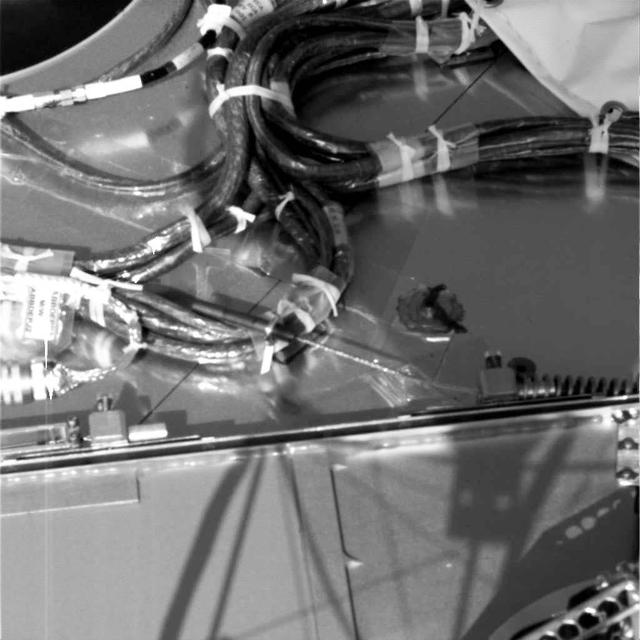

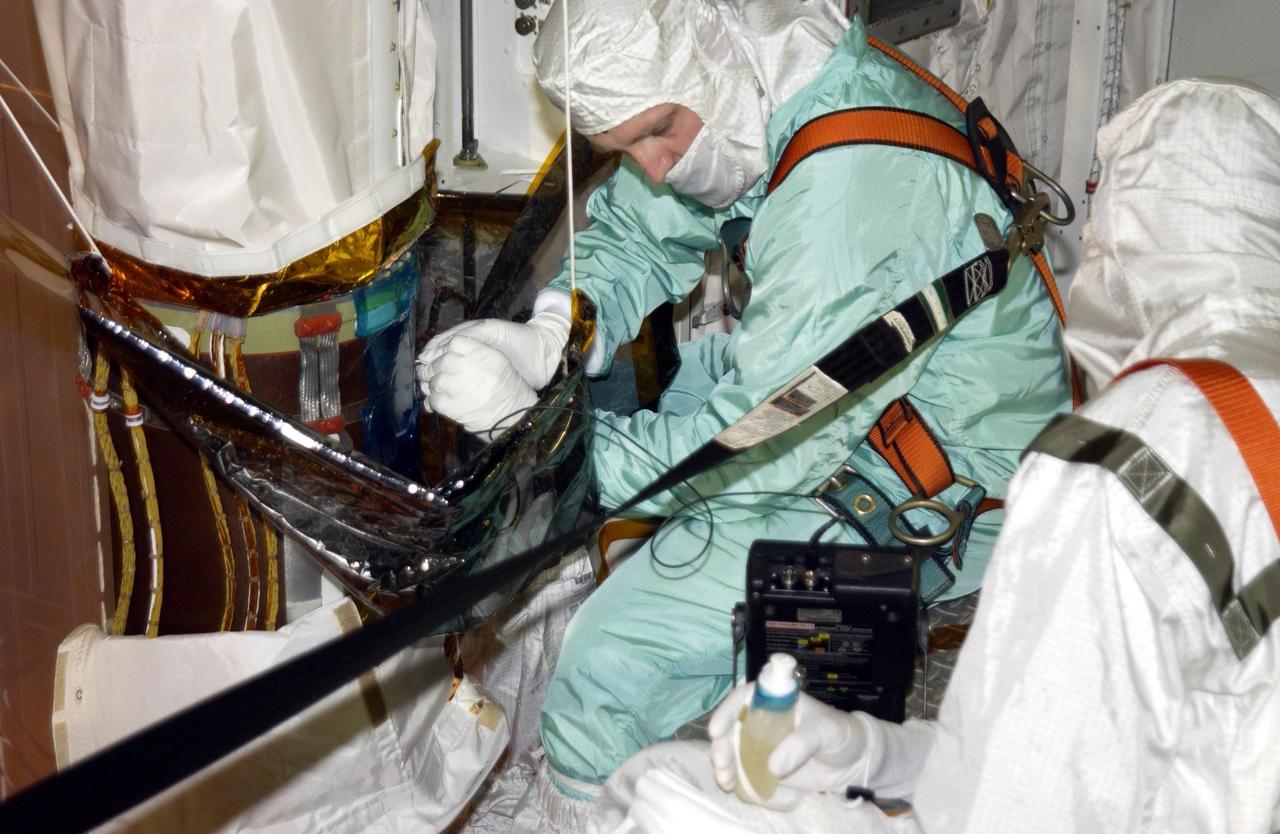
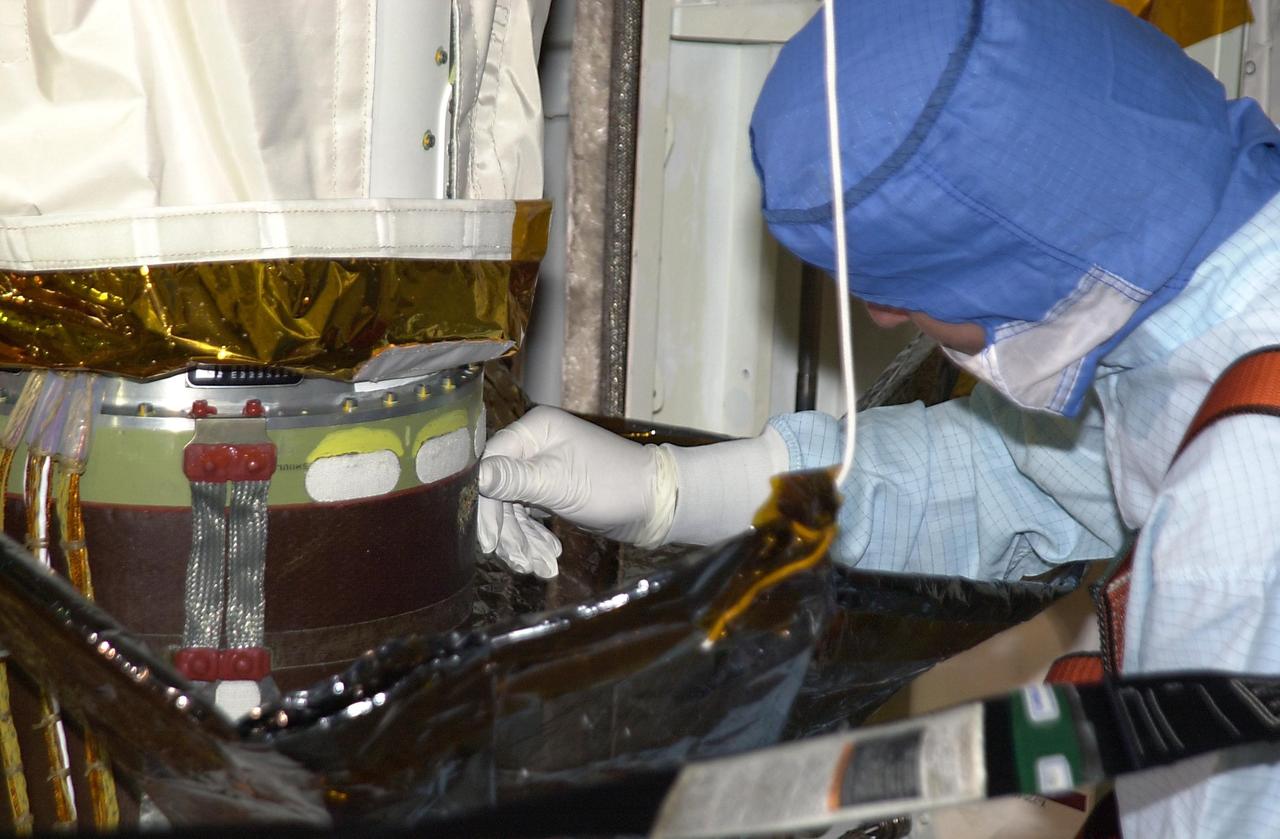
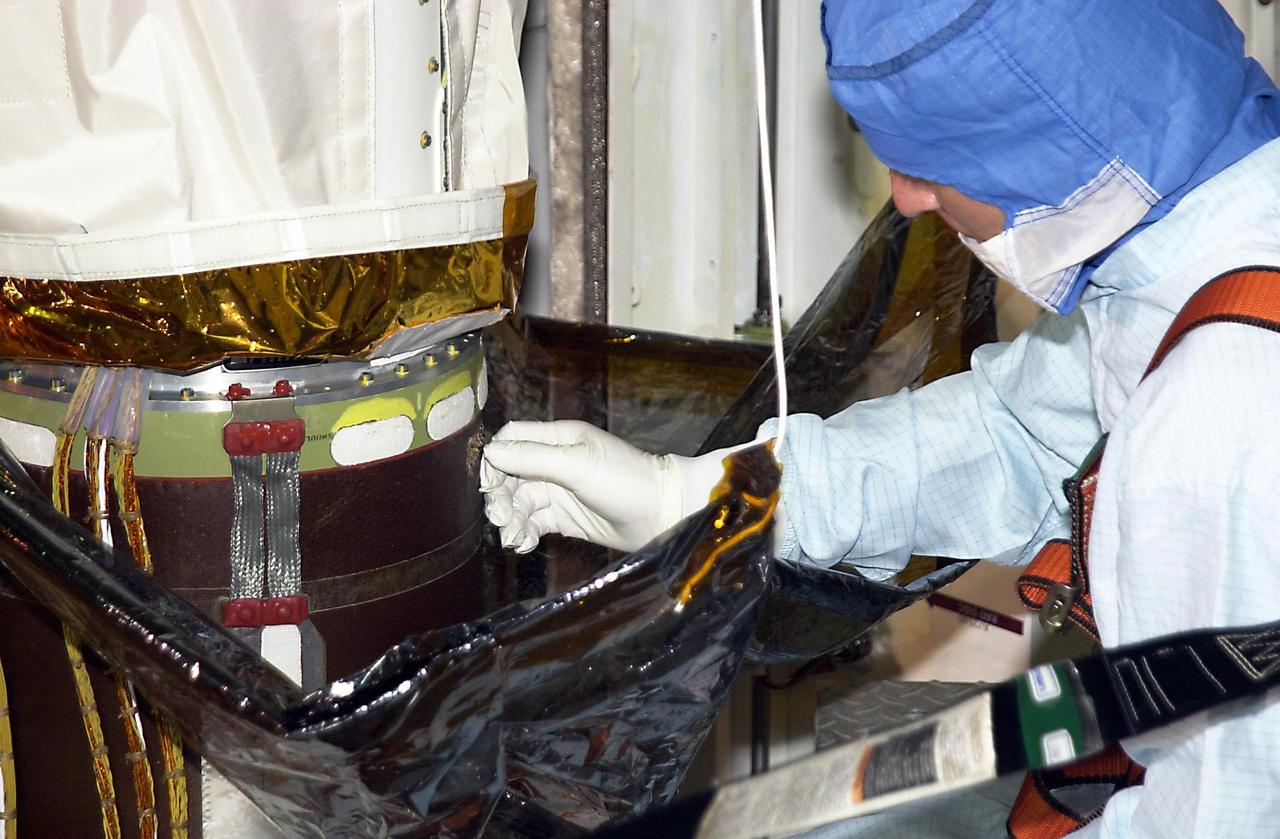
Robotic Arm Biobarrier Cable
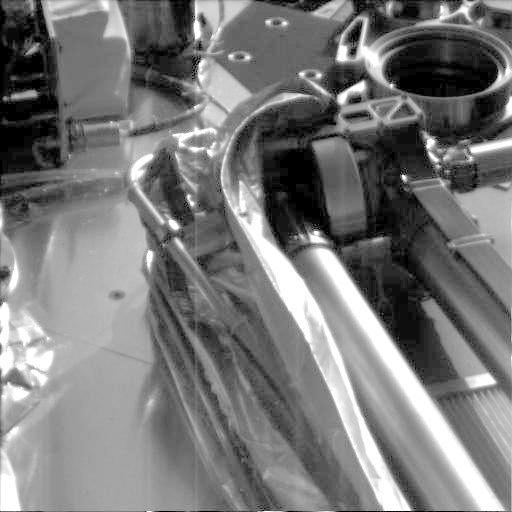
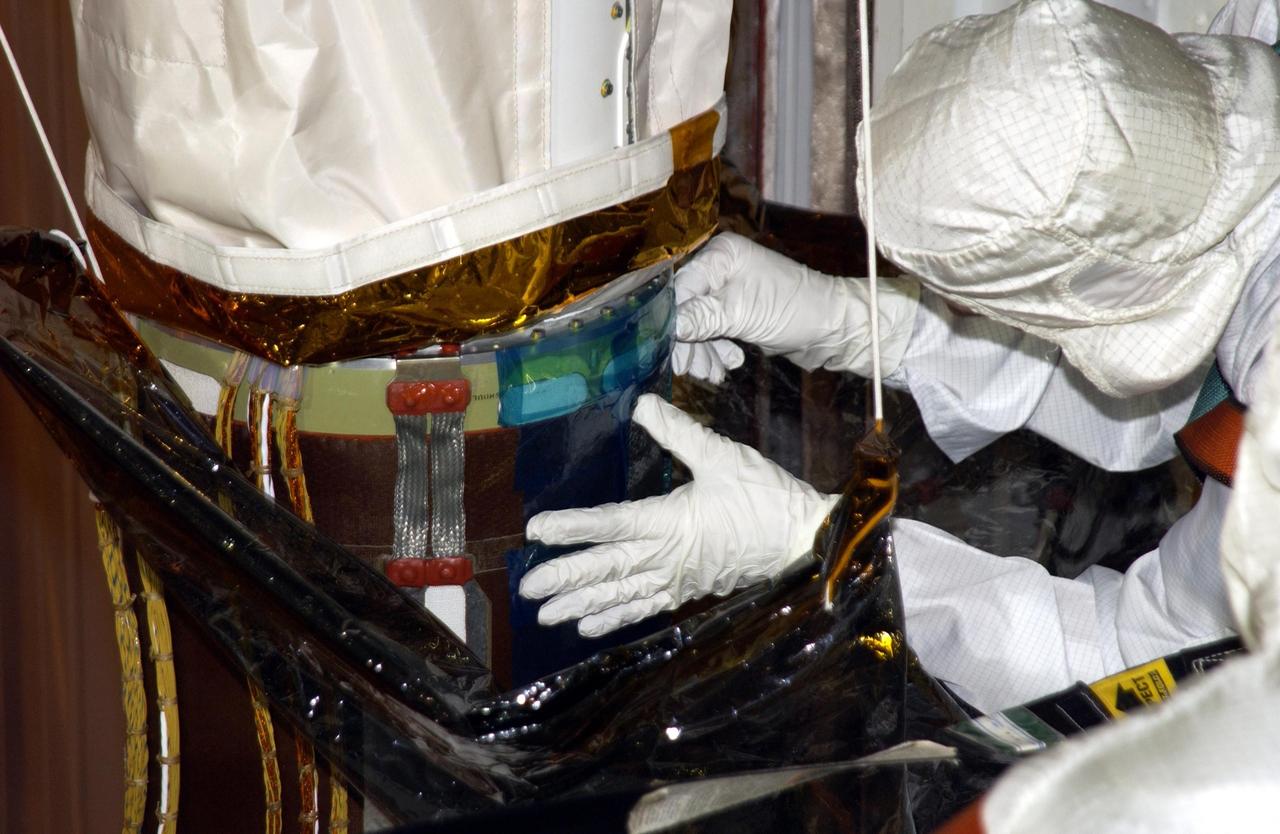
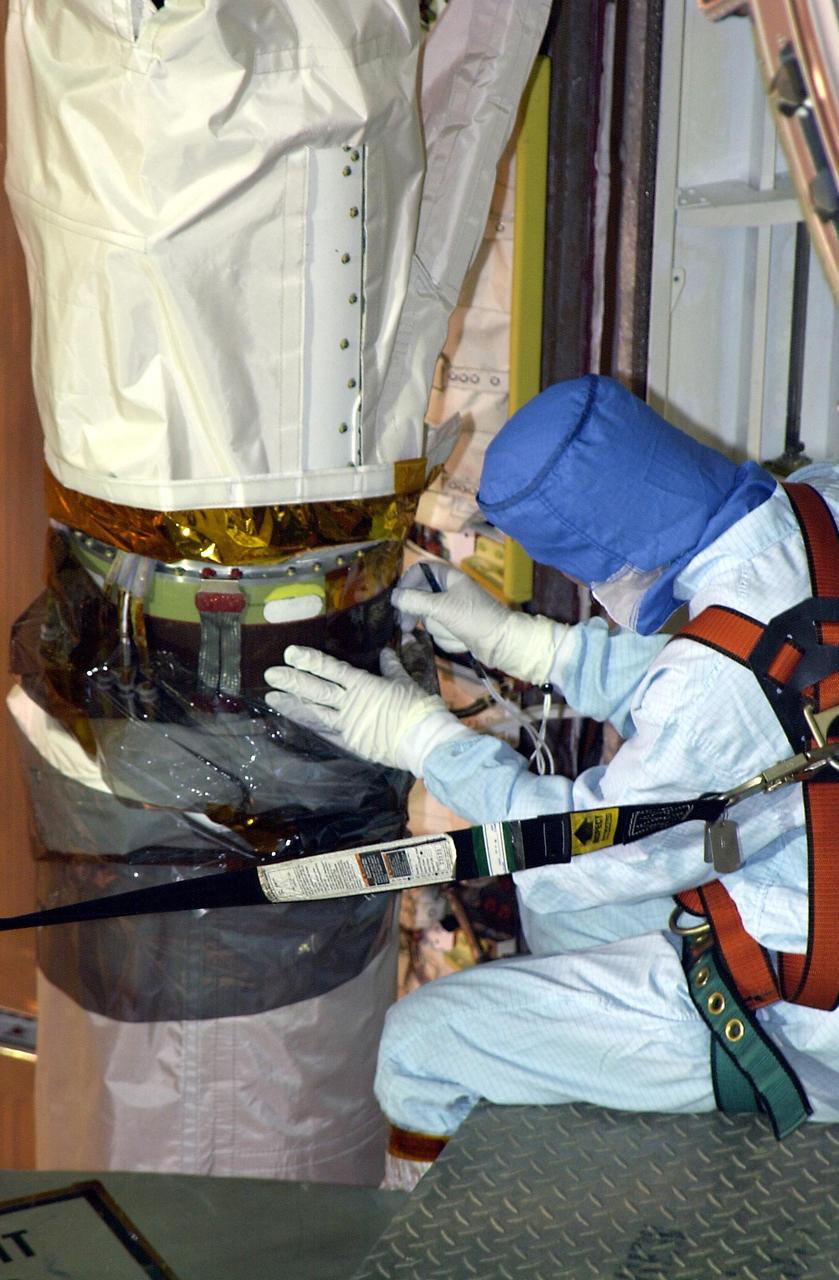
Robotic Arm Unwrapped
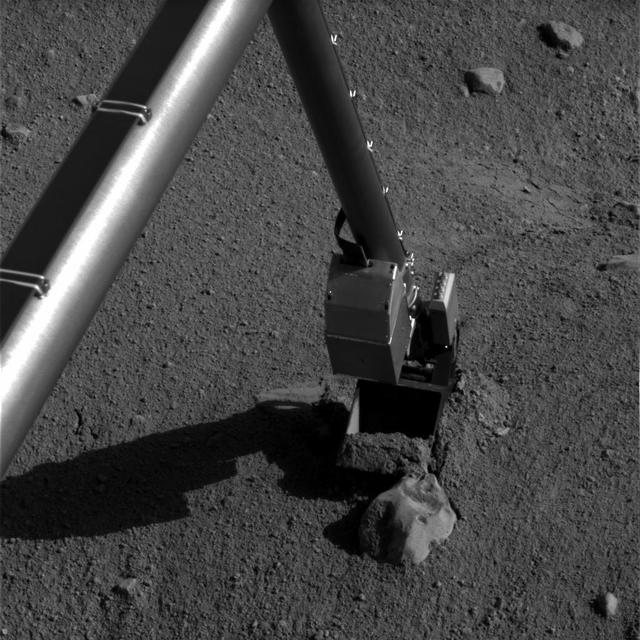

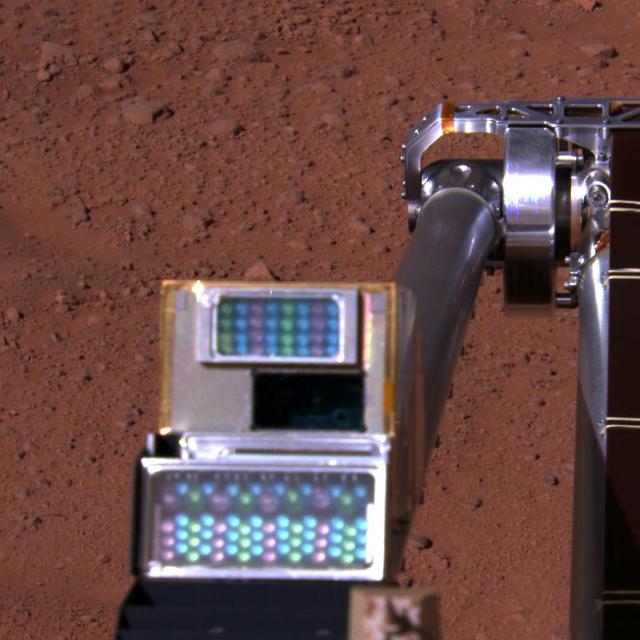
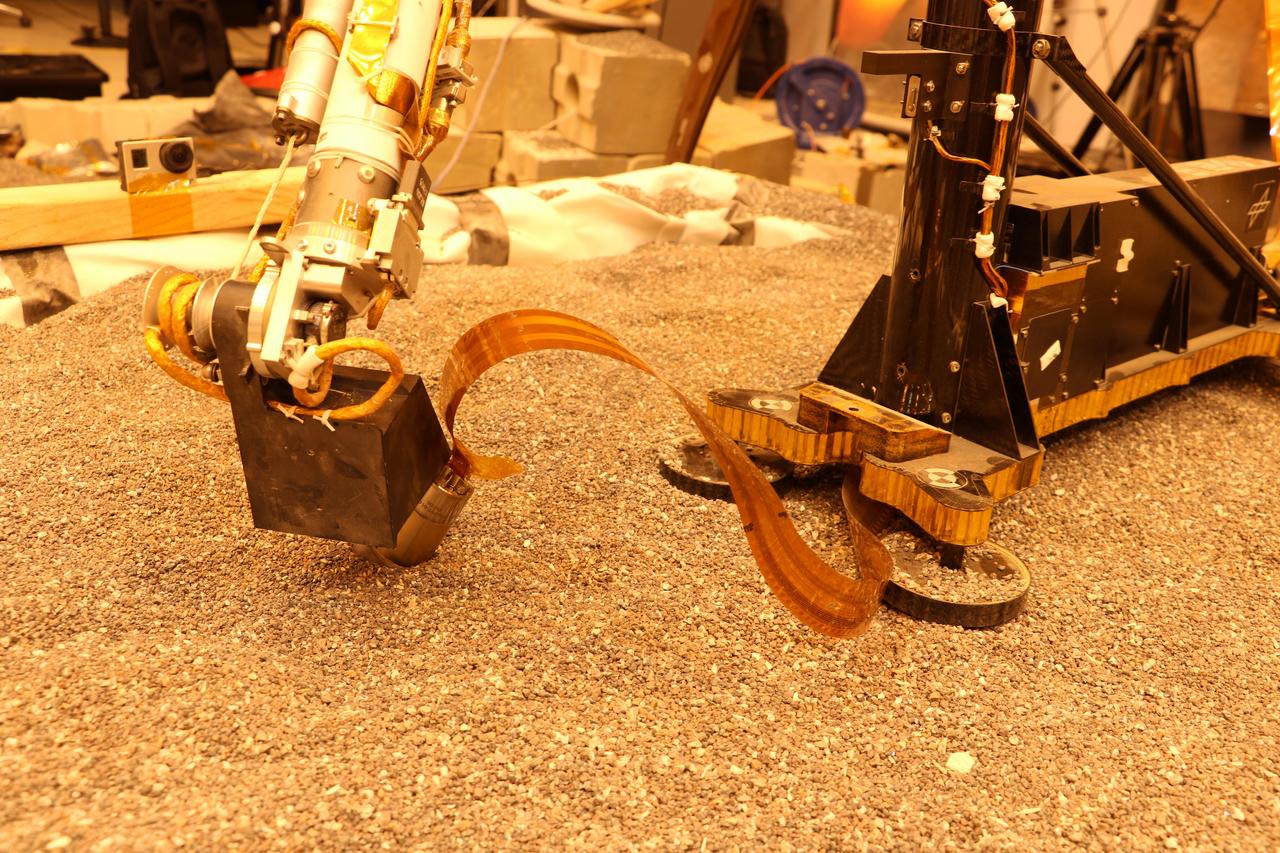
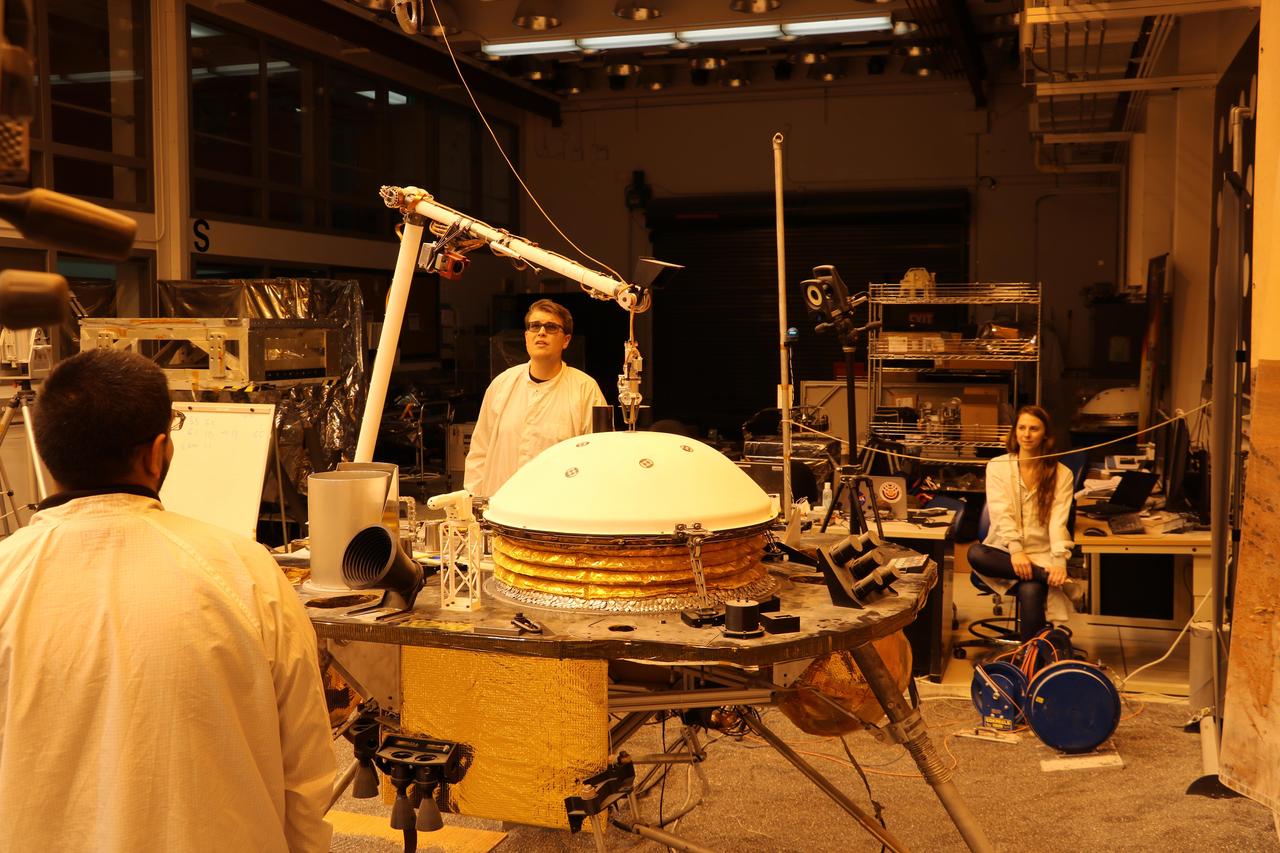
Phoenix Robotic Arm connects with Alice
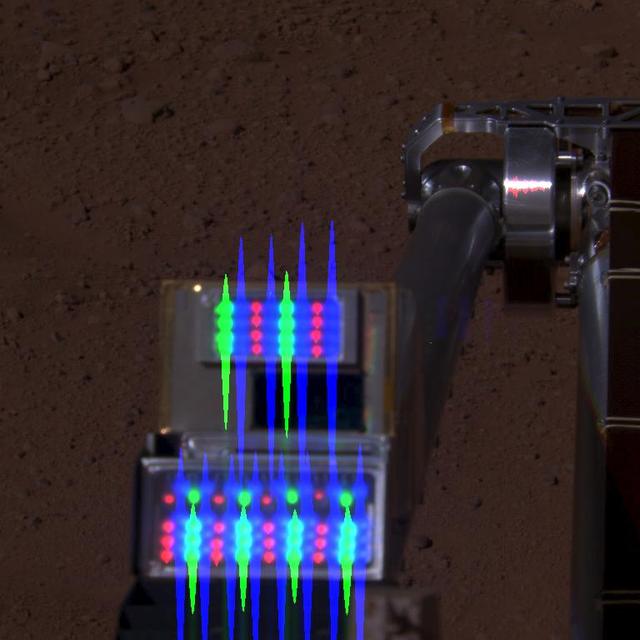
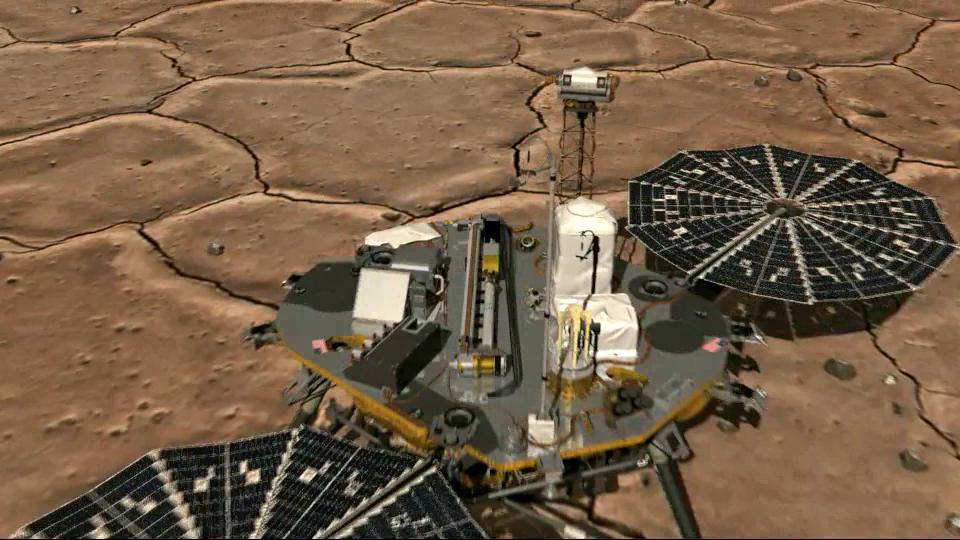
Robotic Arm Camera on Mars with Lights On
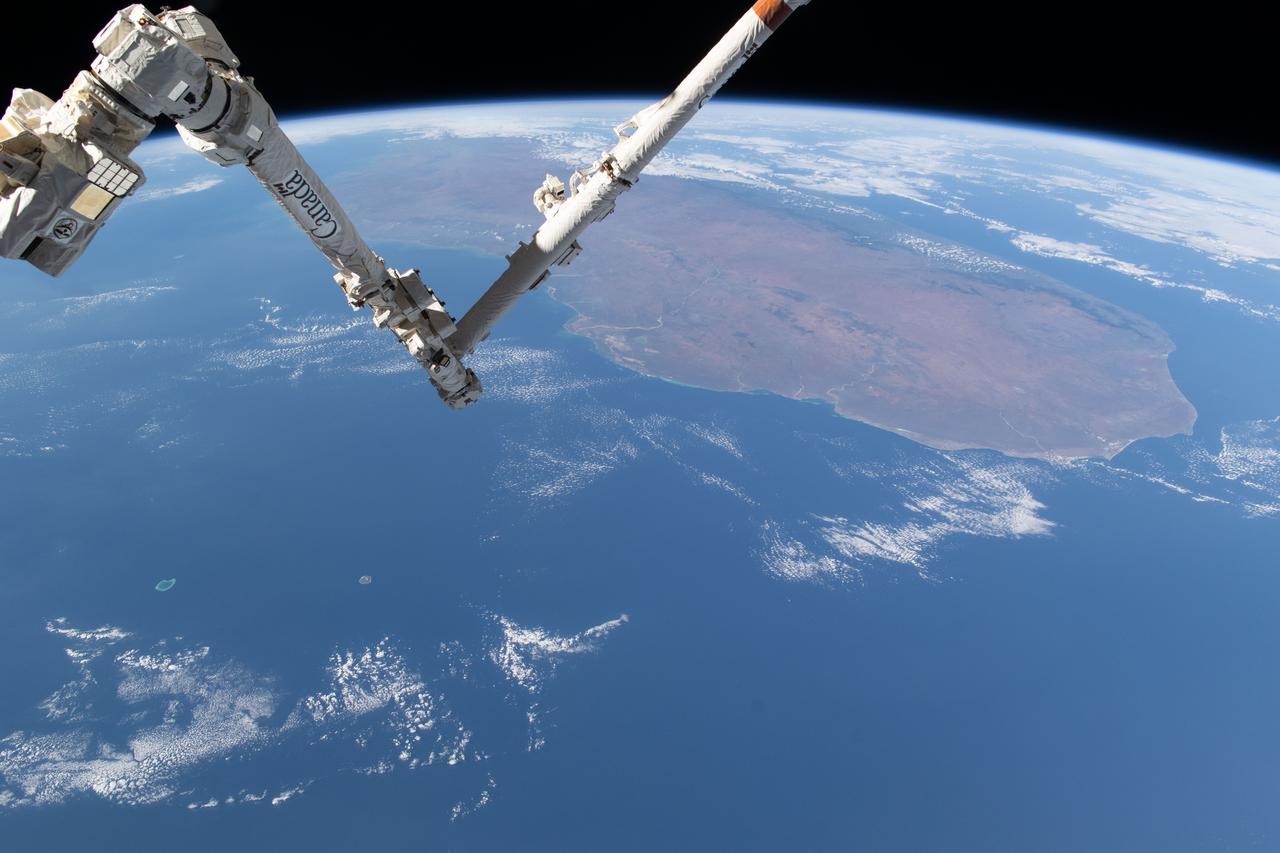

iss071e361950 (July 15, 2024) --- The International Space Station's 57.7-foot-long Canadarm2 robotic arm crosses the foreground as the orbital outpost soared 265 miles above the Mozambique Channel south of the African island nation of Madagascar.
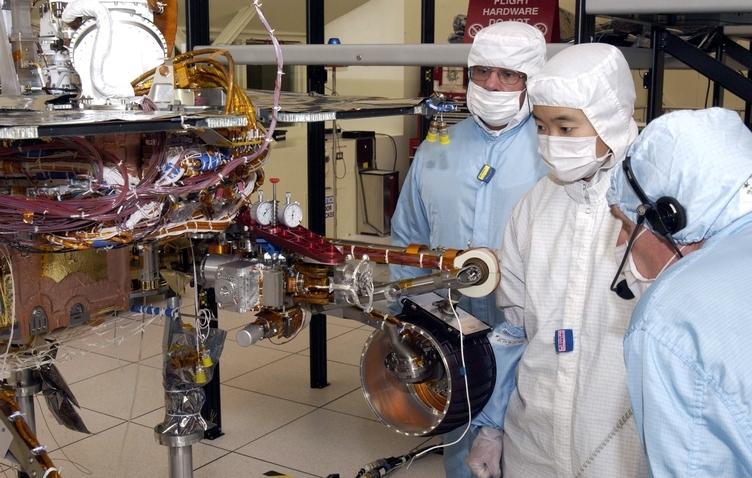
JPL engineers examine the robotic arm of NASA Mars Exploration Rover 1.

