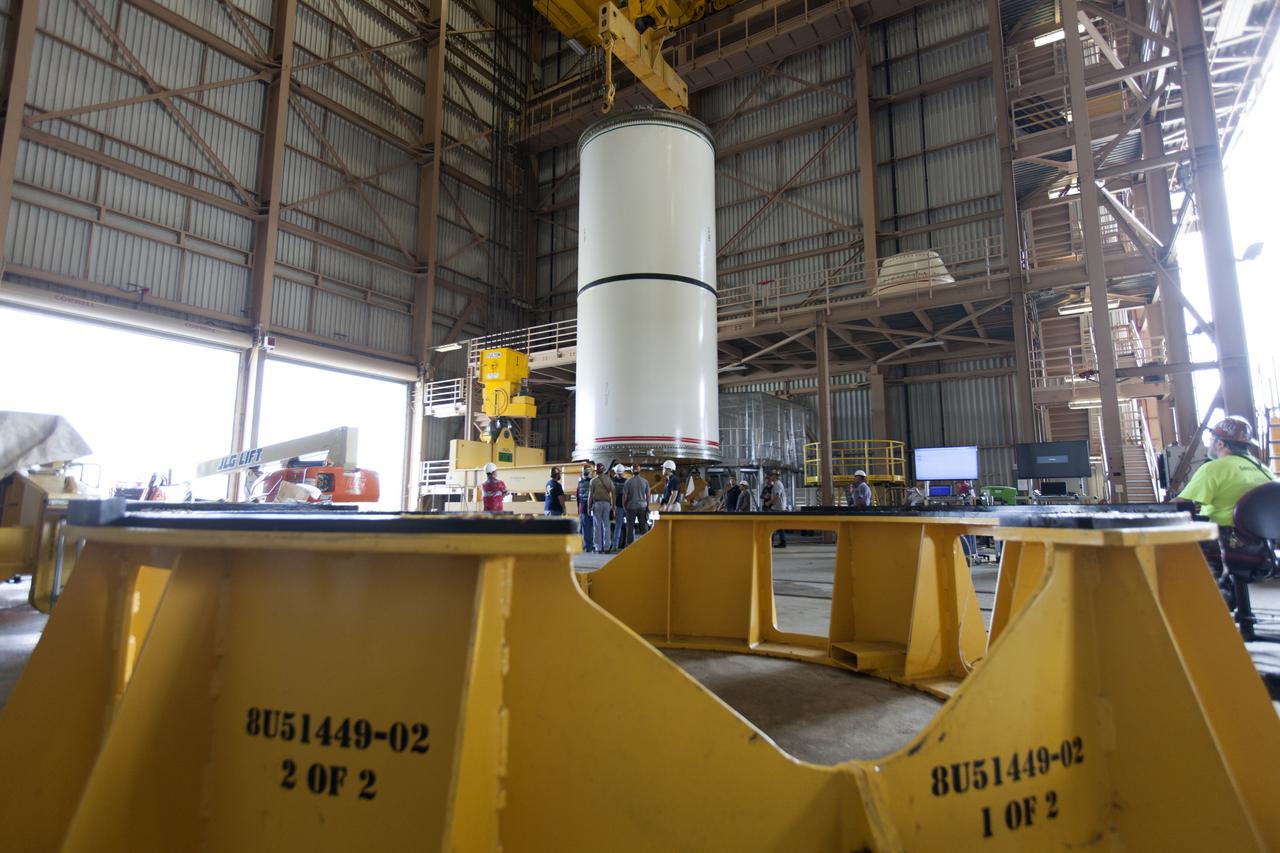

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
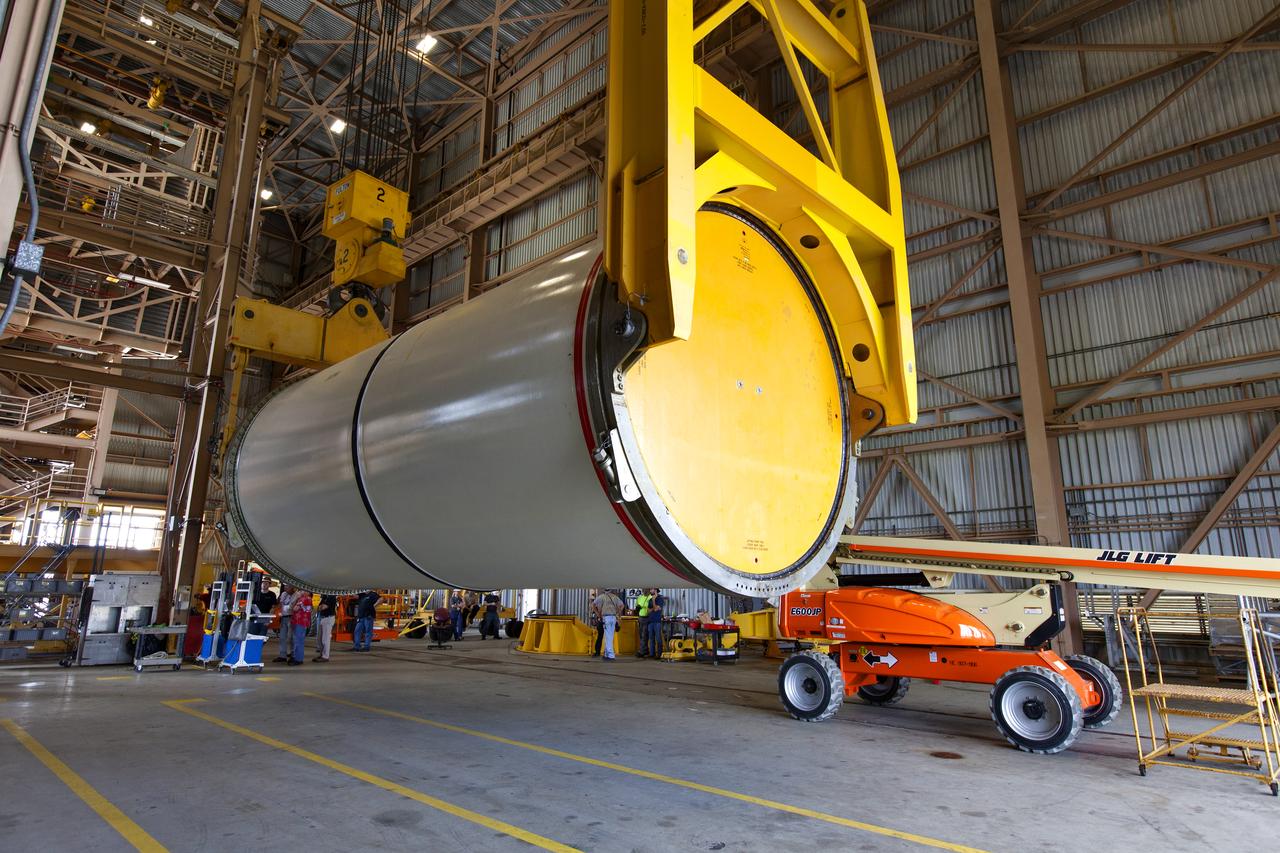

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes were used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
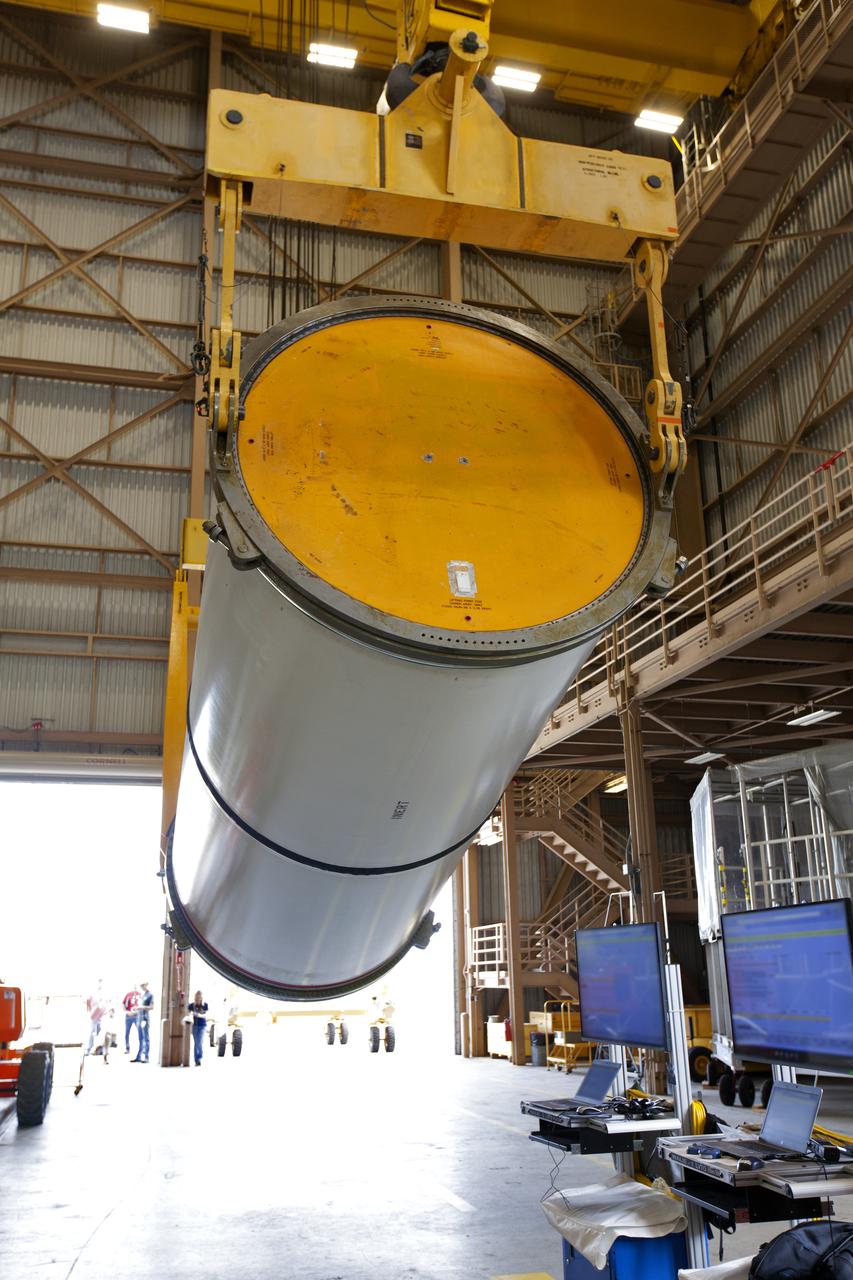

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
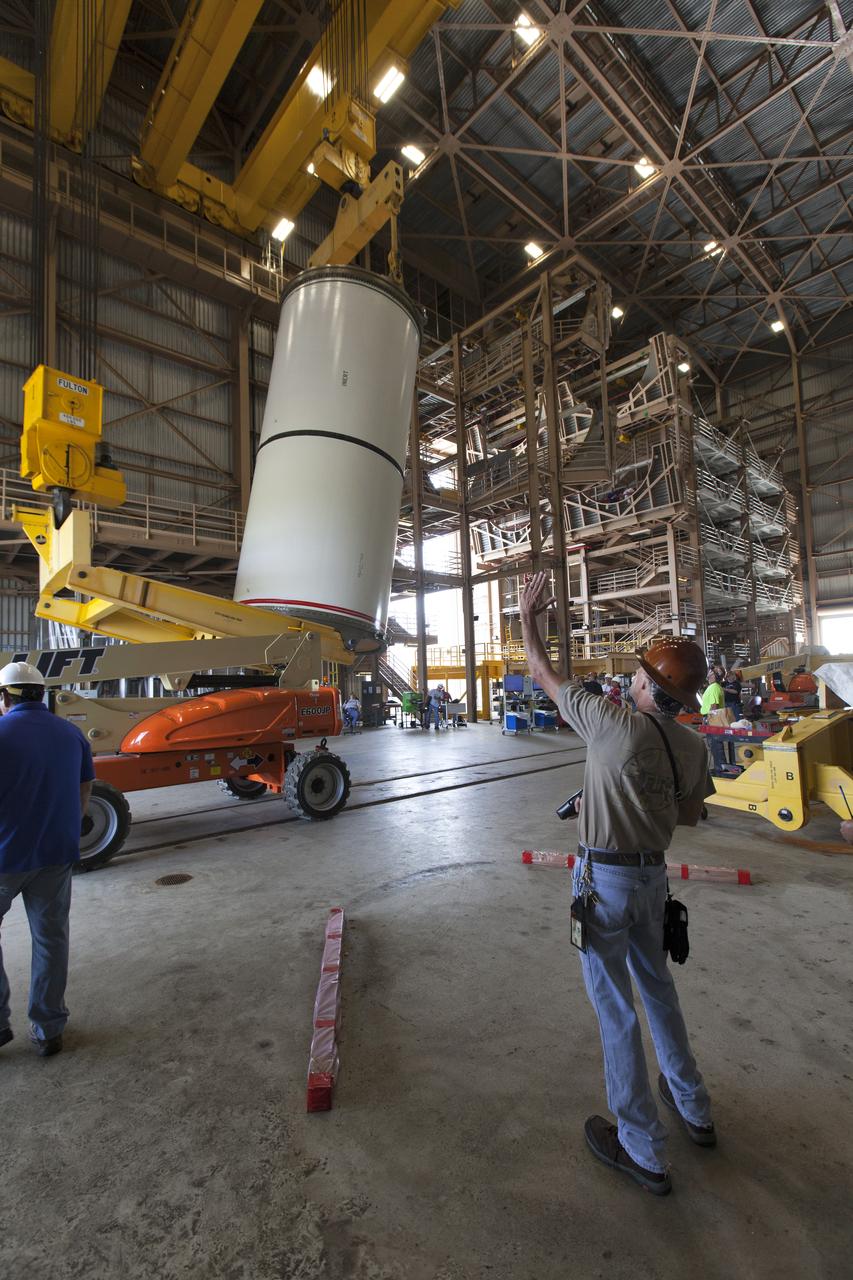

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
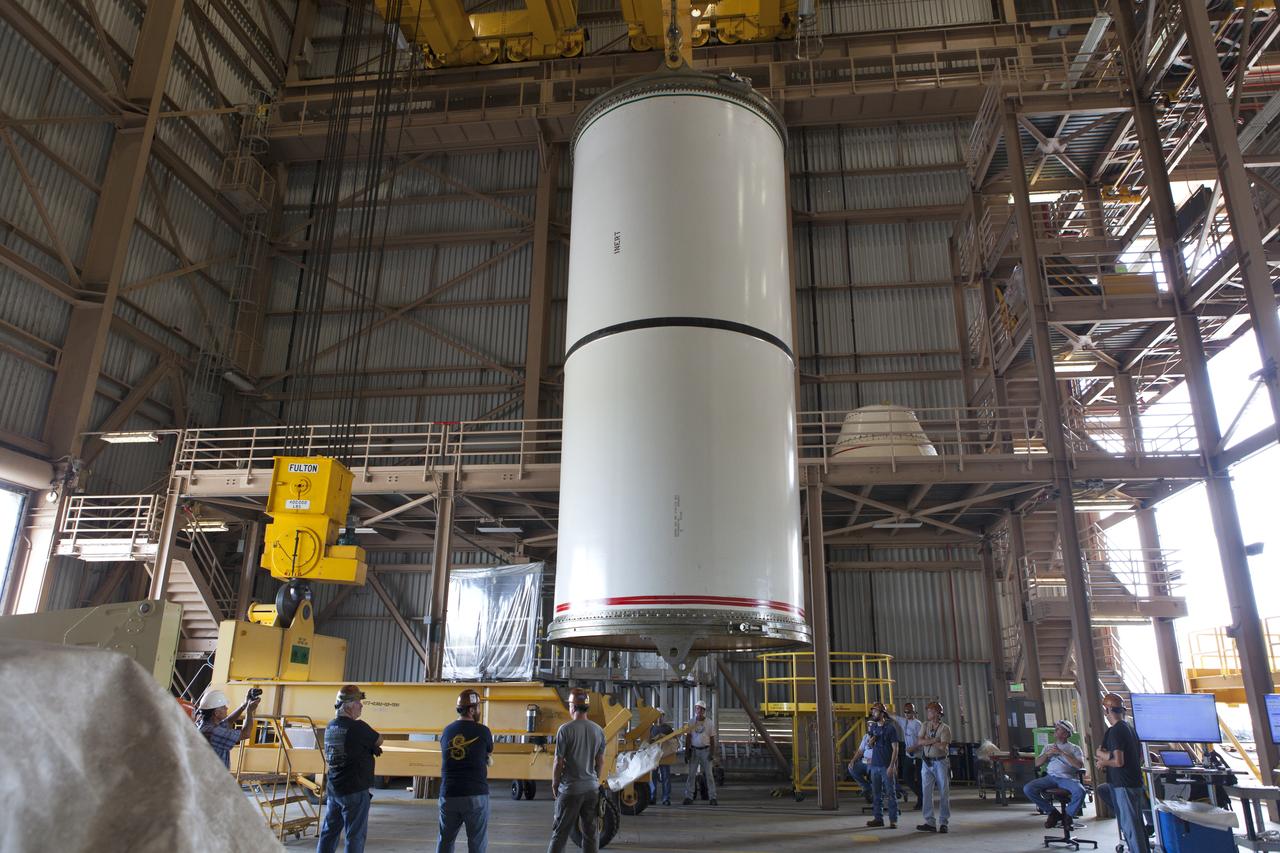

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
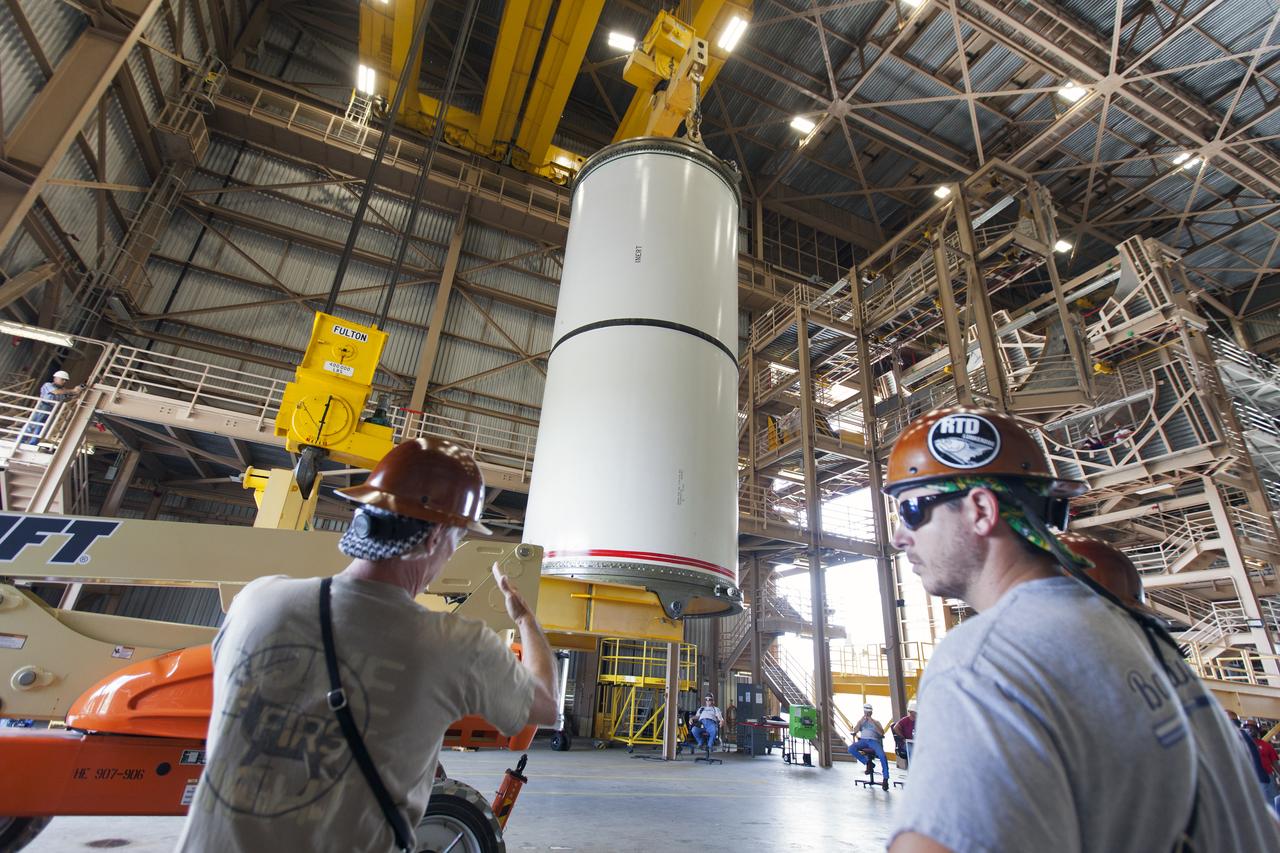

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
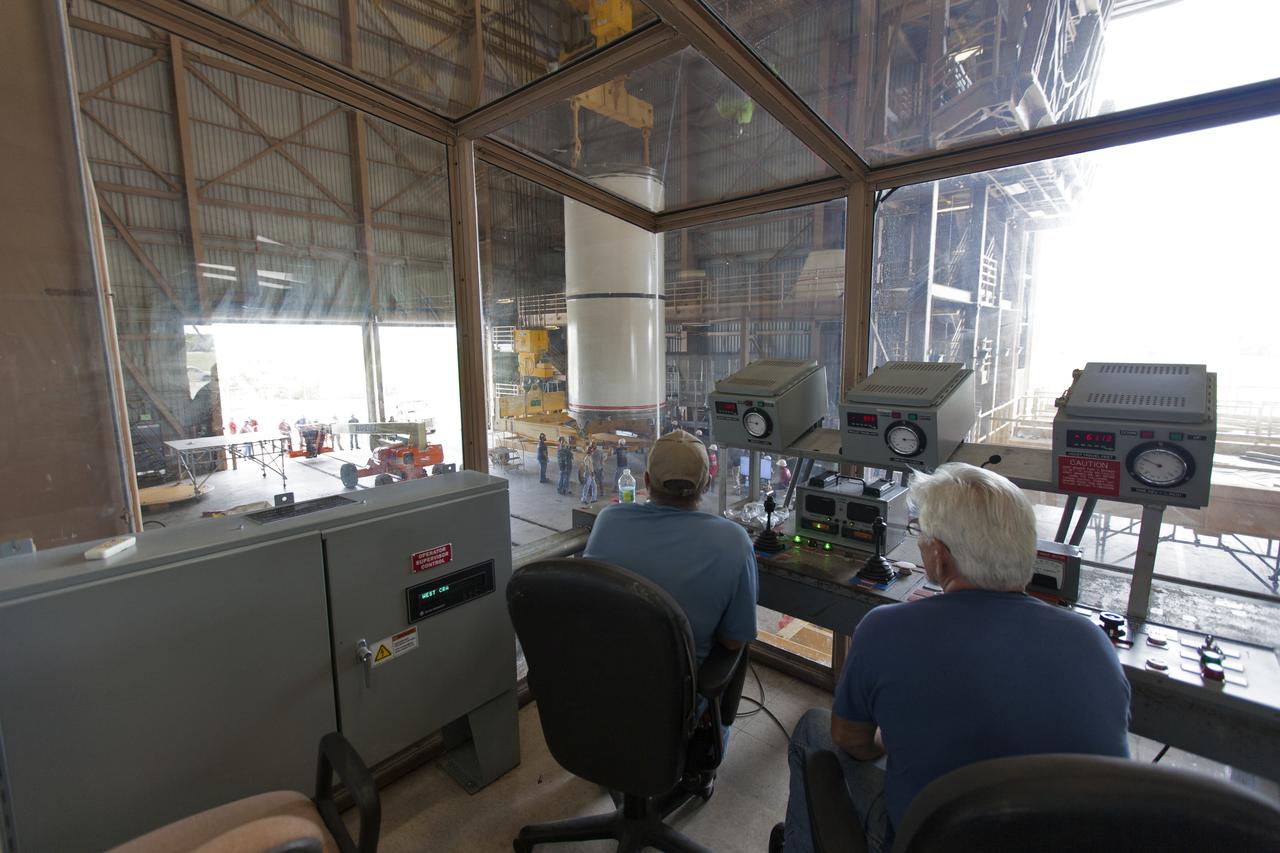

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
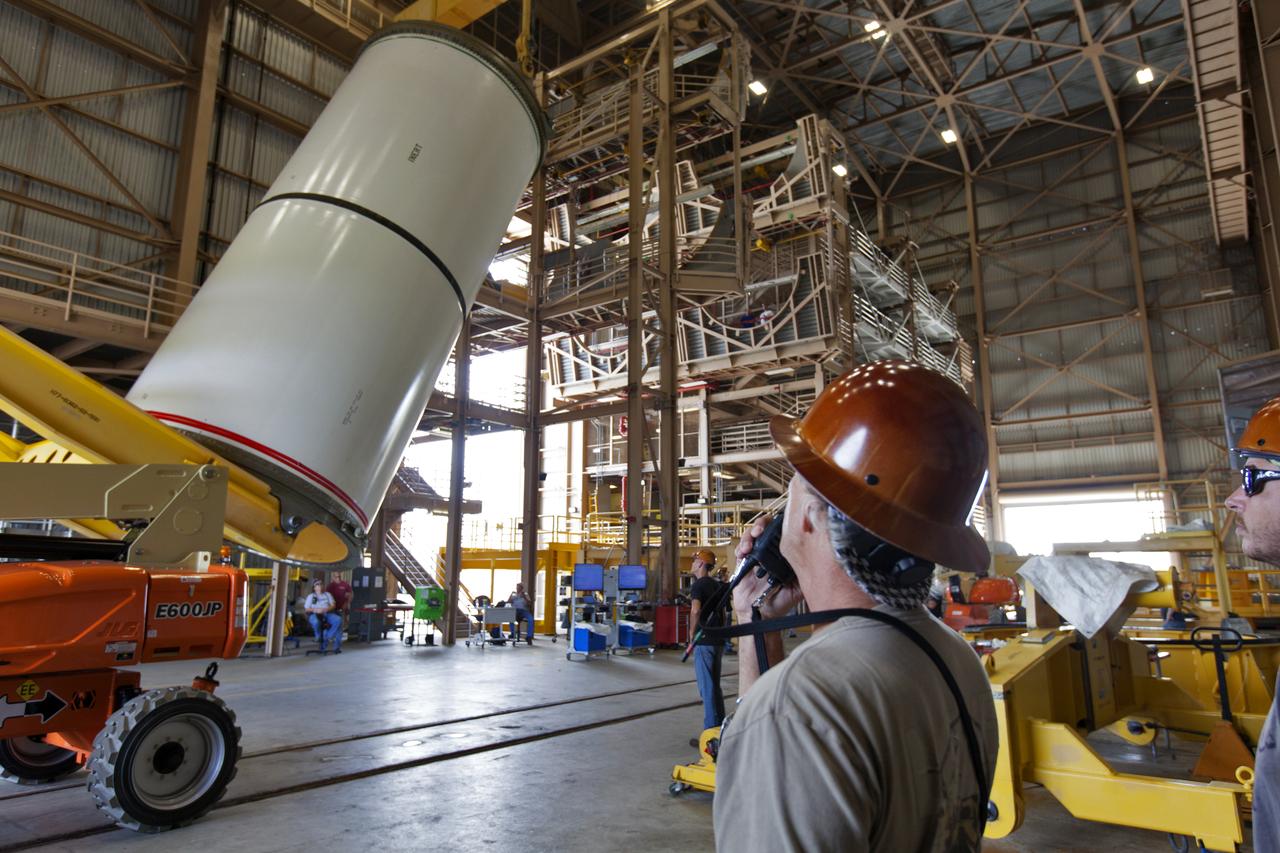

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
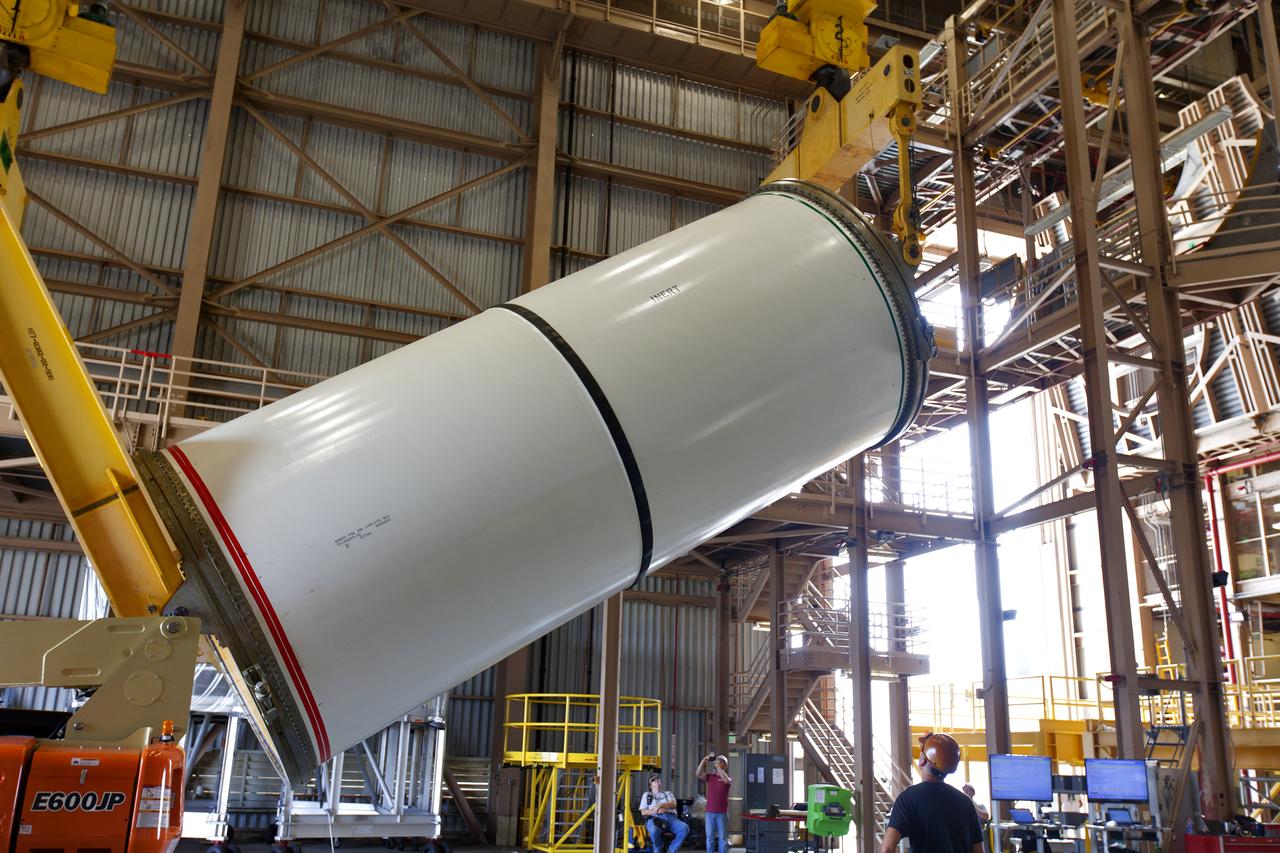

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
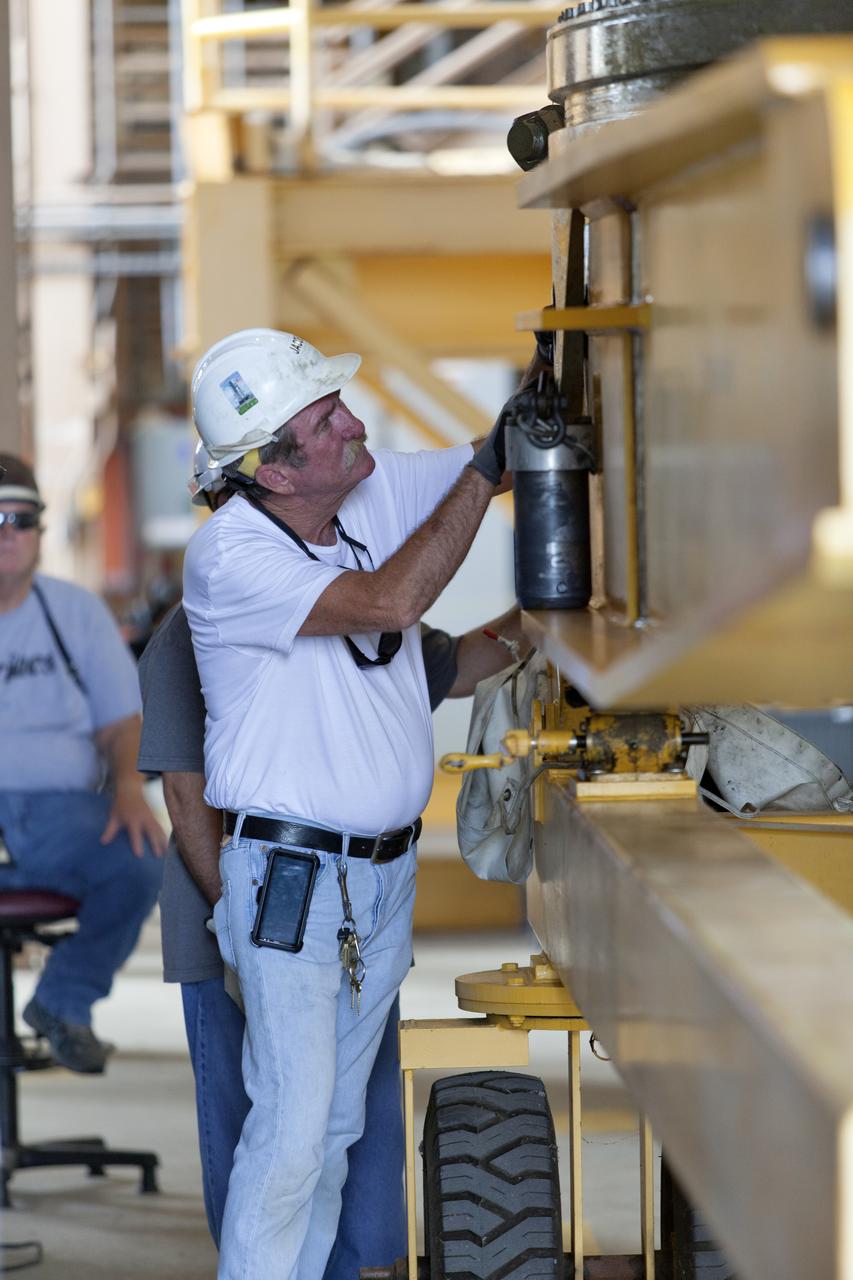

A Jacobs technician, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, checks bolt fittings during practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes will be used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
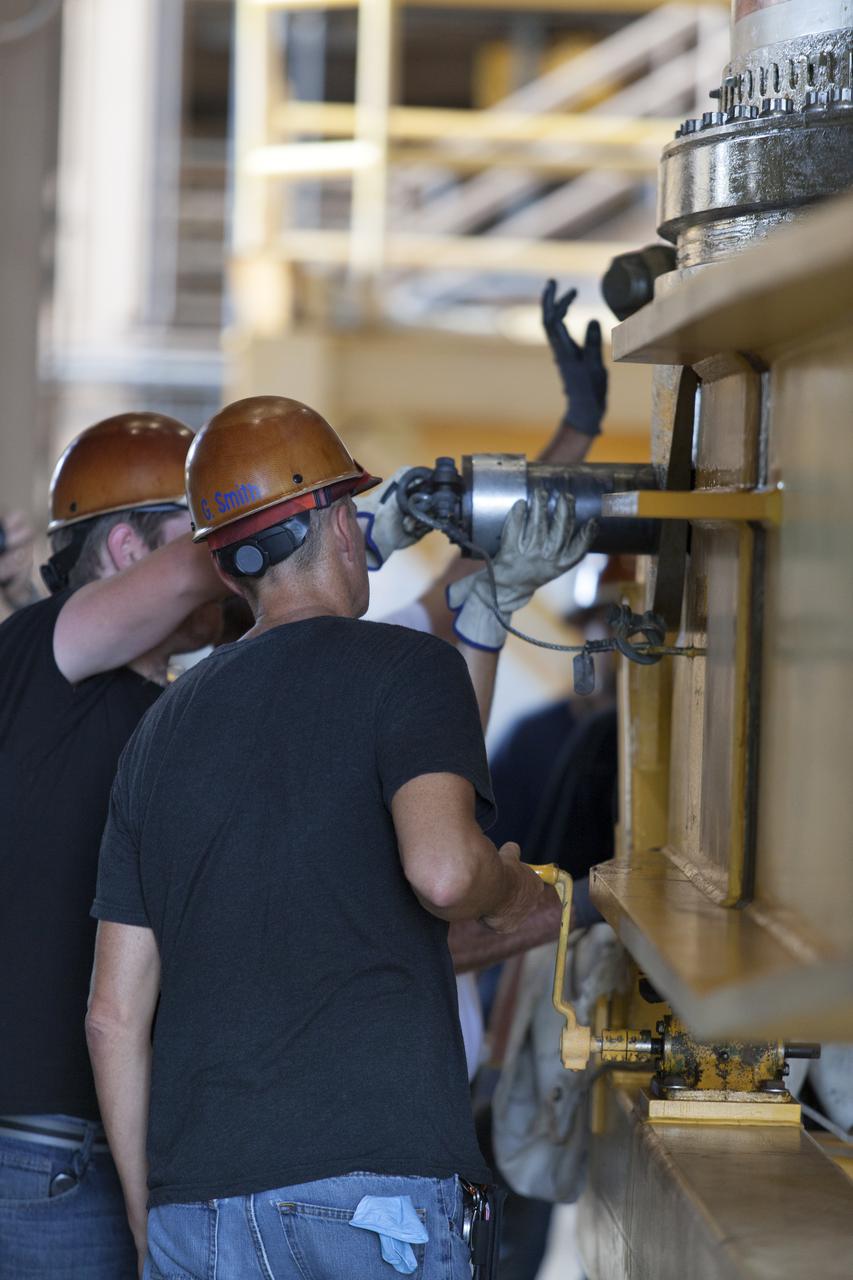

