
Stuart A. Roosa, Apollo 14 Command Module pilot, undergoes a final space suit check prior to liftoff. The Apollo 14, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Roosa; Alan B. Shepard, Jr., Mission Commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, Lunar Module pilot, lifted off from launch complex 39A at KSC on January 31, 1971. It was the third manned lunar landing, the first manned landing in exploration of the lunar highlands, and it demonstrated pinpoint landing capability. The major goal of Apollo 14 was the scientific exploration of the Moon in the foothills of the rugged Fra Mauro region. The lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Shepard and Mitchell included setting up an automated scientific laboratory called Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP), and collecting a total of about 95 pounds (43 kilograms) of Moon rock and soil for a geological investigation back on the Earth. Apollo 14 safely returned to Earth on February 9, 1971.

Portrait of Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, Apollo 14 lunar landing mission Command Module pilot in civilian clothes.

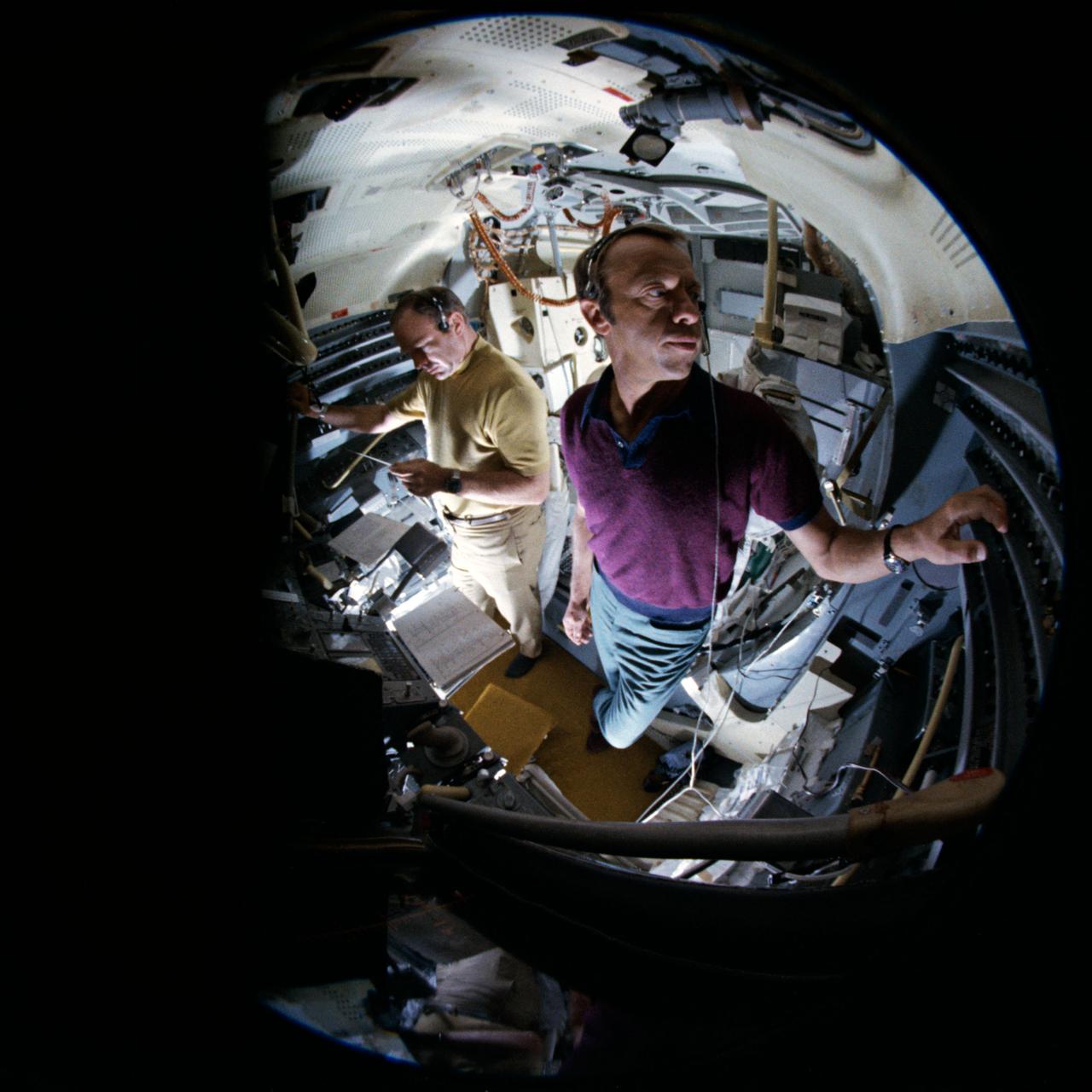
Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

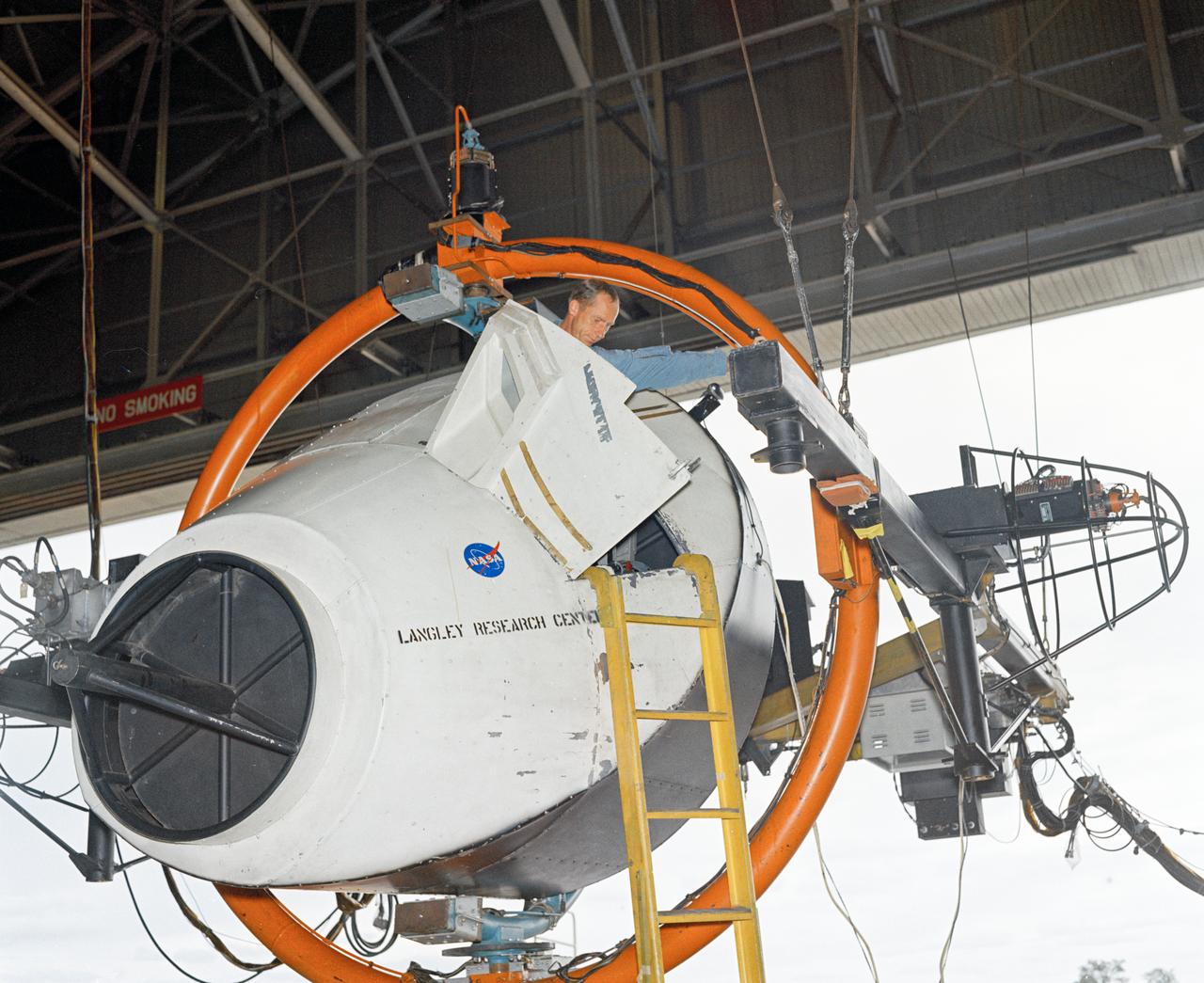
Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

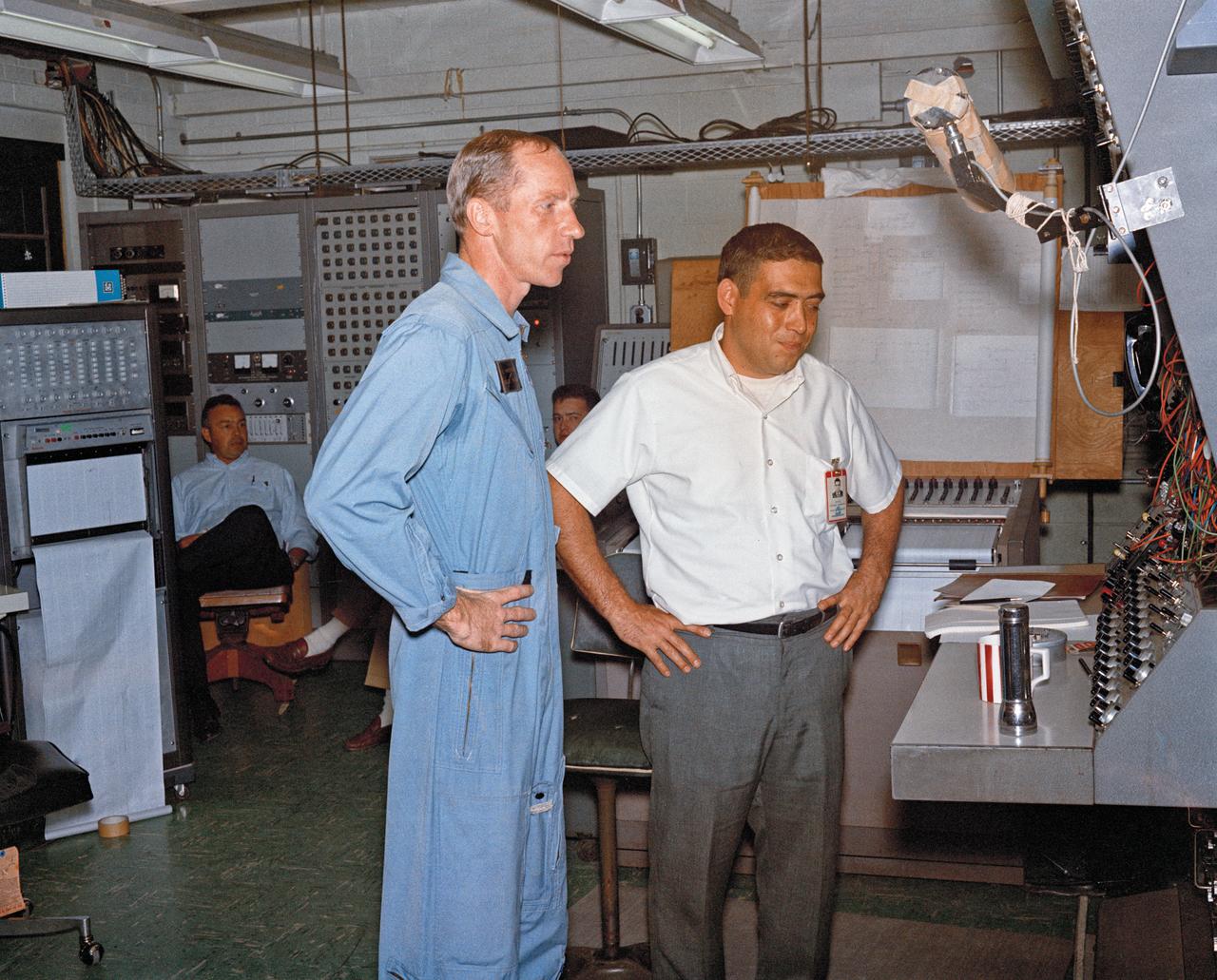
Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
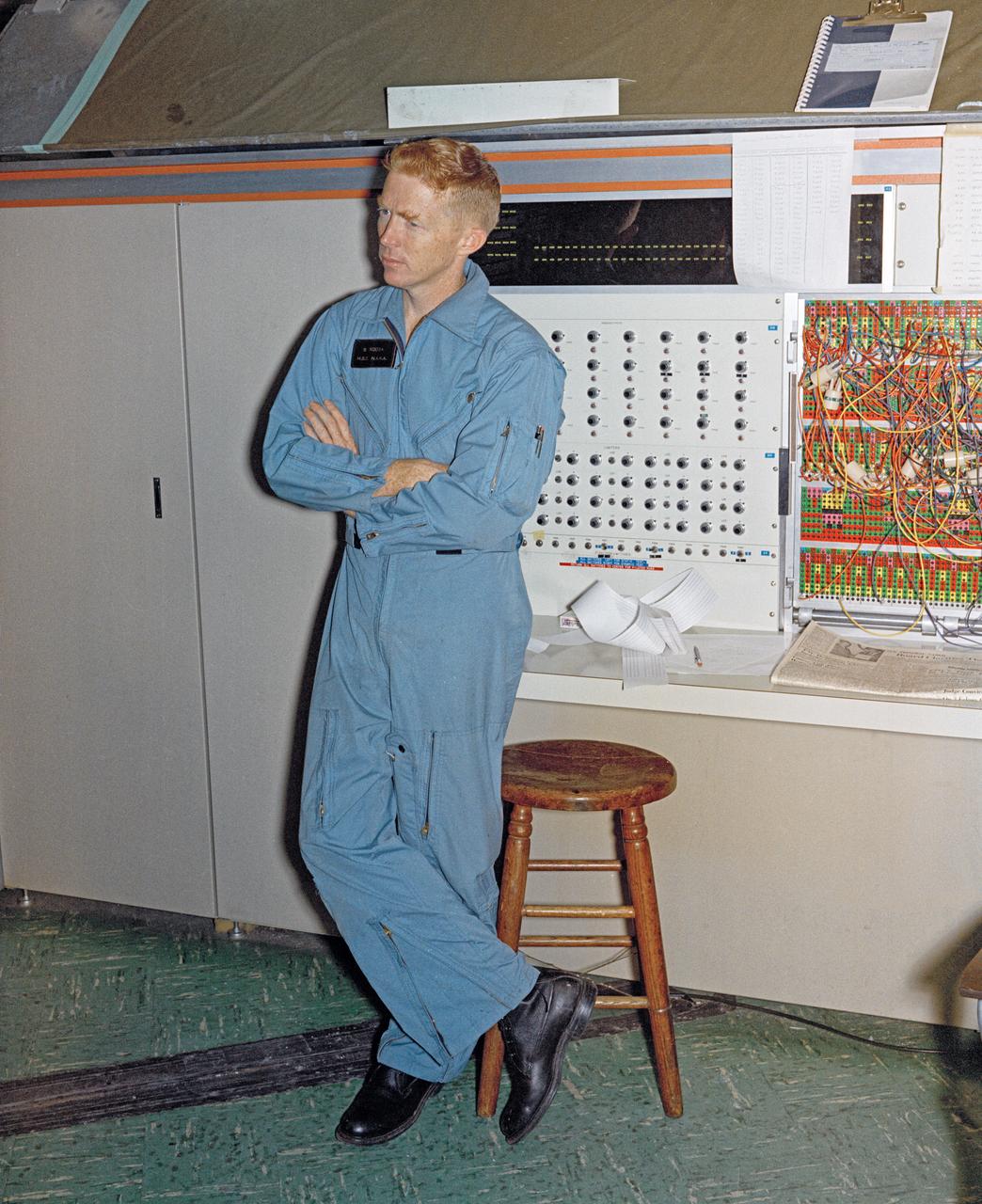

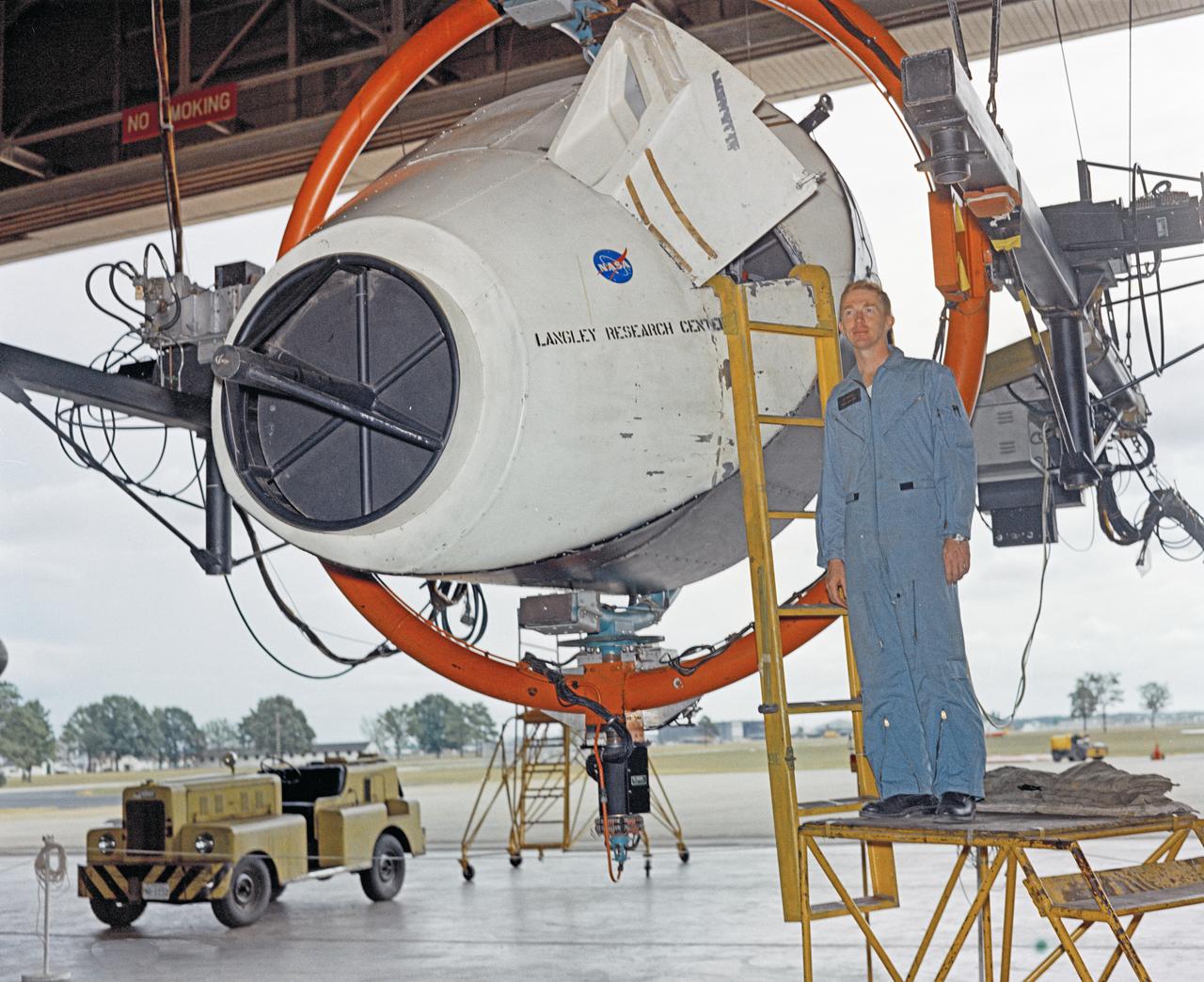
Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
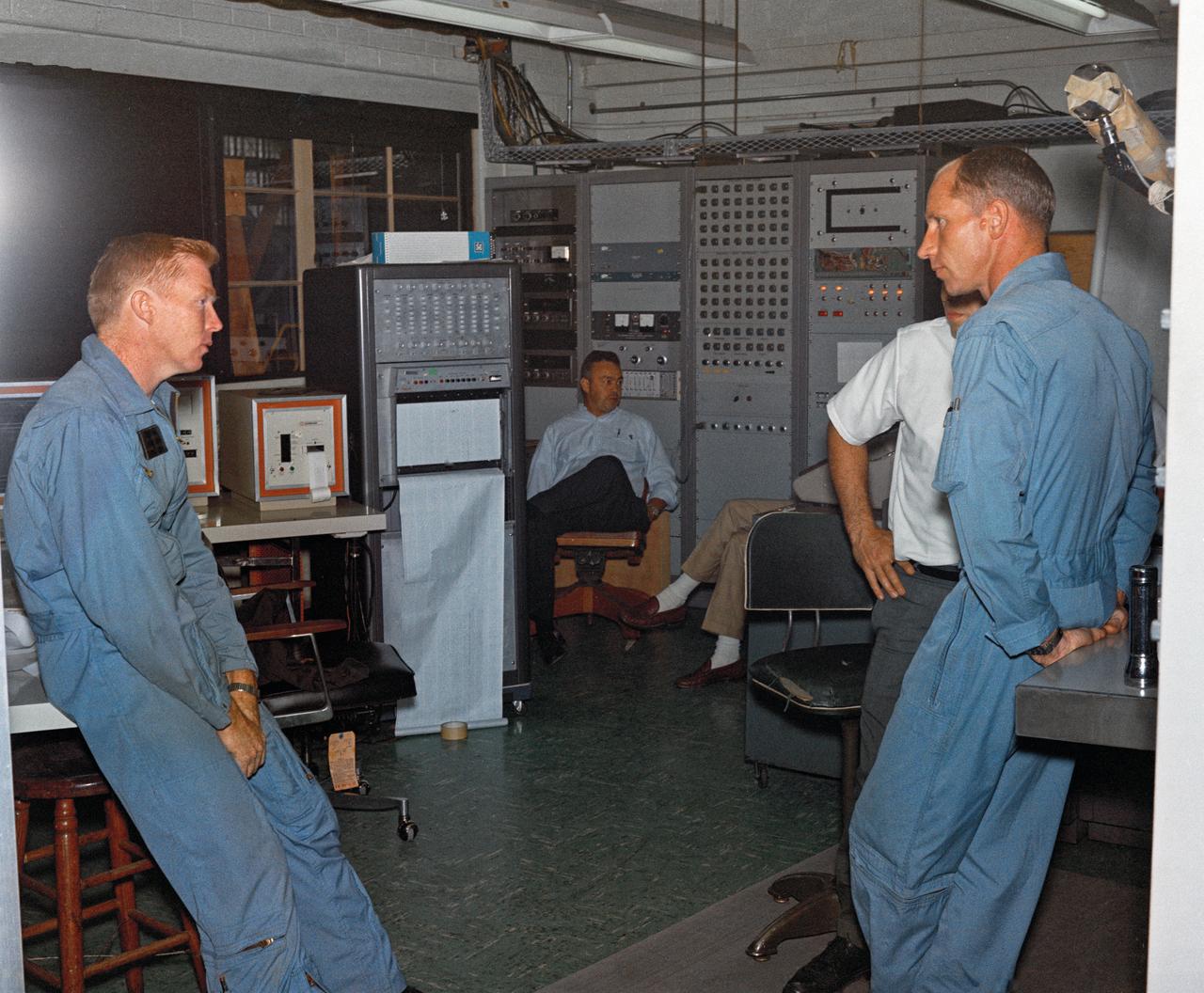

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
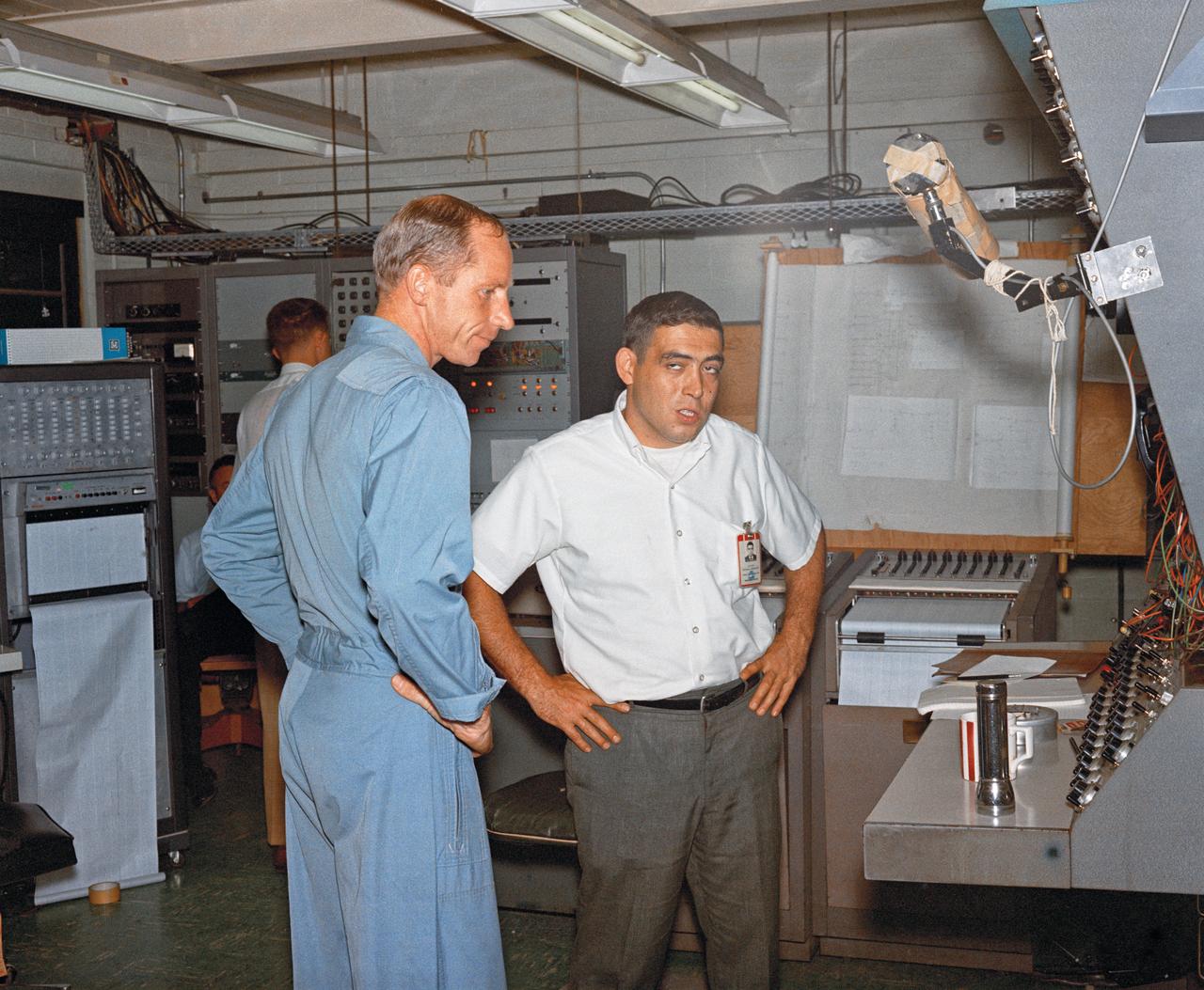

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
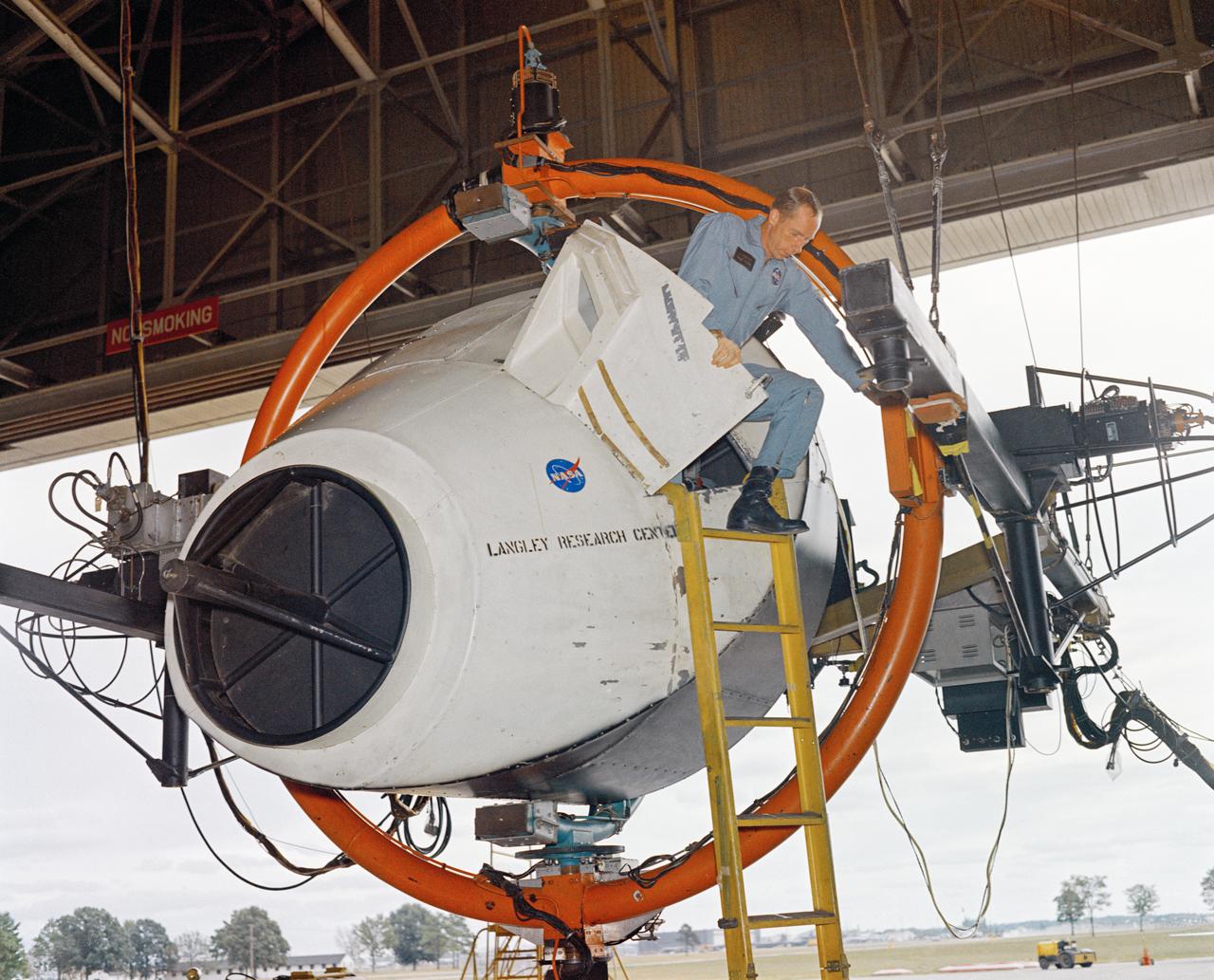

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
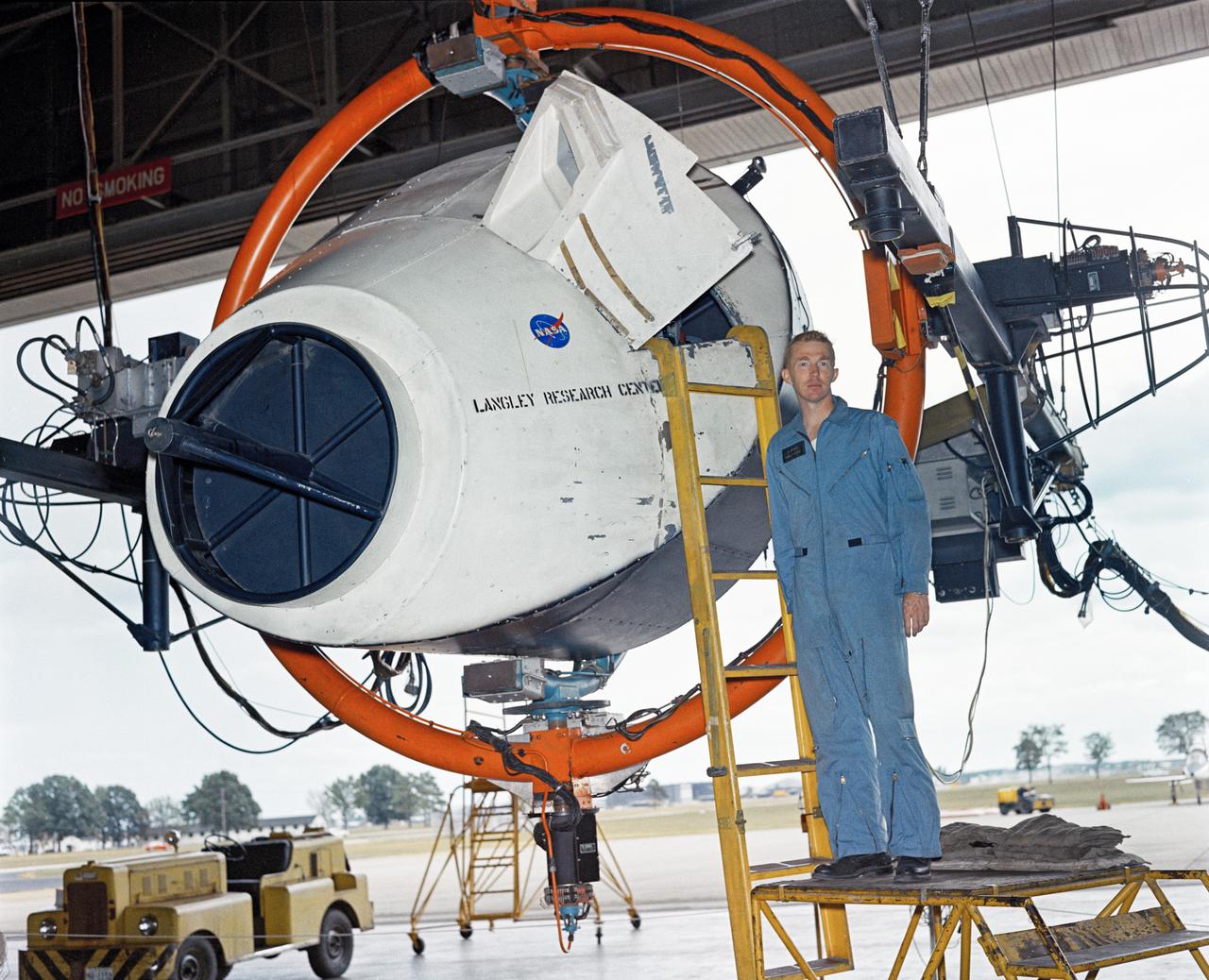

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
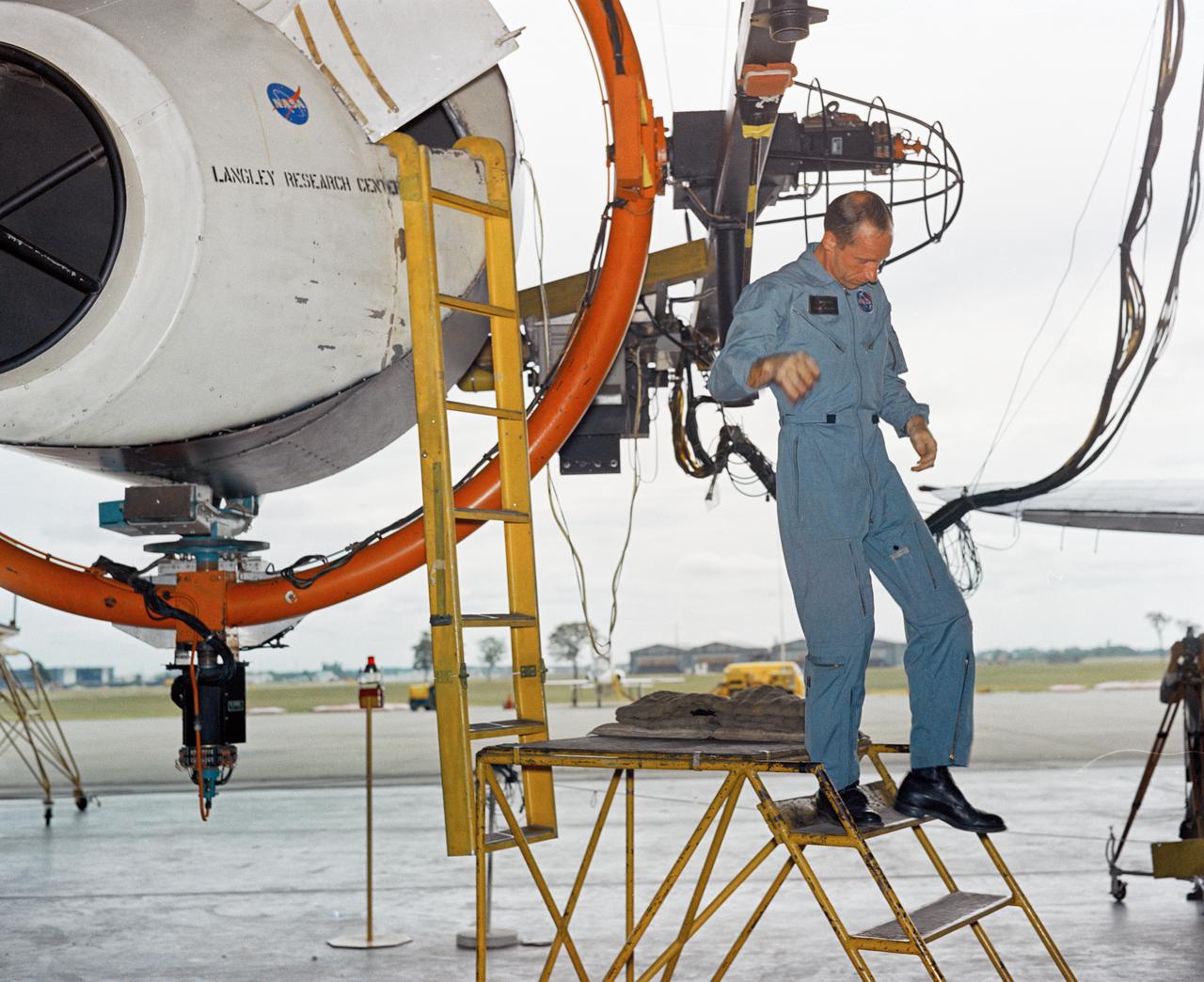

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
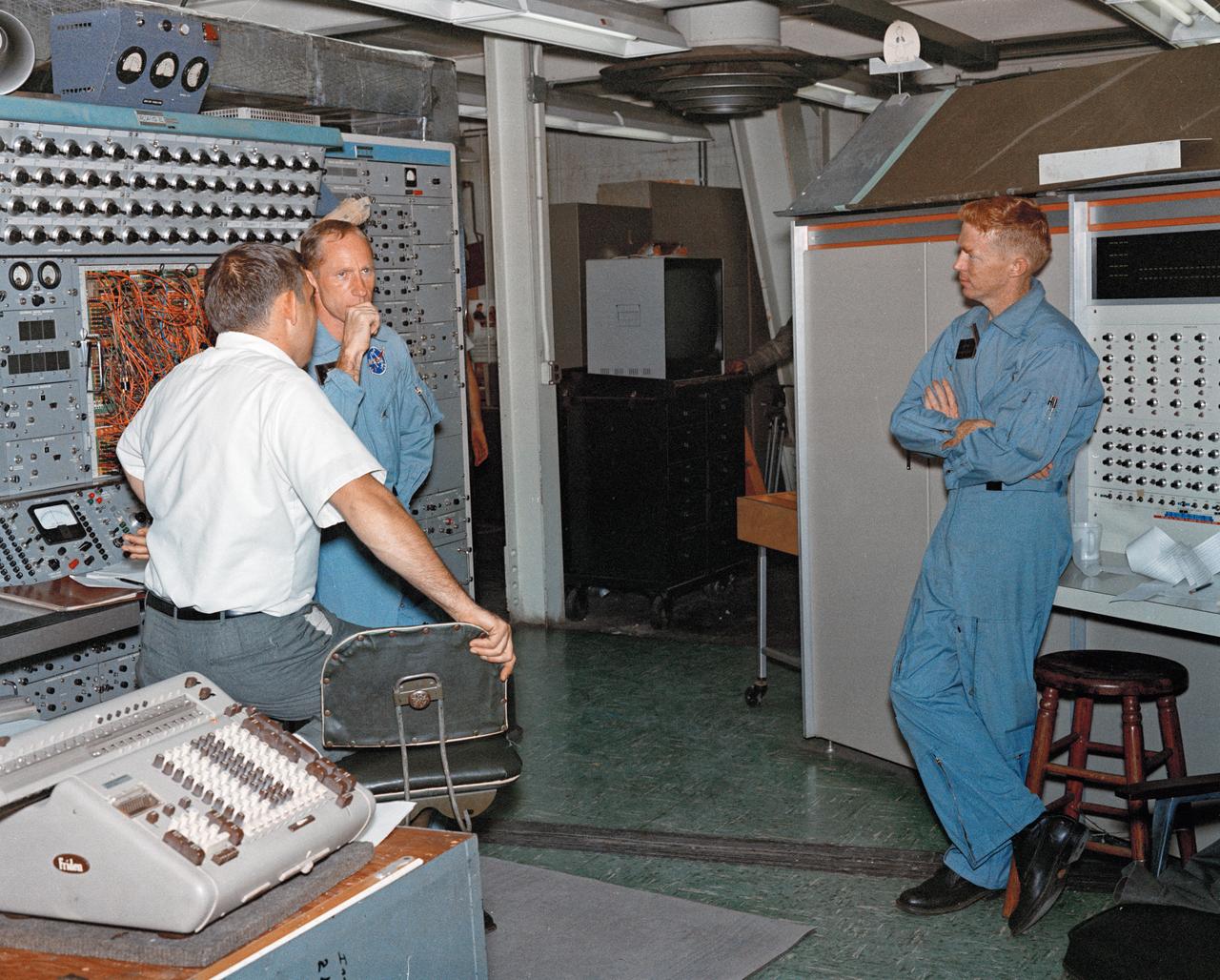

