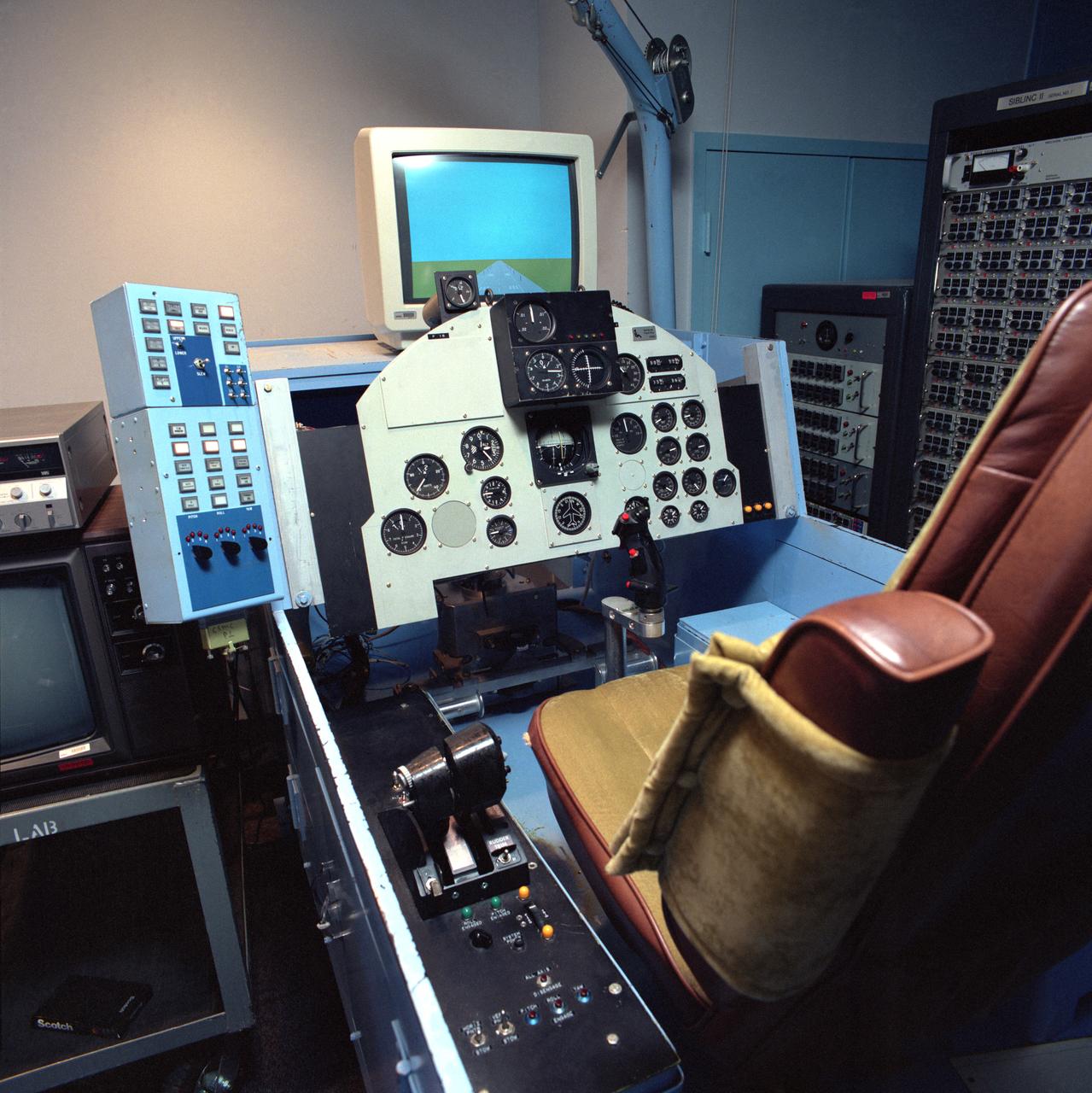

F-15 Propulsion Controlled Aircraft (PCA) simulation cockpit
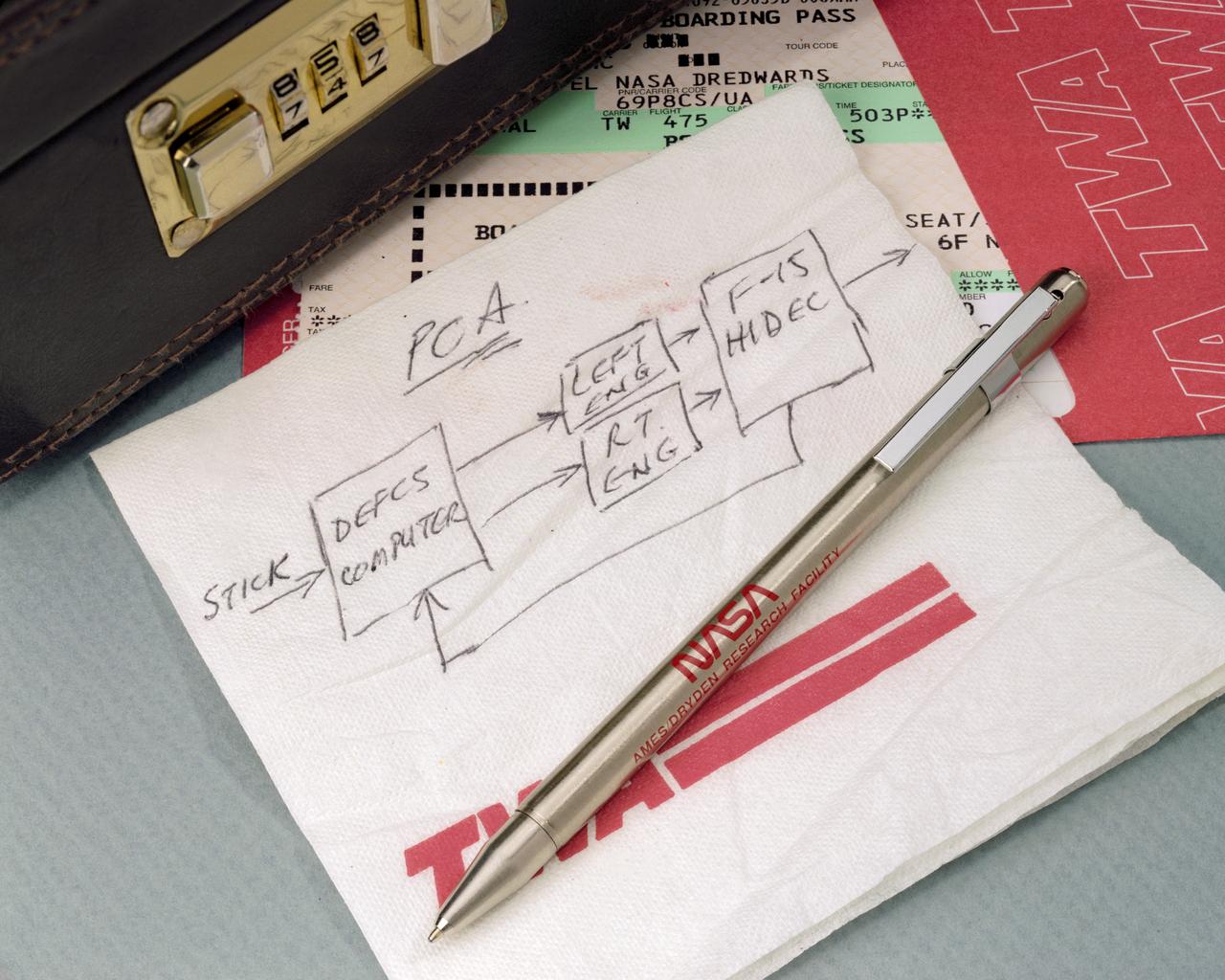
A simple sketch on a TWA napkin by NASA Dryden engineer Frank W. "Bill" Burcham led to development and validation of the Propulsion-Controlled Aircraft concept.
This image shows the X-59 aircraft’s lower empennage structure, or tail section of the plane, that was installed. The stabilators, the outer surfaces also seen in the photo, attach to the lower empennage and are used to help regulate the aircraft pitch which controls the up and down movement of the motion of the plane. The 13-foot engine will pack 22,000 pounds of propulsion and energy and power the X-plane to its planned cruising speed of Mach 1.4. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
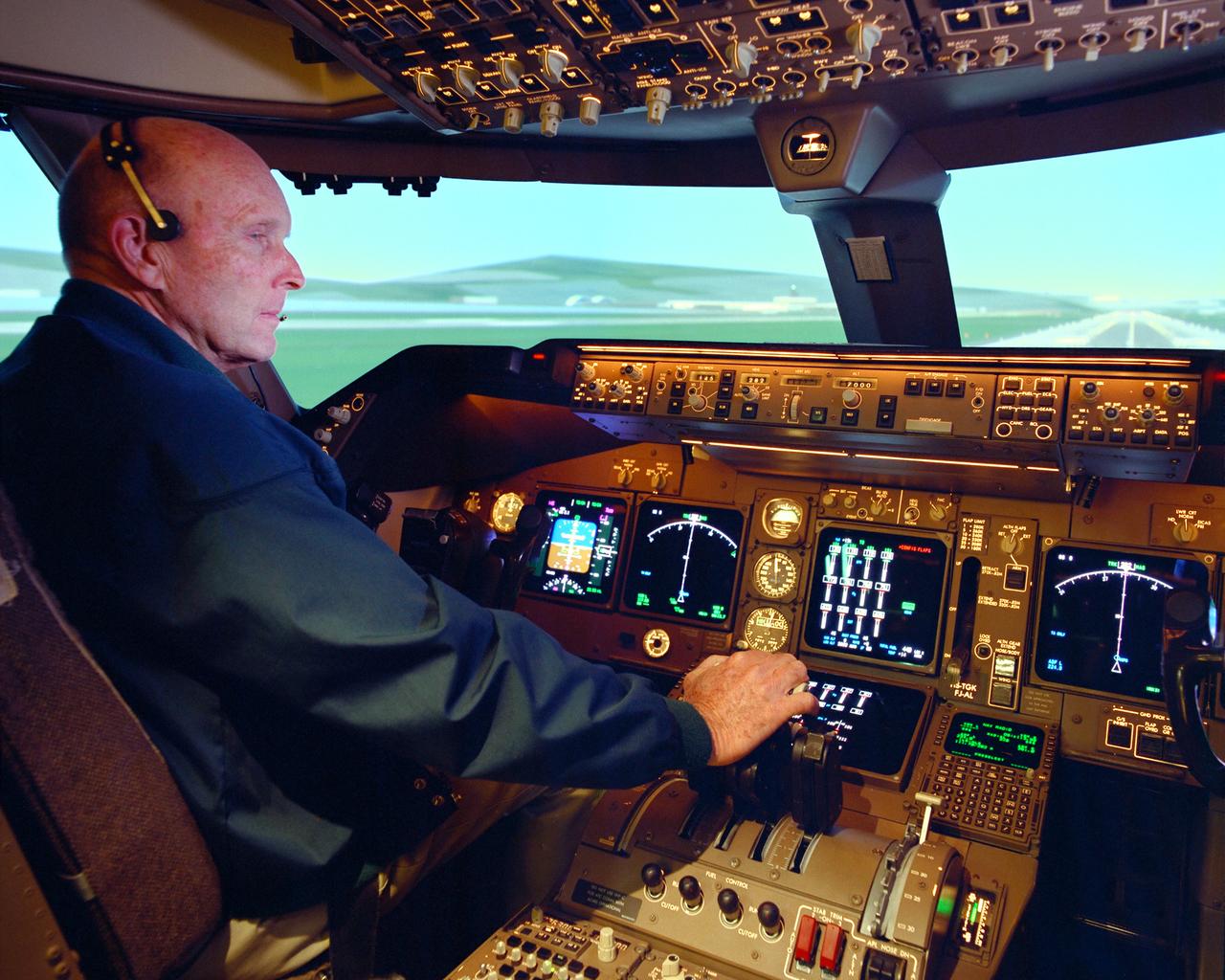

NASA research pilot Gordon Fullerton checked out how the PCA software worked in the multi-engine simulator at NASA Ames before fight-testing PCA in an MD-11.
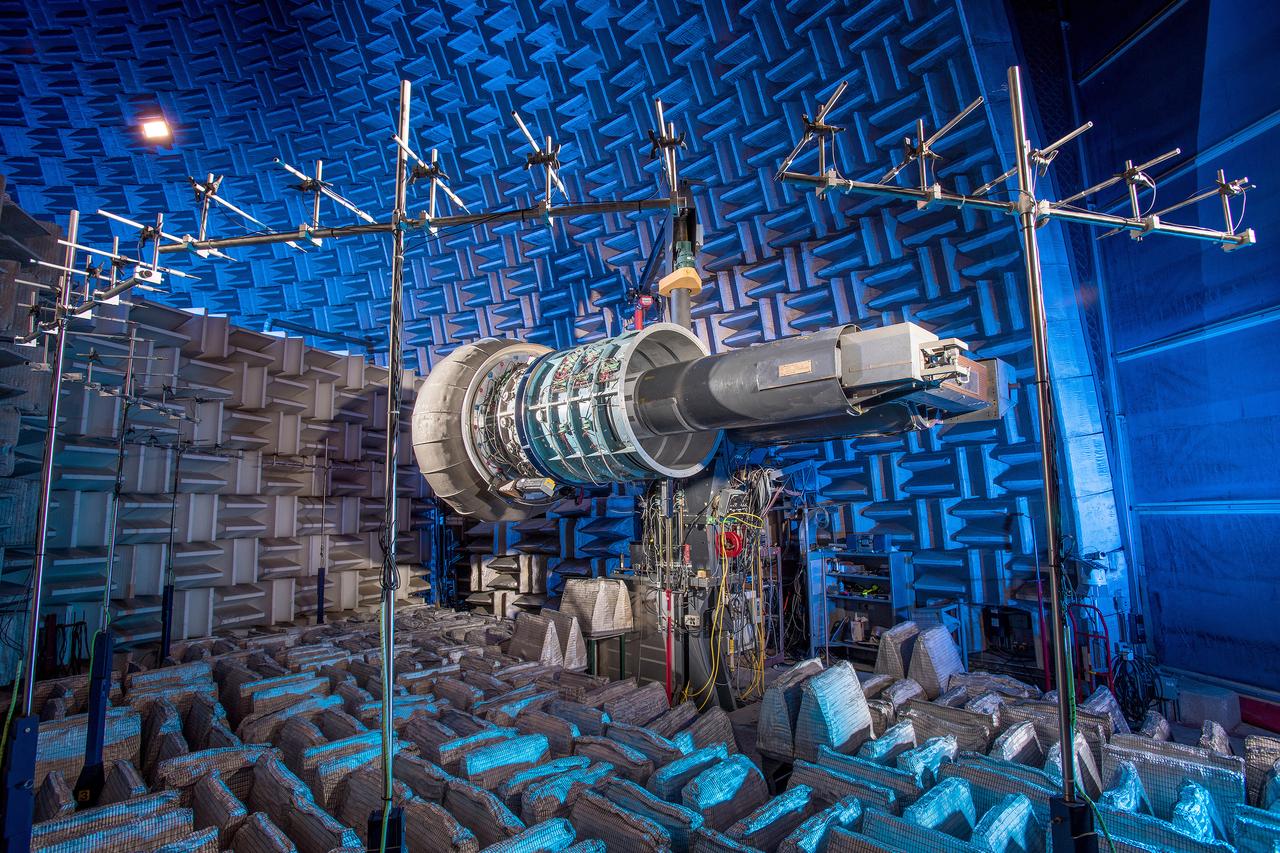
The Advanced Noise Control Fan shown here is located in NASA Glenn’s Aero-Acoustic Propulsion Laboratory. The 4-foot diameter fan is used to evaluate innovate aircraft engine noise reduction concepts less expensively and more quickly.
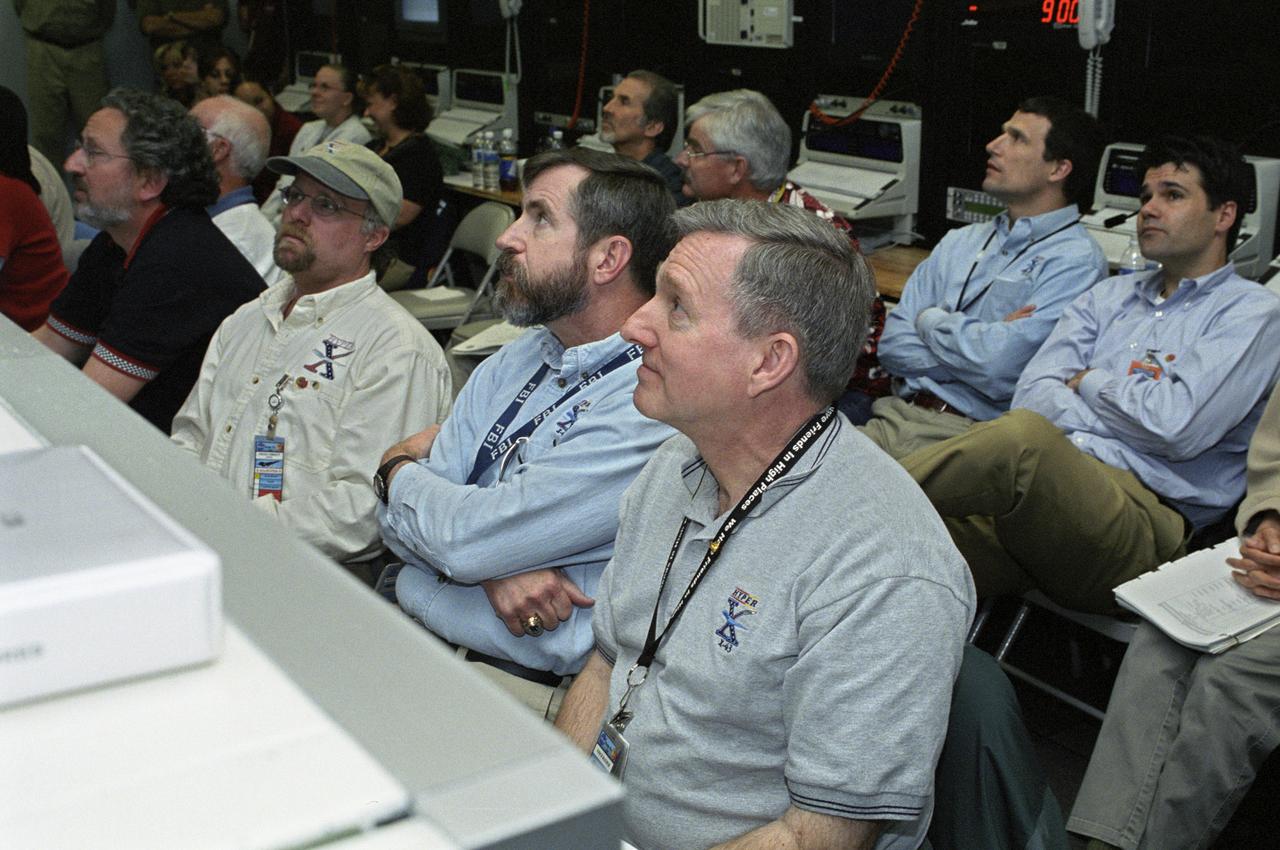

NASA personnel in a control room during the successful second flight of the X-43A aircraft. front row, left to right: Randy Voland, LaRC Propulsion; Craig Christy, Boeing Systems; Dave Reubush, NASA Hyper-X Deputy Program Manager; and Vince Rausch, NASA Hyper-X Program Manager. back row, left to right: Bill Talley, DCI/consultant; Pat Stoliker, DFRC Director (Acting) of Research Engineering; John Martin, LaRC G&C; and Dave Bose, AMA/Controls.
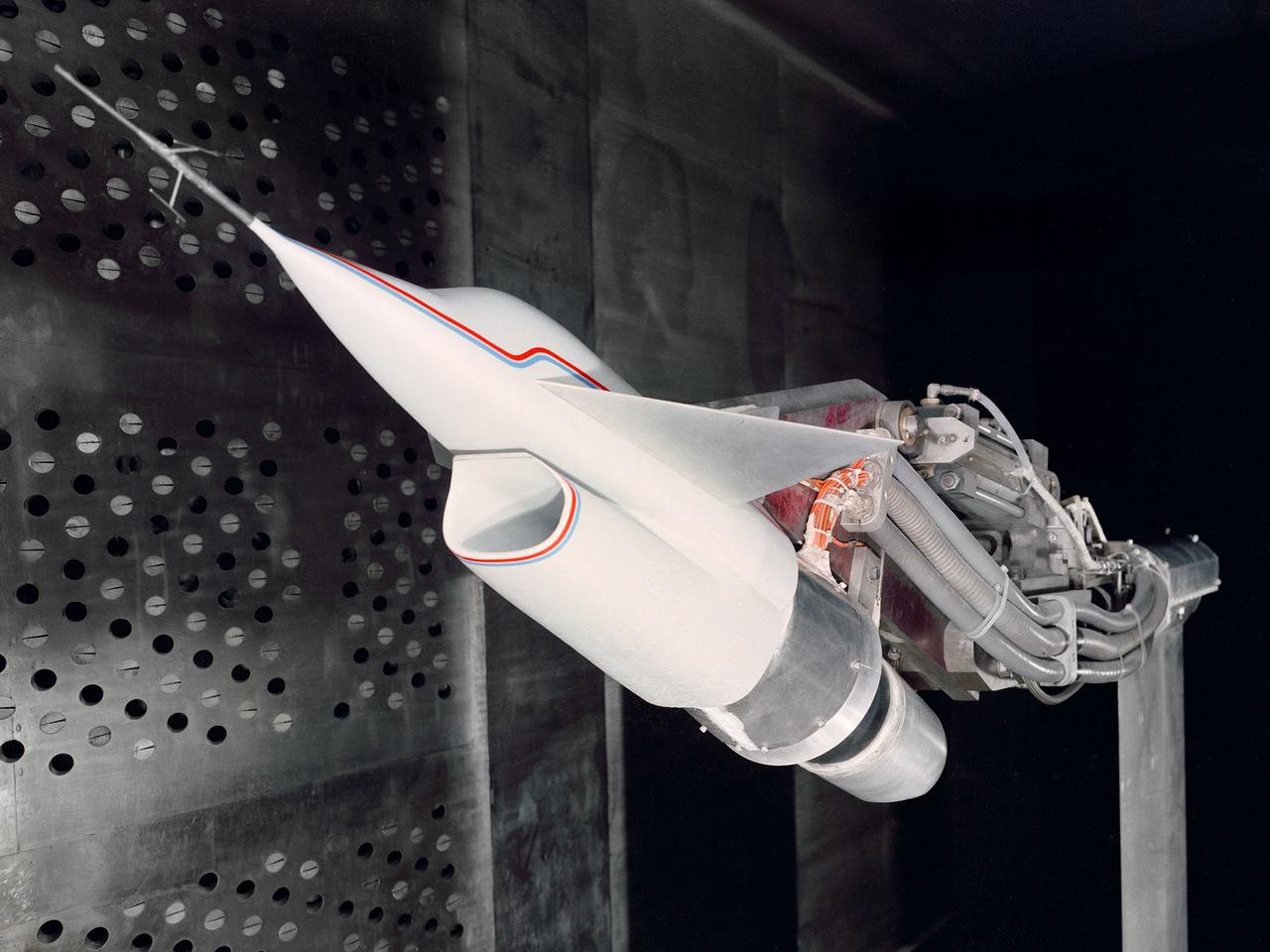
A Highly Maneuverable Aircraft Technology (HiMAT) inlet model installed in the test section of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Engineers at the Ames Research Center, Dryden Flight Research Center, and Rockwell International designed two pilotless subscale HiMAT vehicles in the mid-1970s to study new design concepts for fighter aircraft in the transonic realm without risking the lives of test pilots. The aircraft used sophisticated technologies such as advanced aerodynamics, composite materials, digital integrated propulsion control, and digital fly-by-wire control systems. In late 1977 NASA Lewis studied the HiMAT’s General Electric J85-21 jet engine in the Propulsion Systems Laboratory. The researchers charted the inlet quality with various combinations anti-distortion screens. HiMAT employed a relatively short and curved inlet compared to actual fighter jets. In the spring of 1979, Larry Smith led an in-depth analysis of the HiMAT inlet in the 8- by 6 tunnel. The researchers installed vortex generators to battle flow separation in the diffuser. The two HiMAT aircraft performed 11 hours of flying over the course of 26 missions from mid-1979 to January 1983 at Dryden and Ames. Although the HiMAT vehicles were considered to be overly complex and expensive, the program yielded a wealth of data that would validate computer-based design tools.
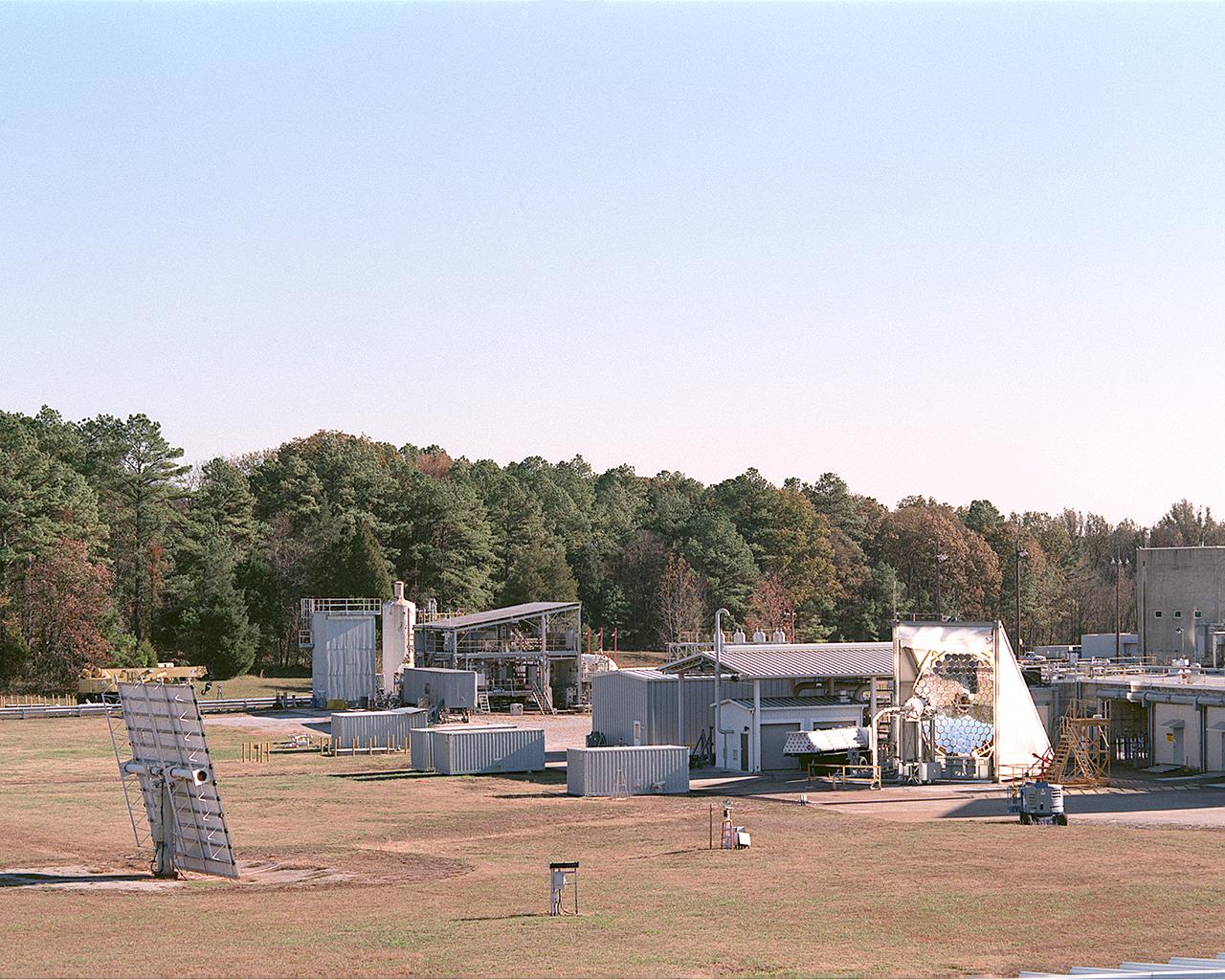

This photograph shows an overall view of the Solar Thermal Propulsion Test Facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The 20-by 24-ft heliostat mirror, shown at the left, has dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on an 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror (right). The concentrator mirror then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber, shown at the front of concentrator mirror. Researchers at MSFC have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than chemical a combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propell nt. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth-orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
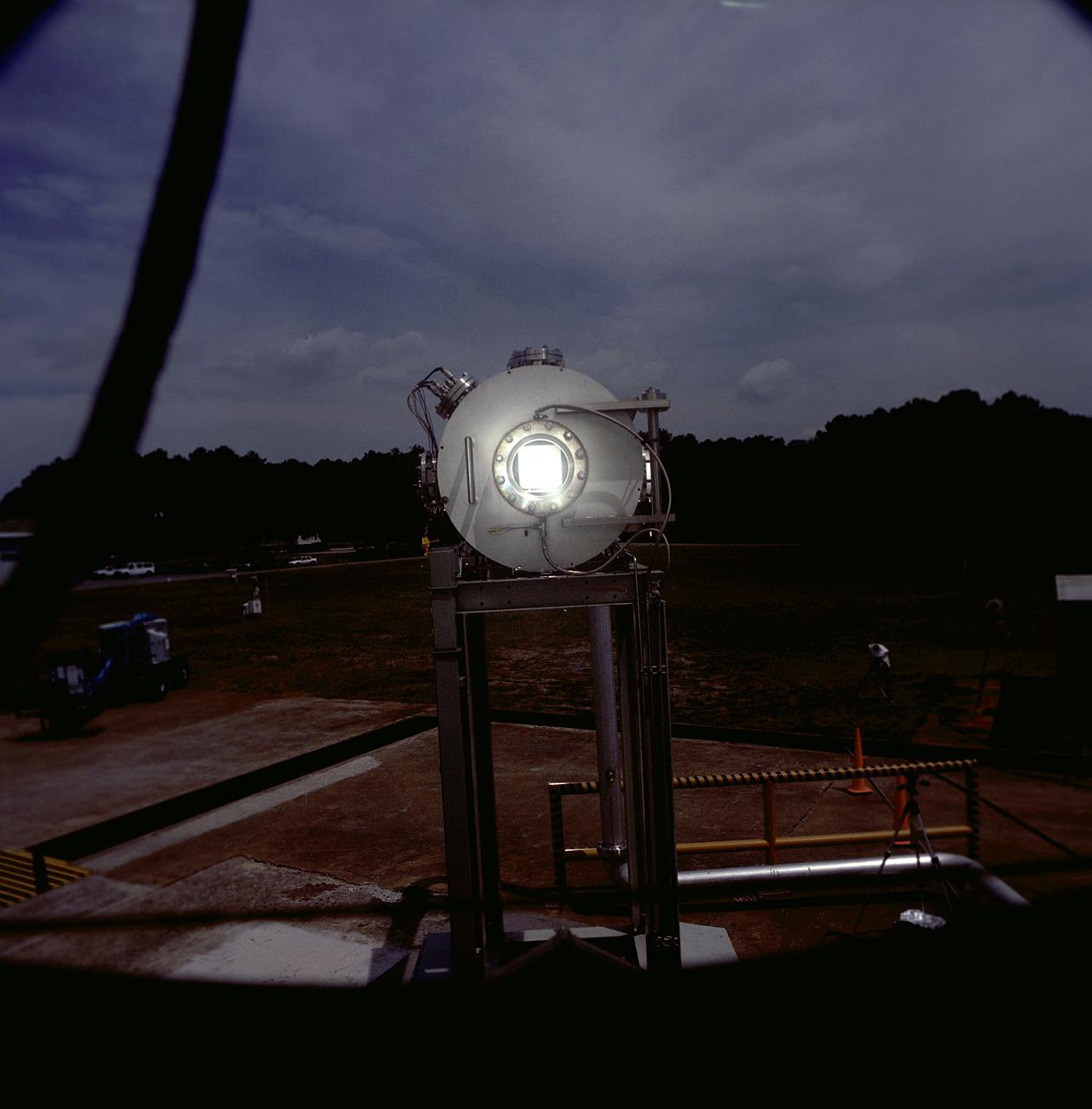

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on an 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. This photograph is a close-up view of a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber at the MSFC Solar Thermal Propulsion Test facility. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
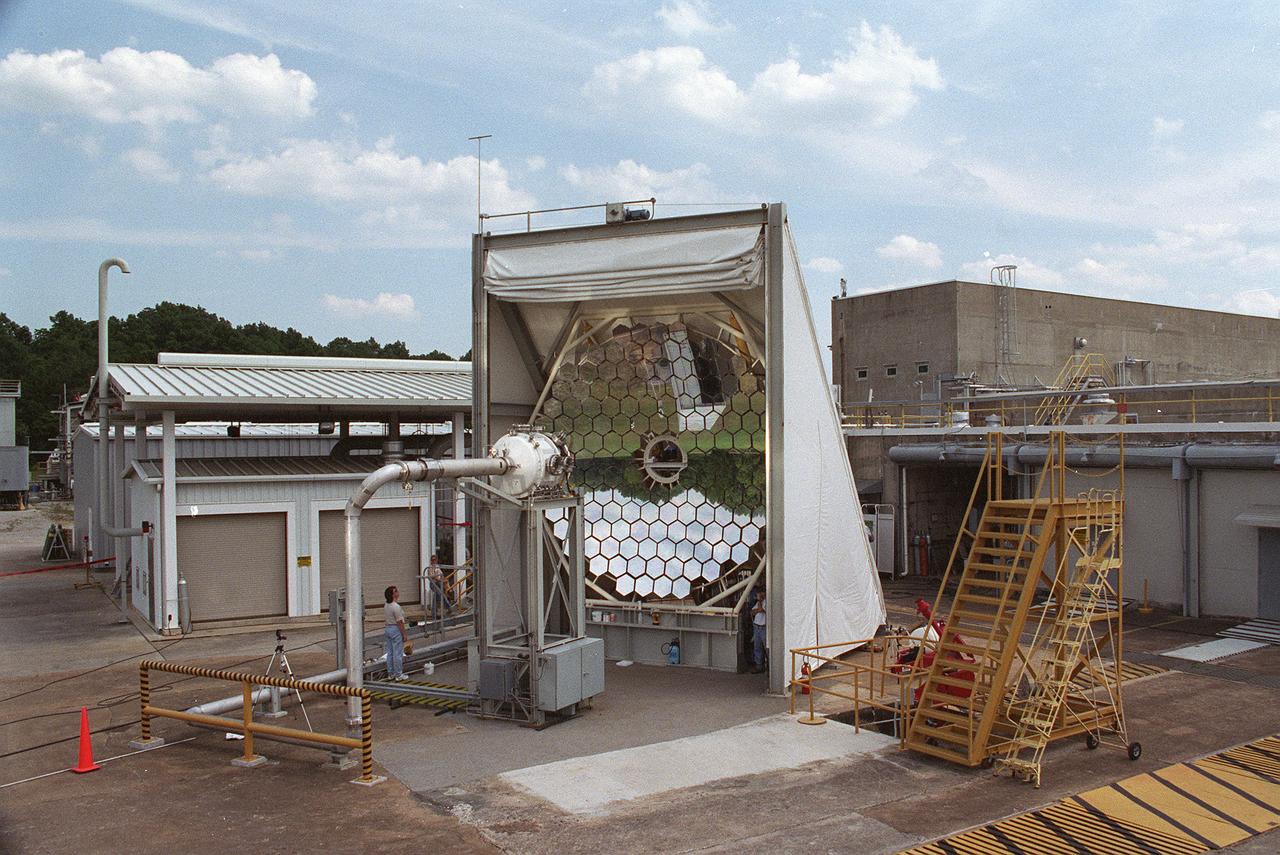