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, check bolt fittings as they practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
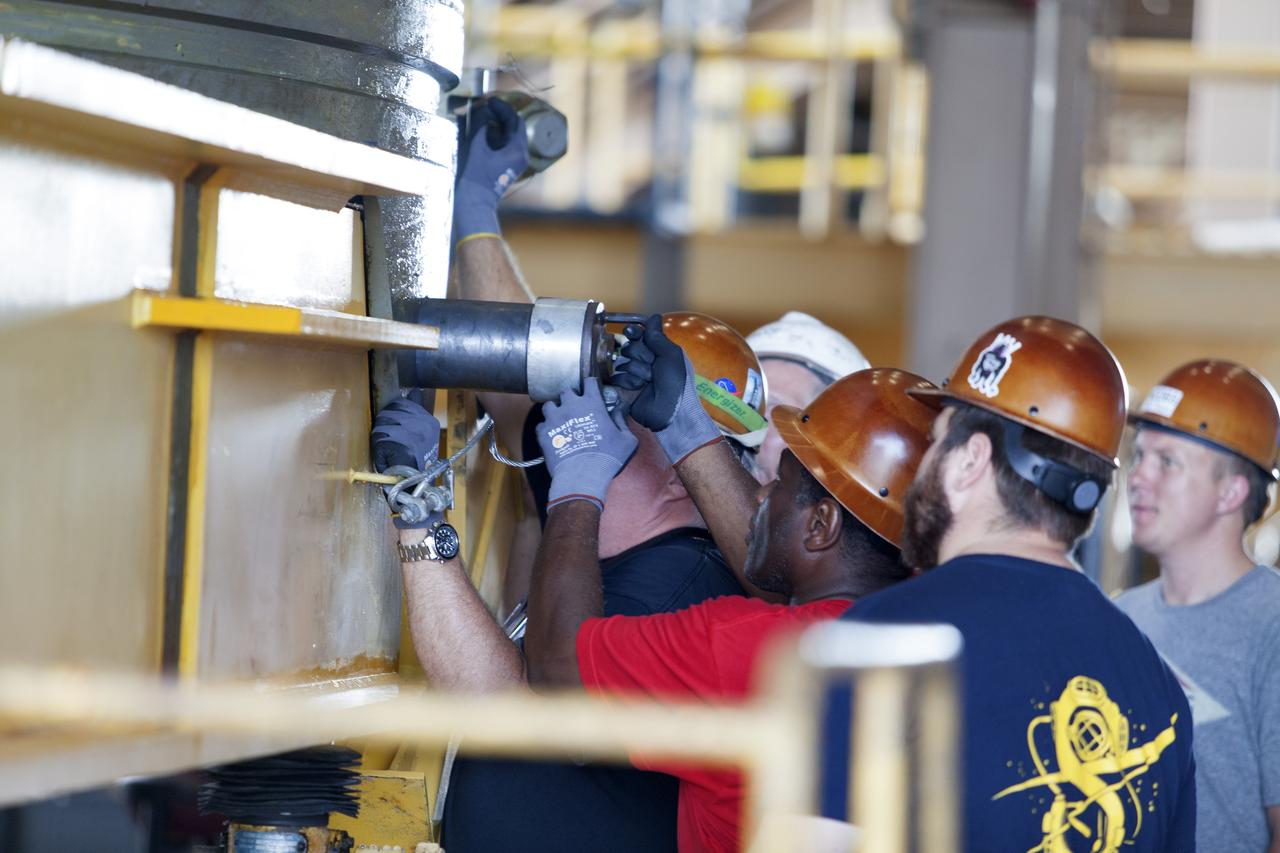

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, check bolt fittings as they practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
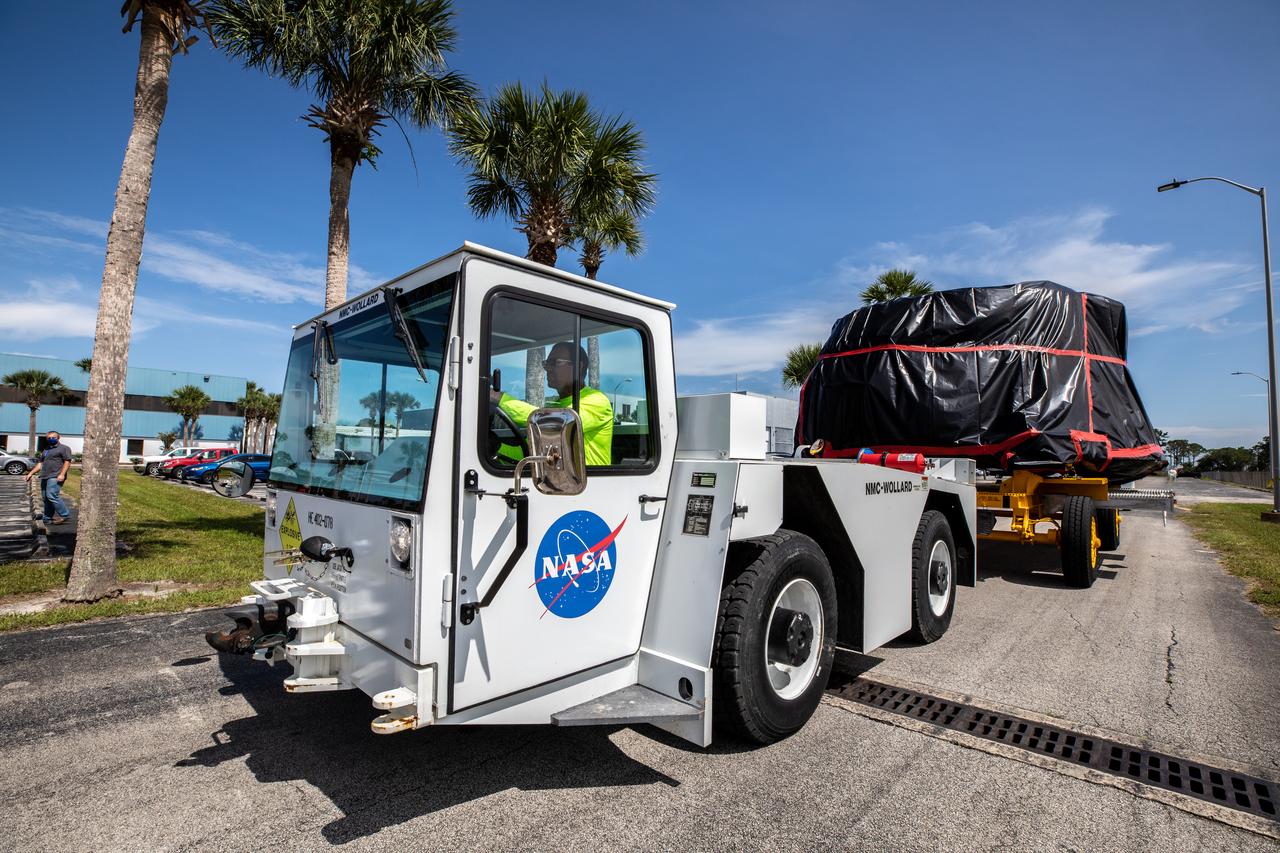

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are transported to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
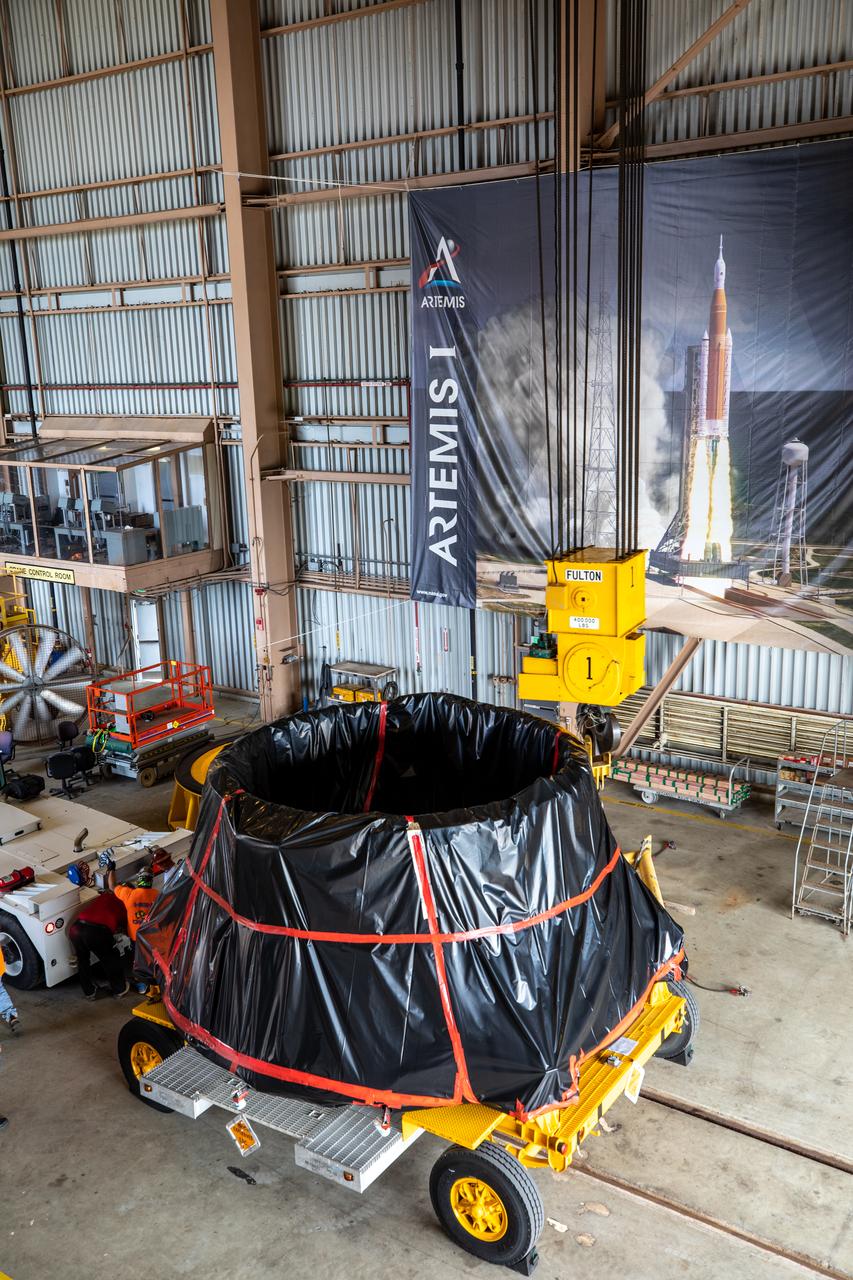

The first of two Artemis I aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters is moved into the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
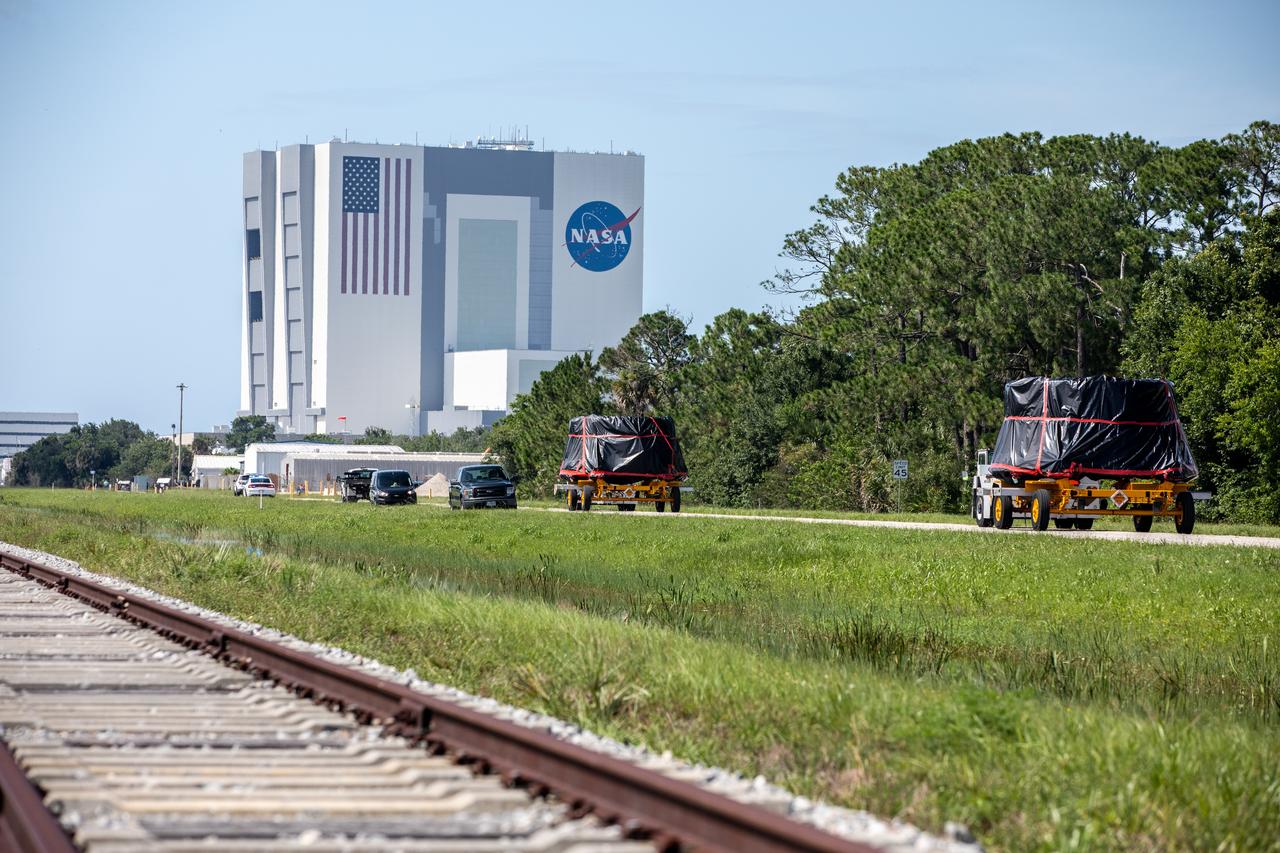

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved along the road to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The aft skirts will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
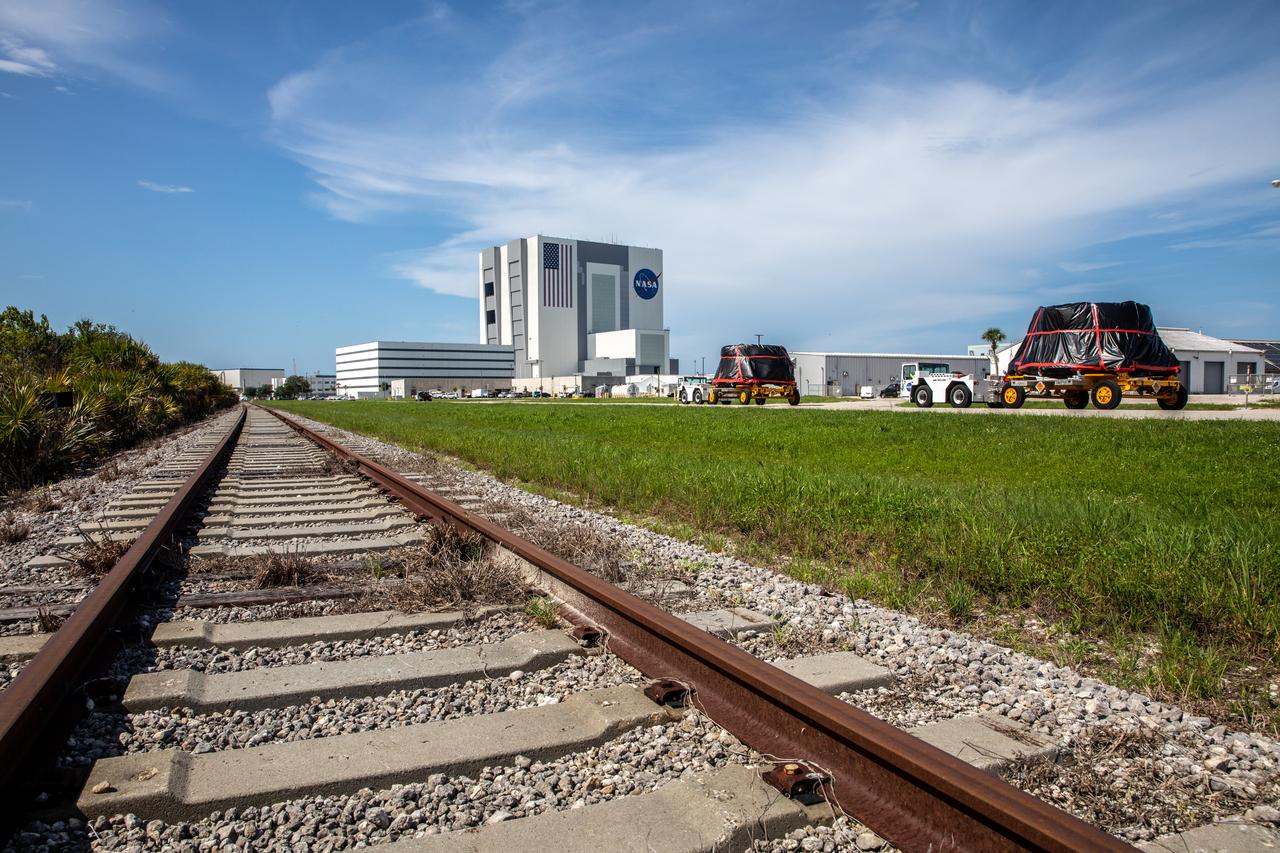

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved along the road to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The aft skirts will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are transported to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are transported to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
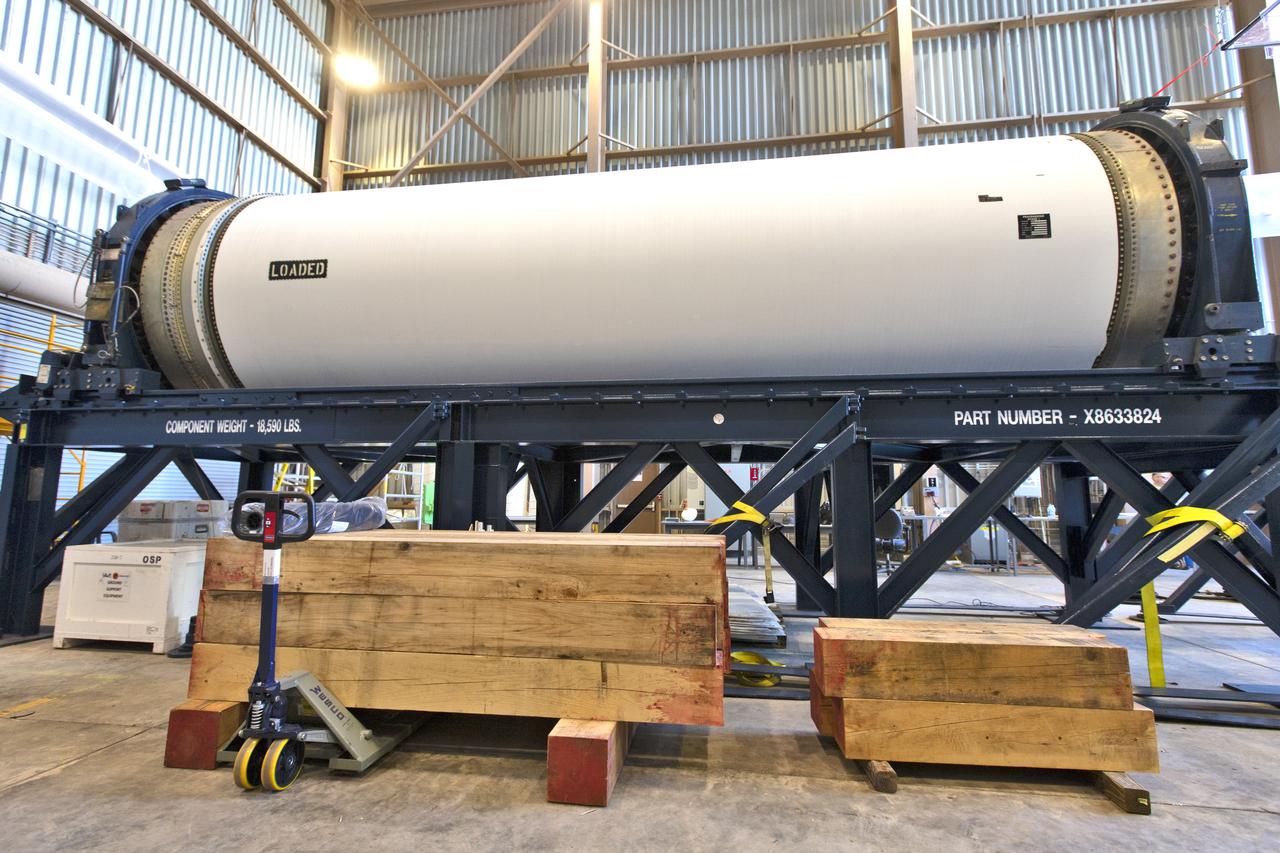

The Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
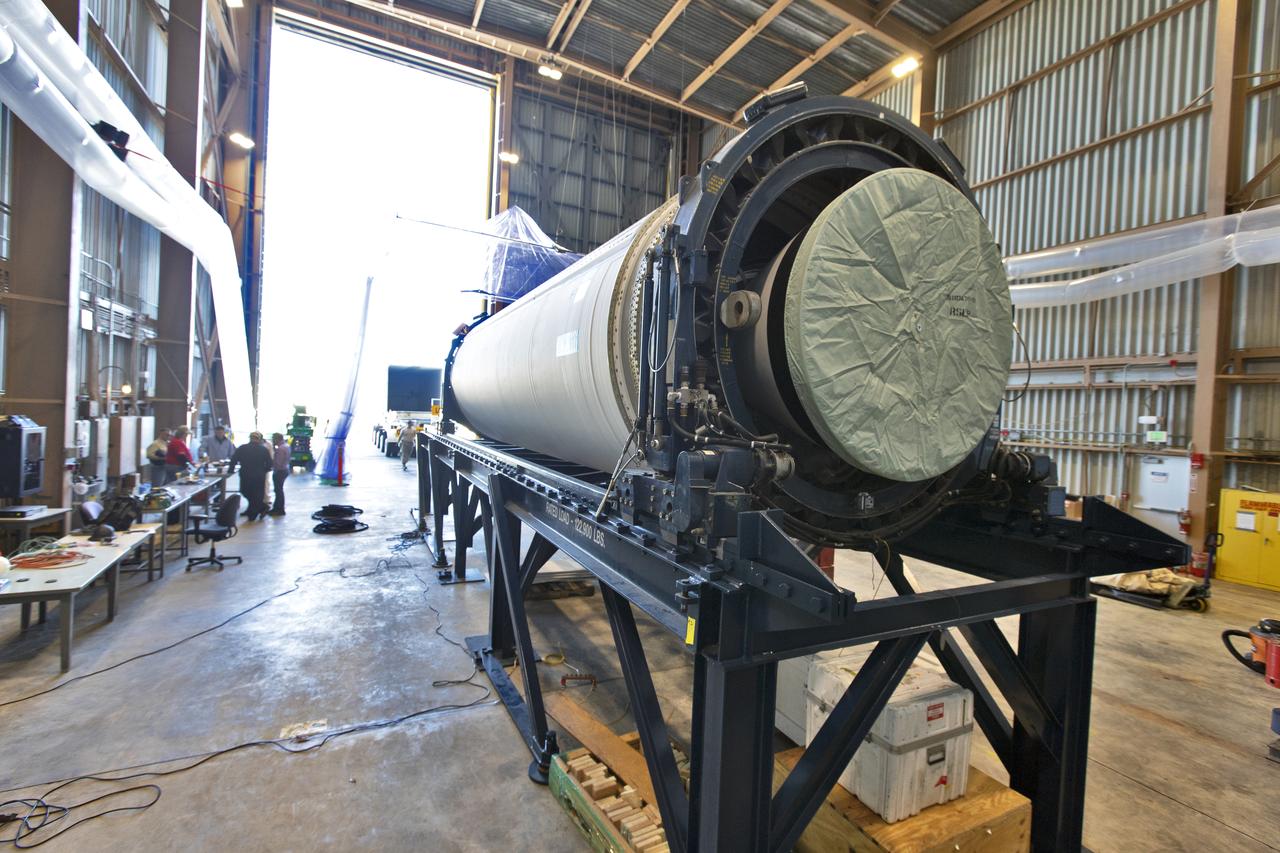

The Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.

The Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
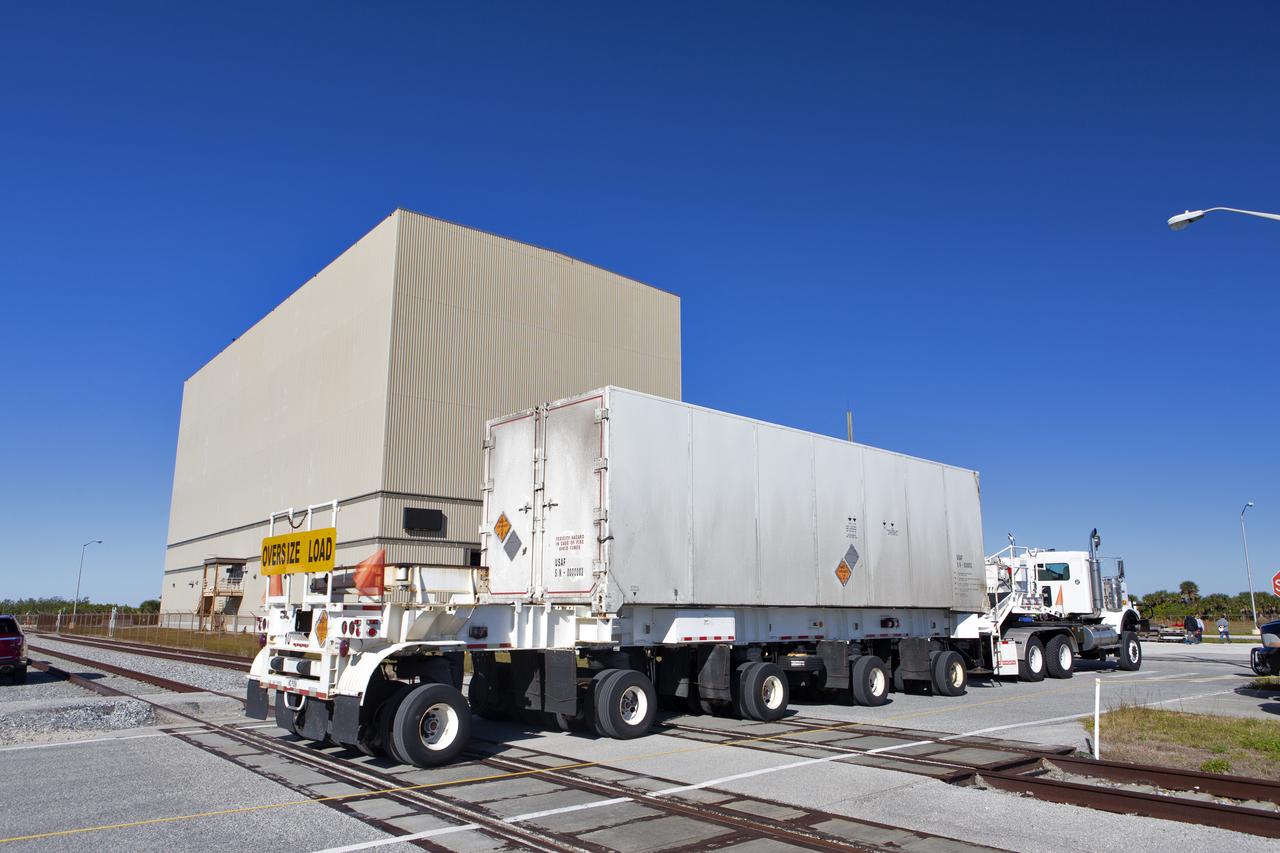

A heavy transport truck containing the Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be unloaded and moved into the RPSF where it will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
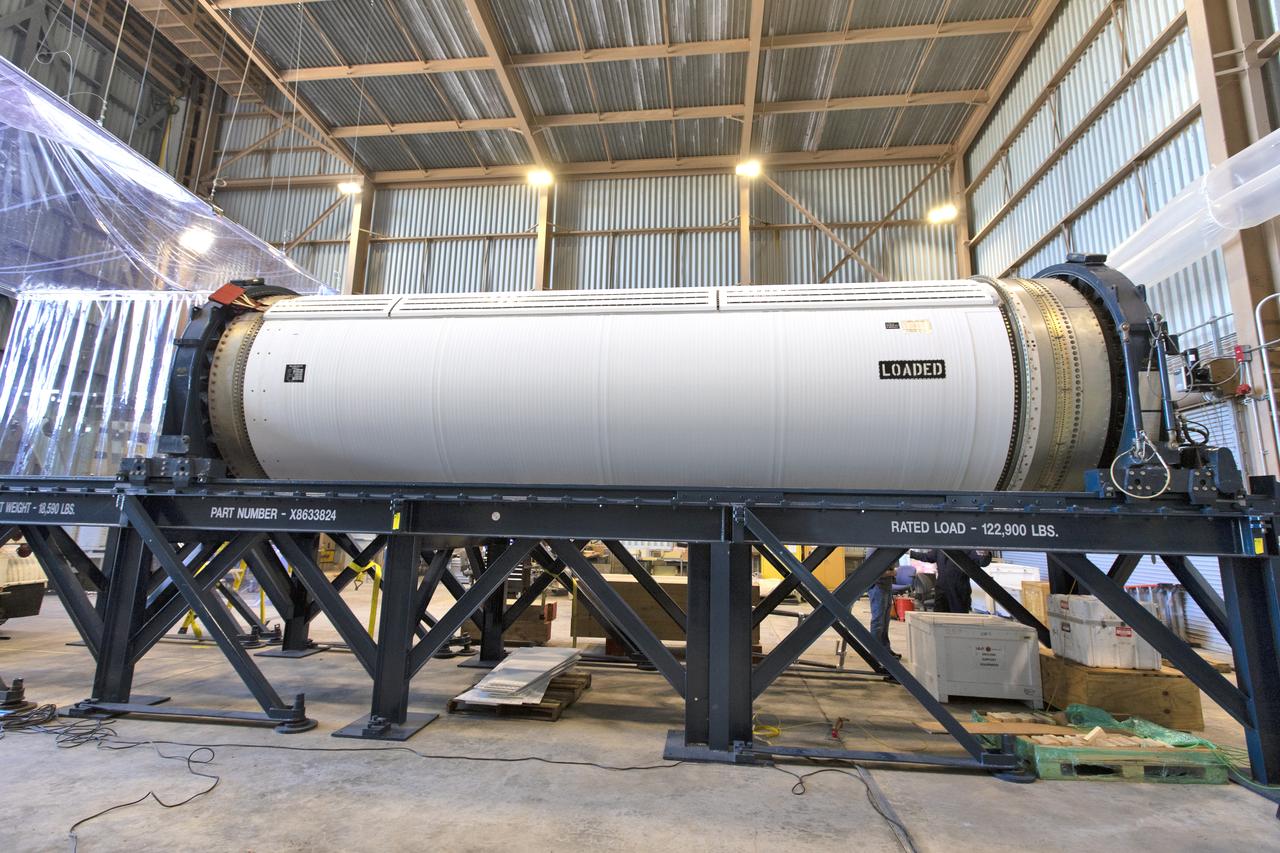

The Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
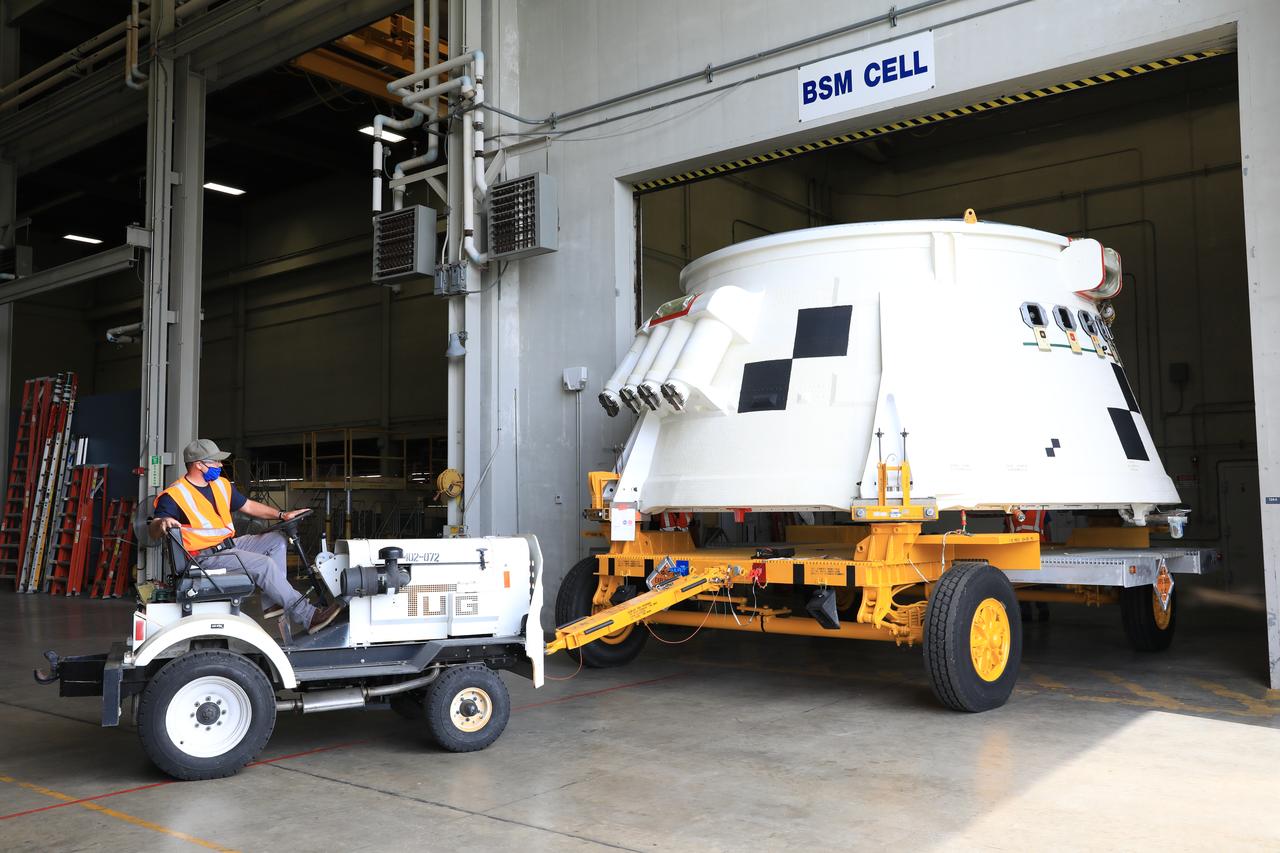

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view, the left aft skirt assembly is attached to a move vehicle and moved out of a test cell. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
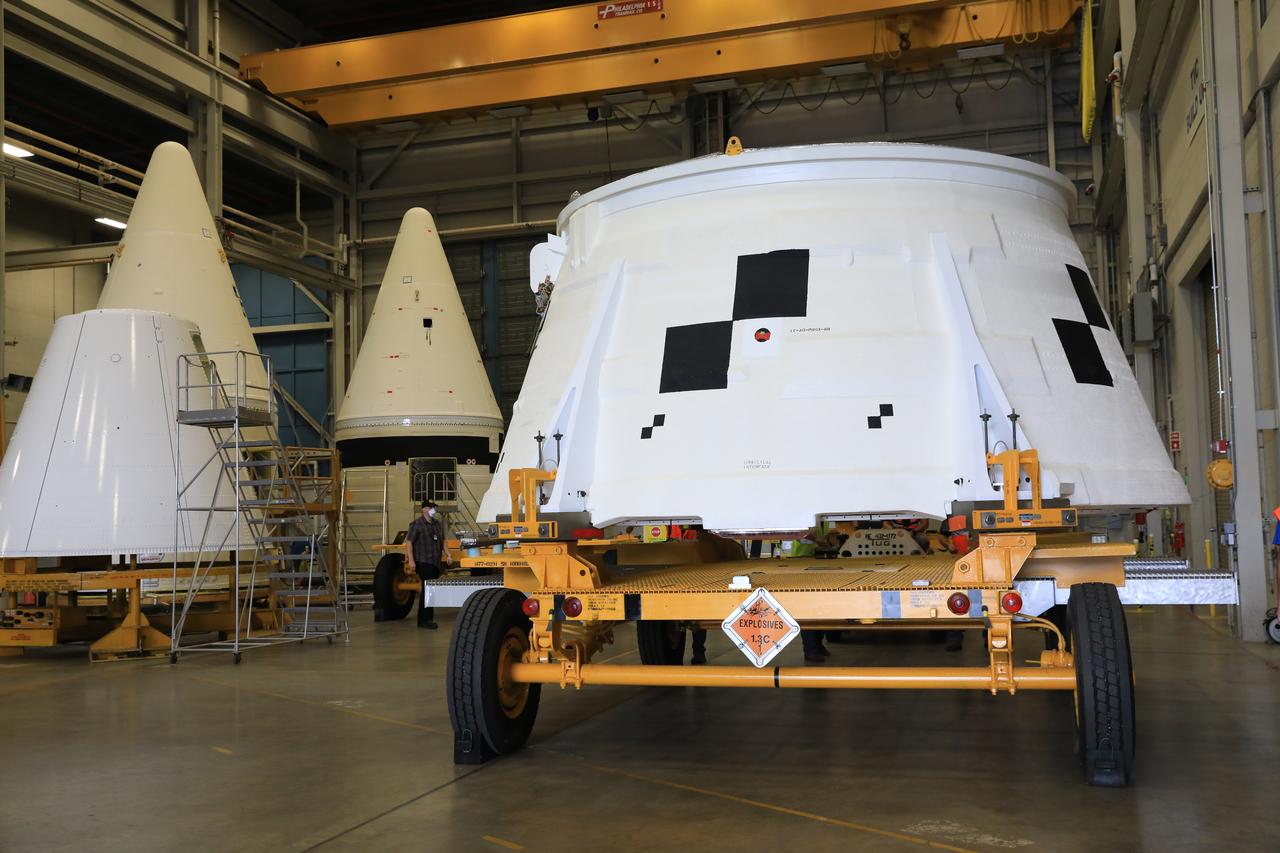