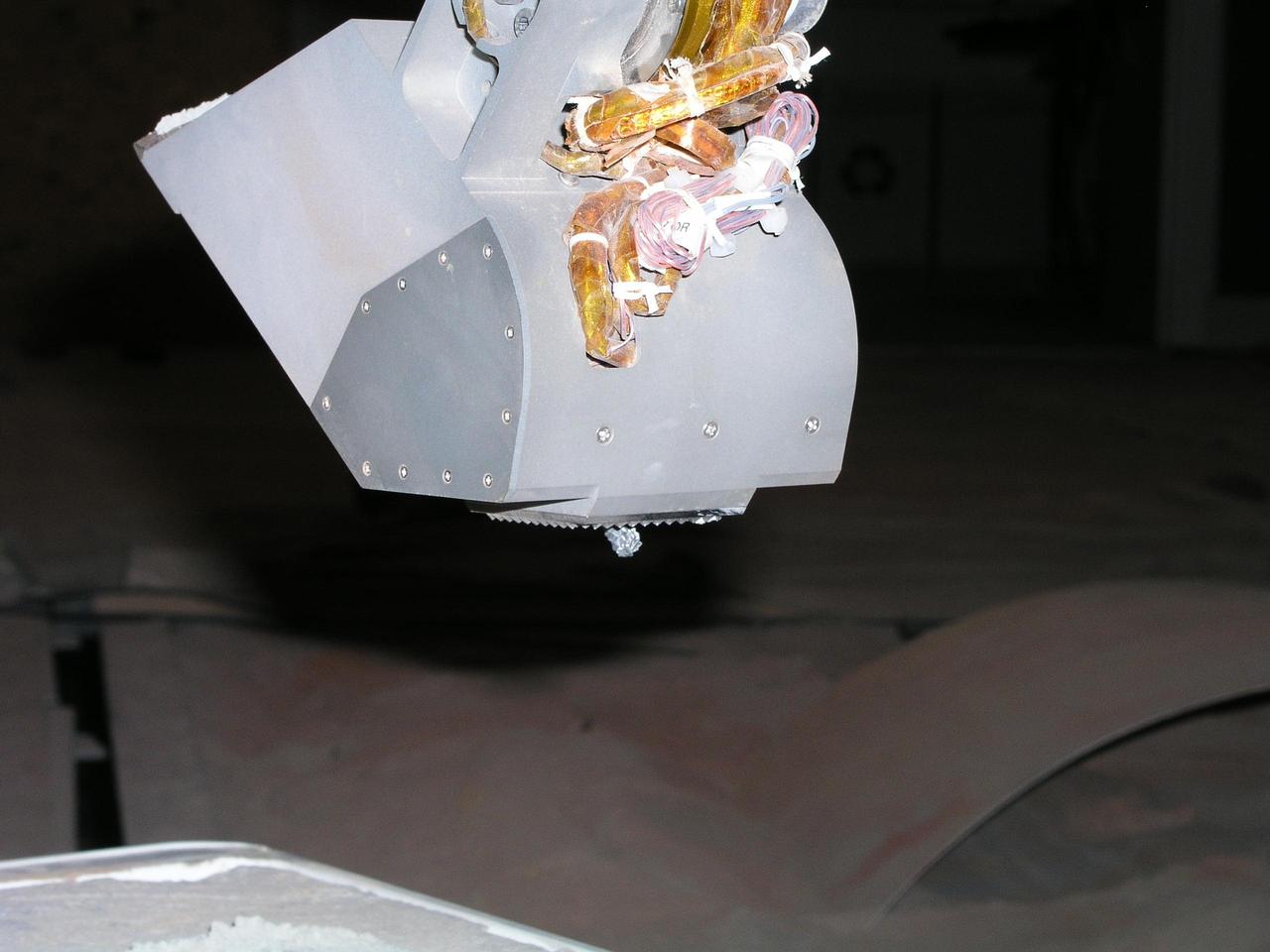
Martian Soil Inside Phoenix Robotic Arm Scoop

Robotic Arm Camera on Mars, with Lights Off
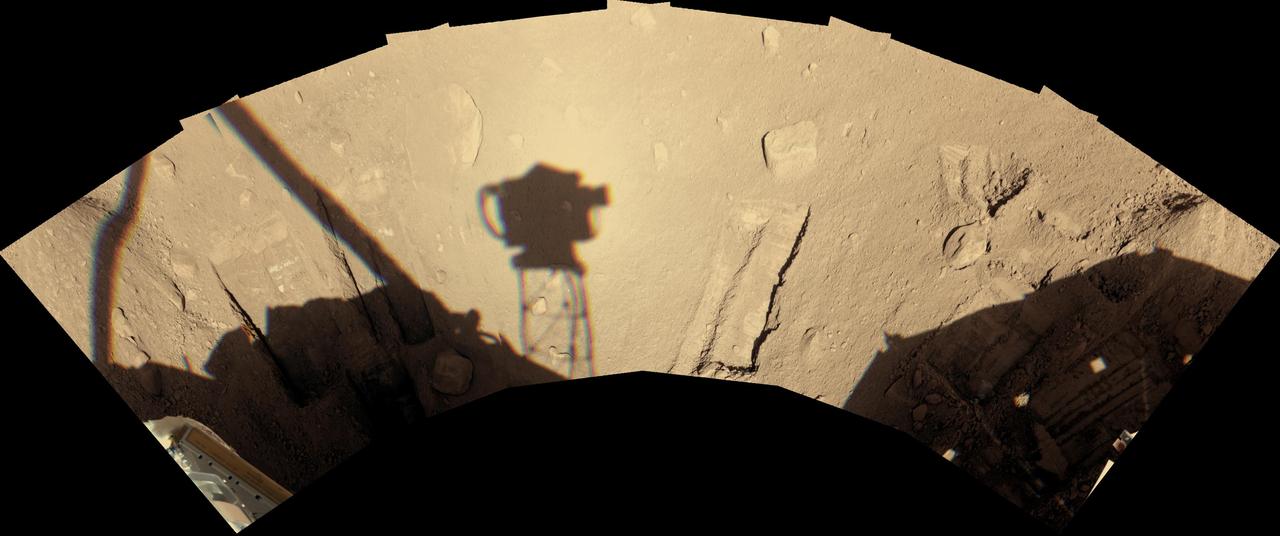

Phoenix Robotic Arm Workspace After 90 Sols

Members of NASA Phoenix Mars Mission Robotic Arm engineering team test the arm motorized rasp in the Payload Interoperability Testbed at the University of Arizona, Tucson.
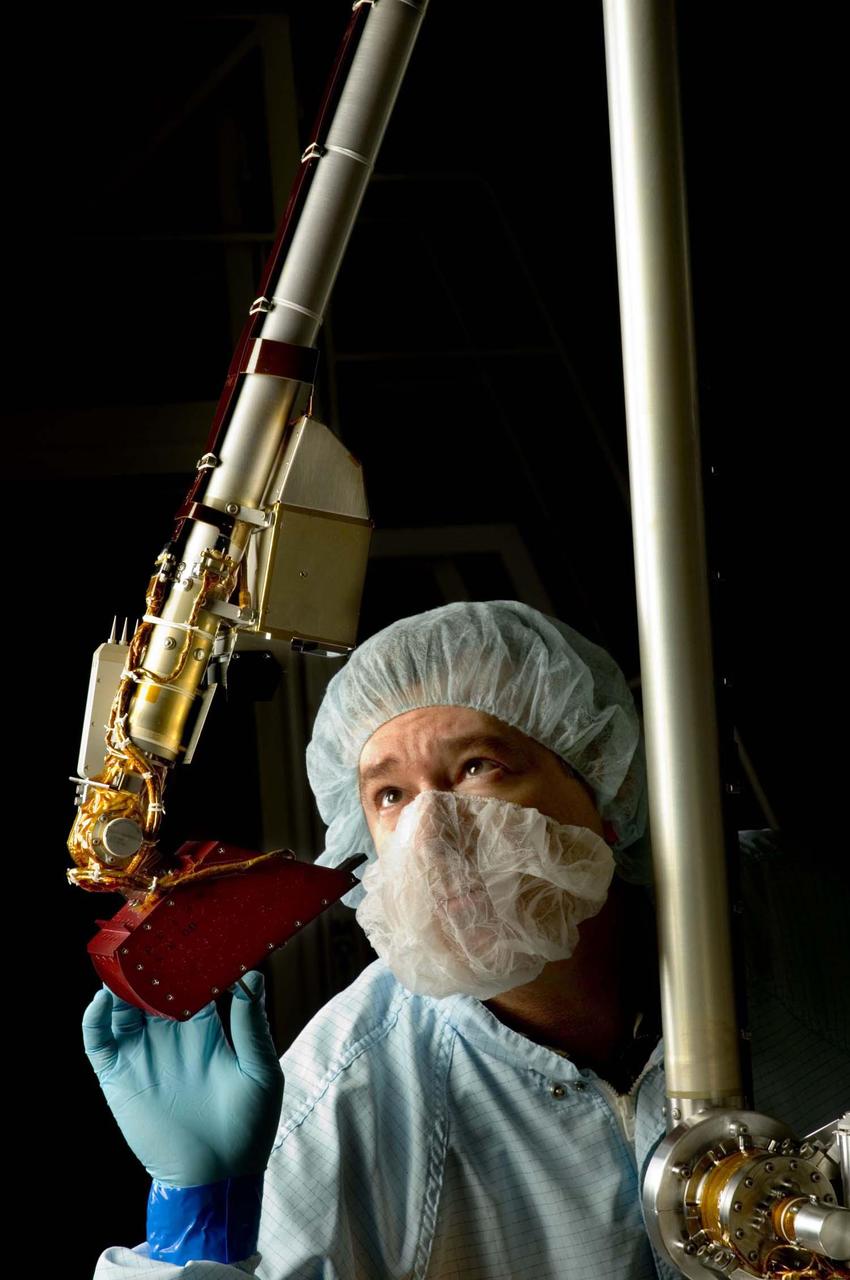
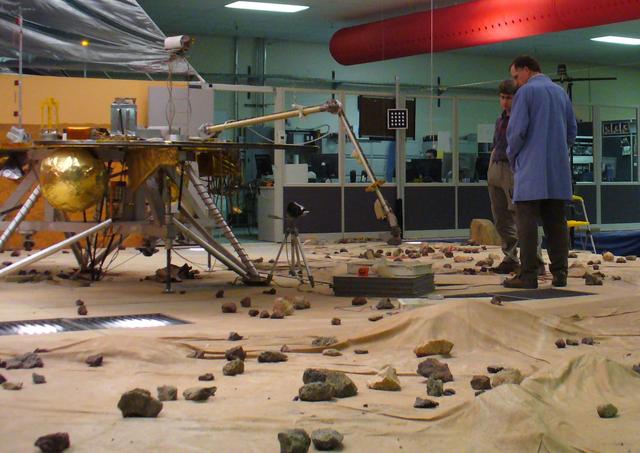
A spacecraft technician inspected the vital robotic arm of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander during the assembly phase of the mission
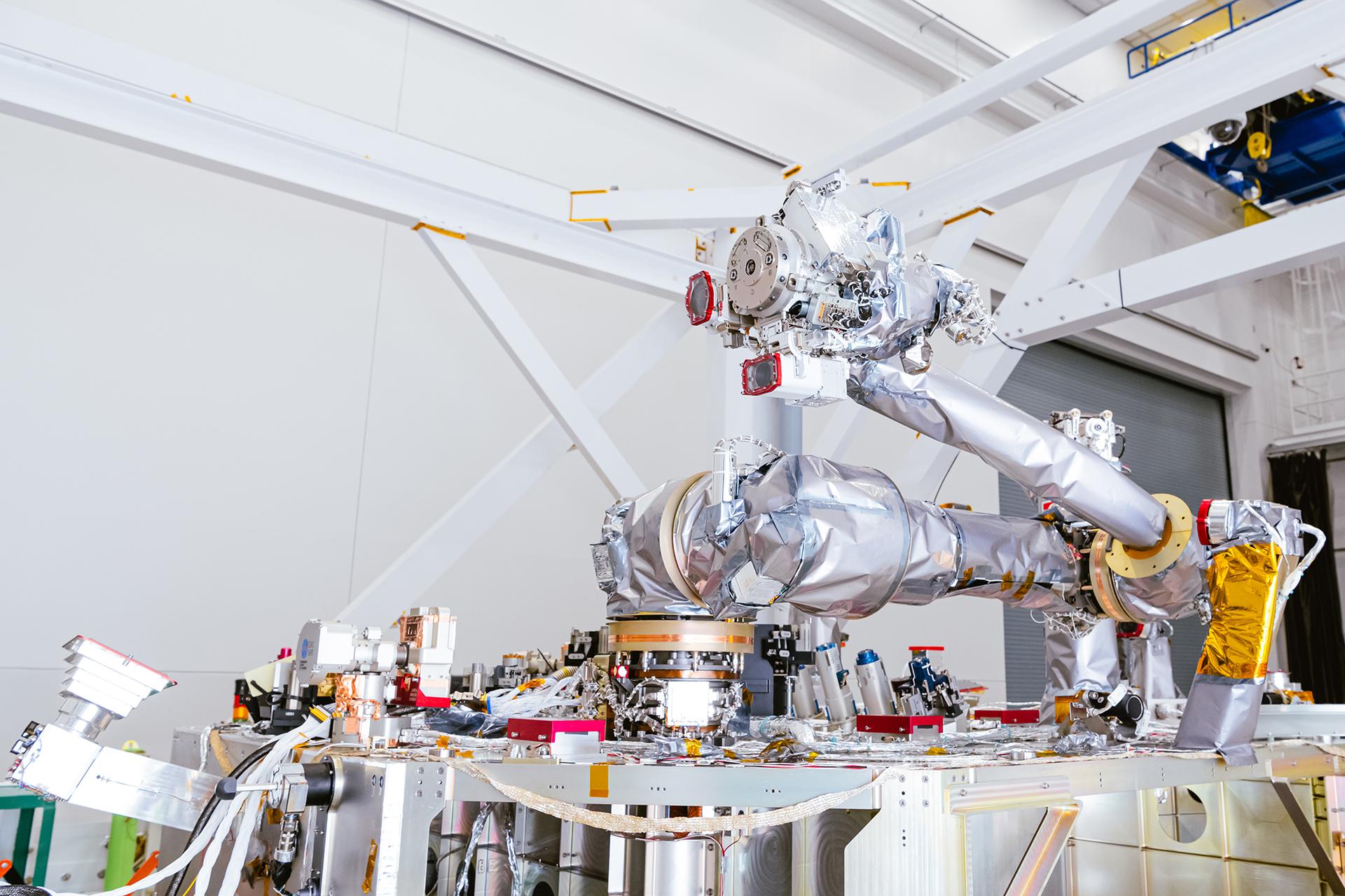
A detail view of one of the OSAM-1 robotic arms after being integrated onto the flight payload top-deck at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt., Md Oct 4, 2024. This photo has been approved for public release. NASA/Mike Guinto

In this image, engineers from NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory test and flex Curiosity robotic arm and tools. A video can be viewed at the Photojournal.
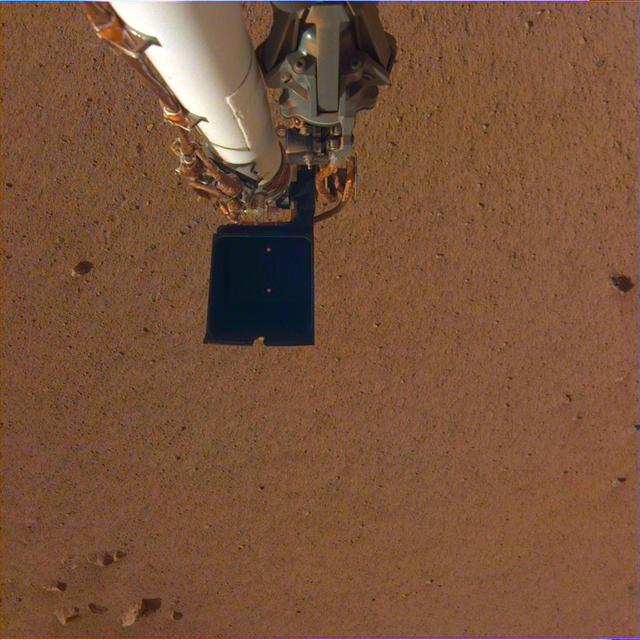
NASA's InSight spacecraft took a color-calibrated image of its robotic arm using its Instrument Deployment Camera on Dec. 4, 2018 (Sol 8). The camera still has a transparent dust cover on it, but the robotic arm can clearly be seen above the Martian soil. There is a dark scoop at the end of the arm. Above the scoop is the stowed grapple, the claw that InSight will use to grab and move its instruments from its deck onto the planet's surface. InSight will be the first Mars mission to use a robotic arm to grasp objects and deploy them onto the surface of another planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22872
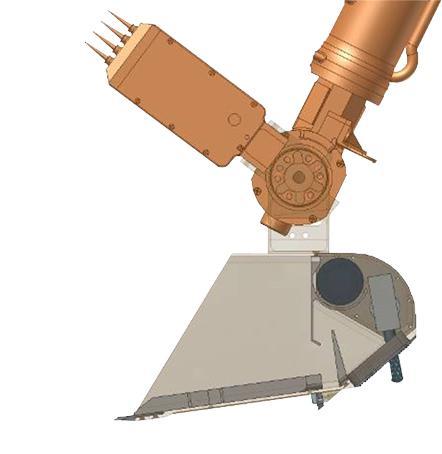
This illustration shows some of the components on and near the end of the robotic arm on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander. Primary and secondary blades on the scoop that aided in the collection of soil samples.

This photograph shows the rasp protruding from the back of the scoop on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander Robotic Arm engineering model in the Payload Interoperability Testbed at the University of Arizona, Tucson.
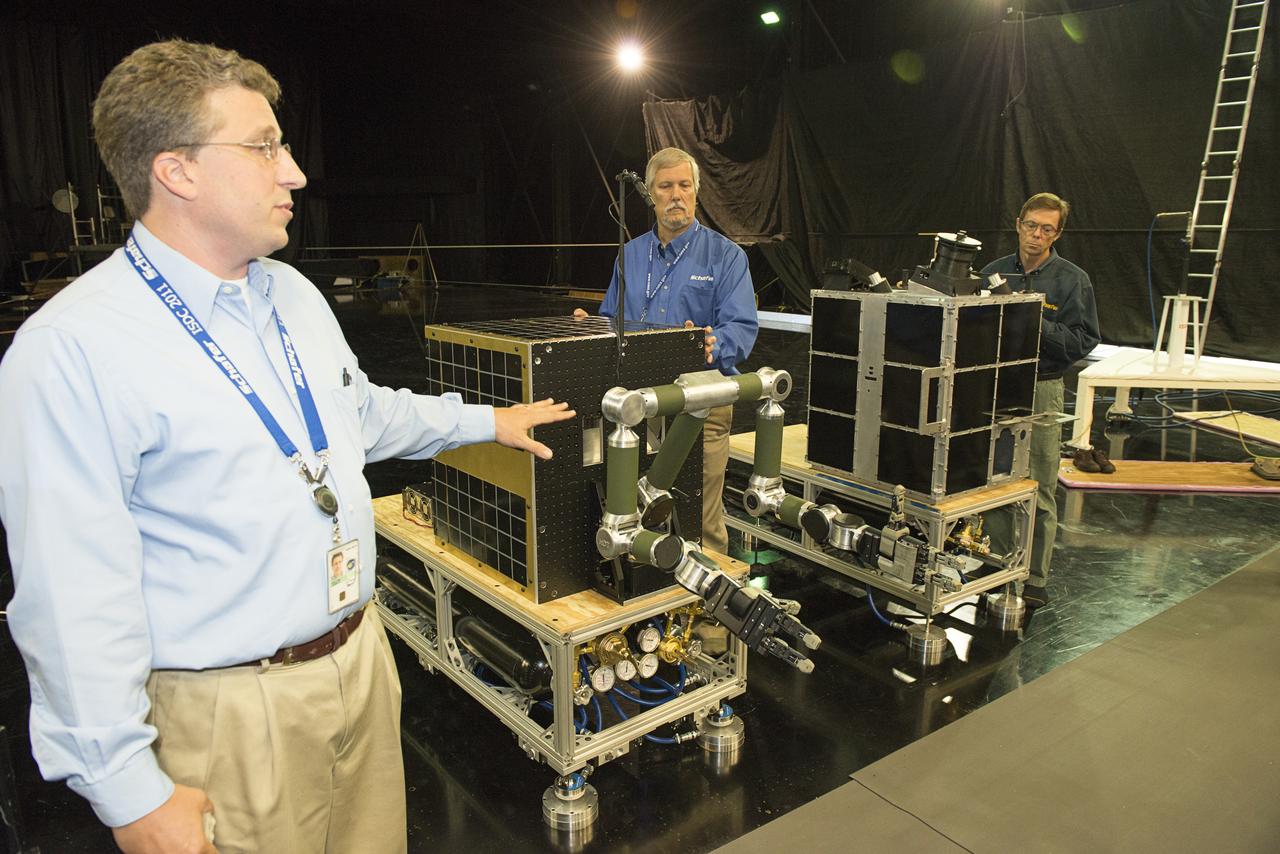

FINAL DEMONSTRATION OF A WIRELESS DATA TASK SUPPORTED BY SLS ADVANCED DEVELOPMENT USED TO DEMONSTRATE REAL-TIME VIDEO OVER WIRELESS CONNECTIONS ALONG WITH DATA AND COMMANDS AS DEMONSTRATED VIA THE ROBOTIC ARMS. THE ARMS AND VIDEO CAMERAS WERE MOUNTED ON FREE FLOATING AIR-BEARING VEHICLES TO SIMULATE CONDITIONS IN SPACE. THEY WERE USED TO SHOW HOW A CHASE VEHICLE COULD MOVE UP TO AND CAPTURE A SATELLITE, SUCH AS THE FASTSAT MOCKUP DEMONSTRITING HOW ROBOTIC TECHNOLOGY AND SMALL SPACECRAFT COULD ASSIST WITH ORBITAL DEBRIS MITIGATION
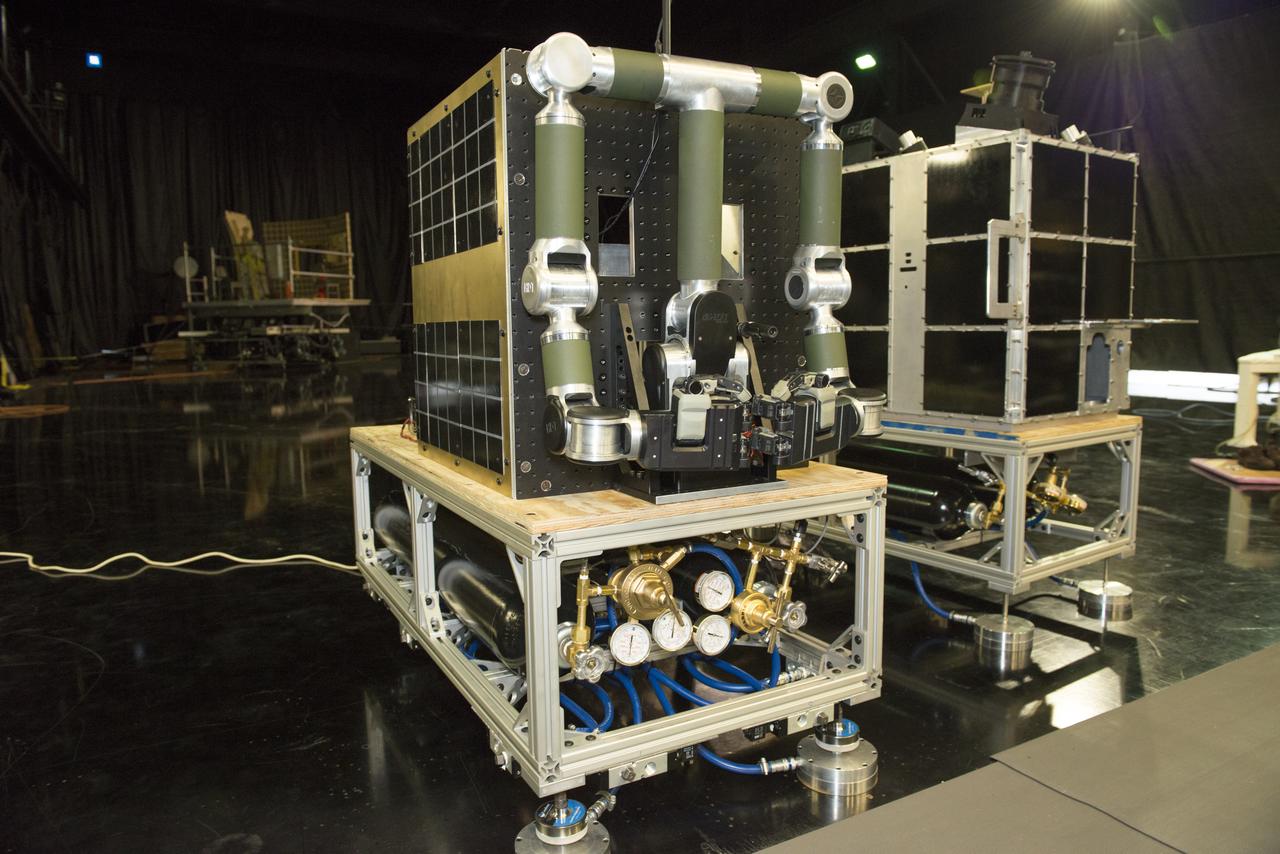

FINAL DEMONSTRATION OF A WIRELESS DATA TASK SUPPORTED BY SLS ADVANCED DEVELOPMENT USED TO DEMONSTRATE REAL-TIME VIDEO OVER WIRELESS CONNECTIONS ALONG WITH DATA AND COMMANDS AS DEMONSTRATED VIA THE ROBOTIC ARMS. THE ARMS AND VIDEO CAMERAS WERE MOUNTED ON FREE FLOATING AIR-BEARING VEHICLES TO SIMULATE CONDITIONS IN SPACE. THEY WERE USED TO SHOW HOW A CHASE VEHICLE COULD MOVE UP TO AND CAPTURE A SATELLITE, SUCH AS THE FASTSAT MOCKUP DEMONSTRITING HOW ROBOTIC TECHNOLOGY AND SMALL SPACECRAFT COULD ASSIST WITH ORBITAL DEBRIS MITIGATION
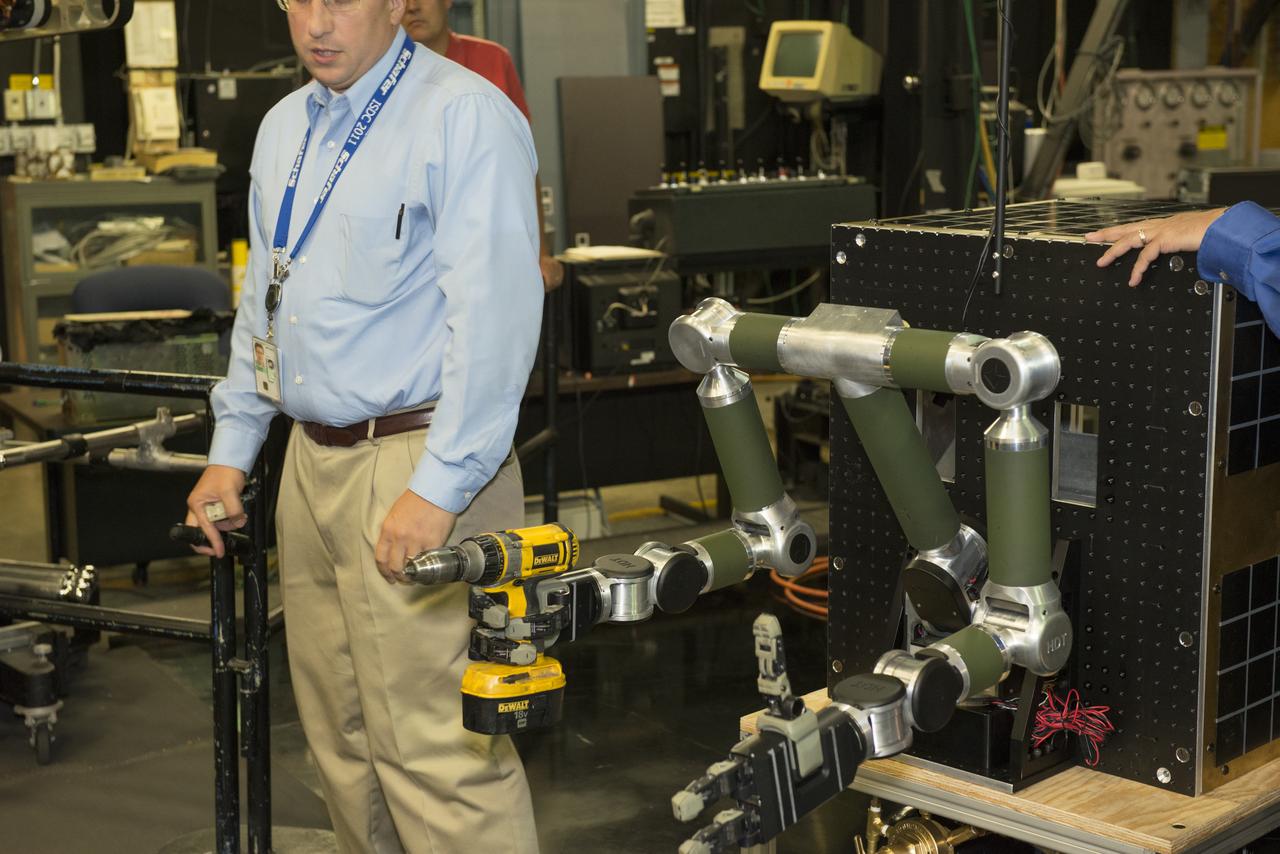

FINAL DEMONSTRATION OF A WIRELESS DATA TASK SUPPORTED BY SLS ADVANCED DEVELOPMENT USED TO DEMONSTRATE REAL-TIME VIDEO OVER WIRELESS CONNECTIONS ALONG WITH DATA AND COMMANDS AS DEMONSTRATED VIA THE ROBOTIC ARMS. THE ARMS AND VIDEO CAMERAS WERE MOUNTED ON FREE FLOATING AIR-BEARING VEHICLES TO SIMULATE CONDITIONS IN SPACE. THEY WERE USED TO SHOW HOW A CHASE VEHICLE COULD MOVE UP TO AND CAPTURE A SATELLITE, SUCH AS THE FASTSAT MOCKUP DEMONSTRITING HOW ROBOTIC TECHNOLOGY AND SMALL SPACECRAFT COULD ASSIST WITH ORBITAL DEBRIS MITIGATION
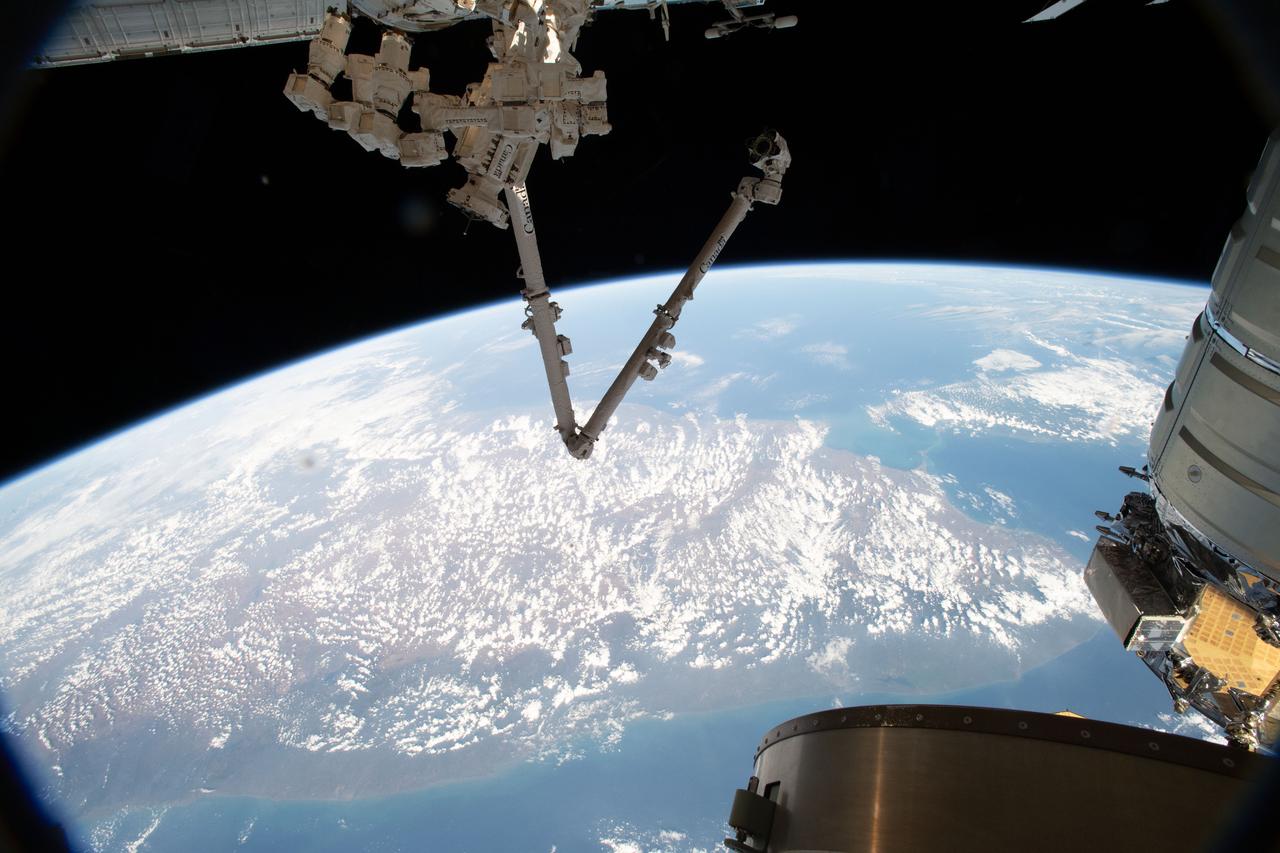

iss058e005961 (Jan. 26, 2019) --- The International Space Station's Canadarm2 robotic arm and its Dextre robotic hand are seen as the orbital complex flew 252 miles above the Arabian Sea off the coast of India.
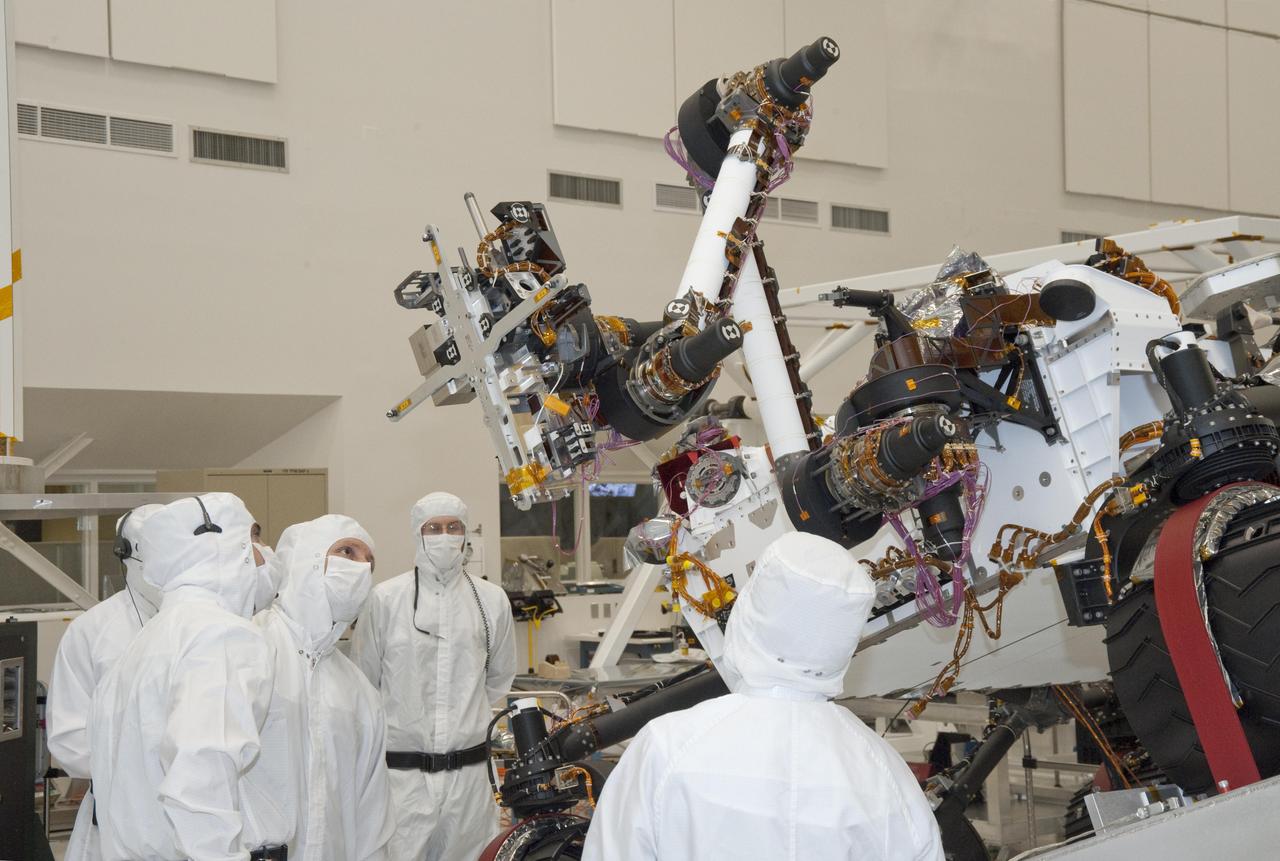