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
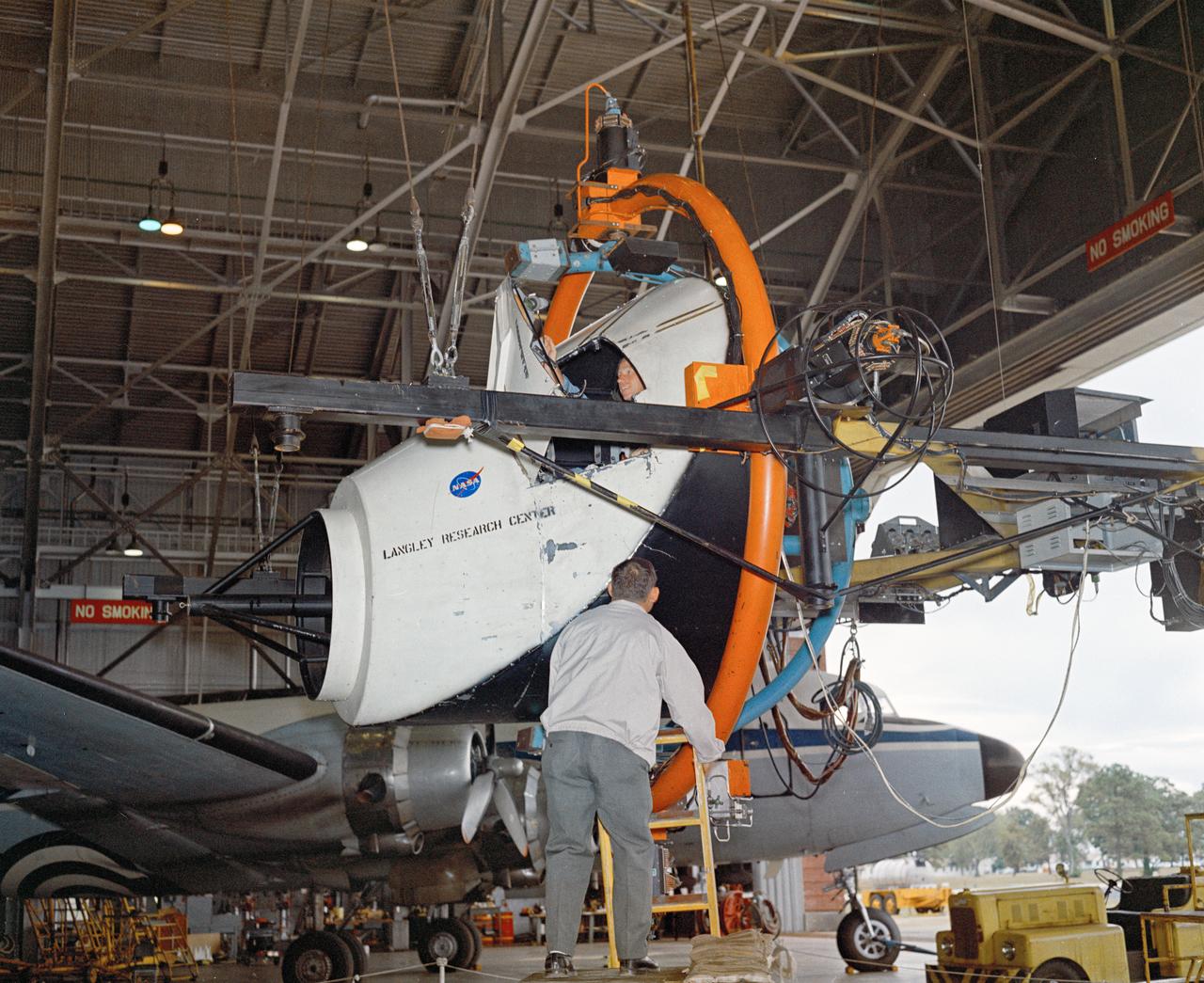

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
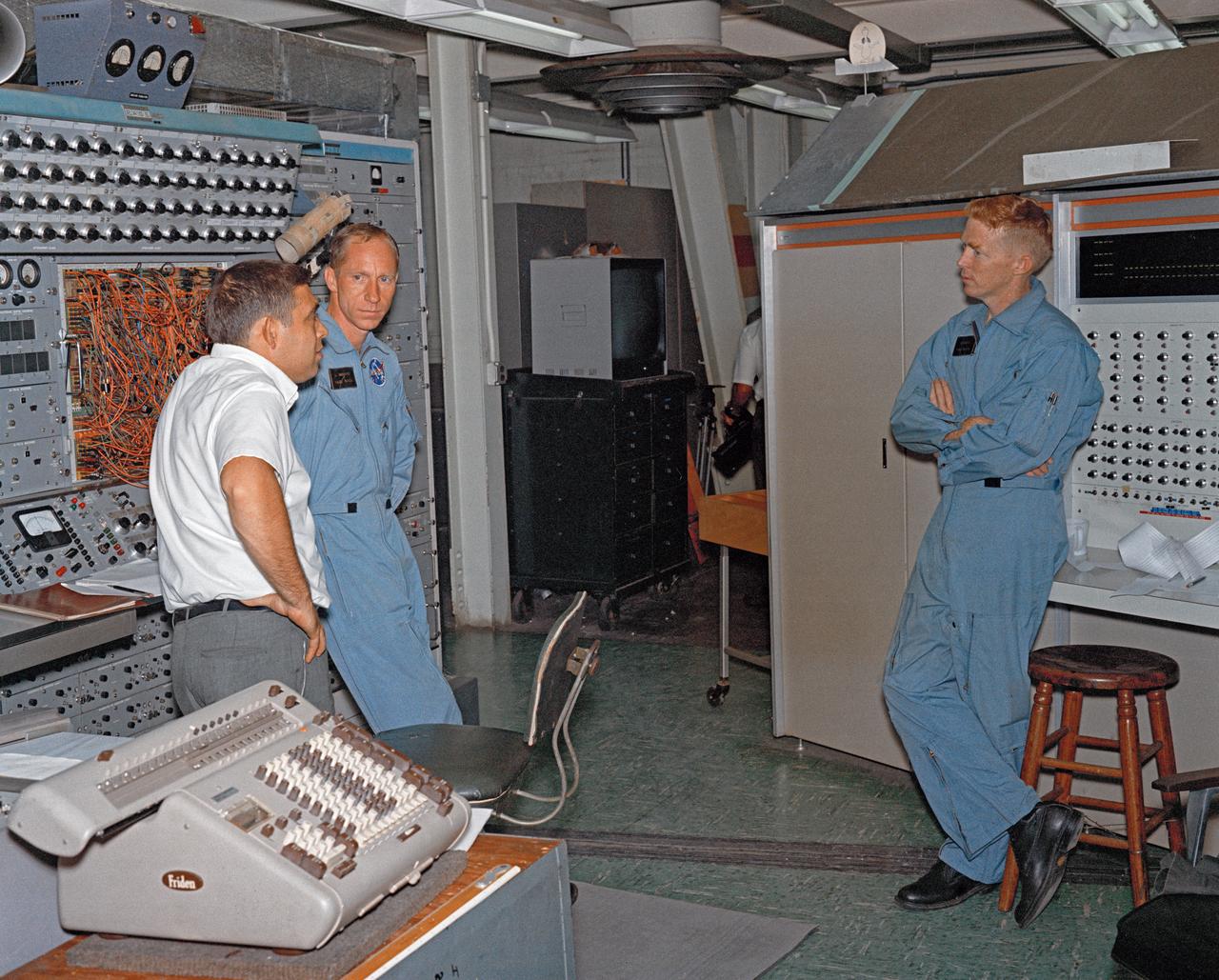

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
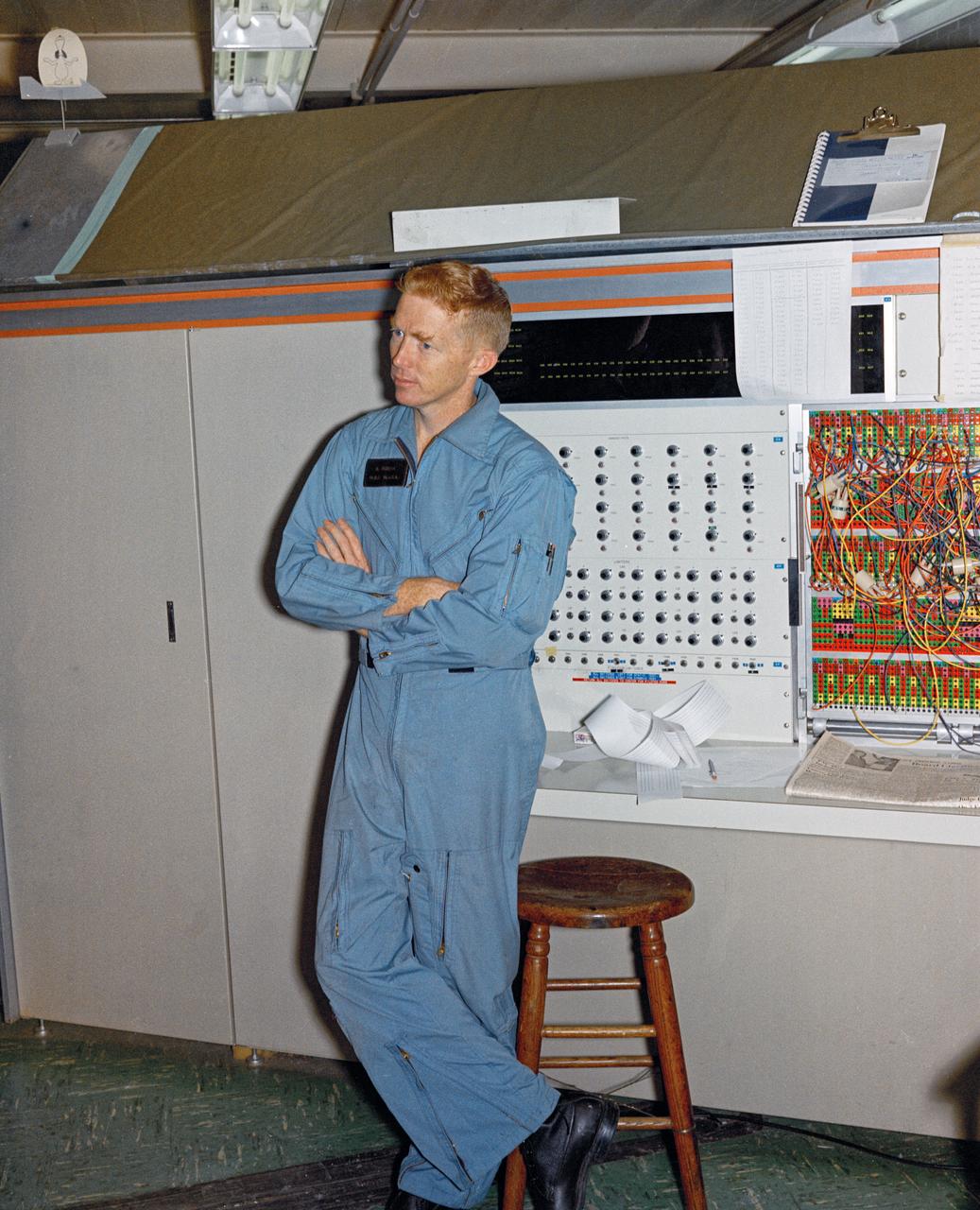

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
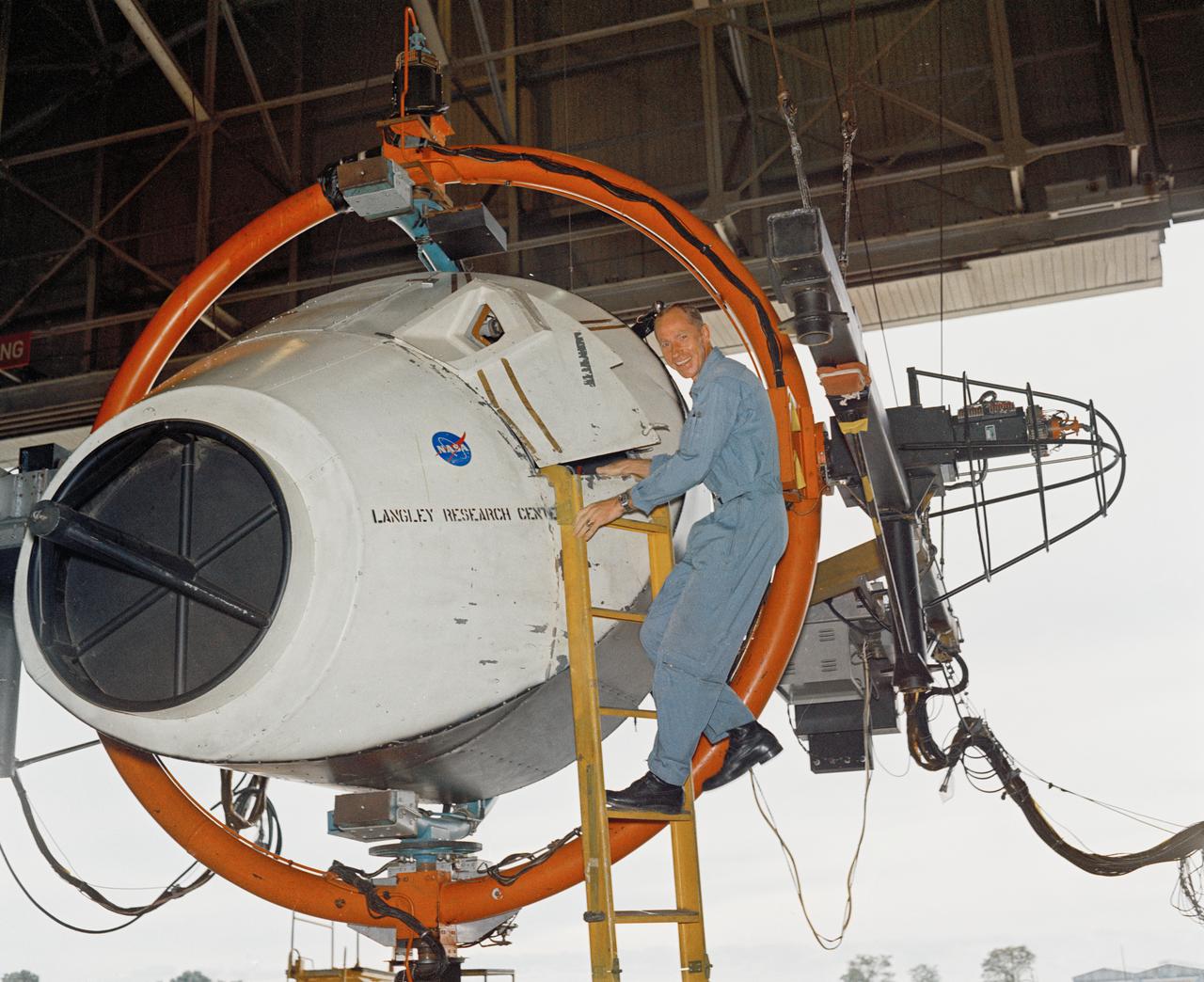

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
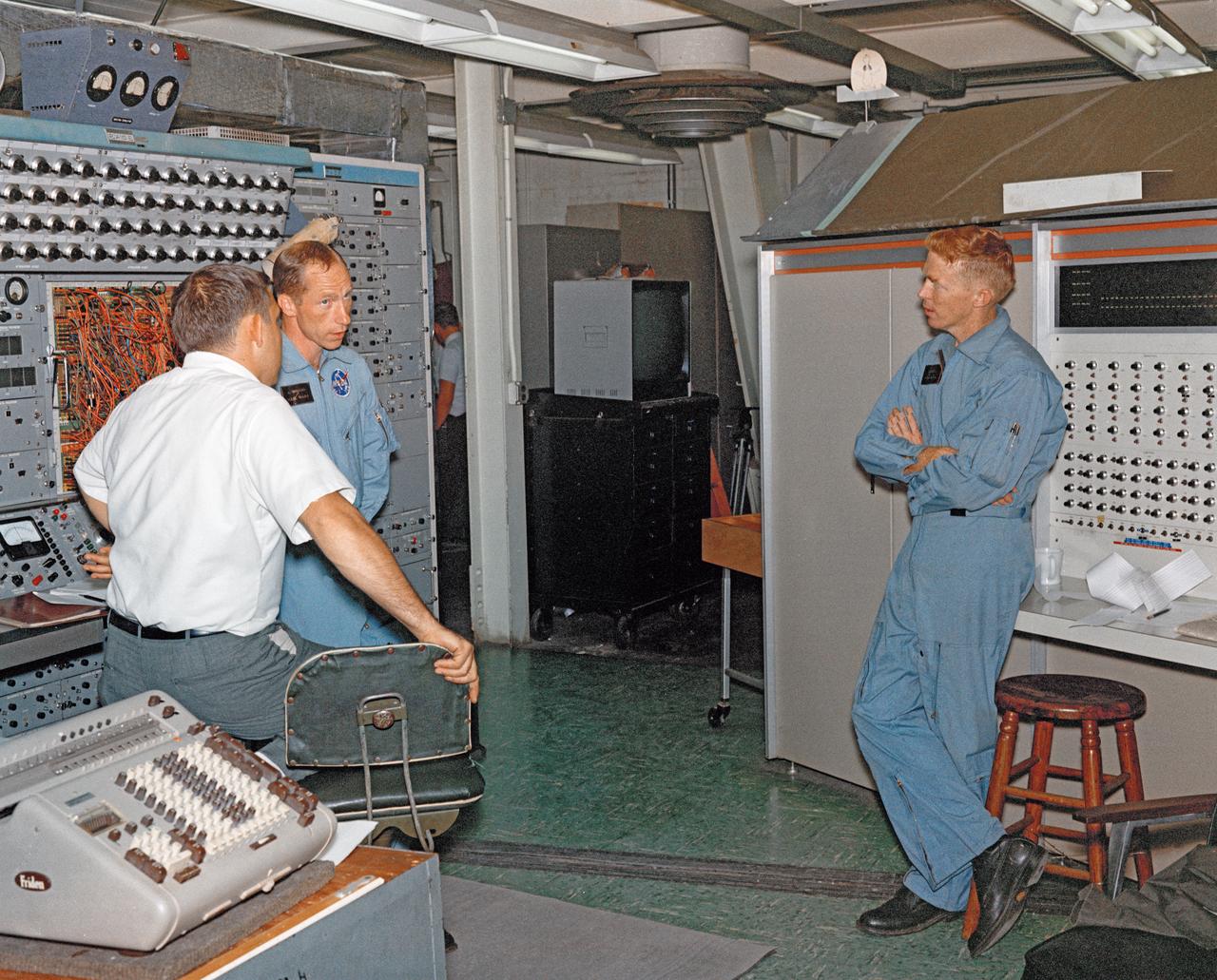

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
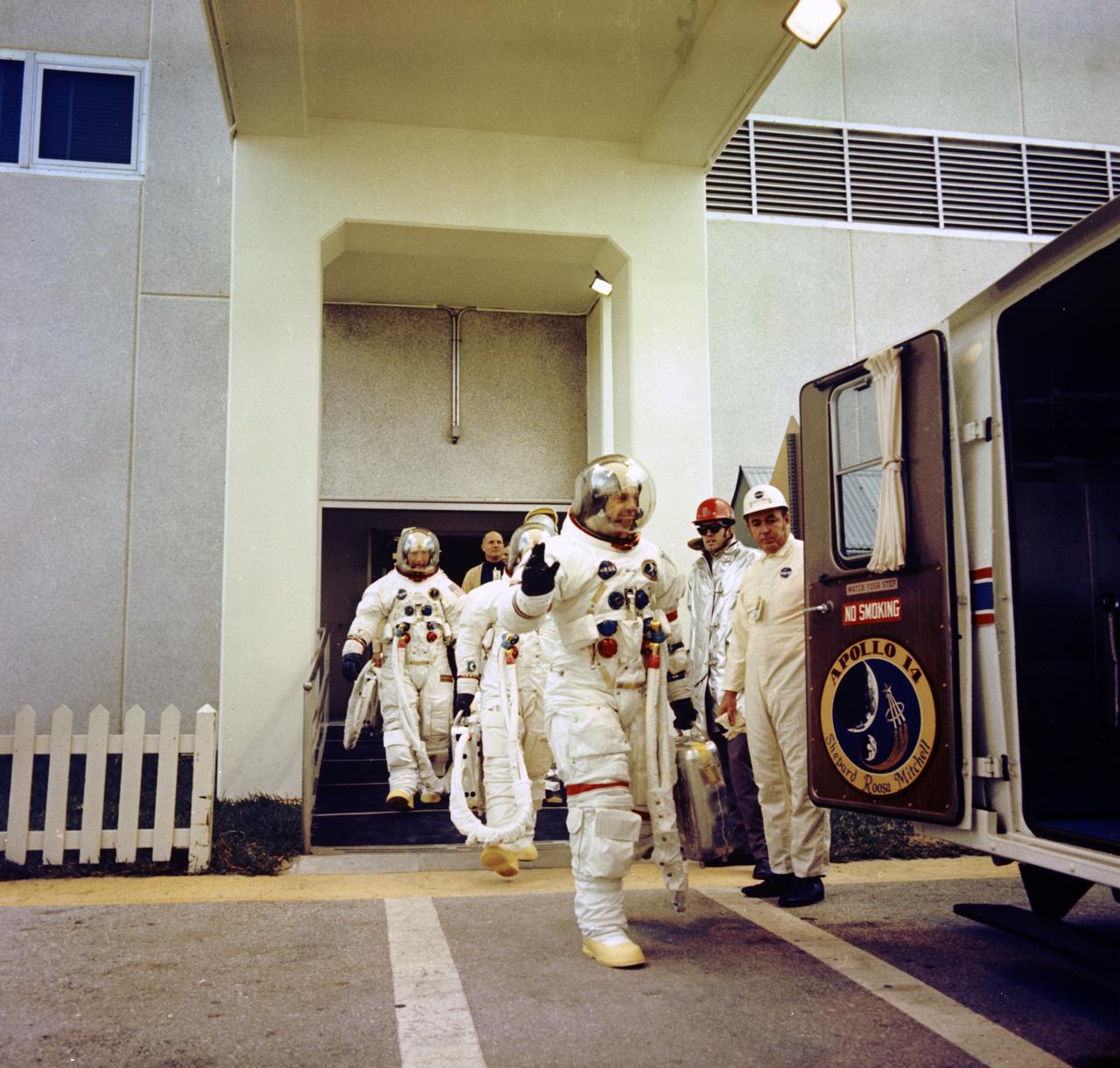

Apollo 14 Mission Commander, Alan B. Shepard, Jr., waves to well-wishers as he and astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, Command Module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, Lunar Module pilot, walk to the transfer van during the countdown demonstration test. The Apollo 14, carrying the crew of three lifted off from launch complex 39A at KSC on January 31, 1971. It was the third manned lunar landing, the first manned landing in exploration of the lunar highlands, and it demonstrated pinpoint landing capability. The major goal of Apollo 14 was the scientific exploration of the Moon in the foothills of the rugged Fra Mauro region. The lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Shepard and Mitchell included setting up an automated scientific laboratory called Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP), and collecting a total of about 95 pounds (43 kilograms) of Moon rock and soil for a geological investigation back on the Earth. Apollo 14 safely returned to Earth on February 9, 1971.
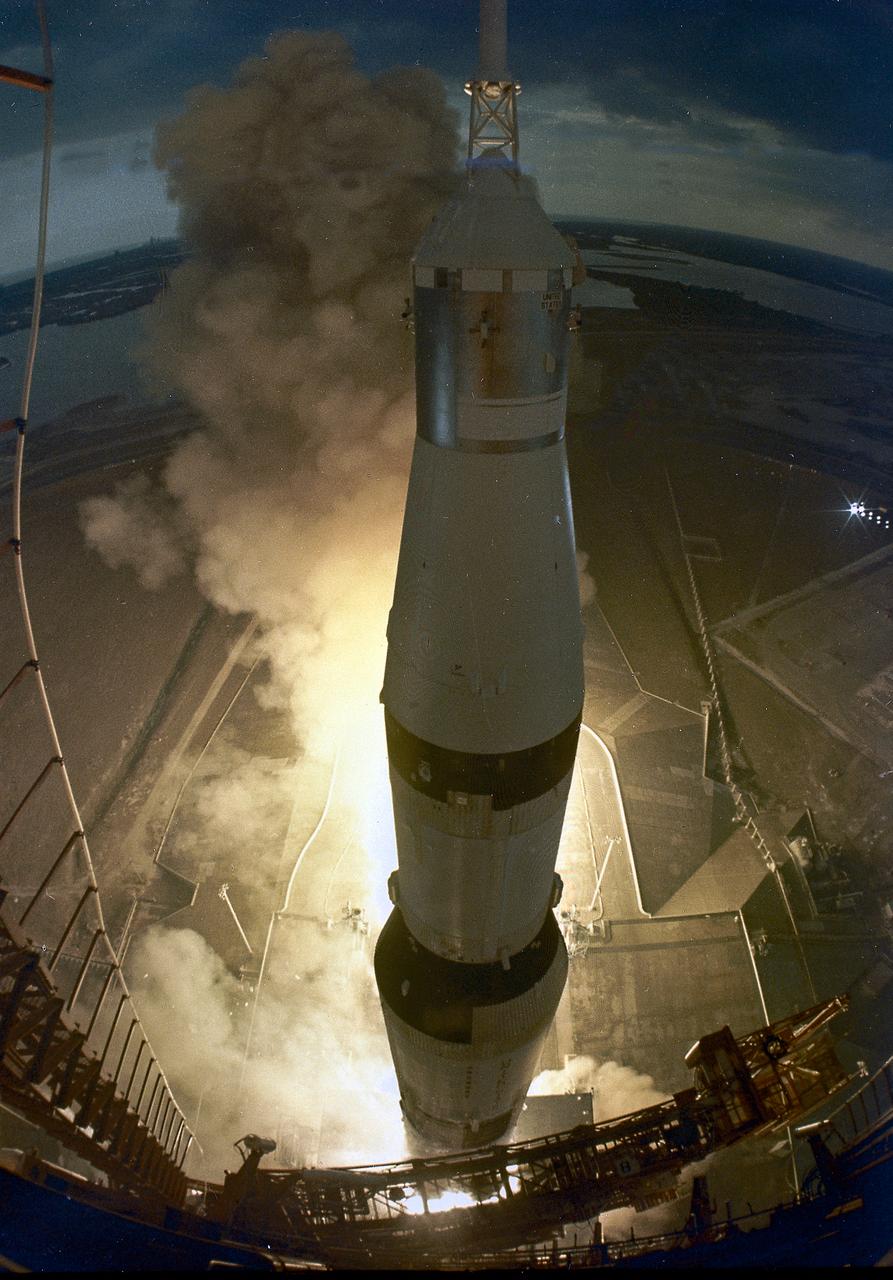

This is a view from sequential photographs of the Apollo 14 liftoff taken by a remote camera atop the 360-foot gantry level of Launch Complex 39A. The Apollo 14, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Mission commander Alan B. Shepard Jr., Command Module pilot Stuart A. Roosa, and Lunar Module pilot Edgar D. Mitchell, lifted off from launch complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center on January 31, 1971. It was the third manned lunar landing, the first manned landing in exploration of the lunar highlands, and it demonstrated pinpoint landing capability. The major goal of Apollo 14 was the scientific exploration of the Moon in the foothills of the rugged Fra Mauro region. Activities of astronauts Shepard and Mitchell, during extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface, included setting up an automated scientific laboratory called Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP), and collecting a total of about 95 pounds (43 kilograms) of Moon rock and soil for a geological investigation back on the Earth.
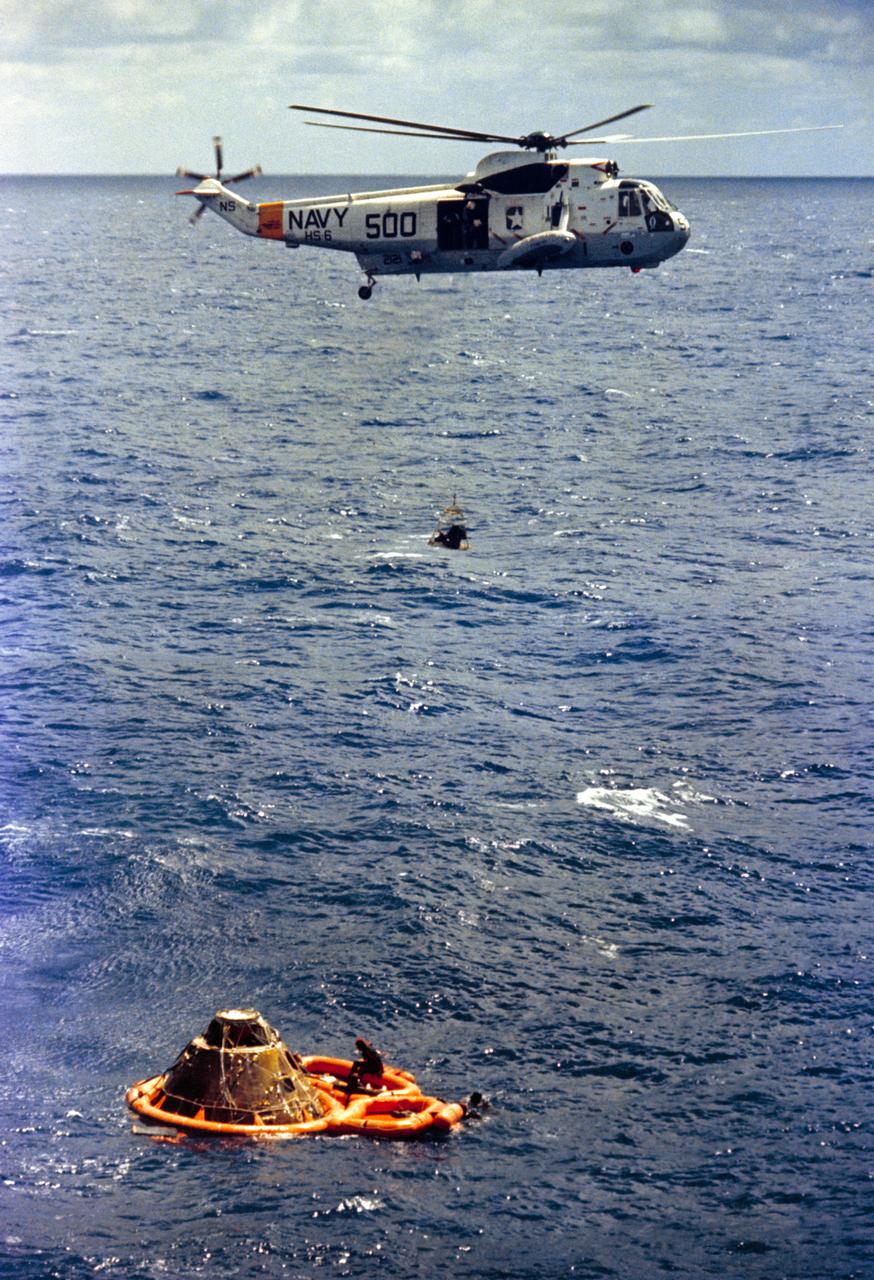

S71-19476 (9 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, is hoisted inside a Billy Pugh net to a U.S. Navy helicopter assisting in Apollo 14 recovery operations in the South Pacific Ocean. Visible in a life raft beside the Command Module (CM) are astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, back to camera; and Edgar D. Mitchell (partially obscured by the spacecraft), lunar module pilot. Three U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmers who assisted in the recovery operations are pictured in and around the life raft. Apollo 14 splashdown occurred at 3:04:39 p.m. (CST), Feb. 9, 1971, approximately 765 nautical miles south of American Samoa in the South Pacific Ocean.
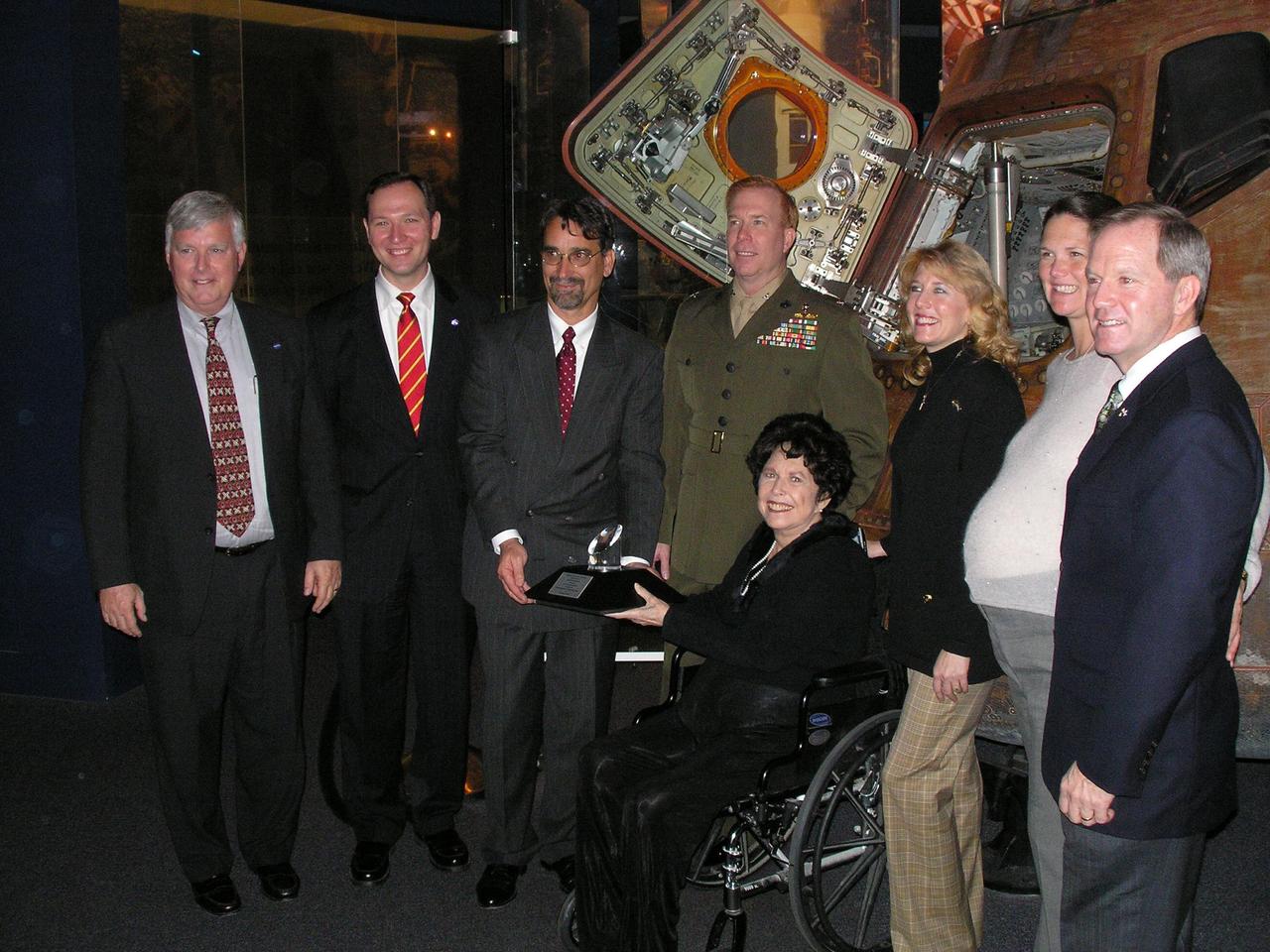

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Apollo 14 astronaut Stuart Roosa's family recently was presented with the NASA Ambassador of Exploration Award, recognizing the sacrifices and dedication of the Apollo, Gemini and Mercury astronauts. Attending the ceremony, seen here (from left), are James Kennedy, director, NASA Kennedy Space Center; Jeffrey Jezierski (J. T.), White House liaison, NASA; Daniel Gruenbaum, general manager of the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame; and Roosa's family, his son Col. Christopher Roosa, USMC; his widow Joan Roosa, (in wheelchair); his daughter Rosemary Roosa; and daughter-in-law Whitney and his son Allen Roosa. Each of the honored astronauts or their surviving families was presented with a lunar sample, part of the 842 pounds of moon rocks and soil returned during the six lunar expeditions from 1969 to 1972. Roosa's family chose to display the award that featured a small piece of the moon at the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame in Titusville, Fla.
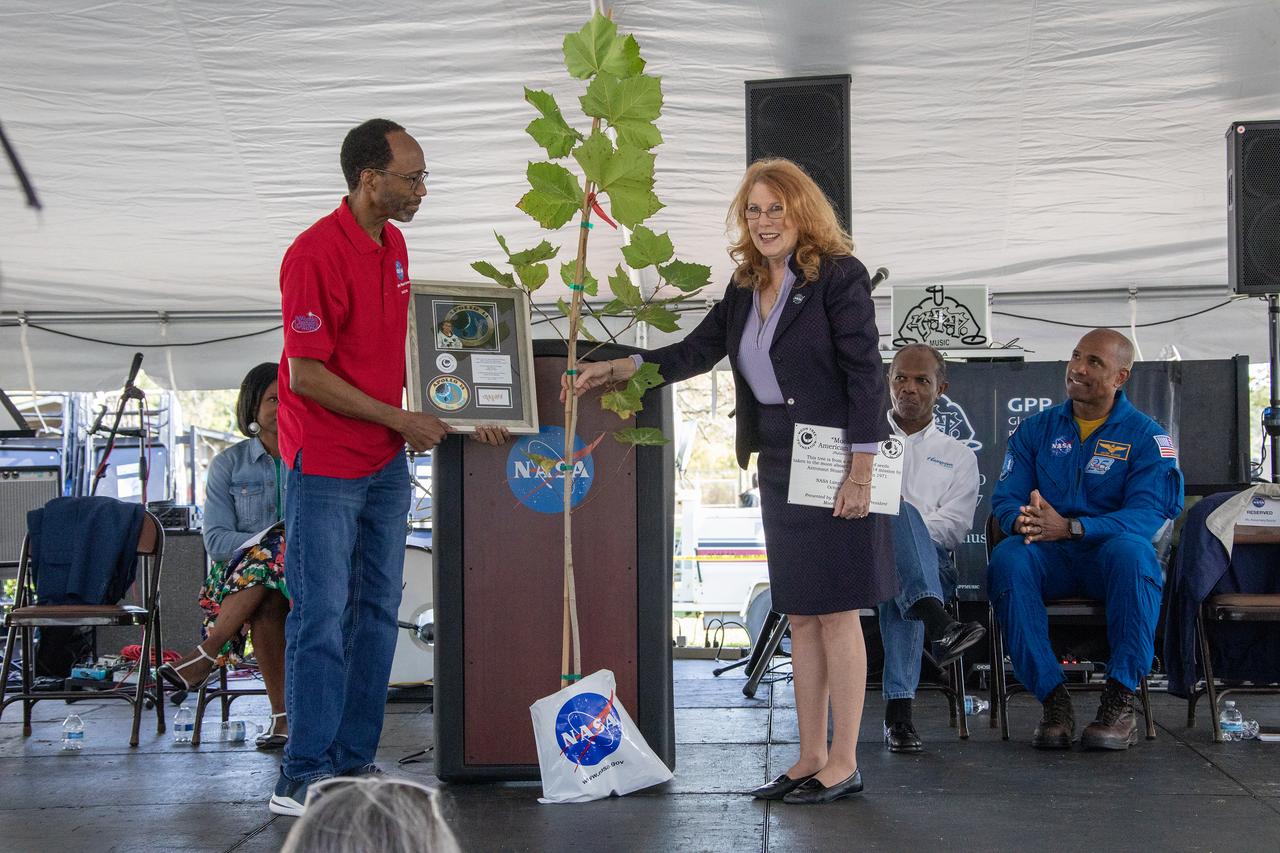

"Moon Tree" American Sycamore tree presented to Langley Center Director Clayton Moore by Rosemary Roosa, President of Moon Tree Foundation. More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
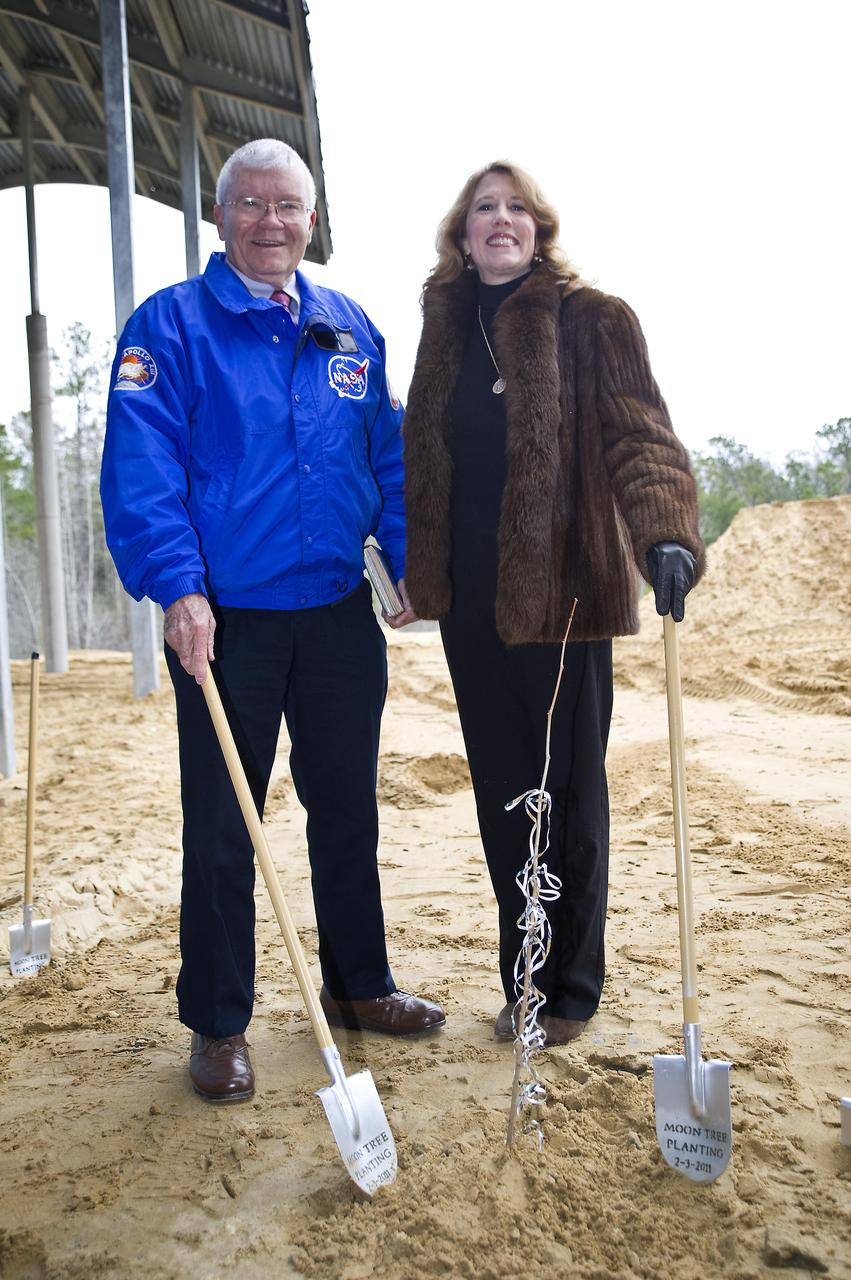

Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise stands with Rosemary Roosa, daughter of late Apollo 14 astronaut Stuart Roosa, beside a 'moon tree' planted at the INFINITY science center on Feb. 3, 2011. The moon tree is a descendent of seeds carried into space by Stuart Roosa on the Apollo 14 mission in 1971.

Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise stands with Rosemary Roosa, daughter of late Apollo 14 astronaut Stuart Roosa, beside a 'moon tree' planted at the INFINITY science center on Feb. 3, 2011. The moon tree is a descendent of seeds carried into space by Stuart Roosa on the Apollo 14 mission in 1971.

Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise stands with Rosemary Roosa, daughter of late Apollo 14 astronaut Stuart Roosa, beside a 'moon tree' planted at the INFINITY science center on Feb. 3, 2011. The moon tree is a descendent of seeds carried into space by Stuart Roosa on the Apollo 14 mission in 1971.
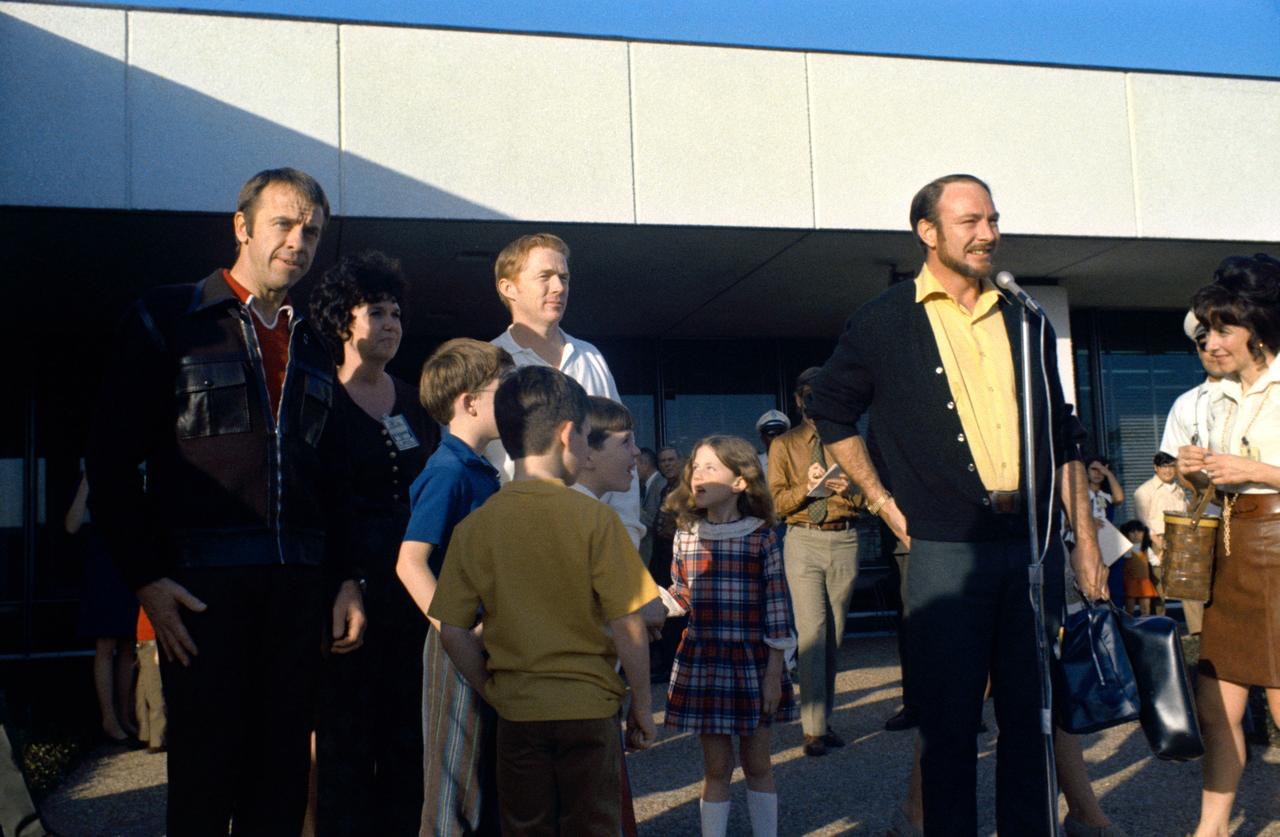

S71-22028 (26 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, right, the Apollo 14 lunar module pilot, addresses NASA-MSC personnel and news media representatives and other visitors soon after he and his fellow crewmen were released from a 15-day confinement period in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory. Pictured with Mitchell in front of the LRL, MSC Building 37, are astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., left, commander; and Stuart A Roosa, command module pilot, Mrs. Mitchell is at right and Mrs. Roosa, near left. Roosa is flanked by his four children, left to right, Christopher A., Stuart A. Roosa Jr., John D. and Rosemary D.
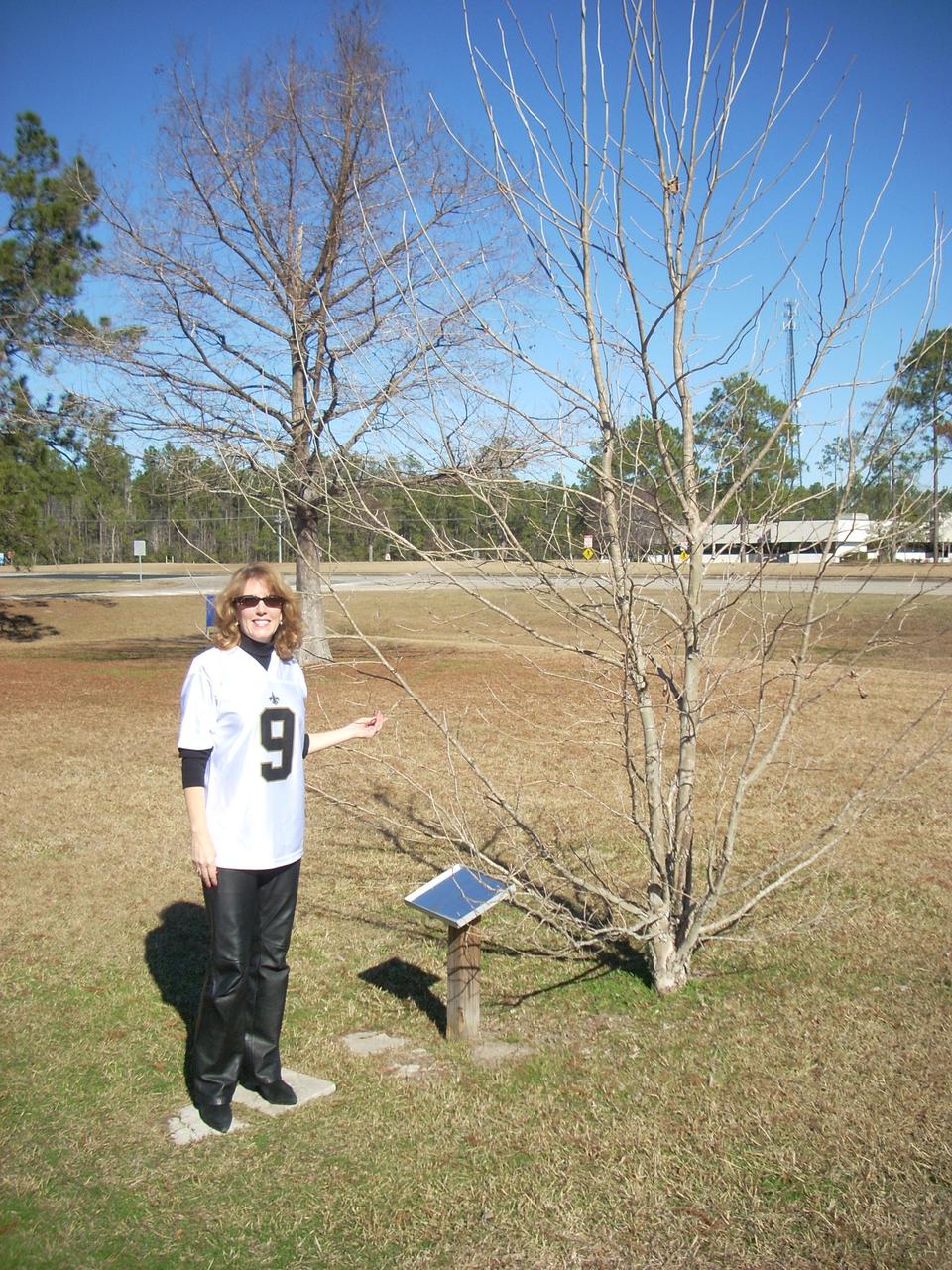

: An image from Jan. 7, 2011, shows Rosemary Roosa, daughter of the late Apollo 14 astronaut Stuart Roosa, standing beside the Moon tree outside of StenniSphere, the previous museum and visitor center at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The Moon tree is grown from seeds carried to the Moon and back by astronaut Stuart Roosa on the Apollo 14 mission.
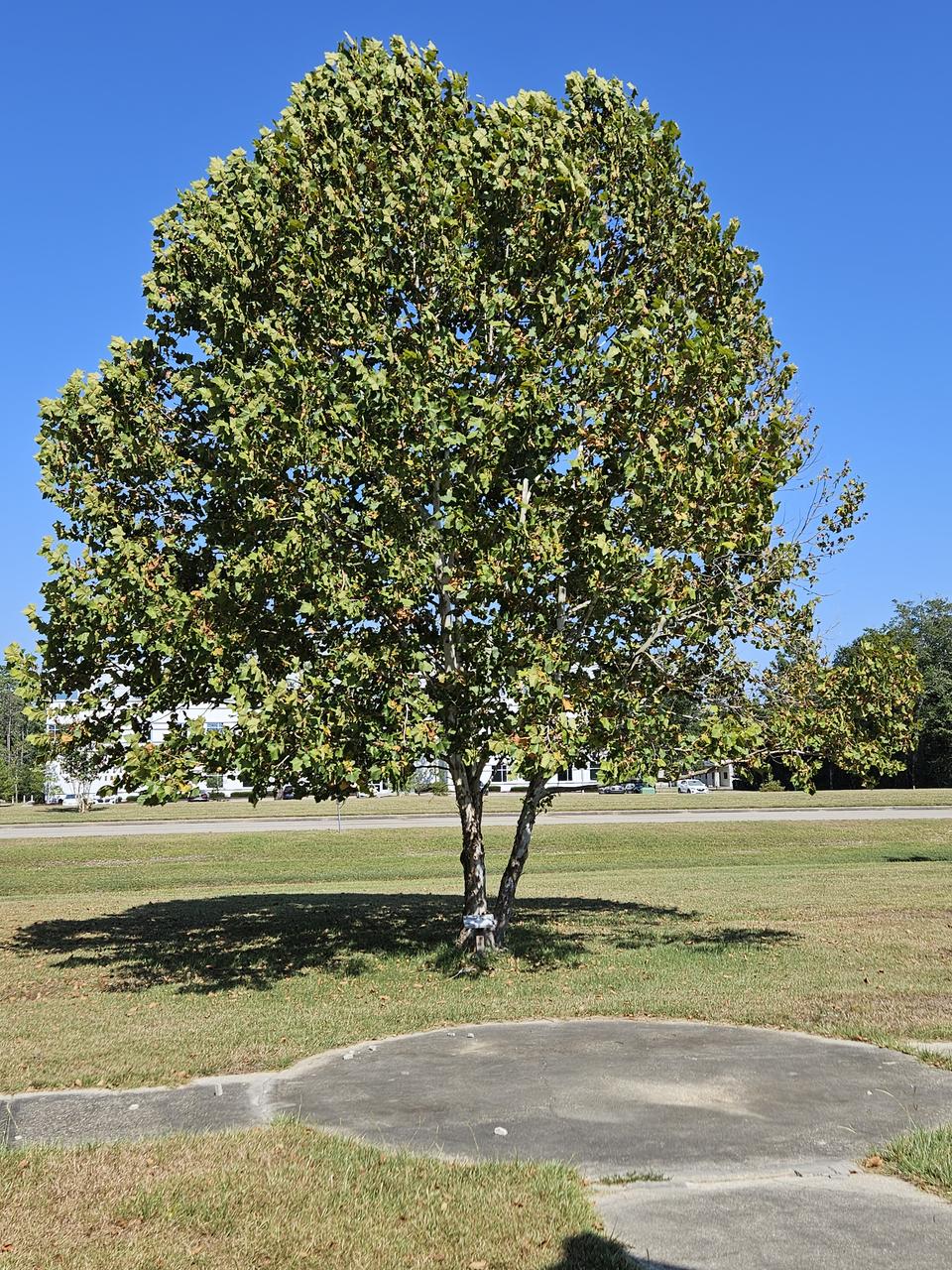

An image from 2023 image shows the growth of a Moon tree planted in 2004 to honor the Apollo 11 mission. The seeds for the tree were carried to the Moon and back by astronaut Stuart Roosa on the Apollo 14 mission.

The Moon tree, planted on July 20, 2004 at NASA Stennis, is a descendant of seeds carried to the Moon and back by the late Apollo 14 astronaut and longtime Mississippi Coast resident, Stuart Roosa, as he orbited the Moon in the command module, “Kitty Hawk.”

S70-55635 (December 1970) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. Left to right, are Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot. The Apollo 14 emblem is in the background.
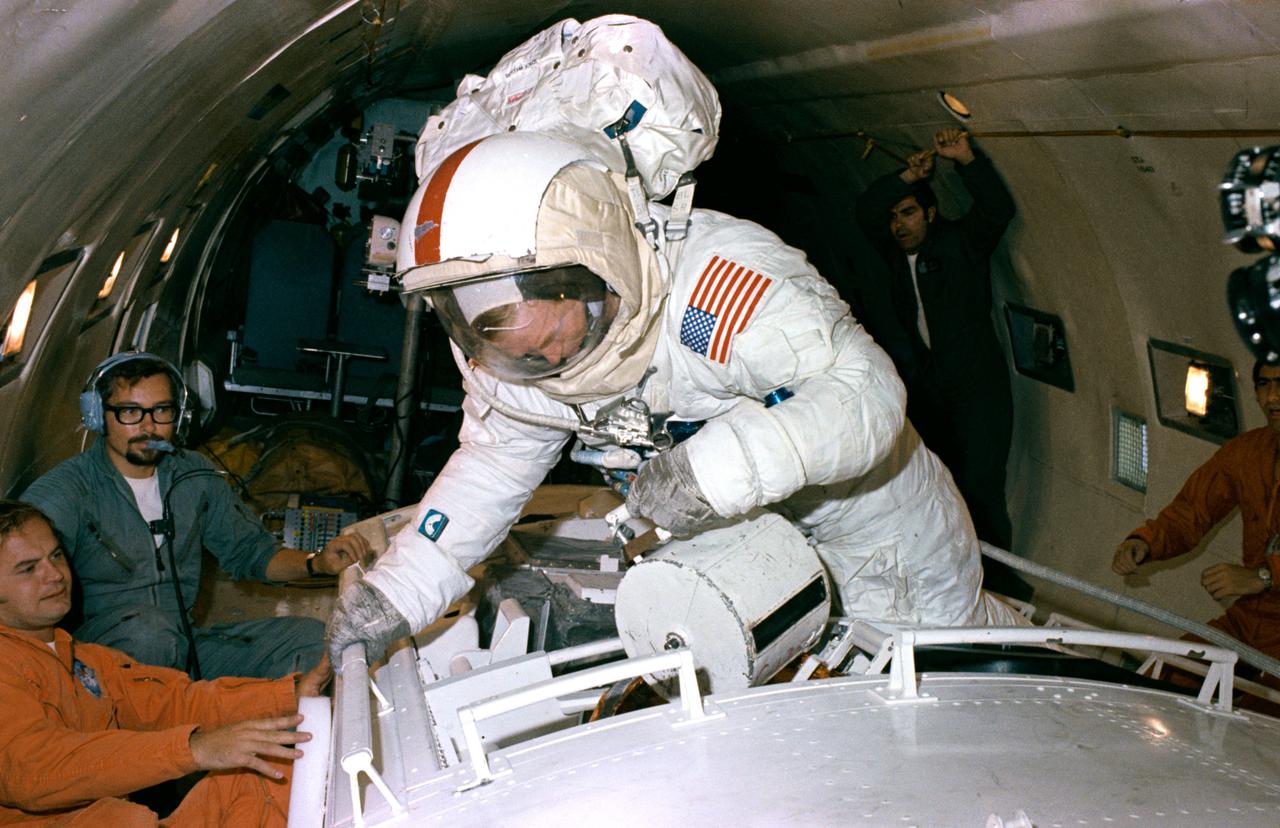

S72-50271 (September 1972) --- Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, backup crew command module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission, participates in extravehicular activity simulation training under zero-gravity conditions aboard a U. S. Air Force KC-135 aircraft. A mock-up of the Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module is used in the exercise. Here, Roosa simulates retrieving the film cassette of the Mapping Camera from the SIM bay. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, Apollo 17 prime crew command module pilot, is scheduled to receive film cassettes from the Mapping Camera, Panoramic Camera, and Lunar Sounder during Apollo 17 trans-Earth extravehicular activity.
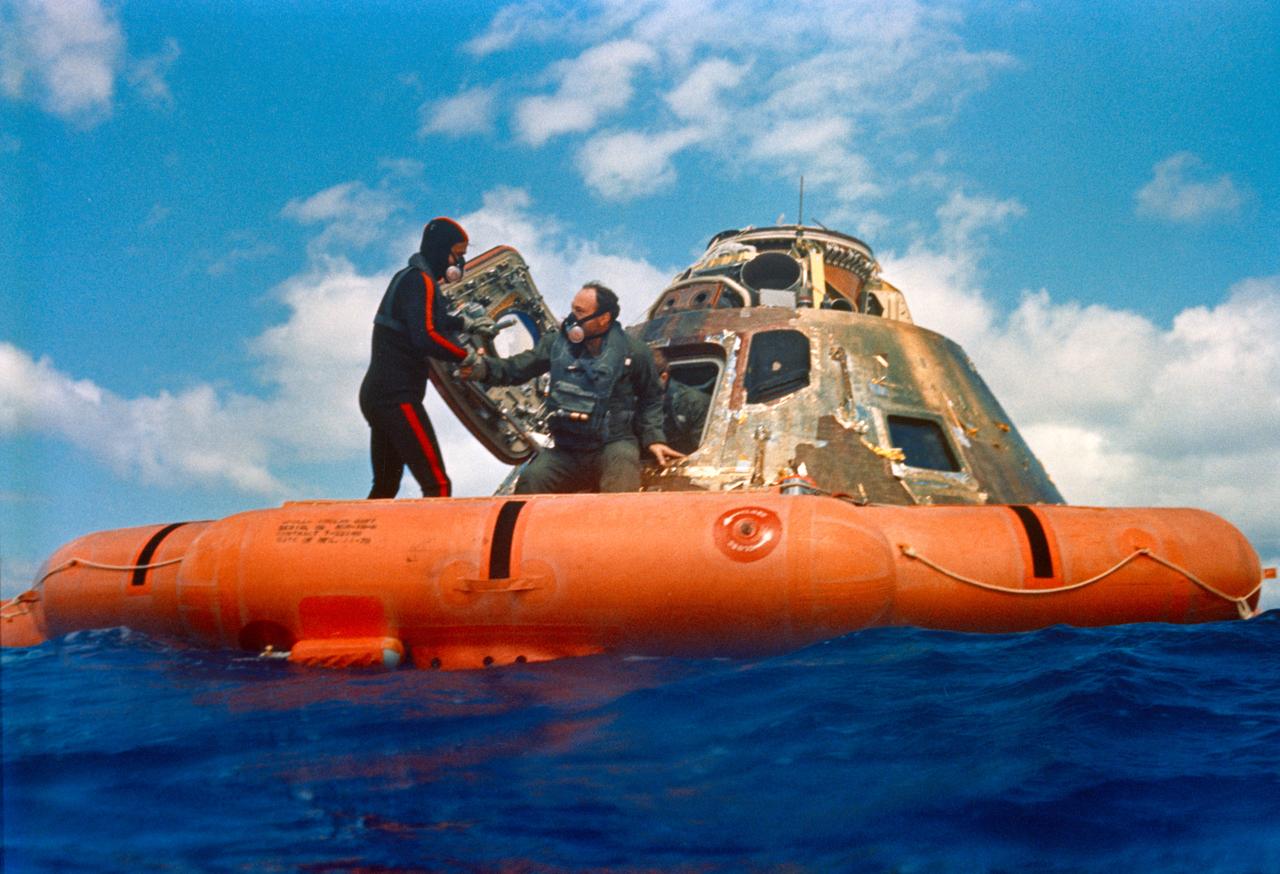

S71-19474 (9 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, is assisted out of the Command Module (CM) by a U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmer during the Apollo 14 recovery operations in the South Pacific Ocean. Mitchell was followed out of the spacecraft by astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot. Roosa is partially visible behind Mitchell. The Apollo 14 splashdown occurred at 3:04:39 p.m. (CST), Feb. 9, 1971, in the South Pacific Ocean, approximately 765 nautical miles from American Samoa. They were transported by U.S. Navy helicopter to the USS New Orleans, prime recovery vessel.
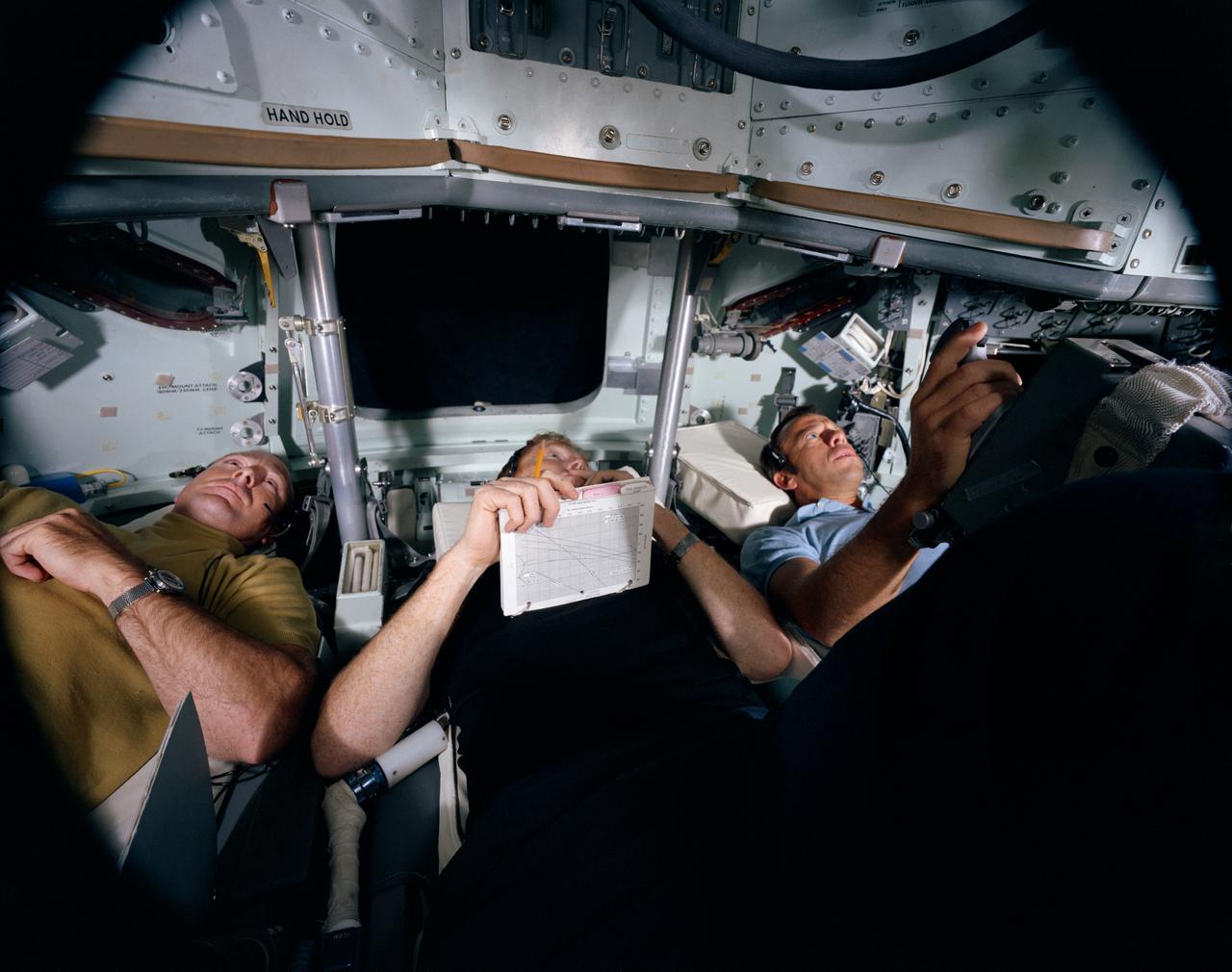

S70-45580 (July 1970) --- The members of the prime crew of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission participate in Command Module (CM) simulation training at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Left to right are astronauts Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander.
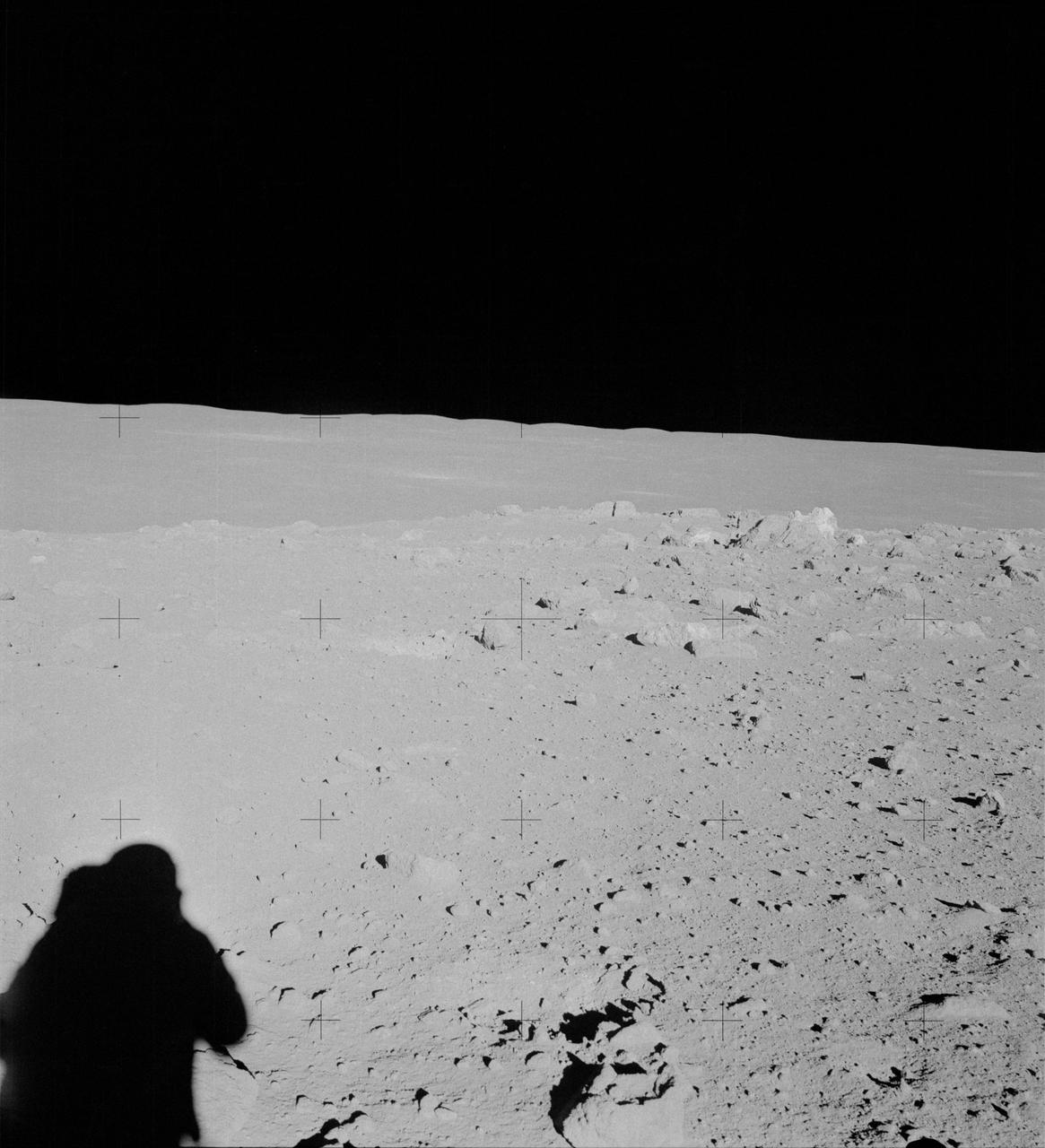

AS14-64-9099 (6 Feb. 1971) --- An Apollo 14 crew member (note shadow) photographs this field of boulders located on the flank of Cone Crater during the second extravehicular activity (EVA). This view is looking just north of west. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, were exploring the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, was maneuvering the Apollo 14 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
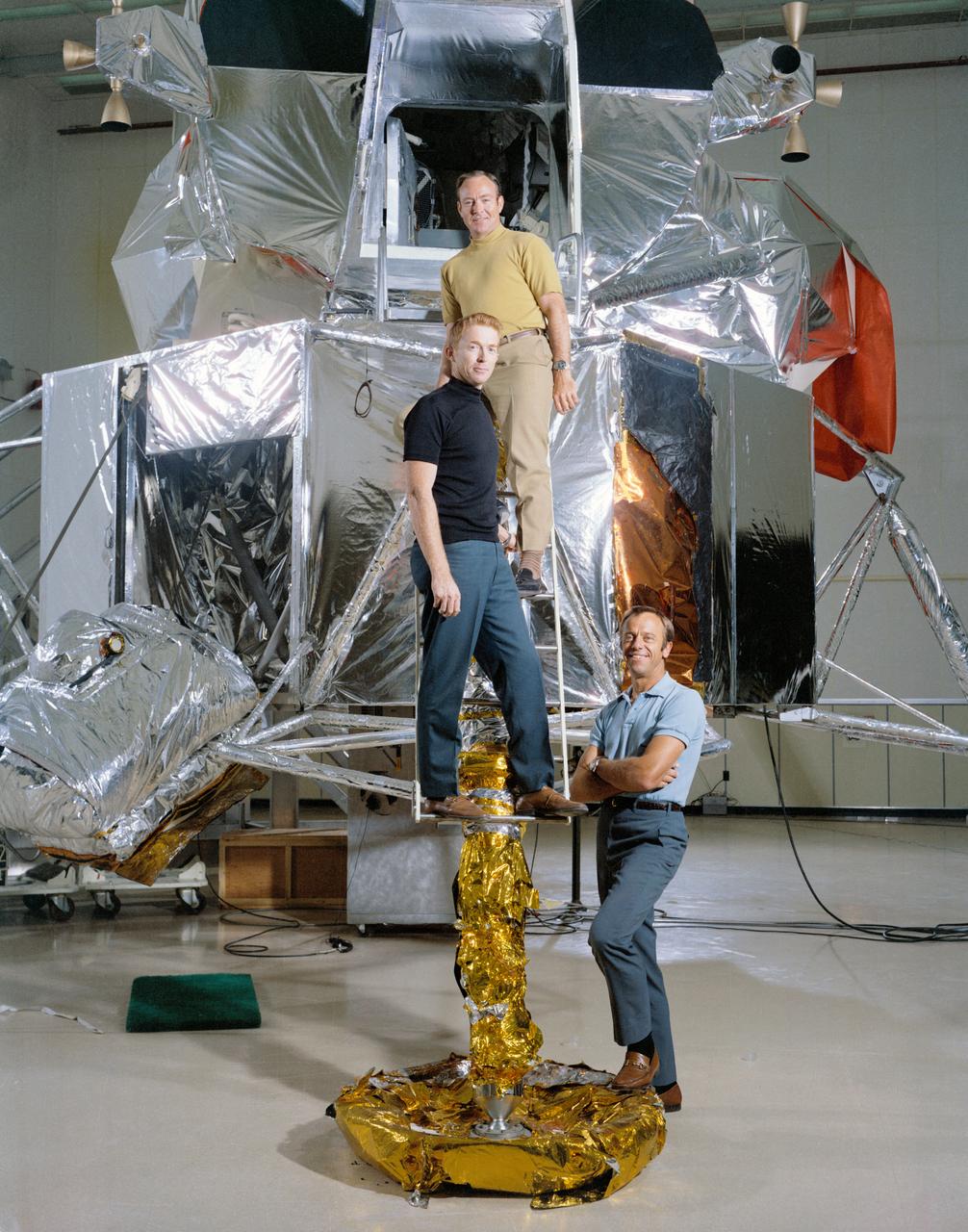

S70-45581 (July 1970) --- The members of the prime crew of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission are photographed during training activity at the Kennedy Space Center. From foreground are astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot. They are standing in front of a Lunar Module mock-up.
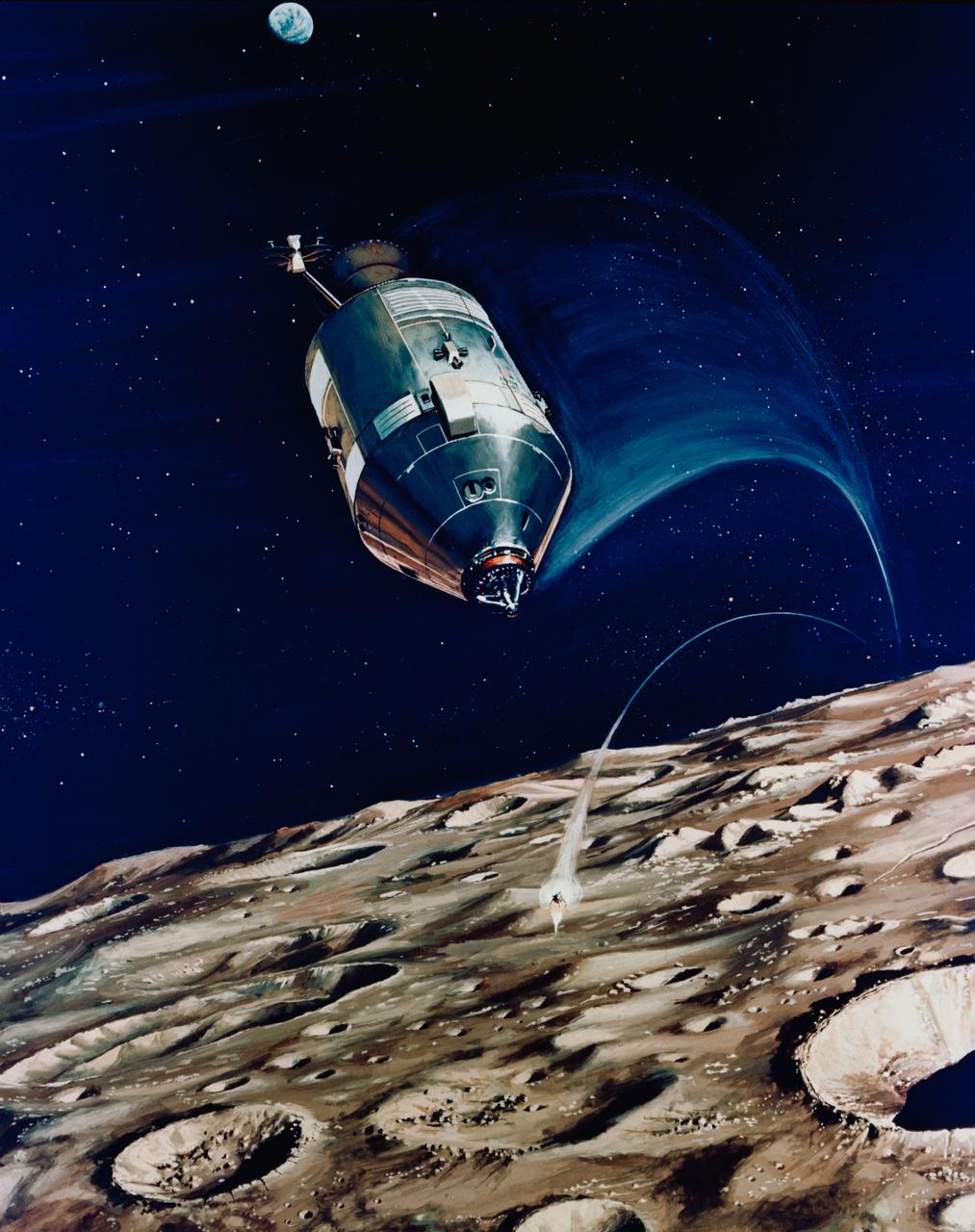

