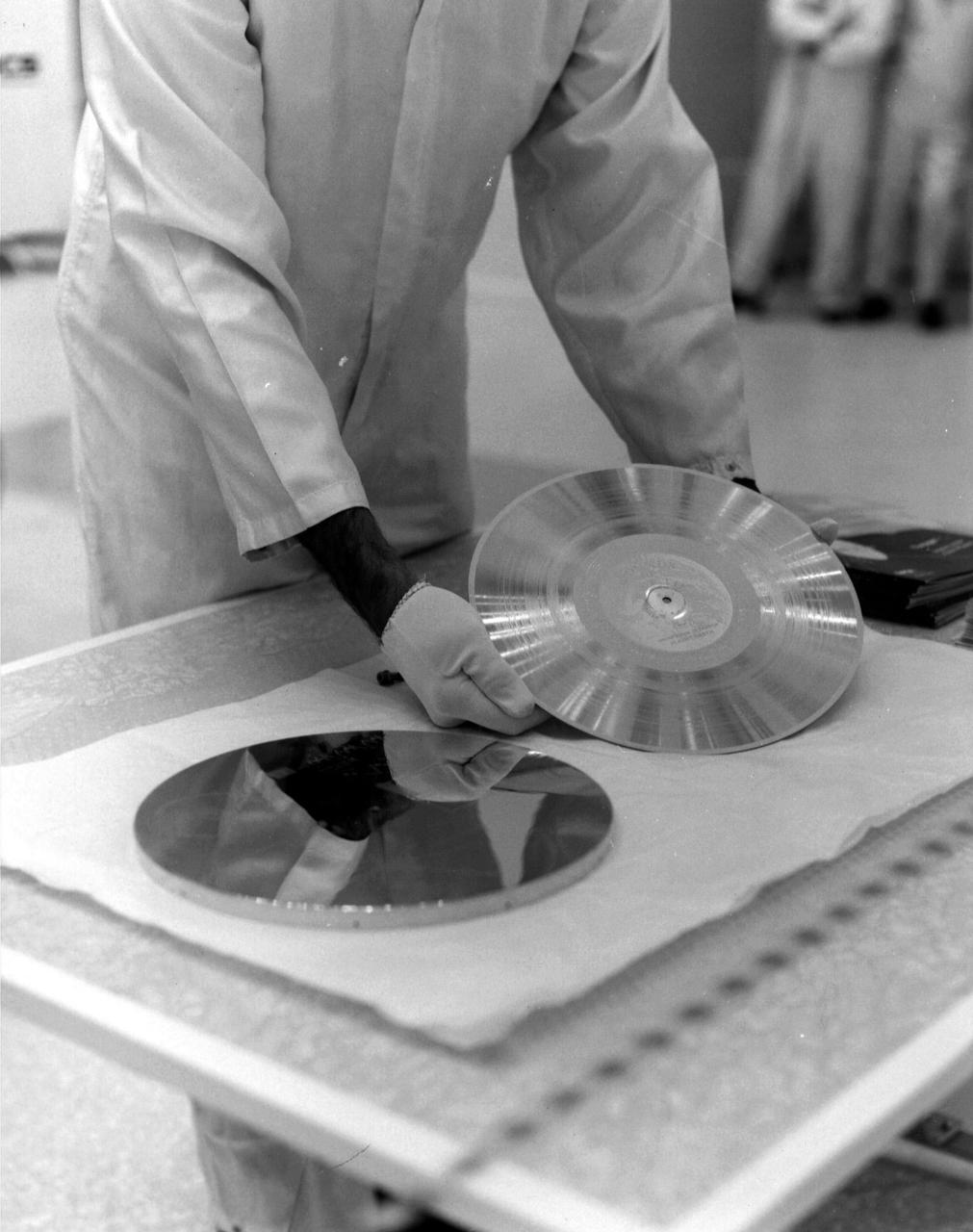

The Voyager 1 Golden Record is prepared for installation on the spacecraft in this archival image from 1977. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21741
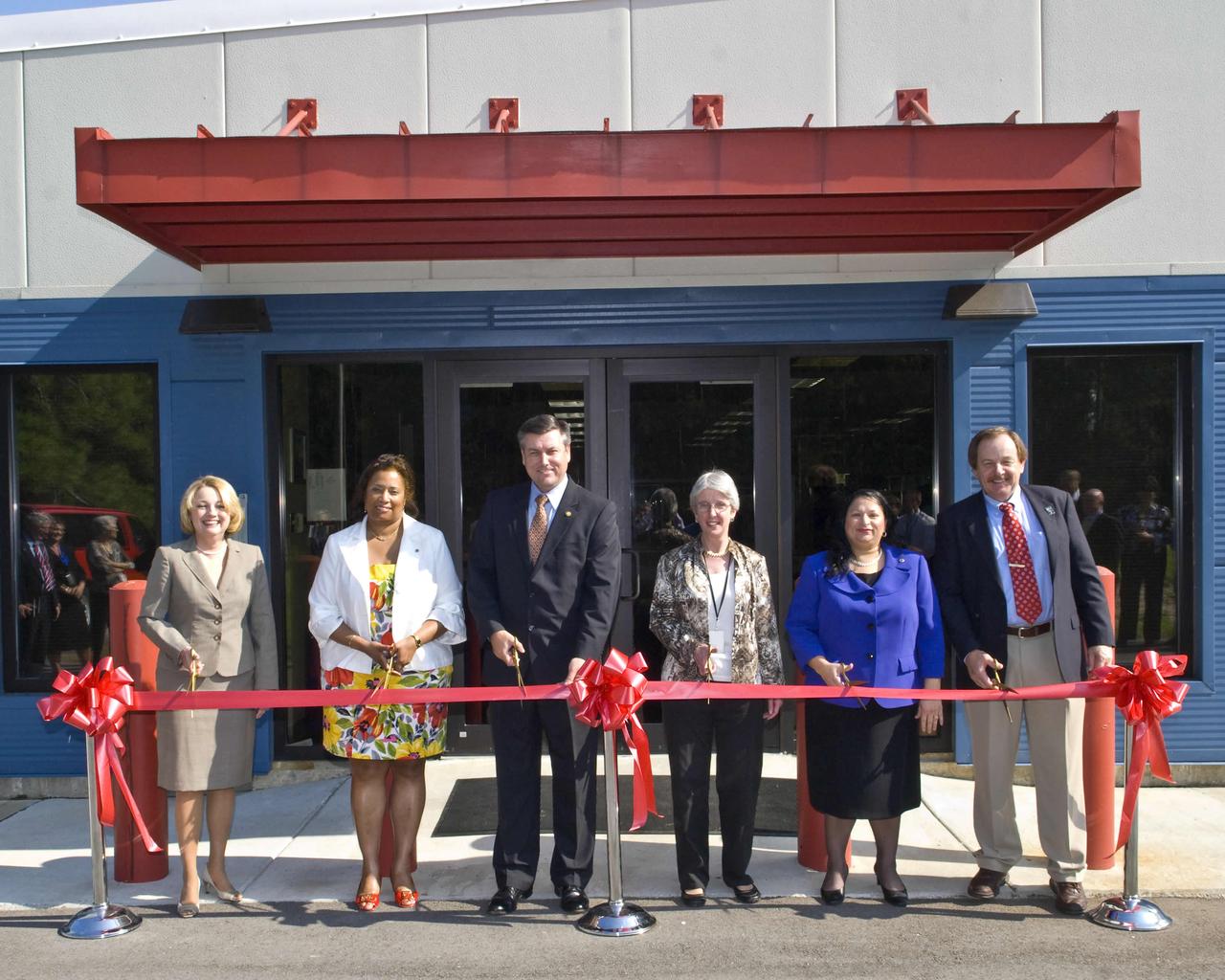

NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center cut the ribbon Aug. 24 on a new, storm-resistant Records Retention Facility that consolidates and protects records storage at the nation's premier rocket engine test facility. This facility will also house history office operations. Participants in the ribbon-cutting included: (l to r) Gay Irby, Center Operations deputy director at Stennis; Linda Cureton, NASA chief information officer; Patrick Scheuermann, Stennis director; Jane Odom, NASA chief archivist; Dinna Cottrell, Stennis chief information officer; and James Cluff, Stennis records manager.
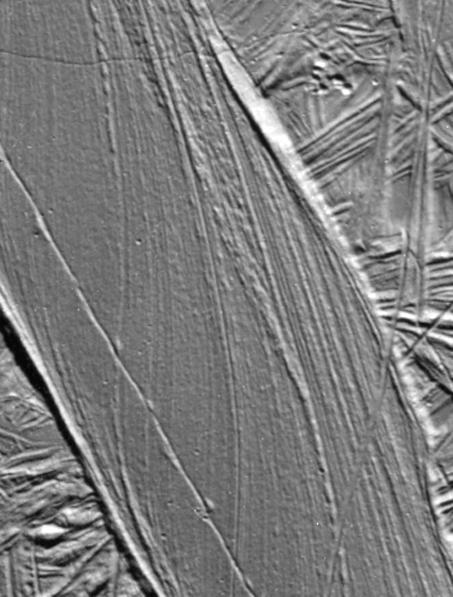
A Record of Crustal Movement on Europa

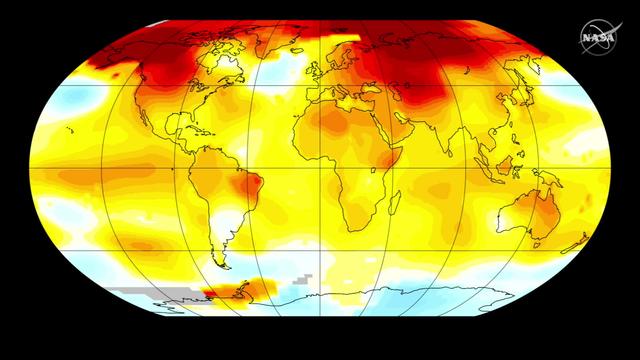
The year 2014 now ranks as the warmest on record since 1880, according to an analysis by NASA scientists. Nine of the 10 warmest years since modern records began have now occurred since 2000, according to a global temperature analysis by scientists at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York. 2014’s record-breaking warmth continues a long-term trend of a warming climate. The global average temperature has increased about 1.4 degrees Fahrenheit (0.8 degrees Celsius) since 1880, with most of that warming occurring during the last three to four decades. The warming trend is largely driven by the increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide and other heat-trapping greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, caused by human emissions. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1znaGfS" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1znaGfS</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
Two key climate change indicators -- global surface temperatures and Arctic sea ice extent -- have broken numerous records through the first half of 2016, according to NASA analyses of ground-based observations and satellite data. Each of the first six months of 2016 set a record as the warmest respective month globally in the modern temperature record, which dates to 1880, according to scientists at NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York. The six-month period from January to June was also the planet's warmest half-year on record, with an average temperature 1.3 degrees Celsius (2.4 degrees Fahrenheit) warmer than the late nineteenth century. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/29SQngq" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/29SQngq</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
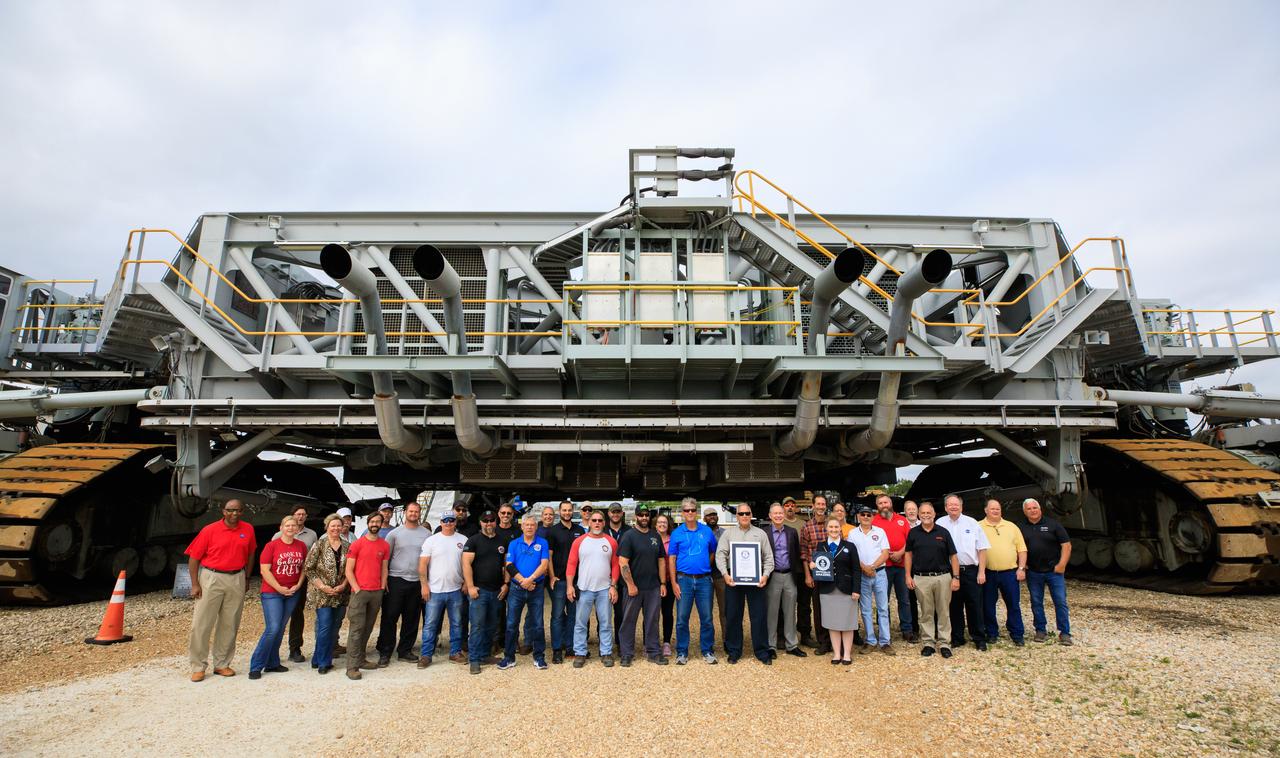

Guinness World Records officially designated NASA’s Crawler Transporter 2 as the heaviest self-powered vehicle, weighing approximately 6.65 million pounds. During a March 29, 2023, ceremony at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Guinness World Records presented a certificate to teams with the Exploration Ground Systems Program and Kennedy leadership. The crawler is responsible for carrying the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for the Artemis missions to and from the launch pad.
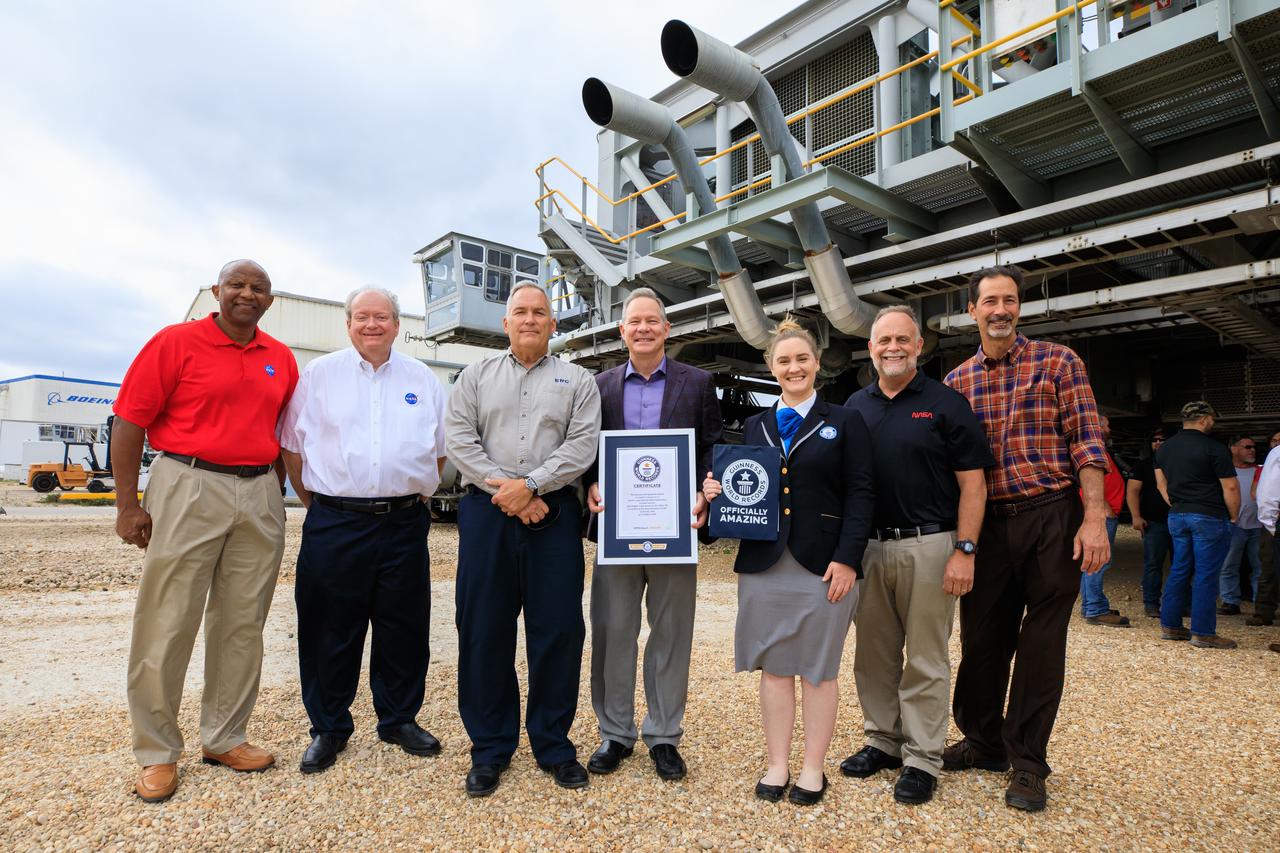

Guinness World Records officially designated NASA’s Crawler Transporter 2 as the heaviest self-powered vehicle, weighing approximately 6.65 million pounds. During a March 29, 2023, ceremony at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Guinness World Records presented a certificate to teams with the Exploration Ground Systems Program and Kennedy leadership. Pictured, from left, are: Kelvin Manning, Kennedy deputy director; Burt Summerfield, Kennedy associate director, management; Brett Raulerson, Jacobs TOSC Crawlers, Transporters and Structures group manager; Gary Casteel, Jacobs director, Ground Systems Support; Hannah Ortman, Guinness World Records adjudicator; Shawn Quinn, NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems manager; and John Giles, NASA’s Crawler Element Operations manager.
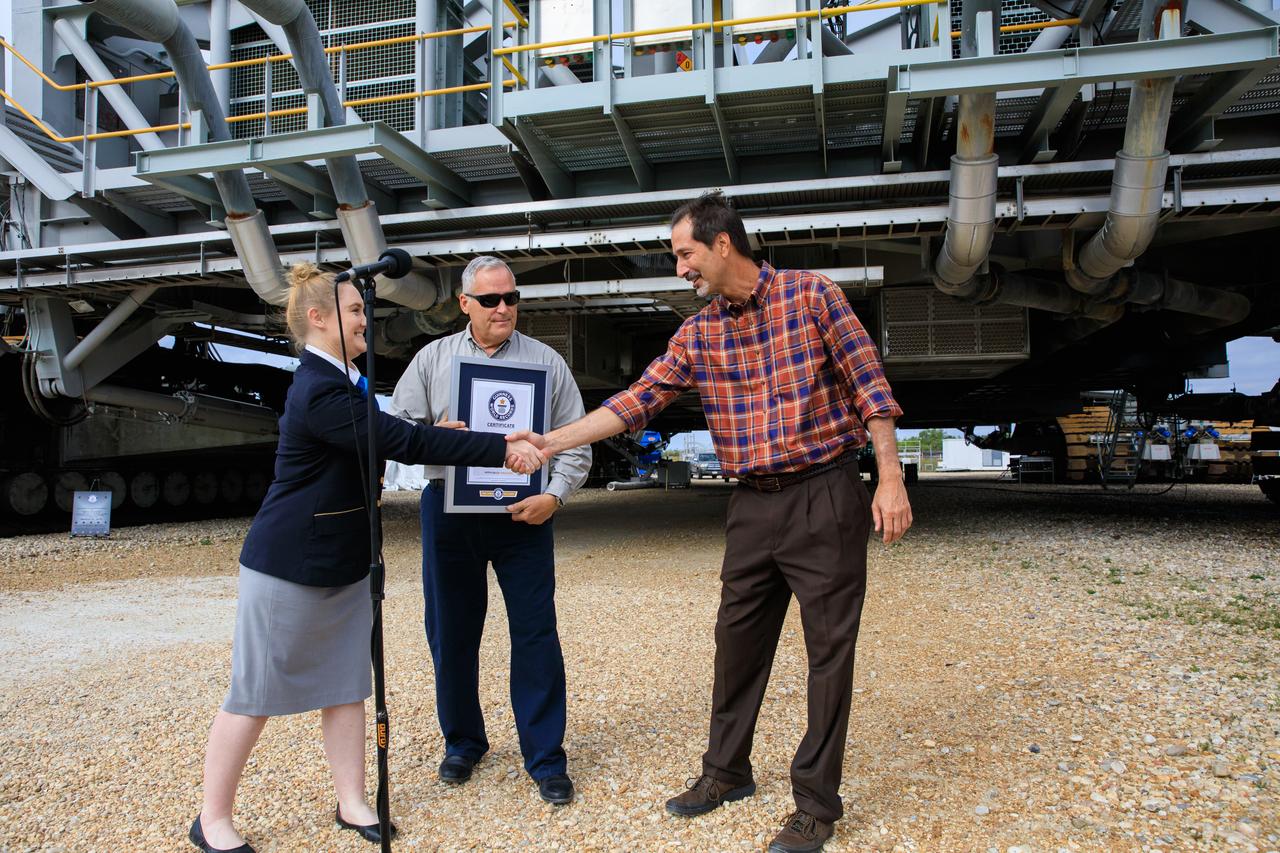

Guinness World Records adjudicator Hannah Ortman shakes hands NASA’s Crawler Element Operations Manager John Giles during a ceremony on March 29, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Also in the photo is Brett Raulerson, Jacobs TOSC Crawlers, Transporters and Structures group manager. Guinness World Records officially designated NASA’s Crawler Transporter 2 as the heaviest self-powered vehicle, weighing approximately 6.65 million pounds. The crawler is responsible for carrying the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for the Artemis missions to and from the launch pad.

Guinness World Records adjudicator Hannah Ortman shakes hands with Brett Raulerson, Jacobs TOSC Crawlers, Transporters and Structures group manager, left, and John Giles, NASA’s Crawler Element Operations manager, during a ceremony on March 29, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Guinness World Records officially designated NASA’s Crawler Transporter 2 as the heaviest self-powered vehicle, weighing approximately 6.65 million pounds. The crawler is responsible for carrying the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for the Artemis missions to and from the launch pad.
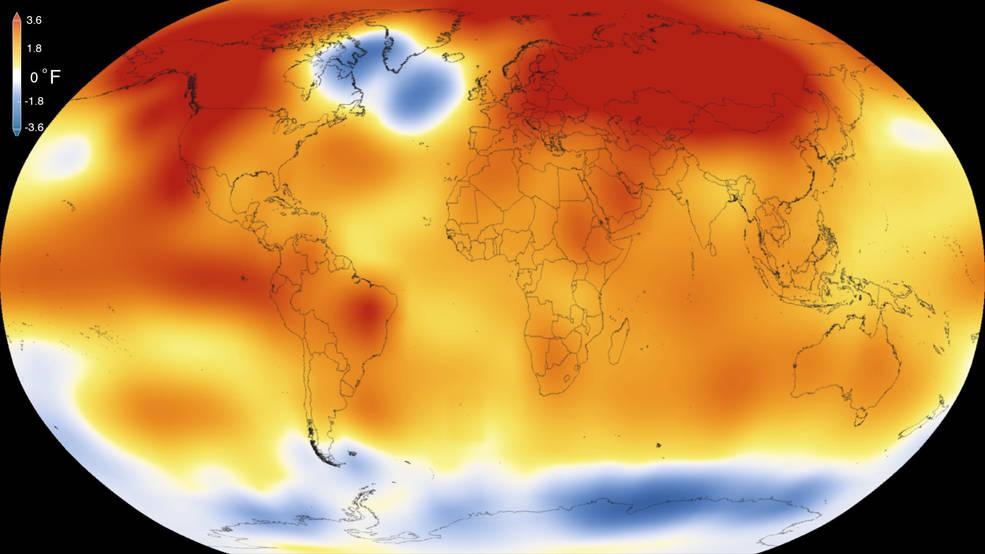
2015 was the warmest year since modern record-keeping began in 1880, according to a new analysis by NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies. The record-breaking year continues a long-term warming trend — 15 of the 16 warmest years on record have now occurred since 2001. Credits: Scientific Visualization Studio/Goddard Space Flight Center Details: Earth’s 2015 surface temperatures were the warmest since modern record keeping began in 1880, according to independent analyses by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Globally-averaged temperatures in 2015 shattered the previous mark set in 2014 by 0.23 degrees Fahrenheit (0.13 Celsius). Only once before, in 1998, has the new record been greater than the old record by this much. The 2015 temperatures continue a long-term warming trend, according to analyses by scientists at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York (GISTEMP). NOAA scientists agreed with the finding that 2015 was the warmest year on record based on separate, independent analyses of the data. Because weather station locations and measurements change over time, there is some uncertainty in the individual values in the GISTEMP index. Taking this into account, NASA analysis estimates 2015 was the warmest year with 94 percent certainty. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-noaa-analyses-reveal-record-shattering-global-warm-temperatures-in-2015" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-noaa-analyses-reveal-reco...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Record Drive Day, Opportunity Sol 383 vertical
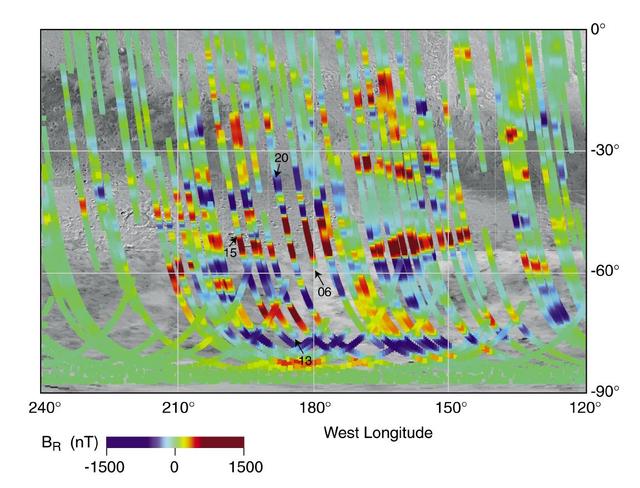
Magnetic Strips Preserve Record of Ancient Mars
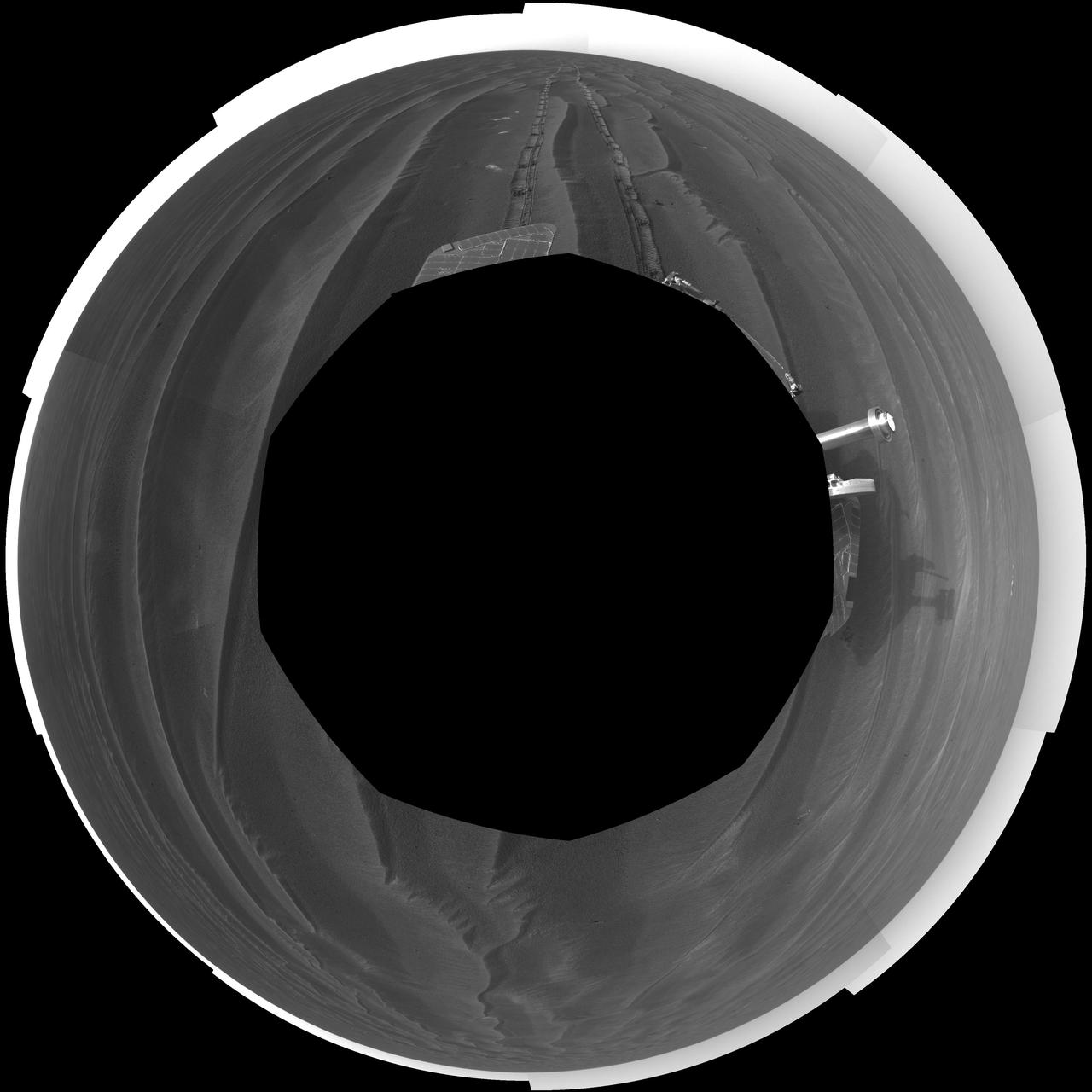
Record Drive Day, Opportunity Sol 383 polar

Record Drive Day, Opportunity Sol 383
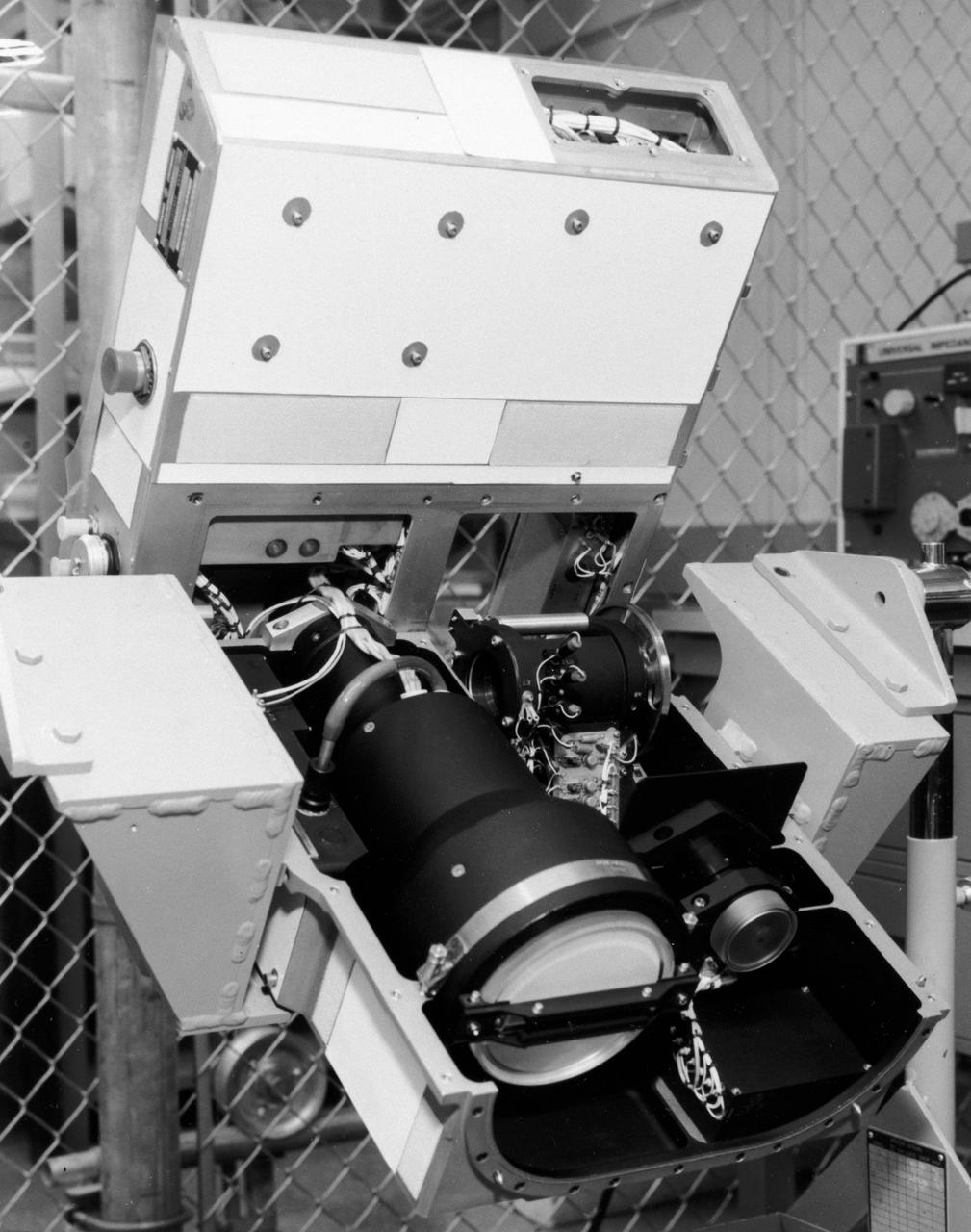

S72-49482 (November 1972) --- The Optical Recorder of the Lunar Sounder Experiment (S-209) which will be mounted in the SIM bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module. The three functional parts of the Lunar Sounder are the optical recorder, the coherent synthetic aperture radar, and the antennas, a retractable dipole for HF and a yagi for VHF. The Lunar Sounder will probe three-quarters of a mile below the moon's surface from the orbiting Apollo 17 spacecraft. Electronic data recorded on film will be retrieved by the crew during trans-Earth EVA. Geologic information on the lunar interior obtained by the sounder will permit scientific investigation of underground rock layers, lava flow patterns, rille (canyon) structures, mascon properties, and any areas containing water. A prototype lunar sounder has been flight tested in aircraft over selected Earth sites to confirm the equipment design and develop scientific analysis techniques. The Lunar Sounder Experiment was developed by North American Rockwell's (NR) Space Division for NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center to provide data for a scientific investigation team with representatives from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, University of Utah, University of Michigan, U.S. Geological Survey, and NASA Ames Research Center.
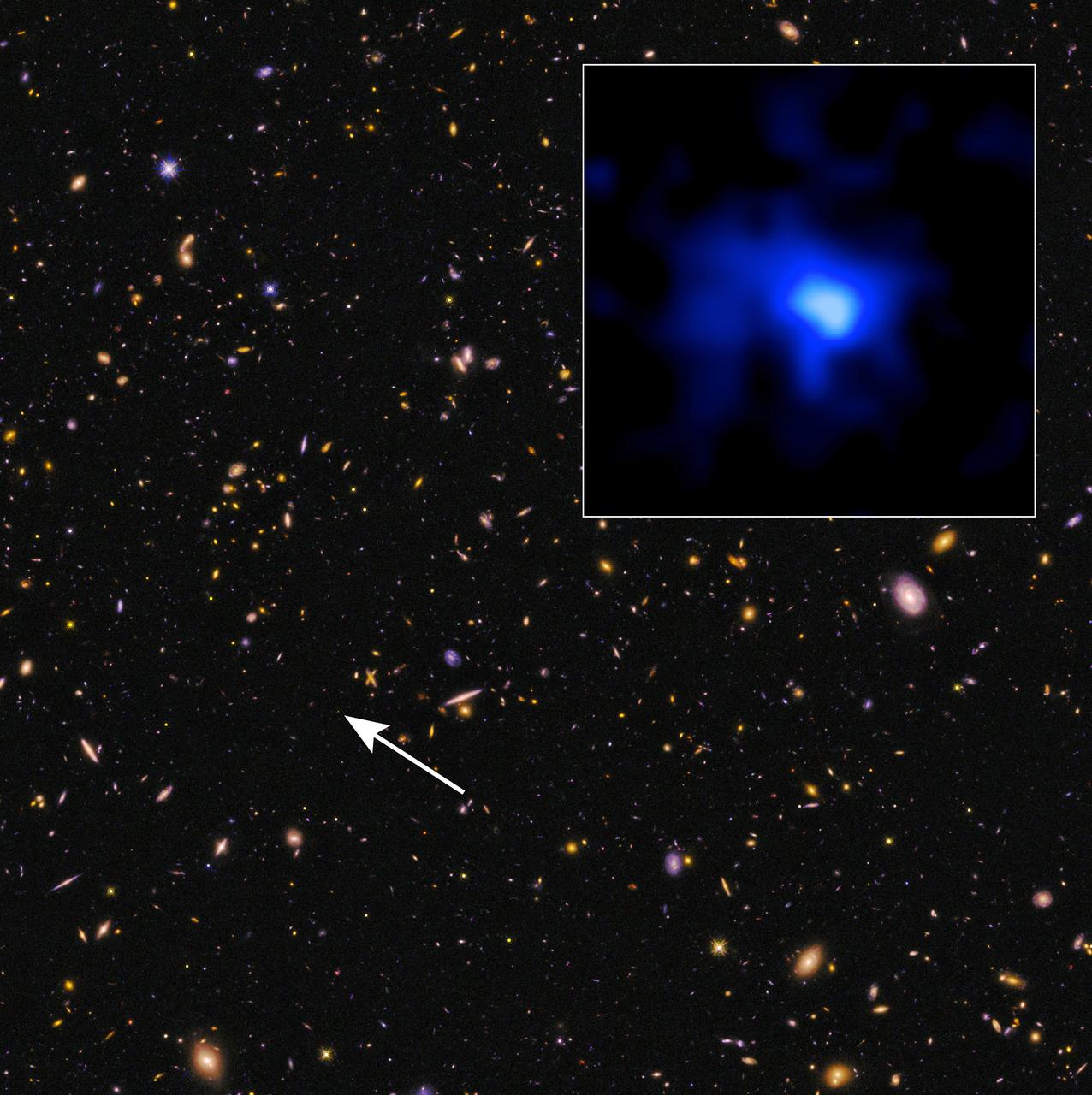

