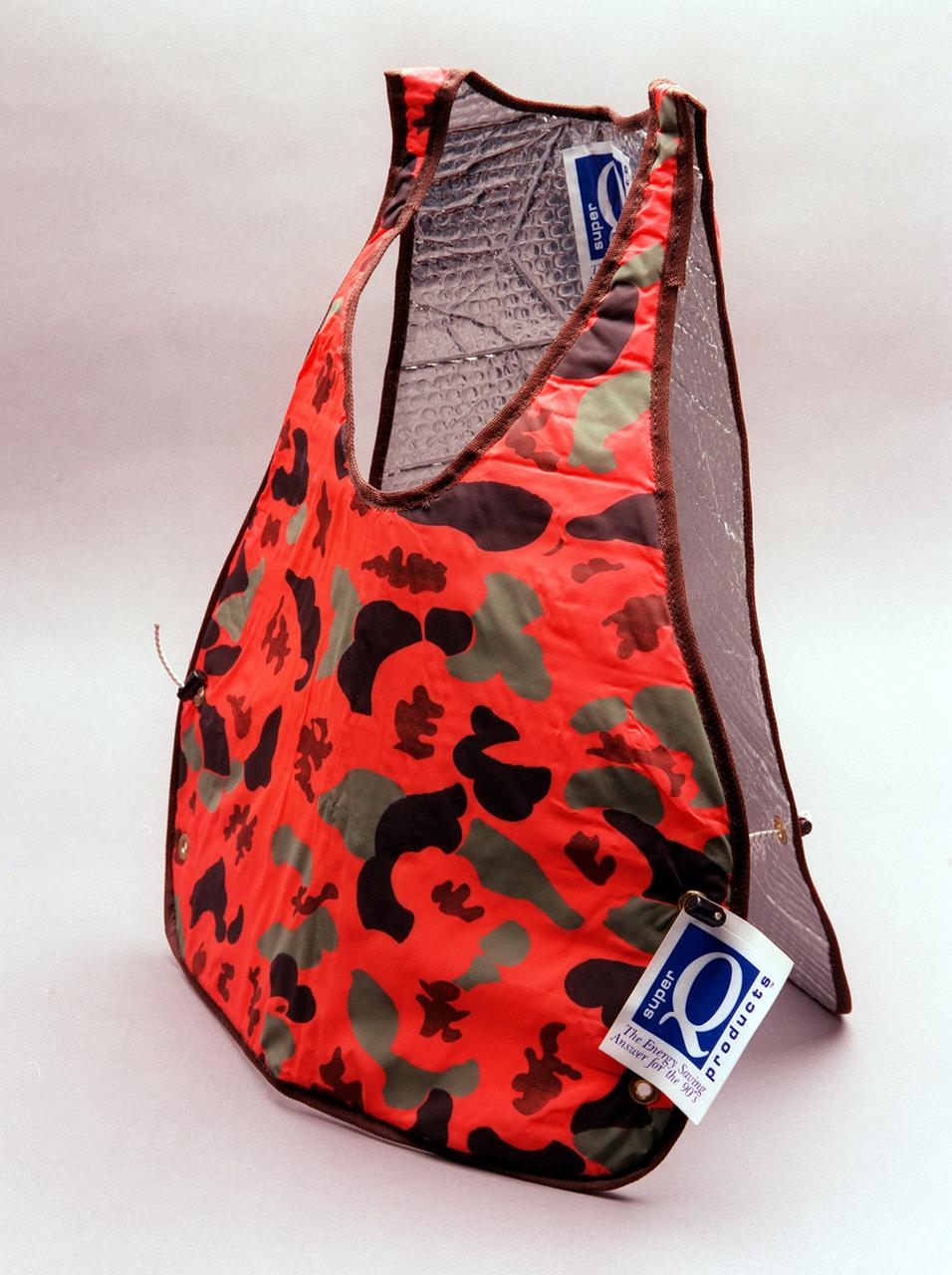

Radiation insulation technology from Apollo and subsequent spacecraft was used to develop superinsulators, used by makers of cold weather apparel, to make parkas, jackets, boots and outdoor gear such as sleeping bags. The radiant barrier technology offers warmth retention at minimal weight and bulk.
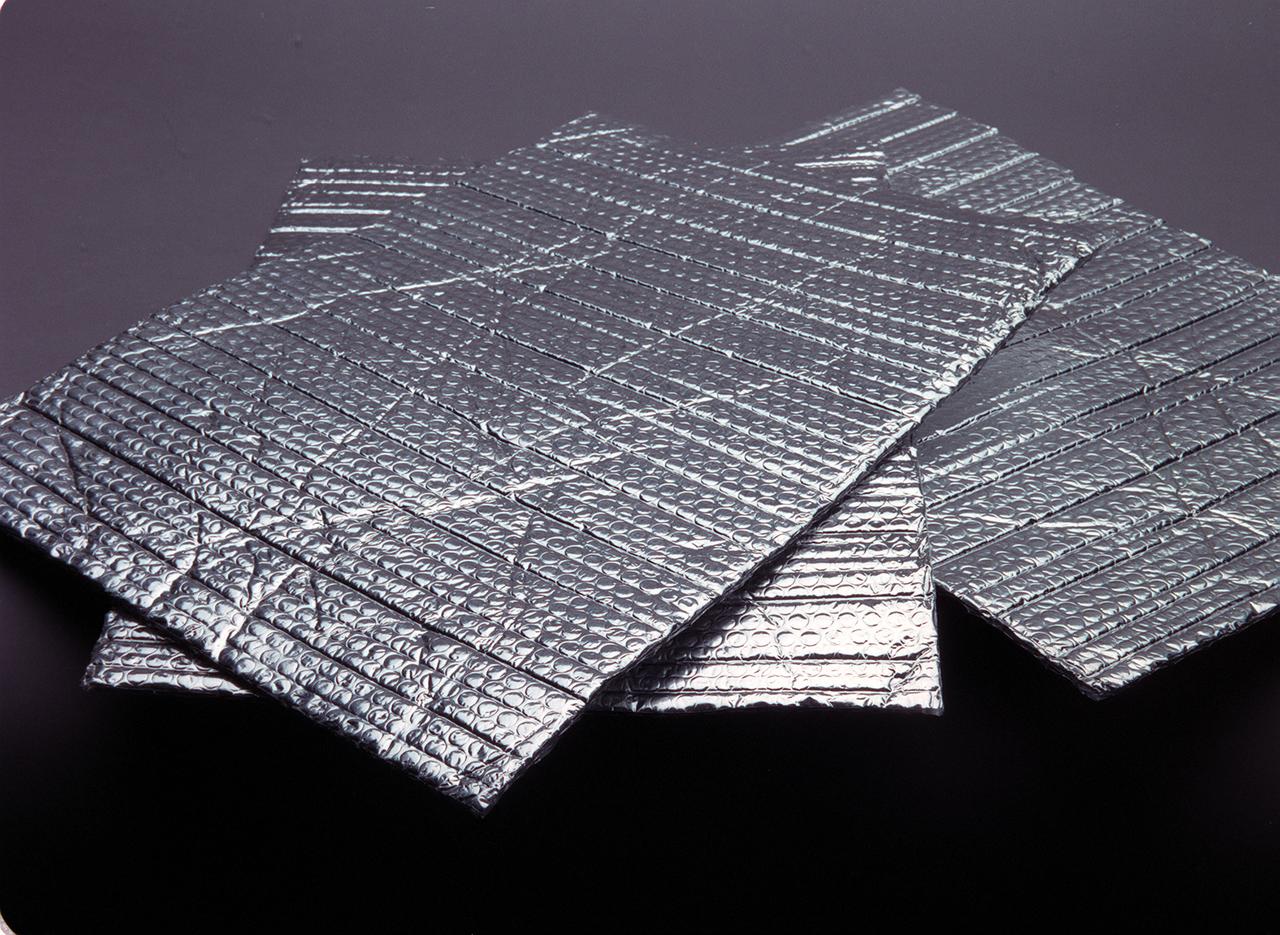

Radiation insulation technology from Apollo and subsequent spacecraft was used to develop superinsulators, used by makers of cold weather apparel, to make parkas, jackets, boots and outdoor gear such as sleeping bags. The radiant barrier technology offers warmth retention at minimal weight and bulk.
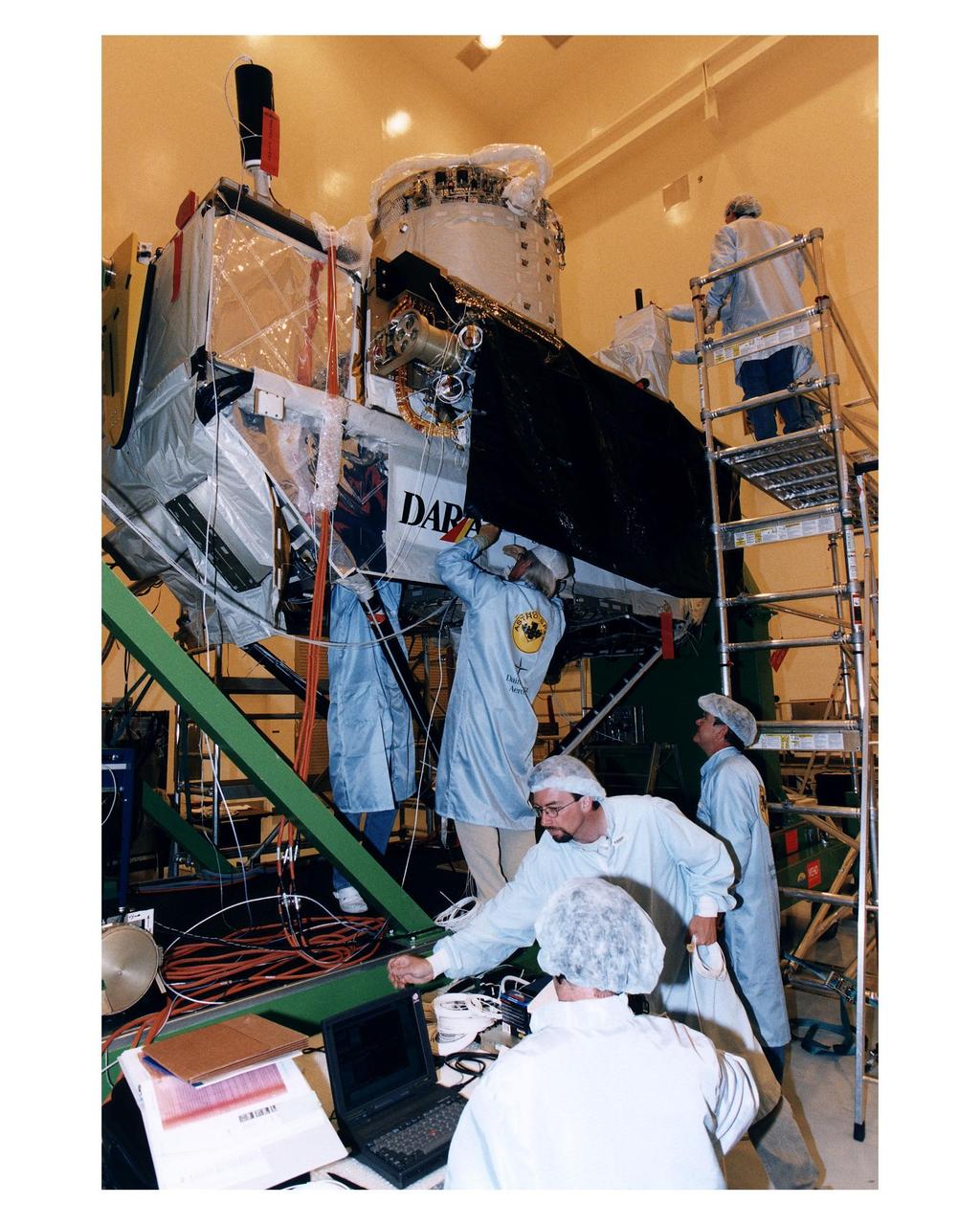