Testing of the robotic arm on NASA Mars rover Curiosity on Sept. 3, 2010, included movements of the arm while the rover was on a table tilted to 20 degrees to simulate a sloped surface on Mars.
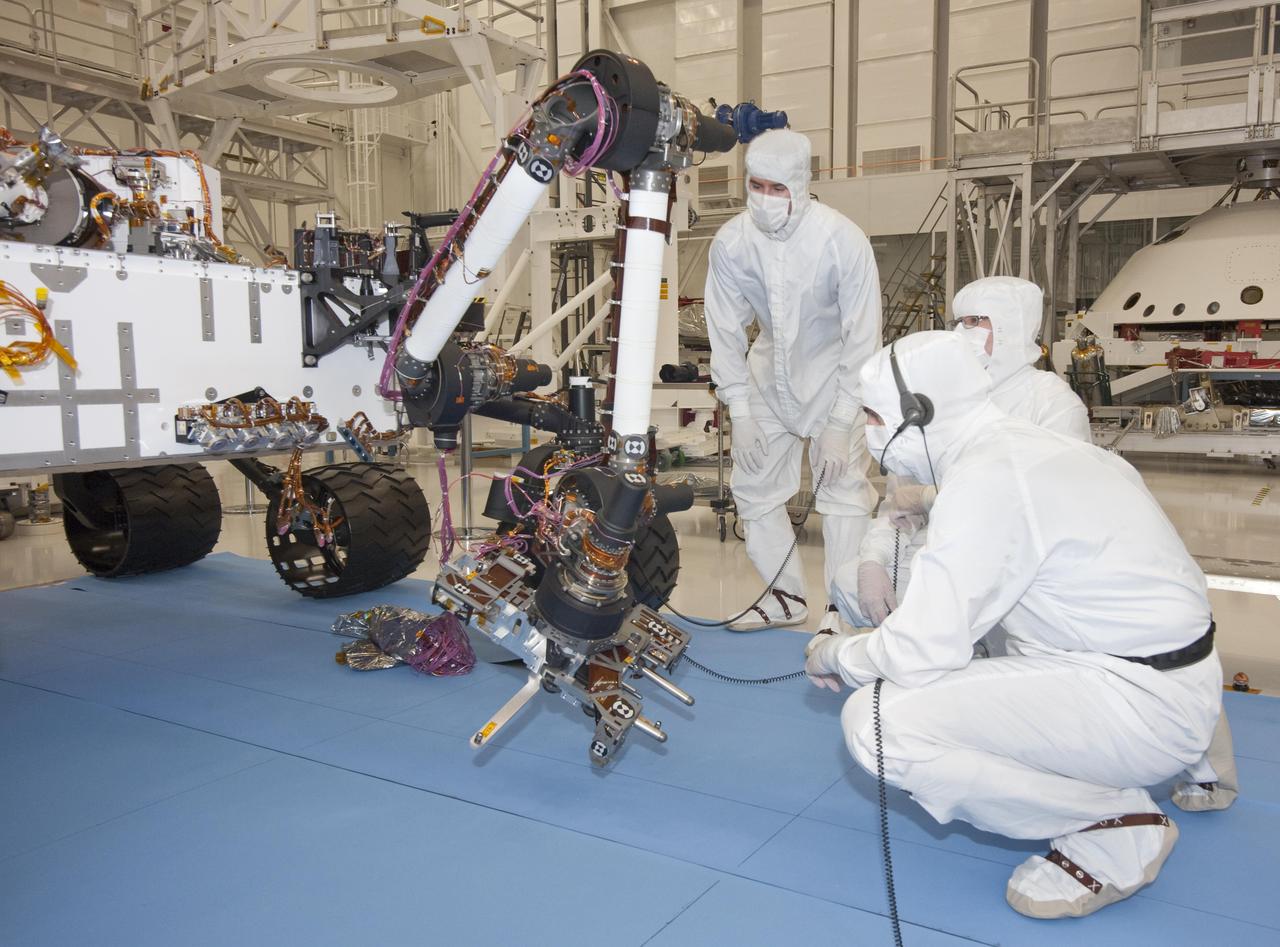

Test operators in a clean room at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory monitor some of the first motions by the robotic arm on the Mars rover Curiosity after installation in August 2010. The arm is shown in a partially extended position.

Engineers at Lockheed Martin Space, Denver, Colorado, test the robotic arm on NASA's InSight lander several months before launch. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22741
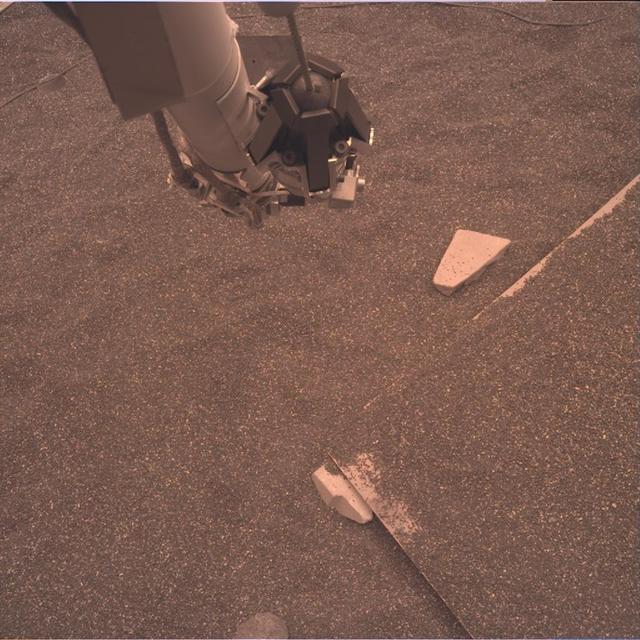

This test image from an engineering model of NASA's InSight lander shows part of the lander's robotic arm and the simulated Martian ground at a testbed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The testbed aims to mimic the environment InSight will encounter at Mars so engineers can prepare for the spacecraft operations to come. This image is expected to be similar to the raw or unprocessed images that InSight will send back to Earth. It was taken by the instrument deployment camera attached to InSight's robotic arm. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22827
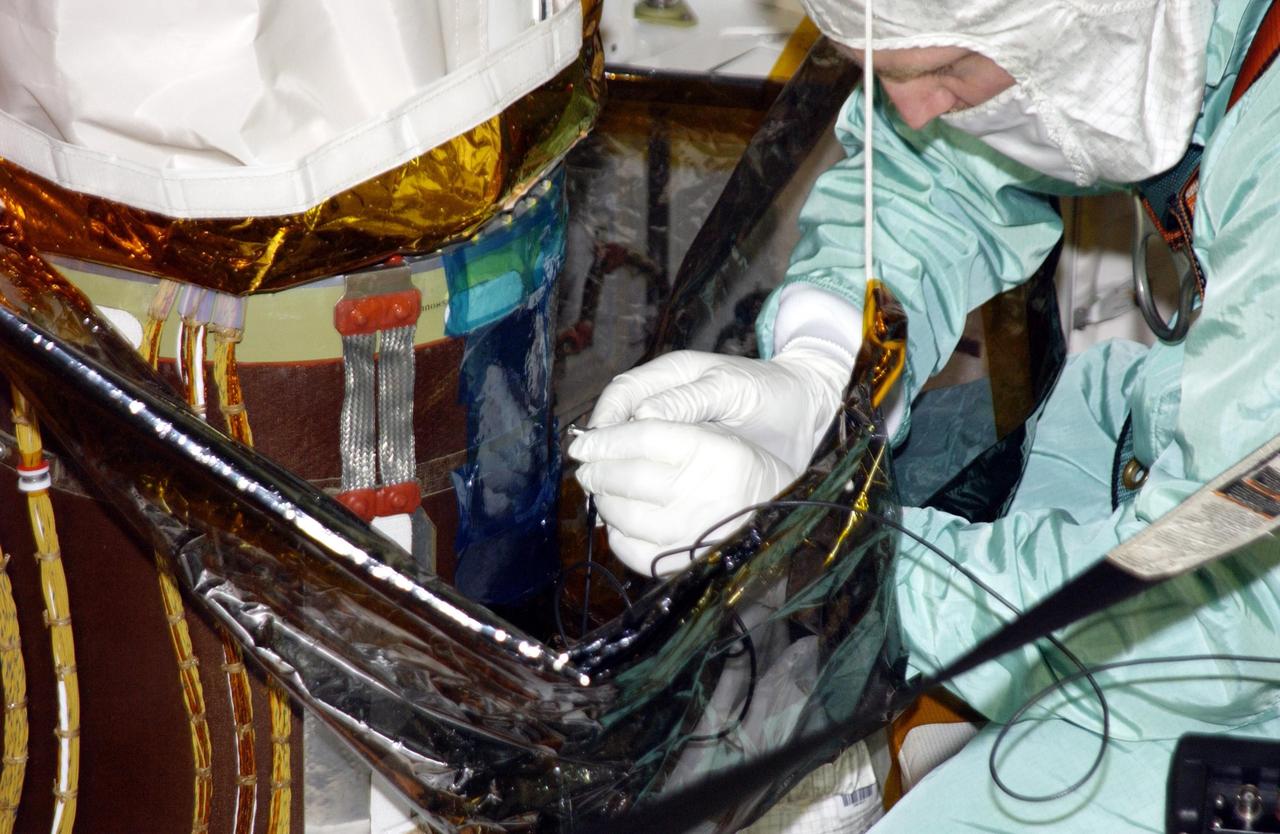

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Robotic arm experts get ready for ultrasound testing on Endeavour's robotic arm. A scrape of the honeycomb shell around the arm occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Robotic arm experts get ready for ultrasound testing on Endeavour's robotic arm. A scrape of the honeycomb shell around the arm occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Robotic arm experts begin inspection of a scrape on the surface of the honeycomb shell on Endeavour's robotic arm. The scrape occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Robotic arm experts begin inspection of a scrape on the surface of the honeycomb shell on Endeavour's robotic arm. The scrape occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22..

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Robotic arm experts begin inspection of a scrape on the surface of the honeycomb shell on Endeavour's robotic arm. The scrape occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.

This test using an engineering model of the InSight lander here on Earth shows how the spacecraft on Mars will use its robotic arm to press on a digging device, called the "mole." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23619

This artist image of an imaginary camera zooming in from above shows the location of the Robotic Arm Camera on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander as it acquires an image of the scoop at the end of the arm

NASA's InSight mission tests an engineering version of the spacecraft's robotic arm in a Mars-like environment at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The five-fingered grapple on the end of the robotic arm is lifting up the Wind and Thermal Shield, a protective covering for InSight's seismometer. The test is being conducted under reddish "Mars lighting" to simulate activities on the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22806
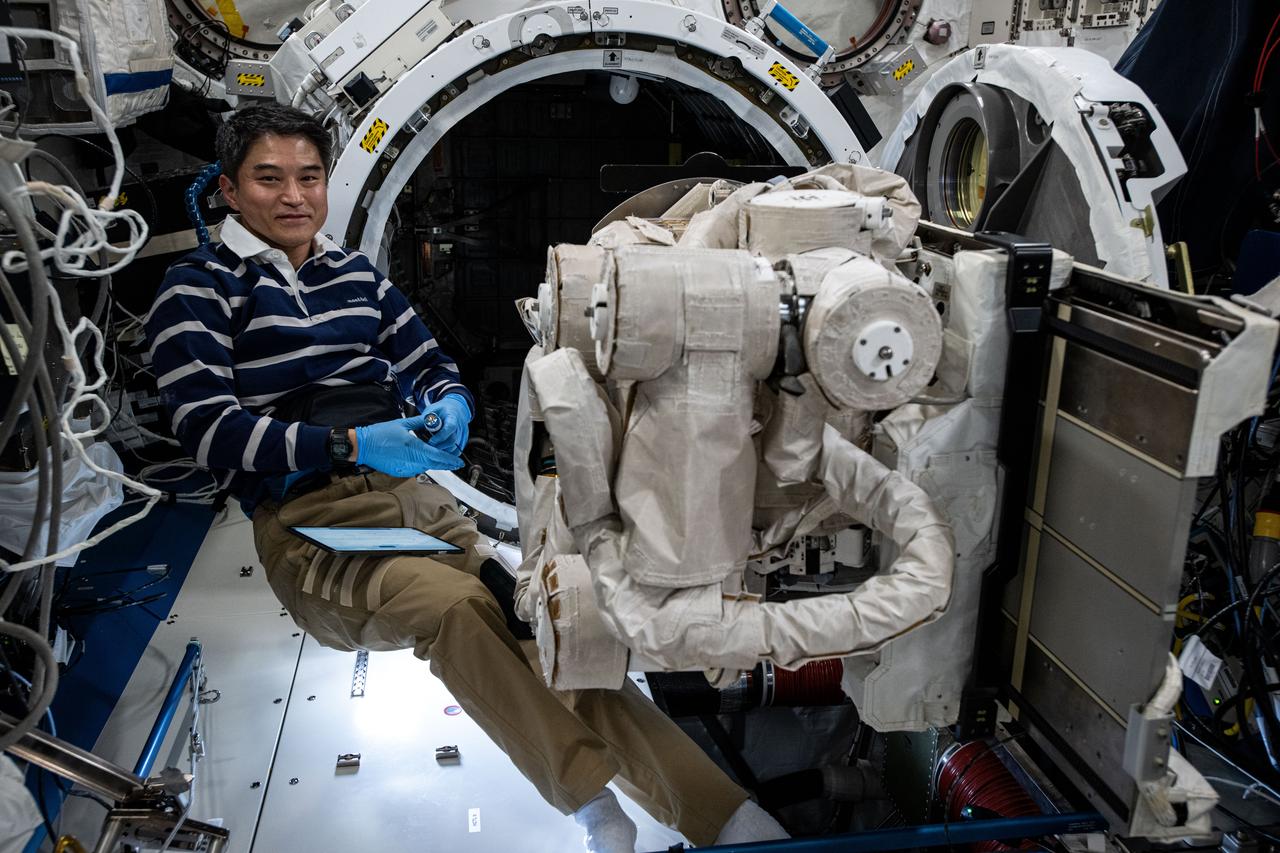

iss073e0133686 (June 3, 2025) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 73 Commander is pictured during maintenance operations on the Japanese robotic arm's Small Fine Arm inside the Kibo laboratory module. The Small Fine Arm is used for precise and dexterous robotic maneuvers when grappling small components or payloads on the outside of the International Space Station. There are two other robotic arms on the outside of the orbital outpost including the Canadarm2 robotic arm and the European robotic arm (ERA). Canadarm2 can be used to maneuver spacecraft, spacewalkers, and large payloads. ERA can also be used to maneuver spacewalkers and space station components.
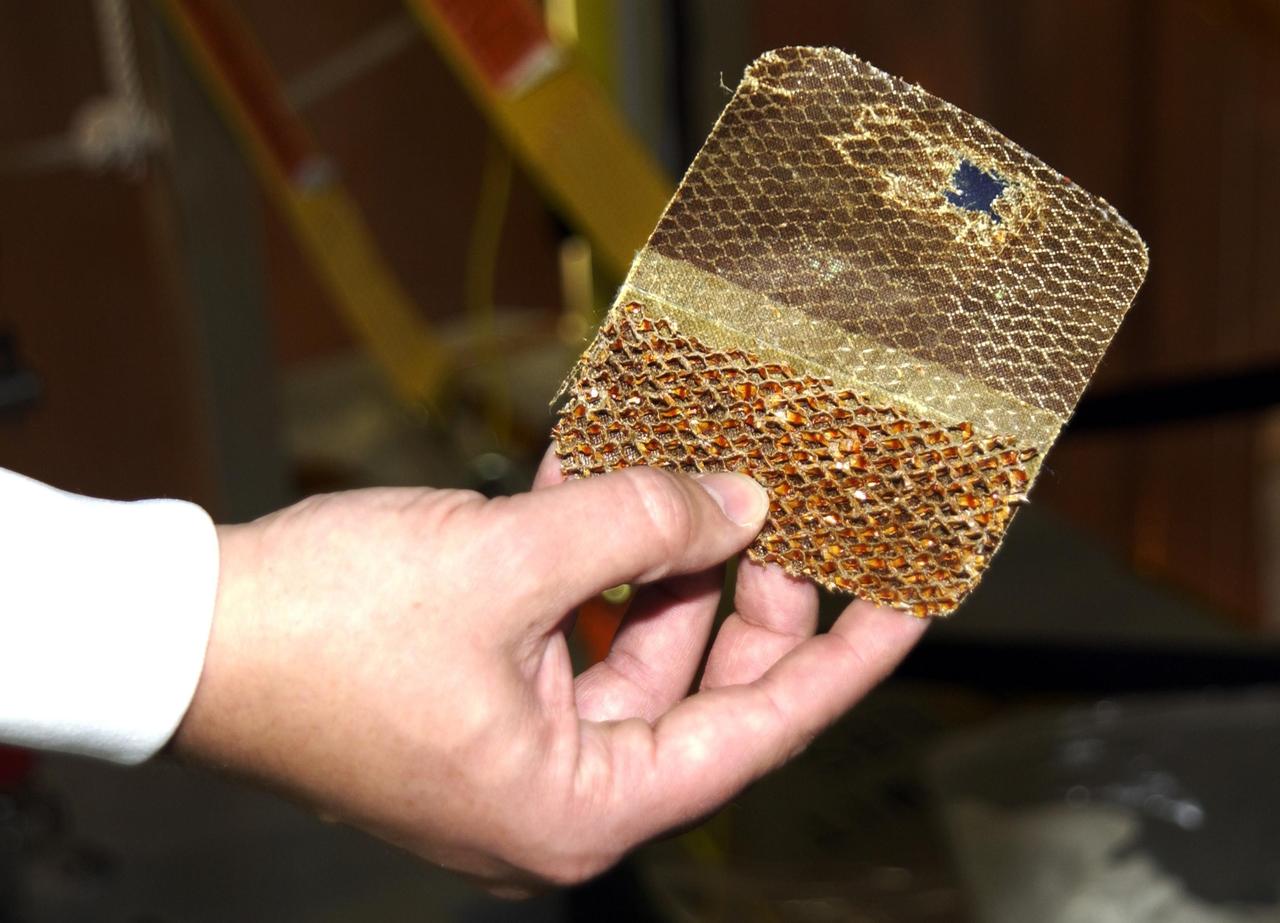

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A piece of the honeycomb shell around Endeavour's robotic arm has been cut to inspect the arm. A scrape of the shell occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.
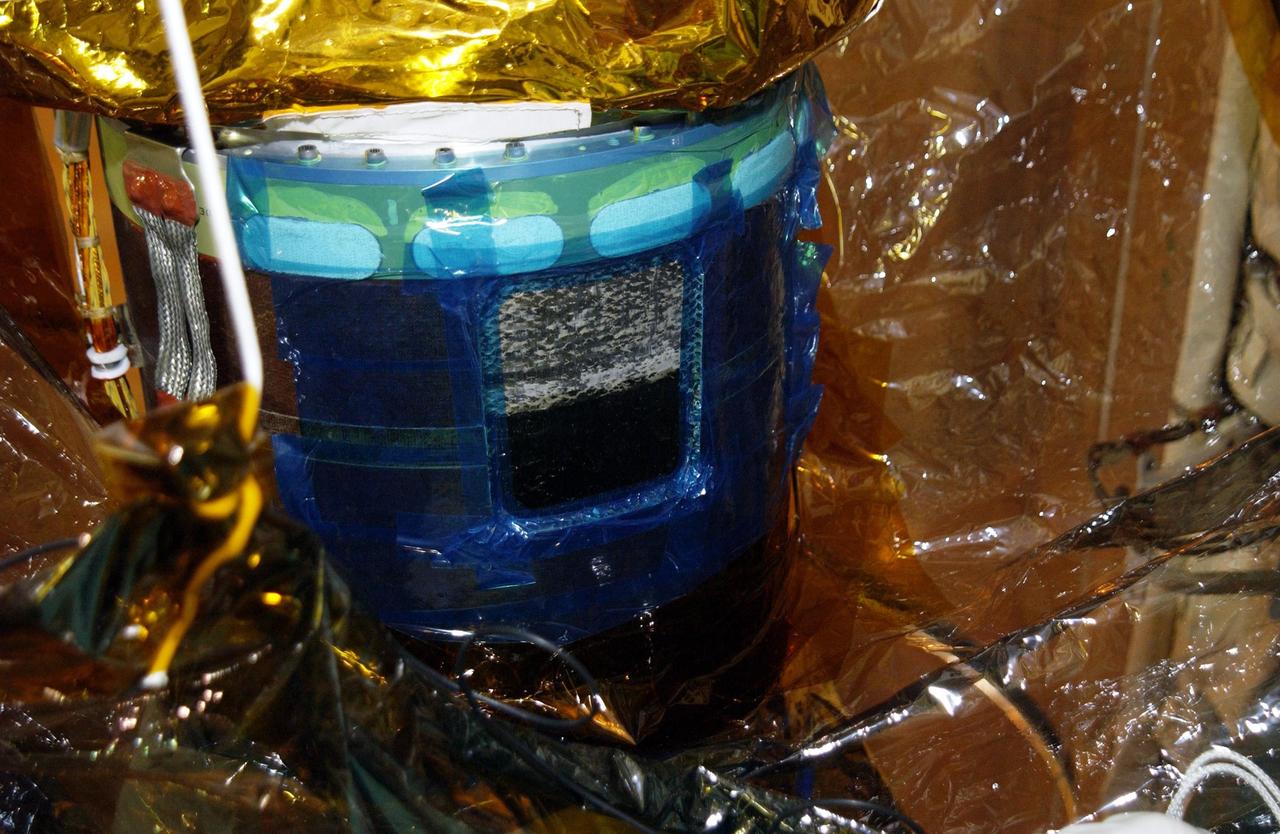
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The opening shown here is the site where the honeycomb shell around Endeavour's robotic arm has been cut to inspect the arm. A scrape of the shell occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.
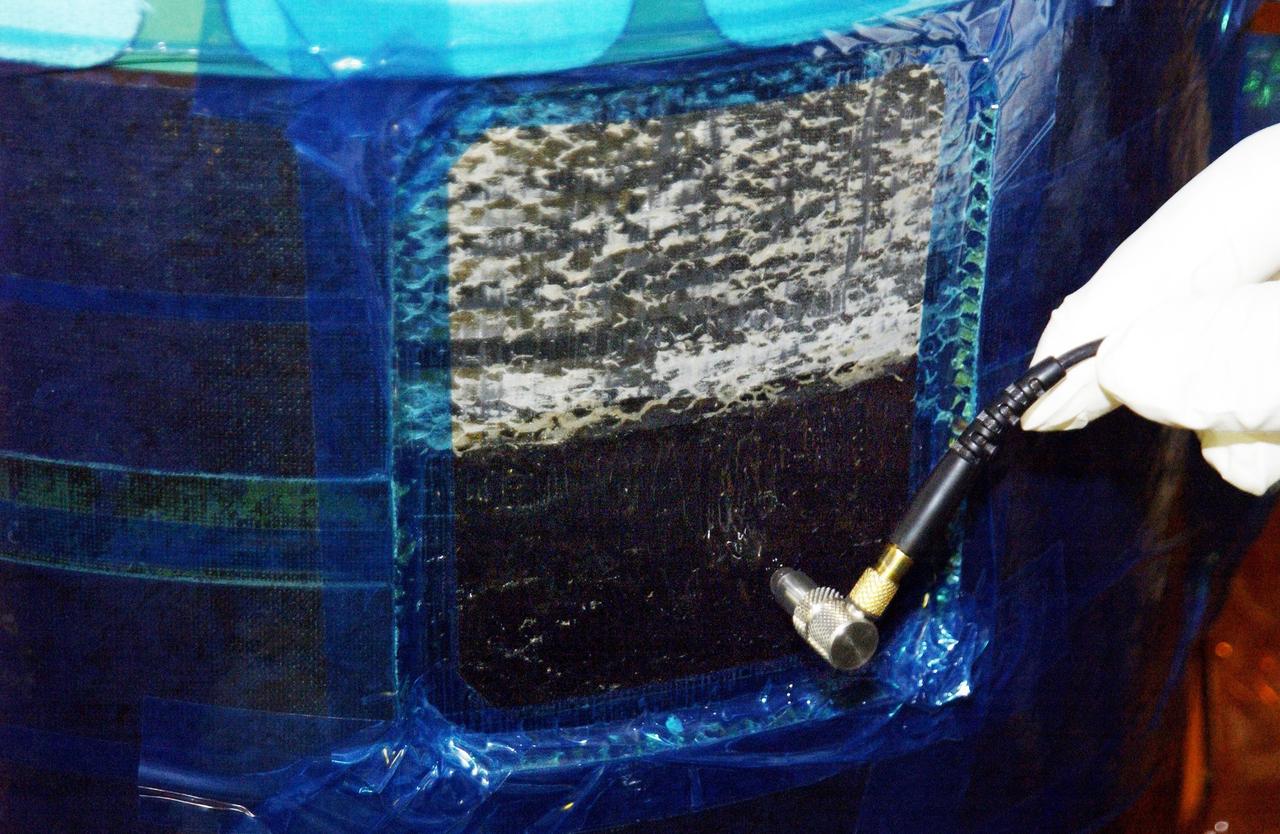

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An ultrasound device is held at the site where the honeycomb shell around Endeavour's robotic arm has been cut to inspect the arm. A scrape of the shell occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One of a team of robotic experts looks at the site of the scrape on the surface of the honeycomb shell on the robotic arm that occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. The site will be cut out and ultrasound testing will be done on the structure underneath. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One of a team of robotic experts looks at the site of the scrape on the surface of the the robotic arm's honeycomb shell. The scrape occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in Endeavour's mid-body. The site will be cut out and ultrasound testing will be done on the structure underneath. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One of a team of robotic experts prepares the site scraped on the robotic arm for removal. The scrape occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. The site will be cut out and ultrasound testing will be done on the structure underneath. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One of a team of robotic experts looks at the site of the scrape on the surface of the the robotic arm's honeycomb shell. The scrape occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in Endeavour's mid-body. The site will be cut out and ultrasound testing will be done on the structure underneath. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.
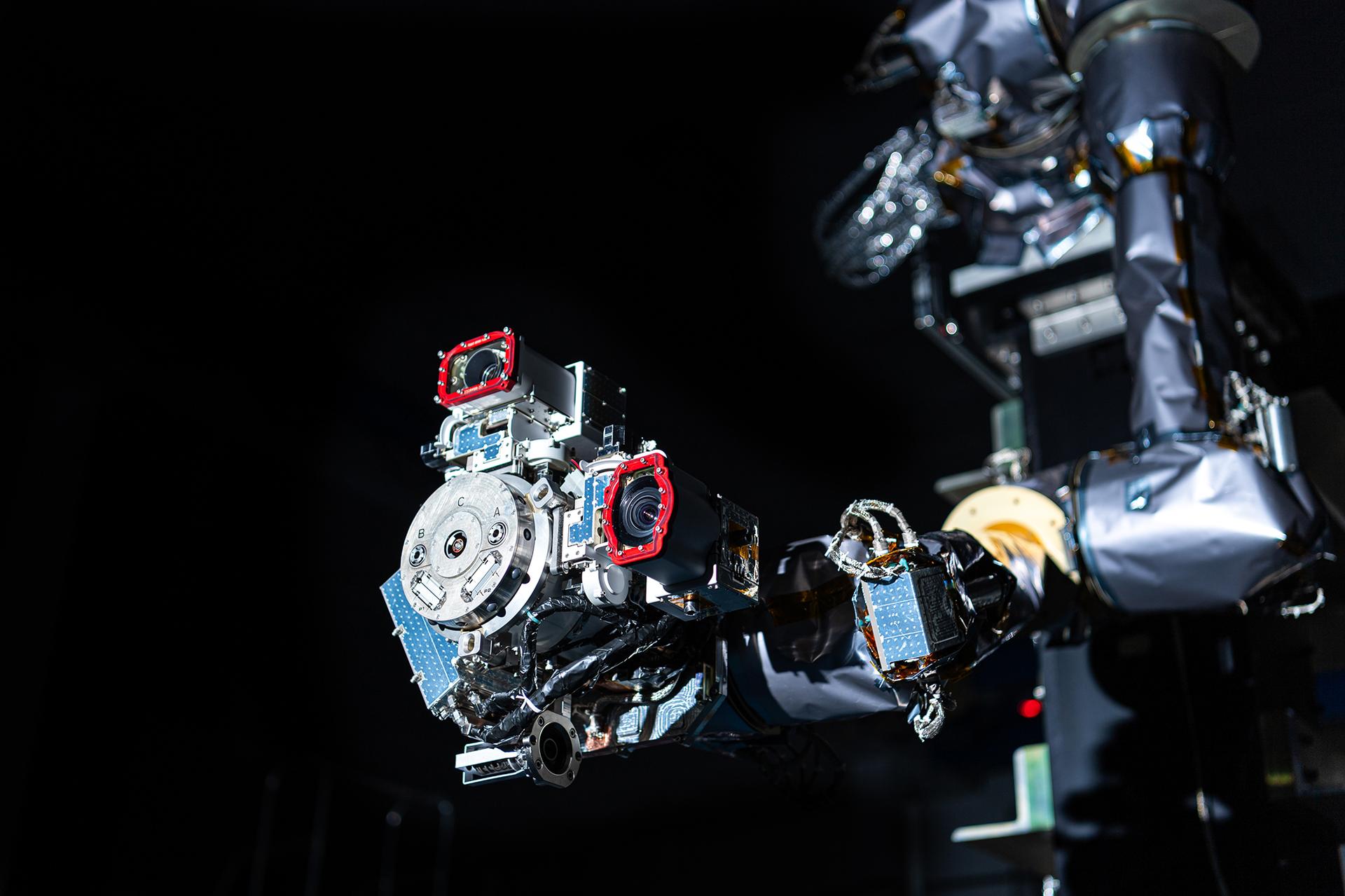
One of the OSAM-1 Robot Arms is seen, mounted onto ground support equipment used for testing inside the cleanroom at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Md., Apr 17, 2024. This photo has been reviewed by Maxar, OSAM1 project management, and the Export Control Office and is released for public view. NASA/Mike Guinto
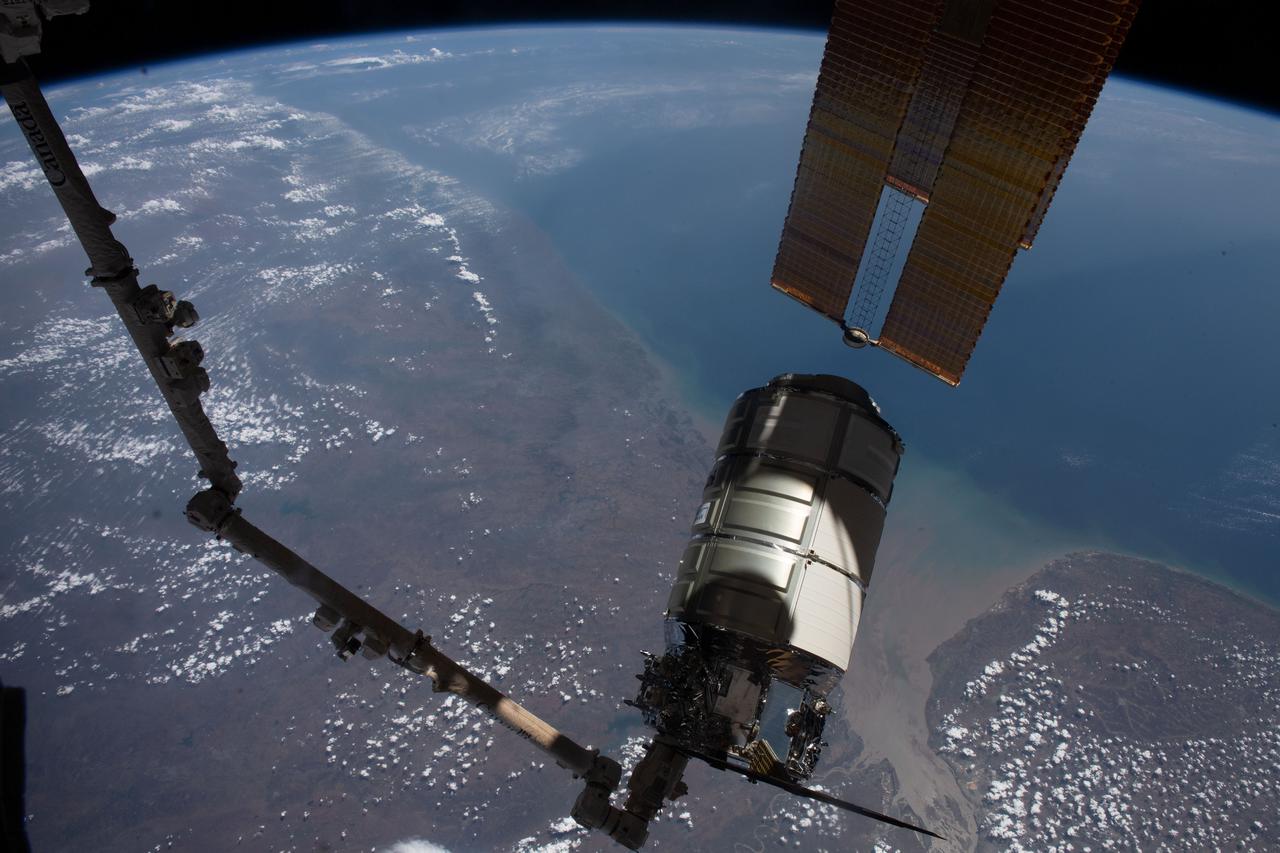

iss069e004909 (April 21, 2023) --- The Cygnus space freighter from Northrop Grumman is pictured in the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm as the International Space Station orbited 258 miles above the Arabian Sea coast of India.
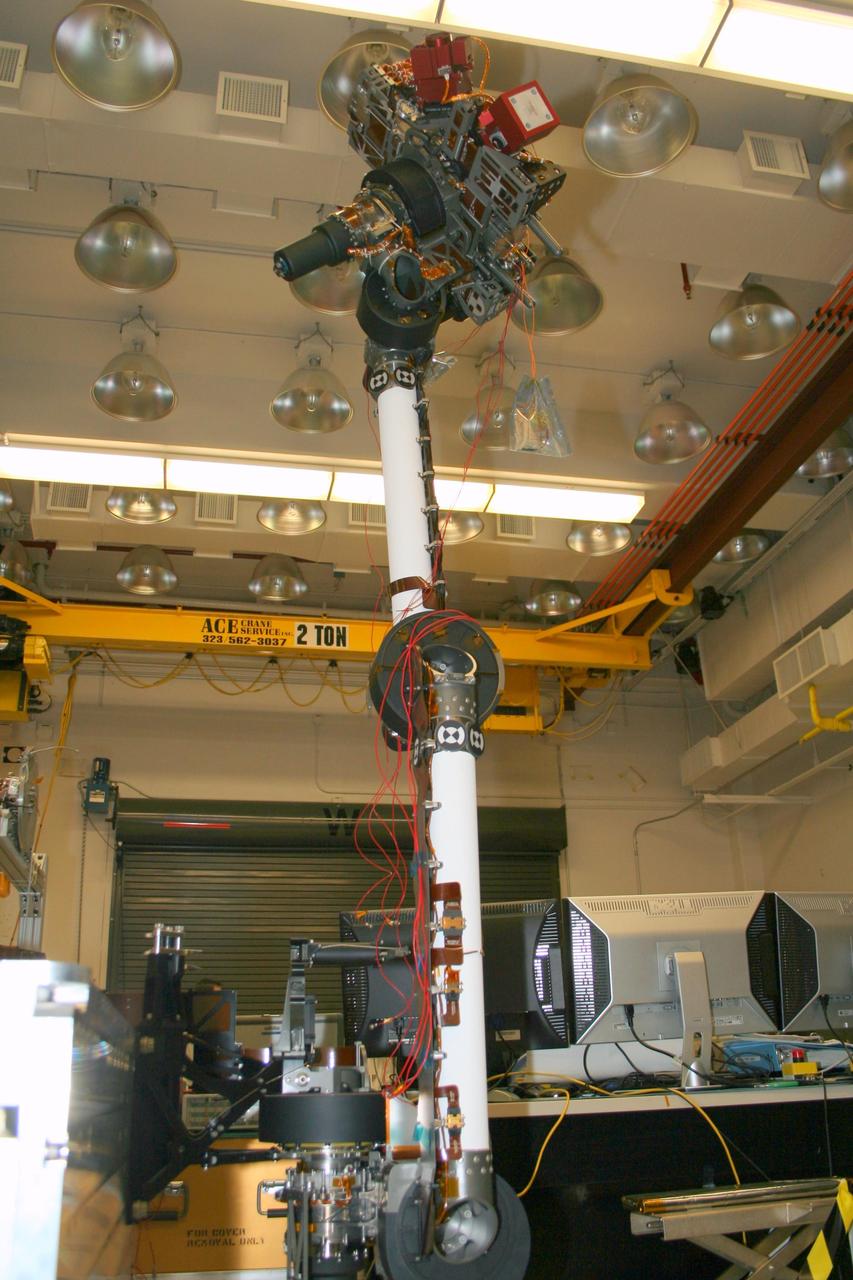