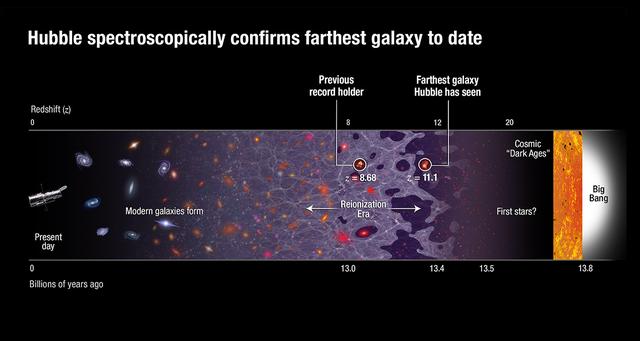
This is a Hubble Space Telescope image of the farthest spectroscopically confirmed galaxy observed to date (inset). It was identified in this Hubble image of a field of galaxies in the CANDELS survey (Cosmic Assembly Near-infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey). NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope also observed the unique galaxy. The W. M. Keck Observatory was used to obtain a spectroscopic redshift (z=7.7), extending the previous redshift record. Measurements of the stretching of light, or redshift, give the most reliable distances to other galaxies. This source is thus currently the most distant confirmed galaxy known, and it appears to also be one of the brightest and most massive sources at that time. The galaxy existed over 13 billion years ago. The near-infrared light image of the galaxy (inset) has been colored blue as suggestive of its young, and hence very blue, stars. The CANDELS field is a combination of visible-light and near-infrared exposures. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/astronomers-set-a-new-galaxy-distance-record" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/astronomers-set-a-new-galaxy...</a> Credits: NASA, ESA, P. Oesch (Yale U.) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
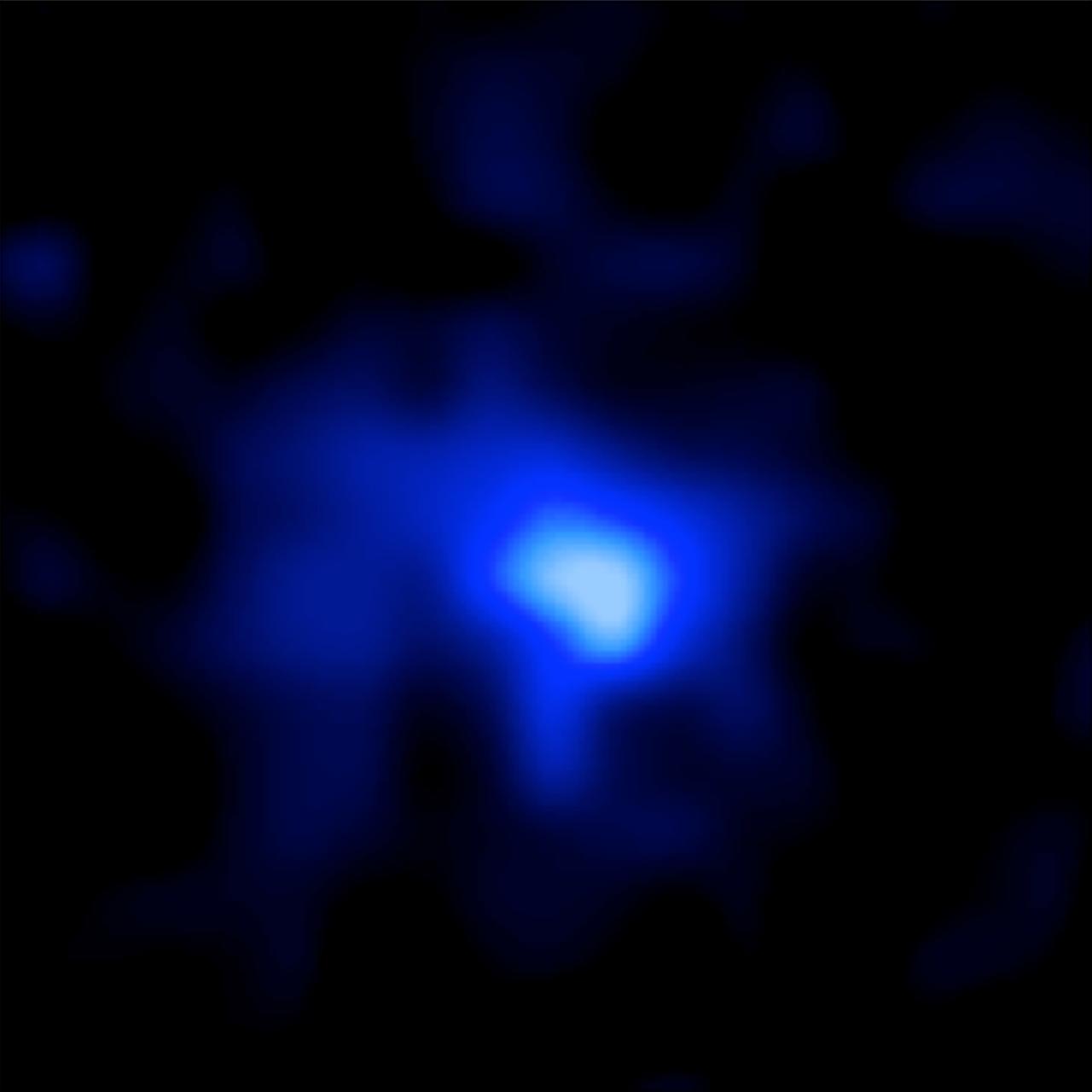
This is a Hubble Space Telescope image of the farthest spectroscopically confirmed galaxy observed to date (inset). It was identified in this Hubble image of a field of galaxies in the CANDELS survey (Cosmic Assembly Near-infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey). NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope also observed the unique galaxy. The W. M. Keck Observatory was used to obtain a spectroscopic redshift (z=7.7), extending the previous redshift record. Measurements of the stretching of light, or redshift, give the most reliable distances to other galaxies. This source is thus currently the most distant confirmed galaxy known, and it appears to also be one of the brightest and most massive sources at that time. The galaxy existed over 13 billion years ago. The near-infrared light image of the galaxy (inset) has been colored blue as suggestive of its young, and hence very blue, stars. The CANDELS field is a combination of visible-light and near-infrared exposures. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/astronomers-set-a-new-galaxy-distance-record" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/astronomers-set-a-new-galaxy...</a> Credits: NASA, ESA, P. Oesch (Yale U.) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
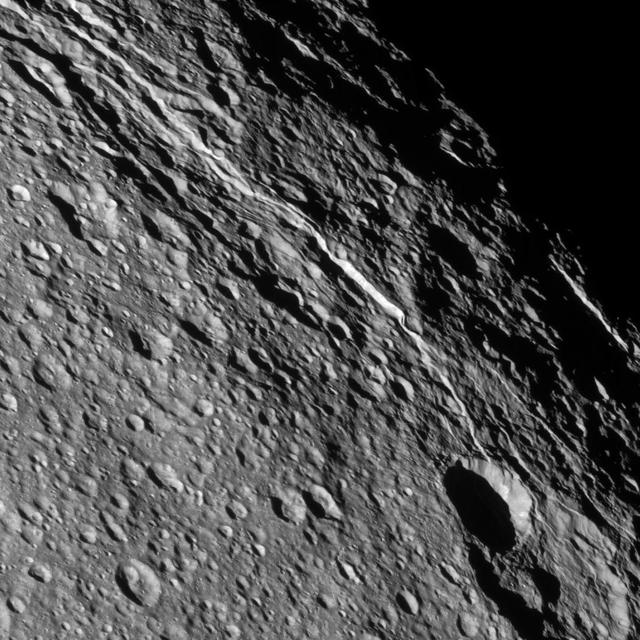

The surface of Saturn moon Rhea bears witness to its violent history. Each crater seen here by NASA Cassini spacecraft records an impact in the moon past.
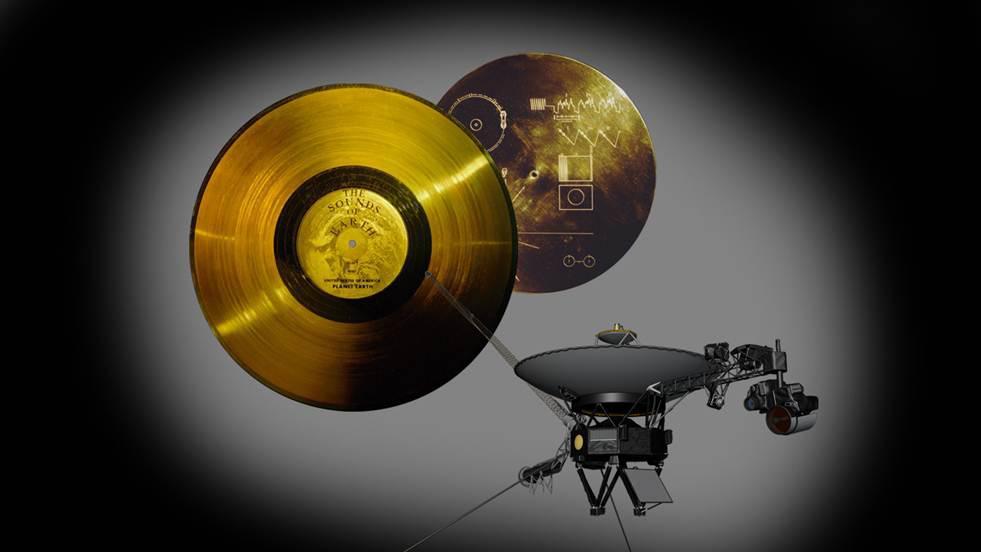

This image highlights the special cargo onboard NASA Voyager spacecraft: the Golden Record. Each of the two Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977 carry a 12-inch gold-plated phonograph record with images and sounds from Earth.
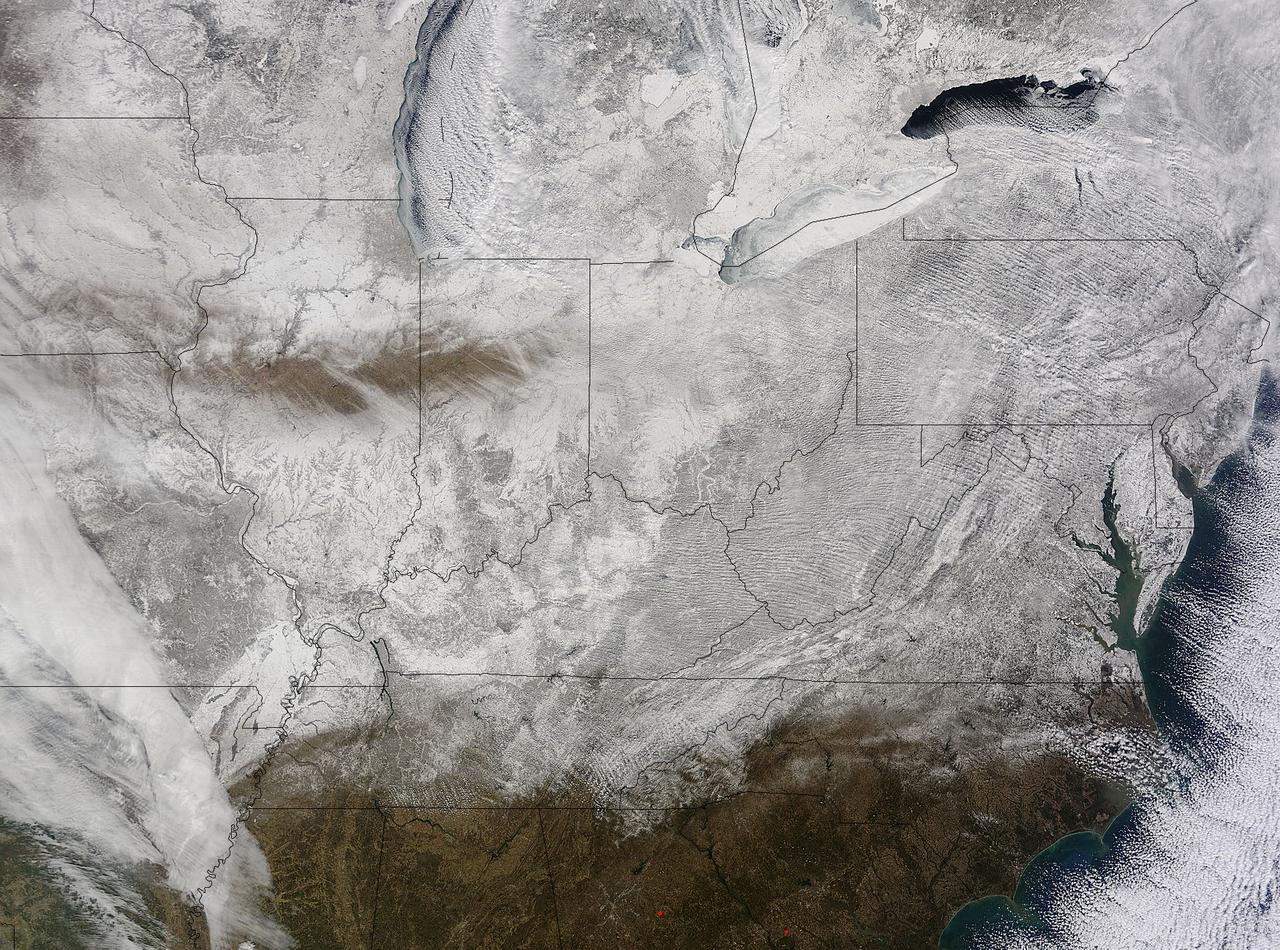

NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of the snow-covered eastern U.S. that looks like the states have been sitting in a freezer. In addition to the snow cover, Arctic and Siberian air masses have settled in over the Eastern U.S. triggering many record low temperatures in many states. On Feb. 19 at 16:40 UTC (11:40 a.m. EST), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a picture of the snowy landscape. The snow cover combined with the frosty air mass made the eastern U.S. feel like the inside of freezer. The MODIS image was created at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. On the morning of Feb. 20, NOAA's Weather Prediction Center (WPC) noted, "There were widespread subzero overnight lows Thursday night (Feb. 19) extending from Illinois to western Virginia, and numerous record lows were set. Bitterly-cold arctic air is setting numerous temperature records across the eastern U.S. and will keep temperatures well below normal on Friday (Feb. 20)." In Baltimore, Maryland, a low temperature of 1F broke the record low for coldest morning recorded at the Thurgood Marshall Baltimore Washington-International Airport. In Louisville, Kentucky, temperatures dropped to -6F, breaking the old record low of 0F, according to meteorologist Brian Goode of WAVE-TV. Meanwhile, Richmond Kentucky bottomed out at a frigid -32F. In North Carolina, a record low temperature was set at Charlotte where the overnight temperature bottomed out at 7F breaking the old record of 13F in 1896. In Asheville, temperatures dropped to just 4F breaking the old record of 10F in 1979. Temperature records for Asheville extend back to 1876. Several records were also broken in Georgia, according to Matt Daniel, a meteorologist at WMAZ-TV, Macon Georgia, who cited data from the National Weather Service. Daniel said that Macon set a new record low when the temperature dropped to 18F, beating the previous record of 21F set in 1958. Athens broke a new record low, too dropping to 14F and beating the old record of 18F set in 1958/1928. NOAA's NPC noted that "Highs on Friday (Feb. 20) will struggle to get out of the teens from the Ohio Valley to the Mid-Atlantic region. After Friday, temperatures are forecast to moderate and get closer to February averages as a storm system approaches from the west." Image Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
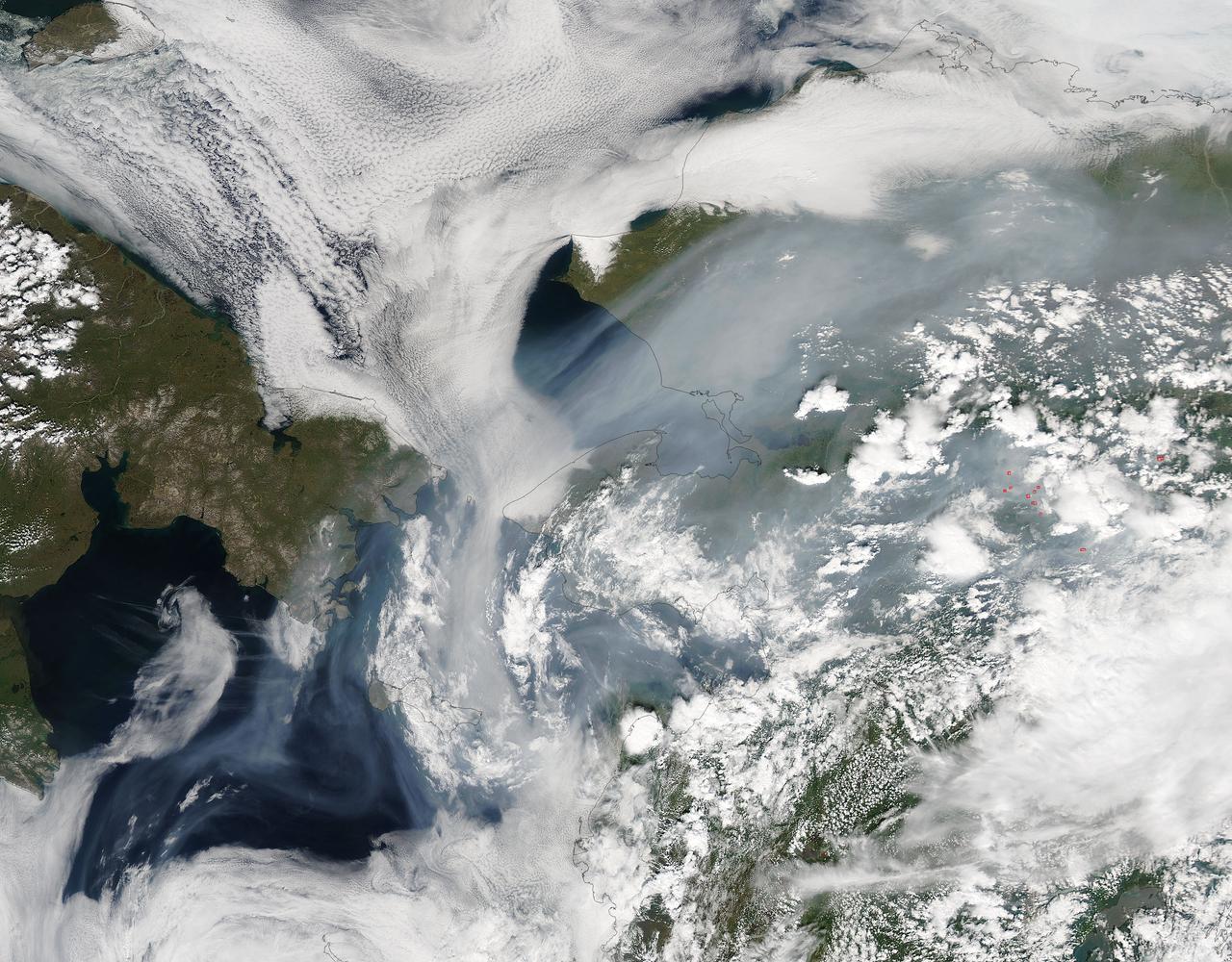
Fires have raged throughout Alaska in 2015. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite acquired this image on July 14, 2015. Actively burning areas, detected by the thermal bands on MODIS, are outlined in red. According to the most recent update (July 16, 2015) from the Alaska Interagency Coordination Center, about 304 fires were actively burning when MODIS imaged the area. To date, fires have charred a total of 4,854,924 acres in Alaska. The worst fire season in Alaska's history was in 2004. At this point in time, 2015 is a month ahead of the totals in 2004 putting it on track surpass the fire totals in 2004. The amount of acreage burned in Alaska during June 2015 shattered the previous acreage record set in June 2004 by more than 700,000 acres delivering a sobering piece of news for Alaskan residents. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
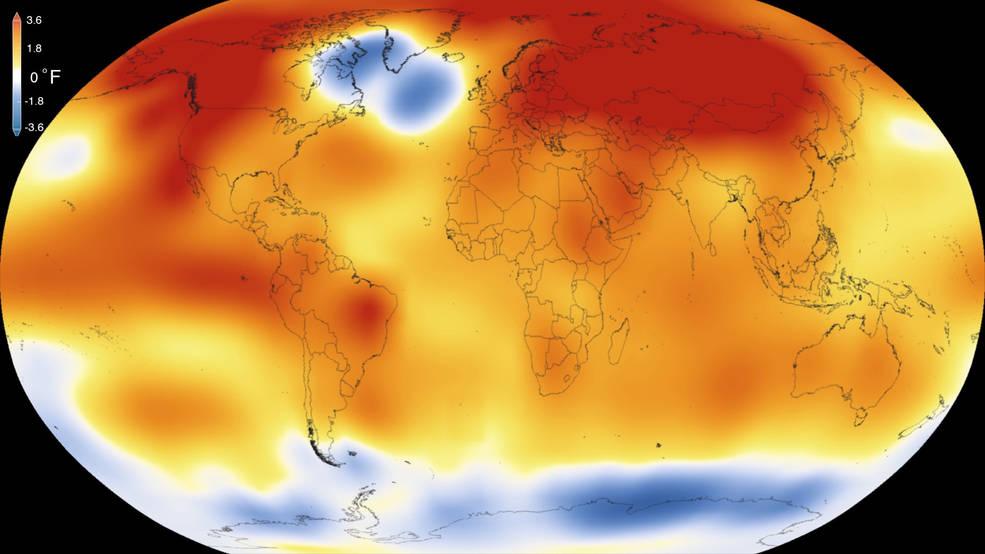
2015 was the warmest year since modern record-keeping began in 1880, according to a new analysis by NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies. The record-breaking year continues a long-term warming trend — 15 of the 16 warmest years on record have now occurred since 2001. Credits: Scientific Visualization Studio/Goddard Space Flight Center Details: Earth’s 2015 surface temperatures were the warmest since modern record keeping began in 1880, according to independent analyses by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Globally-averaged temperatures in 2015 shattered the previous mark set in 2014 by 0.23 degrees Fahrenheit (0.13 Celsius). Only once before, in 1998, has the new record been greater than the old record by this much. The 2015 temperatures continue a long-term warming trend, according to analyses by scientists at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York (GISTEMP). NOAA scientists agreed with the finding that 2015 was the warmest year on record based on separate, independent analyses of the data. Because weather station locations and measurements change over time, there is some uncertainty in the individual values in the GISTEMP index. Taking this into account, NASA analysis estimates 2015 was the warmest year with 94 percent certainty.
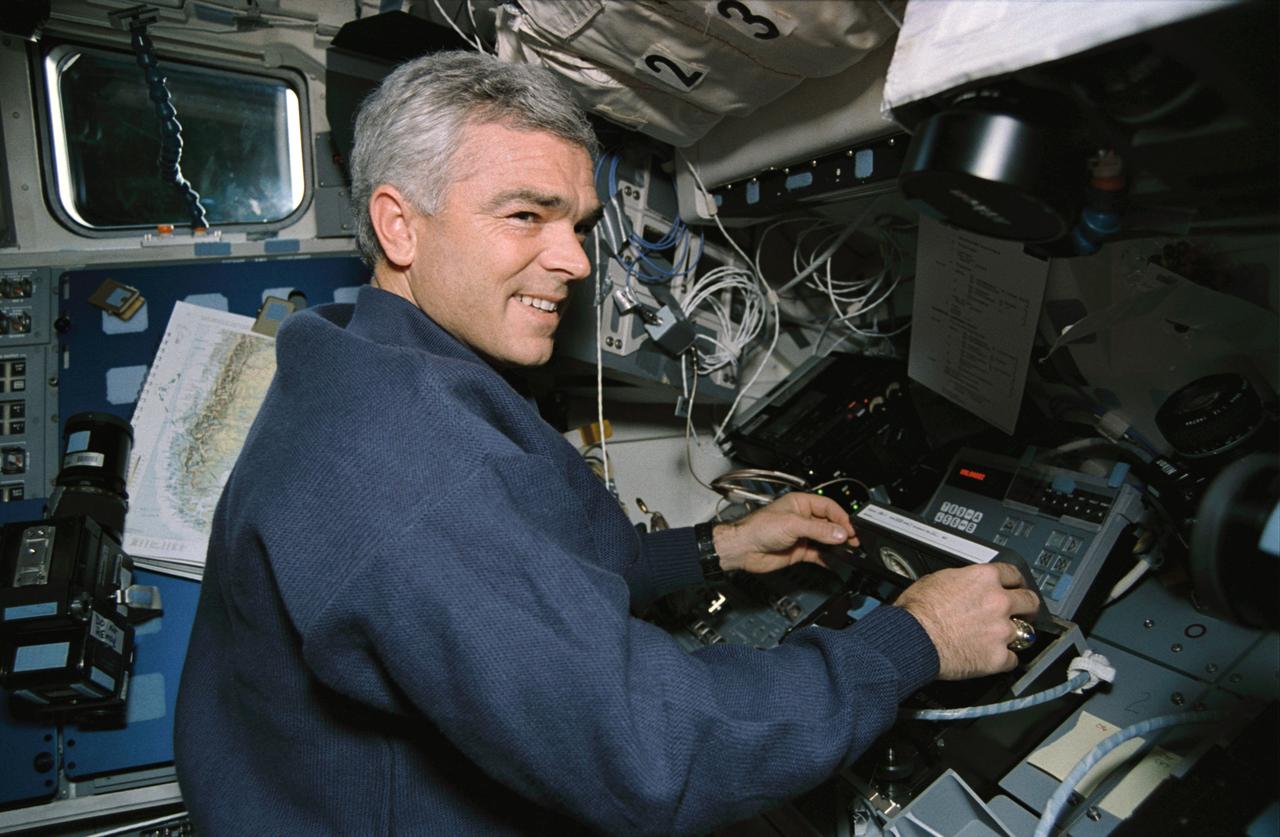

STS059-09-012 (9-20 April 1994) --- On the Space Shuttle Endeavour's aft flight deck, astronaut Michael R. (Rich) Clifford, mission specialist, inserts a tape in the payload high rate recorder. Three of these state-of-the-art recorders captured four times the amount of data that could be radioed to the ground. The 183 tapes, each containing 40 megabytes of data, will be turned into images over the next year, and analyzed over the next decade. Clifford was joined in space by five other NASA astronauts for a week and a half of support to the Space Radar Laboratory (SRL-1)/STS-59 mission.
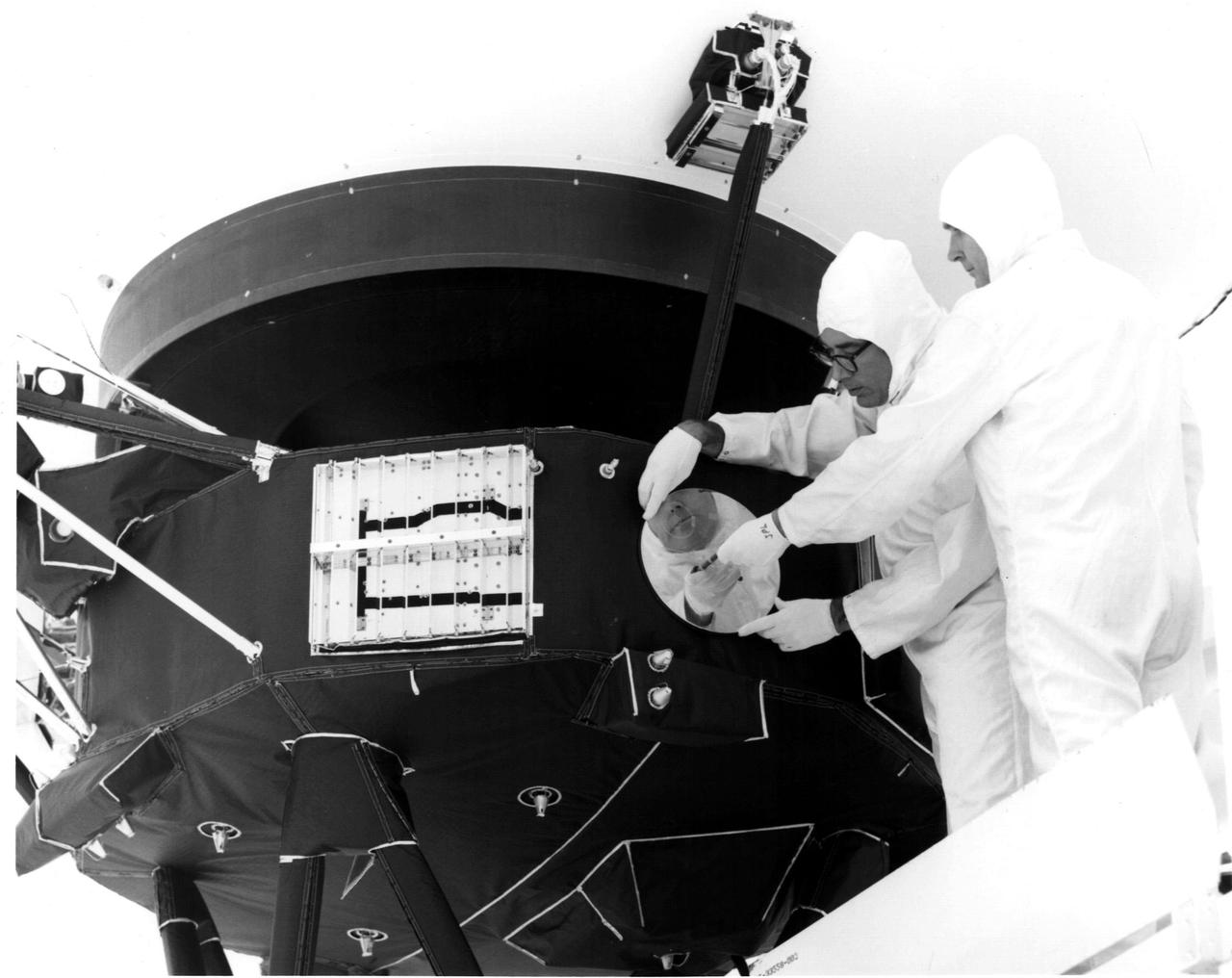

Engineers secure the cover over the Voyager 1 Golden Record in this archival image from 1977. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21740

New Record Five-Wheel Drive, Spirit Sol 1856
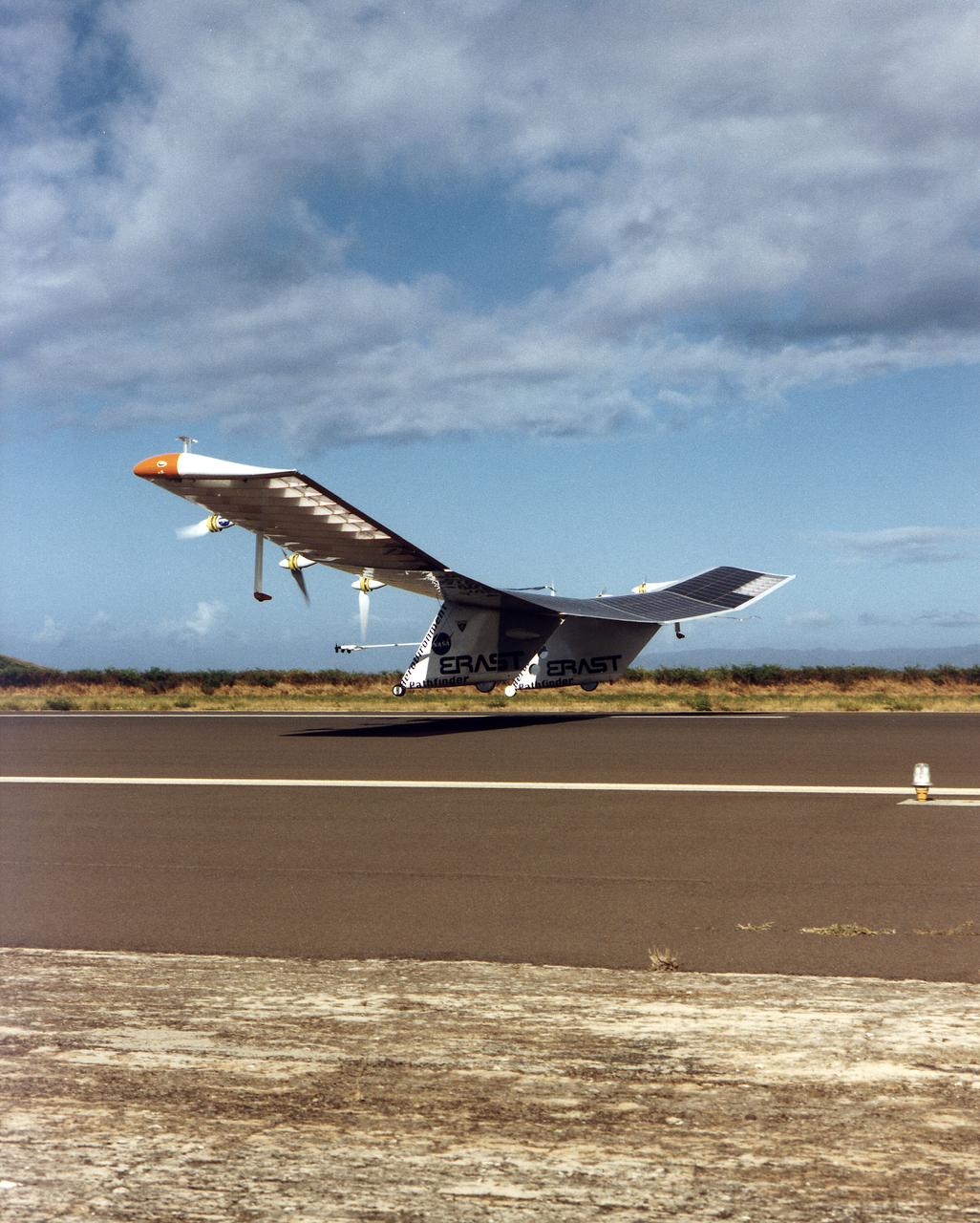

The Pathfinder aircraft has set a new unofficial world record for high-altitude flight of over 71,500 feet for solar-powered aircraft at the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility, Kauai, Hawaii. Pathfinder was designed and manufactured by AeroVironment, Inc, of Simi Valley, California, and was operated by the firm under a jointly sponsored research agreement with NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. Pathfinder's record-breaking flight occurred July 7, 1997. The aircraft took off at 11:34 a.m. PDT, passed its previous record altitude of 67,350 feet at about 5:45 p.m. and then reached its new record altitude at 7 p.m. The mission ended with a perfect nighttime landing at 2:05 a.m. PDT July 8. The new record is the highest altitude ever attained by a propellor-driven aircraft. Before Pathfinder, the altitude record for propellor-driven aircraft was 67,028 feet, set by the experimental Boeing Condor remotely piloted aircraft.
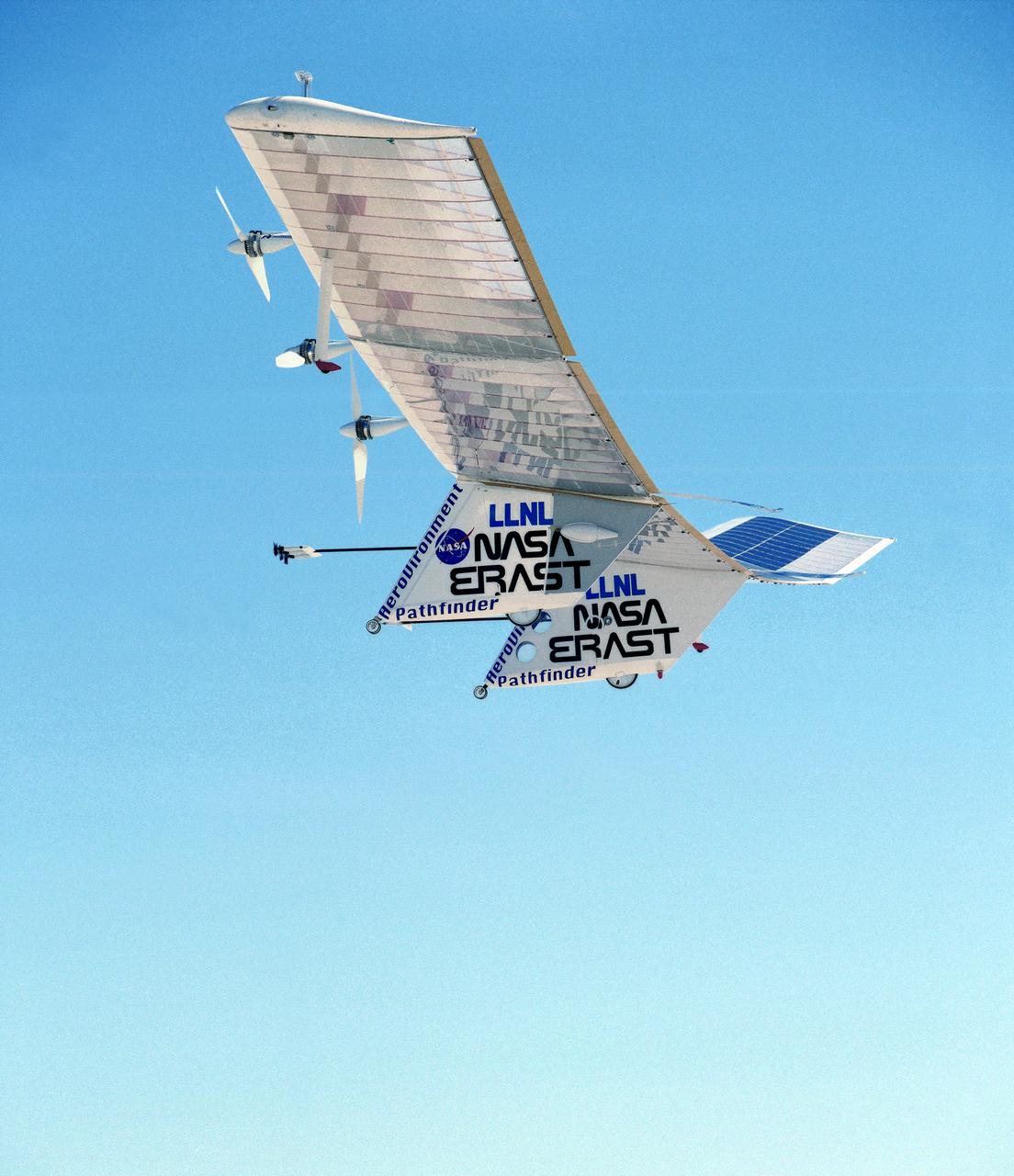

