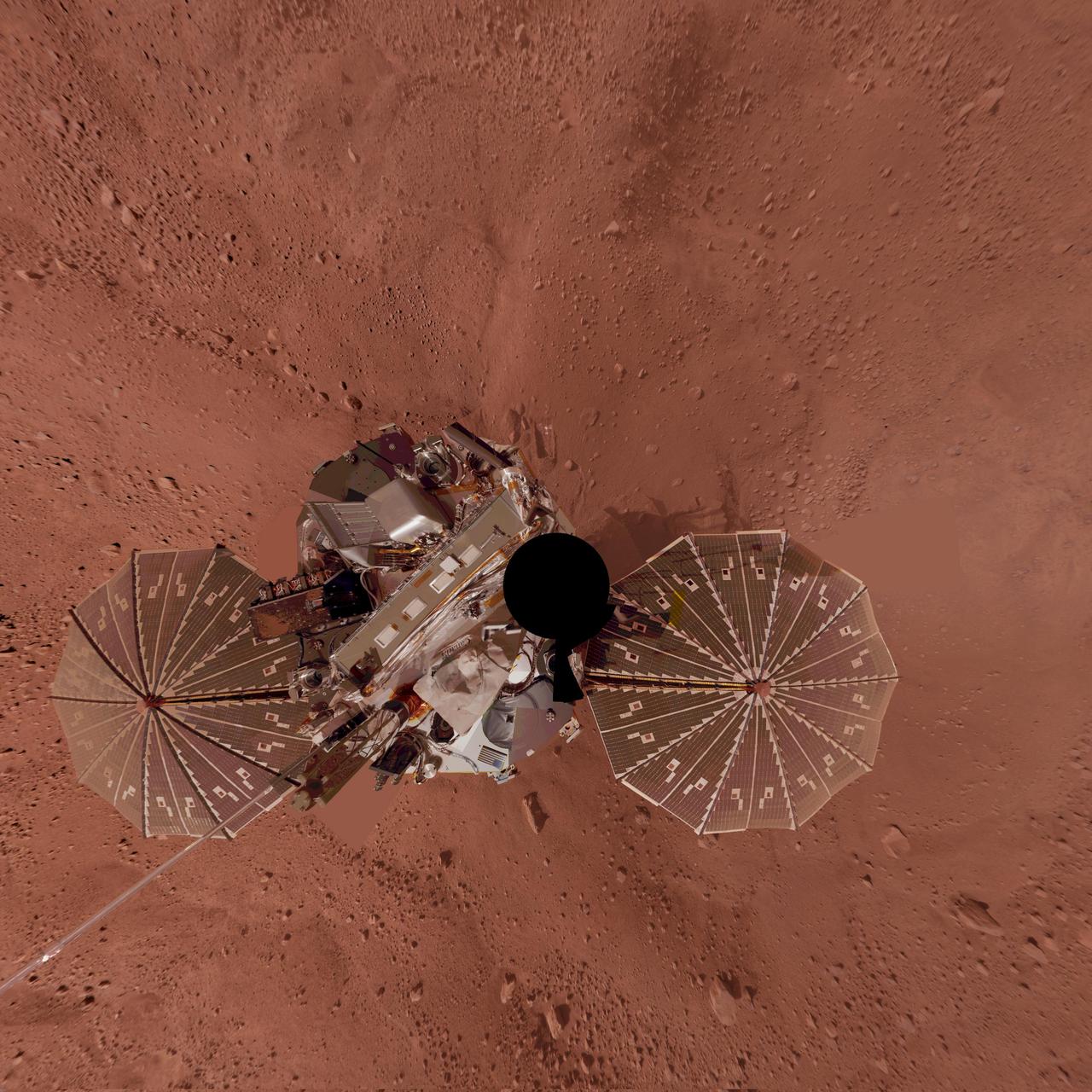

Phoenix Lander Self Portrait on Mars, Vertical Projection
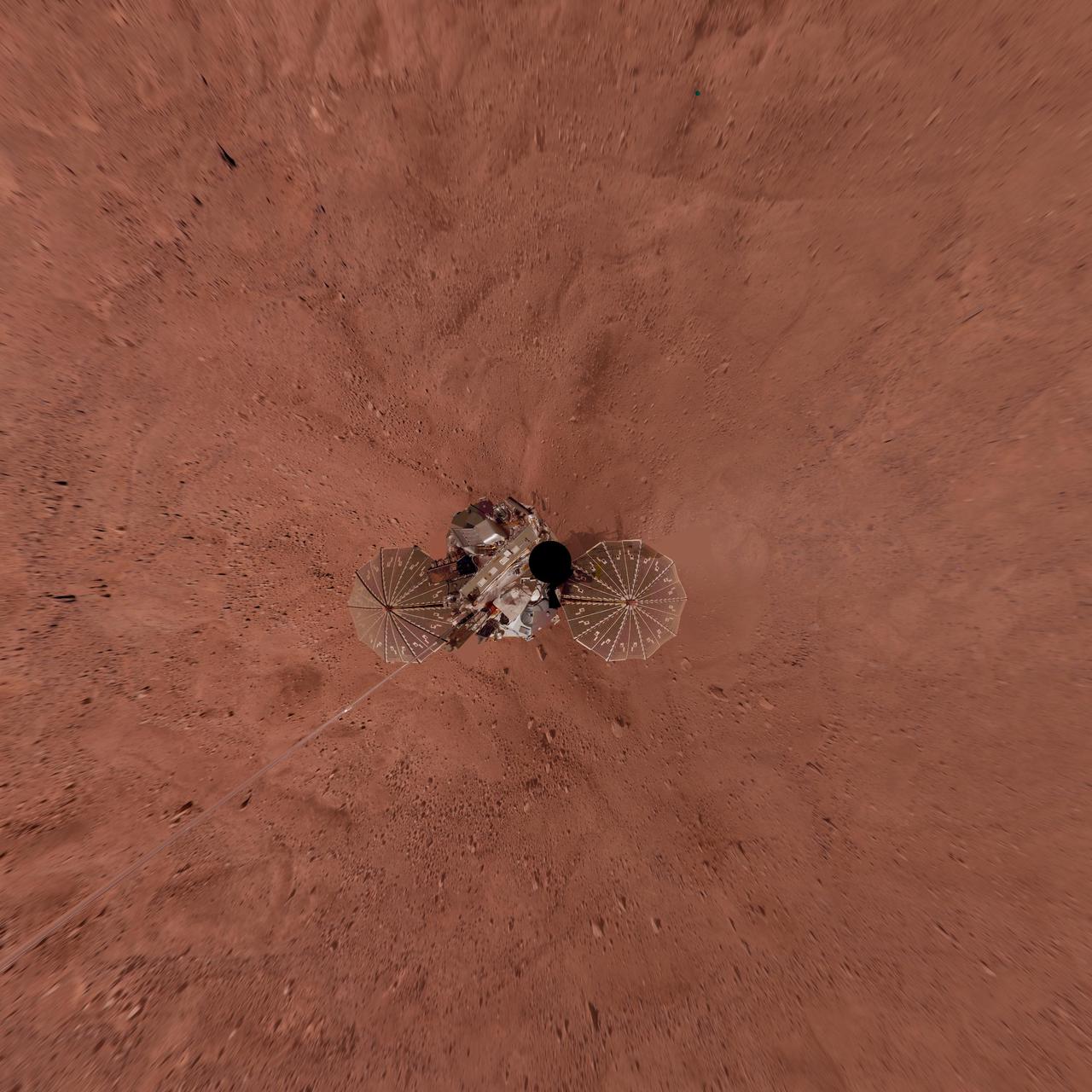

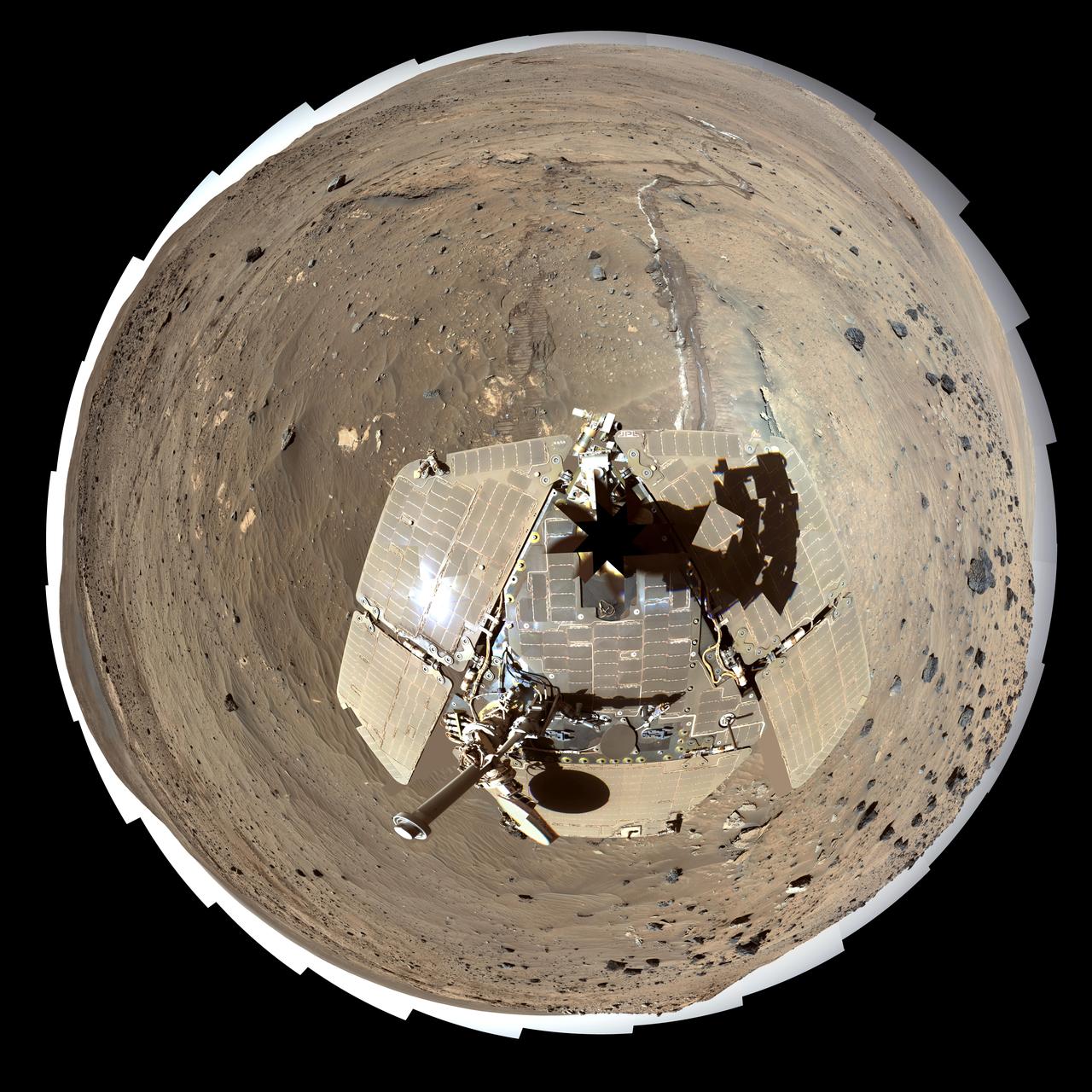
Phoenix Lander on Mars with Surrounding Terrain, Vertical Projection

Dr. Stephen Petranek, MARS scientific advisor and co-executive producer speaks on a panel after a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Gareth Edwards, film director, Rogue One: A Star Wars Story, speaks on a panel after a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

A guest uses some virtual reality viewers before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films winners and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
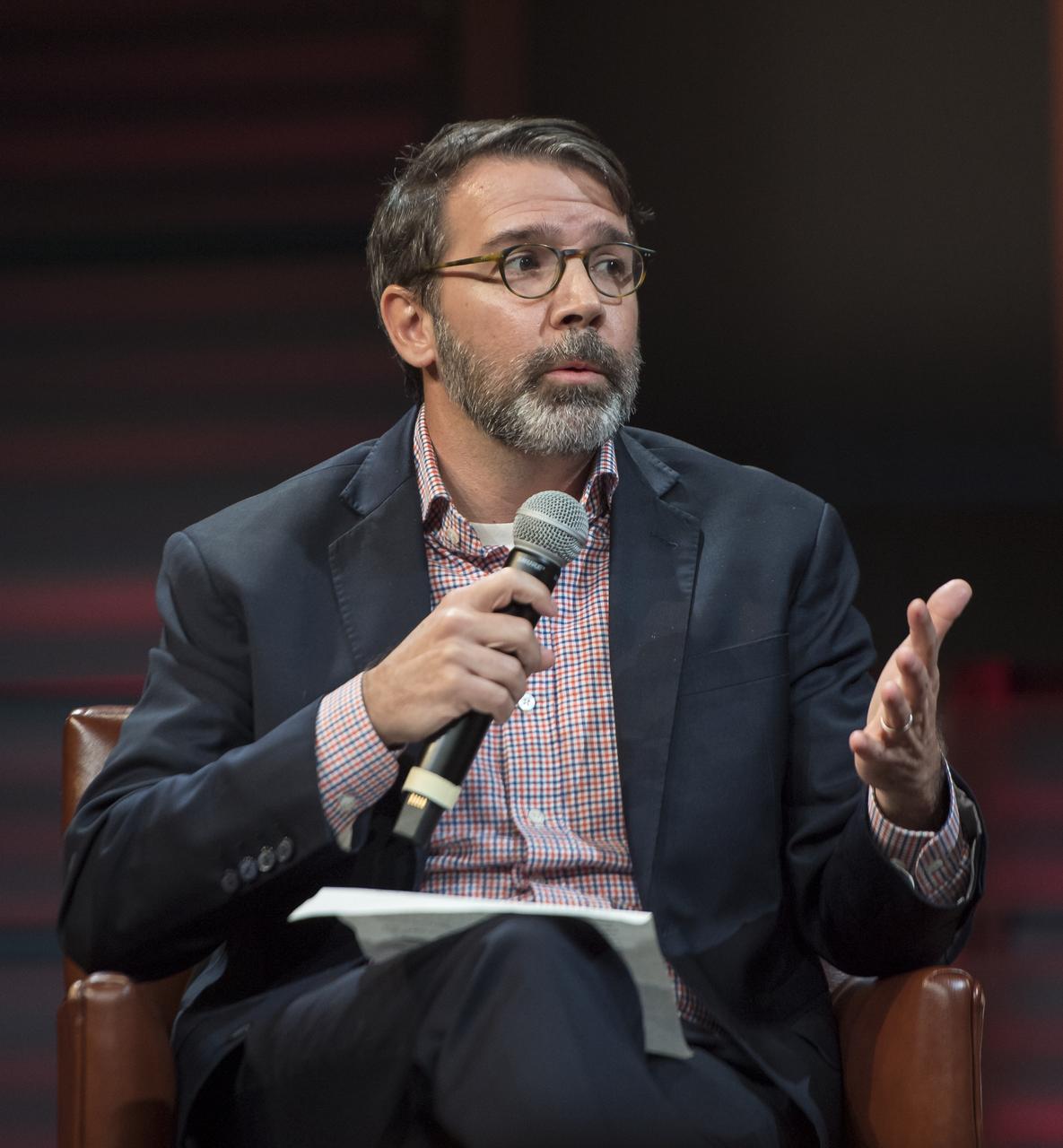

Chris Davenport, Washington Post space reporter, moderates a panel after a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
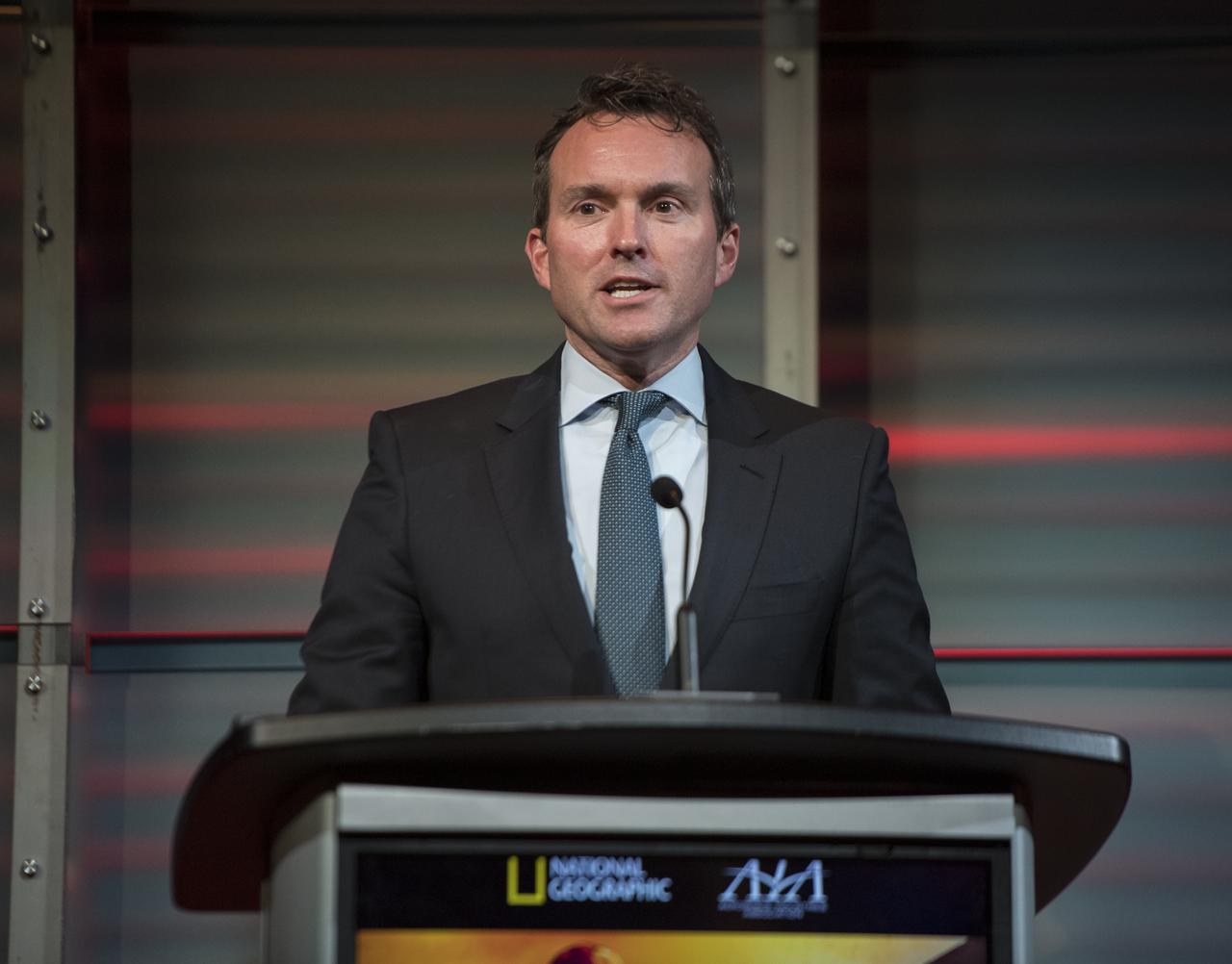

Eric Fanning, AIA President and CEO speaks before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films winners and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
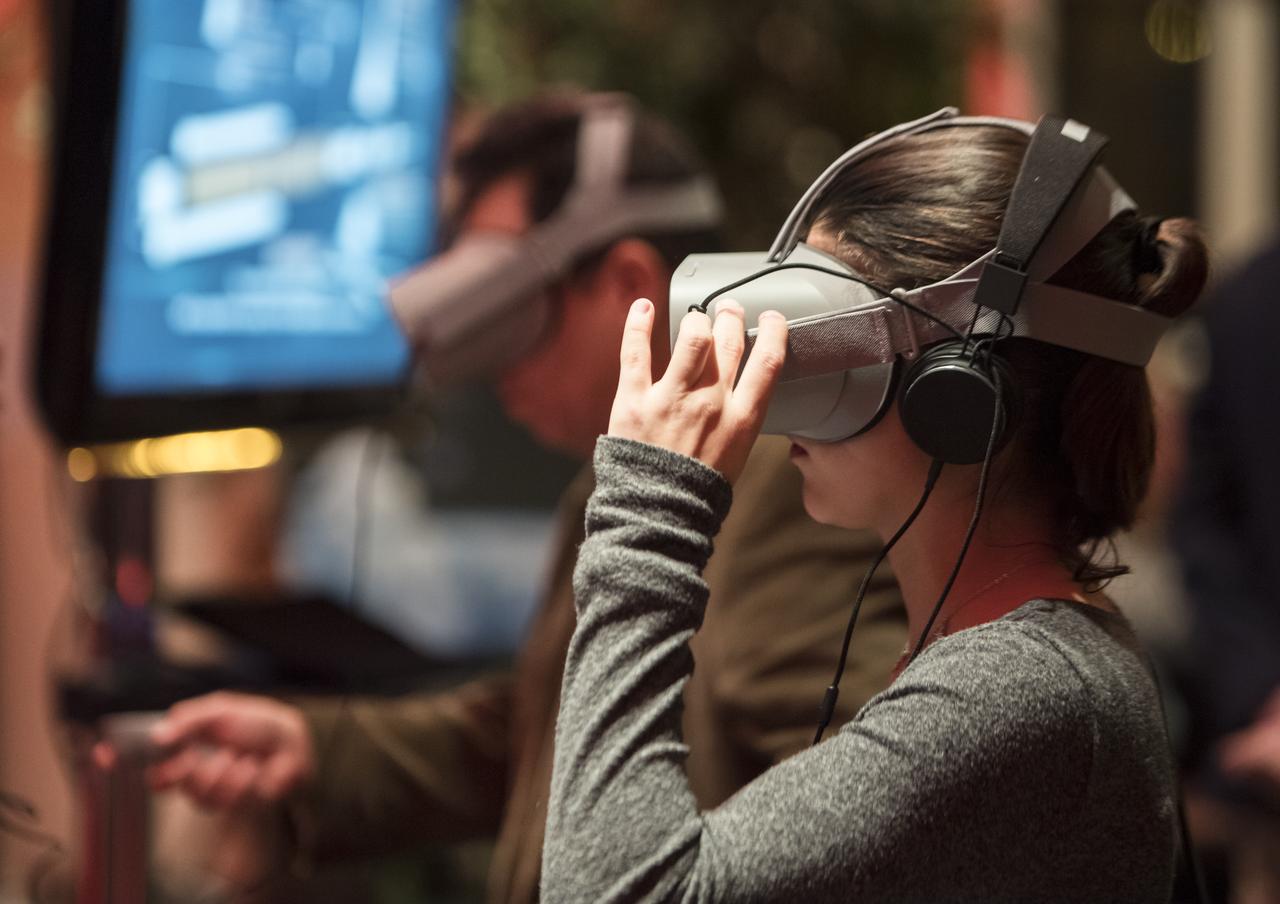

A guest uses some virtual reality viewers before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films winners and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
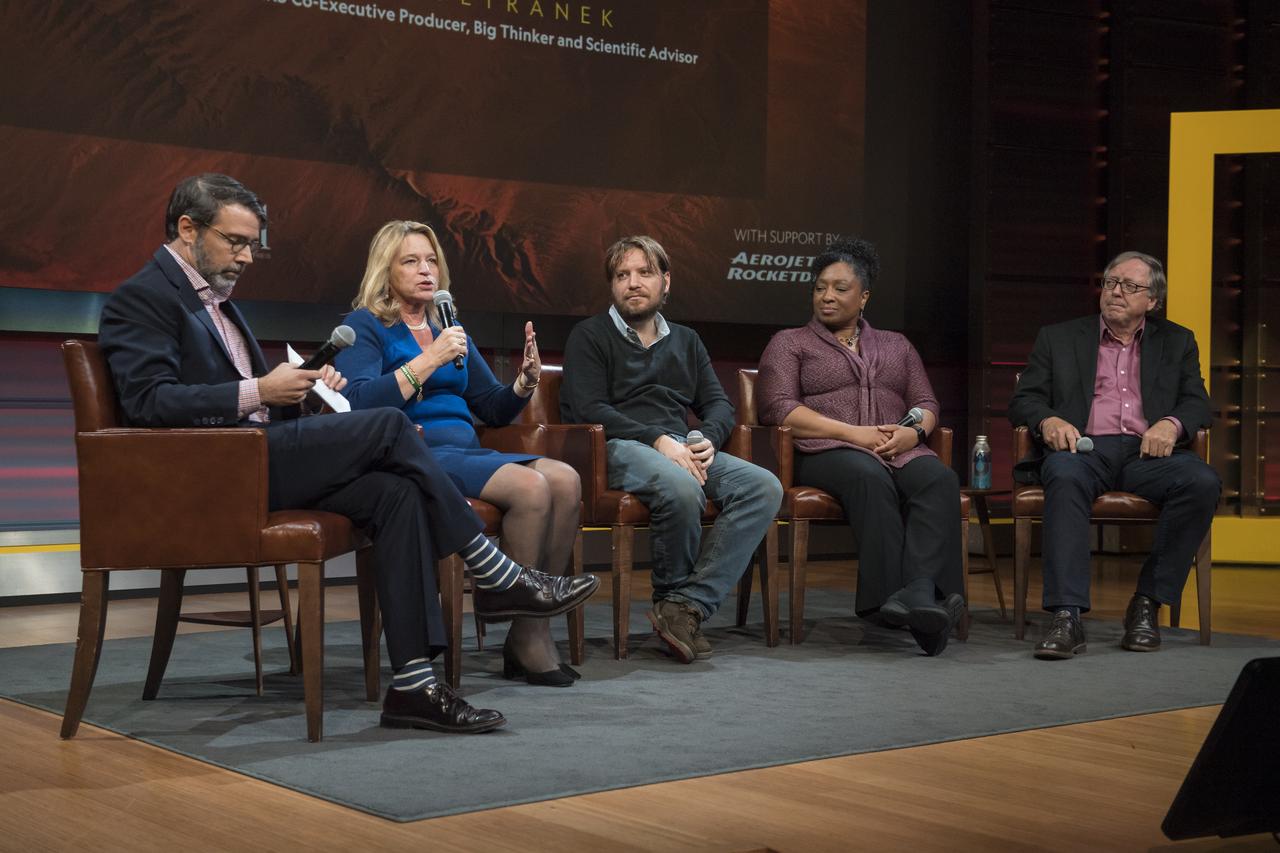

Ellen Stofan, director, Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum, speaks on a panel after a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
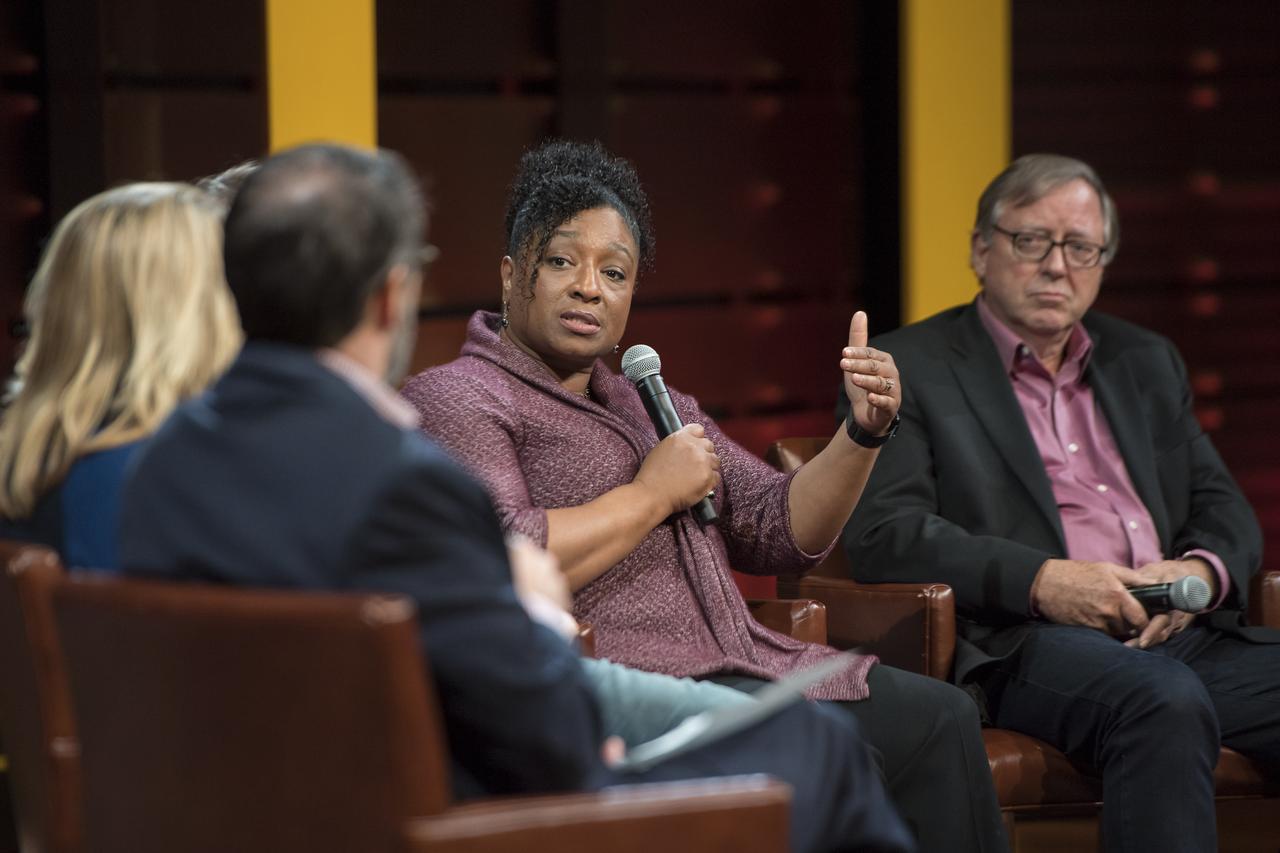

Christyl Johnson, deputy director for technology and research investments, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, second from right, speaks on a panel after a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
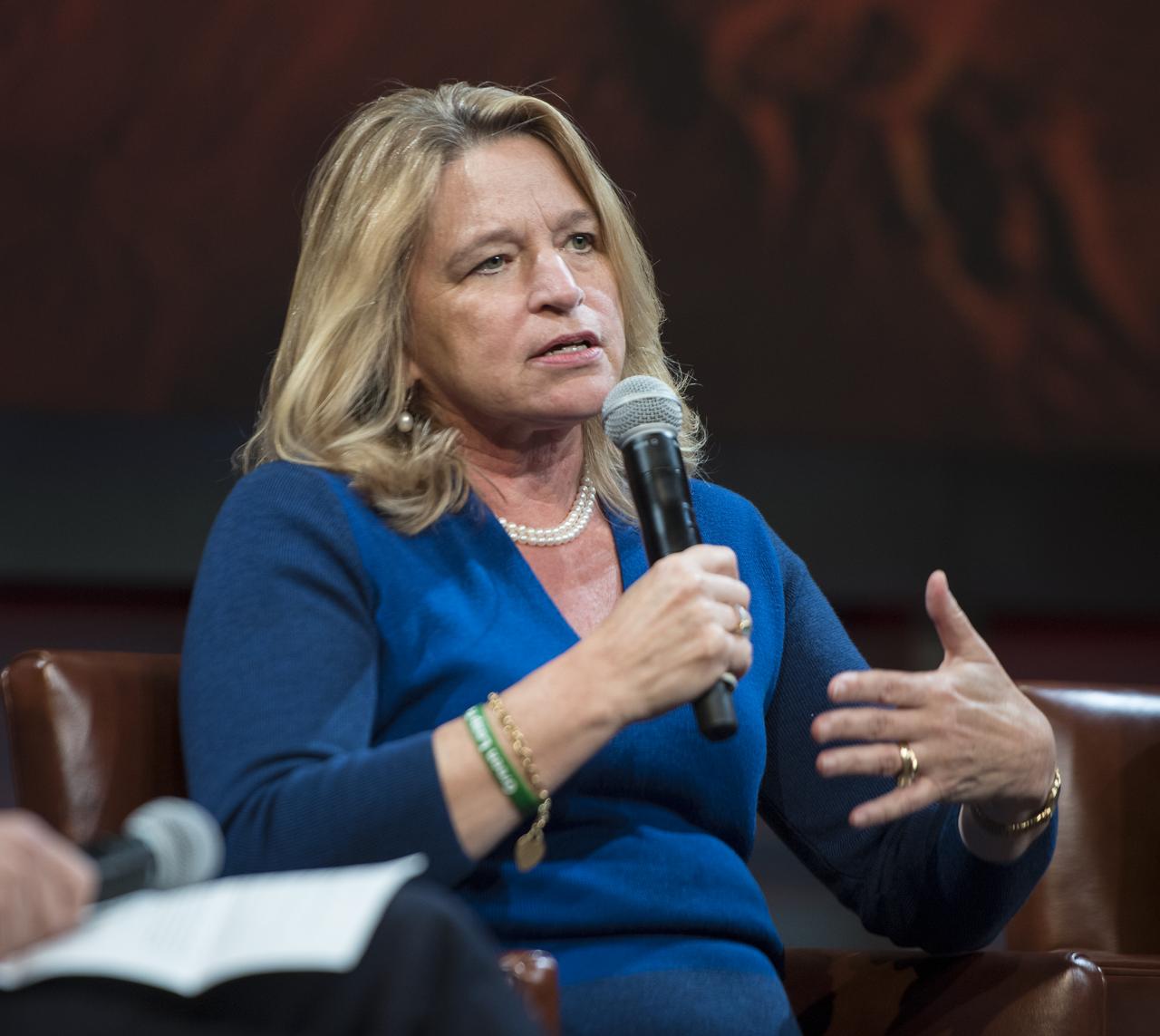

Ellen Stofan, director, Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum, speaks on a panel after a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
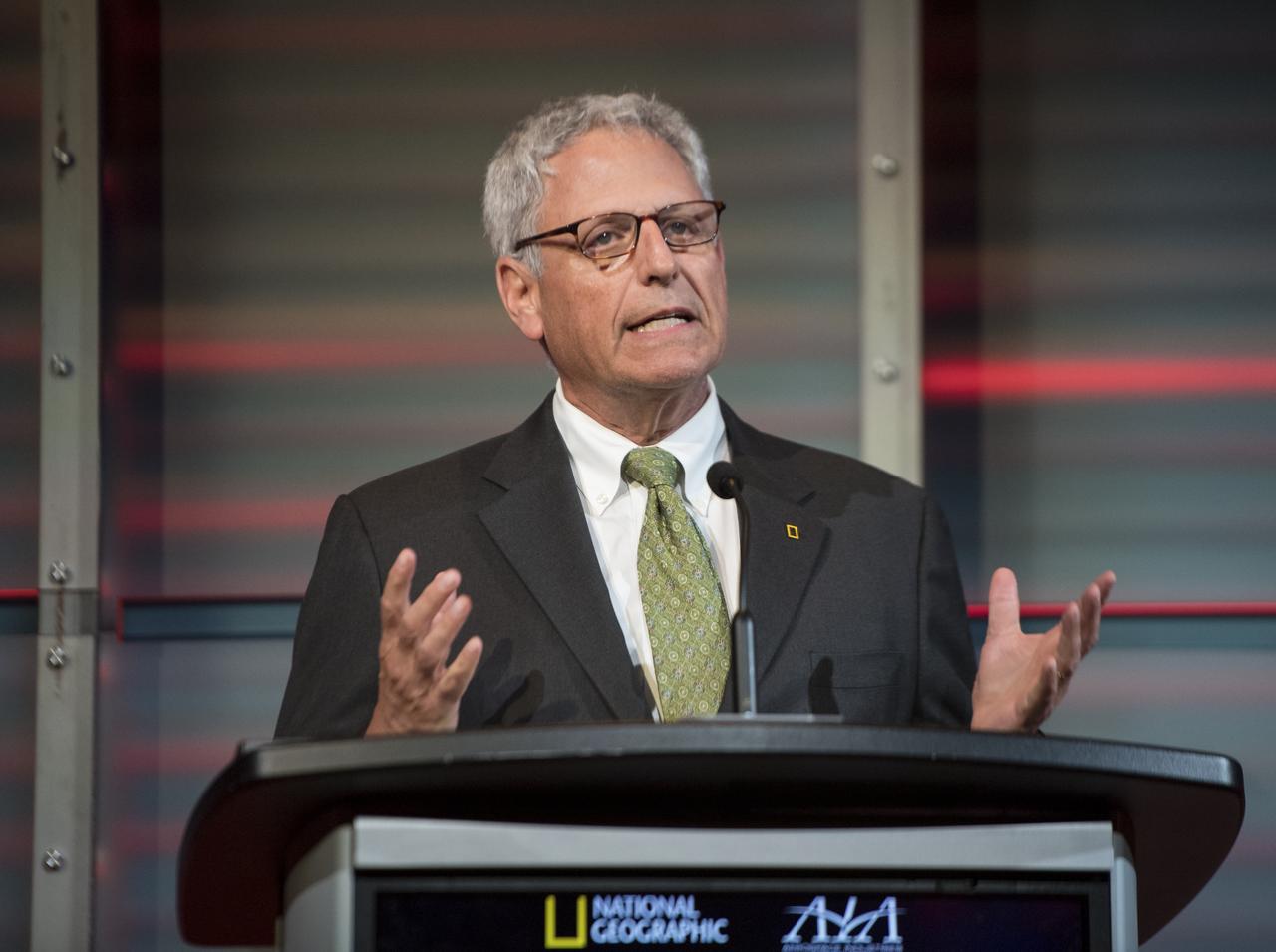

