
Astronaut L. Gordon Cooper, Jr., one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The MA-9 mission, boosted by the Mercury-Atlas launch vehicle, was the last flight of the Mercury Project. The Faith 7 spacecraft orbited the Earth 22 times in 1-1/2 days.

Astronaut John H. Glenn, one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The MA-6 mission, boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, was the first manned orbital launch by the United States, and carried Astronaut Glenn aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft to orbit the Earth.

Christopher Kraft, flight director during Project Mercury, works at his console inside the Flight Control area at Mercury Mission Control.

Astronaut Alan B. Shepard, one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The Freedom 7 spacecraft boosted by Mercury-Redstone vehicle for the MR-3 mission made the first marned suborbital flight and Astronaut Shepard became the first American in space.

Astronaut Walter M. "Wally" Schirra, one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The MA-8 (Mercury-Atlas) mission with Sigma 7 spacecraft was the third marned orbital flight by the United States, and made the six orbits in 9-1/4 hours.

Astronaut Virgil I. "Gus" Grissom, one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The MR-4 mission, boosted by the Mercury-Redstone vehicle, made the second marned suborbital flight. The capsule, Liberty Bell 7, sank into the sea after the splashdown.

The original seven astronauts for the Mercury Project pose in front of an Air Force Jet. From left to right: Scott Carpenter, L. Gordon Cooper, John H. Glenn, Virgil I. Gus Grissom, Walter M. Wally Schirra, Alan B. Shepard, and Donald K. Deke Slayton.

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz
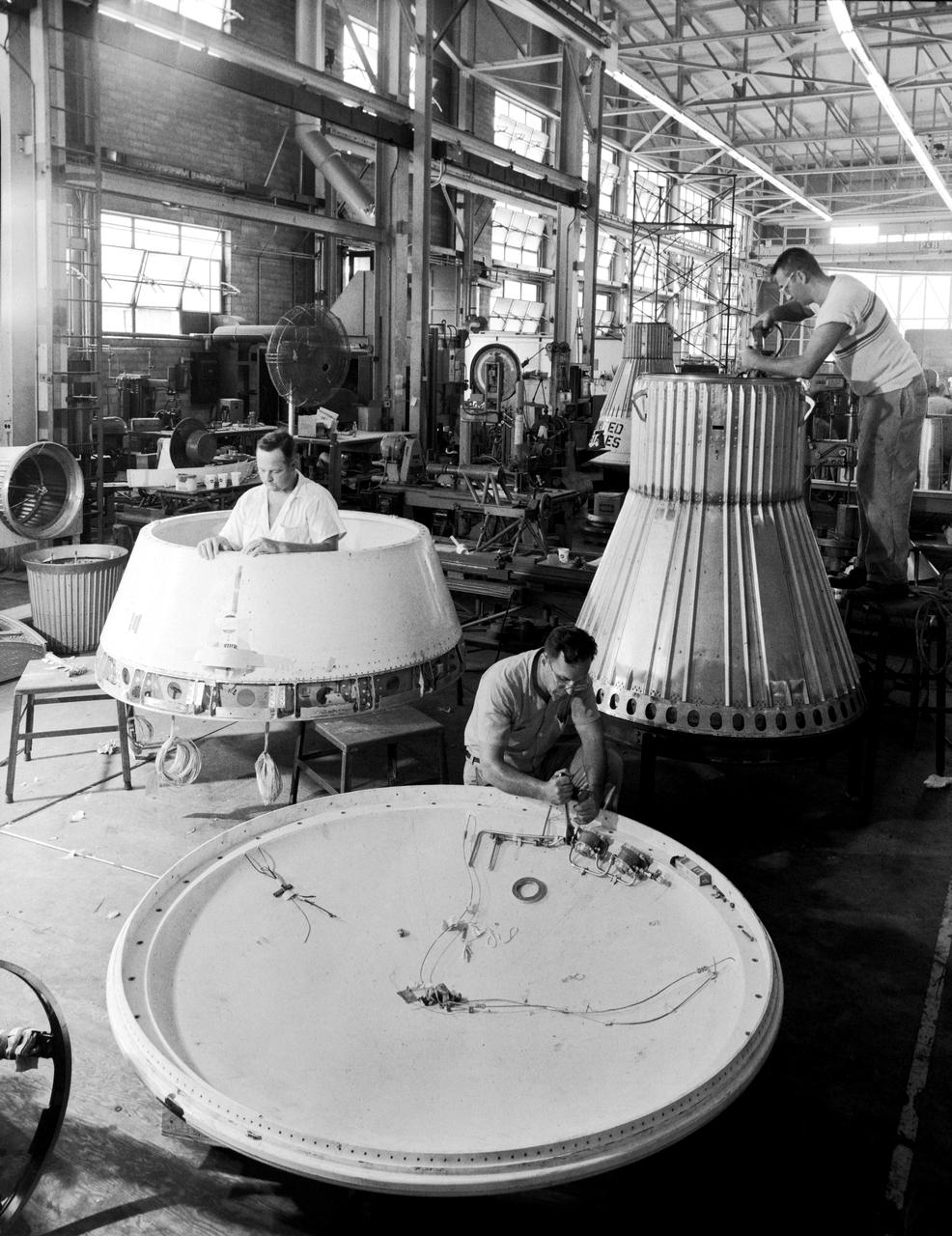

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz
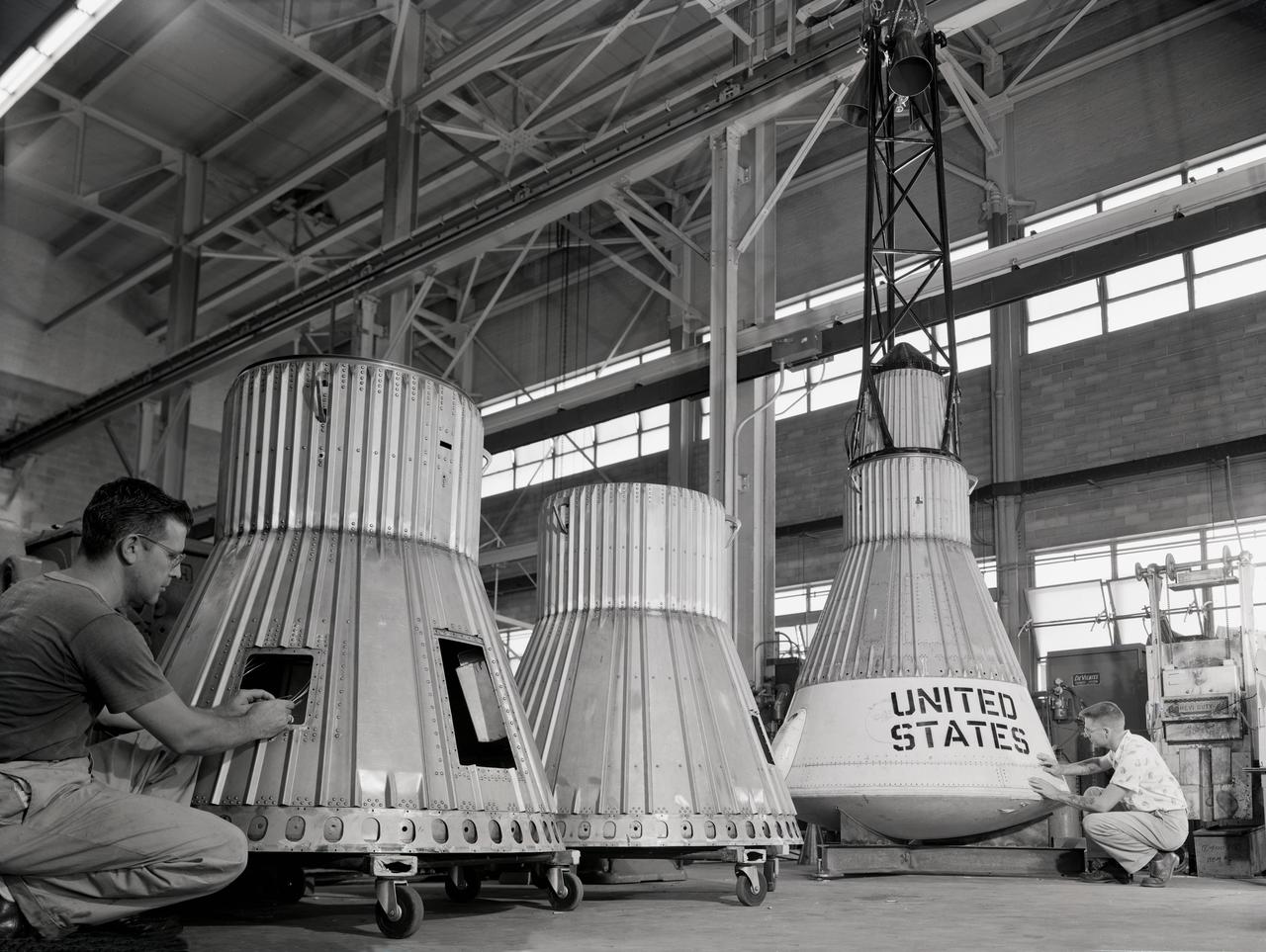

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz

Assembling the Little Joe capsules. The capsules were manufactured in-house by Langley technicians. Three capsules are shown here in various stages of assembly. The escape tower and rocket motors shown on the completed capsule would be removed before shipping and finally assembly for launching at Wallops Island. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 32): Design of the Little Joe capsules began at Langley before McDonnell started on the design of the Mercury capsule and was, therefore, a separate design. Although it was not designed to carry a man, it did have to carry a monkey. It had to meet the weight and center of gravity requirements of Mercury and withstand the same aerodynamic loads during the exit trajectory. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. Project Mercury: Little Joe: Boilerplate Mercury spacecraft undergo fabrication at the shops of the Langley Research Center. They will launched atop Little Joe rockets to test the spacecraft recovery systems. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition. L59-4947 Technicians prepare a Little Joe launch vehicle prototype for the Mercury space program, 1959. Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, page 76, by James Schultz
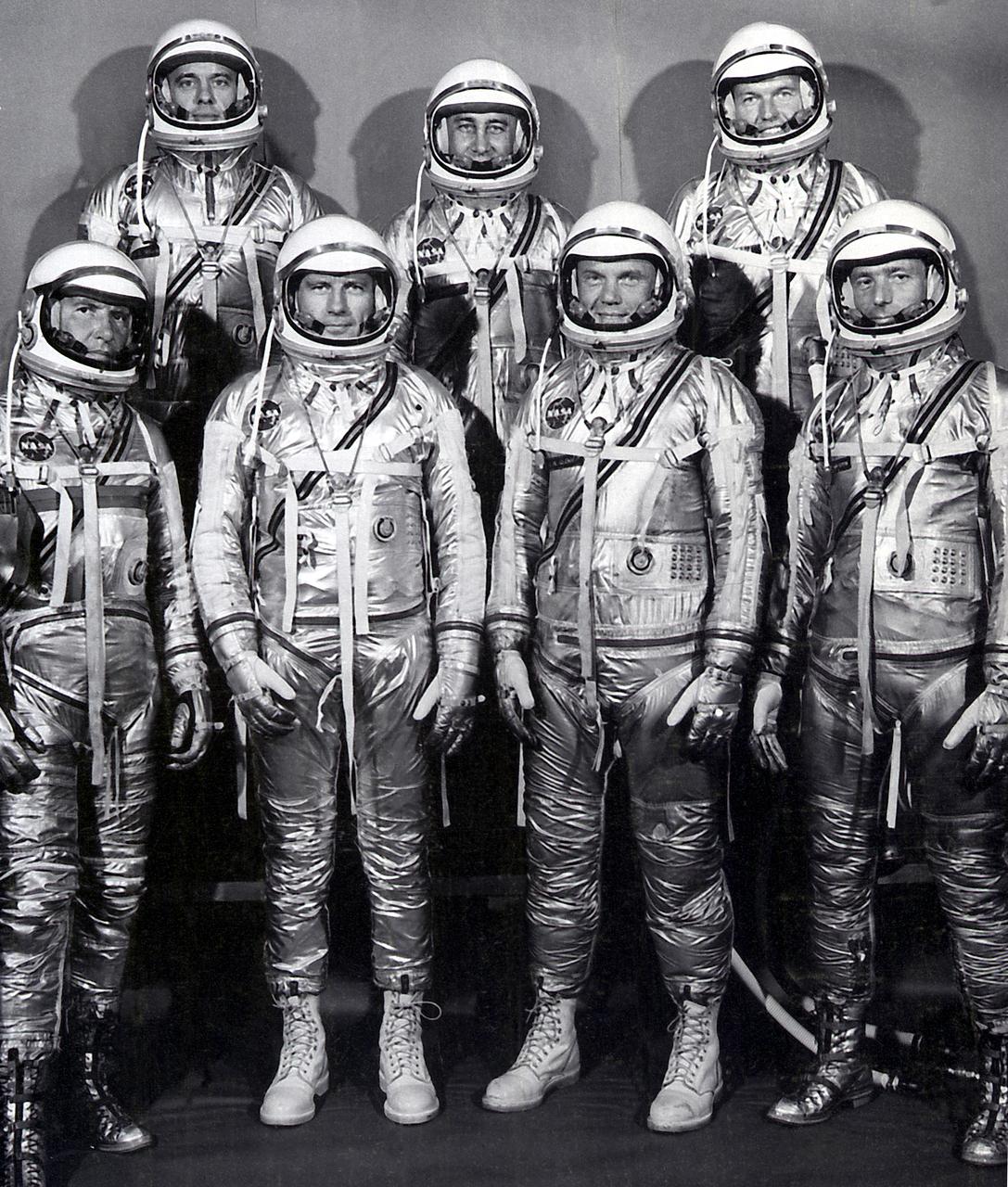

The group portrait of the original seven astronauts for the Mercury Project. NASA selected its first seven astronauts on April 27, 1959. Left to right at front: Walter M. Wally Schirra, Donald K. Deke Slayton, John H. Glenn, Jr., and Scott Carpenter. Left to right at rear: Alan B. Shepard, Virgil I. Gus Grissom, and L. Gordon Cooper, Jr.
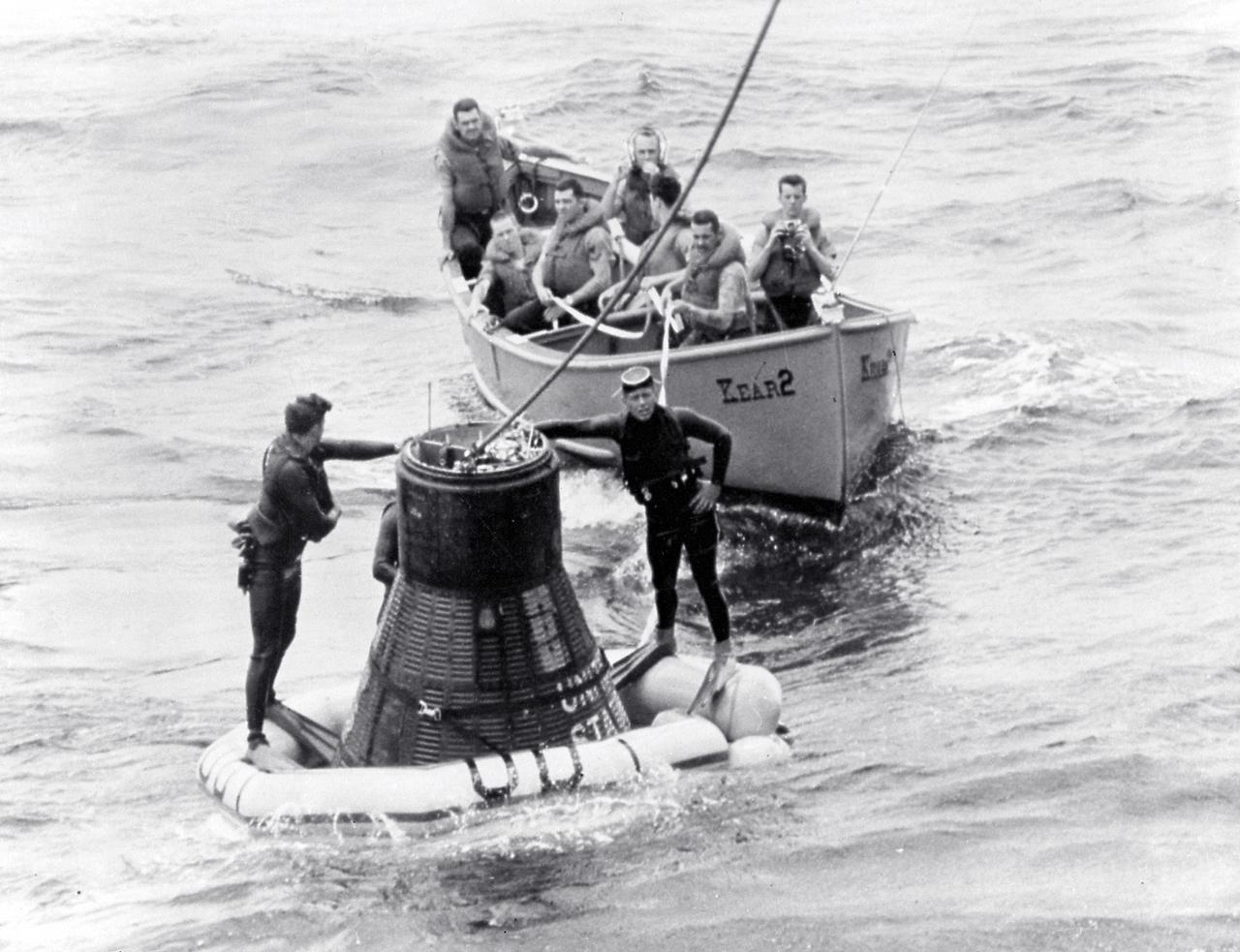

The recovery operation of the Faith 7 spacecraft after the completion of the 1-1/2 day orbital flight (MA-9 mission) with Astronaut Gordon Cooper. Navy frogmen attach the flotation collar to the spacecraft. The MA-9 mission was the last flight of the Mercury Project and launched on May 15, 1963 boosted by The Mercury-Atlas launch vehicle.
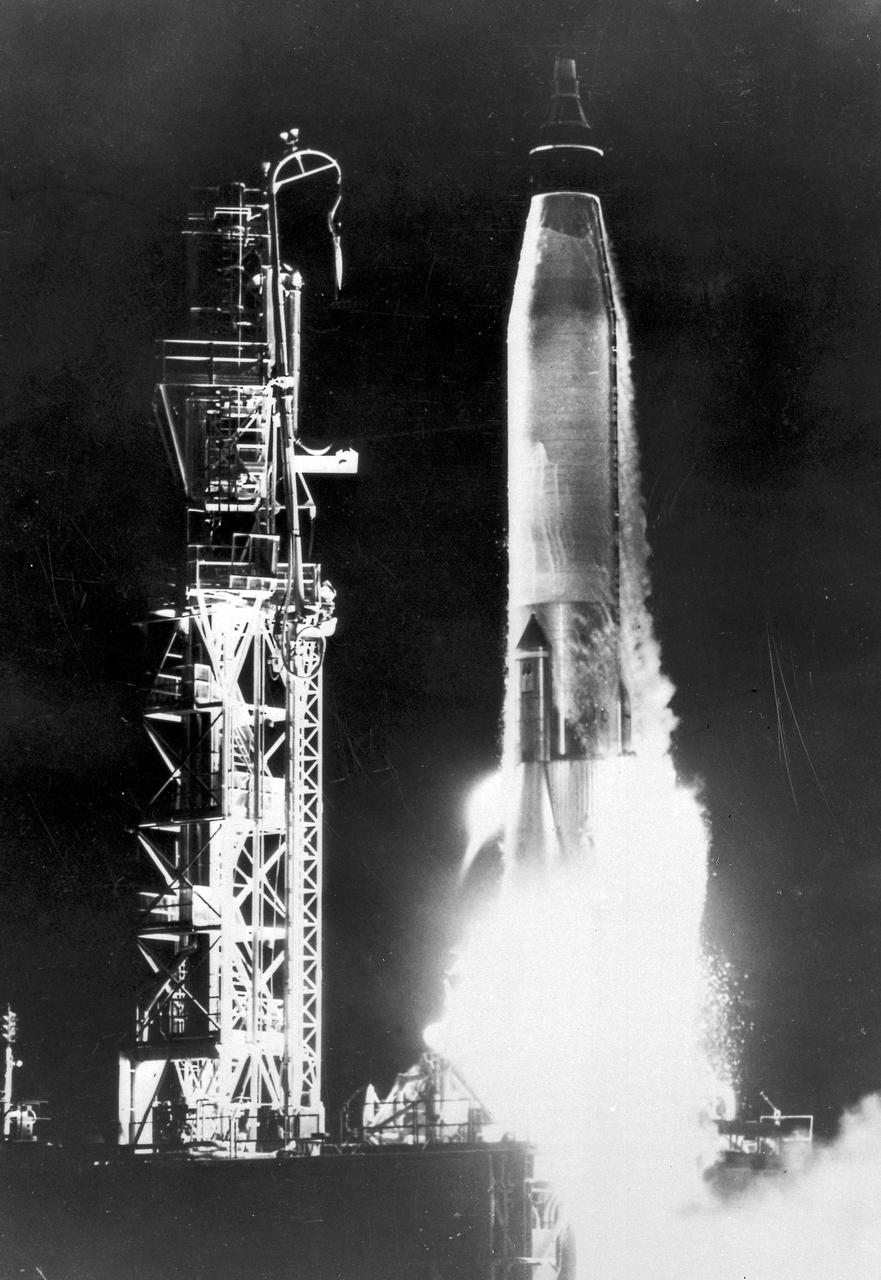

An Atlas launch vehicle carrying the Big Joe capsule leaves its launching pad on a 2,000-mile ballistic flight to the altitude of 100 miles. The Big Joe capsule is a boilerplate model of the marned orbital capsule under NASA's Project Mercury. The capsule was recovered and studied for the effect of re-entry heat and other flight stresses.
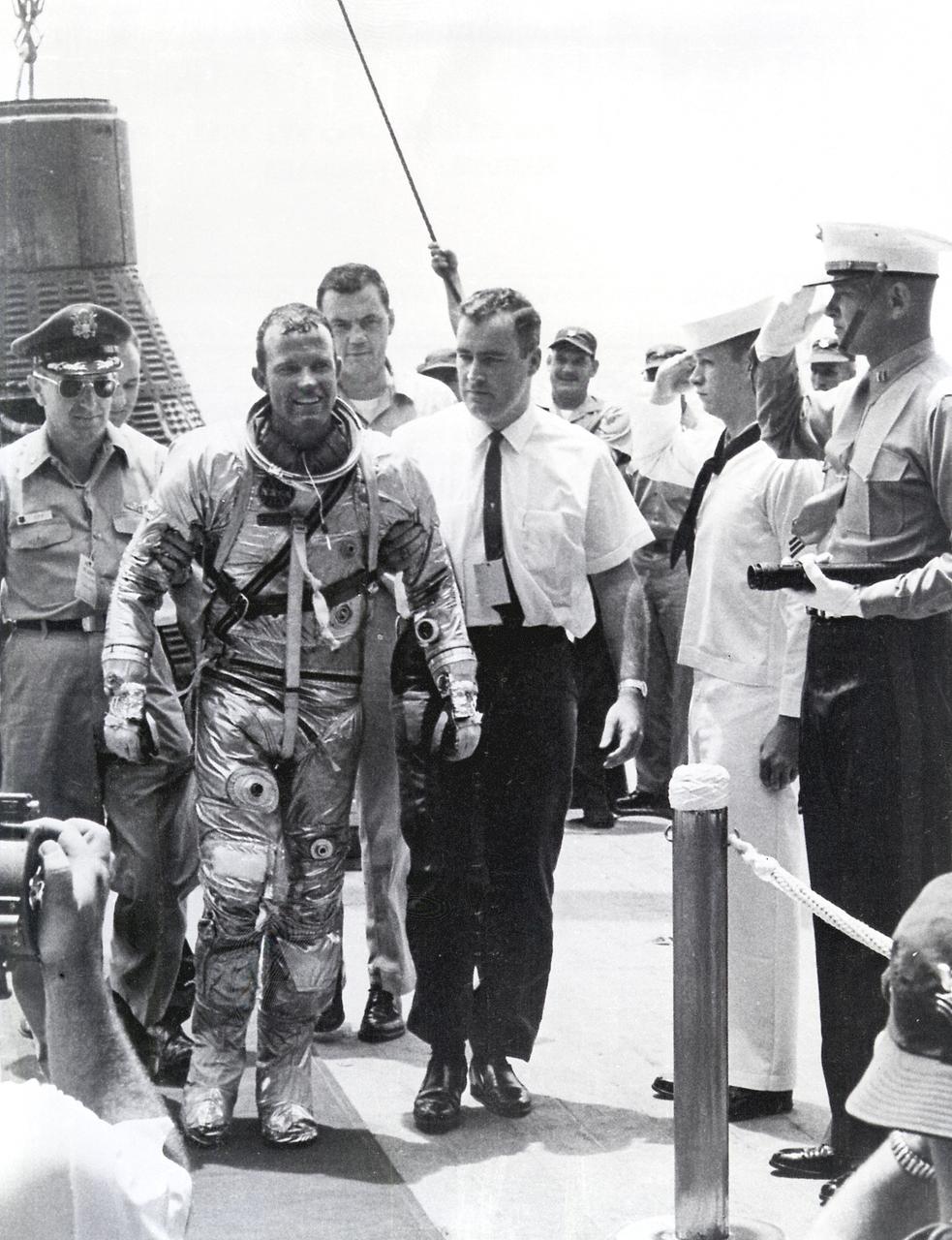

Astronaut Gordon Cooper leaves the Faith 7 (MA-9) spacecraft after a successful recovery operation. The MA-9 mission, the last flight of the Mercury Project, was launched on May 15, 1963, orbited the Earth 22 times, and lasted for 1-1/2 days.
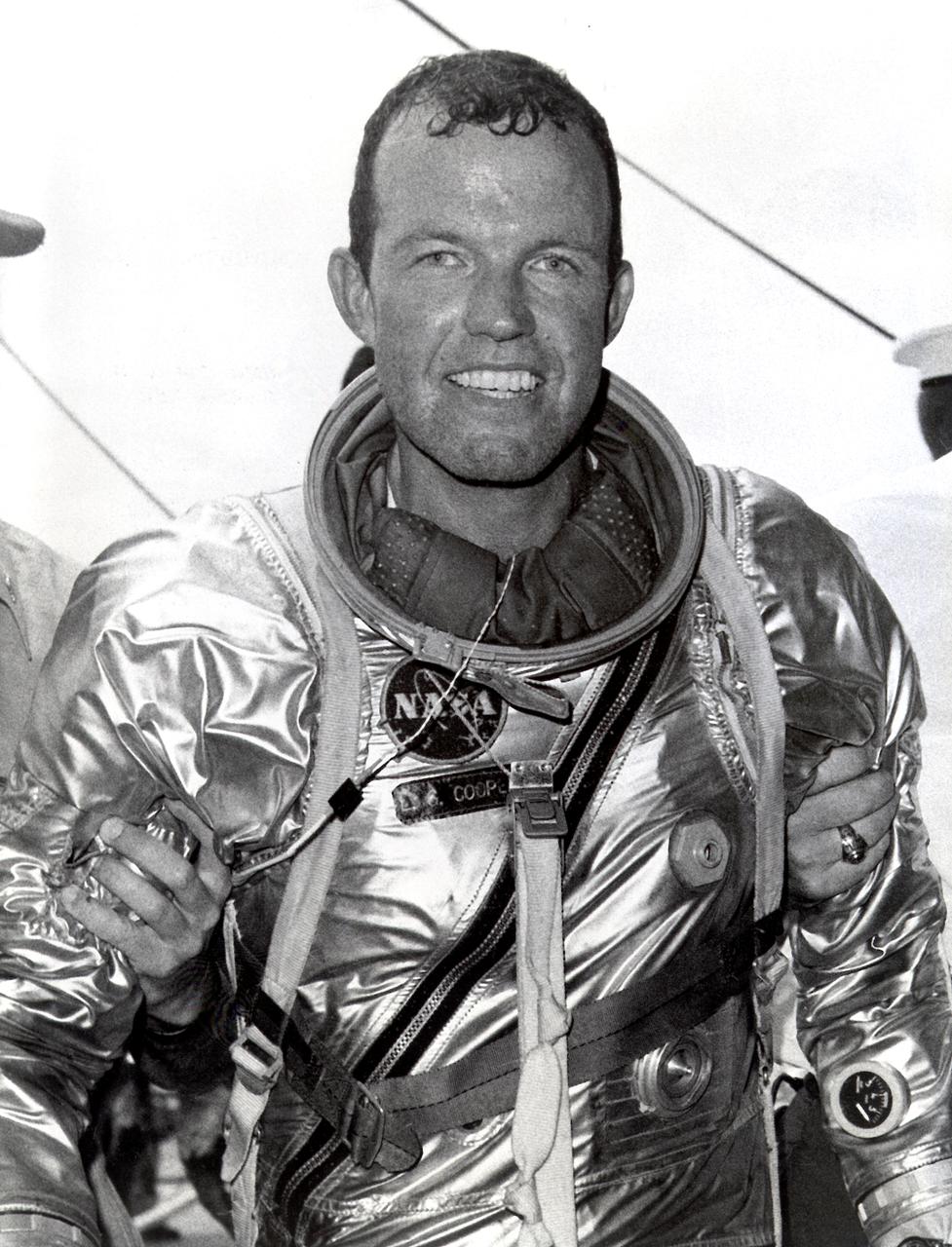

Astronaut Gordon Cooper leaves the Faith 7 (MA-9) spacecraft after a successful recovery operation. The MA-9 mission, the last flight of the Mercury Project, was launched on May 15, 1963, orbited the Earth 22 times, and lasted for 1-1/2 days.