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved out of their test cells and are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view at right is the right aft skirt. In view at left are the two Artemis I forward assemblies. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
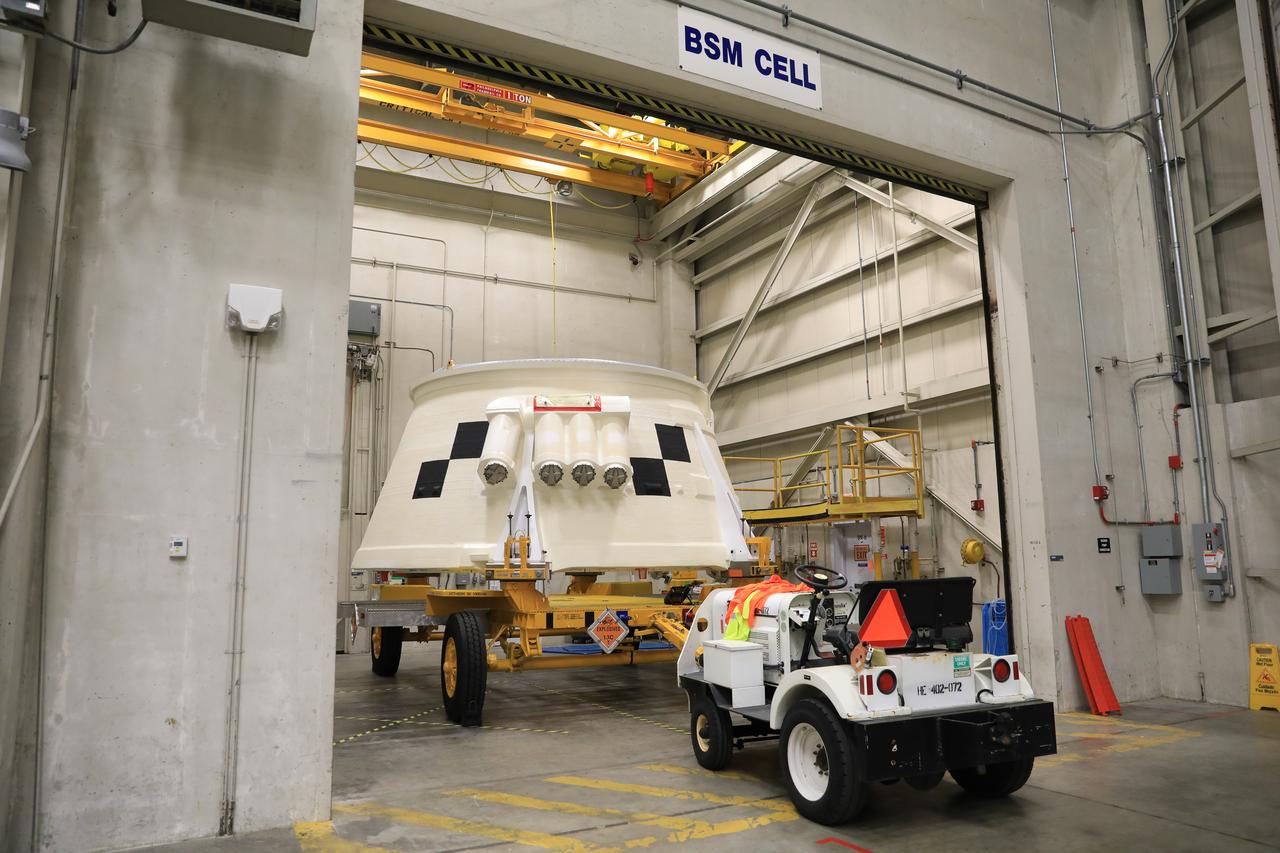

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view, the left aft skirt assembly is attached to a move vehicle in a test cell. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
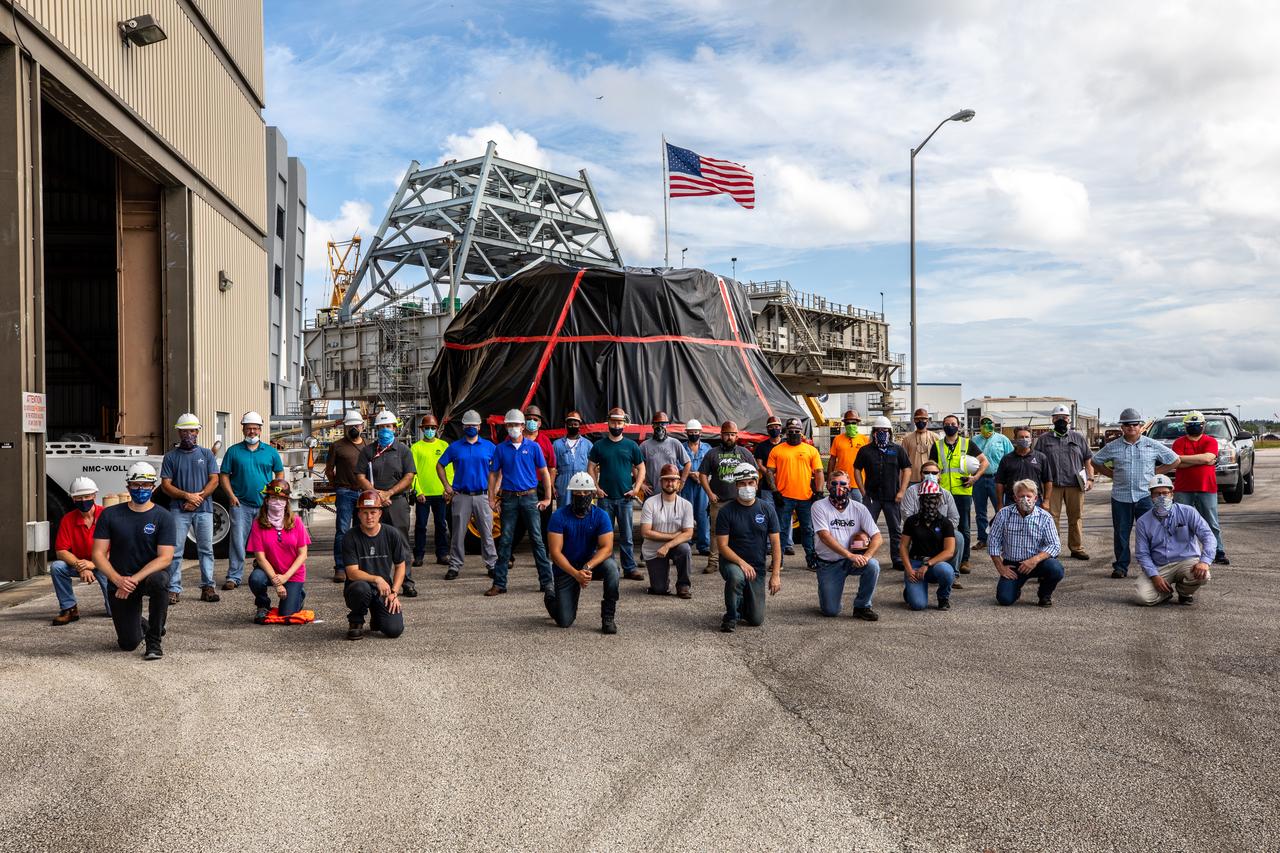

Exploration Ground Systems workers gather in front of the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020, to mark the arrival of the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters. The aft skirts were moved from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
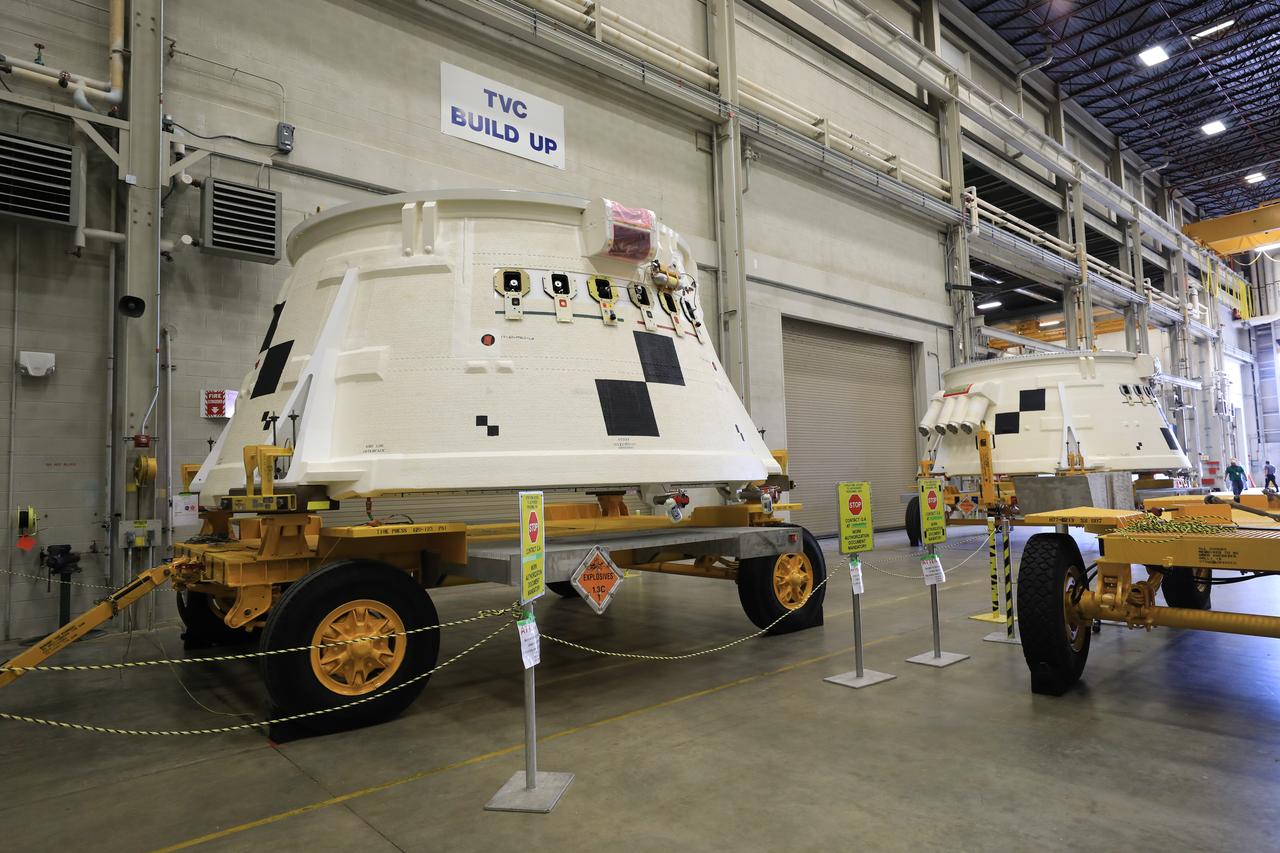

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view at left is the left aft skirt assembly, and at far right is the right aft skirt assembly. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
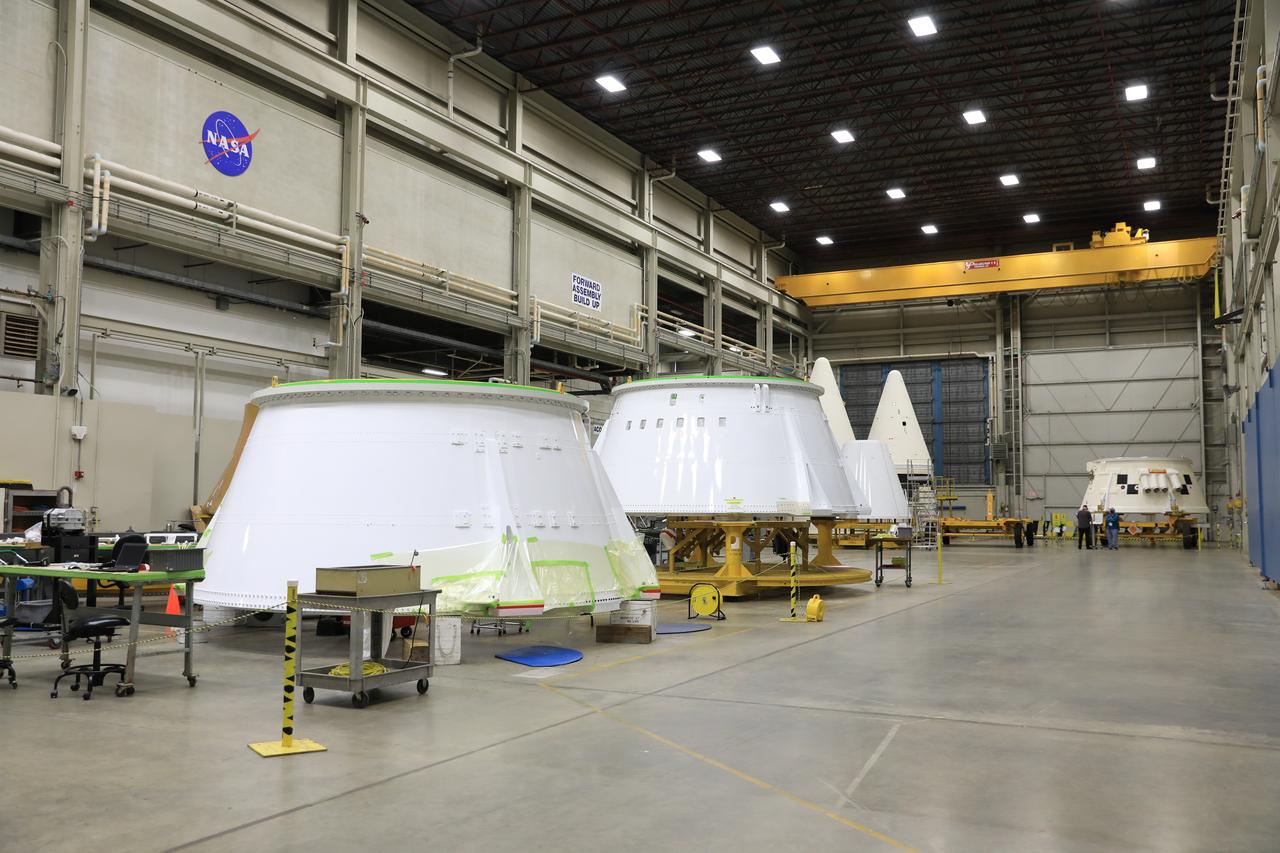

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility (BFF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis II aft skirt structures for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are in view at left. Behind them are the two Artemis I forward assemblies. At far right, in the distance, is the right aft skirt assembly. In the BFF, the two aft skirt assemblies are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
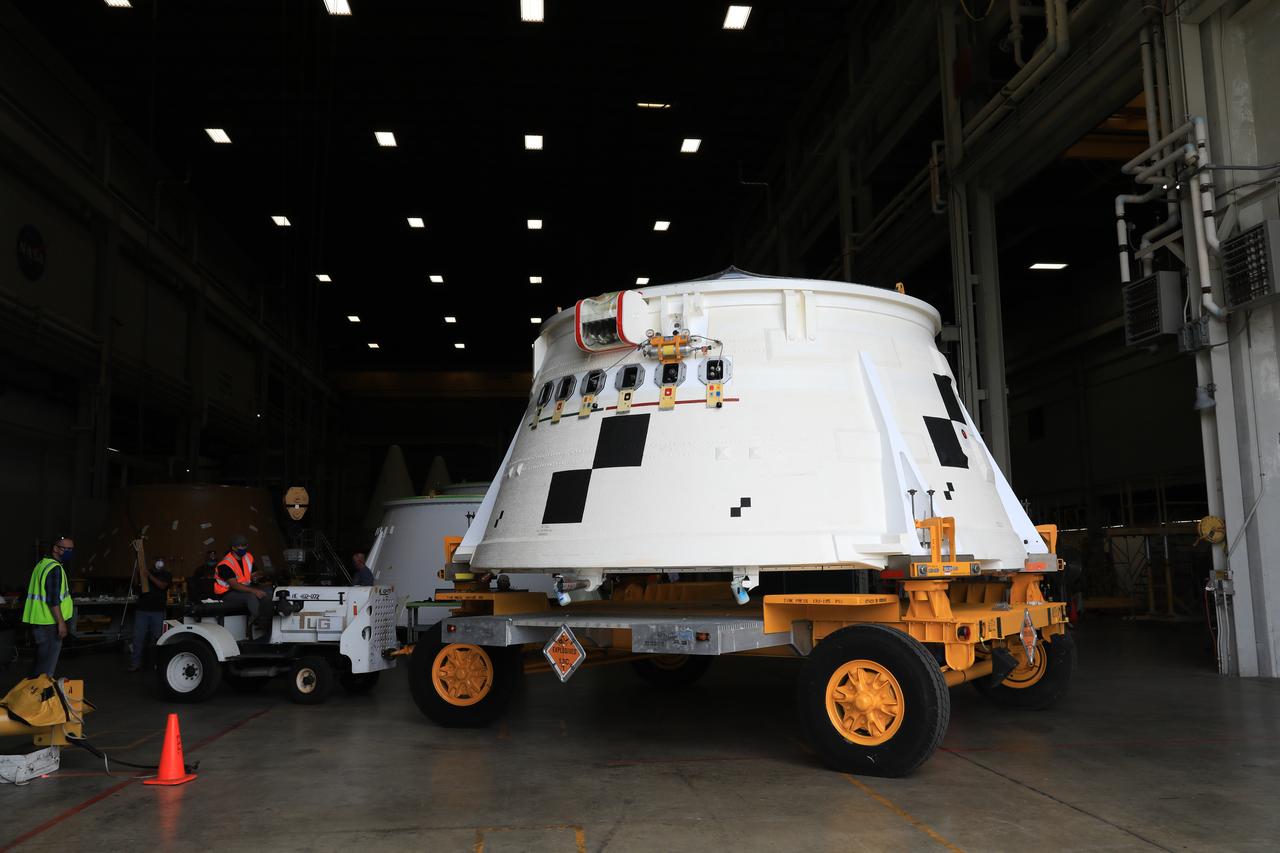

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view, the left aft skirt assembly is attached to a move vehicle and moved out of a test cell. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view at left is the left aft skirt assembly. Behind it to the right is the right aft skirt assembly. Also in view at far right, are the Artemis I forward assemblies, with the left assembly in front and the right assembly behind it. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
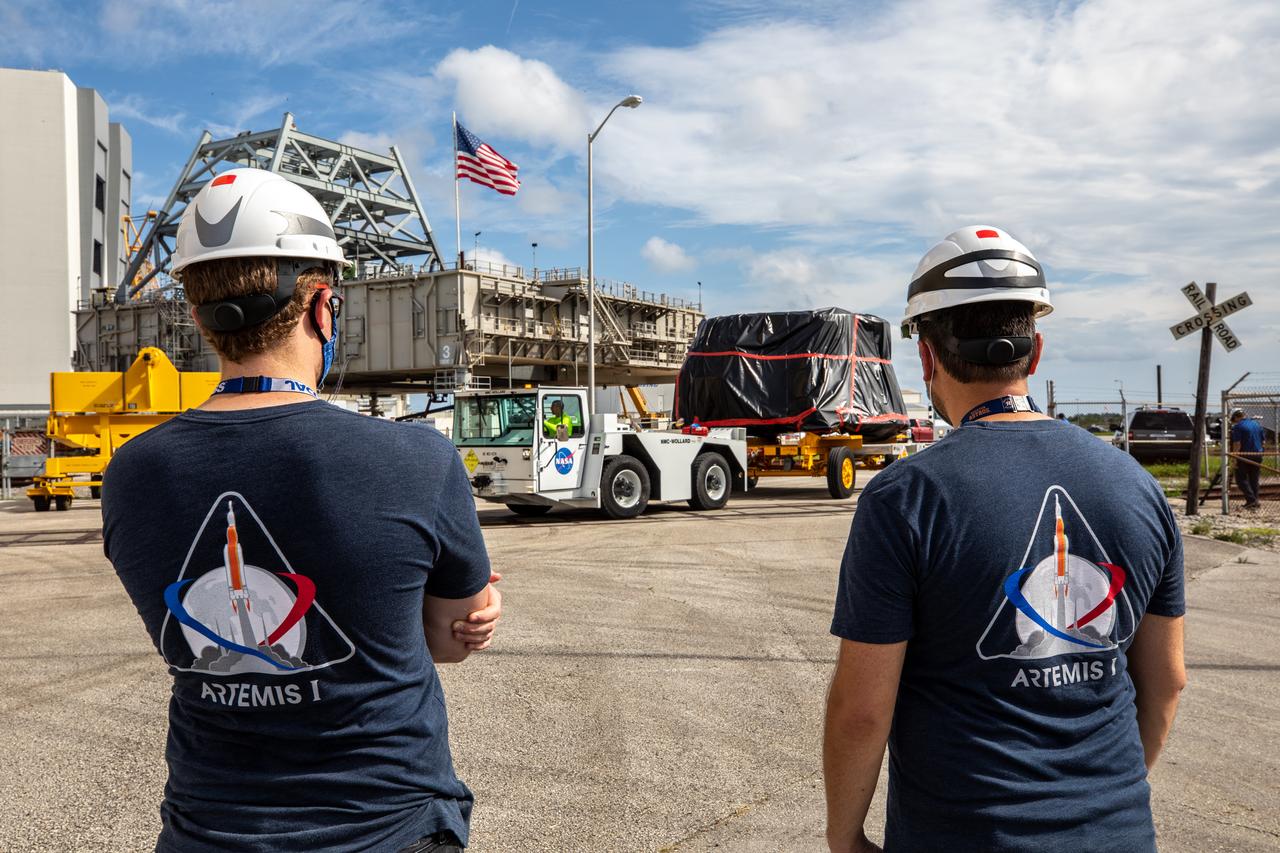

Exploration Ground Systems workers watch as the first of two Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters crosses a railroad track on its way to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. They were transported from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
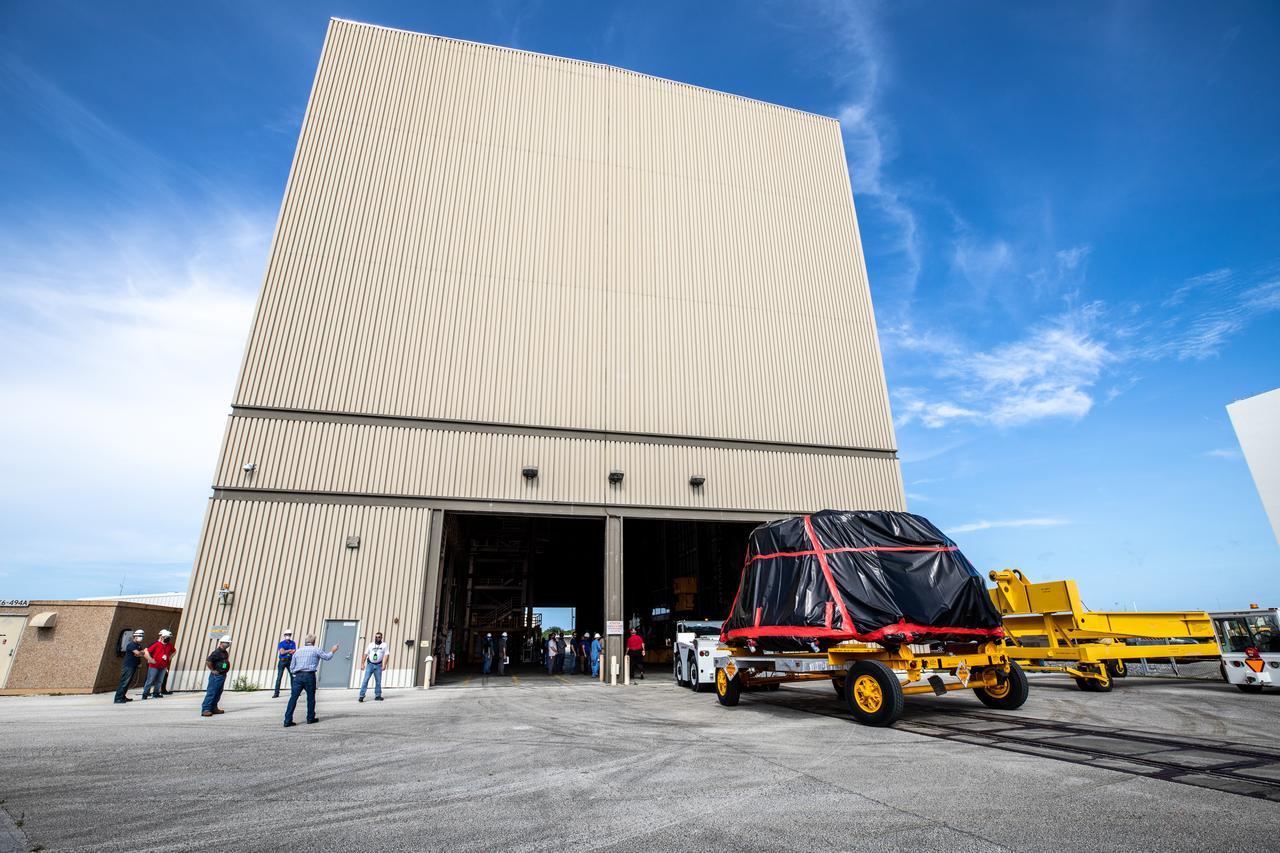

The first of two Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. They were transported from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
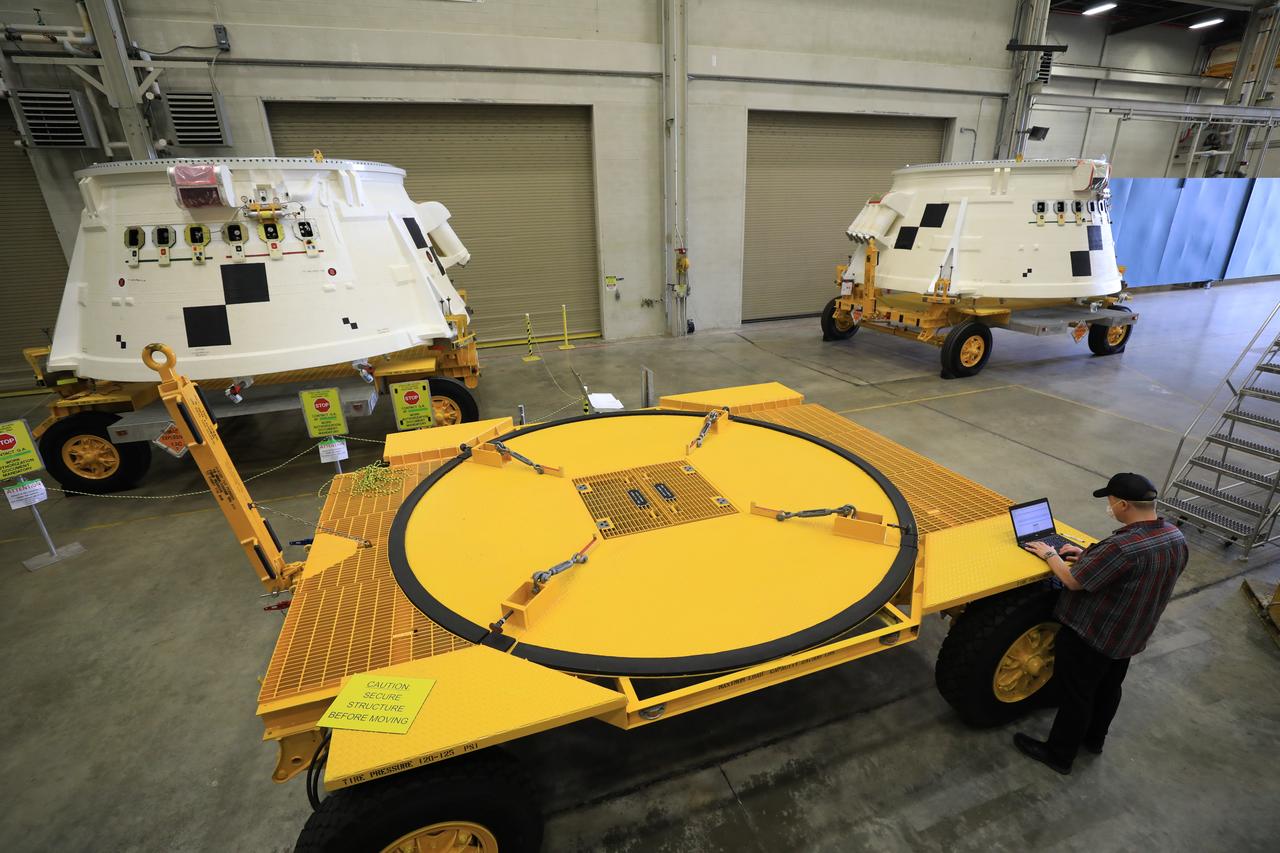

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view at left is the left aft skirt assembly, and at right is the right aft skirt assembly. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
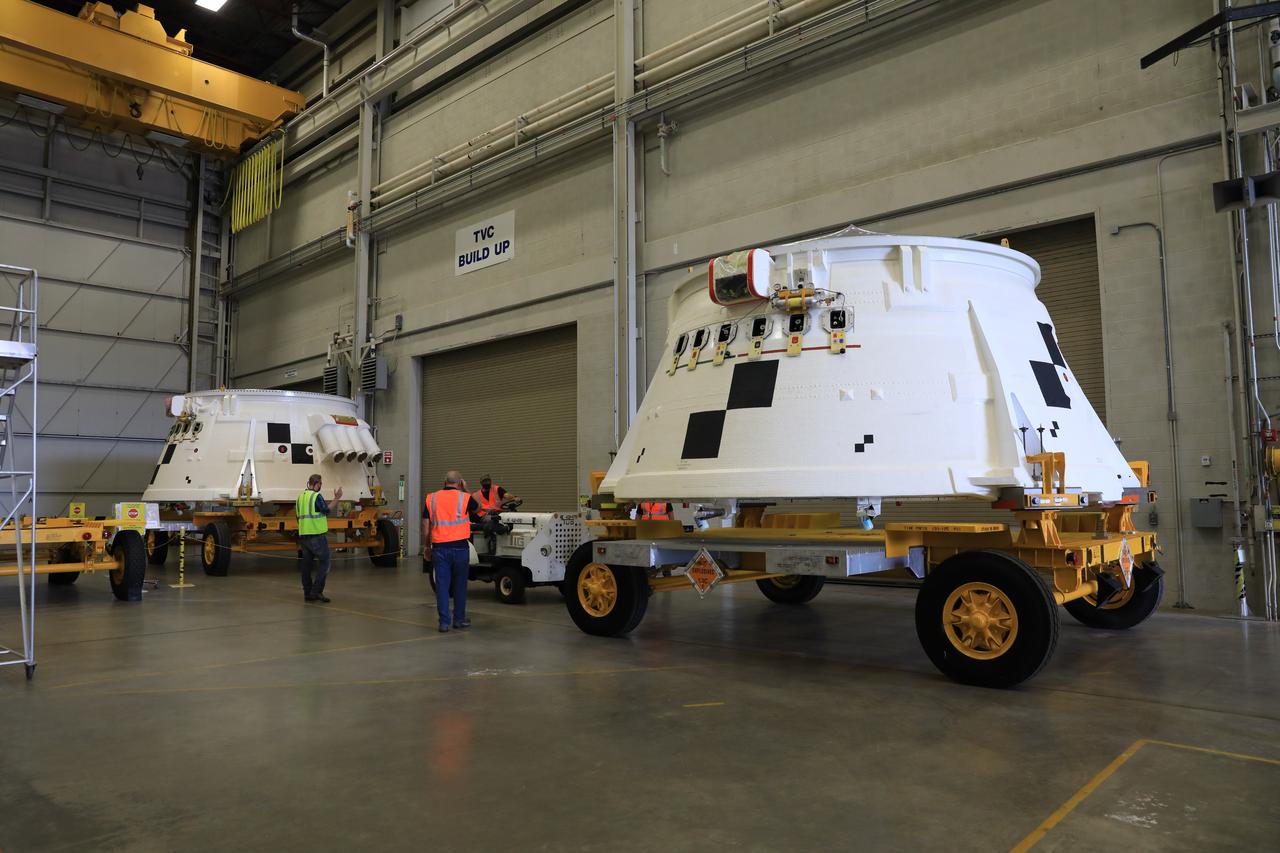

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved out of their test cells and are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
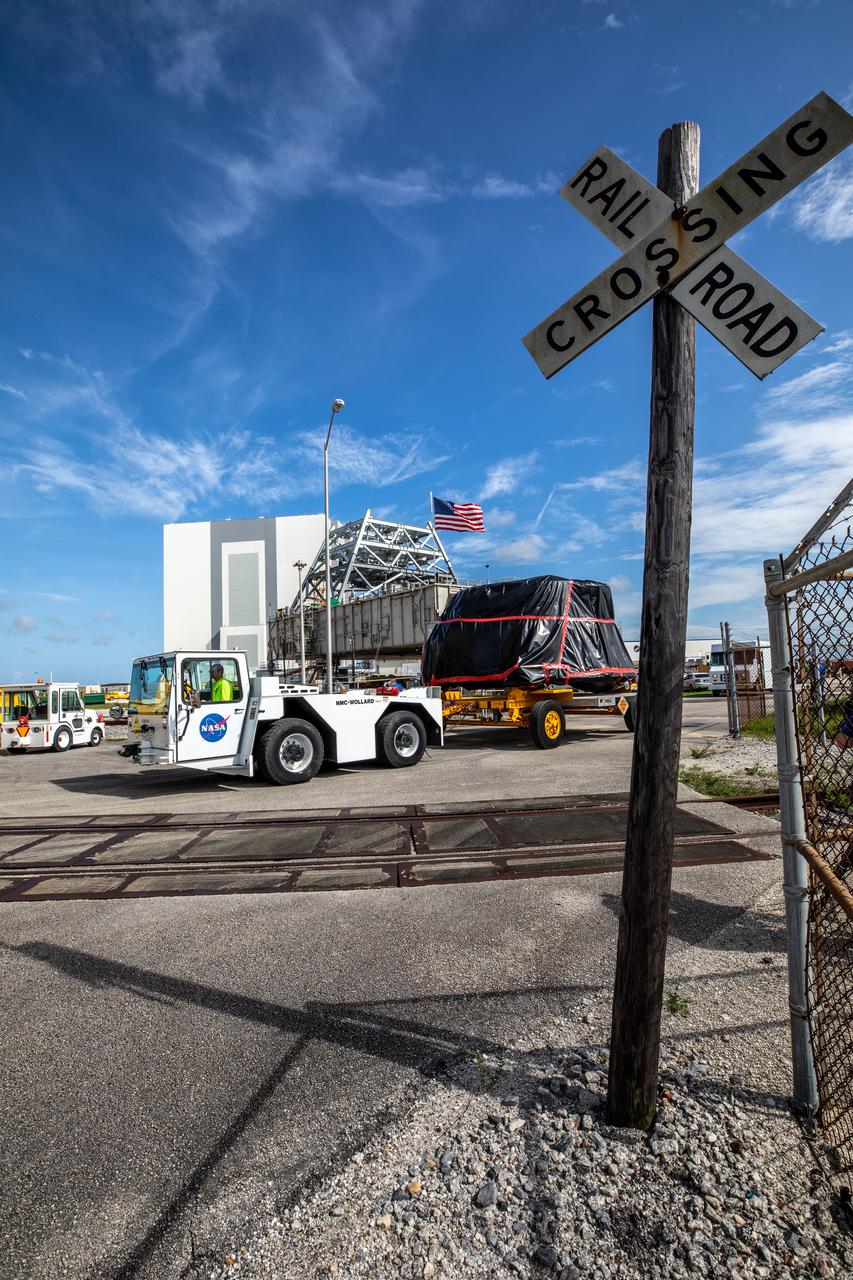

One of two Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters crosses a railroad track on its way to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. They were transported from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
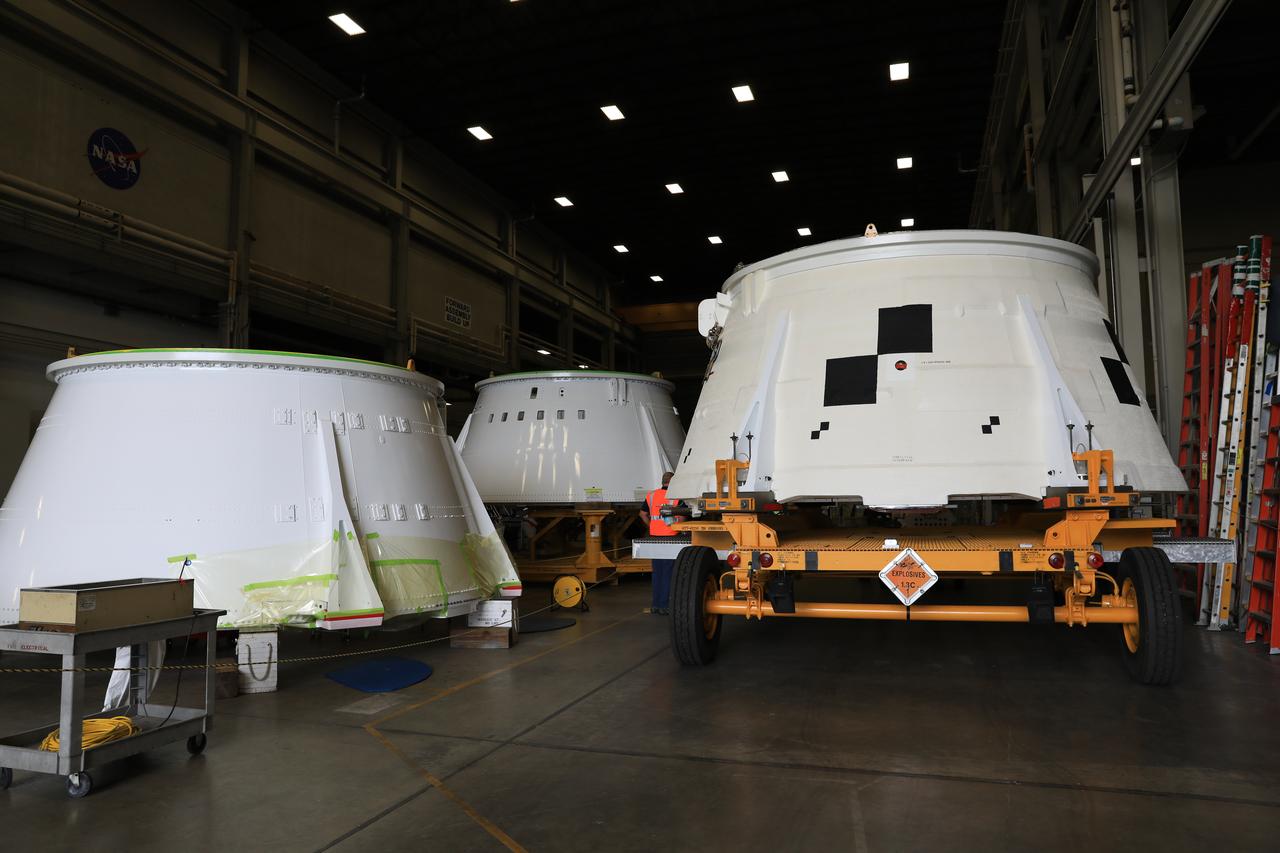

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view, the left aft skirt assembly is attached to a move vehicle and moved out of a test cell. The Artemis II aft skirt structures are in view at left. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.

