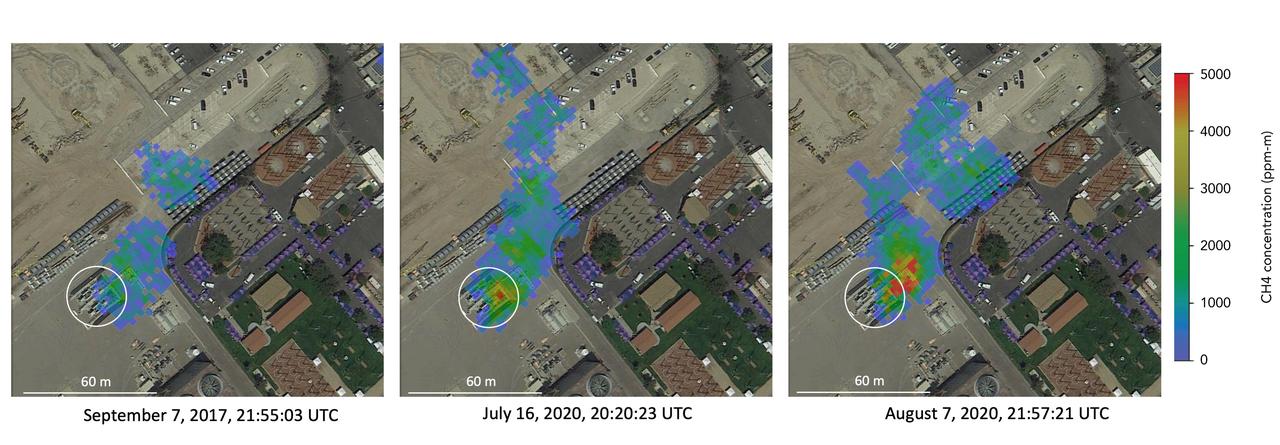
Atmospheric methane is a potent greenhouse gas and an important contributor to air quality. Future instruments on orbiting satellites can help improve our understanding of important methane emission sources. NASA conducts periodic methane studies using the next-generation Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS-NG) instrument. These studies are determining the locations and magnitudes of the largest methane emission sources across California, including those associated with landfills, refineries, dairies, wastewater treatment plants, oil and gas fields, power plants, and natural gas infrastructure. These three images show concentrations of methane in a natural gas plume relative to background air measured by AVIRIS-NG, overlaid on true-color land surface images (source: Google Earth). The aircraft was flying at an altitude of about 10,000 feet (3,000 meters) above ground level and the AVIRIS-NG image pixels are each about 10 feet (3 meters) across. The plume shape varies with changing emission rate, wind speed and direction. The methane plume originates from a compressor — circled in each image — at Valley Generating Station, a natural gas-fired power plant near Los Angeles. The color scale indicates the concentration of methane in each pixel relative to background methane concentrations in the surrounding atmosphere. The plume was initially detected by a single overflight in September 2017 but assumed at the time to be due to normal operations (intermittent venting). The plume was detected by AVIRIS-NG again on six flights in July-August 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24019

This image depicts a firing of a single H-1 engine at the Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC’s) Power Plant test stand. This 1950s test stand, inherited from the Army, was used to test fire engines until the Test Area was completed in the latter 1960s. The H-1 engine was the workhorse of the first Saturn launch vehicles and used in the Saturn I, Block 1 and II, and in the Saturn IB. The eight H-1 engines were attached to a thrust frame on the vehicle’s aft end in two different ways. Four engines are rigidly attached to the inboard position and canted at a three degree angle to the long axis of the booster. The other four engines, mounted in the outboard position, are canted at six degrees.
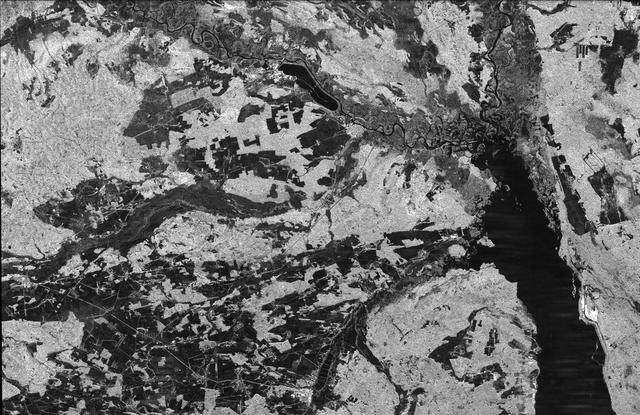

This is an image of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant and its surroundings, centered at 51.17 north latitude and 30.15 west longitude.
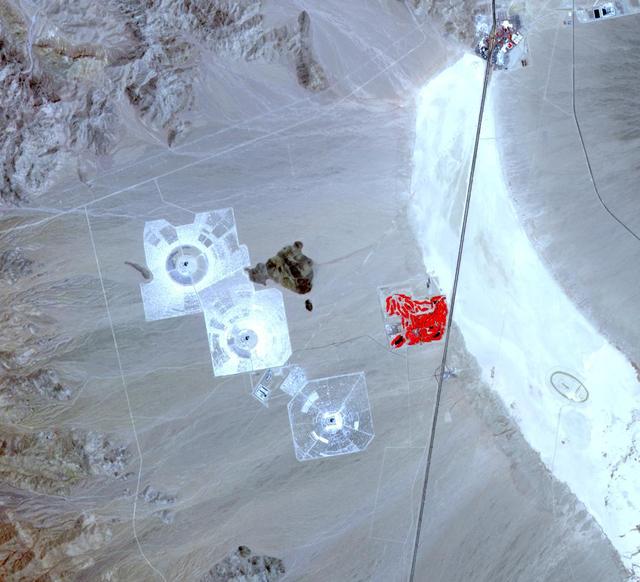

On May 30, 2013, NASA Terra spacecraft acquired this image of the largest solar plant of its kind in the world started producing power in southern California Mojave Desert near the Nevada border.
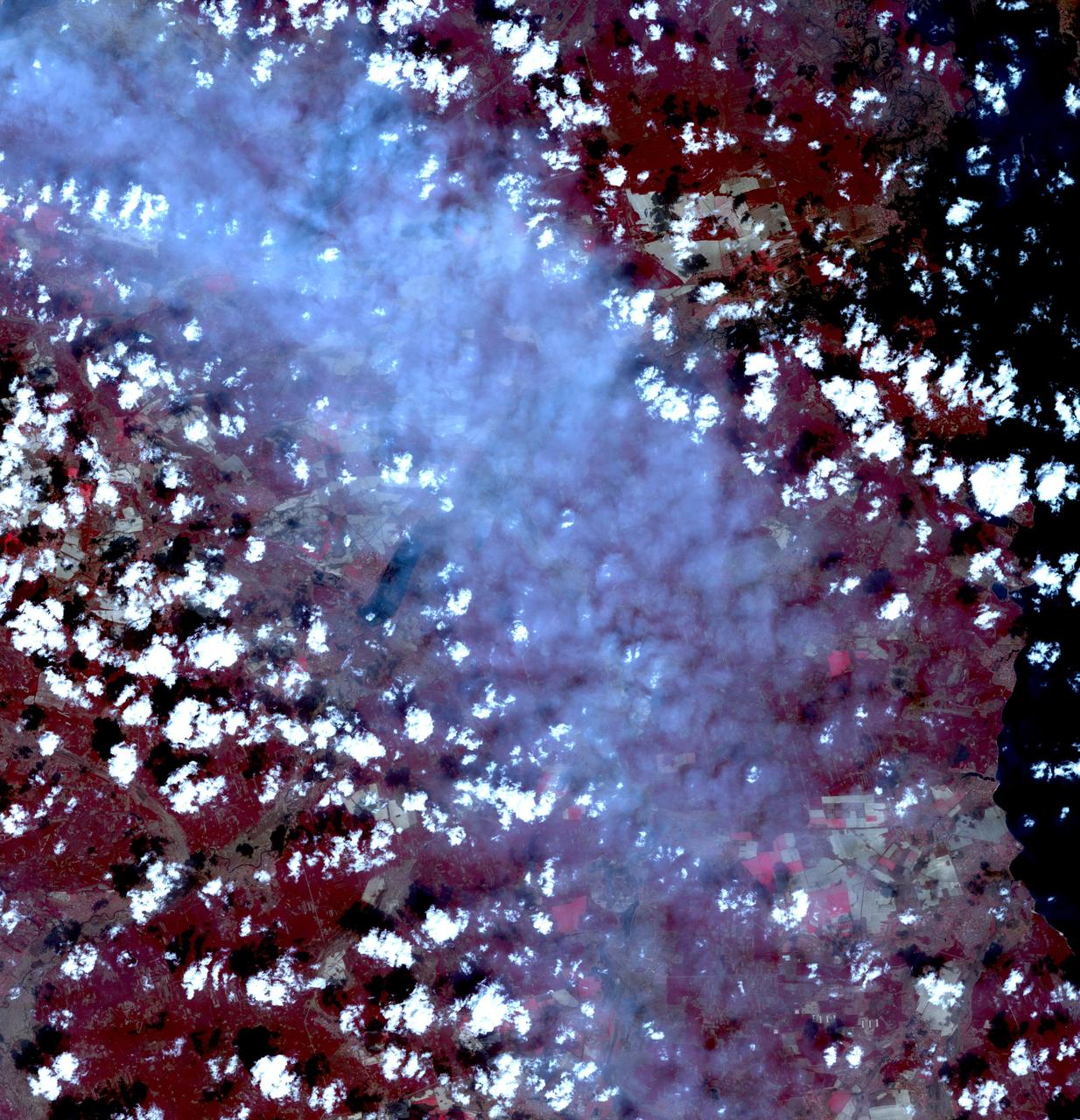

Fires began near the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine April 4, 2020. By April 14, the fires were nearly extinguished. On April 16, new fires erupted, sending large, dark gray clouds of smoke traveling over 750 km to the southeast. The ASTER image, acquired April 18, shows part of the billowing smoke plume. The image covers an area of 59.2 by 61.4 km, and is located near 51 degrees north, 30.1 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23911
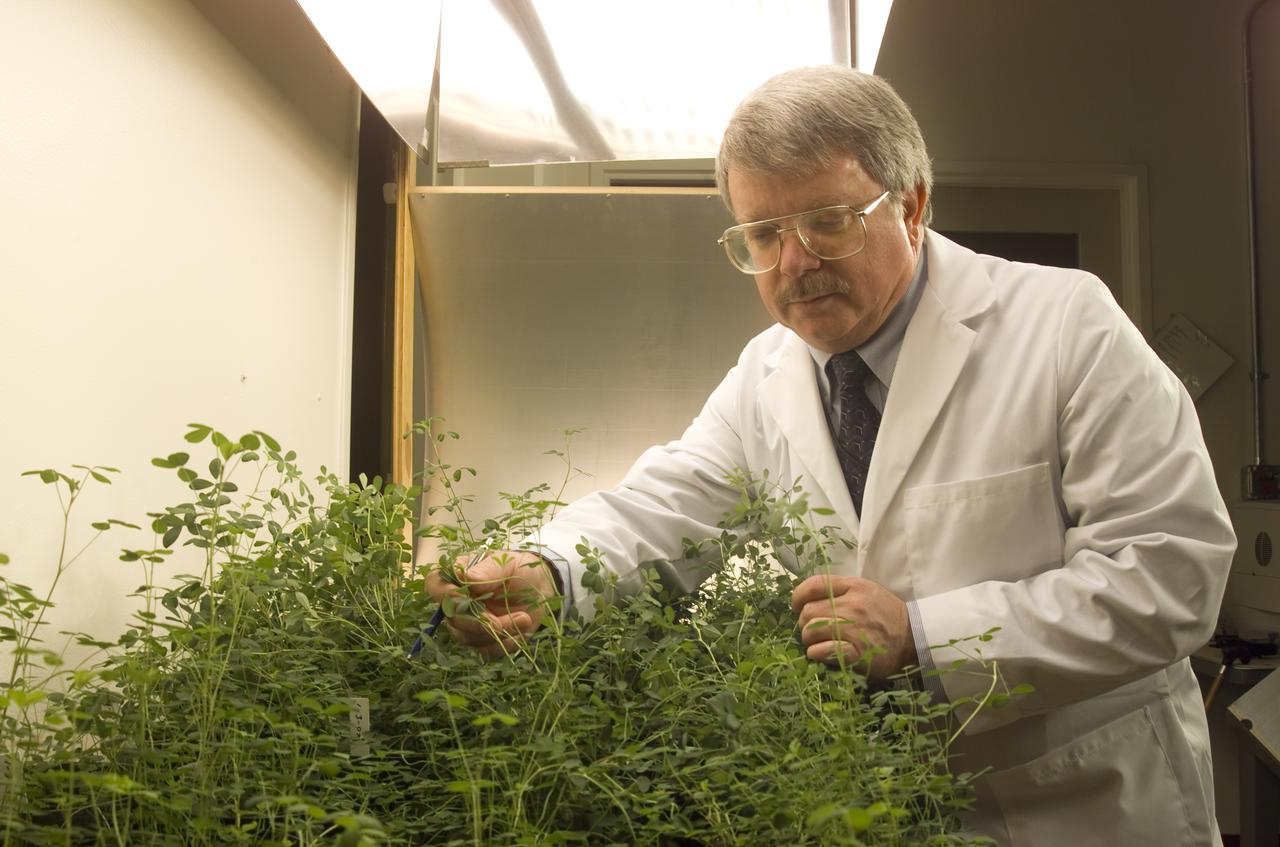

Microvave effects on plant growth (alfalfa), shown here is Dr. Jay Skiles of NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. NASA scientists are about to test that hypothesis by evaluating the effects of continuously beaming weak microwaves on alfalfa plants during laboratory tests. Microwaves derived from solar power and transmitted by orbiting satellites to electric power stations on Earth may someday enable U.S. energy self-sufficiency, but is this method safe for local plant life?
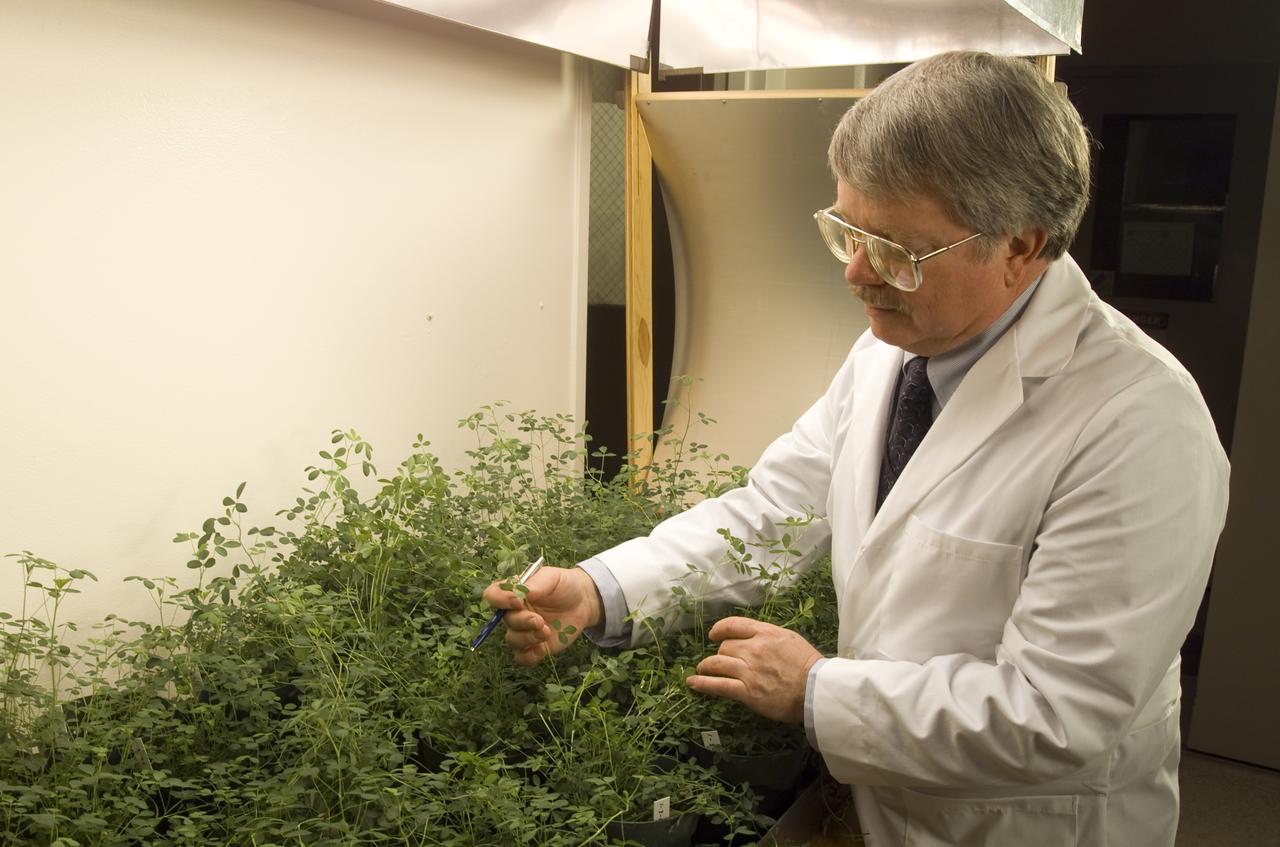

Microvave effects on plant growth (alfalfa), shown here is Dr. Jay Skiles of NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. NASA scientists are about to test that hypothesis by evaluating the effects of continuously beaming weak microwaves on alfalfa plants during laboratory tests. Microwaves derived from solar power and transmitted by orbiting satellites to electric power stations on Earth may someday enable U.S. energy self-sufficiency, but is this method safe for local plant life?
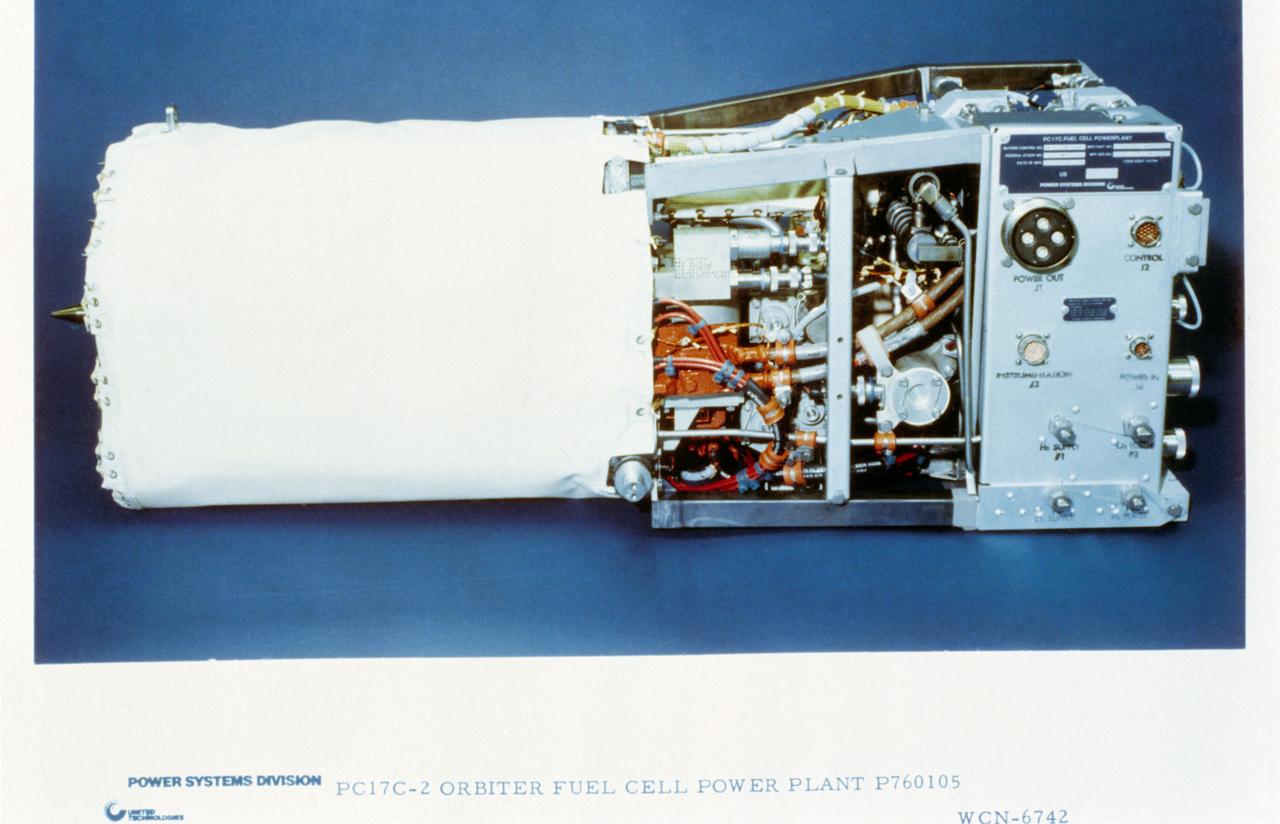
View of the PC17C-2 Orbiter Fuel Cell Power Plant P760105 From United Technologies Hamilton-Standard.

This artist's concept from 1962 show a three hundred-sixty ton spaceship, powered by a forty-megawatt nuclear-electric power plant, transporting a three-man crew to Mars. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center engineers, a five-ship convoy would make the round trip journey in about five hundred days.
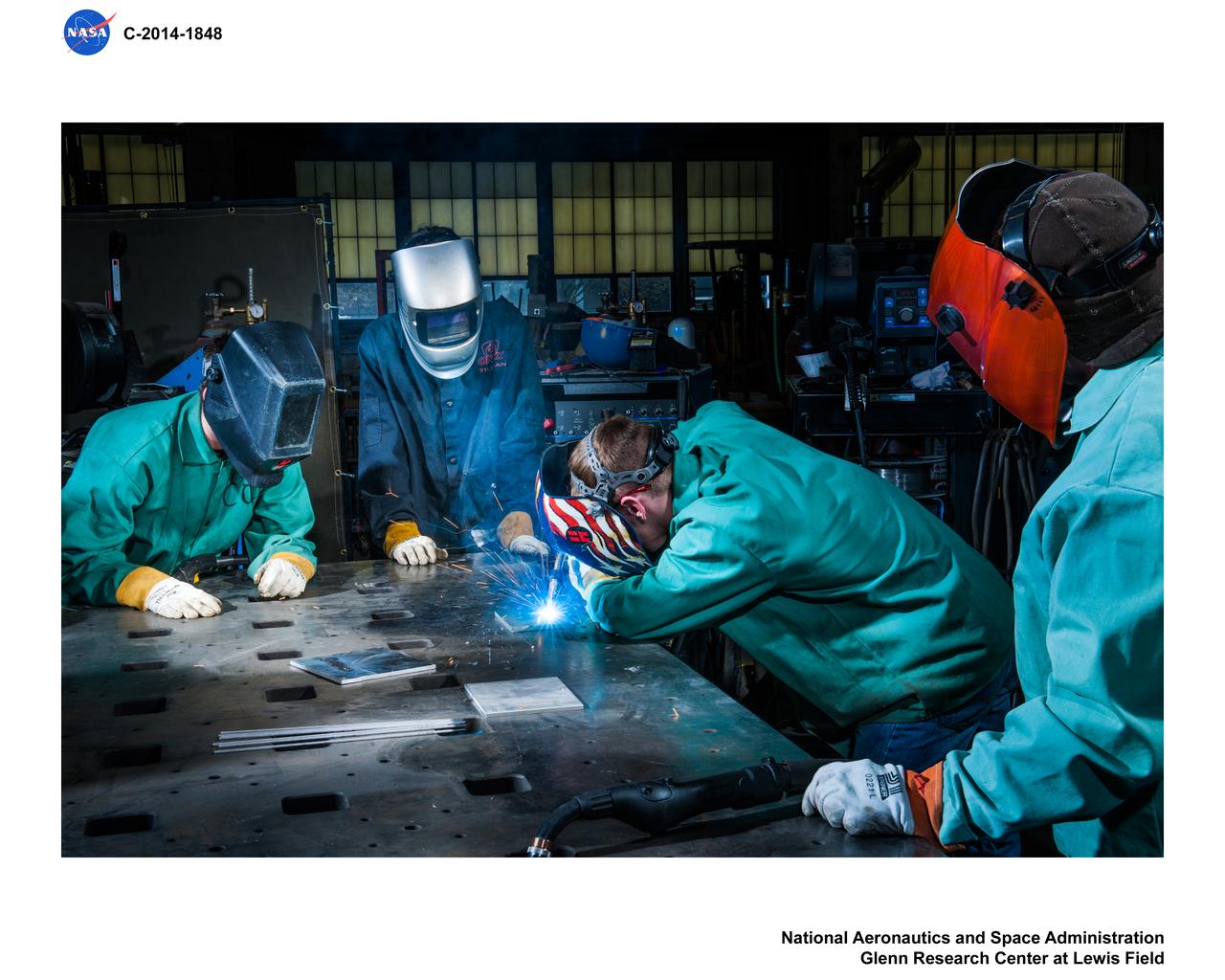

Visit to the Manufacturing Facility by Administration, Faculty and Students from the Erie Huron Ottawa Vocational Education Career Center, EHOVE in support of the 3KVA Mobile Photovoltaic Power Plant Project

On February 15, 2015 the Desert Sunlight solar project in California’s Mojave Desert became operational. This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows the 550-megawatt plant generates enough electricity to power 160,000 average homes. Covering an area of 16 km2, the 8.8 million cadmium telluride photovoltaic modules take advantage of the more than 300 days of sunshine. Desert Sunlight joins the similar-sized Topaz Solar Farm in San Luis Obispo County, CA, that became operational in June, 2014. The Desert Sunlight image (left) was acquired March 12, 2015 and is located at 33.8 degrees north, 115.4 degrees west; the Topaz image (right) was acquired September 11, 2014 and is located at 35.4 degrees north, 120.1 degrees west. Each image covers an area of 10.5 x 12 km. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19268
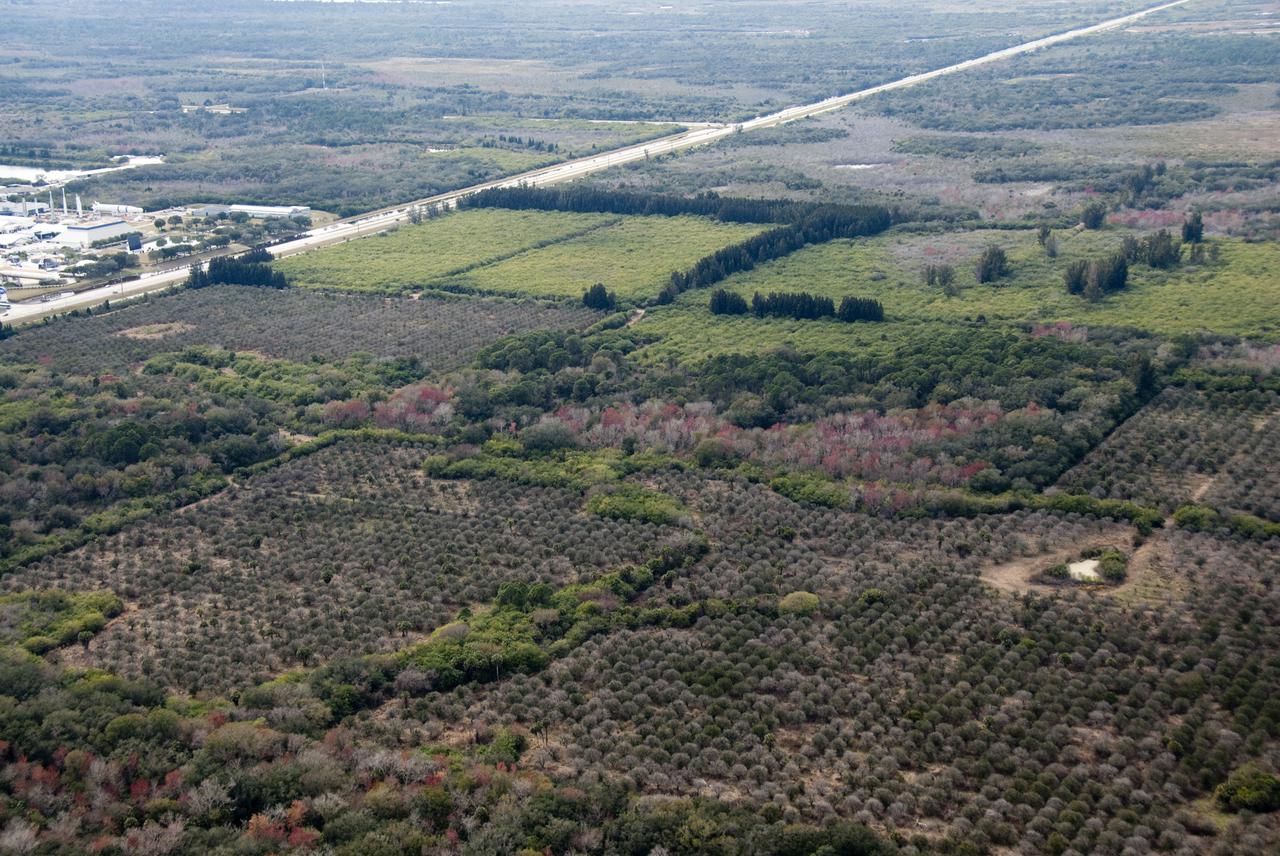

