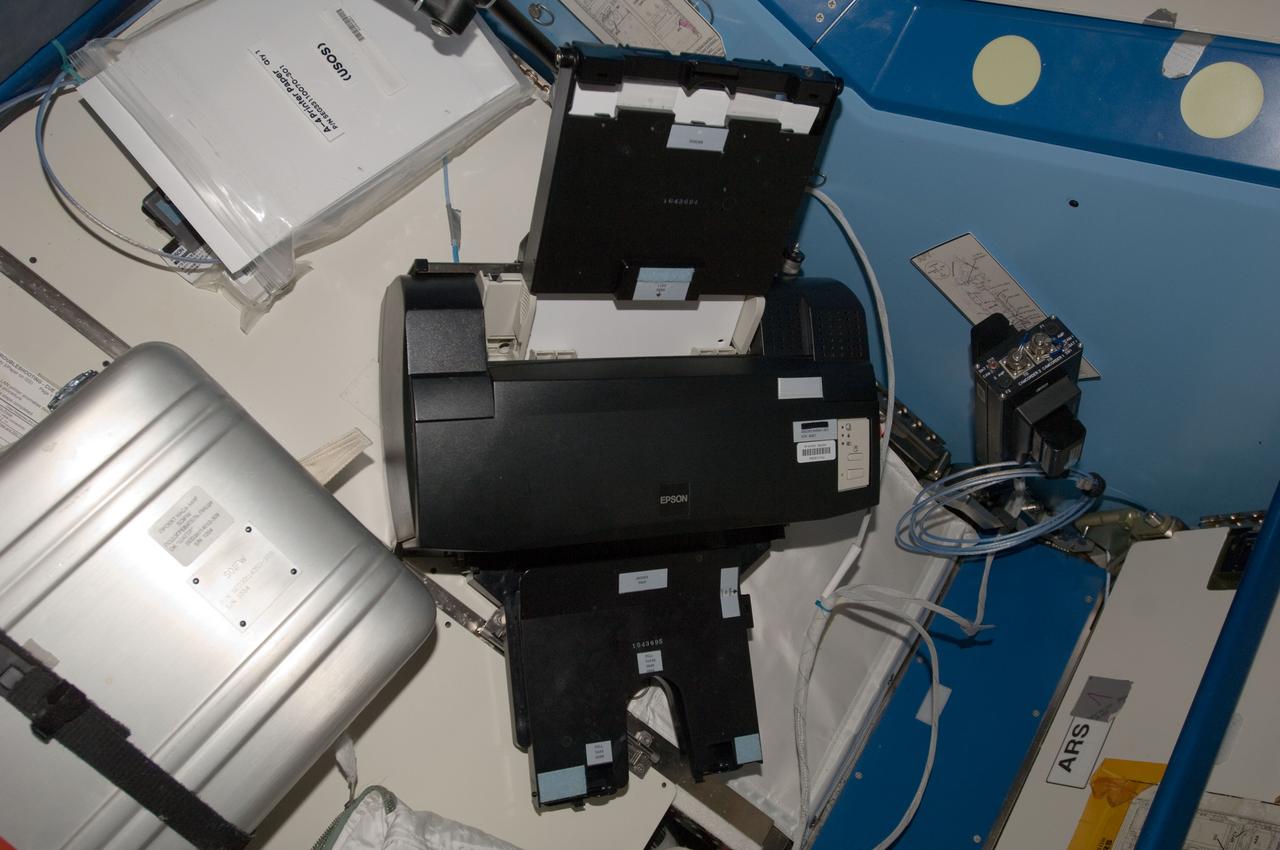

View of Epson Printer, Barcode: POC91113J. Photo was taken during Expedition 34.
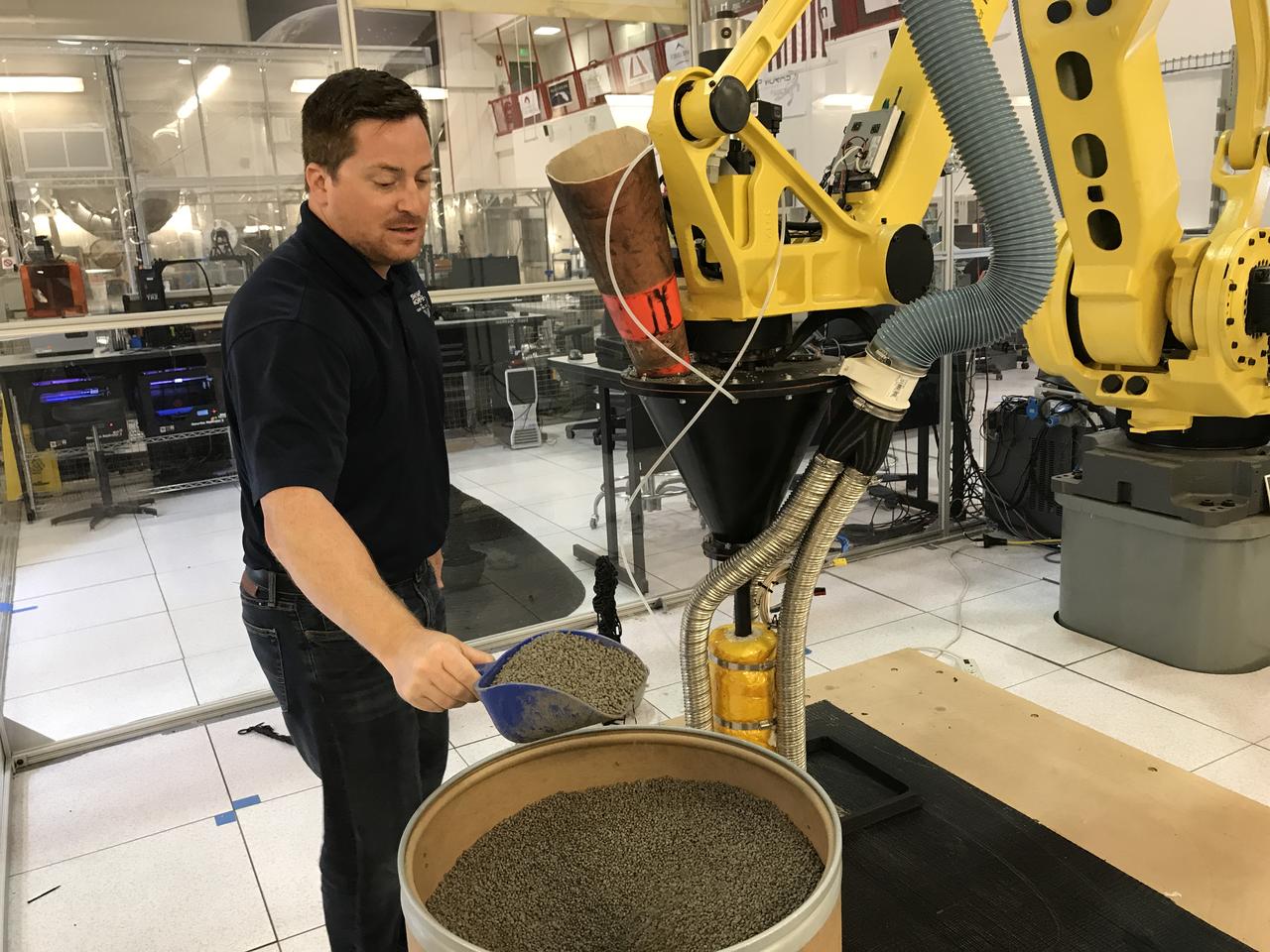

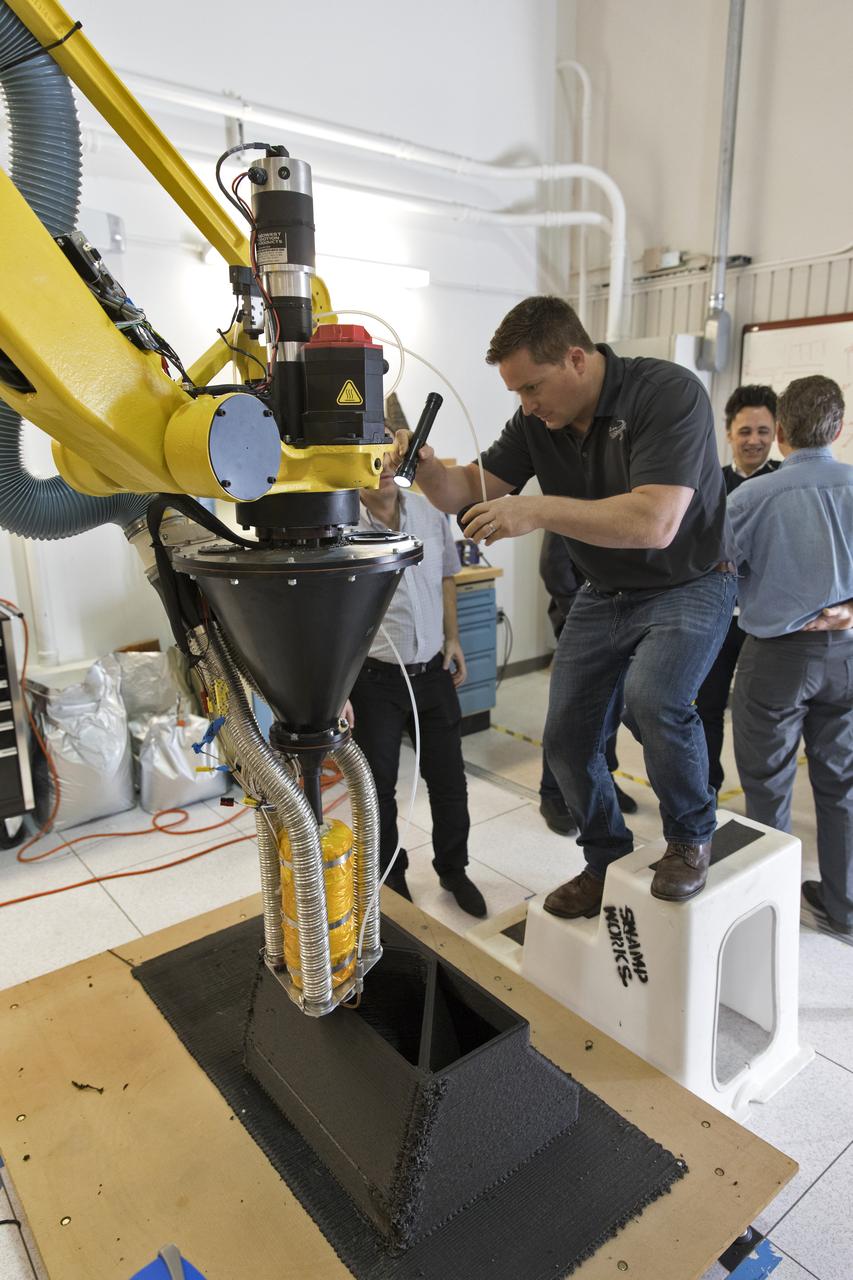
Nathan Gelino, a research engineer, manually loads materials into the Zero Launch Mass 3-D Printer at Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works Tuesday. The 3-D printer heated the pellets to about 600 degrees F and extruded them to produce specimens for material strength properties testing. Automated pellet delivery system will be added to the printer soon.
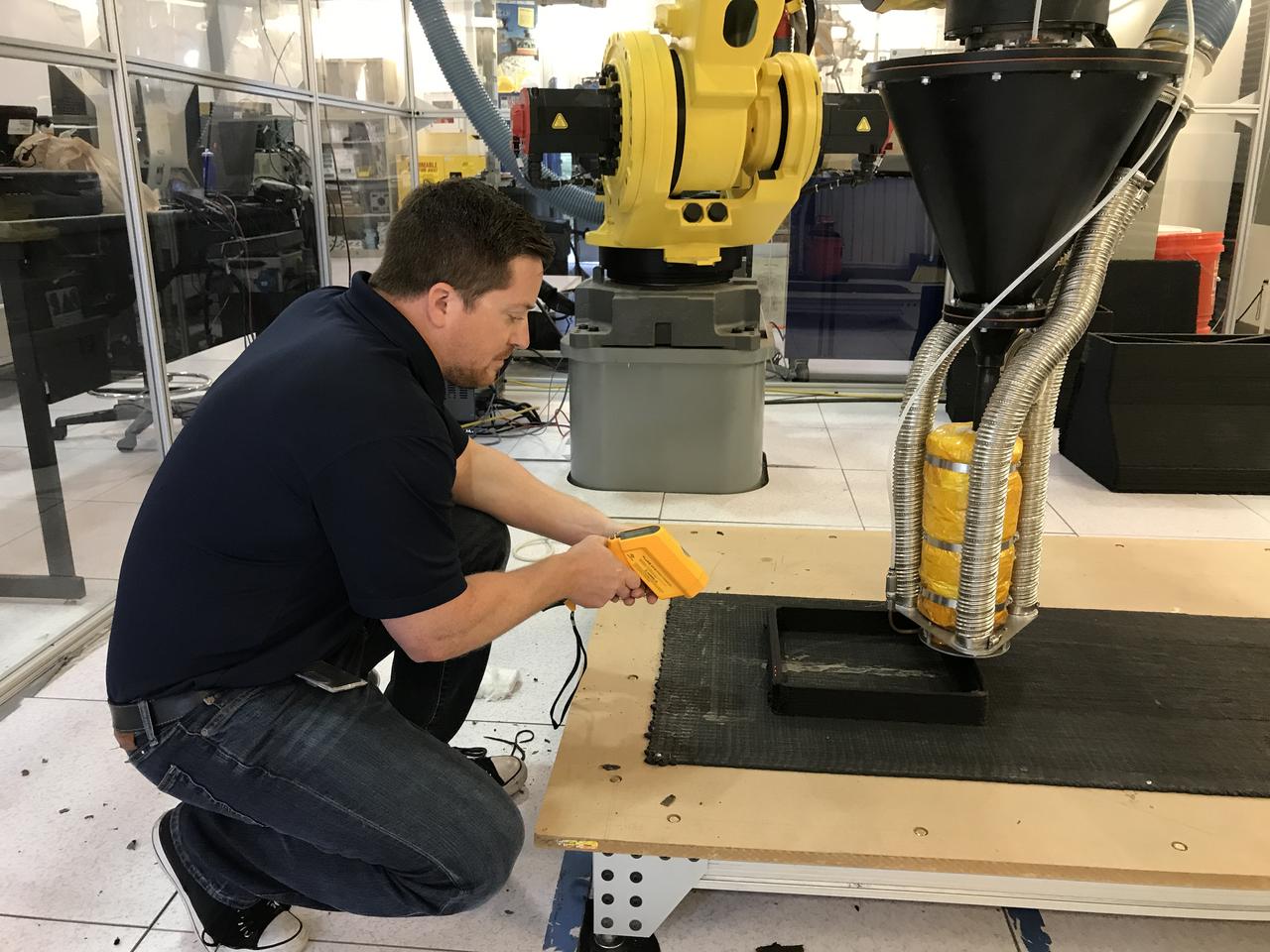

Packing light is the idea behind the Zero Launch Mass 3-D Printer. Instead of loading up on heavy building supplies, a large scale 3-D printer capable of using recycled plastic waste and dirt at the destination as construction material would save mass and money when launching robotic precursor missions to build infrastructure on the Moon or Mars in preparation for human habitation. To make this a reality, Nathan Gelino, a researcher engineer with NASA’s Swamp Works at Kennedy Space Center, measured the temperature of a test specimen from the 3-D printer Tuesday as an early step in characterizing printed material strength properties. Material temperature plays a large role in the strength of bonds between layers.
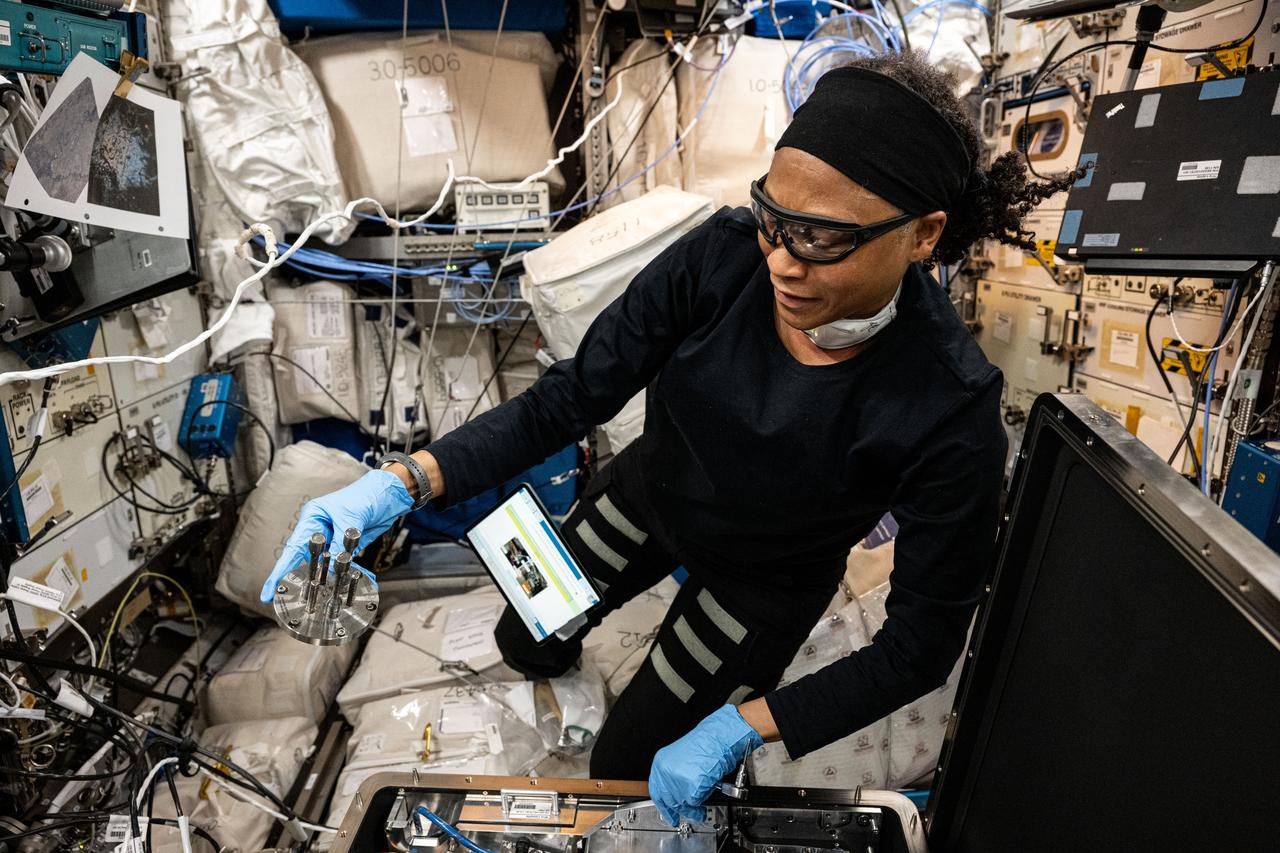

iss071e522127 (Aug. 21, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Jeanette Epps configures the Metal 3D printer that manufactures experimental samples printed with stainless steel aboard the International Space Station's Columbus laboratory module. Researchers are exploring how the Metal 3D printer operates in the microgravity conditions of weightlessness and radiation as well as its ability to manufacture tools and parts on demand during space missions.
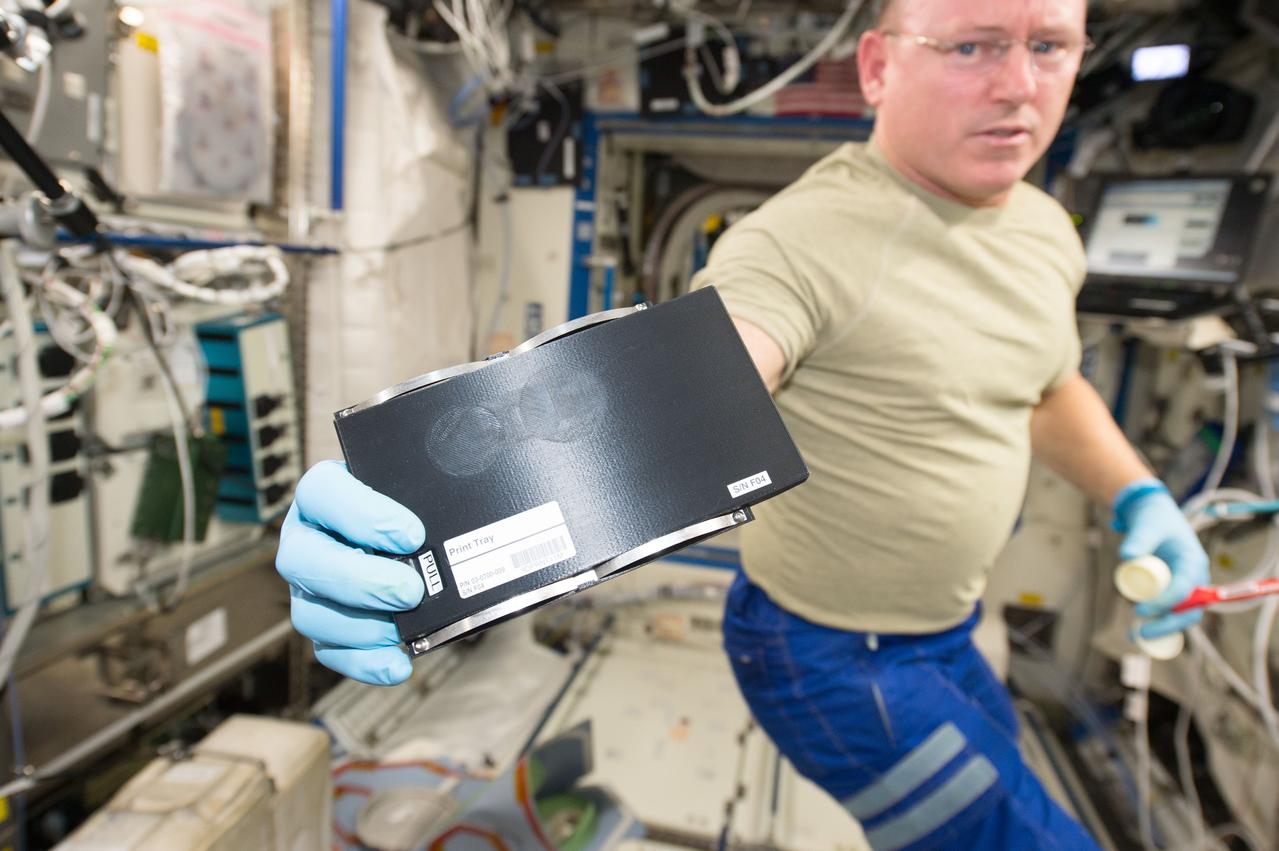

iss042e031282 (12/09/2014) ---US Astronaut Barry (Butch) Wilmore holding a 3D coupon works with the new 3D printer aboard the International Space Station. The 3D Printing experiment in zero gravity demonstrates that a 3D printer works normally in space. In general, a 3D printer extrudes streams of heated plastic, metal or other material, building layer on top of layer to create 3 dimensional objects. Testing a 3D printer using relatively low-temperature plastic feedstock on the International Space Station is the first step towards establishing an on-demand machine shop in space, a critical enabling component for deep-space crewed missions and in-space manufacturing.
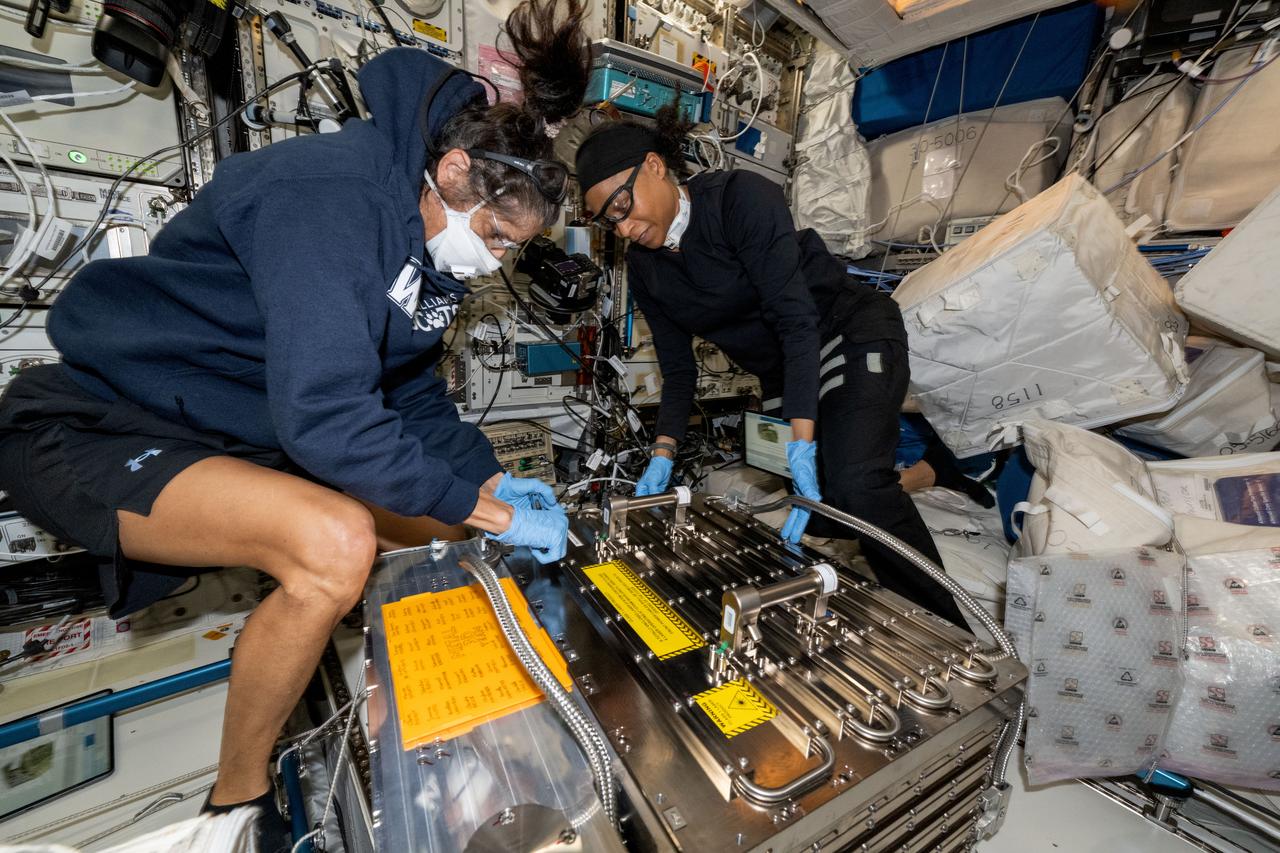

iss071e523326 (Aug. 21, 2024) --- NASA astronauts (from left) Suni Williams, Pilot for Boeing's Crew Flight Test, and Jeanette Epps, Expedition 71 Flight Engineer, configure the Metal 3D printer inside the Columbus laboratory module. They retrieved an experimental sample printed with stainless steel, replaced a substrate in the advanced manufacturing hardware, then reinstalled the 3D printer back in Columbus' European Drawer Rack-2. Researchers are exploring how the Metal 3D printer operates in the microgravity conditions of weightlessness and radiation as well as its ability to manufacture tools and parts on demand during space missions.
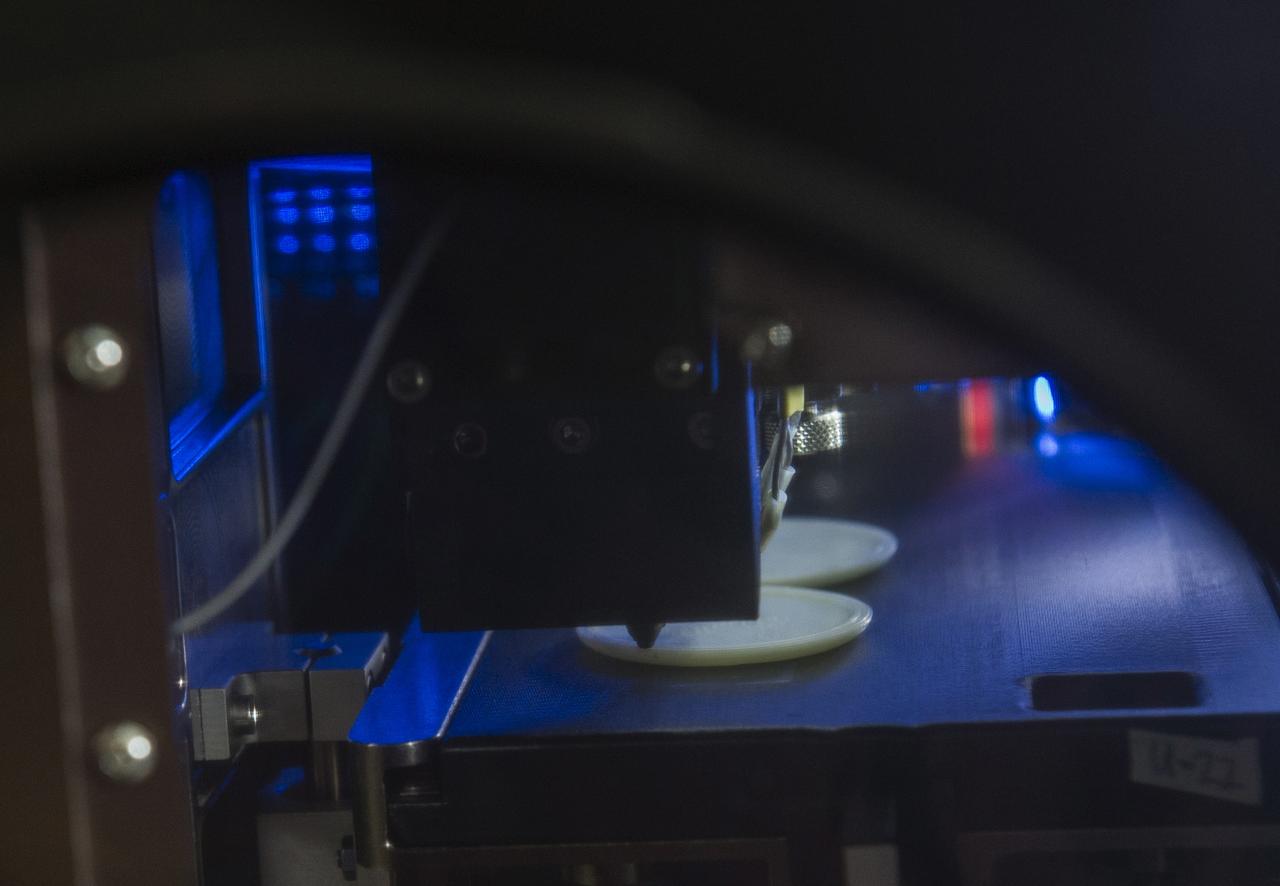
MADE IN SPACE” 3D PRINTER PRINTING TEST SAMPLES WHILE PRINTER IS IN MICROGRAVITY GLOVE BOX
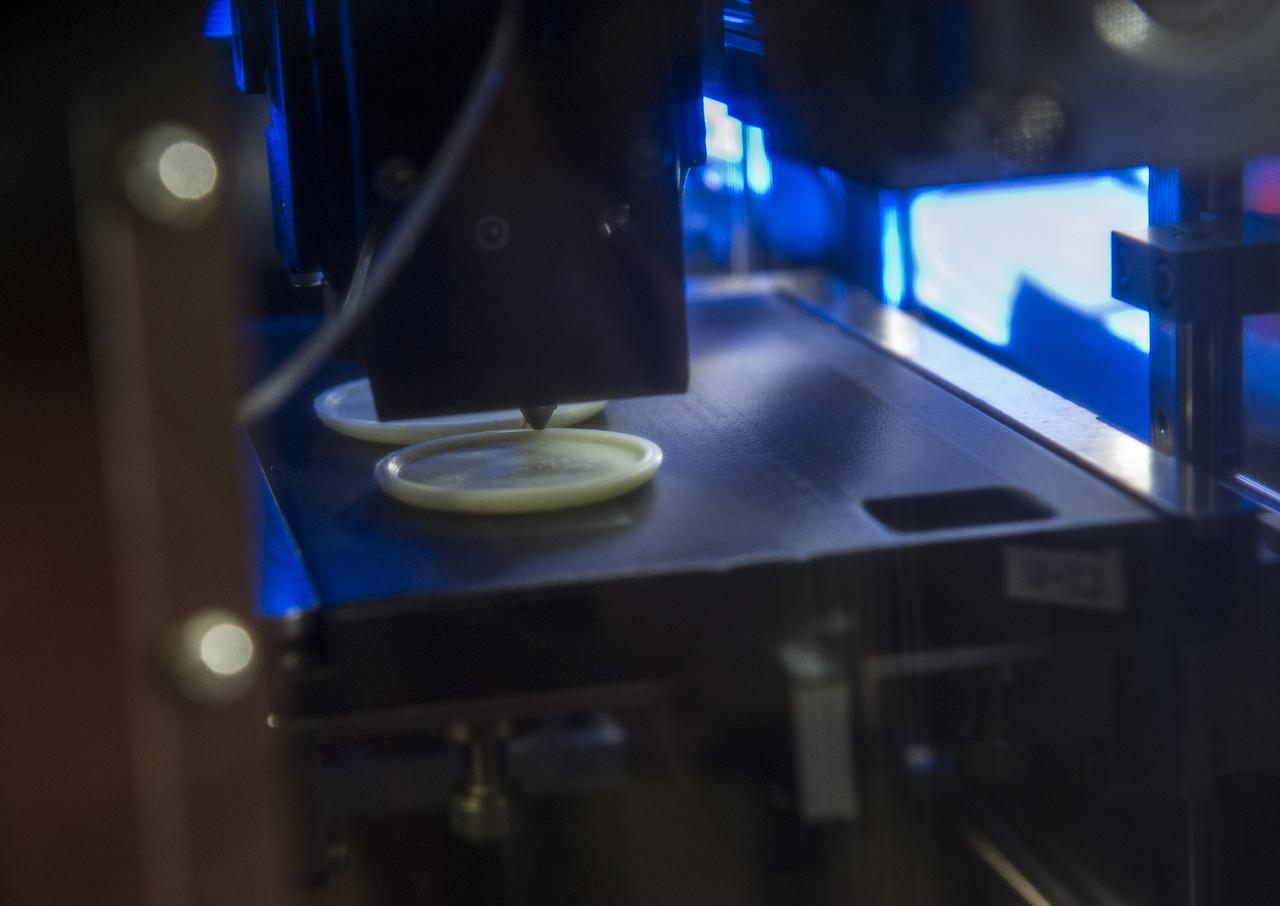
MADE IN SPACE” 3D PRINTER PRINTING TEST SAMPLES WHILE PRINTER IS IN MICROGRAVITY GLOVE BOX
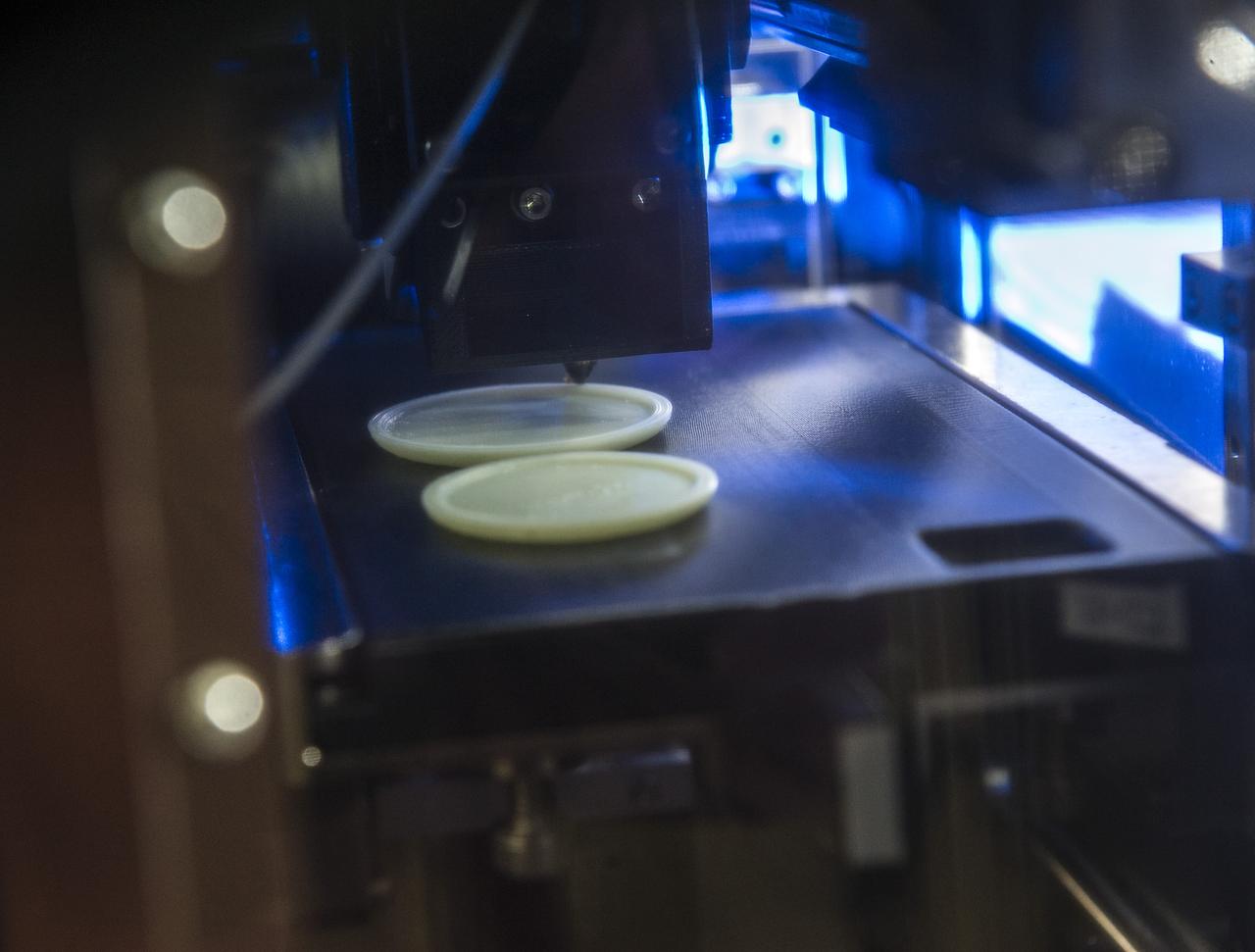
MADE IN SPACE” 3D PRINTER PRINTING TEST SAMPLES WHILE PRINTER IS IN MICROGRAVITY GLOVE BOX
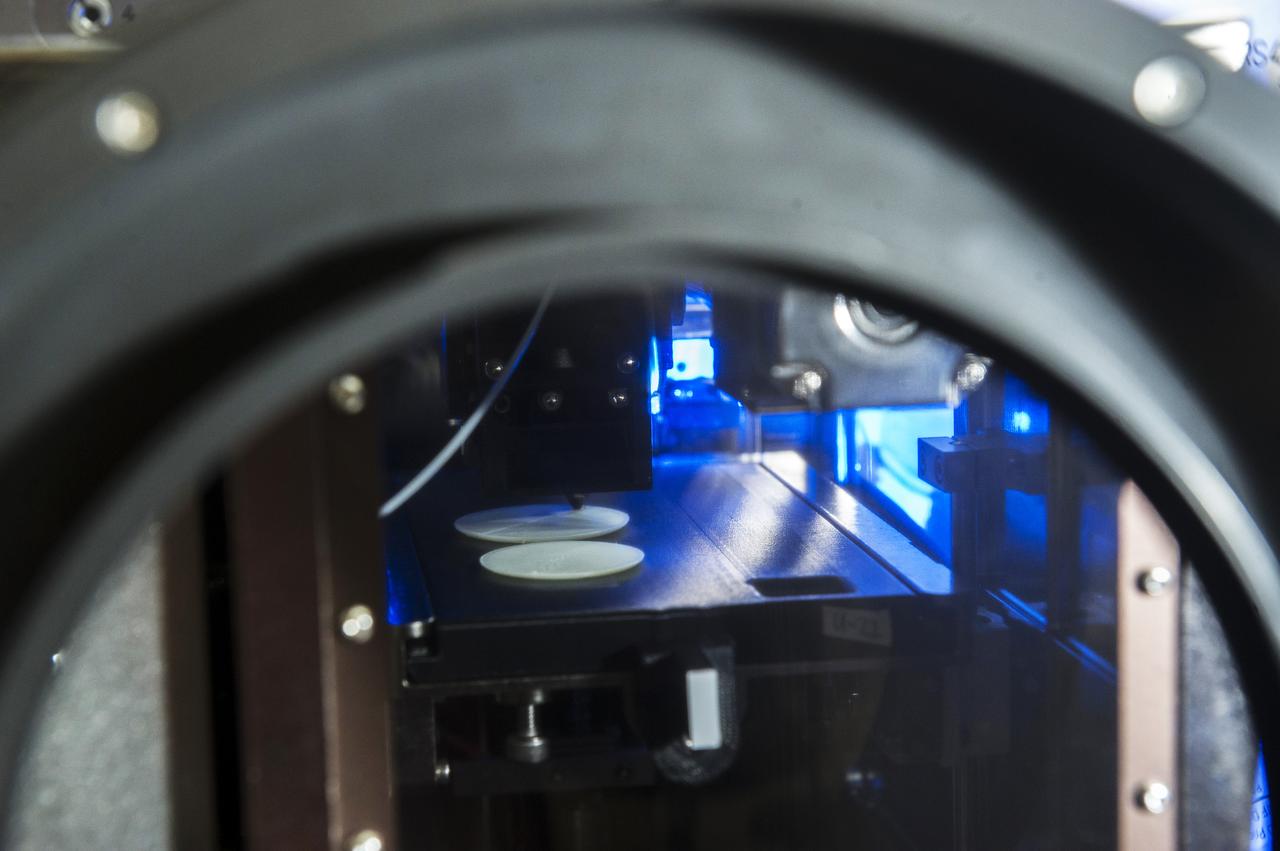
MADE IN SPACE” 3D PRINTER PRINTING TEST SAMPLES WHILE PRINTER IS IN MICROGRAVITY GLOVE BOX
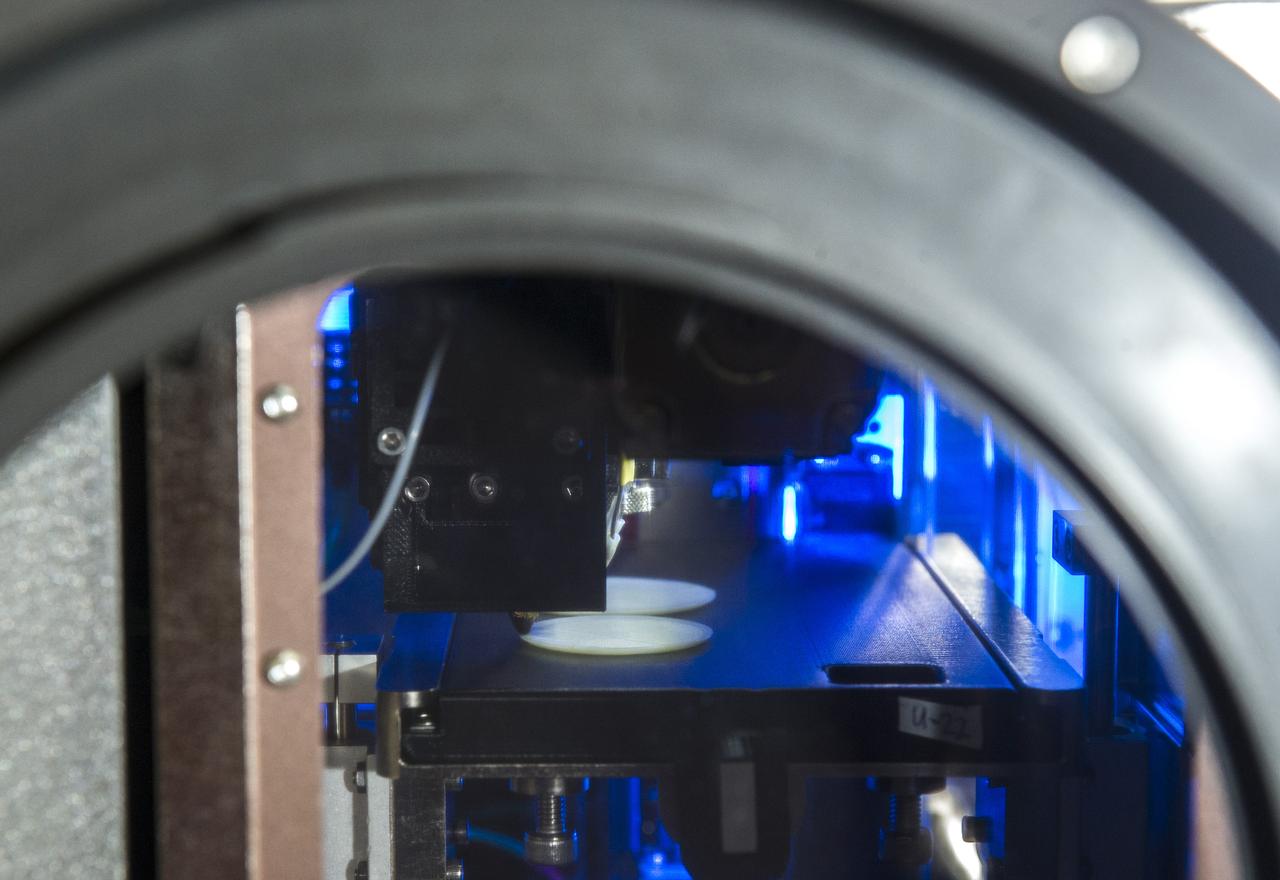
MADE IN SPACE” 3D PRINTER PRINTING TEST SAMPLES WHILE PRINTER IS IN MICROGRAVITY GLOVE BOX
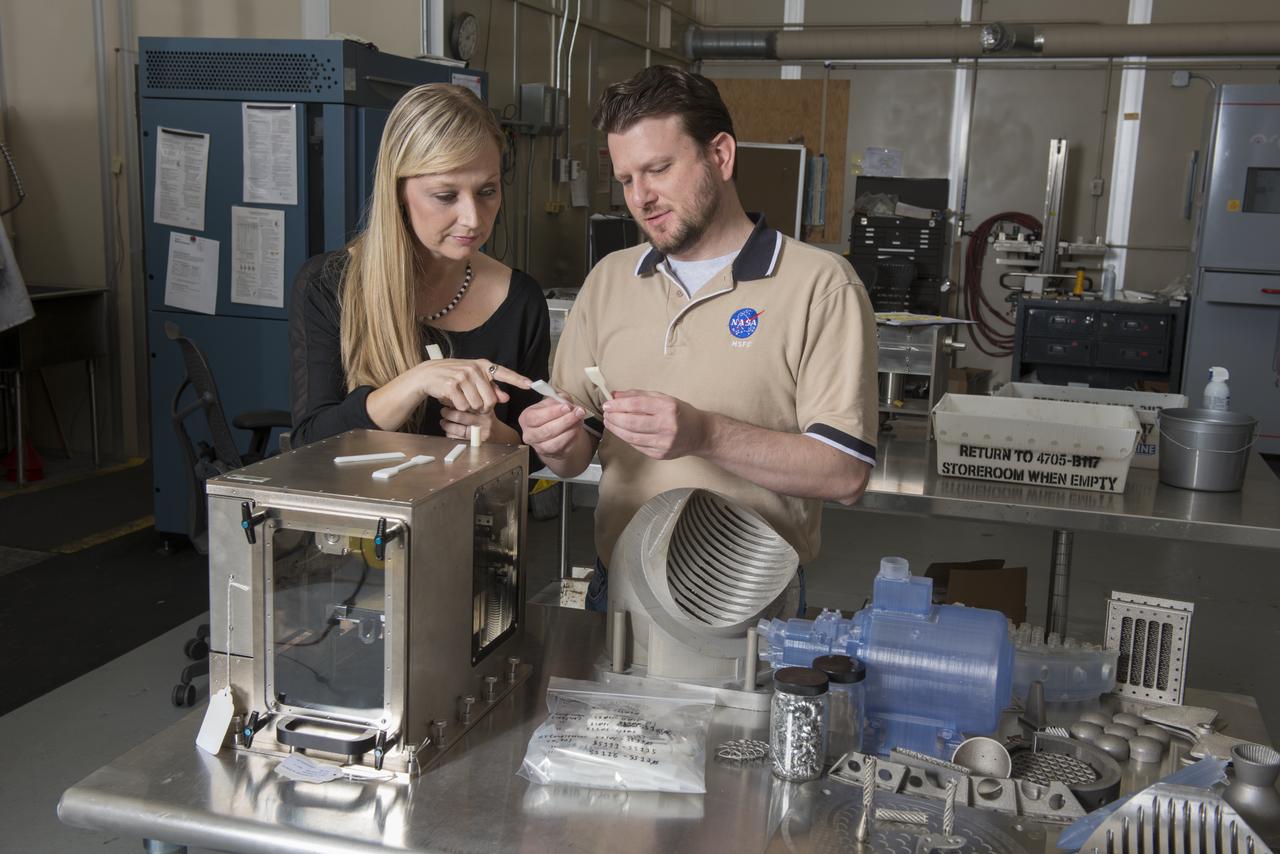

