrives at the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Sept. 3, 2024. The European Service Module, which is assembled by Airbus in Bremen, Germany, from parts made in 10 European countries and the United States, acts as the driving force behind Orion for deep space exploration, providing essential propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power.
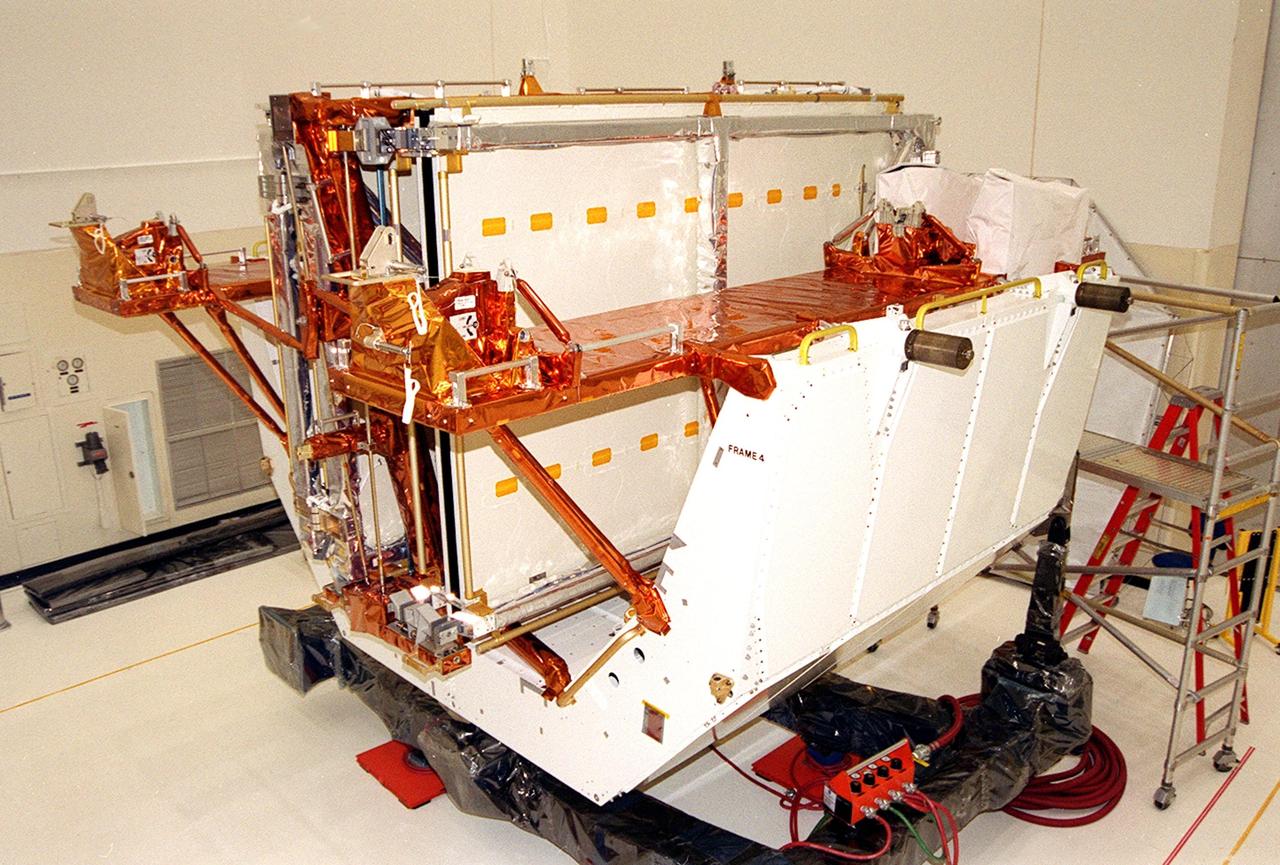
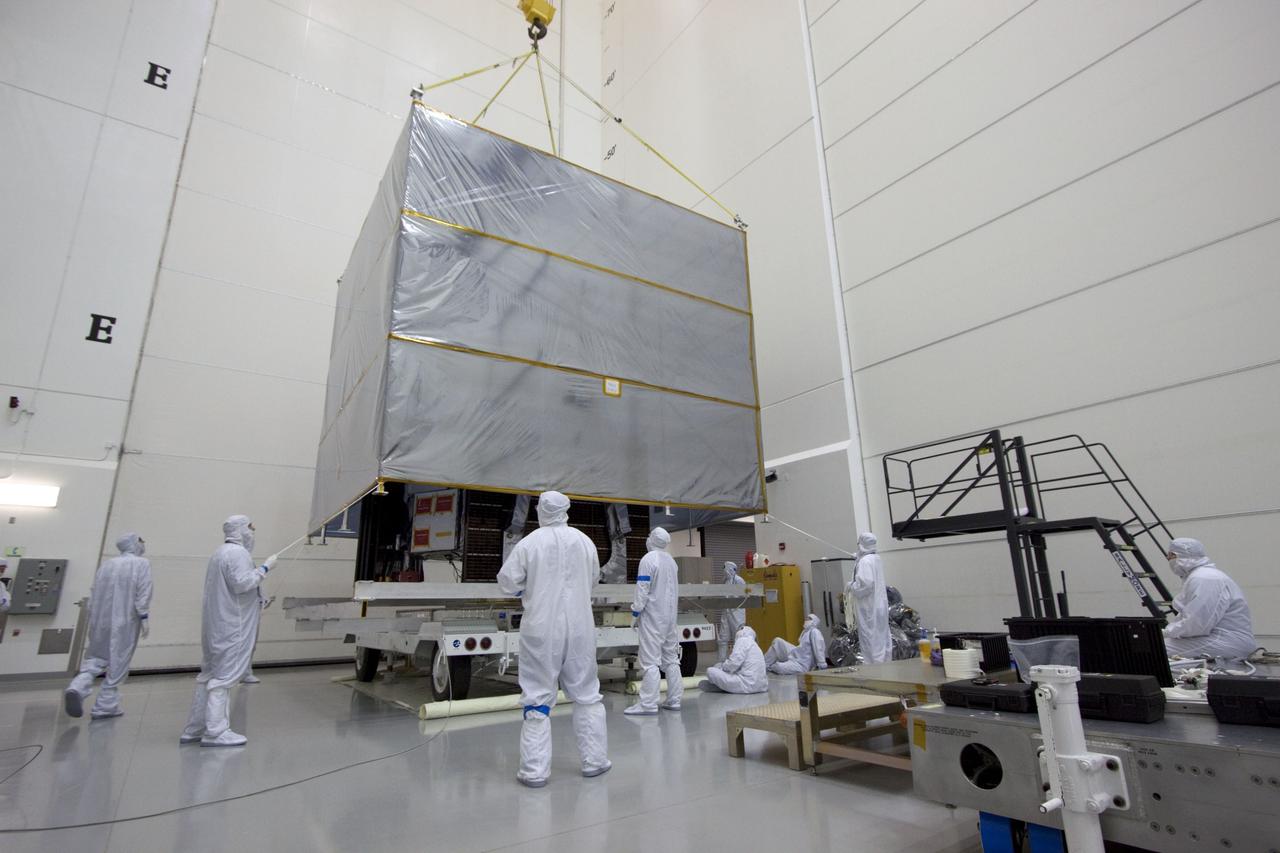
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Solar arrays part of the payload for the Hubble Servicing Mission, STS-109, await processing in the Vertical Processing Facility. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
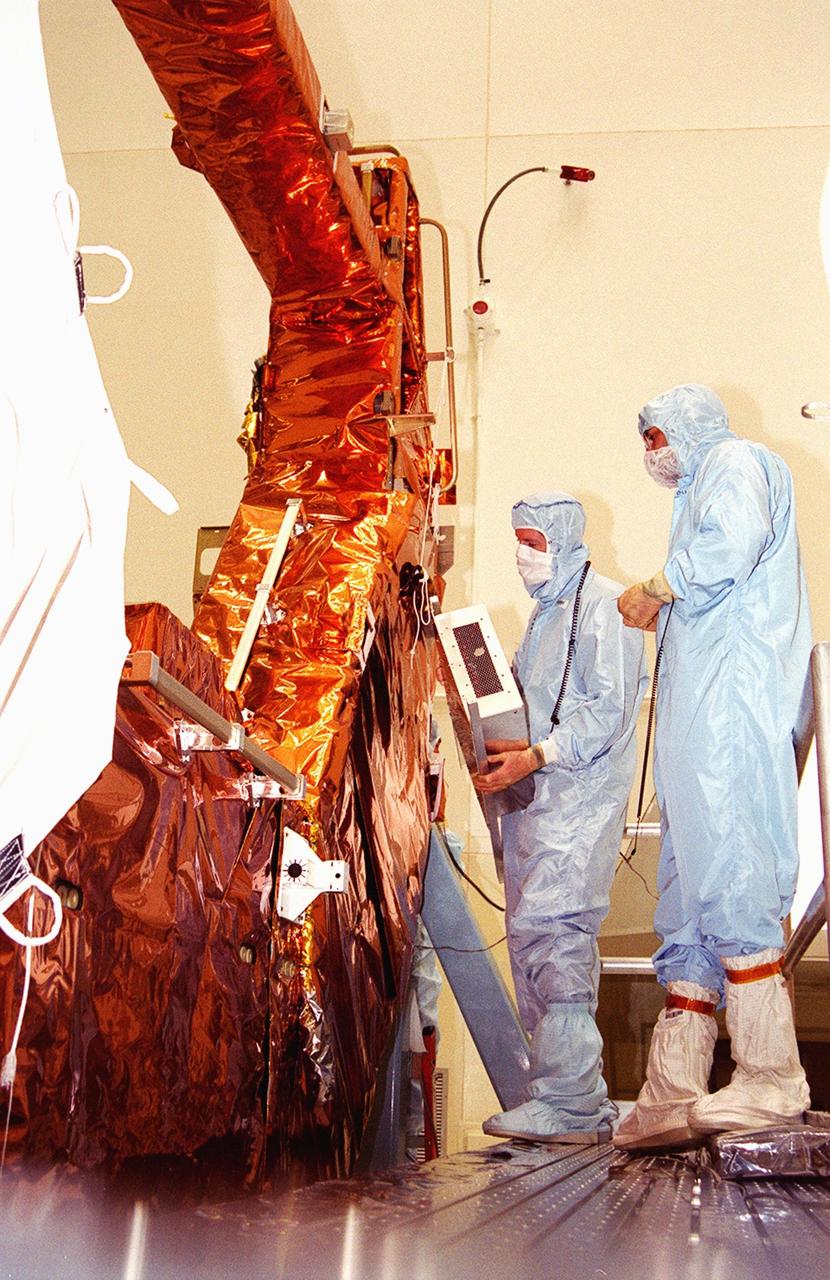

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility check over part of the payload for the Hubble Servicing Mission, STS-109. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
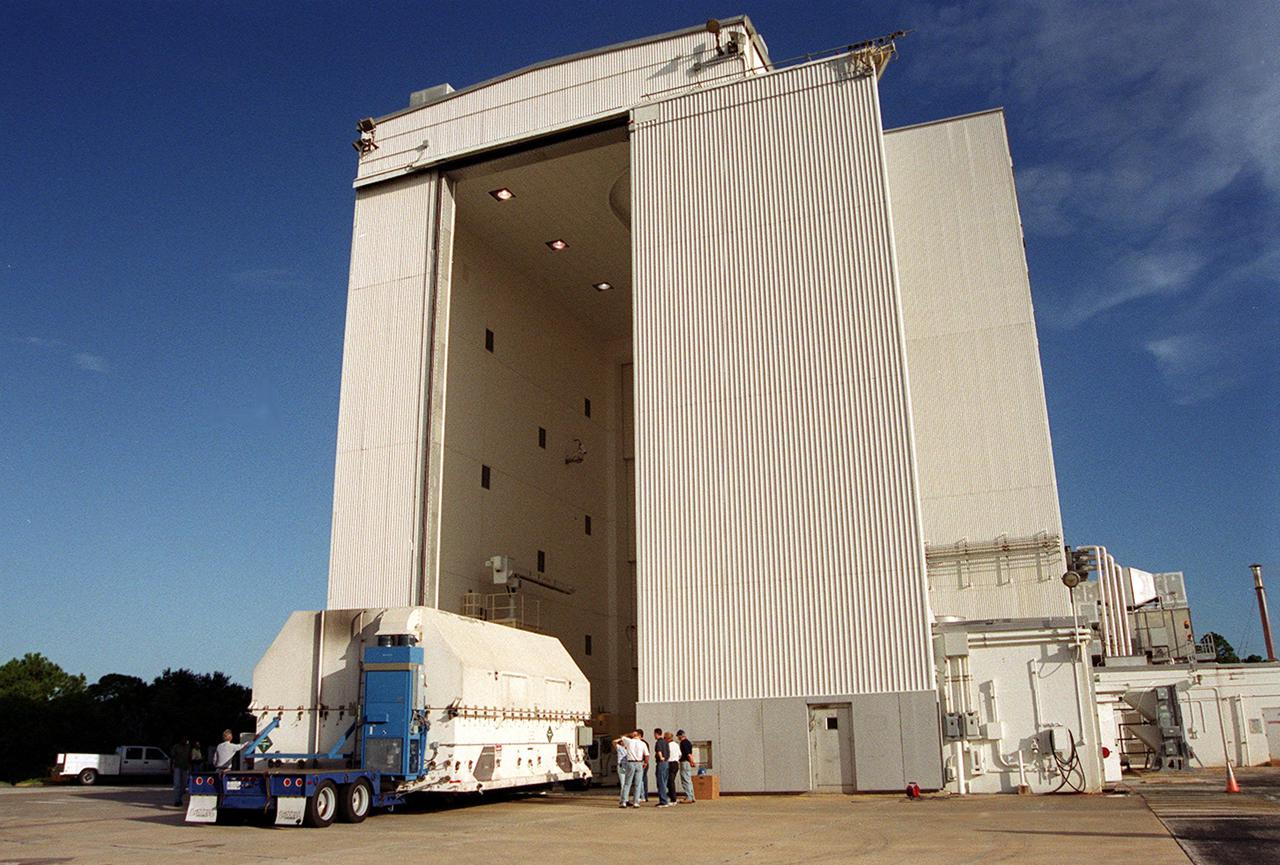

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, is moved into a facility at KSC. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
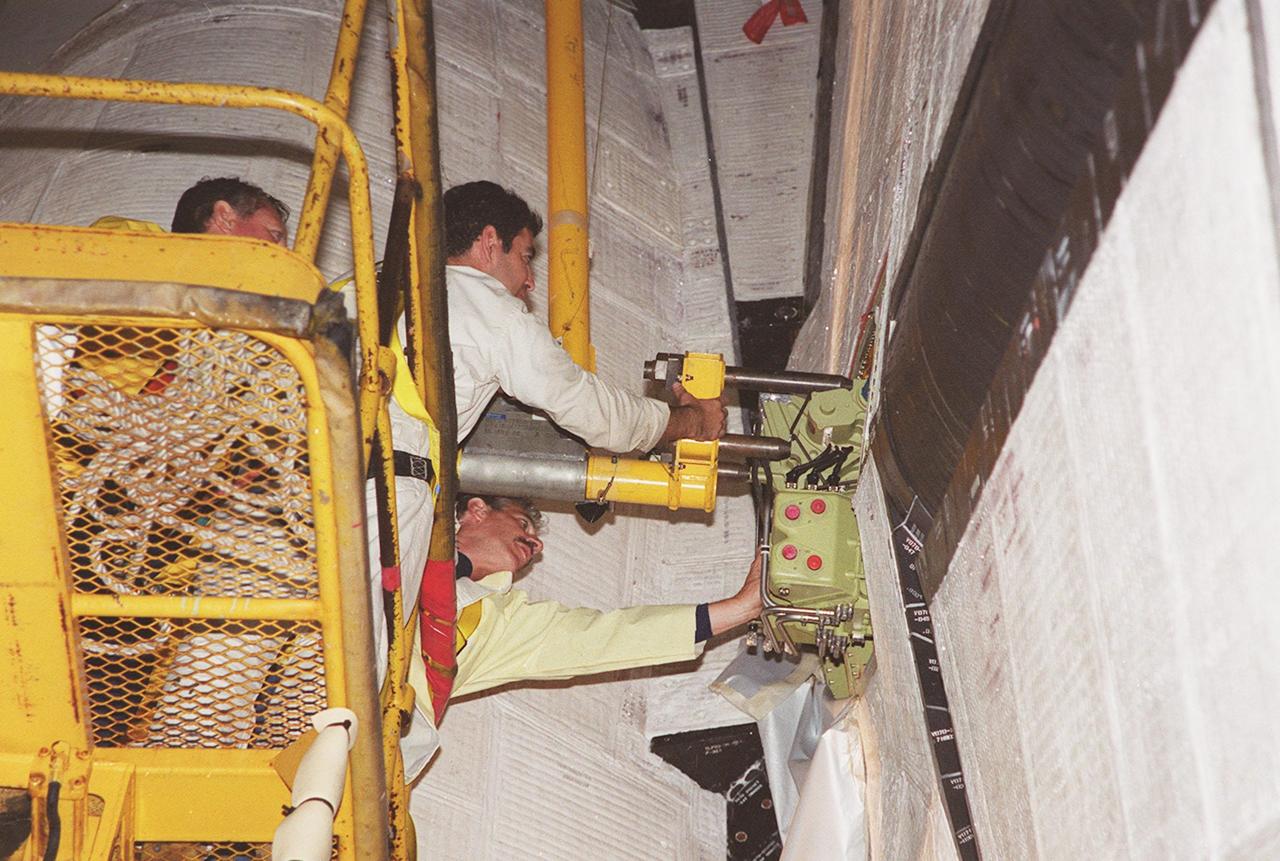

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers move the replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) into the body of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
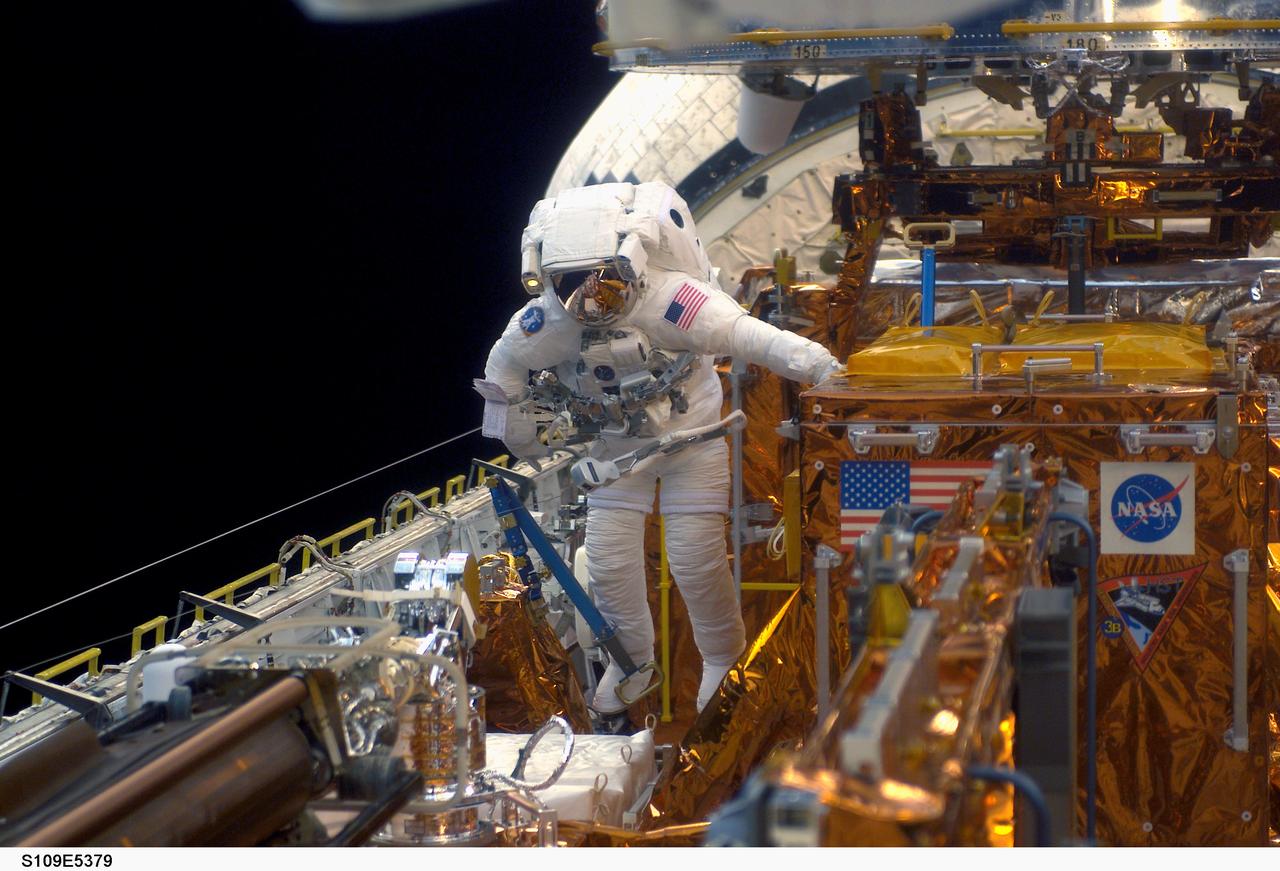