Gary Knell, CEO, National Geographic Partners speaks before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films winners and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine gives keynote remarks before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
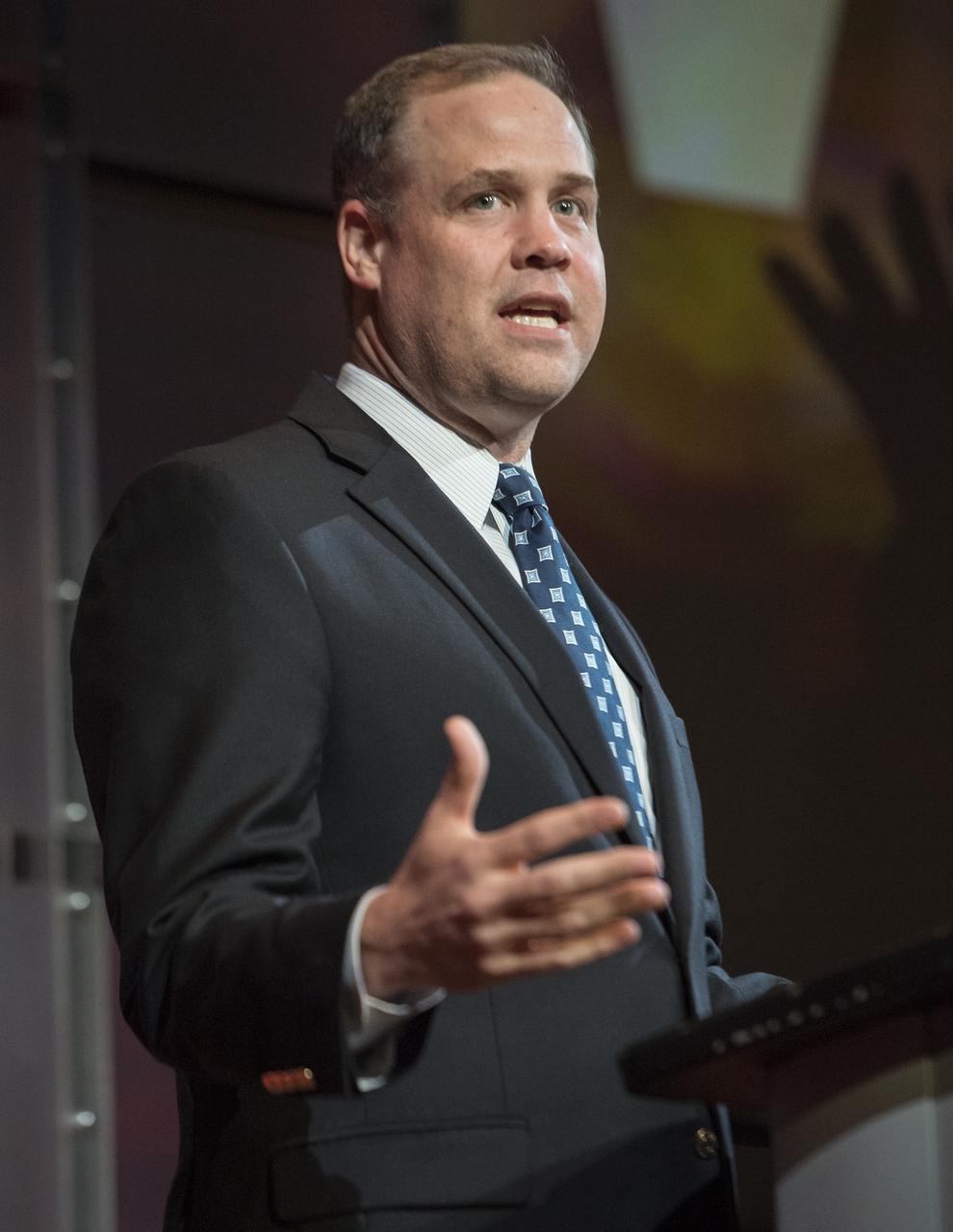

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine gives keynote remarks before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
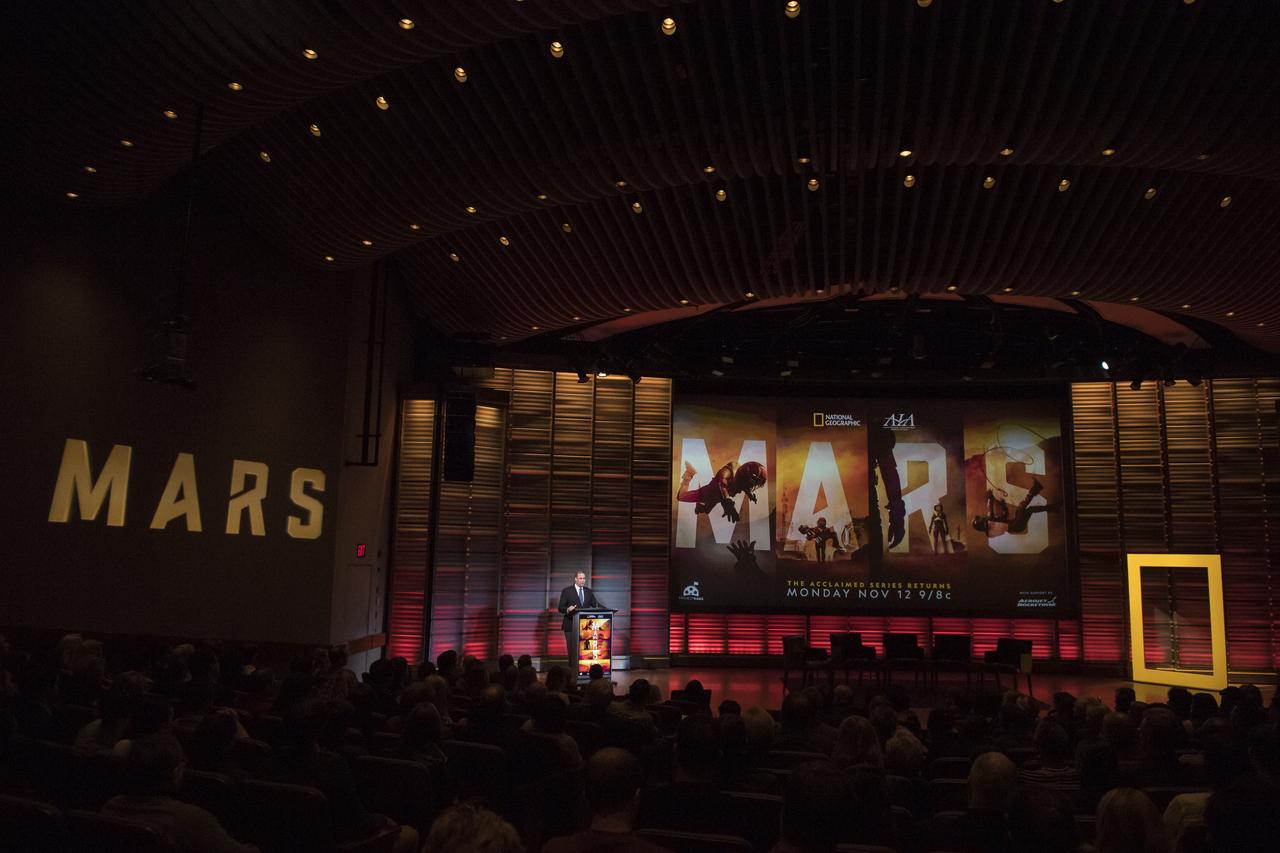

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine gives keynote remarks before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
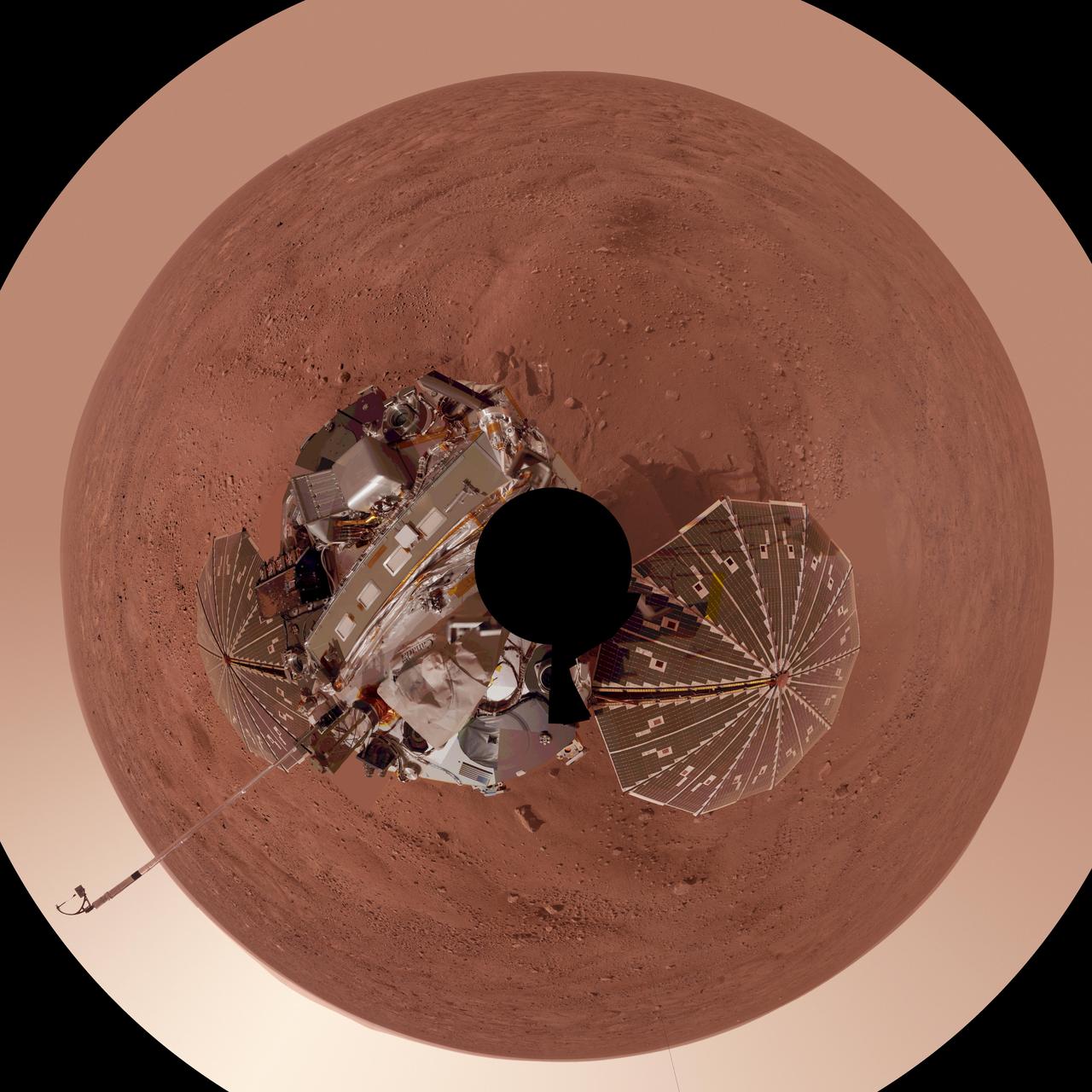
This view is a polar projection that combines more than 500 exposures taken by the Surface Stereo Imager camera on NASA Mars Phoenix Lander and projects them as if looking down from above.

From left to right, Eric Fanning, AIA President and CEO; Christyl Johnson, deputy director for technology and research investments, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center; Dr. Stephen Petranek, MARS scientific advisor and co-executive producer; Ellen Stofan, director, Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum; Gareth Edwards, film director, Rogue One: A Star Wars Story; and Chris Davenport, Washington Post space reporter pose for a photo before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films winners and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
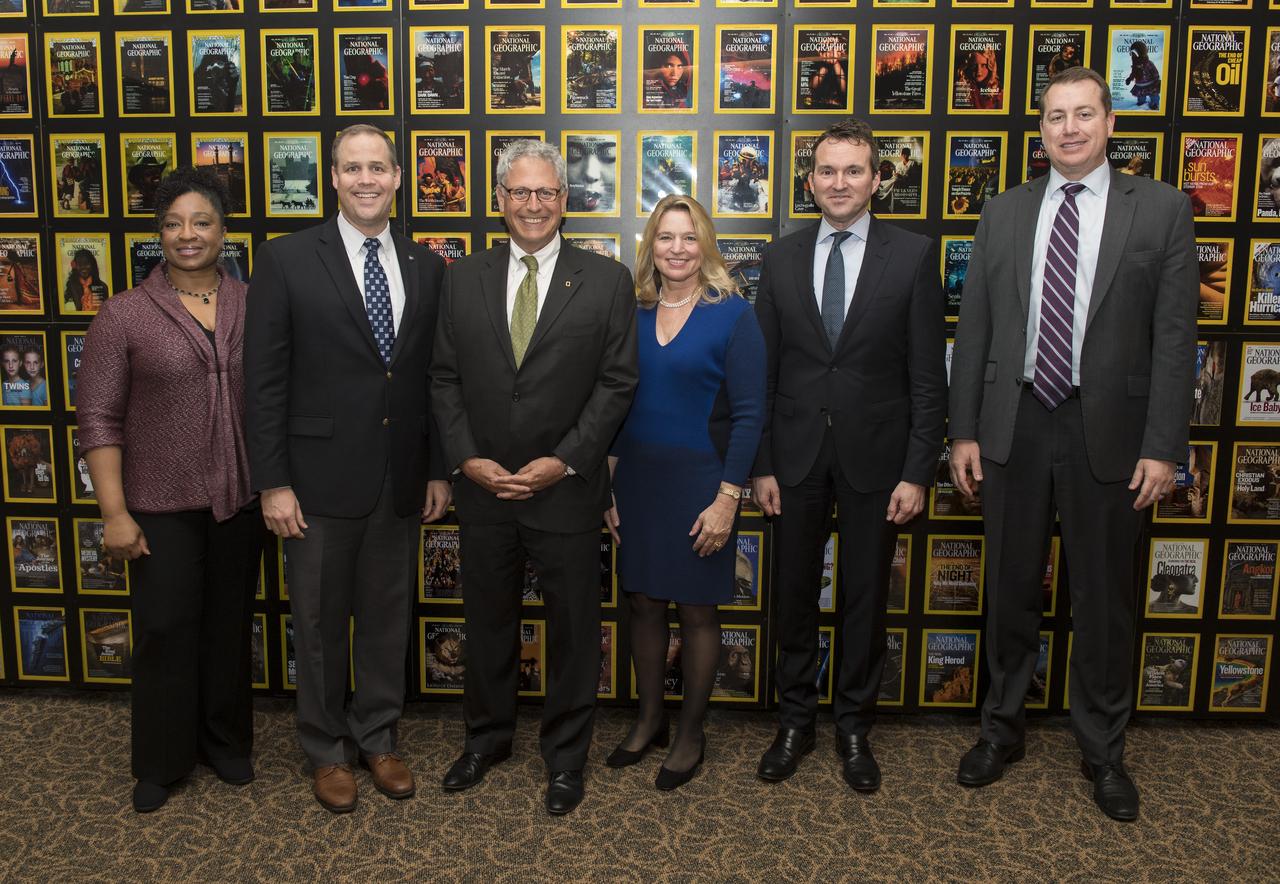

From left to right, Christyl Johnson, deputy director for technology and research investments, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center; NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine; Gary Knell, CEO, National Geographic Partners; Ellen Stofan, director, Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum; Eric Fanning, AIA President and CEO; and Jeff DeWitt, NASA Chief Financial Officer, pose for a photo before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films winners and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
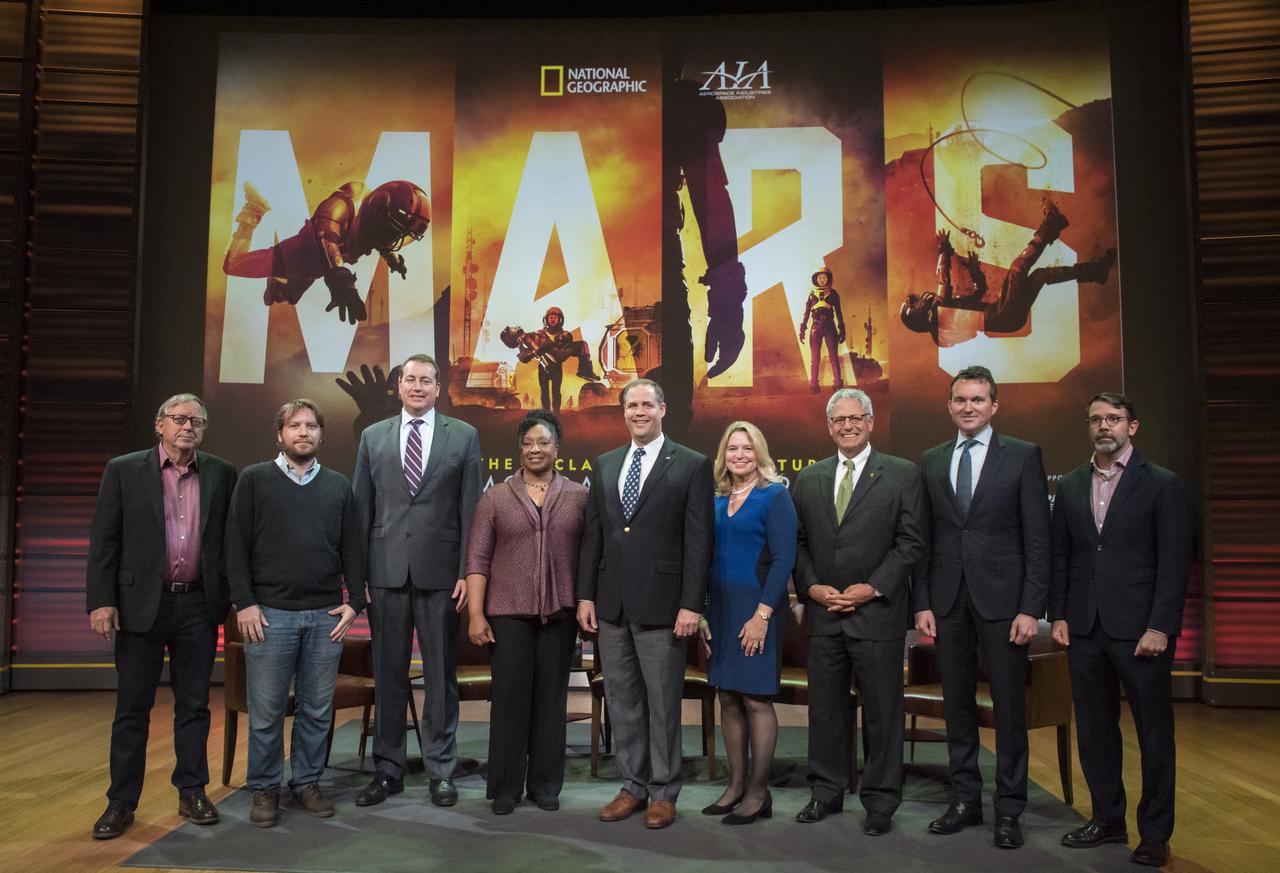

From left to right, Dr. Stephen Petranek, MARS scientific advisor and co-executive producer; Gareth Edwards, film director, Rogue One: A Star Wars Story; Jeff DeWitt, NASA chief financial officer; Christyl Johnson, deputy director for technology and research investments, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center; NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine; Ellen Stofan, director, Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum; Gary Knell, CEO, National Geographic Partners; Eric Fanning, AIA President and CEO; and Chris Davenport, Washington Post space reporter, pose for a photo before a showing of the Project Mars Competition's short films winners and the Mars series, Monday, November 5, 2018 at National Geographic Society Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
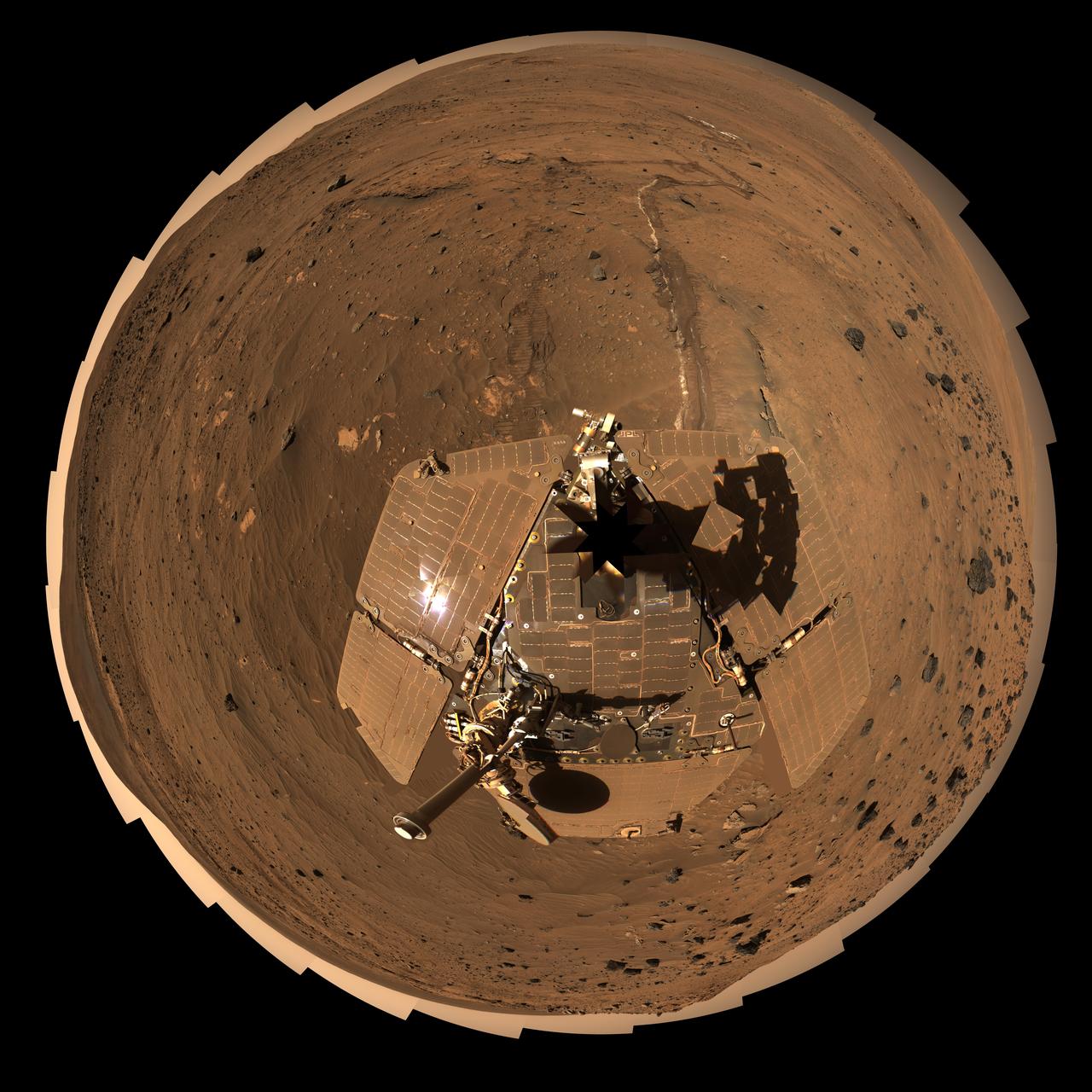

This self-portrait of NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit is a polar projection of the 360-degree McMurdo panorama made from images taken by Spirit from April through October 2006.
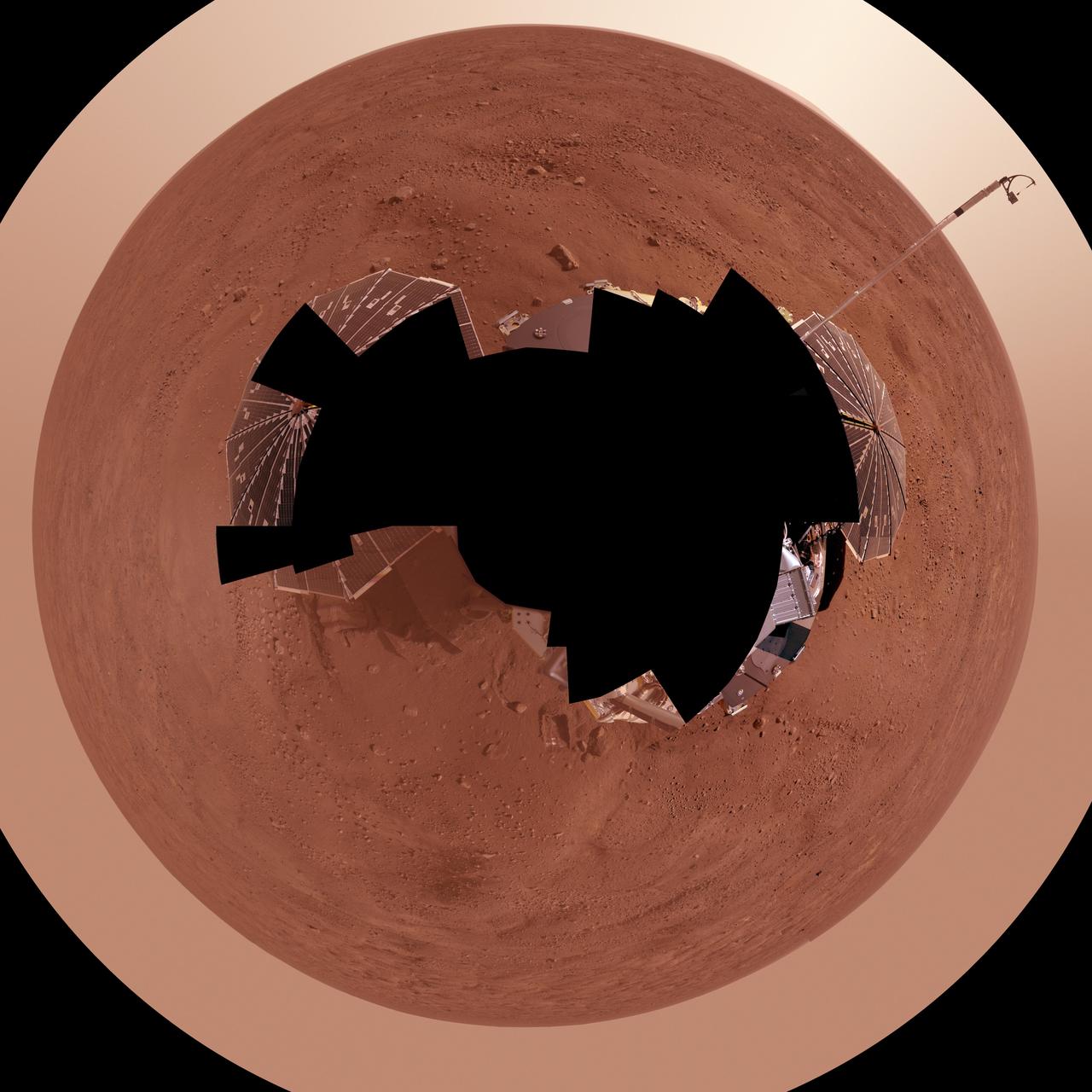
Full-Circle Color Panorama of Phoenix Landing Site on Northern Mars, Polar Projection
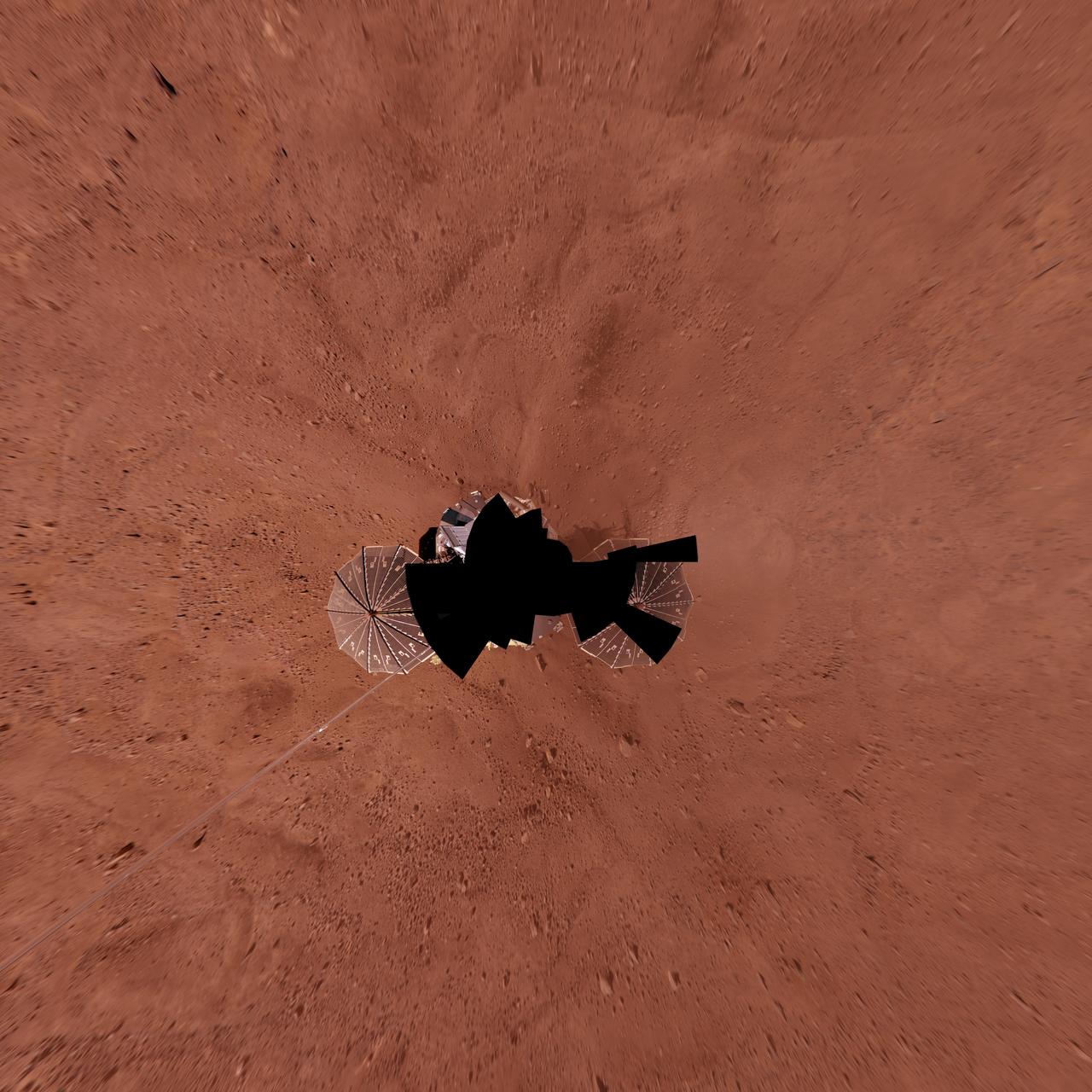

Full-Circle Color Panorama of Phoenix Landing Site on Northern Mars, Vertical Projection
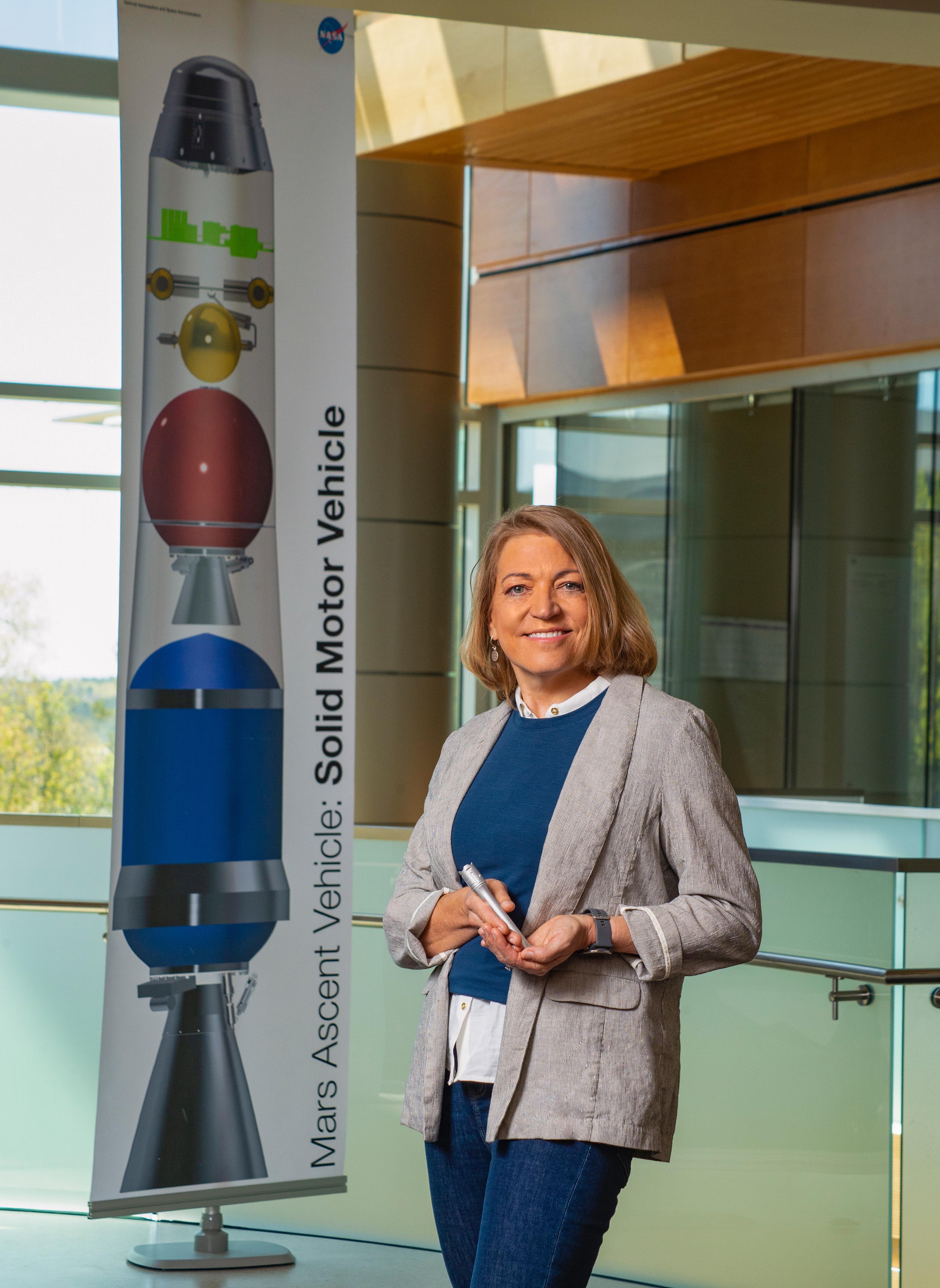

Angie Jackman, manager of the Mars Ascent Vehicle (MAV) project, holds a 3D-printed model of the tubes NASA's Perseverance rover is already filling with Martian rock and soil samples. Set to be the first rocket to launch from another planet, the MAV is designed to carry the sealed samples into orbit around Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25074