NASA Project Mercury astronaut.
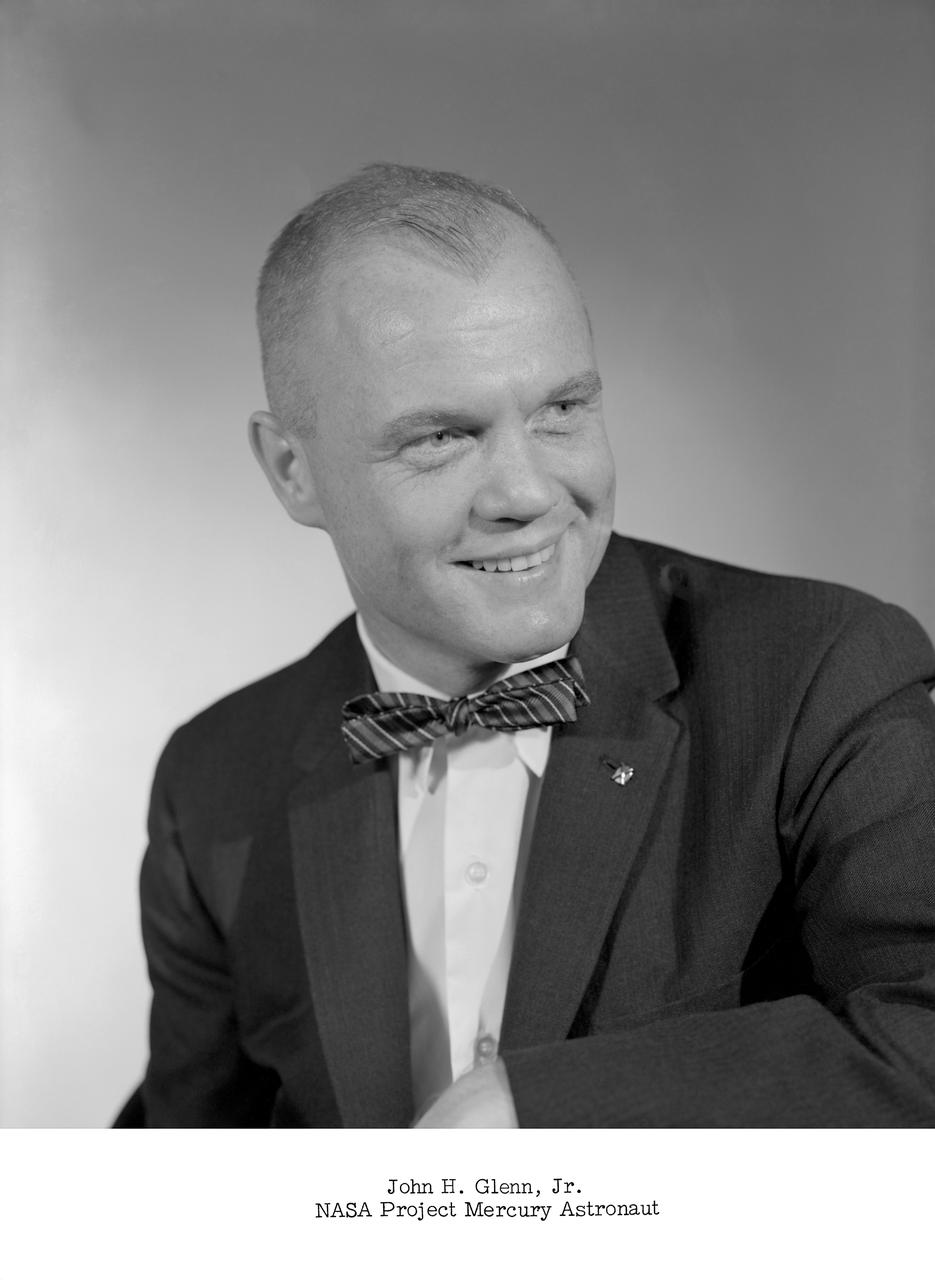

NASA Project Mercury astronaut.
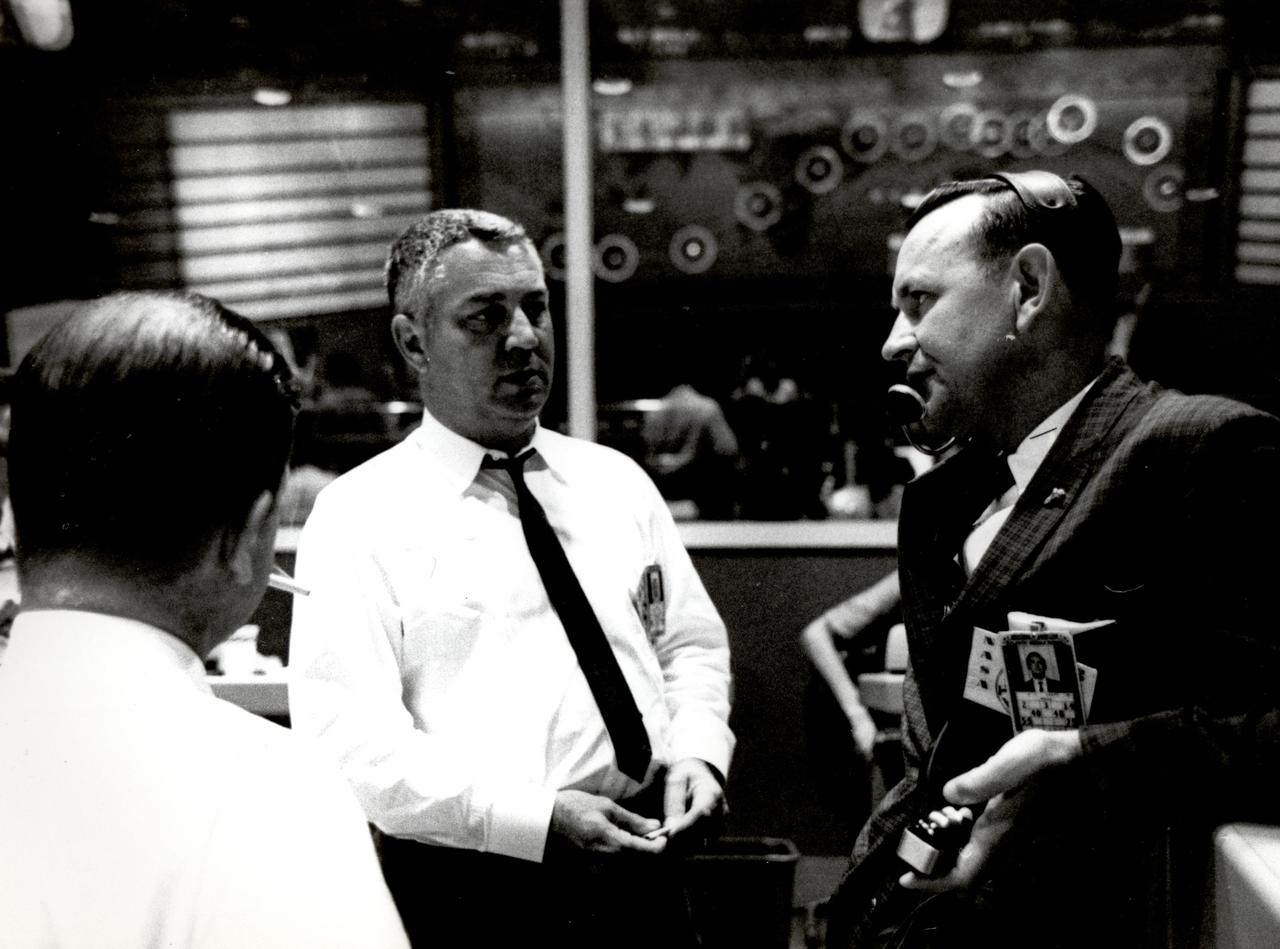

Inside Mercury flight control, Walter C. Williams, associate director for Project Mercury operations (center) listens to Christopher Kraft, flight director (right).
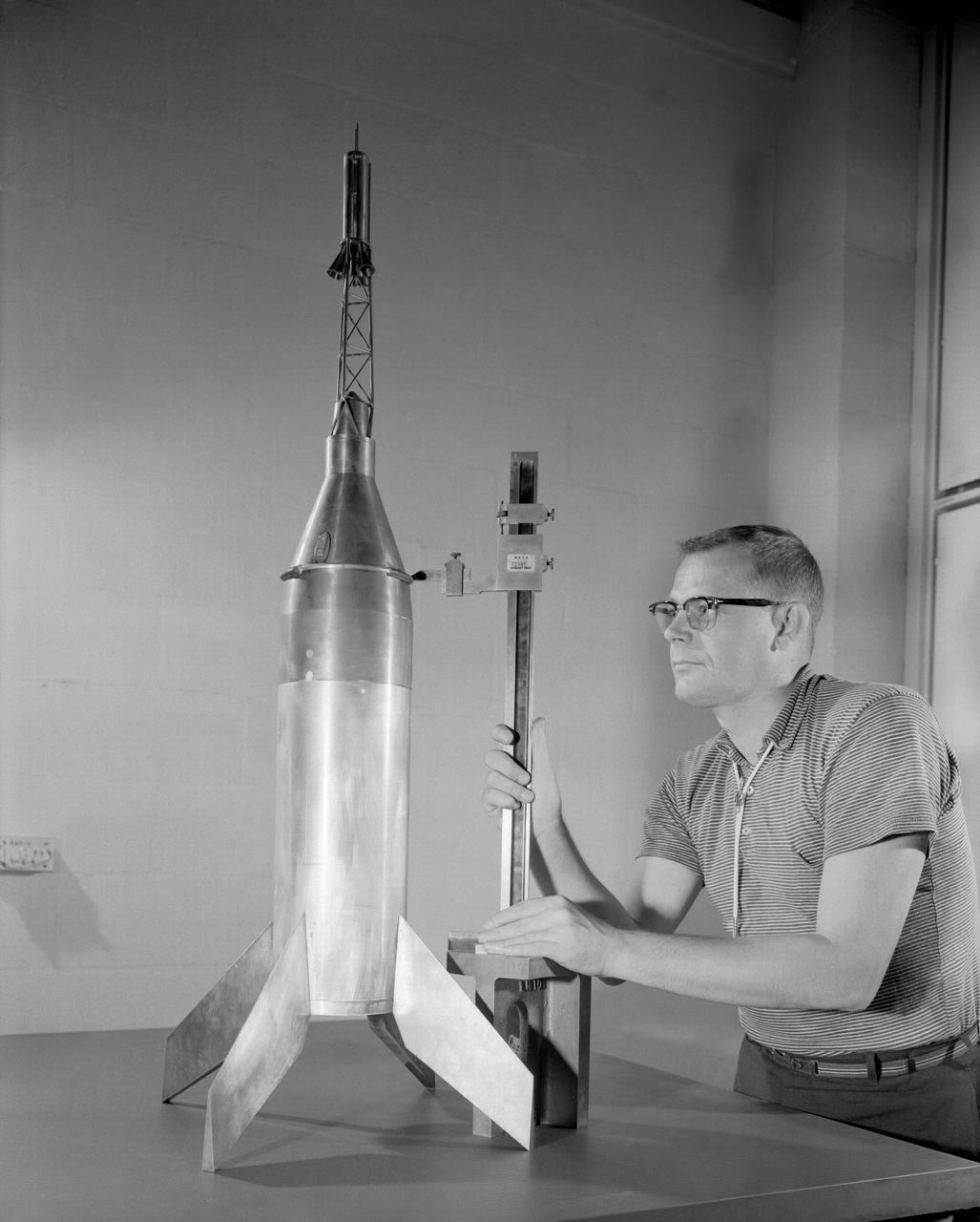

Publicity photograph of a technician measuring a wind tunnel model of the Little Joe test vehicle. Joseph Shortal noted that (vol. 3, p. 29): The largest project at Wallops in support of Mercury was the Little Joe project, designed to qualify the abort-escape system under flight conditions. James Hansen (p. 47) writes: STG engineers Max Faget and Paul Purser, then of Langley's PARD, had conceived Little Joe as a space capsule test vehicle even before the establishment of NASA and the formation of the STG. Girlruth understood the importance of the Little Joe tests: We had to be sure there were no serious performance and operational problems that we had simply not thought of in such a new and radical type of flight vehicle. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 47 Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
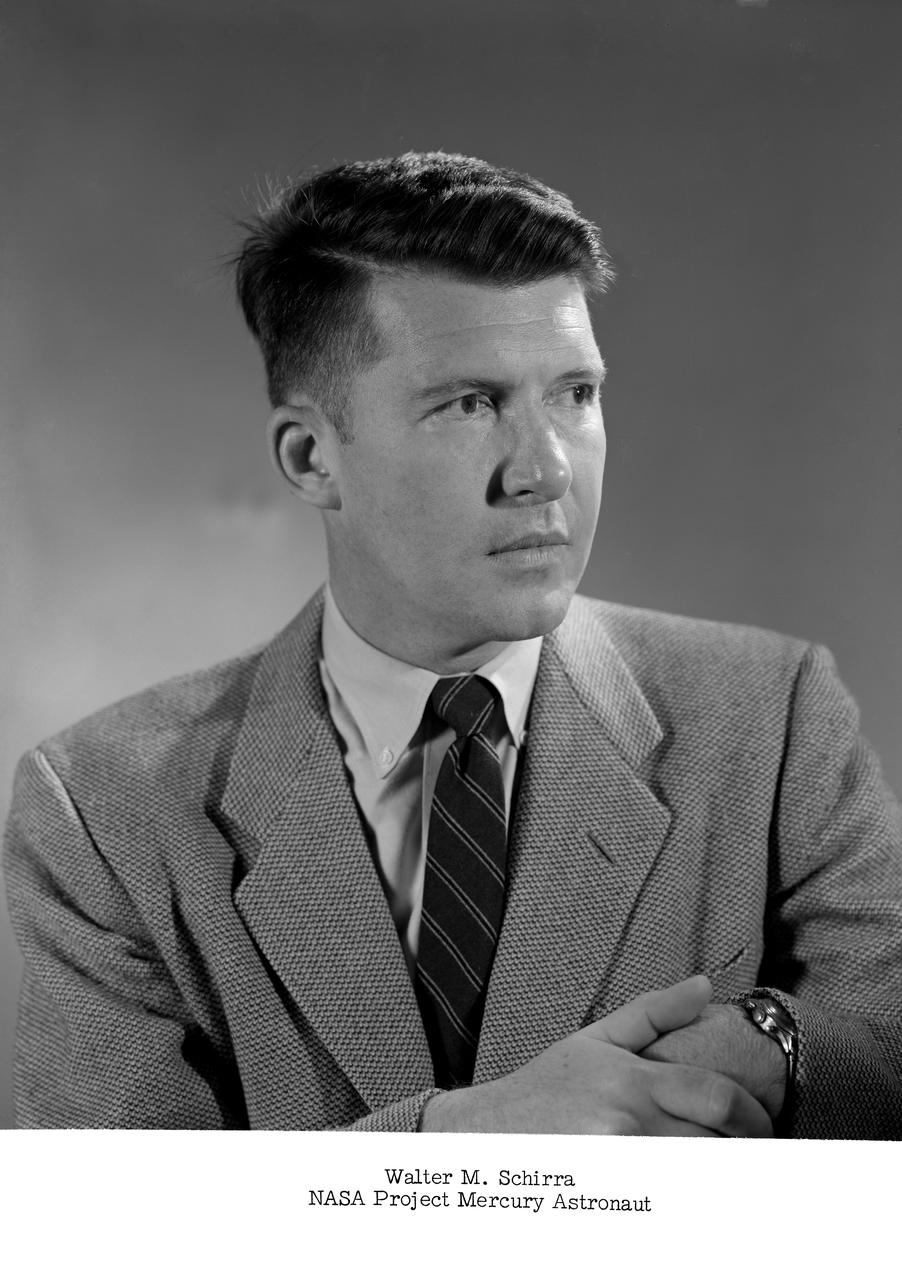

NASA Project Mercury astronaut. -- Schirra was later known as Wally .
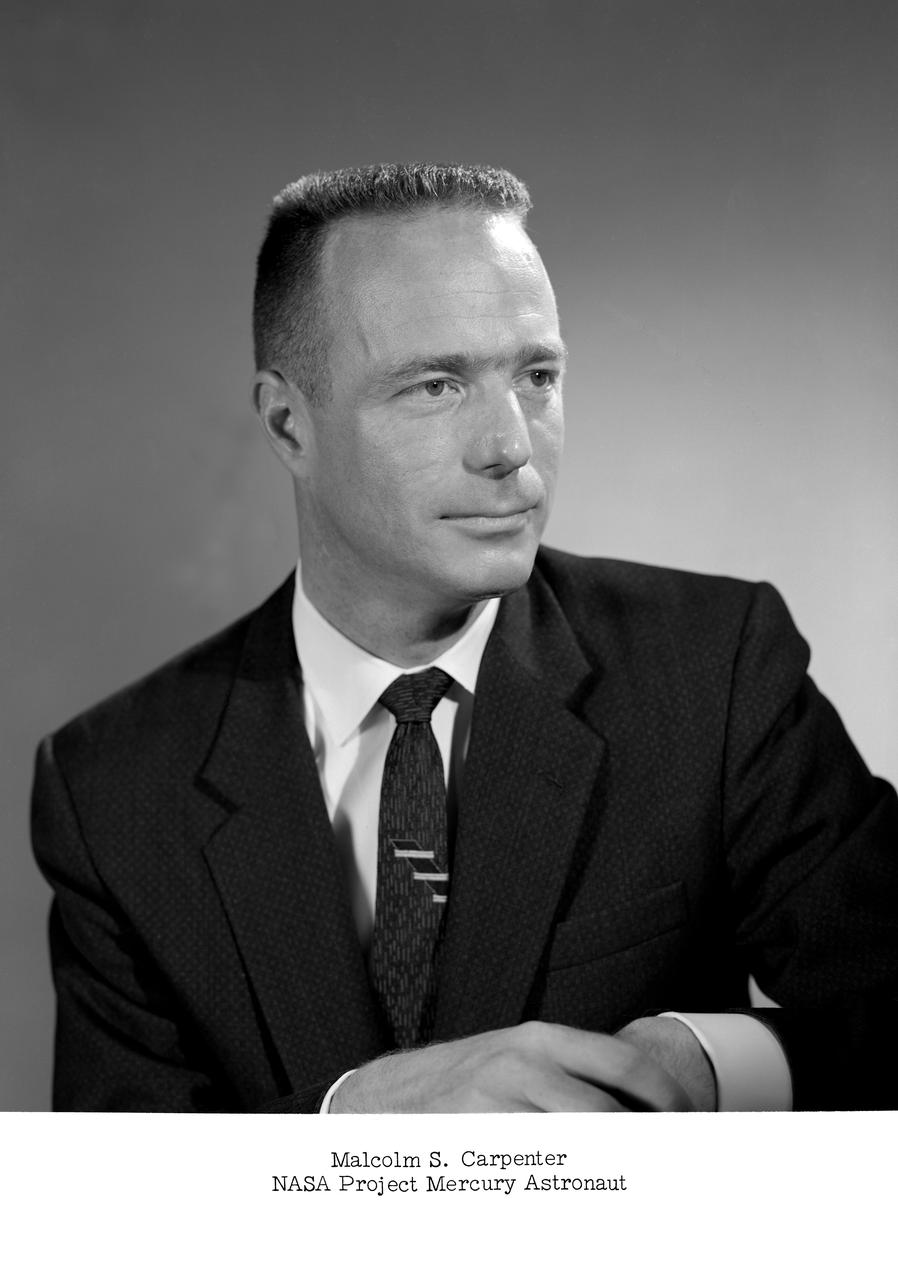

NASA Project Mercury astronaut. -- Carpenter was later known as M. Scott Carpenter.
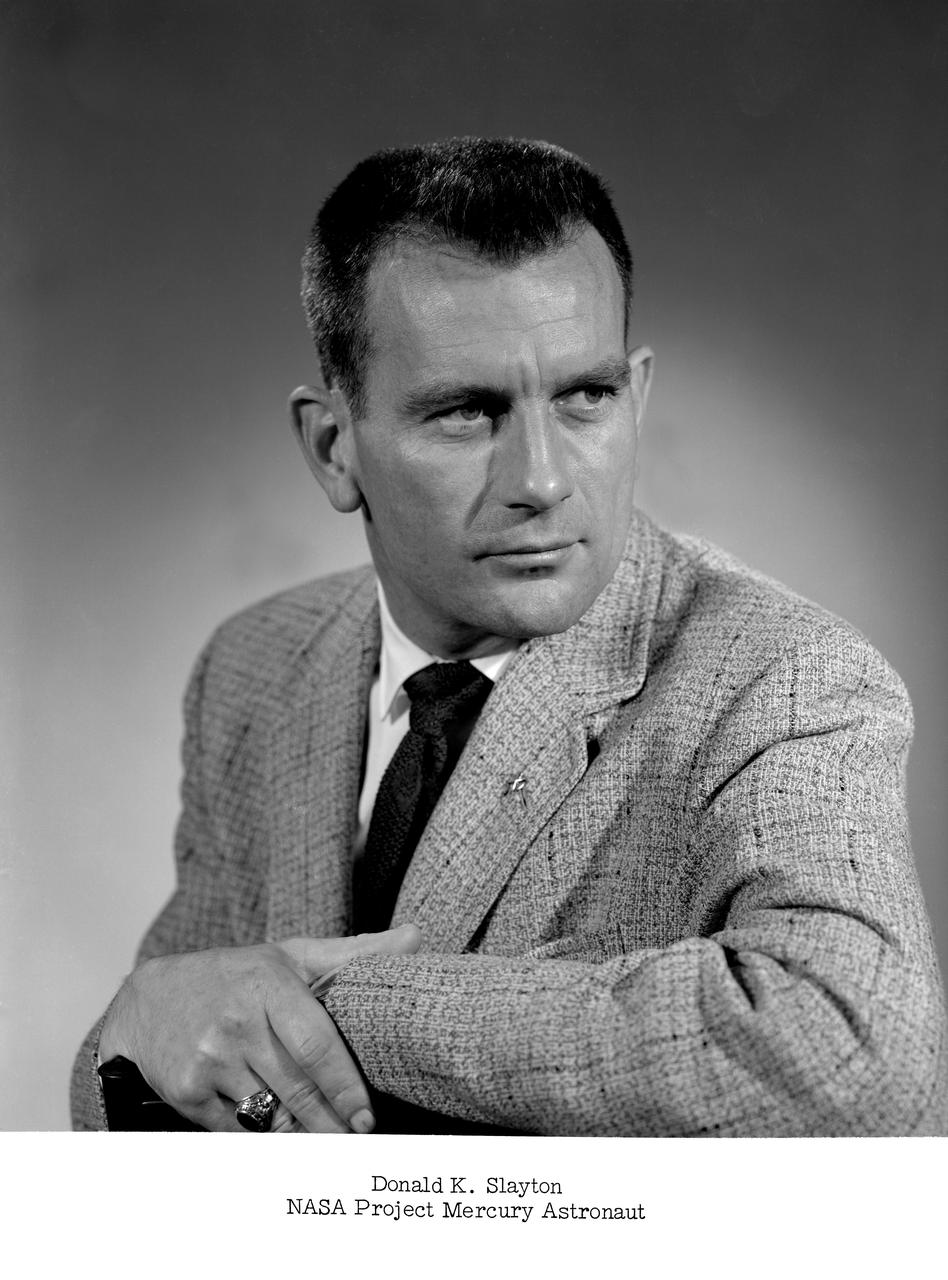

NASA Project Mercury astronaut -- Slayton was later known as Deke.
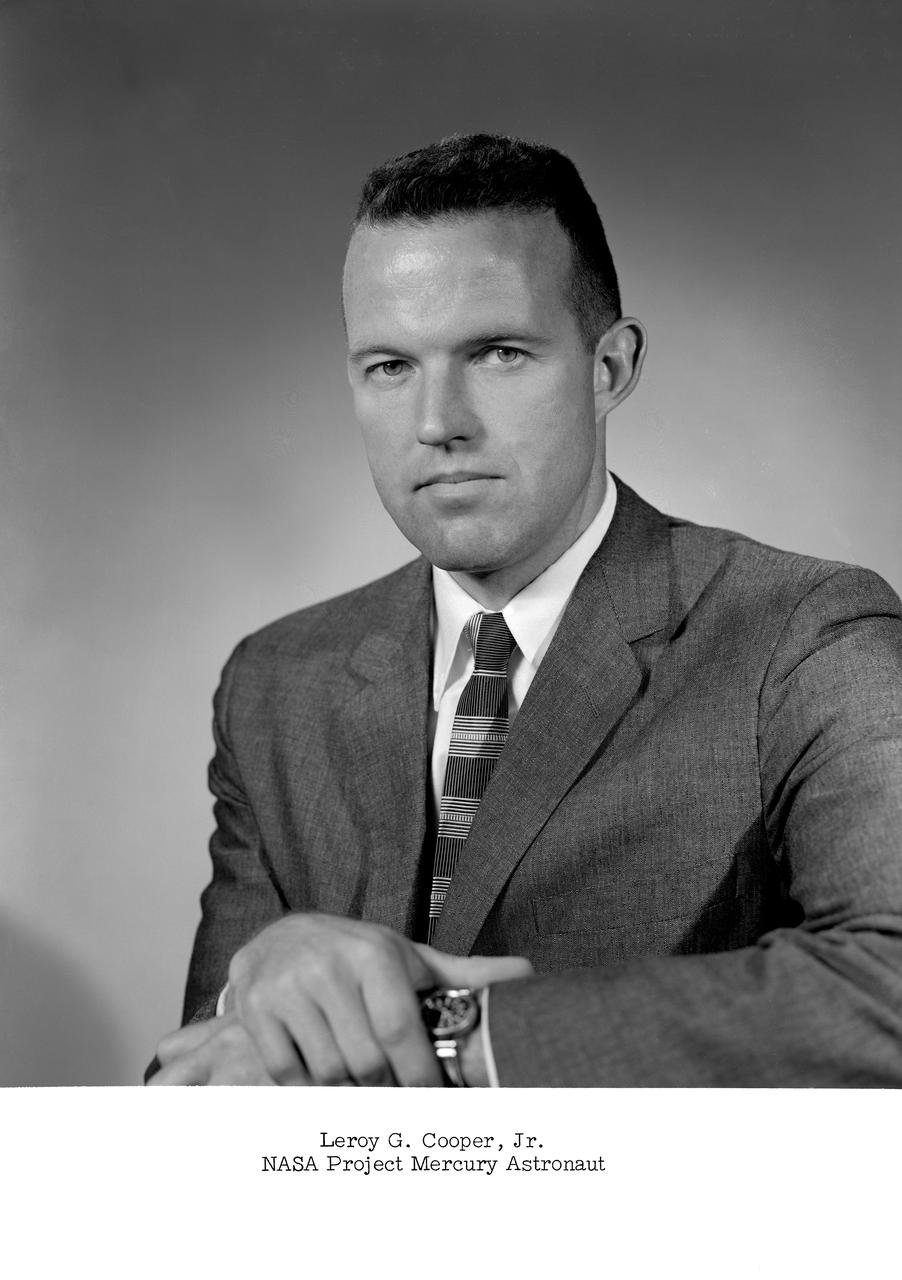

NASA Project Mercury astronaut. -- Cooper was later known as L. Gordon Cooper.
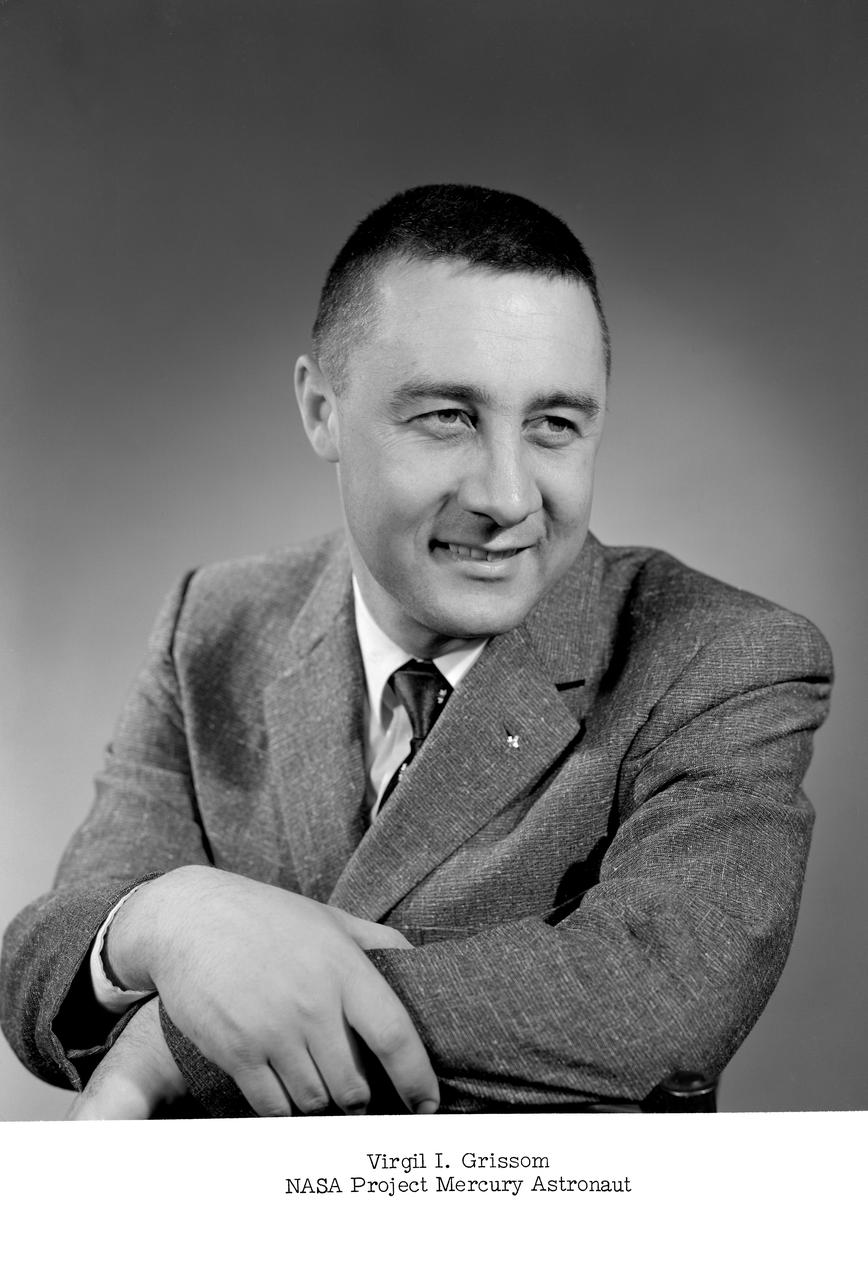

NASA Project Mercury astronaut. -- Grissom was later known as Gus .
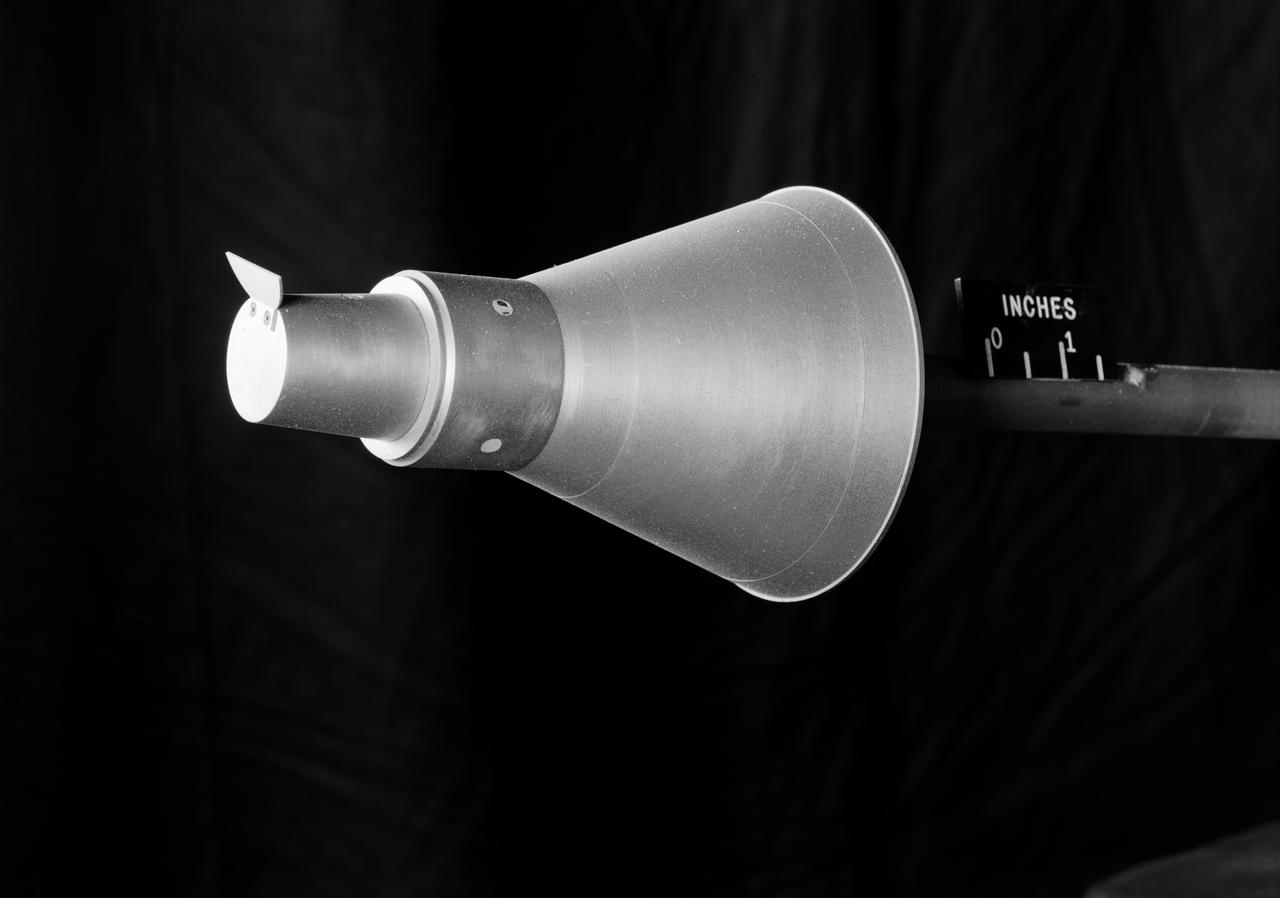

Model of Mercury capsule used for wind tunnel testing.
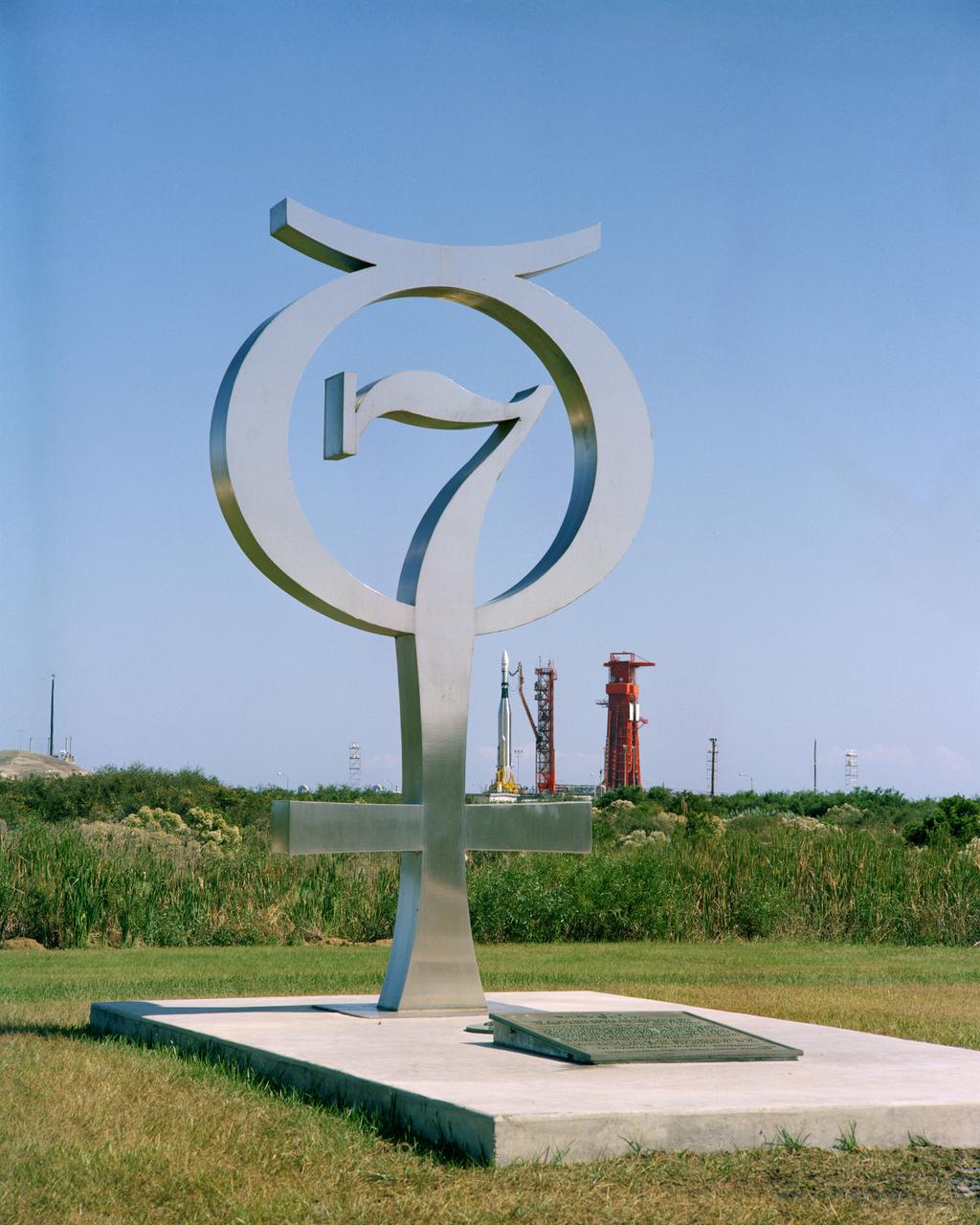

S66-59963 (9 Nov. 1966) --- Monument at Pad 14 honoring Project Mercury. The Arabic number seven represents the seven original astronauts. The other figure is the astronomical symbol of the Planet Mercury. In background is the Gemini-12 Agena Target Docking Vehicle atop its Atlas launch vehicle at Cape Kennedy, Florida. Photo credit: NASA
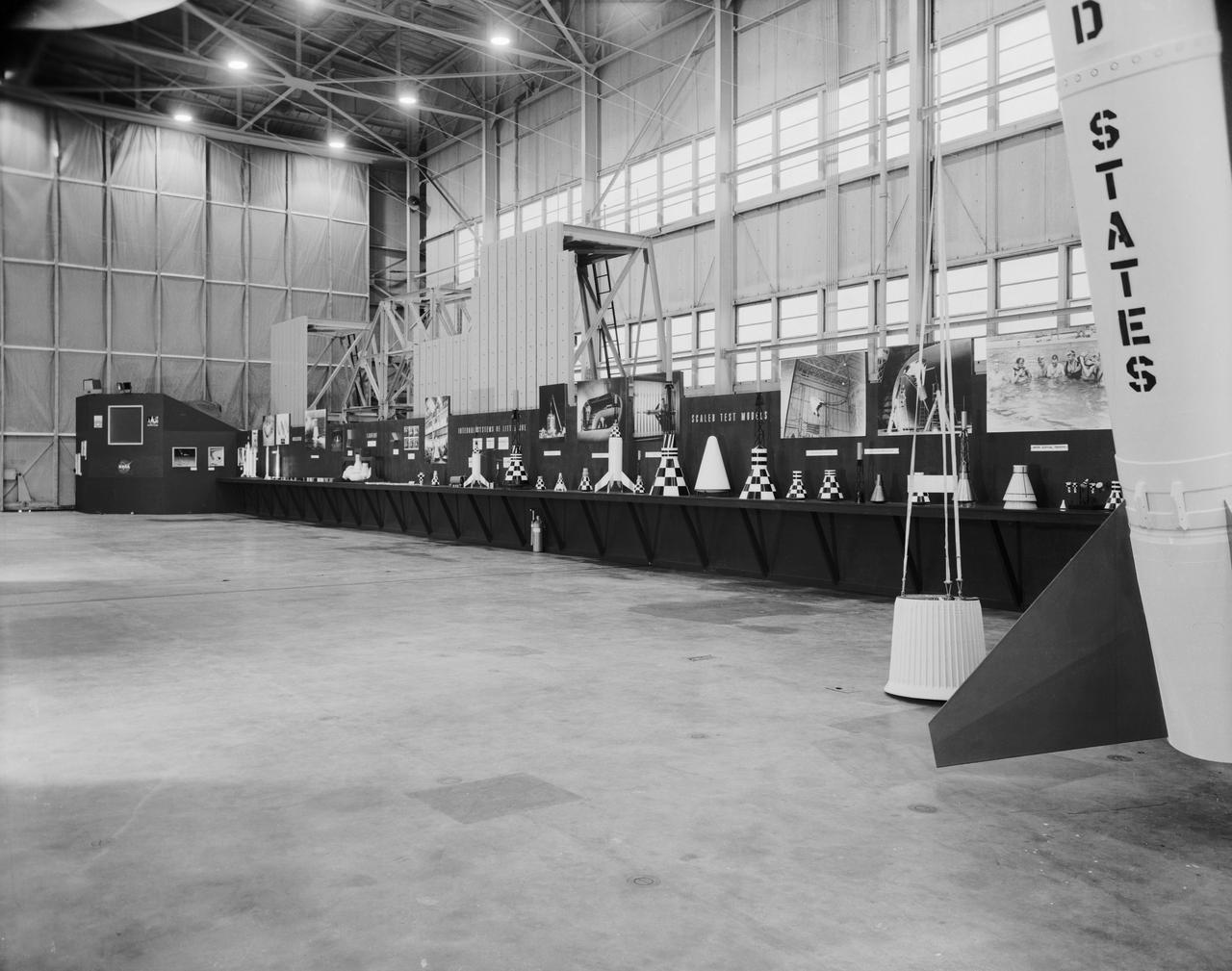