STS109-E-5379 (6 March 2002) --- Astronaut Richard M. Linnehan, mission specialist, works on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Columbia during the STS-109 mission's third space walk. The primary purpose of the extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Linnehan and John M. Grunsfeld was to replace the Power Control Unit on the giant telescope. The image was recorded with a digital still camera by one of Linnehan's crew mates inside Columbia's crew cabin.
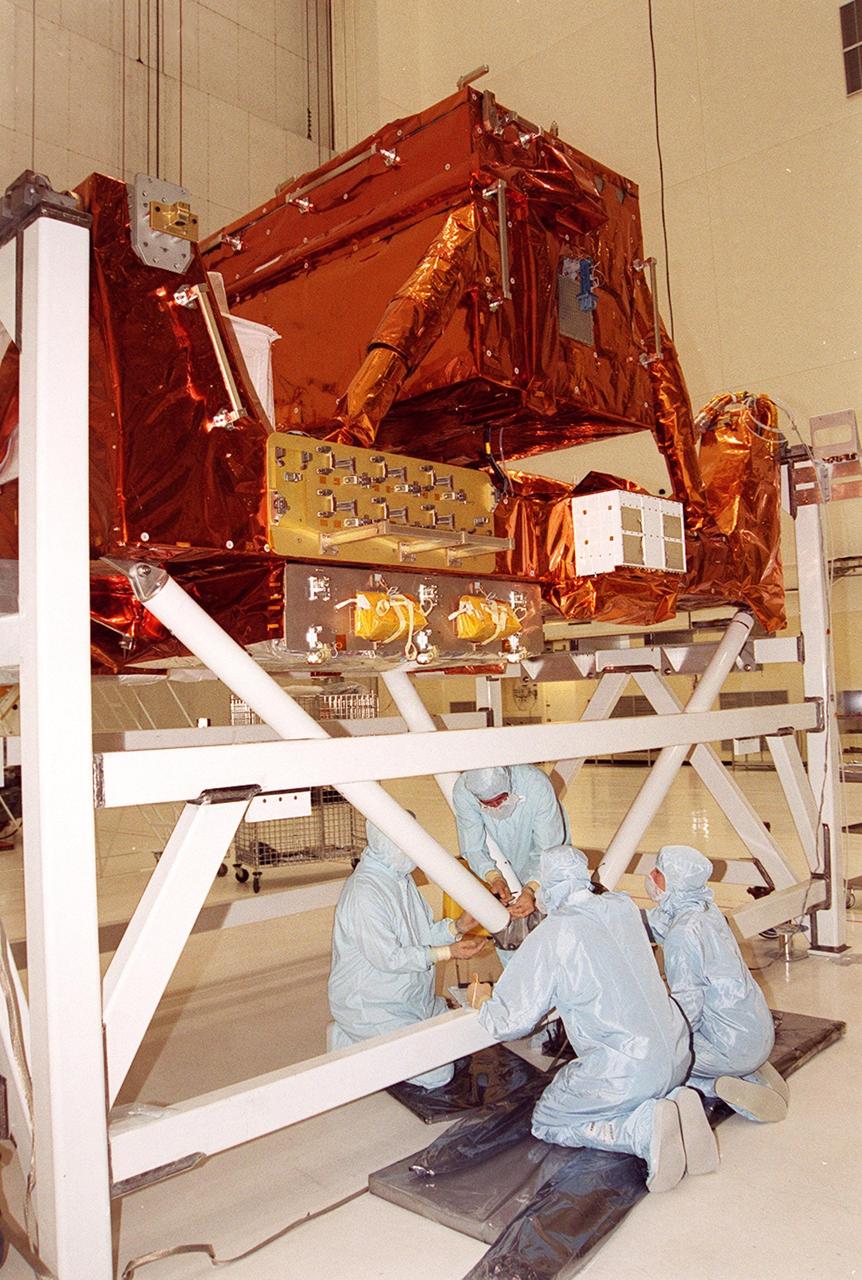
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers begin preparations for testing part of the payload (behind them) for the Hubble Servicing Mission, STS-109. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
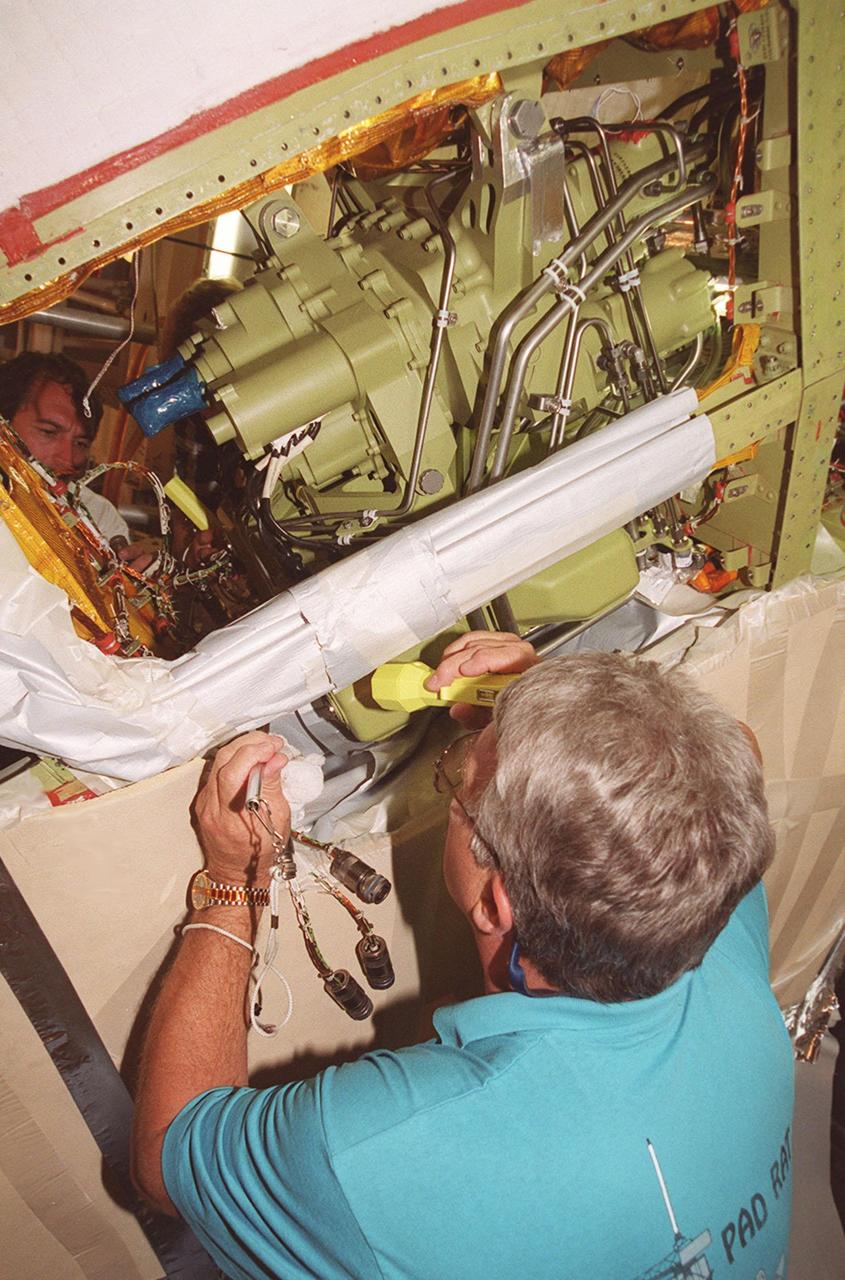

At Launch Pad 39A, Greg Lohning, who is with NASA, inspects the wiring on the newly installed Power Drive Unit (PDU) in Space Shuttle Atlantis. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
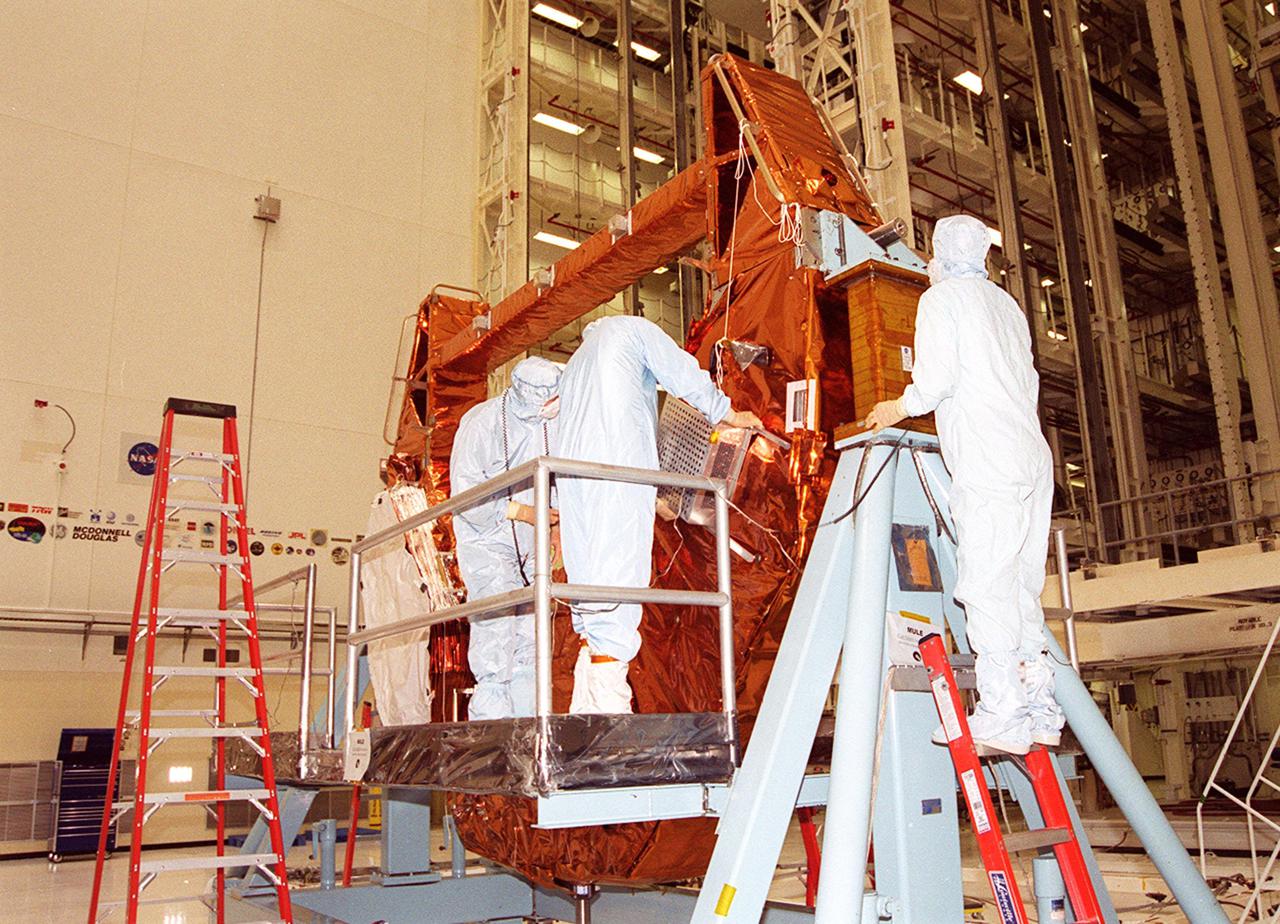

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility check out equipment that is part of the payload for the Hubble Servicing Mission, STS-109. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the NICMOS Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
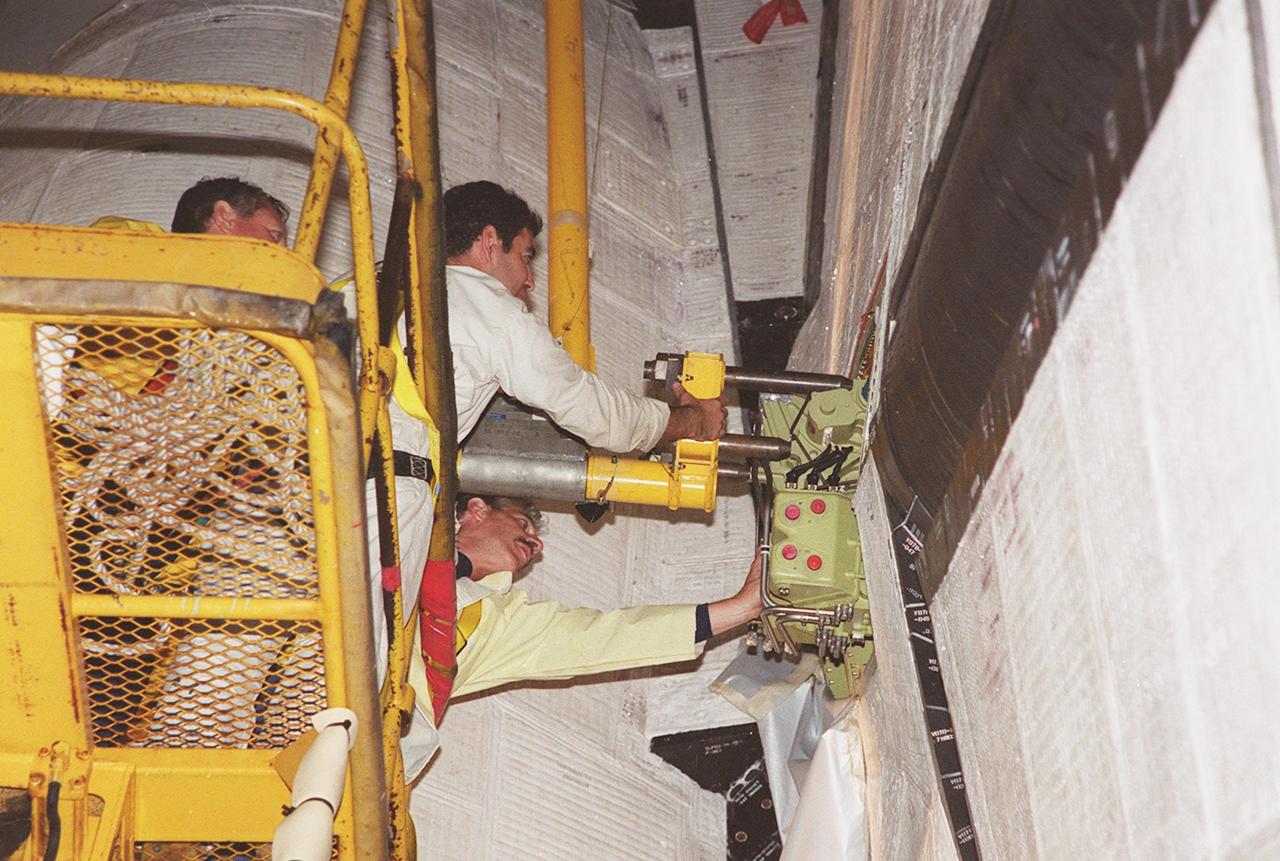

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers move the replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) into the body of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
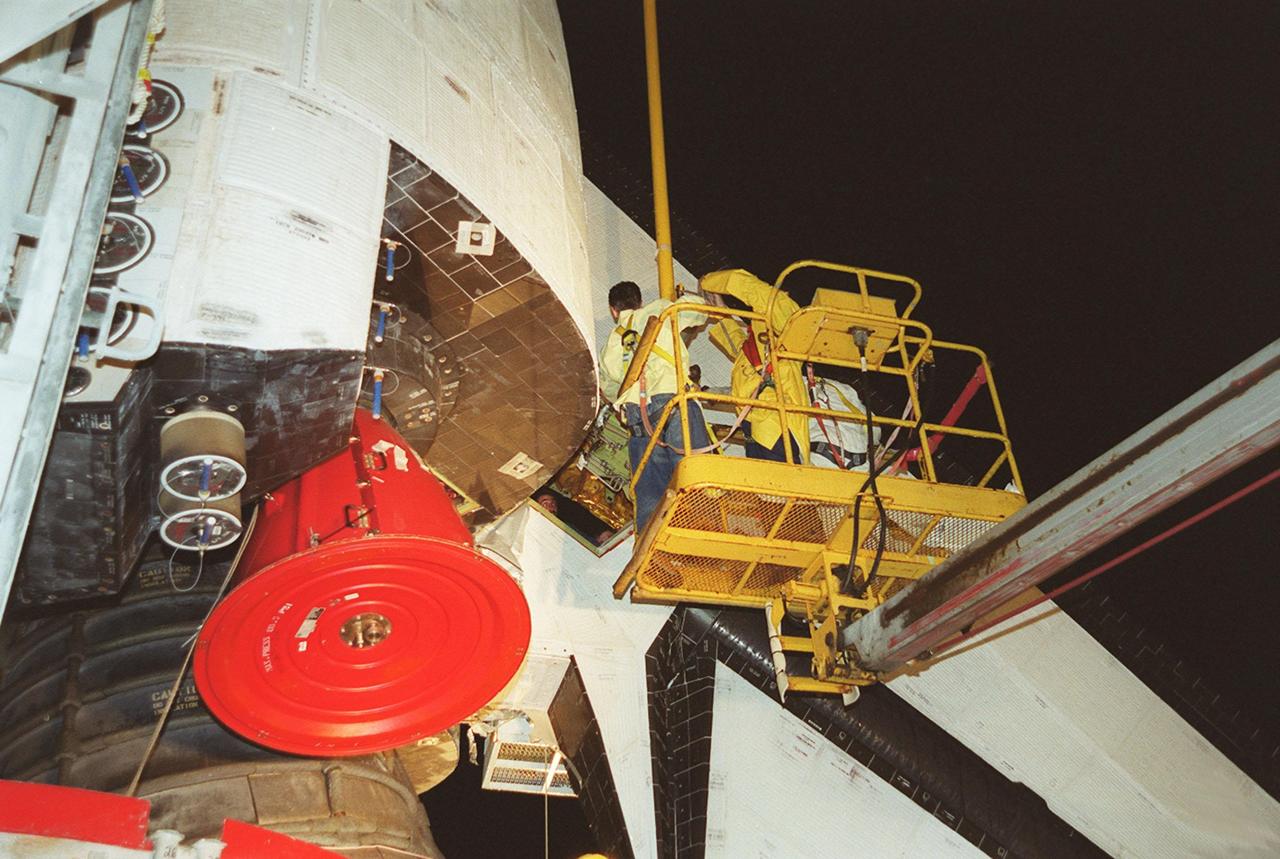

