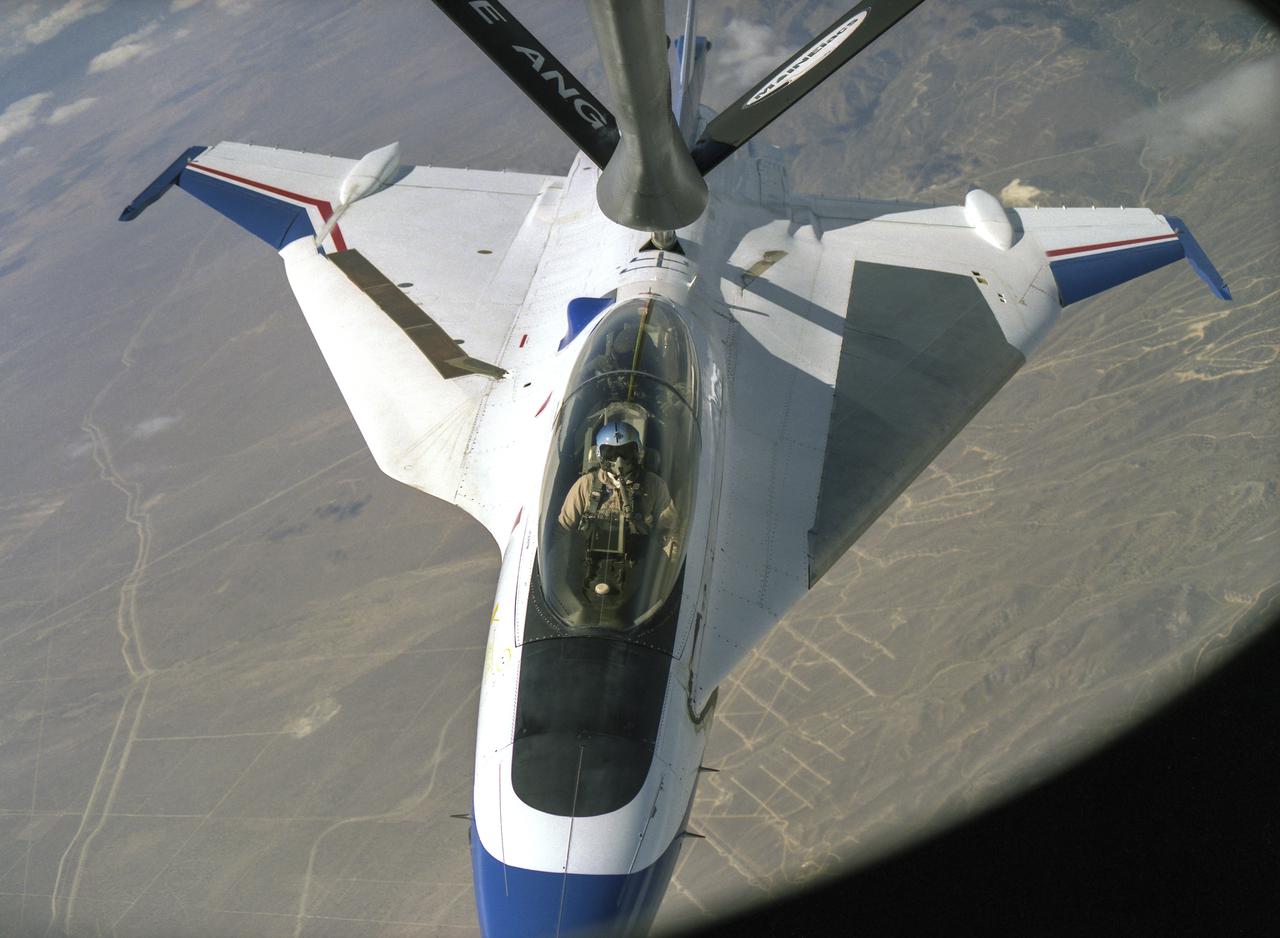

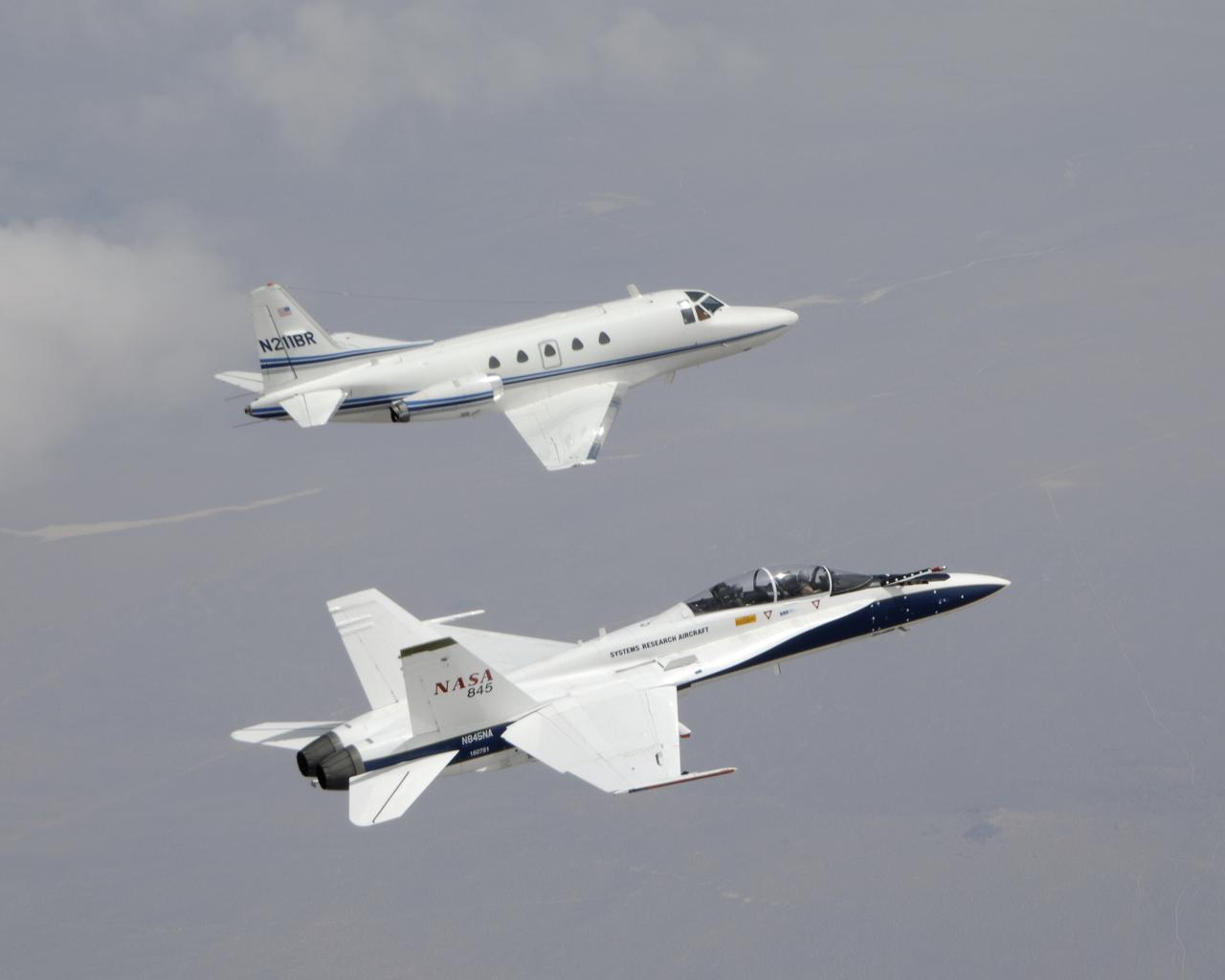
An F-16XL refuels in-flight. Only two XLs were built, and NASA eventually operated both for experimental purposes, including an active supersonic laminar flow experiment.

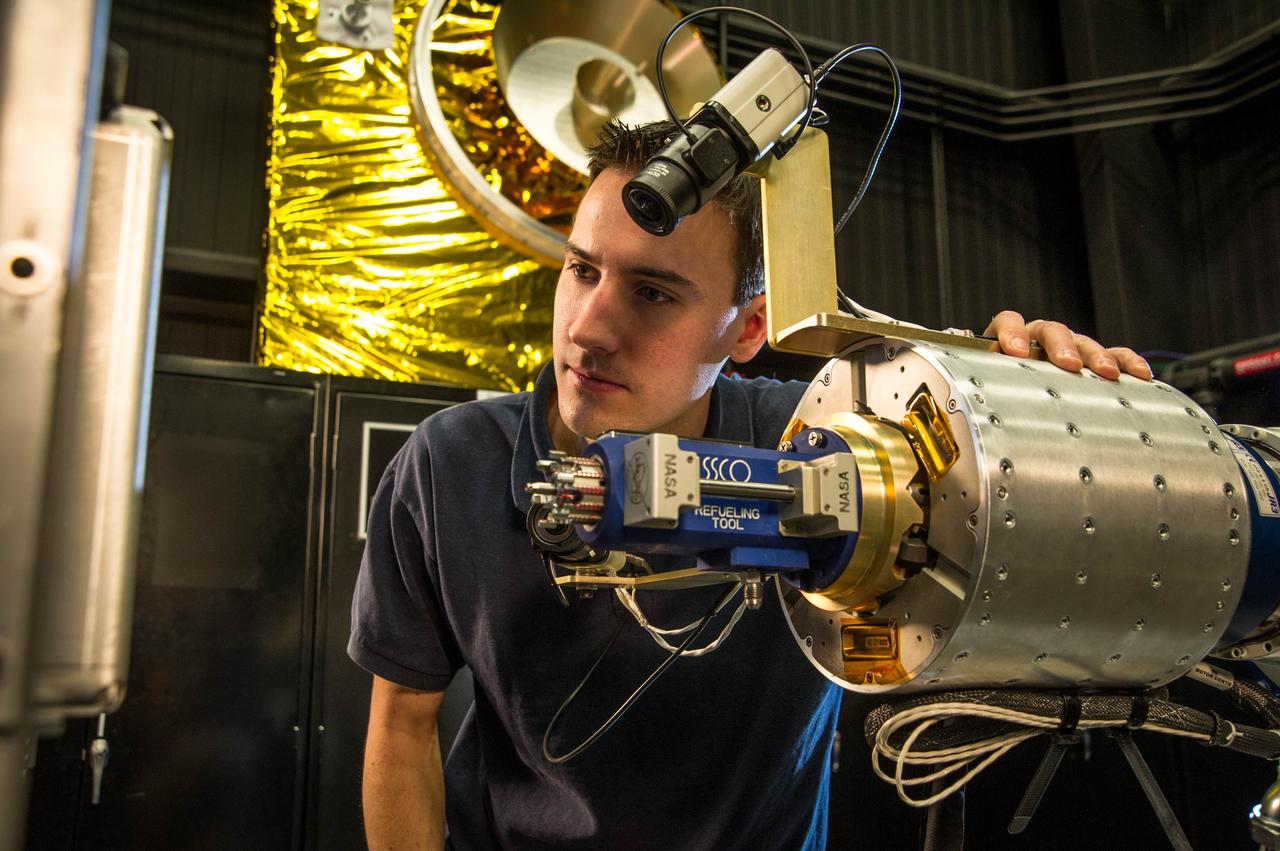
Goddard's Ritsko Wins 2011 SAVE Award The winner of the 2011 SAVE Award is Matthew Ritsko, a Goddard financial manager. His tool lending library would track and enable sharing of expensive space-flight tools and hardware after projects no longer need them. This set of images represents the types of tools used at NASA. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/people/features/ritsko-save.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/people/features/ritsko-save.html</a> The engineering mockup of the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module is currently on display within the press building at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The RRM mission is a joint effort between NASA and the Canadian Space Agency designed to demonstrate and test the tools, technologies, and techniques needed to robotically refuel satellites in space. Reporters have the opportunity to get a close-up view of the replica module and tools that are a part of the final shuttle mission payload. SSCO engineers test an RRM tool. To learn more about the RRM go to: <a href="http://ssco.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">ssco.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagr.am/p/E_05l/" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) builds on the first two phases of International Space Station (ISS) technology demonstrations that tested tools, technologies and techniques to refuel and repair satellites in orbit. RRM3, which arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on May 8, is planned to launch to the ISS later this year.
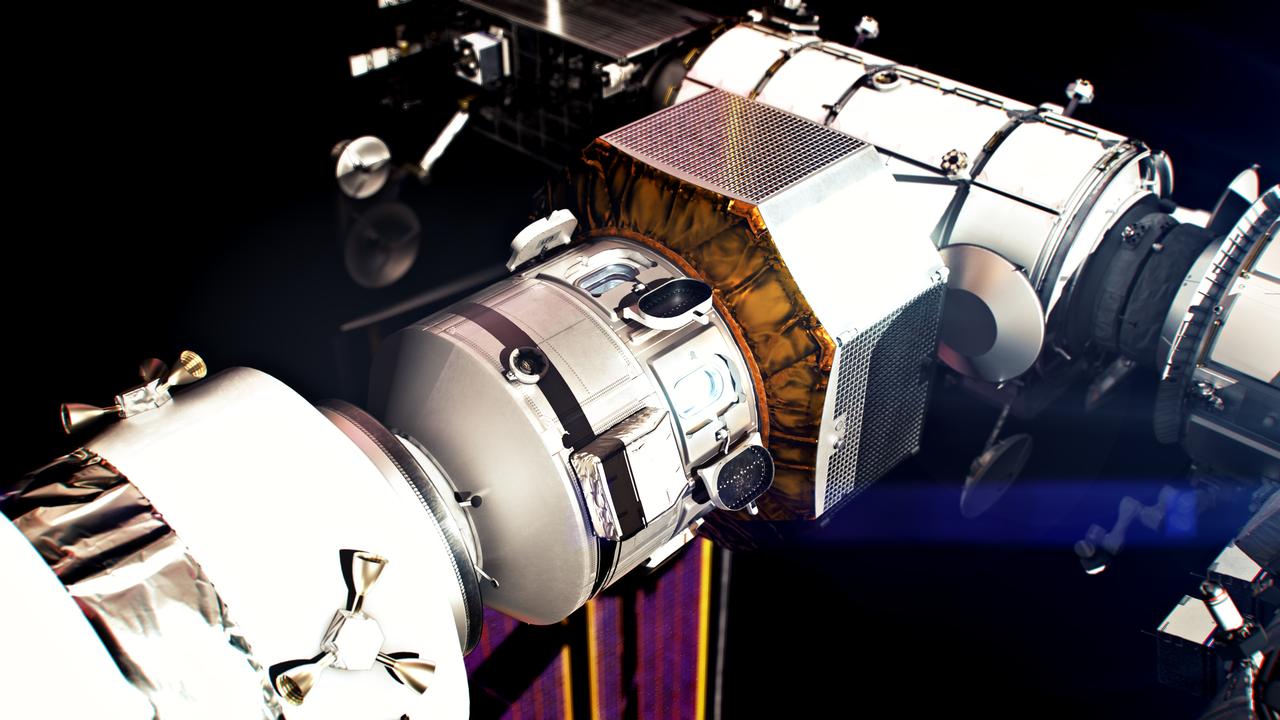

Gateway's ESPRIT Refueling Module, or ERM, will provide refueling capabilities for the space station, cargo storage, and windows for stunning views of the Earth, Moon and deep space. ERM will be delivered to Gateway by the crewed Orion spacecraft on the Artemis V mission after launching on an Space Launch System (SLS) Block 1B rocket.
RROxiTT lead roboticist Alex Janas stands with the Oxidizer Nozzle Tool as he examines the work site. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn NASA has successfully concluded a remotely controlled test of new technologies that would empower future space robots to transfer hazardous oxidizer – a type of propellant – into the tanks of satellites in space today. Concurrently on the ground, NASA is incorporating results from this test and the Robotic Refueling Mission on the International Space Station to prepare for an upcoming ground-based test of a full-sized robotic servicer system that will perform tasks on a mock satellite client. Collectively, these efforts are part of an ongoing and aggressive technology development campaign to equip robots and humans with the tools and capabilities needed for spacecraft maintenance and repair, the assembly of large space telescopes, and extended human exploration. Read more here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-tests-new-robotic-refueling-technologies/#.UxeLyyRkLH4" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-tests-new-robotic-refue...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on May 8. The fluid transfer module will demonstrate innovative methods to store, transfer and freeze standard cryogenic fluid in space. RRM3 is scheduled to launch to the International Space Station later this year.

The technology to replenish crucial satellite supplies in space currently does not exist. NASA is looking to help change that with Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3). The fluid transfer module arrived at Kennedy Space Center on May 8, and is planned to launch to the International Space Station later this year.

NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on May 8. The mission, which is scheduled to launch to the International Space Station later this year, will advance satellite servicing capabilities that will enable long duration, deep space exploration.
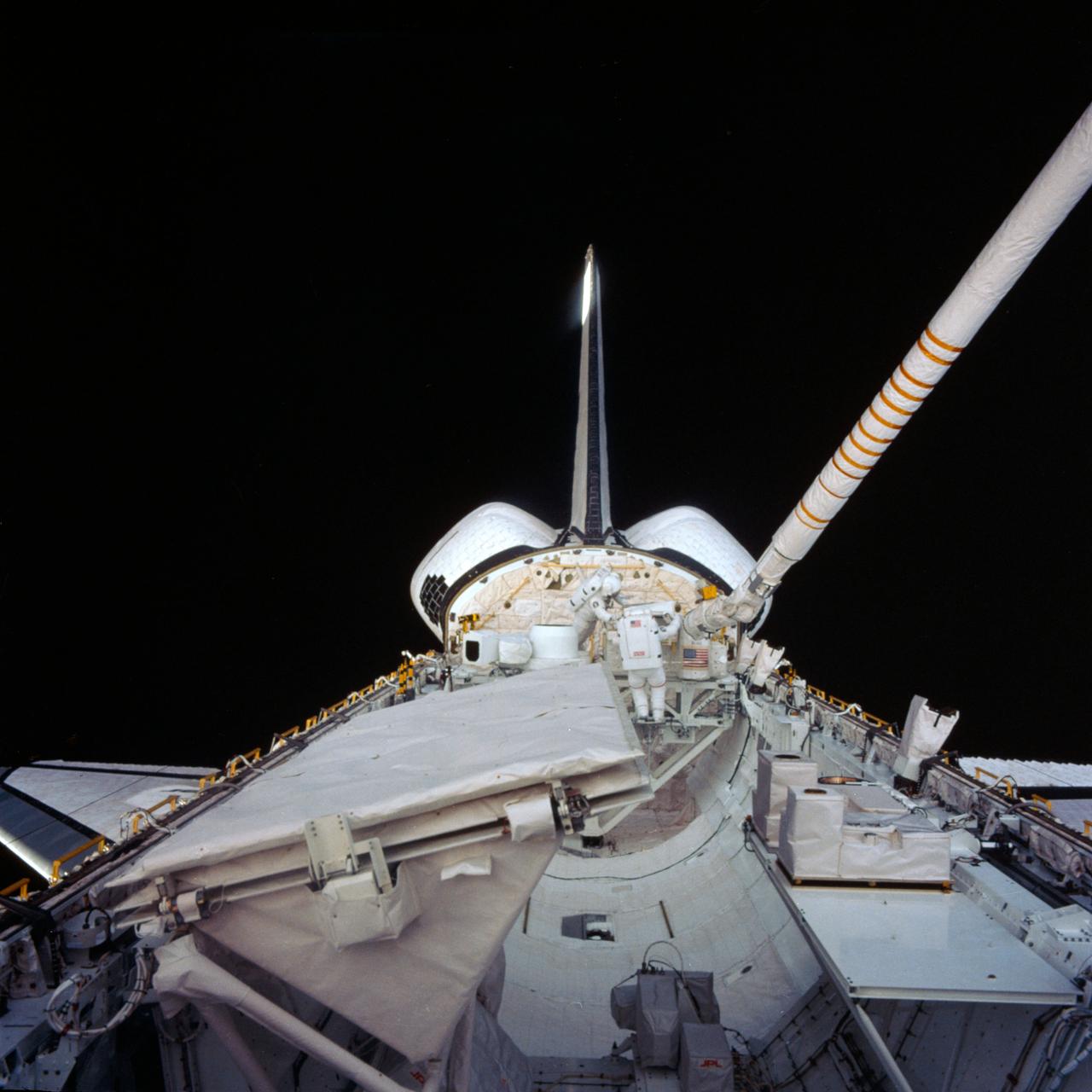

S84-43432 (11 Oct. 1984) --- Appearing small in the center background of this image, astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan, left, and David C. Leestma, both 41-G mission specialists, perform an in-space simulation of refueling another spacecraft in orbit. Their station on the space shuttle Challenger is the orbital refueling system (ORS), positioned on the mission peculiar support structure (MPR ESS). The Large Format Camera (LFC) is left of the two mission specialists. In the left foreground is the antenna for the shuttle imaging radar (SIR-B) system onboard. The Canadian-built remote manipulator system (RMS) is positioned to allow close-up recording capability of the busy scene. A 50mm lens on a 70mm camera was used to photograph this scene. Photo credit: NASA
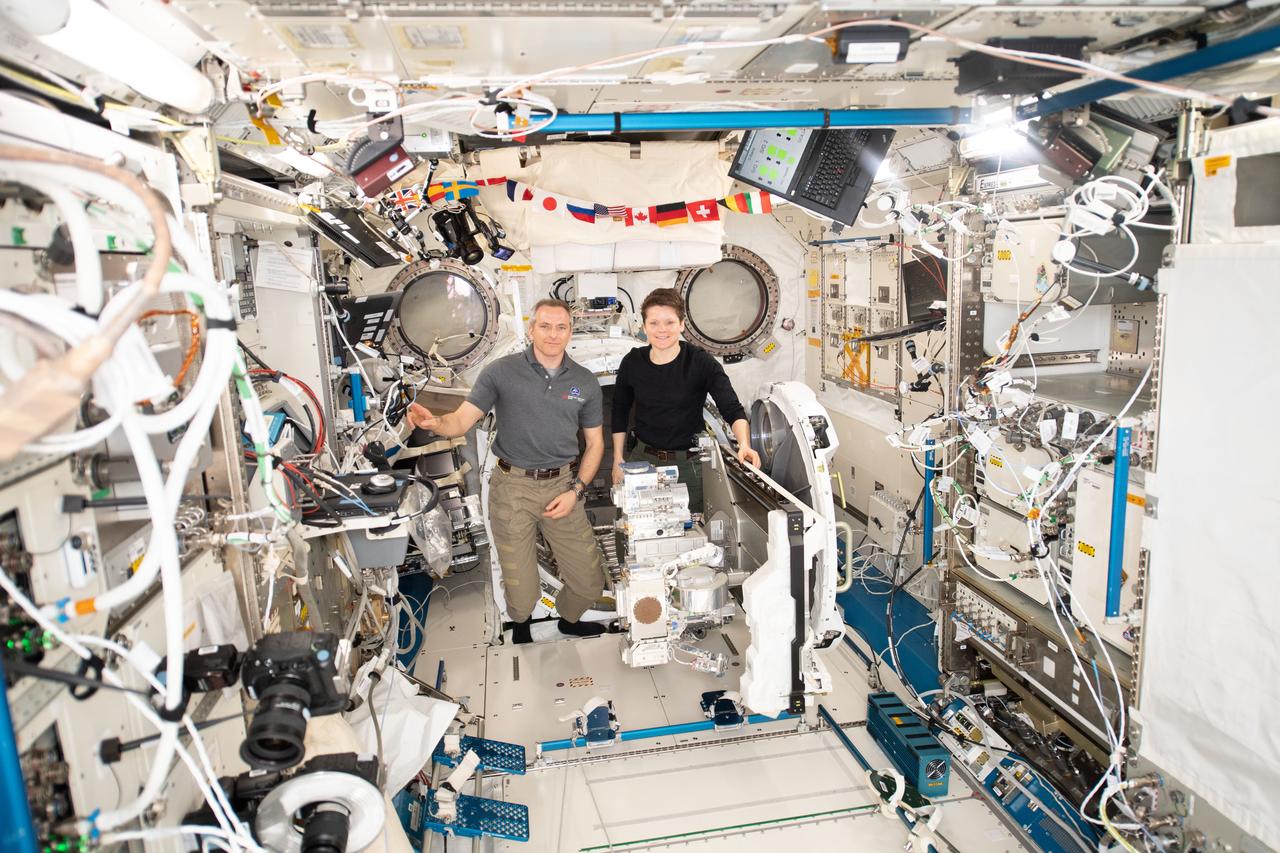

iss058e015664 (2/19/2019) --- NASA astronaut Anne McClain and Canadian Space Agency (CSA) astronaut David Saint-Jacques shown during the installation of the Robotics Refueling Mission (RRM)-3 on the JEM Airlock slide table in the KIBO module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) demonstrates the first transfer and long term storage of liquid methane, a cryogenic fluid, in microgravity. The ability to replenish and store cryogenic fluids, which can function as a fuel or coolant, can help enable long duration journeys to destinations like the Moon and Mars.
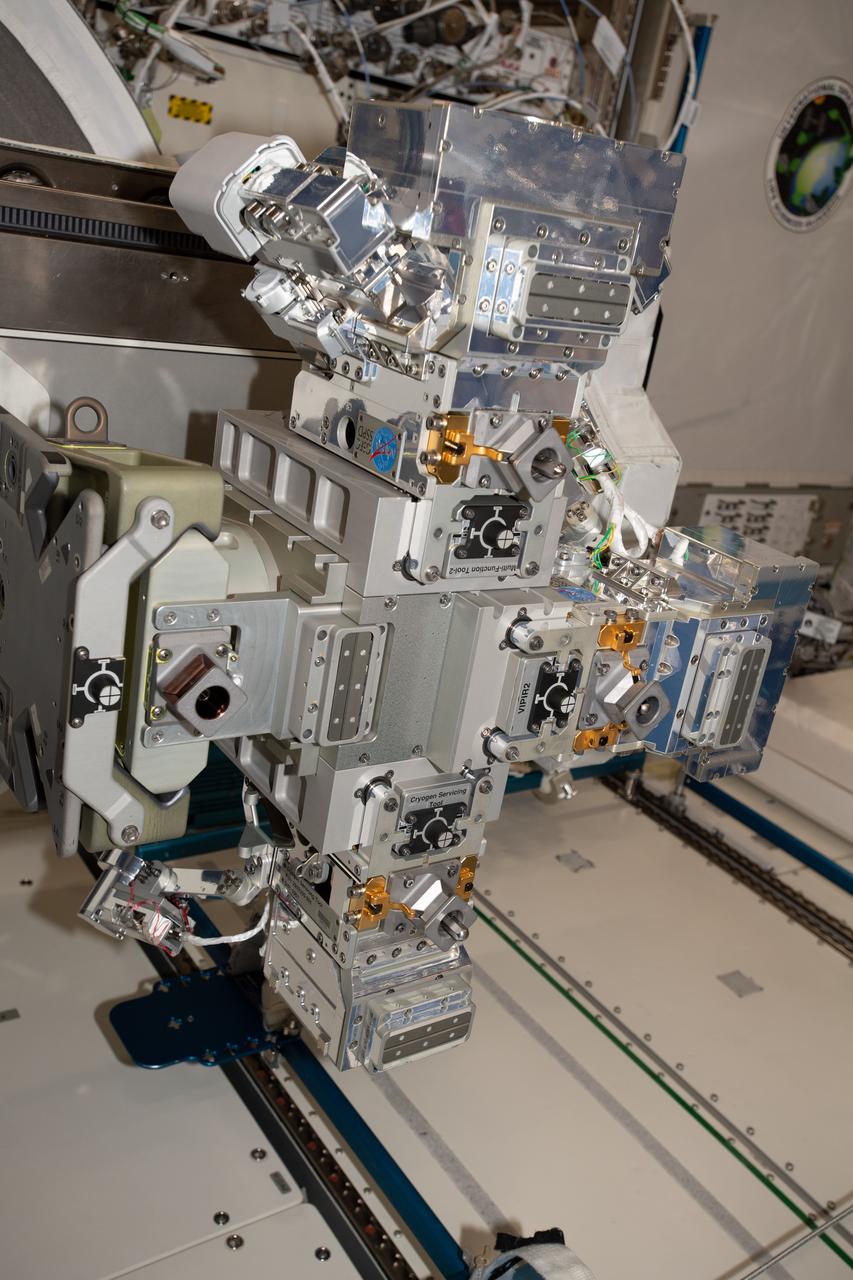

iss058e015157 (2/19/2019) --- Photo documentation of the Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) hardware in the KIBO module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) demonstrates the first transfer and long term storage of liquid methane, a cryogenic fluid, in microgravity. The ability to replenish and store cryogenic fluids, which can function as a fuel or coolant, can help enable long duration journeys to destinations like the Moon and Mars.
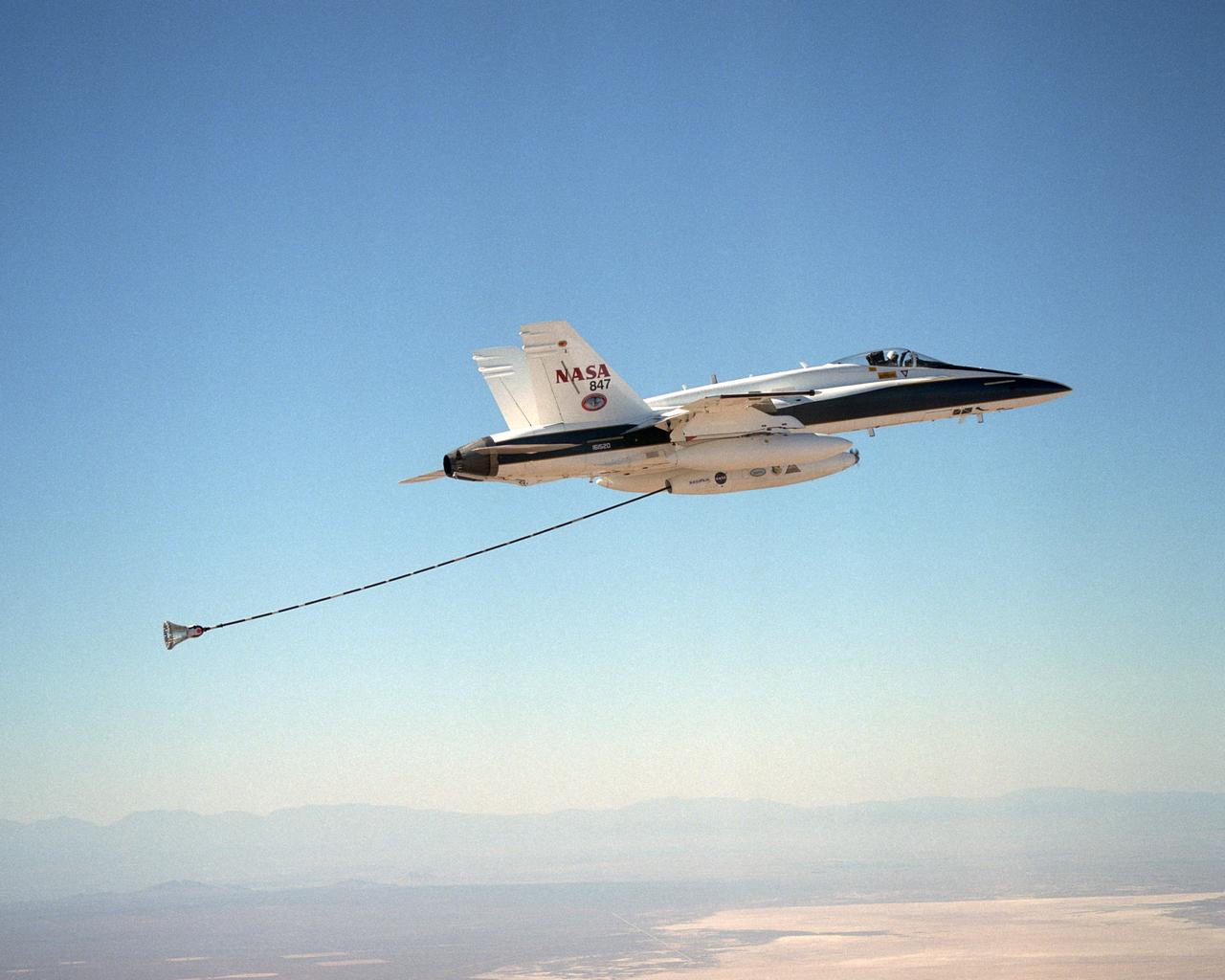

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
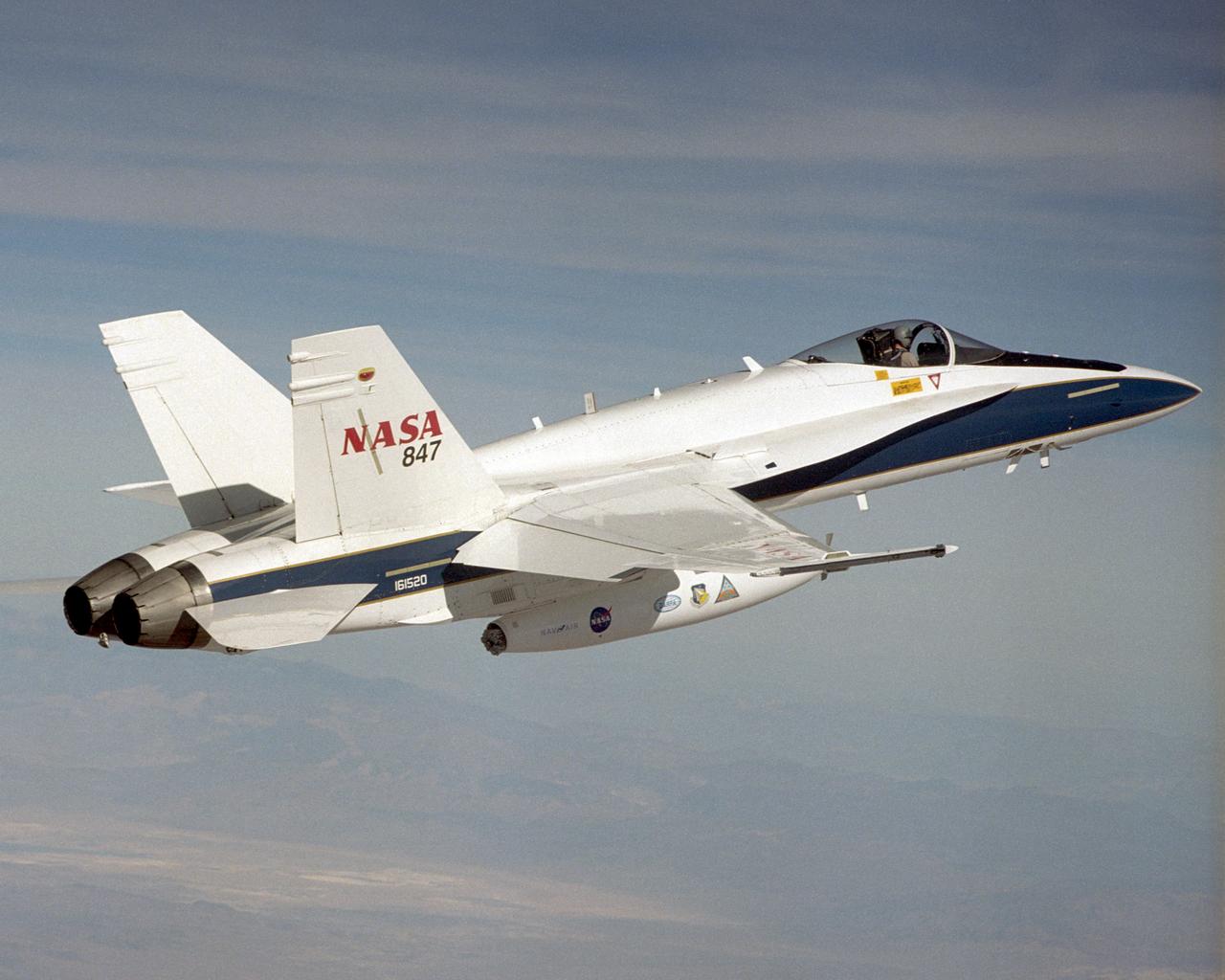

A NASA F/A-18 flies over the Dryden Flight Research Center and Rogers Dry Lake on December 11, 2002. The aircraft participated in the Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project. The 300-gallon aerial refueling store seen on the belly of the aircraft carries fuel and a refueling drogue. This aircraft acted as a tanker in the study to develop an aerodynamic model for future automated aerial refueling, especially of unmanned vehicles.
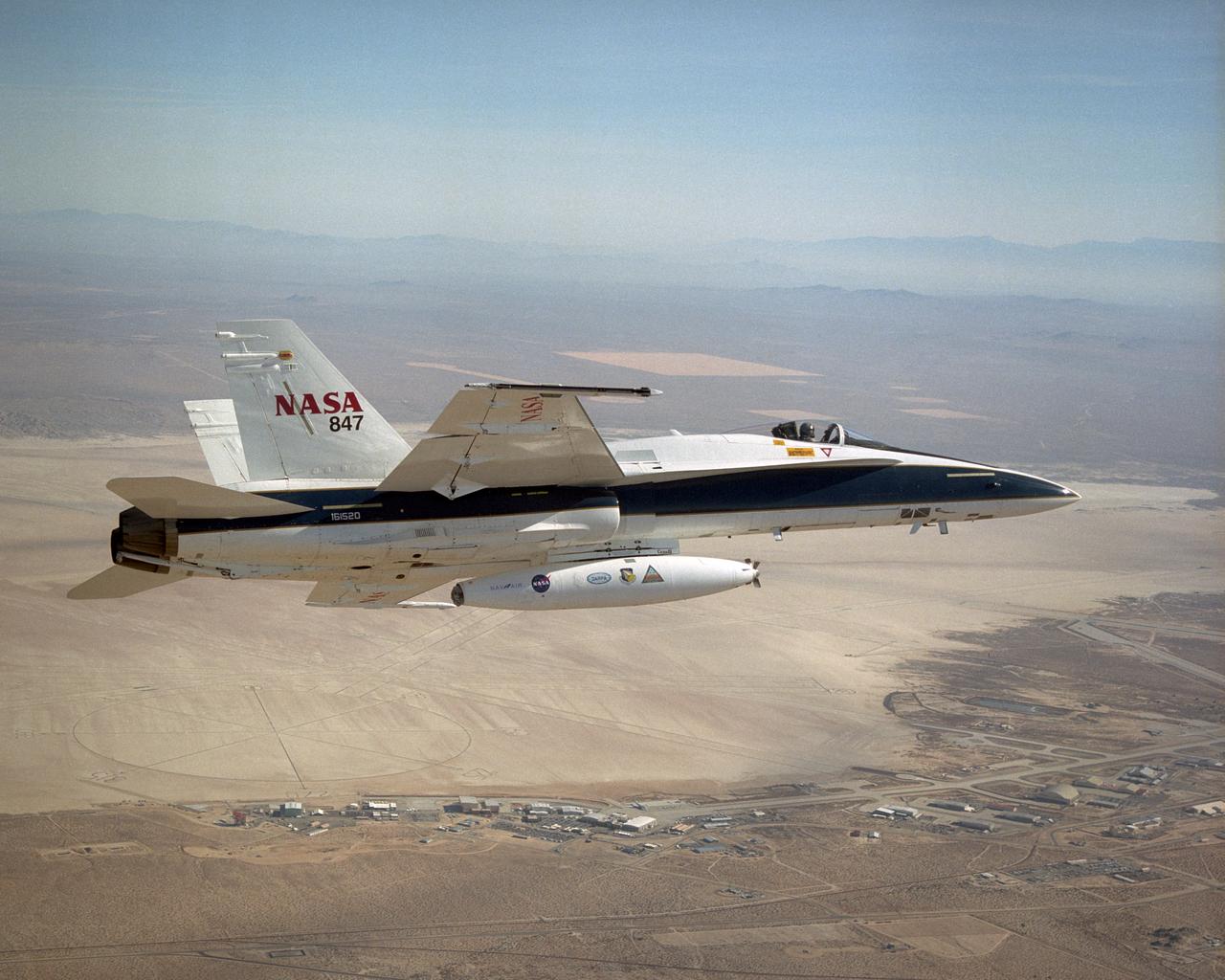