The Pathfinder solar-powered remotely piloted aircraft climbs to a record-setting altitude of 50,567 feet during a flight Sept. 11, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
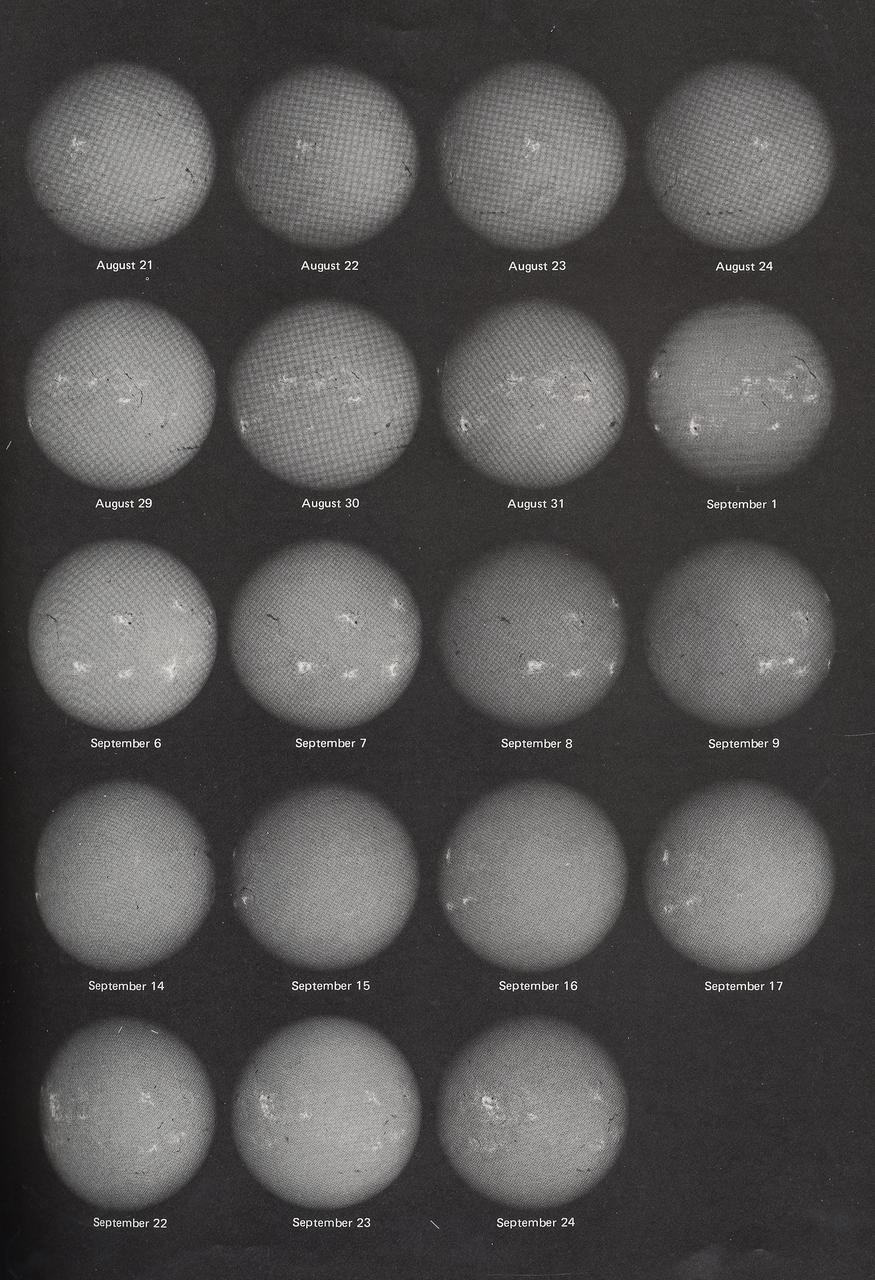
This montage shows changing faces of the Sun, recorded daily during the 59 days spent in orbit by Skylab's second crew. The Sun spun more than two full turns around its axis. Solar rotation is apparent in these daily portraits, as are real changes on the Sun. Bright features are centers of activity on the Sun. This image contains daily records from September 6, 1973 through September 24, 1973.
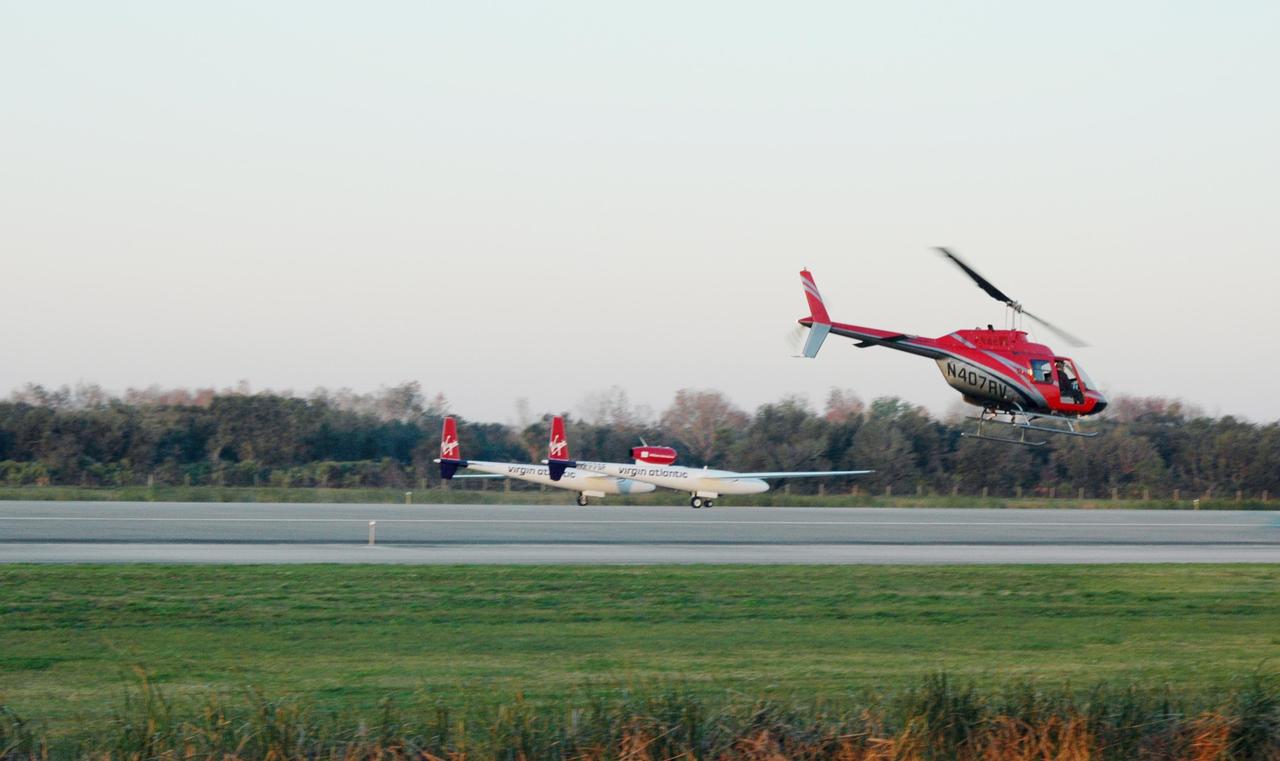

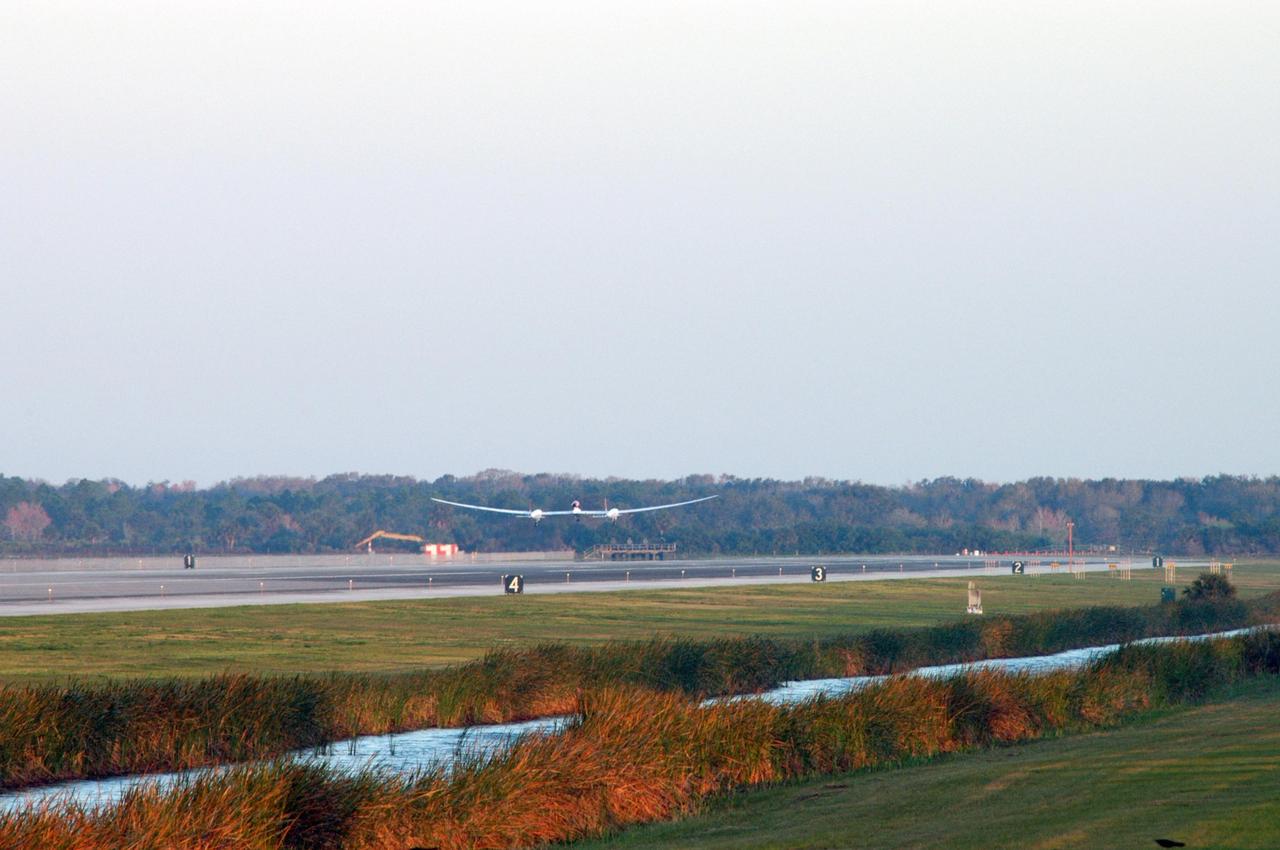
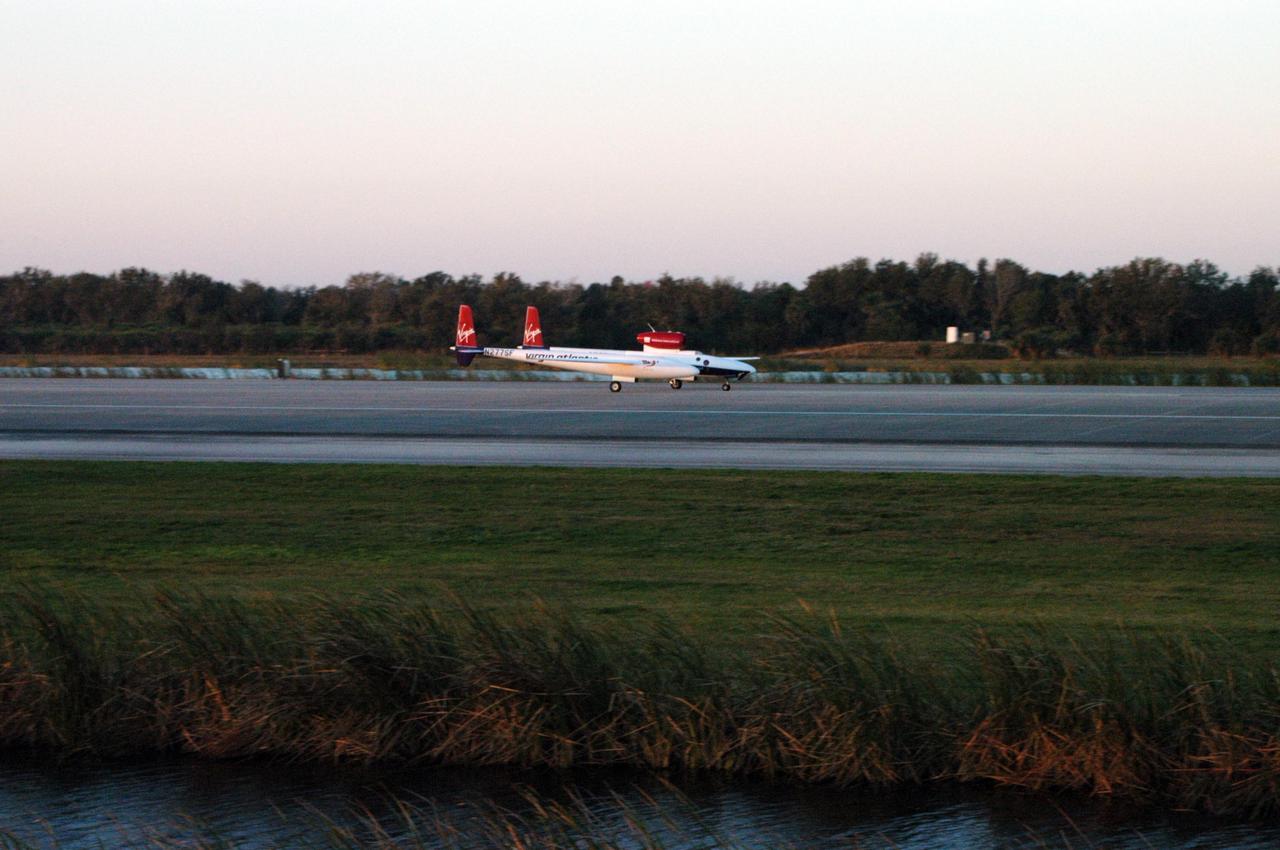
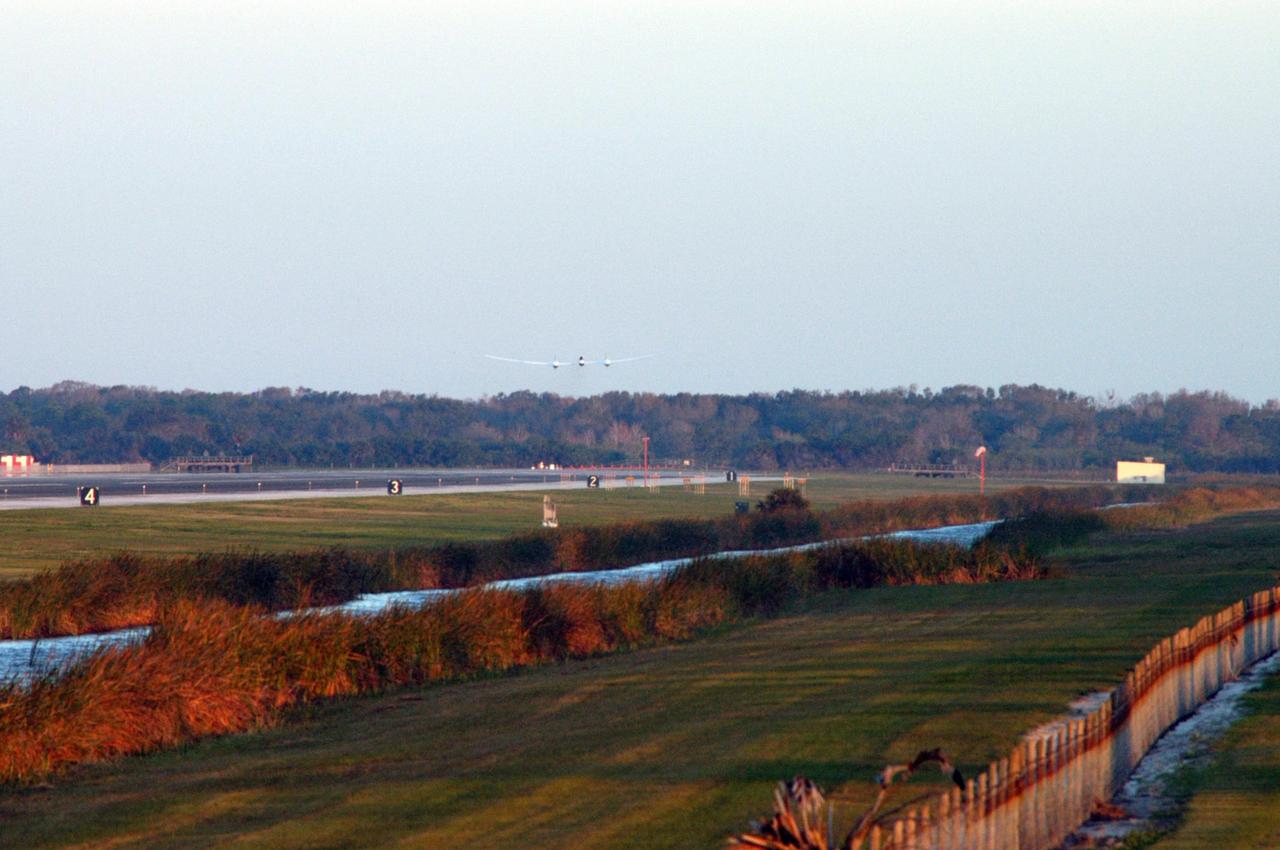
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff as a nearby helicopter films the historic event for audiences in the United Kingdom. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.
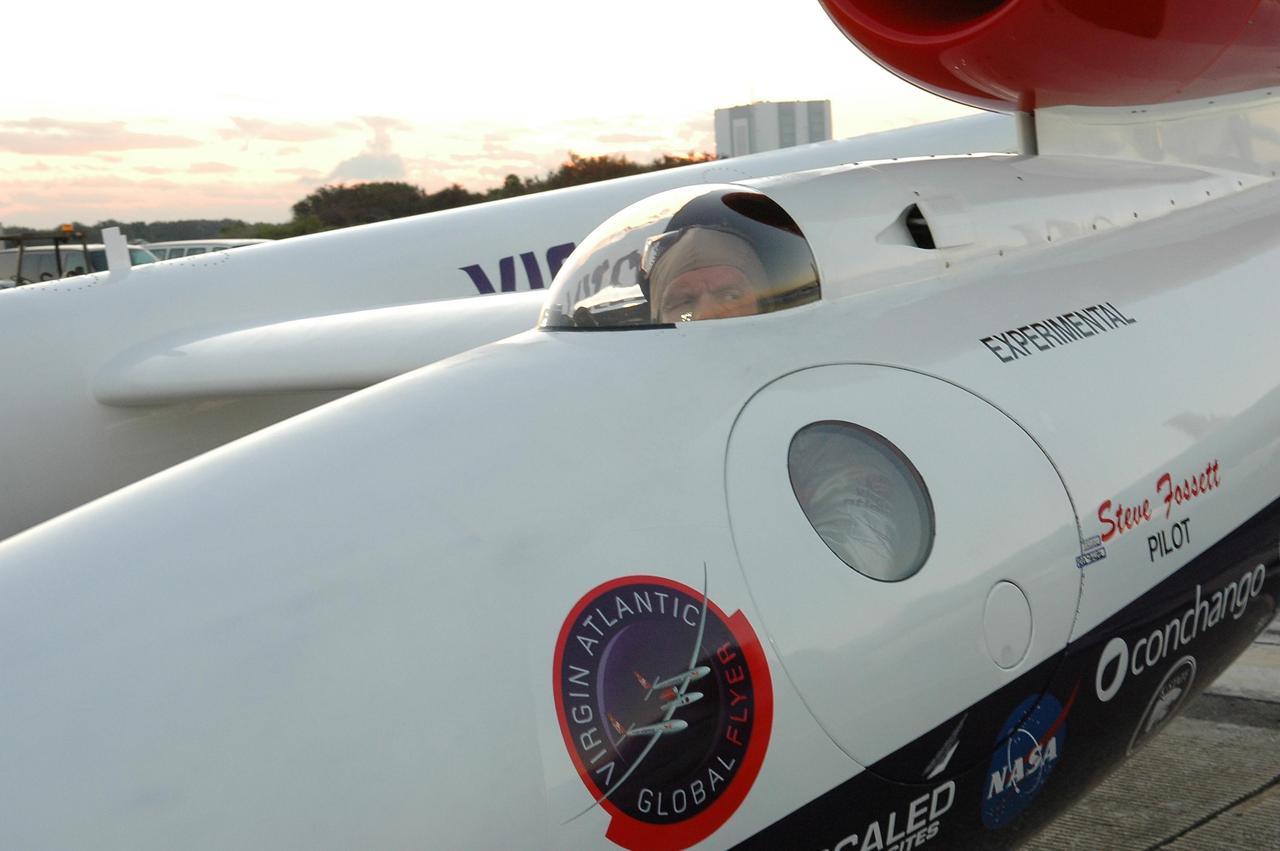

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, the door is closed on the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer as pilot Steve Fossett looks out the cockpit window. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff as a nearby helicopter films the event for audiences in the United Kingdom. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.
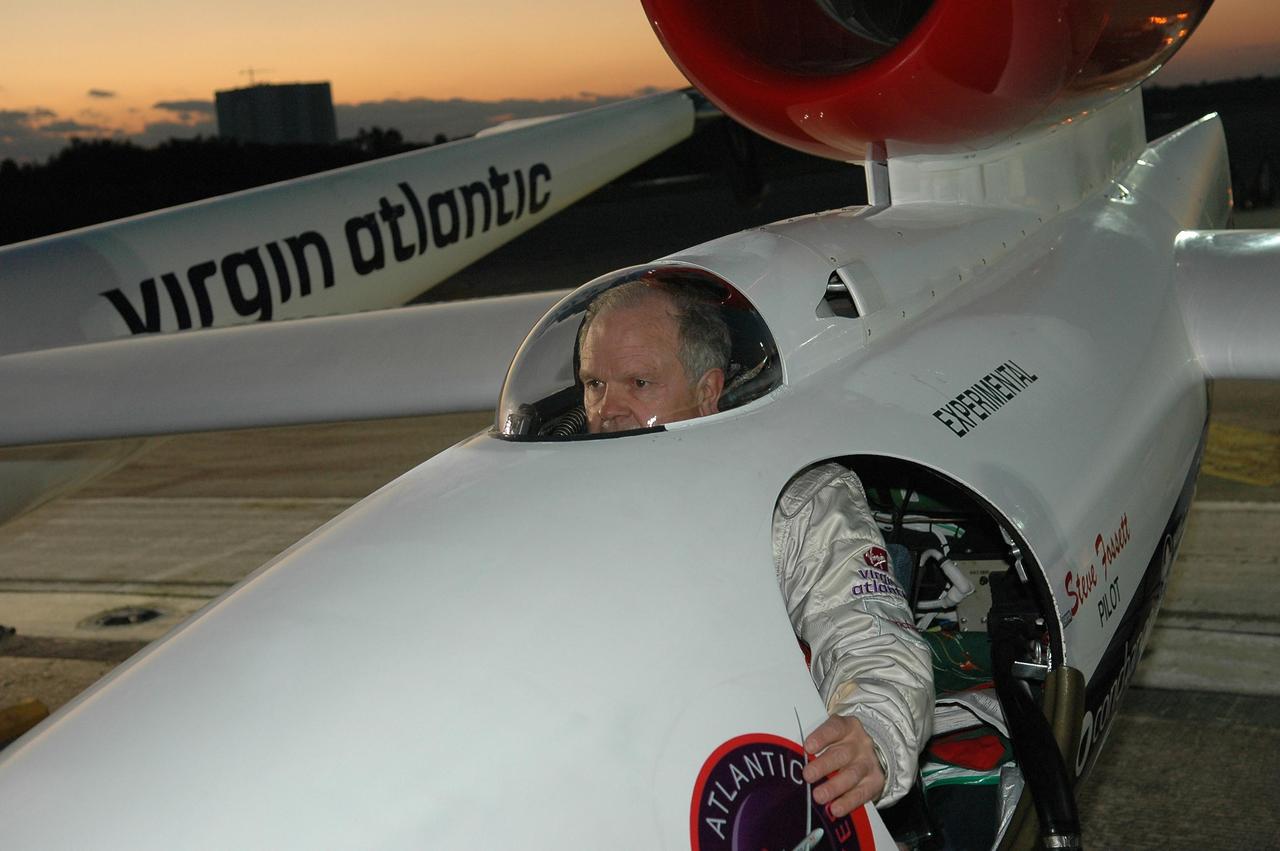

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett, seated in the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer cockpit, checks visibility and head space. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at dawn, Steve Fossett (left) gets ready to climb into the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer parked on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
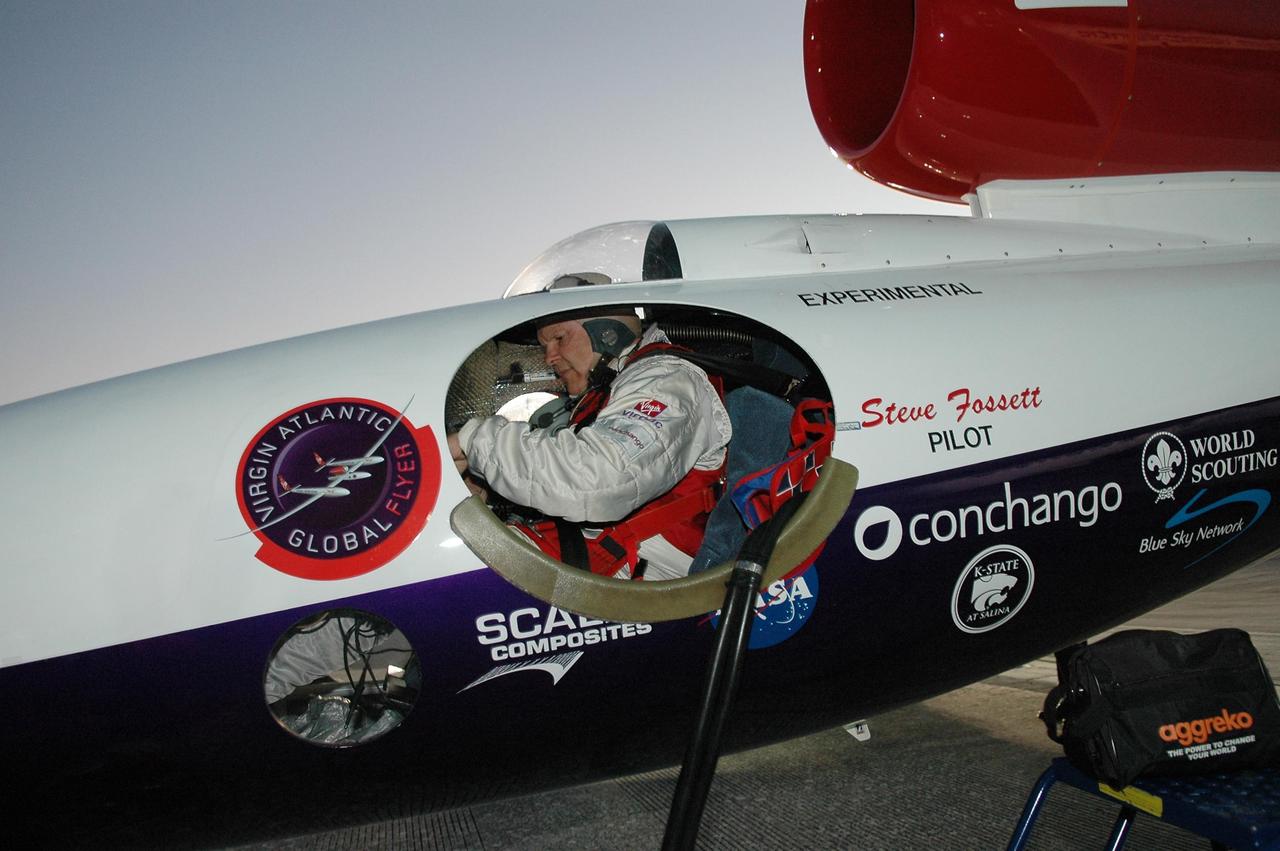

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett, seated in the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer cockpit, completes the checkout before takeoff. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
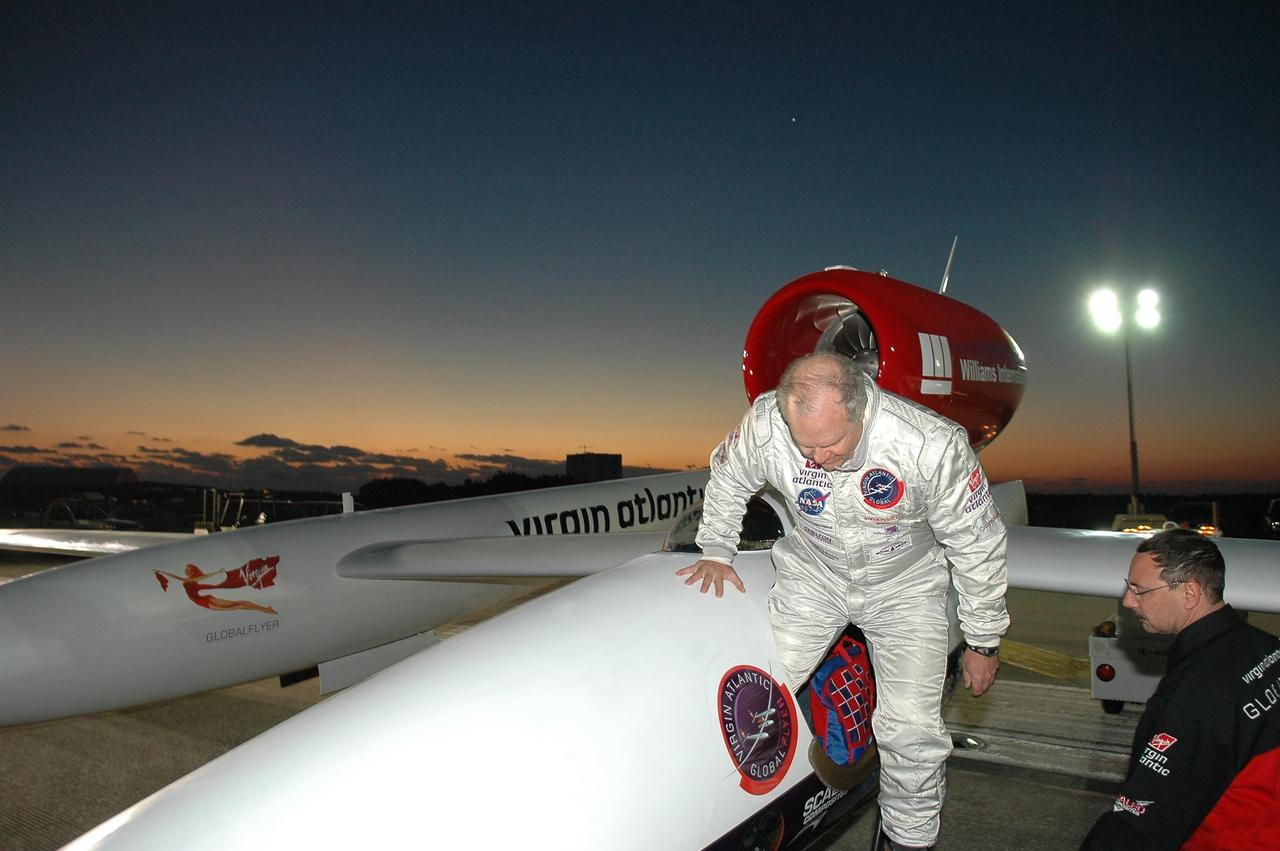

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at dawn, Steve Fossett (left) climbs into the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer parked on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
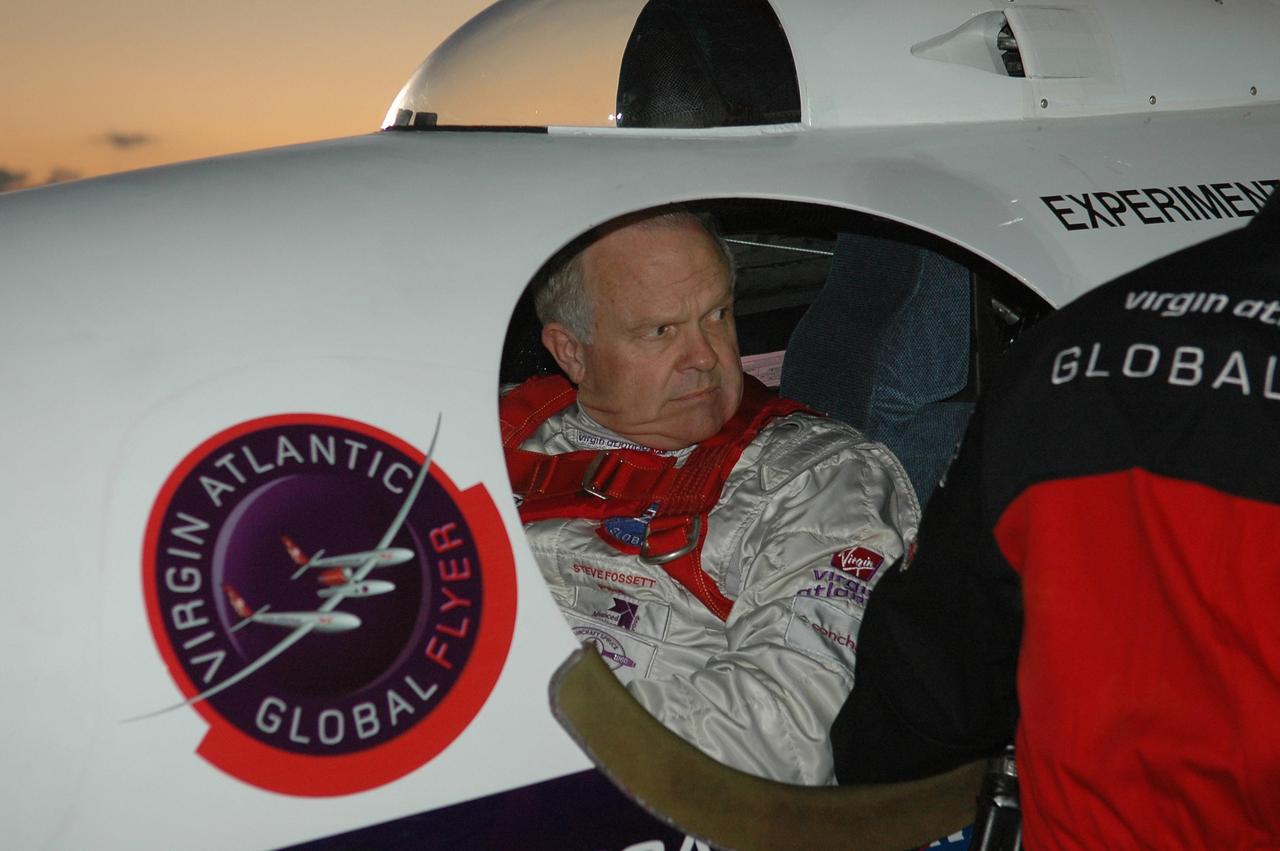