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers help guide the replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis into place. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
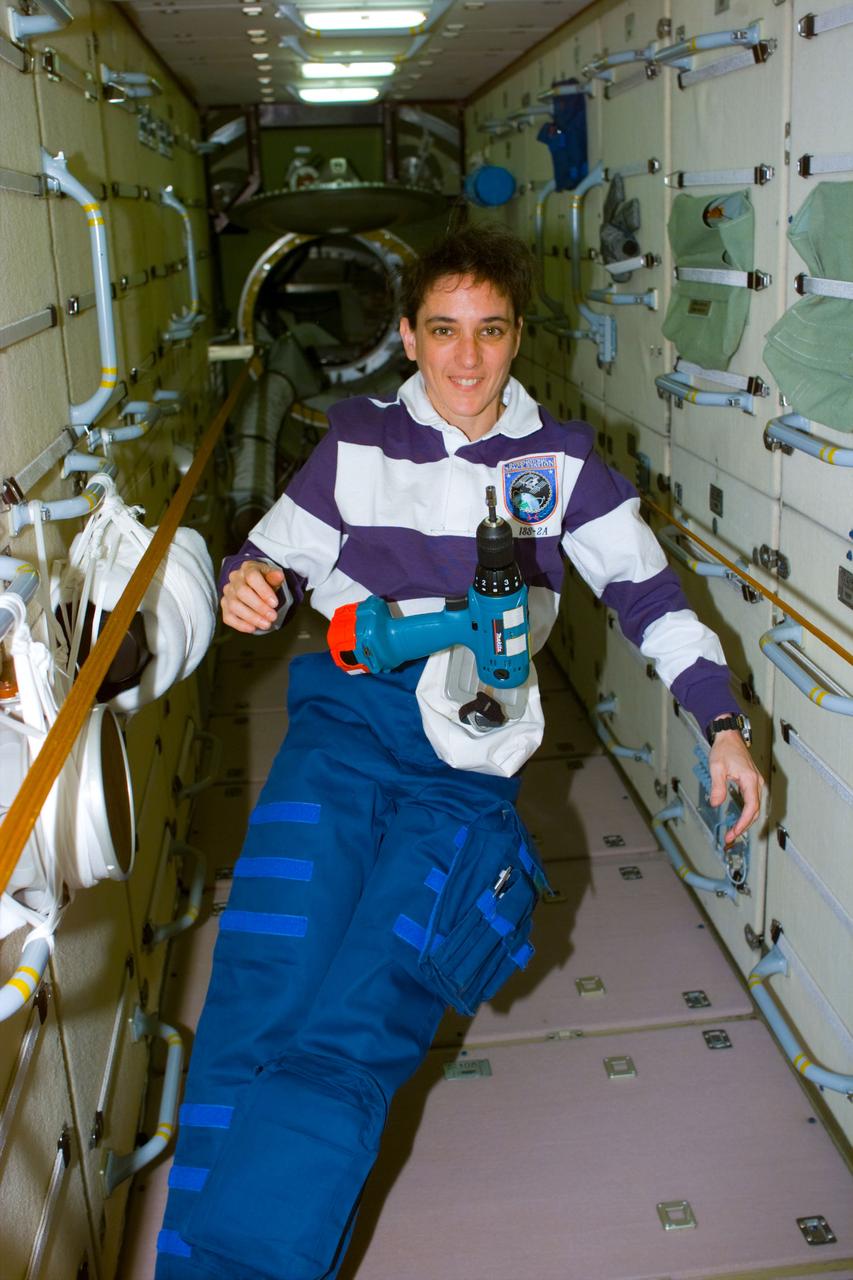

S88-E-5083 (12-11-98) --- Astronaut Nancy J. Currie, mission specialist, with a rechargeable power tool on Zarya. One of Currie's tasks was to replace a faulty unit which controls the discharging of stored energy from one of the Russian-built module's six batteries. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 05:24:08 GMT, Dec. 11.
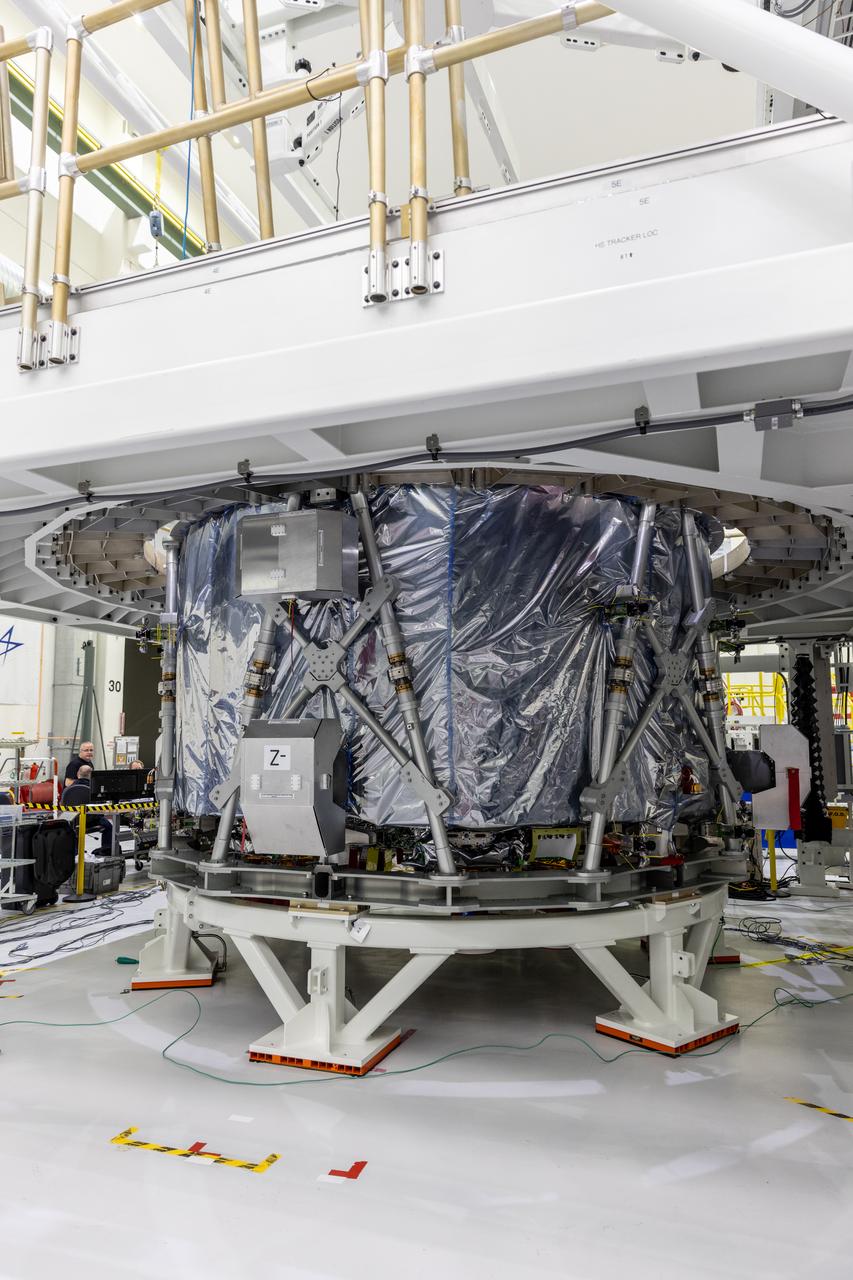

The transport carrier containing the European Service Module for NASA’s Artemis III mission arrives at the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Sept. 3, 2024. The European Service Module, which is assembled by Airbus in Bremen, Germany, from parts made in 10 European countries and the United States, acts as the driving force behind Orion for deep space exploration, providing essential propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power.

The transport carrier containing the European Service Module for NASA’s Artemis III mission arrives at the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Sept. 3, 2024. The European Service Module, which is assembled by Airbus in Bremen, Germany, from parts made in 10 European countries and the United States, acts as the driving force behind Orion for deep space exploration, providing essential propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power.
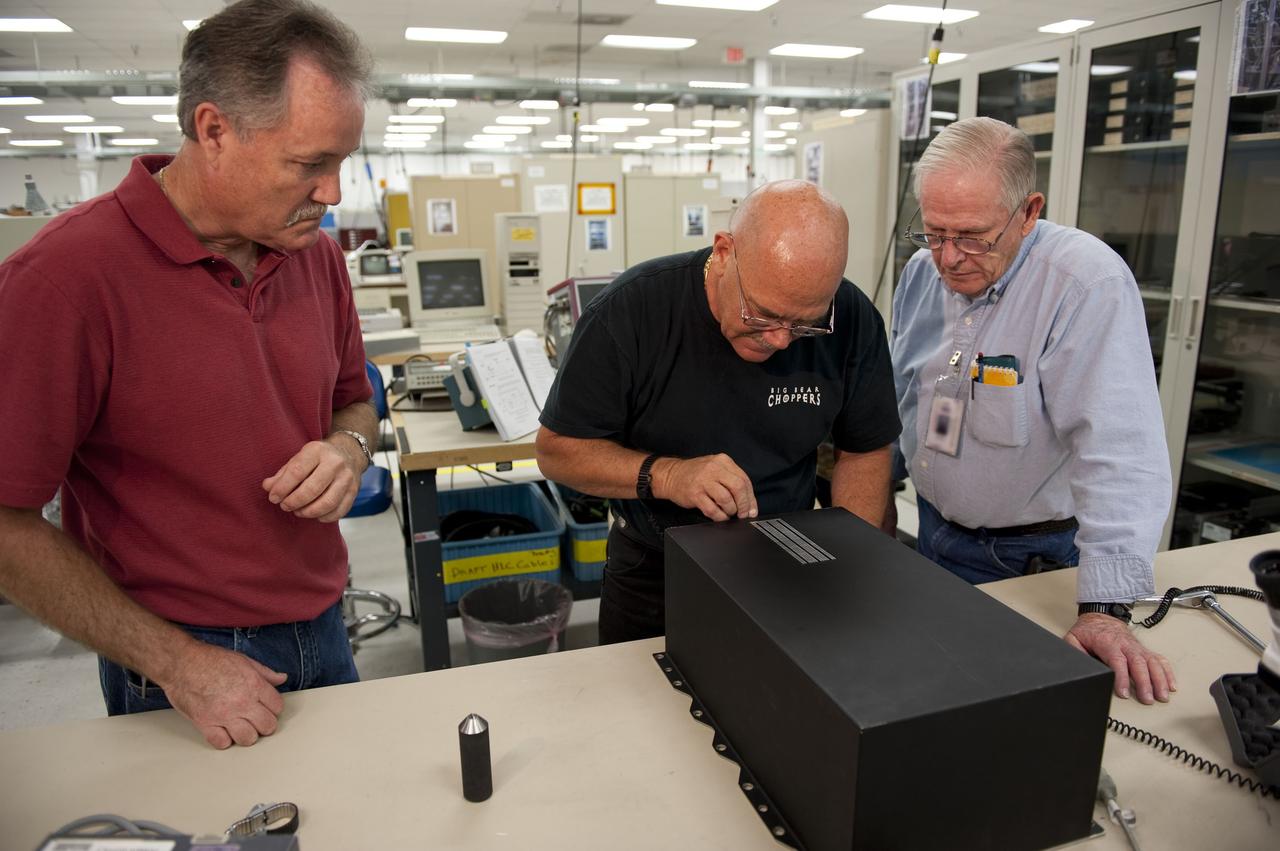

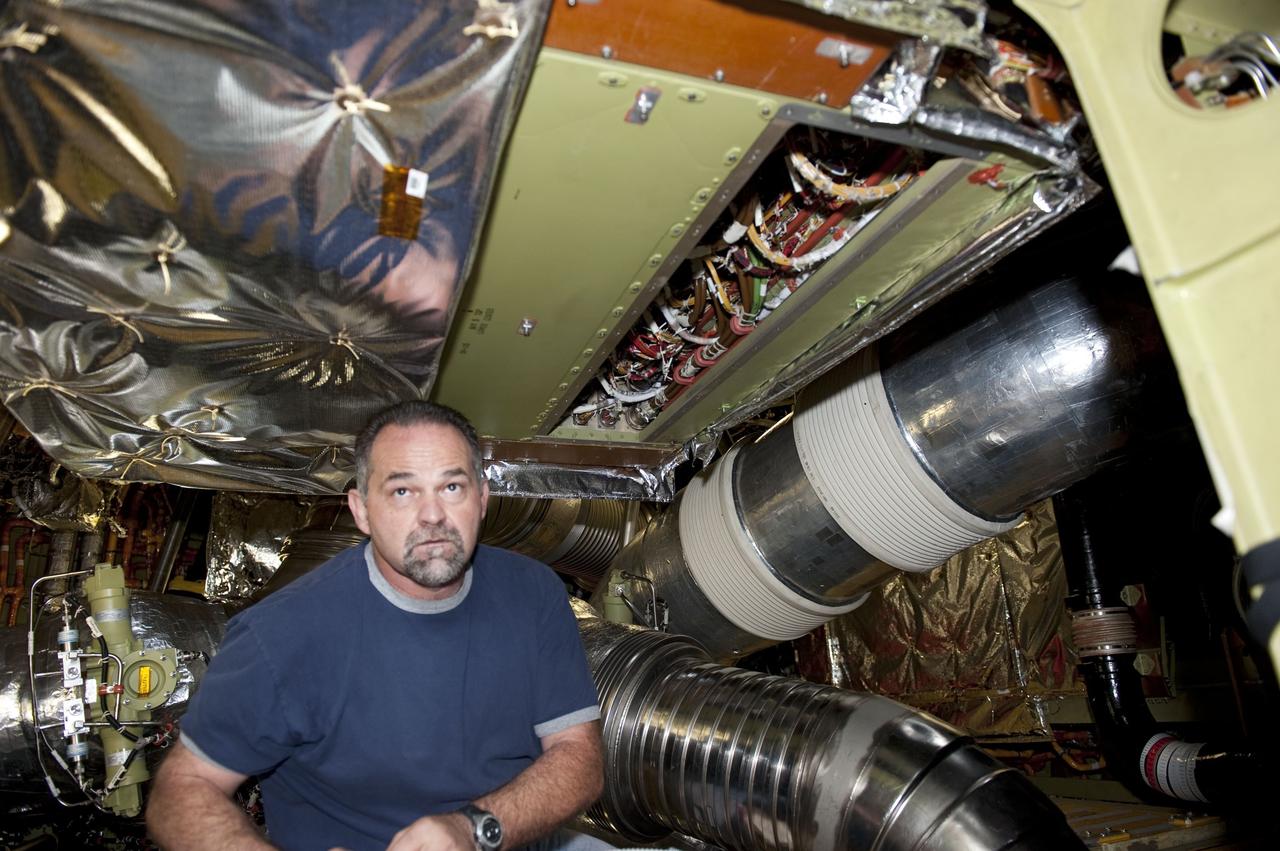
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, technicians remove the cover on the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) to begin the testing process. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
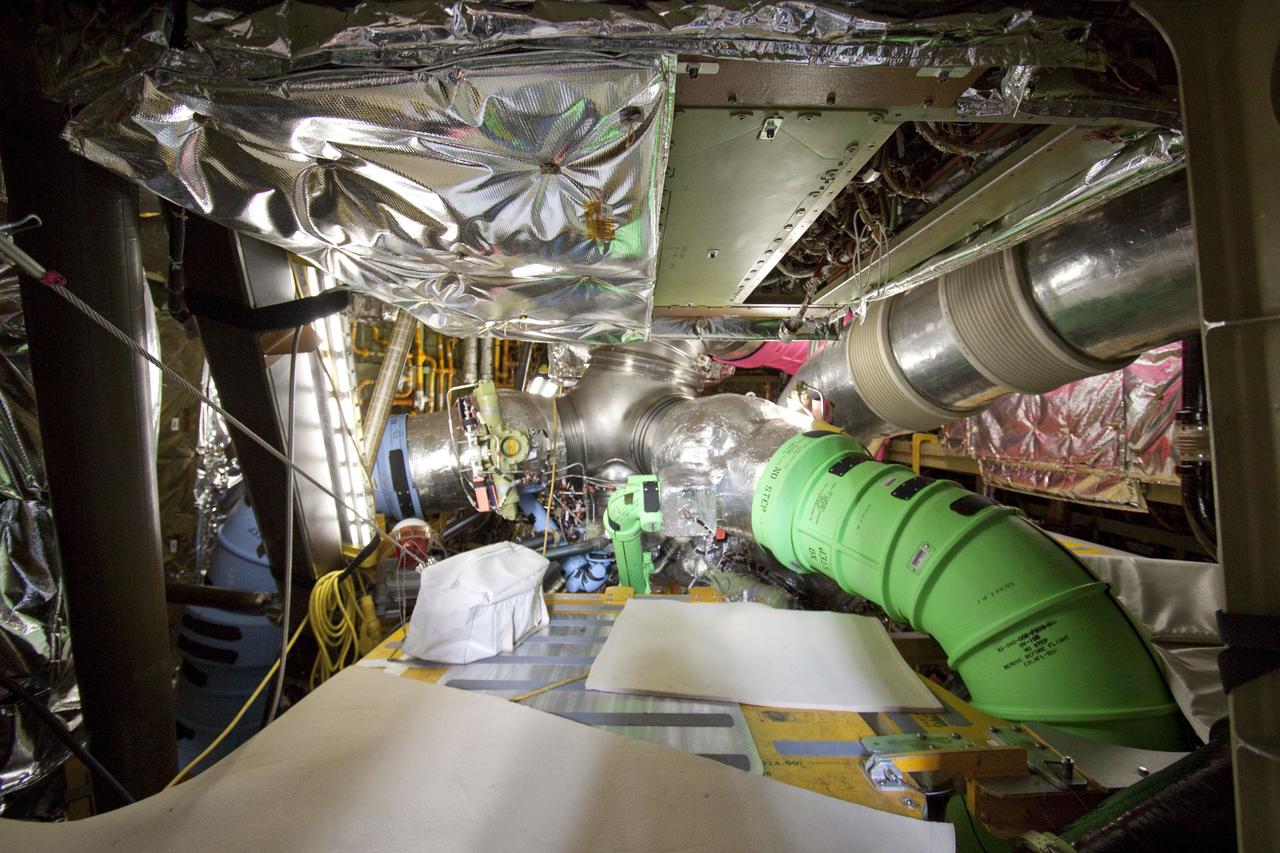

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) has been replaced inside of space shuttle Endeavour. Located in Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission and has been replaced. Systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, technicians remove the cover on the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) to begin the testing process. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