S71-16574 (11 Jan. 1971) --- An artist's concept depicting the Apollo 14 Command and Service Modules (CSM) circling the moon as the Lunar Module (LM) heads toward a lunar landing. While astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remains with the CSM in lunar orbit, astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, will descend in the LM to explore an area in the rugged Fra Mauro highlands.
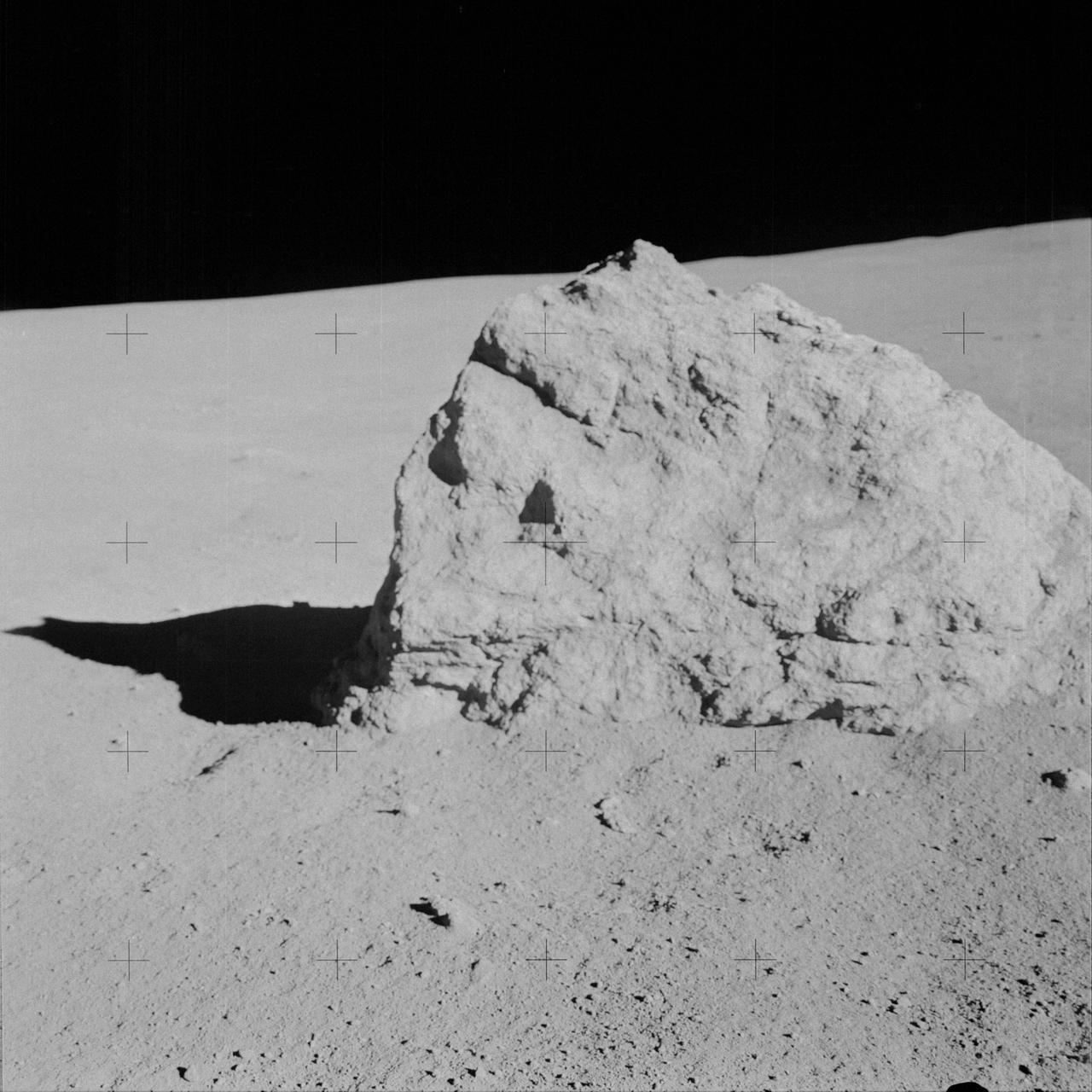

AS14-64-9135 (6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, took this close-up view of a large boulder, approximately five feet long, during the second extravehicular activity (EVA), on Feb. 6, 1971. Astronauts Shepard and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
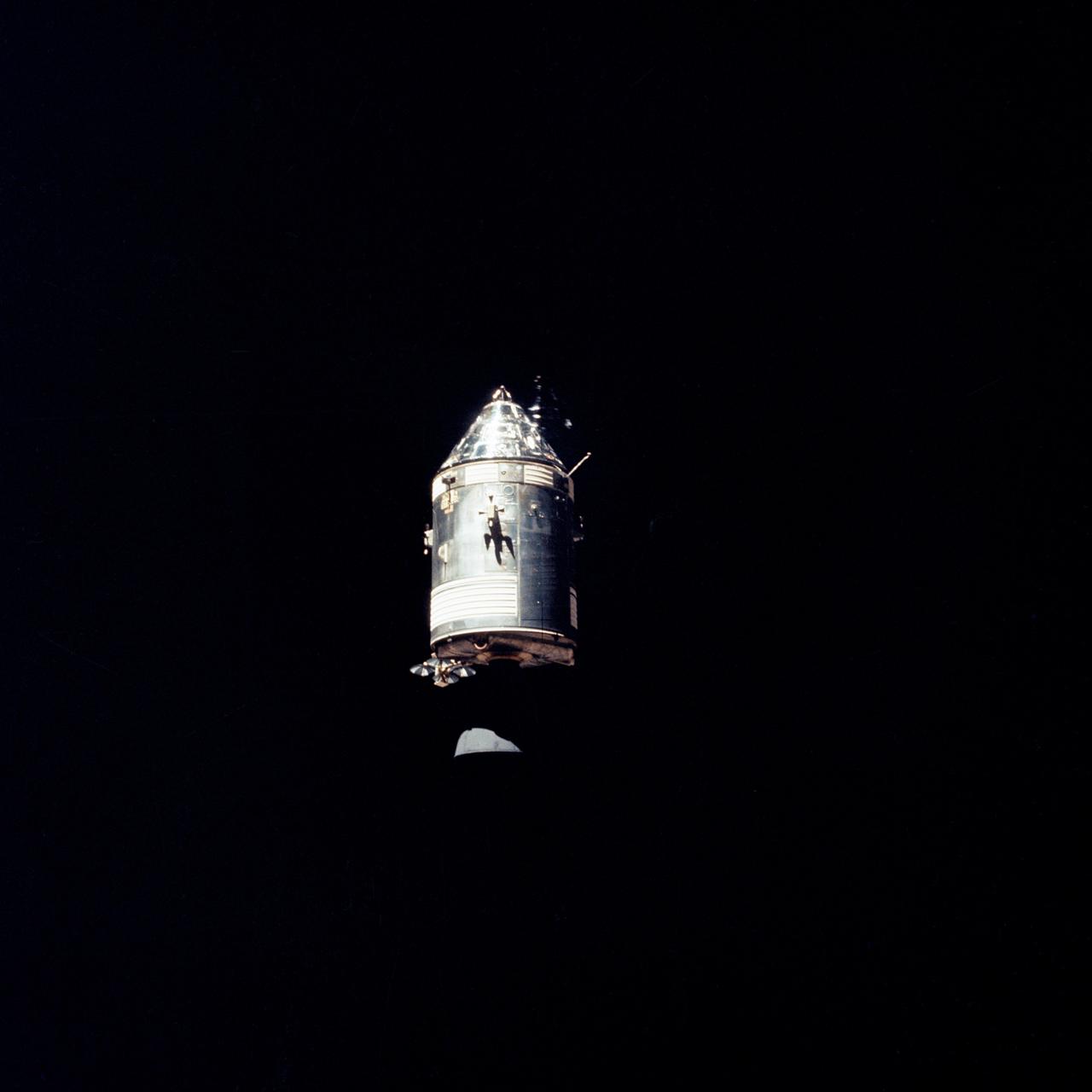

AS14-66-9344 (February 1971) --- The Apollo Command and Service Modules (CSM) are photographed against a black sky background from the Lunar Module (LM) above the moon. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM "Antares" to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa , command module pilot, remained with the CSM "Kitty Hawk" in lunar orbit.
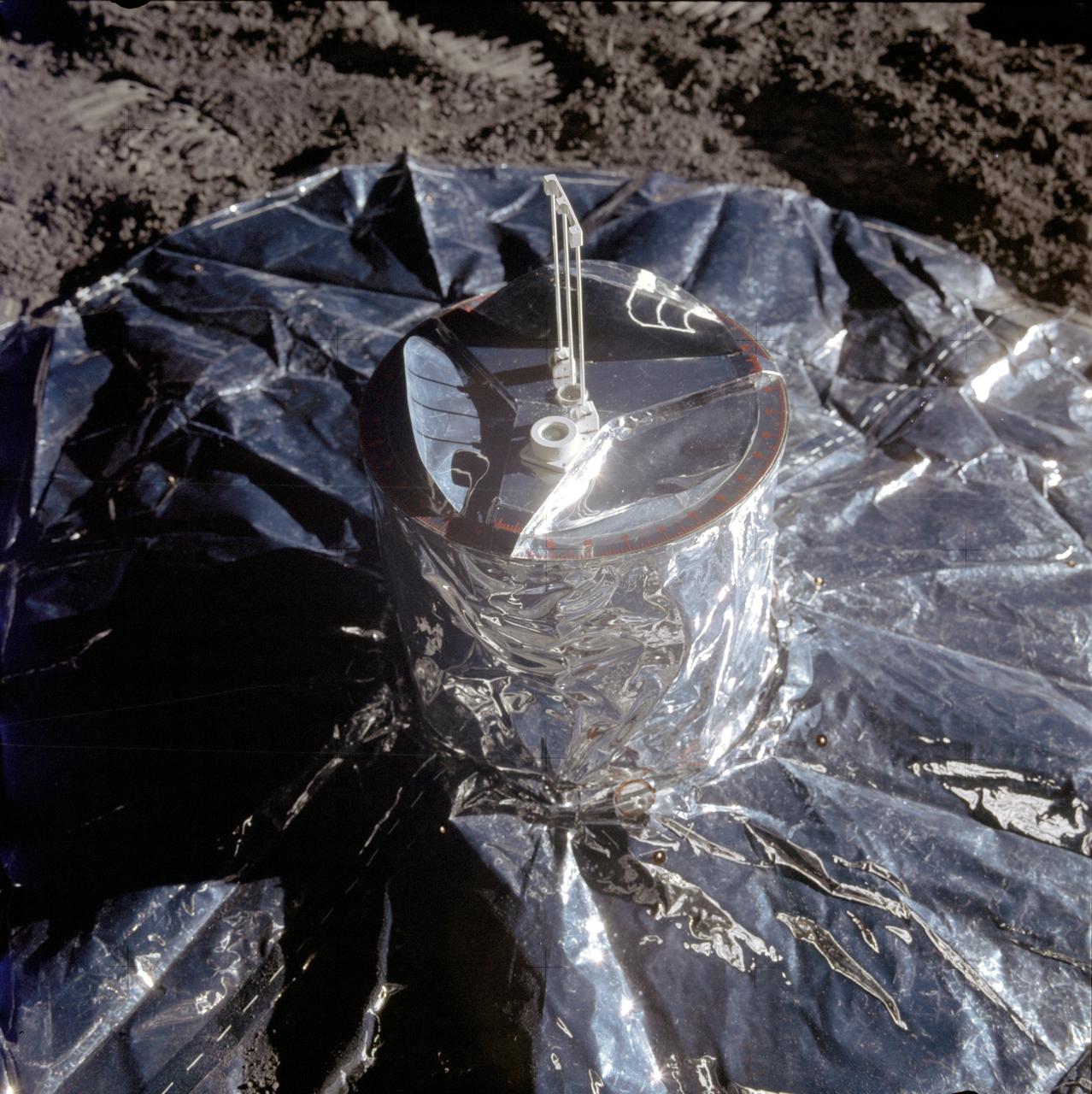

AS14-67-9362 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the passive seismic experiment (PSE), a component of the Apollo lunar surface experiments package (ALSEP), which was deployed on the moon by the Apollo 14 astronauts during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
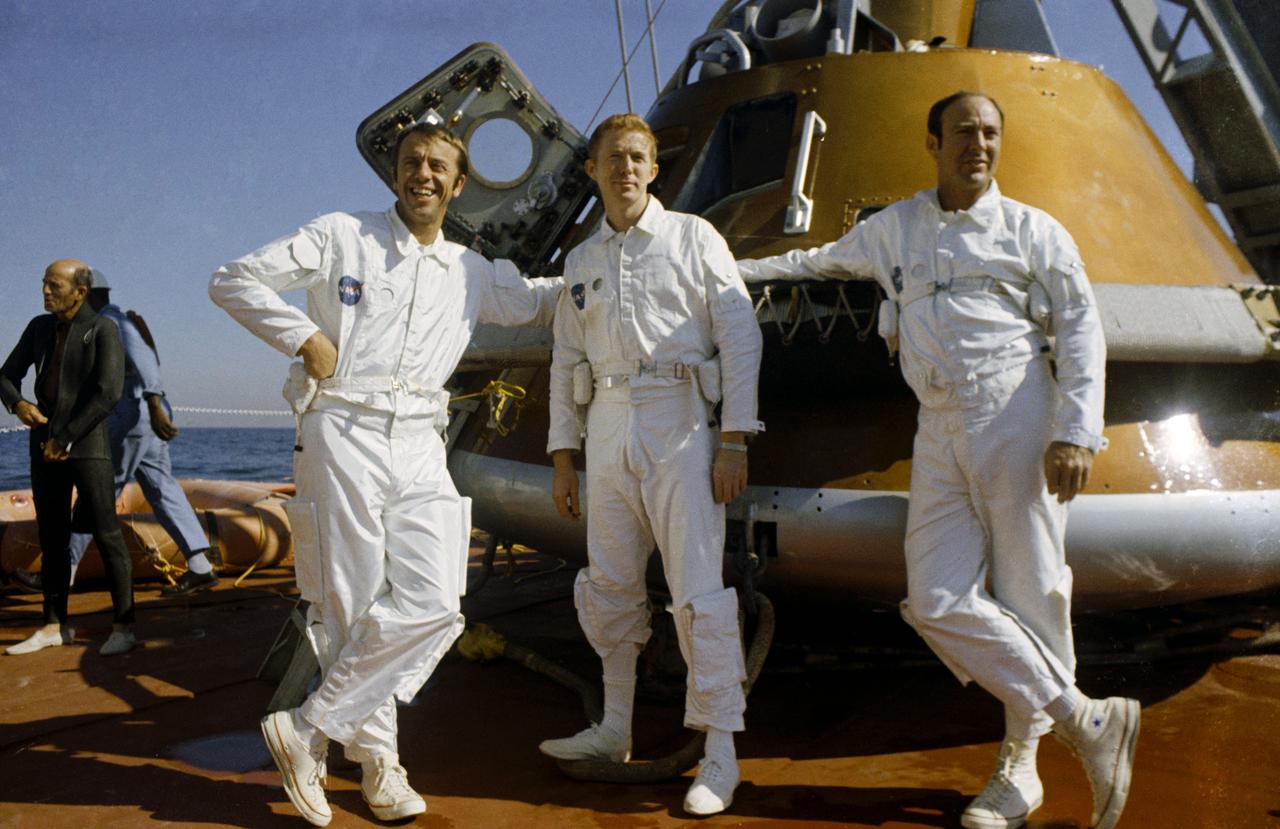

S70-51699 (24 Oct. 1970) --- The prime crew of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission relaxes aboard the NASA motor vessel retriever, prior to participating in water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. Left to right are astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot. They are standing by a Command Module (CM) trainer which was used in the exercises.

AS14-64-9181 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- A view of the lunar terrain at the Apollo 14 Fra Mauro landing site as photographed through the left window of the Lunar Module (LM). Note the clump of lunar soil in the foreground, and a crater in the center on the horizon. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
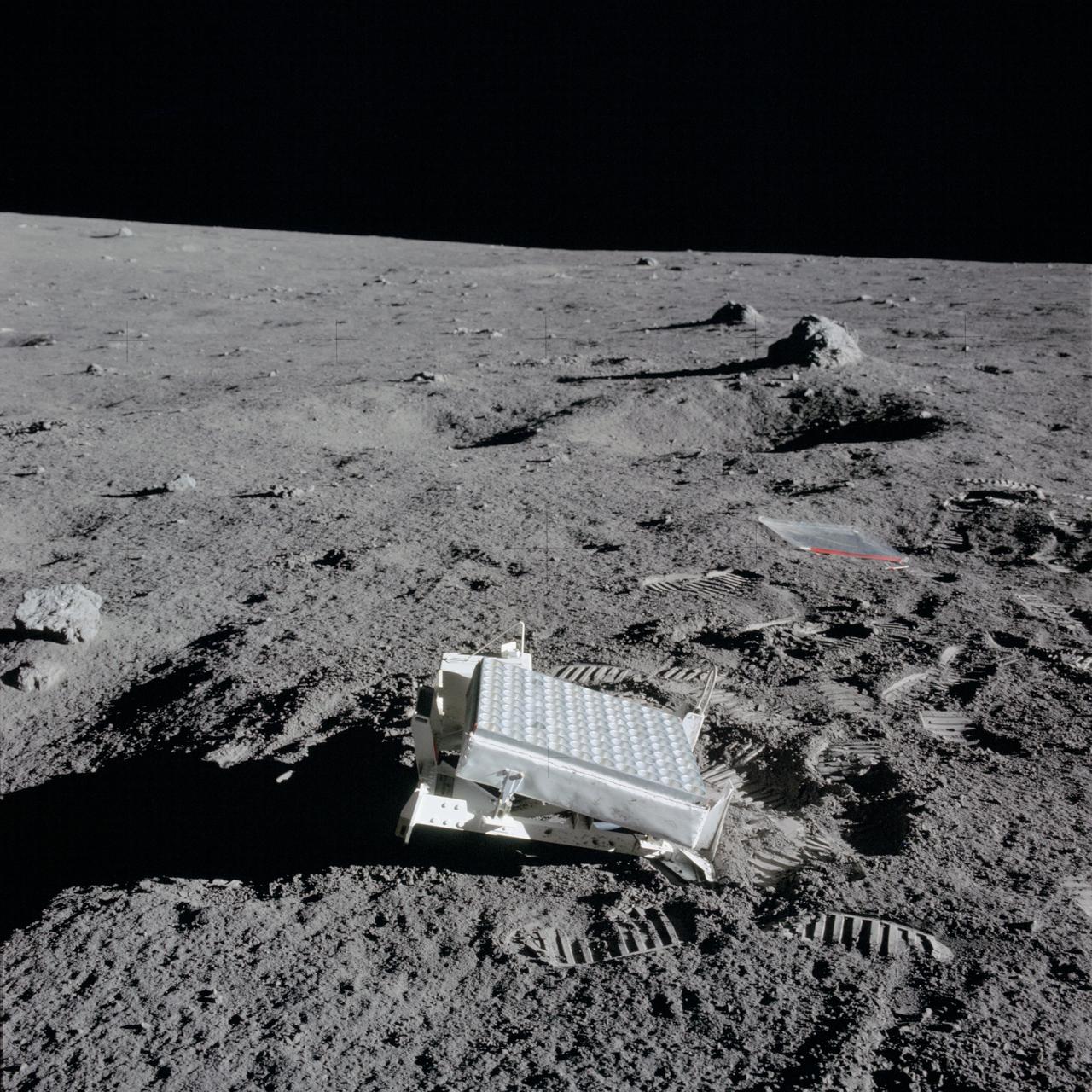
AS14-67-9386 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the laser ranging retro reflector (LR3) which the Apollo 14 astronauts deployed on the moon during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
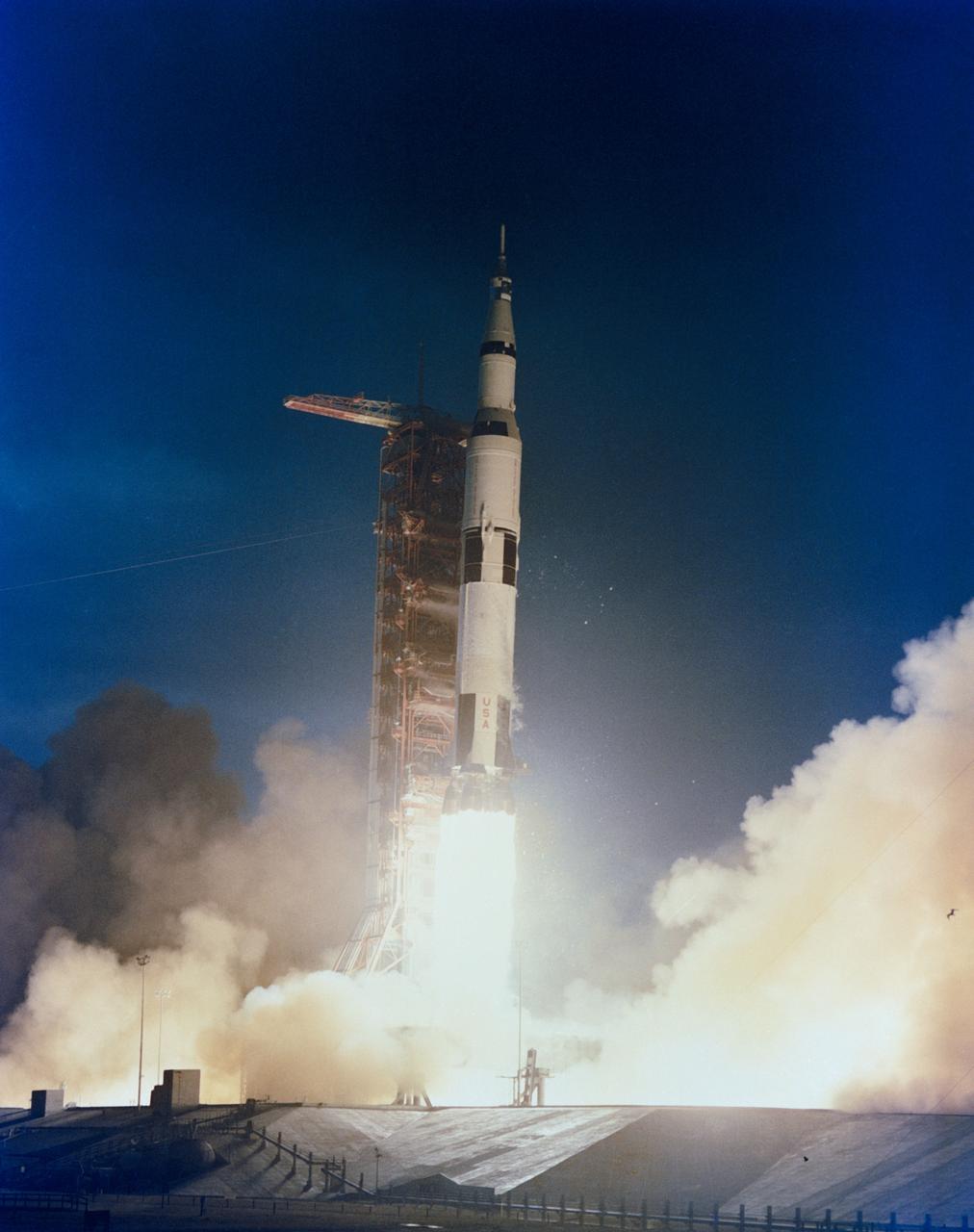

S71-17621 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1981, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.

AS14-66-9241 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, makes a pan with the lunar surface television camera during an extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. This photograph was taken by fellow astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander. While Shepard and Mitchell descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
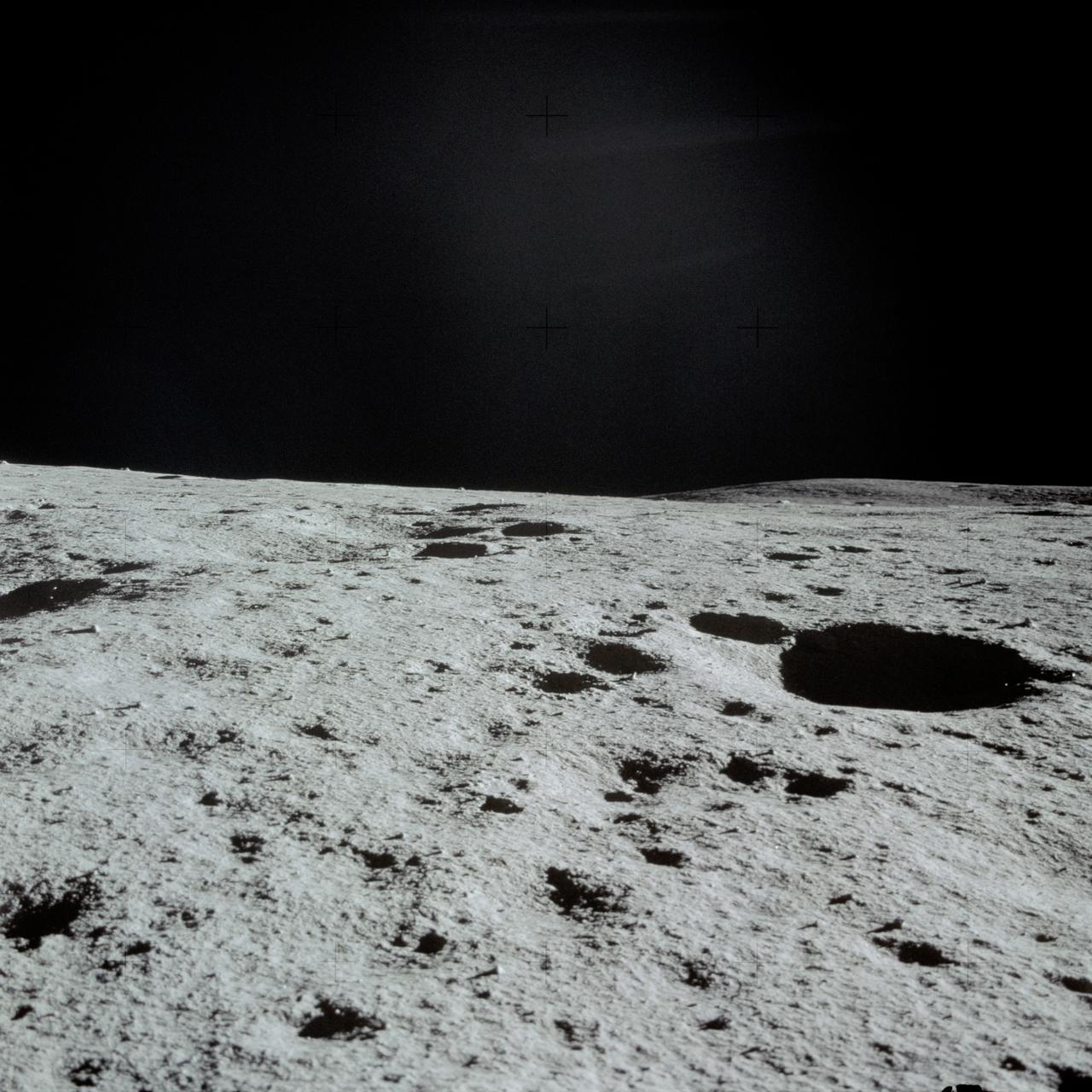

AS14-66-9244 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- An excellent view of the lunar terrain looking through the right window of the Lunar Module (LM), photographed by one of the Apollo 14 astronauts during their stay on the lunar surface. Pothole-sized craters can be seen in the foreground. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
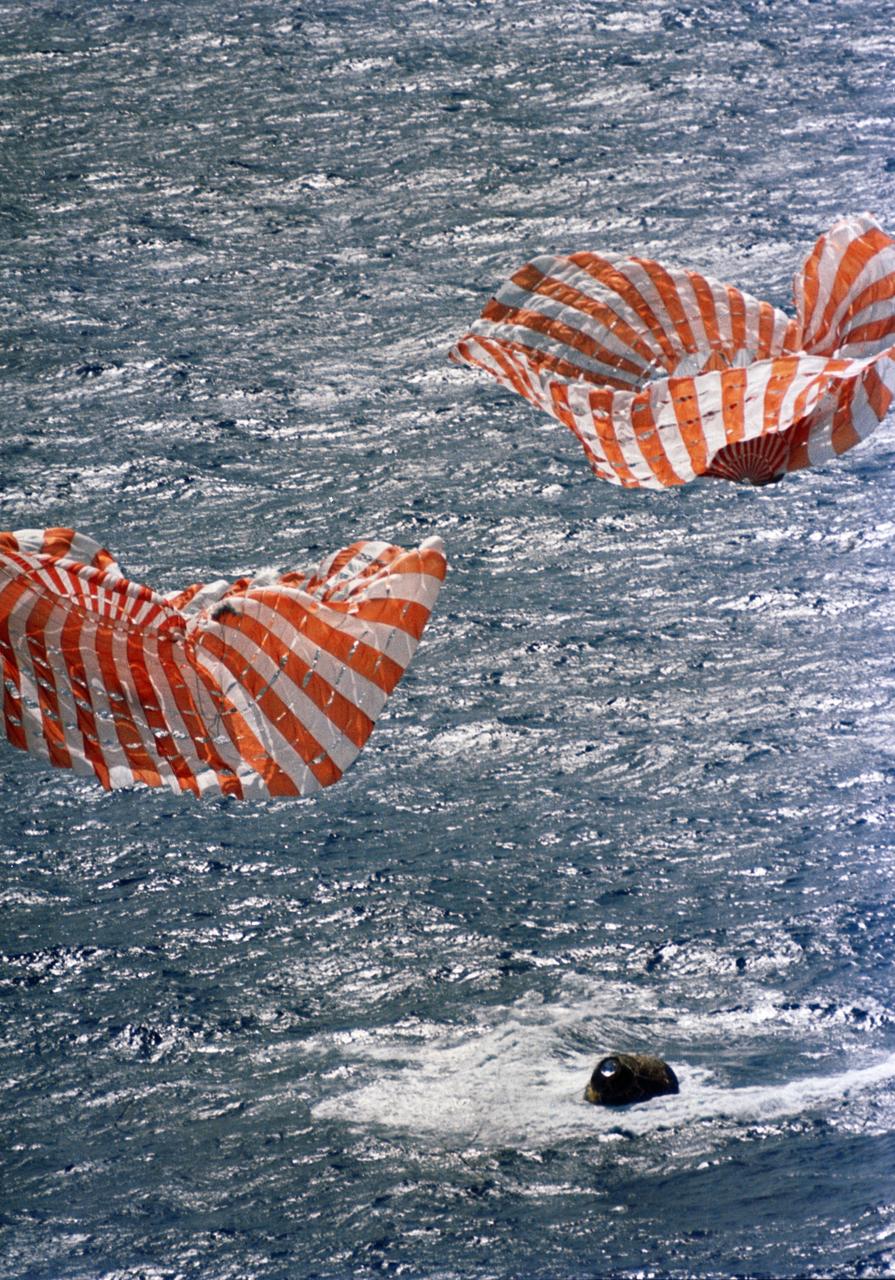

S71-19472 (9 Feb. 1971) --- The Apollo 14 Command Module (CM) splashes down and two of its three main parachutes can be seen collapsing, as the 10-day mission comes to a safe and successful end. The Apollo 14 spacecraft, with astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, aboard, splashed down at 3:04:39 p.m. (CST) approximately 765 nautical miles southeast of American Samoa.
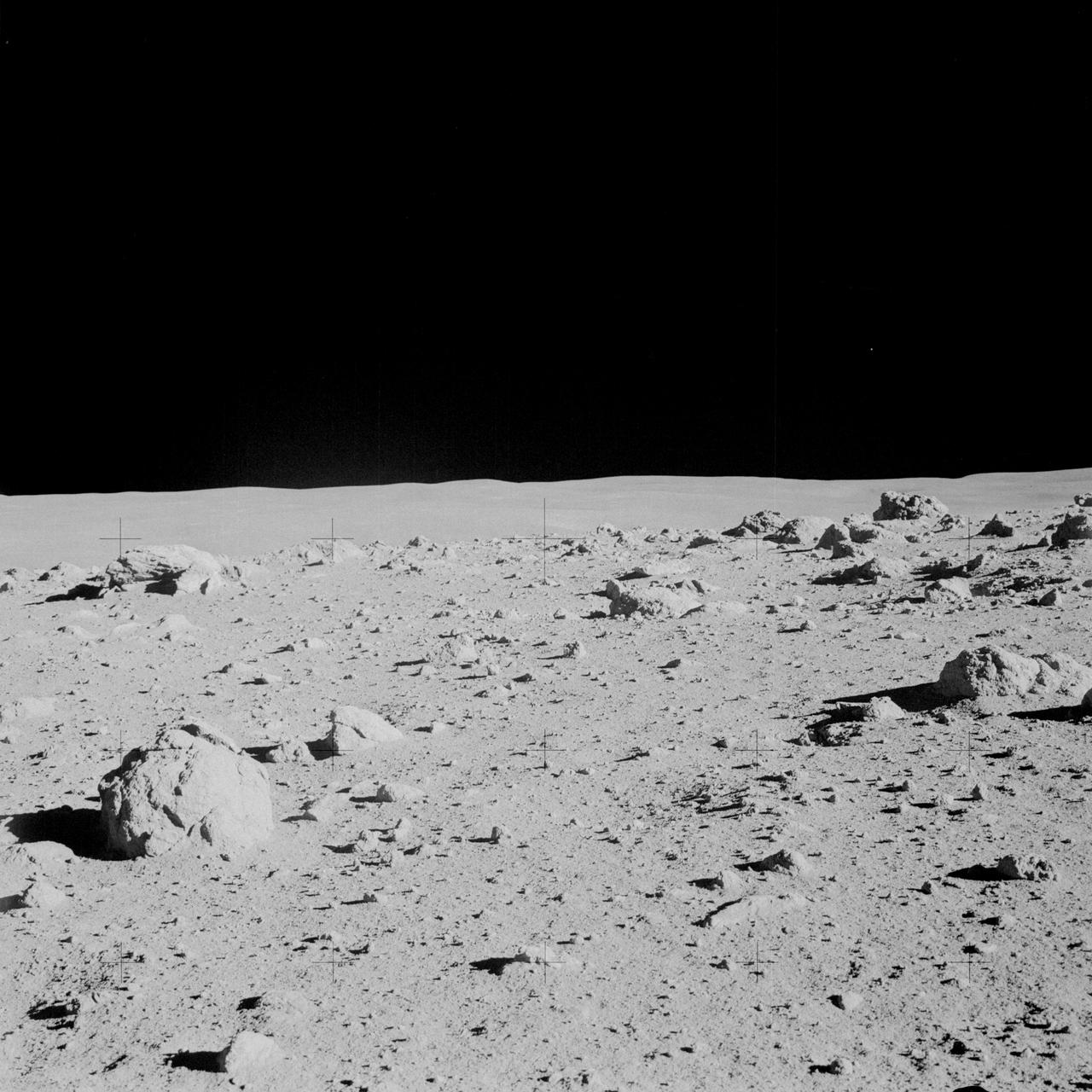

AS14-64-9103 (6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, photographed this overall view of a field of boulders on the flank of Cone Crater during the second extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, joined Shepard in exploring the moon, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
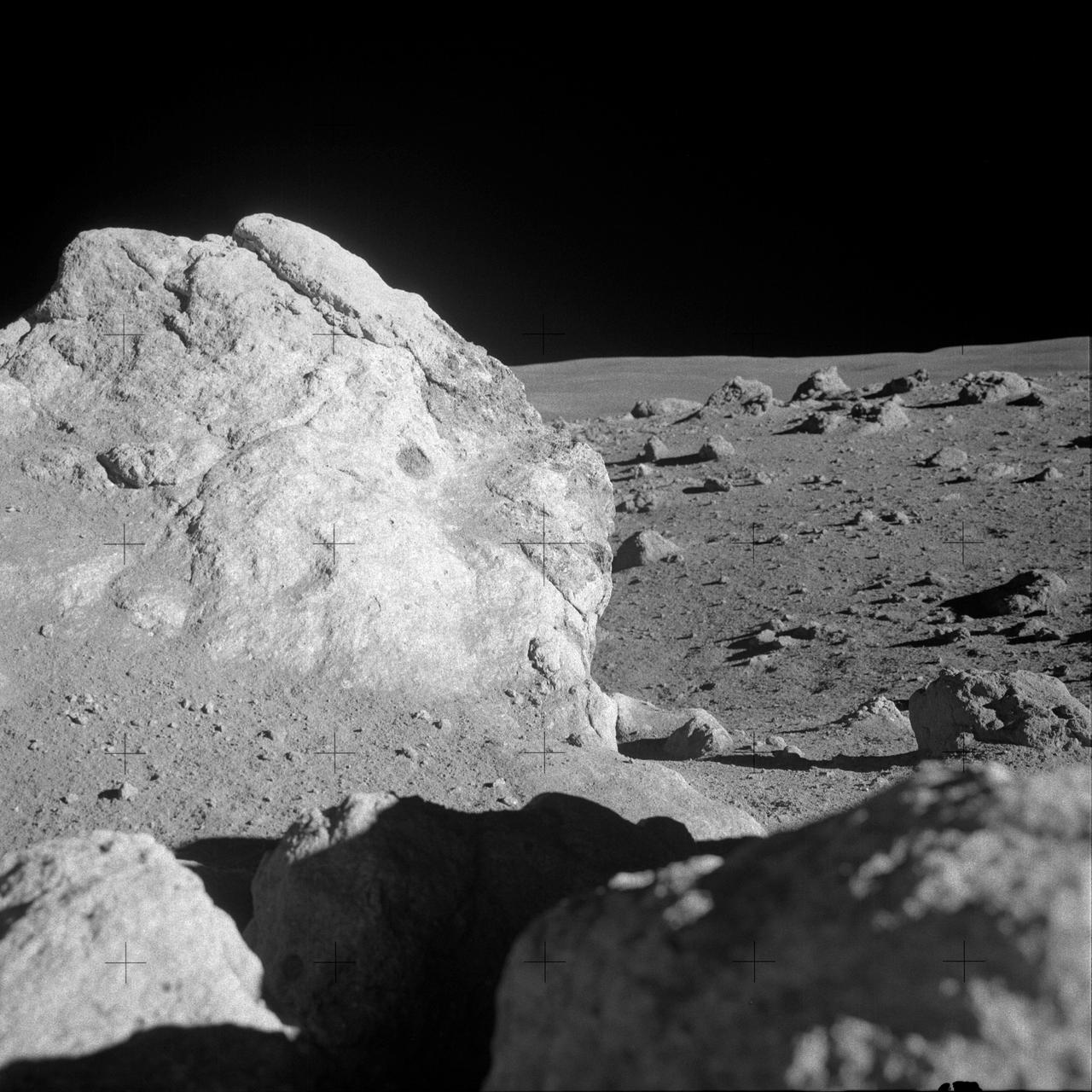

AS14-68-9451 (6 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of a large boulder in a field of boulders near the rim of Cone Crater, which was photographed by the Apollo 14 moon-explorers during the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) to explore the lunar surface while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
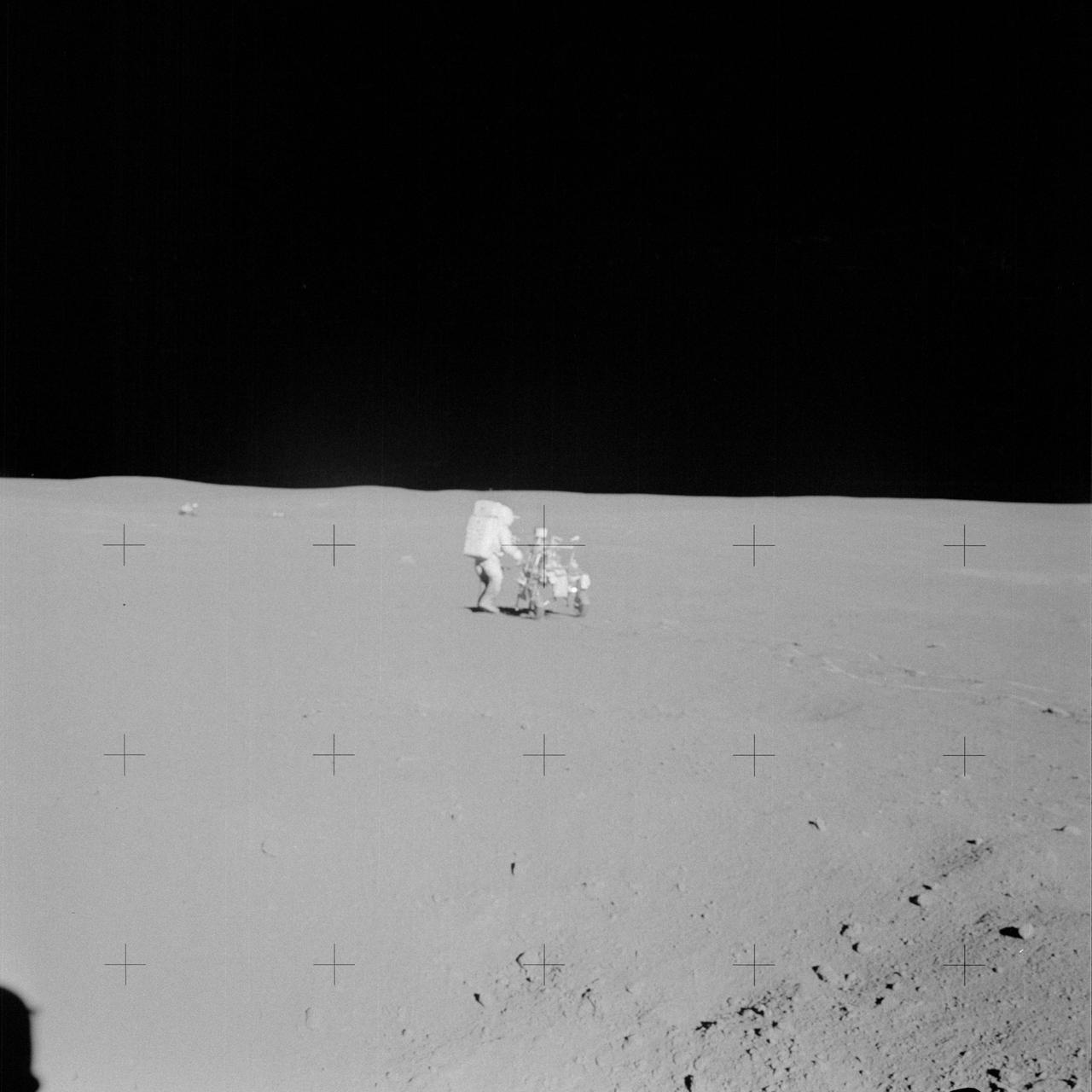