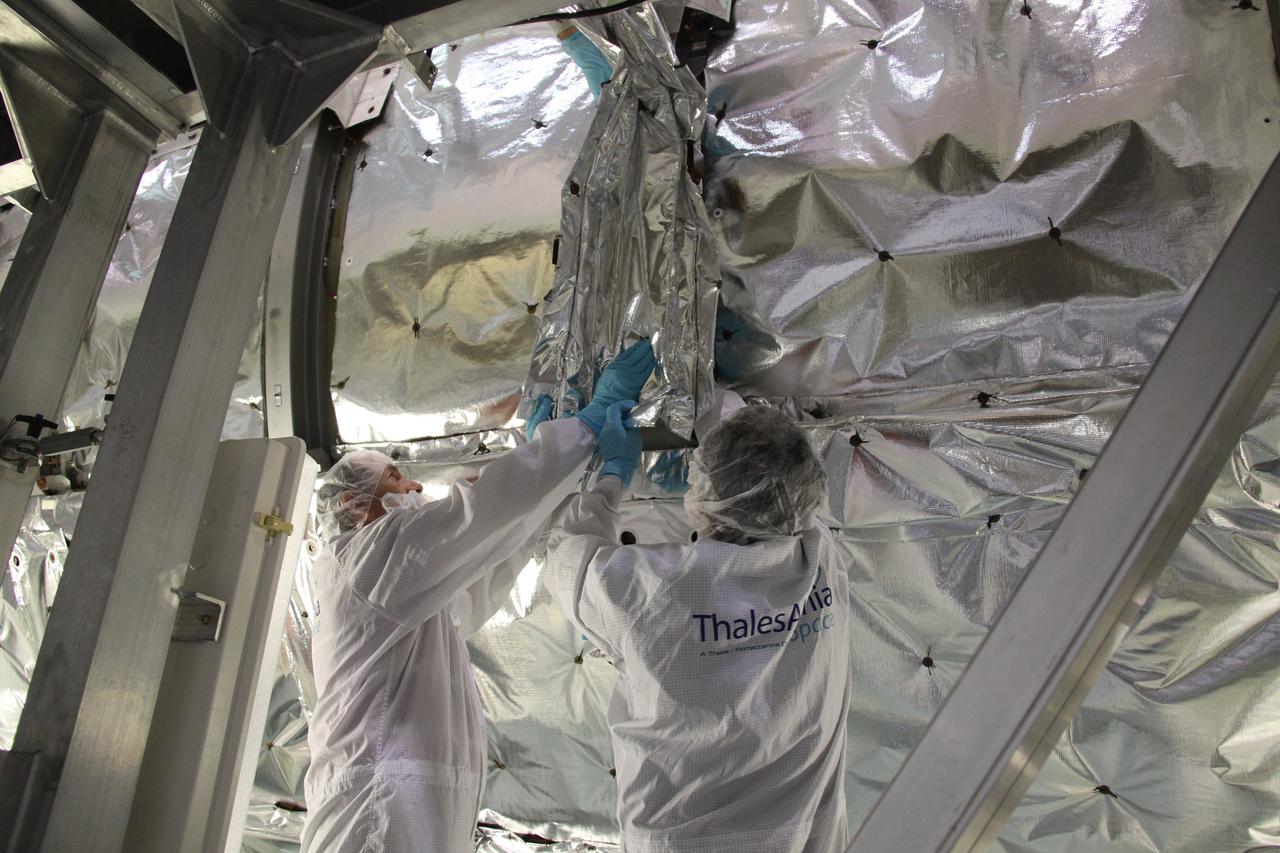
Employees of Daimler-Benz Aerospace in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility install insulation on the Cryogenic Infrared Spectro-meters and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) payload for the STS-85 mission. The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11- day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere
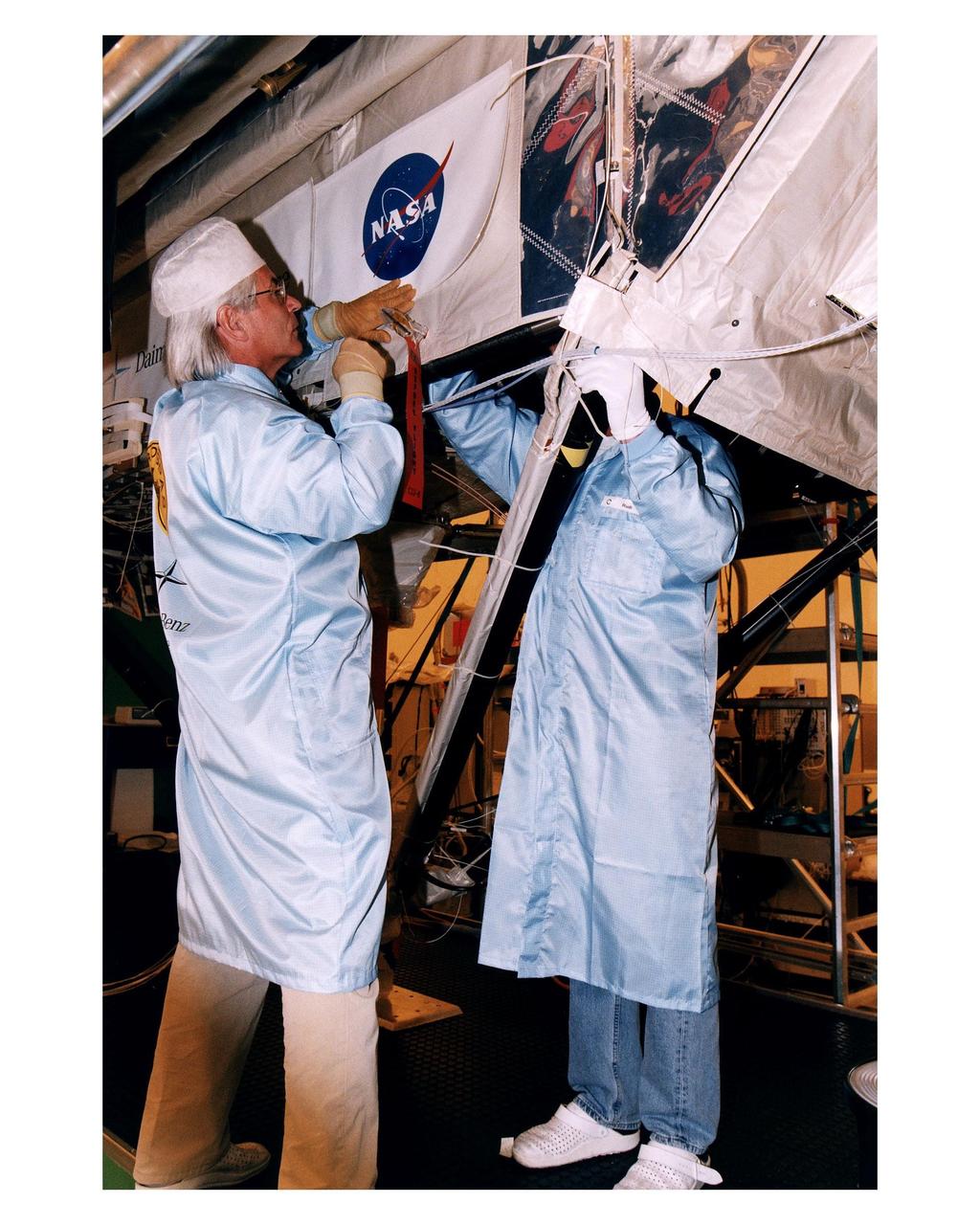

Employees of Daimler-Benz Aerospace in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility install insulation on the Cryogenic Infrared Spectro-meters and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) payload for the STS-85 mission. The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11- day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere
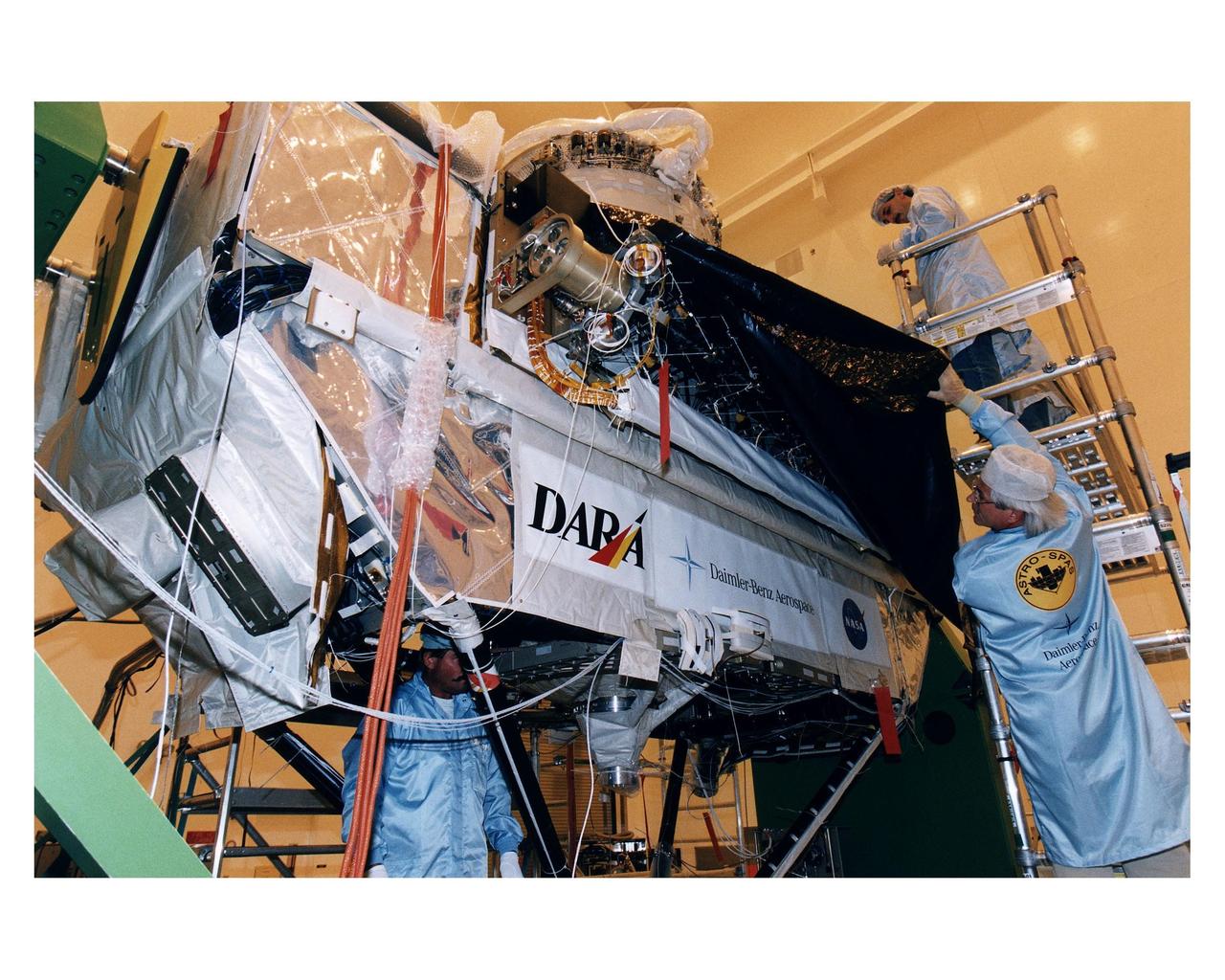
Employees of Daimler-Benz Aerospace in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility install insulation on the Cryogenic Infrared Spectro-meters and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2) payload for the STS-85 mission. The CRISTA is a system of three telescopes and four spectrometers to measure infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s middle atmosphere. During the 11- day mission, the CRISTA-SPAS-2 free-flying satellite will be deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery and retrieved later in the flight. Also onboard the satellite will be the Middle Atmosphere High Resolution Spectrograph Investigation (MAHRSI) to measure ultraviolet radiation emitted and scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere
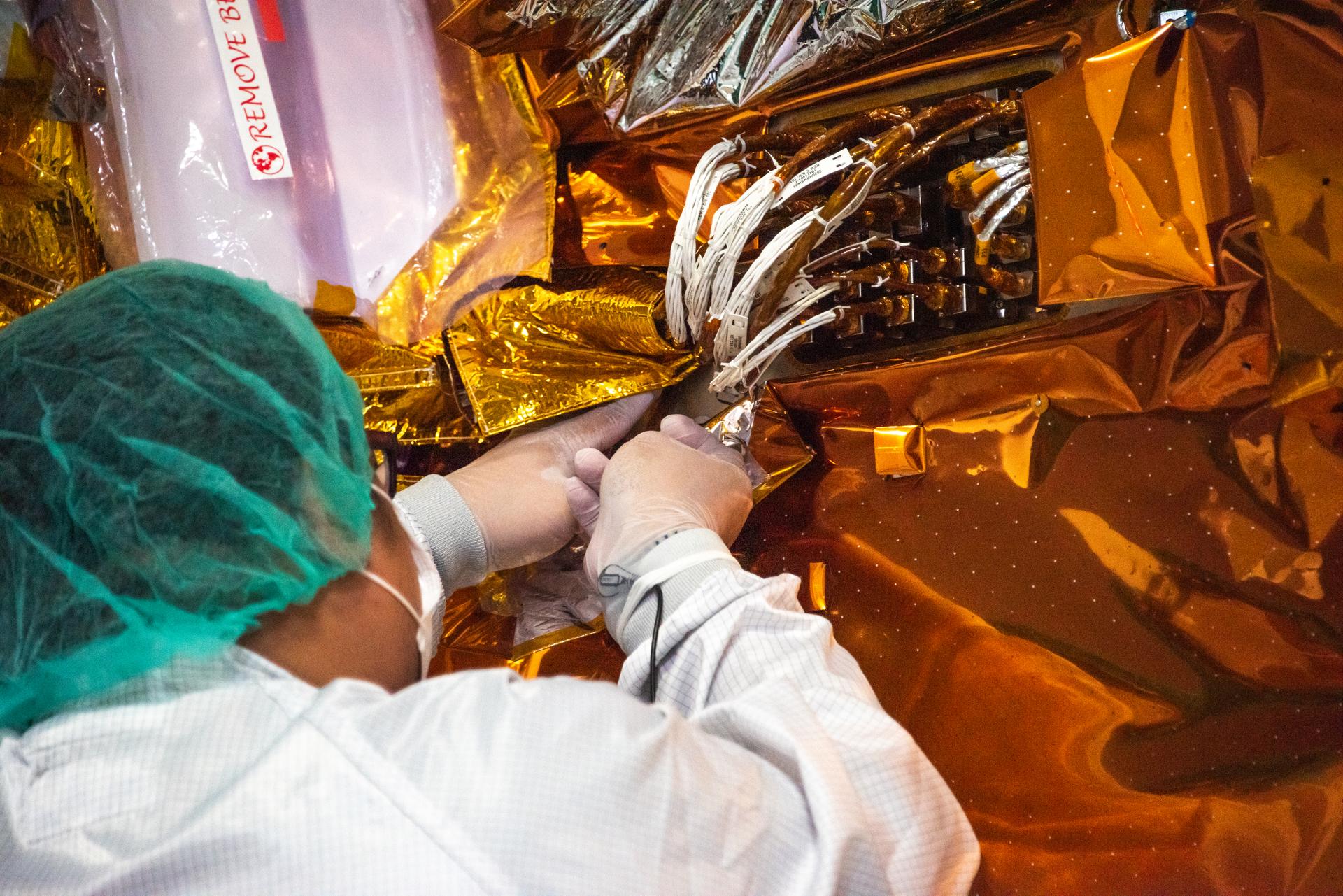