A NASA F/A-18 flies over the Dryden Flight Research Center and Rogers Dry Lake on December 11, 2002. The aircraft participated in the Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project. The 300-gallon aerial refueling store seen on the belly of the aircraft carries fuel and a refueling drogue. This aircraft acted as a tanker in the study to develop an aerodynamic model for future automated aerial refueling, especially of unmanned vehicles.
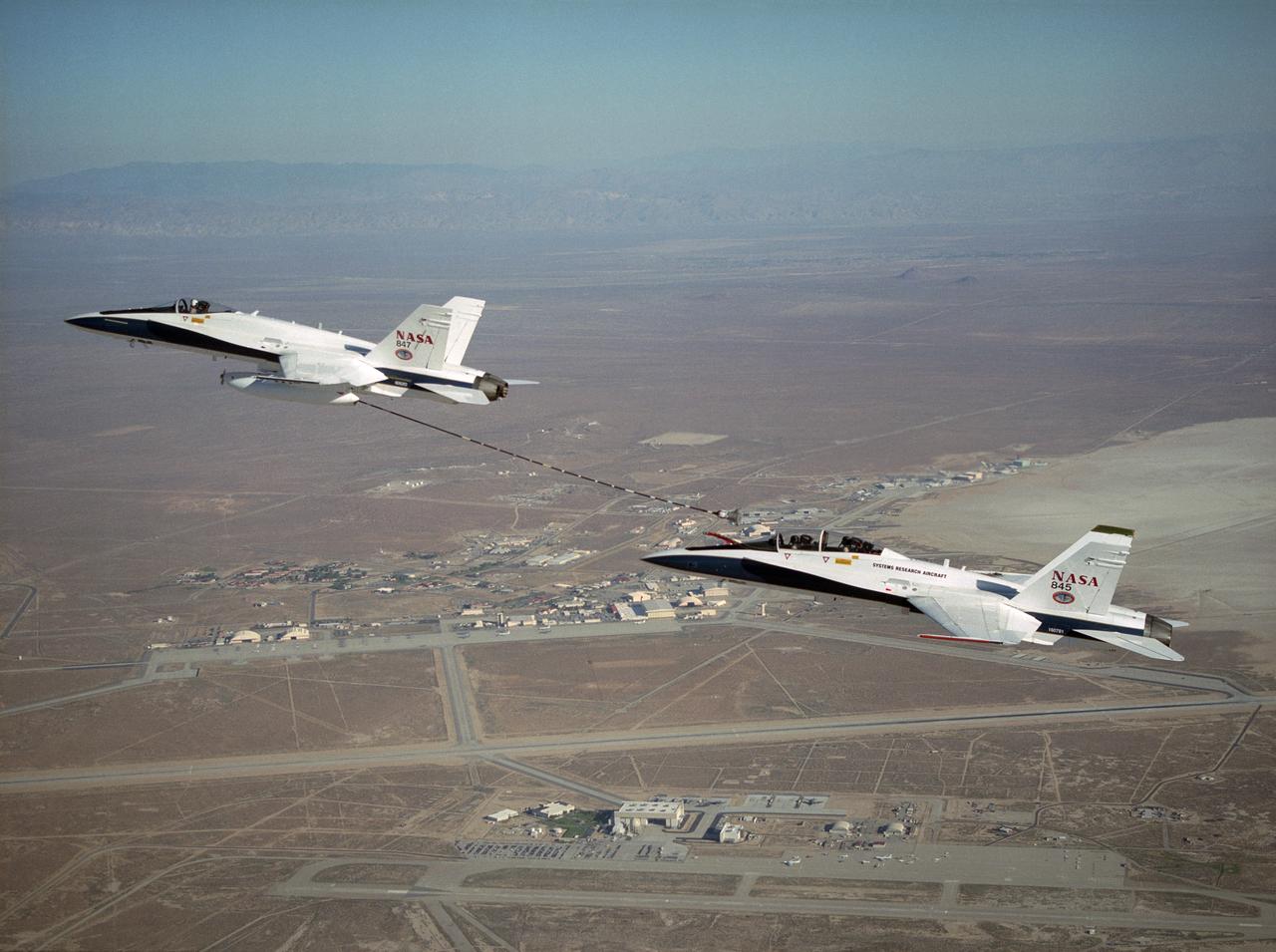

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
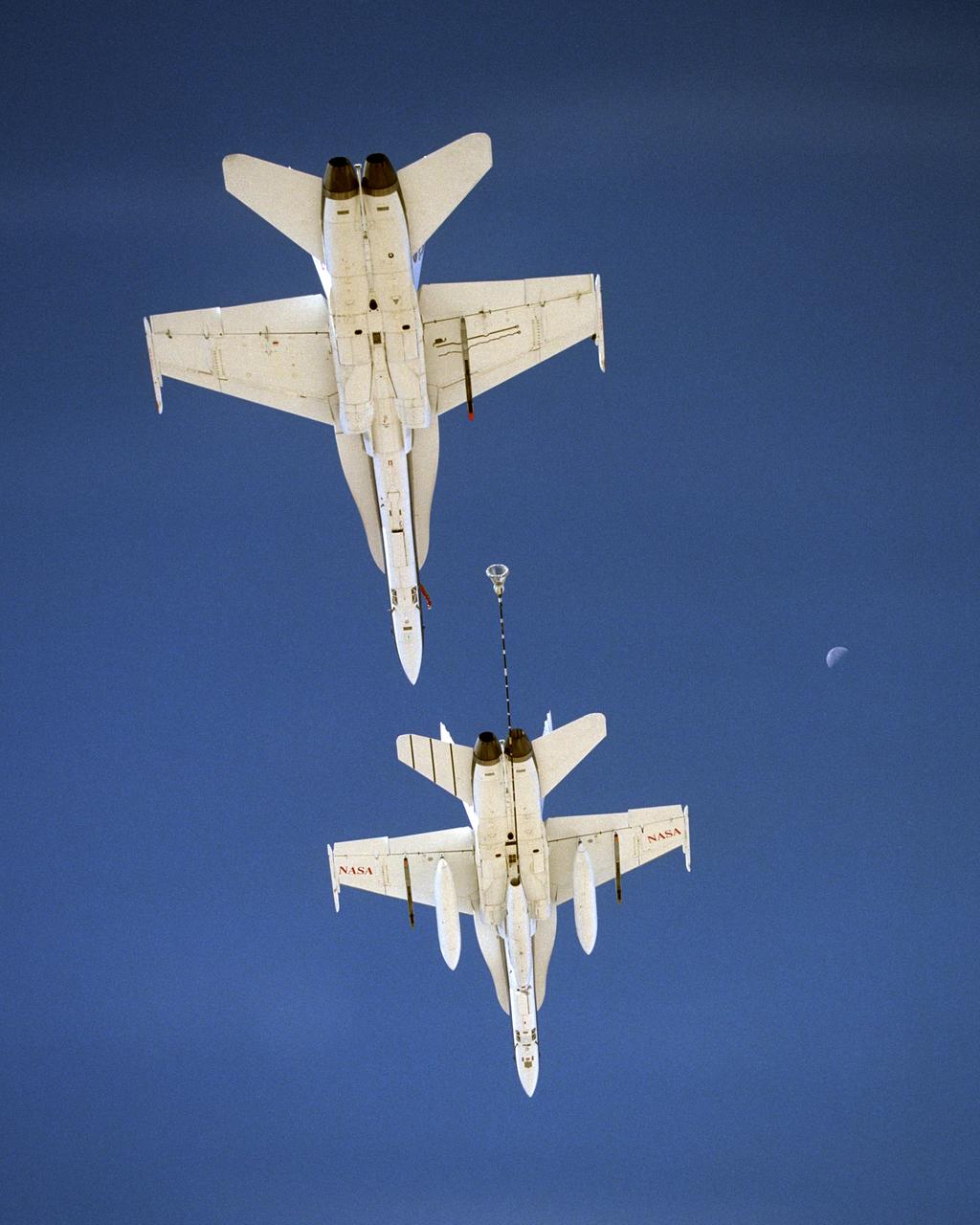

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.

A NASA F/A-18 flies over the Dryden Flight Research Center and Rogers Dry Lake on December 11, 2002. The aircraft participated in the Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project. The 300-gallon aerial refueling store seen on the belly of the aircraft carries fuel and a refueling drogue. This aircraft acted as a tanker in the study to develop an aerodynamic model for future automated aerial refueling, especially of unmanned vehicles.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module demonstration. Seen here speaking with media are Dewayne Washington from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland, moderator (left); Frank Cepollina, project manager with NASA's Satellite Servicing Capabilities Office and Mathieu Caron, Mission Operations manager with the Canadian Space Agency. Space shuttle Atlantis will fly the RRM on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Once in place the RRM will use the station's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre, to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. Atlantis and its crew of four are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the RRM and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
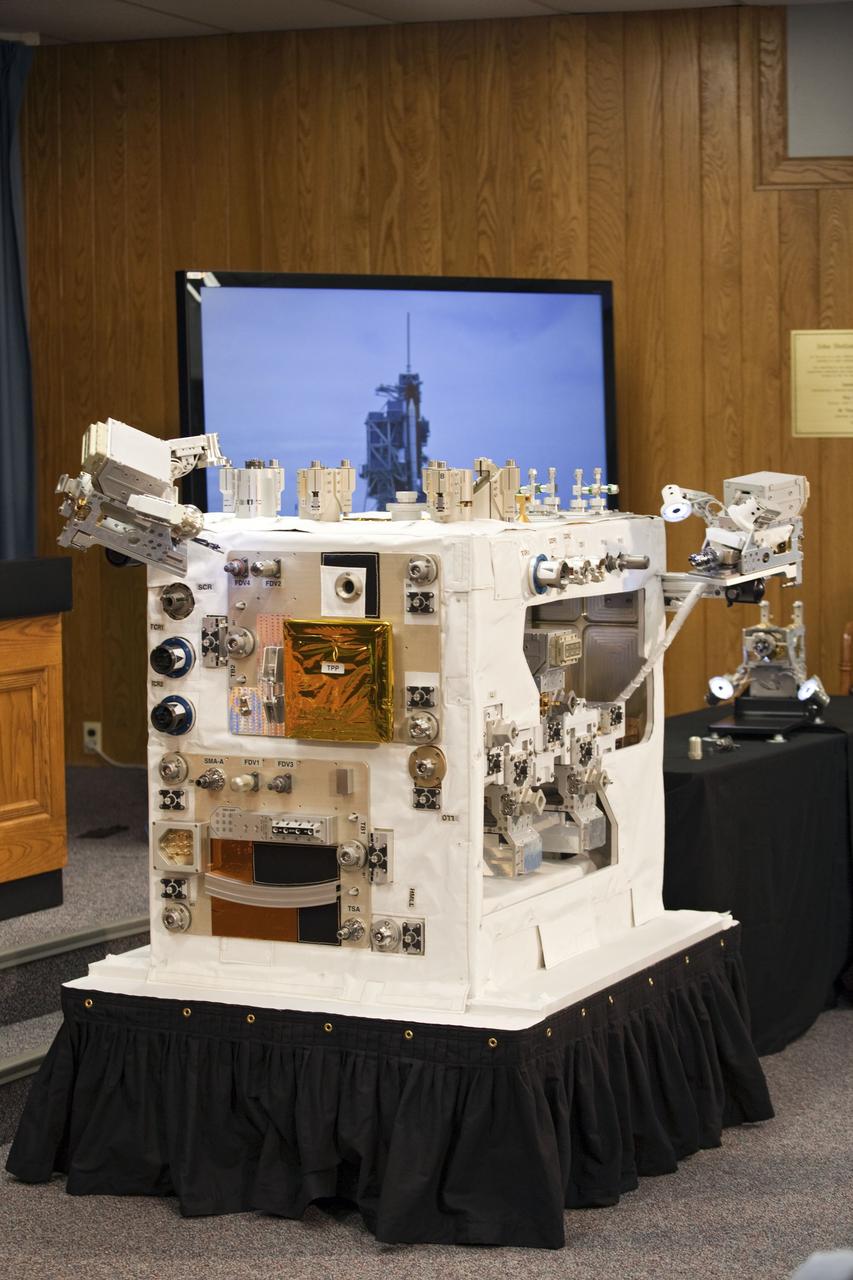

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module demonstration. Seen here is a demo version of the experiment that will fly on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Once in place, the RRM will use the station's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre, to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. Atlantis and its crew of four are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the RRM and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
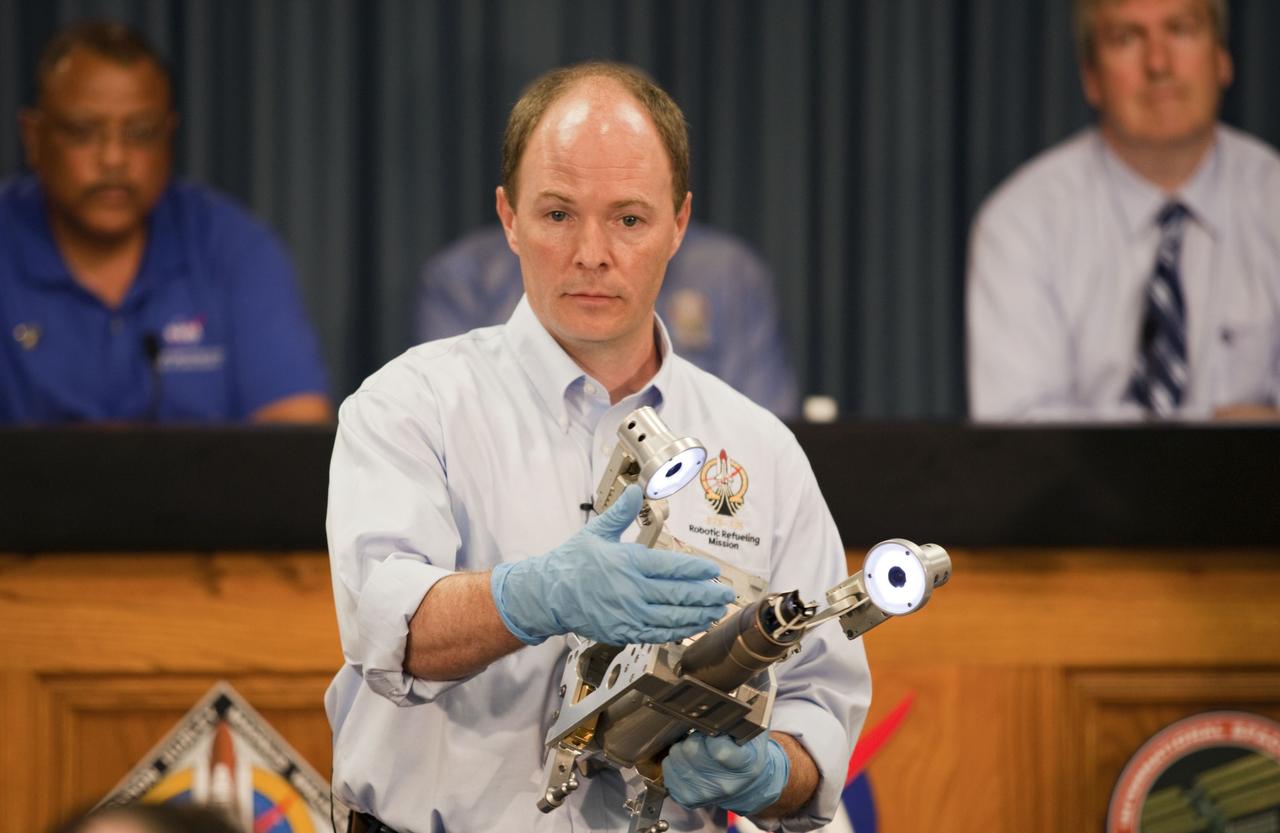

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module demonstration. Seen here is Benjamin Reed, deputy project manager with NASA's Satellite Servicing Capabilities Office, giving media an overview of the RRM. Space shuttle Atlantis will fly the RRM on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Once in place, the RRM will use the station's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre, to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. Atlantis and its crew of four are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the RRM and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
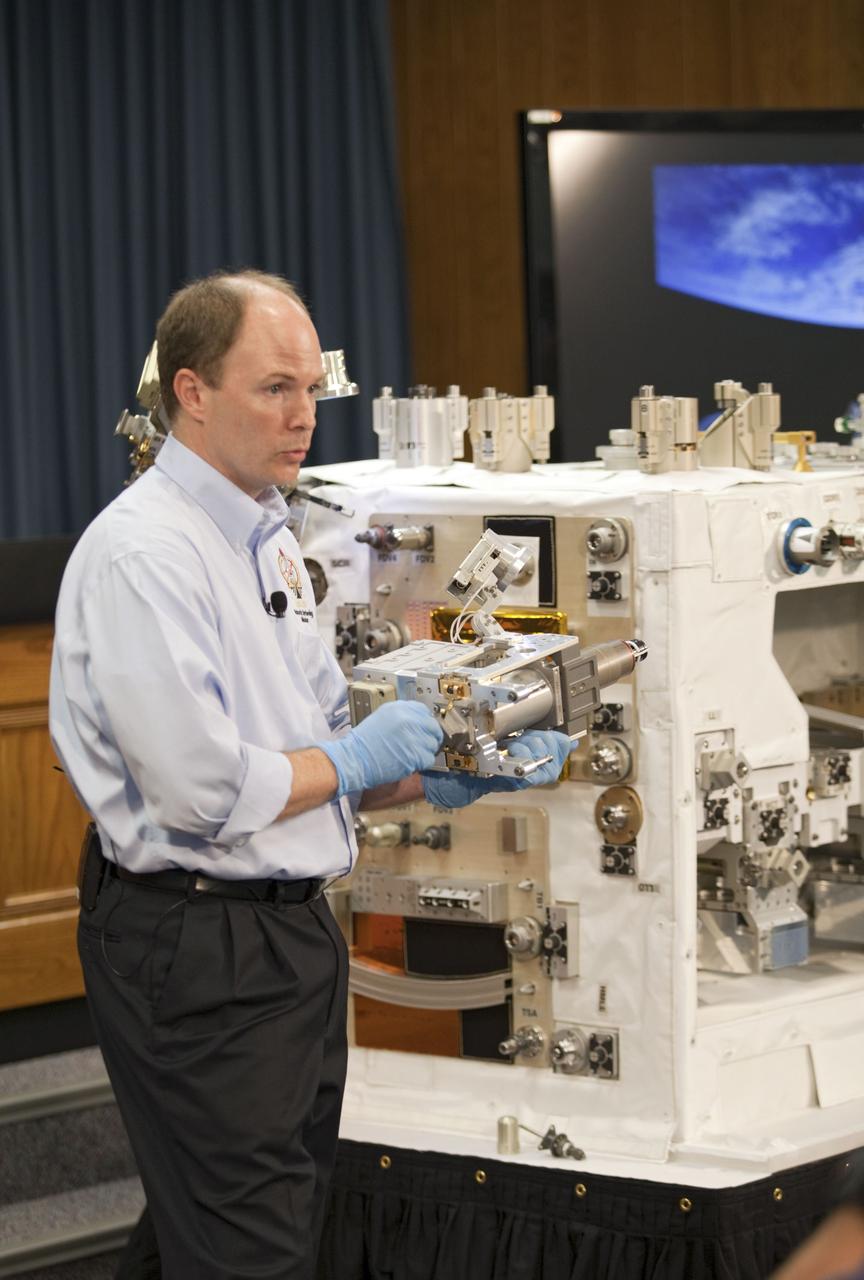

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module demonstration. Seen here is Benjamin Reed, deputy project manager with NASA's Satellite Servicing Capabilities Office, giving media an overview of the RRM. Space shuttle Atlantis will fly the RRM on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Once in place, the RRM will use the station's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre, to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. Atlantis and its crew of four are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the RRM and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
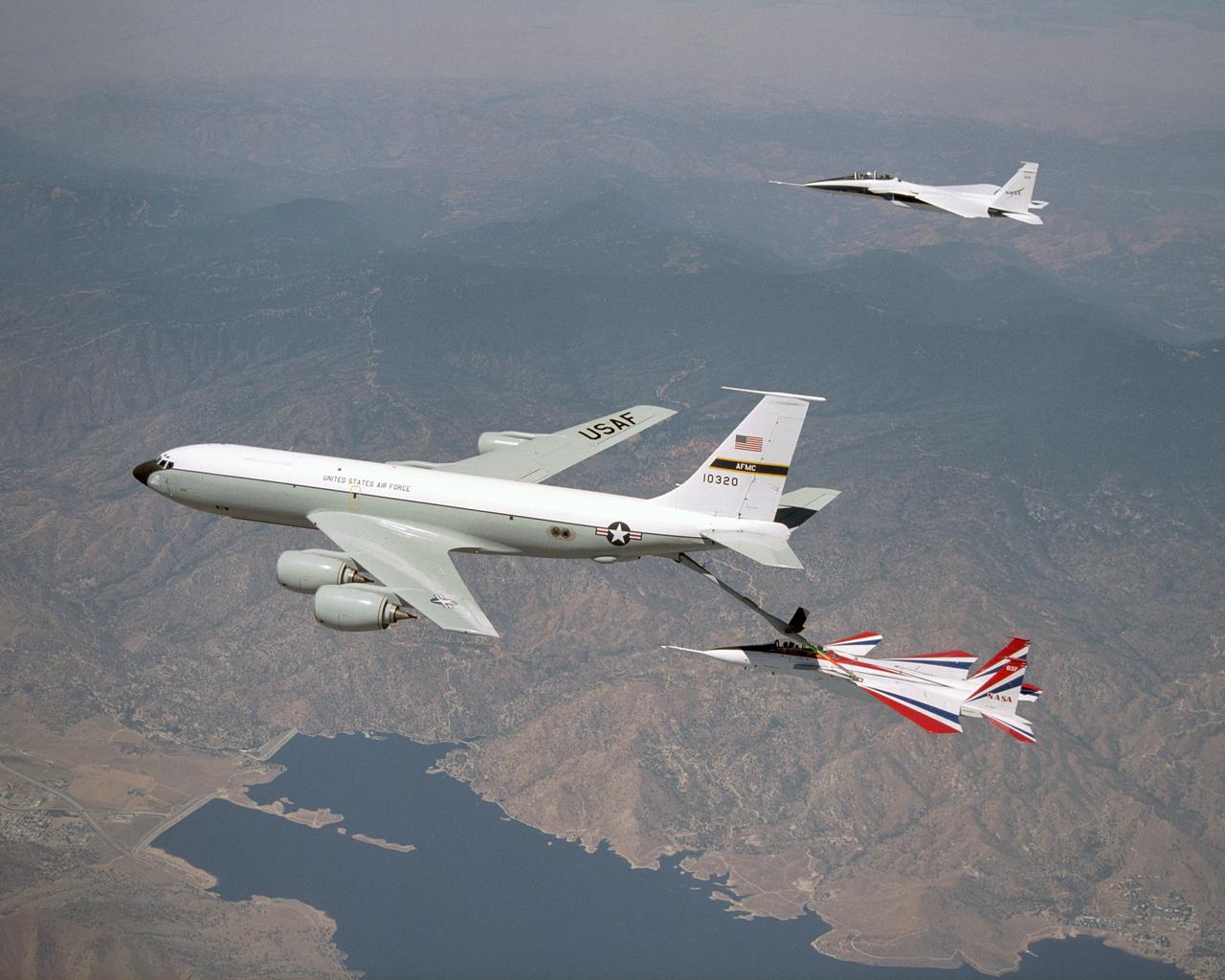

One of NASA's two F-15 research aircraft gets refueled in mid-air over Lake Isabella from a USAF KC-135 tanker while NASA's other F-15 flies chase alongside.
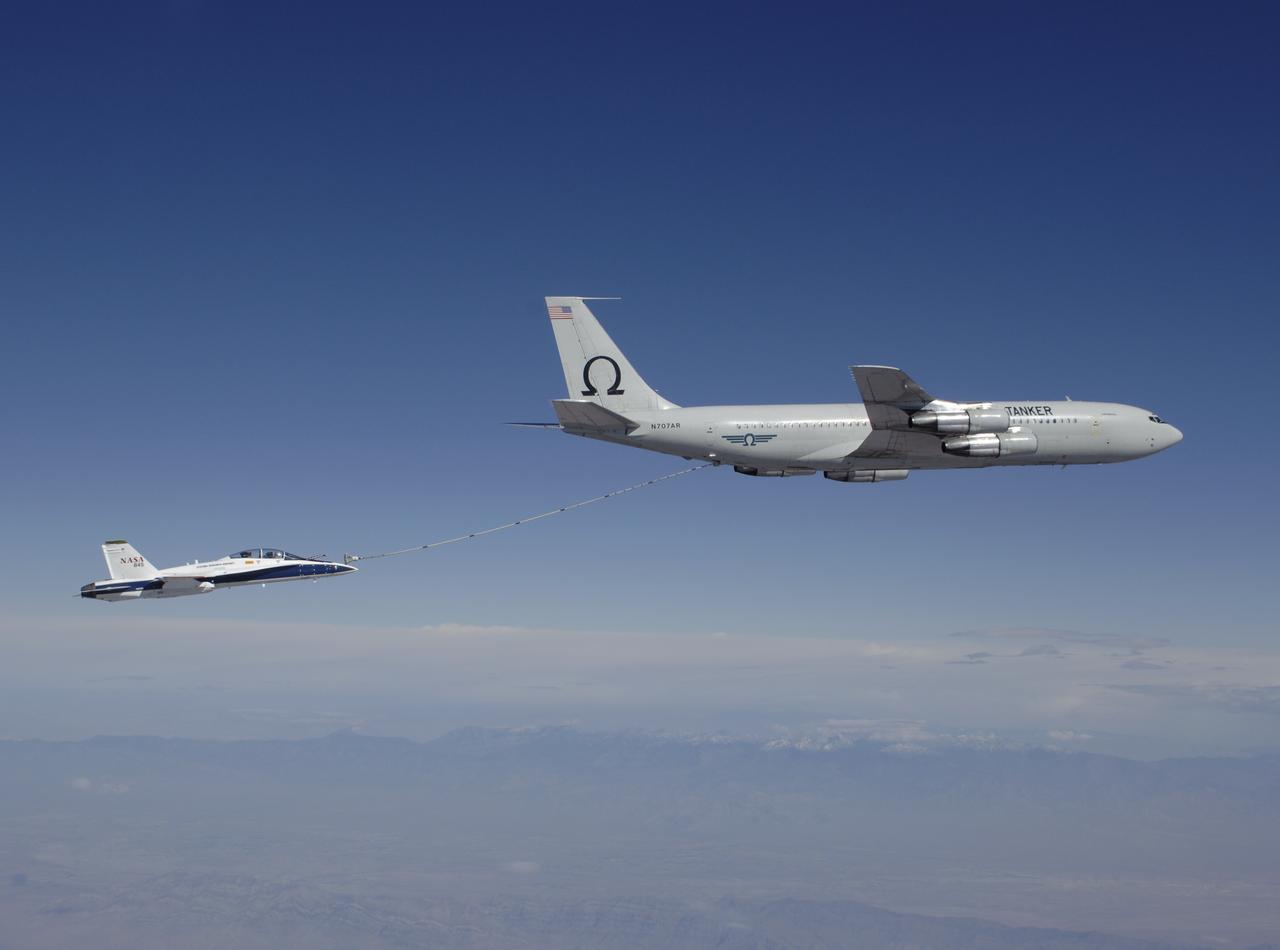

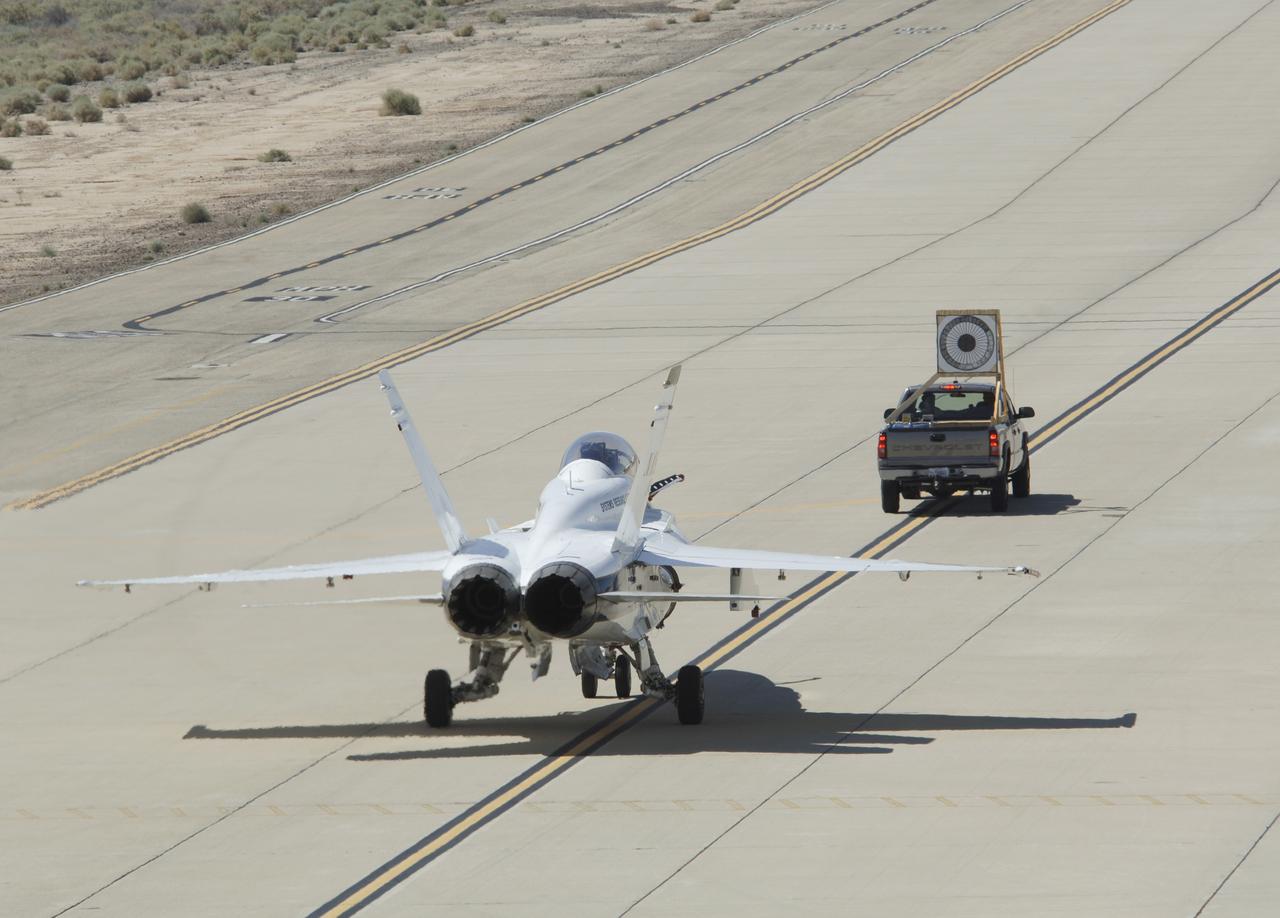
F/A-18 #845 behind an Omega Air Boeing 707 tanker during an Autonomous Airborne Refueling Demonstration (AARD) flight.
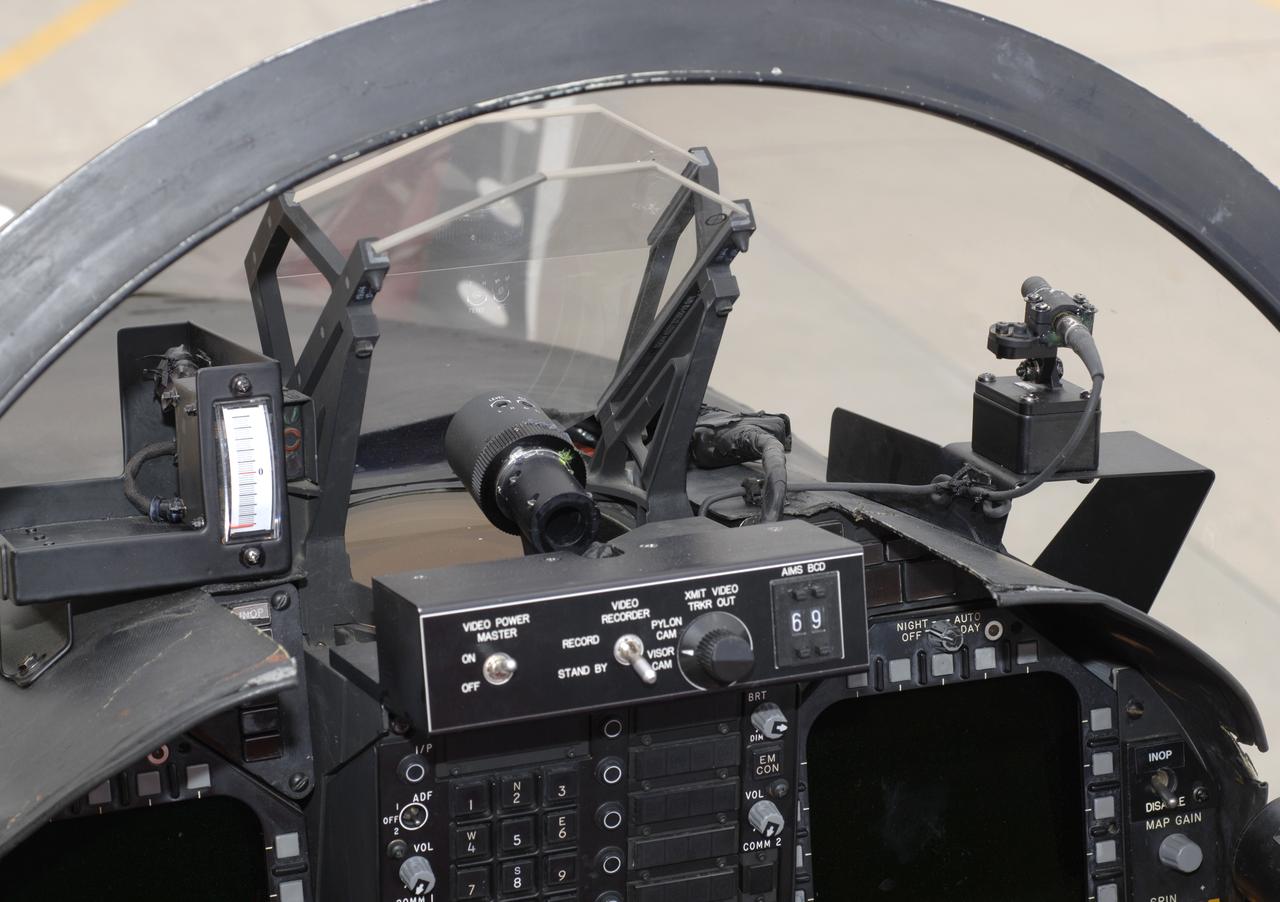