Mock-up of the Mercury capsule on display at the first NASA inspection held on October 24, 1959.
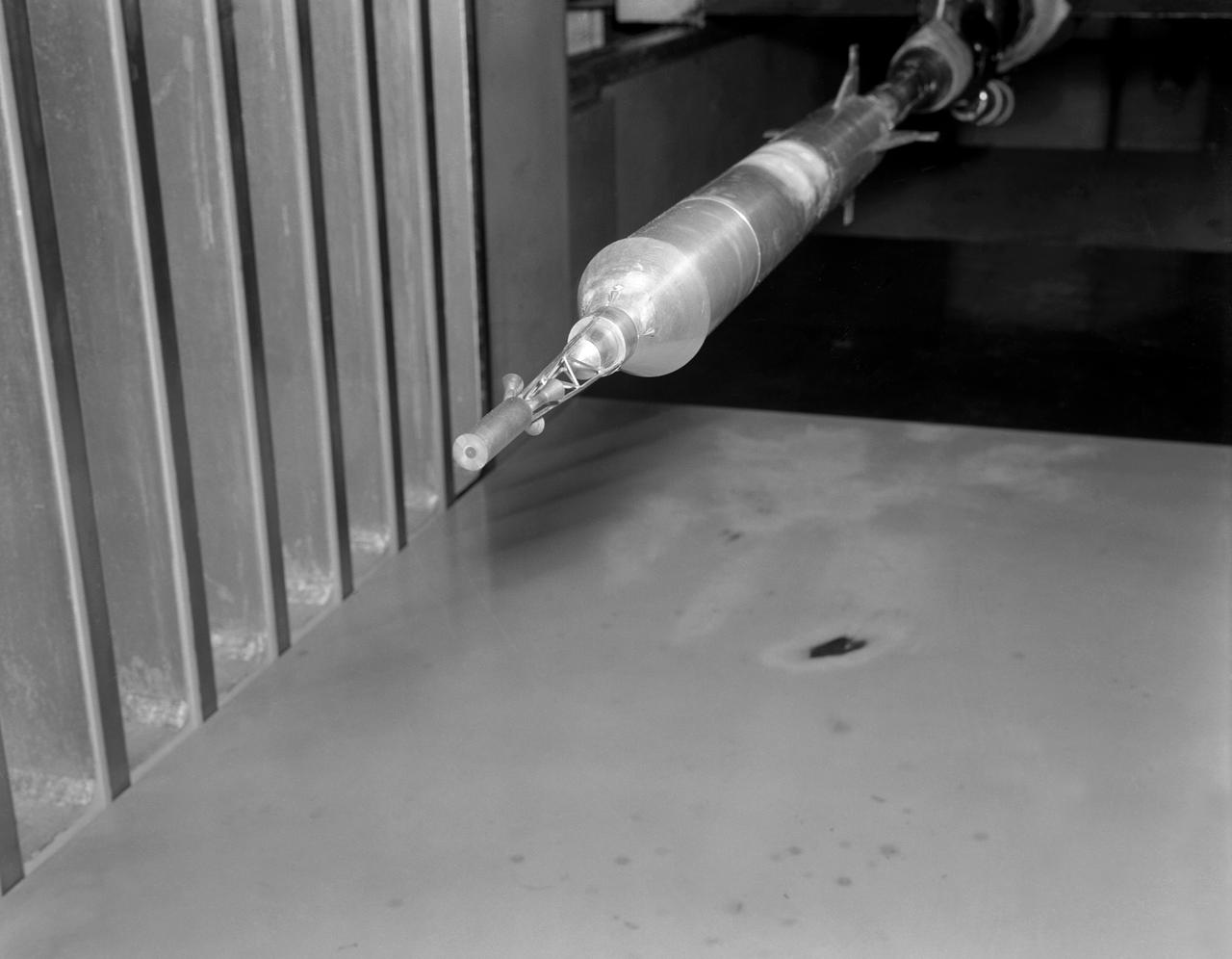

Model of Mercury being tested in the Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel.
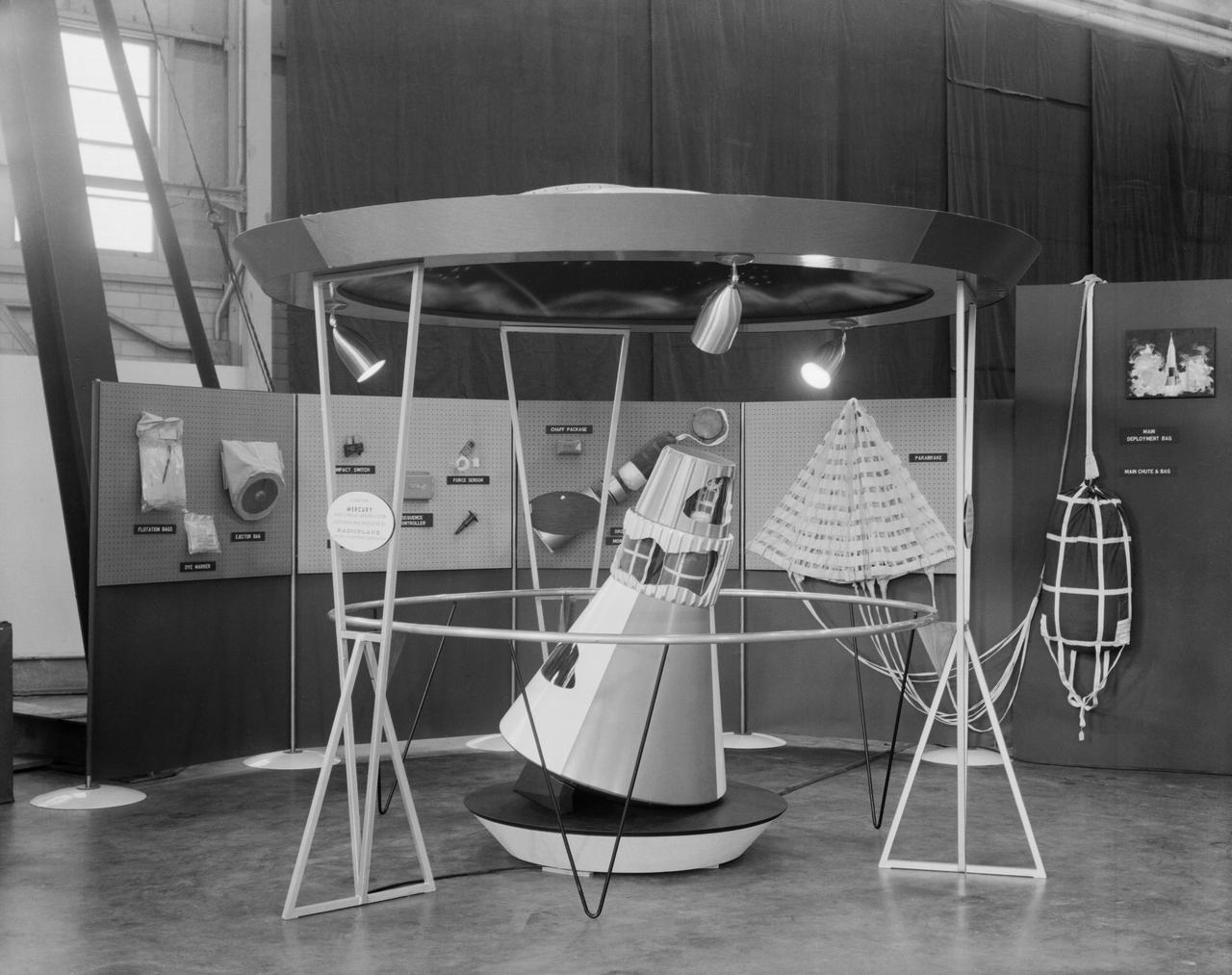

Mock-up of the Mercury capsule on display at the first NASA inspection held on October 24, 1959.
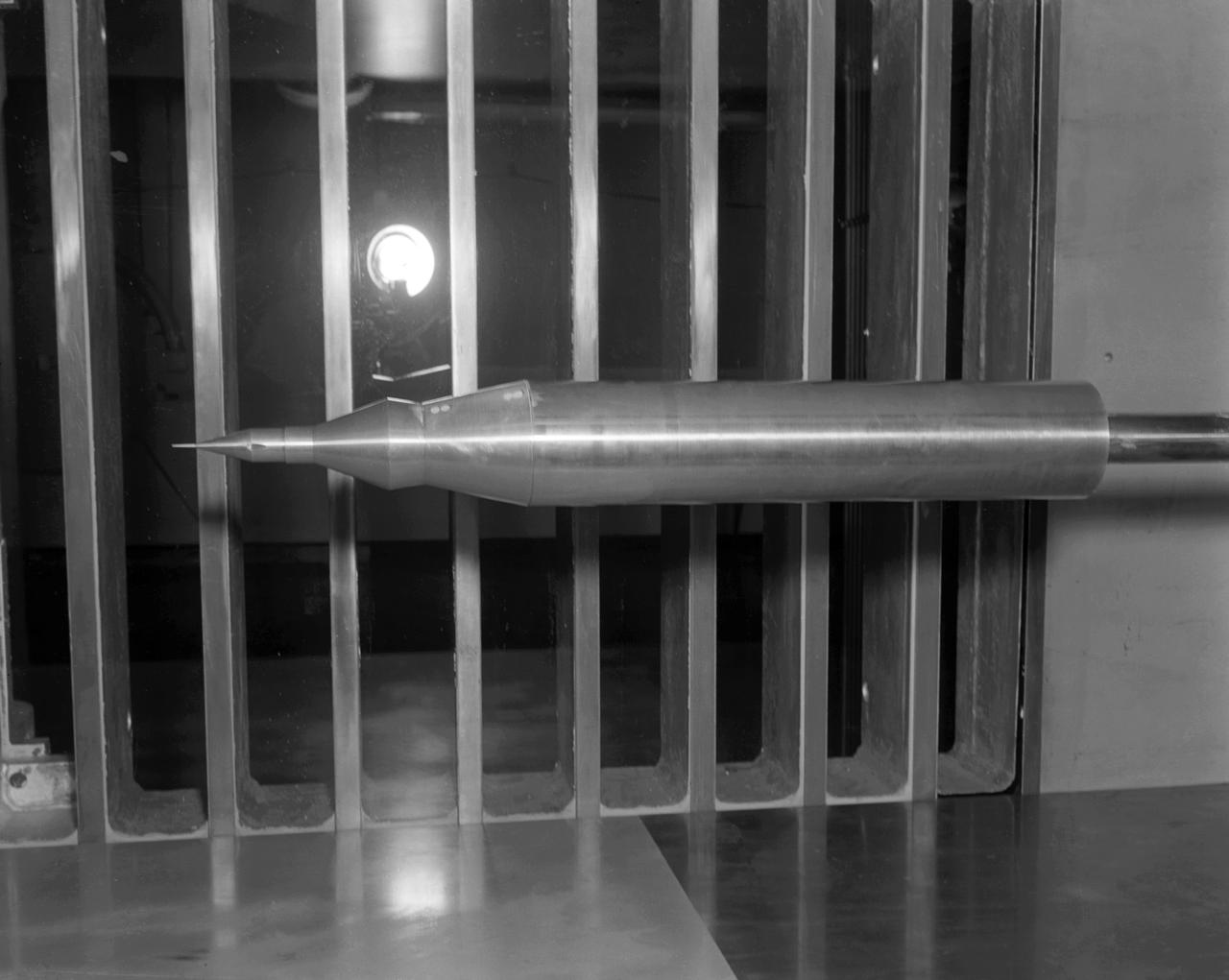

Model of Mercury (Redstone booster) carrying the spacecraft in the Unitary Plan wind tunnel for testing.

Model of Mercury (Redstone booster) carrying the spacecraft in the Unitary Plan wind tunnel for testing.
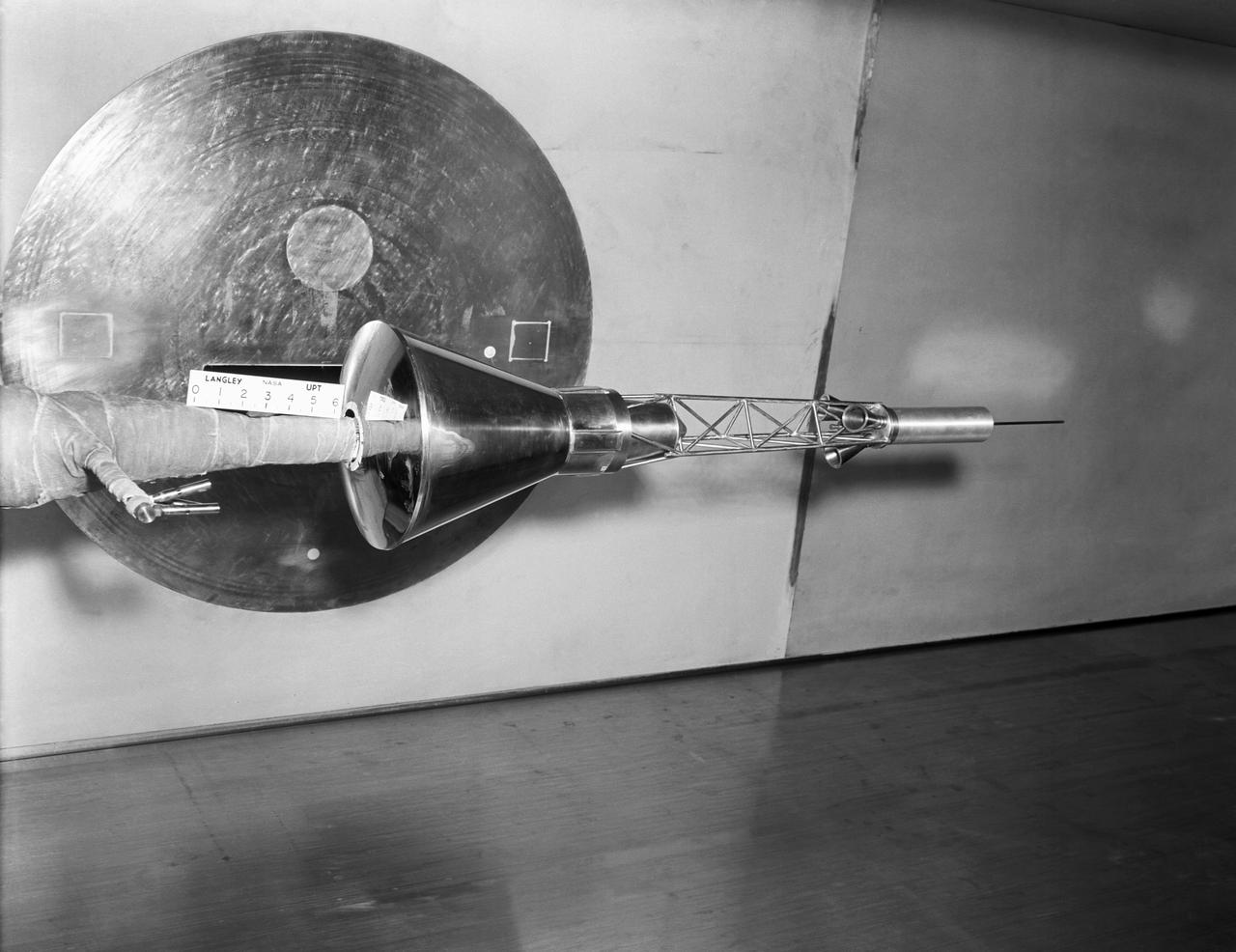
A one-sixth scale model of the Mercury capsule being tested in the 300-mph 7 x 10-foot wind tunnel.
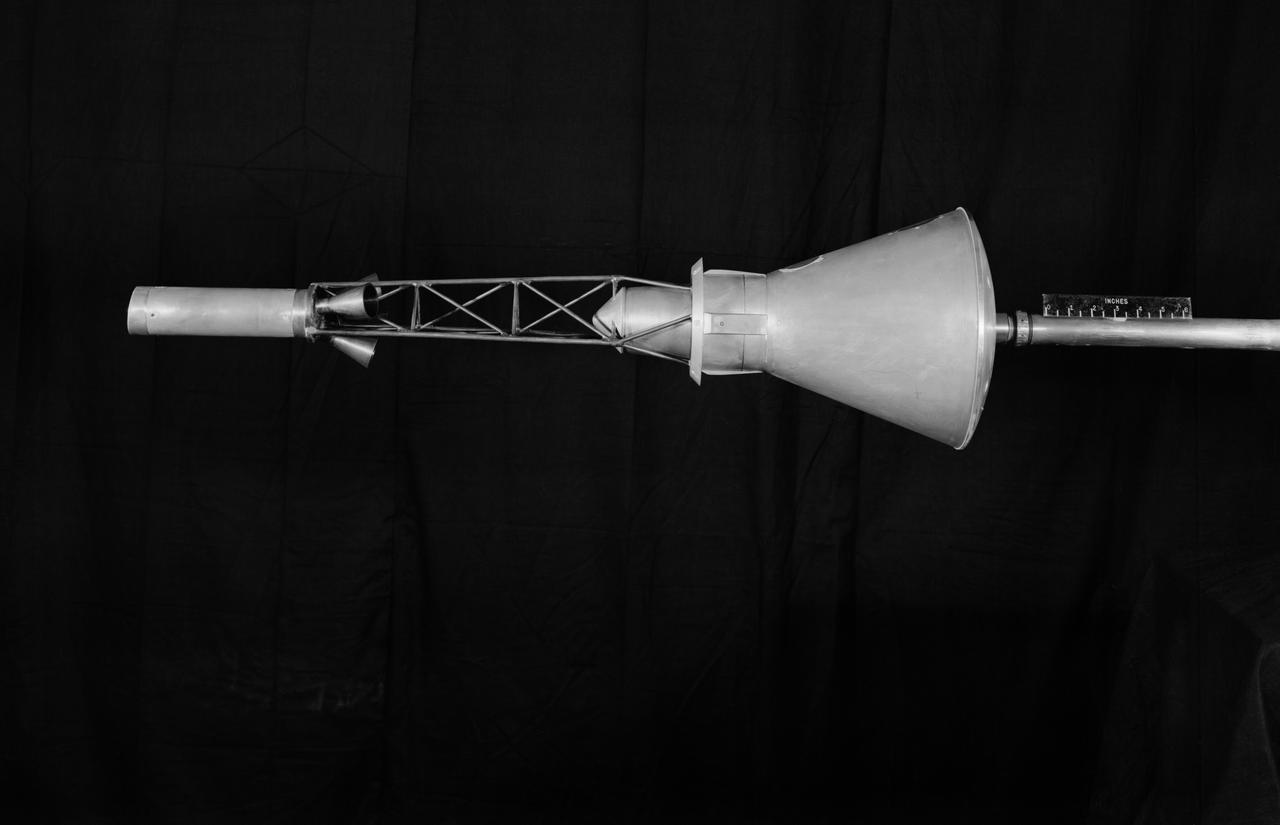

One-sixth scale model of Mercury space capsule model used in wind tunnel testing.

A Mercury capsule is mounted inside the Altitude Wind Tunnel for a test of its escape tower rockets at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. In October 1959 NASA’s Space Task Group allocated several Project Mercury assignments to Lewis. The Altitude Wind Tunnel was quickly modified so that its 51-foot diameter western leg could be used as a test chamber. The final round of tests in the Altitude Wind Tunnel sought to determine if the smoke plume from the capsule’s escape tower rockets would shroud or compromise the spacecraft. The escape tower, a 10-foot steel rig with three small rockets, was attached to the nose of the Mercury capsule. It could be used to jettison the astronaut and capsule to safety in the event of a launch vehicle malfunction on the pad or at any point prior to separation from the booster. Once actuated, the escape rockets would fire, and the capsule would be ejected away from the booster. After the capsule reached its apex of about 2,500 feet, the tower, heatshield, retropackage, and antenna would be ejected and a drogue parachute would be released. Flight tests of the escape system were performed at Wallops Island as part of the series of Little Joe launches. Although the escape rockets fired prematurely on Little Joe’s first attempt in August 1959, the January 1960 follow-up was successful.
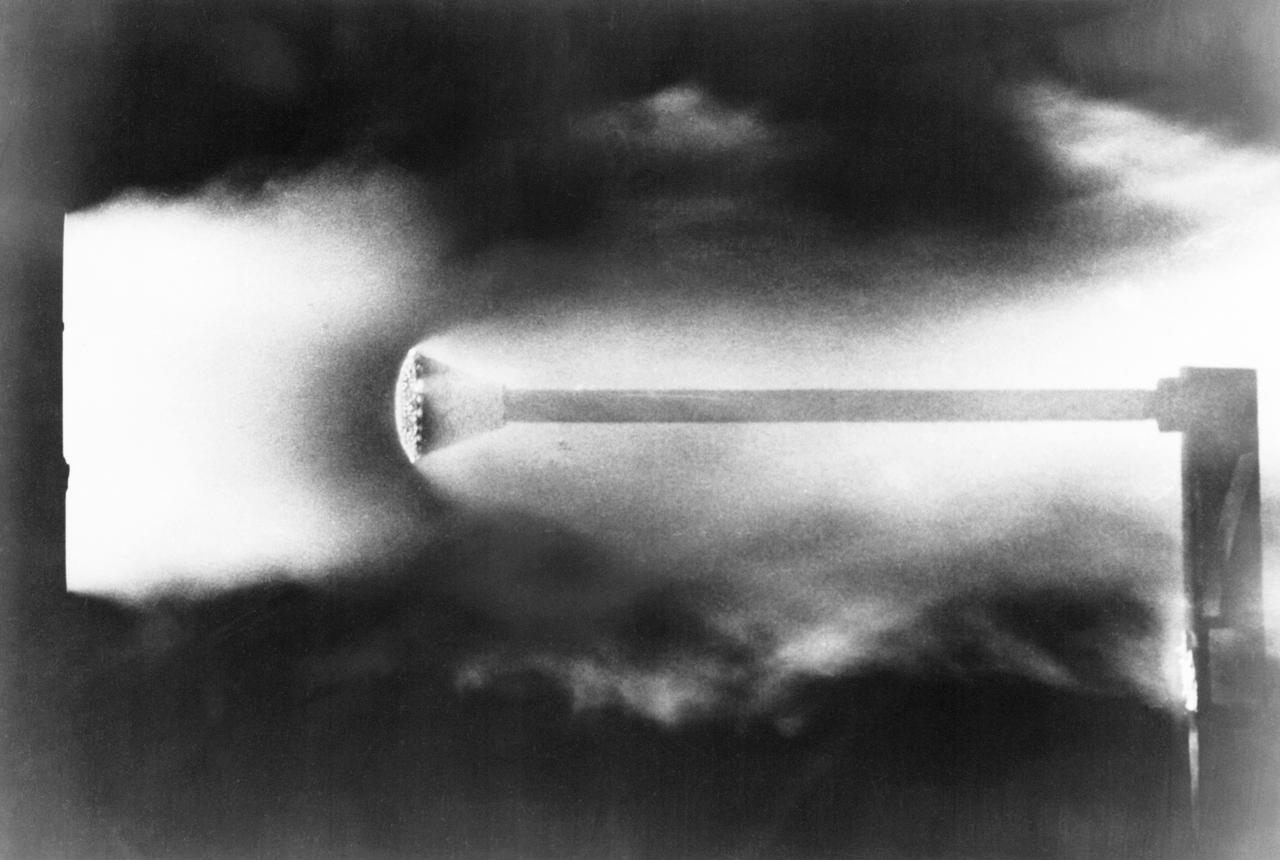
A hot jet research facility, used extensively in the design and development of the reentry heat shield on the Project Mercury spacecraft. The electrically-heated arc jet simulates the friction heating encountered by a space vehicle as it returns to the earth's atmosphere at high velocities. The arc jet was located in Langley's Structures Research Laboratory. It was capable of heating the air stream to about 9,000 degrees F. -- Published in Taken from an October 5, 1961 press release entitled: Hot Jet Research Facility used in Reentry Studies will be demonstrated at NASA Open House, October 7.
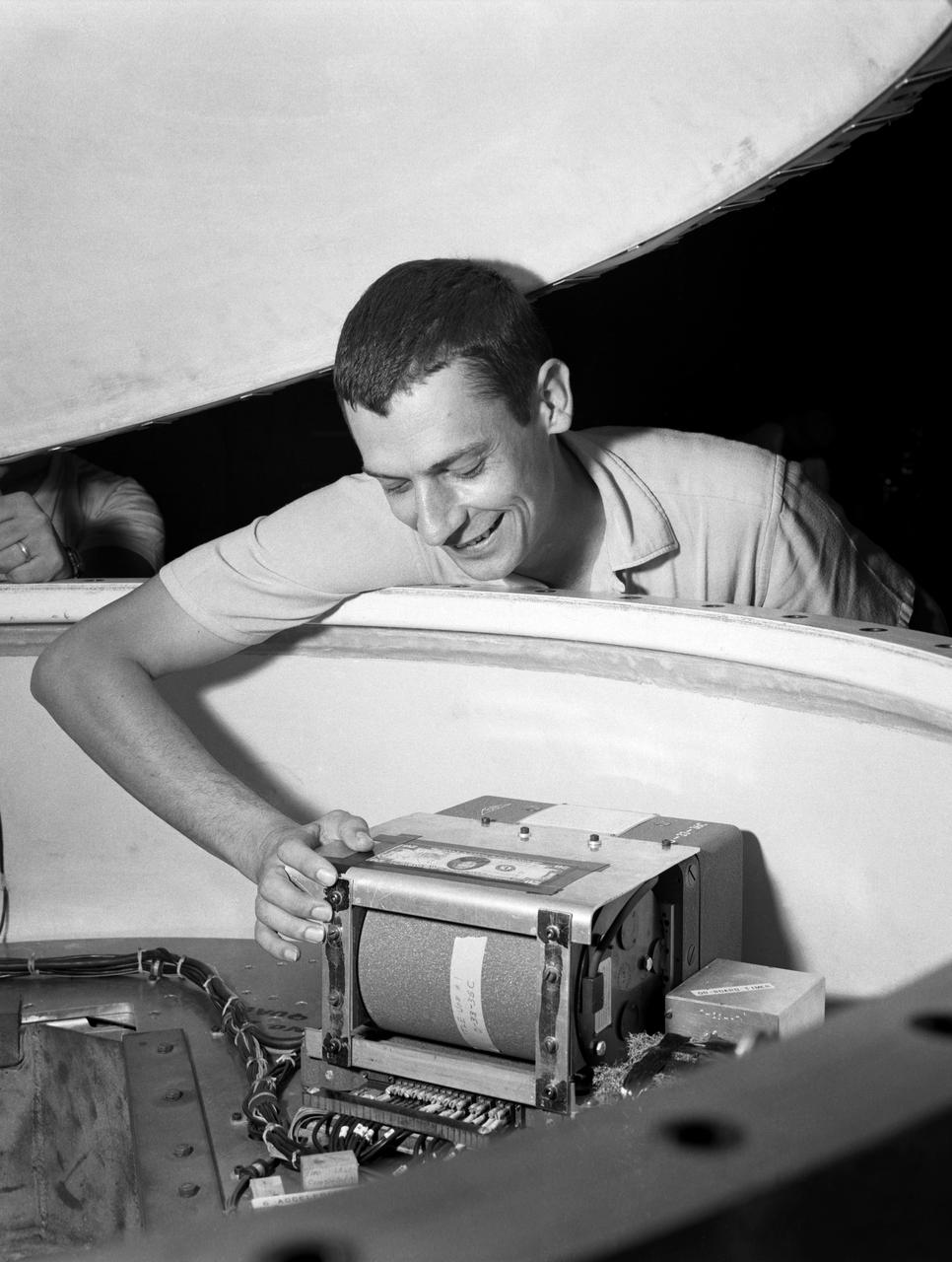

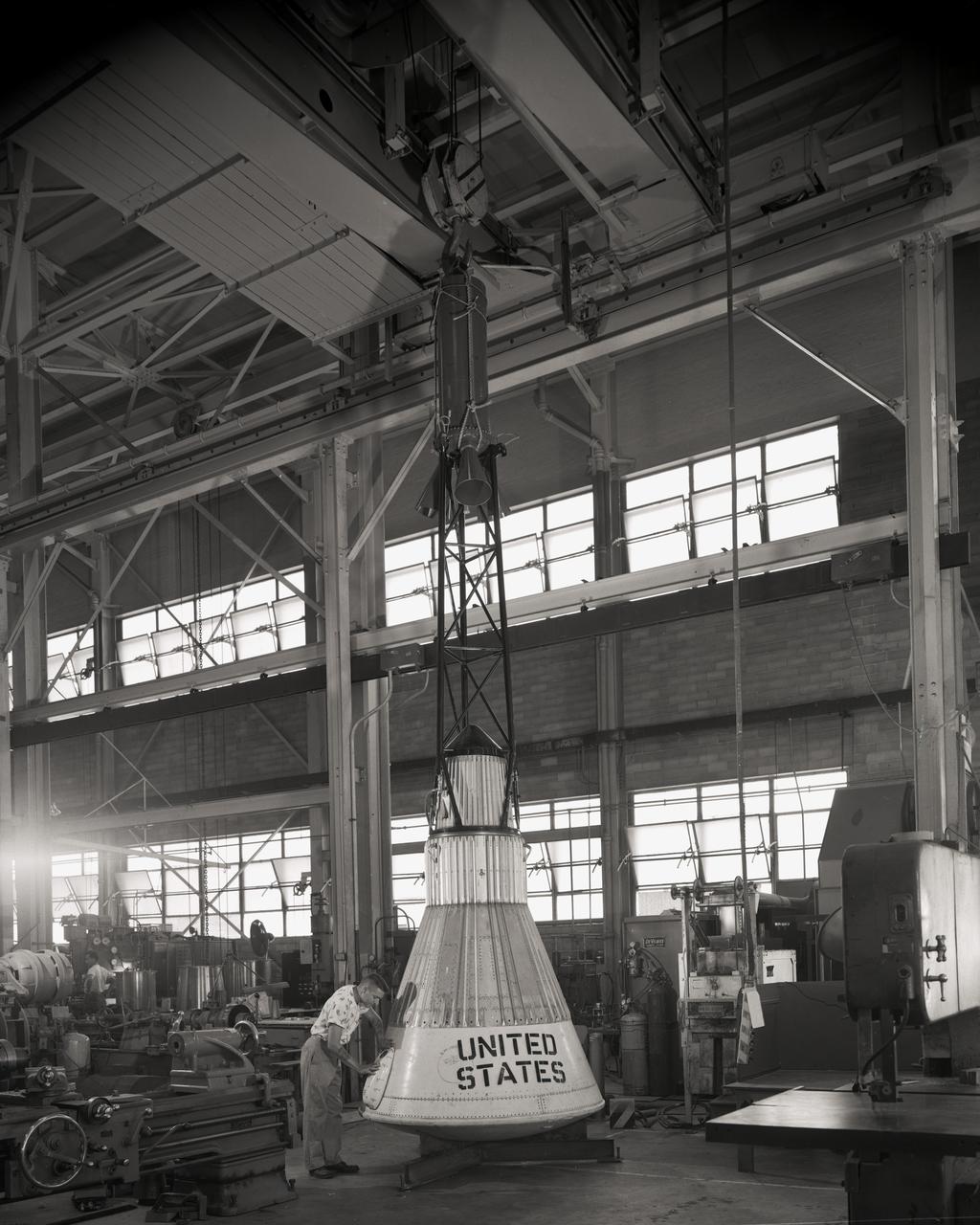
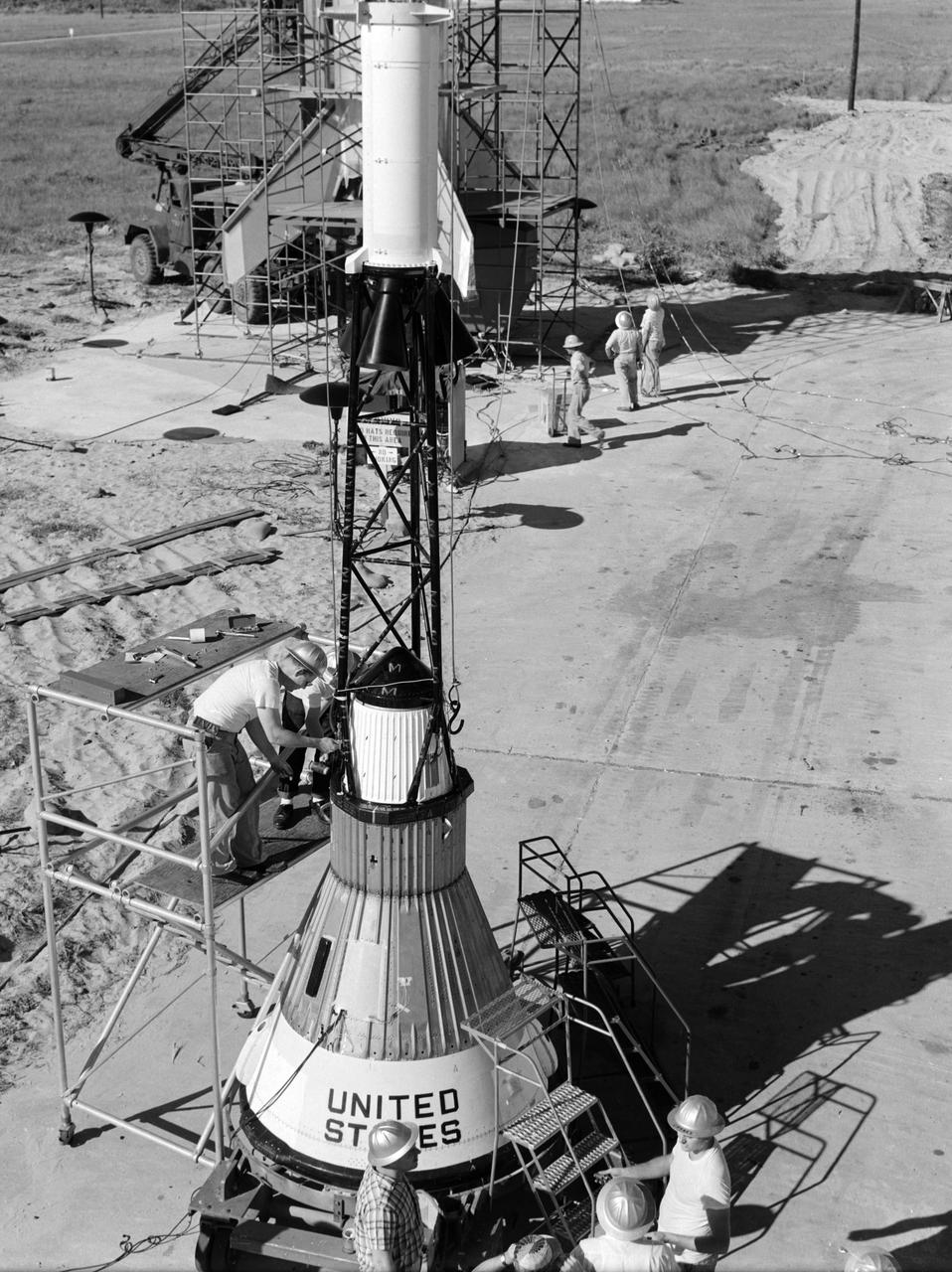
Technicians adjust the rocket motor during the attachment of the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.