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
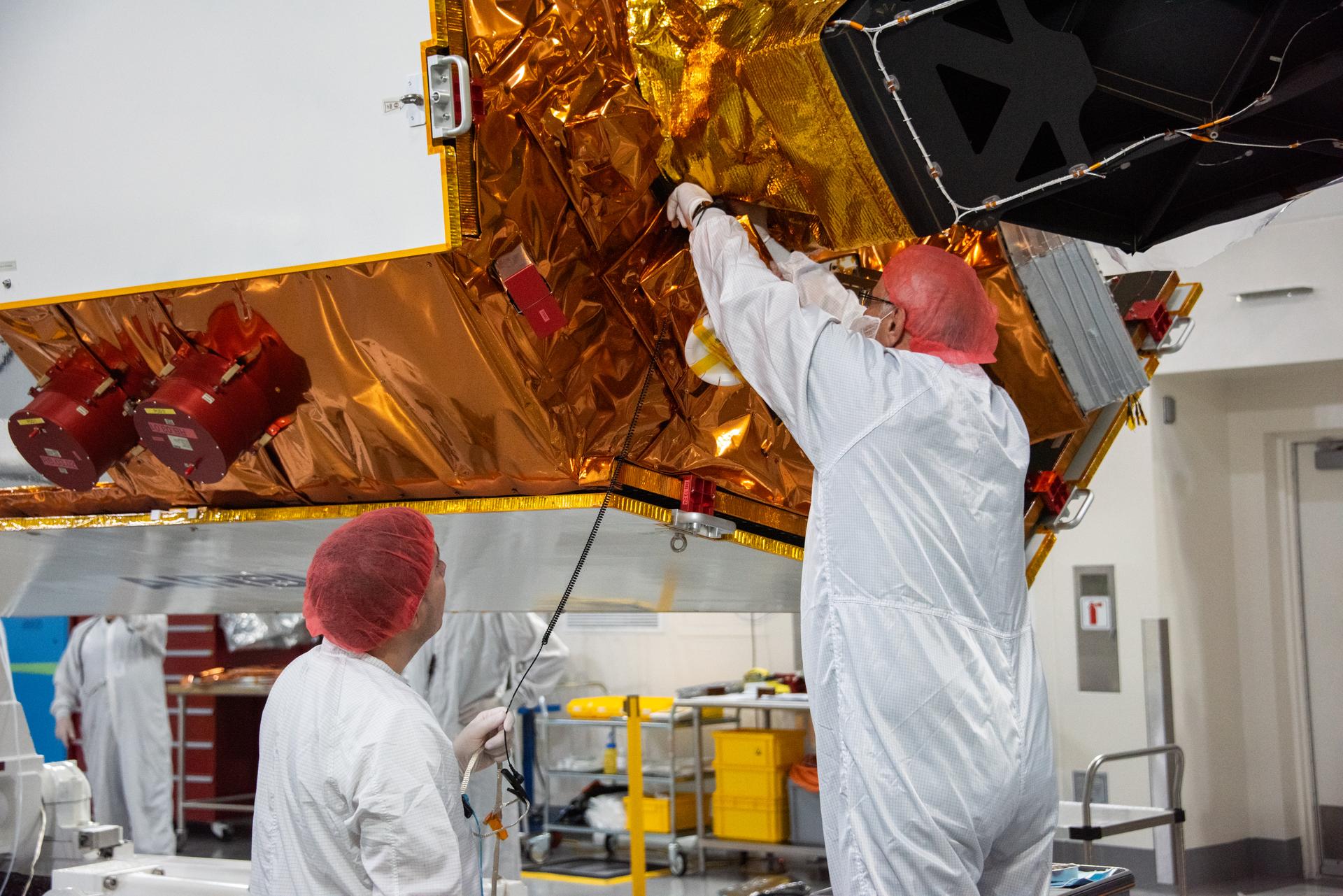

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
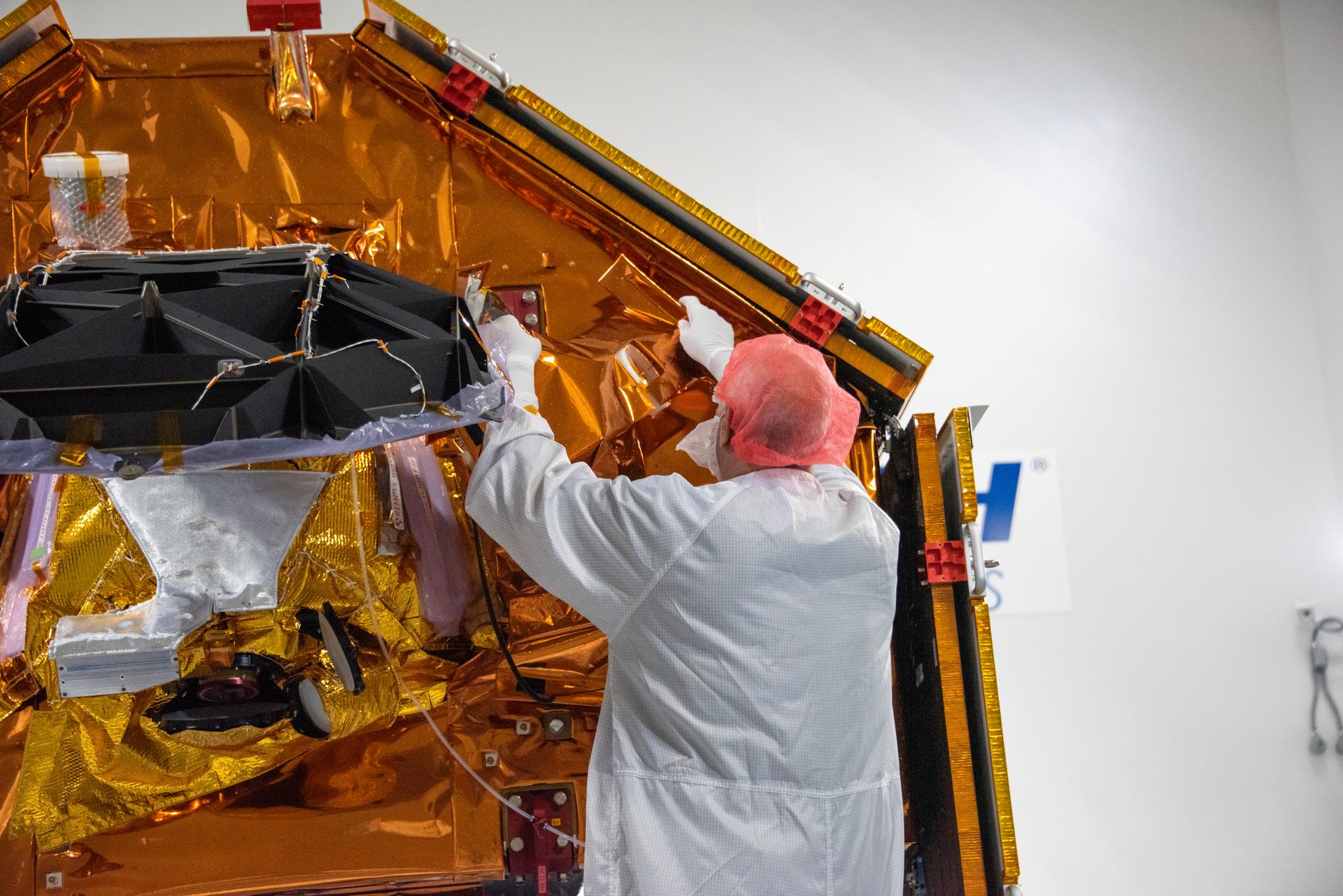

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
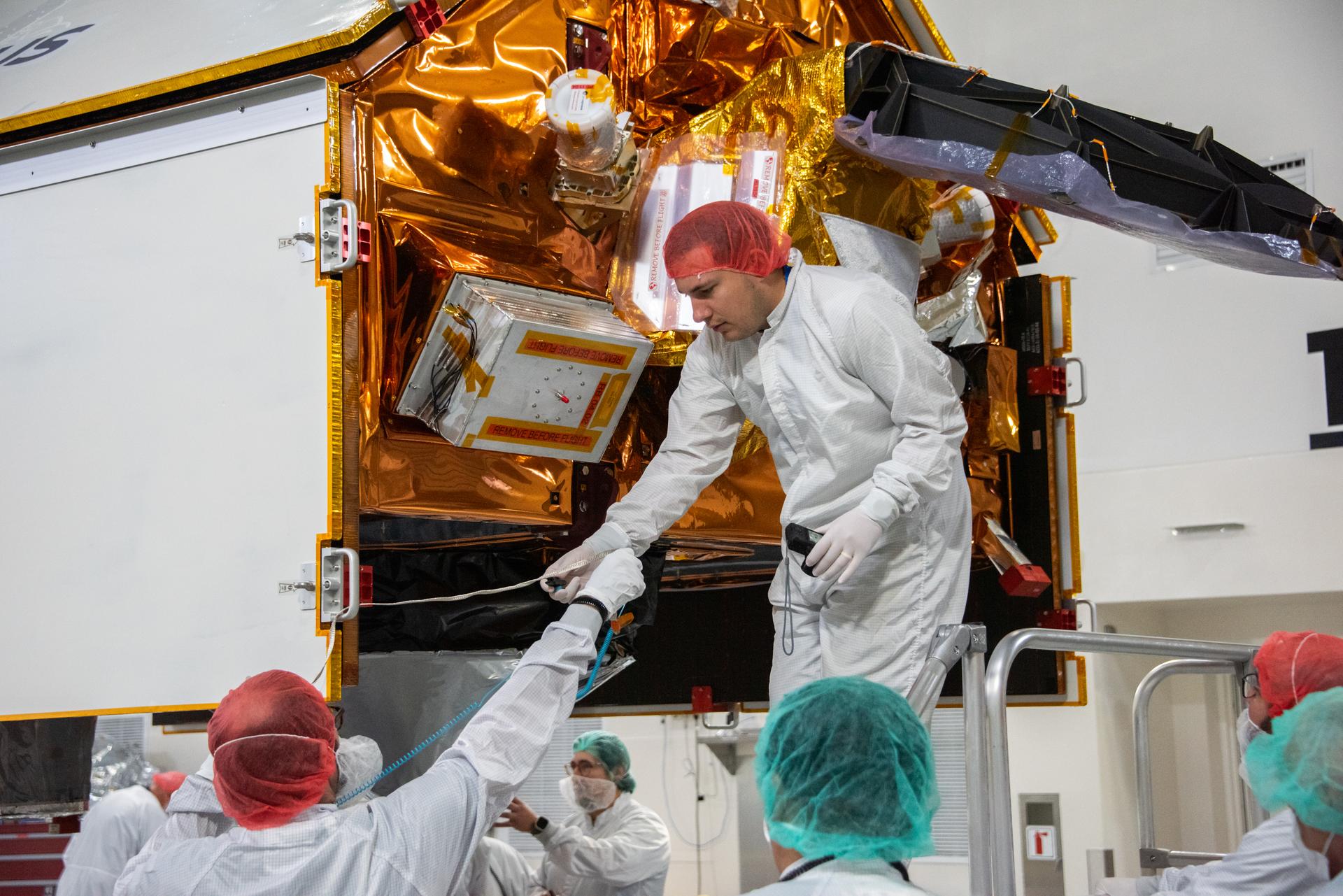

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
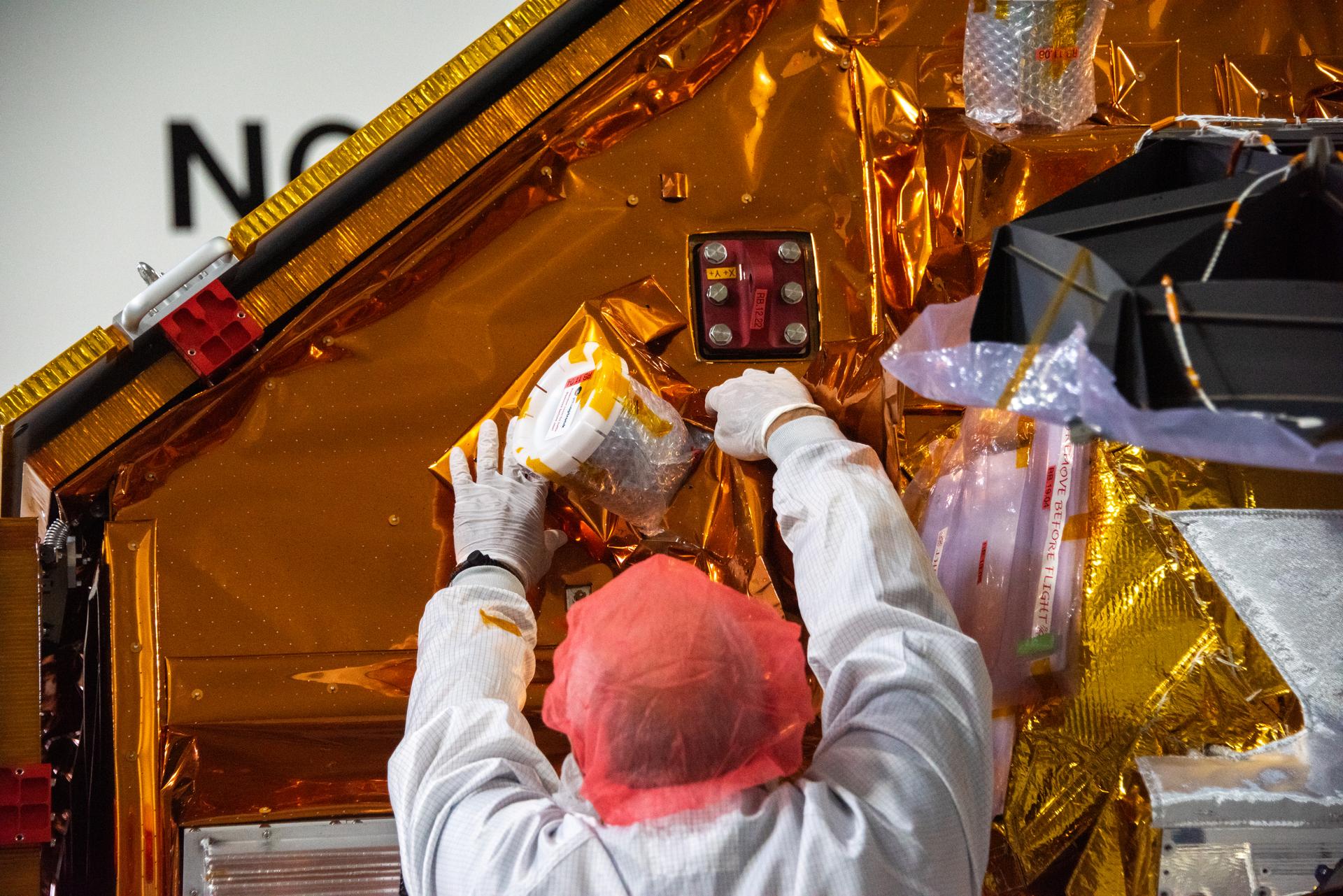

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
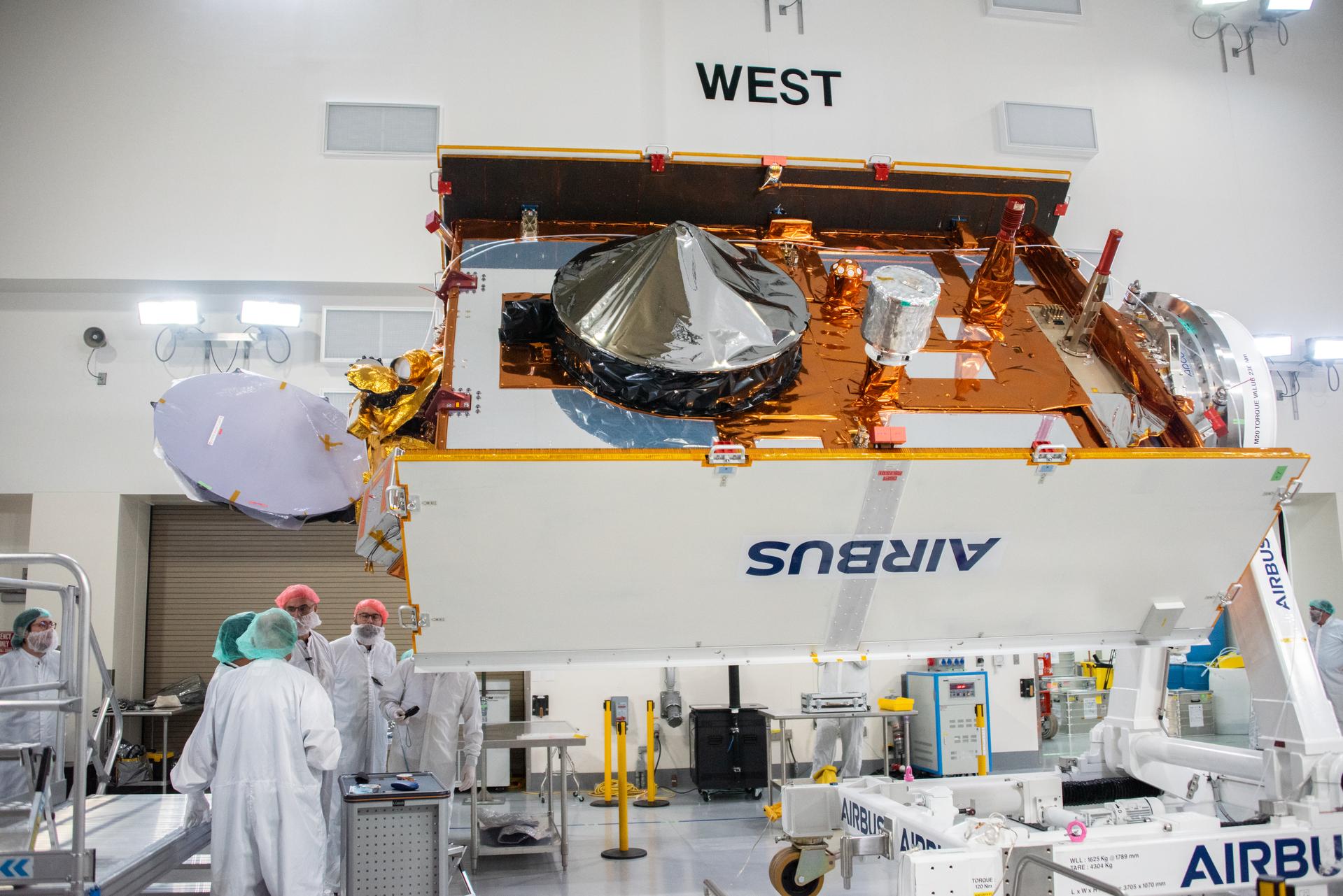

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
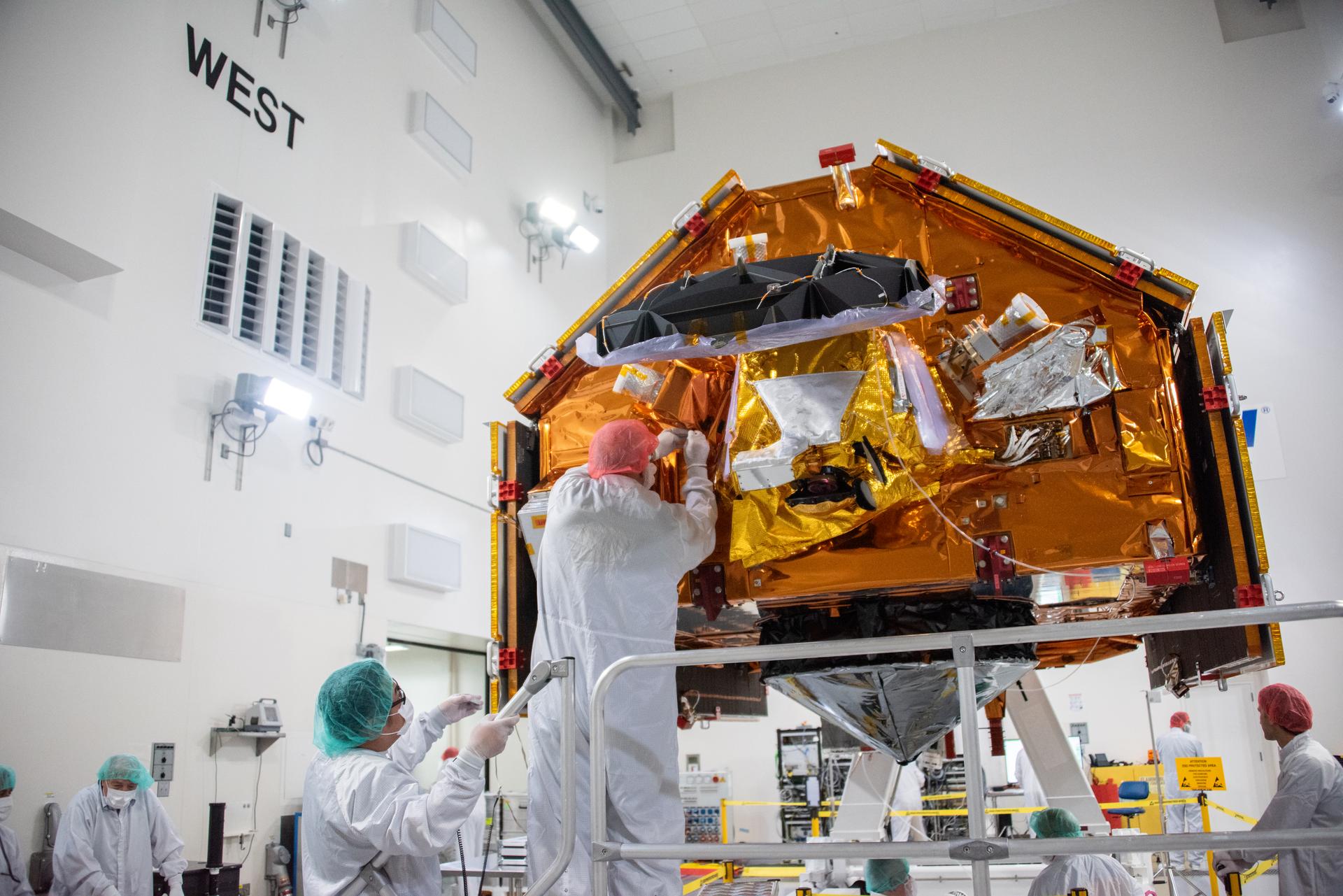

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
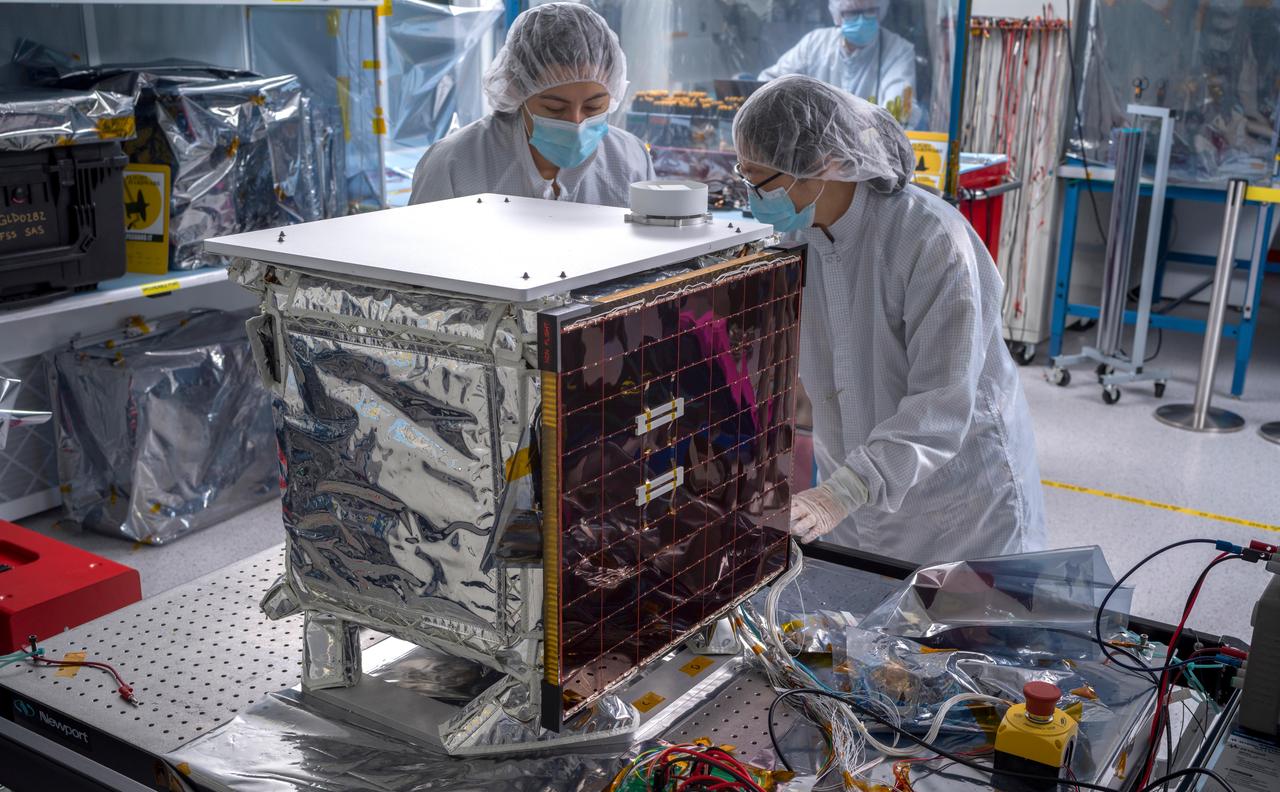

In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in March 2024, engineers and technicians work to prepare the agency's Farside Seismic Suite (FSS) for environmental testing to simulate conditions it will encounter in space. Along with being placed in a vacuum chamber and subjected to extreme temperatures, the instrument suite will undergo severe shaking that mimics the rocket's motion during launch. The cube-shaped payload contains two instruments that will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. The two seismometers are packaged together with a large battery, a computer, and electronics inside a cube structure that's surrounded by several layers of insulation and suspended within an outer protective cube, which is in turn covered with a shiny insulating blanket. The suite's single solar panel can be seen at center. On top is a white radiator that will allow the suite to shed heat generated by its electronics during the hot lunar daytime hours. The puck-like object atop the radiator is the suite's antenna, for communicating with two small relay satellites that will orbit the Moon and send data to Earth. Pictured (from left): Joanna Farias, and Bert Turney, and Hsin-Yi Hao. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26299
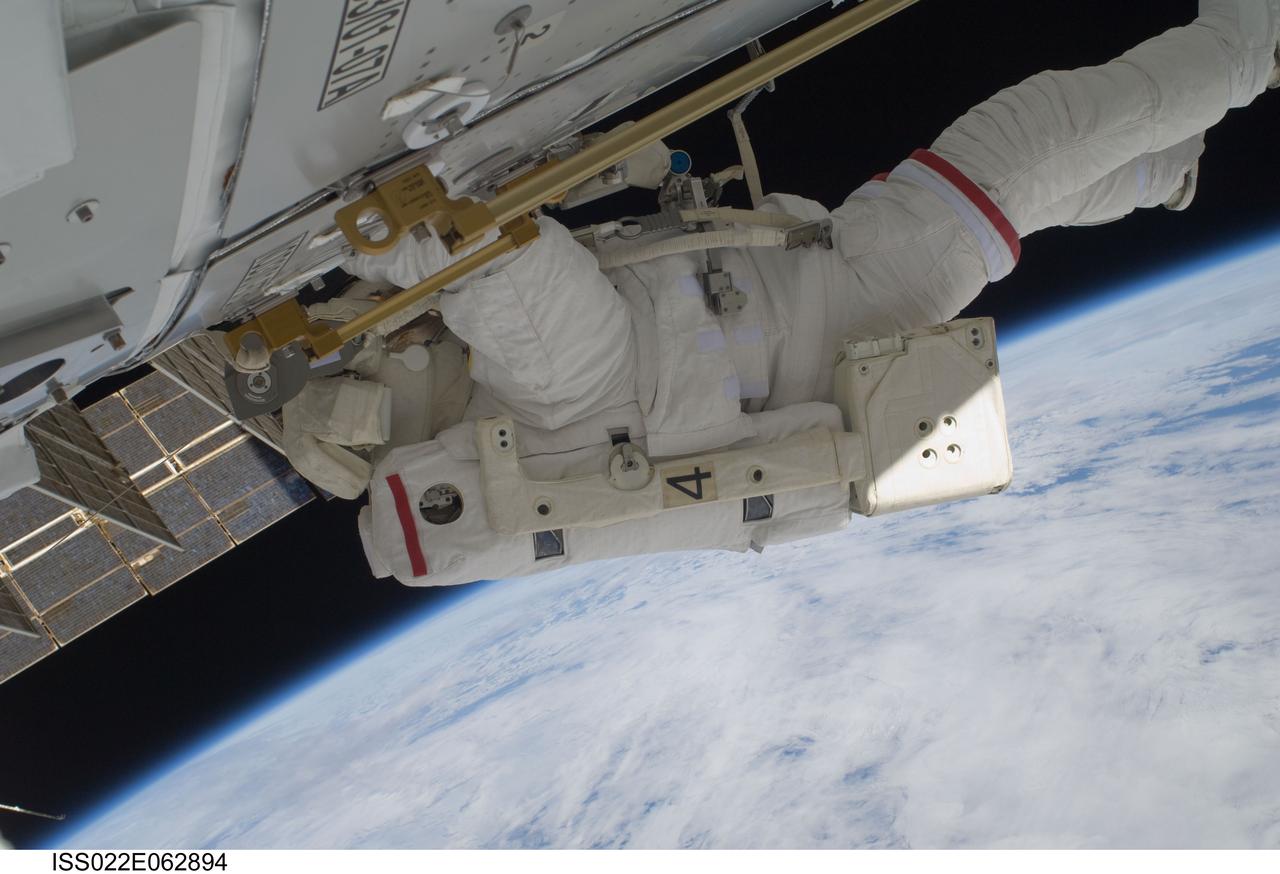

ISS022-E-062894 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Robert Behnken, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and astronaut Nicholas Patrick (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station?s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station?s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station?s cooling radiators during the mission?s second spacewalk.
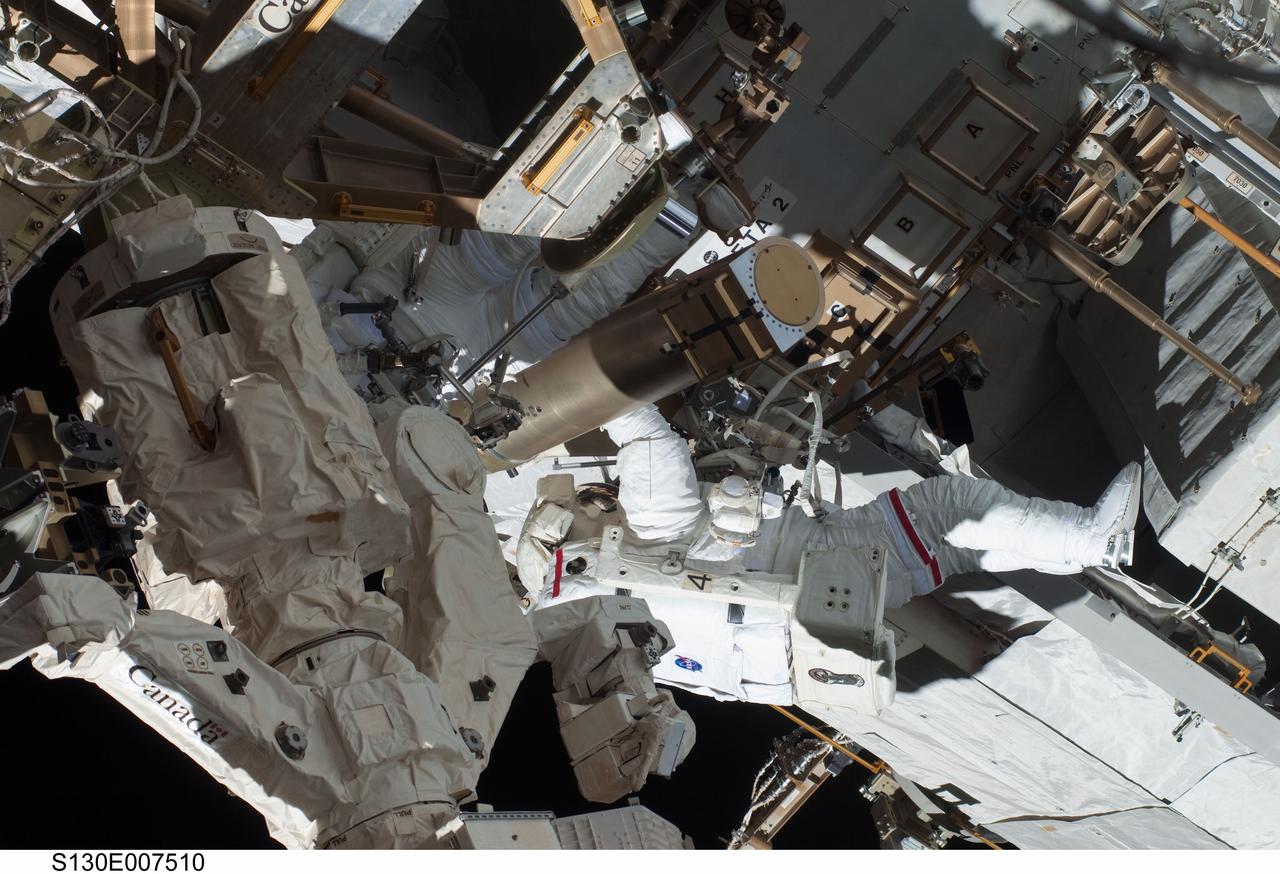

S130-E-007510 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Nicholas Patrick (partially obscured at left), both STS-130 mission specialists, participate in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and Patrick relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
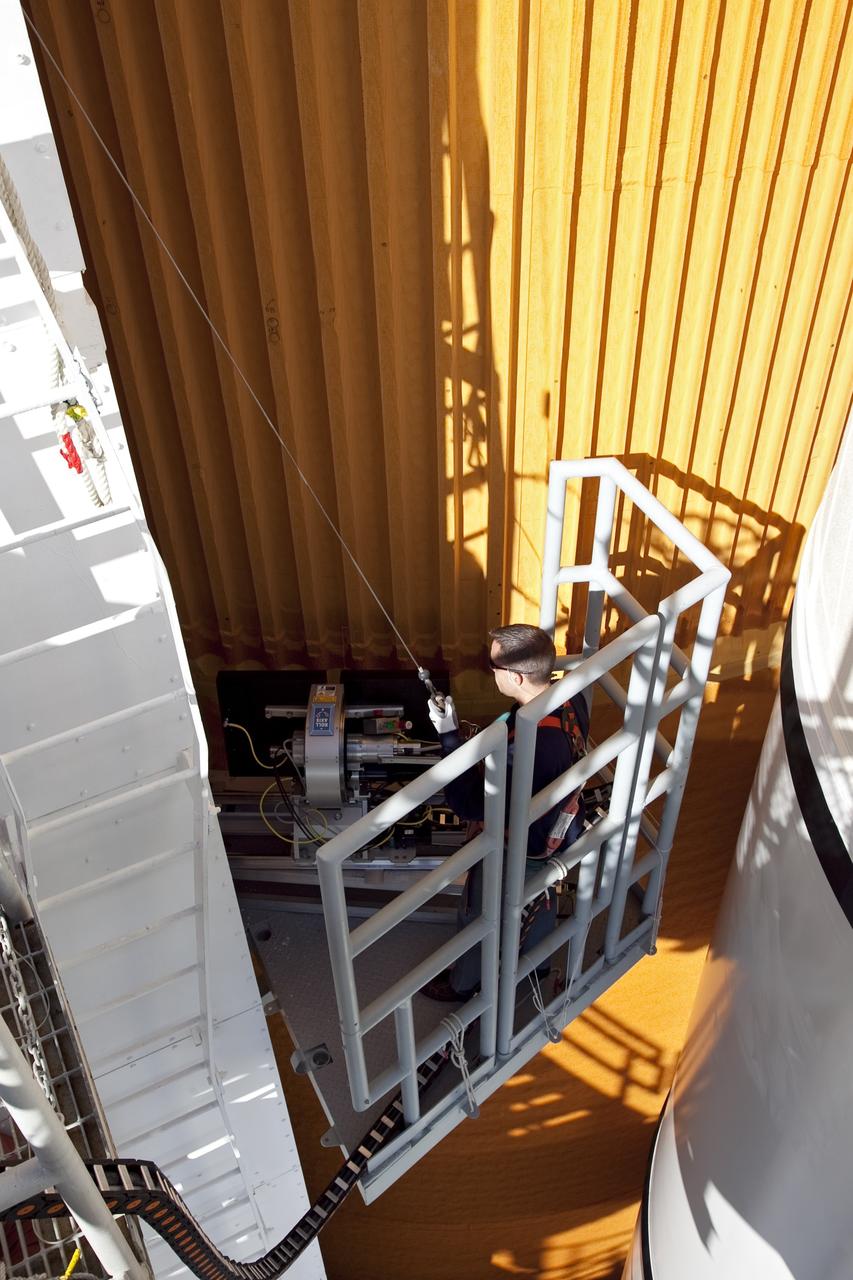

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An engineer uses a backscatter device to examine space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
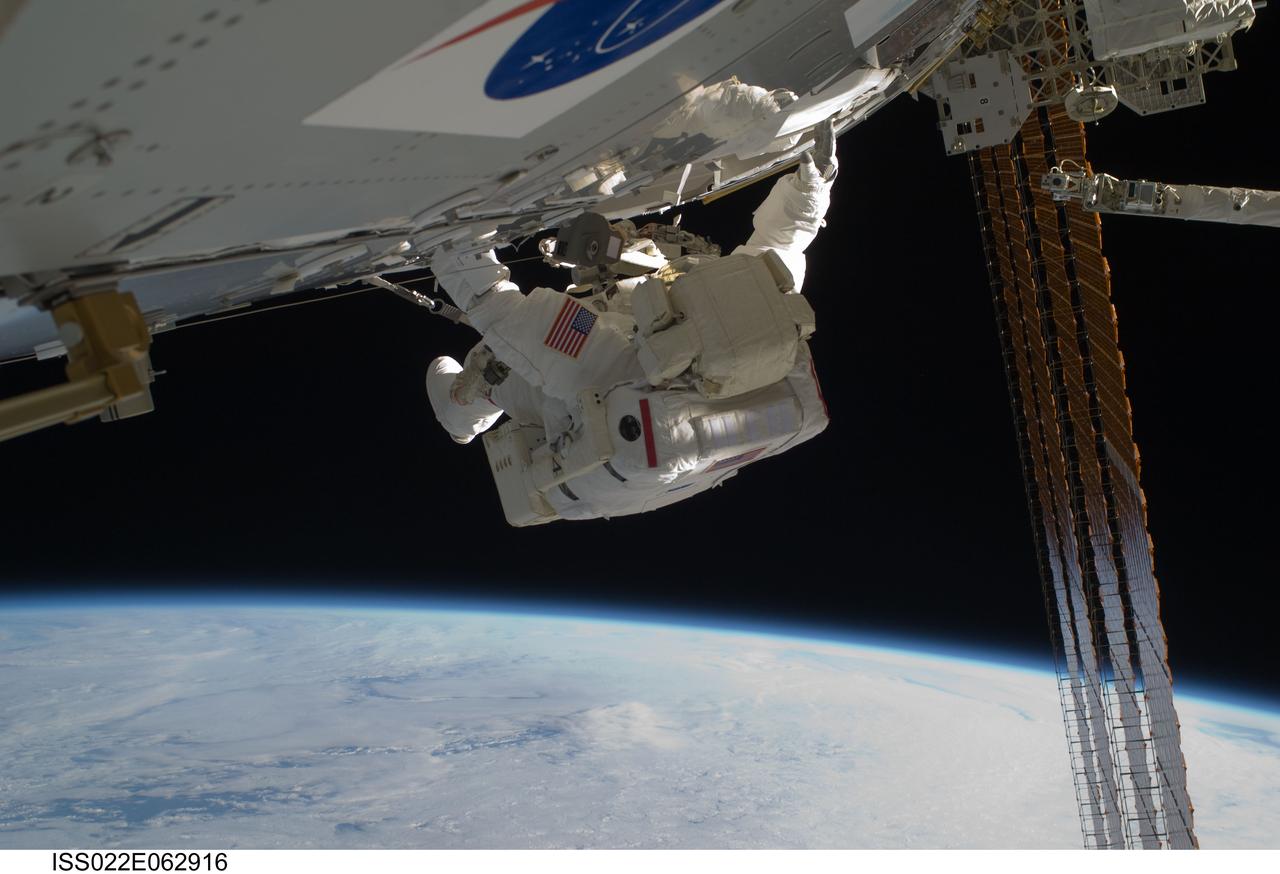

ISS022-E-062916 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Robert Behnken, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and astronaut Nicholas Patrick (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station?s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station?s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station?s cooling radiators during the mission?s second spacewalk.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Meteoroids and Debris Protective Shield of the Permanent Multipurpose Module, or PMM. The reflective silver mesh is Mylar, which is aluminized to protect hardware aboard the International Space Station from solar thermal radiation. The Leonardo multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, is being modified to become the PMM that will carry supplies and critical spare parts to the station aboard space shuttle Discovery’s STS-133 mission. Discovery, targeted to launch Nov. 1, will leave the module behind so it can be used for microgravity experiments in fluid physics, materials science, biology and biotechnology. Photo credit: NASA_Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An engineer uses a backscatter device to examine space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
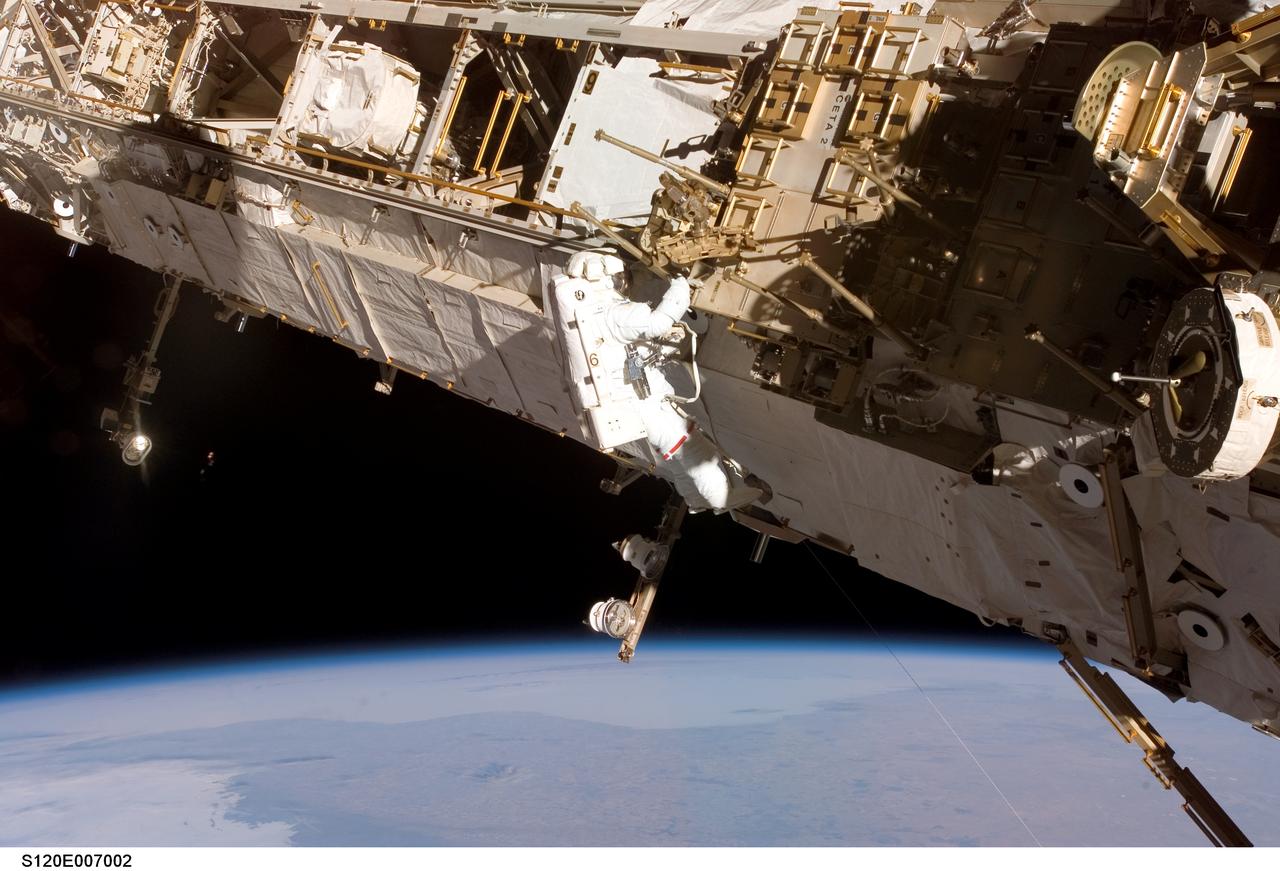

S120-E-007002 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
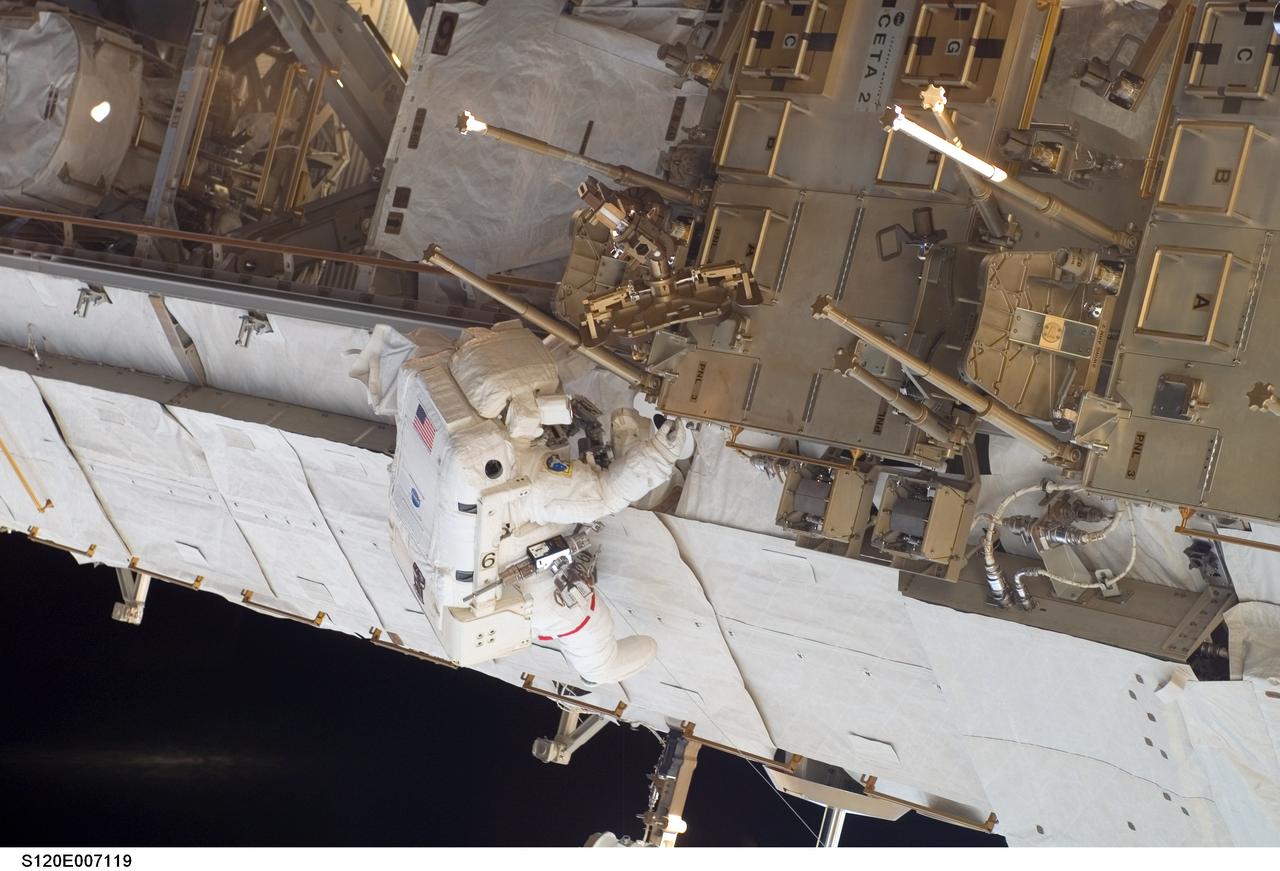

S120-E-007119 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
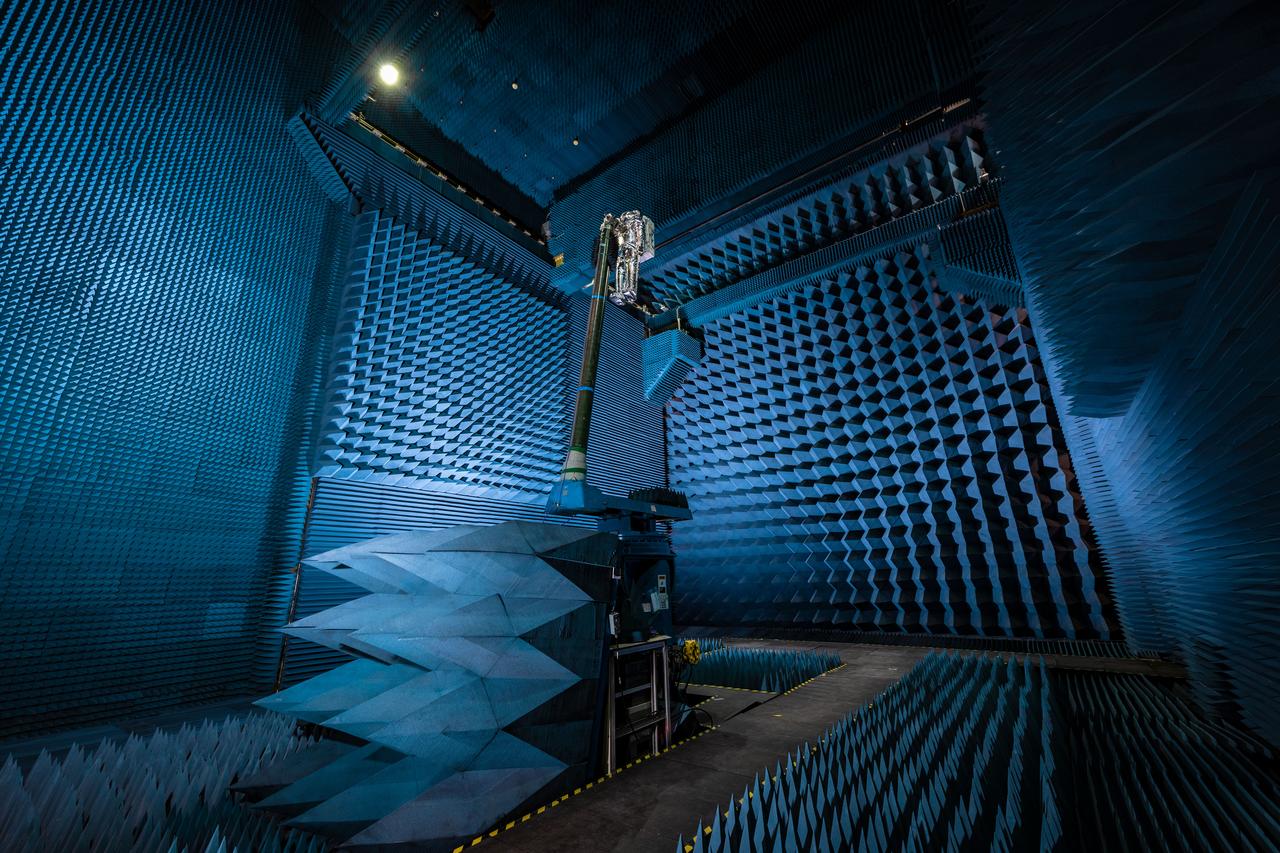

jsc2021e022487 (June 11, 2021) --- NASA’s Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (xEMU) spacesuit undergoes antenna testing in NASA Johnson Space Center’s anechoic chamber to inspect multi-layer insulation keep-out zones for the Wi-Fi and ultra-high-frequency antennas that are part of the spacesuit’s communication system. The xEMU test article is named xGUS, the successor to the Extravehicular Mobility Unit test article (also named GUS), which was named after NASA astronaut Gus Grissom and his iconic silver spacesuit. This image was taken from where the "horn," or source antenna, is located that sends out radio frequency signals to the spacesuit. The anechoic chamber walls are covered with a material that absorbs electromagnetic energy allowing the anechoic chamber to simulate a space environment. The antenna test facility is utilized to test antenna radiation distribution pattern performance for spaceflight applications in electromagnetic environments.
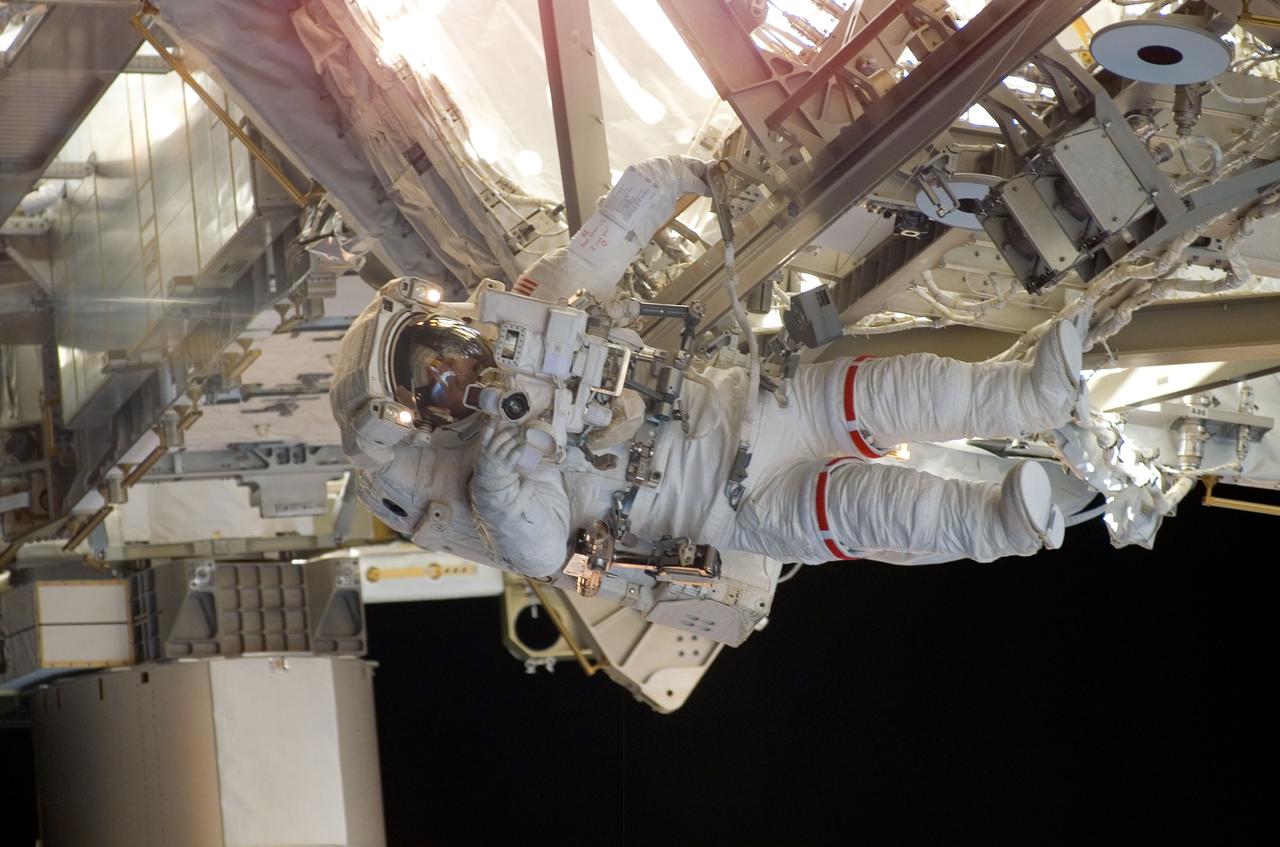

S120-E-007100 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.

jsc2021e022515 (June 11, 2021) --- NASA’s Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (xEMU) spacesuit undergoes antenna testing in NASA Johnson Space Center’s anechoic chamber to inspect multi-layer insulation keep-out zones for the Wi-Fi and ultra-high-frequency antennas that are part of the spacesuit’s communication system. The xEMU test article is named xGUS, the successor to the Extravehicular Mobility Unit test article (also named GUS), which was named after NASA astronaut Gus Grissom and his iconic silver spacesuit. This image was taken from where the "horn," or source antenna, is located that sends out radio frequency signals to the spacesuit. The anechoic chamber walls are covered with a material that absorbs electromagnetic energy allowing the anechoic chamber to simulate a space environment. The antenna test facility is utilized to test antenna radiation distribution pattern performance for spaceflight applications in electromagnetic environments. Pictured in the photo is antenna test engineer Will Bond.
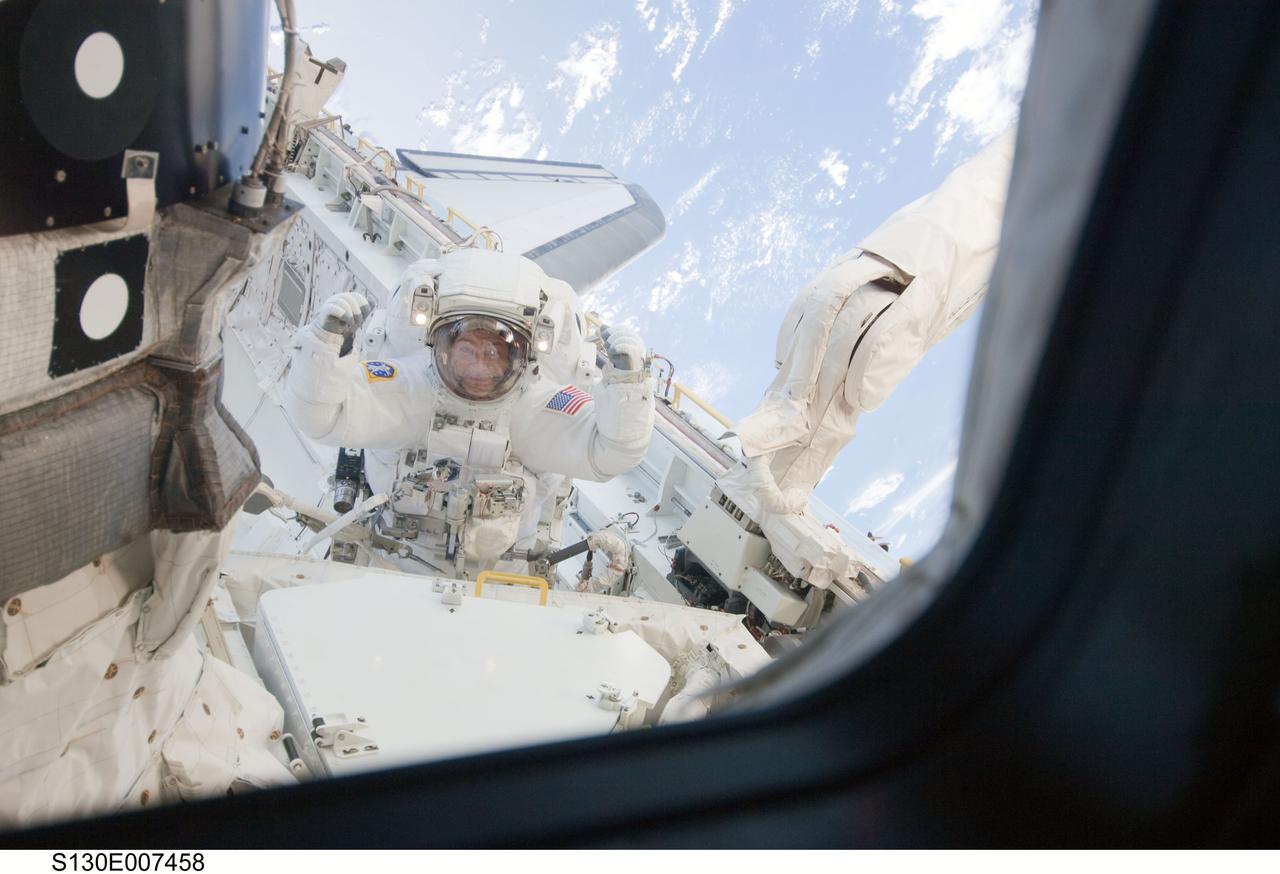