NIKKI WERKHEISER AND QUINCY BEAN, MEMBERS OF THE 3-D PRINTER TEAM EXAMINE PARTS PRODUCED ON A PROTOTYPE OF THE FIRST 3-D PRINTER TO BE SENT TO THE ISS
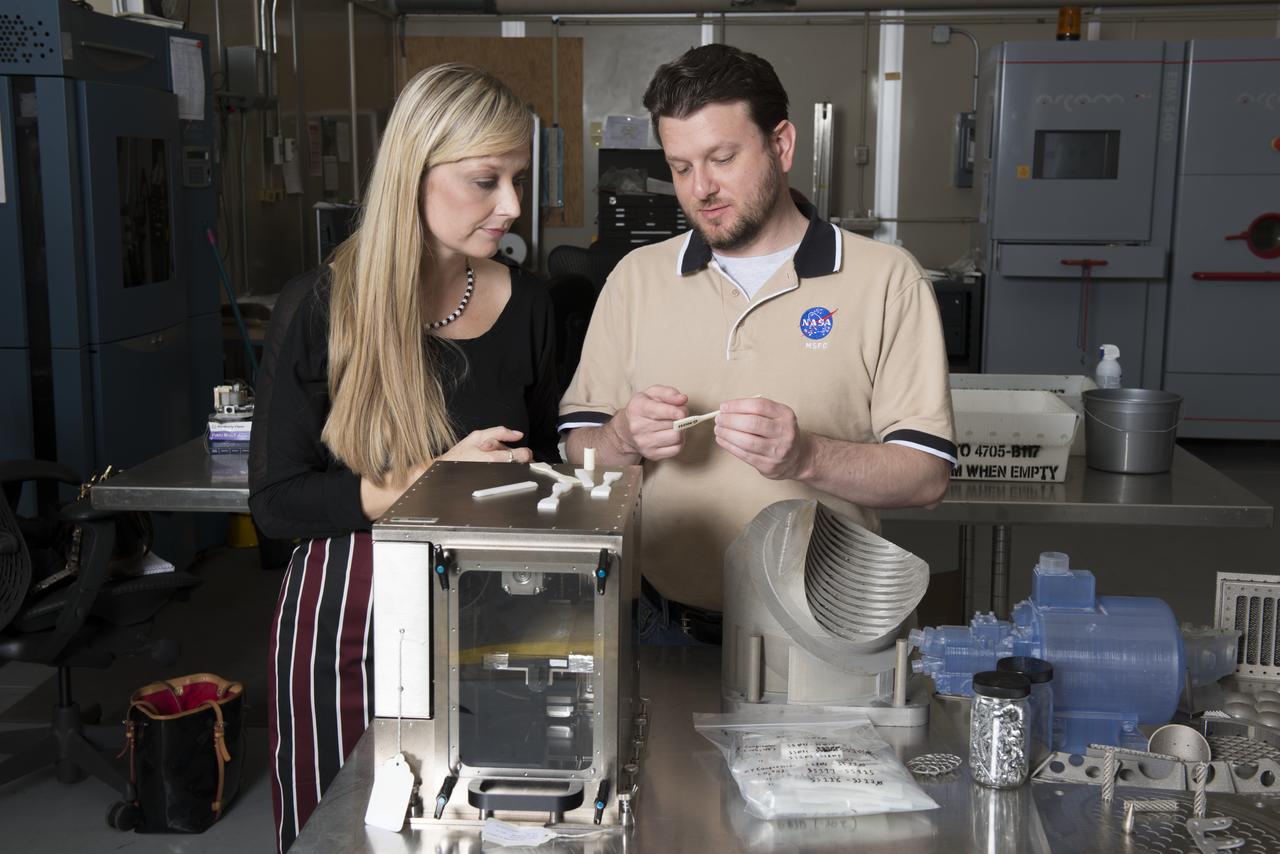

NIKKI WERKHEISER AND QUINCY BEAN, MEMBERS OF THE 3-D PRINTER TEAM EXAMINE PARTS PRODUCED ON A PROTOTYPE OF THE FIRST 3-D PRINTER TO BE SENT TO THE ISS
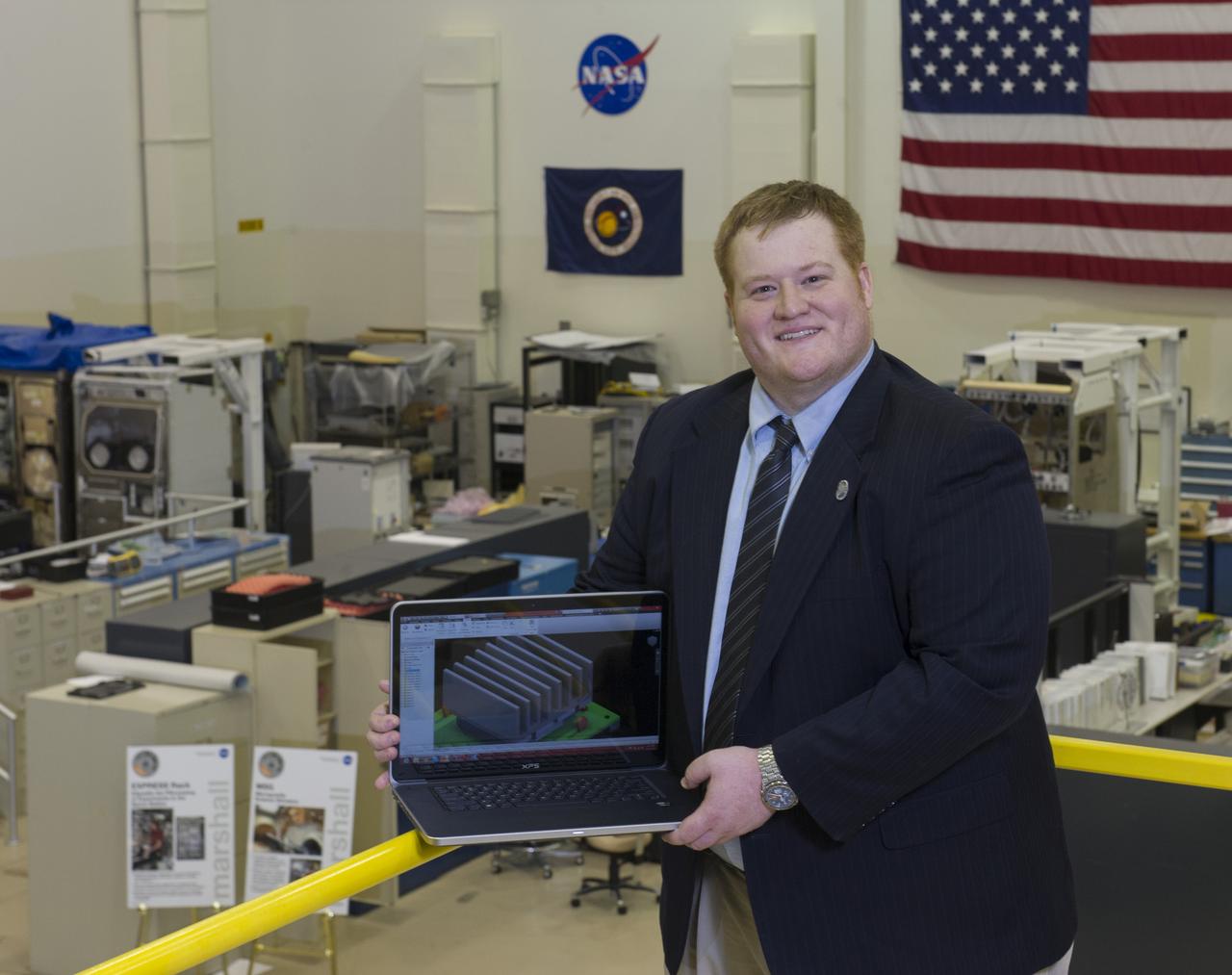

MICHAEL SNYDER, DIRECTOR OF R&D AND LEAD ENGINEER FOR MADE IN SPACE, SHOWS A CAD RENDERING OF A VITAL COMPONENT OF THE 3D PRINTER HEADED FOR THE ISS DURING TESTING AT MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER.-
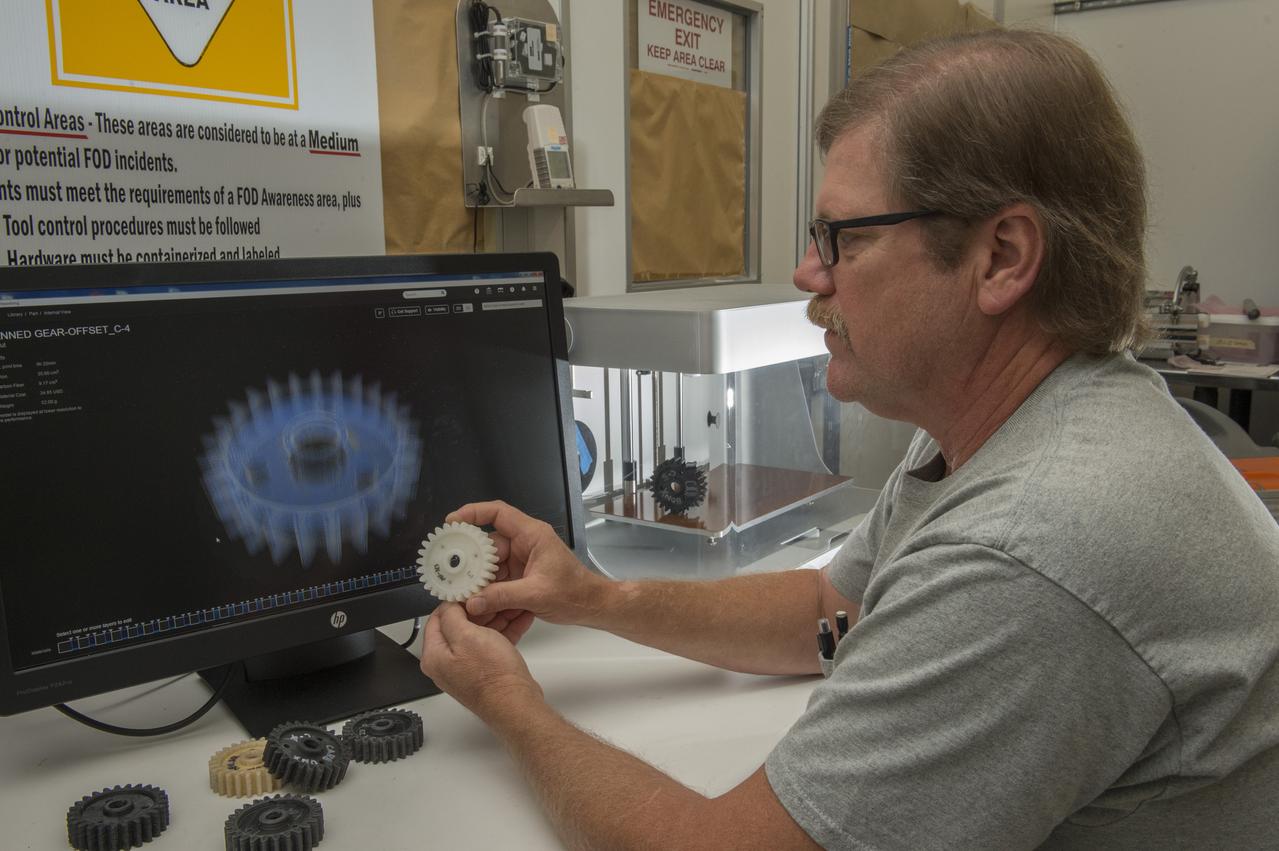

Phillip Steele (EM42/ESSSA) examines composite material gears printed with Marshall’s MarkForged® 3D Printer (background).
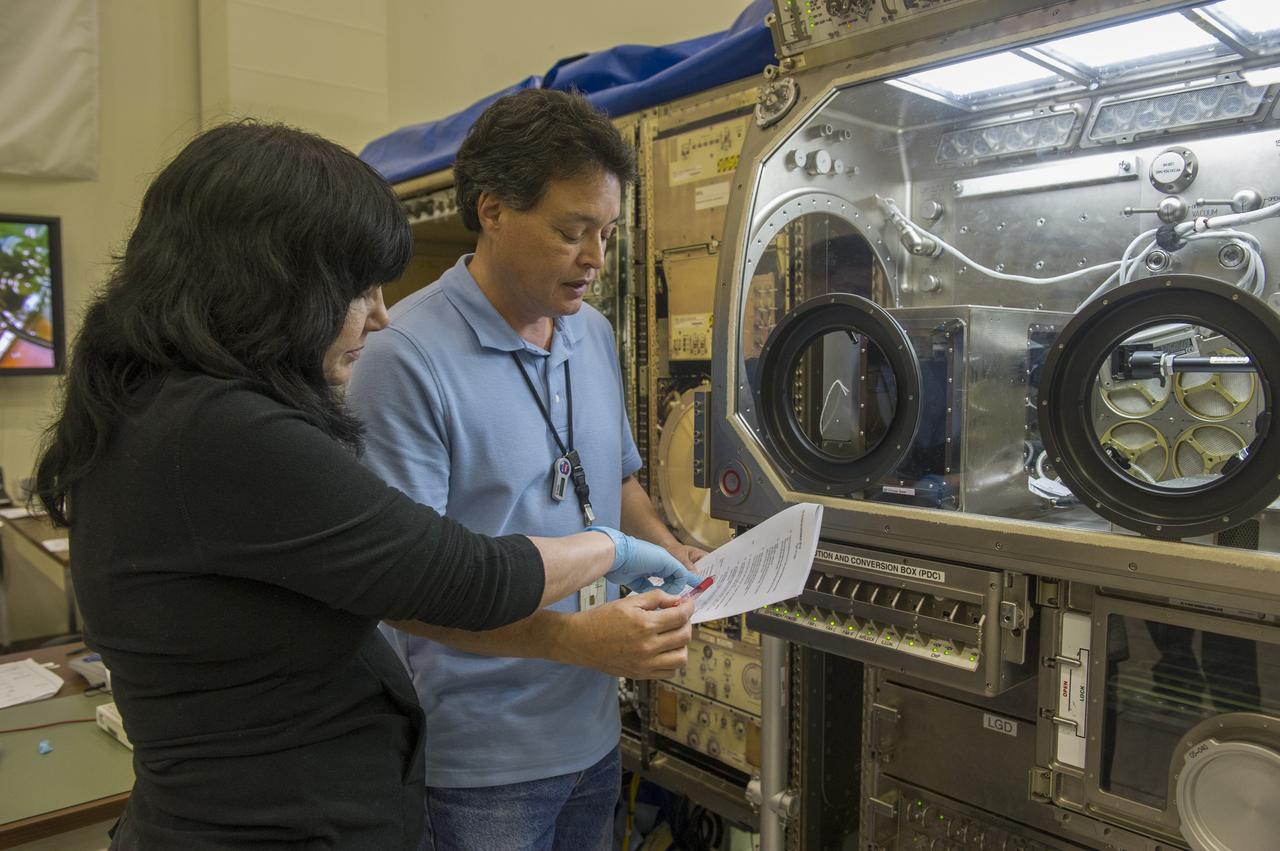

CINDY AZZARITA AND CHARLIE SCOTT, 3D PRINT OPERATIONS LEAD, WRITE THE CREW PROCEDURES FOR ON ORBIT INSTALL AND STOW OF 3D PRINTER
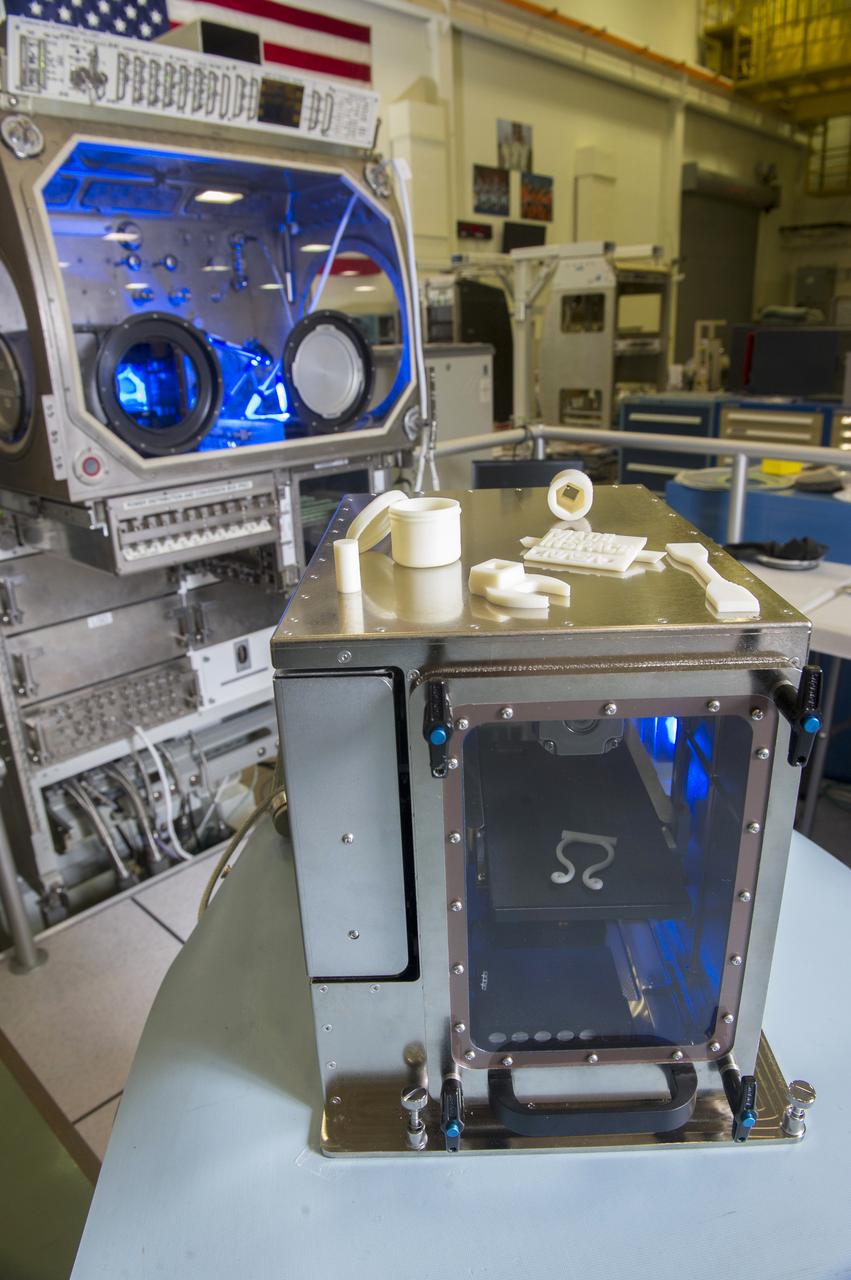

“MADE IS SPACE” 3D PRINTER IN FOREGROUND WITH MICROGRAVITY GLOVEBOX IN BACKGROUND, COVER PHOTO FOR NASA TECH BRIEFS MAGAZINE, JUNE 2014 ISSUE
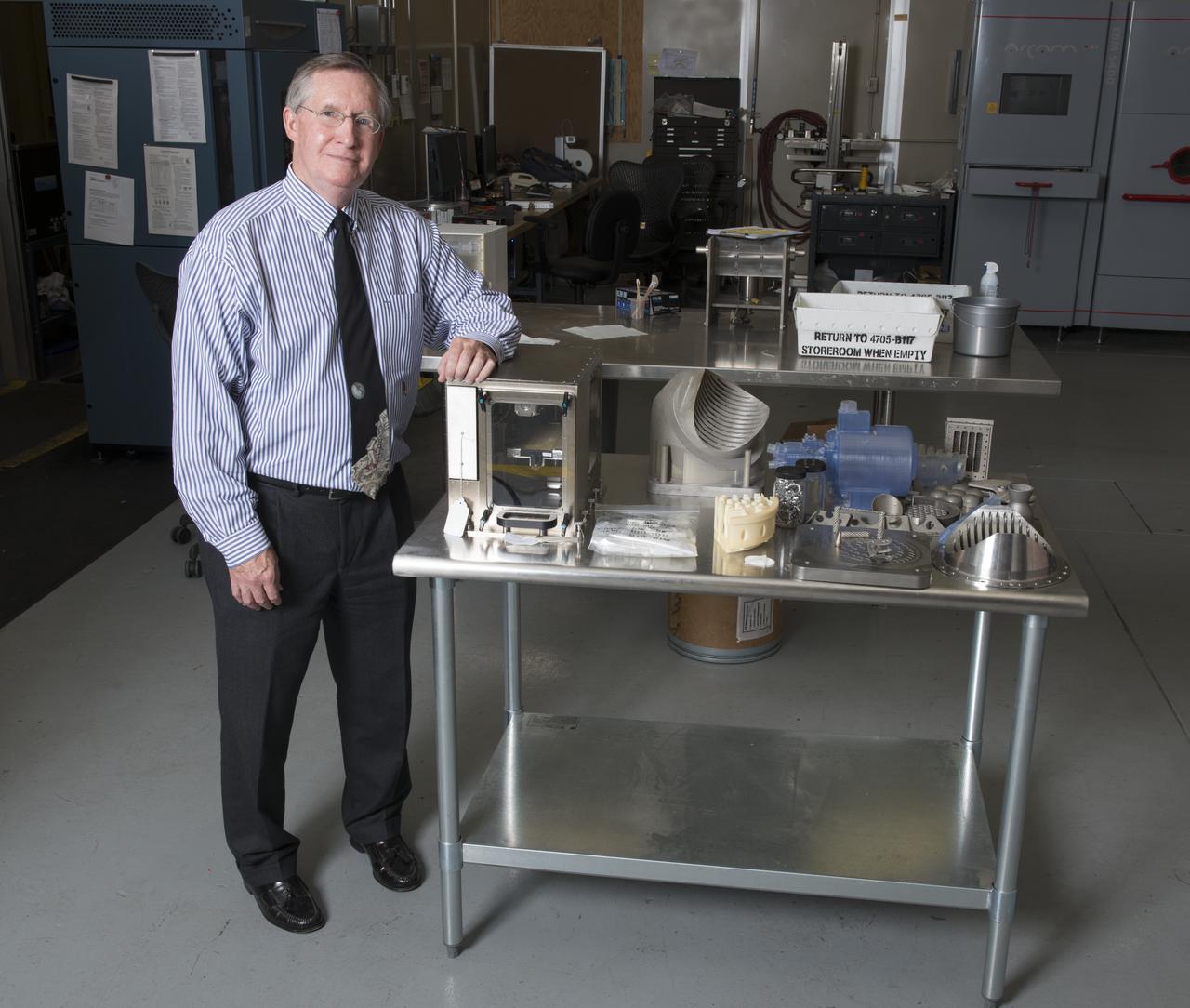

RAYMOND G. (CORKY) CLINTON WITH A WORKING MODEL OF THE FIRST 3-D PRINTER TO BE SENT TO THE ISS, ALONG WITH OTHER PRODUCTS FROM THE ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING LAB IN BUILDING 4707.
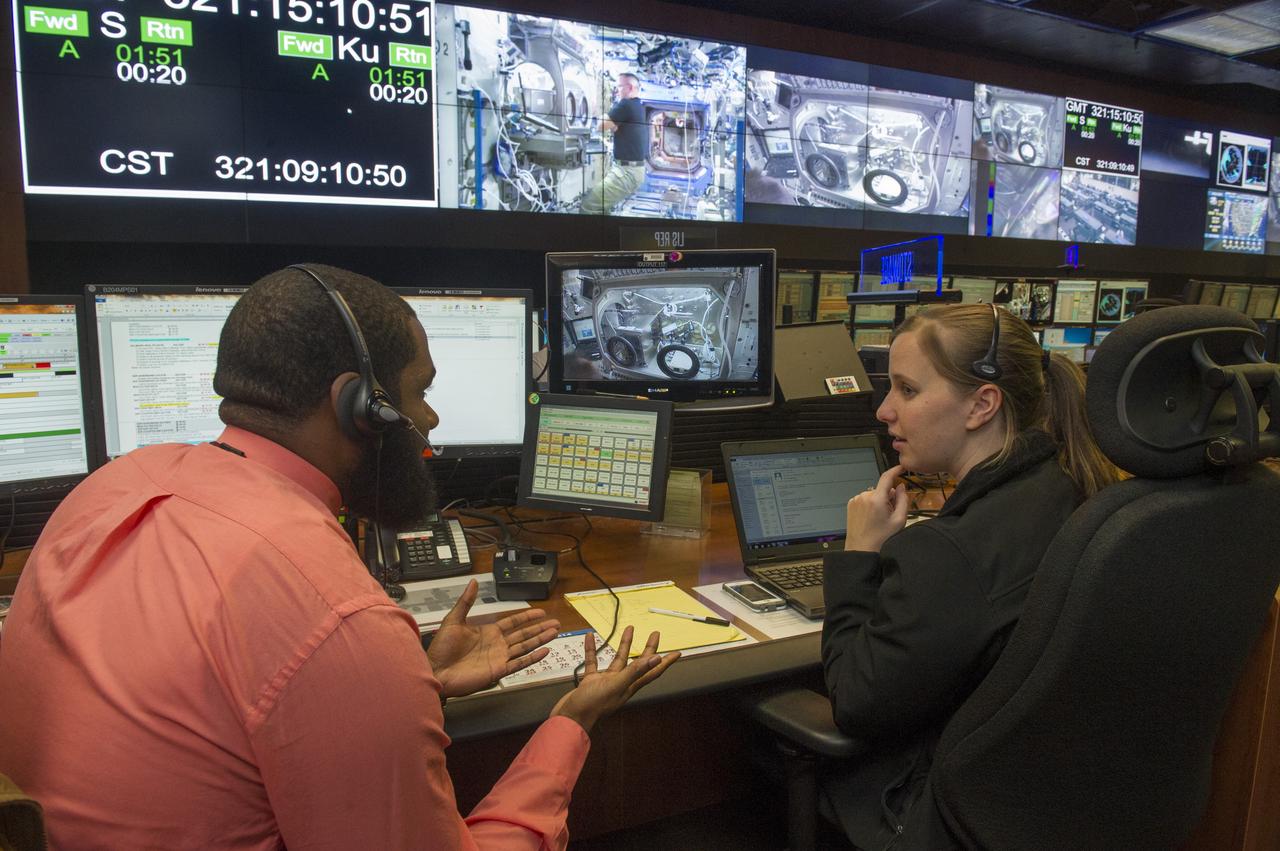

DARIAN BRYANT, LEFT, AND MELISSA HOPPER, STOWAGE ENGINEERS WITH THE PAYLOAD OPERATIONS INTEGRATION CENTER AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER WORK WITH NASA ASTRONAUT BARRY "BUTCH" WILMORE TO CALIBRATE THE FIRST 3-D PRINTER FLOWN ON THE INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION.
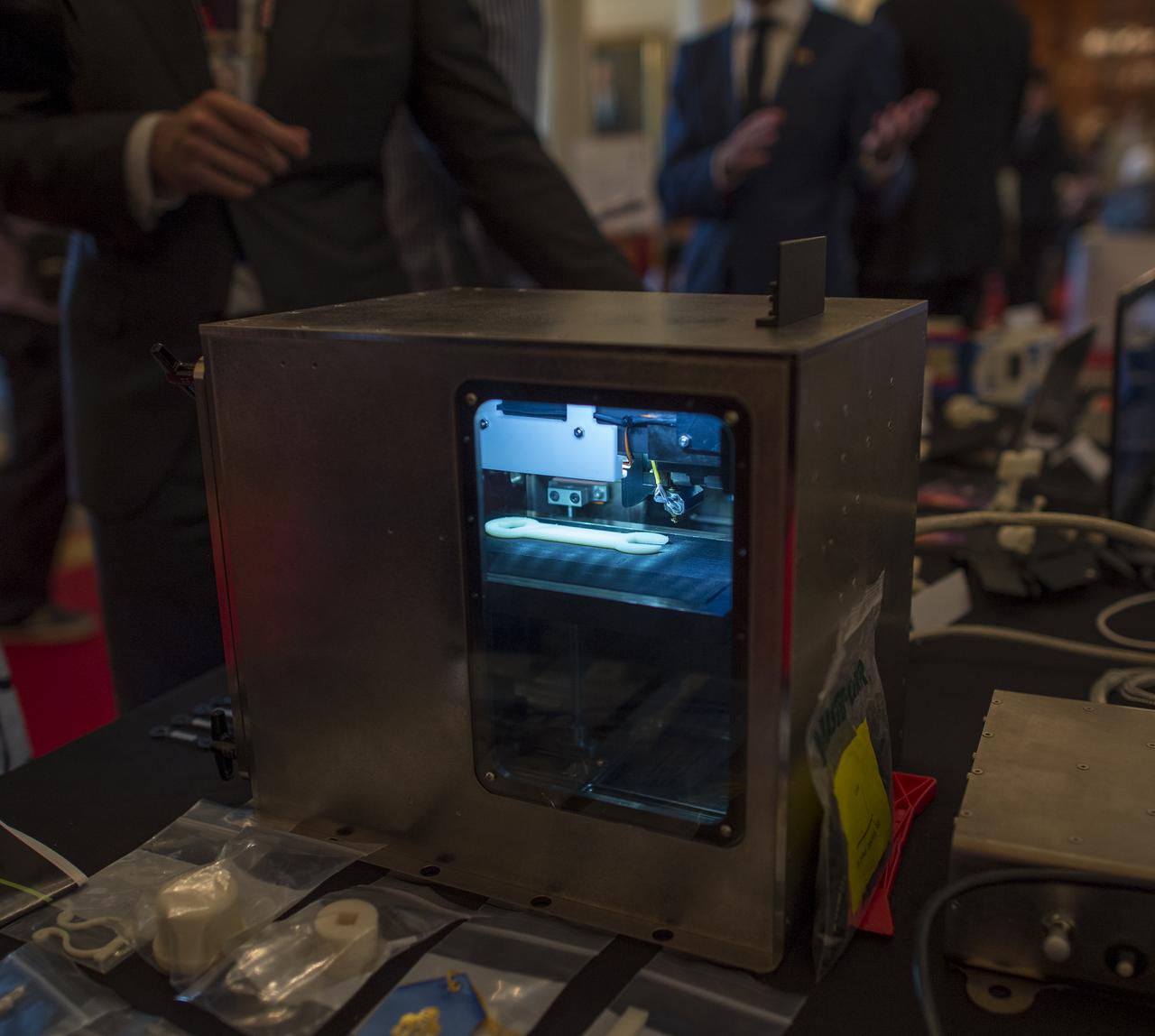

A prototype model of the Made In Space 3D printer is on display during the first ever White House Maker Faire which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. The Made In Space 3D printer was just approved by NASA to be tested onboard the International Space Station (ISS), and NASA announced a challenge for students to design items that would be printed by this first 3D printer to fly in space. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
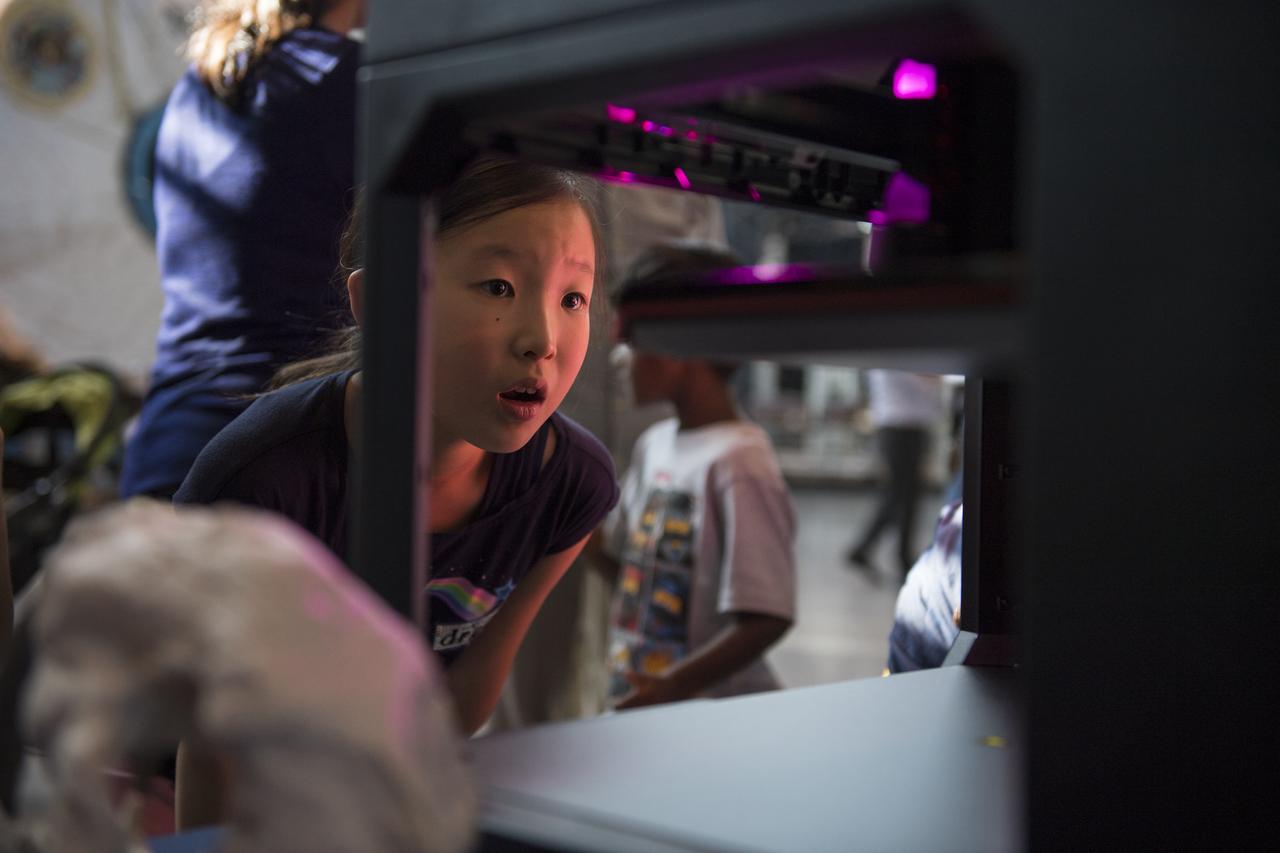