In the middle of this image taken at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the long robotic arm of NASA Mars Science Laboratory rises straight up toward the ceiling of the lab where it is being tested.

iss069e004825 (April 21, 2023) --- The Cygnus space freighter from Northrop Grumman is poised for release from the Canadarm2 robotic arm as the International Space Station orbited 263 miles above the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Ireland.
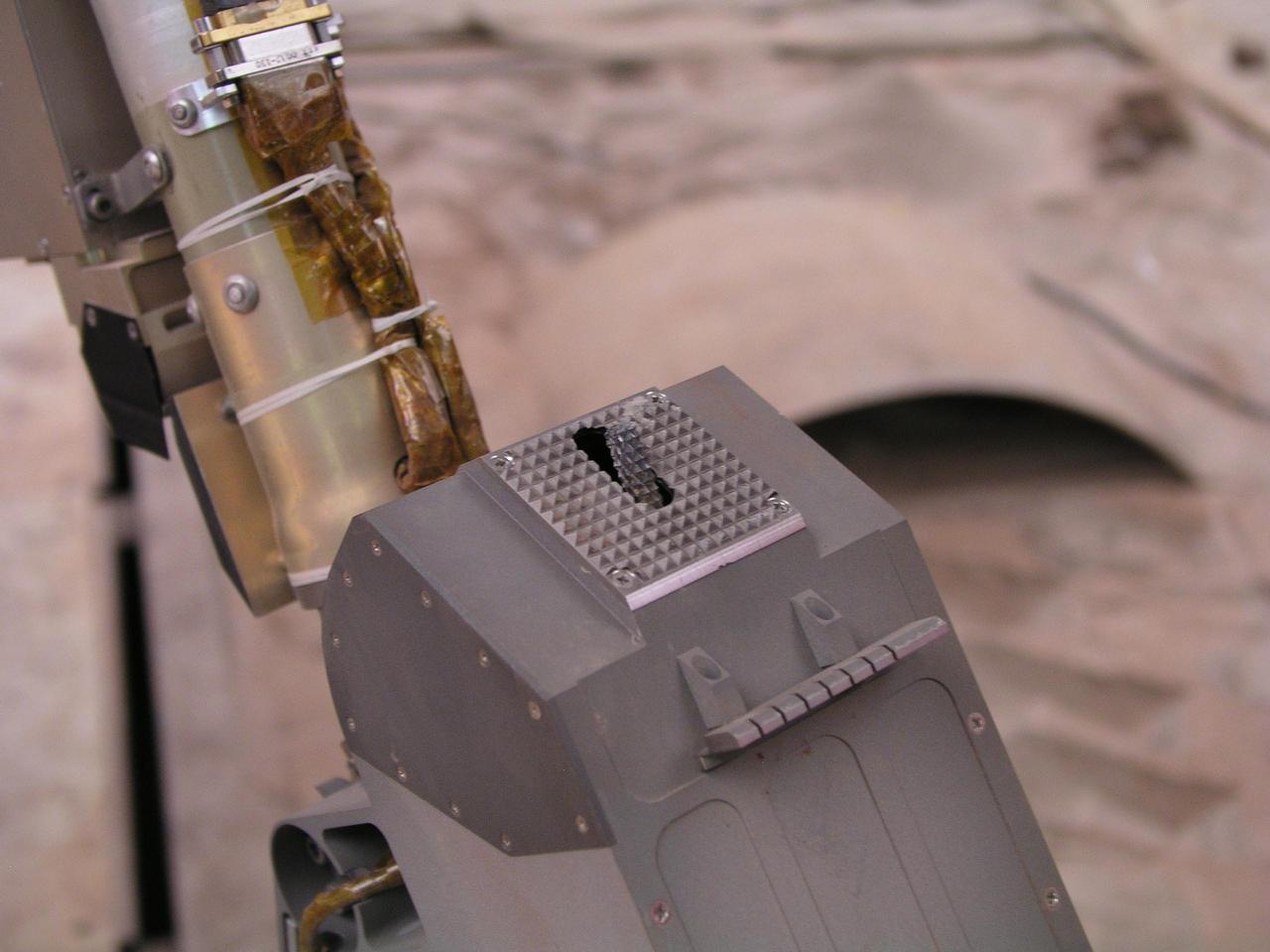
This close-up photograph taken at the Payload Interoperability Testbed at the University of Arizona, Tucson, shows the motorized rasp protruding from the bottom of the scoop on the engineering model of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander Robotic Arm.
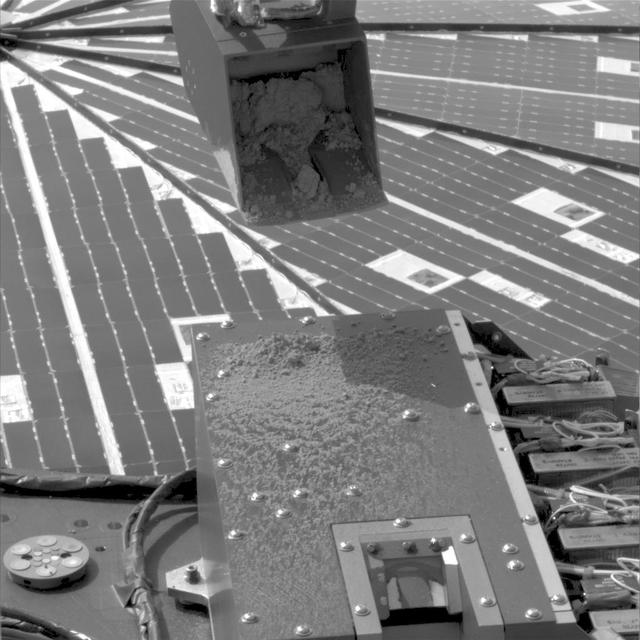

NASA Phoenix Mars Lander used its Robotic Arm during the mission 15th Martian day since landing June 9, 2008 to test a prinkle method for delivering small samples of soil to instruments on the lander deck.
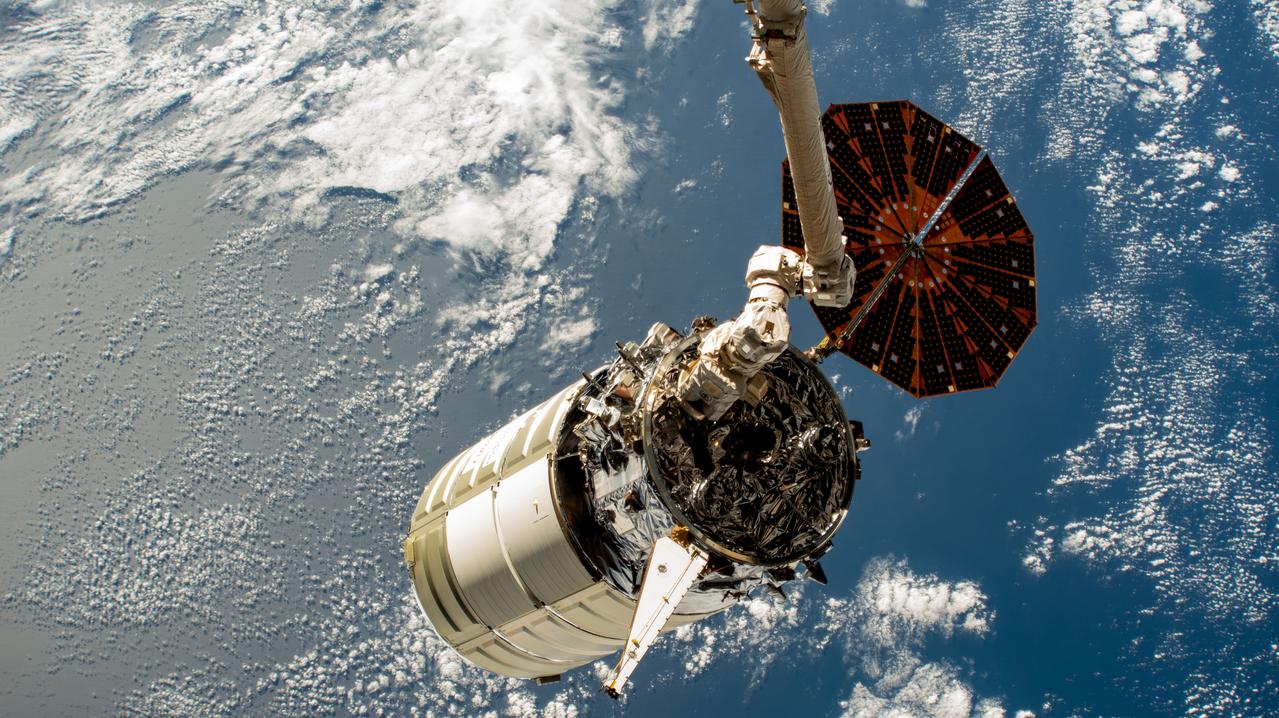

iss069e004821 (April 21, 2023) --- The Cygnus space freighter from Northrop Grumman is poised for release from the Canadarm2 robotic arm as the International Space Station orbited 262 miles above the north Atlantic Ocean.
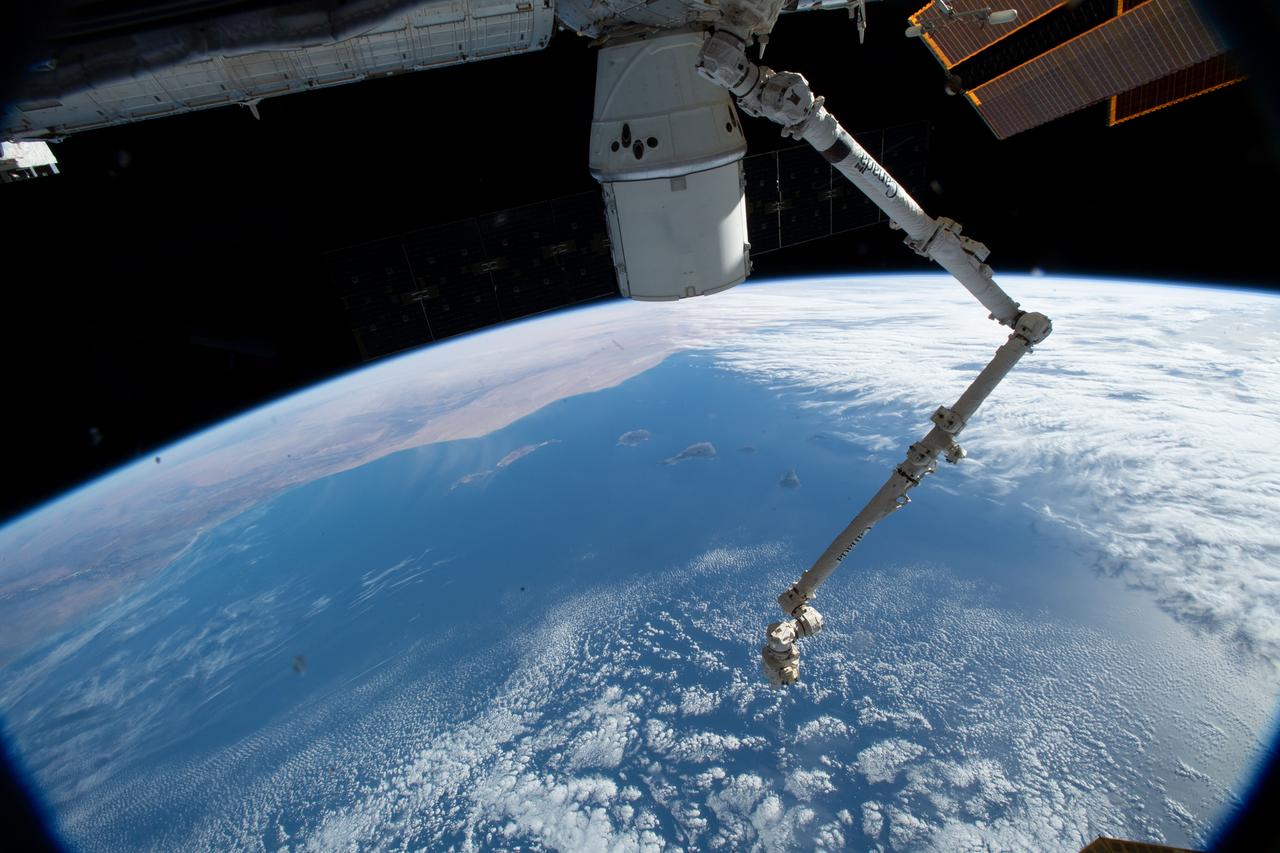

iss058e000081 (Dec. 22, 2018) --- The SpaceX Dragon cargo craft and the Canadarm2 robotic arm are pictured attached to the International Space Station as the orbital complex was 251 miles above the Atlantic Ocean about to fly over Morocco.
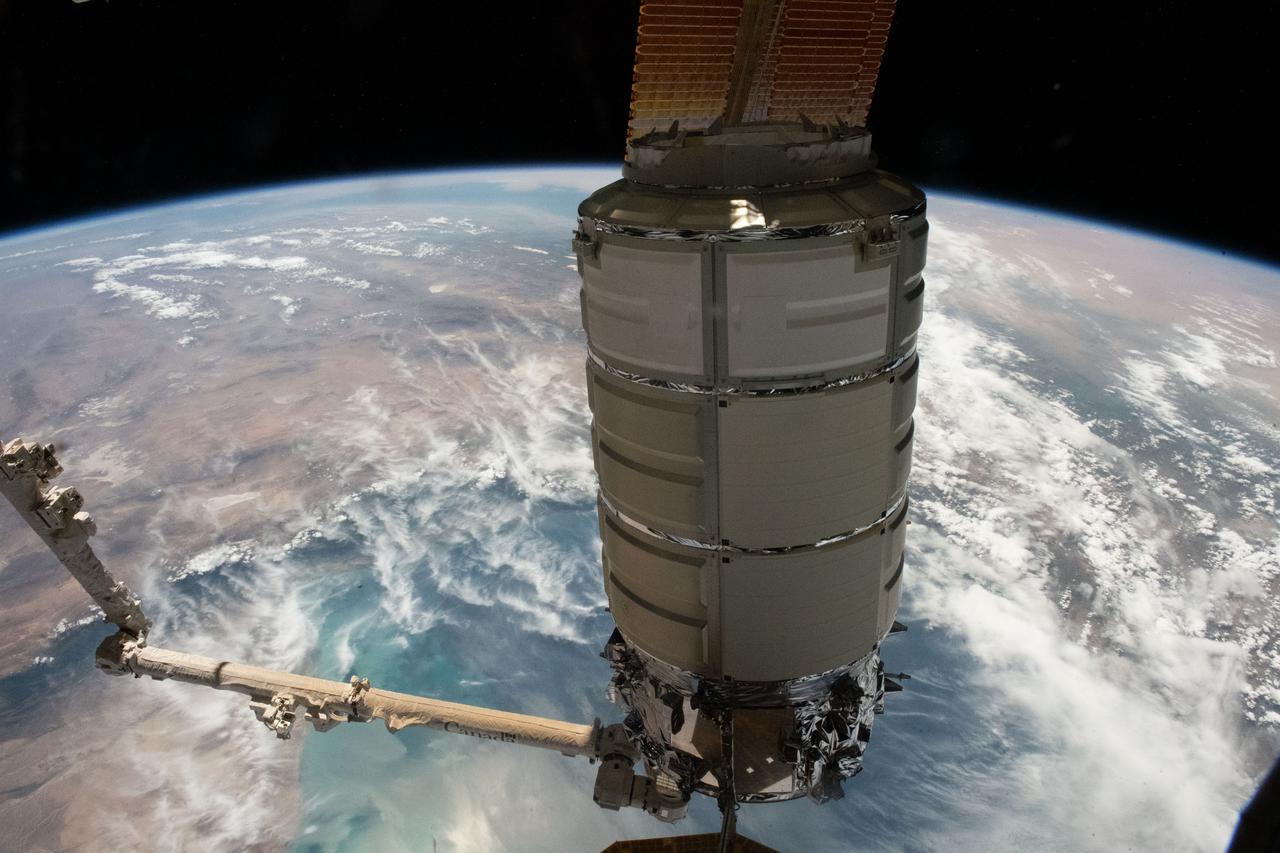

iss069e004895 (April 21, 2023) --- The Cygnus space freighter from Northrop Grumman is pictured in the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm as the International Space Station orbited 261 miles above the Caspian Sea off the coast of Turkmenistan.
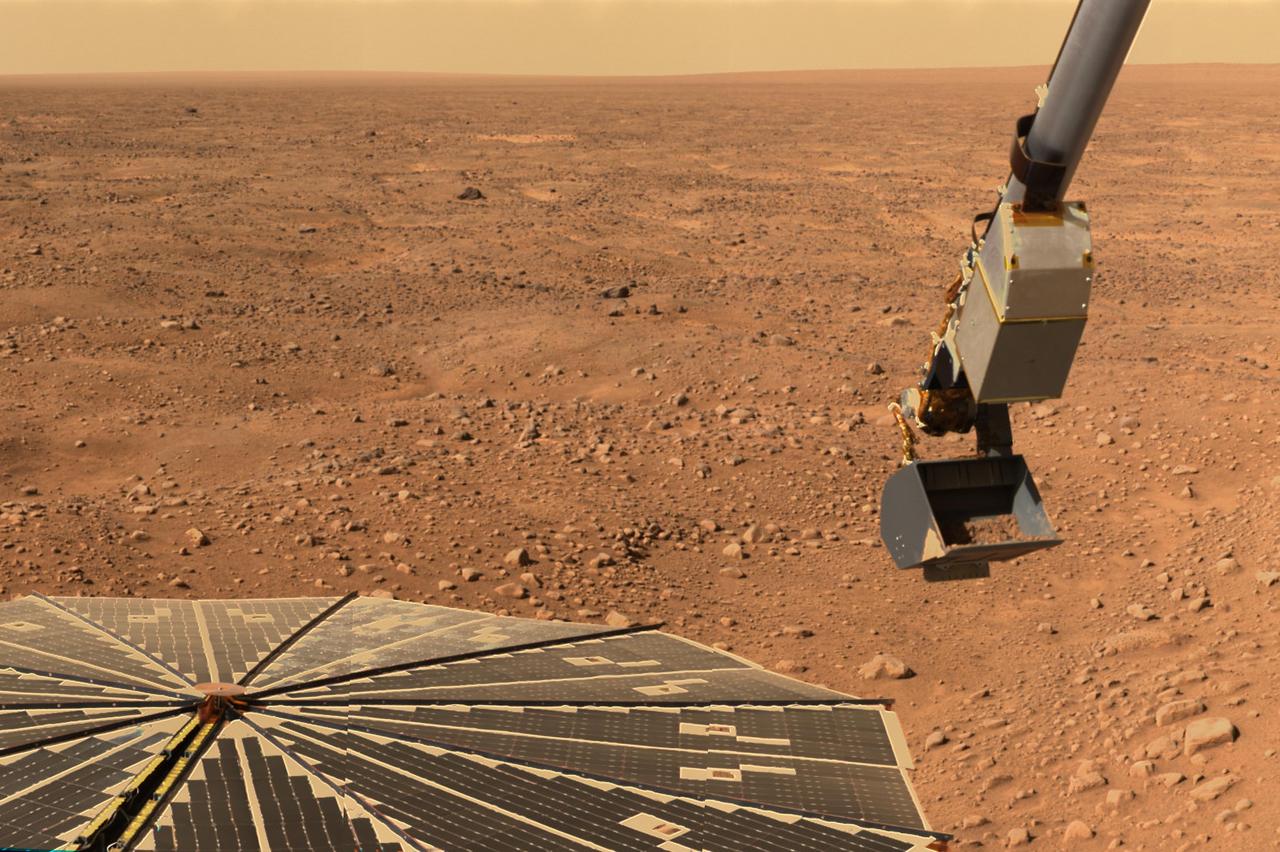
This panorama image of NASA’s Phoenix Mars Lander’s solar panel and the lander’s Robotic Arm with a sample in the scoop. The image was taken just before the sample was delivered to the Optical Microscope.

This set of images shows parts of the robotic arm on NASA's Perseverance rover flexing and turning during its first checkout after landing on Mars. These images were taken by Perseverance's Navigation Cameras on March 3, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24338
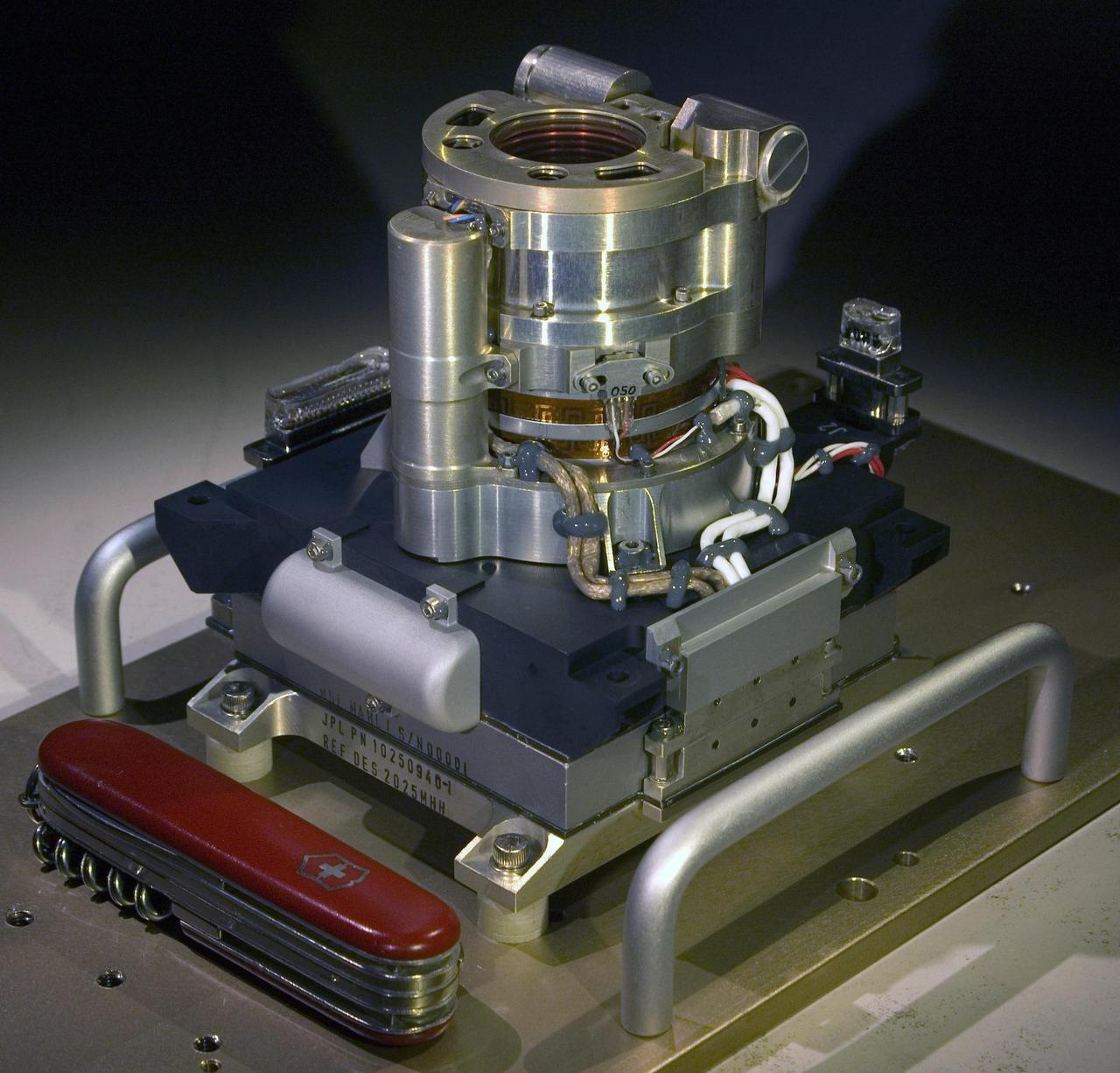
The Mars Hand Lens Imager MAHLI camera will fly on NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission, launching in late 2011. This photo of the camera was taken before MAHLI November 2010 installation onto the robotic arm of the mission Mars rover, Curiosity.
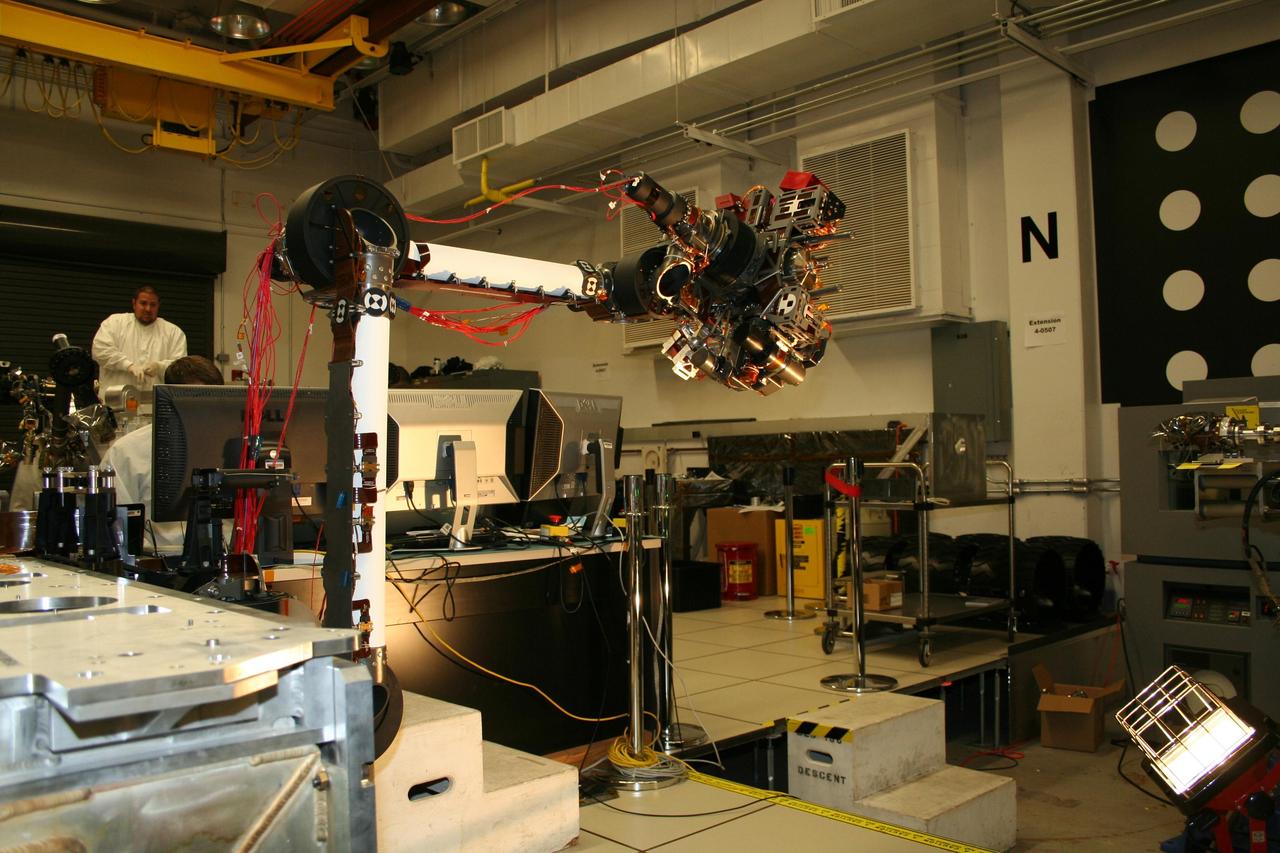

In the middle of this image taken at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the long robotic arm of NASA Mars Science Laboratory is bent at nearly a 90-degree angle.
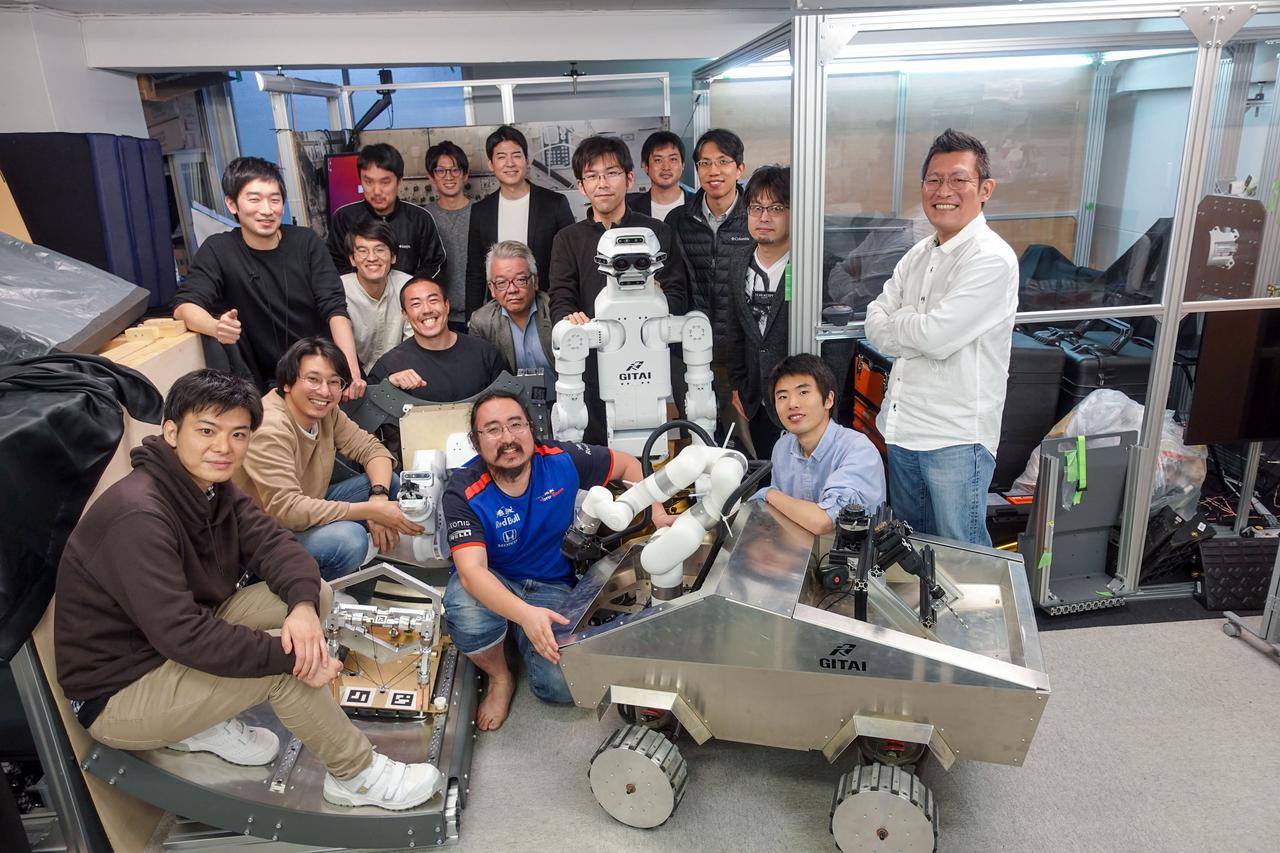
jsc2021e036655 (8/11/2021) --- The GITAI team. The GITAI S1 Robotic Arm Tech Demo (Nanoracks-GITAI Robotic Arm) demonstrates the versatility and dexterity in microgravity of a robot designed by GITAI Japan Inc. For the demonstration, the robot conducts common crew activities and tasks via supervised autonomy and teleoperations from the ground.