Technicians adjust the rocket motor during the attachment of the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.

Technicians adjust the rocket motor during the attachment of the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.

Technicians adjust the rocket motor during the attachment of the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.

Technicians adjust the rocket motor during the attachment of the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
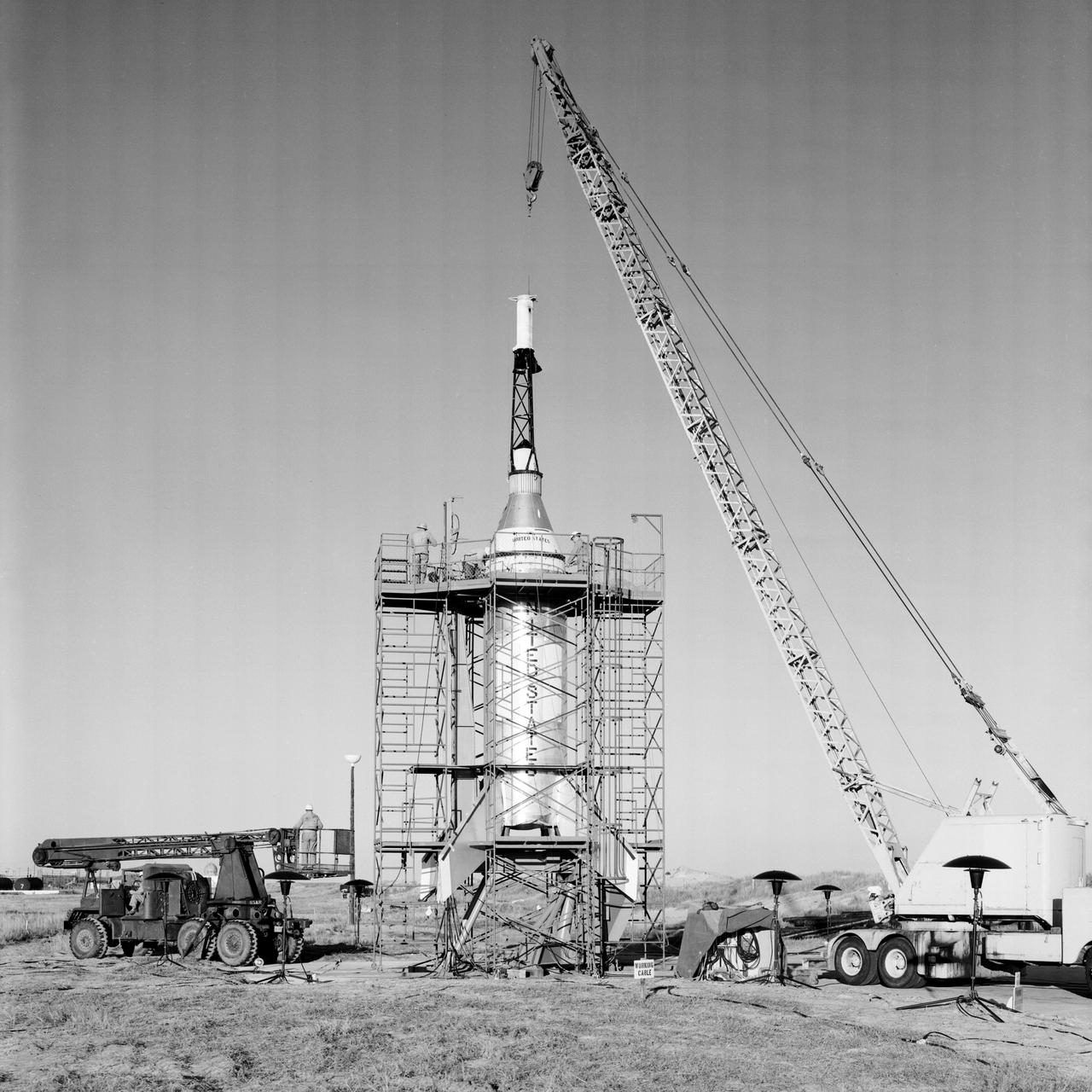

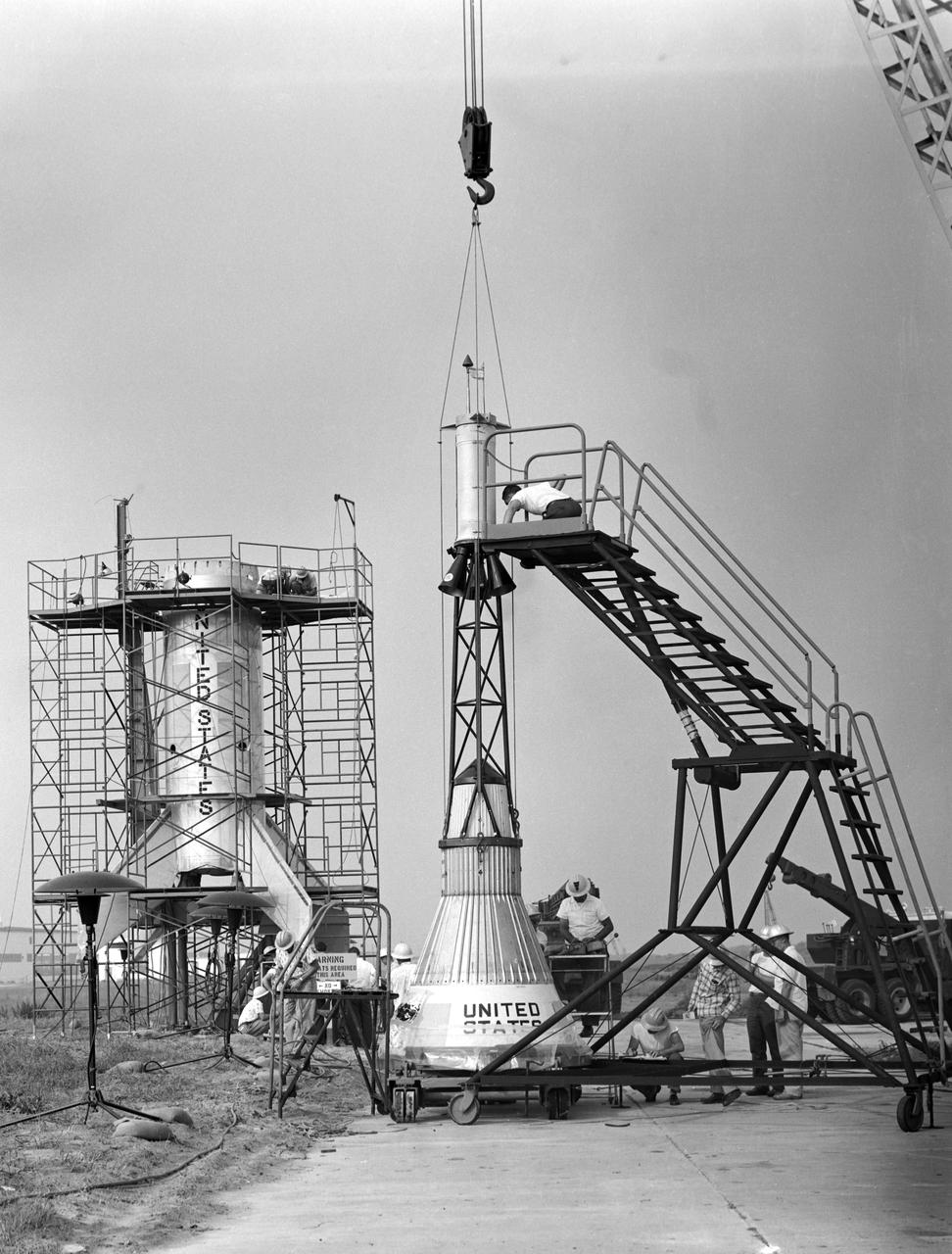
The Mercury capsule and escape tower are being lowered onto the Little Joe booster for launch on August 21, 1959. Joseph Shortal described this as follows (vol. 3, p. 33): The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.

The Mercury capsule and escape tower are being lowered onto the Little Joe booster for launch on August 21, 1959. Joseph Shortal described this as follows (vol. 3, p. 33): The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
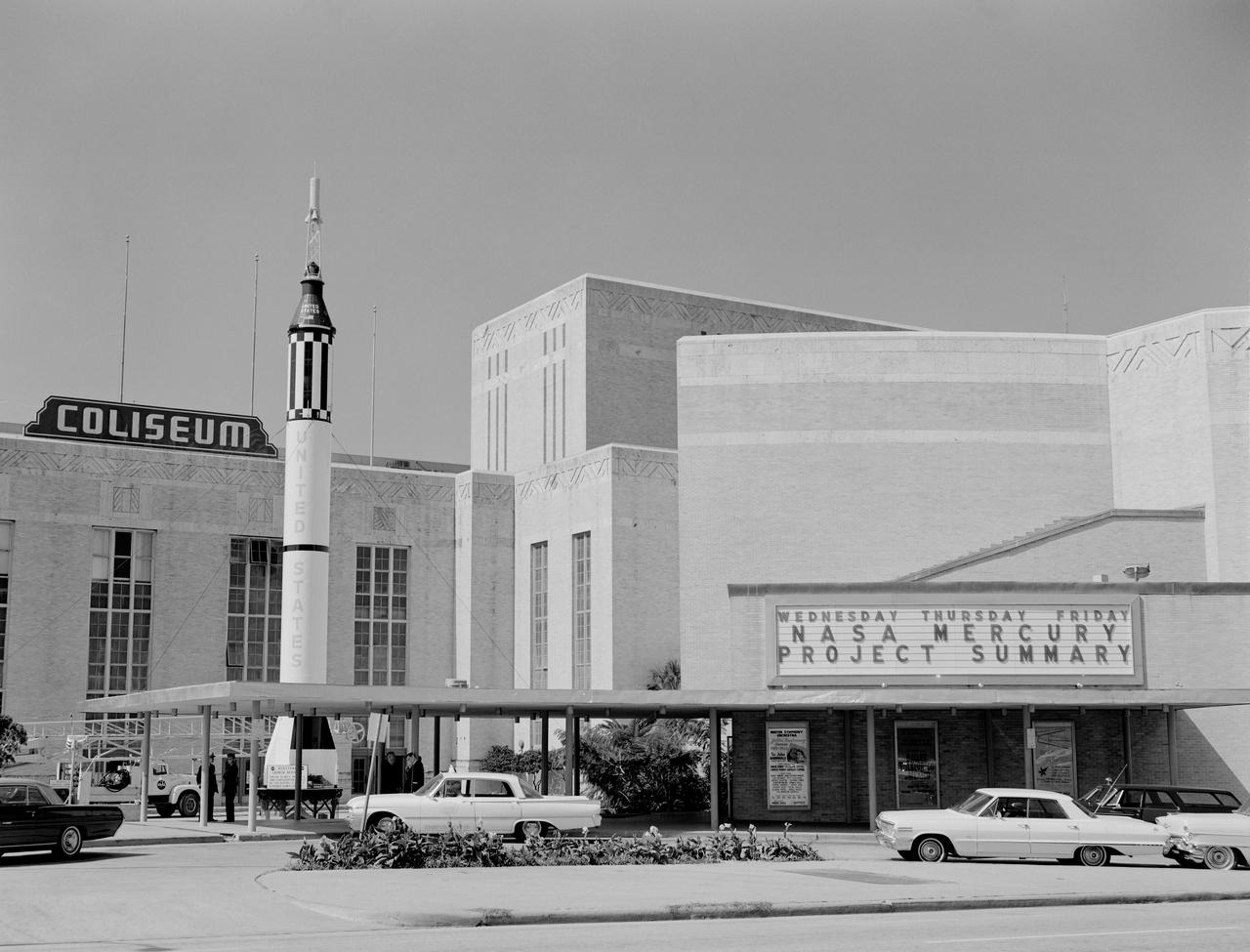

In October 1963, the Project Mercury Summary Conference was held in the Houston, TX, Coliseum. This series of 44 photos is documentation of that conference. A view of the Houston, TX, Coliseum, and parking area in front with a Mercury Redstone Rocket setup in the parking lot for display (S63-16451). A view of an Air Force Atlas Rocket, a Mercury Redstone Rocket, and a Mercury Spacecraft on a test booster on display in the front area of the Coliseum (S63-16452). A view an Air Force Atlas Rocket and a Mercury Redstone Rocket set up for display with the Houston City Hall in the background (S63- 16453). This view shows the Atlas Rocket, Mercury Redstone, and Mercury Test Rocket with the Houston, TX, Coliseum in the background (S63- 16454). A balcony view, from the audience right side, of the attendees looking at the stage (S63-16455). A view of the NASA Space Science Demonstration with equipment setup on a table, center stage and Space Science Specialist briefing the group as he pours Liquid Oxygen into a beaker (S63-16456). View of the audience from the balcony on the audience right showing the speakers lecturn on stage to the audience left (S63-16457). A view of attendees in the lobby. Bennet James, MSC Public Affairs Office is seen to the left of center (S63-16458). Another view of the attendees in the lobby (S63- 16459). In this view, Astronaut Neil Armstrong is seen writing as others look on (S63-16460). In this view of the attendees, Astronauts Buzz Aldrin and Walt Cunningham are seen in the center of the shot. The October Calendar of Events is visable in the background (S63-16461). Dr. Charles Berry is seen in this view to the right of center, seated in the audience (S63-16462). View of " Special Registration " and the five ladies working there (S63-16463). A view from behind the special registration table, of the attendees being registered (S63-16464). A view of a conference table with a panel seated. (R-L): Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, Hugh L. Dryden, Walter C. Williams, and an unidentified man (S63- 16465). A closeup of the panel at the table with Dr. Gilruth on the left (S63-16466). About the same shot as number S63-16462, Dr. Berry is seen in this shot as well (S63-16467). In this view the audio setup is seen. In the audience, (L-R): C. C. Kraft, Vernon E. (Buddy) Powell, Public Affairs Office (PAO); and, in the foreground mixing the audio is Art Tantillo; and, at the recorder is Doyle Hodges both of the audio people are contractors that work for PAO at MSC (S63-16468). In this view Maxime Faget is seen speaking at the lecturn (S63-16469). Unidentified person at the lecturn (S63-16470). In this view the motion picture cameras and personel are shown documenting the conference (S63-16471). A motion picture cameraman in the balcony is shown filming the audience during a break (S63- 16472). Family members enjoy an exhibit (S63-16473). A young person gets a boost to look in a Gemini Capsule on display (S63-16474). A young person looks at the Gemini Capsule on display (S63-16475). Dr. Robert R. Gilruth is seen at the conference table (S63-16476). Walt Williams is seen in this view at the conference table (S63-16477). Unidentified man sitting next to Walt Williams (S63-16478). (L-R): Seated at the conference table, Dr. Robert Gilruth, Hugh L. Dryden, and Walt Williams (S63- 16479). Group in lobby faces visable, (L-R): Walt Williams, unidentified person, Dr. Robert Gilruth, Congressman (S63-16480). Man in uniform at the lecturn (S63-16481). Astronaut Leroy Gordon Cooper at the lecturn (S63-16482). Astronaut Cooper at the lecturn with a picture on the screen with the title, " Astronaut Names for Spacecraft " (S63-16483). Dr. Gilruth at the lecturn (S63-16484). Walt Williams at the lecturn (S63-16485). Unidentified man at the lecturn (S63-16486). John H. Boynton addresses the Summary Conference (S63-16487). (L-R): Astronaut Leroy Gordon Cooper, Mrs. Cooper, Senator Cris Cole, and Mrs. Cole (S63- 16488). In this view in the lobby, Senator and Mrs. Cris Cole, with Astronaut Gordon Cooper standing near the heatshield, and Mrs. Cooper; next, on the right is a press photographer (S63-16489). (L-R): Astronaut L. Gordon Cooper and Mrs. Cooper, unidentified man, and Senator Walter Richter (S63-16490). (L-R): Eugene Horton, partially obscured, briefs a group on the Mercury Spacecraft, an unidentified person, Harold Ogden, a female senator, Senator Chris Cole, Mrs. Cole, an unidentified female, Senator Walter Richter, Jim Bower, and an unidentified female (S63-16491). In this view, Mrs. Jim Bates is seen in the center, and Senator Walter Richter to the right (S63- 16492). The next three (3) shots are 4X5 CN (S63-16493 - S63-16495). In this view a NASA Space Science Demonstration is seen (S63-16493). In this view a shot of the conference table is seen, and, (L-R): Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, Hugh L. Dryden, Mr. Walter Williams, and an unidentfied man (S63-16494 - S63-16495). HOUSTON, TX

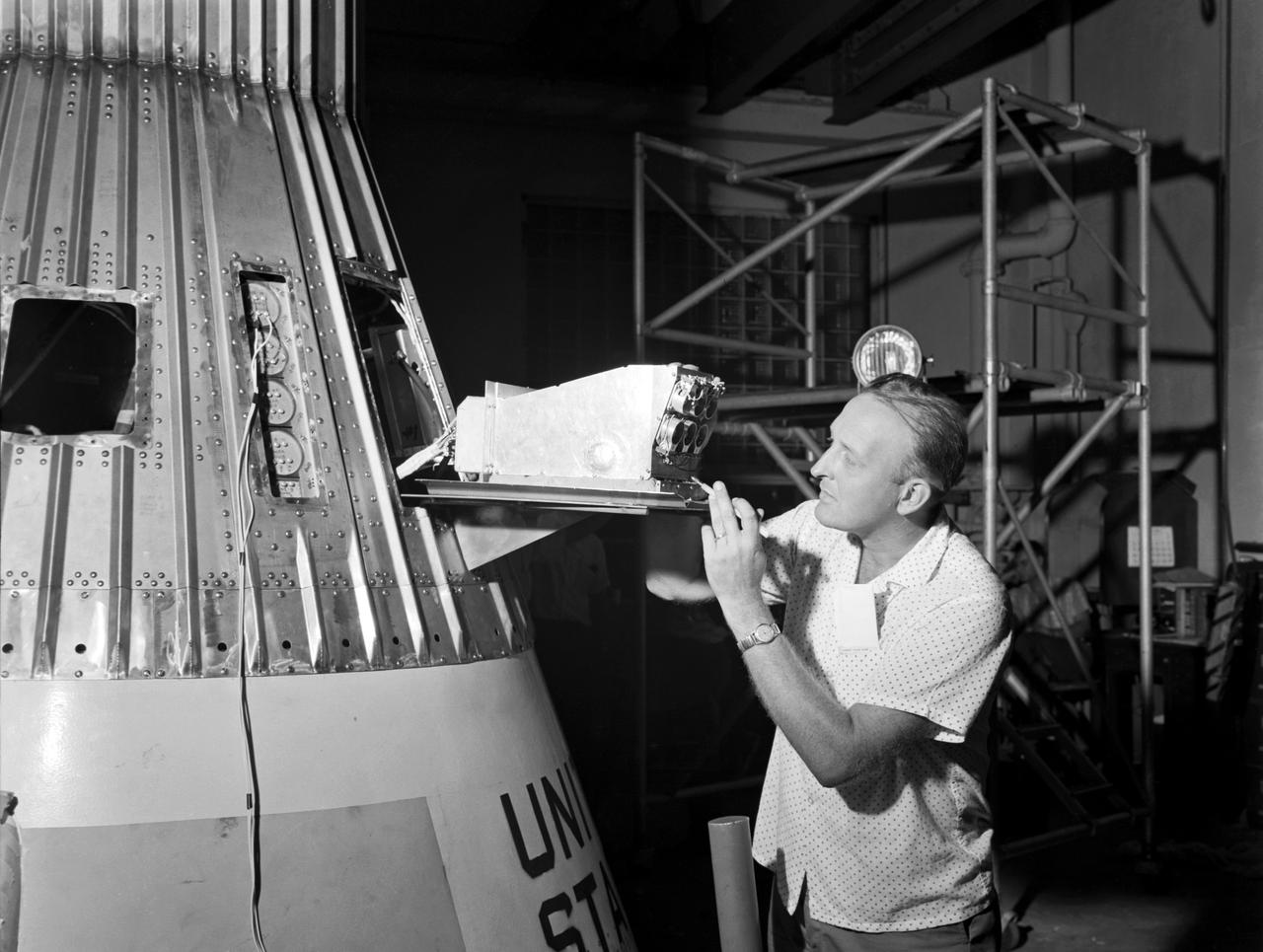
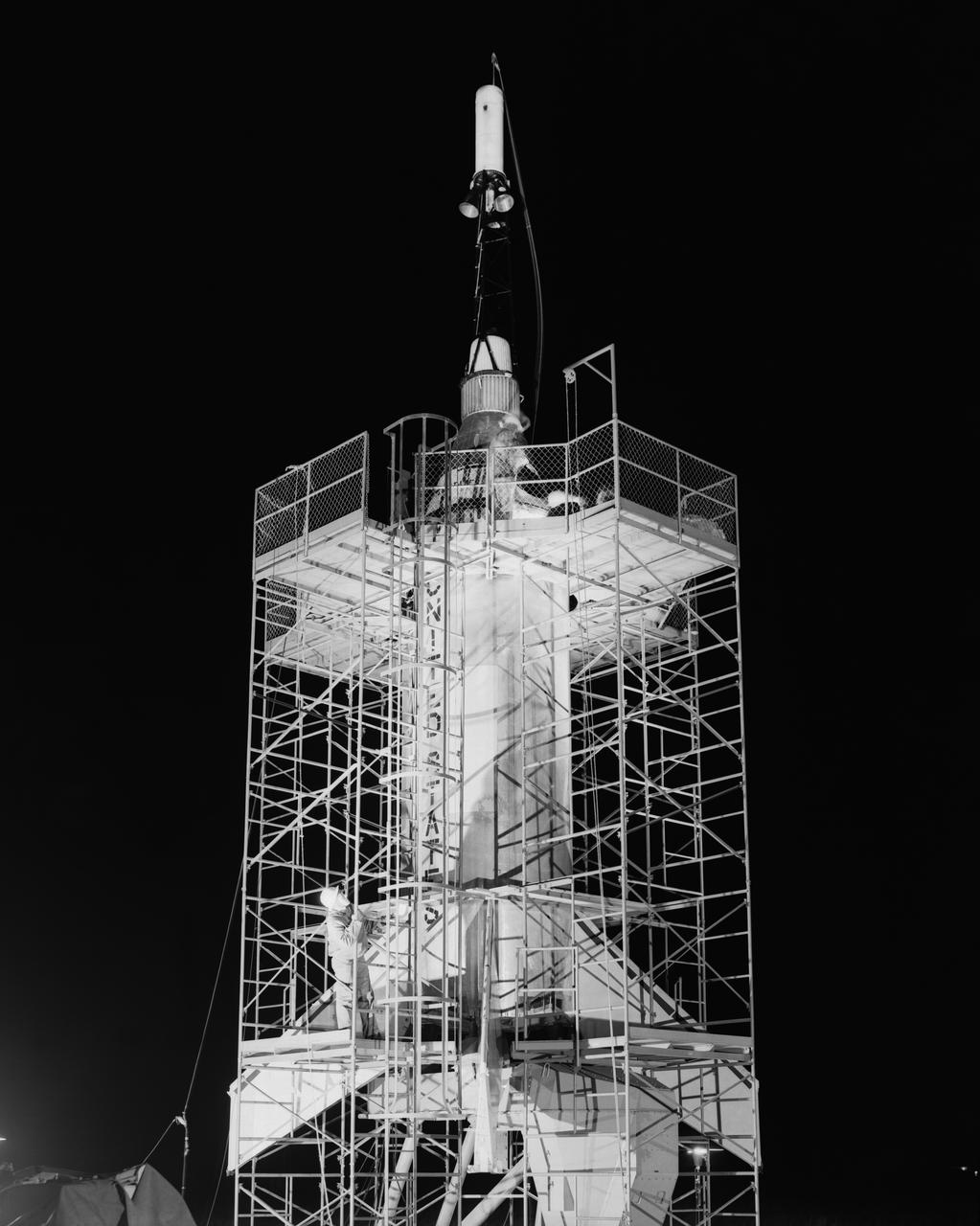
Technicians attach the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal describe this as follows (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
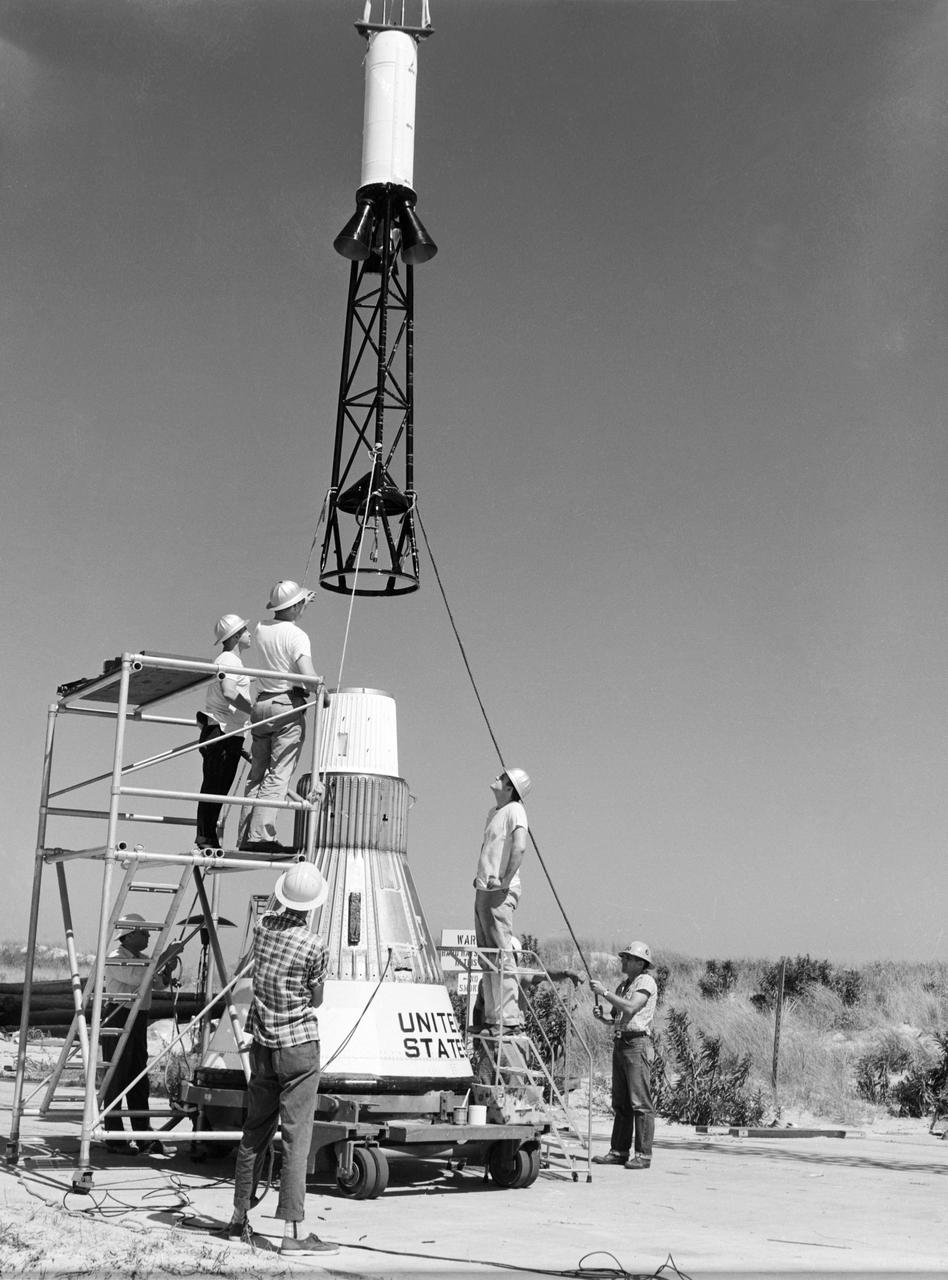

Technicians attach the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal describe this as follows (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.

Technicians attach the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal describe this as follows (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.

Assisted by Astronaut John Glenn, Astronaut Virgil Grissom enters the Mercury capsule, Liberty Bell 7, for the MR-4 mission on July 21, 1961. Boosted by the Mercury-Redstone vehicle, the MR-4 mission was the second manned suborbital flight.

Astronaut John Glenn enters the Mercury spacecraft, Friendship 7, prior to the launch of MA-6 on February 20, 1961 and became the first American who orbited the Earth. The MA-6 mission was the first manned orbital flight boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, a modified Atlas ICBM (Intercontinental Ballistic Missile), lasted for five hours, and orbited the Earth three times.
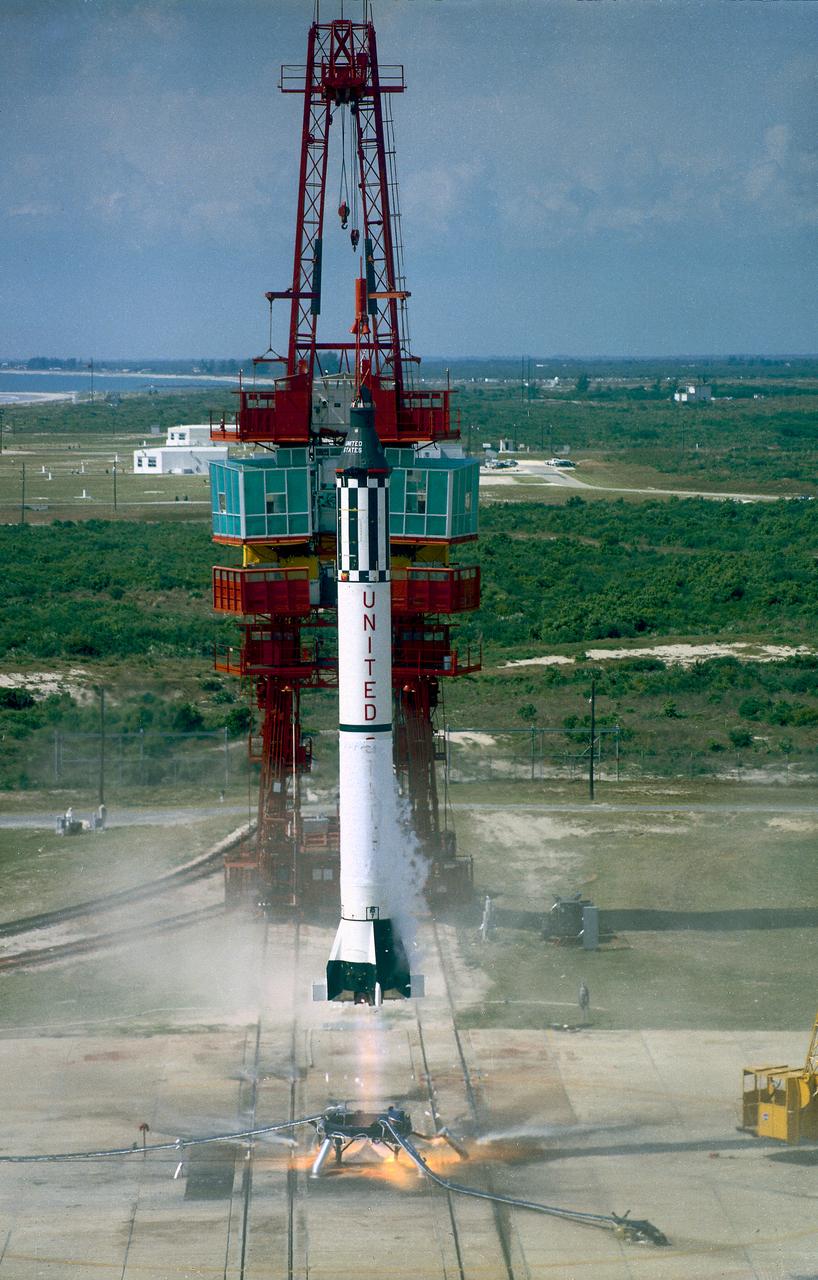

The launch of the Mercury-Redstone (MR-3), Freedom 7. MR-3 placed the first American astronaut, Alan Shepard, in suborbit on May 5, 1961.
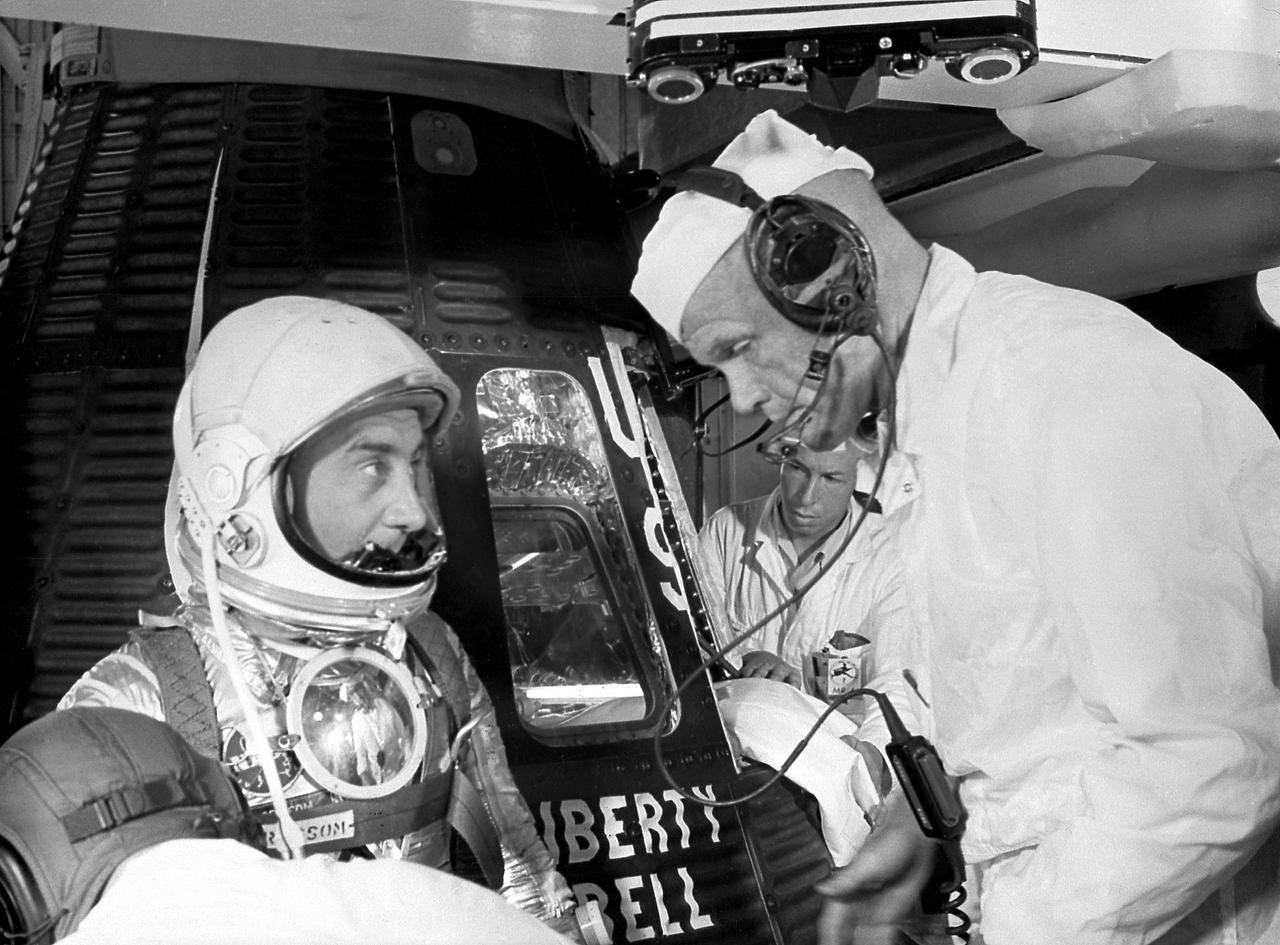