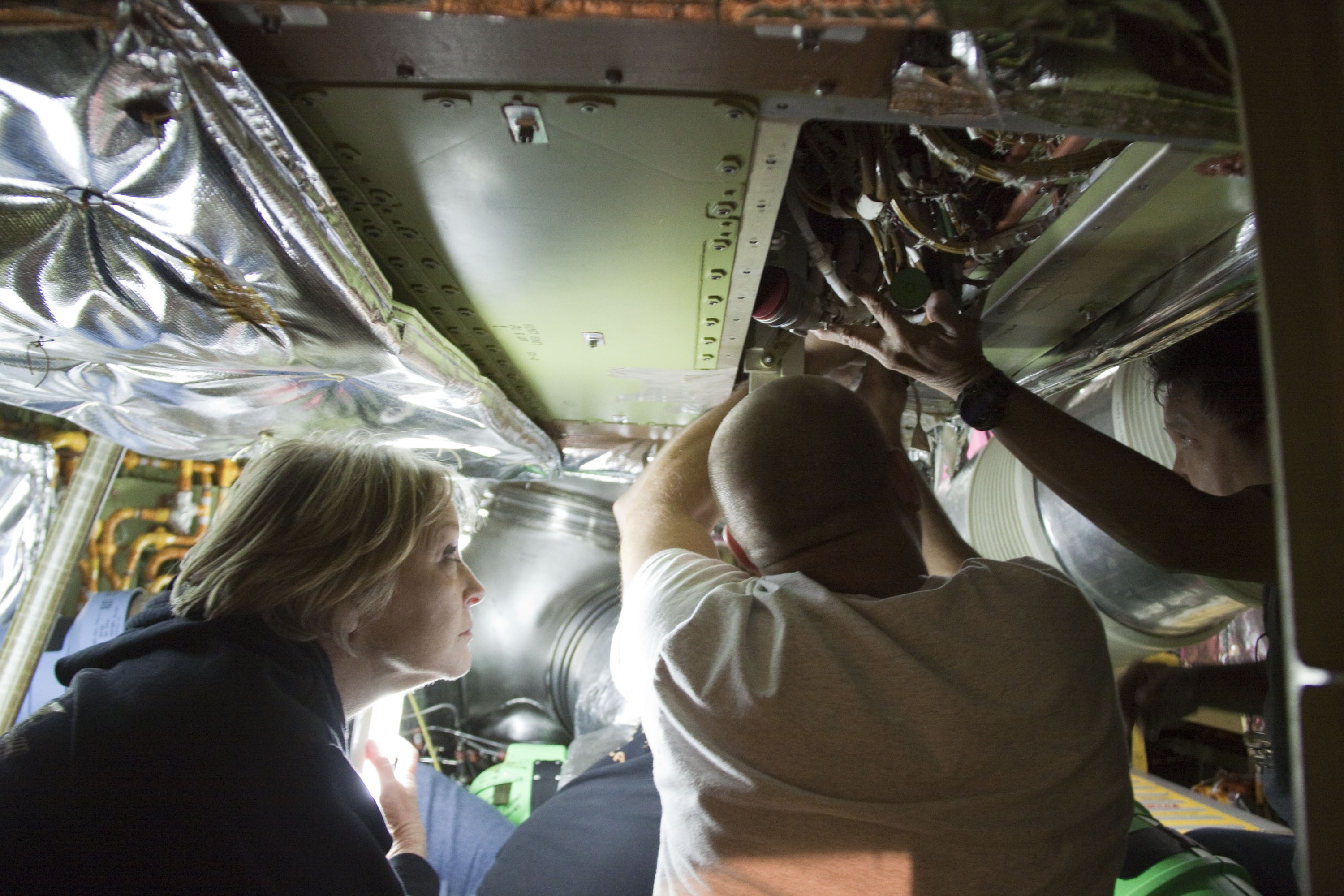
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removes a cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is removed from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A work station, a worker inspects the replacement Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) which is being prepared for installation into Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. --The Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is outside at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A after it was removed from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removed a cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, technicians work to remove the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, technicians carefully remove the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) from a cart for testing. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) has been replaced inside of space shuttle Endeavour. Located in Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission and has been replaced. Systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removes a cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, technicians begin to remove the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
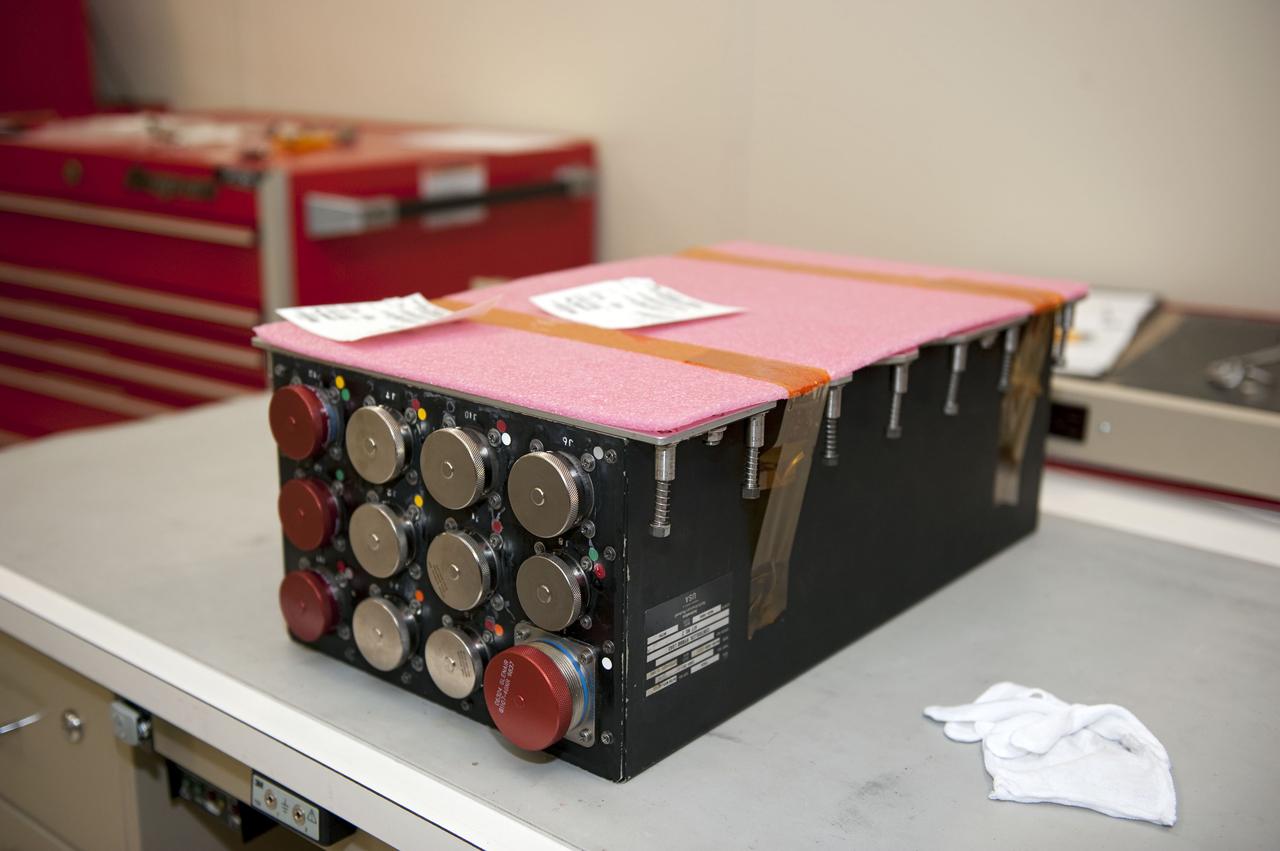

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A work station, a replacement Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is being prepared for installation into Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
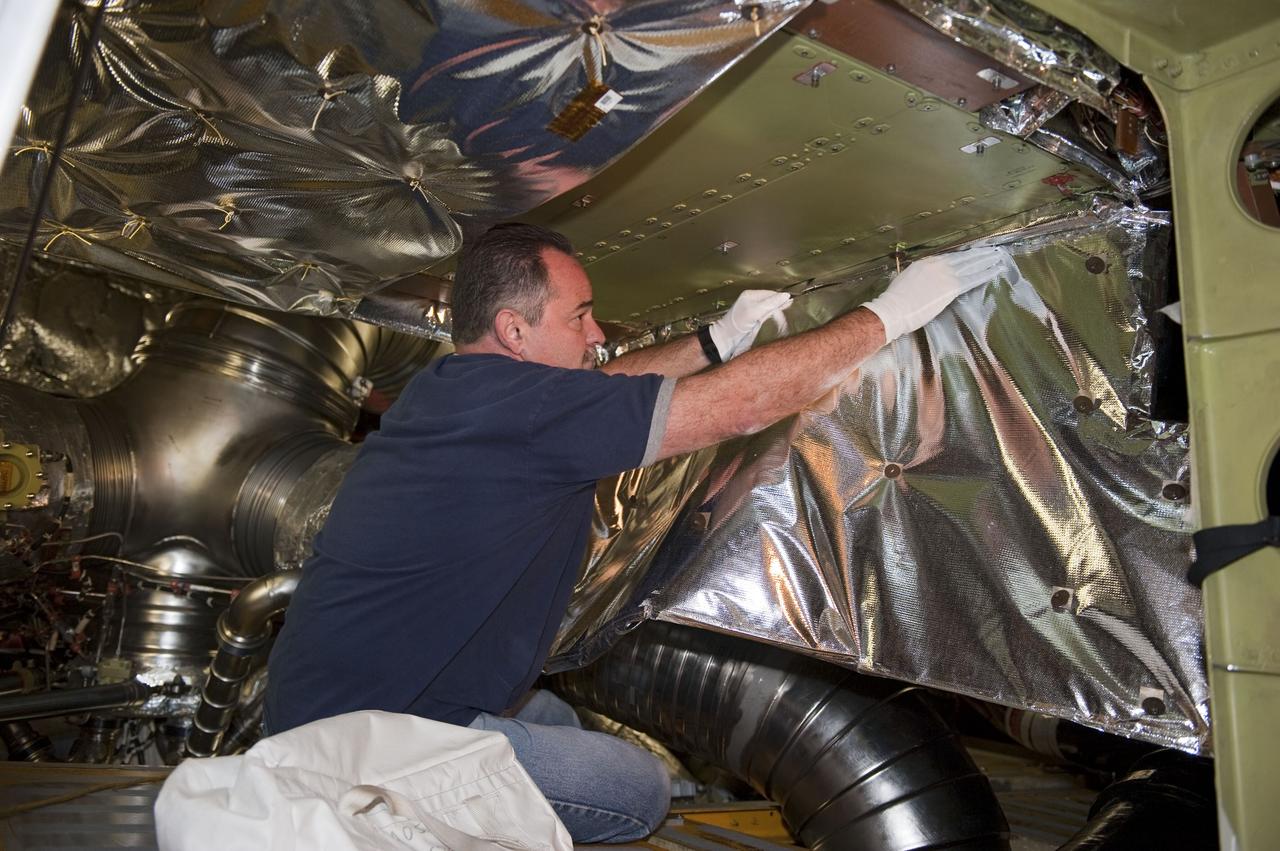

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removes an insulating blanket and cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
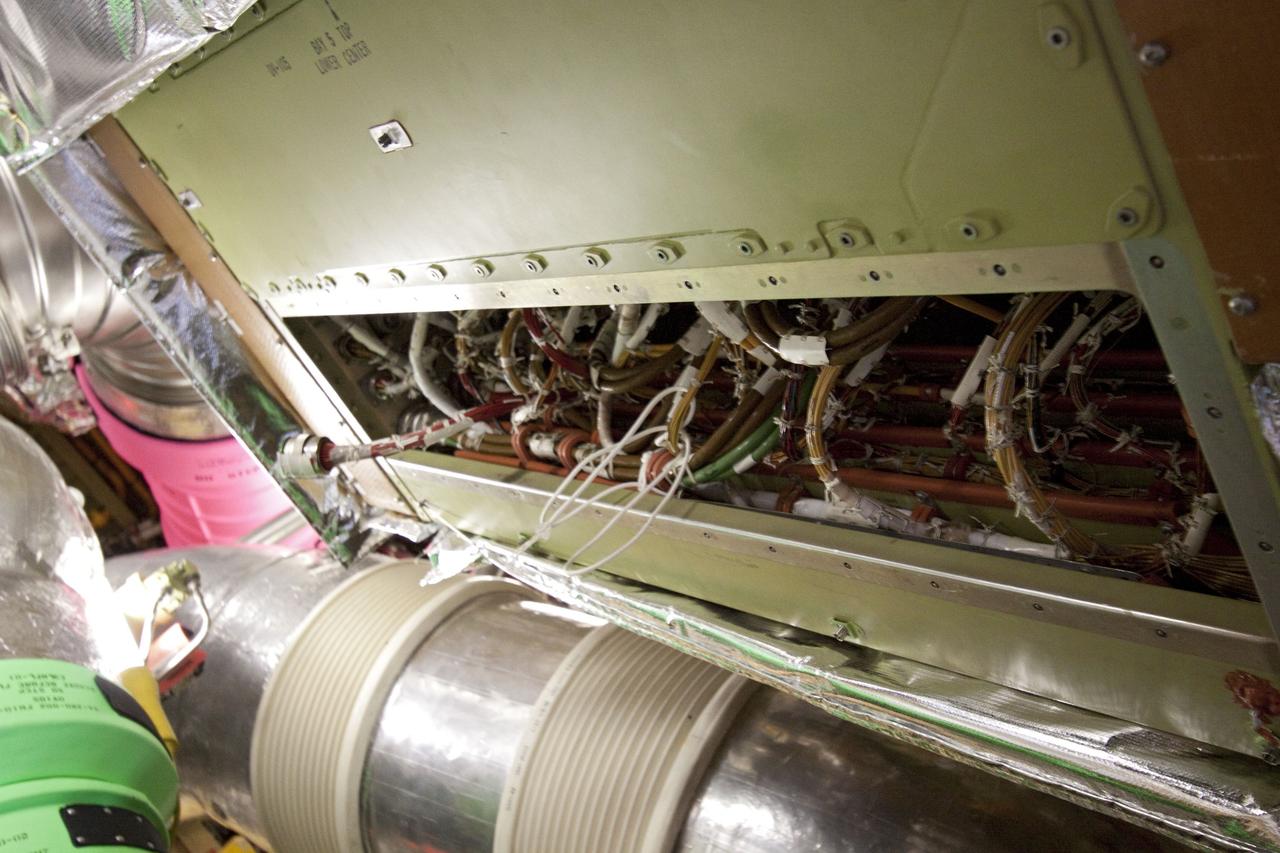

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) has been replaced inside of space shuttle Endeavour. Located in Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission and has been replaced. Systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is uncovered for testing. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
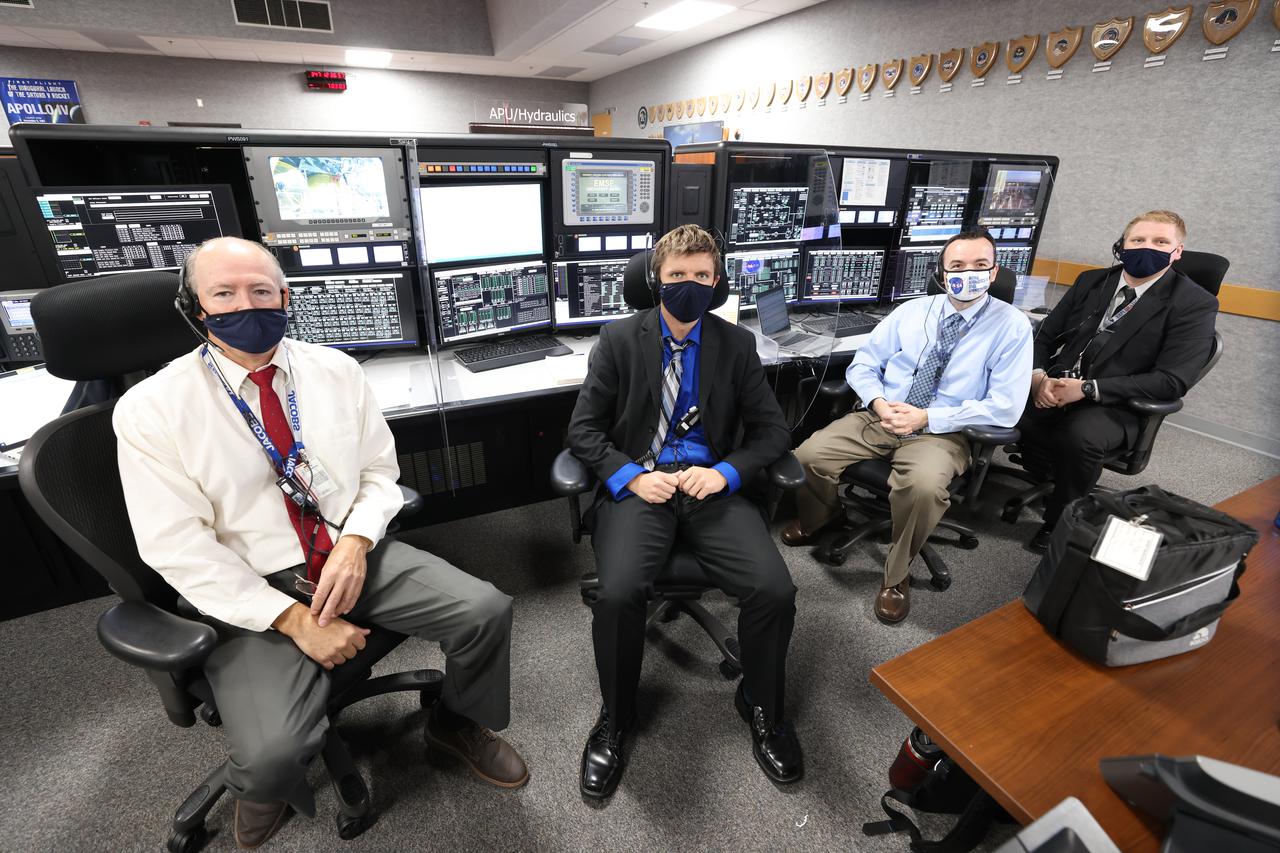