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover captured this view of its robotic arm during sunset on Sept. 16, 2025, the 4,661st Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This series of six images shows the rover's 7-foot-long (2.5-meter-long) arm setting its turret, a rotating platform for science instruments, onto rock targets nicknamed "Turbio" and "Rio Aguas Blancas." The front hazard cameras, located on the front of the rover's chassis, took the images between 3:55 and 4:51 p.m. local Mars time, showcasing the lengthening shadows at the end of the day. The sun finally set at 4:54 p.m. local Mars time. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26673

Robotic Arm Camera Image of the South Side of the Thermal and Evolved-Gas Analyzer Door TA4 receiving sample
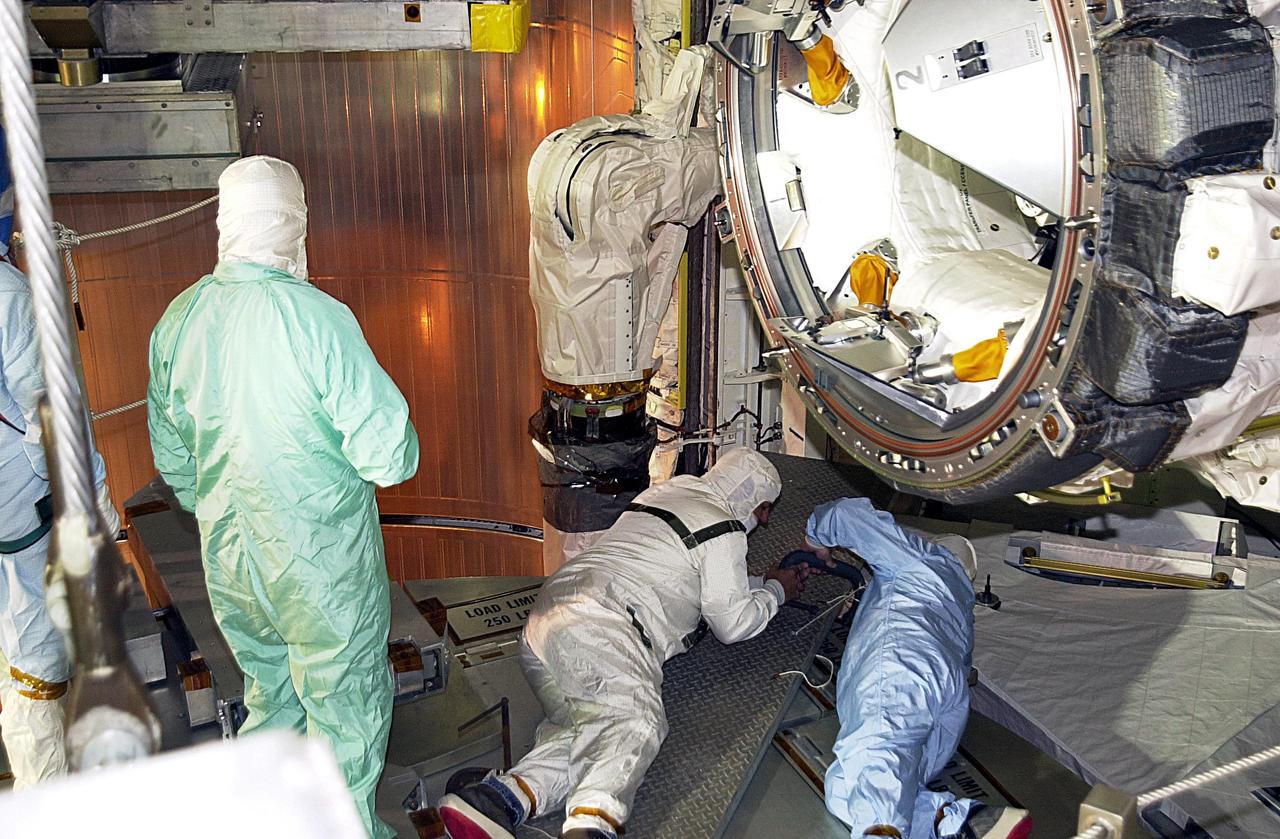

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in Endeavour's payload bay look at the site of the scrape on the surface of the honeycomb shell on the robotic arm that occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. The site will be cut out and ultrasound testing will be done on the structure underneath. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.
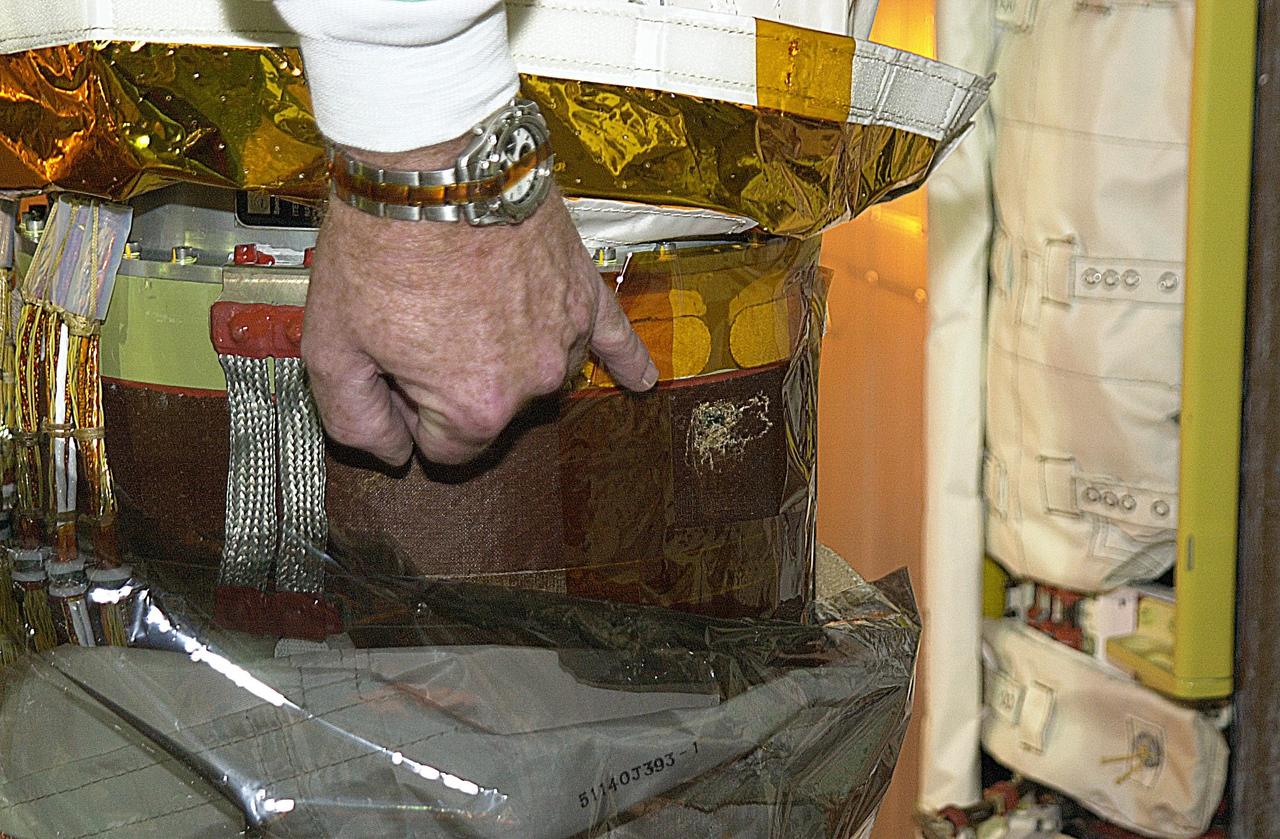

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The site being identified in the photo is the scrape on the surface of the honeycomb shell on Endeavour's robotic arm. The scrape occurred while work platforms were being installed to gain access to repair the oxygen leak in the Shuttle's mid-body. The site will be cut out and ultrasound testing will be done on the structure underneath. Launch of Endeavour on mission STS-113 has been postponed until no earlier than Nov. 22.
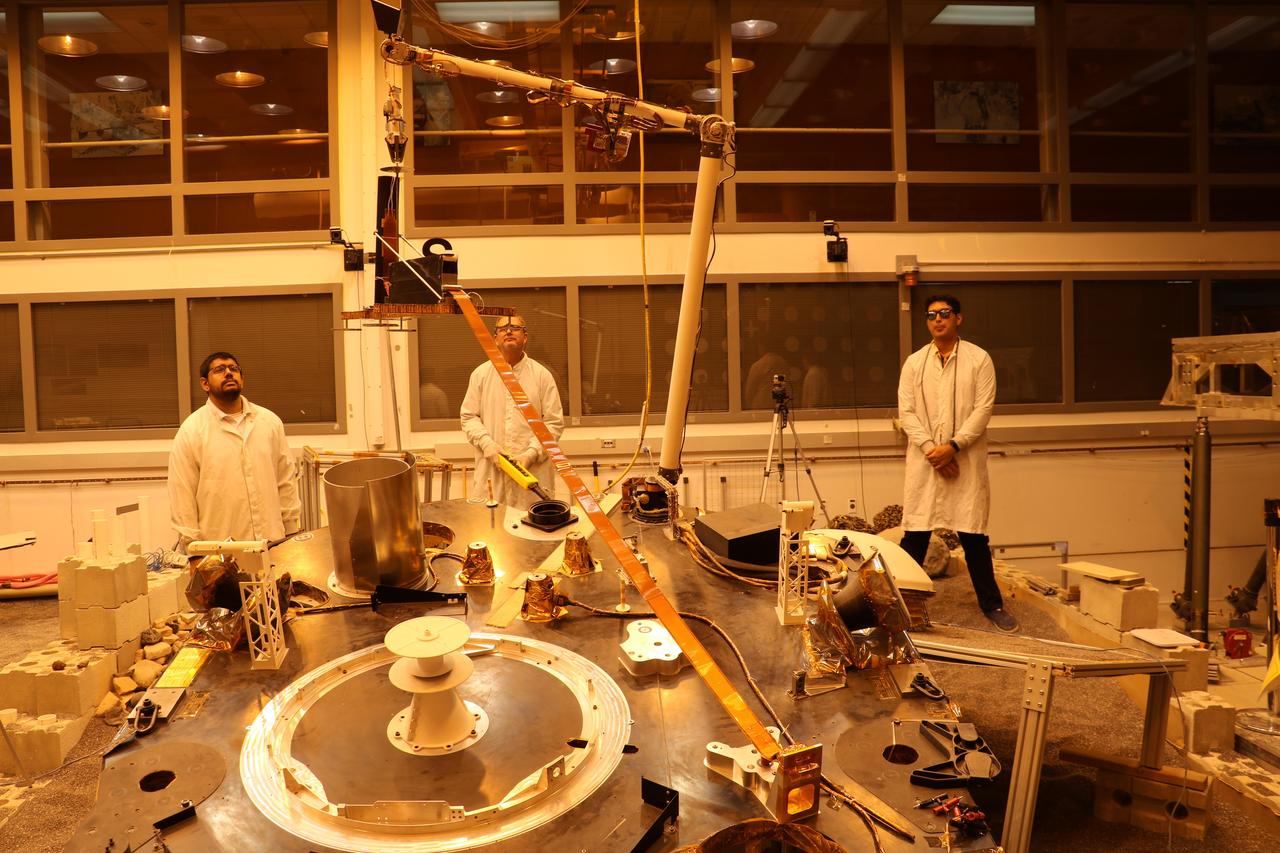

An engineering version of the robotic arm on NASA's InSight mission lifts the engineering version of the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Probe (HP3) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This test was conducted by InSight team members in a Mars-like environment, including reddish lighting, to simulate conditions InSight will encounter on the Red Planet. The orange tape-like tail behind HP3 is a tether that connects the HP3 support structure to the instrument's back-end electronics box on the lander. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22807

Inside a massive clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland the James Webb Space Telescope team is steadily installing the largest space telescope mirror ever. Unlike other space telescope mirrors, this one must be pieced together from segments using a high-precision robotic arm. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1ROaT4G" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1ROaT4G</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
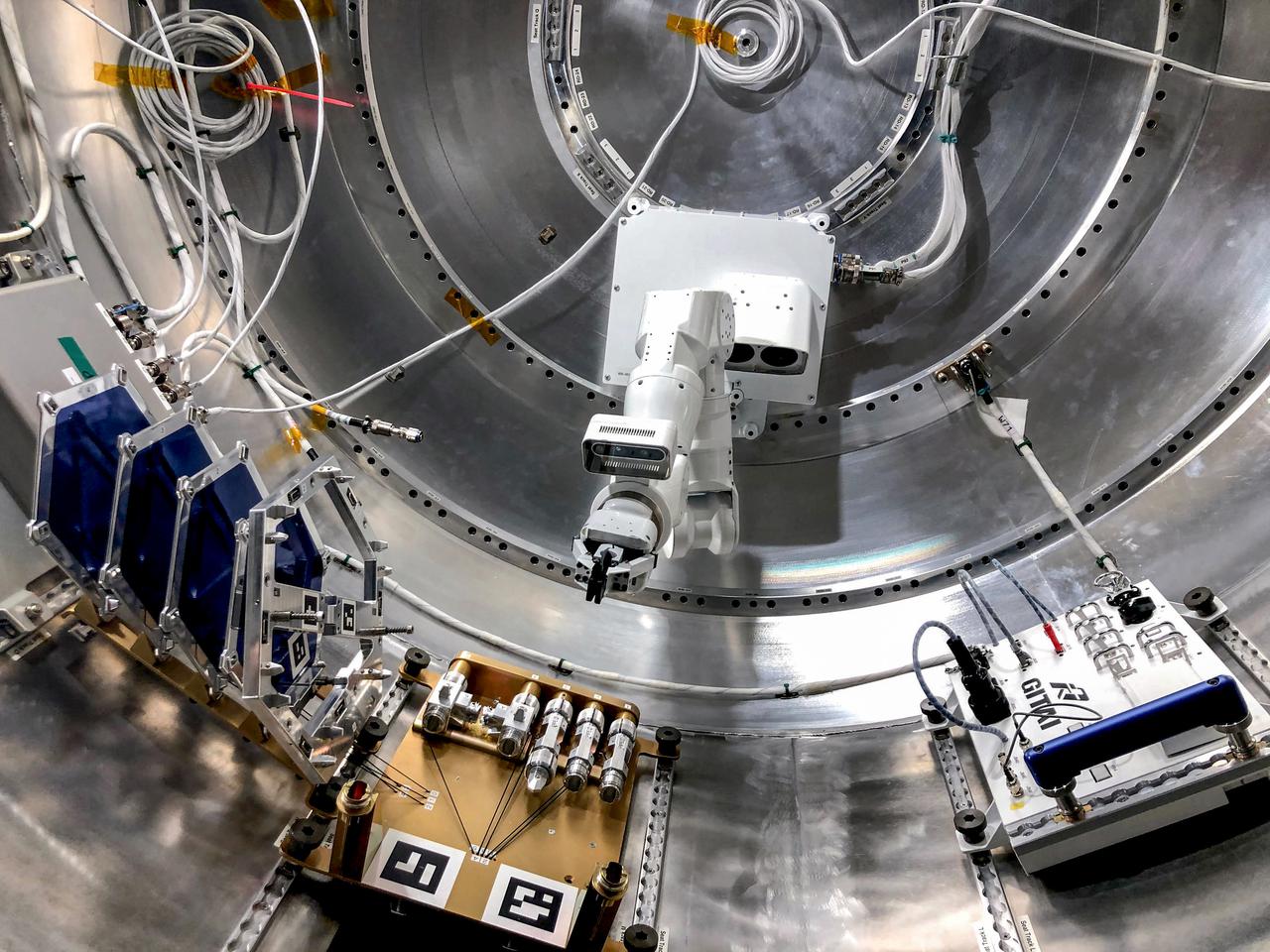
jsc2021e036656 (4/2/2021) --- Complete configuration of the GITAI S1 inside the Bishop airlock mock-up. The GITAI S1 Robotic Arm Tech Demo (Nanoracks-GITAI Robotic Arm) demonstrates the versatility and dexterity in microgravity of a robot designed by GITAI Japan Inc. For the demonstration, the robot conducts common crew activities and tasks via supervised autonomy and teleoperations from the ground.
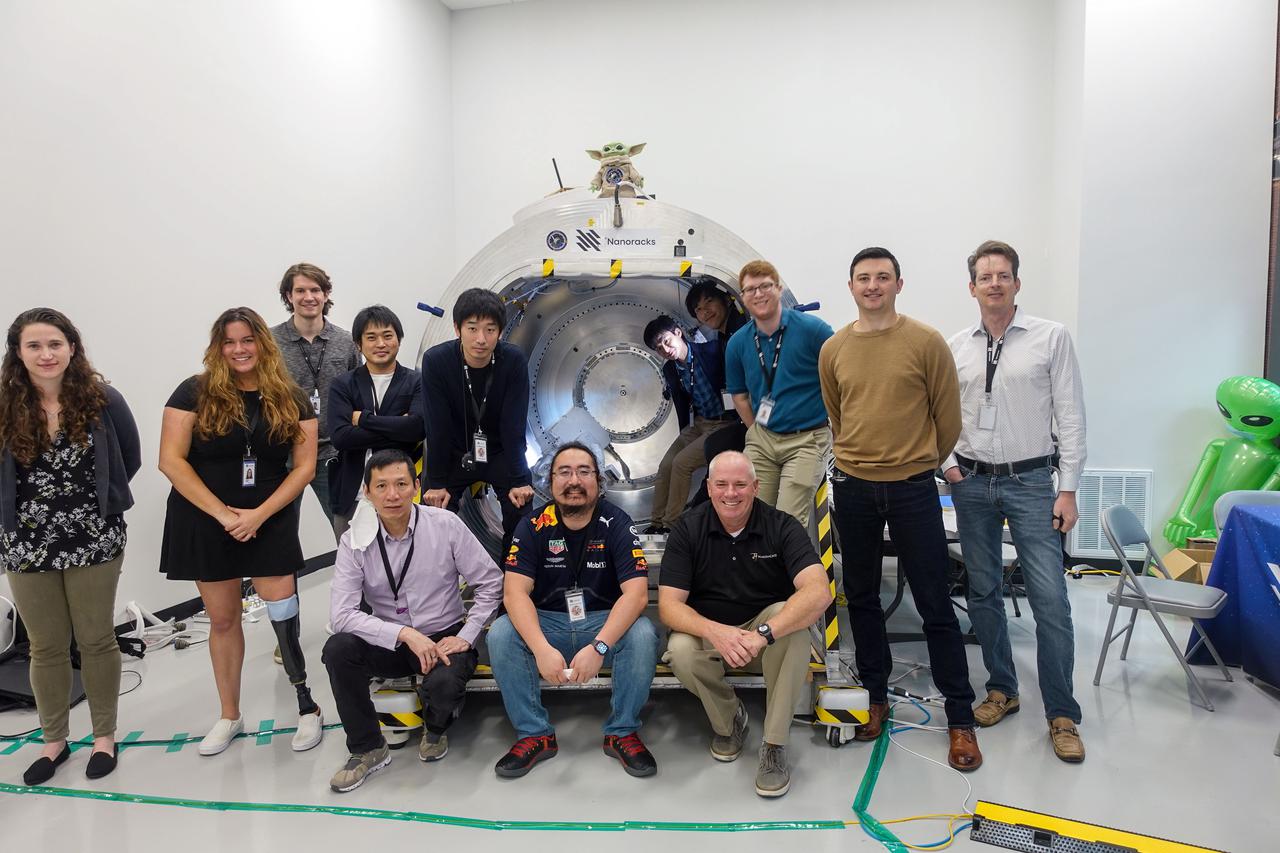
jsc2021e036652 (8/11/2021) --- The GITAI and Nanoracks team group photo. The GITAI S1 Robotic Arm Tech Demo (Nanoracks-GITAI Robotic Arm) demonstrates the versatility and dexterity in microgravity of a robot designed by GITAI Japan Inc. For the demonstration, the robot conducts common crew activities and tasks via supervised autonomy and teleoperations from the ground.
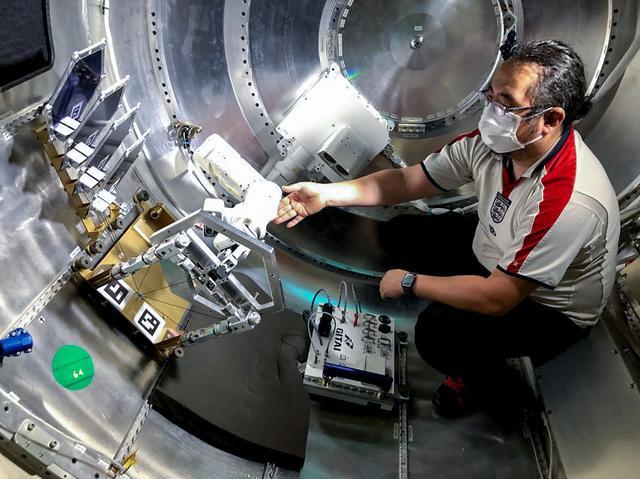

jsc2021e036653 (8/11/2021) --- Final checks of the GITAI S1 Flight Model. The GITAI S1 Robotic Arm Tech Demo (Nanoracks-GITAI Robotic Arm) demonstrates the versatility and dexterity in microgravity of a robot designed by GITAI Japan Inc. For the demonstration, the robot conducts common crew activities and tasks via supervised autonomy and teleoperations from the ground.
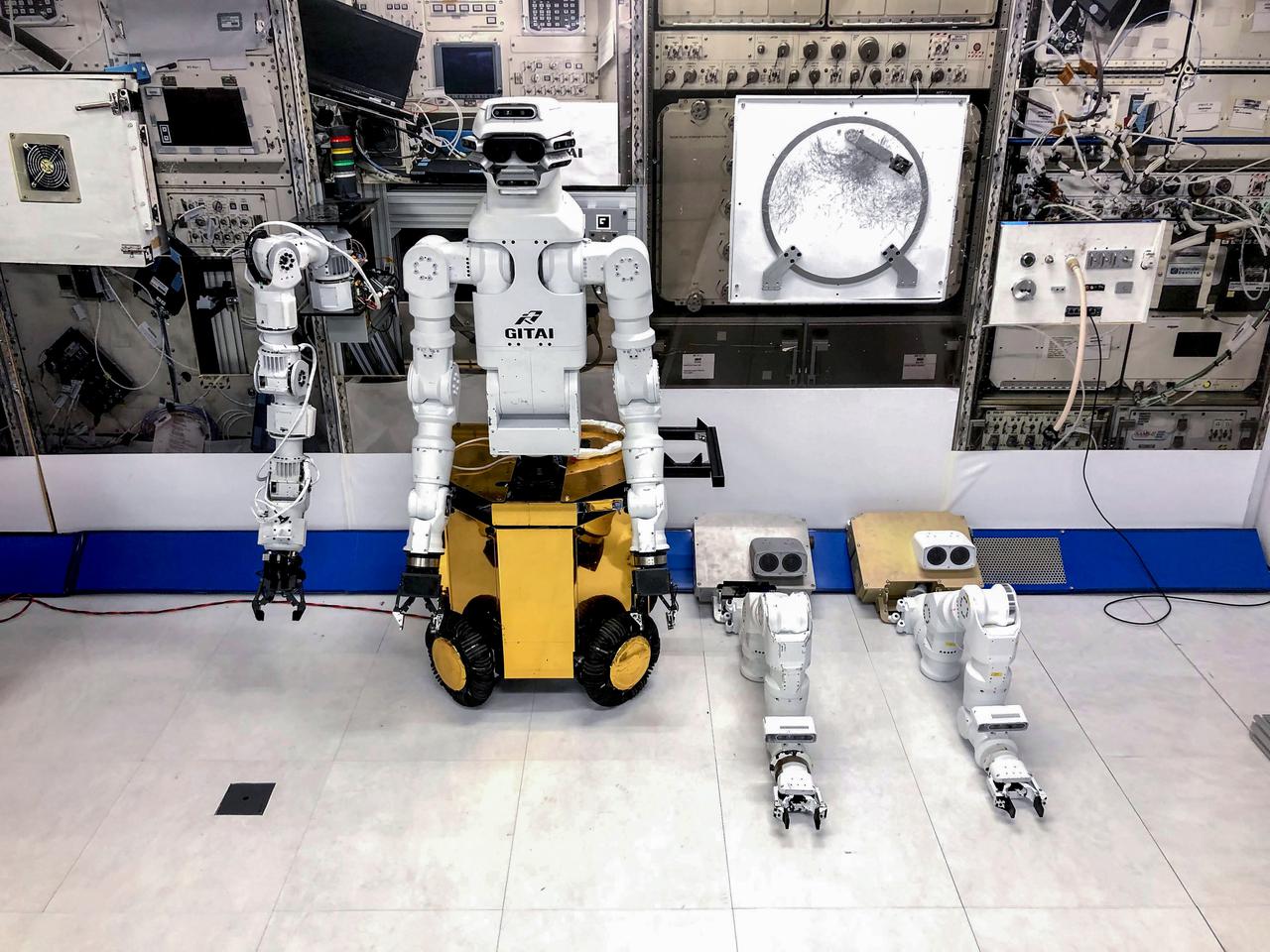
jsc2021e036654 (12/12/2020) --- Final checks of the GITAI S1 Flight Model. The GITAI S1 Robotic Arm Tech Demo (Nanoracks-GITAI Robotic Arm) demonstrates the versatility and dexterity in microgravity of a robot designed by GITAI Japan Inc. For the demonstration, the robot conducts common crew activities and tasks via supervised autonomy and teleoperations from the ground.
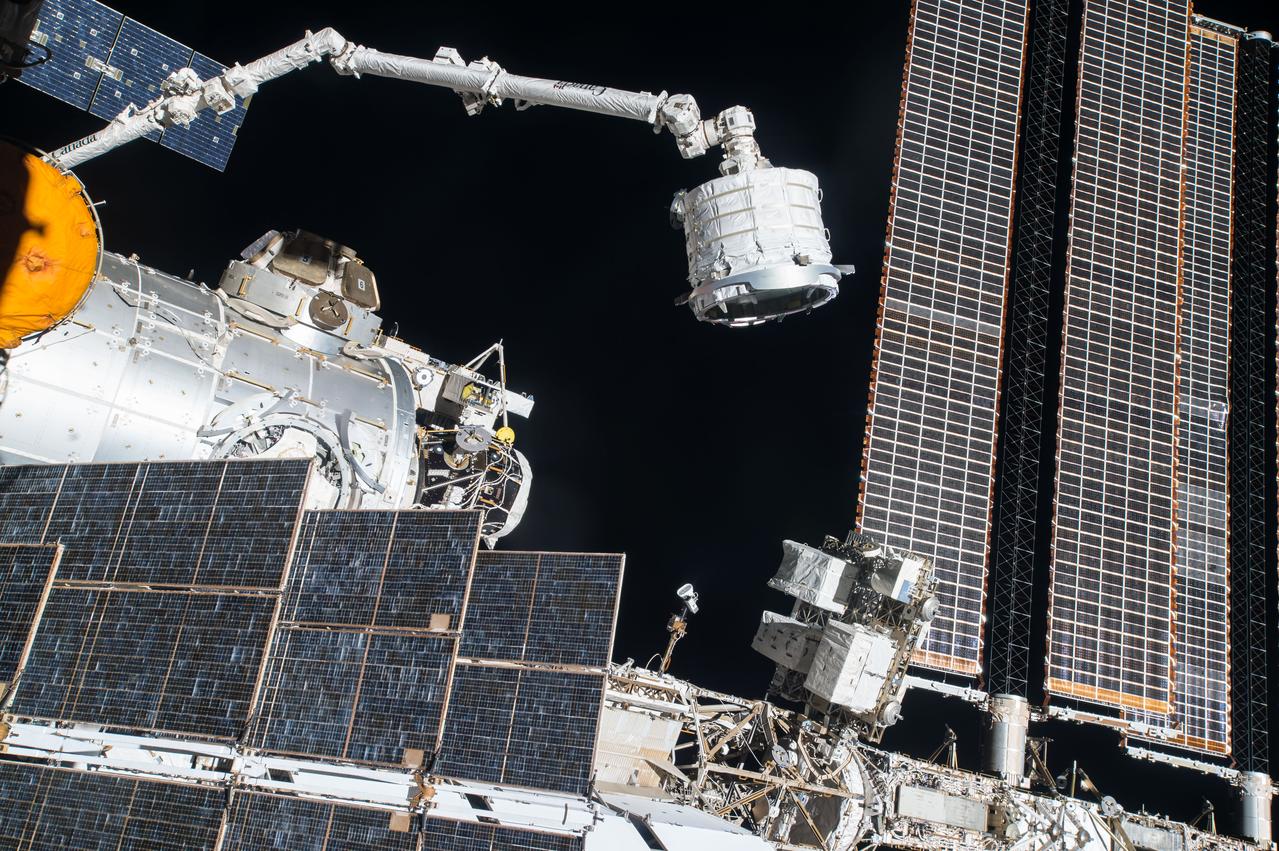

iss047e061107 (4/16/2016) --- View of Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) attached to Canadarm2 Robotic Arm. The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is an experimental expandable capsule that docks with the International Space Station (ISS). After docking, BEAM inflates to roughly 13 feet long and 10.5 feet in diameter to provide a habitable volume where a crew member can enter.
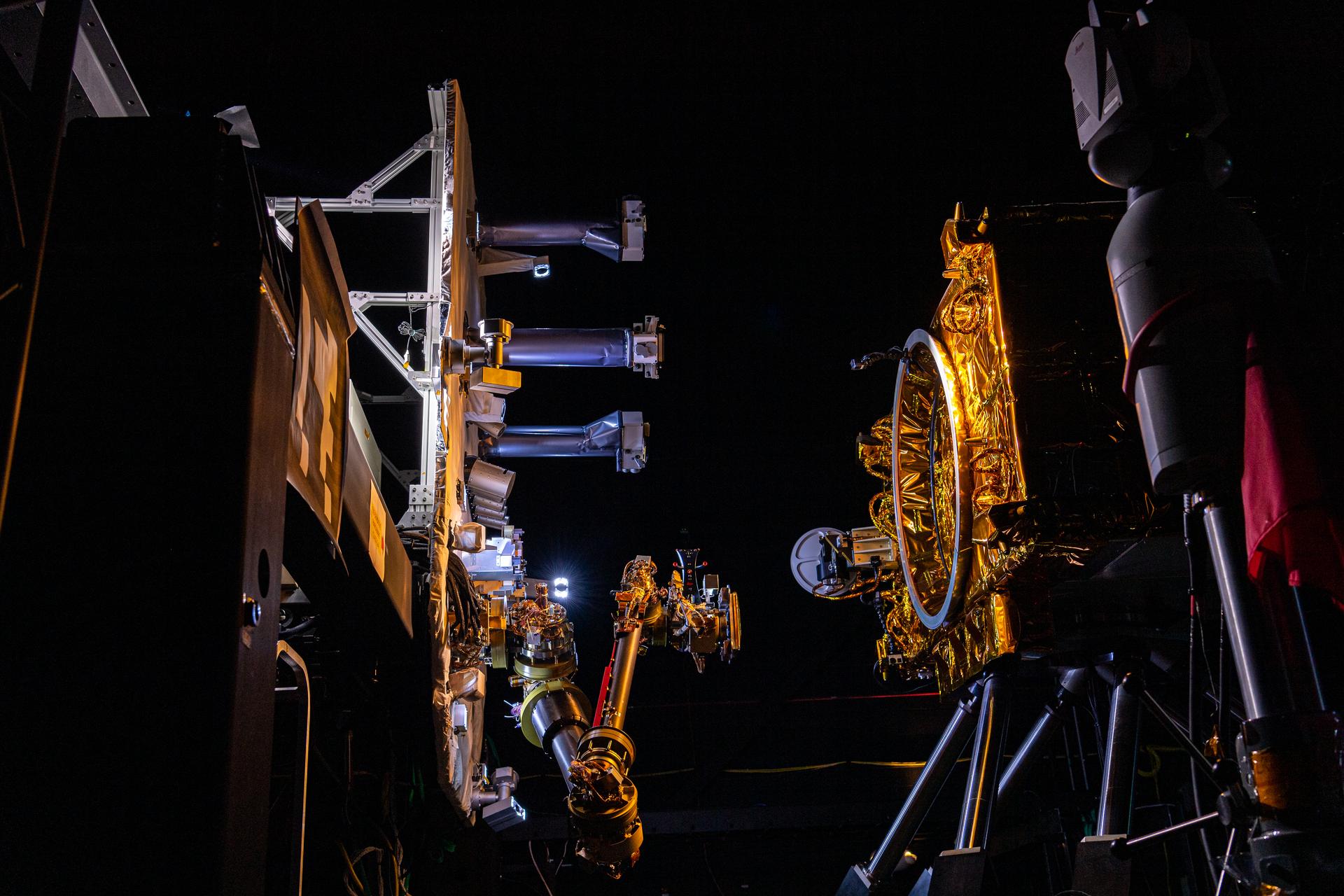

Detail shot of the OSAM-1 auto-capture test bed performing a test of the robot arm inside the robotics operations center at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Md., Feb 23, 2023. This photo has been approved for public release. NASA/Mike Guinto
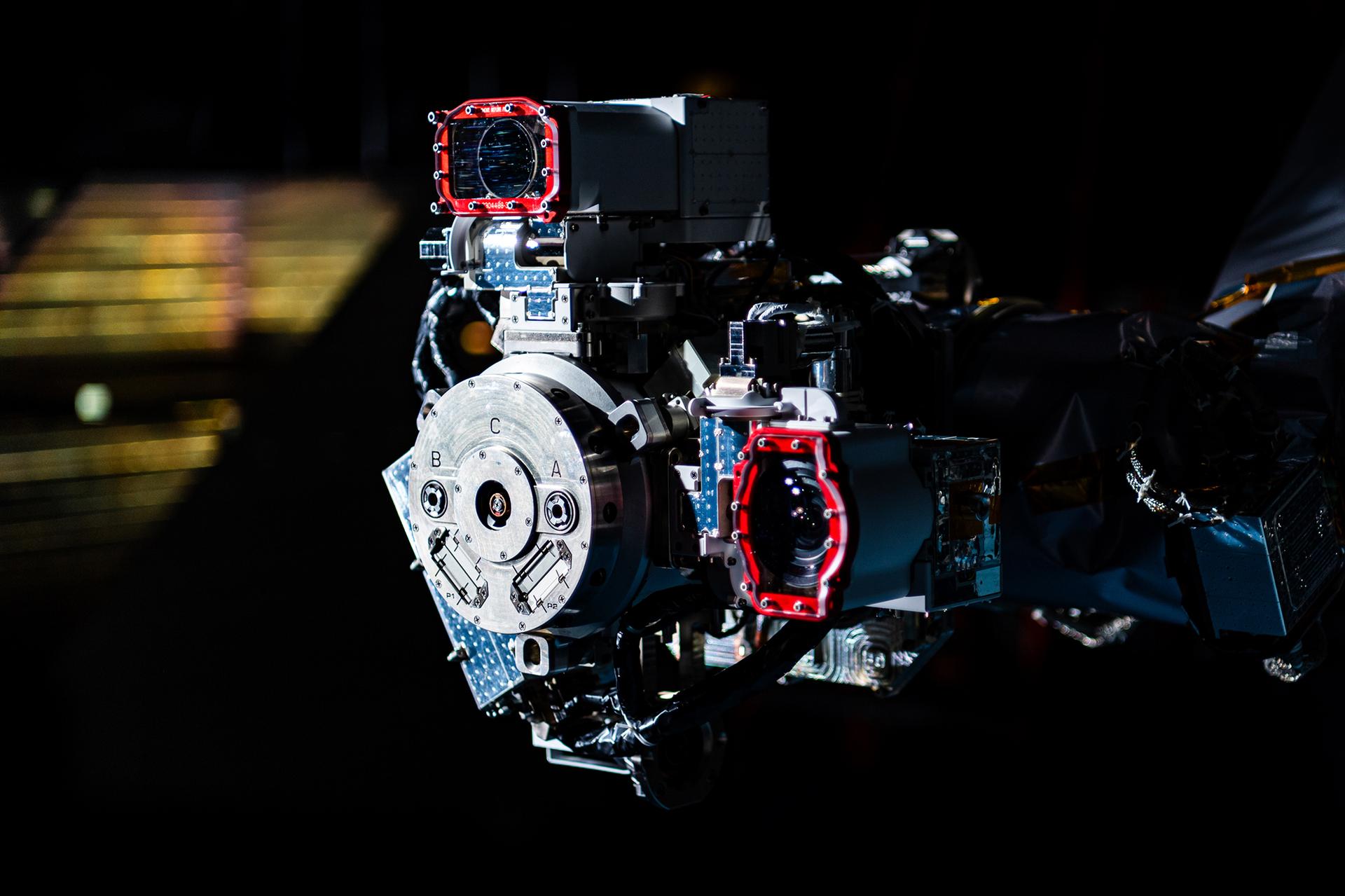
One of the OSAM-1 Robot Arms is seen, mounted onto ground support equipment used for testing inside the cleanroom at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Md., Apr 17, 2024. This photo has been reviewed by Maxar, OSAM1 project management, and the Export Control Office and is released for public view. NASA/Mike Guinto
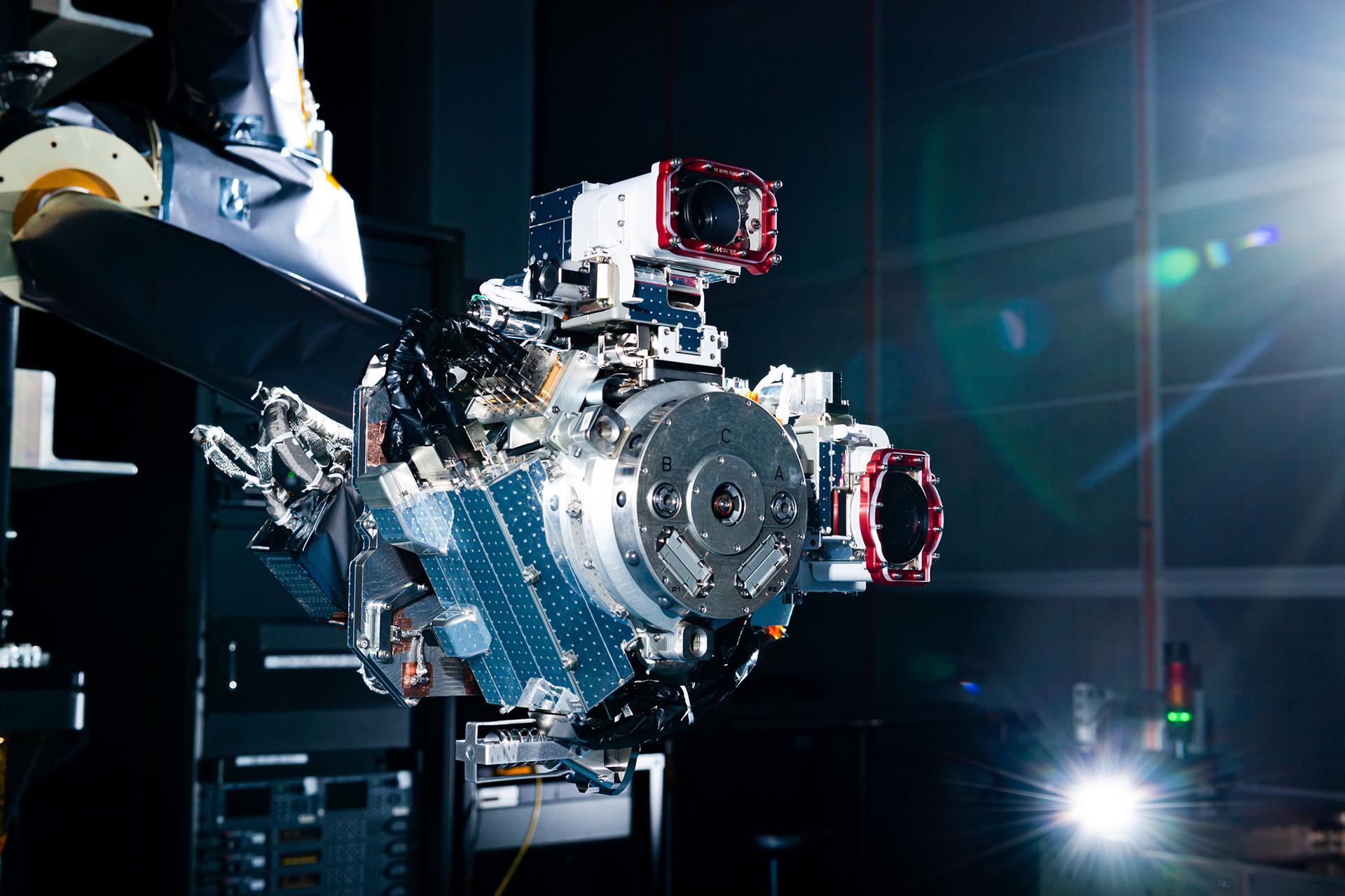
One of the OSAM-1 Robot Arms is seen, mounted onto ground support equipment used for testing inside the cleanroom at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Md., Apr 17, 2024. This photo has been reviewed by Maxar, OSAM1 project management, and the Export Control Office and is released for public view. NASA/Mike Guinto
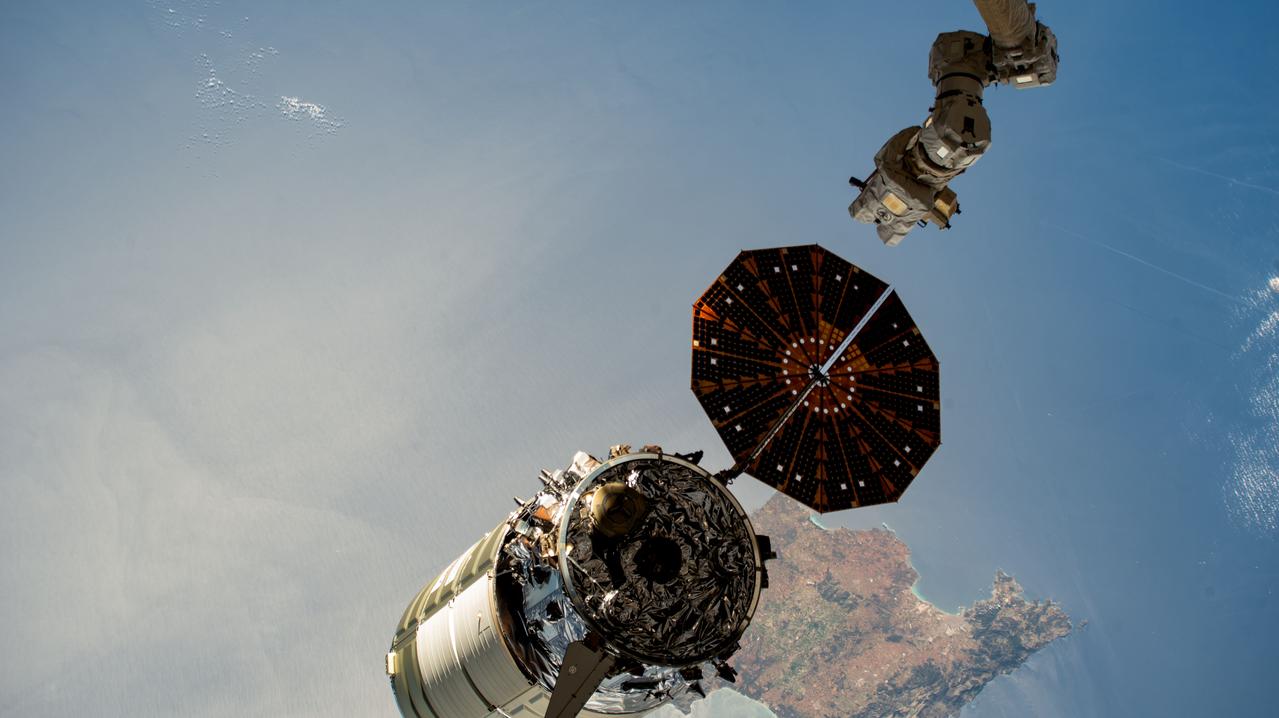

iss069e004822 (April 21, 2023) --- The Cygnus space freighter from Northrop Grumman is pictured moments after its release from the Canadarm2 robotic arm as the International Space Station orbited 262 miles above the Mediterranean Sea near the Spanish island of Mallorca.
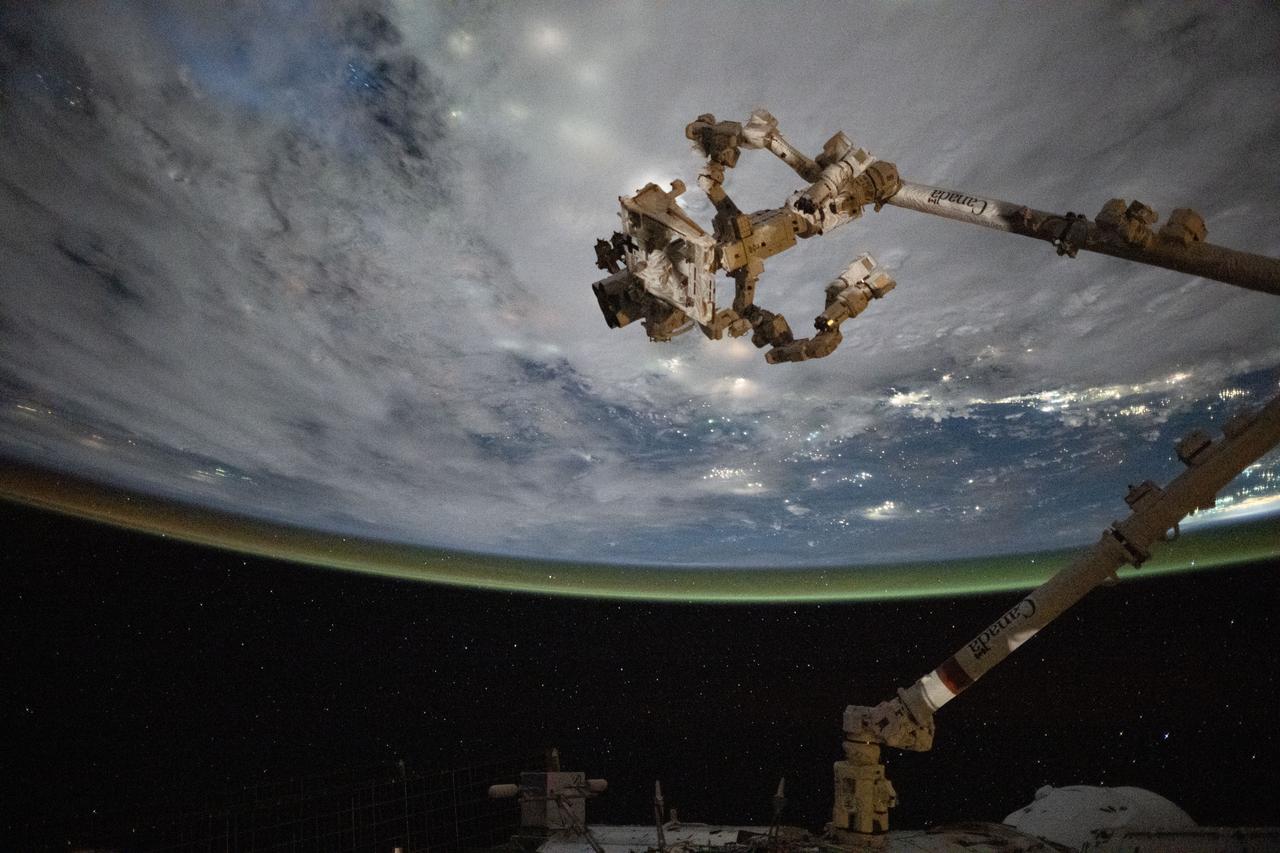

iss073e0695937 (Sept. 1, 2025) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm with Dextre, its fine-tuned robotic hand attached, is pictured extending from the International Space Station as it orbited 258 miles above the coast of Cambodia on a cloudy Gulf of Thailand.
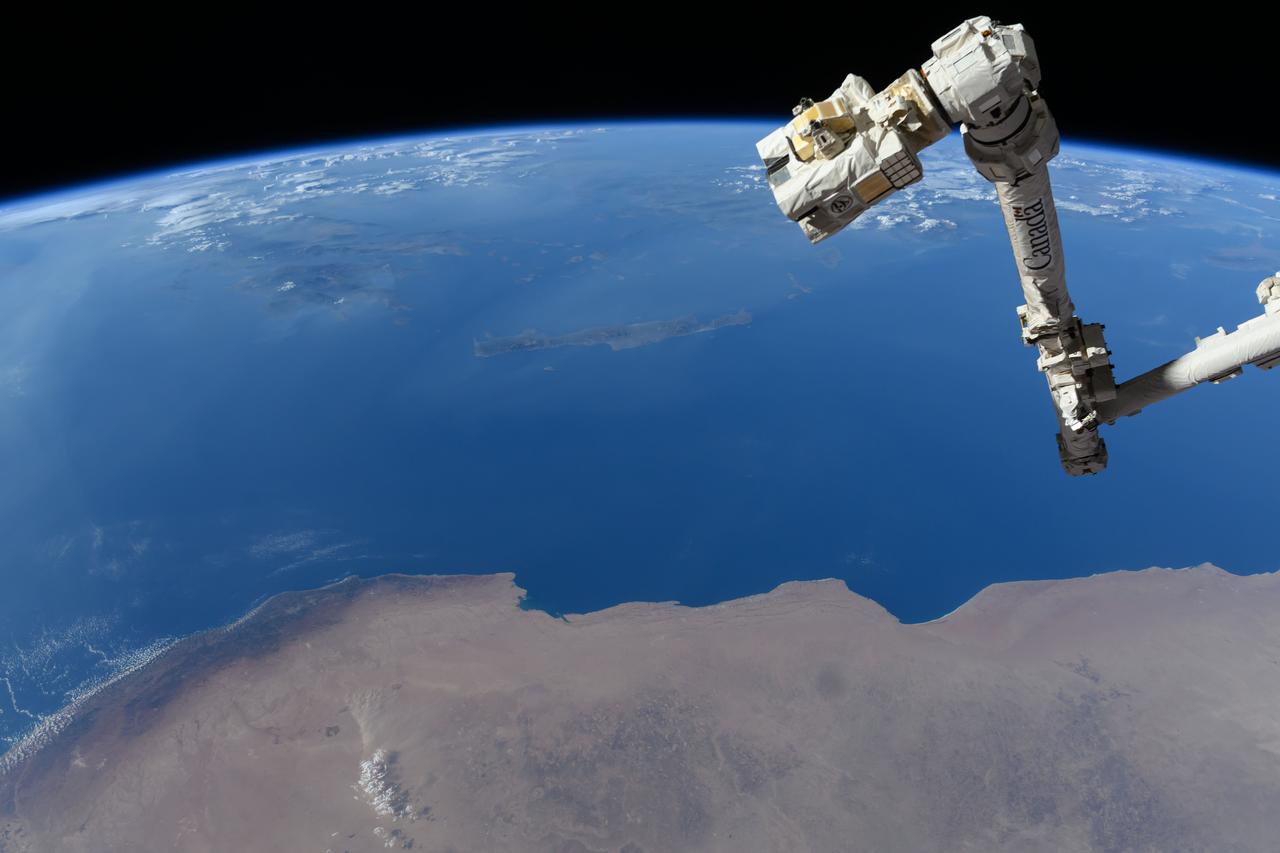

iss071e384199 (July 17, 2024) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm's latching end effector, or LEE, is used to grapple fixtures on the International Space Station, as well as capture the approaching Cygnus cargo craft from Northrop Grumman and attach it to the Unity module for cargo transfer operations. 256 miles below the outpost is the Mediterranean coast of Libya and Egypt and the Greek island of Crete.

iss072e157843 (Nov. 11, 2024) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm with its fine-tuned robotic hand Dextre, or the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, attached is pictured after maneuvering and installing scientific hardware on the International Space Station. Dextre is remotely operated by robotics controllers on the ground providing precise handling capabilities reducing the need for spacewalks giving astronauts more time to conduct science.
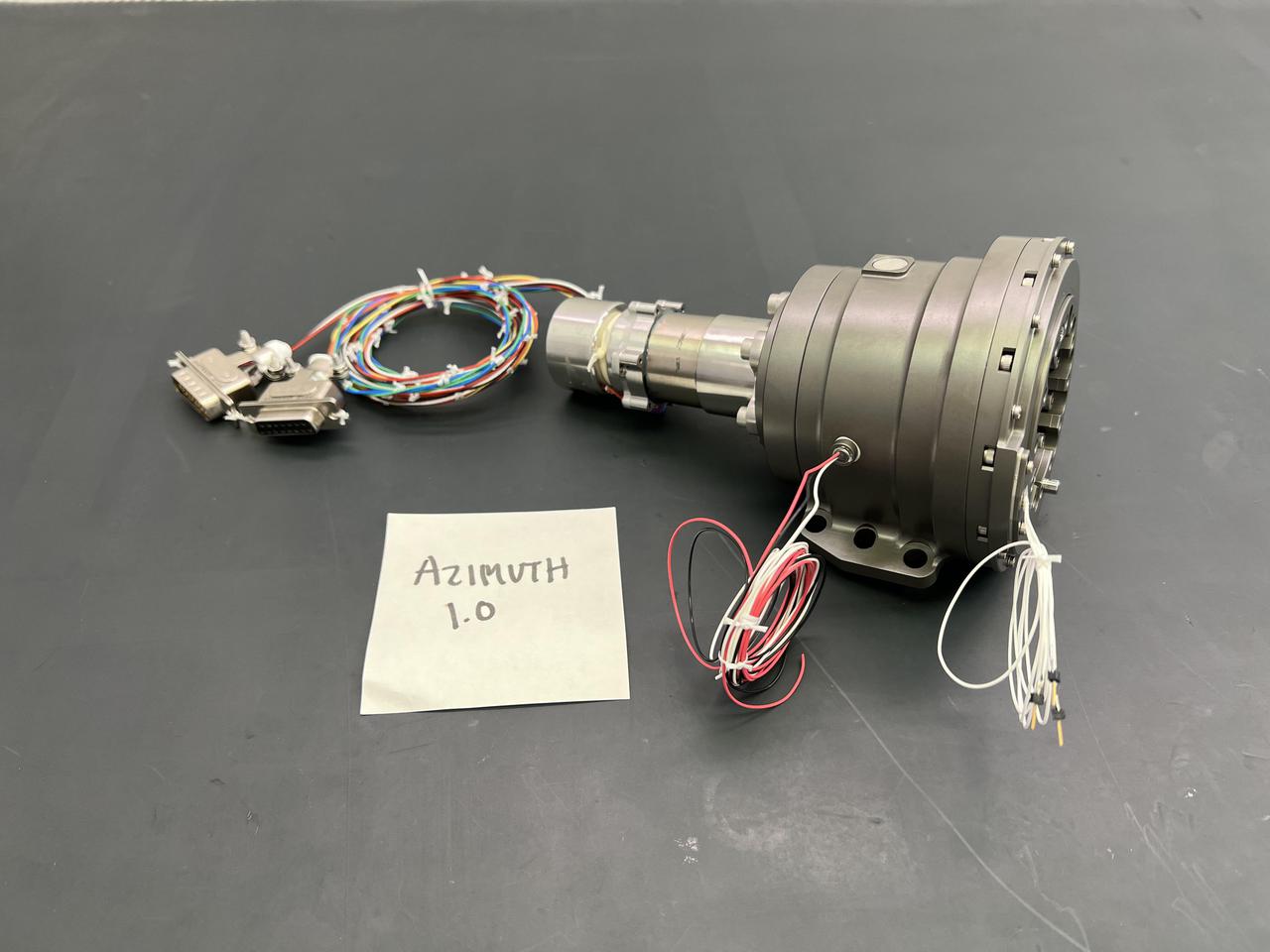

In early 2022, the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) project – led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California – successfully integrated special gears into pieces of a robotic arm that is planned to perform a robot-controlled lunar surface experiment with imagery in the coming years. These bulk metallic glass (BMG) gears, integrated into COLDArm's joints and actuators, were developed through the Game Changing Development bulk metallic glass gears project to operate at extreme temperatures below minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). The gear alloys have a disordered atomic-scale structure, making them both strong and elastic enough to withstand these exceptionally low temperatures. Typical gearboxes require heating to operate at such cryogenic temperatures. The BMG gear motors have been tested and successfully operated at roughly minus 279 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius) without heating assistance. This gear motor is one of the key technologies to enable the robotic arm to operate in extremely cold environments, such as during lunar night. Each of the four joints containing BMG gears will be tested once the arm is fully assembled, which is scheduled for spring of 2022. Robotic joint testing will include dynamometer testing to measure torque/rotational speed, as well as cryogenic thermal vacuum testing to understand how the equipment would perform in an environment similar to space. Once proven, the BMG gears and COLDArm capabilities will enable future missions to work in extreme environments on the Moon, Mars, and ocean worlds. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24567
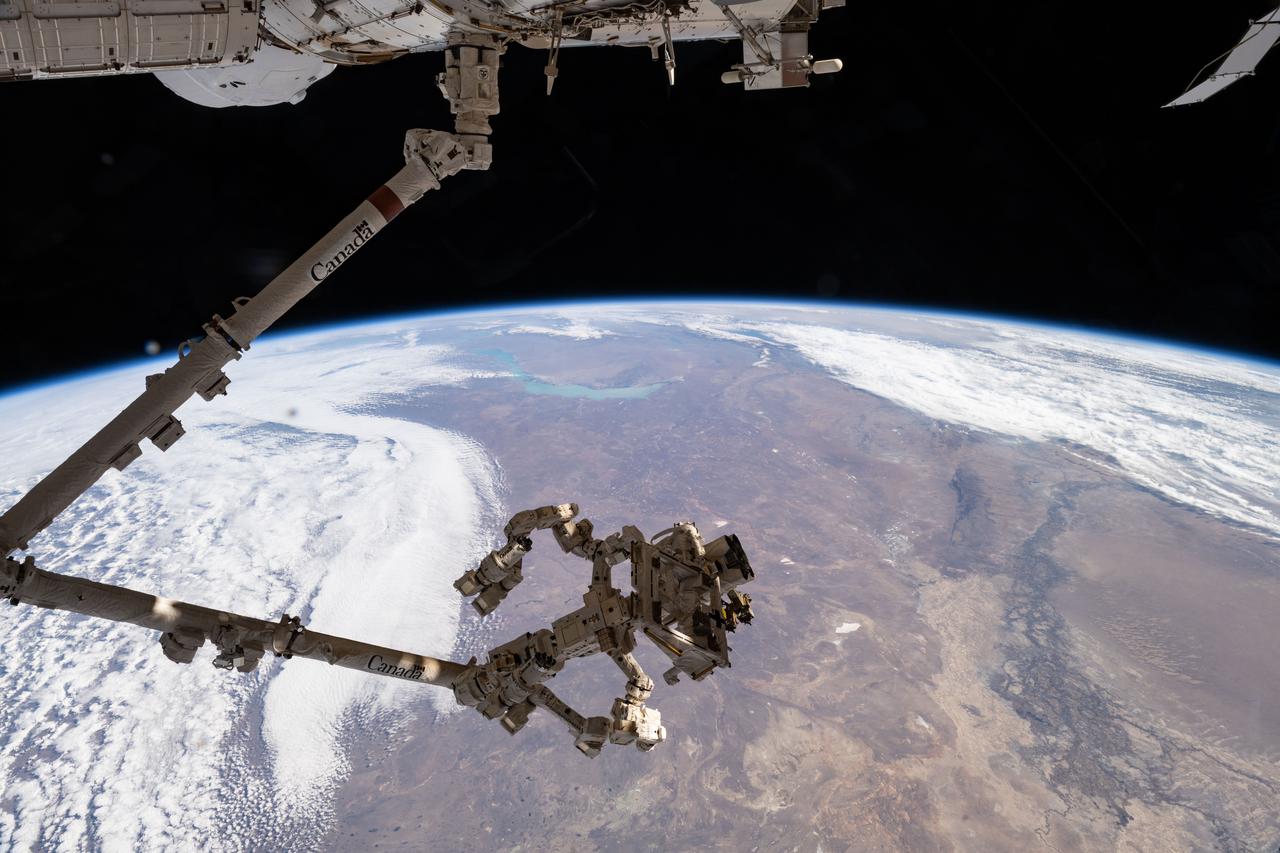

iss073e0819948 (Oct. 2, 2025) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm, with Dextre—its fine-tuned robotic hand—attached, extends from the International Space Station’s Harmony module as the orbital outpost soars 263 miles above Kazakhstan. At upper center is Lake Balkhash, notable for its two distinct segments: the western portion contains freshwater, while the eastern portion holds saltwater due to a combination of geography, hydrology, and limited water circulation.
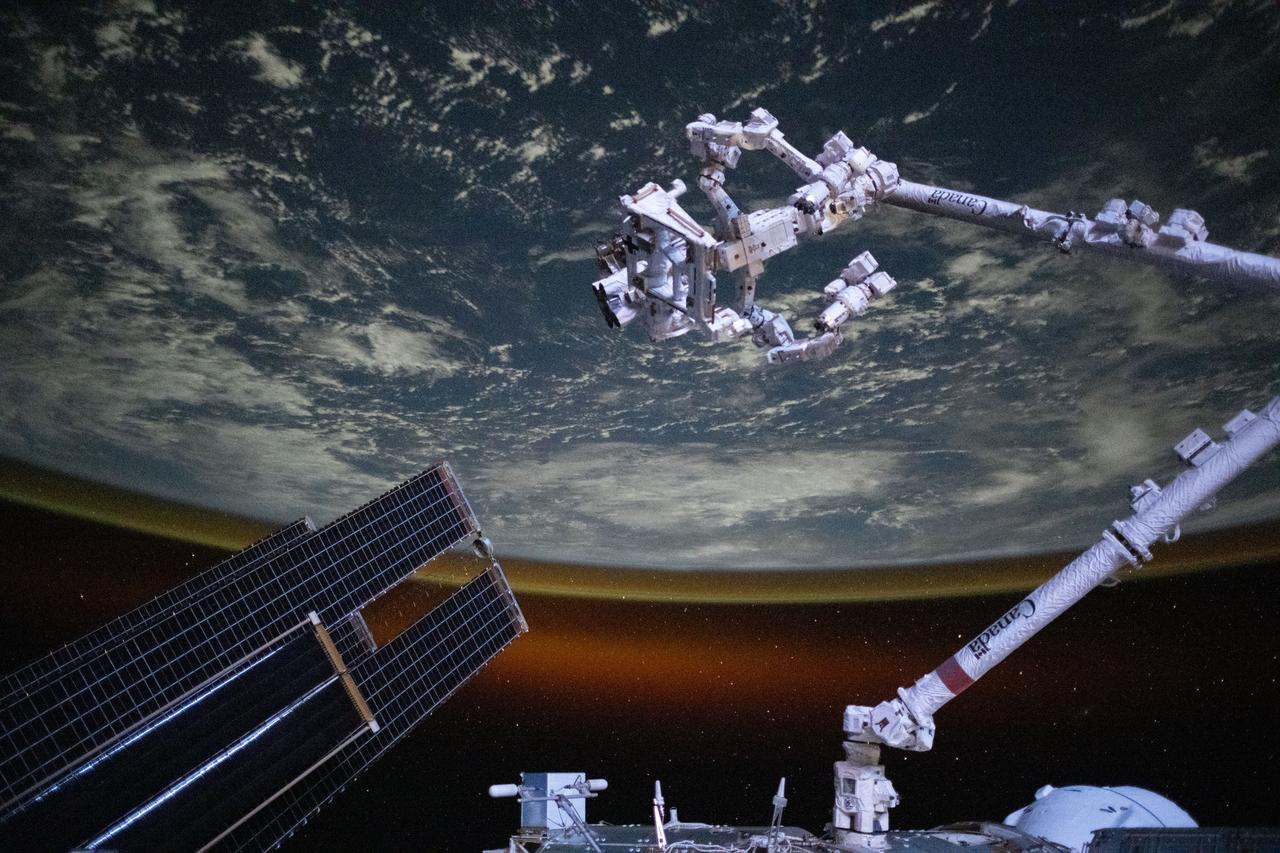

iss073e0695491 (Sept. 1, 2025) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm with Dextre, its fine-tuned robotic hand attached, is pictured extending from the International Space Station as it orbited 258 miles above the Indian Ocean southwest of the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The Earth's horizon is highlighted by the atmospheric glow with a set of the orbital outpost's main solar arrays and a partially obscured SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft in the foreground.
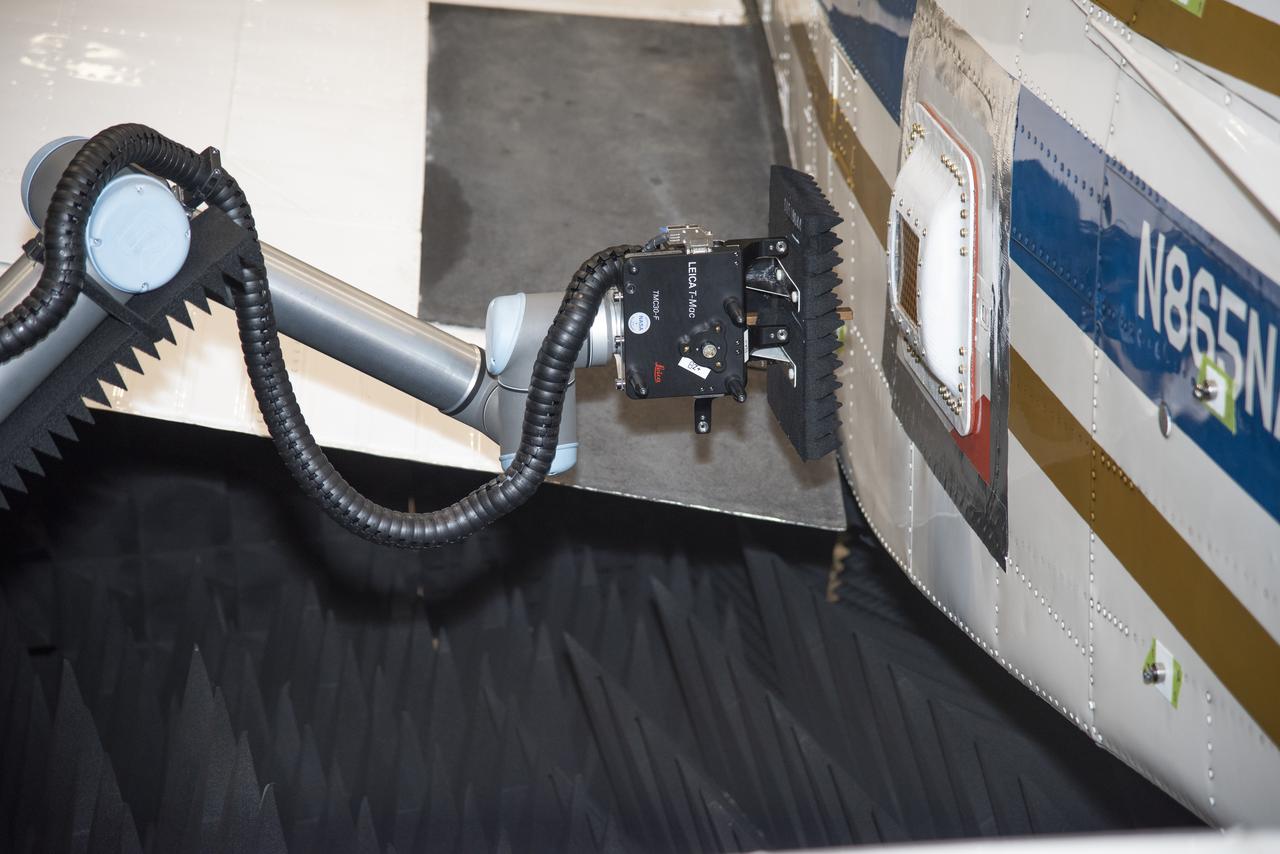

Tests were conducted with a robotic antenna scanner at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. The scanner was used to test the in-situ radiation pattern of the conformal antenna to verify its performance parameters before being tested on an aircraft.
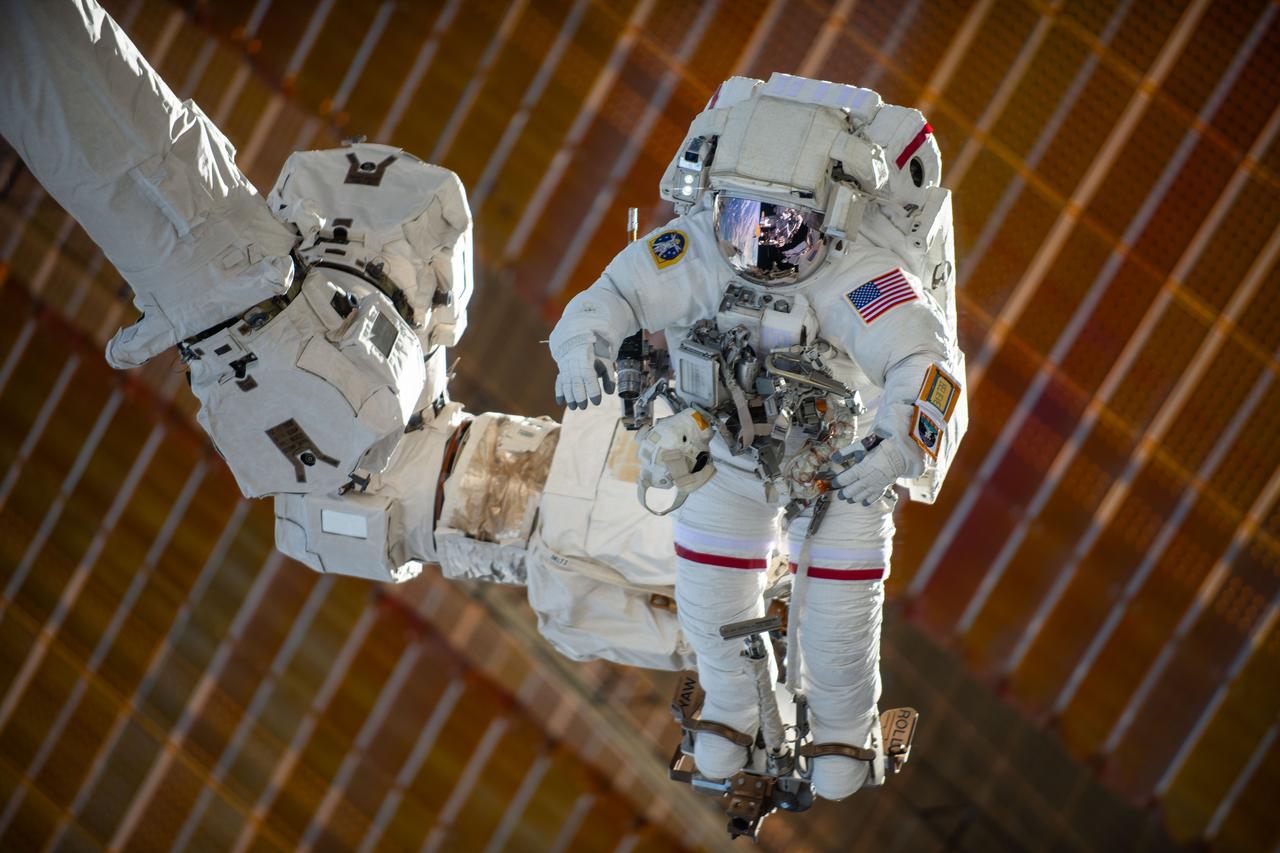

iss072e595426 (Jan. 30, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams is attached to the Canadarm2 robotic arm's latching end effector while being maneuvered to her worksite 264 miles above the South Pacific Ocean. Williams removed and stowed a radio frequency group antenna assembly during the five-hour and 26-minute spacewalk outside the International Space Station.

iss072e595424 (Jan. 30, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams is attached to the Canadarm2 robotic arm's latching end effector while being maneuvered to her worksite 264 miles above the South Pacific Ocean. Williams removed and stowed a radio frequency group antenna assembly during the five-hour and 26-minute spacewalk outside the International Space Station.
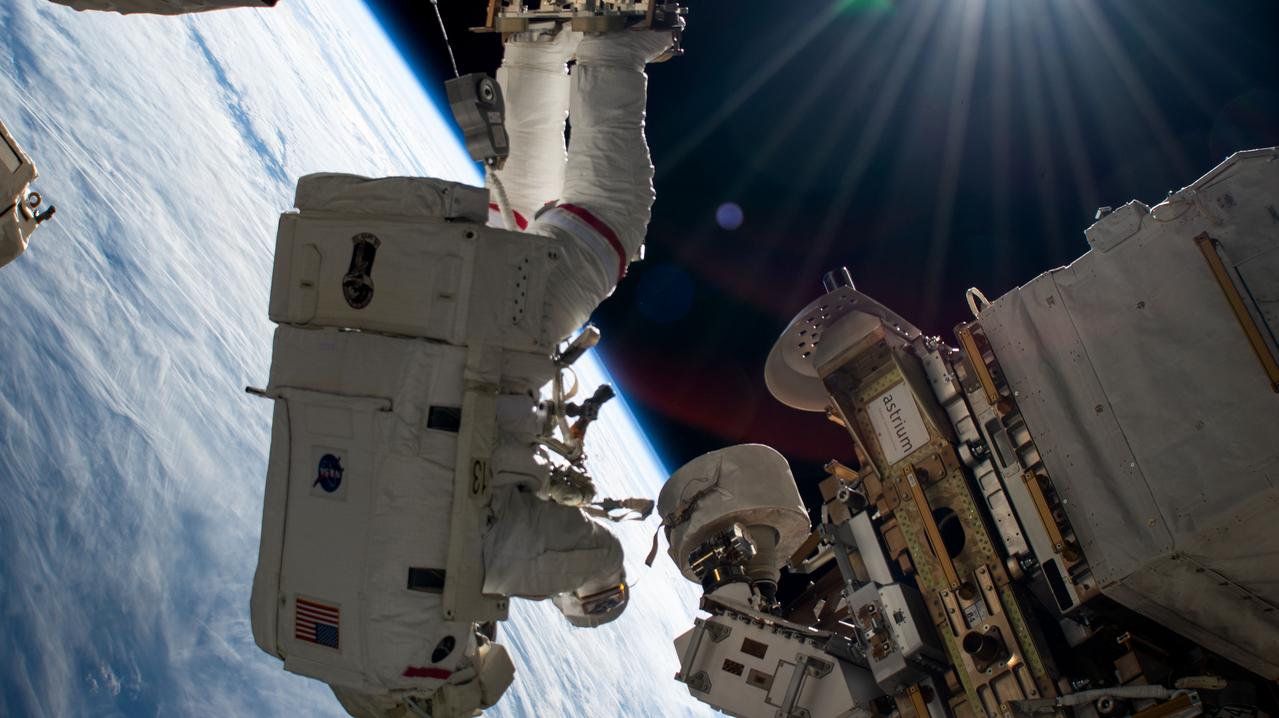

iss072e574908 (Jan. 30, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams seemingly hangs upside down while attached to the Canadarm2 robotic arm's latching end effector during a five-hour and 26 minute spacewalk to remove and stow a radio frequency group antenna assembly. The orbital outpost was soaring 260 miles above Russia near the Sea of Azov at the time of this photograph.
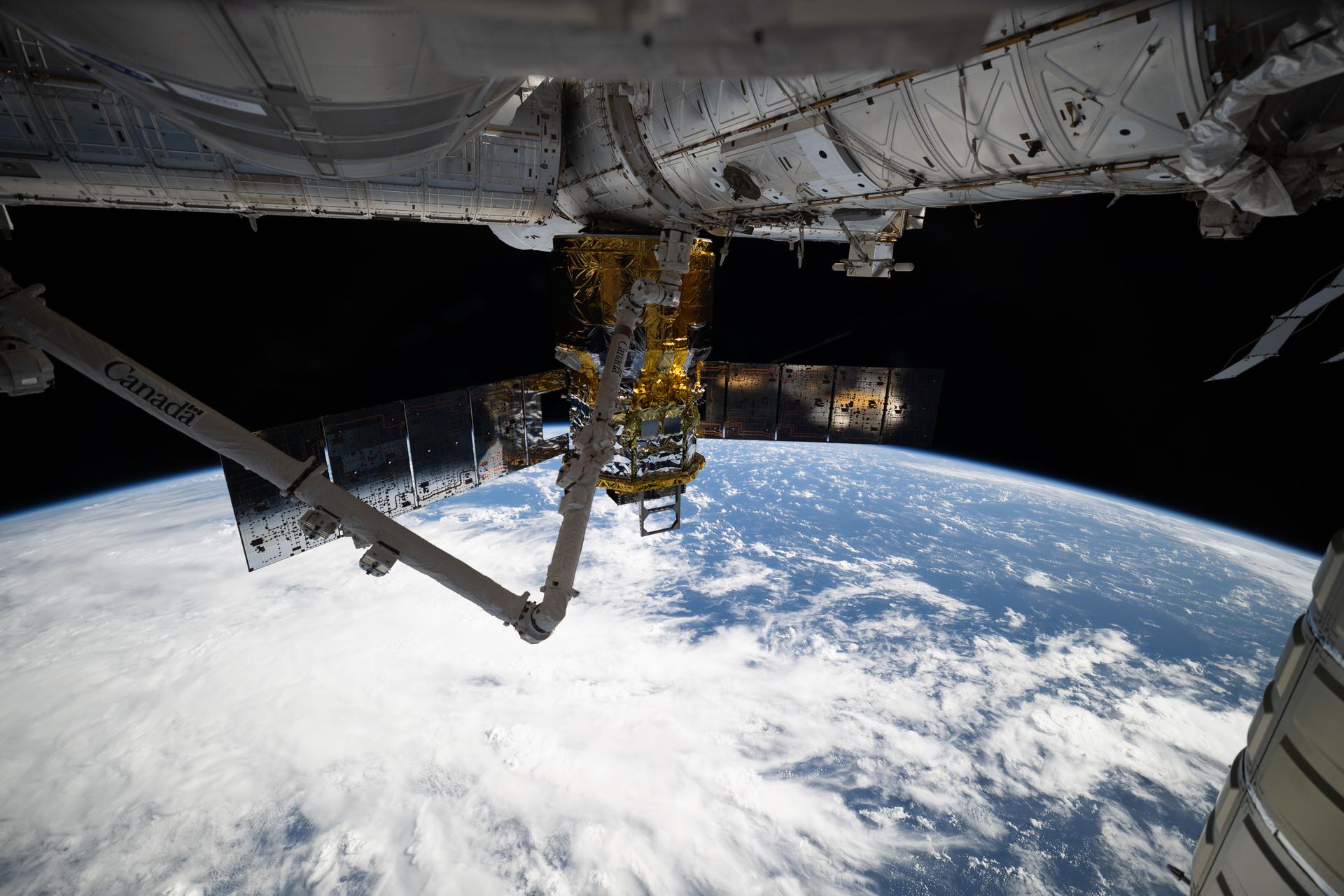

iss074e0319321 (Feb. 19, 2026) --- JAXA’s (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) HTV-X1 cargo craft, with the Canadarm2 robotic arm perched on a portable data grapple fixture in front, is pictured berthed to the Earth-facing port of the International Space Station’s Harmony module. At the time of this photograph, the orbital outpost was soaring 263 miles above a cloudy Indian Ocean northeast of Madagascar. Credit: NASA/Chris Williams
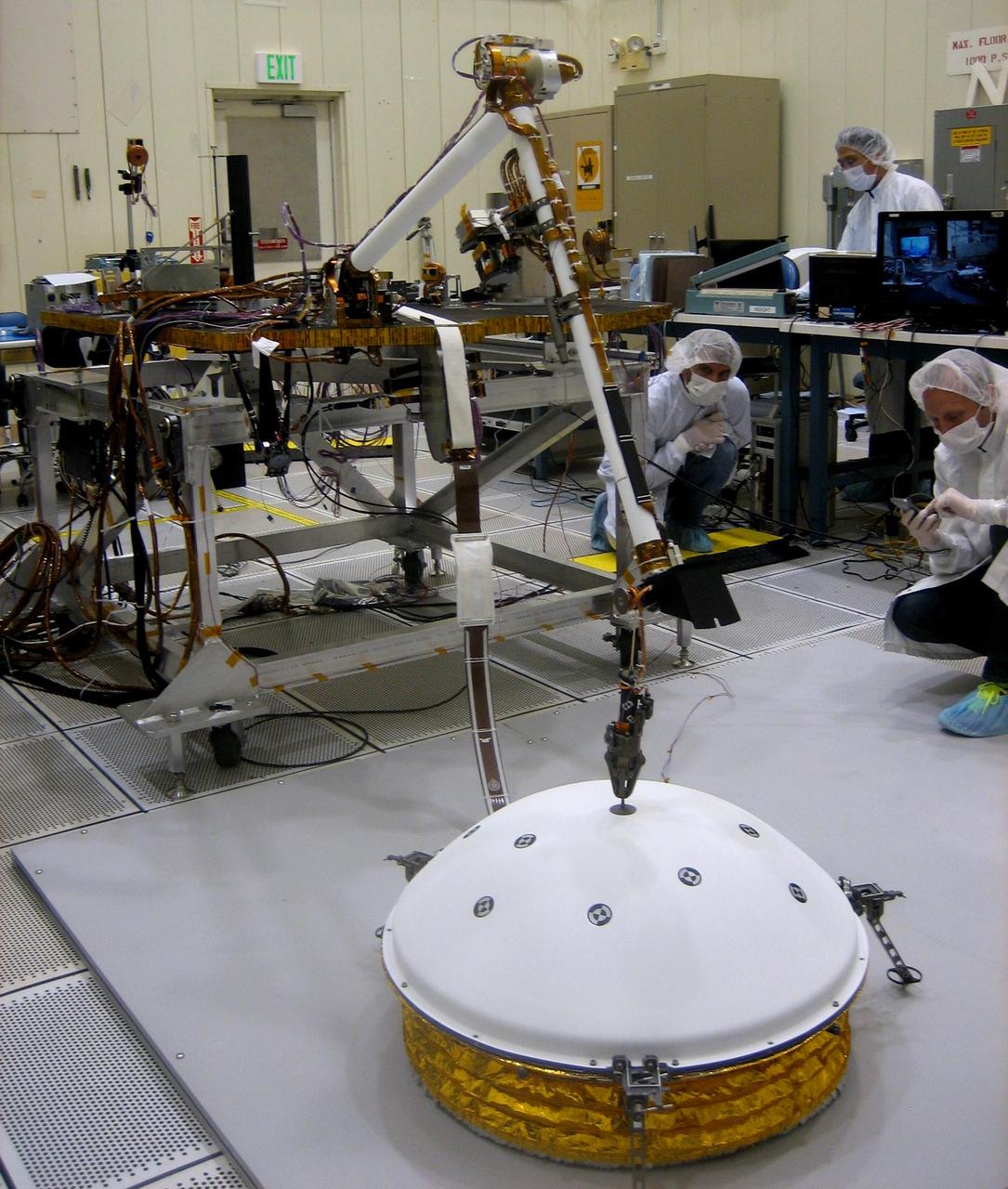

In the weeks after NASA's InSight mission reaches Mars in September 2016, the lander's arm will lift two key science instruments off the deck and place them onto the ground. This image shows testing of InSight's robotic arm inside a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, about two years before it will perform these tasks on Mars. InSight -- an acronym for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport -- will launch in March 2016. It will study the interior of Mars to improve understanding of the processes that formed and shaped rocky planets, including Earth. One key instrument that the arm will deploy is the Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure, or SEIS. It is from France's national space agency (CNES), with components from Germany, Switzerland, the United Kingdom and the United States. In this scene, the arm has just deployed a test model of a protective covering for SEIS, the instrument's wind and thermal shield. The shield's purpose is to lessen disturbances that weather would cause to readings from the sensitive seismometer. Note: After thorough examination, NASA managers have decided to suspend the planned March 2016 launch of the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission. The decision follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak in a section of the prime instrument in the science payload. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19144
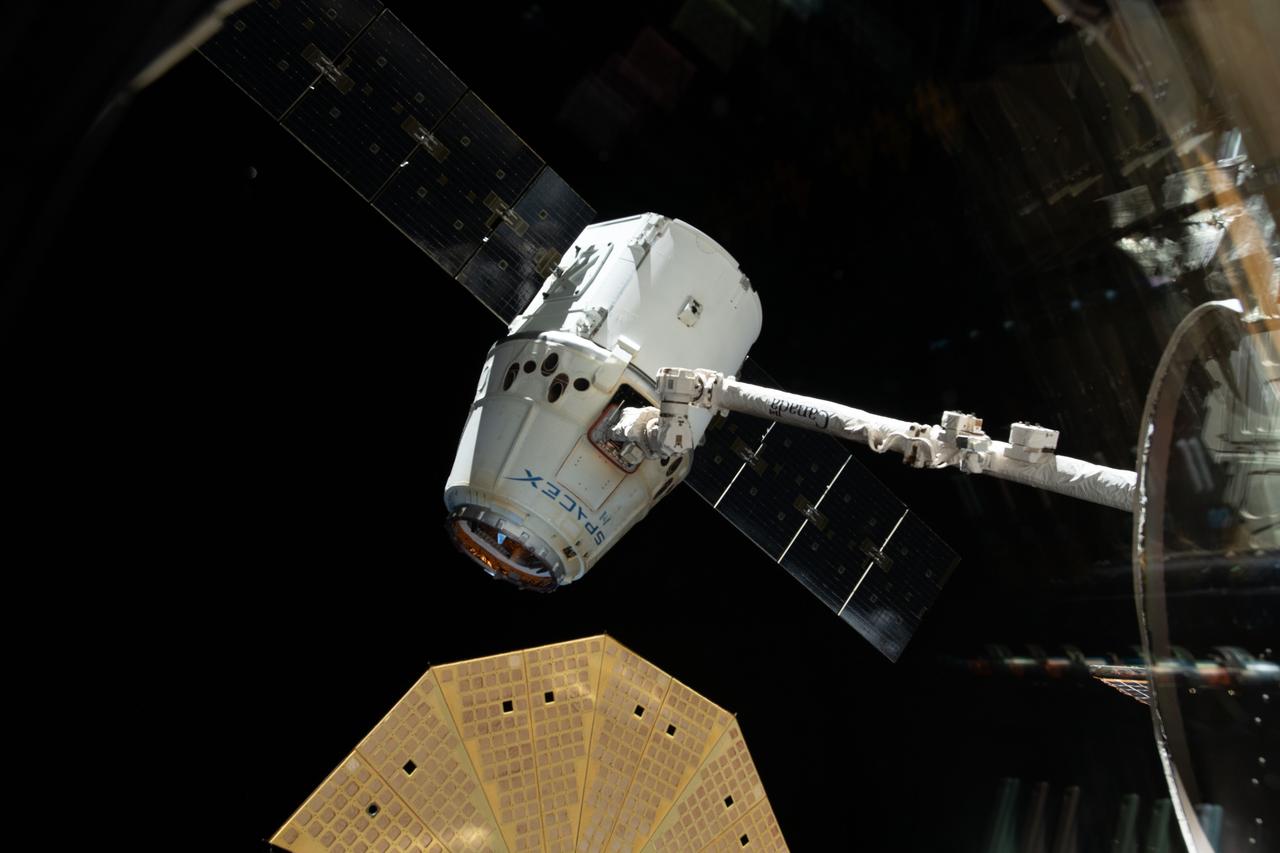

iss058e002666 (Jan. 13, 2019) --- The SpaceX Dragon cargo craft is pictured in the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm before its release and departure from the International Space Station. Featured prominently in the lower foreground is one of two cymbal-shaped UltraFlex solar arrays attached to the Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply ship. The orbital complex was orbiting 254 miles above East Asia at the time this photograph was taken.
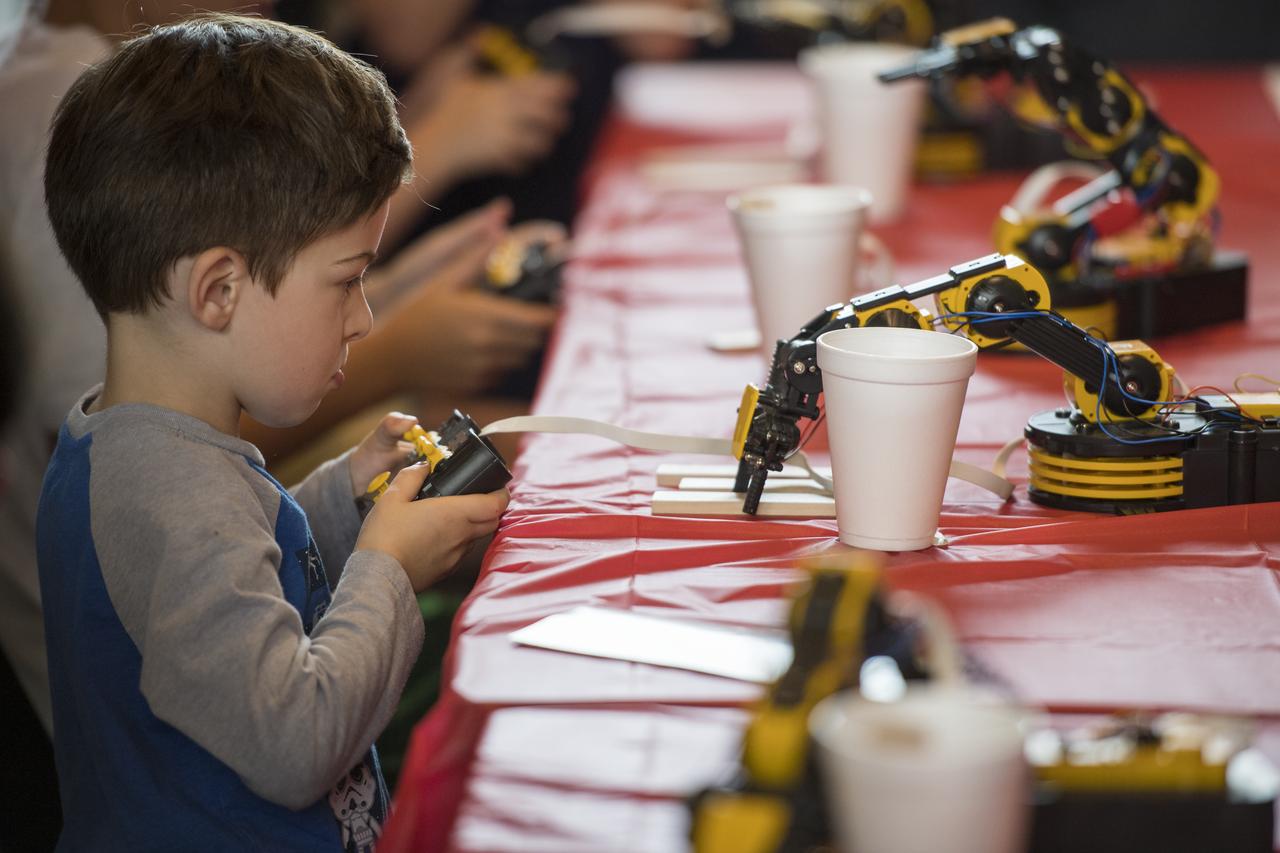

Visitors operate robotic arms at the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Mars Day, an annual event celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

iss071e403651 (July 21, 2024) --- The 57.7-foot-long Canadarm2 robotic arm extends from the International Space Station's Harmony module as the orbital outpost soared 261 miles above the coast of Peru. Partially obscured in the top background, is the Boeing Starliner spacecraft docked to Harmony's forward port.
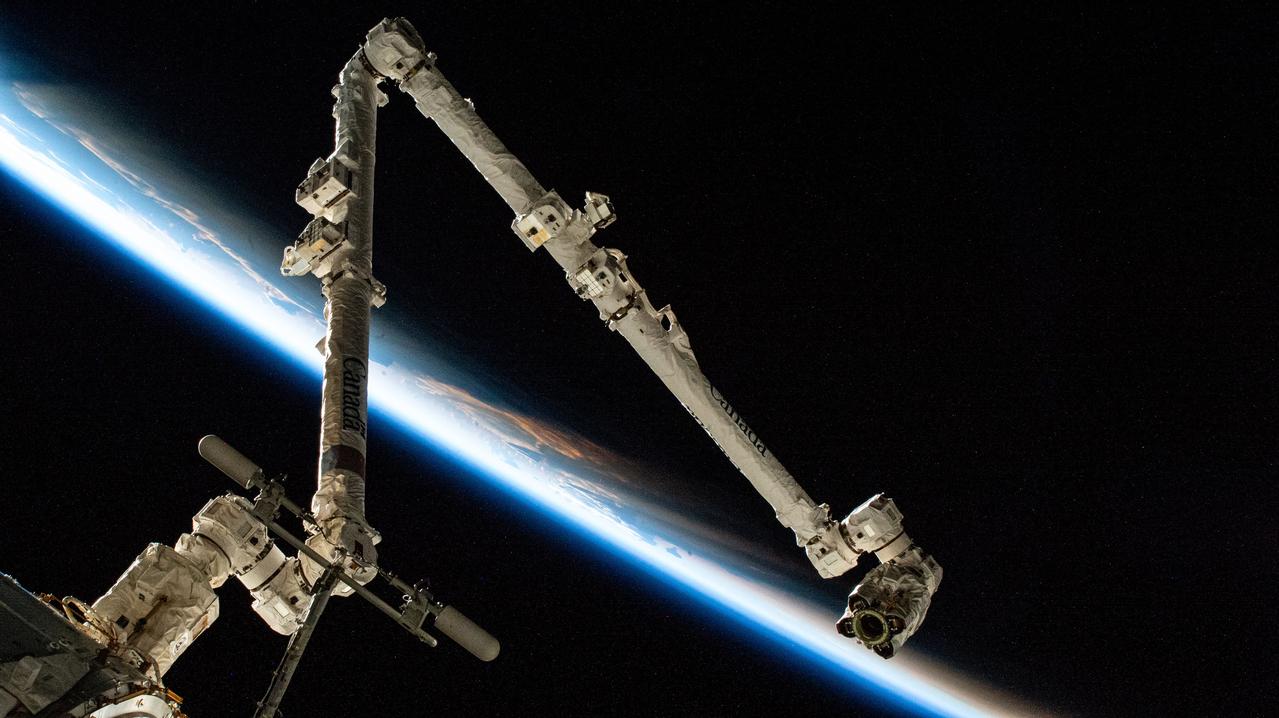

iss073e0657546 (Sept. 8, 2025) --- The 57.7-foot-long Canadarm2 robotic arm extends from a grapple fixture on the International Space Station as it soared into an orbital sunrise 260 miles above the Philippine Sea at approximately 4:04 a.m. local time.
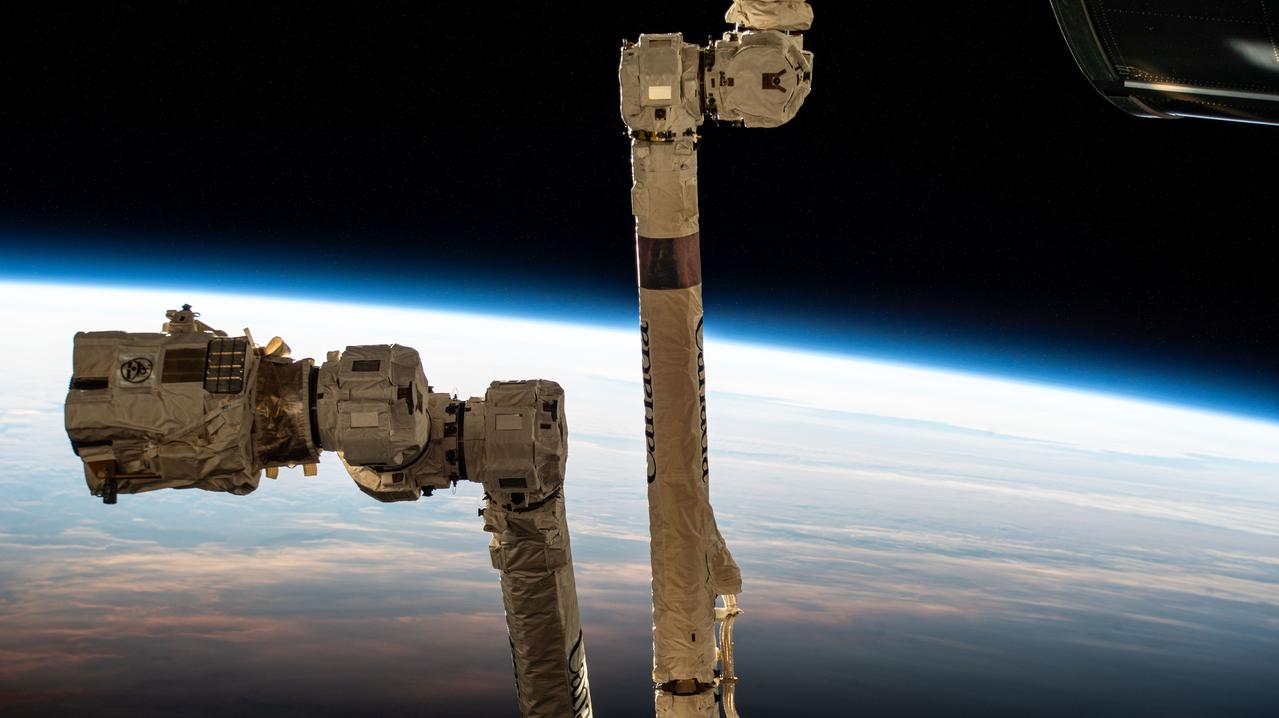

iss072e576480 (Jan. 31, 2025) --- The 57.7-foot-long Canadarm2 robotic arm with its latching end effector that can grapple spacecraft or maneuver spacewalkers is pictured as the International Space Station orbited into daylight 267 miles above the South Pacific Ocean just south of New Zealand's Auckland Islands.
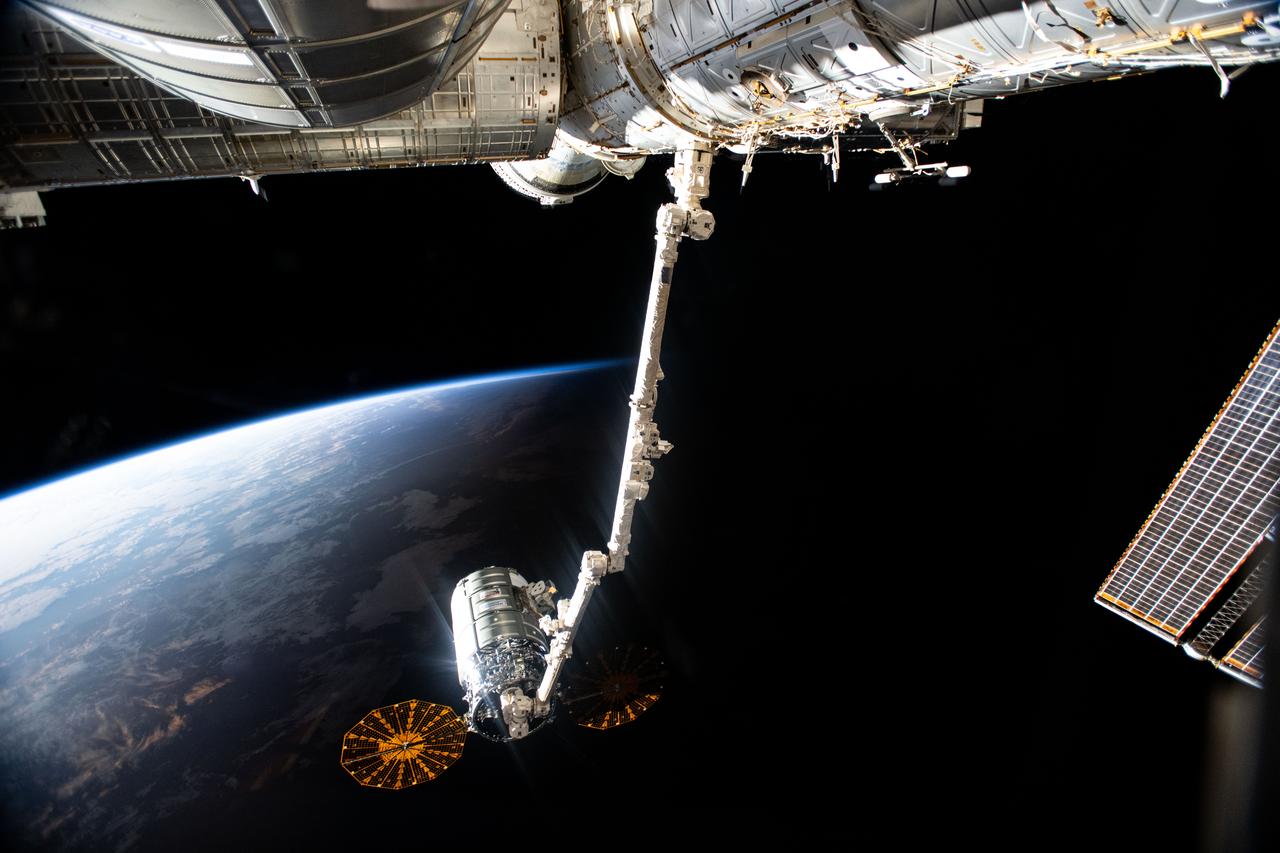

iss071e329922 (July 12, 2024) -- Northrop Grumman's Cygnus space freighter is pictured attached to the Canadarm2 robotic arm ahead of its release from the International Space Station's Unity module. The orbiting lab and Cygnus were soaring into orbital daytime as this photo was taken.

iss073e0920711 (Oct. 21, 2025) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm releases Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus XL cargo craft after it was installed on the Earth-facing port of the Unity module. The International Space Station was soaring into an orbital sunrise 269 miles above the Atlantic Ocean southwest of Cape Town, South Africa, at the time of this photgraph.
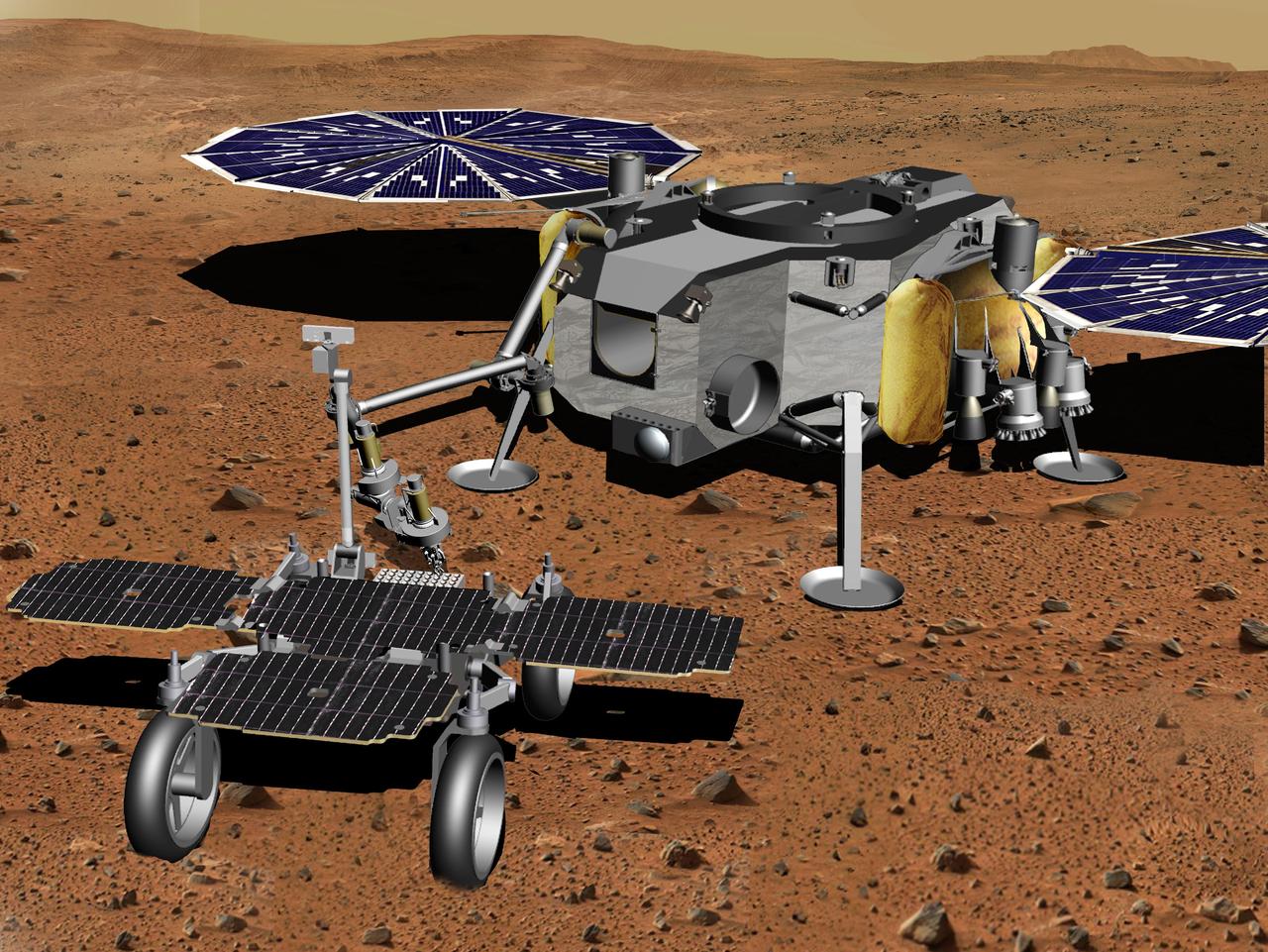
In this illustration of a Mars sample return mission concept, a robotic arm transfers samples of Martian rock and soil from a fetch rover onto a lander. NASA and the European Space Agency are solidifying concepts for a Mars sample return mission after NASA's Mars 2020 rover collects rock and soil samples and stores them in sealed tubes on the planet's surface for potential future return to Earth. NASA will deliver a Mars lander in the vicinity of Jezero Crater, where Mars 2020 will have collected and cached samples. The lander will carry a NASA rocket (the Mars Ascent Vehicle) along with ESA's Sample Fetch Rover that is roughly the size of NASA's Opportunity Mars rover. The fetch rover will gather the cached samples and carry them back to the lander for transfer to the ascent vehicle; additional samples could also be delivered directly by Mars 2020. The ascent vehicle will then launch from the surface and deploy a special container holding the samples into Mars orbit. ESA will put a spacecraft in orbit around Mars before the ascent vehicle launches. This spacecraft will rendezvous with and capture the orbiting samples before returning them to Earth. NASA will provide the payload module for the orbiter. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23495
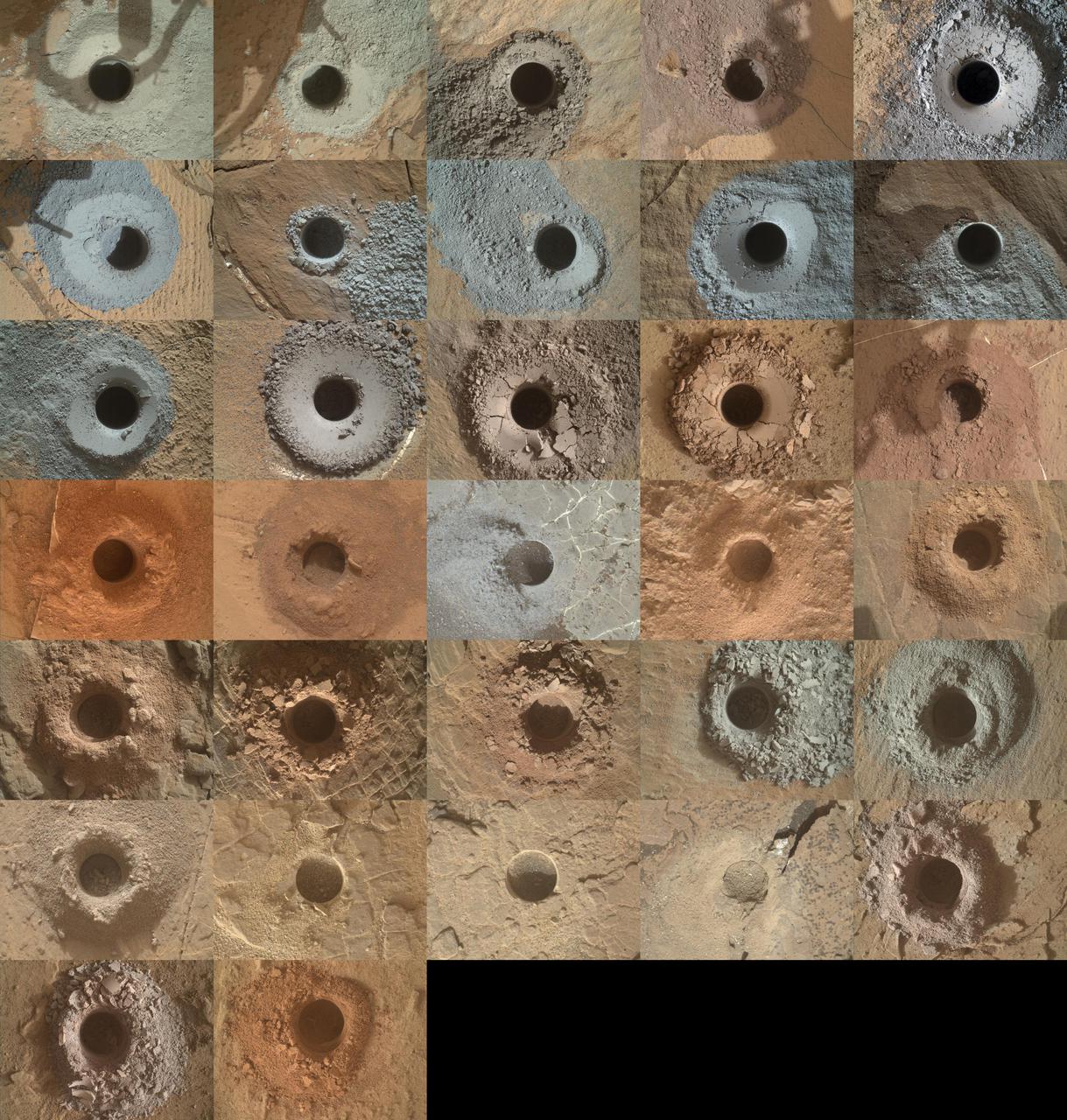

