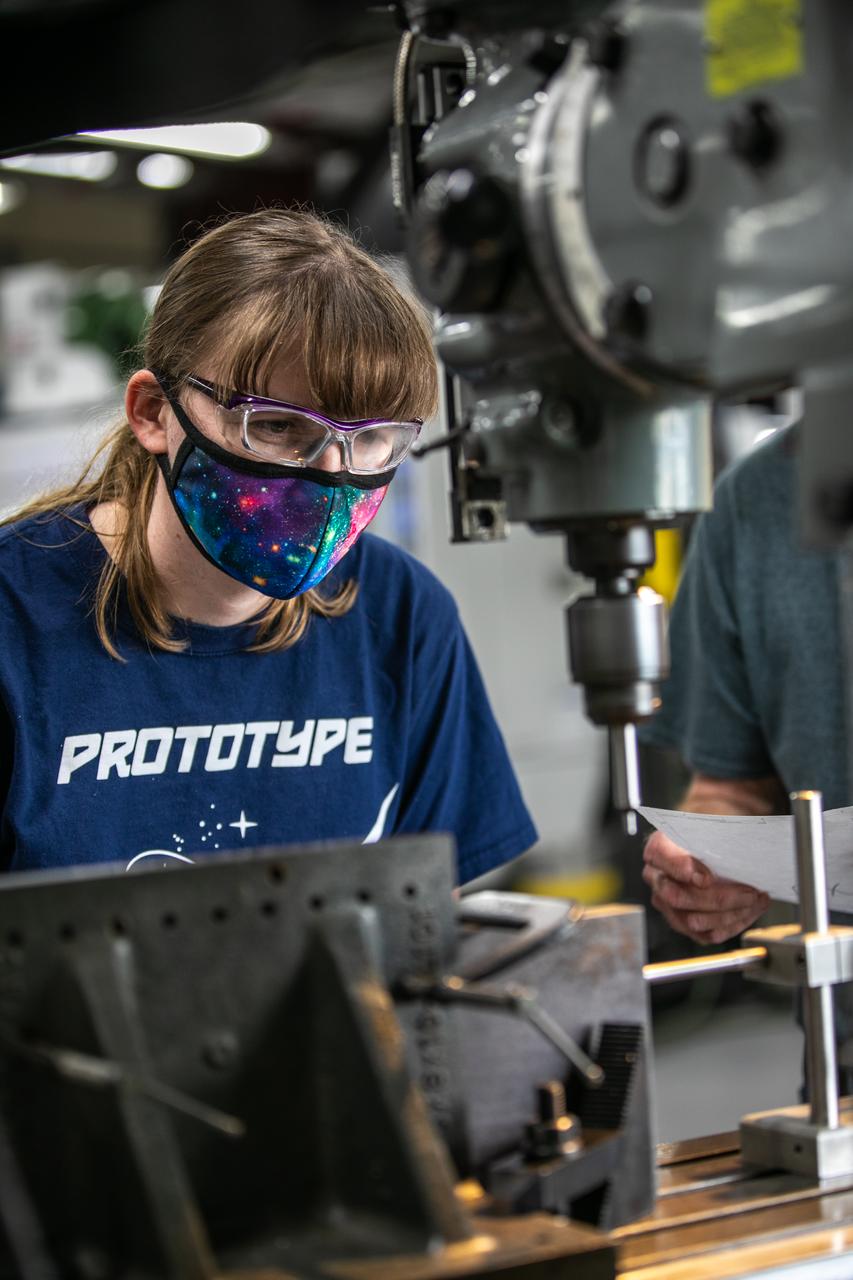

Katie Mortensen, a mechanical engineering technician, machines test article materials inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. The prototype laboratory designs, fabricates, and tests prototypes, test articles and test support equipment. It has a long history of providing fast solutions to complex operations problems. The lab’s teams of engineers use specialized equipment to produce exacting, one-of-a-kind items made from a range of materials depending on the design. The lab supports projects at Kennedy and at the agency level.
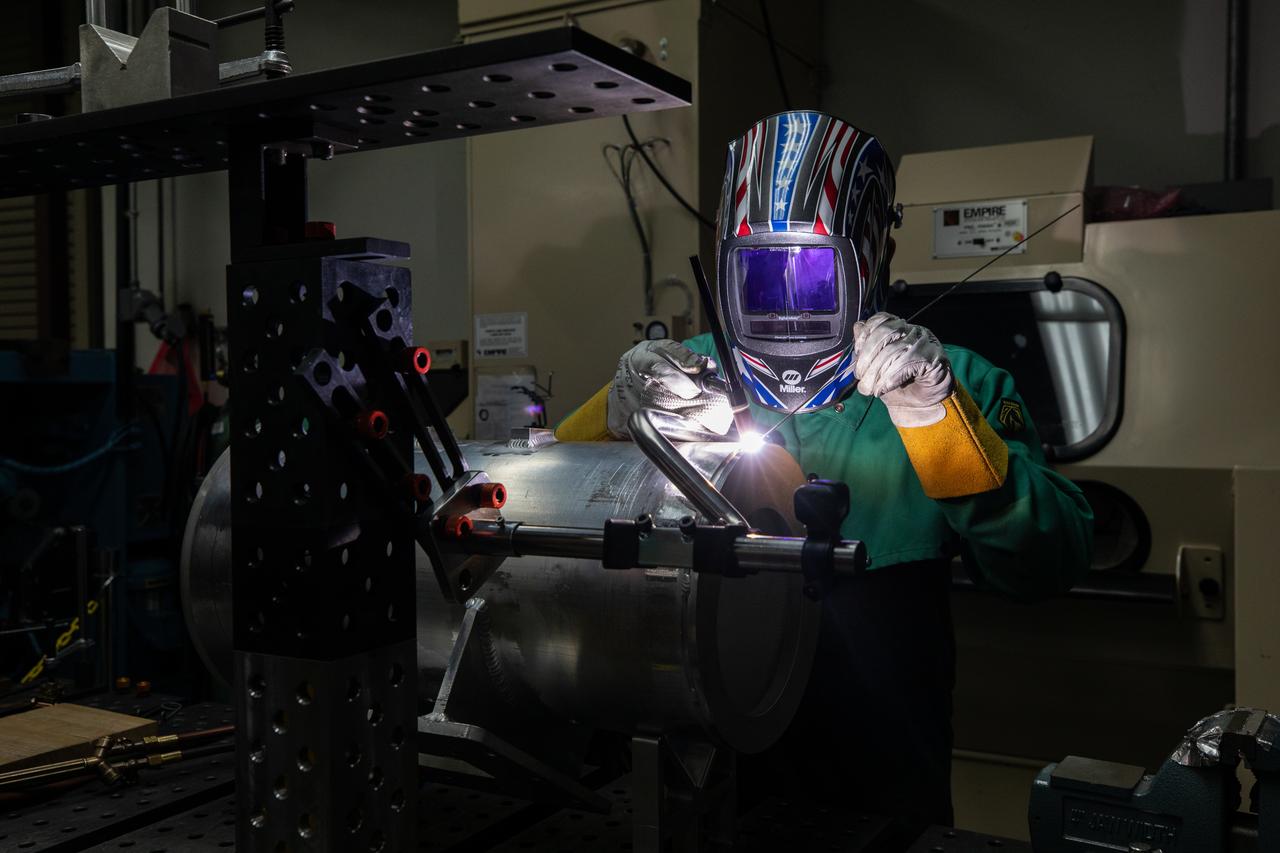

Spencer Wells, a mechanical engineering technician, welds a part of a camera enclosure which will be used at Launch Complex 39B inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. The prototype laboratory designs, fabricates, and tests prototypes, test articles and test support equipment. It has a long history of providing fast solutions to complex operations problems. The lab’s teams of engineers use specialized equipment to produce exacting, one-of-a-kind items made from a range of materials depending on the design. The lab supports projects at Kennedy and at the agency level.
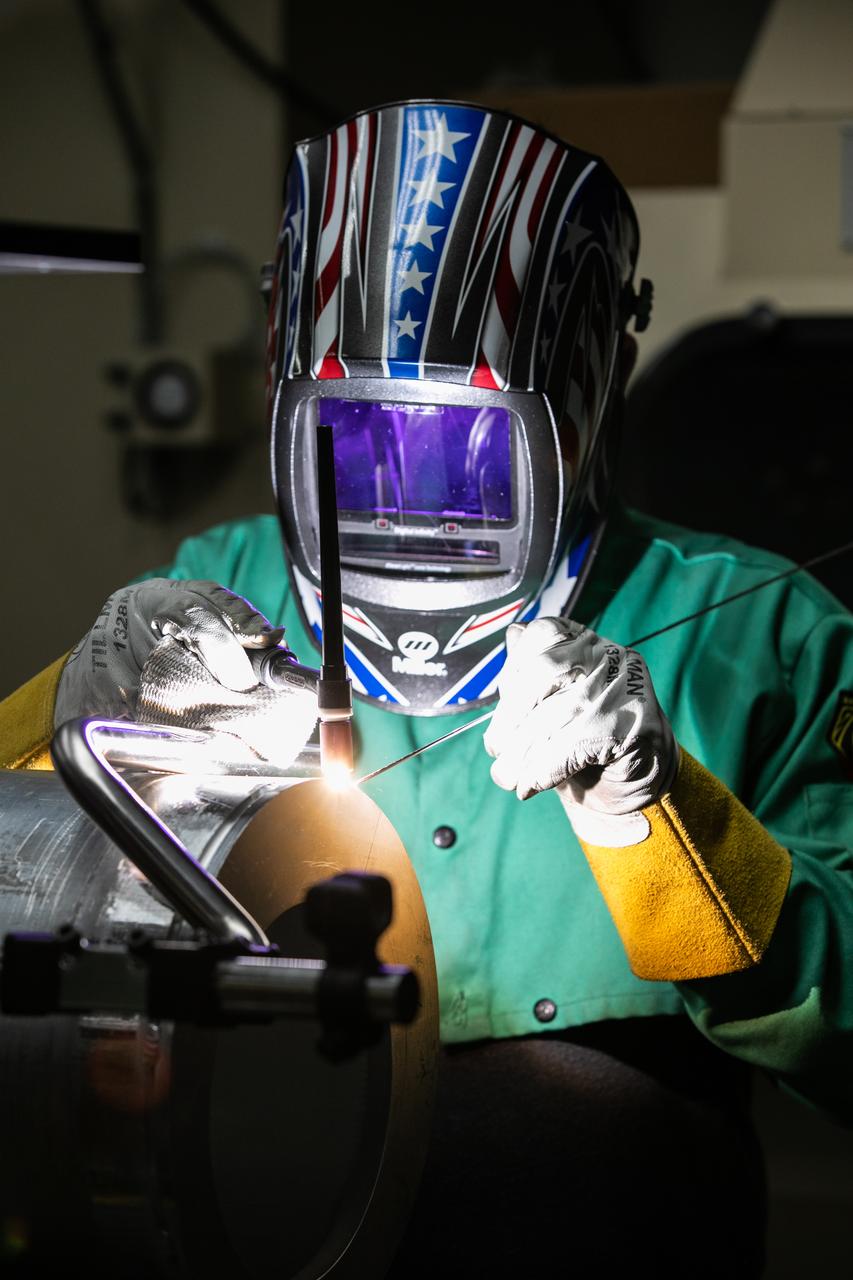

Spencer Wells, a mechanical engineering technician, welds a part of a camera enclosure which will be used at Launch Complex 39B inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. The prototype laboratory designs, fabricates, and tests prototypes, test articles and test support equipment. It has a long history of providing fast solutions to complex operations problems. The lab’s teams of engineers use specialized equipment to produce exacting, one-of-a-kind items made from a range of materials depending on the design. The lab supports projects at Kennedy and at the agency level.
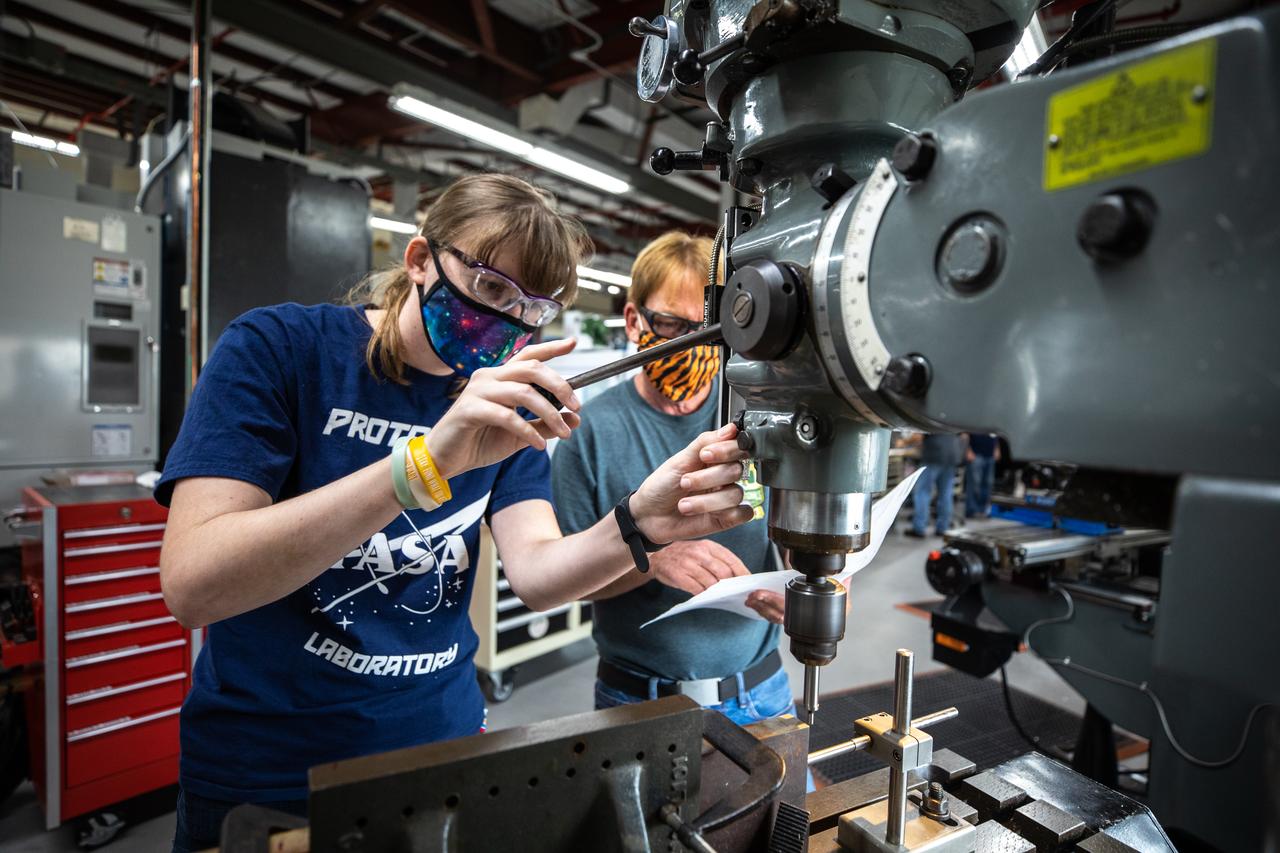

From left, mechanical engineering technicians Katie Mortensen and Jim Niehoff machine test article material inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. The prototype laboratory designs, fabricates, and tests prototypes, test articles and test support equipment. It has a long history of providing fast solutions to complex operations problems. The lab’s teams of engineers use specialized equipment to produce exacting, one-of-a-kind items made from a range of materials depending on the design. The lab supports projects at Kennedy and at the agency level.
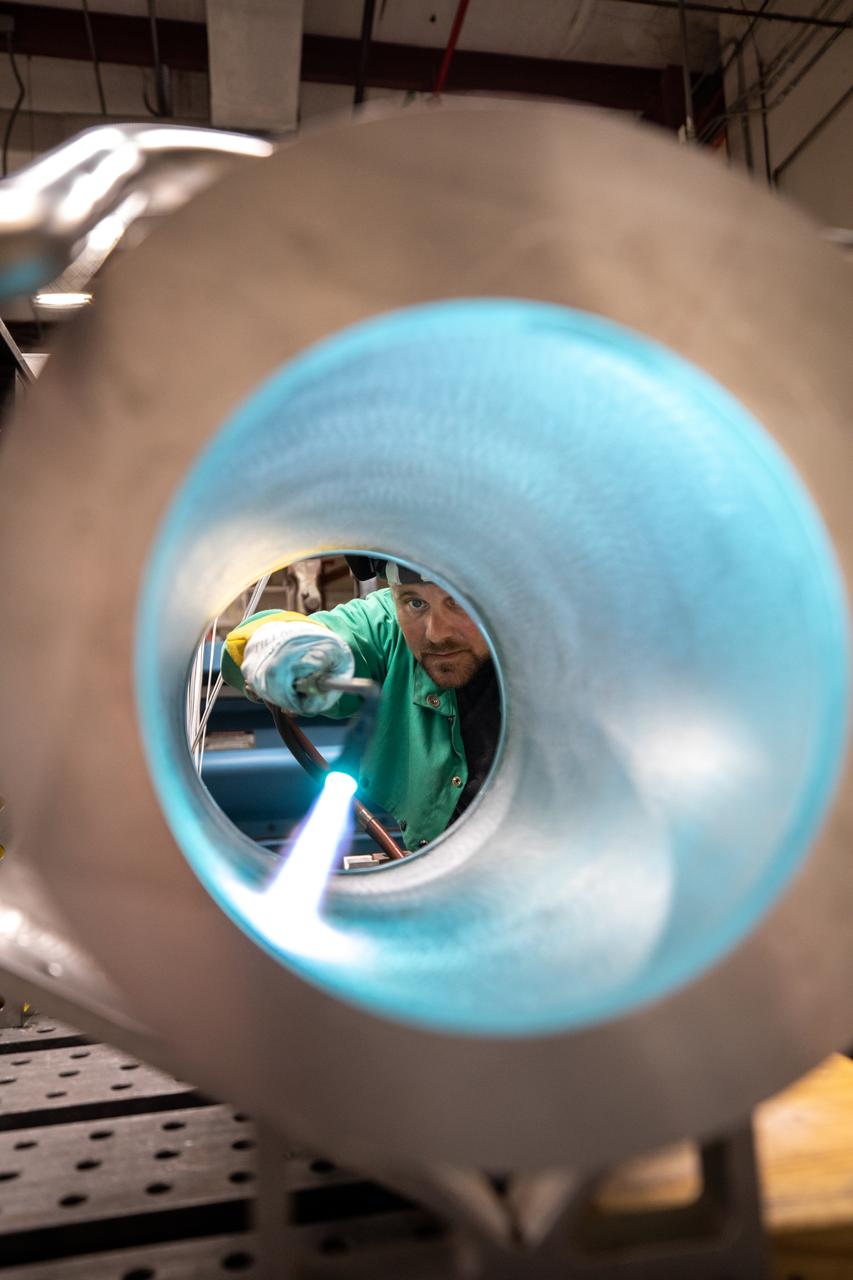

Spencer Wells, a mechanical engineering technician, examines the interior of a camera enclosure for Launch Complex 39B inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. The prototype laboratory designs, fabricates, and tests prototypes, test articles and test support equipment. It has a long history of providing fast solutions to complex operations problems. The lab’s teams of engineers use specialized equipment to produce exacting, one-of-a-kind items made from a range of materials depending on the design. The lab supports projects at Kennedy and at the agency level.
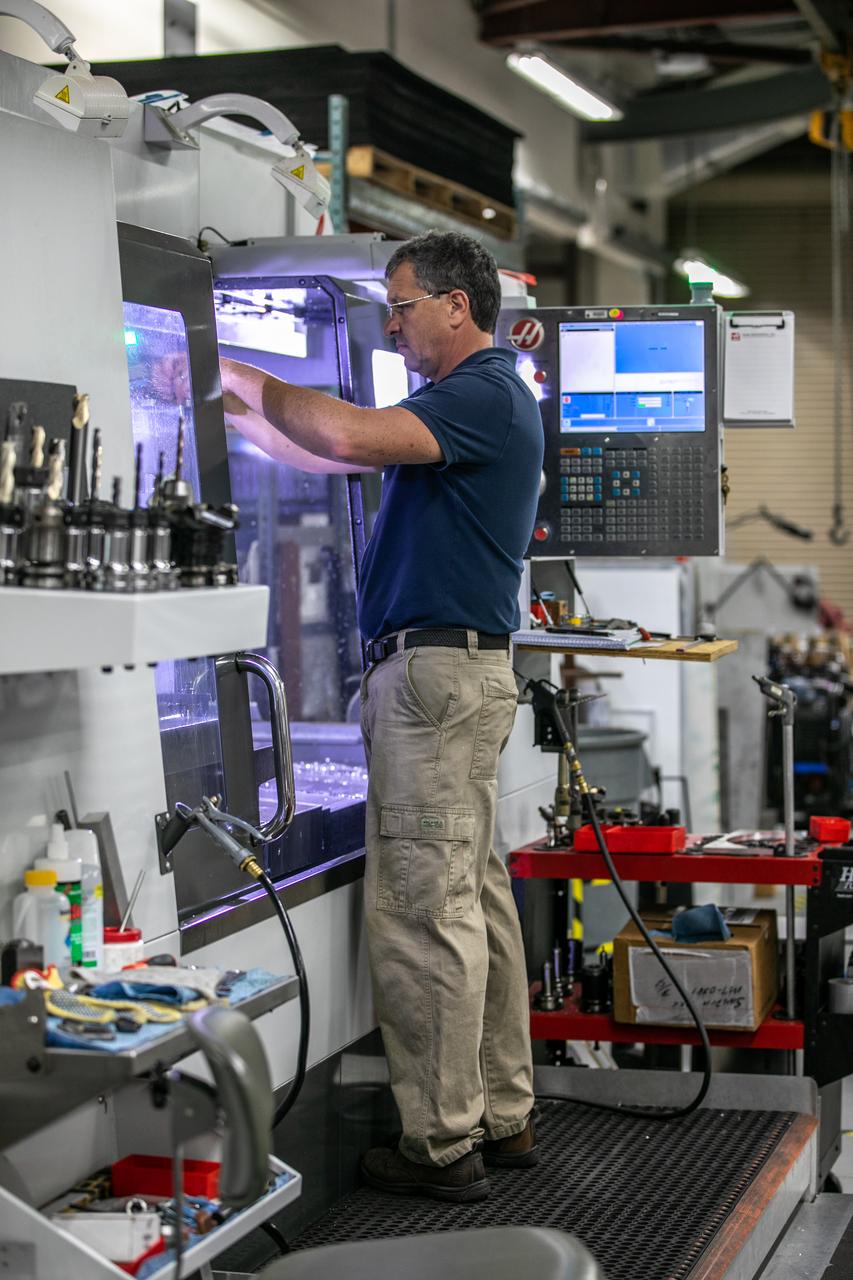

Tim Evans, a mechanical engineering technician, uses a computer numerical control (CNC) machine to machine a part for a Launch Pad 39B camera enclosure inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. The prototype laboratory designs, fabricates, and tests prototypes, test articles and test support equipment. It has a long history of providing fast solutions to complex operations problems. The lab’s teams of engineers use specialized equipment to produce exacting, one-of-a-kind items made from a range of materials depending on the design. The lab supports projects at Kennedy and at the agency level.
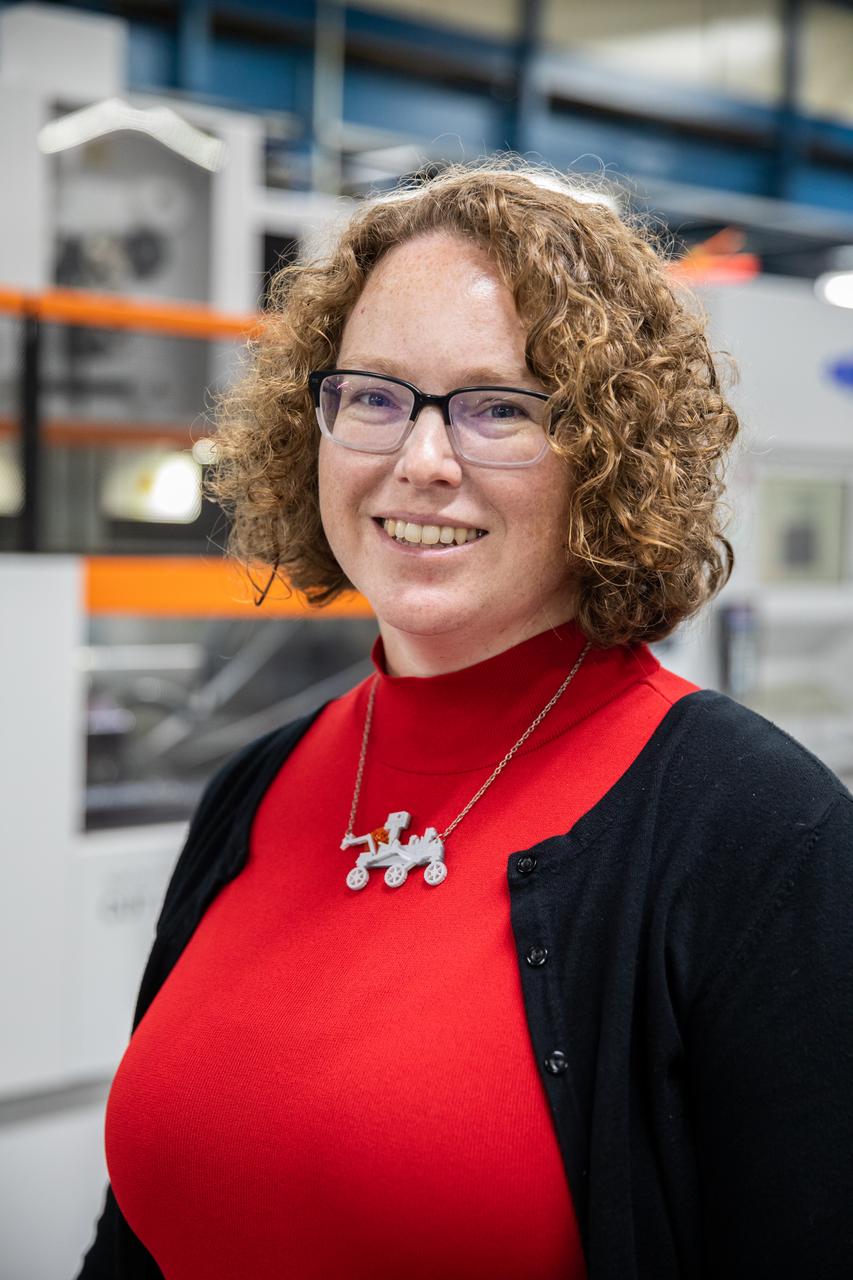

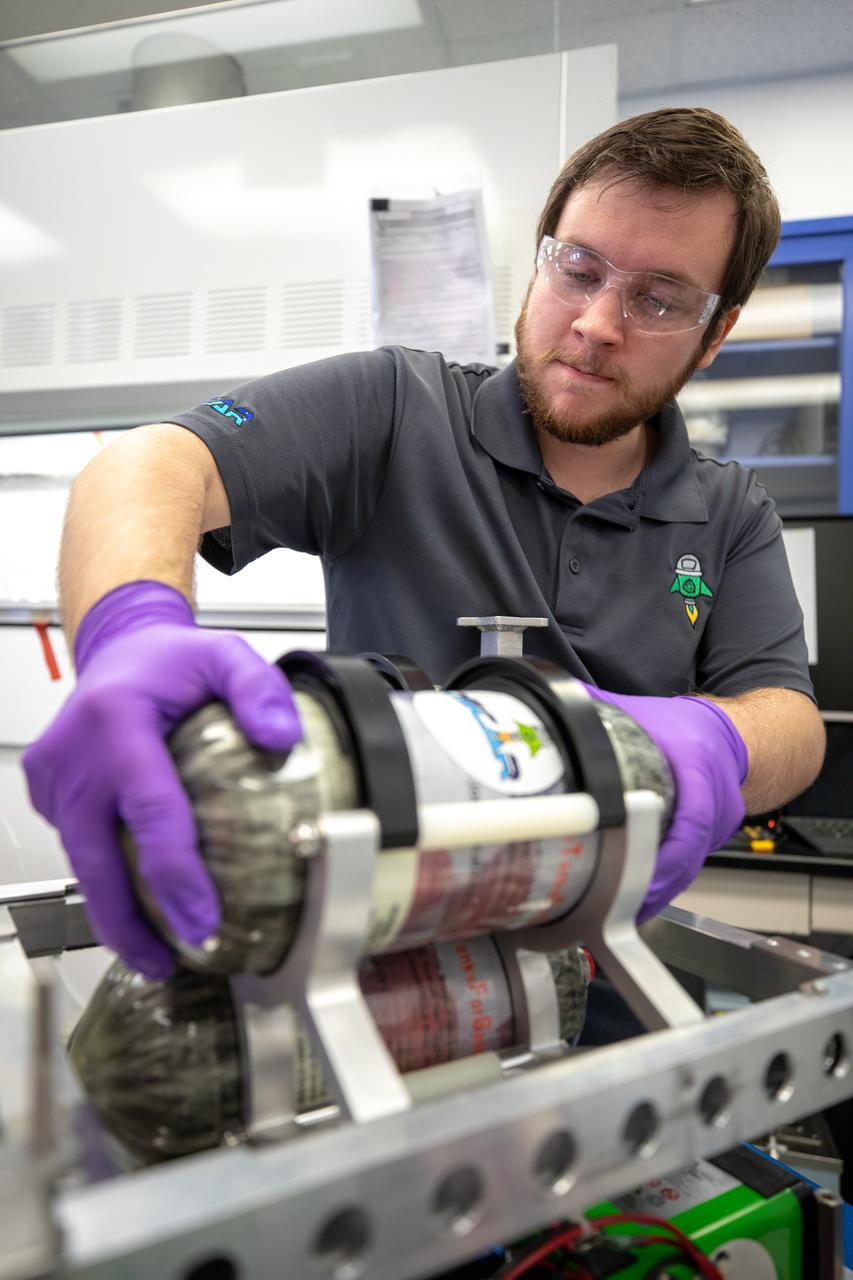
Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, is inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to begin testing on the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied to spacecraft and launch vehicles.
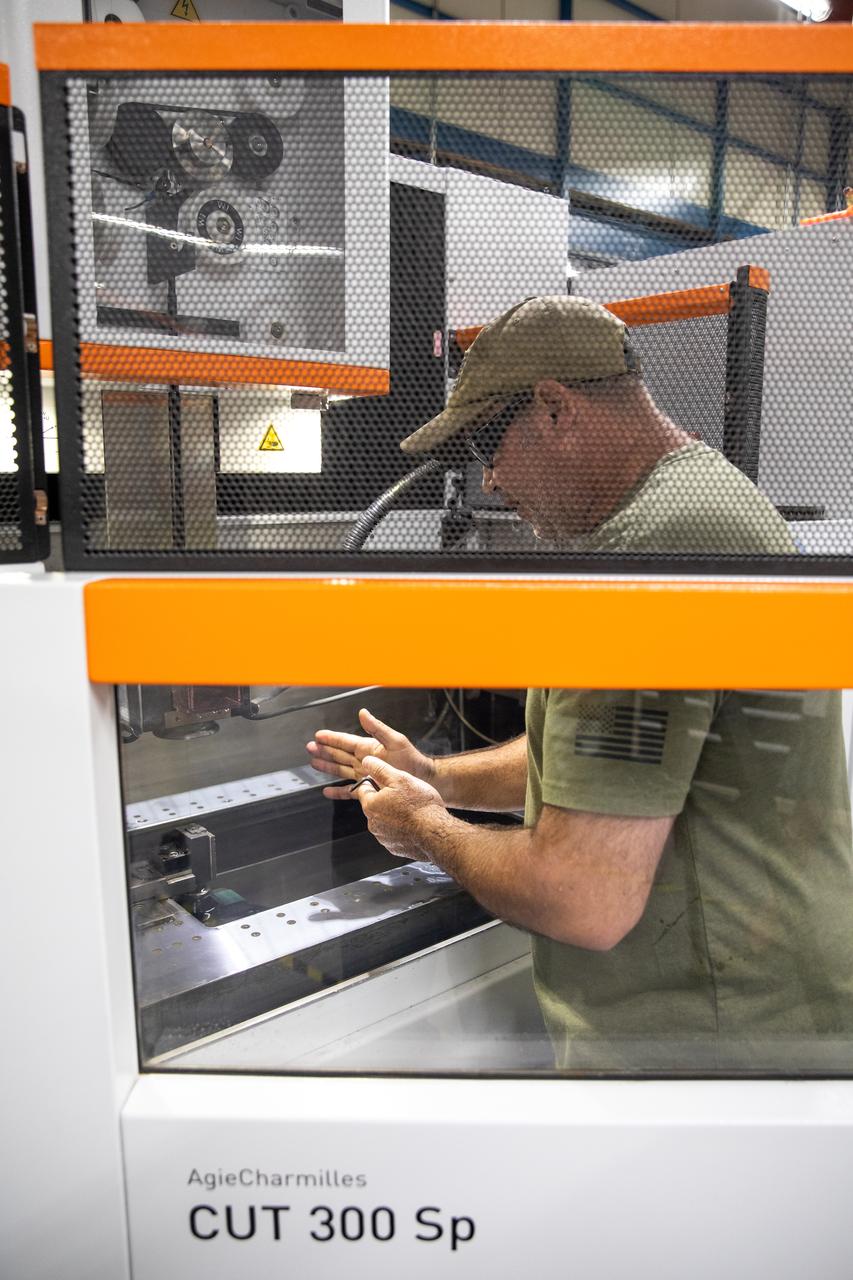

Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician with NASA, handles a sample that is being prepared for fatigue and corrosion testing for the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a ten percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
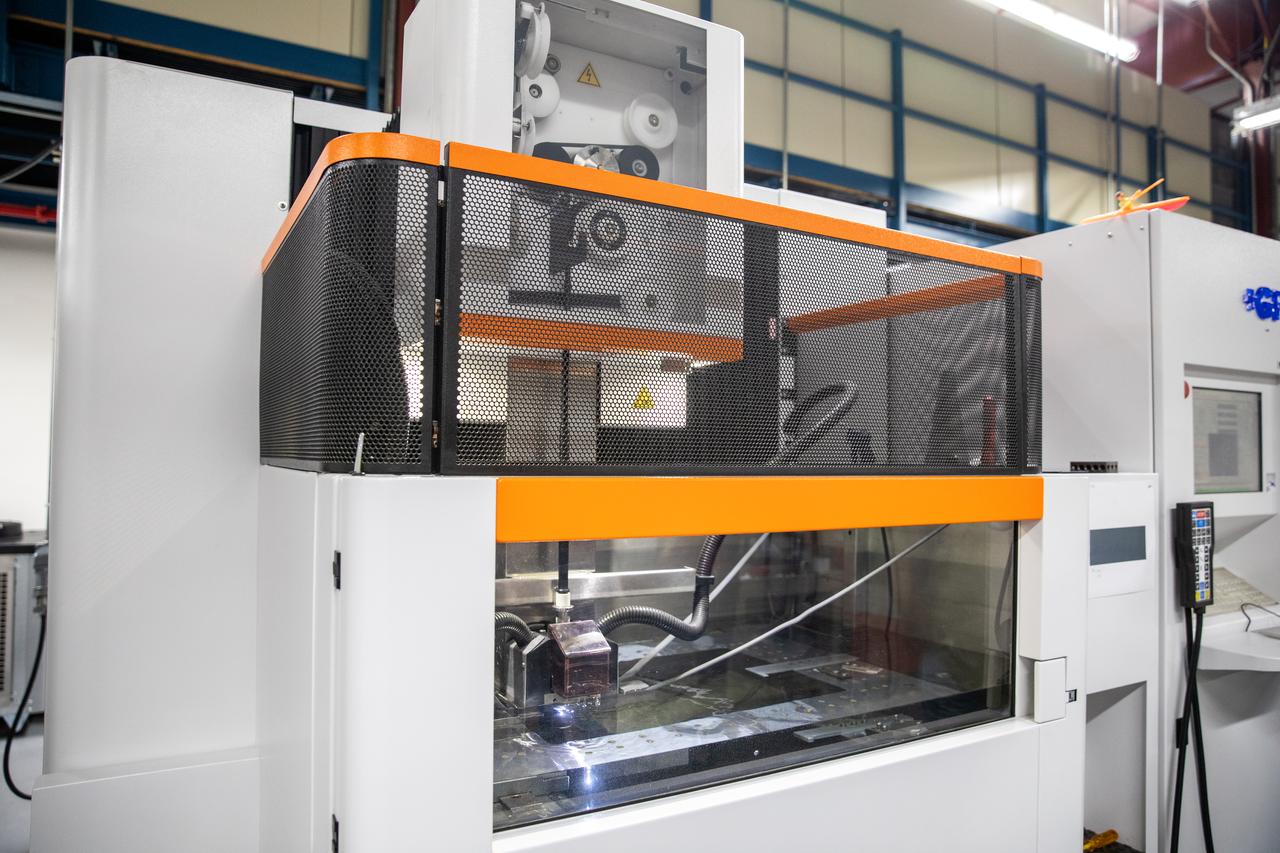

Testing of the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiment is underway inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a ten percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
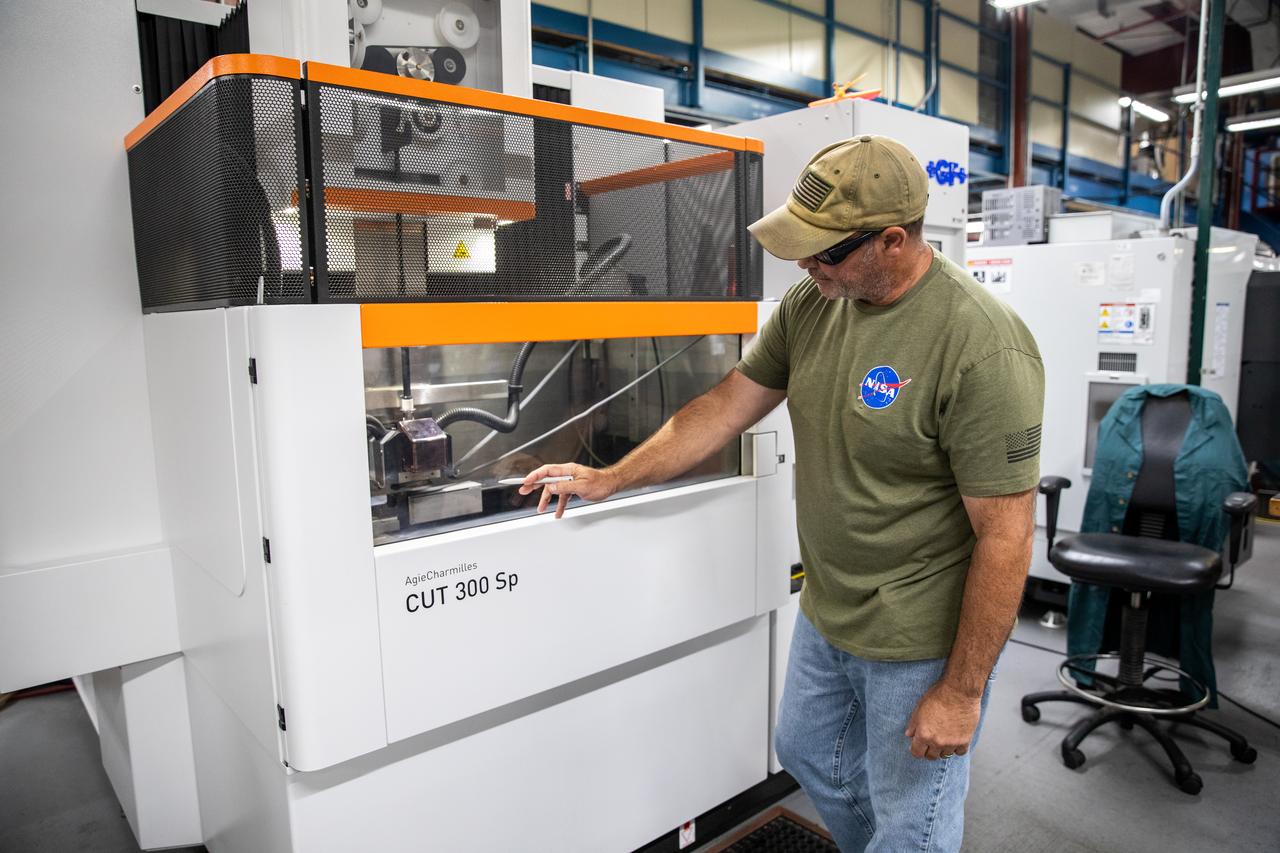

Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician with NASA, prepares the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) specimens for testing inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
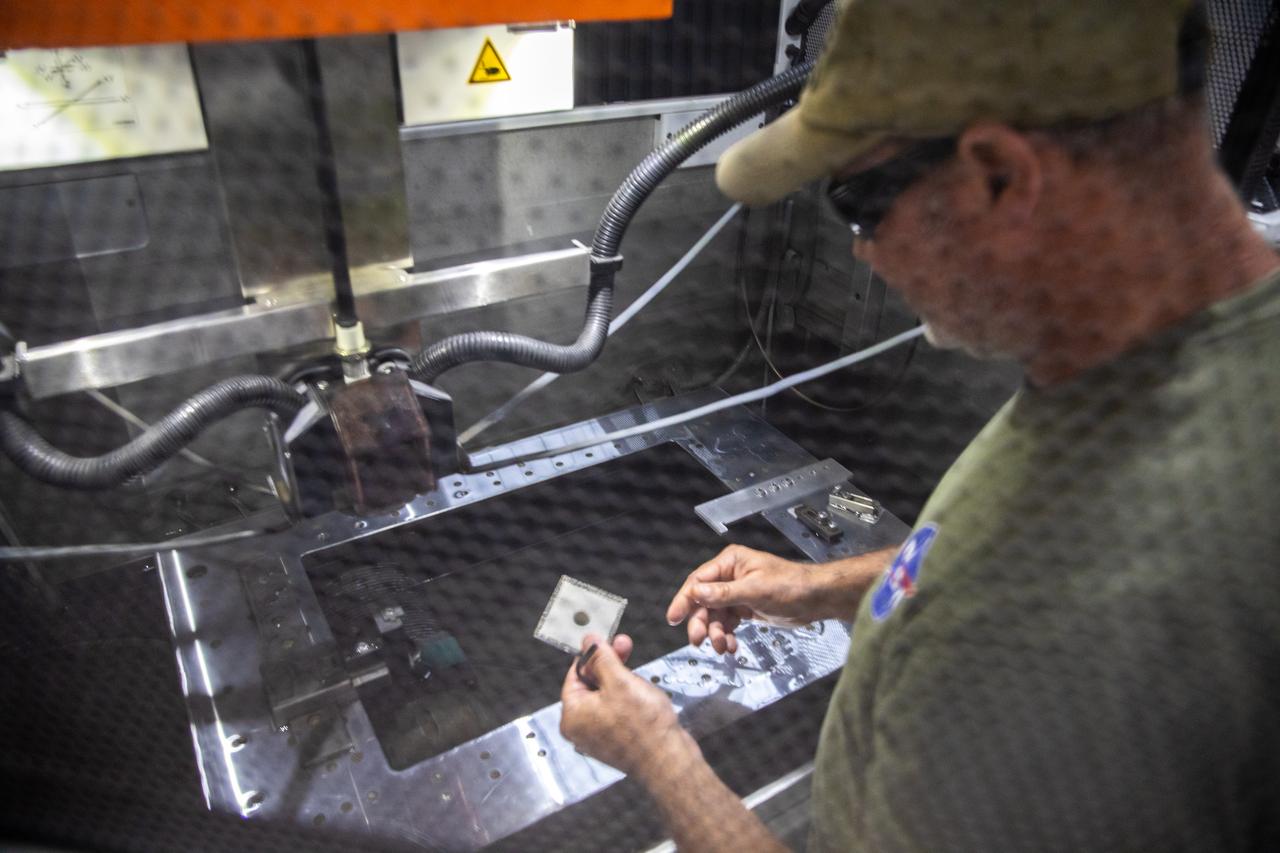

Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician with NASA, prepares a sample for testing for the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
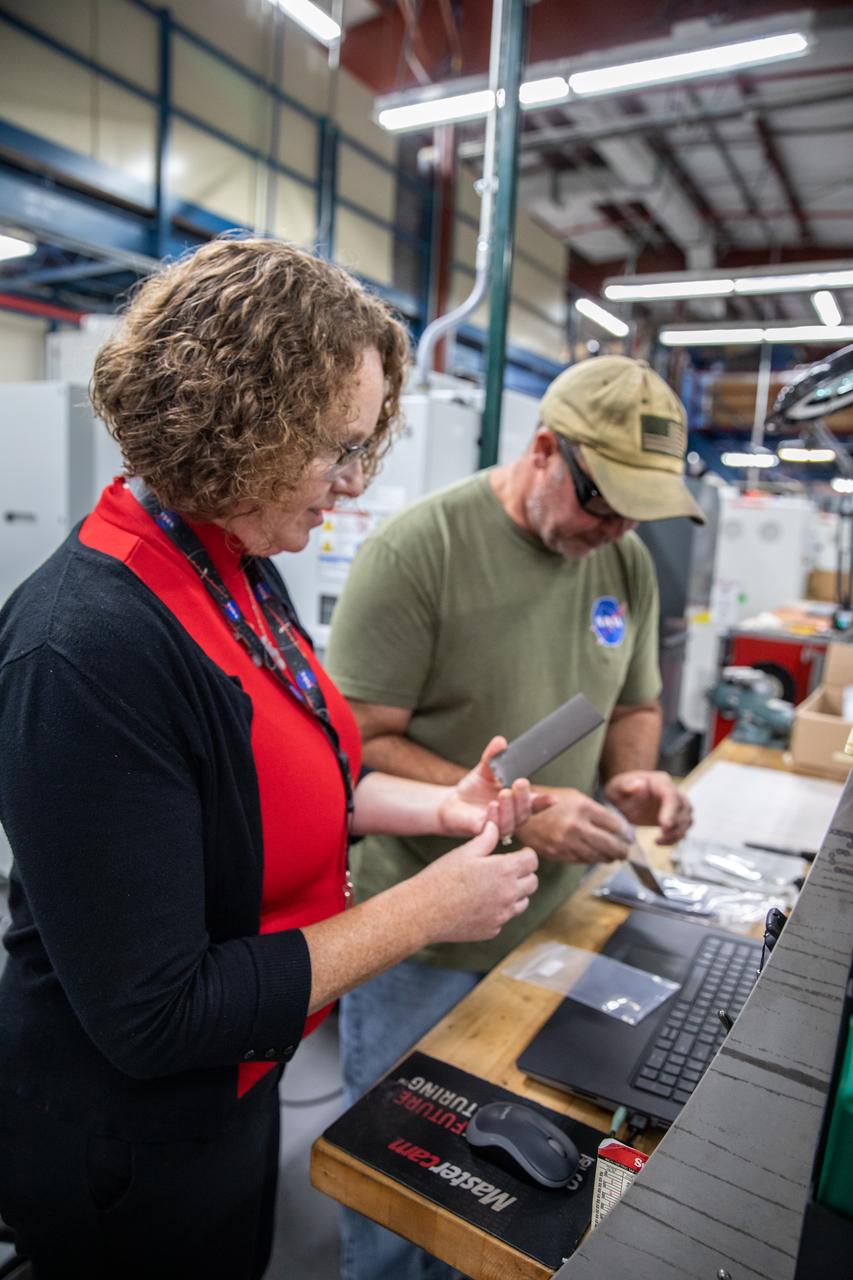

From left, Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, and Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician, inspect specimens prepared forthe Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiment inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied used on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
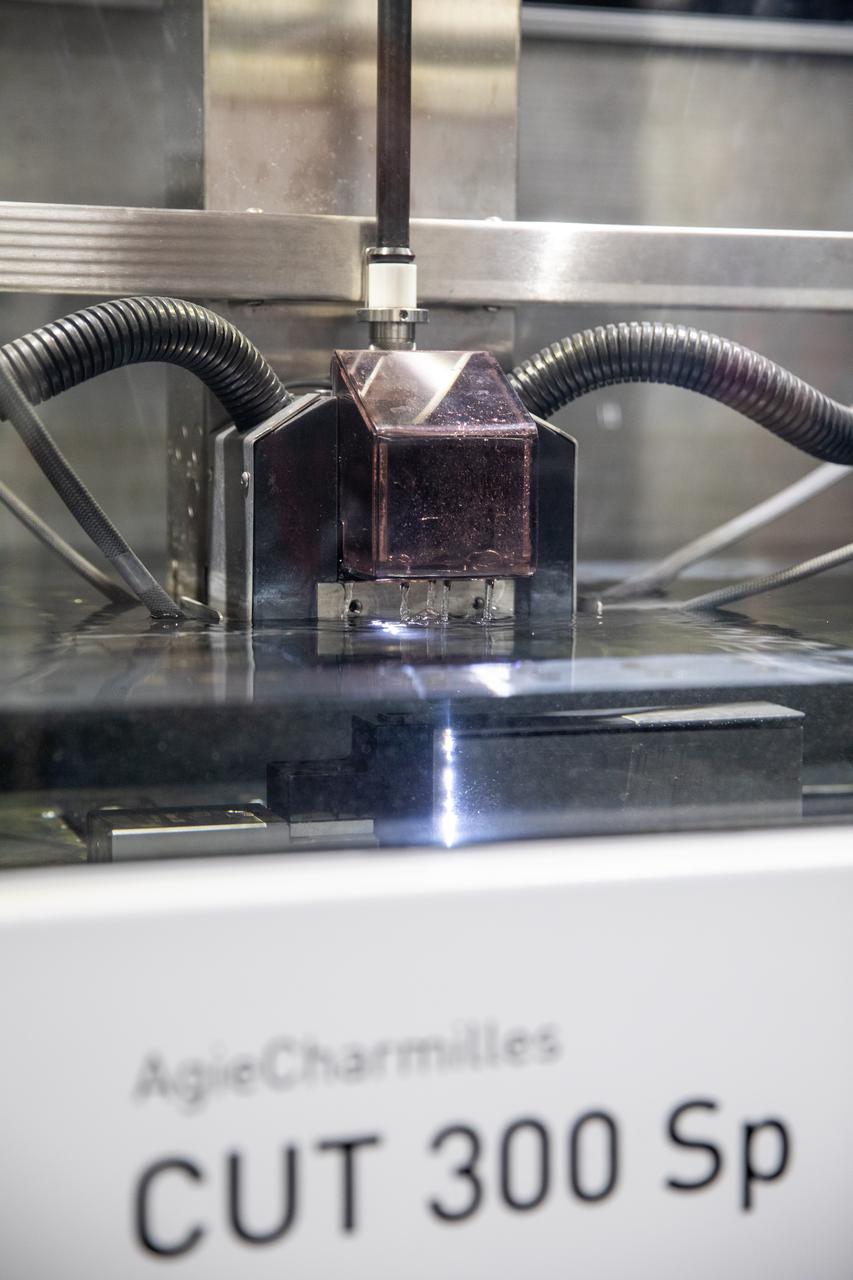
Testing of the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiment is underway inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
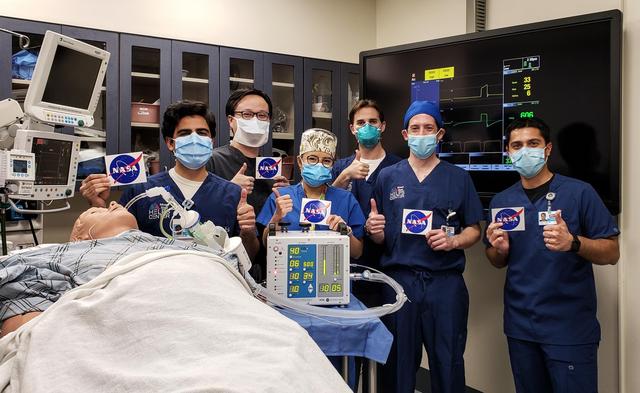
After testing a ventilator prototype developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, doctors in the Department of Anesthesiology and the Human Simulation Lab at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City give a thumbs up. Developed in response to the coronavirus outbreak, the device, called VITAL (Ventilator Intervention Technology Accessible Locally), requires far fewer parts than traditional ventilators, making it cheaper to build and ideal for rapid manufacture. Lying on the bed is a human patient simulator used to test the device. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23772

A furled first prototype starshade developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, shown in technology partner Astro Aerospace/Northrup Grumman's facility in Santa Barbara, California, in 2013. This design shows petals that are more extreme in shape, which properly diffracts starlight for smaller telescopes. For launch, the petals of the starshade will be wrapped around the spacecraft, then unfurled into the familiar flower-like design once in space. As shown by this 66-foot (20-meter) model, starshades can come in many shapes and sizes. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20905
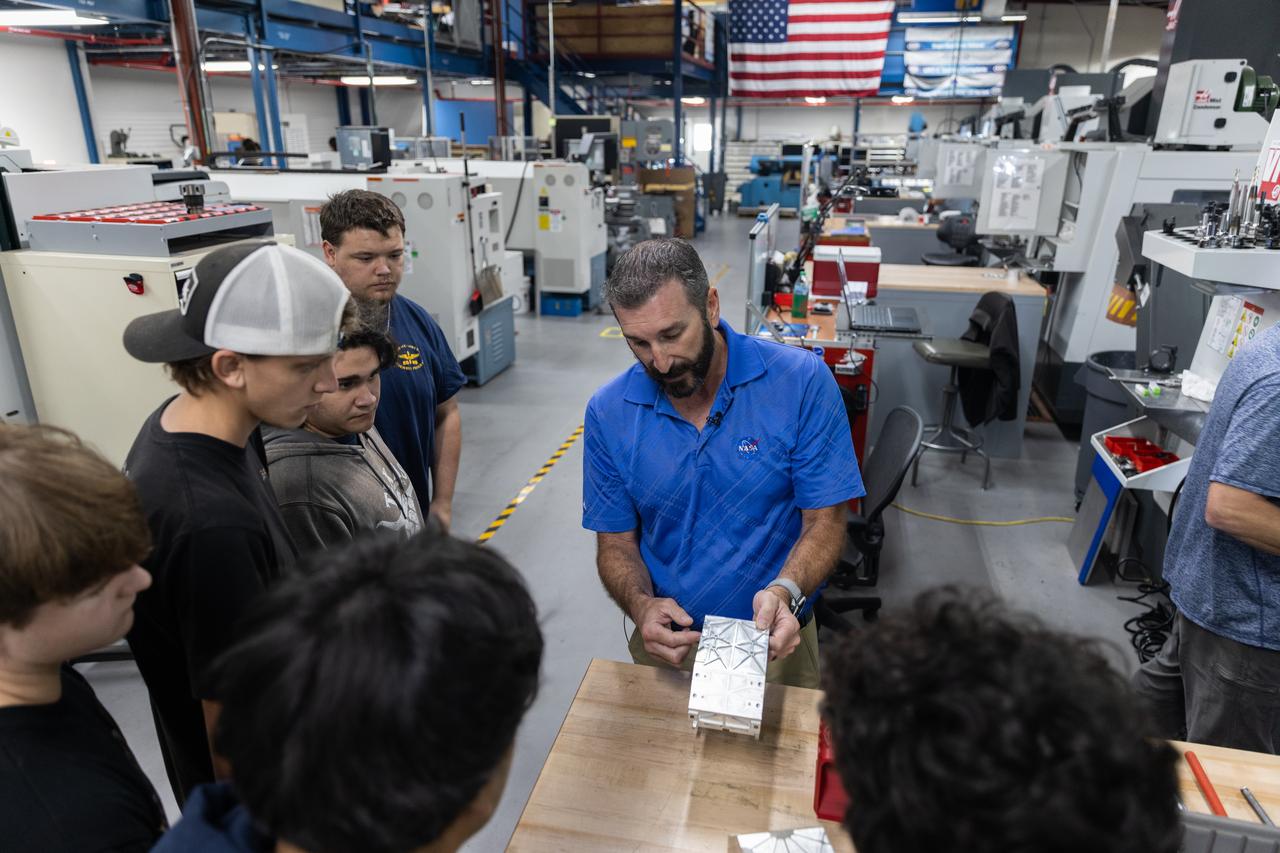

Students from Eau Gallie High School in Melbourne, Florida, visited the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, April 28, 2025. The STEM participants have an interest in technical trades and learned about the technicians at the Prototype Development Laboratory who design, fabricate, and test protypes, test articles, and test support equipment.
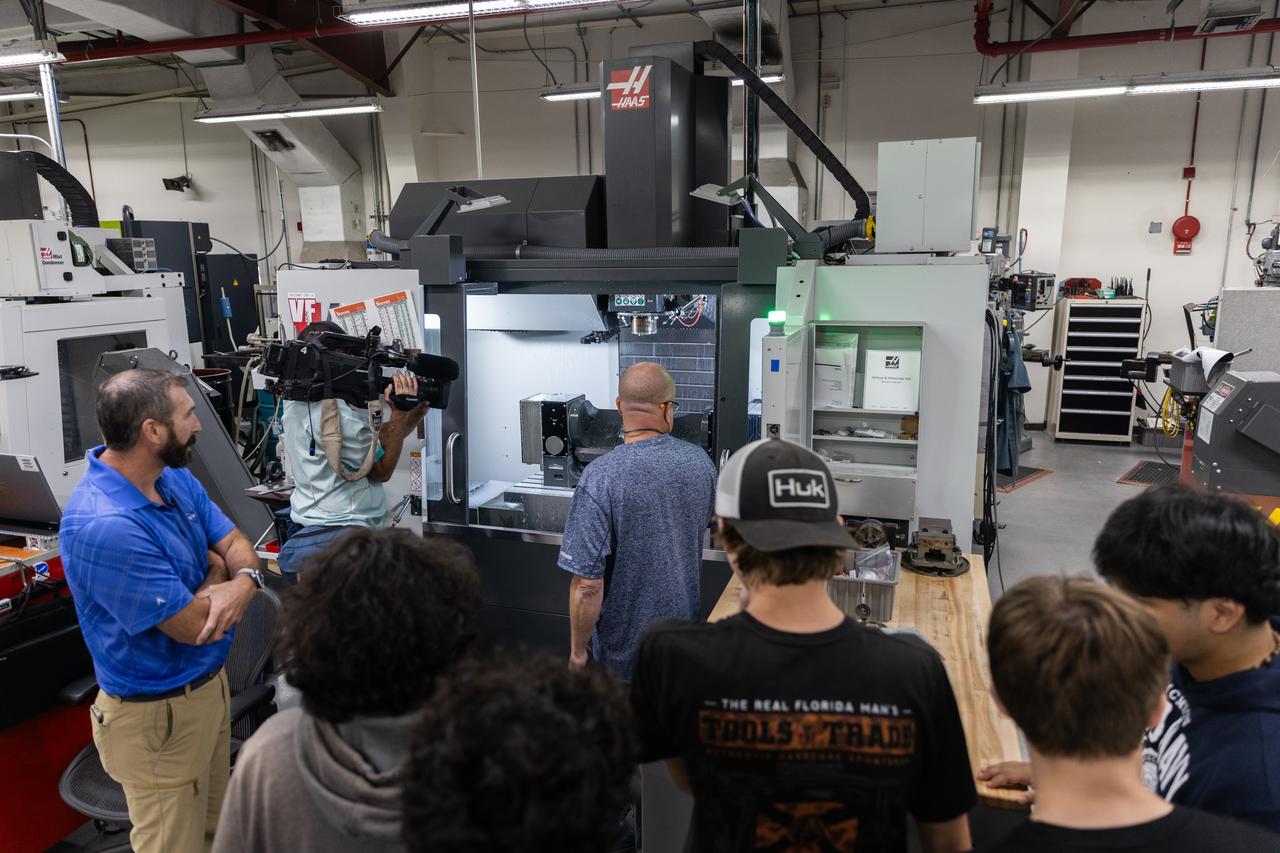

Students from Eau Gallie High School in Melbourne, Florida, visited the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, April 28, 2025. The STEM participants have an interest in technical trades and learned about the technicians at the Prototype Development Laboratory who design, fabricate, and test protypes, test articles, and test support equipment.
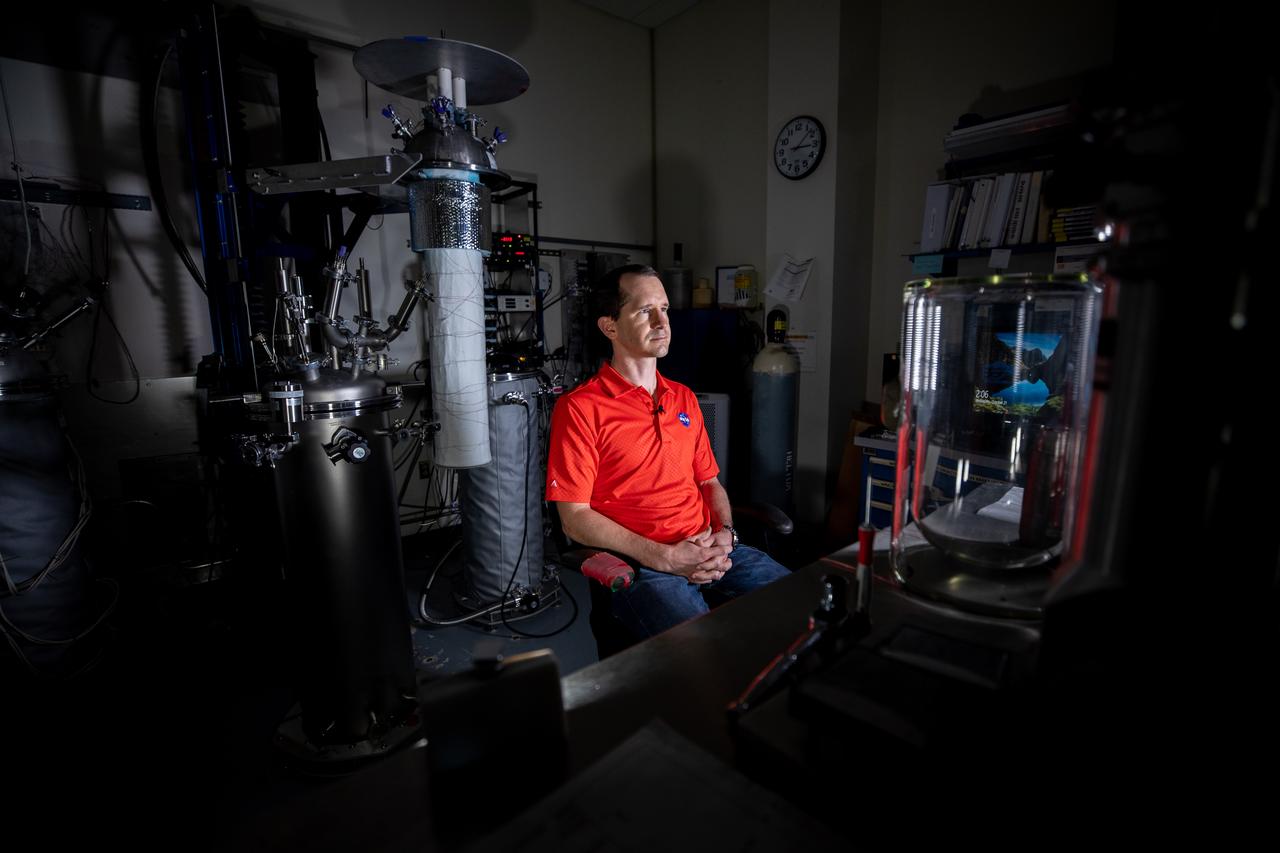

Adam Swanger, NASA engineer, is inside the Cryogenics Test Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. Established in 2000, the Cryogenics Test Laboratory provides a one-of-a kind capability for research, development and application of cross-cutting technologies to meet the needs of industry and government. The test lab provides cryogenic expertise, experimental testing, technical standards development, prototype construction and practical problem-solving for technology development with research institutions and commercial partners.
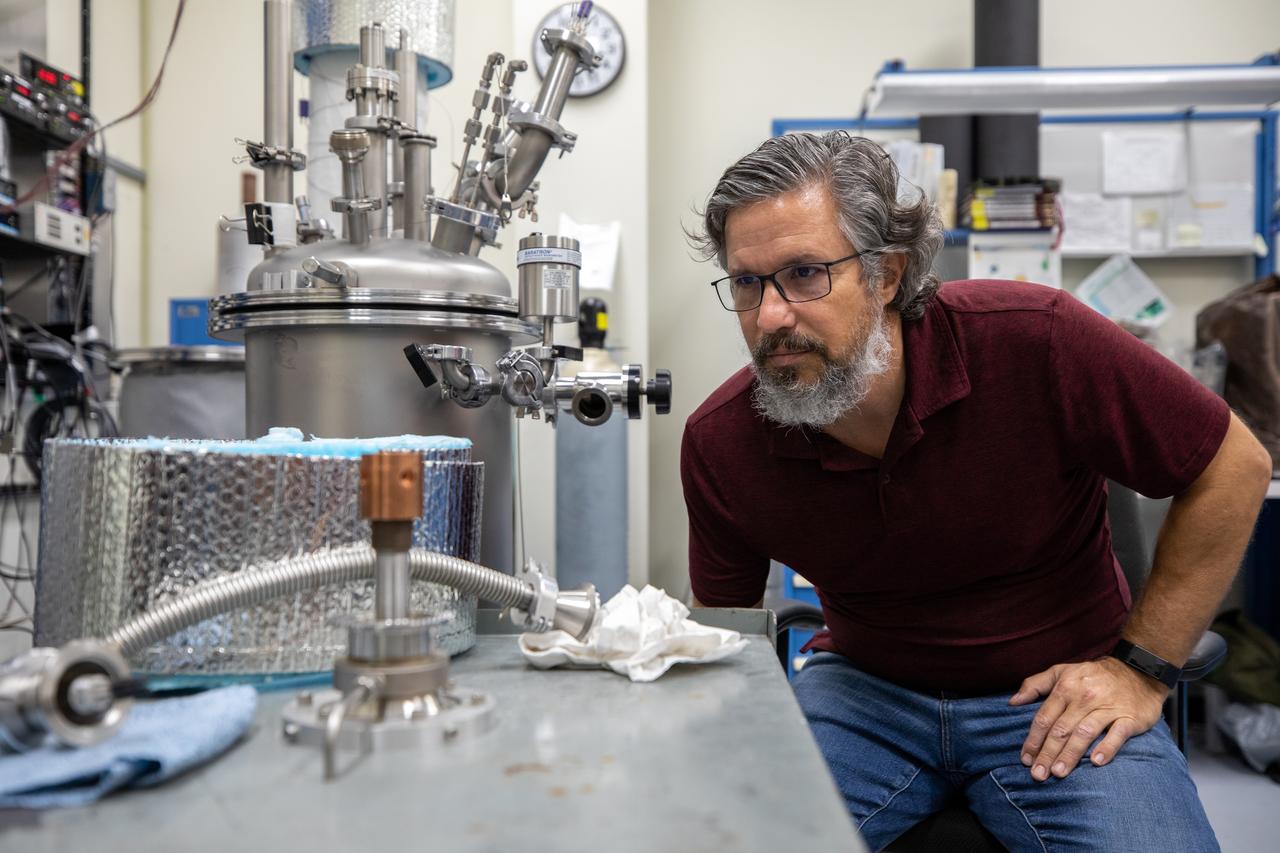
Jared Sass, NASA engineer, monitors a test inside the Cryogenics Test Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. Established in 2000, the Cryogenics Test Laboratory provides a one-of-a kind capability for research, development and application of cross-cutting technologies to meet the needs of industry and government. The test lab provides cryogenic expertise, experimental testing, technical standards development, prototype construction and practical problem-solving for technology development with research institutions and commercial partners.
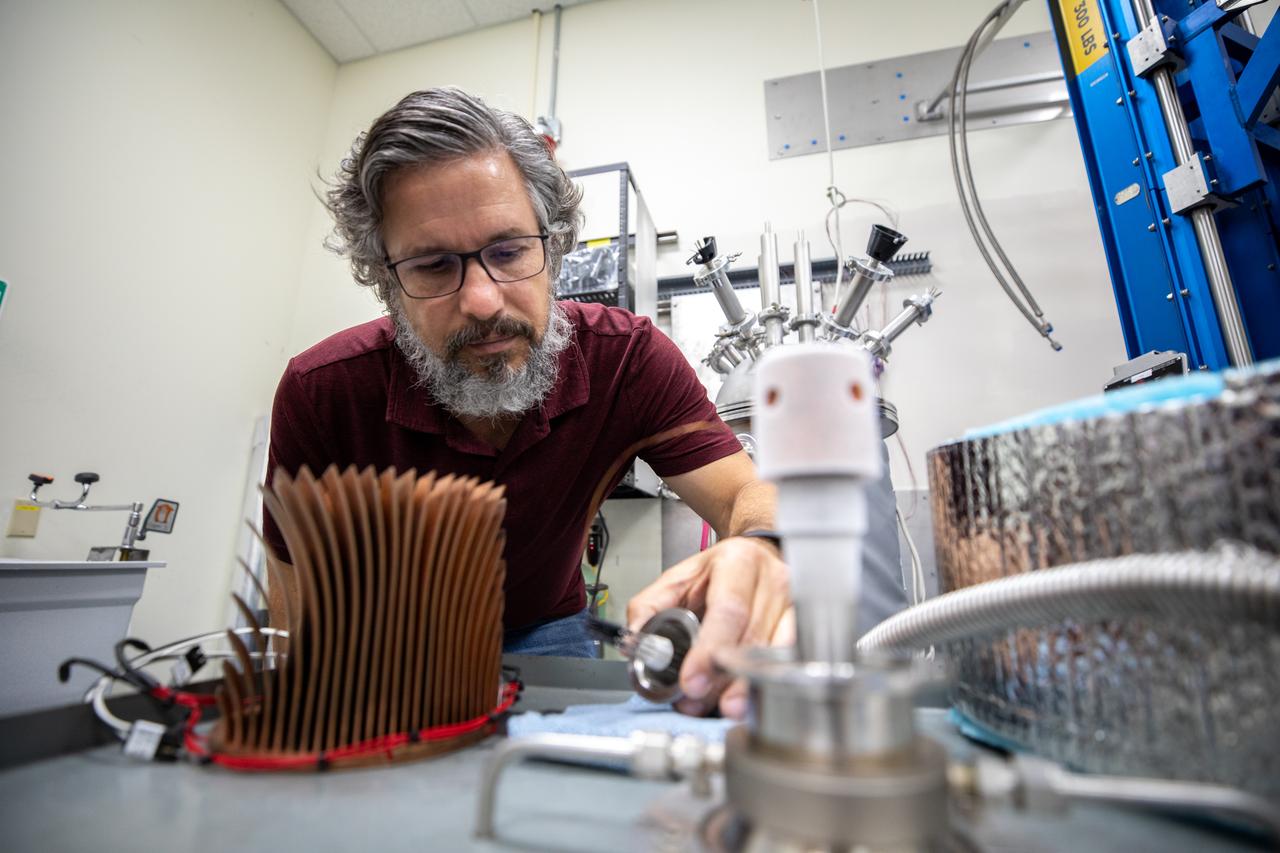
Jared Sass, NASA engineer, monitors a test inside the Cryogenics Test Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. Established in 2000, the Cryogenics Test Laboratory provides a one-of-a kind capability for research, development and application of cross-cutting technologies to meet the needs of industry and government. The test lab provides cryogenic expertise, experimental testing, technical standards development, prototype construction and practical problem-solving for technology development with research institutions and commercial partners.
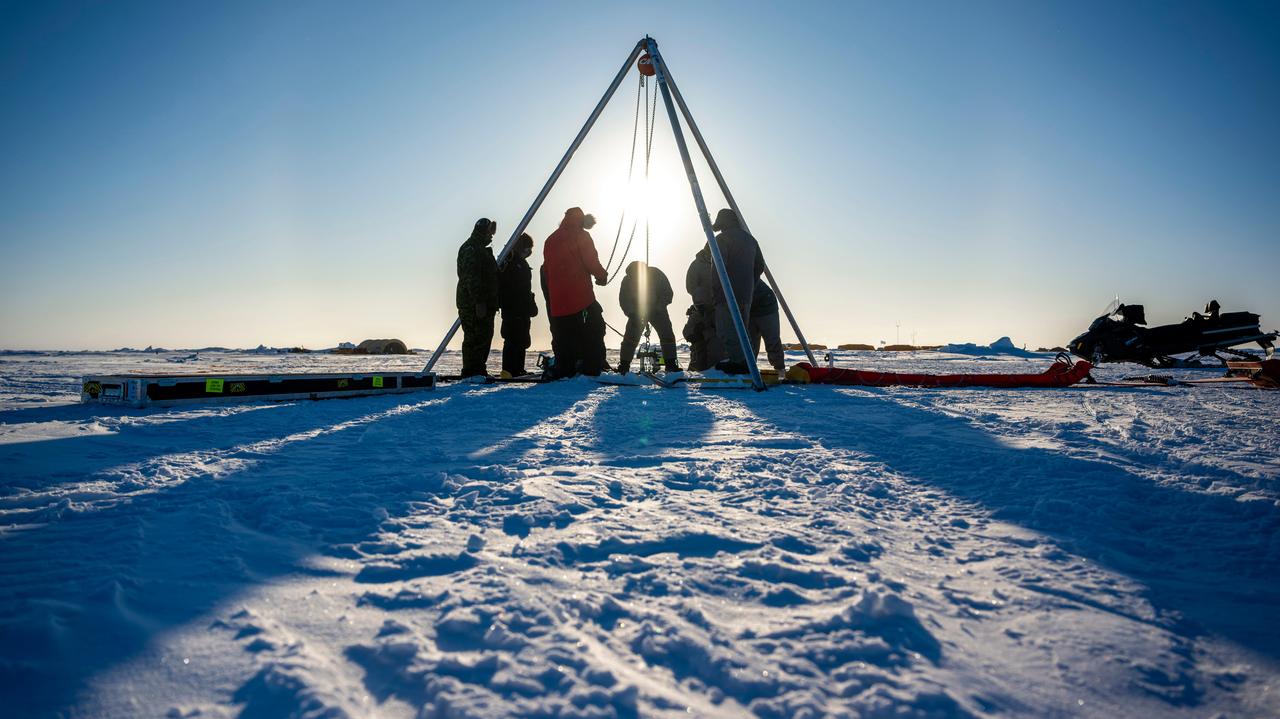

A prototype of an autonomous robot, part of a project called IceNode being developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, was tested in the Beaufort Sea north of Alaska in March 2024. The project envisions a fleet of such robots to venture beneath Antarctic ice shelves and gather data that would help scientists calculate how rapidly the ice shelves there are melting – and how fast that melting could cause global sea levels to rise. This image, as well as Figures A and B, shows the team lowering the prototype through a borehole in the sea ice. During this Arctic field test, the robot descended on a tether about 330 feet (100 meters) into the ocean, where its instruments gathered salinity, temperature, and flow data. The team also conducted tests to determine adjustments that would enable them to take the robot off-tether. Each about 8 feet (2.4 meters) long and 10 inches (25 centimeters) in diameter, the robots use three-legged "landing gear" that springs out from one end to attach the robot to the underside of the ice. Rather than using propulsion, the robots would autonomously position themselves with the help of novel algorithms based on models of ocean currents. Released from a borehole or a vessel in the open ocean, the robots would ride those currents on a long journey beneath an ice shelf. They would target the underwater area known as the "grounding zone," where floating ice shelves, ocean, and land meet, deep inside unmapped cavities where the ice may be melting the fastest. Each robot would detach a ballast and rise up to affix itself to the underside of the ice, where their suite of sensors would measure how fast warm, salty ocean water is circulating up to melt the ice, and how quickly cold meltwater is sinking. As conceived, the IceNode fleet would operate for up to a year, continuously capturing data, including seasonal fluctuations. Then the robots would detach themselves from the ice, drift back out to open ocean, and transmit their data via satellite. This test was conducted through the U.S. Navy Arctic Submarine Laboratory's biennial Ice Camp, a three-week operation that provides researchers a temporary base camp from which to conduct field work in the harsh Arctic environment. IceNode has been funded through JPL's internal research and technology development program and its Earth Science and Technology Directorate. JPL is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26349
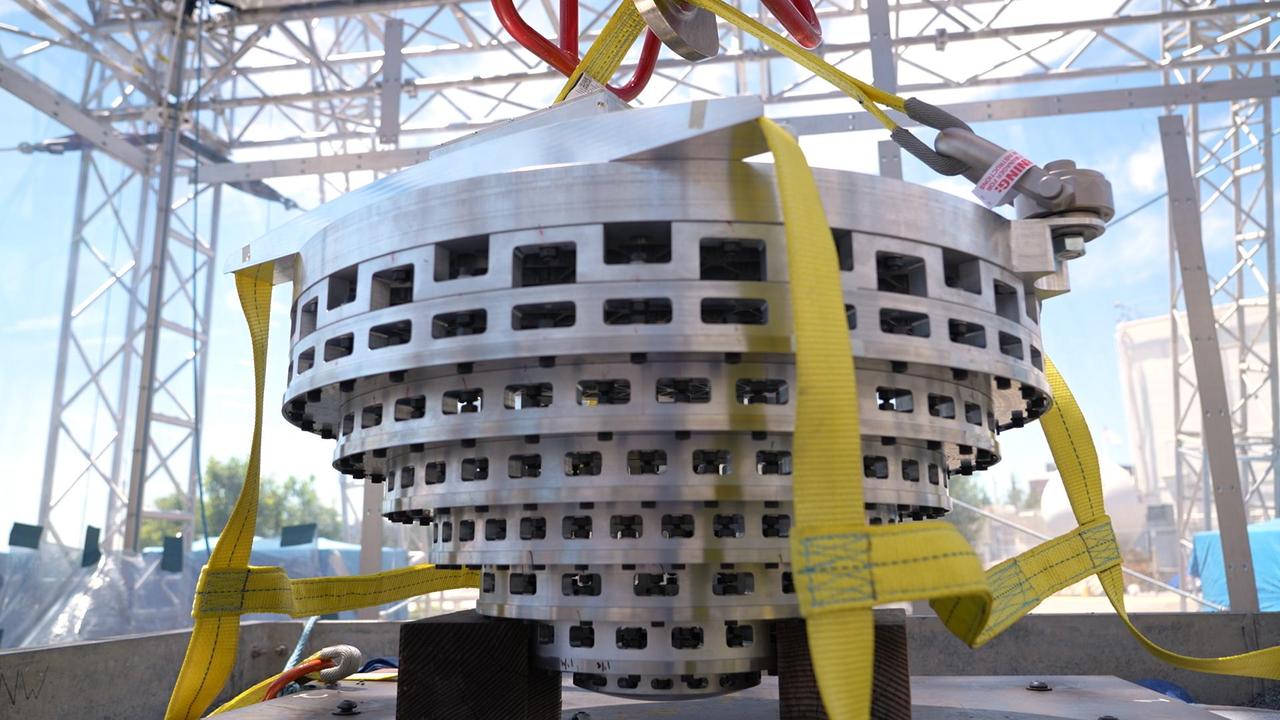
This prototype of a collapsible Mars lander base is part of SHIELD (Simplified High Impact Energy Landing Device), a project aimed at developing spacecraft that would intentionally crash land on the Red Planet, using an accordion-like, collapsible base that acts like the crumple zone of a car to absorb the energy of a hard impact. The design could drastically reduce the cost of landing on Mars by simplifying the harrowing entry, descent, and landing process and expanding options for possible landing sites. Developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, the prototype was attached to a drop tower on Aug. 12, 2022, at JPL. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25420
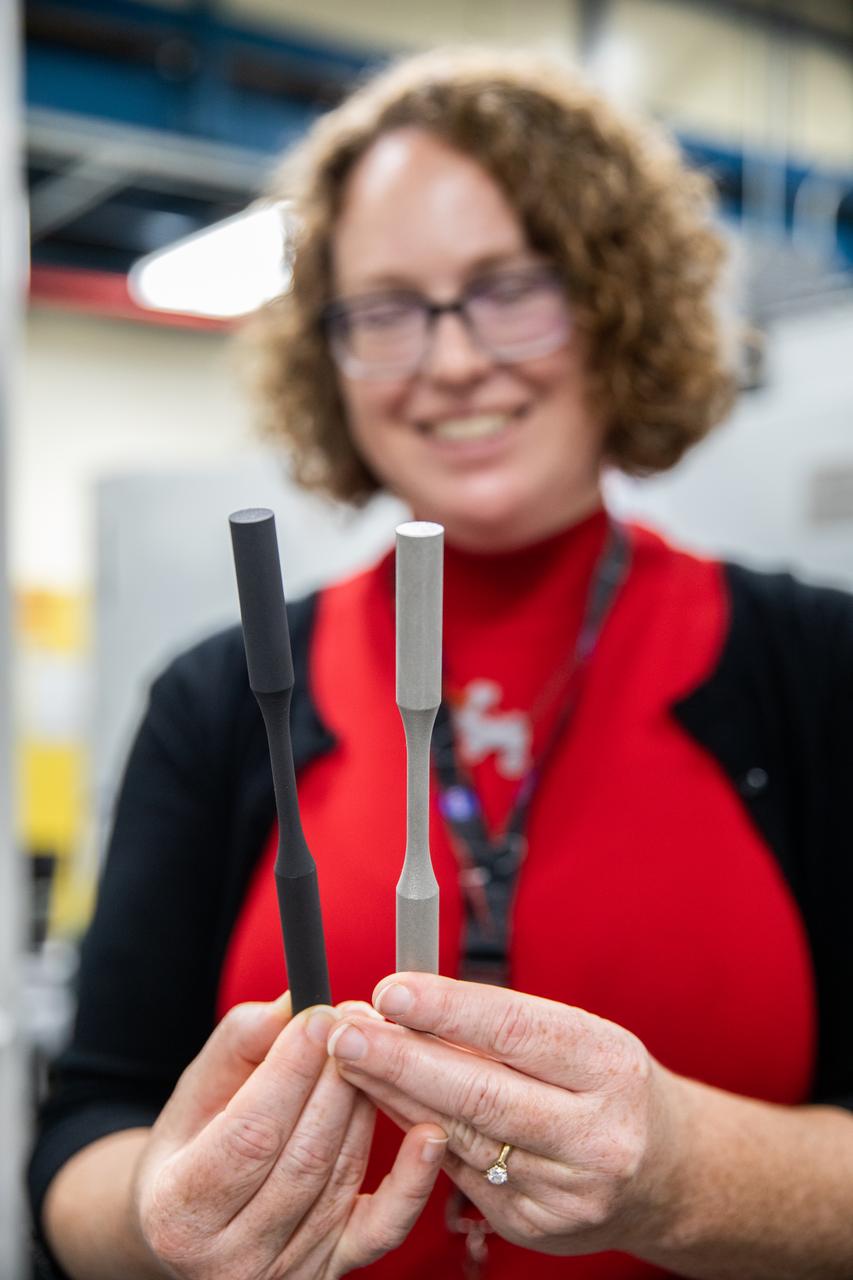

Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, displays two fatigue samples that will be tested in the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiments inside the Prototype Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied to spacecraft and launch vehicles.
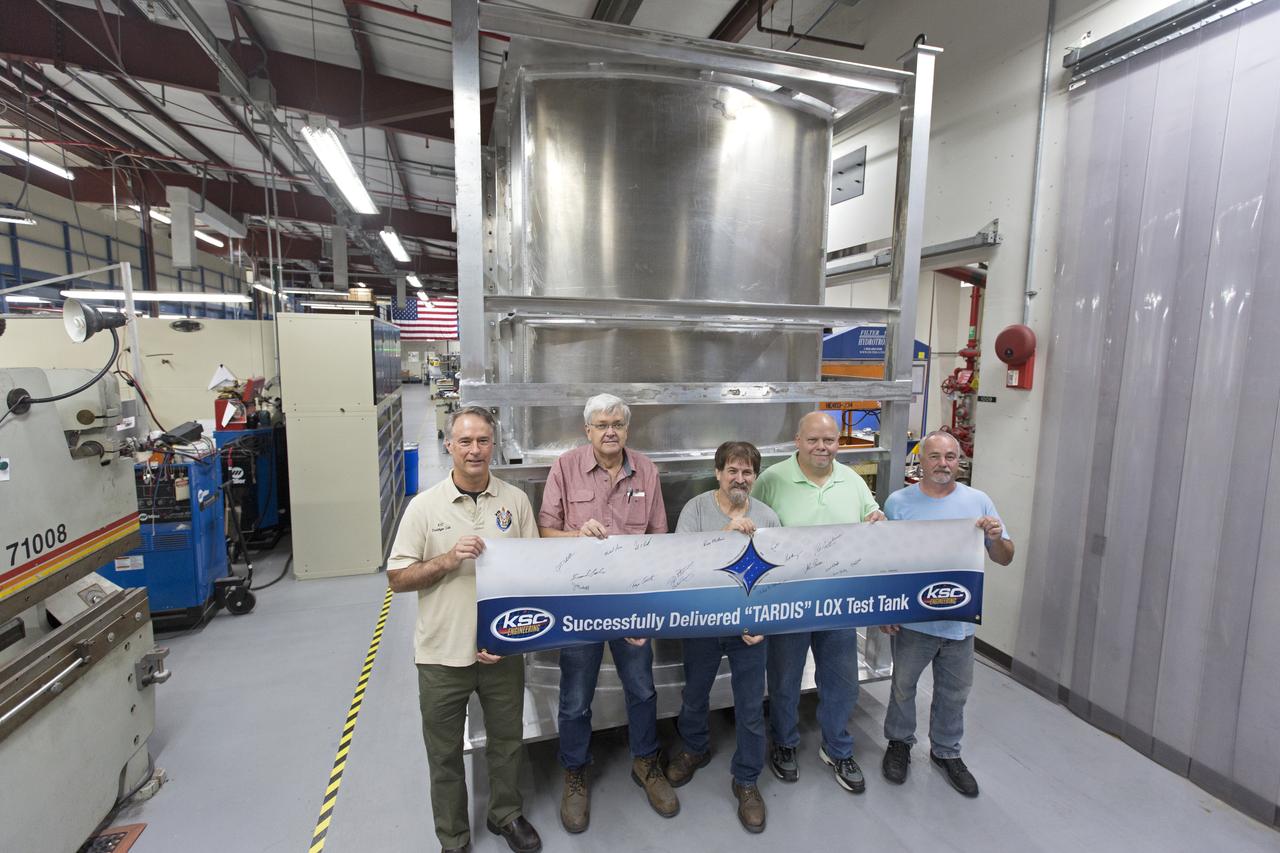

Inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, engineers and technicians hold a banner marking the successful delivery of a liquid oxygen test tank called Tardis. From left, are Todd Steinrock, chief, Fabrication and Development Branch, Prototype Development Lab; David McLaughlin, electrical engineering technician; Phil Stroda, mechanical engineering technician; Perry Dickey, lead electrical engineering technician; and Harold McAmis, lead mechanical engineering technician. Engineers and technicians worked together to develop the tank and build it at the lab to support cryogenic testing at Johnson Space Center's White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The 12-foot-tall, 3,810-pound aluminum tank will be shipped to White Sands for testing.
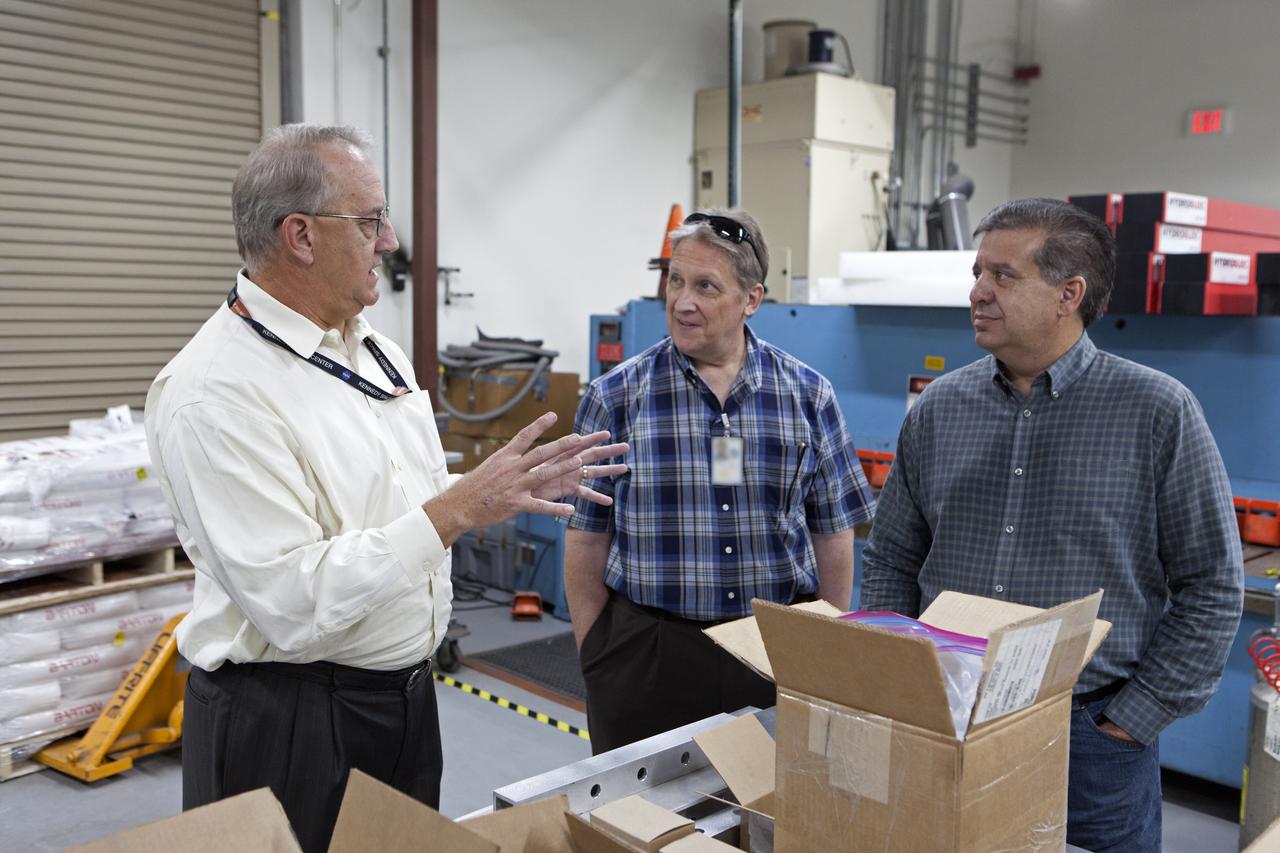

NASA Kennedy Space Center's Engineering Director Pat Simpkins, at left, talks with Michael E. Johnson, a project engineer; and Emilio Cruz, deputy division chief in the Laboratories, Development and Testing Division, inside the Prototype Development Laboratory. A banner signing event was held to mark the successful delivery of a liquid oxygen test tank, called Tardis. Engineers and technicians worked together to develop the tank and build it at the lab to support cryogenic testing at Johnson Space Center's White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The 12-foot-tall, 3,810-pound aluminum tank will be shipped to White Sands for testing.
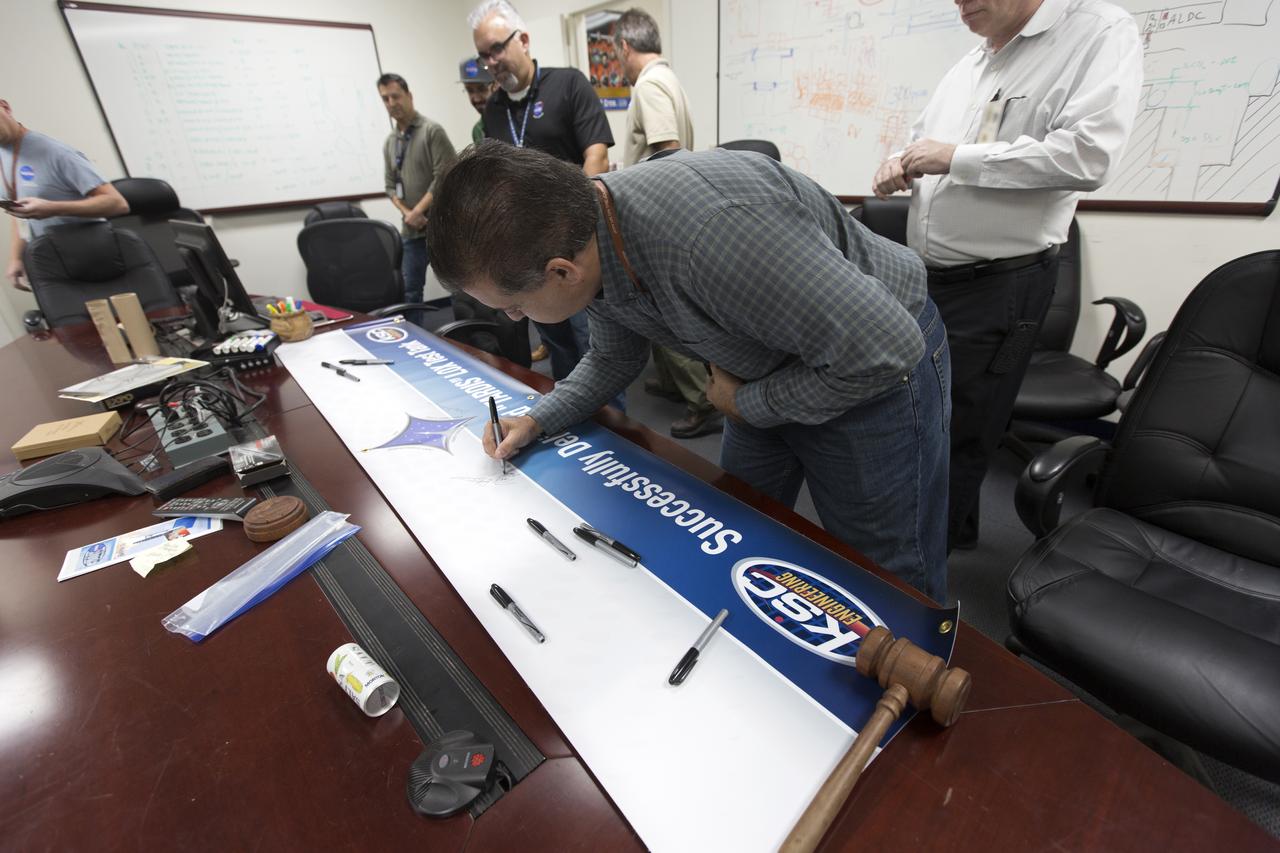

Workers sign the banner marking the successful delivery of a liquid oxygen test tank, called Tardis, in the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Engineers and technicians worked together to develop the tank and build it at the lab to support cryogenic testing at Johnson Space Center's White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The 12-foot-tall, 3,810-pound aluminum tank will be shipped to White Sands for testing.

Inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers in the lab hold a banner marking the successful delivery of a liquid oxygen test tank called Tardis. Engineers and technicians worked together to develop the tank to build it at the lab to support cryogenic testing at Johnson Space Center's White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The 12-foot-tall, 3,810-pound aluminum tank will be shipped to White Sands for testing.
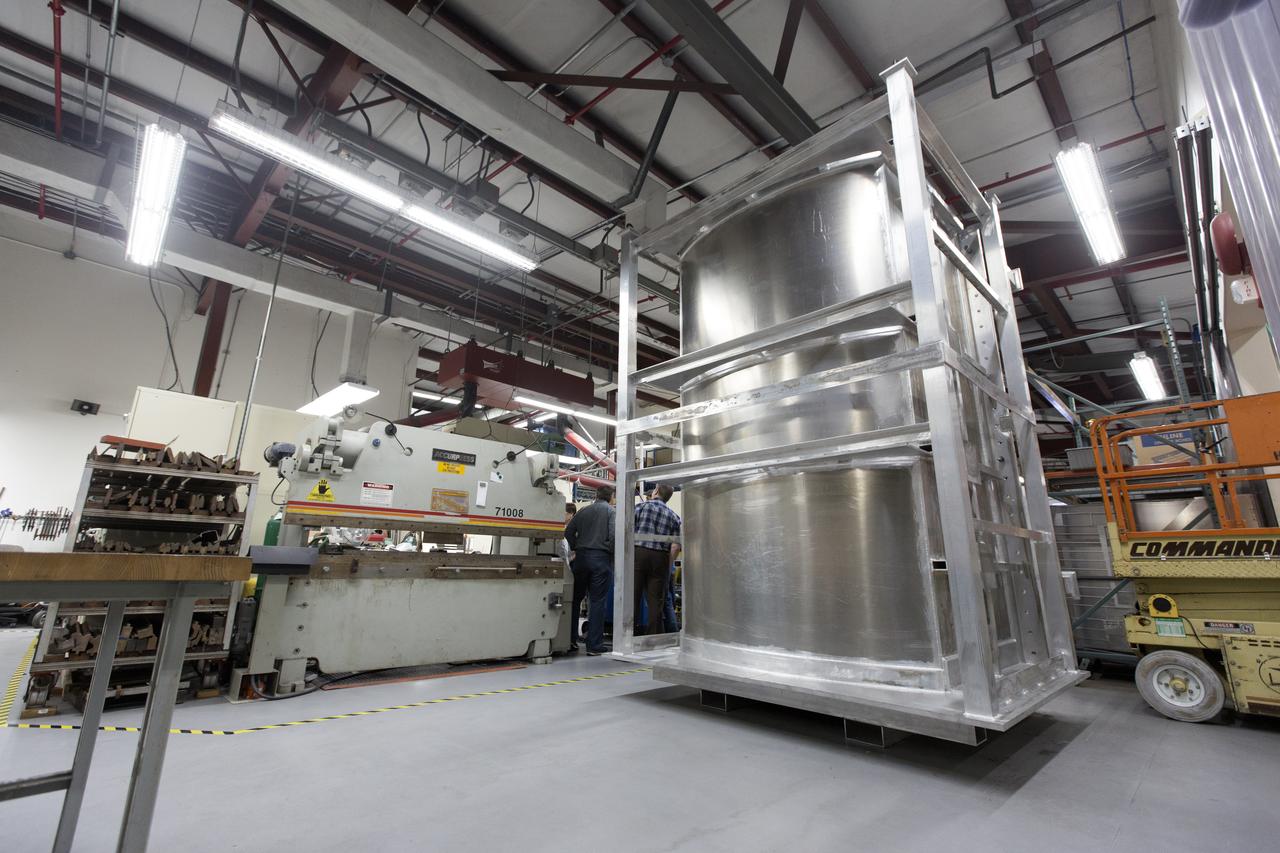

A liquid oxygen test tank was completed in the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A banner signing event marked the successful delivery of the tank called Tardis. Engineers and technicians worked together to develop the tank and build it at the lab to support cryogenic testing at Johnson Space Center's White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The 12-foot-tall, 3,810-pound aluminum tank will be shipped to White Sands for testing.
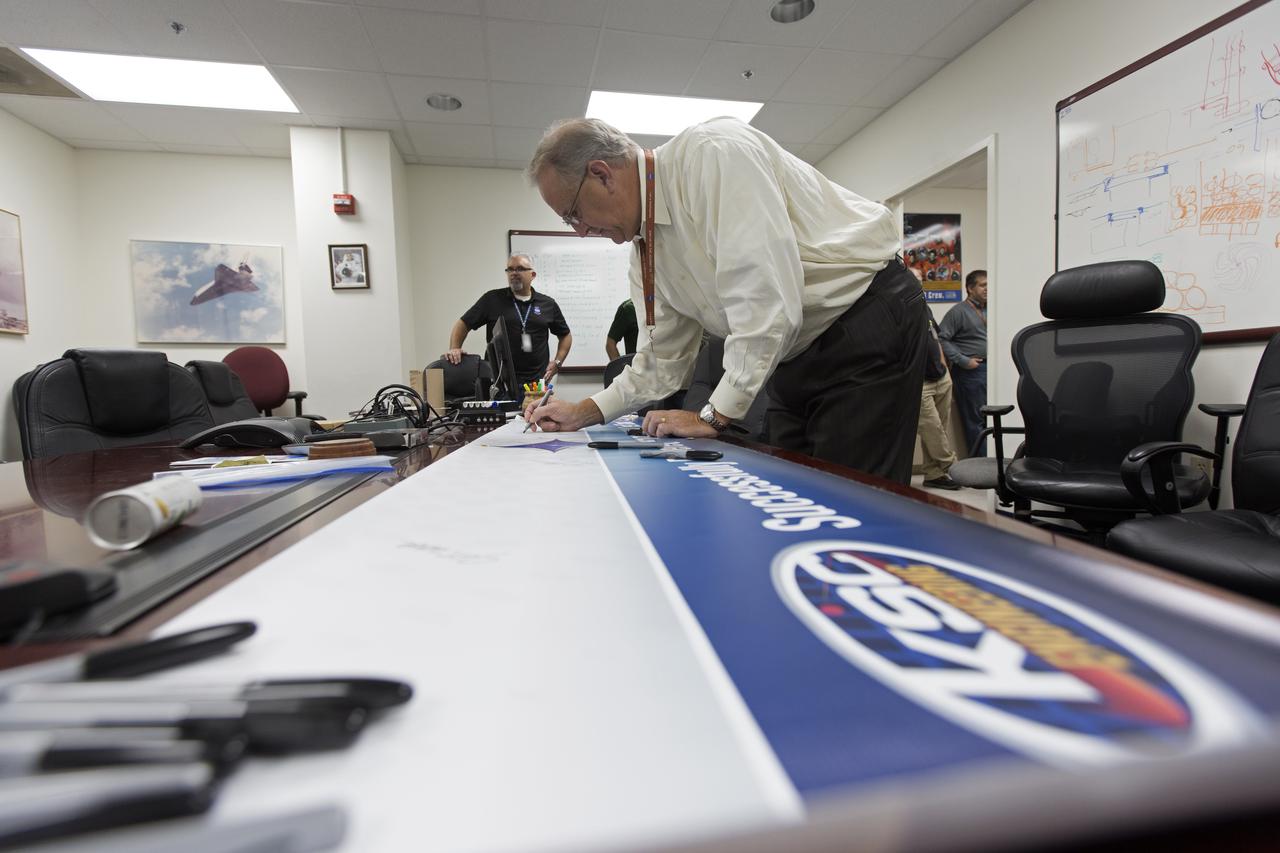

NASA Kennedy Space Center's Engineering Director Pat Simpkins signs the banner marking the successful delivery of a liquid oxygen test tank, called Tardis, in the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Engineers and technicians worked together to develop the tank and build it to support cryogenic testing at Johnson Space Center's White Stands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The 12-foot-tall, 3,810-pound aluminum tank will be shipped to White Sands for testing.

NASA Kennedy Space Center's Engineering Directorate held a banner signing event in the Prototype Development Laboratory to mark the successful delivery of a liquid oxygen test tank, called Tardis. Engineers and technicians worked together to develop the tank and build it to support cryogenic testing at Johnson Space Center's White Stands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The 12-foot-tall, 3,810-pound aluminum tank will be shipped to White Sands for testing.
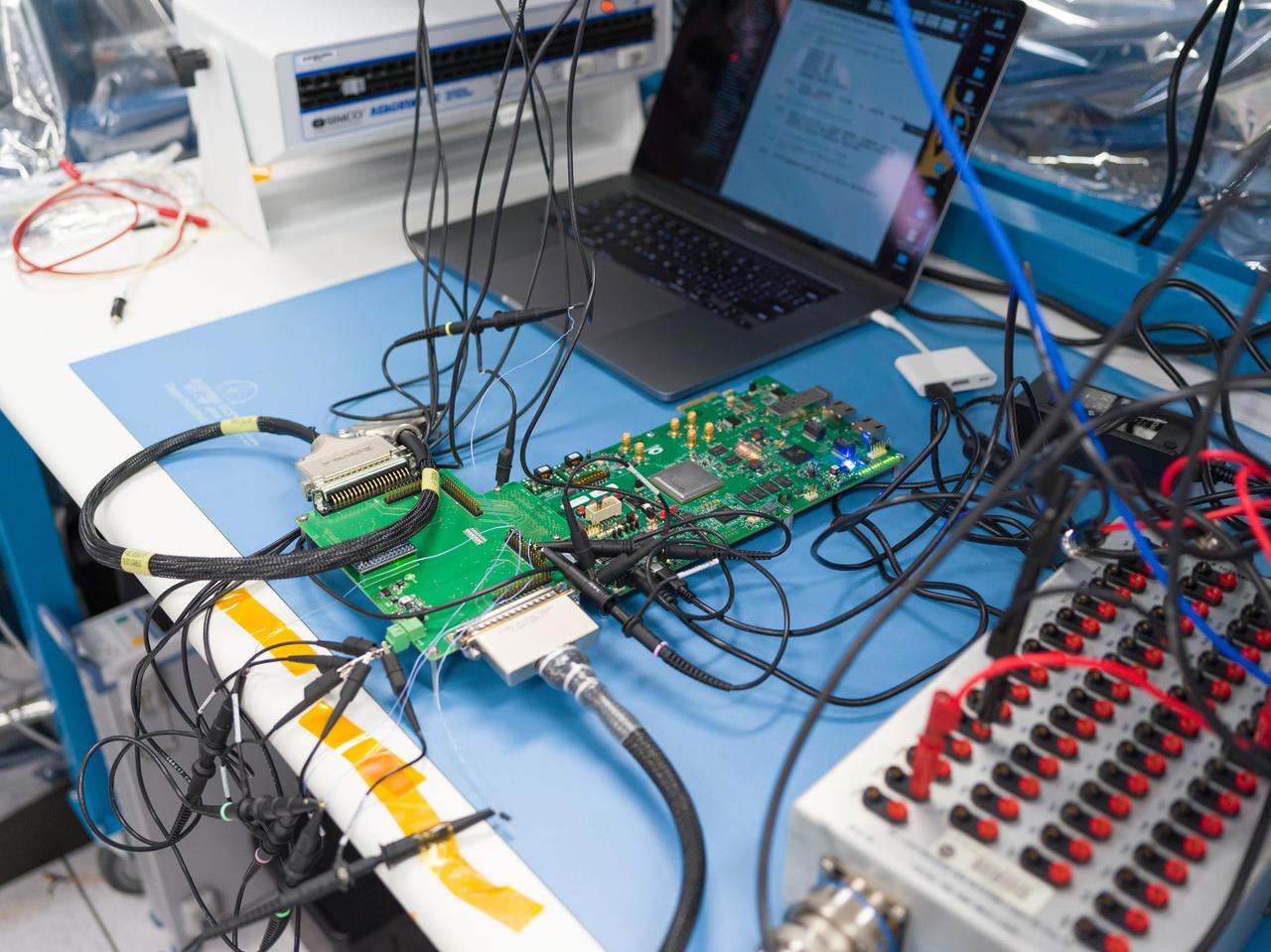
Seen here in March 2023, prototype hardware for the Venus Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (VISAR) underwent interface testing at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. VISAR is being developed at JPL for NASA's Venus Emissivity Radio Science, InSAR, Topography & Spectroscopy (VERITAS) mission that will launch within a decade to explore Earth's twin. These early interface tests are the first in a series to be run by JPL and Thales Alenia Space Italy (TASI), an international partner of the VERITAS mission that is contributing hardware to the instrument. Figure A shows TASI engineers Luca Di Marco Napini and Gabriel Mihu working in a JPL cleanroom on the VISAR prototype hardware. When VERITAS arrives in orbit, it will use VISAR to create detailed 3D global maps of Venus. The spacecraft will also carry a near-infrared spectrometer to figure out what the surface is made of. Together, the instruments will offer clues about the planet's past and present geologic processes, help reveal how the paths of Venus and Earth diverged, and how Venus lost its potential as a habitable world. VERITAS is managed by JPL. VERITAS and NASA's Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging (DAVINCI) mission were selected in 2021 under NASA's Discovery Program as the agency's next missions to Venus. The Discovery Program is managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, for the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25832
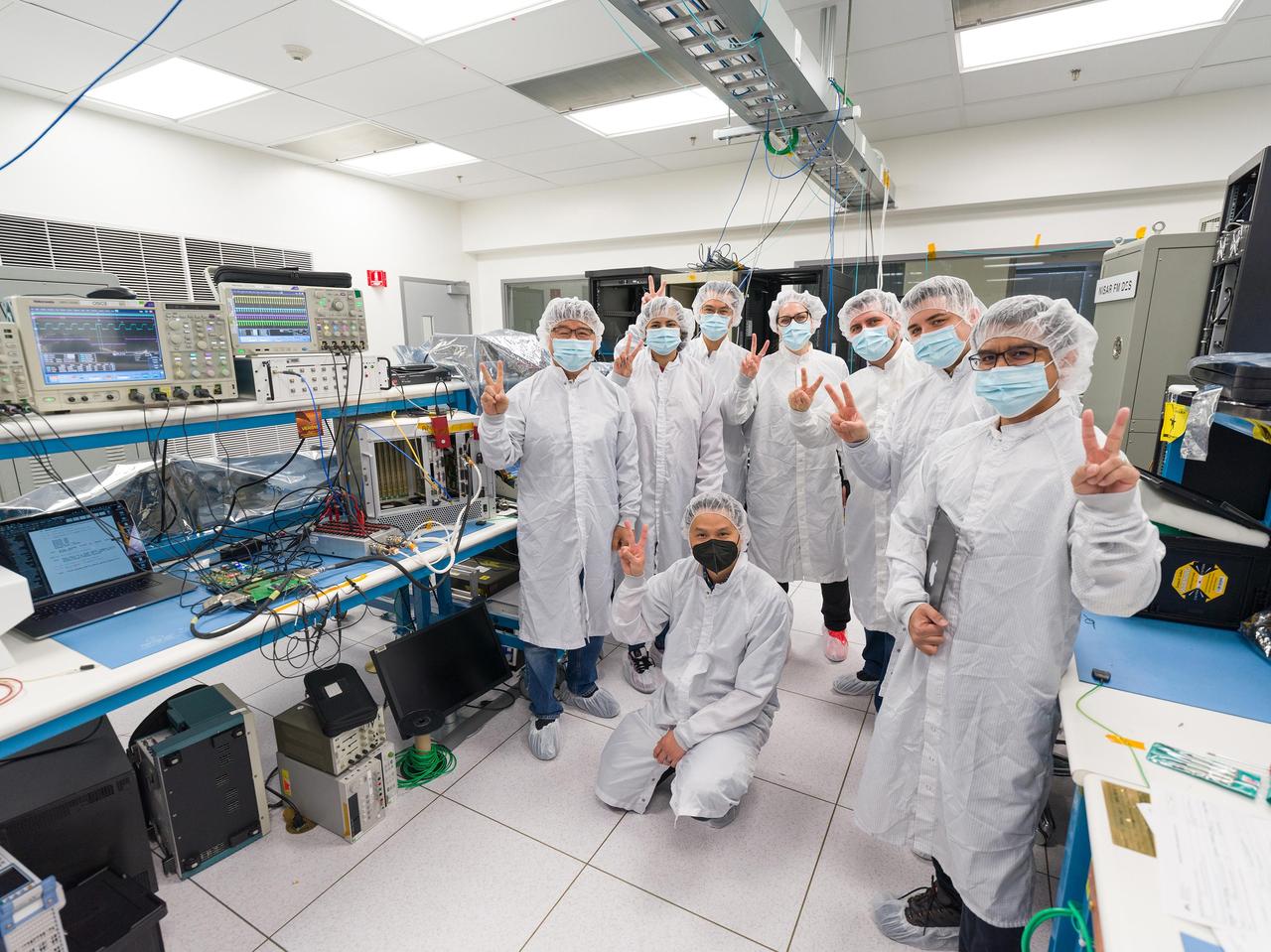

Seen here are members of the international team that participated in recent tests on prototype hardware for the Venus Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (VISAR) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. VISAR is being developed at JPL for NASA's Venus Emissivity Radio Science, InSAR, Topography & Spectroscopy (VERITAS) mission that will launch within a decade to explore Earth's twin. In March 2023, the hardware underwent early interface tests in a JPL clean room, representing the first in a series to be run by JPL and Thales Alenia Space Italy (TASI), an international partner of the VERITAS mission that is contributing hardware to the instrument. Dressed in gowns to minimize the risk of contamination with sensitive electronics, the JPL VISAR digital team and TASI engineers pose for a photograph next to the laboratory benches where the tests took place. Figure A shows the same personnel without gowns for a team photo. From left to right: Marvin Cruz (JPL), Chester Lim (JPL), Tim Noh (JPL), Hana Haideri (JPL), Luca Di Marco Napini (TASI), Ernie Chuang (JPL), Dragana Perkovic-Martin (JPL), and Gabriel Mihu (TASI). JPL's Michael Burke, Anusha Yarlagadda, Duane Clark, and TASI's Antonio Delfino also participated in the tests but are not pictured. When VERITAS arrives in orbit, it will use VISAR to create detailed 3D global maps of Venus. The spacecraft will also carry a near-infrared spectrometer to figure out what the surface is made of. Together, the instruments will offer clues about the planet's past and present geologic processes, help reveal how the paths of Venus and Earth diverged, and how Venus lost its potential as a habitable world. VERITAS is managed by JPL. VERITAS and NASA's Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging (DAVINCI) mission were selected in 2021 under NASA's Discovery Program as the agency's next missions to Venus. The Discovery Program is managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, for the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25833
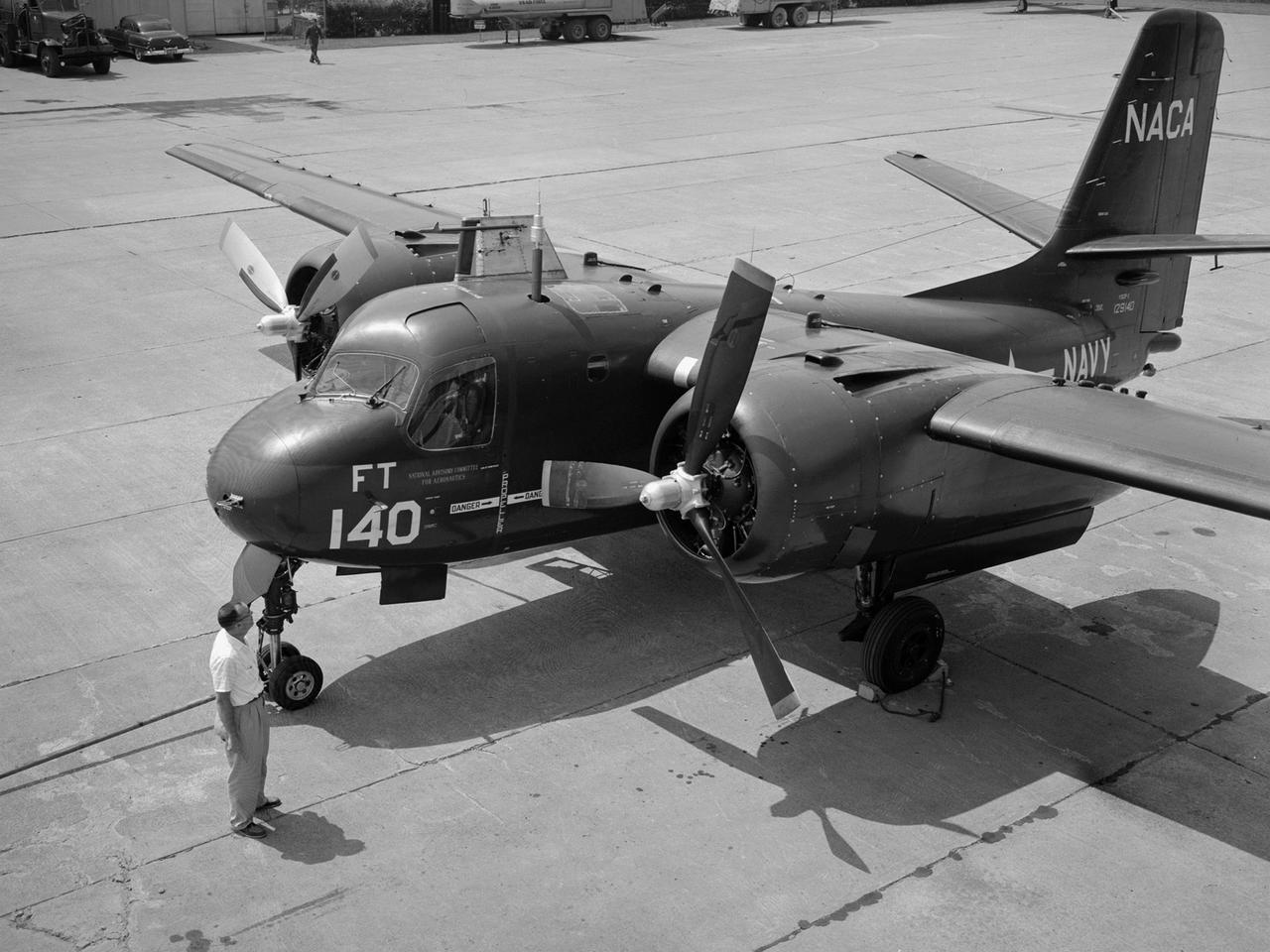

The NACA’s Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory acquired the Grumman S2F-1 Tracker from the Navy in 1955 to study icing instrumentation. Lewis’s icing research program was winding down at the time. The use of jet engines was increasing thus reducing the threat of ice accumulation. Nonetheless Lewis continued research on the instrumentation used to detect icing conditions. The S2F-1 Tracker was a carrier-based submarine hunter for the Navy. Grumman developed the Tracker as a successor to its Korean War-era Guardian patrol aircraft. Prototypes first flew in late 1952 and battle-ready versions entered Naval service in early 1954. The Navy utilized the Trackers to protect fleets from attack.

The first prototype starshade developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, shown in technology partner Astro Aerospace/Northrup Grumman's facility in Santa Barbara, California, in 2013. As shown by this 66 foot (20-meter) model, starshades can come in many shapes and sizes. This design shows petals that are more extreme in shape which properly diffracts starlight for smaller telescopes. Each petal is covered in a high-performance plastic film that resembles gold foil. On a starshade ready for launch, the thermal gold foil will only cover the side of the petals facing away from the telescope, with black on the other, so as not to reflect other light sources such as the Earth into its camera. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20906
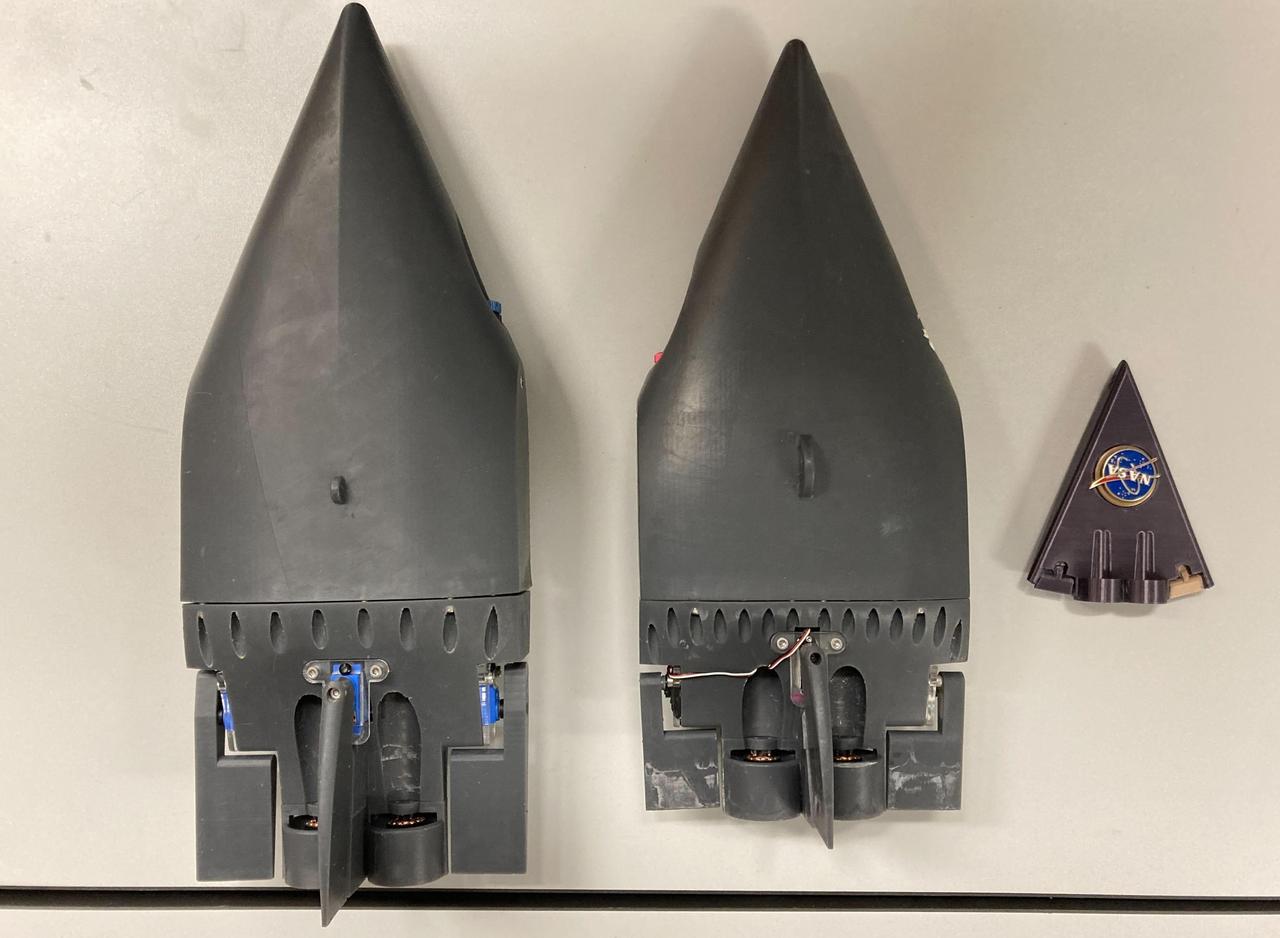

Two prototypes for a NASA mission concept called SWIM (short for Sensing With Independent Micro-swimmers) are arranged beside a much smaller nonfunctioning model representing the final envisioned size of the robot: about 5 inches (12 centimeters) long. The plastic prototypes were built at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to demonstrate the feasibility of the concept, a swarm of dozens of self-propelled, cellphone-size robots exploring the waters of icy moons like Jupiter's Europa and Saturn's Enceladus. Delivered to the subsurface ocean by an ice-melting cryobot, the tiny robots would zoom away to look for chemical and temperature signals that could point to life. The prototypes were used in more that 20 rounds of underwater testing in a pair of tanks at JPL and in a competition swimming pool at Caltech in Pasadena. Relying on low-cost, commercially made motors and electronics, the robots are pushed along by two propellers and use two to four flaps for steering. The prototype in the center of the image weighs 3.7 pounds (1.7 kilograms) and is 14.5 inches (37 centimeters) long, 6 inches (15 centimeters) wide, and 2.5 inches (6.5 centimeters) tall, with a volume of 104 cubic inches (1.7 liters). The upgraded prototype at left is slightly bigger: 16.5 inches (42 centimeters) long, 3 inches (7.5 centimeters) tall, with a weight of 5 pounds (2.3 kilograms) and a volume of 140 cubic inches (2.3 liters). In pool tests, the prototype at left demonstrated controlled maneuvering, the ability to stay on and correct its course, and a back-and-forth "lawnmower" exploration pattern. It managed all of this autonomously, without the team's direct intervention. The robot even spelled out "J-P-L." As conceived for spaceflight and represented by the model at right, the robots would have dimensions about three times smaller than these prototypes – tiny compared to existing remotely operated and autonomous underwater scientific vehicles. The swimmers would feature miniaturized, purpose-built parts and employ a novel wireless underwater acoustic communication system for transmitting data and triangulating their positions. Several years more of work would be needed to make such an advanced concept ready for spaceflight. Led by JPL, SWIM development took place from spring 2021 to fall 2024. The project was supported by Phase I and II funding from NASA's Innovative Advanced Concepts program under the agency's Space Technology Mission Directorate. JPL is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26425
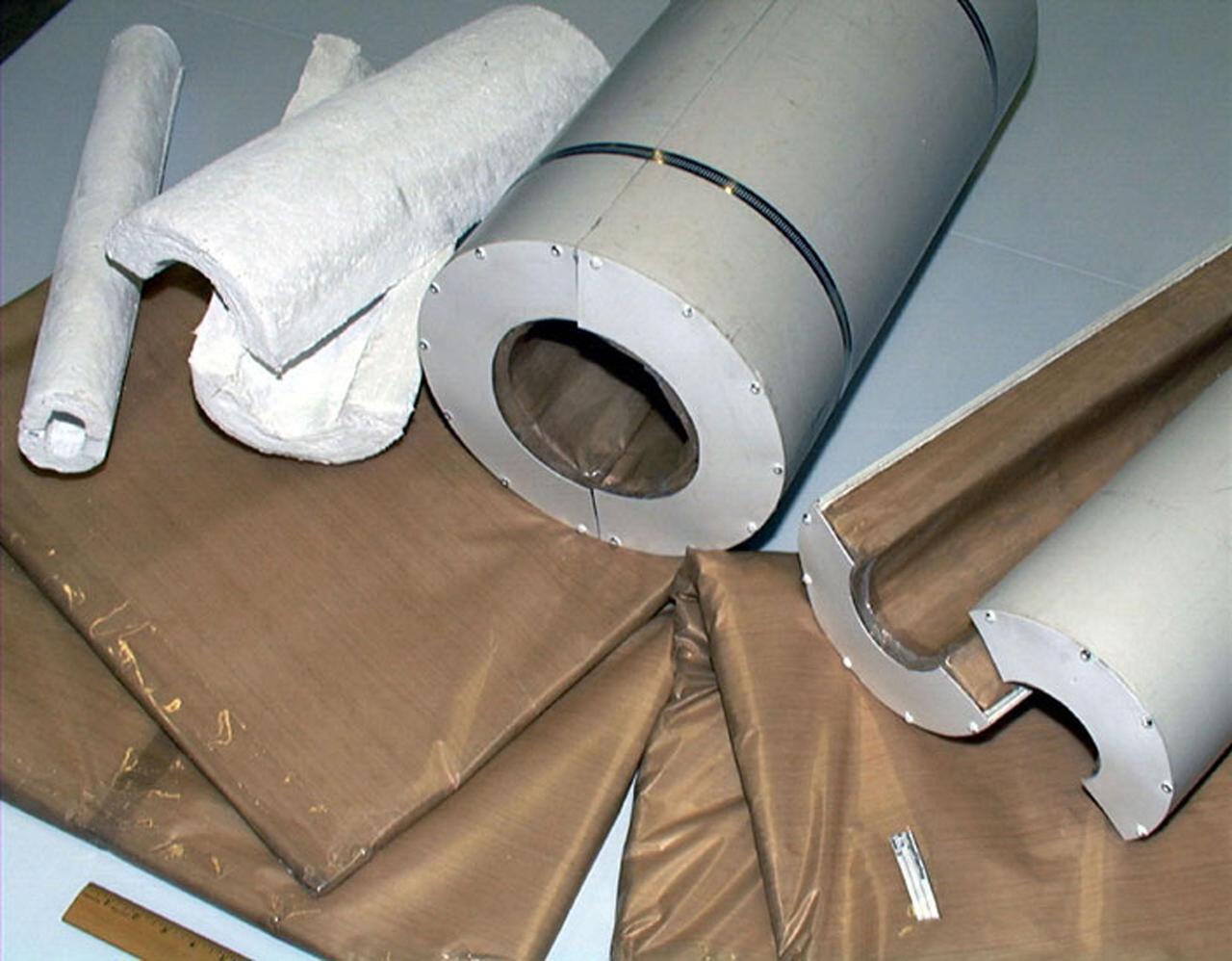

Various materials are ready for testing in the Kennedy Space Center's cryogenics test bed laboratory. The cryogenics laboratory is expanding to a larger test bed facility in order to offer research and development capabilities that will benefit projects originating from KSC, academia and private industry. Located in KSC's industrial area, the lab is equipped with a liquid nitrogen flow test area to test and evaluate cryogenic valves, flow-meters and other handling equipment in field conditions. A 6,000-gallon tank supplies liquid to low-flow and high-flow test sections. KSC engineers and scientists can also build system prototypes and then field test and analyze them with the center's unique equipment. Expanded cryogenic infrastructure will posture the Space Coast to support biological and medical researchers who use liquid nitrogen to preserve and store human and animal cells and to destroy cancer tissue using cryosurgery; hospitals that use superconductive magnets cooled in liquid helium for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); the food industry, which uses liquid nitrogen for freezing and long-term storage; as well as the next generation of reusable launch vehicles currently in development
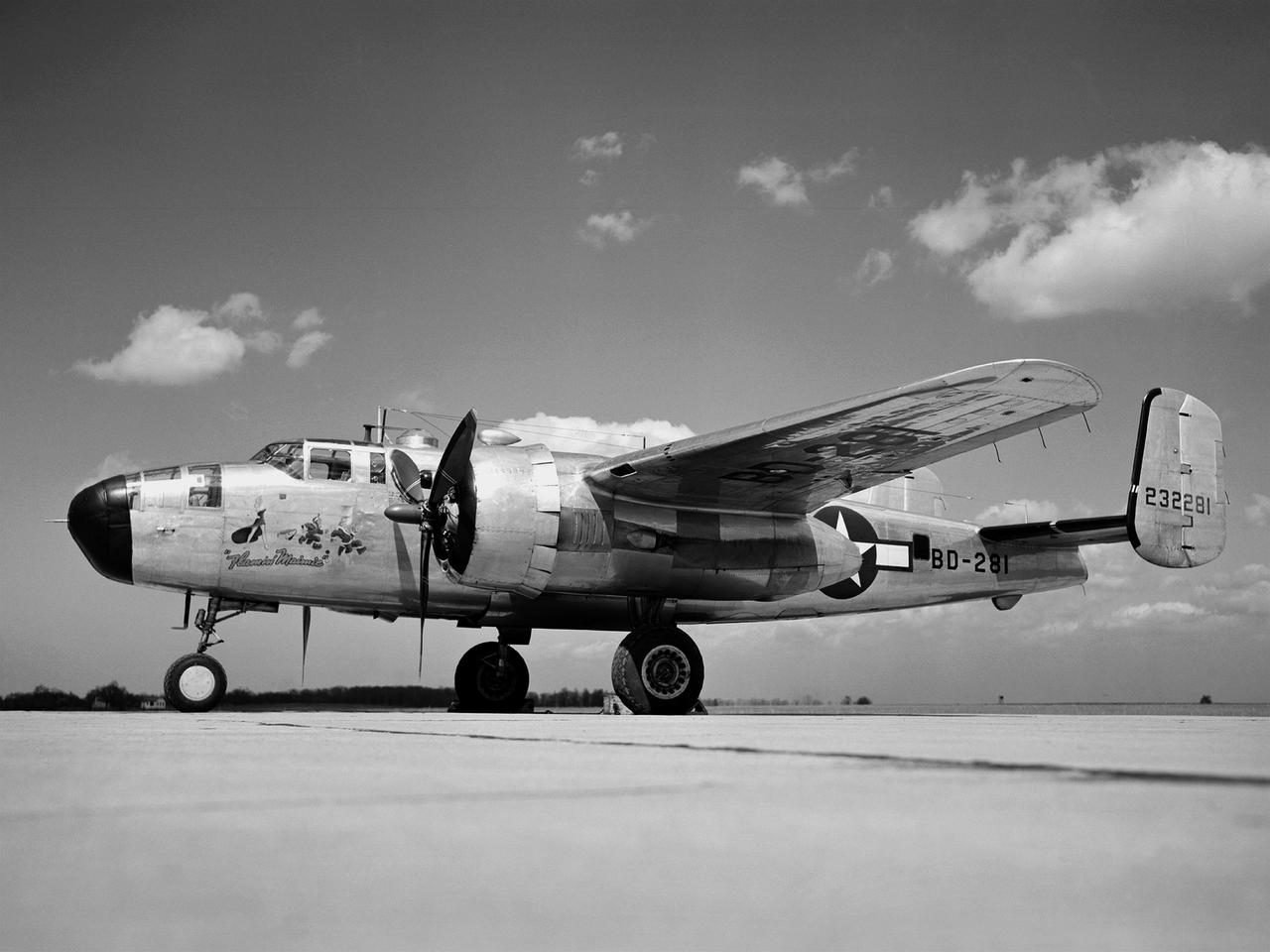

In 1946 the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory became the NACA’s official icing research center. In addition to the Icing Research Tunnel, the lab possessed several aircraft modified for icing work, including a Consolidated B-24M Liberator and a North American XB-25E Mitchell, seen here. The XB-25E’s frequent engine fires allegedly resulted in its “Flamin’ Maimie” nickname. The aircraft’s nose art, visible in this photograph, includes a leather-jacketed mechanic with an extinguisher fleeing a fiery woman. North American developed the B-25 in the mid-1930s as a transport aircraft, but it was hurriedly reconfigured as a medium bomber for World War II. This XB-25E was a single prototype designed in 1942 specifically to test an exhaust gas ice prevention system developed by NACA researcher Lewis Rodert. The system circulated the engines’ hot bleed air to the wings, windshield, and tail. The XB-25E was utilized at the NACA’s Ames Aeronautical Laboratory for two years before being transferred to Cleveland in July 1944. NACA Lewis mechanics modified the aircraft further by installing electrical heating in the front fuselage, propellers, inboard sing, cowls, and antennae. Lewis pilots flew the B-24M and XB-25E into perilous weather conditions all across the country to study both deicing technologies and the physics of ice-producing clouds. These dangerous flights led to advances in weather sensing instruments and flight planning.

Materials are being tested in the Kennedy Space Center's cryogenics test bed laboratory. The cryogenics laboratory is expanding to a larger test bed facility in order to offer research and development capabilities that will benefit projects originating from KSC, academia and private industry. Located in KSC's industrial area, the lab is equipped with a liquid nitrogen flow test area to test and evaluate cryogenic valves, flow-meters and other handling equipment in field conditions. A 6,000-gallon tank supplies liquid to low-flow and high-flow test sections. KSC engineers and scientists can also build system prototypes and then field test and analyze them with the center's unique equipment. Expanded cryogenic infrastructure will posture the Space Coast to support biological and medical researchers who use liquid nitrogen to preserve and store human and animal cells and to destroy cancer tissue using cryosurgery; hospitals that use superconductive magnets cooled in liquid helium for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); the food industry, which uses liquid nitrogen for freezing and long-term storage; as well as the next generation of reusable launch vehicles currently in development

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, installs OSCAR to the flight hardware that will carry it on its suborbital flight test. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees have worked on constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
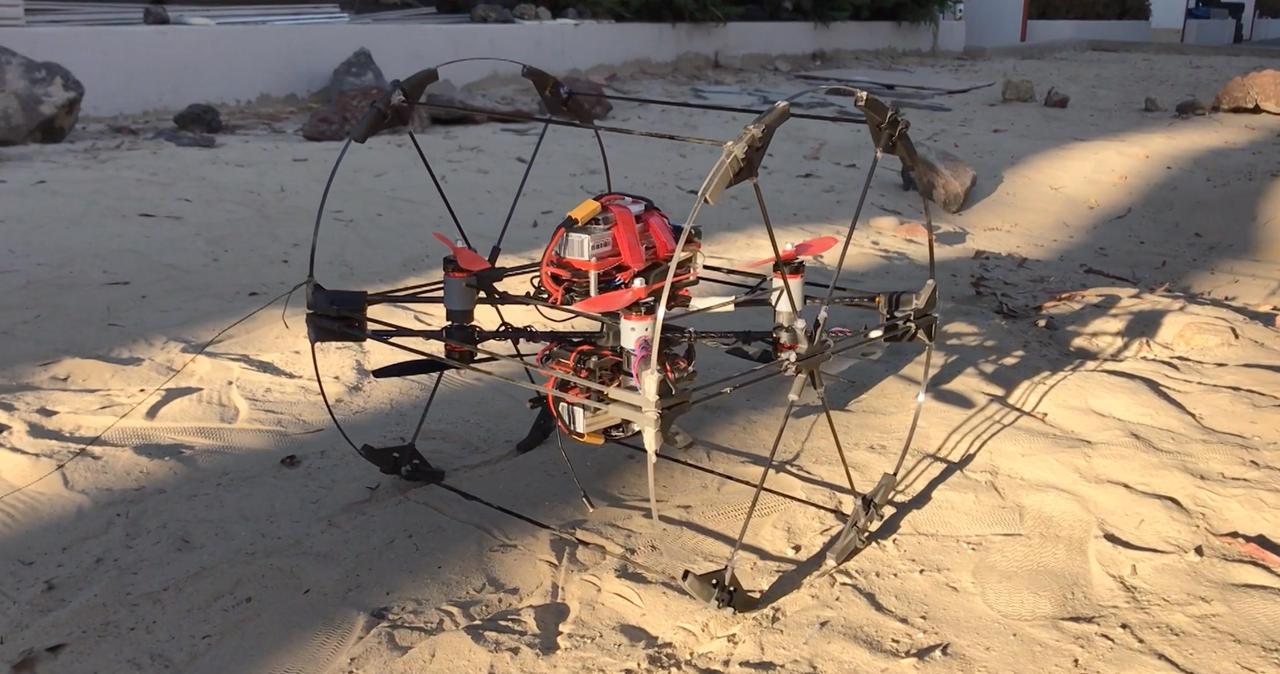

A prototype of the transforming robot Shapeshifter is tested in the robotics yard at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Shapeshifter is made of smaller robots that can morph into rolling spheres, flying drones, swimming submersibles and more. Shapeshifter is a developing concept for a transformational vehicle to explore treacherous, distant worlds. The flying amphibious robot is part of the early-stage research program NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC), which offers several phases of funding to visionary concepts, helping turn ideas that sound like science fiction into science fact. JPL Principle Investigator Ali Agha envisions Shapeshifter as a mission to Saturn's moon Titan, the only other world in the solar system known to have liquid in the form of methane lakes, rivers and seas on its surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23433
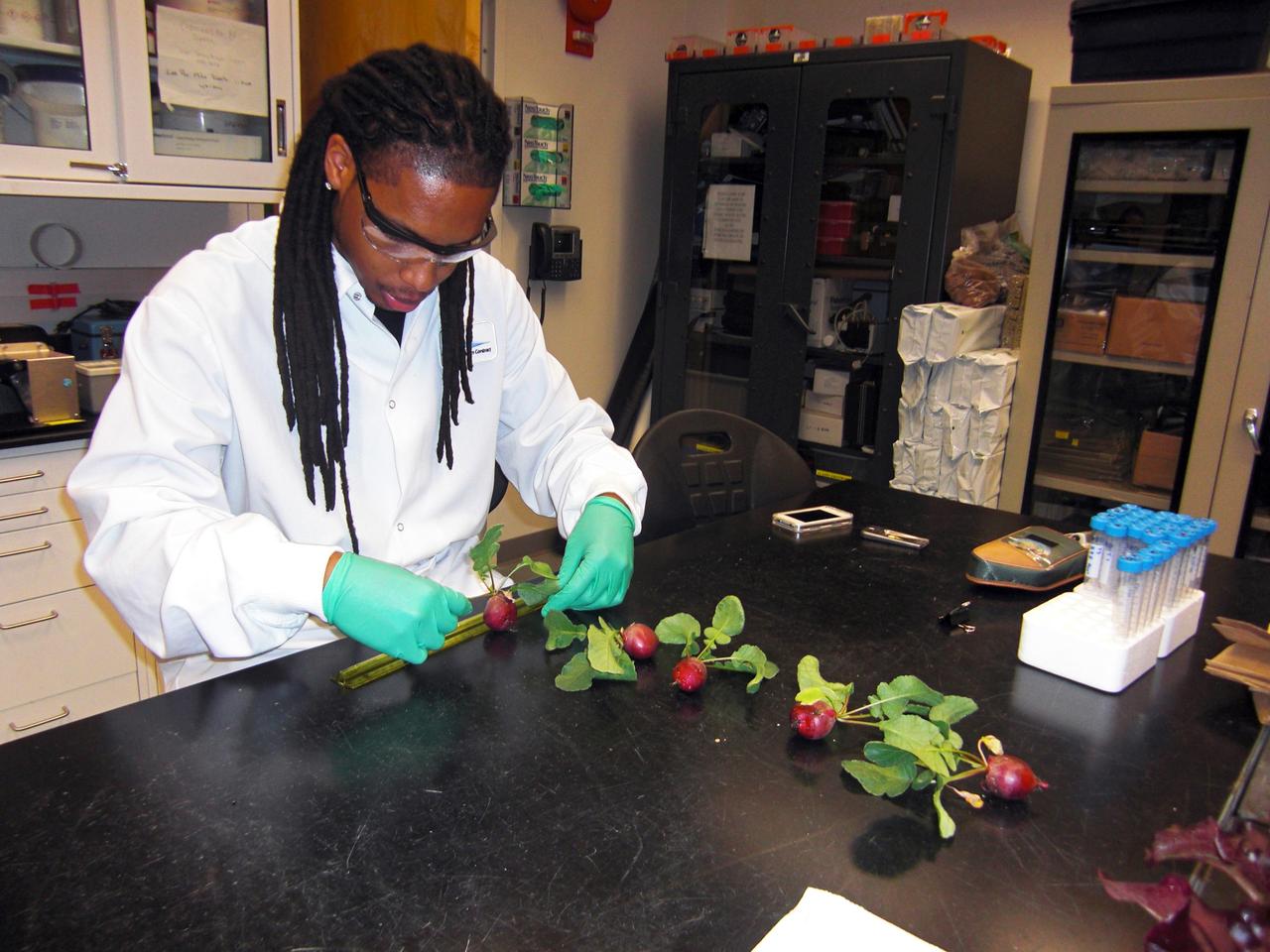

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. Matthew Mickens, a plant biologist from North Carolina Agriculture and Technical State University in North Carolina, measures radish plants that were just harvested from a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales
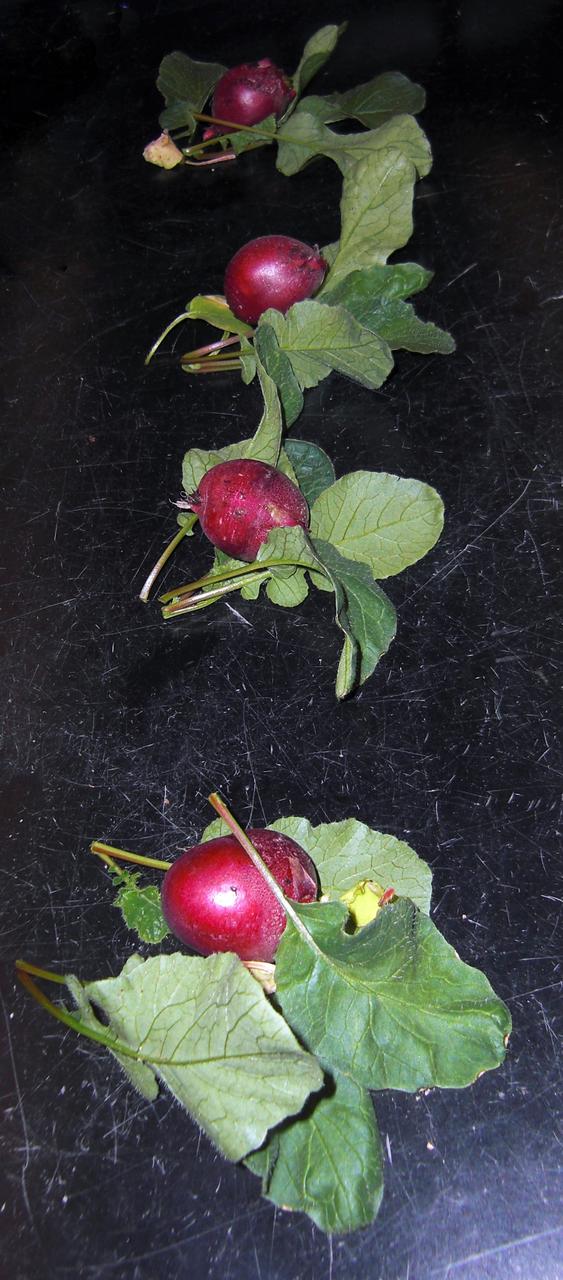

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, radish plants were harvested from a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales
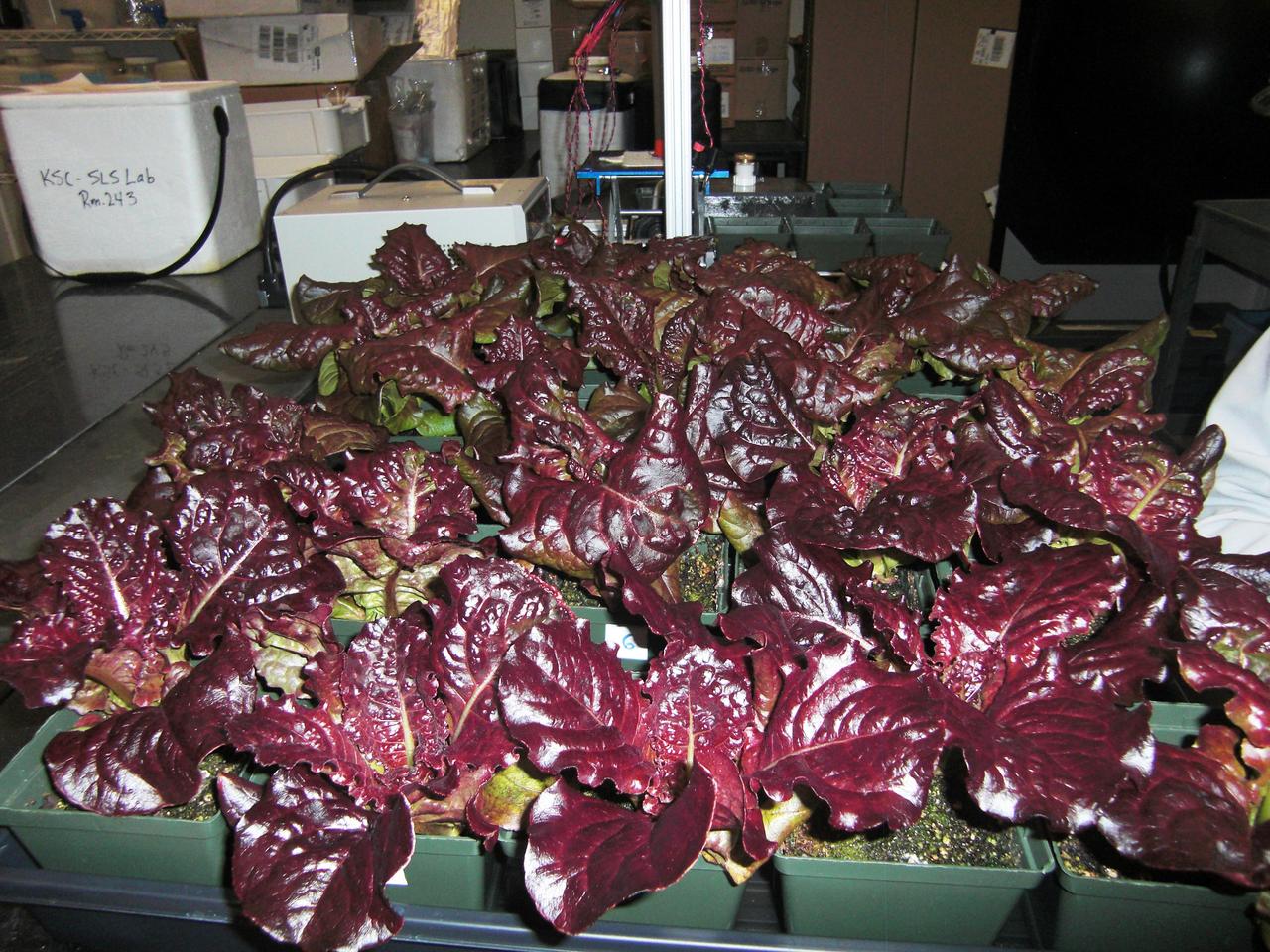

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, red leaf lettuce plants were harvested from a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales
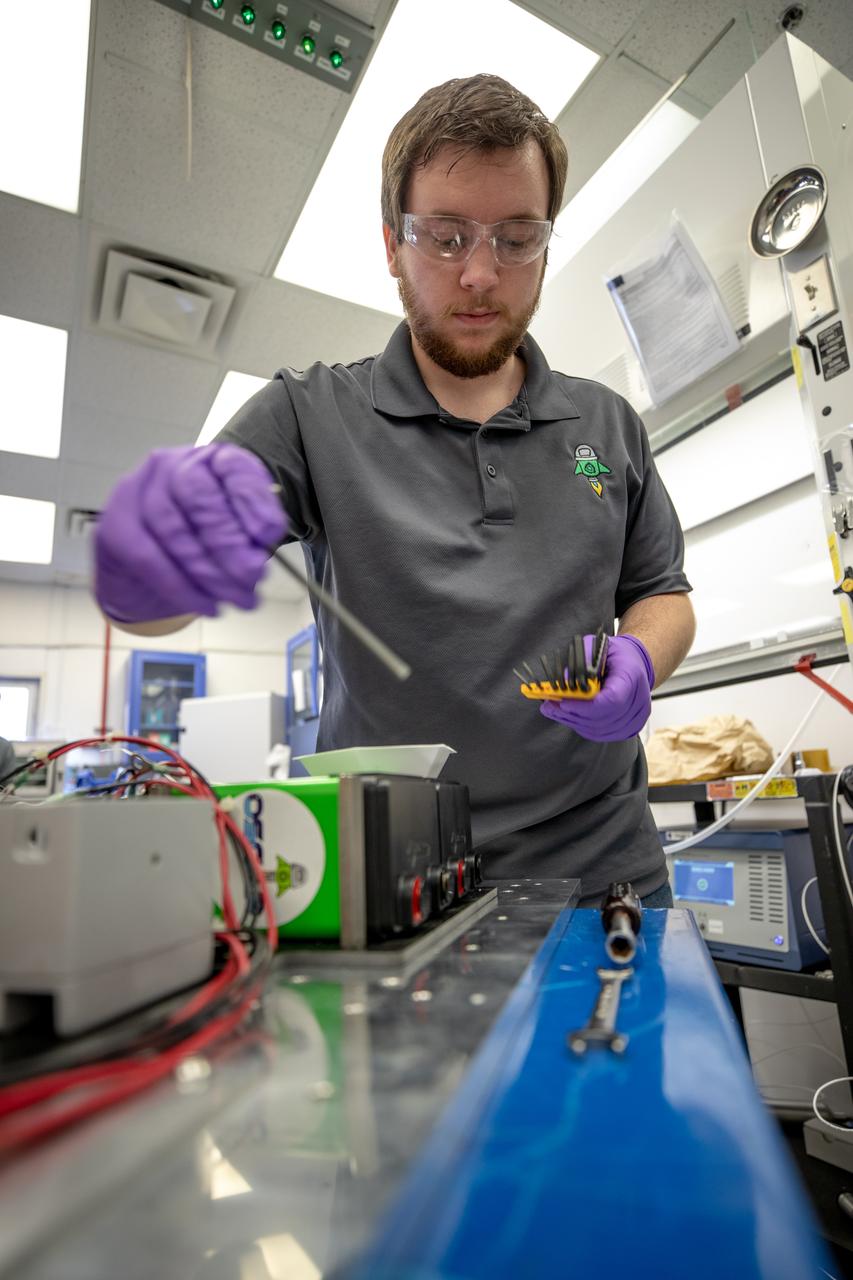

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assembles the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
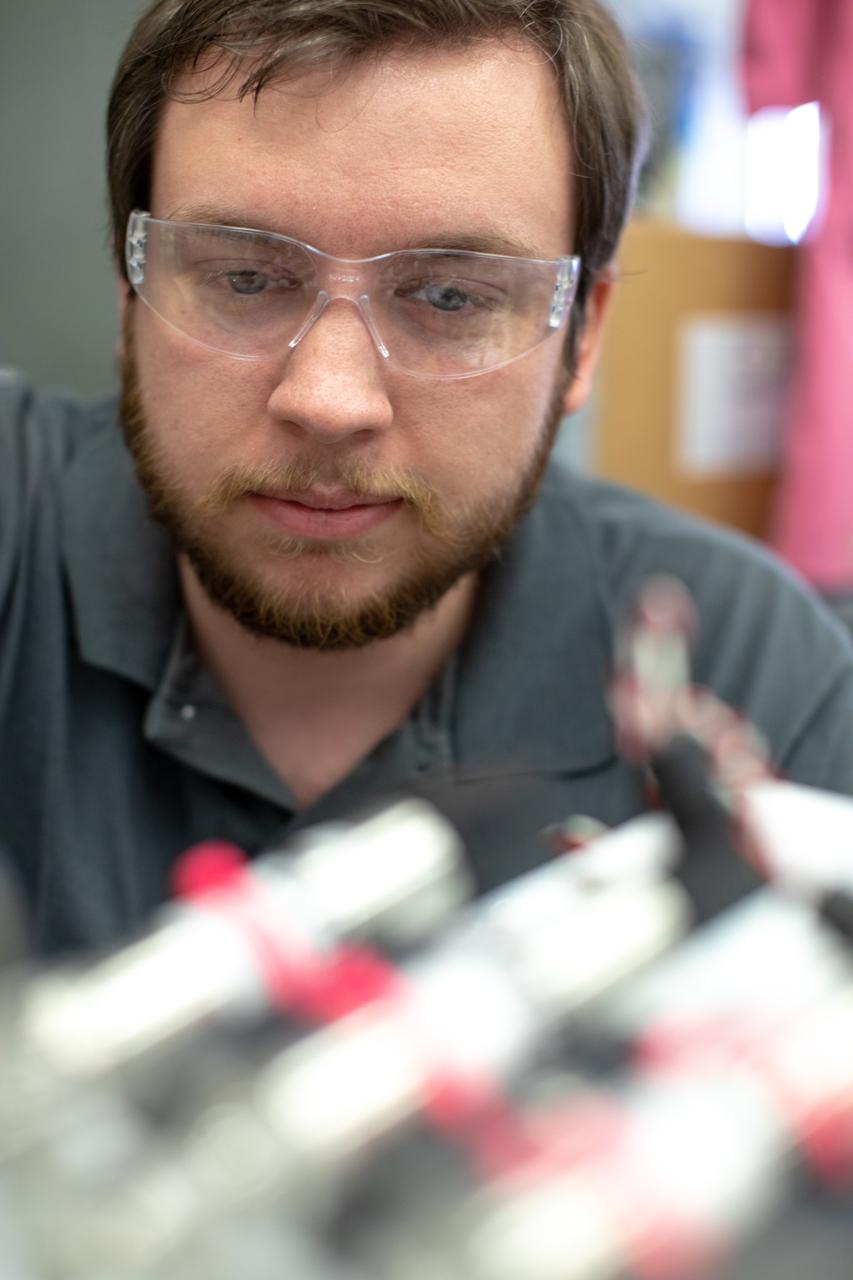

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assembles the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
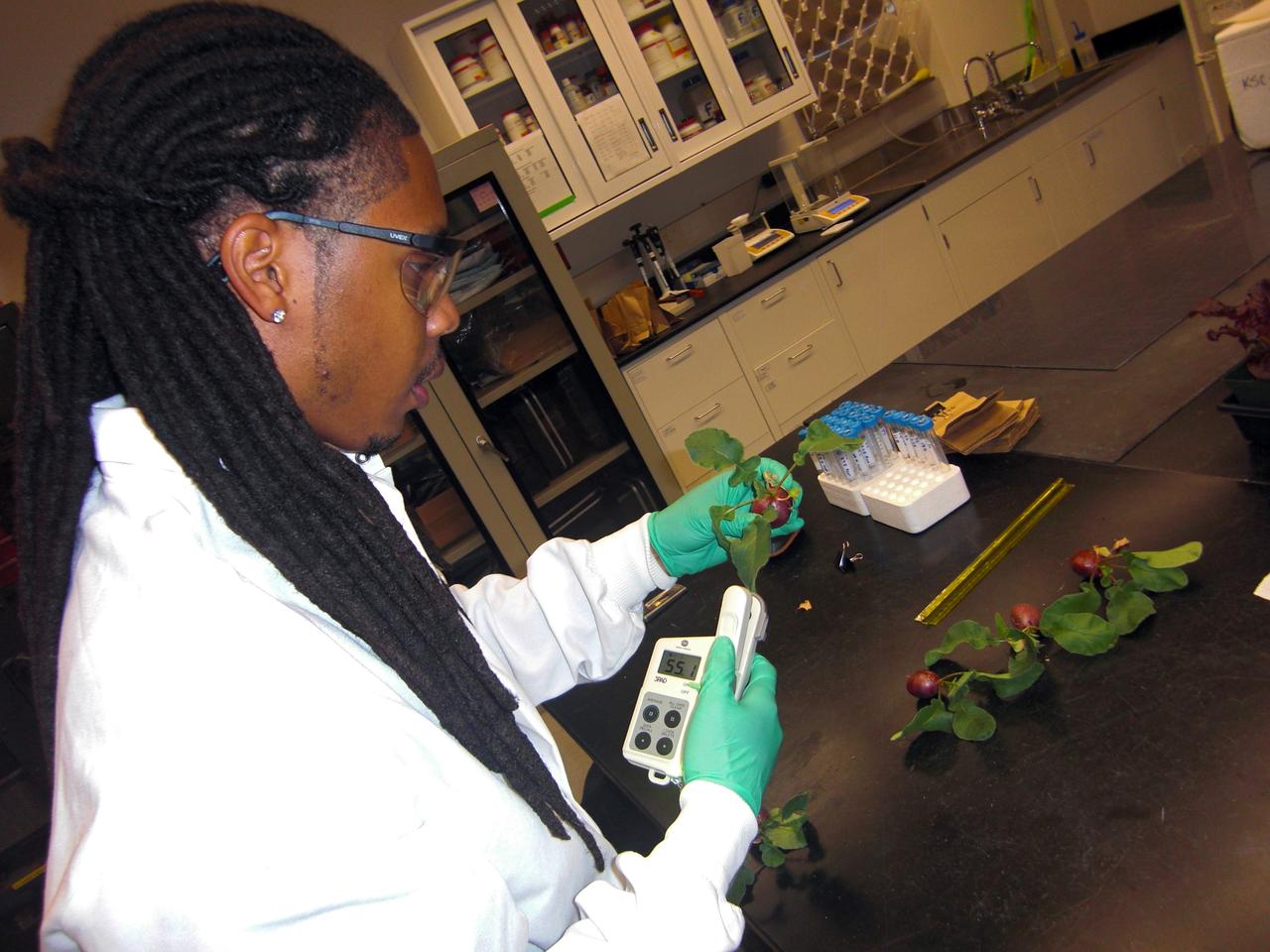

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. Matthew Mickens, a plant biologist from North Carolina Agriculture and Technical State University in North Carolina, measures radish plants that were just harvested from a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales
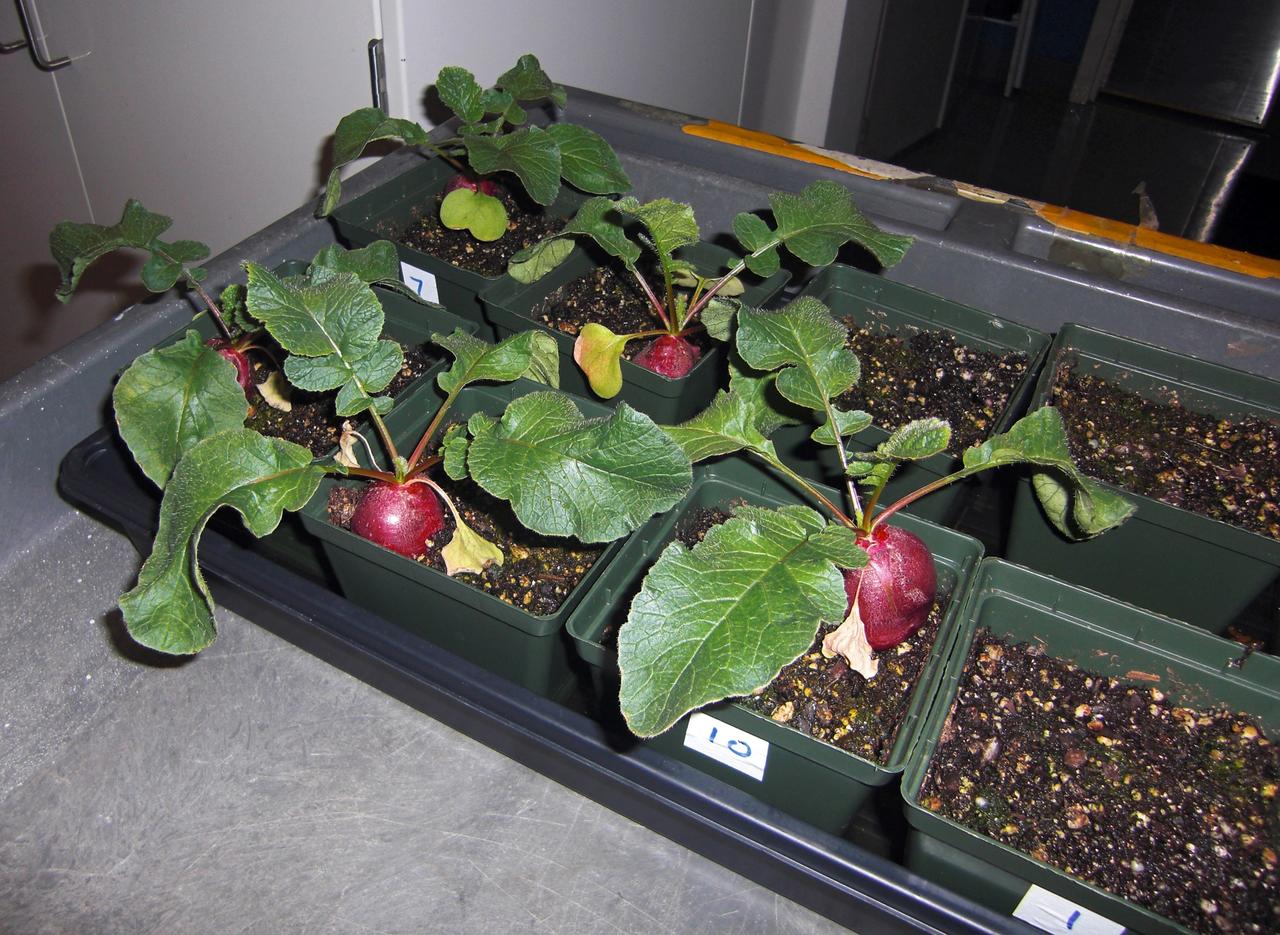

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, radish plants are being harvested in a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales
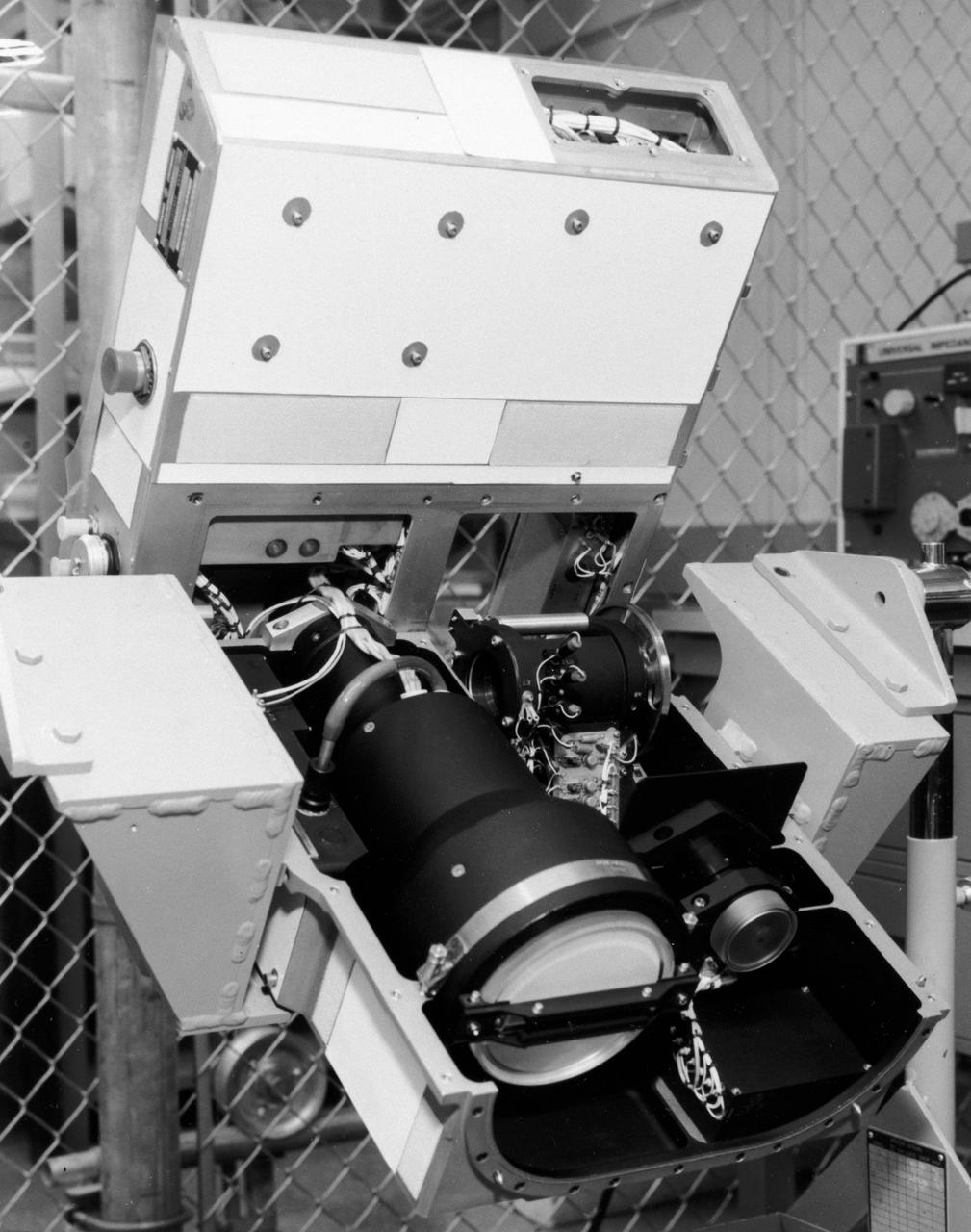

S72-49482 (November 1972) --- The Optical Recorder of the Lunar Sounder Experiment (S-209) which will be mounted in the SIM bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module. The three functional parts of the Lunar Sounder are the optical recorder, the coherent synthetic aperture radar, and the antennas, a retractable dipole for HF and a yagi for VHF. The Lunar Sounder will probe three-quarters of a mile below the moon's surface from the orbiting Apollo 17 spacecraft. Electronic data recorded on film will be retrieved by the crew during trans-Earth EVA. Geologic information on the lunar interior obtained by the sounder will permit scientific investigation of underground rock layers, lava flow patterns, rille (canyon) structures, mascon properties, and any areas containing water. A prototype lunar sounder has been flight tested in aircraft over selected Earth sites to confirm the equipment design and develop scientific analysis techniques. The Lunar Sounder Experiment was developed by North American Rockwell's (NR) Space Division for NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center to provide data for a scientific investigation team with representatives from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, University of Utah, University of Michigan, U.S. Geological Survey, and NASA Ames Research Center.
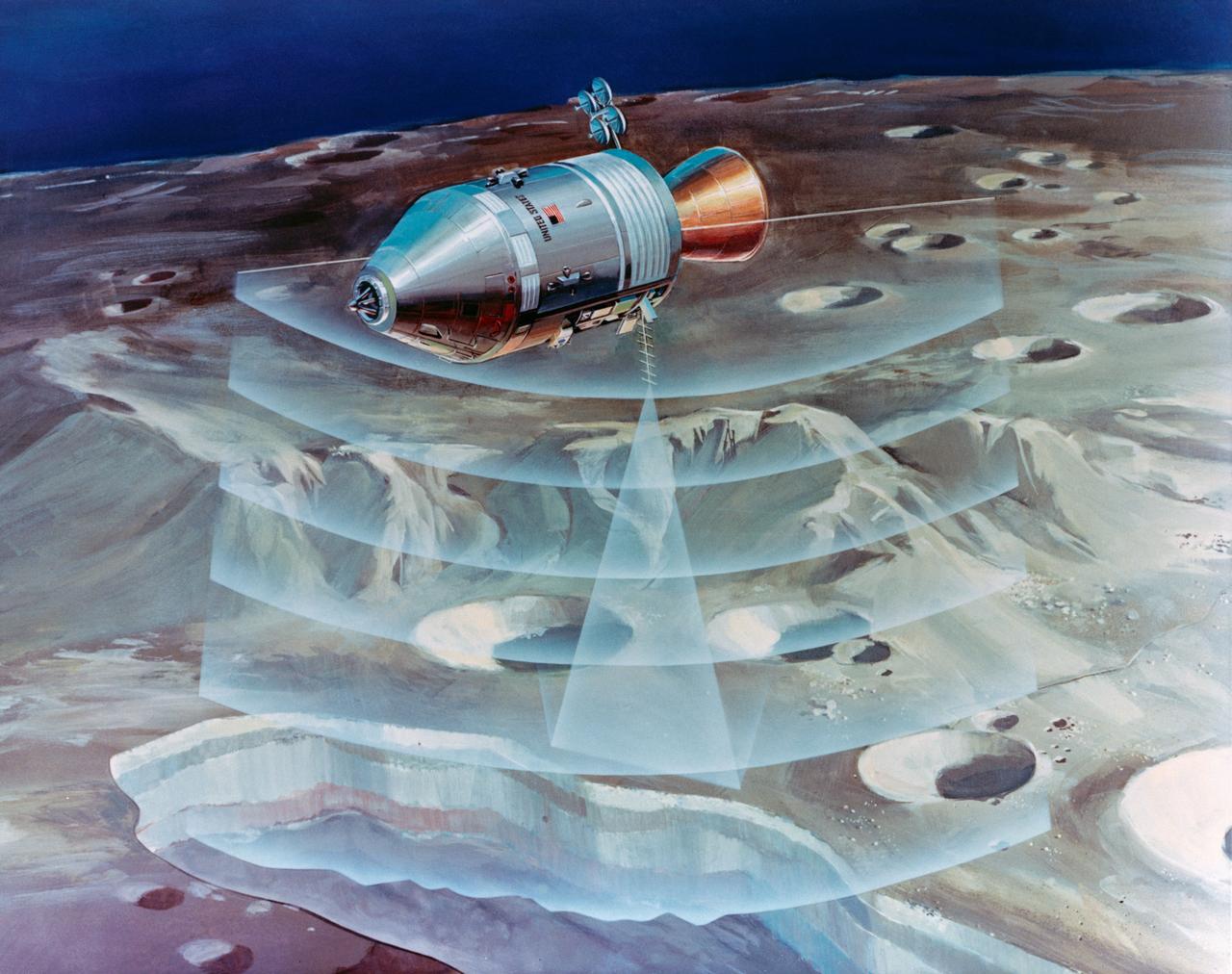

S72-53472 (November 1972) --- An artist's concept illustrating how radar beams of the Apollo 17 lunar sounder experiment will probe three-quarters of a mile below the moon's surface from the orbiting spacecraft. The Lunar Sounder will be mounted in the SIM bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module. Electronic data recorded on film will be retrieved by the crew during trans-Earth EVA. Geologic information on the lunar interior obtained by the sounder will permit scientific investigation of underground rock layers, lava flow patterns, rille (canyon) structures, mascon properties, and any areas containing water. A prototype lunar sounder has been flight tested in aircraft over selected Earth sites to confirm the equipment design and develop scientific analysis techniques. The Lunar Sounder Experiment (S-209) was developed by North American Rockwell's (NR) Space Division for NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center to provide data for a scientific investigation team with representatives from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, University of Utah, University of Michigan, U.S. Geological Survey, and NASA Ames Research Center.
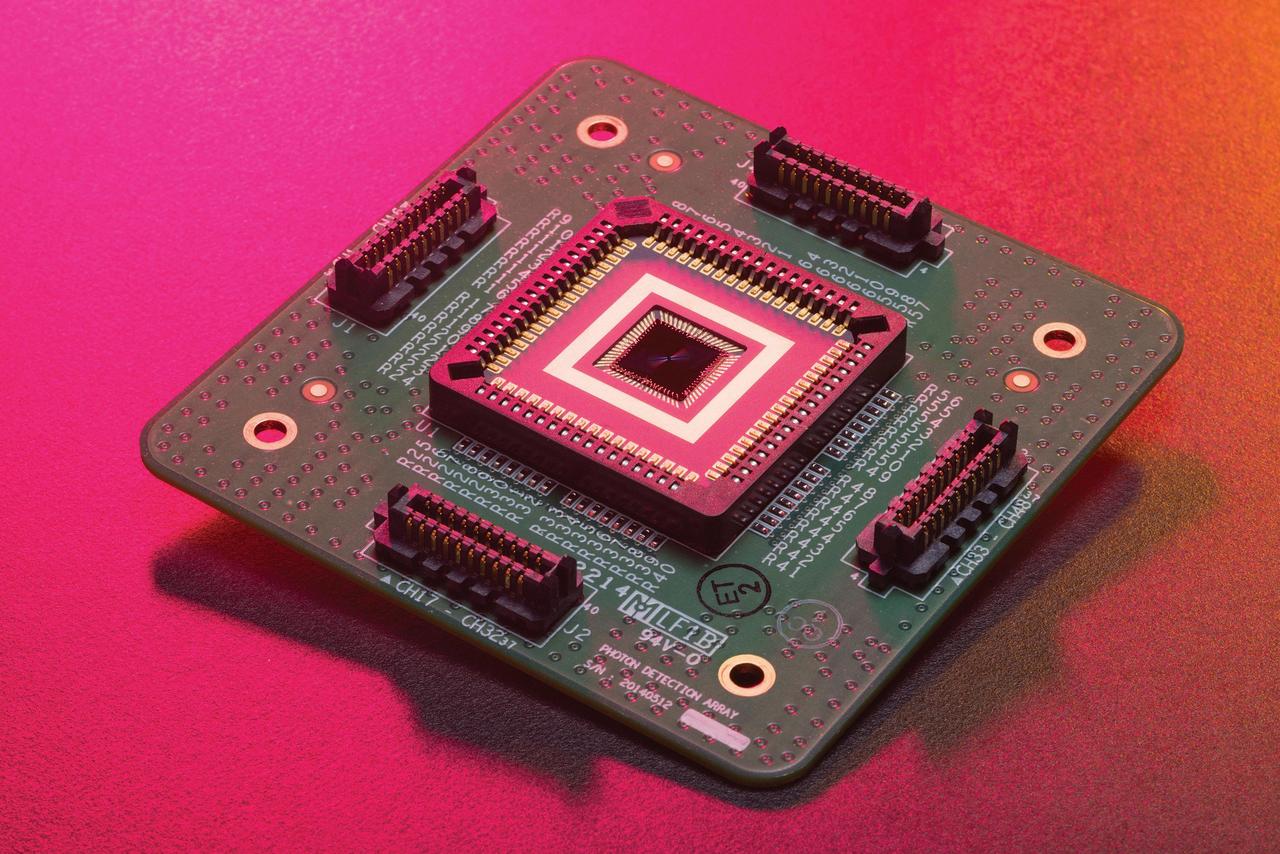
Shown here is a prototype of the Deep Space Optical Communications, or DSOC, ground receiver detector built by the Microdevices Laboratory at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The prototype superconducting nanowire single-photon detector was used by JPL technologists to help develop the detector that – from a station on Earth – will receive near-infrared laser signals from the DSOC flight transceiver traveling with NASA's Psyche mission in deep space. DSOC will test key technologies that could enable high-bandwidth optical, or laser, communications from Mars distances. Bolted to the side of the spacecraft and operating for the first two years of Psyche's journey to the asteroid of the same name, the DSOC flight laser transceiver will transmit high-rate data to Caltech's Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California, which houses the 200-inch (5.1-meter) Hale Telescope. The downlink detector converts optical signals to electrical signals, which can be processed and decoded. The detector is designed to be both sensitive enough to detect single photons (quantum particles of light) and able to detect many photons arriving all at once. At its farthest point during the technology demonstration's operations period, the transceiver will be up to 240 million miles (390 million kilometers) away, meaning that by the time its weak laser pulses arrive at Earth, the detector will need to efficiently detect a trickle of single photons. But when the spacecraft is closer to Earth and the flight transceiver is delivering its highest bit rate to Palomar, the detector is capable of detecting very high numbers of photons without becoming overwhelmed. Because data is encoded in the timing of the laser pulses, the detector must also be able to determine the time of a photon's arrival with a precision of 100 picoseconds (one picosecond is one trillionth of a second). DSOC is the latest in a series of optical communication technology demonstrations funded by NASA's Technology Demonstrations Missions (TDM) program and the agency's Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) program. JPL, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages DSOC for TDM within NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate and SCaN within the agency's Space Operations Mission Directorate. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25840
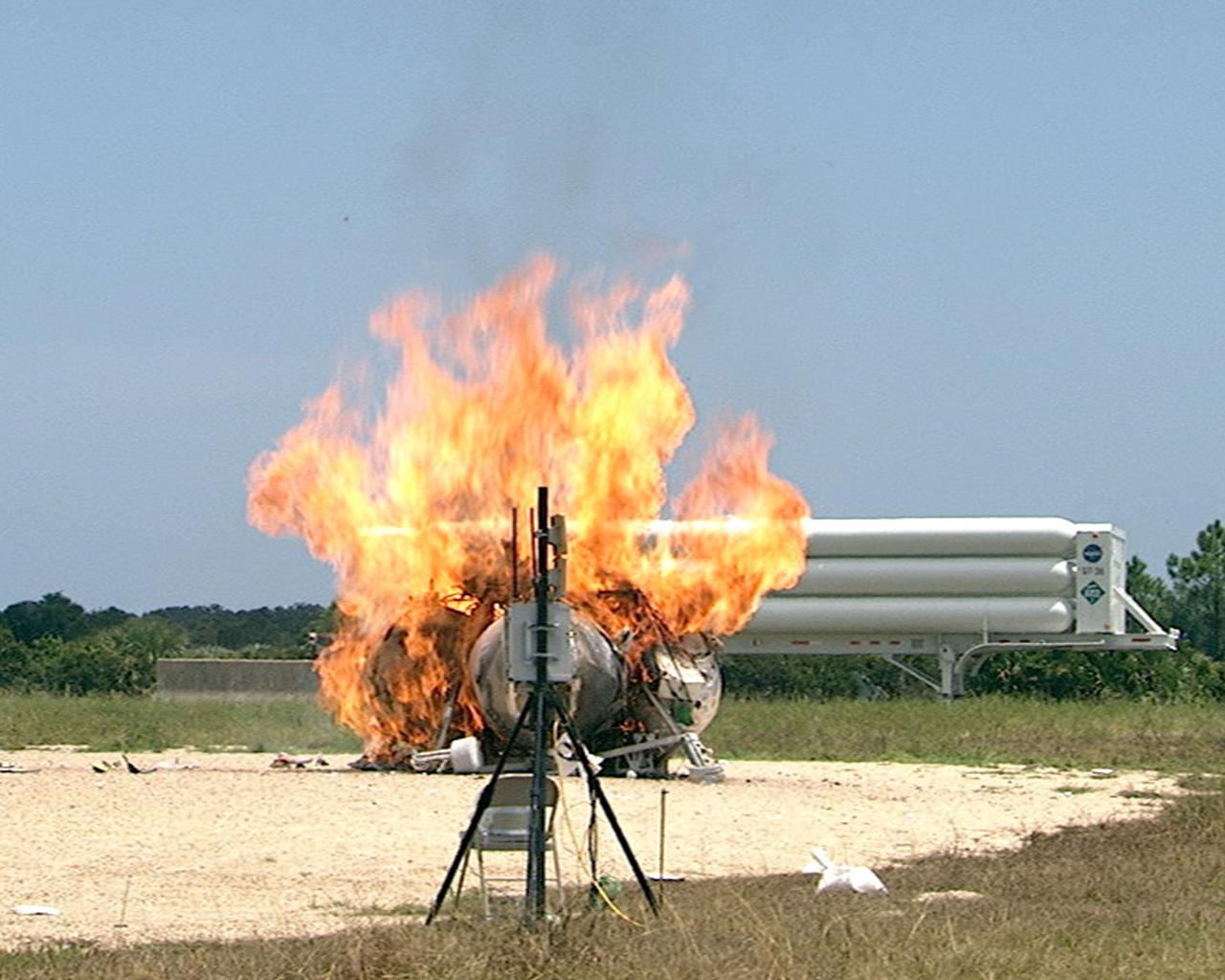

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a free-flight test of the Project Morpheus vehicle at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the vehicle lifted off the ground and then experienced a hardware component failure, which prevented it from maintaining stable flight. No one was injured and the resulting fire was extinguished by Kennedy fire personnel. Engineers are looking into the test data and the agency will release information as it becomes available. Failures such as these were anticipated prior to the test, and are part of the development process for any complex spaceflight hardware. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. Morpheus was manufactured and assembled at JSC and Armadillo Aerospace. Morpheus is large enough to carry 1,100 pounds of cargo to the moon – for example, a humanoid robot, a small rover, or a small laboratory to convert moon dust into oxygen. The primary focus of the test is to demonstrate an integrated propulsion and guidance, navigation and control system that can fly a lunar descent profile to exercise the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, safe landing sensors and closed-loop flight control. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a free-flight test of the Project Morpheus vehicle at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the vehicle lifted off the ground and then experienced a hardware component failure, which prevented it from maintaining stable flight. Engineers are looking into the test data and the agency will release information as it becomes available. Failures such as these were anticipated prior to the test, and are part of the development process for any complex spaceflight hardware. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. Morpheus was manufactured and assembled at JSC and Armadillo Aerospace. Morpheus is large enough to carry 1,100 pounds of cargo to the moon – for example, a humanoid robot, a small rover, or a small laboratory to convert moon dust into oxygen. The primary focus of the test is to demonstrate an integrated propulsion and guidance, navigation and control system that can fly a lunar descent profile to exercise the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, safe landing sensors and closed-loop flight control. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA
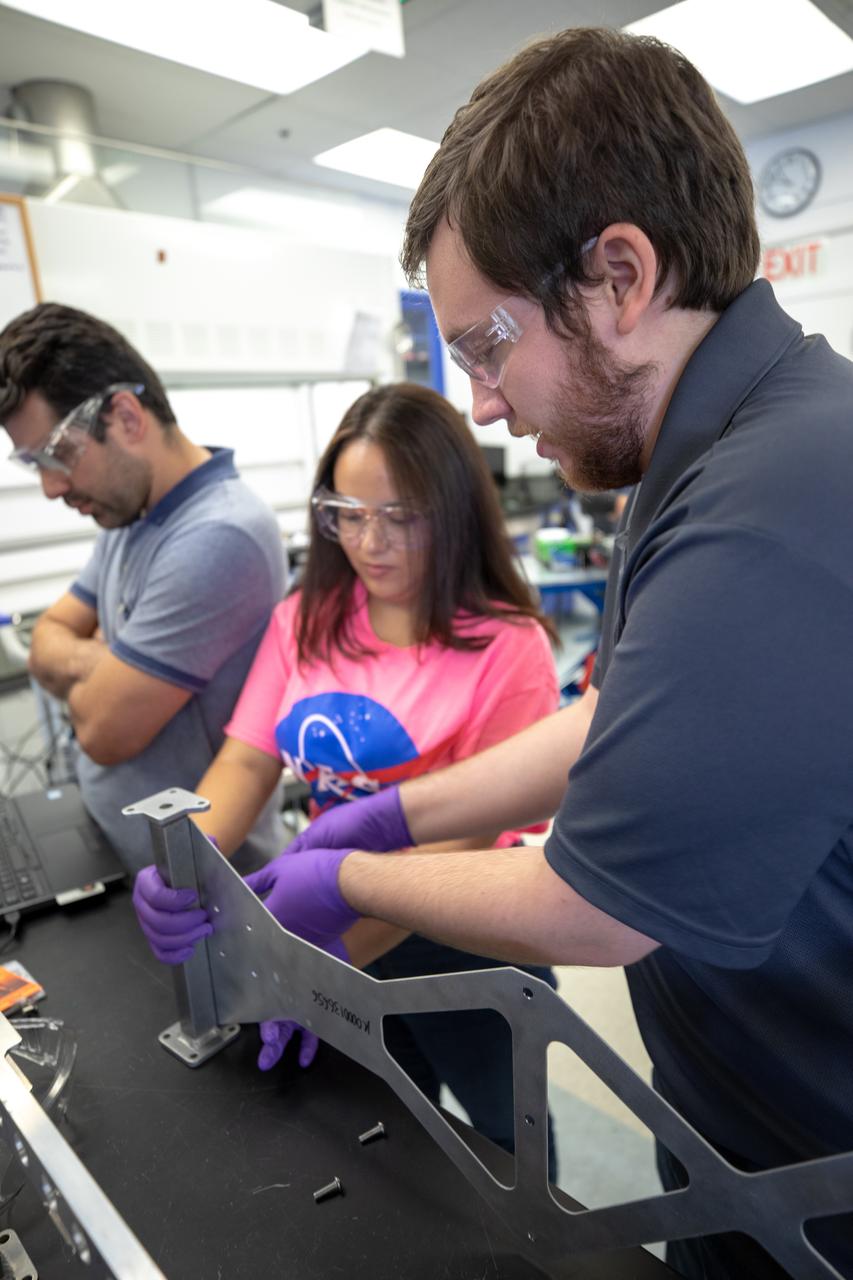

From left, Kennedy Space Center Mechanical Engineer Jaime Toro, NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) data acquisition and testing; Brianna Sandoval, OSCAR intern; and Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy employee providing support for OSCAR under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assemble the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
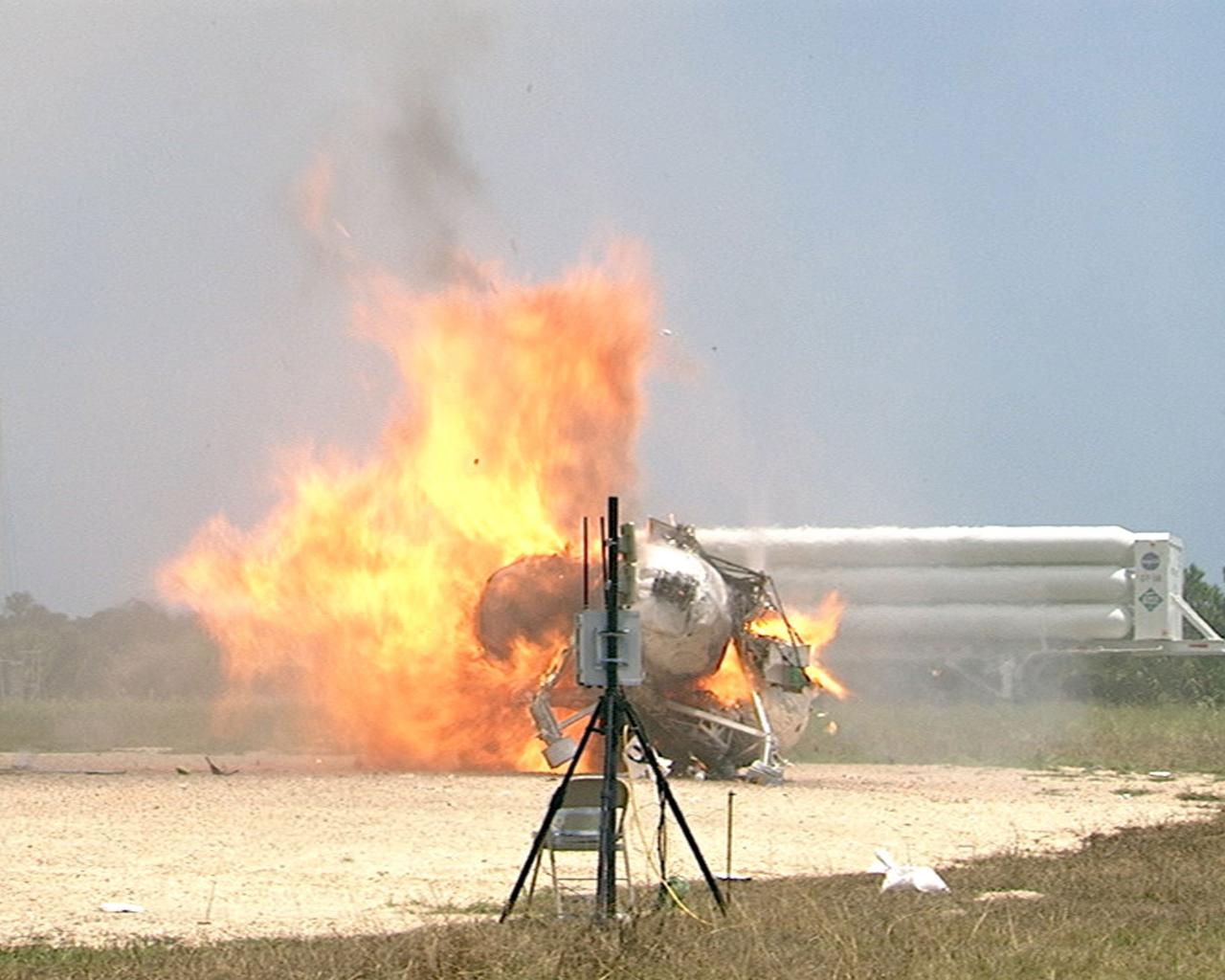

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a free-flight test of the Project Morpheus vehicle at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the vehicle lifted off the ground and then experienced a hardware component failure, which prevented it from maintaining stable flight. No one was injured and the resulting fire was extinguished by Kennedy fire personnel. Engineers are looking into the test data and the agency will release information as it becomes available. Failures such as these were anticipated prior to the test, and are part of the development process for any complex spaceflight hardware. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. Morpheus was manufactured and assembled at JSC and Armadillo Aerospace. Morpheus is large enough to carry 1,100 pounds of cargo to the moon – for example, a humanoid robot, a small rover, or a small laboratory to convert moon dust into oxygen. The primary focus of the test is to demonstrate an integrated propulsion and guidance, navigation and control system that can fly a lunar descent profile to exercise the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, safe landing sensors and closed-loop flight control. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA
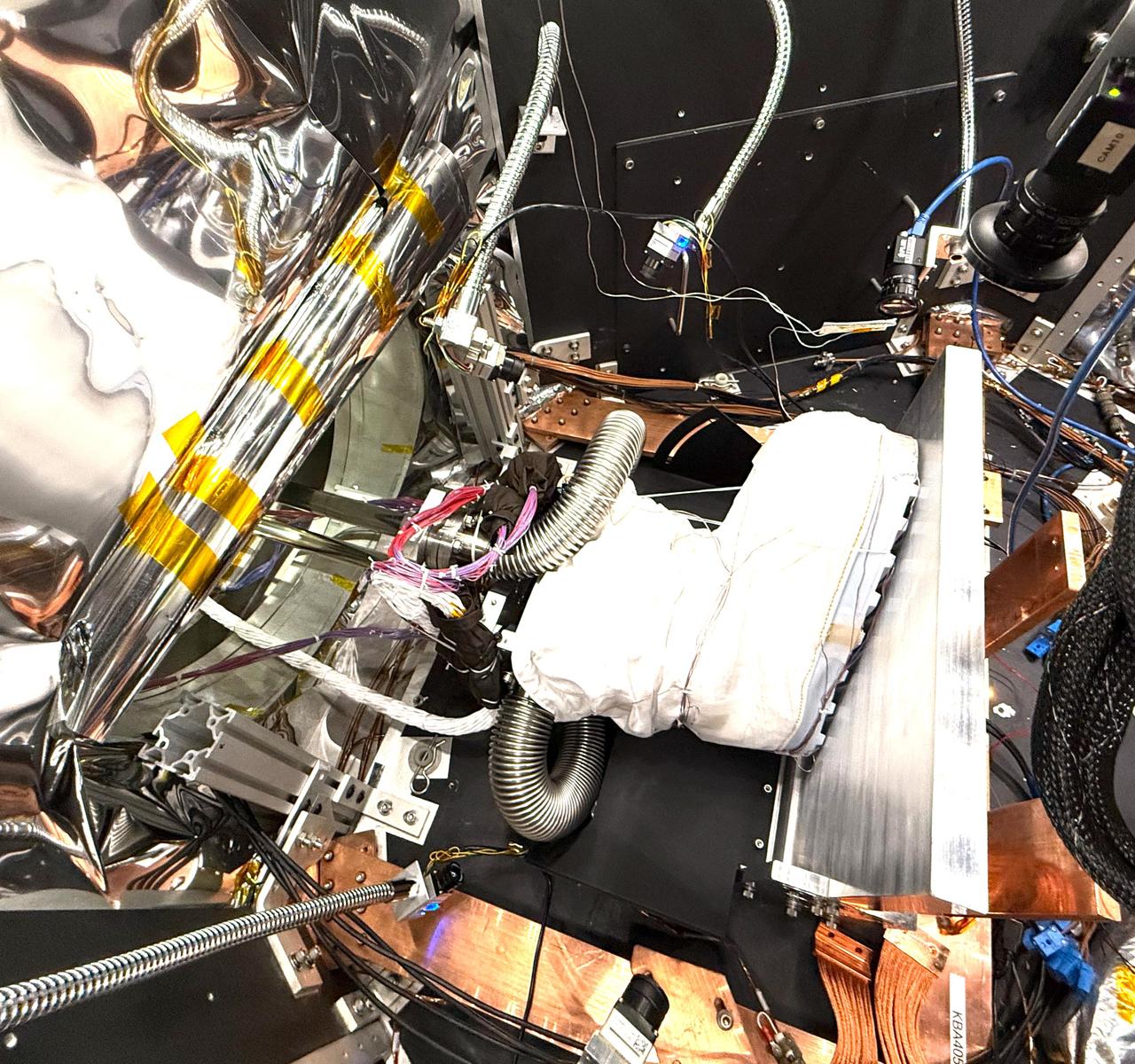
A boot that's part of a NASA lunar surface spacesuit prototype is readied for testing inside a thermal vacuum chamber called CITADEL at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Nov. 8, 2024. The thick aluminum plate at right stands in for the frigid surface of the lunar South Pole, where Artemis III astronauts will confront conditions more extreme than any previously experienced by humans. Built to prepare potential future robotic spacecraft for the frosty, low-pressure conditions on ocean worlds like Jupiter's frozen moon Europa, CITADEL (Cryogenic Ice Testing, Acquisition Development, and Excavation Laboratory) has also proven key to evaluating how astronaut gloves and boots hold up in extraordinary cold. It can reach temperatures as low as low as minus 370 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 223 degrees Celsius), approximating conditions in permanently shadowed regions that astronauts will explore. Figure A, showing the outer boot sole, was taken from inside CITADEL on Nov. 13, 2024. The boot is positioned in a load lock, one of four small drawer-like chambers through which test materials are inserted into the larger chamber. Initiated by the Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center, the boot testing took place from October 2024 to January 2025. The boot is part of a NASA spacesuit called the Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit, or xEMU. Results haven't yet been fully analyzed. In addition to spotting vulnerabilities with existing suits, the experiments are intended to help NASA develop this unique test capability and prepare criteria for standardized, repeatable, and inexpensive test methods for the next-generation lunar suit being built by Axiom Space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26592
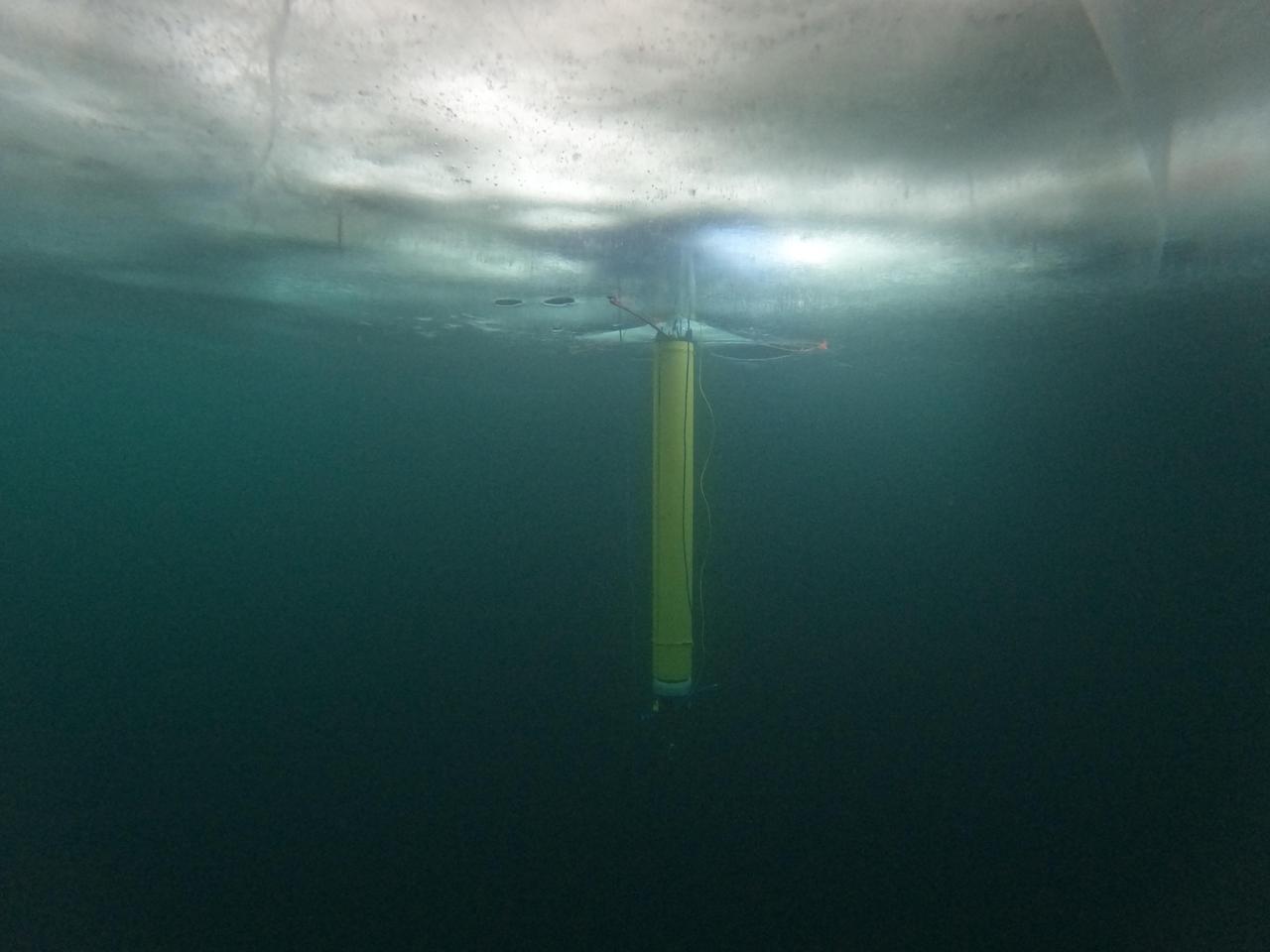

A prototype of an autonomous robot, part of a project called IceNode being developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, is seen from beneath the frozen surface of Lake Superior, off Michigan's Upper Peninsula. The three thin legs of the robot's "landing gear" affix it to the icy ceiling. A remote camera captured the image during a field test in 2022. The IceNode project envisions a fleet of such robots to venture beneath Antarctic ice shelves and gather data that would help scientists calculate how rapidly the ice shelves there are melting – and how fast that melting could cause global sea levels to rise. Each about 8 feet (2.4 meters) long and 10 inches (25 centimeters) in diameter, the robots use three-legged "landing gear" that springs out from one end to attach the robot to the underside of the ice. Rather than using propulsion, the robots would autonomously position themselves with the help of novel algorithms based on models of ocean currents. Released from a borehole or a vessel in the open ocean, the robots would ride those currents on a long journey beneath an ice shelf. They would target the underwater area known as the "grounding zone," where floating ice shelves, ocean, and land meet, deep inside unmapped cavities where the ice may be melting the fastest. Each robot would detach a ballast and rise up to affix itself to the underside of the ice, where their suite of sensors would measure how fast warm, salty ocean water is circulating up to melt the ice, and how quickly cold meltwater is sinking. As conceived, the IceNode fleet would operate for up to a year, continuously capturing data, including seasonal fluctuations. Then the robots would detach themselves from the ice, drift back out to open ocean, and transmit their data via satellite. This test was conducted through the U.S. Navy Arctic Submarine Laboratory's biennial Ice Camp, a three-week operation that provides researchers a temporary base camp from which to conduct field work in the harsh Arctic environment. IceNode has been funded through JPL's internal research and technology development program and its Earth Science and Technology Directorate. JPL is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26421
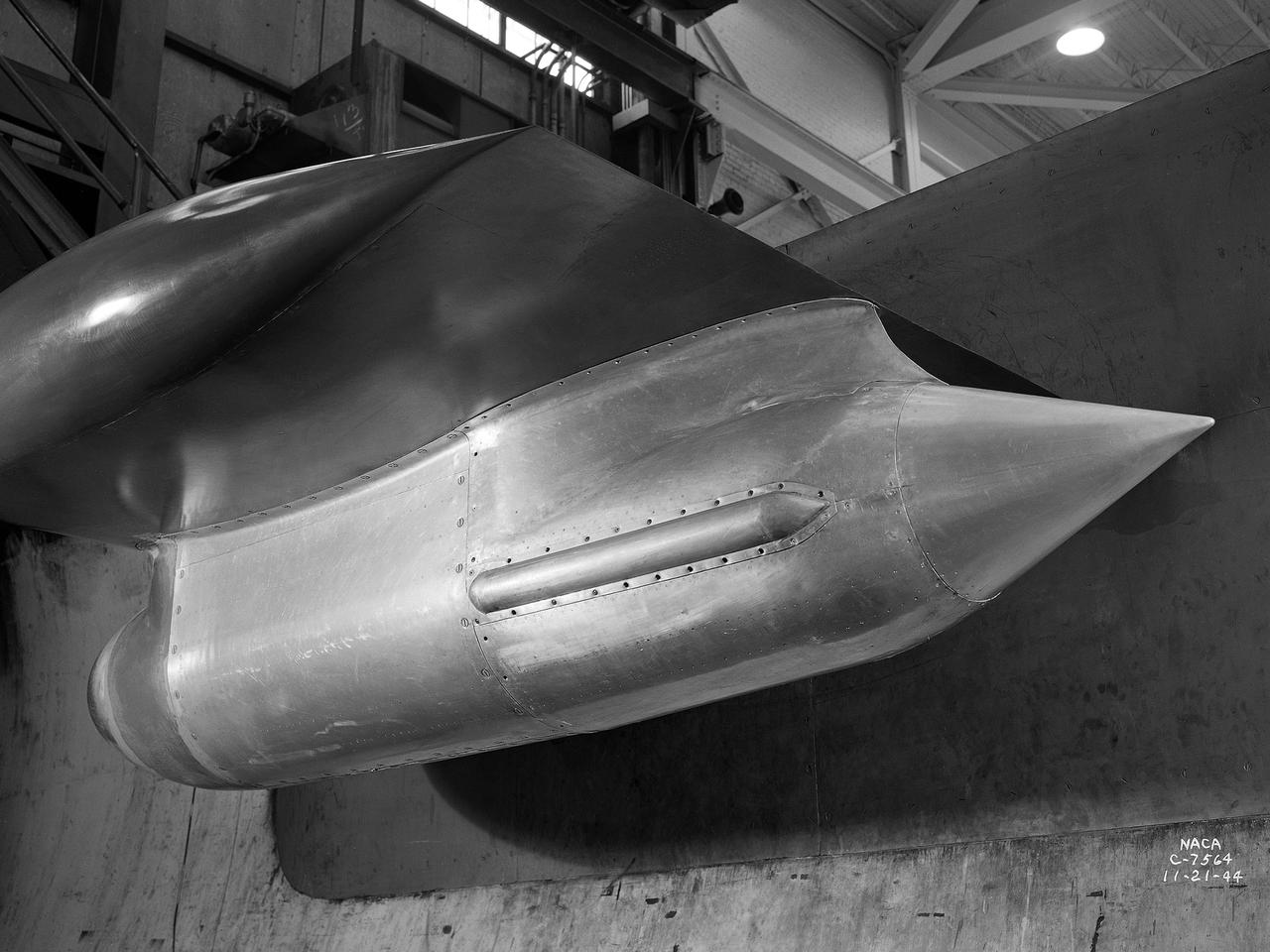

The Westinghouse 19XB turbojet seen from the side in the Altitude Wind Tunnel (AWT) test section at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. Westinghouse started the development of a series of relatively small axial-flow turbojets for the Navy shortly after Pearl Harbor. In 1943 the 19A engine became both the first operational US-designed jet engine and the only U.S. turbojet incorporated into an aircraft during the war in Europe. In March 1943 Westinghouse agreed to create an improved six-stage 1400-pound thrust version, the 19B. The engine underwent its first test run a year later in March 1944. Almost immediately the navy agreed to Westinghouse’s proposal for the even larger 10-stage, 1600-pound-thrust 19XB prototype. By July 1944 the navy had contracted with the NACA for the testing of both engines in the AWT. The tunnel was the nation’s only facility for studying full-scale engines in simulated altitude conditions. The wind tunnel investigations, which began on September 9, 1944, revealed the superiority of the previously untested 19XB over the 19B. The 19B engines failed to restart consistently and suffered combustion blowouts above 17,000 feet. The 19XB, however, performed well and restarted routinely at twice that altitude. Two months later on January 26, 1945, two 19Bs powered a McDonnell XFD–1 Phantom, the US Navy’s first fighter jet, on its initial flight. Following its exceptional performance in the AWT, the 19XB engines soon replaced the 19Bs in the Phantom.