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - This aerial view combines NASA's Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex (left) and the proposed 500-acre site for one of the largest solar power plants of its kind. The planned 100-megawatt photovoltaic solar plant would use similar panels to those already built at Kennedy by the SunPower Corp. The energy produced by the proposed facility would be used to provide power to Florida Power and Light customers. Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, FPL Vice President and Chief Development Officer Eric Silagy and a SunPower Corp. representative made a joint announcement regarding the new construction during a ceremony held in November 2009 to commission a 1-megawatt solar plant. Included in the announcement were plans to establish a permanent renewable energy research and development center at Exploration Park, Kennedy's new business complex. The dedicated RandD facility proposed for Exploration Park could result in at least 50 high-salary science and engineering positions permanently established at Kennedy by SunPower and FPL's other partners, a potential for solar panel manufacturing located nearby and as many as 1,000 new construction jobs. FPL and Kennedy have initiated environmental studies and a plan to support the next project, which could be initiated before the end of 2010. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
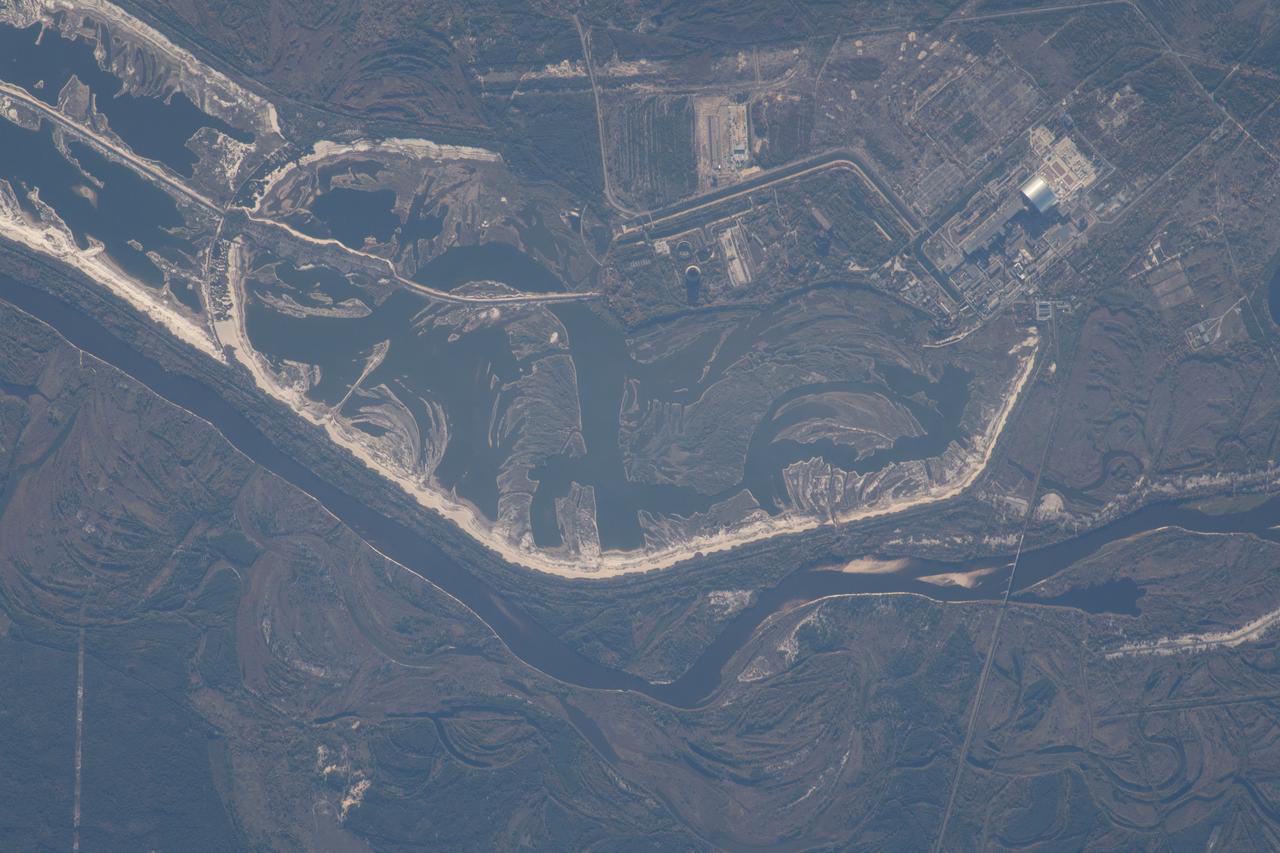

iss057e051419 (Oct. 14, 2018) --- The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant on the Pripyat River in northern Ukraine was pictured as the International Space Station orbited 257 miles above Eastern Europe. Across the Ukrainian border in Belarus, the Polesie State Radioecological Reserve was created to enclose territory most affected by radioactive fallout from the Chernobyl disaster.
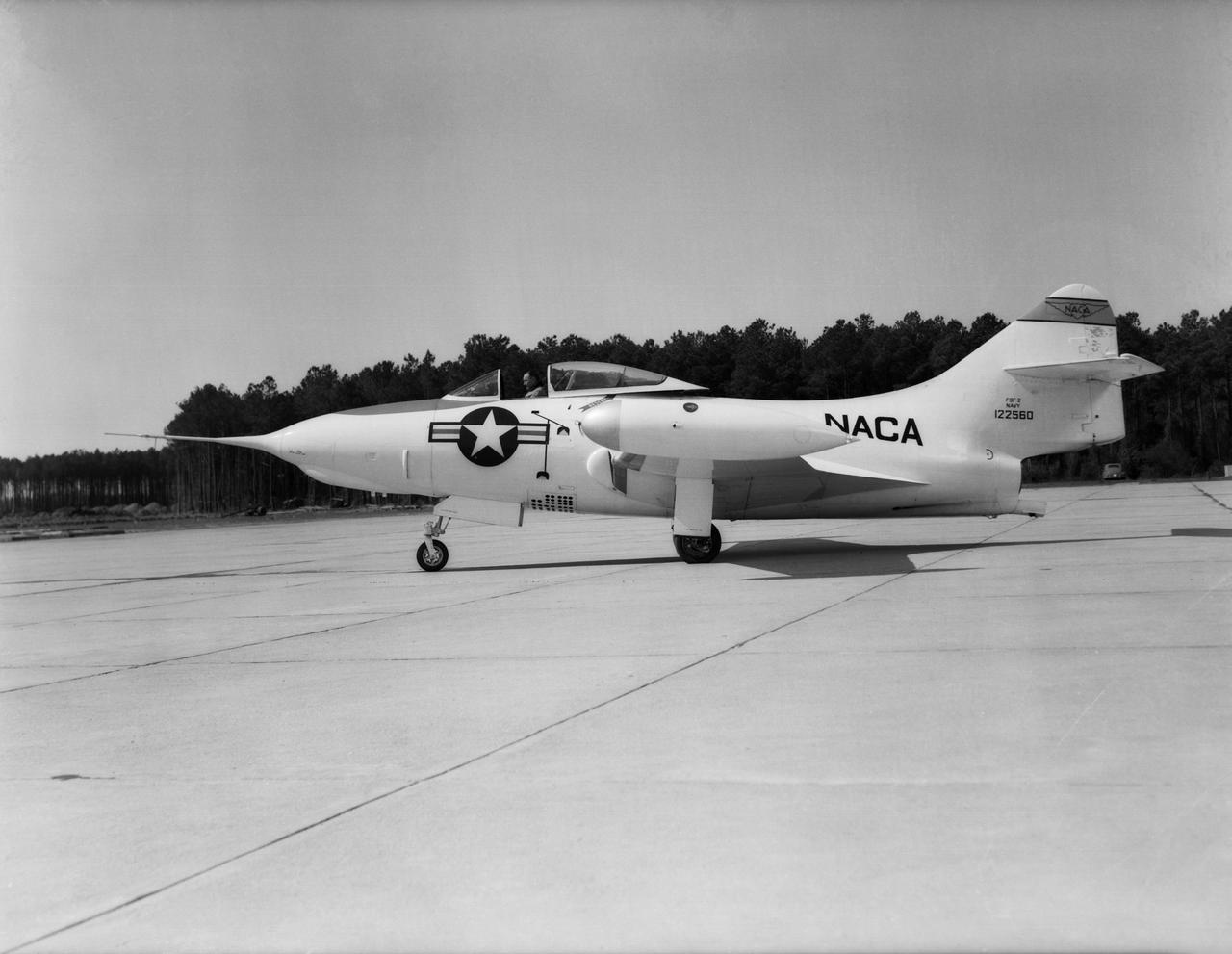

Grumman F9F-2 Panther: Originally built as a F9F-3, this Grumman F9F-2 Panther has a Pratt and Whitney J42 turbojet power plant, hence the designation change. This Panther underwent handling quality tests, serving long enough at Langley to witness the change from the NACA to NASA.

iss048e049821 (8/5/2016) --- NASA astronaut Jeff Williams is photographed with two canisters for the Biological Research in Canisters - Natural Product under Microgravity (BRIC-NP) experiment. Image was taken in the Destiny U.S. Laboratory aboard the International space Station (ISS). In the BRIC-NP investigation, fungal strains isolated from the Chernobyl nuclear power plant (ChNPP) accident are screened for the secretion of natural products that could be beneficial for biomedical and agricultural applications.
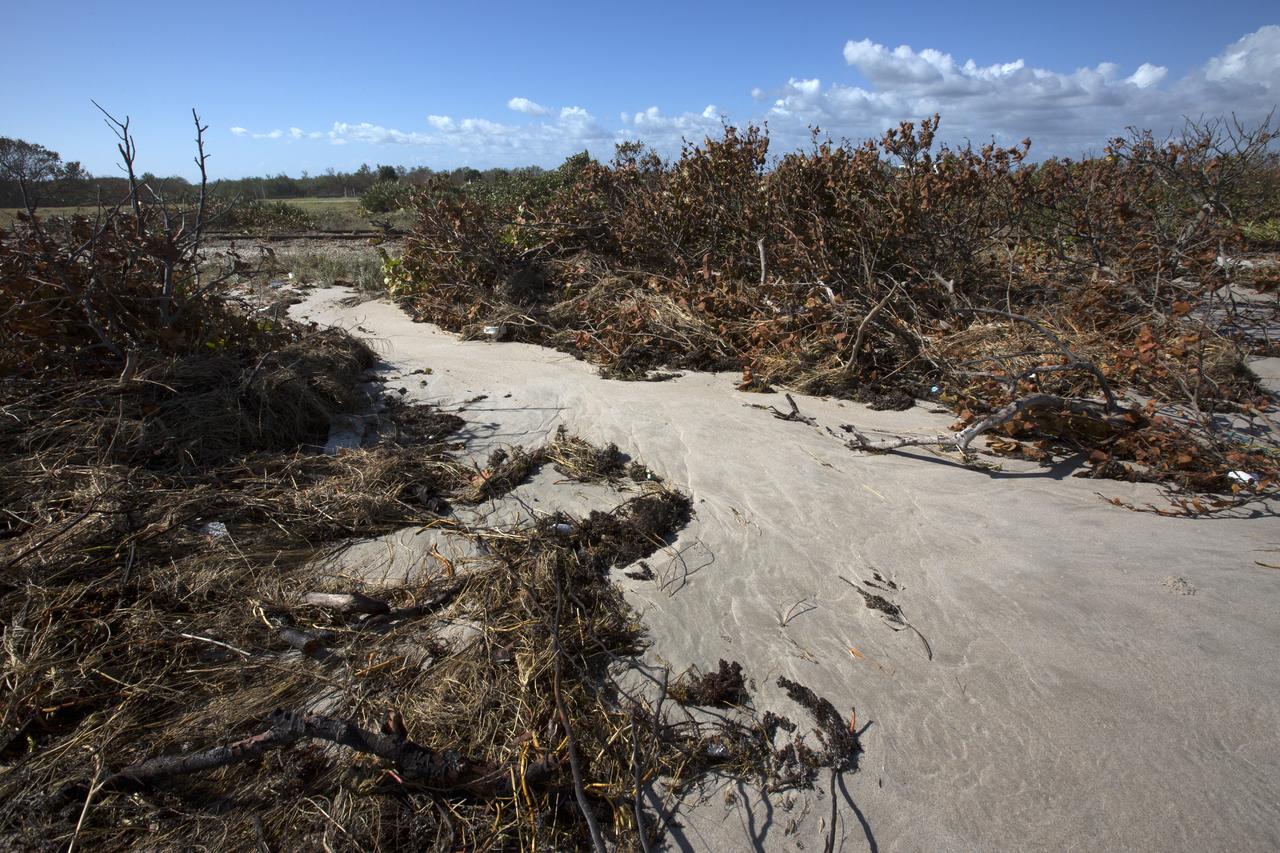

Plant debris caused by Hurricane Matthew is strewn across the dune line along the Atlantic shoreline at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Although some sections of shoreline suffered erosion, recently restored portions of beach fared well. Hurricane Matthew, a Category 3 storm, passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion.
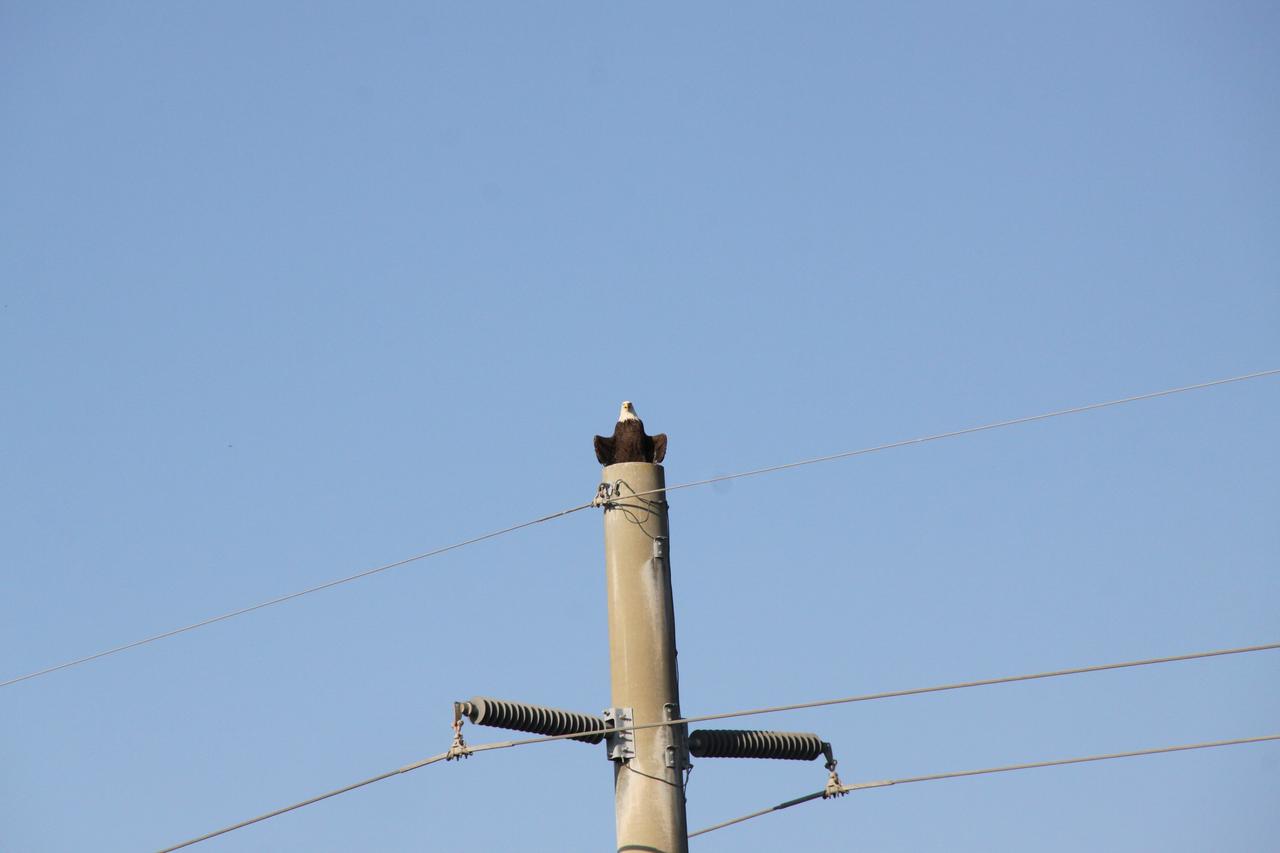

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A bald eagle surveys NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida from a power pole along the Kennedy Parkway, which runs parallel to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge coexists with Kennedy and provides a habitat for 330 species of birds. A variety of other wildlife, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and plants, also inhabit the refuge. For information on the refuge, visit www.fws.gov/merrittisland/Index.html. For information on Kennedy, visit www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
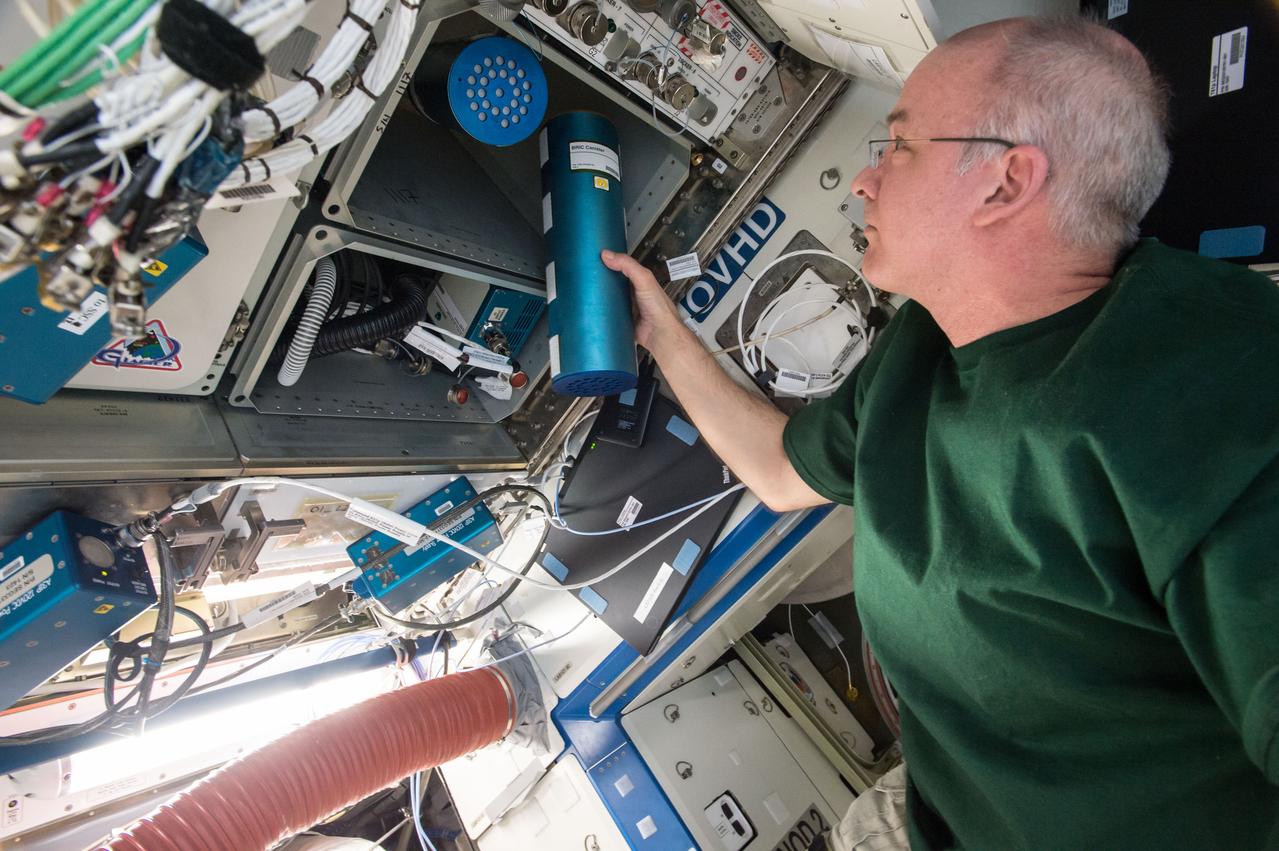

iss048e049824 (8/5/2016) --- NASA astronaut Jeff Williams transfers two canisters for the Biological Research in Canisters - Natural Product under Microgravity (BRIC-NP) experiment to ExPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Rack 2 Locker 6, LAB1O1-D2, in the Destiny U.S. Laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS). In the BRIC-NP investigation, fungal strains isolated from the Chernobyl nuclear power plant (ChNPP) accident are screened for the secretion of natural products that could be beneficial for biomedical and agricultural applications.
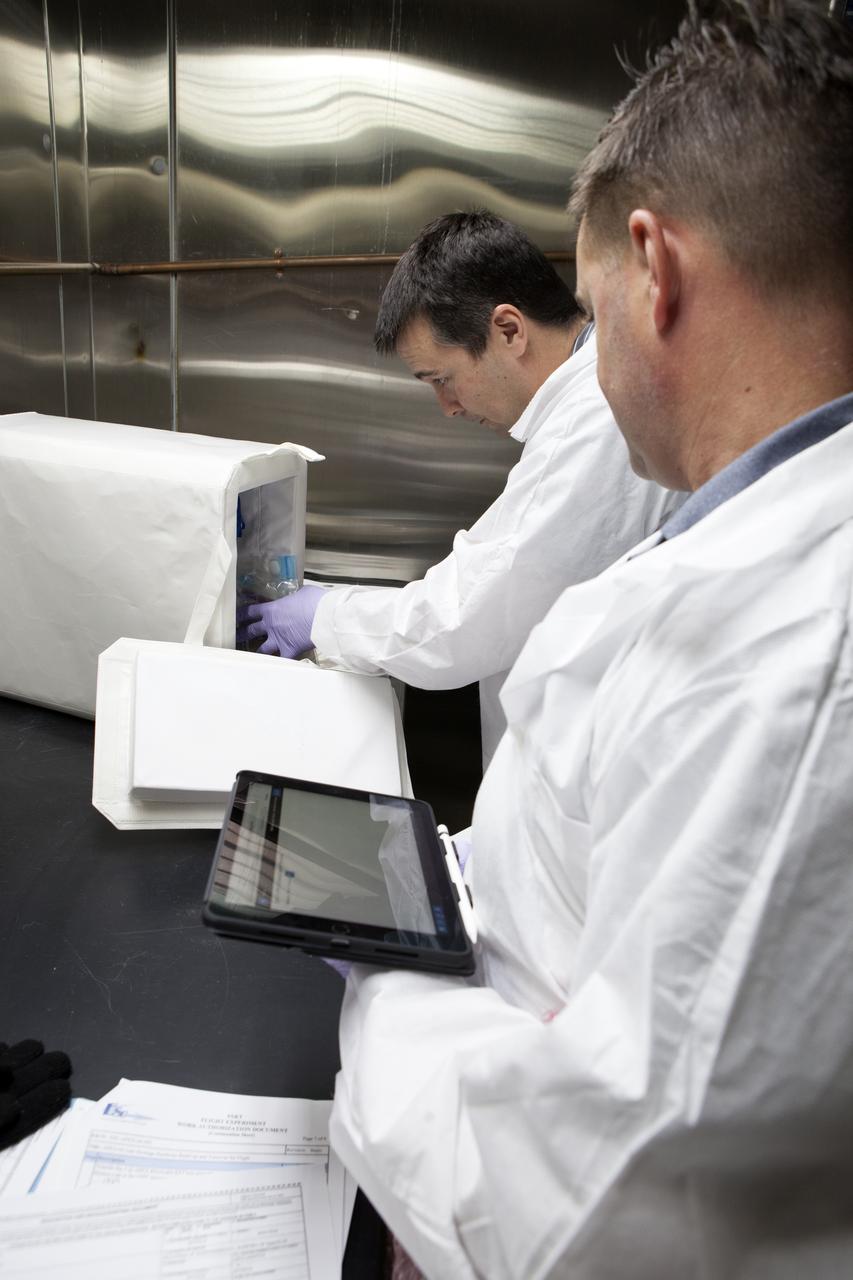

APEX-04, or Advanced Plant EXperiments-04, is being prepared in a cold room in the Kennedy Space Center Processing Facility for SpaceX-10. Eric Morris from the cold stowage group fits items into the Double Cold Bag (DCB) which is a non-powered container that keeps the APEX petri plates at +4 degrees Celsius during launch and ascent.. Dr. Anna Lisa Paul of the University of Florida is the principal investigator for APEX-04. Apex-04 is an experiment involving Arabidopsis in petri plates inside the Veggie facility aboard the International Space Station. Since Arabidopsis is the genetic model of the plant world, it is a perfect sample organism for performing genetic studies in spaceflight. The experiment is the result of a grant from NASA’s Space Life and Physical Sciences division.
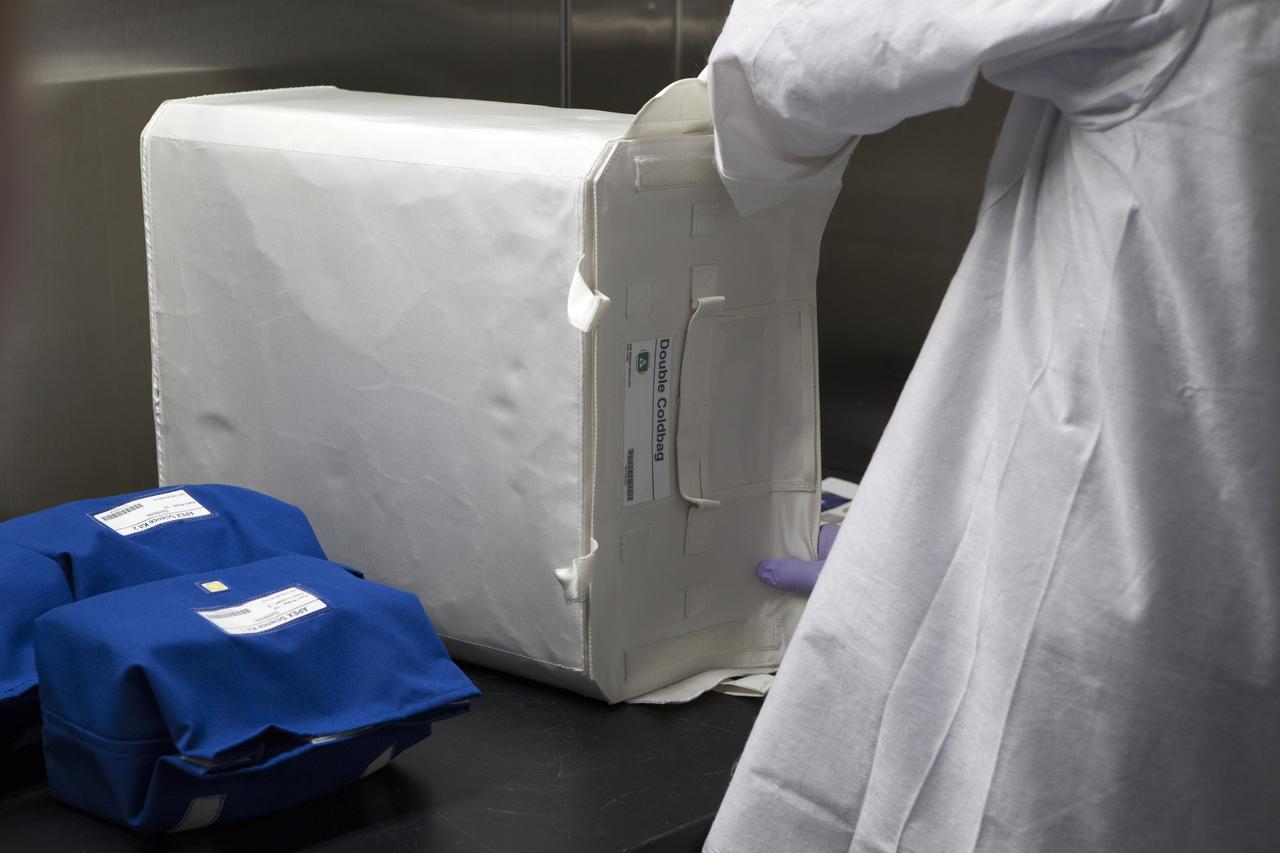