Astronaut Virgil Grissom chats with Astronaut John Glenn prior to entering the Liberty Bell 7 capsule for the MR-4 Mission. The MR-4 mission was the second manned suborbital flight using the Mercury-Redstone booster, which was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
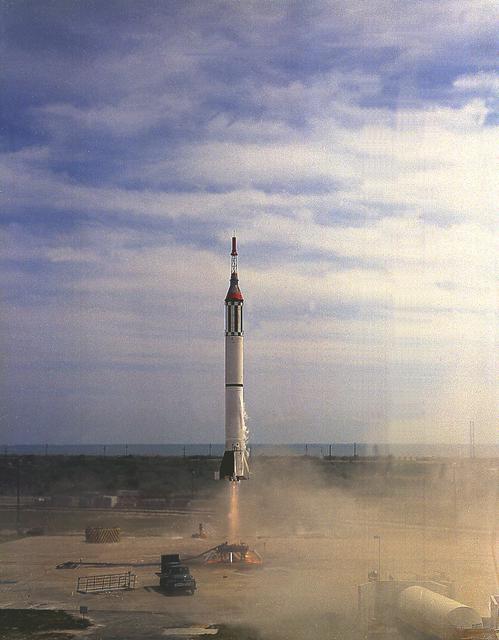

The Mercury-Redstone Booster Development vehicle (MR-BD) lifts off from Cape Canaveral March 24, 1961. This test flight evaluated changes incorporated in the booster designed to reduce vehicle oscillations and vibrations. The Mercury-Redstone launch vehicle was developed by Dr. Wernher von Braun and the rocket team in Huntsville, Alabama.
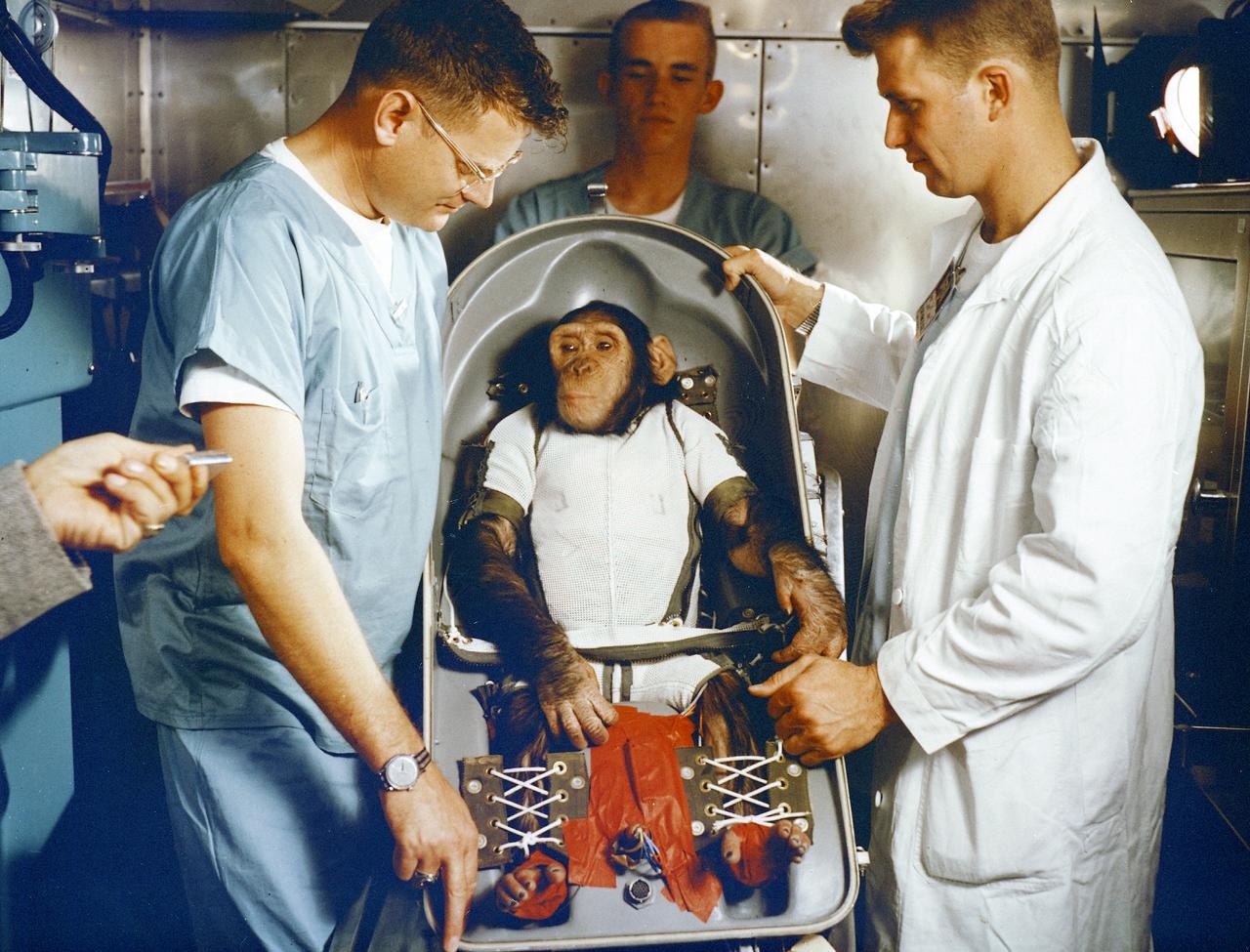

A three-year-old chimpanzee, named Ham, in the biopack couch for the MR-2 suborbital test flight. On January 31, 1961, a Mercury-Redstone launch from Cape Canaveral carried the chimpanzee "Ham" over 640 kilometers down range in an arching trajectory that reached a peak of 254 kilometers above the Earth. The mission was successful and Ham performed his lever-pulling task well in response to the flashing light. NASA used chimpanzees and other primates to test the Mercury Capsule before launching the first American astronaut Alan Shepard in May 1961. The successful flight and recovery confirmed the soundness of the Mercury-Redstone systems.

Astronaut John Glenn enters the Mercury spacecraft, Friendship 7, prior to the launch of MA-6 on February 20, 1961 and became the first American who orbited the Earth. The MA-6 mission was the first manned orbital flight boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, a modified Atlas ICBM (Intercontinental Ballistic Missile), lasted for five hours, and orbited the Earth three times.
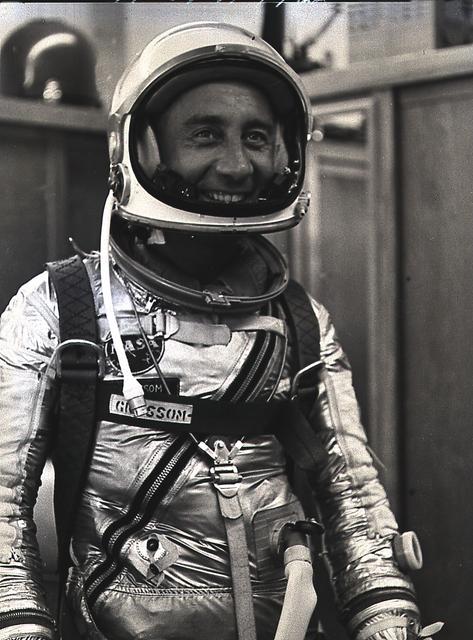

Astronaut Virgil Gus Grissom awaits America's second marned space mission, Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) on July 21, 1961. During the 15-minute suborbital flight, the Liberty Bell 7 Mercury spacecraft reached an altitude of 118 miles and traveled 303 miles downrange. It was the fourth flight of the Mercury-Redstone launch vehicle (MR-4), developed by Dr. Wernher von Braun and the rocket team in Huntsville, Alabama.
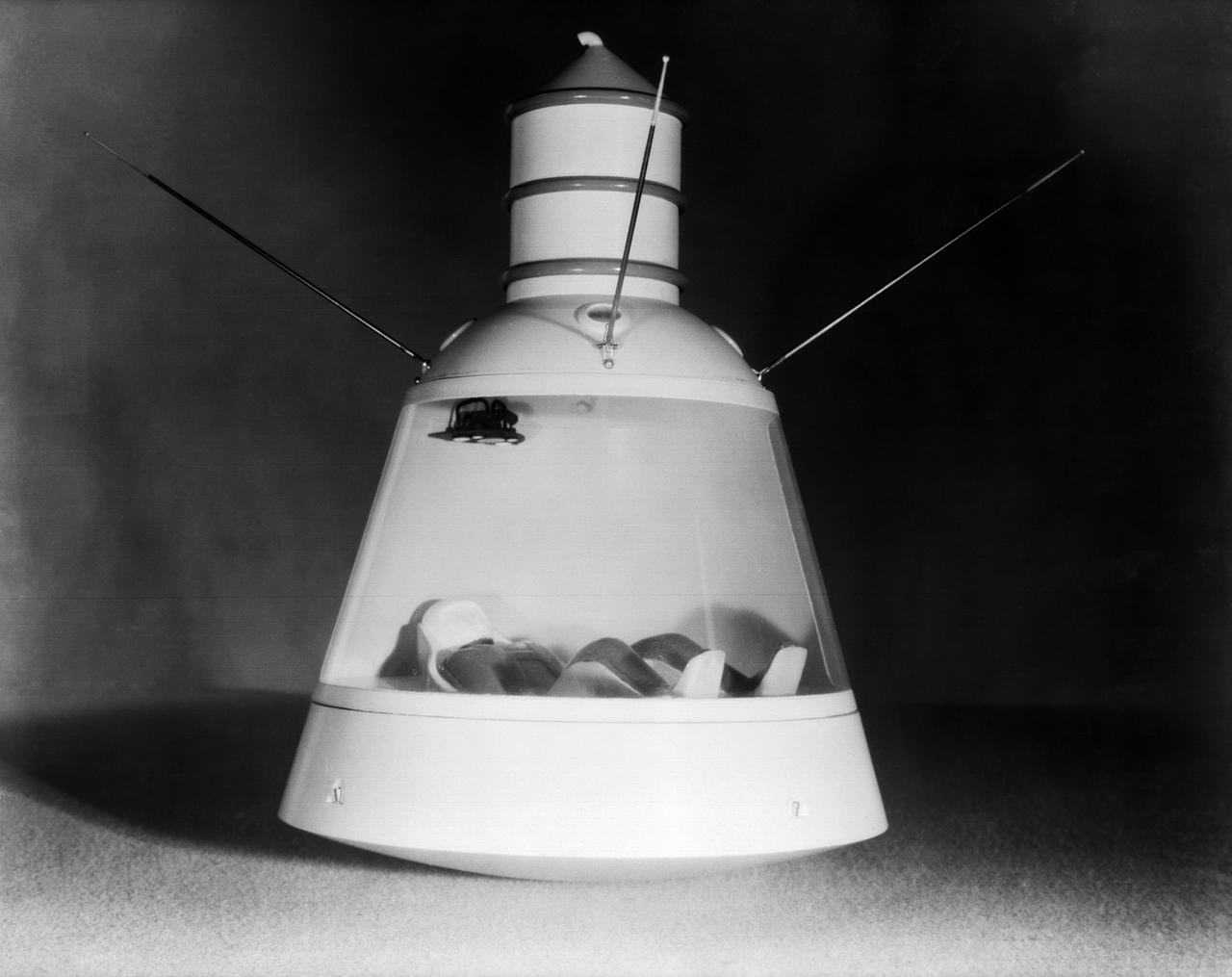
Scale model of Mercury capsule shape A, indicating the position of the astronaut.
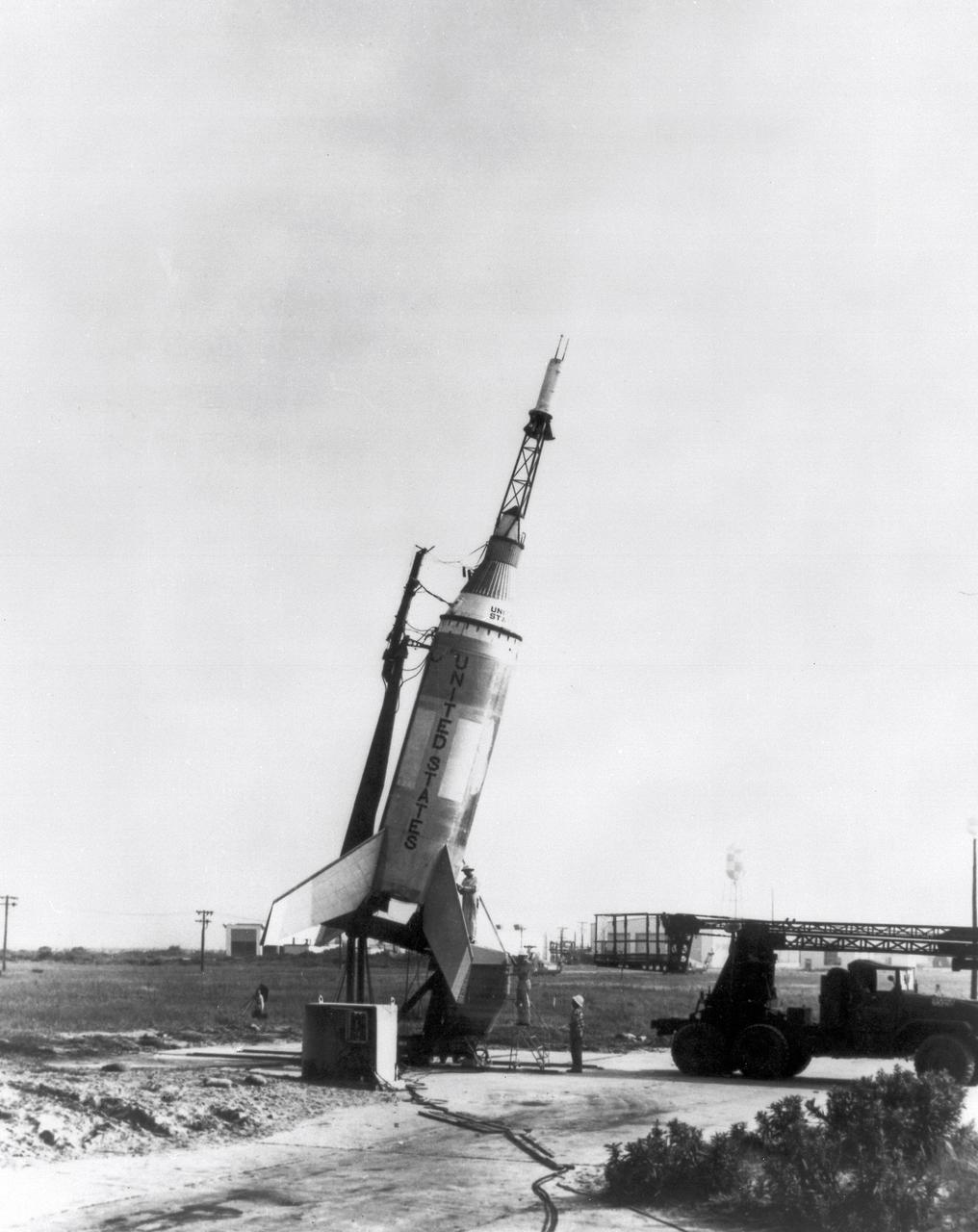

The Little Joe launch vehicle for the LJ1 mission on the launch pad at the wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Virginia, on January 21, 1960. This mission achieved the suborbital Mercury cupsule test, testing of the escape system, and biomedical tests by using a monkey, named Miss Sam.
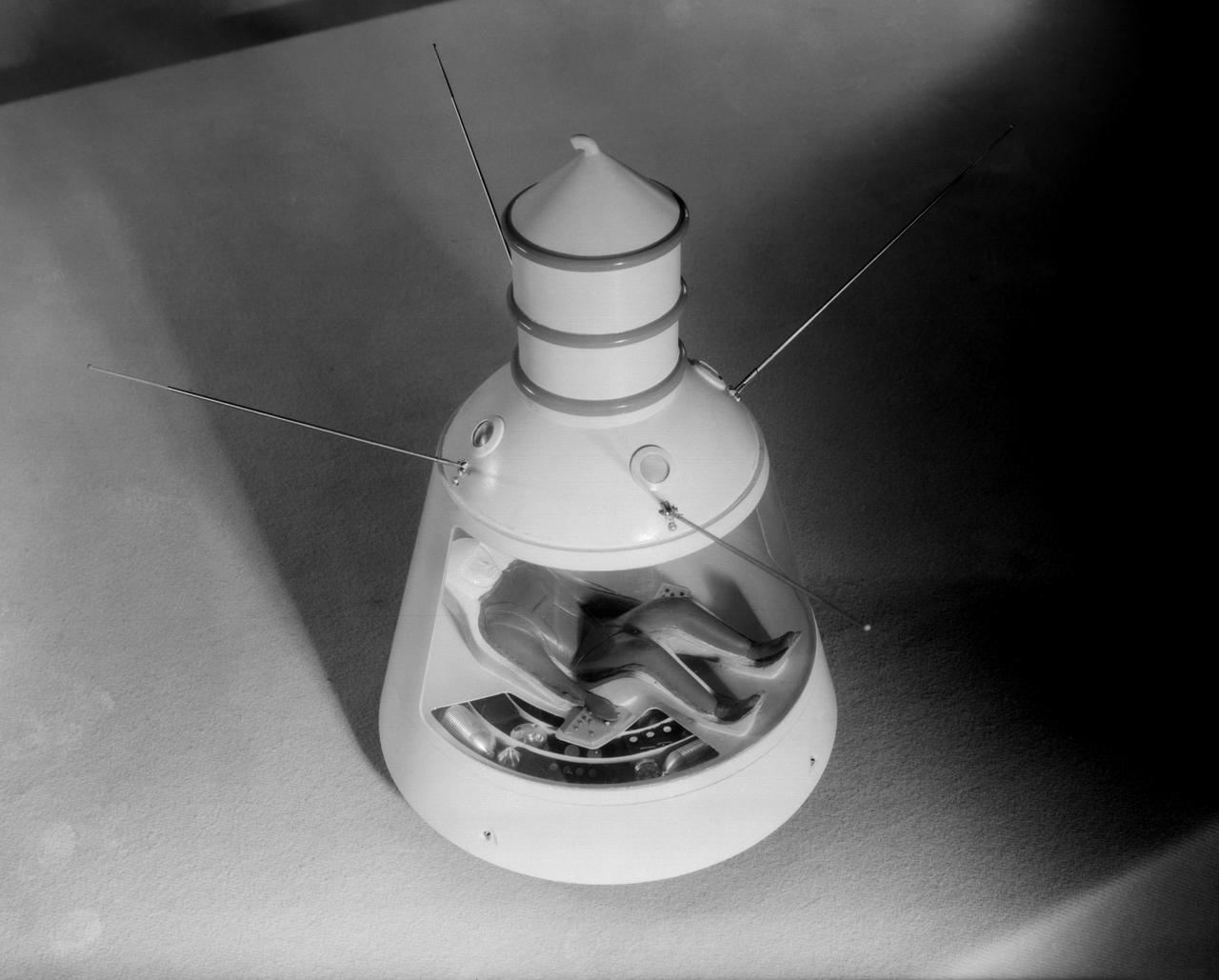

Scale model of Mercury capsule shape A, indicating the position of the astronaut.
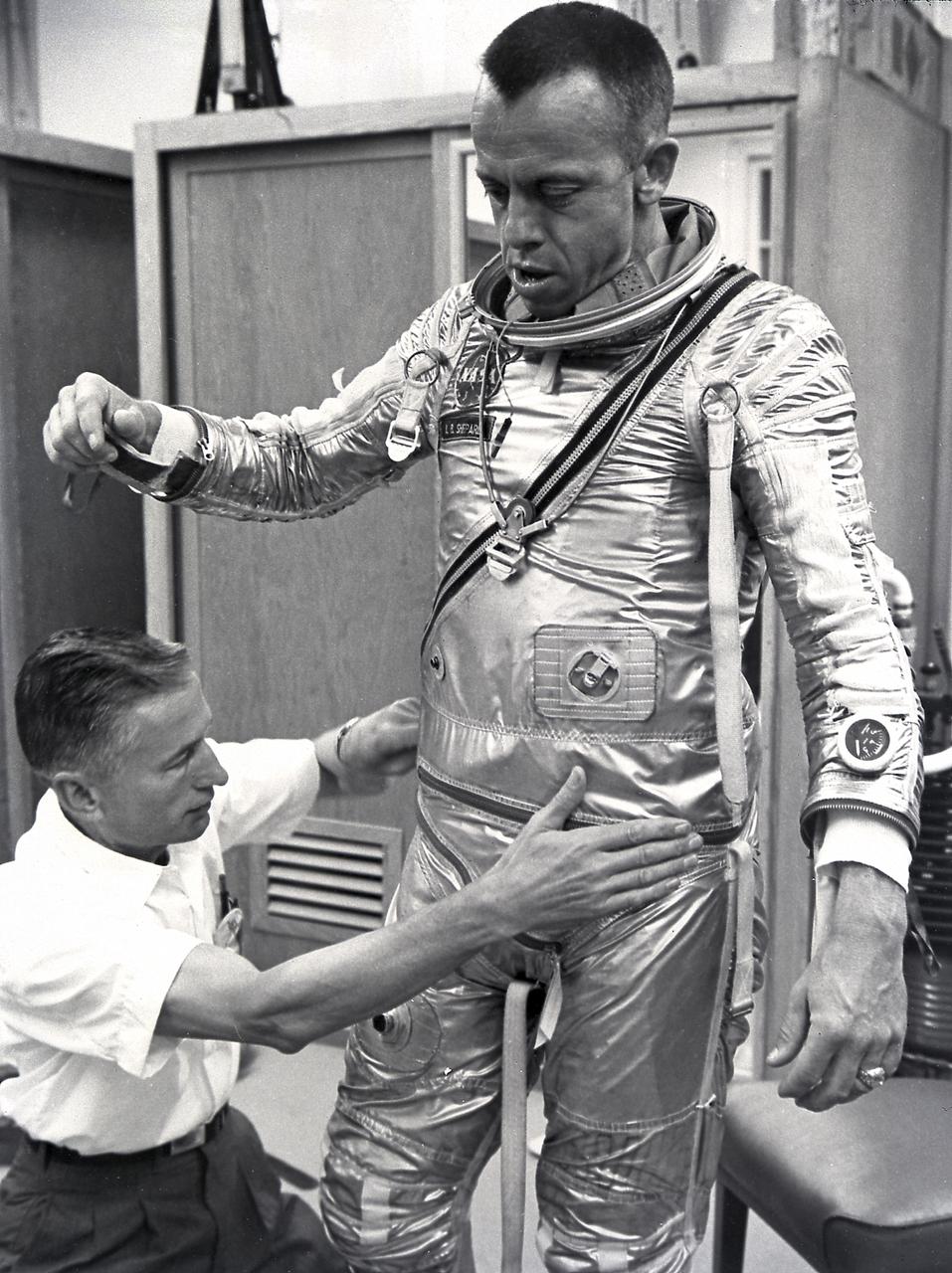

Astronaut Alan Shepard fitted with space suit prior to the first marned suborbital flight. Freedom 7, carrying Astronaut Alan Shepard, boosted by the Mercury-Redstone launch vehicle, lifted off on May 5, 1961. Astronaut Shepard became the first American in space.
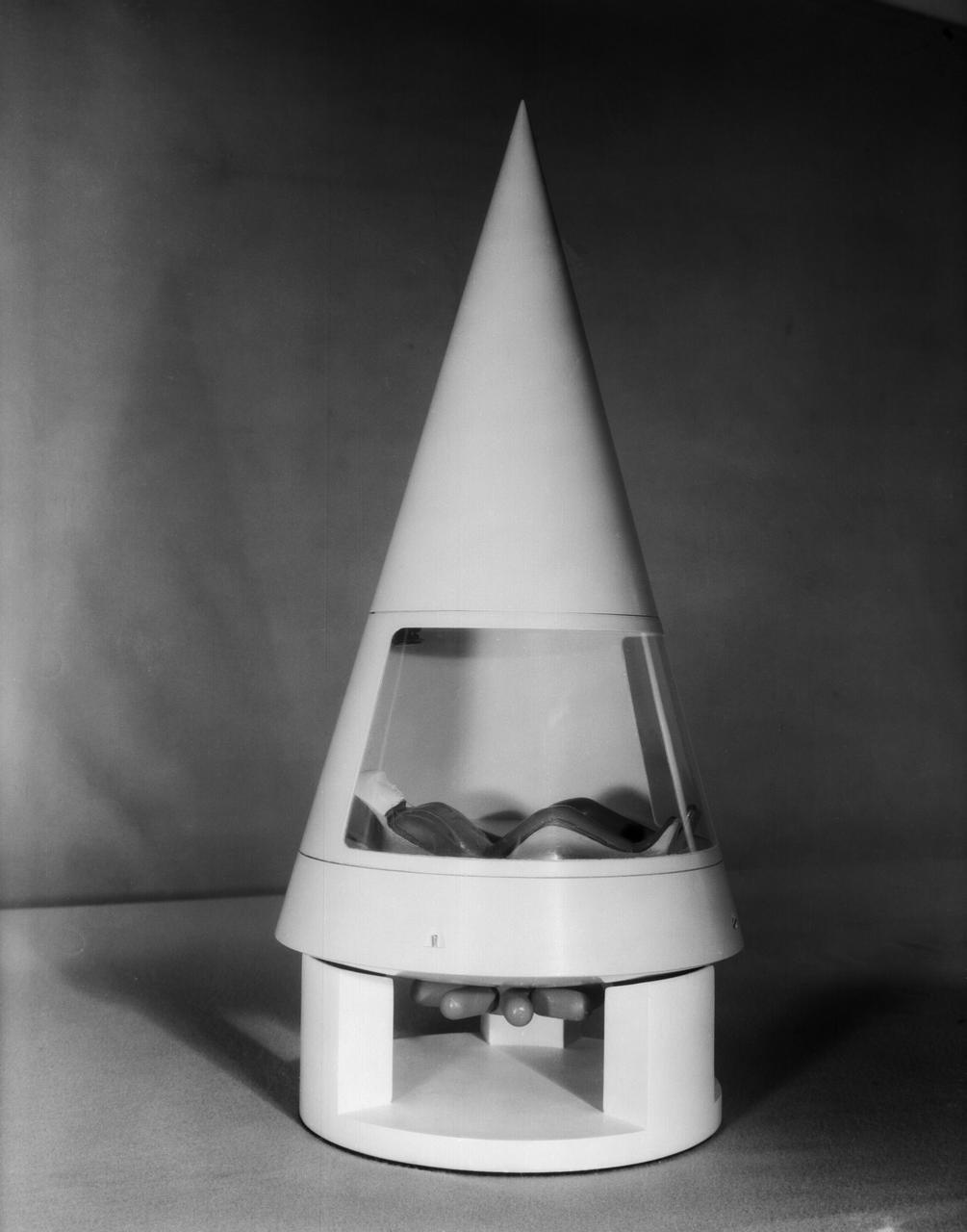

Scale model of Mercury capsule shape A, indicating the position of the astronaut.
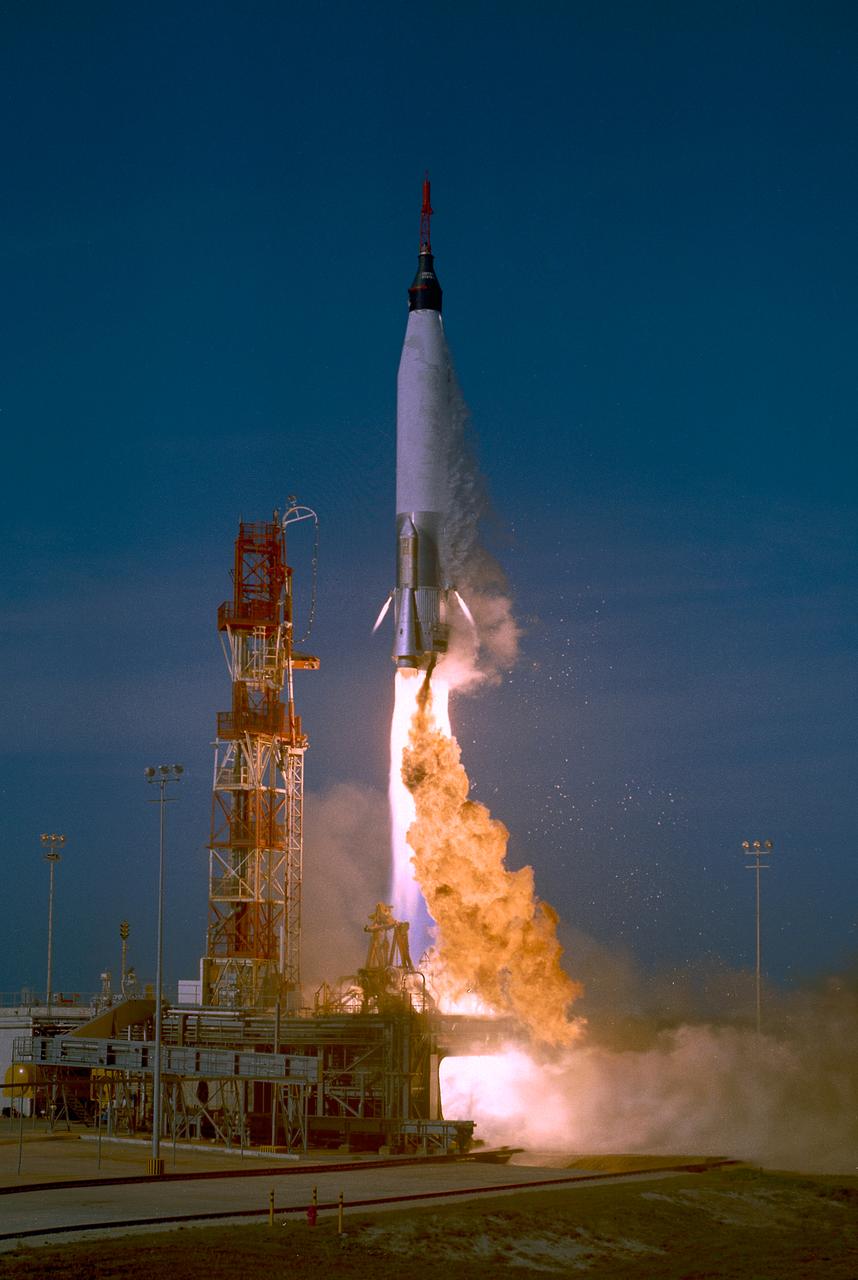

The launch of the Mercury Atlas (MA-2), an unmarned suborbital Mercury capsule test on February 24, 1961.
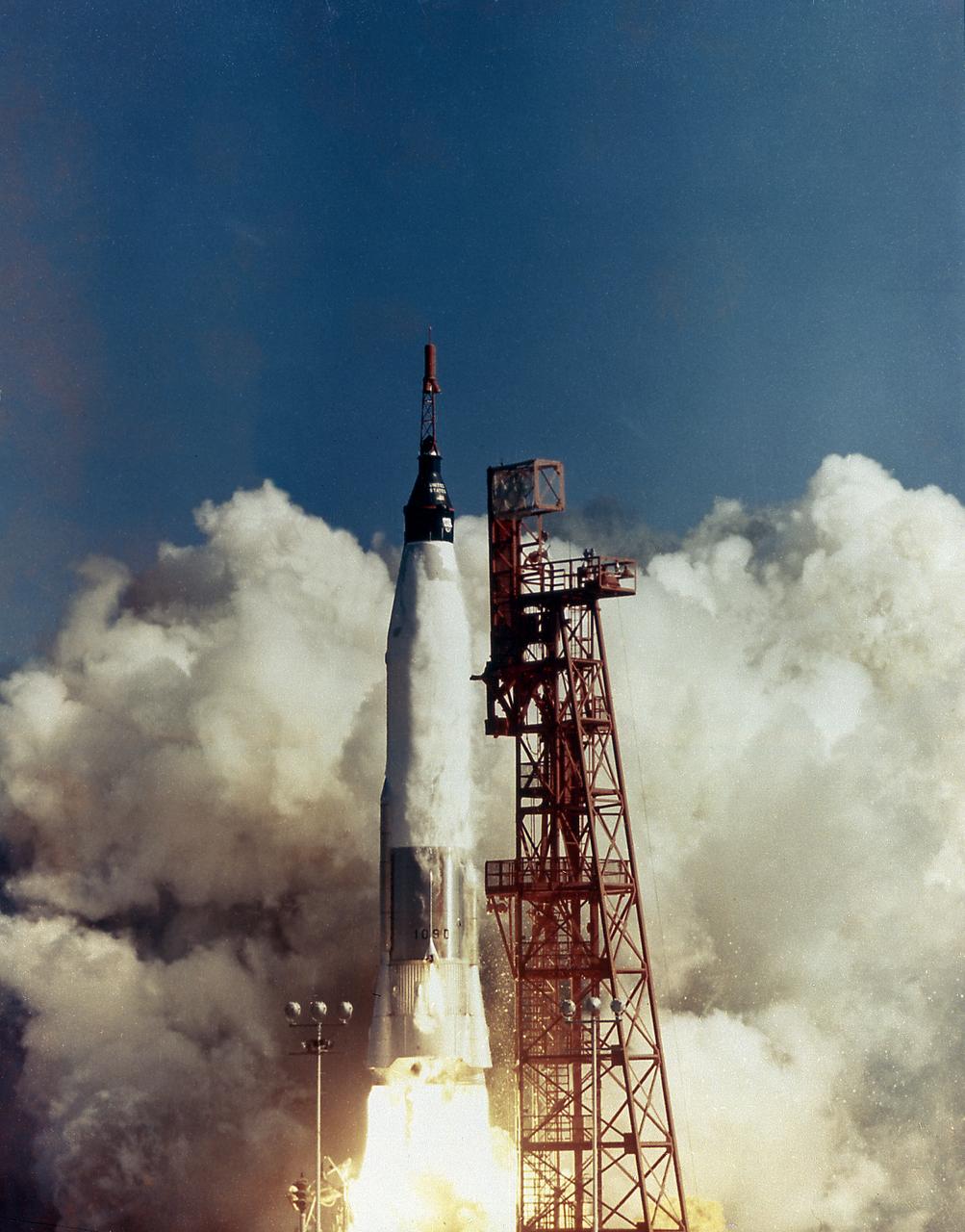