AS14-64-9140 (6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, participates in the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA). He is standing near the modularized equipment transporter (MET). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Mitchell descended in the Apollo 14 LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
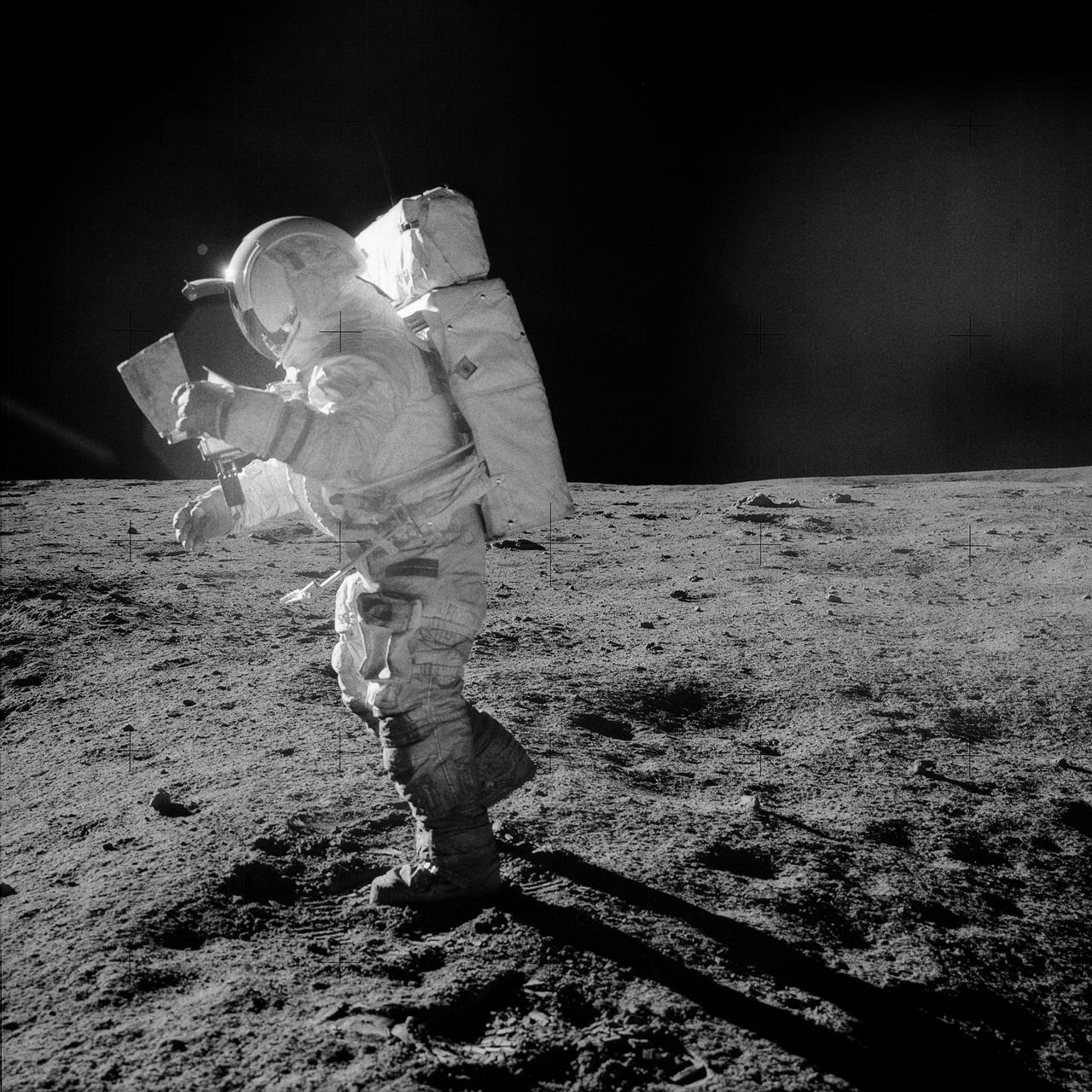

AS14-64-9089 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, moves across the lunar surface as he looks over a traverse map during an extravehicular activity (EVA). Lunar dust can be seen clinging to the boots and legs of the space suit. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Mitchell explored the lunar surface while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, orbited the moon in the Command and Service Modules (CSM).
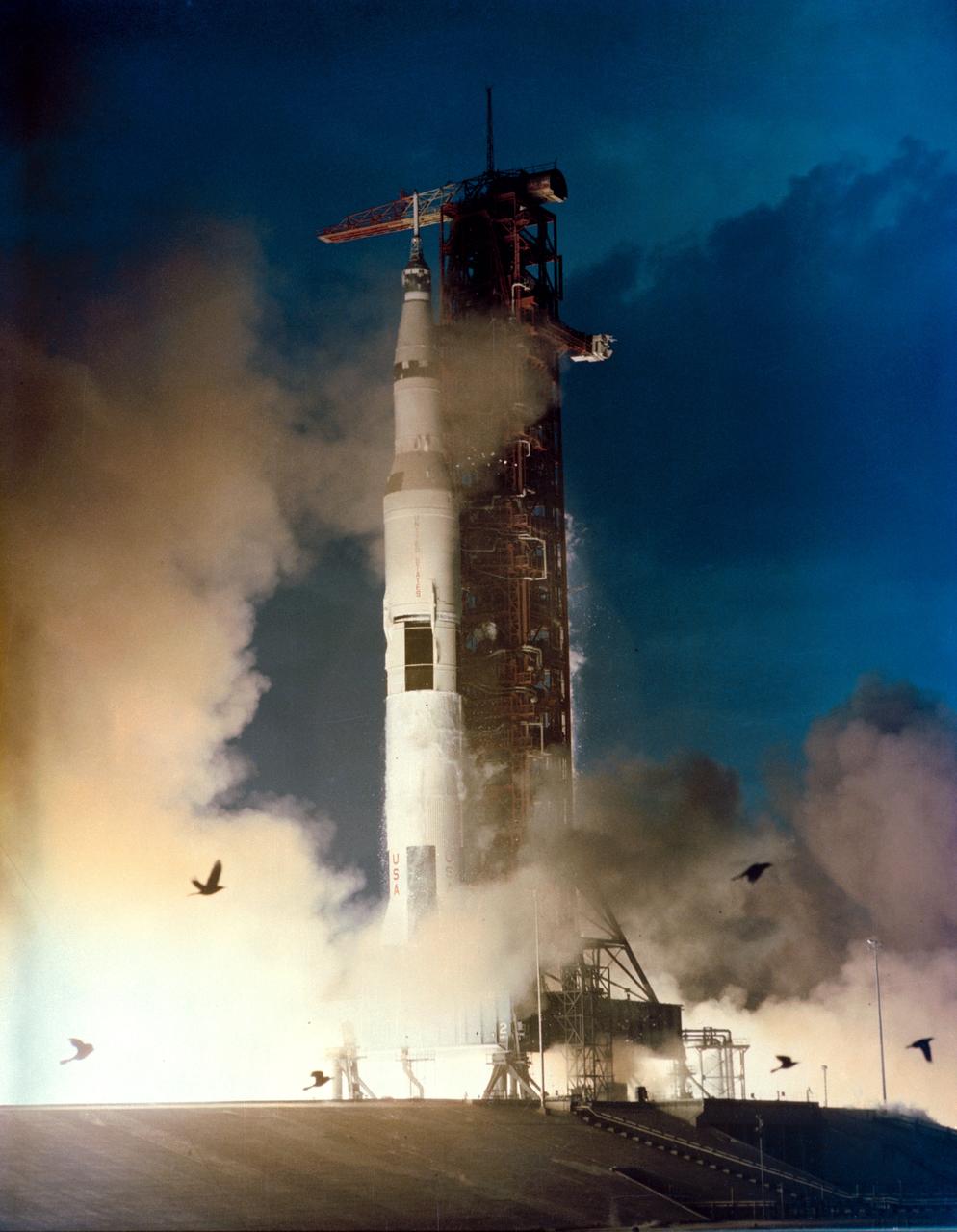

S71-18395 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
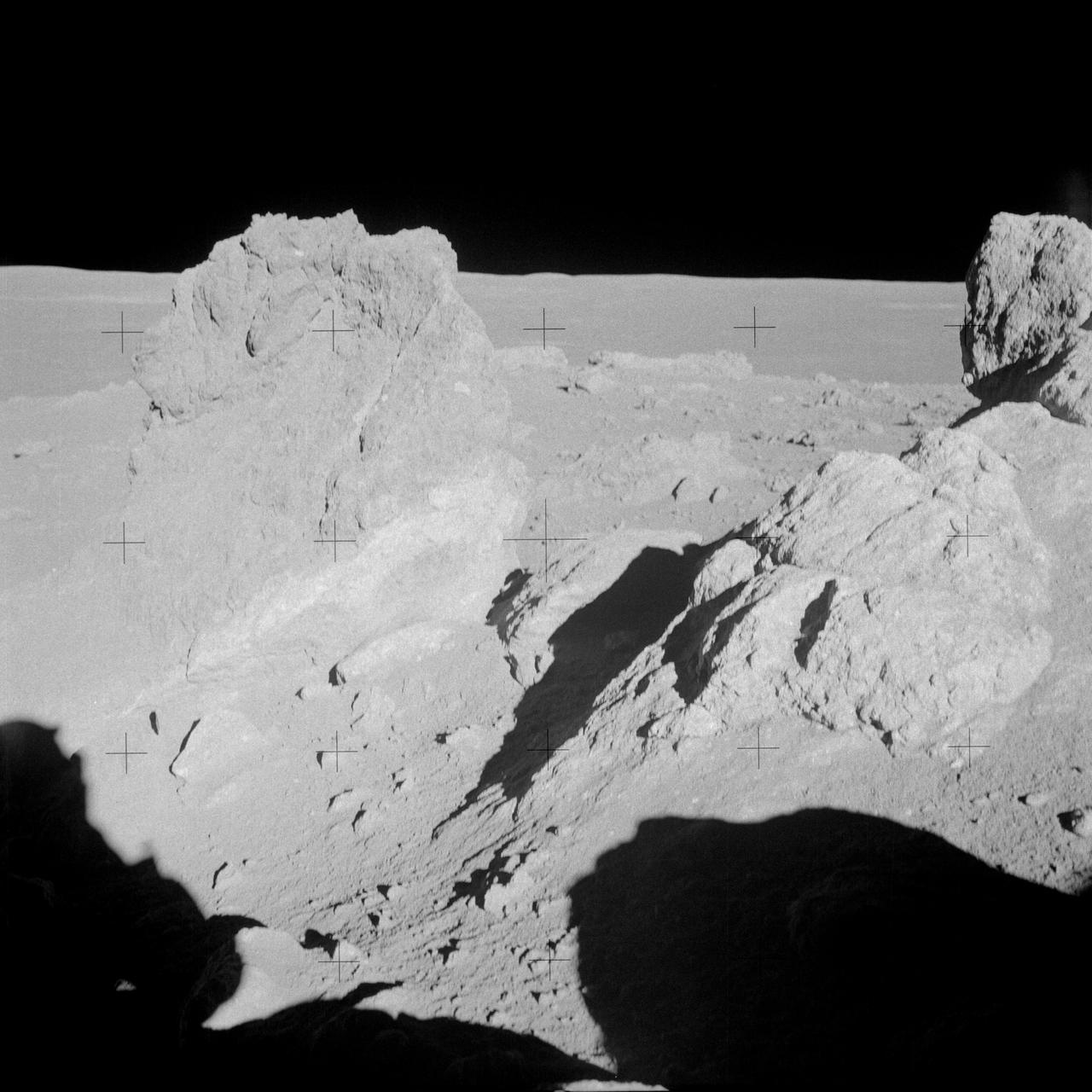

AS14-68-9449 (6 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of a group of large boulders near the rim of Cone Crater photographed by the Apollo 14 astronauts during their second extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS14-66-9278 (5 Feb. 1971) --- An excellent view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) on the moon, as photographed during the first Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
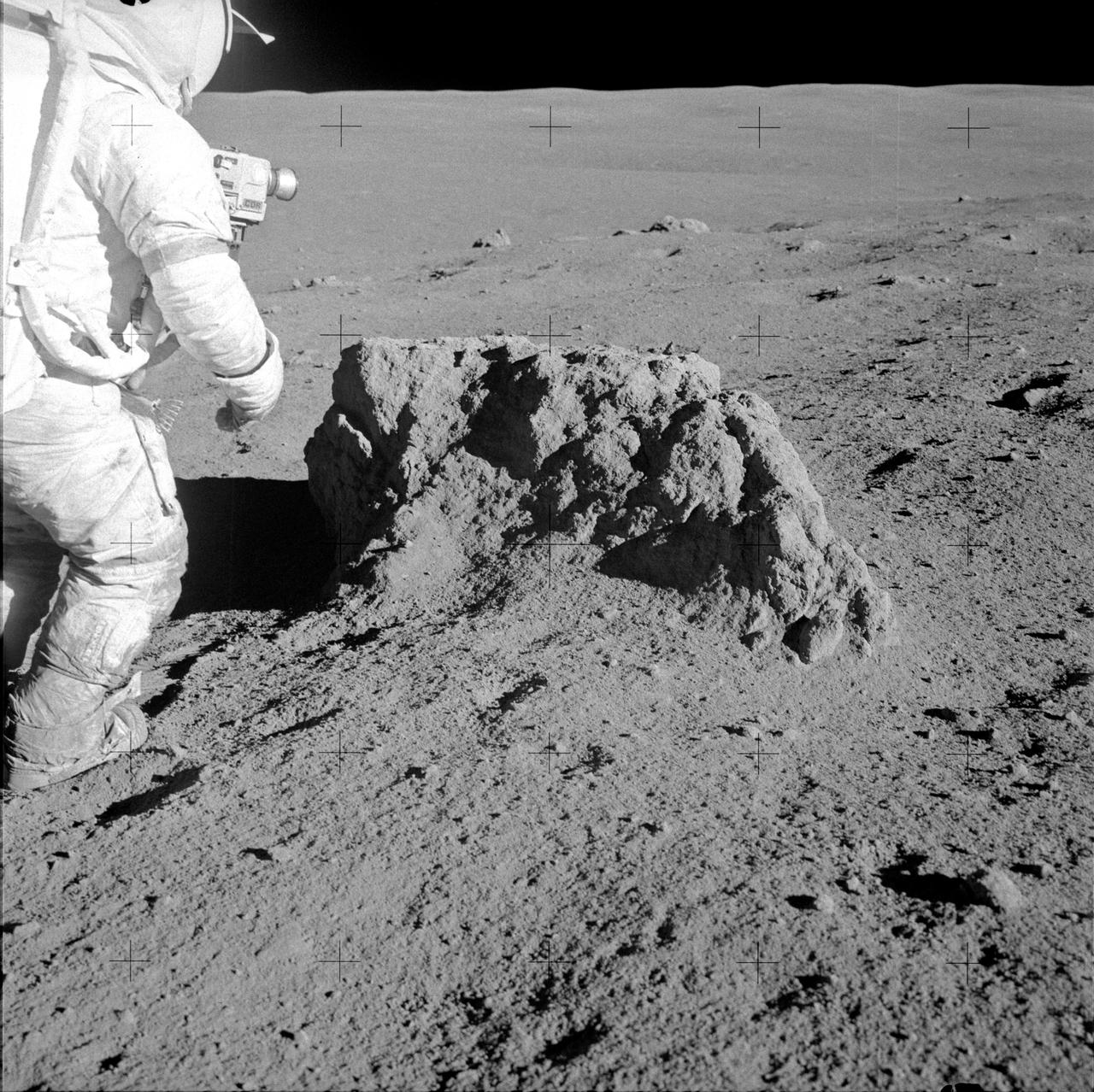

AS14-68-9414 (6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., Apollo 14 commander, stands beside a large boulder on the lunar surface during the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA), on Feb. 6, 1971. Note the lunar dust clinging to Shepard's space suit. Astronauts Shepard and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, explored the lunar surface while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, orbited the moon in the Command and Service Modules (CSM).
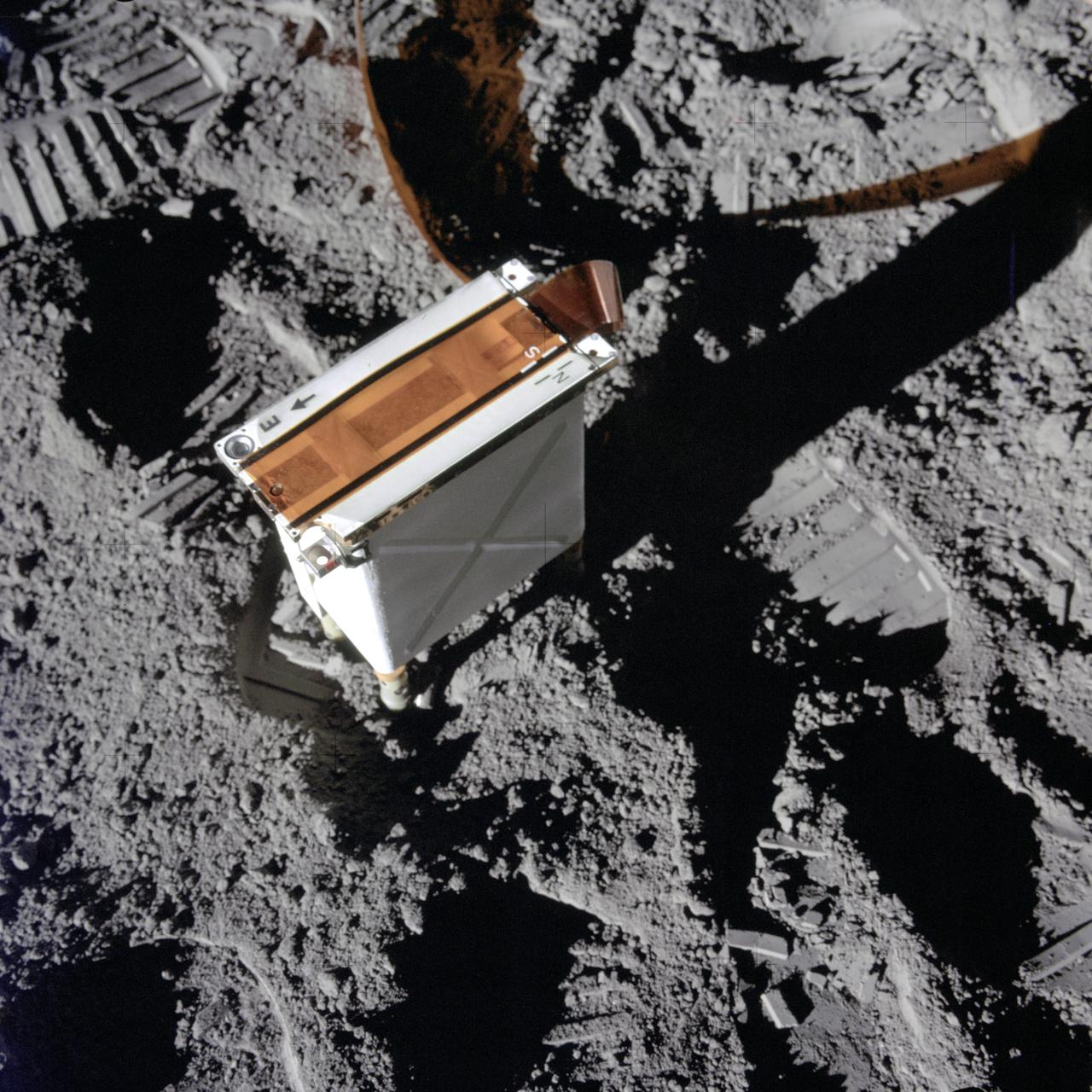

AS14-67-9364 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the charged particle lunar environment experiment (CPLEE), a component of the Apollo lunar surface experiments package (ALSEP) which was deployed on the moon by the Apollo 14 astronauts. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
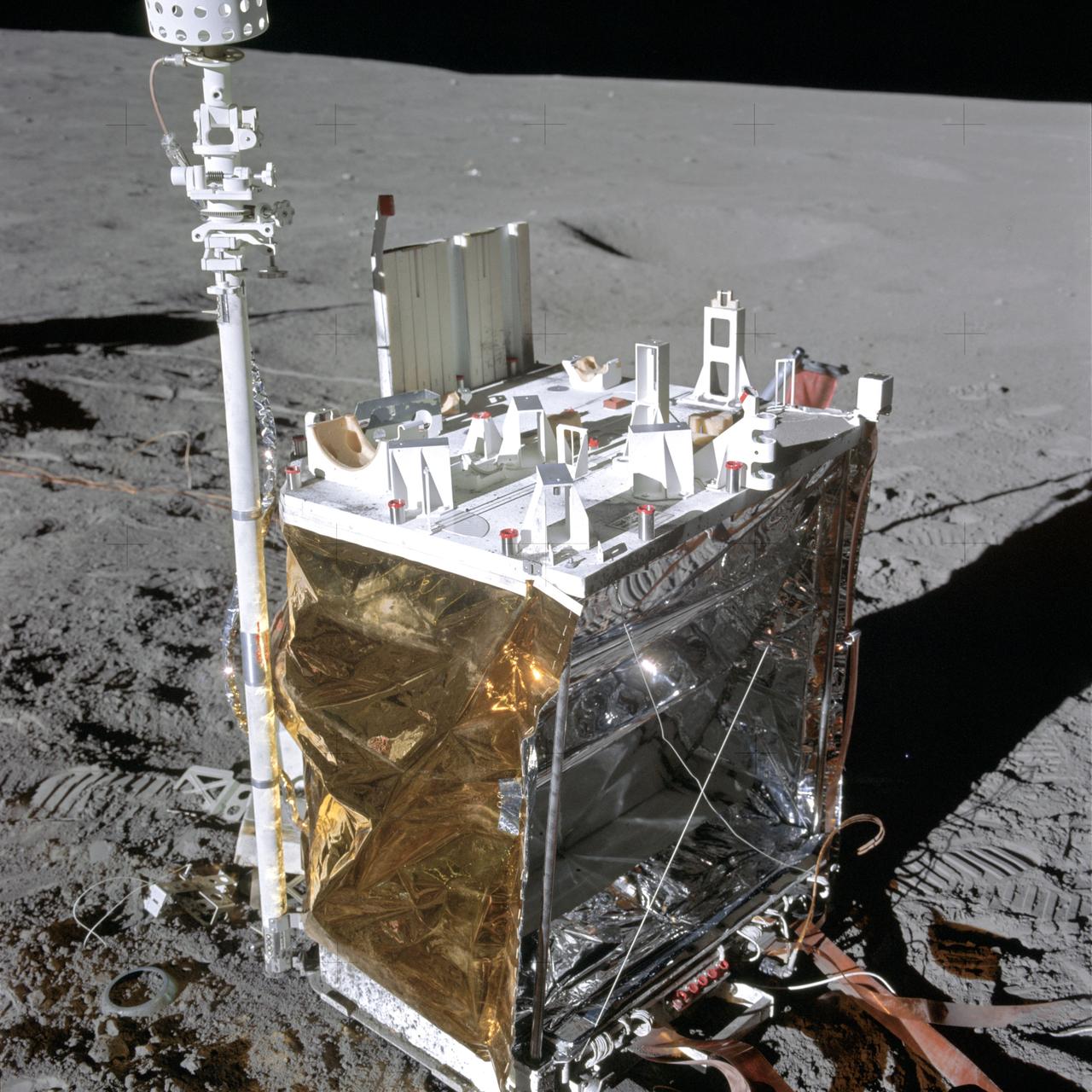
AS14-67-9379 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the central station (CS) of the Apollo lunar surface experiments package (ALSEP), which was deployed on the moon by the Apollo 14 astronauts during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
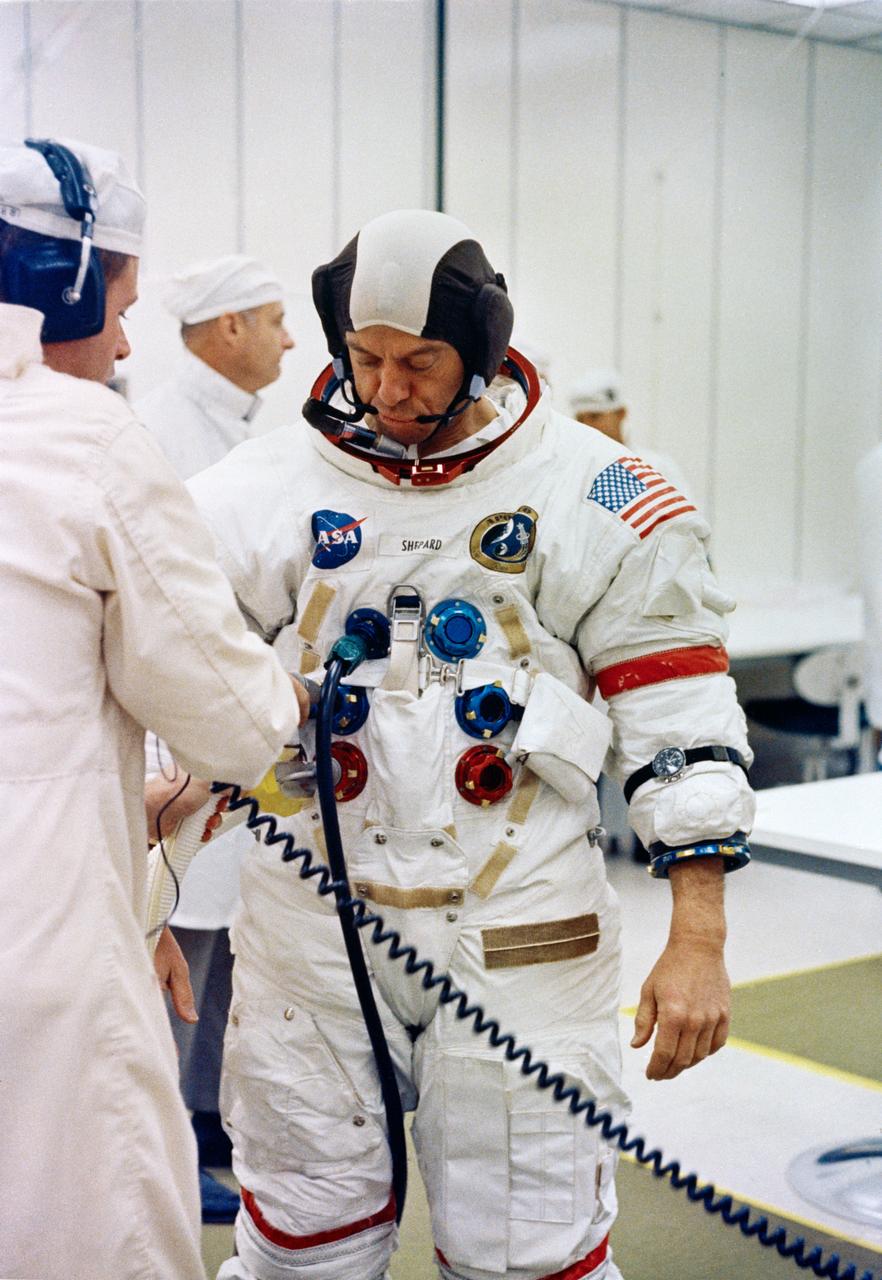

S71-16638 (31 Jan. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, undergoes suiting up operations at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) during the Apollo 14 prelaunch countdown. Apollo 14, with astronauts Shepard; Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; and Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; aboard was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39 at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971.
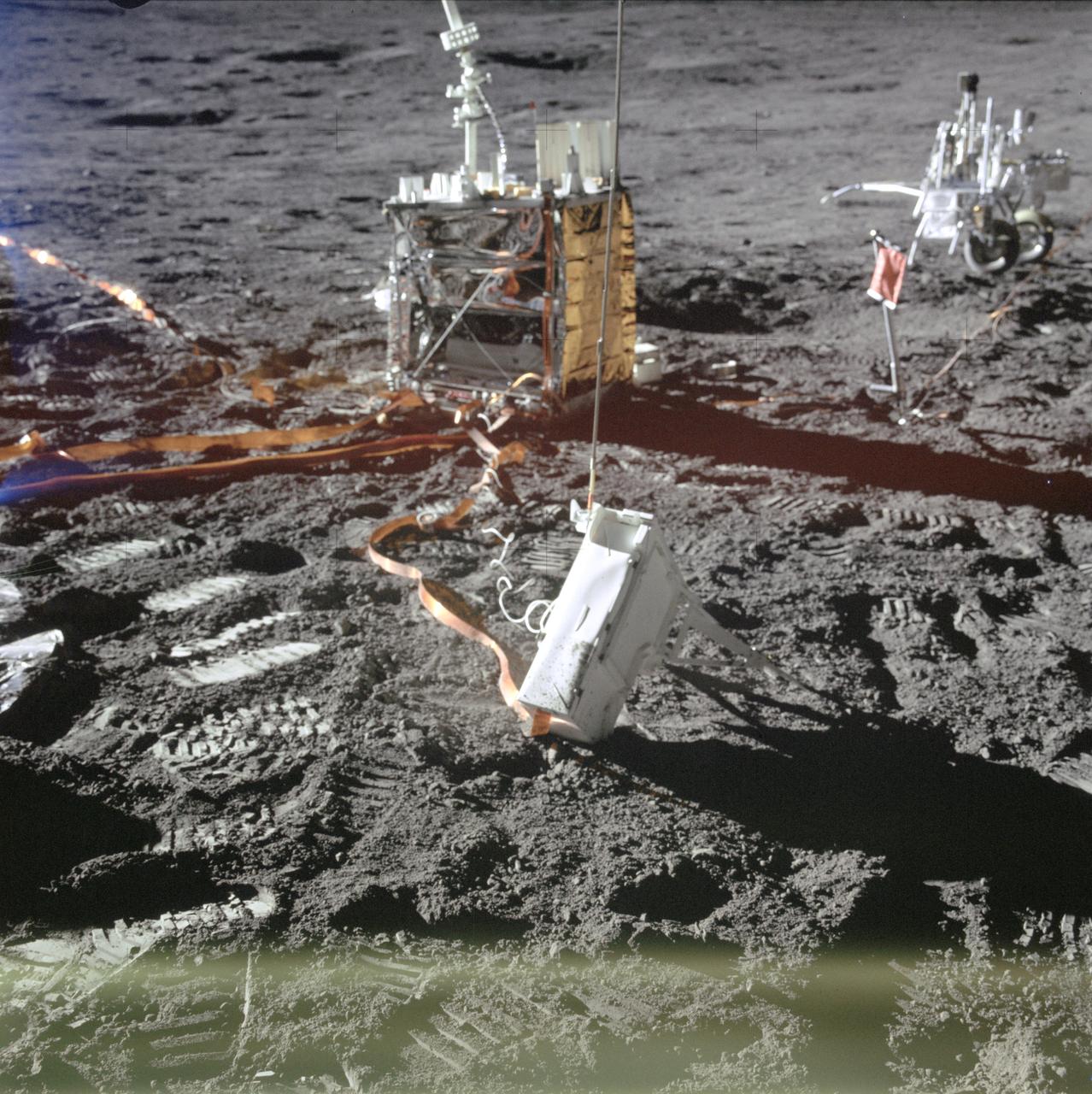
AS14-67-9361 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of two components of the Apollo lunar surface experiments package (ALSEP) which the Apollo 14 astronauts deployed on the moon during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). In the center background is the ALSEP's central station (CS); and in the foreground is the mortar package assembly of the ALSEP's active seismic experiment (ASE). The modularized equipment transporter (MET) can be seen in the right background. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
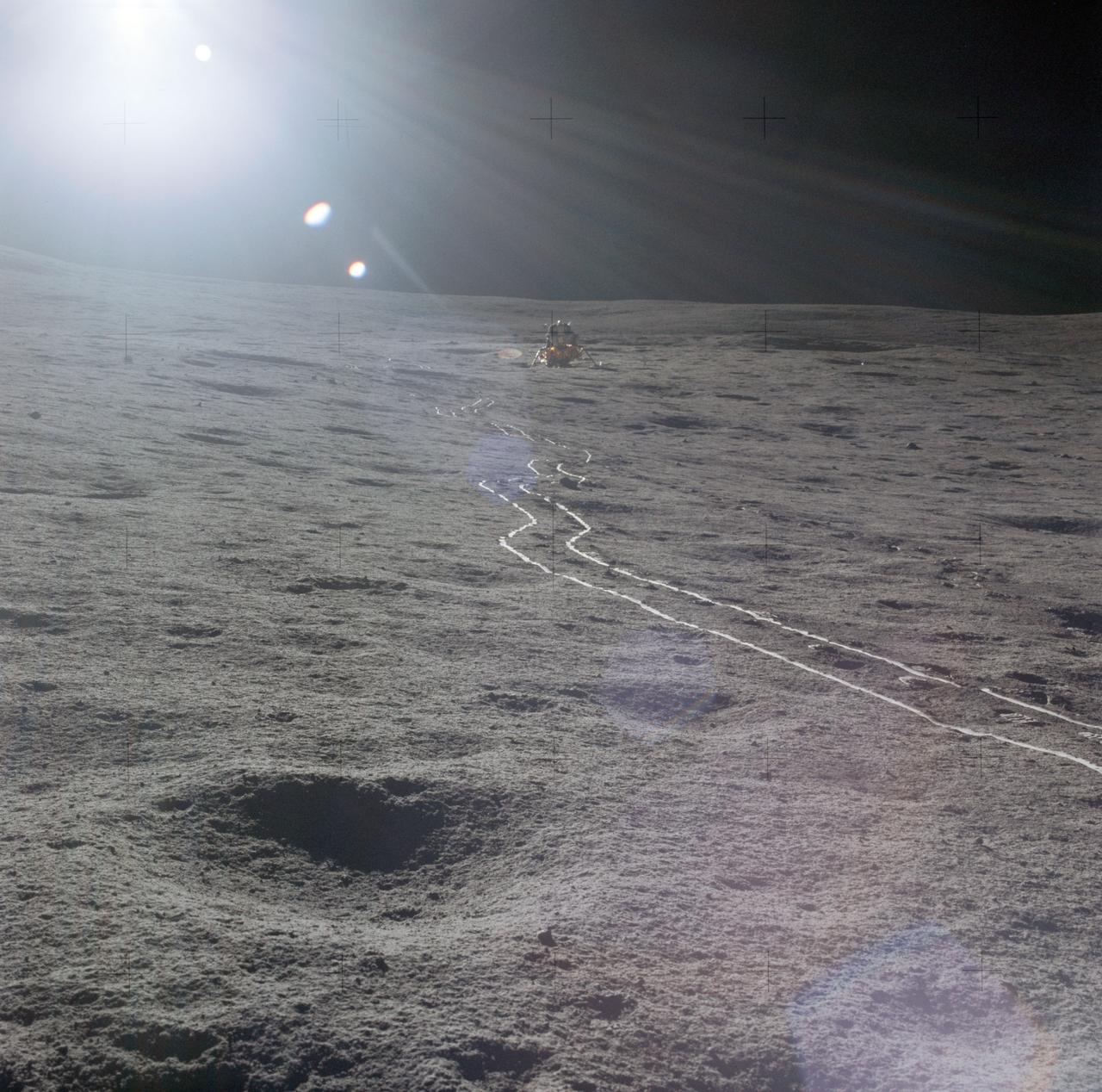

AS14-67-9367 (5 Feb. 1971) --- The Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) as seen by the two moon-exploring crewmen of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, photographed against a brilliant sun glare during the first extravehicular activity (EVA). A bright trail left in the lunar soil by the two-wheeled modularized equipment transporter (MET) leads from the LM. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, were exploring the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, was maneuvering the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
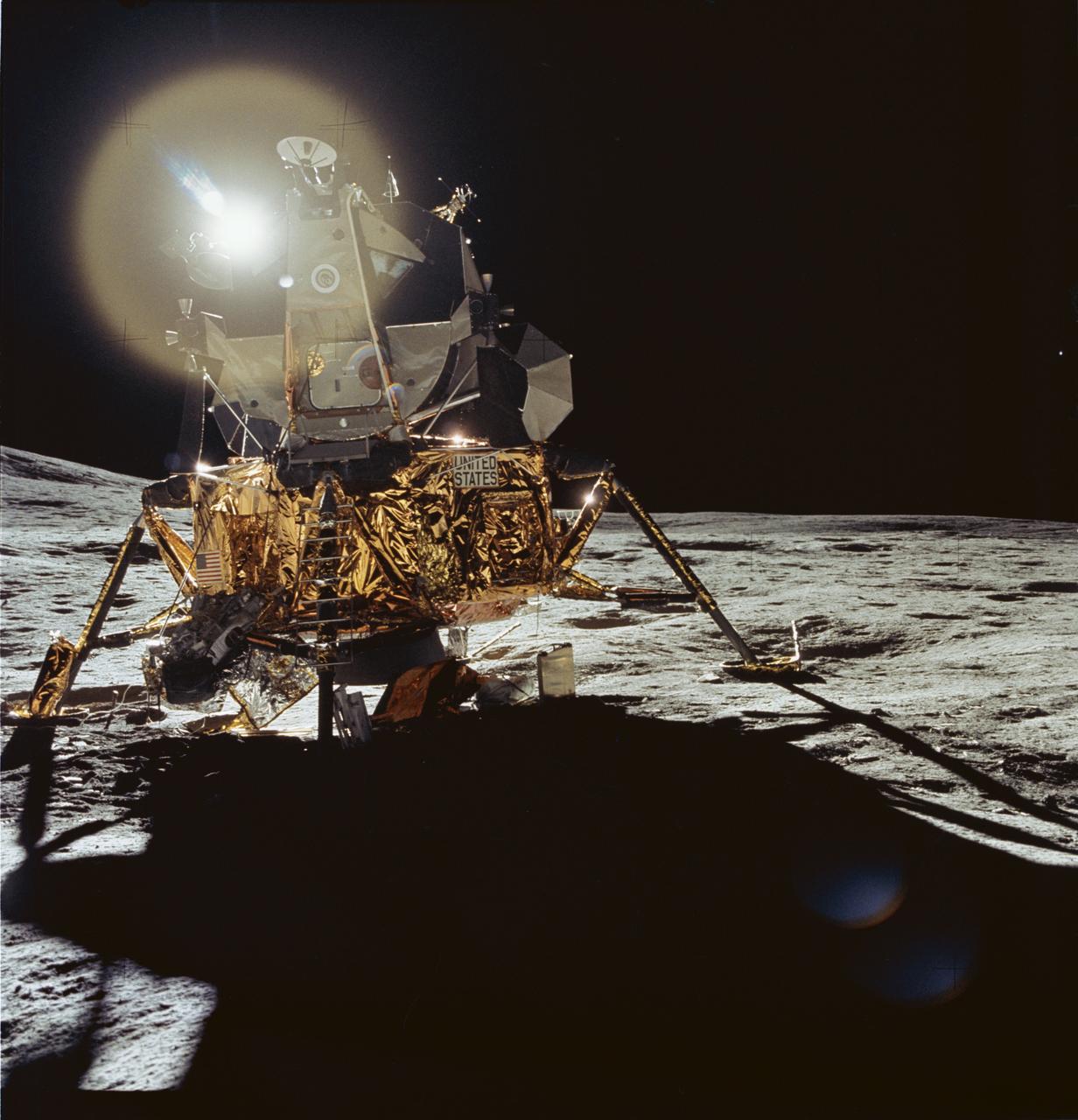

AS14-66-9306 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A front view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM), which reflects a circular flare caused by the brilliant sun, as seen by the two moon-exploring crew men of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). The unusual ball of light was said by the astronauts to have a jewel-like appearance. At the extreme left the lower slope of Cone Crater can be seen. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
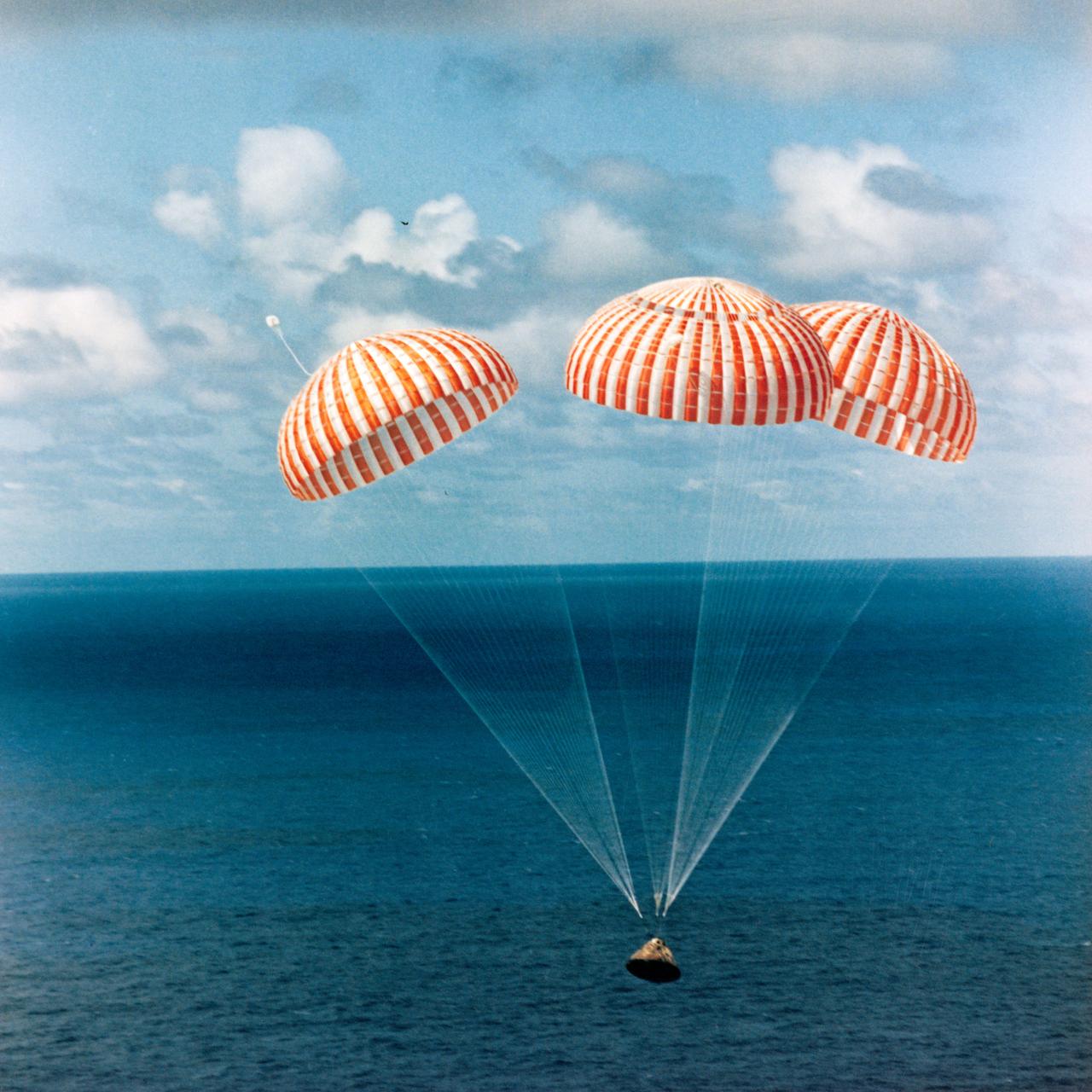