F/A-18 #845 HUD and video camera setup for Autonomous Airborne Refueling Demonstration (AARD) project
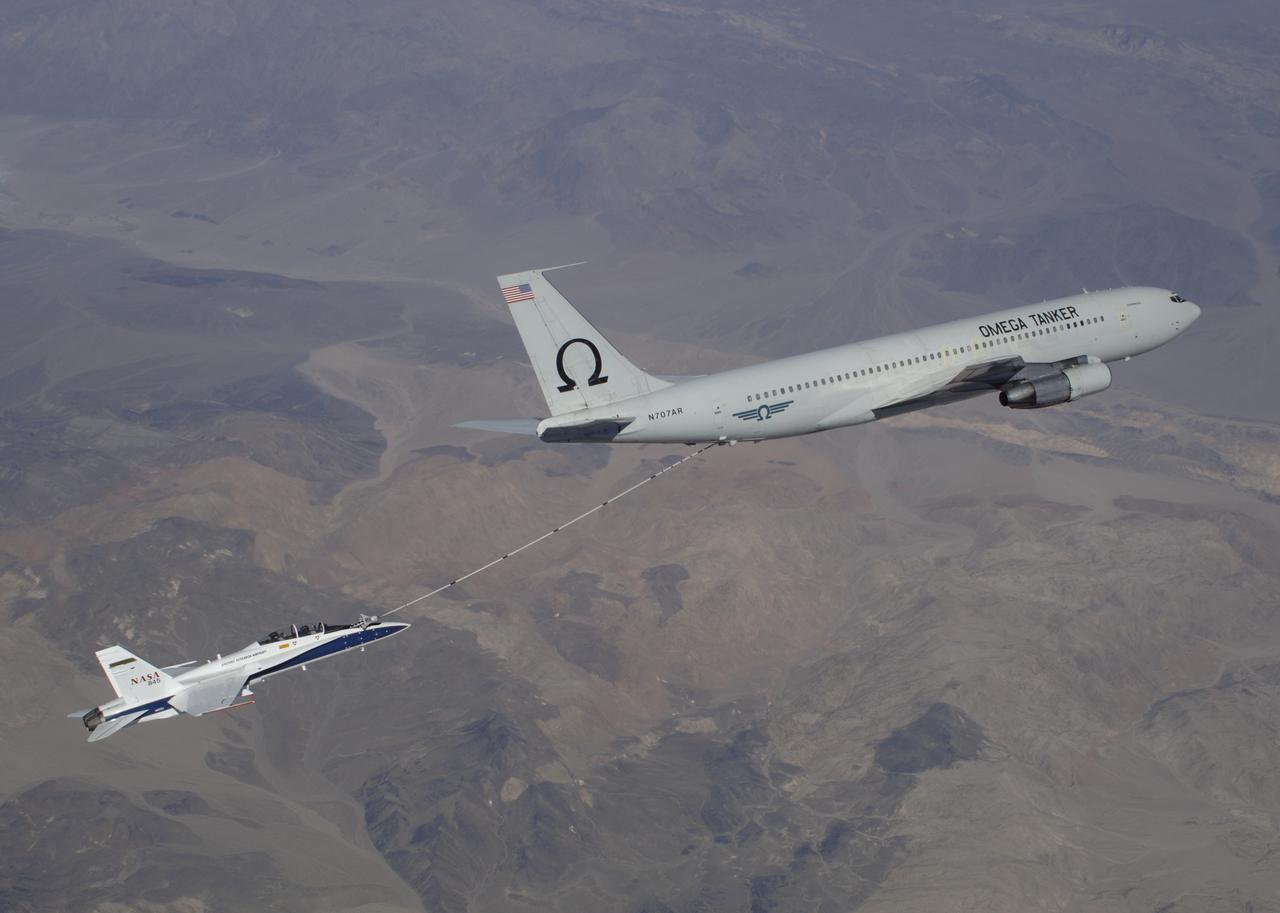

F/A-18 #845 behind an Omega Air Boeing 707 tanker during an Autonomous Airborne Refueling Demonstration (AARD) flight.
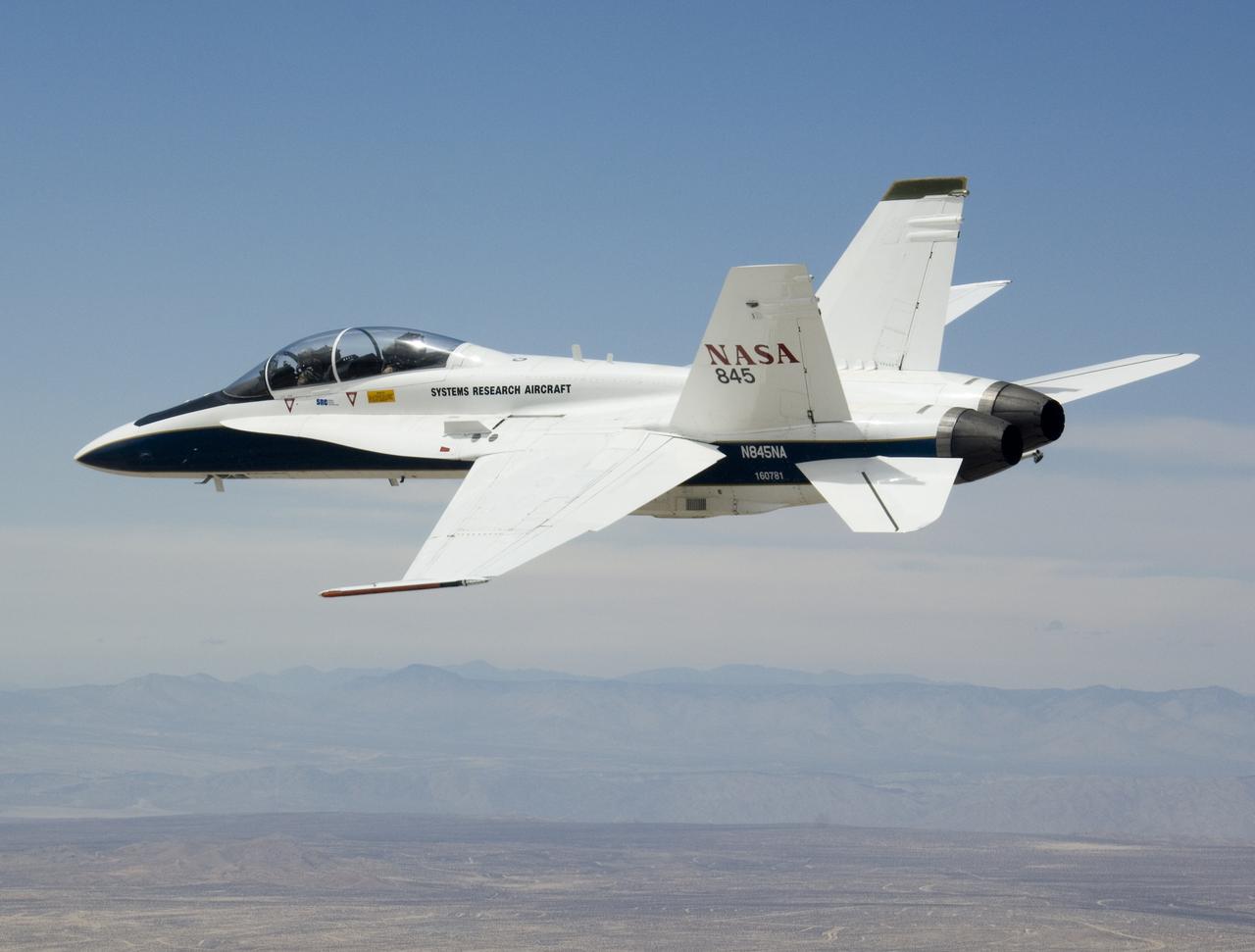

NASA's F/A-18B #845 was captured by the photographer as it returned from its final flight in the Autonomous Airborne Refueling Demonstration research project.
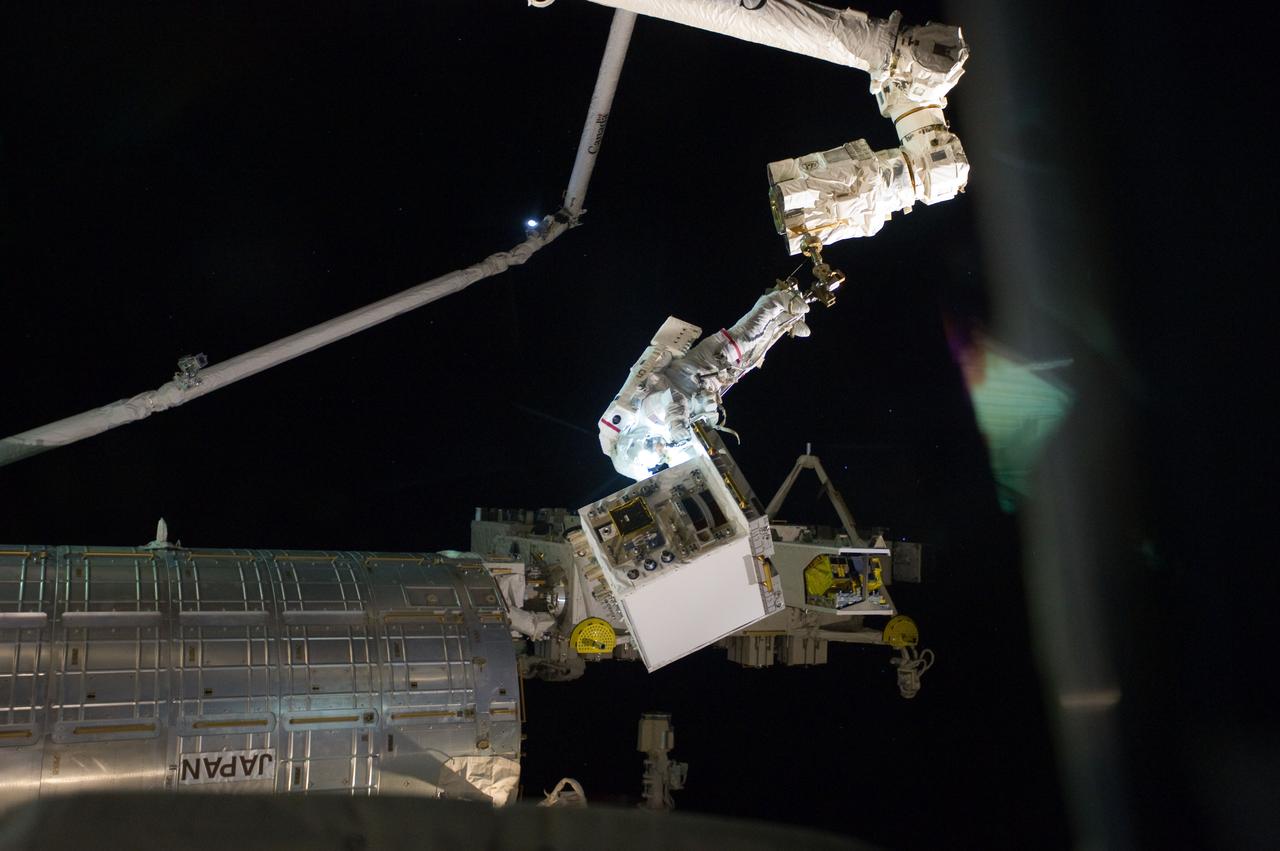

S135-E-007535 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system’s robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum, is holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. NASA astronaut Ron Garan, also a station flight engineer, who shared the spacewalk with Fossum, is out of frame. Photo credit: NASA
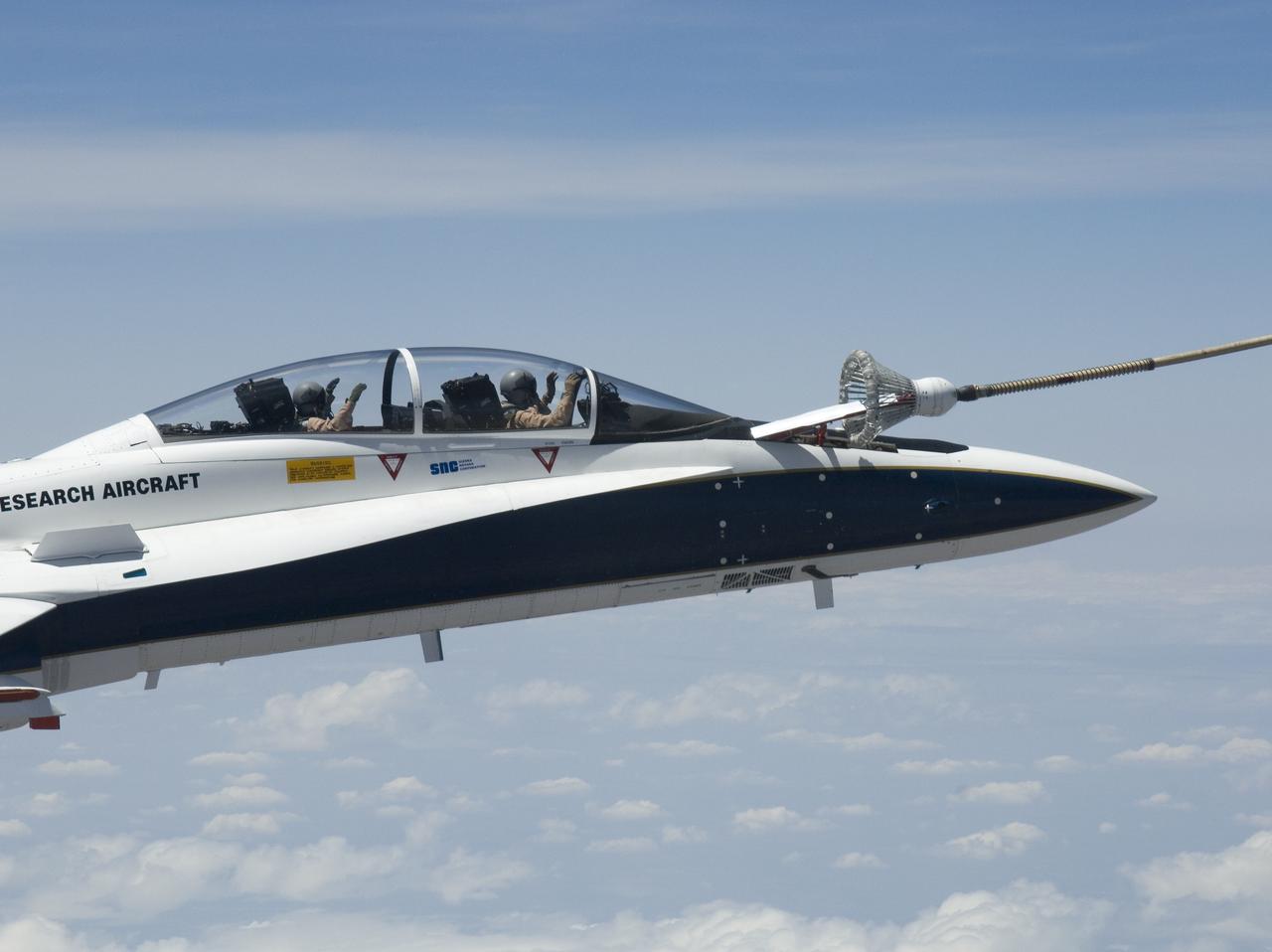

Pilot Dick Ewers and flight test engineer Leslie Molzahn were hands-off as NASA F/A-18 #845 flew itself into the drogue on an autonomous refueling demonstration.
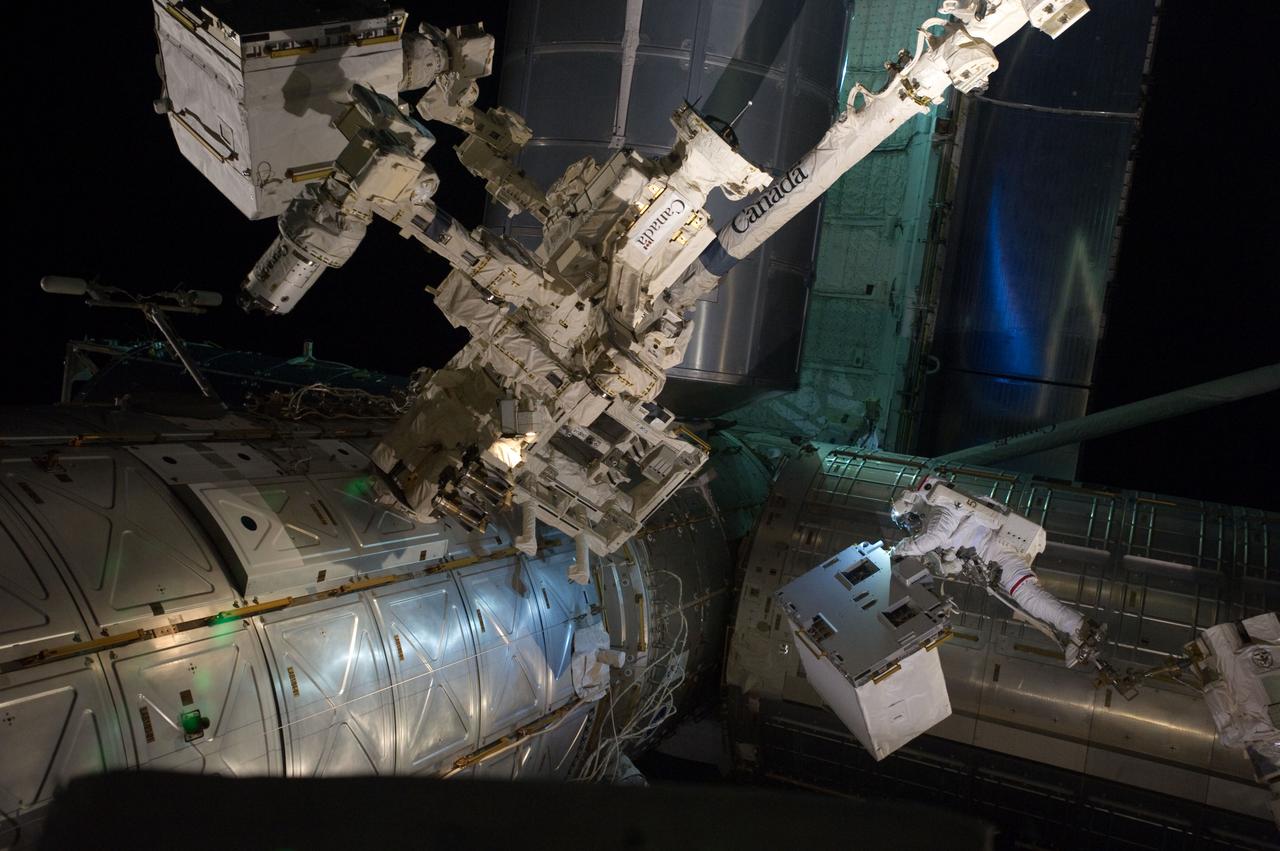

S135-E-007551 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system's robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum (lower right side of frame) holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. The failed pump module is with DEXTRE in the upper left corner of the photo. NASA astronauts Fossum and Ron Garan performed the six-hour, 31-minute spacewalk, which represents the final scheduled extravehicular activity during shuttle missions. Photo credit: NASA
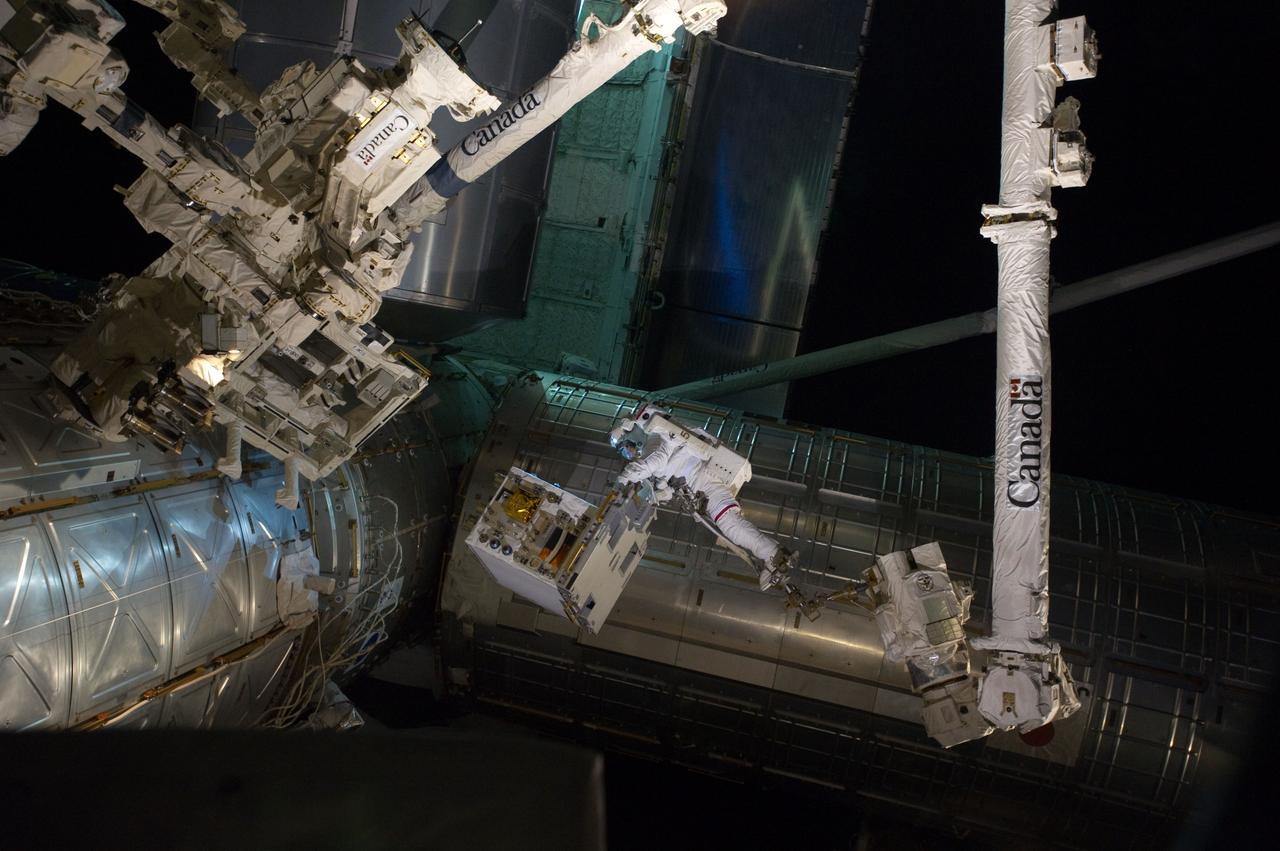

S135-E-007547 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system's robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum (frame center) holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. The failed pump module is with DEXTRE on left side of the photo. NASA astronauts Fossum and Ron Garan performed the six-hour, 31-minute spacewalk, which represents the final scheduled extravehicular activity during shuttle missions. Photo credit: NASA
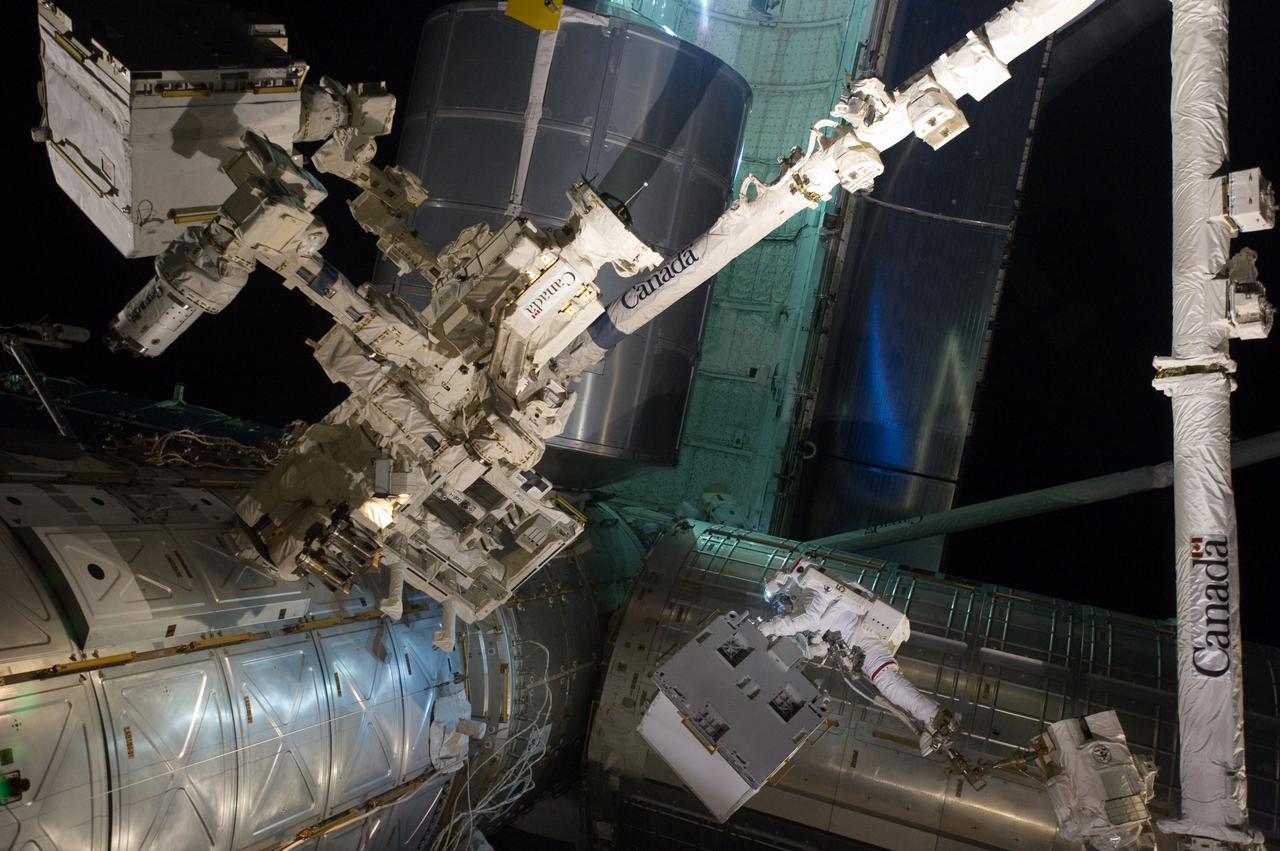
S135-E-007549 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system's robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum (lower right side of frame) holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. The failed pump module is with DEXTRE in the upper left corner of the photo. NASA astronauts Fossum and Ron Garan performed the six-hour, 31-minute spacewalk, which represents the final scheduled extravehicular activity during shuttle missions. Photo credit: NASA
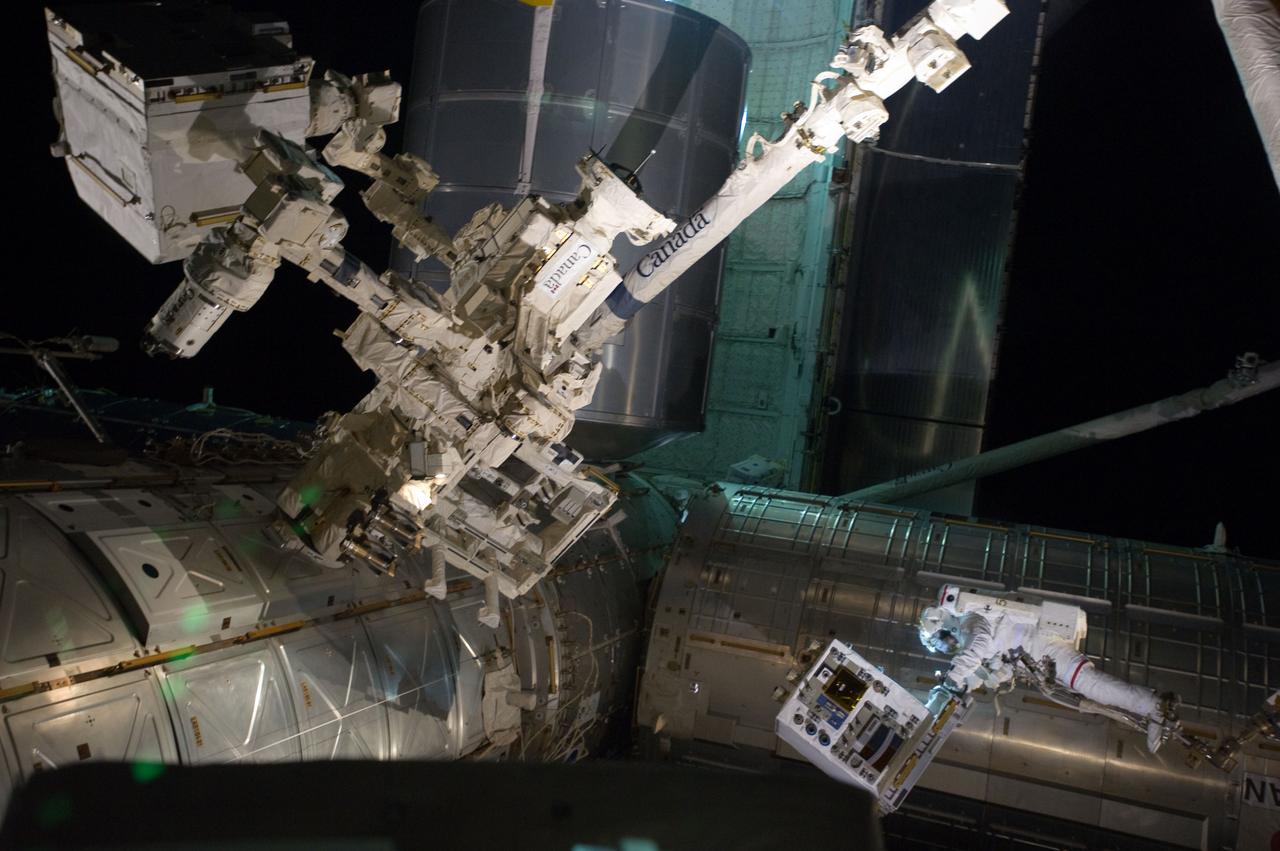

S135-E-007544 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system's robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum (lower right side of frame) holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. The failed pump module is with DEXTRE in the upper left corner of the photo. NASA astronauts Fossum and Ron Garan performed the six-hour, 31-minute spacewalk, which represents the final scheduled extravehicular activity during shuttle missions. Photo credit: NASA
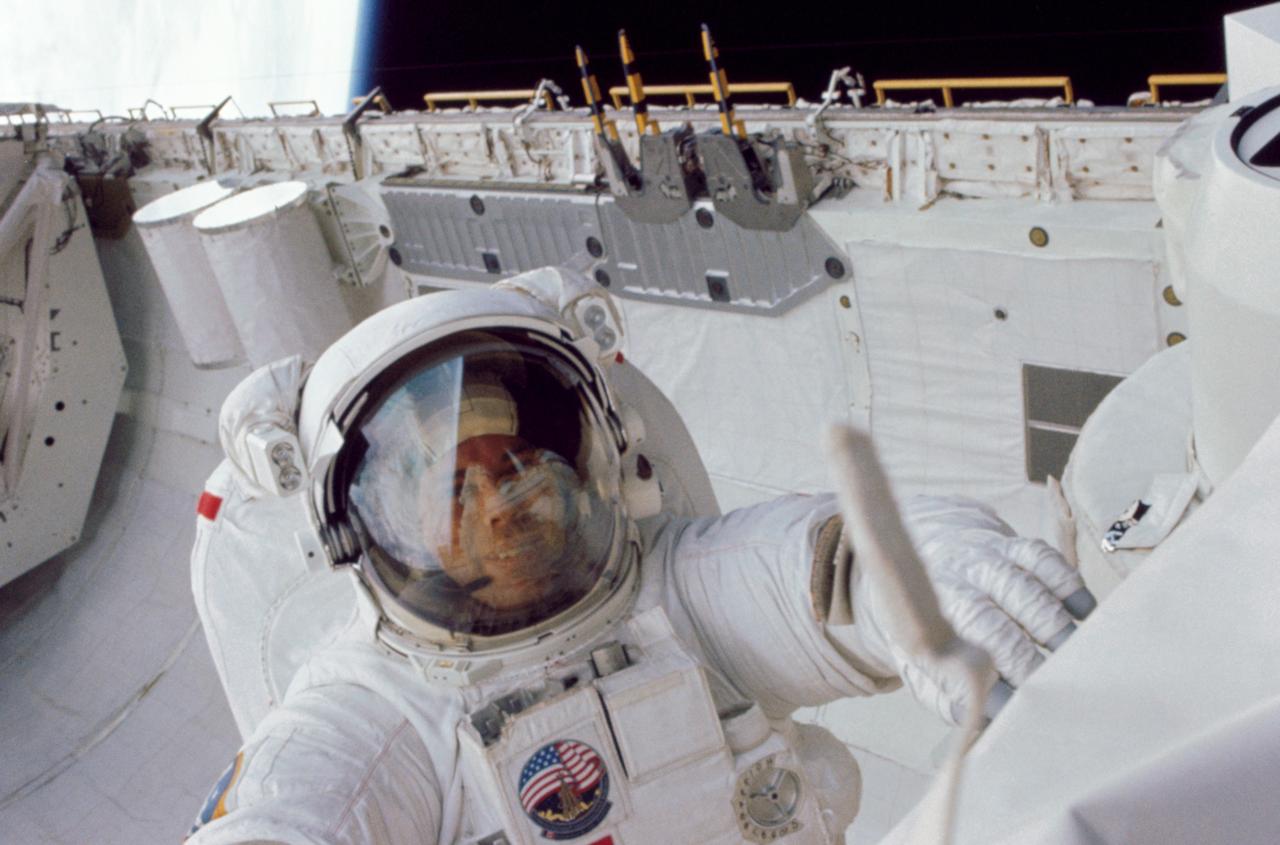

41G-101-014 (13 October 1984) --- Astronaut David C. Leestma, in a 35mm frame exposed by fellow mission specialist, Astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan, participates in extravehicular activity of Oct. 11 in the Challenger's aft cargo bay. Leestma's right hand (out of frame) was inside a special work station called the orbital refueling system (ORS).
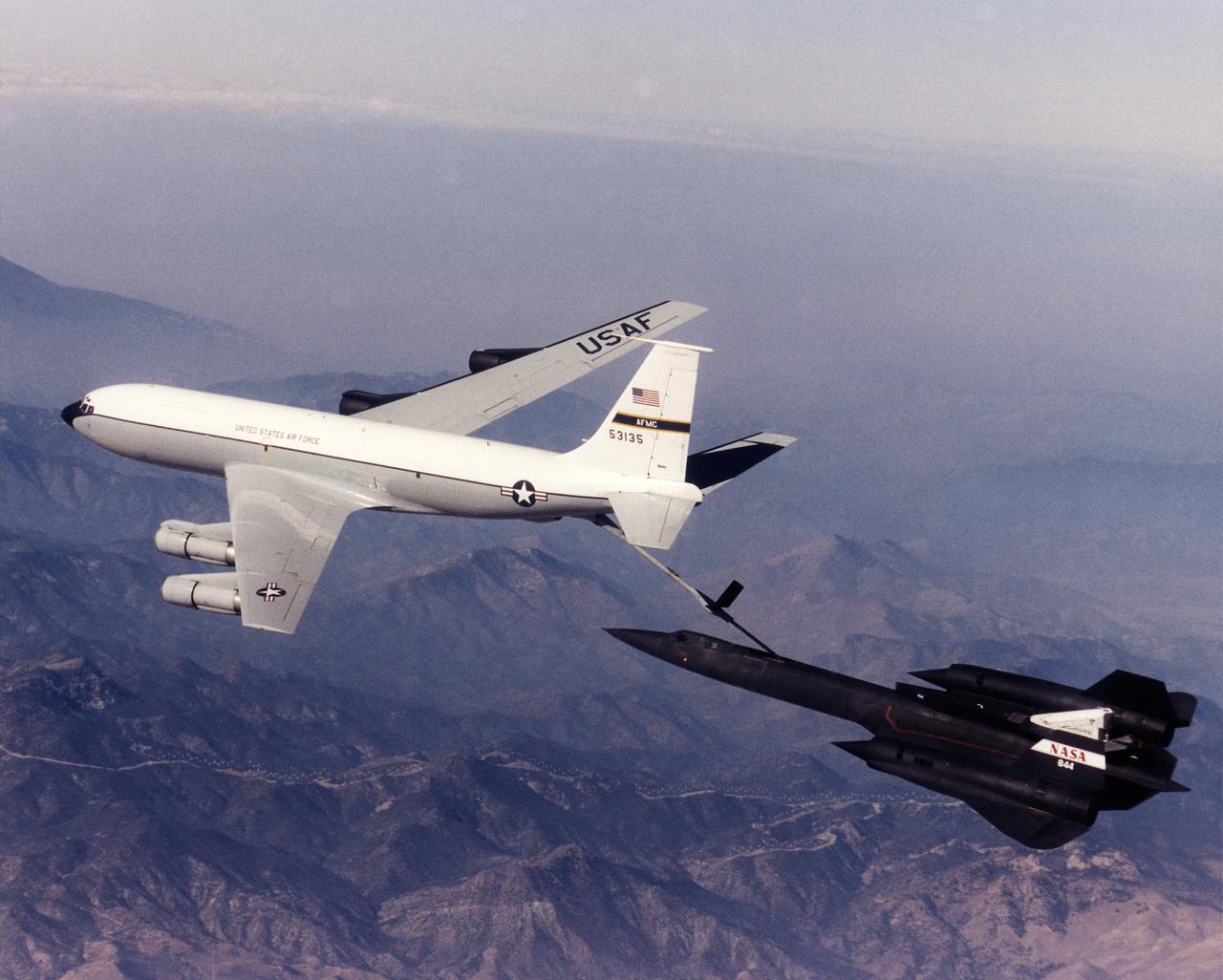

A NASA SR-71 refuels with an Edwards Air Force Base KC-135 during the first flight of the NASA/Rocketdyne/ Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE). The flight took place Oct. 31 at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
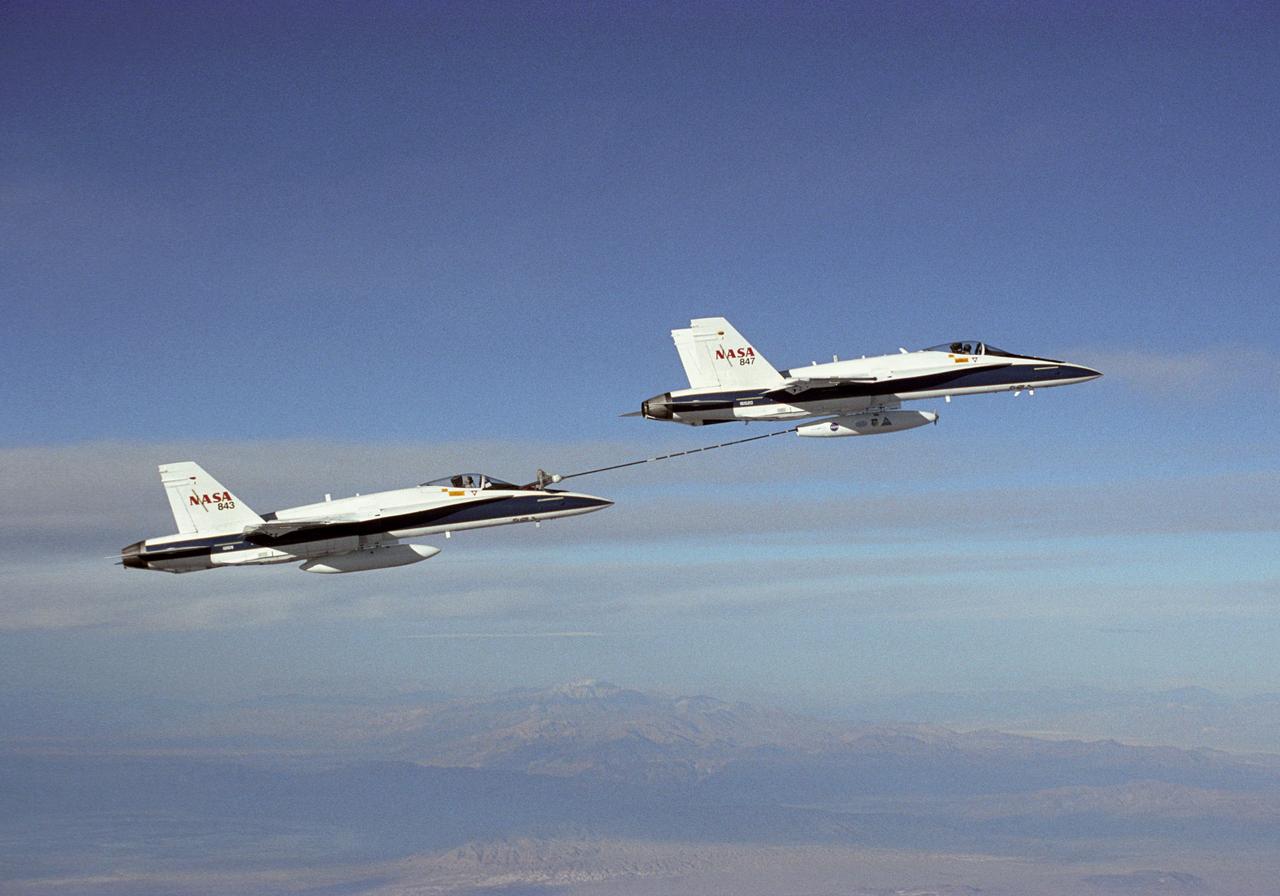