This self-portrait of NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit is a false color polar projection of the 360-degree McMurdo panorama made from images taken by Spirit from April through October 2006.
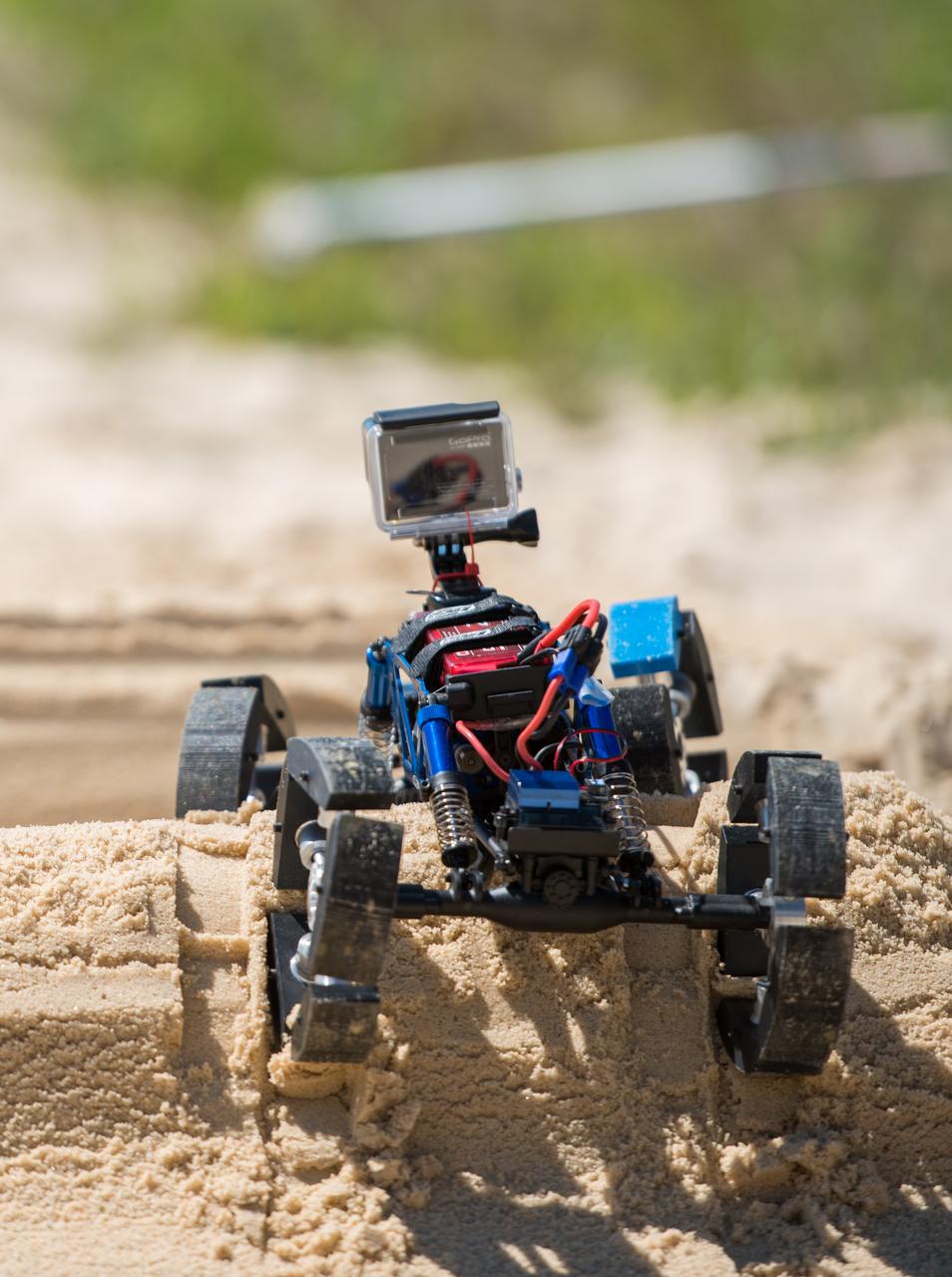

Toledo, Bowser and Scott High School Students, Mars and Moon Wheel, Engineering Design Project, Hardware Test on the Dunes
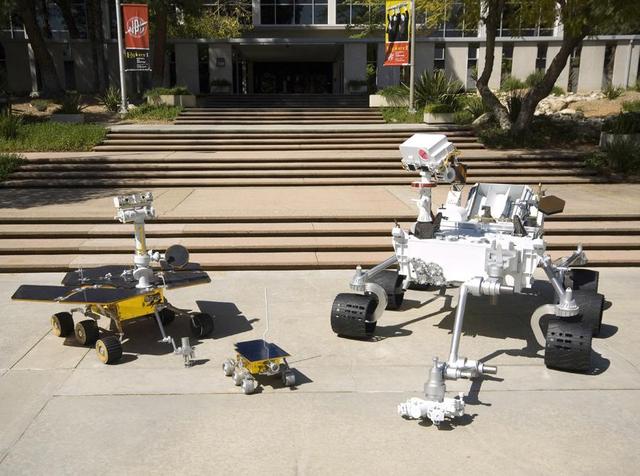

Full-scale models of three generations of NASA Mars rovers show the increase in size from the Sojourner rover of the Mars Pathfinder project, to the twin Mars Exploration Rovers Spirit and Opportunity, to the Mars Science Laboratory rover.
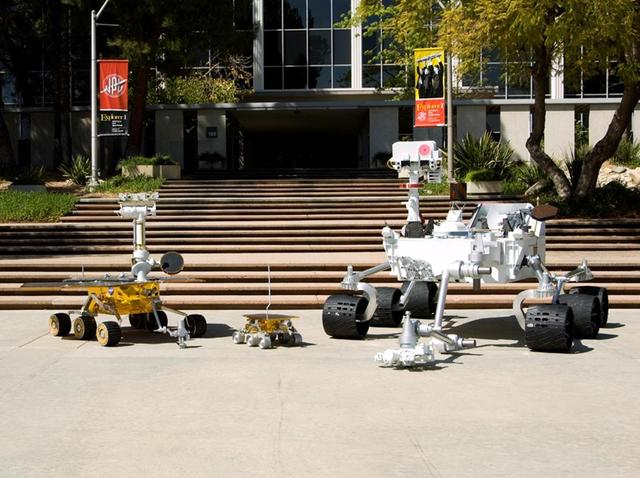

Full-scale models of three generations of NASA Mars rovers show the increase in size from the Sojourner rover of the Mars Pathfinder project, to the twin Mars Exploration Rovers Spirit and Opportunity, to the Mars Science Laboratory rover.
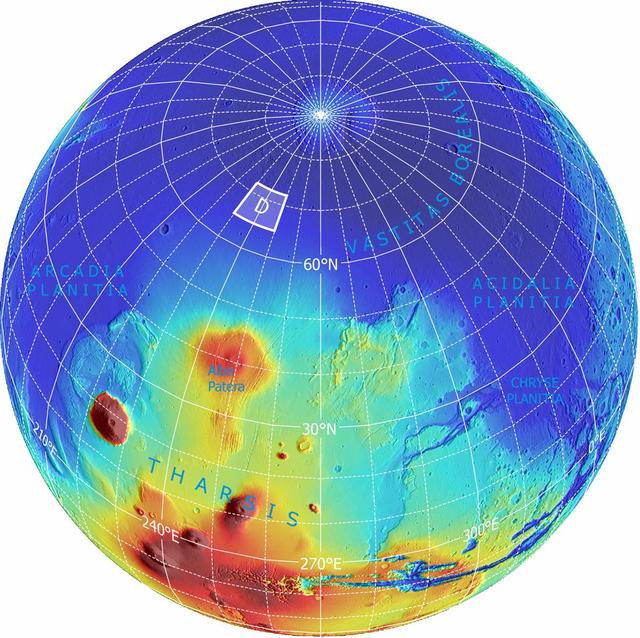
This is an orthographic projection with color-coded elevation contours and shaded relief based on data from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter on NASA Mars Global Surveyor orbiter.

Members of NASA's Mars 2020 project take a moment after attaching the remote sensing mast to the Mars 2020 rover. The image was taken on June 5, 2019, in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility's High Bay 1 clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23267

NASA Viking Project found a place in history when it became the first U.S. mission to land a spacecraft successfully on the surface of Mars.
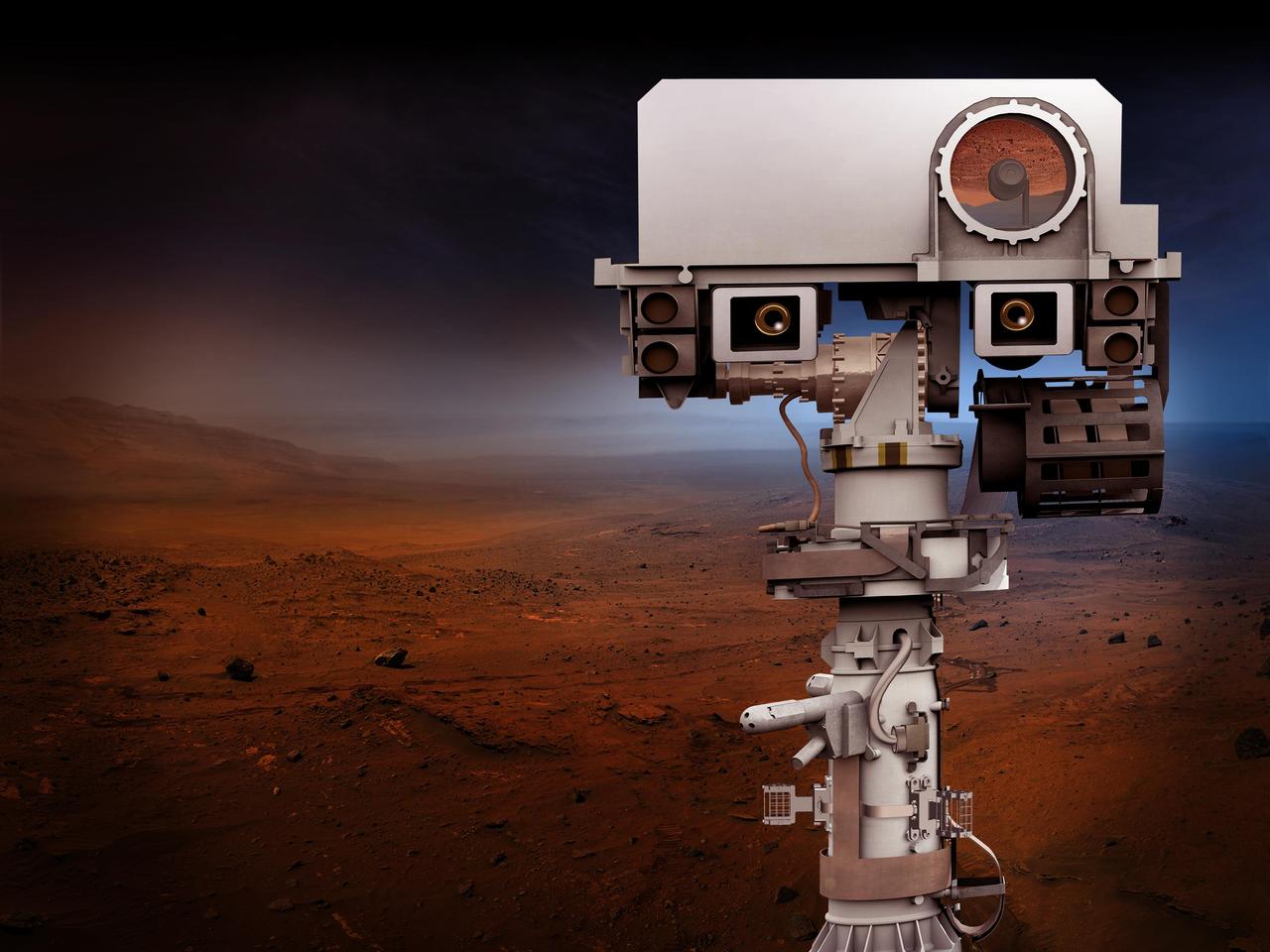

NASA's Mars 2020 Project will re-use the basic engineering of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory/Curiosity to send a different rover to Mars, with new objectives and instruments. This artist's concept depicts the top of the 2020 rover's mast. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20760
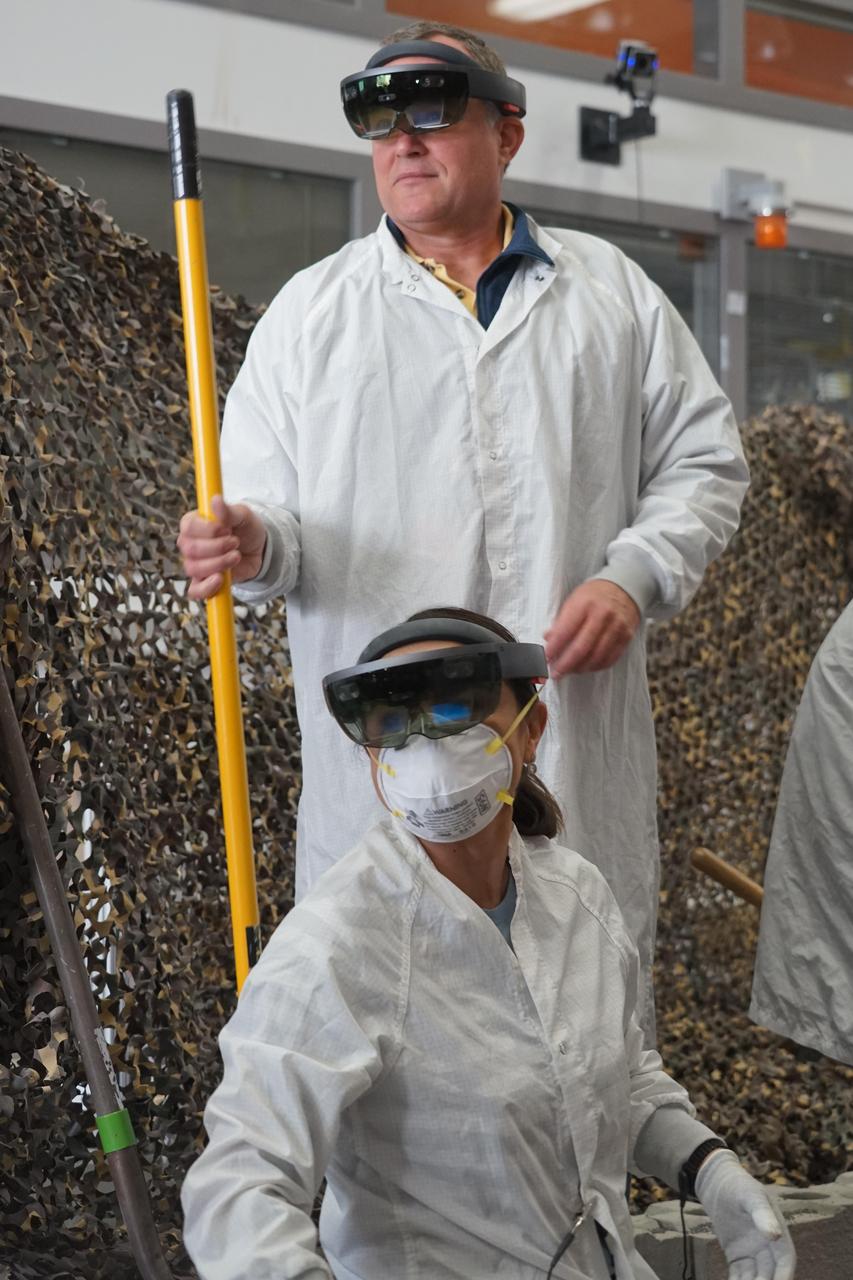

InSight Project Manager Tom Hoffman (standing) and engineer Marleen Sundgaard wear Microsoft HoloLens augmented reality headsets, which project digital terrain models of InSight's landing location on Mars over a lab space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22951

This view of Lyot Crater is a combined mapping by NASA Project Viking with elevation information from Mars Global Surveyor showing at least one of the nine craters in the northern lowlands of Mars with exposures of hydrated minerals detected from orbit.
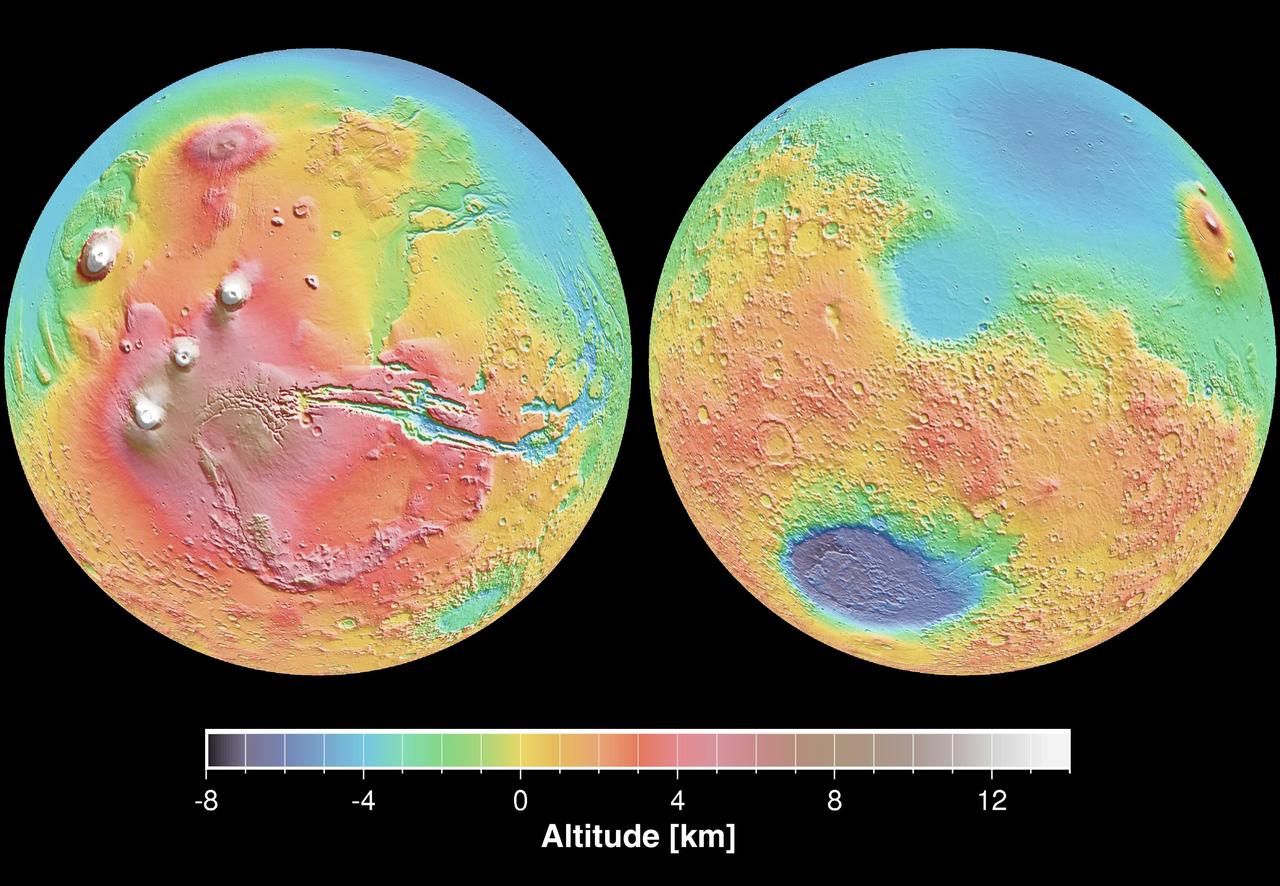
These maps are global false-color topographic views of Mars at different orientations from NASA Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter MOLA. The maps are orthographic projections that contain over 200,000,000 points and about 5,000,000 altimetric crossovers.
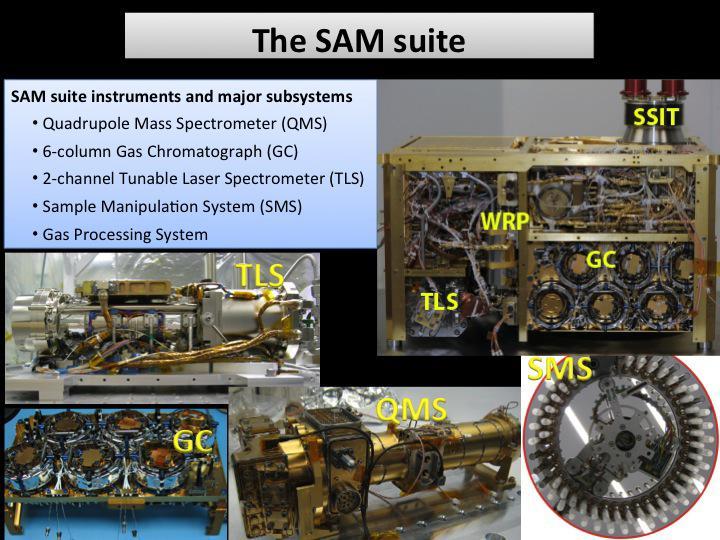
This illustration shows the instruments and subsystems of the Sample Analysis at Mars SAM suite on the Curiosity Rover of NASA Mars Science Laboratory Project. SAM analyzes the gases in the Martian atmosphere.
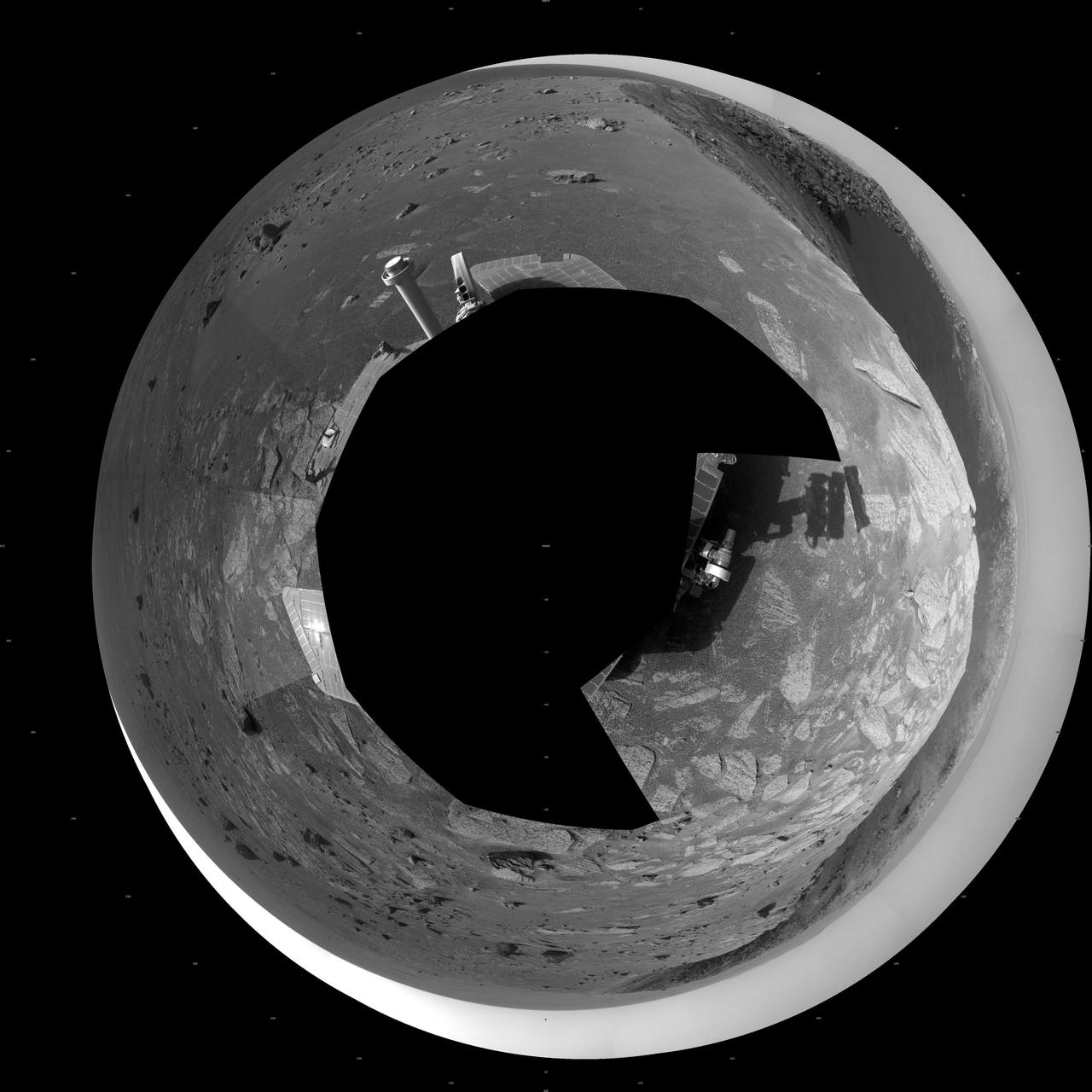

A football-field-size crater, informally named Santa Maria, dominates the scene in this polar projection from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity.
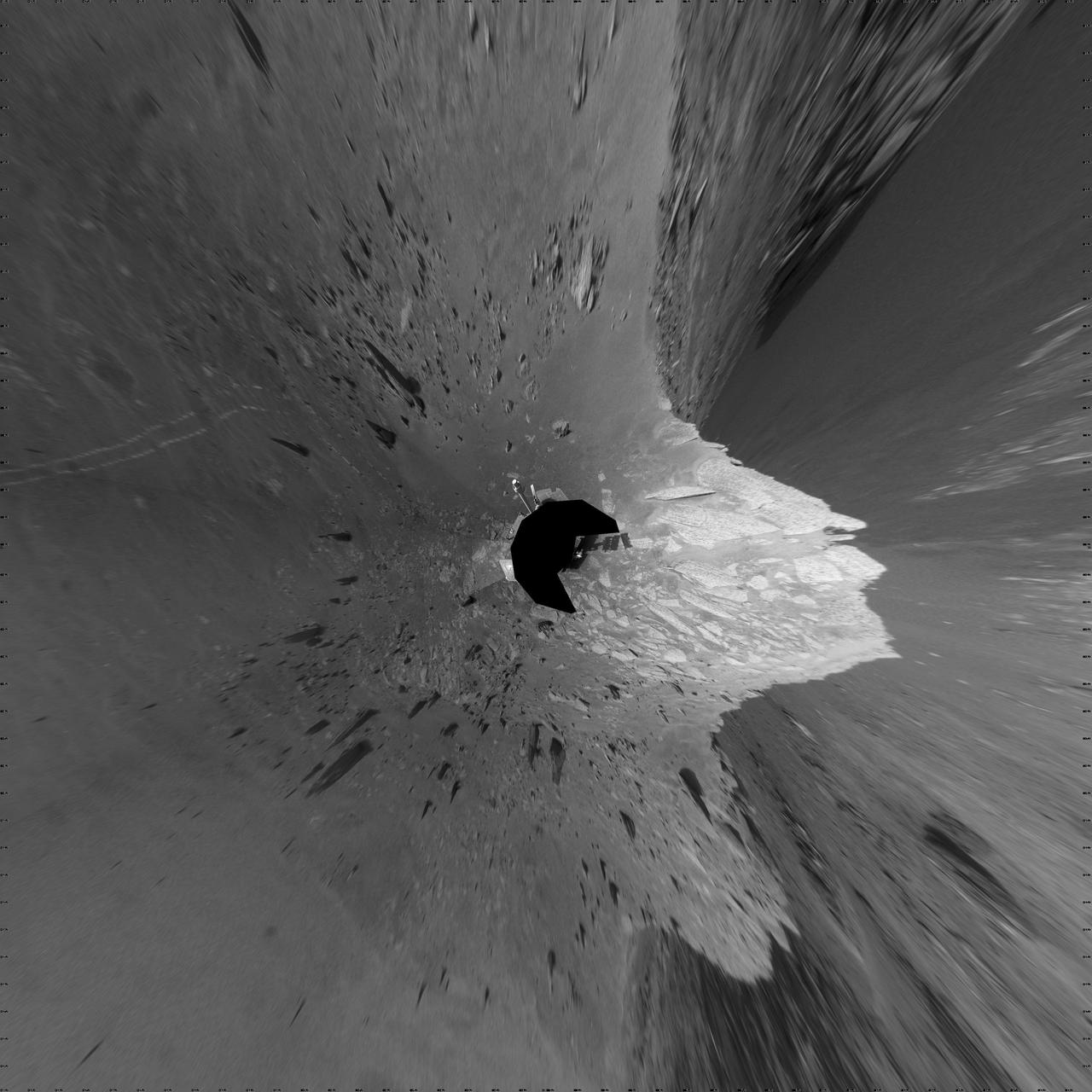

This vertical projection view is of a football-field-size crater, informally named Santa Maria, as seen by NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity.
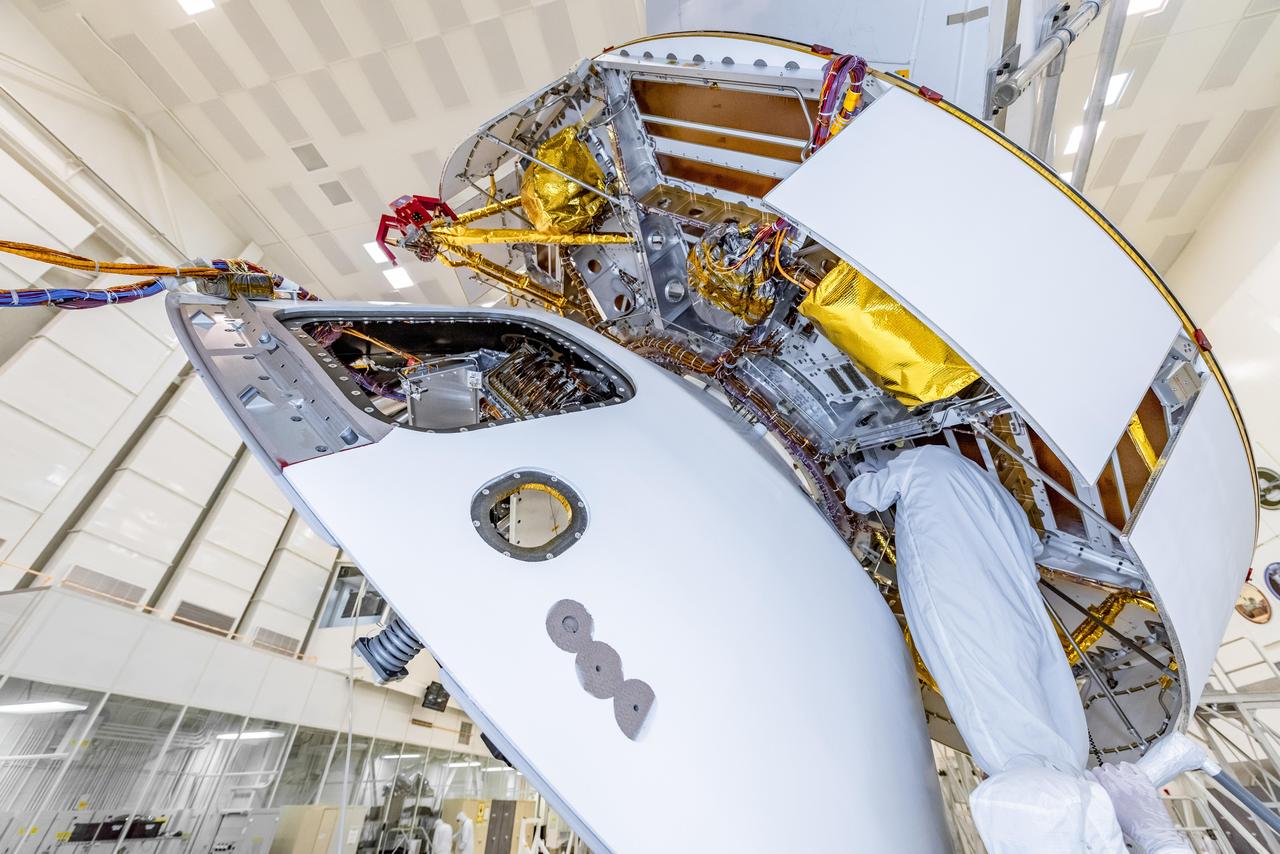

A member of NASA's Mars 2020 project checks connections between the spacecraft's back shell and cruise stage. The image was taken on March 26, 2019, in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility's High Bay 1 clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, California. During the mission's voyage to Mars, the cruise stage houses the hardware that steers and provides power to the spacecraft. The back shell, along with the heatshield (not pictured), protects the 2020 rover and the sky crane landing system during Mars atmospheric entry. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23163

Bob Balaram, Teddy Tzanetos and Havard Grip from the NASA Mars Helicopter project discuss the sequence of events for the day's flight testing. The image was taken Jan. 18, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23162
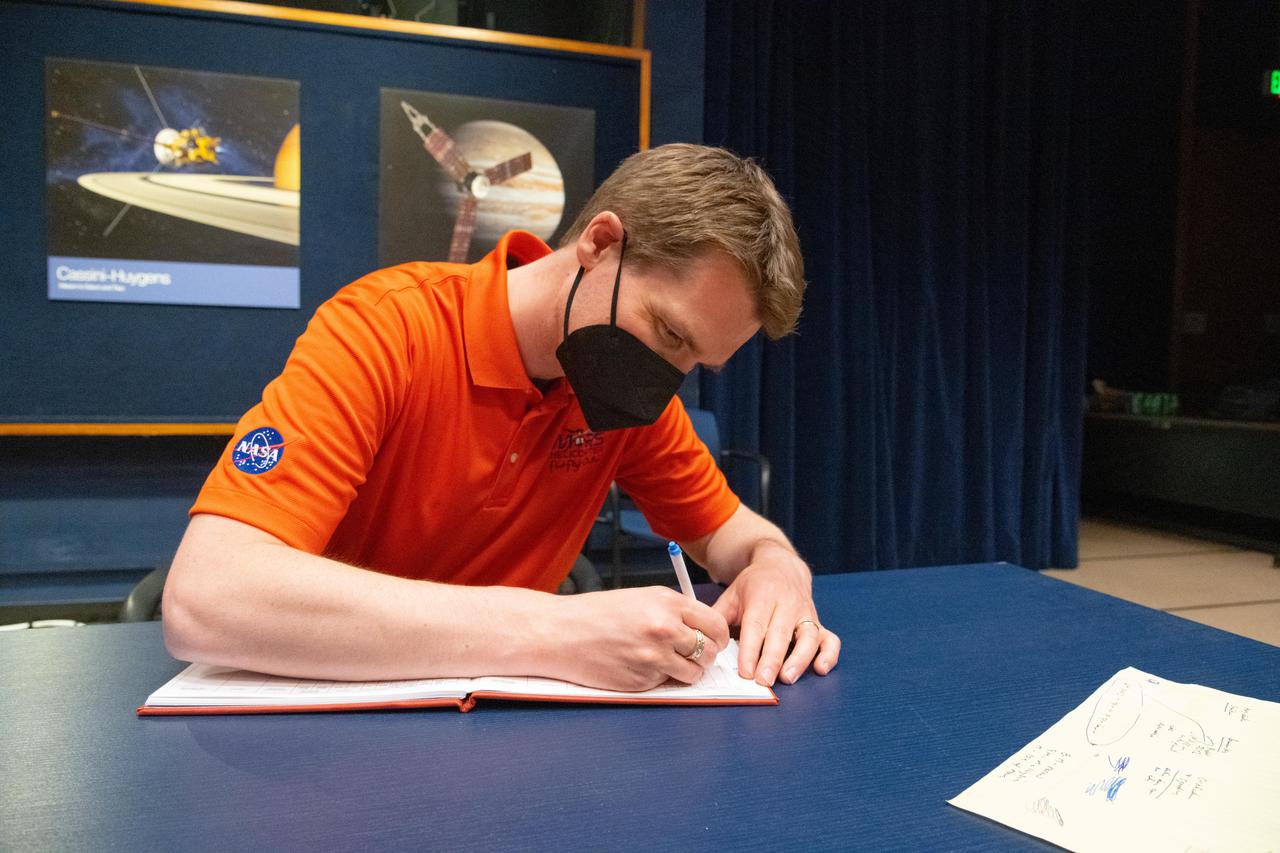