Launch team members are seated at the Auxiliar Power Units/Hydraulics consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
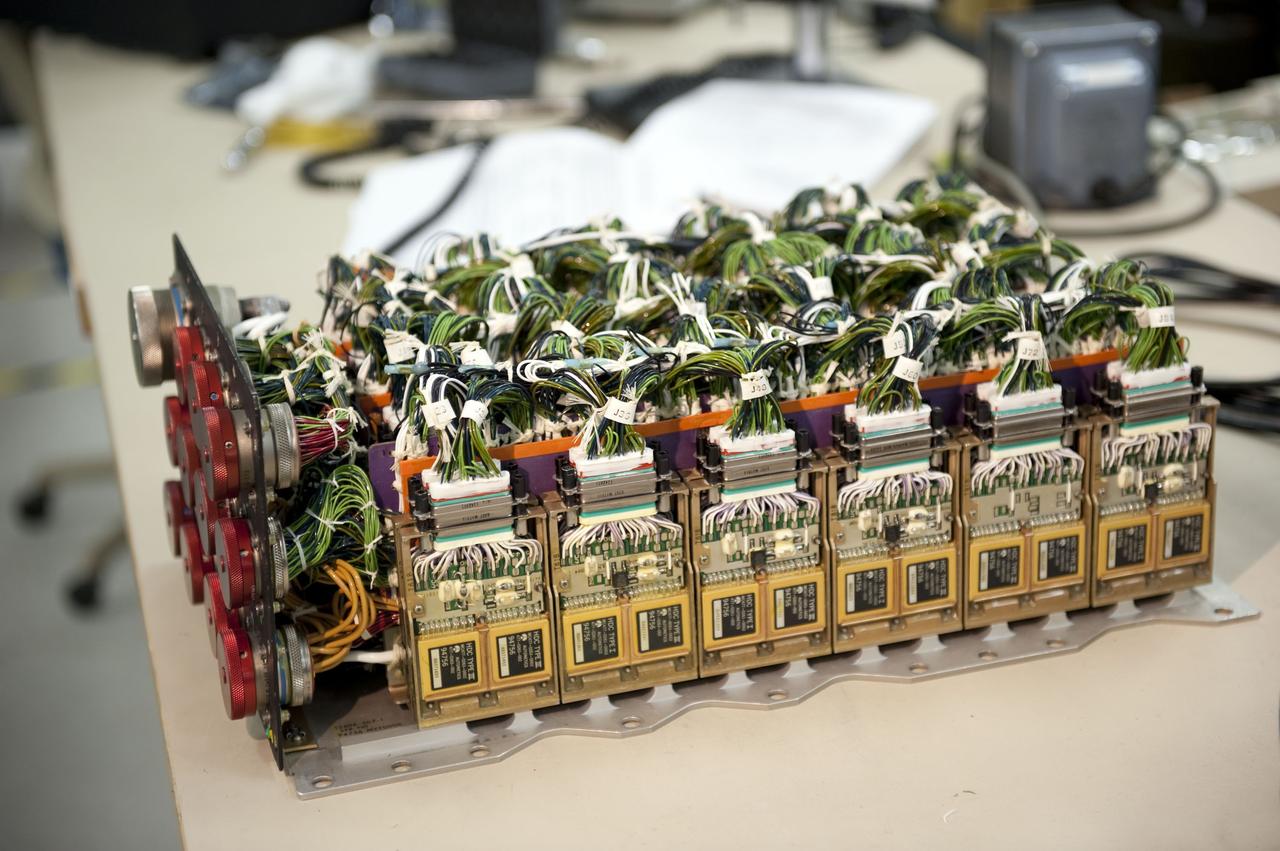
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is uncovered for testing. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
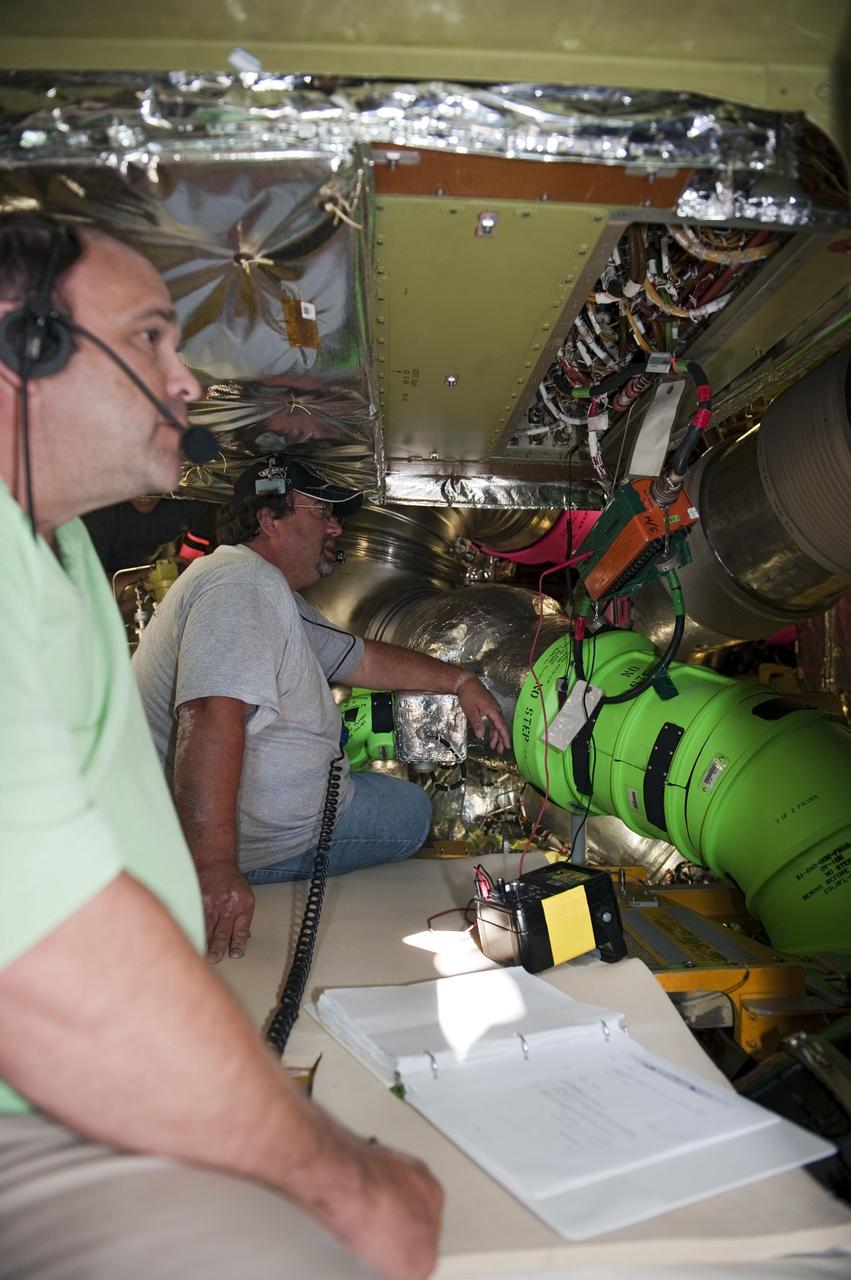

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, technicians inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section test the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
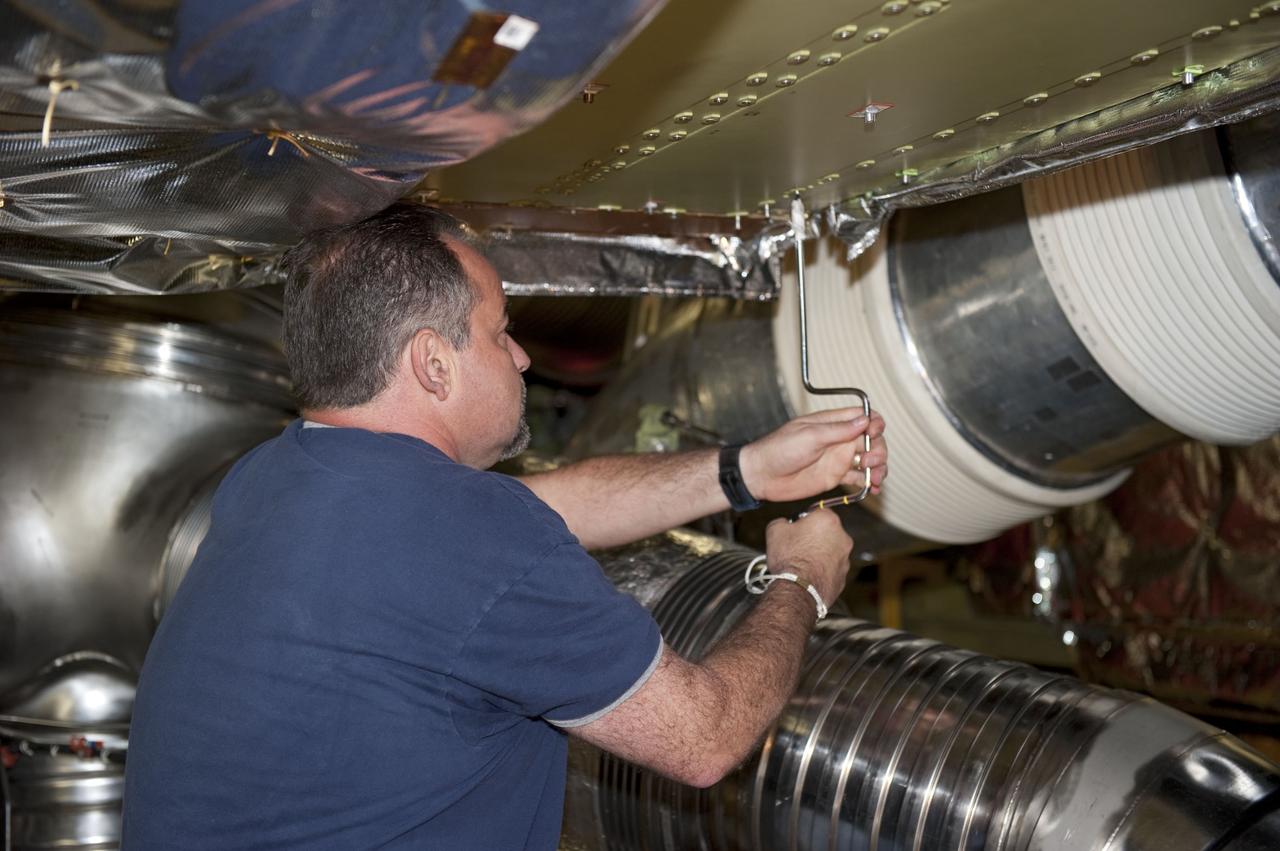

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removes a cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
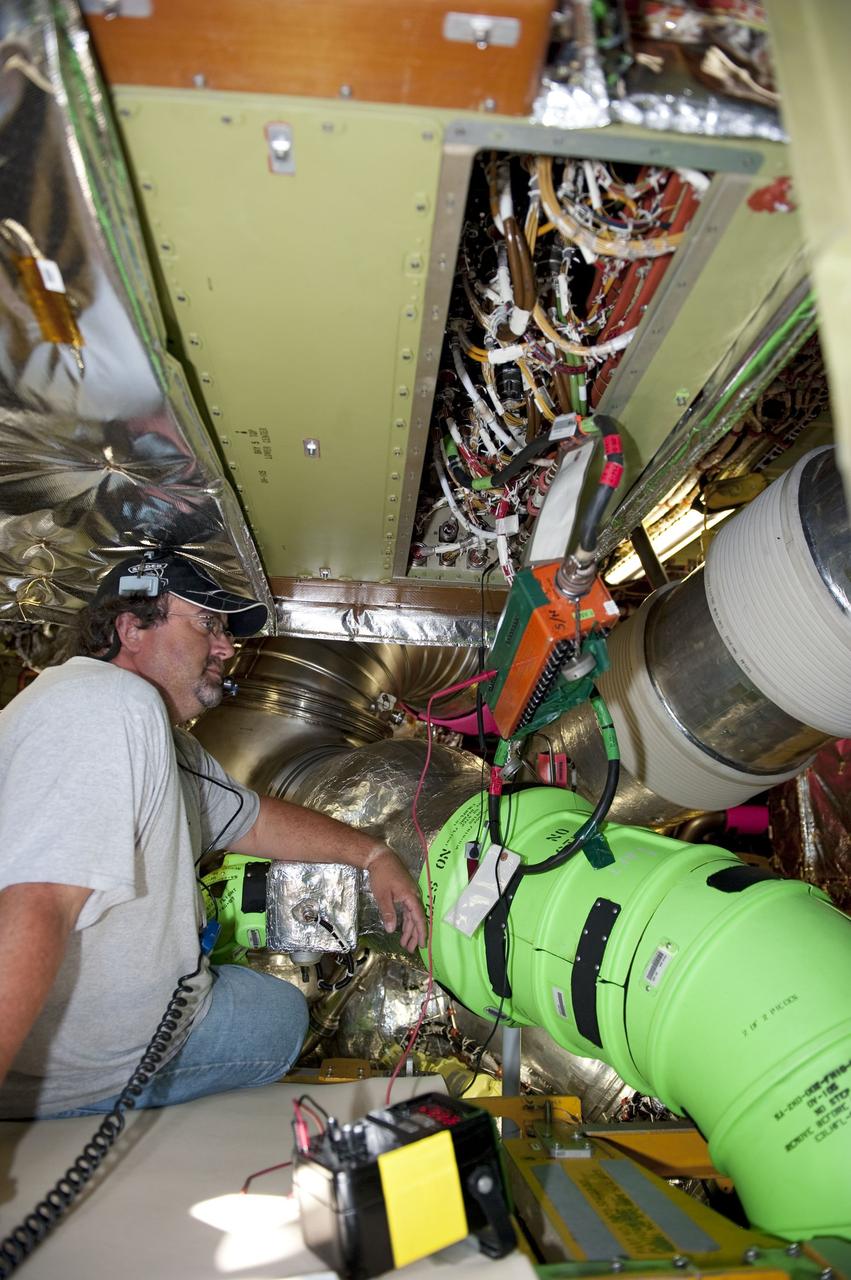

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, technicians inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section test the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
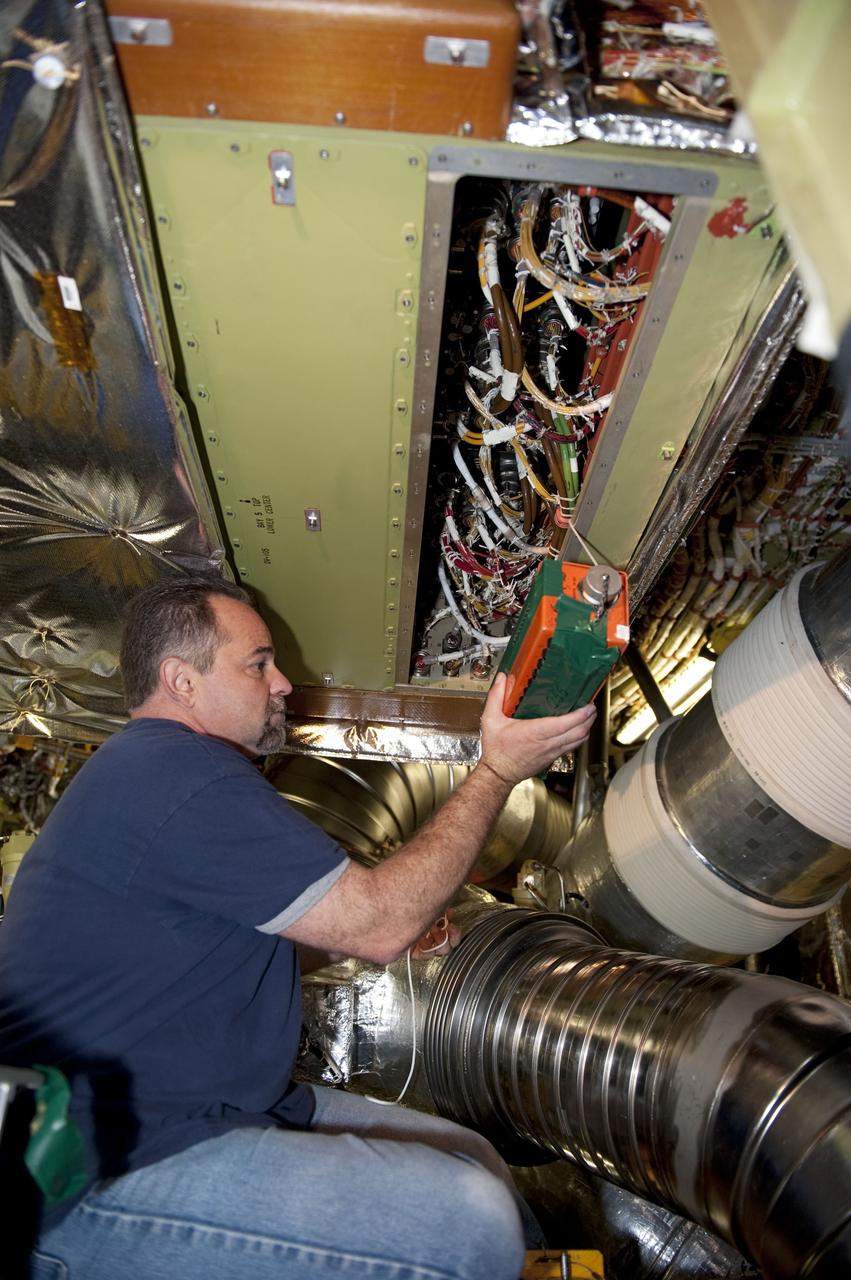

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section is testing the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) for replacement. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
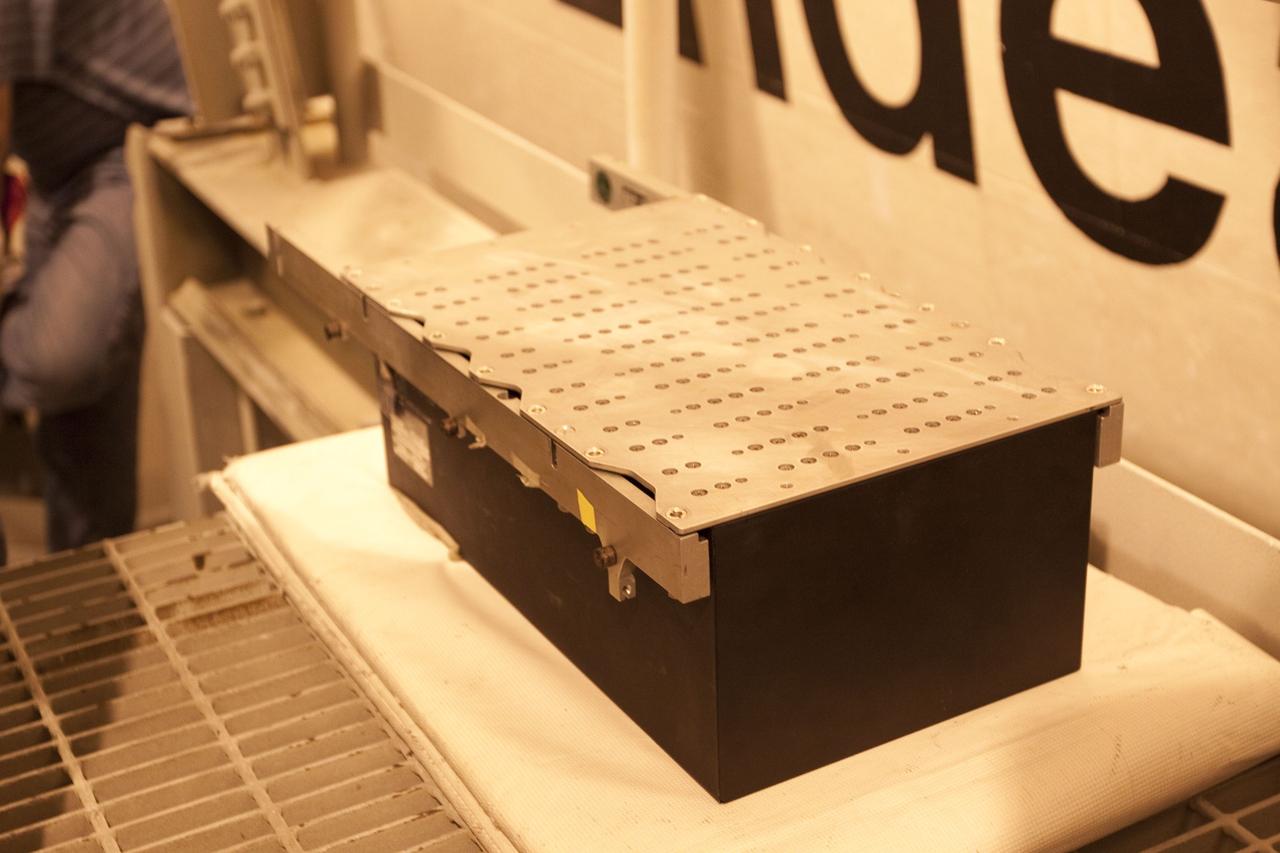
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is outside at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A after it was removed from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
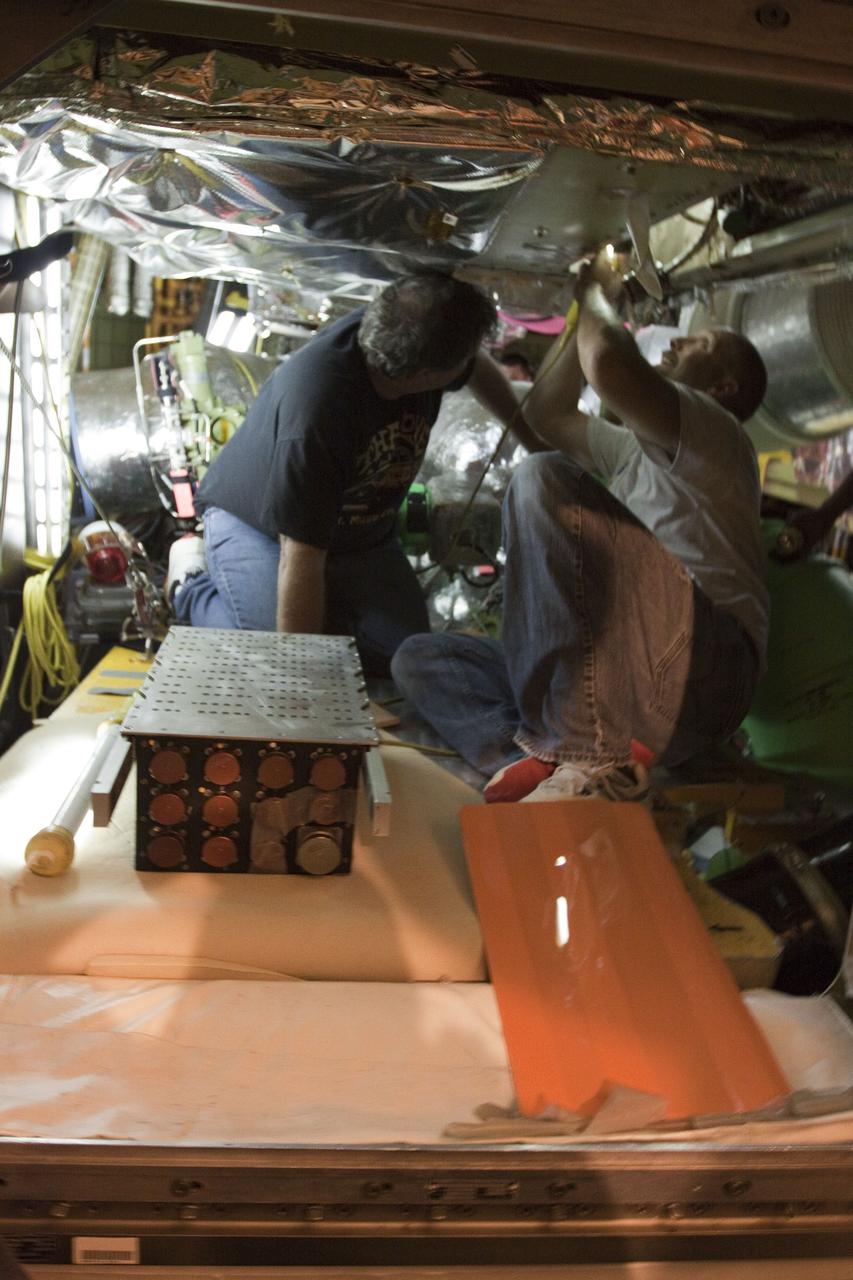