S71-18753 (9 Feb. 1971) --- The Apollo 14 Command Module (CM), with astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, aboard, approaches touchdown in the South Pacific Ocean to successfully end a 10-day lunar landing mission. The splashdown occurred at 3:04:39 p.m. (CST), Feb. 9, 1971, approximately 765 nautical miles south of American Samoa. The three crew men were flown by helicopter to the USS New Orleans prime recovery ship.
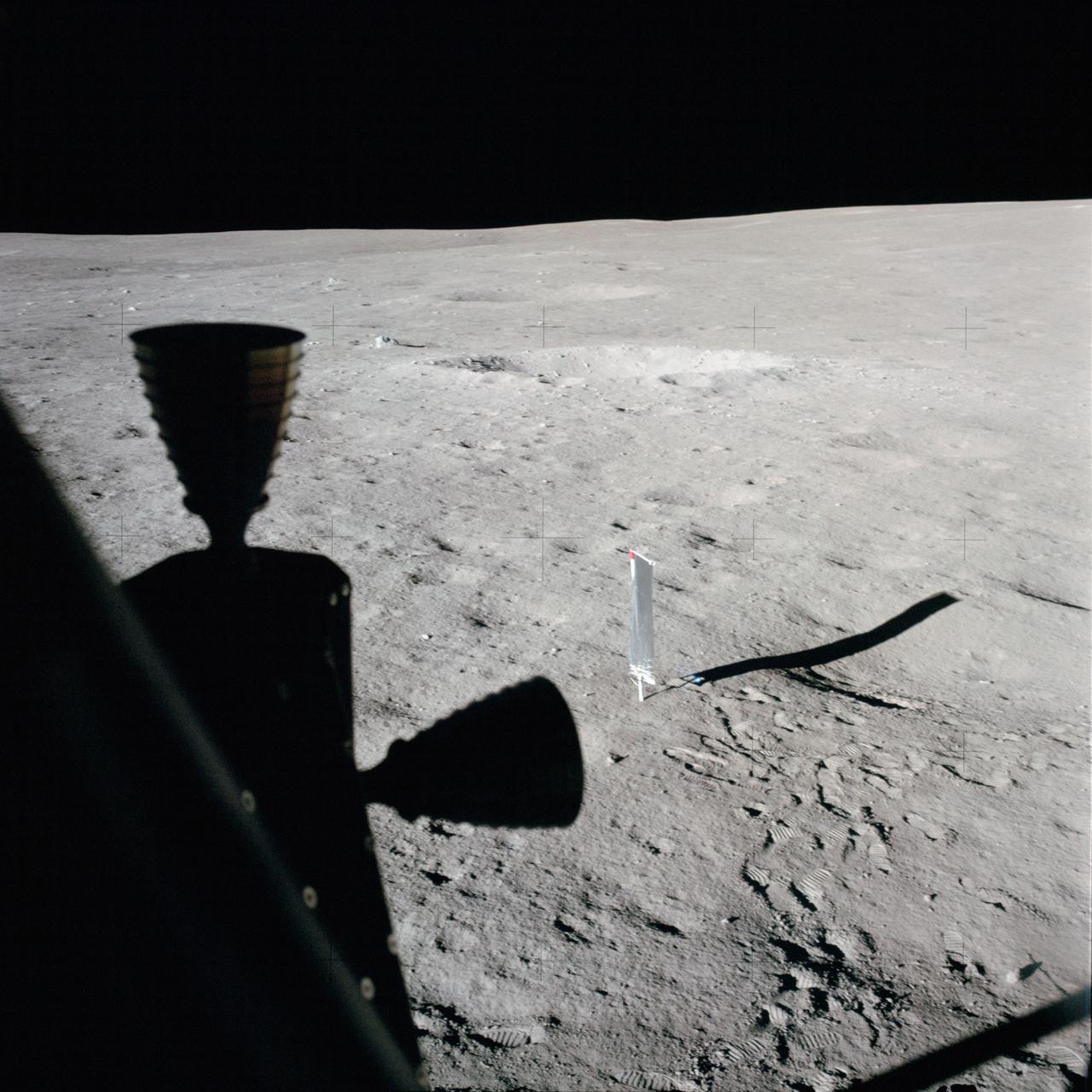

AS14-66-9322 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- This photograph taken through a window of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM), on the moon, shows an excellent view of the nearby terrain. In the center background is the deployed solar wind composition (SWC) experiment. Two LM RCS thrusters are silhouetted in the left foreground. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

S71-16637 (January 1971) --- A close-up view of the plaque which the Apollo 14 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Antares". Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The seven by nine inch stainless steel plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the LM's descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 astronauts.
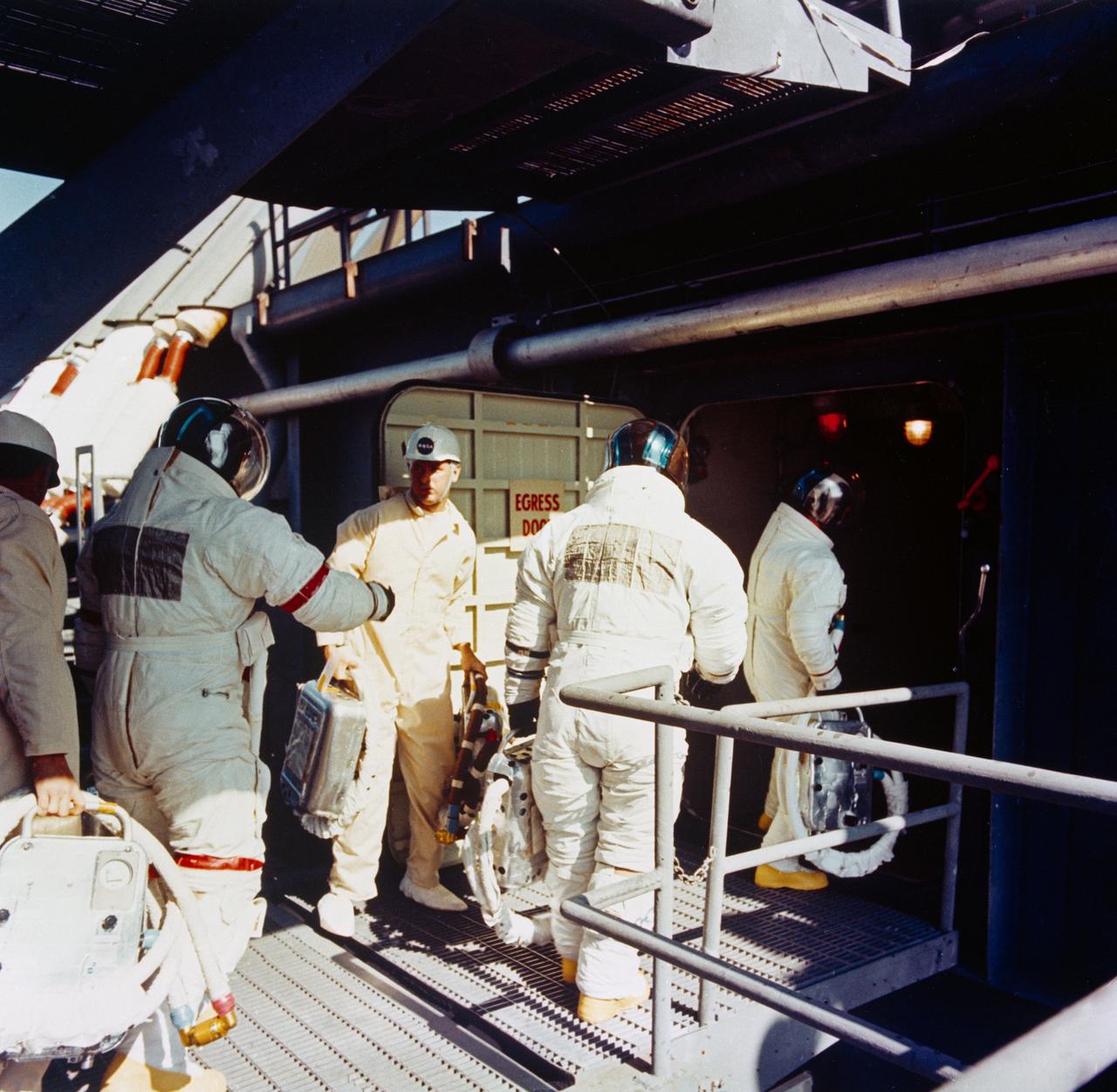

S71-16635 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The three Apollo 14 astronauts arrive at the White Room atop Pad A, Launch Complex 39, during the Apollo 14 prelaunch countdown. Apollo 14, with Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, aboard was launched at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Note identifying bands on the sleeve and leg of Shepard. Standing in the center foreground is astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, chief of the MSC Astronaut Office.

S71-18557 (9 Feb. 1971) --- Sealed inside a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF), Apollo 14 astronauts greet newsmen and crew men aboard the USS New Orleans, Apollo 14 prime recovery ship. They are from left to right, astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot. Apollo 14 splashdown occurred at 3:04:39 p.m. (CST), Feb. 9, 1971, in the South Pacific Ocean, approximately 765 nautical miles from American Samoa.
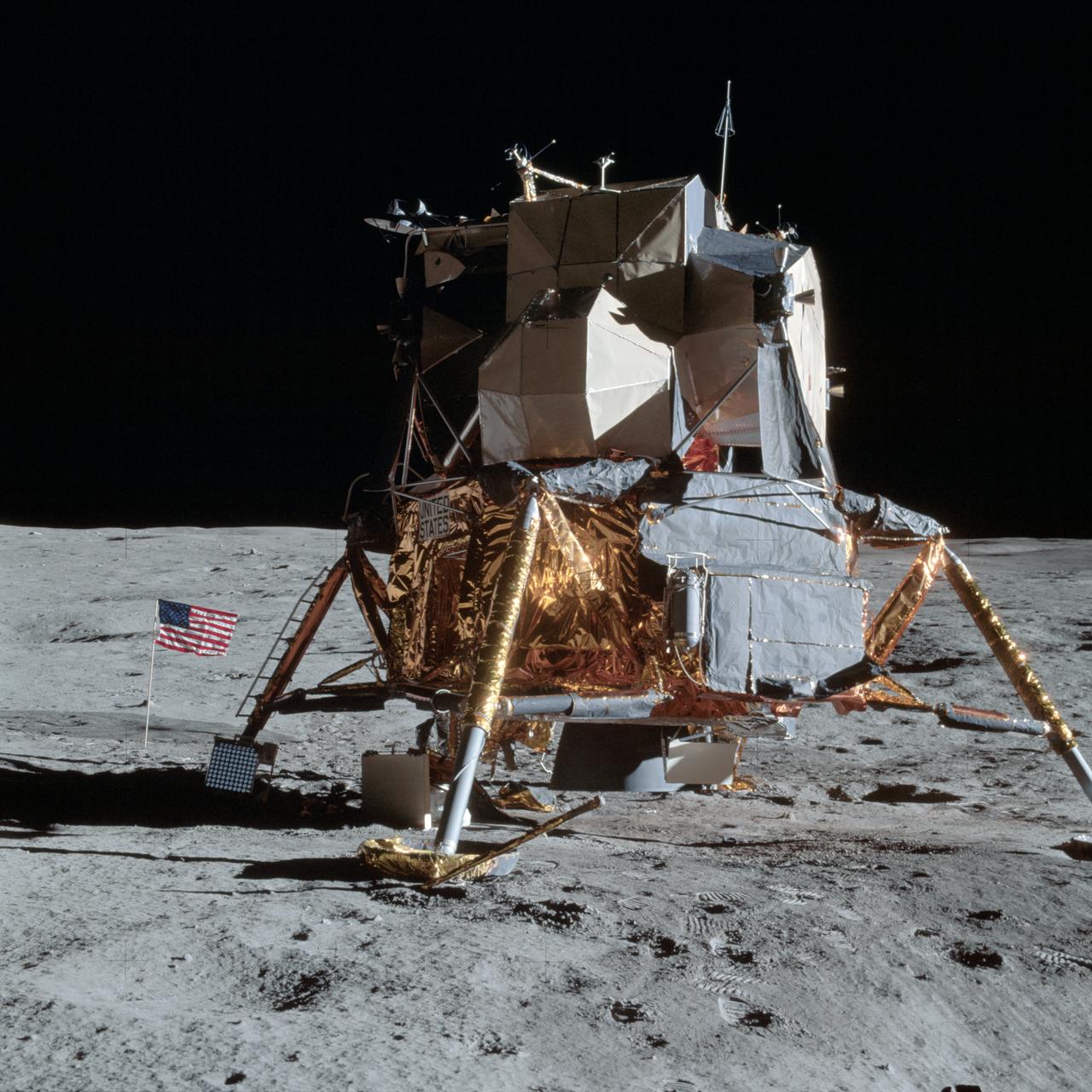
AS14-66-9277 (5 Feb. 1971) --- An excellent view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) on the moon, as photographed during the first Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The astronauts have already deployed the U.S. flag. Note the laser ranging retro reflector (LR-3) at the foot of the LM ladder. The LR-3 was deployed later. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
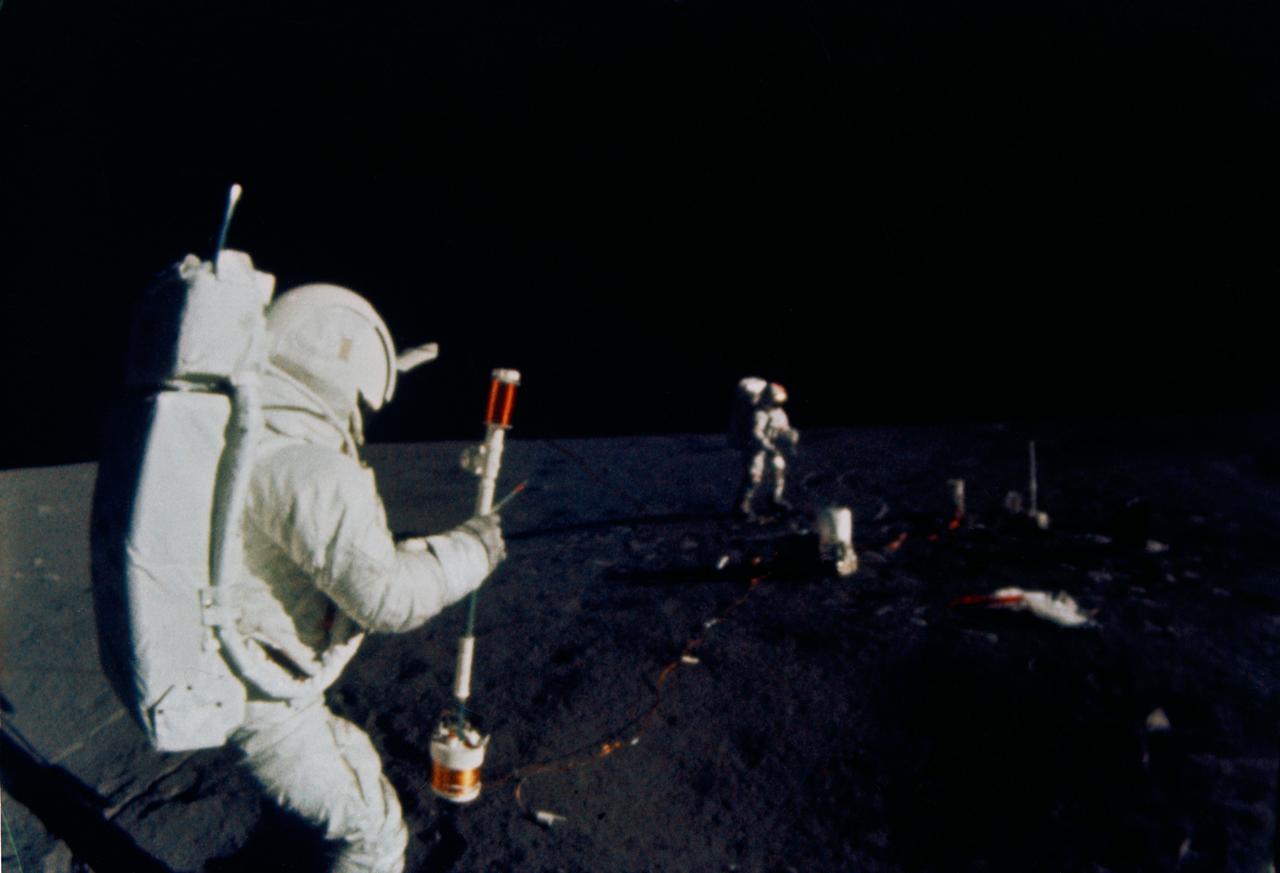

S71-19509 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, operates the Active Seismic Experiment's (ASE) thumper during the first Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, walks near deployed components of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) in the background. This photograph was taken by an automatic 16mm camera mounted on the Apollo lunar hand tool carrier aboard the Modularized Equipment Transporter (MET). While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
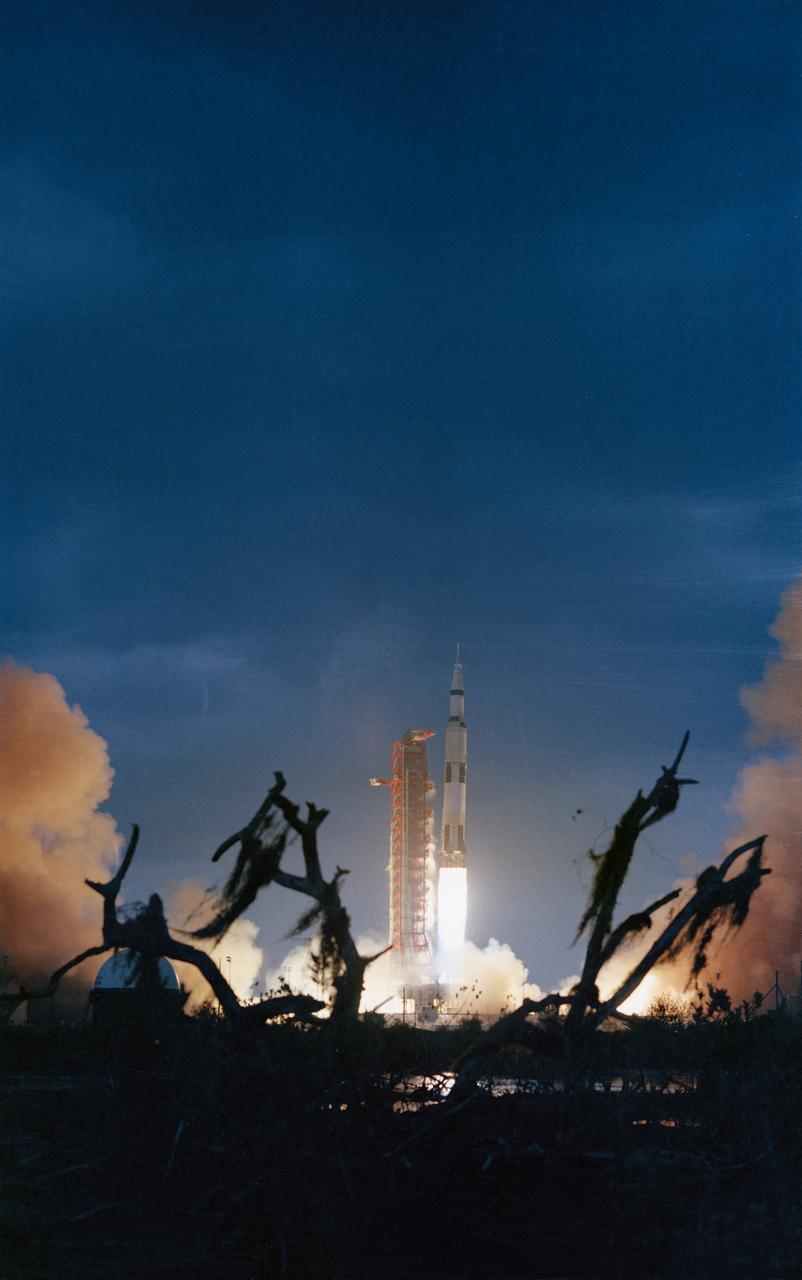

S71-18399 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. This view is framed by moss-covered dead trees in the dark foreground. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
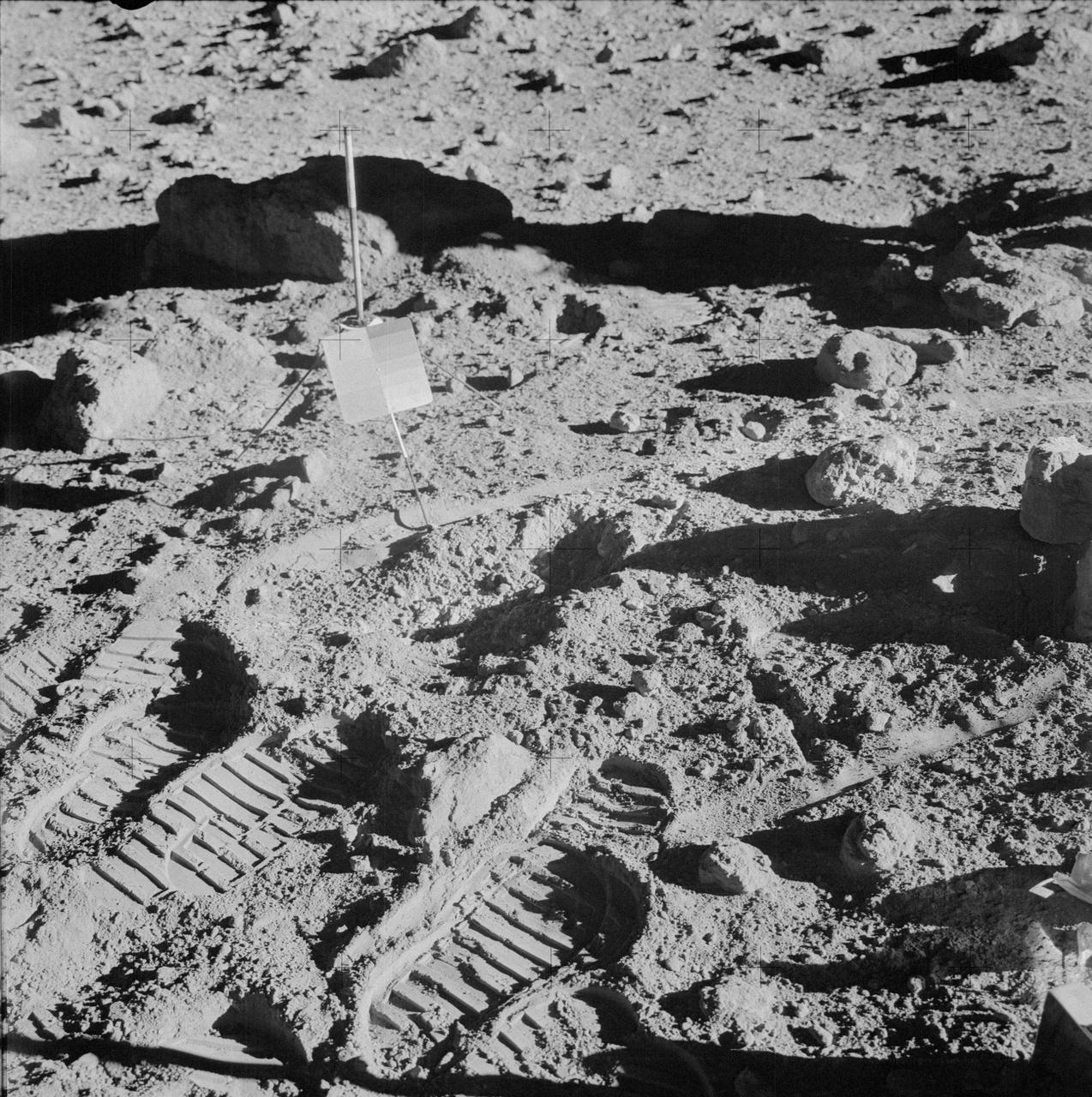

AS14-64-9127 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of lunar soil, showing bootprints made by the Apollo 14 astronauts during extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. Also visible are tracks made by the modularized equipment transporter (MET) and deployed gnomon. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
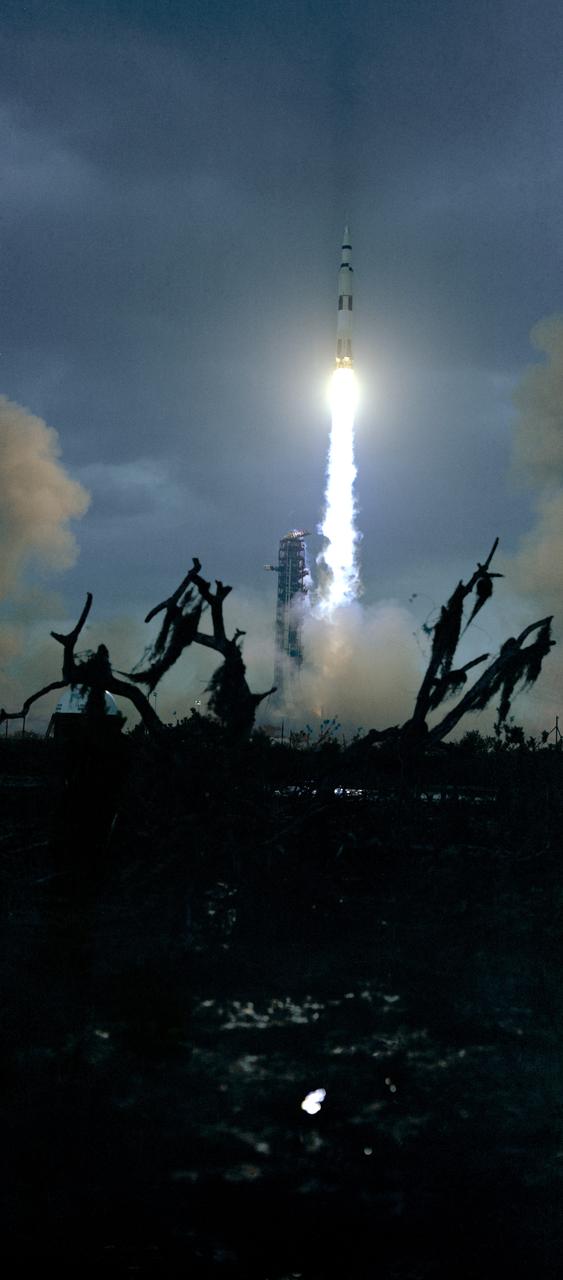

S71-18398 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. This view is framed by moss-covered dead trees in the dark foreground. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
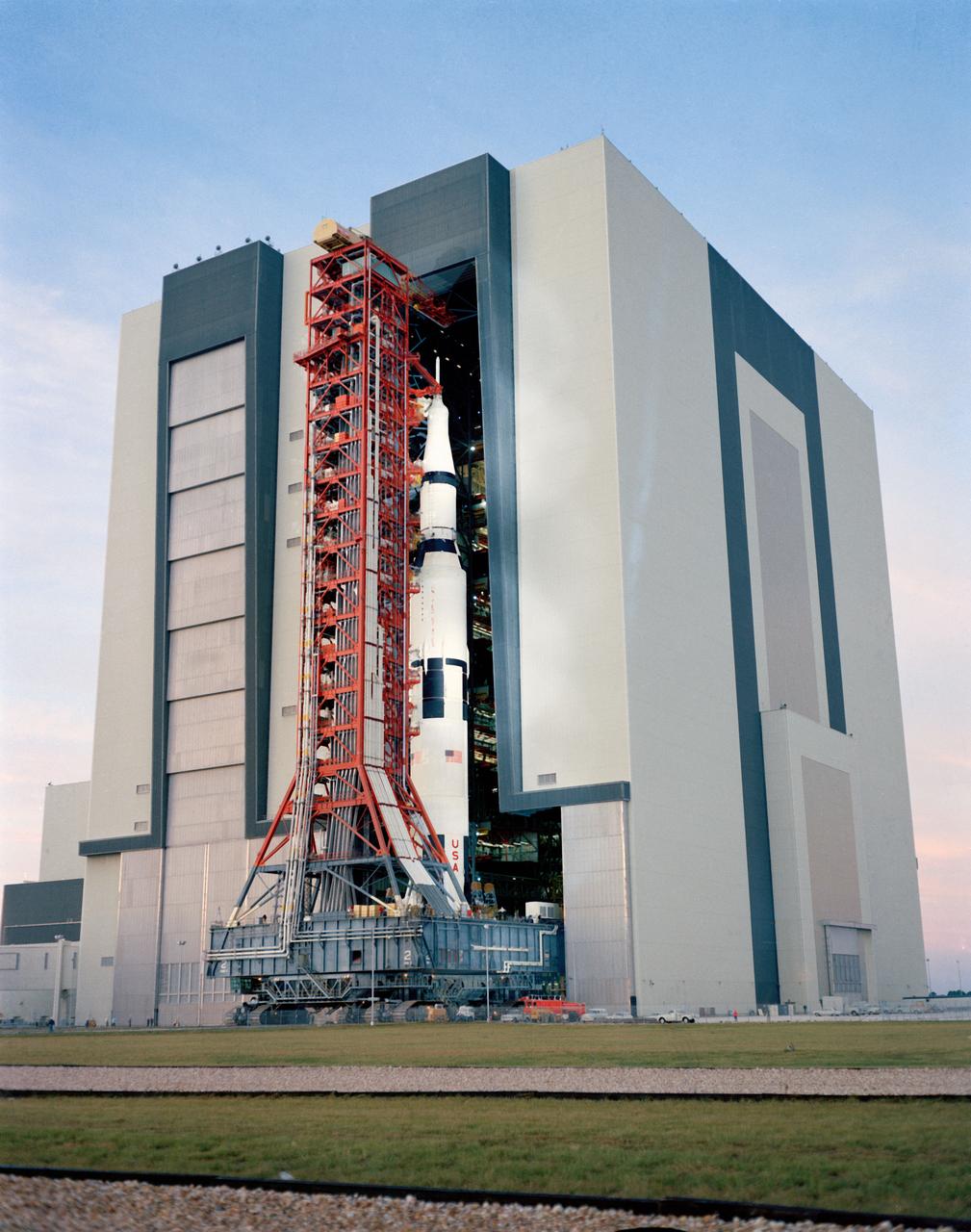

S70-54121 (9 Nov. 1970) --- A ground level view at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), showing the Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle leaving the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower, atop a huge crawler-transporter, were rolled out to Pad A. The Apollo 14 crewmen will be astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
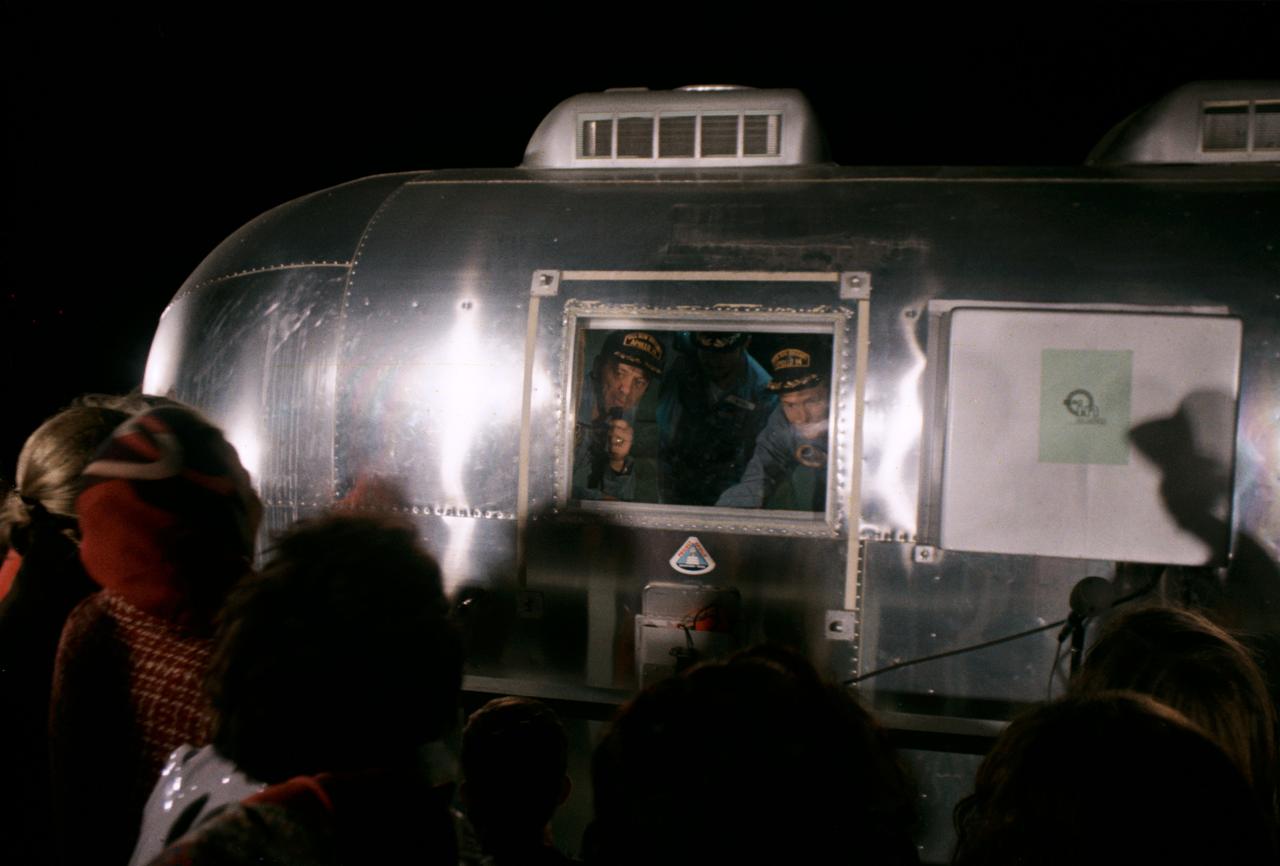

S71-19508 (12 Feb. 1971) --- Separated by aluminum and glass of their Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF), the Apollo 14 crew members visit with their families and friends upon arriving at Ellington Air Force Base in the early morning hours of Feb. 12, 1971. Looking through the MQF window are astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr. (left), commander; Stuart A. Roosa (right), command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot. The crew men were brought to Houston aboard a C-141 transport plane from Pago Pago, American Samoa. The USS New Orleans had transported the crew to American Samoa from the recovery site in the South Pacific.
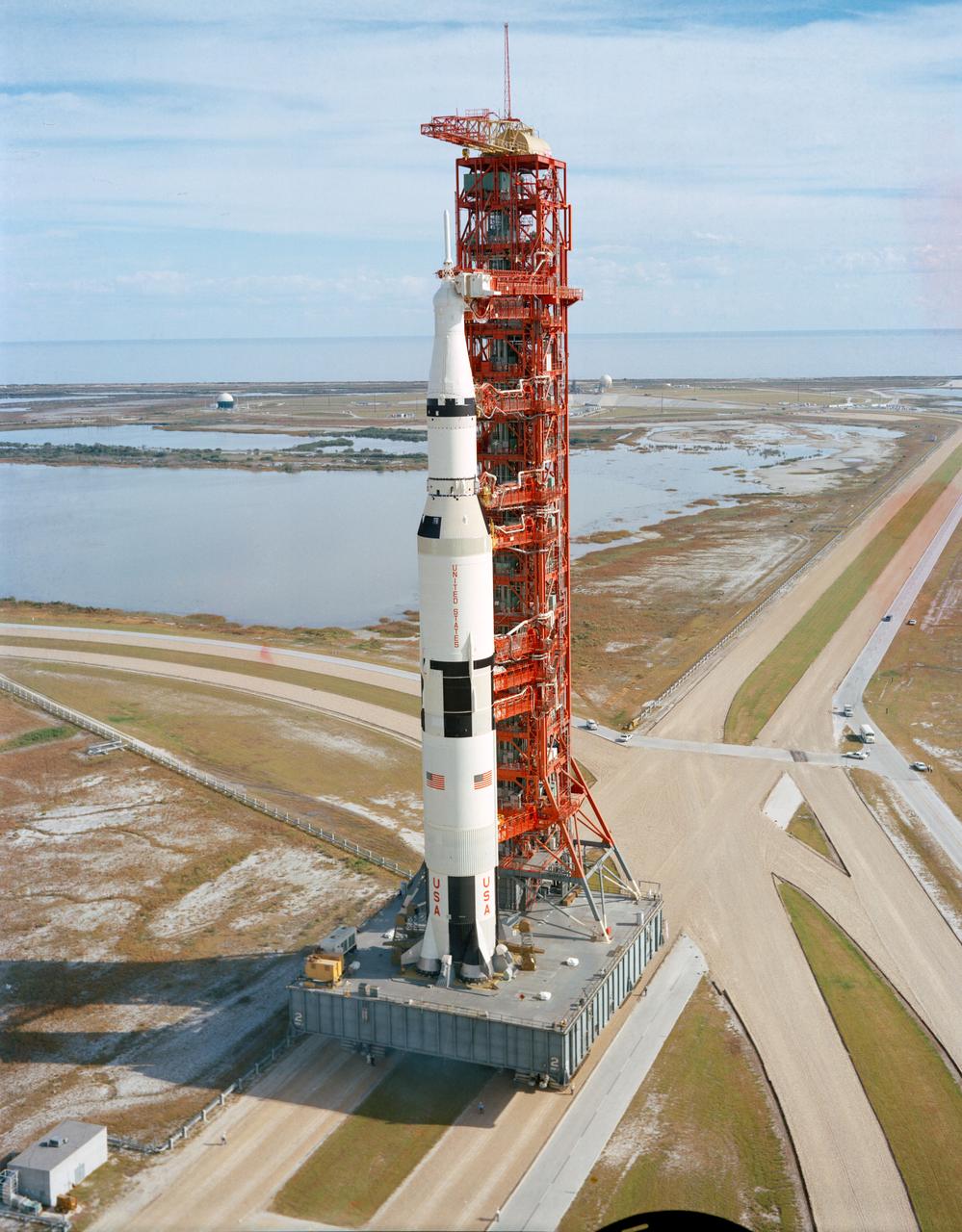