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett is strapped into the cockpit of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer waiting for takeoff. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
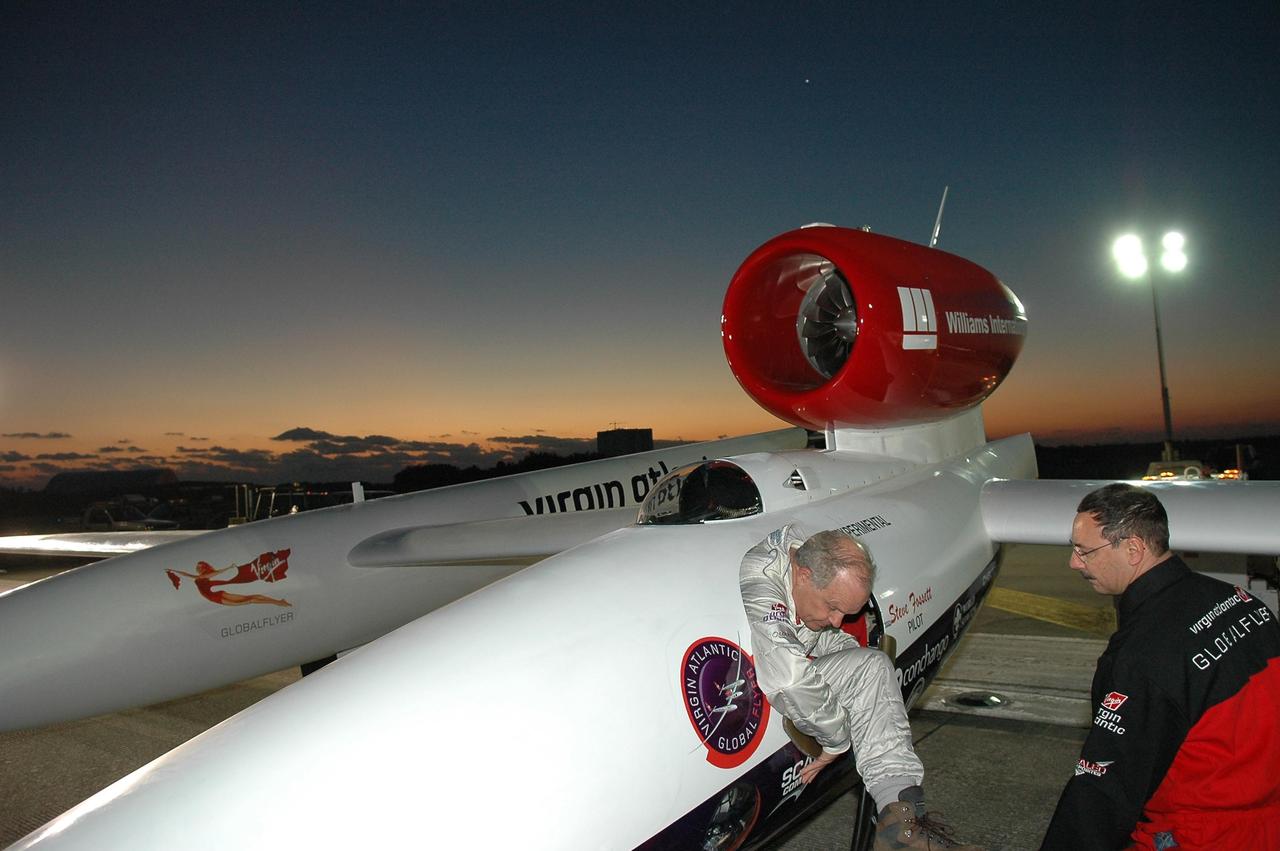

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at dawn, Steve Fossett (left) climbs into the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer parked on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

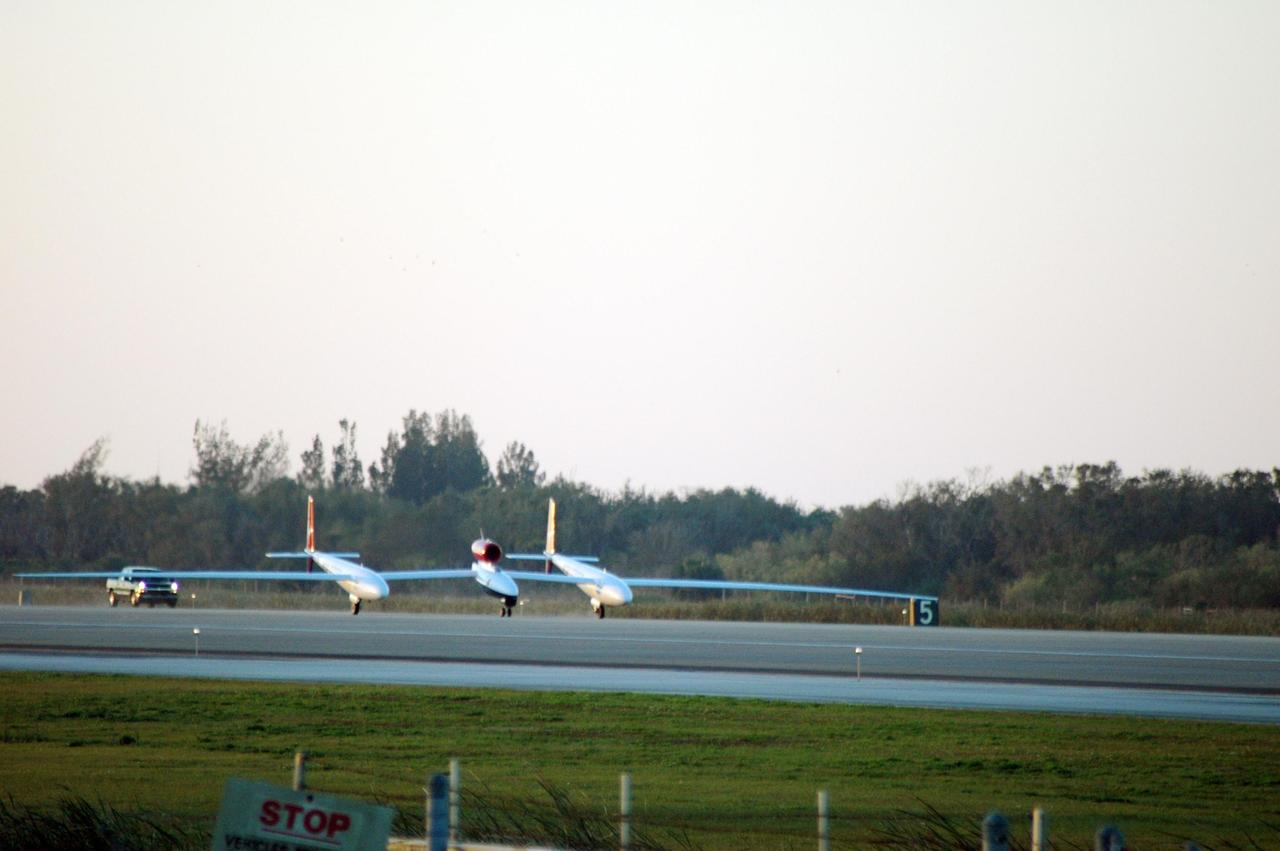
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, lifts off the ground. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - From NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, is airborne. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
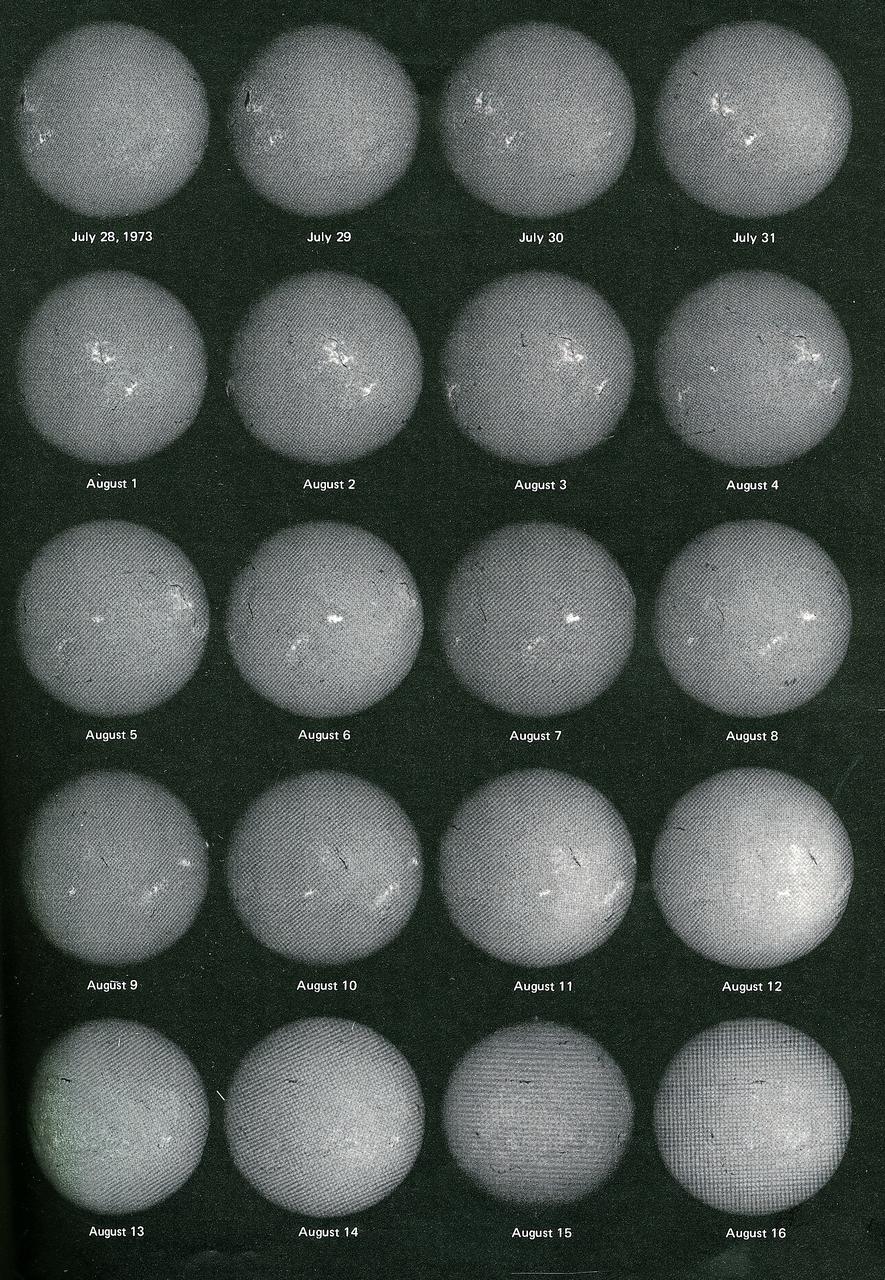
This montage shows changing faces of the Sun, recorded daily during the 59 days spent in orbit by Skylab's second crew. The Sun spun more than two full turns around its axis. Solar rotation is apparent in these daily portraits, as are real changes on the Sun. Bright features are centers of activity on the Sun. This image contains daily records from July 28, 1973 through August 16, 1973.
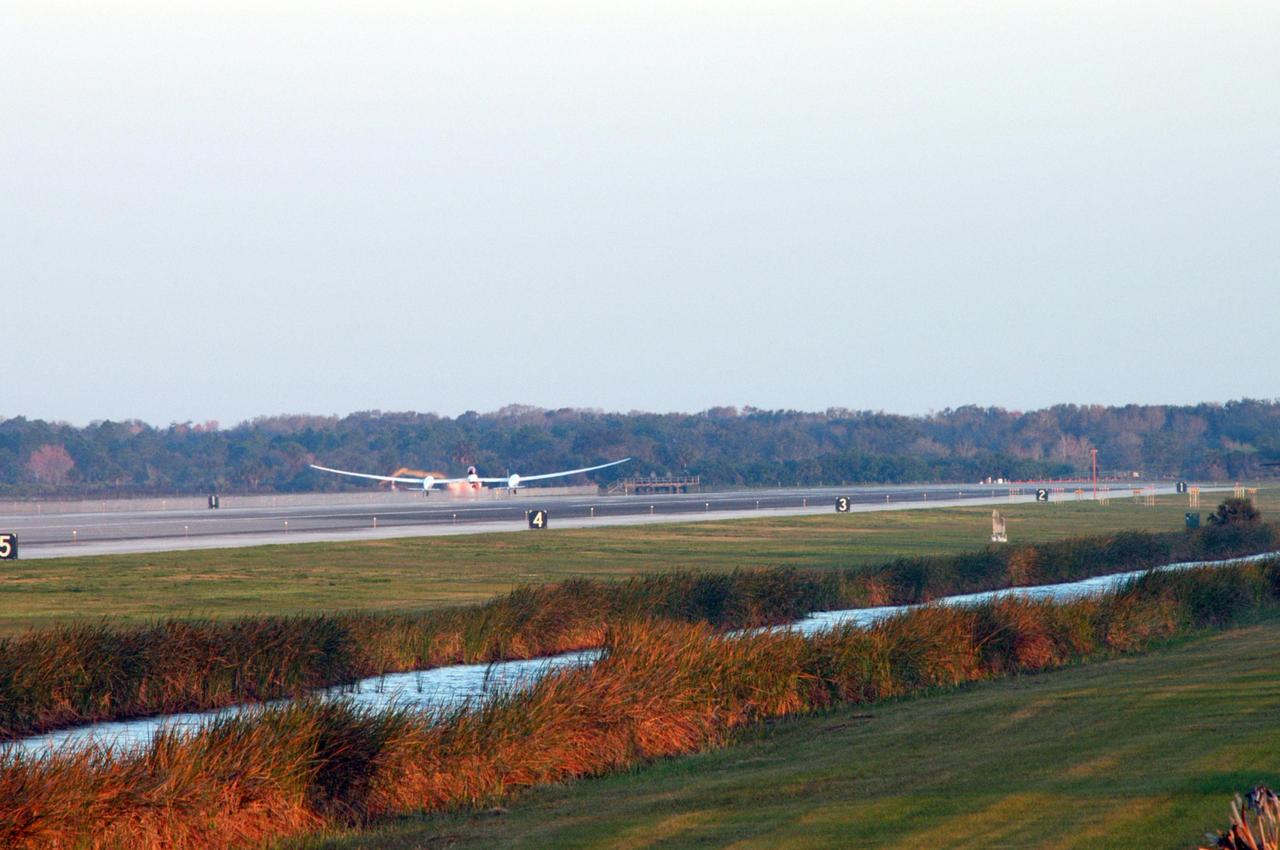

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

This montage shows changing faces of the Sun, recorded daily during the 59 days spent in orbit by Skylab's second crew. The Sun spun more than two full turns around its axis. Solar rotation is apparent in these daily portraits, as are real changes on the Sun. Bright features are centers of activity on the Sun. This image contains daily records from August 17, 1973 through September 5, 1973.
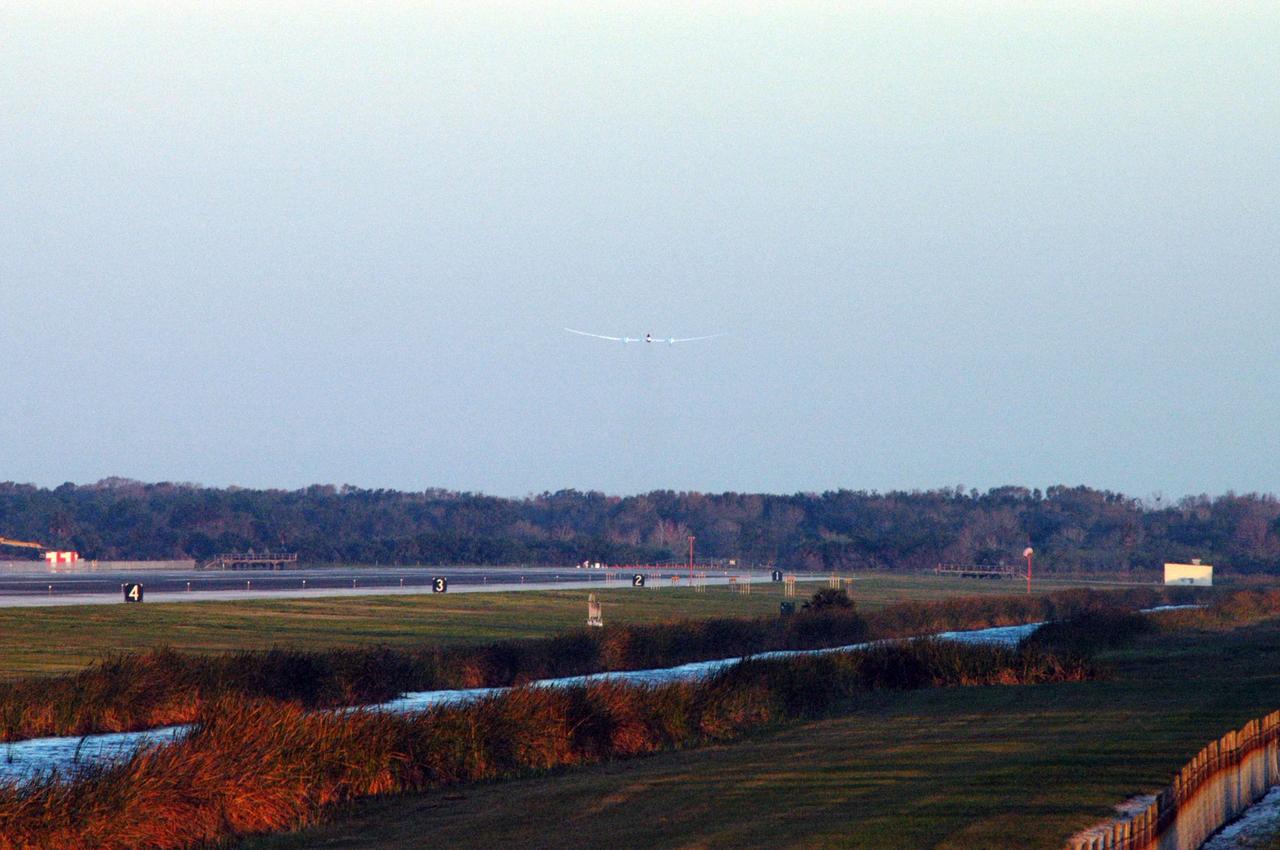

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - With little runway to spare, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, is airborne from NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
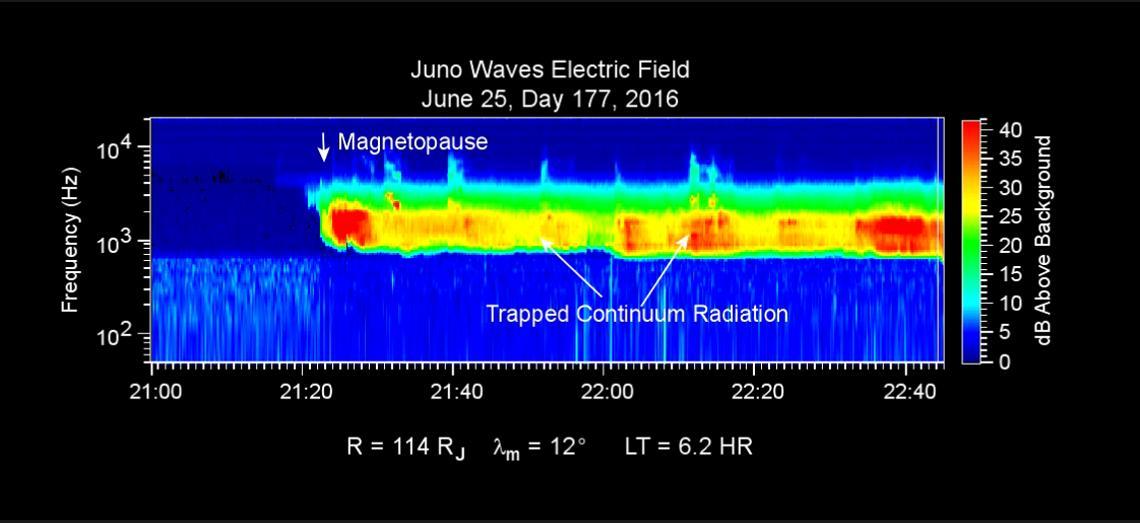
This chart presents data that the Waves investigation on NASA's Juno spacecraft recorded as the spacecraft crossed the bow shock just outside of Jupiter's magnetosphere on June 24, 2016, while approaching Jupiter. Audio accompanies the animation, with volume and pitch correlated to the amplitude and frequency of the recorded waves. The graph is a frequency-time spectrogram with color coding to indicate wave amplitudes as a function of wave frequency (vertical axis, in hertz) and time (horizontal axis, with a total elapsed time of two hours). During the hour before Juno reached the bow shock, the Waves instrument was detecting mainly plasma oscillations just below 10,000 hertz (10 kilohertz). The frequency of these oscillations is related to the local density of electrons; the data yield an estimate of approximately one electron per cubic centimeter (about 16 per cubic inch) in this region just outside Jupiter's bow shock. The broadband burst of noise marked "Bow Shock" is the region of turbulence where the supersonic solar wind is heated and slowed by encountering the Jovian magnetosphere. The shock is analogous to a sonic boom generated in Earth's atmosphere by a supersonic aircraft. The region after the shock is called the magnetosheath. The vertical bar to the right of the chart indicates the color coding of wave amplitude, in decibels (dB) above the background level detected by the Waves instrument. Each step of 10 decibels marks a tenfold increase in wave power. When Juno collected these data, the distance from the spacecraft to Jupiter was about 5.56 million miles (8.95 million kilometers), indicated on the chart as 128 times the radius of Jupiter. Jupiter's magnetic field is tilted about 10 degrees from the planet's axis of rotation. The note of 22 degrees on the chart indicates that at the time these data were recorded, the spacecraft was 22 degrees north of the magnetic-field equator. The "LT" notation is local time on Jupiter at the longitude of the planet directly below the spacecraft, with a value of 6.2 indicating approximately dawn. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20753
By pushing NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope to its limits, an international team of astronomers has shattered the cosmic distance record by measuring the farthest galaxy ever seen in the universe. This surprisingly bright infant galaxy, named GN-z11, is seen as it was 13.4 billion years in the past, just 400 million years after the Big Bang. GN-z11 is located in the direction of the constellation of Ursa Major. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1oSqHad" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1oSqHad</a>
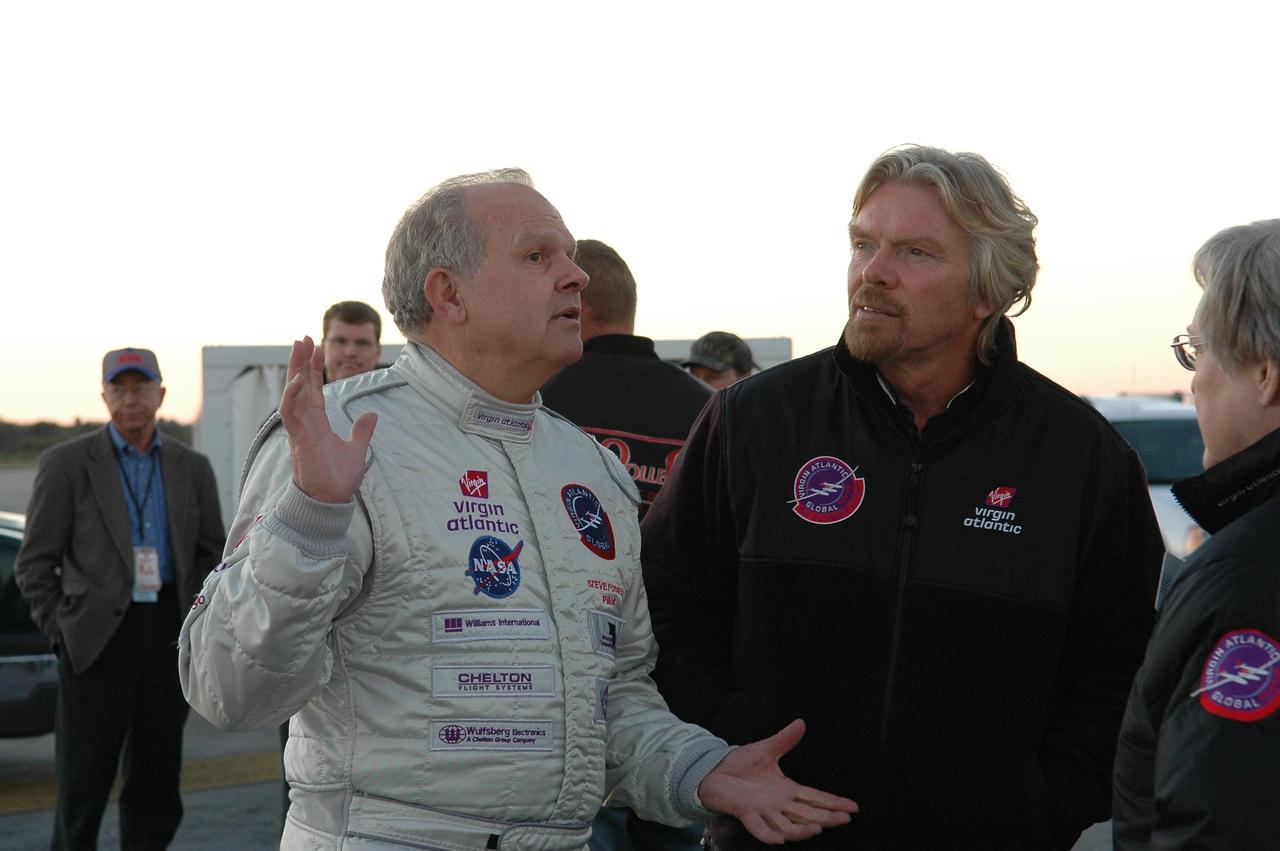

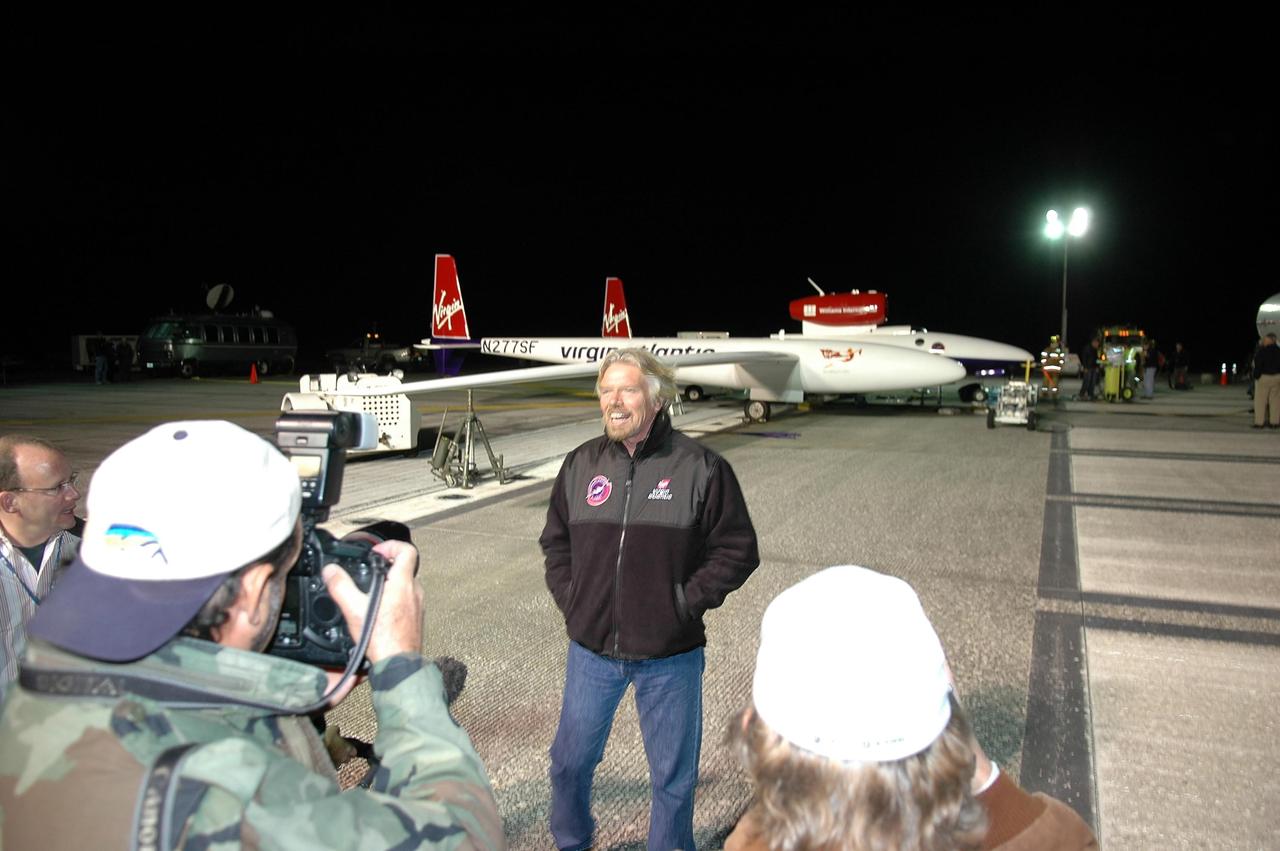
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Pilot Steve Fossett (left) and Sir Richard Branson (right) talk with Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer team members about the fuel leak detected in the aircraft. Branson is chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett was expected to take off from the KSC SLF before the takeoff was postponed due to the fuel leak that appeared in the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Before dawn on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF), Steve Fossett talks to the media about the anticipated flight of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
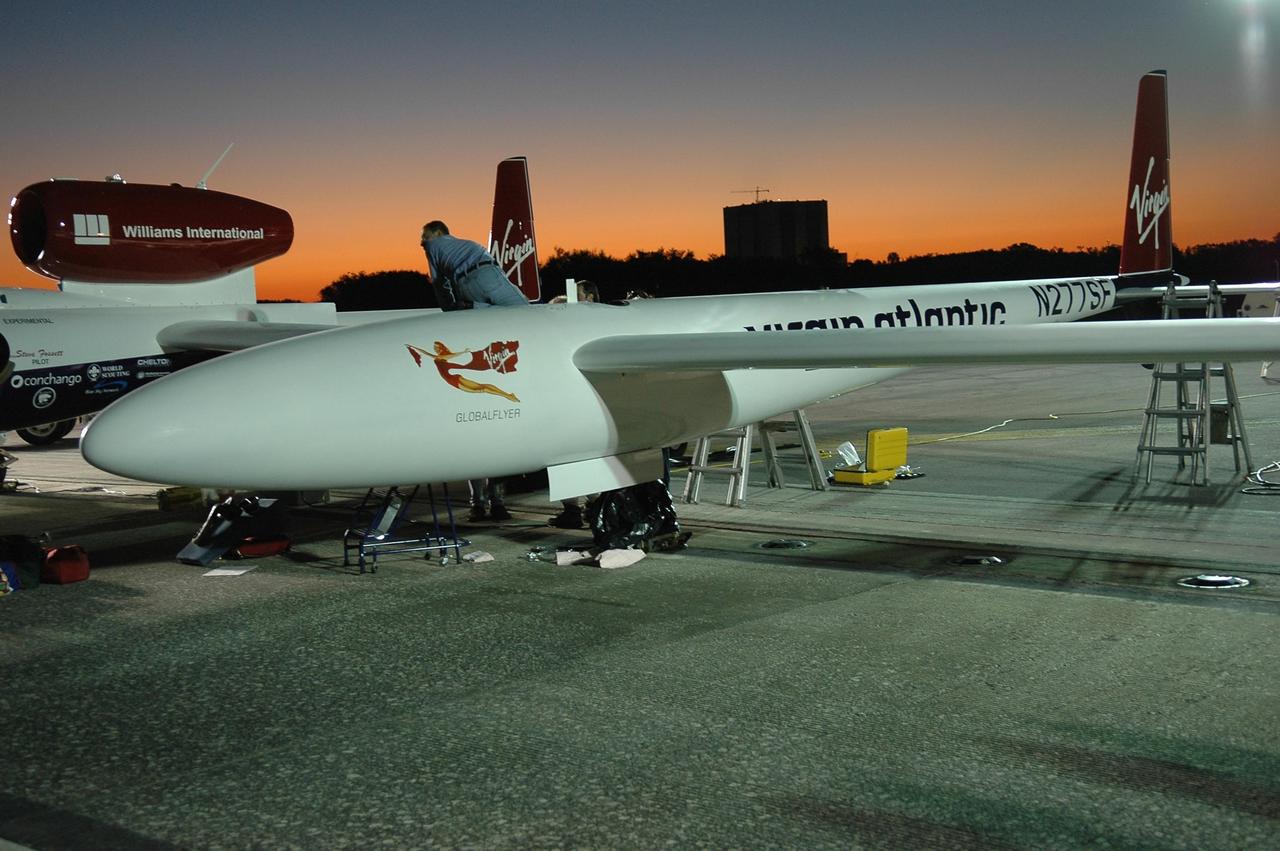

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - As a rosy dawn creeps over the horizon, team members check the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer before its early morning launch from NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF). Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
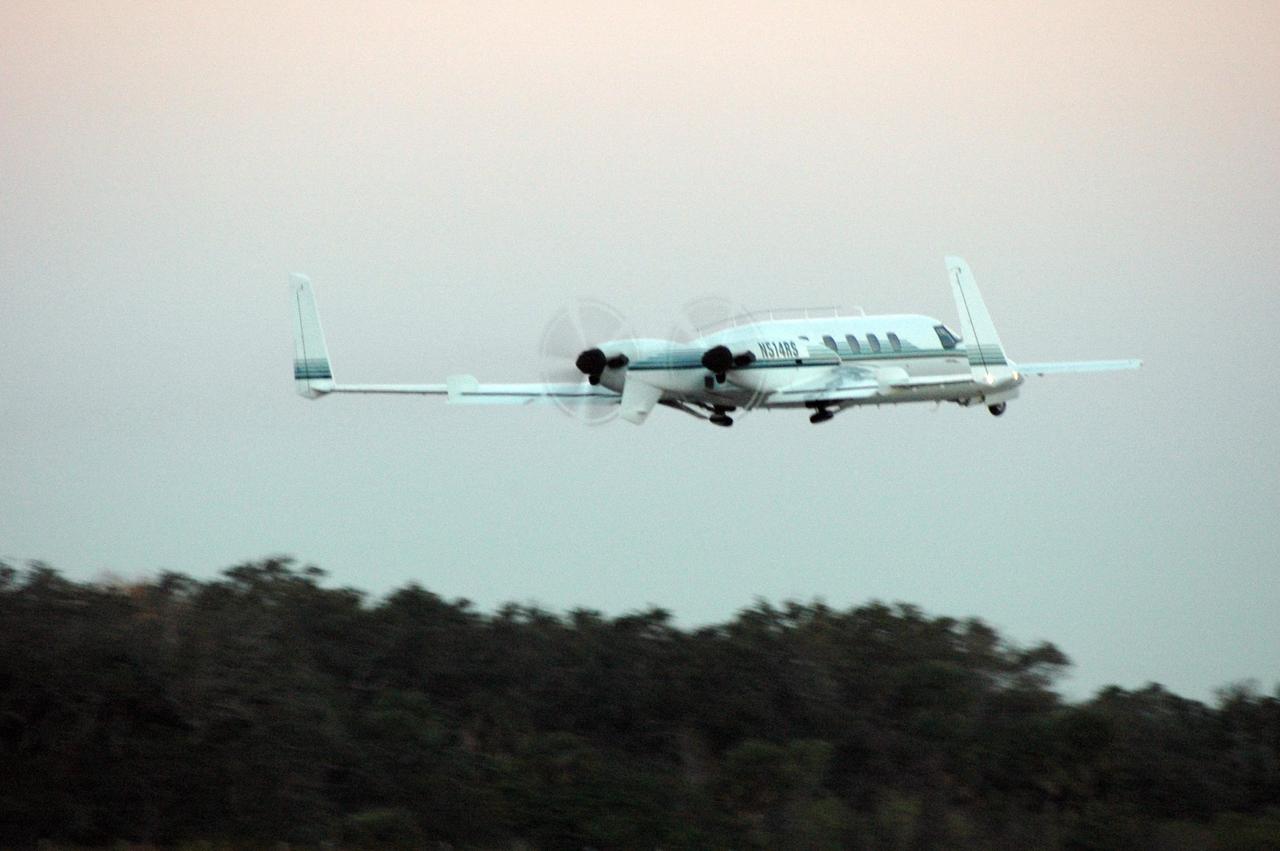