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
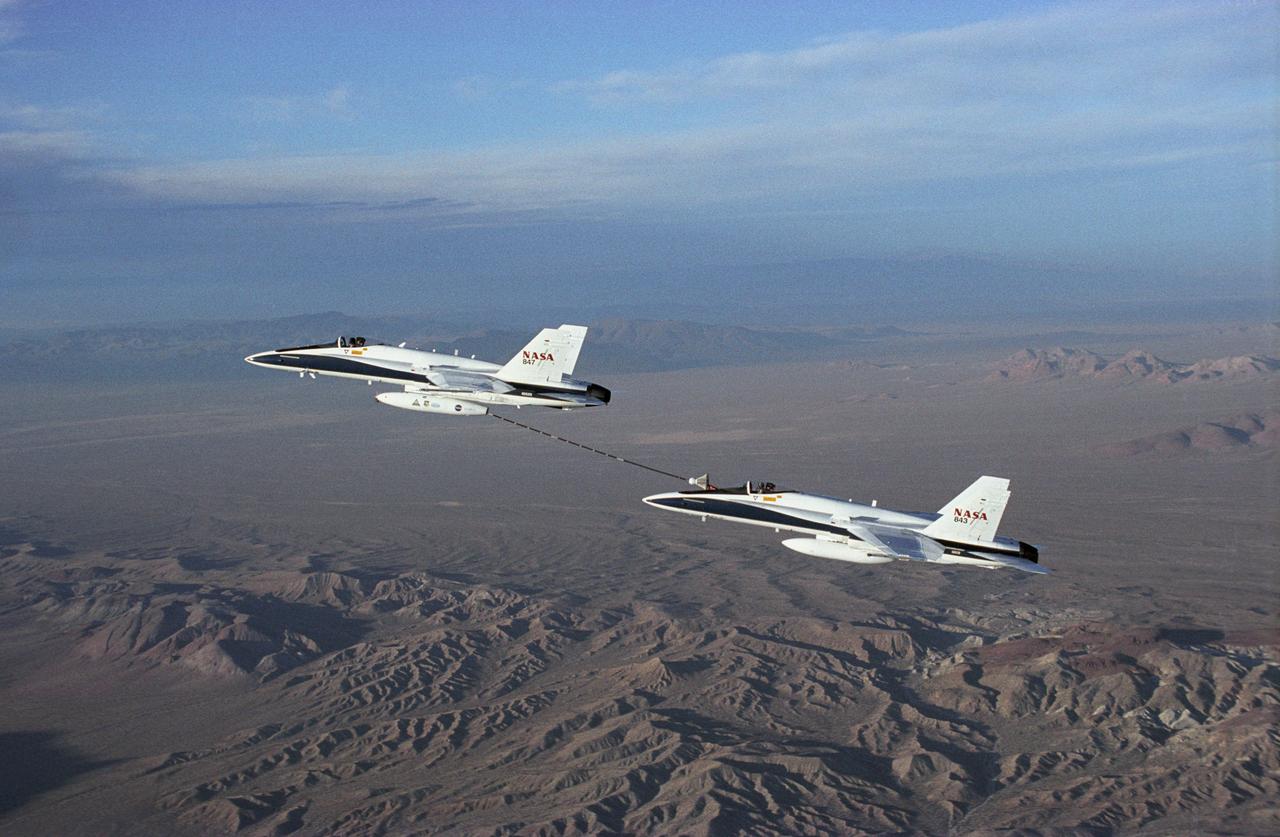

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
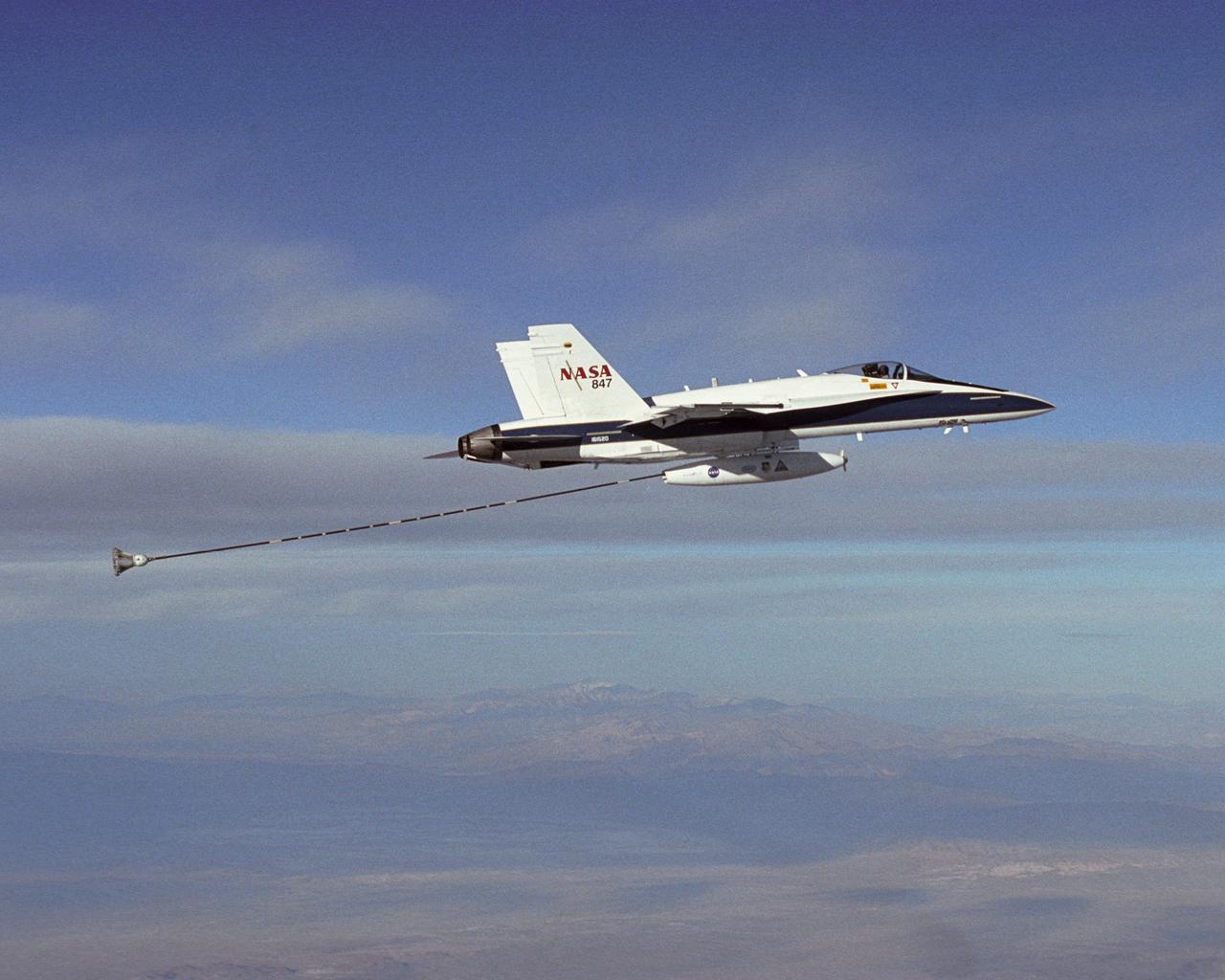

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
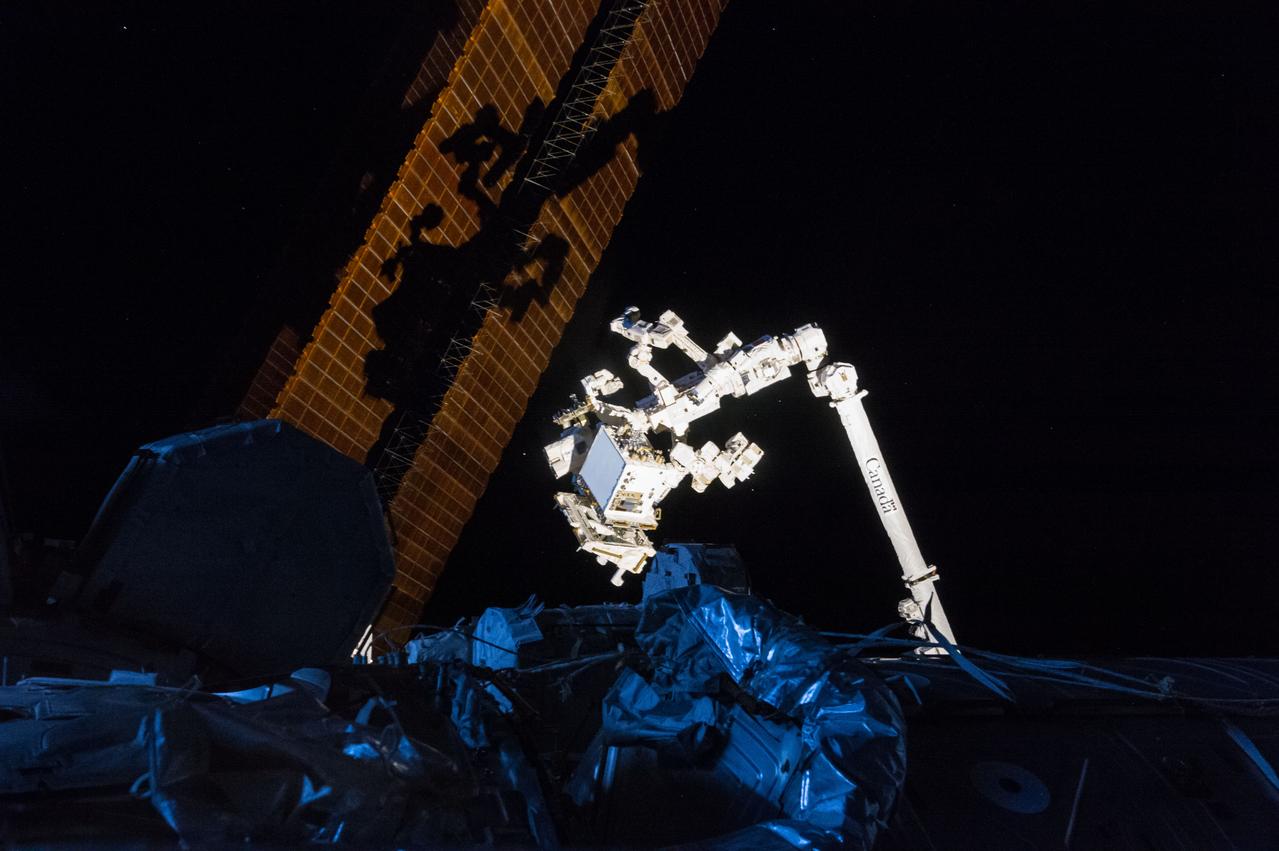

iss050e056301 (3/8/2017) --- A view of the Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS) during Robotic Refueling Mission-Phase 2 (RRM-P2) operations. NASA's Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) is an external International Space Station (ISS) investigation that demonstrates and tests the tools, technologies and techniques needed to robotically refuel, repair, and upgrade satellites in space, especially satellites that were not designed to be serviced. A joint effort between NASA and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), RRM is the first in-orbit attempt to test robotic refueling and servicing techniques for spacecraft not built with in-orbit servicing in mind.
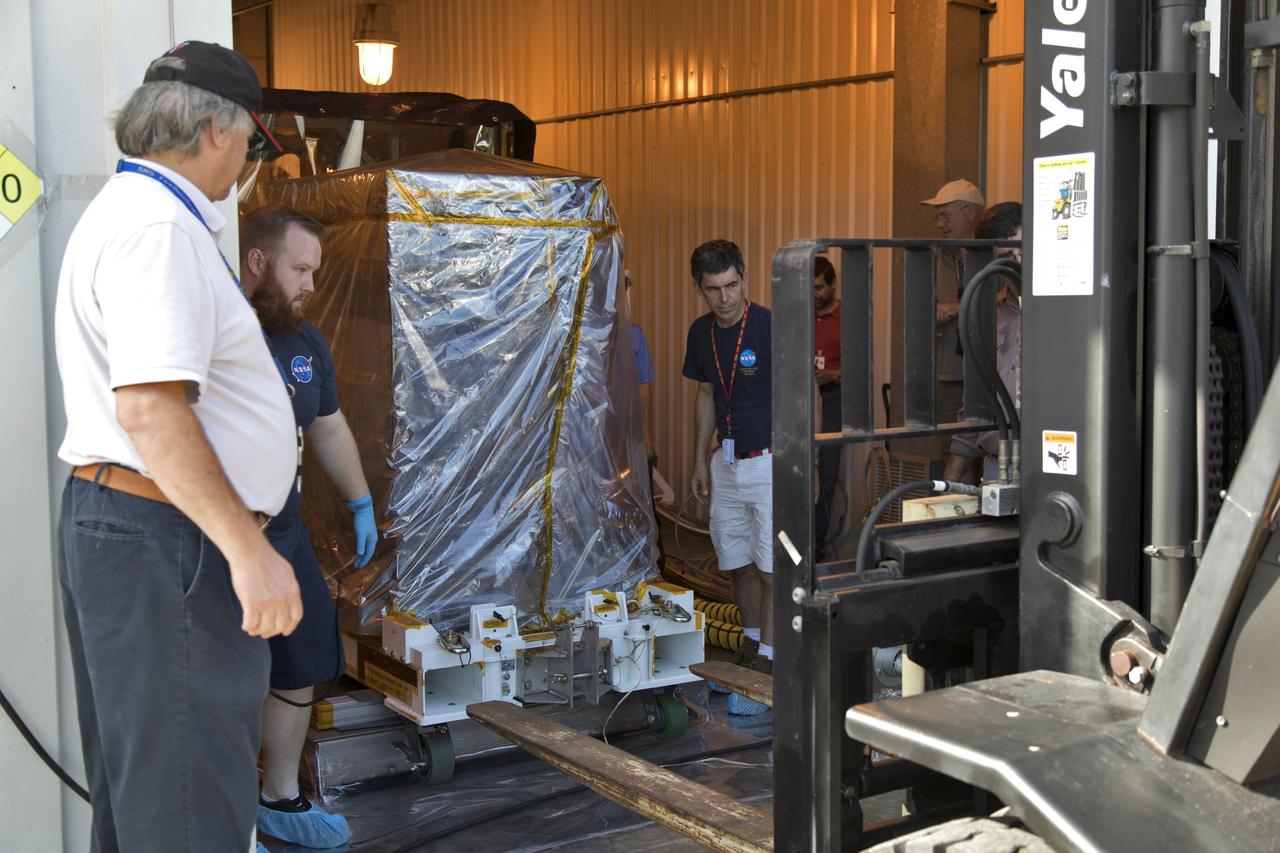

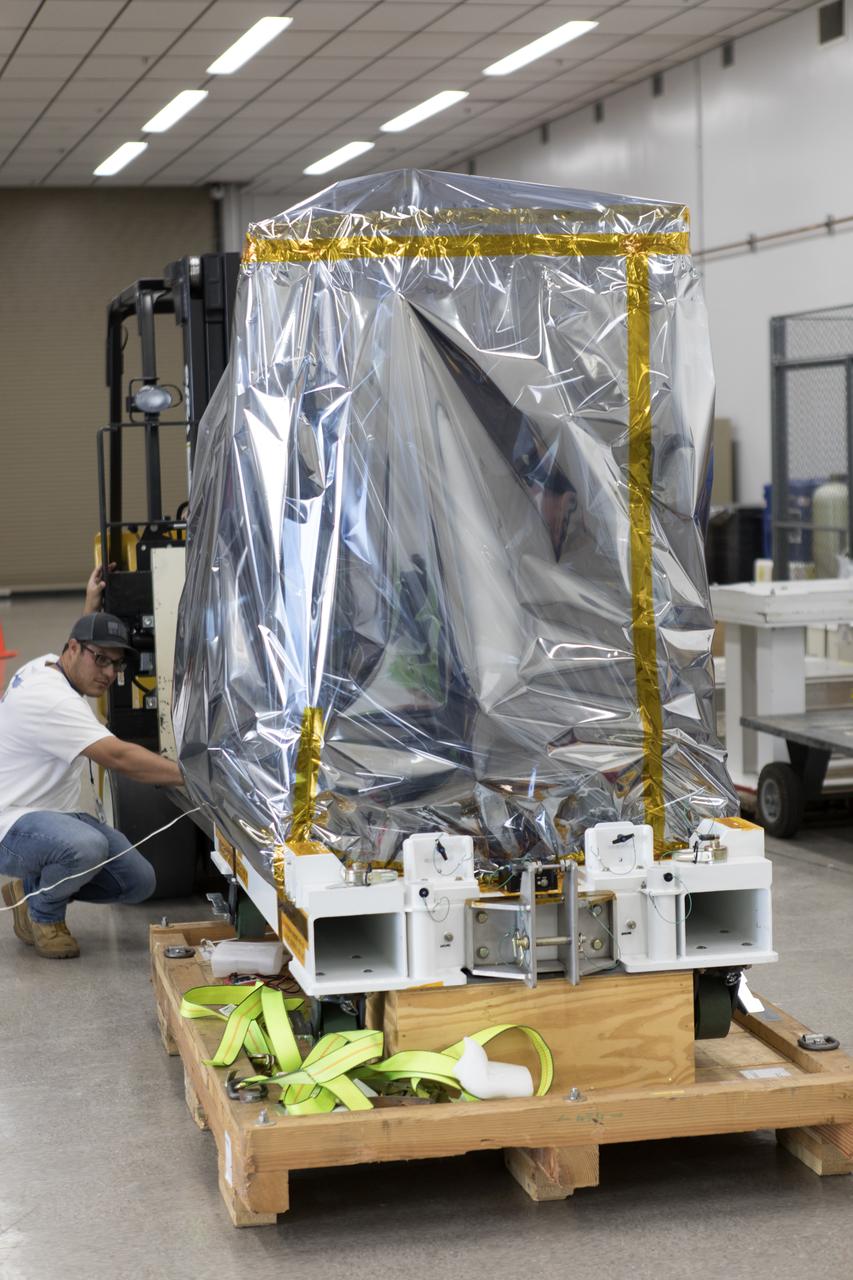
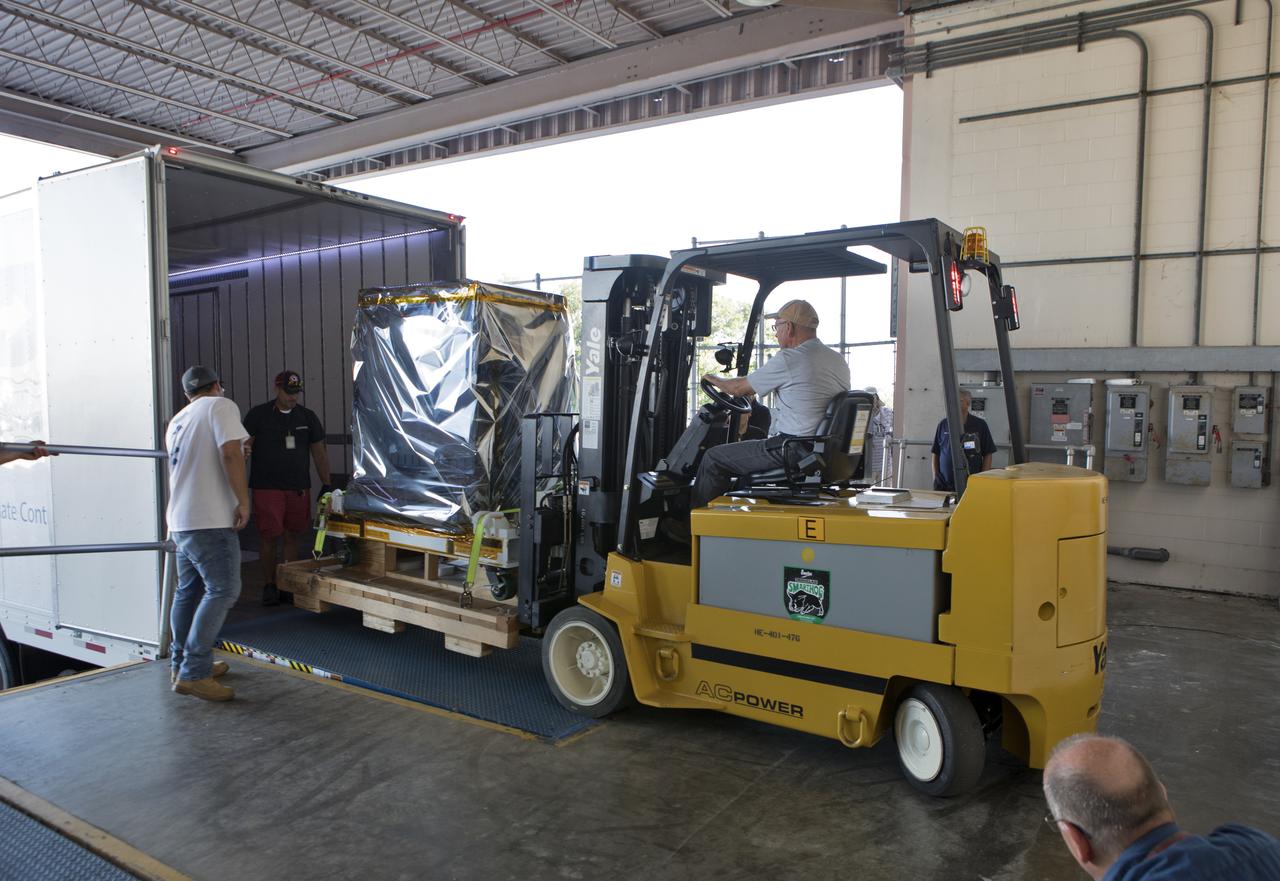
The Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload is unloaded from a forklift inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
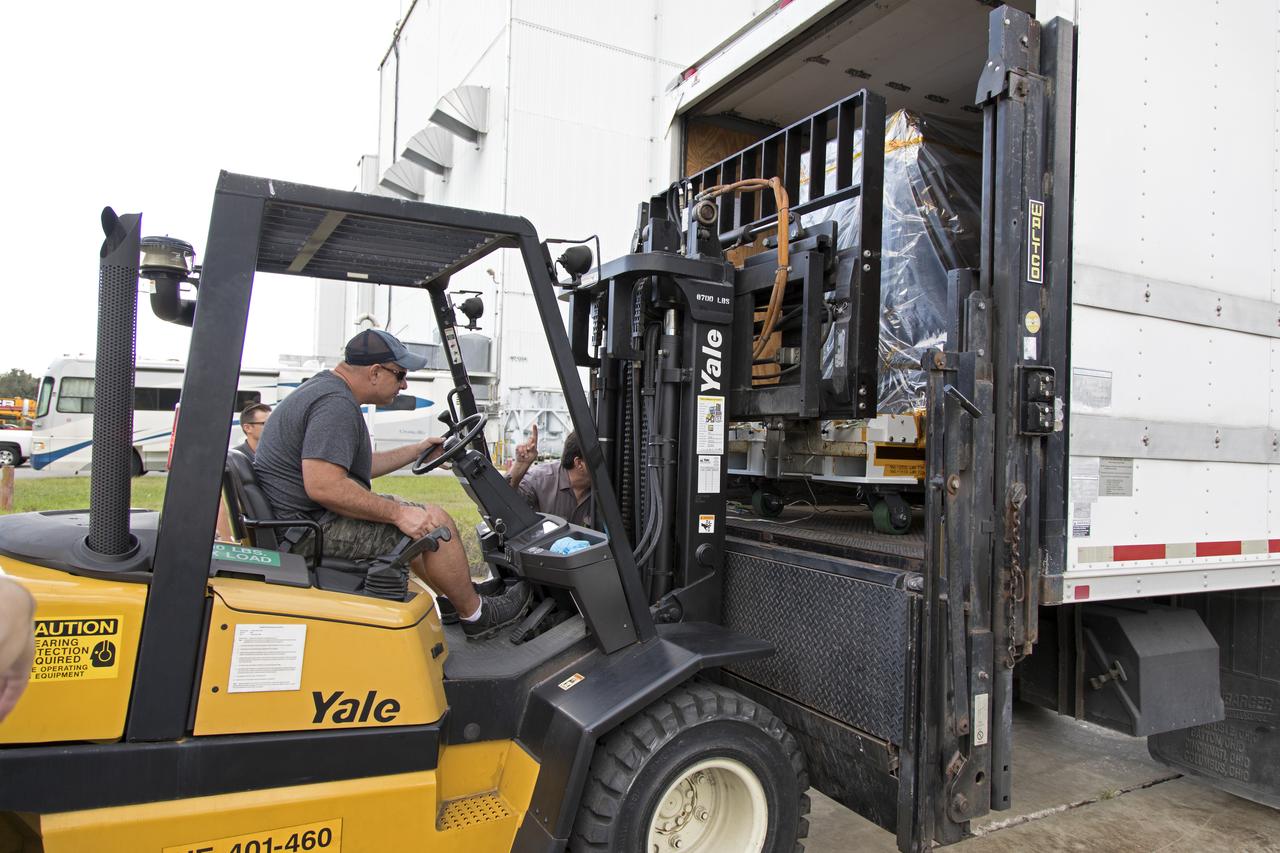

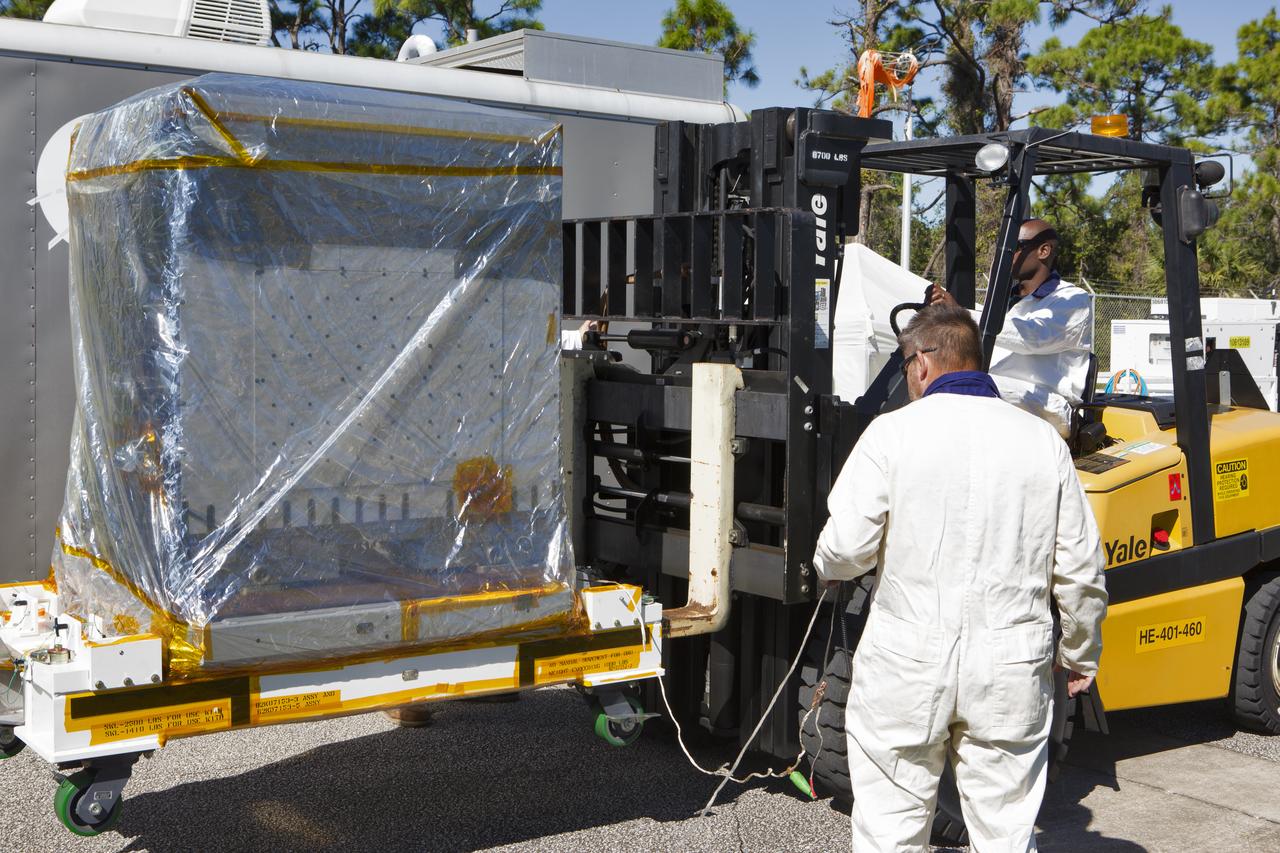
A worker uses a forklift to unload the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload from a truck at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

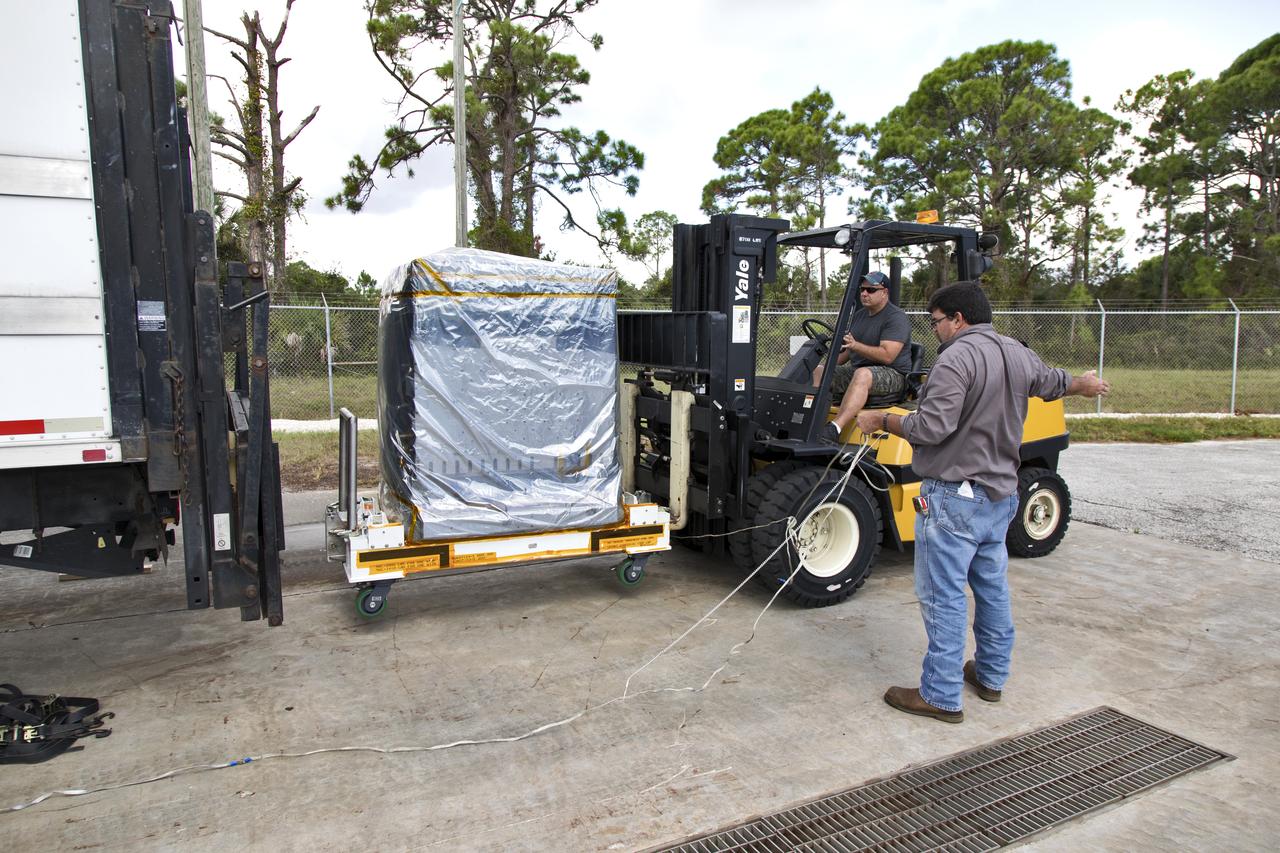
The Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload is being prepared to be moved from the Fuel Transfer Building to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

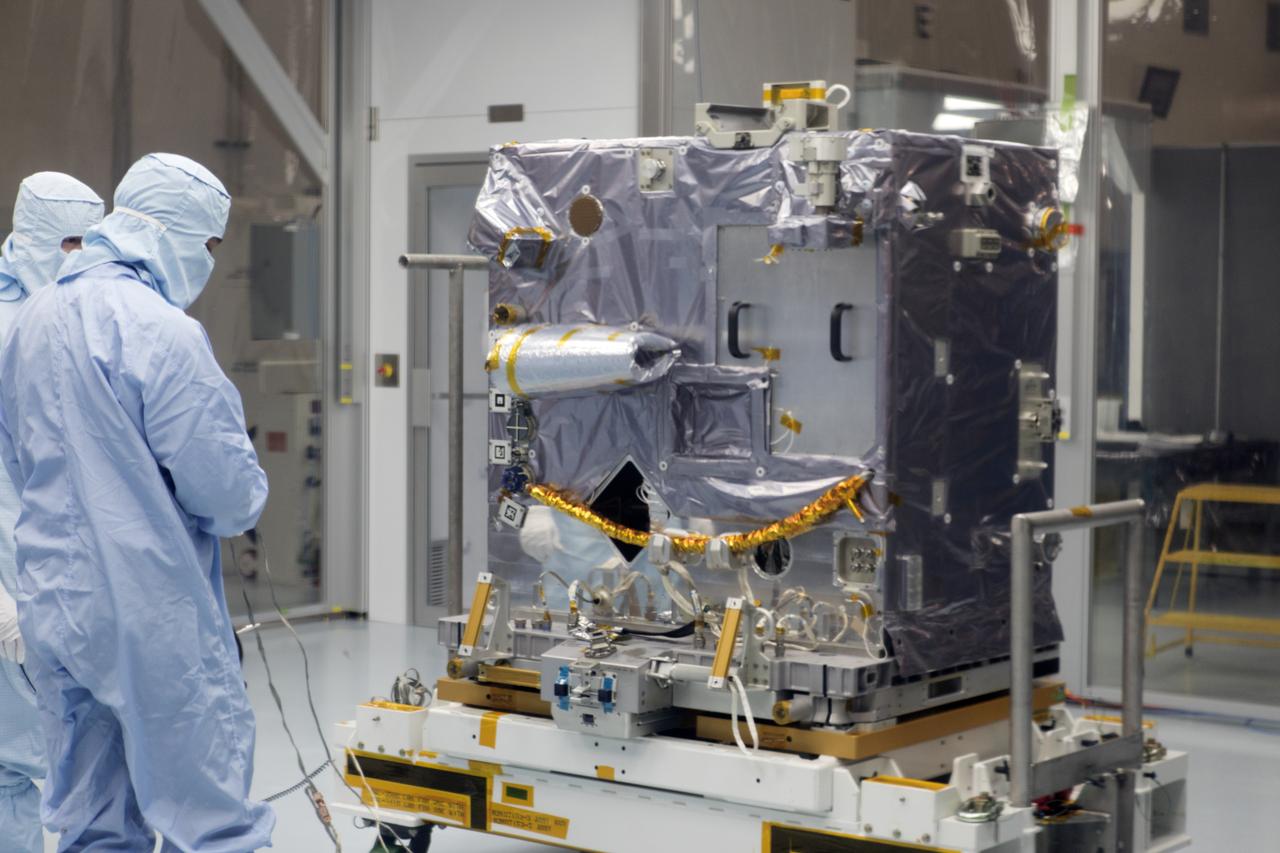
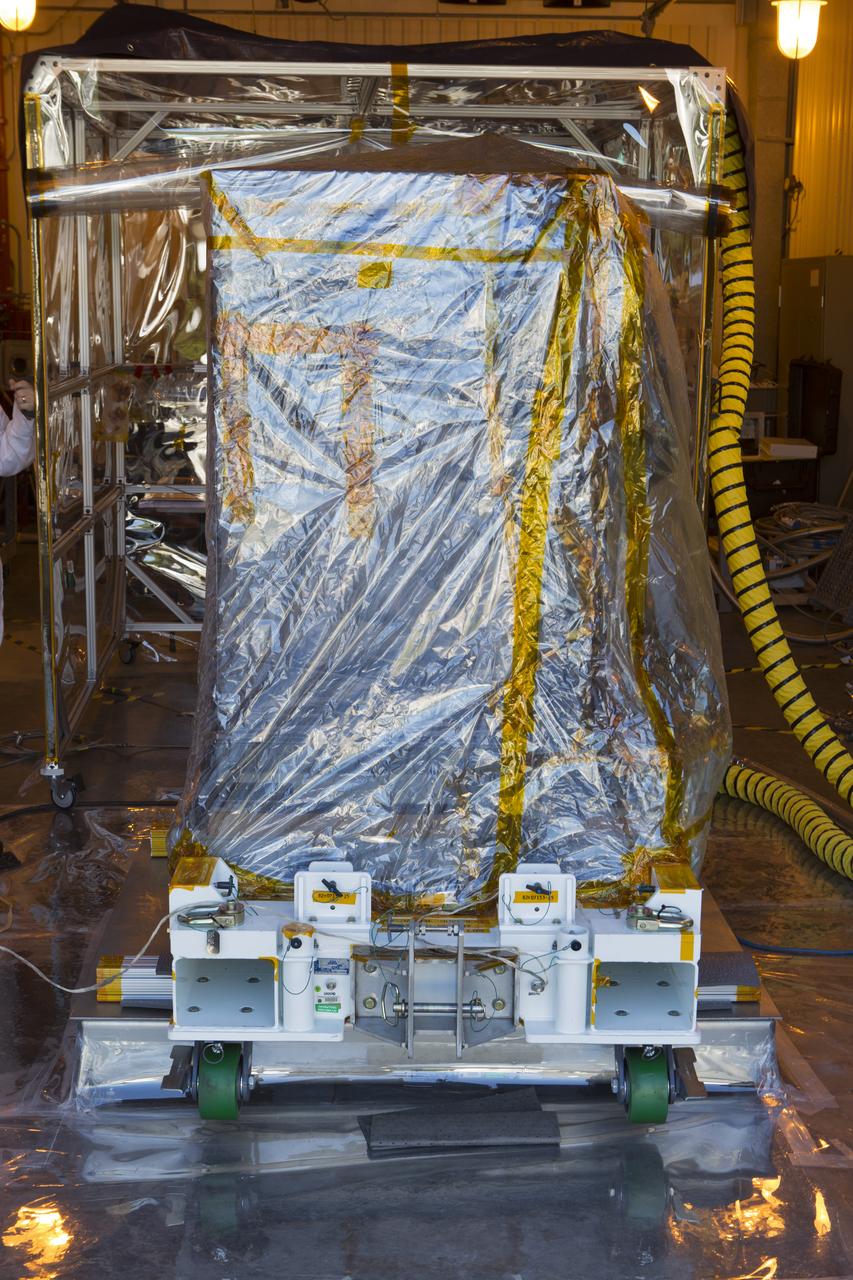
The Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload is inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