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. This photograph, taken at MSFC's Solar Thermal Propulsion Test Facility, shows a concentrator mirror, a combination of 144 mirrors forming this 18-ft diameter concentrator, and a vacuum chamber that houses the focal point. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has a dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on the 18-foot diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth-orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
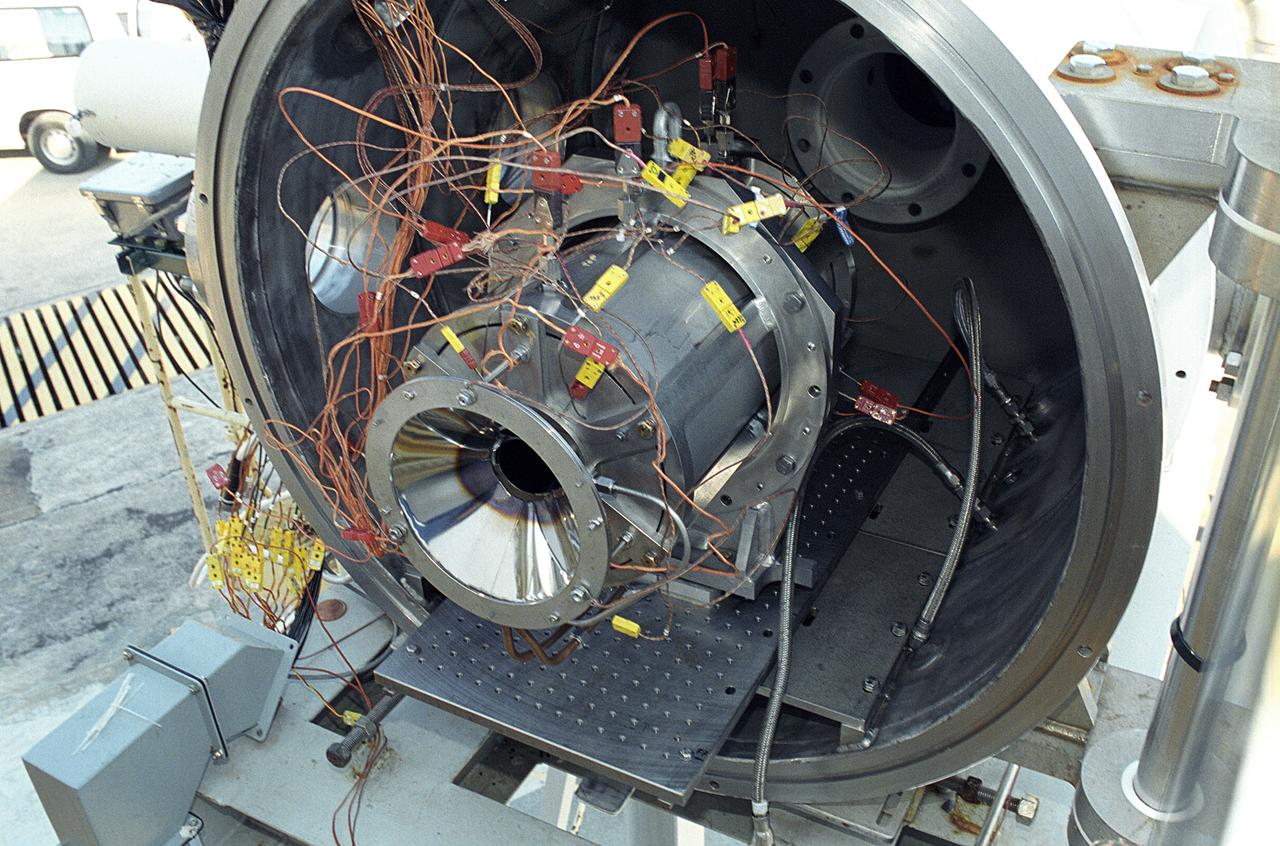

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. This photograph shows a fully assembled solar thermal engine placed inside the vacuum chamber at the test facility prior to testing. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has a dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on the 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move theNation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
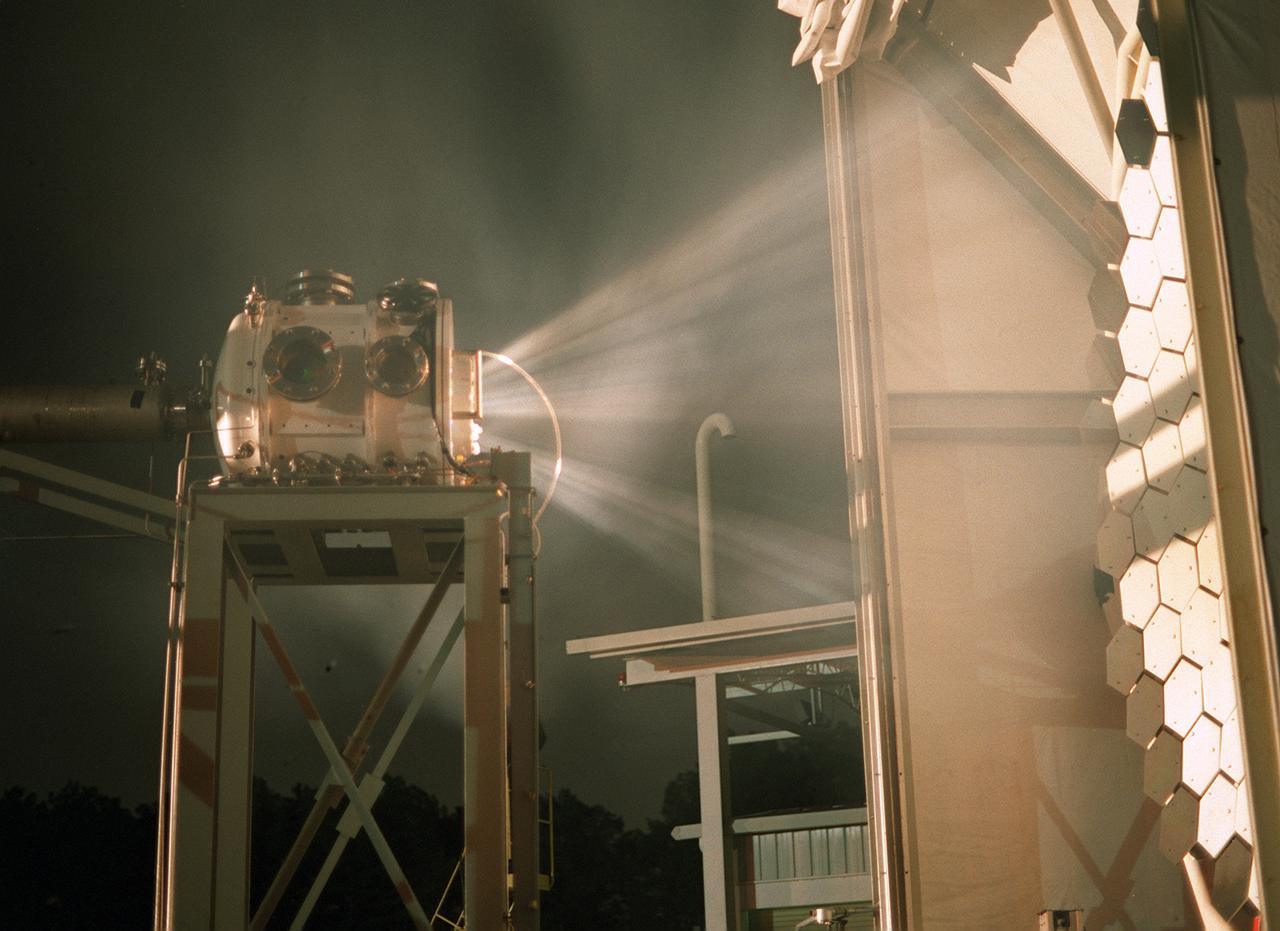

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has a dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on the 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. This image, taken during the test, depicts the light being concentrated into the focal point inside the vacuum chamber. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
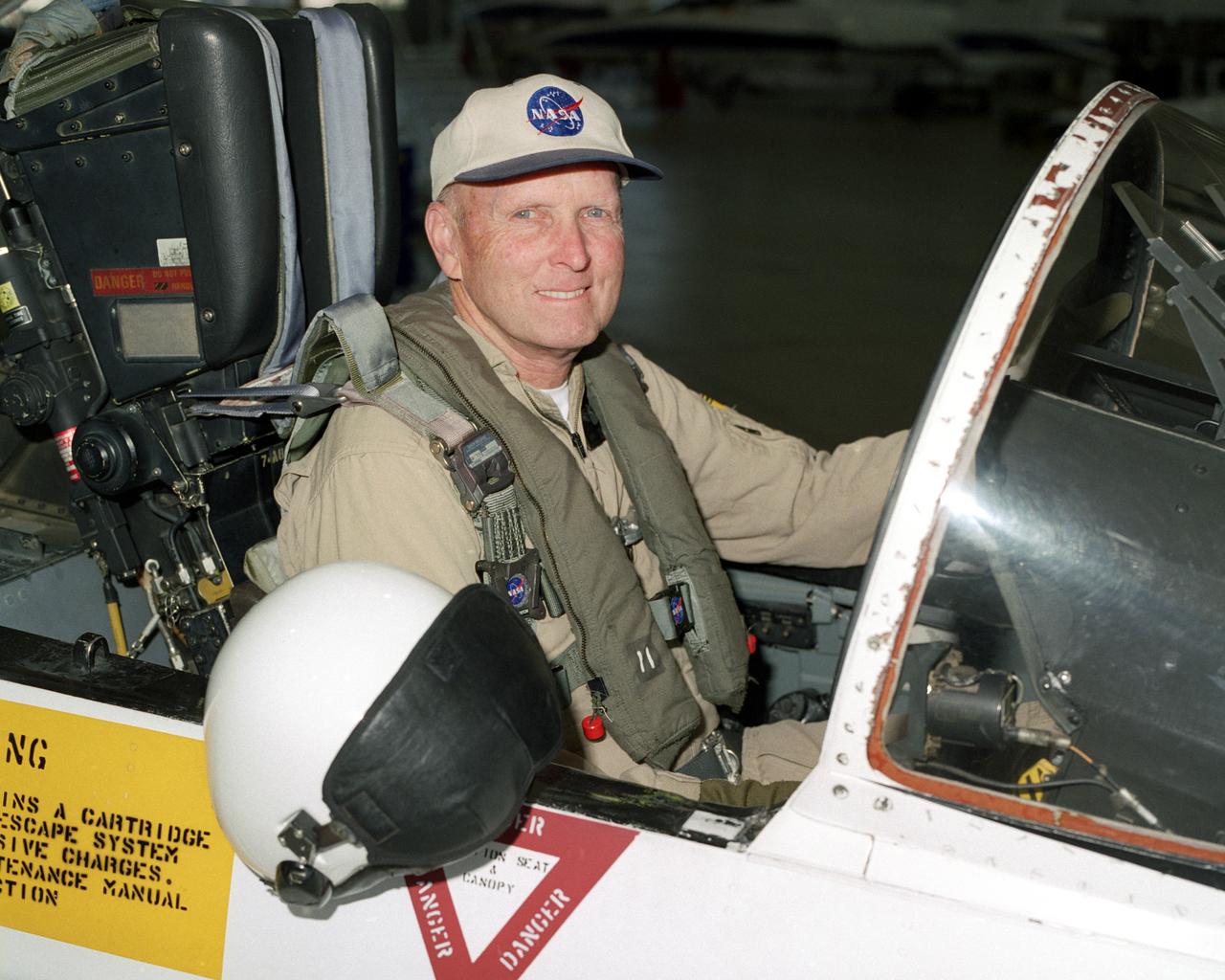

Former NASA astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton, seated in the cockpit of an F/A-18, is a research pilot at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif. Since transferring to Dryden in 1986, his assignments have included a variety of flight research and support activities piloting NASA's B-52 launch aircraft, the 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), and other multi-engine and high performance aircraft. He flew a series of development air launches of the X-38 prototype Crew Return Vehicle and in the launches for the X-43A Hyper-X project. Fullerton also flies Dryden's DC-8 Airborne Science aircraft in support a variety of atmospheric physics, ground mapping and meteorology studies. Fullerton also was project pilot on the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft program, during which he successfully landed both a modified F-15 and an MD-11 transport with all control surfaces neutralized, using only engine thrust modulation for control. Fullerton also evaluated the flying qualities of the Russian Tu-144 supersonic transport during two flights in 1998, one of only two non-Russian pilots to fly that aircraft. With more than 15,000 hours of flying time, Fullerton has piloted 135 different types of aircraft in his career. As an astronaut, Fullerton served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16, and 17 lunar missions. In 1977, Fullerton was on one of the two flight crews that piloted the Space Shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test Program at Dryden. Fullerton was the pilot on the STS-3 Space Shuttle orbital flight test mission in 1982, and commanded the STS-51F Spacelab 2 mission in 1985. He has logged 382 hours in space flight. In July 1988, he completed a 30-year career with the U.S. Air Force and retired as a colonel.
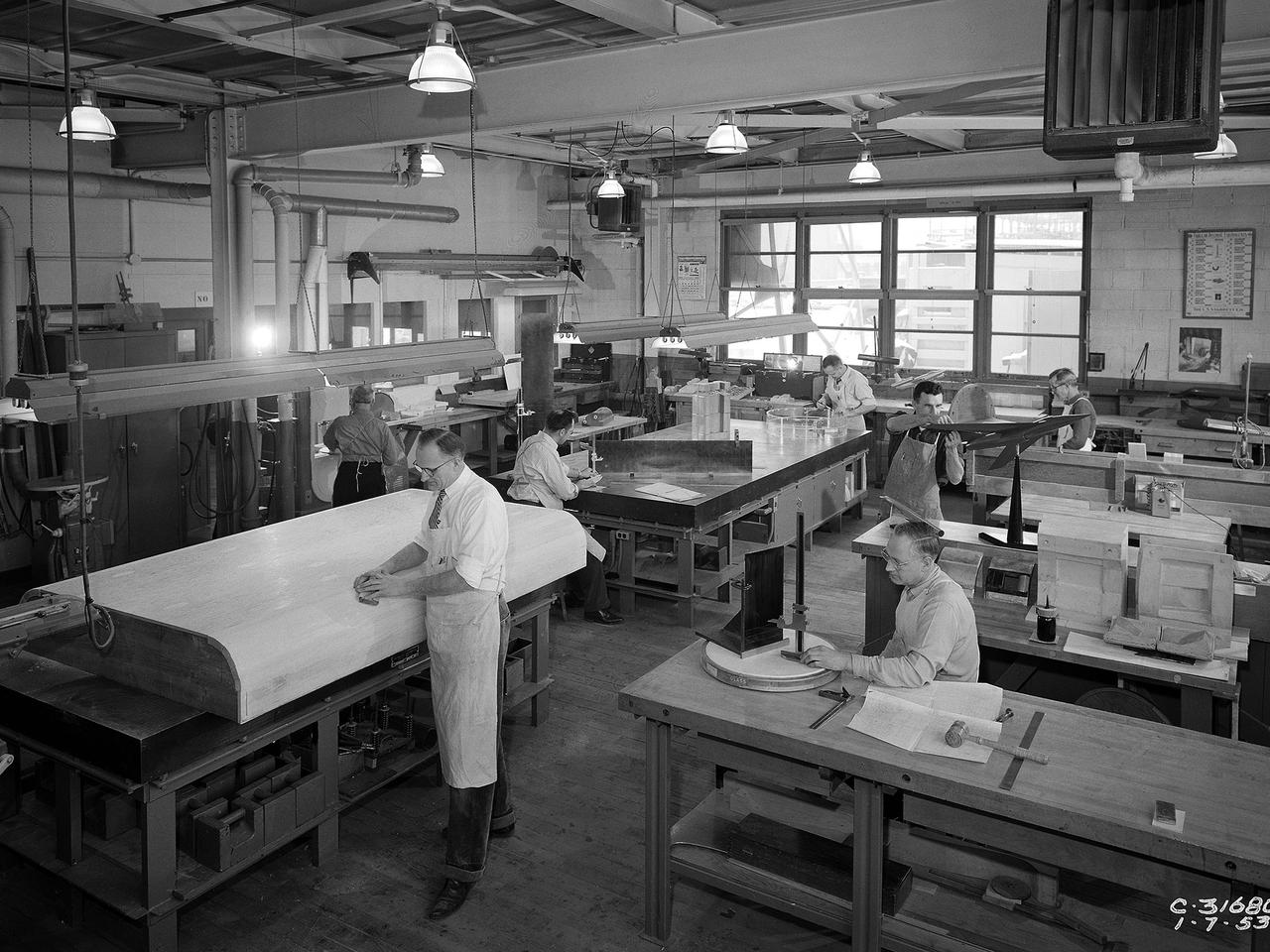

Craftsmen work in the wood model shop at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The Fabrication Division created almost all of the equipment and models used at the laboratory. The Fabrication Shop building contained a number of specialized shops in the 1940s and 1950s. These included a Machine Shop, Sheet Metal Shop, Wood Model and Pattern Shop, Instrument Shop, Thermocouple Shop, Heat Treating Shop, Metallurgical Laboratory, and Fabrication Office. The Wood Model and Pattern Shop created everything from control panels and cabinets to aircraft models molds for sheet metal work.
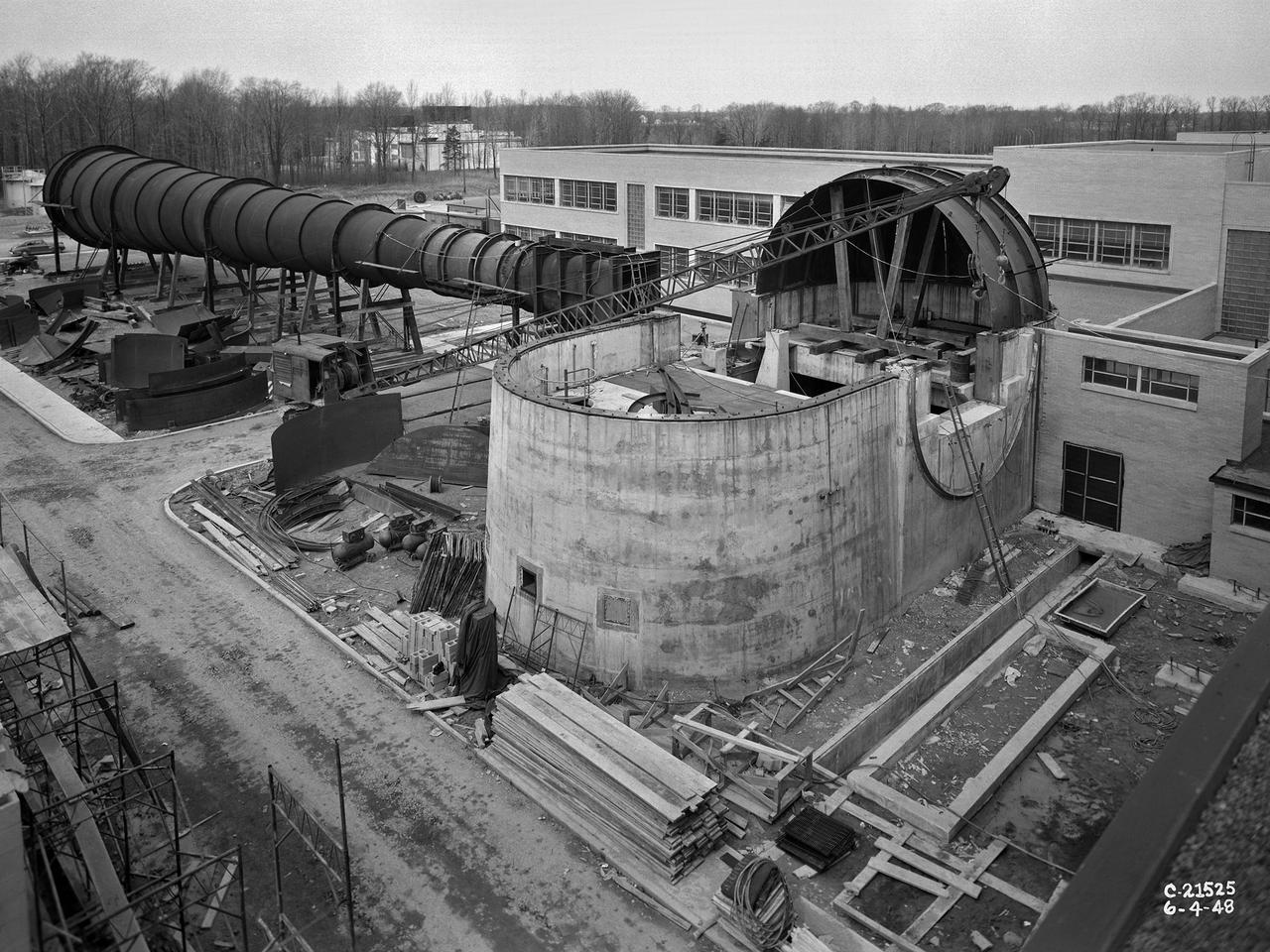

The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory was the nation’s largest supersonic facility when it began operation in April 1949. The emergence of new propulsion technologies such as turbojets, ramjets, and rockets during World War II forced the NACA and the aircraft industry to develop new research tools. In late 1945 the NACA began design work for new large supersonic wind tunnels at its three laboratories. The result was the 4- by 4-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory, 6- by 6-foot supersonic wind tunnel at Ames Aeronautical Laboratory, and the largest facility, the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel in Cleveland. The two former tunnels were to study aerodynamics, while the 8- by 6 facility was designed for supersonic propulsion. The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel was used to study propulsion systems, including inlets and exit nozzles, combustion fuel injectors, flame holders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet engines. Flexible sidewalls alter the tunnel’s nozzle shape to vary the Mach number during operation. A seven-stage axial compressor, driven by three electric motors that yield a total of 87,000 horsepower, generates air speeds from Mach 0.36 to 2.0. A section of the tunnel is seen being erected in this photograph.
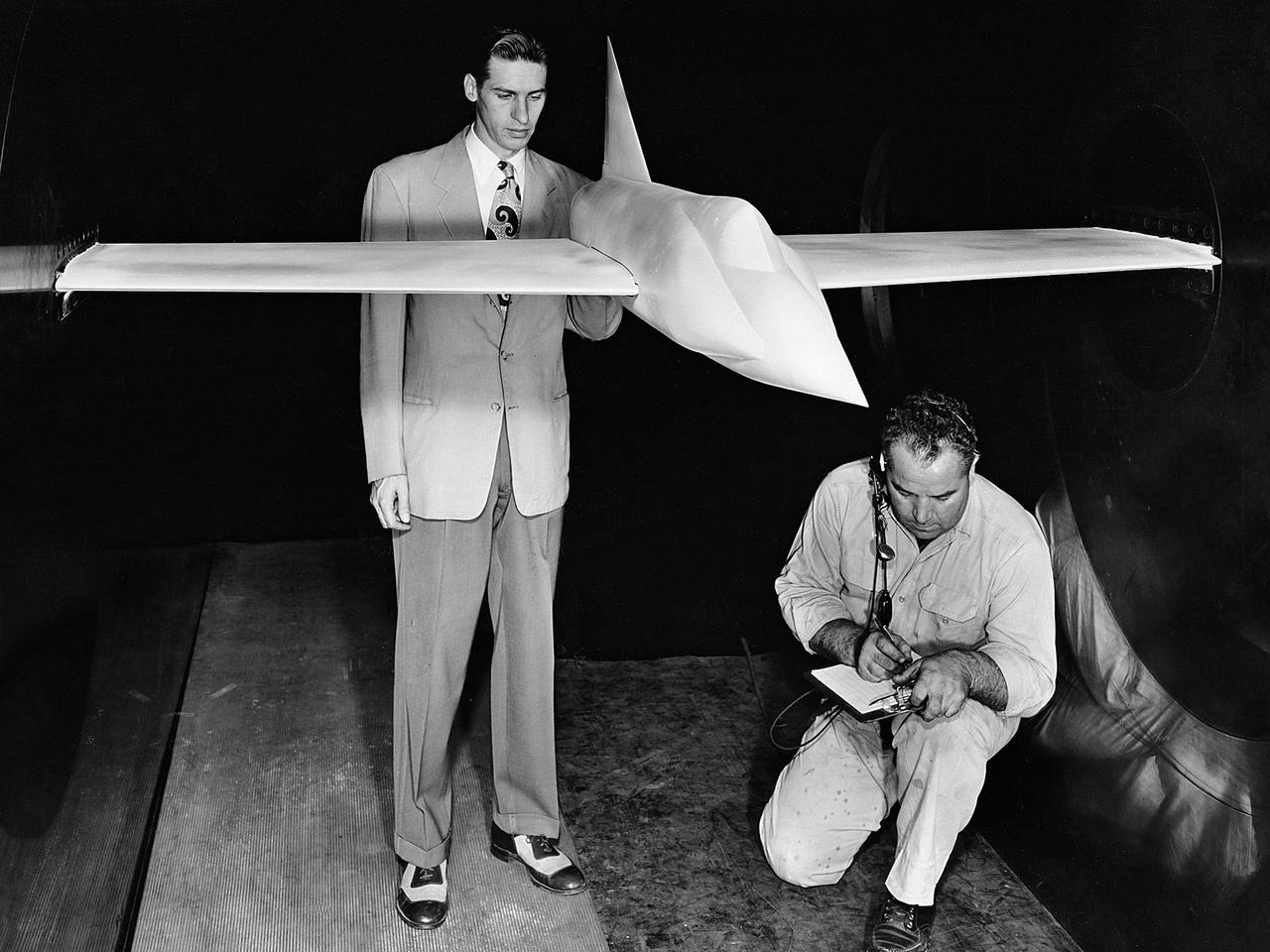

A .10-scale model of Convair’s XF-102 in the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory for jet exit studies. The XF-102 was a prototype of the F-102 Delta Dagger. The F-102 served as an interceptor against long range bombers from the Soviet Union. The aircraft was powered by a Pratt and Whitney J57 turbojet. The first prototype crashed two weeks after is first flight on October 24, 1953, just months after this photograph. Engineers then incorporated the fixed-wing design to reduce drag at supersonic speeds. The production model F-102 became the first delta-wing supersonic aircraft in operation. The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel is used to study propulsion systems, including inlets and exit nozzles, combustion fuel injectors, flame holders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet engines. Flexible sidewalls alter the tunnel’s nozzle shape to vary the Mach number during operation. A seven-stage axial compressor, driven by three electric motors that yield a total of 87,000 horsepower, generates air speeds from Mach 0.36 to 2.0.
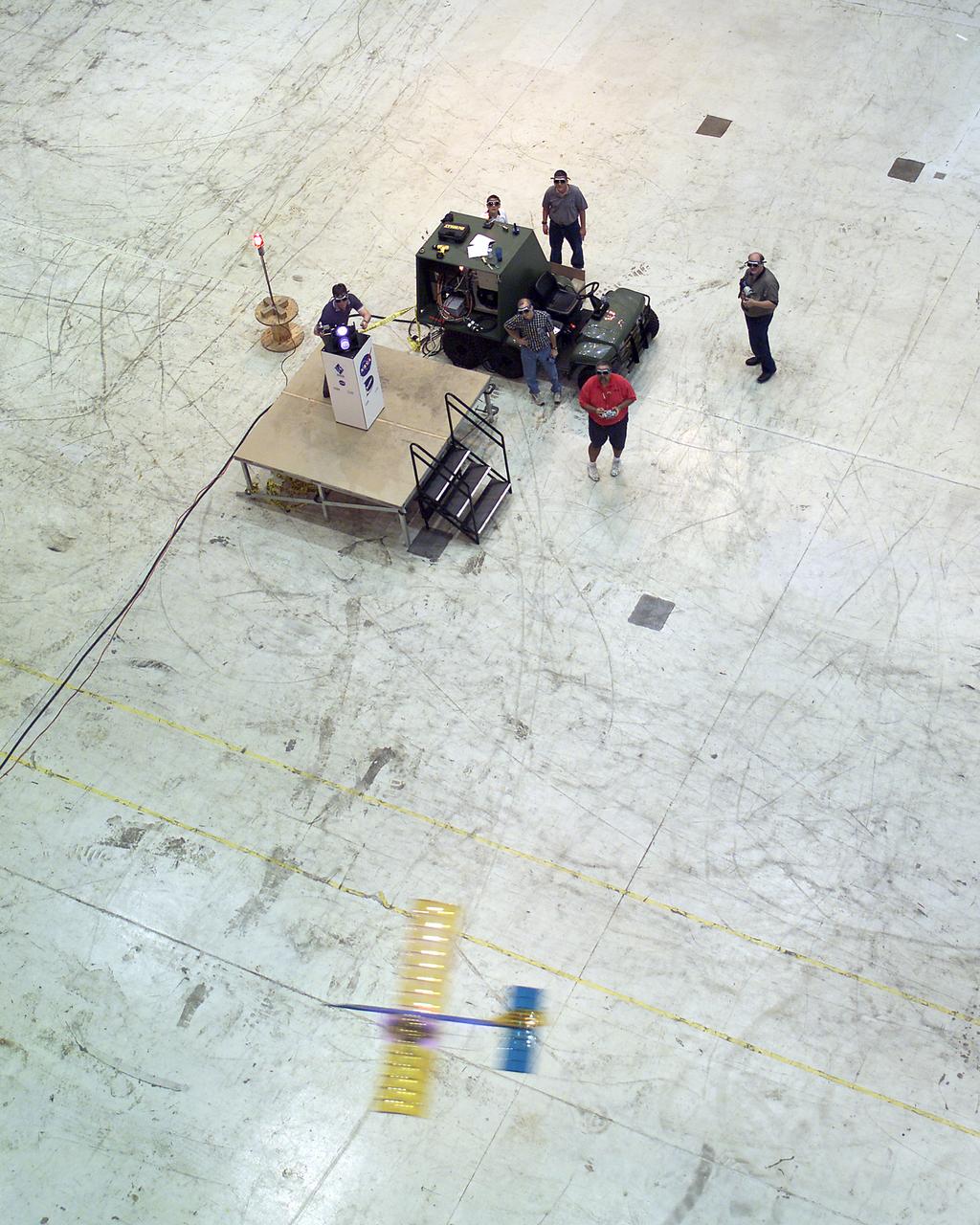

Powered by a laser beam directed at it from a center pedestal, a lightweight model plane makes the first flight of an aircraft powered by laser energy inside a building at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center.
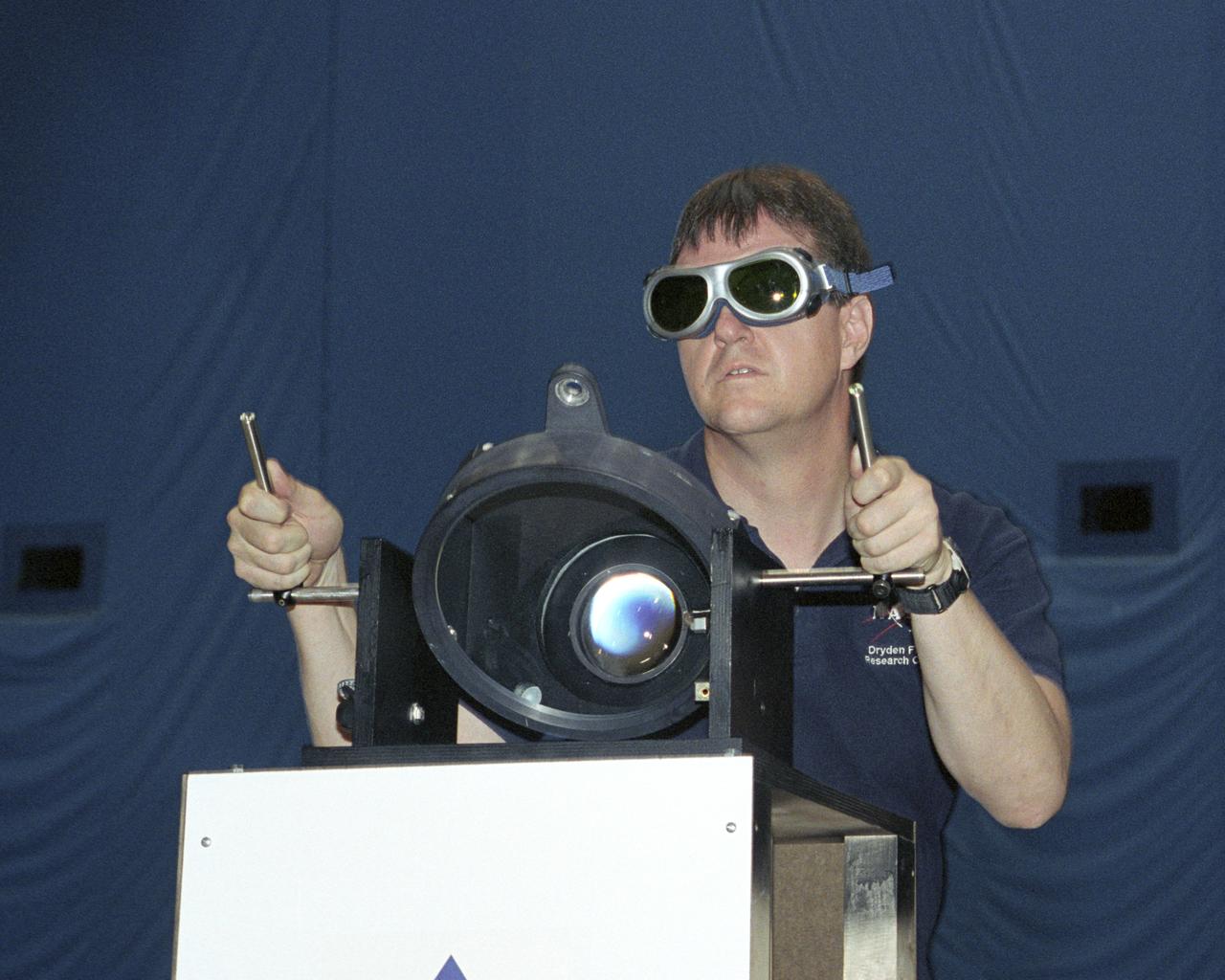