A visitor watches as a rocket is printed by a Makerbot 3D printer at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
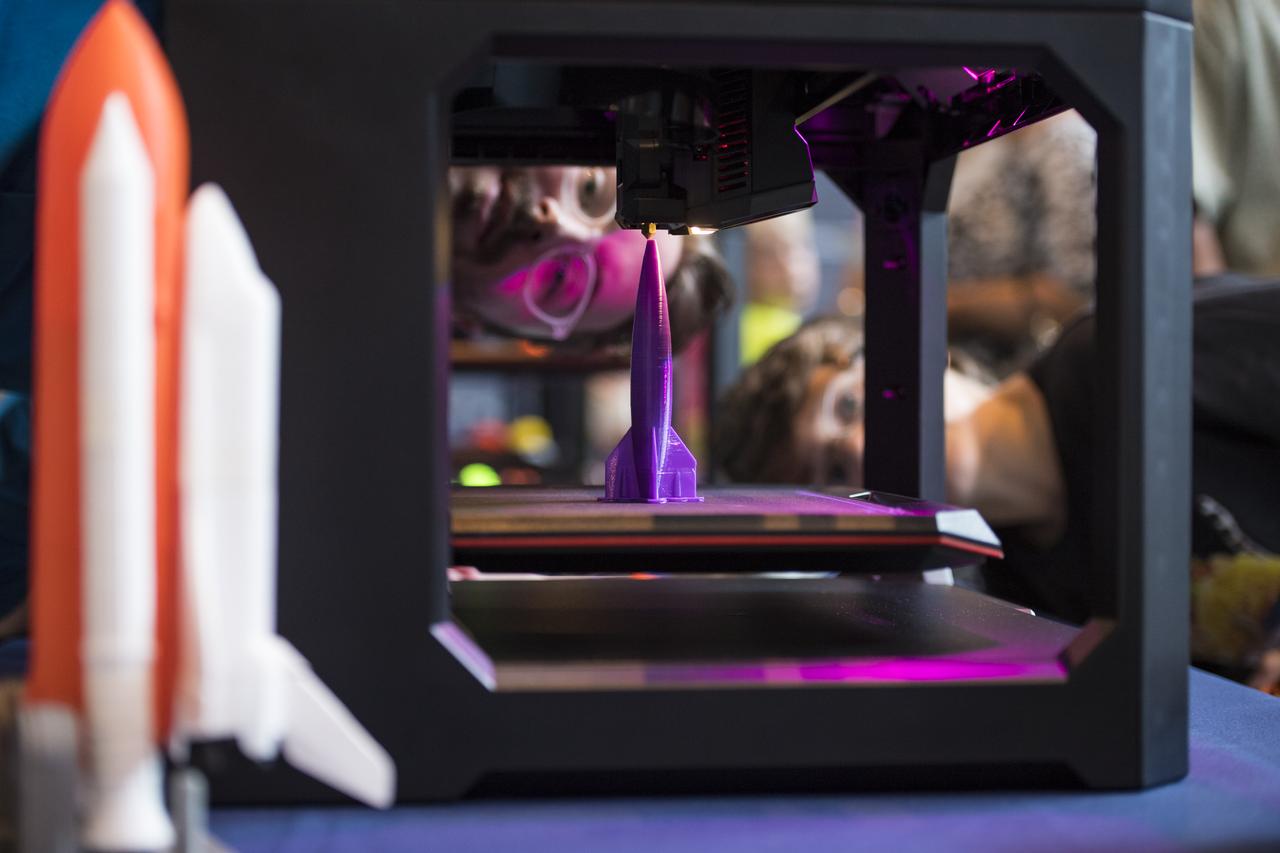

Visitors watch as a rocket is printed by a Makerbot 3D printer at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
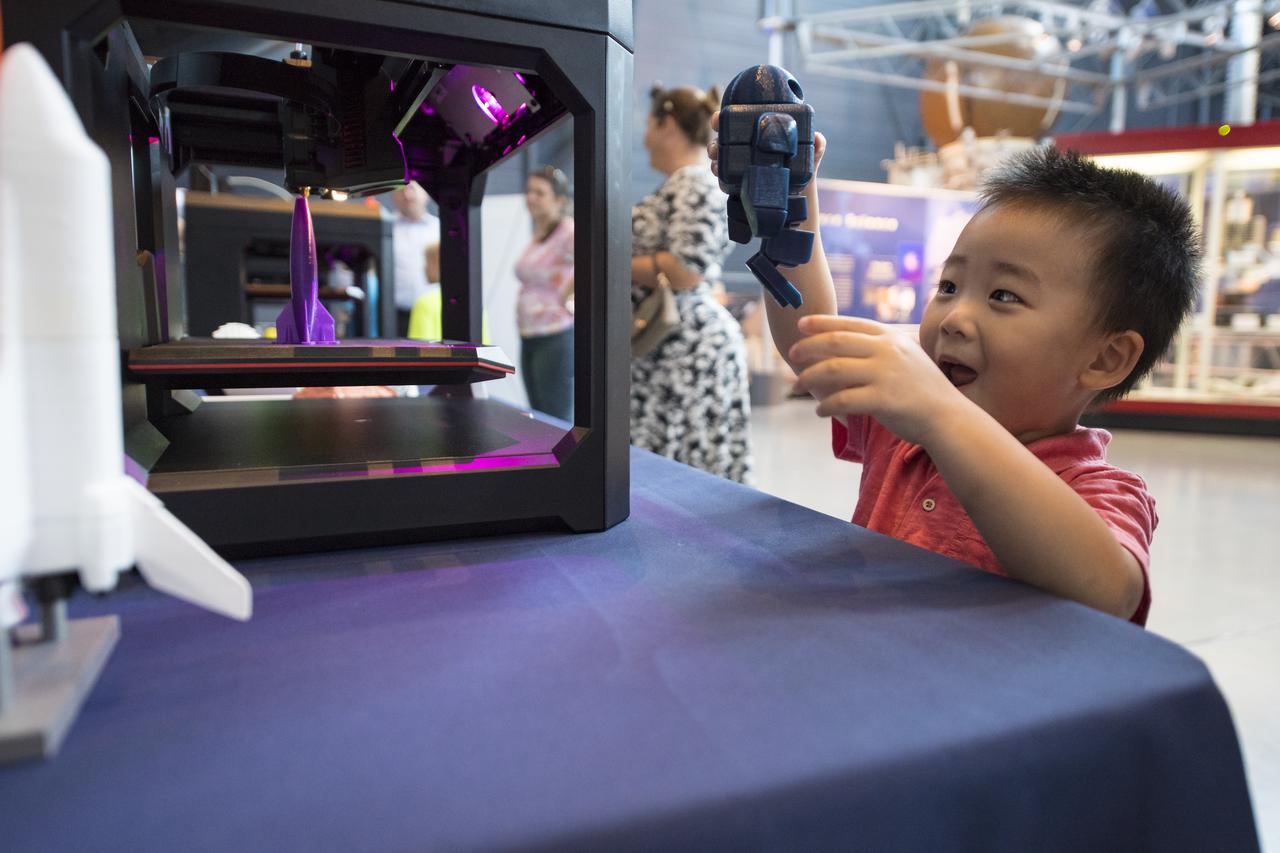

A visitor plays with a robot printed by a 3D printer at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
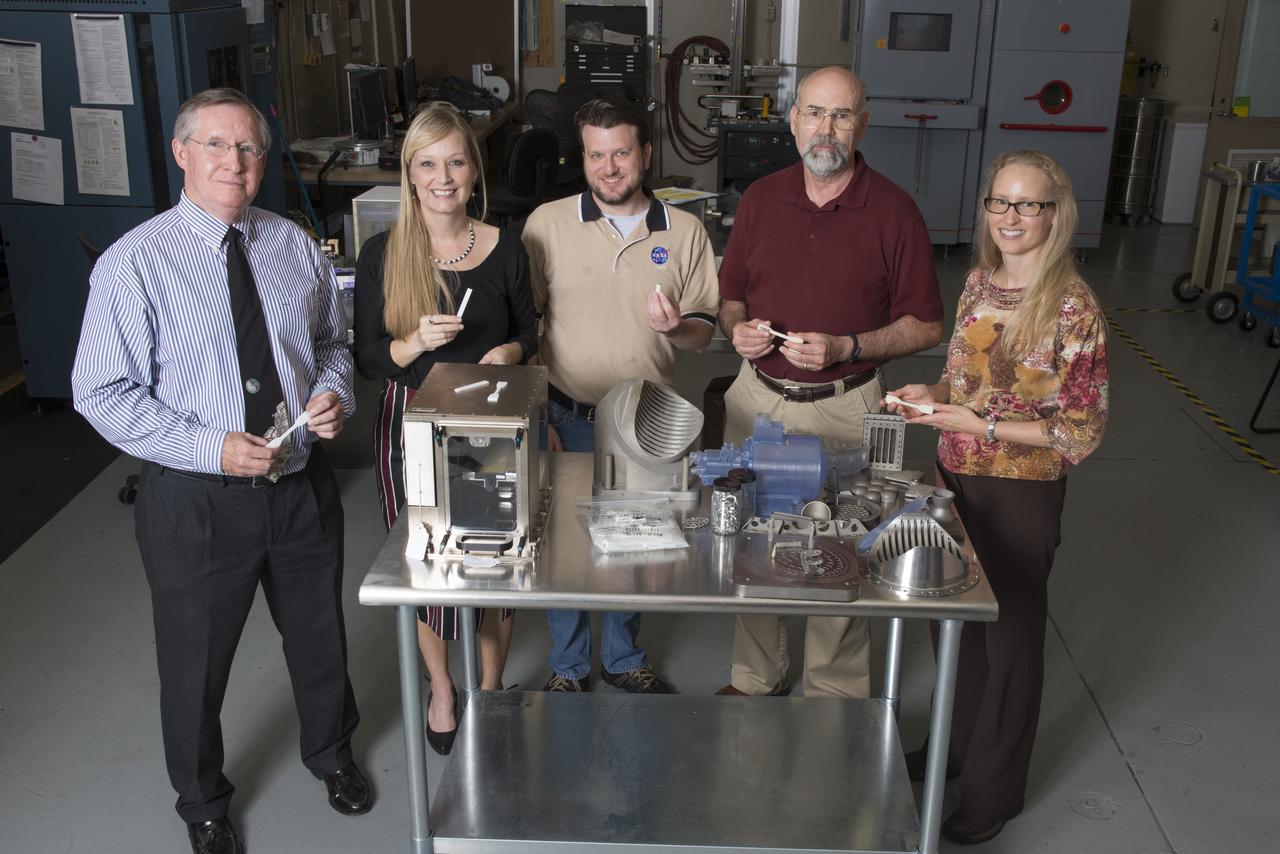

GROUP PHOTOGRAPH OF MEMBERS OF THE 3-D PRINTER TEAM IN THE ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING LAB IN BUILDING 4707. (L TO R) RAYMOND (CORKY) CLINTON, NIKKI WERKHEISER; QUINCY BEAN; RICK RYAN; AND JENNIFER EDMUNSON
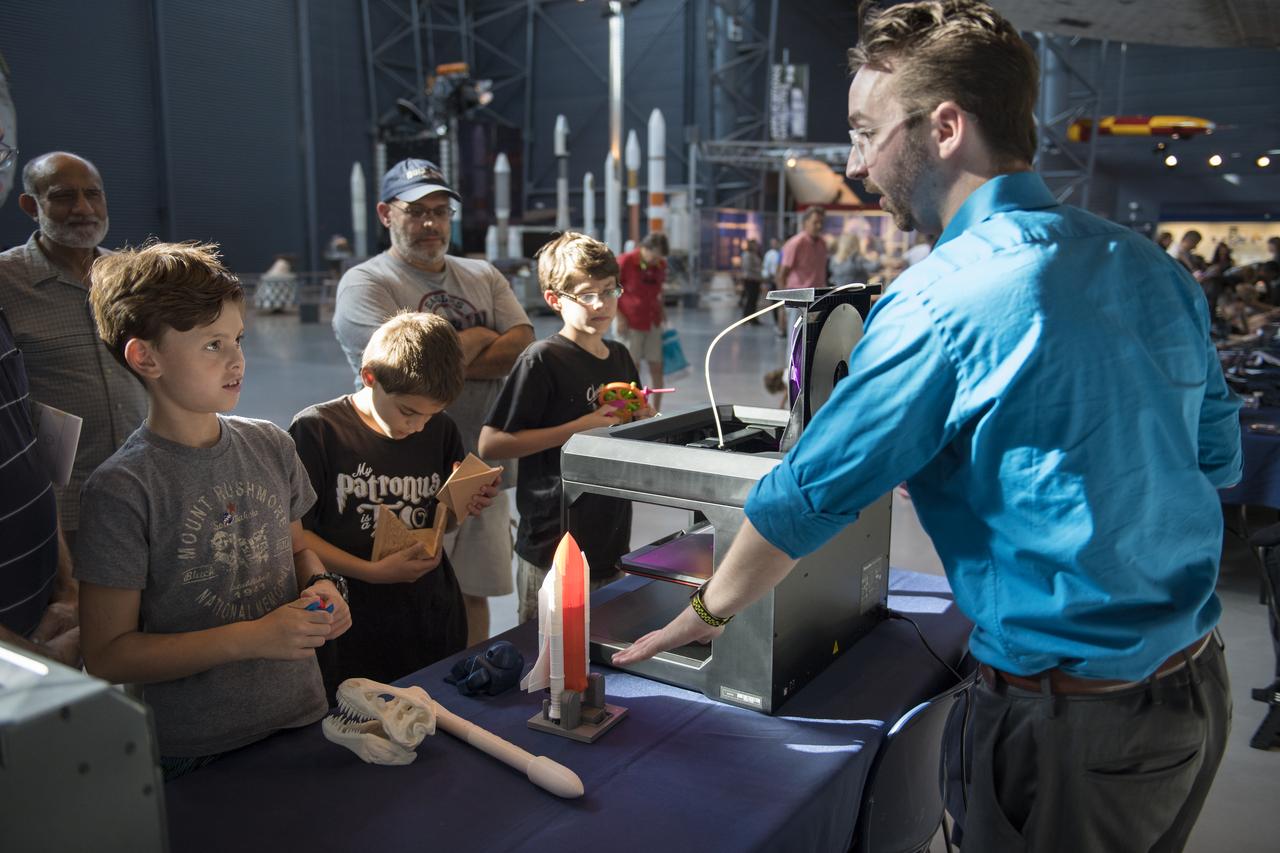

Visitors learn about 3D printing at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
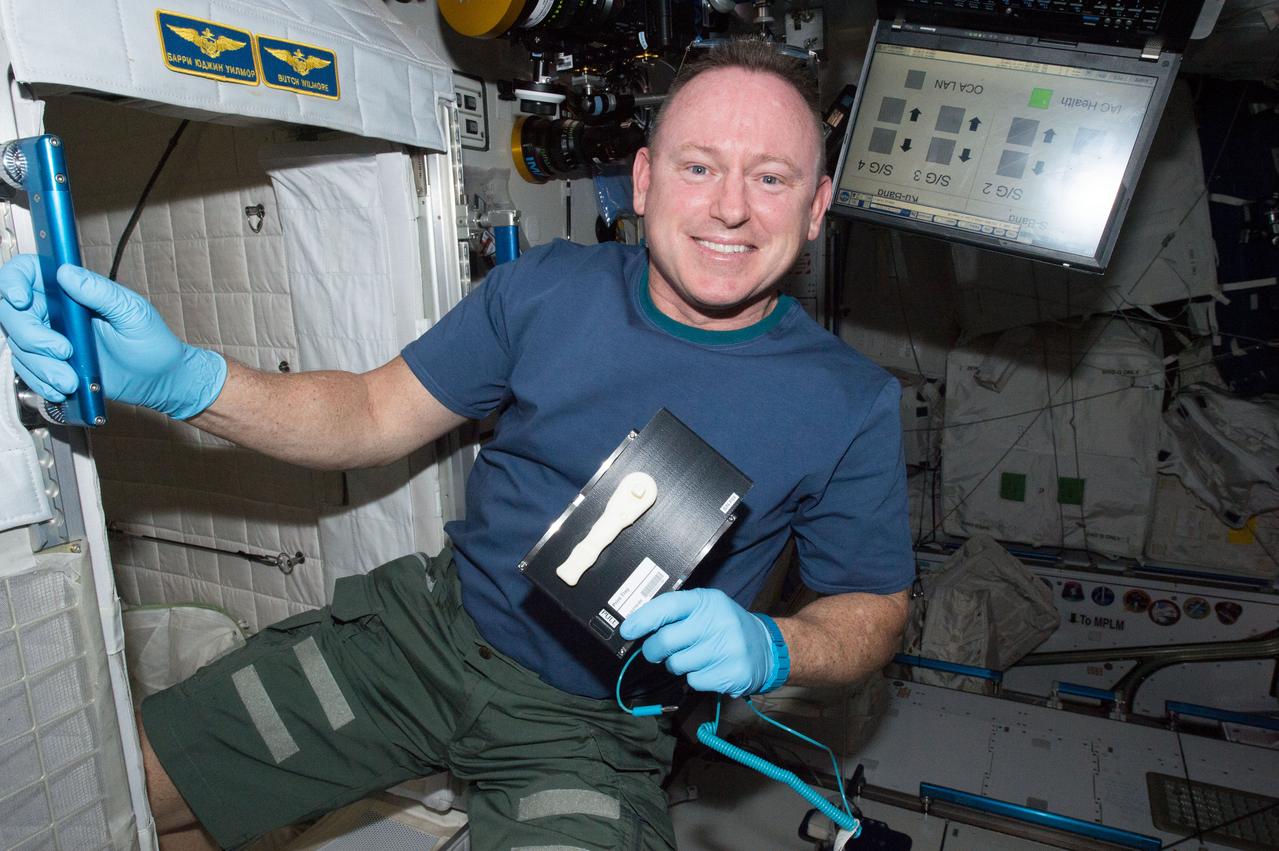

iss042e046041 (12/16/14) --- NASA Astronaut Barry (Butch) Wilmore holds a 3-D printed ratchet wrench and plate from the new 3-D printer aboard the International Space Station. The printer completed the first phase of a NASA technology demonstration by printing a tool with a design file that was transmitted from the ground to the printer.
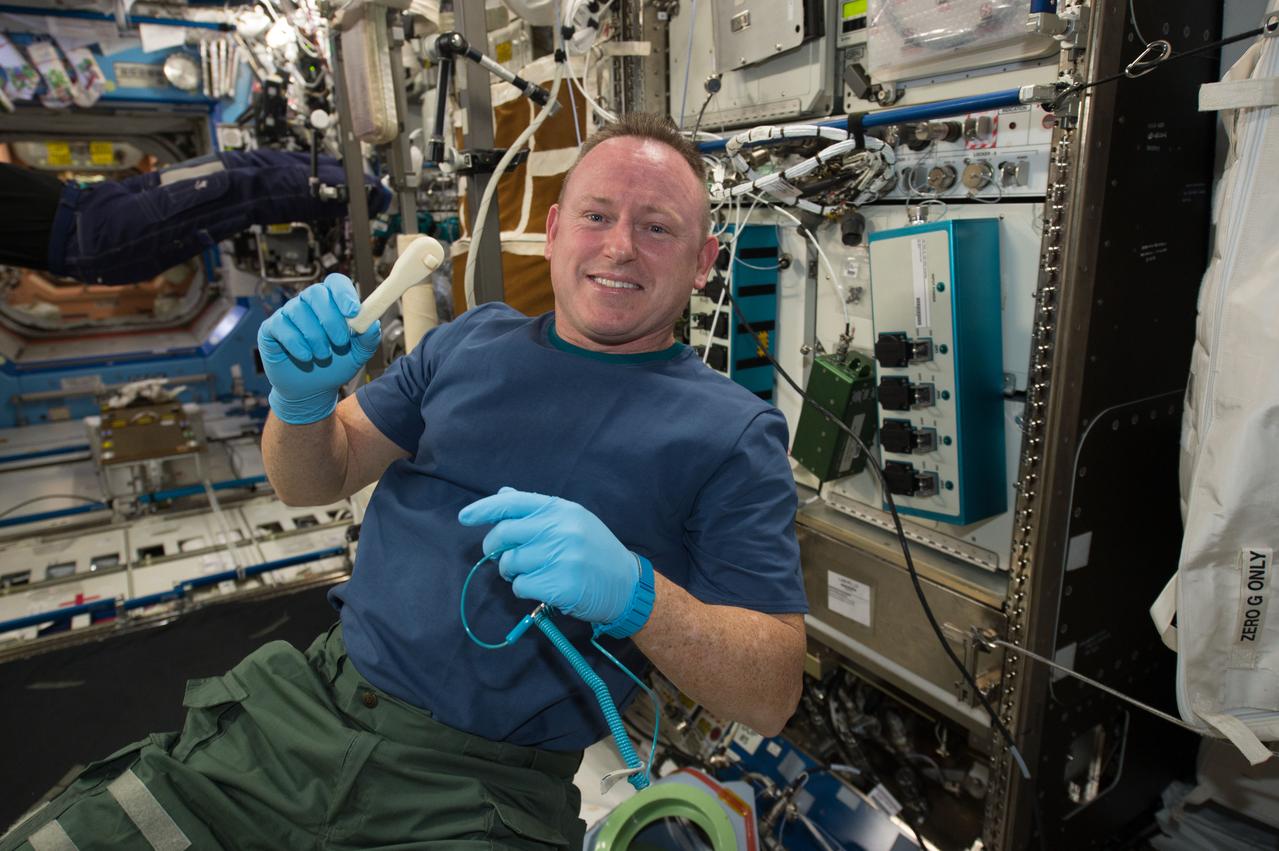

iss042e046048 (12/16/14) --- NASA Astronaut Barry (Butch) Wilmore holds a 3-D printed ratchet wrench from the new 3-D printer aboard the International Space Station. The printer completed the first phase of a NASA technology demonstration by printing a tool with a design file that was transmitted from the ground to the printer.
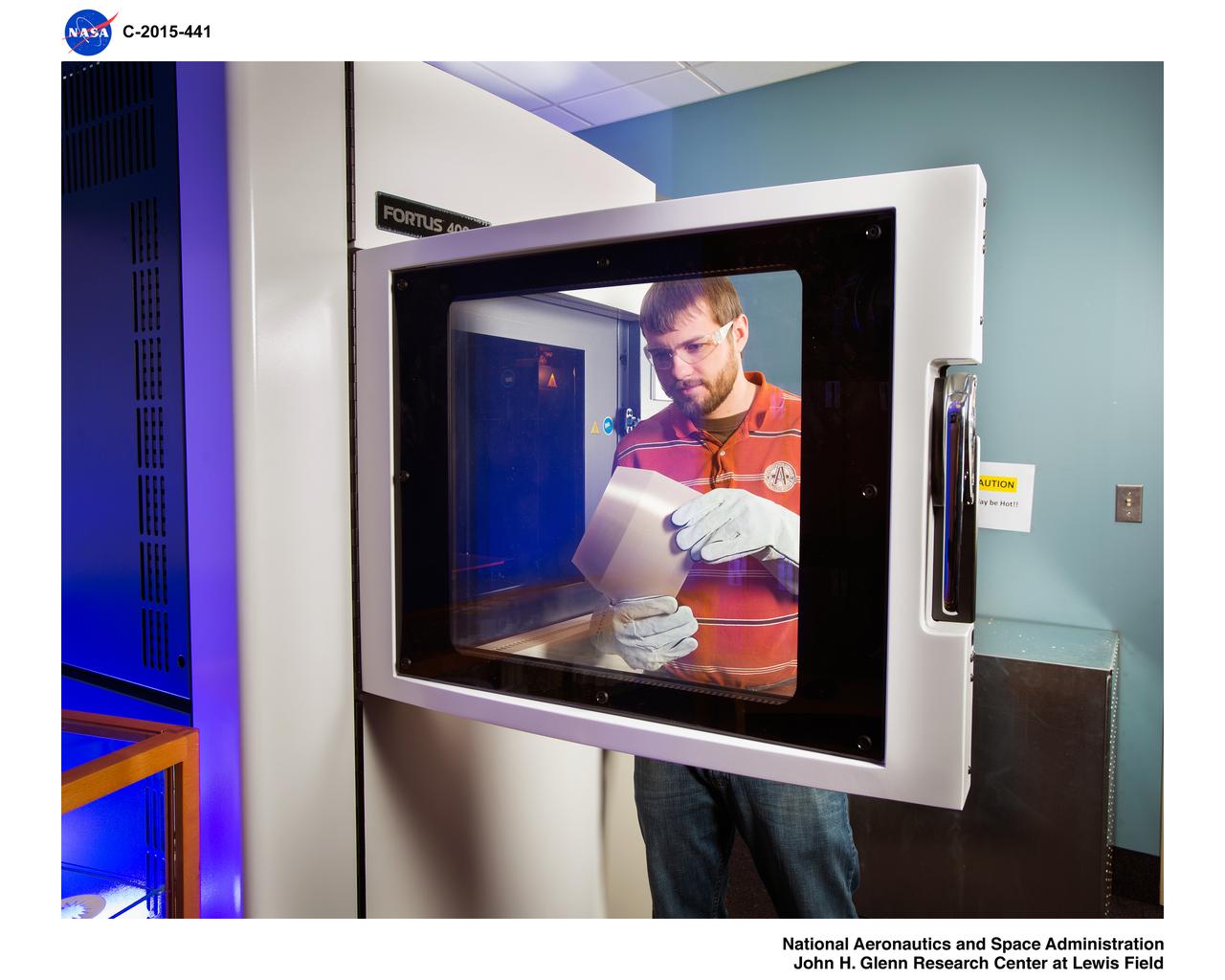

3-D Printer and Products for Manufacturing Division Code FM
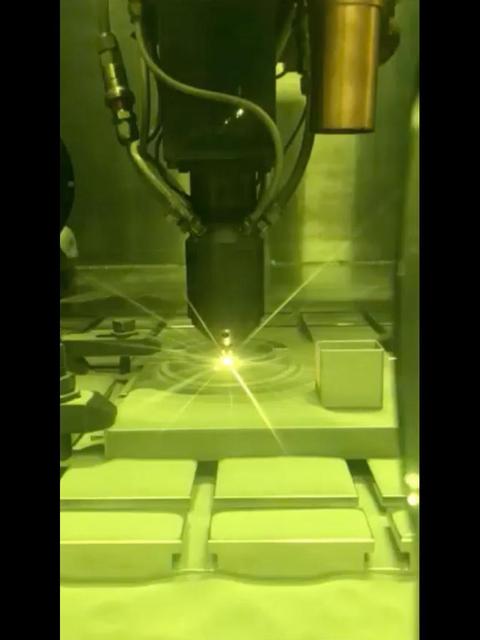

This video clip shows a 3D printing technique where a printer head scans over each layer of a part, blowing metal powder that is melted by a laser. It's one of several ways parts are 3D printed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, but was not used to create the parts aboard the Perseverance rover. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23972
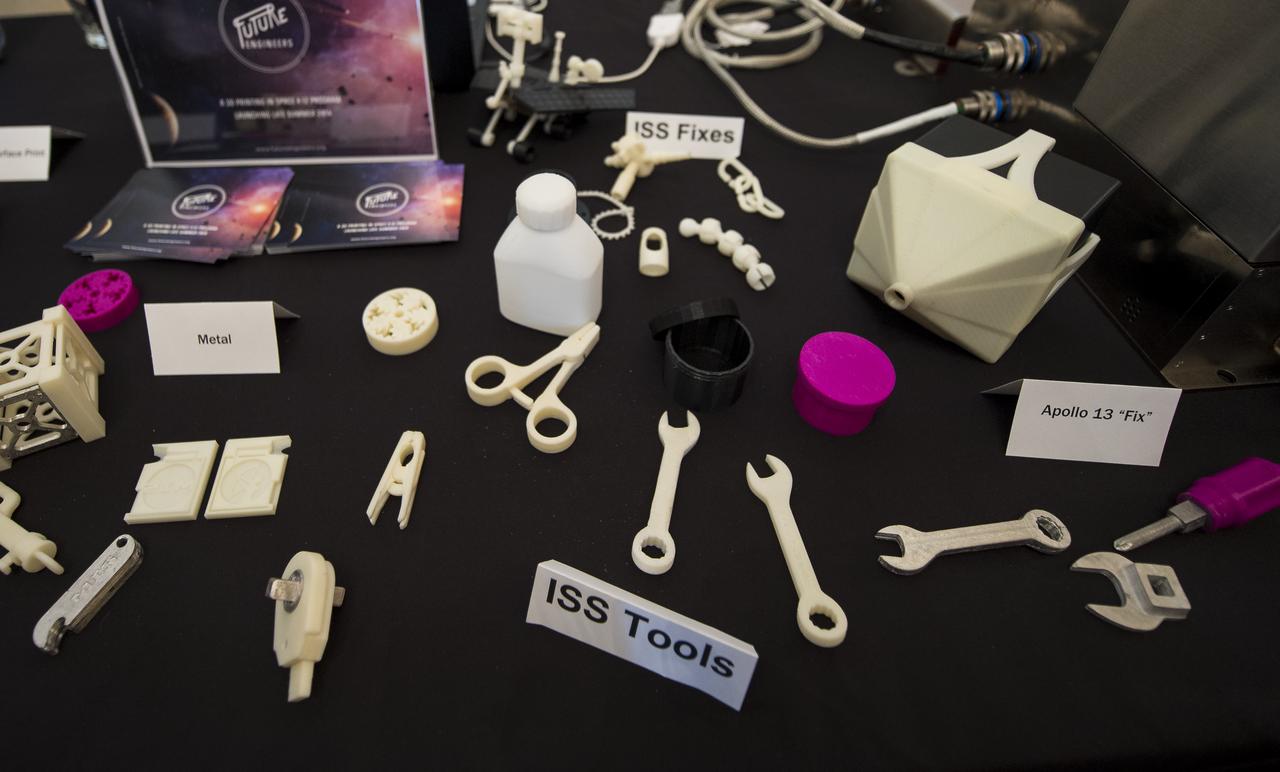

The Made In Space company displays some of the tools that can be made by their 3D printer during the first ever White House Maker Faire which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. The Made In Space 3D printer was just approved by NASA to be tested onboard the International Space Station (ISS), and NASA announced a challenge for students to design items that would be printed by this first 3D printer to fly in space. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
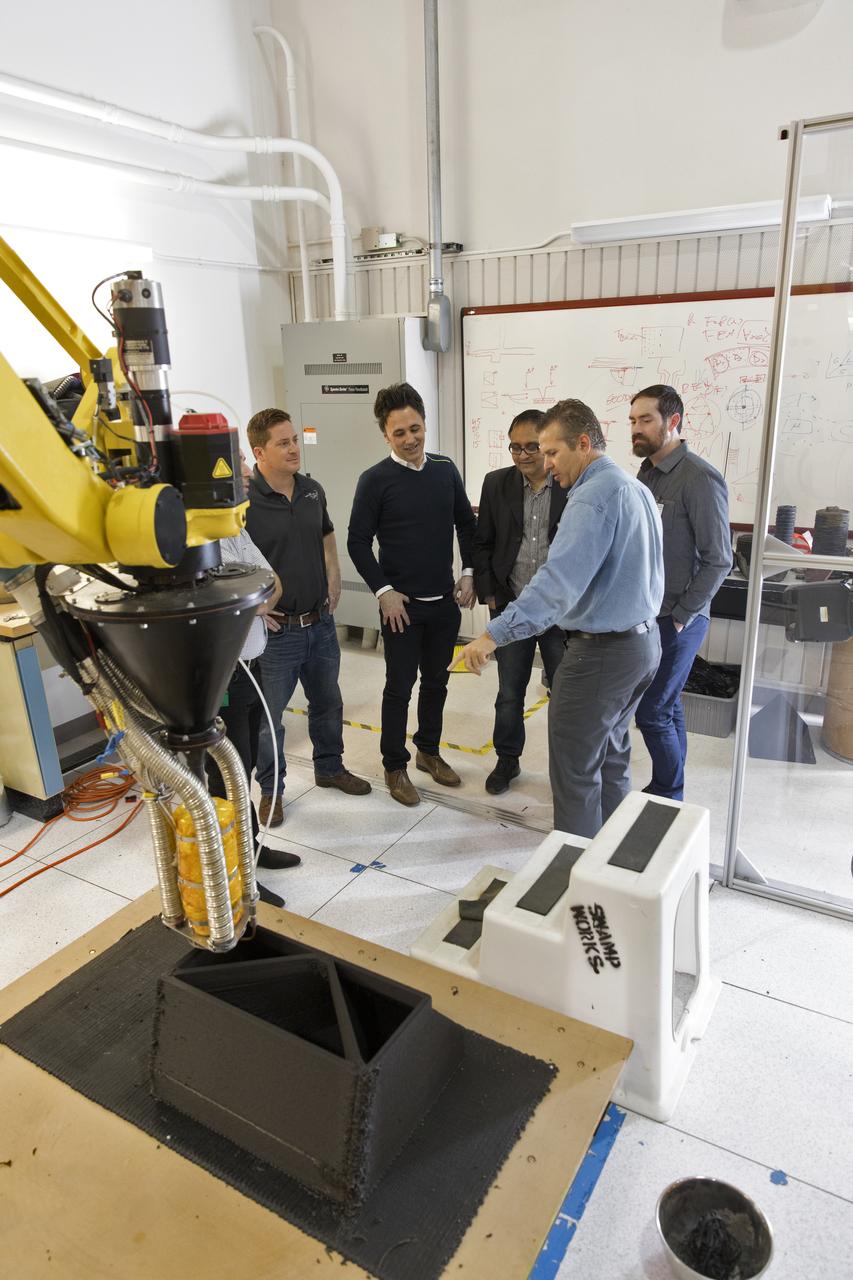

Researchers at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida are developing a Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer at the center's Swamp Works. The printer can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers. This will prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. The Kennedy team is working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.

A Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer is being developed by researchers in Swamp Works at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The printer can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers. This will prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. The Kennedy team is working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.
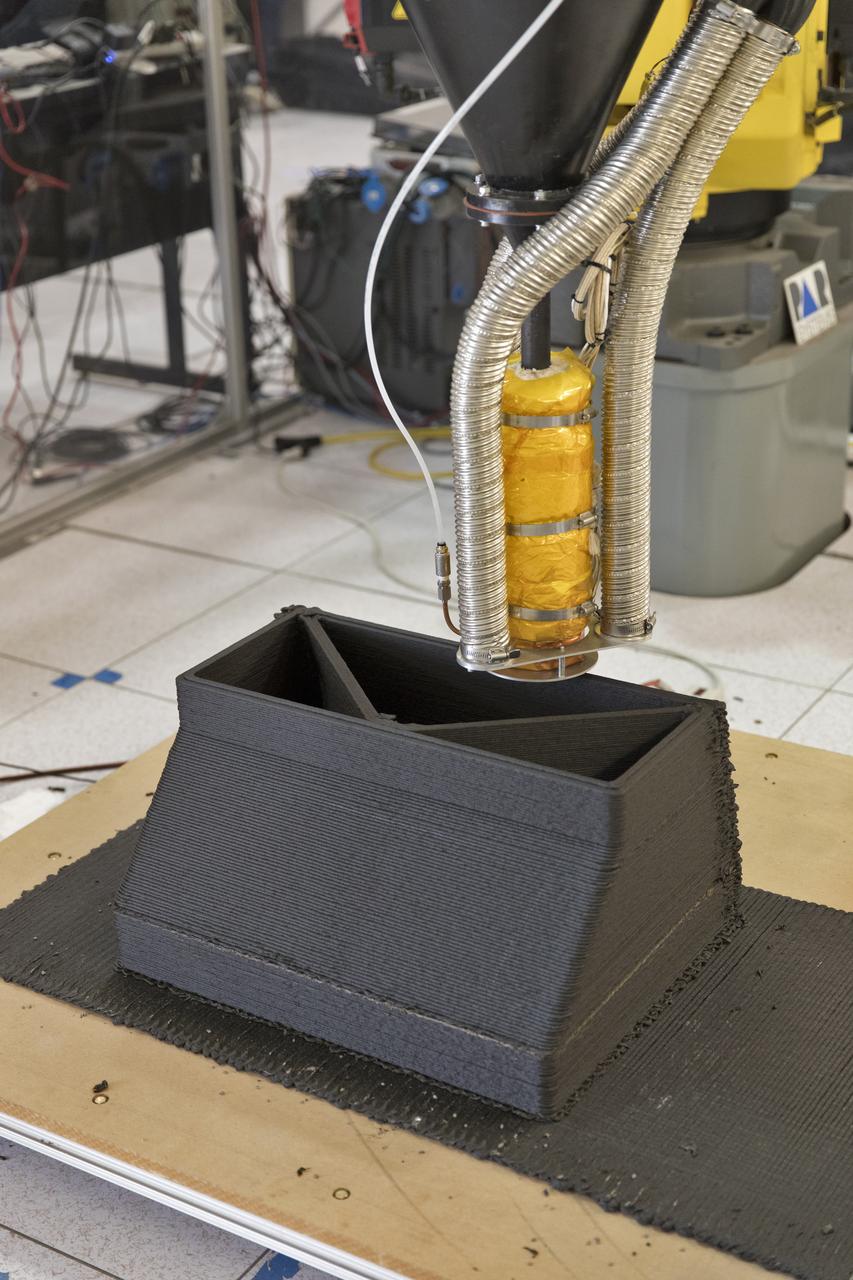
A Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer is being tested at the Swamp Works at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The printer can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers. This will prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. The Kennedy team is working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.
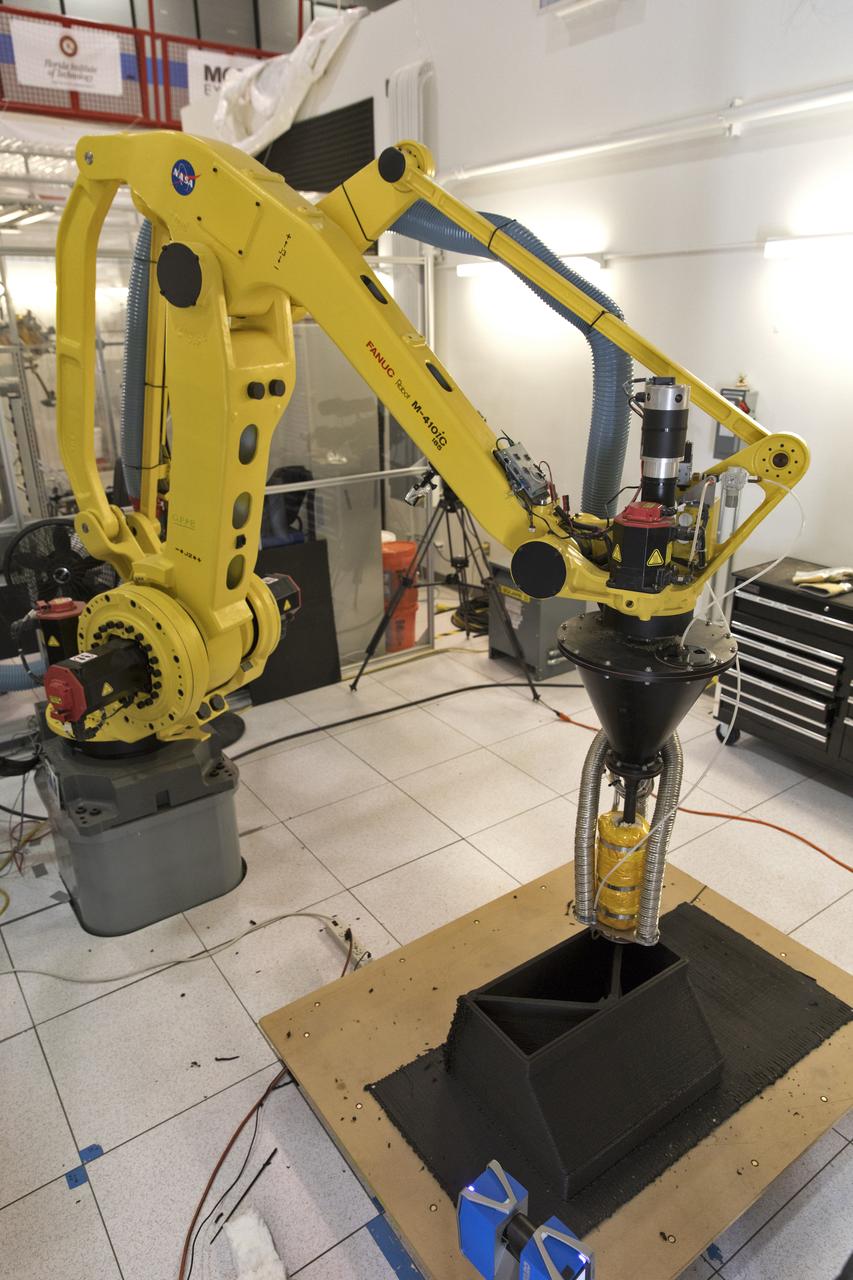

Researchers demonstrate a Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer in Swamp Works at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The printer can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers. This will prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. The Kennedy team is working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.

NIKKI WERKHEISER EXAMINES THE RAW MATERIAL USED IN THE FIRST 3-D PRINTER TO BE SENT TO THE ISS WHICH IS DESIGNED TO BE A TEST BED FOR MANUFACTURING SMALL AS ARTICLES AS NEEDED.

jsc2019e053733 (9/12/2019) --- Preflight imagery of the Made in Space - Recycler. The Made in Space - Recycler will utilize polymer materials to produce filament that is transferred to Manufacturing Device to perform printing operations. This experiment shows the value of closing the loop between the printer and recycling materials utilized by the printer. This has implications for space conservation and deep space missions. Image courtesy of: Made In Space, Inc.