Ingenuity Mars chief pilot Håvard Grip records data of the first flight of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter into the official pilot's logbook for the project — the "Nominal Pilot's Logbook for Planets and Moons." The image was taken at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on April 19, 2021. Pilot logbooks are used by aviators to provide a record of their flights, including current and accumulated flight time, number and locations of takeoffs and landings, as well as unique operating conditions and certifications. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24591
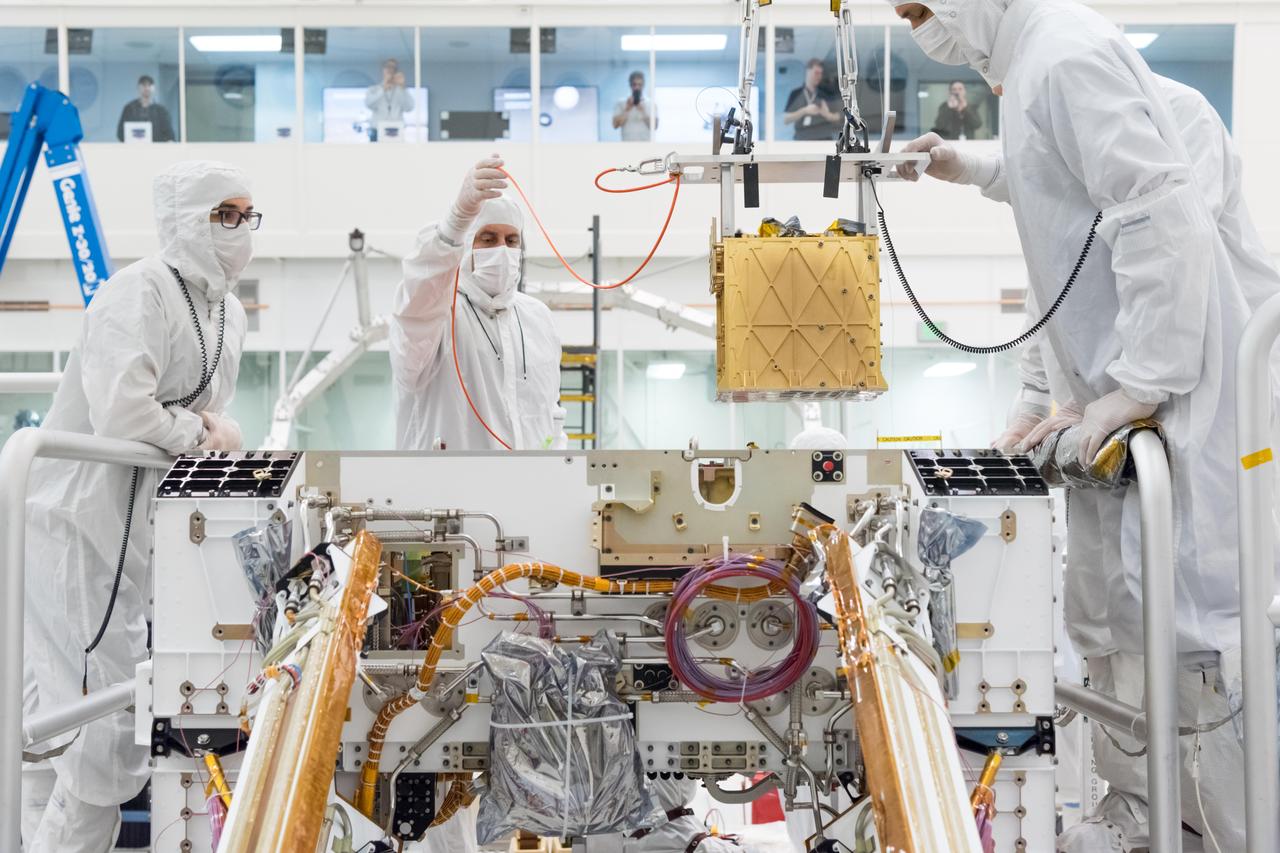
Members of NASA's Mars 2020 project install the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) into the chassis of NASA's next Mars rover. MOXIE will demonstrate a way that future explorers might produce oxygen from the Martian atmosphere for propellant and for breathing. The car-battery-sized instrument does this by collecting carbon dioxide (CO2) from the Martian atmosphere and electrochemically splitting the carbon dioxide molecules into oxygen and carbon monoxide molecules. The oxygen is then analyzed for purity before being vented back out to the Martian atmosphere along with the carbon monoxide and other exhaust products. The image was taken on March 20, 2019, in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility's High Bay 1 Cleanroom at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23154
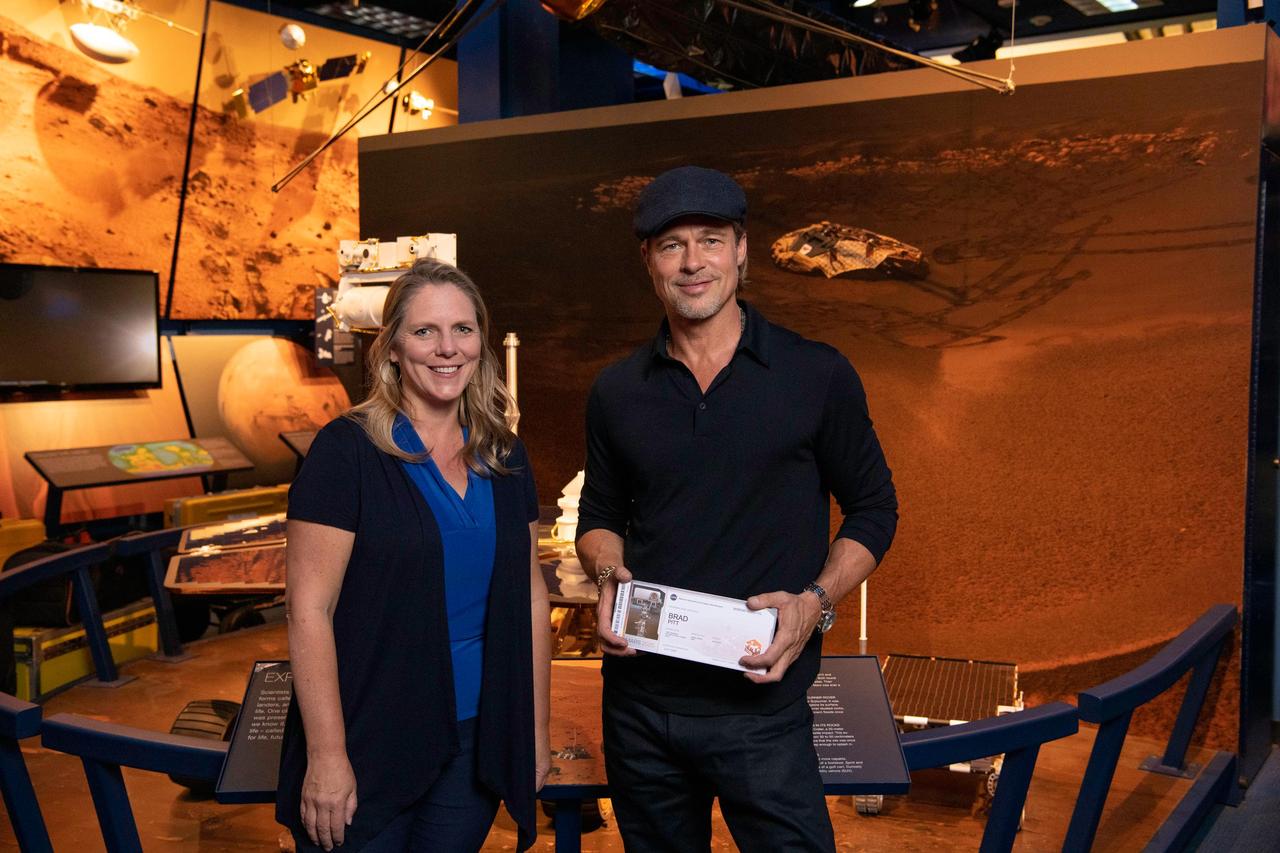

The actor Brad Pitt (right) shows off his "boarding pass" for Mars with Jennifer Trosper (left), the Mars 2020 project systems engineer and a veteran of several NASA Mars missions, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, on Sept. 6, 2019. Members of the public can join the actor in sending their names to Mars aboard NASA's Mars 2020 rover at https://go.nasa.gov/mars2020pass. Names can be submitted until Sept. 30, 2019. Pitt visited JPL to learn about real space technology after filming his space-themed movie "Ad Astra." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23279
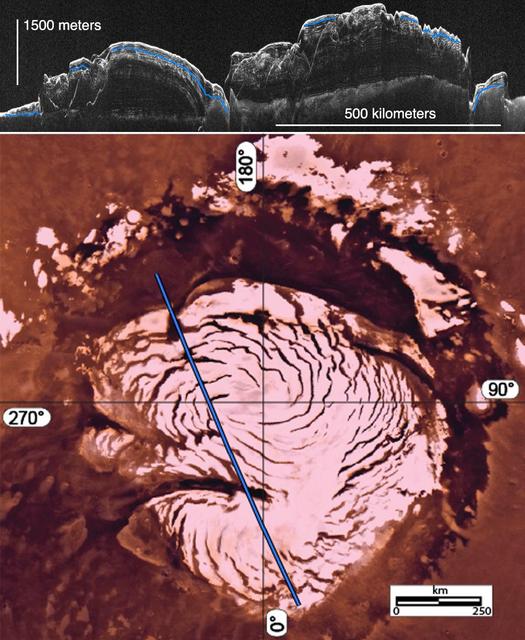
This image montage features a two-dimensional radar cross section of Mars north polar cap collected by SHARAD instrument on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft top, and a color image mosaic of the polar cap from NASA Viking project bottom
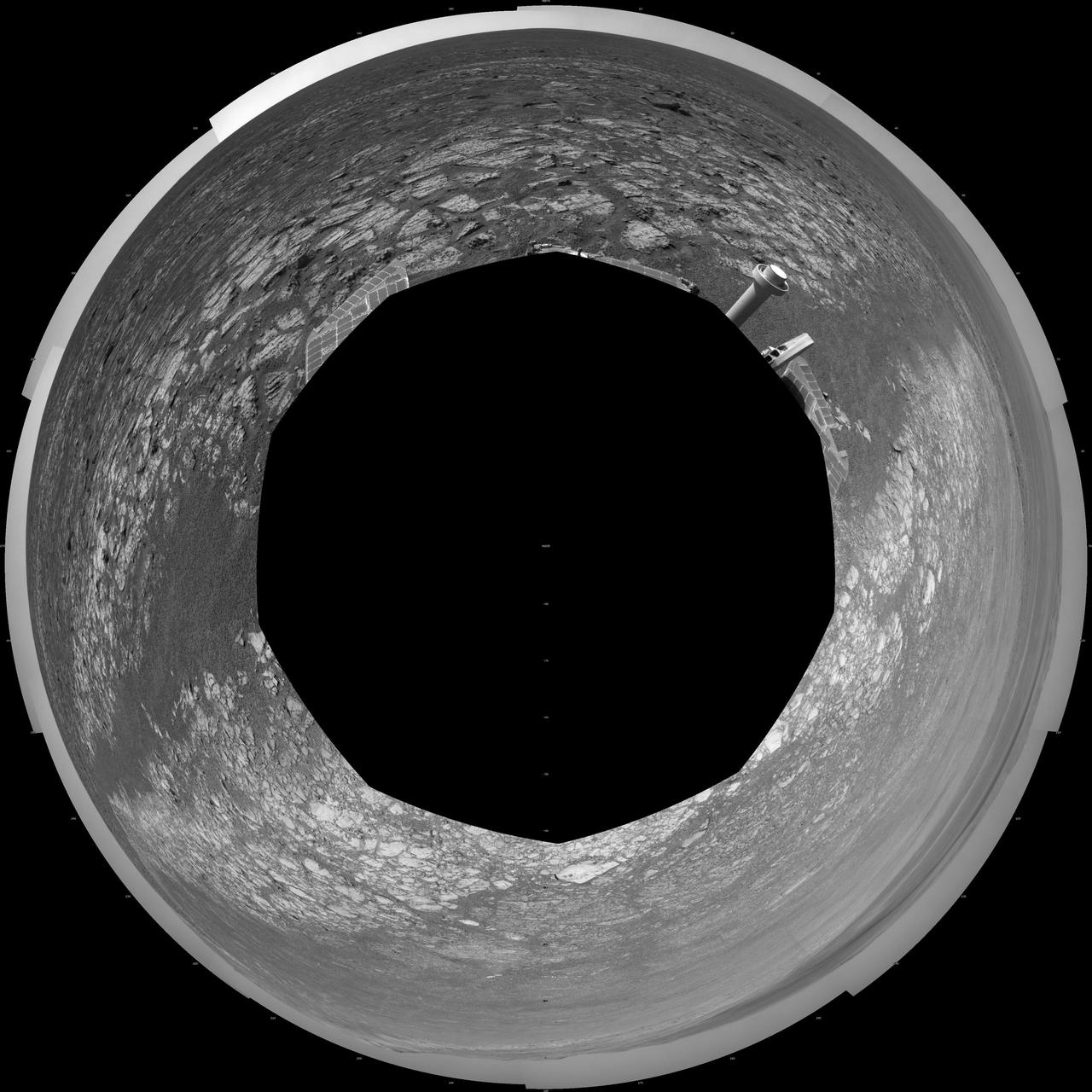
This 360-degree polar projection was assembled from images taken by the navigation camera on NASA Mars Exporation Rover Opportunity shows terrain surrounding the position where the rover spent its 3,000th Martian day.
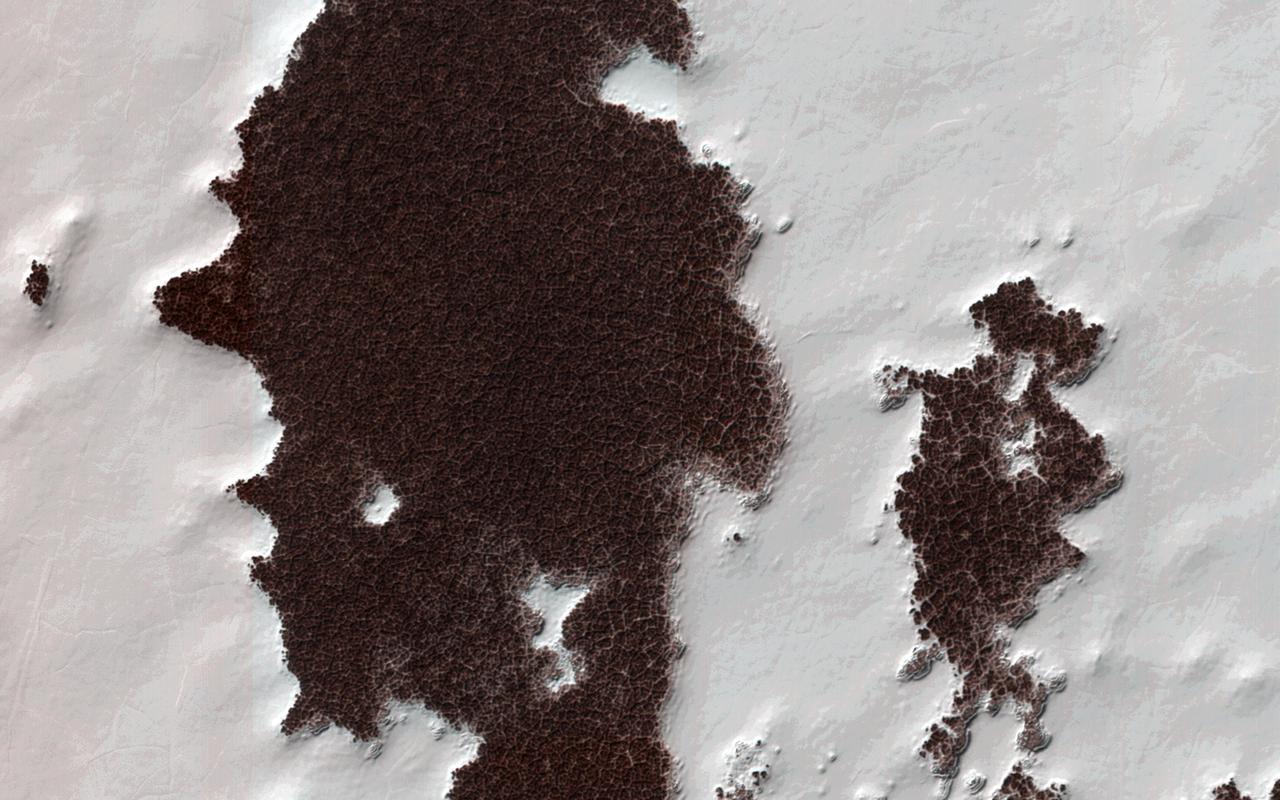

The white portions of this observation are part of the South Polar residual ice cap, with the sunlight is coming from roughly the bottom of this non-map projected image captured by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
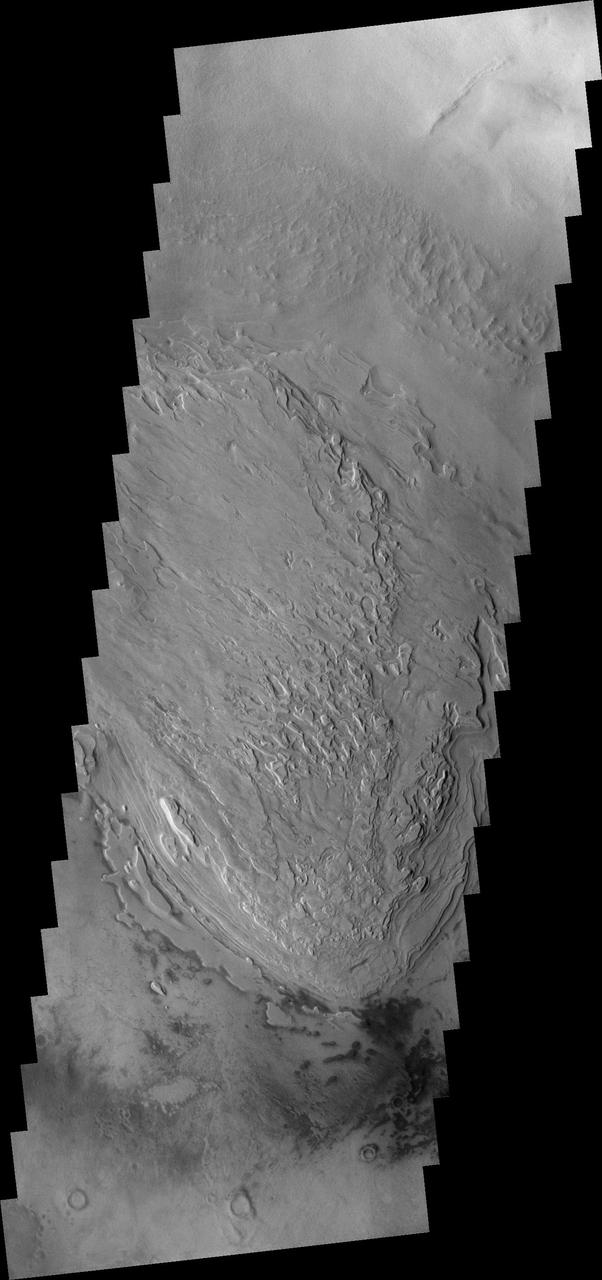

Taken by one of the Mars Student Imaging Project MSIP teams, these are the unusual floor deposits in Spallanzani Crater. The wind may have affected the surface of the layered deposit. Small dunes have formed near the southern margin
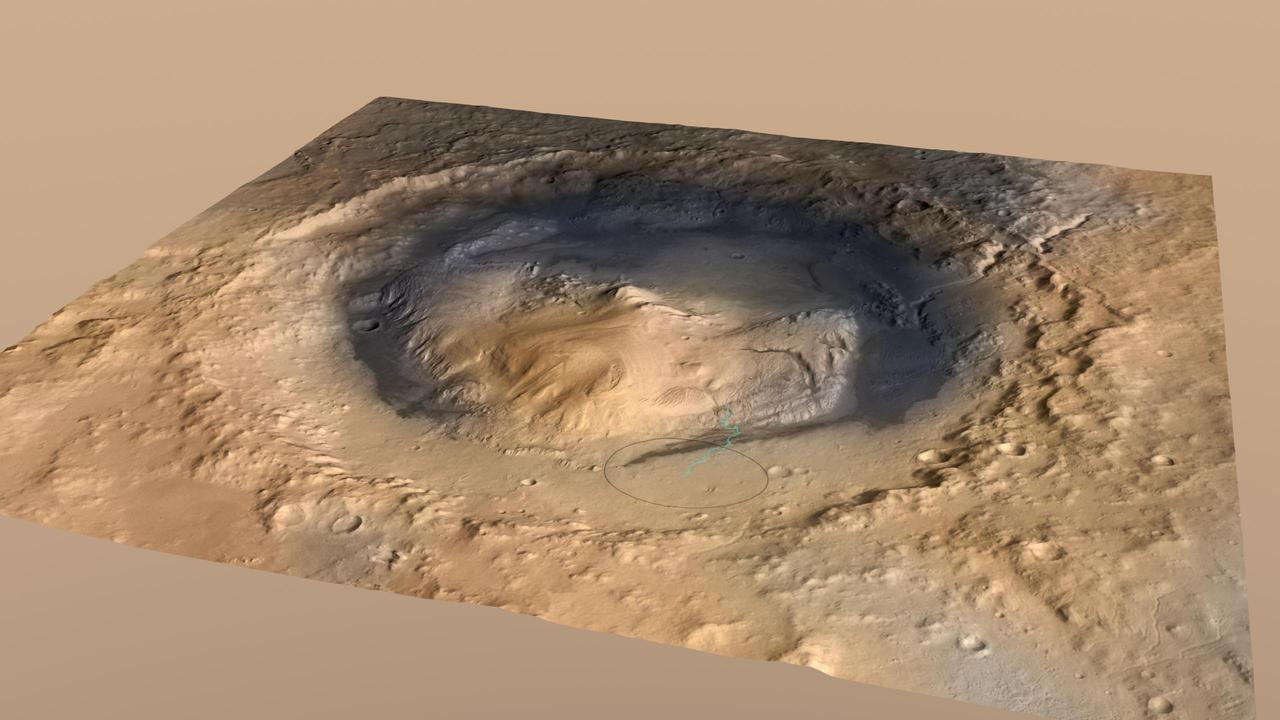

Curiosity, the big rover of NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission, will land in August 2012 near the foot of a mountain inside Gale Crater. The mission project science group is calling the mountain Mount Sharp.

This 360-degree mosaic of images from the navigation camera on NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity shows the view from the western rim of Santa Maria crater is presented as a vertical projection, with north at the top.
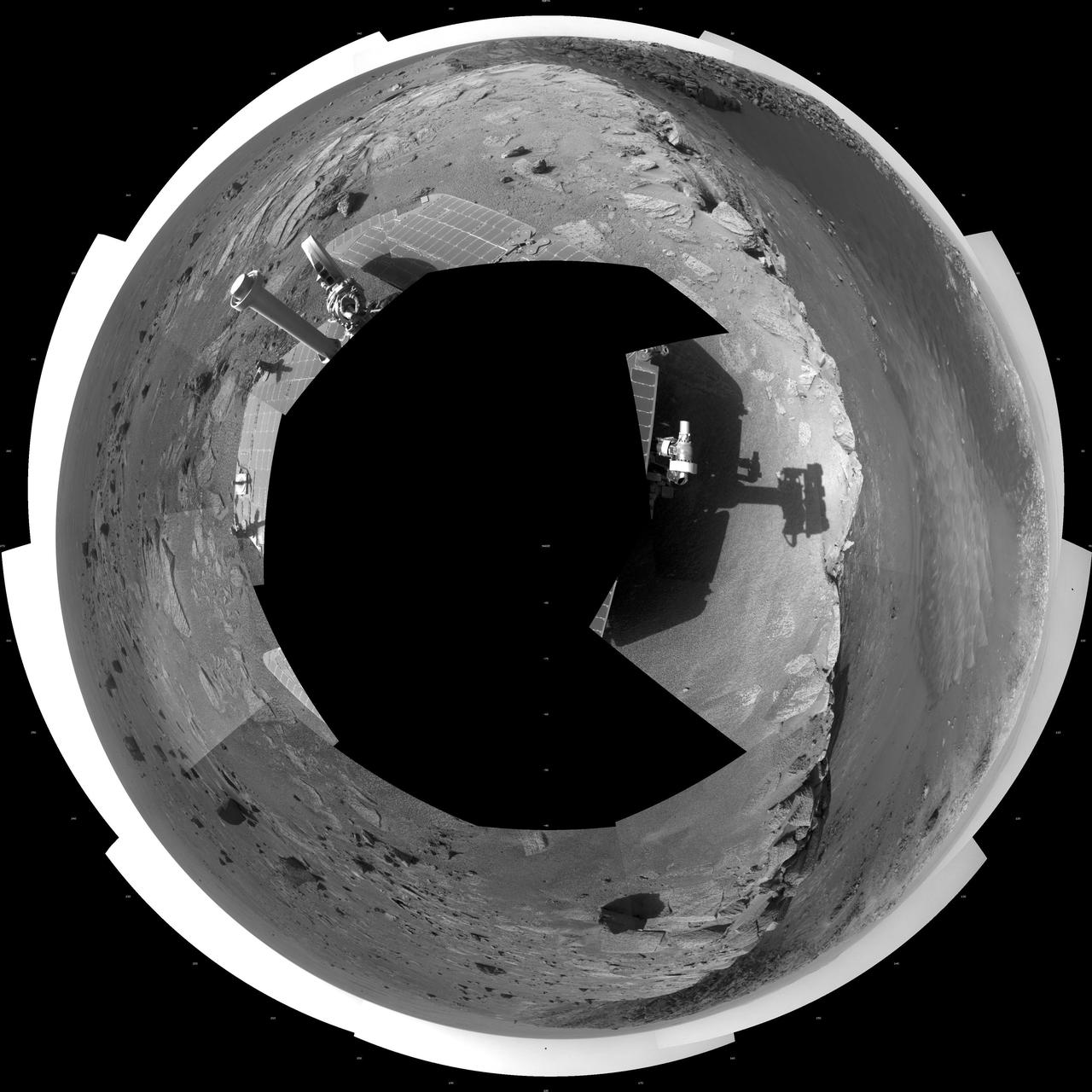

This 360-degree mosaic of images from the navigation camera on NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity shows the view from the western rim of Santa Maria crater is presented as a polar projection, with north at the top.
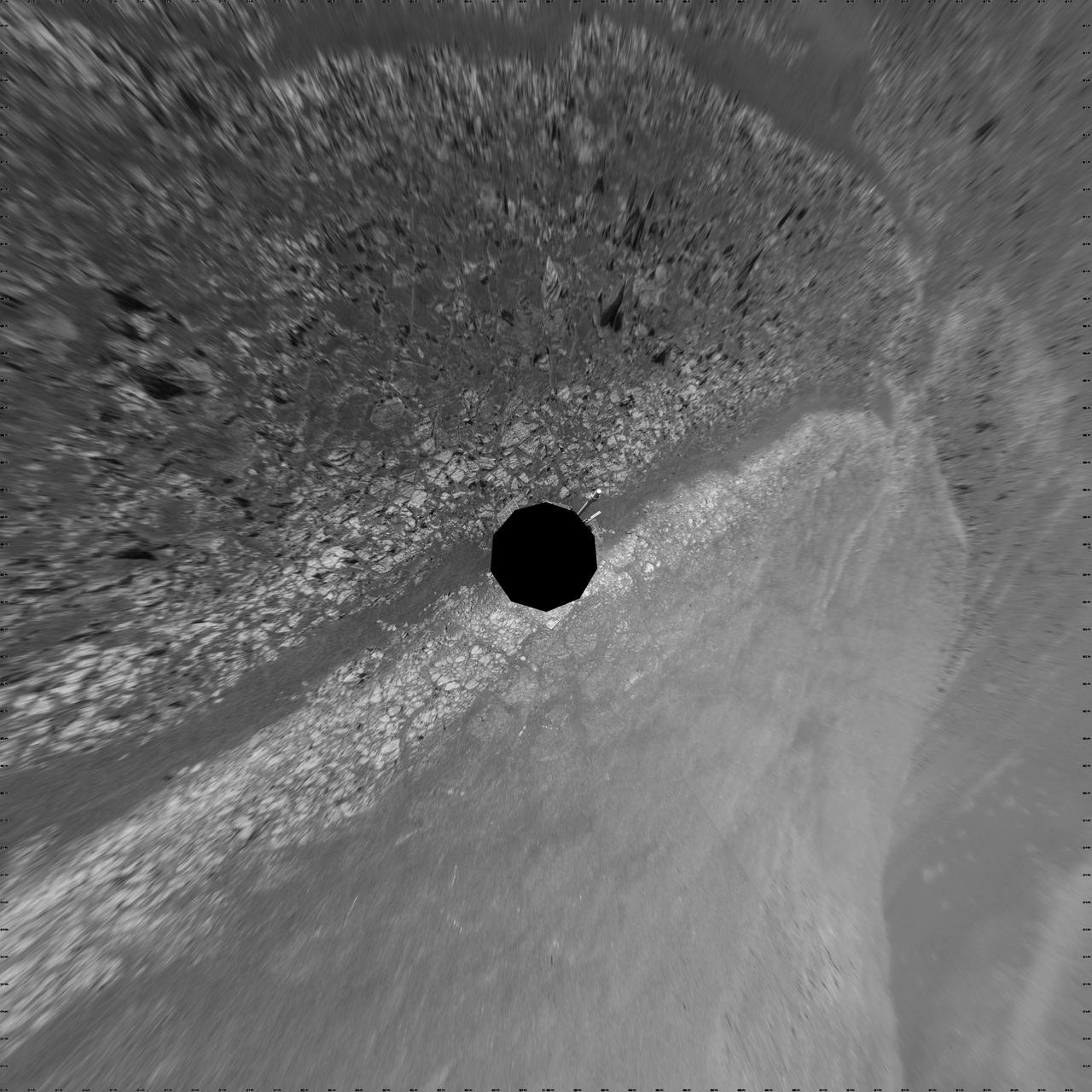

This 360-degree vertical projection was assembled from images taken by the navigation camera on NASA Mars Exporation Rover Opportunity shows terrain surrounding the position where the rover spent its 3,000th Martian day.
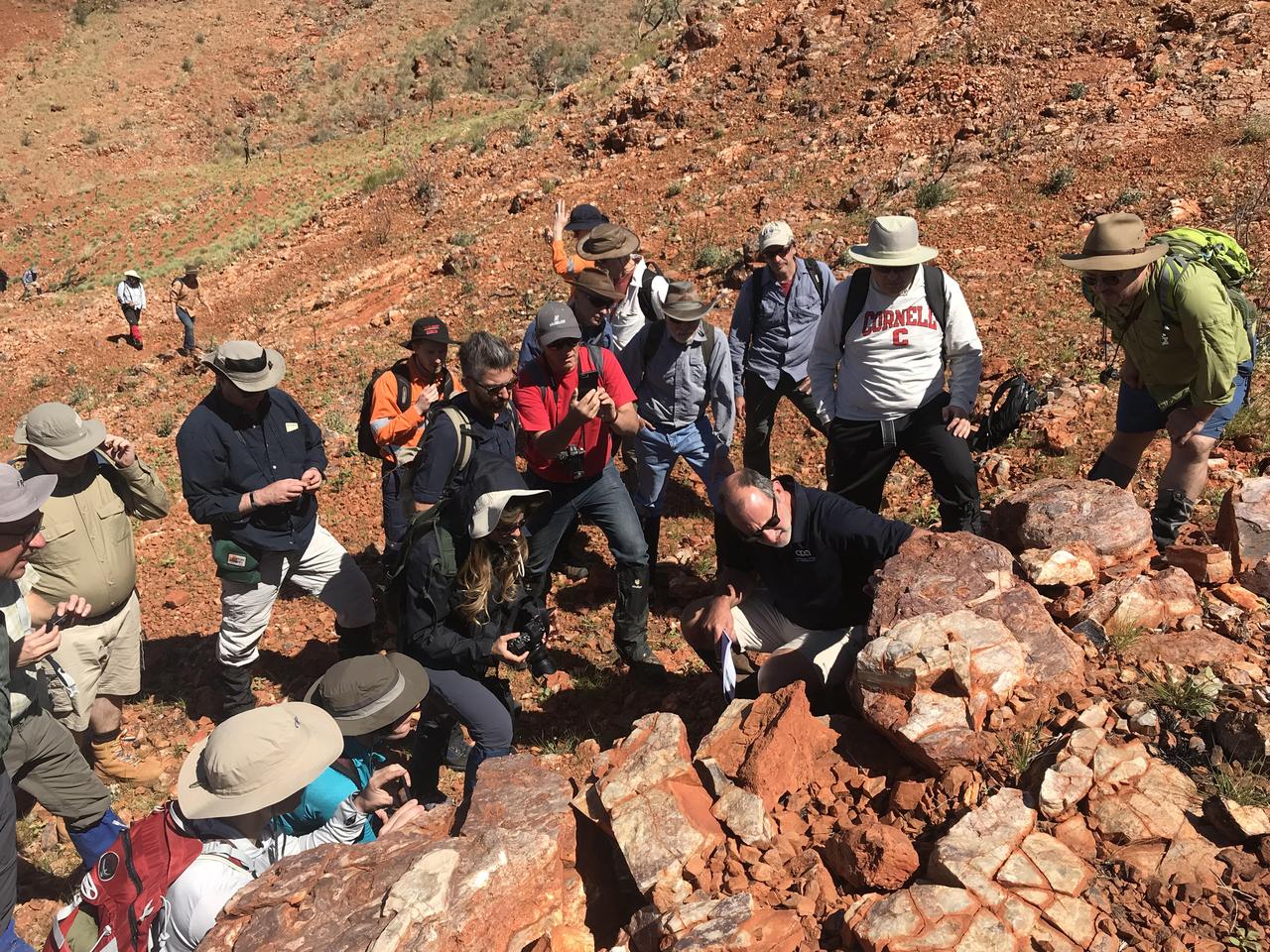

Scientists from NASA's Mars 2020 and ESA's ExoMars projects study stromatolites, the oldest confirmed fossilized lifeforms on Earth, in the Pilbara region of North West Australia. The image was taken on Aug. 19, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23551
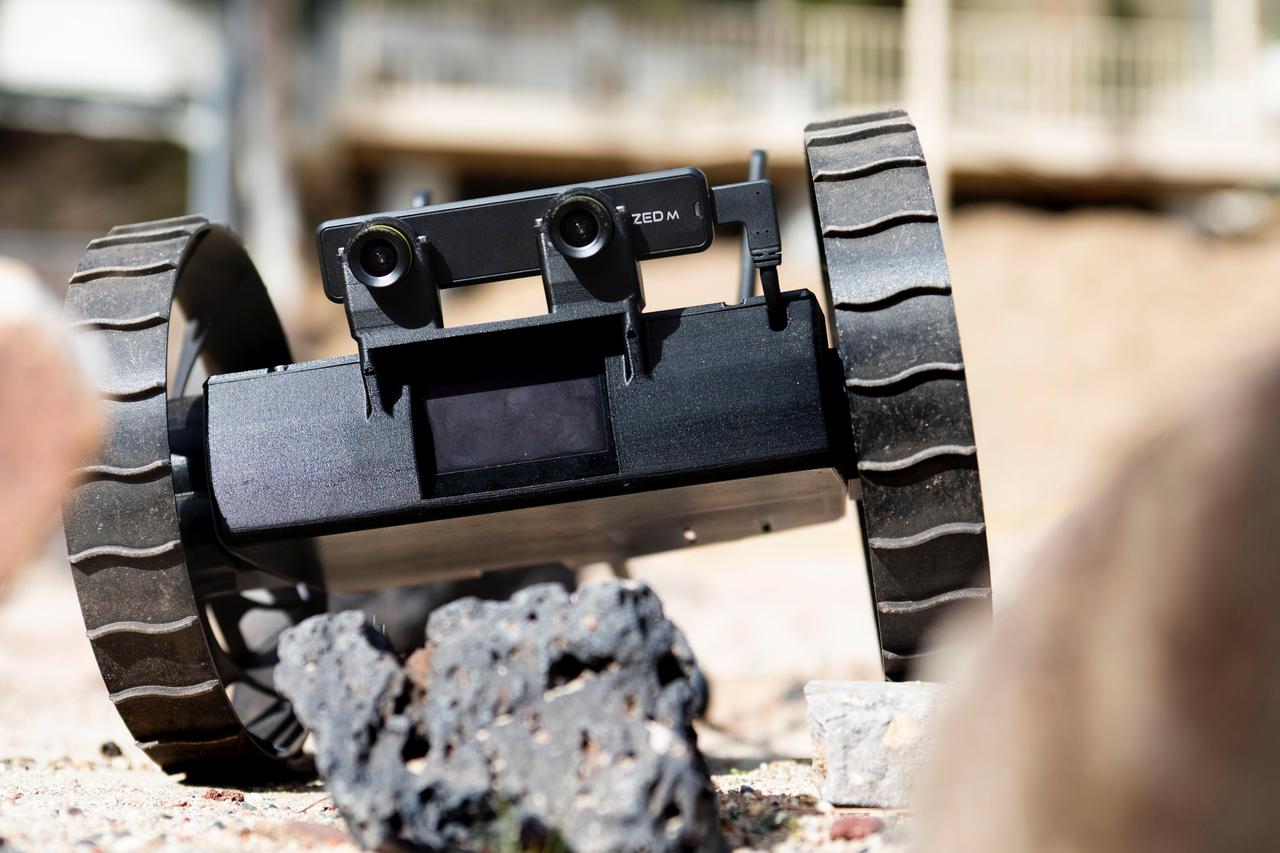