S70-54127 (9 Nov. 1970) --- A high-angle view at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), showing the Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle on the way from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to Pad A. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower sit atop a huge crawler-transporter. The Apollo 14 crewmen will be astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
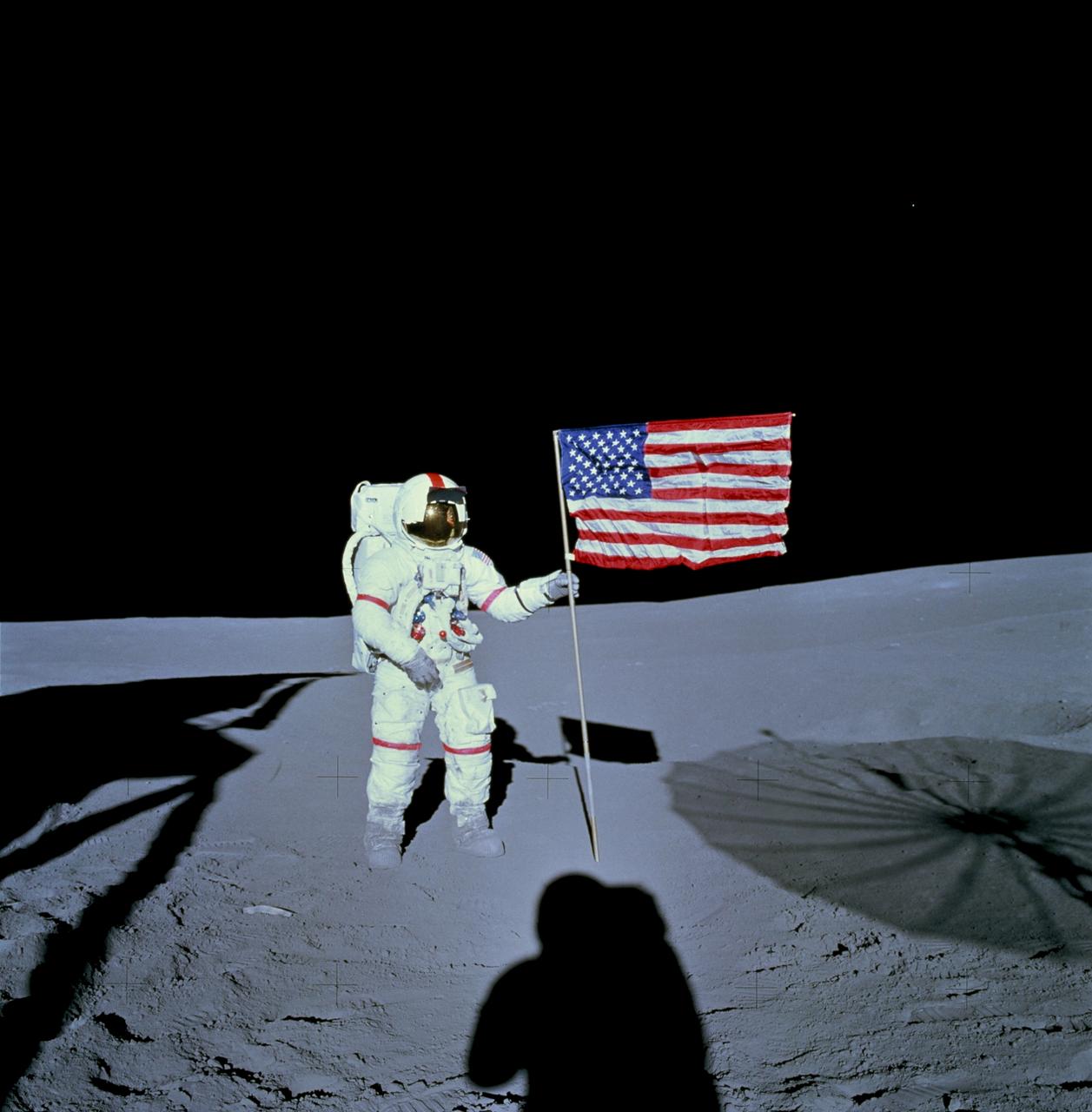

AS14-66-9232 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, stands by the deployed United States flag on the lunar surface during the early moments of the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the mission. Shadows of the Lunar Module (LM), astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, and the erectable S-Band Antenna surround the scene of the third flag implanting to be performed on the lunar surface. While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the LM ?Antares? to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) ?Kitty Hawk? in lunar orbit.
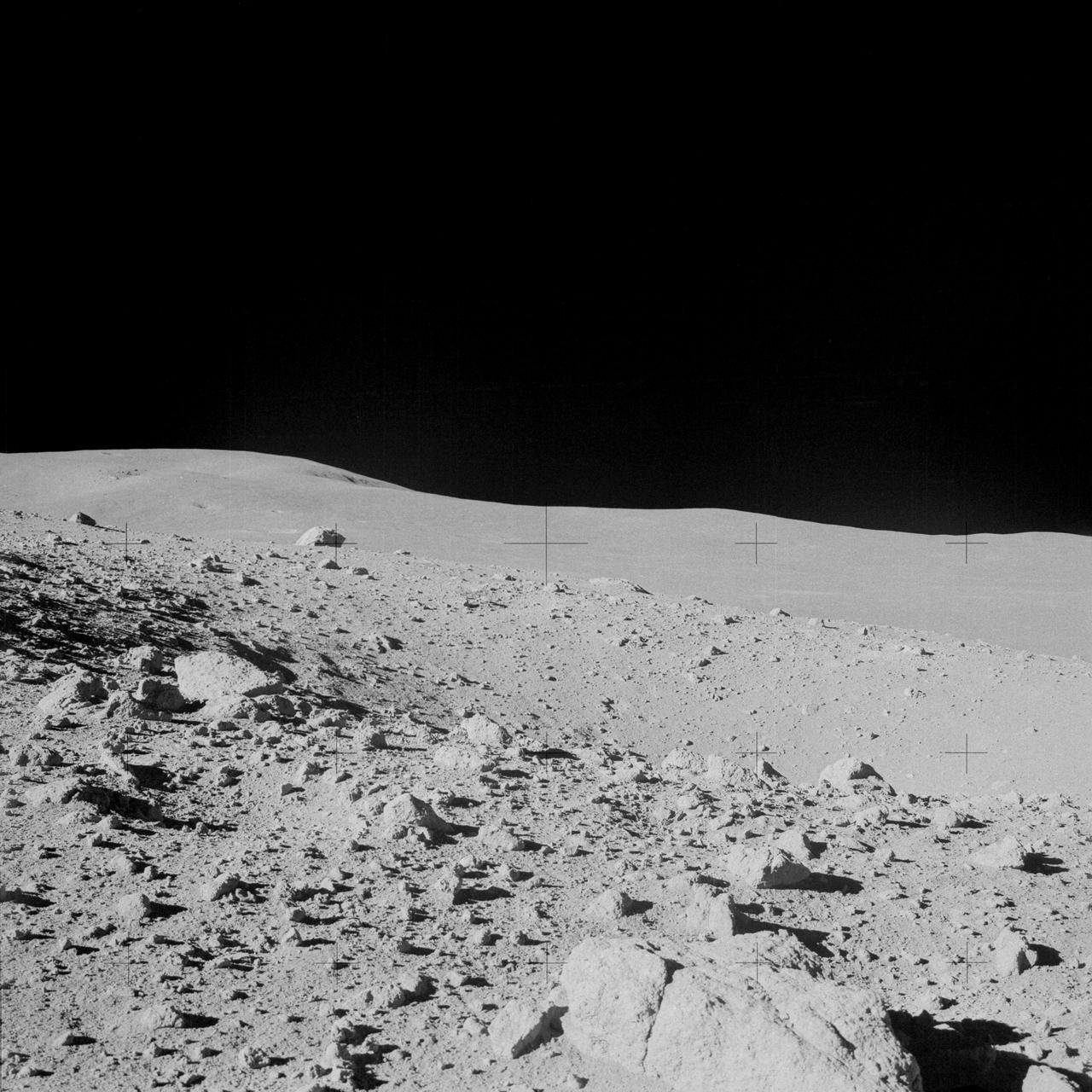

AS14-64-9118 (6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, photographed this overall view of a field of boulders on the flank of Cone Crater, during the second extravehicular activity (EVA), on Feb. 6, 1971. The view is looking south across the lunar valley through which the Apollo 14 moon-explorers flew their Lunar Module (LM) during the final approach to the landing. Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, joined Shepard in exploring the moon, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
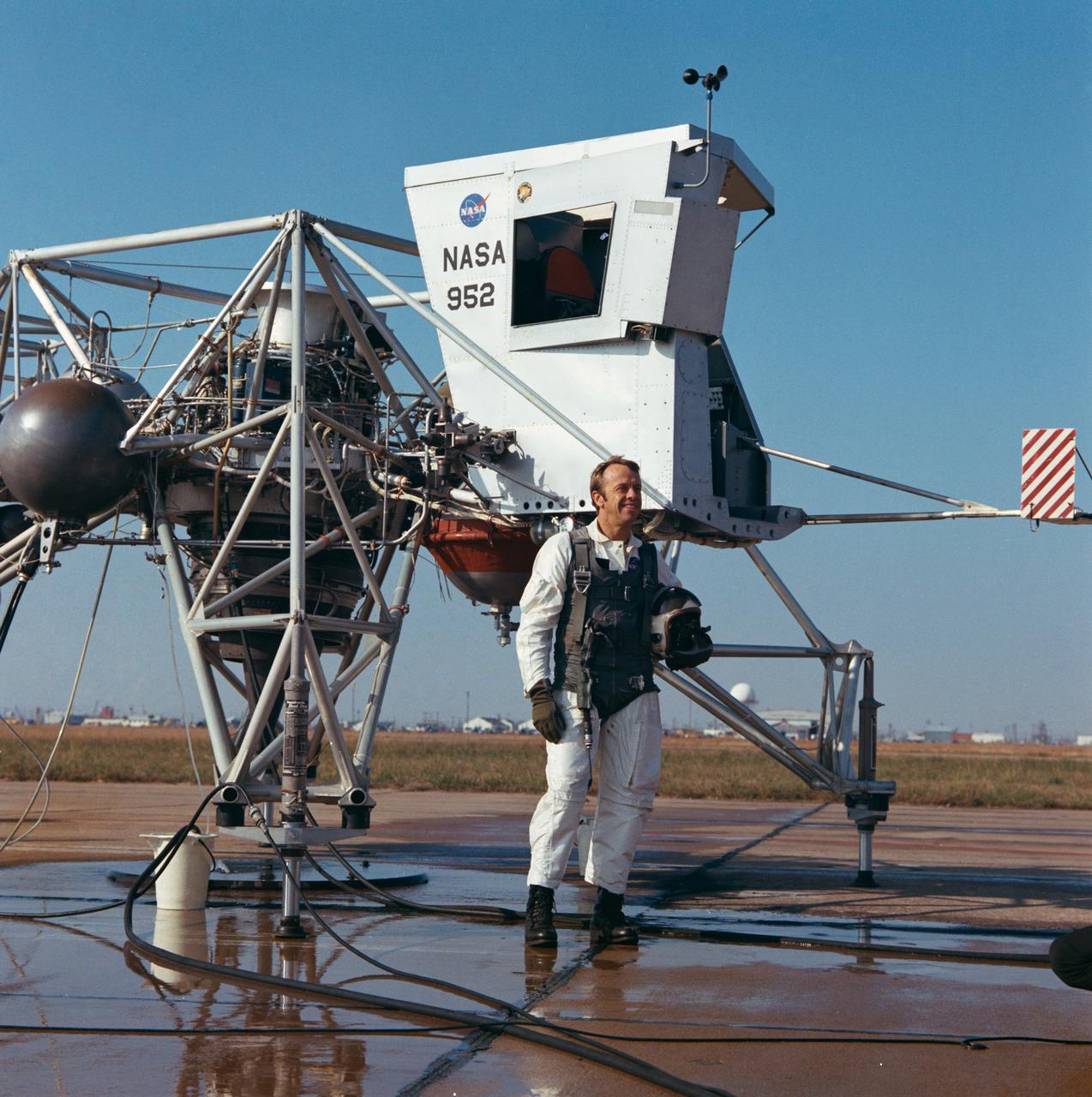

S70-56287 (14 Dec. 1970) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, stands near a Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV) prior to a test flight at Ellington Air Force Base, Houston, on Dec. 14, 1970. Shepard will be at the controls of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) when it lands on the moon in the highlands near Fra Mauro. Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Shepard and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descend in the LM to explore the moon.
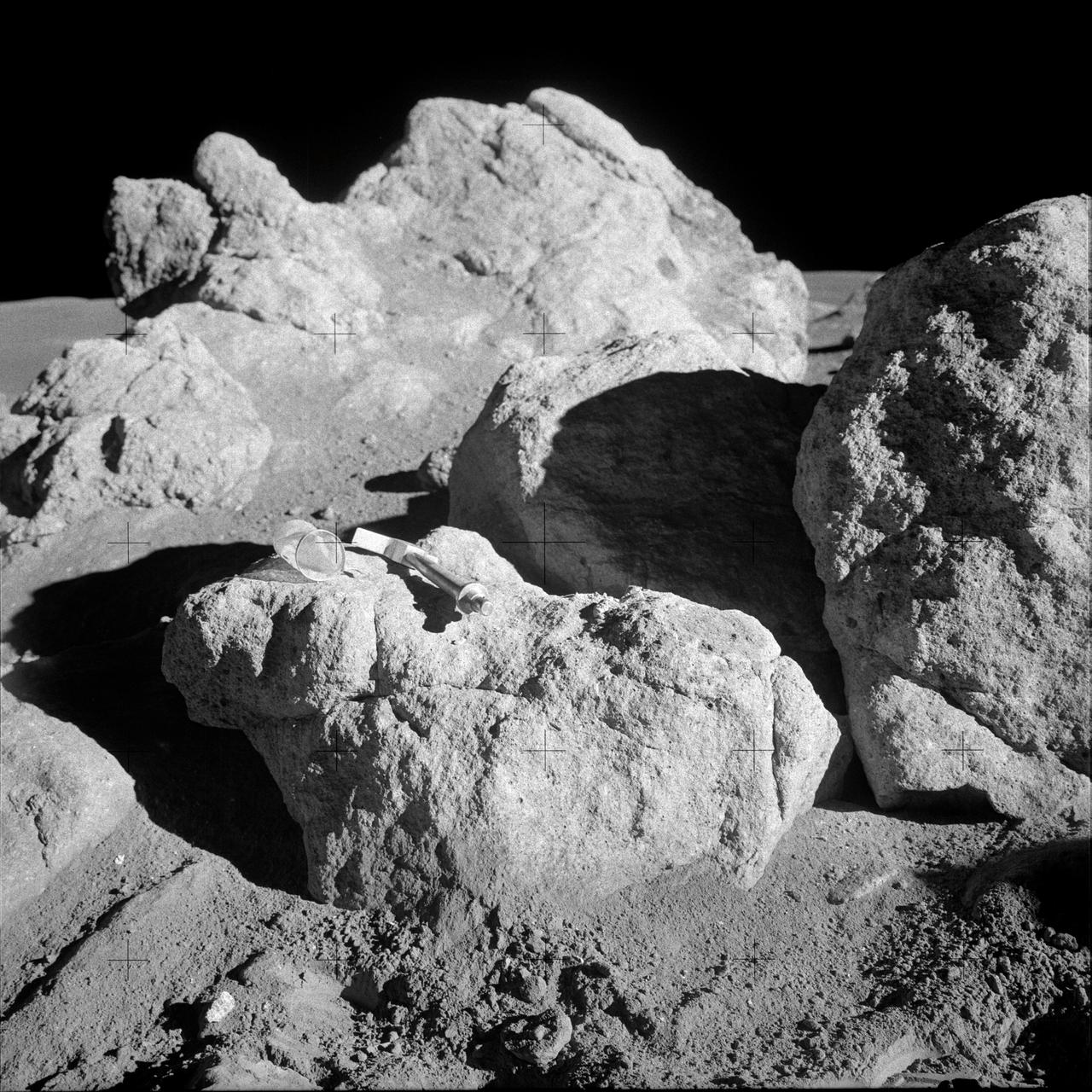

AS14-68-9452 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- A hammer and a small collection bag lie atop a lunar boulder to give some indication of size in this view of several boulders clustered together. This is one of the white rocks from which samples were taken by the two moon-exploring crew men of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, were exploring the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

S71-19473 (9 Feb. 1971) --- The Apollo 14 crew members step aboard the USS New Orleans, after exiting a U.S. Navy helicopter which retrieved the three from their splashdown site not far away. From left to right, are astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; and Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander. They will be sealed inside a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) aboard the prime recovery ship. Apollo 14 splashdown occurred at 3:04:39 p.m. (CST) in the South Pacific Ocean, approximately 765 nautical miles from American Samoa.
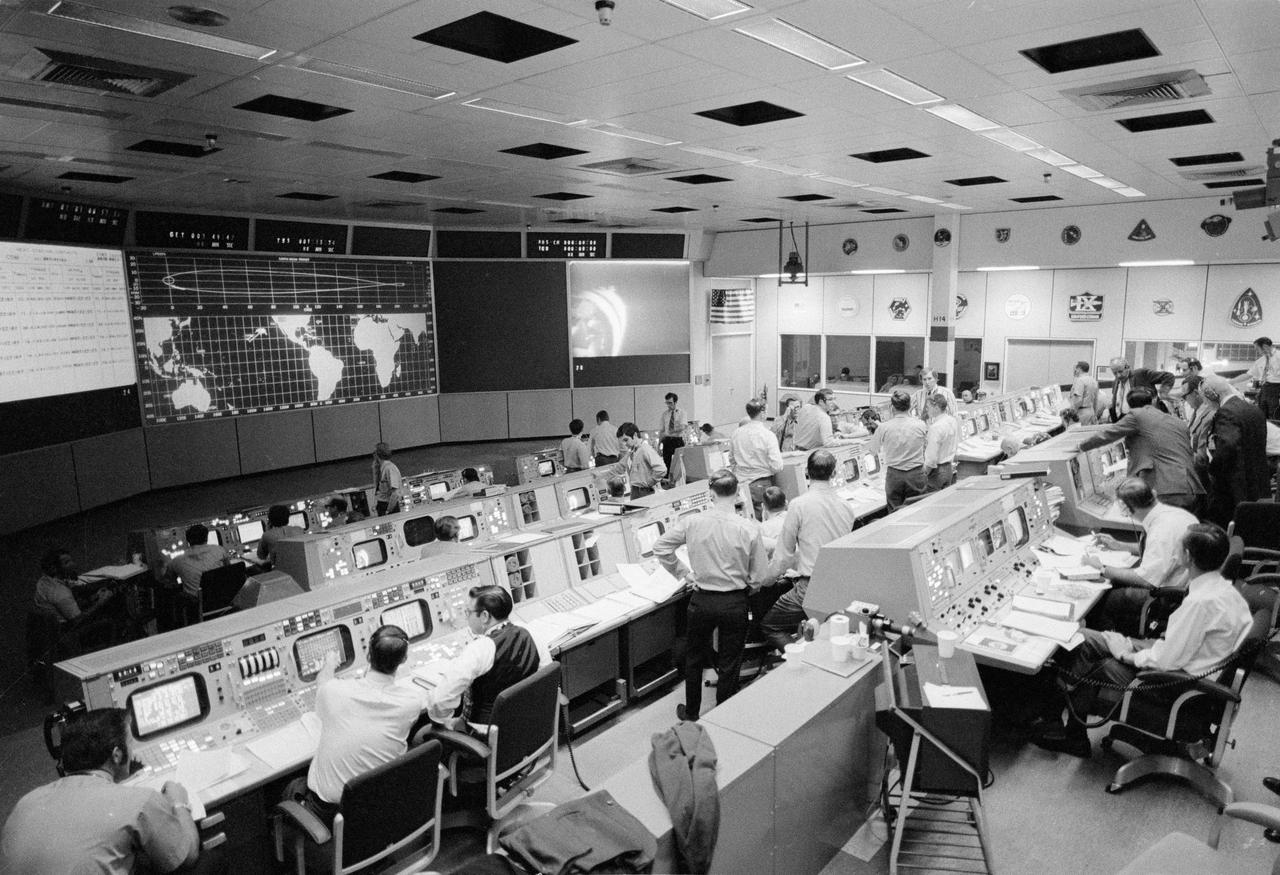

S71-16879 (31 Jan. 1971) --- Overall view of activity in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center during the Apollo 14 transposition and docking maneuvers. The Apollo 14 Lunar Module, still attached to the Saturn IVB stage, can be seen on the large television monitor. Due to difficulty with the docking mechanism six attempts were made before a successful "hard dock" of the Command Module with the Lunar Module was accomplished. Aboard the Command Module were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., Stuart A. Roosa, and Edgar D. Mitchell.
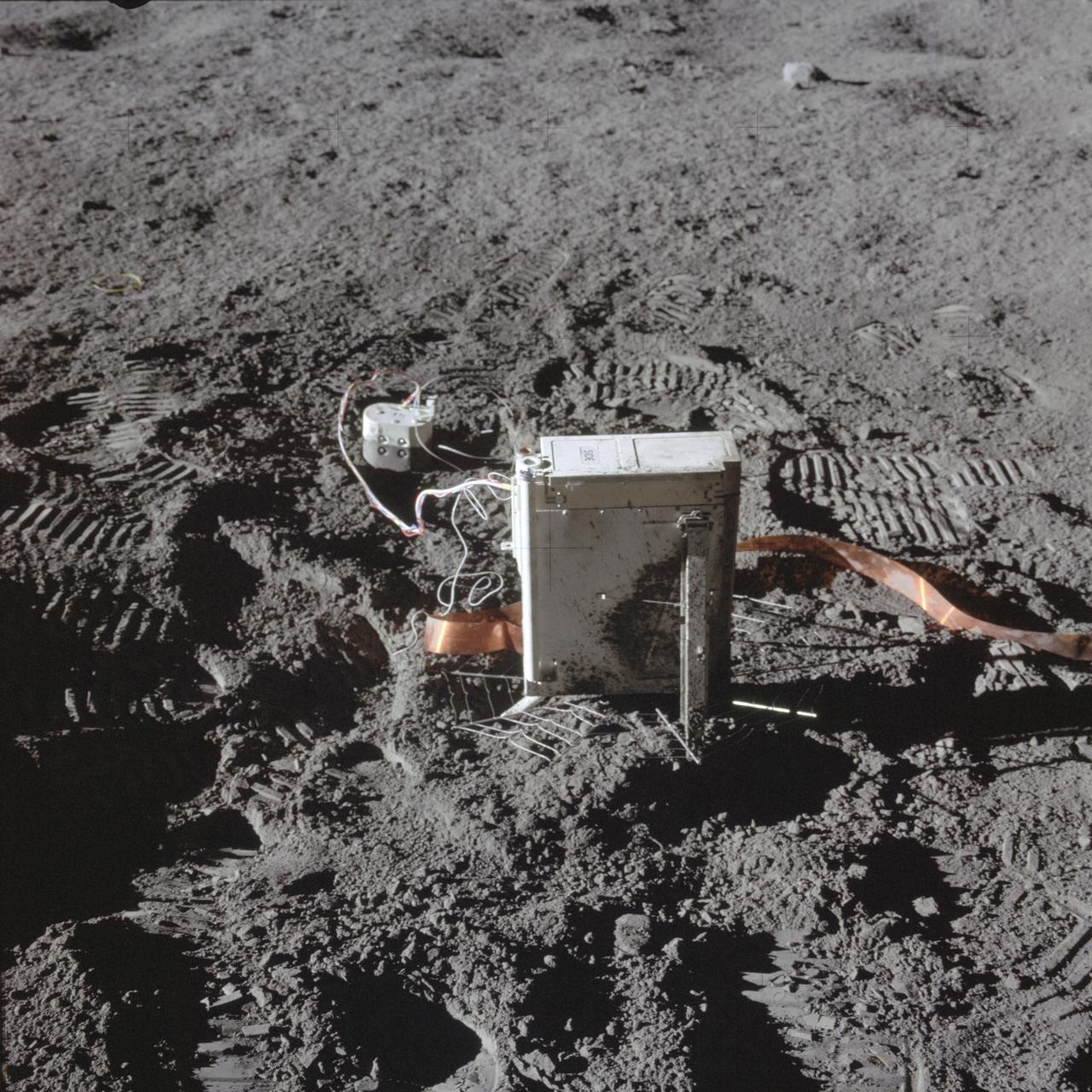
AS14-67-9369 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the Suprathermal ion detector experiment (SIDE), foreground, and cold cathode ion gauge (CCIG), smaller object in background, components of the Apollo lunar surface experiments package (ALSEP), which was deployed on the moon by the Apollo 14 astronauts during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr. and Edgar D. Mitchell descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
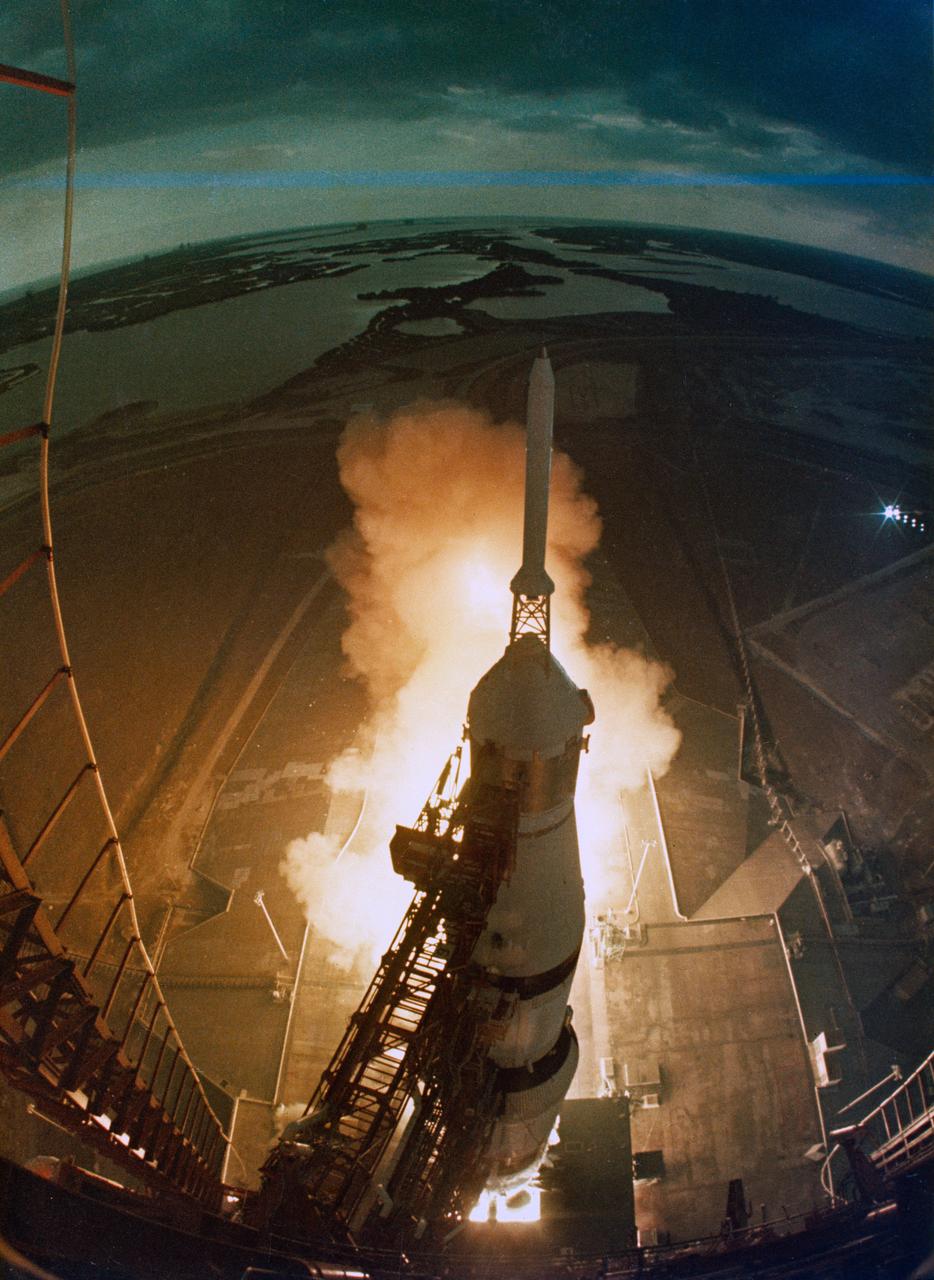

S71-17620 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1981, on a lunar landing mission. This view of the liftoff was taken by a camera mounted on the mobile launch tower. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
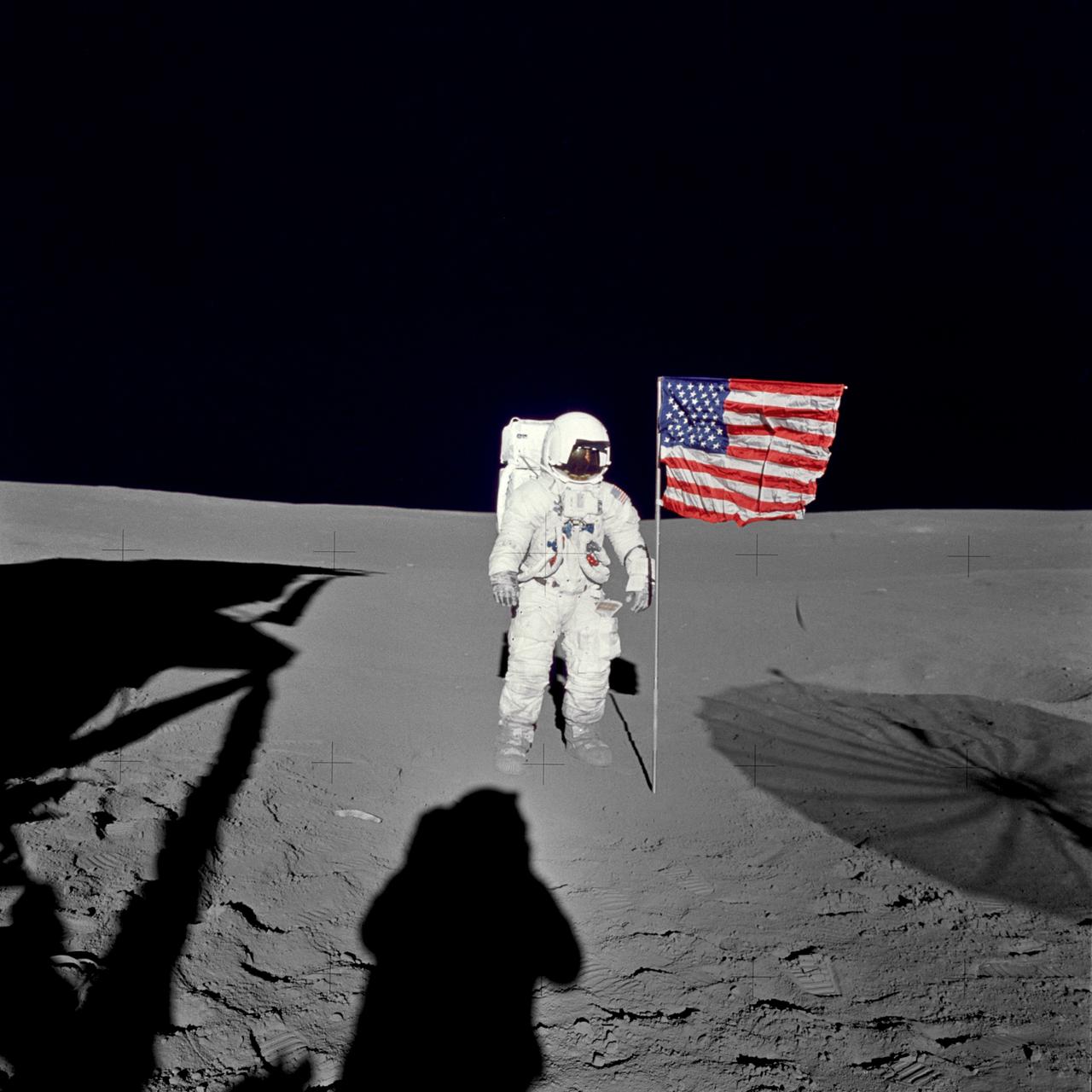

AS14-66-9233 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, stands by the deployed U.S. flag on the lunar surface during the early moments of the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the mission. He was photographed by astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., mission commander, using a 70mm modified lunar surface Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Antares" to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Kitty Hawk" in lunar orbit.
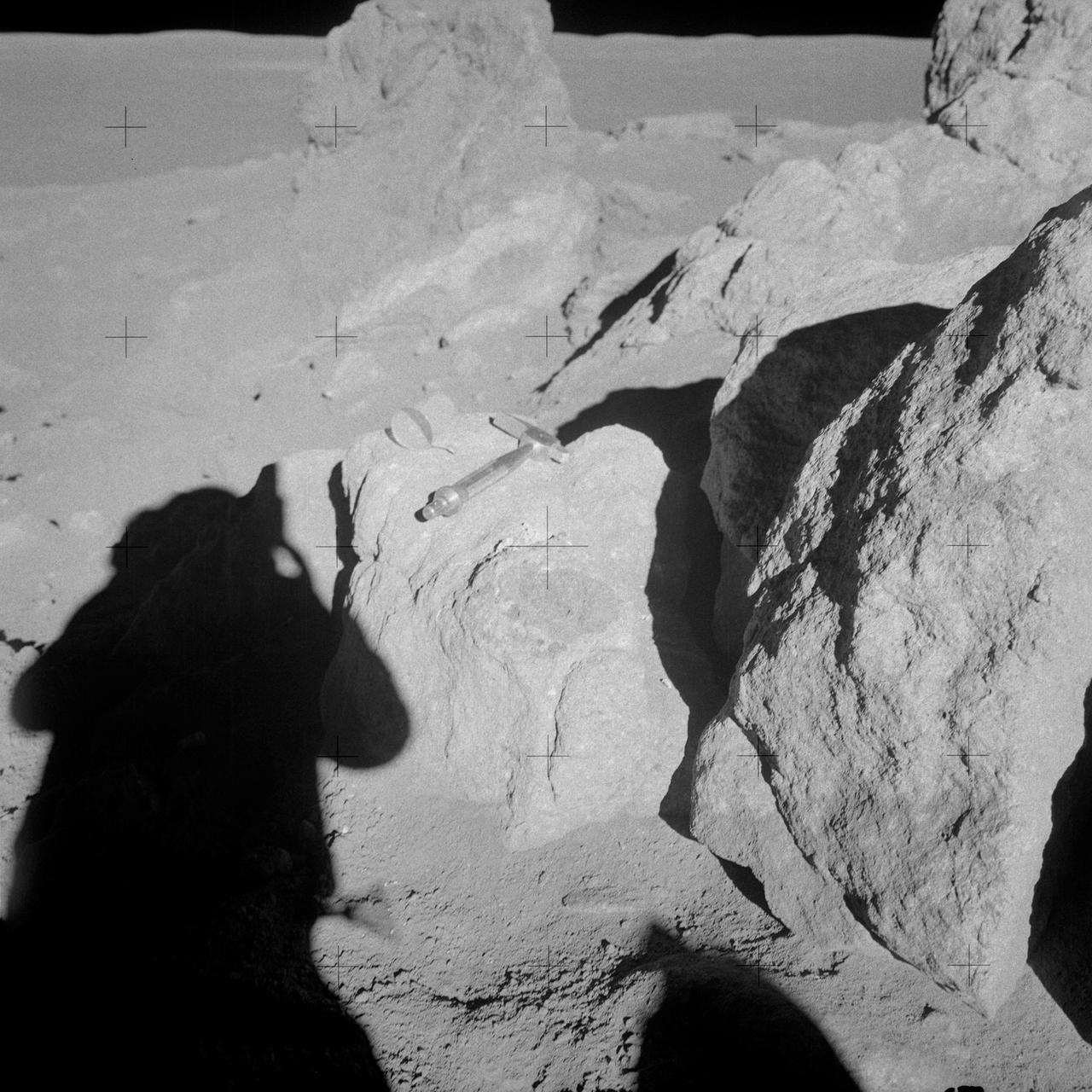

AS14-68-9453 (6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, whose shadow is in the foreground, photographs a group of large boulders near the rim of Cone Crater. An interesting feature is the white and brown rock in the boulder. Mitchell removed a sample where the hammer is lying. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Mitchell descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Antares" to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Kitty Hawk" in lunar orbit.
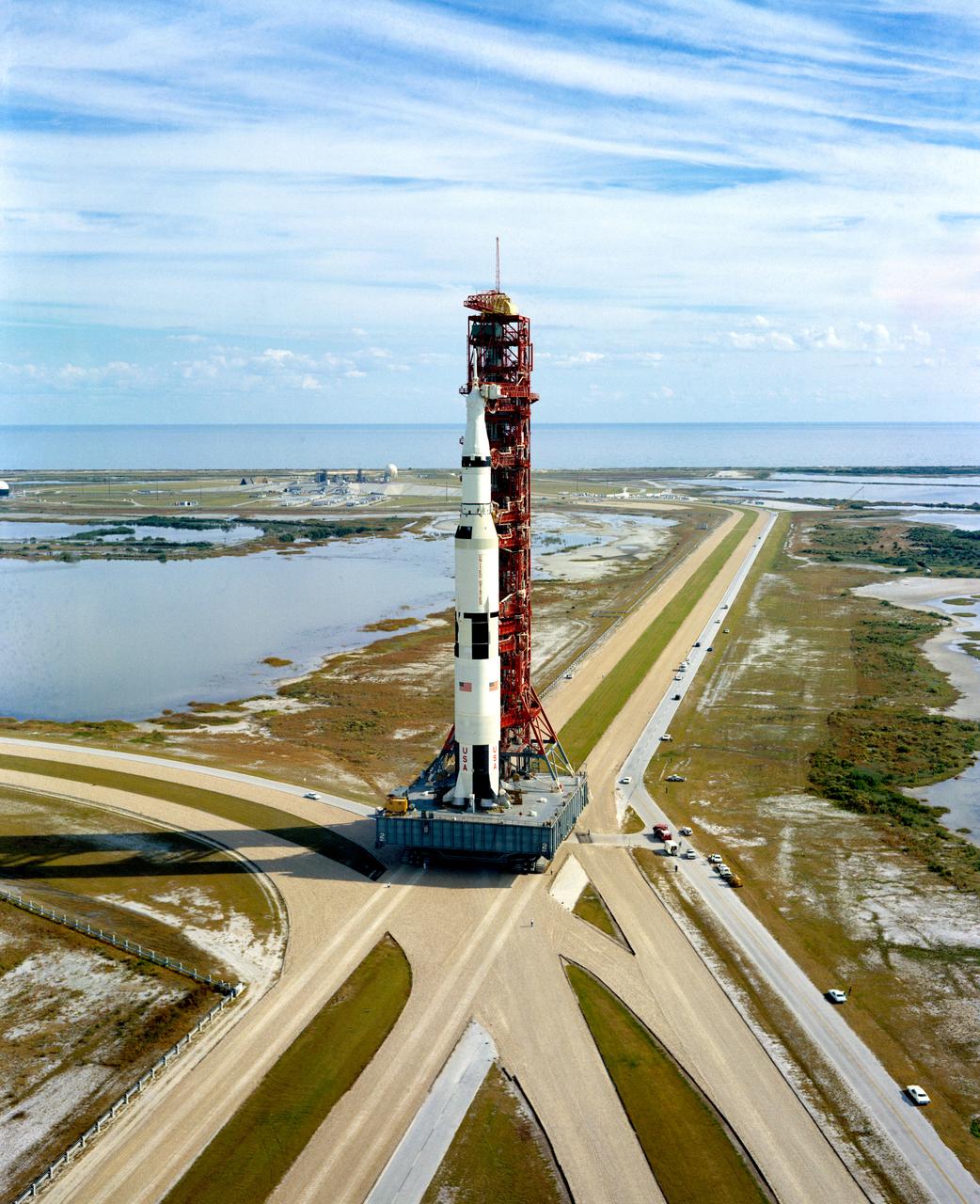

S70-54119 (9 Nov. 1970) --- A high-angle view at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), showing the Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle on the way from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to Pad A. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower sit atop a huge crawler-transporter. The Apollo 14 crewmen will be astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.