APEX-04, or Advanced Plant EXperiments-04, is being prepared in a cold room in the Kennedy Space Center Processing Facility for SpaceX-10. Eric Morris from the cold stowage group places the APEX-04 science kits into the Double Cold Bag (DCB), which is a non-powered container that keeps the APEX petri plates at +4 degrees Celsius during launch and ascent. The cold bricks in the lower right of the photo are placed in the DCB prior to closure. Dr. Anna Lisa Paul of the University of Florida is the principal investigator for APEX-04. Apex-04 is an experiment involving Arabidopsis in petri plates inside the Veggie facility aboard the International Space Station. Since Arabidopsis is the genetic model of the plant world, it is a perfect sample organism for performing genetic studies in spaceflight. The experiment is the result of a grant from NASA’s Space Life and Physical Sciences division.
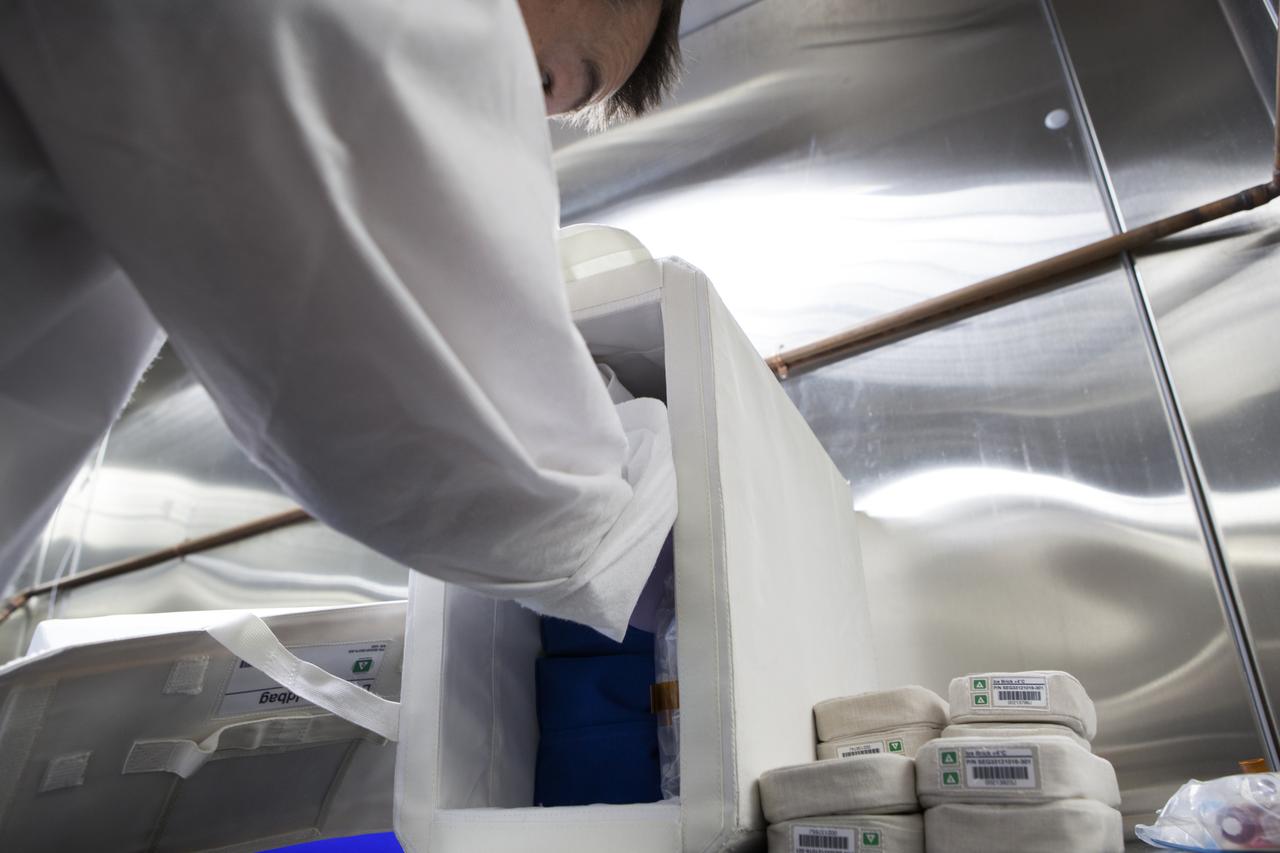

APEX-04, or Advanced Plant EXperiments-04, is being prepared in a cold room in the Kennedy Space Center Processing Facility for SpaceX-10. Eric Morris from the cold stowage group fits items into the Double Cold Bag (DCB) which is a non-powered container that keeps the APEX petri plates at +4 degrees Celsius during launch and ascent.. Dr. Anna Lisa Paul of the University of Florida is the principal investigator for APEX-04. Apex-04 is an experiment involving Arabidopsis in petri plates inside the Veggie facility aboard the International Space Station. Since Arabidopsis is the genetic model of the plant world, it is a perfect sample organism for performing genetic studies in spaceflight. The experiment is the result of a grant from NASA’s Space Life and Physical Sciences division.
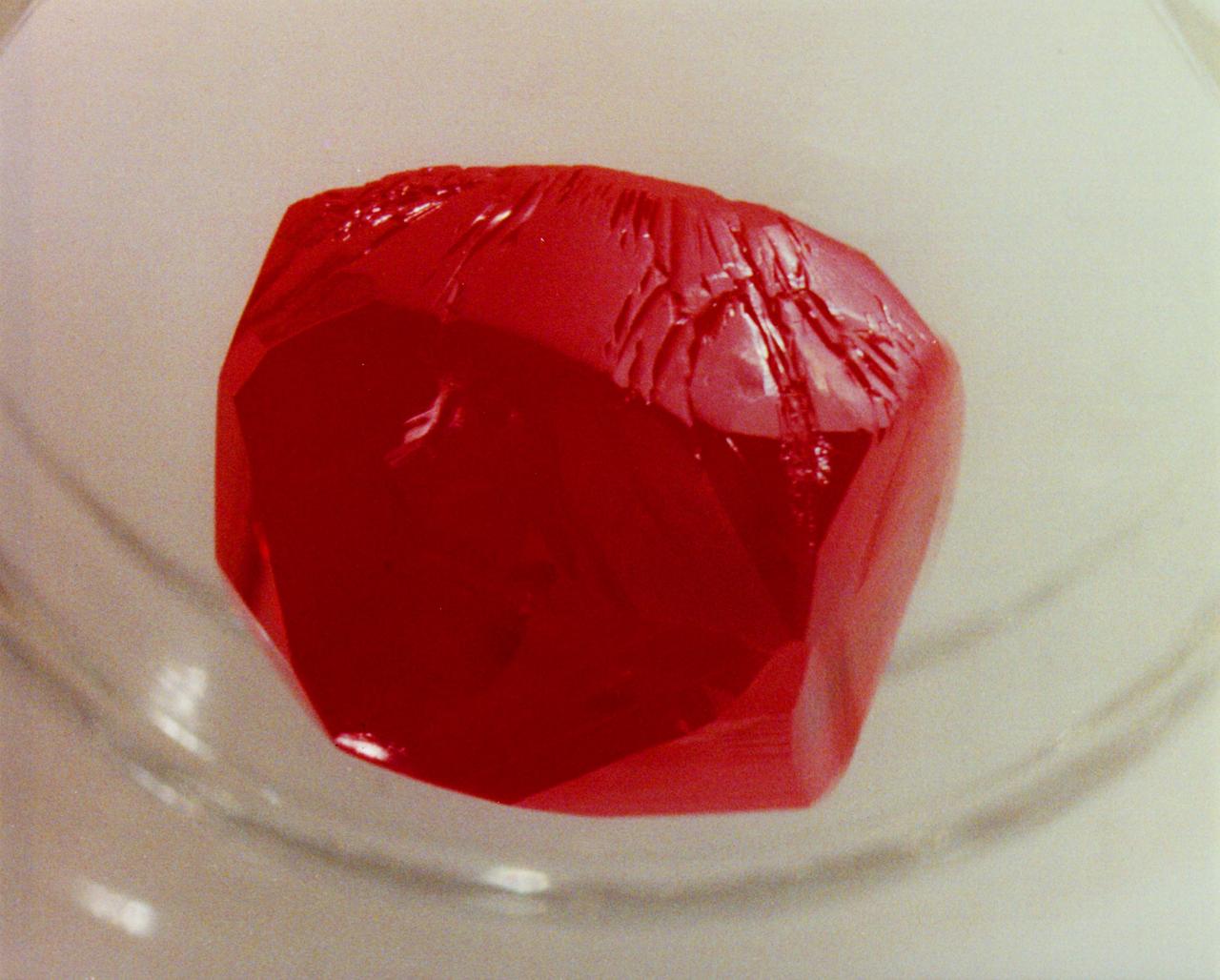

Vapor Crystal Growth System developed in IML-1, Mercuric Iodide Crystal grown in microgravity FES/VCGS (Fluids Experiment System/Vapor Crystal Growth Facility). During the mission, mercury iodide source material was heated, vaporized, and transported to a seed crystal where the vapor condensed. Mercury iodide crystals have practical uses as sensitive X-ray and gamma-ray detectors. In addition to their excellent optical properties, these crystals can operate at room temperature, which makes them useful for portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications, and astronomical observing.
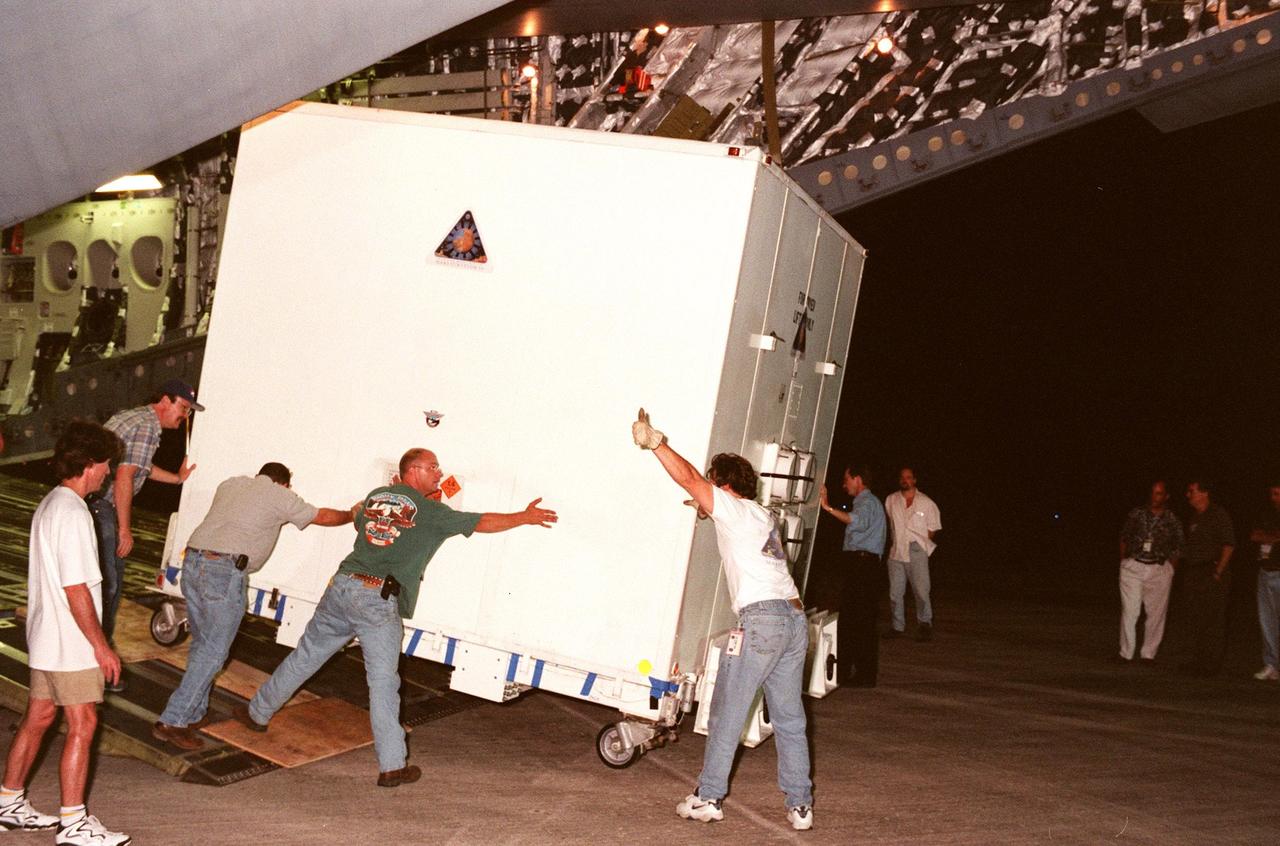

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the Mars Polar Lander is rolled from the Air Force C-17 cargo plane that carried it from the Lockheed Martin Astronautics plant in Denver, CO. The Mars Polar Lander is targeted for launch from Cape Canaveral Air Station aboard a Delta II rocket on Jan. 3, 1999. The solar-powered spacecraft is designed to touch down on the Martian surface near the northern-most boundary of the south pole in order to study the water cycle there. The lander also will help scientists learn more about climate change and current resources on Mars, studying such things as frost, dust, water vapor and condensates in the Martian atmosphere
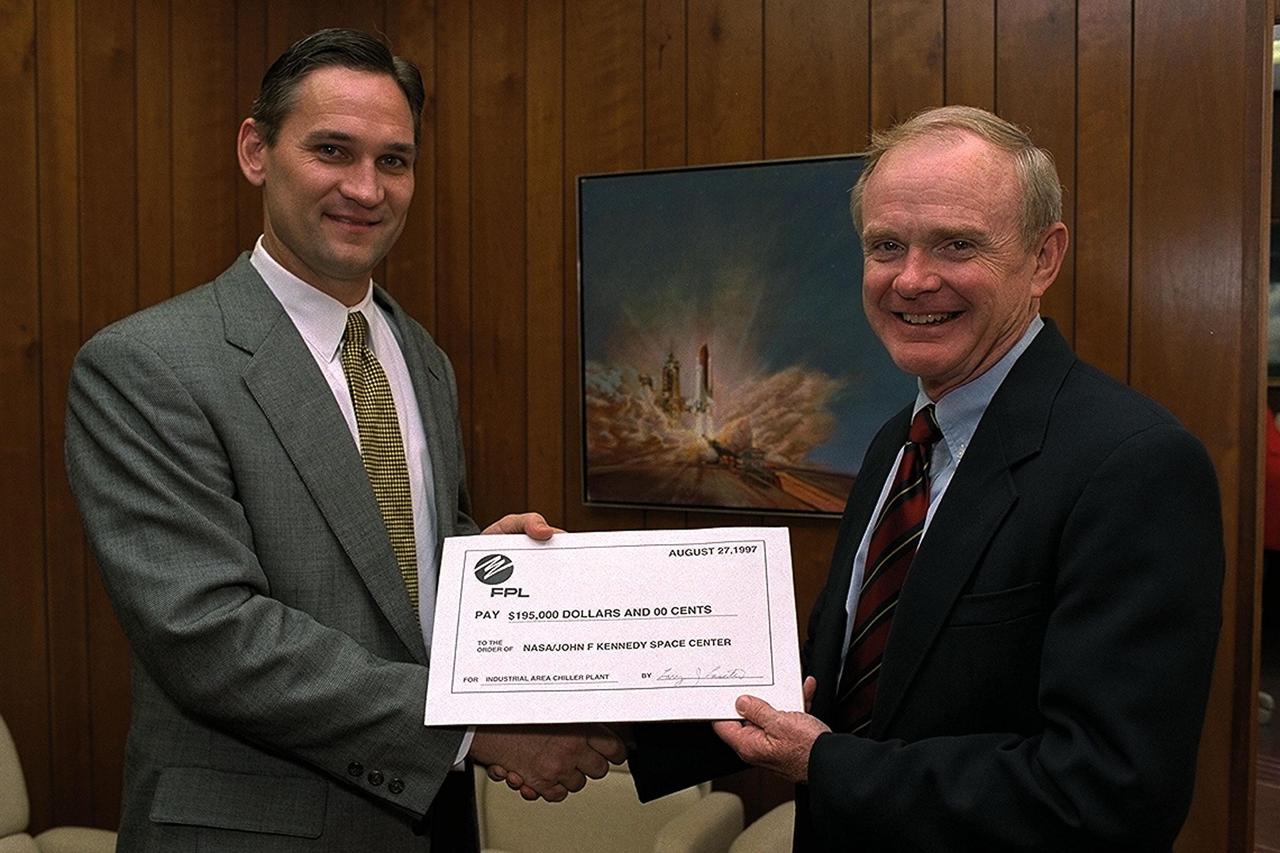

Larry Laseter (left), vice president of Sales and Marketing for the Florida Power & Light (FPL) Company, presents Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Director Roy Bridges Jr., with a rebate check for $195,000, recognizing KSC's commitment to reducing overall energy consumption and costs now and in the future. The energy savings realized by KSC come as a direct result of installing new chilled water systems hardware in the KSC Industrial Area Chiller Plant. KSC has received FPL rebates for its energy-saving efforts since 1993, but this check is the largest single-project rebate to date
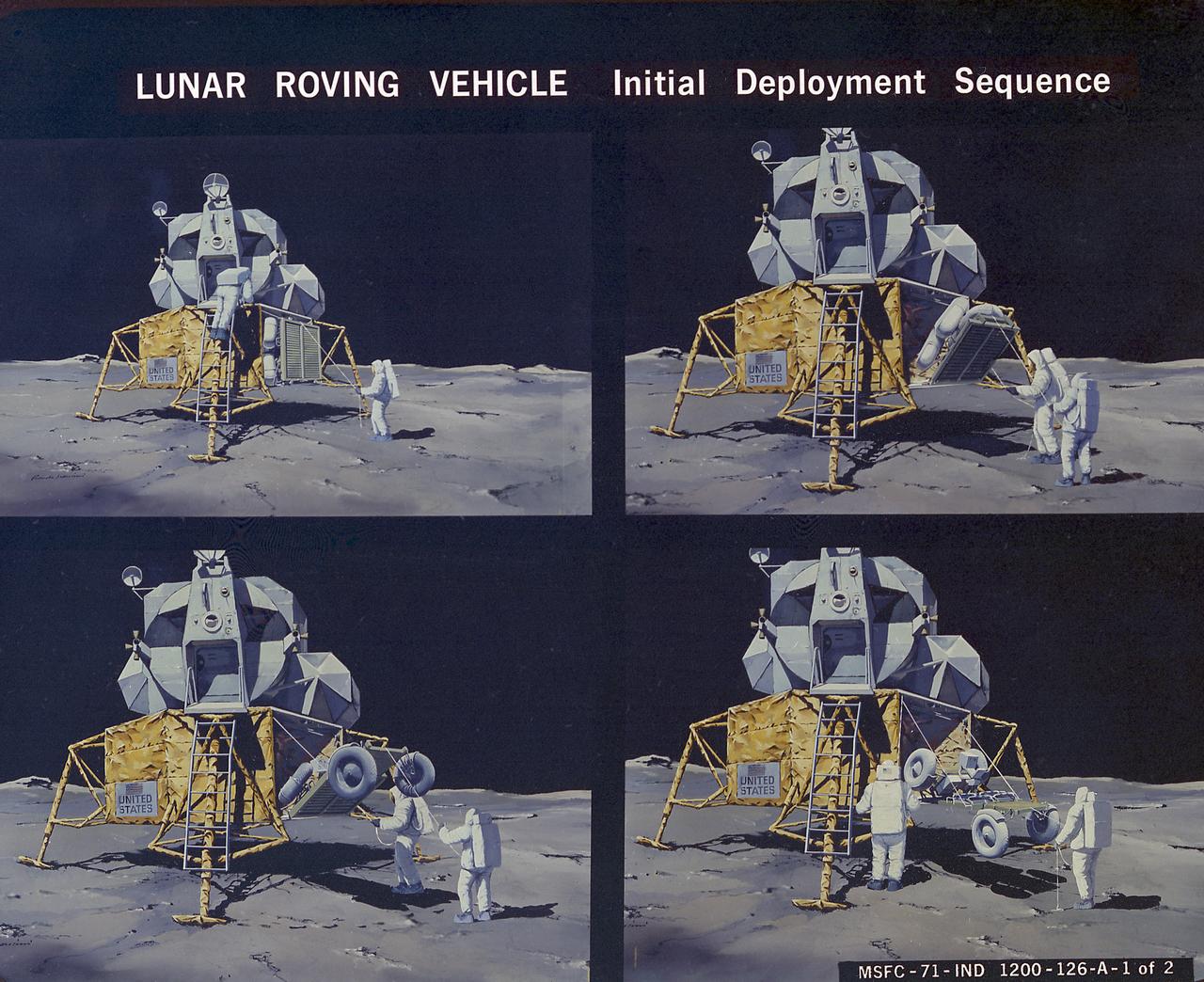
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
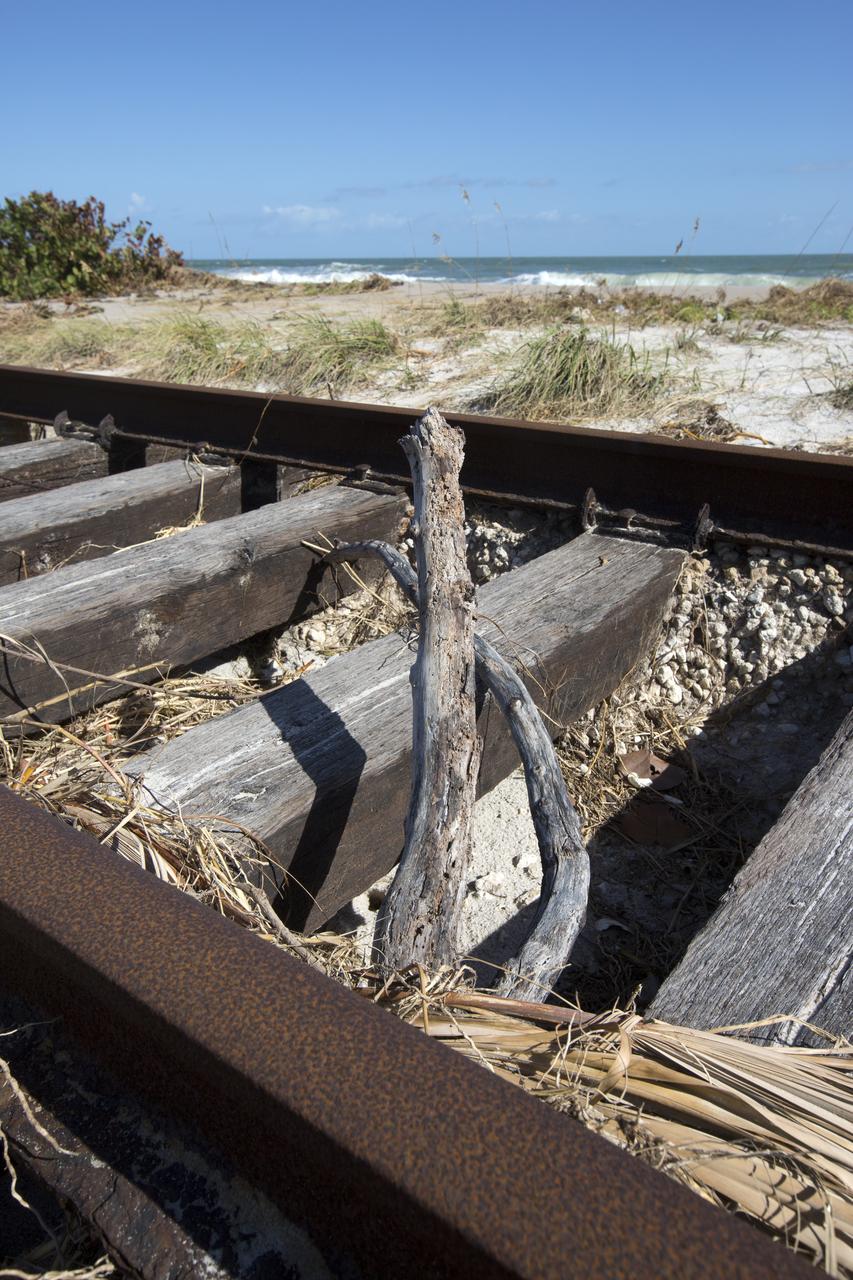

Plant debris and ground erosion left behind by Hurricane Matthew affect a stretch of the NASA Railroad at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A portion of the line near the ocean was used during the Apollo era, although some portions were used to deliver commodities to the nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station through the end of the Titan program. NASA determined it was financially and ecologically advantageous to leave the tracks in place. Hurricane Matthew, a Category 3 storm, passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
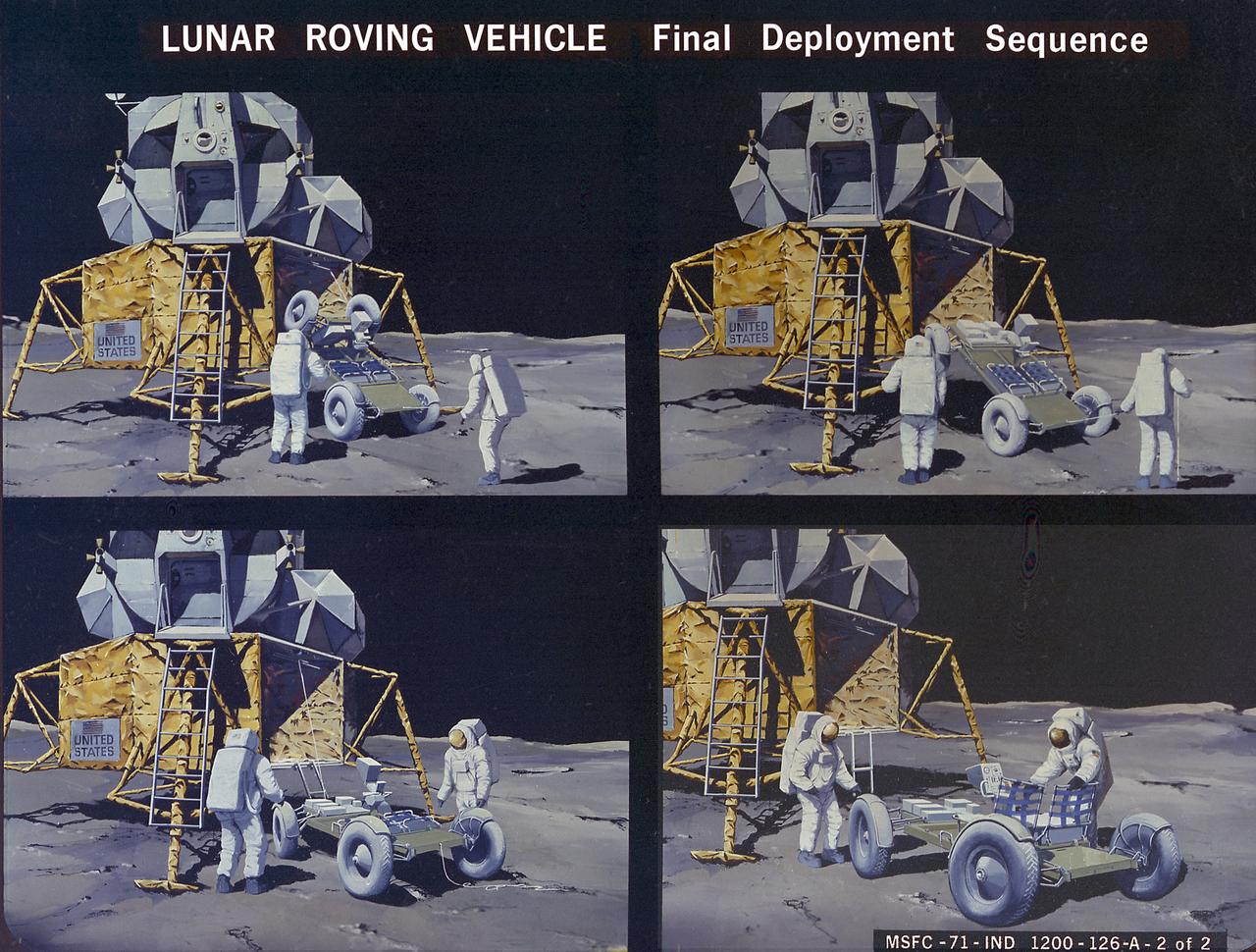
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.