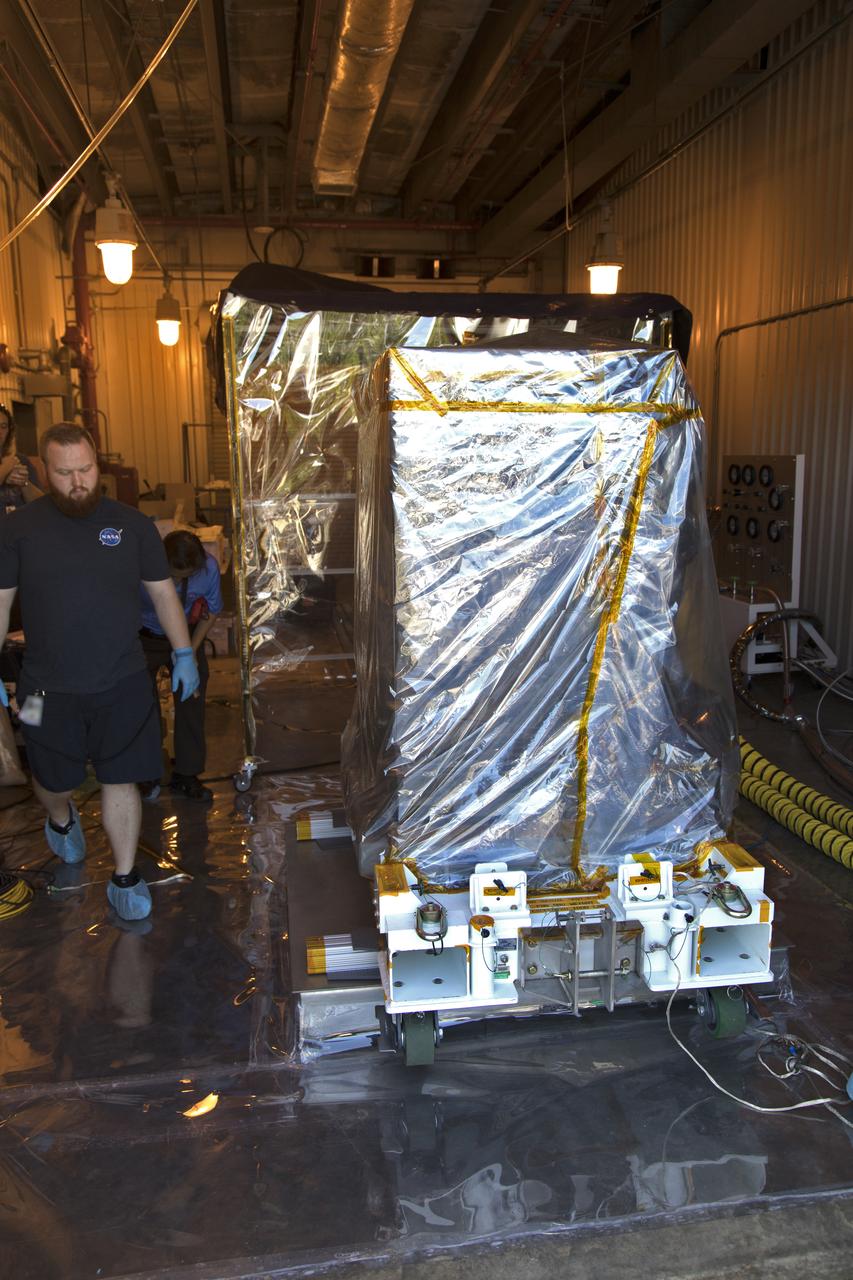
Workers prepare the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload for transport from the Fuel Transfer Building to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

A worker uses a forklift to unload the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload from a truck at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
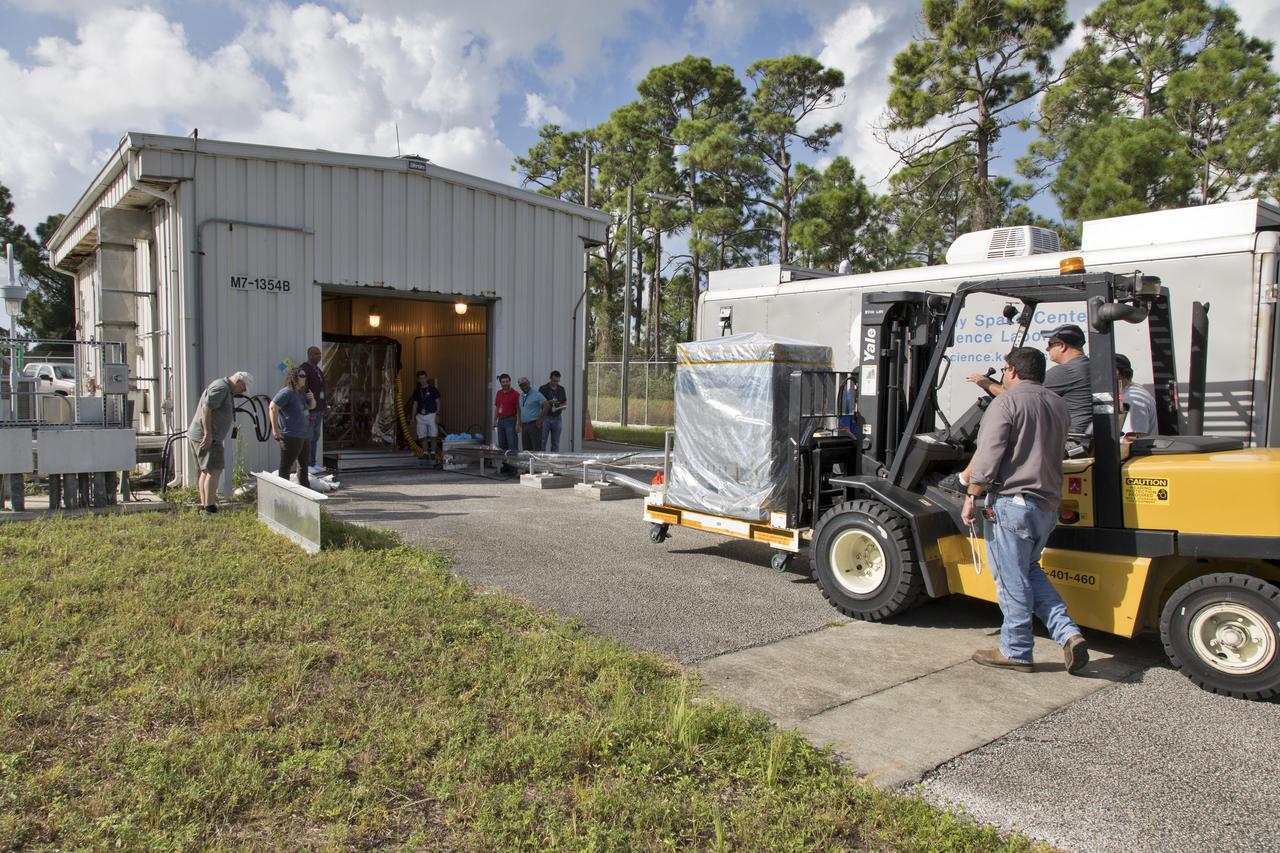

A worker uses a forklift to carry the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload to the entrance of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
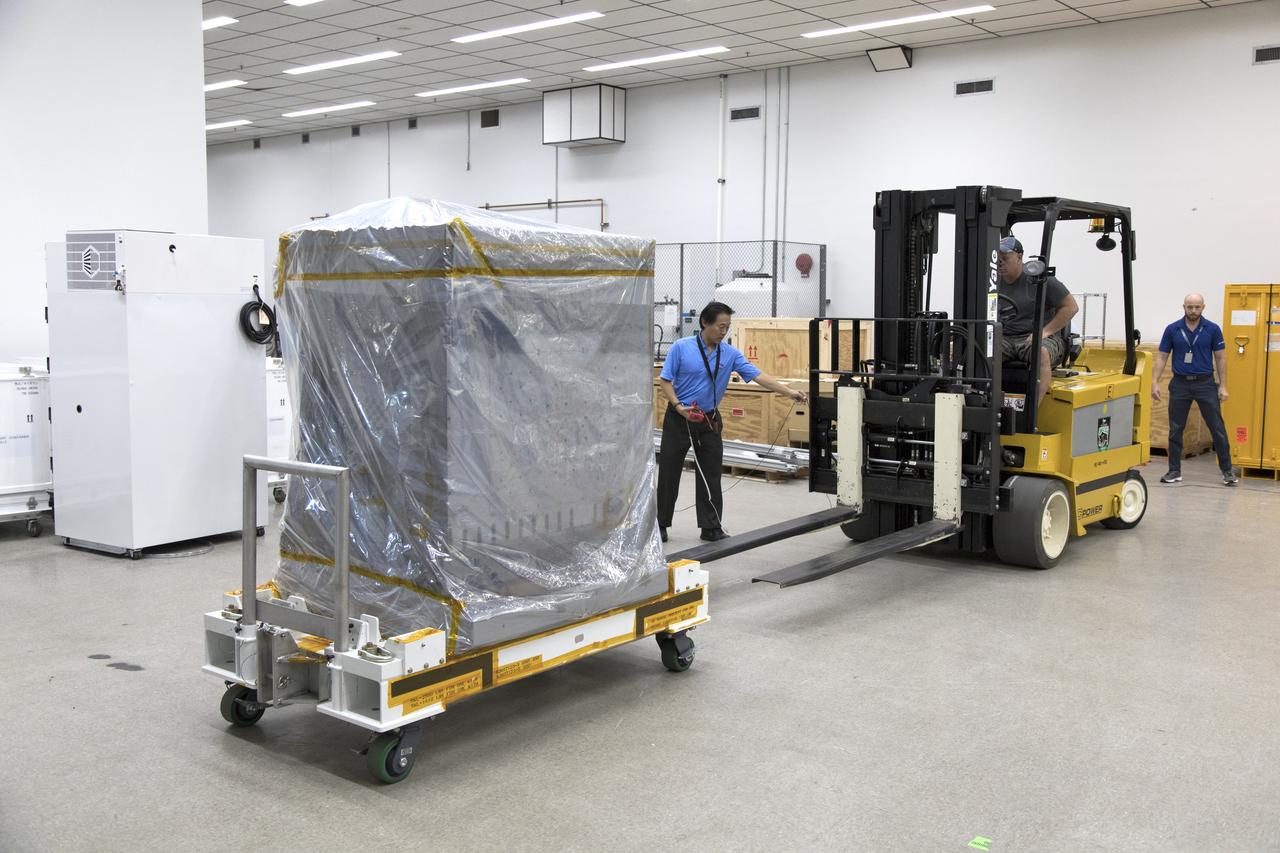

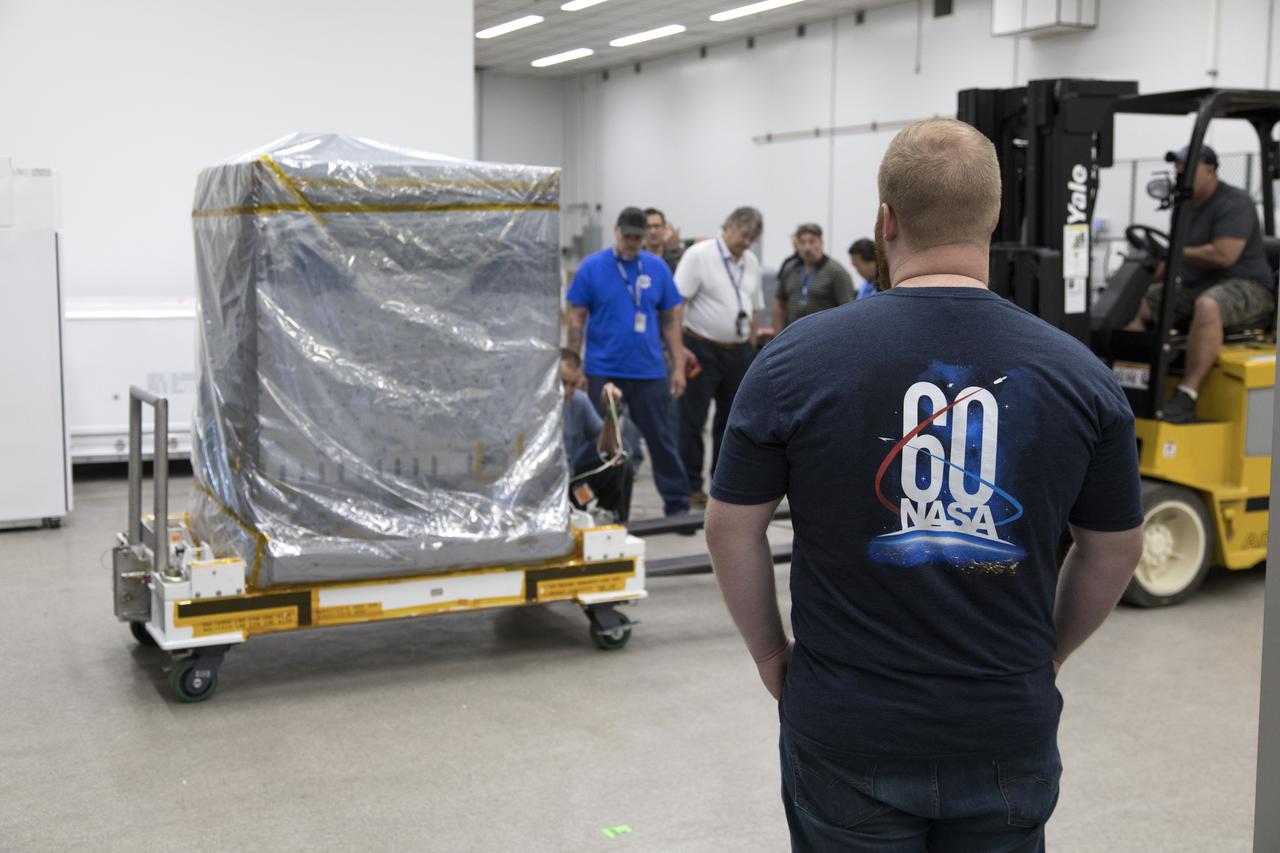
Workers prepare the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload to be transferred from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

Workers prepare to transfer the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

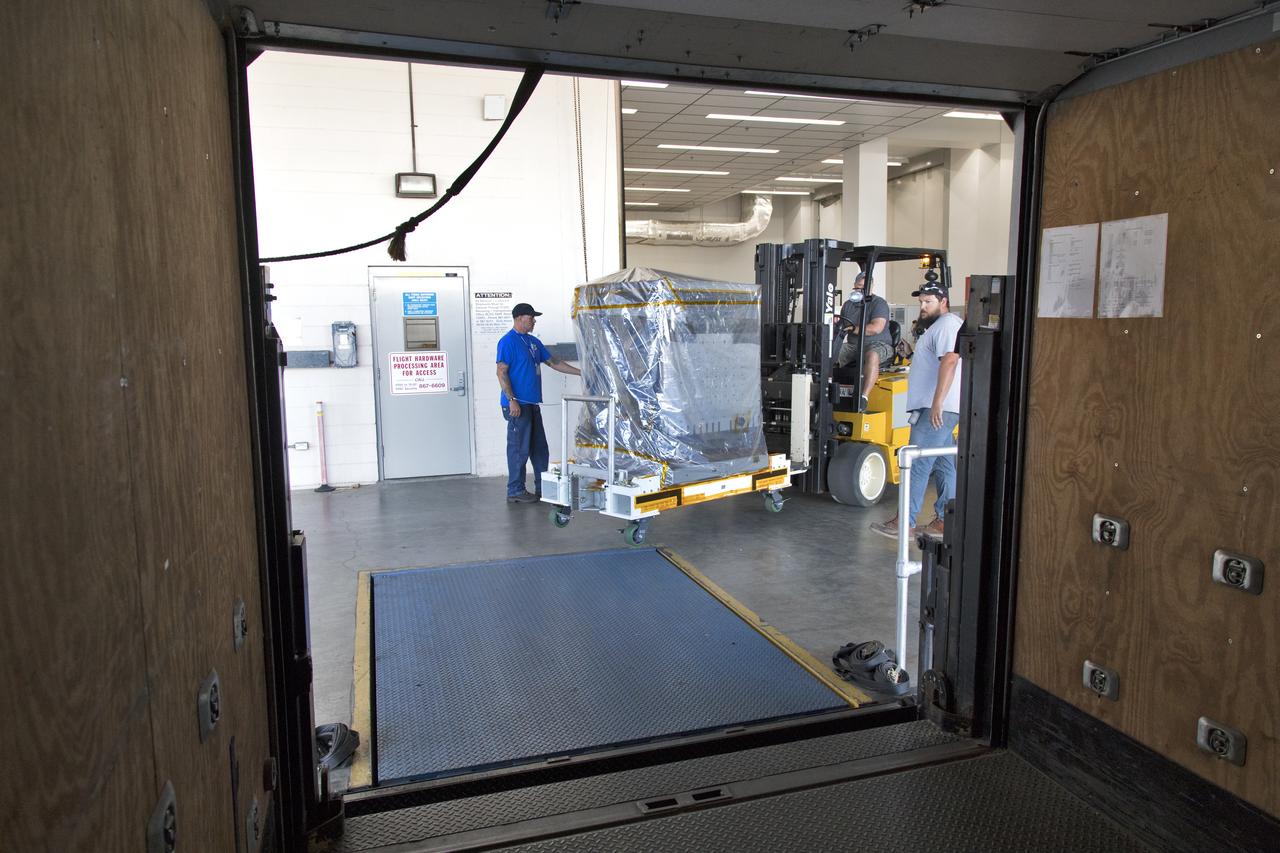
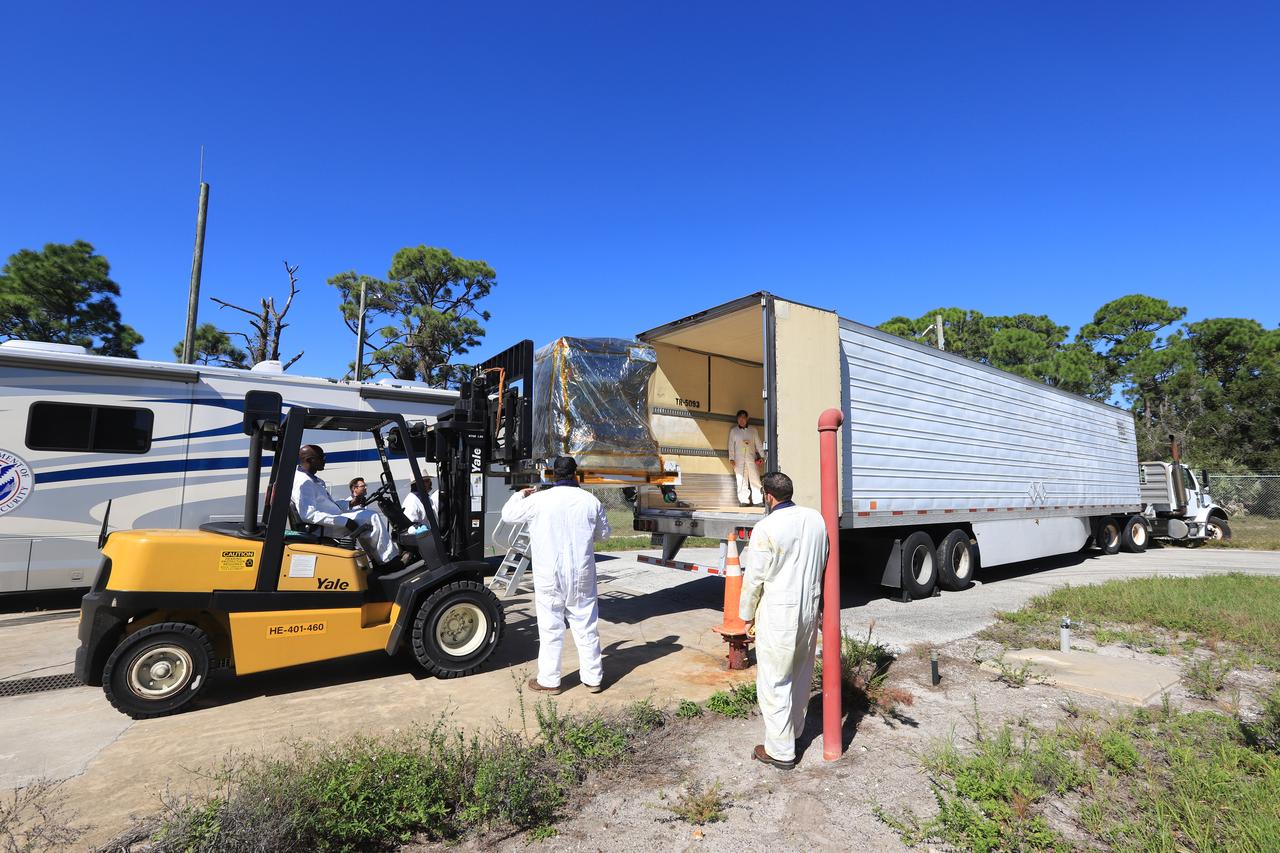
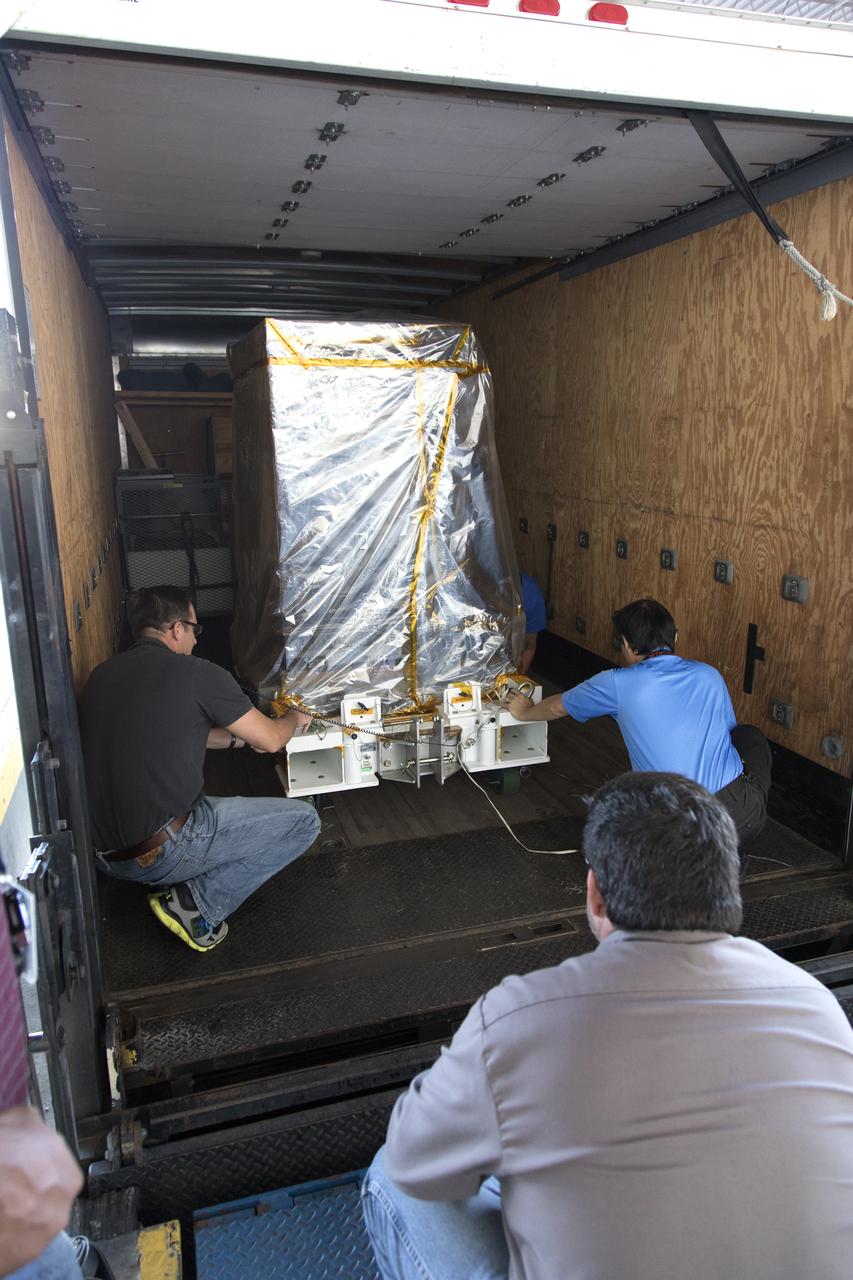
A truck containing the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload departs the Fuel Transfer Building near the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for transport to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

Workers prepare the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload to be transferred from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

A forklift is used to load the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload onto a truck at the Fuel Transfer Building for transport to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

Workers load the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload onto a truck at the Space Station Processing Facility for transfer to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

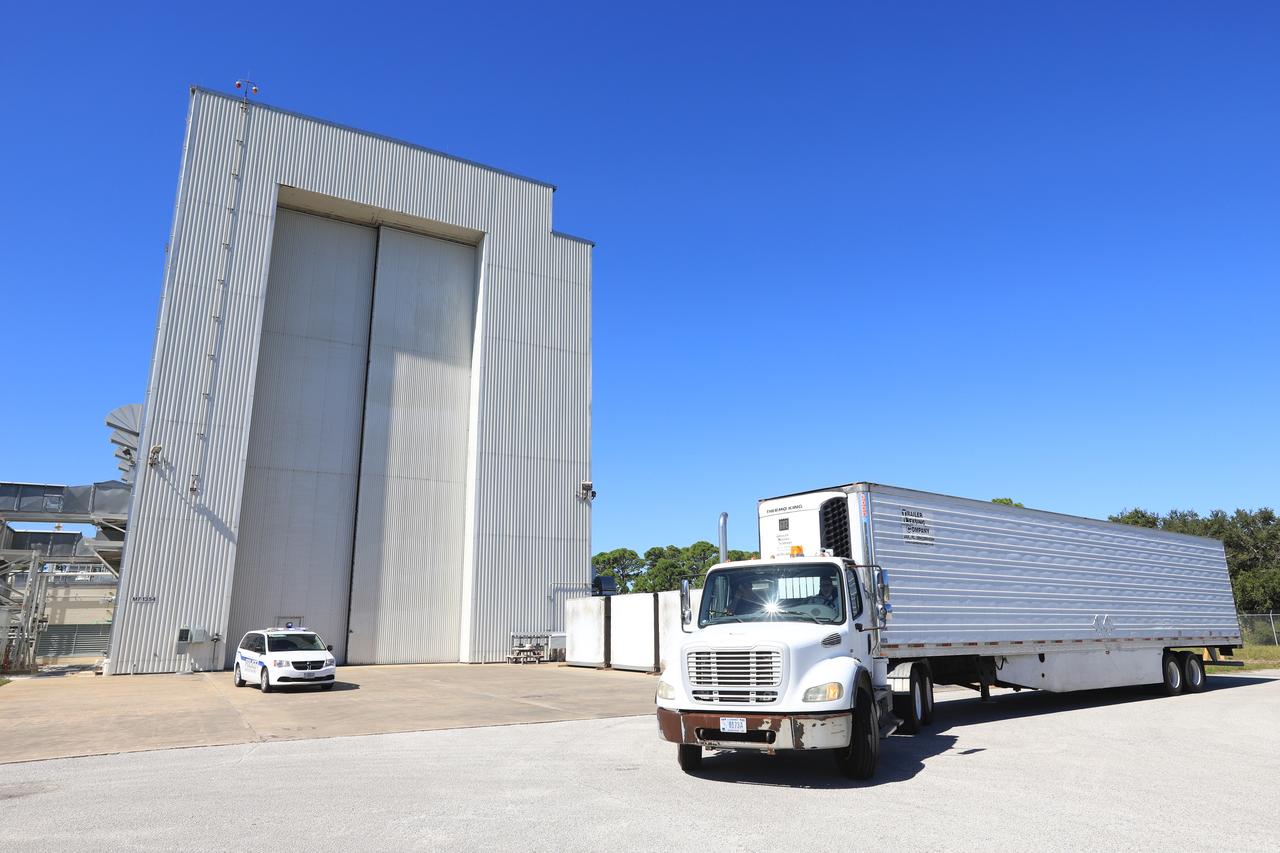
A truck carrying the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload departs from the Space Station Processing Facility on its way to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
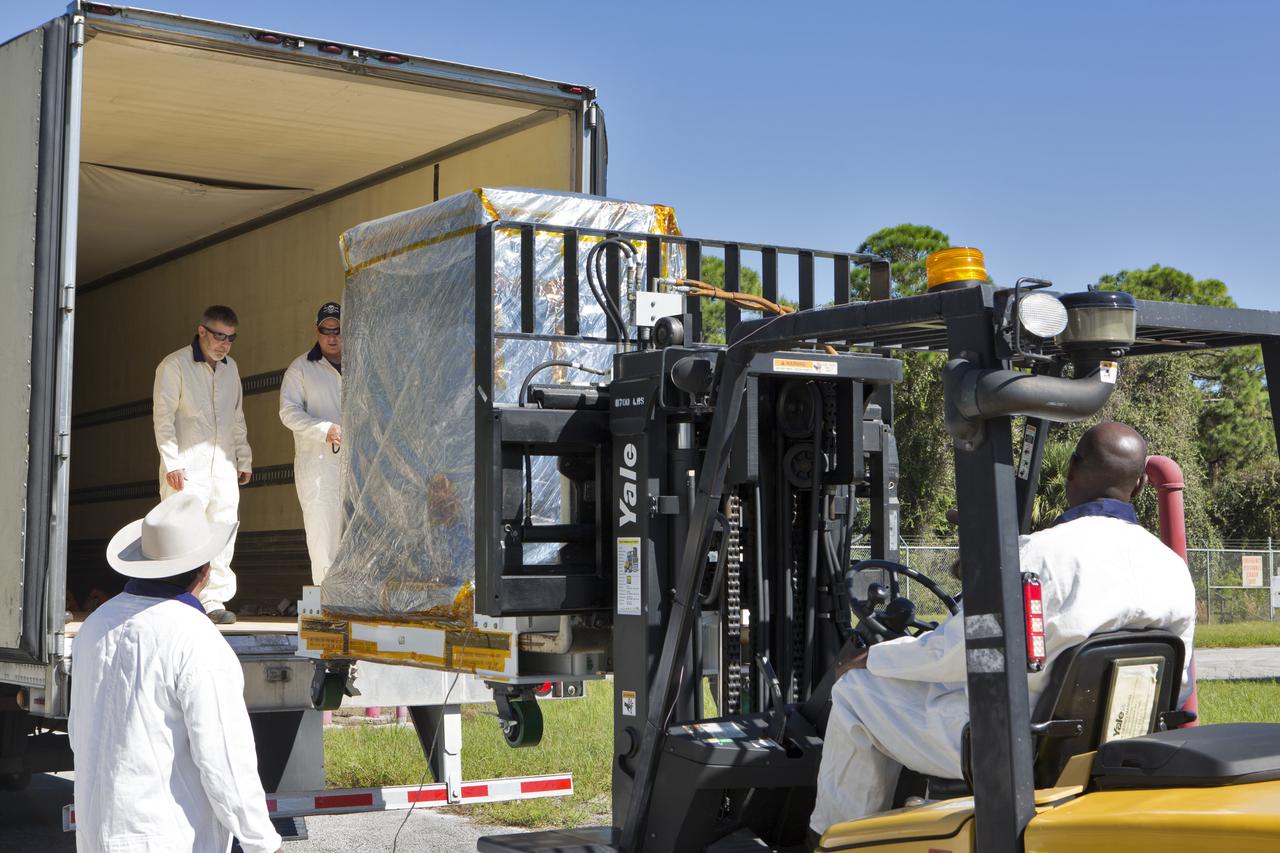

A forklift is used to load the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload onto a truck at the Fuel Transfer Building for transport to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
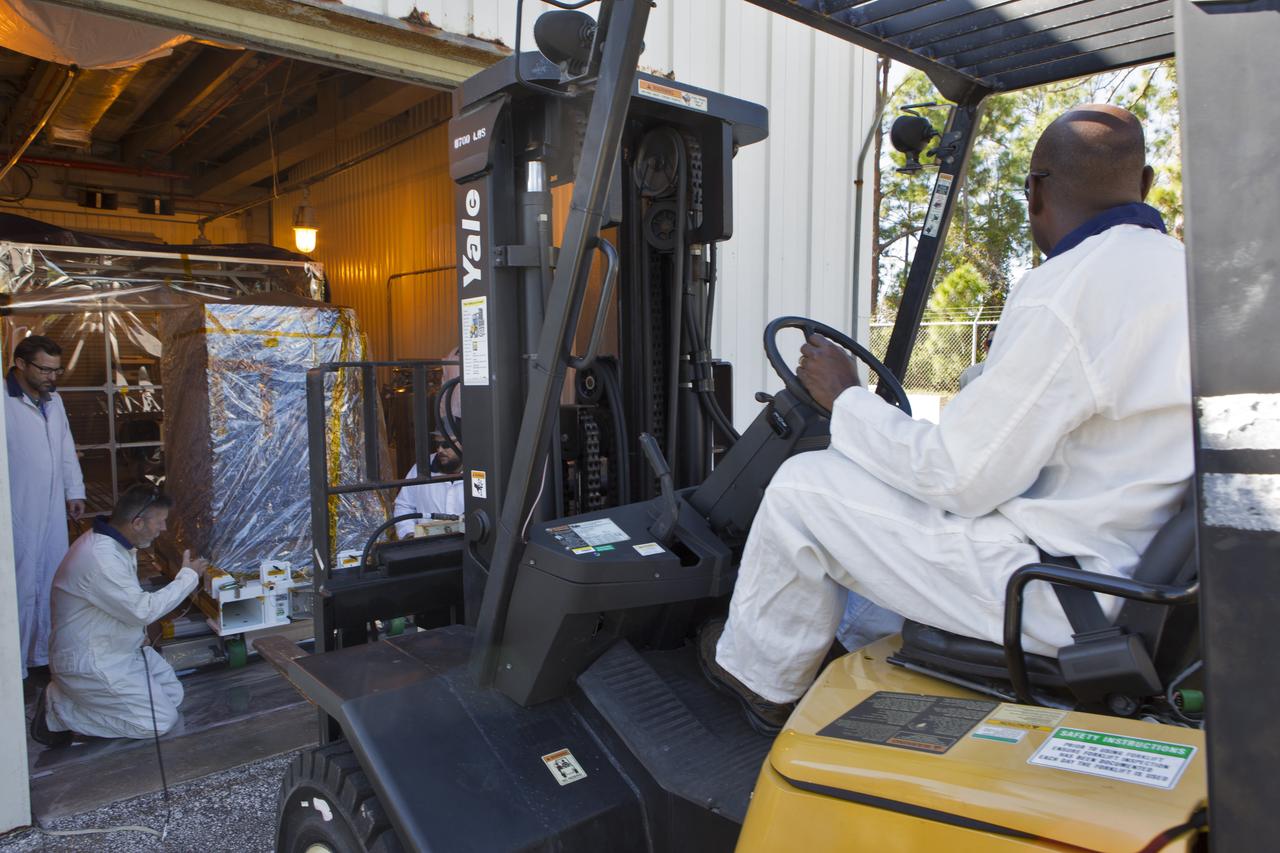