The Artemis I aft skirts for the NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved along the road to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. In the background is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The aft skirts will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the VAB. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
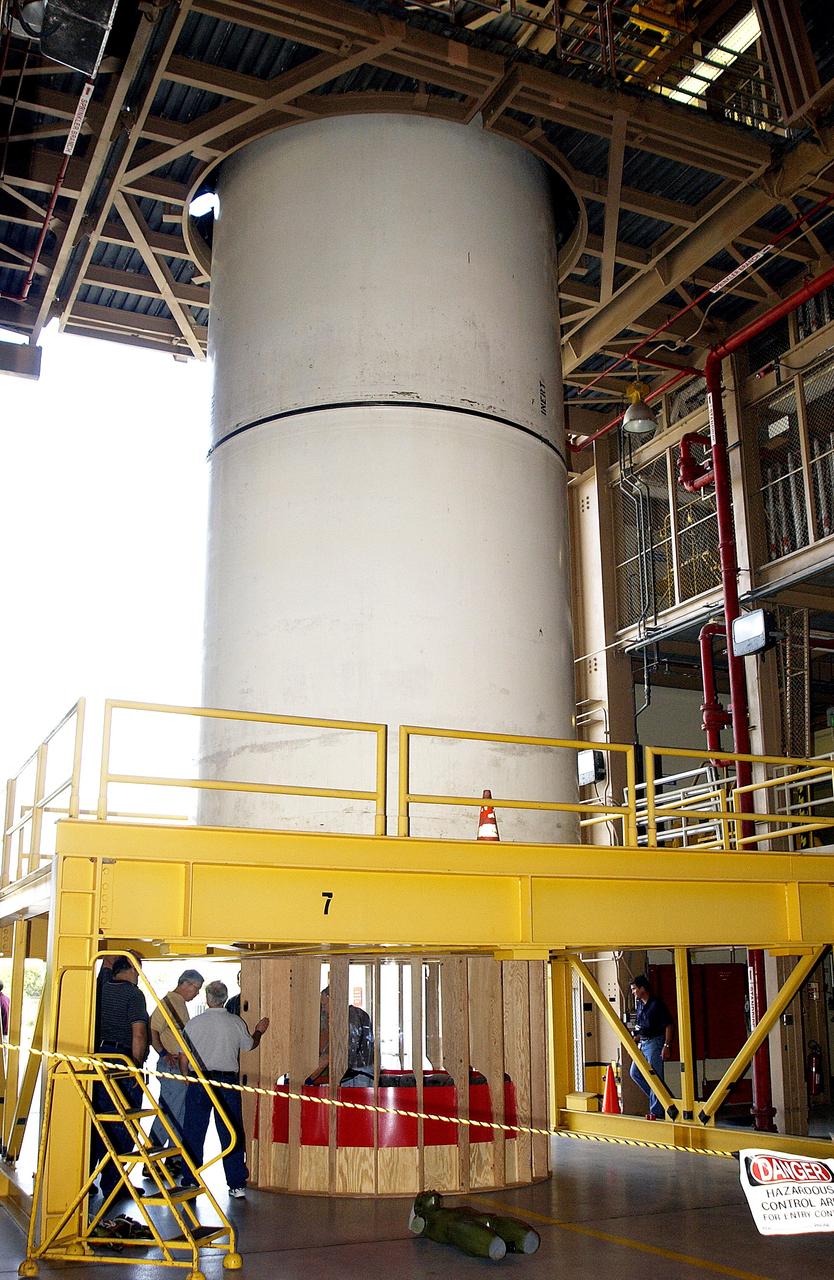

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility stand a mockup of two segments of a solid rocket booster (SRB) being used to test the feasibility of a vertical SRB propellant grain inspection, required as part of safety analysis.
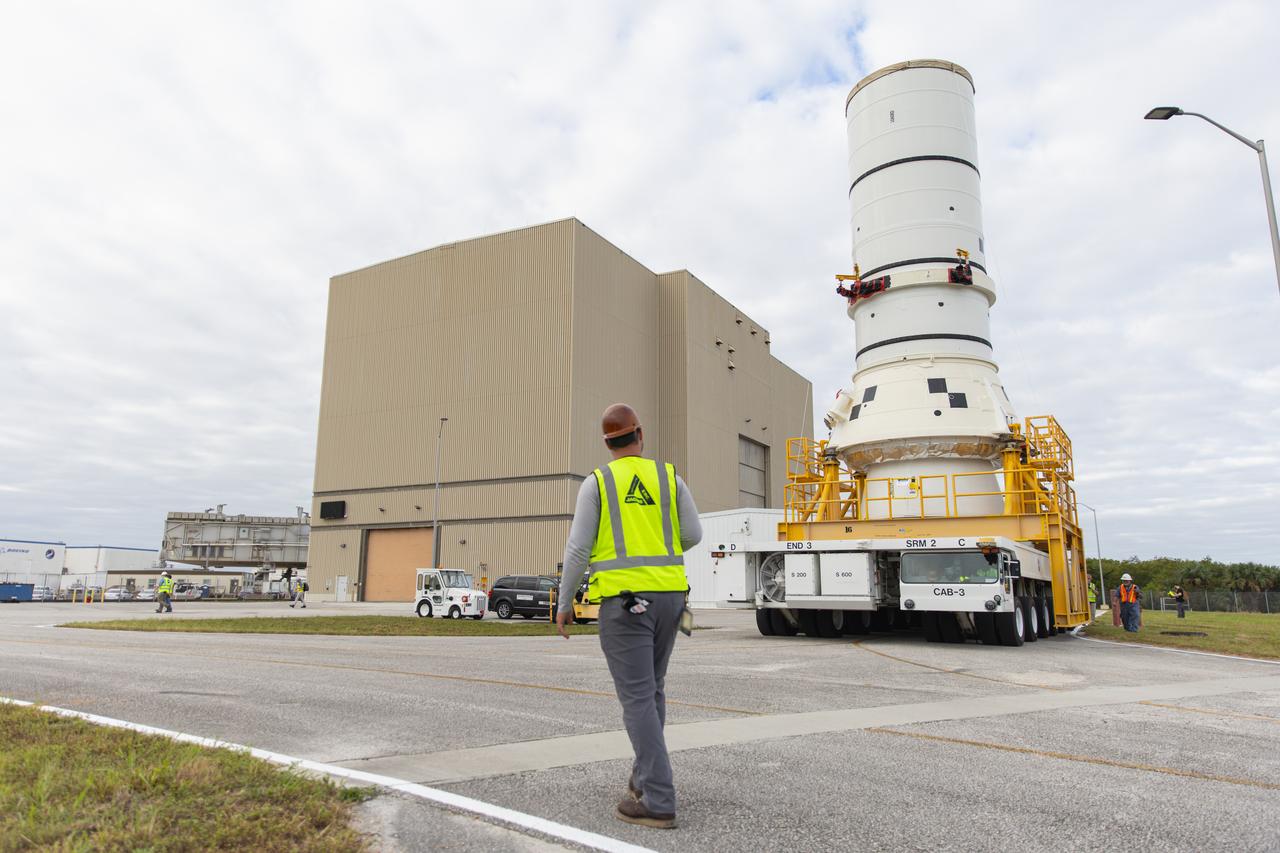

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
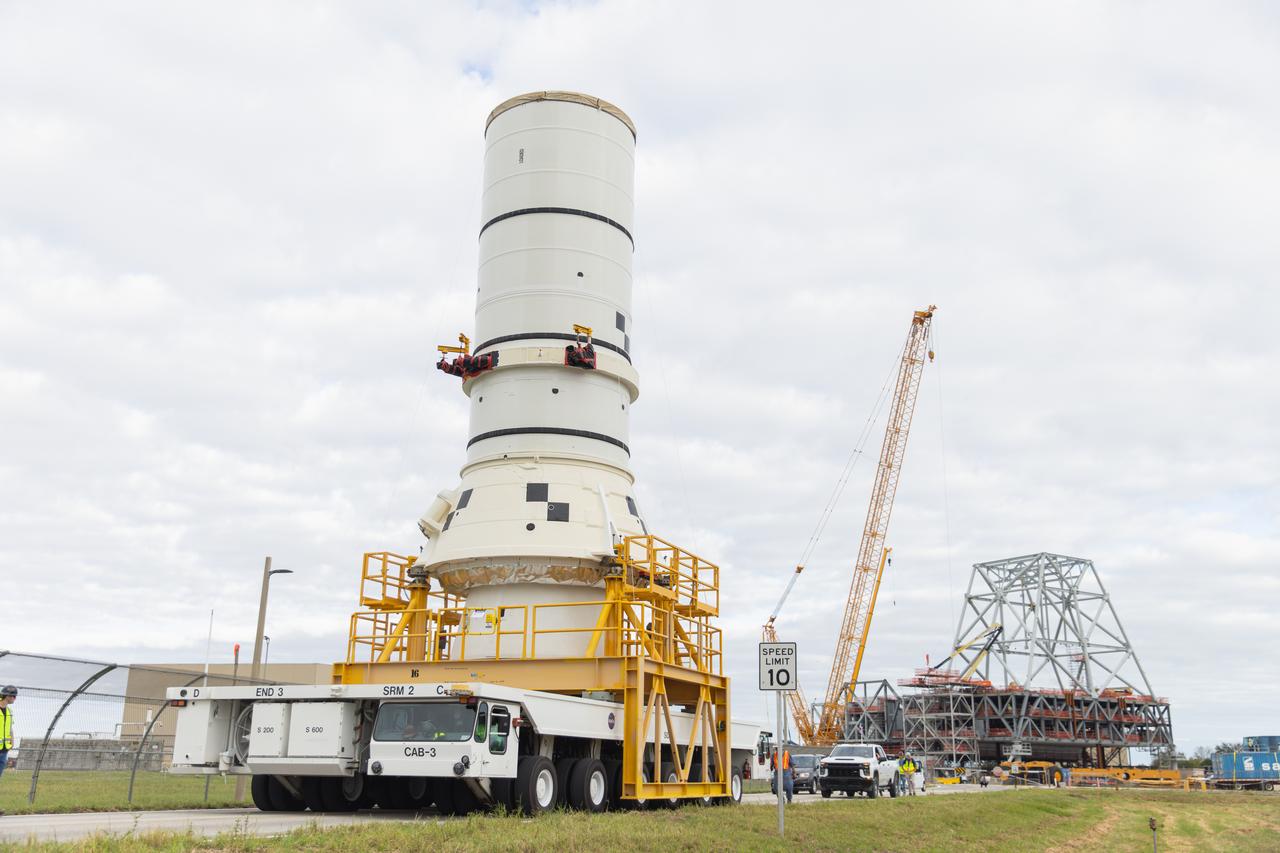

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
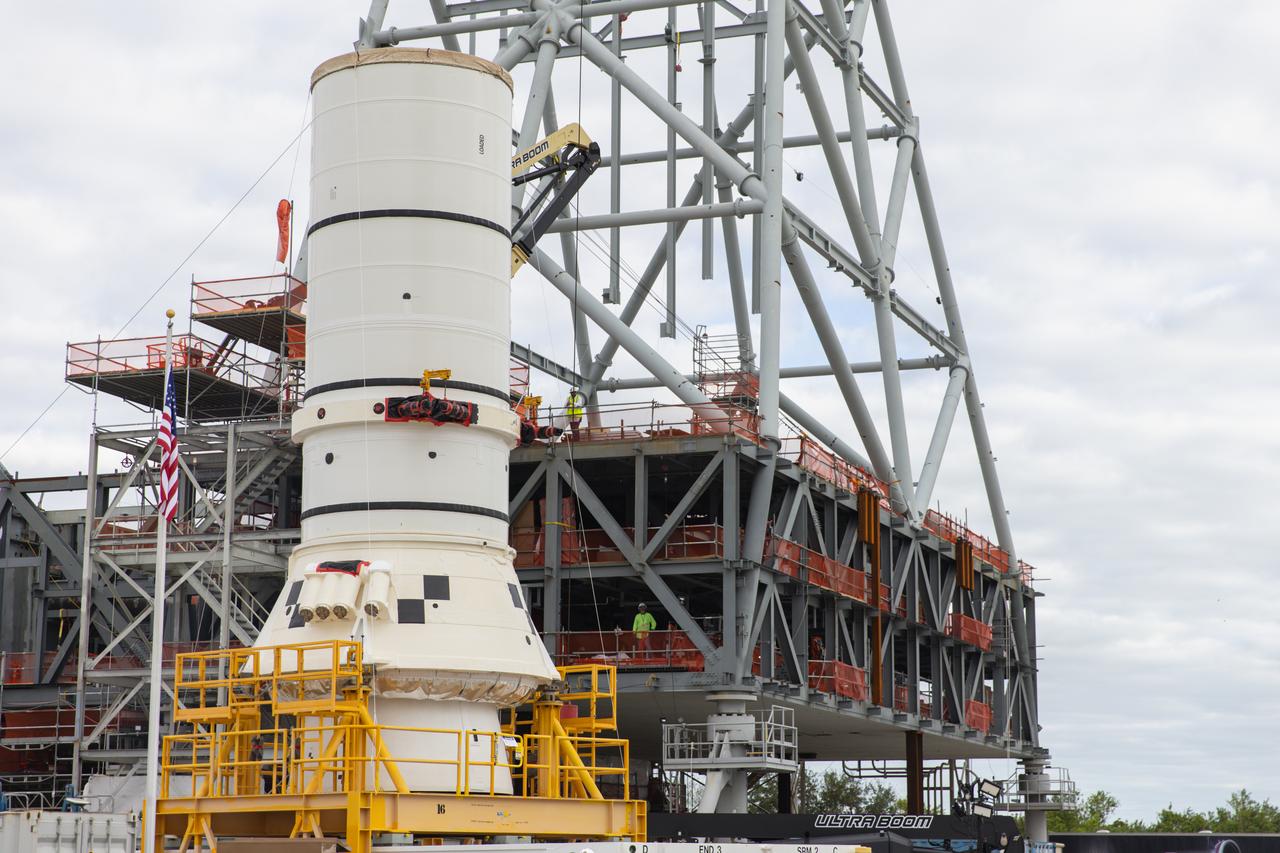

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.

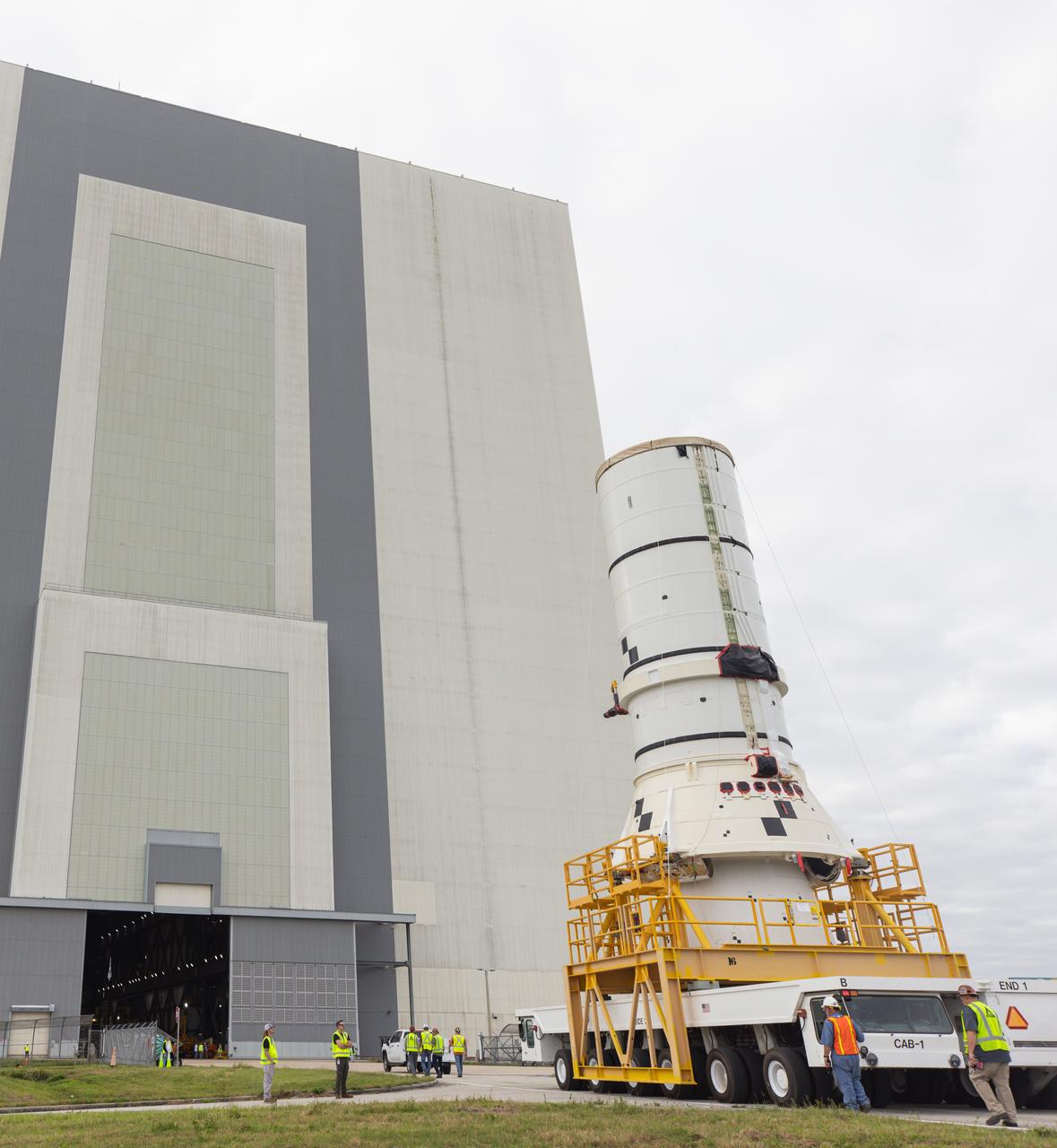
The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
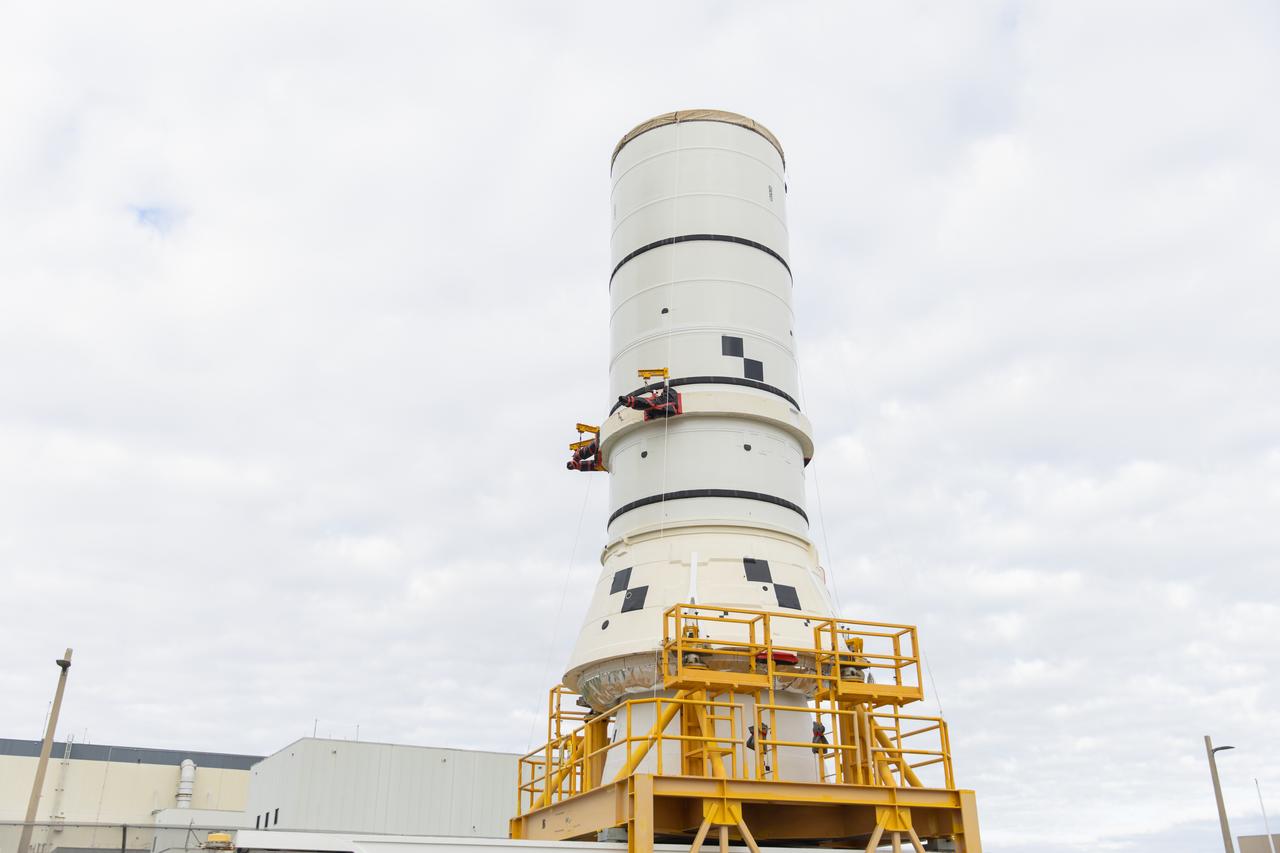

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
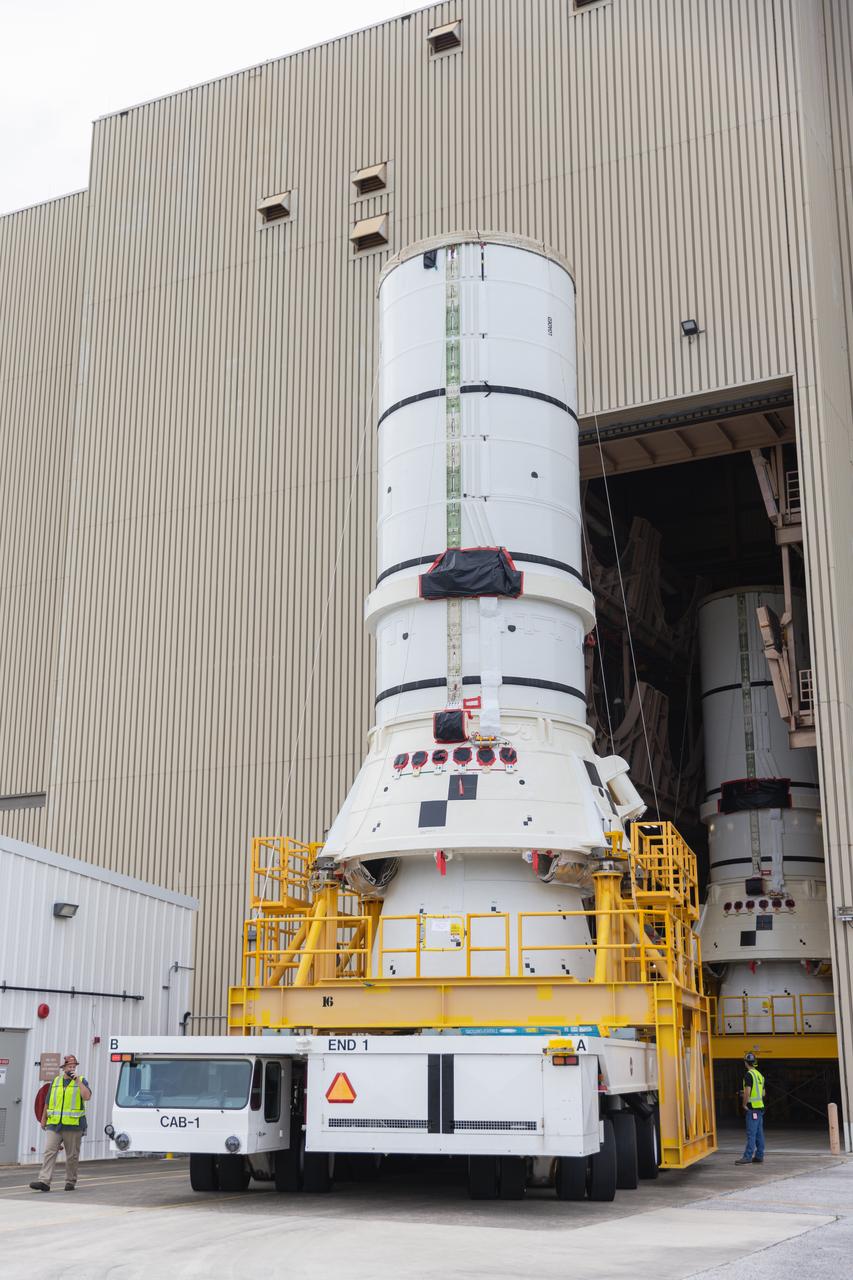

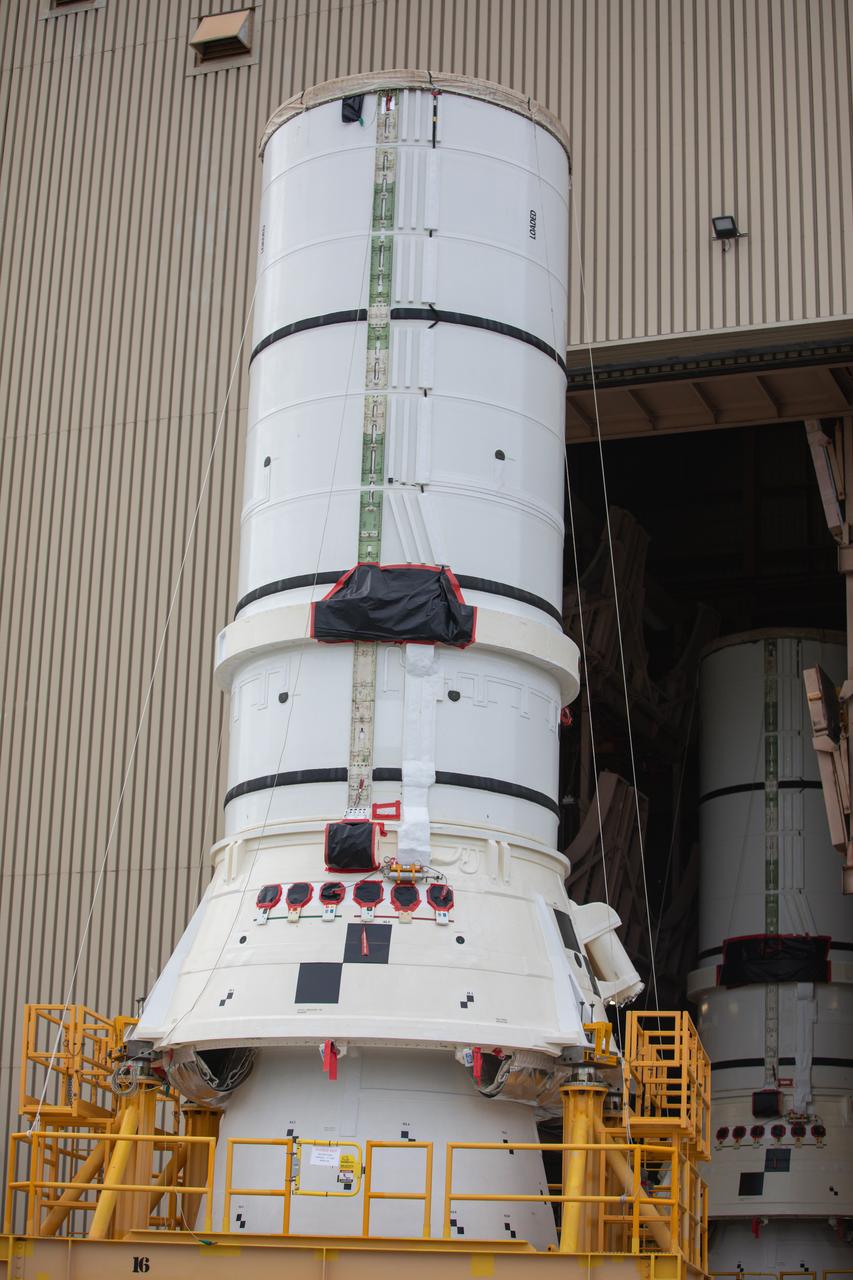
The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
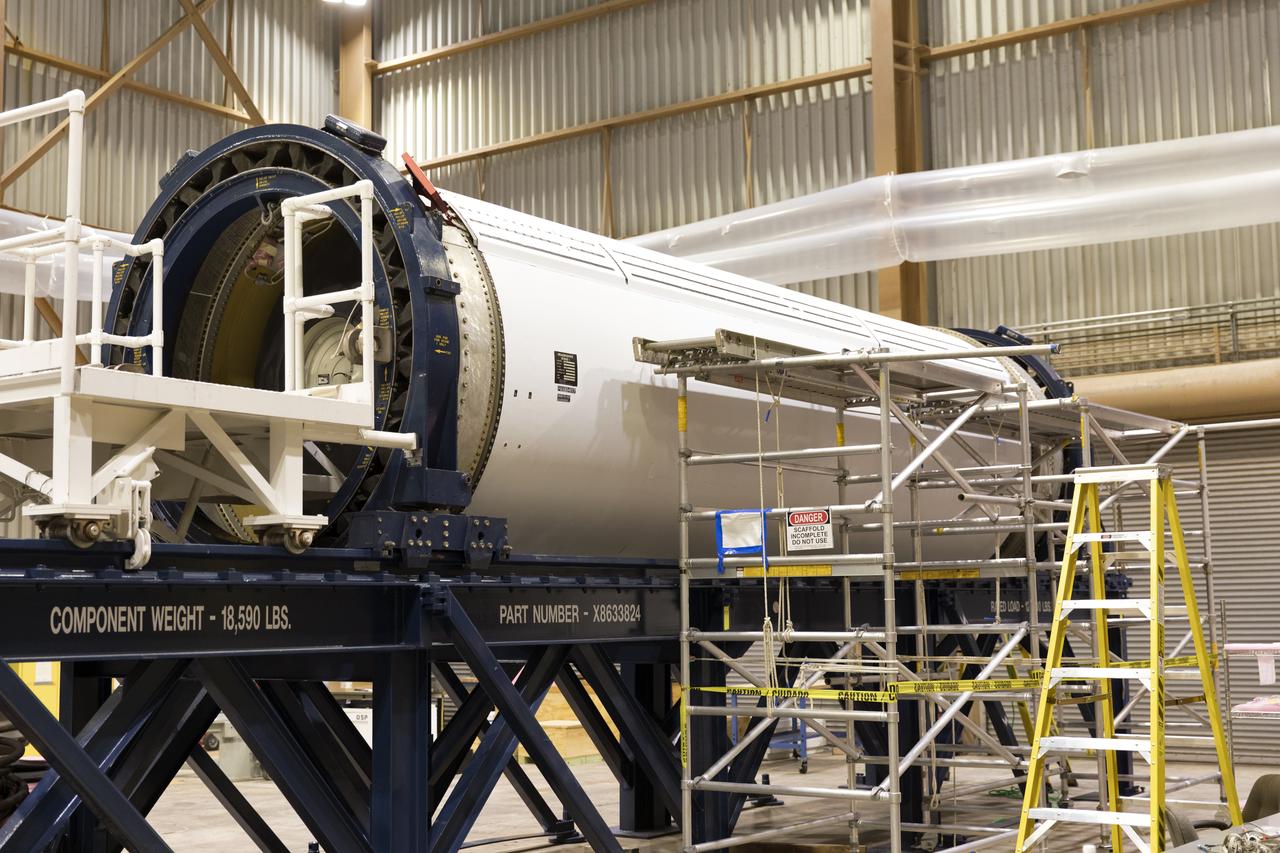

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
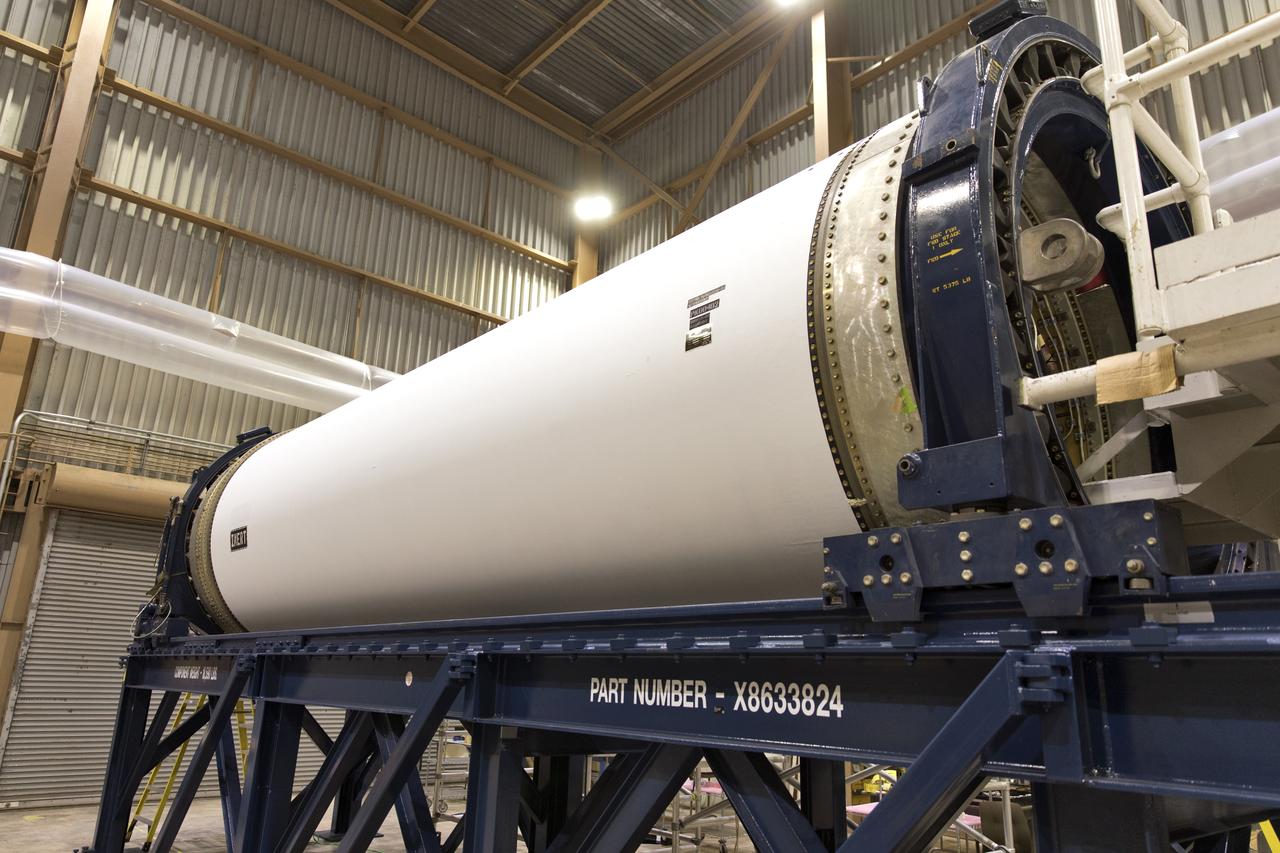

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
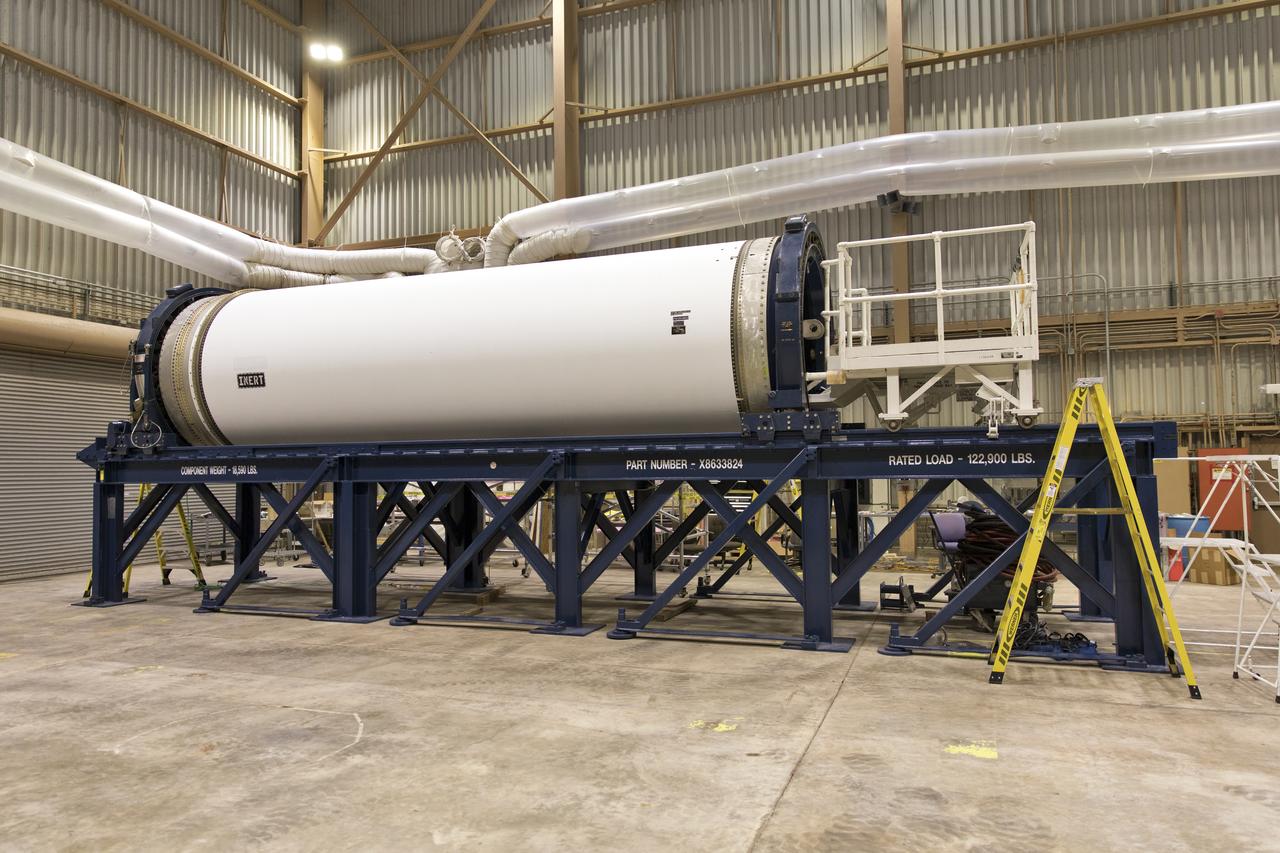