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Beechcraft Starship aircraft precedes the takeoff of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer from NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Photographers on board the Beachcraft will capture the historic event from the air. Pilot Steve Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Before dawn on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF), Steve Fossett looks over the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer in preparation for flight.. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
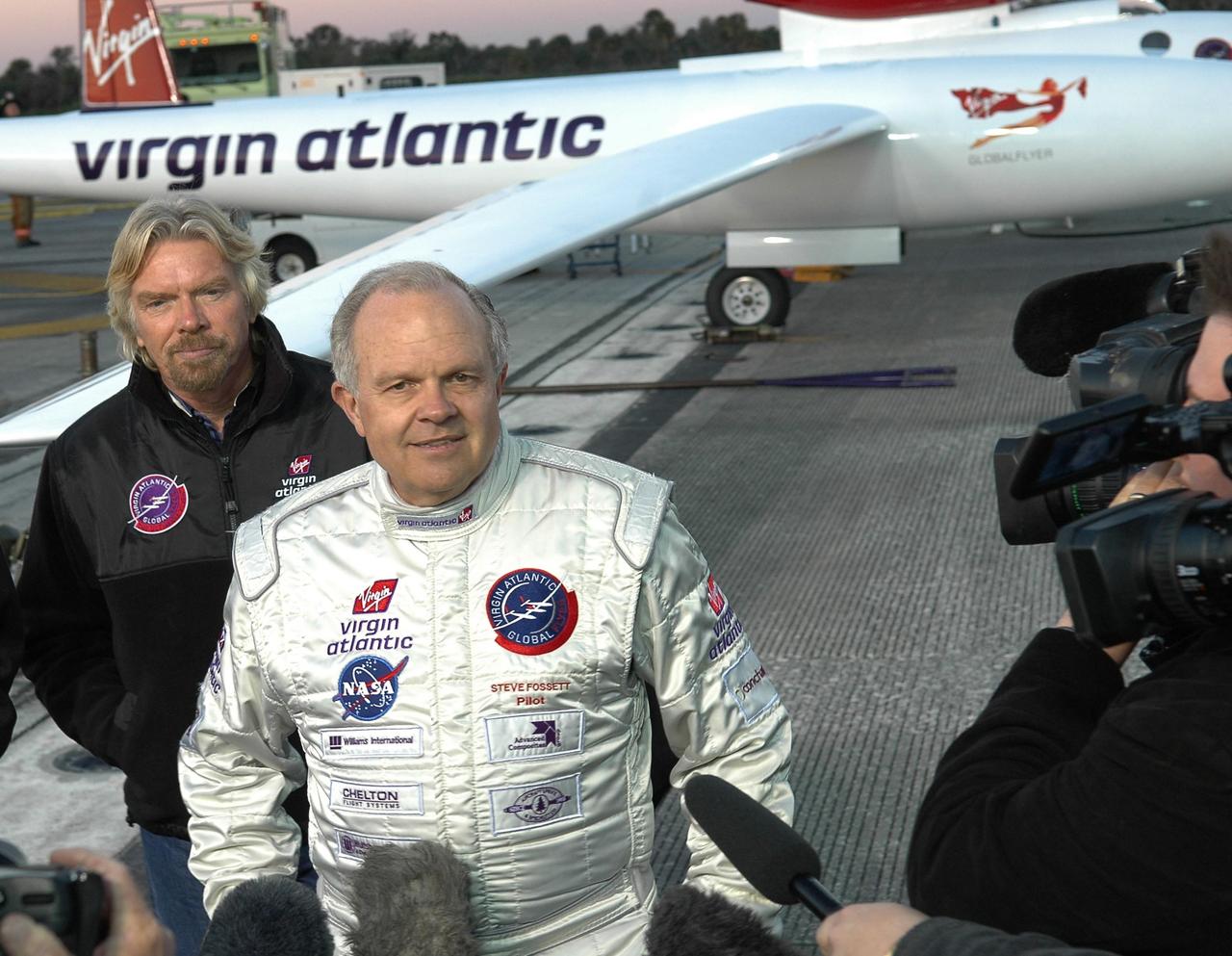

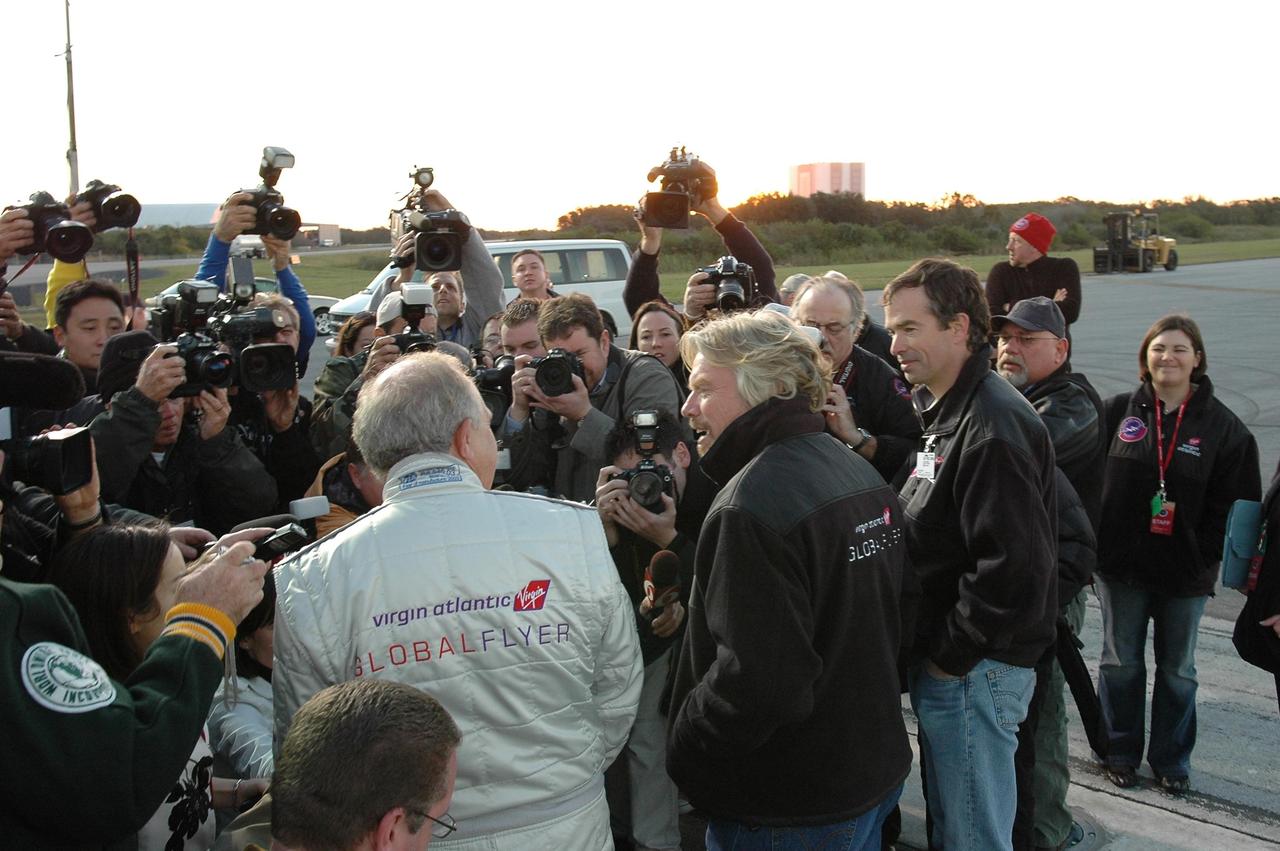
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Pilot Steve Fossett talks to the media about the reason the takeoff of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer was postponed. Behind Fossett is Sir Richard Branson, chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic. Behind both is the GlobalFlyer aircraft. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett was expected to take off from the KSC SLF before the takeoff was postponed due to the fuel leak that appeared in the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
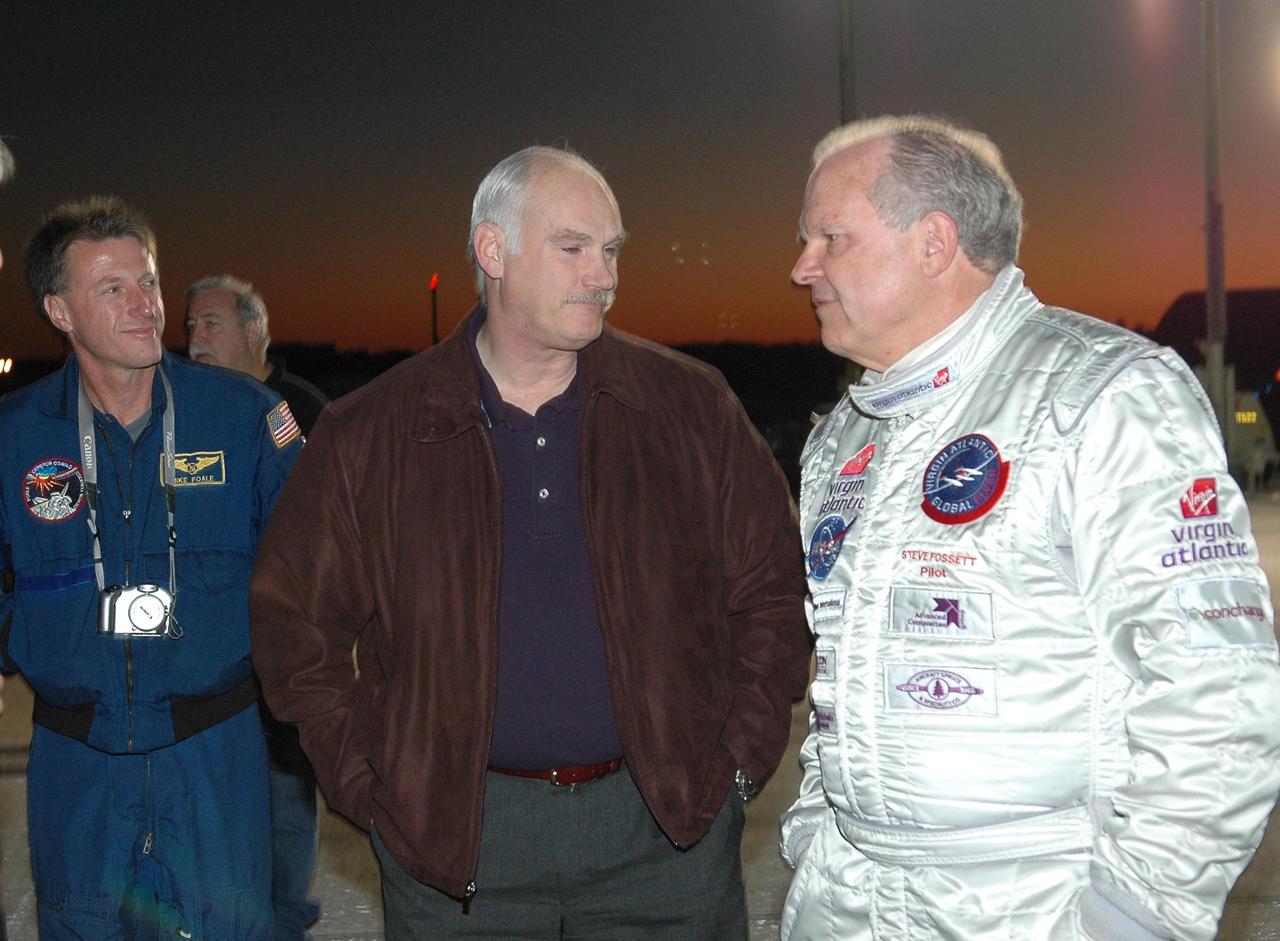

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - As a rosy dawn creeps over the horizon, Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Operations Michael Foale (left) and astronaut Bill Readdy (center) talk to Steve Fossett about the anticipated flight of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
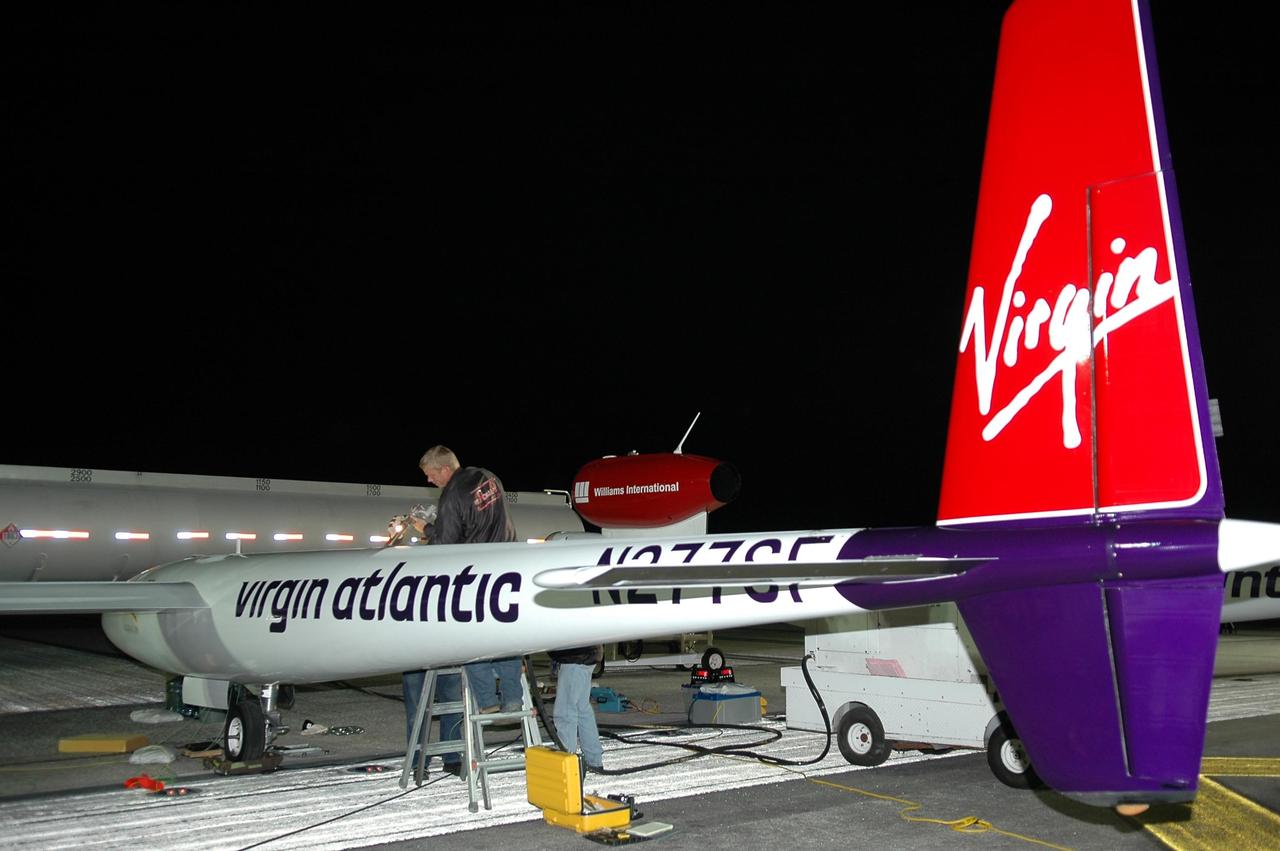

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Before dawn, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer is being fueled on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF). Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
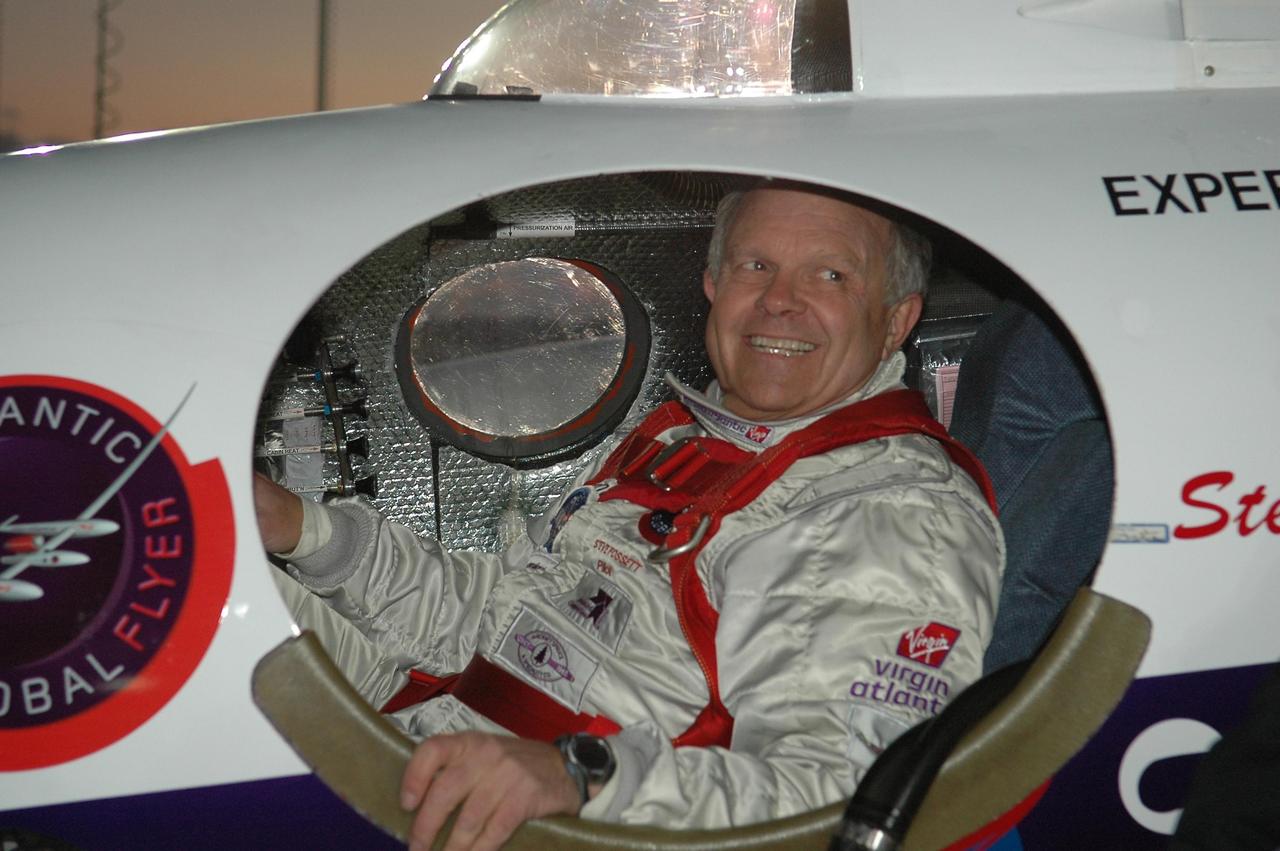

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett is happy and eager to start what he hopes will be a historic flight in the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer he is strapped into. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
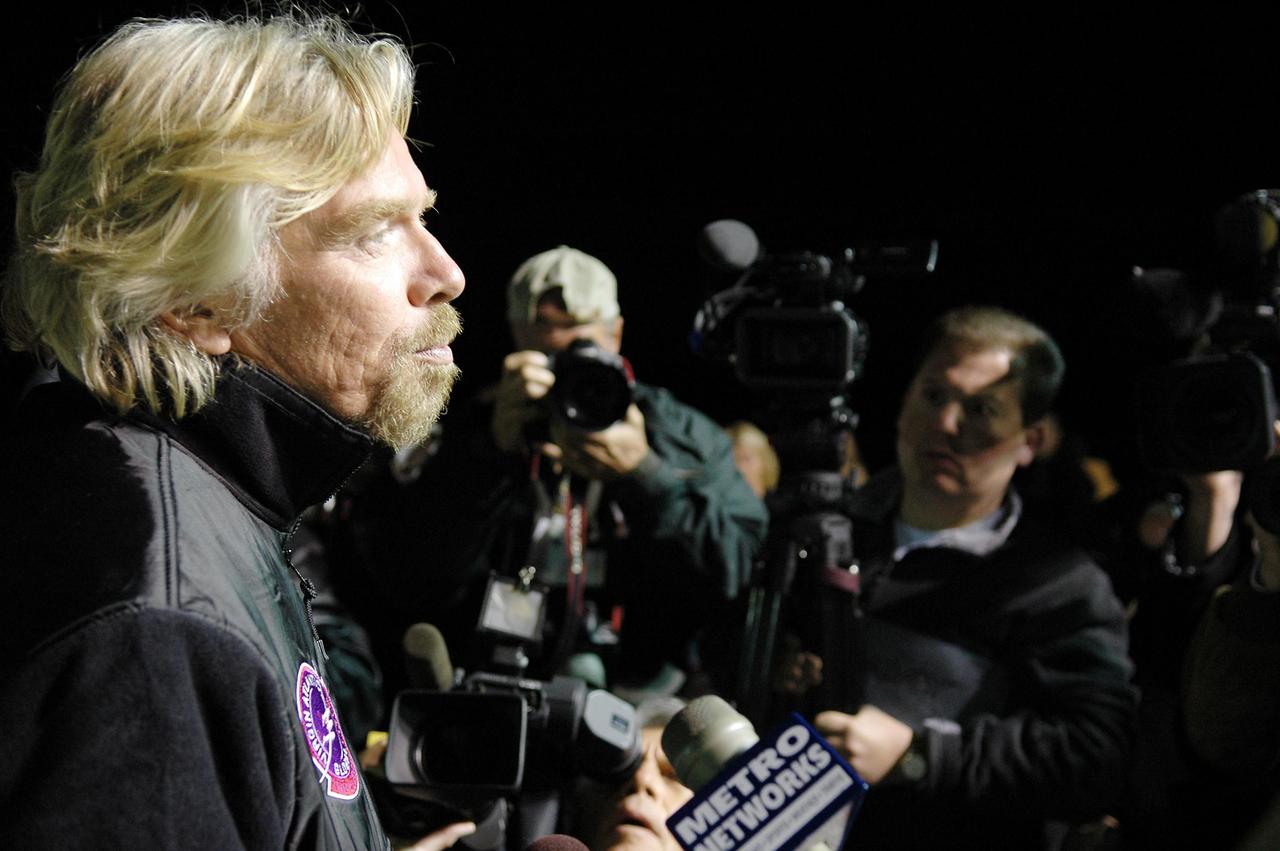

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Before dawn on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF), Sir Richard Branson talks to the media. Branson is chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic, which is sponsoring the GlobalFlyer. Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
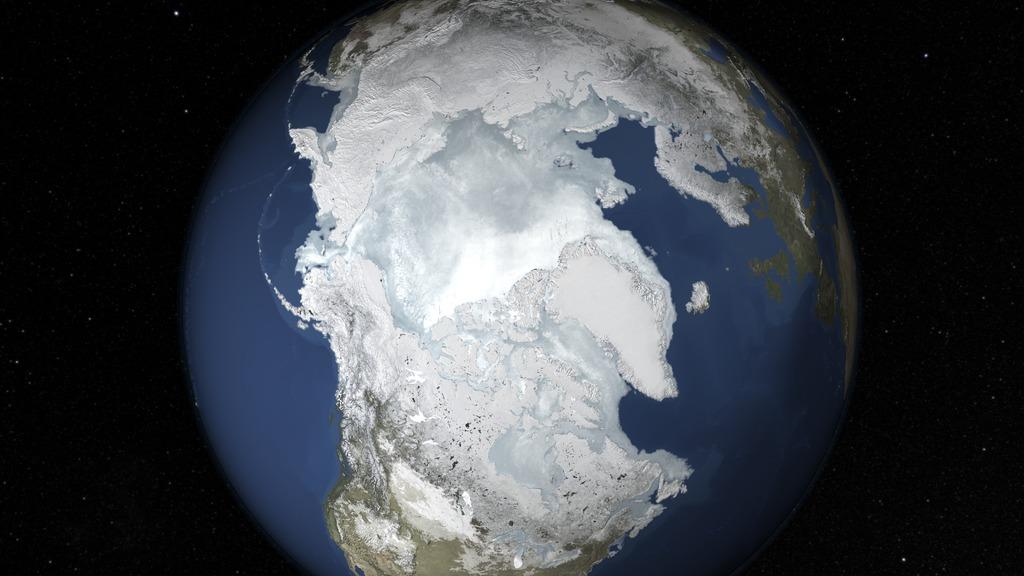

The sea ice cap of the Arctic appeared to reach its annual maximum winter extent on Feb. 25, according to data from the NASA-supported National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the University of Colorado, Boulder. At 5.61 million square miles (14.54 million square kilometers), this year’s maximum extent was the smallest on the satellite record and also one of the earliest. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1Eyvelz" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1Eyvelz</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
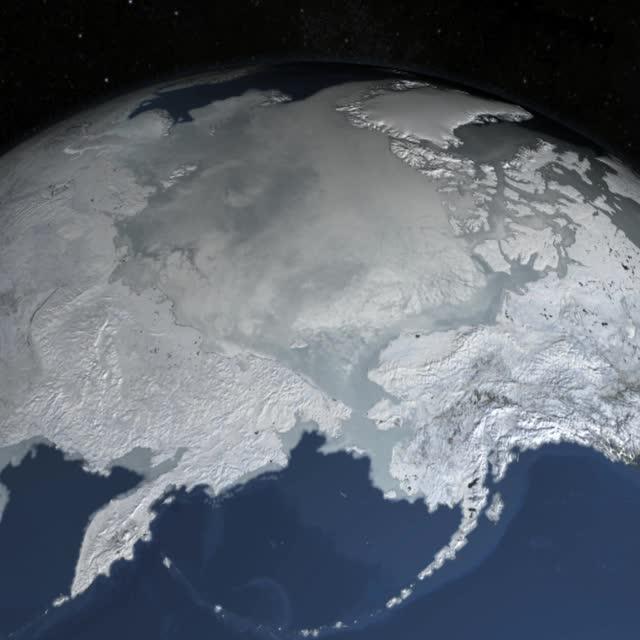

The sea ice cap of the Arctic appeared to reach its annual maximum winter extent on February 25, according to data from the NASA-supported National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the University of Colorado, Boulder. At 5.61 million square miles (14.54 million square kilometers), this year’s maximum extent was the smallest on the satellite record and also one of the earliest. Credit: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
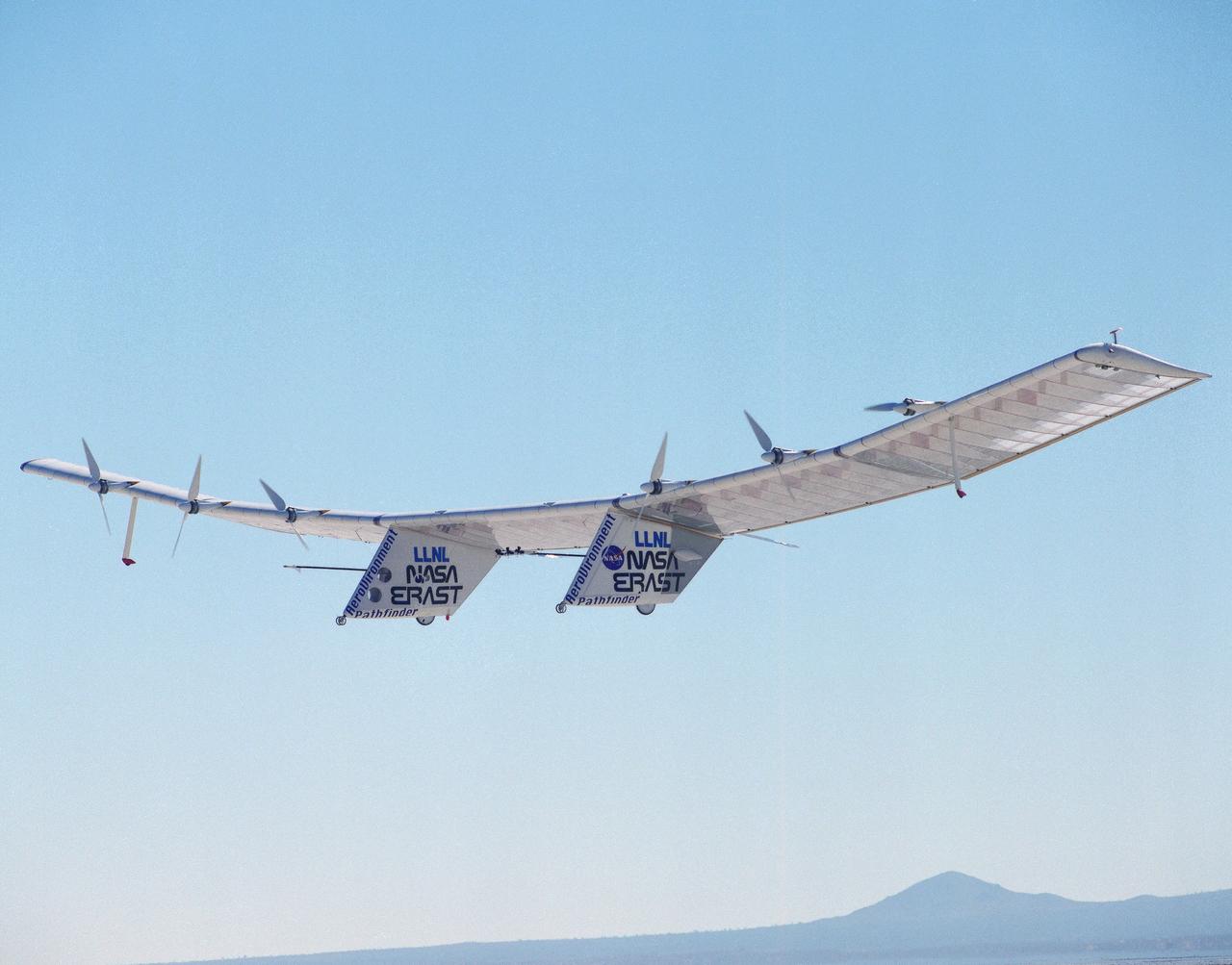

The Pathfinder solar-powered remotely piloted aircraft climbs to a record-setting altitude of 50,567 feet during a flight Sept. 11, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The flight was part of the NASA ERAST (Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology) program. The Pathfinder was designed and built by AeroVironment Inc., Monrovia, California. Solar arrays cover nearly all of the upper wing surface and produce electricity to power the aircraft's six motors.
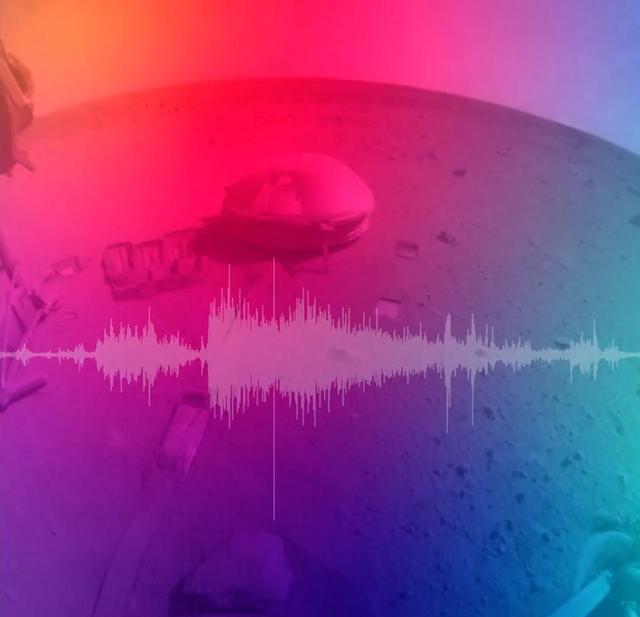

NASA's InSight Mars lander detected a giant meteoroid strike on Dec. 24, 2021, the 1,094th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. InSight's seismometer recorded seismic signals that are not in the range of human hearing. In order to make the signals audible, the data was sped up 100 times. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25582
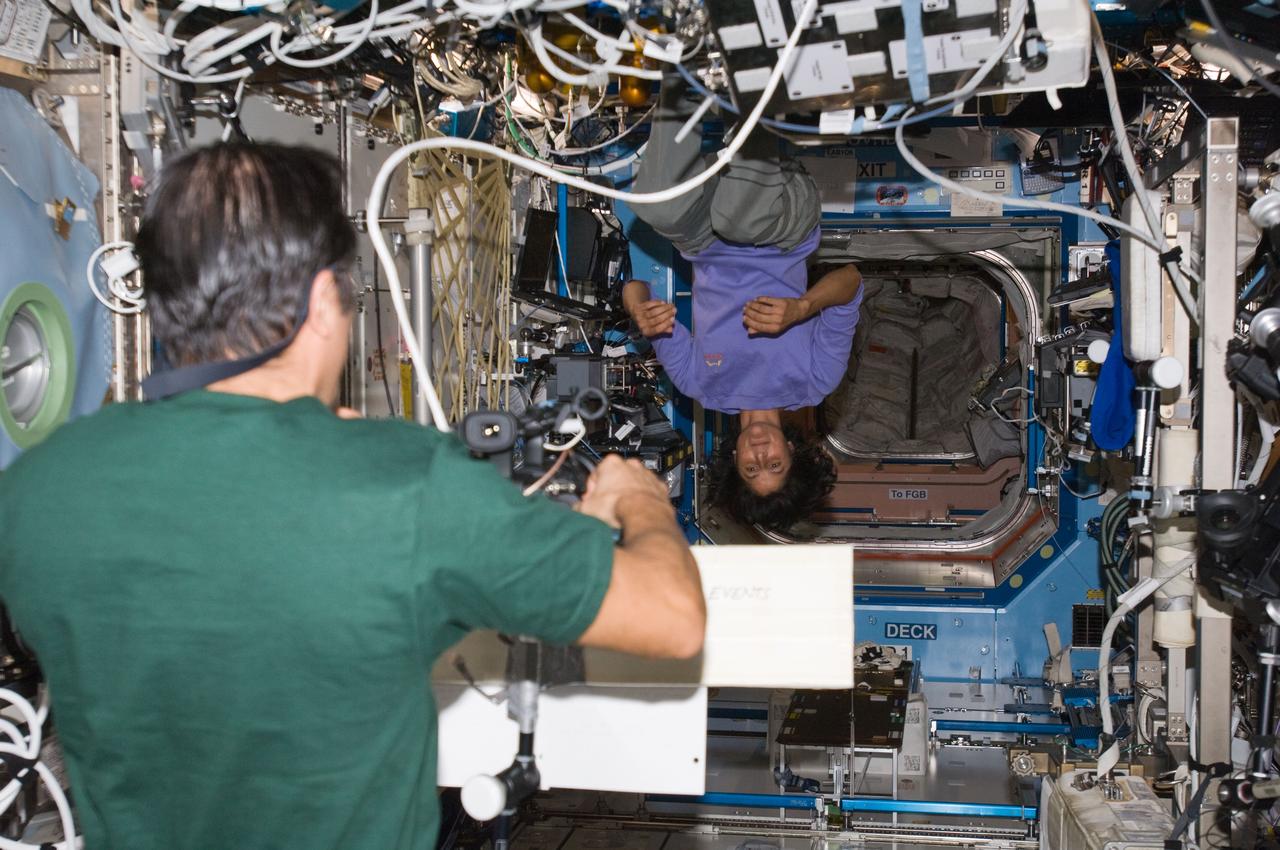

ISS032-E-009061 (25 July 2012) --- NASA astronauts Joe Acaba and Sunita Williams, both Expedition 32 flight engineers, perform video message recording in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
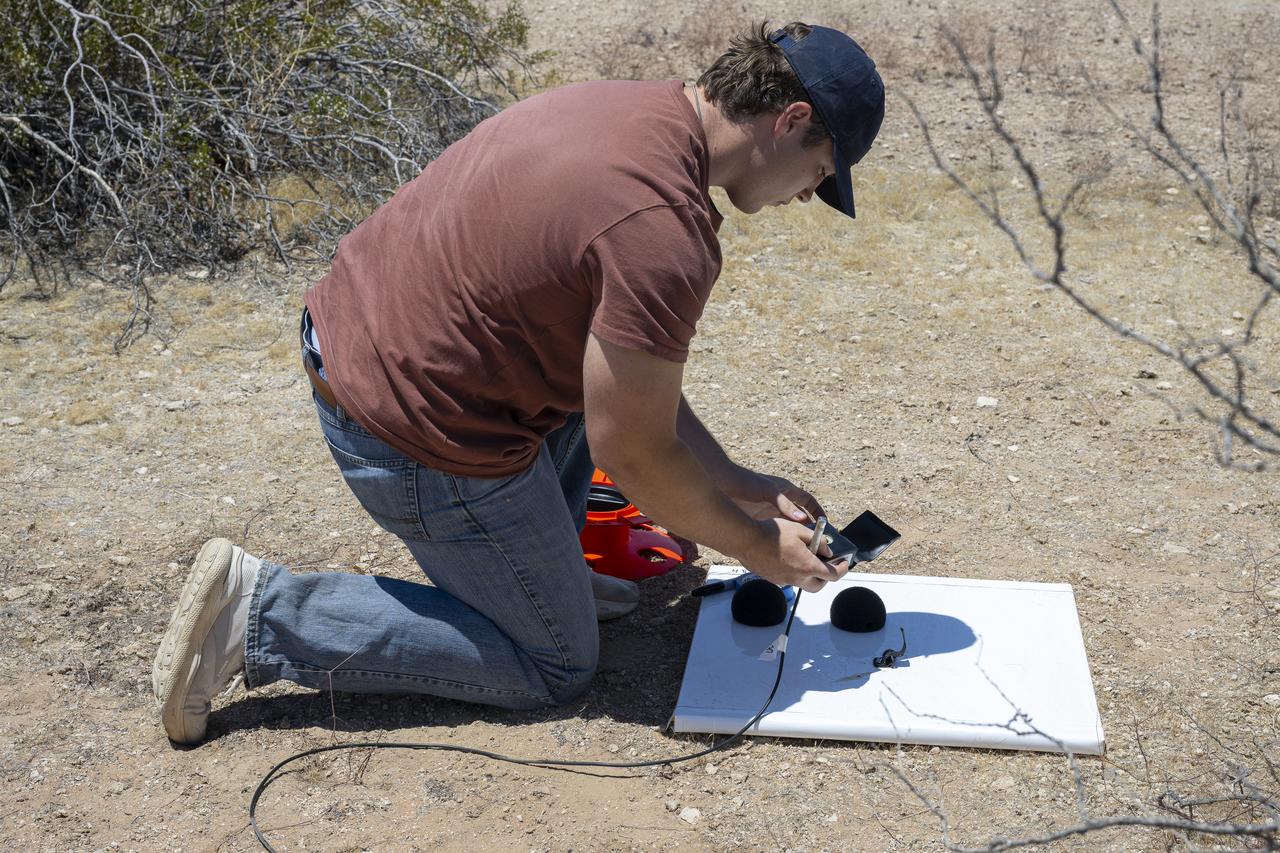