Shown is a Zero Launch Mass 3D printer on July 28, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works. A team at the Florida spaceport tested the printer as part of the Relevant Environment Additive Construction Technology (REACT) project. Among the key objectives of the project is developing an architectural and structural design for a shelter that provides protection to habitable assets on the lunar surface. Testing REACT derives from NASA’s 2020 Announcement of Collaboration Opportunity with AI SpaceFactory – an architectural and construction technology company and winner of NASA’s 3D Printed Habitat Challenge.

iss071e522120 (8/21/2024) ---A view the Metal 3D printer that manufactures experimental samples printed with stainless steel aboard the International Space Station's Columbus laboratory module. Researchers are exploring how the Metal 3D printer operates in the microgravity conditions of weightlessness and radiation as well as its ability to manufacture tools and parts on demand during space missions.
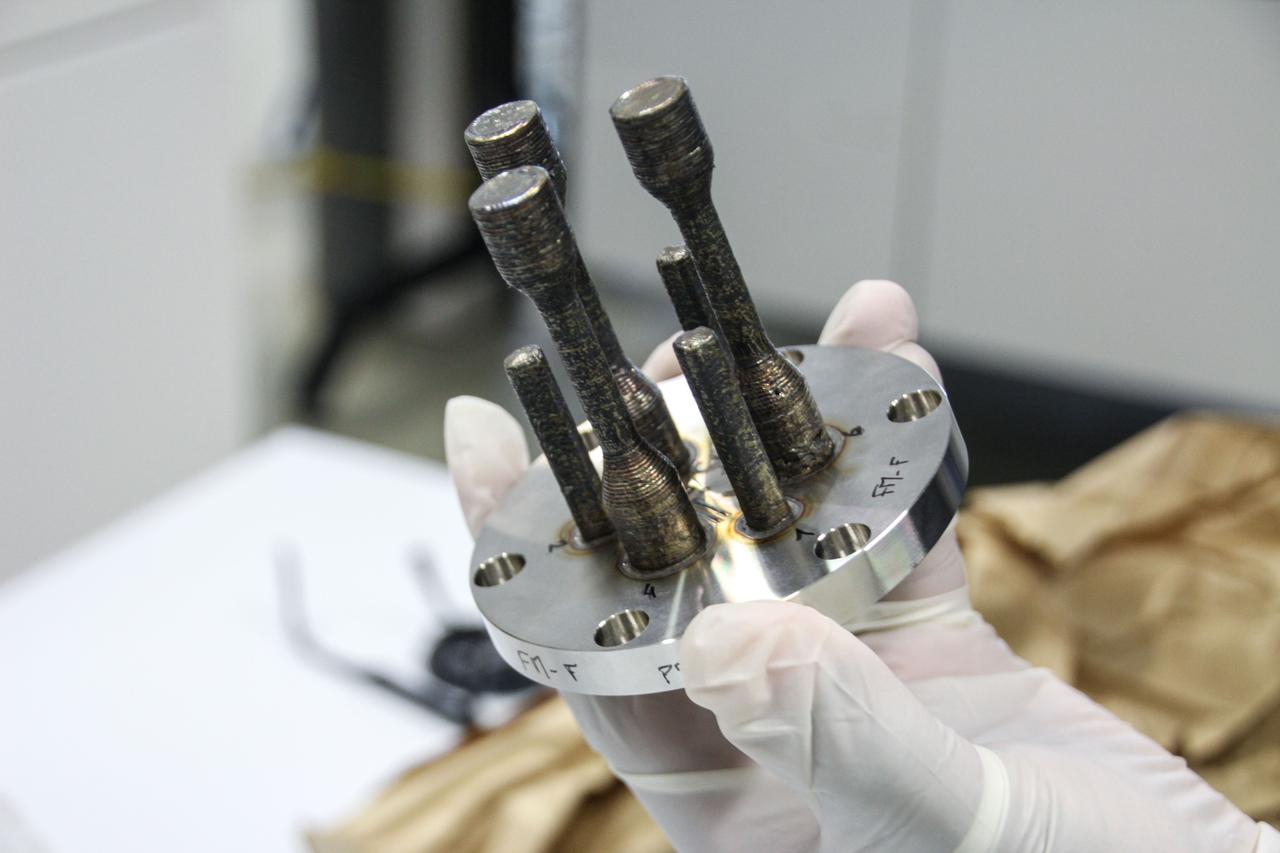

jsc2024e005971 (3/21/2023) --- A preflight image for Metal 3D printer shows one of the stainless steel specimens after printing on the ground. A team member holds the sample at the ESA (European Space Agency) materials laboratory. Metal 3D printer evaluates in-space additive manufacturing for potential use in maintenance and long-duration missions to the Moon or Mars. Image courtesy of ESA/Airbus.
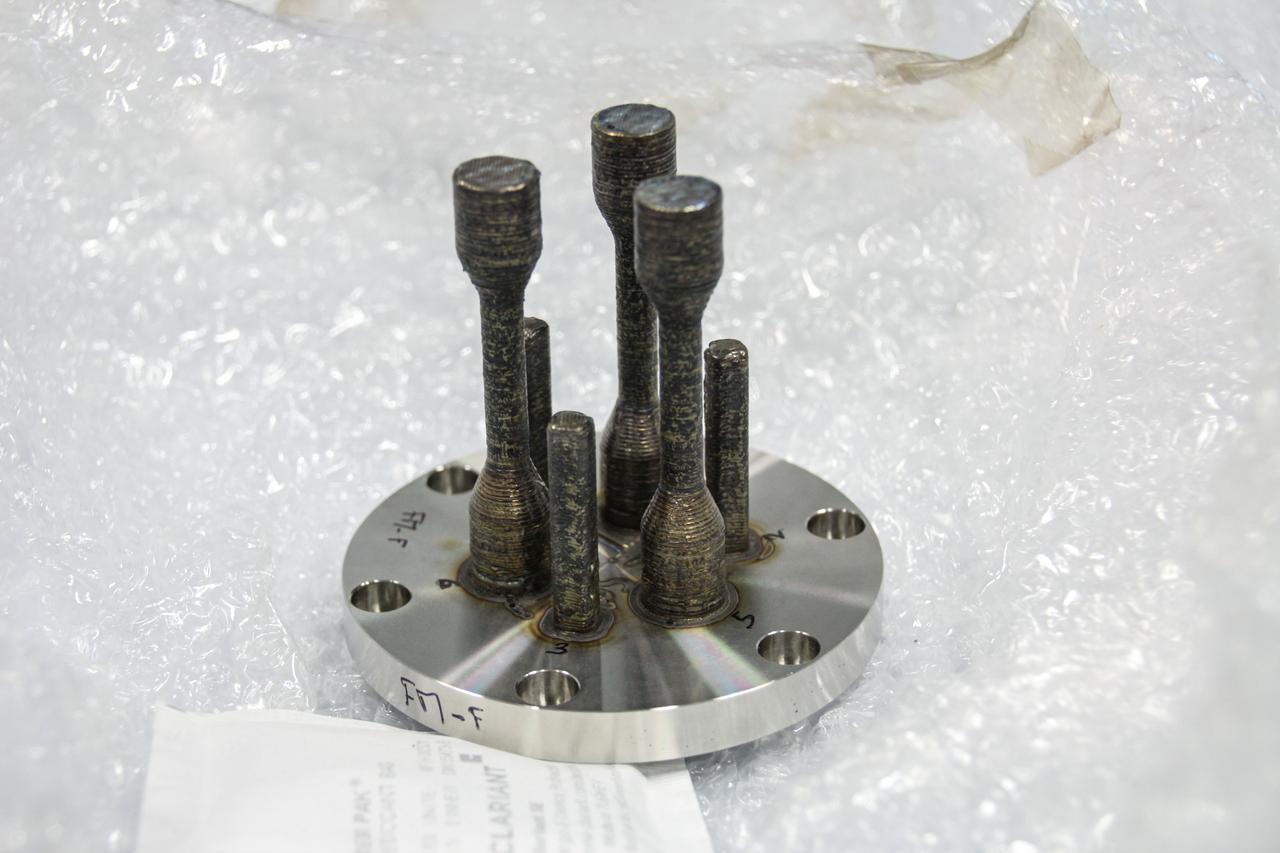

jsc2024e005970 (3/21/2023) --- A preflight image for Metal 3D printer shows one of the specimens after printing on the ground. The specimen was made from stainless steel at the ESA (European Space Agency) materials laboratory. Metal 3D printer evaluates in-space additive manufacturing for potential use in maintenance and long-duration missions to the Moon or Mars. Image courtesy of ESA/Airbus.
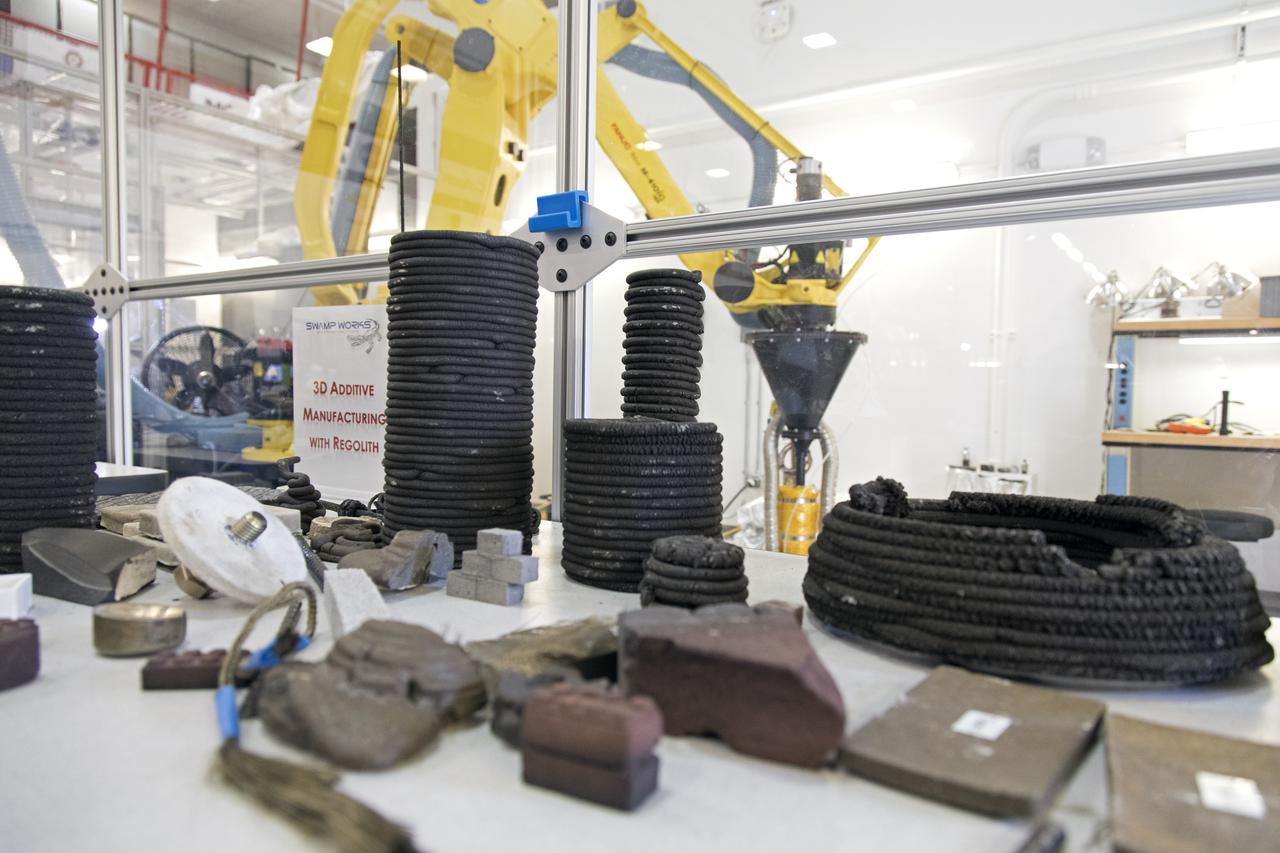

Research engineers at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida are working on a Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer at the center's Swamp Works. The printer can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars, and even for troops in remote locations on Earth. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers to prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. The group is working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.
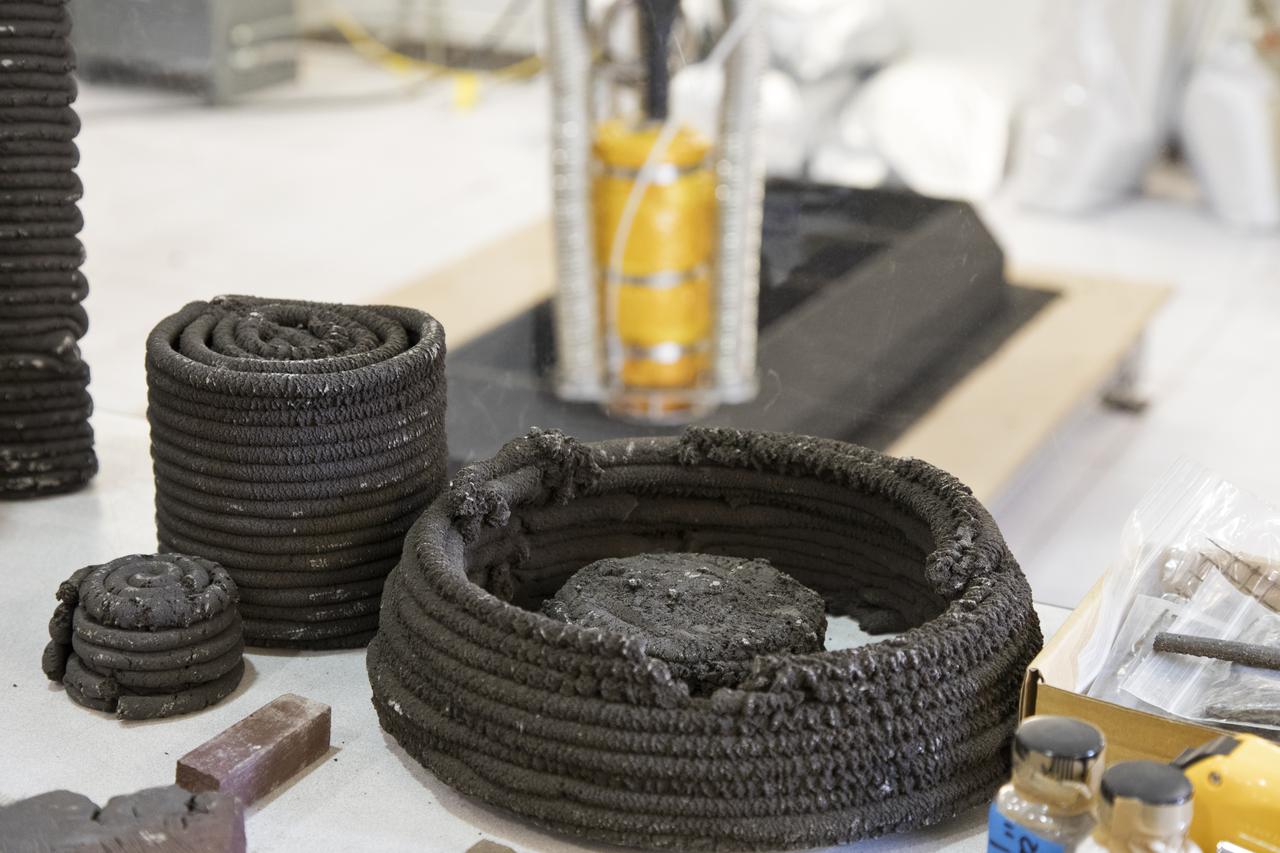

Pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers are being used to test a Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer in the Swamp Works at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The printer can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars, and even for troops in remote locations on Earth. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses these pellets to prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. The group is working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.

Research engineers at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida are working on a Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer at the center's Swamp Works. The printer can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars, and even for troops in remote locations on Earth. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers to prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. The group is working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.
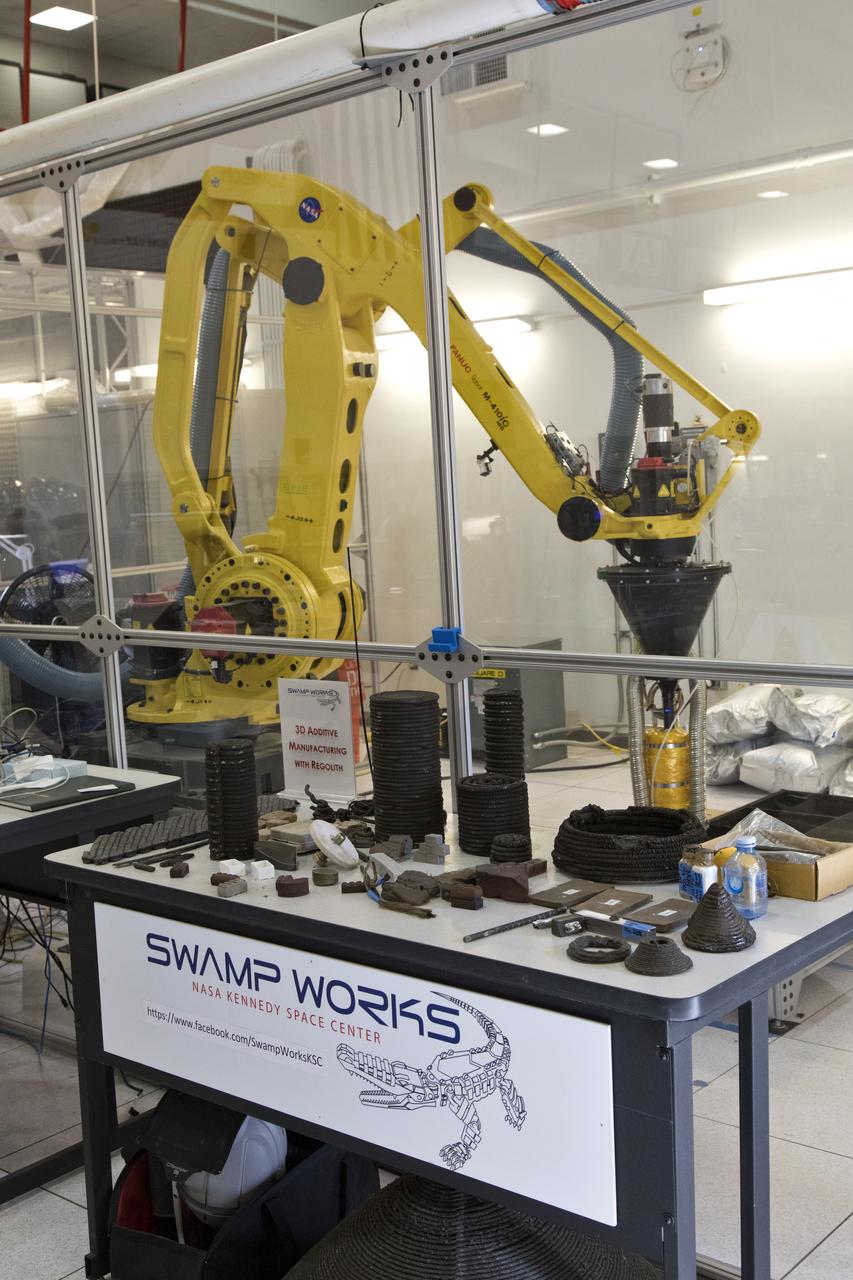

A Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer is being tested at the Swamp Works at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The printer can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars, and even for troops in remote locations on Earth. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers to prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. The group is working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.
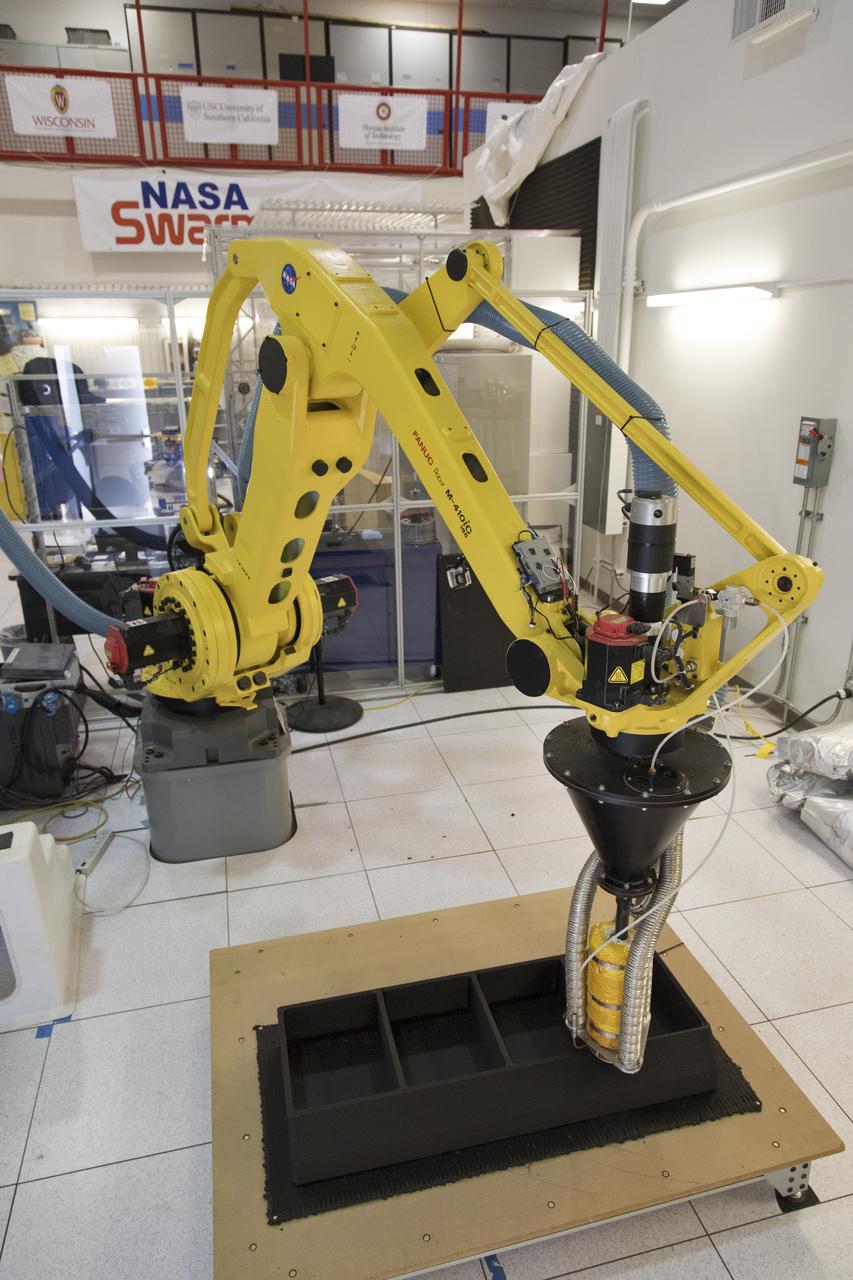

A Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer is being tested at the Swamp Works at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The printer can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars, and even for troops in remote locations on Earth. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers to prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. The group is working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.
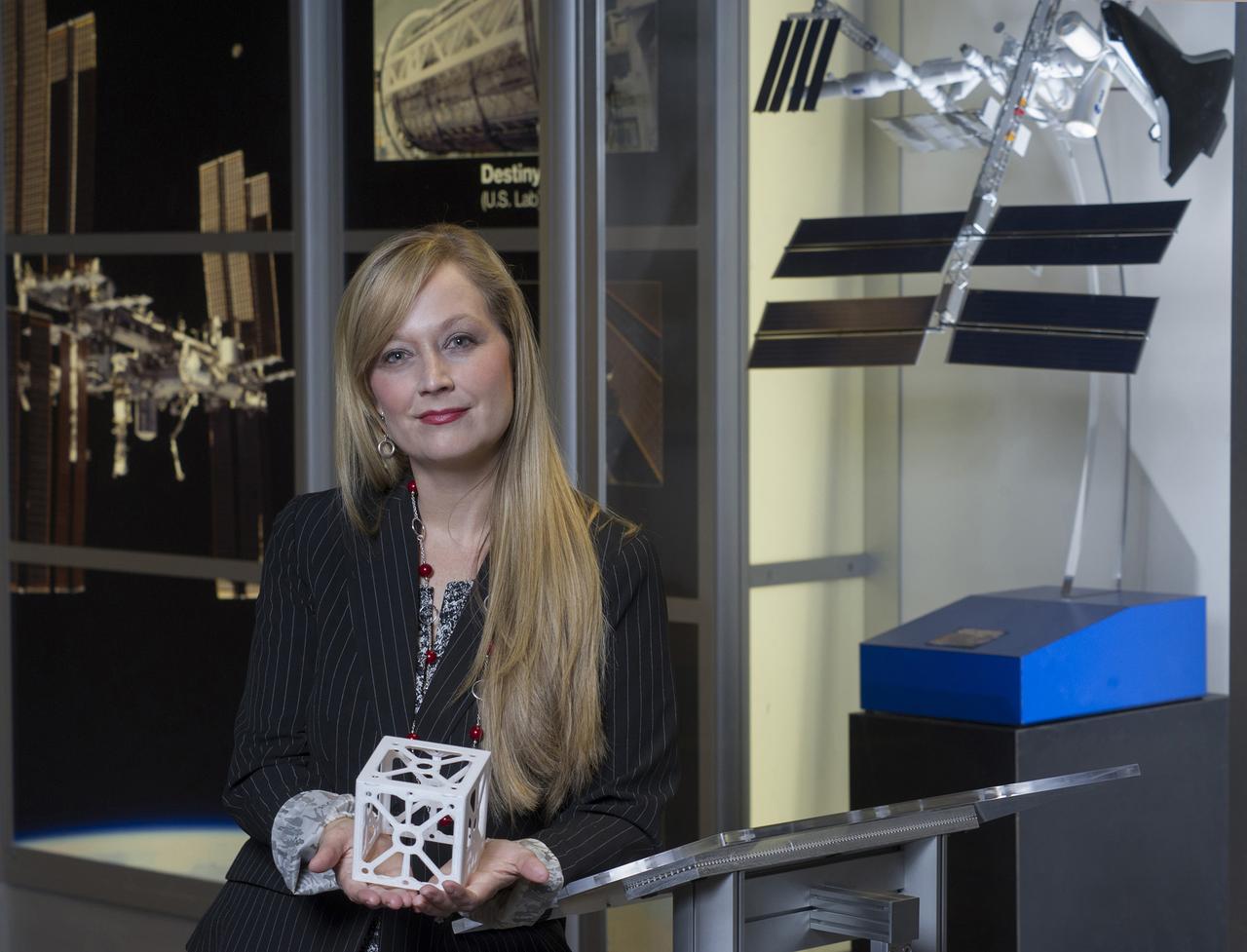

NIKI WERKHEISER, NASA'S 3D PRINTING IN ZERO-G PROJECT MANAGER, HOLDS A 3D PRINTED CUBESAT STRUCTURE WHICH IS JUST ONE OF THE MANY POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS THAT AN IN-SPACE MANUFACTURING CAPABILITY WILL PROVIDE

iss060e043926 (Aug. 23, 2019) --- Expedition 60 Flight Engineer Christina Koch of NASA conducts science operations for the BioFabrication Facility experiment researching the effectiveness of using 3D biological printers to produce usable human organs in microgravity.
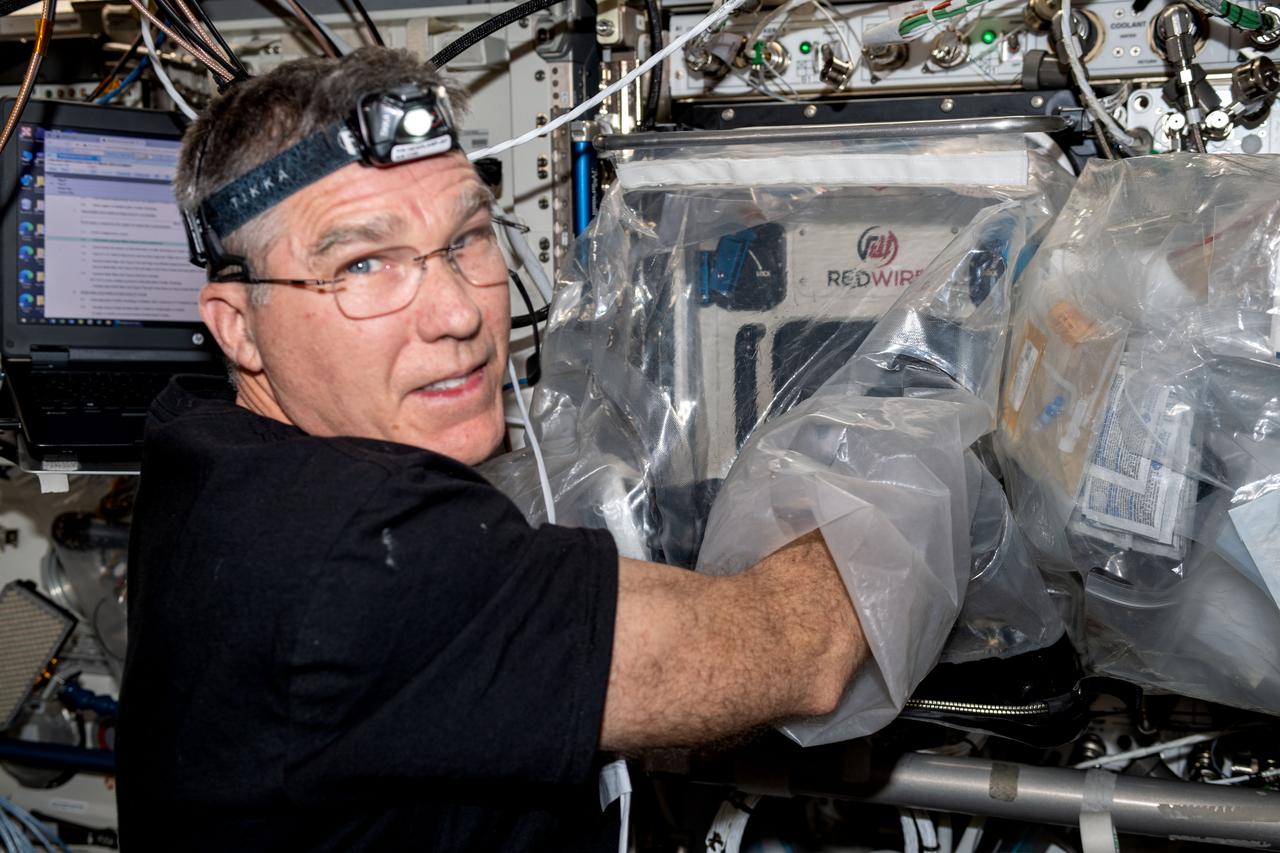

iss069e038872 (July 28, 2023) -- NASA astronaut Stephen Bowen works with the BioFabrication Facility which uses 3D printers to investigate the feasibility of printing organ-like tissues in microgravity.
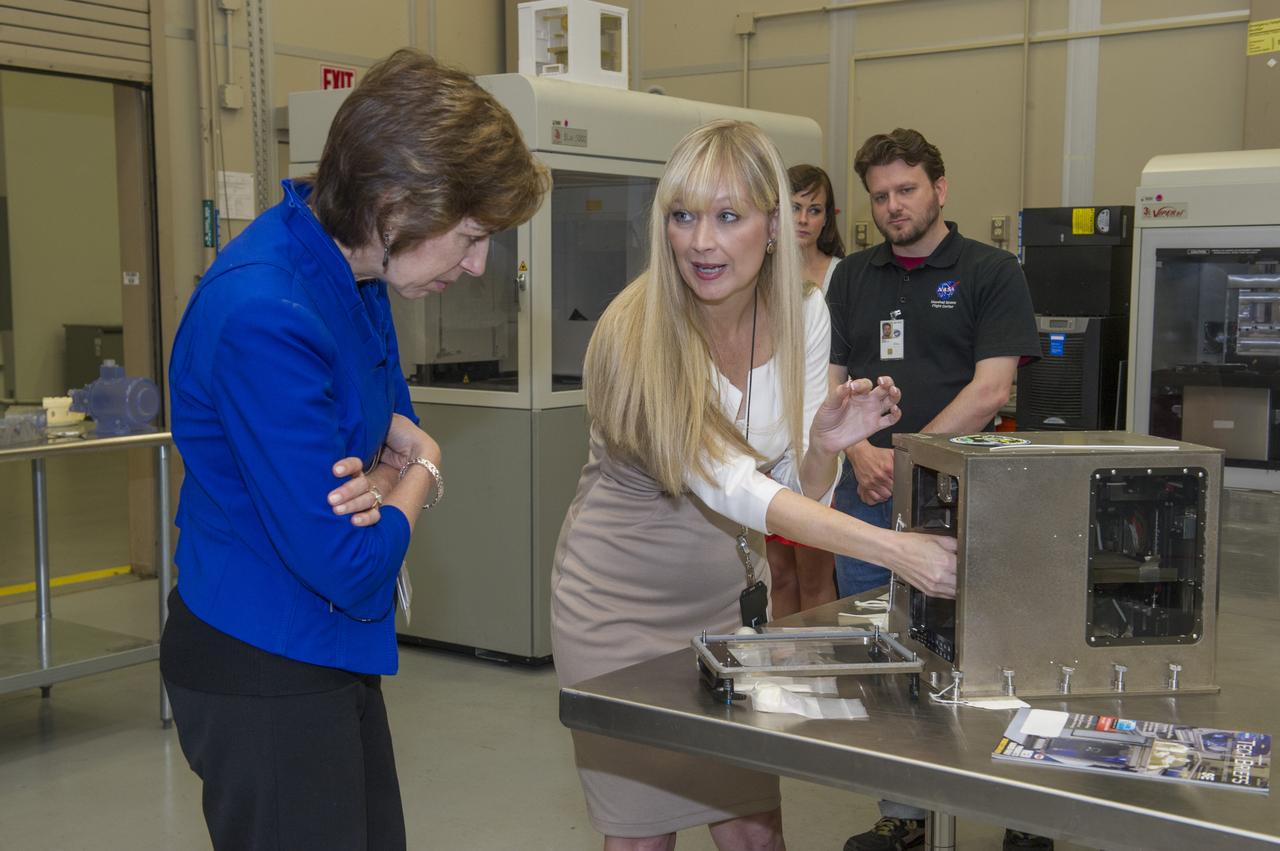

NIKI WERKHEISER - 3D PRINTING ZERO-G PROJECT MANAGER, DISCUSSES 3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY WITH DR. ELLEN OCHOA.1401414 THE ISS NOW HAS A 3D PRINTER, WHICH THE TECHNOLOGY WAS TESTED AT THE MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER
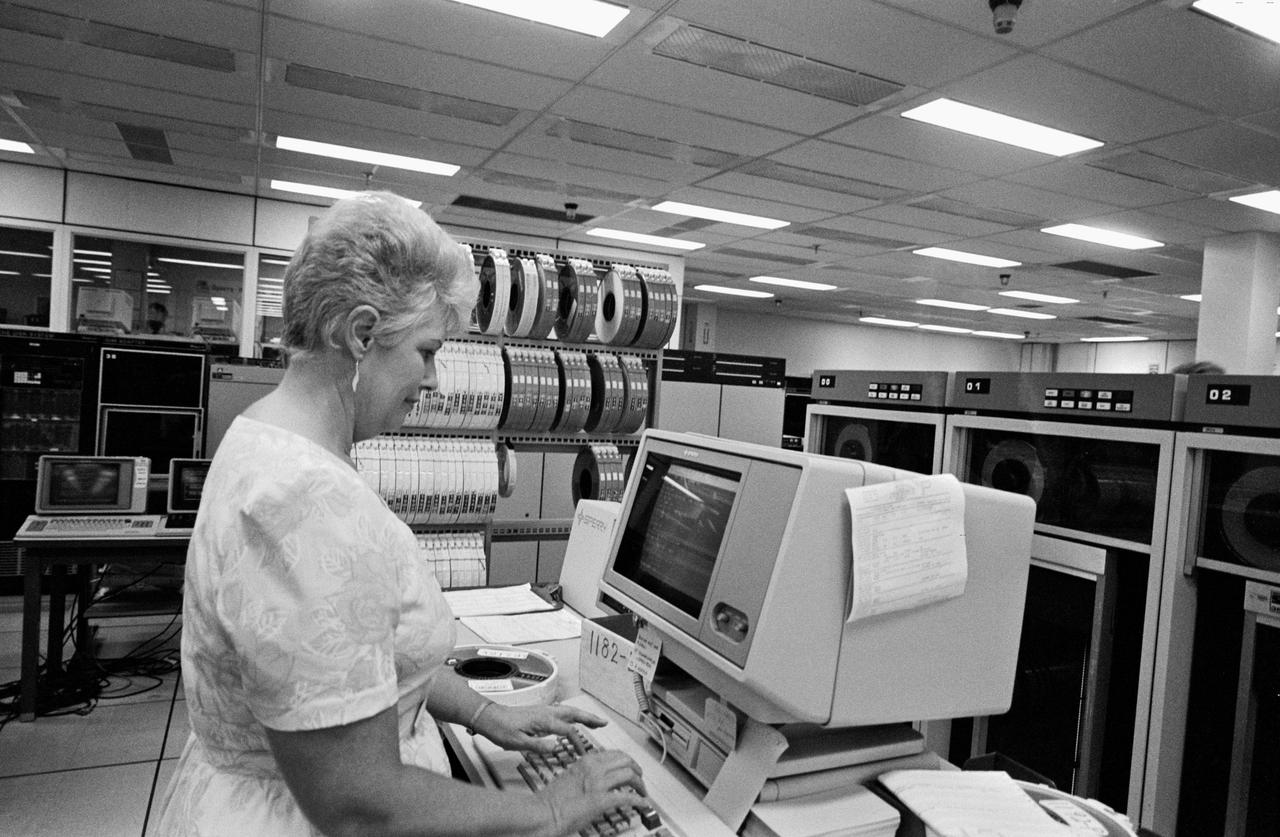

S86-30337 (4 April 1986) --- Digital data from the MADS tape is sent from Larue Forbes’ terminal to a hard copy printer in another facility at JSC.
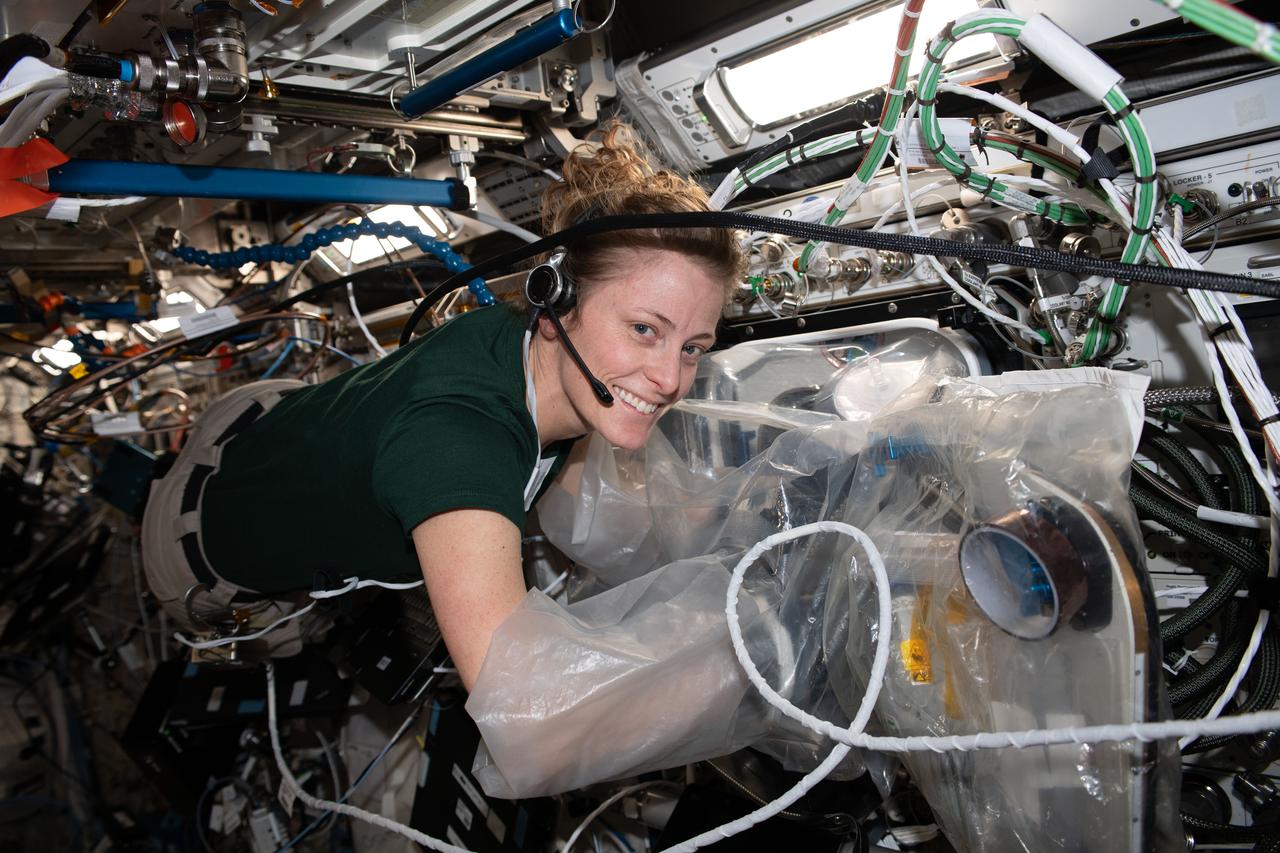

iss070e023971 (Nov. 13, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Loral O'Hara uses a portable glovebag to replace components on a biological printer, the BioFabrication Facility (BFF), that is testing the printing of organ-like tissues in microgravity.
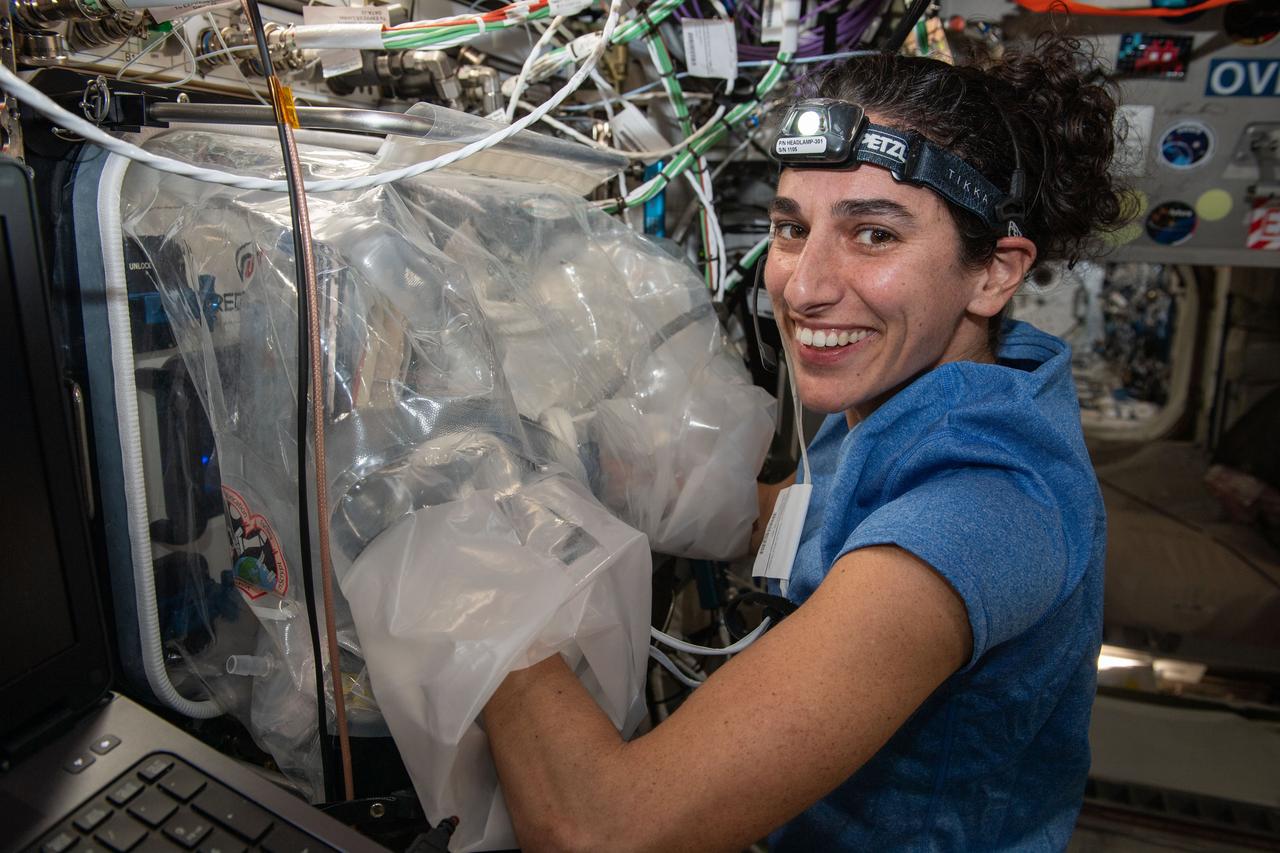