NASA Dryden project engineer Dave Bushman carefully aims the optics of a laser device at a solar cell panel on a model aircraft during the first flight demonstration of an aircraft powered by laser light.
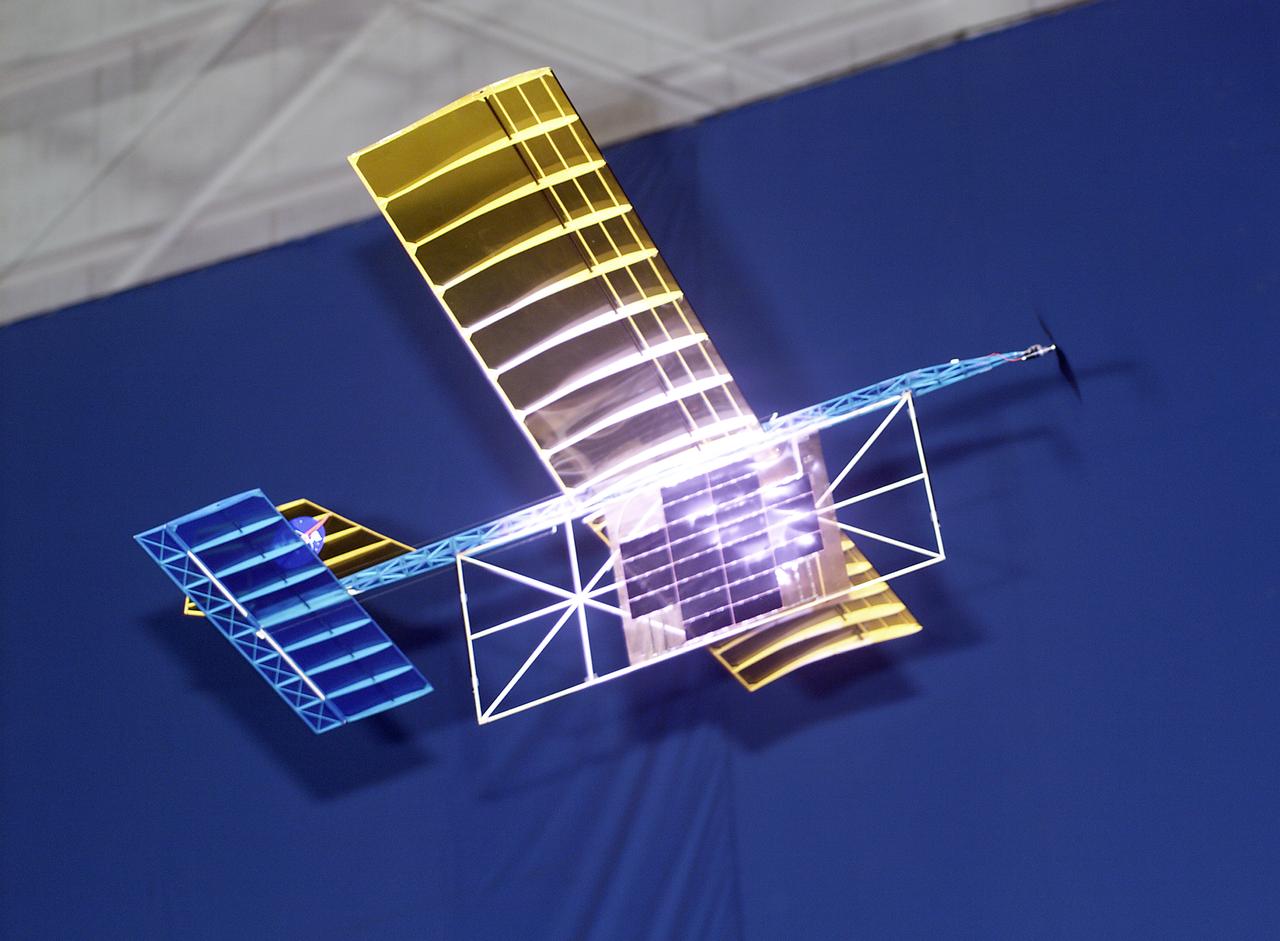
With a laser beam centered on its panel of photovoltaic cells, a lightweight model plane makes the first flight of an aircraft powered by a laser beam inside a building at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center.
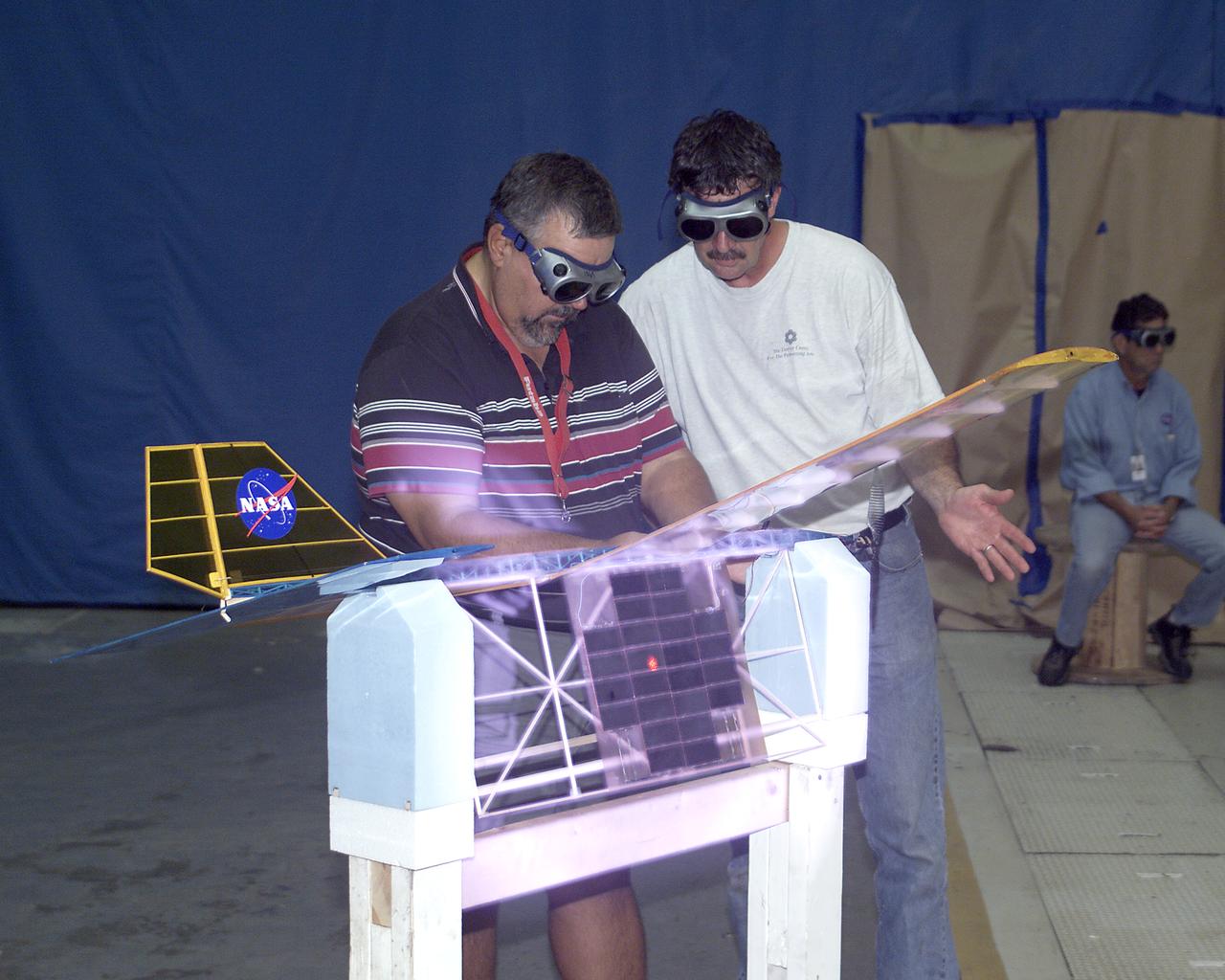

With a laser beam centered on its solar panel, a lightweight model aircraft is checked out by technician Tony Frakowiak and researcher Tim Blackwell before its power-beamed demonstration flight.
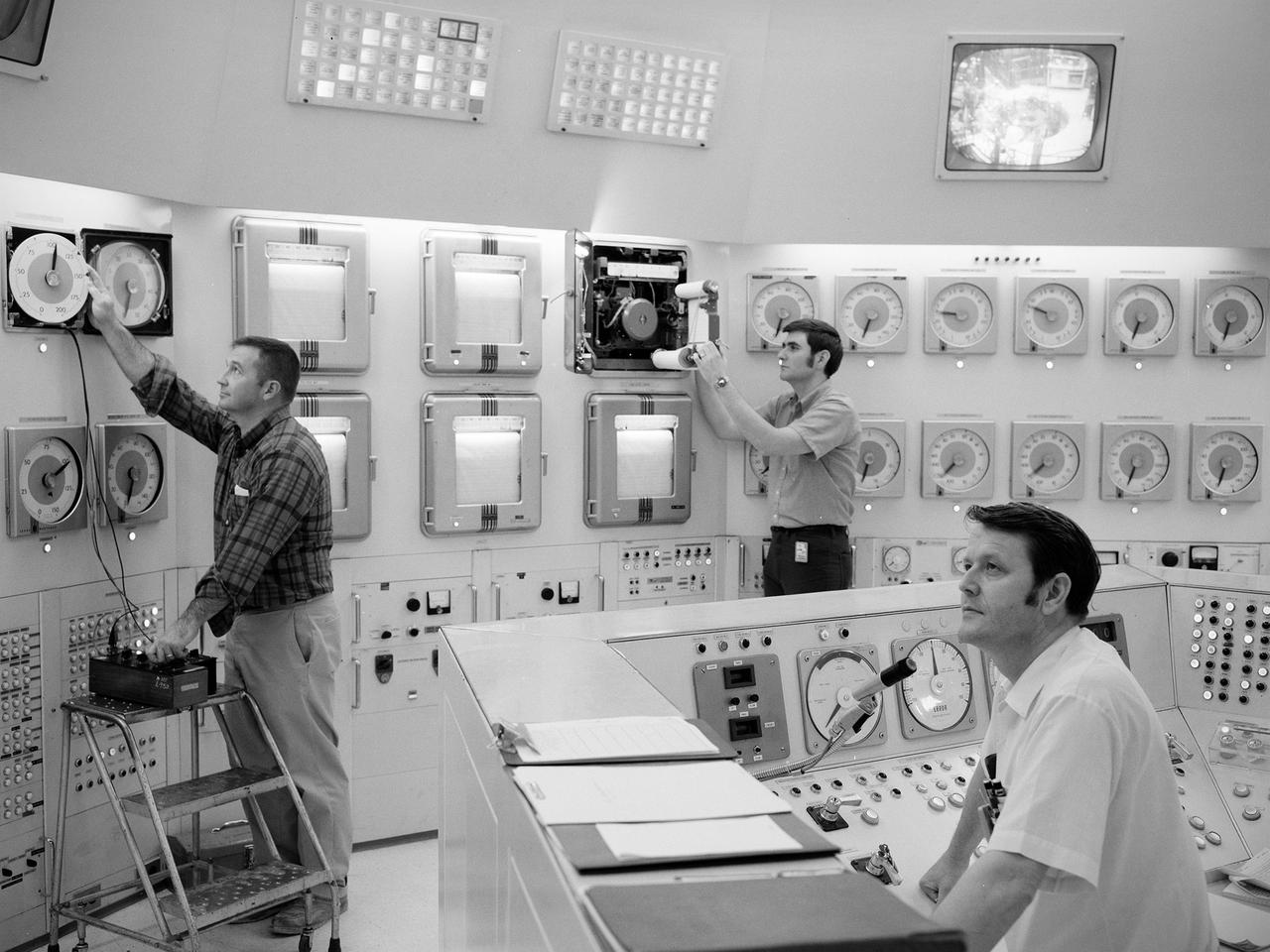

Donald Rhodes, left, and Clyde Greer, right, monitor the operation of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Reactor Facility from the control room. The 60-megawatt test reactor, NASA’s only reactor, was the eighth largest test reactor in the world. The facility was built by the Lewis Research Center in the late 1950s to study the effects of radiation on different materials that could be used to construct nuclear propulsion systems for aircraft or rockets. The reactor went critical for the first time in 1961. For the next two years, two operators were on duty 24 hours per day working on the fission process until the reactor reached its full-power level in 1963. Reactor Operators were responsible for monitoring and controlling the reactor systems. Once the reactor was running under normal operating conditions, the work was relatively uneventful. Normally the reactor was kept at a designated power level within certain limits. Occasionally the operators had to increase the power for a certain test. The shift supervisor and several different people would get together and discuss the change before boosting the power. All operators were required to maintain a Reactor Operator License from the Atomic Energy Commission. The license included six months of training, an eight-hour written exam, a four-hour walkaround, and testing on the reactor controls.
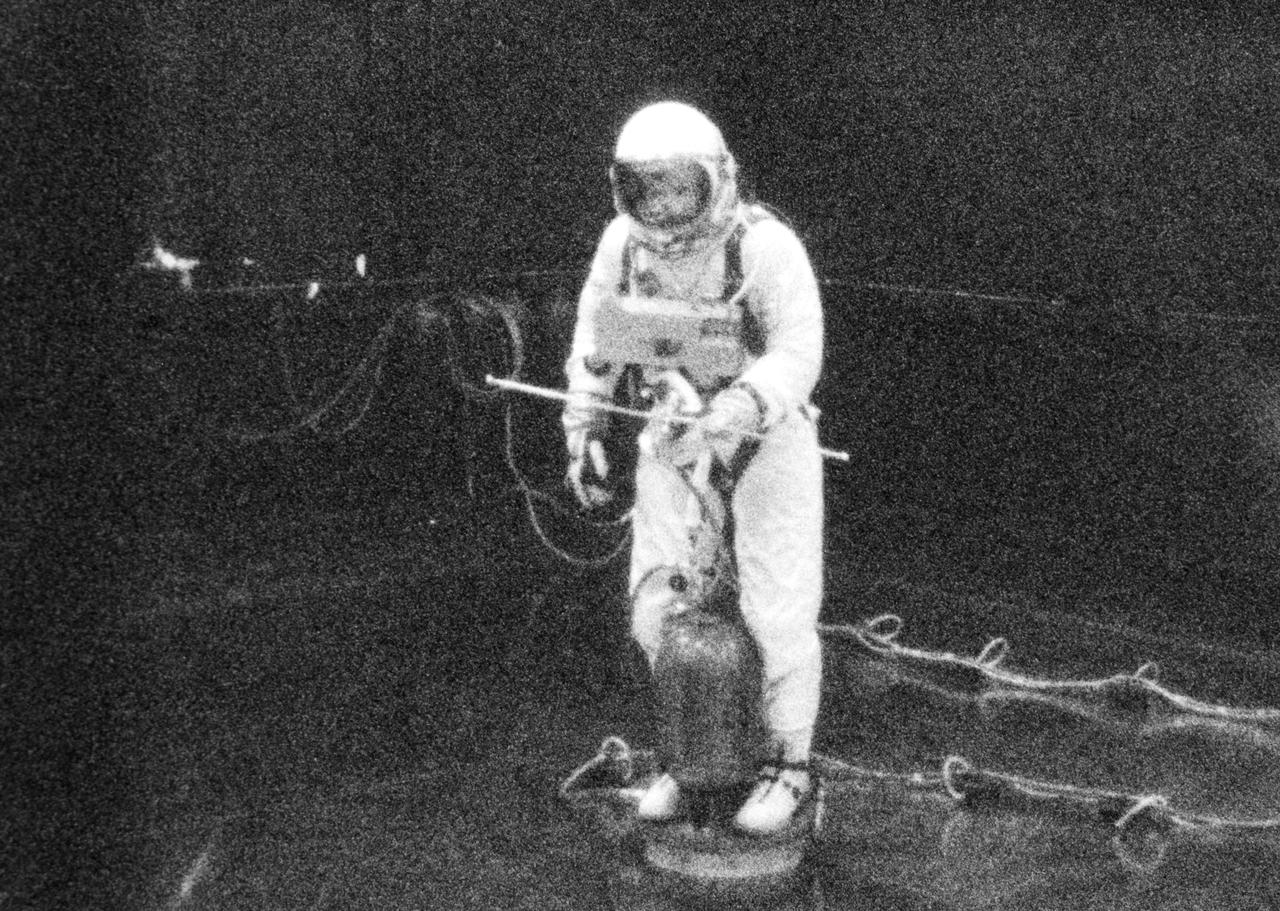

S65-19504 (28 May 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 prime crew, is pictured during an extravehicular exercise in the Building 4 laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas. White is controlling about the yaw (vertical) axis while translating. He stands on a Balance Extravehicular Training Aircraft which is separated from the level steel floor by a .001th-inch cushion of air. In his right hand White holds a zero-gravity integral propulsion unit which is a self-maneuvering device used by an astronaut in a zero-gravity environment. This condition is simulated in this training exercise. White's spacesuit is pressurized to create a realistic training condition. The simulated umbilical line is floated on air with the aid of eleven small air pads.
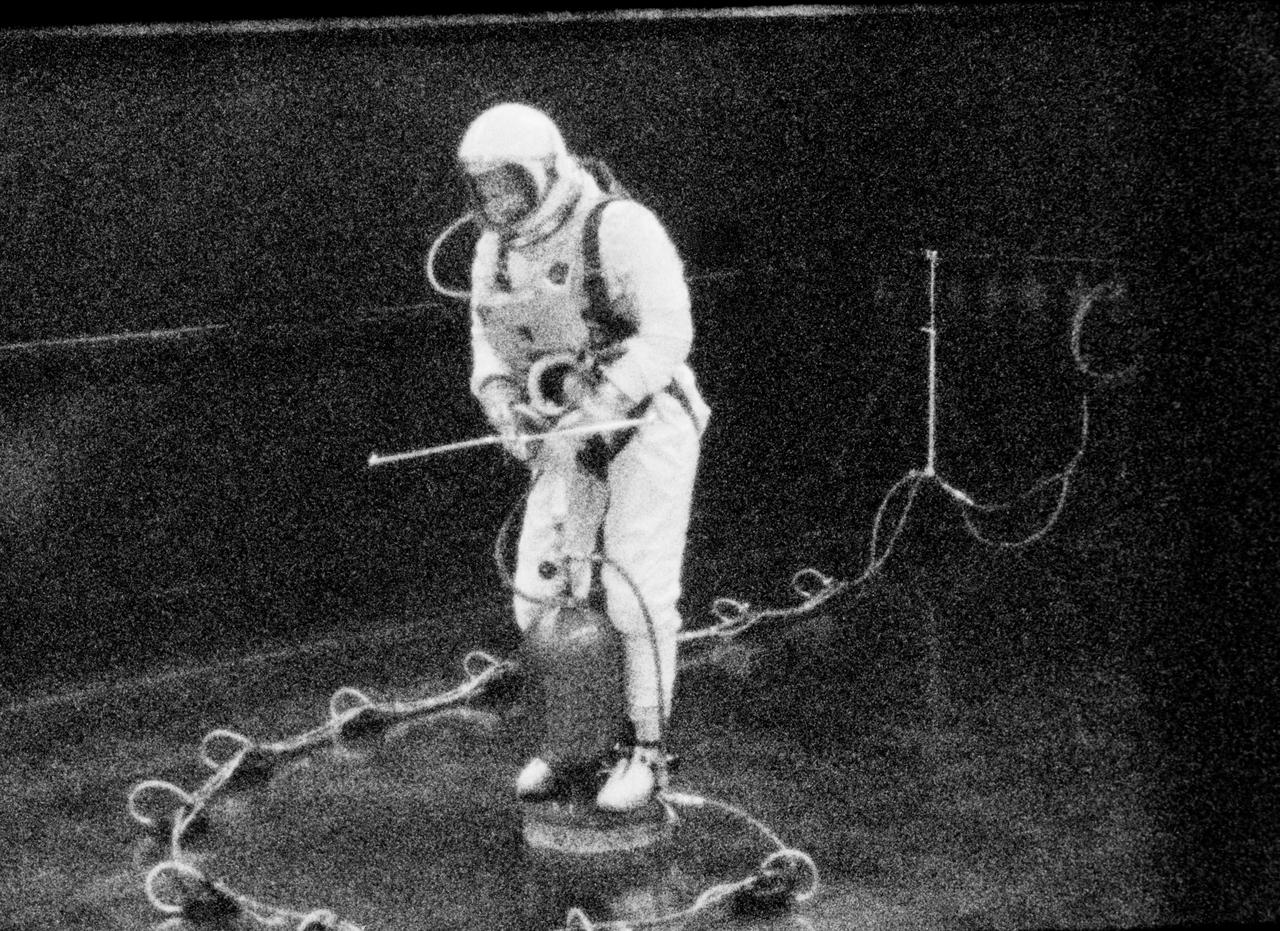
S65-19505 (28 May 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 prime crew, is pictured during an extravehicular exercise in the Building 4 laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas. White is controlling about the yaw (vertical) axis while translating. He stands on a Balance Extravehicular Training Aircraft which is separated from the level steel floor by a .001th-inch cushion of air. In his right hand White holds a zero-gravity integral propulsion unit which is a self-maneuvering device used by an astronaut in a zero-gravity environment. This condition is simulated in this training exercise. White's spacesuit is pressurized to create a realistic training condition. The simulated umbilical line is floated on air with the aid of eleven small air pads.
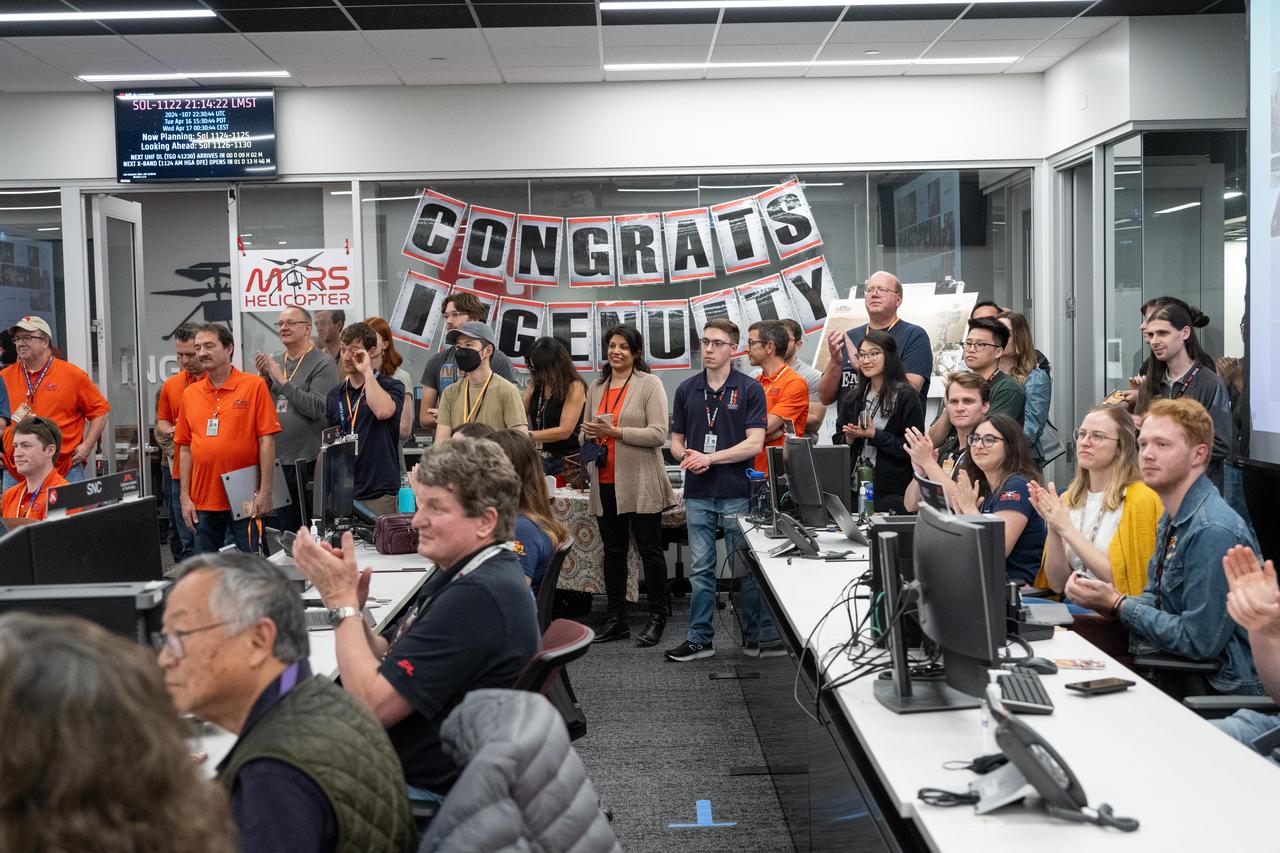

Engineers working on NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter gathered together in a control room for one last time to monitor a transmission from the history-making helicopter at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on April 16, 2024. The transmission confirmed the operation of a software patch that will allow Ingenuity to act as a stationary testbed and collect data that could benefit future explorers of the Red Planet. Originally designed as short-lived technology demonstration mission that would perform up to five experimental test flights over 30 days, the first aircraft on another world operated from the Martian surface for almost three years, flew more than 14 times farther than planned, and logged more than two hours of total flight time. Its 72nd and final flight was Jan. 18, 2024. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26318

A mechanic and apprentice work on a wooden impeller in the Fabrication Shop at the NACA Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The 260-person Fabrication Division created almost all of the equipment and models used at the laboratory. The Technical Services Building, referred to as the “Fab Shop”, contained a number of specialized shops in the 1940s and 1950s. These included a Machine Shop, Sheet Metal Shop, Wood and Pattern Shop, Instrument Shop, Thermocouple Shop, Heat Treating Shop, Metallurgical Laboratory, and Fabrication Office. The Machine Shop fabricated research equipment not commercially available. During World War II these technicians produced high-speed cameras for combustion research, impellers and other supercharger components, and key equipment for the lab’s first supersonic wind tunnel. The Wood and Pattern Shop created everything from control panels and cabinets to aircraft model molds for sheet metal work. The Sheet Metal Shop had the ability to work with 0.01 to 4-inches thick steel plates. The Instrument Shop specialized in miniature parts and instrumentation, while the Thermocouple Shop standardized the installation of pitot tubes and thermocouples. The Metallurgical Laboratory contained a control lab for the Heat Treating Shop and a service lab for the NACA Lewis research divisions. The Heat Treating Shop heated metal parts to optimize their physical properties and contained a Precision Castings Foundry to manufacture equipment made of heat resisting alloys.
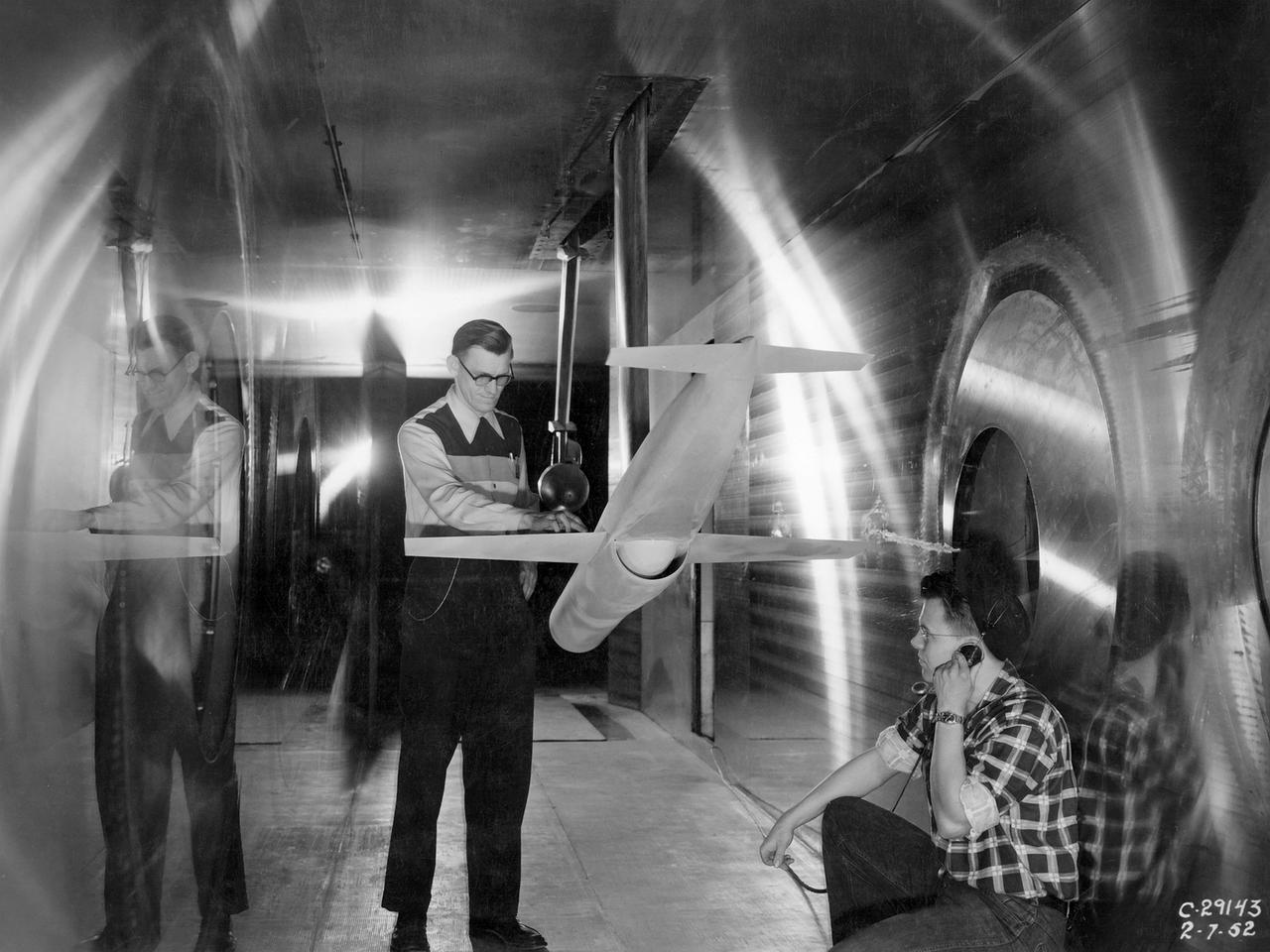

A researcher at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory checks the setup of a RJM-2 ramjet model in the test section of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel. The 8- by 6 was not only the laboratory’s first large supersonic wind tunnel, but it was also the NACA’s first facility capable of testing an operating engine at supersonic speeds. The 8- by 6-foot tunnel has been used to study engine inlets, fuel injectors, flameholders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet propulsion systems. The 8-foot wide and 6-foot tall test section consisted of 1-inch thick steel plates with hatches on the floor and ceiling to facilitate the installation of the test article. The two windows seen on the right wall allowed photographic equipment to be set up. The test section was modified in 1956 to accommodate transonic research. NACA engineers drilled 4,700 holes into the test section walls to reduce transonic pressure disturbances and shock waves. NACA Lewis undertook an extensive research program on ramjets in the 1940s using several of its facilities. Ramjets provide a very simple source of propulsion. They are basically a tube which ingests high speed air, ignites it, and then expels the heated air at a significantly higher velocity. Ramjets are extremely efficient and powerful but can only operate at high speeds. Therefore, they require a booster rocket or aircraft drop to accelerate them to high speeds before they can operate.
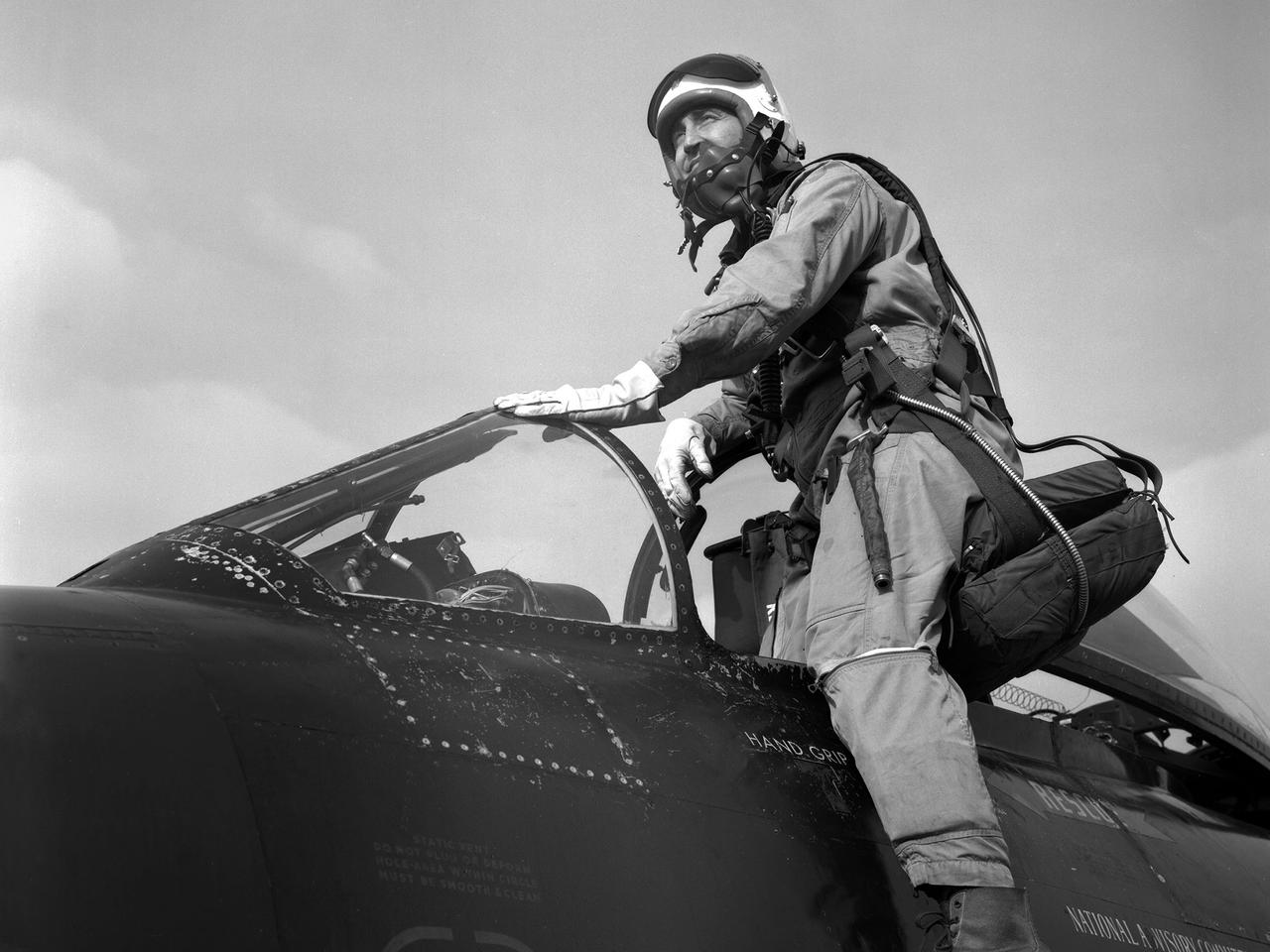

Pilot Joe Algranti climbs into the cockpit of a McDonnell F2H-2B Banshee on the tarmac at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. Nine months later the laboratory became part of the new National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and the NACA logo was permanently removed from the hangar. Algranti served as a Navy fighter pilot from 1946 to 1947 and earned a Physics degree from the University of North Carolina. He joined the NACA Lewis staff in 1951 witnessed the technological transformation from high speed flight to space. At Lewis Algranti piloted icing research flights, operated the liquid-hydrogen pump system for Project Bee, and served as the primary test subject for the Multi-Axis Space Test Inertia Facility (MASTIF). The MASTIF was a device used to train the Mercury astronauts how to control a spinning capsule. In 1960, Algranti and fellow Lewis pilots Warren North and Harold Ream transferred to NASA’s Space Task Group at Langley to actively participate in the space program. Two years later, Algranti became the Chief of Aircraft Operations and Chief Test Pilot at NASA’s new Manned Space Center in Houston. Algranti earned notoriety in 1968 when he test flew the first Lunar Landing Training Vehicle. He operated the vehicle four minutes before being forced to eject moments before it impacted the ground. Algranti also flew the NASA’s modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, the Super Guppy, and the KC-135 "Vomit Comet" training aircraft. He retired in 1992 with over 40 years of NASA service.
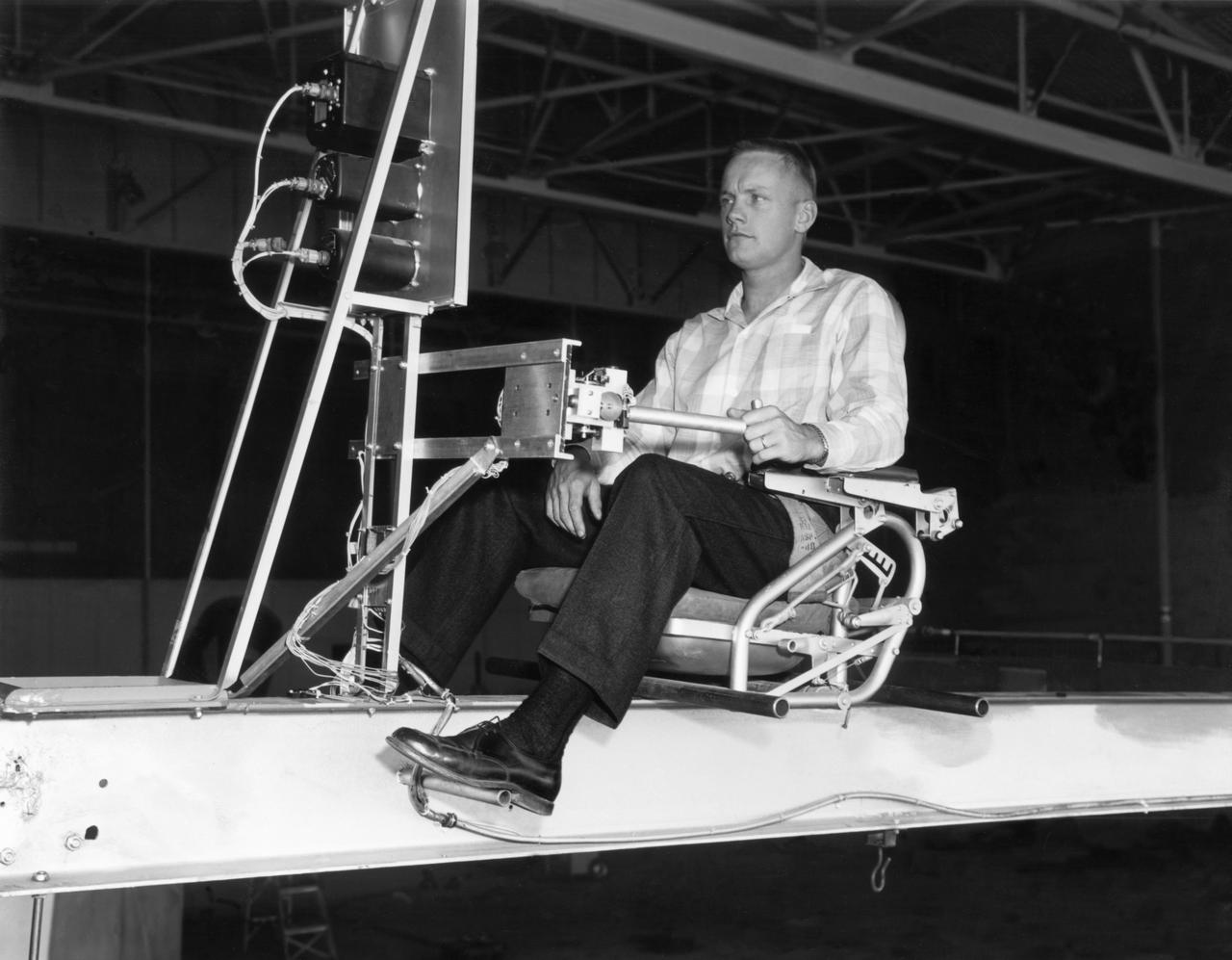