The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
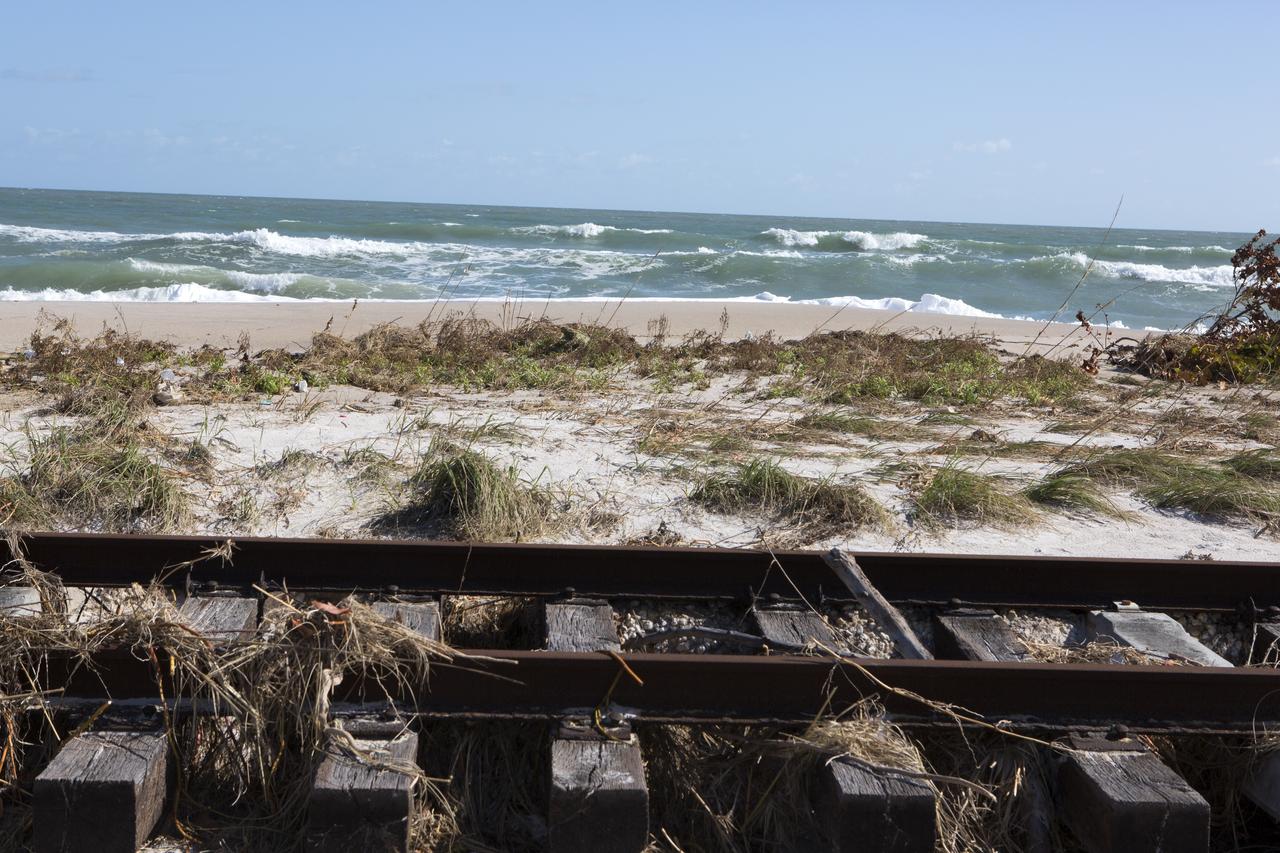

Plant debris left behind by Hurricane Matthew covers a stretch of the NASA Railroad near Launch Pads 39A and B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A portion of the line near the ocean was used during the Apollo era, although some portions were used to deliver commodities to the nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station through the end of the Titan program. NASA determined it was financially and ecologically advantageous to leave the tracks in place. Hurricane Matthew, a Category 3 storm, passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
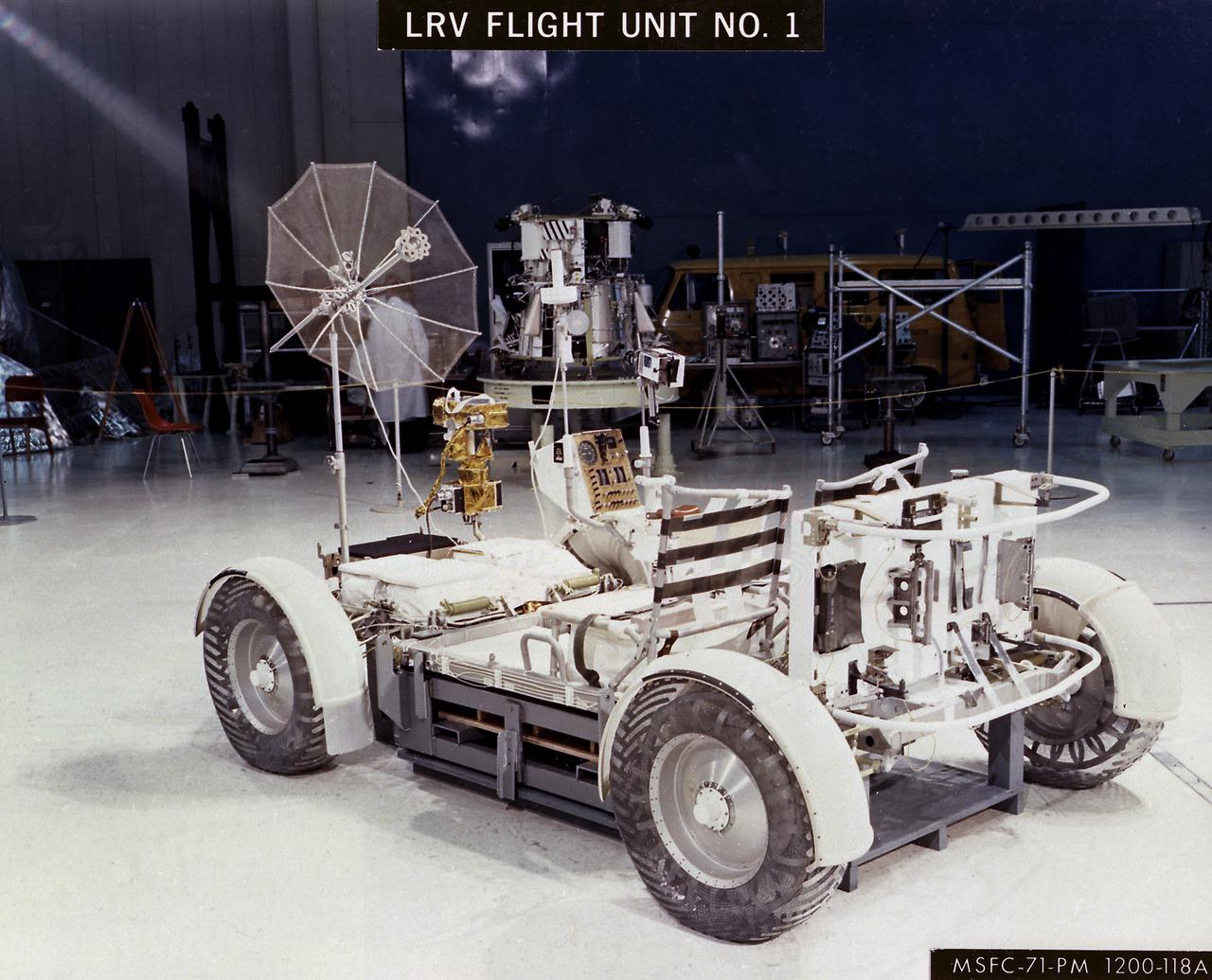
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crews to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
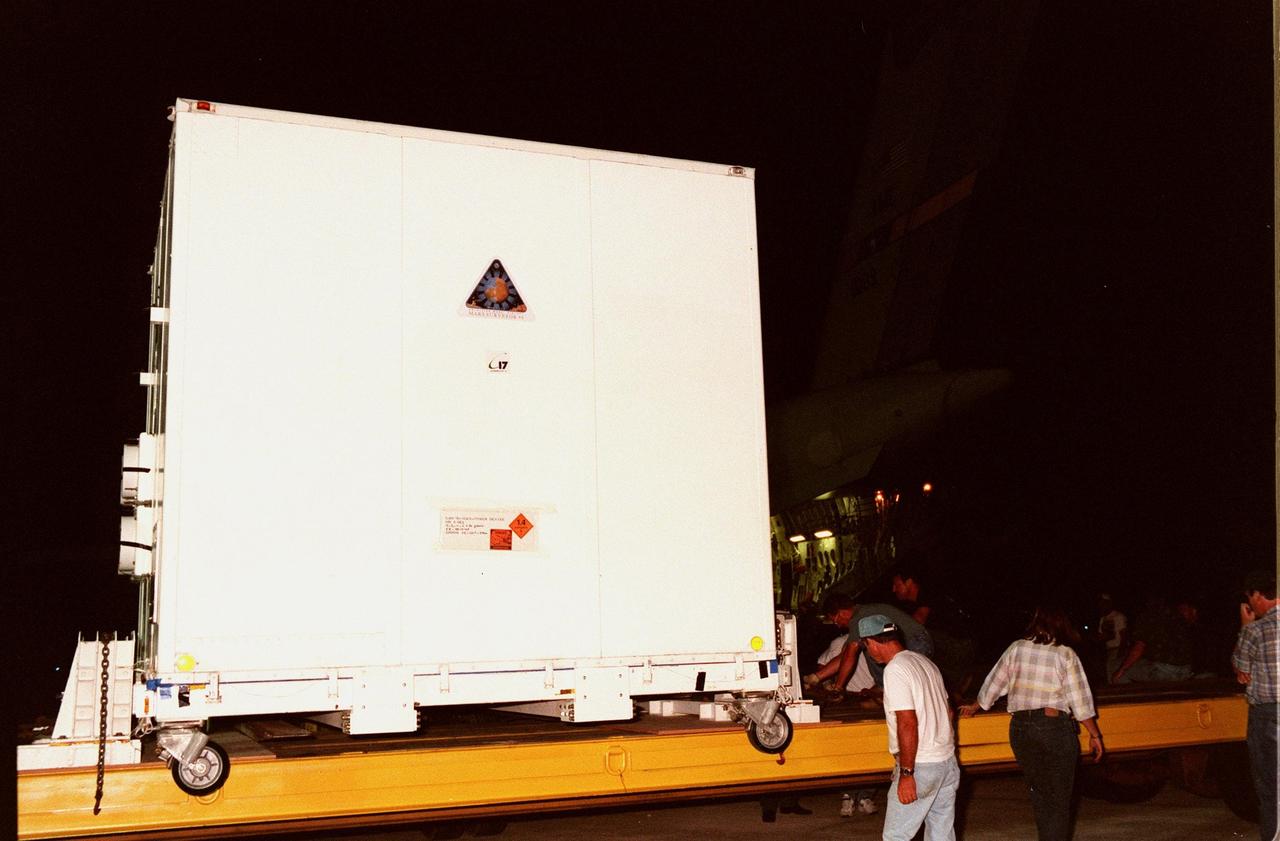

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the Mars Polar Lander is loaded onto a truck after its flight aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo plane that carried it from the Lockheed Martin Astronautics plant in Denver, CO. The lander is being transported to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2(SAEF-2) in the KSC Industrial Area for testing, including a functional test of the science instruments and the basic spacecraft subsystems. The solar-powered spacecraft is designed to touch down on the Martian surface near the northern-most boundary of the south pole in order to study the water cycle there. The lander also will help scientists learn more about climate change and current resources on Mars, studying such things as frost, dust, water vapor and condensates in the Martian atmosphere. The Mars Polar Lander spacecraft is planned for launch from Cape Canaveral Air Station aboard a Delta II rocket on Jan. 3, 1999

Plant debris left behind by Hurricane Matthew covers a stretch of the NASA Railroad at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A portion of the line near the ocean was used during the Apollo era, although some portions were used to deliver commodities to the nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station through the end of the Titan program. NASA determined it was financially and ecologically advantageous to leave the tracks in place. Hurricane Matthew, a Category 3 storm, passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.

This photograph depicts the flight article of the Airlock Module (AM) Flight Article being mated to the Fixed Airlock Shroud and aligned in a clean room of the McDornell Douglas Plant in St. Louis, Missouri. The AM enabled crew members to conduct extravehicular activities outside Skylab as required for experiment support. Separated from the Workshop and the Multiple Docking Adapter by doors, the AM could be evacuated for egress or ingress of a space-suited astronaut through a side hatch. Oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks needed for Skylab's life support system were mounted on the external truss work of the AM. Major components in the AM included Skylab's electric power control and distribution station, environmental control system, communication system, and data handling and recording systems. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for the design and development of the Skylab hardware and experiment management.
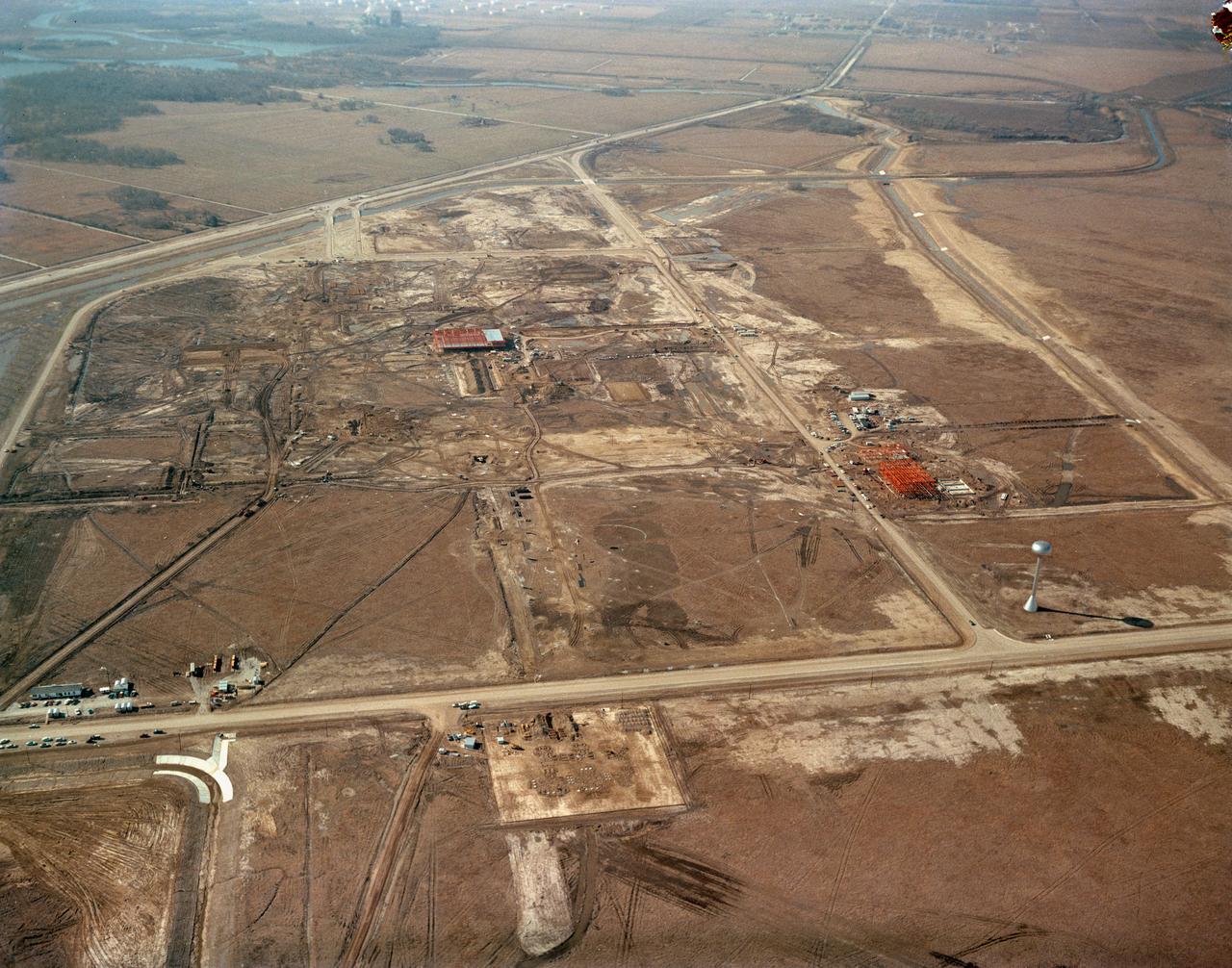

S63-00950 (1963) --- An aerial view of Site 1, the Manned Spacecraft Center, in 1963 during early construction. The view faces the southwest. Highway 528 is at the top of the picture. Second Street runs basically north and south on the right side of the image, to the right or west and running parallel to that avenue is a drainage ditch. Winding through the site a Houston Lighting and Power Co. canal crosses over the drainage ditch near the top of the frame. Twin bridges over the canal are pictured at upper left which were constructed to allow traffic to enter and leave through MSC's secondary gateway. The unfinished red structure to the right of center and roughly 100 yards south of the elevated water storage tank is the Central Heating and Cooling Plant. In the upper left quadrant of the frame, construction appears very far along on the Central Data Office.
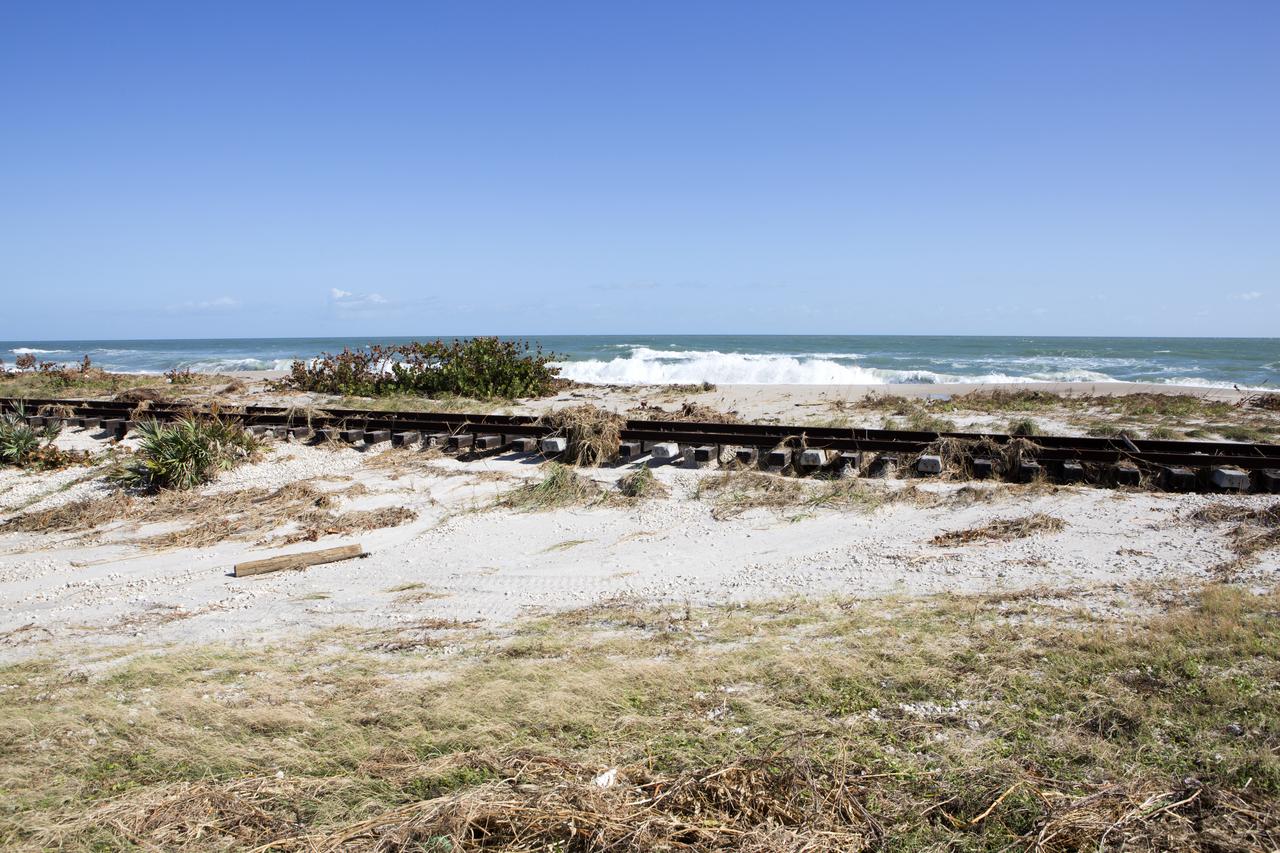

Plant debris left behind by Hurricane Matthew covers a stretch of the NASA Railroad near Launch Pads 39A and B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A portion of the line near the ocean was used during the Apollo era, although some portions were used to deliver commodities to the nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station through the end of the Titan program. NASA determined it was financially and ecologically advantageous to leave the tracks in place. Hurricane Matthew, a Category 3 storm, passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
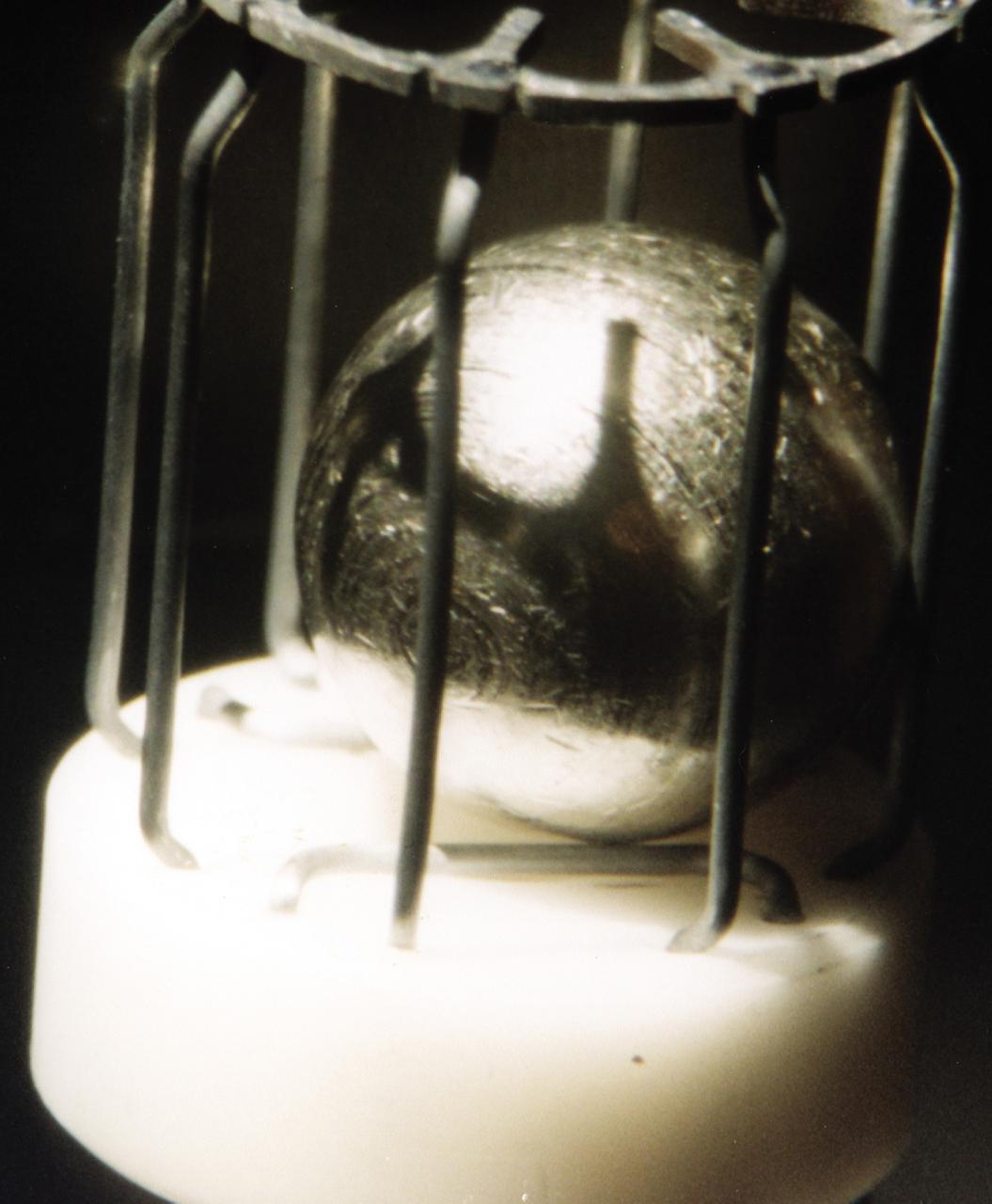
This metal sample, which is approximately 1 cm in diameter, is typical of the metals that were studied using the German designed electromagnetic containerless processing facility. The series of experiments that use this device is known as TEMPUS which is the acronym that stands for the German Tiegelfreies Elektromanetisches Prozessieren Unter Schwerelosigkeit. Most of the TEMPUS experiments focused on various aspects of undercooling liquid metal and alloys. Undercooling is the process of melting a material and then cooling it to a temperature that is below its normal freezing or solidification point. The TEMPUS experiments that used the metal cages as shown in the photograph, often studied bulk metallic glass, a solid material with no crystalline structures. We study metals and alloys not only to build things in space, but to improve things that are made on Earth. Metals and alloys are everywhere around us; in our automobiles, in the engines of aircraft, in our power-plants, and elsewhere. Despite their presence in everyday life, there are many scientific aspects of metals that we do not understand.
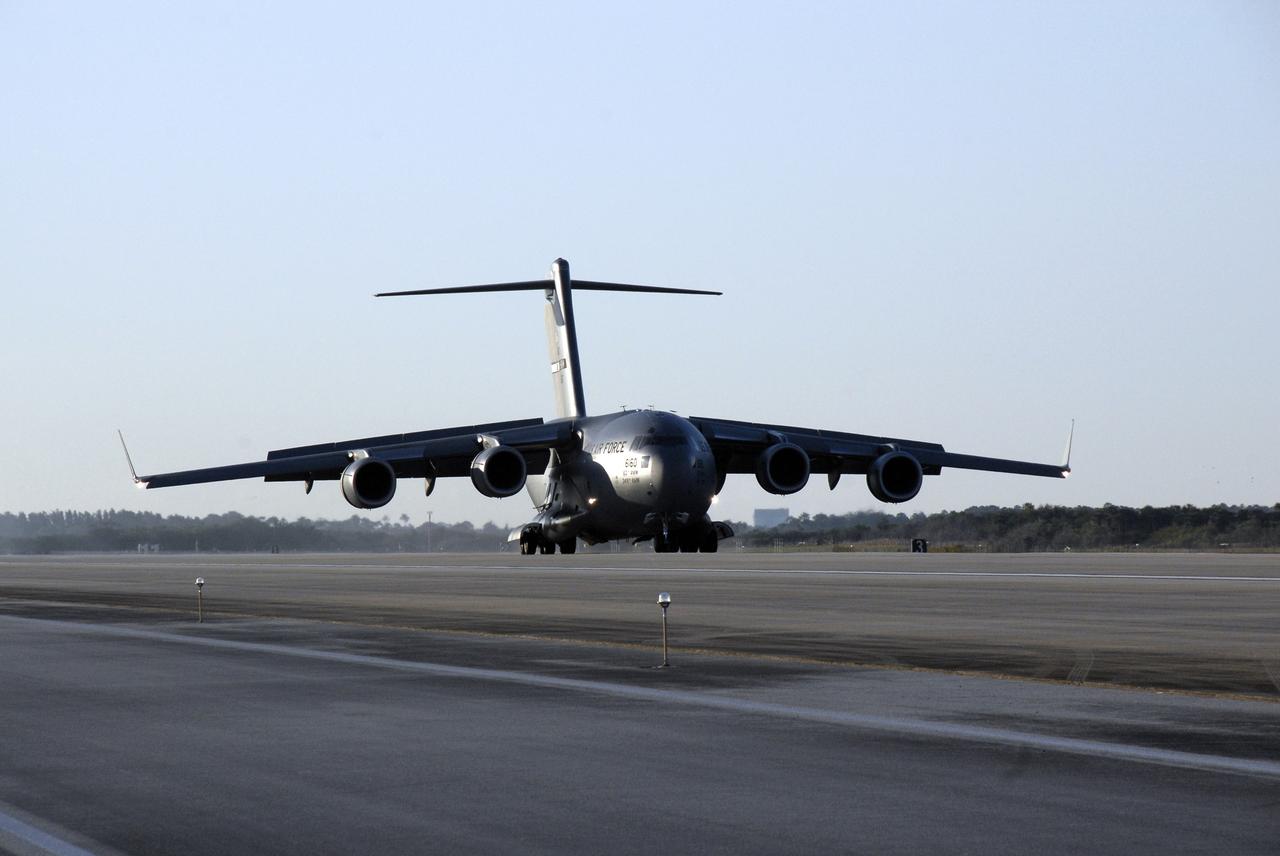