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover has used the drill on its robotic arm to take 32 rock samples to date. The Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI), a camera on the end of the robotic arm, provided the images in this mosaic. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24764

A partial view of the deck of NASA's InSight lander, where it stands on the Martian plains Elysium Planitia. The color-calibrated image was received on Dec. 4, 2018 (Sol 8). InSight's robotic arm with its stowed grapple can be seen above the deck, and jutting out from the front of the deck is one of the boxy attitude control system thrusters that helped control the spacecraft's landing. The circular silver inset of the propellant tank can also be seen in the middle of the image, as well as one of the connections for the aeroshell and parachute, which looks like a cupholder in the foreground. Next to the propellant tank is the UHF antenna, which helps the lander communicate with Earth. In the background, part of one of InSight's solar panels is visible. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22873
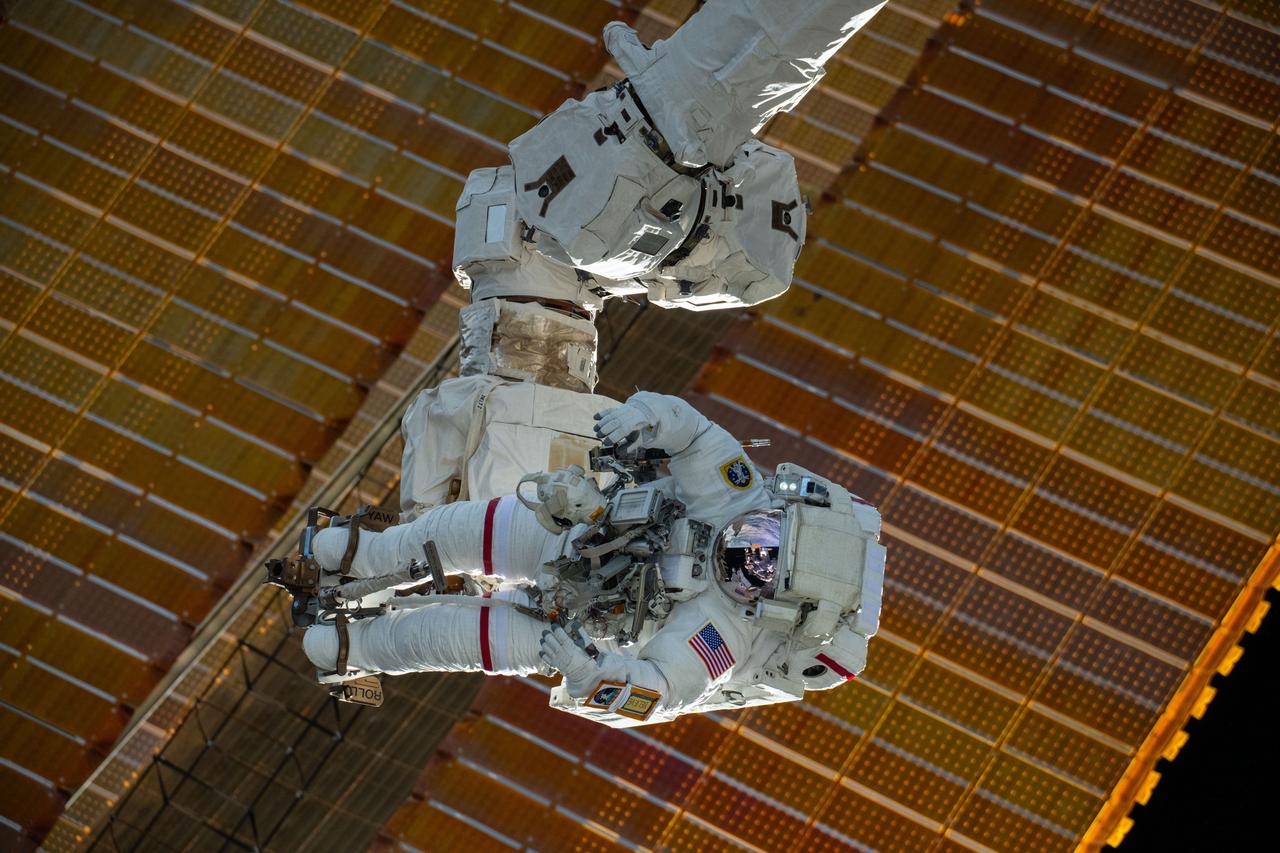

iss072e595502 (Jan. 30, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams is attached to the Canadarm2 robotic arm's latching end effector while being maneuvered to her worksite 264 miles above the South Pacific Ocean. Williams removed and stowed a radio frequency group antenna assembly during the five-hour and 26-minute spacewalk outside the International Space Station.
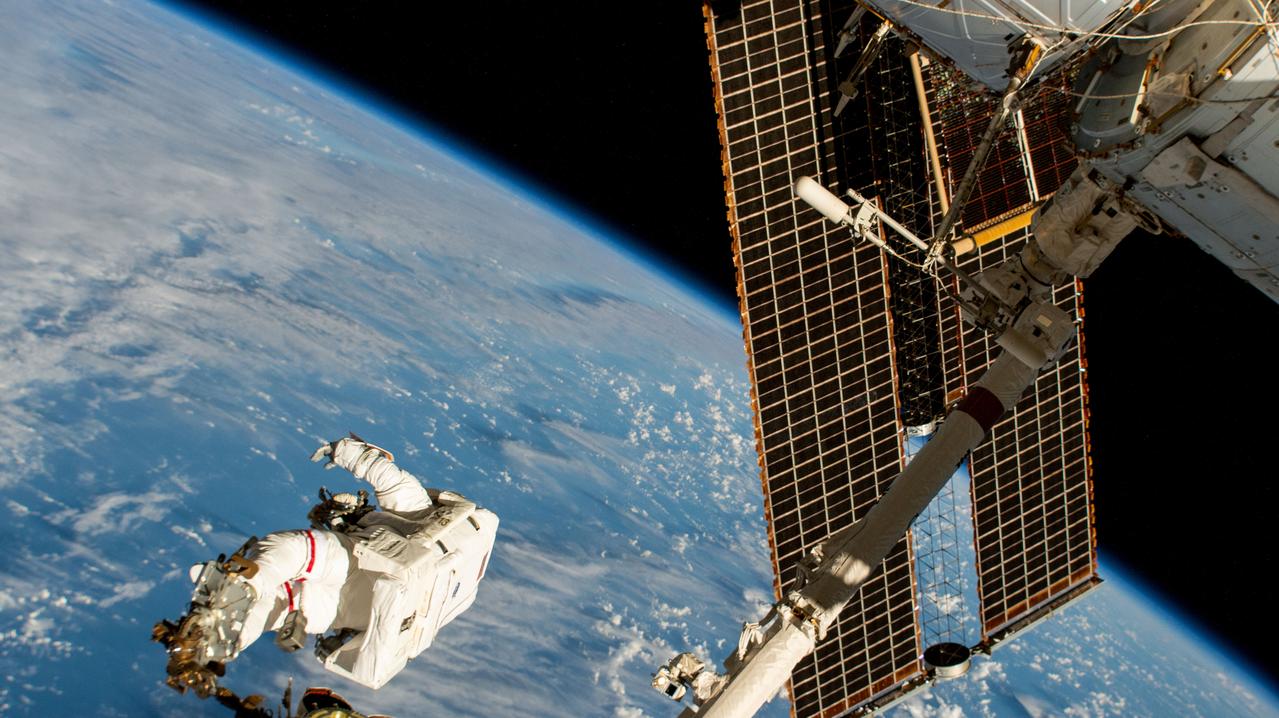

iss072e574907 (Jan. 30, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams is attached to the Canadarm2 robotic arm's latching end effector while being maneuvered to her worksite 264 miles above the South Pacific Ocean. Williams removed and stowed a radio frequency group antenna assembly during the five-hour and 26-minute spacewalk outside the International Space Station.
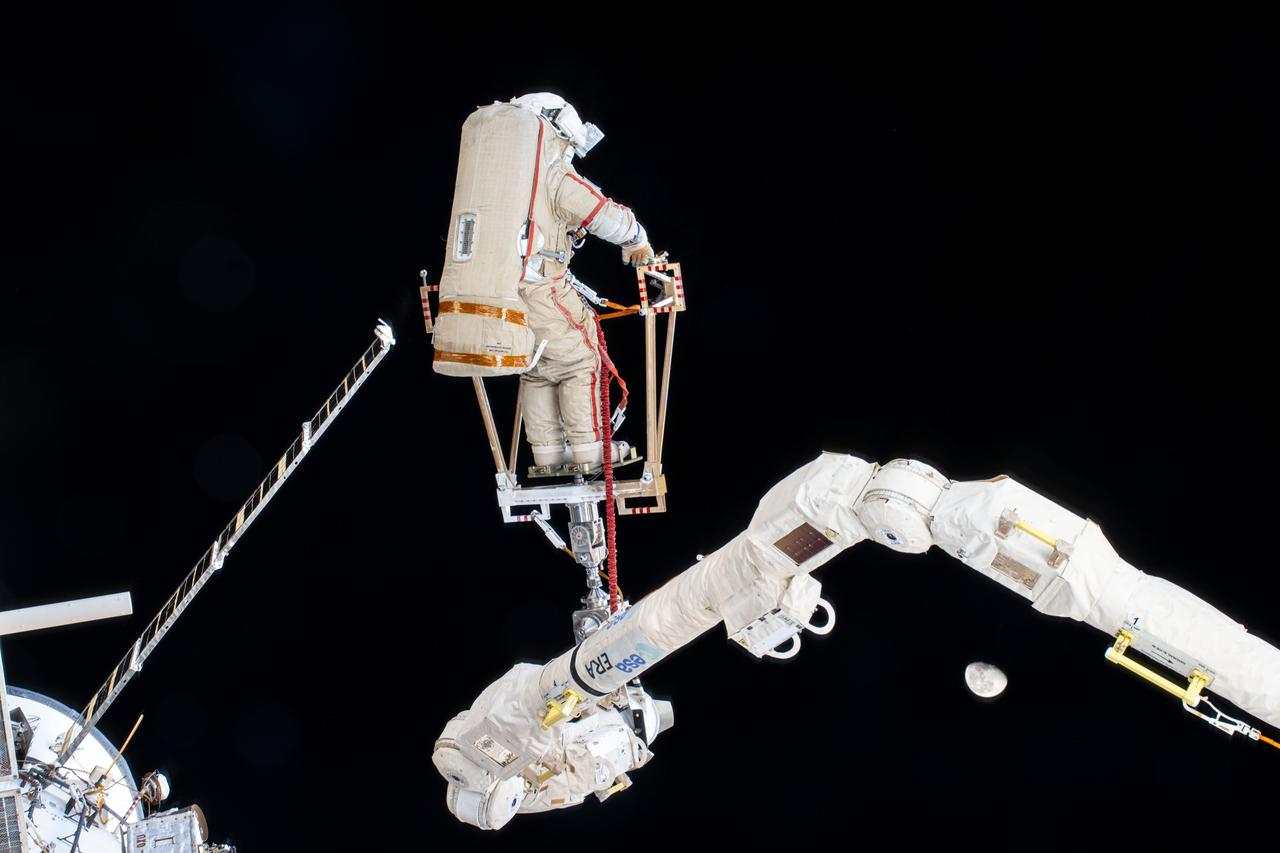

iss072e397366 (Dec. 19, 2024) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Alexey Ovchinin is maneuvered using the European robotic arm during a seven-hour and 17-minute spacewalk. He and fellow Flight Engineer Ivan Vagner (not pictured) partnered together in the vacuum of space on Dec.19 installing a celestial X-ray experiment and removng other scientific hardware on the exterior of the International Space Station. The waning gibbous Moon is at lower right as the orbital outpost soared 262 miles above the Pacific Ocean.
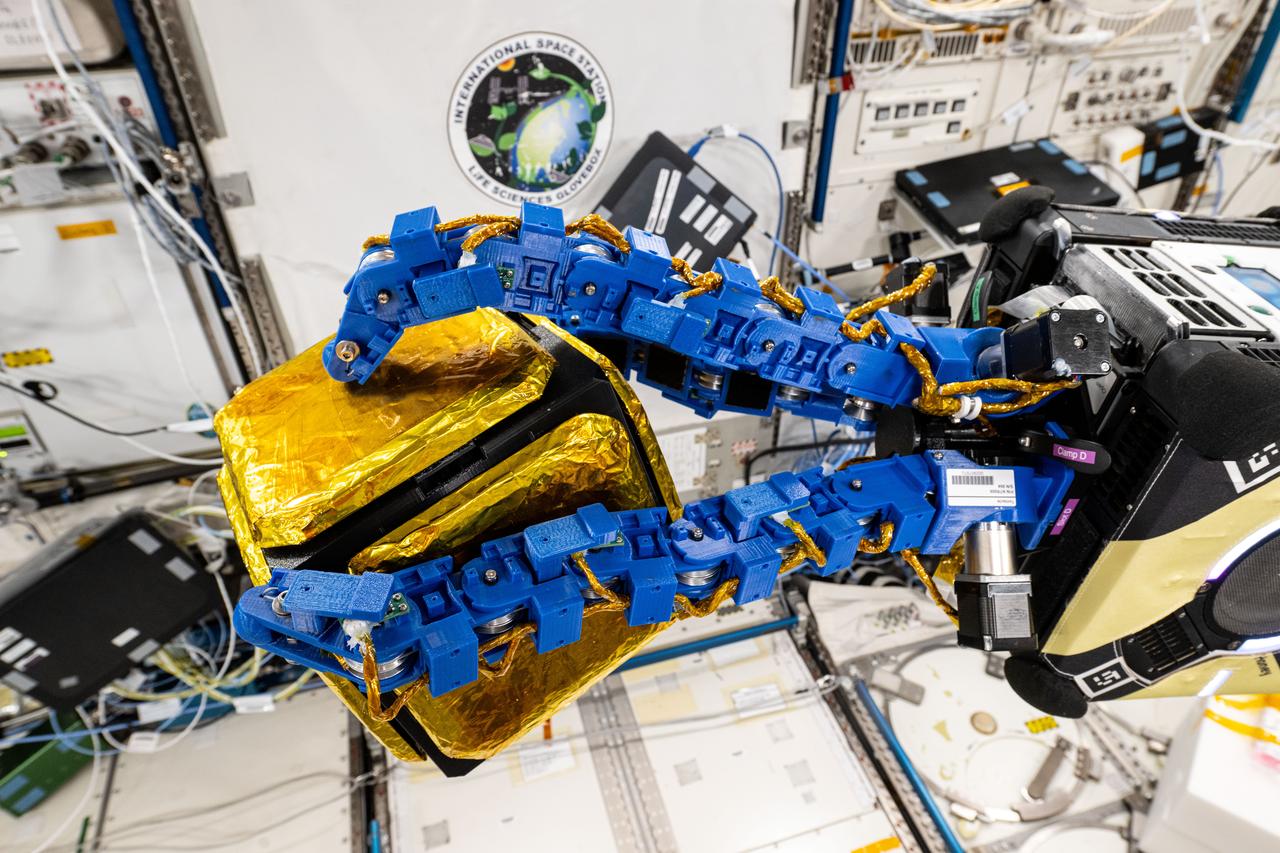
iss072e593717 (Feb. 4, 2025) --- The blue tentacle-like arms containing gecko-like adhesive pads, attached to an Astrobee robotic free-flyer, reach out and grapple a "capture cube" inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The experimental grippers, outfitted on the toaster-sized Astrobee, demonstrated autonomous detection and capture techniques that may be used to remove space debris and service satellites in low Earth orbit.
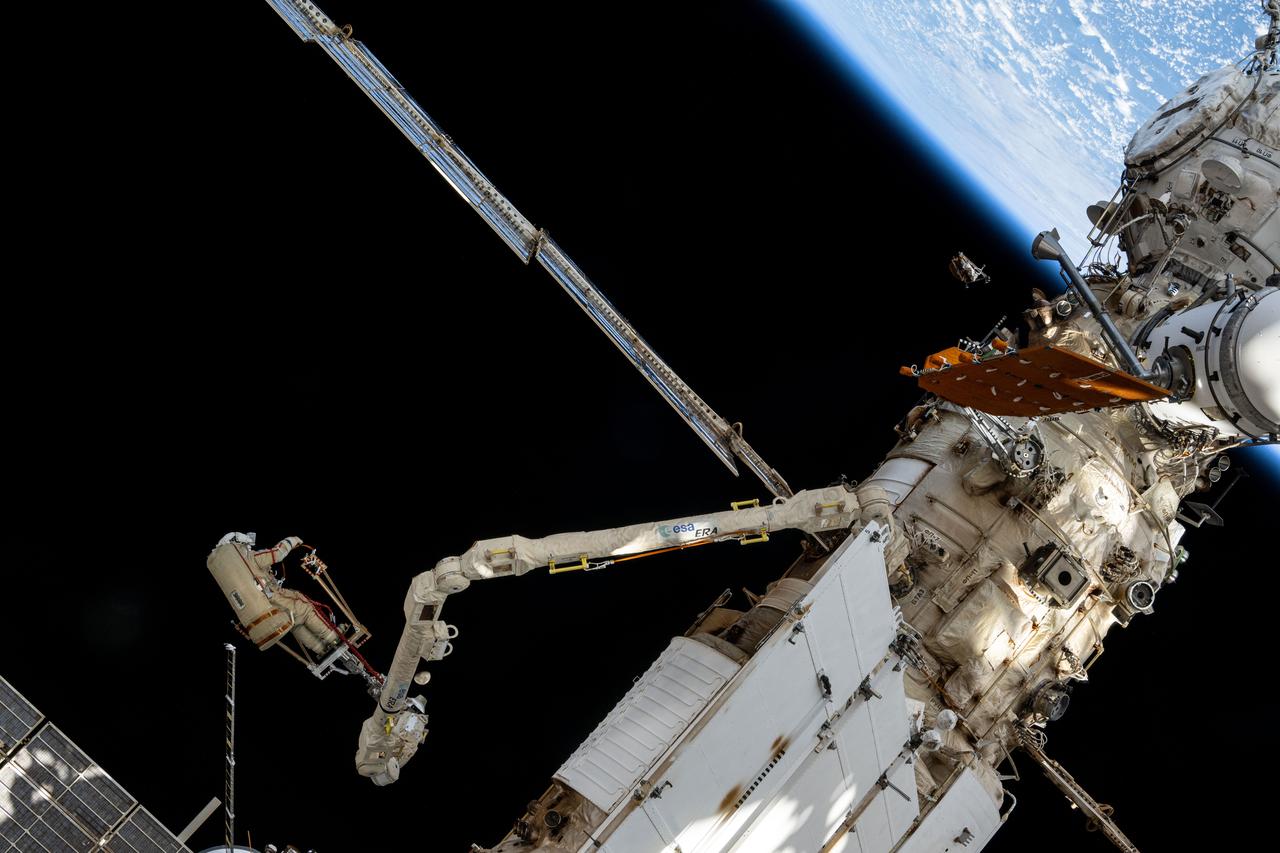

iss072e397516 (Dec. 19, 2024) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Alexey Ovchinin is maneuvered using the European robotic arm during a seven-hour and 17-minute spacewalk. He and fellow Flight Engineer Ivan Vagner (not pictured) partnered together in the vacuum of space on Dec.19 installing a celestial X-ray experiment and removng other scientific hardware on the exterior of the International Space Station.
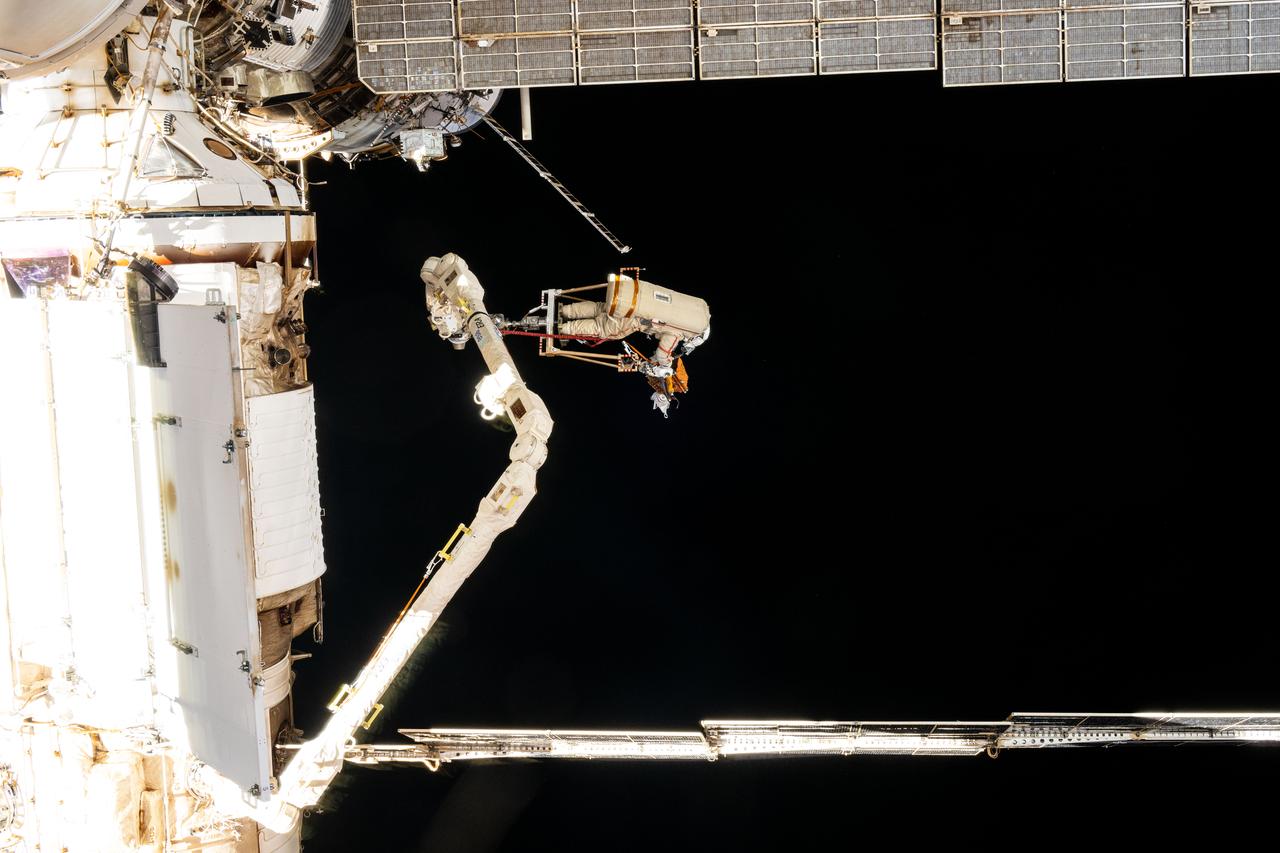

iss072e397475 (Dec. 19, 2024) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Alexey Ovchinin is maneuvered using the European robotic arm during a seven-hour and 17-minute spacewalk. He and fellow Flight Engineer Ivan Vagner (not pictured) partnered together in the vacuum of space on Dec.19 installing a celestial X-ray experiment and removng other scientific hardware on the exterior of the International Space Station.
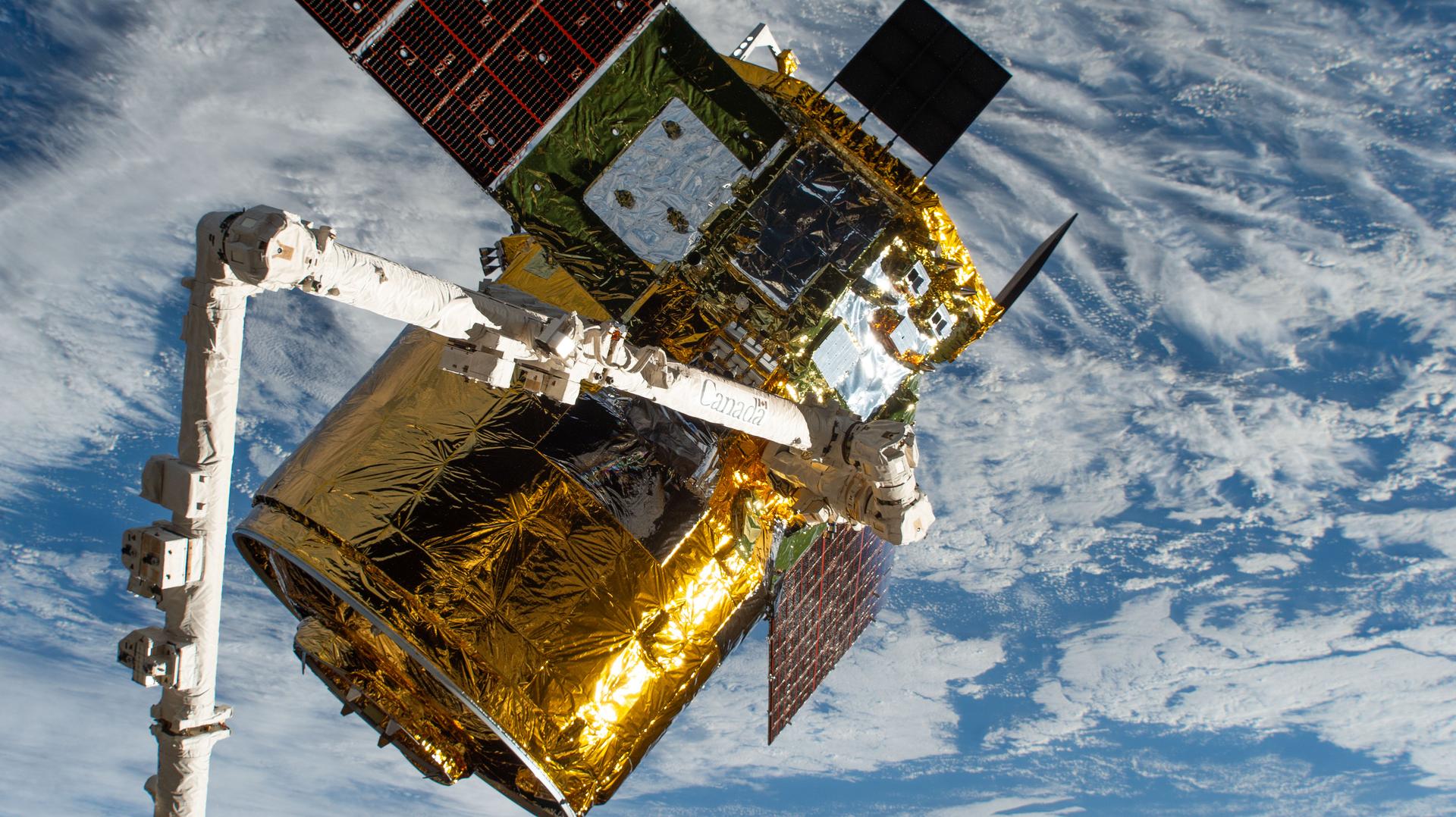

iss073e0988465 (Oct. 29, 2025) --- The new HTV-X1 cargo spacecraft from JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), carrying about 12,800 pounds of science, supplies, and hardware for the Expedition 73 crew, is pictured in the grip of the Canadarm2 robotic arm. JAXA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Kimiya Yui (not pictured) commanded Canadarm2 to gently reach out and capture HTV-X1 when the spacecraft reached a point about 10 meters away from the International Space Station.
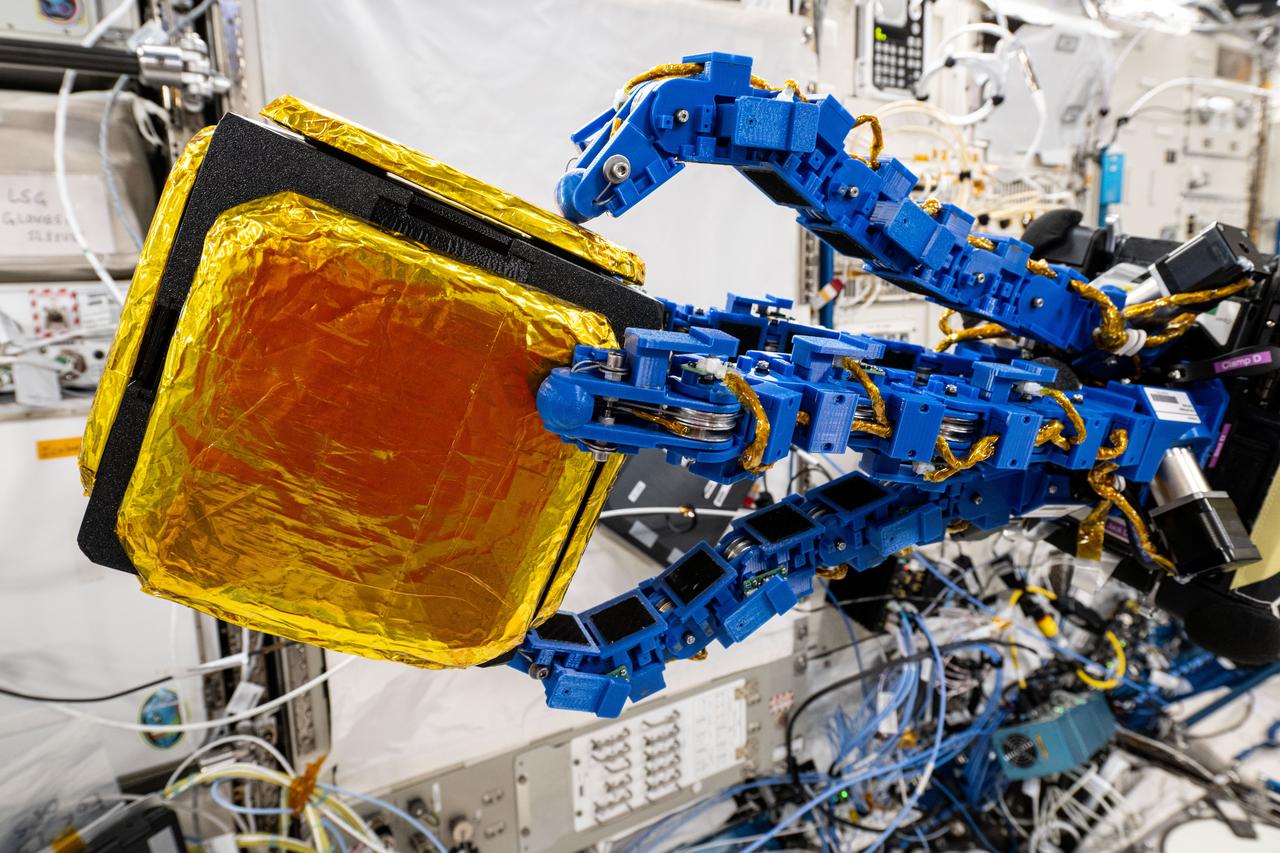
iss072e593737 (Feb. 4, 2025) --- The blue tentacle-like arms containing gecko-like adhesive pads, attached to an Astrobee robotic free-flyer, reach out and grapple a "capture cube" inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The experimental grippers, outfitted on the toaster-sized Astrobee, demonstrated autonomous detection and capture techniques that may be used to remove space debris and service satellites in low Earth orbit.
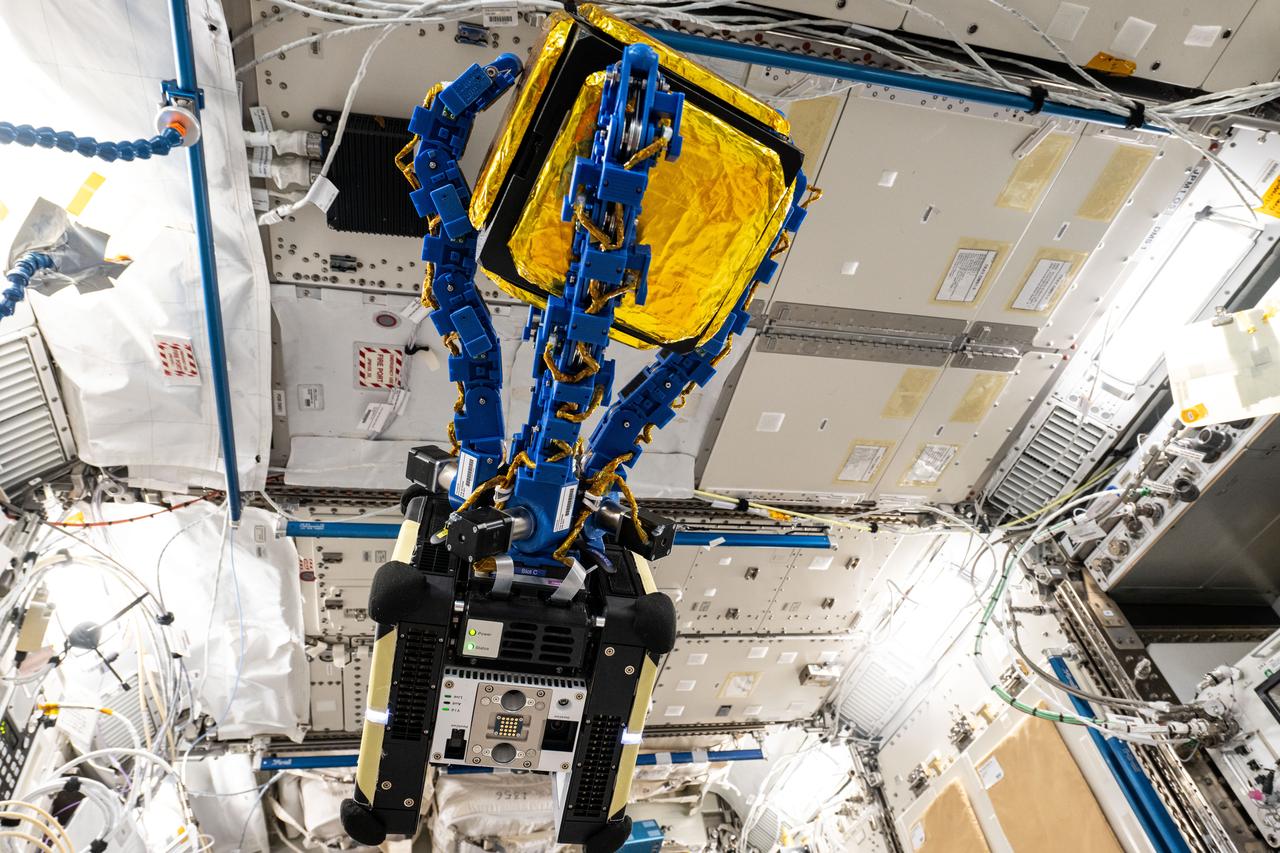

iss072e593734 (Feb. 4, 2025) --- The blue tentacle-like arms containing gecko-like adhesive pads, attached to an Astrobee robotic free-flyer, reach out and grapple a "capture cube" inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The experimental grippers, outfitted on the toaster-sized Astrobee, demonstrated autonomous detection and capture techniques that may be used to remove space debris and service satellites in low Earth orbit.