Famed astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, the first man to set foot on the moon during the historic Apollo 11 space mission in July 1969, served for seven years as a research pilot at the NACA-NASA High-Speed Flight Station, now the Dryden Flight Research Center, at Edwards, California, before he entered the space program. Armstrong joined the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) at the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory (later NASA's Lewis Research Center, Cleveland, Ohio, and today the Glenn Research Center) in 1955. Later that year, he transferred to the High-Speed Flight Station at Edwards as an aeronautical research scientist and then as a pilot, a position he held until becoming an astronaut in 1962. He was one of nine NASA astronauts in the second class to be chosen. As a research pilot Armstrong served as project pilot on the F-100A and F-100C aircraft, F-101, and the F-104A. He also flew the X-1B, X-5, F-105, F-106, B-47, KC-135, and Paresev. He left Dryden with a total of over 2450 flying hours. He was a member of the USAF-NASA Dyna-Soar Pilot Consultant Group before the Dyna-Soar project was cancelled, and studied X-20 Dyna-Soar approaches and abort maneuvers through use of the F-102A and F5D jet aircraft. Armstrong was actively engaged in both piloting and engineering aspects of the X-15 program from its inception. He completed the first flight in the aircraft equipped with a new flow-direction sensor (ball nose) and the initial flight in an X-15 equipped with a self-adaptive flight control system. He worked closely with designers and engineers in development of the adaptive system, and made seven flights in the rocket plane from December 1960 until July 1962. During those fights he reached a peak altitude of 207,500 feet in the X-15-3, and a speed of 3,989 mph (Mach 5.74) in the X-15-1. Armstrong has a total of 8 days and 14 hours in space, including 2 hours and 48 minutes walking on the Moon. In March 1966 he was commander of the Gemini 8 or
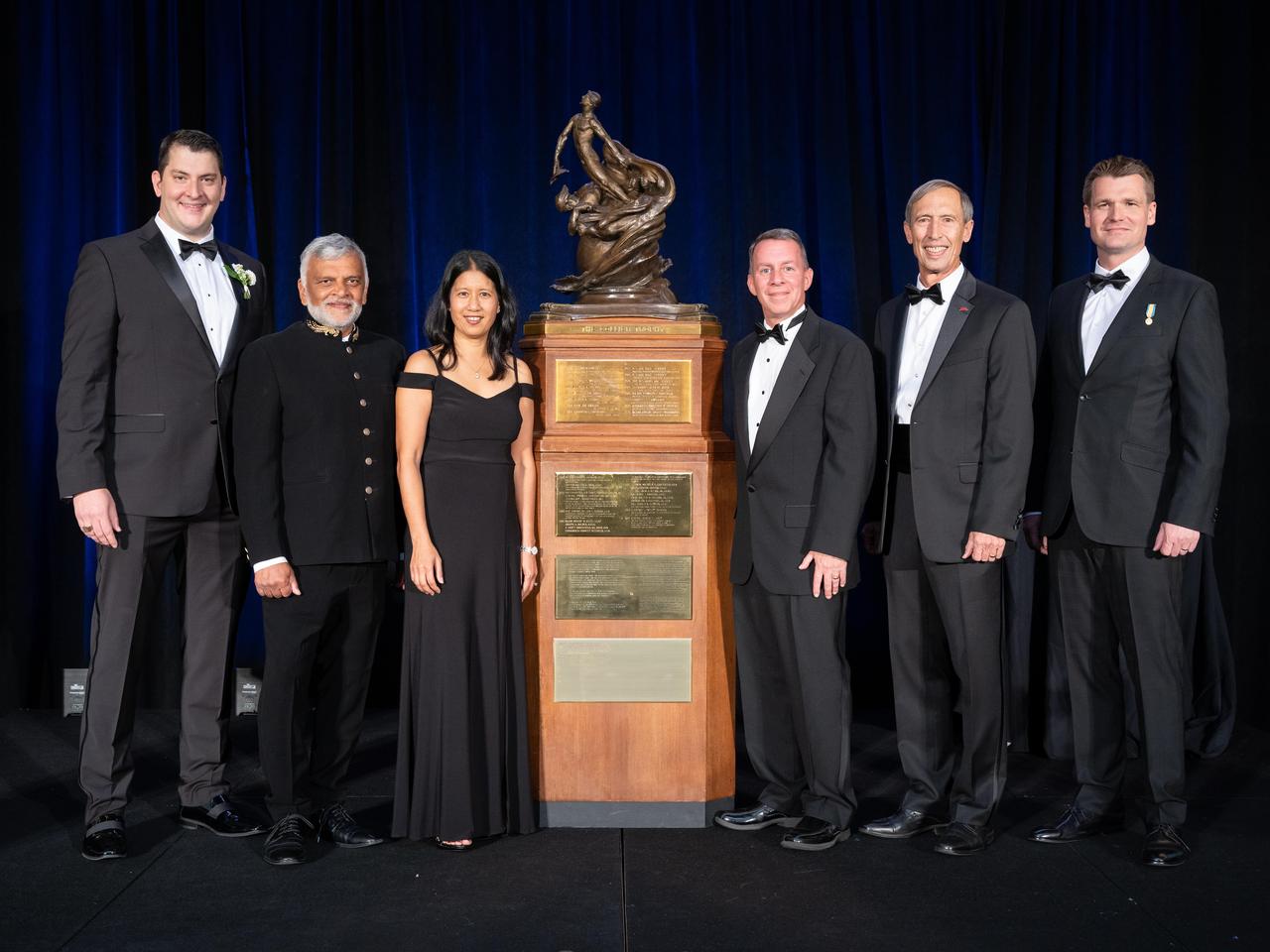

Members of NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter team stand next to the Collier Trophy during the Robert J. Collier Dinner in Washington on June 9, 2022. The team was awarded the 2021 Collier Trophy "for the first powered, controlled flight of an aircraft on another planet, thereby opening the skies of Mars and other worlds for future scientific discovery and exploration," the award citation states. From left to right: Teddy Tzanetos, Ingenuity team lead at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Bob Balaram, Ingenuity emeritus chief engineer at JPL; MiMi Aung, former Ingenuity project manager at JPL; Bobby Braun, former director for Planetary Science at JPL; Larry James, deputy director at JPL; Håvard Grip, Ingenuity chief pilot at JPL. This historic trophy – which is on permanent display at the Smithsonian Air and Space Museum in Washington – is awarded annually by the National Aeronautic Association "for the greatest achievement in aeronautics or astronautics in America, with respect to improving the performance, efficiency, and safety of air or space vehicles, the value of which has been thoroughly demonstrated by actual use during the preceding year." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25323
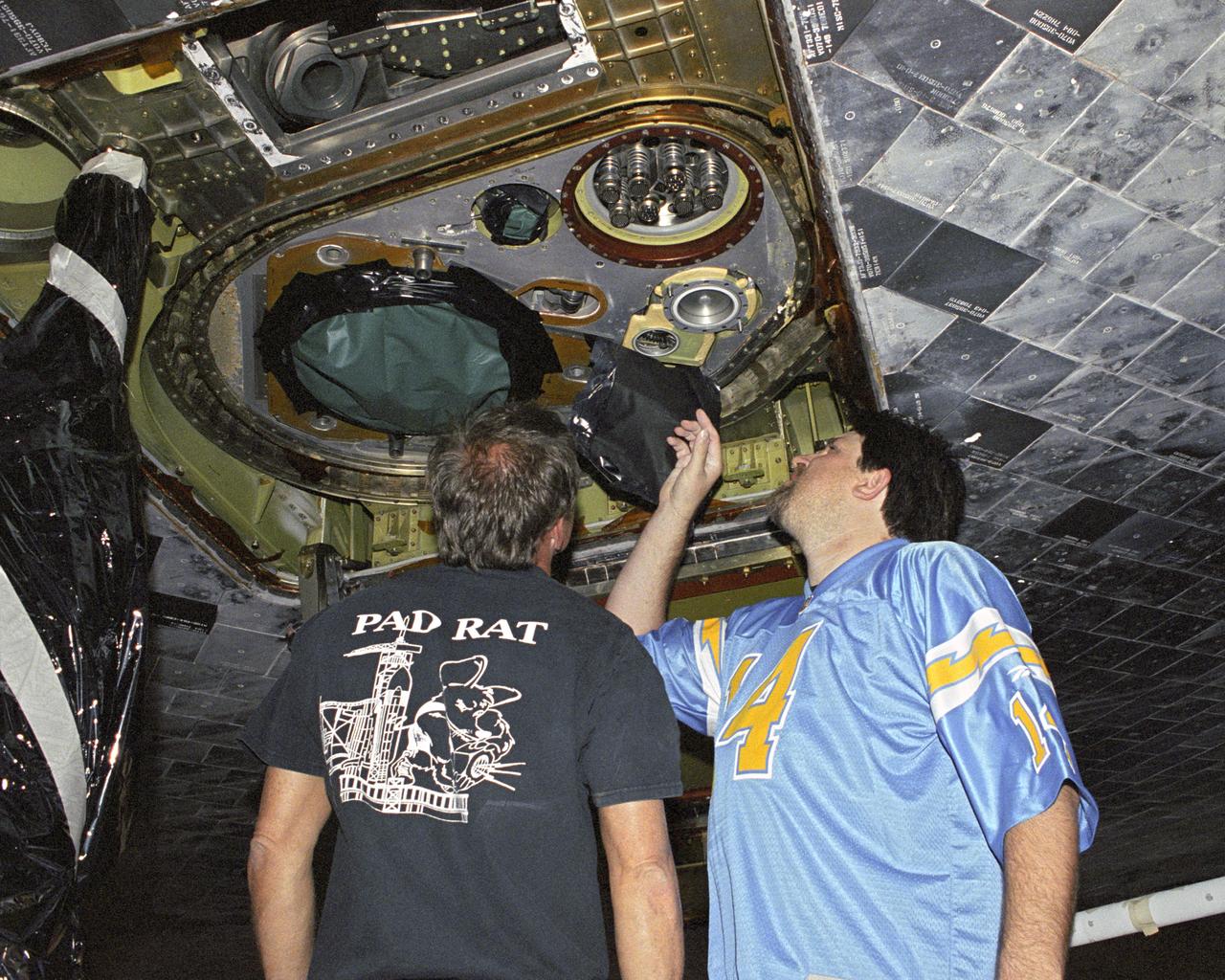

Robert 'Skip' Garrett; main propulsion advanced systems technician, and Chris Jacobs; main propulsion systems engineering technician, inspect external tank attachment fittings on the Space Shuttle Discovery as part of it's post-flight processing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The Space Shuttles receive post-flight servicing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) following landings at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle pa
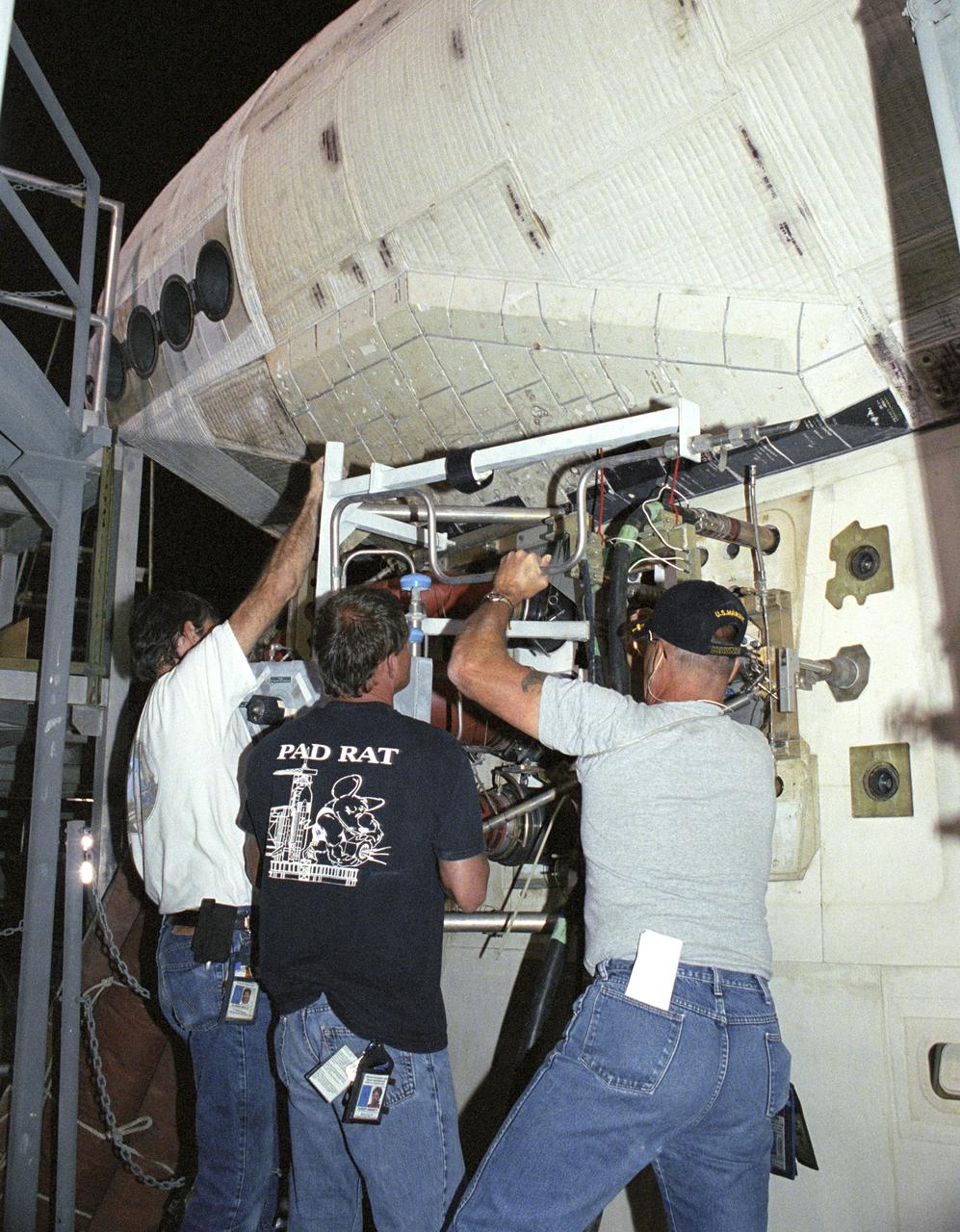

Todd Viddle; APU advanced systems technician, Robert 'Skip' Garrett; main propulsion advanced systems technician, and Dan McGrath; main propulsion systems engineer technician, remove a servicing unit from the Space Shuttle Discovery as part of it's post-flight processing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The Space Shuttles receive post-flight servicing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) following landings at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items

Title: W-8 Fan Acoustic Casing Treatment Test on the Source Diagnostic Test Rotor Alone Hardware Program: Advanced Air Vehicles Program (AAVP) Project: Advanced Air Transport Technology (AATT) Sub-project: Aircraft Noise Reduction (ANR) Weekly Highlight: · Acoustic Casing Treatment Testing Completed in the W-8 Single Stage Axial Compressor Facility: Testing of Acoustic Casing Treatments on the Source Diagnostic Test (SDT) rotor alone hardware which had begun in early January was completed on Thursday, February 16th. Four different over-the-rotor acoustic casing treatment concepts were tested along with two baseline configurations. Testing included steady-aerodynamic measurements of fan performance, hotfilm turbulence measurements, and inlet acoustic measurements with an in-duct array. These measurements will be used to assess the aerodynamic and acoustic impact of fan acoustic casing treatments on a high bypass ratio fan at TRL 3. This test was the last of 3 planned tests of potential over-the-rotor acoustic casing treatments. The first treatment test was completed in the Normal Incidence Tube (NIT) at Langley Research Center (LaRC) in Fall 2015 and the second was completed on the Advanced Noise Control Fan (ANCF) in the Aero-Acoustic Propulsion Laboratory (AAPL) in Winter 2016. This work is supported by the Aircraft Noise Reduction (ANR) subproject of the Advanced Air Transport Technology (AATT) Project. (POC: LTV/ Rick Bozak 3-5160)
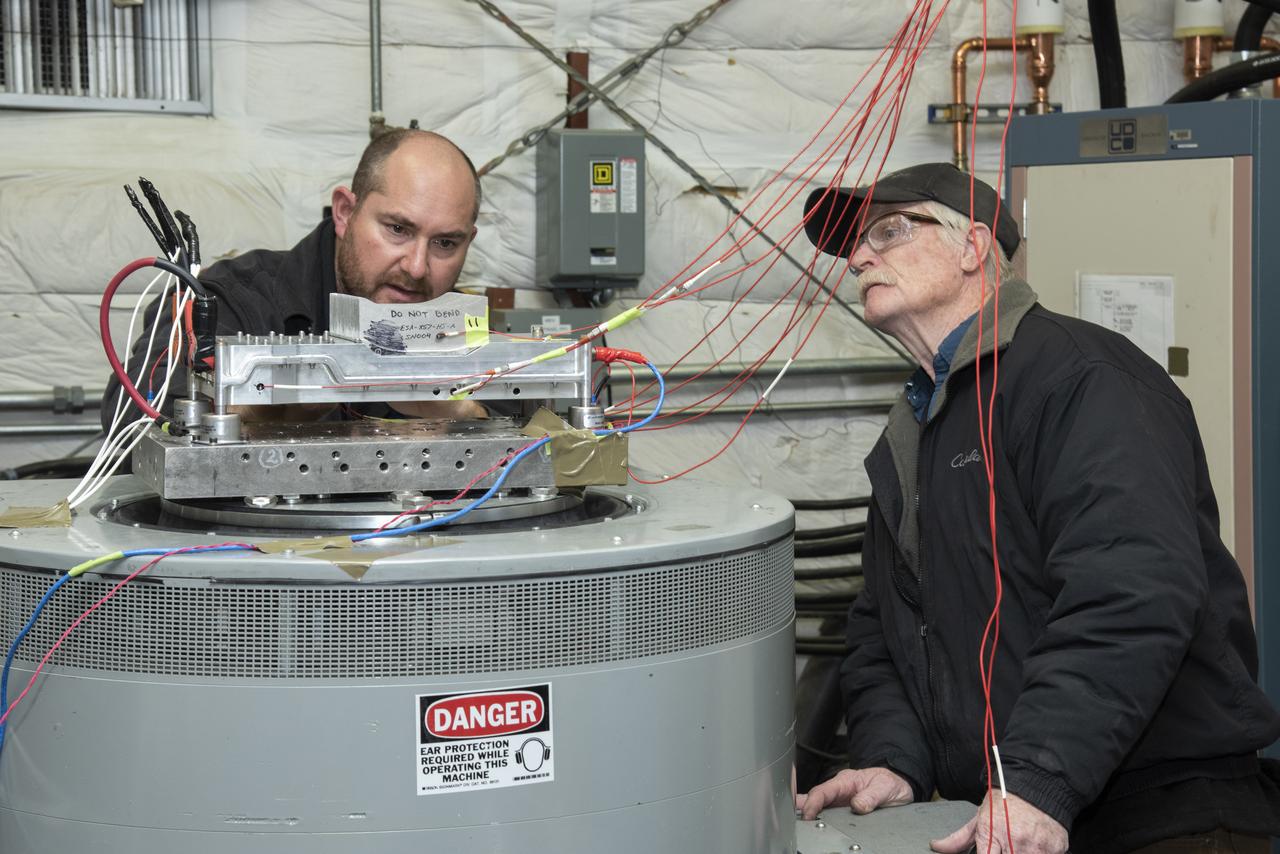

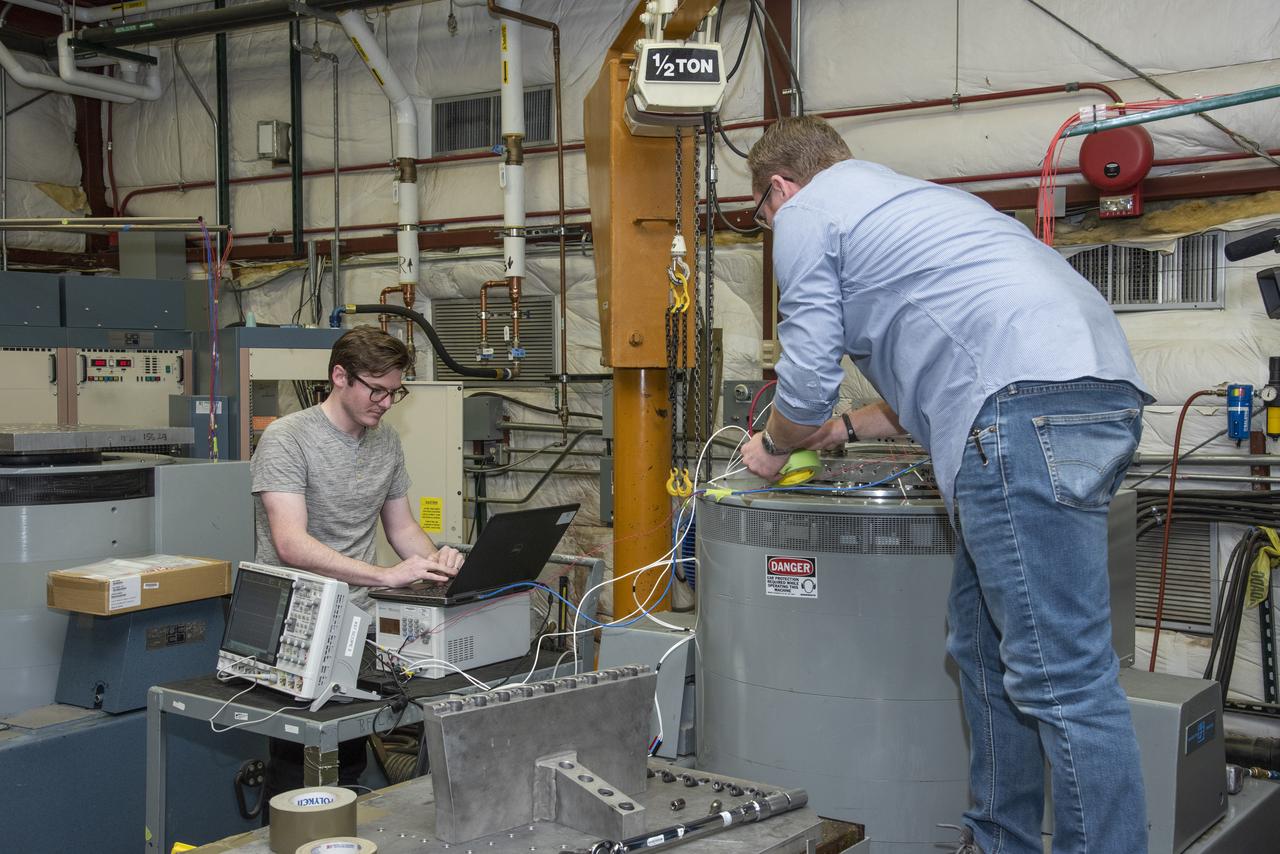
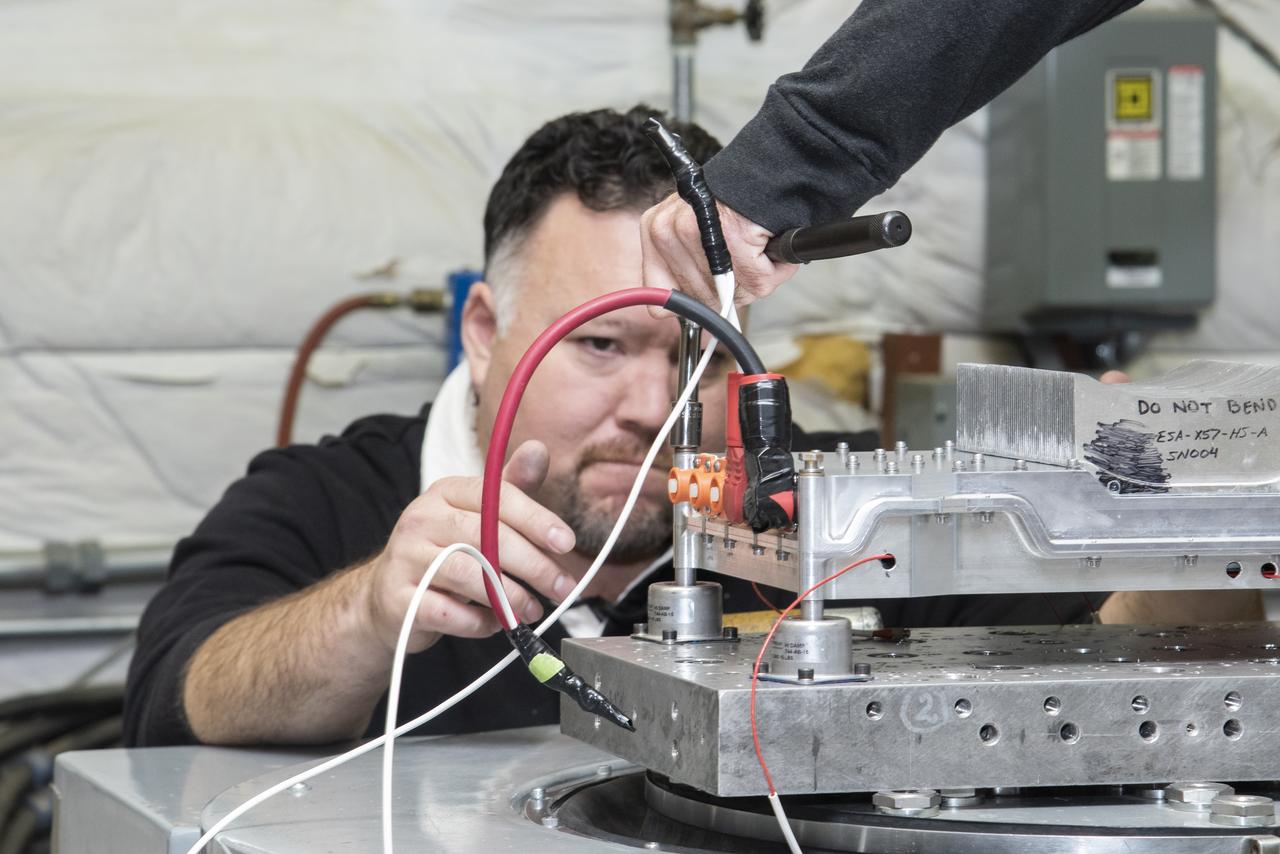
Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASAs first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

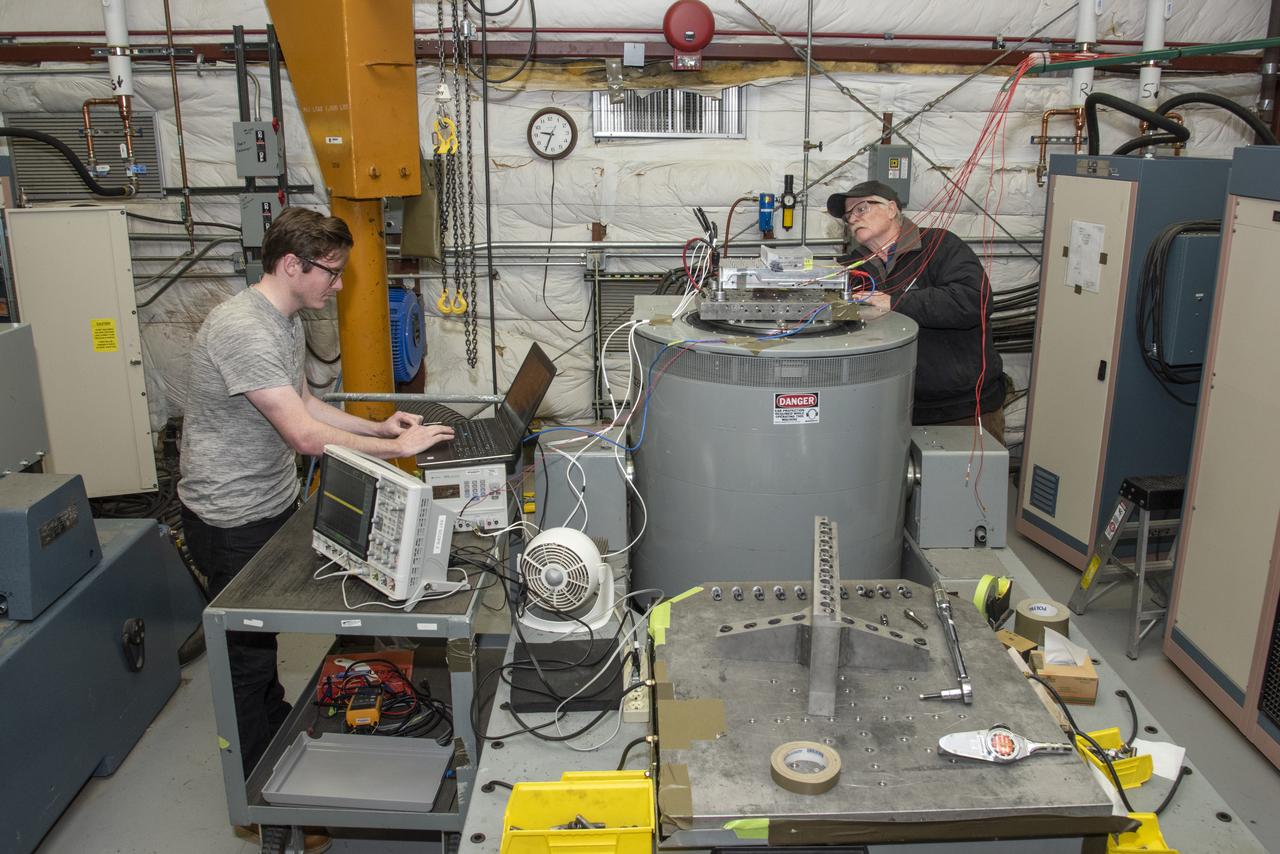
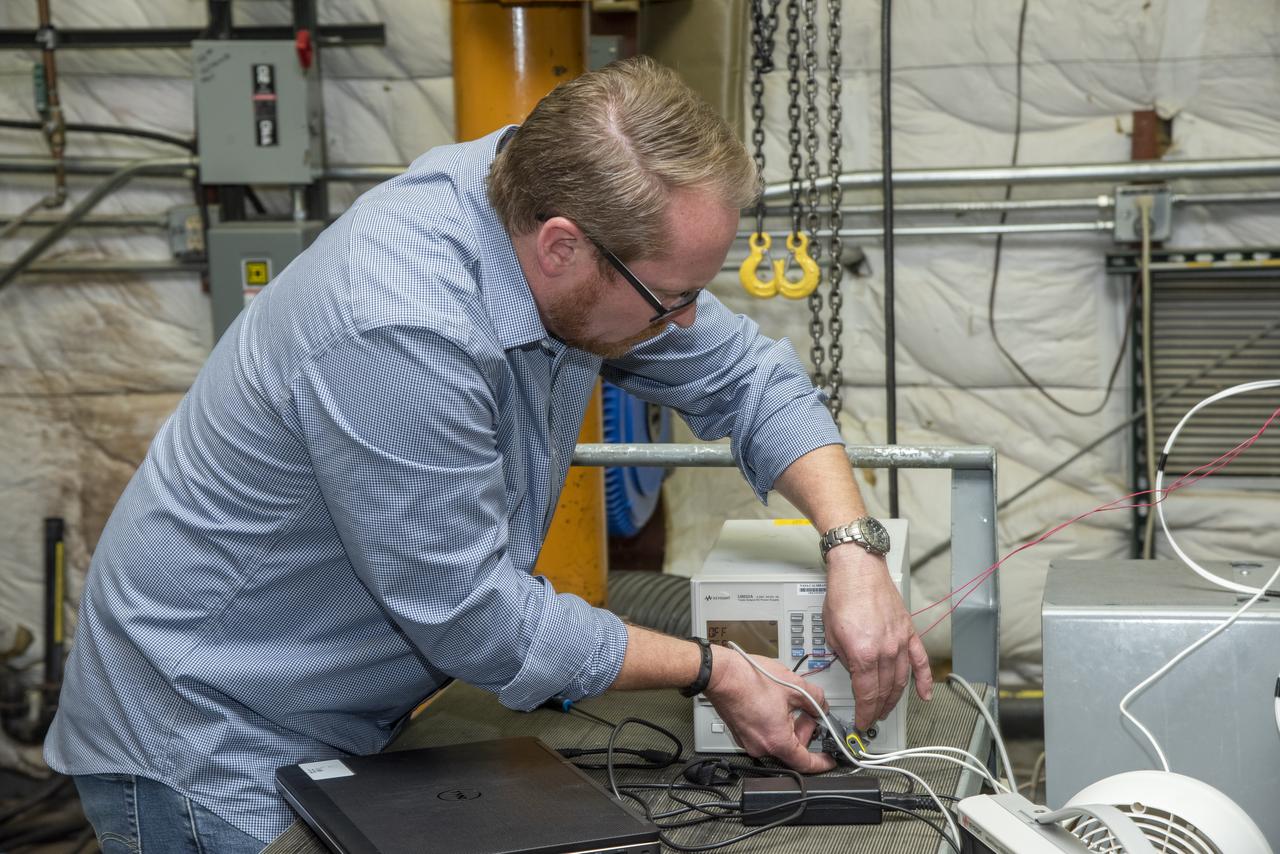
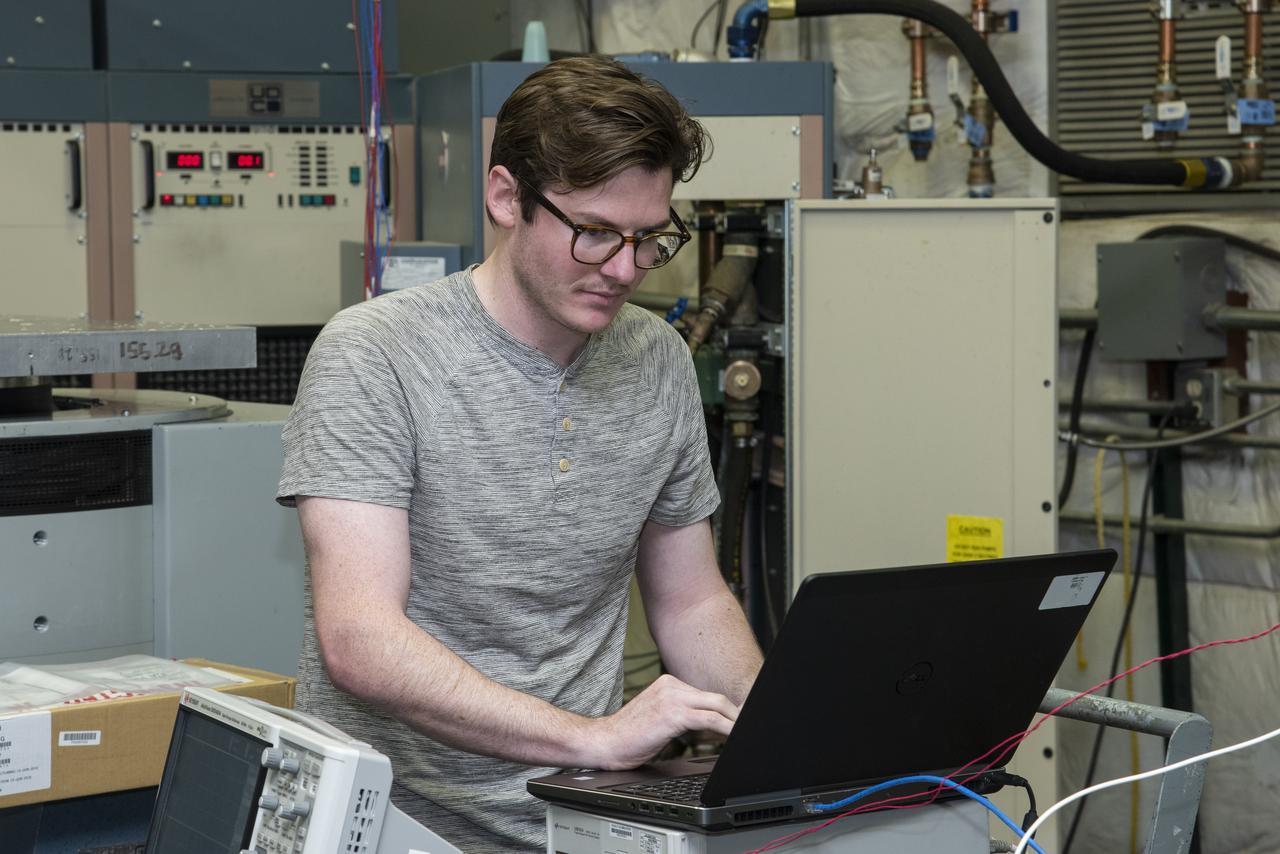
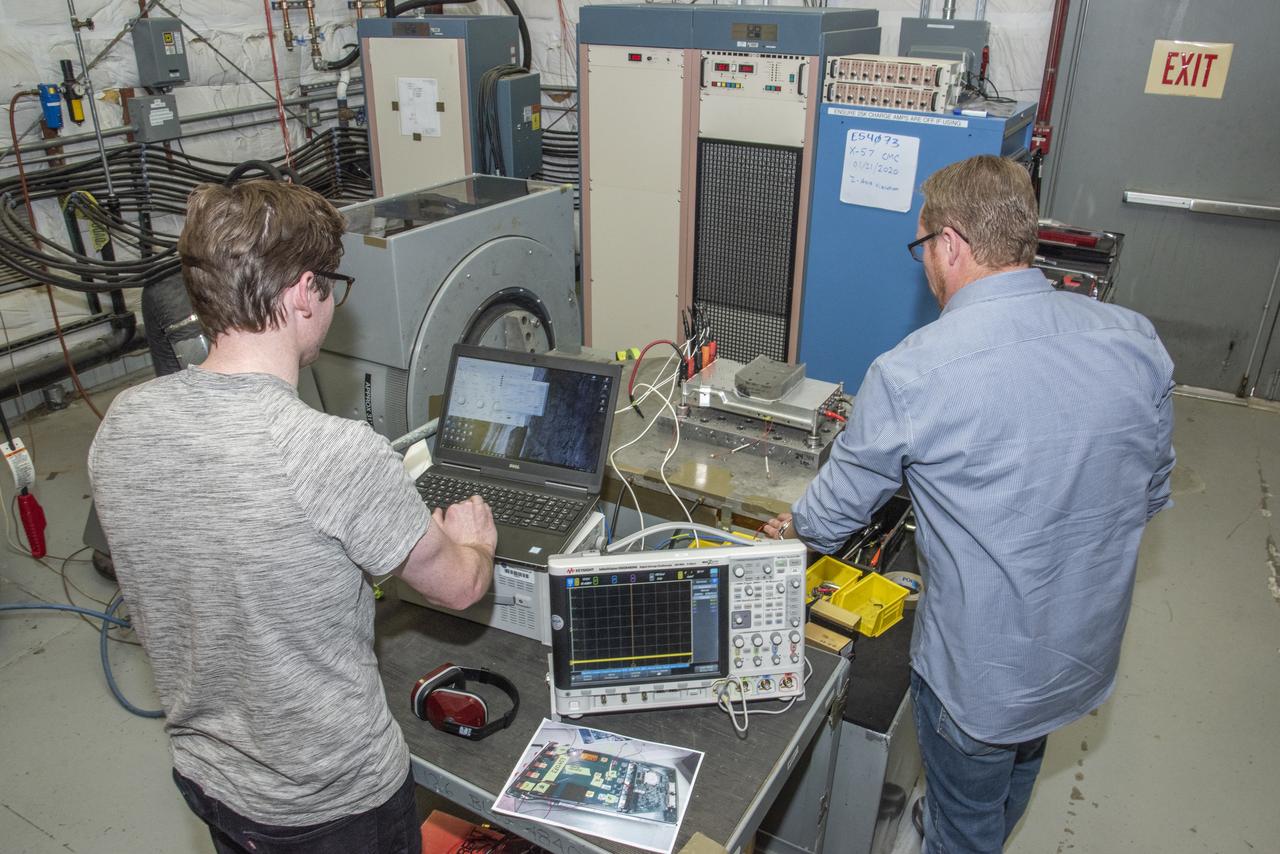
Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