iss070e030135 (Nov. 24, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Jasmin Moghbeli uses a portable glovebag to swap components inside the BioFabrication Facility (BFF) located in the International Space Station's Columbus laboratory module. The BFF is a biological printer that is testing the printing of organ-like tissues in microgravity.
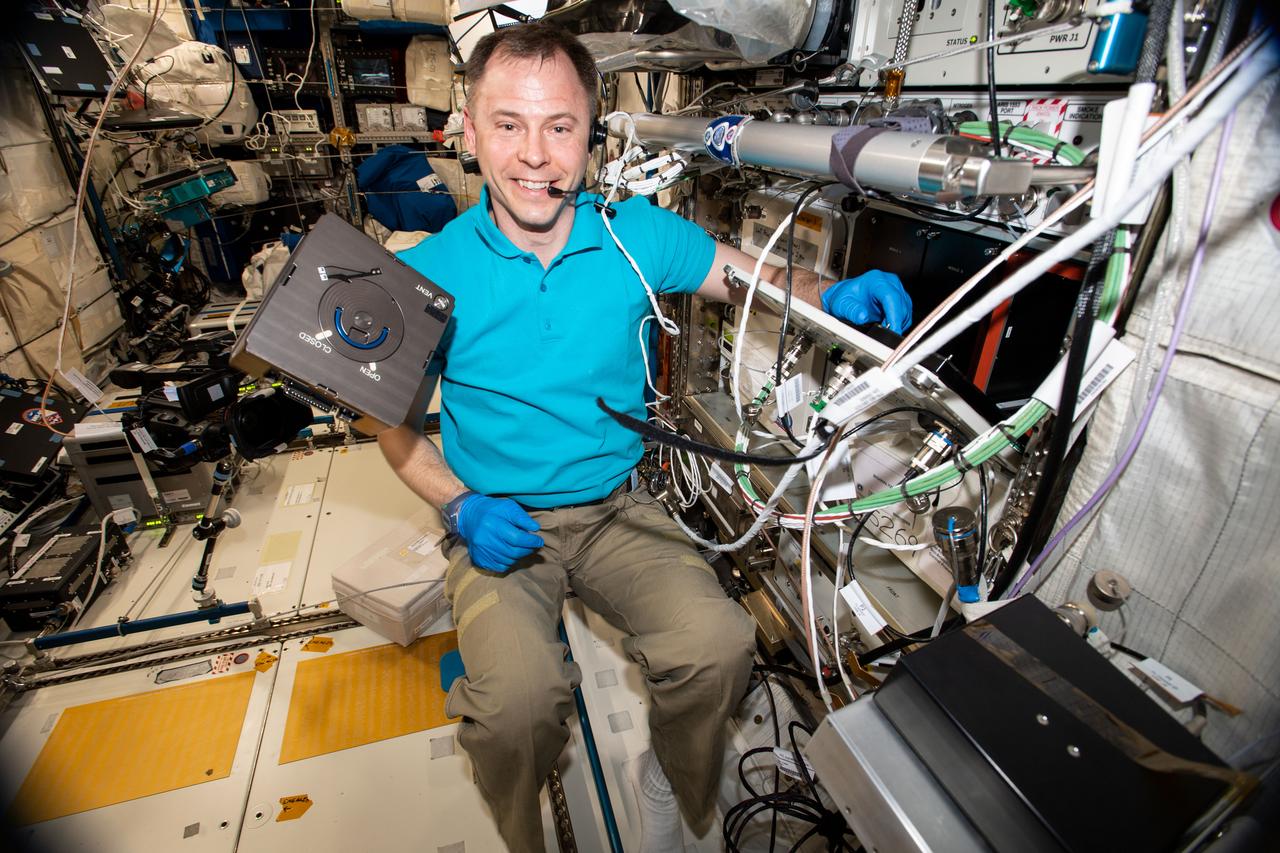

iss060e035050 (Aug. 12, 2019) --- Expedition 60 Flight Engineer Nick Hague of NASA conducts science operations inside Europe's Columbus Laboratory module for the BioFabrication Facility experiment. The study is investigating the effectiveness of using 3D biological printers to produce usable human organs in microgravity.
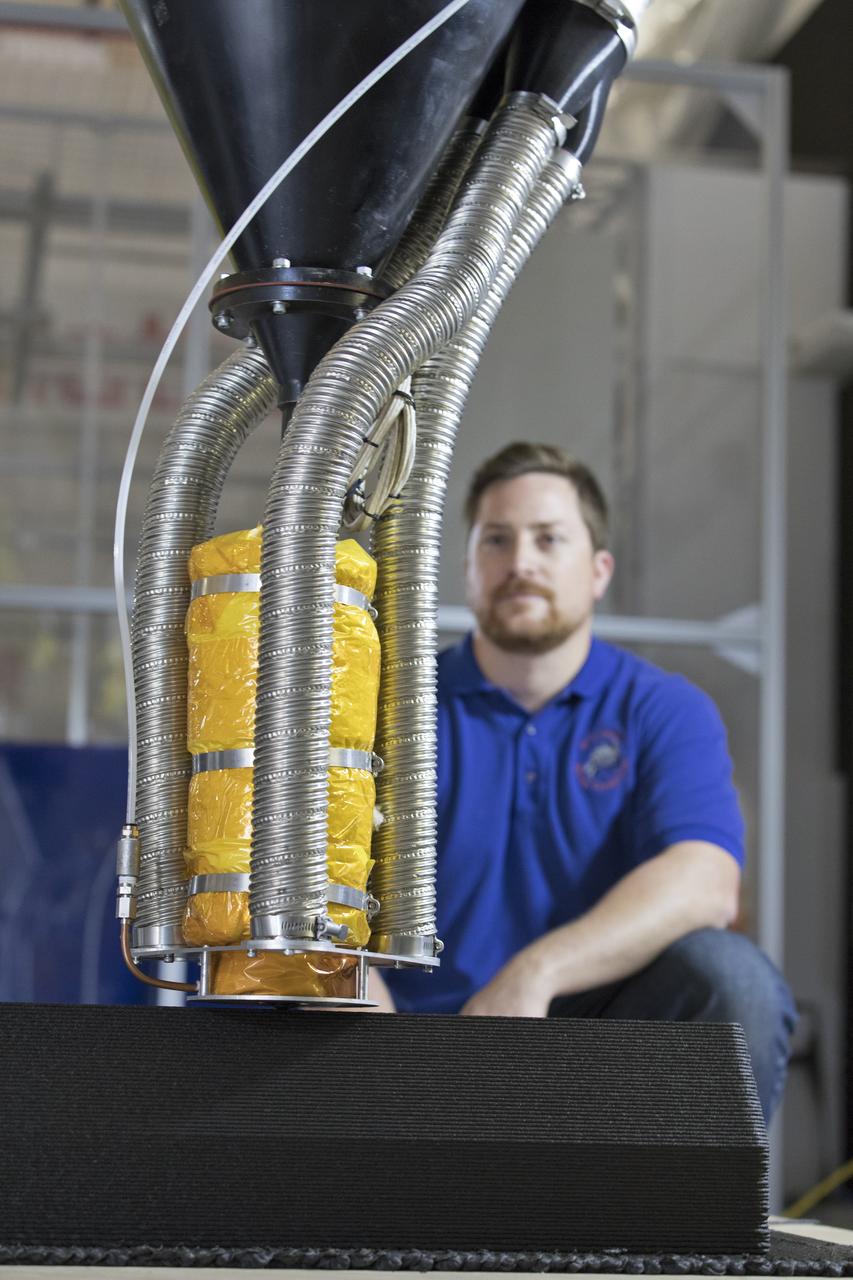

Nathan Gelino, a NASA research engineer at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is working on a Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer in the center's Swamp Works that can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars, and even for troops in remote locations here on Earth. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses pellets made from simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers to prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. Gelino and his team are working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.
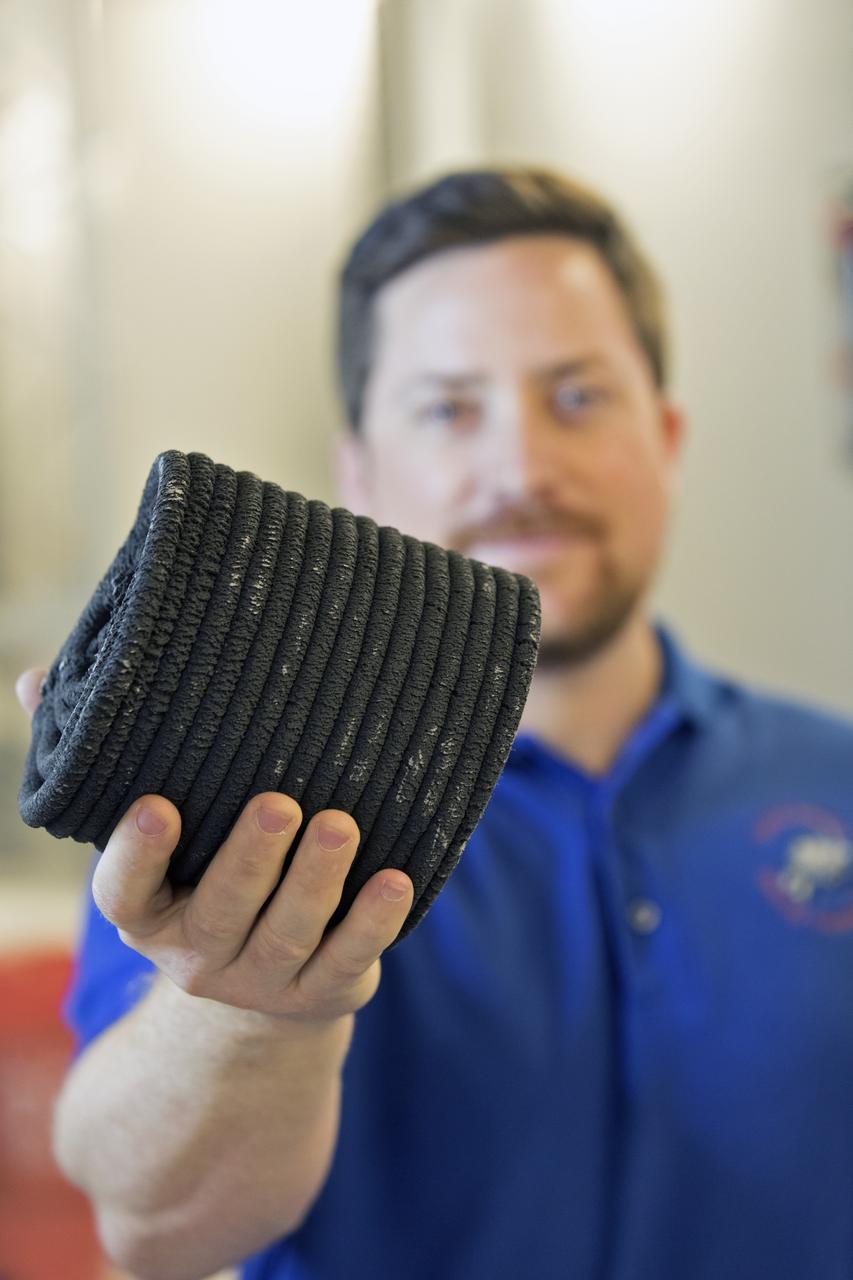

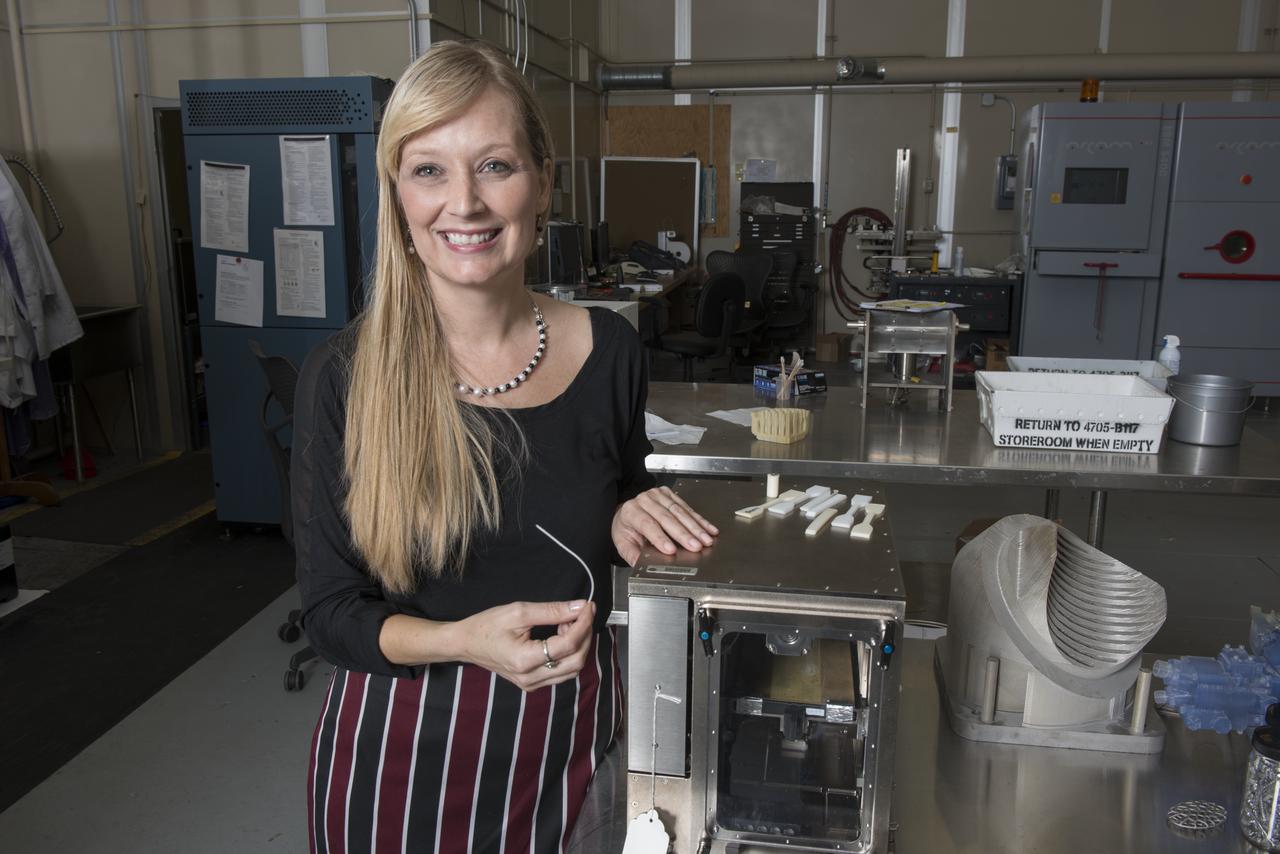
Nathan Gelino, a NASA research engineer at Kennedy Space Center in Florida displays a 3-D printed cylinder used for compression testing. Engineers at the center’s Swamp Works measured how much force it takes to break the structure before moving on to 3-D printing with a simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers. Next, Gelino and his group are working on a Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer that can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars, even for troops in remote locations here on Earth. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses these pellets to prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. Gelino and his team are working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.
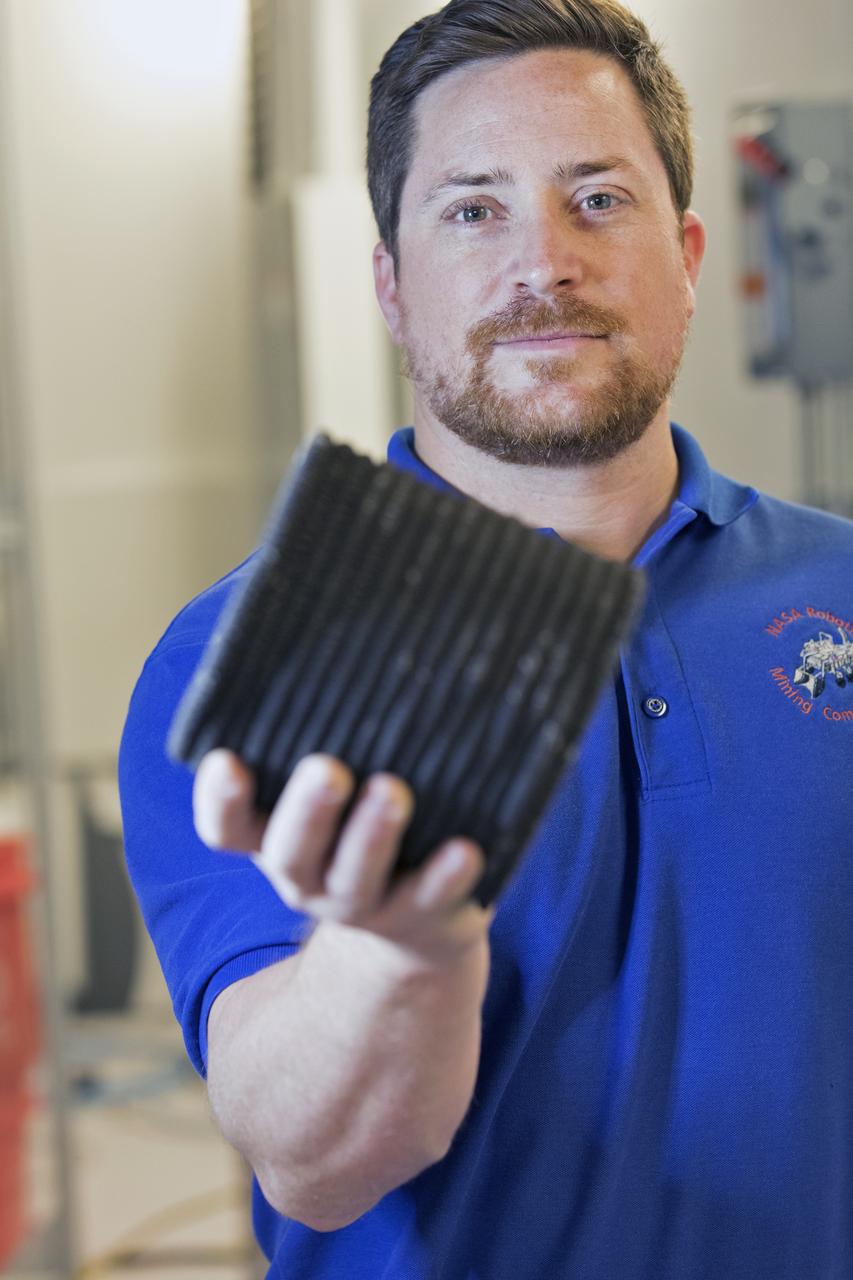

Nathan Gelino, a NASA research engineer at Kennedy Space Center in Florida displays a 3-D printed cylinder used for compression testing. Engineers at the center’s Swamp Works measured how much force it takes to break the structure before moving on to 3-D printing with a simulated lunar regolith, or dirt, and polymers. Next, Gelino and his group are working on a Zero Launch Mass 3-D printer that can be used for construction projects on the Moon and Mars, even for troops in remote locations here on Earth. Zero launch mass refers to the fact that the printer uses these pellets to prove that space explorers can use resources at their destination instead of taking everything with them, saving them launch mass and money. Gelino and his team are working with Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to develop a system that can 3-D print barracks in remote locations on Earth, using the resources they have where they are.
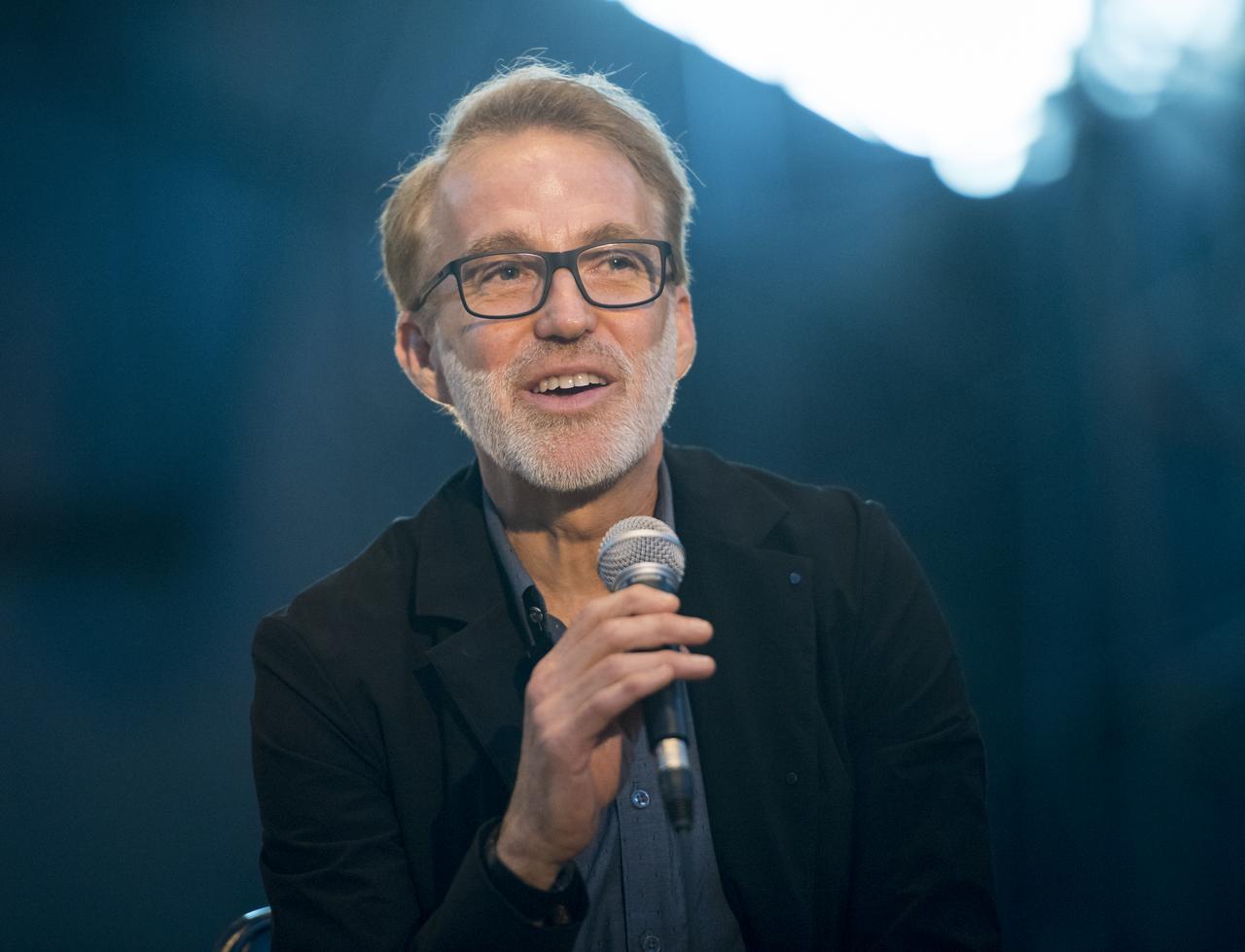

Michael Painter, senior program officer, Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, speaks on a panel on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
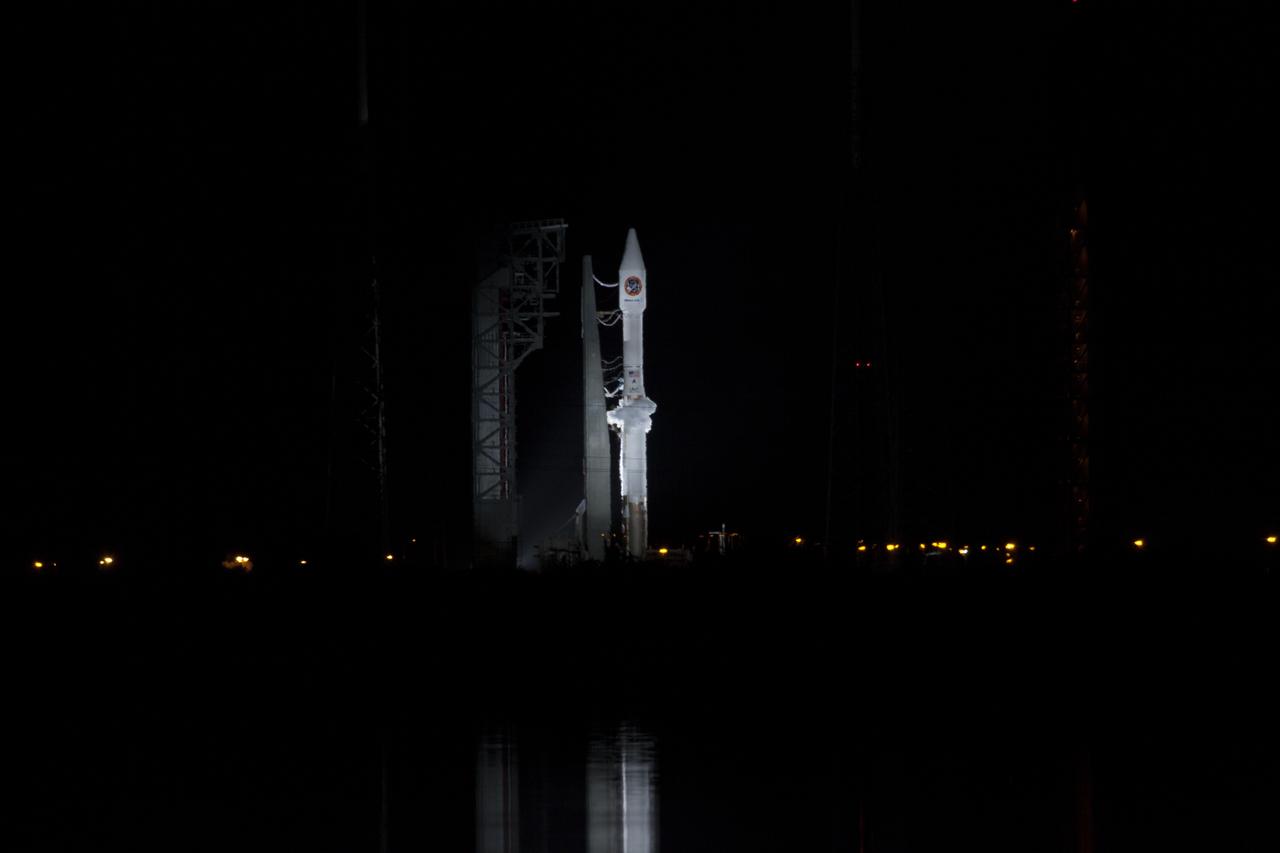

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
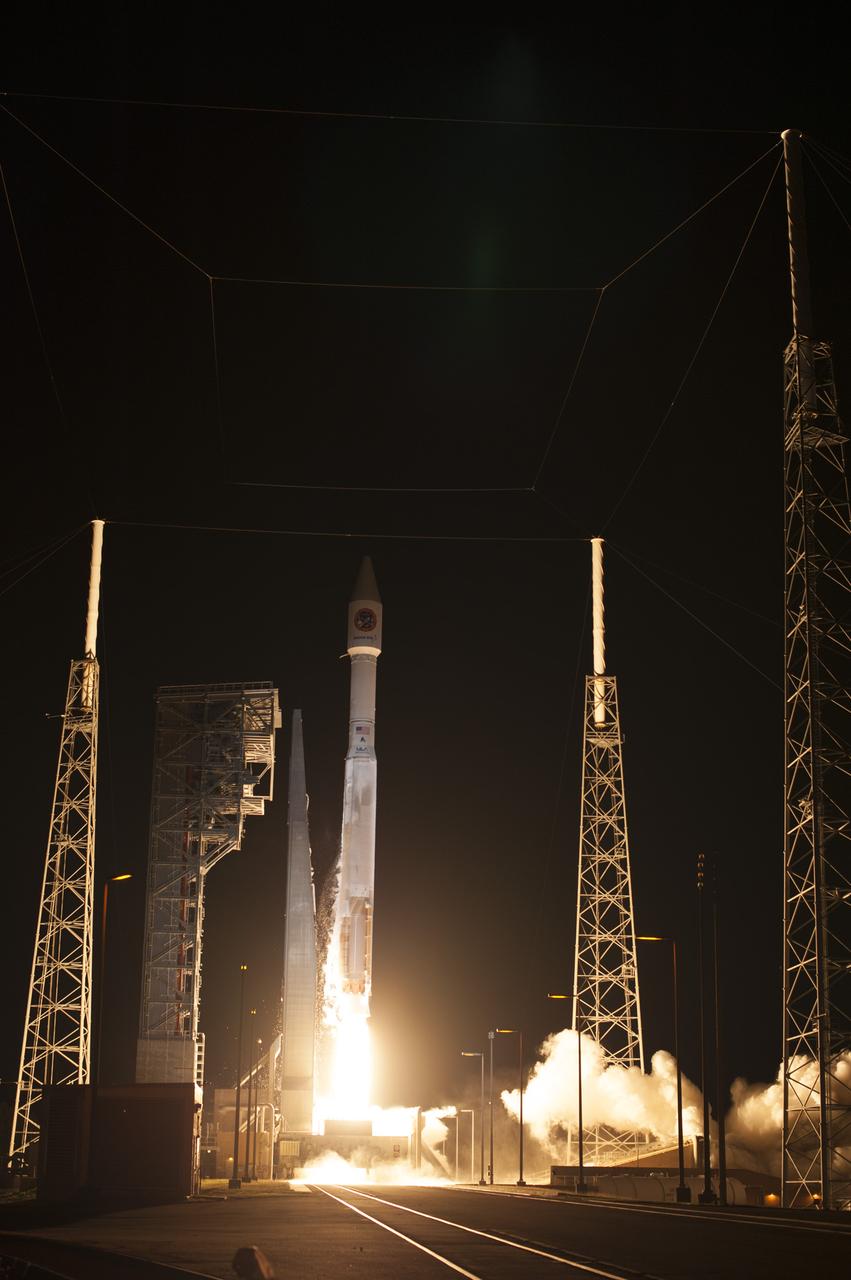

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
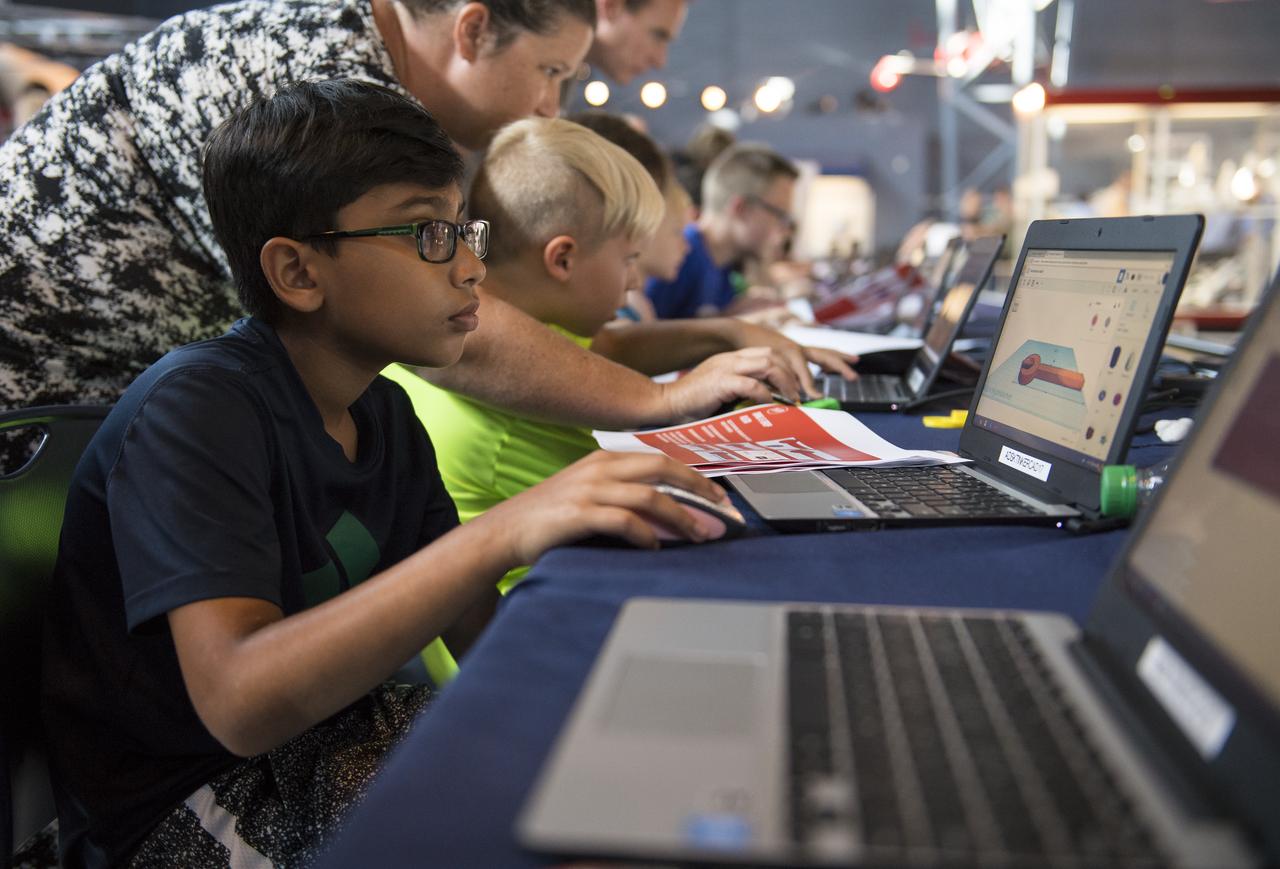

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
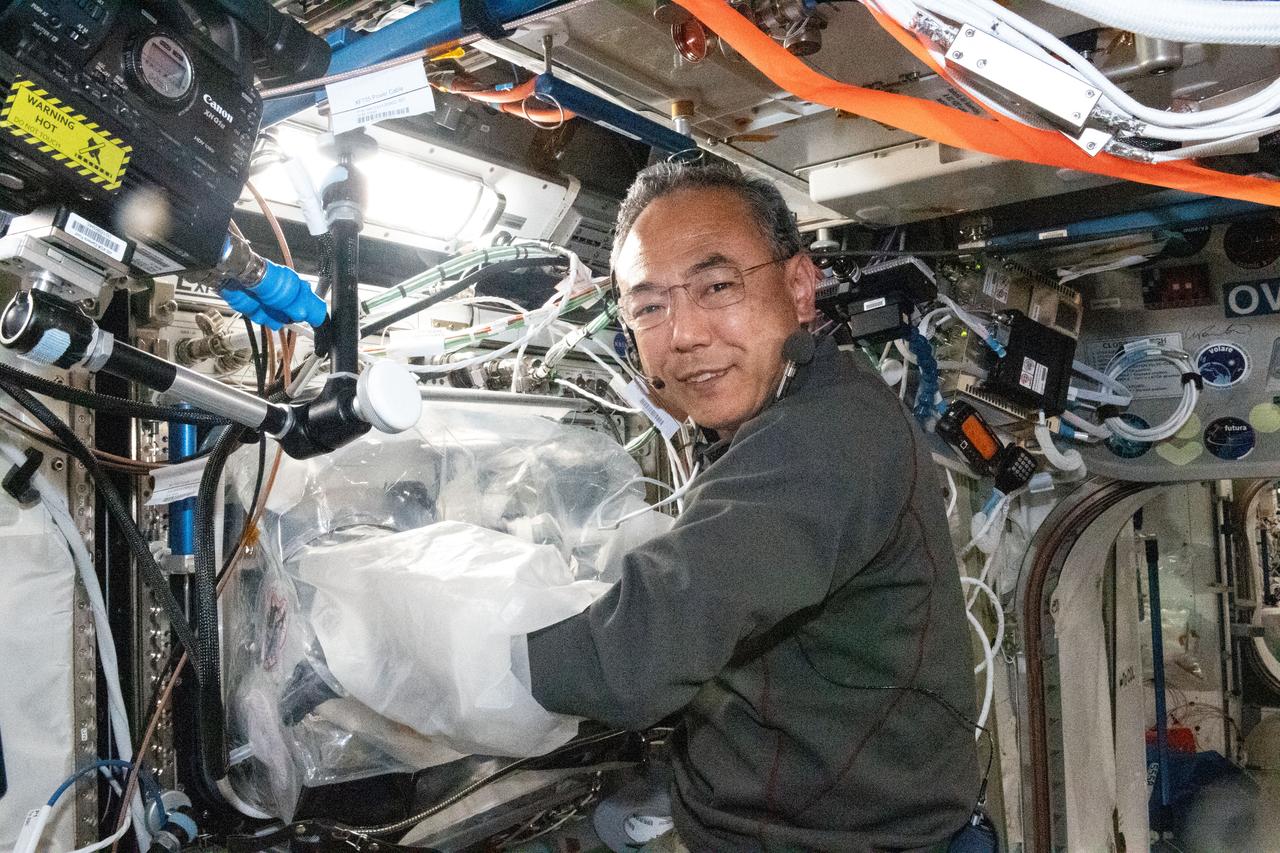

iss069e086005 (Sept. 6, 2023) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Satoshi Furukawa replaces components on the BioFabrication Facility (BFF). The 3D biological printer, located in the International Space Station's Columbus laboratory module, is testing printing organ-like tissues in microgravity with an eye to manufacturing whole human organs in space in the future.
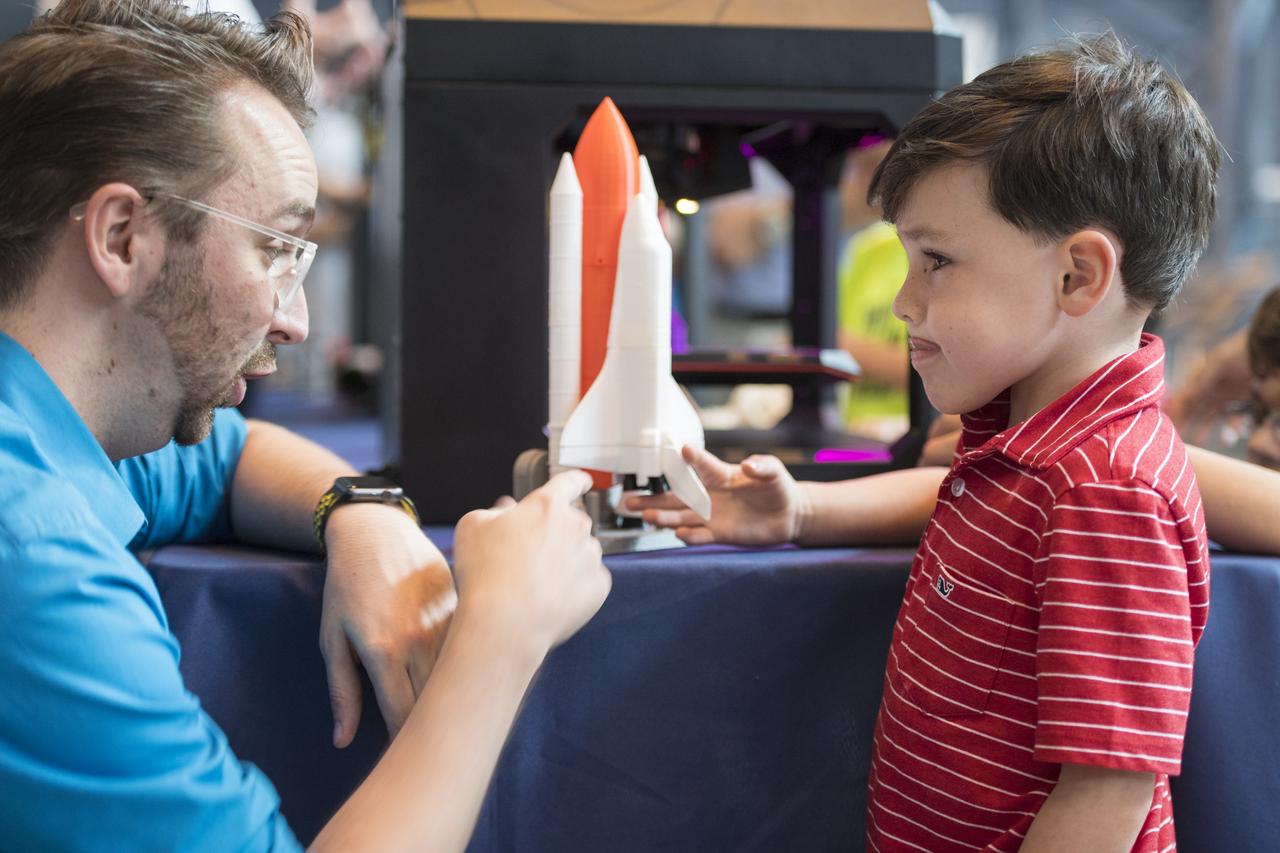

A visitor learns about 3D printing at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
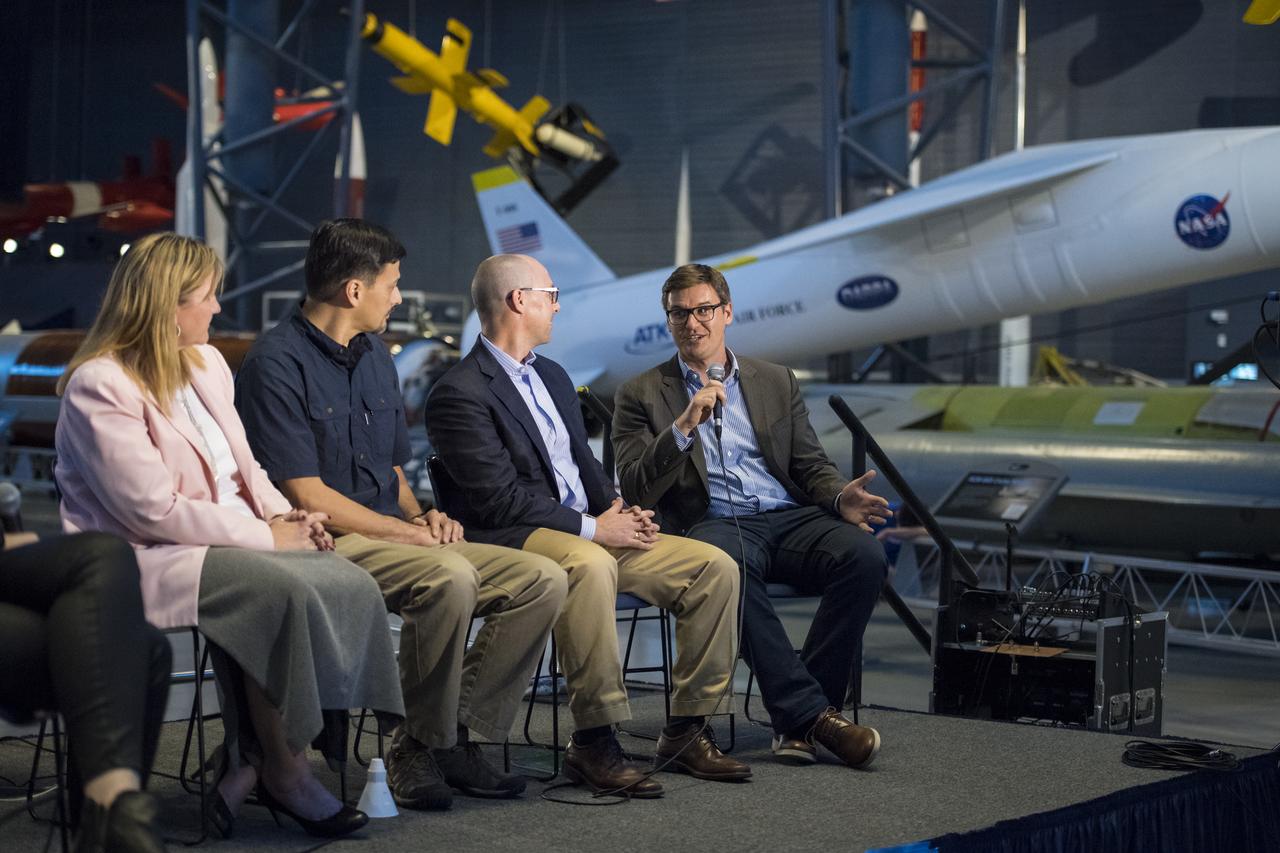

Paul Scott, interim executive director, The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), speaks on a panel on "igniting NOVA K-12 engineering and maker education", at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and ASME, at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
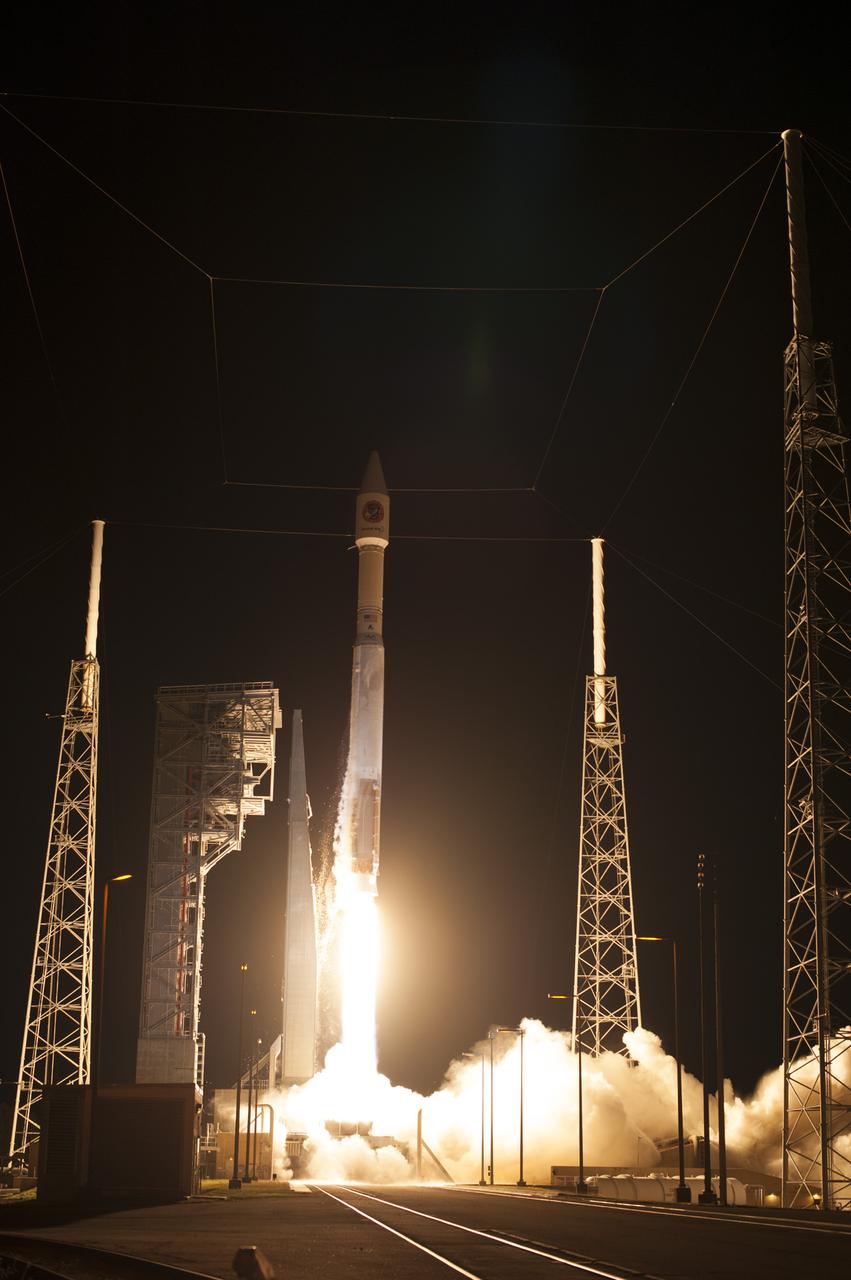

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
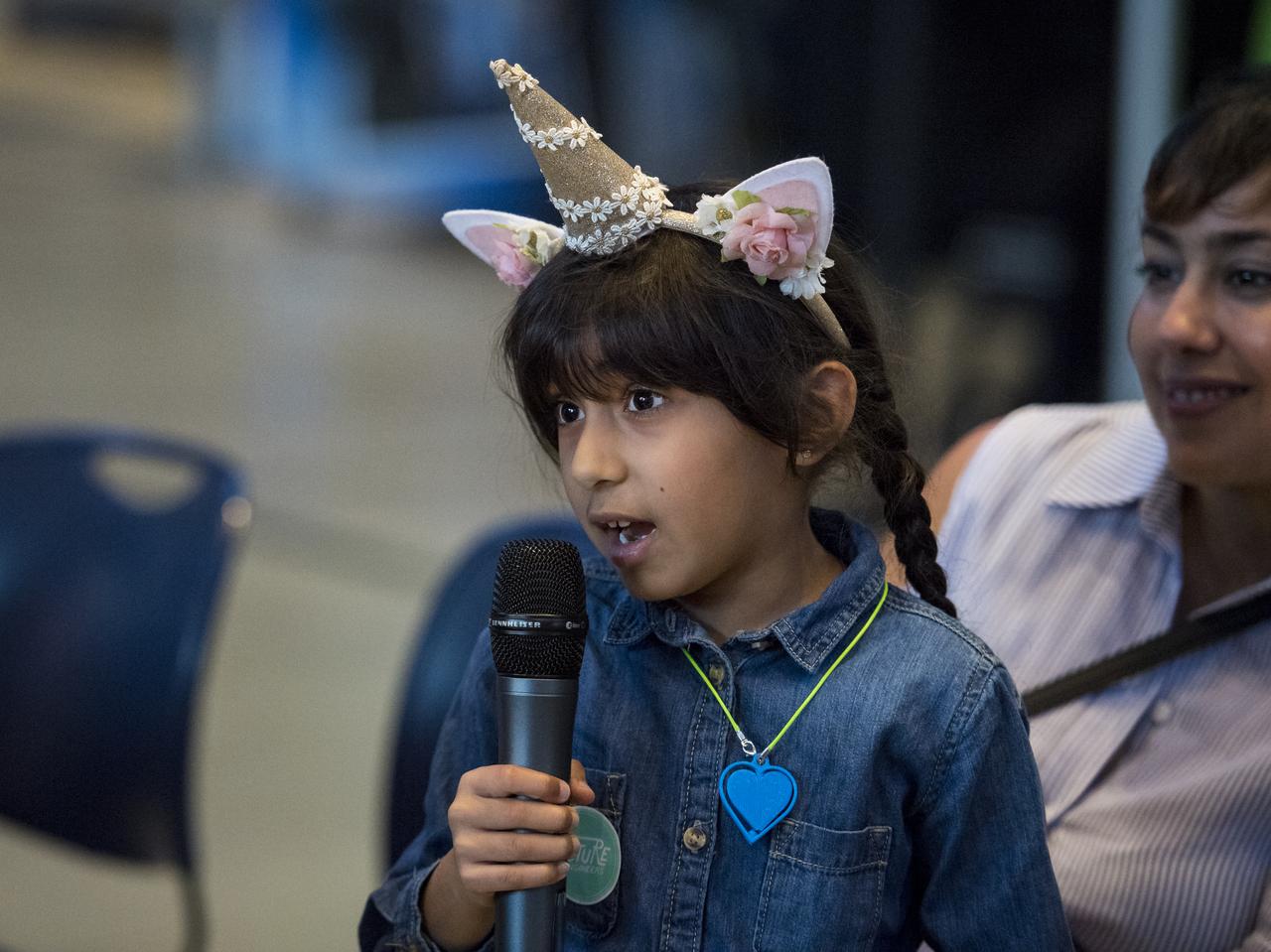

A young audience member asks the panel a question during a discussion on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
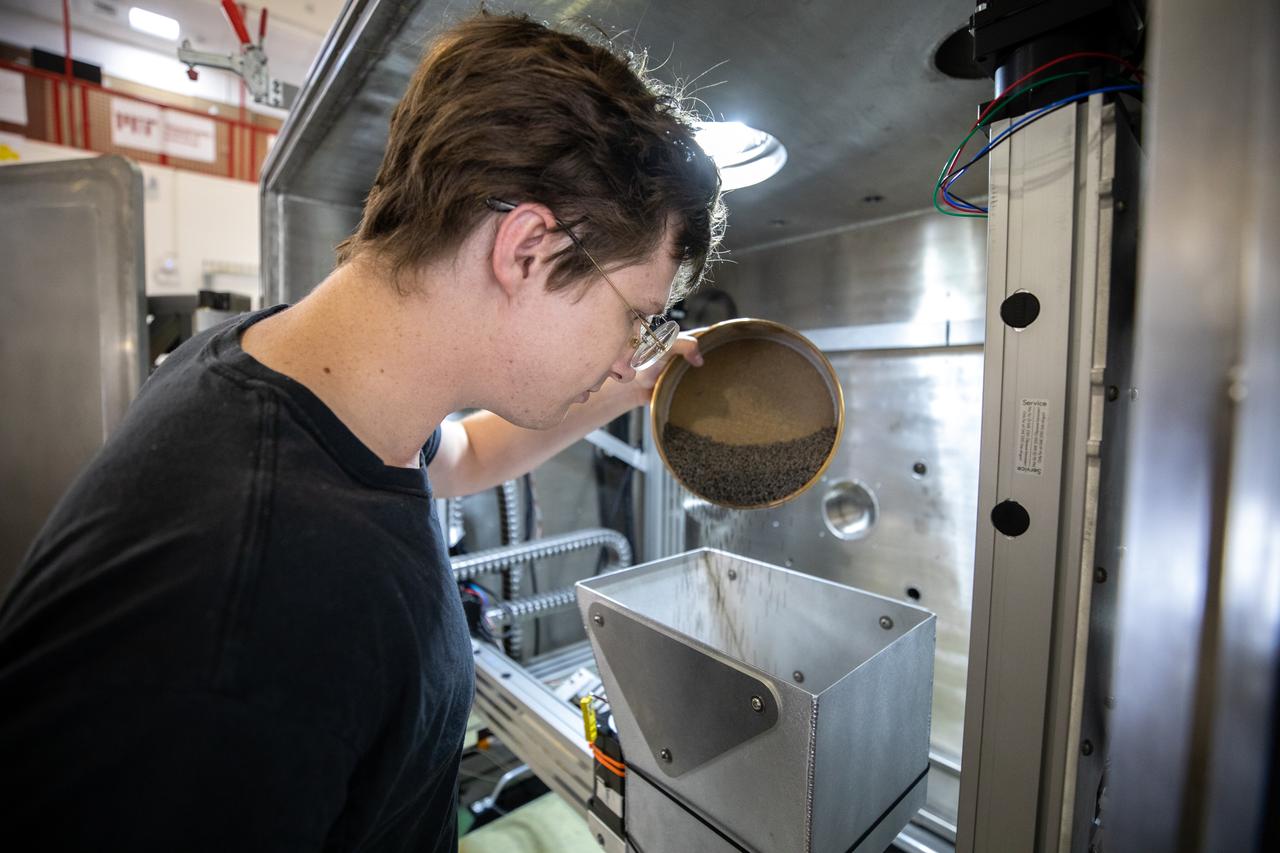

Materials engineer Thomas Lipscomb tests a 3D printer on July 28, 2022, at Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as part of the Relevant Environment Additive Construction Technology (REACT) project. Among the key objectives of the project is developing an architectural and structural design for a shelter that provides protection to habitable assets on the lunar surface. Testing REACT derives from NASA’s 2020 Announcement of Collaboration Opportunity with AI SpaceFactory – an architectural and construction technology company and winner of NASA’s 3D Printed Habitat Challenge.
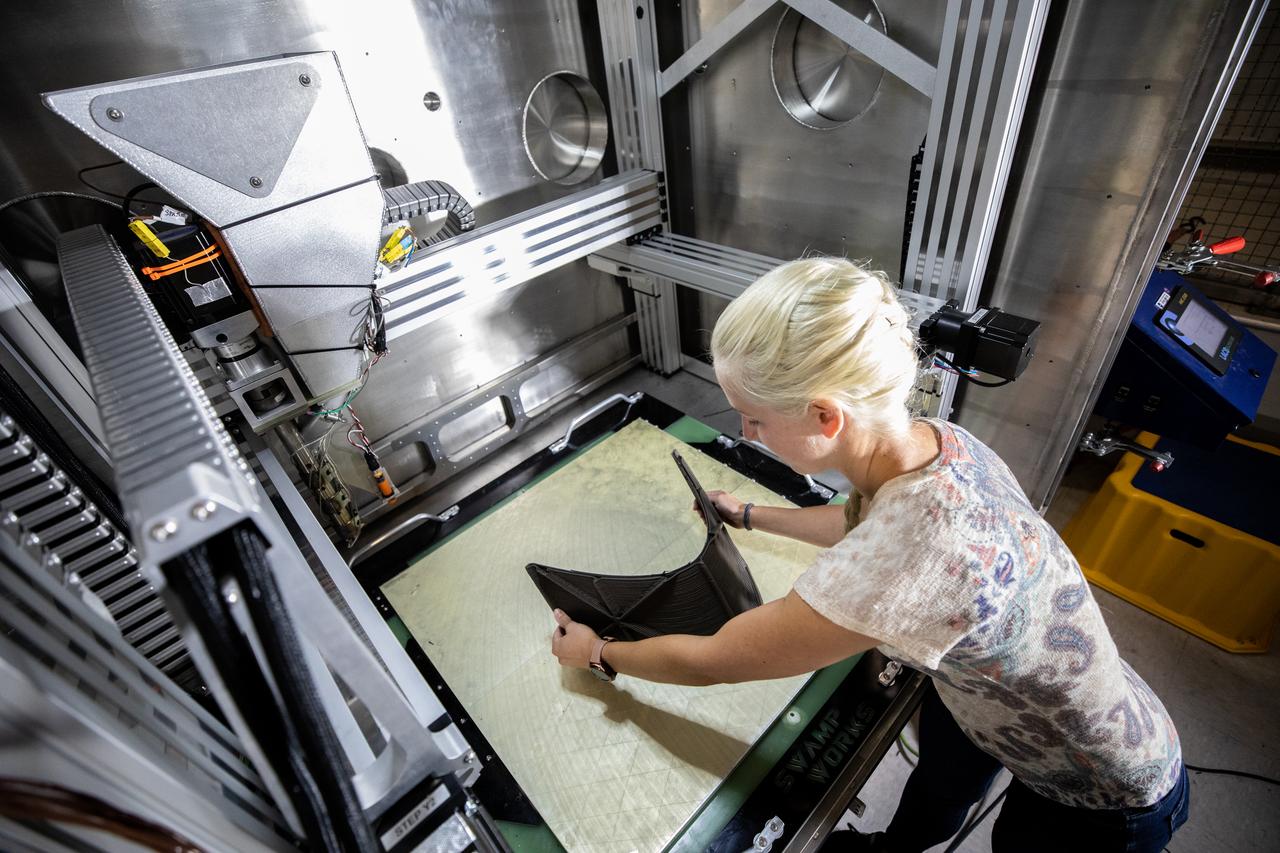

Chemist Tesia Irwin tests a 3D printer on July 28, 2022, at Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as part of the Relevant Environment Additive Construction Technology (REACT) project. Among the key objectives of the project is developing an architectural and structural design for a shelter that provides protection to habitable assets on the lunar surface. Testing REACT derives from NASA’s 2020 Announcement of Collaboration Opportunity with AI SpaceFactory – an architectural and construction technology company and winner of NASA’s 3D Printed Habitat Challenge.
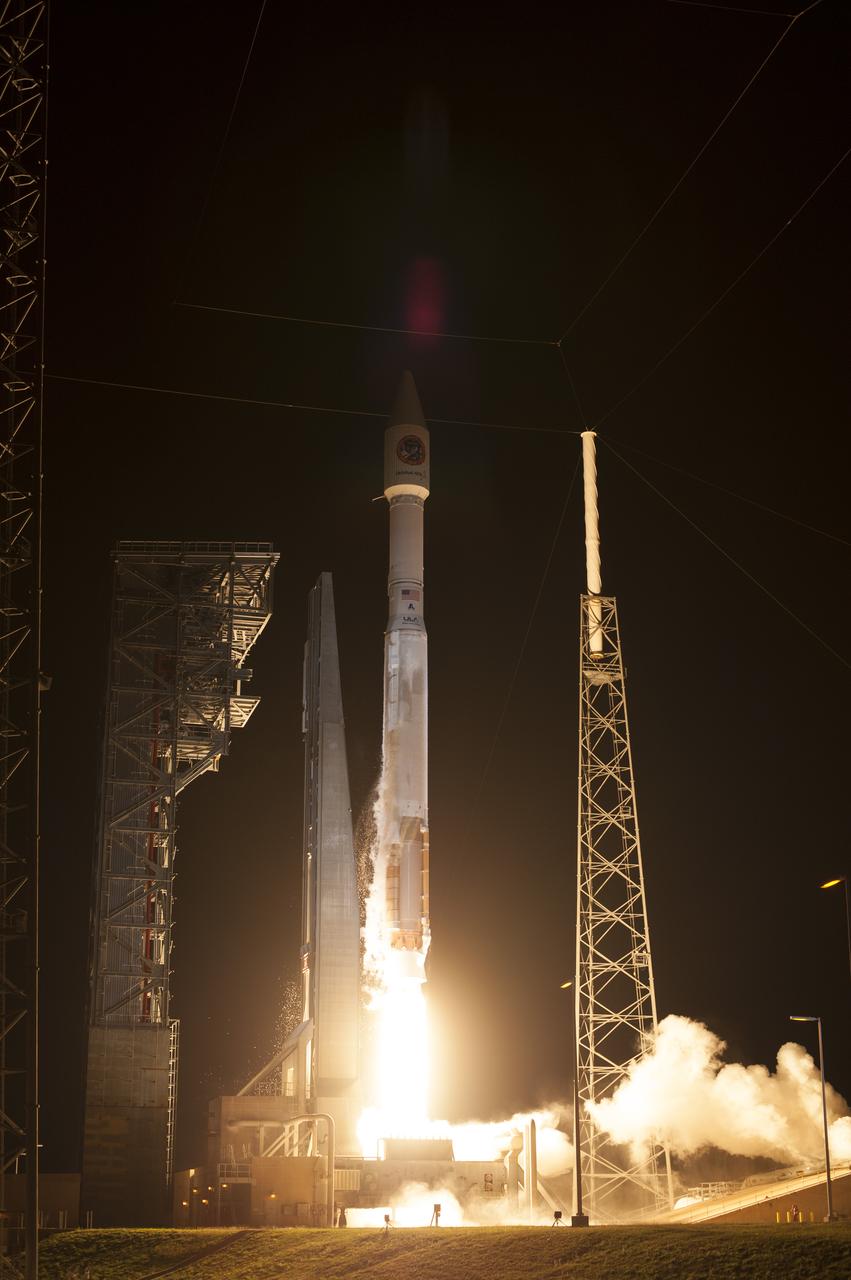

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
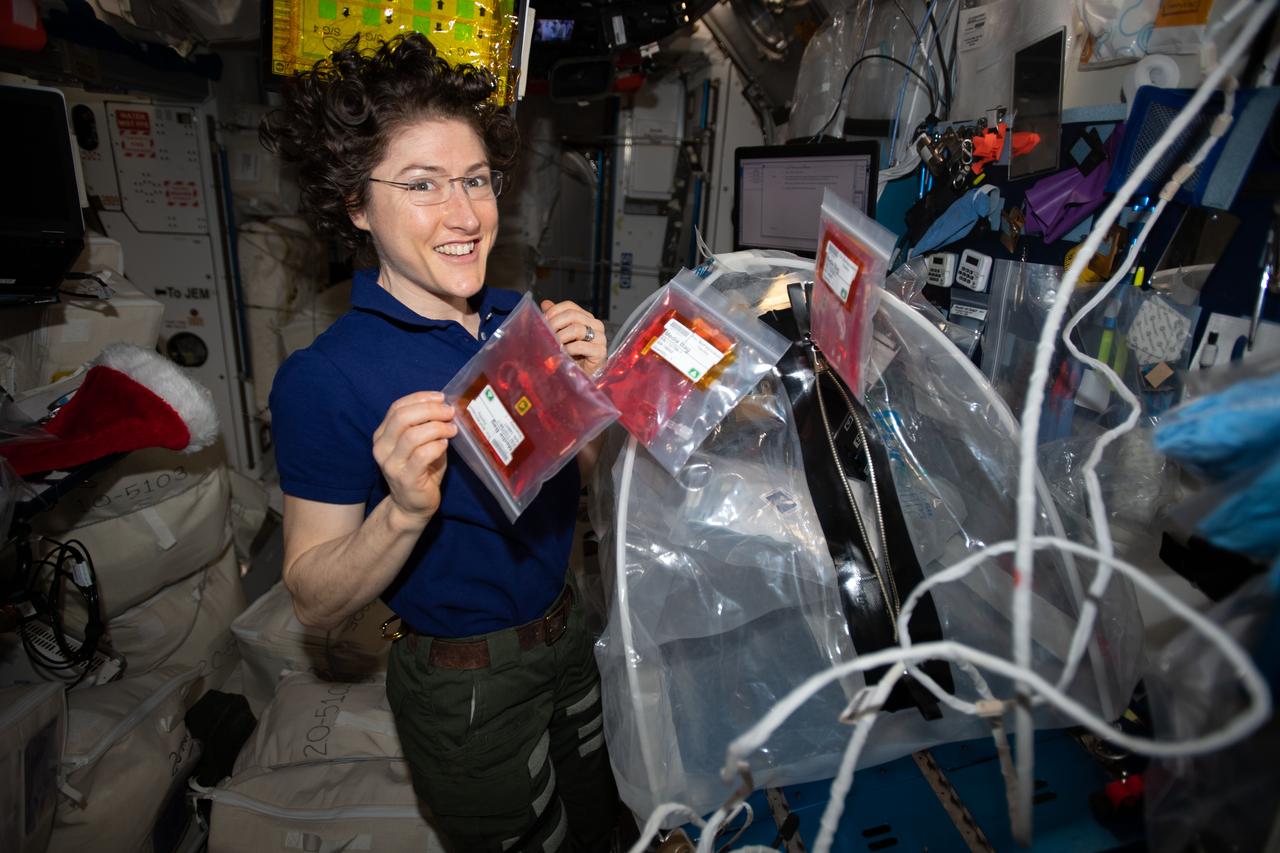

iss061e093848 (Dec. 22, 2019) --- Expedition 61 Flight Engineer and NASA astronaut Christina Koch handles media bags that enable the manufacturing of organ-like tissues using the the BioFabrication Facility (BFF), a 3-D biological printer. The BFF could become a part of a larger system capable of manufacturing whole, fully-functioning human organs from existing patient cells in microgravity.
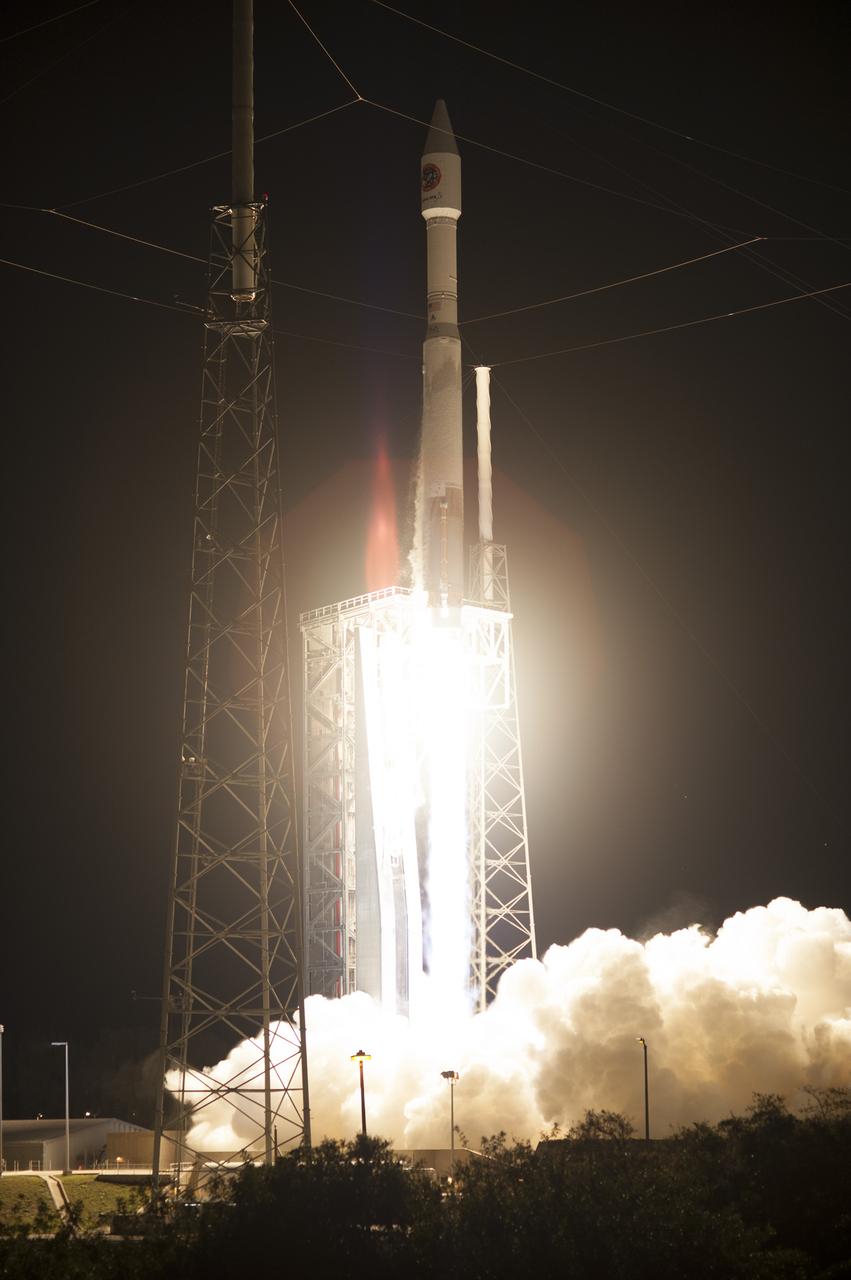

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
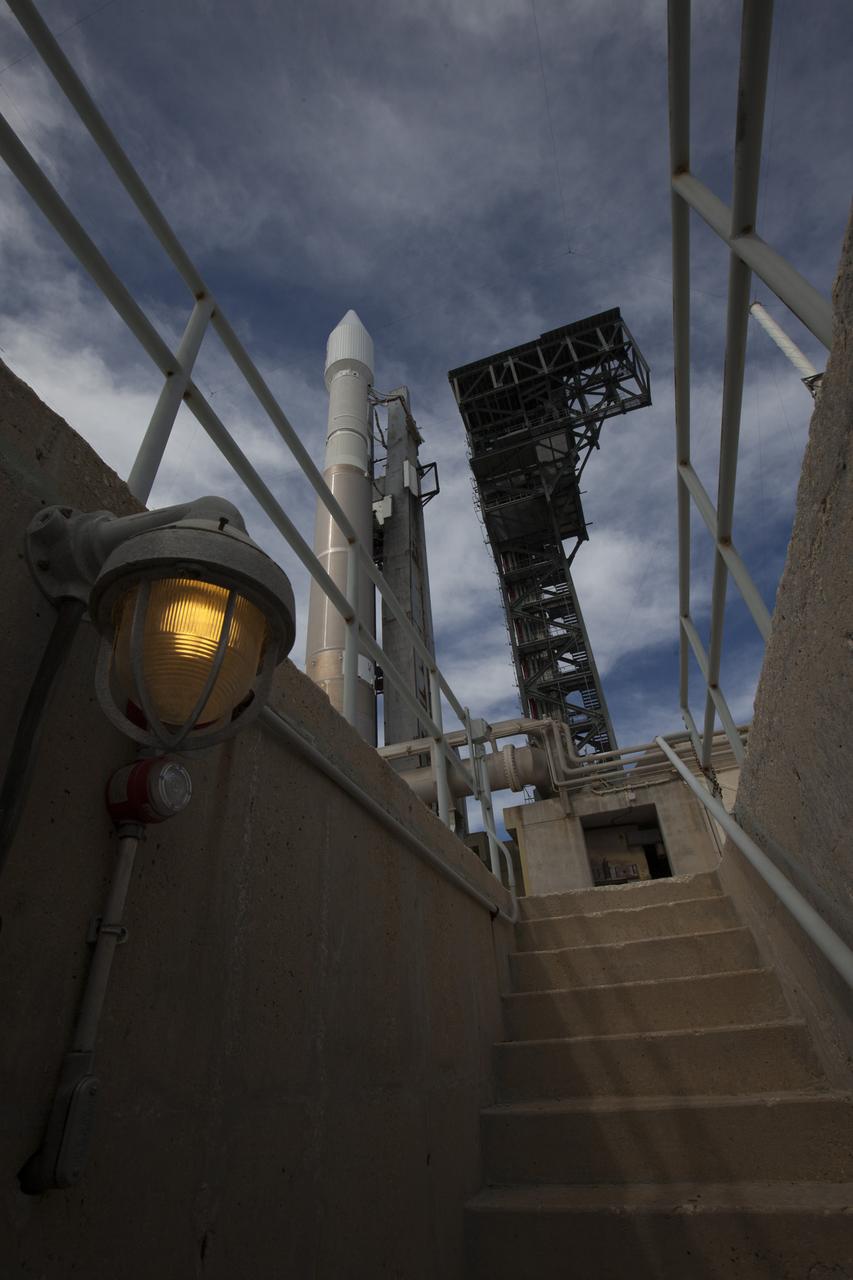

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
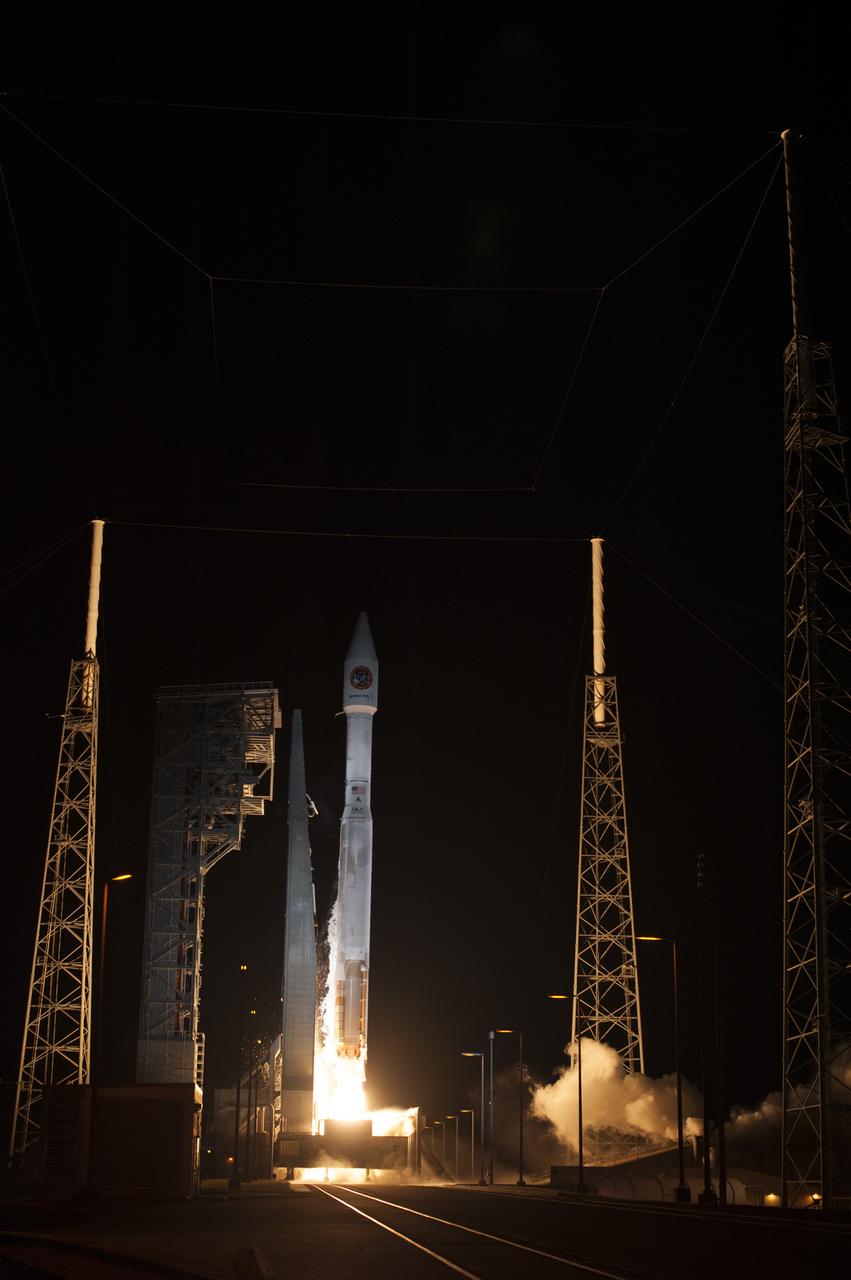

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
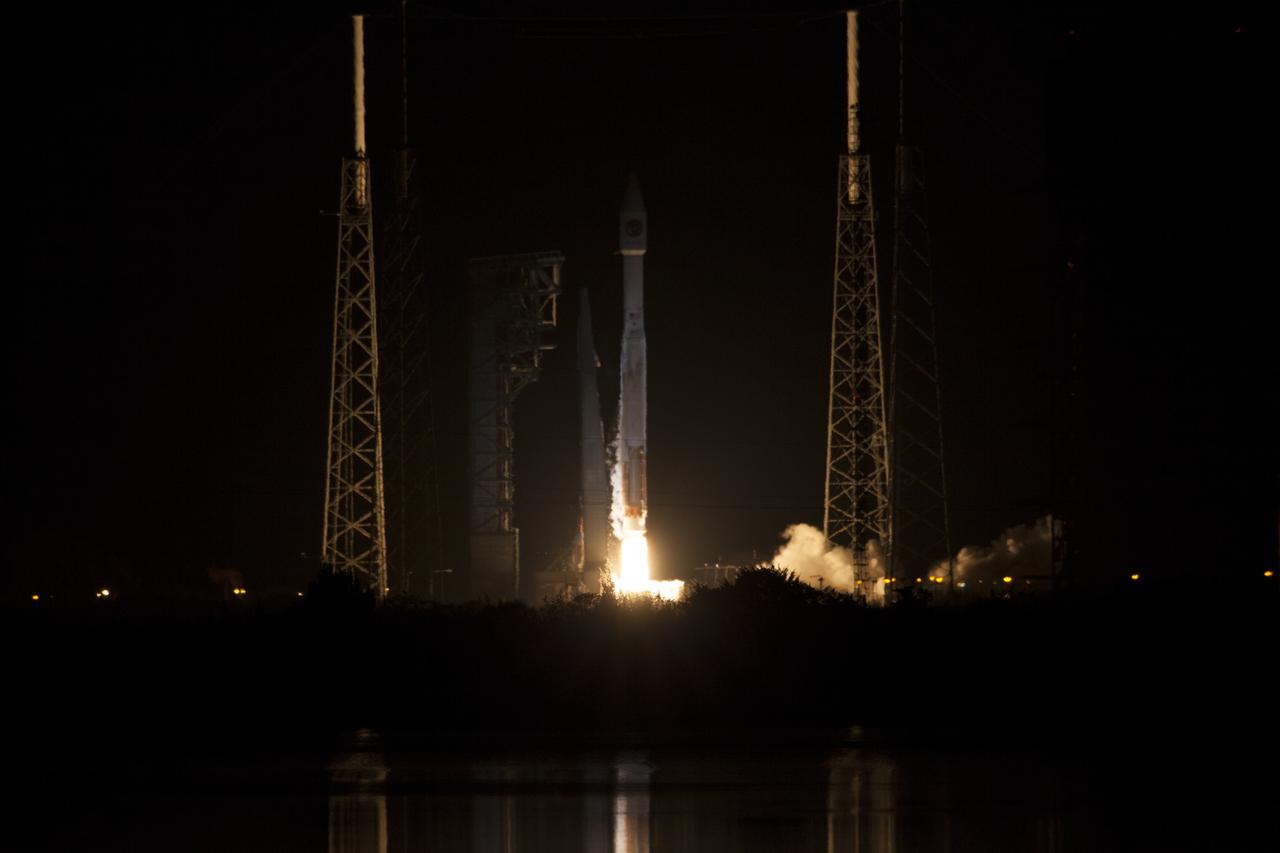

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
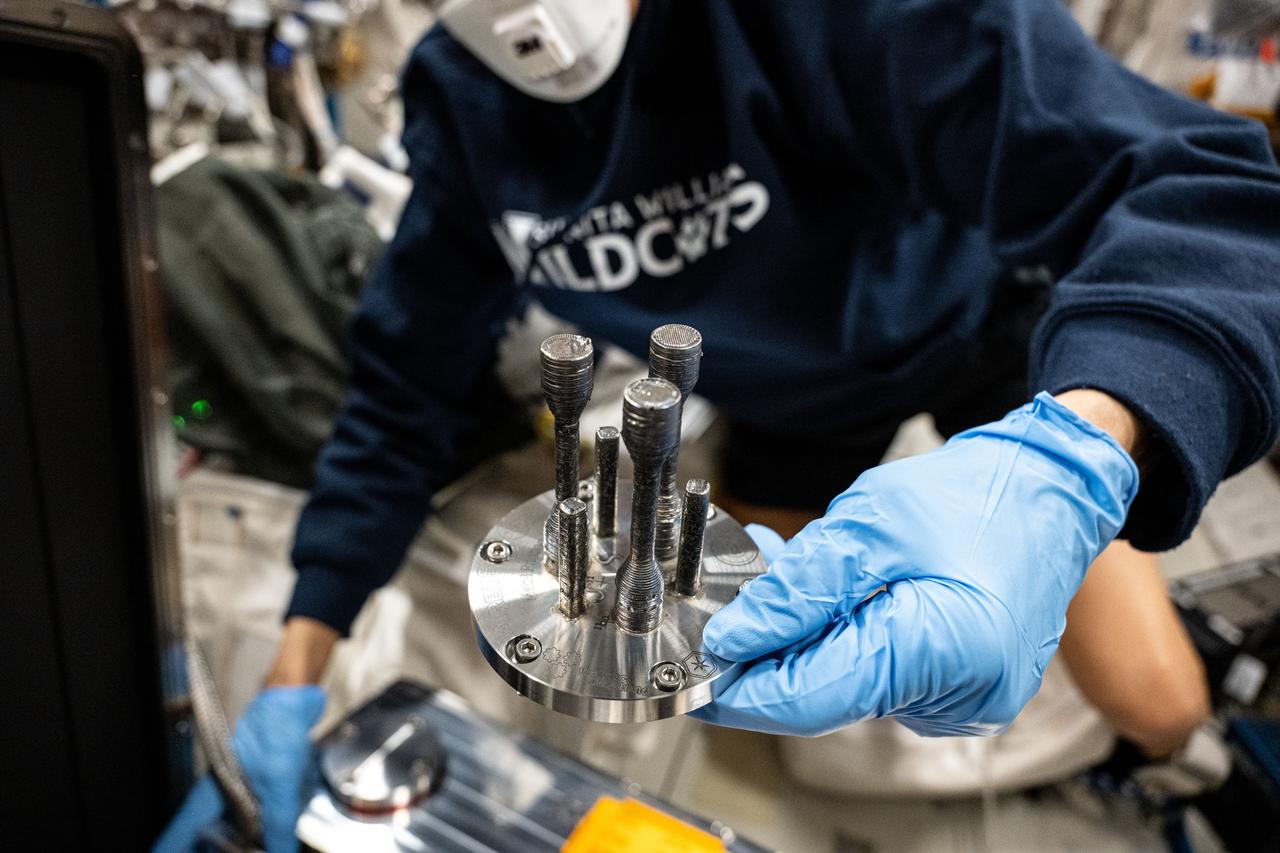

iss071e522123 (8/21/2024) --- A metal specimen 3D printed in space for ESA’s Metal 3D Printer investigation. Researchers successfully produced the first metal parts printed in space and found their quality in line with expectations and now plan to print additional specimens in space. Resupply becomes challenging as mission duration and distance from Earth increase, and 3D printing could provide a way to make parts for repairs and dedicated tools on demand, increasing mission autonomy.