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

Aerial View of Proposed RPSF Area, November 9, 1964
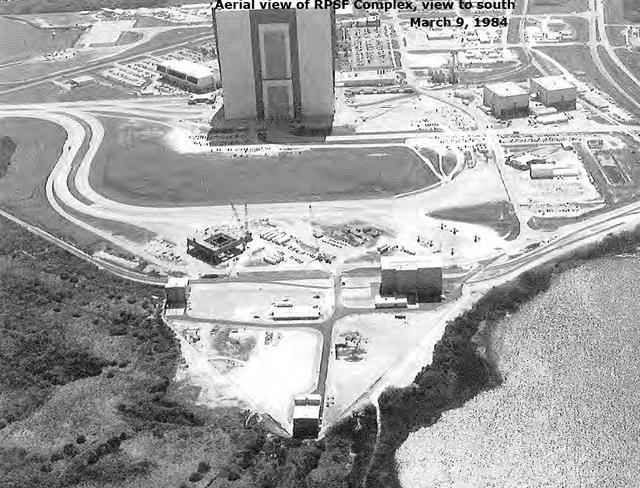

Aerial View of RPSF Complex, view to the south, March 9, 1984
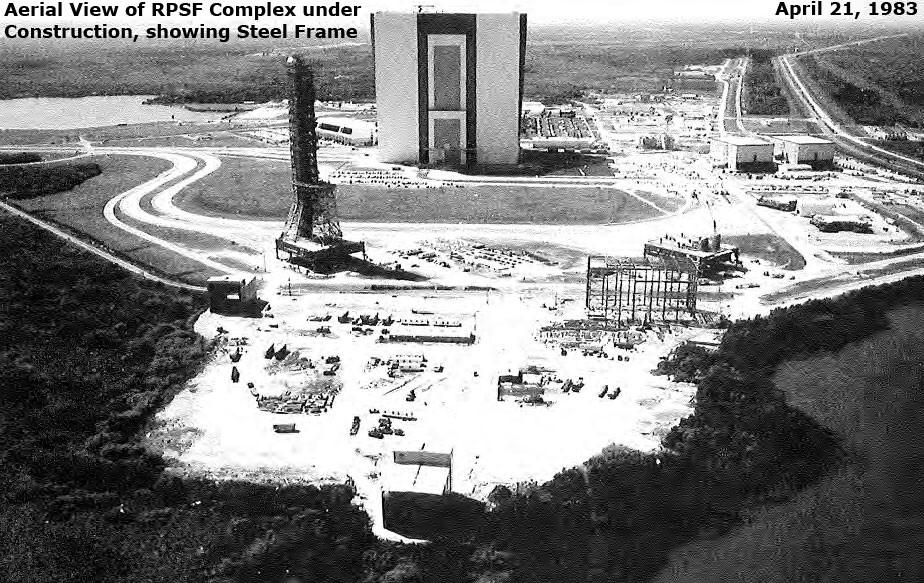
Aerial View of RPSF Complex under construction showing steel frame, April 21, 1983
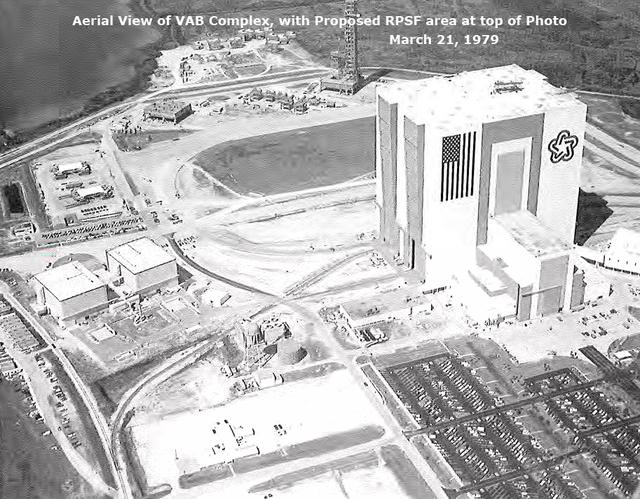

Aerial View of VAB Complex, with Proposed RPSF Area, March 21, 1979

View of VAB southwest wall in Assembly Area, July 6, 1966
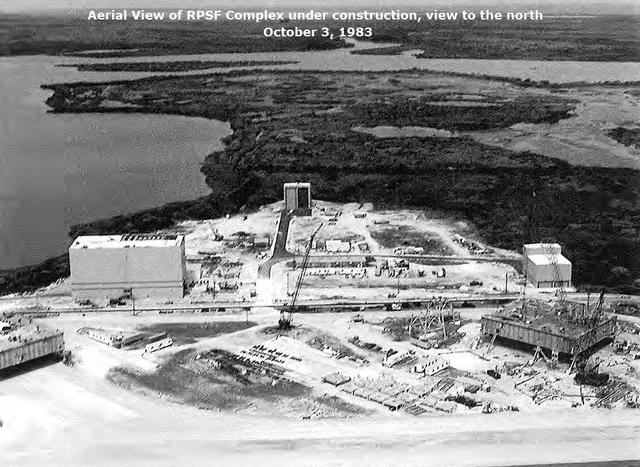

Aerial View of RPSF Complex under construction view to the north, October 3, 1983

Aerial View of Proposed RPSF Area, January 7, 1966
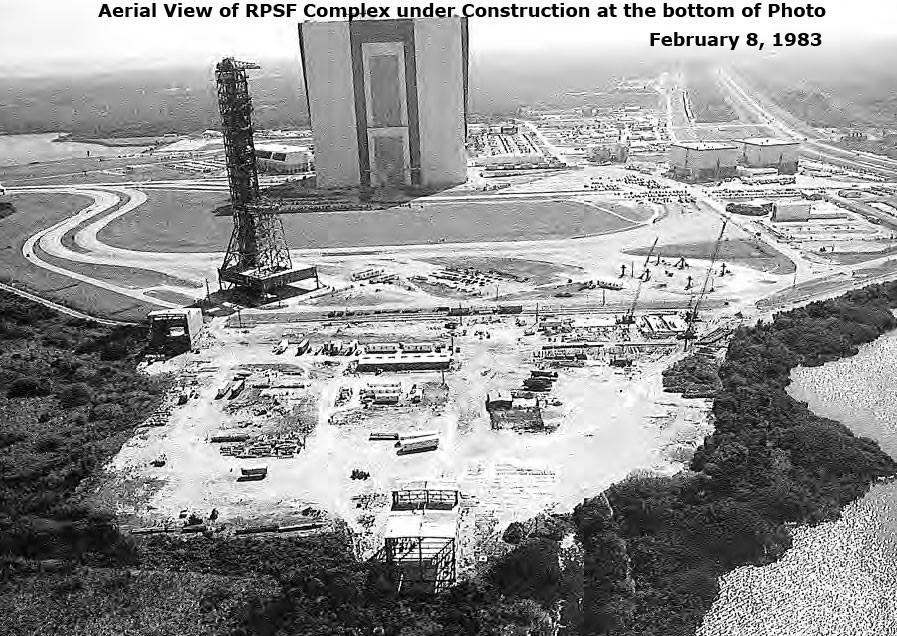

Aerial View of RPSF Complex under construction, February 8, 1983
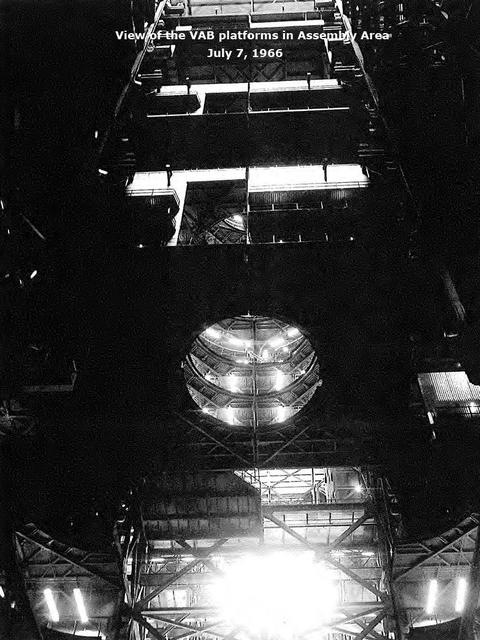
View of the VAB platforms in Assembly Area, July 7, 1966
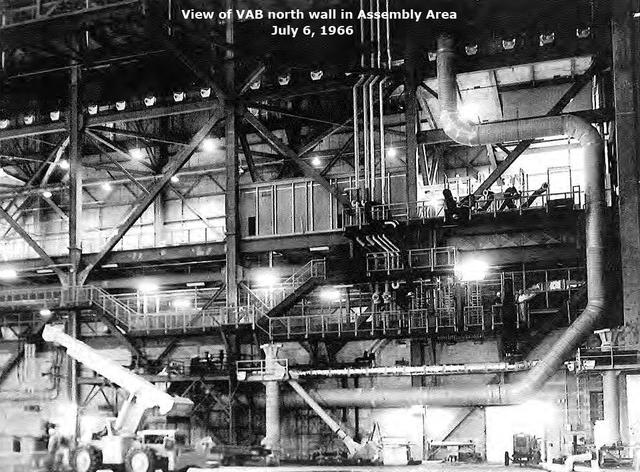

View of VAB north wall in Assembly Area, July 6, 1966
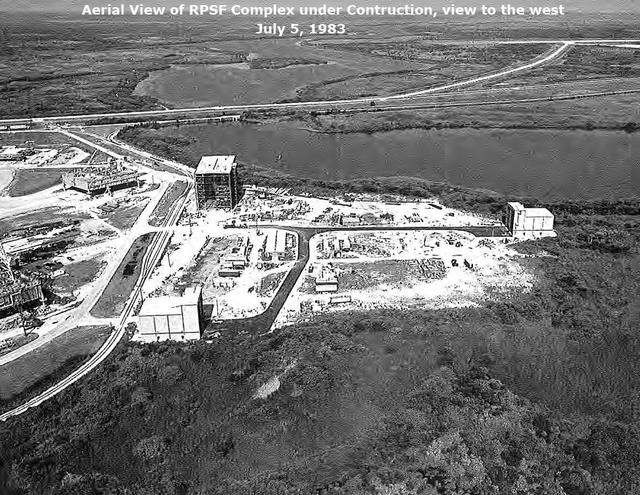

Aerial View of RPSF Complex under construction view to the west, July 5, 1983
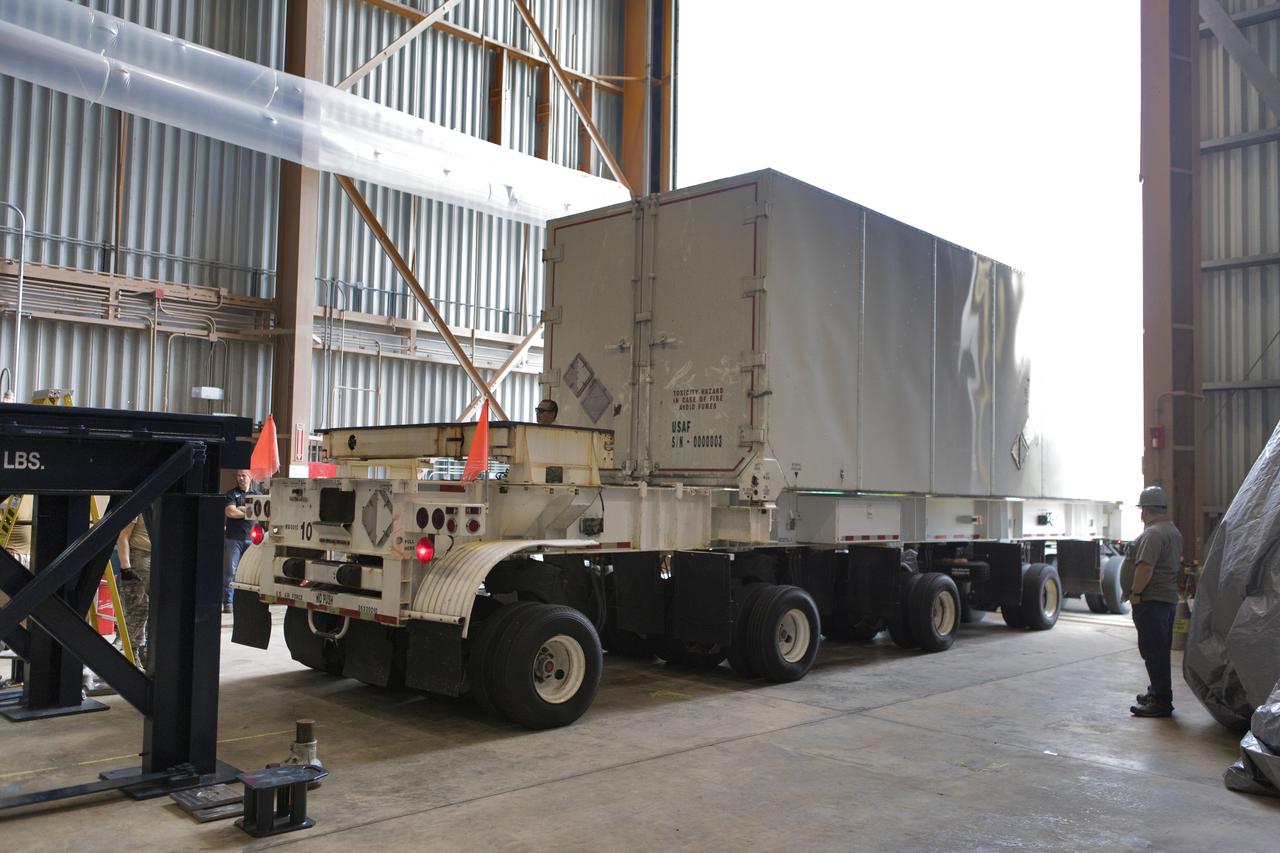

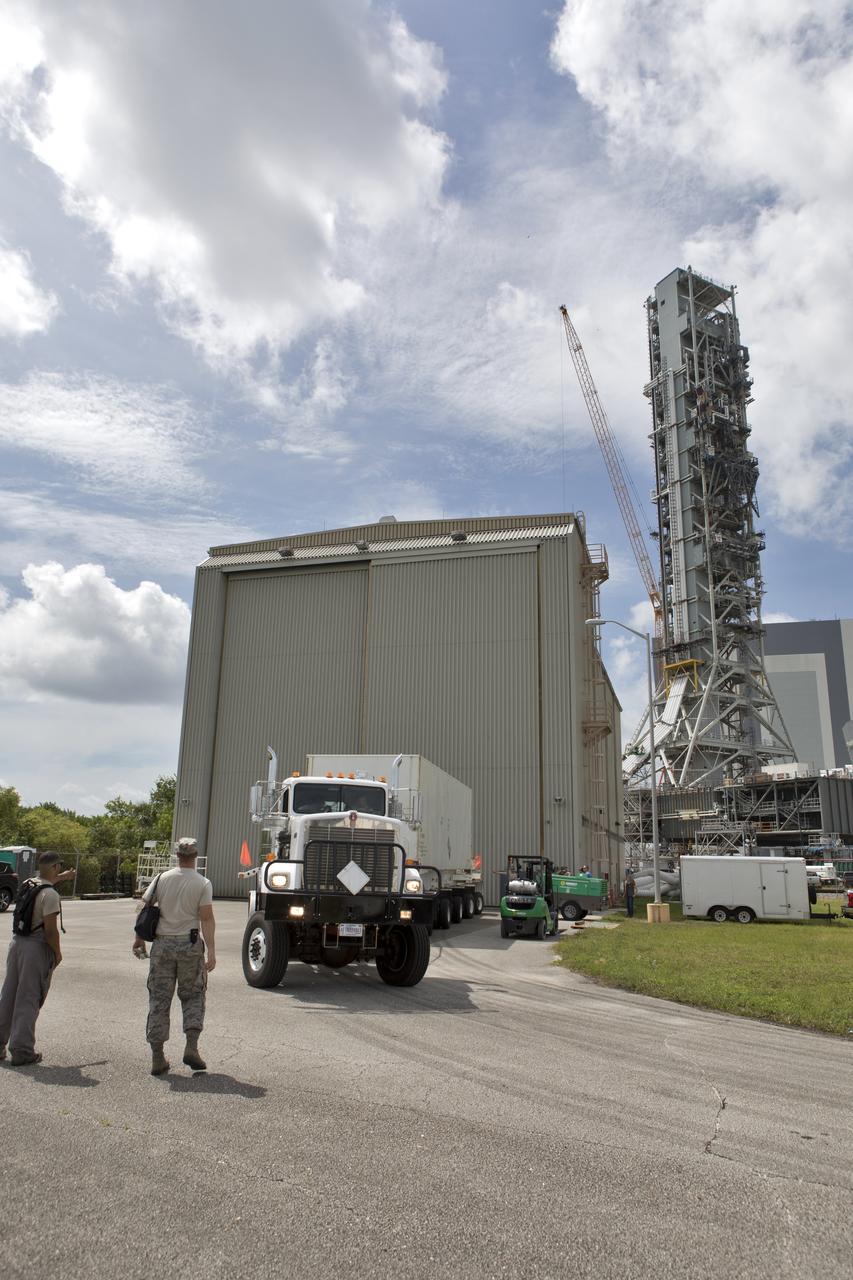
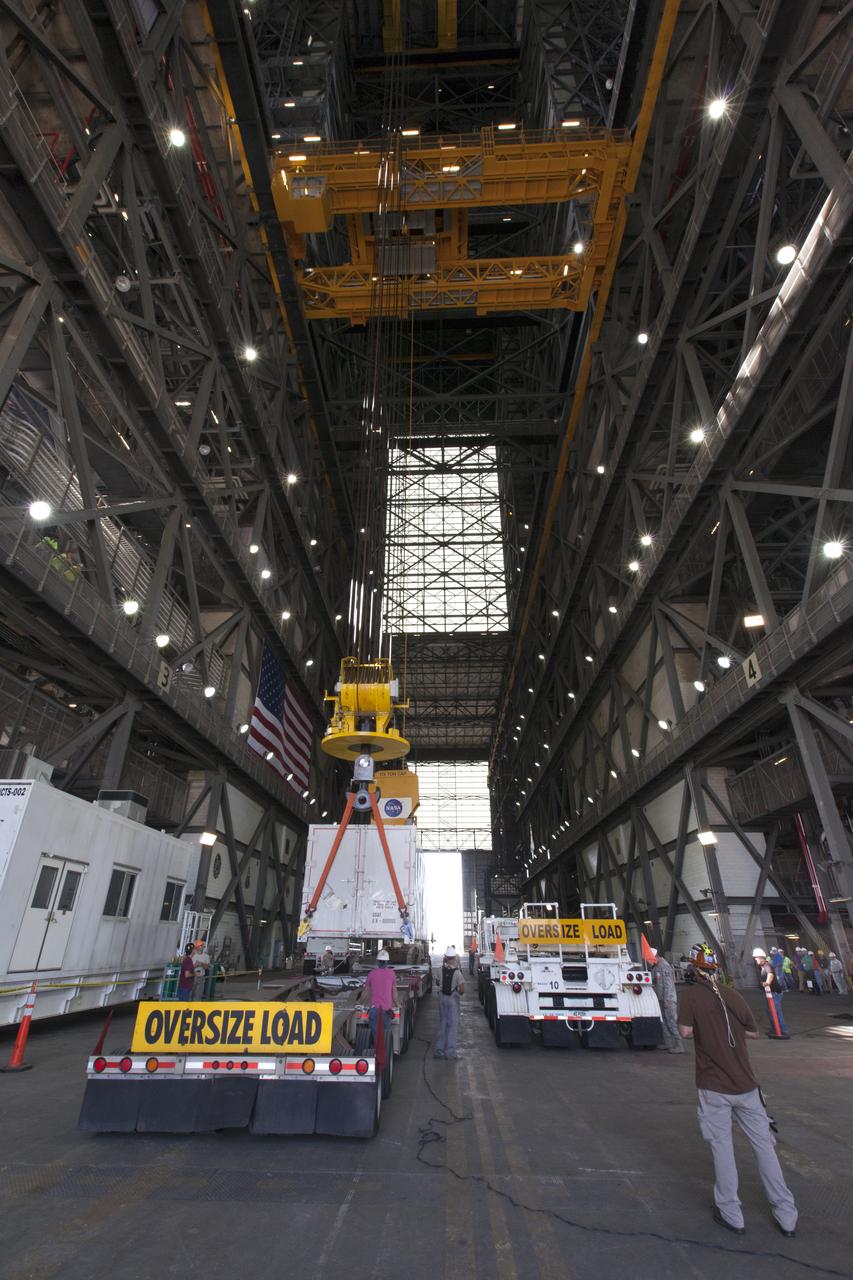
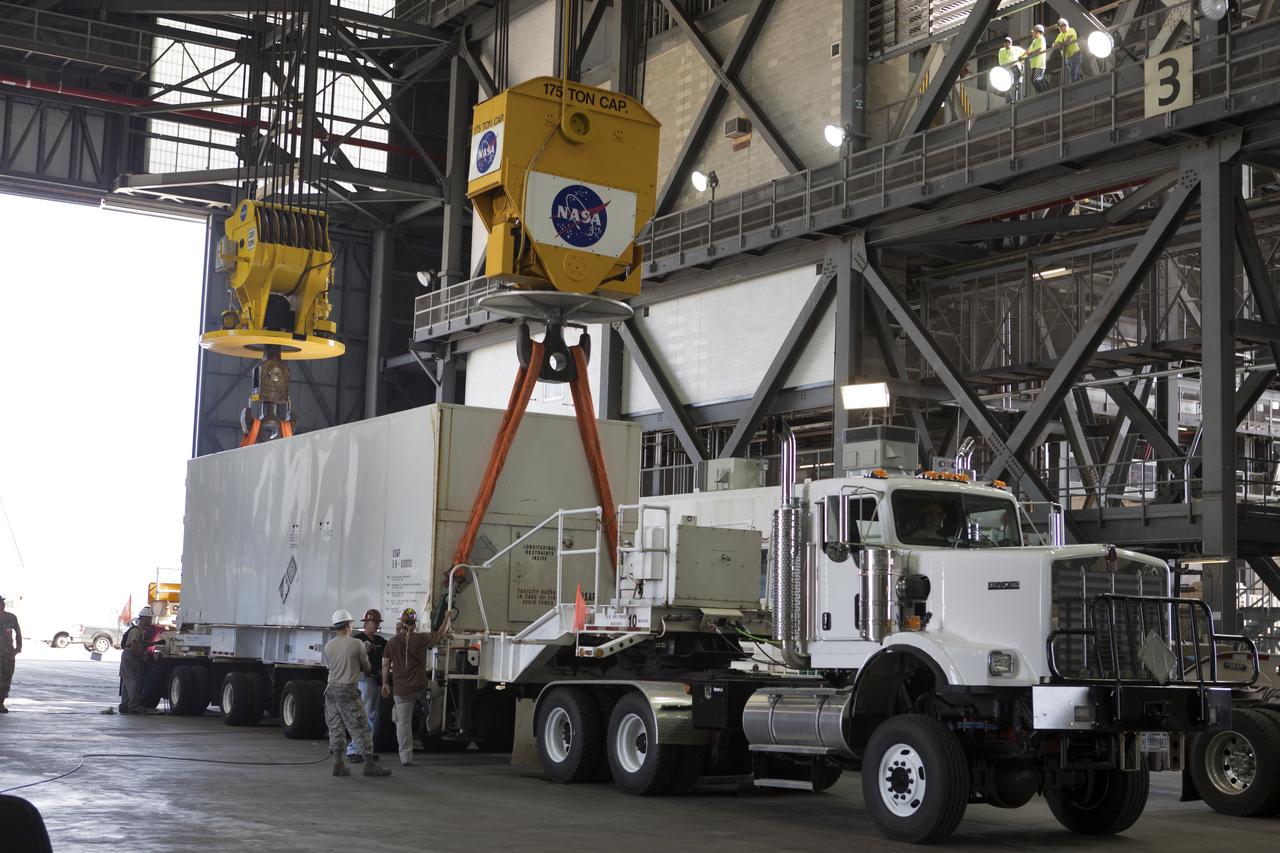
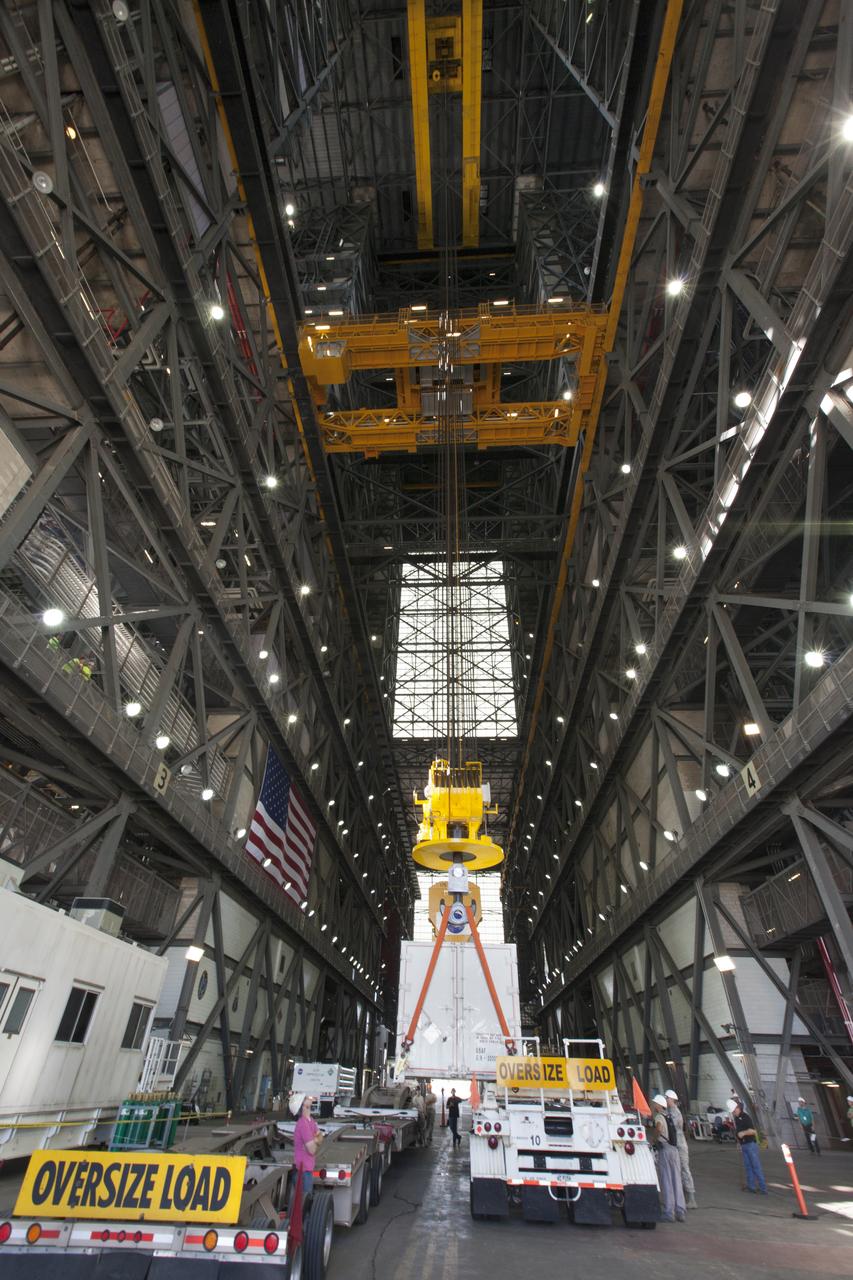
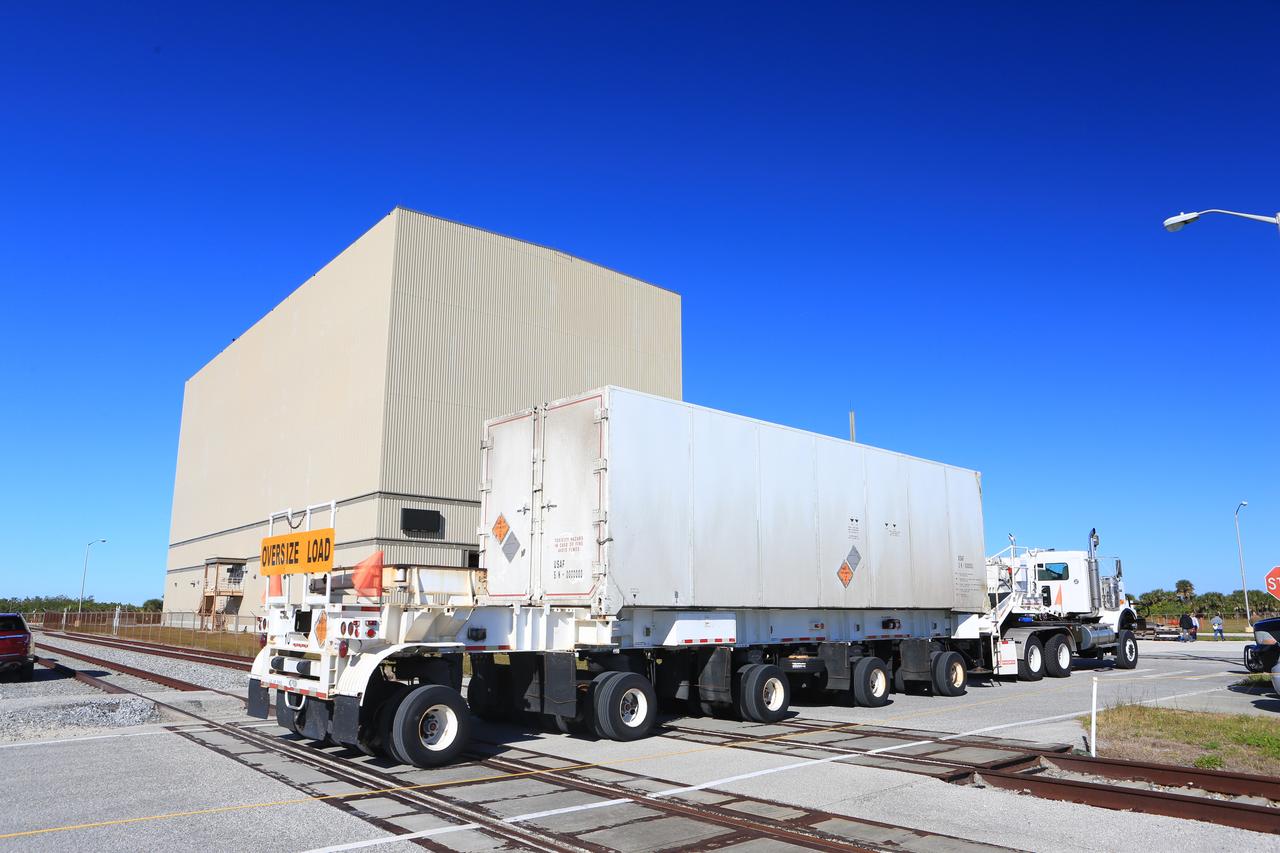
Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
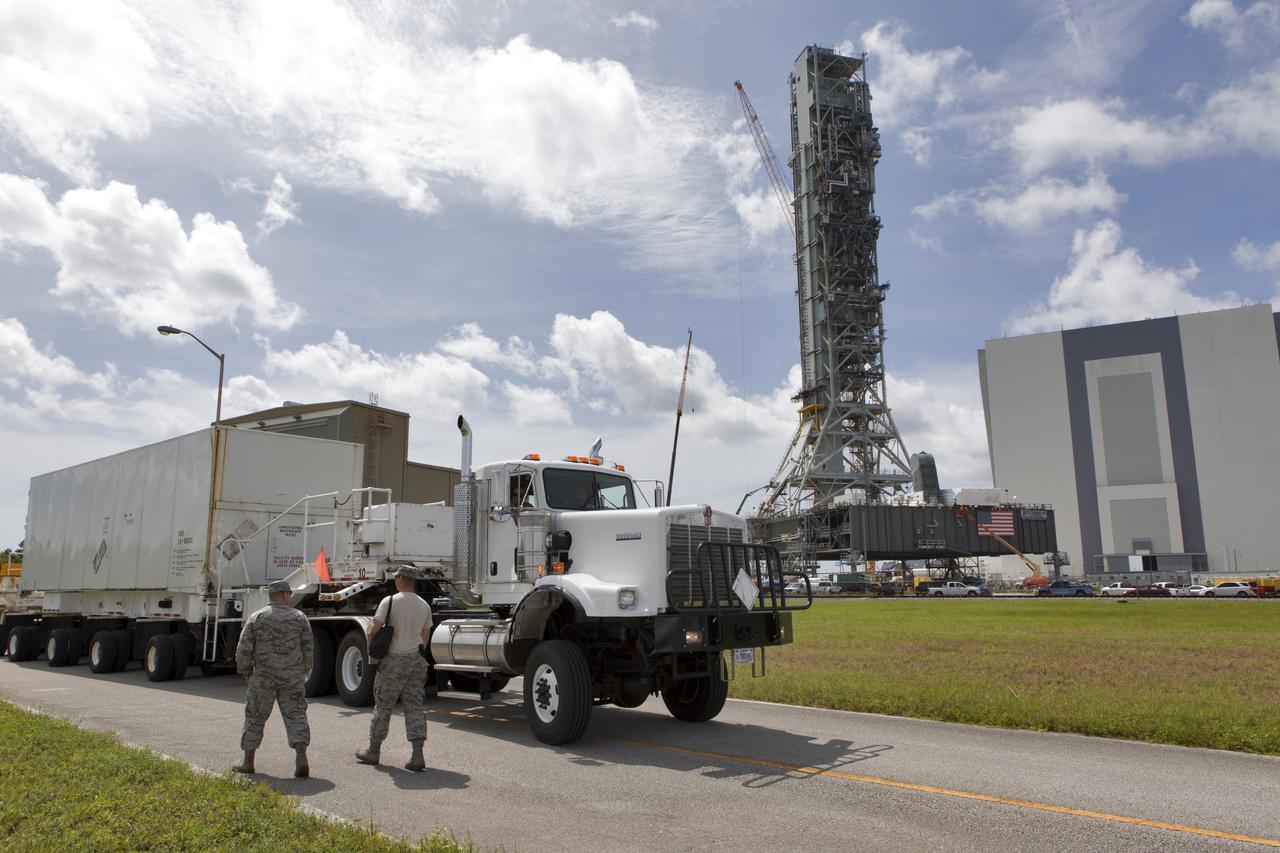

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
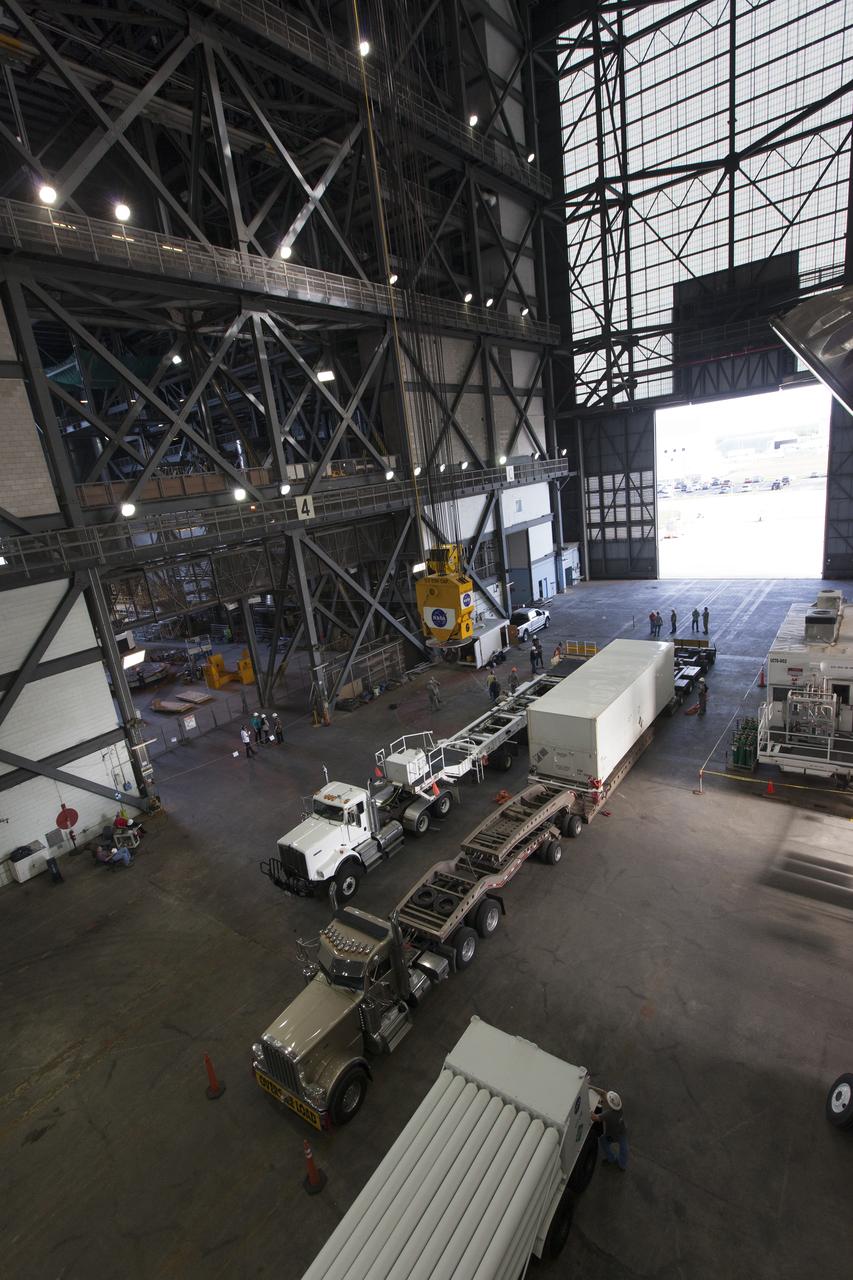