The launch of the MA-6, Friendship 7, on February 20, 1962. Boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, a modified Atlas Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM), Friendship 7 was the first U.S. marned orbital flight and carried Astronaut John H. Glenn into orbit. Astronaut Glenn became the first American to orbit the Earth.
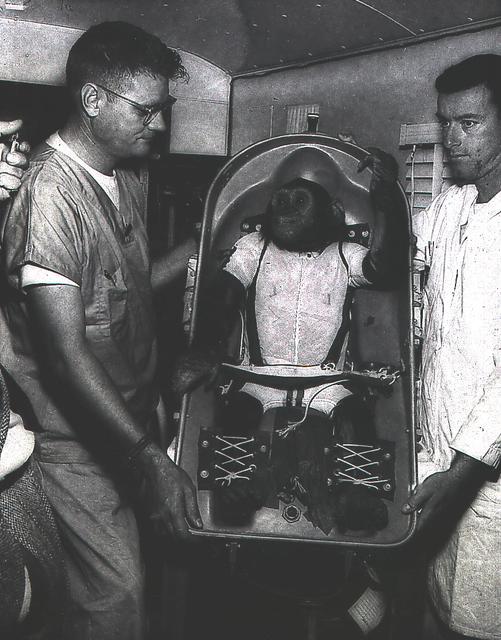
A three-year-old chimpanzee, named Ham, in the biopack couch for the MR-2 suborbital test flight. On January 31, 1961, a Mercury-Redstone launch from Cape Canaveral carried the chimpanzee "Ham" over 640 kilometers down range in an arching trajectory that reached a peak of 254 kilometers above the Earth. The mission was successful and Ham performed his lever-pulling task well in response to the flashing light. NASA used chimpanzees and other primates to test the Mercury Capsule before launching the first American astronaut Alan Shepard in May 1961. The successful flight and recovery confirmed the soundness of the Mercury-Redstone systems.
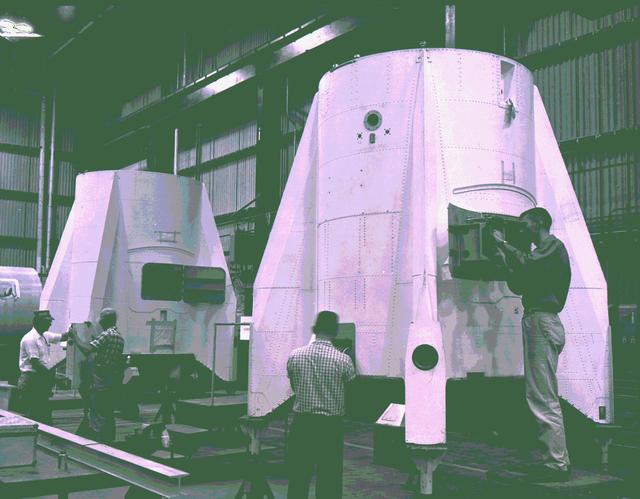

In this 1959 photograph, technicians prepare tail sections for Mercury-Redstone vehicles in Building 4706 at Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama. Developed by Dr. Wernher von Braun and the rocket team at Redstone, the Mercury-Redstone launched the first two marned U.S. missions.
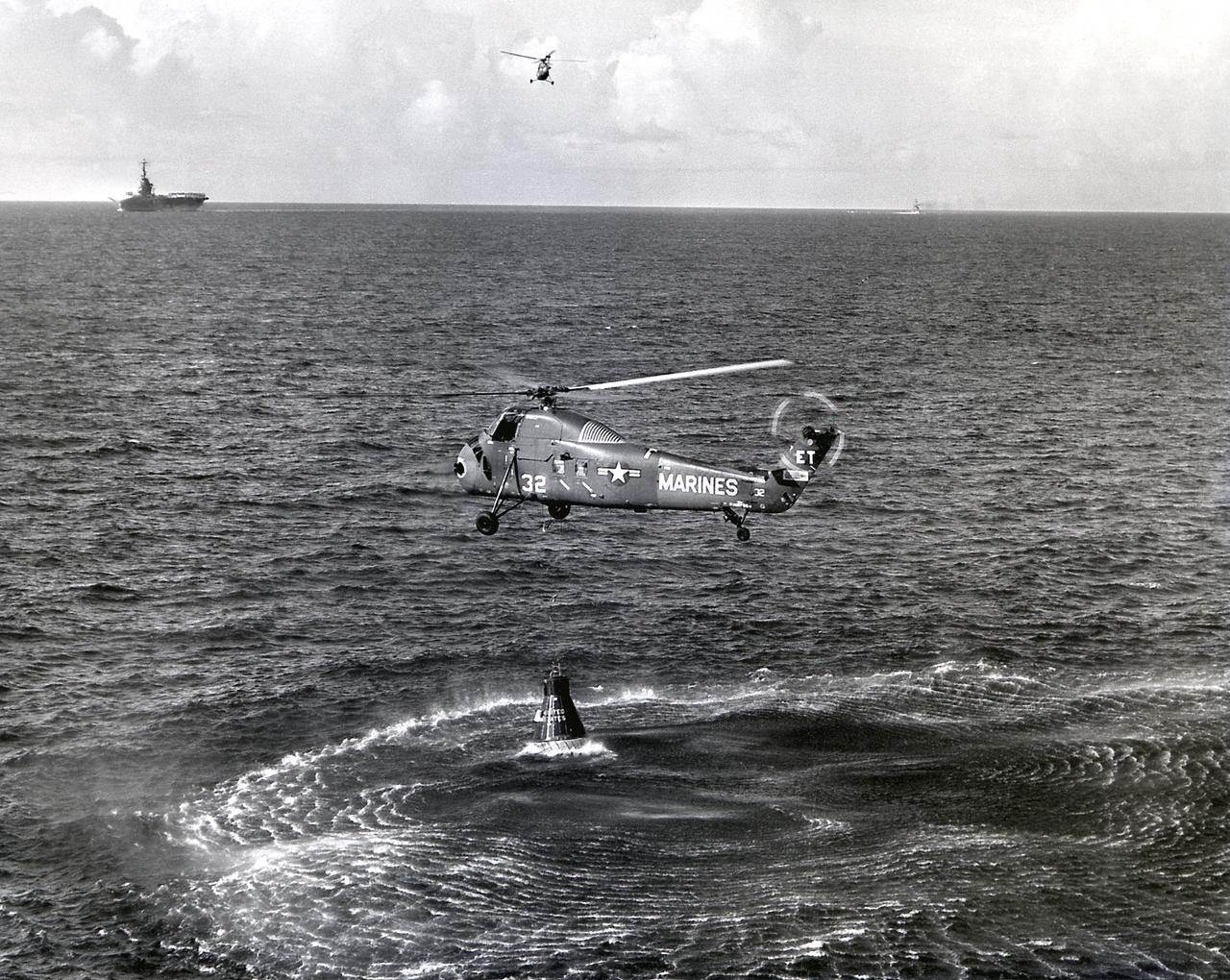

A U.S. Marine helicopter attempts to retrieve the sinking capsule, Liberty Bell 7, of the MR-4 mission. The attempt failed and the capsule sank. The MR-4 mission marned by Astronaut Virgil Grissom was the second manned orbital flight boosted by the Mercury-Redstone vehicle. The Recovery ship is in the background.
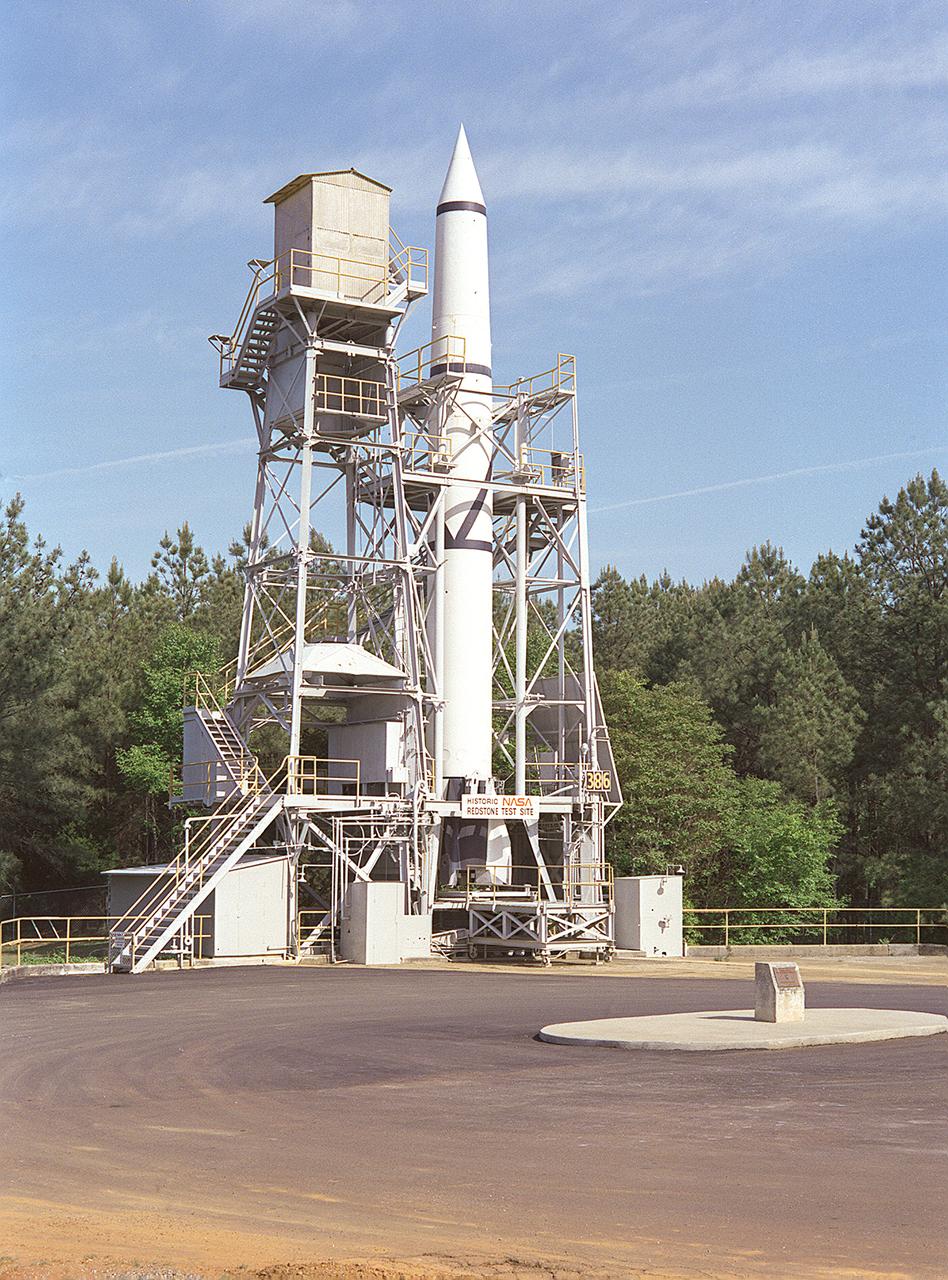

The Redstone Test Stand was used during the 1950s in early development of the Redstone missile propulsion system. This was the test stand where the modified Redstone missile that launched into space the first American, Alan Shepard, was static tested as the last step before the flight occurred.
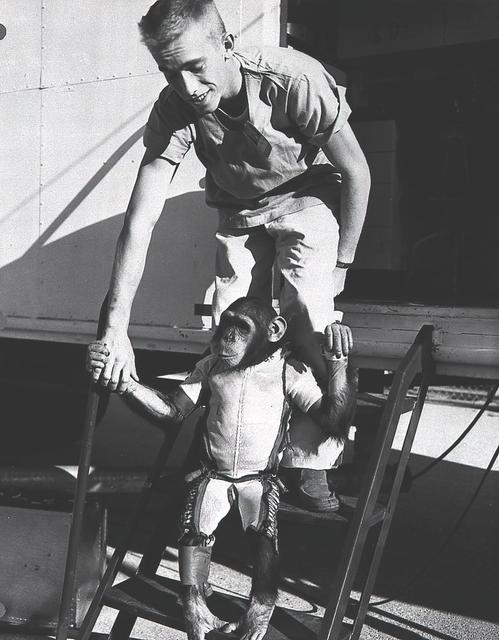

Ham, a three-year-old chimpanzee, in the spacesuit he would wear for the second Mercury- Redstone (MR-2) suborbital test flight in January, 1961. NASA used chimpanzees and other primates to test the Mercury capsule before launching the fisrt American astronaut, Alan Shepard, in May 1961. The Mercury capsule rode atop a modified Redstone rocket, developed by Dr. Wernher von Braun and the German Rocket Team in Huntsville, Alabama.
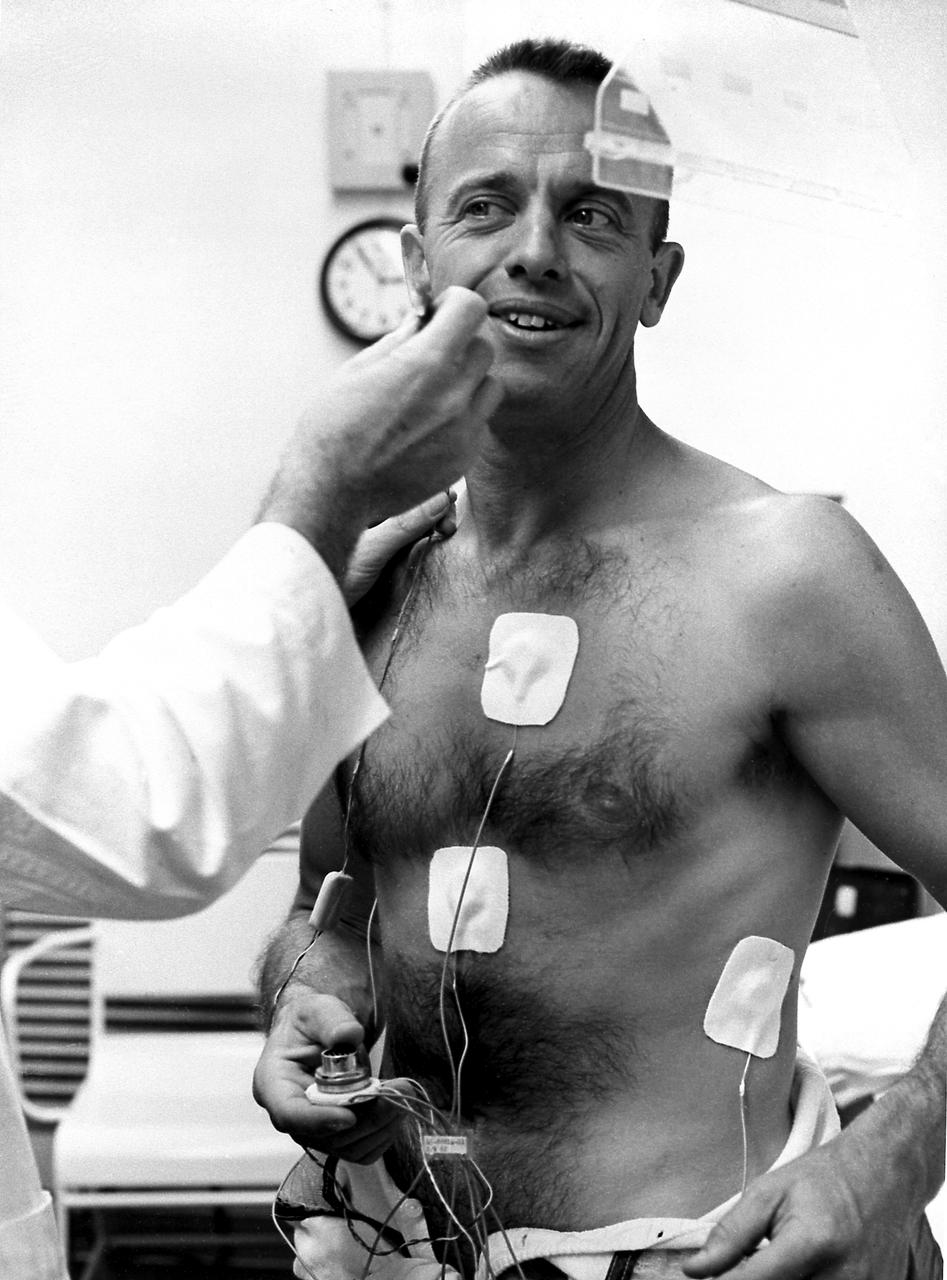
Astronaut Alan Shepard underwent a physical examination prior to the first marned suborbital flight. Freedom 7 carrying Astronaut Alan Shepard, boosted by the Mercury-Redstone launch vehicle, lifted off on May 5, 1961. Astronaut Shepard became the first American in space.
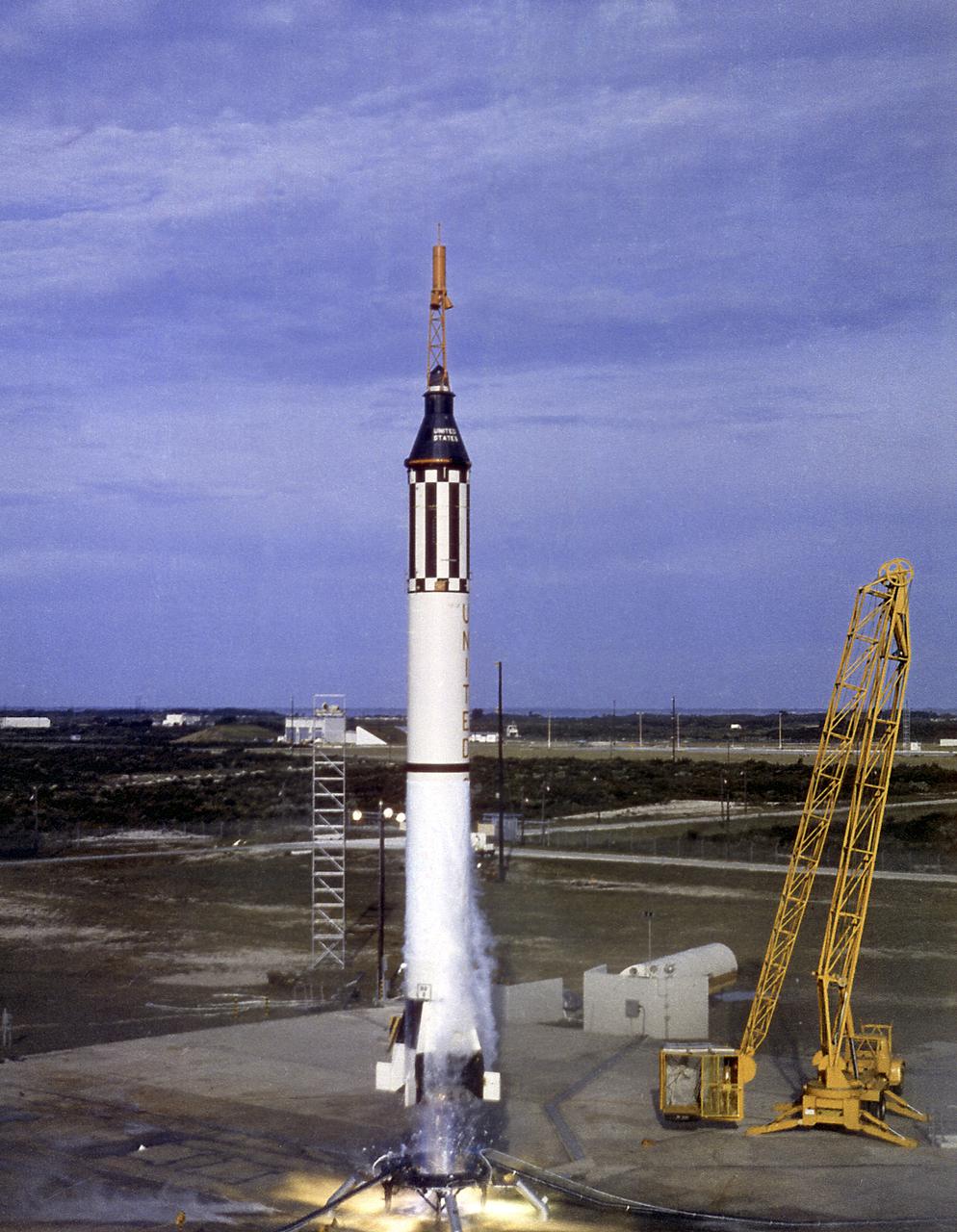
Liftoff of MR-4 (Mercury-Redstone), Liberty Bell 7, on July 21, 1961. MR-4 mission was the second marned suborbital flight and carried Astronaut Virgil Grissom aboard the Liberty Bell 7 spacecraft in space for a duration of 15-1/2 minutes.
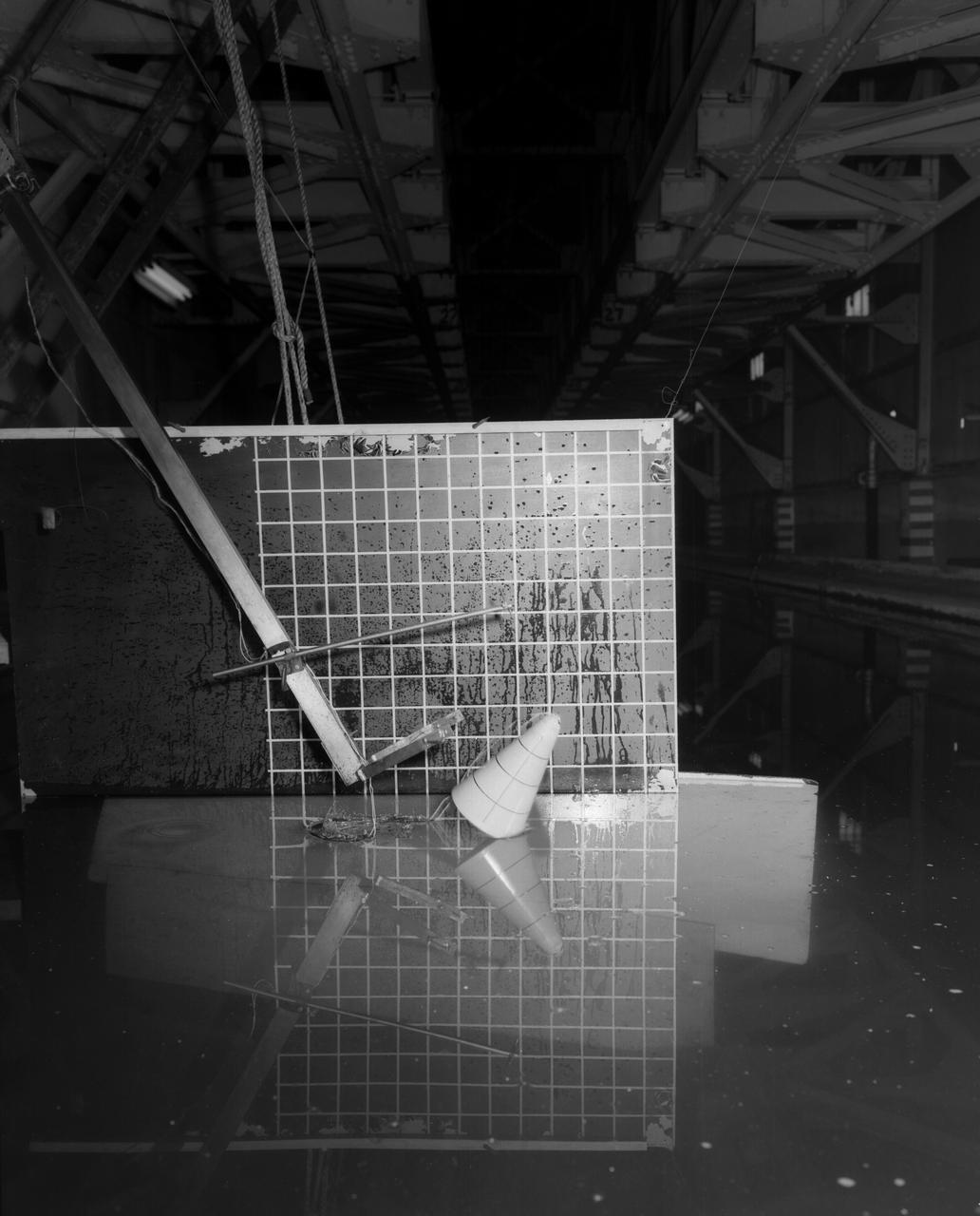

Testing of Mercury Capsule Shape A by the Hydrodynamics Division of Langley. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 19): The Hydrodynamics Division provided assistance in determining landing loads. In this connection, after PARD engineers had unofficially approached that division to make some water impact tests with the boilerplate capsule, J.B. Parkinson, Hydrodynamics Chief visited Shortal to find out if the request had his support. Finding out that it did, Parkinson said, Its your capsule. If you want us to drop it in the water, we will do it. From Shortal (Vol. 3, p. 16): The basic design of the capsule was made by M.A. Faget and his coworkers at PARD during the winter of 1957-1958. It was natural, then, that extensive use was made of the facilities at Wallops during the development of the spacecraft. The tests at Wallops consisted of 26 full-size capsules, either launched from the ground by rocket power or dropped from airplanes at high altitude and 28 scaled models, either rocket boosted or released from balloons. Emphasis in the Wallops program was on dynamic stability and aerodynamic heating of the capsule, and effectiveness of the pilot-escape and parachute-recovery systems. The biggest part of the Wallops program was the series of full-size capsules, rocket launched with the Little Joe booster, developed especially for Mercury. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
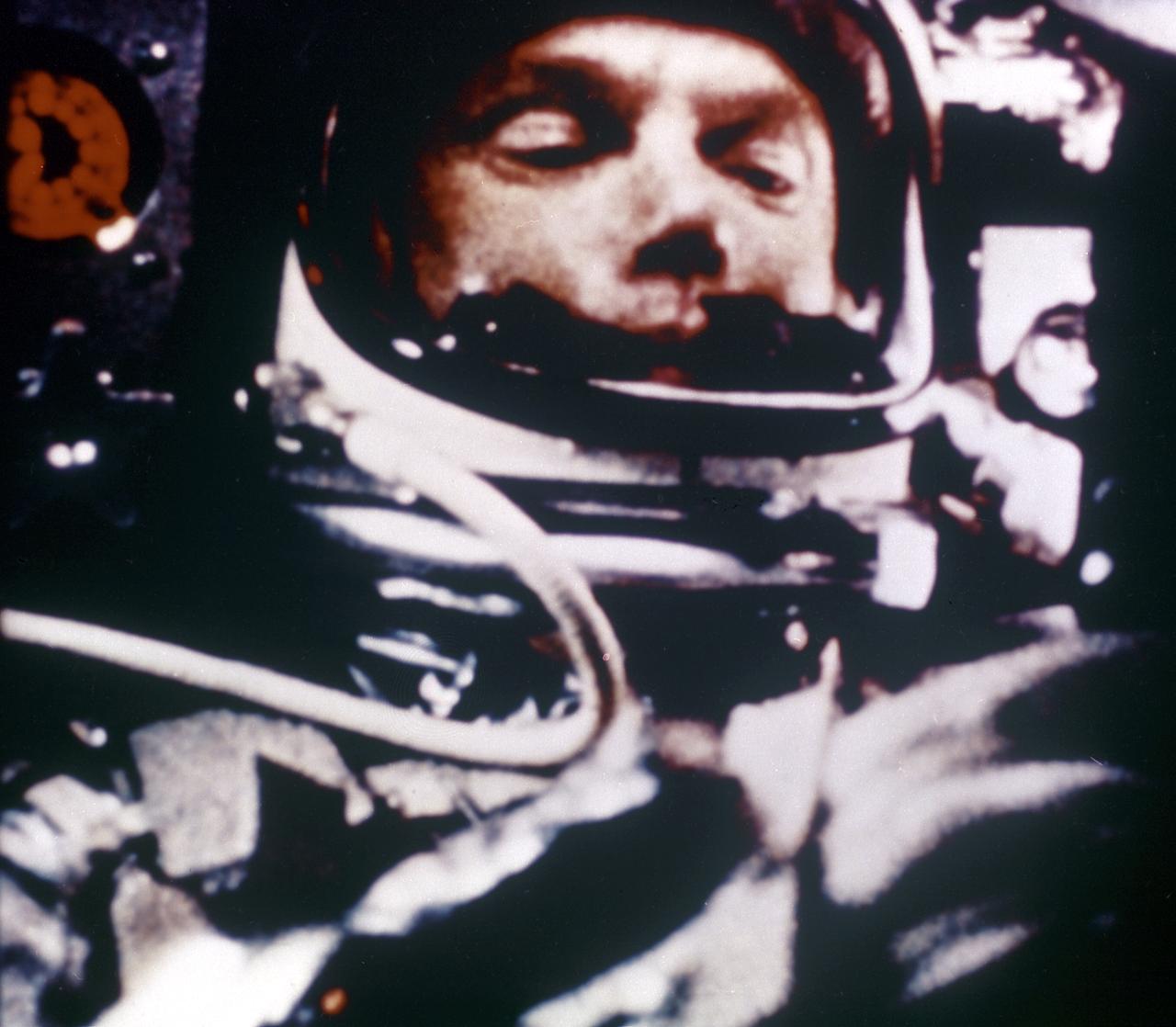

Astronaut John Glenn in the Friendship 7 capsule during the first manned orbital flight, the MA-6 mission. Boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, a modified Atlas (intercontinental ballistic missile), the MA-6 mission lasted for 5 hours and orbited the Earth three times.

Dr. von Braun addresses a crowd celebrating in front of the Madison County Alabama Courthouse following the successful launch of Astronaut Alan Shepard (America's first astronaut in space) into space on a Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle, Freedom 7. Shepard's Mercury Spacecraft, was launched from Cape Canaveral. He reached a speed of 5200 mph. His flight lasted 15-1/2 minutes. May 5, 1961 (Photo: Courtesy of Huntsville/Madison County Public Library)
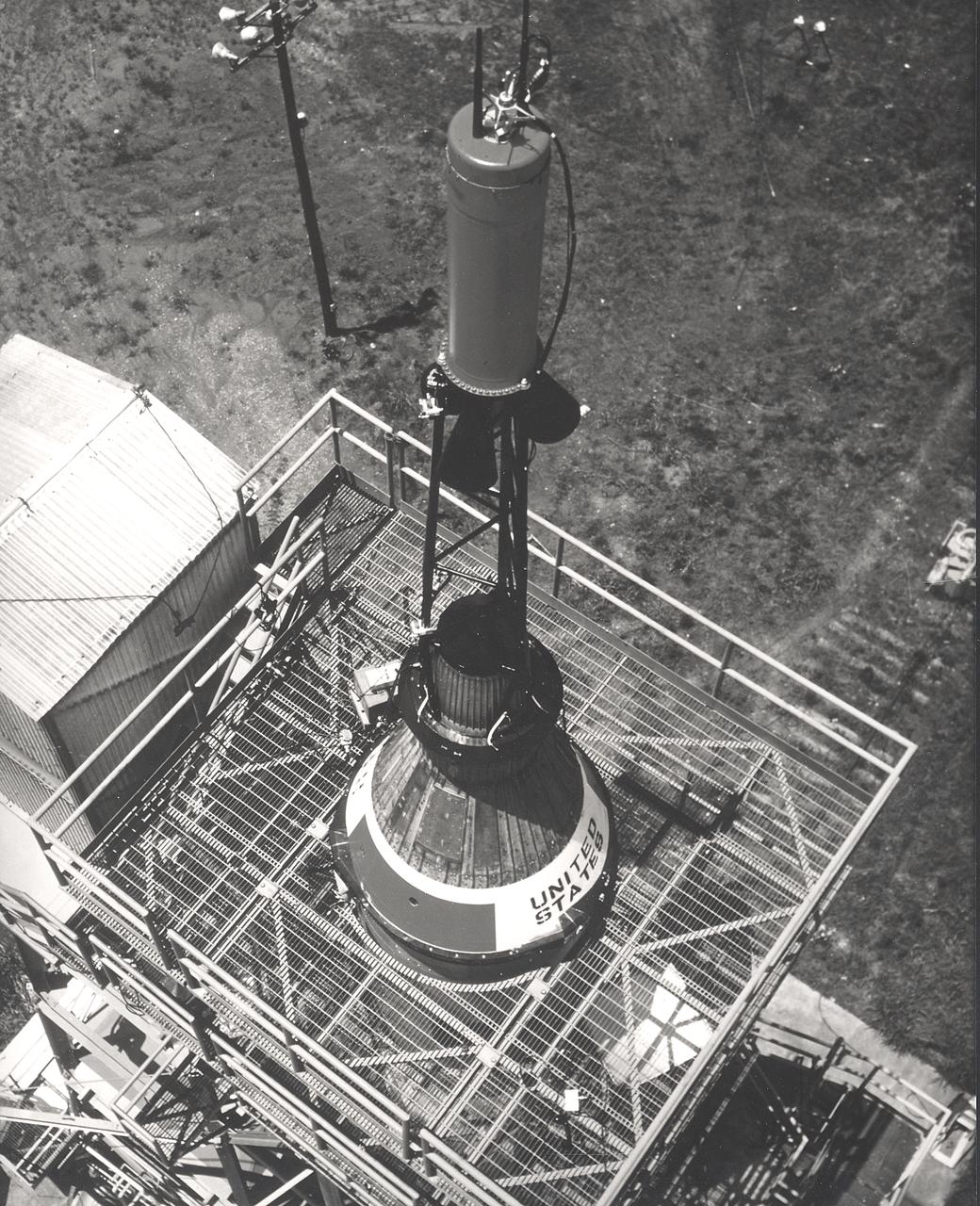

This photograph depicts installation of the Mercury capsule and escape system on top of a booster prior to test firing of the Mercury-Redstone launch vehicle at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
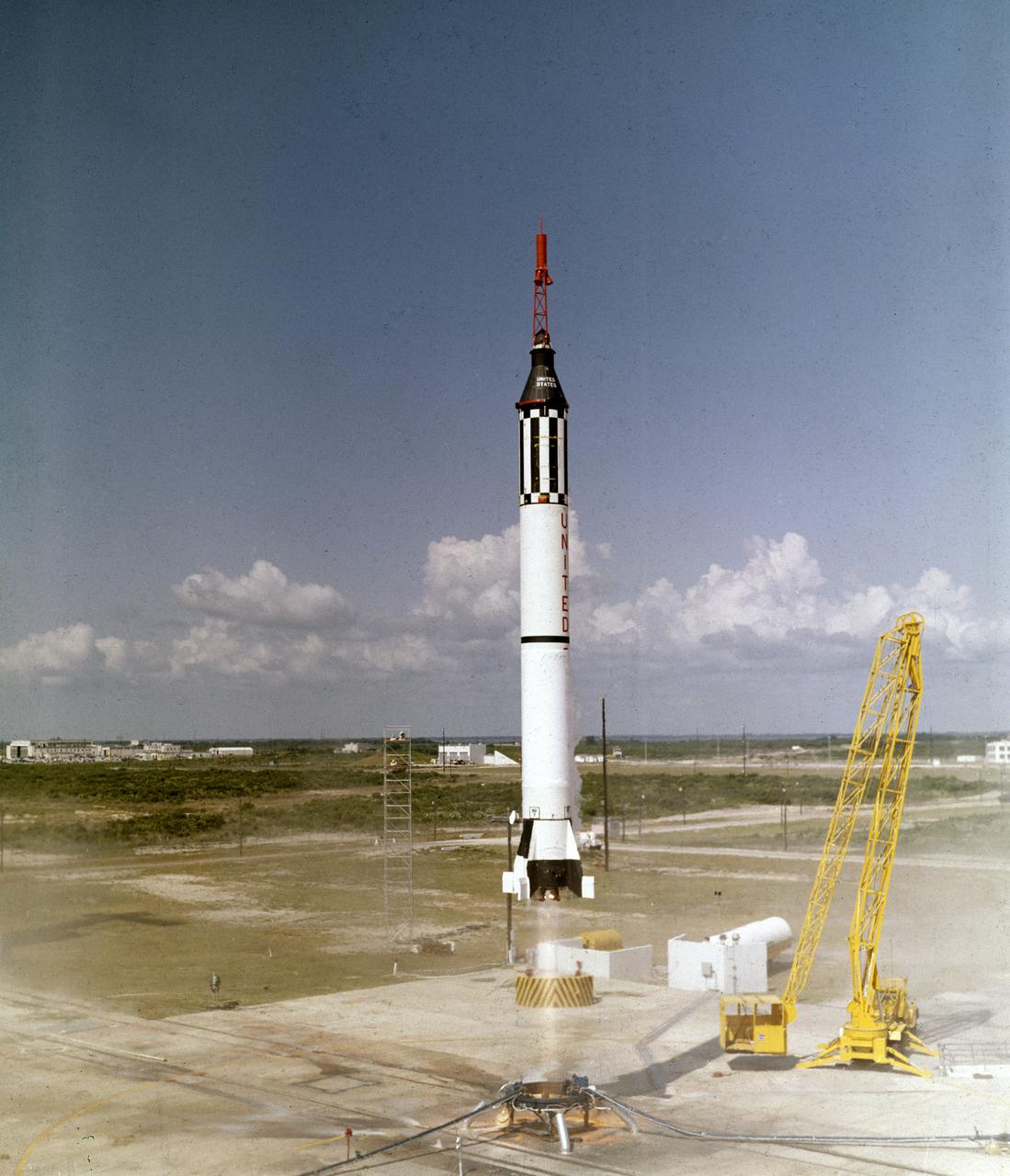