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES, arrives on a C-17 military cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida from its manufacturing plant in El Segundo, Calif. Developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA, the GOES-O satellite is targeted to launch April 28 onboard a United Launch Alliance Delta IV expendable launch vehicle. Once in orbit, GOES-O will be designated GOES-14, and NASA will provide on-orbit checkout and then transfer operational responsibility to NOAA. GOES-O will be placed in on-orbit storage as a replacement for an older GOES satellite. After arriving, the satellite was transported to Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., where final testing of the imaging system, instrumentation, communications and power systems will be performed. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
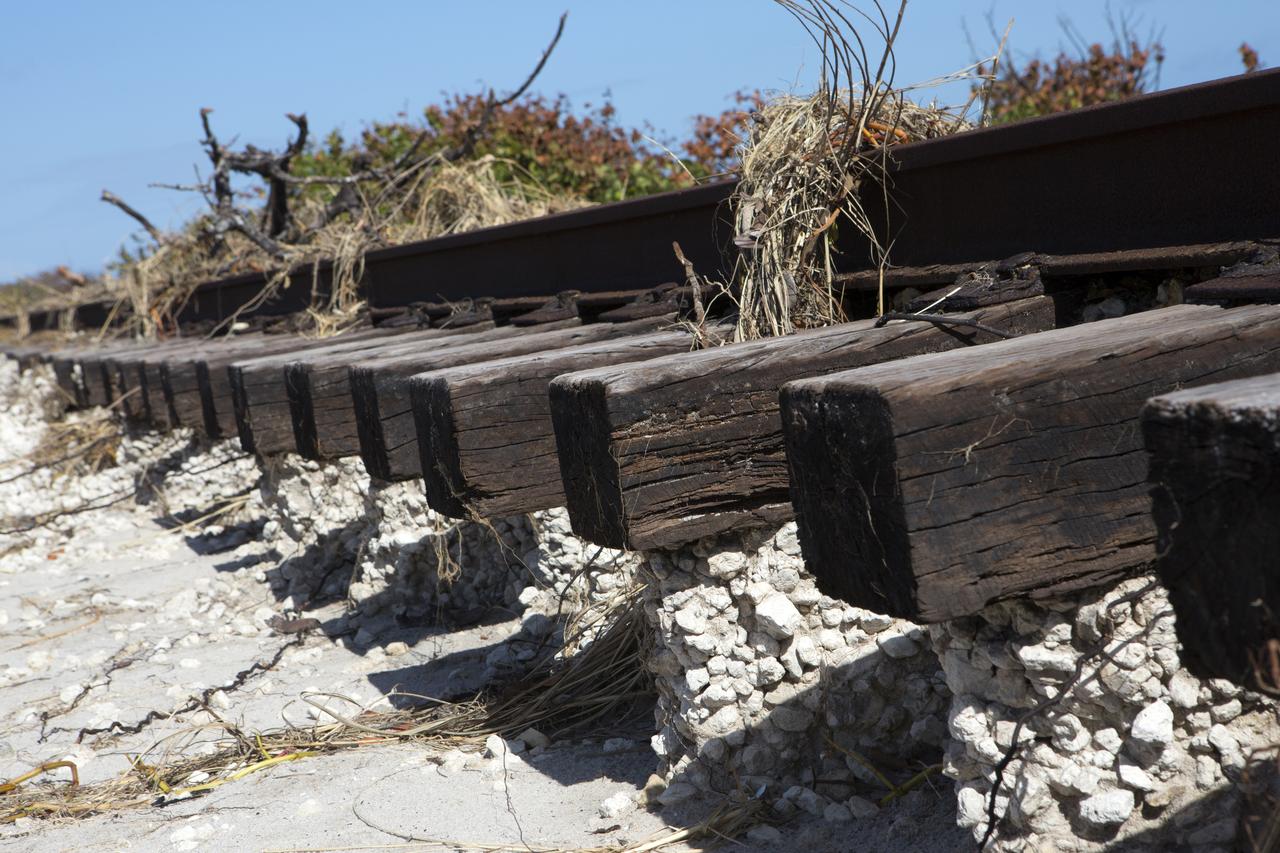

Plant debris and ground erosion left behind by Hurricane Matthew affect a stretch of the NASA Railroad at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A portion of the line near the ocean was used during the Apollo era, although some portions were used to deliver commodities to the nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station through the end of the Titan program. NASA determined it was financially and ecologically advantageous to leave the tracks in place. Hurricane Matthew, a Category 3 storm, passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
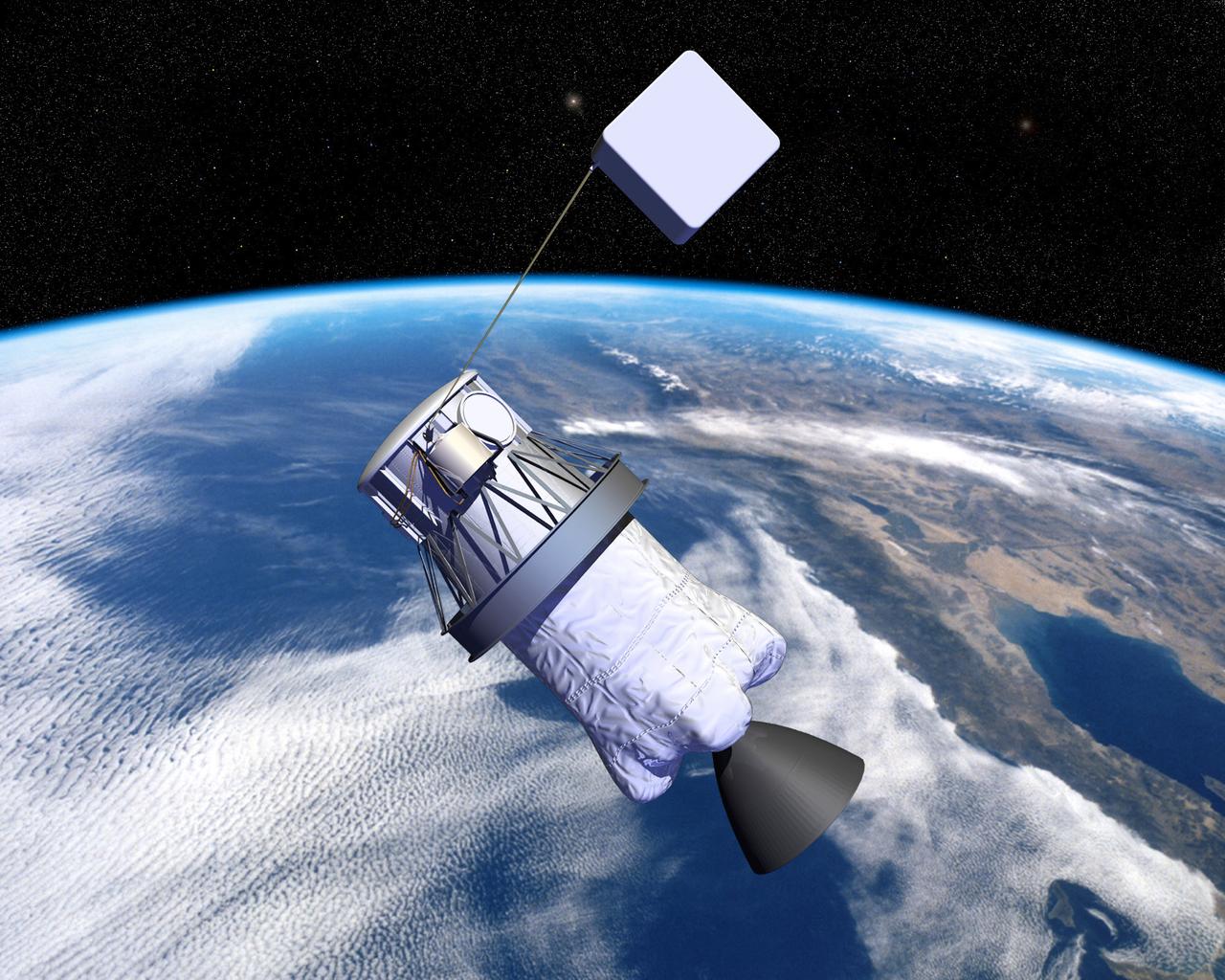

Pictured is an artist's concept of NASA's Propulsive Small Expendable Deployer System experiment (ProSEDS). ProSEDS will demonstrate the use of an electrodynamic tether, basically a long, thin wire, for propulsion. An electrodynamic tether uses the same principles as electric motors in toys, appliances and computer disk drives, and generators in automobiles and power plants. When electrical current is flowing through the tether, a magnetic field is produced that pushes against the magnetic field of the Earth. For ProSEDS, the current in the tether results by virtue of the voltage generated when the tether moves through the Earth's magnetic field at more than 17,000 mph. This approach can produce drag thrust generating useable power. Since electrodynamic tethers require no propellant, they could substantially reduce the weight of the spacecraft and provide a cost-effective method of reboosting spacecraft. The initial flight of ProSEDS is scheduled to fly aboard an Air Force Delta II rocket in summer of 2002. In orbit, ProSEDS will deploy from a Delta II second stage. It will be a 3.1-mile (5 kilometer) long, ultrathin base-wire tether cornected with a 6.2-mile (10 kilometer) long nonconducting tether. The ProSEDS experiment is managed by the Space Transportation Directorate at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
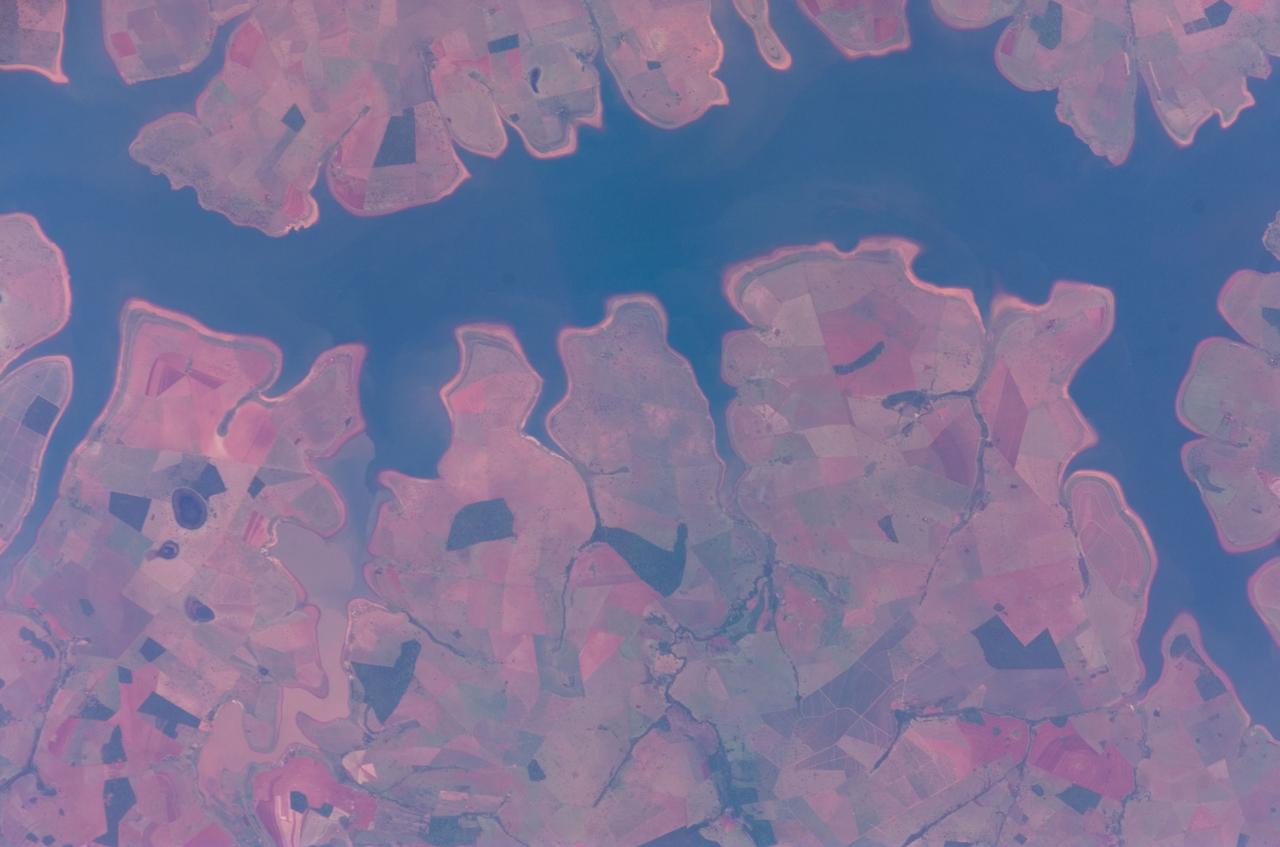

ISS016-E-011999 (22 Nov. 2007) --- Sao Simao Reservoir, Brazil is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 16 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). The Sao Simao reservoir, near the confluence of the Rio Paranaiba and Rio Verde in Brazil, is the featured subject in a milestone image of Earth. This colorful, patchwork image is the 300,000th image of Earth downlinked from the space station. There are now over 745,000 images of Earth taken by astronaut crews, beginning with the Mercury missions in 1961 and continuing to the present day on the ISS. The Sao Simao reservoir is located on the border between the states of Goias and Minas Gerais (near the geographic coordinates of 18.7S 50.4W). Though the town of Sao Simao was founded around 1935, major growth occurred when the hydroelectric power plant and dam were built - forming the reservoir -- in 1975. The reservoir is part of a major navigation link that allows transport of goods and commerce between central Brazil, the Prata River and the South Atlantic. With 600,000 square kilometers of surface area, the reservoir also serves as a tourist destination for fishing, swimming and boating. In addition to hydroelectric power production, the economy of the region is based in agribusiness. The image highlights agricultural fields of various kinds and in different stages of cultivation. The major commodities include corn, soybeans, sesame seeds, sugarcane, beans, manioc, coffee and meat production.
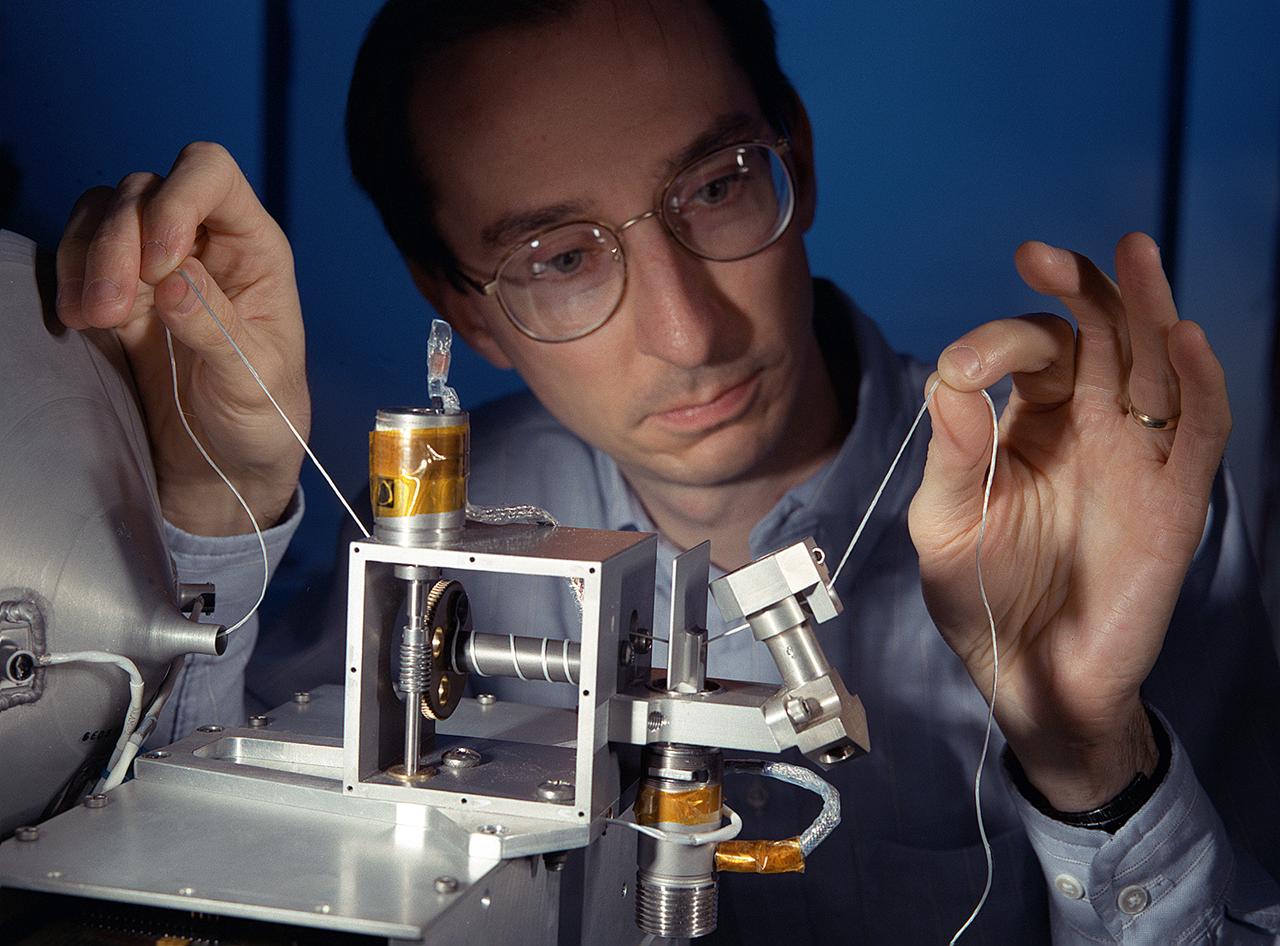

NASA's Propulsive Small Expendable Deployer System experiment (ProSEDS) will demonstrate the use of an electrodynamic tether, basically a long, thin wire, for propulsion. An electrodynamic tether uses the same principles as electric motors in toys, appliances and computer disk drives, and generators in automobiles and power plants. When electrical current is flowing through the tether, a magnetic field is produced that pushes against the magnetic field of the Earth. For ProSEDS, the current in the tether results by virtue of the voltage generated when the tether moves through the Earth's magnetic field at more than 17,000 mph. This approach can produce drag thrust generating useable power. Since electrodynamic tethers require no propellant, they could substantially reduce the weight of the spacecraft and provide a cost-effective method of reboosting spacecraft. The initial flight of ProSEDS is scheduled to fly aboard an Air Force Delta II rocket in the summer of 2002. In orbit, ProSEDS will deploy from a Delta II second stage. It will be a 3.1-mile (5 kilometer) long, ultrathin base-wire cornected with a 6.2-mile (10 kilometer) long nonconducting tether. This photograph shows Less Johnson, a scientist at MSFC inspecting the nonconducting part of a tether as it exits a deployer similar to the one to be used in the ProSEDS experiment. The ProSEDS experiment is managed by the Space Transportation Directorate at MSFC.
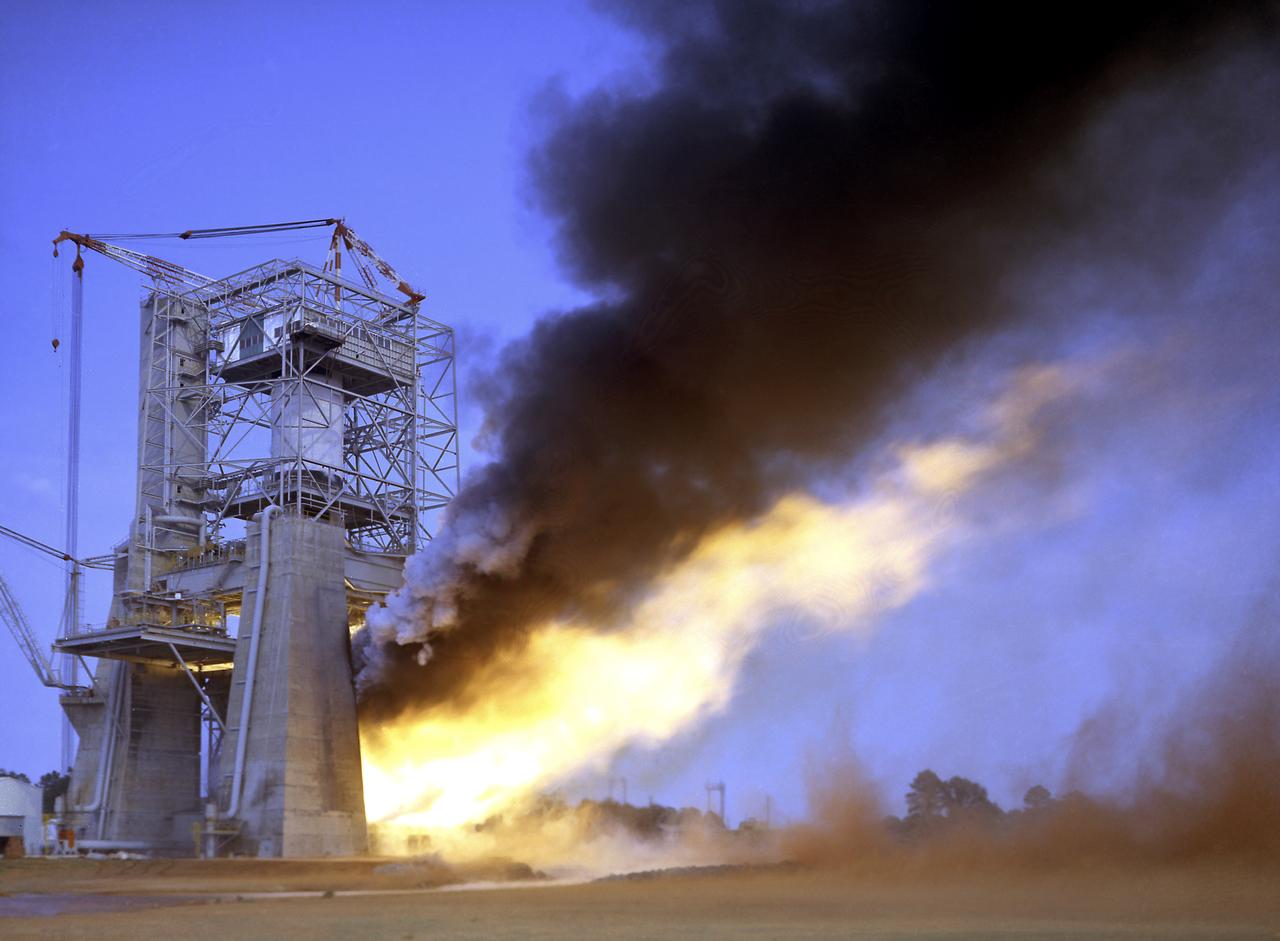

This photograph depicts a view of the test firing of all five F-1 engines for the Saturn V S-IC test stage at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S-IC stage is the first stage, or booster, of a 364-foot long rocket that ultimately took astronauts to the Moon. Operating at maximum power, all five of the engines produced 7,500,000 pounds of thrust. The S-IC Static Test Stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level, and was required to hold down the brute force of the 7,500,000-pound thrust. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the up position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. When the Saturn V S-IC first stage was placed upright in the stand , the five F-1 engine nozzles pointed downward on a 1,900-ton, water-cooled deflector. To prevent melting damage, water was sprayed through small holes in the deflector at the rate 320,000 gallons per minutes.
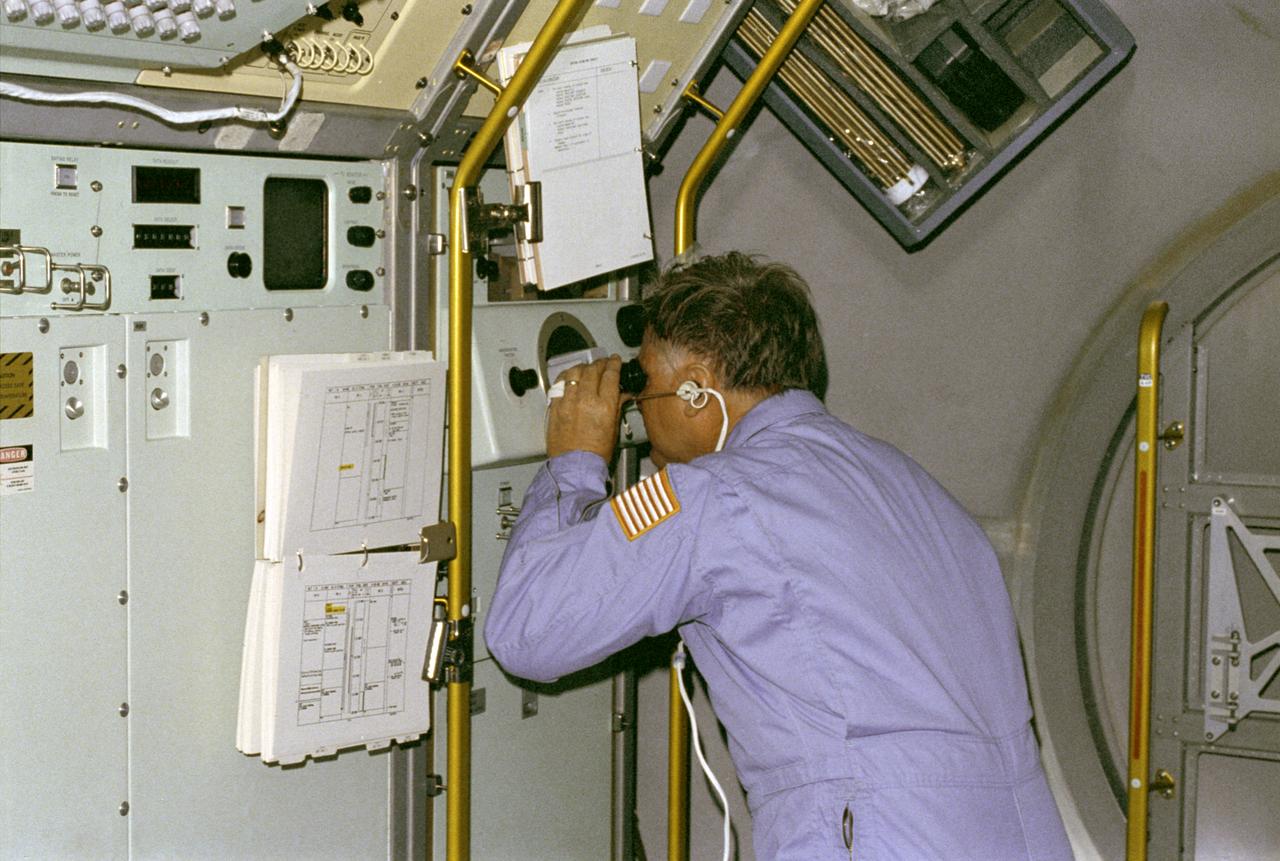