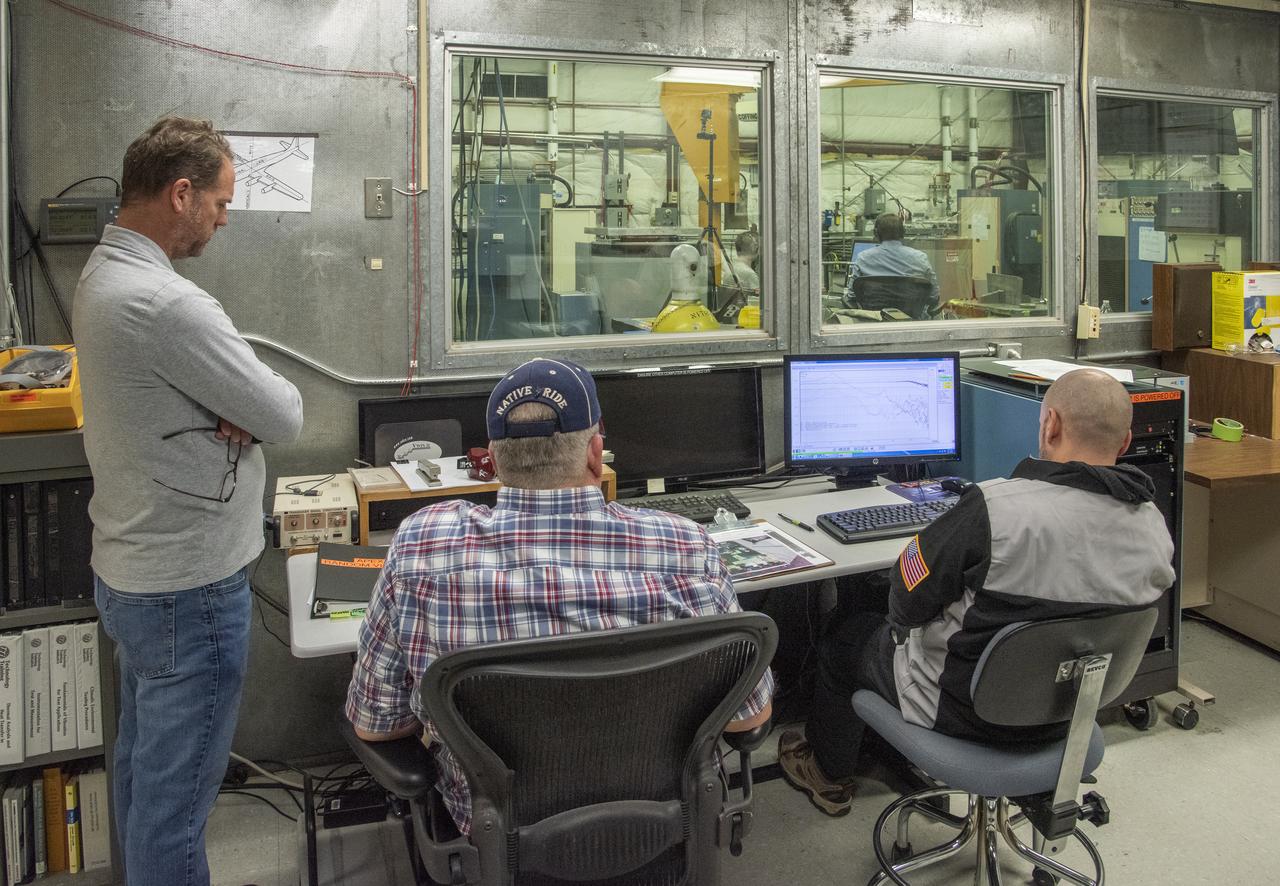
Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
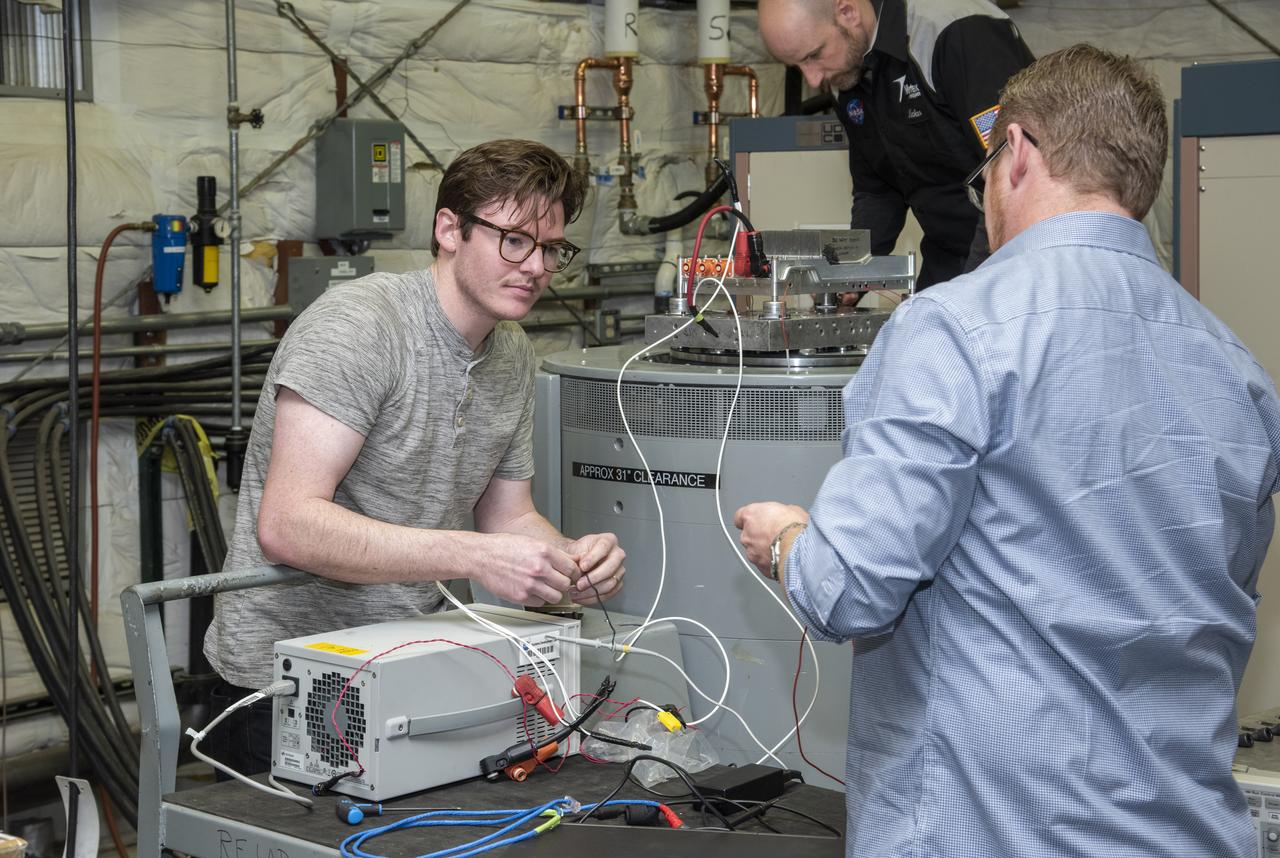
Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
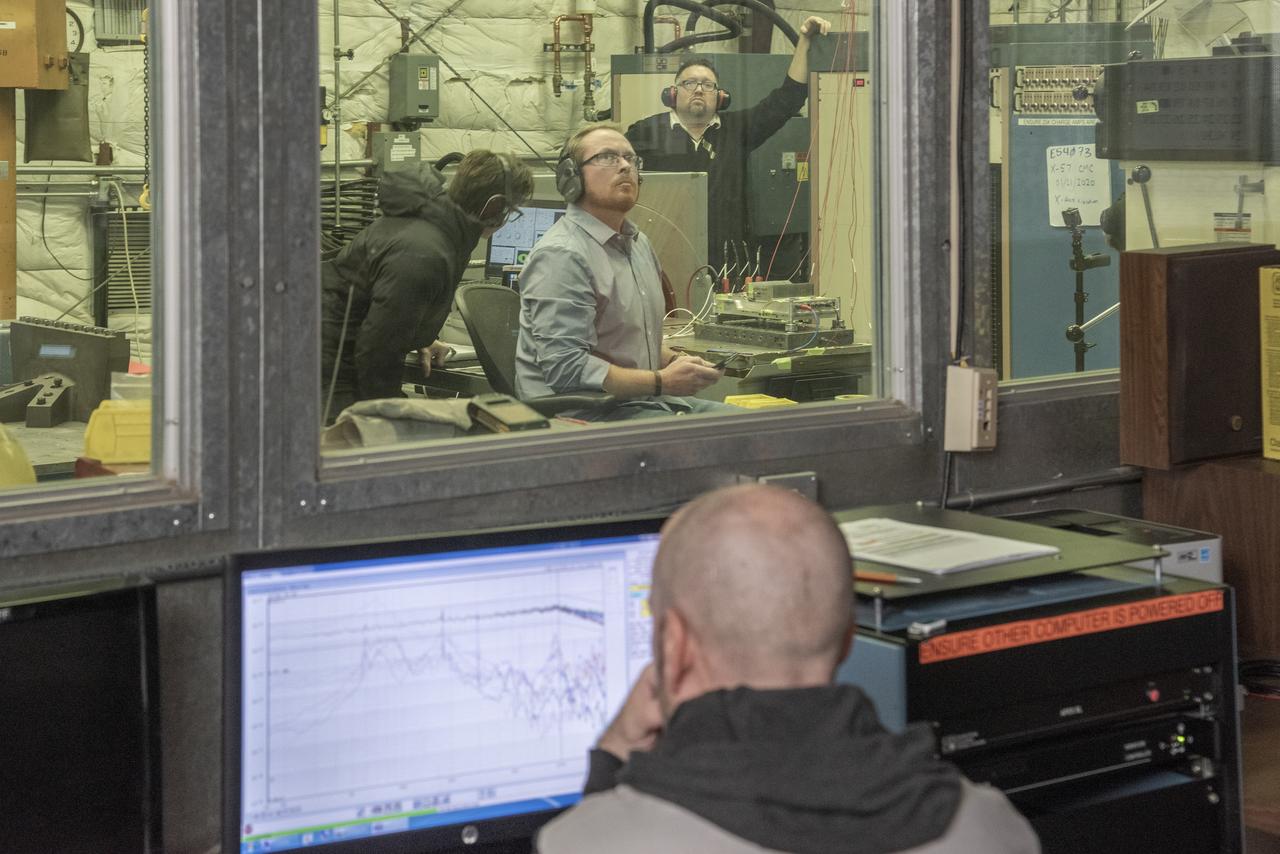

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
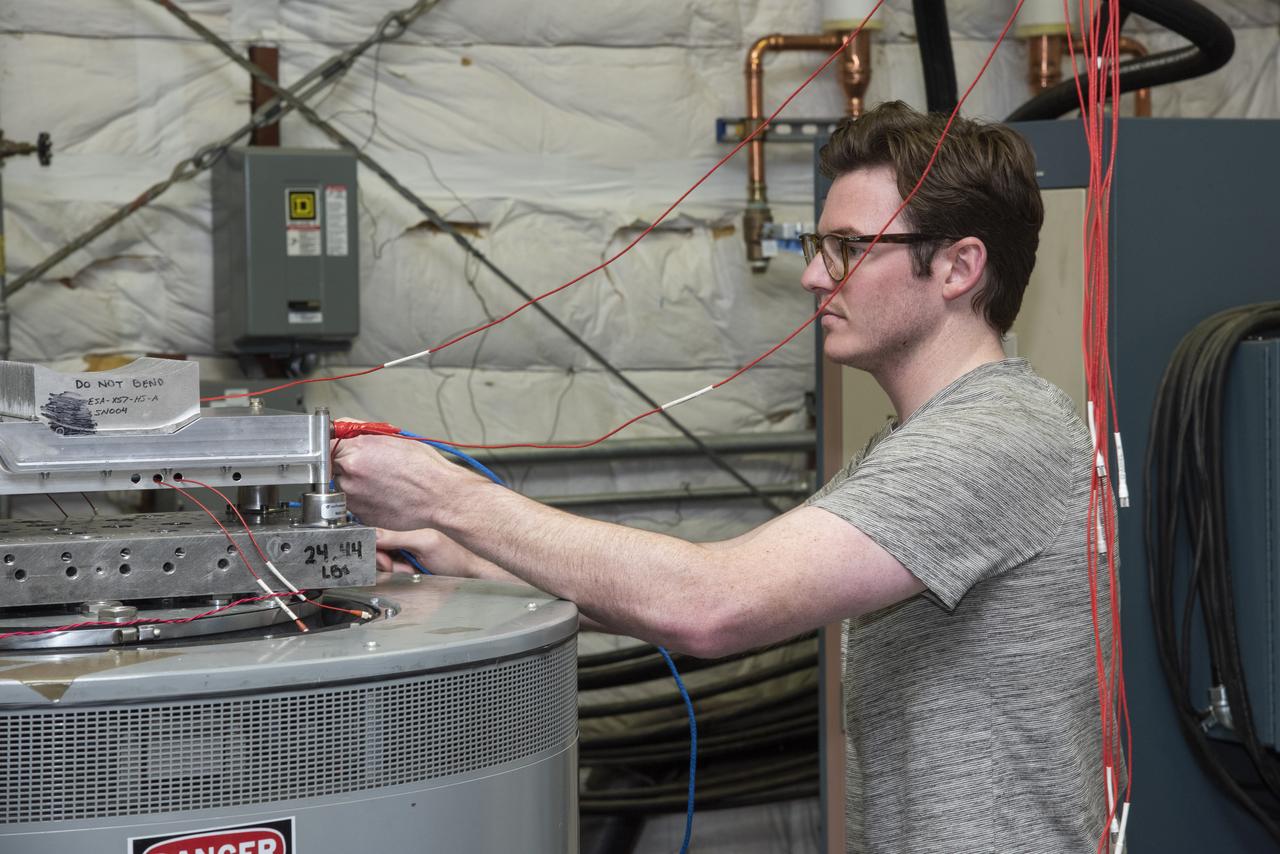

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
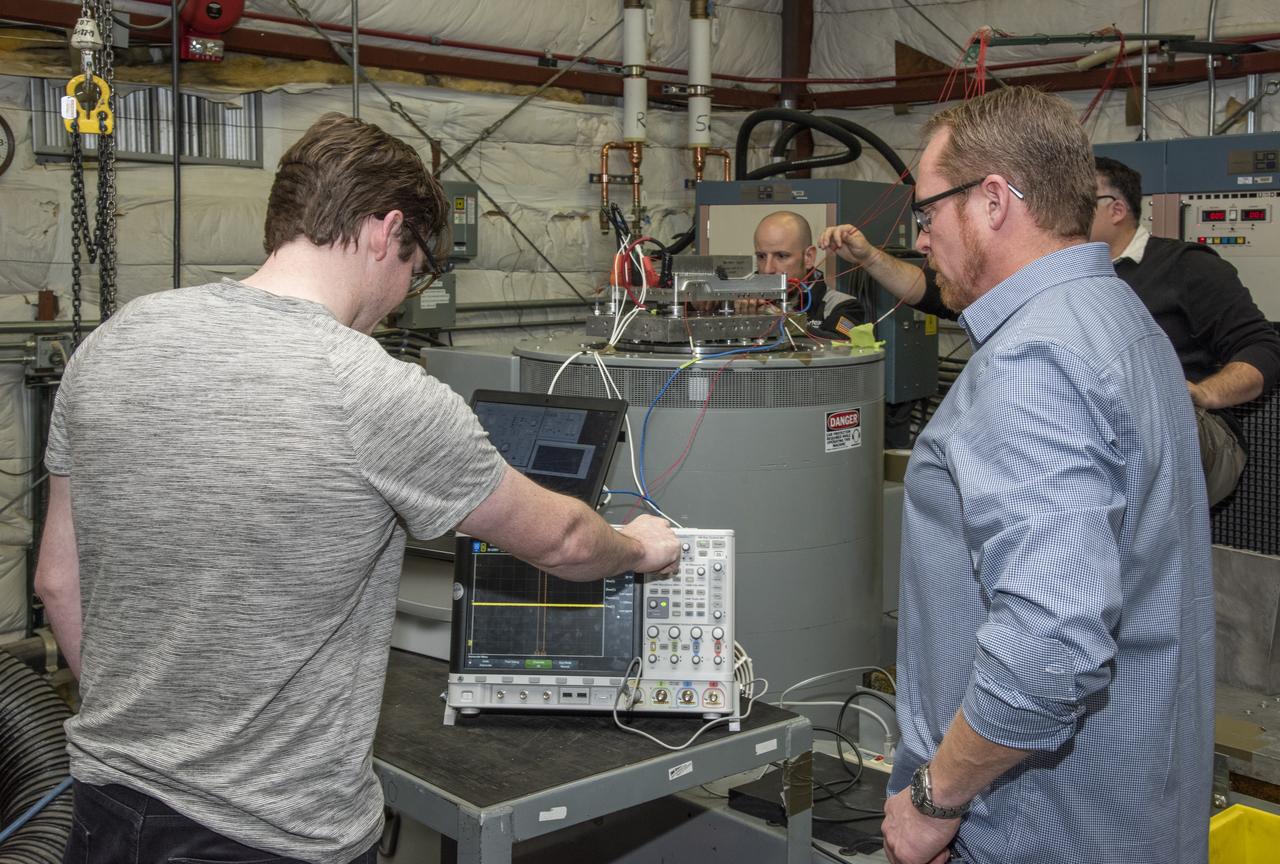

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
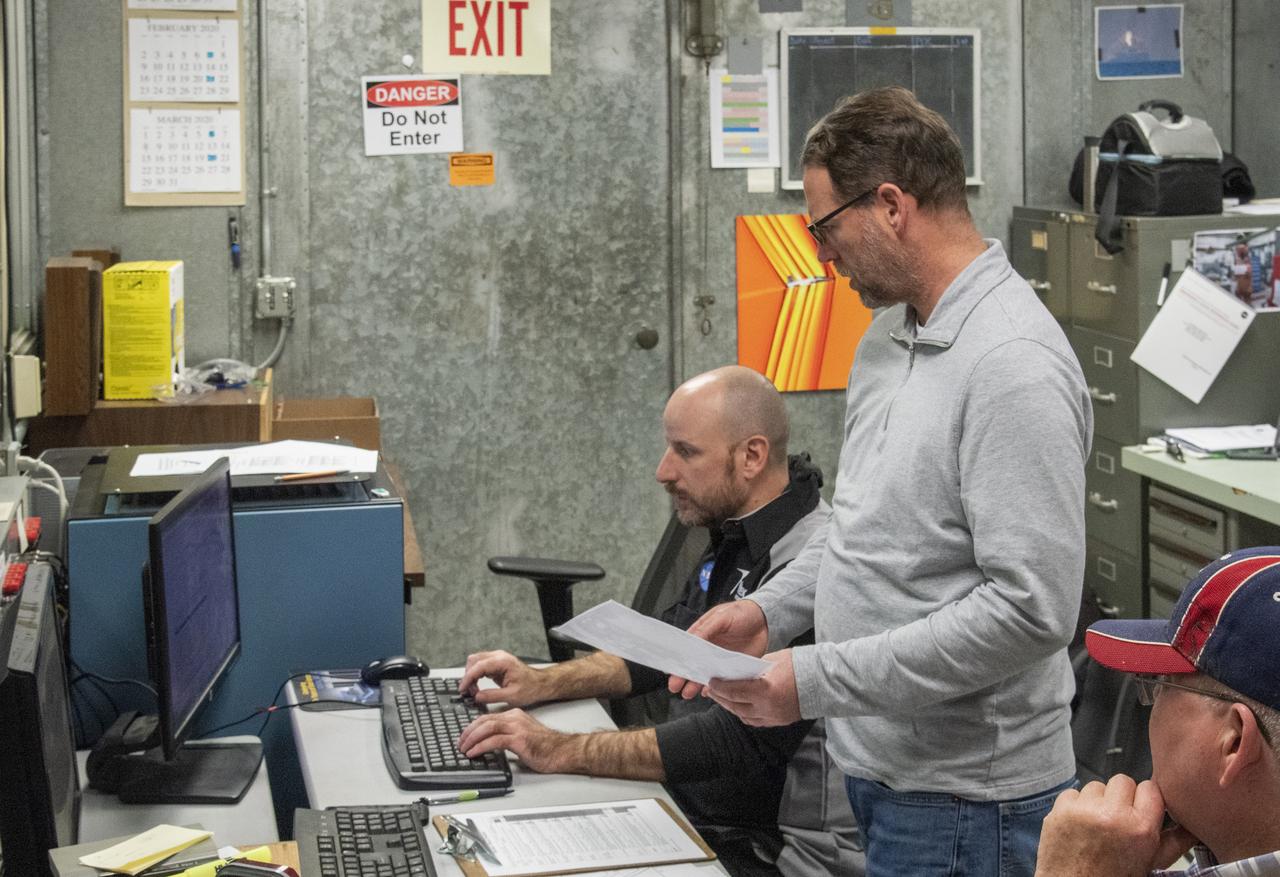

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
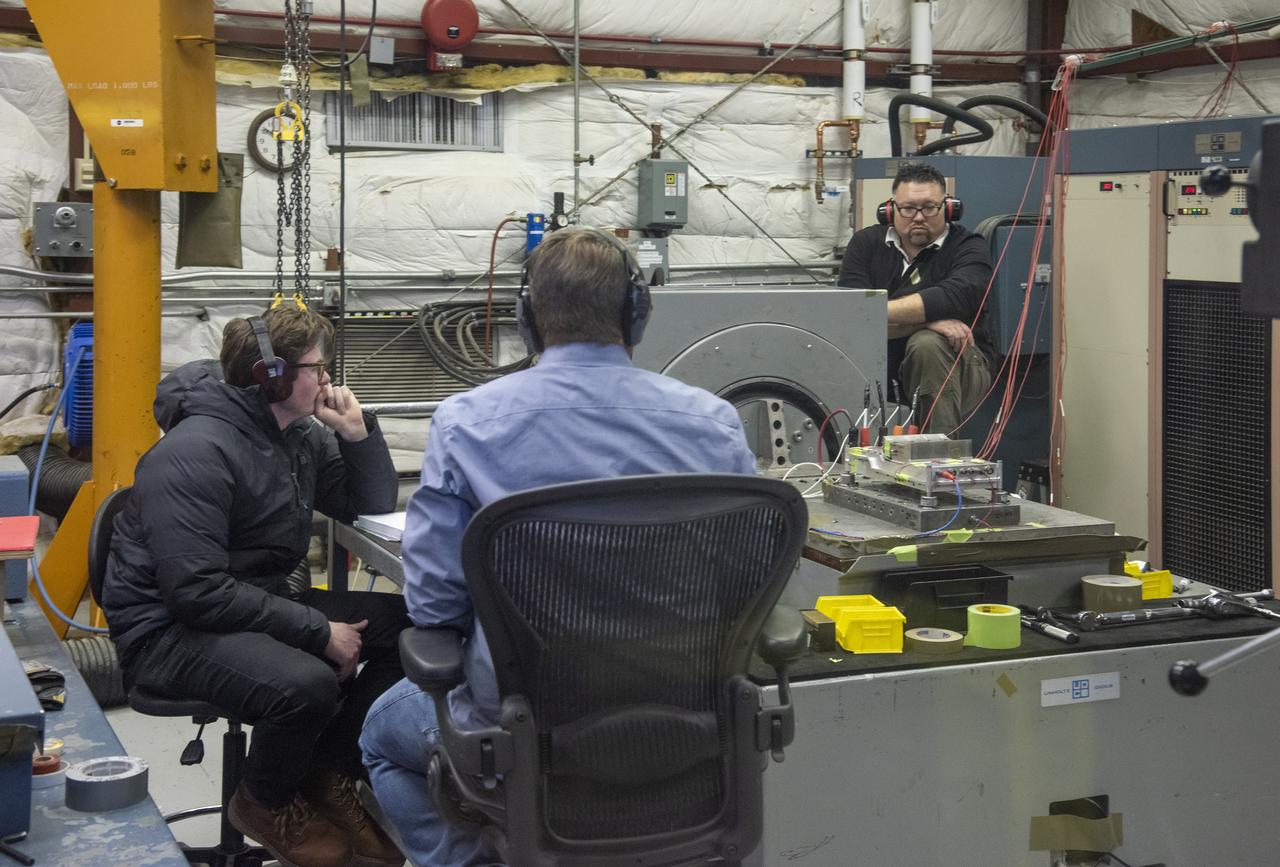

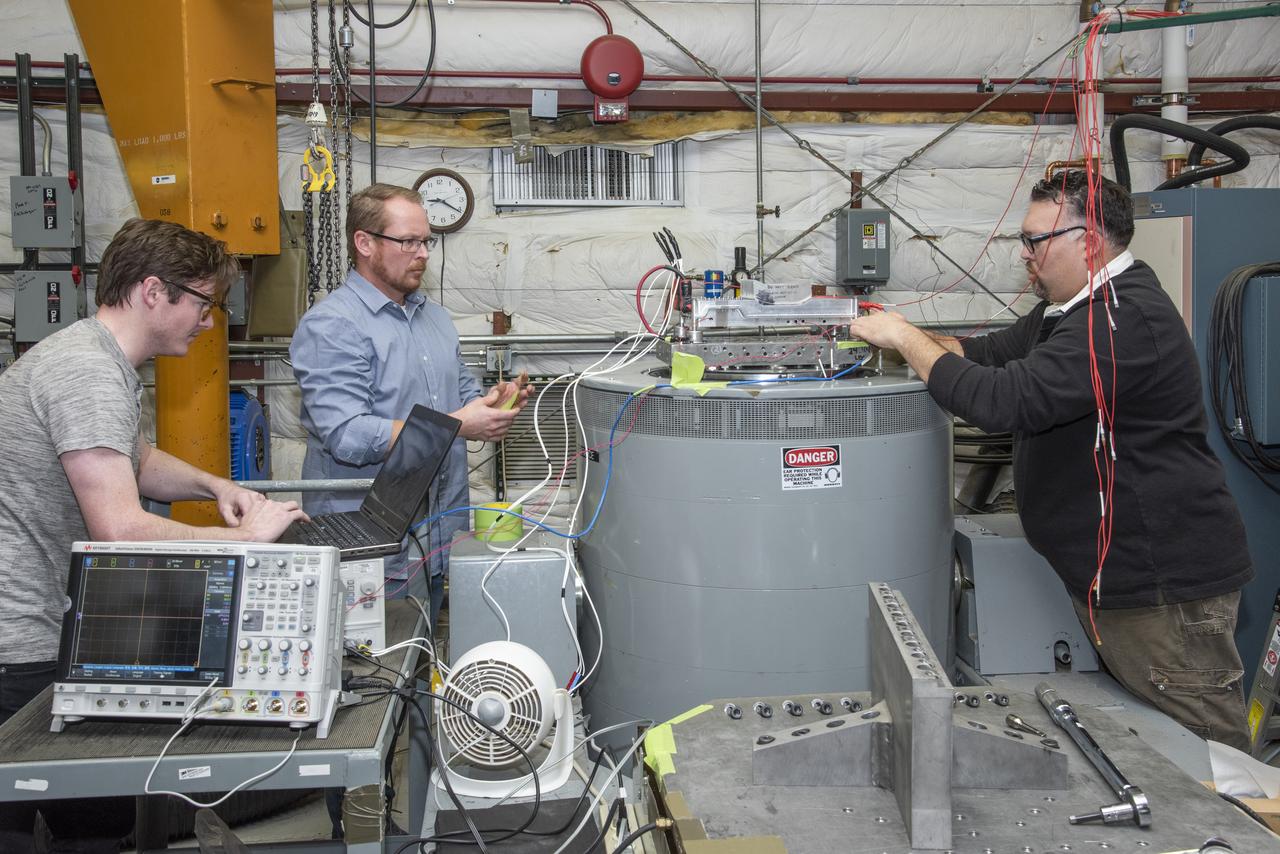
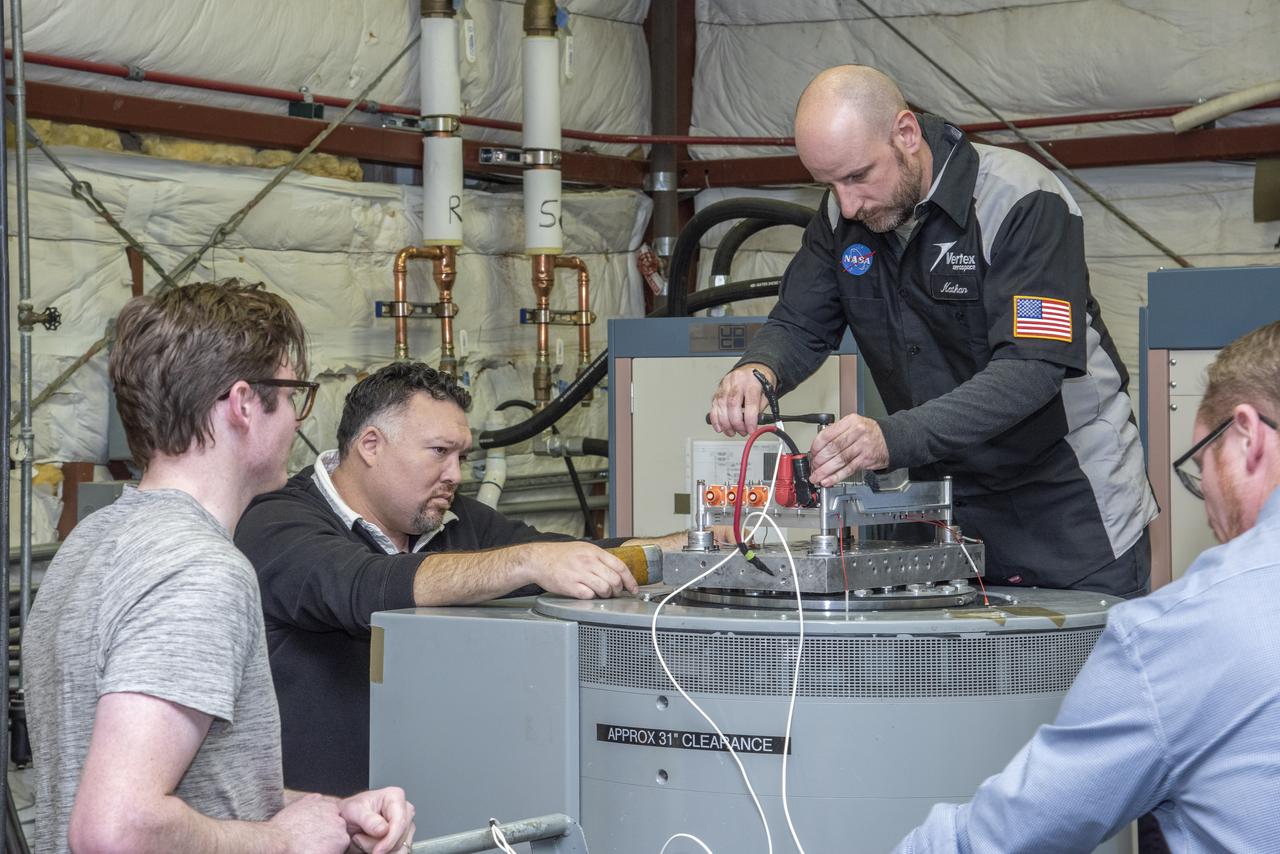
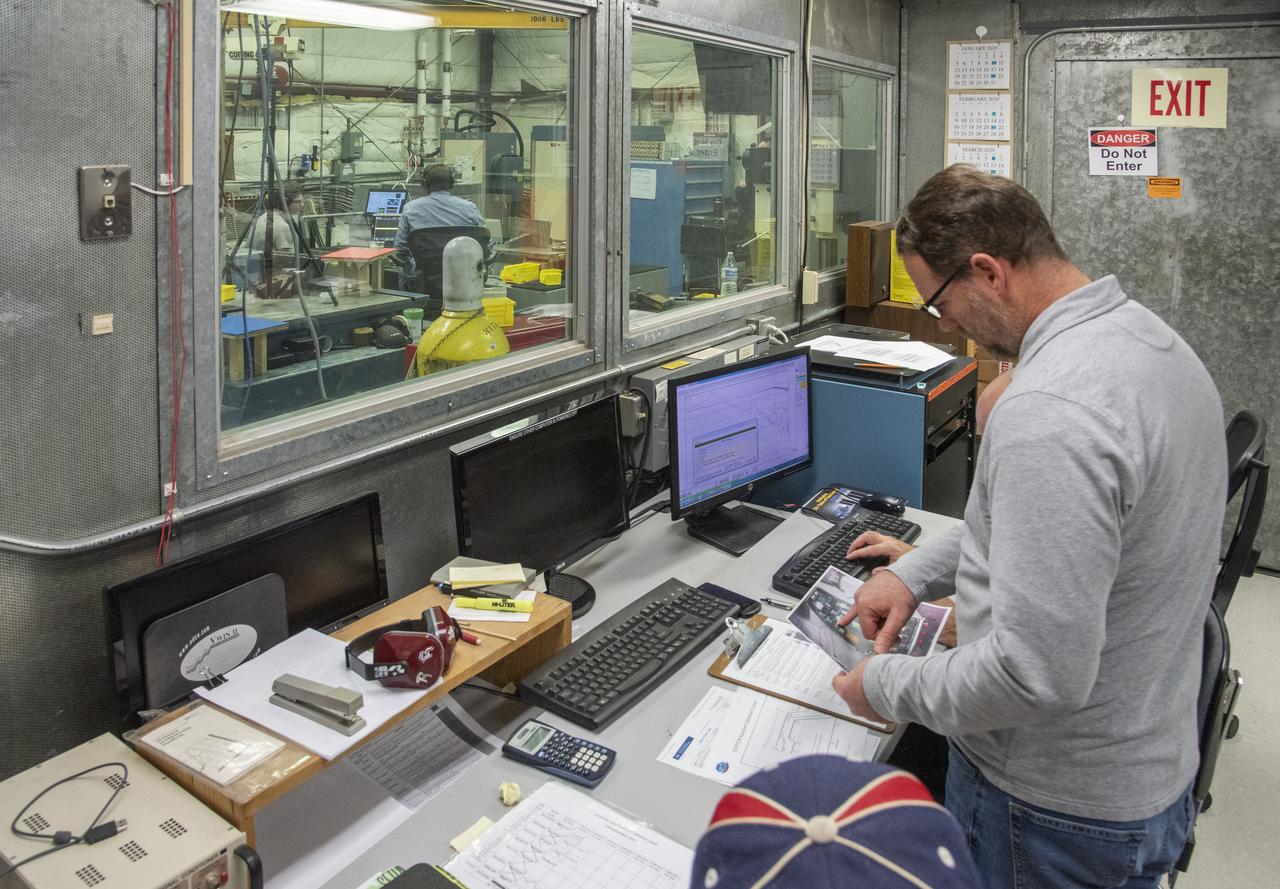
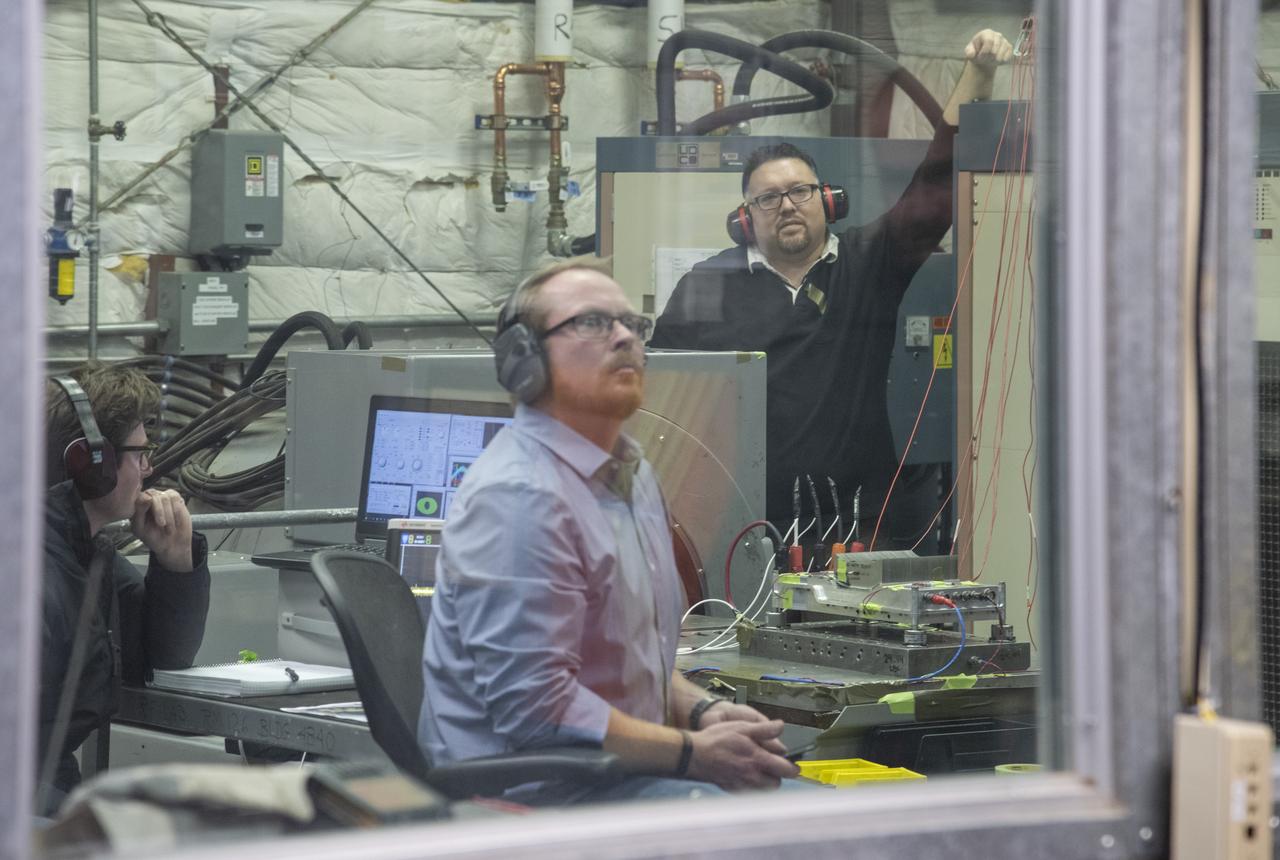
A cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane, undergoes vibration testing at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab. The cruise motor controller is exposed to two levels of vibration on three different axes, helping NASA to examine the integrity of the controller for flight conditions. The cruise motor controller will be a critical component for providing power to X-57’s motors when the aircraft takes to the skies in 2020.
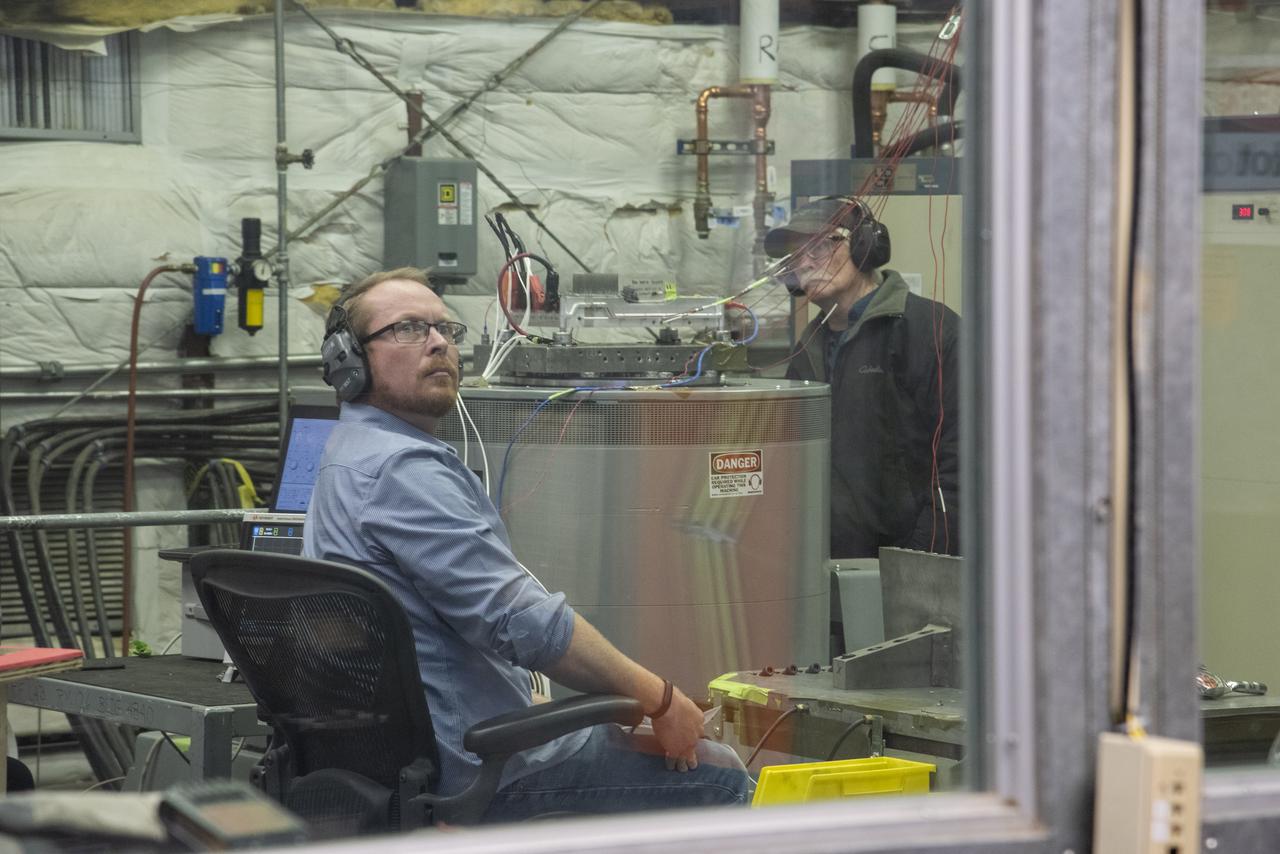