A shoebox-sized wheeled robot explores the rugged terrain on the surface of the Mars Yard at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory during recent tests of the Autonomous Pop-Up Flat Folding Explorer Robot (A-PUFFER) project. The robots are designed to work in groups, and could form roving teams of small robots that might one day explore the surface of the Moon or Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23793
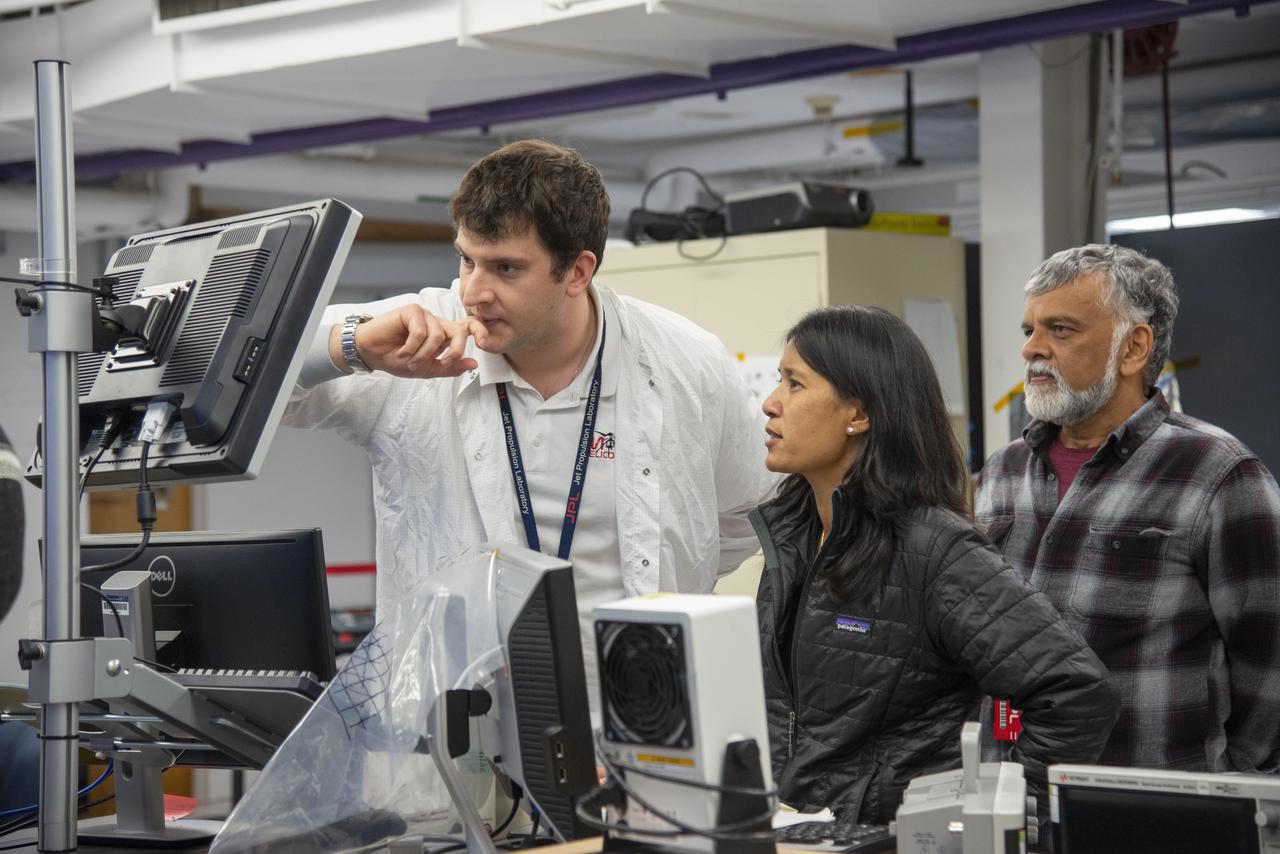

Teddy Tzanetos, MiMi Aung and Bob Balaram of NASA's Mars Helicopter project observe a flight test. The image was taken on Jan. 18, 2019 as the flight model of the Mars Helicopter was tested in the Space Simulator, a 25-foot-wide (7.62 meter-wide) vacuum chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23161
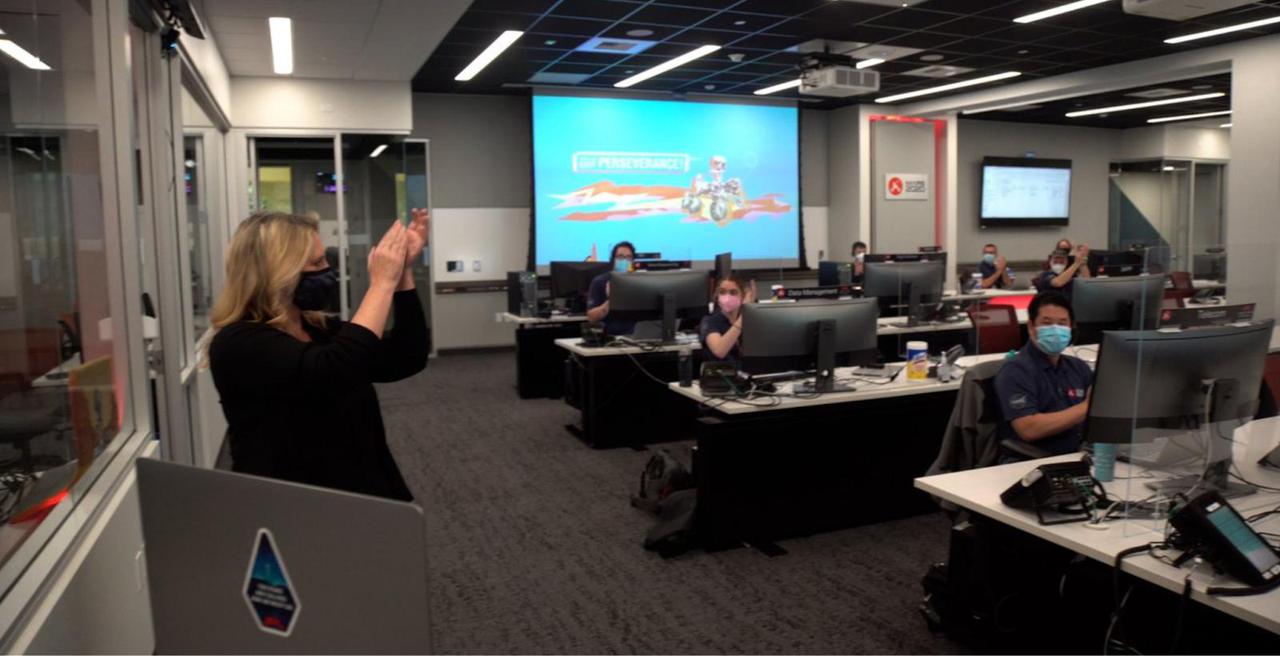

Jennifer Trosper, Mars Perseverance project manager, leads rover team members at JPL in a round of applause for students who were honored through the "You've Got Perseverance" campaign for overcoming obstacles in pursuit of their educational goals. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25272
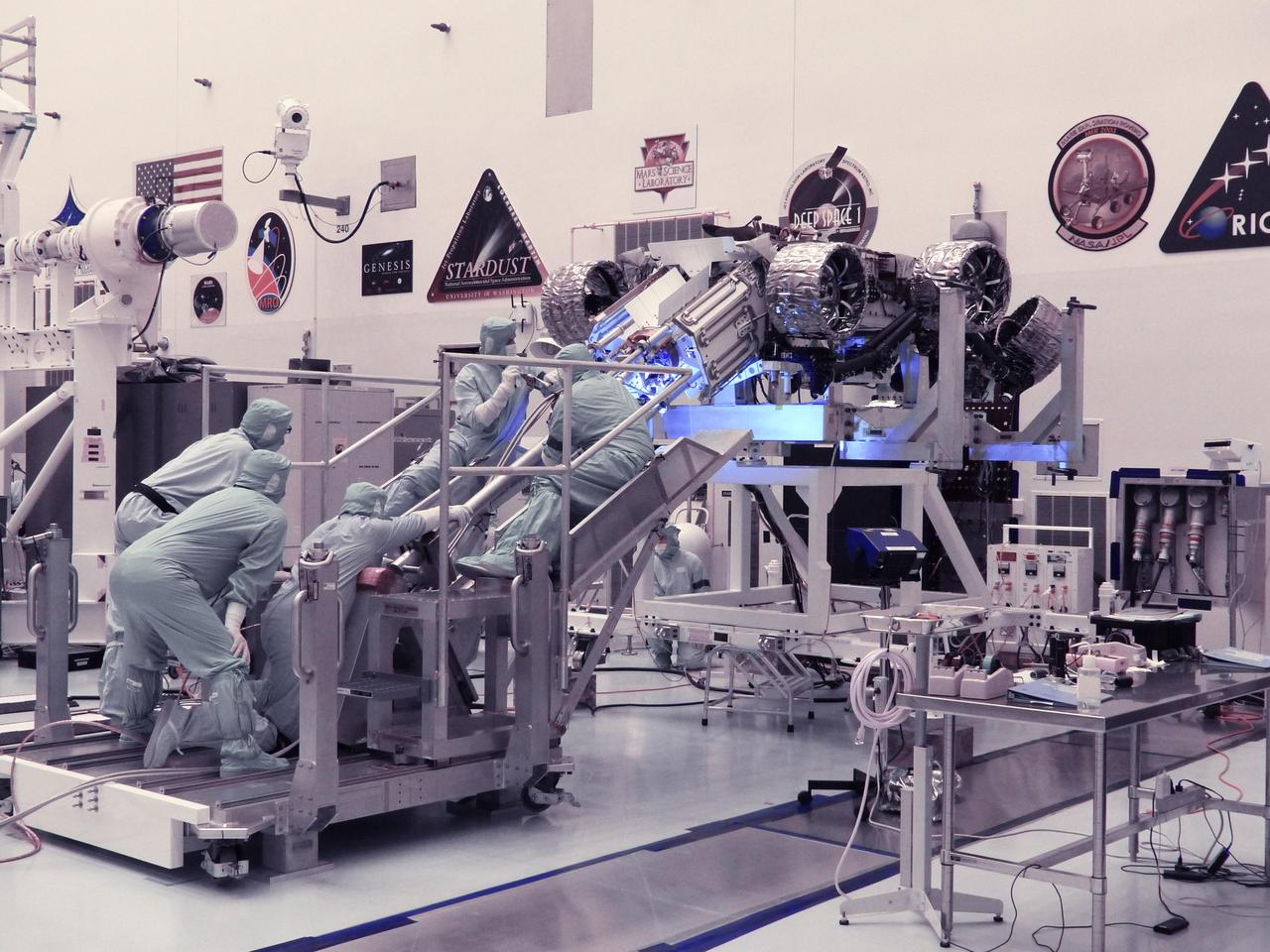
Technicians in the payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida perform a fit check between NASA'S Mars 2020 Perseverance rover and its Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator on April 16-17, 2020. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is designed and built by the U.S. Department of Energy, and provided to NASA as part of the space agency's Radioisotope Power Systems Program. It arrived at NASA KSC in April 2020 following its final assembly and transport from the Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory. The fit check is the first time that the fueled flight generator is connected to the rover. After the successful fit check, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator was disconnected; it will be connected to the rover for the final time on the launch pad atop the mission's Atlas V launch vehicle in July, before the planned launch of the Mars 2020 mission. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is a space nuclear power system that produces about 110 watts of electrical power to run the rover's systems and science instruments, and extra heat to keep them warm during the frigid Martian nights and winter seasons. It converts the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium dioxide into electricity using thermocouples with no moving parts. The choice of a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator as the rover's power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover's landing site and in planning its surface operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23827
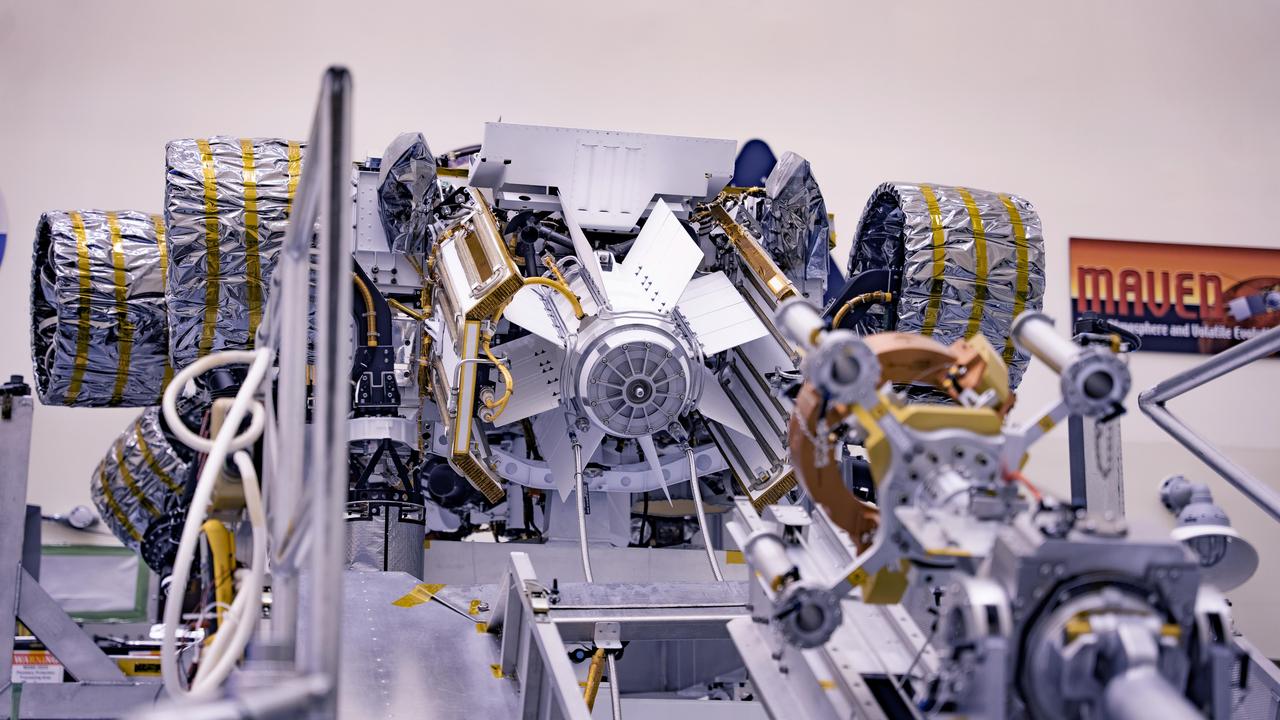
The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator for NASA'S Mars 2020 Perseverance rover is shown during a fit check with the rover in a payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 16-17, 2020. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is designed and built by the U.S. Department of Energy, and provided to NASA as part of the space agency's Radioisotope Power Systems Program. It arrived at NASA KSC in April 2020 following its final assembly and transport from the Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory. The fit check is the first time that the fueled flight generator is connected to the rover. After the successful fit check, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator was disconnected; it will be connected to the rover for the final time on the launch pad atop the mission's Atlas V launch vehicle in July, before the planned launch of the Mars 2020 mission. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is a space nuclear power system that produces about 110 watts of electrical power to run the rover's systems and science instruments, and extra heat to keep them warm during the frigid Martian nights and winter seasons. It converts the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium dioxide into electricity using thermocouples with no moving parts. The choice of a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator as the rover's power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover's landing site and in planning its surface operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23981
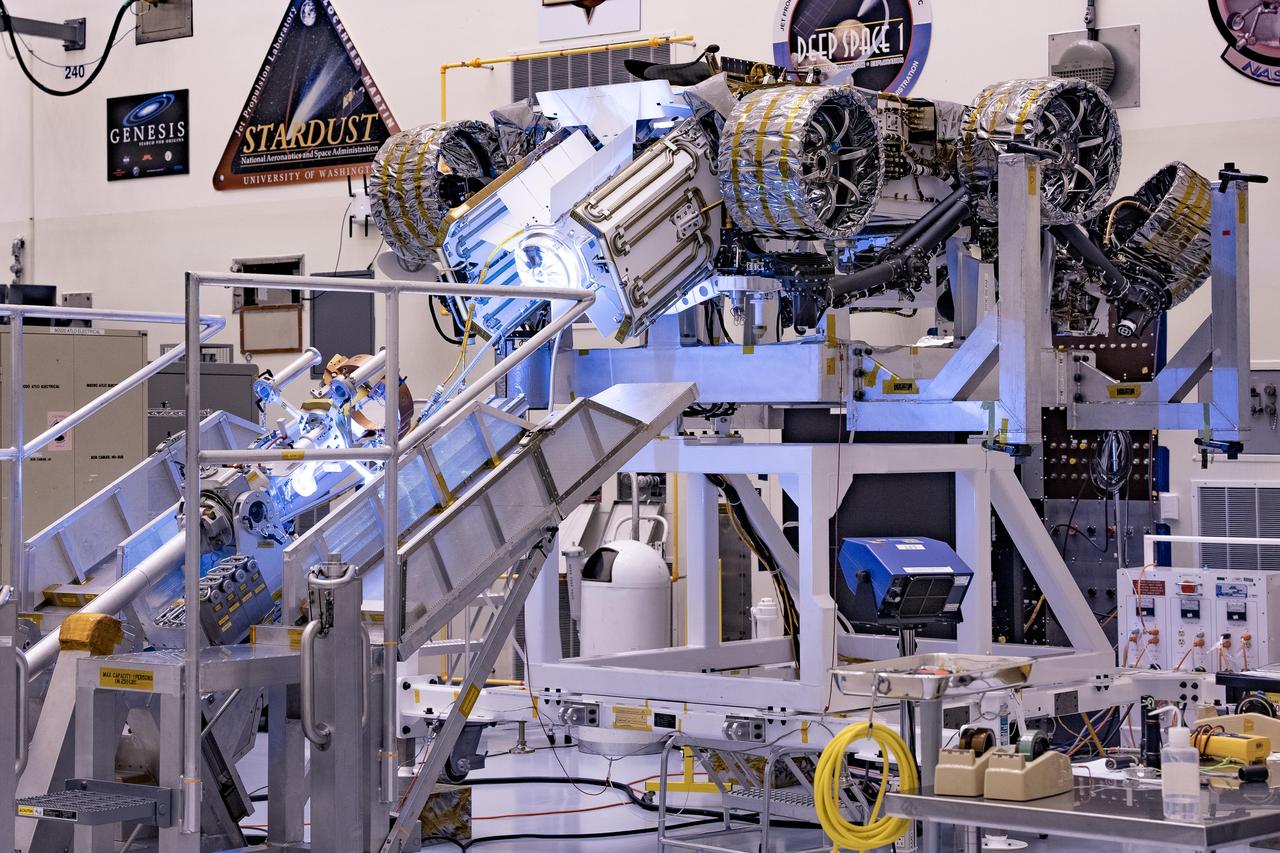

This image shows the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator for NASA'S Mars 2020 Perseverance rover during a fit check with the rover in the payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 16-17, 2020. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is designed and built by the U.S. Department of Energy, and provided to NASA as part of the space agency's Radioisotope Power Systems Program. It arrived at NASA KSC in April 2020 following its final assembly and transport from the Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory. The fit check is the first time that the fueled flight generator is connected to the rover. After the successful fit check, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator was disconnected; it will be connected to the rover for the final time on the launch pad atop the mission's Atlas V launch vehicle in July, before the planned launch of the Mars 2020 mission. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is a space nuclear power system that produces about 110 watts of electrical power to run the rover's systems and science instruments, and extra heat to keep them warm during the frigid Martian nights and winter seasons. It converts the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium dioxide into electricity using thermocouples with no moving parts. The choice of a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator as the rover's power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover's landing site and in planning its surface operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23982
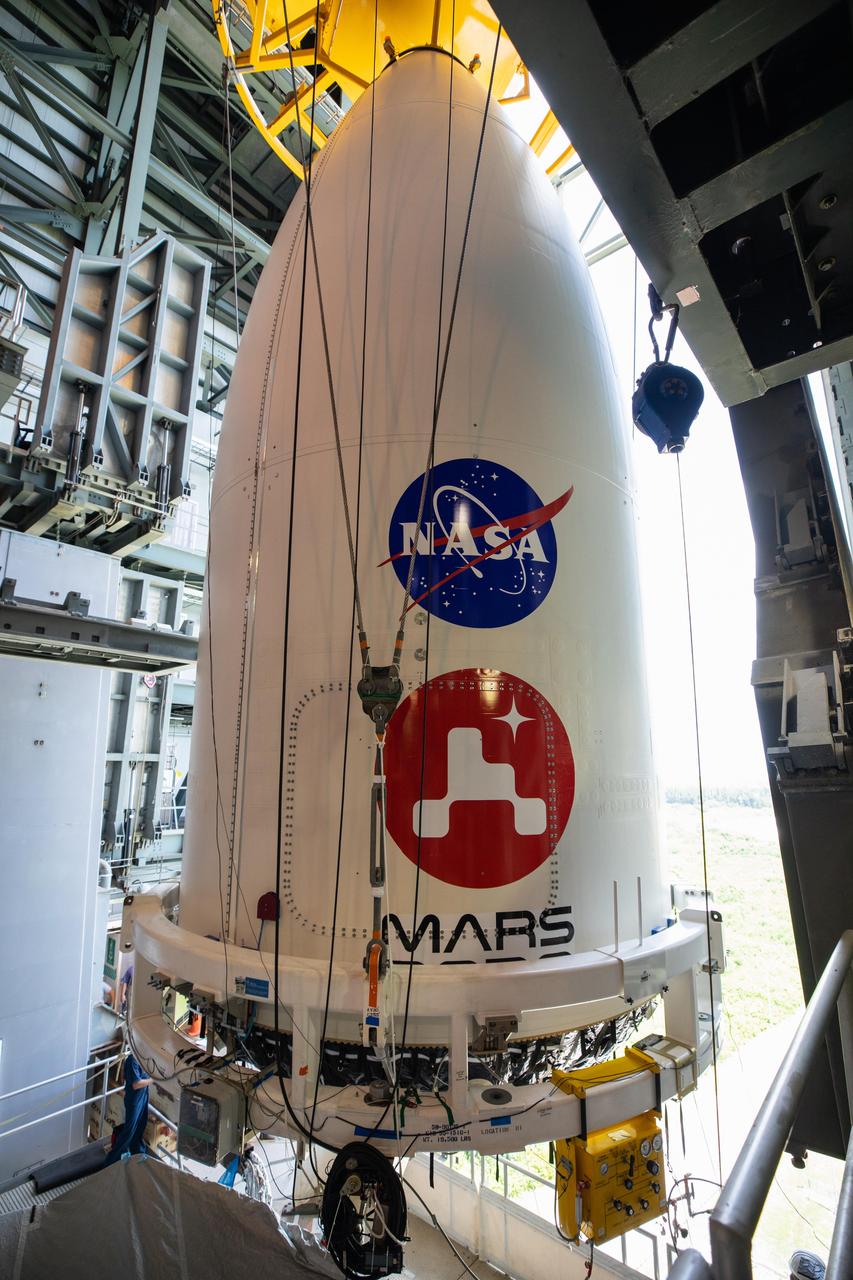

The payload fairing, or nose cone, containing NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover is maneuvered into place atop the Atlas V rocket that will hurl it toward Mars. The image was taken on July 7, 2020, inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23986
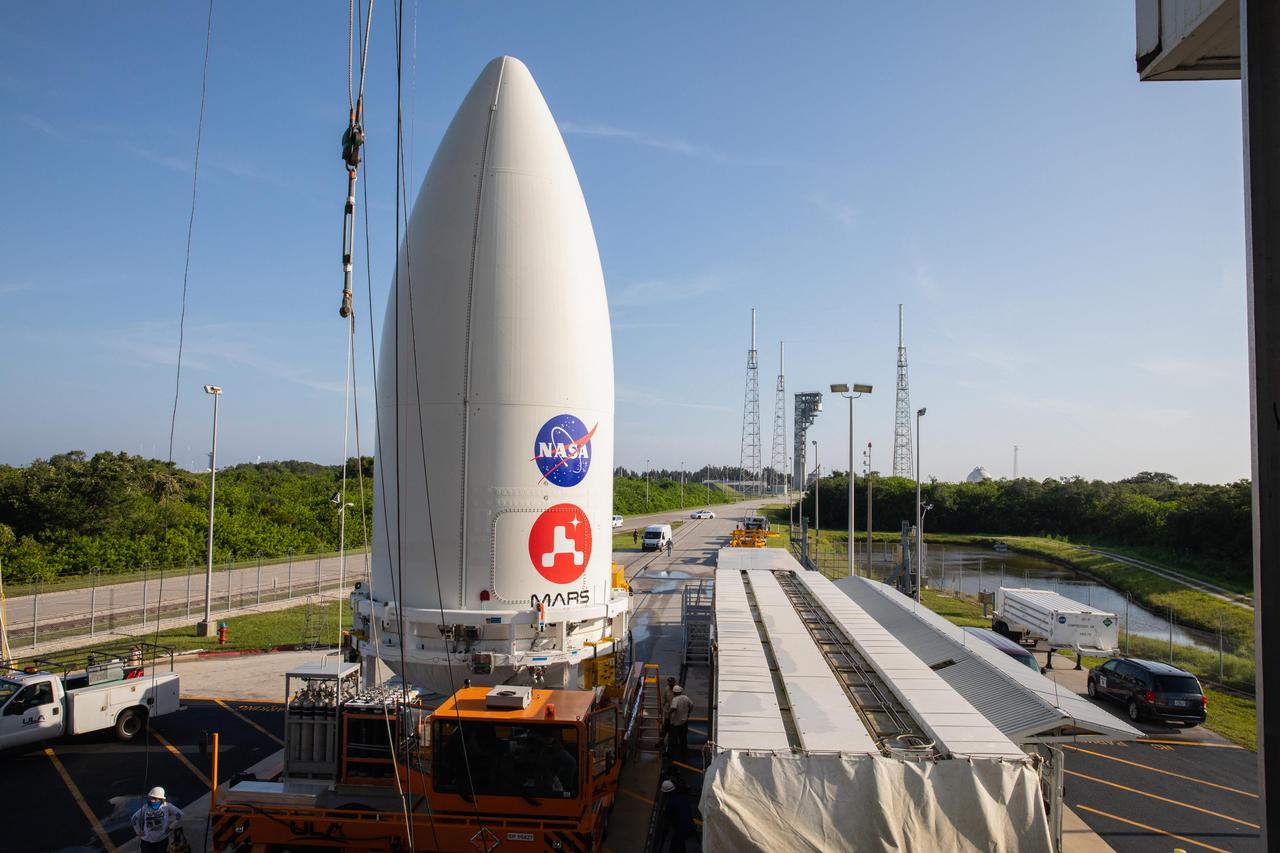

The payload fairing, or nose cone, containing the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover sits atop the motorized payload transporter that will carry it to Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The image was taken on July 7, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23985

One investigation on NASA's Mars 2020 rover will extract oxygen from the Martian atmosphere. It is called MOXIE, for Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment. In this image, MOXIE Principal Investigator Michael Hecht, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, is in the MOXIE development laboratory at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. Mars' atmosphere is mostly carbon dioxide. Demonstration of the capability for extracting oxygen from it, under Martian environmental conditions, will be a pioneering step toward how humans on Mars will use the Red Planet's natural resources. Oxygen can be used in the rocket http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20761
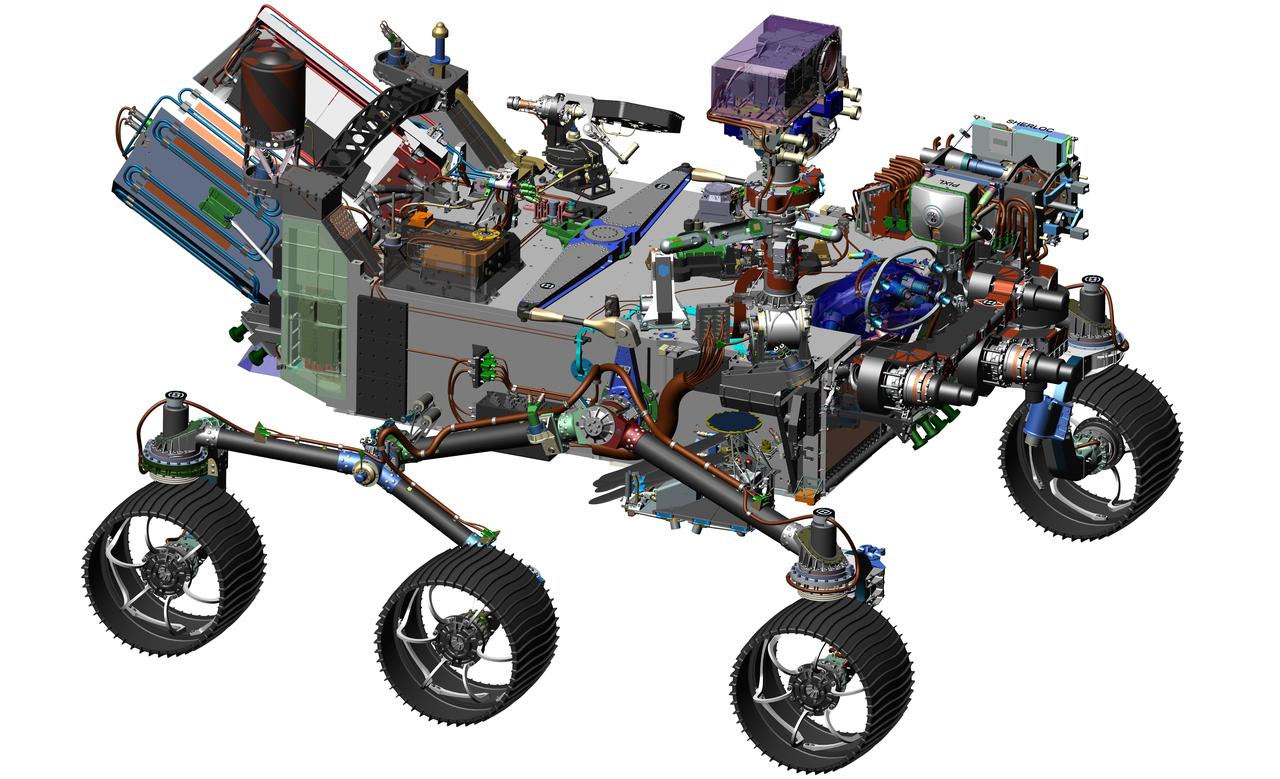
NASA's 2020 Mars rover mission will go to a region of Mars thought to have offered favorable conditions long ago for microbial life, and the rover will search for signs of past life there. It will also collect and cache samples for potential return to Earth, for many types of laboratory analysis. As a pioneering step toward how humans on Mars will use the Red Planet's natural resources, the rover will extract oxygen from the Martian atmosphere. This 2016 image comes from computer-assisted-design work on the 2020 rover. The design leverages many successful features of NASA's Curiosity rover, which landed on Mars in 2012, but it adds new science instruments and a sampling system to carry out the new goals for the mission. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20759
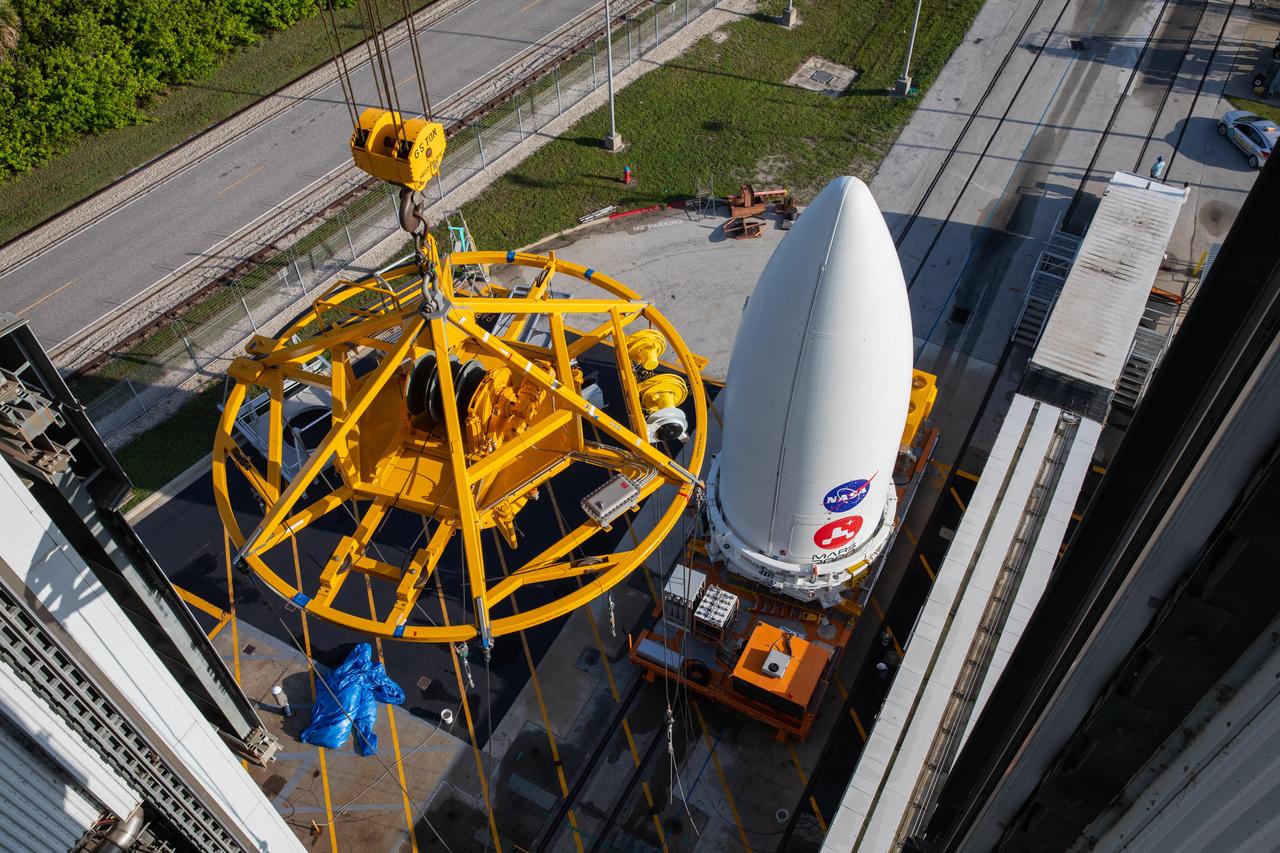