A forklift is being used to lift the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload out of the Fuel Transfer Building on Oct. 30, 2018, to be transported to the SpaceX facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
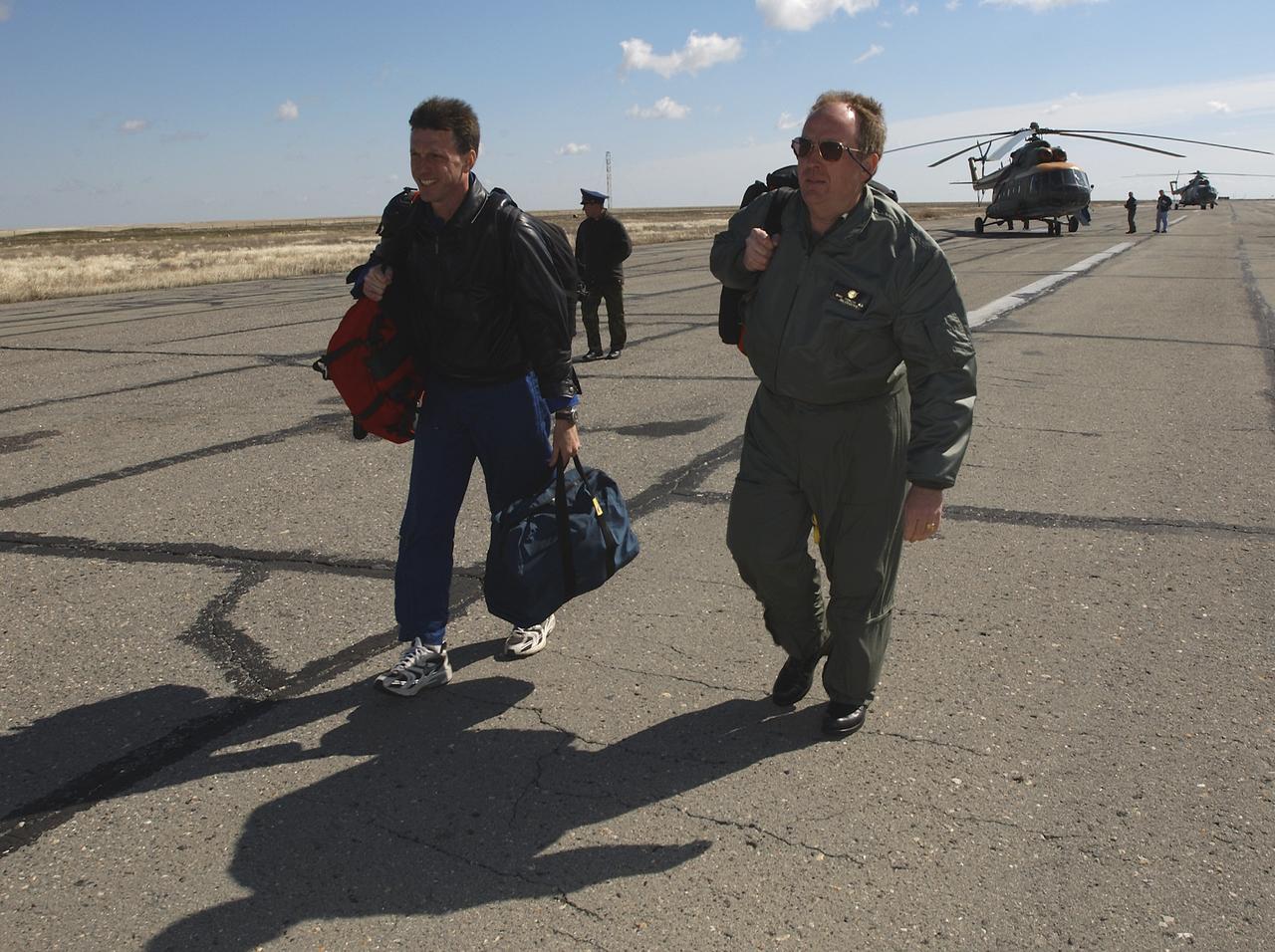

Astronaut Michael Foale, left, and Mike Duncan, Expedition 6 Lead Flight Surgeon, move to another helicopter after the landing team helicopters returned for refueling, Tuesday, May 4, 2003, in Kazakhstan. Foale and Duncan went on from the refueling to meet the crew of Expedition 6 at the landing site. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
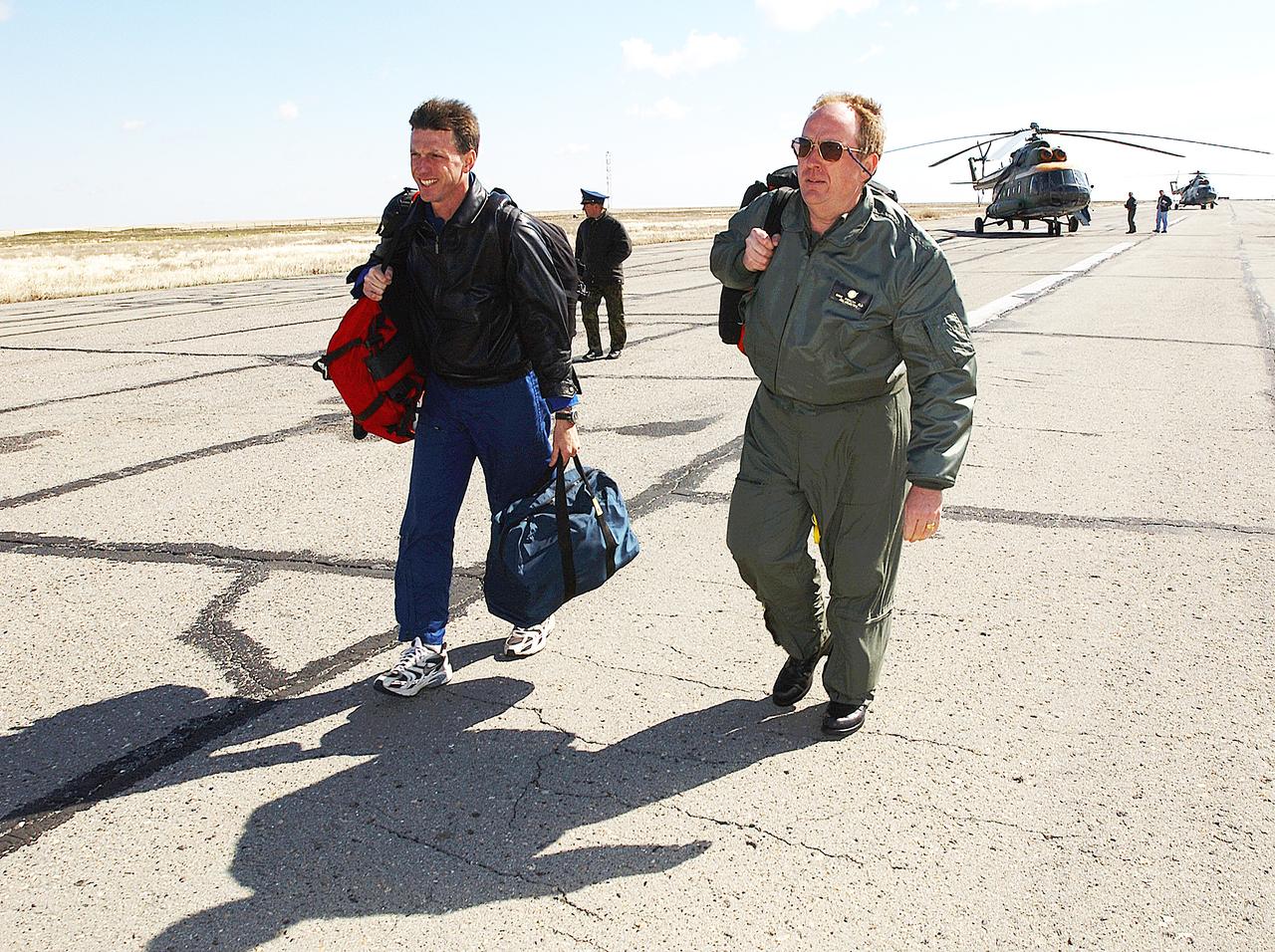

May 4, 2003, Kazakhstan. Astronaut Michael Foale (L) and Mike Duncan (R), Expedition Six Lead Flight Surgeon move to the lead helicopter after the landing team helicopters needed to return for refueling. Foale and Duncan went on from the refueling to meet the crew of Expedition Six at the landing site. Photo Credit: "NASA/Bill Ingalls"
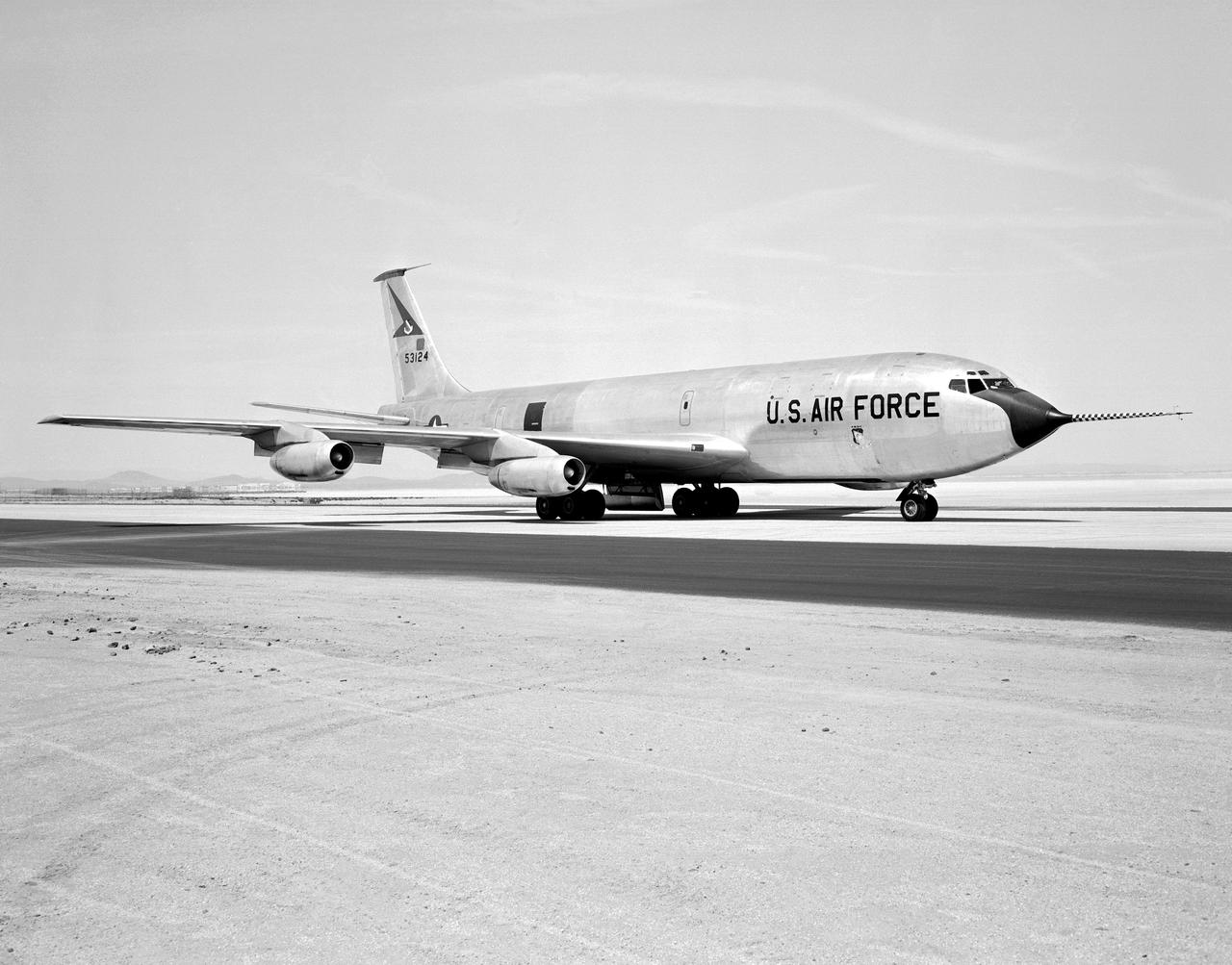

The Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker, besides being used extensively in its primary role as an inflight aircraft refueler, has assisted in several projects at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. In 1957 and 1958, Dryden was asked by what was then the Civil Aeronautics Administration (later absorbed into the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in 1958) to help establish new approach procedure guidelines on cloud-ceiling and visibility minimums for Boeing's first jet airliner, the B-707. Dryden used a KC-135 (the military variant of the 707), seen here on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, to aid the CAA in these tests. In 1979 and 1980, Dryden was again involved with general aviation research with the KC-135. This time, a special wingtip "winglet", developed by Richard Whitcomb of Langley Research Center, was tested on the jet aircraft. Winglets are small, nearly vertical fins installed on an airplane's wing tips to help produce a forward thrust in the vortices that typically swirl off the end of the wing, thereby reducing drag. This winglet idea was tested at the Dryden Flight Research Center on a KC-135A tanker loaned to NASA by the Air Force. The research showed that the winglets could increase an aircraft's range by as much as 7 percent at cruise speeds. The first application of NASA's winglet technology in industry was in general aviation business jets, but winglets are now being incorporated into most new commercial and military transport jets, including the Gulfstream III and IV business jets, the Boeing 747-400 and MD-11 airliners, and the C-17 military transport. In the 1980's, a KC-135 was used in support of the Space Shuttle program. Since the Shuttle was to be launched from Florida, researchers wanted to test the effect of rain on the sensitive thermal tiles. Tiles were mounted on special fixtures on an F-104 aircraft and a P-3 Orion. The F-104 was flown in actual rain conditions, and also behind the KC-135 spray tanker as it rel
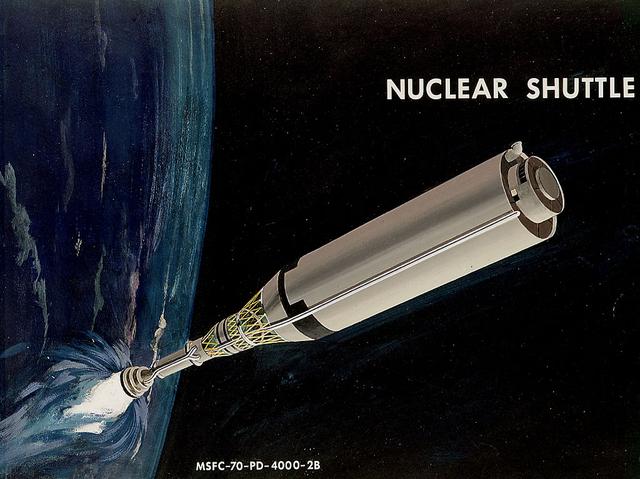

This 1970 artist's concept shows a Nuclear Shuttle in flight. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development engineers, the Nuclear Shuttle would deliver payloads to lunar orbit or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling and additional missions.
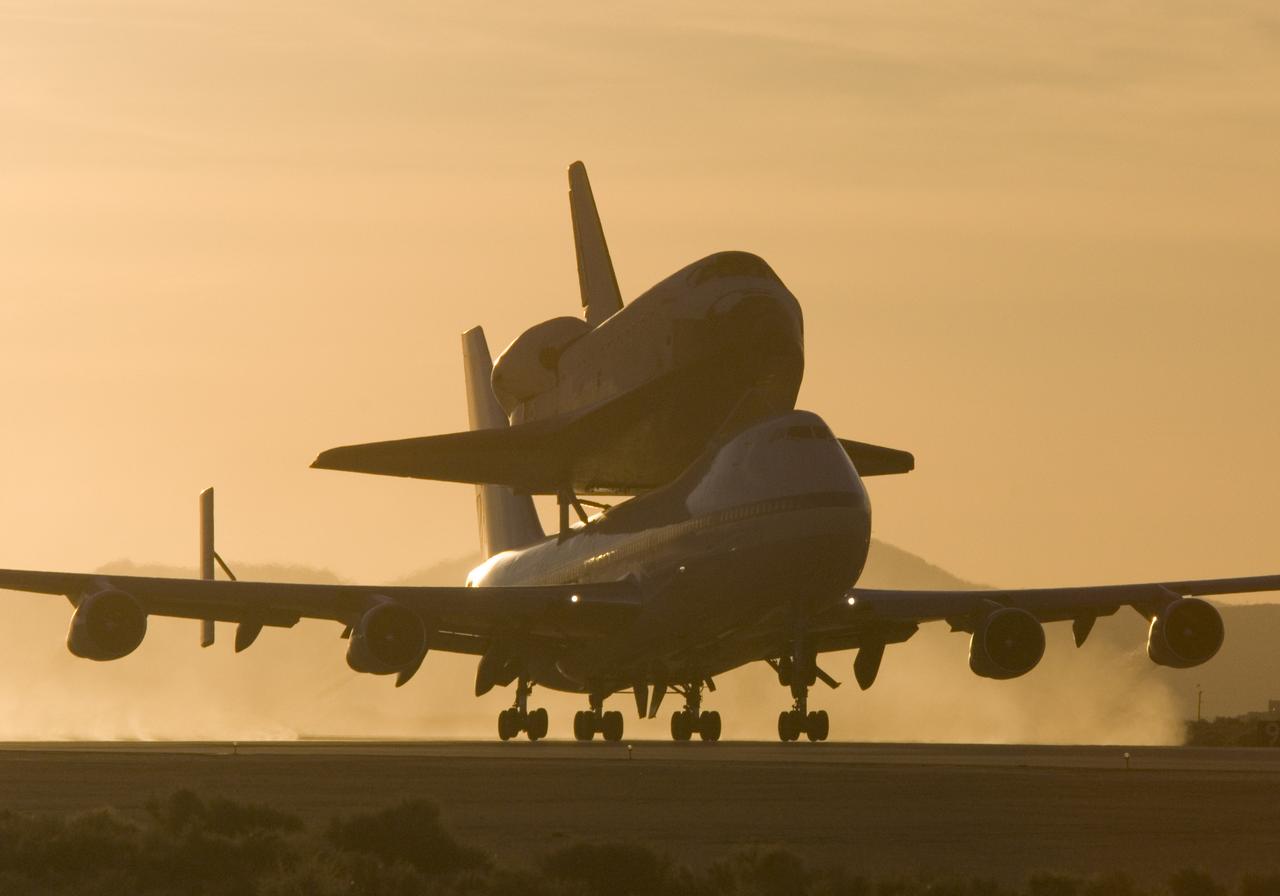

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Atlantis on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take approximately two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling.
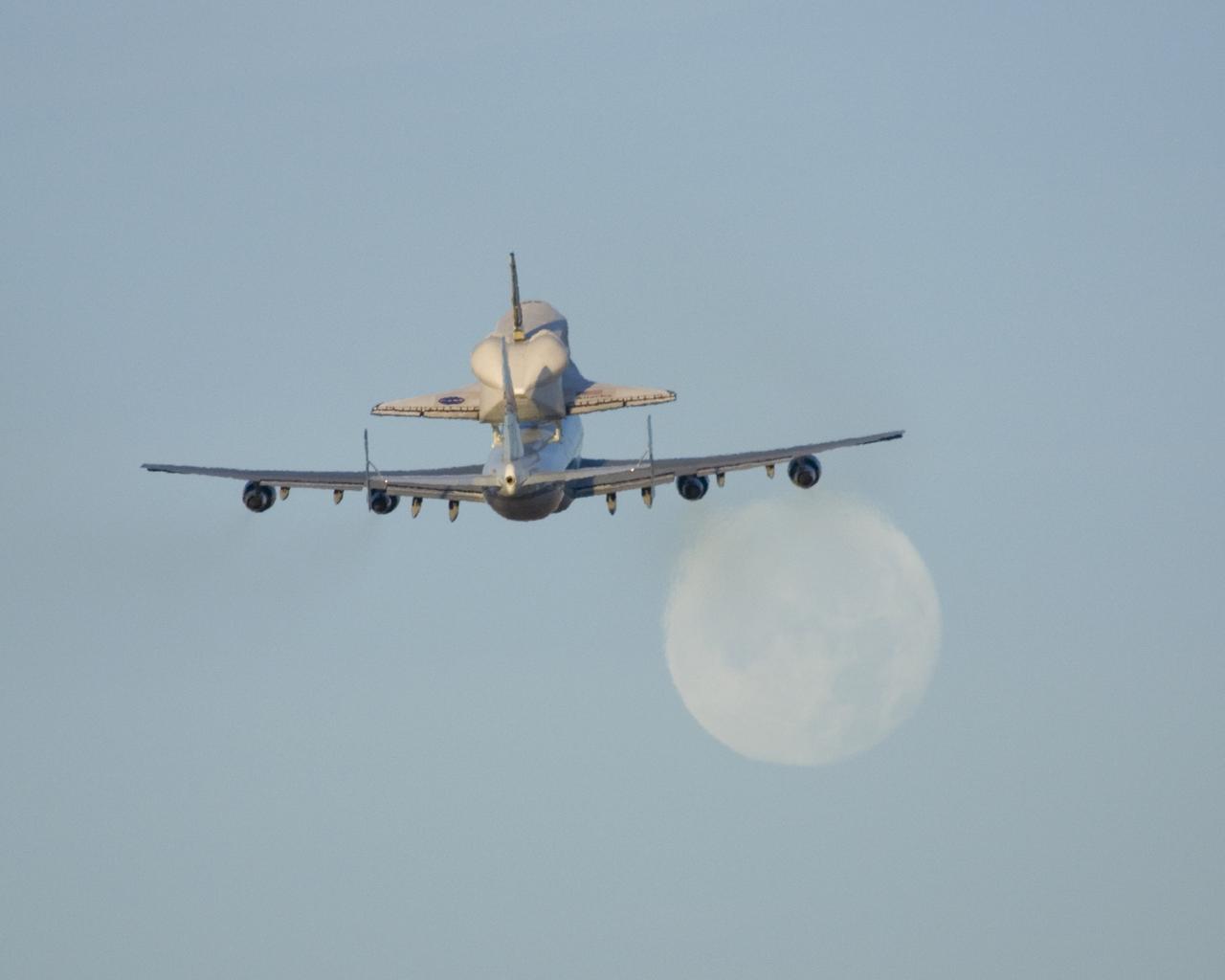

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Atlantis on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take approximately two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling.
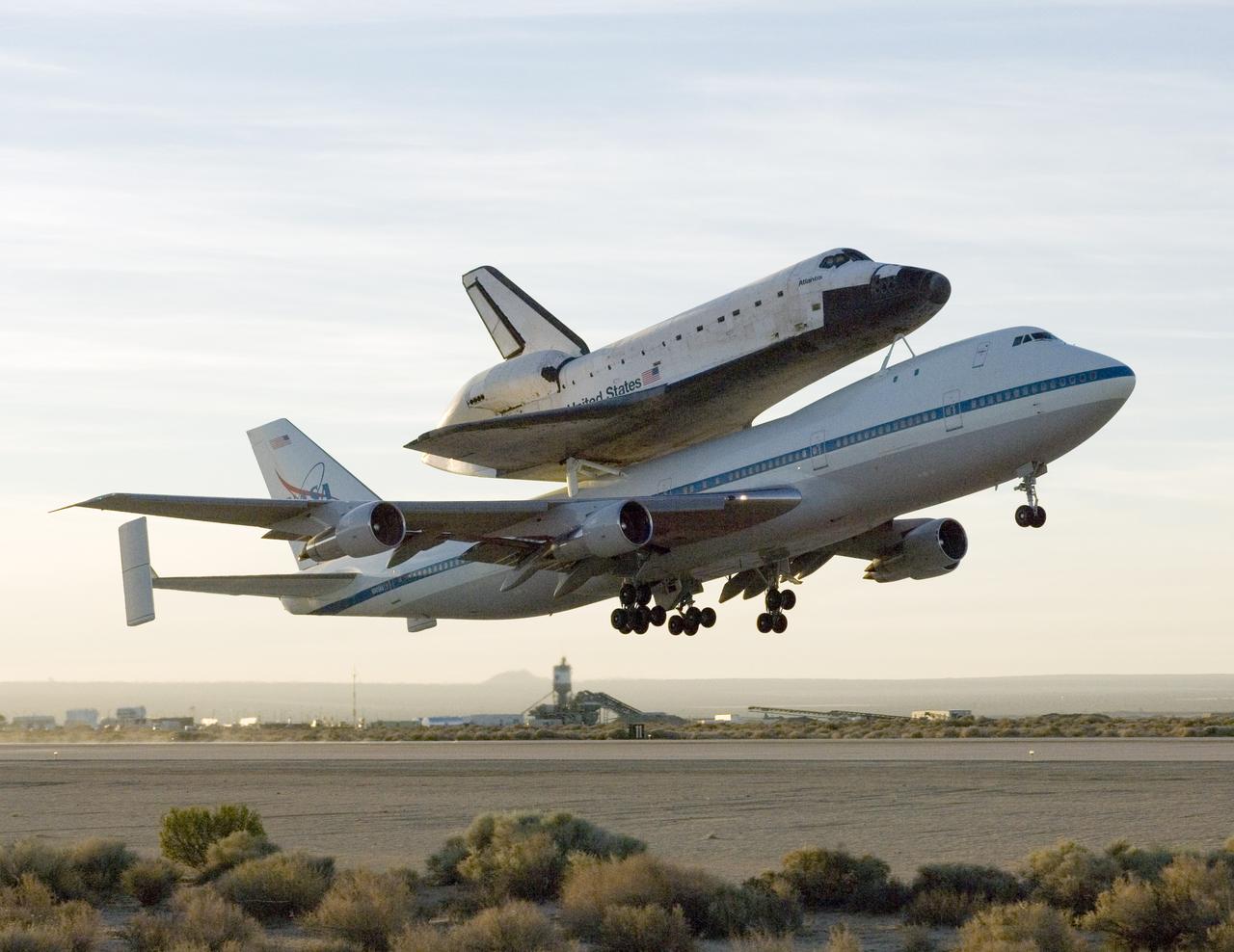

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Atlantis on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take approximately two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling.
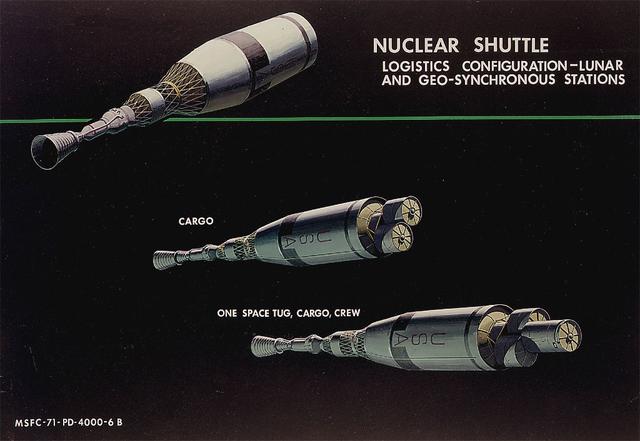
This 1971 artist's concept shows the Nuclear Shuttle in both its lunar logistics configuraton and geosynchronous station configuration. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development persornel, the Nuclear Shuttle would deliver payloads to lunar orbits or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling and additional missions.

As part of the Space Task Group's recommendations for more commonality and integration in America's space program, Marshall Space Flight Center engineers proposed an orbiting propellant storage facility to augment Space Shuttle missions. In this artist's concept from 1969 an early version of the Space Shuttle is shown refueling at the facility.
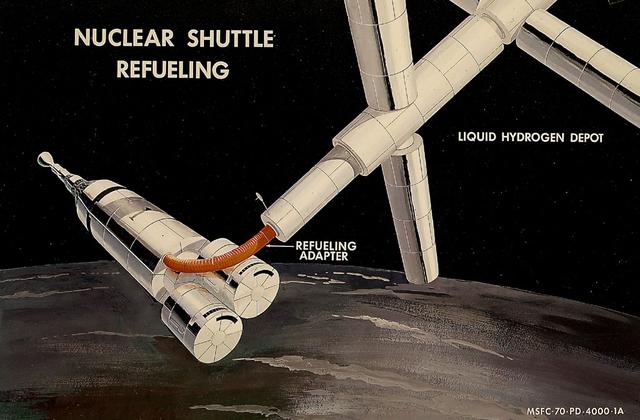
This artist's concept from 1970 shows a Nuclear Shuttle taking on fuel from an orbiting Liquid Hydrogen Depot. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development persornel, the Nuclear Shuttle would deliver payloads to lunar orbit or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling and additional missions.

Cape Canaveral, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis soars into a layer of thin clouds at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida moments after lifting off on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/ Jim Grossmann Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim will lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: Jim Grossmann
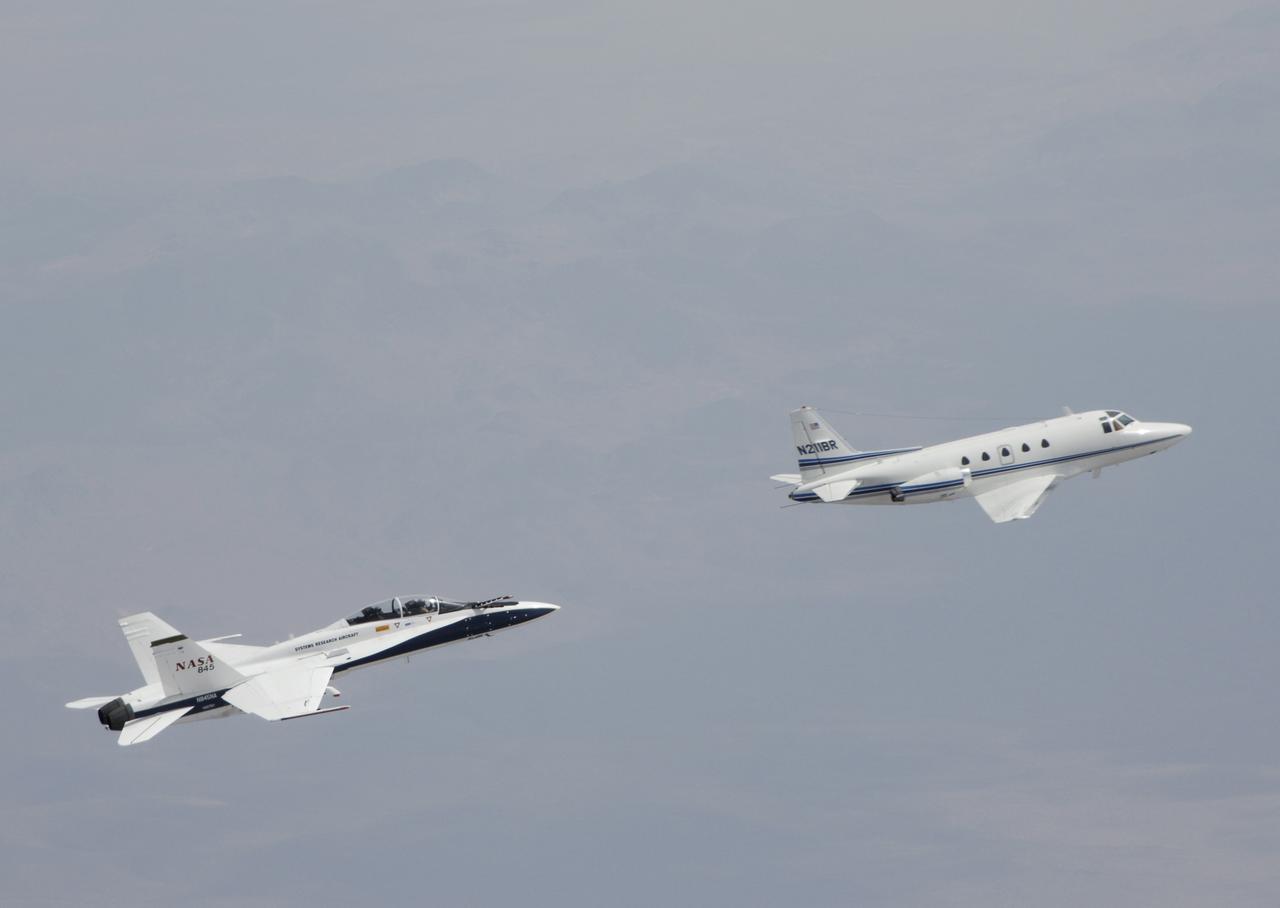

Testing autonomous software for AARD program using a NASA F/A-18 #845 following a chartered Sabreliner.
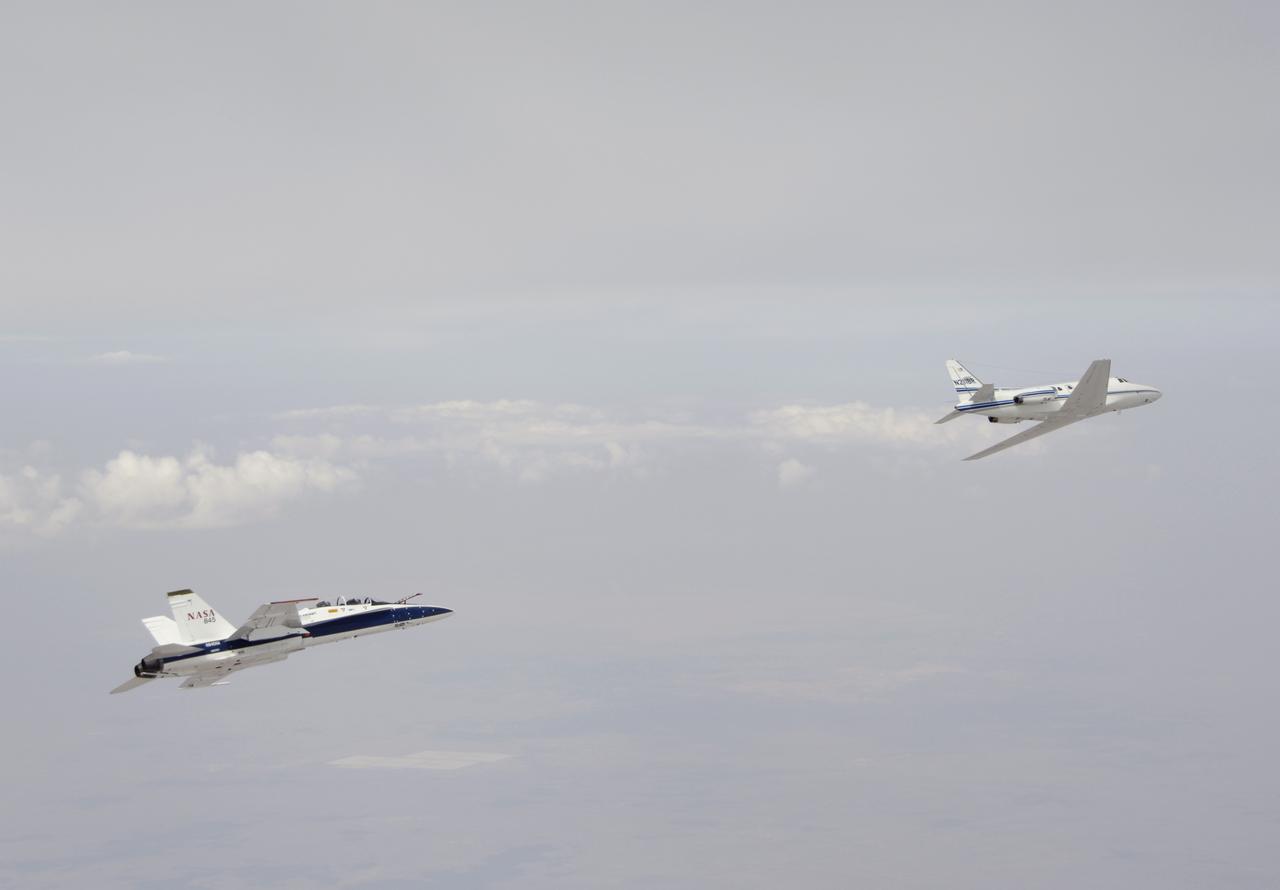

Testing autonomous software for AARD program using a NASA F/A-18 #845 following a chartered Sabreliner.

Testing autonomous software for AARD program using a NASA F/A-18 #845 following a chartered Sabreliner.

View from F/A-18 #845 behind Omega Air Boeing 707 tanker during an AARD flight showing probe and drogue.

F/A-18 #845 testing autonomous system for AARD project by following a pickup with an airborne tanker drogue illustration.

iss072e423785 (1/3/2025) — A view of the CLINGERS Cubesat connection mechanism aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Flight Tech Demo of Docking/Undocking Cubesats Inside ISS (CLINGERS) uses the International Space Station’s Astrobee robots to demonstrate an adaptor for docking and close approach sensing to connect both active and passive objects in space. These are critical functions to enable applications such as satellite servicing, orbital refueling, spacecraft repair and upgrade, and in-orbit manufacturing.
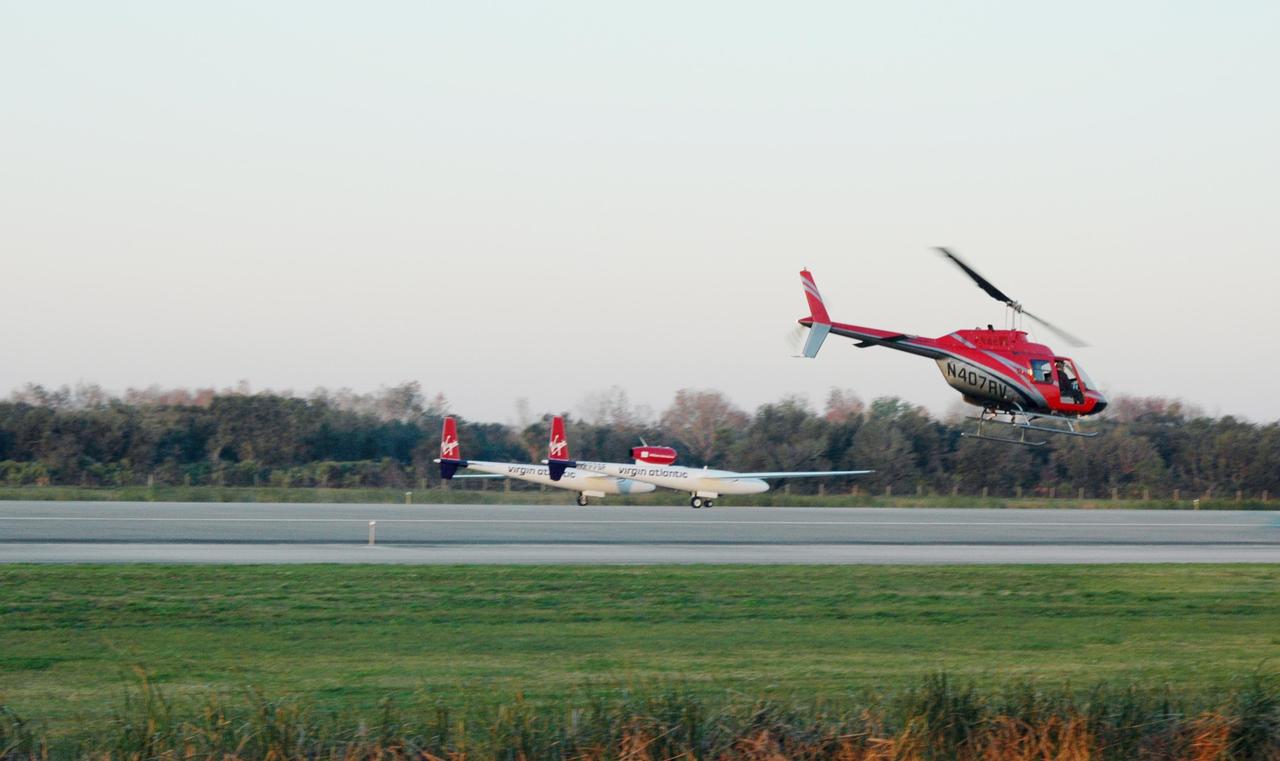

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff as a nearby helicopter films the historic event for audiences in the United Kingdom. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.