The primary purpose of the Spacelab-3 mission was to conduct materials science experiments in a stable low-gravity environment. In addition, the crew performed research in life sciences, fluid mechanics, atmospheric science, and astronomy. Spacelab-3 was equipped with several new minilabs, special facilities that would be used repeatedly on future flights. Two elaborate crystal growth furnaces, a life support and housing facility for small animals, and two types of apparatus for the study of fluids were evaluated on their inaugural flight. In this photograph, astronaut Don Lind observes the mercuric iodide growth experiment through a microscope at the vapor crystal growth furnace. The goals of this investigation were to grow near-perfect single crystals of mercuric iodide and to gain improved understanding of crystal growth by a vapor process. Mercuric iodide crystals have practical use as sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray detectors, and in portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications in diagnosis and therapy, and in astronomical instruments. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, Spacelab-3 (STS-51B) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on April 29, 1985.
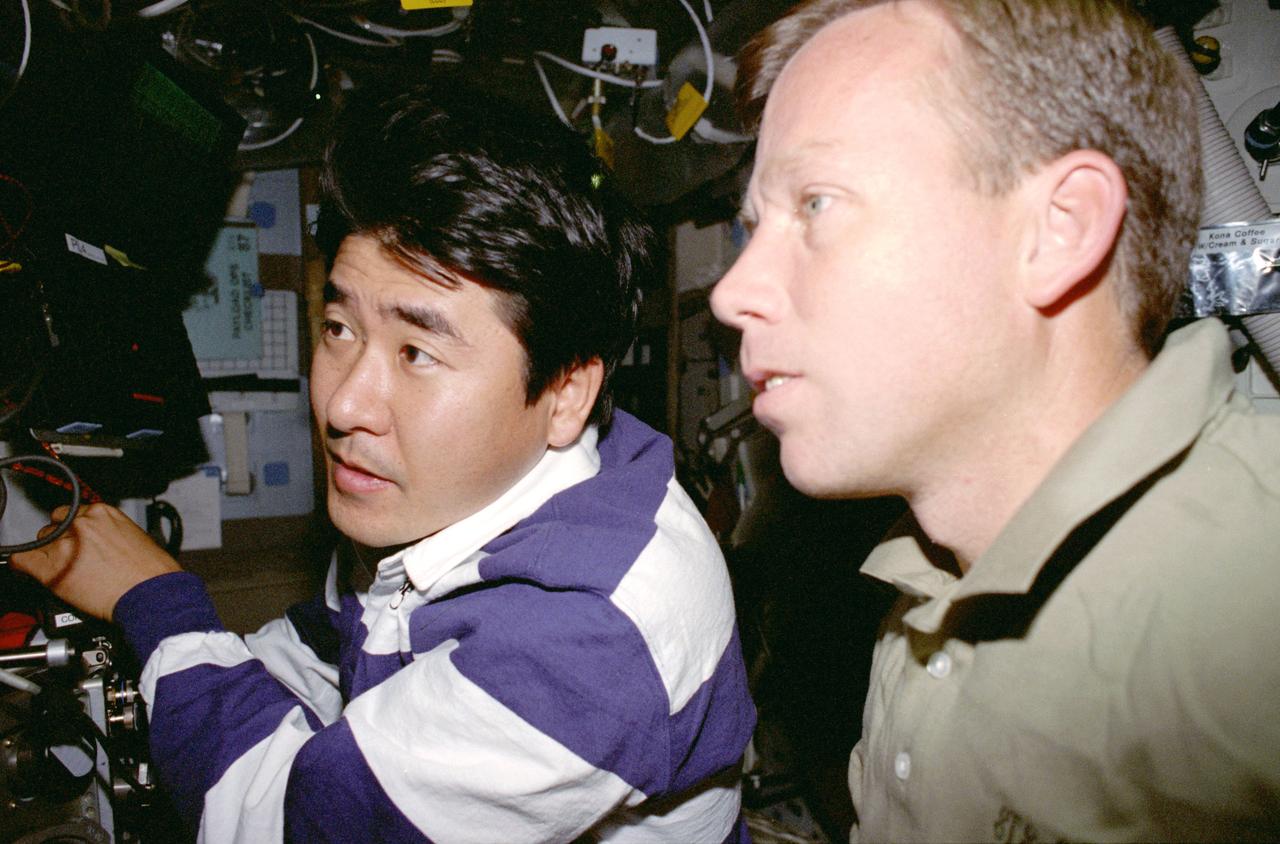

STS087-330-009 (19 November – 5 December 1997) --- Astronauts Takao Doi (left) and Steven W. Lindsey check out the Enclosed Laminar Flames (ELF) experiment on the mid-deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. ELF has been designed to examine the effect of different air flow velocities on the stability of laminar (non-turbulent) flames. Enclosed laminar flames are commonly found in combustion systems such as power plant and gas turbine combustors, and jet engine afterburners. It is hoped that results of this investigation may help to optimize the performance of industrial combustors, including pollutant emissions and heat transfer. The microgravity environment of space makes a perfect setting for a laboratory involving combustion, an activity that creates convection in normal gravity. In microgravity, scientists can study subtle processes ordinarily masked by the effects of gravity. Doi is an international mission specialist representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA) and Lindsey is the pilot. Both are alumni of NASA's 1995 class of Astronaut Candidates (ASCAN).
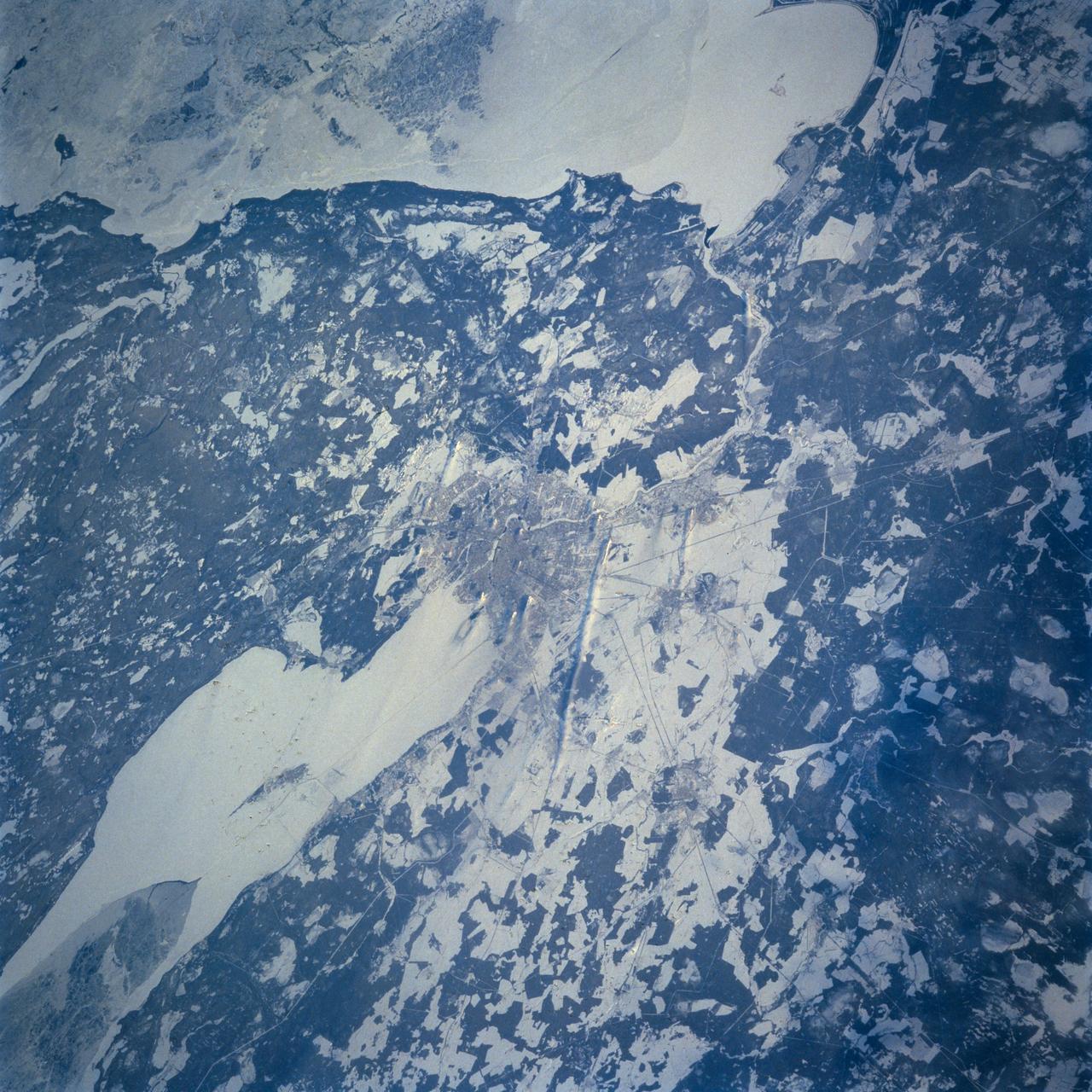

STS060-103-055 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- This wintertime photograph shows the large city of St. Petersburg Russia at the head of the Gulf of Finland. The city, built by Peter the Great, is situated in the former swampy delta of the Neva River which connects the large Lake Ladoga (the frozen white surface on the edge of the photograph) to the Gulf of Finland. An interesting feature of St. Petersburg which can be discerned in this photograph is the new storm surge barrier built from both sides of the Gulf of Finland out to the island of Kronstadt in the middle. This barrier, similar to that which was built on the Thames River south of London to protect it from storm surges out of the North Sea, was constructed to protect St. Petersburg from storm surges coming out of the Baltic Sea and being magnified by the topography and hydrography of the Gulf of Finland. Also visible as a thin line between Kronstadt and St. Petersburg is the ice-free shipping channel kept open much of the winter. Power plant plumes are also visible on the frame. St. Petersburg is the home of the Russian cosmonaut, Sergei Krikalev, who flew aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery during STS-60.
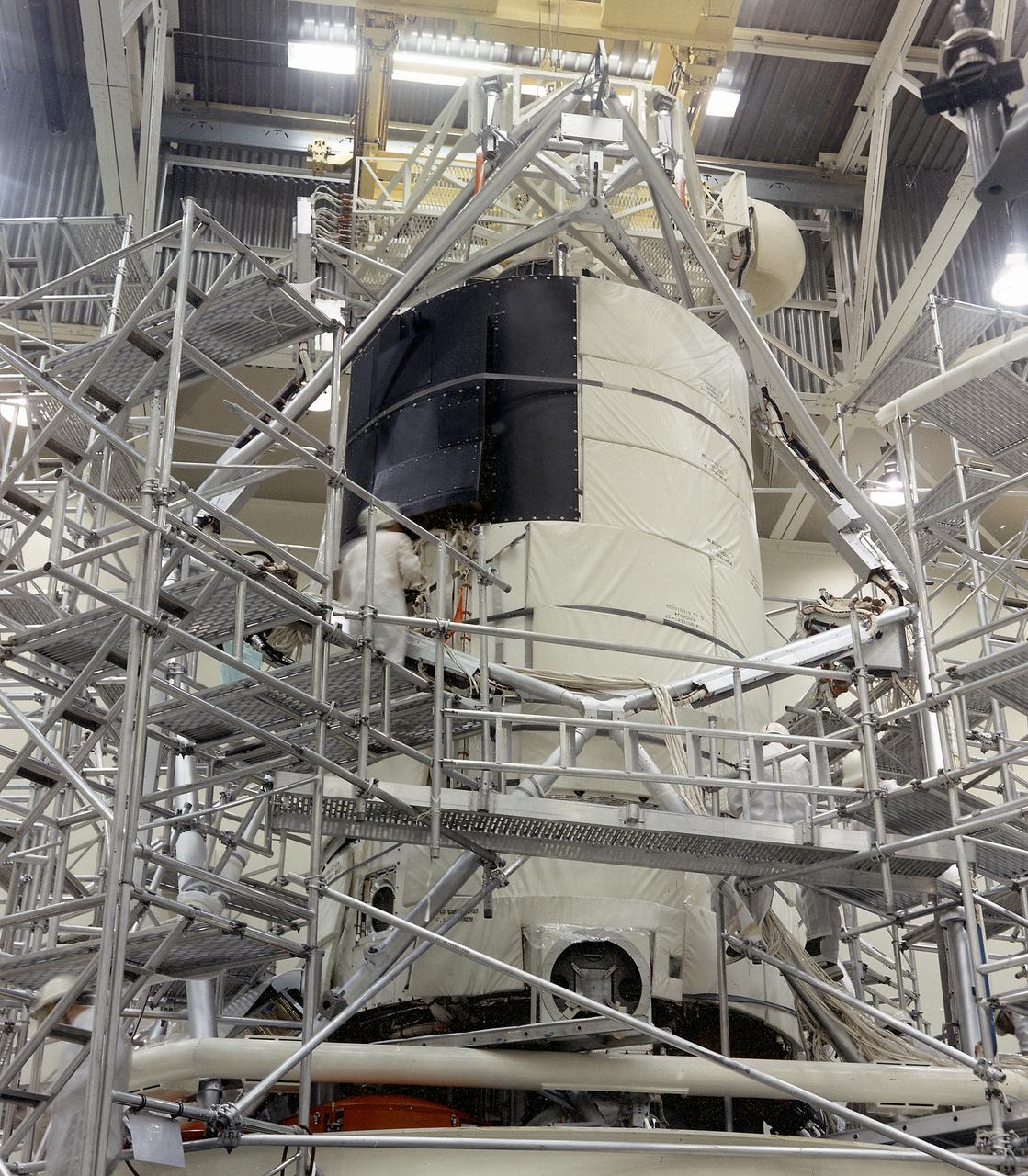

This photograph shows the flight article of the Airlock Module (AM)/Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) assembly being readied for testing in a clean room at the McDornell Douglas Plant in St. Louis, Missouri. Although the AM and the MDA were separate entities, they were in many respects simply two components of a single module. The AM enabled crew members to conduct extravehicular activities outside Skylab as required for experiment support. Oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks needed for Skylab's life support system were mounted on the external truss work of the AM. Major components in the AM included Skylab's electric power control and distribution station, environmental control system, communication system, and data handling and recording systems. The MDA, forward of the AM, provided docking facilities for the Command and Service Module. It also accommodated several experiment systems, among them the Earth Resource Experiment Package, the materials processing facility, and the control and display console needed for the Apollo Telescope Mount solar astronomy studies. The AM was built by McDonnell Douglas and the MDA was built by Martin Marietta. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for the design and development of the Skylab hardware and experiment management.
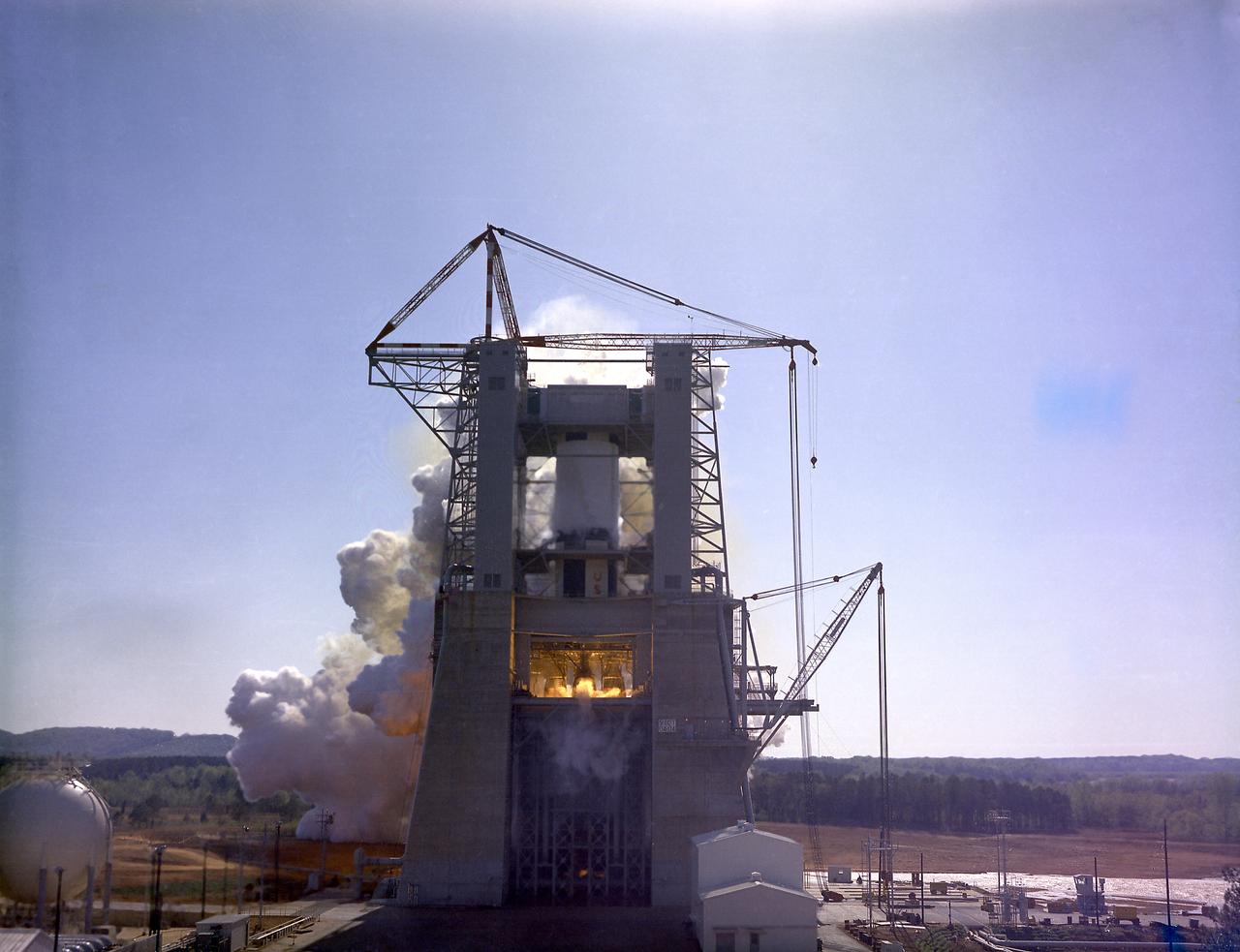

This photograph depicts a dramatic view of the first test firing of all five F-1 engines for the Saturn V S-IC stage at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The testing lasted a full duration of 6.5 seconds. It also marked the first test performed in the new S-IC static test stand and the first test using the new control blockhouse. The S-IC stage is the first stage, or booster, of a 364-foot long rocket that ultimately took astronauts to the Moon. Operating at maximum power, all five of the engines produced 7,500,000 pounds of thrust. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the up position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. When the Saturn V S-IC first stage was placed upright in the stand , the five F-1 engine nozzles pointed downward on a 1,900 ton, water-cooled deflector. To prevent melting damage, water was sprayed through small holes in the deflector at the rate 320,000 gallons per minute.

This photograph depicts a view of the test firing of all five F-1 engines for the Saturn V S-IC test stage at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S-IC stage is the first stage, or booster, of a 364-foot long rocket that ultimately took astronauts to the Moon. Operating at maximum power, all five of the engines produced 7,500,000 pounds of thrust. The S-IC Static Test Stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level, and was required to hold down the brute force of the 7,500,000-pound thrust. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the up position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. When the Saturn V S-IC first stage was placed upright in the stand , the five F-1 engine nozzles pointed downward on a 1,900-ton, water-cooled deflector. To prevent melting damage, water was sprayed through small holes in the deflector at the rate 320,000 gallons per minutes
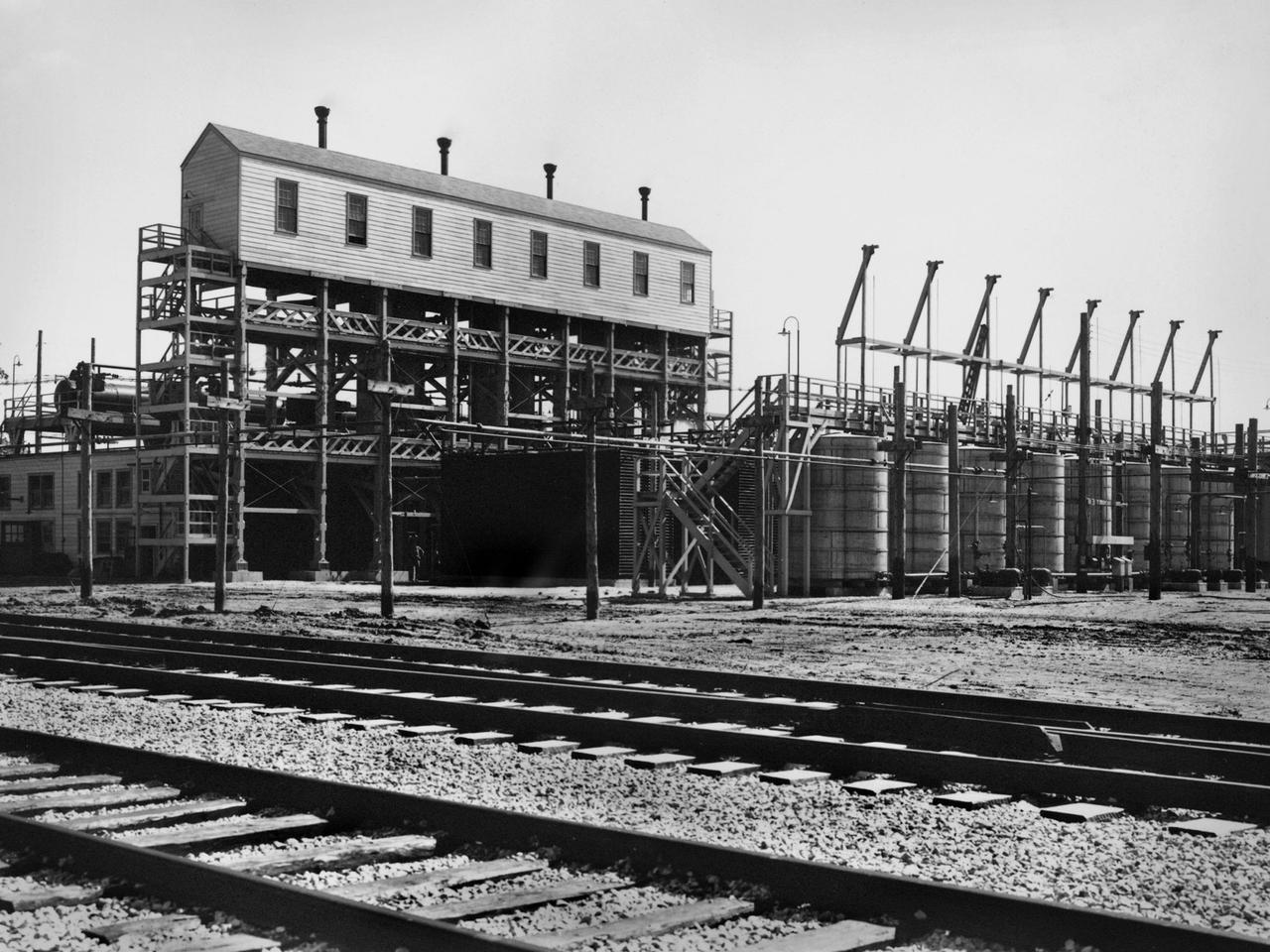

An ammonia oxidation plant at the Plum Brook Ordnance Works near Sandusky, Ohio, which later became the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. During World War II the ordnance works produced trinitroluene (TNT), dinitrotoluene (DNT), and pentolite which were crated and shipped to an arsenal in Ravenna, Ohio. There, the explosives were packed into shells and sent to Allied forces overseas. Plum Brook was the third largest producer of TNT during World War II. Toluene, sulfuric acid, and nitric acid were used to manufacture the TNT. Nitric Acid is made by oxidizing ammonia, adding water, and concentrating it. The facility in this photograph was used for this oxidation. The structure included air compressors, filters, aftercoolers, power recovery systems, air receivers, heaters, ammonia gasifiers, gas mixers, cooler condensers, absorption columns, and bleaching columns. The Plum Brook Ordnance Works was shut down immediately after the war and remained vacant for the next ten years. NASA’s predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), acquired the 500 acres of the site in 1955 to build a nuclear test reactor. By 1963, the agency had acquired the entire 9000 acres from the Army. Almost all of the military facilities were removed in the early 1960s. Plum Brook Station contained over 30 test facilities at its peak in the late 1960s. Today there are four major facilities in operation.
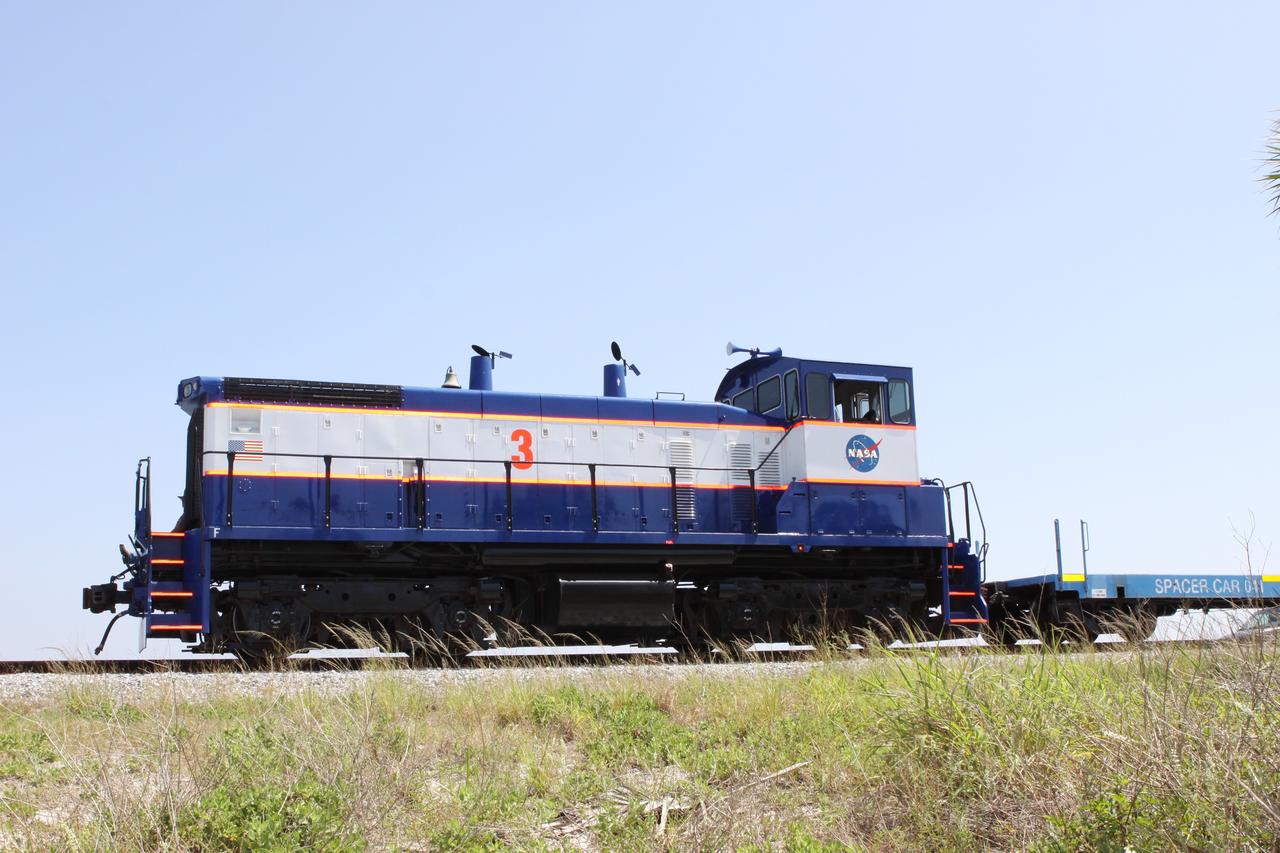