A crane stands at the ready to hoist the payload fairing, or nose cone, containing NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover onto the top of an Atlas V launch vehicle. The image was taken at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23984
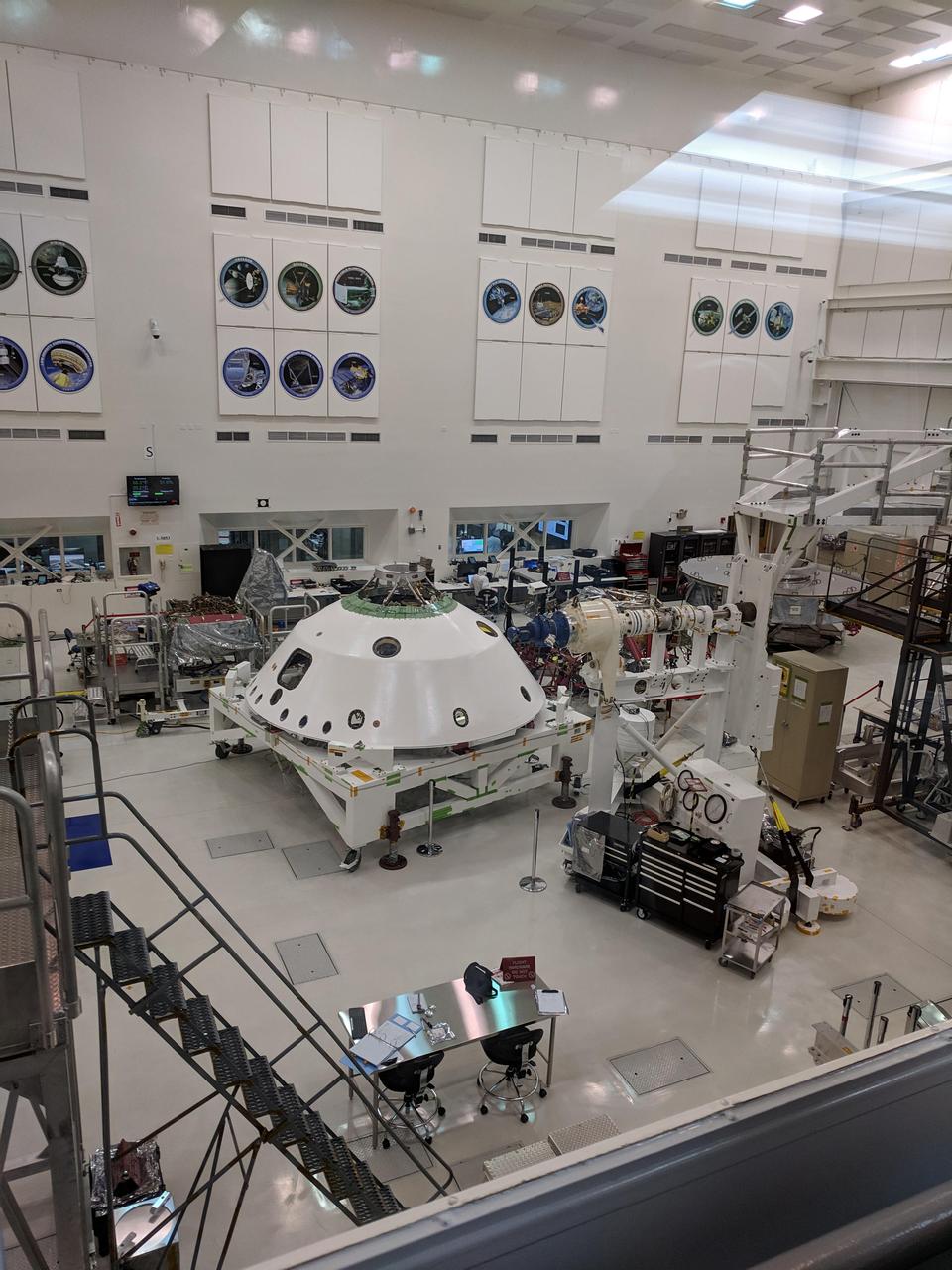

With the backshell that will help protect the Mars 2020 rover during its descent into the Martian atmosphere visible in the foreground, a technician on the project monitors the progress of Systems Test 1. Over two weeks in January 2019, 72 engineers and technicians assigned to the 2020 mission took over the High Bay 1 cleanroom in JPL's Spacecraft Assembly Facility to put the software and electrical systems aboard the mission's cruise, entry capsule, descent stage and rover through their paces. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22966
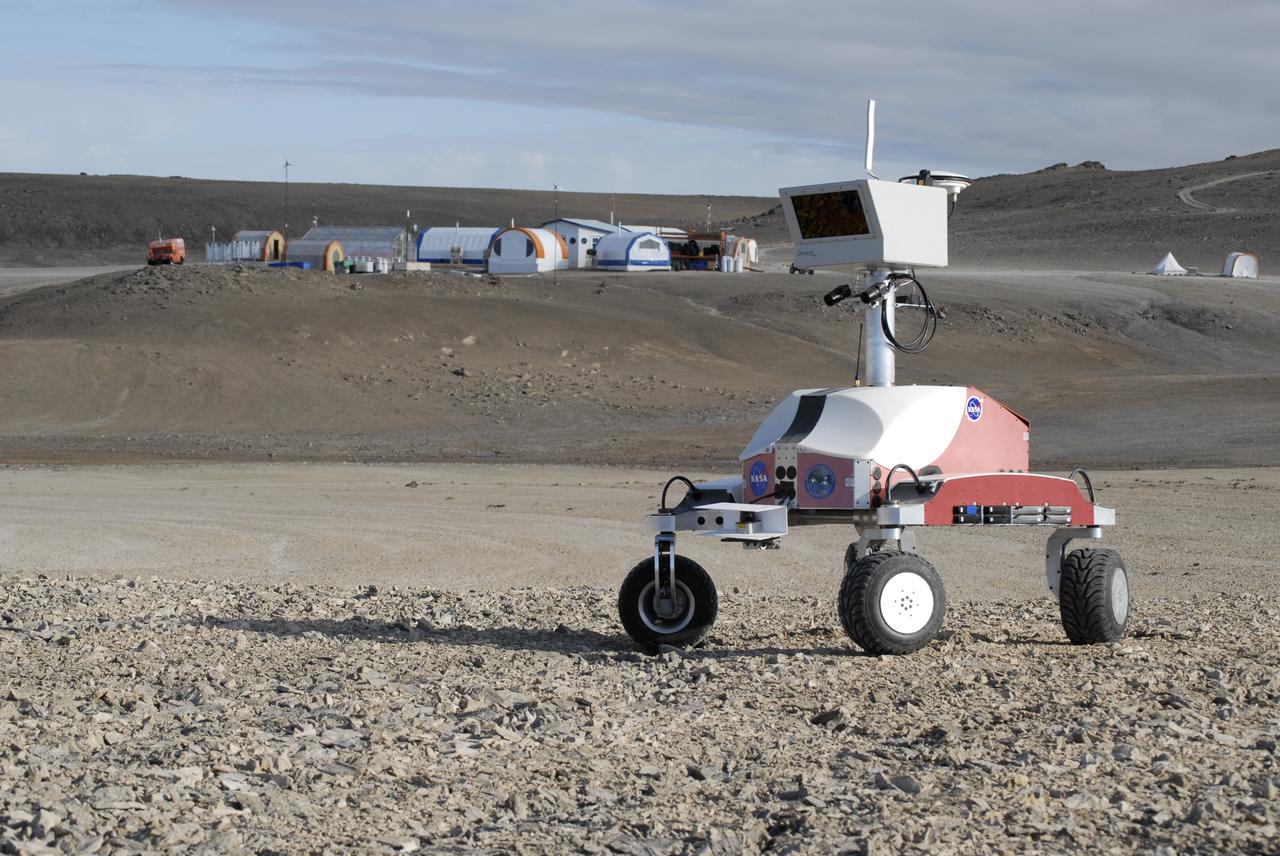

Haughton-Mars Project: - Photo credit to Matt Deans (NASA) K-10 Rover 'Red' base camp at Haughton Creater Devon Island, Nunavut, in the Canadian high arctic. Which lies in the 'frost rubble zone' of the Earth, i.e., in a polar desert environment and is the only crater known to lie in such an environment. Beginning in 1997, the crater and its surroundings are studied as a promising Mars analog by the NASA-led Haughton-Mars Project. (photo reference MCD_0838.JPG)
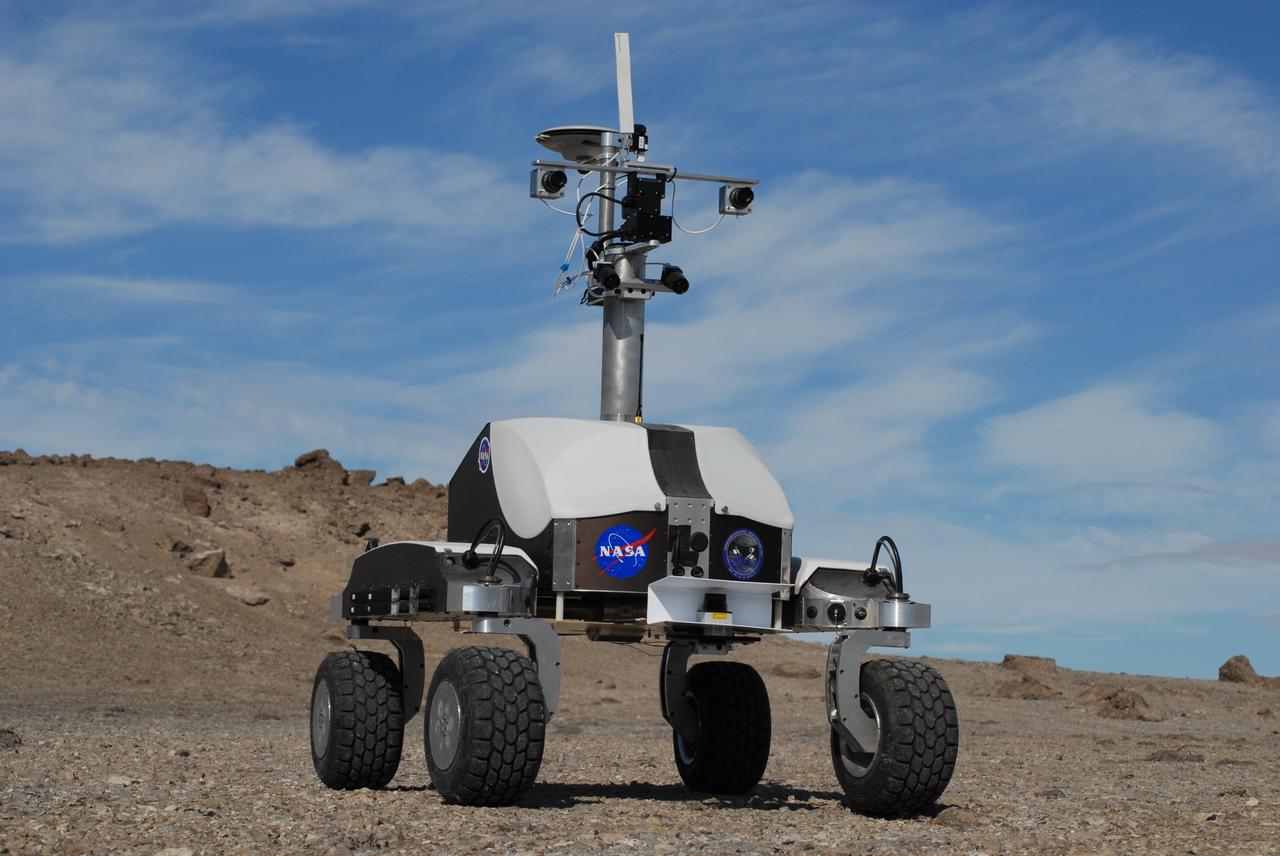

Haughton-Mars Project: - Photo credit to Matt Deans (NASA) K-10 Rover 'Black' operating with ground-penetrating radar at Haughton Creater Devon Island, Nunavut, in the Canadian high arctic. Which lies in the 'frost rubble zone' of the Earth, i.e., in a polar desert environment and is the only crater known to lie in such an environment. Beginning in 1997, the crater and its surroundings are studied as a promising Mars analog by the NASA-led Haughton-Mars Project. (photo reference MCD_0745.JPG

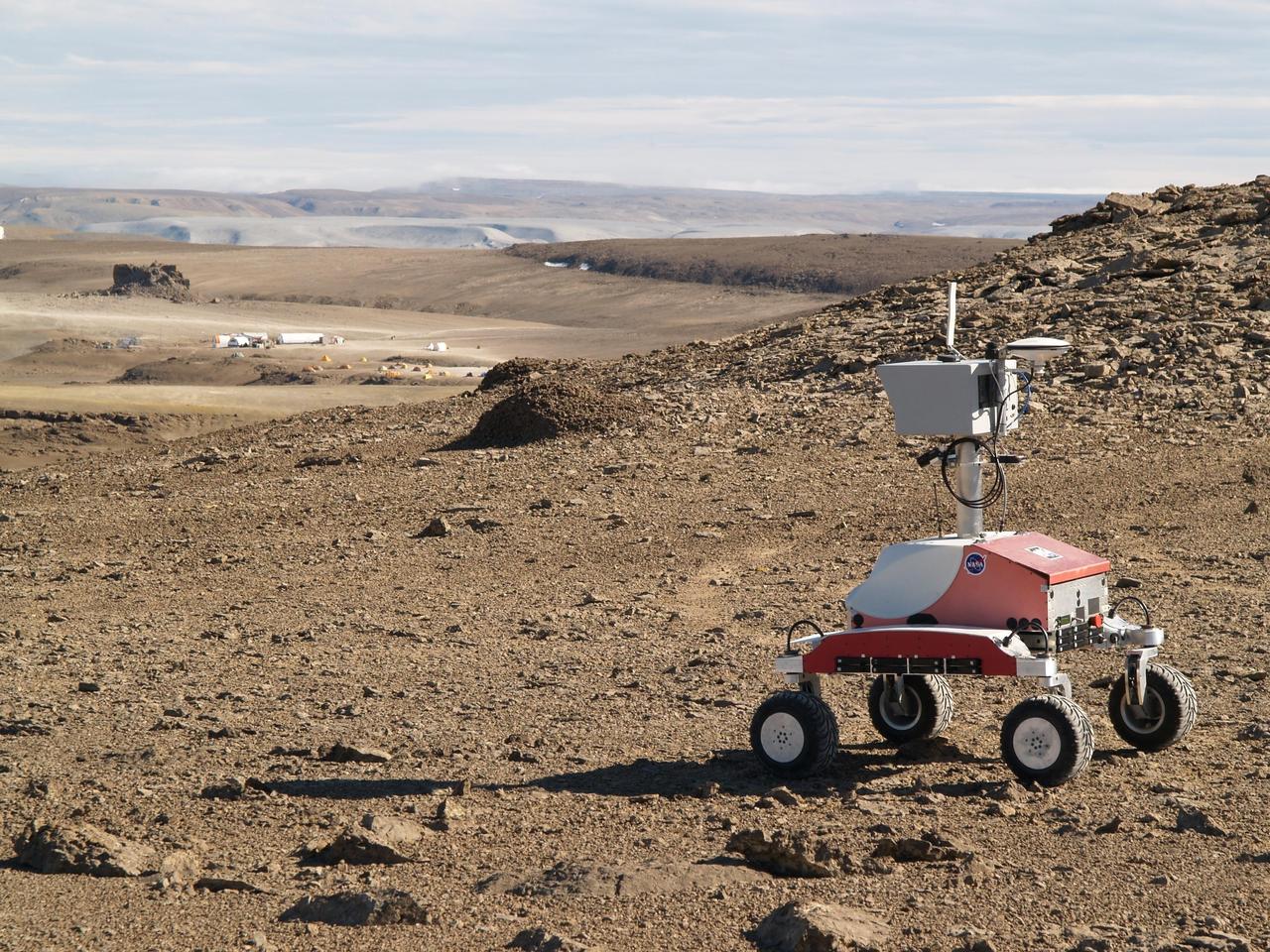
Haughton-Mars Project: - Photo credit to Matt Deans (NASA) K-10 Rover 'Red' base camp at Haughton Creater Devon Island, Nunavut, in the Canadian high arctic. Which lies in the 'frost rubble zone' of the Earth, i.e., in a polar desert environment and is the only crater known to lie in such an environment. Beginning in 1997, the crater and its surroundings are studied as a promising Mars analog by the NASA-led Haughton-Mars Project. (photo reference MCD_0859.JPG)

Haughton-Mars Project: - Photo credit to Lorenzo Flueckiger (CMU West) K-10 Rover 'Red' descending Drill Hill toward base campl at Haughton Creator Devon Island, Nunavut, in the Canadian high arctic. Which lies in the 'frost rubble zone' of the Earth, i.e., in a polar desert environment and is the only crater known to lie in such an environment. Beginning in 1997, the crater and its surroundings are studied as a promising Mars analog by the NASA-led Haughton-Mars Project. (photo reference K10-red-hughton-hill.jpg)
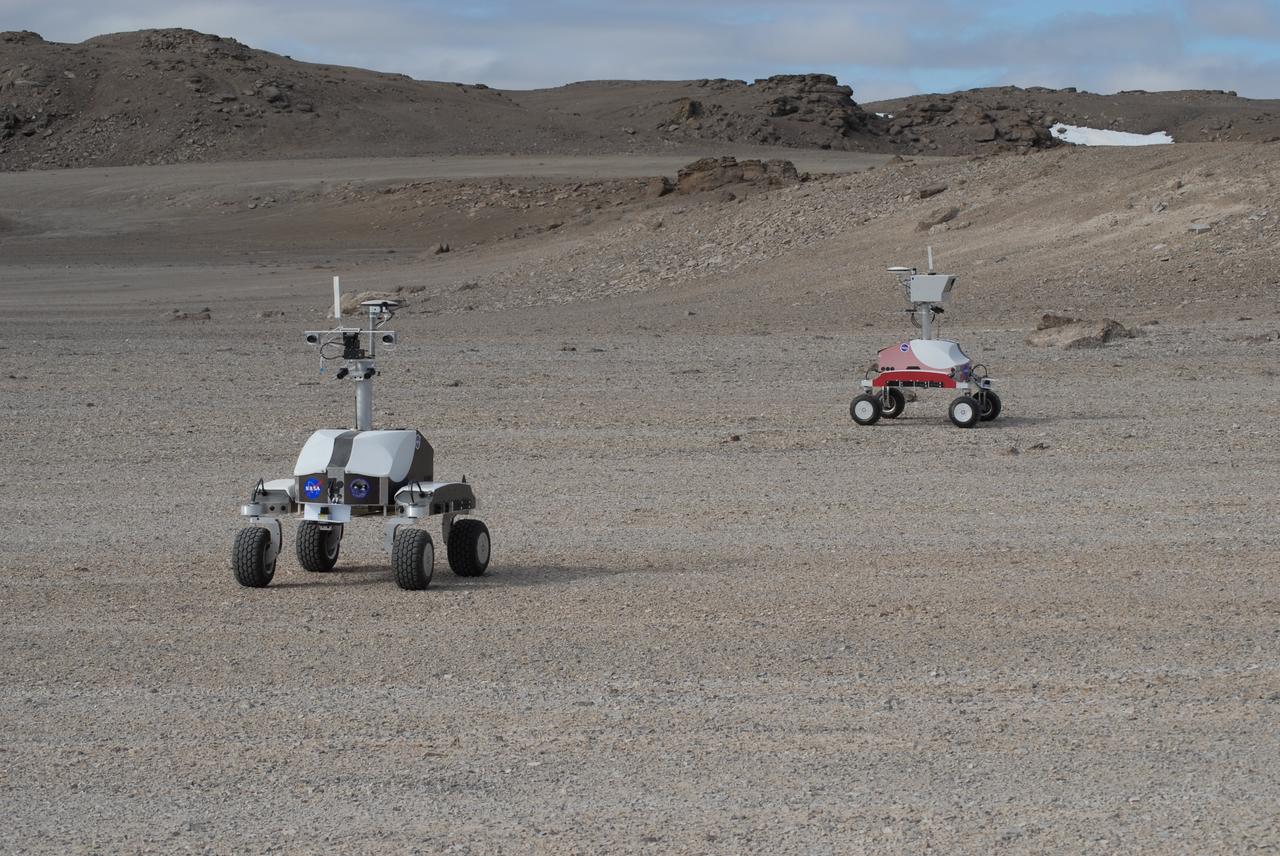

Haughton-Mars Project: - Photo credit to Matt Deans (NASA) K-10 Rover 'Black' and K-10 'RED' conducting systematic site survey at Haughton Creater Devon Island, Nunavut, in the Canadian high arctic. Which lies in the 'frost rubble zone' of the Earth, i.e., in a polar desert environment and is the only crater known to lie in such an environment. Beginning in 1997, the crater and its surroundings are studied as a promising Mars analog by the NASA-led Haughton-Mars Project. (photo reference MCD_0888.JPG)
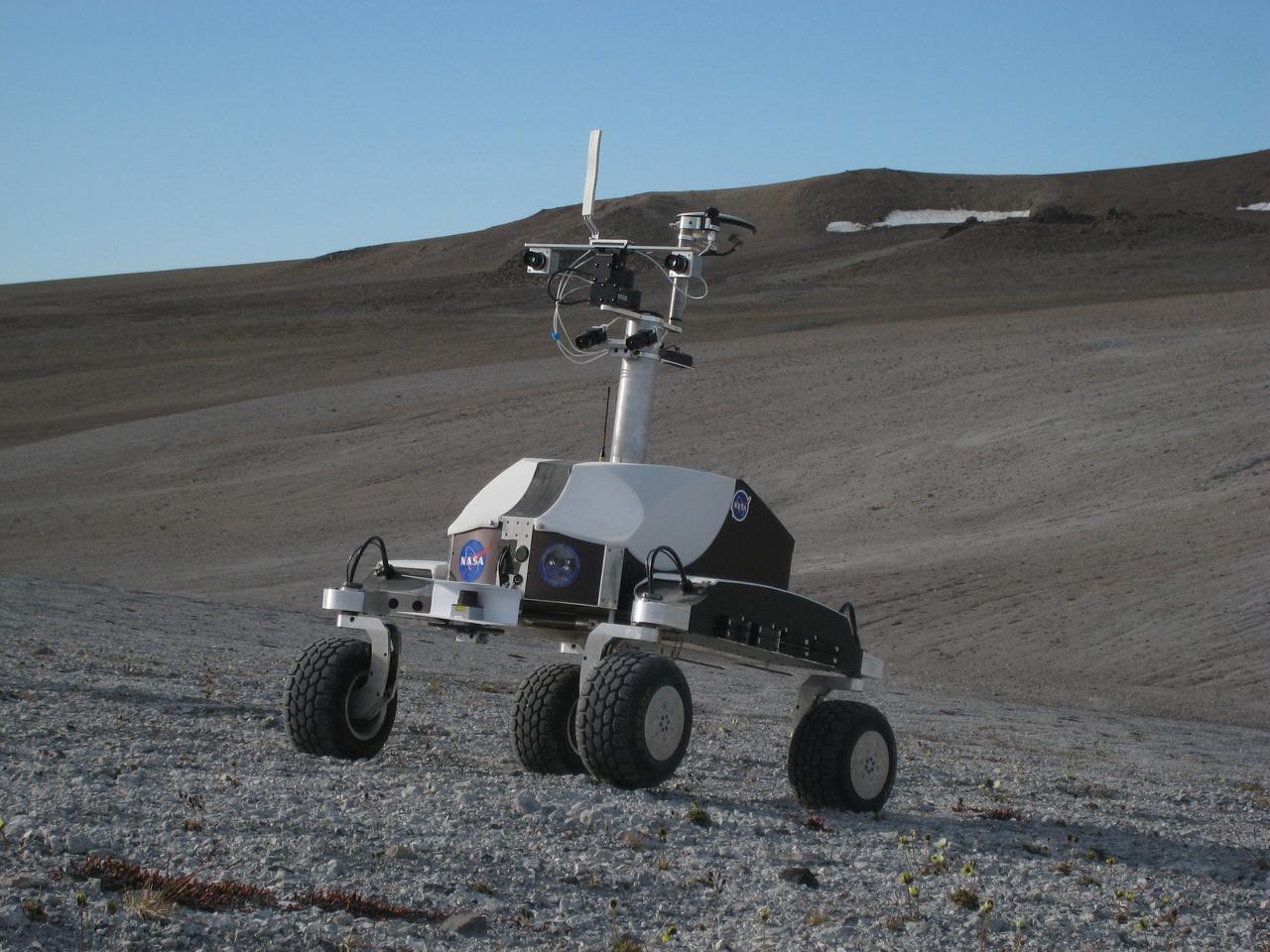

Haughton-Mars Project: - Photo credit to Matt Deans (NASA) K-10 Rover 'Black' driving on 'Drill Hill at Haughton Creater Devon Island, Nunavut, in the Canadian high arctic. Which lies in the 'frost rubble zone' of the Earth, i.e., in a polar desert environment and is the only crater known to lie in such an environment. Beginning in 1997, the crater and its surroundings are studied as a promising Mars analog by the NASA-led Haughton-Mars Project. (photo reference IMG_1278.JPG)
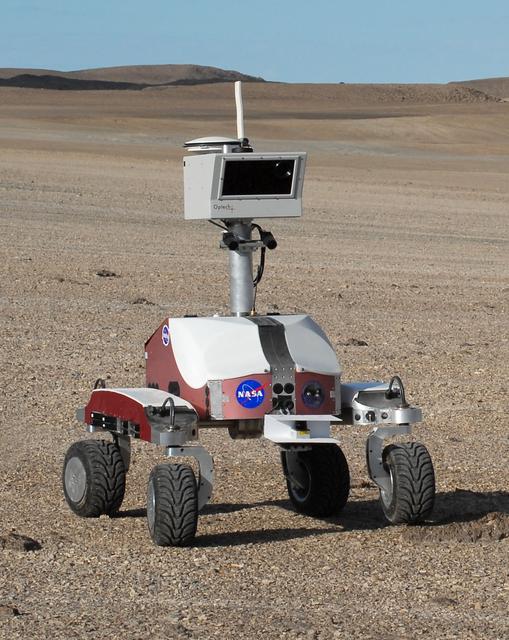

Haughton-Mars Project: - Photo credit to Matt Deans (NASA) K-10 Rover 'Red' base camp at Haughton Creater Devon Island, Nunavut, in the Canadian high arctic. Which lies in the 'frost rubble zone' of the Earth, i.e., in a polar desert environment and is the only crater known to lie in such an environment. Beginning in 1997, the crater and its surroundings are studied as a promising Mars analog by the NASA-led Haughton-Mars Project. (photo reference K10-R-haughton.jpg - crop of ACD07-0170-4 MCD_0859.JPG)

NASA Mars rover Curiosity drove 6.2 feet 1.9 meters during the 100th Martian day, or sol, of the mission Nov. 16, 2012. The view spans from north at the left to south-southeast at the right. It is presented in a cylindrical projection.
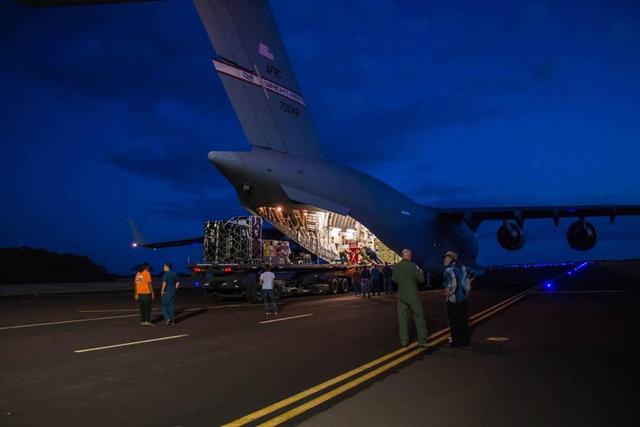

Engineers unload ground support equipment for a June engineering test flight above Kauai, Hawaii. The test flight is part of NASA LDSD project, which is investigating cutting-edge landing technologies that could fly on future Mars missions.
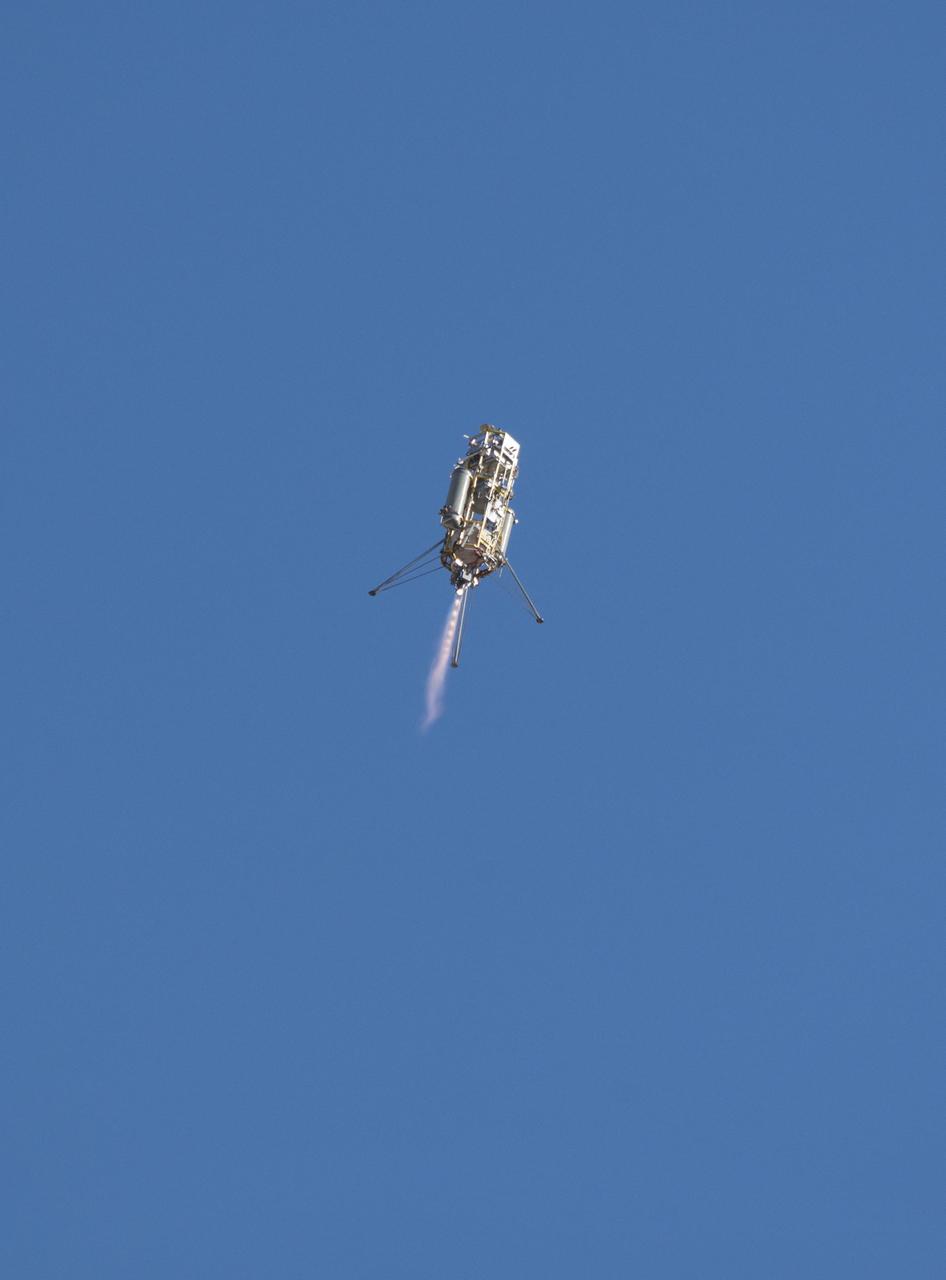

A prototype of the Lander Vision System for NASA Mars 2020 mission was tested in this Dec. 9, 2014, flight of a Masten Space Systems Xombie vehicle at Mojave Air and Space Port in California. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20848
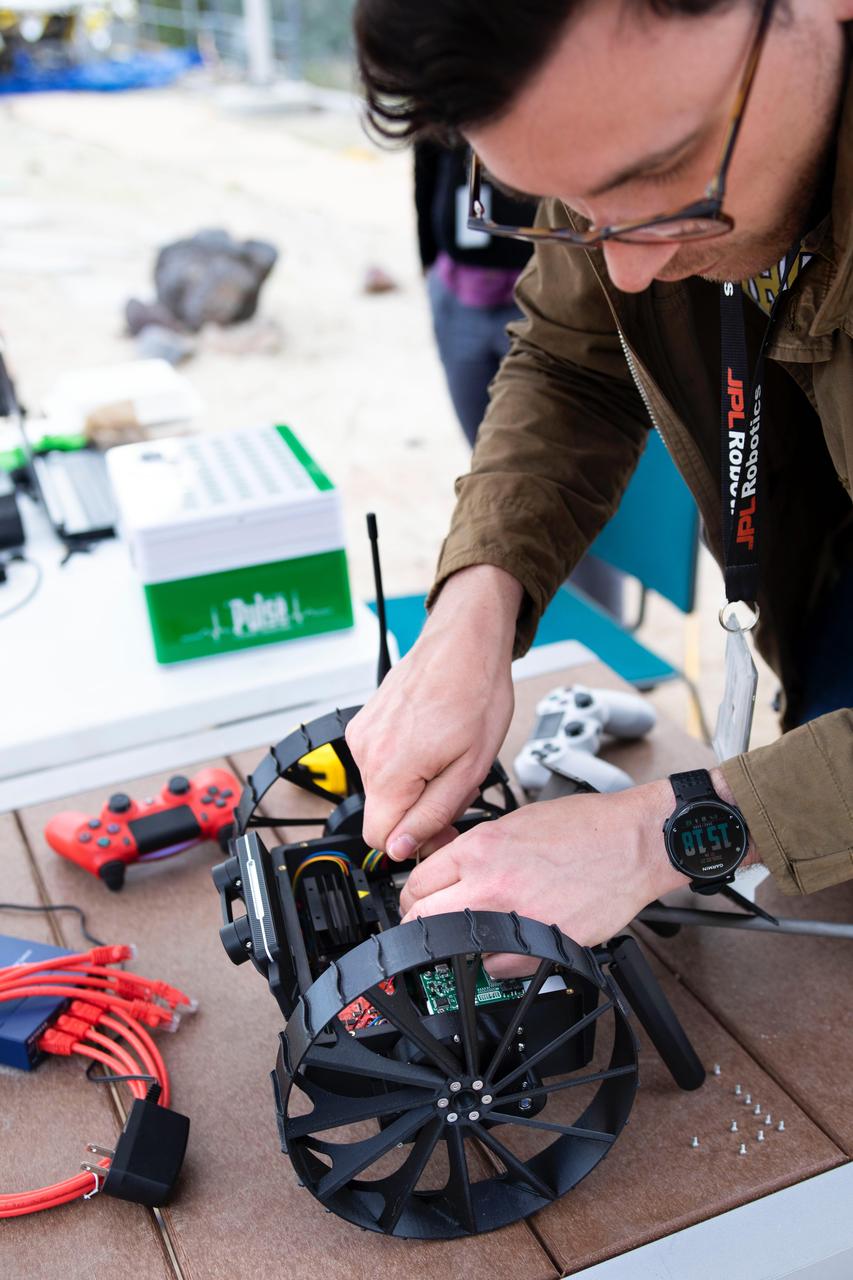

Project manager Jean-Pierre de la Croix works on an Autonomous Pop-Up Flat Folding Explorer Robot (A-PUFFER) during recent trials in the Mars Yard at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This PUFFER is equipped with an onboard computer and stereo camera as well as other sensors to help it autonomously navigate and collaborate with other PUFFERs. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23794
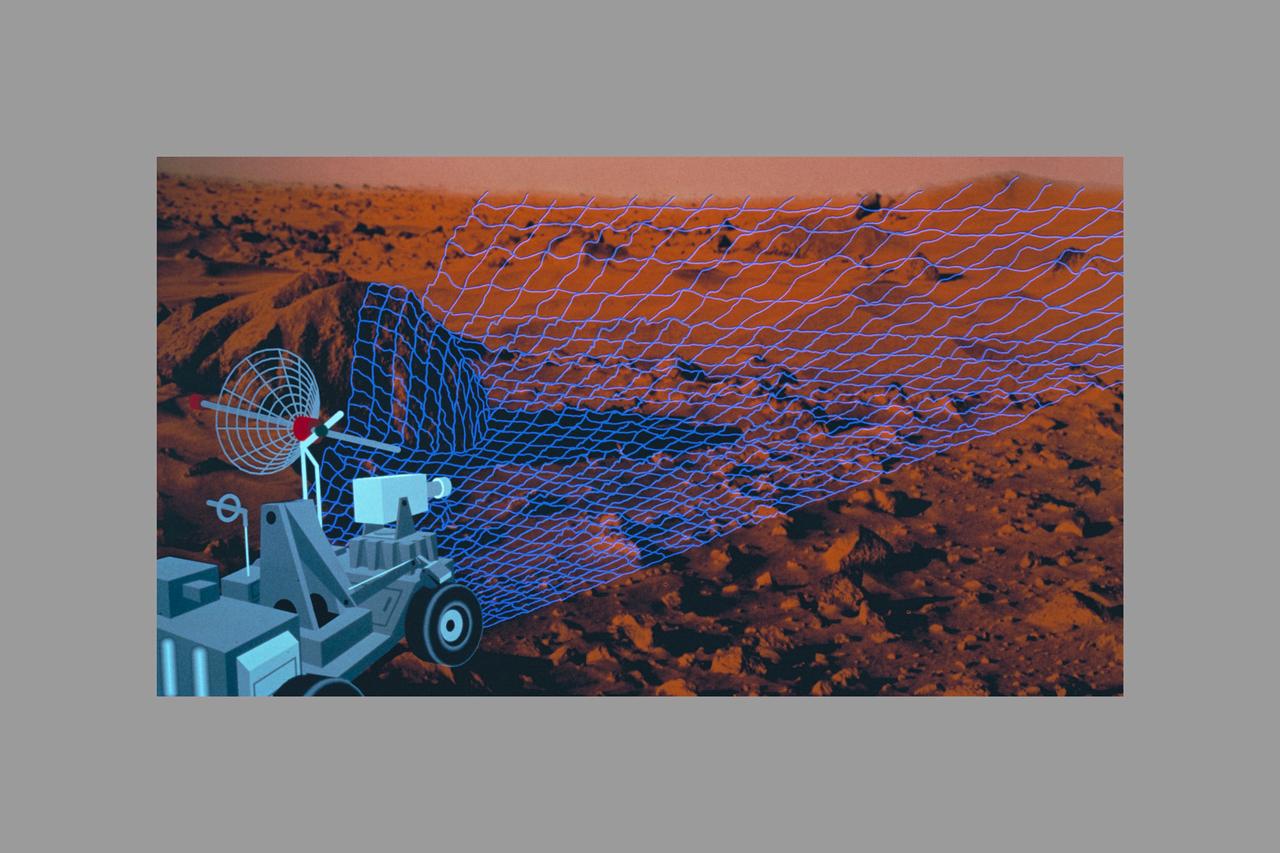