A NASA intern sets up ground recording system (GRS) units in California’s Mojave Desert during a Phase 2 rehearsal of the agency’s Quesst mission. The GRS units were placed across miles of desert terrain to capture the acoustic signature of supersonic aircraft during rehearsal flights and in preparation for the start of the actual tests.
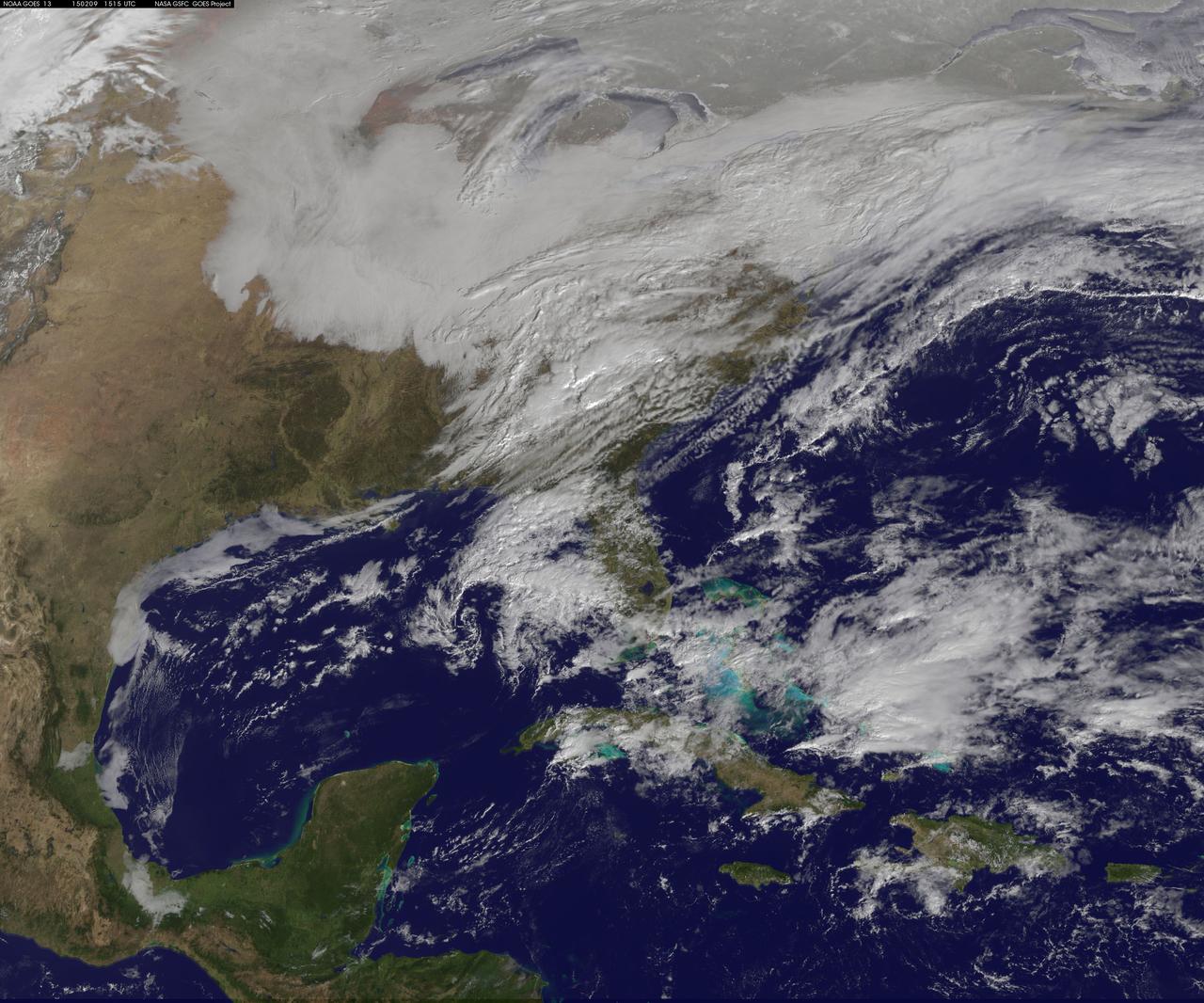

Another large snowstorm affecting New England was dropping more snow on the region and breaking records on February 9, as NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured an image of the clouds associated with the storm system. On Feb. 9, NOAA's National Weather Service in Boston, Massachusetts noted that "The 30-day snowfall total at Boston ending 7 a.m. this morning is 61.6 inches. This exceeds the previous maximum 30 day snowfall total on record at Boston, which was 58.8 inches ending Feb 7 1978." The GOES-East image was created by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It showed a blanket of clouds over the U.S. northeast that stretched down to the Mid-Atlantic where there was no snow on the ground in Washington, D.C. NOAA's National Weather Service Weather Prediction Center provided a look at the extent of the storm system and noted "Heavy snow will impact portions of New York State and New England as the new week begins. Freezing rain will spread from western Pennsylvania to Long Island, with rain for the mid-Atlantic states." The low pressure area bringing the snow to the northeast was located in central Pennsylvania. A cold front extended southward from the low across the Tennessee Valley while a stationary boundary extended eastward from the low across the central mid-Atlantic. To create the image, NASA/NOAA's GOES Project takes the cloud data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite and overlays it on a true-color image of land and ocean created by data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. Together, those data created the entire picture of the storm. NOAA's GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric triggers for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. For updated information about the storm system, visit NOAA's NWS website: <a href="http://www.weather.gov" rel="nofollow">www.weather.gov</a> For more information about GOES satellites, visit: <a href="http://www.goes.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.goes.noaa.gov/</a> or goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">Credit: NOAA/NASA GOES Project</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
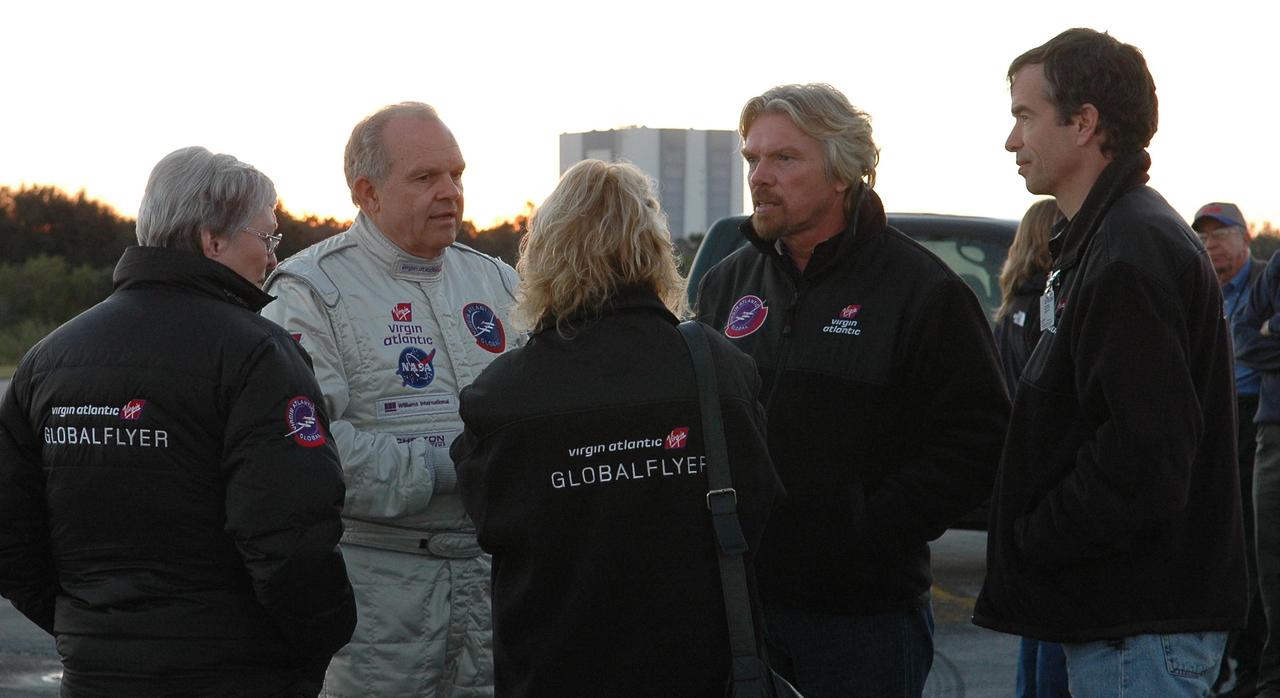

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Pilot Steve Fossett (facing camera, left) and Sir Richard Branson (second from right) talk with Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer team members about the fuel leak detected in the aircraft. Branson is chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic. Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett was expected to take off from the KSC SLF before the takeoff was postponed due to the fuel leak that appeared in the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During fueling of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer before dawn on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF), Sir Richard Branson talks to the media. Branson is chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic. The GlobalFlyer is in the background. Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
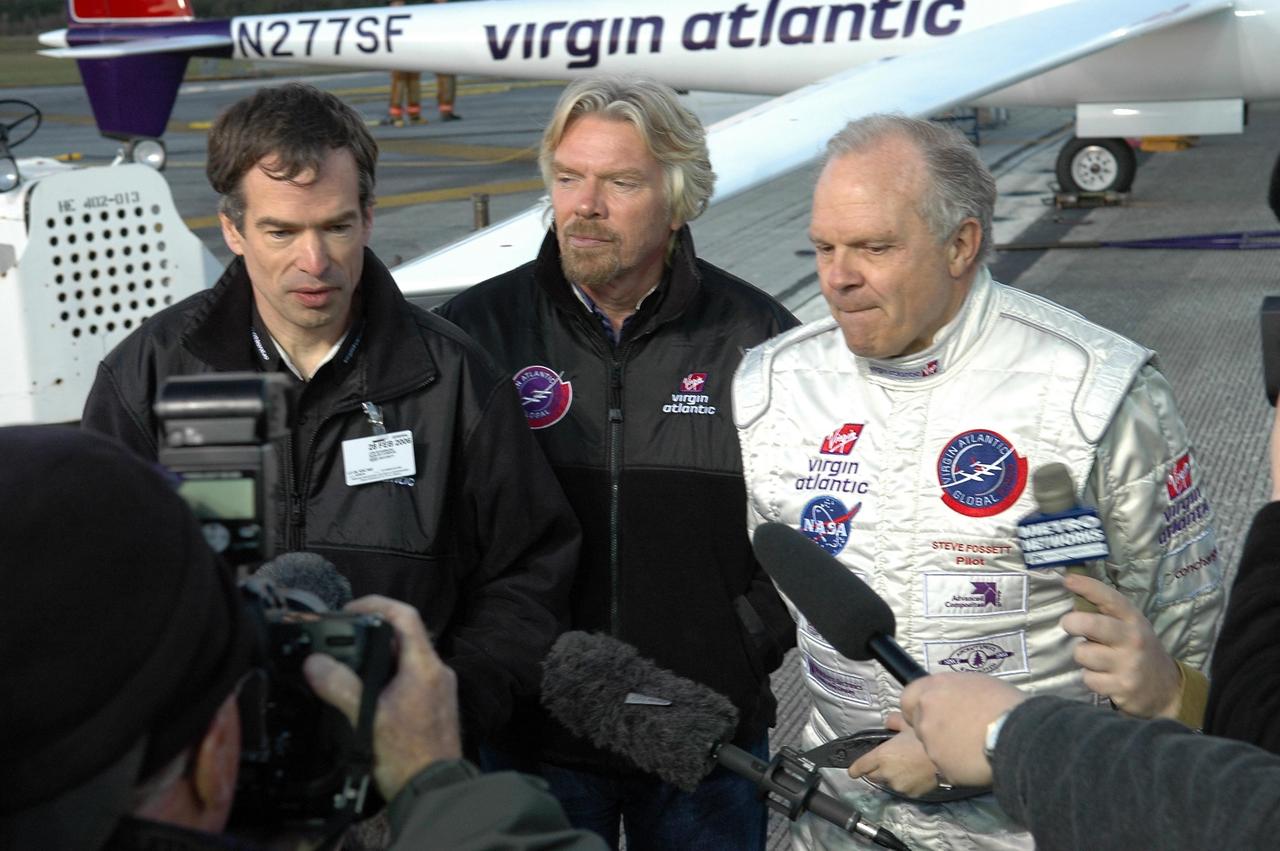

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Pilot Steve Fossett (far right), Sir Richard Branson (center) and Jon Karkow (far left) talk to the media about the reason the takeoff of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer was postponed. Branson is chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic. Karkow, with Scaled Composites, is chief engineer for the GlobalFlyer. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett was expected to take off from the KSC SLF before the takeoff was postponed due to the fuel leak that appeared in the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During fueling of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer before dawn on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF), Sir Richard Branson talks to the media. Branson is chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic. The GlobalFlyer is in the background. Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - (From left, backs to the camera) Pilot Steve Fossett, Sir Richard Branson and Jon Karkow talk with the media about the reason the takeoff of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer was postponed. Branson is chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic. Karkow, with Scaled Composites, is chief engineer for the GlobalFlyer. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett was expected to take off from the KSC SLF before the takeoff was postponed due to the fuel leak that appeared in the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
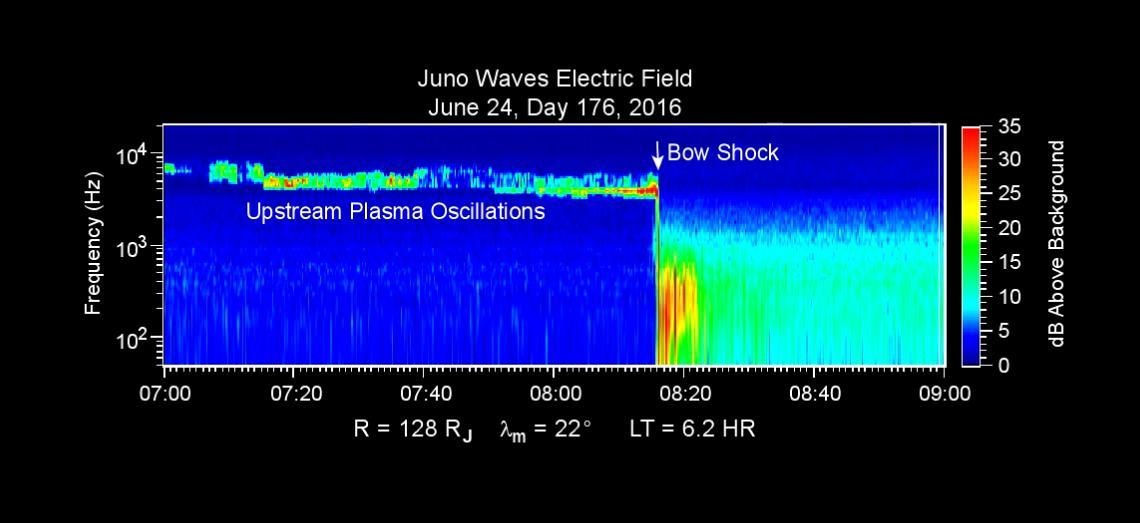
This chart presents data that the Waves investigation on NASA's Juno spacecraft recorded as the spacecraft crossed the bow shock just outside of Jupiter's magnetosphere on June 24, 2016, while approaching Jupiter. Audio accompanies the animation, with volume and pitch correlated to the amplitude and frequency of the recorded waves. The graph is a frequency-time spectrogram with color coding to indicate wave amplitudes as a function of wave frequency (vertical axis, in hertz) and time (horizontal axis, with a total elapsed time of two hours). During the hour before Juno reached the bow shock, the Waves instrument was detecting mainly plasma oscillations just below 10,000 hertz (10 kilohertz). The frequency of these oscillations is related to the local density of electrons; the data yield an estimate of approximately one electron per cubic centimeter (about 16 per cubic inch) in this region just outside Jupiter's bow shock. The broadband burst of noise marked "Bow Shock" is the region of turbulence where the supersonic solar wind is heated and slowed by encountering the Jovian magnetosphere. The shock is analogous to a sonic boom generated in Earth's atmosphere by a supersonic aircraft. The region after the shock is called the magnetosheath. The vertical bar to the right of the chart indicates the color coding of wave amplitude, in decibels (dB) above the background level detected by the Waves instrument. Each step of 10 decibels marks a tenfold increase in wave power. When Juno collected these data, the distance from the spacecraft to Jupiter was about 5.56 million miles (8.95 million kilometers), indicated on the chart as 128 times the radius of Jupiter. Jupiter's magnetic field is tilted about 10 degrees from the planet's axis of rotation. The note of 22 degrees on the chart indicates that at the time these data were recorded, the spacecraft was 22 degrees north of the magnetic-field equator. The "LT" notation is local time on Jupiter at the longitude of the planet directly below the spacecraft, with a value of 6.2 indicating approximately dawn. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20753
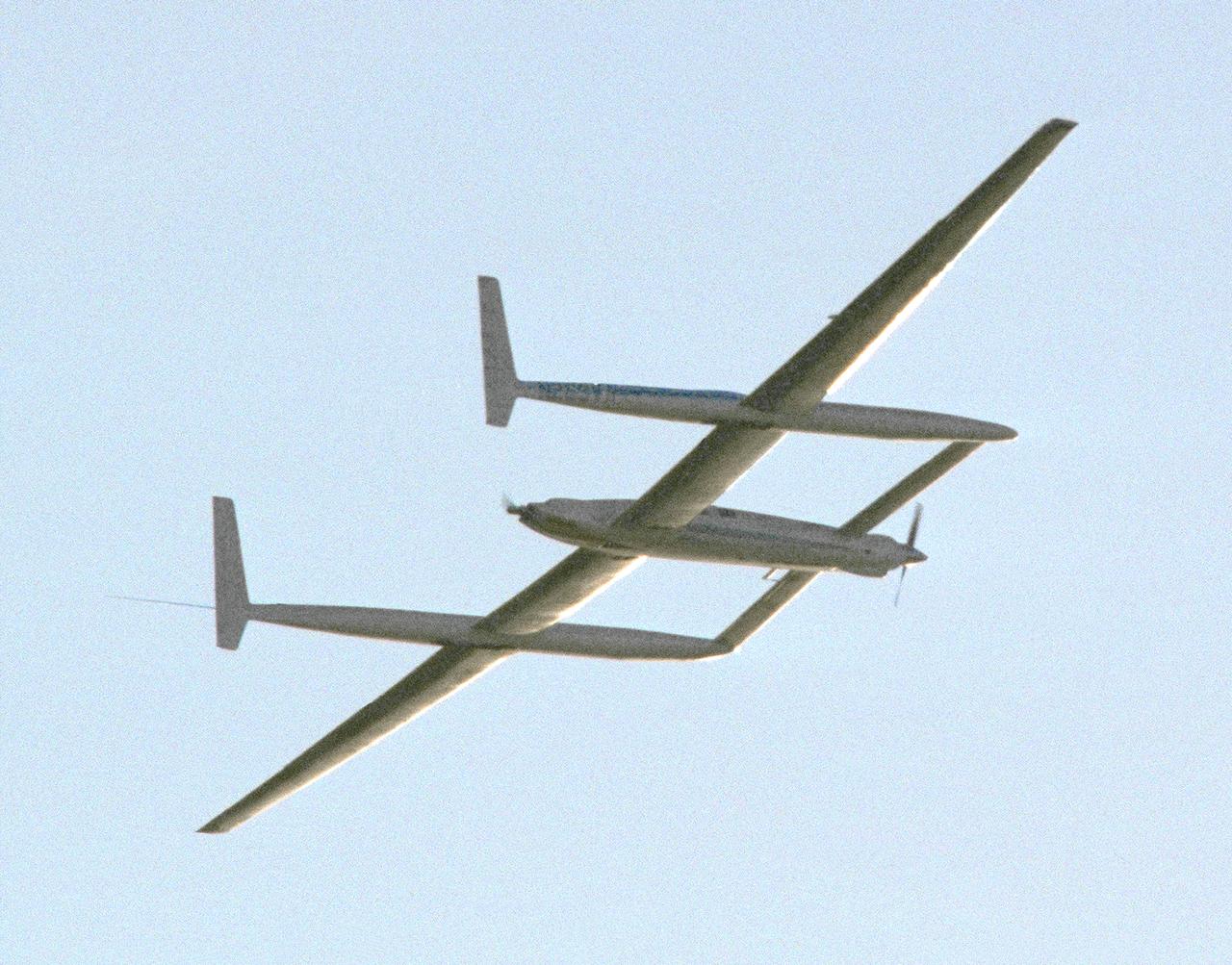

The Voyager aircraft circles before landing at Edwards Air Force Base, Edwards, California, to complete its record breaking, nonstop unfueled flight around the world.
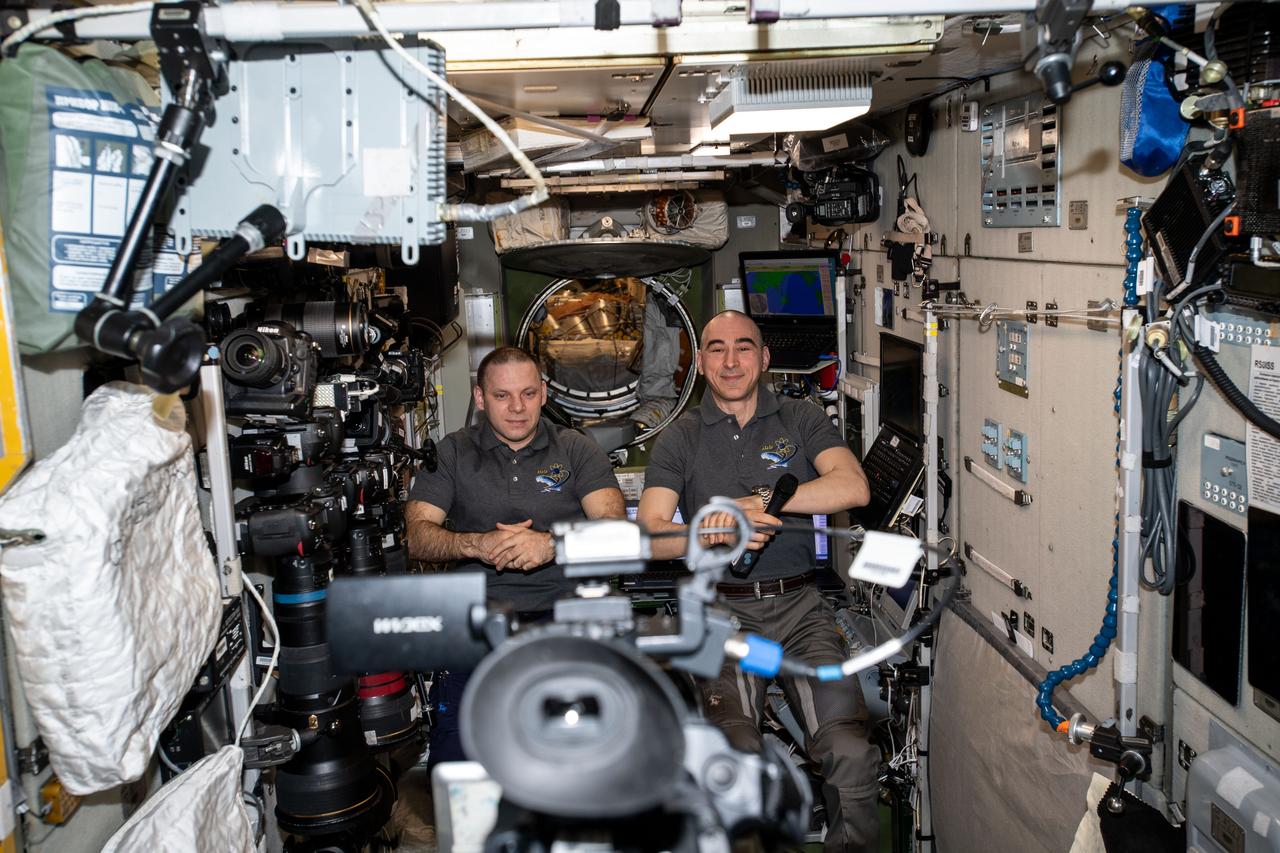

iss063e020091 (May 14, 2020) --- Roscosmos cosmonauts and Expedition 63 Flight Engineers (from left) Ivan Vagner and Anatoly Ivanishin record a public affairs event for Russian media from the International Space Station's Zvezda service module.
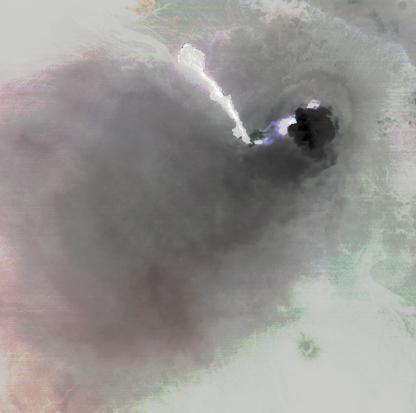

Nabro volcano, Eritrea, in the Horn of Africa, began erupting June 12, 2011, the first-ever recorded eruption of this stratovolcano. This image was acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft on June 19, 2011.

This video and audio show the results of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover using its SuperCam microphone to record the sounds of a Martian dust devil – the first time any such recording has been made. The dust devil passed directly over Perseverance on Sept. 27, 2021, the 215th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. At the same time that SuperCam's microphone recorded the dust devil, Perseverance's weather sensors (measuring wind, pressure, temperature, and dust) and the rover's left navigation camera were on. This allowed scientists to combine sound, image, and atmospheric data. The unique combination of this data, along with atmospheric modeling, allowed the researchers to estimate the dust devil's dimensions: 82 feet (25 meters) wide, at least 387 feet (118 meters) tall, and moving at about 12 mph (19 kph). Capturing a passing dust devil takes some luck. Scientists can't predict when they'll pass by, so rovers like Perseverance and Curiosity routinely monitor in all directions for them. When scientists see them occur more frequently at a certain time of day, or approach from a certain direction, they use that information to focus their monitoring to try to catch a dust devil. The video included here has four rows based on different data sources: The top row is a raw image taken by the left navigation camera's view of the Martian surface. While the camera is capable of color, it takes black-and-white images when searching for dust devils to reduce the amount of data sent back to Earth (since most of the images come back without a dust devil detected). The second row shows the same image processed with change-detection software to indicate where movement occurred over the course of the recording. The color indicates the density of dust, going from blue (lower density) through purple to yellow (highest density). The third row is a graph showing a sudden drop in air pressure recorded by Perseverance's weather sensor suite, called Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer, provided by Centro de Astrobiología (CAB) at the Instituto Nacional de Tecnica Aeroespacial in Madrid. The fourth row indicates sound amplitude from SuperCam's microphone. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25657

By pushing NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope to its limits, an international team of astronomers has shattered the cosmic distance record by measuring the farthest galaxy ever seen in the universe. This surprisingly bright infant galaxy, named GN-z11, is seen as it was 13.4 billion years in the past, just 400 million years after the Big Bang. GN-z11 is located in the direction of the constellation of Ursa Major. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1oSqHad" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1oSqHad</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
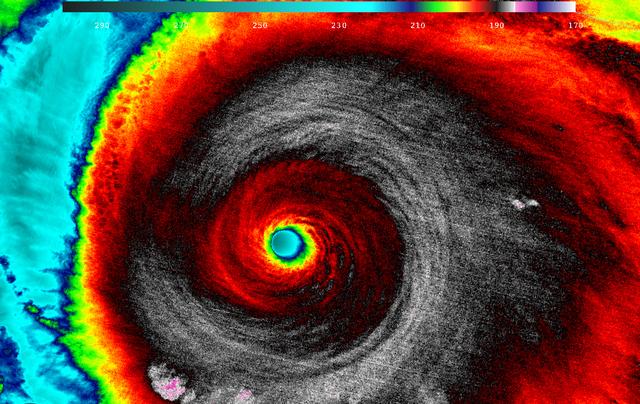
When NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Patricia on October 23 at 5:20 a.m. EDT the VIIRS instrument that flies aboard Suomi NPP looked at the storm in infrared light. Cloud top temperatures of thunderstorms around the eyewall were between 180K (-135.7F/ -93.1C) and 190 Kelvin (-117.7F/ -83.1C). Credit: UW/CIMSS/William Straka III Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/f…/goddard/patricia-eastern-pacific-2015" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/f…/goddard/patricia-eastern-pacific-2015</a>
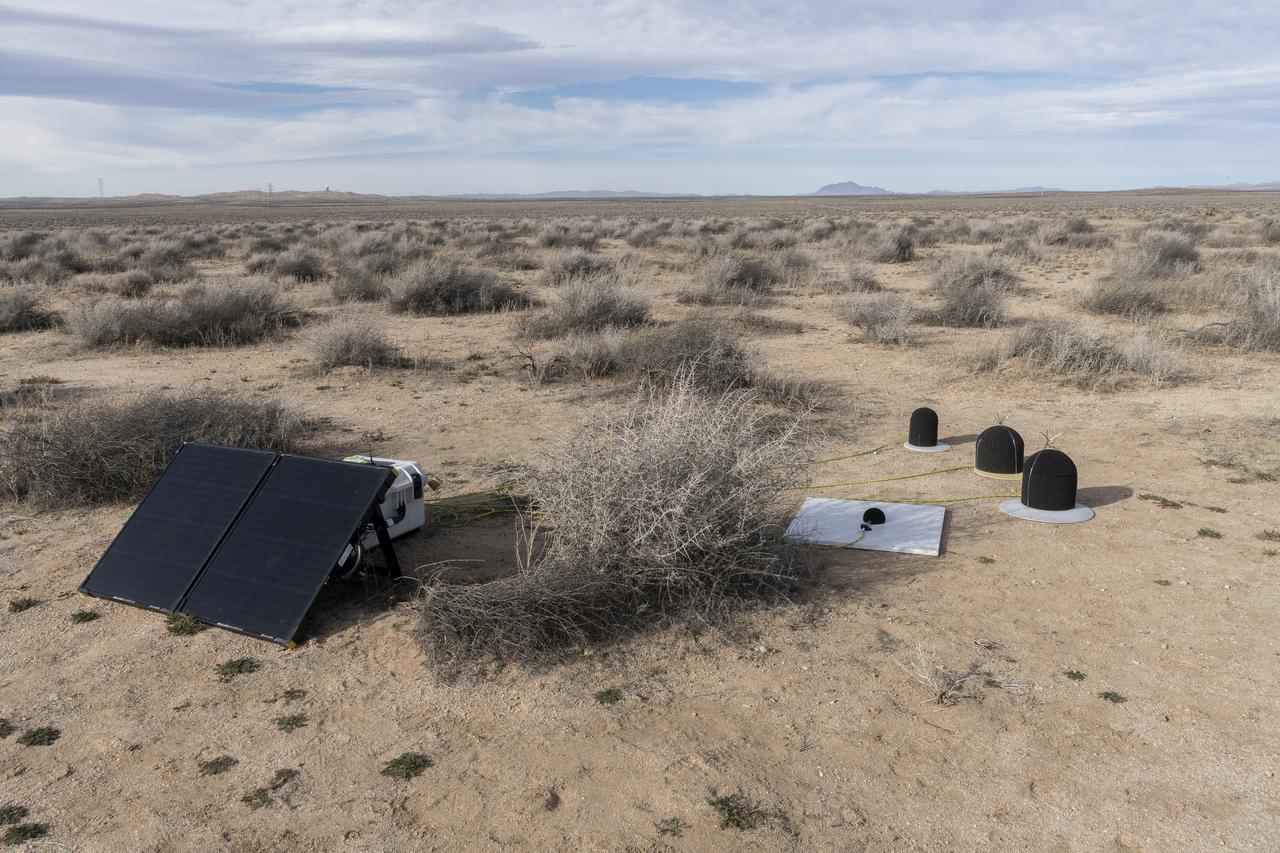

The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. Shown is one of 10 ground recording stations set up along a 30-mile stretch of desert to record sonic booms during the third phase of the of CarpetDIEM, Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems.

Blazar 3C 279's historic gamma-ray flare can be seen in this image from the Large Area Telescope (LAT) on NASA's Fermi satellite. Gamma rays with energies from 100 million to 100 billion electron volts (eV) are shown; for comparison, visible light has energies between 2 and 3 eV. The image spans 150 degrees, is shown in a stereographic projection, and represents an exposure from June 11 at 00:28 UT to June 17 at 08:17 UT. Credit: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration
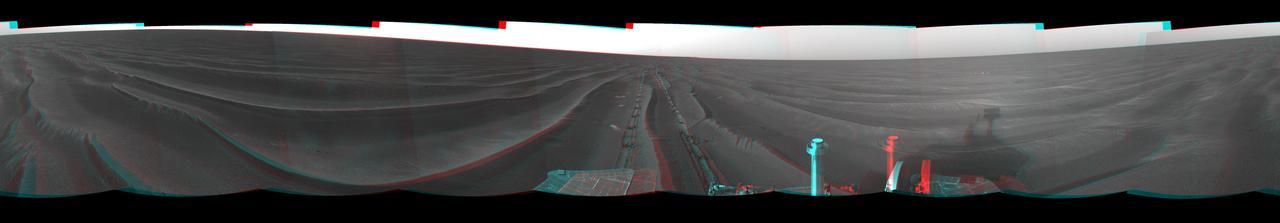
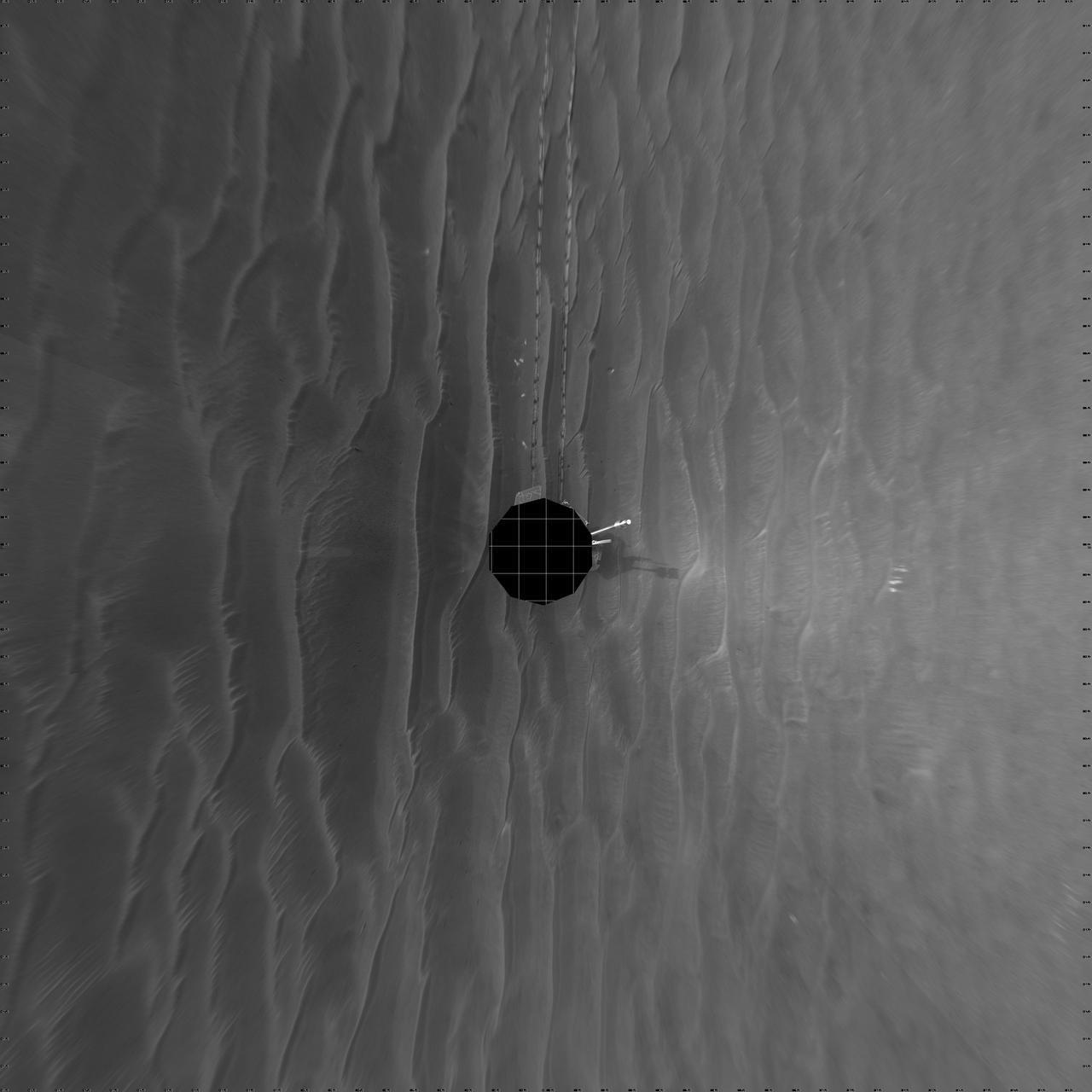
On Feb. 19, 2005, NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity set a one-day distance record for martian driving; Opportunity rolled 177.5 meters 582 feet across the plain of Meridiani. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
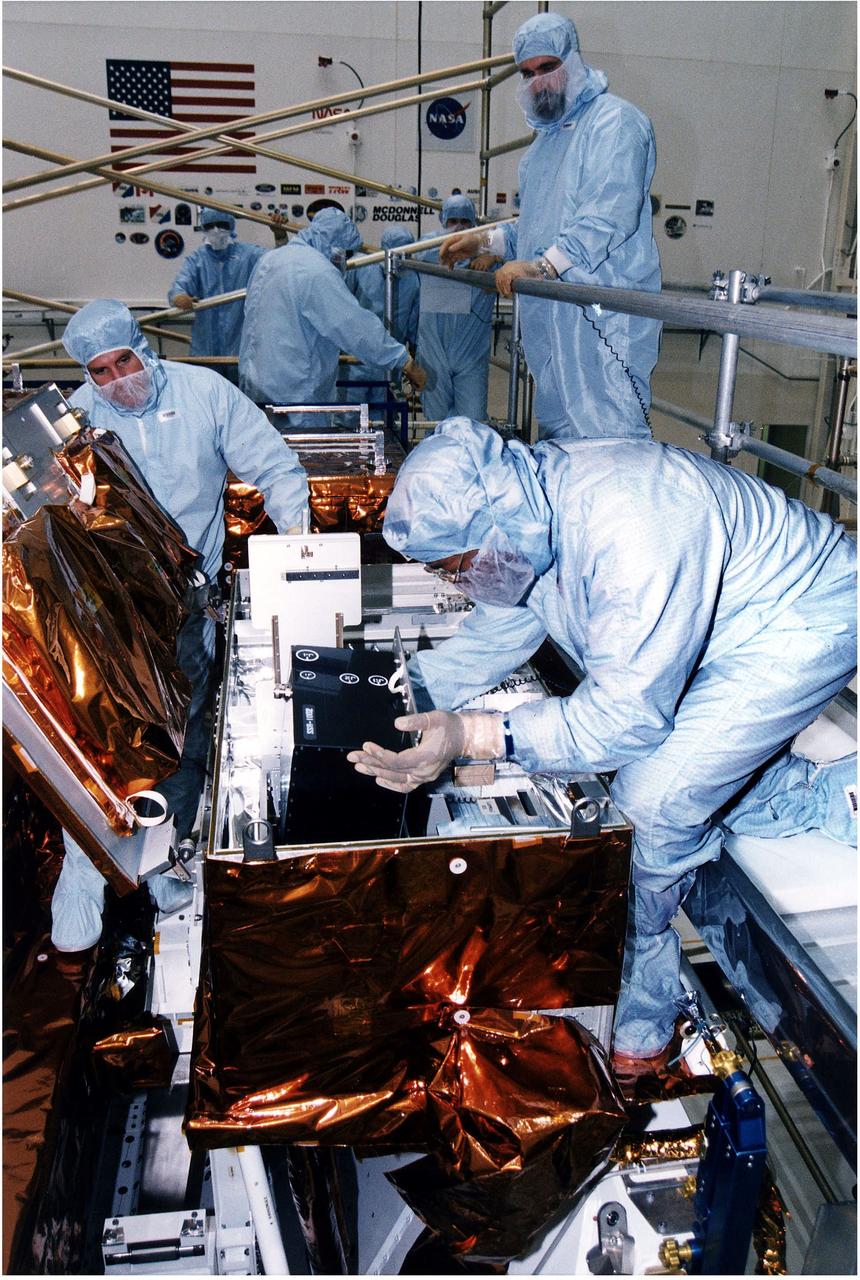