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
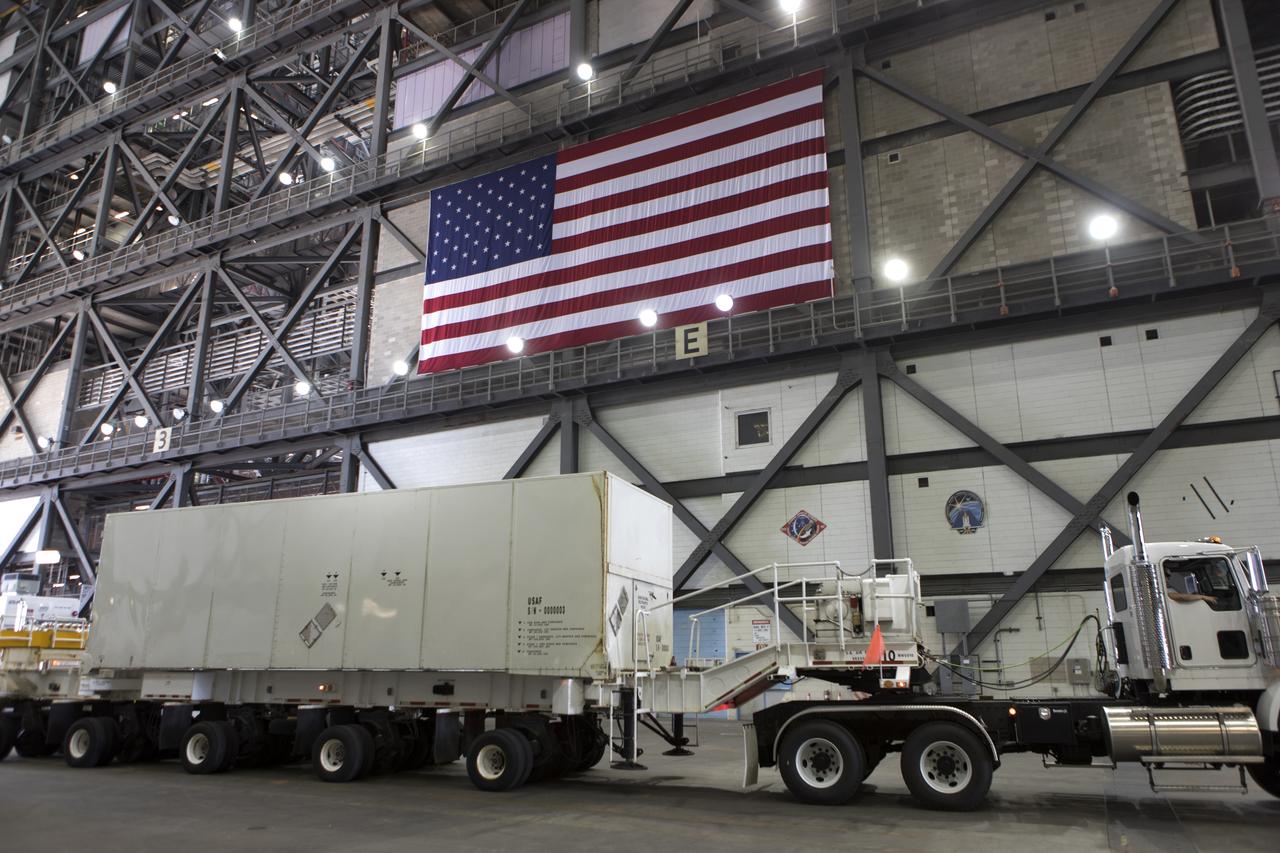

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) will be moved from the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

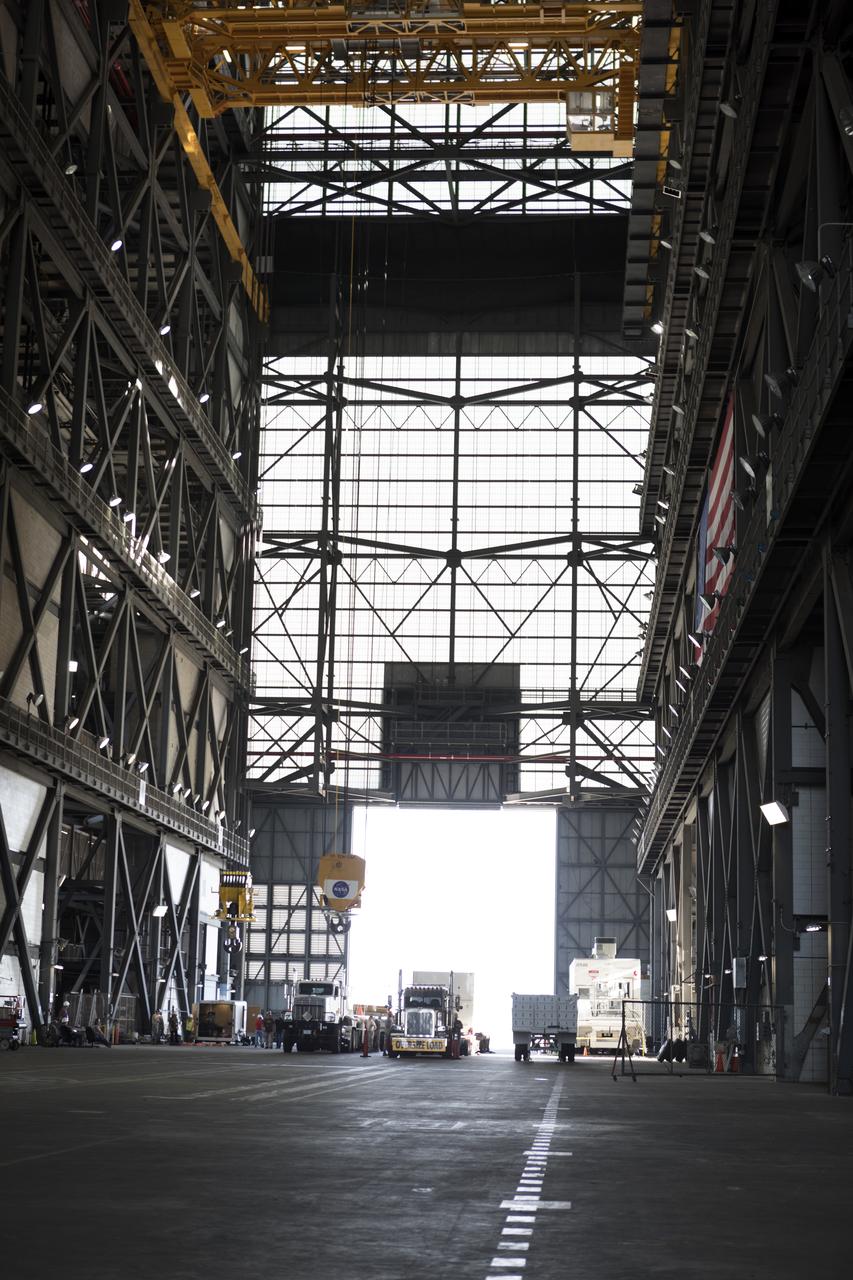
In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside onto another transporter on July 20, 2018. The container will be moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
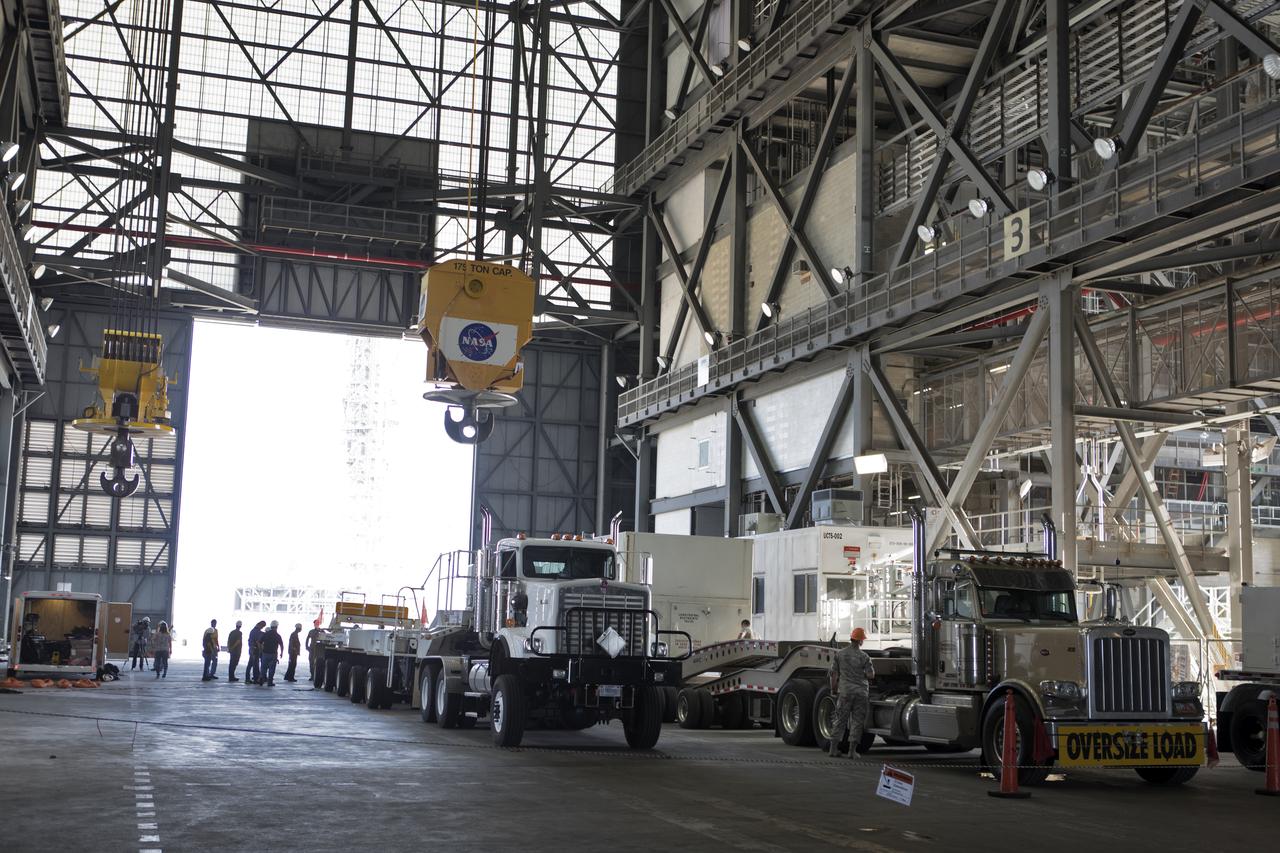

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
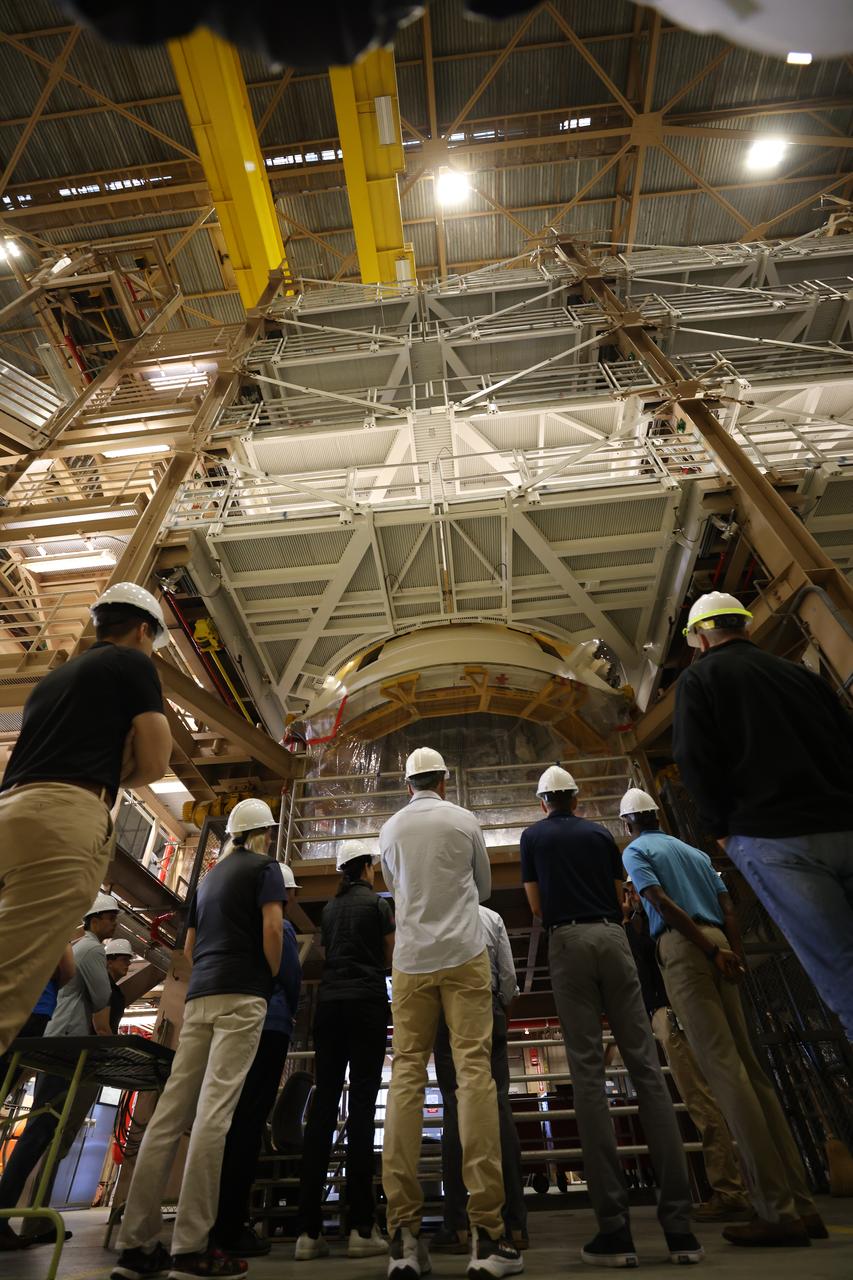

NASA’s 2021 class of astronaut candidates view a booster segment for Artemis II inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility during a familiarization tour of facilities on Tuesday, Oct. 17, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
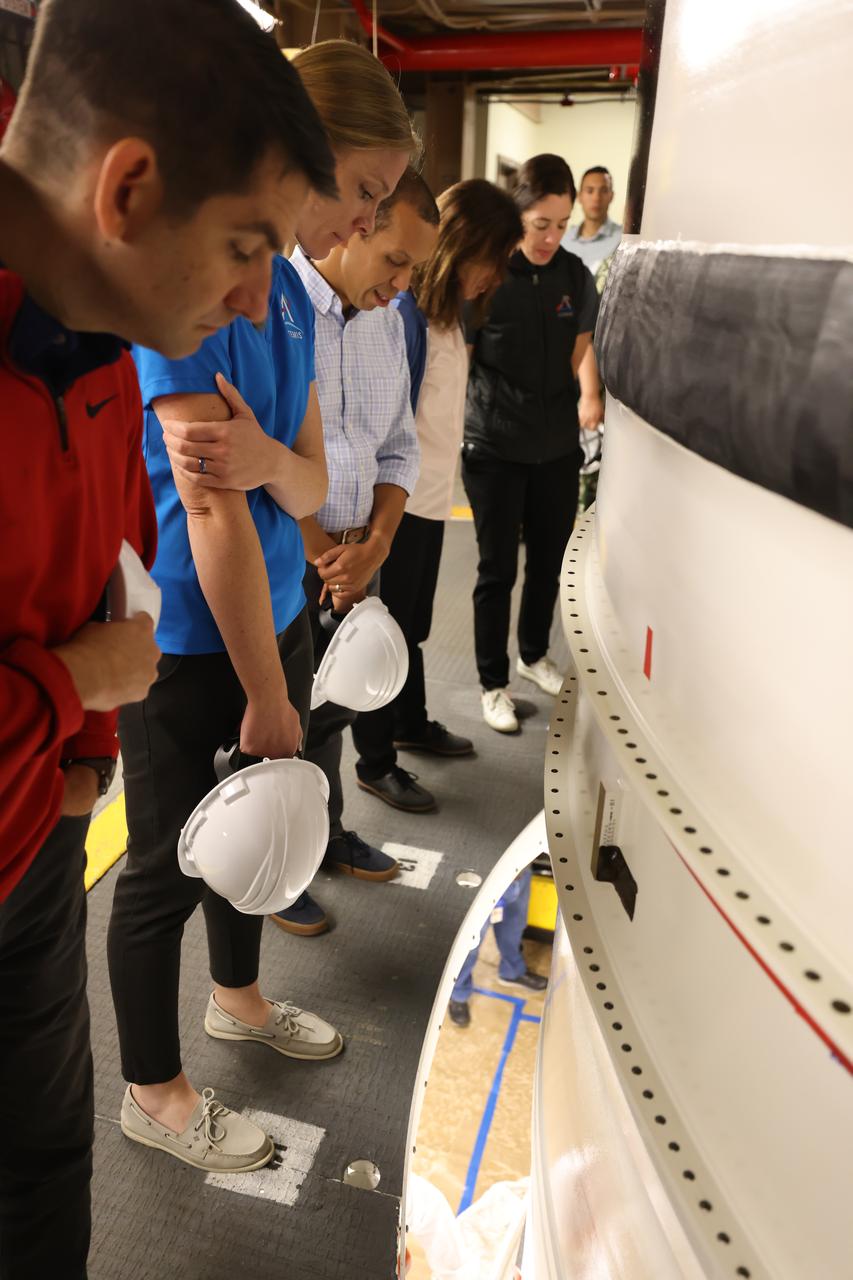

NASA’s 2021 class of astronaut candidates view a booster segment for Artemis II inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility during a familiarization tour of facilities on Tuesday, Oct. 17, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
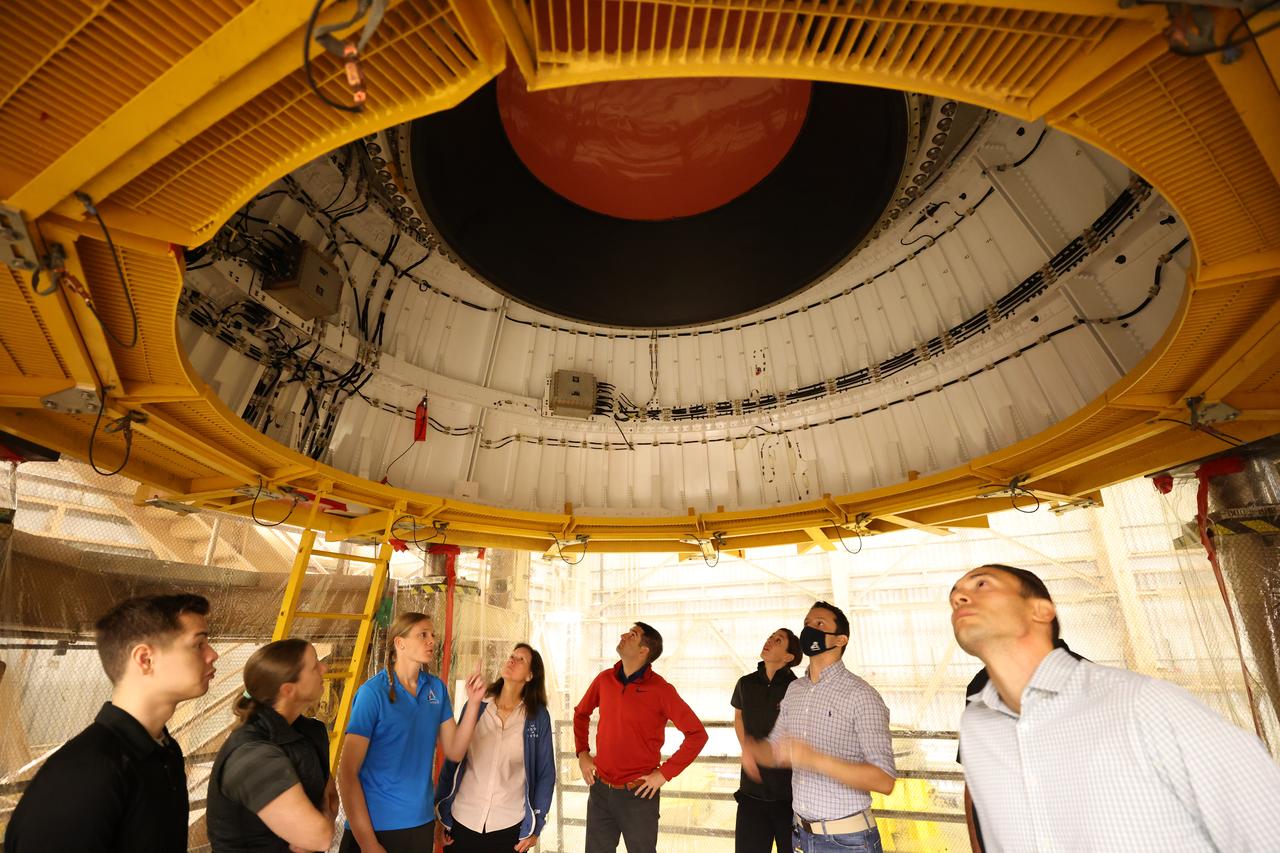

NASA’s 2021 class of astronaut candidates view a booster segment for Artemis II inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility during a familiarization tour of facilities on Tuesday, Oct. 17, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
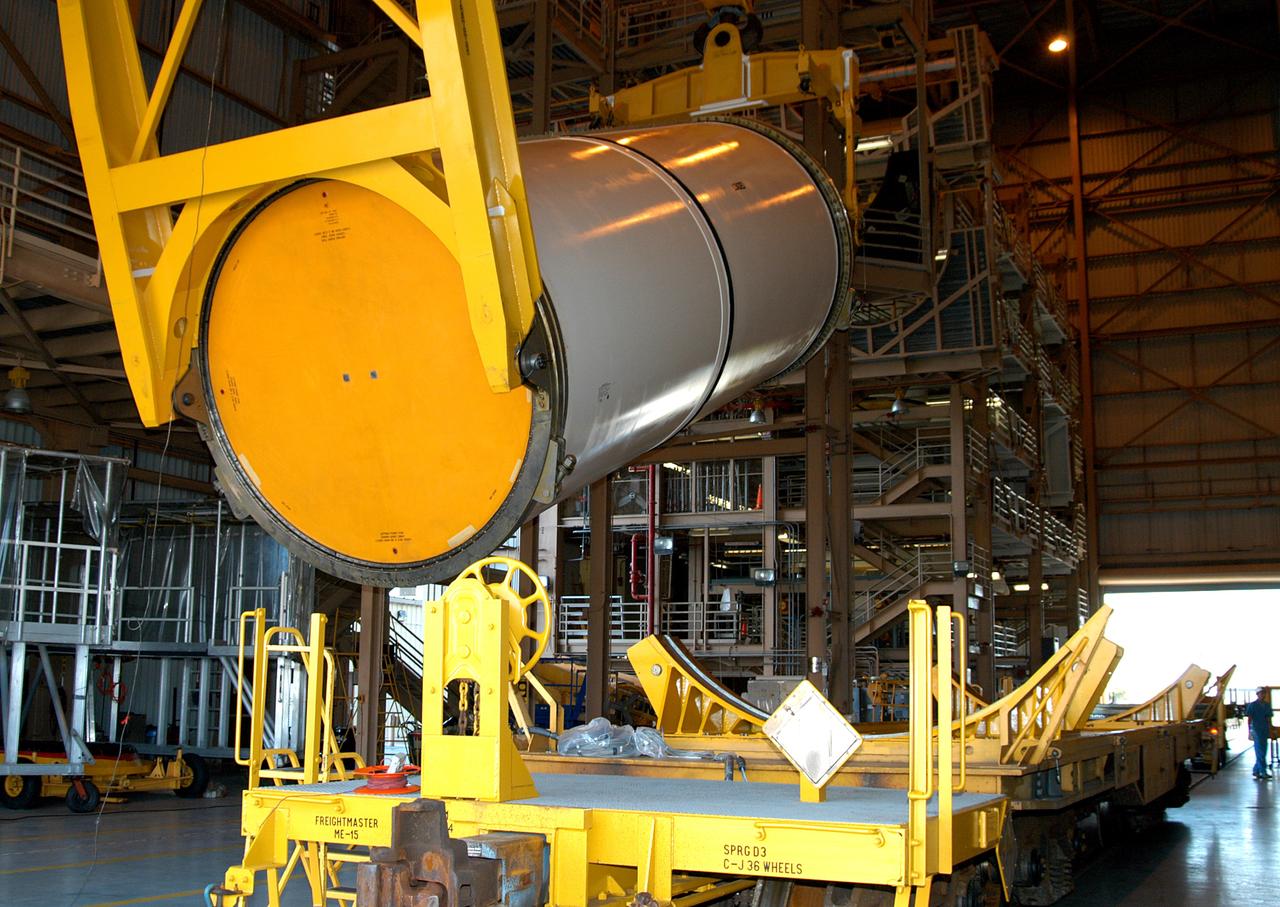

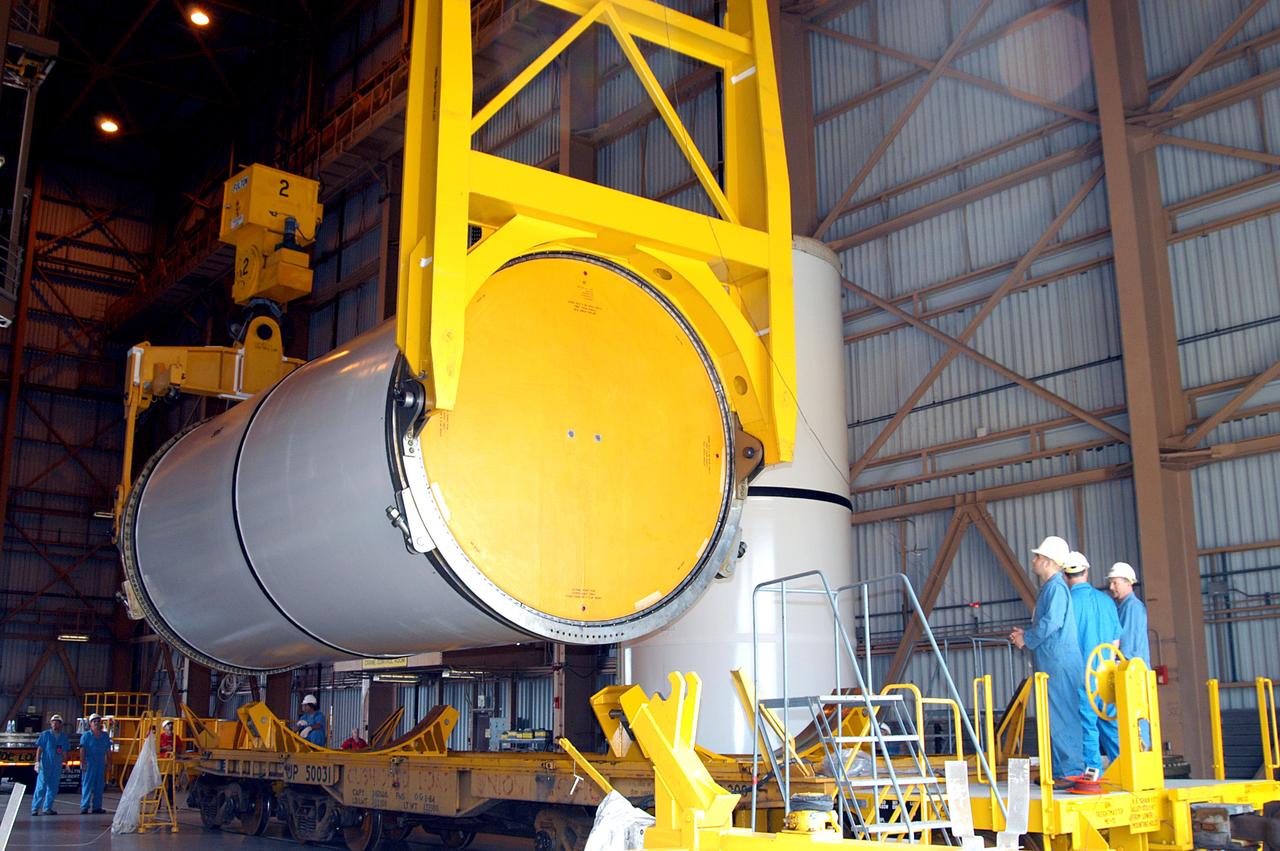
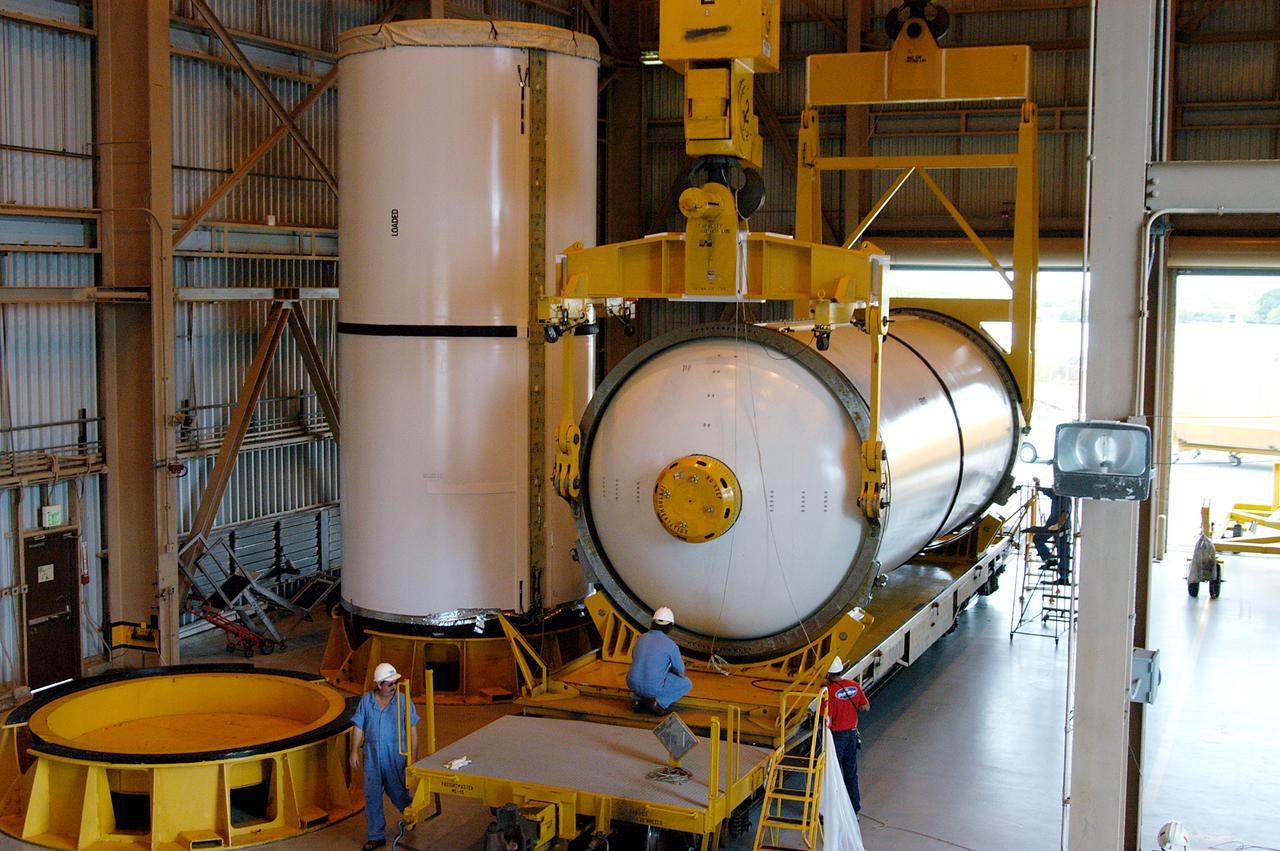
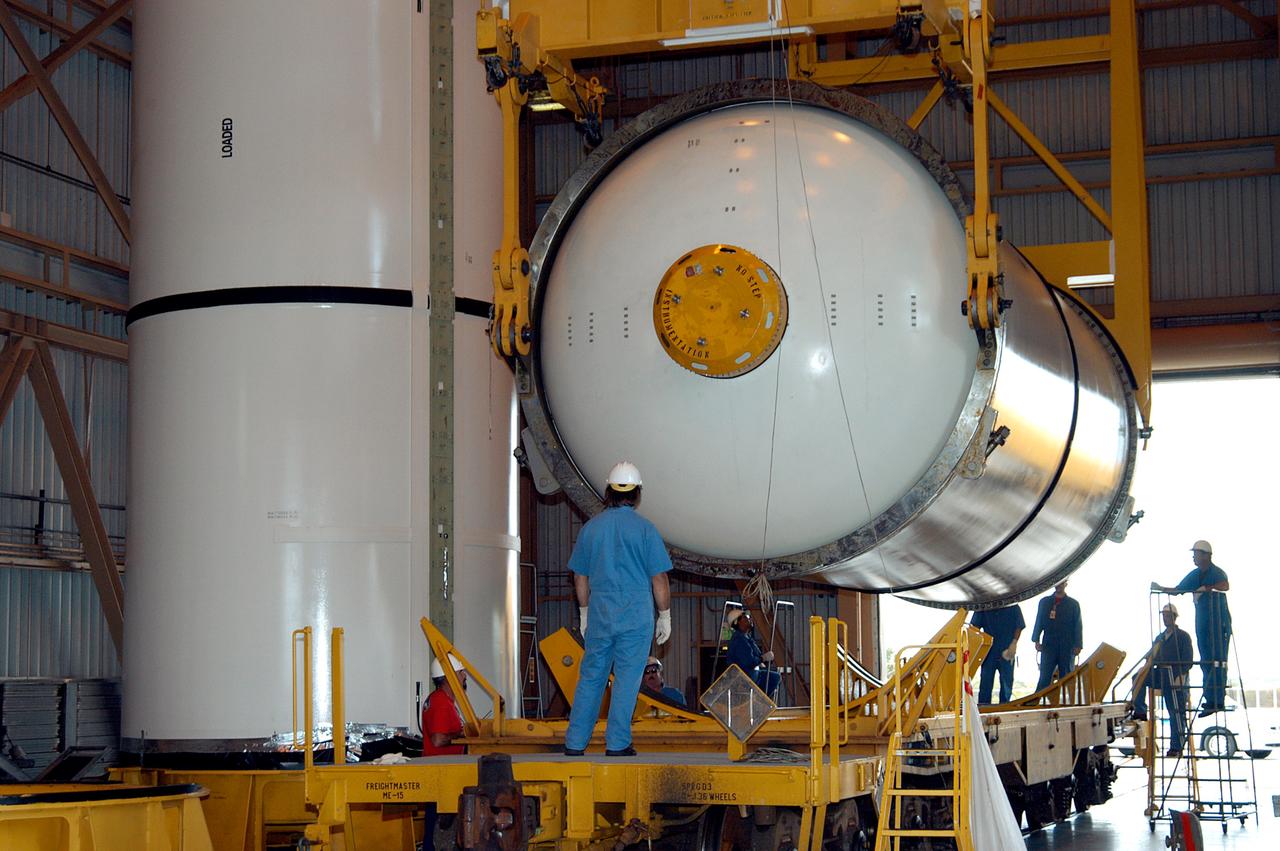
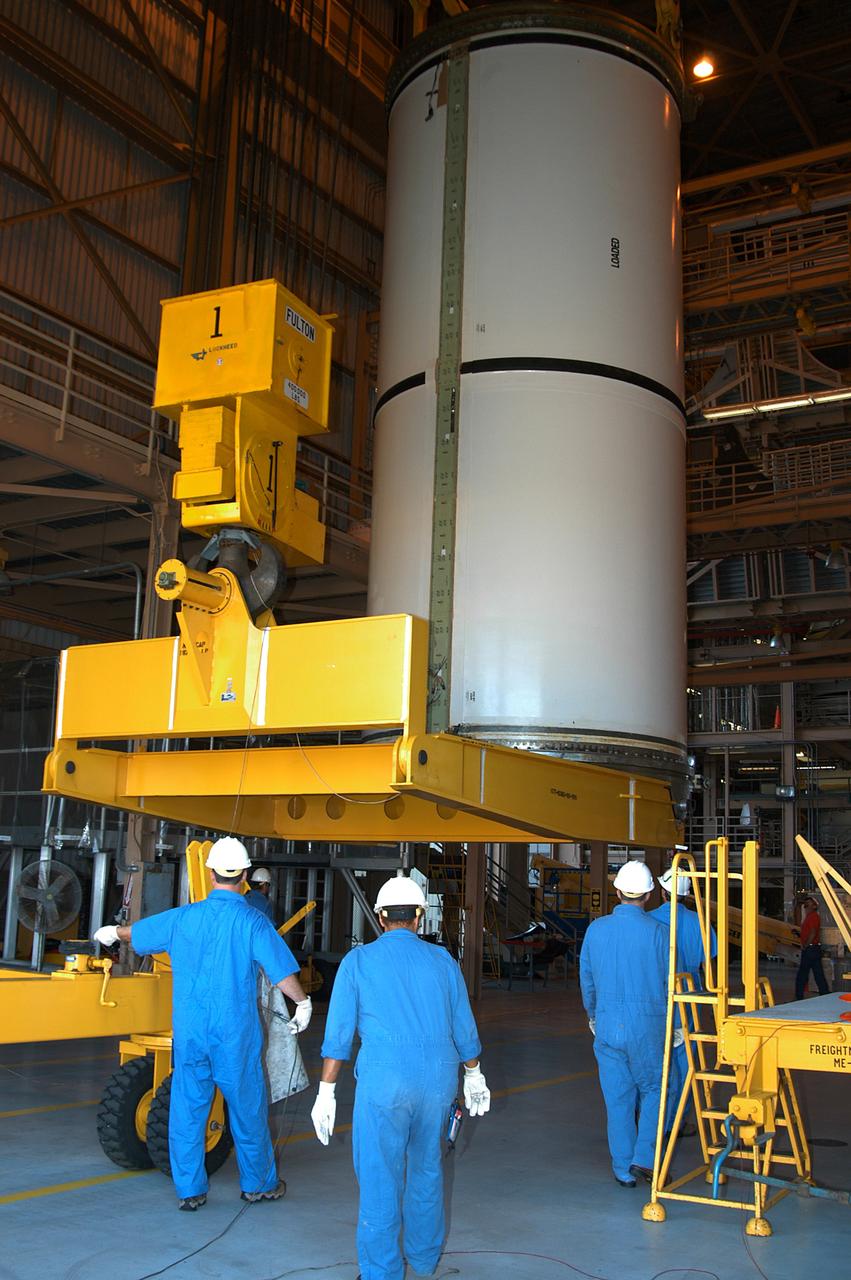
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility, an SRB solid segment is being rotated to horizontal for placement on a rail car. The segment is being shipped to Utah for testing. The segment was part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned to Utah for testing. It will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility, an SRB solid segment is being moved to a rail car for shipment to Utah for testing. The segment was part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned to Utah for testing. It will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.
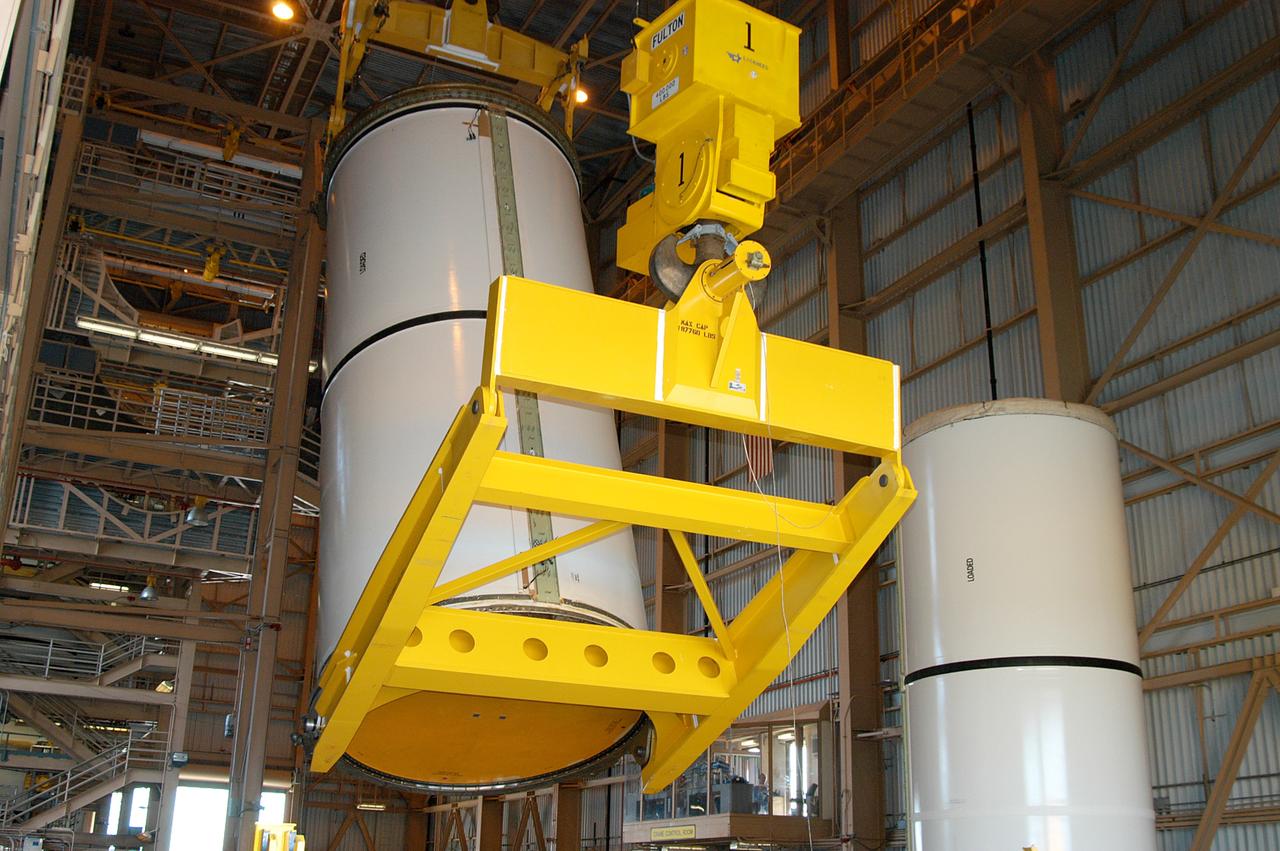

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility, an SRB solid segment is being lifted and moved to a rail car for shipment to Utah for testing. The segment was part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned to Utah for testing. It will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility, an SRB solid segment is lowered onto a rail car for shipment to Utah where it will be tested. The segment was part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned to Utah for testing. It will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.