Autonomous Perception Vision project - Intelligent Systems - Machine Vision, Fusing Photonics and A.I. - Fiber-Optic Probe for Laser Velocimetry (Mars)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Mars Greenhouse is displayed at the Space Life Sciences Lab during a tour of the facility for members of the news media. The Mars Greenhouse project is a collaborative research effort between NASA, University of Florida, Dynamac Corporation, and Rigel Corporation.
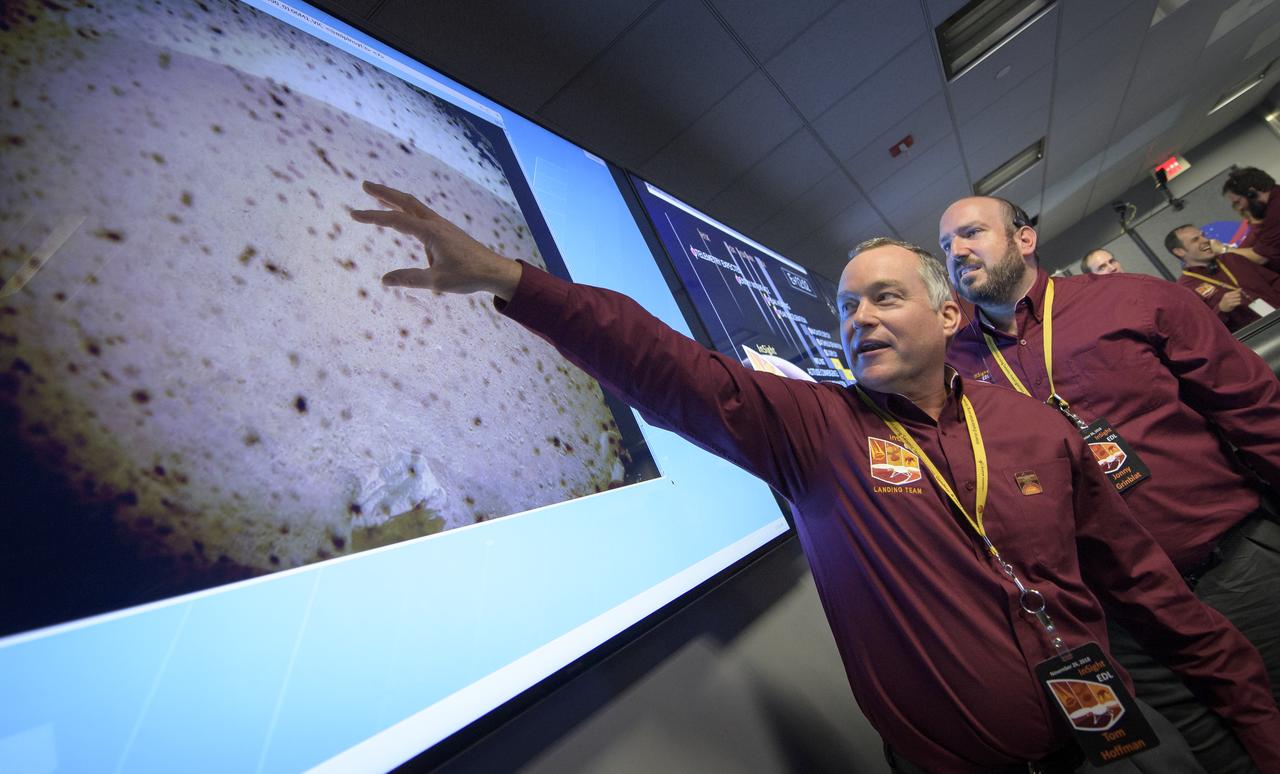

Tom Hoffman, InSight Project Manager, NASA JPL reacts to the first image to be seen from the Mars InSight lander shortly after confirmation of a successful touch down on the surface of Mars, Monday, Nov. 26, 2018 inside the Mission Support Area at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is a Mars lander designed to study the "inner space" of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
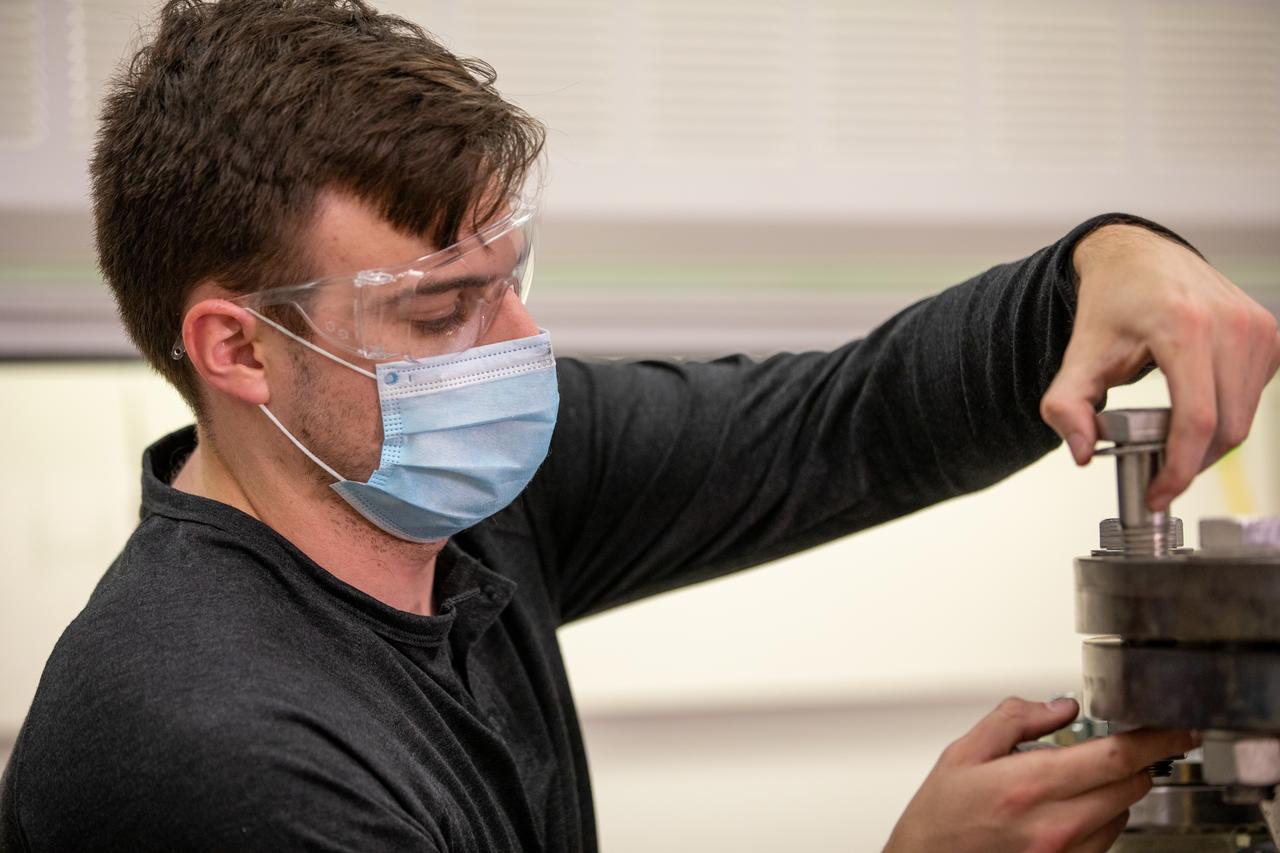
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
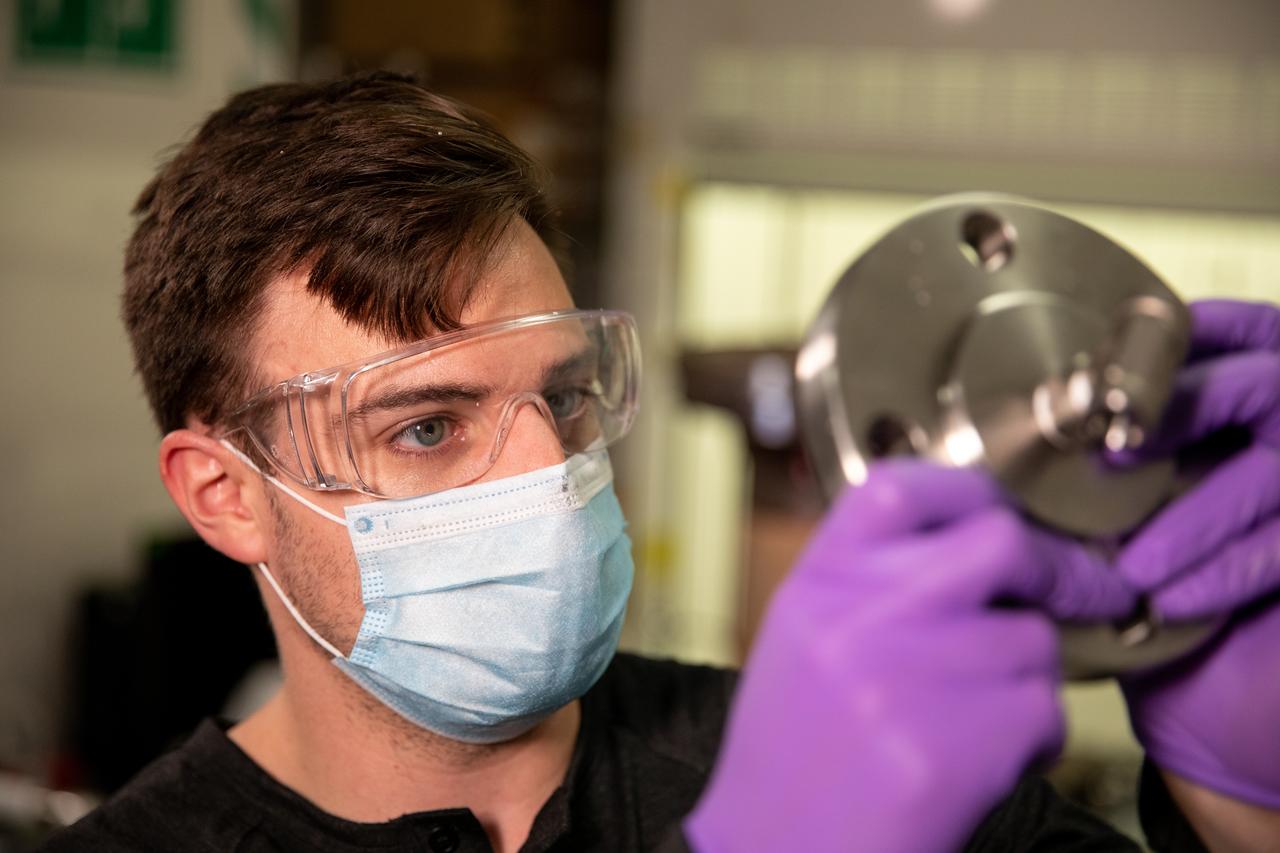

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
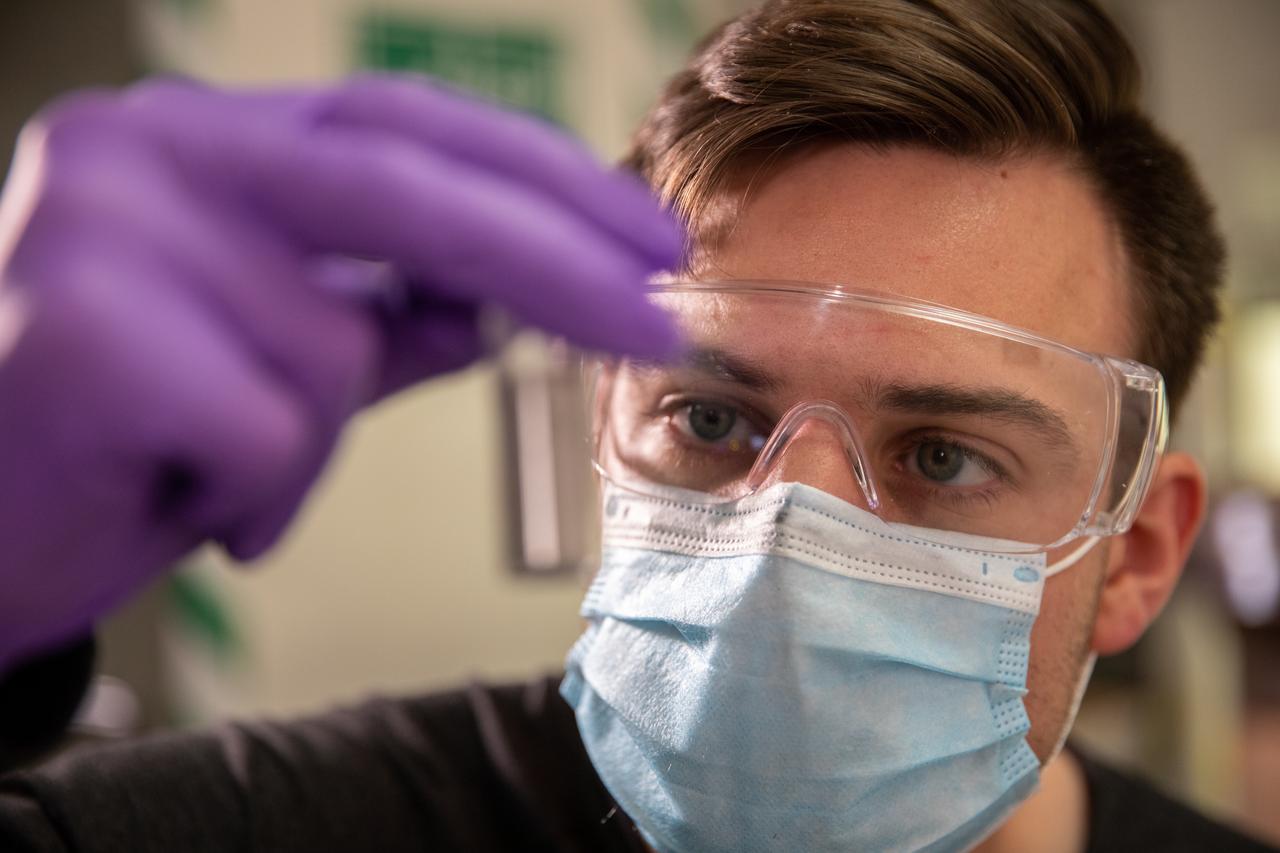
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
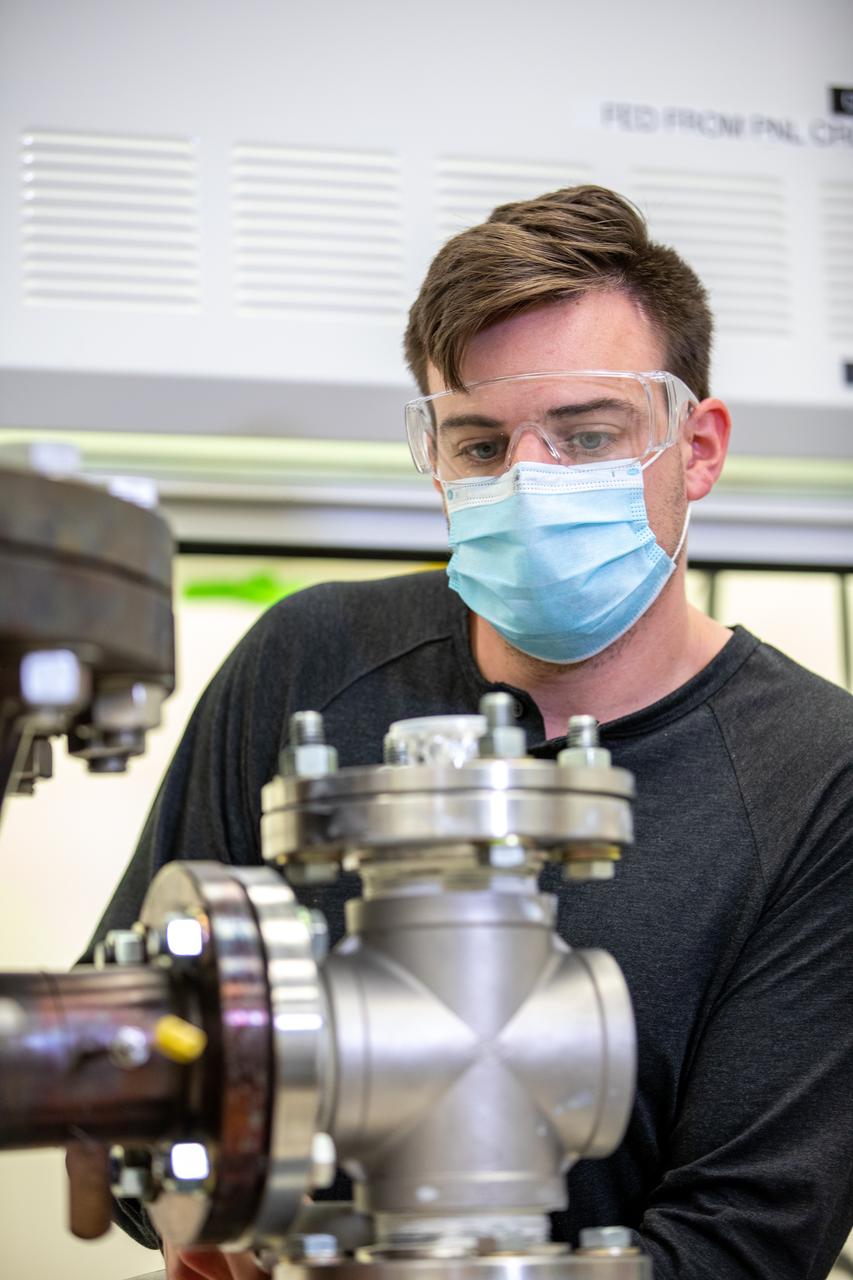

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
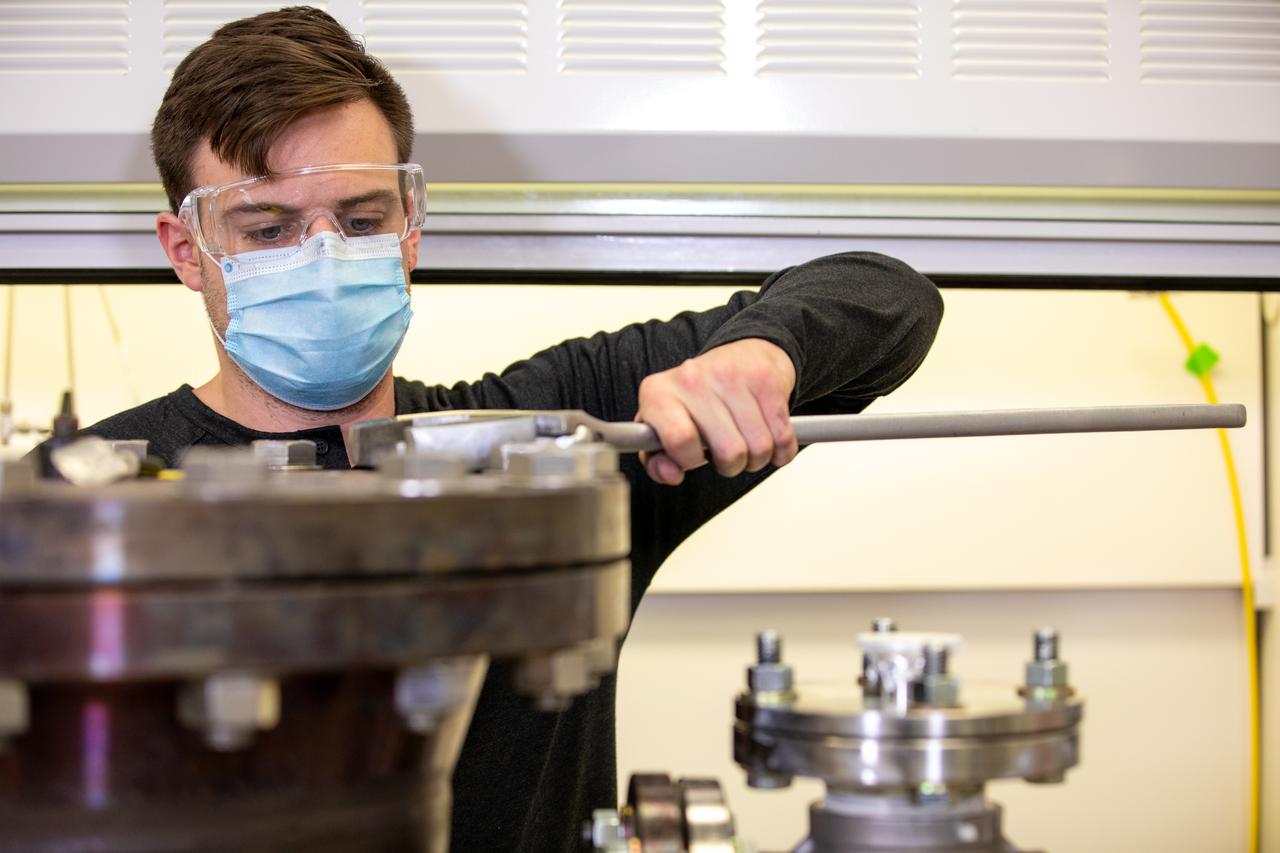

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
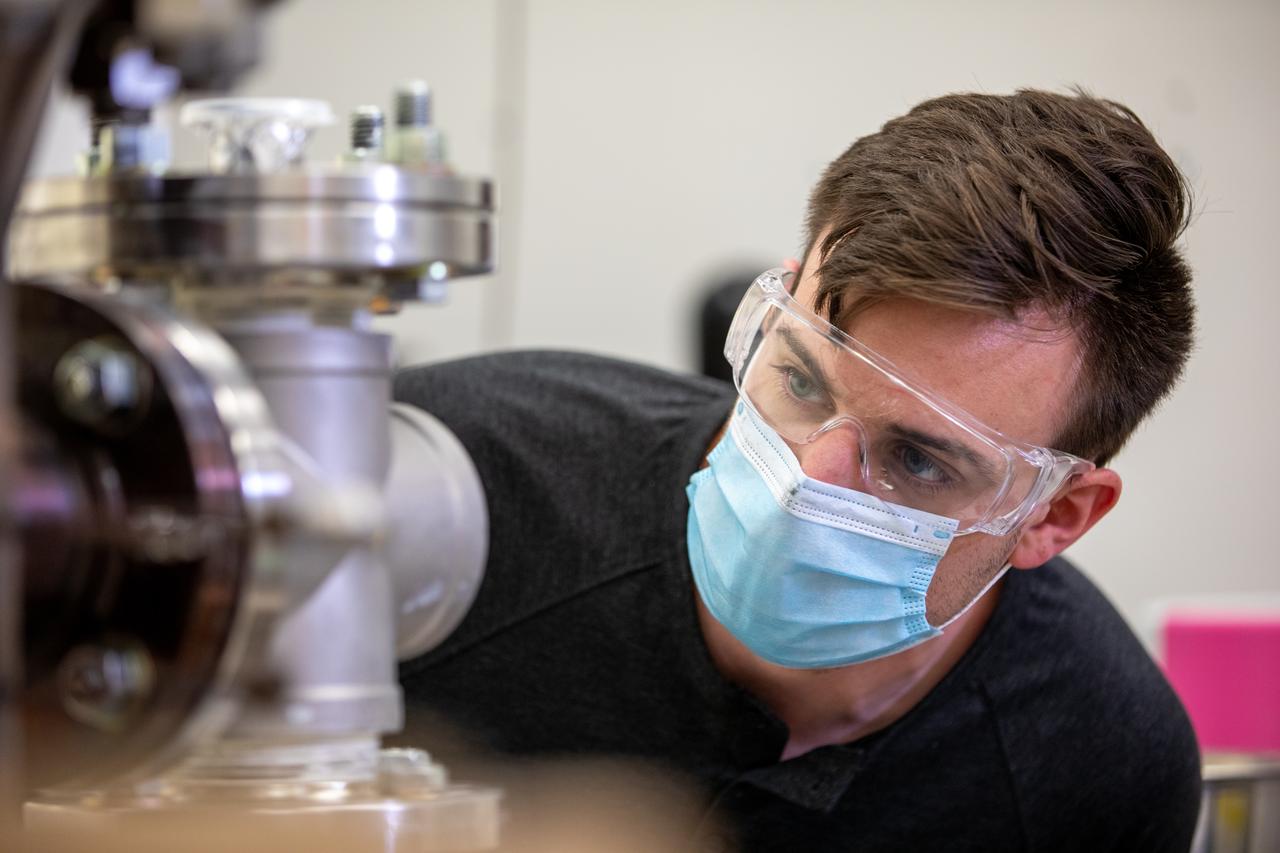

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
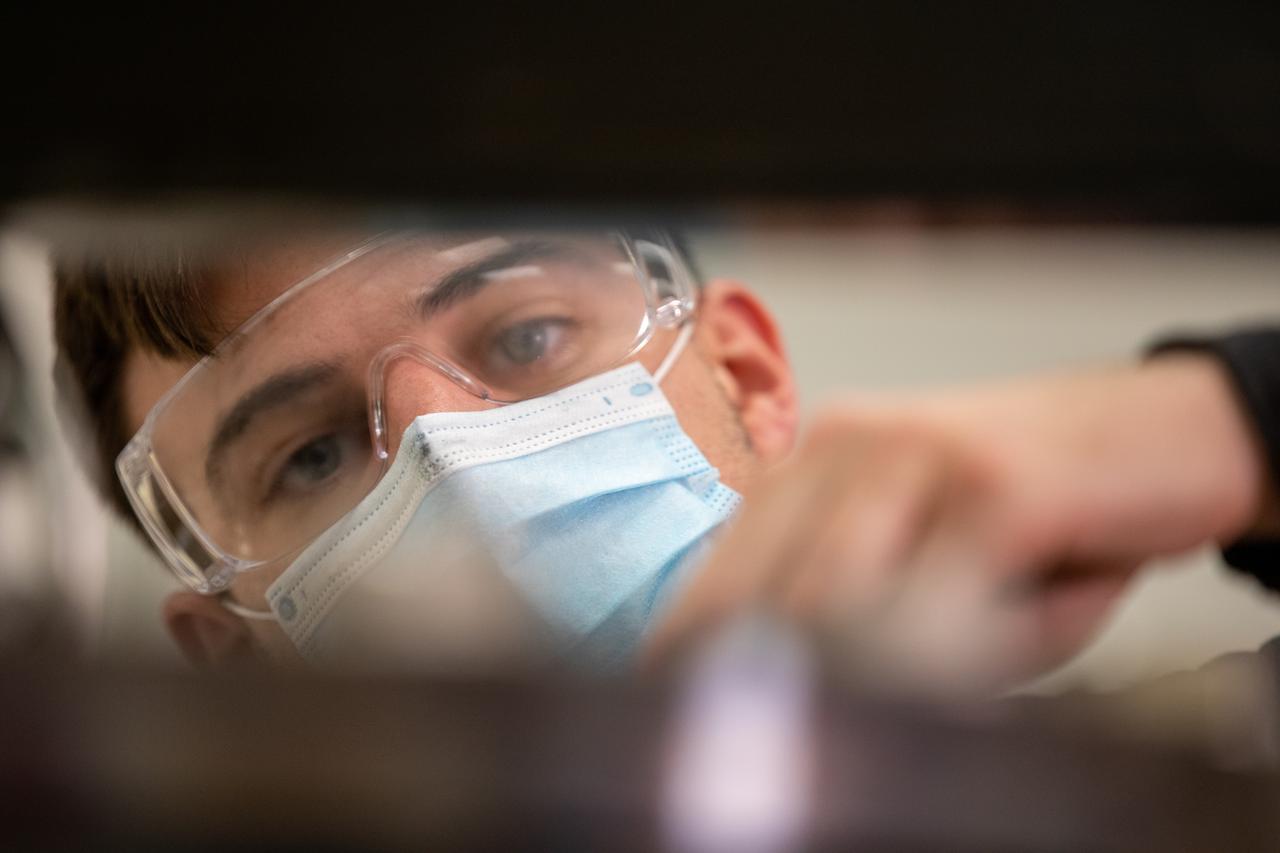

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
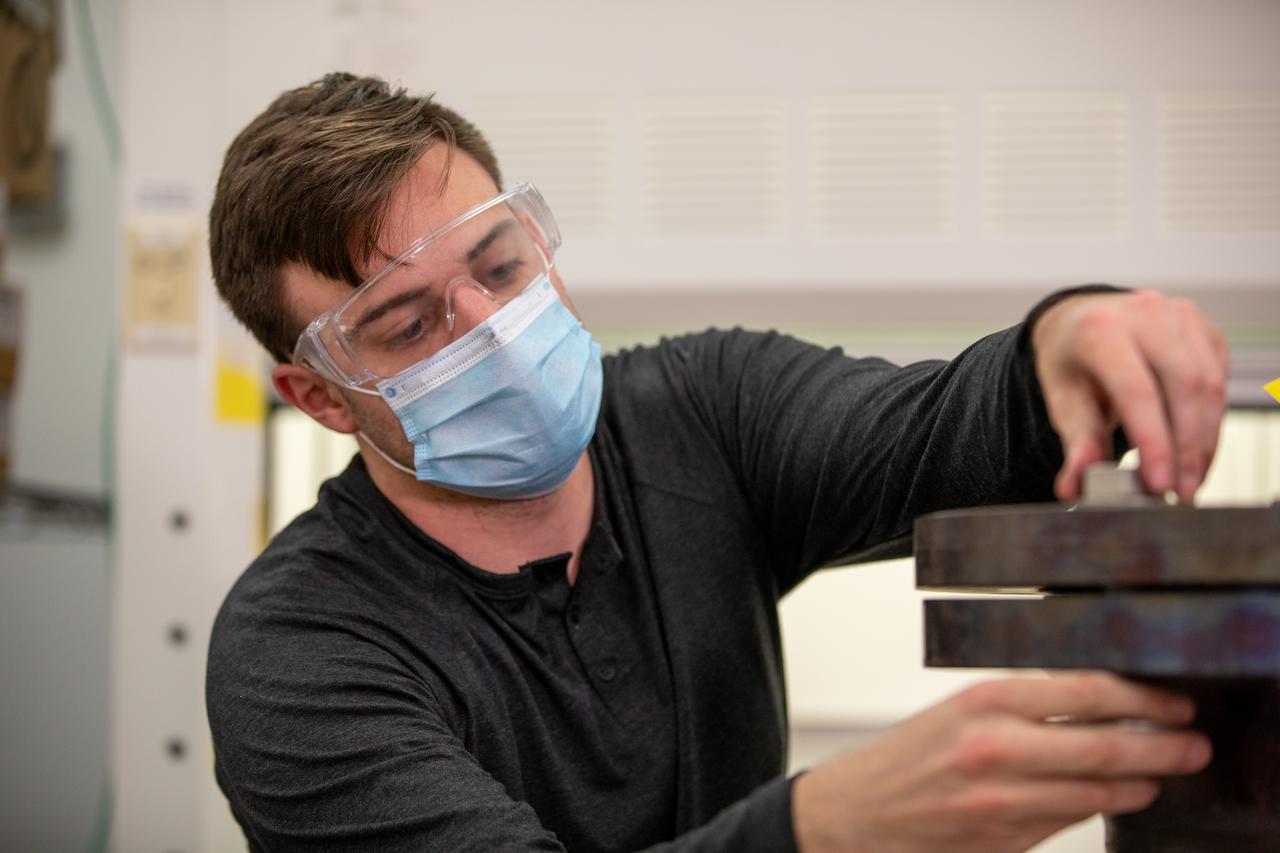