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is removed from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
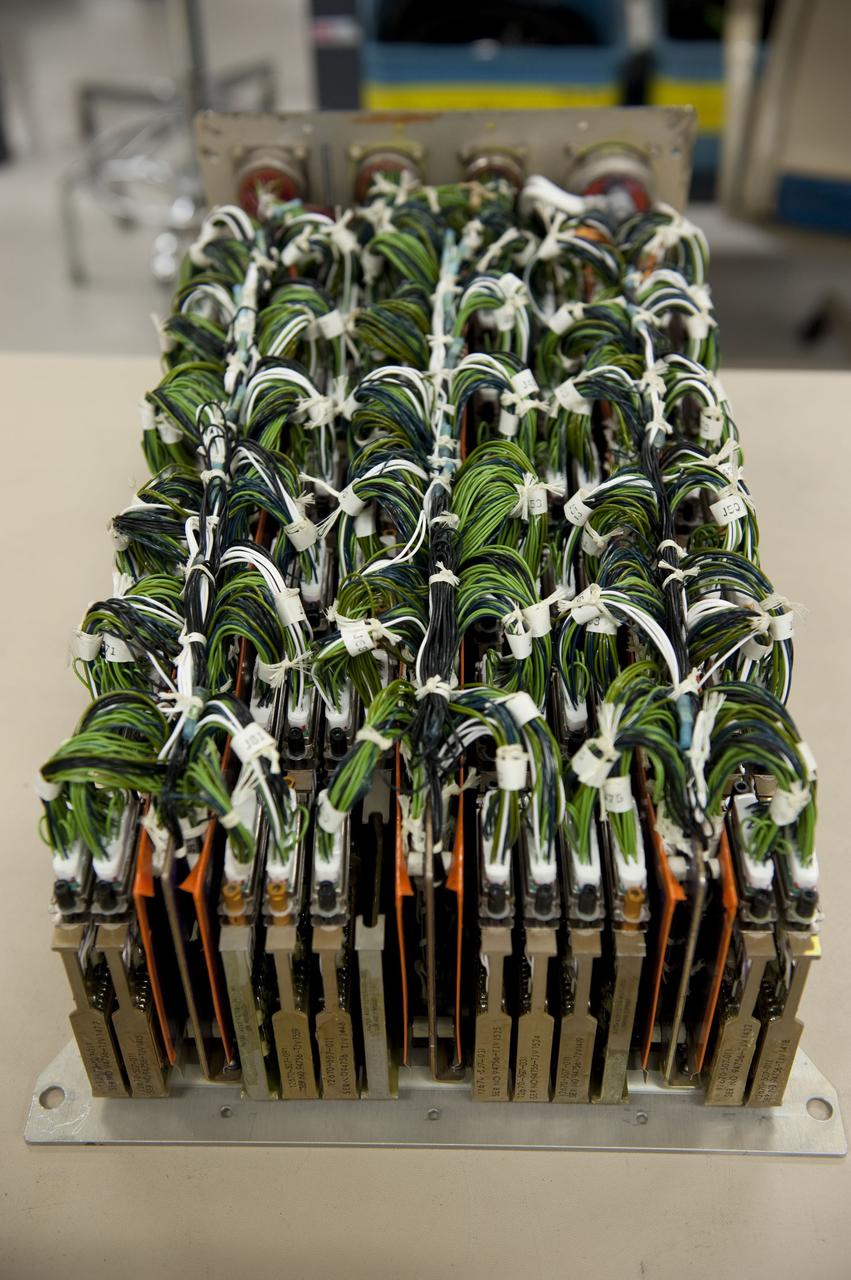
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is uncovered for testing. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is removed from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech's Hazardous Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians use an overhead crane to lift the cover from NASA's Juno spacecraft before its move to a fueling stand where the spacecraft will be loaded with the propellant necessary for orbit maneuvers and the attitude control system. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech's Hazardous Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians disconnect NASA's Juno spacecraft from its transport prior to its move to a fueling stand where the spacecraft will be loaded with the propellant necessary for orbit maneuvers and the attitude control system. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building, overhead cranes are lowered toward the orbiter Columbia. The cranes will lift the orbiter to a vertical position for stacking with the external tank and solid rocket boosters. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech's Hazardous Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians use an overhead crane to lift the cover from NASA's Juno spacecraft before its move to a fueling stand where the spacecraft will be loaded with the propellant necessary for orbit maneuvers and the attitude control system. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
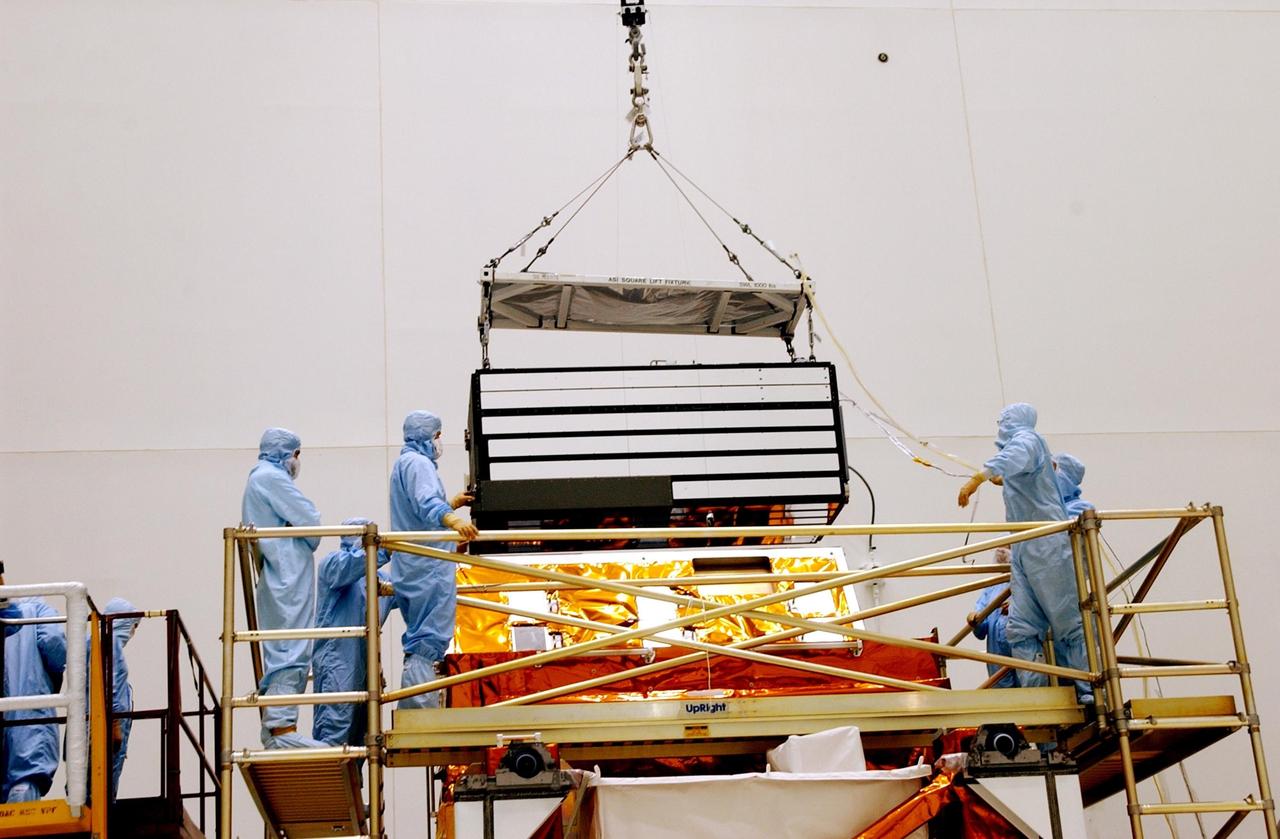

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while an overhead crane lowers the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) toward the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE). The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002
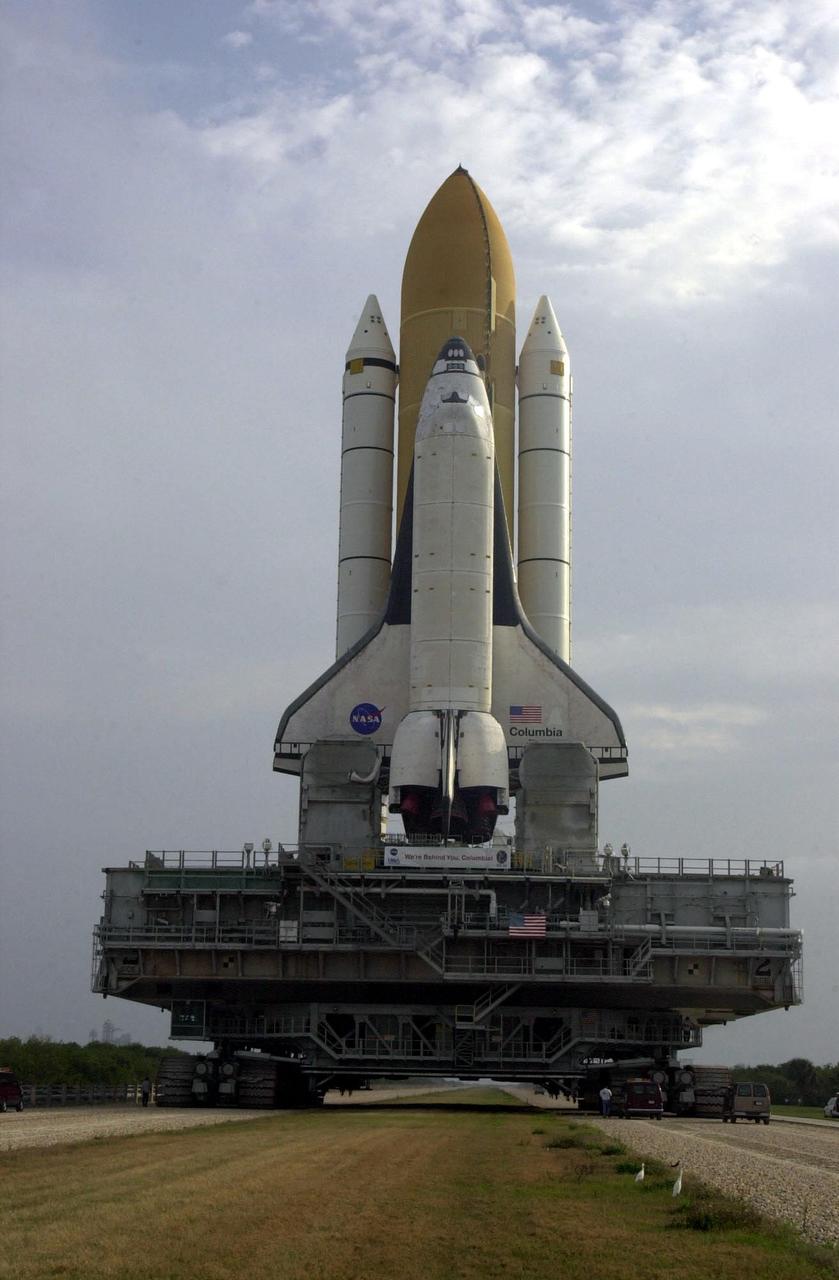

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A grey sky silhouettes Space Shuttle Columbia, atop its Mobile Launcher Platform, as it rolls out to Launch Pad 39A. Underneath is the crawler-transporter, which carries the multi-ton vehicles to the pad. In the grass behind the towering structures are two white herons. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the ACS, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech's Hazardous Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians use an overhead crane to lift the cover from NASA's Juno spacecraft before its move to a fueling stand where the spacecraft will be loaded with the propellant necessary for orbit maneuvers and the attitude control system. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, a worker reaches toward the plastic-covered replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis as it is lifted by crane toward the tail. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
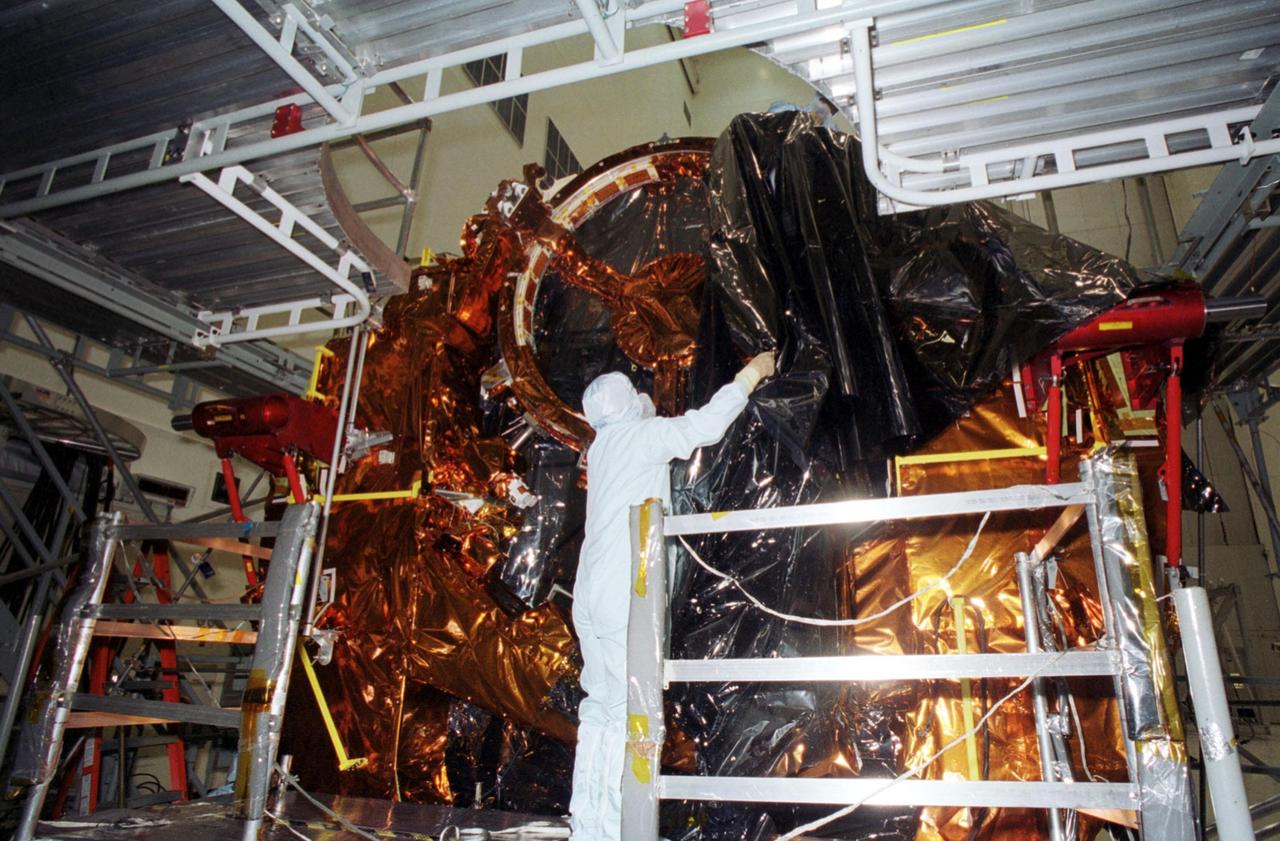