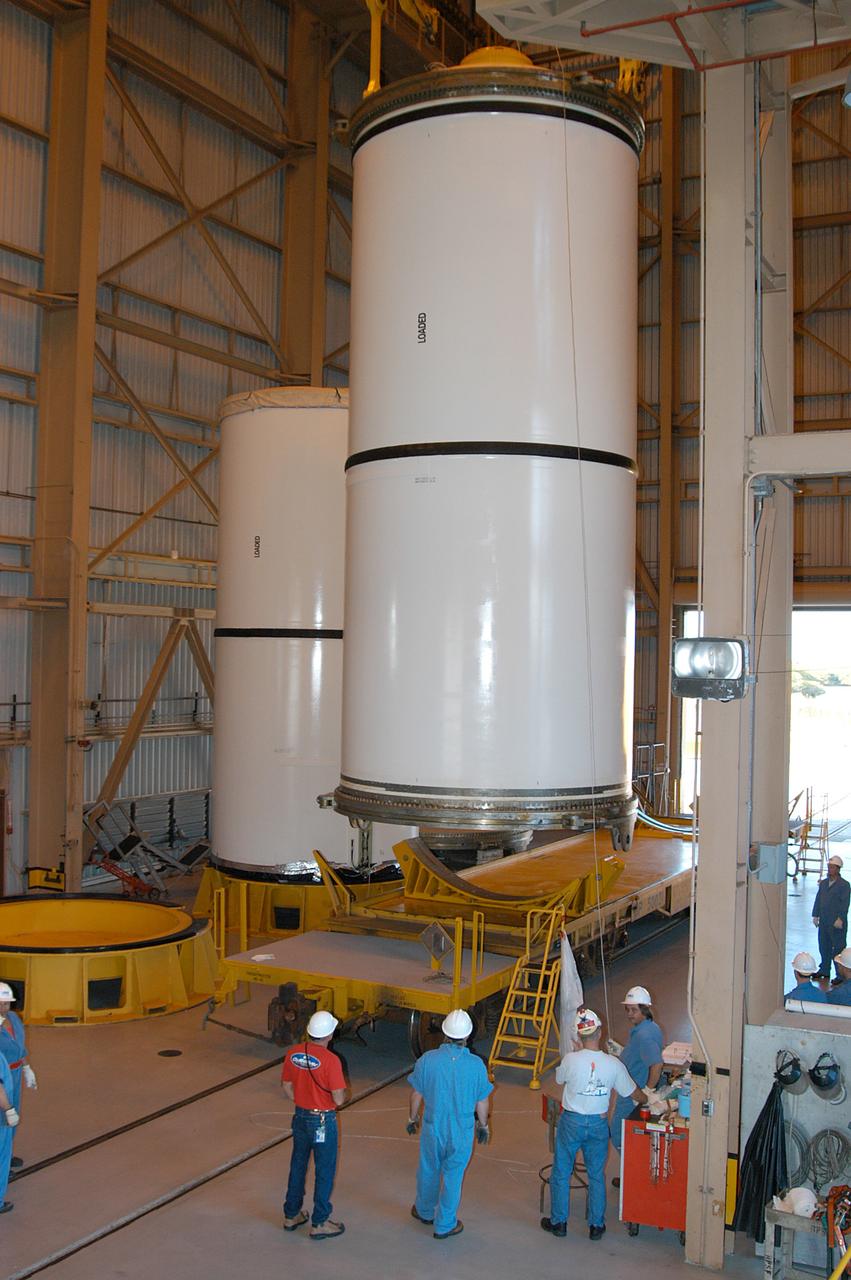
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An engine pulls the container enclosing a segment of a solid rocket booster from the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility. The container will join others on the main track for a trip to Utah where the segments will undergo firing. The segments were part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned for testing. They will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility, an SRB solid segment is lowered onto a rail car for shipment to Utah where it will be tested. The segment was part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned to Utah for testing. It will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility, an SRB solid segment is lowered onto a rail car for shipment to Utah where it will be tested. The segment was part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned to Utah for testing. It will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility, an SRB solid segment is being lifted and moved to a rail car for shipment to Utah for testing. The segment was part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned to Utah for testing. It will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.
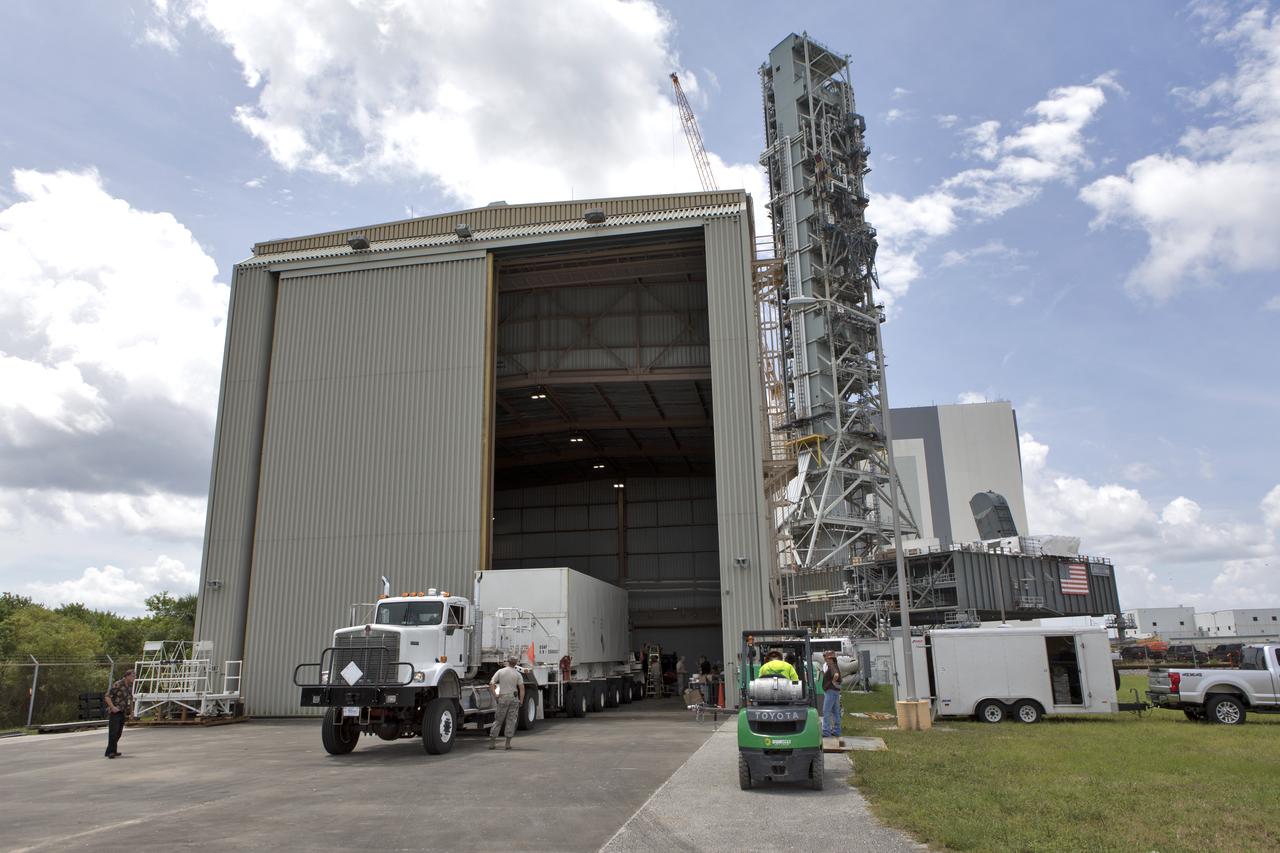

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
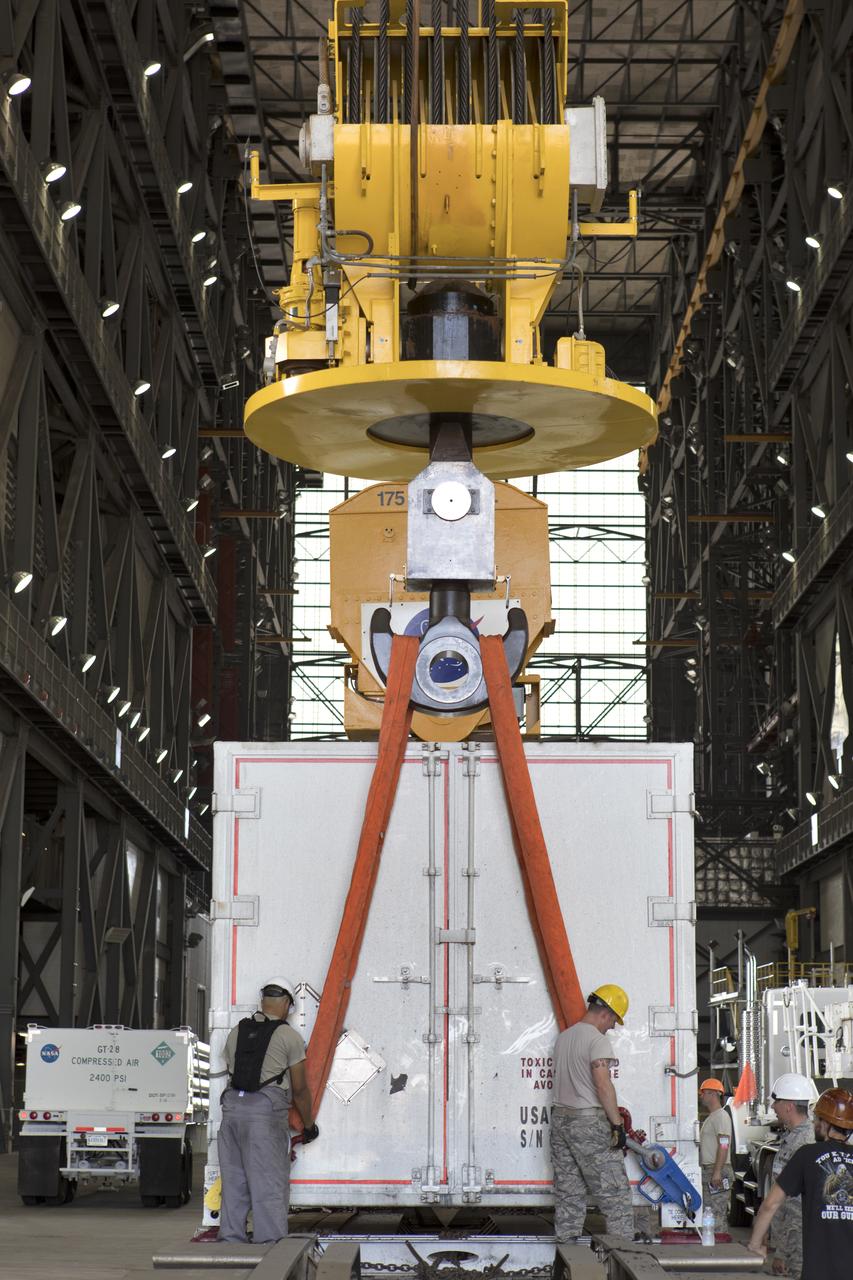

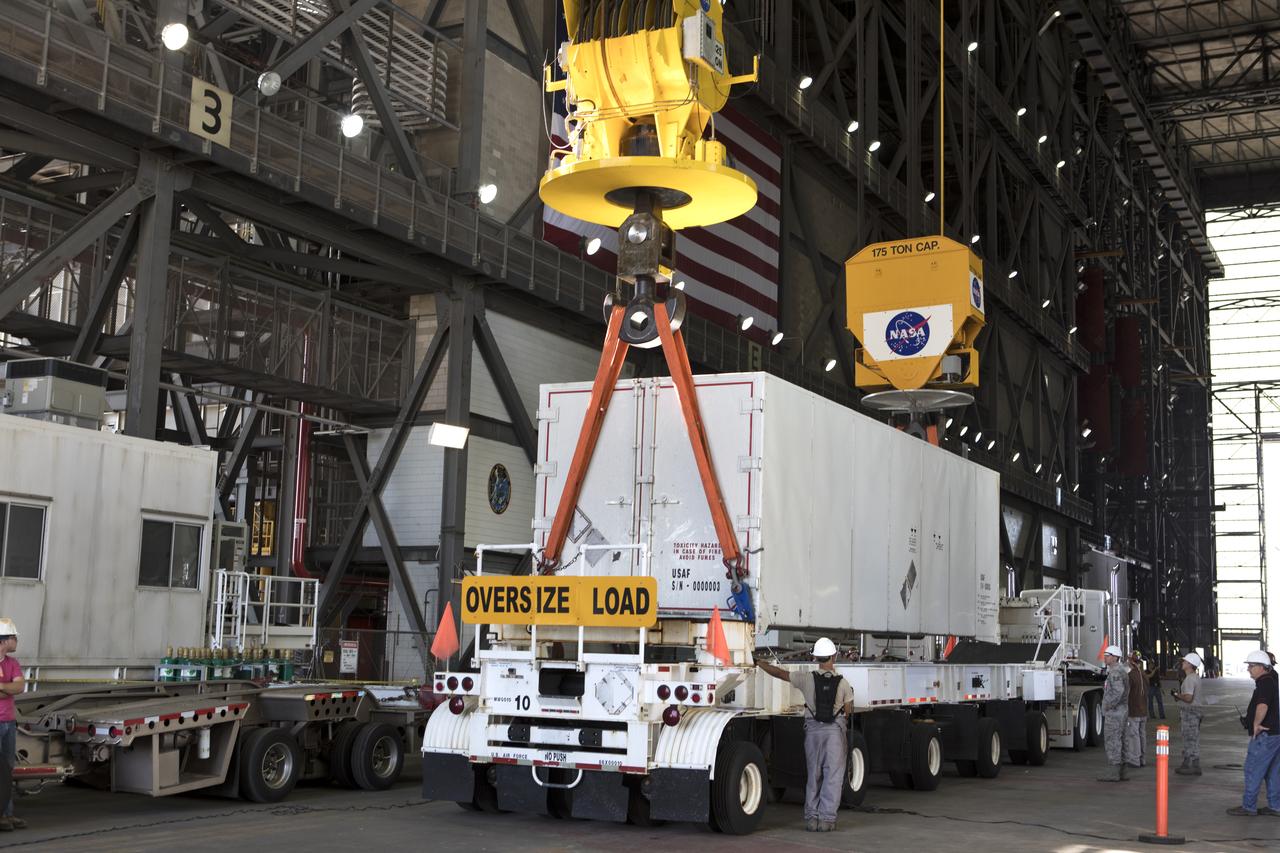
In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacob’s technicians on the Test Operations Support Contract attach a crane to a shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lifted and transferred to another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacob’s technicians attach a crane to a shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lifted and transferred to another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

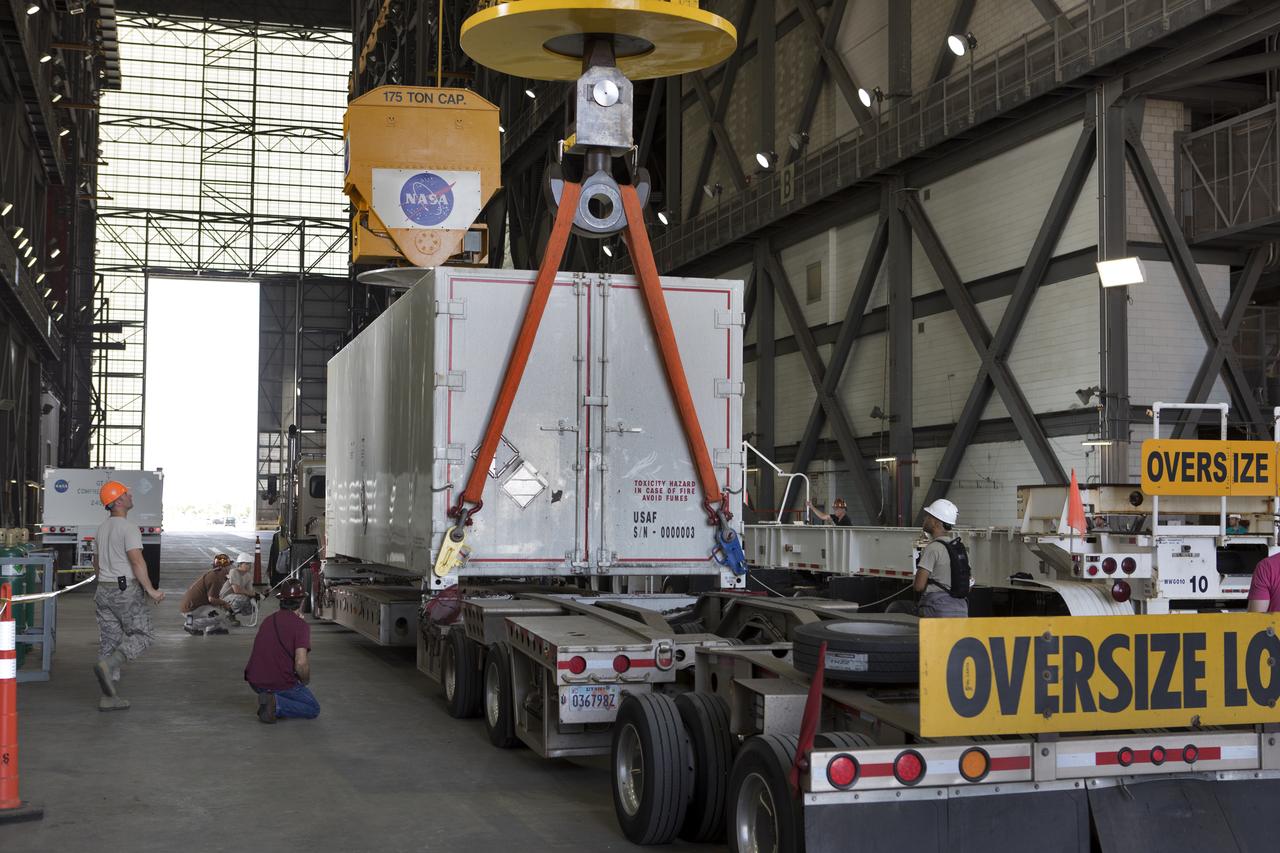
In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lowered onto another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up a shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lifted and transferred to another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

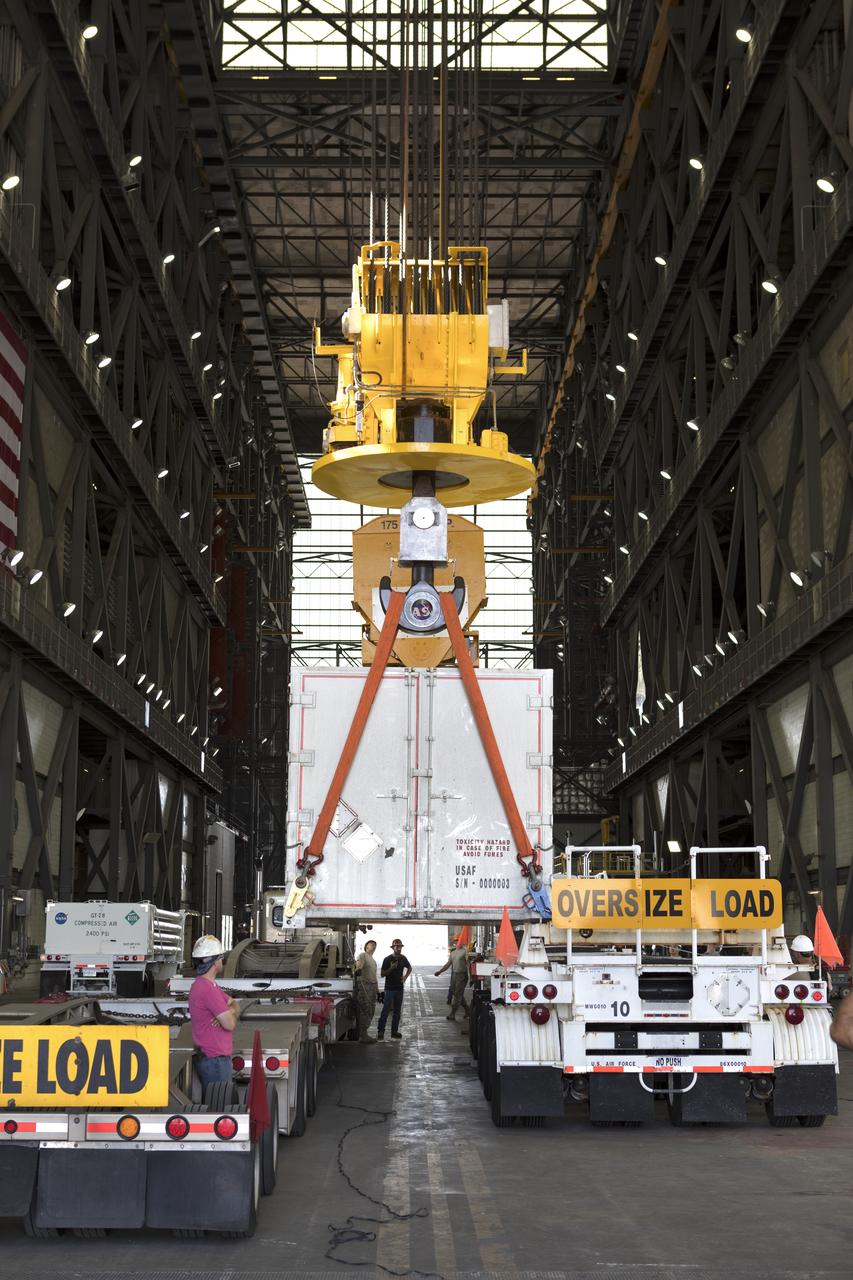
In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane operated by Jacob’s technicians lowers the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside onto another transporter on July 20, 2018. The container will be moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lowered onto another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

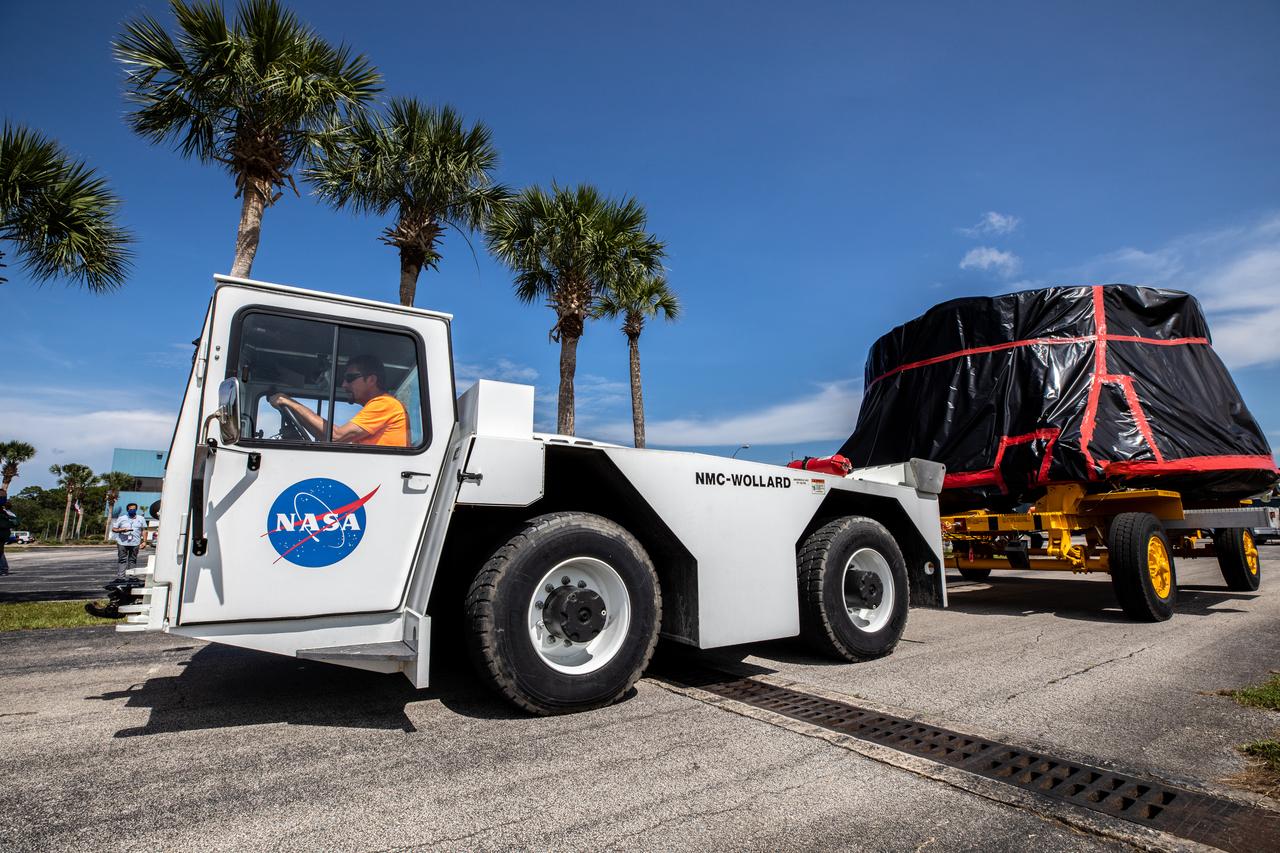
The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.
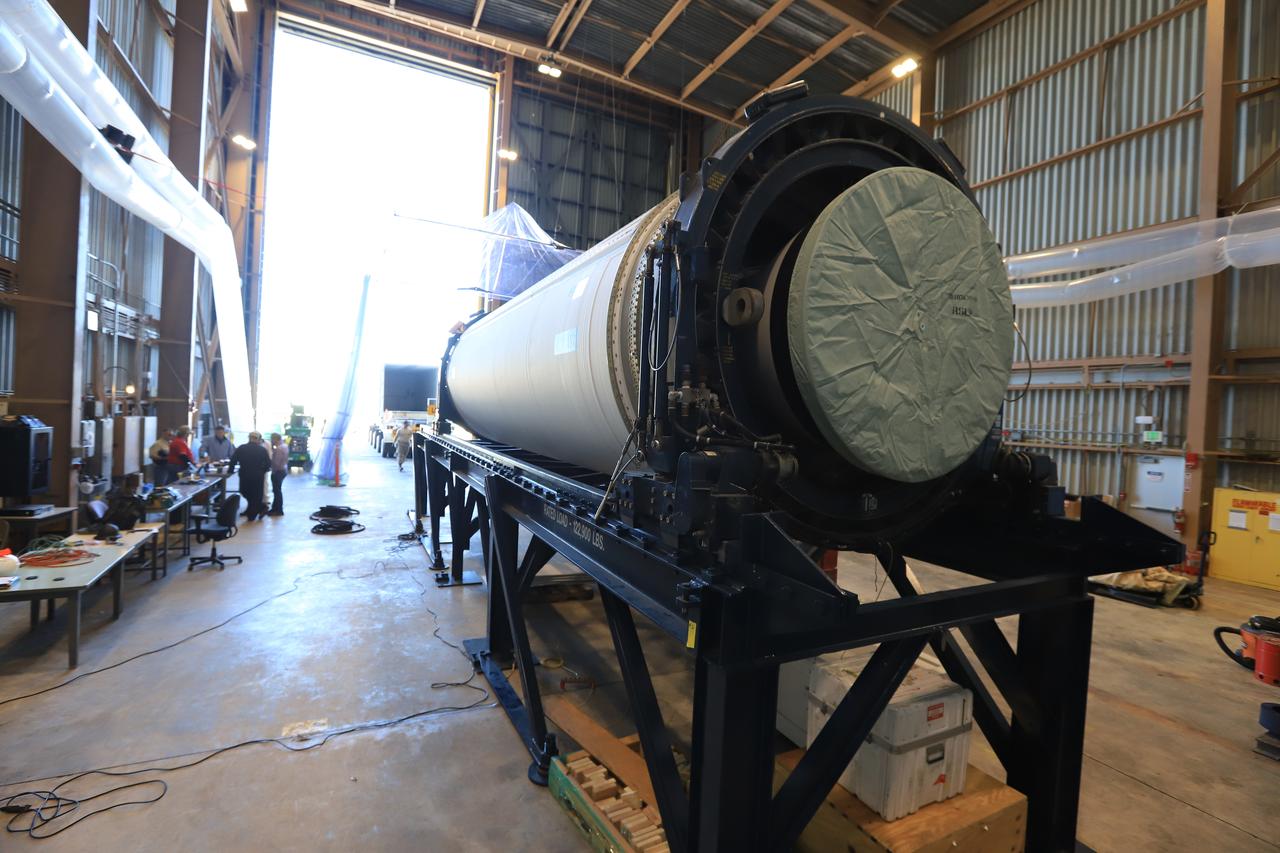

The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.
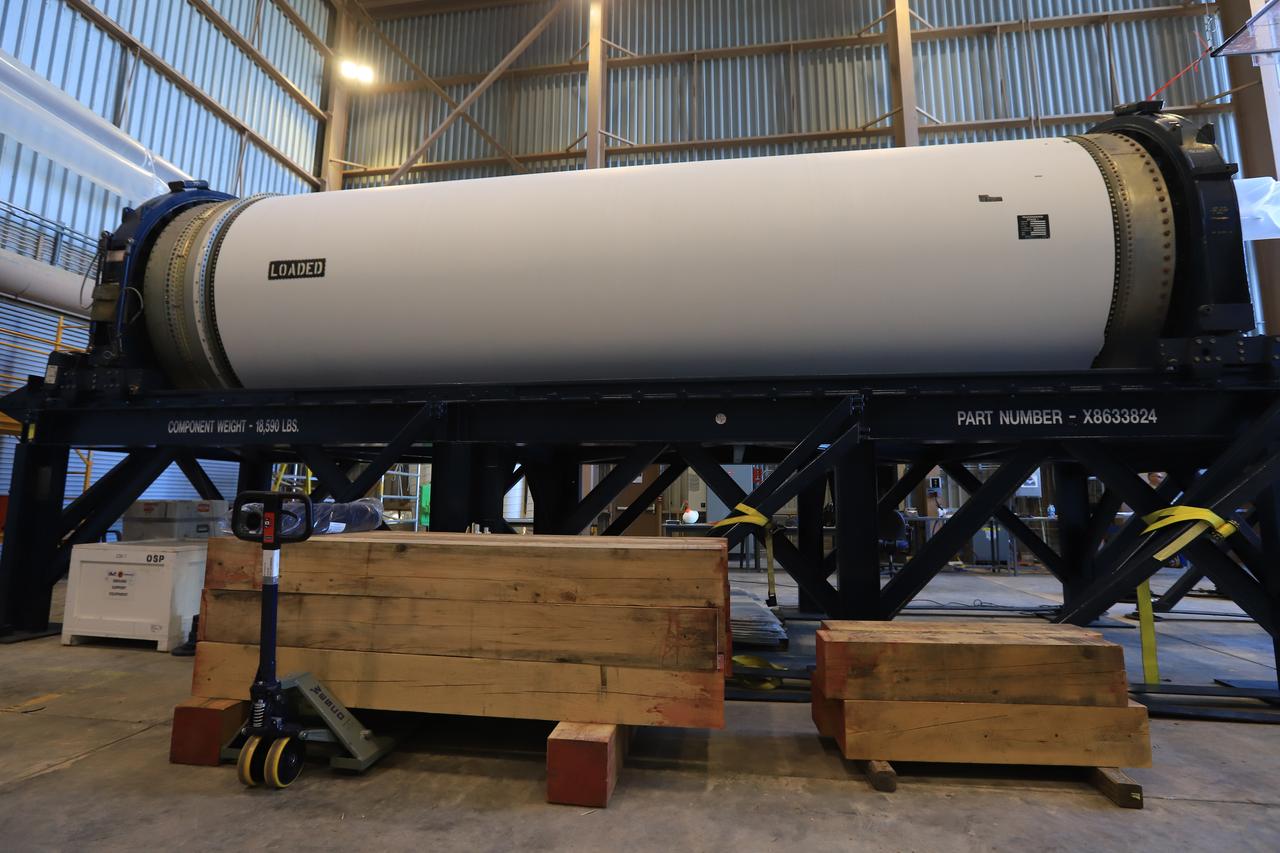

The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.
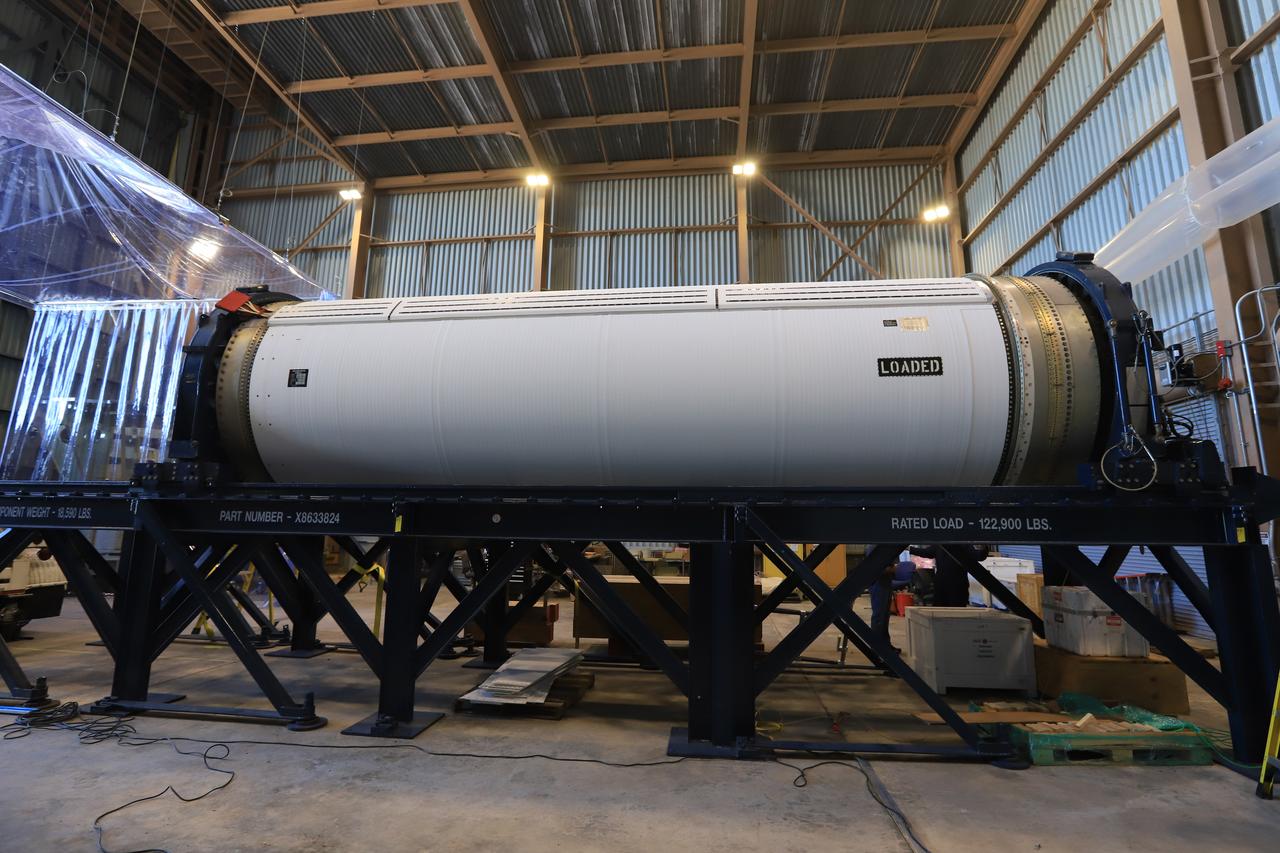