AS14-68-9448 (6 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of a large multi-colored boulder in the boulder field located on the rim of Cone Crater, as photographed by the moon-exploring crew members of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. This view is looking west by southwest. The Lunar Module (LM) can be seen in the background. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, were exploring the moon, after descending in the LM, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
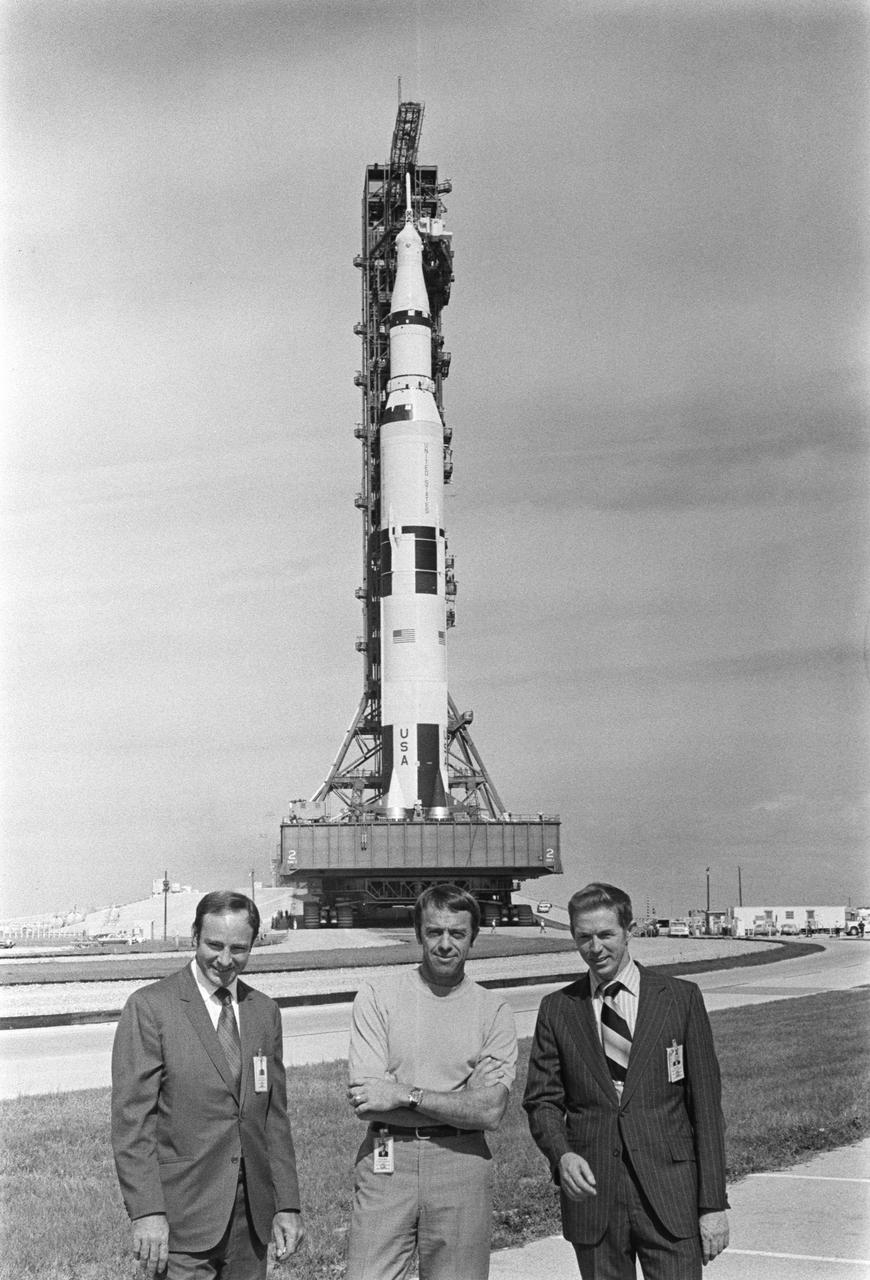

S70-55689 (9 Nov. 1970) --- The Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle arrives at Pad A, Launch Complex 39, during the Apollo 14 roll out from the Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower atop a huge crawler-transporter. The three members of the Apollo 14 prime crew are in the foreground. They are (left to right) astronauts Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot.
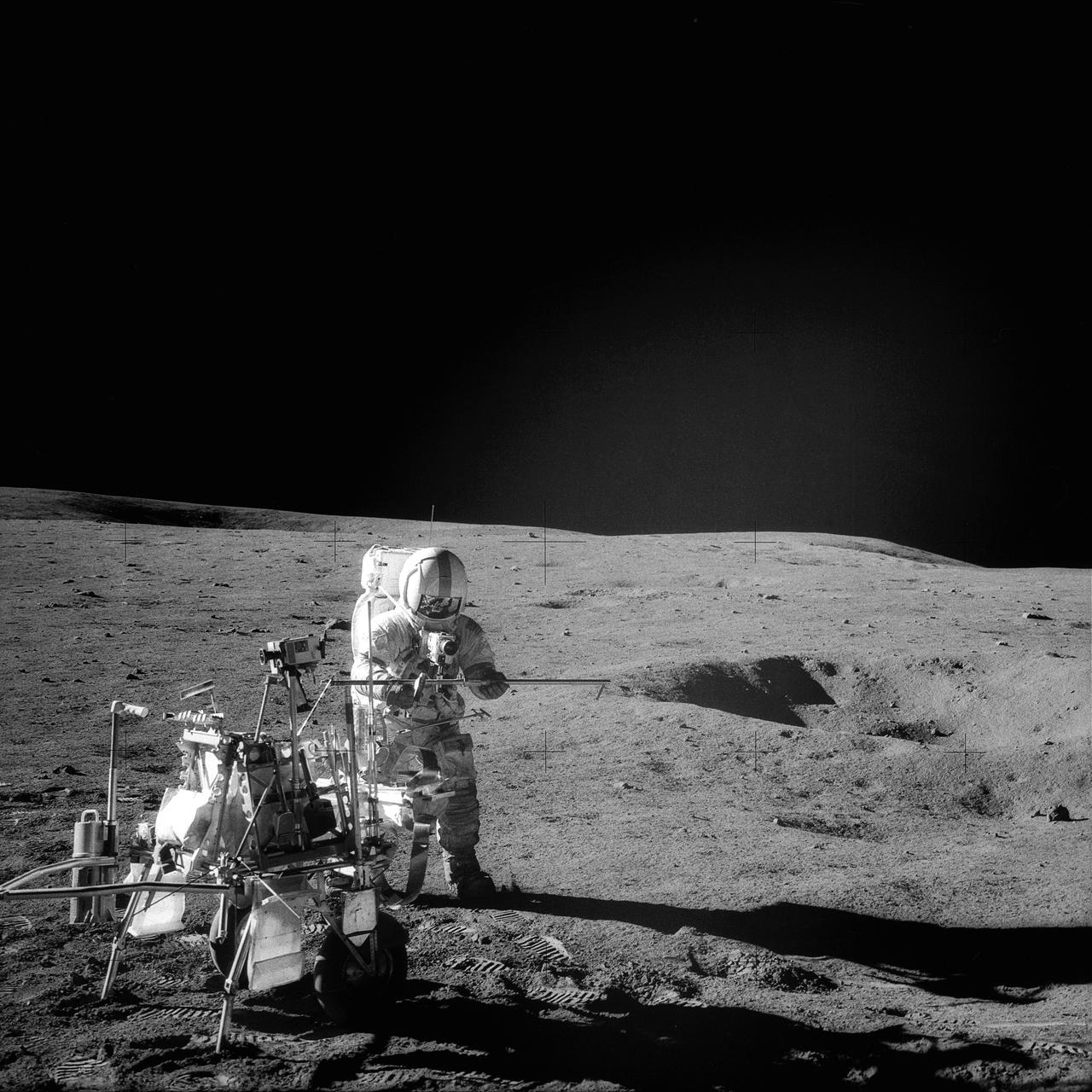

AS14-68-9405 (6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., Apollo 14 commander, assembles a double core tube as he stands beside the rickshaw-type portable workbench or modularized equipment transporter (MET) unique to this mission. The photograph was taken by astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, standing some 170 meters northeast of the Lunar Module (LM), during the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA) on Feb. 6, 1971. While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the LM "Antares" to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Kitty Hawk" in lunar orbit.
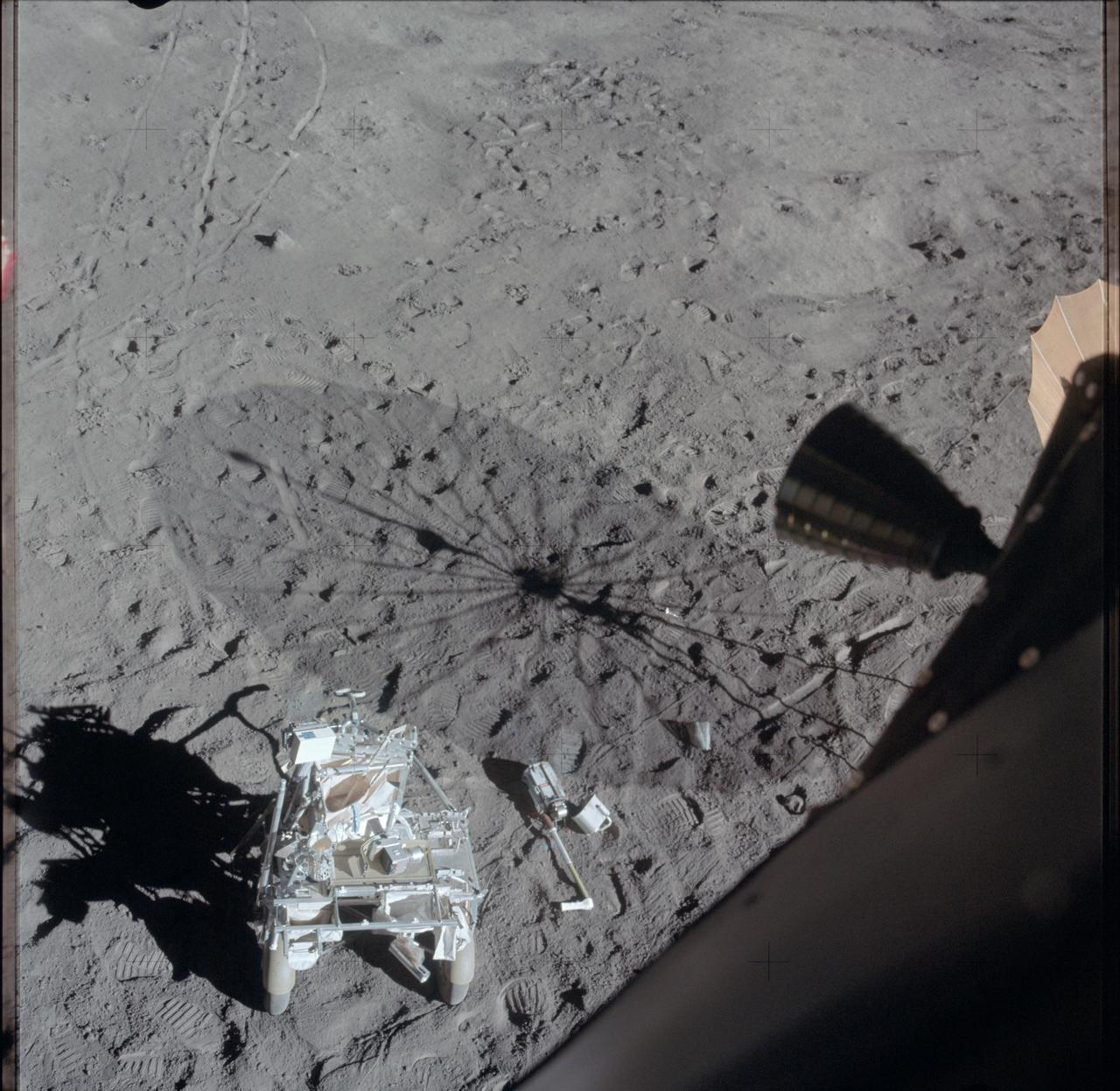

AS14-66-9340 (6 Feb. 1971) --- A view from inside the Lunar Module (LM) following the second Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA). At the left foreground is the modularized equipment transporter (MET). Tracks made by the two-wheeled "Rickshaw"-type cart can be seen in the left background. The Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera lies next to the MET, near a huge shadow of the erectable S-Band antenna. The area is largely covered with bootprints made by astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot. While the pair explored the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
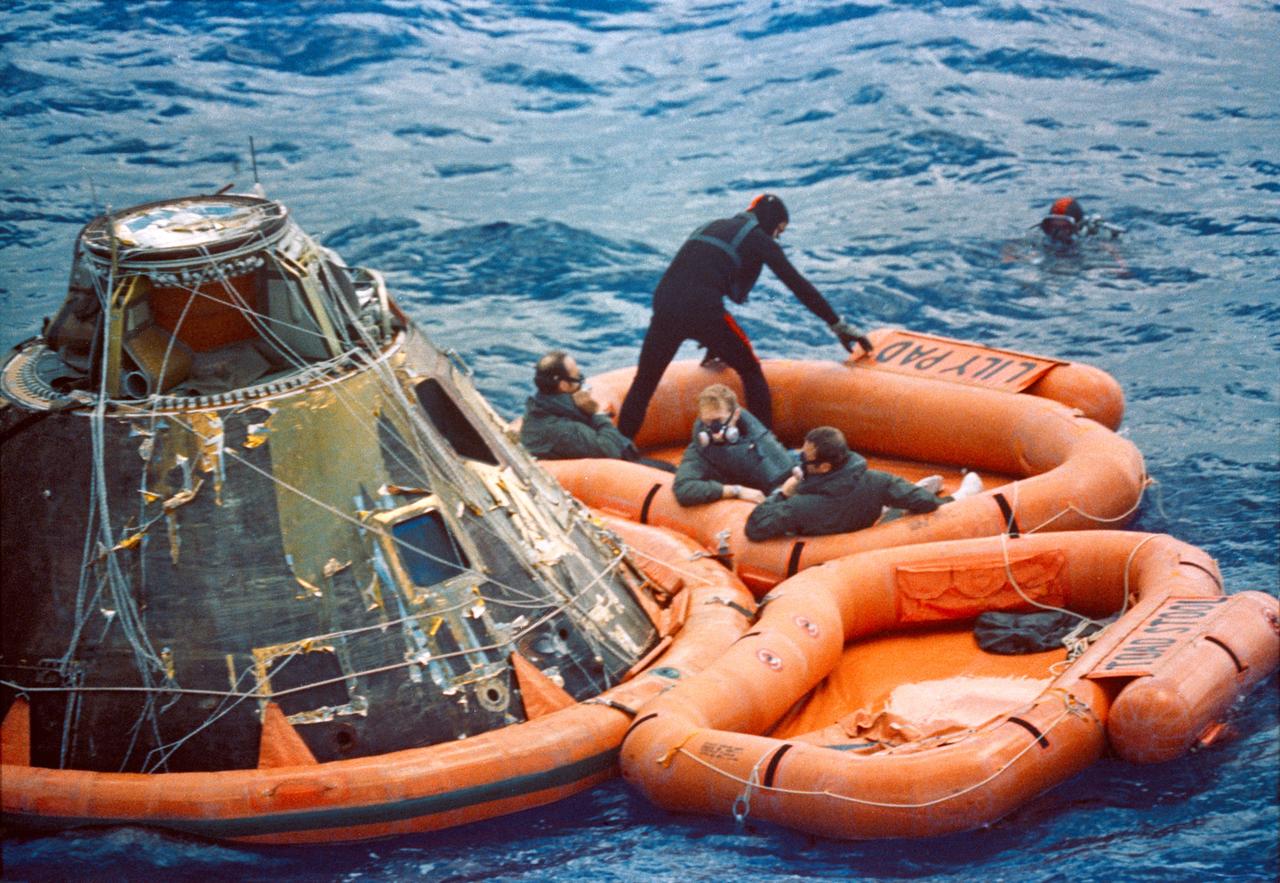

S71-19475 (9 Feb. 1971) --- The Apollo 14 crewmembers sit in a life raft beside their Command Module (CM) in the South Pacific Ocean as they await a U.S. Navy helicopter, which will take them aboard the USS New Orleans, prime recovery ship. The crew men are, from left to right, astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot. Two U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmers (one partially visible in right upper corner) assist in the recovery operations. The Apollo 14 spacecraft splashed down at 3:04:39 p.m. (CST), Feb. 9, 1971, approximately 765 nautical miles from American Samoa in the South Pacific Ocean.
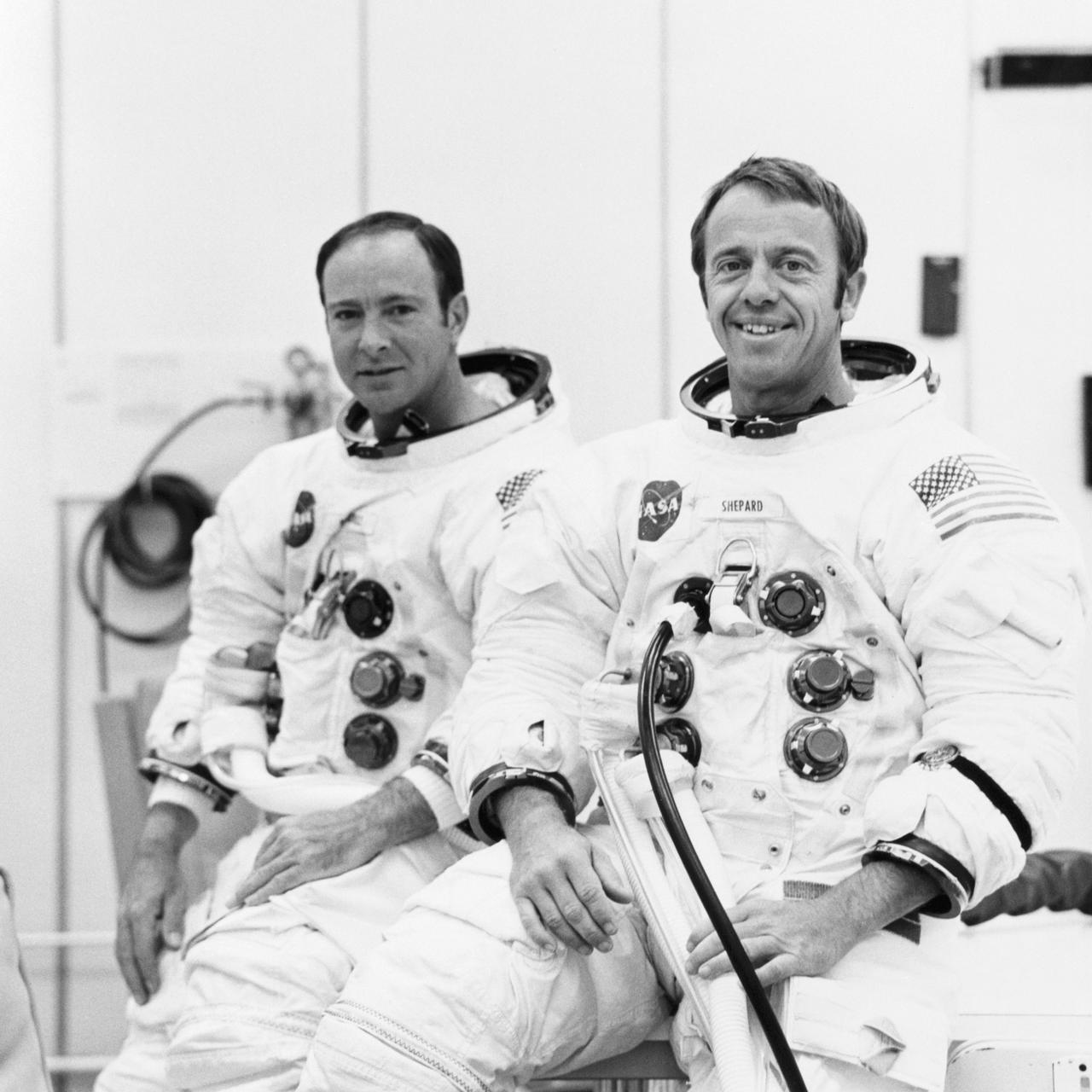

S70-19764 (18 Sept. 1970) --- Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr. (right), commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, are suited up for a manned altitude run in the Apollo 14 Lunar Module. The manned run in a vacuum chamber of the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building was conducted to validate the LM's communications and guidance and navigation systems. Apollo 14 is scheduled for launch from Cape Kennedy on Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar exploration mission which is to carry Shepard and Mitchell down to the moon's rugged Fra Maura highlands region. Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, will remain with the Apollo 14 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while the other two astronauts explore the moon.

The moon bound Apollo 14, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Mission commander Alan B. Shepard Jr., Command Module pilot Stuart A. Roosa, and Lunar Module pilot Edgar D. Mitchell, lifted off from launch complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center on January 31, 1971, and safely returned to Earth on February 9, 1971. It was the third manned lunar landing, the first manned landing in exploration of the lunar highlands, and it demonstrated pinpoint landing capability. The major goal of Apollo 14 was the scientific exploration of the Moon in the foothills of the rugged Fra Mauro region. The extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Shepard and Mitchell included setting up an automated scientific laboratory called Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP), shown here fully deployed. In addition, they collected a total of about 95 pounds (43 kilograms) of Moon rock and soil for a geological investigation back on the Earth.

S70-17851 (September 1970) --- This is the Apollo 14 crew patch designed by astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot. It features the astronaut lapel pin approaching the moon and leaving a comet trail from the liftoff point on Earth. The pin design was adopted by the astronaut corps several years ago. Astronauts who have not yet flown in space wear silver pins. Those who have flown wear gold pins. The NASA insignia design for Apollo flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced.

AS14-66-9305 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A front view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM), which reflects a circular flare caused by the brilliant sun, as seen by the two moon-exploring crew men (out of frame) of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). The unusual ball of light was said by the astronauts to have a jewel-like appearance. In the left background Cone Crater can be seen. In the left foreground are the erectable S-Band antenna and the United States flag. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
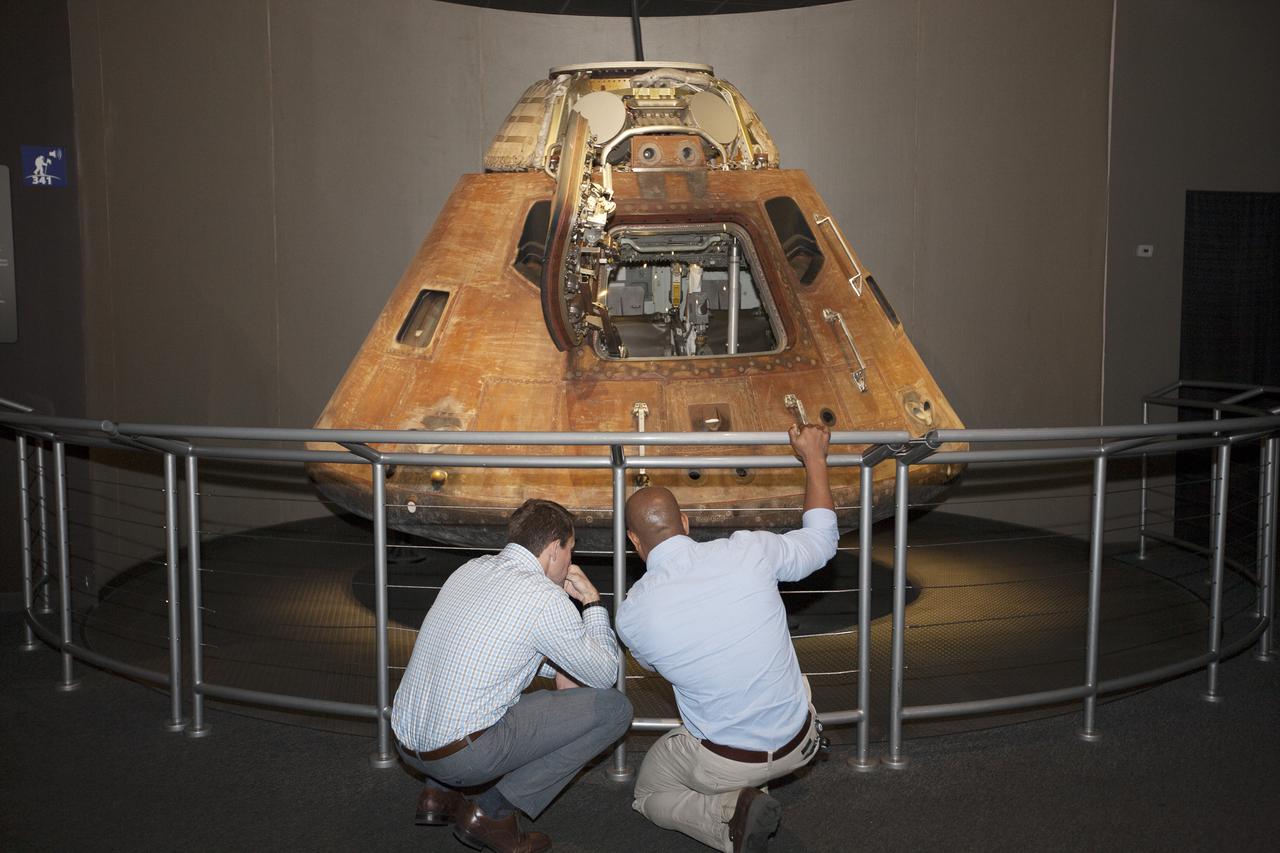

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA astronaut candidates Josh Cassada, left, and Victor Glover observe the Apollo 14 command module which carried astronauts Alan Shepard, Stu Roosa and Edgar Mitchell on their lunar landing mission in 1971.The astronauts toured the Apollo Saturn V Center at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a daylong set of briefings and tours of different facilities at NASA's primary launch center. The astronaut class of 2013 was selected by NASA after an extensive year-and-a-half search. The new group will help the agency push the boundaries of exploration and travel to new destinations in the solar system. To learn more about the astronaut class of 2013, visit: http:__www.nasa.gov_astronauts_2013astroclass.html Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
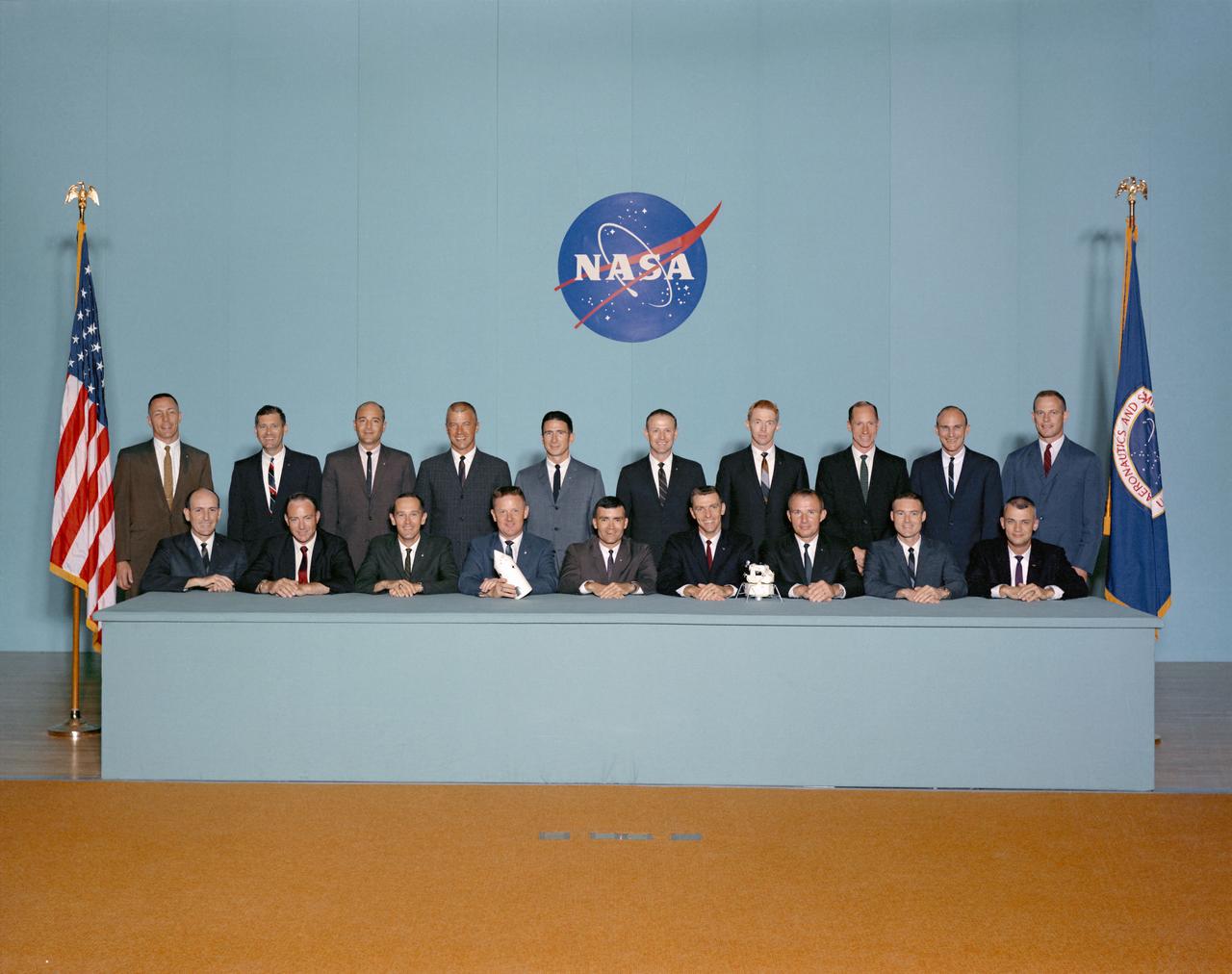

S67-30404 (May 1967) --- Portrait of astronaut group selected April 4, 1966. Seated, left to right, are Edward G. Givens Jr., Edgar D. Mitchell, Charles M. Duke Jr., Don L. Lind, Fred W. Haise Jr., Joe H. Engle, Vance D. Brand, John S. Bull and Bruce McCandless II. Standing, left to right, are John L. Swigert Jr., William R. Pogue, Ronald E. Evans, Paul J. Weitz, James B. Irwin, Gerald P. Carr, Stuart A. Roosa, Alfred M. Worden, Thomas K. Mattingly and Jack R. Lousma. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
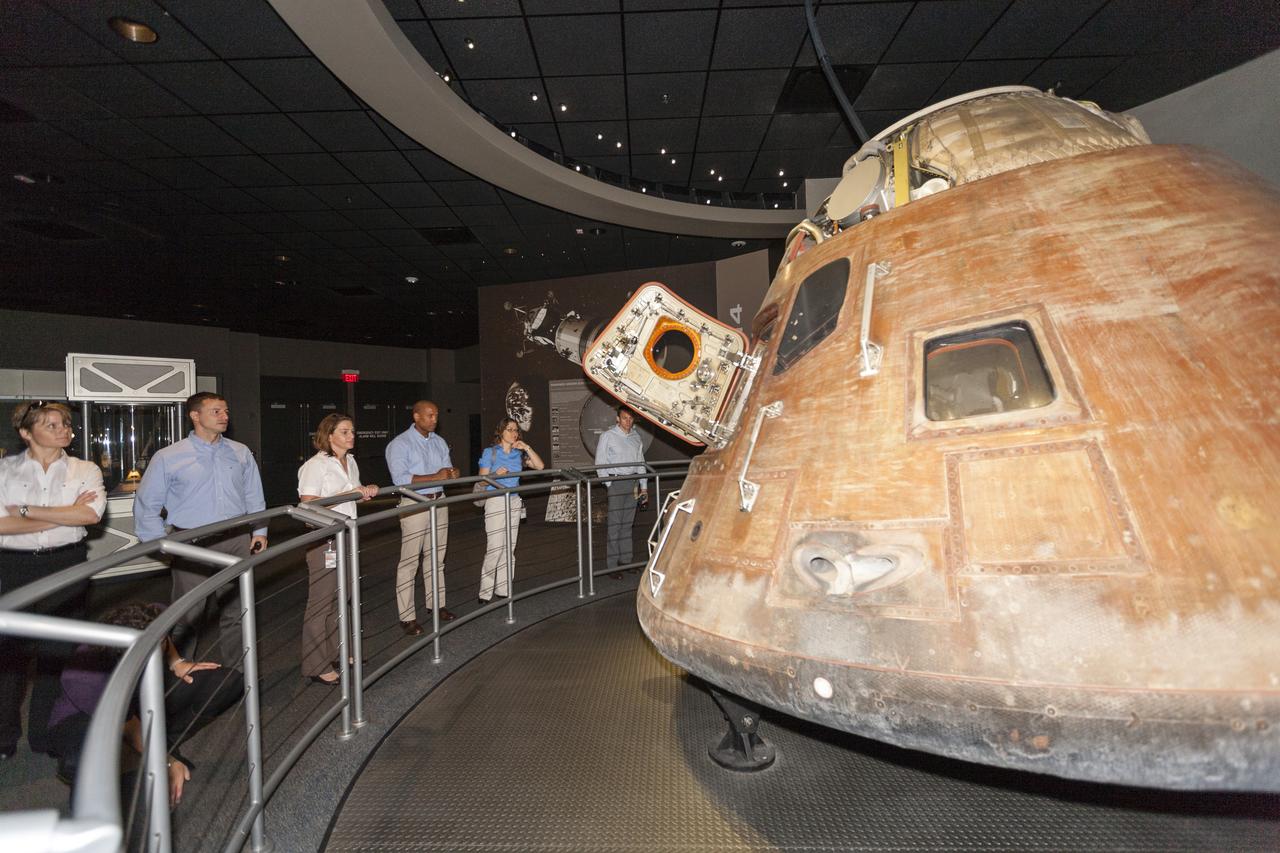

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA astronaut candidates Anne McClain, from left, Andrew Morgan, Nicole Mann, Victor Glover, Christina Hammock and Josh Cassada observe the Apollo 14 command module which carried astronauts Alan Shepard, Stu Roosa and Edgar Mitchell on their lunar landing mission in 1971.The astronauts toured the Apollo Saturn V Center at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a daylong set of briefings and tours of different facilities at NASA's primary launch center. The astronaut class of 2013 was selected by NASA after an extensive year-and-a-half search. The new group will help the agency push the boundaries of exploration and travel to new destinations in the solar system. To learn more about the astronaut class of 2013, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/2013astroclass.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
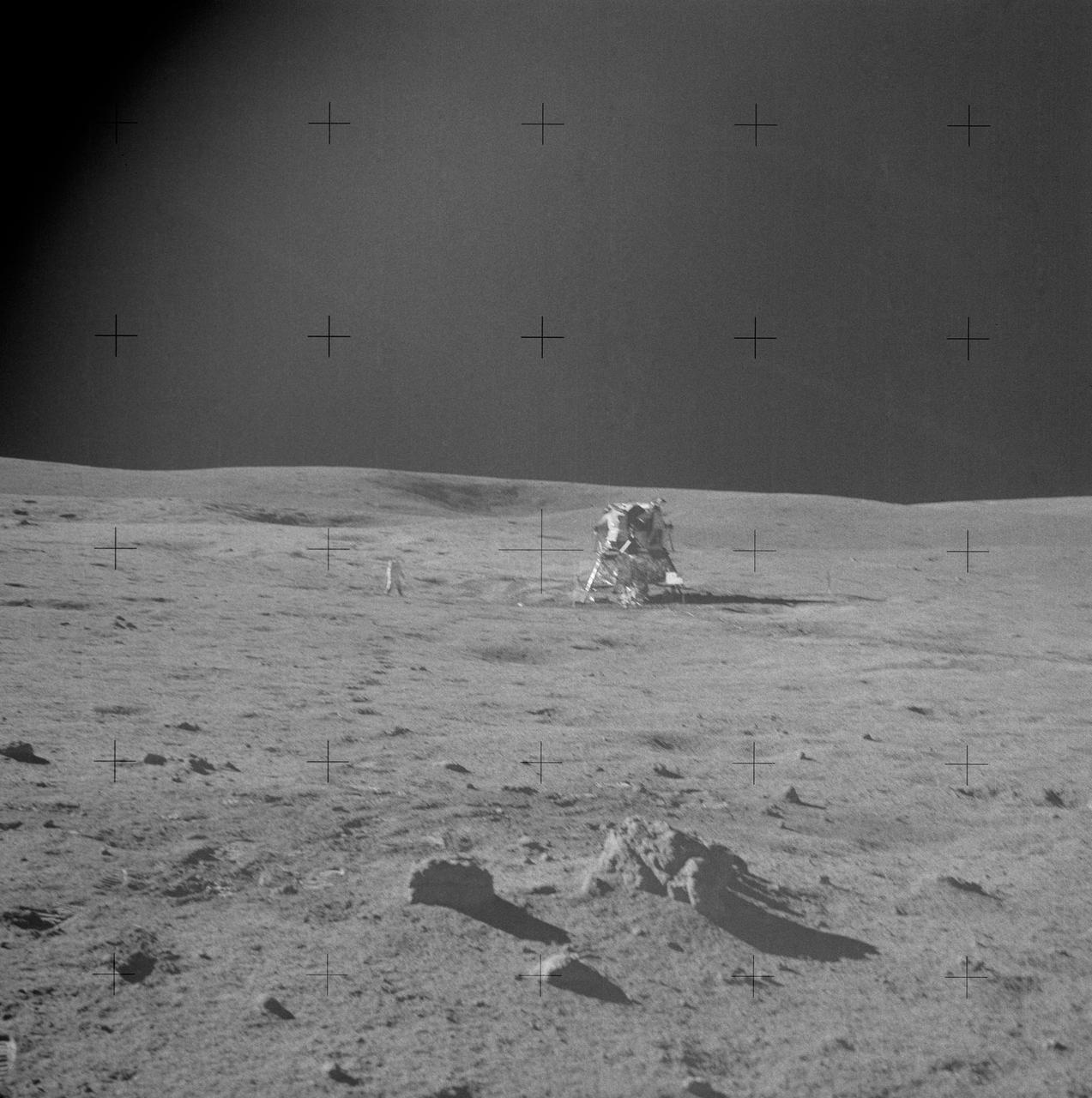

AS14-68-9487 (6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, photographed this sweeping view showing fellow moon-explorer astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., mission commander, and the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM). A small cluster of rocks and a few prints made by the lunar overshoes of Mitchell are in the foreground. Mitchell was standing in the boulder field, located just north by northwest of the LM, when he took this picture during the second Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA), on Feb. 6, 1971. While astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit, Shepard and Mitchell descended in the LM to explore the moon.

S71-20784 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., Apollo 14 commander, can be seen preparing to swing at a golf ball during a television transmission near the close of the second Extravehicular Activity (EVA-2) at the Apollo 14 Fra Mauro landing site. Shepard is using a real golf ball and an actual six iron, attached to the end of the handle for the contingency sample return. Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, looks on. Also visible in the picture is the erectable S-Band antenna (left foreground). Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit, while Shepard and Mitchell descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
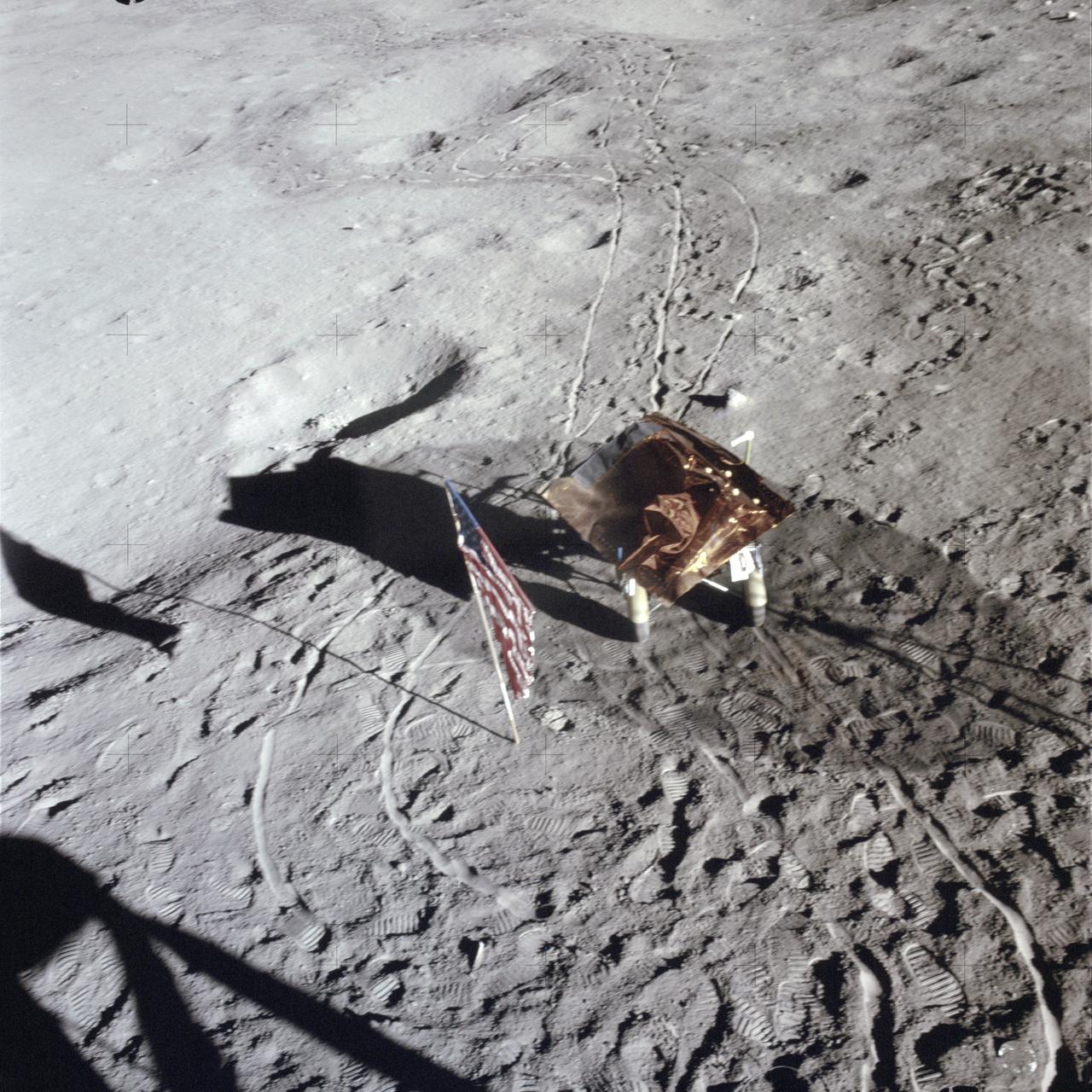

AS14-66-9325 (5 Feb. 1971) --- The third United States flag to be deployed on the lunar surface, footprints, wheel tracks and the "Rickshaw"-type portable workbench, as seen by the two moon-exploring astronauts from inside the Lunar Module (LM), give evidence of a busy first extravehicular activity (EVA) period. The two-wheeled cart is the Apollo modularized equipment transporter (MET), covered with a sheet of foil material to protect the cameras and rock box between EVAs. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

This is the Apollo 14 mission insignia or logo. The Apollo 14, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Stuart A. Roosa, Command Module pilot; Alan B. Shepard, Jr., mission commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, Lunar Module pilot, lifted off from launch complex 39A at KSC on January 31, 1971. It was the third manned lunar landing, the first manned landing in exploration of the lunar highlands, and it demonstrated pinpoint landing capability. The major goal of Apollo 14 was the scientific exploration of the Moon in the foothills of the rugged Fra Mauro region. The lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Shepard and Mitchell included setting up an automated scientific laboratory called Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP), and collecting a total of about 95 pounds (43 kilograms) of Moon rock and soil for a geological investigation back on the Earth. Apollo 14 safely returned to Earth on February 9, 1971.