Two mirrirless Digital Camers, 56mm f1.2 lens, 90mm f2 lens, 35mm f2 lens, 23mm f2 lens, 6x4.5 Medium Format Film Camera, 120 film, Singing Bowl, wirerless instant printer, My 3yr olds Astronaut toy, family photos, Oldest Sons (27) baby shoes for luck, Laptop, Phone (for music), Tablet and Pen, Water Bottle.
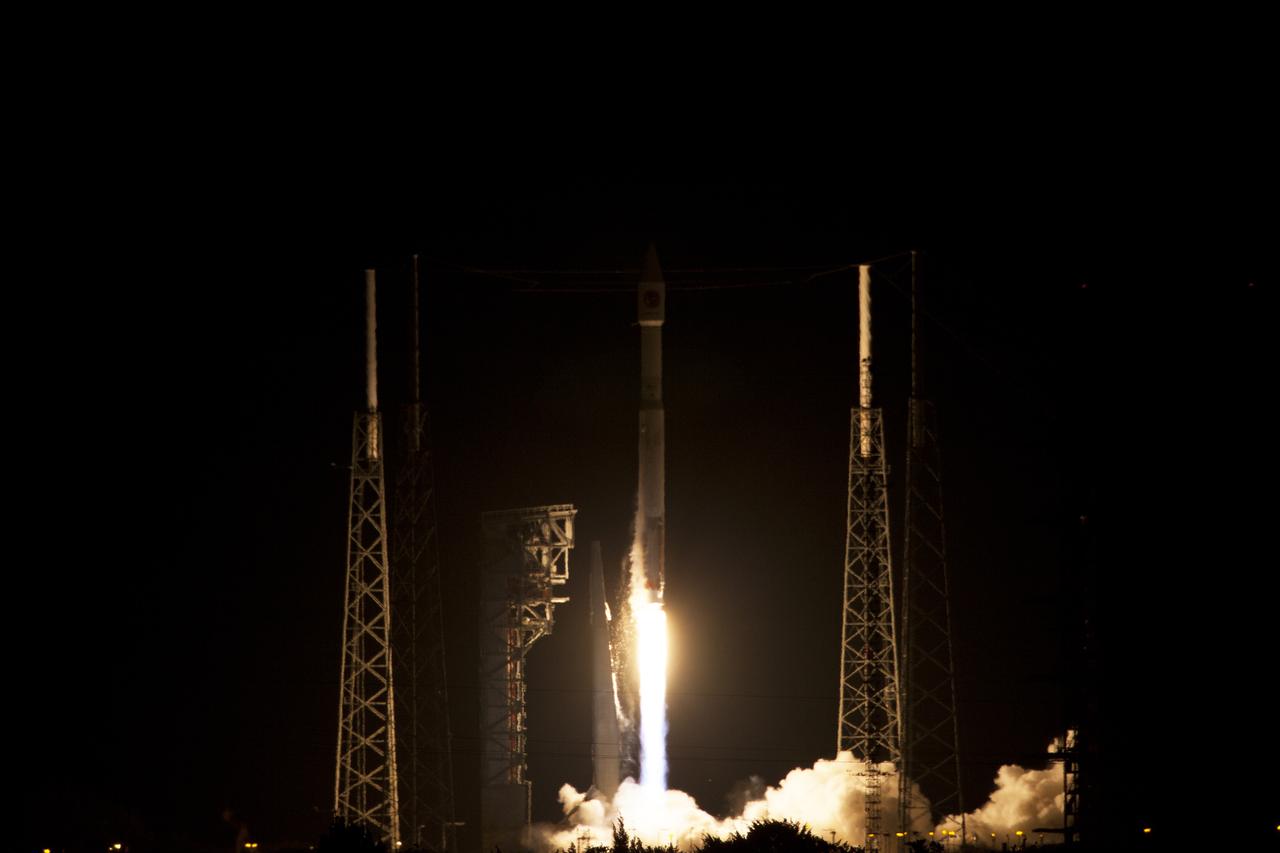

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
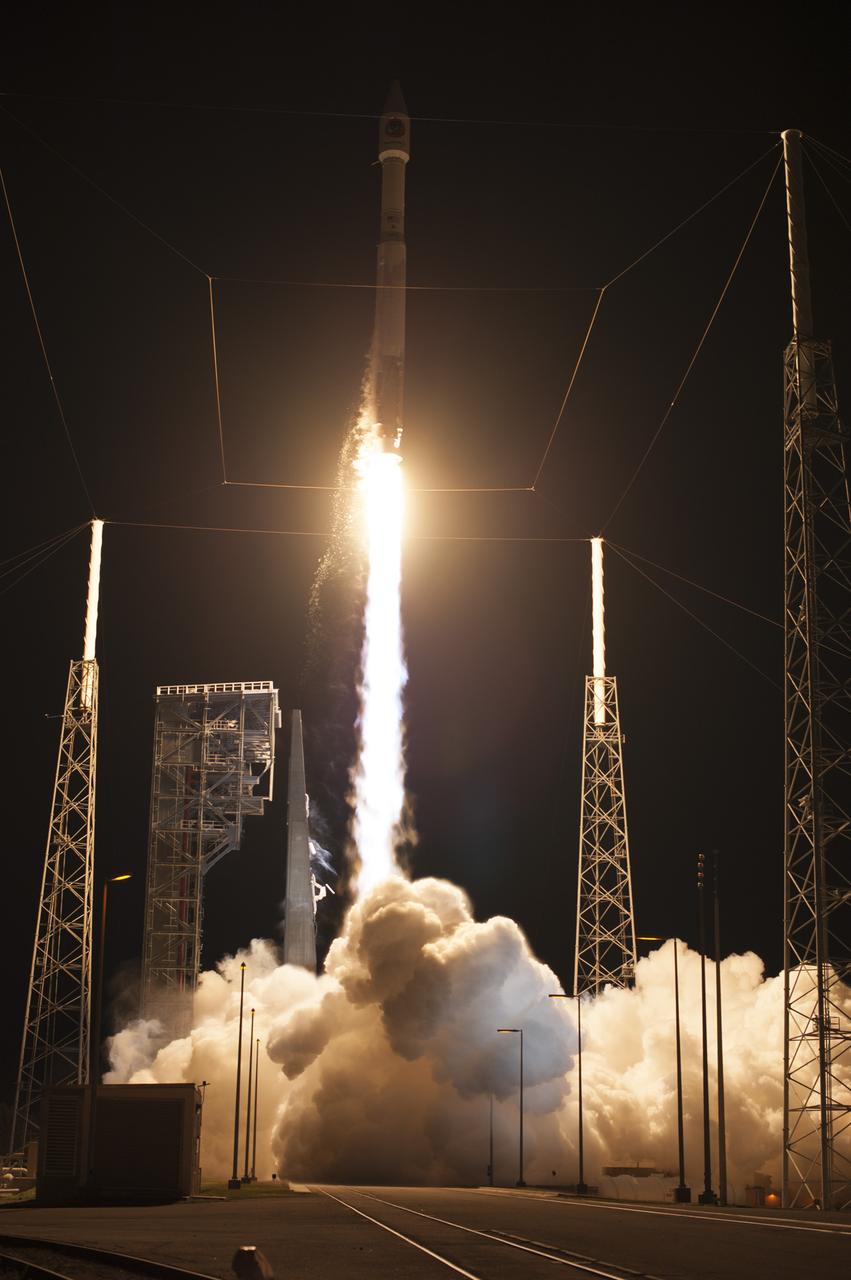

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
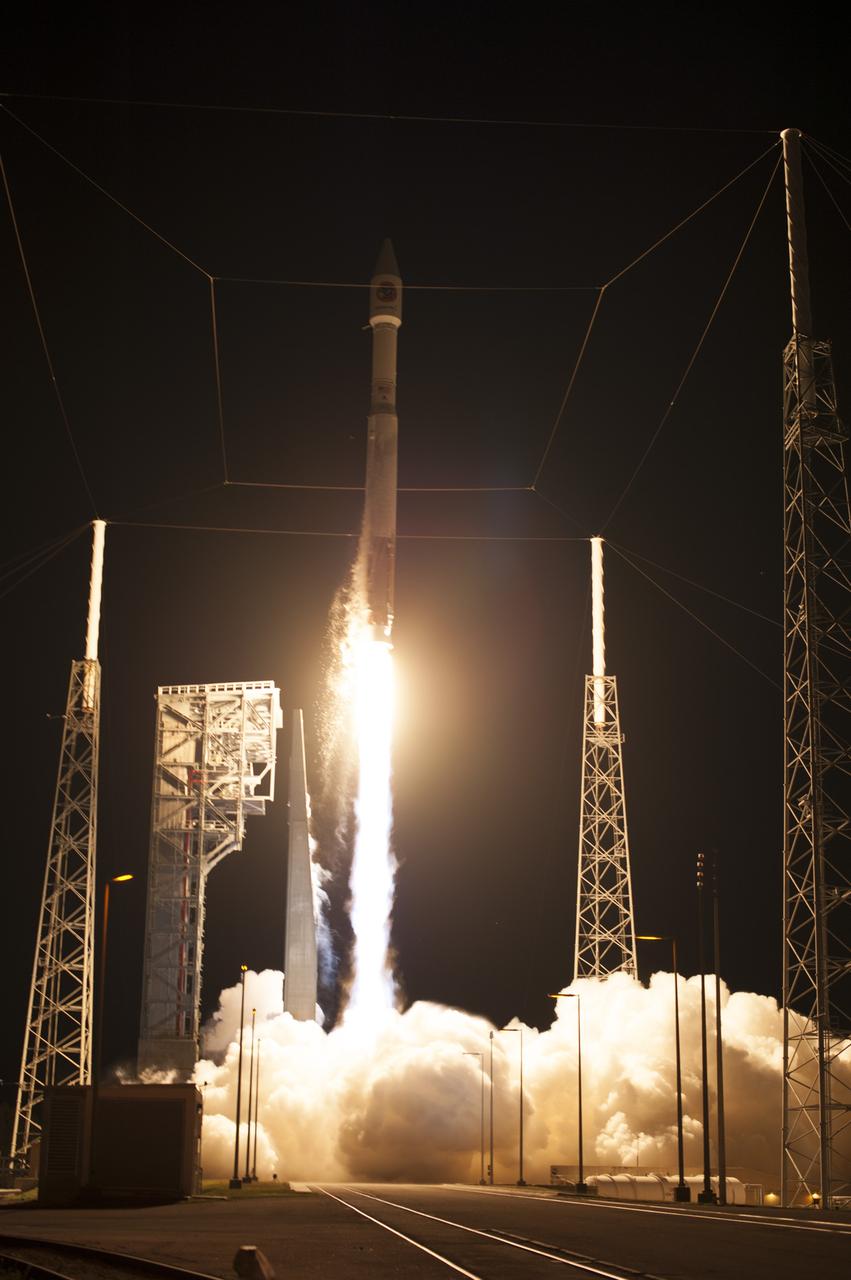

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
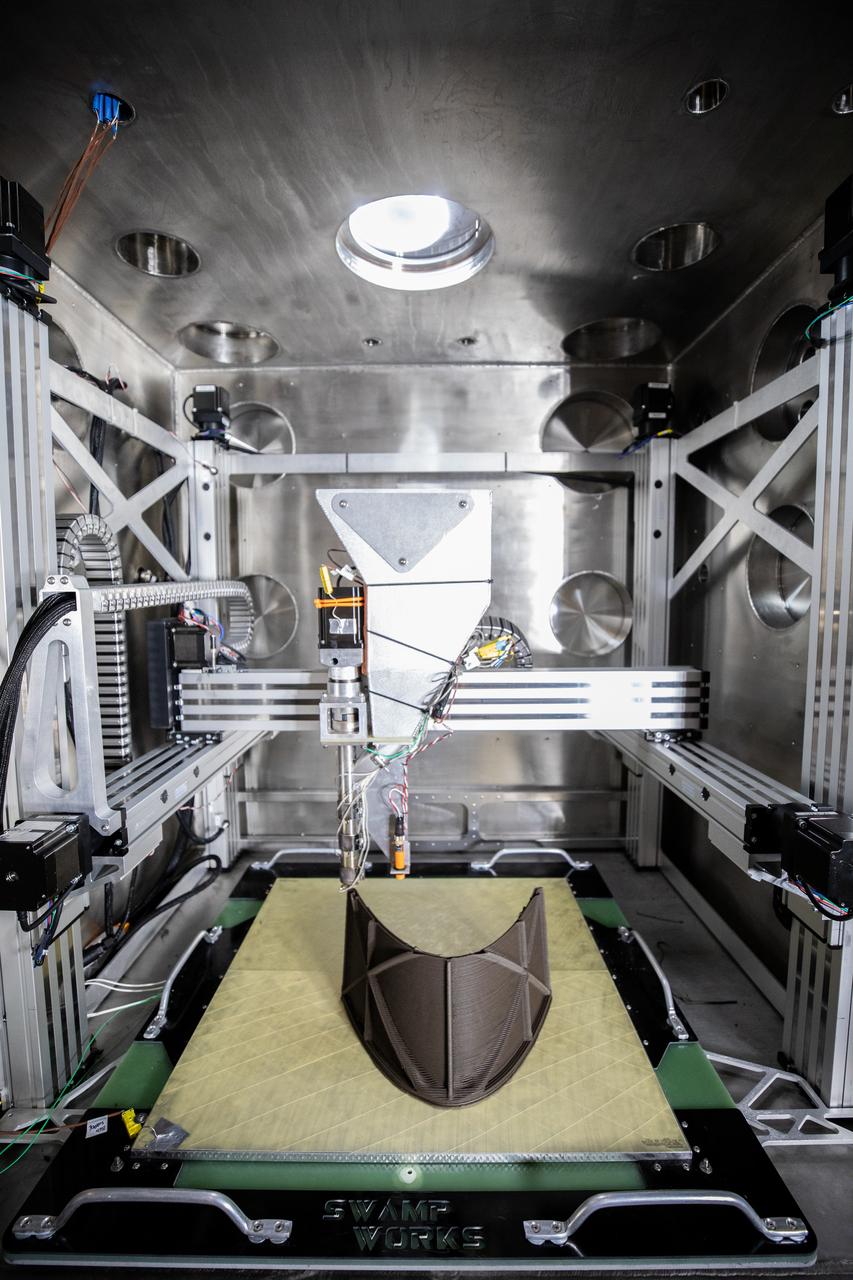

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests a 3D printer on July 28, 2022, at the Florida spaceport’s Swamp Works, as part of the Relevant Environment Additive Construction Technology (REACT) project. Among the key objectives of the project is developing an architectural and structural design for a shelter that provides protection to habitable assets on the lunar surface. Testing REACT derives from NASA’s 2020 Announcement of Collaboration Opportunity with AI SpaceFactory – an architectural and construction technology company and winner of NASA’s 3D Printed Habitat Challenge.
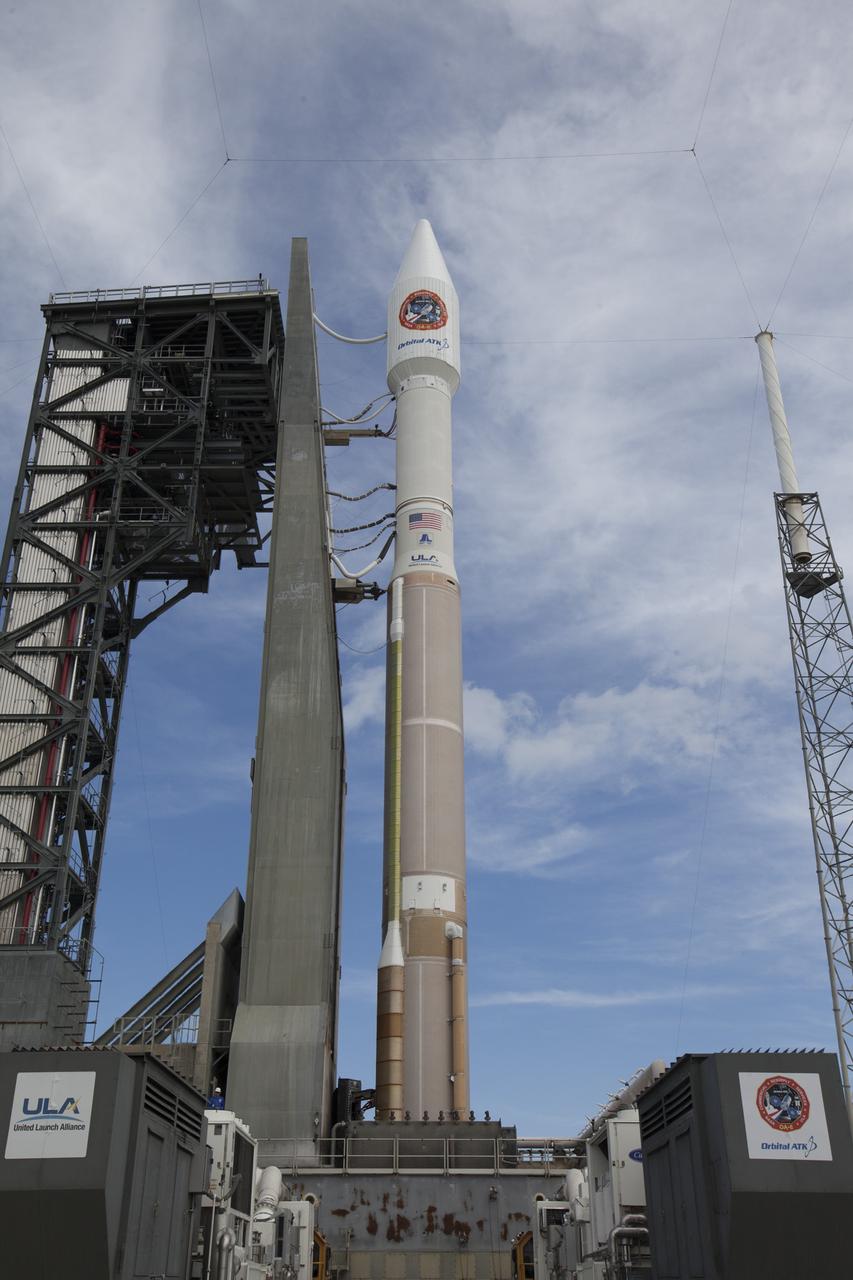

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
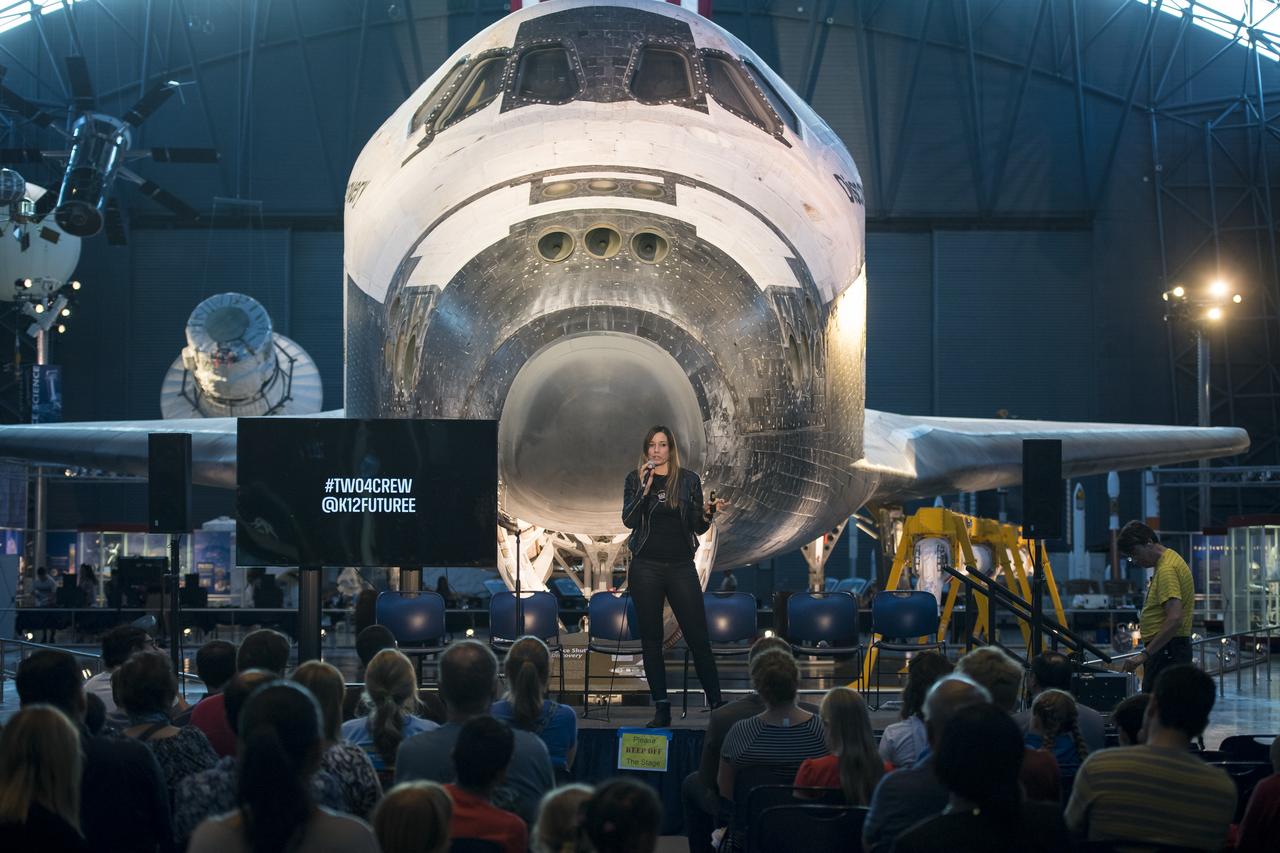

Founder and CEO of Future Engineers, Deanne Bell, speaks at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
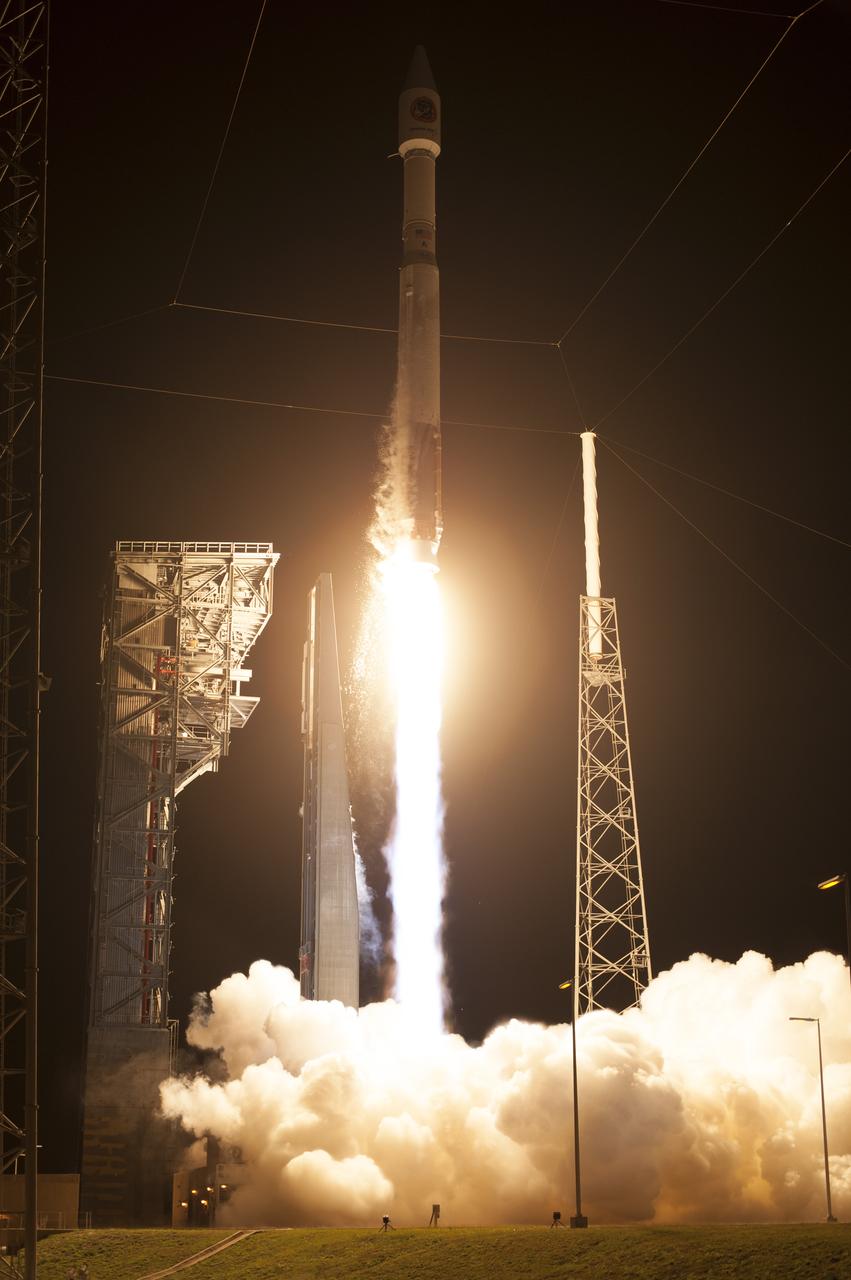

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
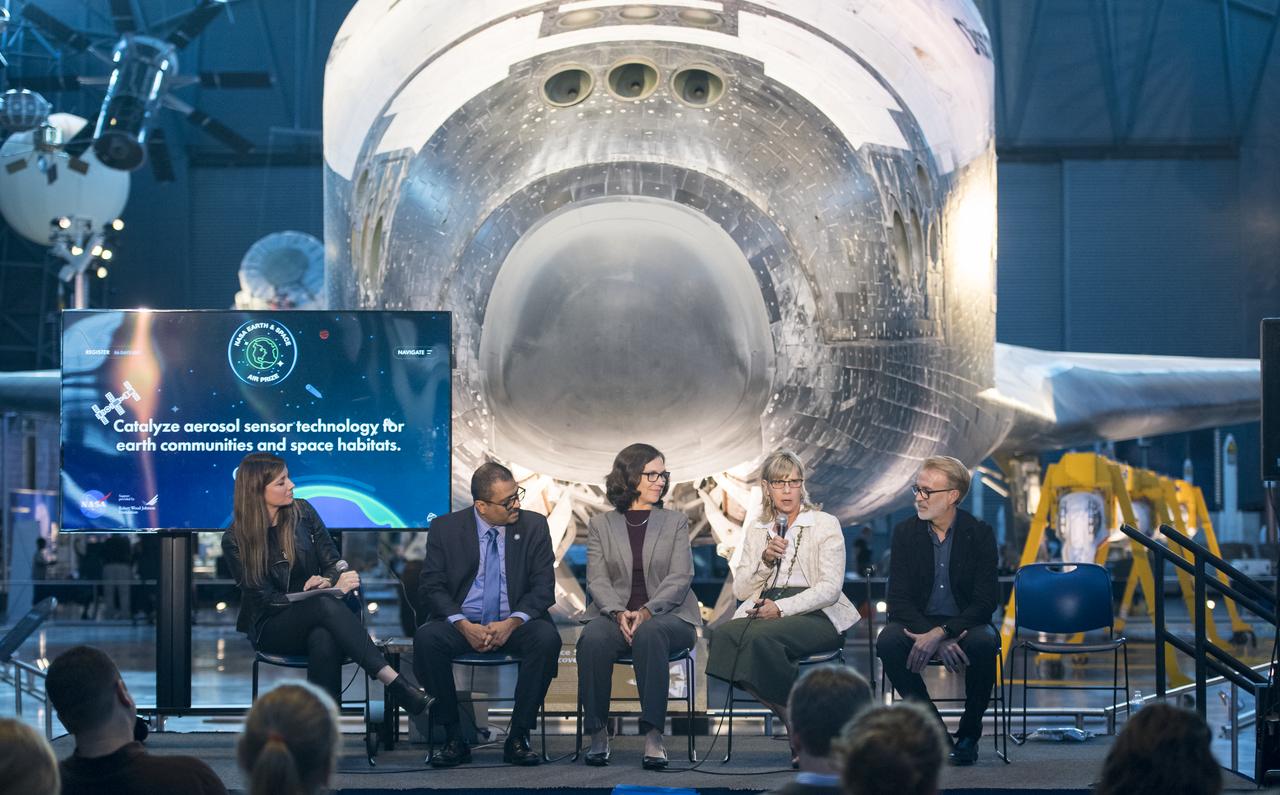

Lynn Buquo, manager, NASA Center of Excellence for Collaborative Innovation, speaks on a panel on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
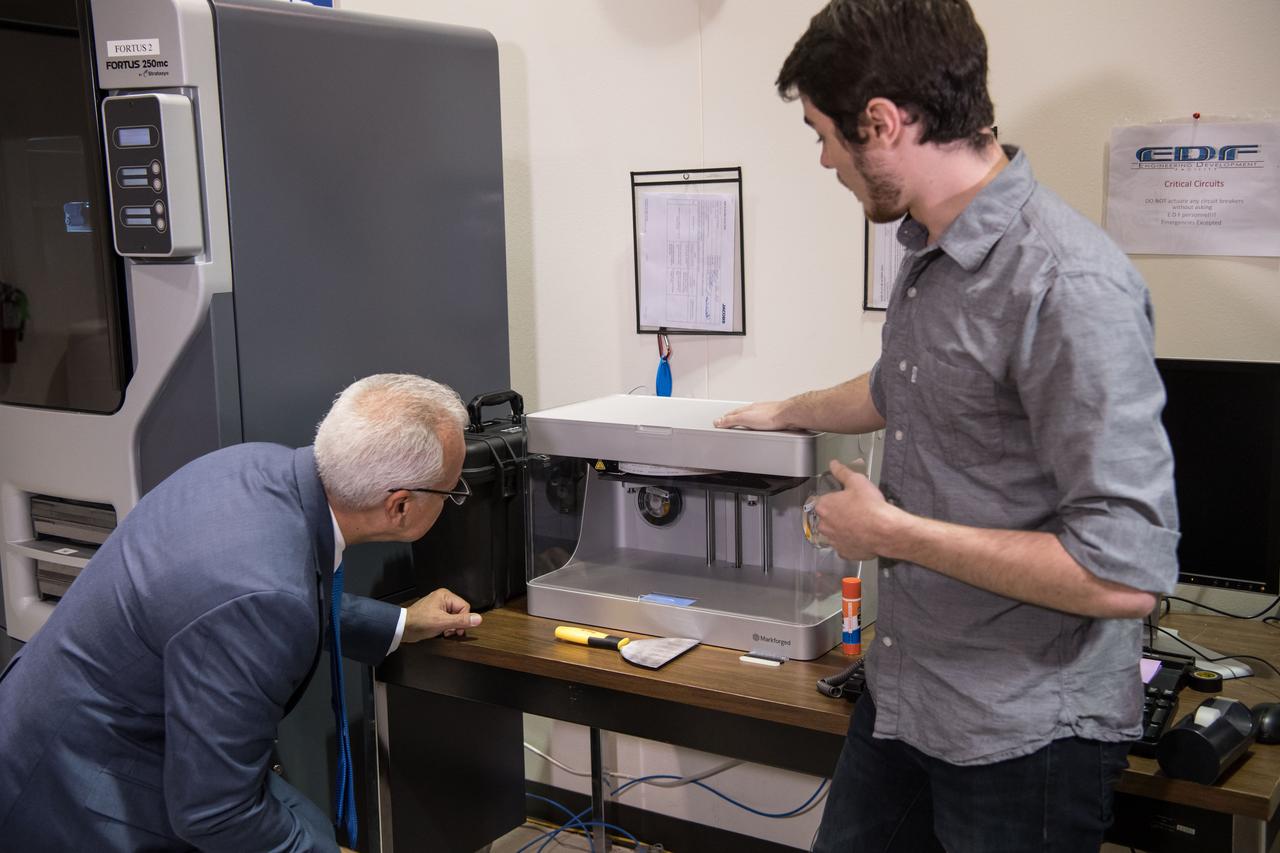

A Jacobs engineer shows NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier how the company uses 3-D printers to create inexpensive physical models of new electronically designed hardware. Date: 08-10-2017 Location: B1 & Jacobs Engineering Subject: NASA Acting Chief Technology Officer Douglas Terrier Tours JSC and Jacobs Photographer: David DeHoyos
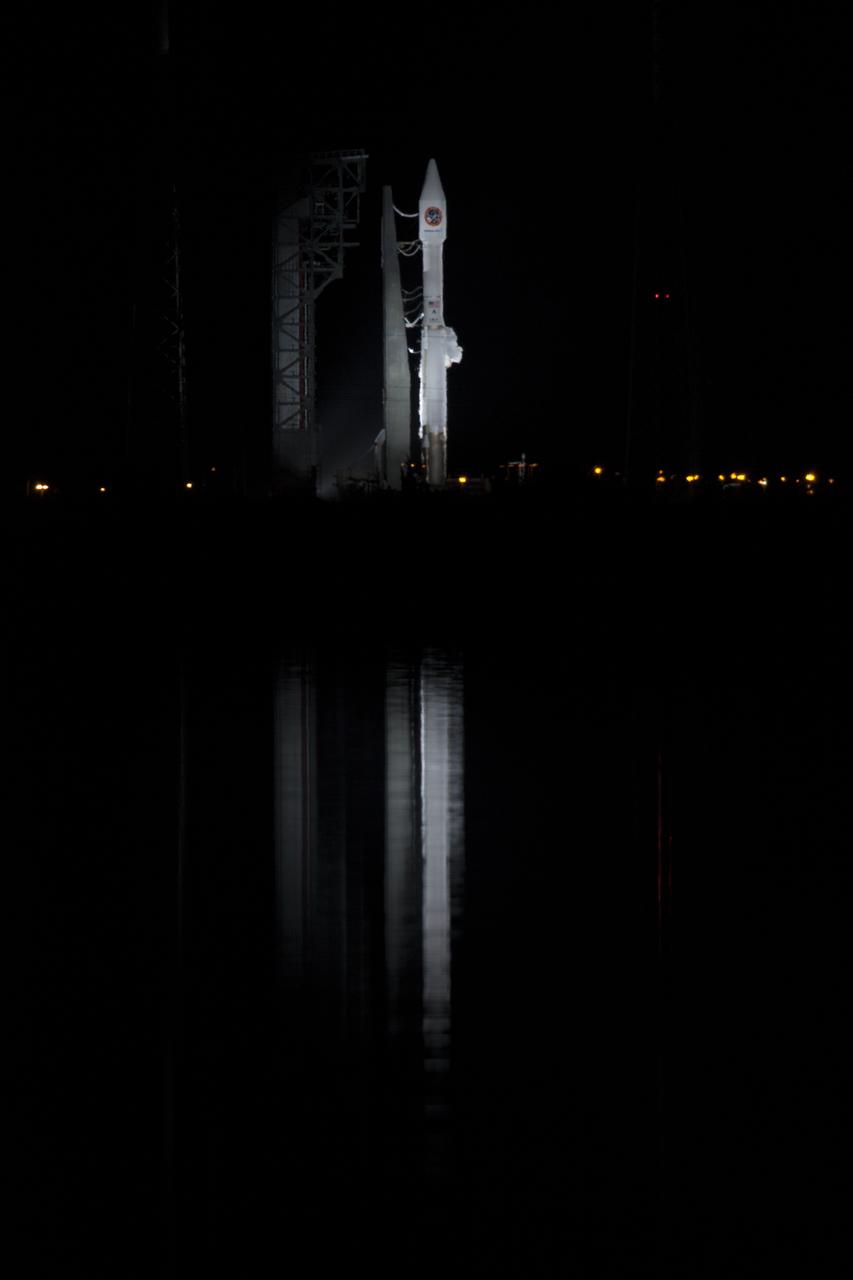

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
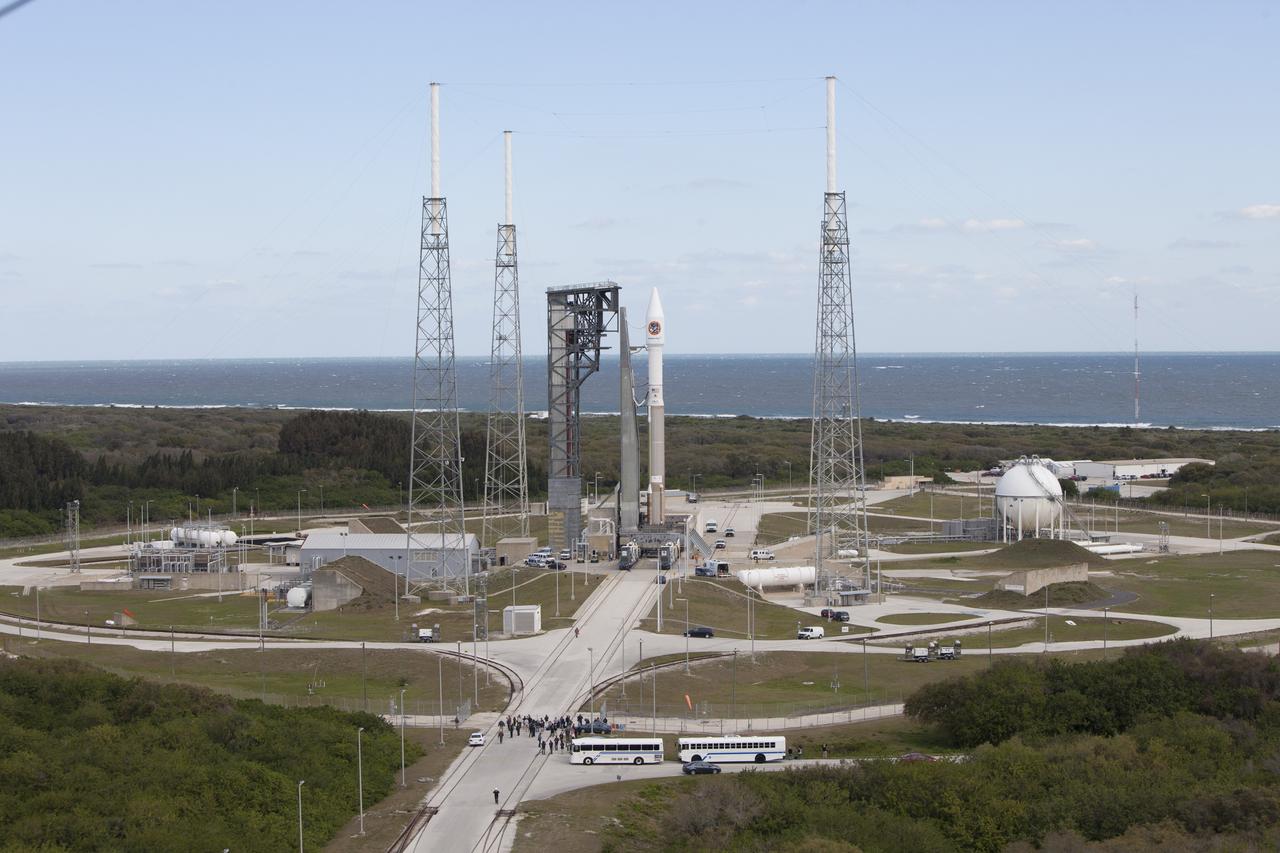

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.

iss061e093837 (Dec. 22, 2019) --- Expedition 61 Flight Engineer and NASA astronaut Christina Koch services the BioFabrication Facility (BFF). The BFF is a 3-D biological printer that manufactures organ-like tissues in microgravity and could become a part of a larger system capable of manufacturing whole, fully-functioning human organs from existing patient cells.
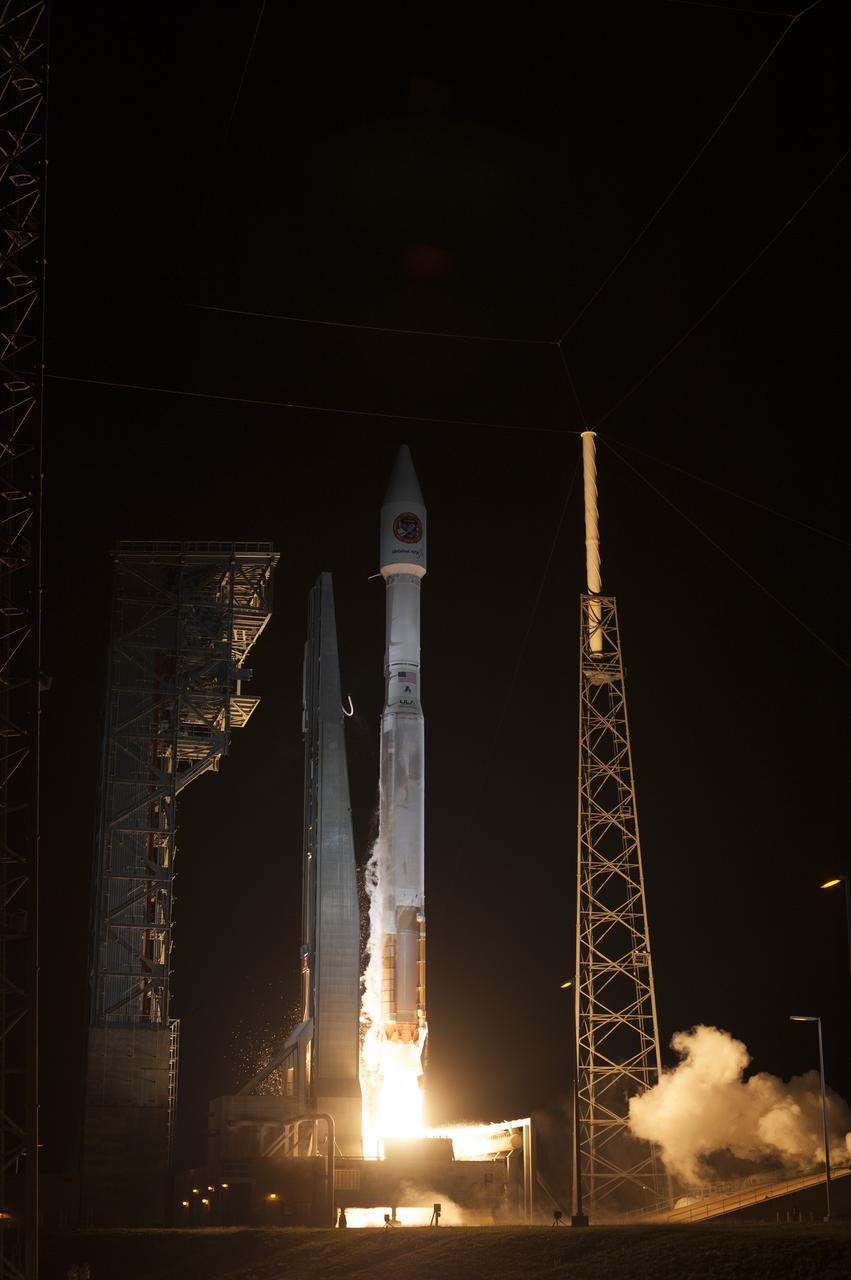