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
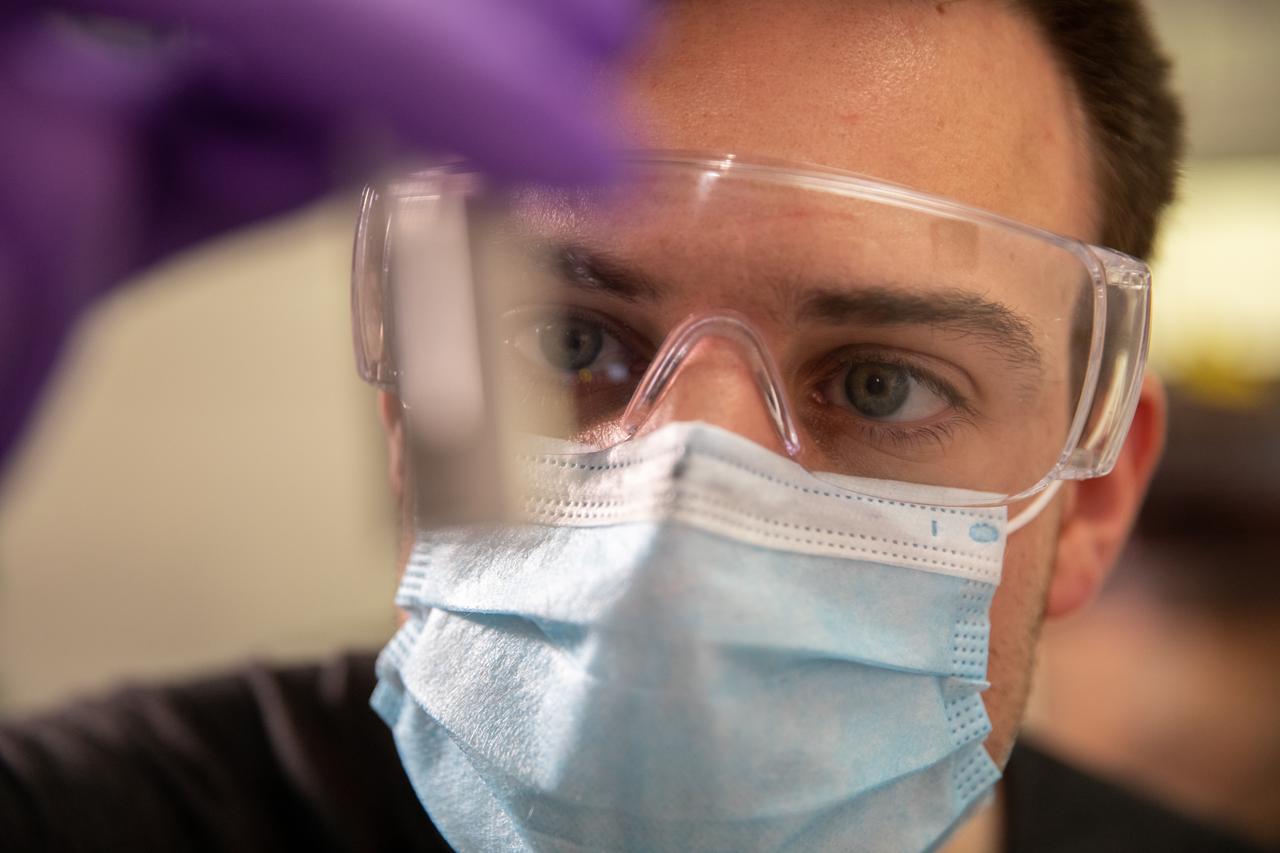
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
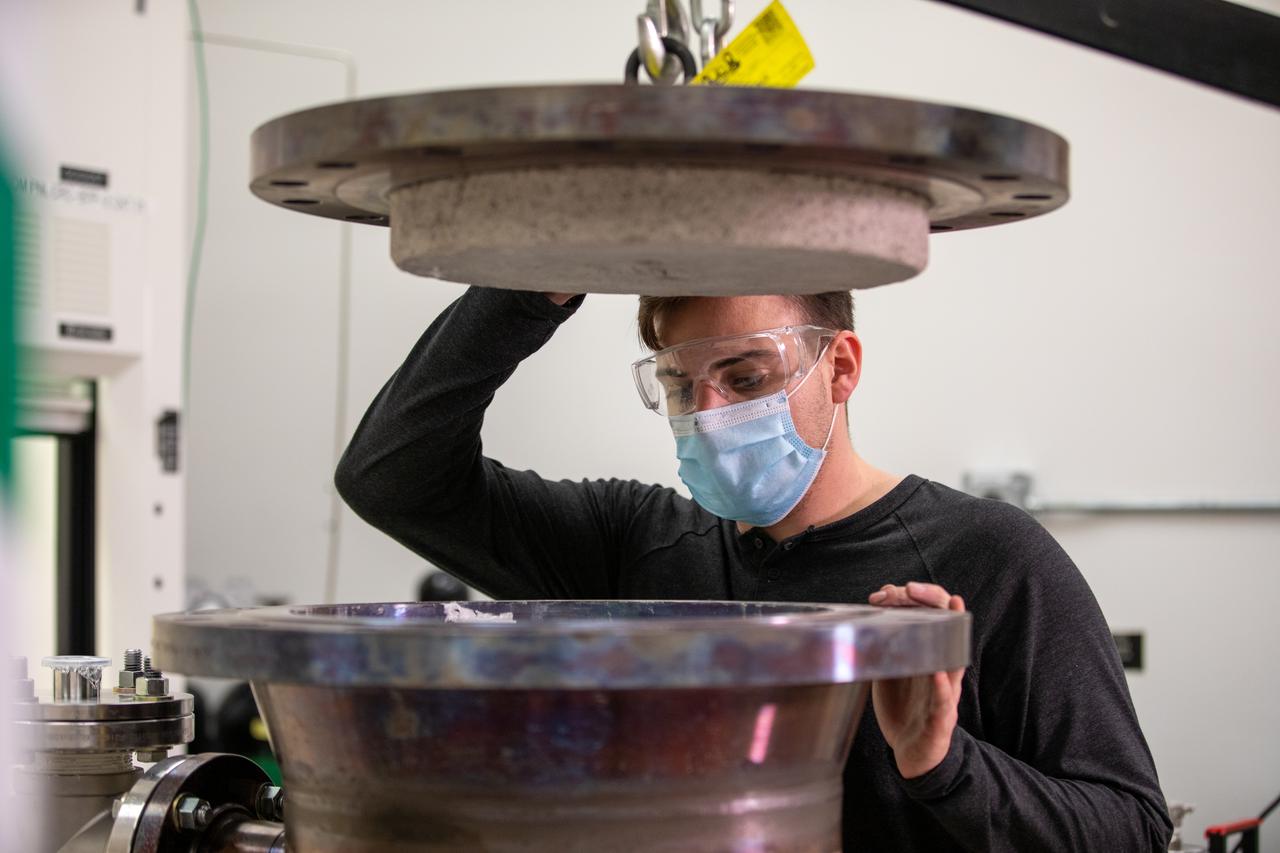

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
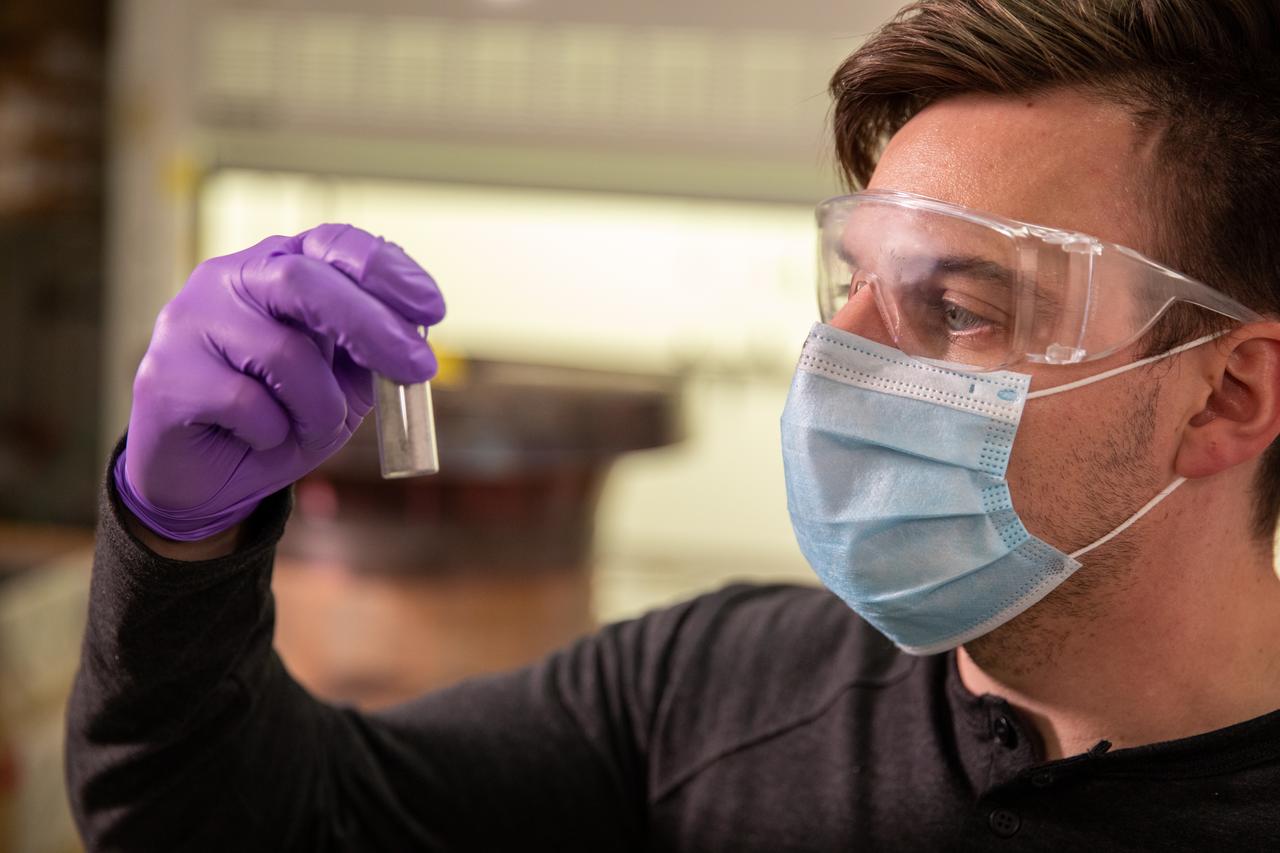

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
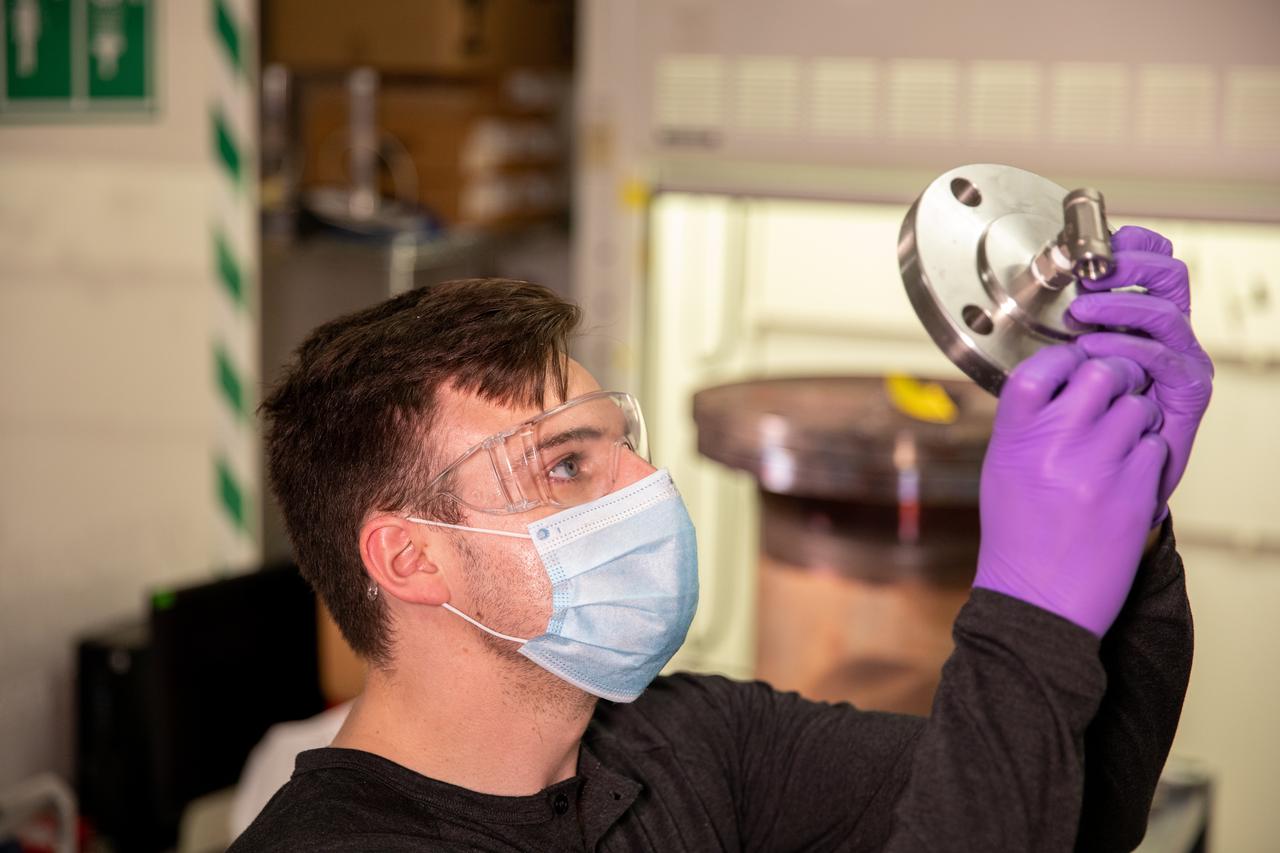

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
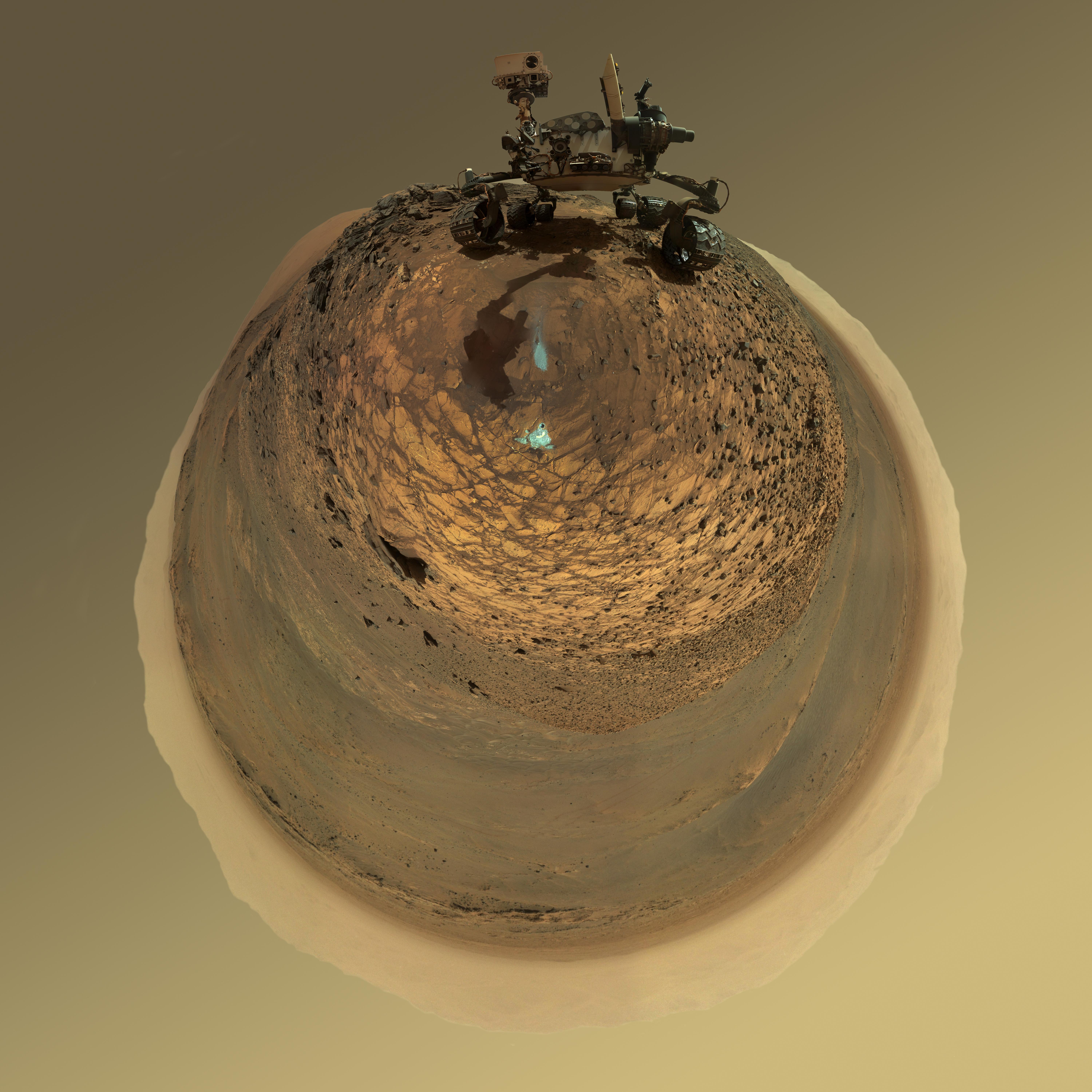
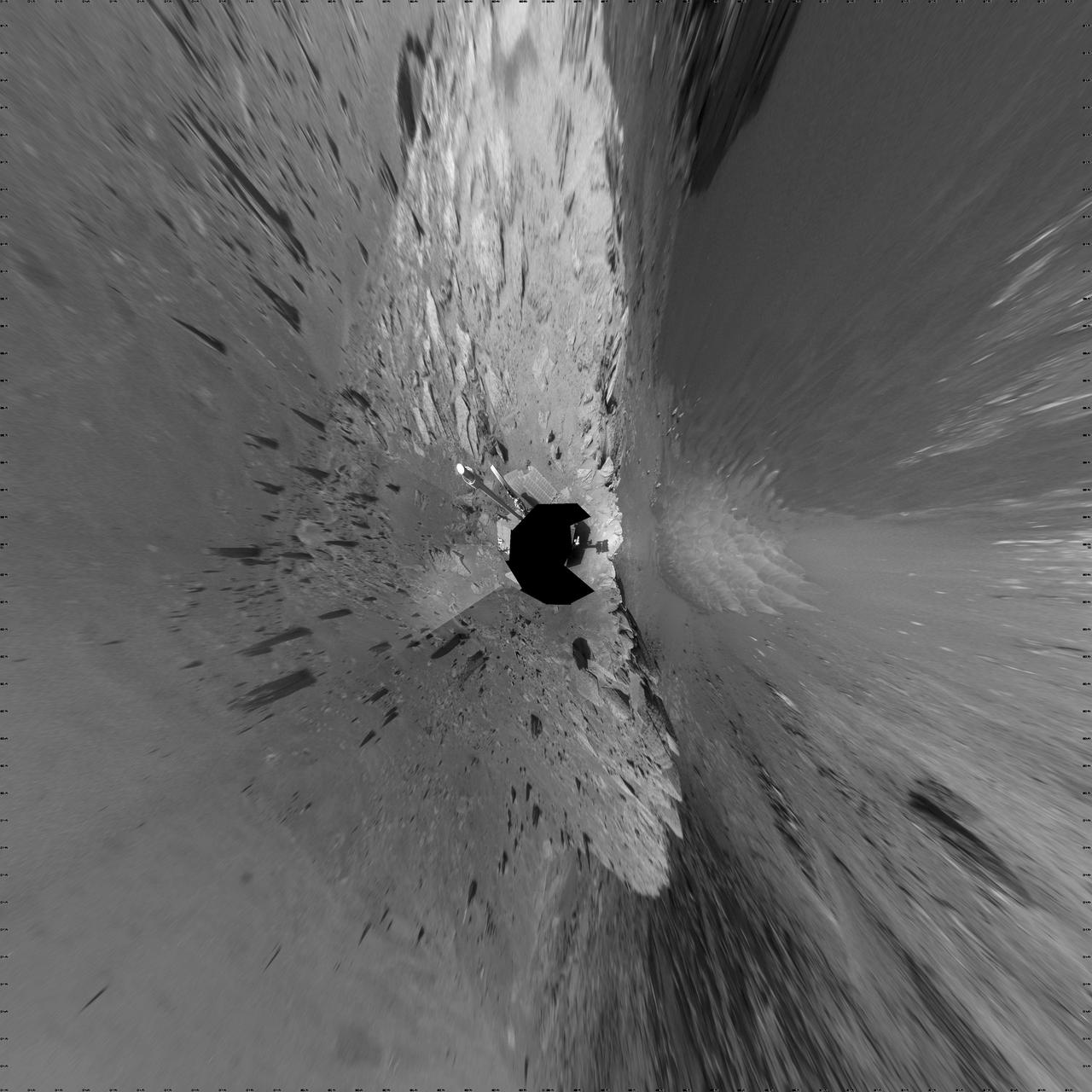
This version of a self-portrait of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover at a drilling site called "Buckskin" on lower Mount Sharp is presented as a stereographic projection, which shows the horizon as a circle. It is a mosaic assembled from the same set of 92 component raw images used for the flatter-horizon version at PIA19807. The component images were taken by Curiosity's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on Aug. 5, 2015, during the 1,065th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. Curiosity drilled the hole at Buckskin during Sol 1060 (July 30, 2015). Two patches of pale, powdered rock material pulled from inside Buckskin are visible in this scene, in front of the rover. The patch closer to the rover is where the sample-handling mechanism on Curiosity's robotic arm dumped collected material that did not pass through a sieve in the mechanism. Sieved sample material was delivered to laboratory instruments inside the rover. The patch farther in front of the rover, roughly triangular in shape, shows where fresh tailings spread downhill from the drilling process. The drilled hole, 0.63 inch (1.6 centimeters) in diameter, is at the upper point of the tailings. The rover is facing northeast, looking out over the plains from the crest of a 20-foot (6-meter) hill that it climbed to reach the "Marias Pass" area. The upper levels of Mount Sharp are visible behind the rover, while Gale Crater's northern rim dominates most of the rest of the horizon.the horizon on the left and right of the mosaic. MAHLI is mounted at the end of the rover's robotic arm. For this self-portrait, the rover team positioned the camera lower in relation to the rover body than for any previous full self-portrait of Curiosity. The assembled mosaic does not include the rover's arm beyond a portion of the upper arm held nearly vertical from the shoulder joint. Shadows from the rest of the arm and the turret of tools at the end of the arm are visible on the ground. With the wrist motions and turret rotations used in pointing the camera for the component images, the arm was positioned out of the shot in the frames or portions of frames used in this mosaic. MAHLI was built by Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed and built the project's Curiosity rover. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19806
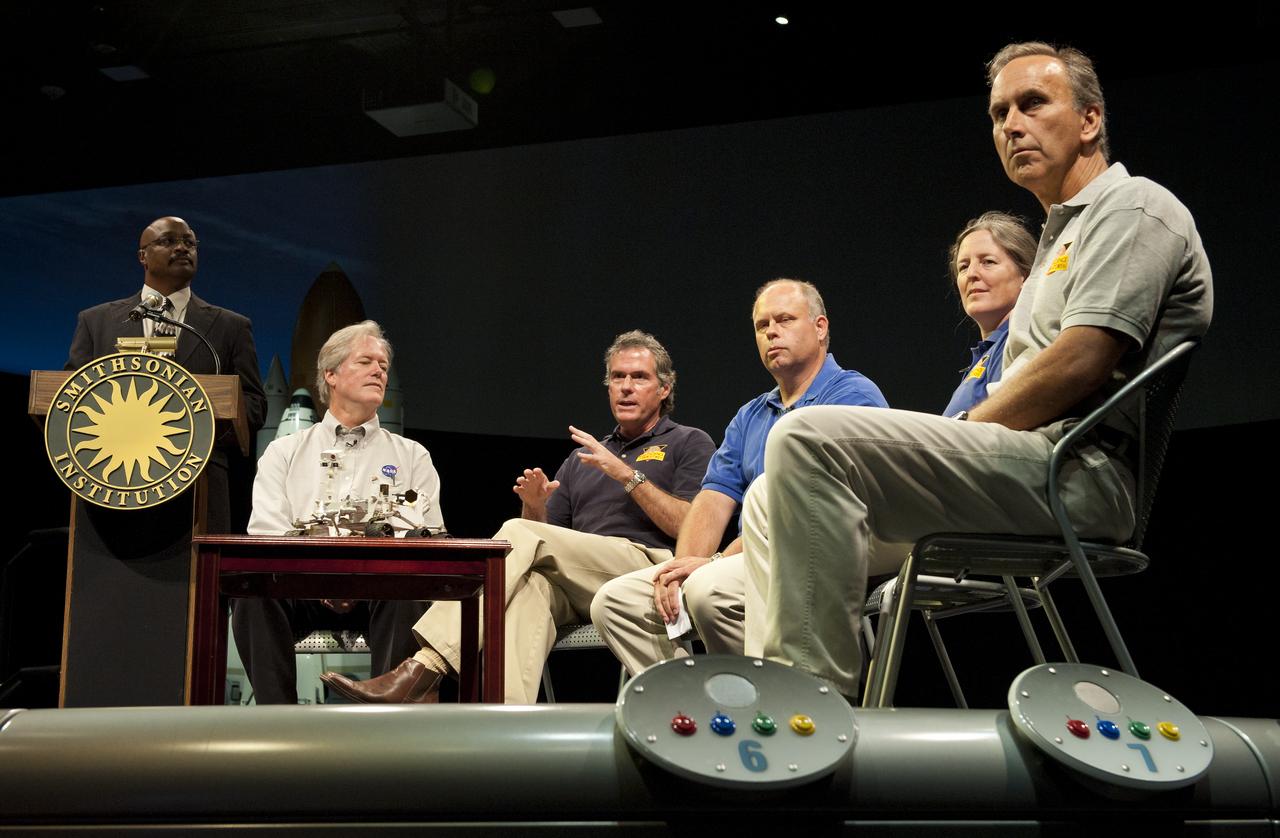

Michael Watkins (third from left), mission manager and project engineer, Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), Jet Propulsion Lab, Pasadena, Calif., speaks at a press conference at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum on Friday, July 22, 2011 in Washington. From left to right, Watkins is joined by Dwayne Brown, NASA Headquarters public affairs officer; Michael Meyer, lead scientist Mars Exploration Program, NASA Headquarters; Watkins; John Grant, geologist, Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington; Dawn Sumner, geologist, University of California, Davis and John Grotzinger, MSL project scientist, JPL. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
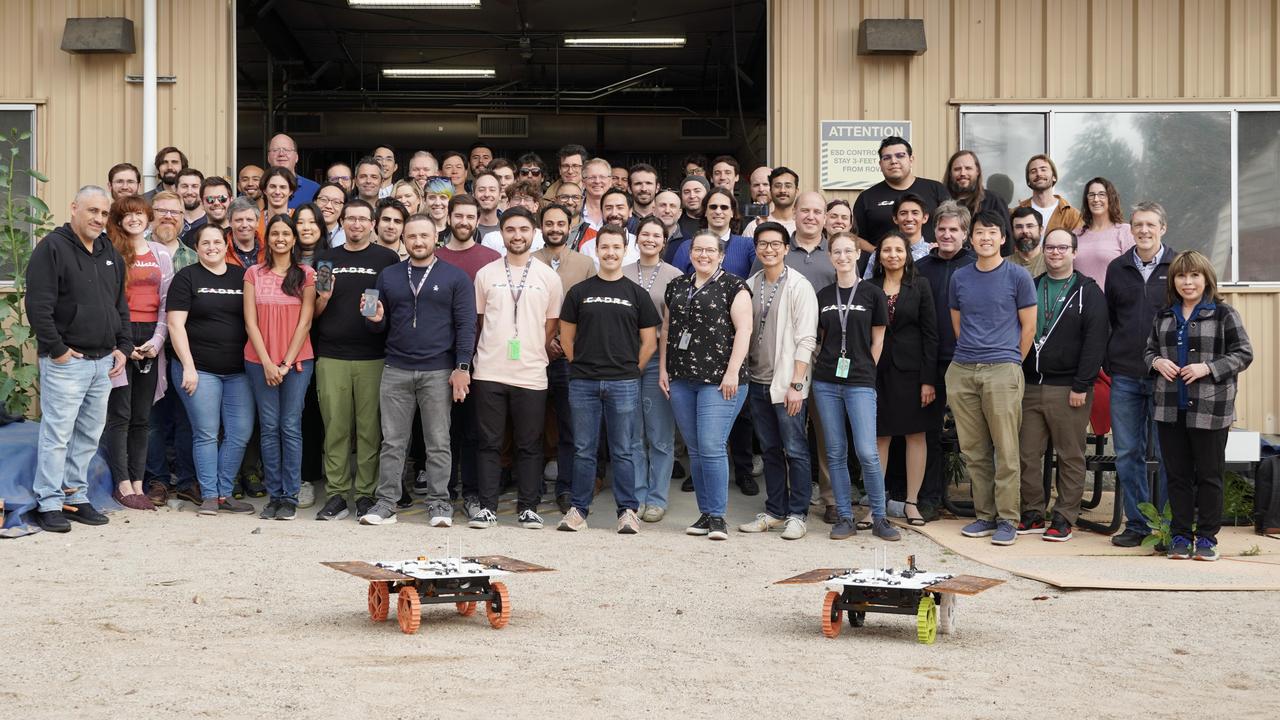

Members of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration team pose with two full-scale development model rovers in the Mars Yard at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in January 2024. The project is designed to show that a group of robotic spacecraft can work together as a team to accomplish tasks and record data autonomously – without explicit commands from mission controllers on Earth. Three small rovers will ride aboard a lunar lander that will carry the project's base station and camera assembly. The rovers shown here are similar in size and appearance to the flight models that will travel to the Moon. Equipped with flight software and autonomy capabilities, these development models were used in a series of Mars Yard tests that helped confirm CADRE hardware and software can work together to accomplish key goals for the project. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26170
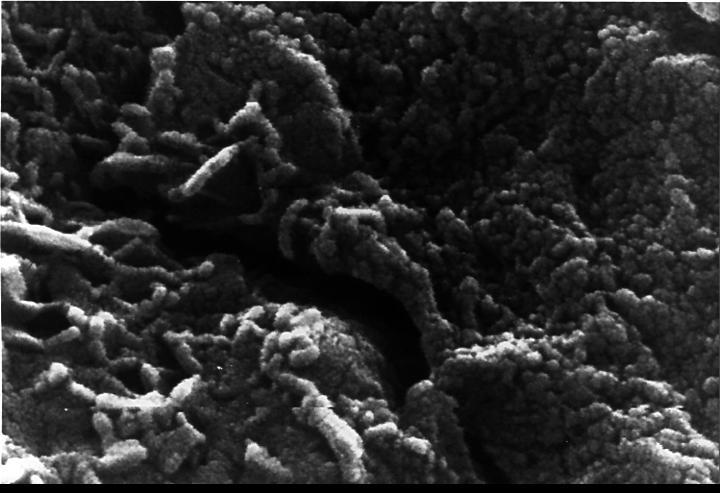

This electron microscope image shows extremely tiny tubular structures that are possible microscopic fossils of bacteria-like organisms that may have lived on Mars more than 3.6 billion years ago. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00285

This 4.5 billion-year-old rock, labeled meteorite ALH84001, is one of 10 rocks from Mars in which researchers have found organic carbon compounds that originated on Mars without involvement of life. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00289
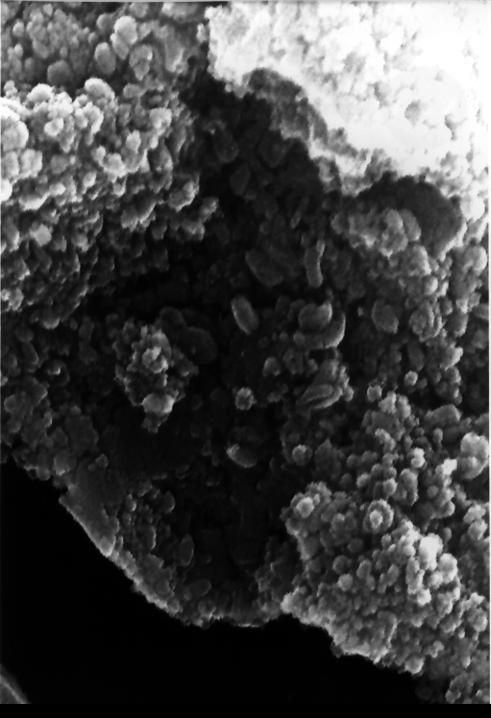
This electron microscope image shows egg-shaped structures, some of which may be possible microscopic fossils of Martian origin as discussed by NASA research published in the Aug. 16, 1996. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00286
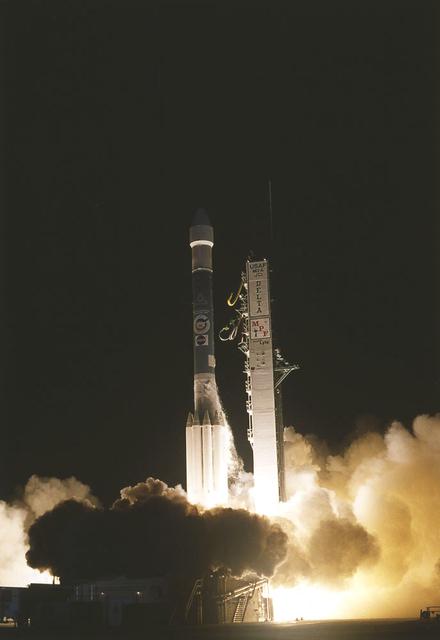

The Mars Pathfinder began the journey to Mars with liftoff atop a Delta II expendable launch vehicle from launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Station. The Mars Pathfinder traveled on a direct trajectory to Mars, and arrived there in July 1997. Mars Pathfinder sent a lander and small robotic rover, Sojourner, to the surface of Mars. The primary objective of the mission was to demonstrate a low-cost way of delivering a science package to the surface of Mars using a direct entry, descent and landing with the aid of small rocket engines, a parachute, airbags and other techniques. In addition, landers and rovers of the future will share the heritage of Mars Pathfinder designs and technologies first tested in this mission. Pathfinder also collected invaluable data about the Martian surface.
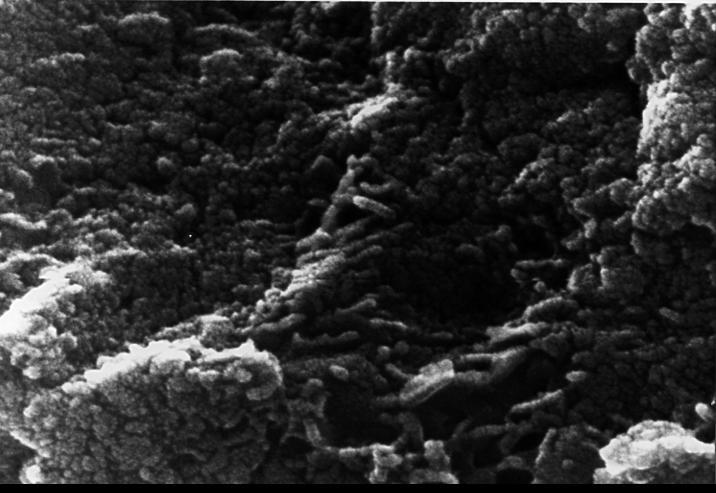
This electron microscope image shows tubular structures of likely Martian origin. These structures are very similar in size and shape to extremely tiny microfossils found in some Earth rocks. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00287
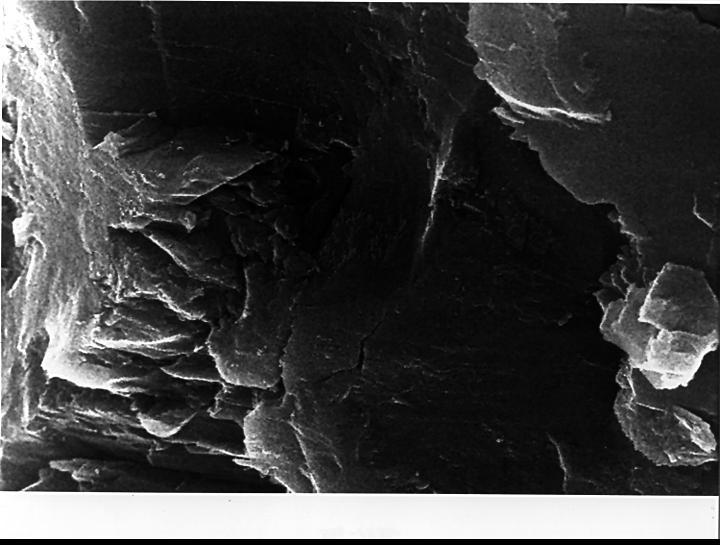
In the center of this electron microscope image of a small chip from a meteorite are several tiny structures that are possible microscopic fossils of primitive, bacteria-like organisms that may have lived on Mars more than 3.6 billion years ago. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00283
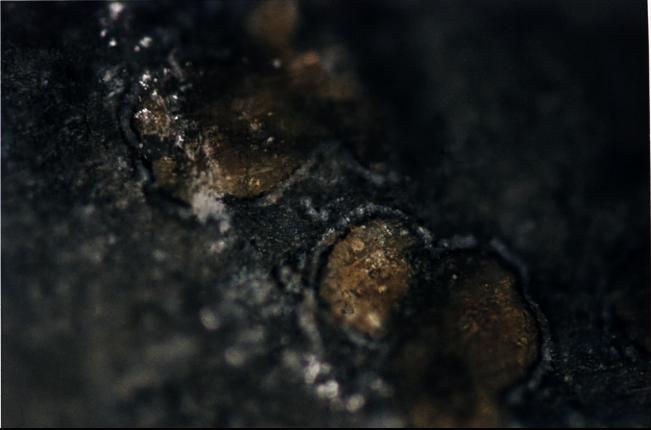

This photograph shows orange-colored carbonate mineral globules found in a meteorite, called ALH84001, believed to have once been a part of Mars. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00290
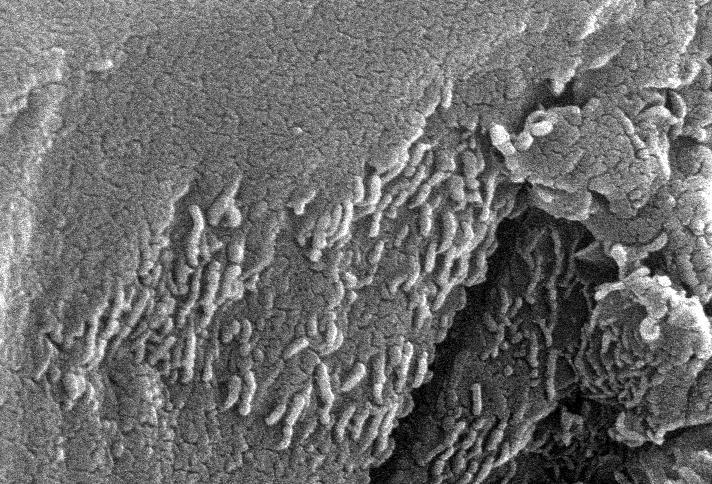
This electron microscope image is a close-up of the center part of photo number S96-12301. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00284