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Railroad locomotive No. 3 delivers tank cars from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the Florida East Coast Railway interchange in Titusville, Fla. The locomotive is one of three NASA Railroad locomotives built for the Toledo, Peoria and Western, or TP&W, between 1968 and 1970. It is a GM Electromotive Division SW-1500 switcher. The locomotive was acquired by NASA from the TP&W in 1984 and painted in the NASA Railroad paint scheme. The power plant was completely overhauled in 2009. The locomotive will pull the train to the interchange in Titusville, where the train’s helium tank cars, a liquid oxygen tank car, and a liquid hydrogen dewar or tank car will be transferred for delivery to the SpaceX engine test complex outside McGregor, Texas. The railroad cars were needed in support of the Space Shuttle Program but currently are not in use by NASA following the completion of the program in 2011. Originally, the tankers belonged to the U.S. Bureau of Mines. At the peak of the shuttle program, there were approximately 30 cars in the fleet. About half the cars were returned to the bureau as launch activity diminished. Five tank cars are being loaned to SpaceX and repurposed to support their engine tests in Texas. Eight cars previously were shipped to California on loan to support the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches from Space Launch Complex-4 on Vandenberg Air Force Base. SpaceX already has three helium tank cars previously used for the shuttle program at Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/spacex. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
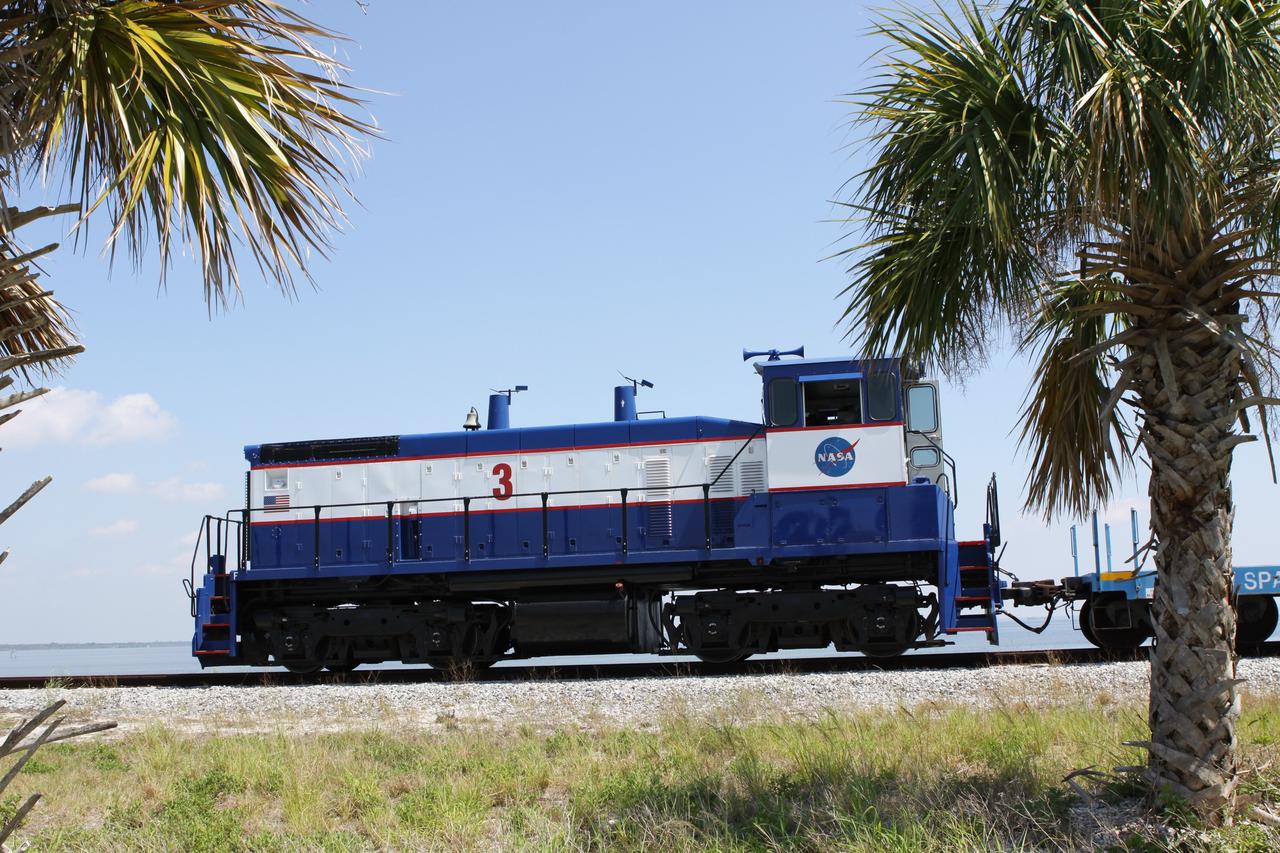

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Railroad locomotive No. 3 delivers tank cars from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the Florida East Coast Railway interchange in Titusville, Fla. The locomotive is one of three NASA Railroad locomotives built for the Toledo, Peoria and Western, or TP&W, between 1968 and 1970. It is a GM Electromotive Division SW-1500 switcher. The locomotive was acquired by NASA from the TP&W in 1984 and painted in the NASA Railroad paint scheme. The power plant was completely overhauled in 2009. The locomotive will pull the train to the interchange in Titusville, where the train’s helium tank cars, a liquid oxygen tank car, and a liquid hydrogen dewar or tank car will be transferred for delivery to the SpaceX engine test complex outside McGregor, Texas. The railroad cars were needed in support of the Space Shuttle Program but currently are not in use by NASA following the completion of the program in 2011. Originally, the tankers belonged to the U.S. Bureau of Mines. At the peak of the shuttle program, there were approximately 30 cars in the fleet. About half the cars were returned to the bureau as launch activity diminished. Five tank cars are being loaned to SpaceX and repurposed to support their engine tests in Texas. Eight cars previously were shipped to California on loan to support the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches from Space Launch Complex-4 on Vandenberg Air Force Base. SpaceX already has three helium tank cars previously used for the shuttle program at Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/spacex. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

ISS015-E-05624 (29 April 2007) --- The Niagara River, eastern end of Lake Erie and western end of Lake Ontario are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. In contrast, an image photographed by an Expedition 14 crewmember just a month earlier on March 21, 2007 (ISS014-E-17999) shows Lake Erie clogged with ice that is pushed against the shore line by the prevailing weather systems from the west. These two images document the breakup of the Lake Erie ice pack, the unofficial signature of spring for residents of Buffalo and Niagara Falls. During the winter months, the ice collects in Lake Erie and is prevented from flowing down the Niagara River (the international boundary between Ontario, Canada and New York State) by the Lake Erie-Niagara River Ice Boom. The 2,680-meter (8,800-foot) boom, administered by the 1909 Boundary Water Treaty's International Niagara Board of Control, is deployed each December. Operational since 1964, the boom serves several functions: it protects the water intakes for the Niagara River power plants, and minimizes ice runs and ice blockages that can create damage and flooding along the river. At the height of winter, the thickness of the ice at the Buffalo harbor can reach 3.5 meters (12 feet). The removal of the ice boom, usually in early April, is now marked by local celebrations. This year the boom was removed in mid-April, a bit later than usual.
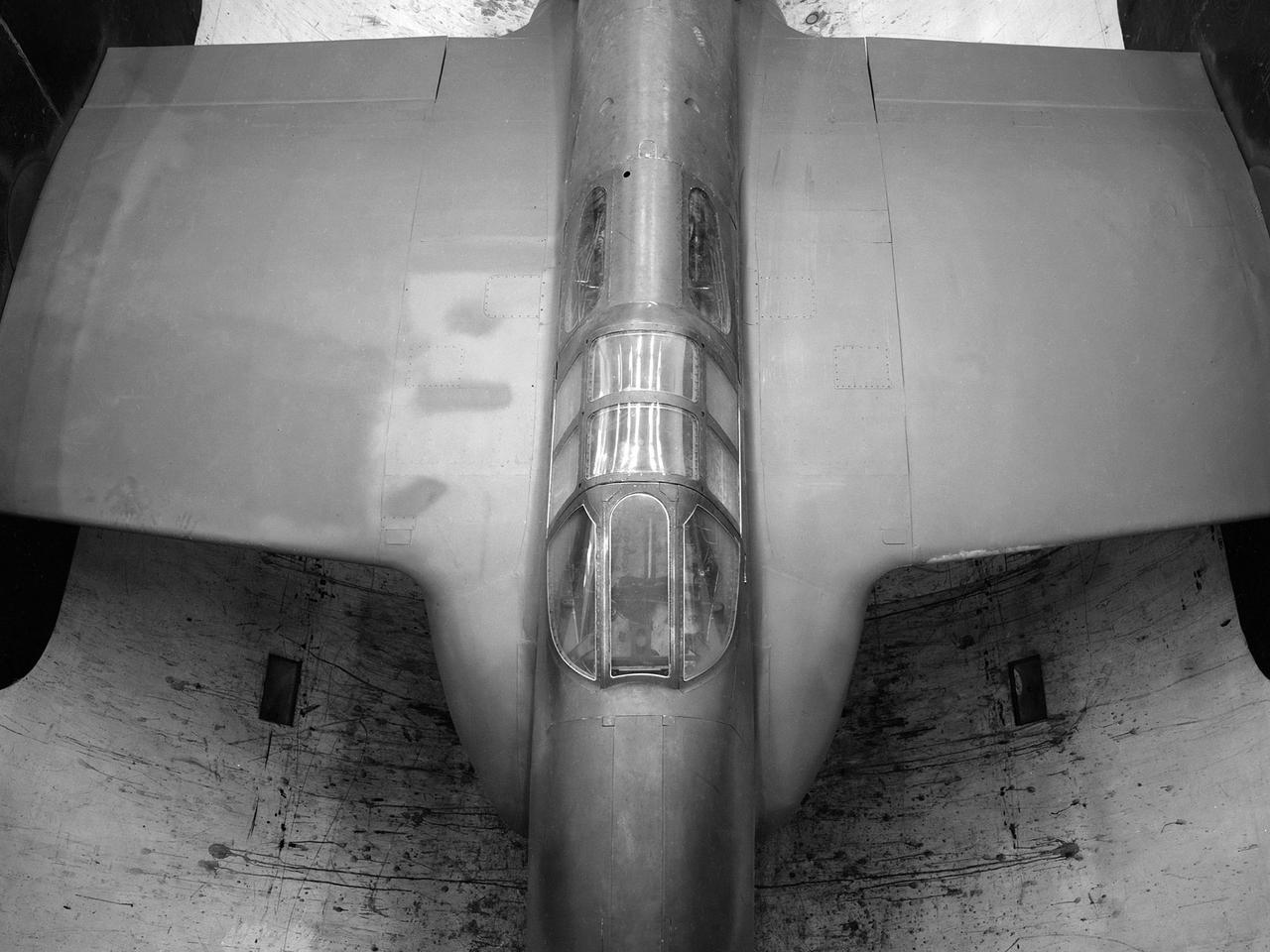

The secret test of the Bell YP–59A Airacomet in the spring of 1944 was the first investigation in the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory’s new Altitude Wind Tunnel (AWT). The Airacomet, powered by two General Electric I–A centrifugal turbojets, was the first US jet aircraft. The Airacomet’s 290-miles per hour speed, however, was dwarfed by the German Messerschmitt Me-262 Schwalbe’s 540 miles per hour. In 1941 and 1942 General Electric built the first US jet engines based on technical drawings from British engineer Frank Whittle. Bell Aircraft was contracted to produce an airframe to incorporate the new engines. The result was the Bell XP–59A Airacomet. The aircraft made its first flight over Muroc Lake, California, on October 2, 1942. The aircraft continued to struggle over the next year and the NACA was asked to test it in the new AWT. A Bell YP–59A was flown from the Bell plant in Buffalo to Cleveland by Bob Stanley, who had piloted the first successful flight of the XP–59A at Muroc in 1942. The wing tips and tail were cut from the aircraft so that it would fit into the AWT’s test section. The study first analyzed the engines in their original configuration and then implemented a boundary layer removal duct, a new nacelle inlet, and new cooling seals. Tests of the modified version showed that the improved airflow distribution increased the I–16’s performance by 25 percent. Despite the improved speed, the aircraft was not stable enough to be used in combat, and the design was soon abandoned.
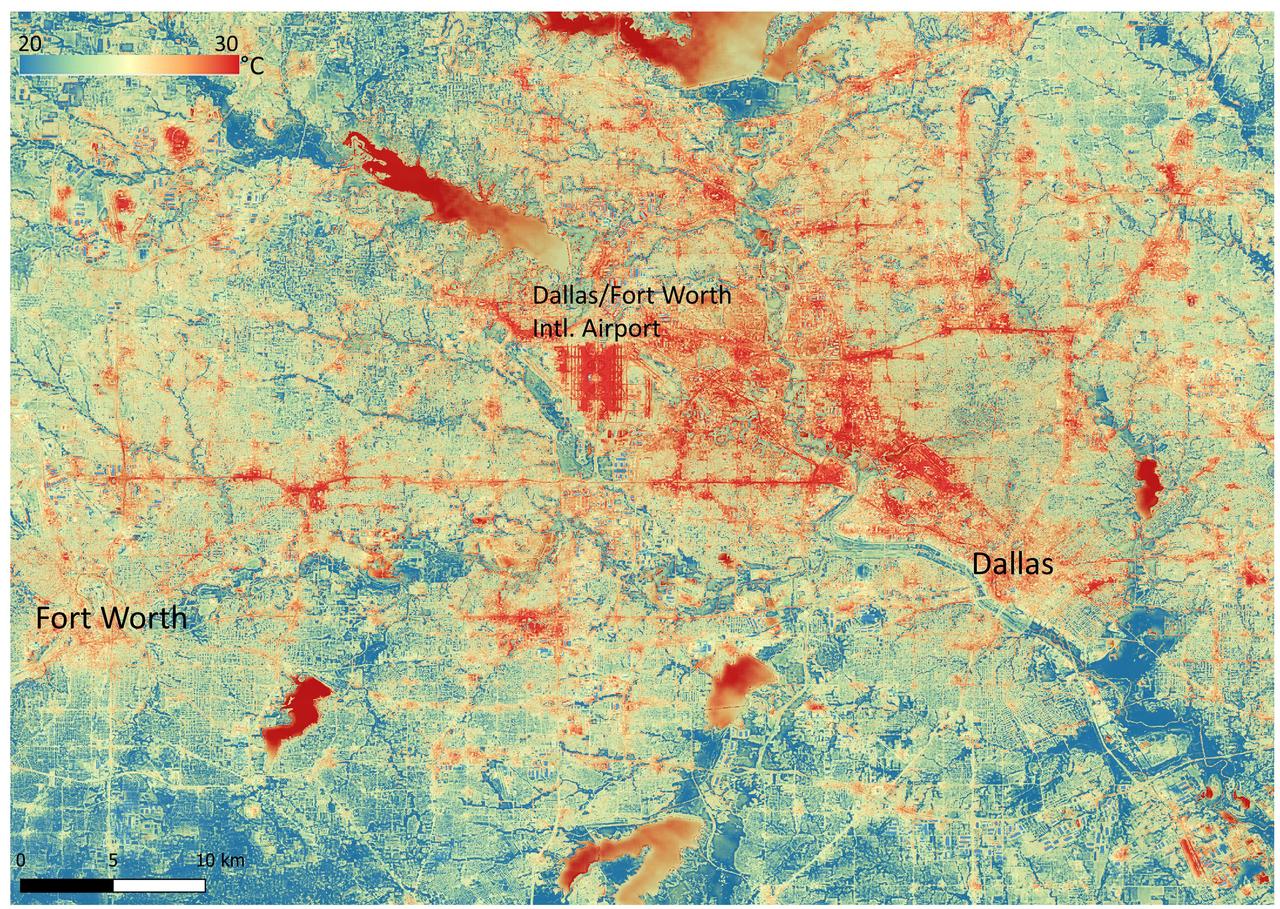
NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS) instrument recorded this image of ground surface temperatures in Dallas and Fort Worth, Texas, on June 20, 2022, at 7:17 a.m. Central Daylight Time. Even early in the day, manmade urban surfaces near city centers and transportation networks – streets, roads, and highways shown in red and orange – are warmer than the outskirts by up to 18 degrees Fahrenheit (10 degrees Celsius). The paved surfaces at Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport, shown in red near the top-center of the image, had the warmest temperatures, exceeding 86 F (30 C). Natural land surfaces such as vegetation and streams in rural areas, shown in green and blue, are cooler than nearby large bodies of water, shown in red and yellow, that tend to retain more heat overnight due to their higher heat capacity. Cities are usually warmer than open land because of human activities and the materials used in building and construction. Streets are often the hottest part of the built environment due to asphalt paving. Dark-colored surfaces absorb more heat from the Sun than lighter-colored ones; asphalt absorbs up to 95% of solar radiation and retains the heat for hours into the nighttime. ECOSTRESS measures the temperature of the ground, which is hotter than the air temperature during the daytime. The instrument launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify plants' thresholds for water use and water stress, giving insight into their ability to adapt to a warming climate. However, ECOSTRESS is also useful for documenting other heat-related phenomena, like patterns of heat absorption and retention. Its high-resolution images, with a pixel size of about 225 feet (70 meters) by 125 feet (38 meters), are a powerful tool for understanding our environment. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25422
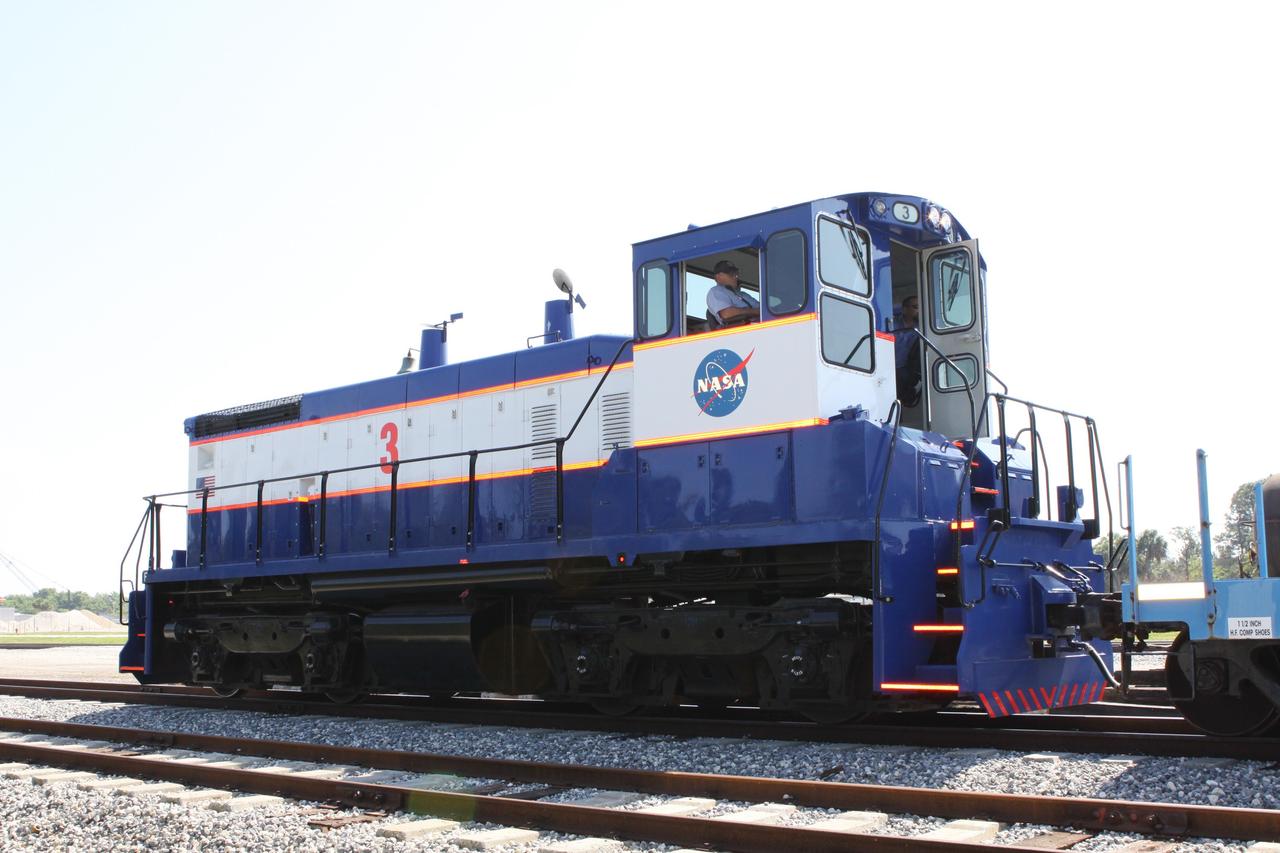

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Railroad locomotive No. 3 is enlisted to deliver tank cars from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the Florida East Coast Railway interchange in Titusville, Fla. The locomotive is one of three NASA Railroad locomotives built for the Toledo, Peoria and Western, or TP&W, between 1968 and 1970. It is a GM Electromotive Division SW-1500 switcher. The locomotive was acquired by NASA from the TP&W in 1984 and painted in the NASA Railroad paint scheme. The power plant was completely overhauled in 2009. The locomotive will pull the train to the interchange in Titusville, where the train’s helium tank cars, a liquid oxygen tank car, and a liquid hydrogen dewar or tank car will be transferred for delivery to the SpaceX engine test complex outside McGregor, Texas. The railroad cars were needed in support of the Space Shuttle Program but currently are not in use by NASA following the completion of the program in 2011. Originally, the tankers belonged to the U.S. Bureau of Mines. At the peak of the shuttle program, there were approximately 30 cars in the fleet. About half the cars were returned to the bureau as launch activity diminished. Five tank cars are being loaned to SpaceX and repurposed to support their engine tests in Texas. Eight cars previously were shipped to California on loan to support the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches from Space Launch Complex-4 on Vandenberg Air Force Base. SpaceX already has three helium tank cars previously used for the shuttle program at Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/spacex. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
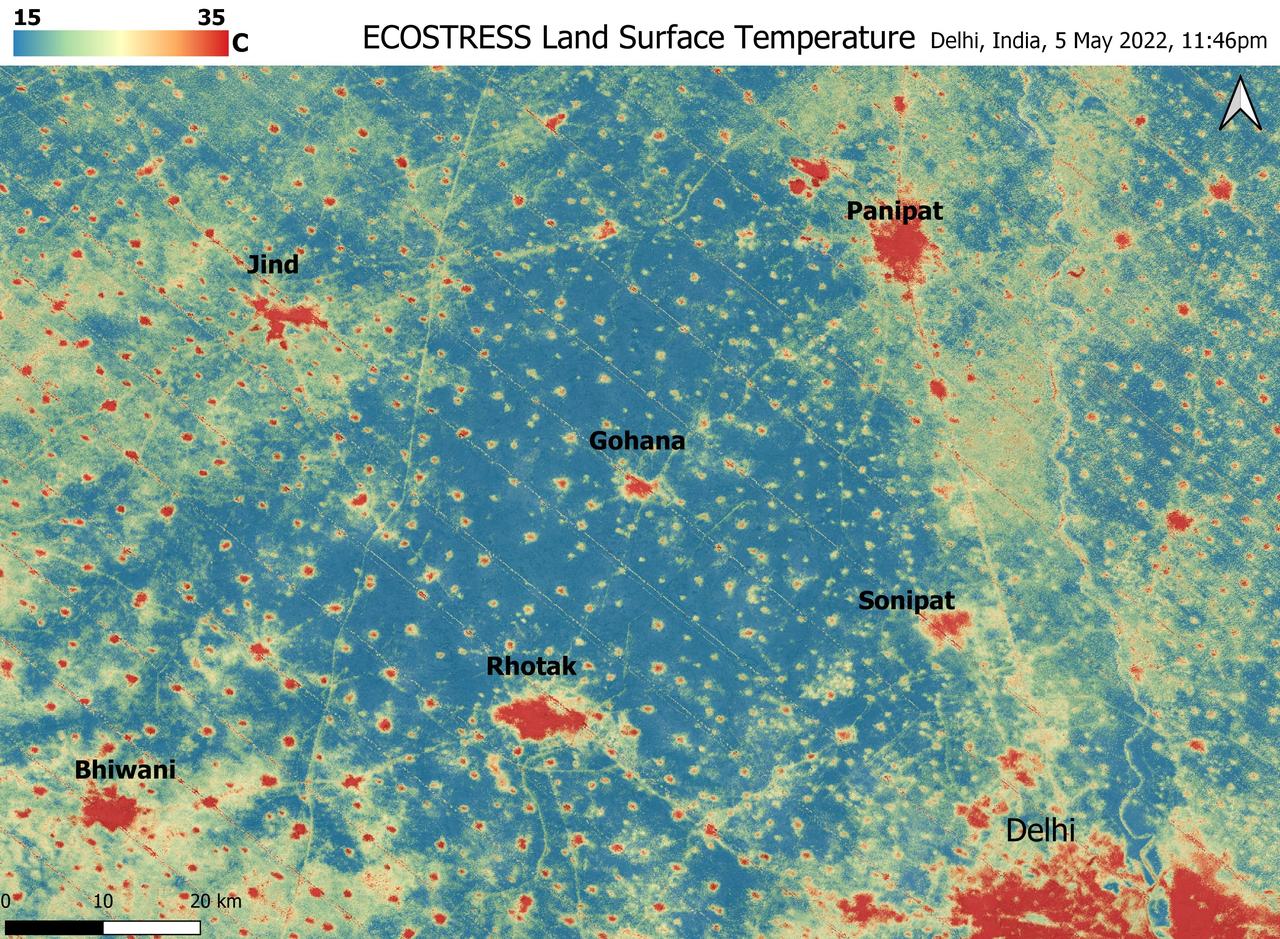
A relentless heat wave has blanketed India and Pakistan since mid-March 2022, causing dozens of deaths, fires, increased air pollution, and reduced crop yields. NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station instrument (ECOSTRESS) has been measuring these temperatures from space, at the highest spatial resolution of any satellite instrument. This image, taken shortly before local midnight on May 5, shows urban areas and agricultural lands northwest of Delhi that are home to about 28 million people. The image covers about 4,800 square miles (12,350 square kilometers). Cities are usually markedly warmer than the surrounding countryside due to human activities and the materials used in the built environment. The image clearly delineates these urban "heat islands." Nighttime temperatures in Delhi and several smaller villages were above 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Celsius), peaking at about 102 degrees F (39 degrees C), while the rural fields nearby had cooled to around 60 degrees F (15 degrees C). This data suggests that city dwellers are experiencing considerably higher temperatures than the average temperatures reported for their regions. ECOSTRESS measures the temperature of the ground itself, which is very similar to air temperature at night (though the ground may be warmer than the air in daylight hours). The instrument launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify plants' thresholds for water use and water stress, giving insight into their ability to adapt to a warming climate. However, ECOSTRESS also records other heat-related phenomena like this heat wave. Its high-resolution images, with a pixel size of about 225 feet (70 meters) by 125 feet (38 meters), are a powerful tool for understanding aspects of the weather event that might be overlooked by traditional observation networks. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24987
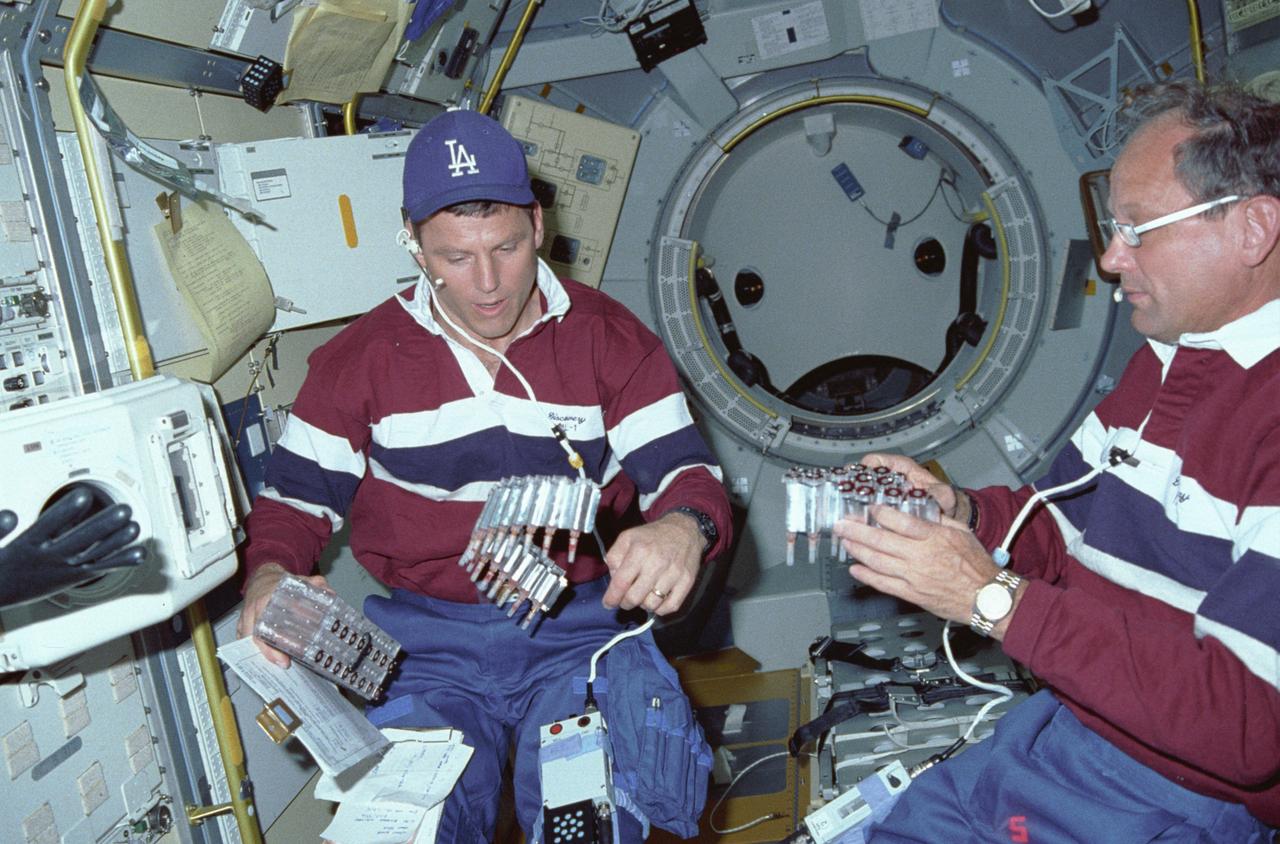