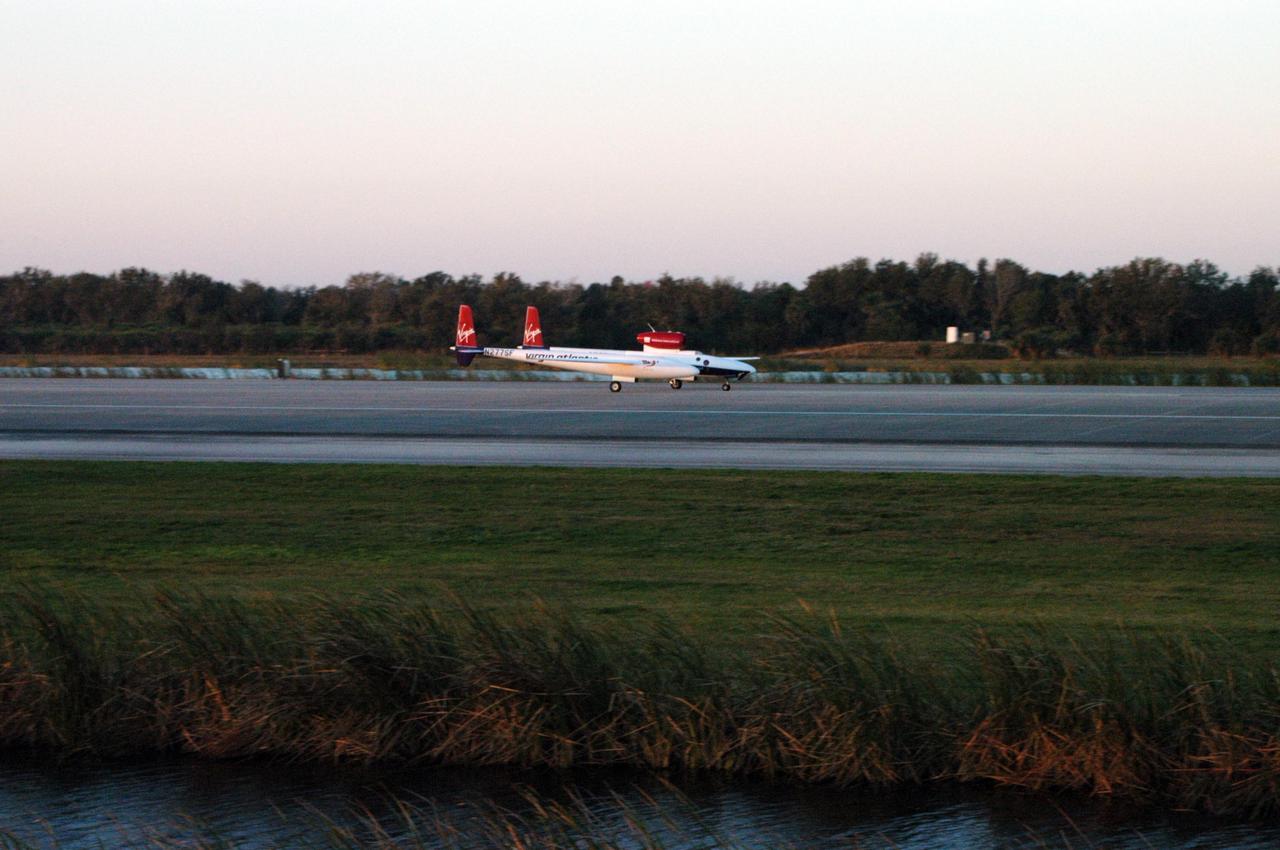
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.
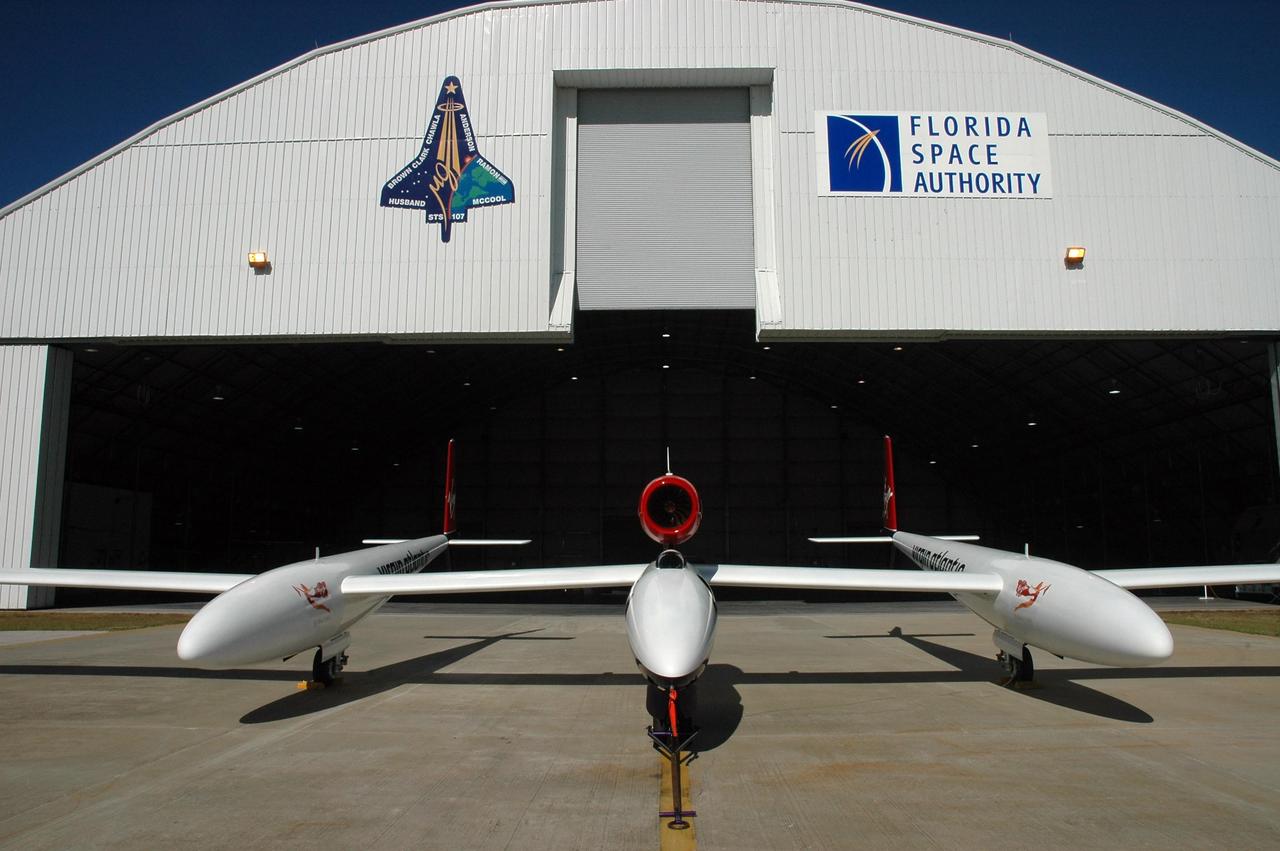

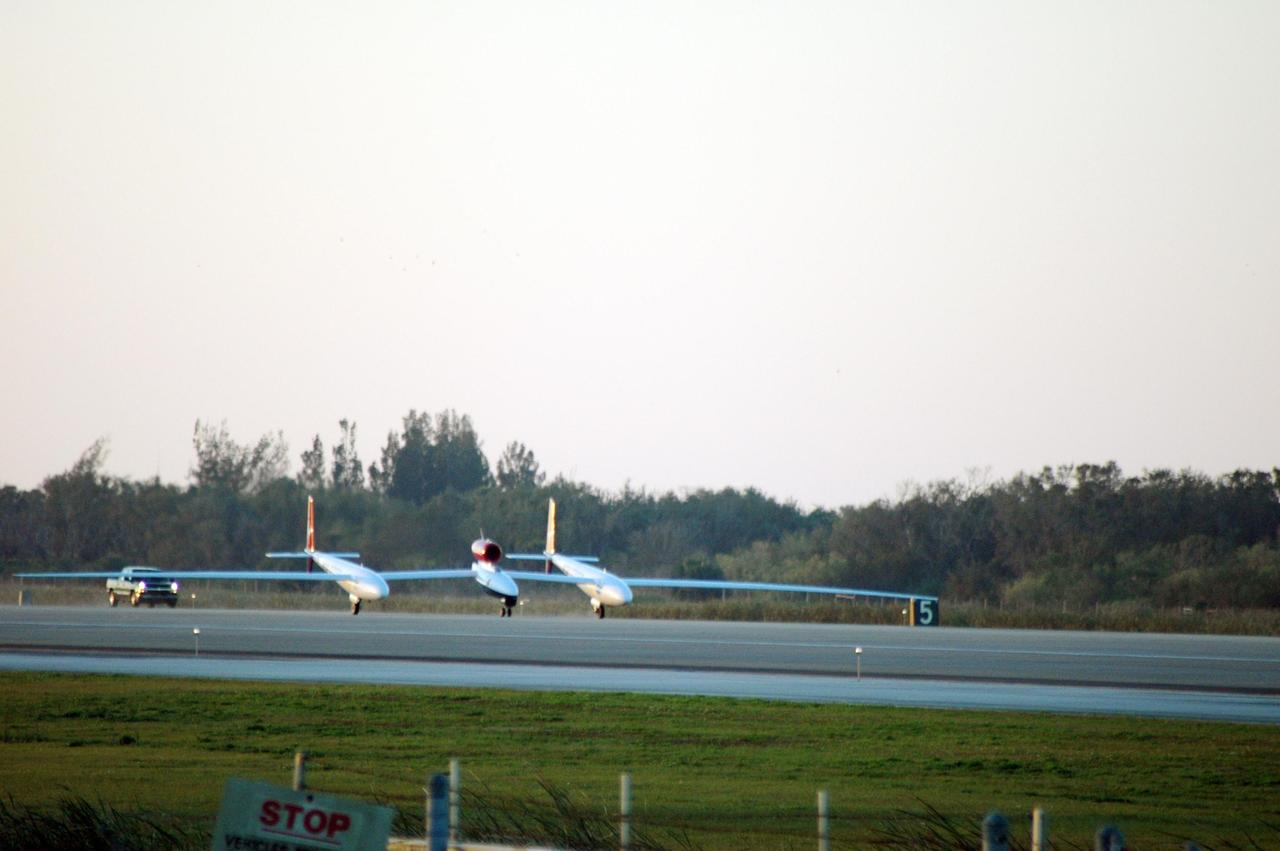
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — The Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer aircraft is on display for employees at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Final preparations are being made at Kennedy before taking off on its record-setting flight, as early as Feb. 1, from Kennedy's Space Shuttle Landing Facility. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
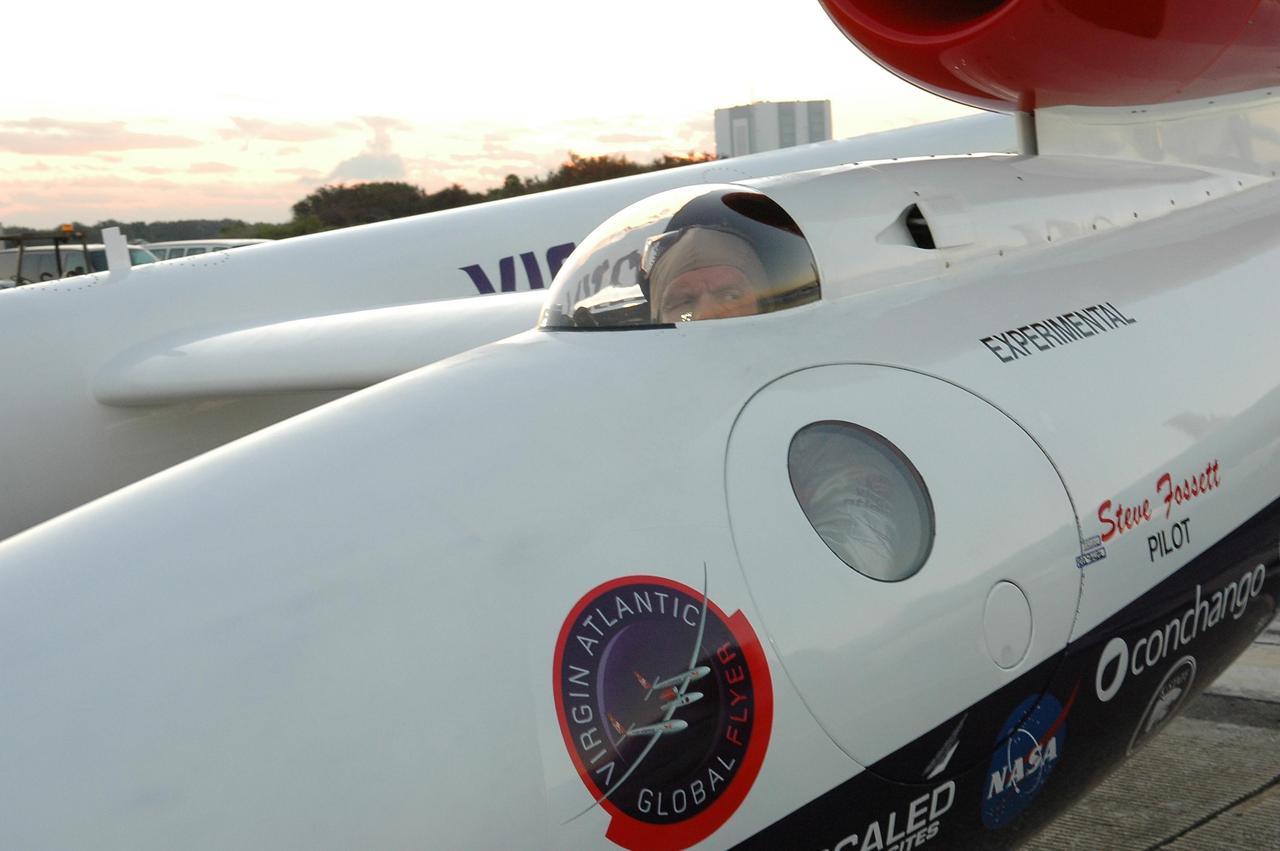

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, the door is closed on the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer as pilot Steve Fossett looks out the cockpit window. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
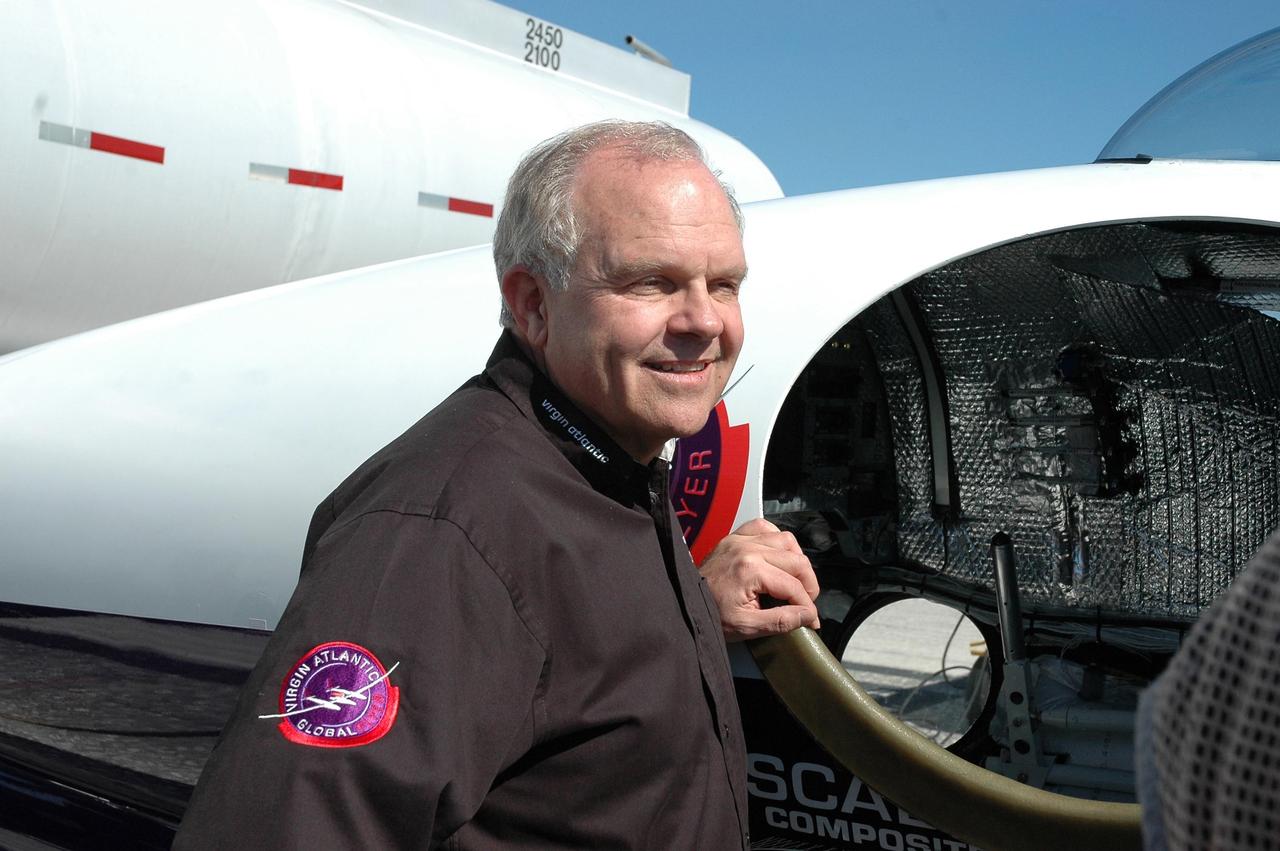

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett stands next to the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer aircraft. Fossett will pilot the aircraft on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility early Tuesday morning. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

S84-43433 (11 Oct 1984) --- Photographed through aft flight deck windows, this 70mm frame shows Astronauts David C. Leestma, left, and Kathryn D. Sullivan at the orbital refueling system (ORS) in the aft cargo bay. A wrist camera on the remote manipulator system (RMS) is perched to record the historic extravehicular activity (EVA). Dr. Sullivan's part of the EVA represented the first such feat for an American woman.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff as a nearby helicopter films the event for audiences in the United Kingdom. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.
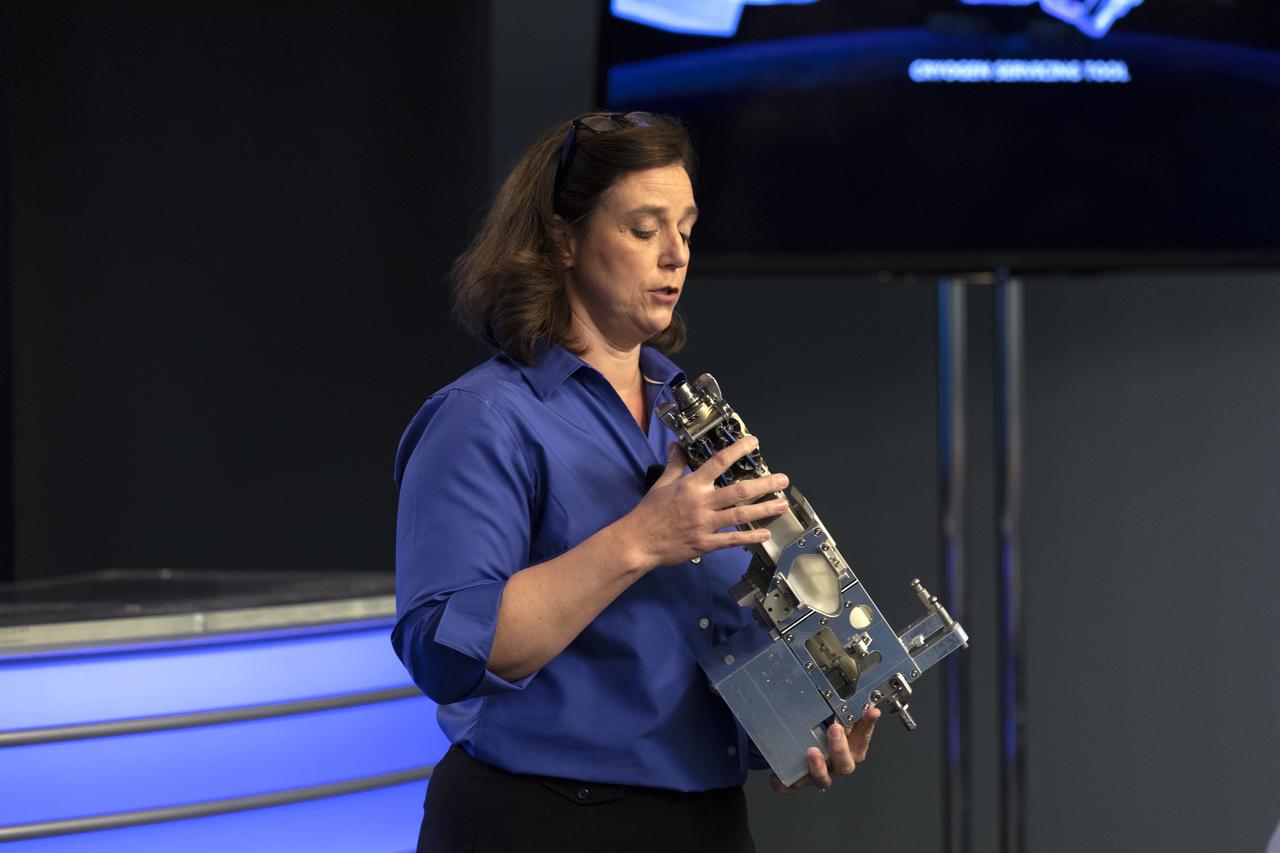

Jill McGuire, project manager for the Robotic Refueling Mission 3, or RRM3, experiment, describes RRM3 hardware for members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
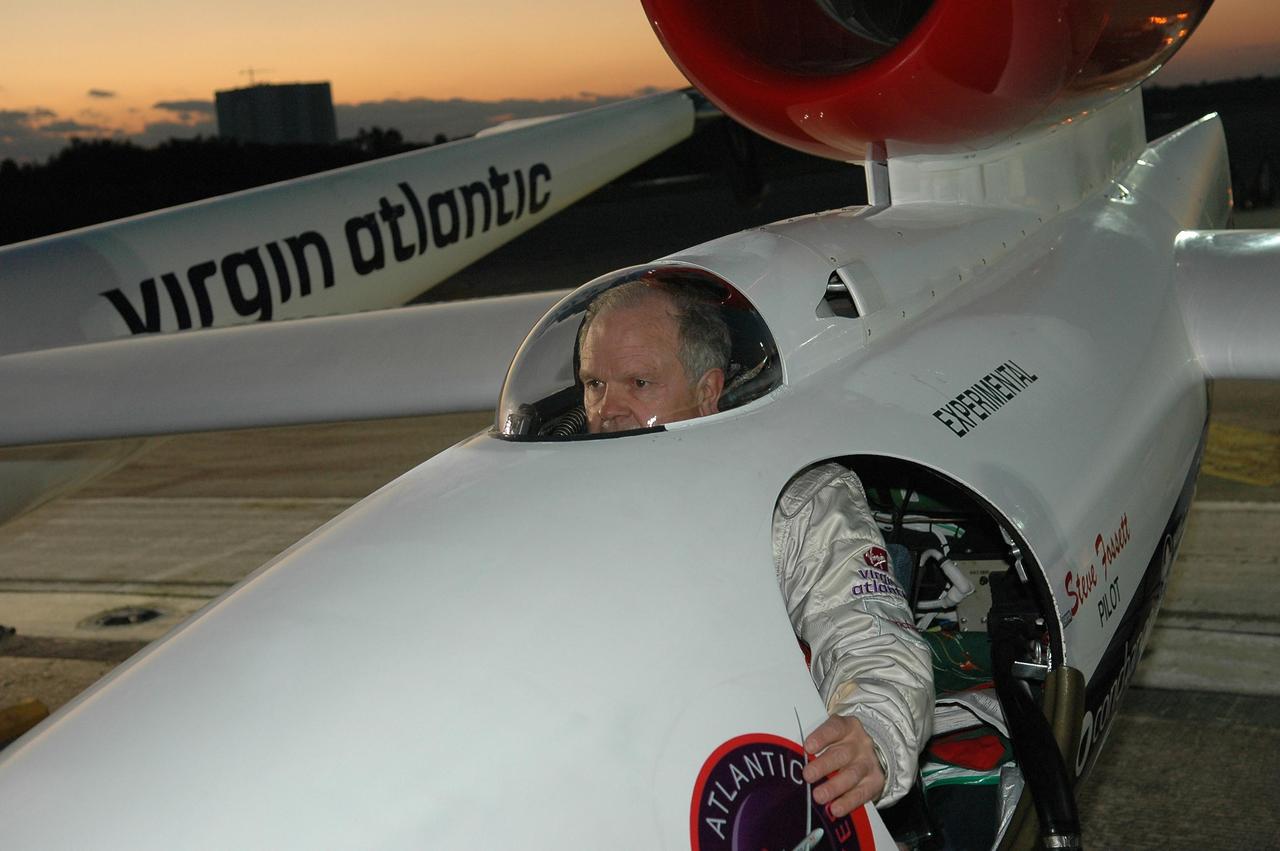

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett, seated in the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer cockpit, checks visibility and head space. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

iss072e747124 (March 18, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers works inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module loading software onto an Astrobee robotic free-flyer. The software is part of a technology investigation demonstrating an adaptor for docking and close approach sensing to connect both active and passive objects in space. Results may enable applications such as satellite servicing, orbital refueling, spacecraft repair and upgrade, and in-orbit manufacturing.
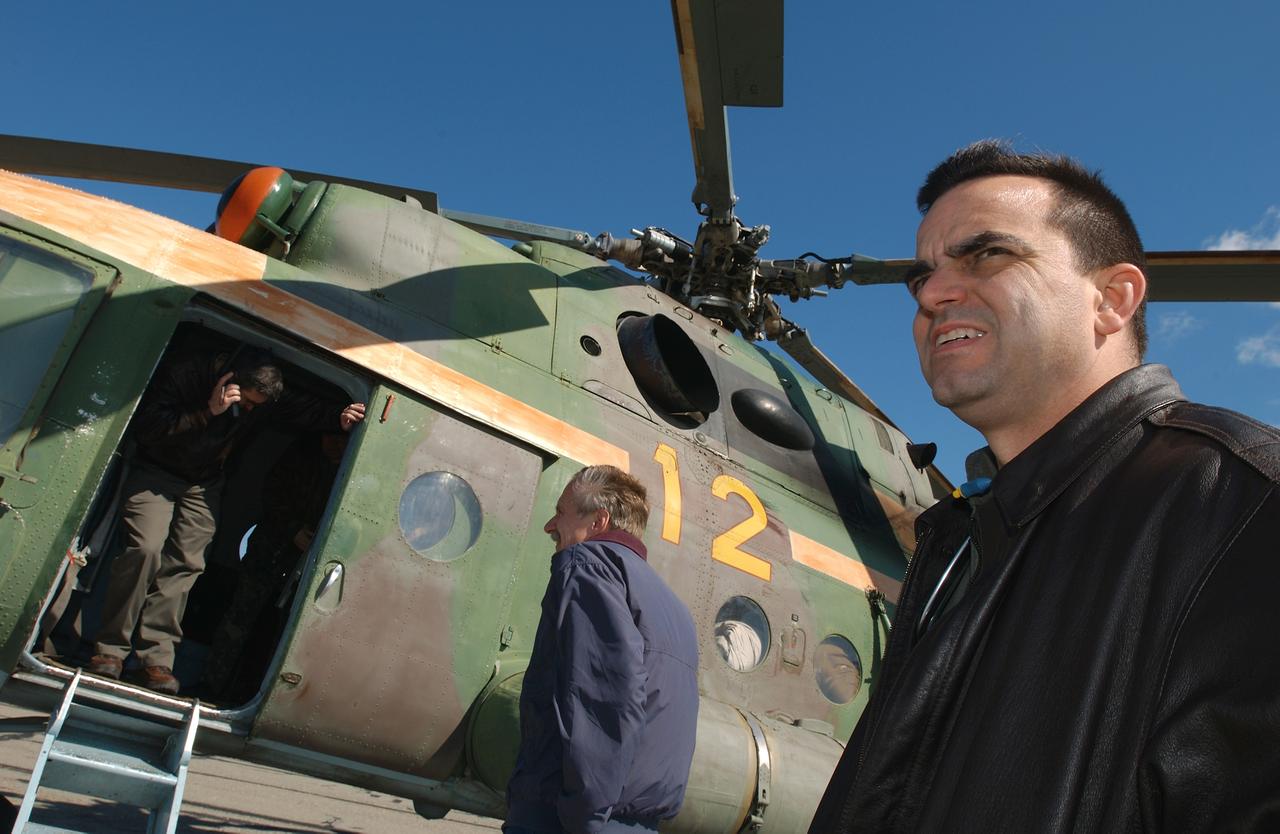

May 4, 2003, Kazakhstan. Bob Cabana (L in door), Director of Flight Crew Operations talks with NASA colleagues on the satellite phone from a Russian helicopter while Bill Gerstenmaier (center), I.S.S. Program Manager and J.D. Polk (R), Expedition Six Flight Surgeon wait to get word if they will be continuing on to the landing site after a refueling stop. Photo Credit: "NASA/Bill Ingalls"
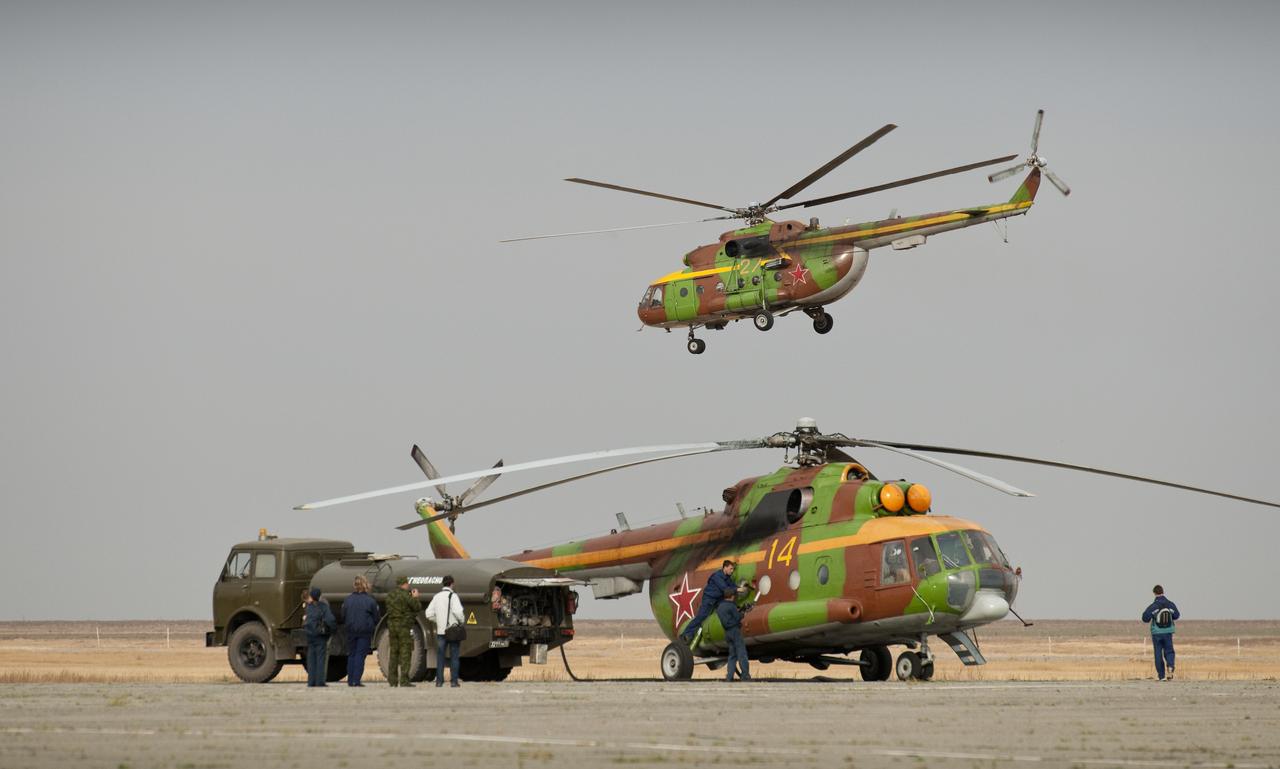

Russian search and rescue helicopters refuel in Arkalyk, Kazakhstan prior to the landing of the Soyuz TMA-18 spacecraft with Expedition 24 Commander Alexander Skvortsov and Flight Engineers Tracy Caldwell Dyson and Mikhail Kornienko on Saturday, Sept. 25, 2010. Russian Cosmonauts Skvortsov and Kornienko and NASA Astronaut Caldwell Dyson, are returning from six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 23 and 24 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
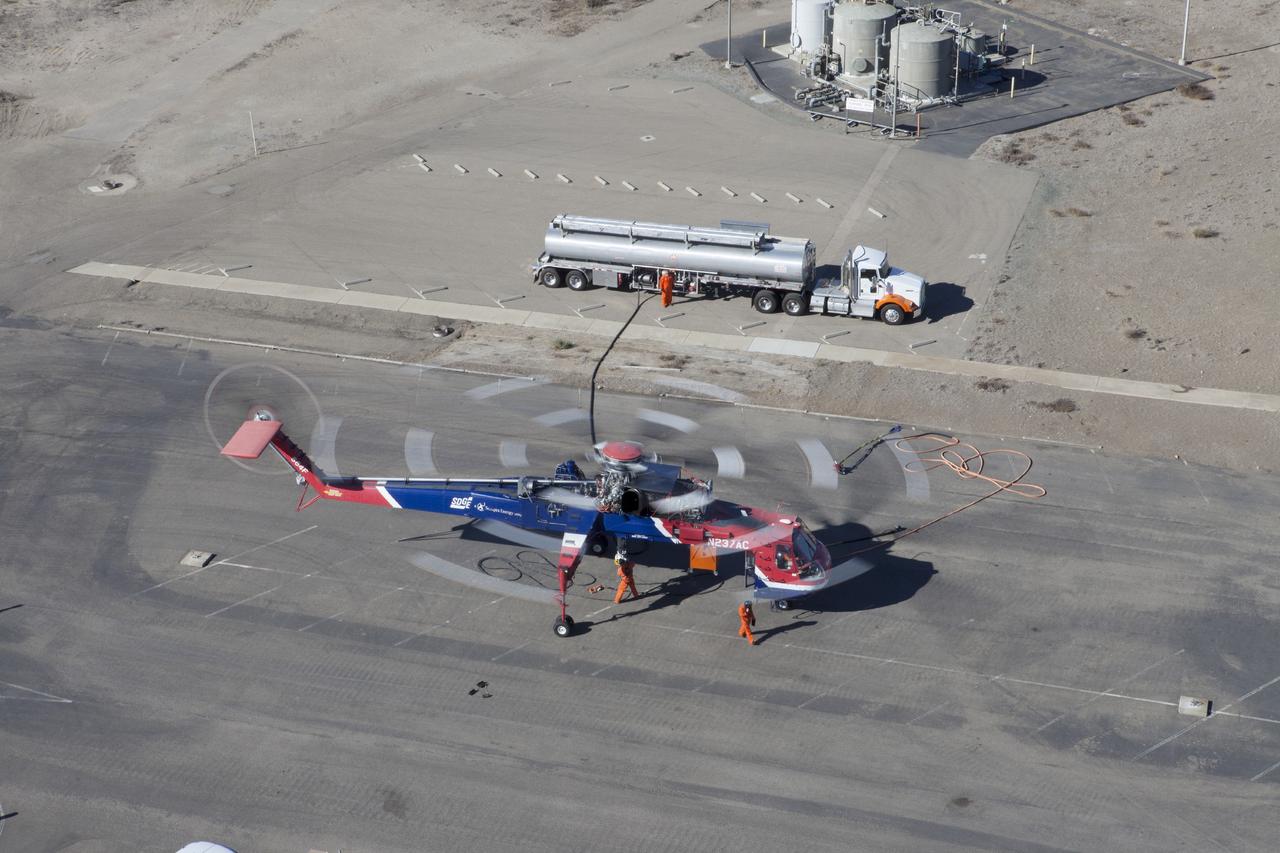