The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.
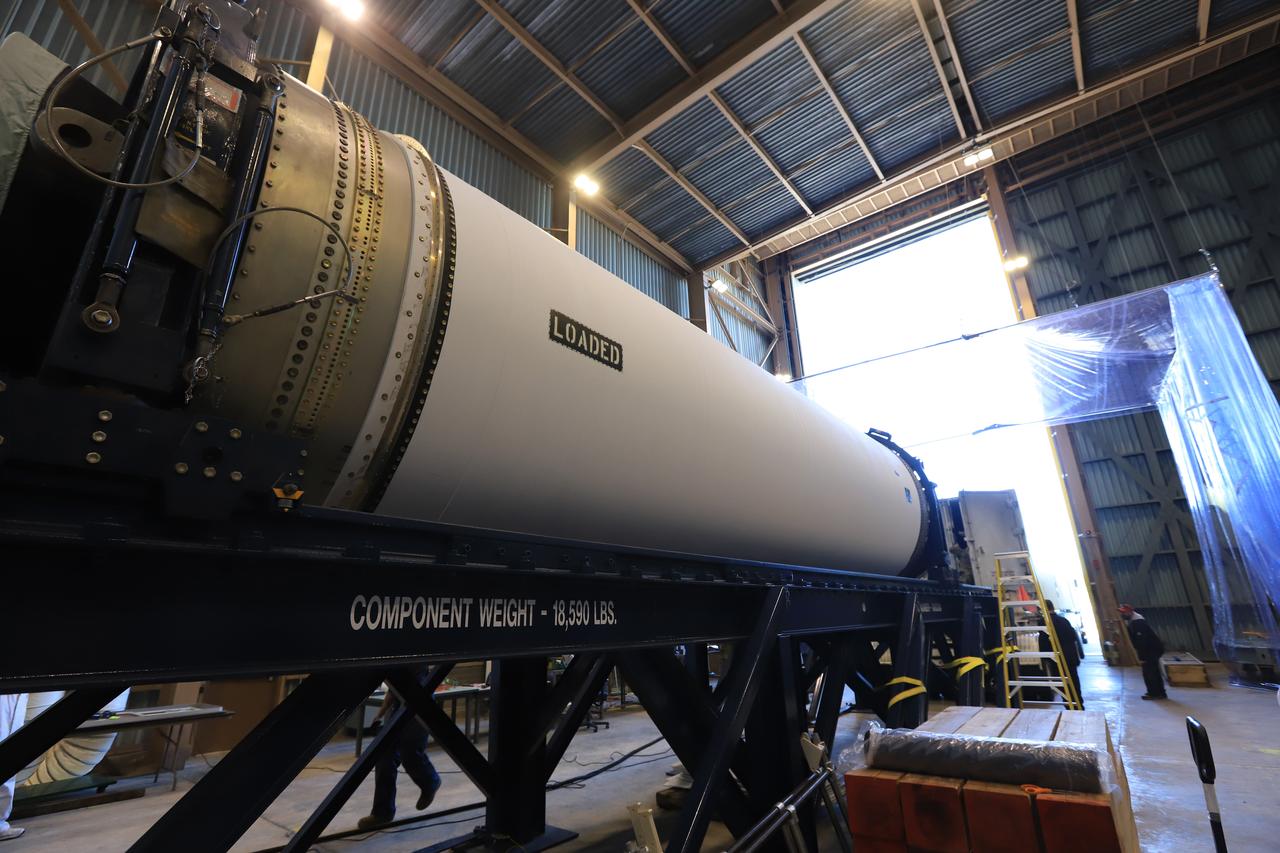

The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.
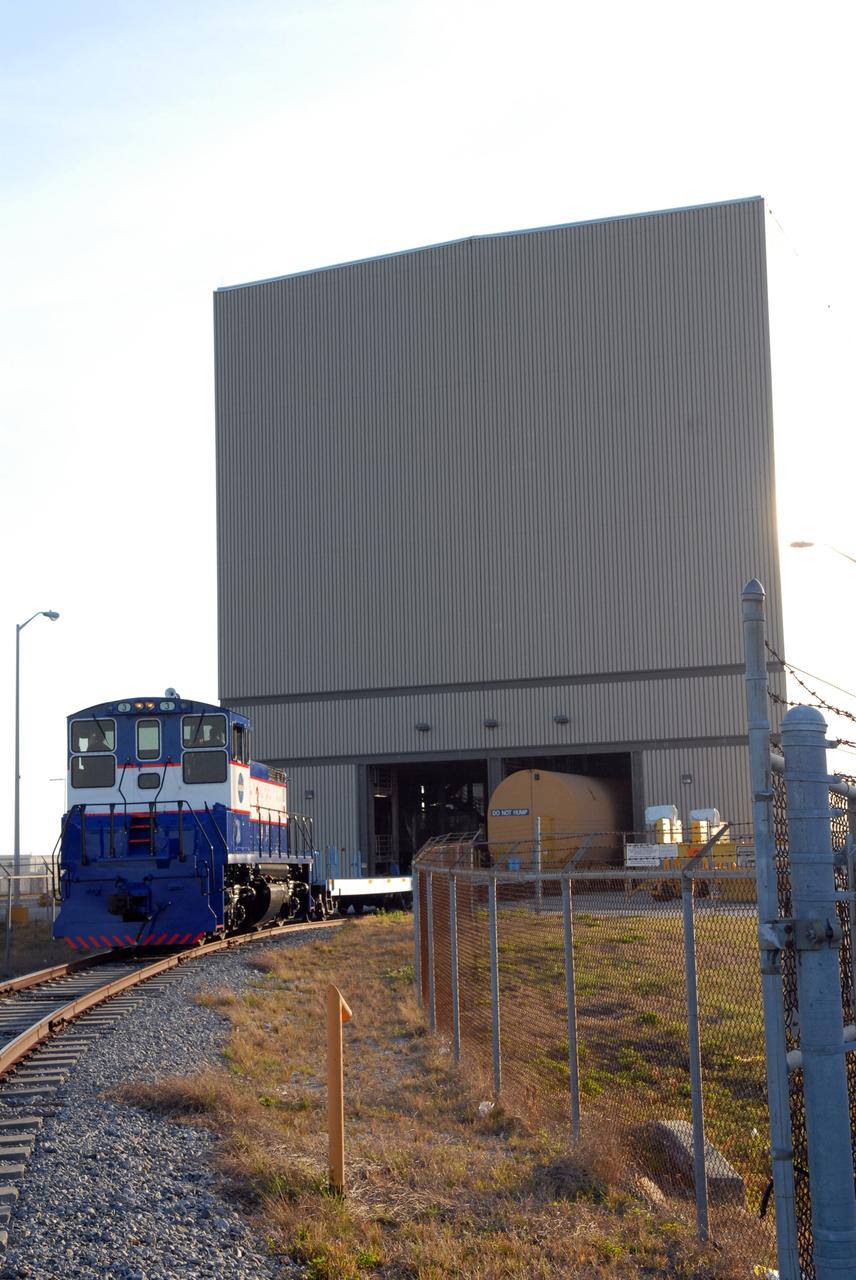

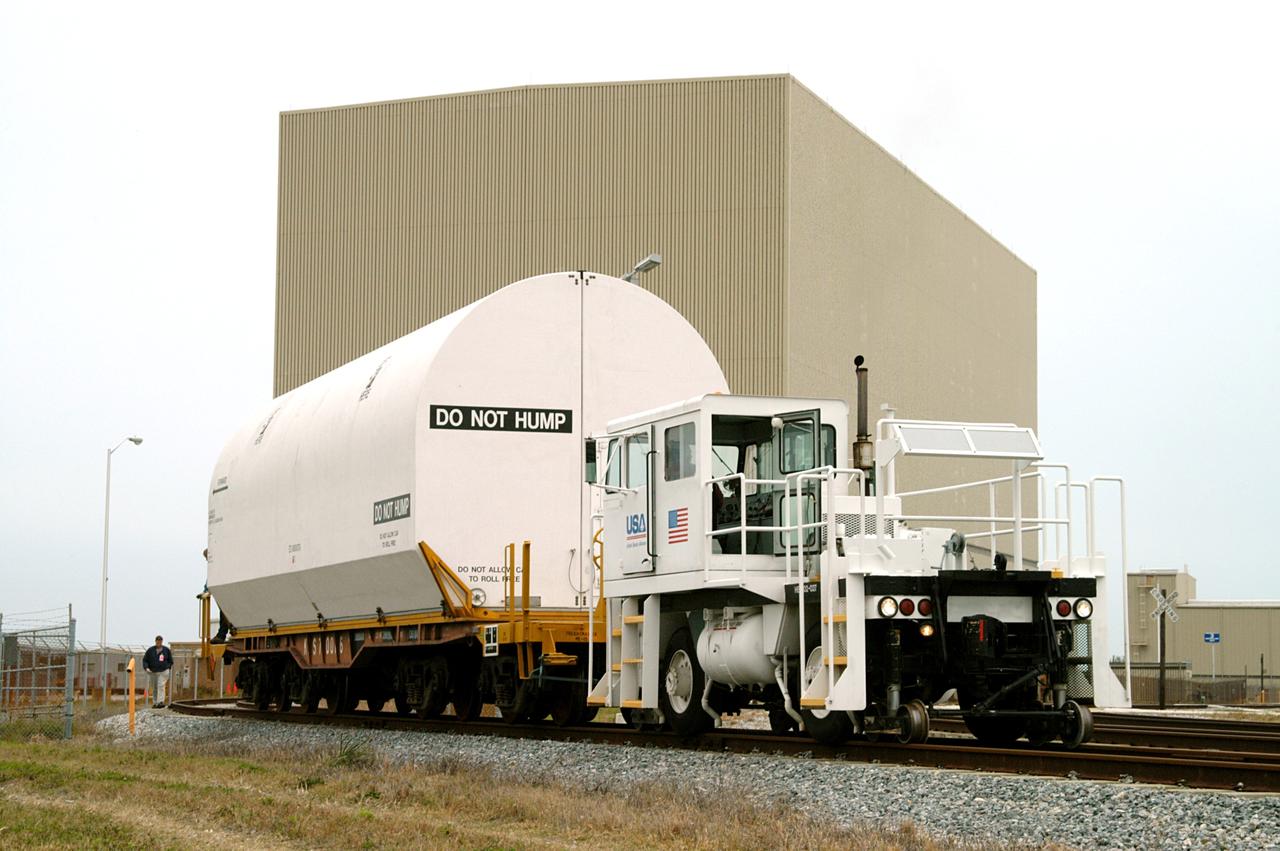
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA Railroad delivers the first Ares I-X segment to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Four reusable motor segments and the nozzle exit cone, manufactured by the Ares I first-stage prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., departed Utah March 12 on the seven-day, cross-country trip to Florida. The segments are being delivered to Kennedy's Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility for final processing and integration. The booster used for the Ares I-X launch is being modified by adding new forward structures and a fifth segment simulator. The motor is the final hardware needed for the rocket's upcoming test flight this summer. The stacking operations are scheduled to begin in the Vehicle Assembly Building in April. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA Railroad delivers the first Ares I-X segment to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Four reusable motor segments and the nozzle exit cone, manufactured by the Ares I first-stage prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., departed Utah March 12 on the seven-day, cross-country trip to Florida. The segments are being delivered to Kennedy's Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility for final processing and integration. The booster used for the Ares I-X launch is being modified by adding new forward structures and a fifth segment simulator. The motor is the final hardware needed for the rocket's upcoming test flight this summer. The stacking operations are scheduled to begin in the Vehicle Assembly Building in April. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

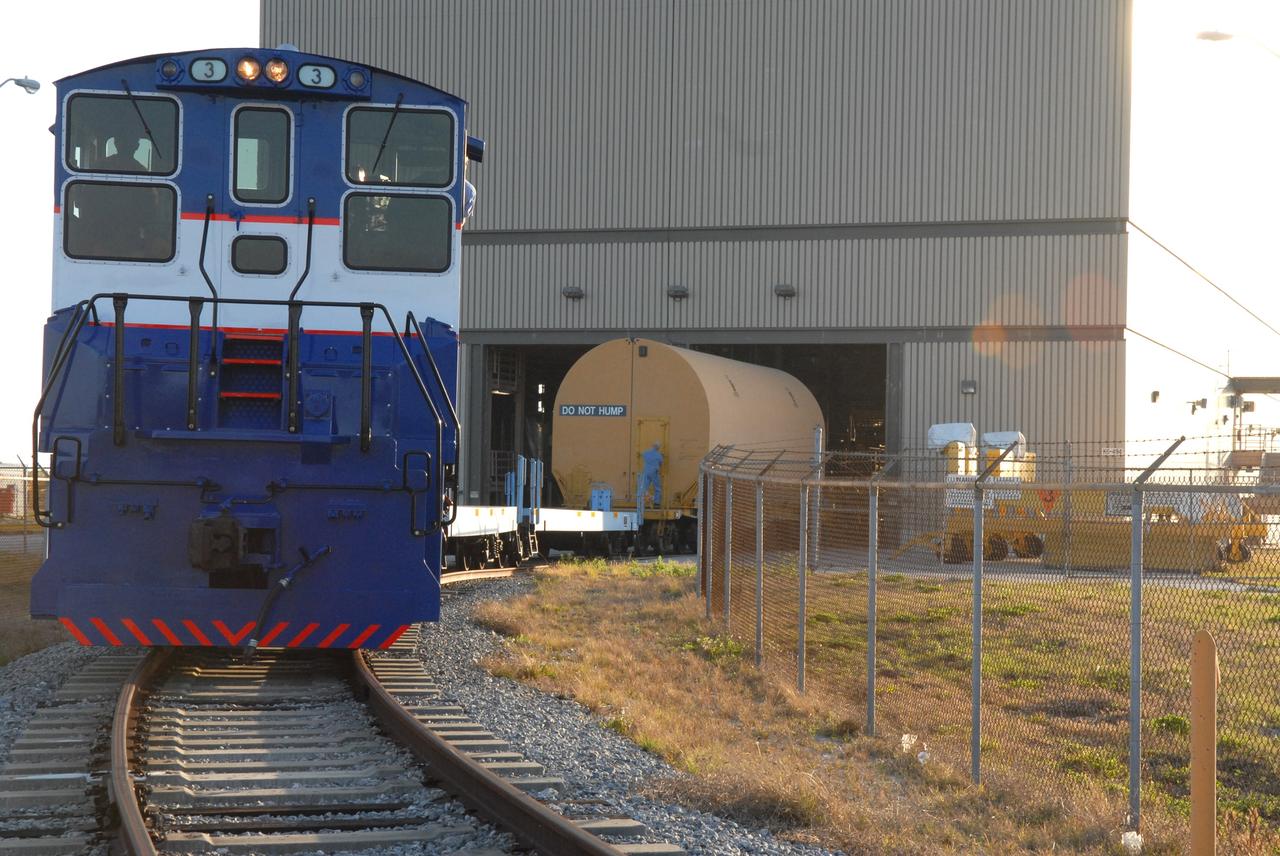
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA Railroad hauls one of the cars with the first Ares I-X segment to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Four reusable motor segments and the nozzle exit cone, manufactured by the Ares I first-stage prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., departed Utah March 12 on the seven-day, cross-country trip to Florida. The segments are being delivered to Kennedy's Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility for final processing and integration. The booster used for the Ares I-X launch is being modified by adding new forward structures and a fifth segment simulator. The motor is the final hardware needed for the rocket's upcoming test flight this summer. The stacking operations are scheduled to begin in the Vehicle Assembly Building in April. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA Railroad hauls one of the cars with the first Ares I-X segment to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Four reusable motor segments and the nozzle exit cone, manufactured by the Ares I first-stage prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., departed Utah March 12 on the seven-day, cross-country trip to Florida. The segments are being delivered to Kennedy's Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility for final processing and integration. The booster used for the Ares I-X launch is being modified by adding new forward structures and a fifth segment simulator. The motor is the final hardware needed for the rocket's upcoming test flight this summer. The stacking operations are scheduled to begin in the Vehicle Assembly Building in April. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
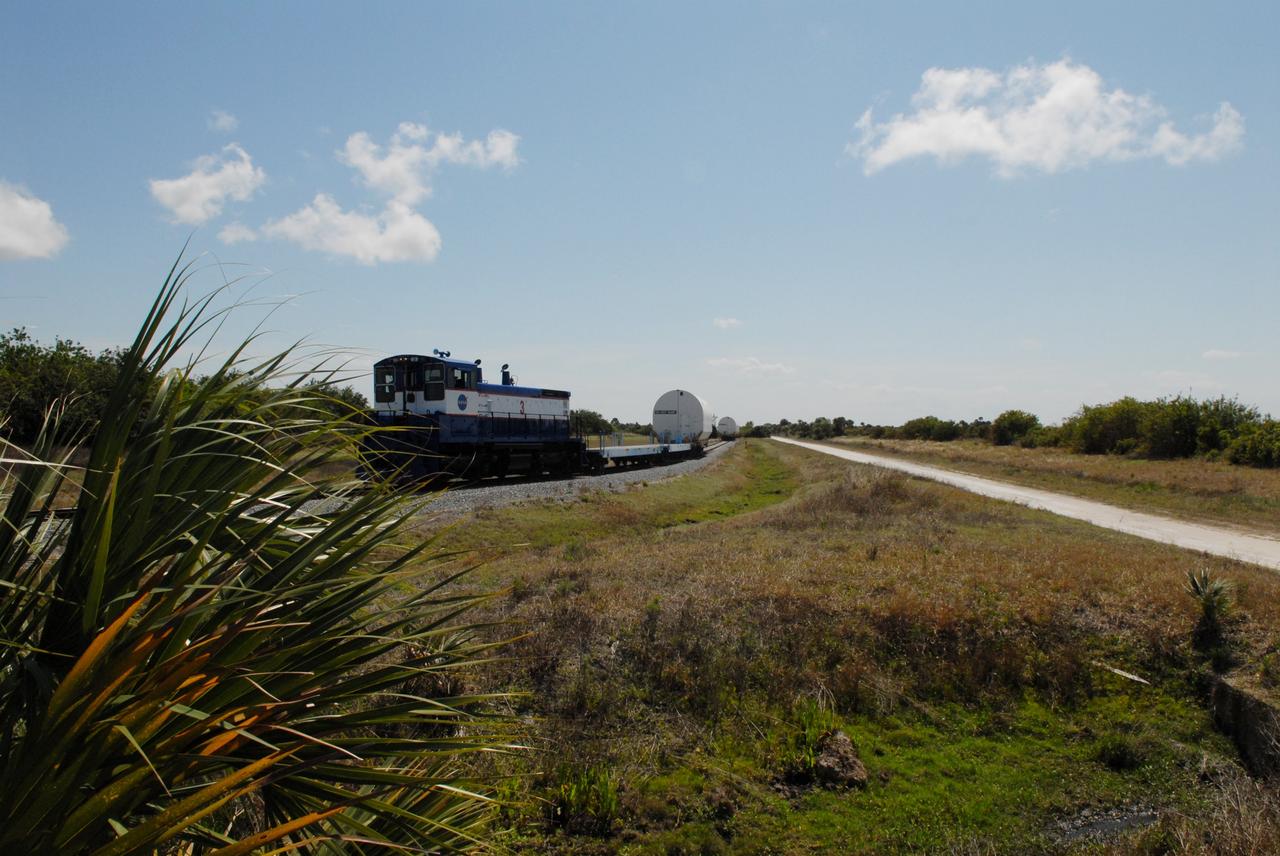

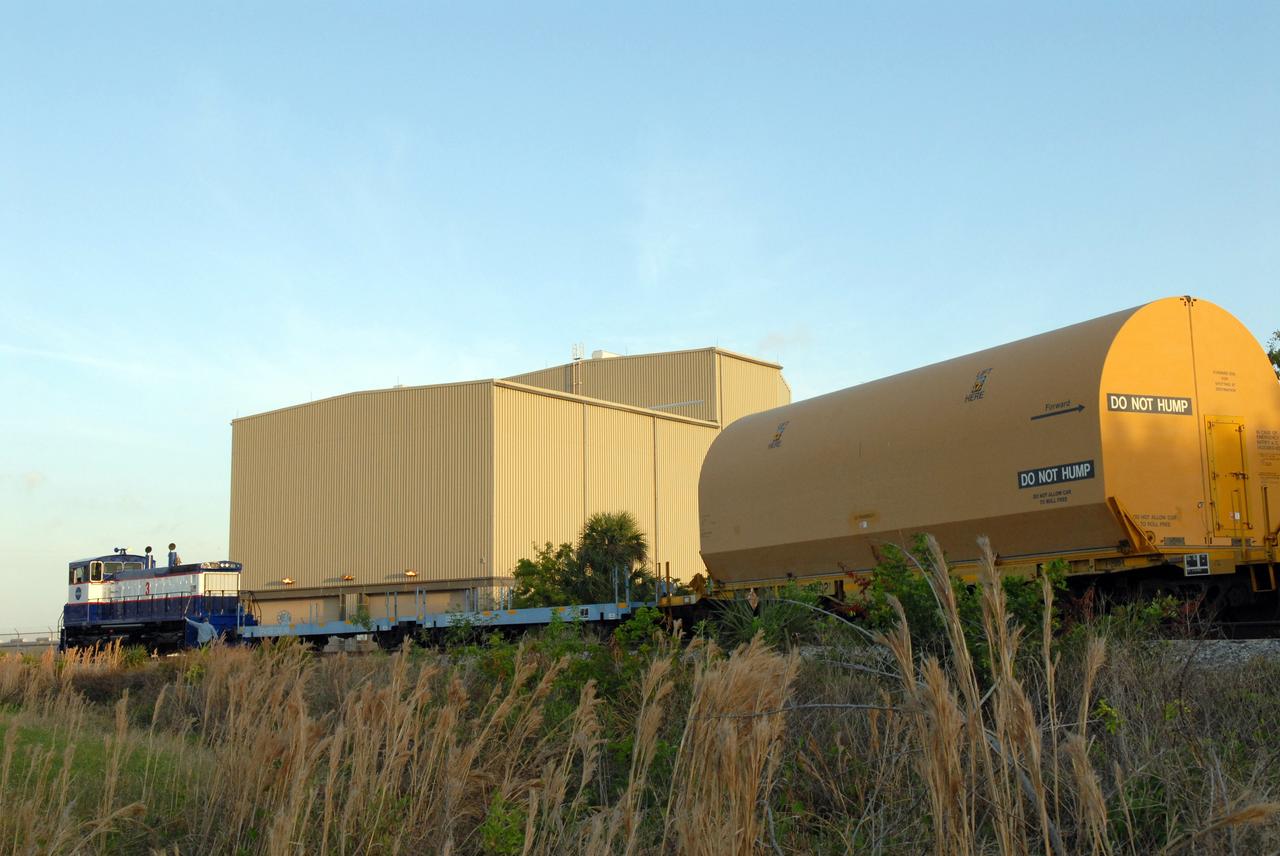
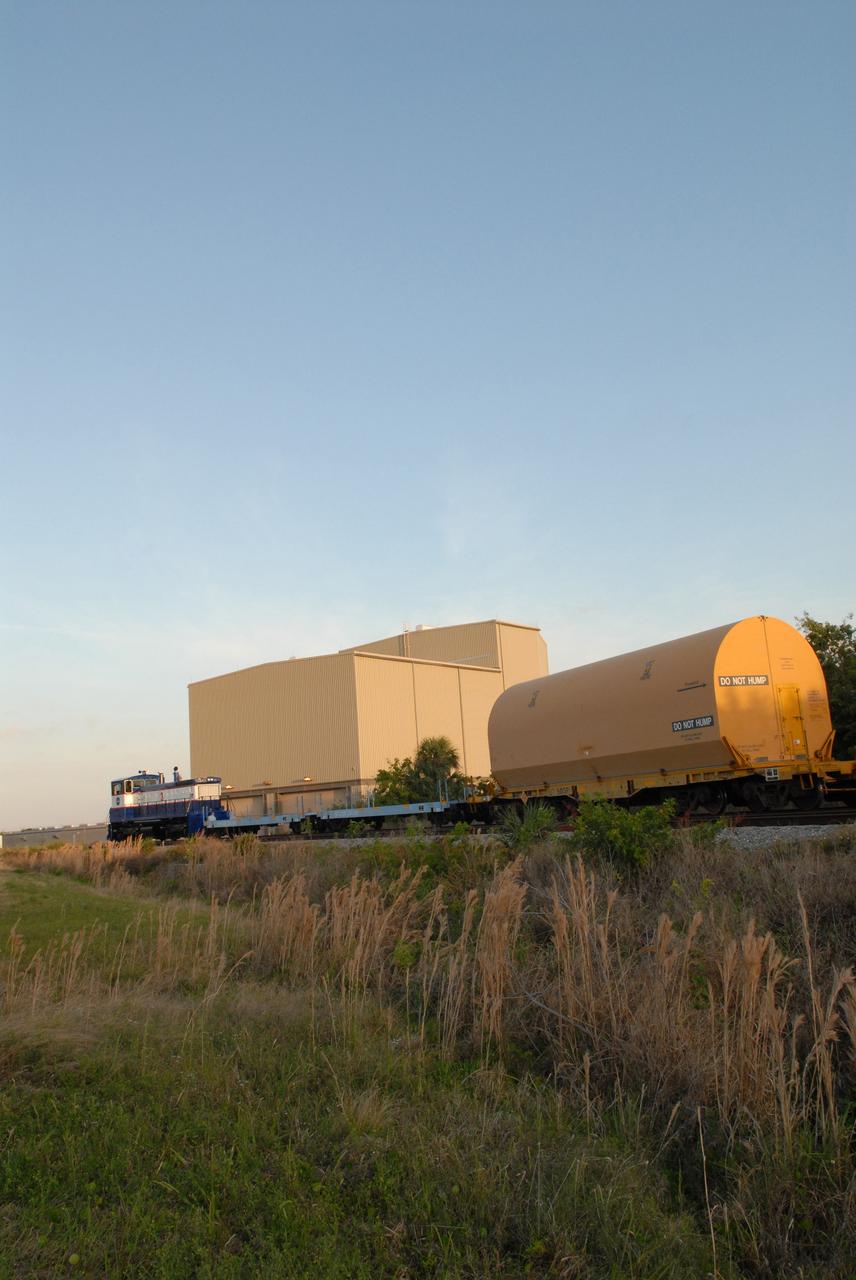
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA Railroad leaves four of the cars with Ares I-X segments at Suspect siding on NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and continues on with the remaining car to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility. The four reusable motor segments and the nozzle exit cone, manufactured by the Ares I first-stage prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, departed Utah March 12 on the seven-day, cross-country trip to Florida. The segments will be delivered to Kennedy's Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility for final processing and integration. The booster used for the Ares I-X launch is being modified by adding new forward structures and a fifth segment simulator. The motor is the final hardware needed for the rocket's upcoming test flight this summer. The stacking operations are scheduled to begin in the Vehicle Assembly Building in April. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
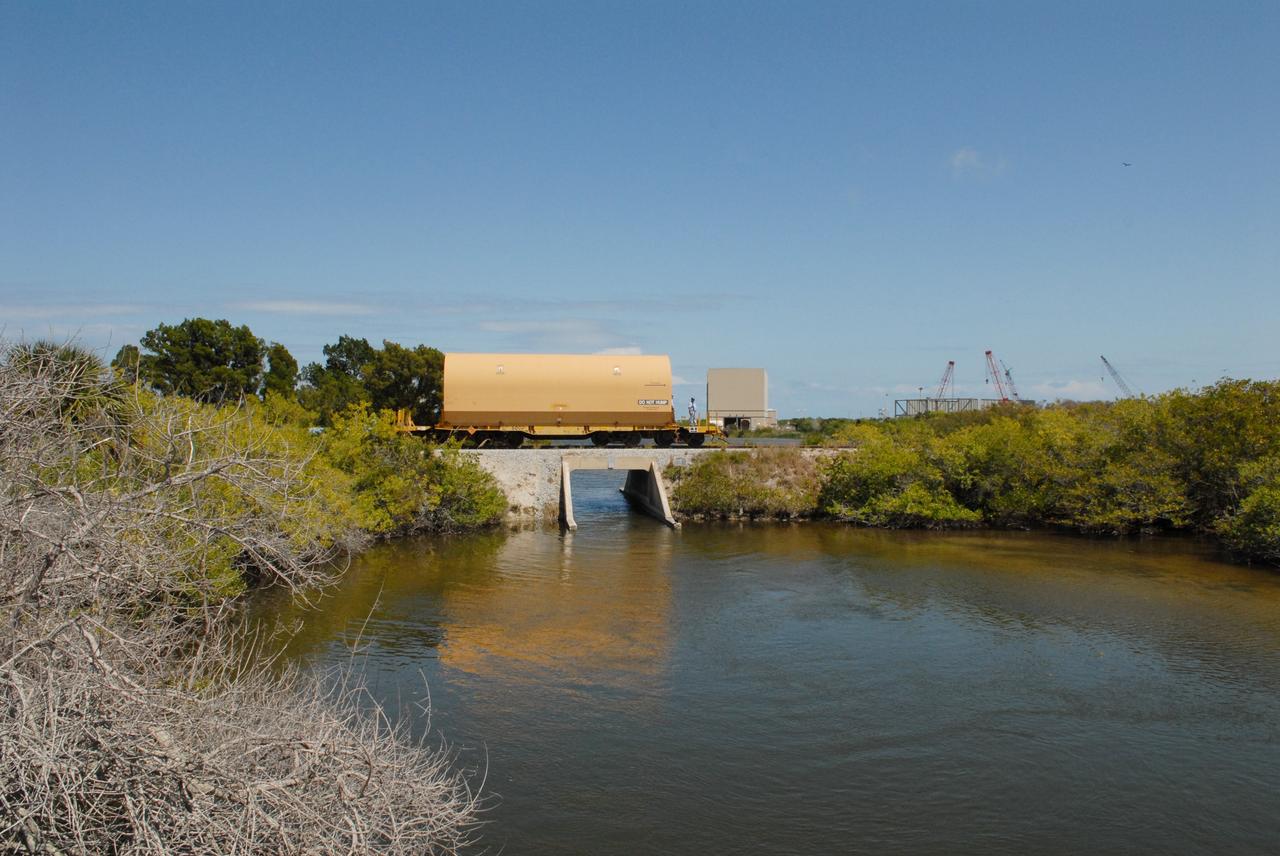

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –The NASA Railroad is hauling one of the cars with an Ares I-X segment to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four reusable motor segments and the nozzle exit cone, manufactured by the Ares I first-stage prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, departed Utah March 12 on the seven-day, cross-country trip to Florida. The segments will be delivered to Kennedy's Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility for final processing and integration. The booster used for the Ares I-X launch is being modified by adding new forward structures and a fifth segment simulator. The motor is the final hardware needed for the rocket's upcoming test flight this summer. The stacking operations are scheduled to begin in the Vehicle Assembly Building in April. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
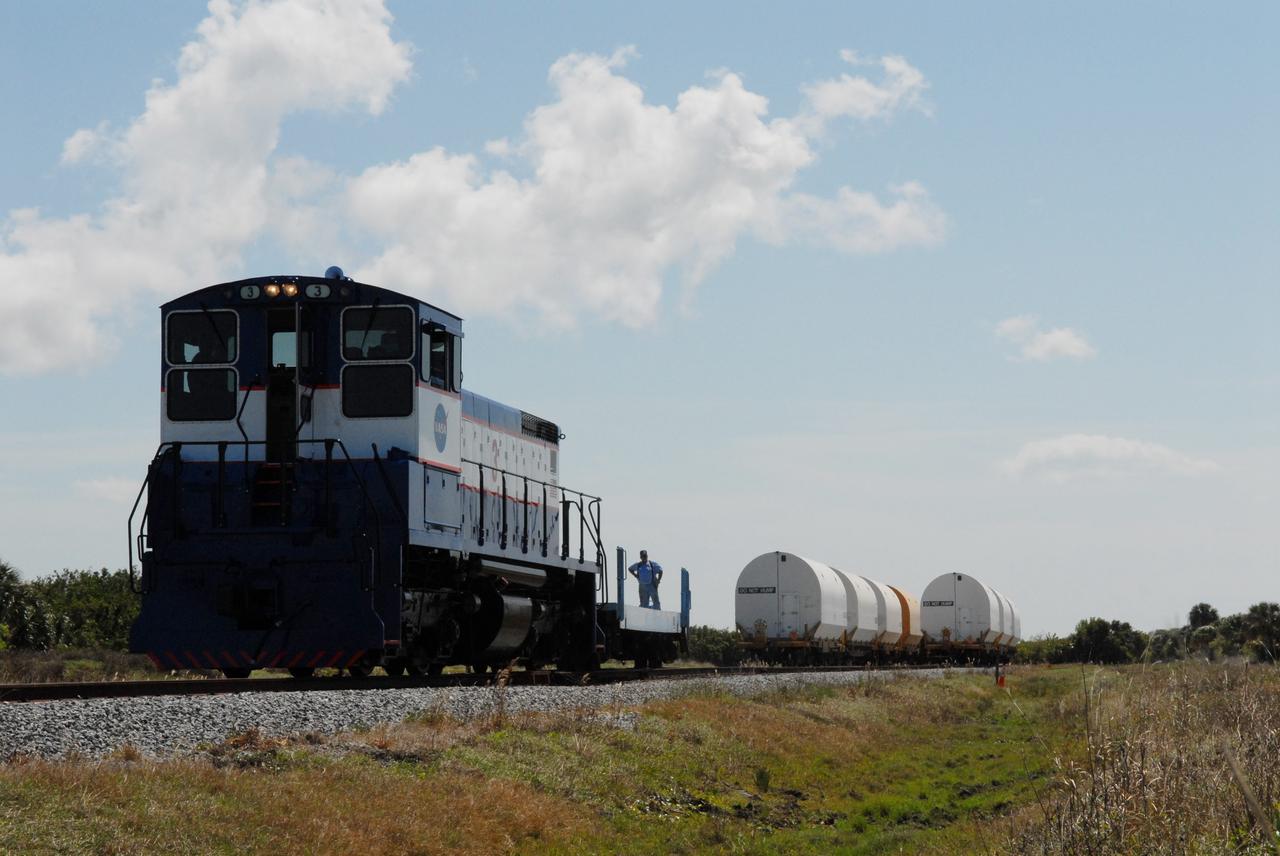

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –The cars on the NASA Railroad are separated for different destinations at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. They carry Ares I-X segments. One of the cars is going to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility. The four reusable motor segments and the nozzle exit cone, manufactured by the Ares I first-stage prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, departed Utah March 12 on the seven-day, cross-country trip to Florida. The segments will be delivered to Kennedy's Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility for final processing and integration. The booster used for the Ares I-X launch is being modified by adding new forward structures and a fifth segment simulator. The motor is the final hardware needed for the rocket's upcoming test flight this summer. The stacking operations are scheduled to begin in the Vehicle Assembly Building in April. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
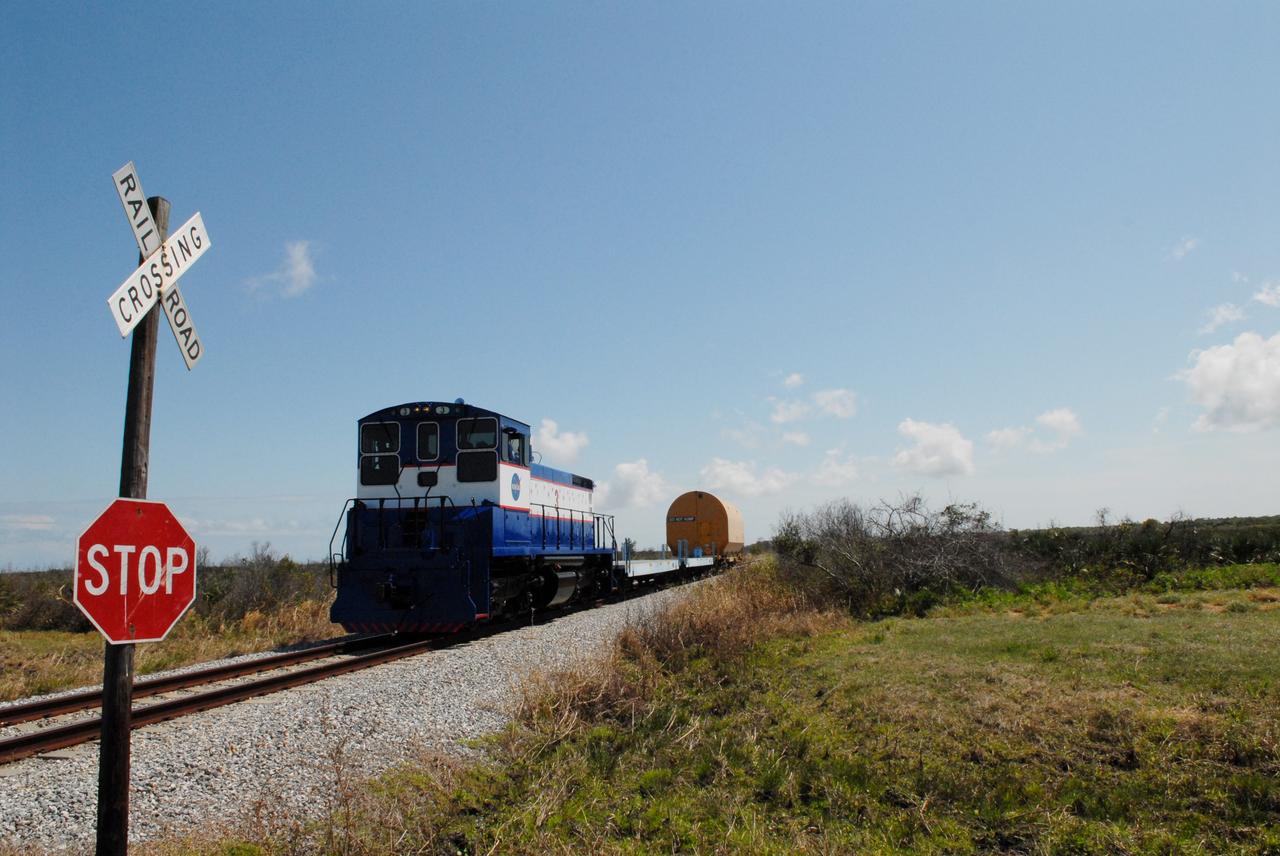

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –This NASA Railroad engine is hauling one of the cars with an Ares I-X segment to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four reusable motor segments and the nozzle exit cone, manufactured by the Ares I first-stage prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, departed Utah March 12 on the seven-day, cross-country trip to Florida. The segments will be delivered to Kennedy's Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility for final processing and integration. The booster used for the Ares I-X launch is being modified by adding new forward structures and a fifth segment simulator. The motor is the final hardware needed for the rocket's upcoming test flight this summer. The stacking operations are scheduled to begin in the Vehicle Assembly Building in April. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller