
This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the dune field on the floor of Rabe Crater. Orbit Number: 65691 Latitude: -43.6749 Longitude: 34.8006 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2016-10-04 20:29 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21183
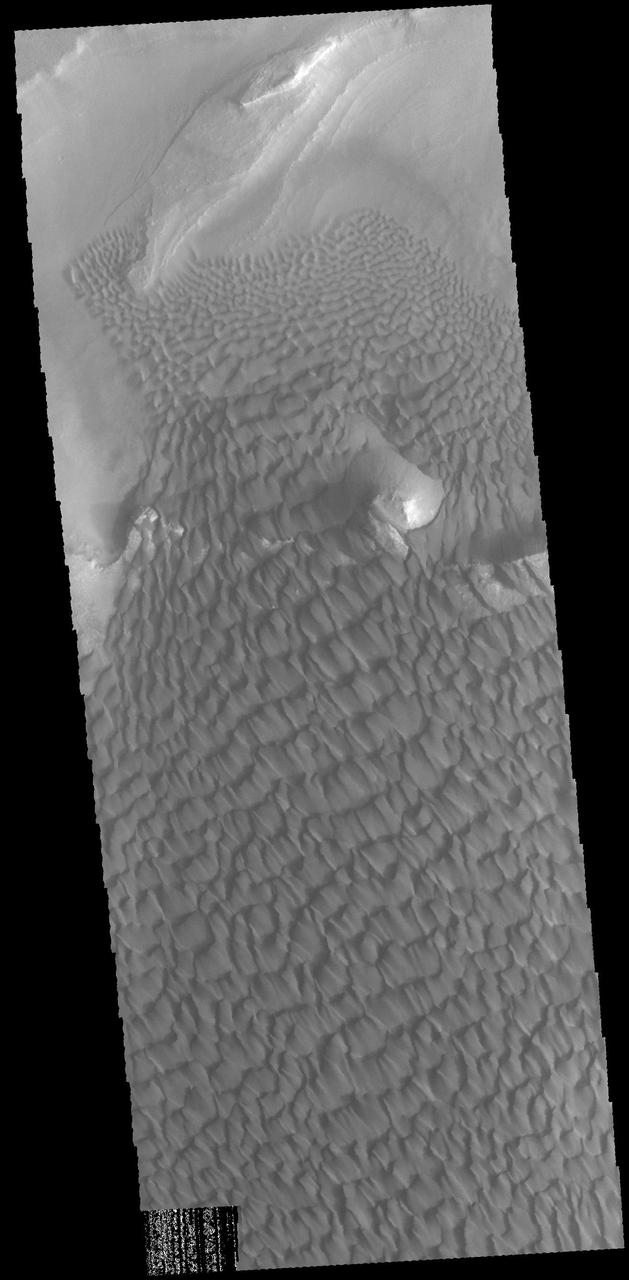

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft show part of the dune field located on the floor of Rabe Crater. Orbit Number: 67412 Latitude: -43.5303 Longitude: 34.6741 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-02-23 15:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21658

This VIS image was collected simultaneously with yesterday's IR image. It shows part of the dune field on the floor of Rabe Crater. Orbit Number: 67144 Latitude: -43.5507 Longitude: 34.5952 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-02-01 12:57 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21520

Rabe Crater Dunes IR
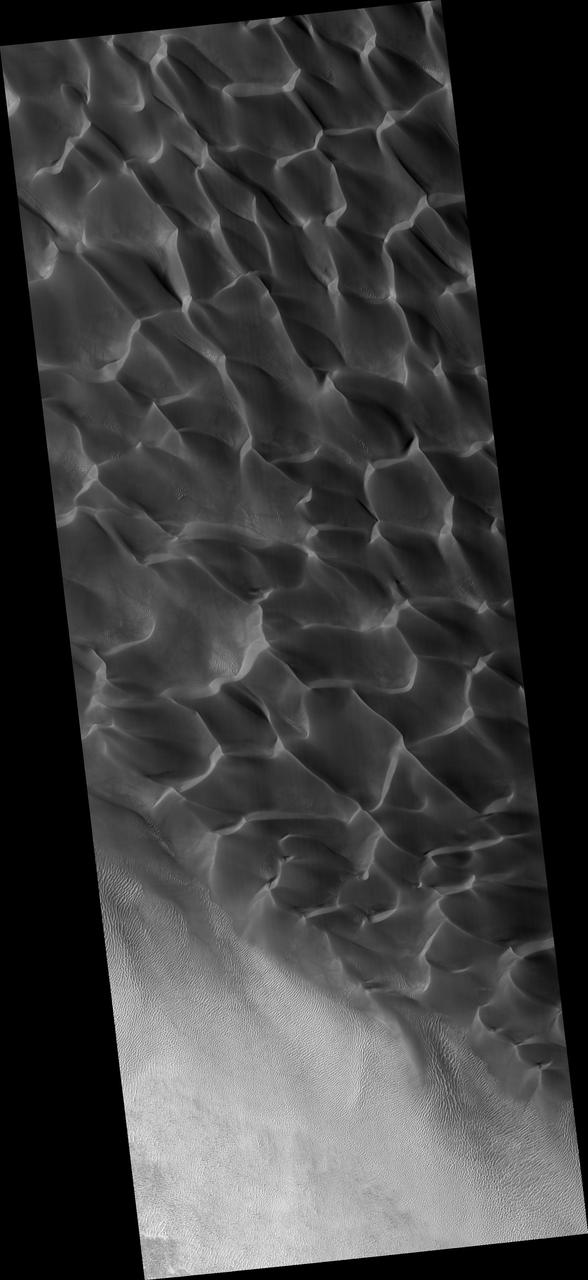
Sand Dunes in Rabe Crater
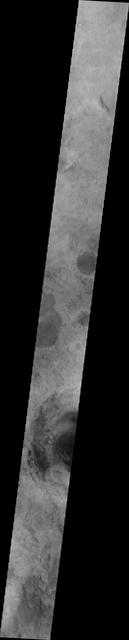
Rabe Crater Dunes
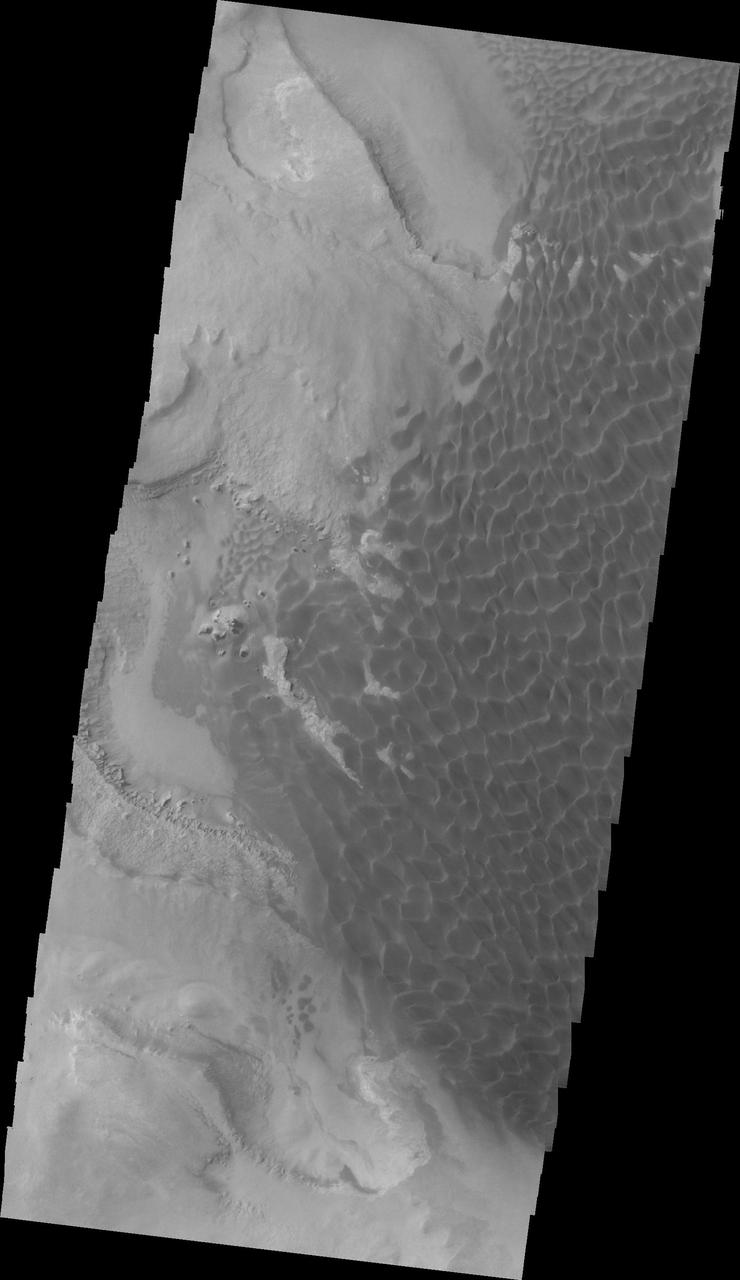

Rabe Crater Dunes VIS
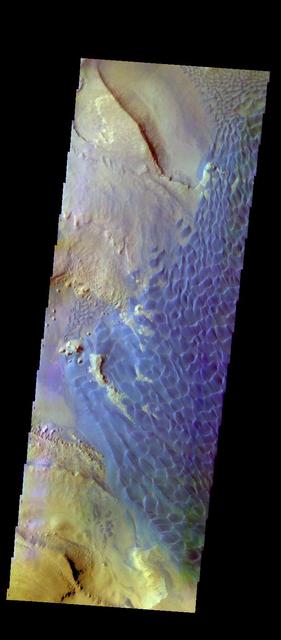
The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the sand dune field on the floor of Rabe Crater. Orbit Number: 51157 Latitude: -43.6787 Longitude: 34.3985 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-06-26 05:33 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21291

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Orbit Number: 52206 Latitude: -43.6573 Longitude: 34.9551 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-09-20 13:07 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21512

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater, including part of the extensive dune field found there. Orbit Number: 52231 Latitude: -43.6665 Longitude: 34.2627 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-09-22 14:29 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21514

This daytime infrared image of Rabe Crater illustrates the warming effect of the sun on sand. The extensive sand sheet and dunes of Rabe crater appear bright in the infrared indicating they are warmer than the surrounding floor and plains materials.

This VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. The floor of Rabe Crater has undergone several surface changing events. At some point after the crater was formed it was partially filled by a material laid down by wind or water action. This material has been eroded, creating a complex depression in the deposited material. The resultant sand has collected into the dunes seen in the image. Orbit Number: 75307 Latitude: -43.5769 Longitude: 34.3041 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-12-06 01:11 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23028

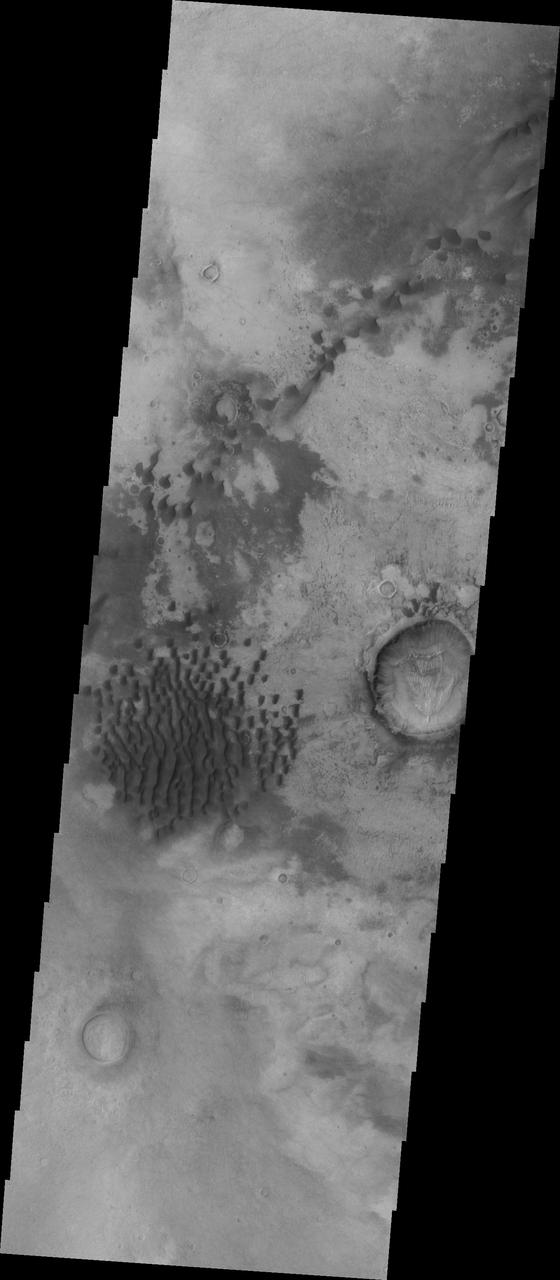
Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 90256 Latitude: -43.5412 Longitude: 34.6619 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-04-19 23:24 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25470

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover halp of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 84884 Latitude: -43.4896 Longitude: 34.4426 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-02-01 15:04 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24736
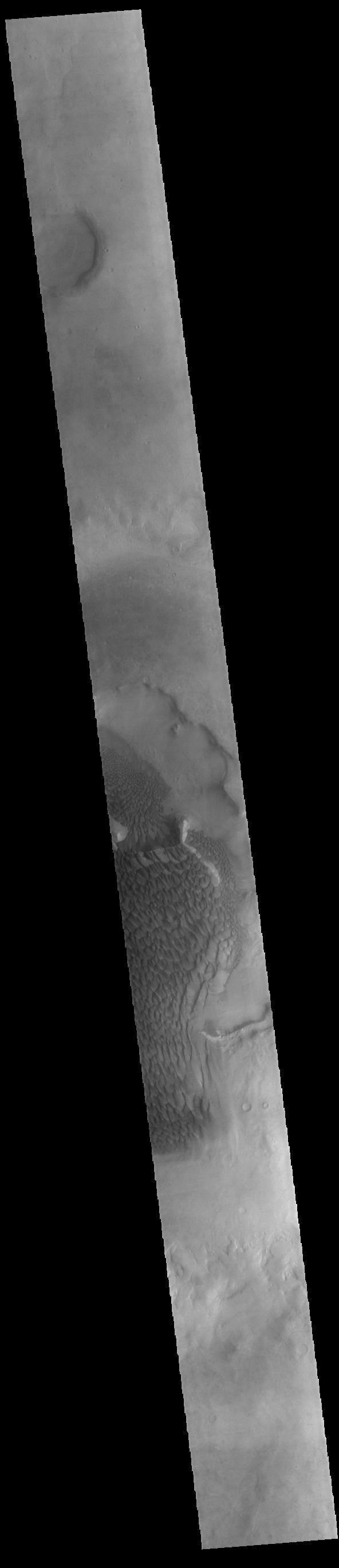

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 84990 Latitude: -43.3123 Longitude: 34.9141 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-02-10 09:02 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24739
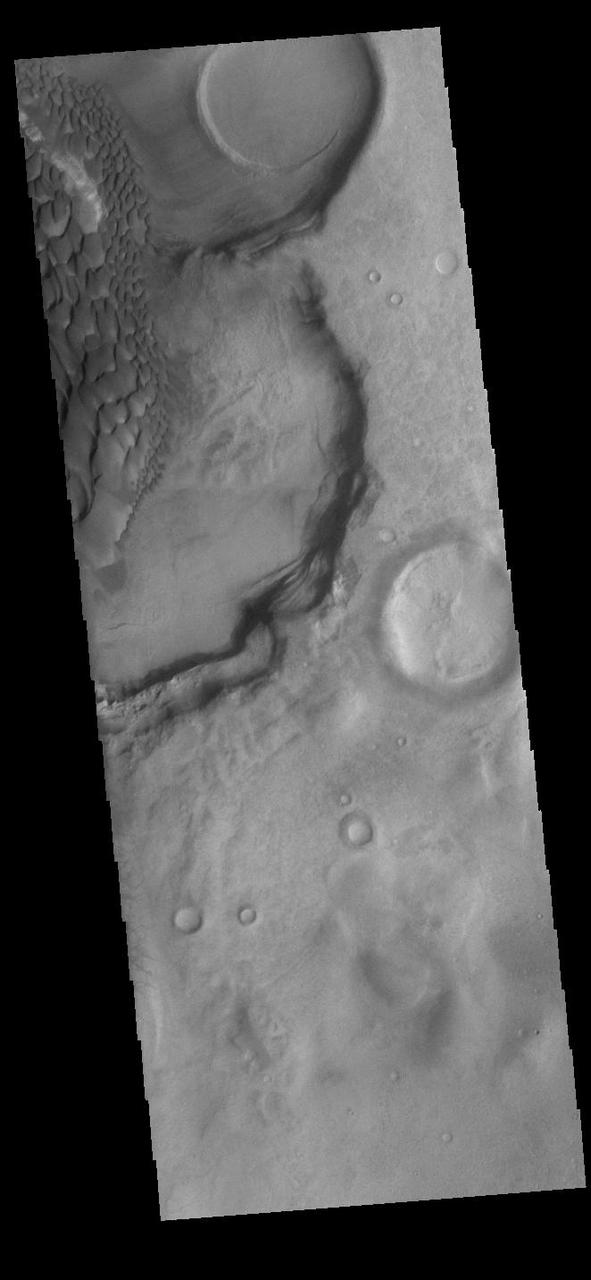

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover only the very upper left of this image of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. The lower elevations at the top of this image are the eroded pit. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated less than the longer side. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming sand dunes. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 91404 Latitude: -43.8048 Longitude: 35.2382 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-07-23 12:03 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25547
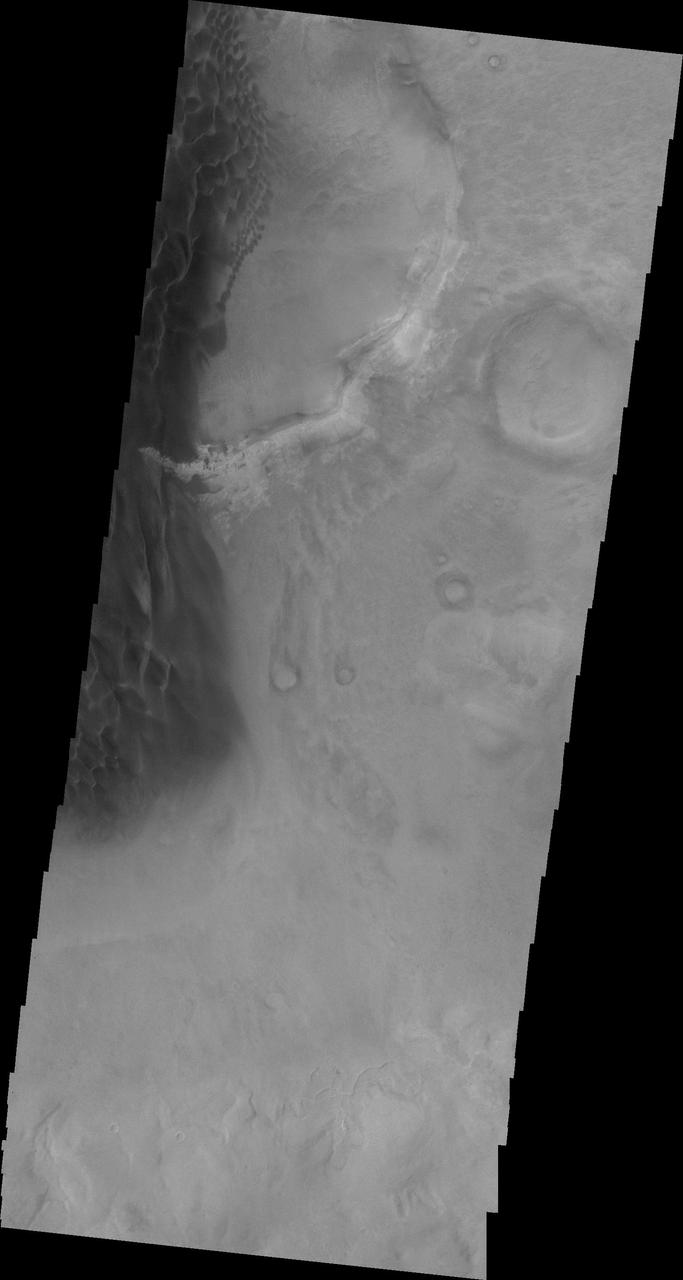
This 2001 Mars Odyssey image shows the eastern margin of the sand sheet and dune field on the floor of Rabe Crater.
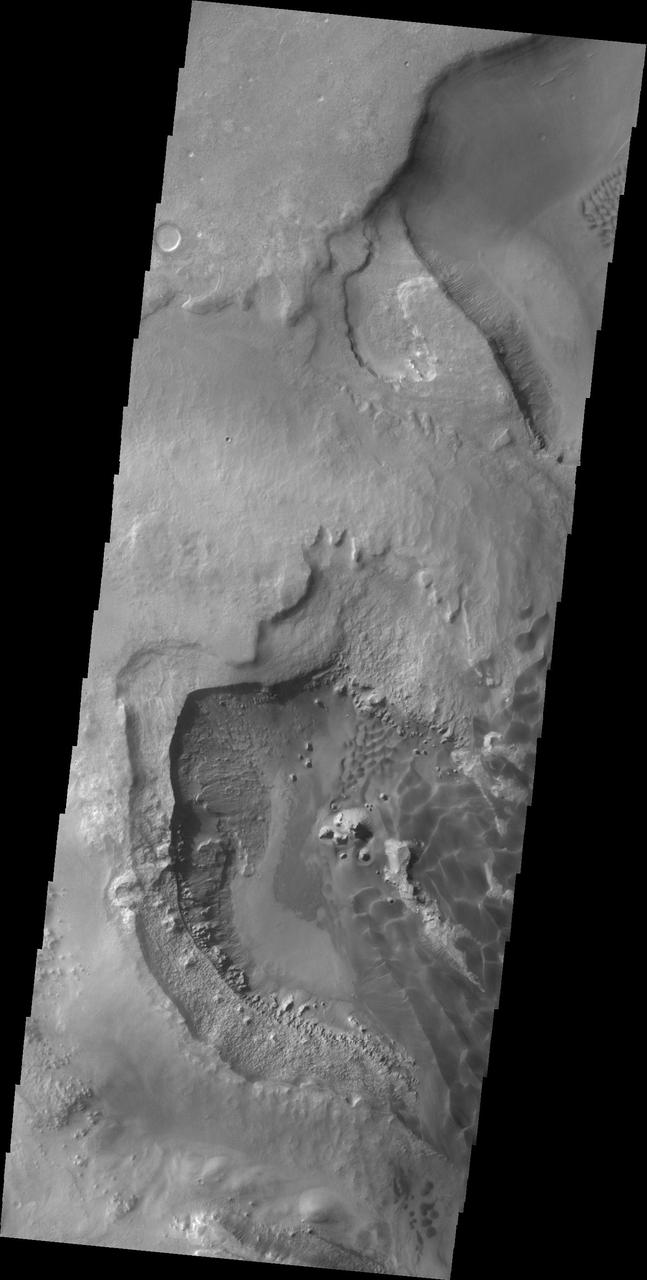

This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows a portion of the depression on the floor of Rabe Crater.
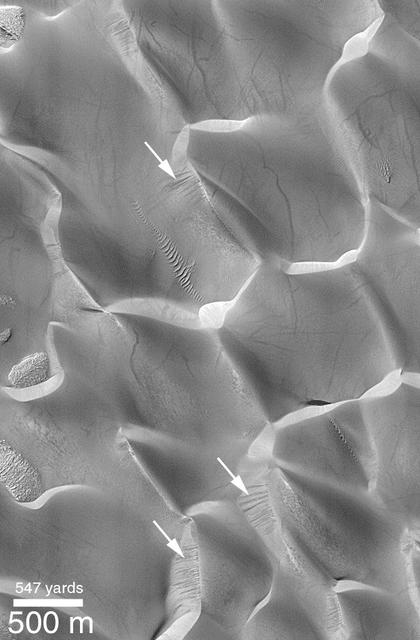
Recent Sand Avalanching on Rabe Crater Dunes

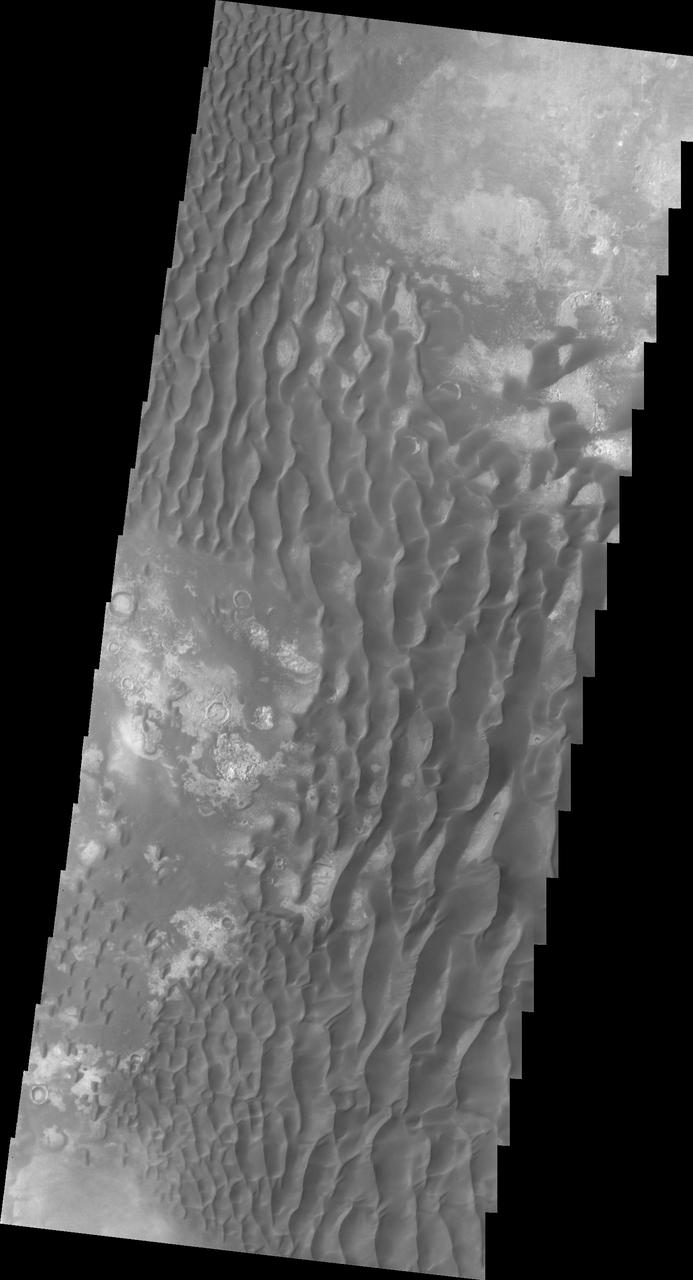
The large sand sheet with surface dune forms seen in this VIS image is located on the complex floor of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. This crater morphology is unique to Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is located in Noachis Terra and is 108km in diameter (67 miles). Orbit Number: 83505 Latitude: -43.6272 Longitude: 34.5903 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-10-11 02:34 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24250
The large sand sheet with surface dune forms seen in this VIS image is located on the complex floor of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. This crater morphology is unique to Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is located in Noachis Terra and is 108km in diameter (67 miles). Orbit Number: 82800 Latitude: -43.81 Longitude: 34.5453 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-08-14 00:54 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24158

The large sand sheet with surface dune forms seen in this VIS image is located on the complex floor of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. This crater morphology is unique to Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is located in Noachis Terra and is 108km in diameter (67 miles). Orbit Number: 82619 Latitude: -43.7003 Longitude: 34.8004 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-07-30 03:43 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24151

The large sand sheet with surface dune forms seen in this VIS image is located on the complex floor of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. This crater morphology is unique to Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is located in Noachis Terra and is 108km in diameter (67 miles). Orbit Number: 84884 Latitude: -43.4896 Longitude: 34.4426 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-02-01 15:04 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24715
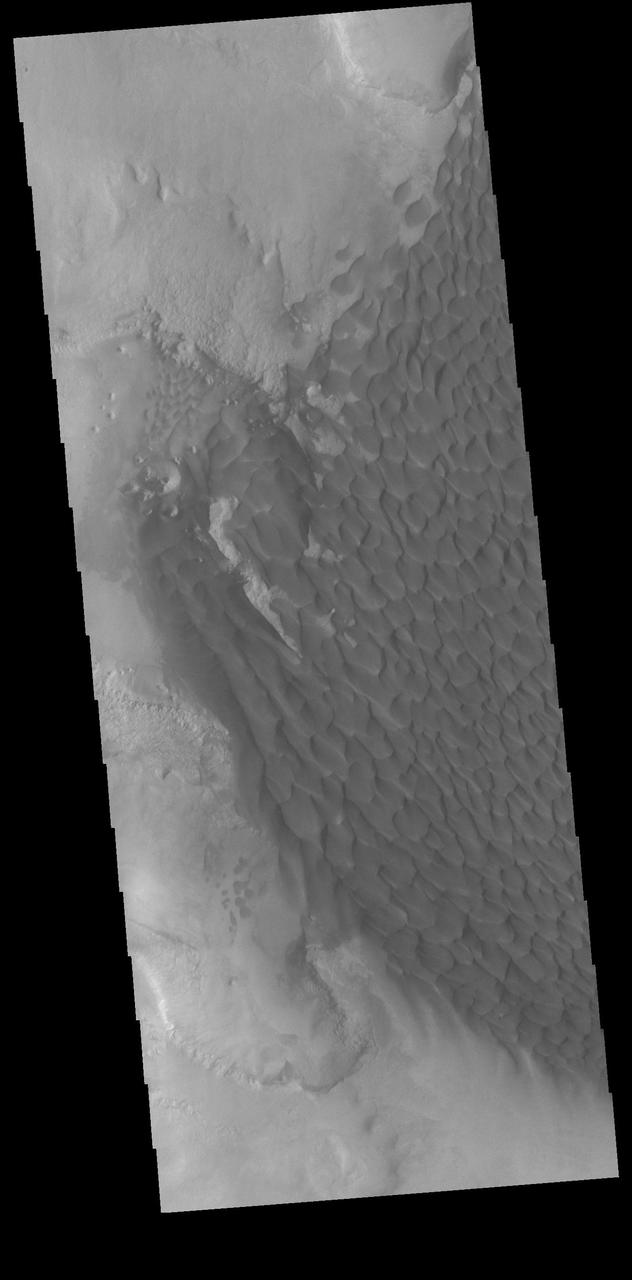

The large sand sheet with surface dune forms seen in this VIS image is located on the complex floor of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. This crater morphology is unique to Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is located in Noachis Terra and is 108km in diameter (67 miles). Orbit Number: 82045 Latitude: -43.8185 Longitude: 34.3876 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-06-12 21:24 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24117

The large sand sheet with surface dune forms seen in this VIS image is located on the complex floor of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. This crater morphology is unique to Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is located in Noachis Terra and is 108km in diameter (67 miles). Orbit Number: 83505 Latitude: -43.6272 Longitude: 34.5903 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-10-11 02:34 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24260

The large sand sheet with surface dune forms seen in this VIS image is located on the complex floor of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. This crater morphology is unique to Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is part of Noachis Terra. Orbit Number: 72201 Latitude: -43.5392 Longitude: 34.6572 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-03-25 04:53 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22501
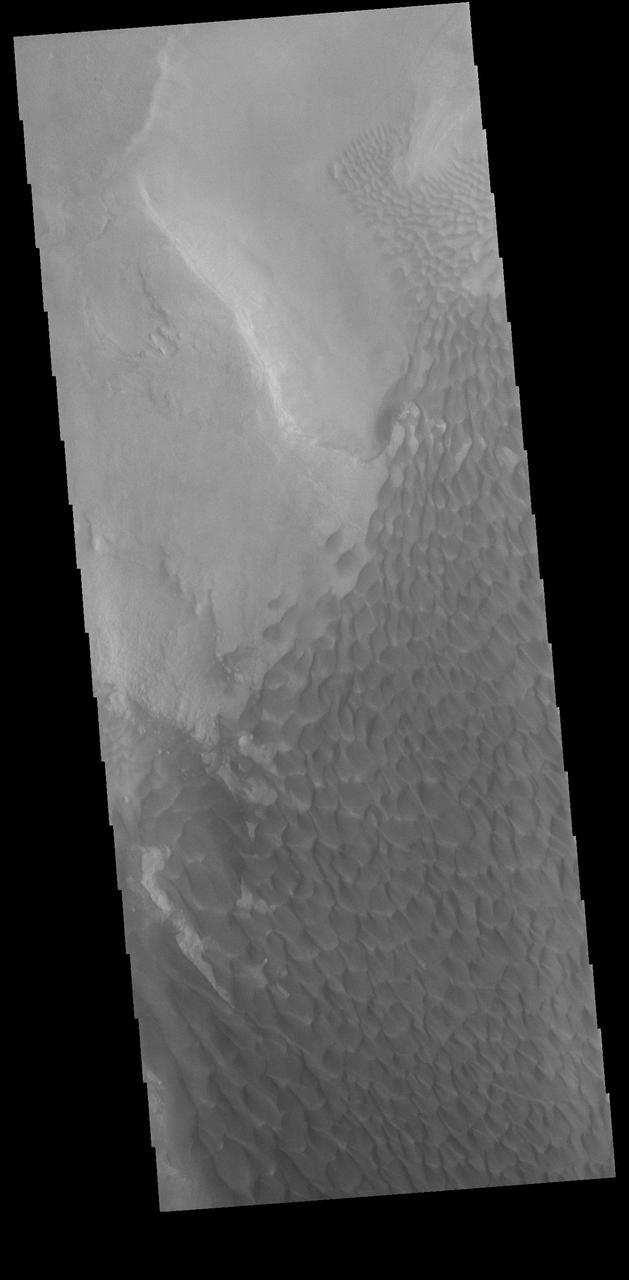

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Sand dunes cover the half of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated less than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 89682 Latitude: -43.5957 Longitude: 34.446 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-03-03 17:05 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25458

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater, including the large dune field. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 93332 Latitude: -43.7011 Longitude: 34.9216 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-12-29 05:34 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25851
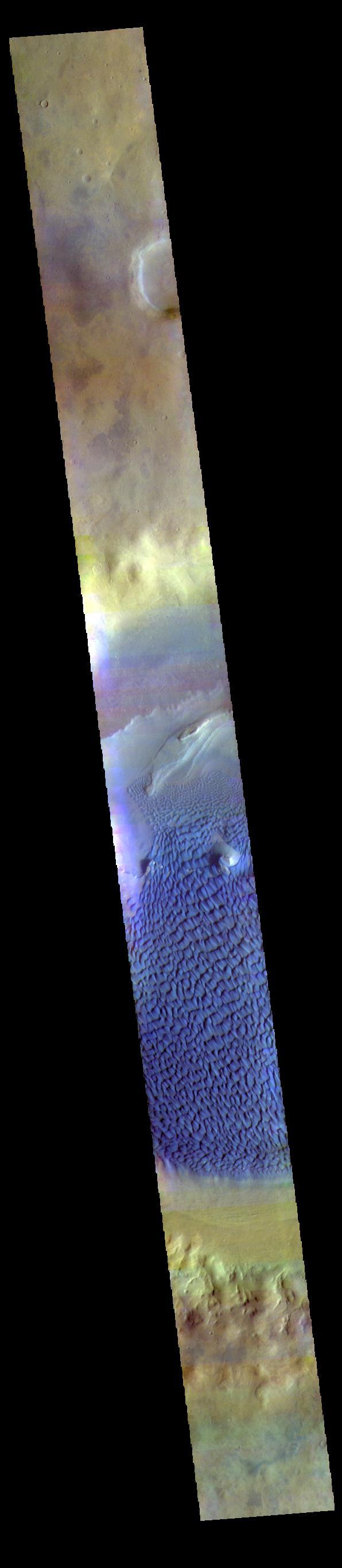

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The movement of the sand is from the lower right towards the upper left. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. Orbit Number: 67013 Latitude: -43.2572 Longitude: 34.5875 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-01-21 18:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24055
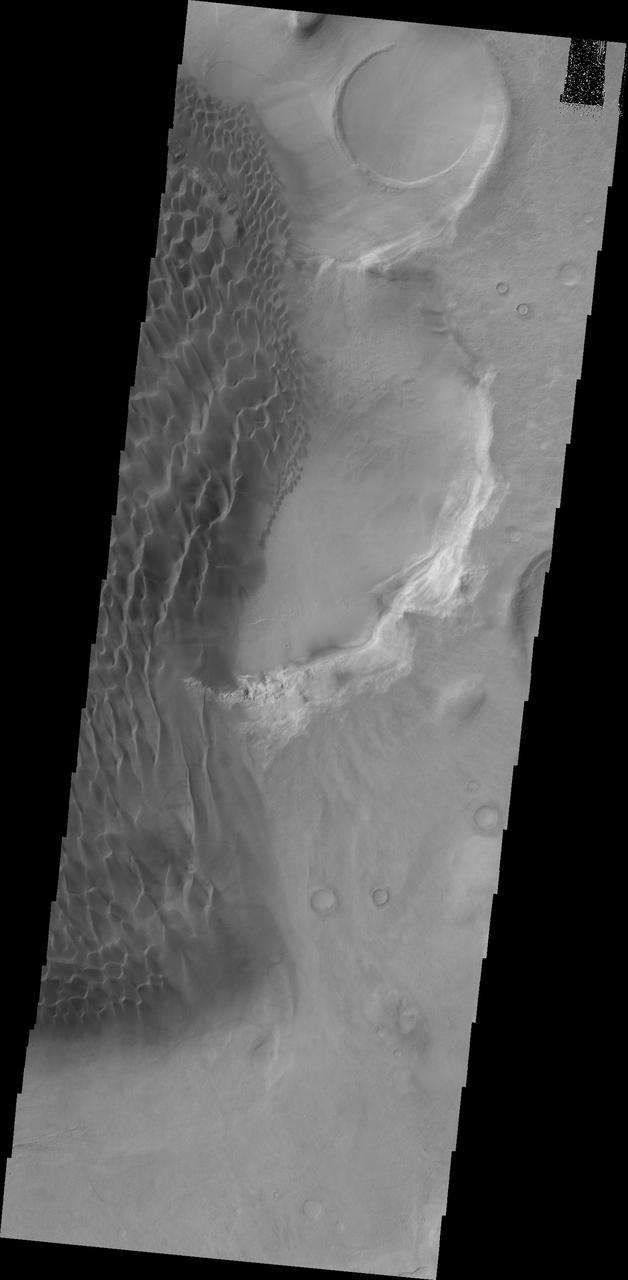

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the dunes on the floor of Rabe Crater.
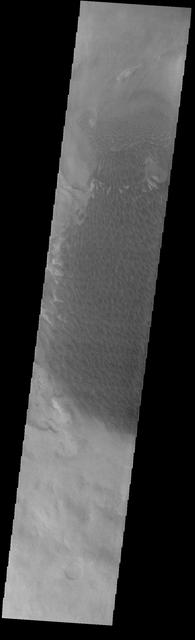
This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey shows the sand sheet with dune forms located on the floor of Rabe Crater.
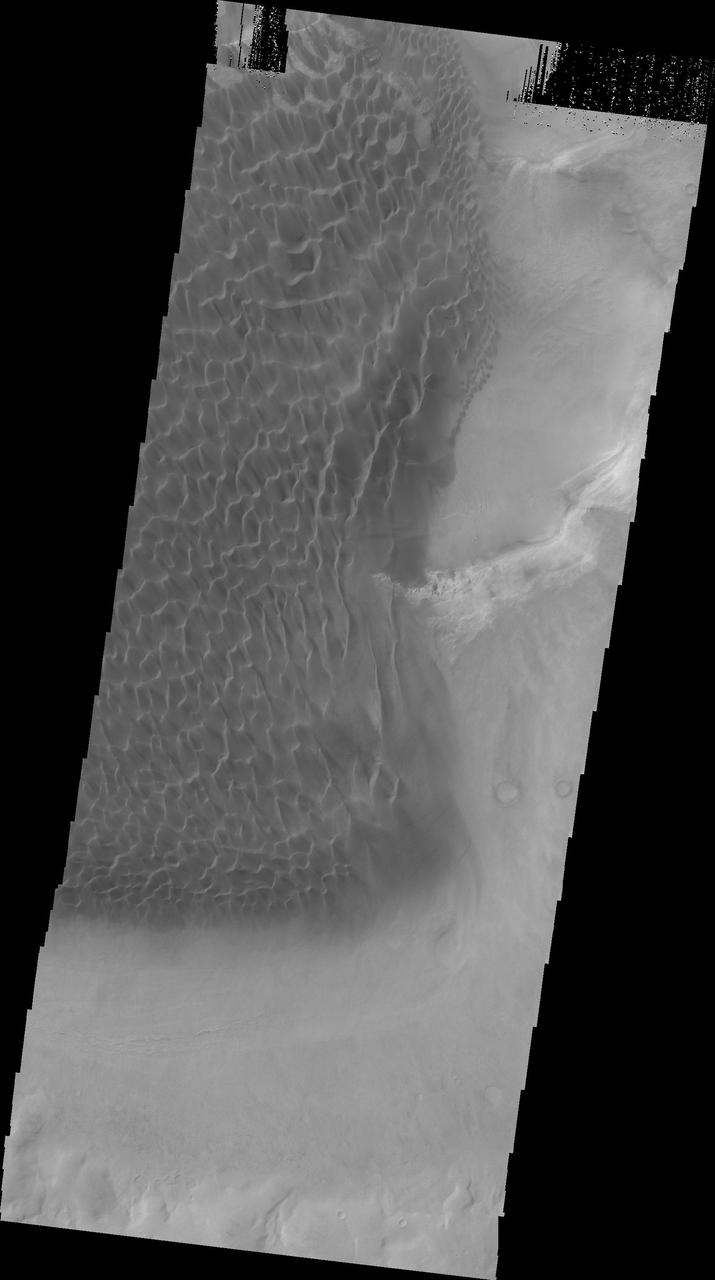

This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey of the dunes on the floor of Rabe Crater was collected simultaneously with yesterday infrared image.

This image shows part of the sand sheet and dunes on the floor of Rabe Crater as seen by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
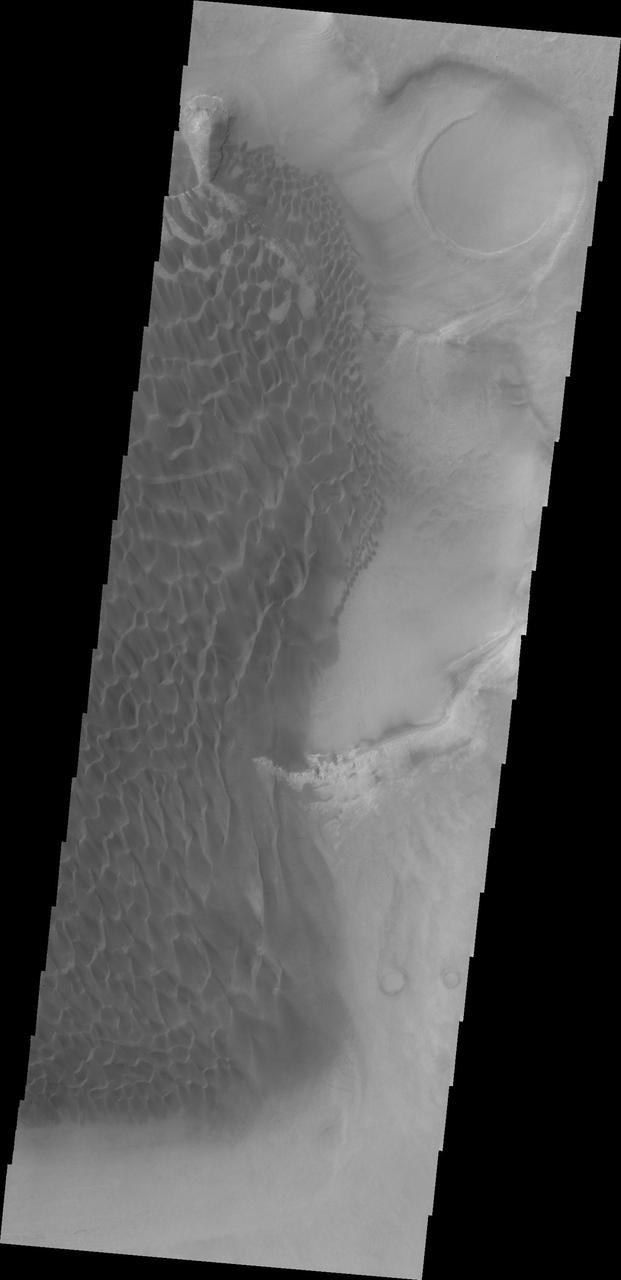

This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the sand sheet and dunes on the floor of Rabe Crater.

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the sand sheet and dunes on the floor of Rabe Crater.
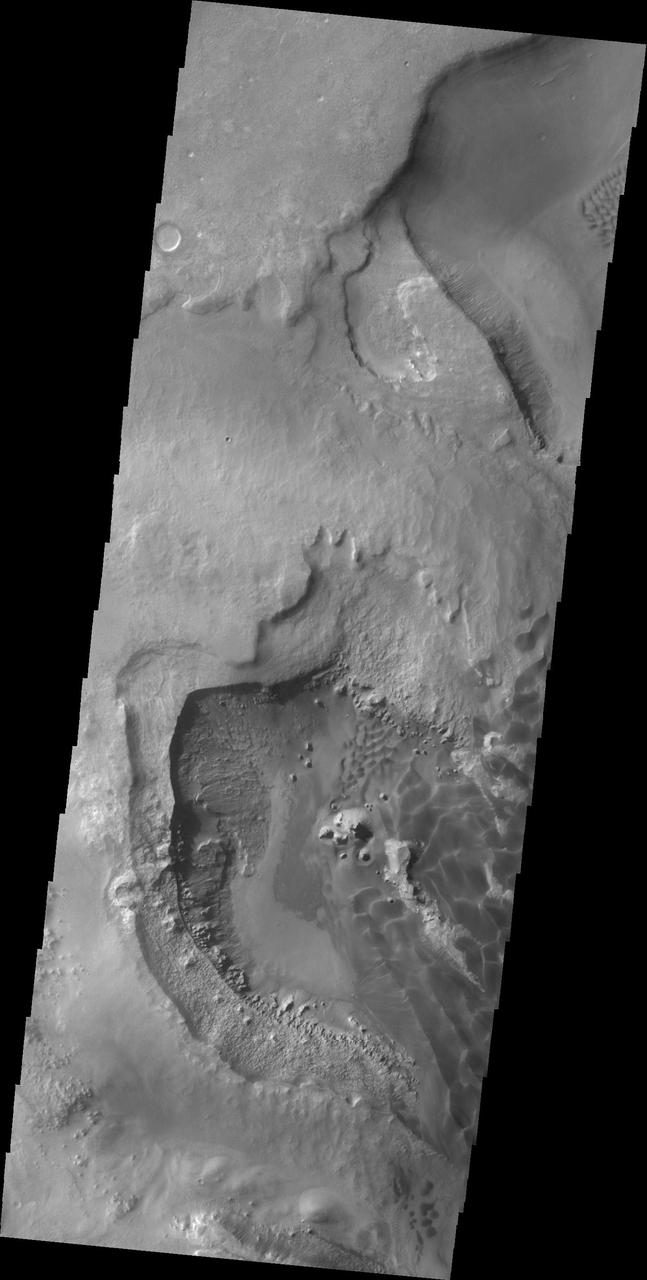

This image shows a portion of the dunes on the floor of Rabe Crater captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
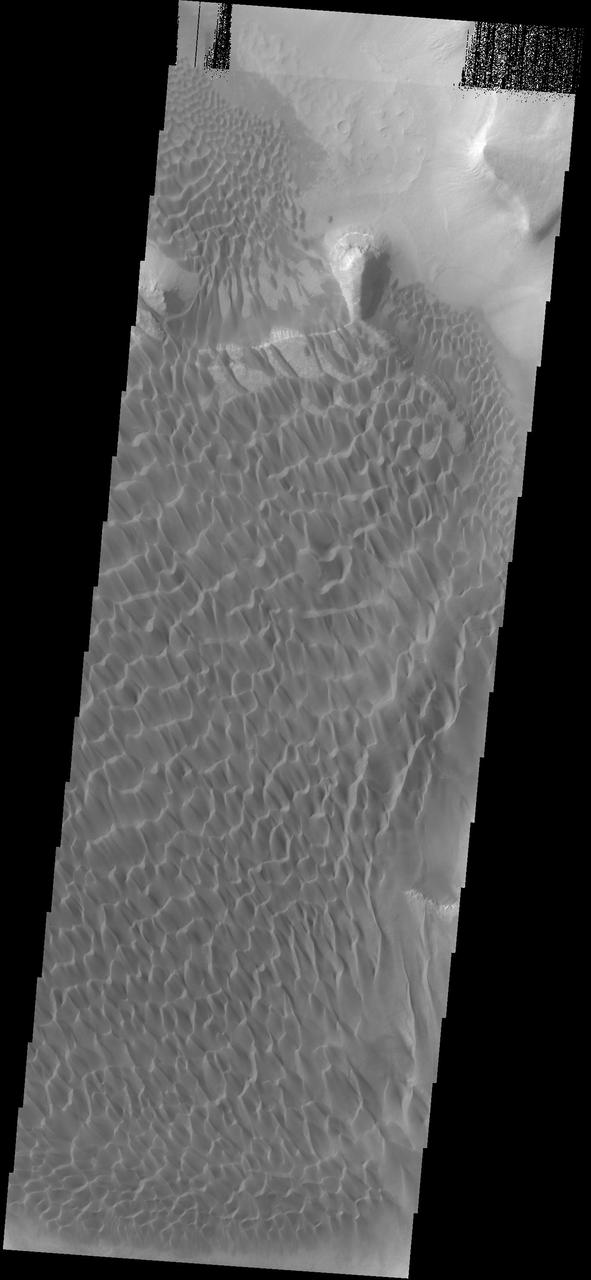

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the dune field located on the floor of Rabe Crater.
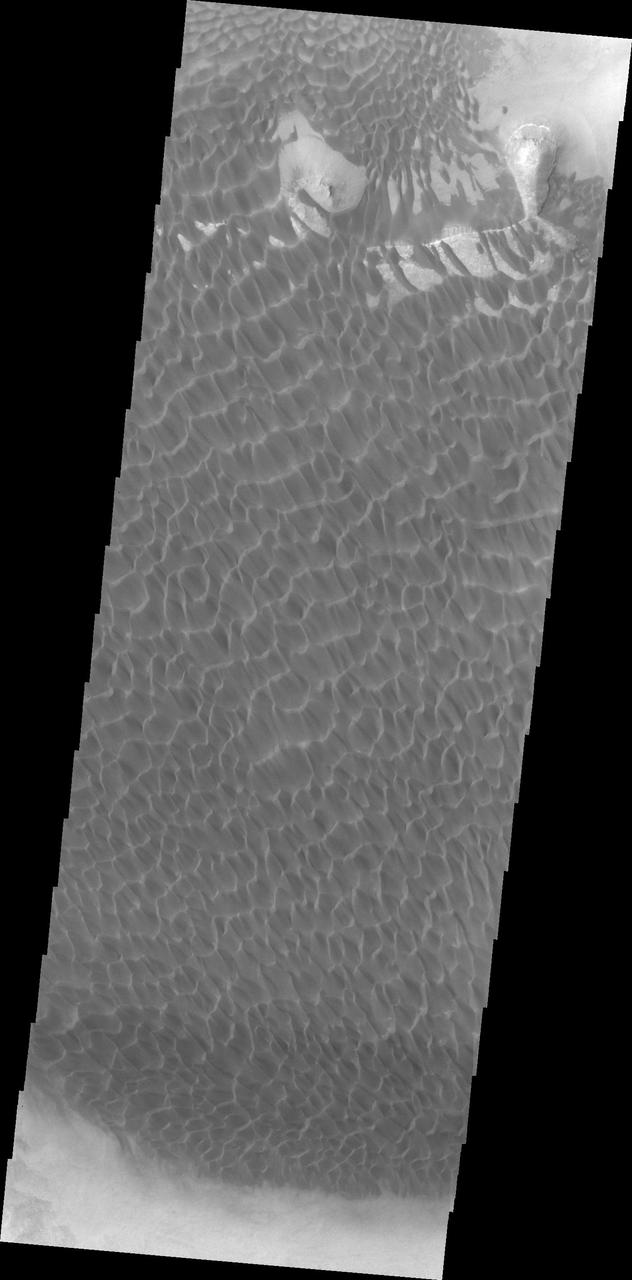
This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the dune field on the floor of Rabe Crater.
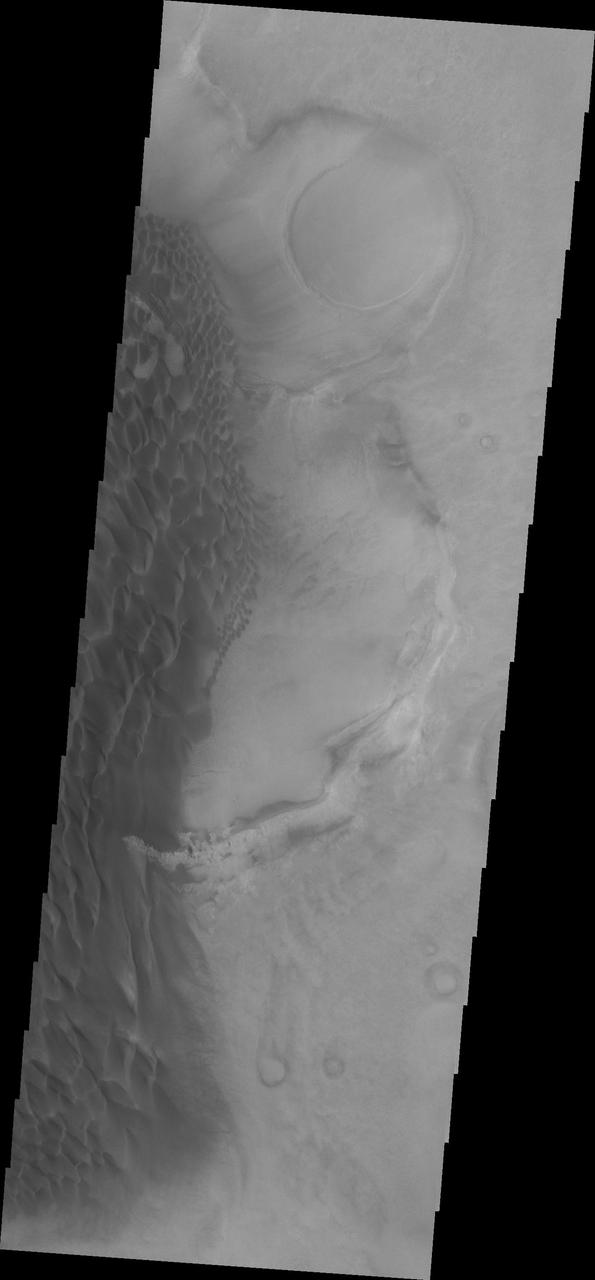

The sand sheet and dune forms in this image from NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft are located on the floor of Rabe Crater.
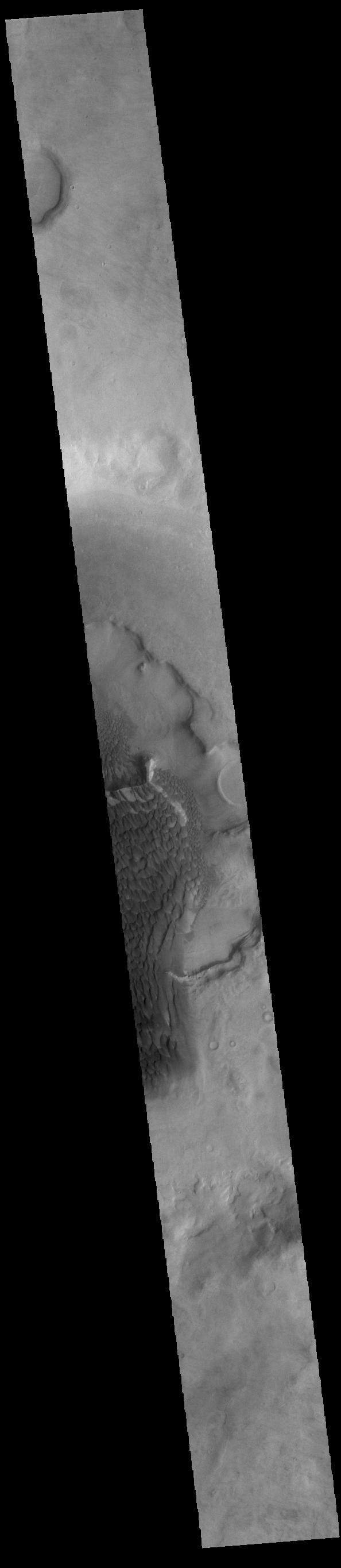

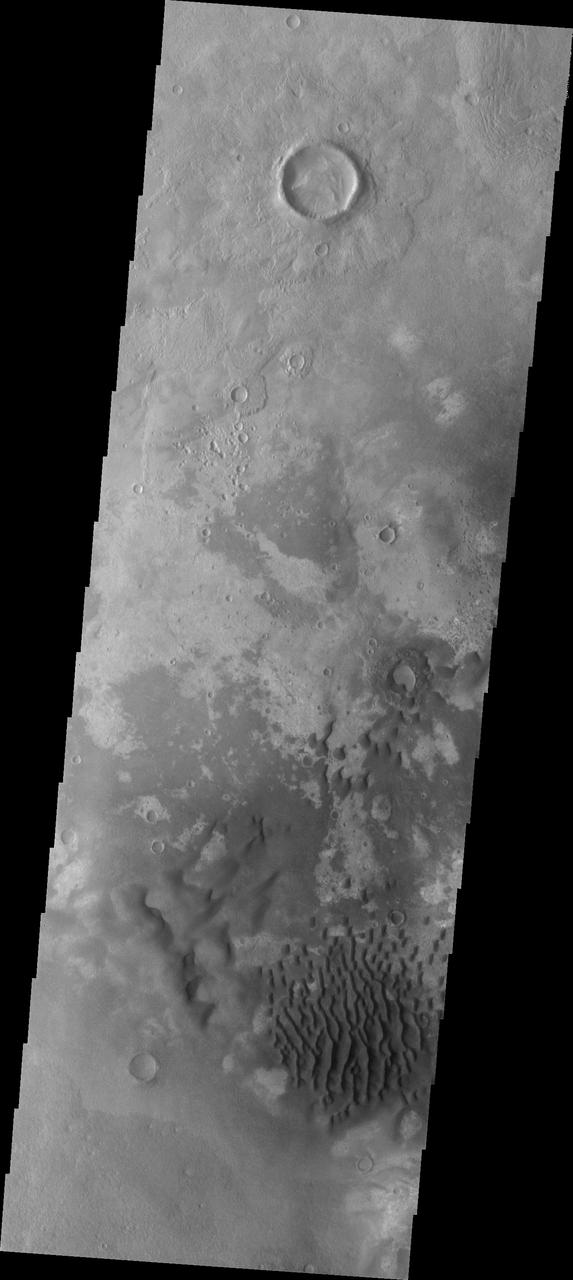
The dunes seen in this VIS image are located on the complex floor of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. Rabe Crater is located in Noachis Terra and is 108km in diameter (67 miles). Orbit Number: 82906 Latitude: -43.447 Longitude: 35.0145 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-08-22 18:52 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24184

The dunes seen in this VIS image are located on the complex floor of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. Rabe Crater is located in Noachis Terra and is 108km in diameter (67 miles). Orbit Number: 84285 Latitude: -44.1162 Longitude: 34.3444 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-12-14 07:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24360

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 67144 Latitude: -43.5512 Longitude: 34.5951 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-02-01 12:57 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24056

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 83505 Latitude: -43.6272 Longitude: 34.5903 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-10-11 02:34 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24709

The Thermal Emission Imaging System aboard NASA Mars Odyssey captured this daytime infrared image of Rabe Crater shows the large dune field located within the crater. Note that the dunes are not confined to the lowest elevation depressions on the
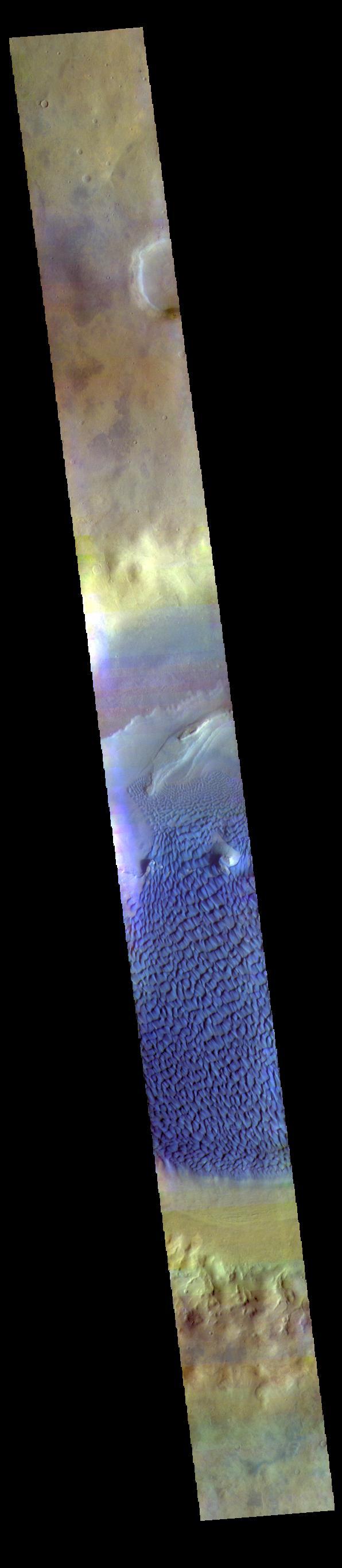

This is a false color image of Rabe Crater. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. This VIS image crosses the entire crater and demonstrates how extensive the dunes are on the floor of Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 67013 Latitude: -43.2572 Longitude: 34.5875 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-01-21 18:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22147
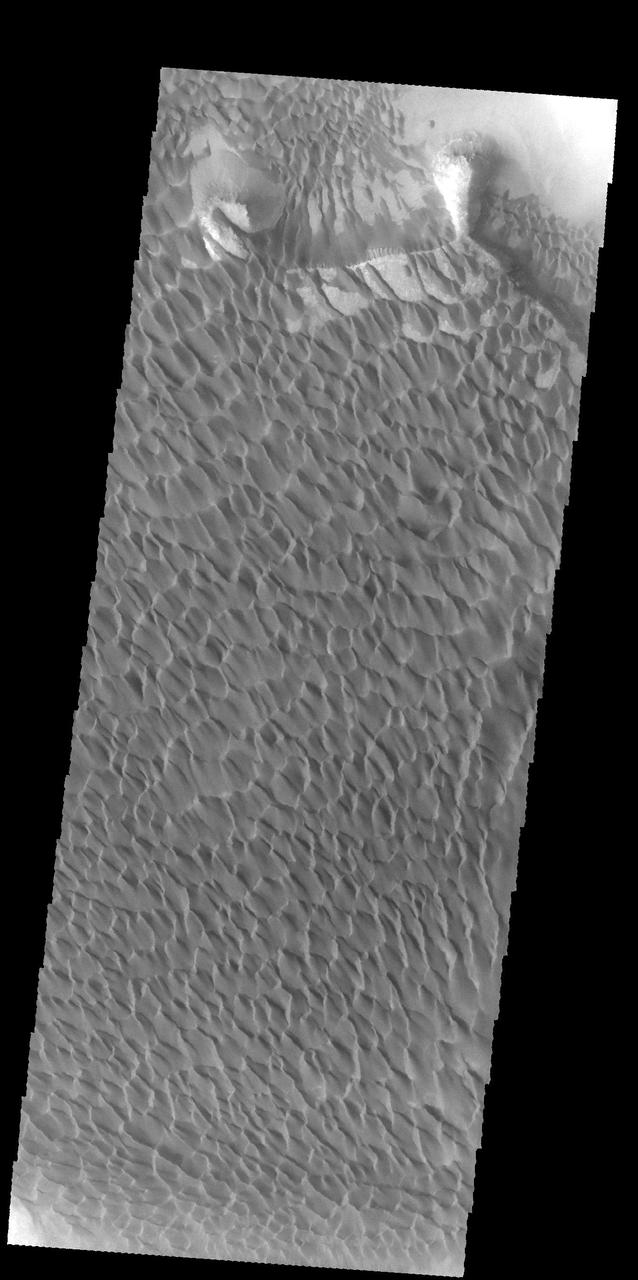

This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows a large portion of the dune field located in the floor of Rabe Crater. Orbit Number: 58024 Latitude: -43.6968 Longitude: 34.8234 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-01-12 09:48 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19207

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the dune field found in a depression on the floor of Rabe Crater. Orbit Number: 57843 Latitude: -43.347 Longitude: 34.6452 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2014-12-28 12:37 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19193

This is a false color image of Rabe Crater. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 67144 Latitude: -43.5512 Longitude: 34.5951 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-02-01 12:57 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22148
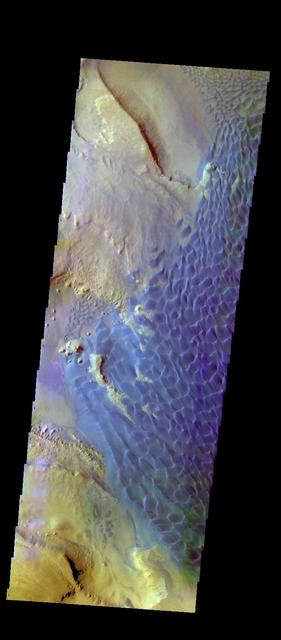
This is a false color image of Rabe Crater. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 51157 Latitude: -43.6787 Longitude: 34.3985 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-06-26 05:33 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22145
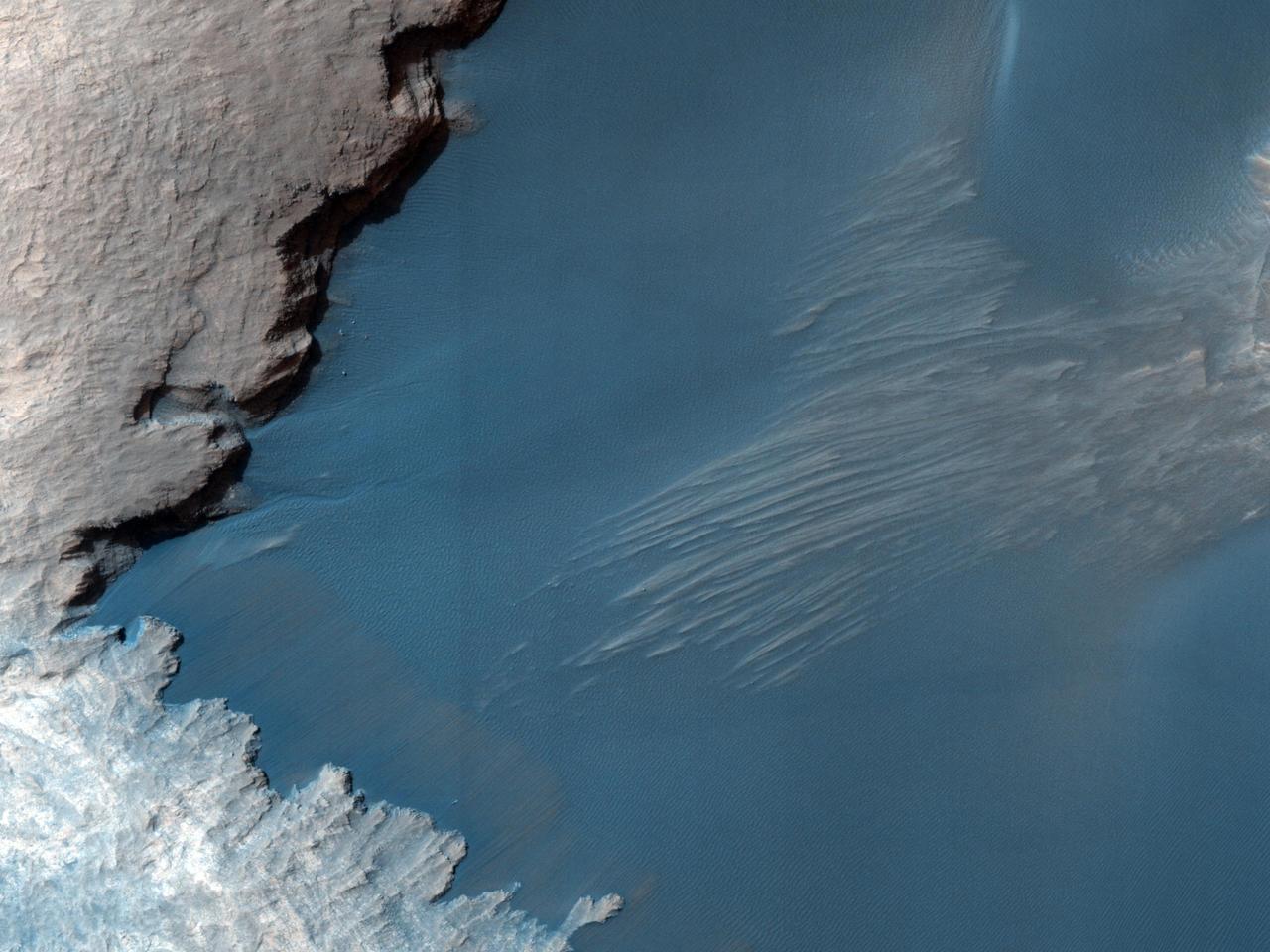

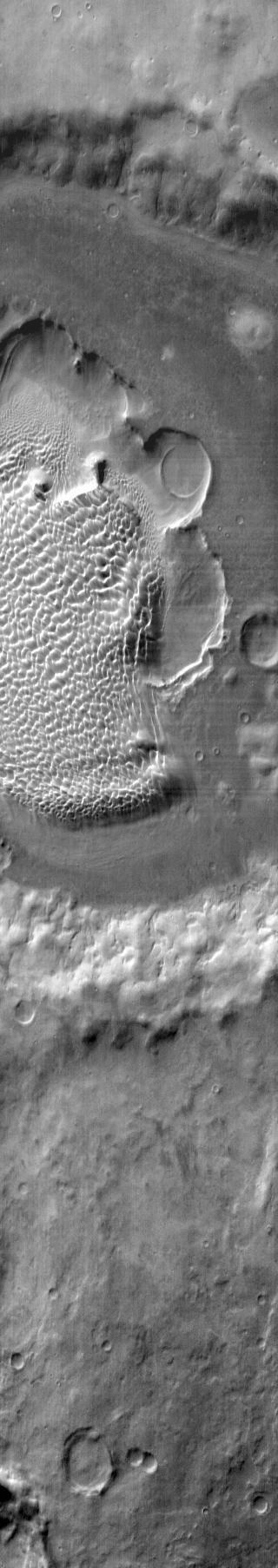
This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater, a large impact crater in the Southern highlands. Dark dunes cover part of crater floor, and contrast with the surrounding bright-colored outcrops.

This daytime IR image from shows NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft part of the dune field on the floor of Rabe Crater. The dunes show up as brighter than the surrounding materials because they are warmer.

This infrared image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the dune field on the floor of Rabe Crater. The dunes are brighter than the surrounding material, indicating that they are warmer.

Today's VIS image shows part of the dune field on the floor and within the pits of Rabe Crater. This crater, and a handful of others in Noachis Terra, have unique floors. At some point after the initial formation of the crater there was an influx of fill material. The later erosion of this material formed a series of large, deep pits in the crater floor. The continued erosion of the floor fill as well as the influx of wind driven sand and dust particles provided the raw materials for the formation of the dunes. The prevailing winds blow from the lower right to the upper left of the image. Orbit Number: 75307 Latitude: -43.5769 Longitude: 34.3041 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-12-06 01:11 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23072

This is a false color image of Rabe Crater. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 52231 Latitude: -43.6665 Longitude: 34.2627 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-09-22 14:29 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22146
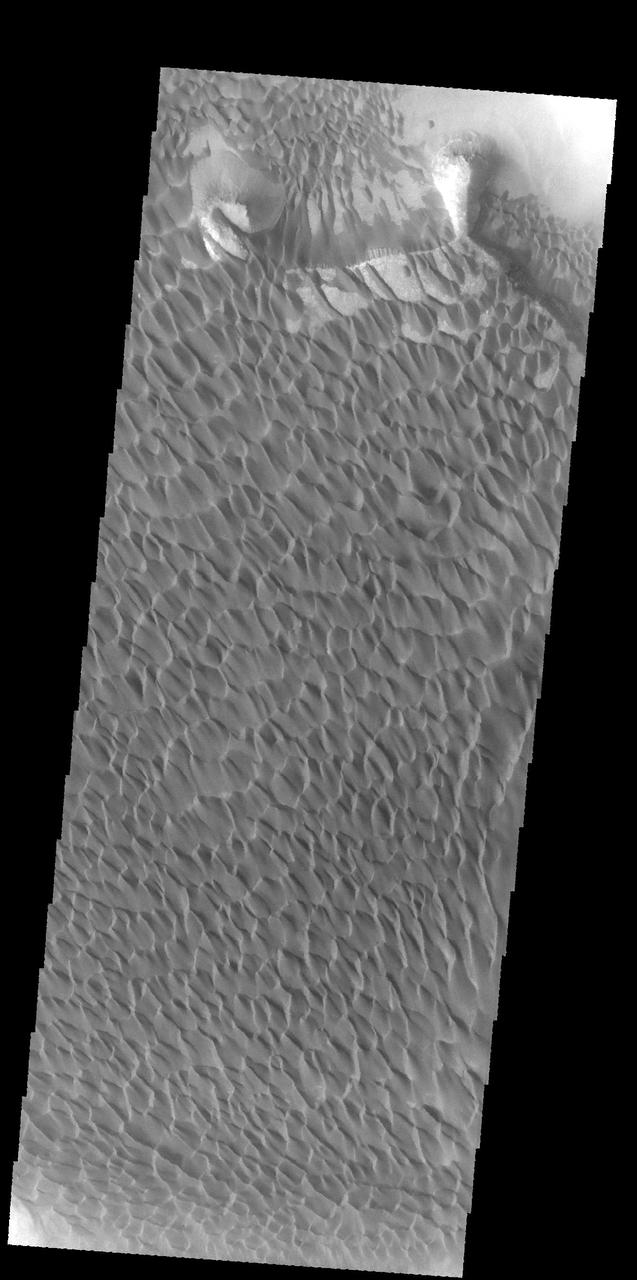

The majority of the dune field in Rabe Crater consists of a sand sheet with dune forms on the surface. The sand sheet is where a thick layer of sand has been concentrated. As continued winds blow across the sand surface it creates dune forms. The depth of the sand sheet prevents excavation to the crater floor and the dune forms all appear connected. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 58024 Latitude: -43.6954 Longitude: 34.8236 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-01-12 09:48 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22144

This VIS image of Rabe Crater is dominated by the extensive dunes that cover the crater floor. To the top of the image part of the pit is visible, as well as a small peninsula that has been eroded into the upper level floor materials. On the upper elevation on the side left of the peninsula the dunes cascade onto the lower pit elevation. There is also a slight arc to the dunes on the pit floor due to how the peninsula changed the wind pattern. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 52206 Latitude: -43.6573 Longitude: 34.9551 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-09-20 13:07 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22142
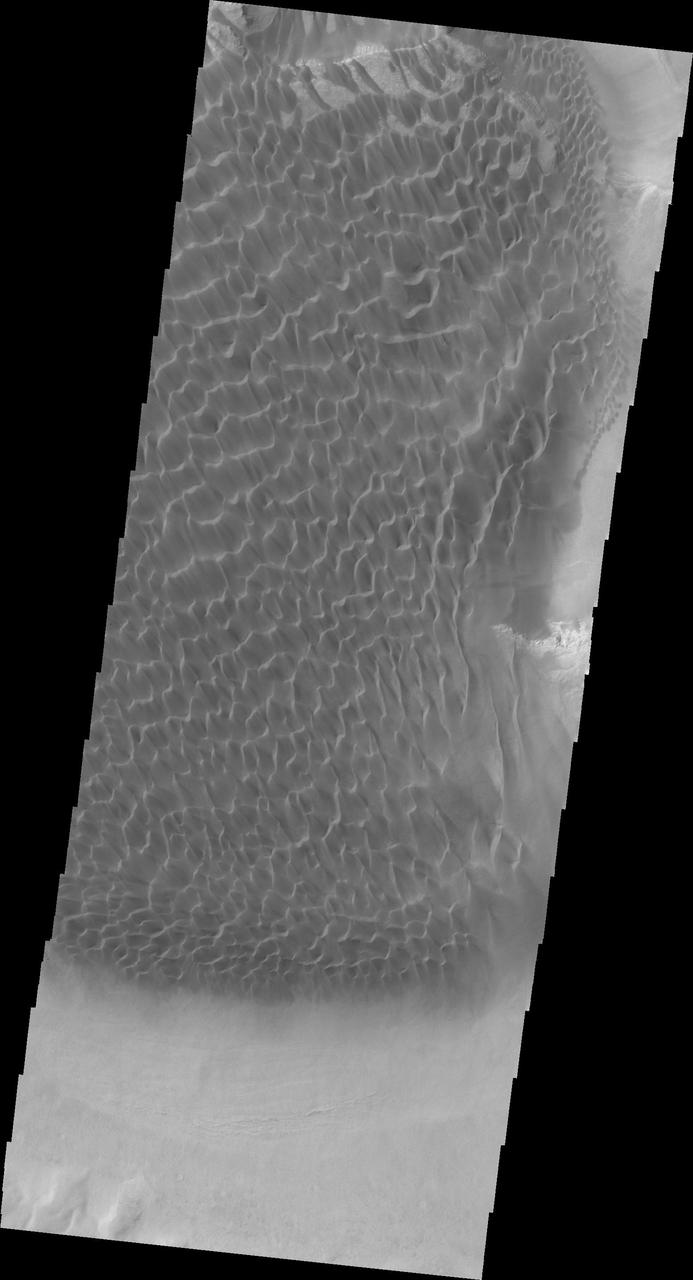
Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 35105 Latitude: -43.8533 Longitude: 34.8802 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-11-12 19:59 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22141
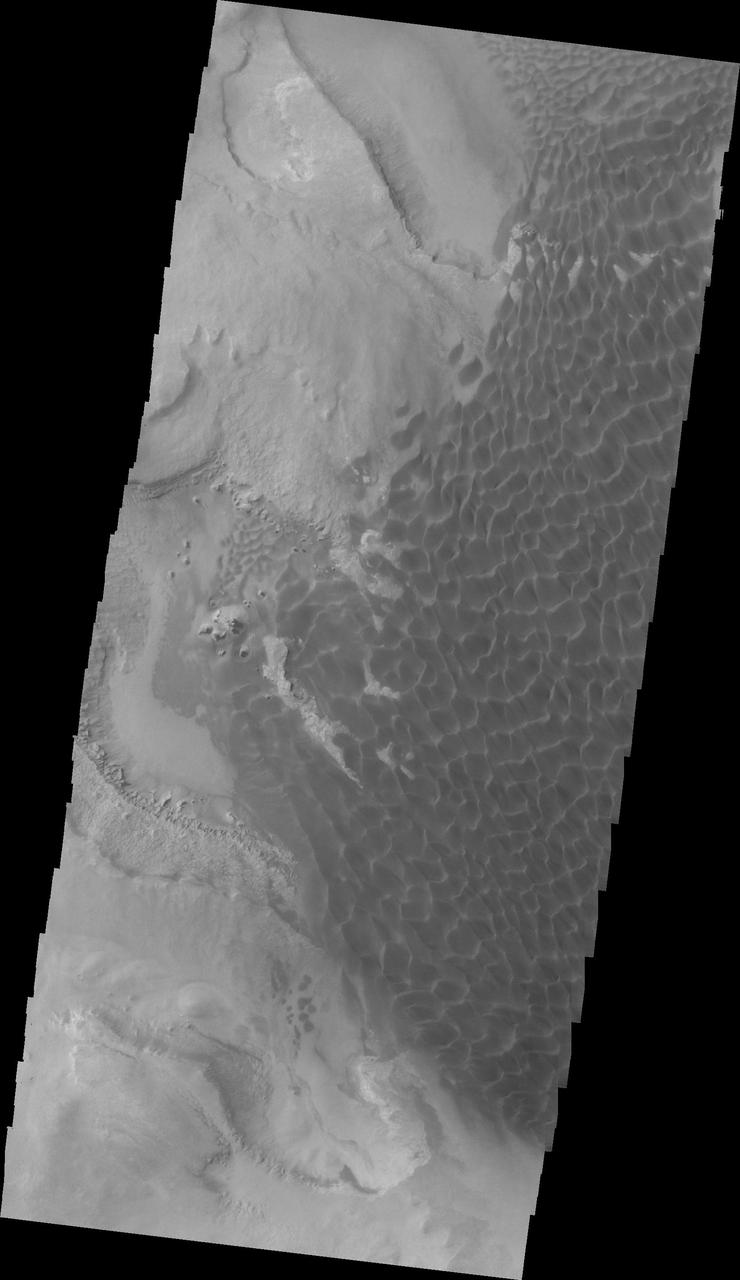

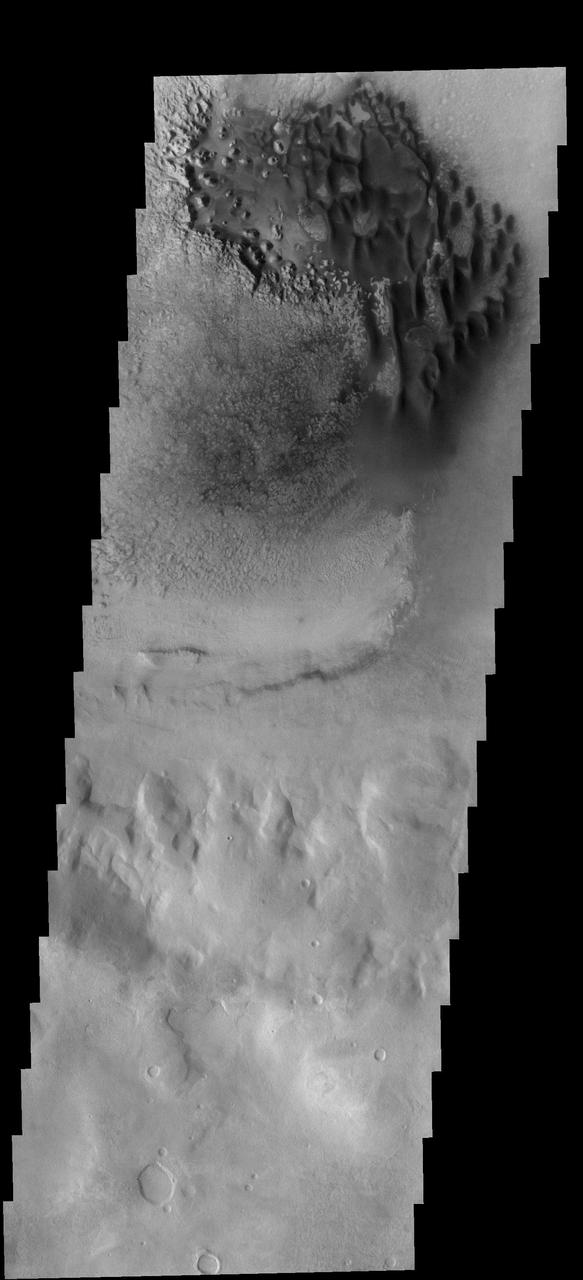
In this VIS image of the floor of Rabe Crater the step down into the pit is visible in the sinuous ridges on the left side of the image. The appearance of the exposed side of the cliffs does not look like a volcanic, difficult to erode material, but rather an easy to erode material such as layered sediments. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 34456 Latitude: -43.7164 Longitude: 34.4056 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-09-20 09:38 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22140
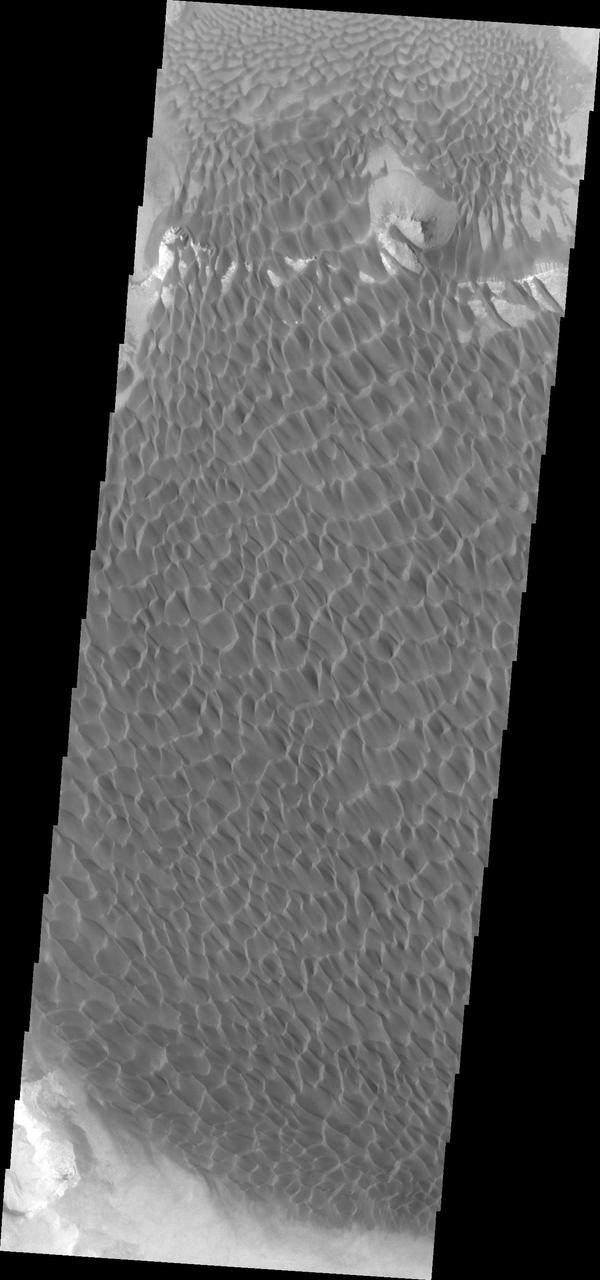
Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. In this VIS image the rim of the pit is visible near the top of the image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 17074 Latitude: -43.6954 Longitude: 34.66 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-10-20 04:05 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22139

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the dune field on the floor of Rabe Crater. Orbit Number: 58467 Latitude: -43.72 Longitude: 35.1415 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-02-17 21:43 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19744

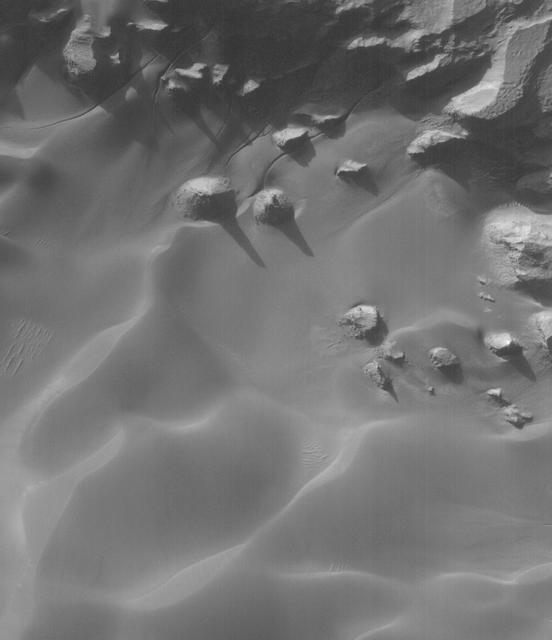
Individual dunes are found on the floor of this unnamed crater located to the north of Rabe Crater in this image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.

This Mars Global Surveyor MGS Mars Orbiter Camera MOC image shows gullies formed in the wall of a depression located on the floor of Rabe Crater west of the giant impact basin, Hellas Planitia

This MOC shows buttes and mesas surrounded by sand dunes on the floor of Rabe Crater, Mars. Gullies of uncertain origin cut sand dune surfaces in the top north quarter of the scene

This image of Rabe Crater and the region around it was collected using the IR (infrared) camera. The brighter the material, the warmer the surface is. Most dunes on Mars are dark in visible wavelengths and bright in infrared. The majority of large craters in the southern hemisphere contain dunes on the crater floor. Orbit Number: 67144 Latitude: -46.329 Longitude: 34.079 Instrument: IR Captured: 2017-02-01 12:57 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21519

Sand dunes on the floor of Rabe Crater are brighter in this infrared image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft than the surrounding materials. This is because the sand is warmer than the surrounding rock. Orbit Number: 57712 Latitude: -43.7612 Longitude: 34.3755 Instrument: IR Captured: 2014-12-17 17:16 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19189

This VIS image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft, compared to yesterday IR image, shows the dunes darker than their surroundings due to cooler temperature.

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows a large dune covered sand sheet on the floor of this unnamed crater in Noachis Terra. Large scale dunes and dune fields cover the floor of many craters in this region west of Hellas Planitia — including Rabe, Proctor, and Matara craters and numerous other unnamed craters. In this false color combination blue indicates basaltic sands. Orbit Number: 67250 Latitude: -49.0136 Longitude: 34.0967 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-02-10 07:02 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24058

This VIS image of Kaiser Crater shows a region of the dunes with varied appearances. The different dune forms developed due to different amounts of available sand, different wind directions, and the texture of the crater floor. Dune size, shape, and spacing is controlled by a variety of factors. Note the dune that fills half of the crater in the center of the image. Kaiser Crater is located in the southern hemisphere in the Noachis region west of Hellas Planitia. Kaiser Crater is just one of several large craters with extensive dune fields on the crater floor. Other nearby dune filled craters are Proctor, Russell, and Rabe. Kaiser Crater is 207 km (129 miles) in diameter. The dunes are located in the southern part of the crater floor. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 14953 Latitude: -46.7919 Longitude: 18.4314 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-04-28 12:59 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22175
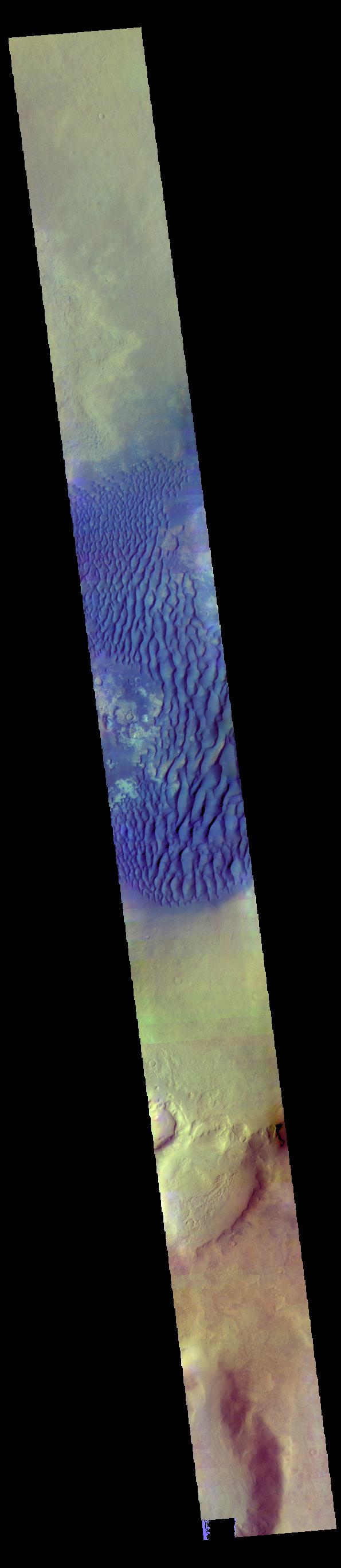
This is a false color image of Kaiser Crater. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. This VIS image crosses 3/4 of the crater and demonstrates how extensive the dunes are on the floor of Kaiser Crater. Kaiser Crater is located in the southern hemisphere in the Noachis region west of Hellas Planitia. Kaiser Crater is just one of several large craters with extensive dune fields on the crater floor. Other nearby dune filled craters are Proctor, Russell, and Rabe. Kaiser Crater is 207 km (129 miles) in diameter. The dunes are located in the southern part of the crater floor. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 66602 Latitude: -47.0551 Longitude: 19.446 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2016-12-18 21:42 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22265

This VIS image of the floor of Kaiser Crater contains a large variety of sand dune shapes and sizes. The "whiter" material is the hard crater floor surface. Kaiser Crater is located in the southern hemisphere in the Noachis region west of Hellas Planitia. Kaiser Crater is just one of several large craters with extensive dune fields on the crater floor. Other nearby dune filled craters are Proctor, Russell, and Rabe. Kaiser Crater is 207 km (129 miles) in diameter. The dunes are located in the southern part of the crater floor. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 35430 Latitude: -46.8699 Longitude: 19.4731 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-12-09 14:09 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22263
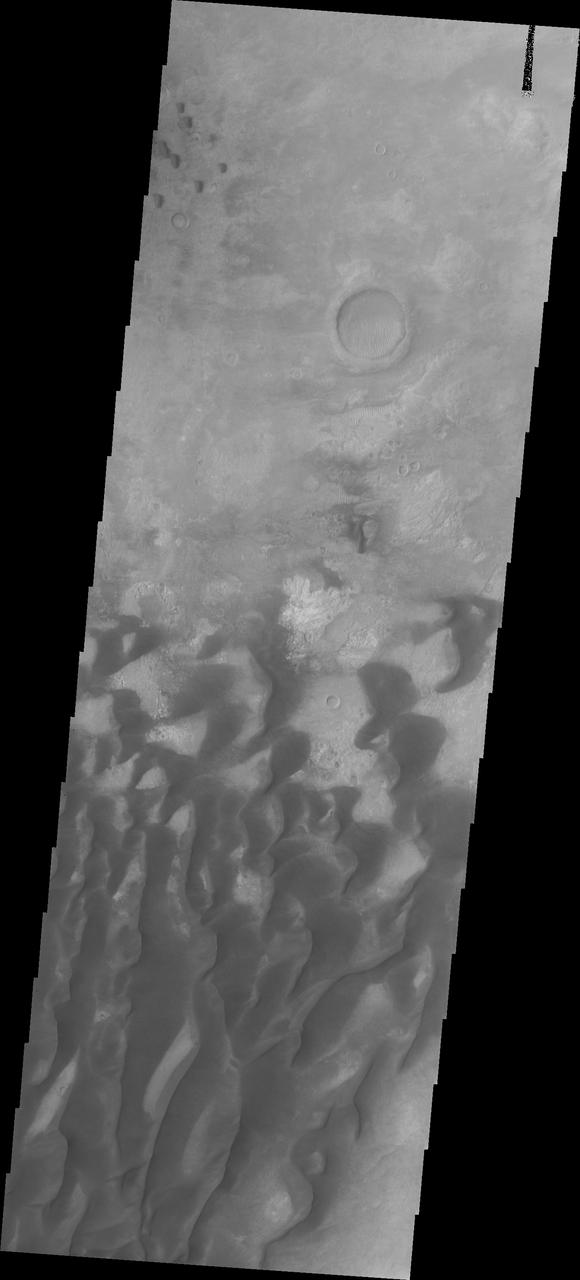

This VIS image of Kaiser Crater shows a region of the dunes with varied appearances. The different dune forms developed due to different amounts of available sand, different wind directions, and the texture of the crater floor. The dune forms change from the bottom to the top of the image - large long connected dunes, to large individual dunes, to the very small individual dunes at the top of the image. Kaiser Crater is located in the southern hemisphere in the Noachis region west of Hellas Planitia. Kaiser Crater is just one of several large craters with extensive dune fields on the crater floor. Other nearby dune filled craters are Proctor, Russell, and Rabe. Kaiser Crater is 207 km (129 miles) in diameter. The dunes are located in the southern part of the crater floor. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 17686 Latitude: -46.6956 Longitude: 19.8394 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-12-09 13:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22261
This VIS image of Kaiser Crater shows individual dunes and where the dunes have coalesced into longer dune forms. The addition of sand makes the dunes larger and the intra-dune areas go from sand-free to complete coverage of the hard surface of the crater floor. With a continued influx of sand the region will transition from individual dunes to a sand sheet with surface dune forms. Kaiser Crater is located in the southern hemisphere in the Noachis region west of Hellas Planitia. Kaiser Crater is just one of several large craters with extensive dune fields on the crater floor. Other nearby dune filled craters are Proctor, Russell, and Rabe. Kaiser Crater is 207 km (129 miles) in diameter. The dunes are located in the southern part of the crater floor. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 1423 Latitude: -46.9573 Longitude: 18.6192 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2002-04-10 16:44 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22173
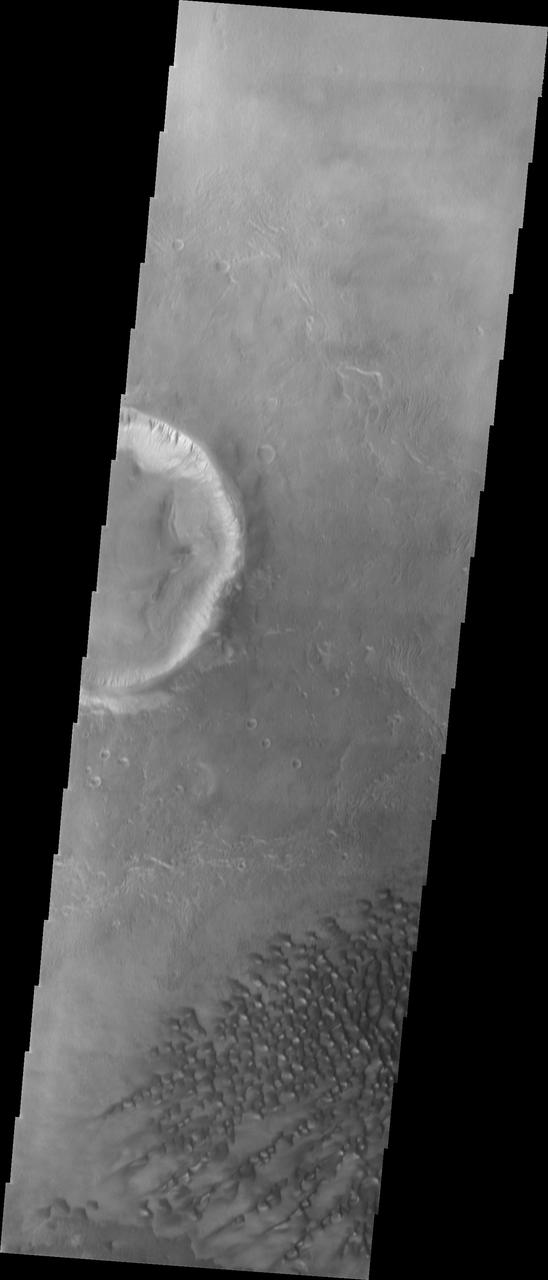

This VIS image of Kaiser Crater shows the central part of the crater floor. At the bottom of the image there is a topographic rise. The change in topography has altered the winds in this region, forming a linear pattern at the edge of the high land. Kaiser Crater is located in the southern hemisphere in the Noachis region west of Hellas Planitia. Kaiser Crater is just one of several large craters with extensive dune fields on the crater floor. Other nearby dune filled craters are Proctor, Russell, and Rabe. Kaiser Crater is 207 km (129 miles) in diameter. The dunes are located in the southern part of the crater floor. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 5505 Latitude: -46.2432 Longitude: 19.028 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2003-03-12 17:05 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22174

This VIS image of the floor of Kaiser Crater contains several sand dune shapes and sizes. The "whiter" material is the hard crater floor surface. Kaiser Crater is located in the southern hemisphere in the Noachis region west of Hellas Planitia. Kaiser Crater is just one of several large craters with extensive dune fields on the crater floor. Other nearby dune filled craters are Proctor, Russell, and Rabe. Kaiser Crater is 207 km (129 miles) in diameter. The dunes are located in the southern part of the crater floor. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 39910 Latitude: -46.9063 Longitude: 19.8112 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2010-12-13 11:17 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22264
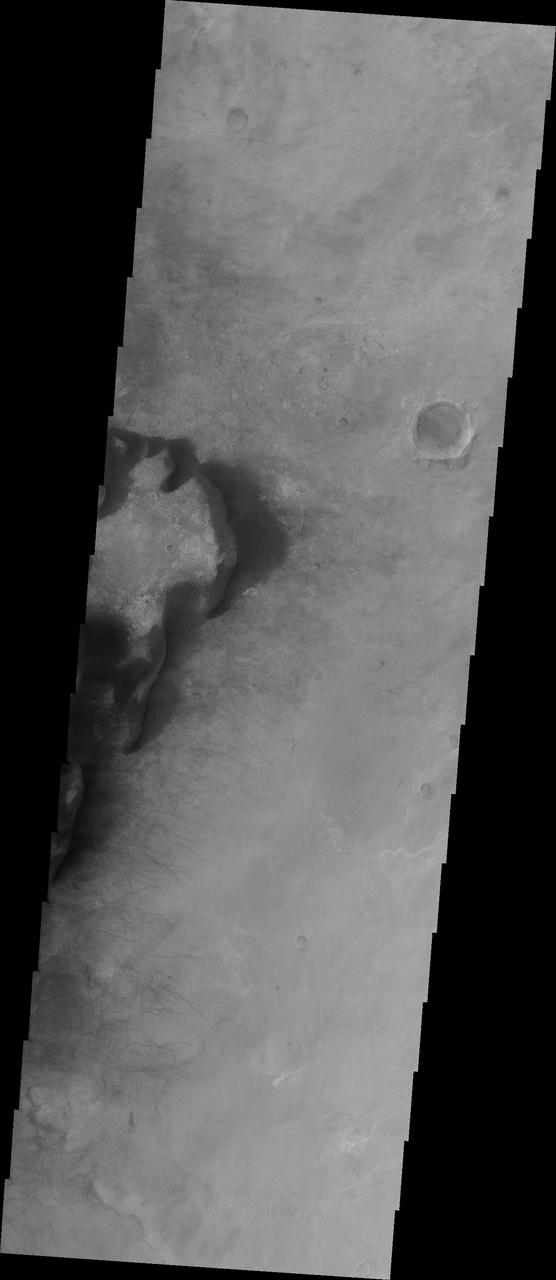

Kaiser Crater is located in the southern hemisphere in the Noachis region west of Hellas Planitia. Kaiser Crater is just one of several large craters with extensive dune fields on the crater floor. Other nearby dune filled craters are Proctor, Russell, and Rabe. Kaiser Crater is 207 km (129 miles) in diameter. The dunes are located in the southeastern part of the crater floor. Most of the individual dunes in Kaiser Crater are barchan dunes. Barchan dunes are crescent shaped with the points of the crescent pointing downwind. The sand is blown up the low angle side of the dune and then tumbles down the steep slip face. This dune type forms on hard surfaces where there is limited amounts of sand. Barchan dunes can merge together over time with increased sand in the local area. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 1036 Latitude: -46.7795 Longitude: 20.2075 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2002-03-09 20:07 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22172
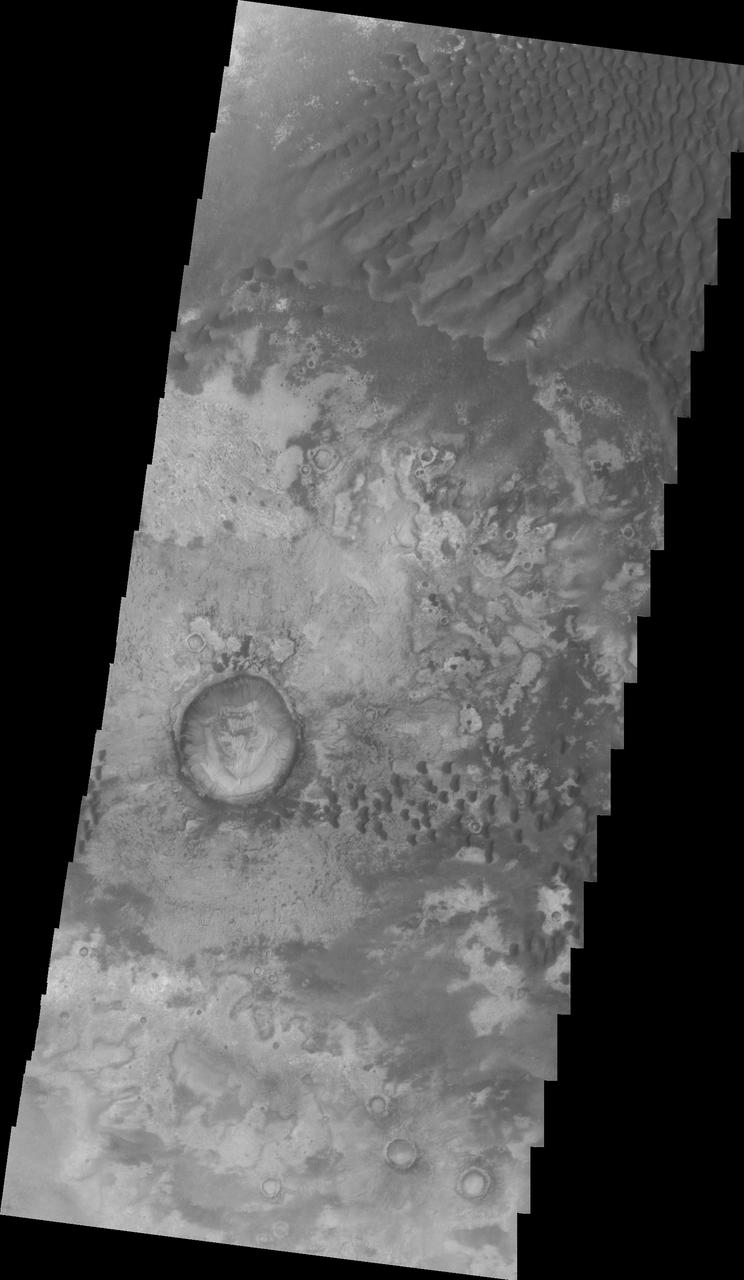

At the top of this VIS image crescent shaped dunes are visible. As the dunes approach a break in elevation the forms change to connect the crescents together forming long aligned dune forms. Kaiser Crater is located in the southern hemisphere in the Noachis region west of Hellas Planitia. Kaiser Crater is just one of several large craters with extensive dune fields on the crater floor. Other nearby dune filled craters are Proctor, Russell, and Rabe. Kaiser Crater is 207 km (129 miles) in diameter. The dunes are located in the southern part of the crater floor. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 34157 Latitude: -46.9336 Longitude: 18.9272 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-08-26 18:49 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22262