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in KSC's Vertical Processing Facility install a solid state recorder into a transport assembly in its protective enclosure as part of the prelaunch preparations for STS-82, the second Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission. The digital solid state recorder will replace one of three engineering/science tape recorders on Hubble. The solid state recorder has no moving parts to wear out. It also is more flexible than a reel-to-reel recorder and can store 10 times as much data. Liftoff aboard Discovery is targeted Feb. 11 with a crew of seven.
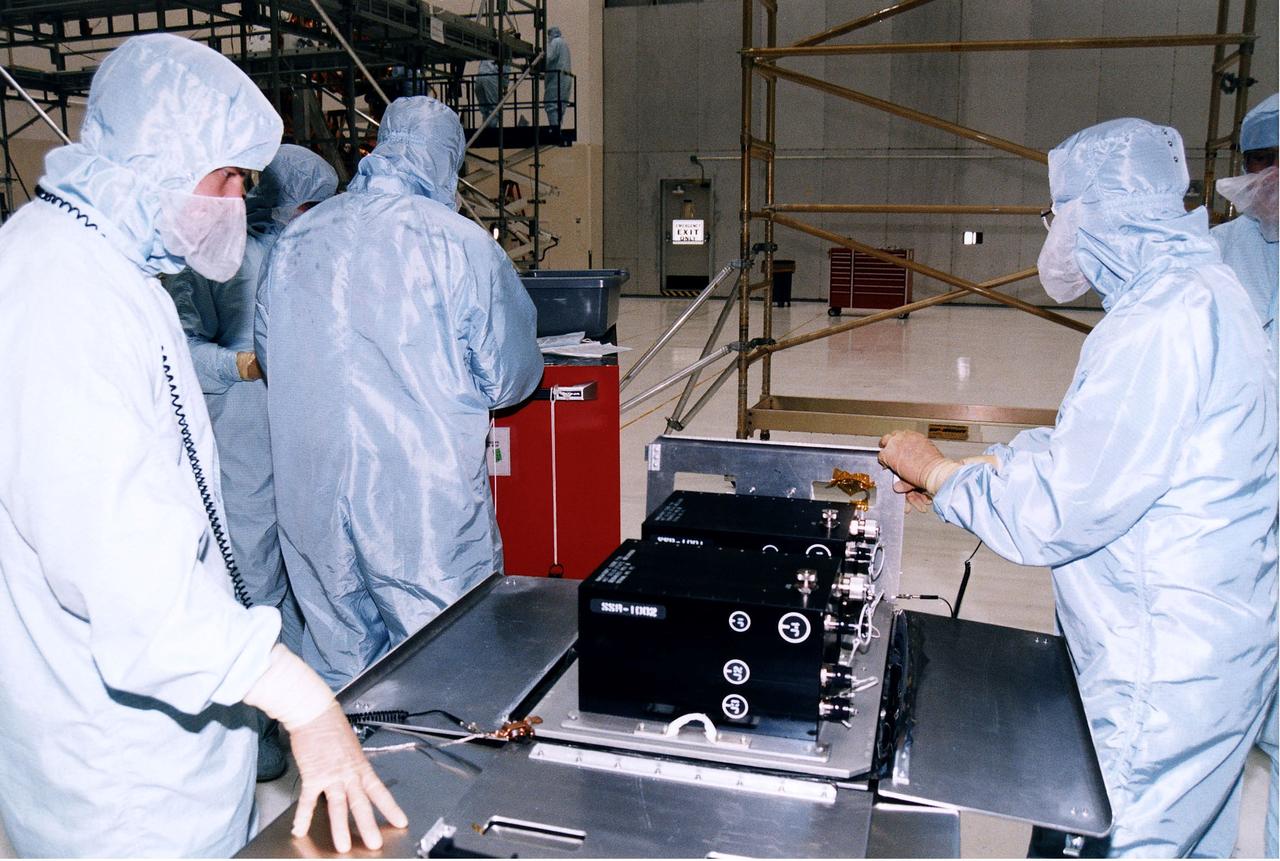

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in KSC's Vertical Processing Facility prepare a solid state recorder for installation in a protective enclosure as part of the prelaunch preparations for STS-82, the second Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission. The digital solid state recorder will replace one of three engineering/science tape recorders on Hubble. The solid state recorder has no moving parts to wear out. It also is more flexible than a reel-to-reel recorder and can store 10 times as much data. Liftoff aboard Discovery is targeted Feb. 11 with a crew of seven.

Researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory have created a series of maps showing land-surface temperatures in the Phoenix area in July 2023, when the city experienced a record-breaking run of hot weather. The images reveal the cumulative effect – overnight and across the month – of relentless daytime heating. The data was captured during overnight hours (around 2 a.m.) on several days in July by an instrument called the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) aboard the NOAA-NASA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite managed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA. The images show how built surfaces – roads, buildings, airport runways, and the like – retain heat, sometimes hovering around 100 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius) for hours after sunset. From July 1 to July 19, the built surfaces in the maps grew progressively hotter, likely the combined effect of the heat wave intensifying and the cumulative heating of those human-made structures. Due to their high heat capacity, these surfaces didn't fully cool overnight before the onset of the next day's heat. At the center of the images is Phoenix's Sky Harbor International Airport, where VIIRS measured the hottest land-surface temperature within the city. The airport is also where Phoenix takes its official air temperature. By those measurements, the city experienced the hottest month on record in July, including a record 31 consecutive days in which the temperature exceeded 110 degrees Fahrenheit (43.3 degrees Celsius). The previous record was 18 days. Land-surface temperatures in cities are usually warmer than in rural and undeveloped areas because of human activities and the materials used for building. Streets – seen in these maps as a grid pattern – are often the hottest part of the built environment due to dark asphalt paving that absorbs more sunlight than lighter-colored surfaces; asphalt absorbs up to 95% of solar radiation. In the images, the mountains near Phoenix are also notably hot due to their angle to the Sun and greater soil exposure from lack of vegetation. The hot surfaces in and around the city stand in contrast to nearby irrigated surfaces such as agricultural fields, golf courses, and parks, which fell as low as 68 degrees Fahrenheit (18.9 degrees Celsius) during the night. The Verde River and other nearby waterways also were significantly cooler. VIIRS is one of five instruments aboard the NOAA-NASA Suomi NPP satellite. Short for Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership, the spacecraft is one of several in the Joint Polar Satellite System. The images were produced from the VNP21IMG Land Surface Temperature product, which is available at NASA's Land, Atmosphere Near-real-time Capability for EOS (LANCE). Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25868
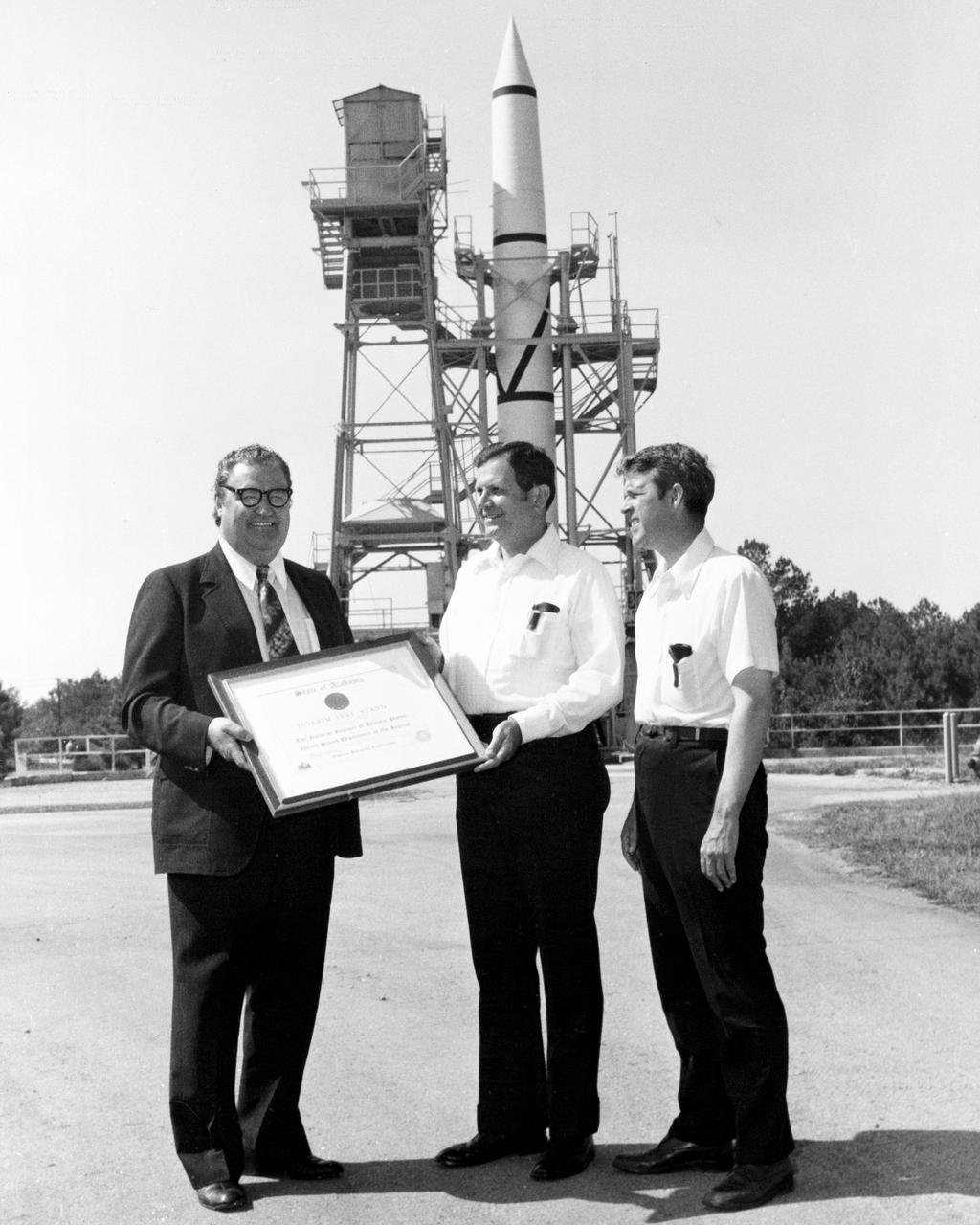

On October 02, 1976, Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) Redstone test stand was received into the National Registry of Historical Places. Photographed in front of the Redstone test stand are Dr. William R. Lucas, MSFC Center Director from June 15, 1974 until July 3, 1986, as he is accepting a certificate of registration from Madison County Commission Chairman James Record, and Huntsville architect Harvie Jones.
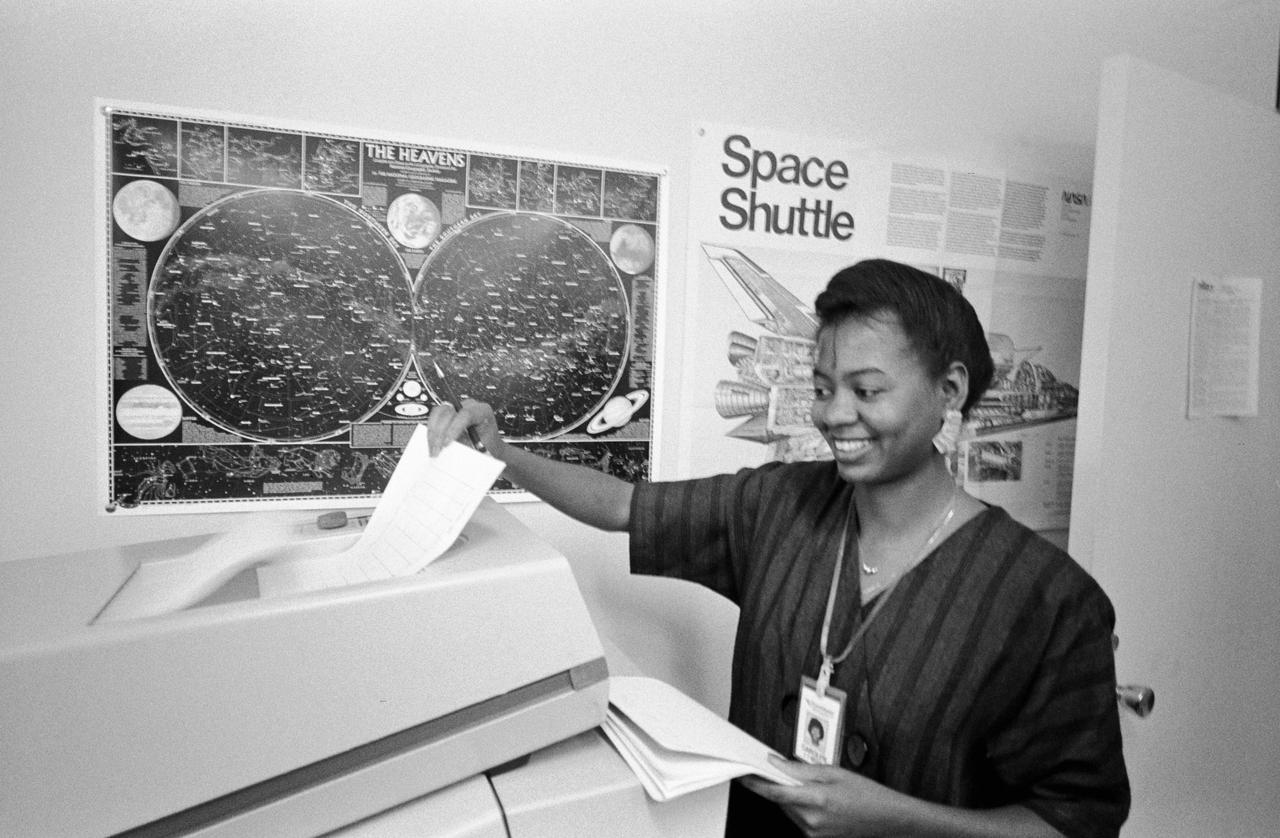

S86-30338 (4 April 1986) --- Carolyn Watson of Lockheed recieves a hard copy print-out of data from the MADS recorder as it is being sent form the termainal in JSC's central data office
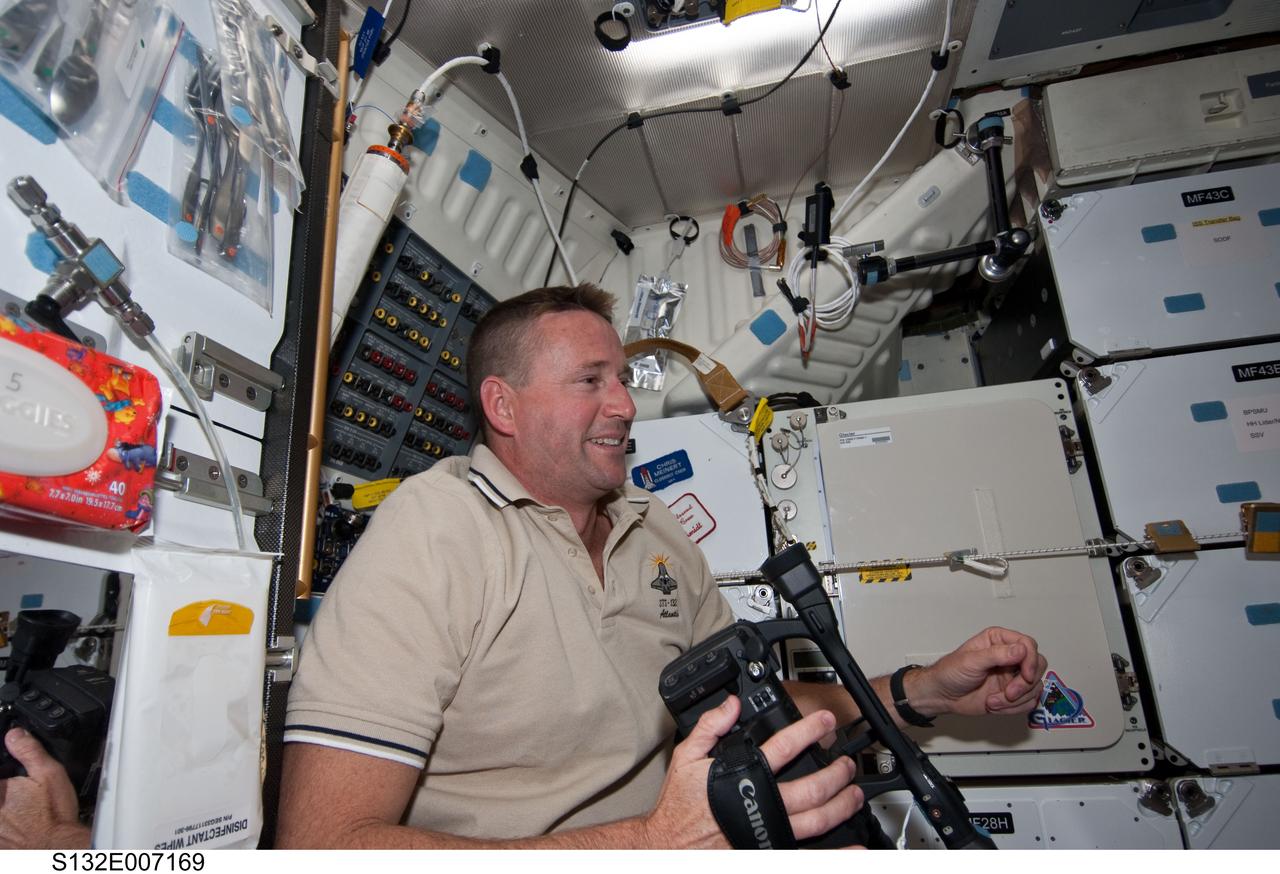

S132-E-007169 (15 May 2010) --- NASA astronaut Ken Ham, STS-132 mission commander, prepares to record some video on the middeck of space shuttle Atlantis during Flight Day 2 activities. Photo credit: National Aeronautics and Space Administration
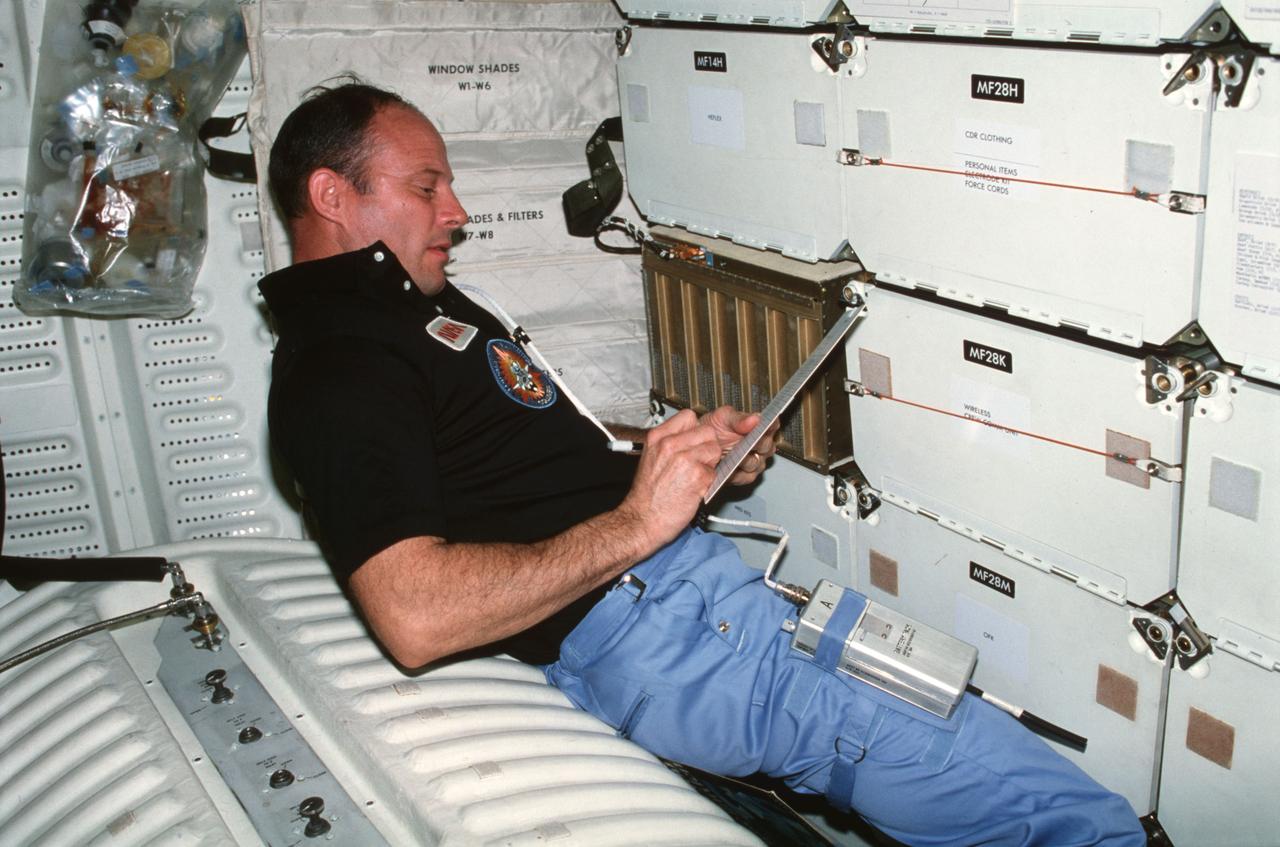

STS003-22-122 (30 March 1982) --- STS-3 Commander Lousma, wearing communications kit assembly (ASSY) mini-headset (HDST), records Plant Growth Unit (PGU) data for the Influence of Weightlessness on Plant Lignification Experiment at forward middeck locker MF14K. The experiment is designed to demonstrate the effect of weightlessness on the quantity and rate of lignin formation in different plant species during early stages of development. Port side bulkhead with window shade and filter kit appears behind Lousma and potable water tank below him. Trash bag also appears in view. Photo credit: NASA
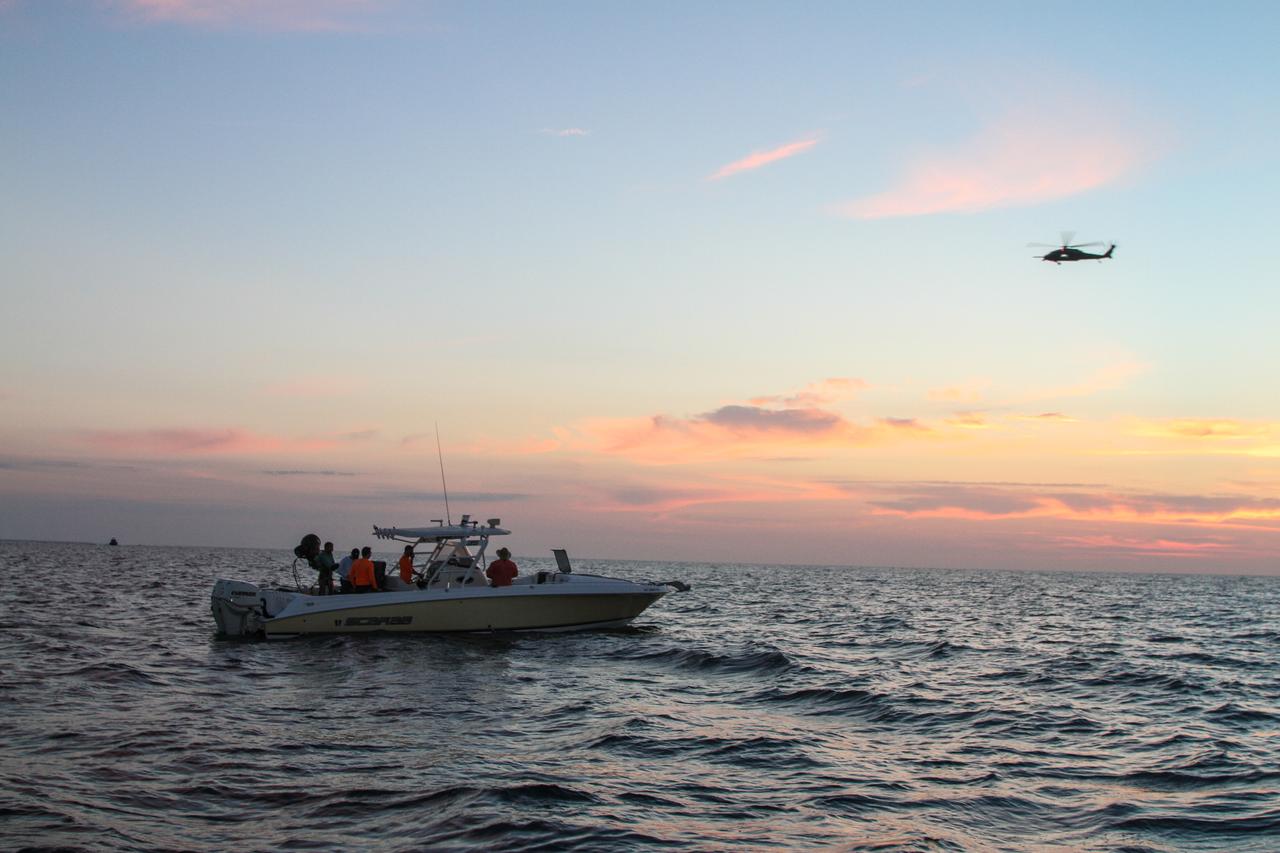

Members of the NASA Ejectable Data Recorder Recovery Team search for the ejectable data recorders in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida on July 2, 2019, after the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test. During AA-2, a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launched atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on July 2, 2019. Liftoff was at 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster sent the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors worked together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test proves that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent. Data from the recorders will be analyzed by engineers.
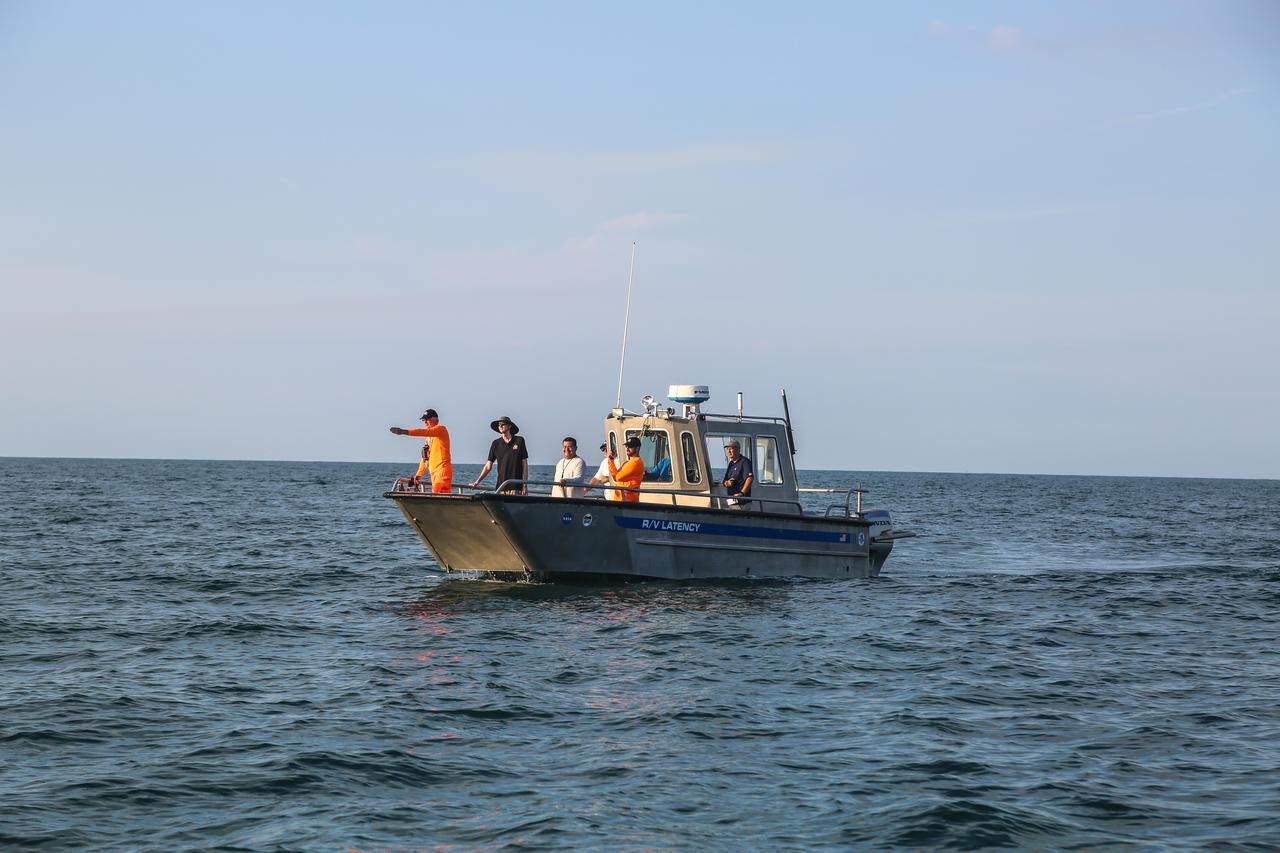

Members of the NASA Ejectable Data Recorder Recovery Team search for the ejectable data recorders in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida on July 2, 2019, after the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test. During AA-2, a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launched atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on July 2, 2019. Liftoff was at 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster sent the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors worked together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test proves that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent. Data from the recorders will be analyzed by engineers.
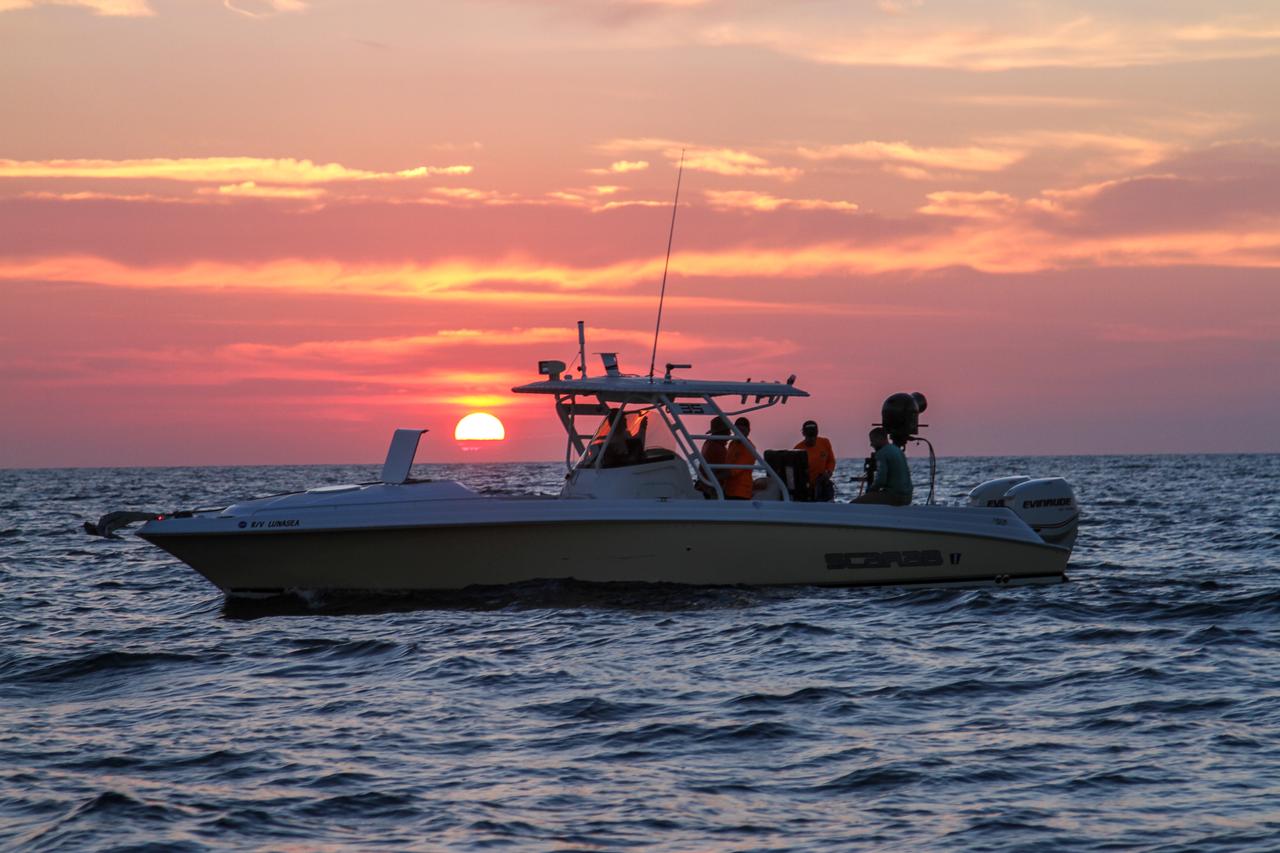

Members of the NASA Ejectable Data Recorder Recovery Team search for the ejectable data recorders in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida on July 2, 2019, after the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test. During AA-2, a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launched atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on July 2, 2019. Liftoff was at 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster sent the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors worked together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test proves that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent. Data from the recorders will be analyzed by engineers.
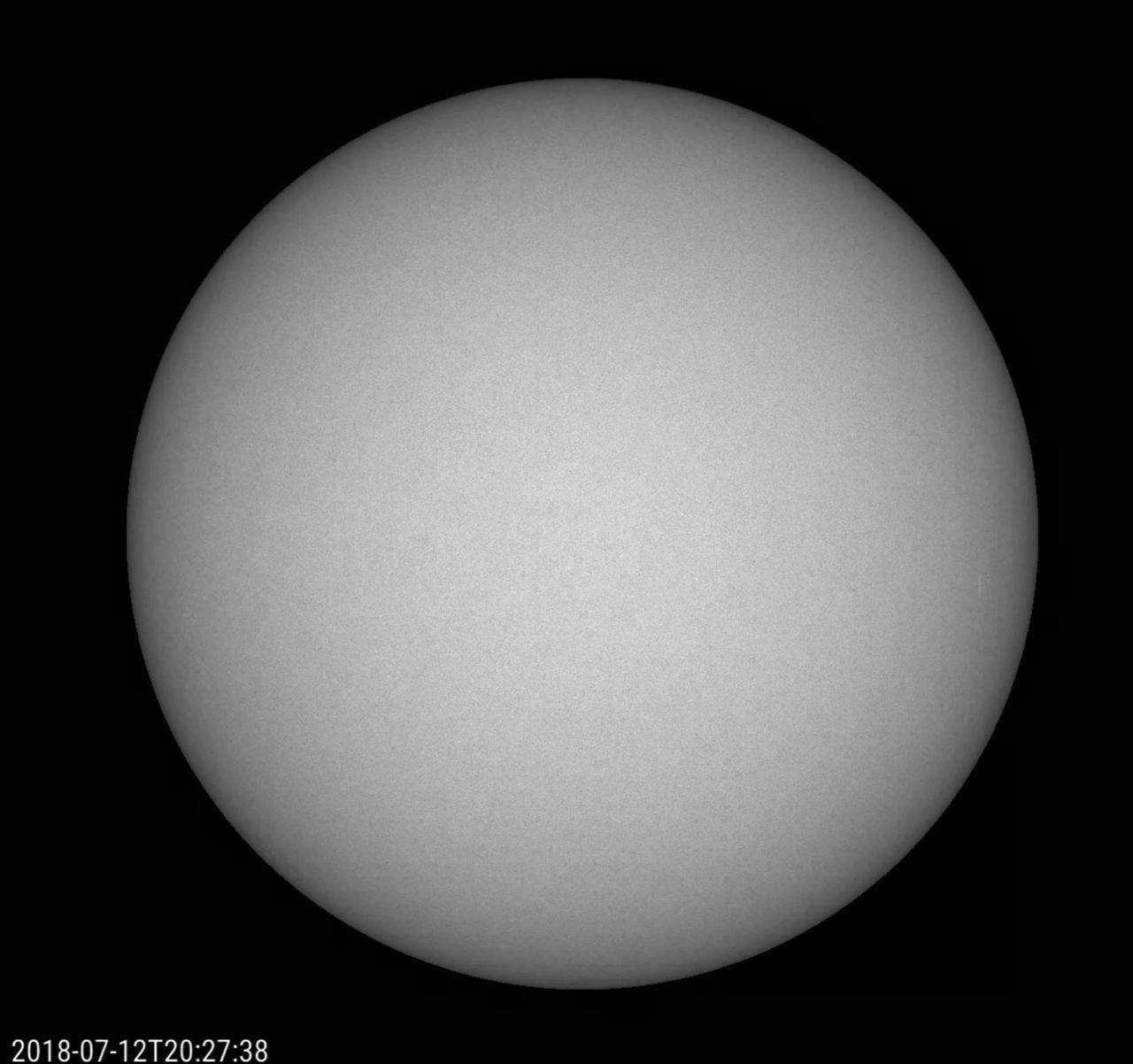