MORRO BAY, Calif. – An Erickson Sky Crane helicopter refuels following splash down of SpaceX Dragon test article. The test enables SpaceX engineers to evaluate the spacecraft's parachute deployment system as part of a milestone under its Commercial Crew Integrated Capability agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The parachute test took place at Morro Bay, Calif. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
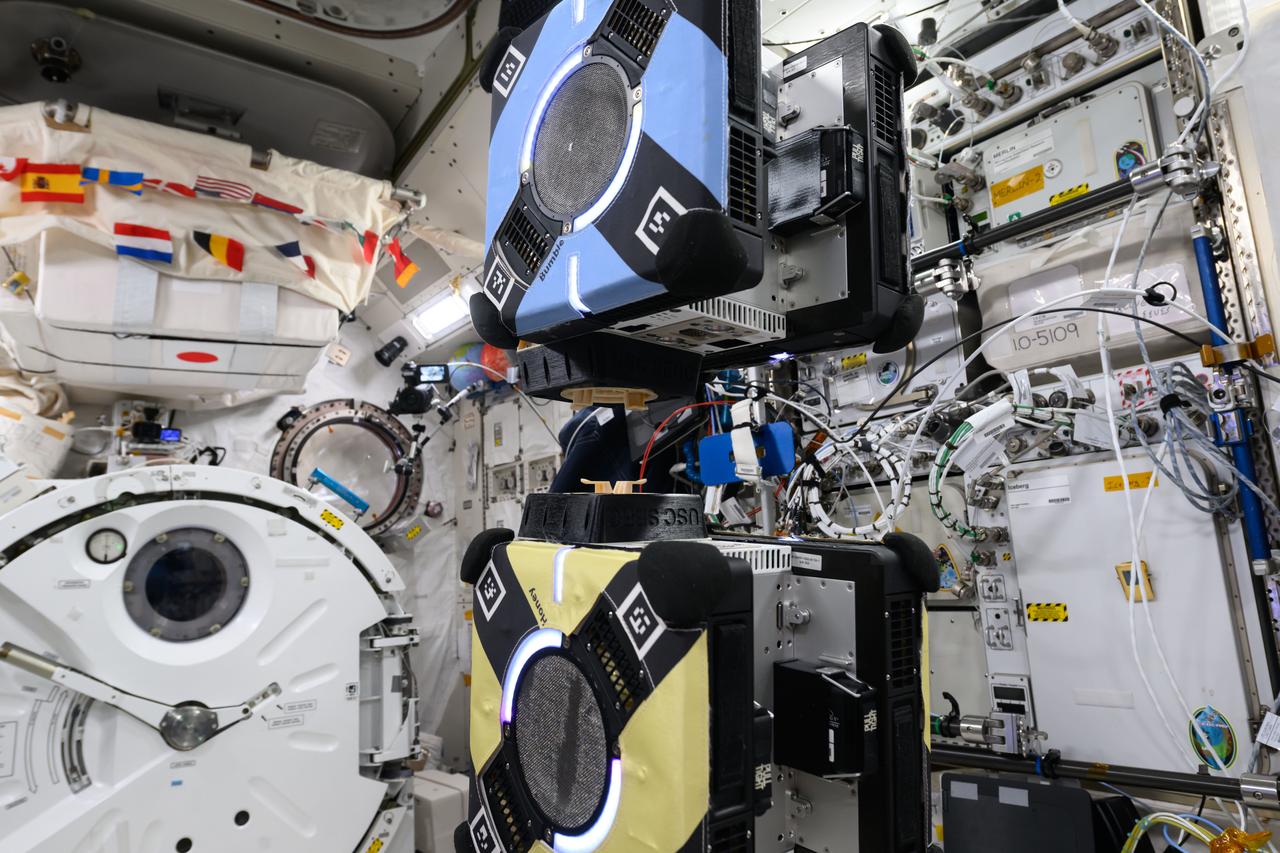

iss072e423875 (1/3/2025) — A view of the CLINGERS Cubesats attached to Astrobee aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Flight Tech Demo of Docking/Undocking Cubesats Inside ISS (CLINGERS) uses the International Space Station’s Astrobee robots to demonstrate an adaptor for docking and close approach sensing to connect both active and passive objects in space. These are critical functions to enable applications such as satellite servicing, orbital refueling, spacecraft repair and upgrade, and in-orbit manufacturing.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at dawn, Steve Fossett (left) gets ready to climb into the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer parked on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Director of Flight Crew Operations Bob Cabana, upper left, talks with NASA colleagues on the satellite phone from a Russian helicopter while International Space Station Program Manager, William Gerstenmaier and J.D. Polk, Expedition 6 Flight Surgeon, right, wait to get word if they will be continuing on to the landing site after a refueling stop, Tuesday, May 4, 2003 in Kazakhstan. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
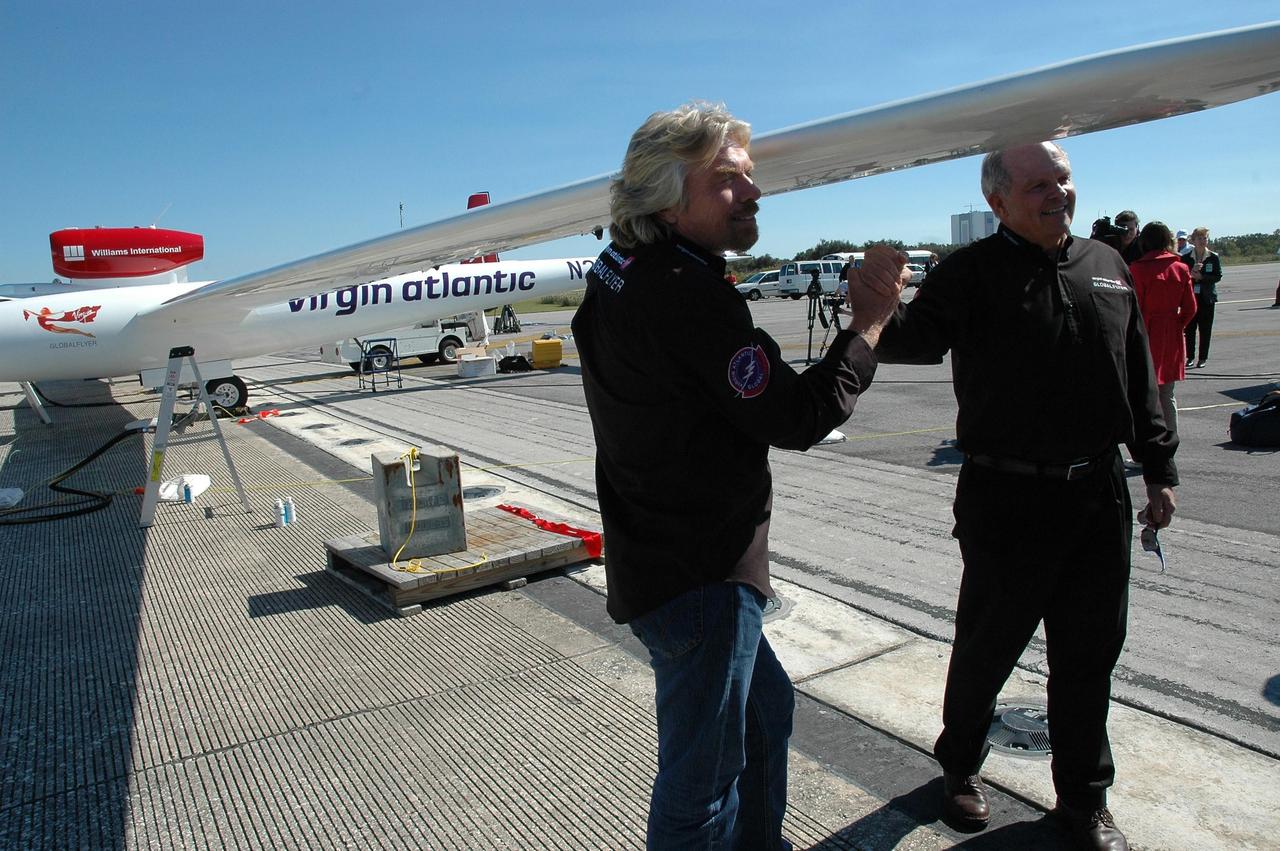

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Sir Richard Branson (left), chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic, talks with Steve Fossett. They are standing next to the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer aircraft, which Fossett will pilot on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility early Tuesday morning. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
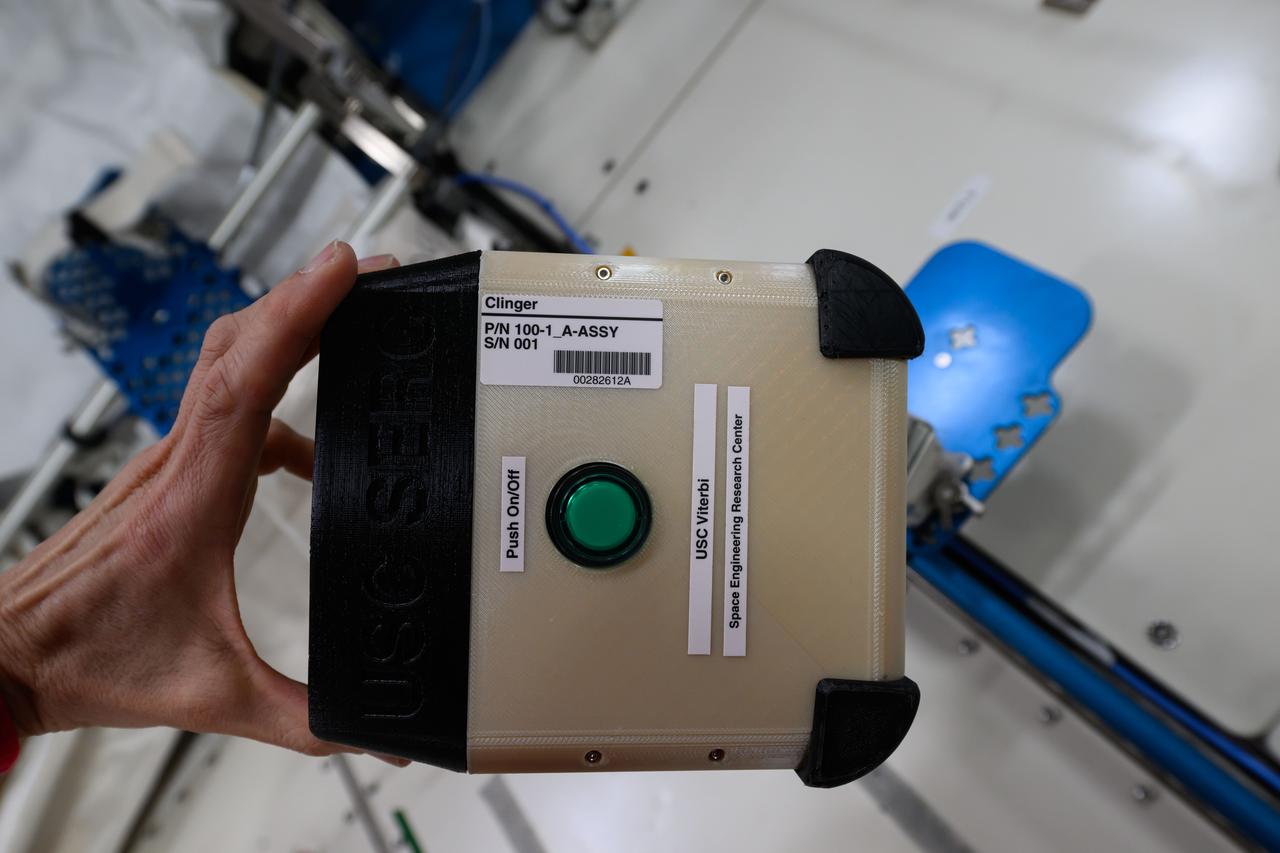

iss072e423784 (1/3/2025) — A view of the CLINGERS Cubesat aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Flight Tech Demo of Docking/Undocking Cubesats Inside ISS (CLINGERS) uses the International Space Station’s Astrobee robots to demonstrate an adaptor for docking and close approach sensing to connect both active and passive objects in space. These are critical functions to enable applications such as satellite servicing, orbital refueling, spacecraft repair and upgrade, and in-orbit manufacturing.
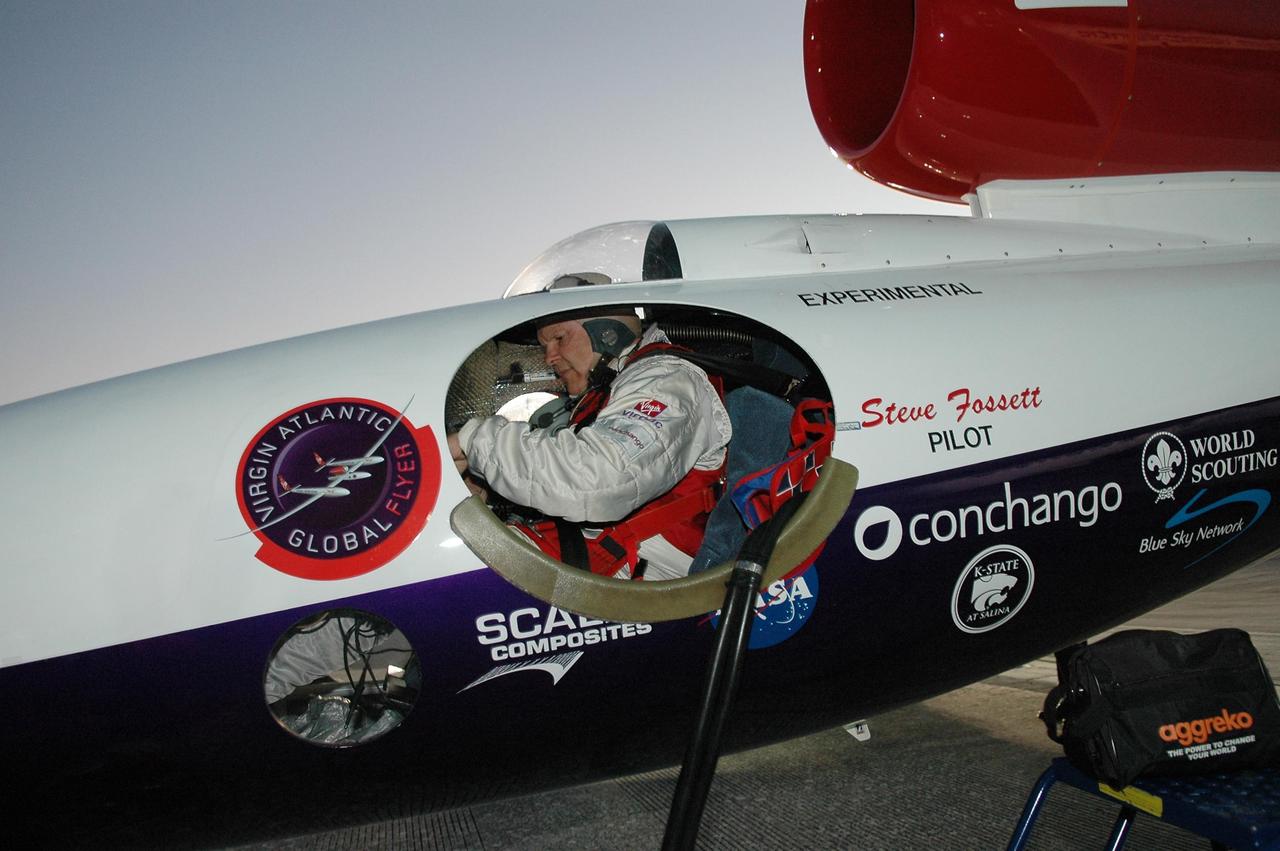

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett, seated in the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer cockpit, completes the checkout before takeoff. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
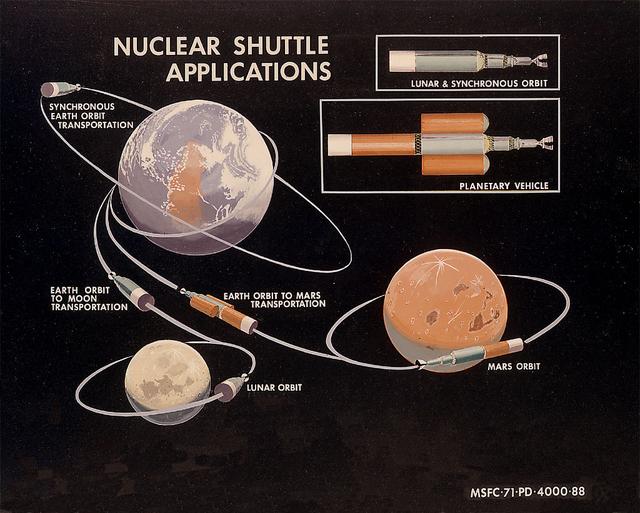
In this 1971 artist's concept, the Nuclear Shuttle is shown in various space-based applications. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development persornel, the Nuclear Shuttle would deliver payloads to geosychronous Earth orbits or lunar orbits then return to low Earth orbit for refueling. A cluster of Nuclear Shuttle units could form the basis for planetary missions.
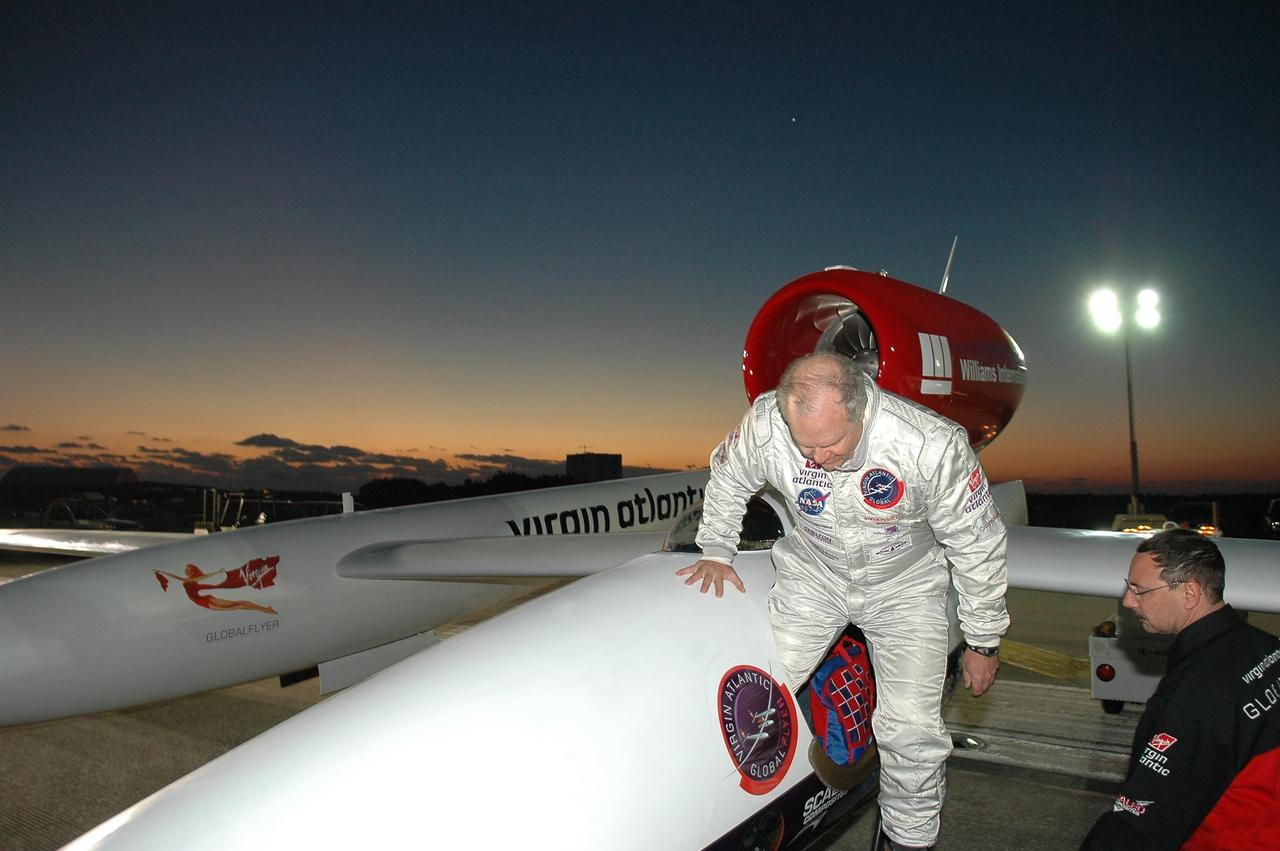

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at dawn, Steve Fossett (left) climbs into the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer parked on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
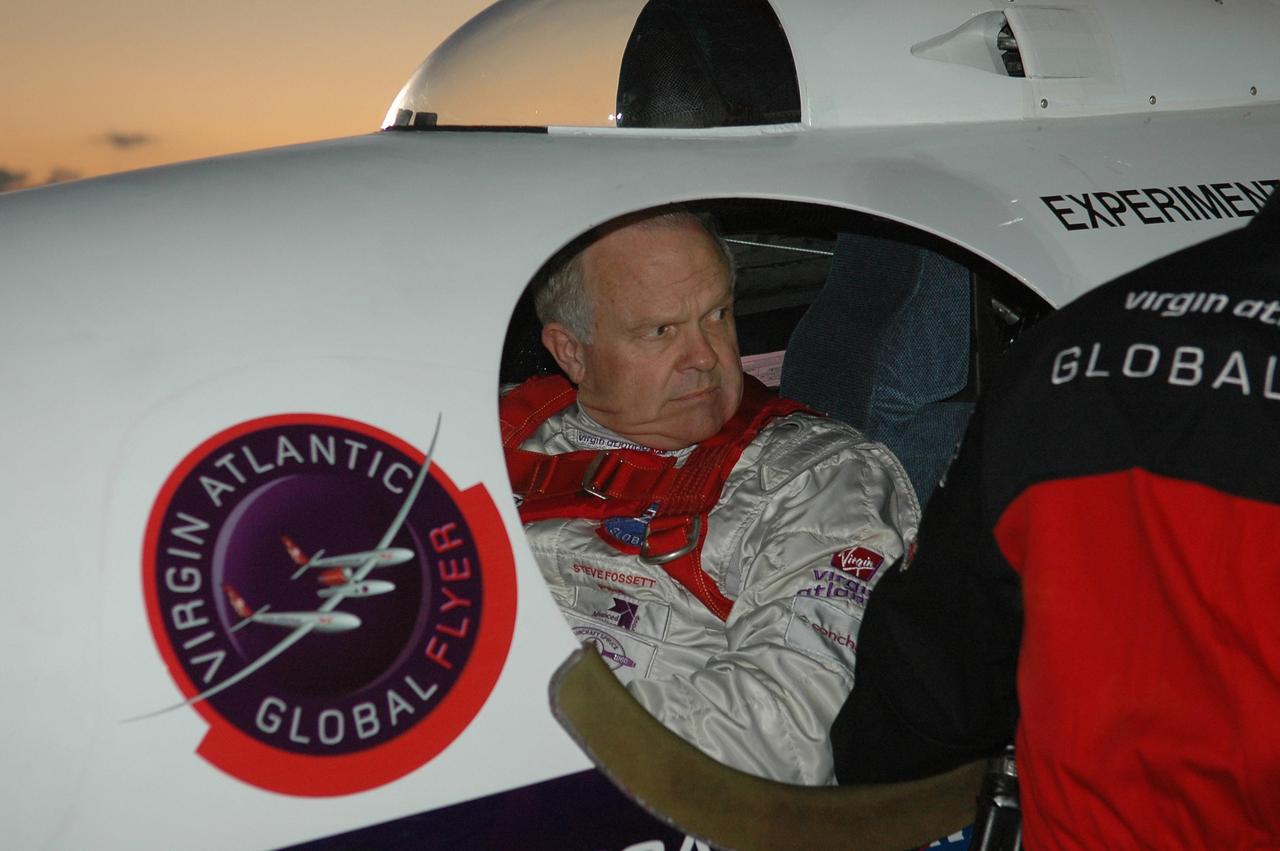

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett is strapped into the cockpit of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer waiting for takeoff. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Jill McGuire, project manager for the Robotic Refueling Mission 3, or RRM3, experiment, describes RRM3 hardware for members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
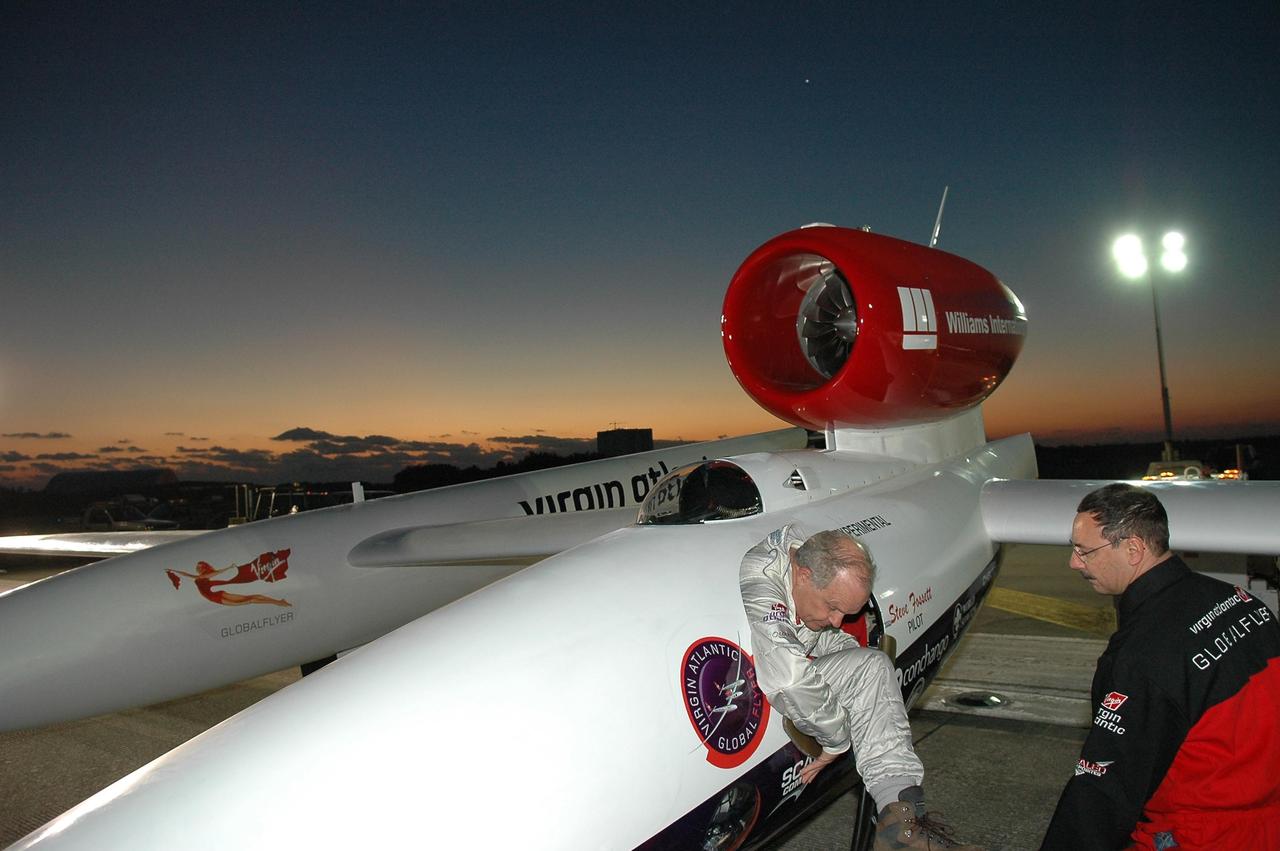

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at dawn, Steve Fossett (left) climbs into the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer parked on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
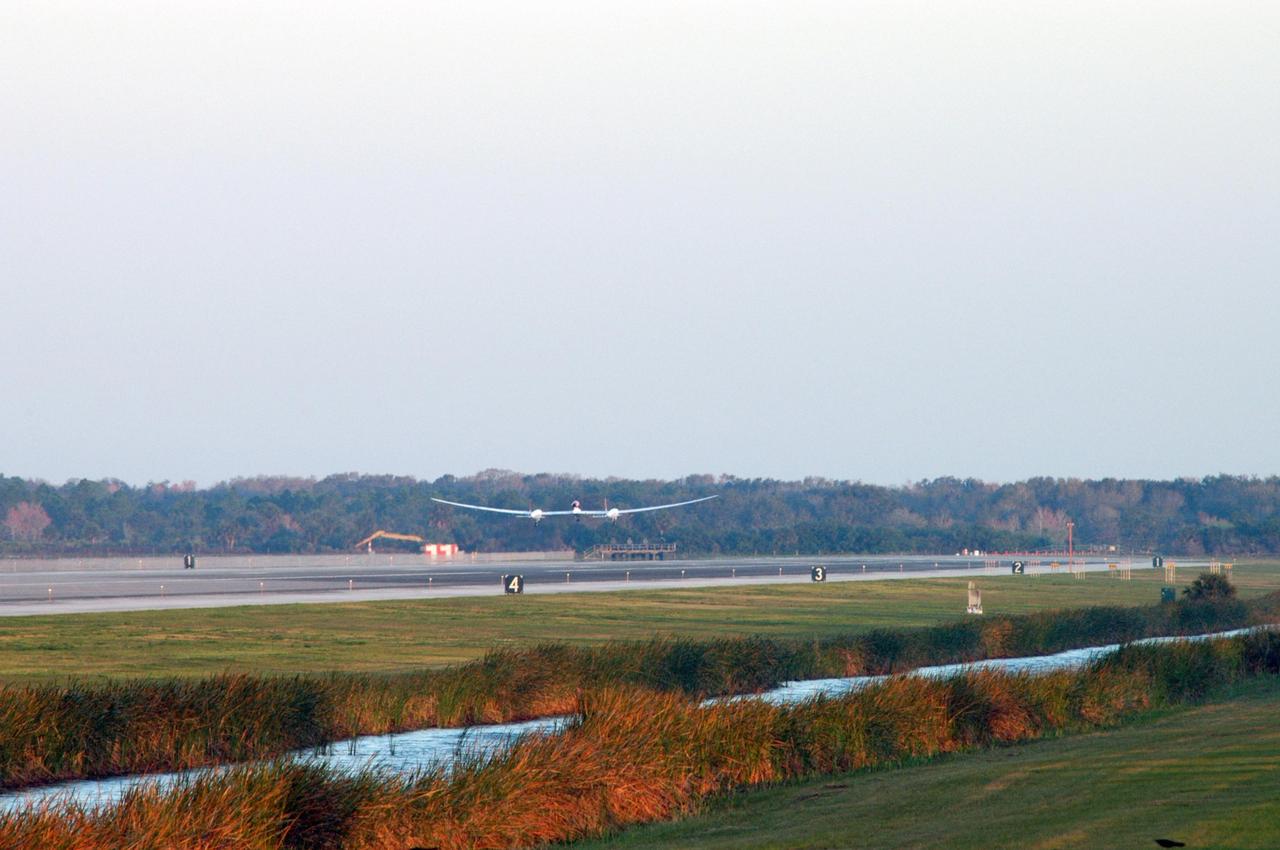

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, lifts off the ground. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
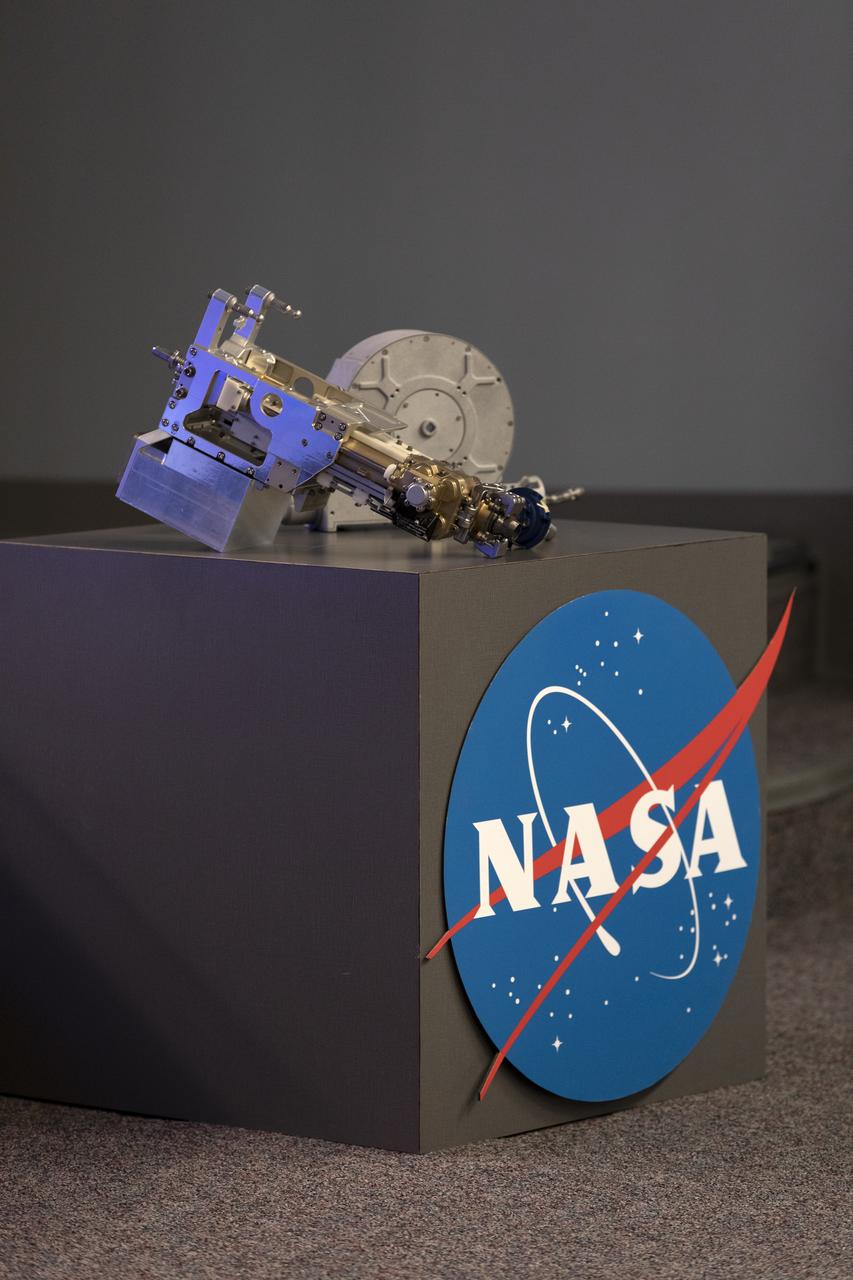

Hardware associated with the Robotic Refueling Mission 3, or RRM3, experiment, ws on display for members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.

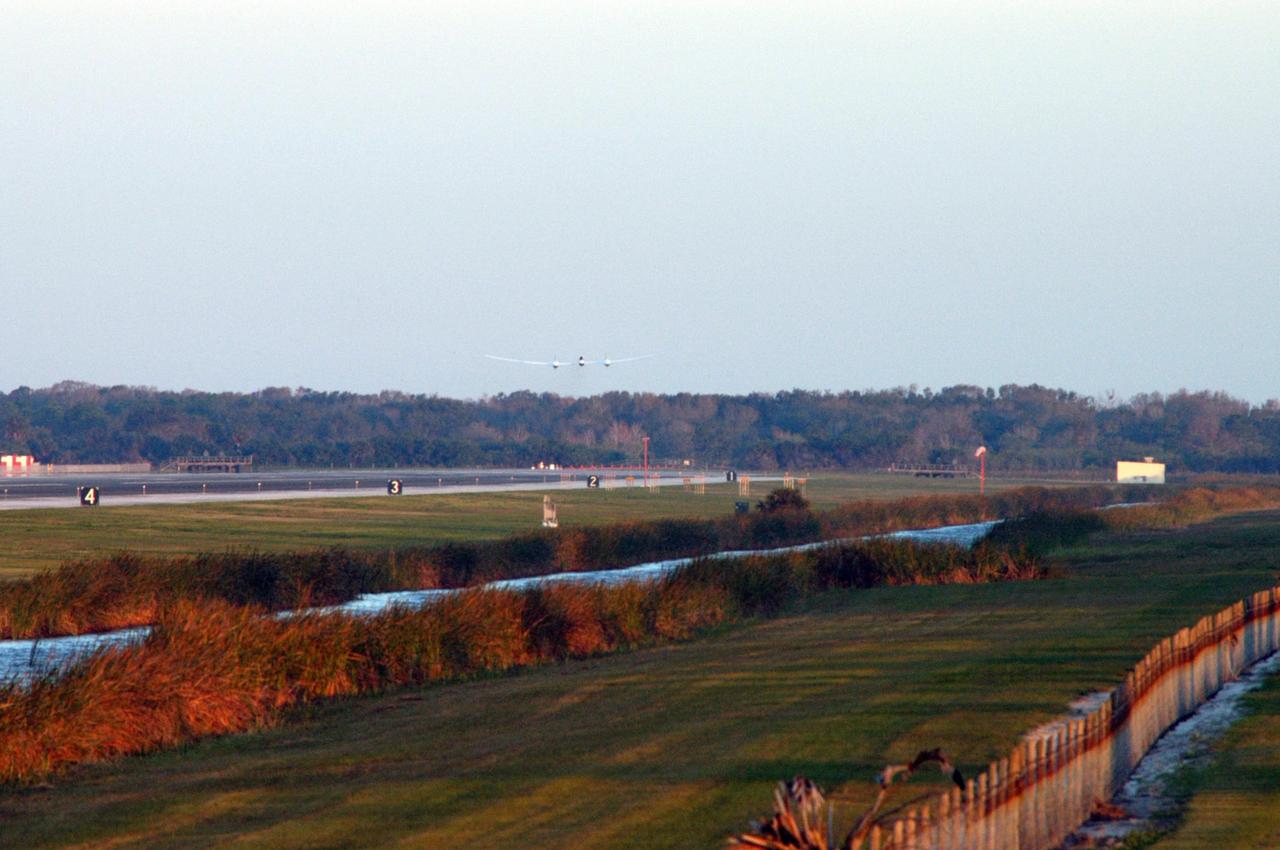
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - From NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, is airborne. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
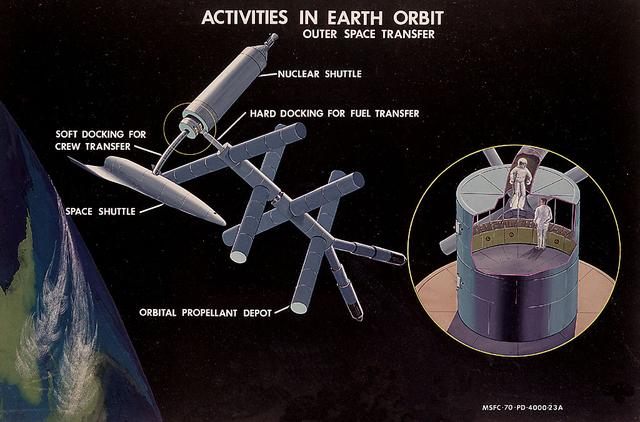
This artist's concept from 1970 shows a Nuclear Shuttle docked to an Orbital Propellant Depot and an early Space Shuttle. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development plarners, the Nuclear Shuttle, in either manned or unmanned mode, would deliver payloads to lunar orbit or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling and additonal missions.