International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Dedicated to the study of life and materials sciences in microgravity, the IML missions explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. In this photograph, Astronauts Stephen S. Oswald and Norman E. Thagard handle ampoules used in the Mercuric Iodide Crystal Growth (MICG) experiment. Mercury Iodide crystals have practical uses as sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray detectors. In addition to their exceptional electronic properties, these crystals can operate at room temperature rather than at the extremely low temperatures usually required by other materials. Because a bulky cooling system is urnecessary, these crystals could be useful in portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications in diagnosis and therapy, and astronomical observation. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).
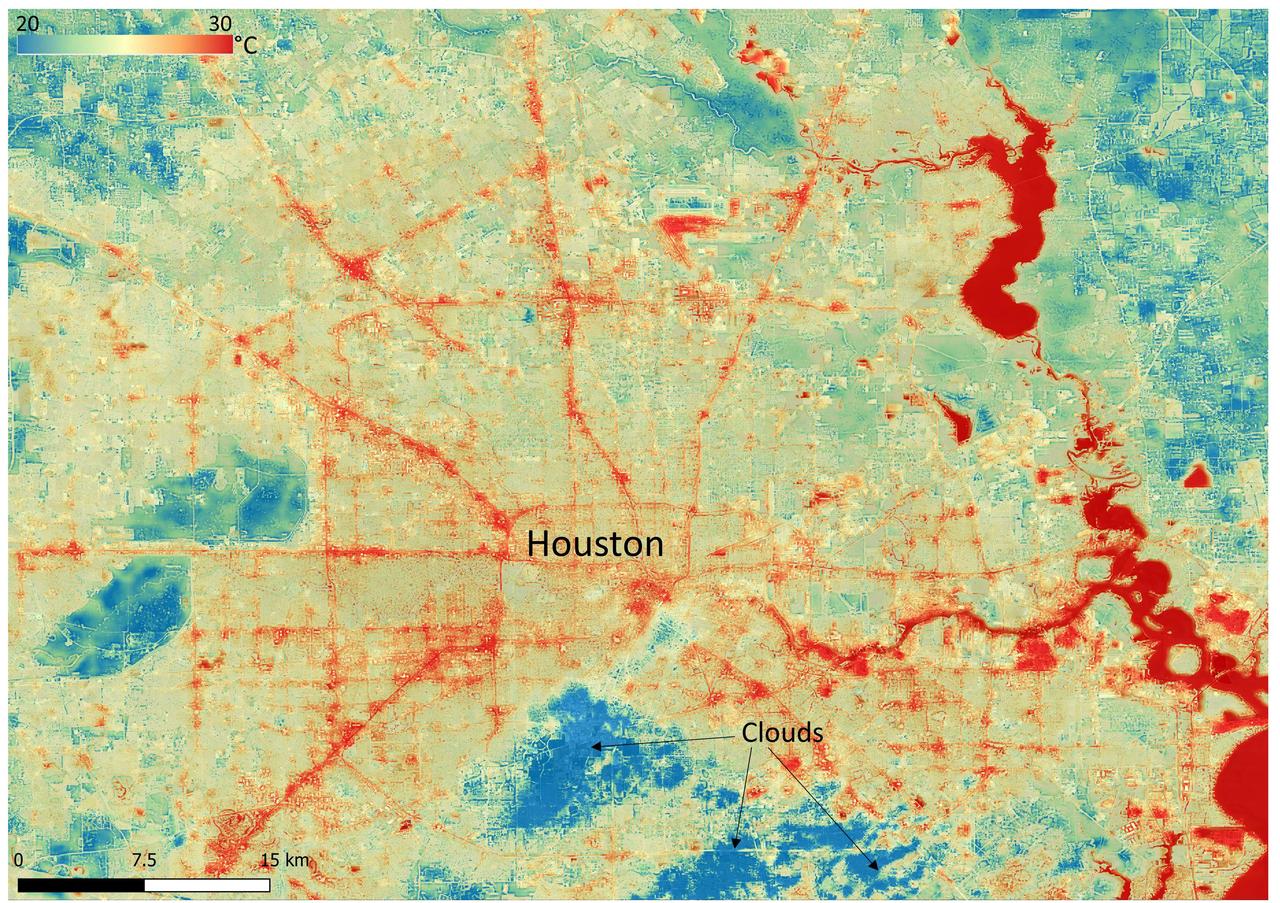
NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS) instrument recorded this image of ground surface temperatures in Houston and its environs on June 20, 2022, at 6:29 a.m. Central Daylight Time. Even just after sunrise, manmade urban surfaces near the city center and transportation networks – streets, roads, and highways shown in red and orange – were significantly warmer than the outskirts by up to 18 degrees Fahrenheit (10 degrees Celsius). Clouds, which are cool compared with the ground, are shown in blue and labeled in the image. Cities are usually warmer than open land because of human activities and the materials used in building and construction. Streets are often the hottest part of the built environment due to asphalt paving. Dark-colored surfaces absorb more heat from the Sun than lighter-colored ones; asphalt absorbs up to 95% of solar radiation and retains the heat for hours into the nighttime. ECOSTRESS measures the temperature of the ground, which is hotter than the air temperature during the daytime. The instrument launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify plants' thresholds for water use and water stress, giving insight into their ability to adapt to a warming climate. However, ECOSTRESS is also useful for documenting other heat-related phenomena, like patterns of heat absorption and retention. Its high-resolution images, with a pixel size of about 225 feet (70 meters) by 125 feet (38 meters), are a powerful tool for understanding our environment. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25421
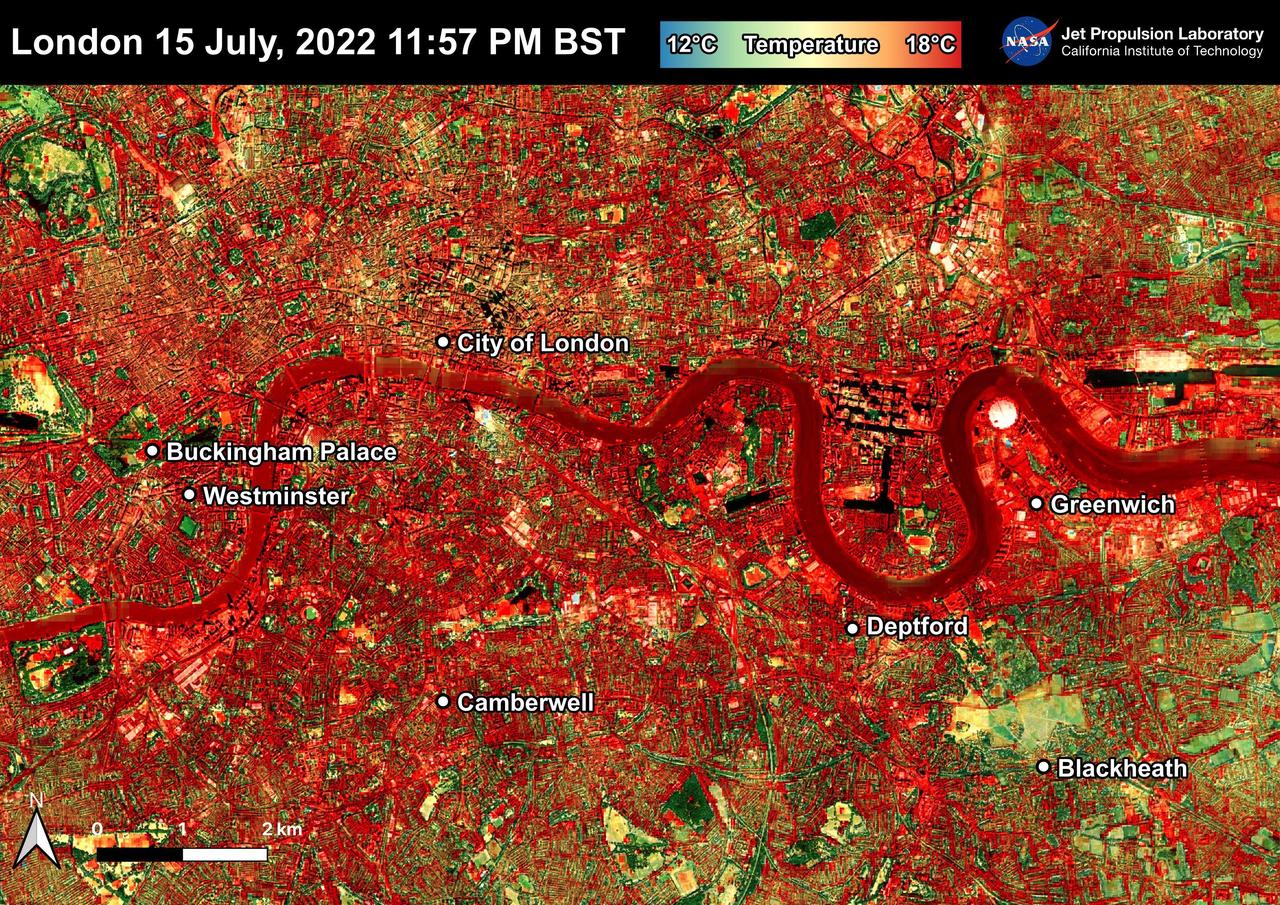
NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS) instrument recorded this image of ground surface temperatures in London and surrounding areas on July 15, 2022, just before midnight local time. It shows surface temperatures exceeding 68 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) at 11:57 p.m. British Summer Time. Parts of Europe in mid-July experienced a record-breaking heat wave. The United Kingdom reaching its highest air temperature on record on July 19, 104.5 F (40.3 C) in Coningsby, about 110 miles (177 kilometers) north of London, which itself saw a high of 104.3 F (40.2 C) the same day. That evening, the overnight low was also a record-breaker: 78.4 F (25.8 C) at Kenley Airfield in Greater London. In this image, the red areas indicate hotter temperatures commonly associated with developed areas. These surfaces – roofs, paved streets, and other built structures – remain warm long after the sun sets. Blue and green areas indicate cooler areas commonly associated with parks and other natural land surfaces. Because this image was acquired at night, it shows bodies of water being warmer than the land surface. This is because water tends to change temperature more slowly, so its temperature stays elevated long after land surfaces have cooled down. Cities are usually warmer than open land with natural surfaces because of human activities as well as the materials used in building and construction. Streets are often the hottest part of the built environment due to asphalt paving. Dark-colored surfaces absorb more heat from the Sun than lighter-colored ones; asphalt absorbs up to 95% of solar radiation and retains the heat for hours into nighttime. This image overlays ECOSTRESS surface temperature data on a Google satellite map for context. ECOSTRESS measures the temperature of the ground, which is hotter than the air temperature during the daytime. The instrument launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify plants' thresholds for water use and water stress, giving insight into their ability to adapt to a warming climate. However, ECOSTRESS is also useful for documenting other heat-related phenomena, like patterns of heat absorption and retention. Its high-resolution images, with a pixel size of about 225 feet (70 meters) by 125 feet (38 meters), are a powerful tool for understanding our environment. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25423
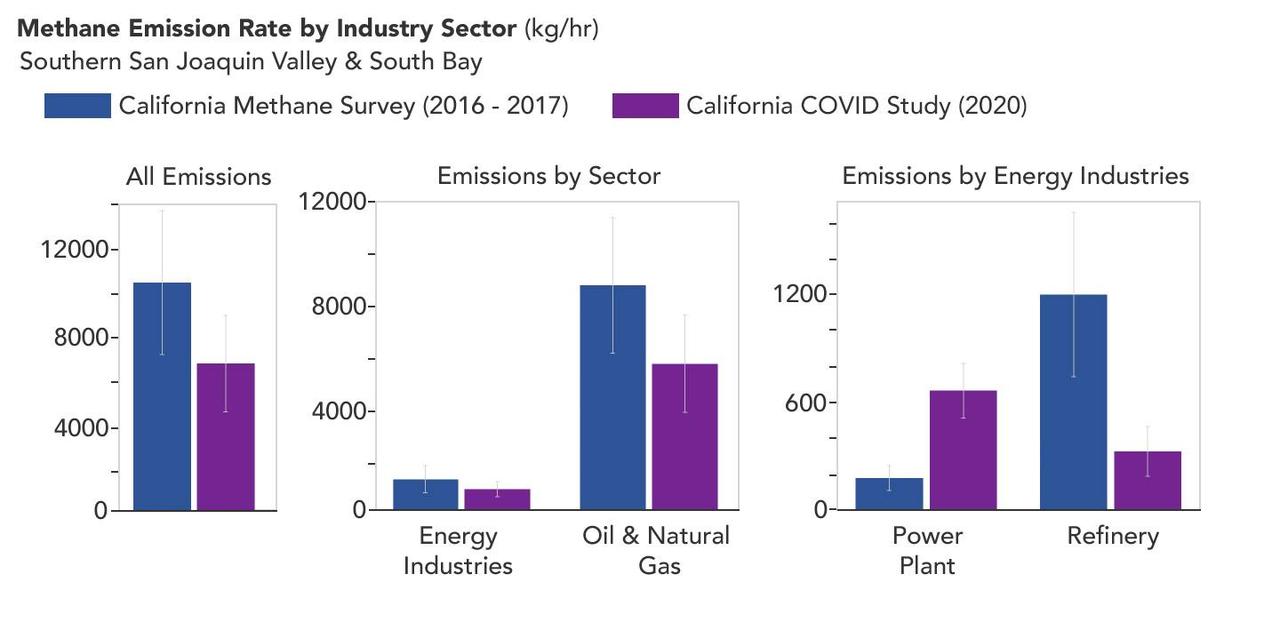
A March 2023 study by researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California compared emissions from a belt of oil refineries across the South Bay area of Los Angeles during the first summer of the COVID-19 pandemic to those observed three years earlier. Using data from a NASA airborne instrument, researchers saw that most of the facilities they identified as methane sources in 2016-17 were no longer emitting the greenhouse gas in 2020, leading to a 73% reduction in measured emissions. The study uses measurements made by an imaging spectrometer called AVIRIS-NG (Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer-Next Generation). Attached to the bottom of an aircraft, the instrument can detect greenhouse gas emissions from individual facilities or even pieces of equipment by looking at how the gases absorb sunlight. In 2016 and 2017, AVIRIS-NG was flown over 22,000 square miles (57,000 square kilometers) of the state as part of the California Methane Survey. From July to September 2020, researchers retraced some of those flight paths over refineries and power plants in Los Angeles County and over oil fields in central California's San Joaquin Valley. The flights were funded by NASA's Earth Science Division, the California Air Resources Board, and the California Energy Commission. The 2020 surveys over Los Angeles identified only 11 plumes from five refinery sources, with a total emissions rate of about 712 pounds (323 kilograms) methane per hour. The 2016 and 2017 flights had found 48 plumes from 33 sources, with a total emissions rate of roughly 2,639 pounds (1,197 kilograms) methane per hour. The drop correlates with an 18% decrease in monthly production in Southern California refineries between the two flight campaigns, the scientists noted, citing data from the California Energy Commission. The study also found that emissions from oil fields in and around the city of Bakersfield in central California fell 34.2%, correlating with a 24.2% drop in oil production. Reduced production during the pandemic due to lower demand for fuel and lower gas prices could have led to the drop in methane emissions, as oil fields and refineries emitted less methane as part of operations. However, researchers said, improved equipment maintenance and mitigation efforts at those facilities between 2016 and 2020 can't be ruled out as a factor. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25864
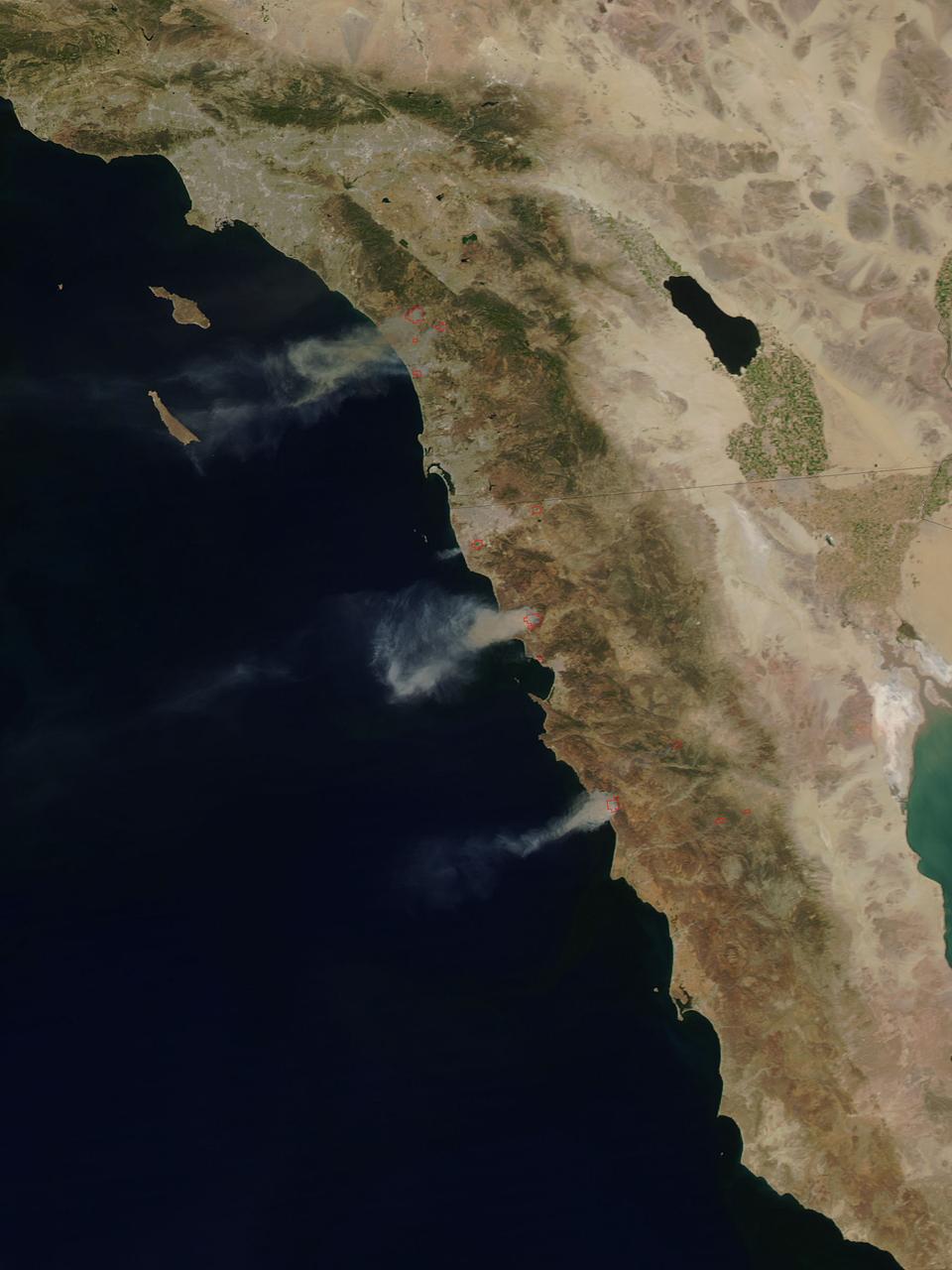

The single fire that ignited and split into nine separate fires still blazes in Southern California today. Firefighters are hoping for a break today (Thursday, May 15, 2014) but it doesn't look like luck may be on their side. Conditions continue to be bone dry with unseasonal heat (98-106 degrees) and the Santa Ana winds are kicking up and allowing these fires to easy jump fire lines. This particular fire started on Wednesday as a single fire and within a day is now nine separate fires which have burned close to 10,000 acres. These fires are threatening more than just landscape in San Diego county, they are also threatening homes, universities, a military base and a nuclear power plant. Day Two of the fires have seen them already destroying dozens of homes and forcing tens of thousands to evacuate. Camp Pendleton has also been partially evacuated due to the blazes as has the popular amusement park, Legoland. The Governor of California has declared a state of emergency. Thousands of firefighters are battling the flames both on the ground and in the air. Seven tankers and 20 military aircraft are also assisting the firefighters with their mission. Temperatures soaring over 100 degrees coupled with 30 mph wind gusts have severely hampered the efforts, however, and fire tornadoes have broken out. Fire tornadoes are caused by crosswinds that create a vortex and produce winds that twist and swirl just like a tornado but with flames that coil upwards in the center of the twister creating a terrifying specter. Although there is no chance of rain in the area for the next several days, the temperatures will start to subside on Friday and into the weekend. Winds are also expected to start to subside, giving firefighters that break that they so desperately need. This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite on May 14, 2014. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS’s thermal bands, are outlined in red. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
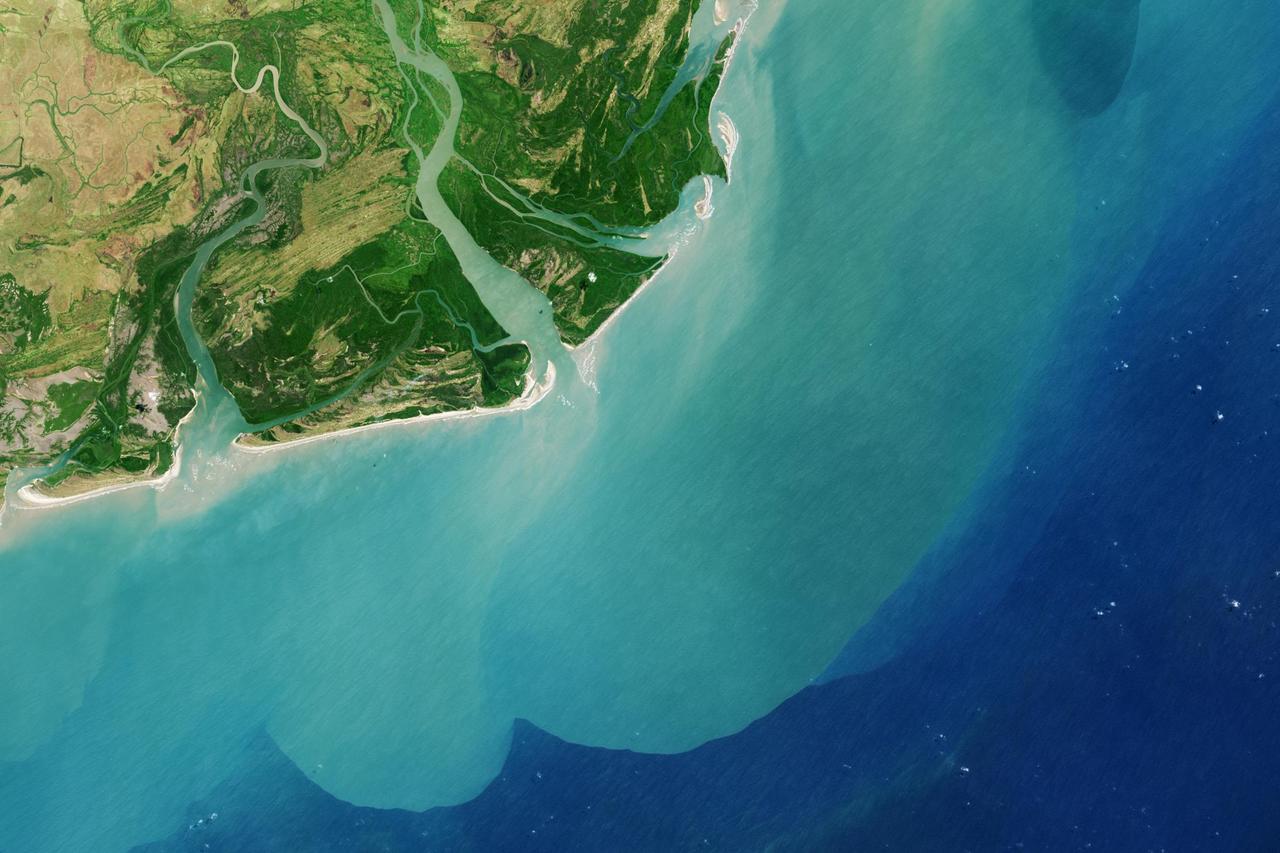

It drains a watershed that spans eight countries and nearly 1.6 million square kilometers 600,000 square miles. The Zambezi also Zambeze is the fourth largest river in Africa, and the largest east-flowing waterway. The Operational Land Imager on the Landsat 8 satellite acquired this natural-color image of the Zambezi Delta on August 29, 2013. Sandbars and barrier spits stretch across the mouths of the delta, and suspended sediment extends tens of kilometers out into the sea. The sandy outflow turns the coastal waters to a milky blue-green compared to the deep blue of open water in the Indian Ocean. The Zambezi Delta includes 230 kilometers of coastline fronting 18,000 square kilometers (7,00 square miles) of swamps, floodplains, and even savannahs (inland). The area has long been prized by subsistence fishermen and farmers, who find fertile ground for crops like sugar and fertile waters for prawns and fish. Two species of endangered cranes and one of the largest concentration of buffalo in Africa -- among many other species of wildlife -- have found a haven in this internationally recognized wetland. However, the past six decades have brought great changes to the Zambezi Delta, which used to pour more water and sediment off of the continent. Hydropower dams upstream-most prominently, the Kariba and the Cahora Bassa-greatly reduce river flows during the wet season; they also trap sediments that would otherwise flow downstream. The result has been less water reaching the delta and the floodplains, which rely on pulses of nutrients and sediments from annual (and mostly benign) natural flooding. The change in the flow of the river affects freshwater availability and quality in the delta. Strong flows push fresh water further out into the sea and naturally keep most of a delta full of fresh (or mostly fresh) water. When that fresh flow eases, the wetlands become drier and more prone to fire. Salt water from the Indian Ocean also can penetrate further into the marsh, upsetting the ecological balance for aquatic plant and animal species. Researchers have found that the freshwater table in the delta has dropped as much as five meters in the 50 years since dams were placed on the river. Less river flow also affects the shape and extent of the delta. Today there is less sediment replenishing the marshes and beaches as they are scoured by ocean waves and tides. "What strikes me in this image is the suspended sediment offshore," said Liviu Giosan, a delta geologist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. "Sediment appears to be transferred from the delta offshore in plumes that not only originate in active river mouths but also from deactivated former mouths, now tidal channels. This shows the power of tidal scouring contributing to the slow but relentless erosion of the delta." http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18155