Over a three-week period (July 3-24, 2018), the Sun produced just one small, short-lived sunspot -- but it tells a big story. Up until July 22, the Sun had no sunspots for 23 consecutive days, the first time that has happened in nine years. The Sun is rapidly approaching solar minimum, a period of very low solar activity in its 11-year cycle -- and doing so more rapidly than many scientists predicted. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22646

NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft will carry a special message when it launches in October 2024 and heads toward Jupiter's moon Europa. The moon shows strong evidence of an ocean under its icy crust, with more than twice the amount of water of all of Earth's oceans combined. A triangular metal plate, seen here, will honor that connection to Earth. The plate is made of tantalum metal and is about 7 by 11 inches (18 by 28 centimeters). Engraved on both sides, it seals an opening in the electronics vault, which houses the spacecraft's sensitive electronics. The side shown here features U.S. Poet Laureate Ada Limón's handwritten "In Praise of Mystery: A Poem for Europa," and will be affixed with a silicon microchip stenciled with more than 2.6 million names submitted by the public. The microchip will be placed at the center of the illustration of a bottle amid the Jovian system – a reference to NASA's "Message in a Bottle" campaign, which invited the public to send their names with the spacecraft. The artwork includes the Drake Equation, which was formulated by astronomer Frank Drake in 1961 to estimate the possibility of finding advanced civilizations beyond Earth. Also featured is a reference to the radio frequencies considered plausible for interstellar communication, symbolizing how humanity uses this radio band to listen for messages from the cosmos. These particular frequencies match the radio waves emitted in space by the components of water and are known by astronomers as the "water hole." On the plate, they are depicted as radio emission lines. The plate includes a portrait of one of the founders of planetary science, Ron Greeley, whose early efforts to develop a Europa mission two decades ago laid the foundation for Europa Clipper. In the spirit of the Voyager spacecraft's Golden Record, which carries sounds and images to convey the richness and diversity of life on Earth, the layered message on Europa Clipper aims to spark the imagination and offer a unifying vision. Europa Clipper, set to launch from Kennedy Space Center in Florida, will arrive at the Jupiter system in 2030 and conduct about 50 flybys of the moon Europa. The mission's main science goal is to determine whether there are places below Europa, that could support life. The mission's three main science objectives are to determine the thickness of the moon's icy shell and its surface interactions with the ocean below, to investigate its composition, and to characterize its geology. The mission's detailed exploration of Europa will help scientists better understand the astrobiological potential for habitable worlds beyond our planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26062
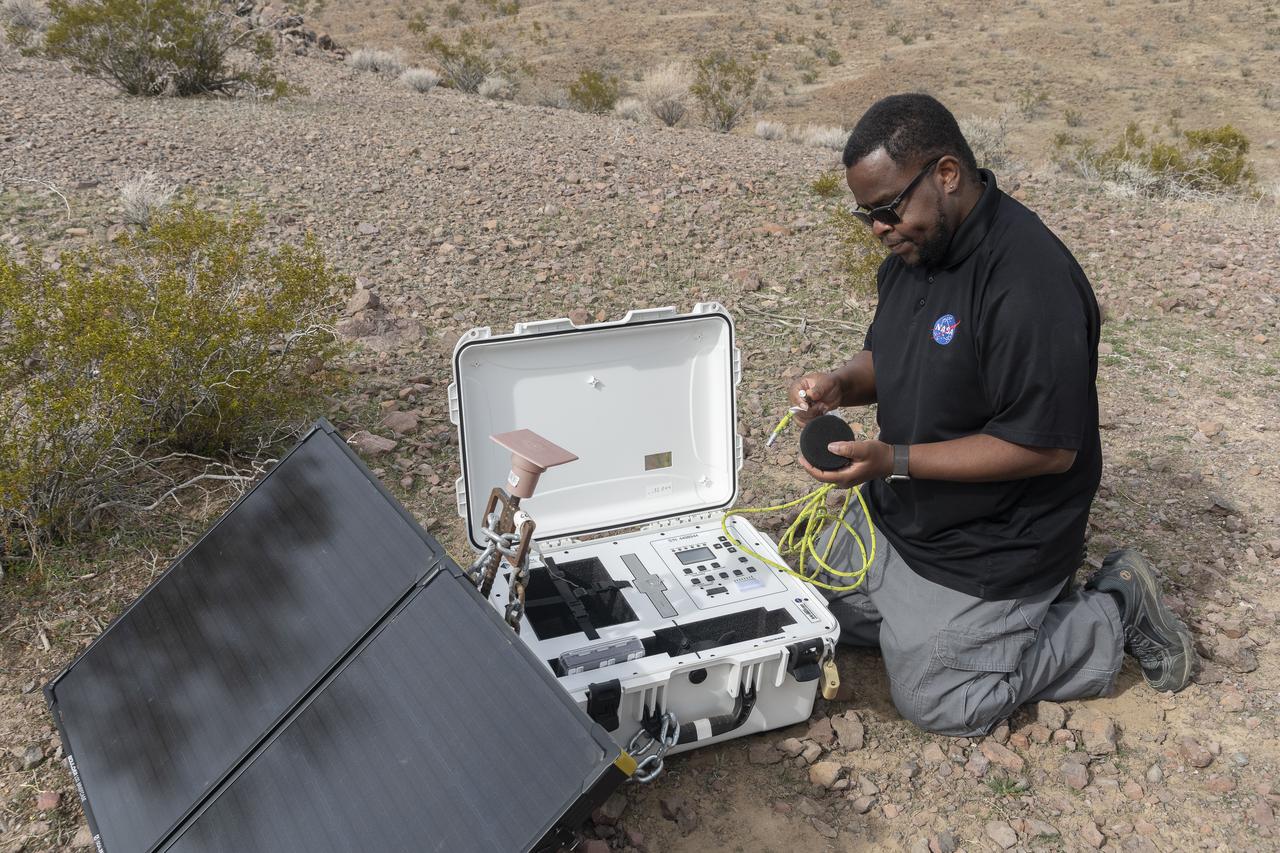

Aerospace engineer Larry Cliatt, Quesst Phase 2 Sub-Project Manager and technical lead for the acoustic validation phase of the Quesst mission, sets up a ground recording system in the California desert. The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. The testing was the third phase of Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights, called CarpetDIEM for short. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems spread out across 30 miles of open desert.
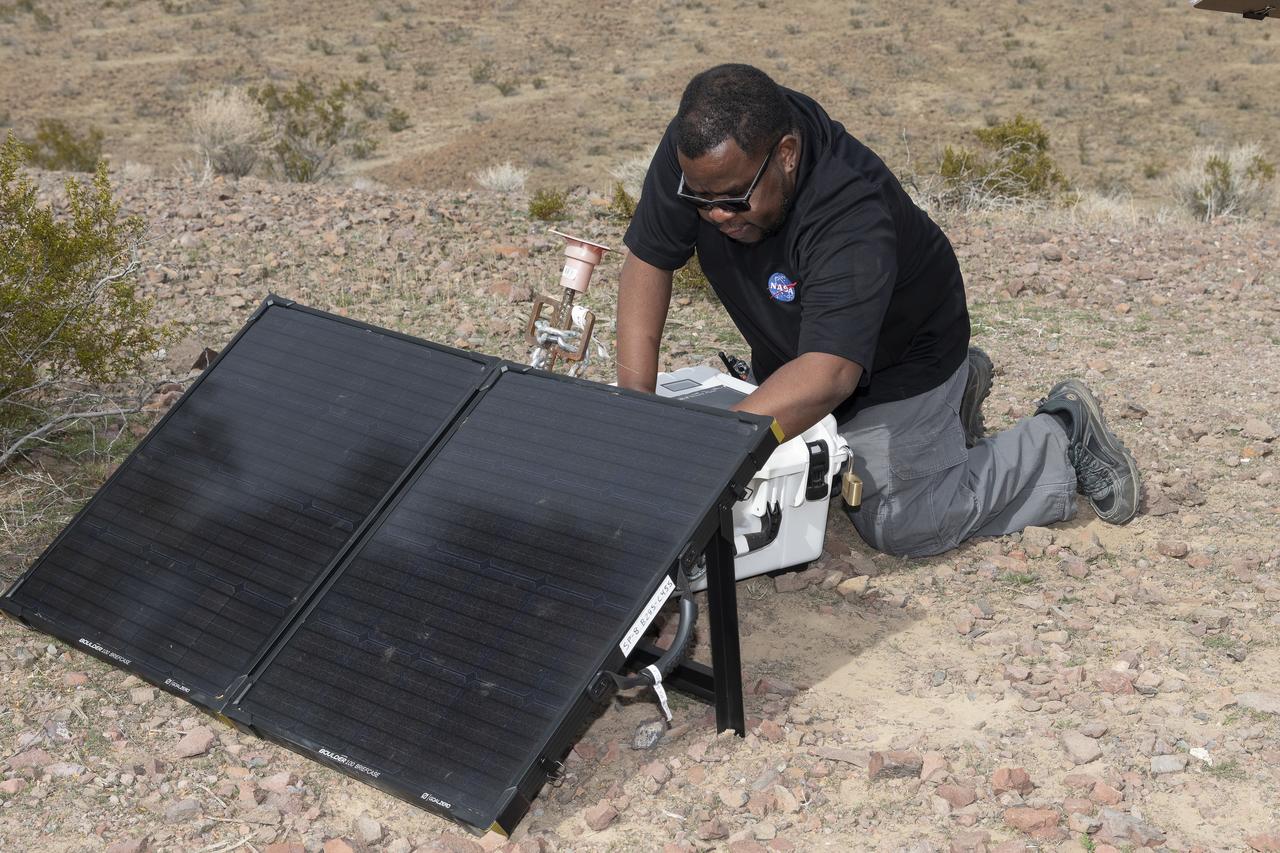

Aerospace engineer Larry Cliatt, Quesst Phase 2 Sub-Project Manager abd technical lead for the acoustic validation phase of the Quesst mission, sets up a ground recording system in the California desert. The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. The testing was the third phase of Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights, called CarpetDIEM for short. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems spread out across 30 miles of open desert.
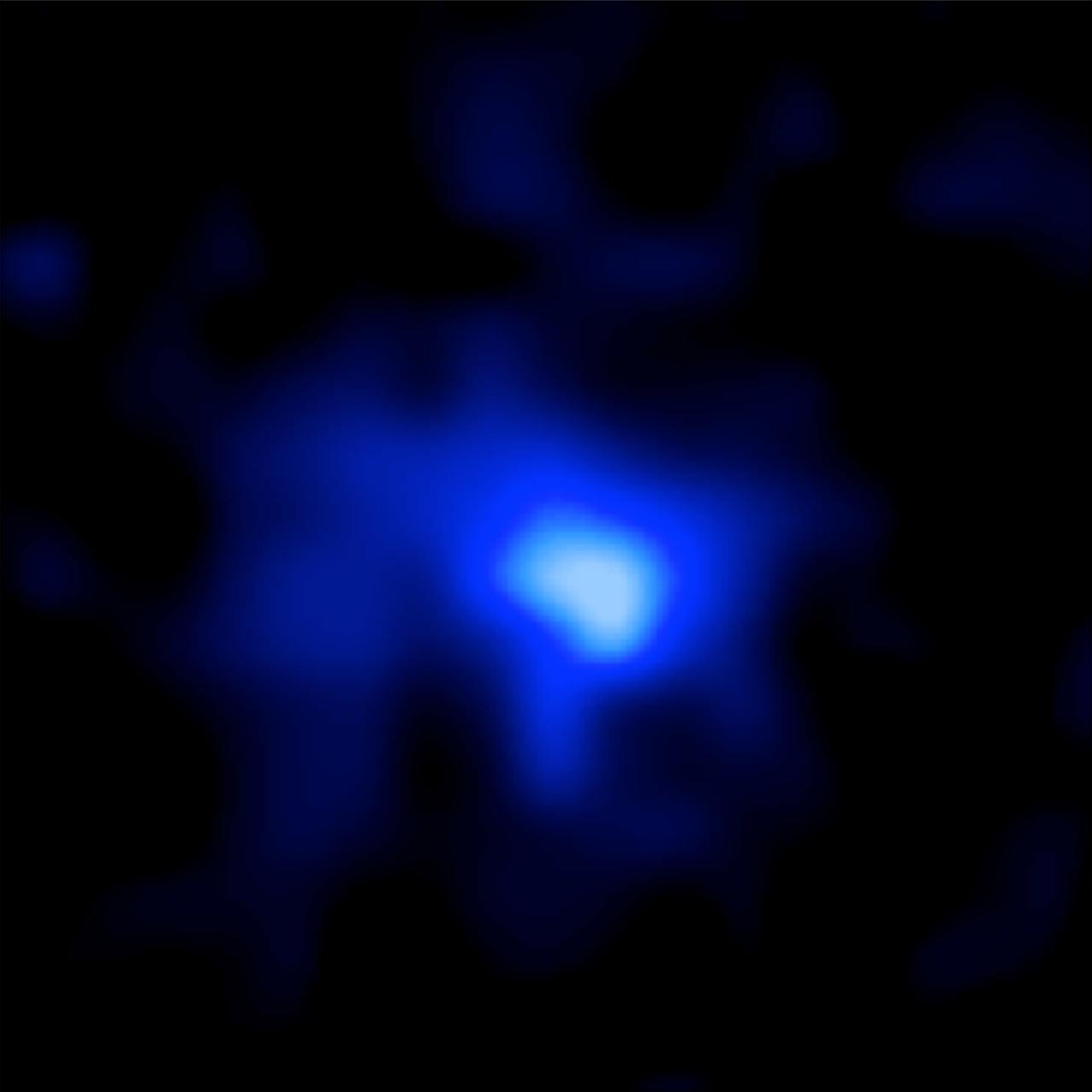
This is a Hubble Space Telescope image of the farthest spectroscopically confirmed galaxy observed to date (inset). It was identified in this Hubble image of a field of galaxies in the CANDELS survey (Cosmic Assembly Near-infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey). NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope also observed the unique galaxy. The W. M. Keck Observatory was used to obtain a spectroscopic redshift (z=7.7), extending the previous redshift record. Measurements of the stretching of light, or redshift, give the most reliable distances to other galaxies. This source is thus currently the most distant confirmed galaxy known, and it appears to also be one of the brightest and most massive sources at that time. The galaxy existed over 13 billion years ago. The near-infrared light image of the galaxy (inset) has been colored blue as suggestive of its young, and hence very blue, stars. The CANDELS field is a combination of visible-light and near-infrared exposures. Credits: NASA, ESA, P. Oesch (Yale U.)
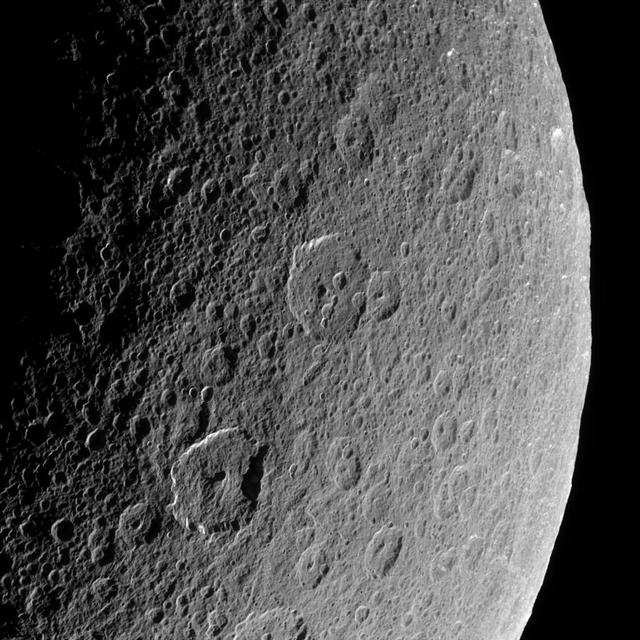

Cassini looks down upon Rhea, whose cratered surface was already ancient before any complex life developed on Earth. The terrain seen here has probably changed little in the past billion years
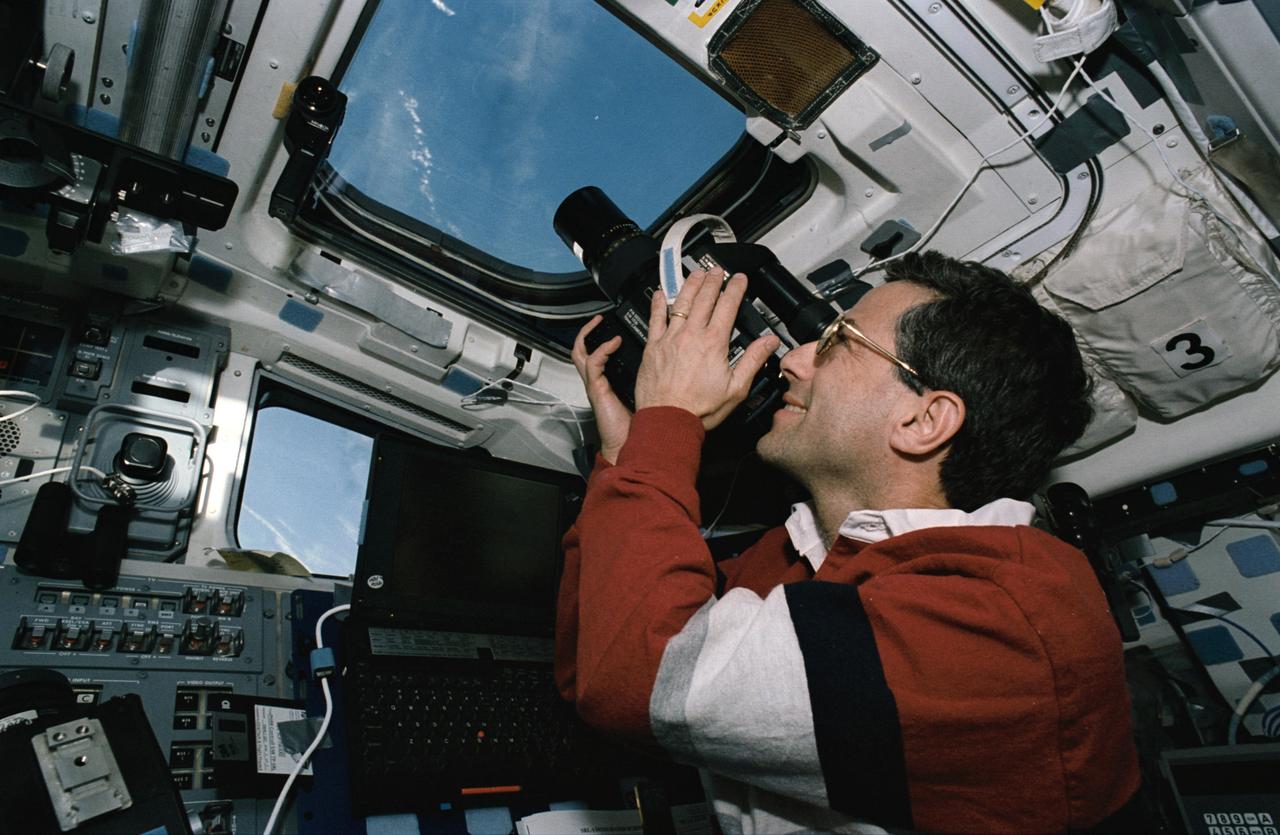

STS059-46-025 (9-20 April 1994) --- On the Space Shuttle Endeavour's aft flight deck astronaut Jerome (Jay) Apt, mission specialist, uses a handheld 70mm Hasselblad camera to record still scenes of Earth. Apt, the commander of Endeavour's Blue Shift, joined five other NASA astronauts for a week and a half in space in support of the Space Radar Laboratory/STS-59 mission.
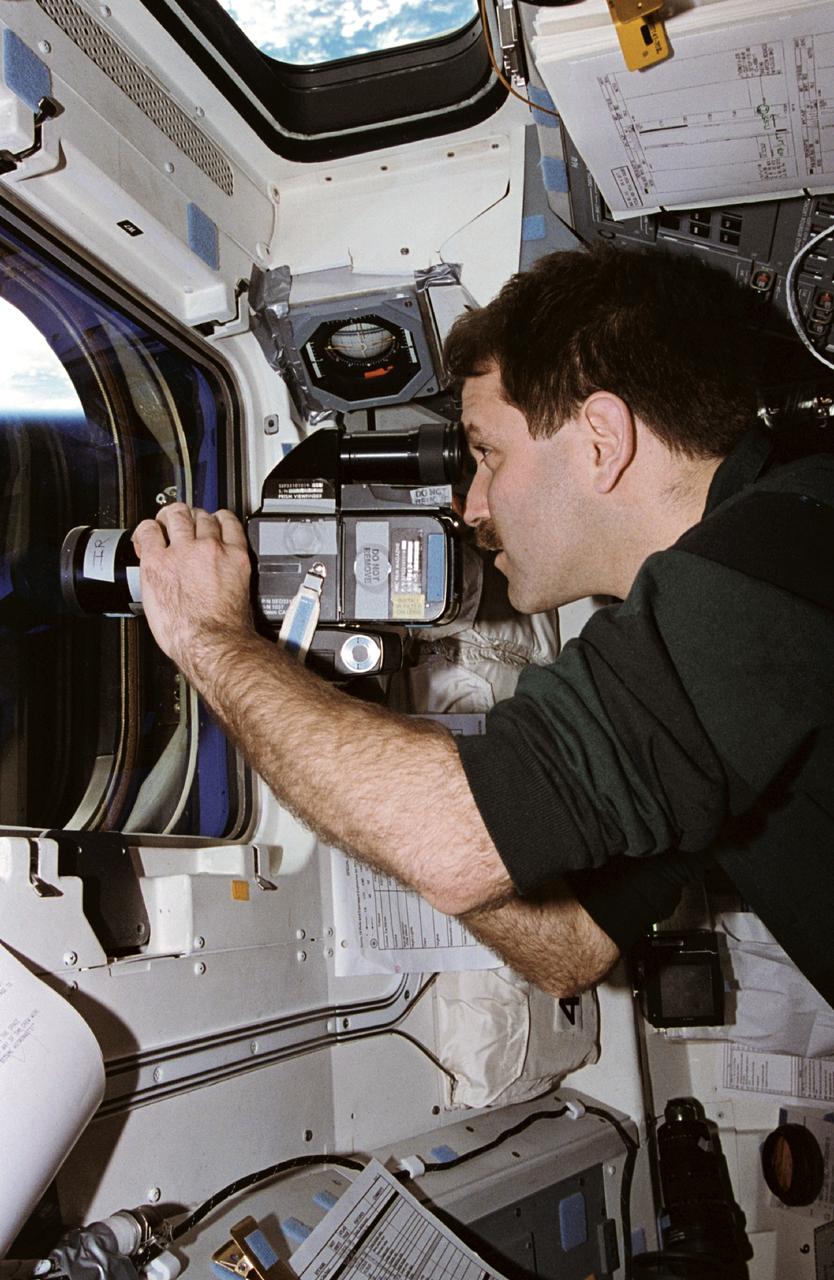

STS067-377-008 (2-18 March 1995) --- Astronaut John M. Grunsfeld, mission specialist, uses a handheld Hasselblad camera to record the Astro-2 payload. Orbiting Earth at 190 nautical miles, Grunsfeld joined four other NASA astronauts and two scientists for almost 17 days conducting research in support of the Astro-2 mission.
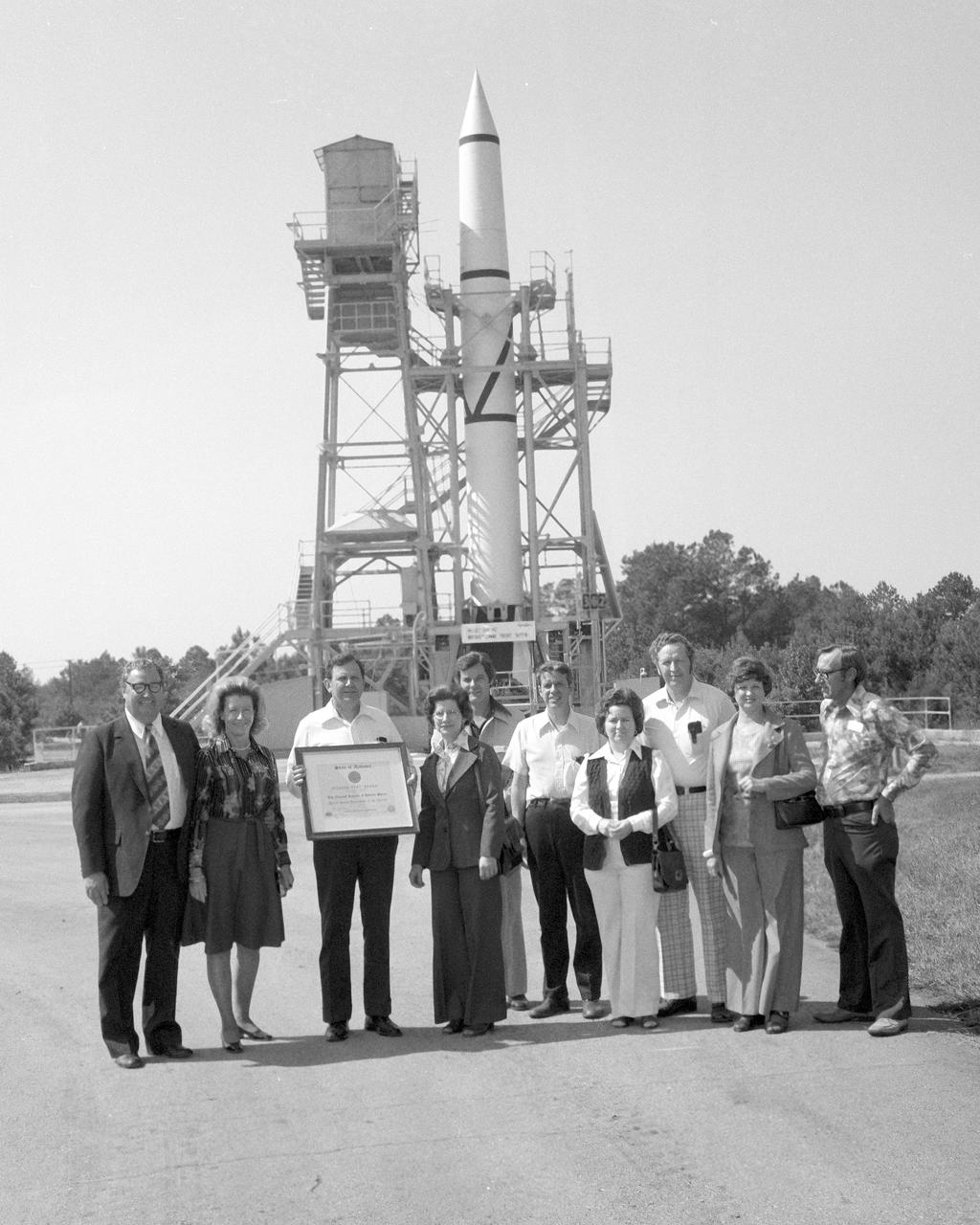

On October 02, 1976, Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) Redstone test stand was received into the National Registry of Historical Places. Photographed in front of the Redstone test stand along with their wives are (left to right), Madison County Commission Chairman James Record, Dr. William R. Lucas, MSFC Center Director from June 15, 1974 until July 3, 1986, (holding certificate), Ed, Buckbee, Space and Rocket Center Director; Harvie Jones, Huntsville Architect; Dick Smith; and Joe Jones.
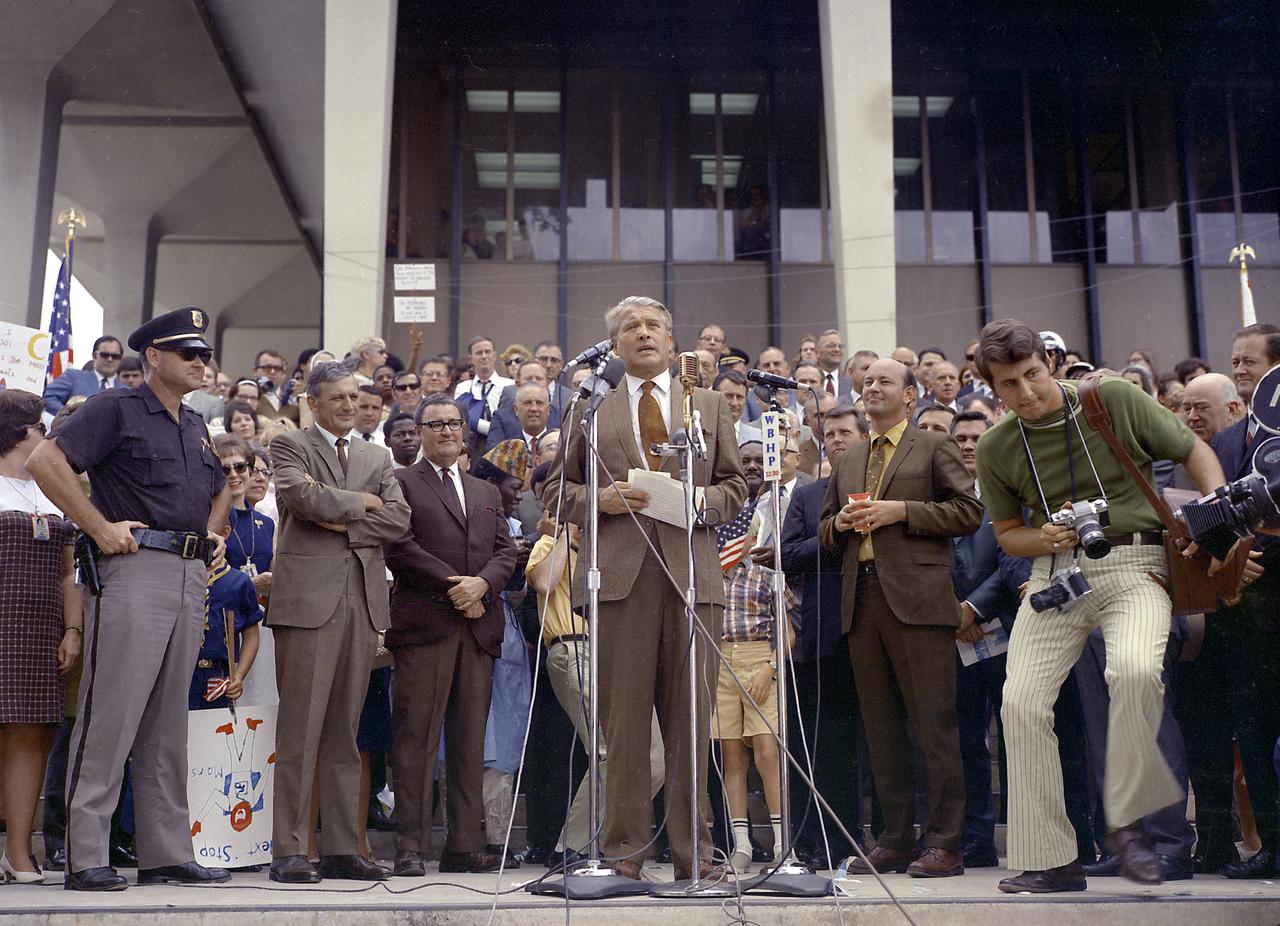

Apollo 11 splashdown celebration in Huntsville, Alabama, on July 24, 1969. Huntsville Alabama is the home of the Marshall Space Flight Center which developed the Saturn vehicles under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The photo shows Dr. von Braun speaking to the crowd at the Madison County Courthouse as Mayor Joe Davis, Madison County Commissioner James Record and City Council President Ken Johnson look on.
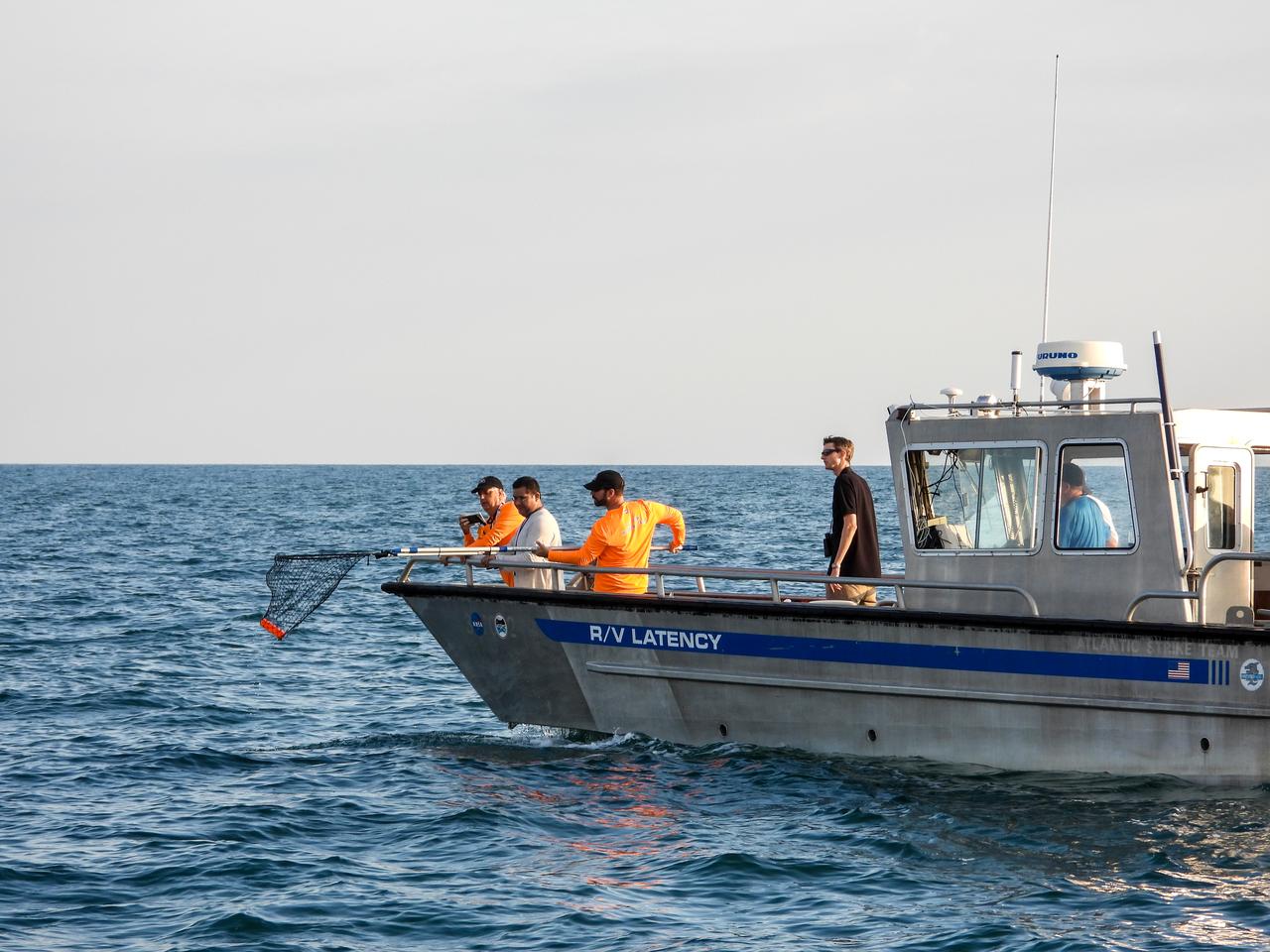

One of the 12 ejectable data recorders from NASA’s Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test is retrieved from the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida by the NASA Ejectable Data Recorder Recovery Team on July 2, 2019. During AA-2, a fully functional Launch Abort System (LAS) with a test version of Orion attached, launched atop a Northrop Grumman provided booster from Launch Pad 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on July 2, 2019. Liftoff was at 7 a.m. EDT. During AA-2, the booster sent the LAS and Orion to an altitude of 31,000 feet, traveling at Mach 1.15 (more than 1,000 mph). The LAS’ three motors worked together to pull the crew module away from the booster and prepare it for splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean. The flight test proves that the abort system can pull crew to safety in the unlikely event of an emergency during ascent. Data from the recorders will be analyzed by engineers.