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility a worker removes the protective covering from the equipment to be used on mission STS-109. The mission is to service the Hubble Space Telescope, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
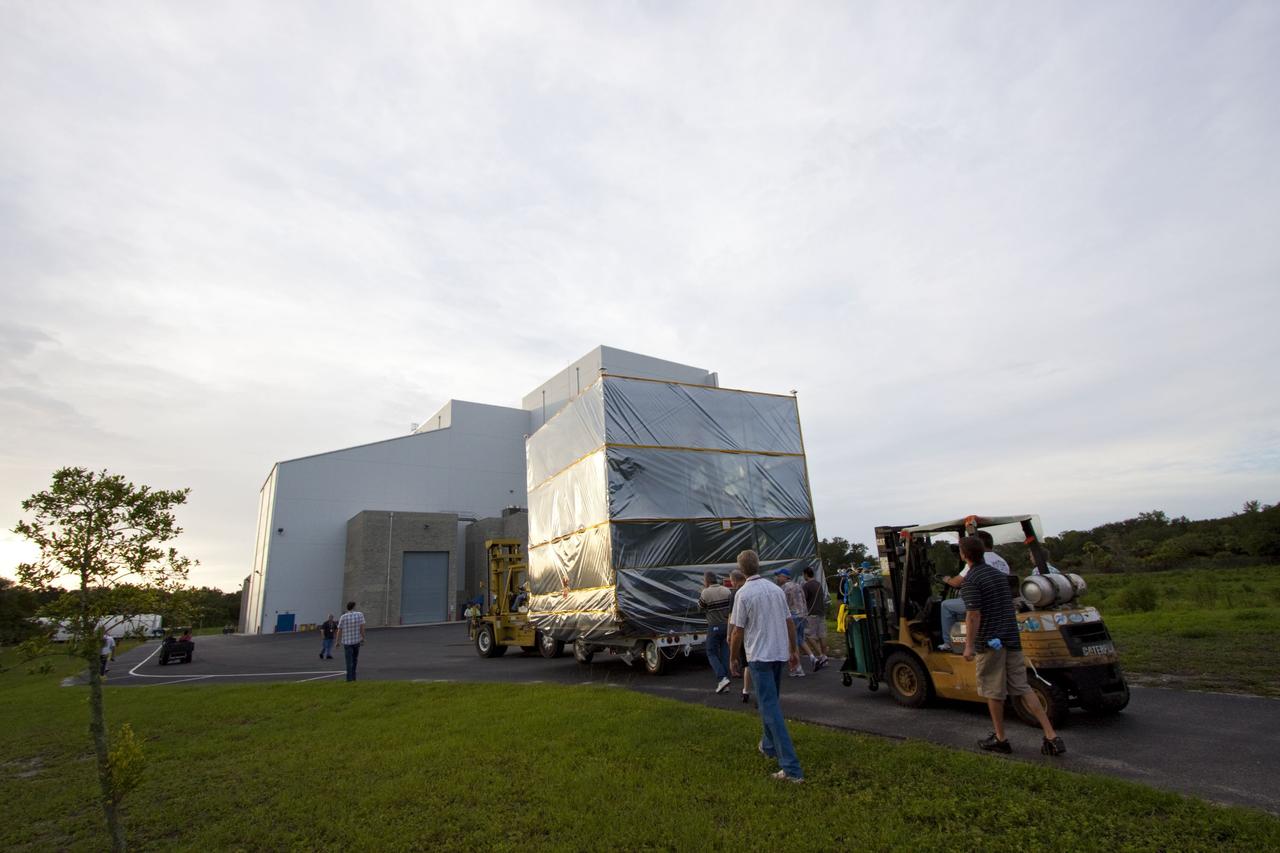

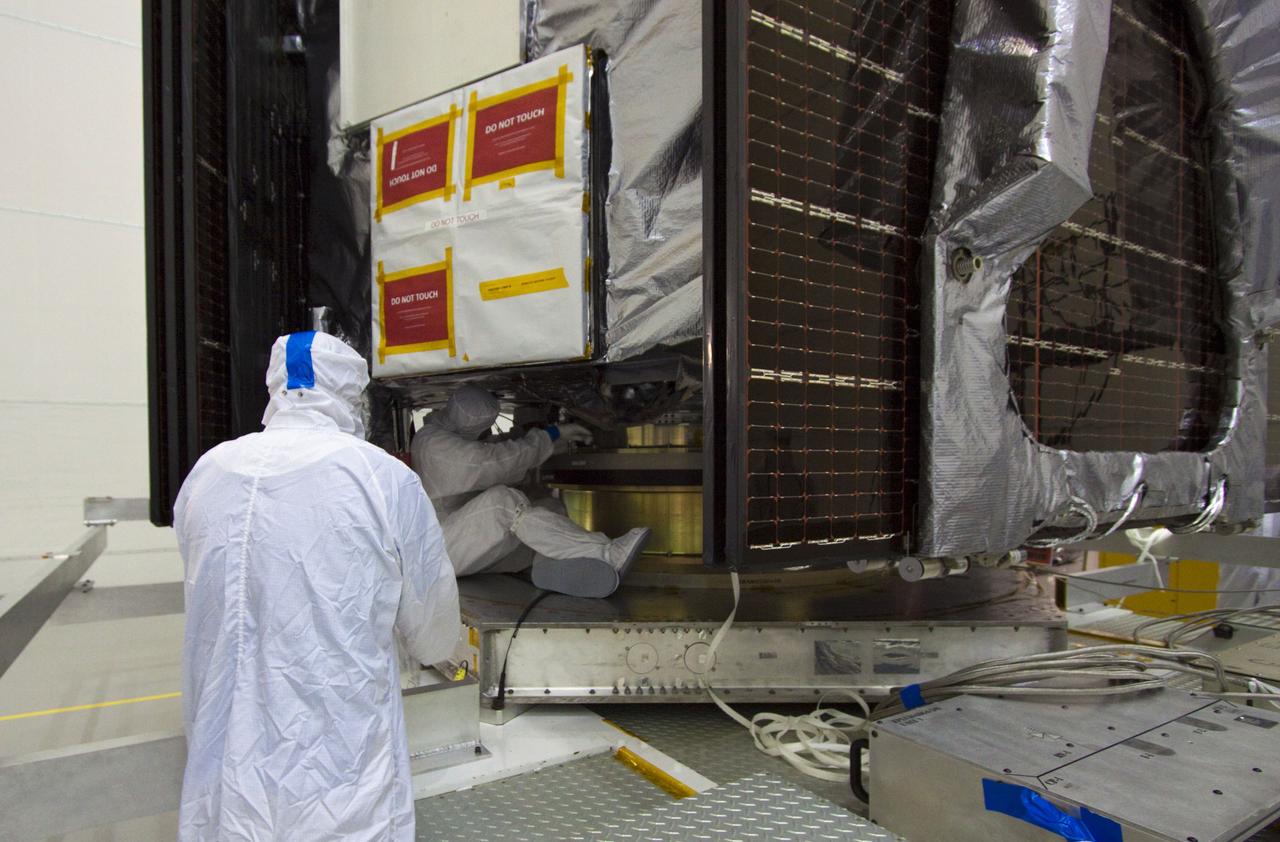
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla., -- Workers transport NASA's Juno spacecraft from Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. The spacecraft will be loaded with the propellant necessary for orbit maneuvers and the attitude control system. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
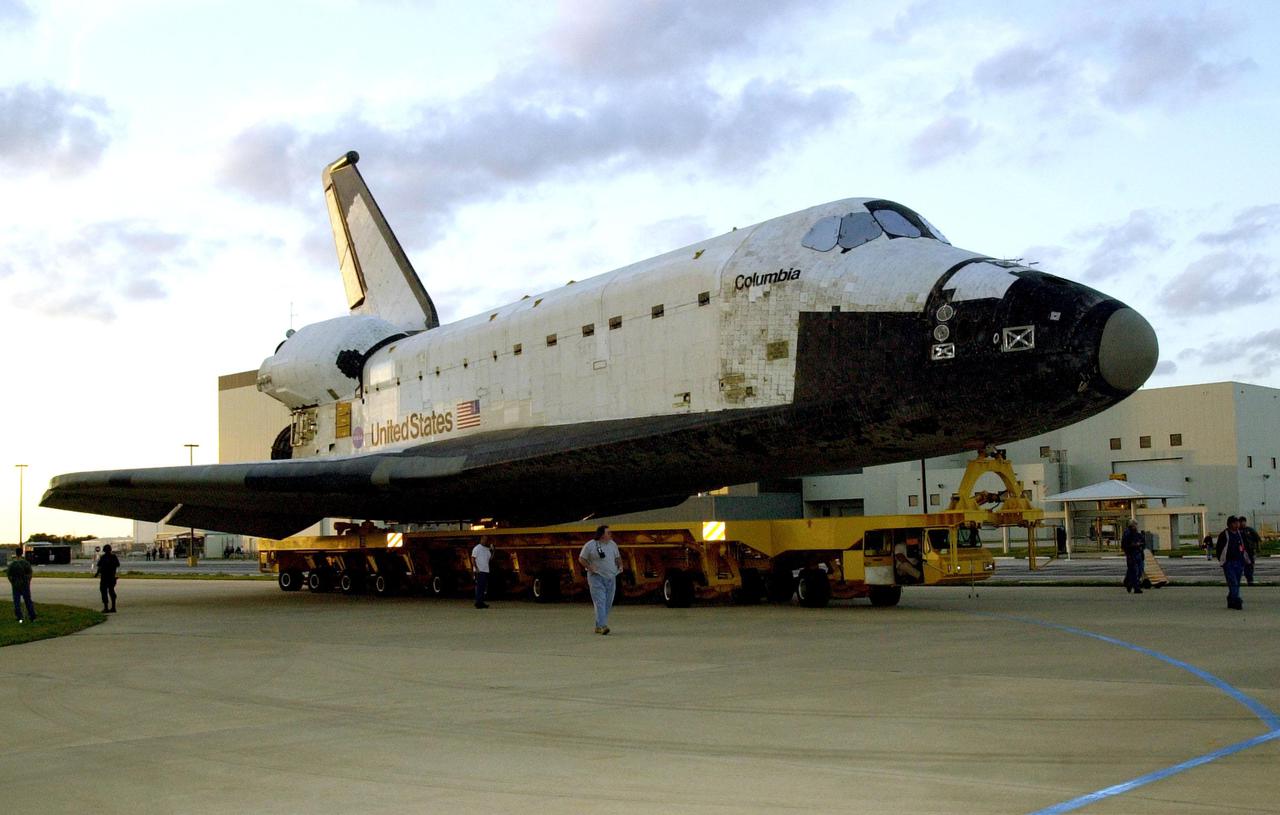

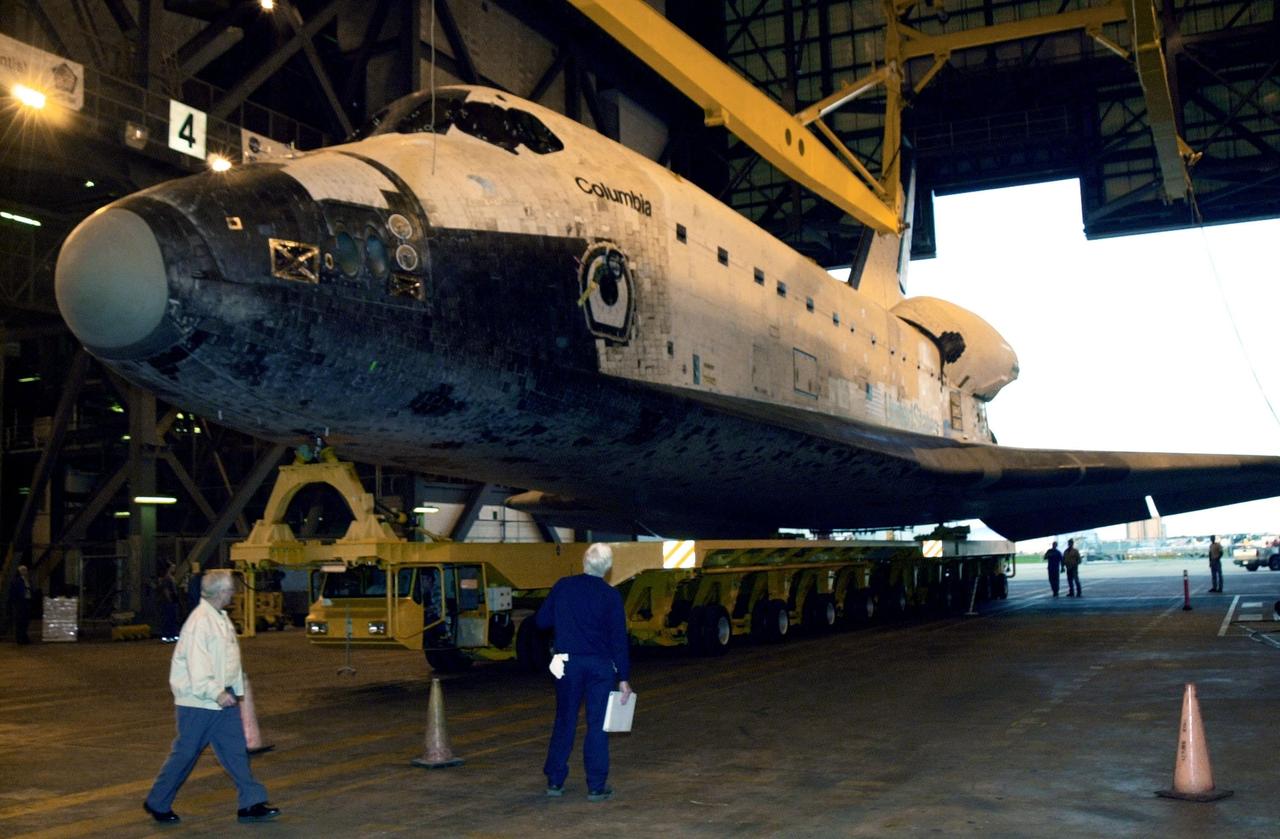
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The orbiter Columbia, atop a transporter, rolls away from the Orbiter Processing Facility on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be mated with the external tank-solid rocket booster stack. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation
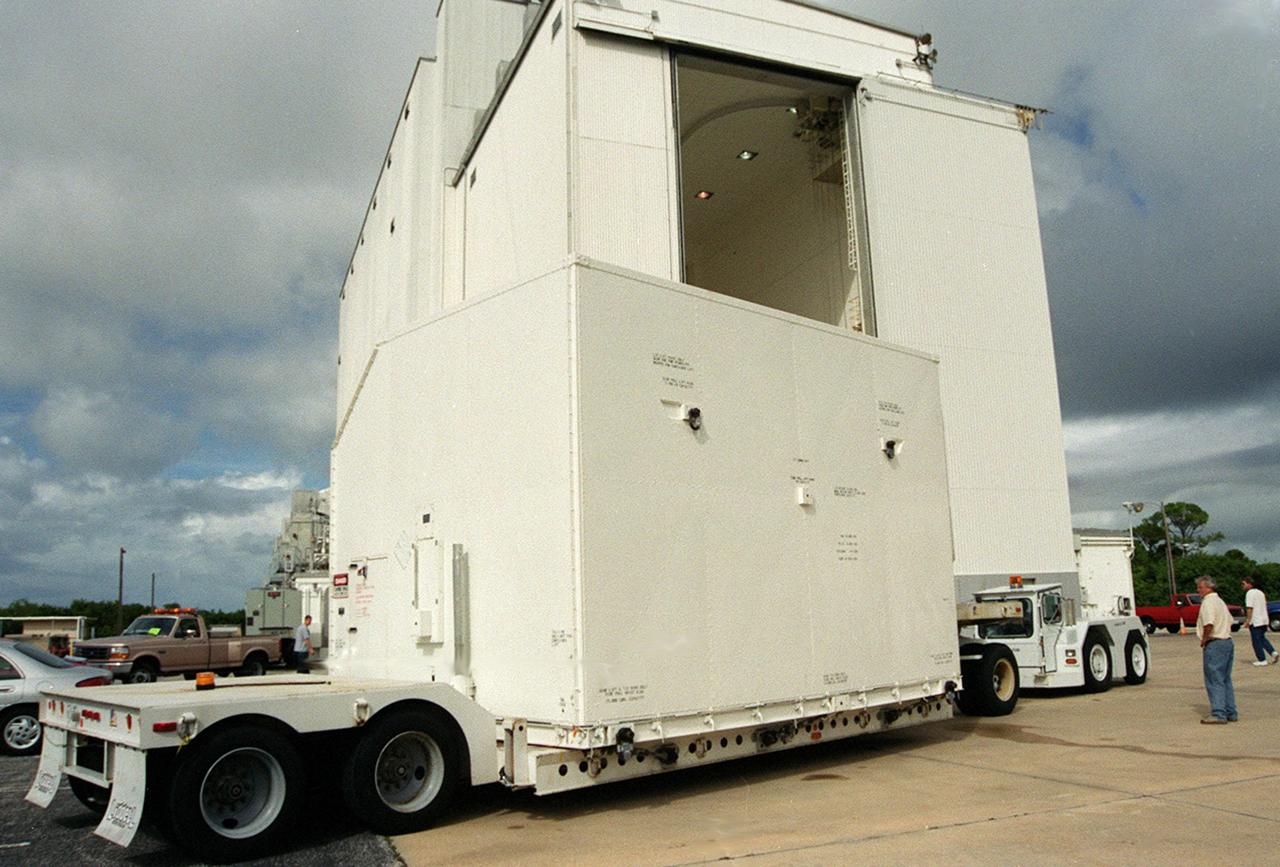

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Part of the equipment to be used on mission STS-109, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, arrives at a facility at KSC. The primary servicing tasks of the mission are to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the Advanced Camera for Surveys, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch in mid-February 2002
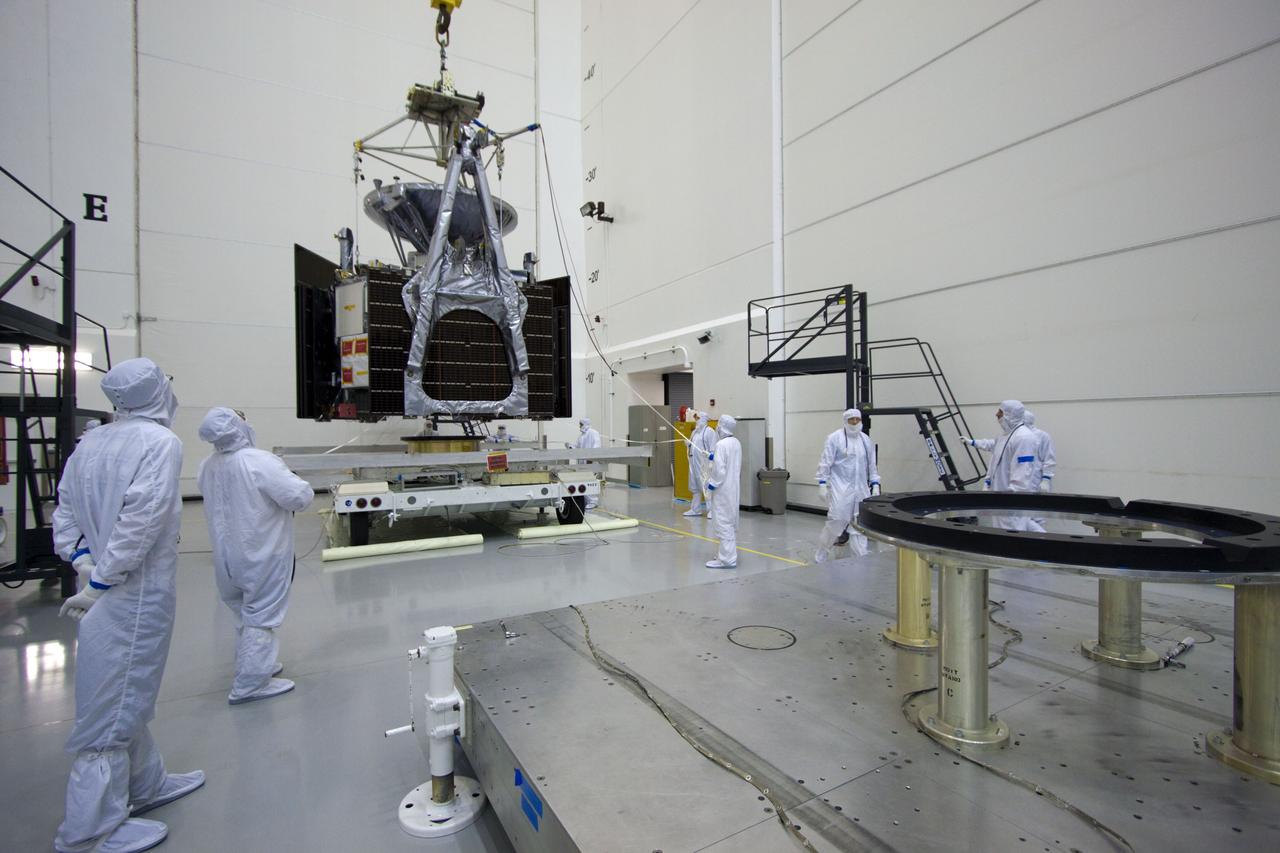