Astronaut Alan B. Shepard, Jr. lifts off in the Freedom 7 Mercury spacecraft on May 5, 1961. This third flight of the Mercury-Redstone (MR-3) vehicle, developed by Dr. Wernher von Braun and the rocket team in Huntsille, Alabama, was the first marned space mission for the United States. During the 15-minute suborbital flight, Shepard reached an altitude of 115 miles and traveled 302 miles downrange.
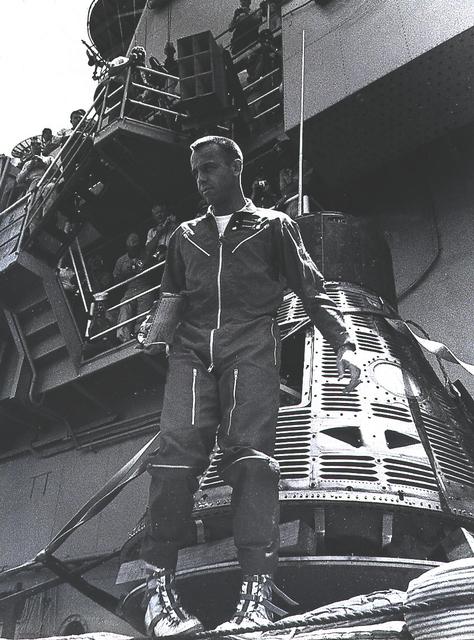
Alan B. Shepard, Jr., America's first astronaut, stands in front of the Freedom 7 spacecraft shortly after completion of the third flight of the Mercury-Redstone (MR-3) vehicle, May 5, 1961. During the 15-minute suborbital flight, the Freedom 7 Mercury spacecraft, launched atop a modified Redstone rocket developed by Dr. Wernher von Braun and the rocket team in Huntsville, Alabama, reached an altitude of 115 miles and traveled 302 miles downrange.
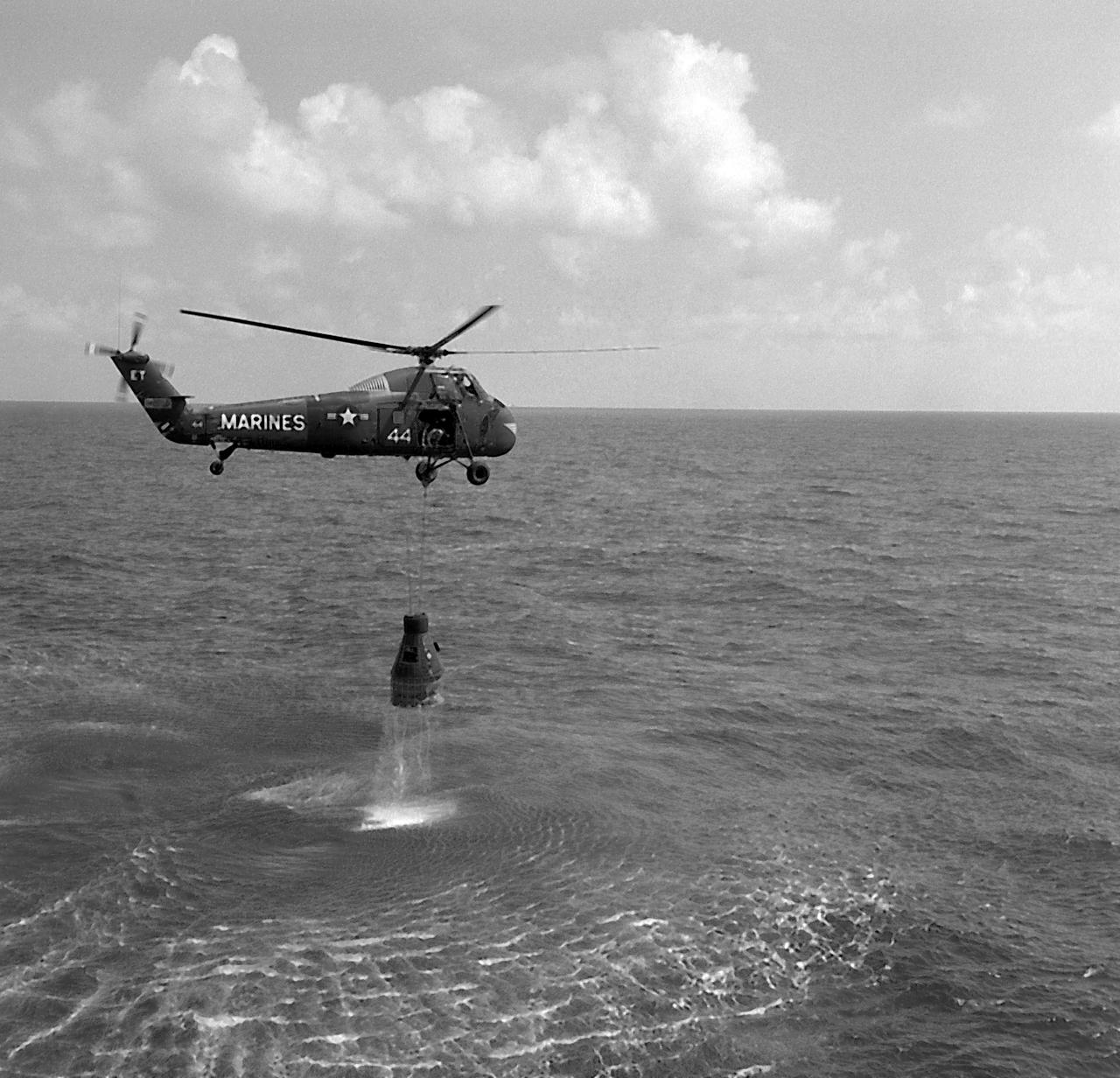

This photo depicts the recovery of the Freedom 7 (MR-3) capsule by a U.S. Marine helicopter. The MR-3 mission successfully placed the first American astronaut, Alan Shepard, in space for 15-1/2 minutes and returned safely to Earth on May 5, 1961.
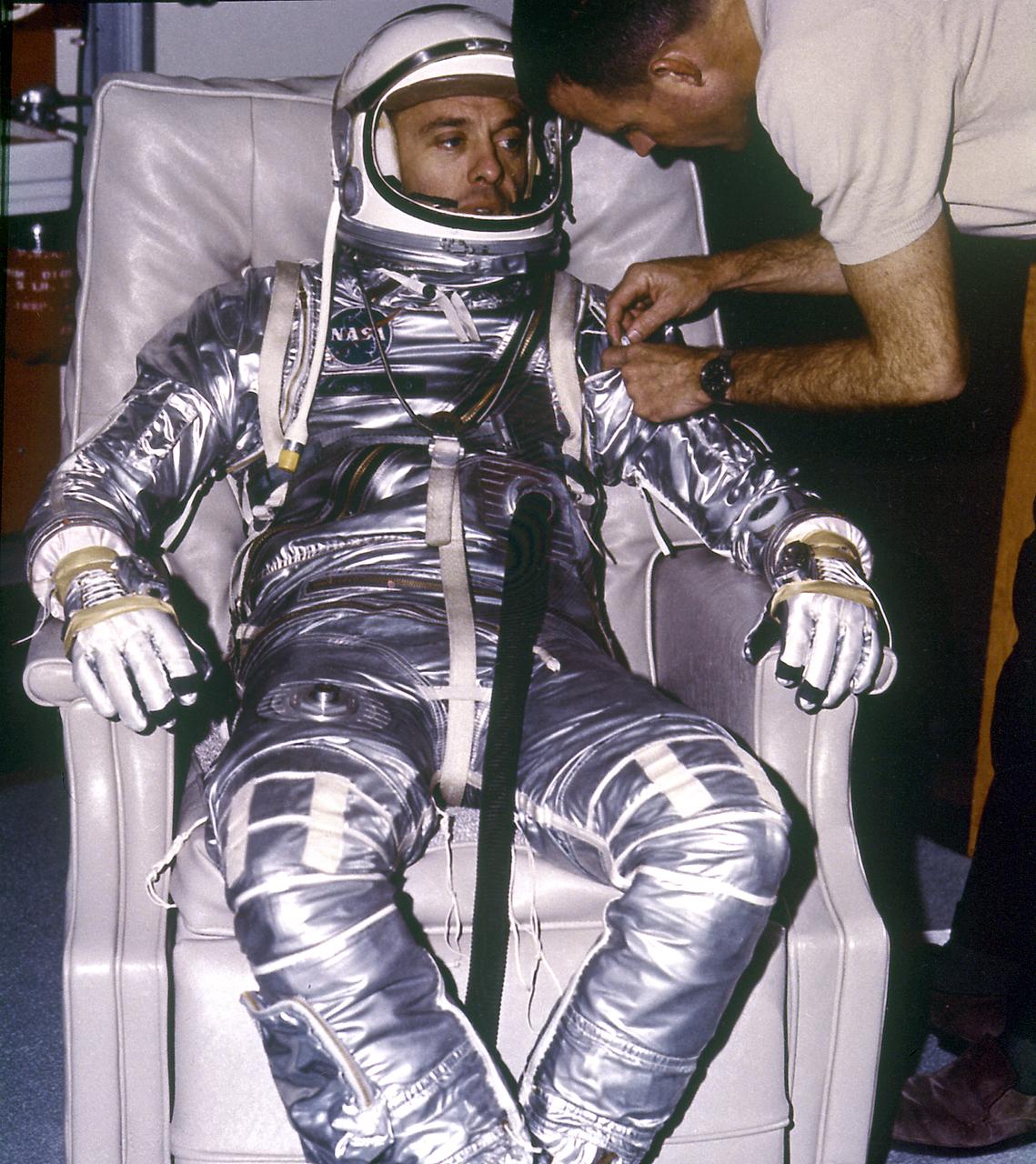

Astronaut Alan B. Shepard, Jr. during suiting for the first manned suborbital flight, MR-3 mission. The Freedom 7 spacecraft, carrying the first American, Astronaut Shepard and boosted by the Mercury-Redstone launch vehicle, lifted off on May 5, 1961.

The launch of the Little Joe booster for the LJ1B mission on the launch pad from the wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Virginia, on January 21, 1960. This mission achieved the suborbital Mercury capsule test, testing of the escape system, and biomedical tests by using a monkey, named Miss Sam.
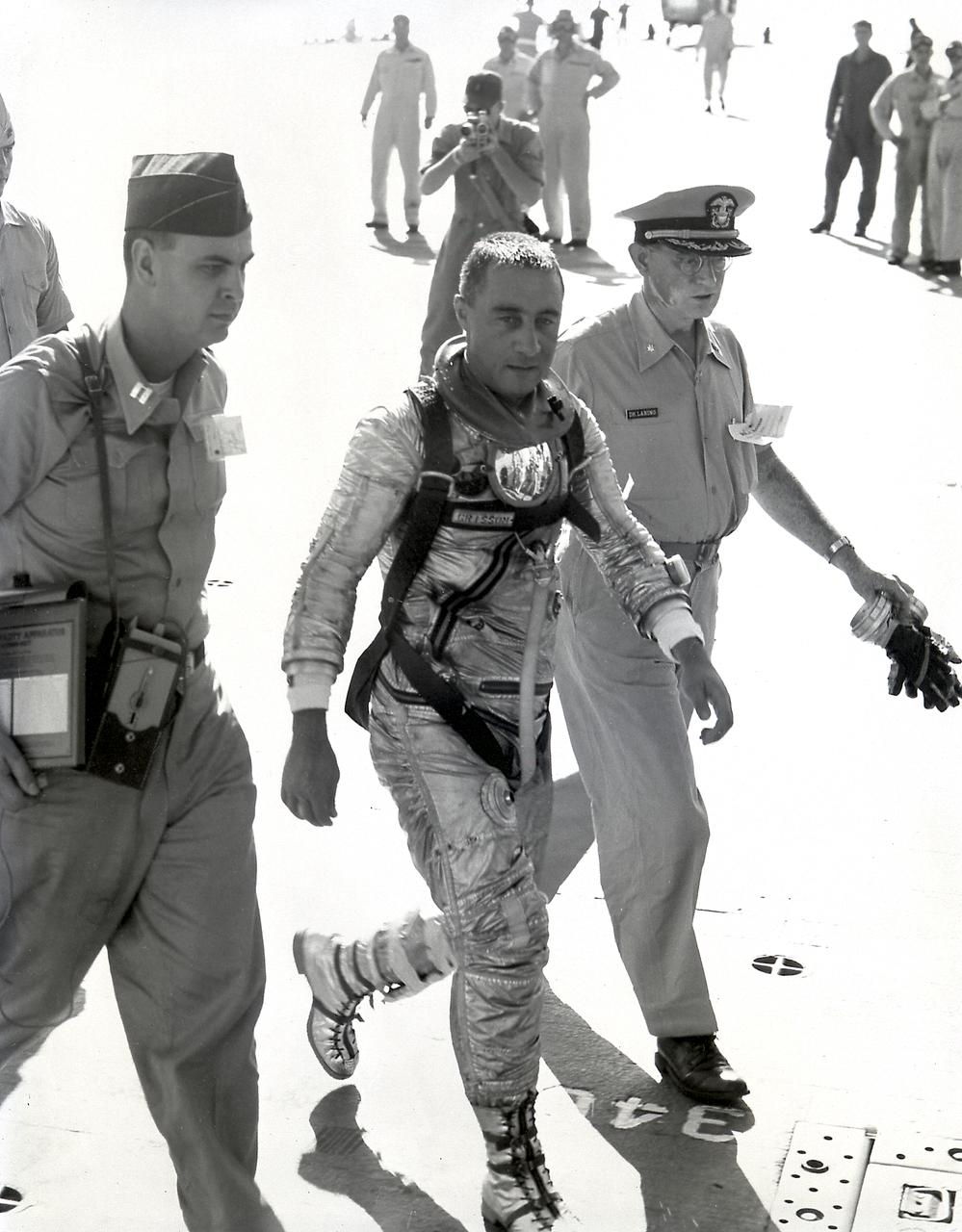

Astronaut Virgil Grissom walks on the recovery ship after completing the 15-1/2-minute suborbital MR-4 mission.
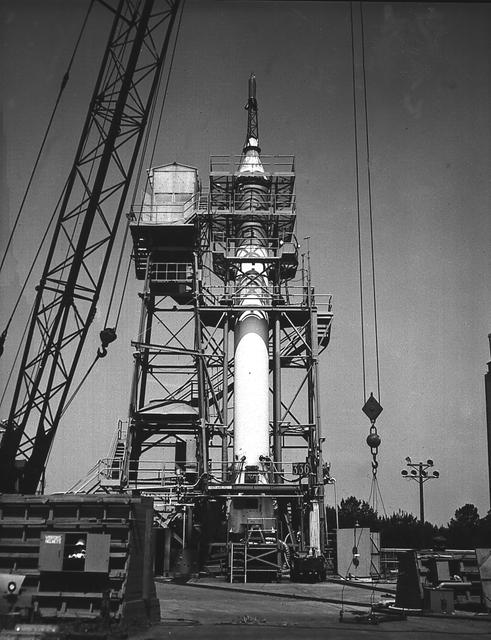

A Mercury-Redstone launch vehicle awaits test-firing in the Redstone Test Stand during the late 1950s. Between 1953 and 1960, the rocket team at Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama performed hundreds of test firings on the Redstone rocket, over 200 on the Mercury-Redstone vehicle configuration alone. It was this configuration which launched America's first two marned space missions, Freedom 7 and Liberty Bell 7,in 1961.
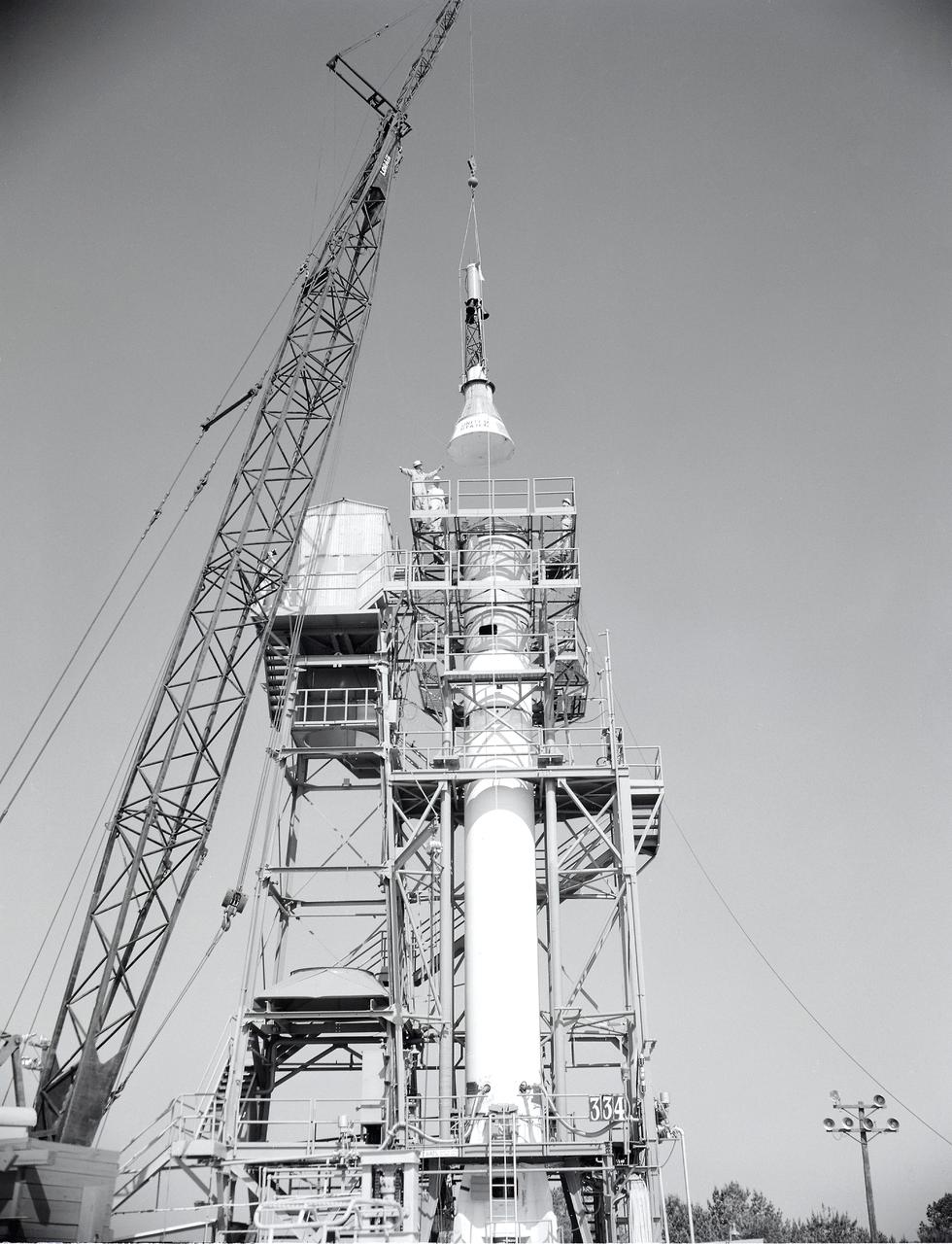

Installation of the Mercury capsule on Redstone booster at the Redstone Test Stand. Assembled at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the Mercury-Redstone launch vehicle was designed to place a marned space capsule into orbital flight around the Earth and recover both safely.

This photograph shows the installation of a Mercury capsule and escape system on top of a booster prior to test firing of the Mercury-Redstone at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) Redstone Test Stand. Assembled by MSFC, the Mercury-Redstone was designed to place a marned space capsule in orbital flight around the Earth and recover both safely.
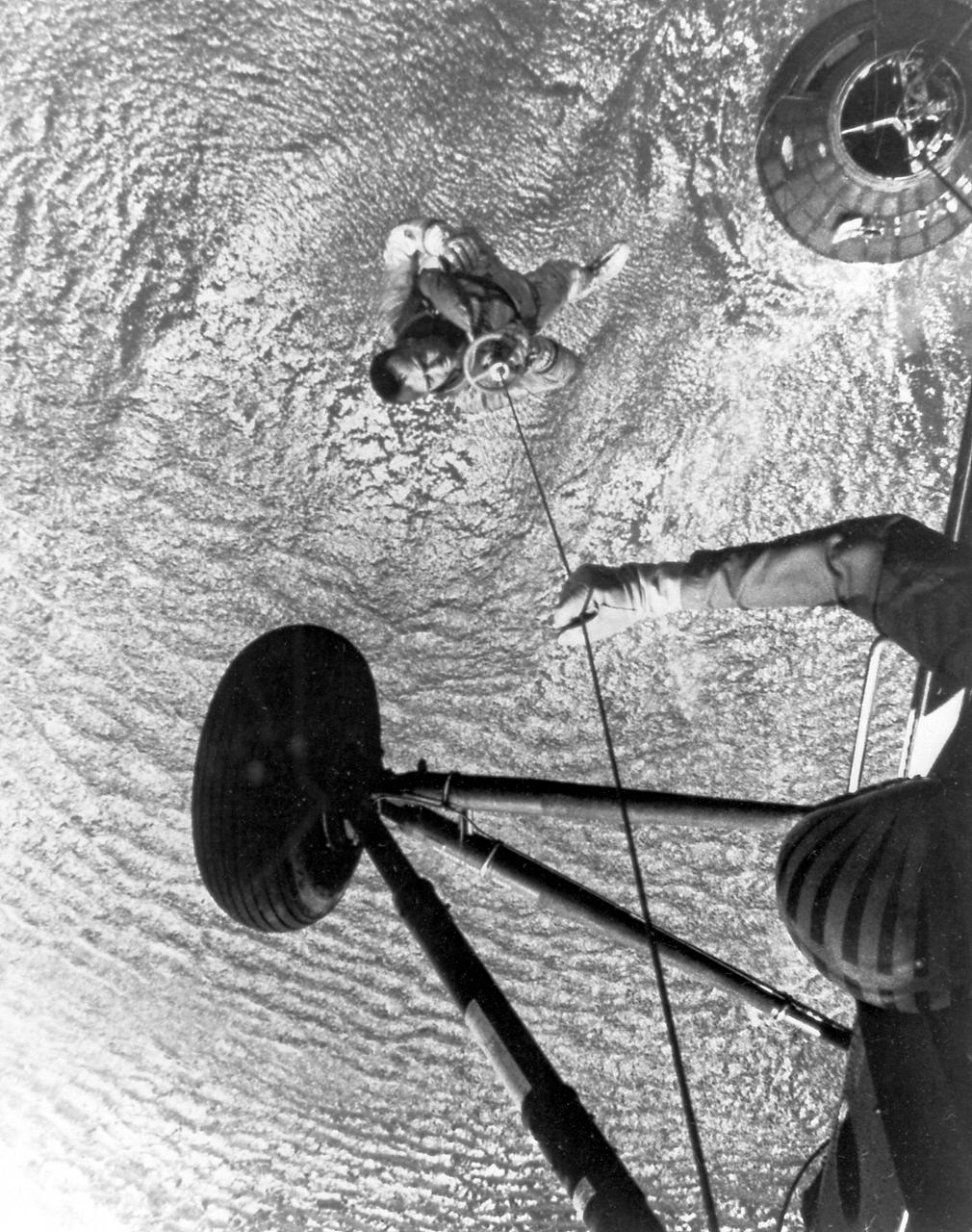

This photo depicts the recovery operations of the MR-3 mission. Astronaut Alan Shepard was picked up by a U.S. Marine helicopter after the completion of the first marned suborbital flight by MR-3 (Mercury-Redstone) with the Freedom 7 capsule.
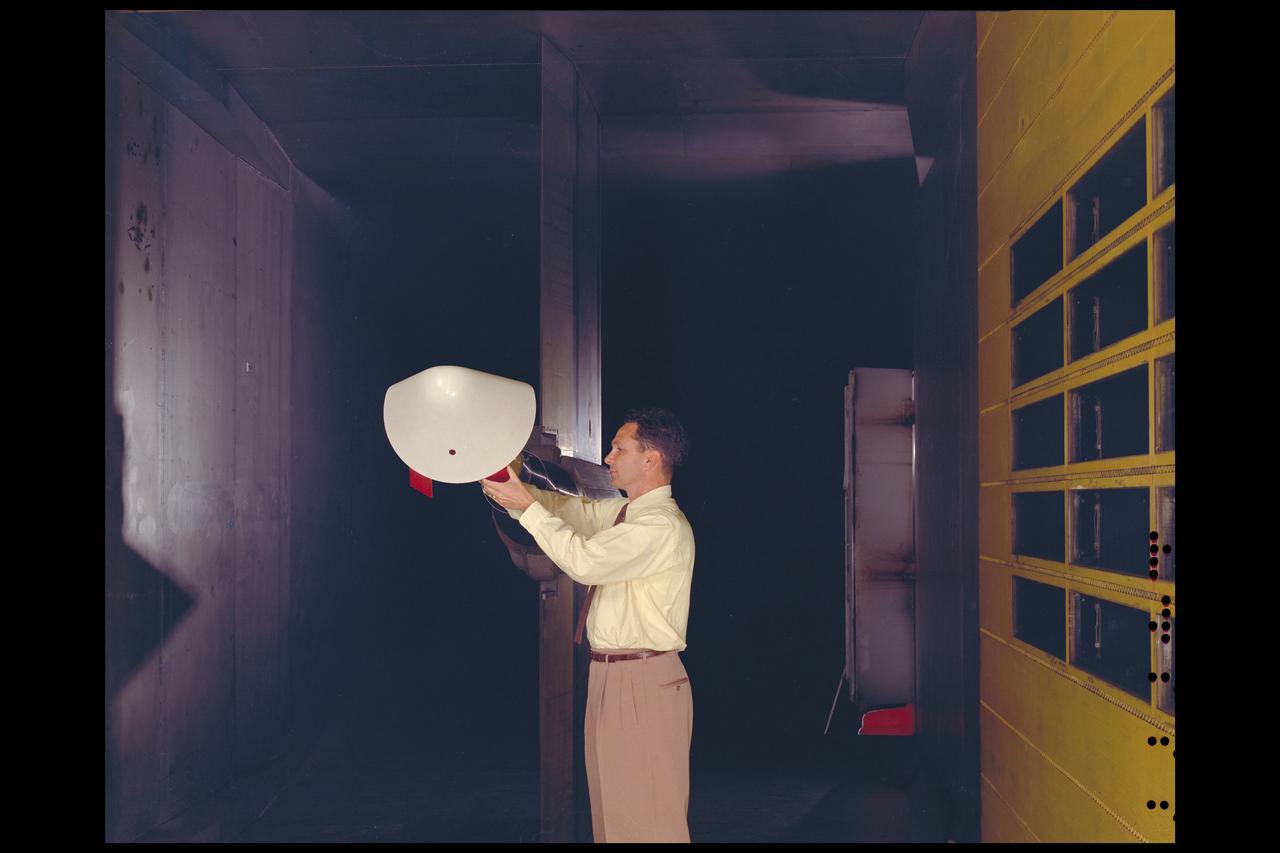

Project Mercury: M-1 model in the 11ft w.t. with engineer

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- CHAMBER TEST - Project Mercury astronaut Virgil I. 'Gus' Grissom, assisted by McDonnell technicians, leaves Mercury spacecraft, dubbed Liberty Bell 7, following simulated flight.
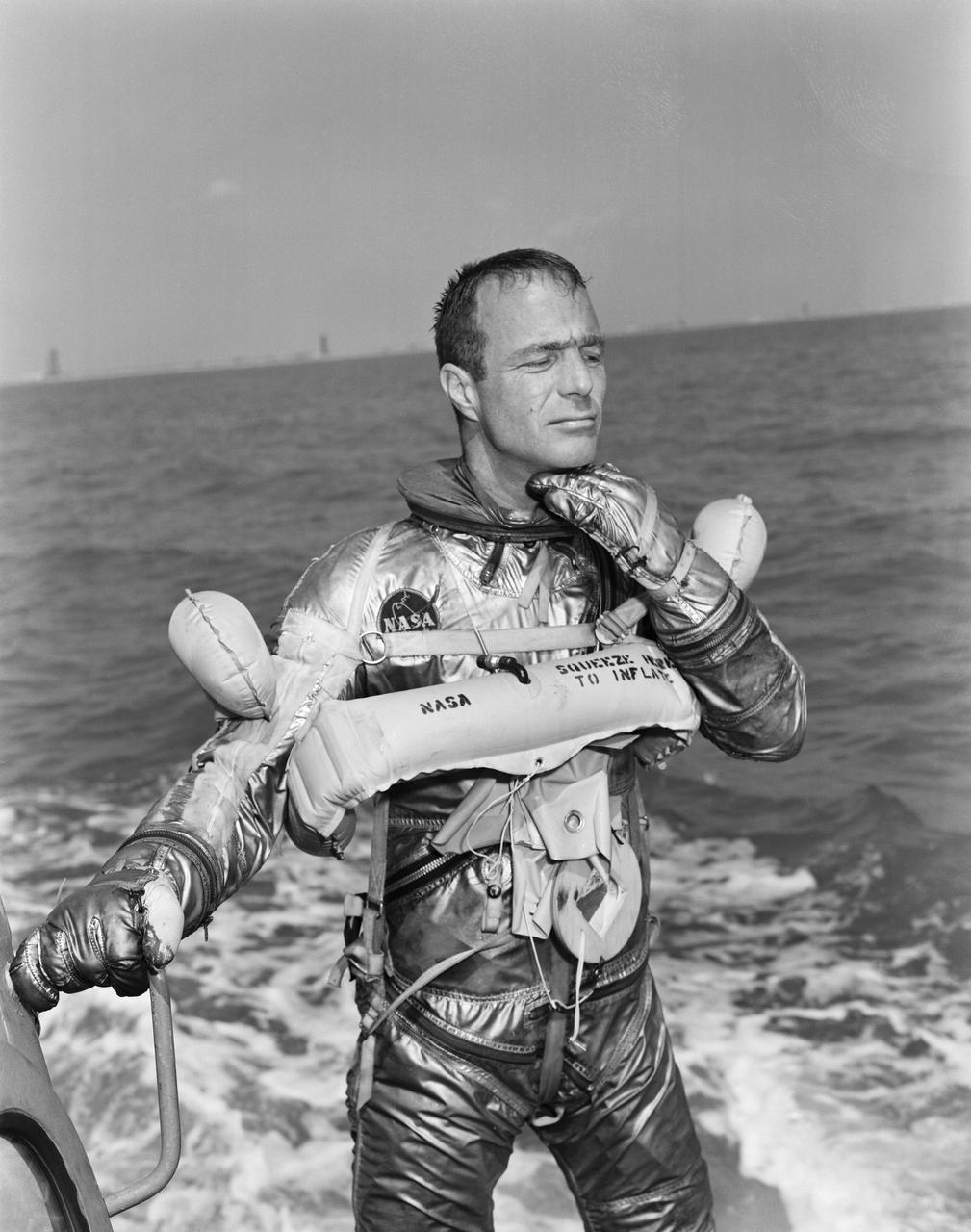

S62-01358 (1962) --- Project Mercury astronaut M. Scott Carpenter, prime pilot of the Mercury-Atlas 7 (MA-7) spaceflight, goes through a water egress test. He is in the Mercury pressure suit, without the helmet, and is wearing a life vest. Photo credit: NASA

This orthographic projection view from NASA MESSENGER spacecraft provides a look at Mercury north polar region. The yellow regions in many of the craters mark locations that show evidence for water ice, as detected by Earth-based radar observations from Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico. MESSENGER has collected compelling new evidence that the deposits are indeed water ice, including imaging within the permanently shaded interiors of some of the craters, such as Prokofiev and Fuller. Instrument: Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) Arecibo Radar Image: In yellow (Harmon et al., 2011, Icarus 211, 37-50) http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19411

Project Mercury: With Project Mercury, the United States gained its first experience in conducting human space missions that provided scientific and engineering knowledge of astronauts in space. Alan Shepard made history May 5, 1961, as America's first man in space. Less than a year later, John Glenn made the nation’s first orbital flight on Feb. 20, 1962. After two suborbital and three orbital missions, Project Mercury ended with a 22-orbit spaceflight on May 16, 1963. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Project Mercury: With Project Mercury, the United States gained its first experience in conducting human space missions that provided scientific and engineering knowledge of astronauts in space. Alan Shepard made history May 5, 1961, as America's first man in space. Less than a year later, John Glenn made the nation’s first orbital flight on Feb. 20, 1962. After two suborbital and three orbital missions, Project Mercury ended with a 22-orbit spaceflight on May 16, 1963. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
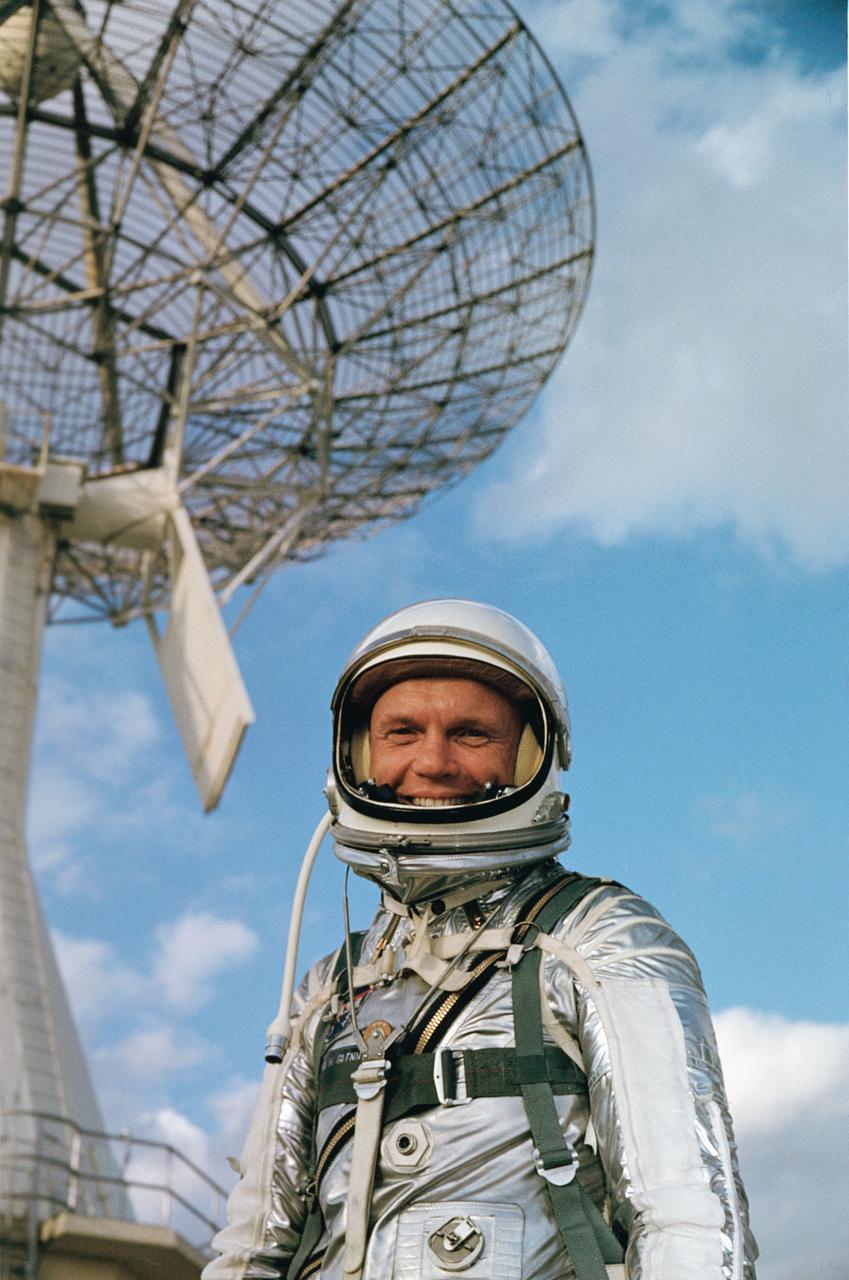