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
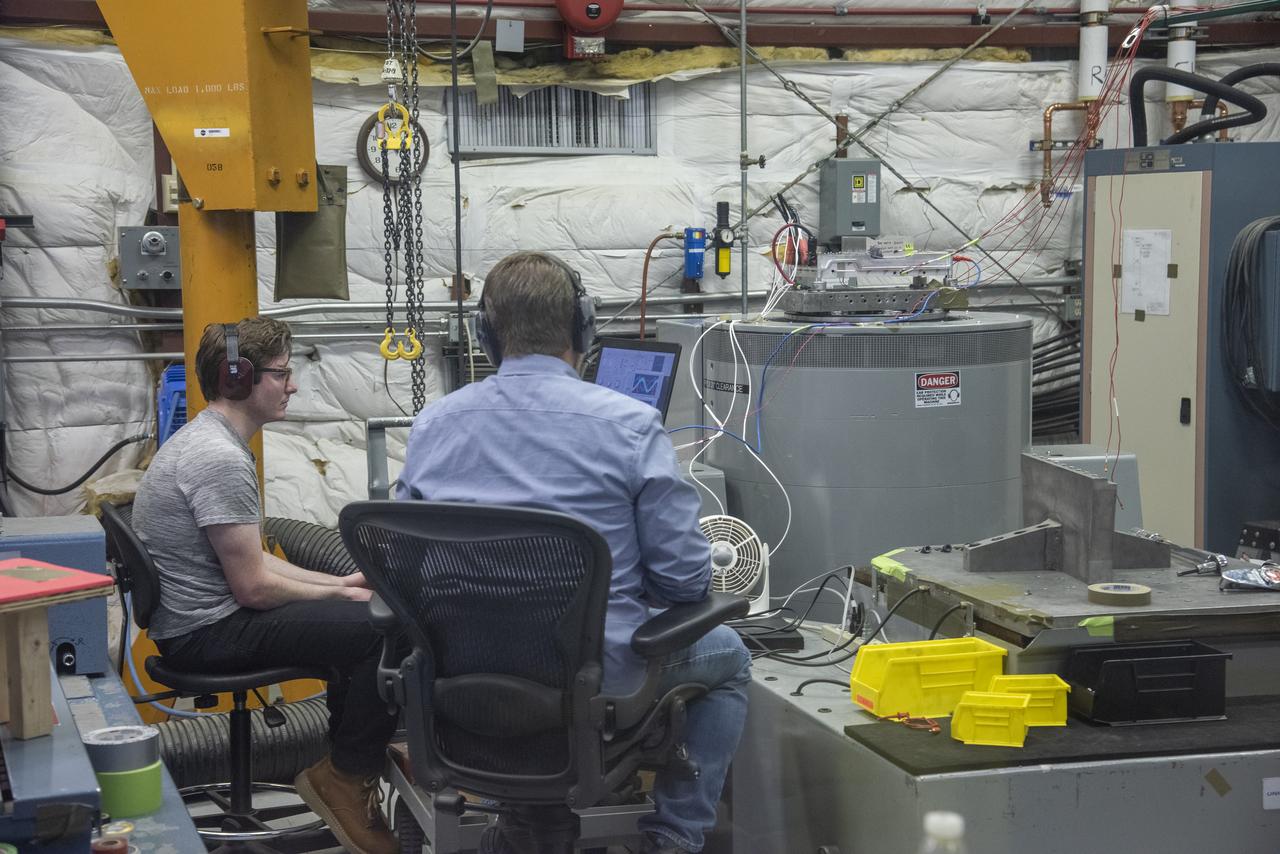
A cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane, undergoes vibration testing at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab. The cruise motor controller is exposed to two levels of vibration on three different axes, helping NASA to examine the integrity of the controller for flight conditions. The cruise motor controller will be a critical component for providing power to X-57's motors when the aircraft takes to the skies in 2020.
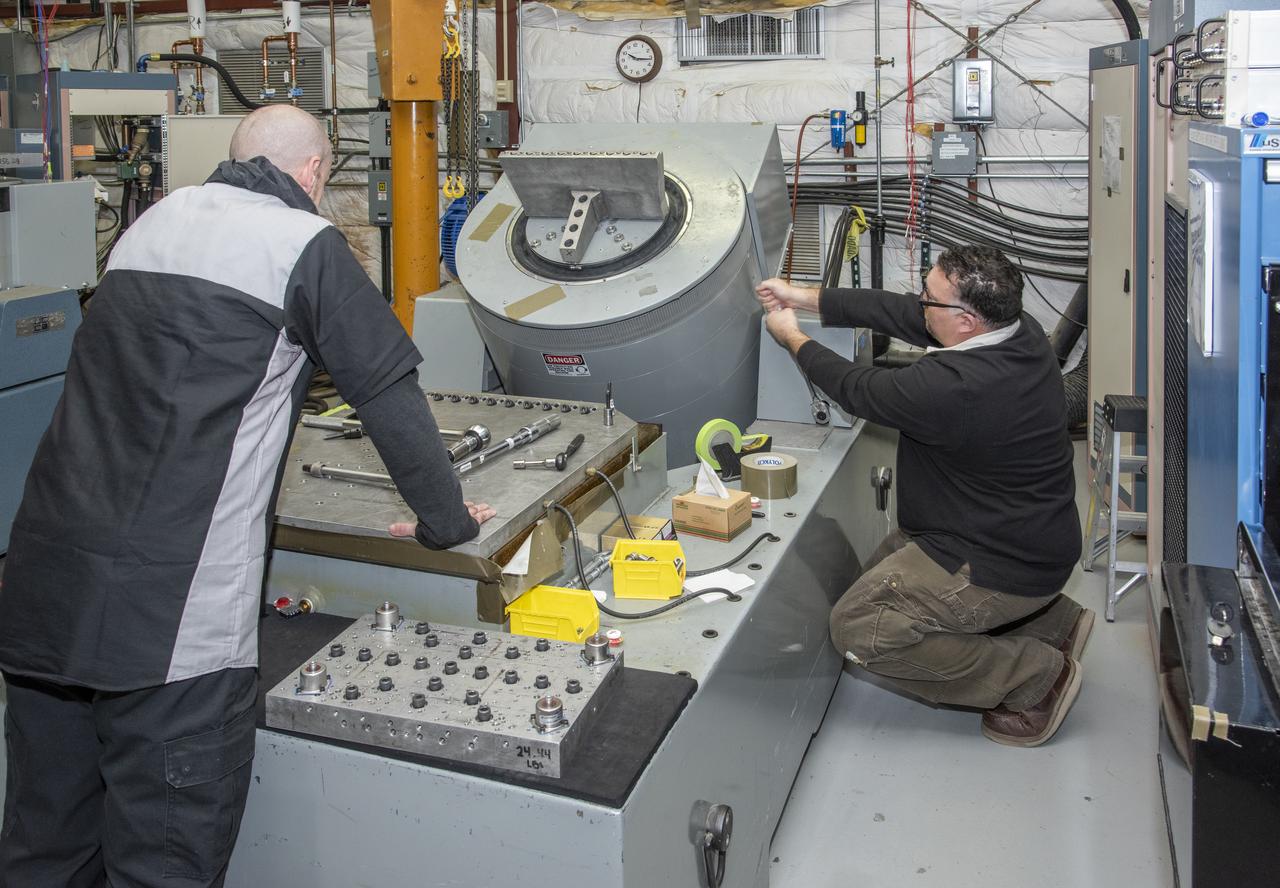

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
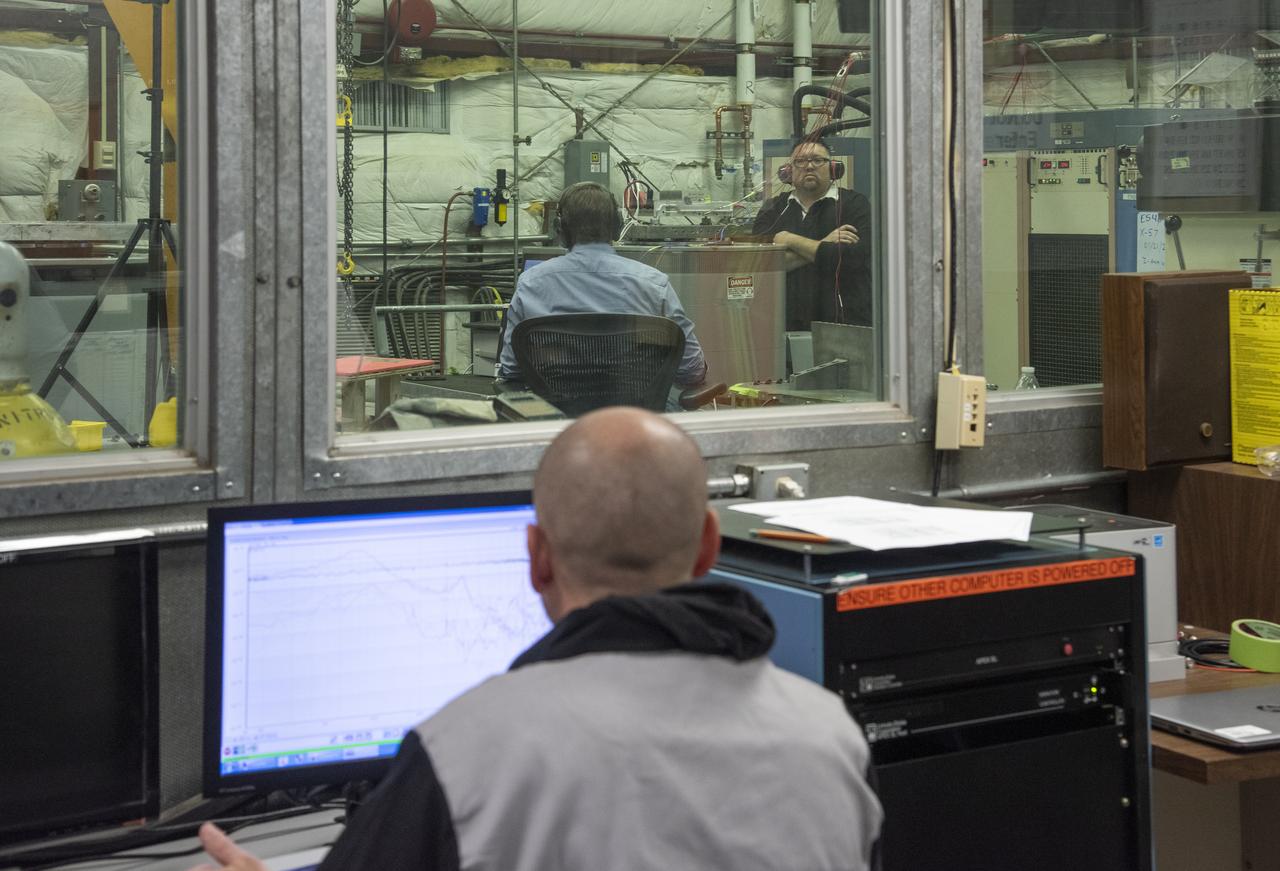

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
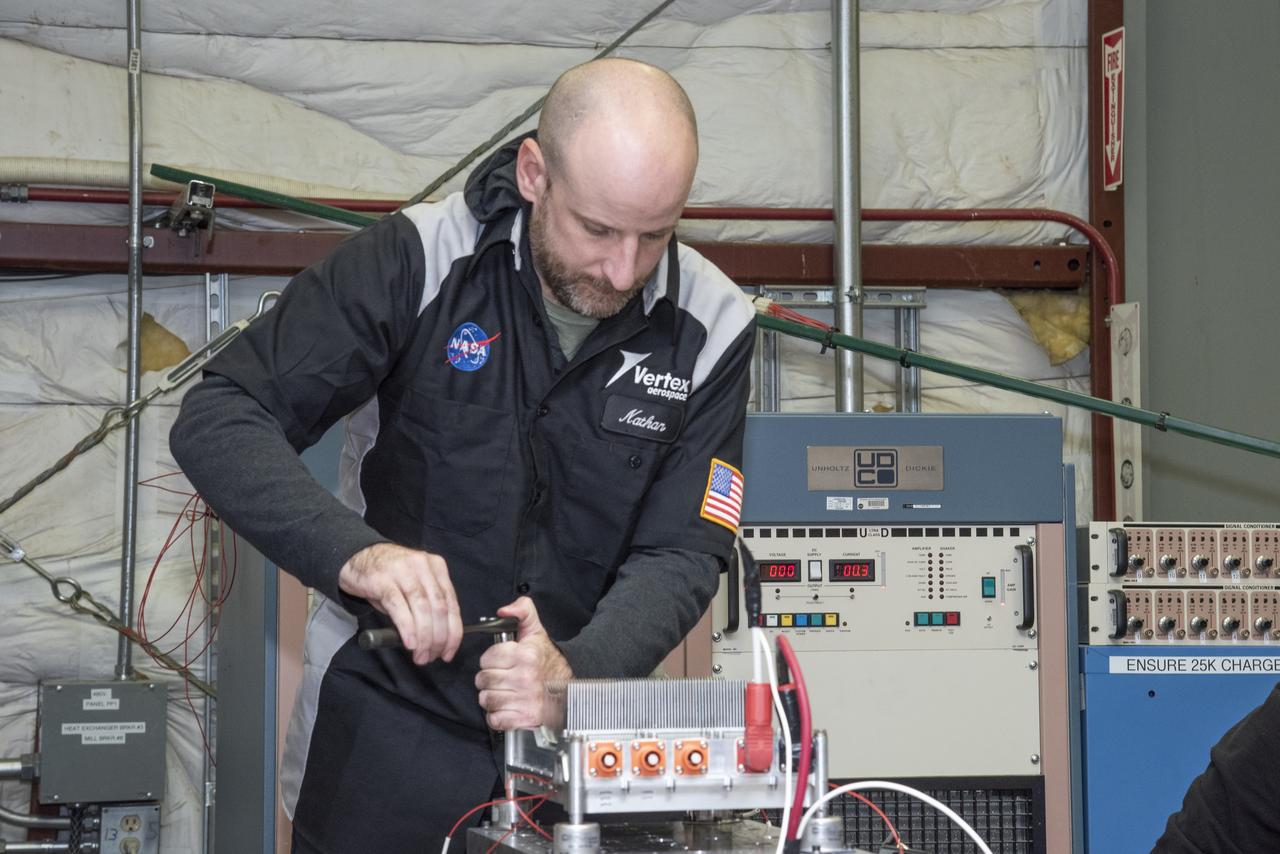

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
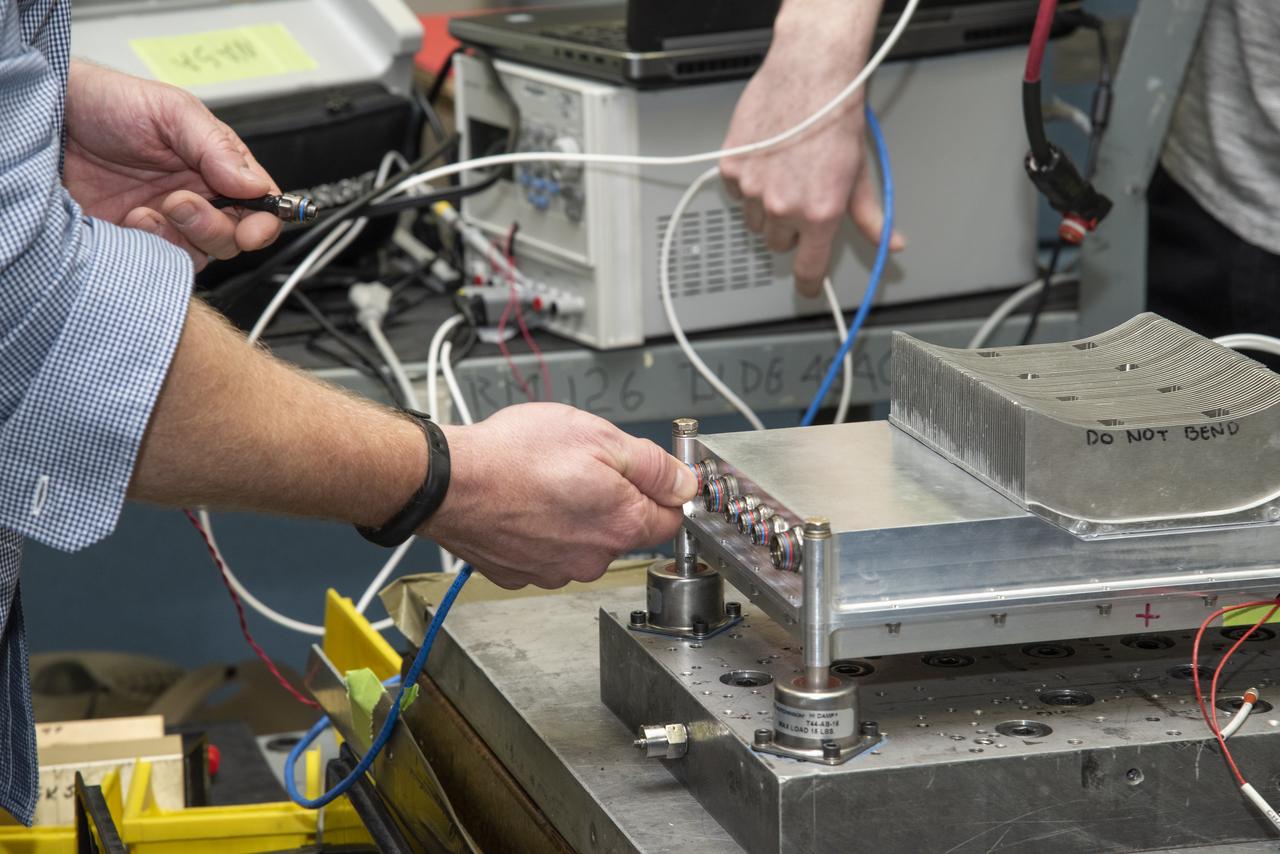
Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
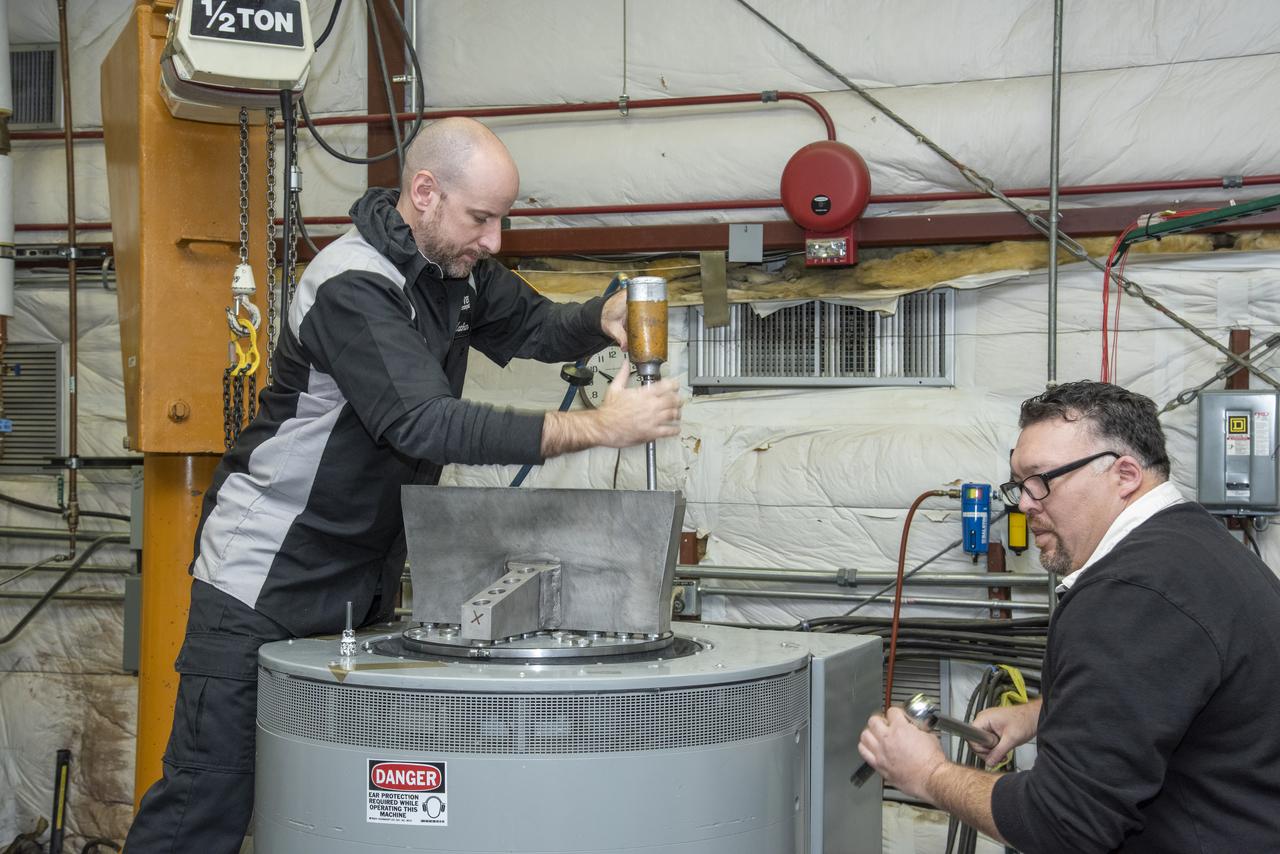

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
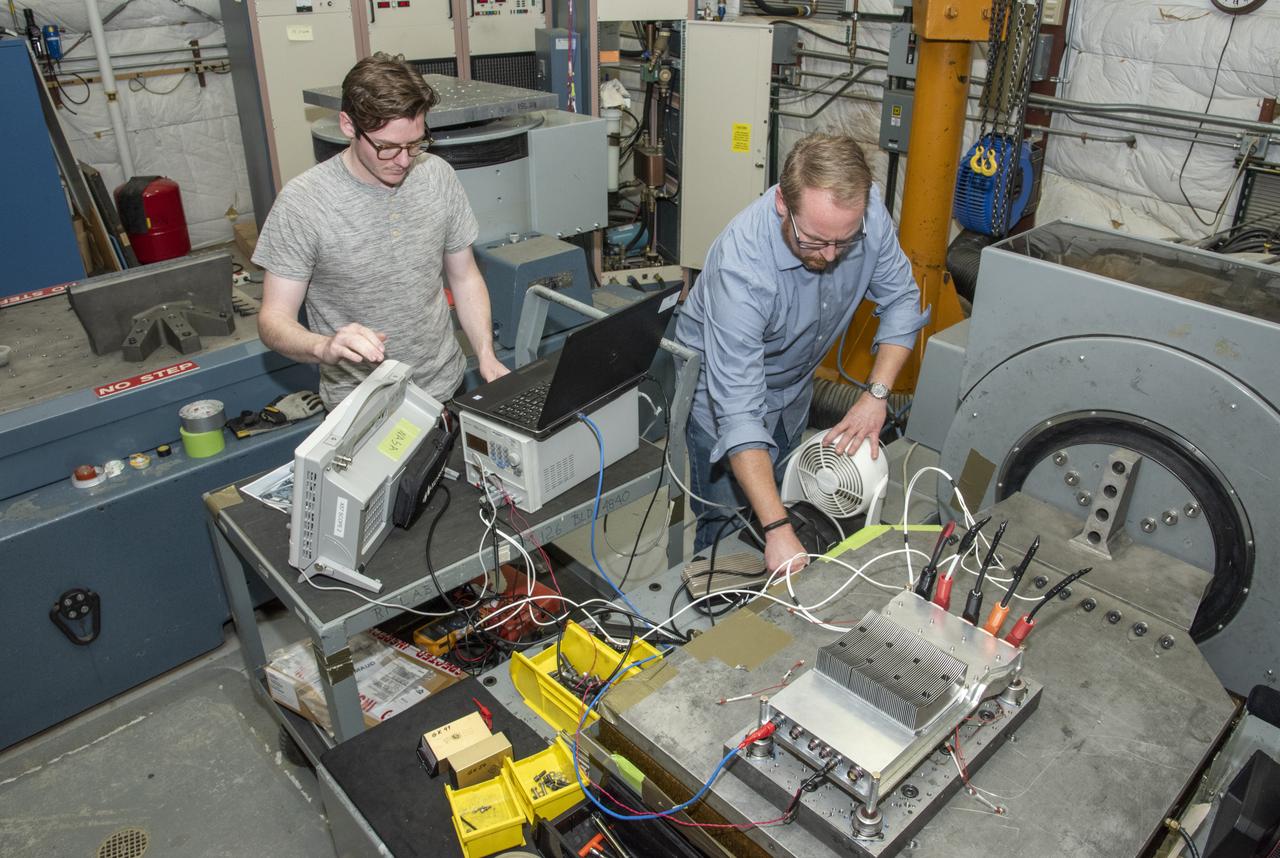

Engineers from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong’s environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project’s first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA’s first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
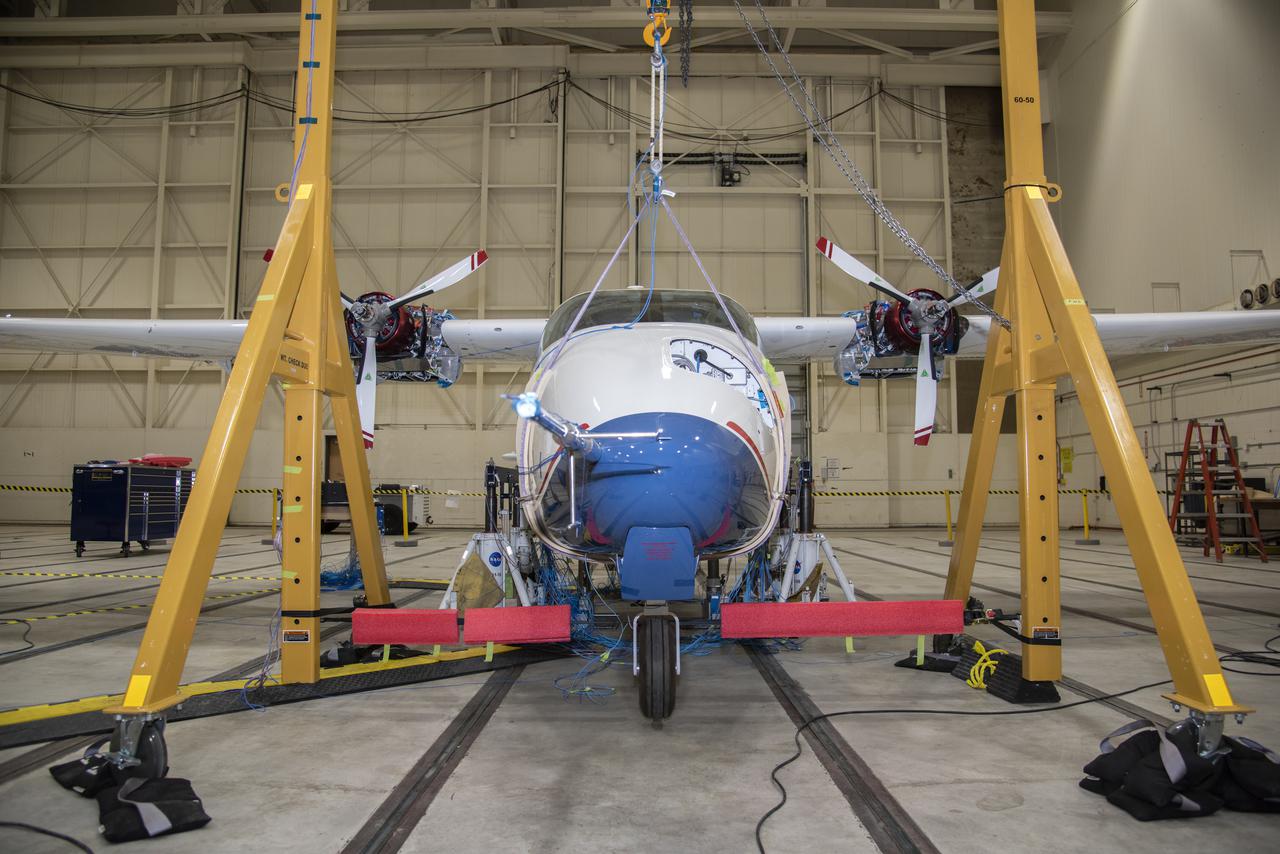

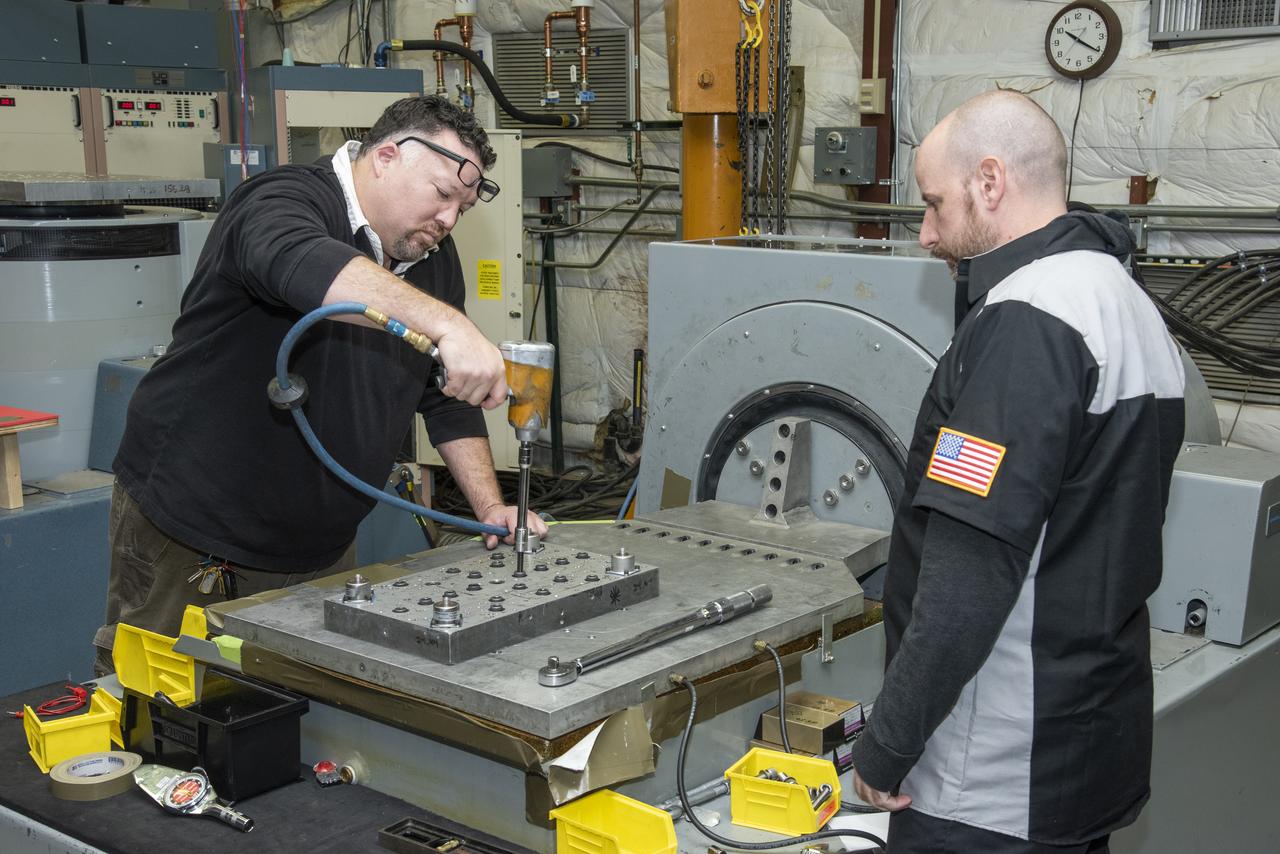
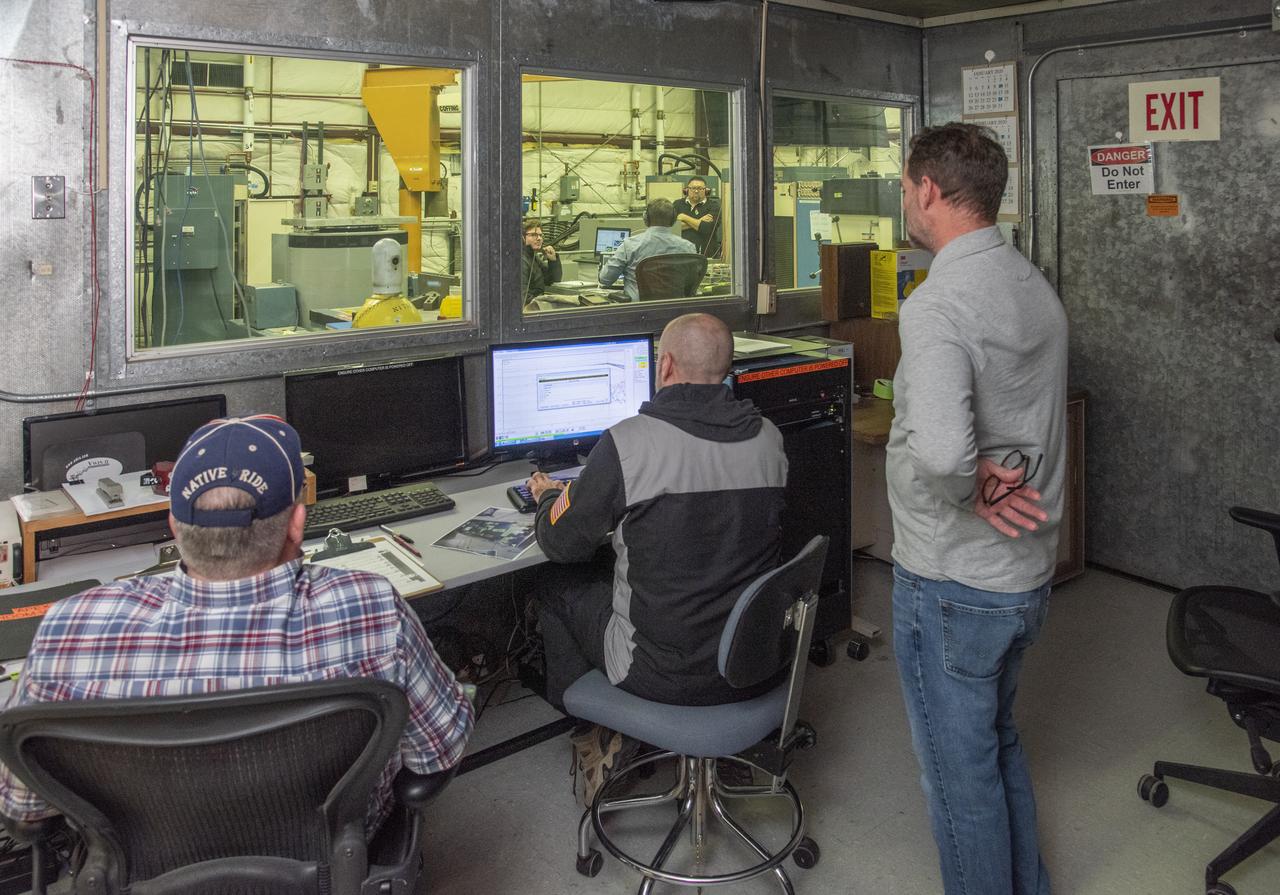
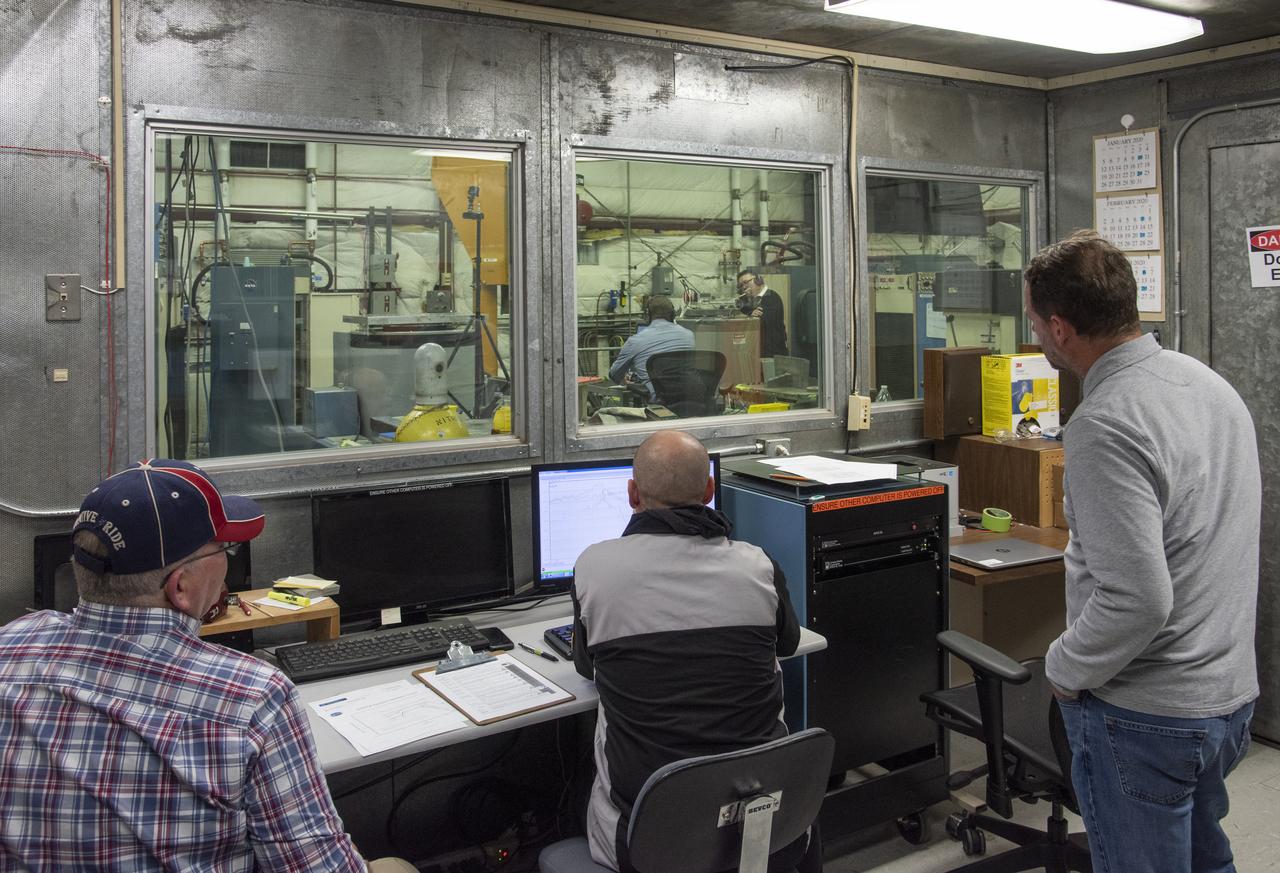
NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell prepares for ground vibration testing, or GVT, at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. Done in parallel with cruise motor controller testing, the GVT tested the vehicle at various vibration levels, helping engineers to examine and validate the integrity of the vehicle for flight conditions. A goal of X-57 is to help the Federal Aviation Administration set certification standards for emerging electric aircraft markets.
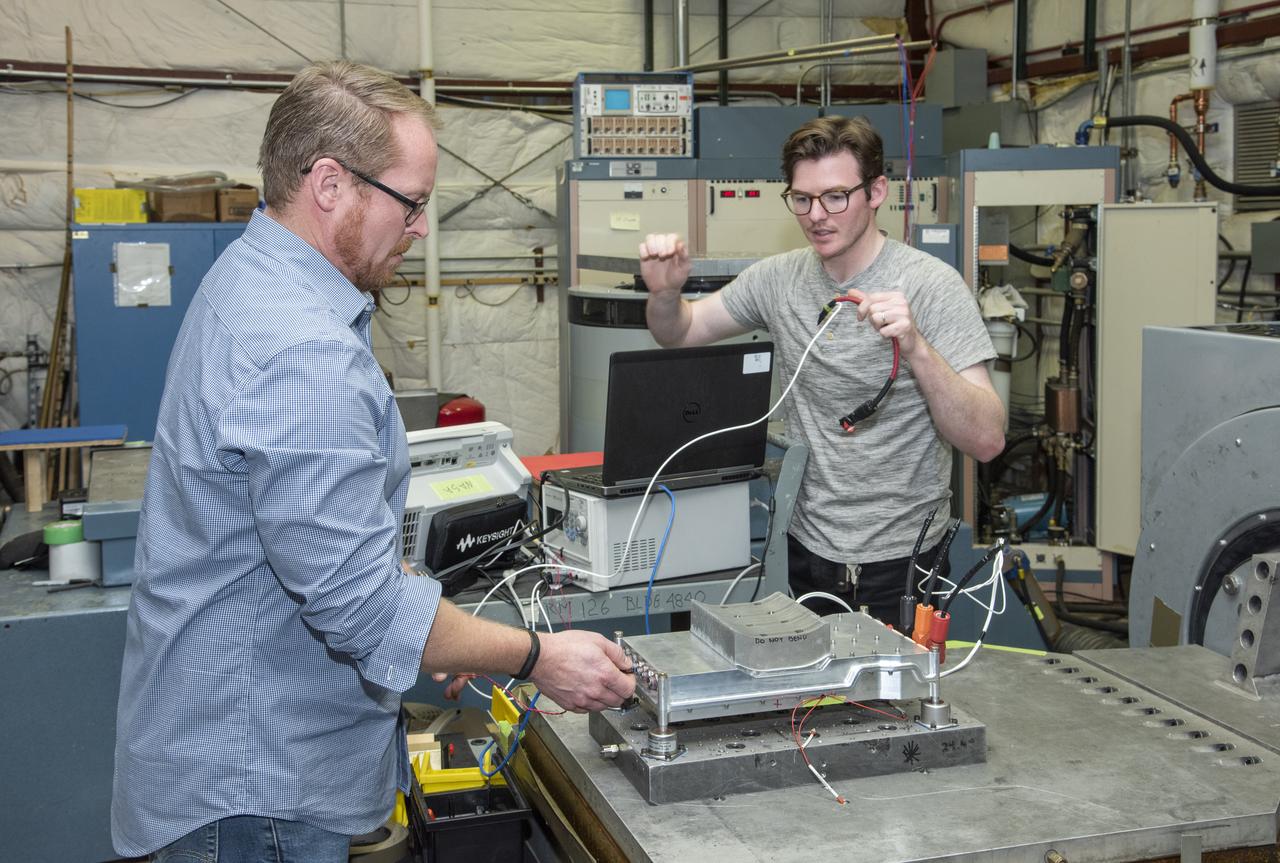

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

Engineers from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong’s environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project’s first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA’s first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong’s environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project’s first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA’s first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
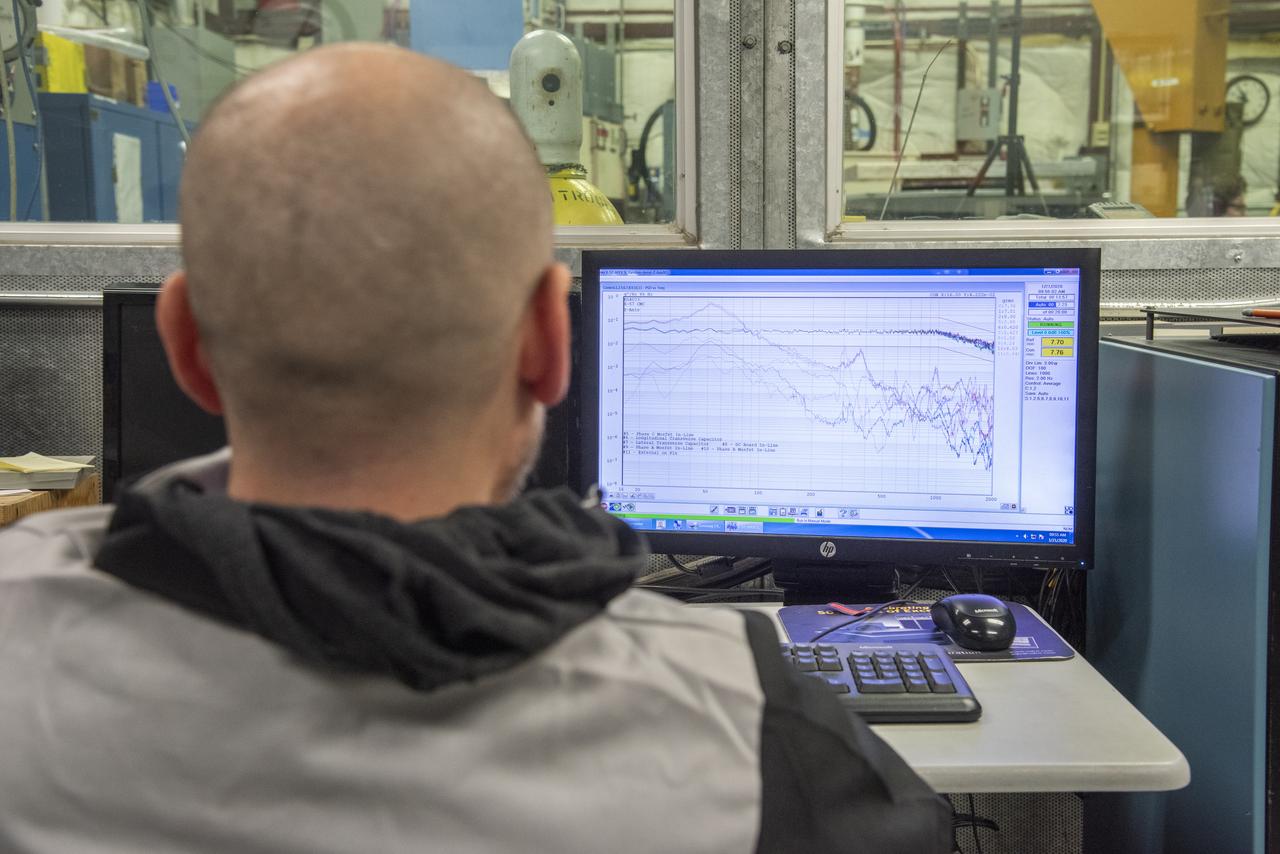

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

A cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane, undergoes vibration testing at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab. The cruise motor controller is exposed to two levels of vibration on three different axes, helping NASA to examine the integrity of the controller for flight conditions. The cruise motor controller will be a critical component for providing power to X-57's motors when the aircraft takes to the skies in 2020.
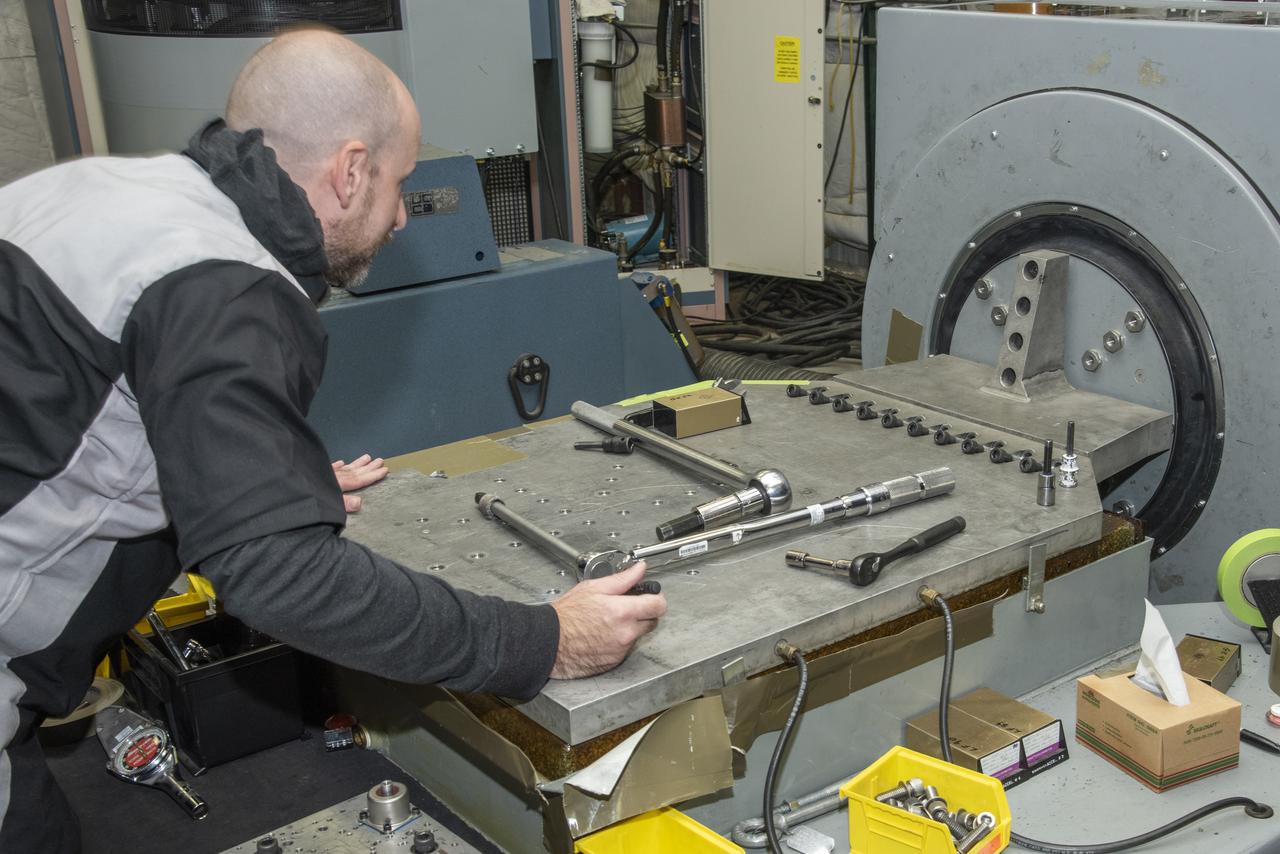

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

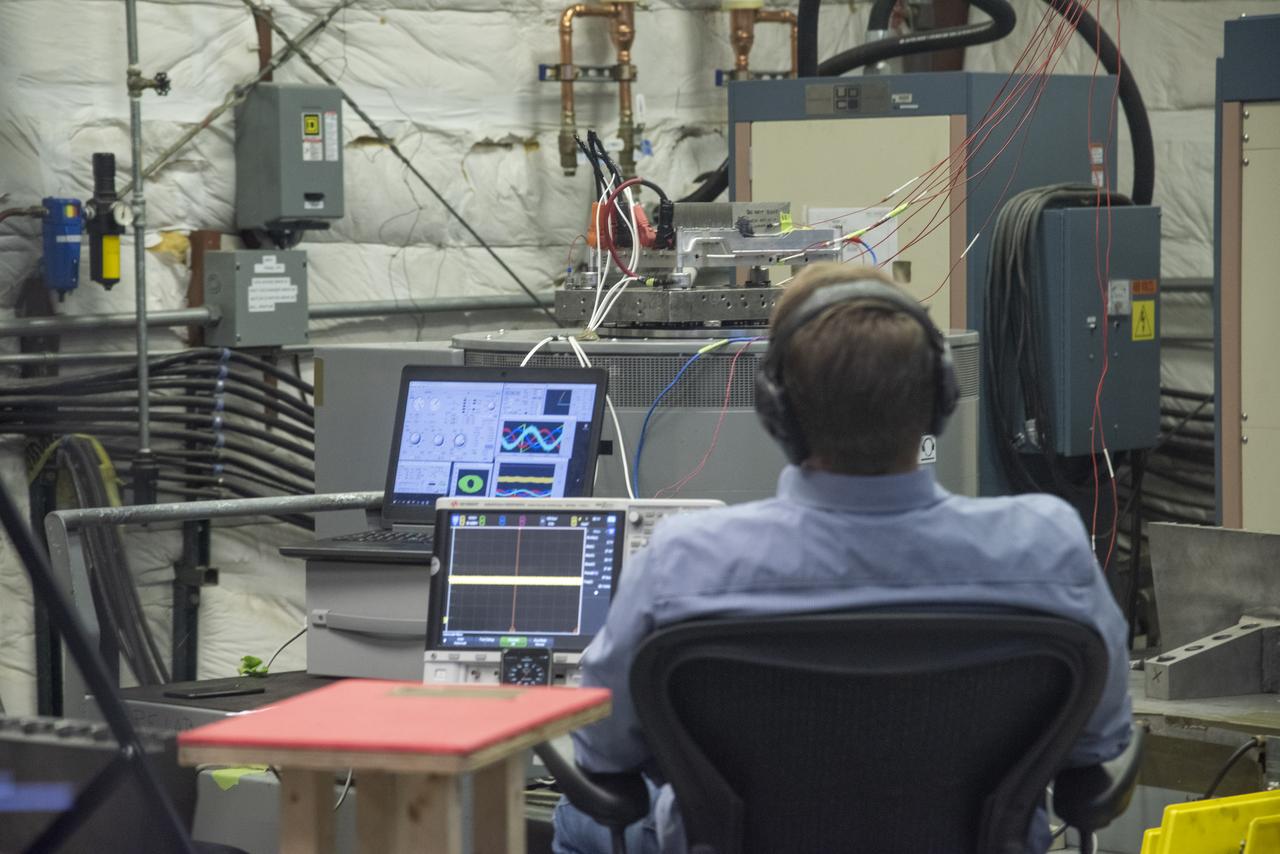
Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
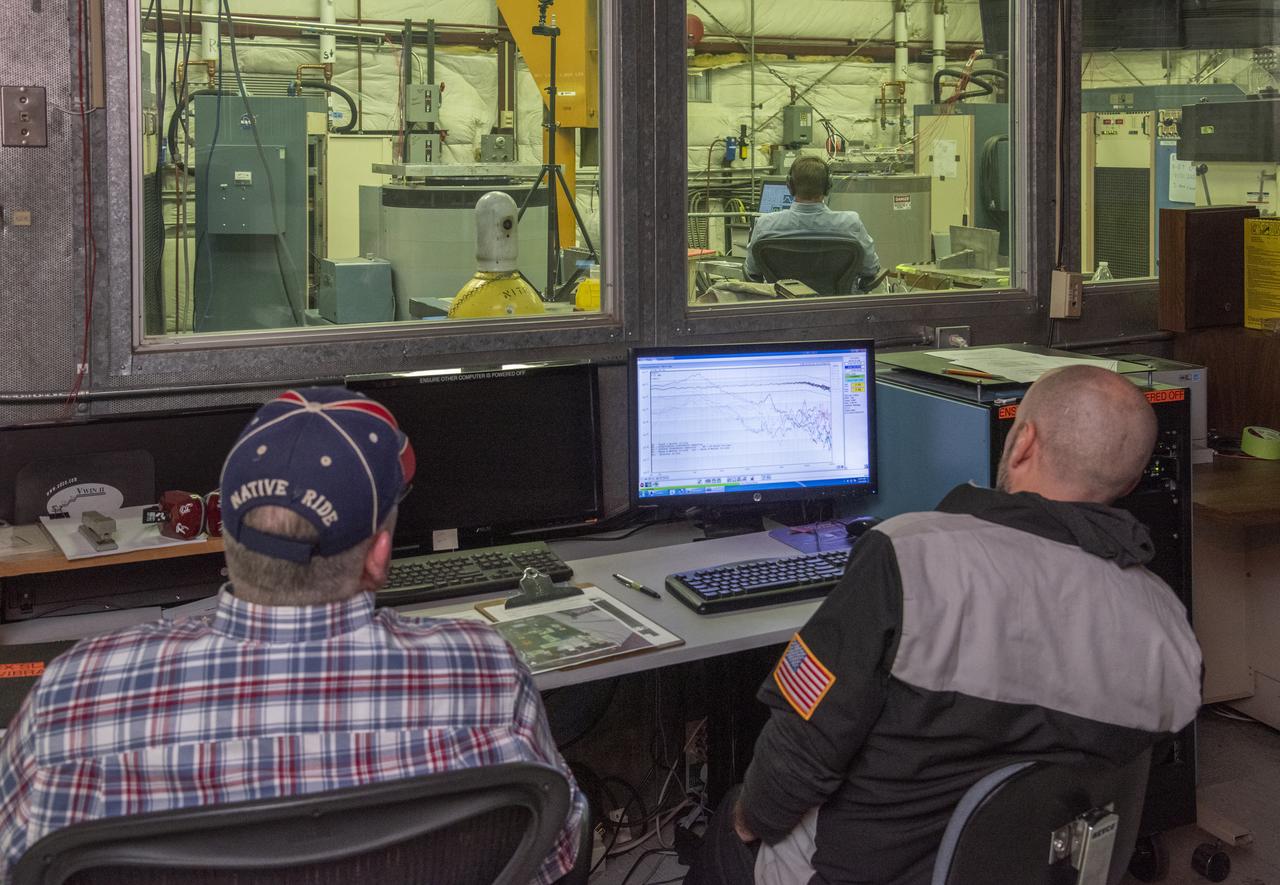

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
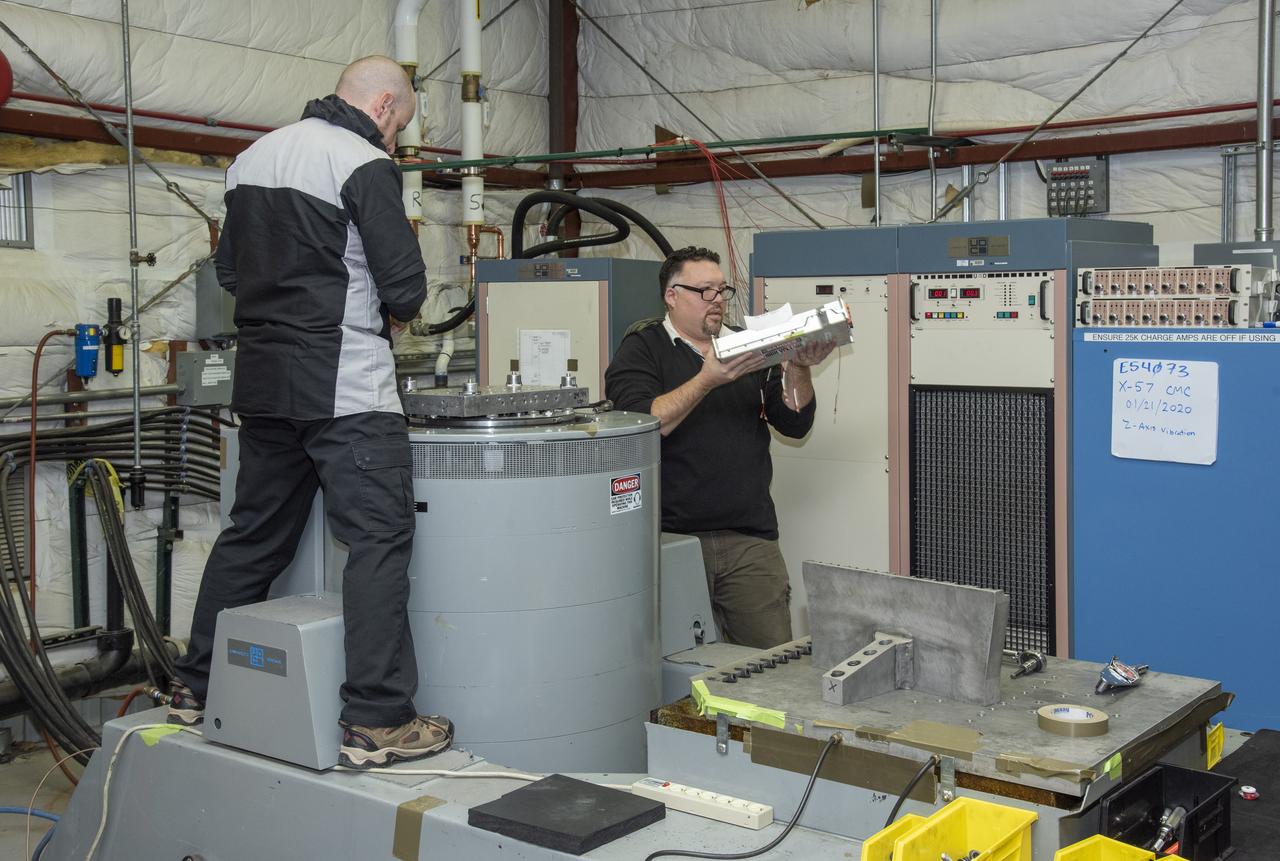

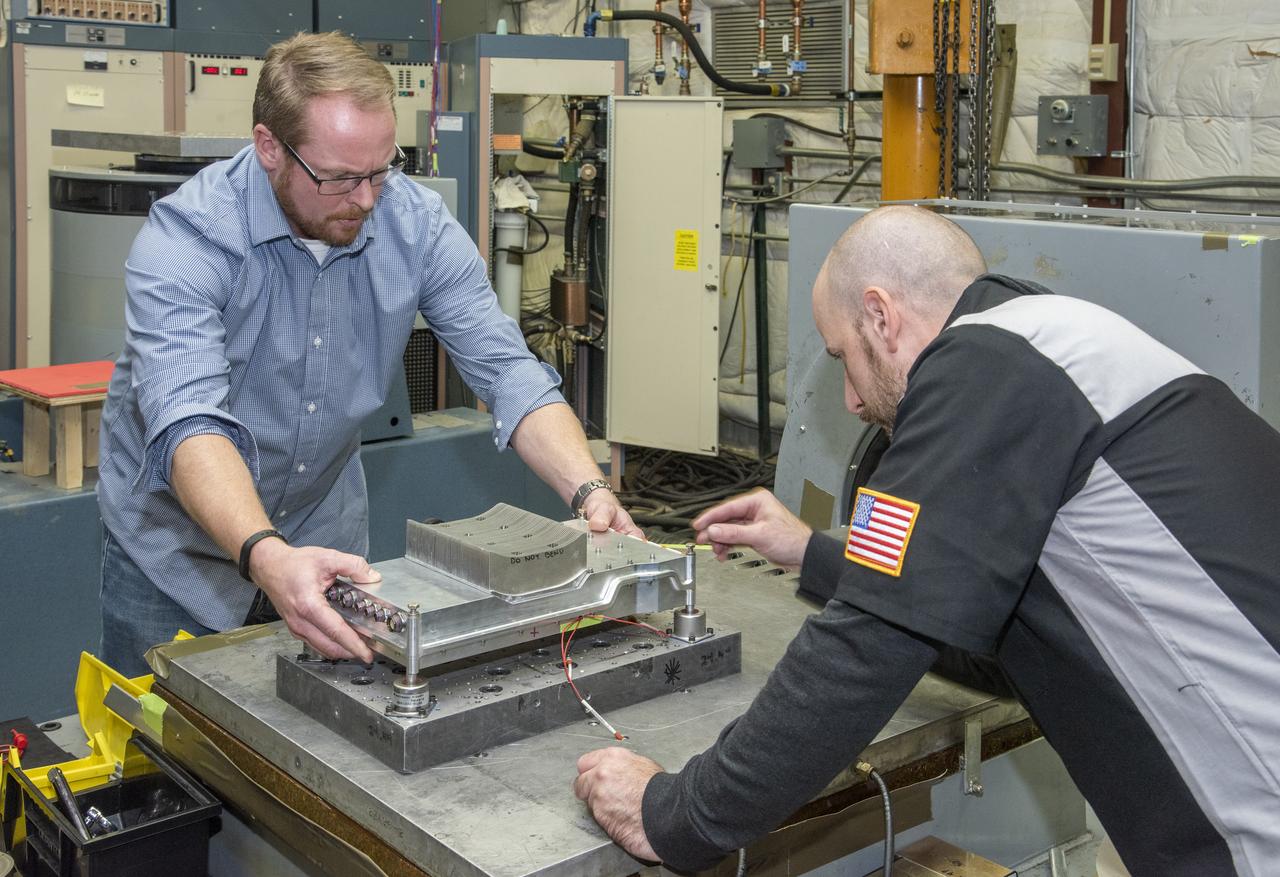
Engineers from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong’s environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project’s first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA’s first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
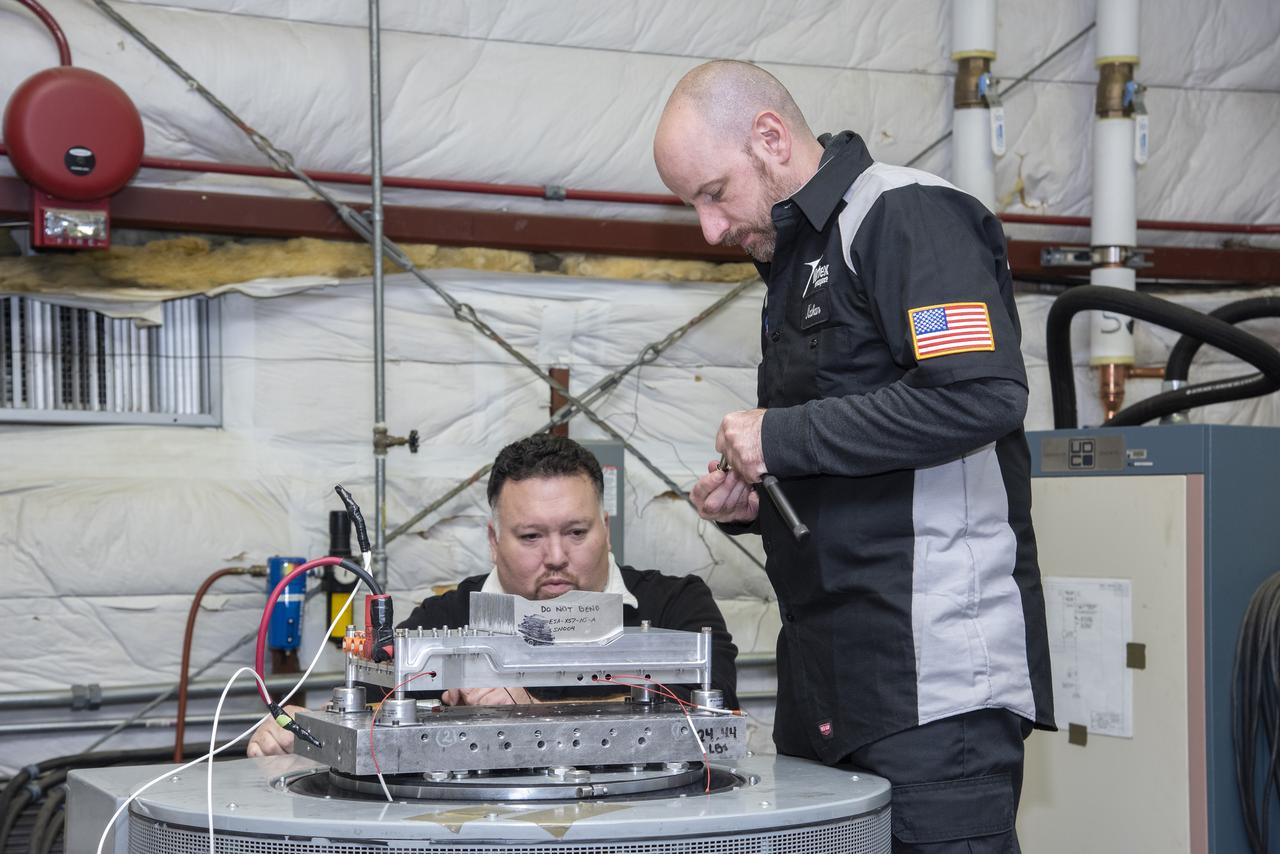

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
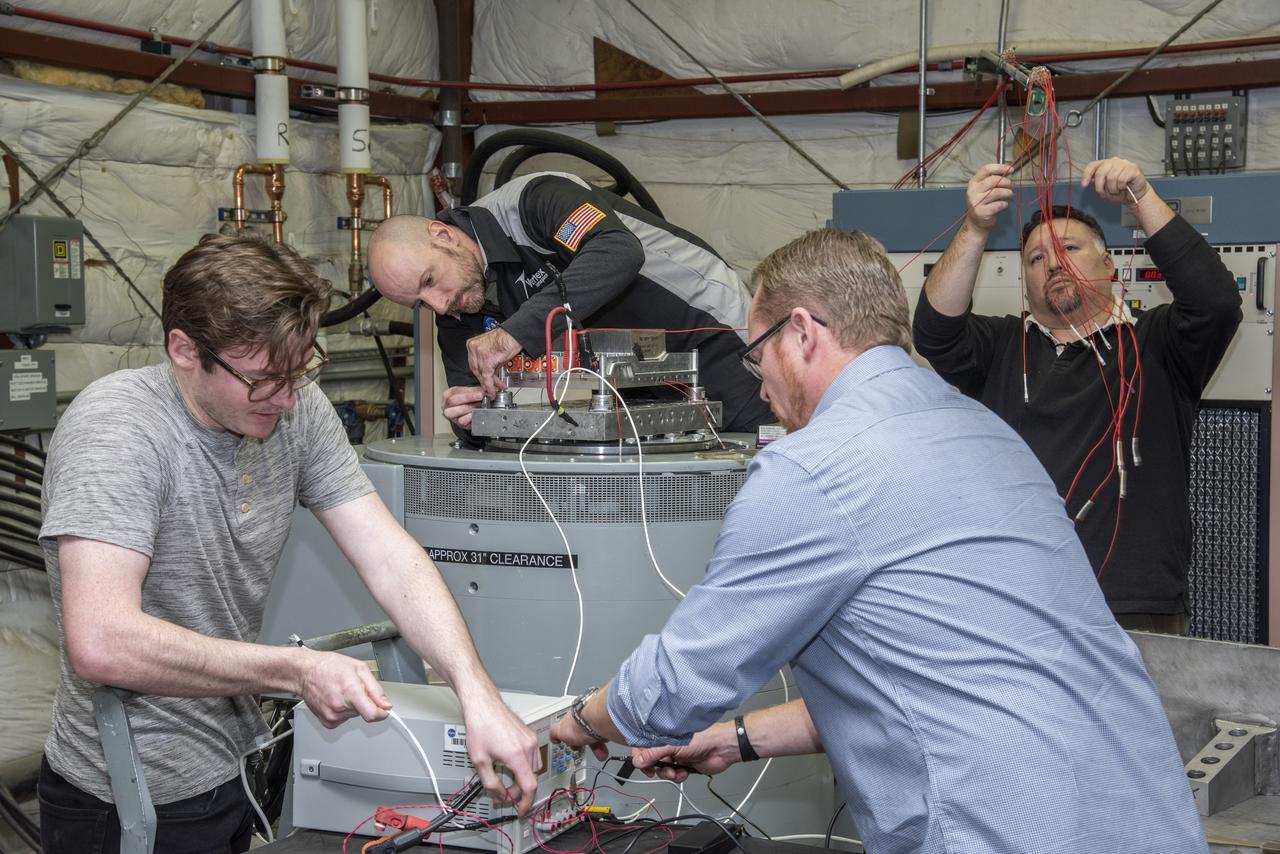

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
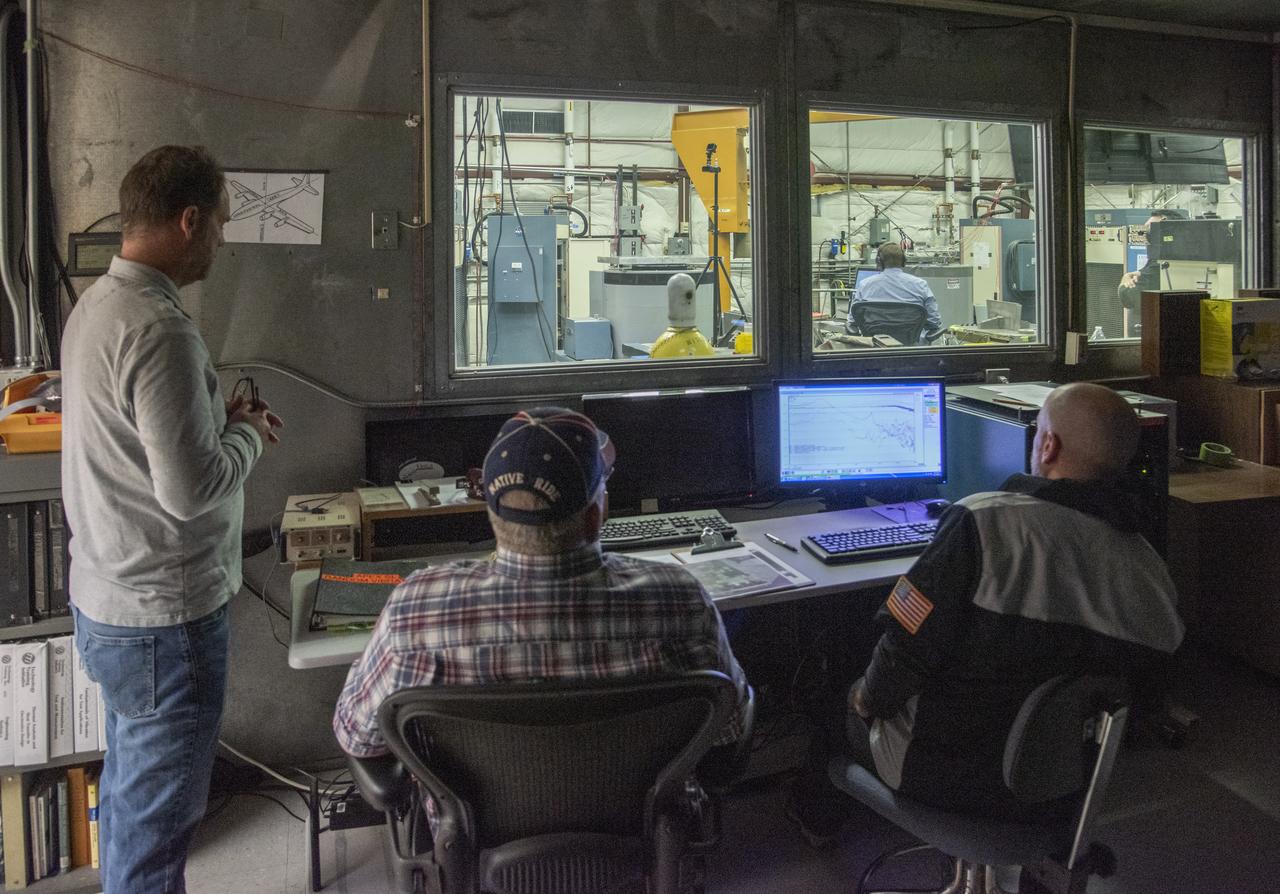

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
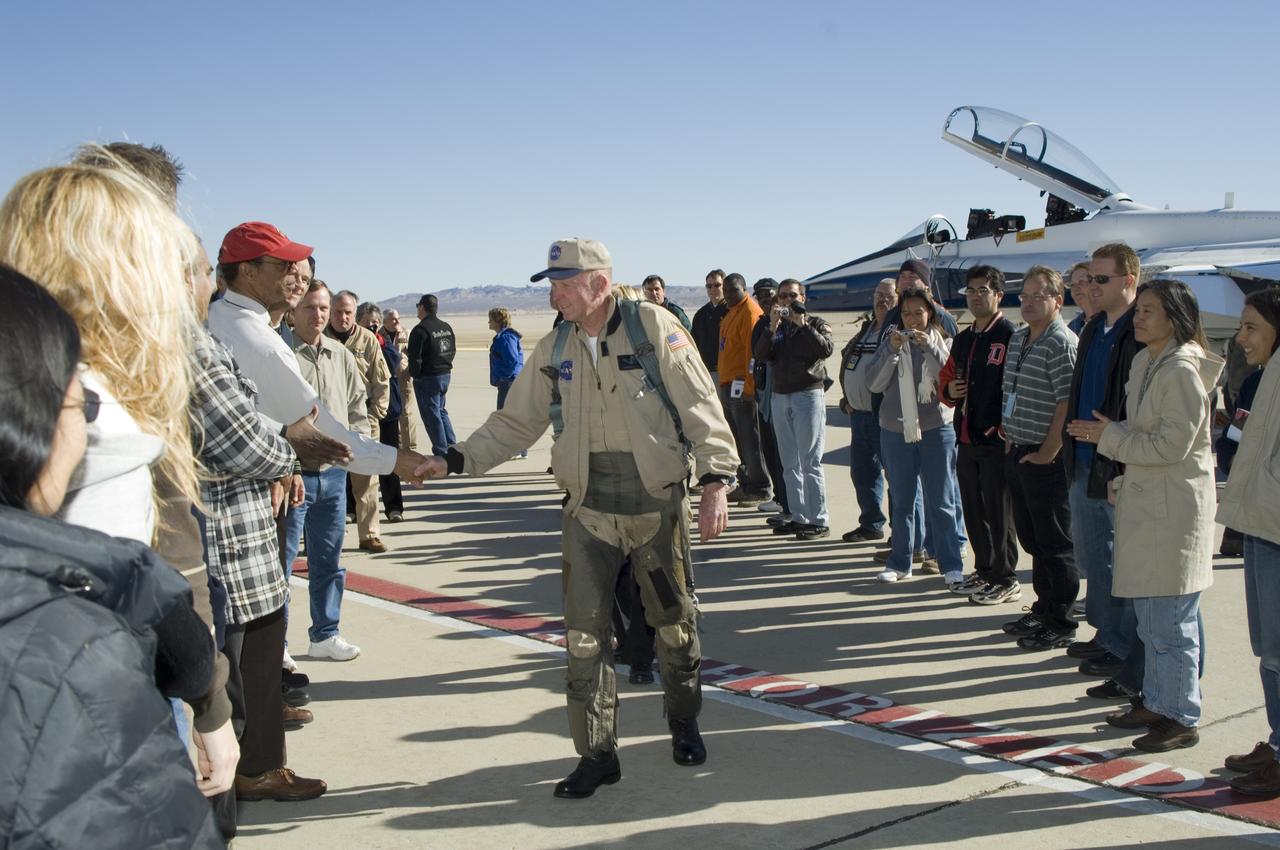

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
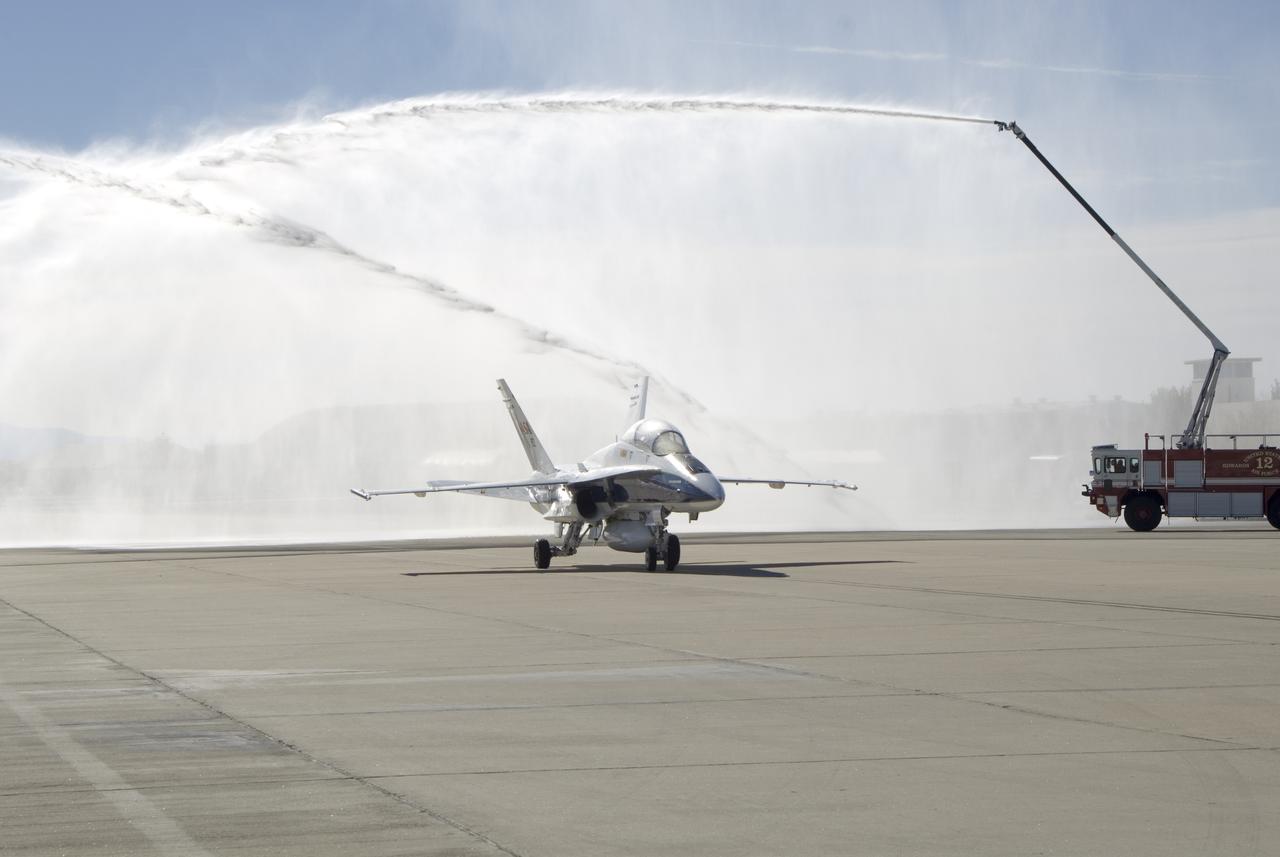

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
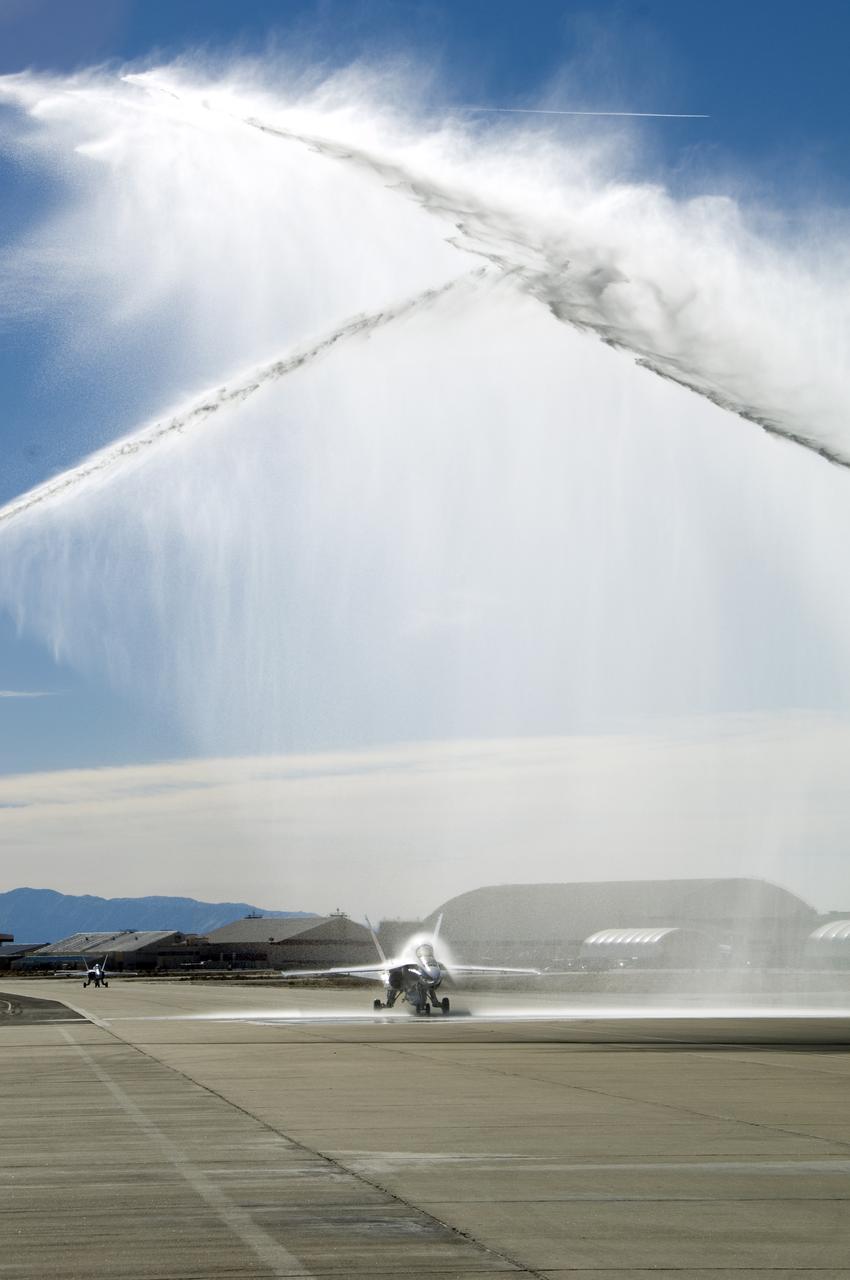

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of sp

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
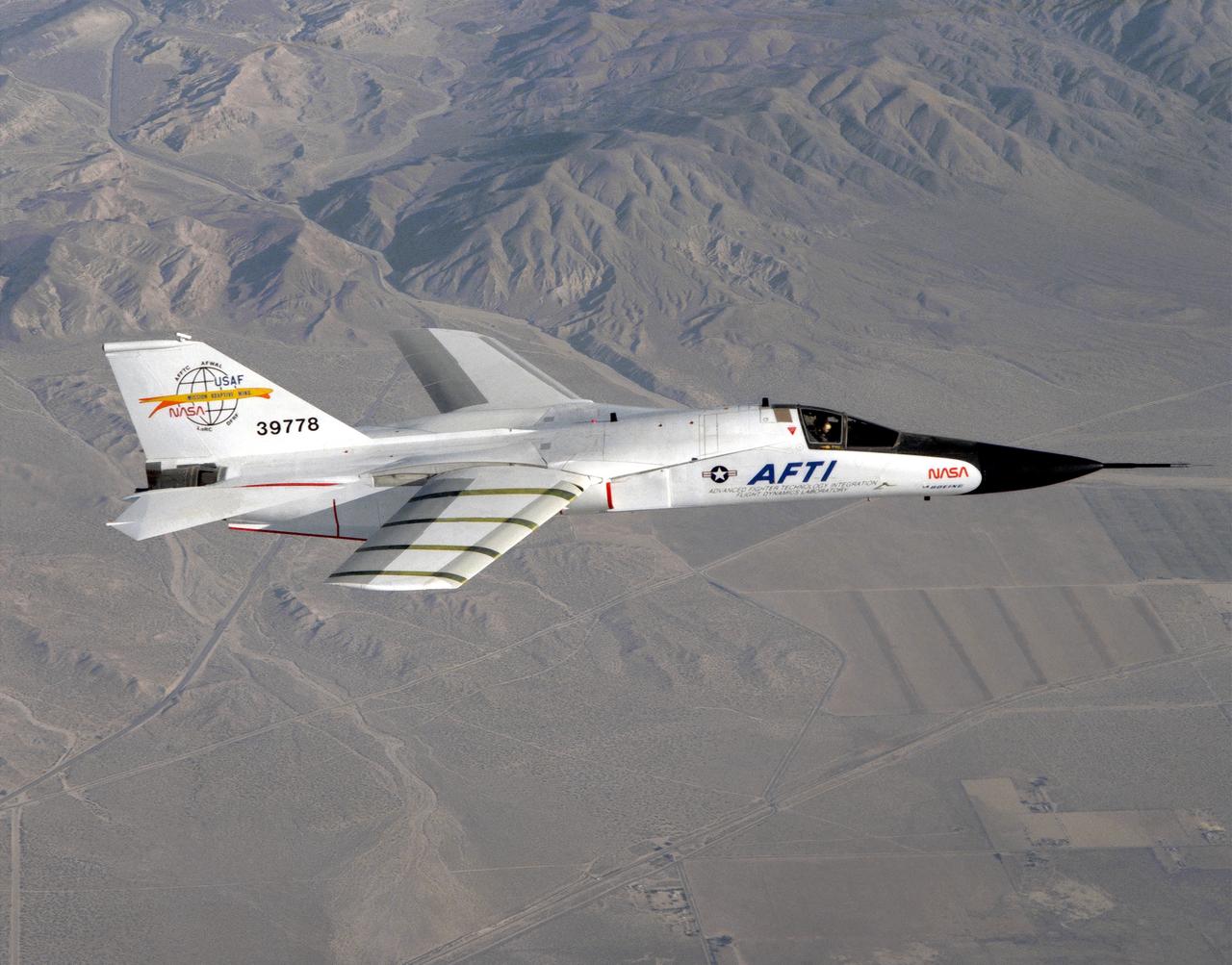

This photograph shows a modified General Dynamics AFTI/F-111A Aardvark with supercritical mission adaptive wings (MAW) installed. The four dark bands on the right wing are the locations of pressure orifices used to measure surface pressures and shock locations on the MAW. The El Paso Mountains and Red Rock Canyon State Park Califonia, about 30 miles northwest of Edwards Air Force Base, are seen directly in the background. With the phasing out of the TACT program came a renewed effort by the Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory to extend supercritical wing technology to a higher level of performance. In the early 1980s the supercritical wing on the F-111A aircraft was replaced with a wing built by Boeing Aircraft Company System called a “mission adaptive wing” (MAW), and a joint NASA and Air Force program called Advanced Fighter Technology Integration (AFTI) was born.
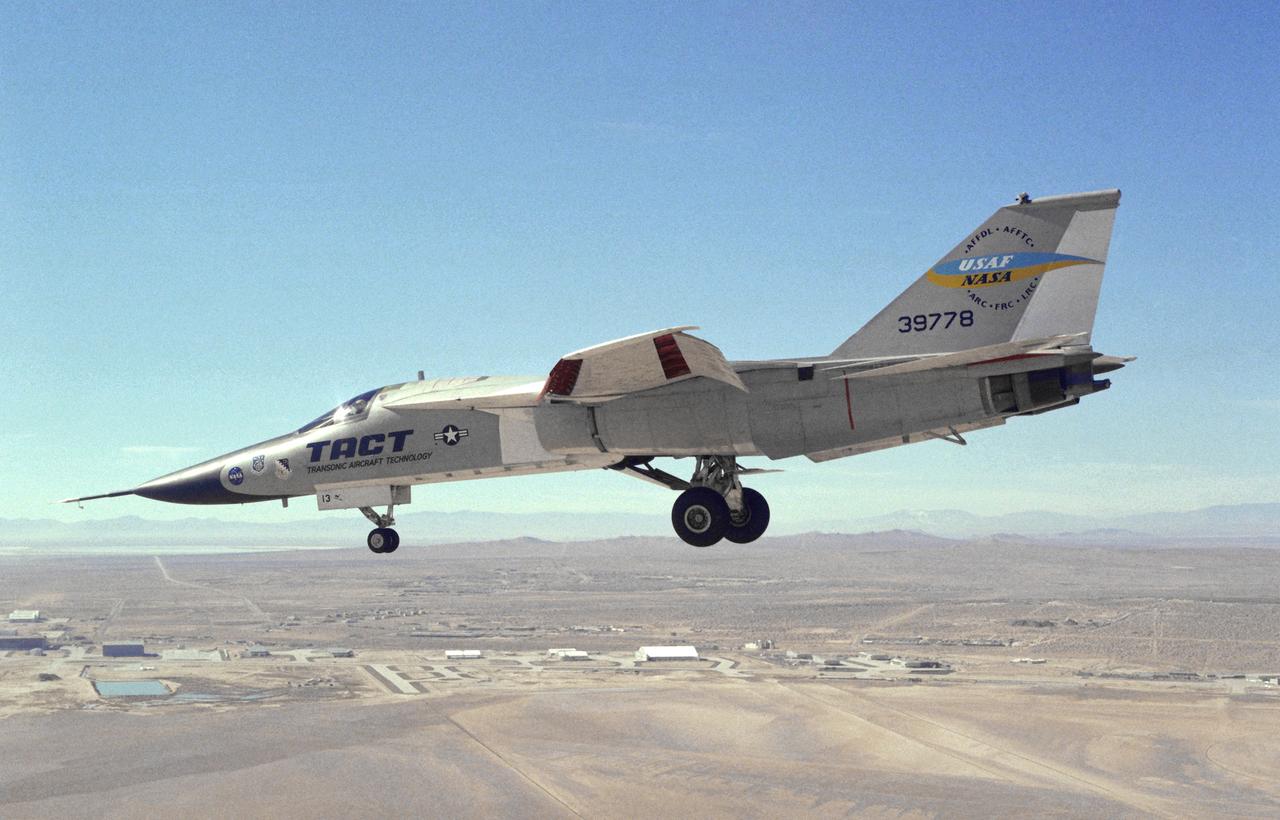

This photograph shows a modified General Dynamics TACT/F-111A Aardvaark with supercritical wings installed. The aircraft, with flaps and landing gear down, is in a decending turn over Rogers Dry Lakebed at Edwards Air Force Base. Starting in 1971 the NASA Flight Research Center and the Air Force undertook a major research and flight testing program, using F-111A (#63-9778), which would span almost 20 years before completion. Intense interest over the results coming from the NASA F-8 supercritical wing program spurred NASA and the Air Force to modify the General Dynamics-Convair F-111A to explore the application of supercritical wing technology to maneuverable military aircraft. This flight program was called Transonic Aircraft Technology (TACT).
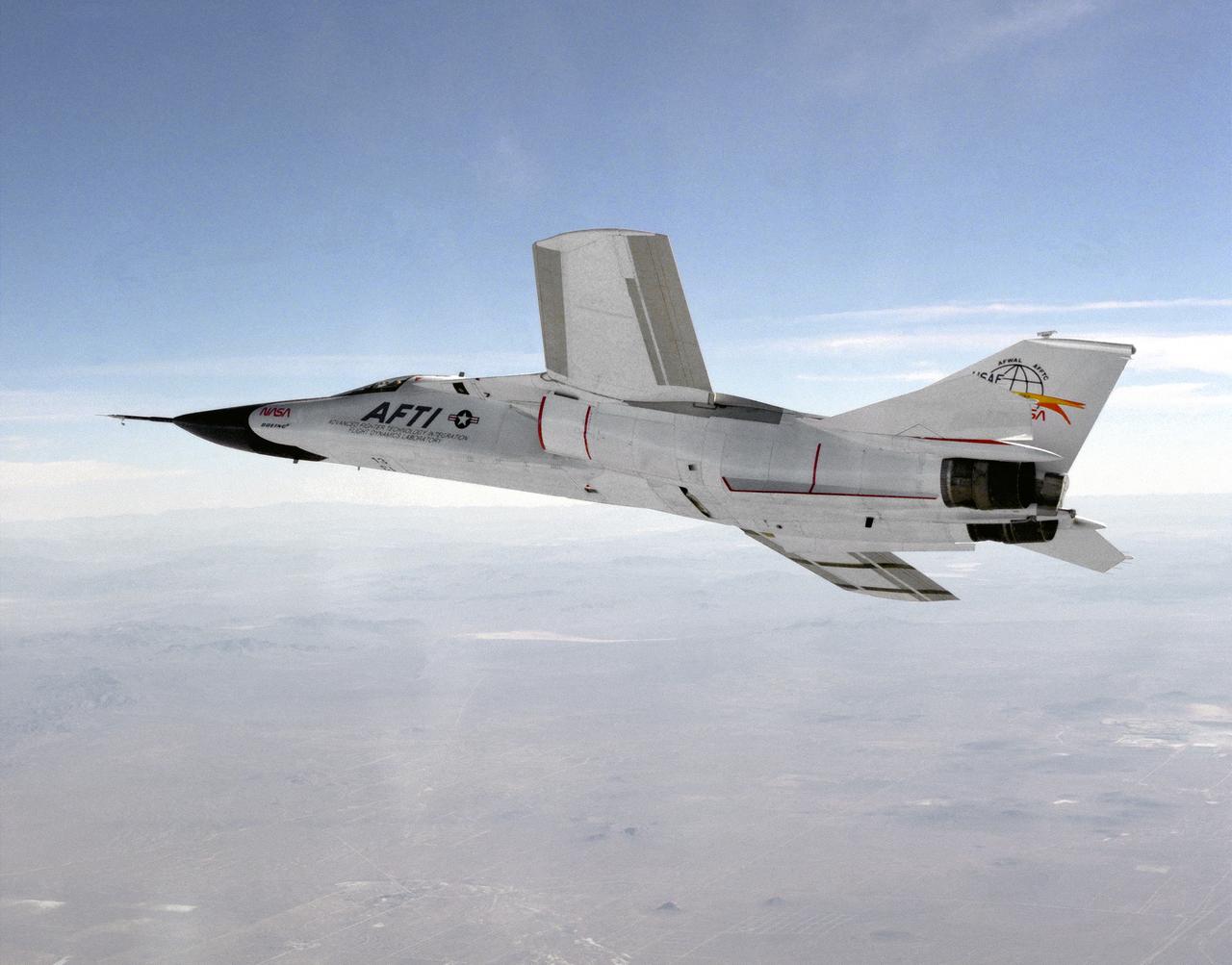

This photograph shows a modified General Dynamics AFTI/F-111A Aardvark with supercritical mission adaptive wings (MAW) installed. The AFTI/F111A is seen banking towards Rodgers Dry Lake and Edwards Air Force Base. With the phasing out of the TACT program came a renewed effort by the Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory to extend supercritical wing technology to a higher level of performance. In the early 1980s the supercritical wing on the F-111A aircraft was replaced with a wing built by Boeing Aircraft Company System called a “mission adaptive wing” (MAW), and a joint NASA and Air Force program called Advanced Fighter Technology Integration (AFTI) was born.
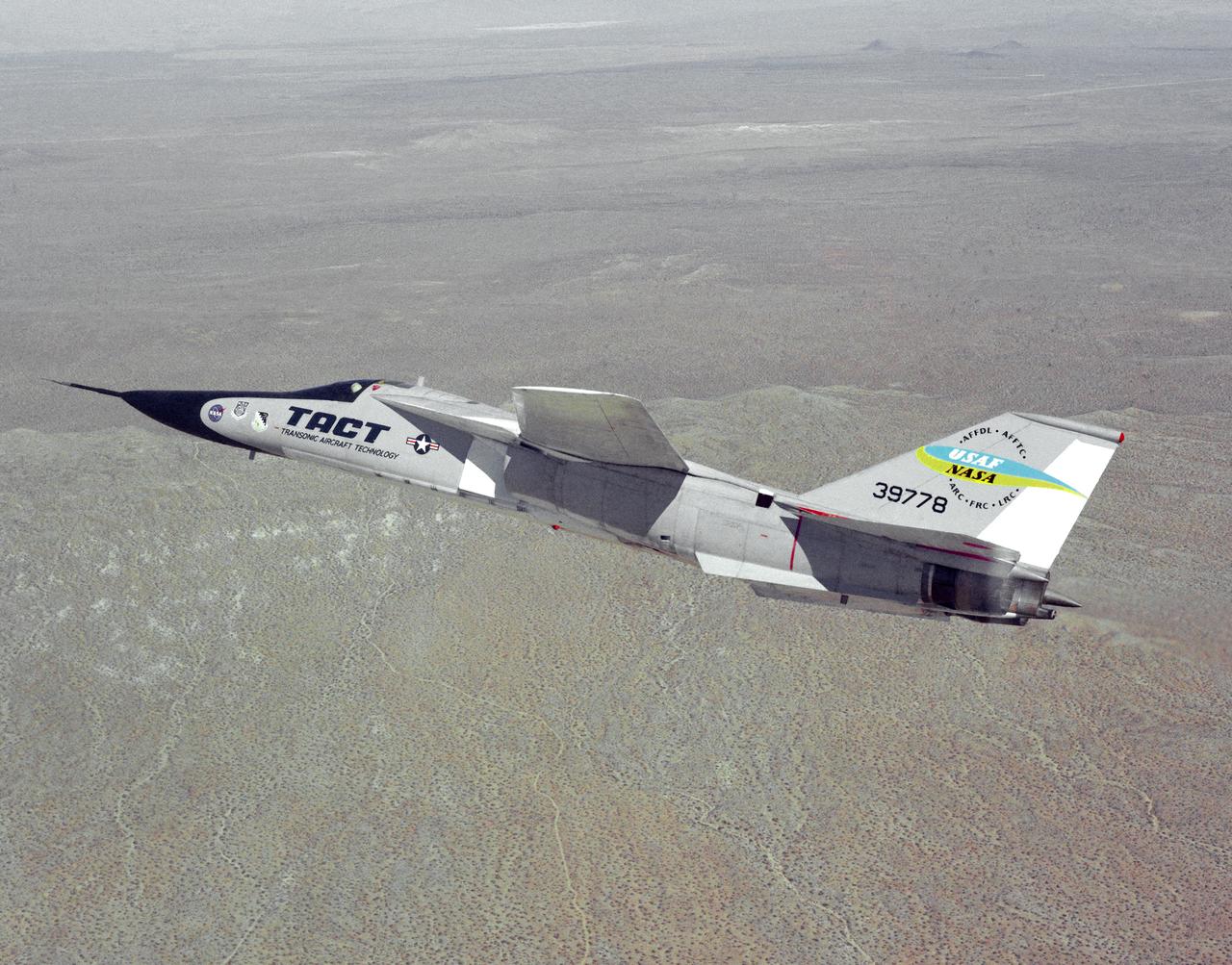

The General Dynamics TACT/F-111A Aardvark is seen In a banking-turn over the California Mojave desert. This photograph affords a good view of the supercritical wing airfoil shape. Starting in 1971 the NASA Flight Research Center and the Air Force undertook a major research and flight testing program, using F-111A (#63-9778), which would span almost 20 years before completion. Intense interest over the results coming from the NASA F-8 supercritical wing program spurred NASA and the Air Force to modify the General Dynamics F-111A to explore the application of supercritical wing technology to maneuverable military aircraft. This flight program was called Transonic Aircraft Technology (TACT).