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech's Hazardous Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians using an overhead crane move NASA's Juno spacecraft to a fueling stand where the spacecraft will be loaded with the propellant necessary for orbit maneuvers and the attitude control system. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
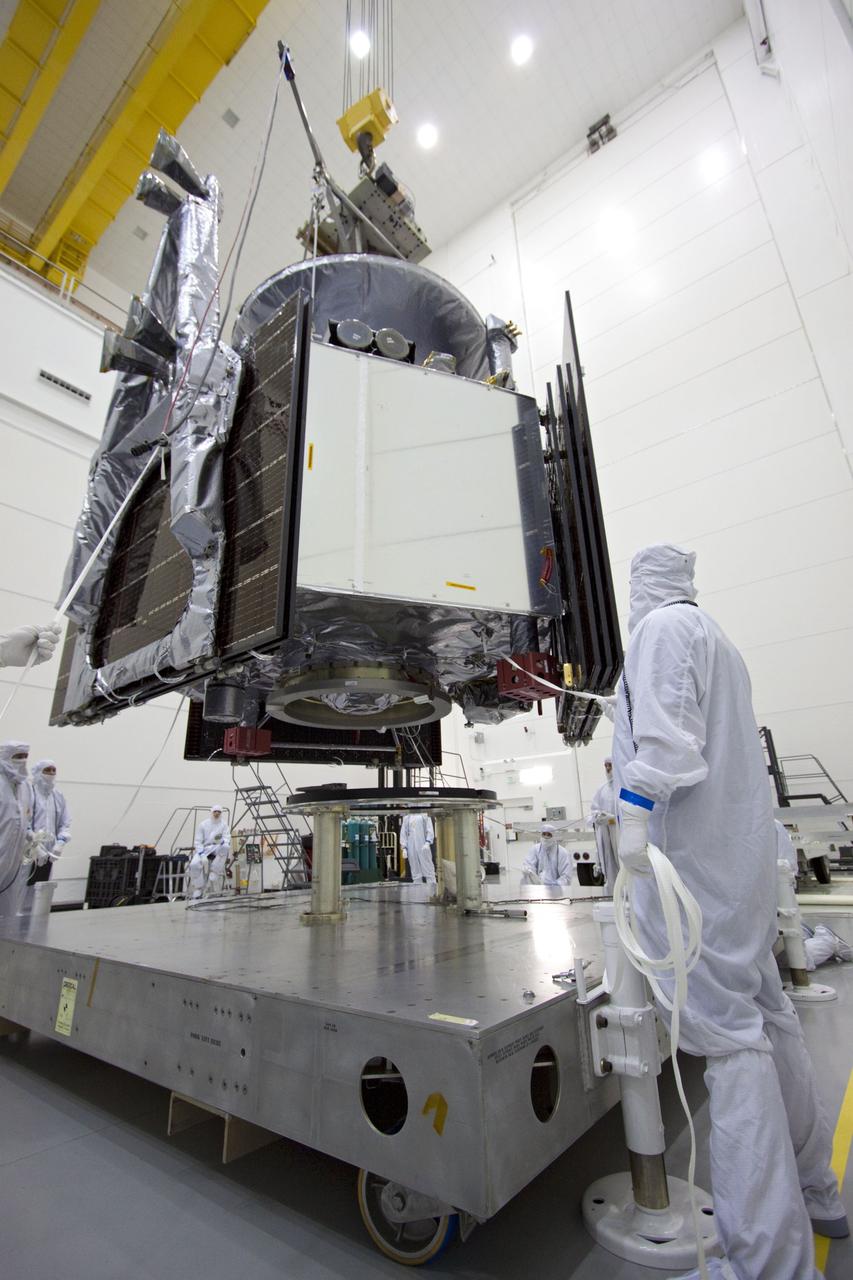

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech's Hazardous Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians using an overhead crane lower NASA's Juno spacecraft to a fueling stand where the spacecraft will be loaded with the propellant necessary for orbit maneuvers and the attitude control system. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
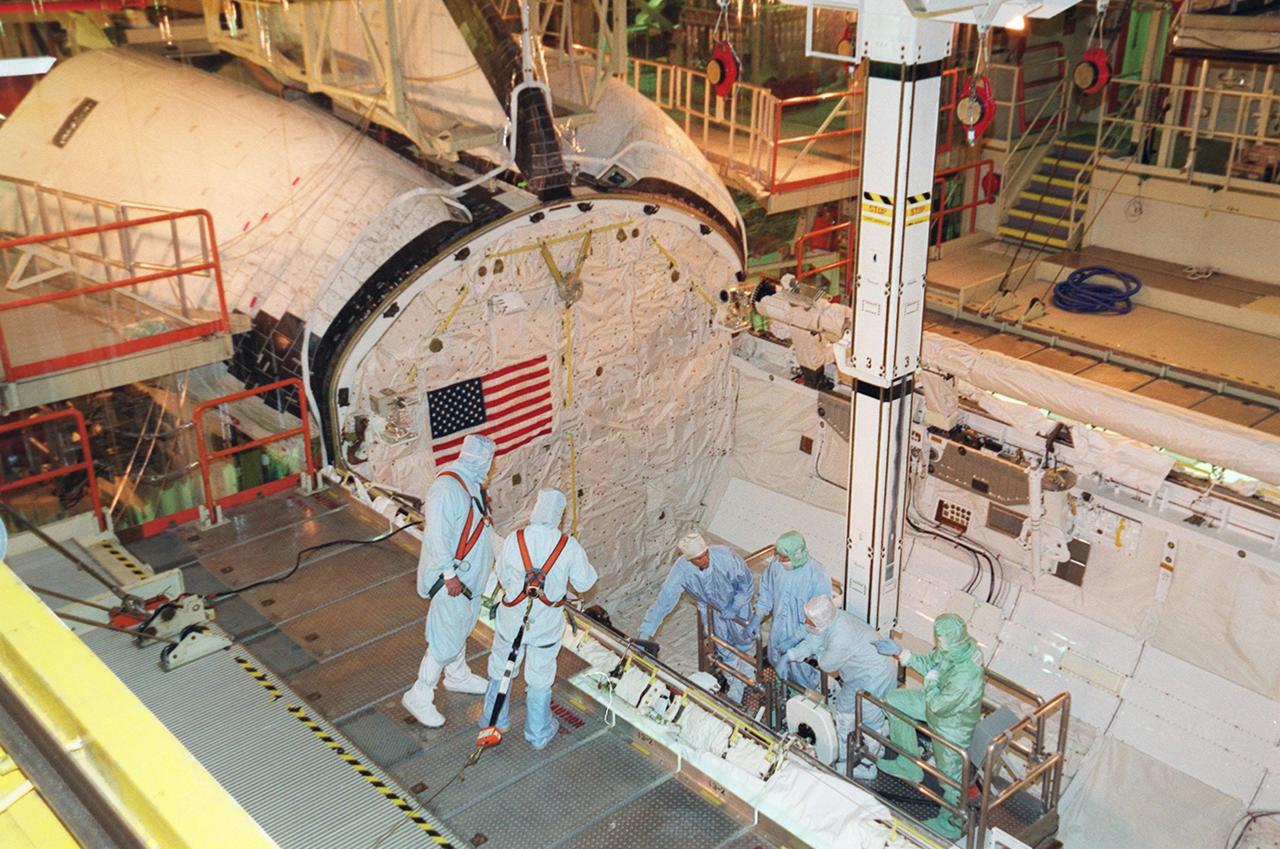
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Members of the STS-109 crew are lowered into the payload bay of orbiter Columbia to check out some of the equipment. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
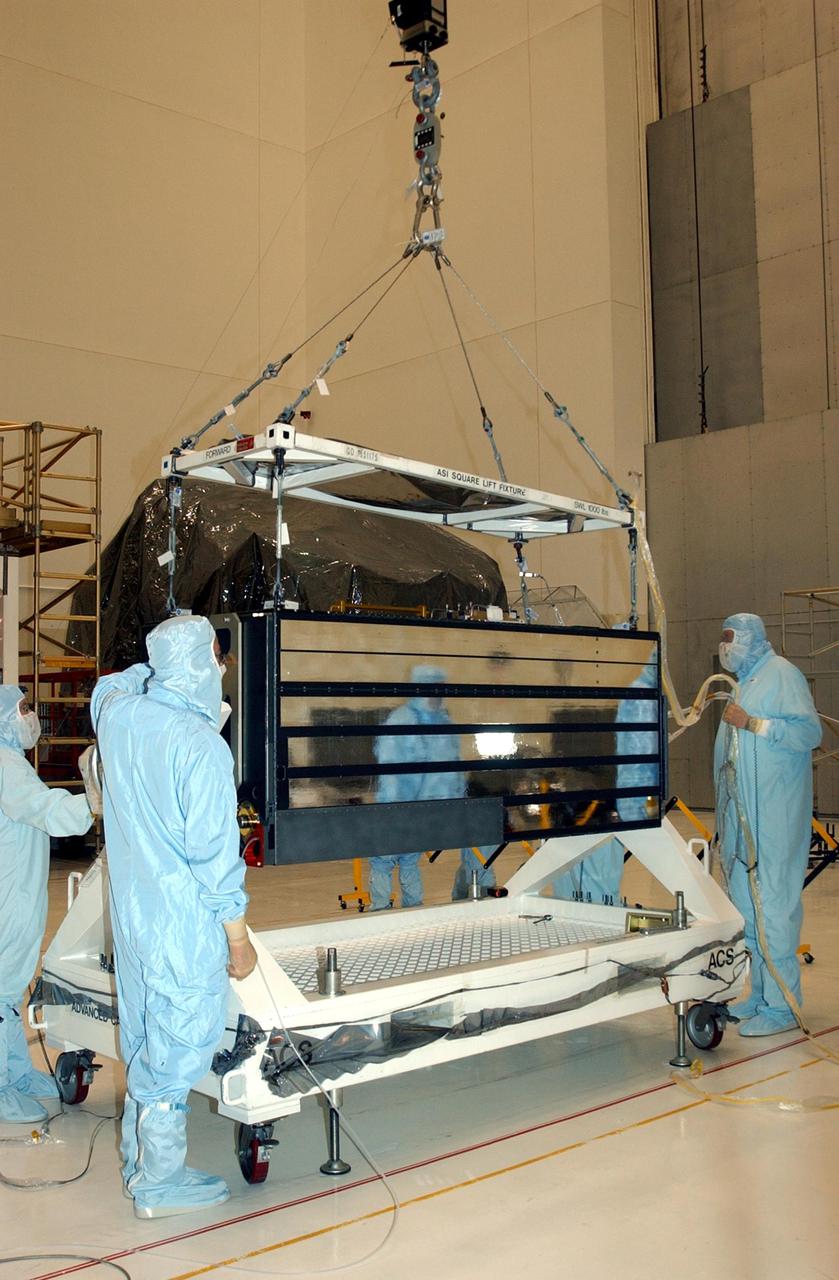

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vertical Processing Facility, workers watch while an overhead crane lifts the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) off the stand. The ACS is part of the payload on the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission, STS-109. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch no earlier than Feb. 21, 2002

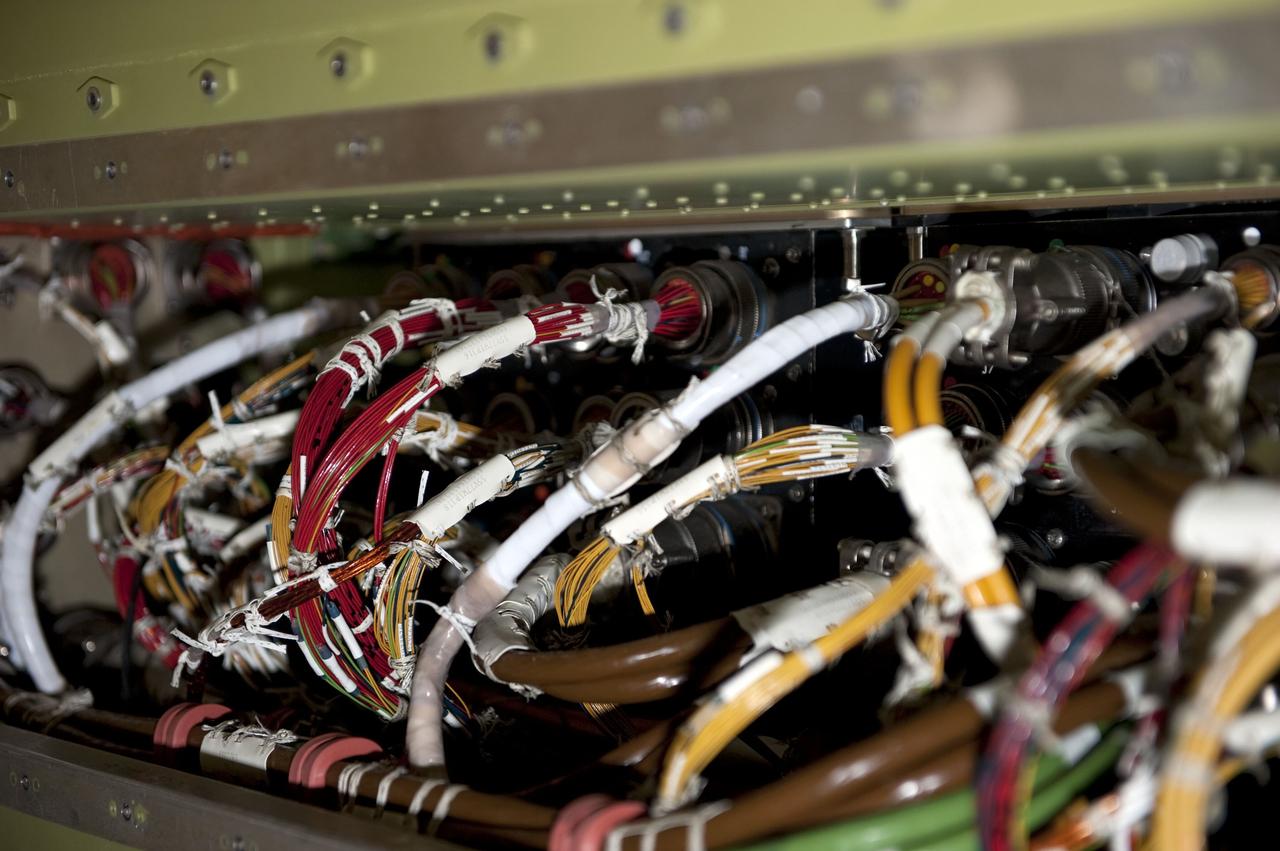
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This diagram of a space shuttle orbiter's avionics bay 5 shows the location of aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2) inside the bay. Space shuttle Endeavour was scheduled to launch on the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on April 29, but that attempt was scrubbed to allow engineers to assess an issue associated with failed heaters on a fuel line for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1). STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Image credit: NASA
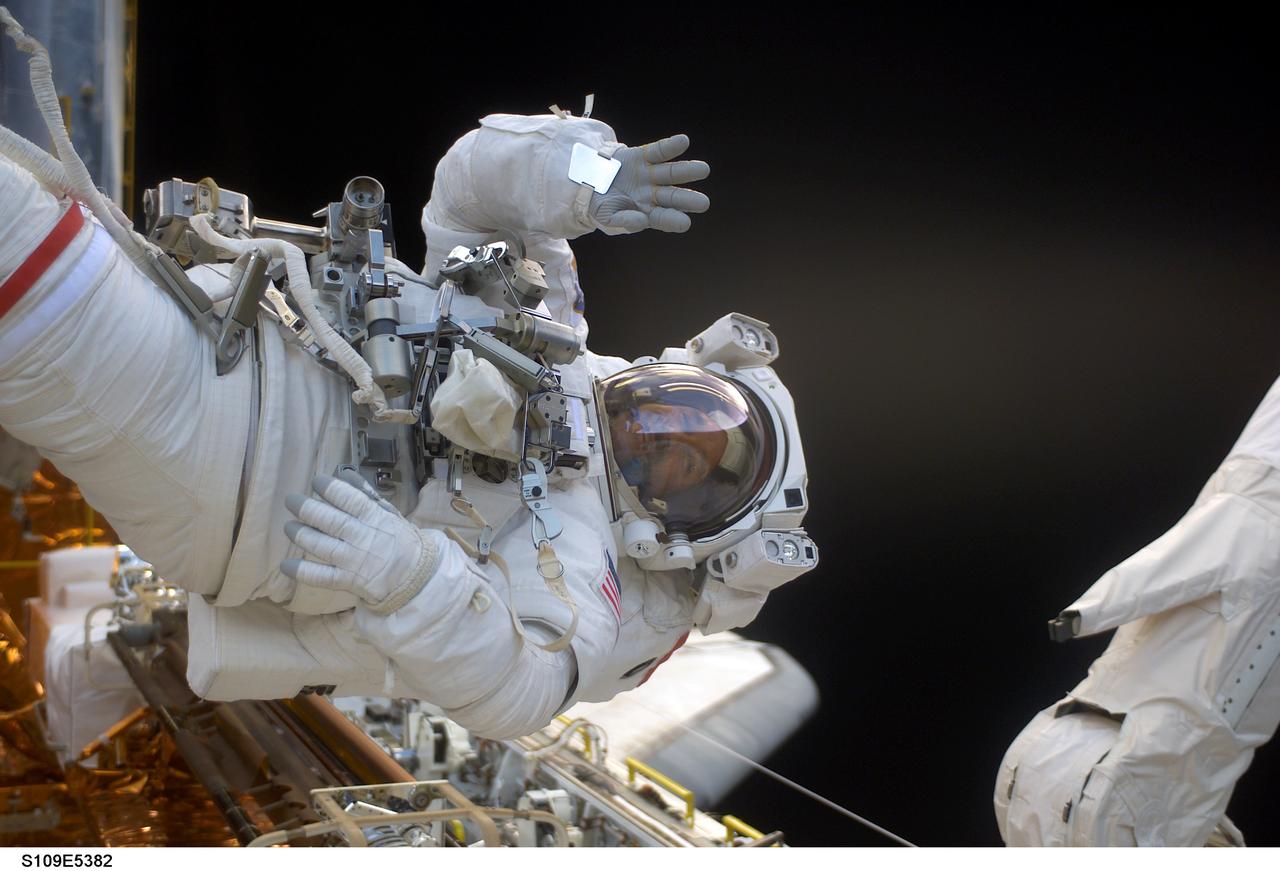

STS109-E-5382 (6 March 2002) --- Astronaut John M. Grunsfeld, payload commander, waves at a crewmate inside Space Shuttle Columbia's crew cabin during a brief break in work on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in the cargo bay of the shuttle during the STS-109 mission's third space walk. The primary purpose of the extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Grunsfeld and Richard M. Linnehan was to replace the Power Control Unit on the giant telescope. The image was recorded with a digital still camera by one of Grunsfeld's crew mates inside Columbia's cabin.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, a worker watches as the plastic-covered replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis is lifted by crane toward the tail. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000