January 1962 -- Project Mercury Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., prime pilot for the MA-6 mission.
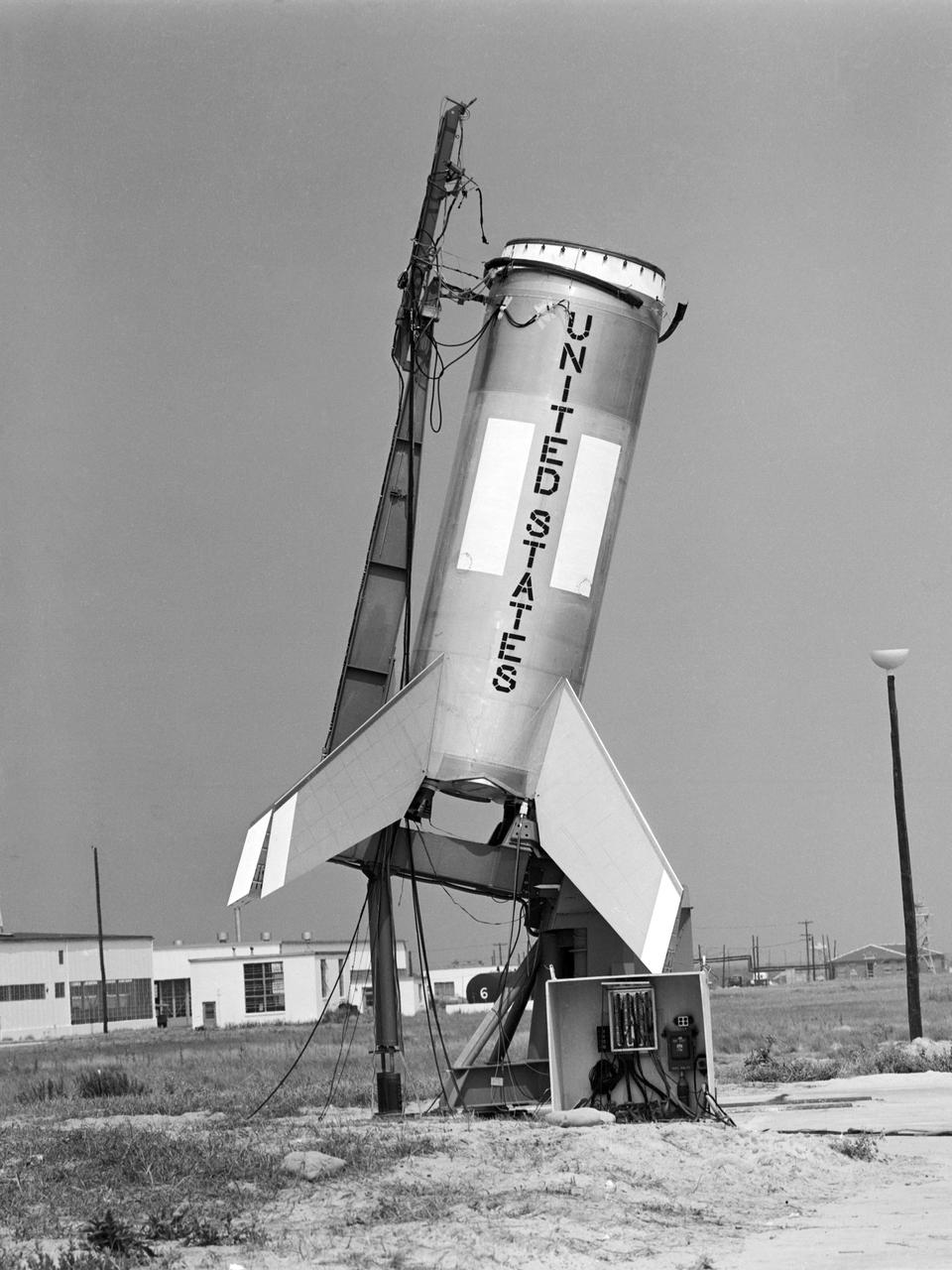

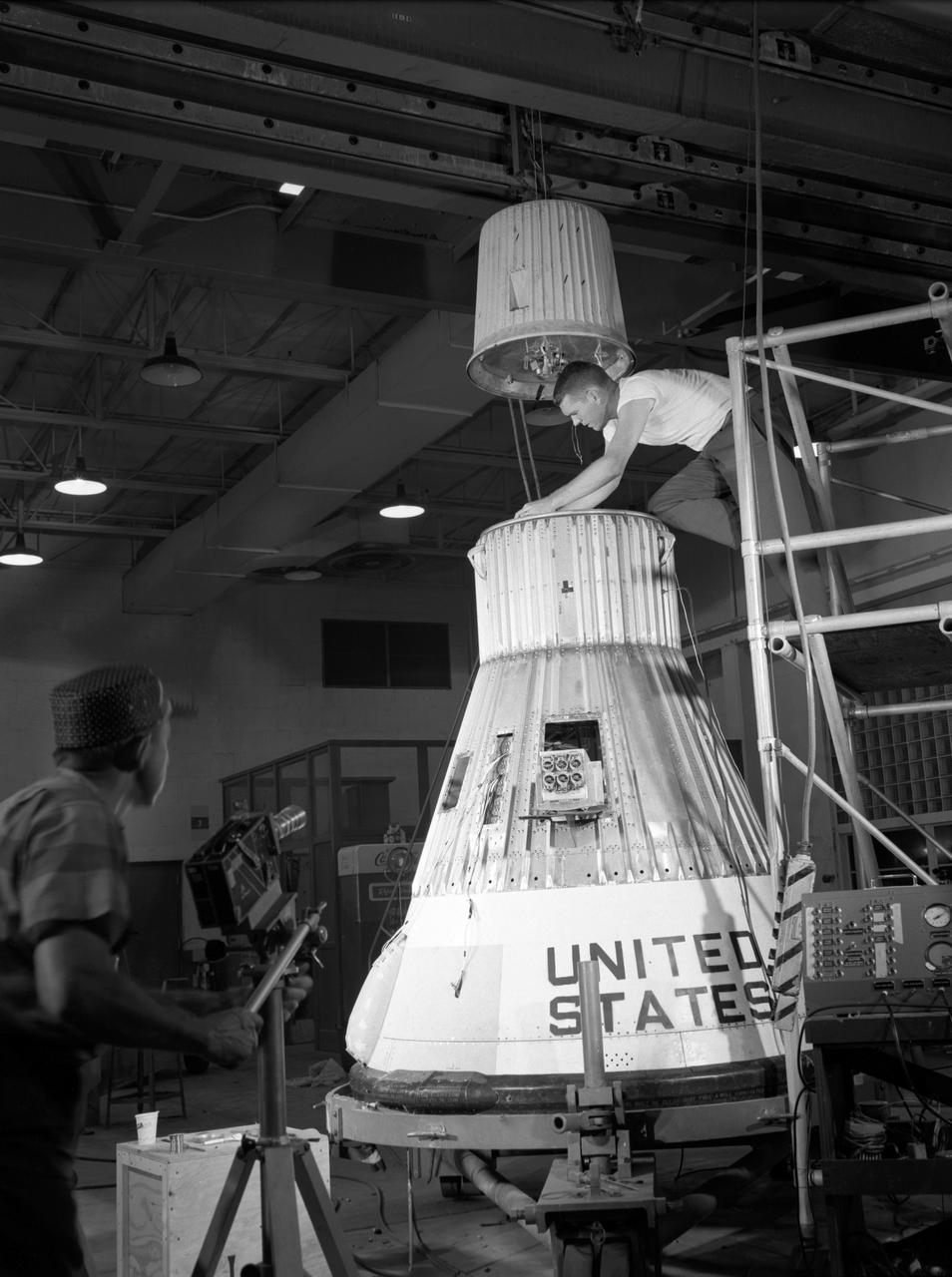
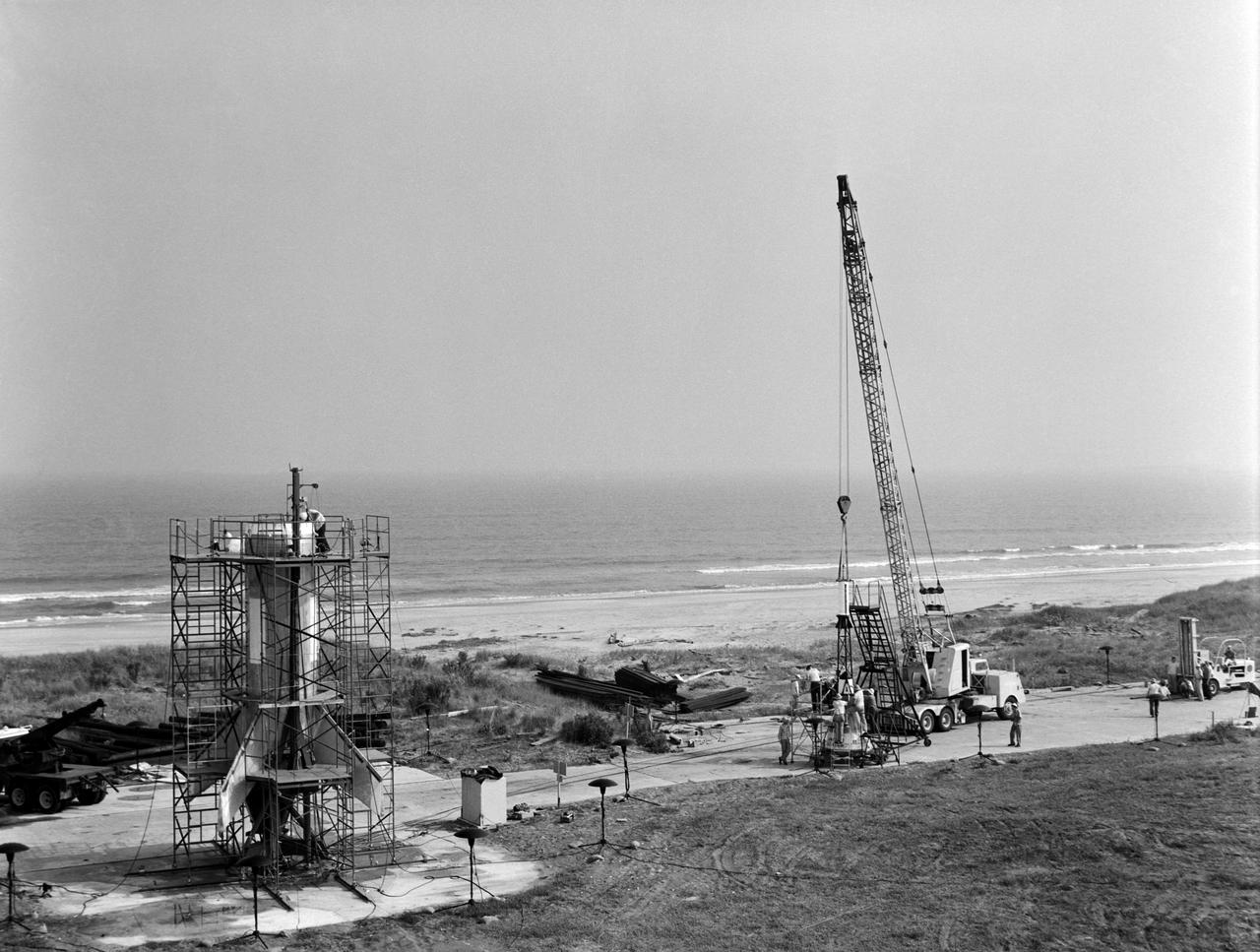
Testing of the Little Joe booster on its launcher. The launcher is positioned at its normal launch angle of 80 degrees. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3, p. 33): The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
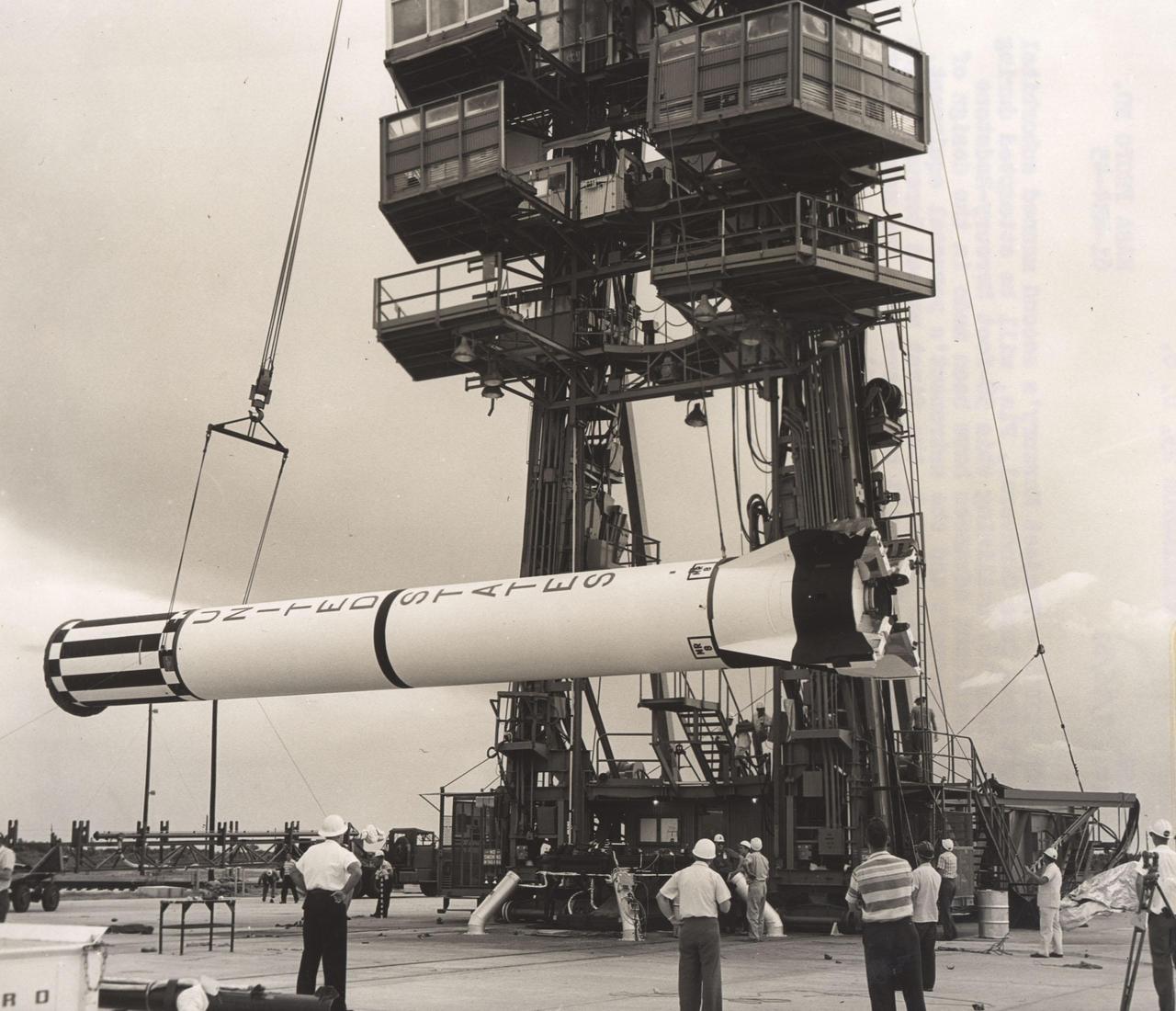

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- READIED FOR FLIGHT - Project Mercury's second manned suborbital space flight, Liberty Bell 7, from Cape Canaveral, Fla., will be attempted during the week of July 16, utilizing this 58-foot Mercury-Redstone vehicle. Significant advances have been made in the design of the Mercury spacecraft and the astronaut's personal equipment. Flight will be similar to MR-3, the first manned Mercury flight May 5, 1961; however, the pilot will have more time for making Earth and celestial observations. (NASA Photo)
/61-mr4-55(s)~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Project Mercury Astronaut Virgil I. Grissom, primary pilot for the Mercury-Redstone 4 manned space flight known as Liberty Bell 7, gets an assist from suit specialist Joe W. Schmidt as he prepares for the Mercury-Redstone 4 manned space flight. The flight, the second manned shot in the Mercury program, was postponed because of bad weather in the launch area. (NASA Photo
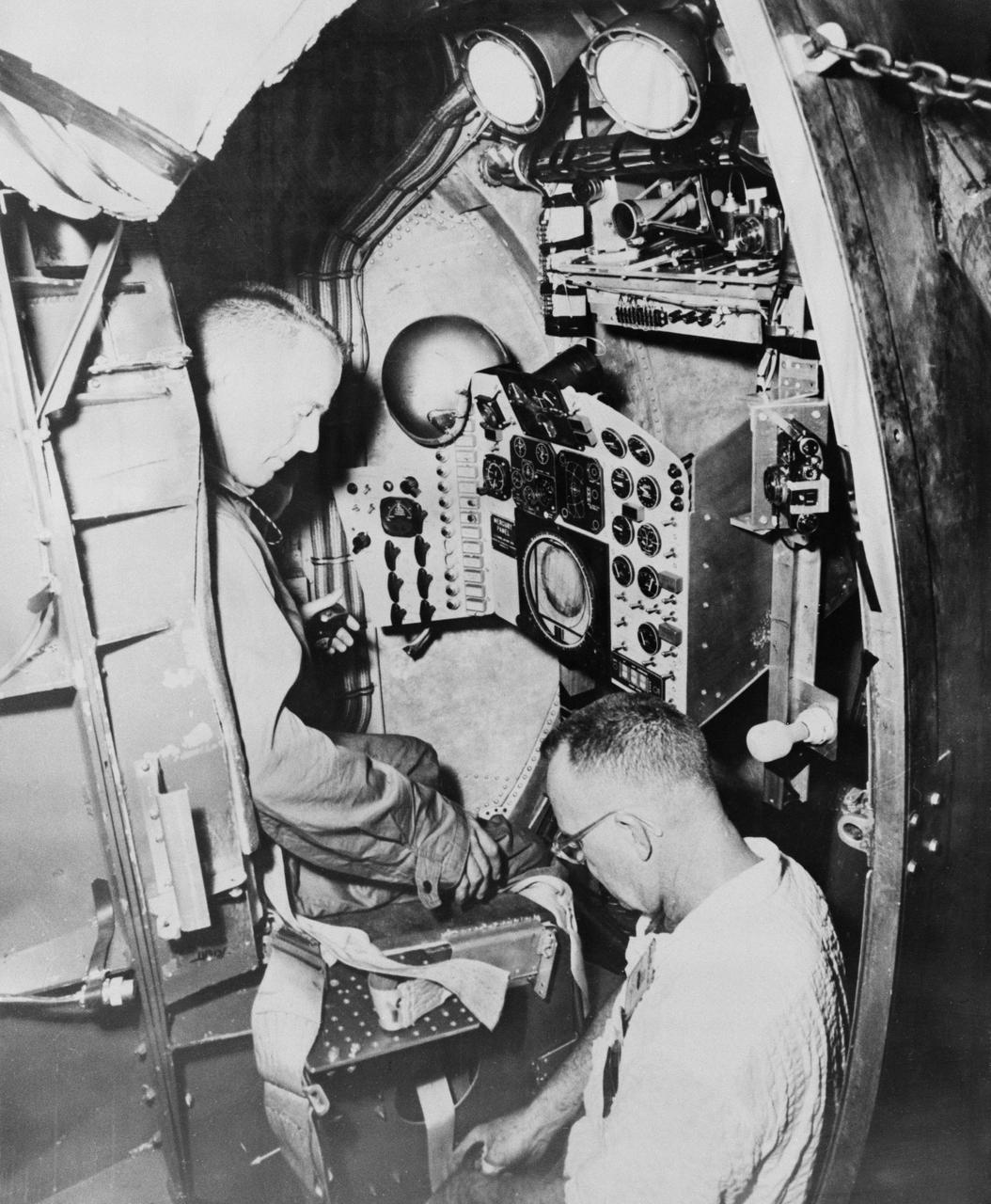

B59-00570 (August 1959) --- Astronaut Scott Carpenter trains at the centrifuge procedures trainer at Wright Field, Johnsville, Pennsylvania, for project Mercury. Photo credit: NASA
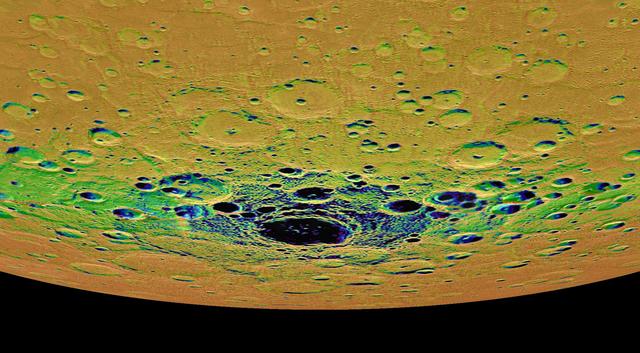
This view from NASA MESSENGER spacecraft is an orthographic projection of Mercury south polar region, colored by an illumination map. The illumination map, created from repeated MDIS imaging, is colored on the basis of the percentage of time that a given area is sunlit. Areas appearing black in the map are regions of permanent shadow. The largest permanently shadowed region near the center of the image is within the interior of the crater Chao Meng-Fu, a location with evidence for hosting considerable amounts of water ice. Instrument: Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) Chao Meng-Fu Center Latitude: -88.4° Chao Meng-Fu Center Longitude: 203.6° E Scale: Chao Meng-Fu has a diameter of roughly 180 kilometers (112 miles) http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19416
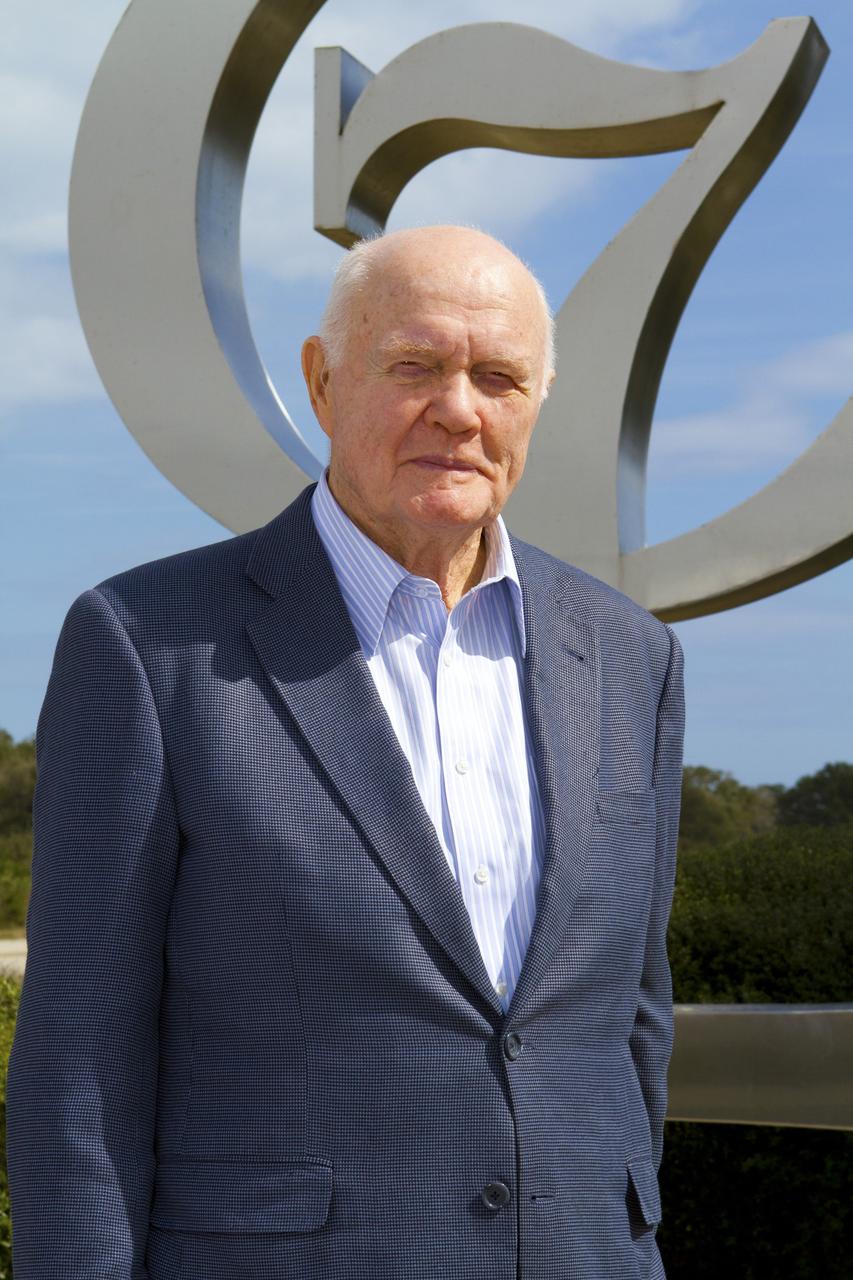

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Mercury astronaut John Glenn poses for a photo in front of the Project Mercury monument at Launch Complex-14 LC-14 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During events at the Cape and NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Glenn is marking the 50th anniversary of being the first American astronaut to orbit the Earth inside the Friendship 7 capsule on Feb. 20, 1962. Glenn's launch aboard an Atlas rocket took with it the hopes of an entire nation and ushered in a new era of space travel that eventually led to Americans walking on the moon by the end of the 1960s. Glenn soon was followed into orbit by Scott Carpenter, Walter Schirra and Gordon Cooper. Their fellow Mercury astronauts Alan Shepard and Virgil "Gus" Grissom flew earlier suborbital flights. Deke Slayton, a member of NASA's original Mercury 7 astronauts, was grounded by a medical condition until the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
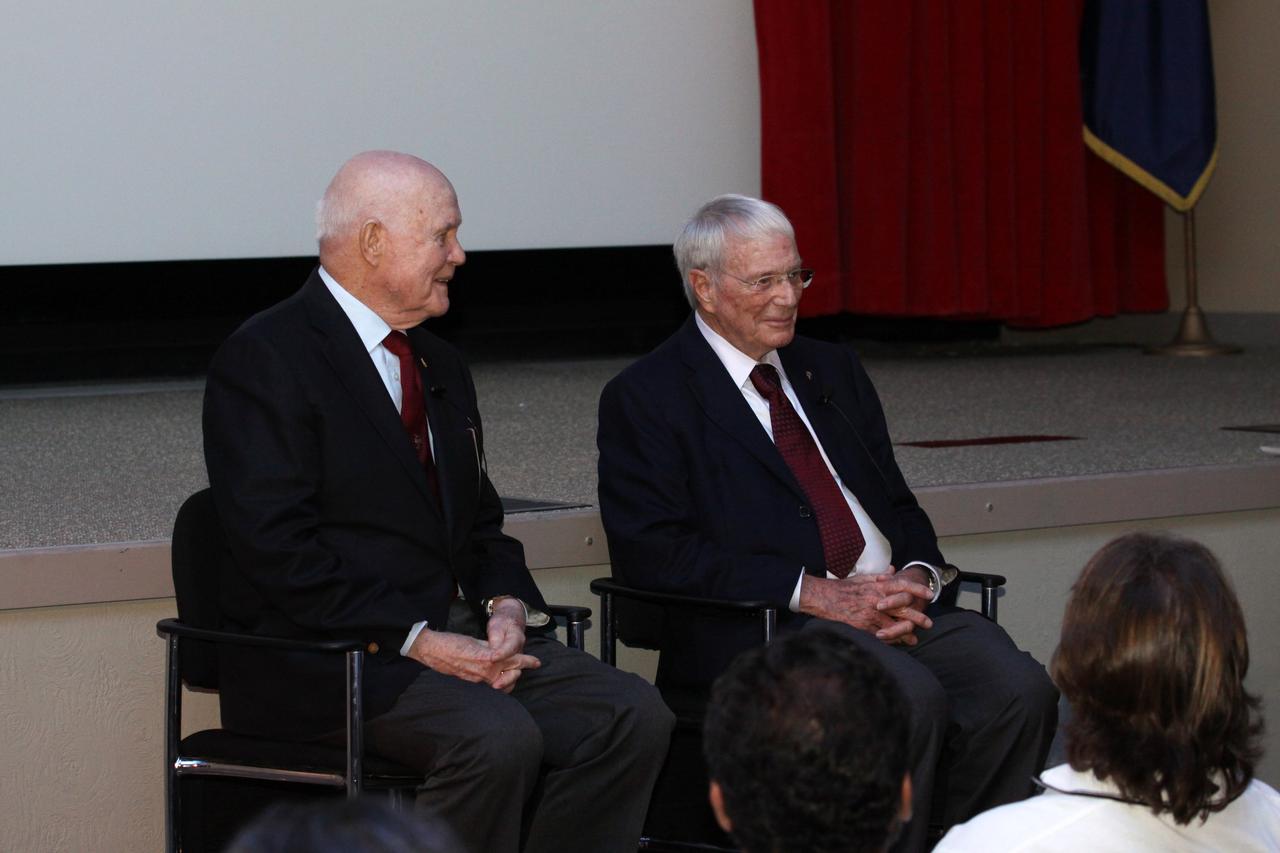

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Mercury astronauts, John Glenn, left, and Scott Carpenter, talk to Mercury Project workers and other guests in the Astronaut Encounter Theater at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. The pair participated in 50th anniversary events at the launch site of Glenn's first orbital flight aboard NASA's Friendship 7 capsule, which launched Feb. 20, 1962, aboard an Atlas rocket. Glenn's launch aboard an Atlas rocket took with it the hopes of an entire nation and ushered in a new era of space travel that eventually led to Americans walking on the moon by the end of the 1960s. Glenn soon was followed into orbit by Carpenter, Walter Schirra and Gordon Cooper. Their fellow Mercury astronauts Alan Shepard and Virgil "Gus" Grissom flew earlier suborbital flights. Deke Slayton, a member of NASA's original Mercury 7 astronauts, was grounded by a medical condition until the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
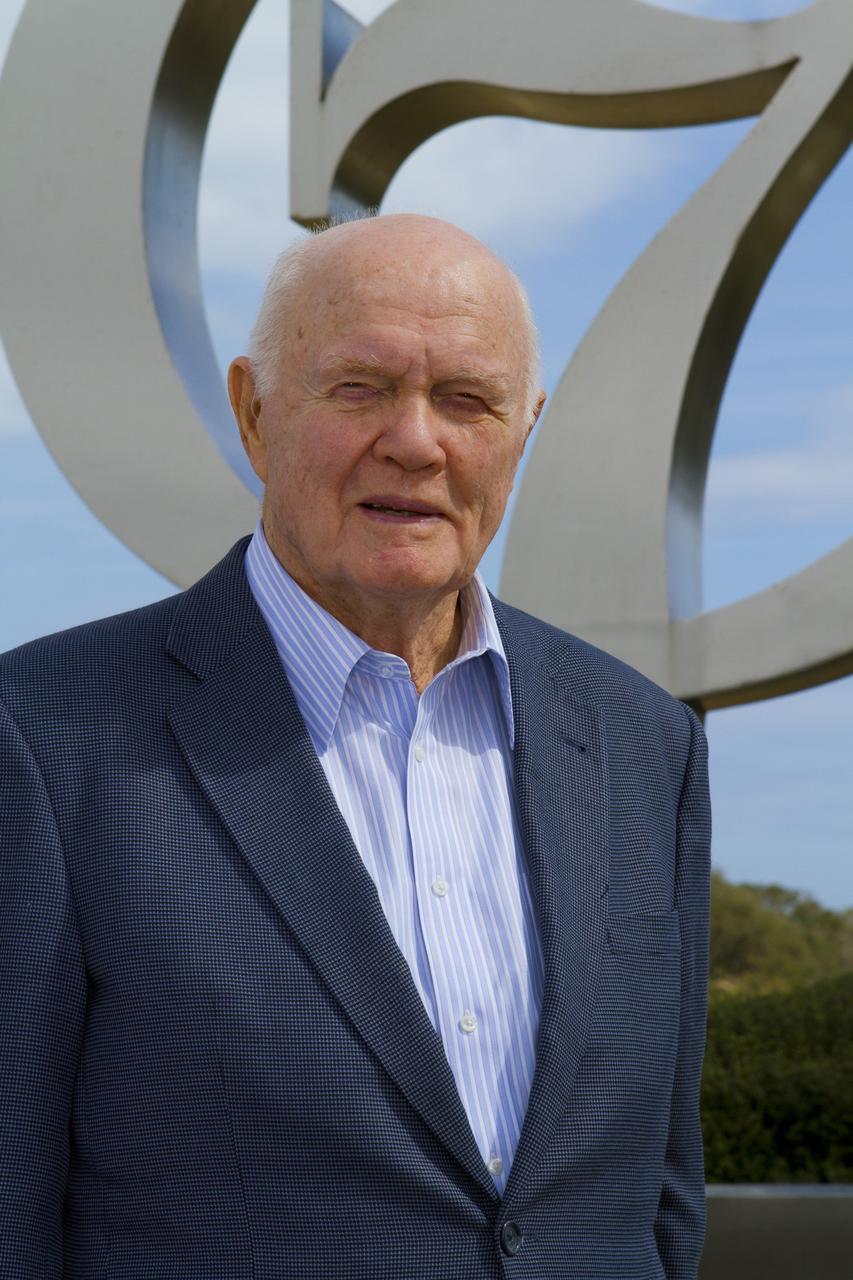

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Mercury astronaut John Glenn poses for a photo in front of the Project Mercury monument at Launch Complex-14 LC-14 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During events at the Cape and NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Glenn is marking the 50th anniversary of being the first American astronaut to orbit the Earth inside the Friendship 7 capsule on Feb. 20, 1962. Glenn's launch aboard an Atlas rocket took with it the hopes of an entire nation and ushered in a new era of space travel that eventually led to Americans walking on the moon by the end of the 1960s. Glenn soon was followed into orbit by Scott Carpenter, Walter Schirra and Gordon Cooper. Their fellow Mercury astronauts Alan Shepard and Virgil "Gus" Grissom flew earlier suborbital flights. Deke Slayton, a member of NASA's original Mercury 7 astronauts, was grounded by a medical condition until the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett