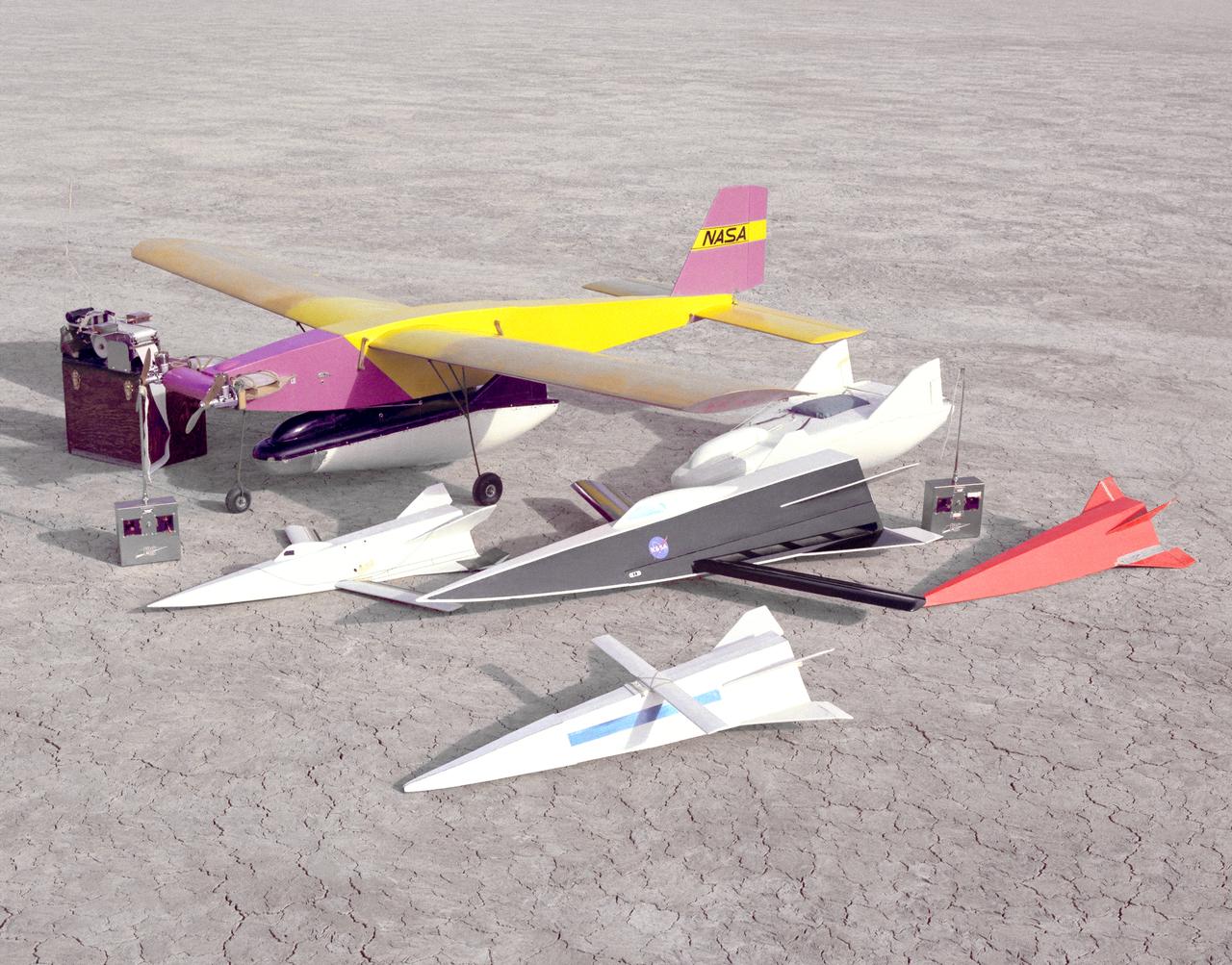

Flight Research Center and Dryden Flight Research Center engineer R. Dale Reed has long used free-flight models to test new concepts. This photo from 1963 shows two different models of the M2-F2 (one under the Mothership) and four Hyper III shapes.
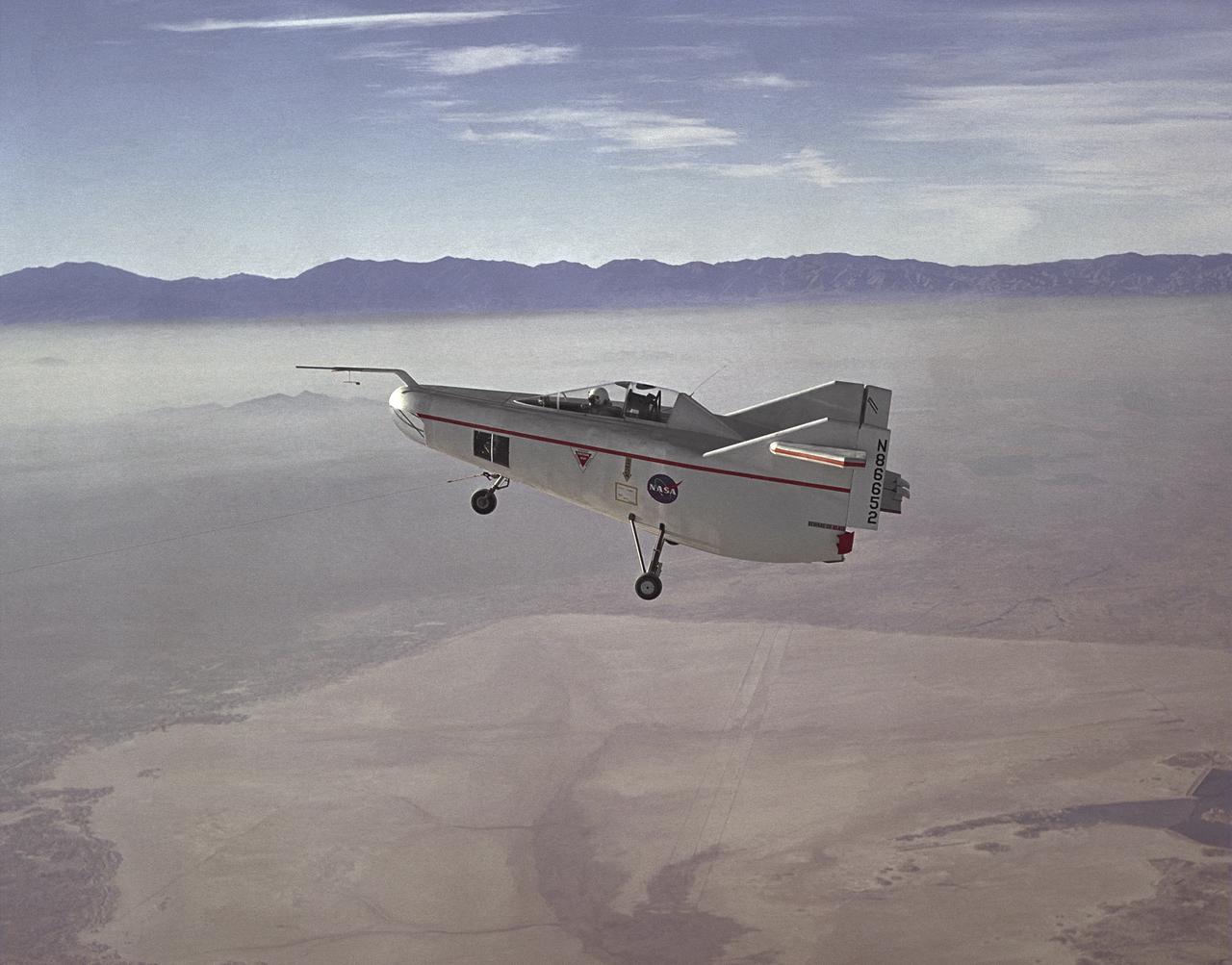

The M2-F1 Lifting Body is seen here under tow, high above Rogers Dry Lake near the Flight Research Center (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California. R. Dale Reed effectively advocated the project with the support of NASA research pilot Milt Thompson. Together, they gained the support of Flight Research Center Director Paul Bikle. After a six-month feasibility study, Bikle gave approval in the fall of 1962 for the M2-F1 to be built.
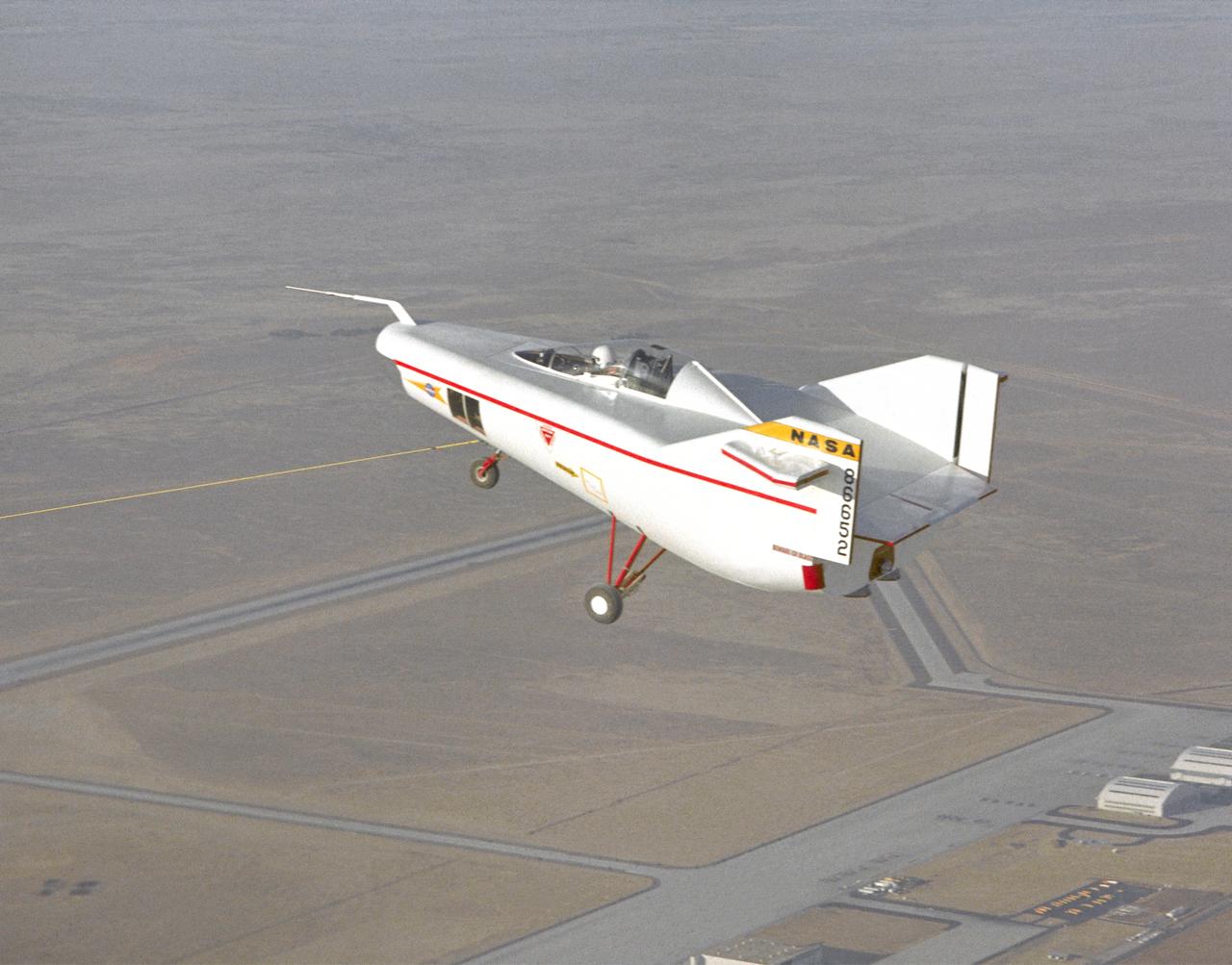

The M2-F1 Lifting Body is seen here under tow by an unseen C-47 at the NASA Flight Research Center (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California. The low-cost vehicle was the first piloted lifting body to be test flown. The lifting-body concept originated in the mid-1950s at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics' Ames Aeronautical Laboratory, Mountain View California. By February 1962, a series of possible shapes had been developed, and R. Dale Reed was working to gain support for a research vehicle.
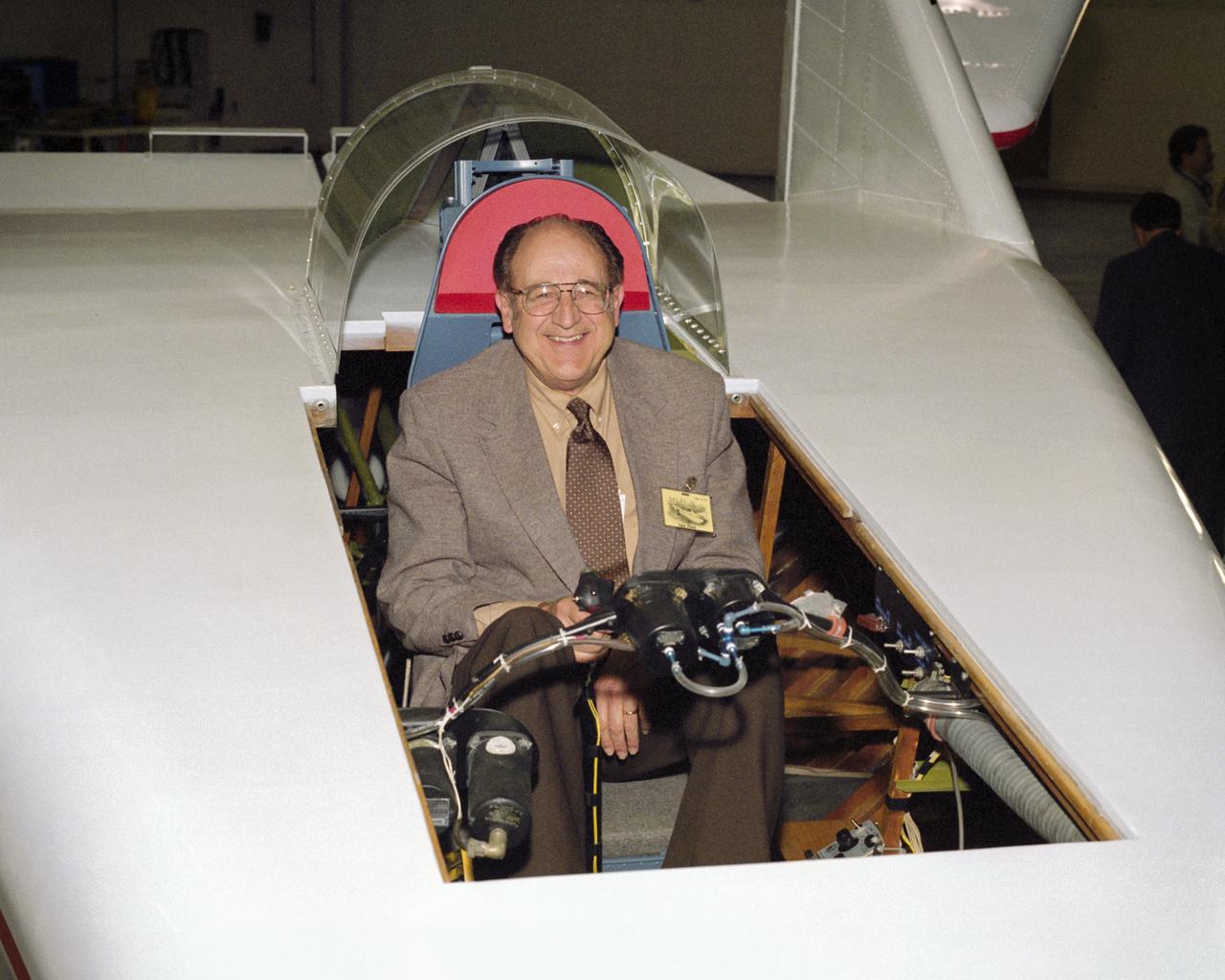

Often called the "Father of the Lifting Bodies," NASA aerospace engineer Dale Reed enjoys a moment in the cockpit of the restored wingless M2-F1 in 1997.
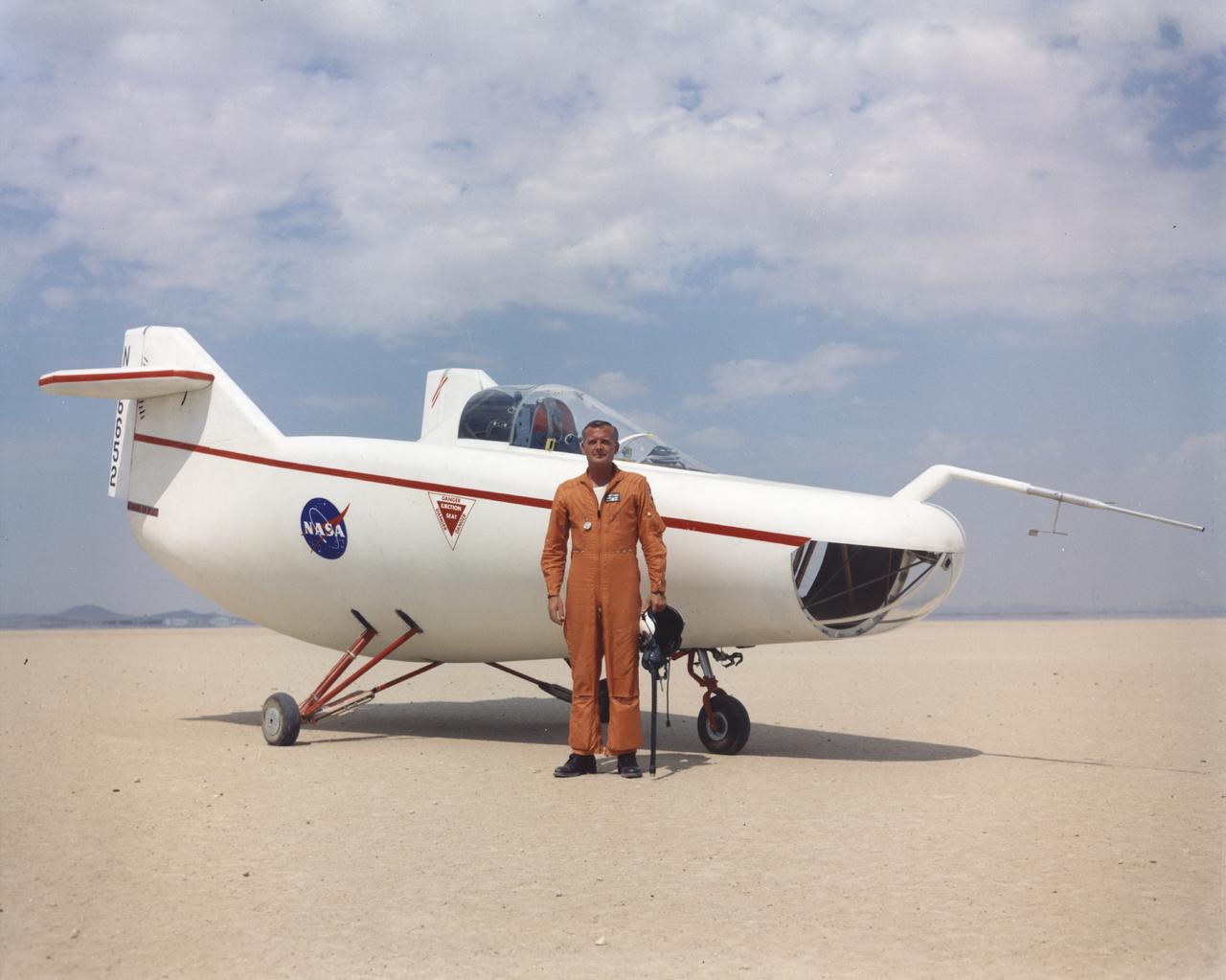

NASA Flight Research Pilot Milt Thompson, shown here on the lakebed with the M2-F1 lifting body, was an early backer of R. Dale Reed's lifting-body proposal. He urged Flight Research Center director Paul Bikle to approve the M2-F1's construction. Thompson also made the first glide flights in both the M2-F1 and its successor, the heavyweight M2-F2.
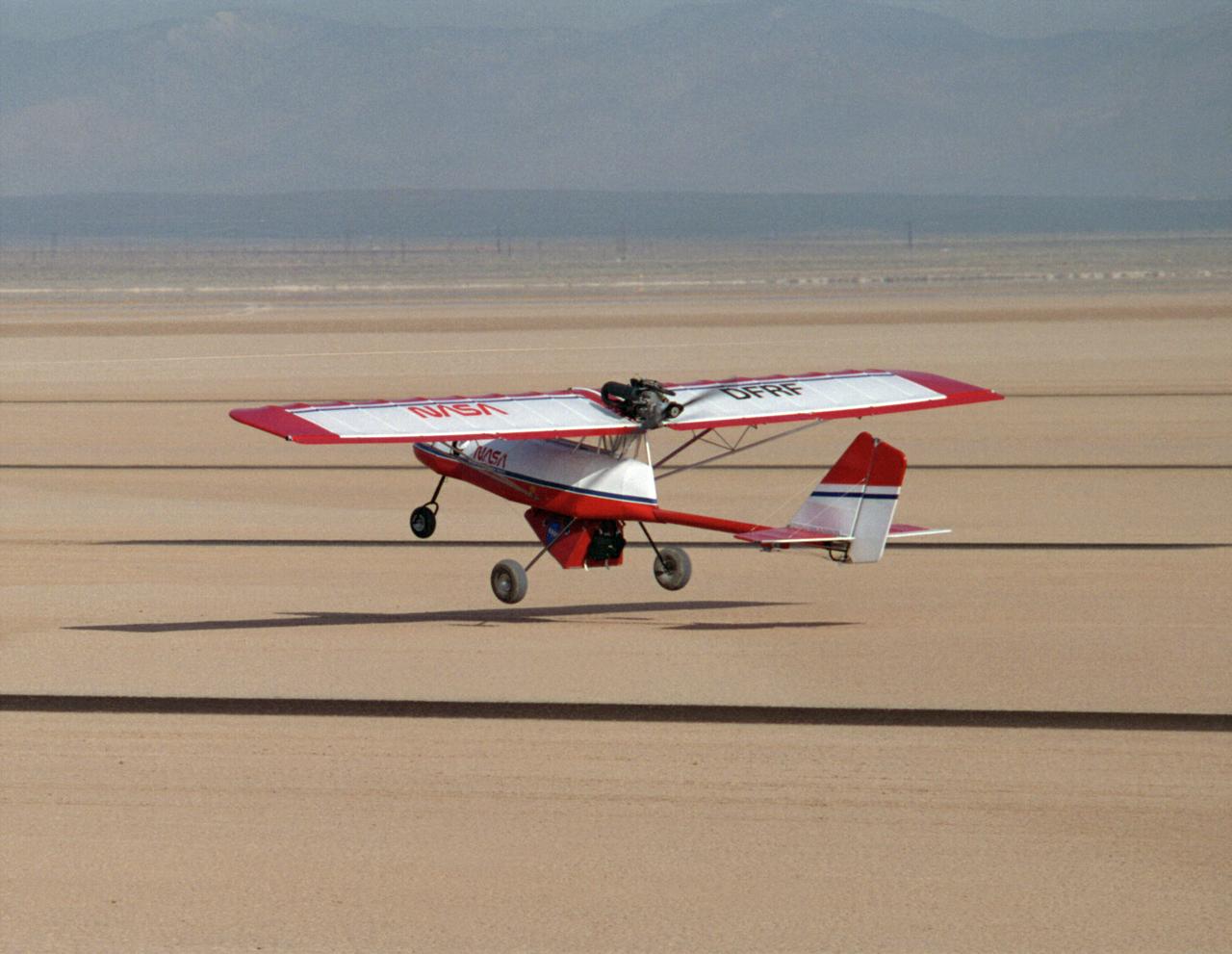

A Rans S-12 remotely piloted "mothership" takes off from a lakebed runway carrying a Spacewedge research model during 1992 flight tests. The Spacewedge was lauched in flight from the Rans S-12 aircraft and then glided back to a landing under a steerable parafoil. Technology tested in the Spacewedge program was used in developing the X-38 research vehicle.
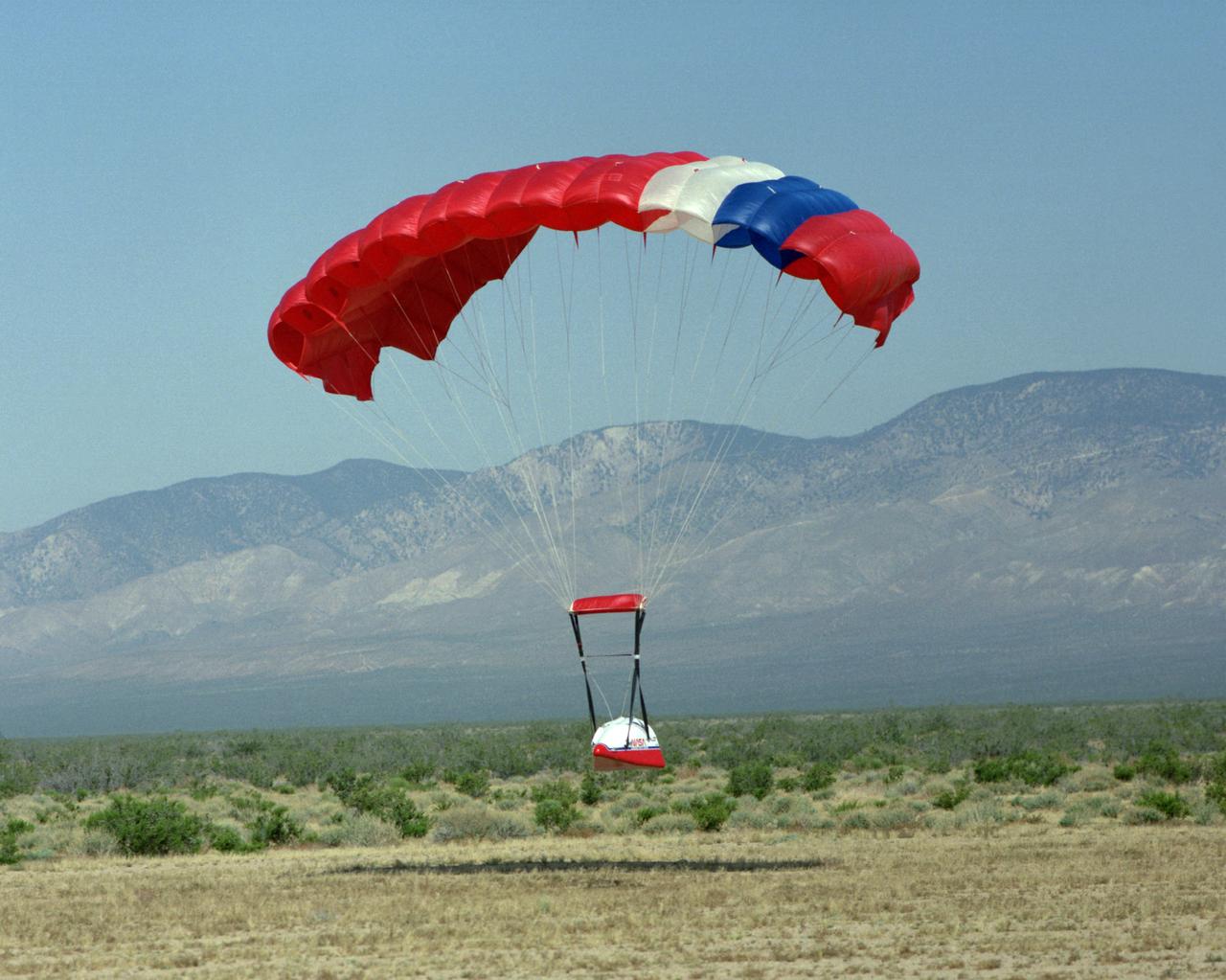

The Spacewedge subscale research model glides in toward a touchdown at a California City landing zone during 1992 flight tests of the vehicle.
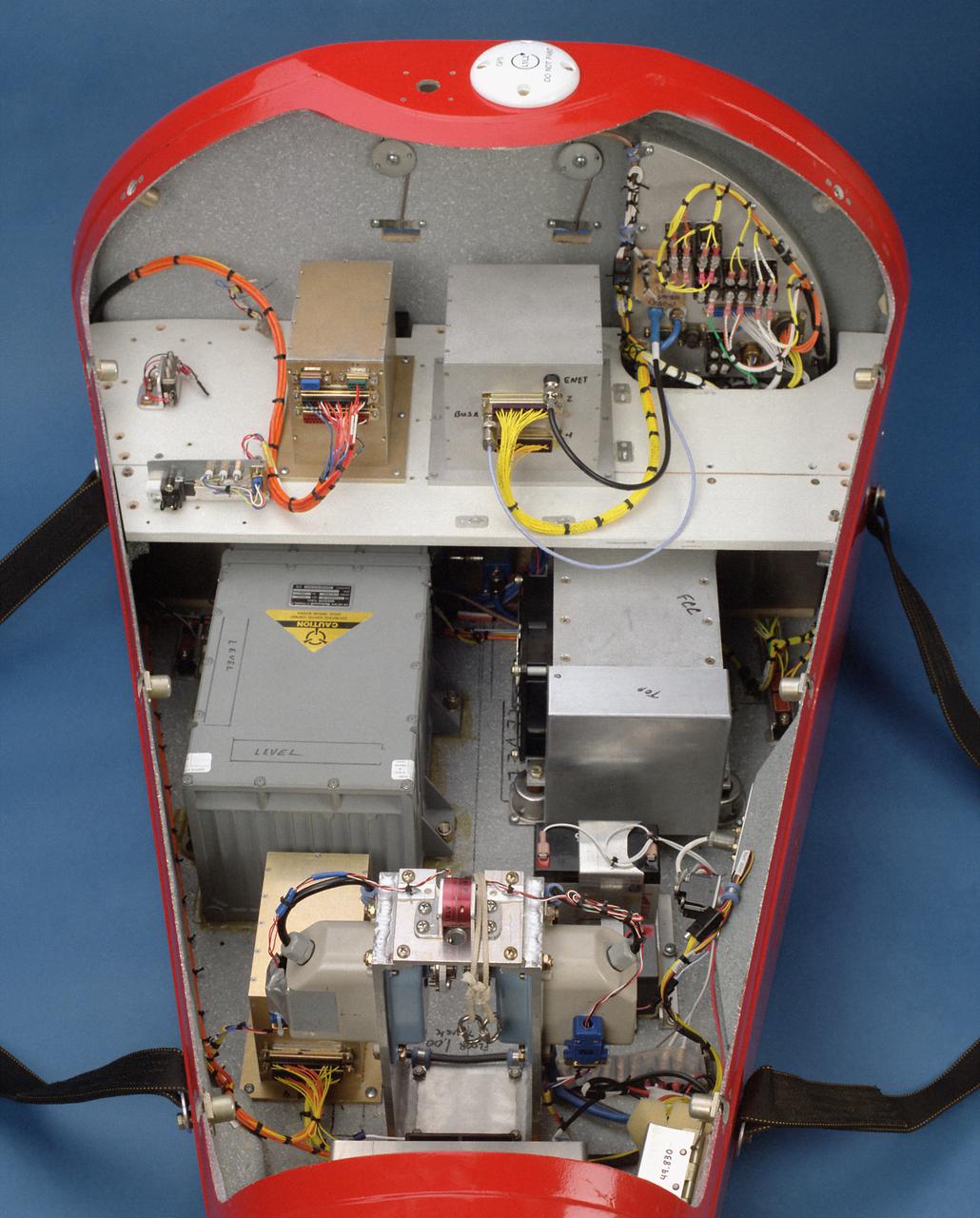
This photo shows the instrumentation and equipment inside the Spacewedge #3, a remotely-piloted research vehicle flown at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, to help develop technology for autonomous return systems for spacecraft as well as methods to deliver large Army cargo payloads to precise landings.
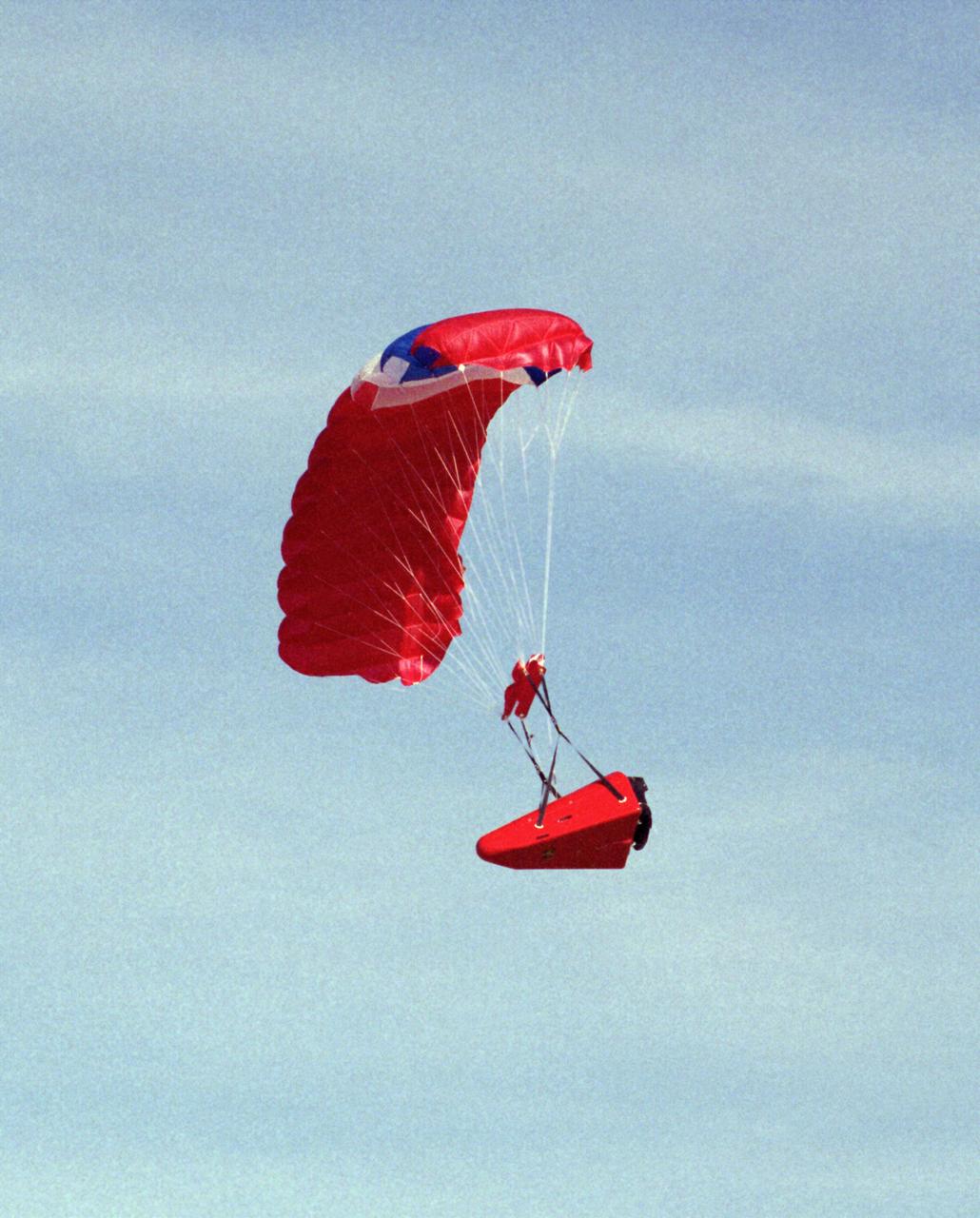

One of the Spacewedge remotely-piloted research vehicles in flight under a steerable parafoil during 1995 research flights conducted by NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center.
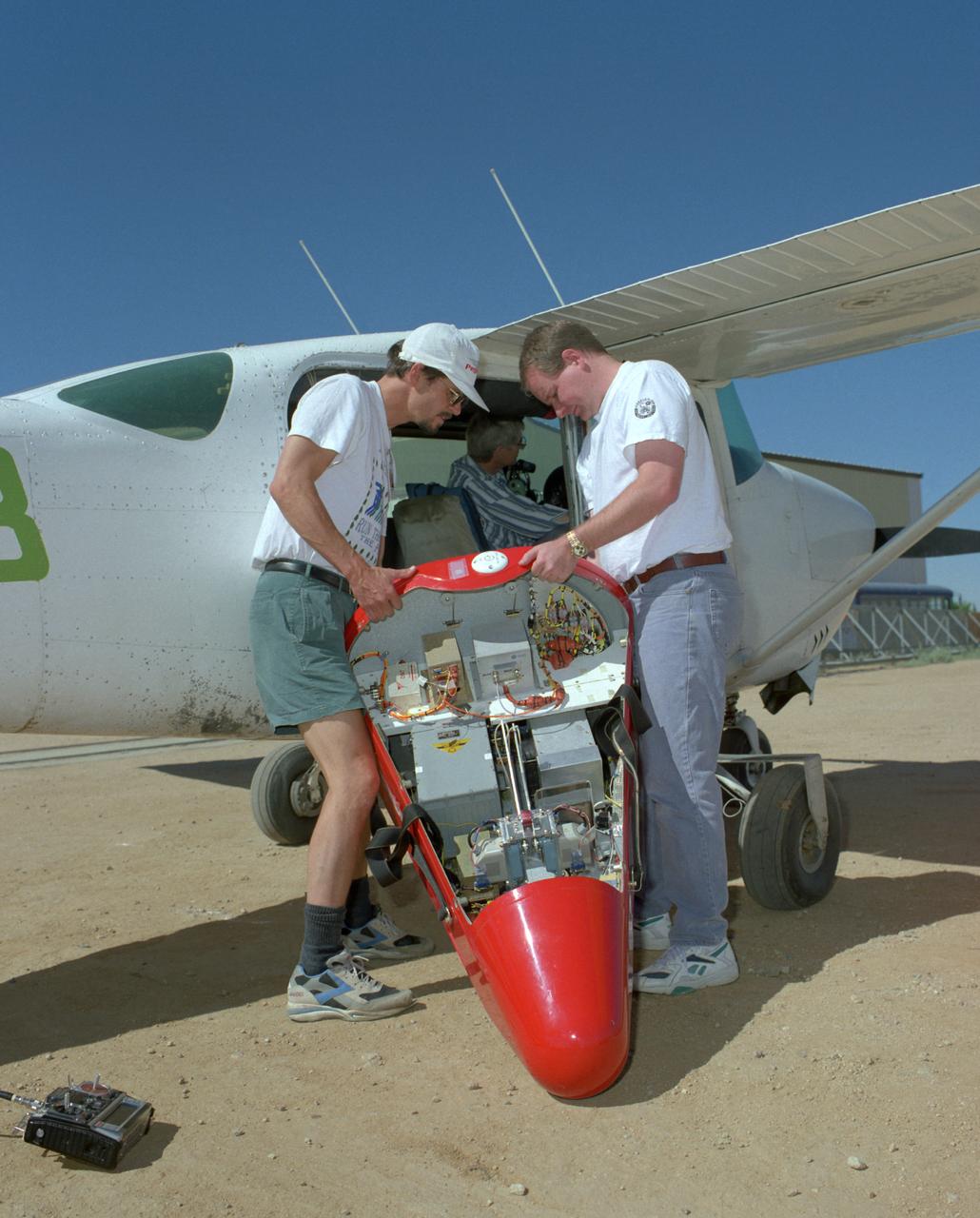

Crew members load a Spacewedge subscale research model into a Cessna aircraft for flight testing in 1996. The Spacewedge was drop-launched from the Cessna and then glided back to a soft landing under a steerable parafoil.
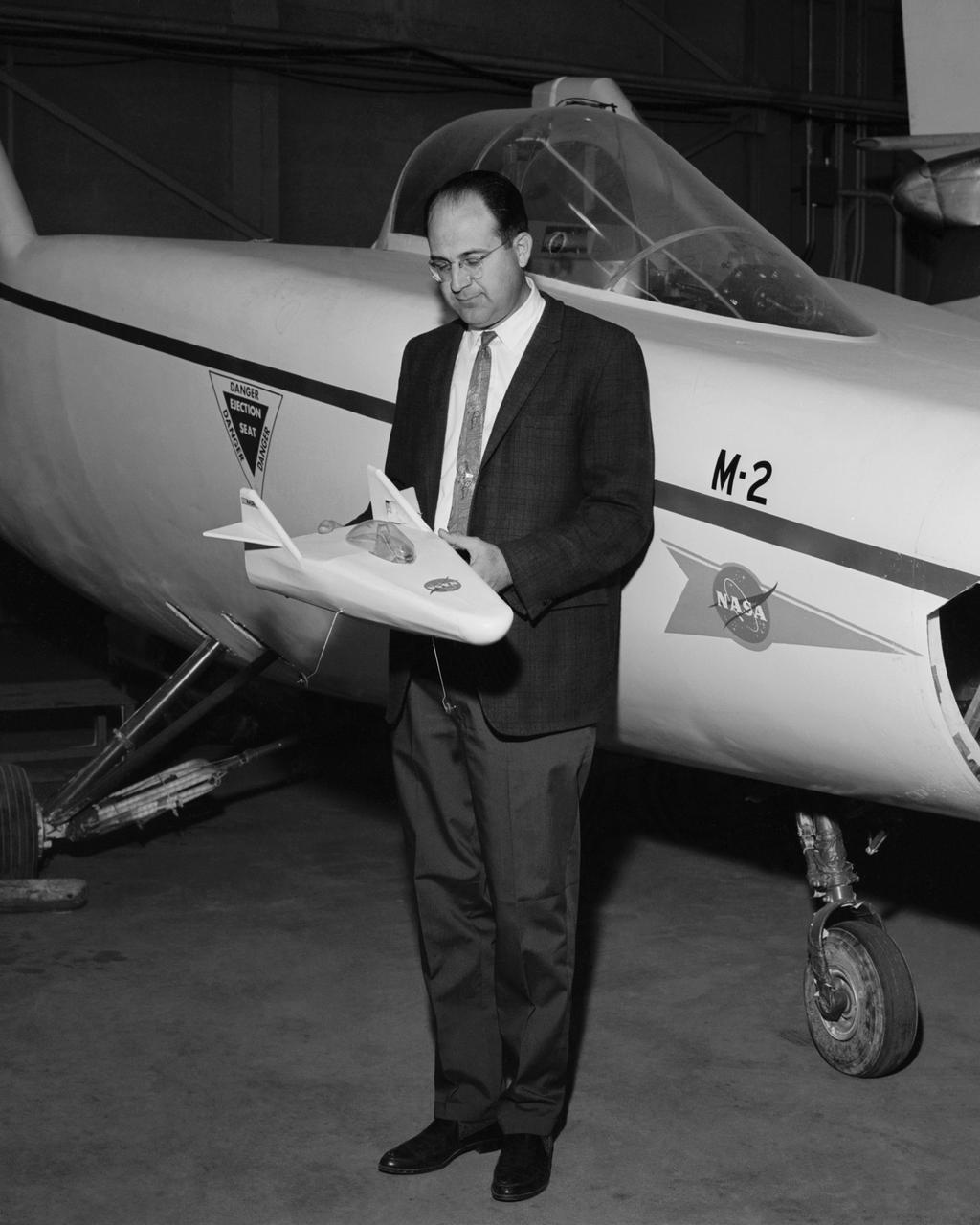

Dale Reed with a model of the M2-F1 in front of the actual lifting body. Reed used the model to show the potential of the lifting bodies. He first flew it into tall grass to test stability and trim, then hand-launched it from buildings for longer flights. Finally, he towed the lifting-body model aloft using a powered model airplane known as the "Mothership." A timer released the model and it glided to a landing. Dale's wife Donna used a 9 mm. camera to film the flights of the model. Its stability as it glided--despite its lack of wings--convinced Milt Thompson and some Flight Research Center engineers including the center director, Paul Bikle, that a piloted lifting body was possible.
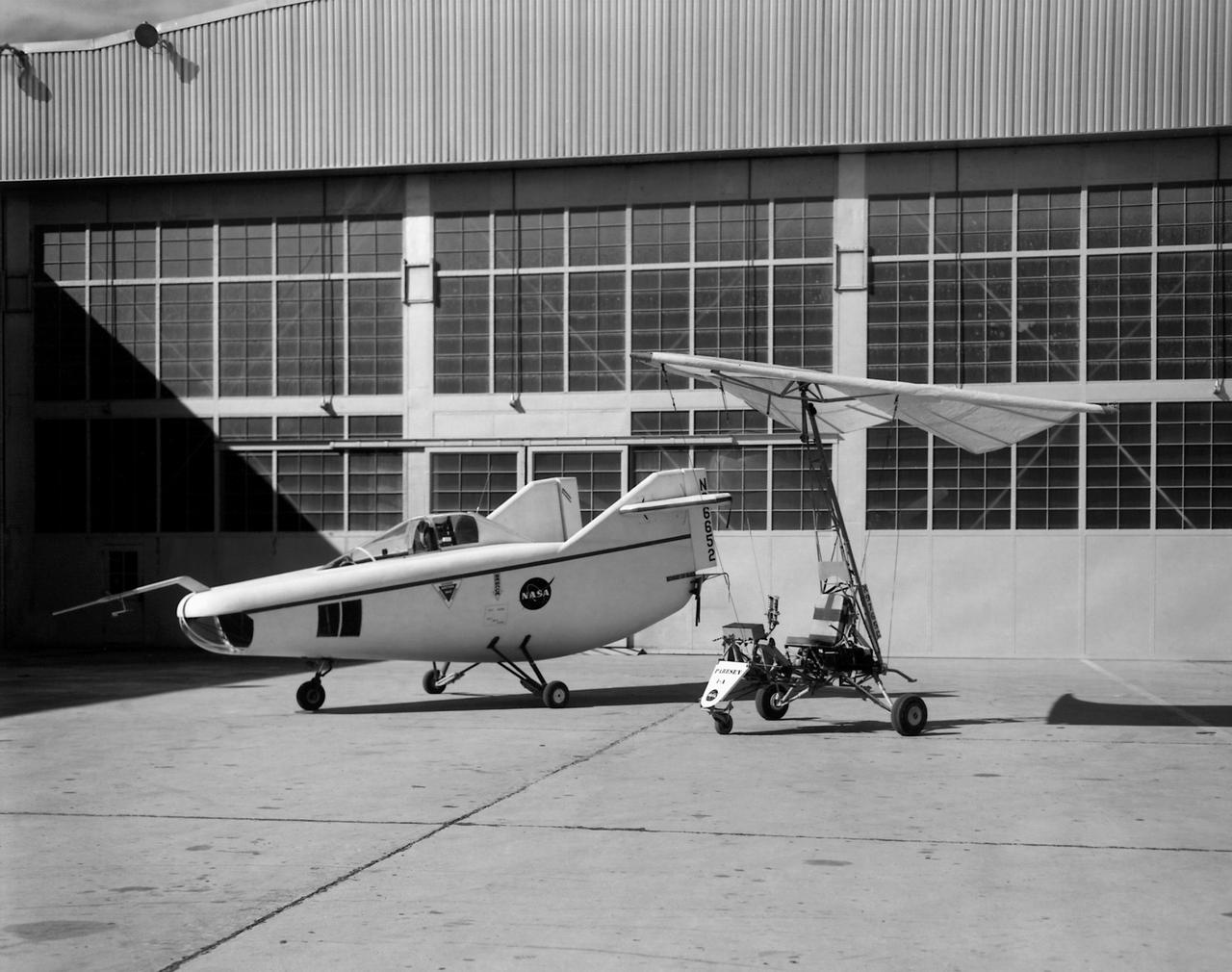

In this photo of the M2-F1 lifting body and the Paresev 1B on the ramp, the viewer sees two vehicles representing different approaches to building a research craft to simulate a spacecraft able to land on the ground instead of splashing down in the ocean as the Mercury capsules did. The M2-F1 was a lifting body, a shape able to re-enter from orbit and land. The Paresev (Paraglider Research Vehicle) used a Rogallo wing that could be (but never was) used to replace a conventional parachute for landing a capsule-type spacecraft, allowing it to make a controlled landing on the ground.