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
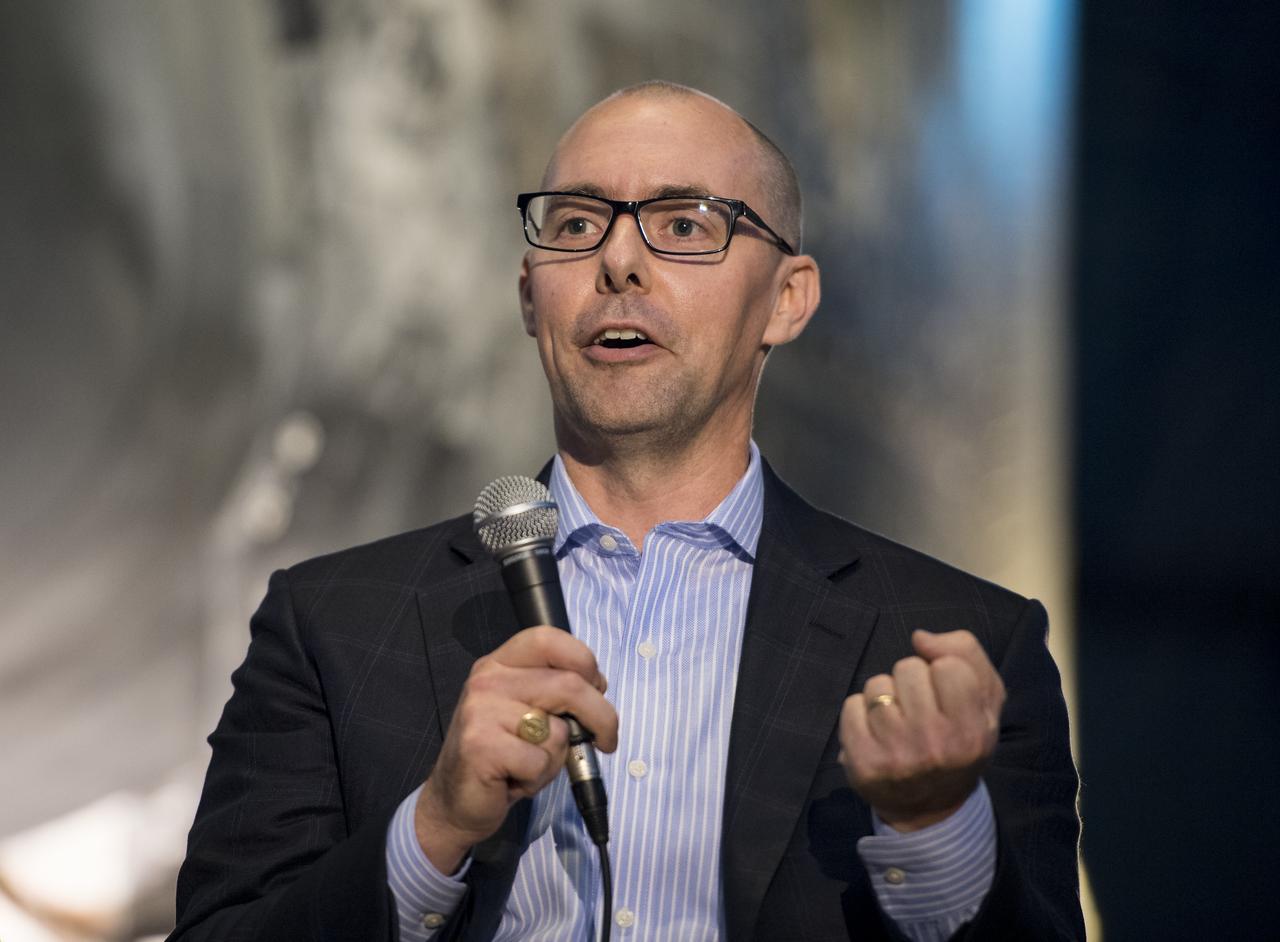

Ryan Heitz, co-founder and head of school, Ideaventions Academy, speaks on a panel on "igniting NOVA K-12 engineering and maker education", at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
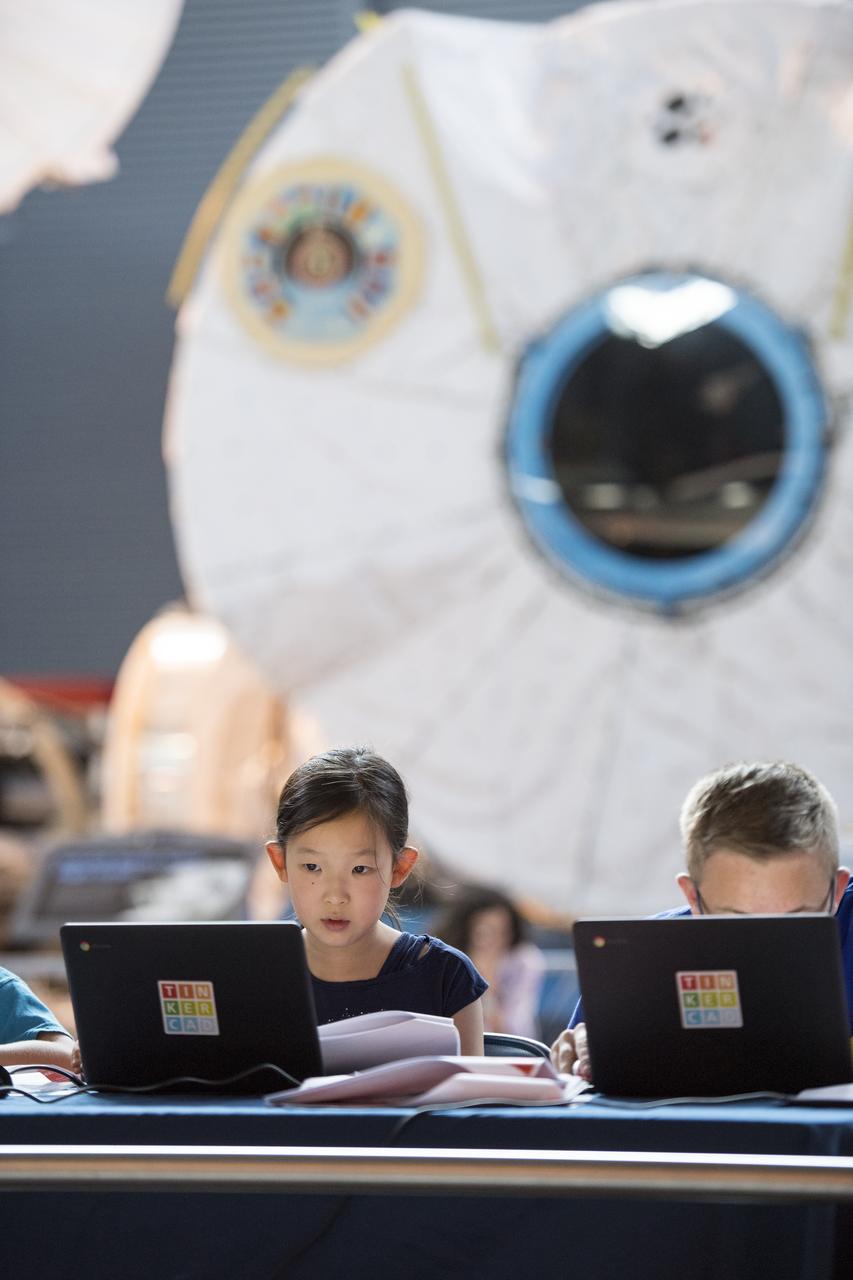

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
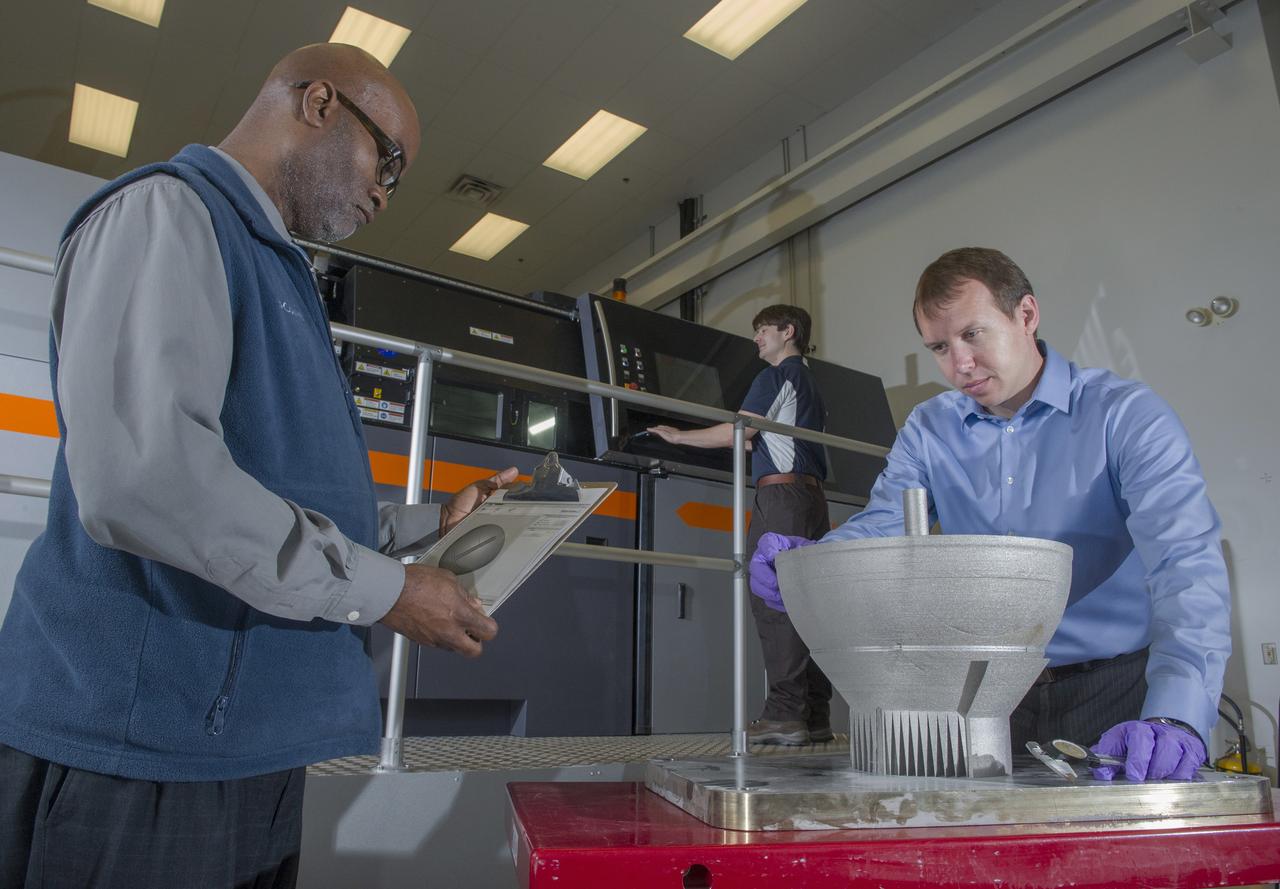

JOHNNIE CLARK, BRIAN WEST, AND ZACK JONES OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH MSFC’S XLINE SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. CURRENTLY ONE OF THE LARGEST METAL 3D PRINTERS, THE XLINE AT MARSHALL IS BEING USED TO DEVELOP AND CERTIFY NICKEL ALLOY 718 MATERIAL PROPERTIES AND LARGE MANUFACTURING TECH DEMOS FOR THE RS25 ENGINE AND THE COMMERCIAL CREWED VEHICLE PROJECTS.
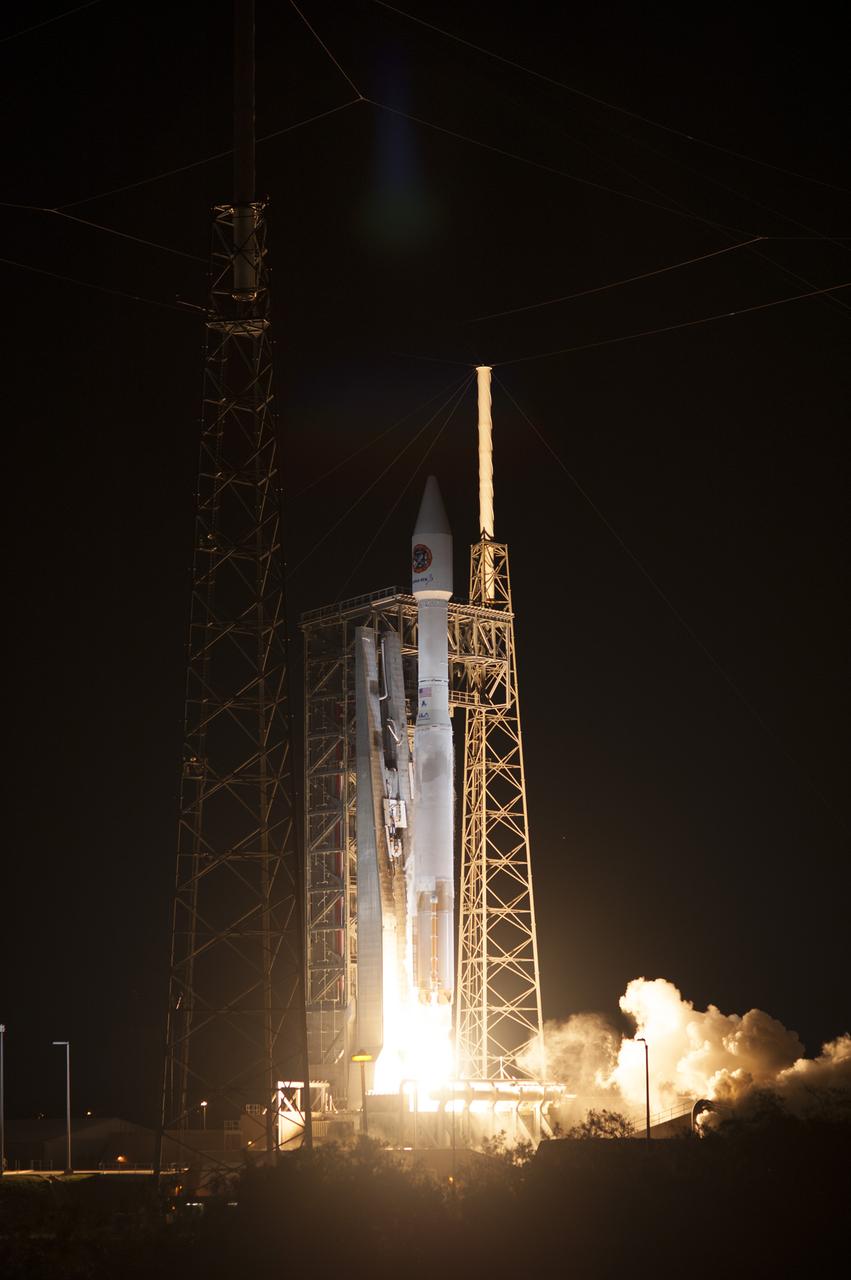

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
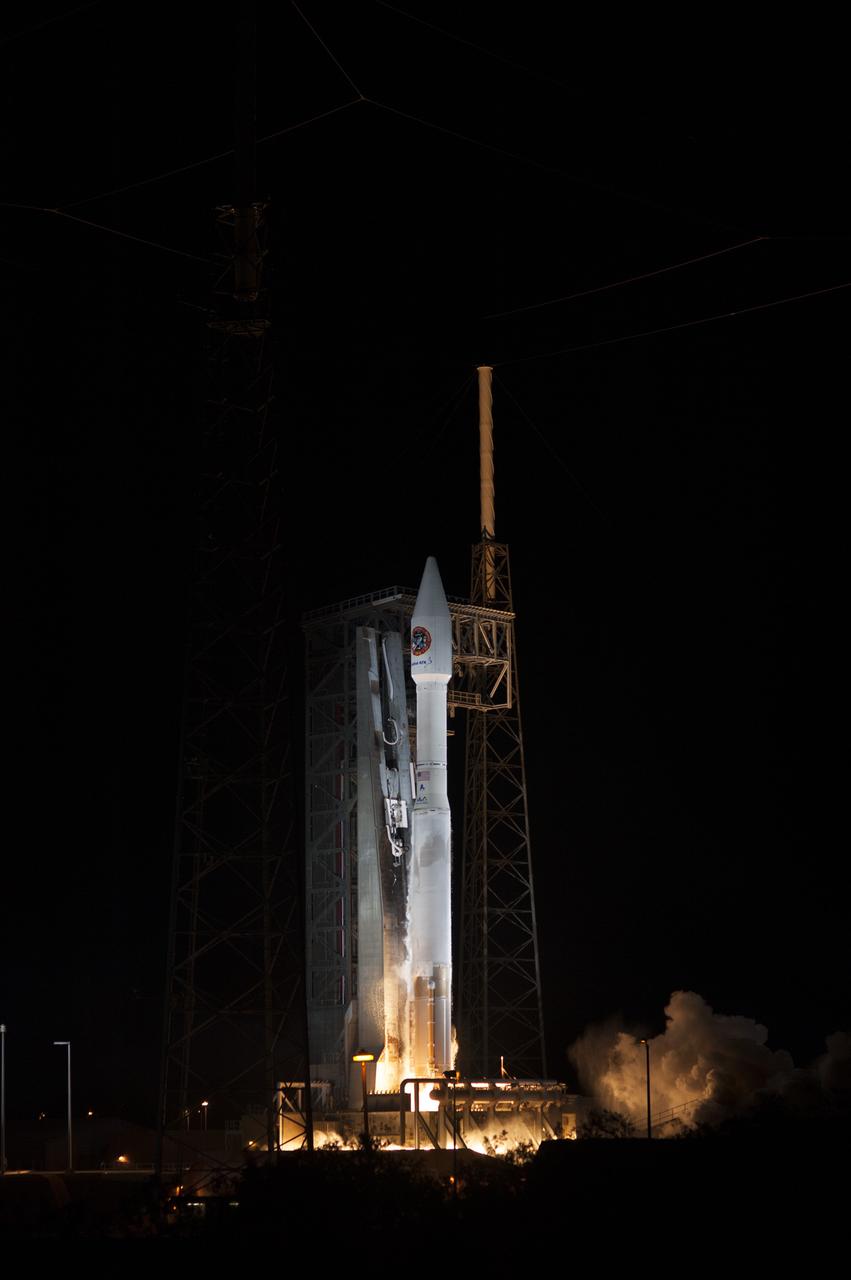

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
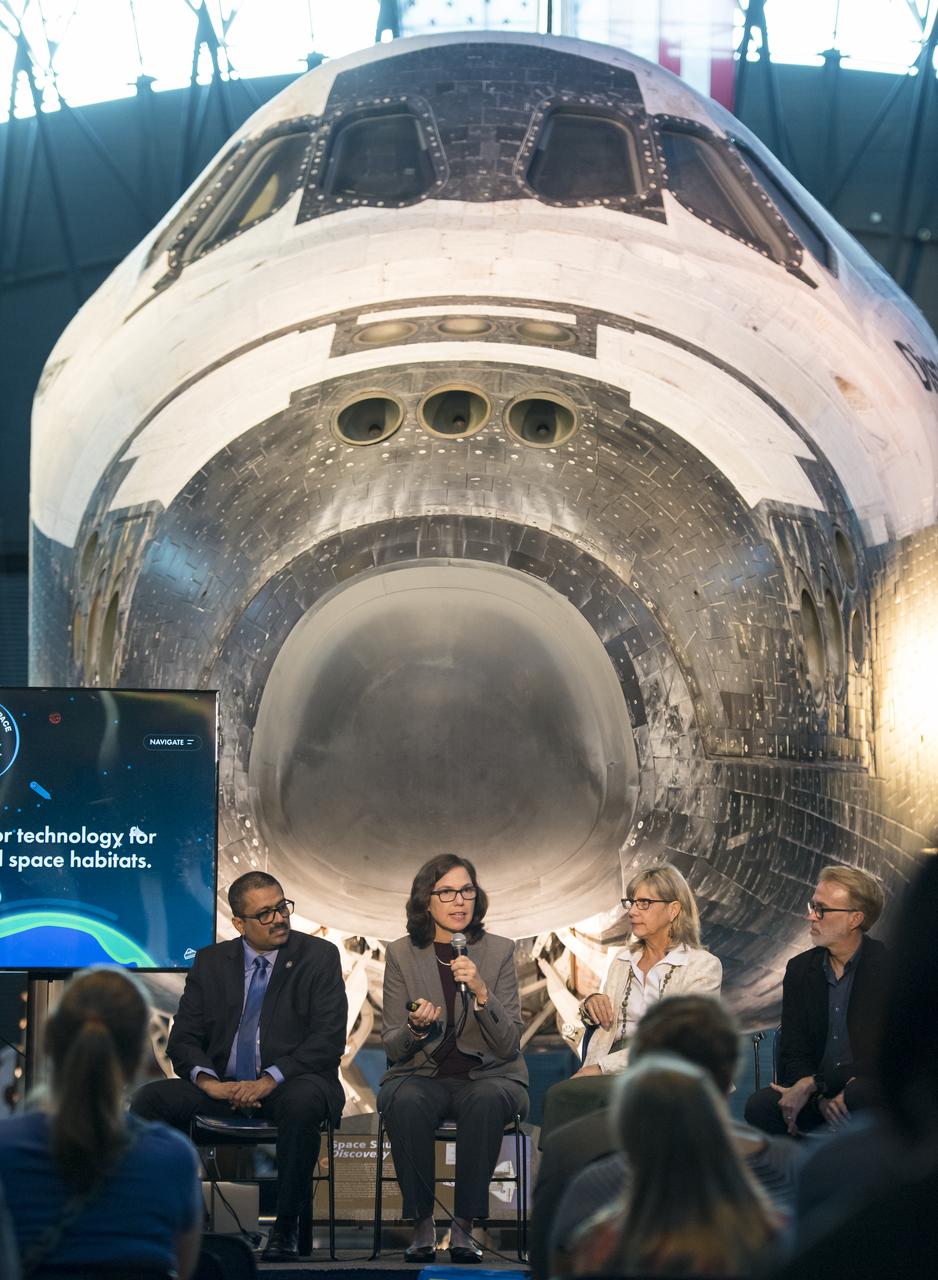

Marit Meyer, research aerospace engineer, Aerosol Science and Instrumentation, NASA, speaks on a panel on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
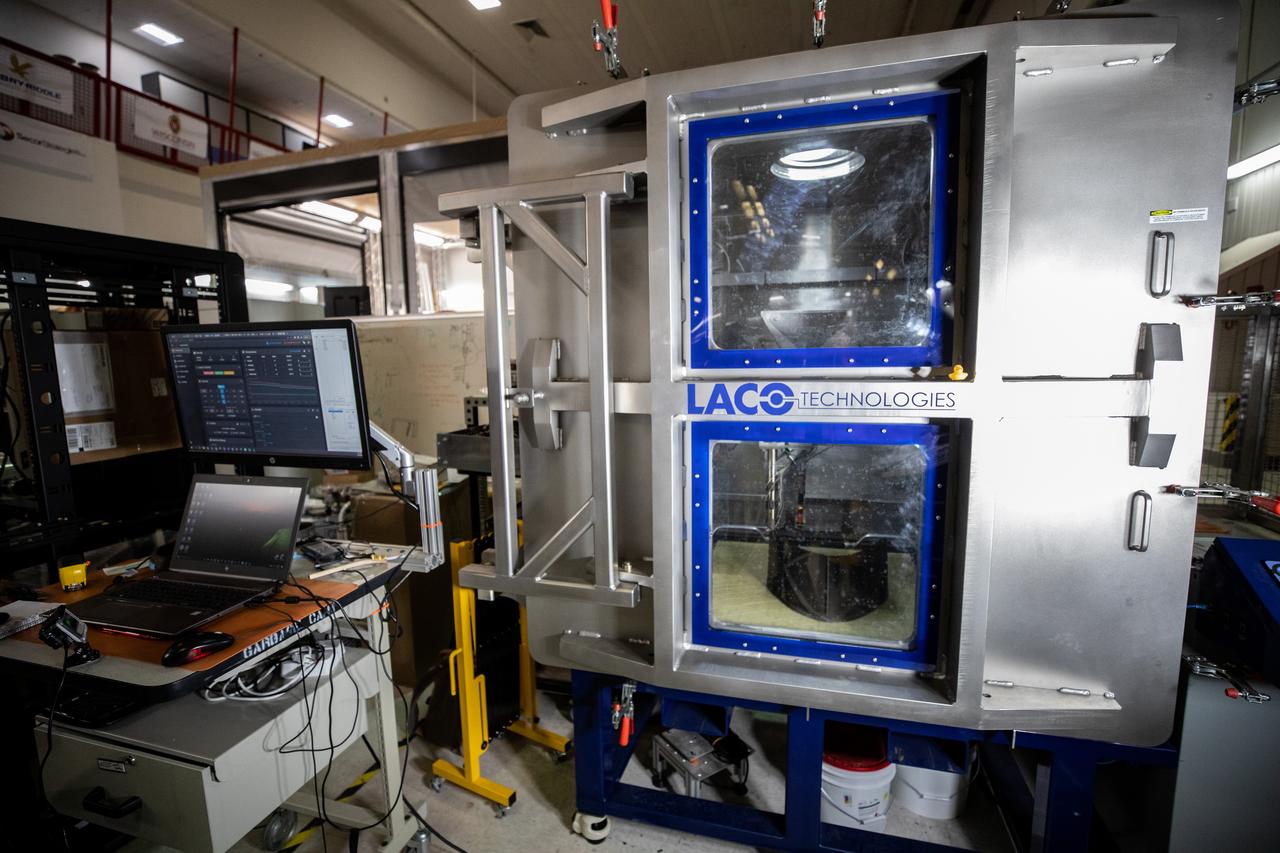

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests a 3D printer on July 28, 2022, at the Florida spaceport’s Swamp Works, as part of the Relevant Environment Additive Construction Technology (REACT) project. Among the key objectives of the project is developing an architectural and structural design for a shelter that provides protection to habitable assets on the lunar surface. Testing REACT derives from NASA’s 2020 Announcement of Collaboration Opportunity with AI SpaceFactory – an architectural and construction technology company and winner of NASA’s 3D Printed Habitat Challenge.
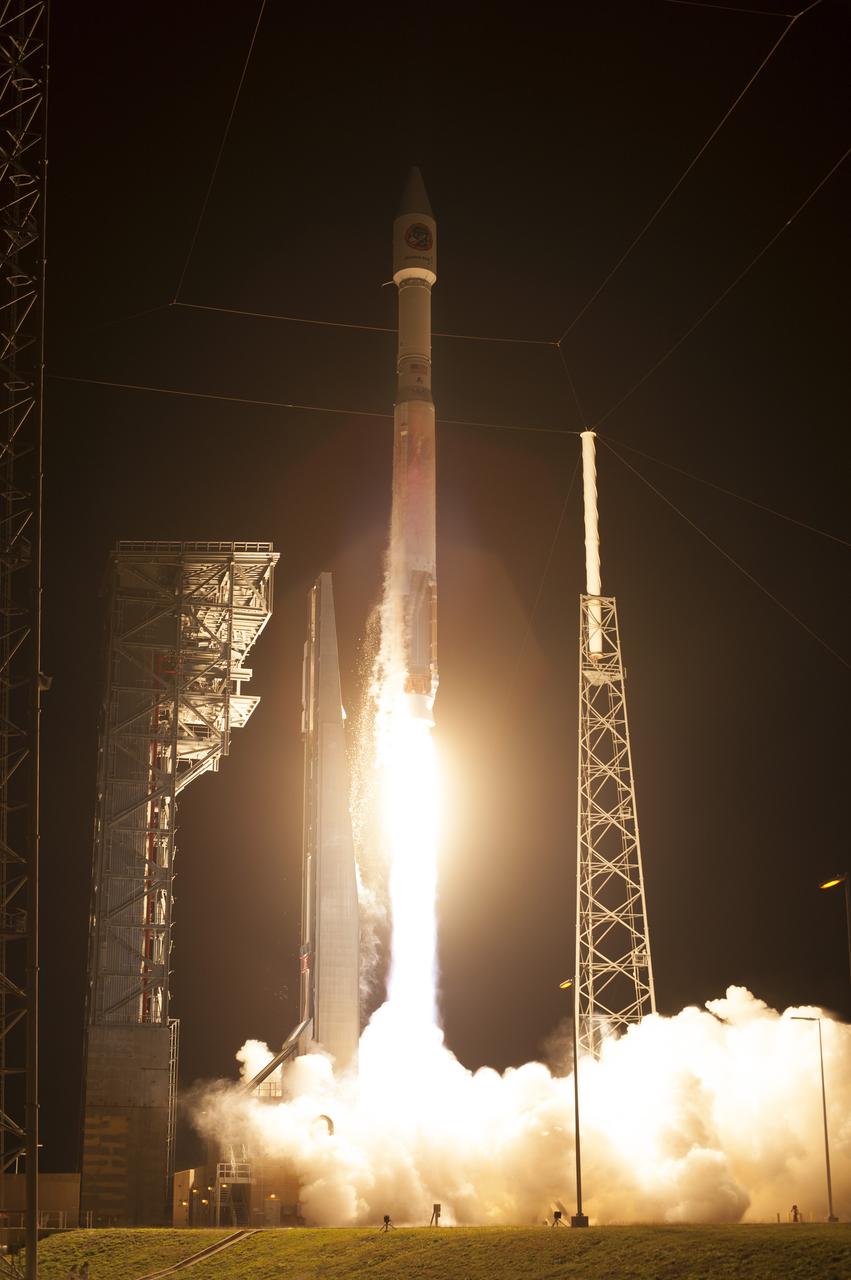

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
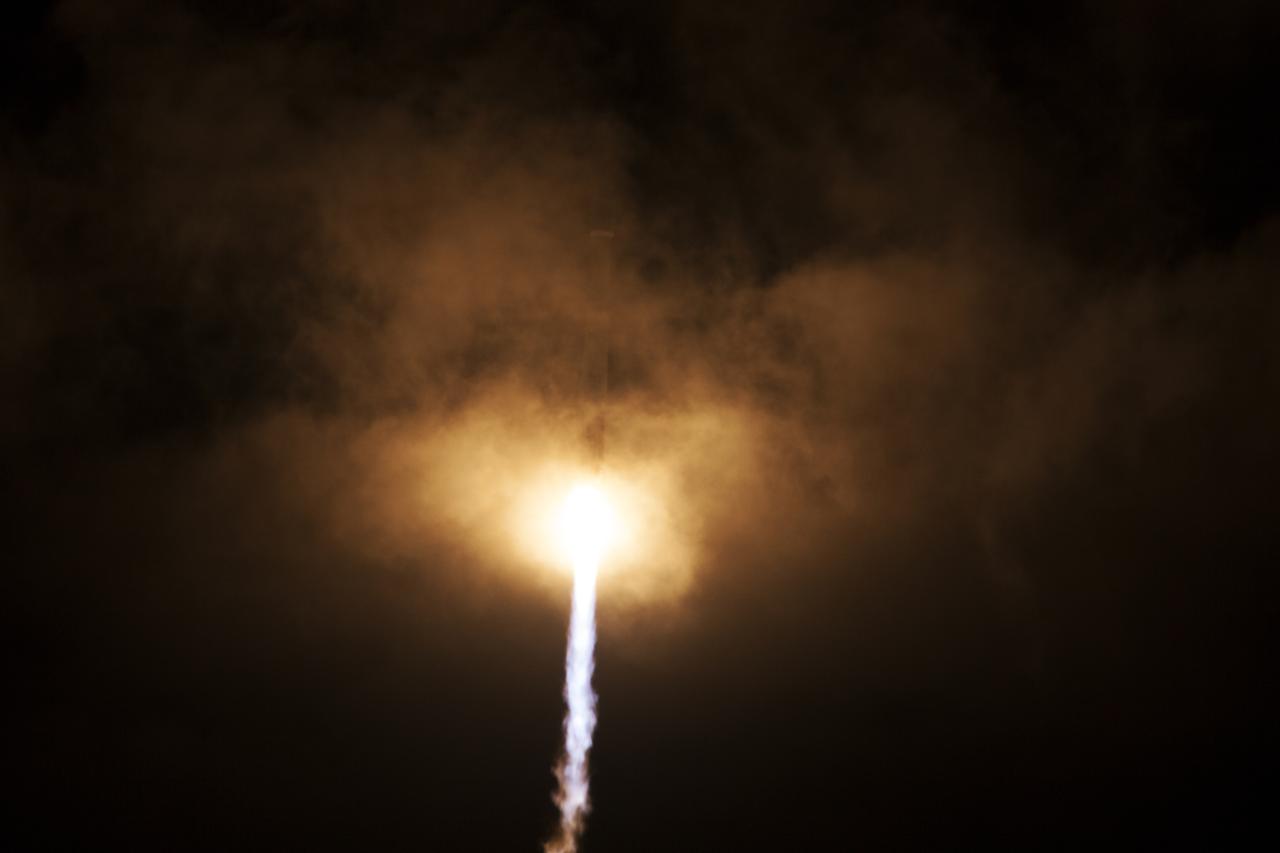

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station carrying an Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply spacecraft on a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:05 p.m. EDT. Cygnus will deliver the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate 3-D printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
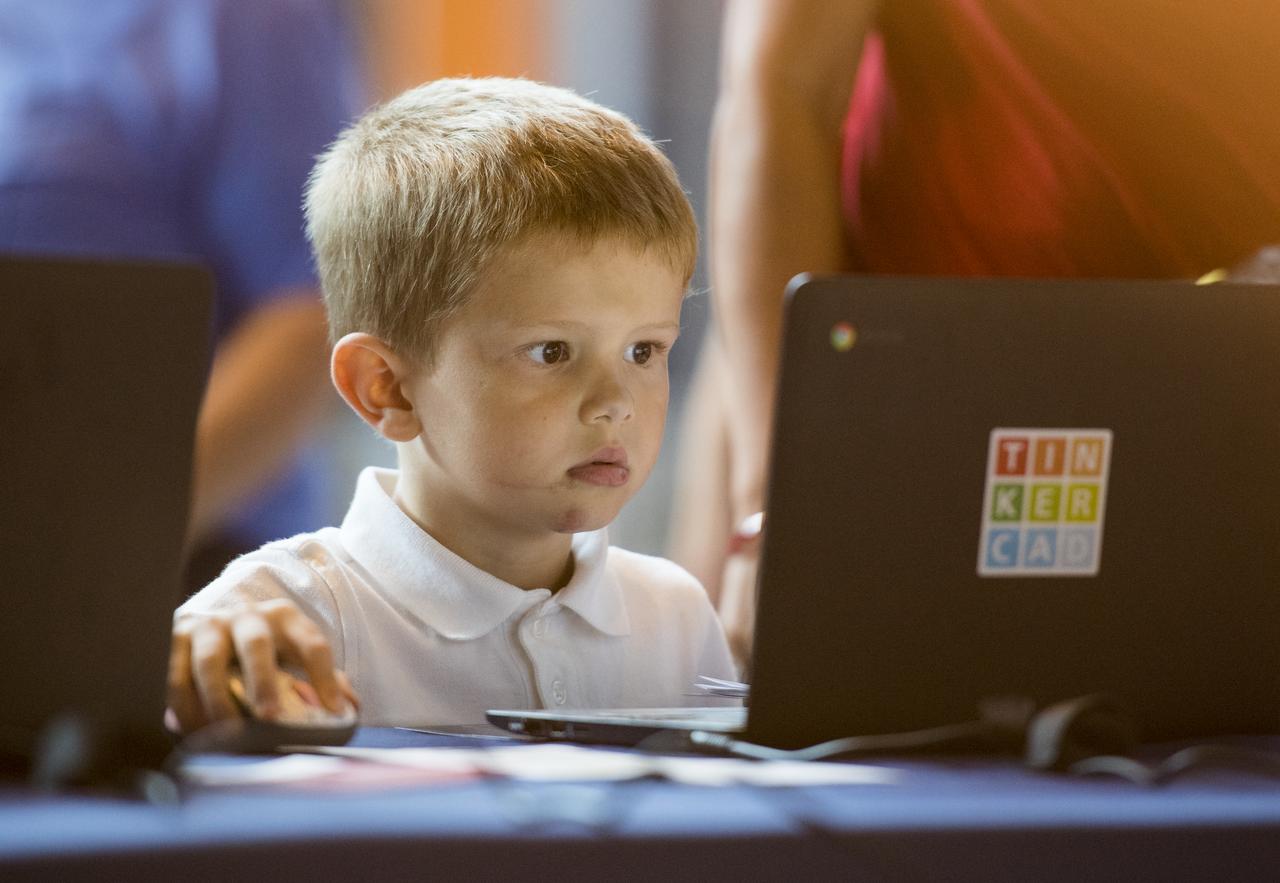

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
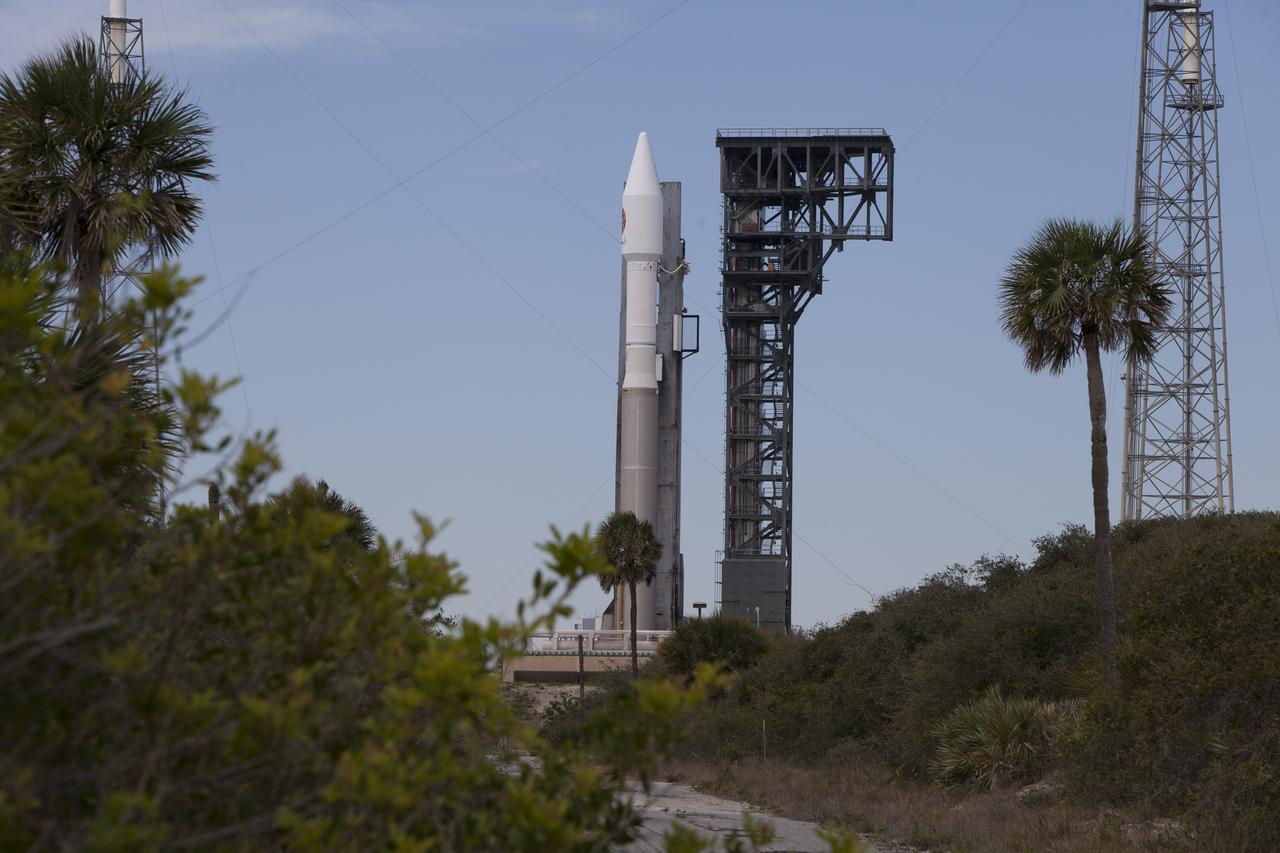

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
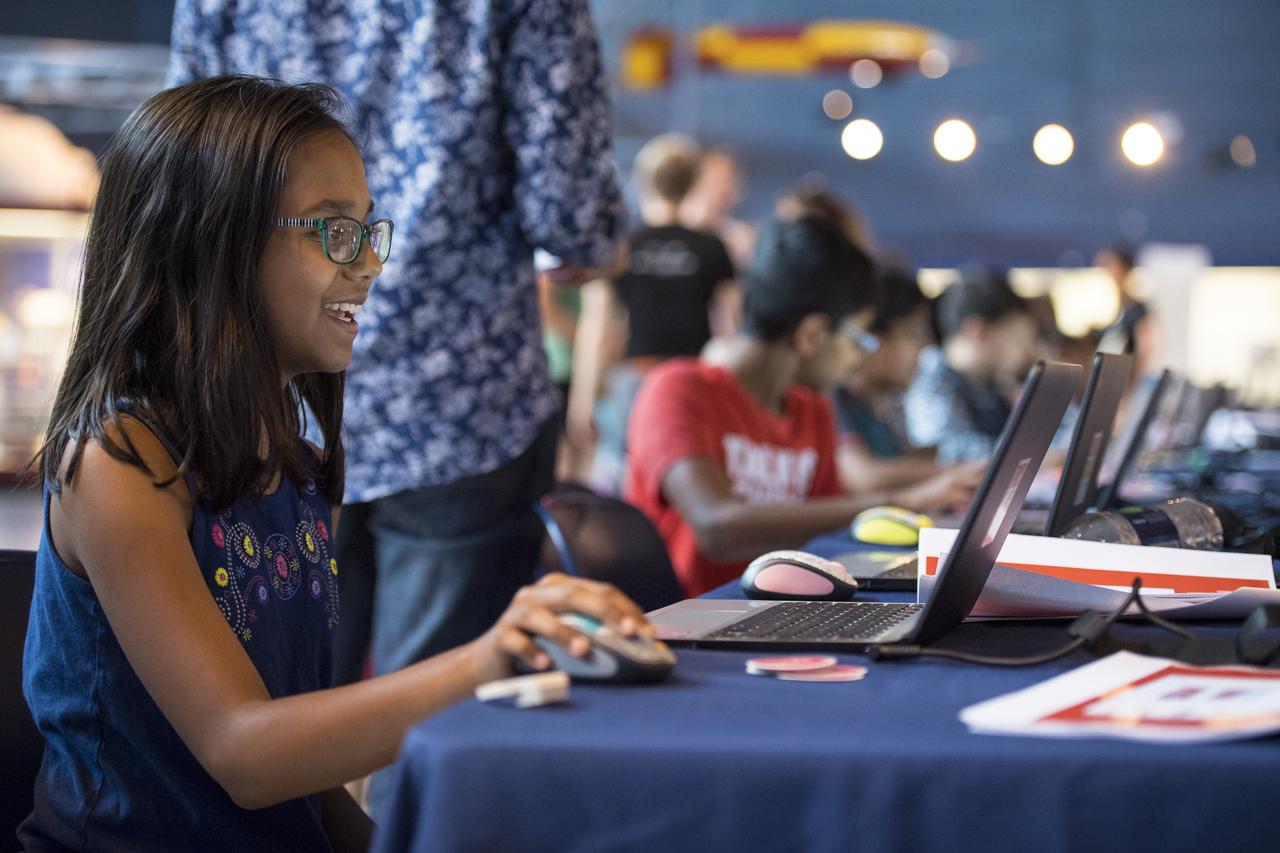

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)