S130-E-007458 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Nicholas Patrick, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Patrick and astronaut Robert Behnken (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
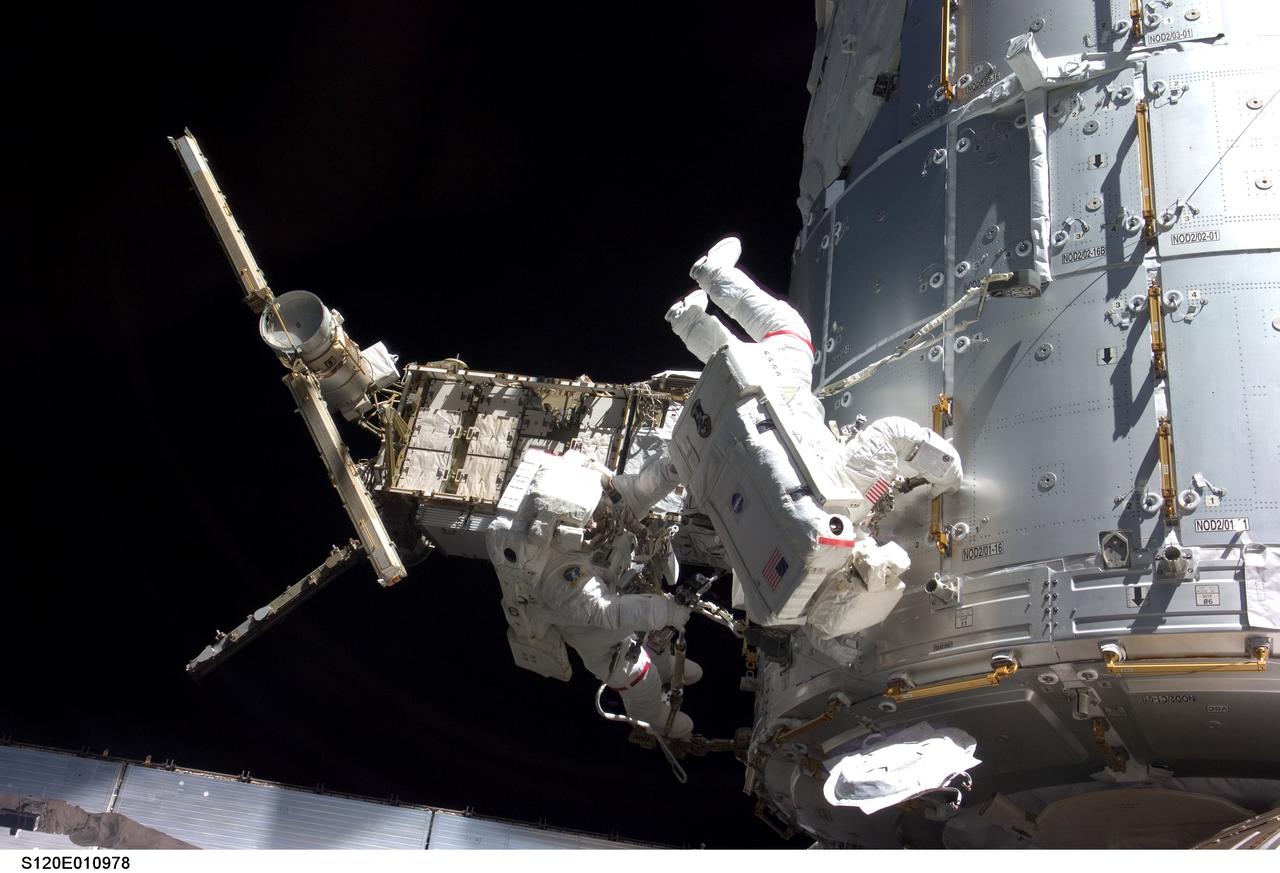

S120-E-010978 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani (left), Expedition 16 flight engineer, and Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participate in the second scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and Parazynski outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. Also the spacewalkers worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers.
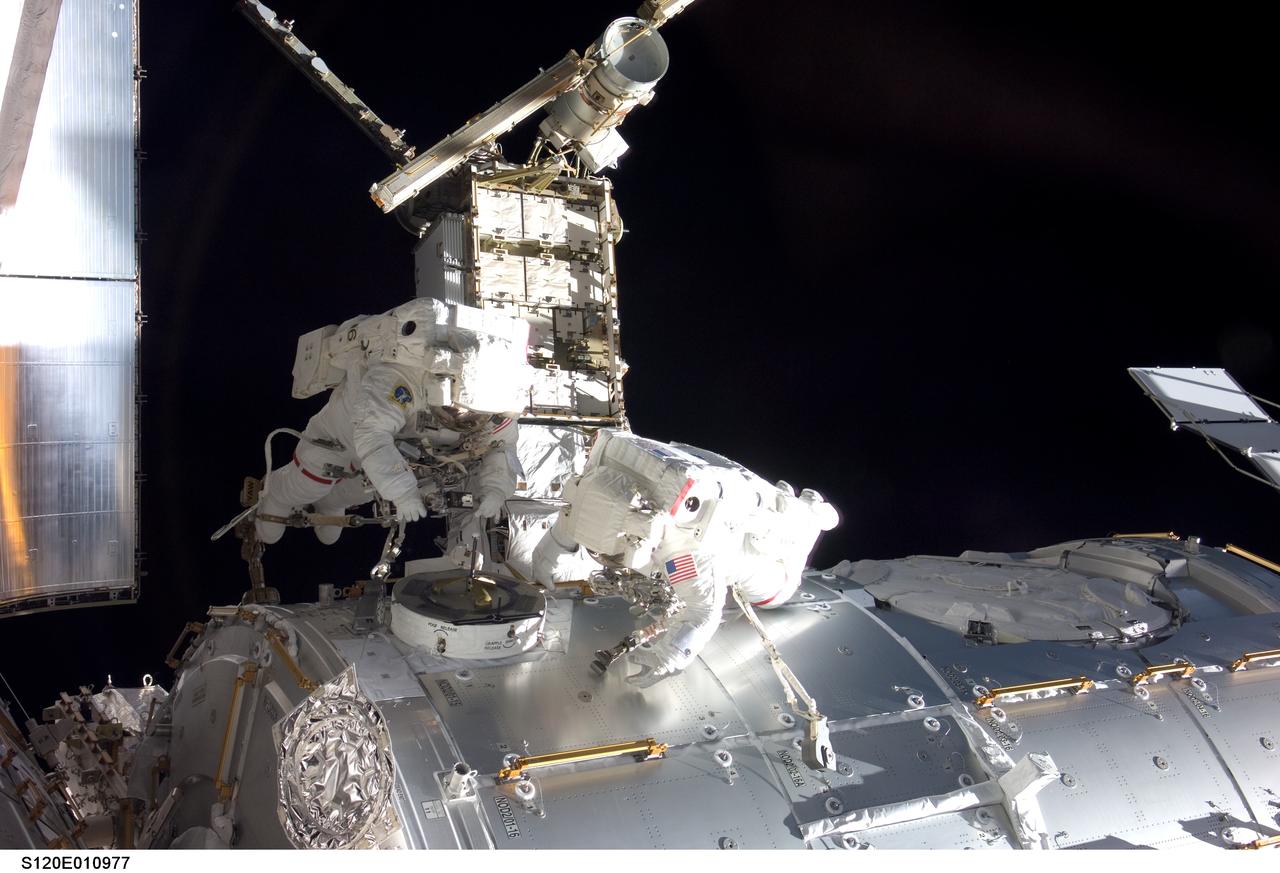
S120-E-010977 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani (left), Expedition 16 flight engineer, and Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participate in the second scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and Parazynski outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. Also the spacewalkers worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers.
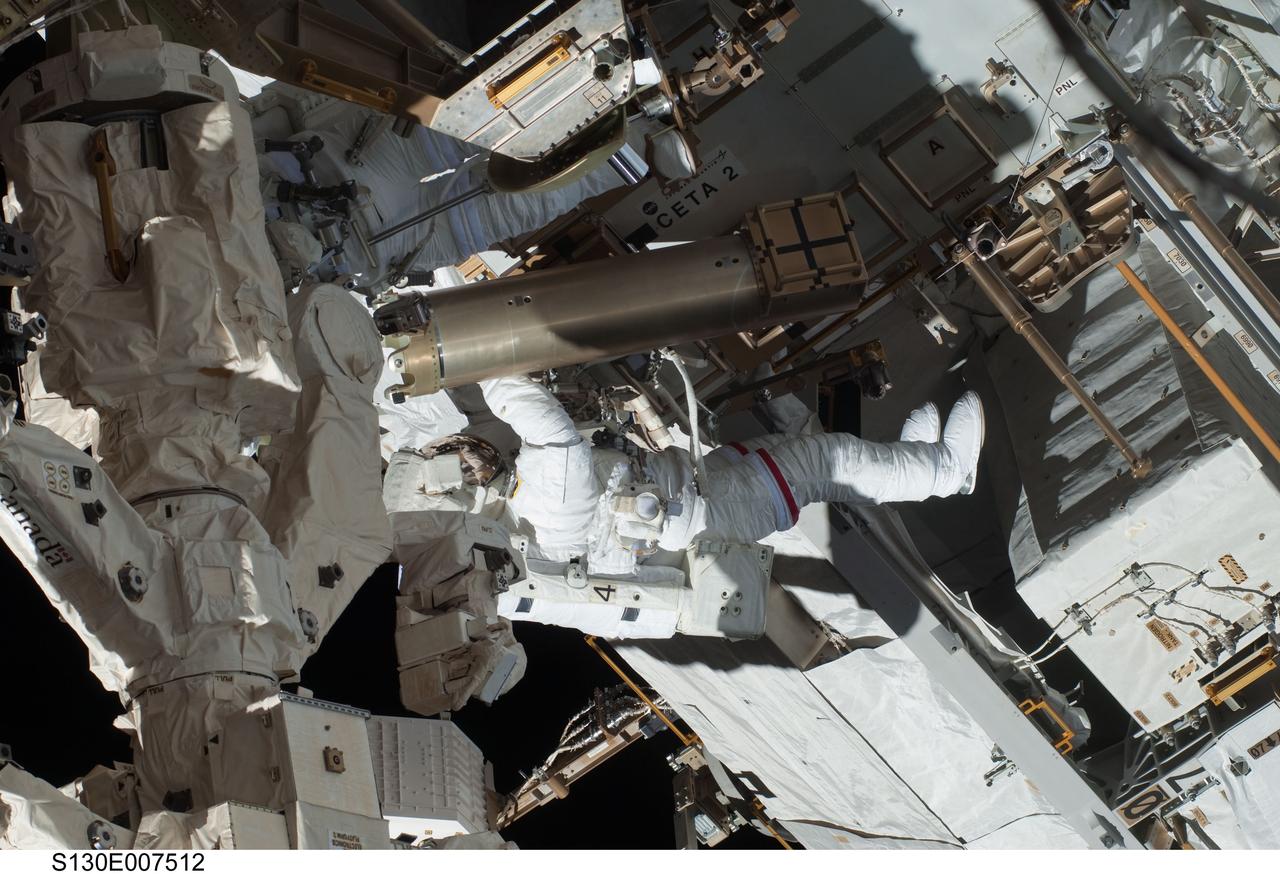

S130-E-007512 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Nicholas Patrick (partially obscured at top left), both STS-130 mission specialists, participate in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and Patrick relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
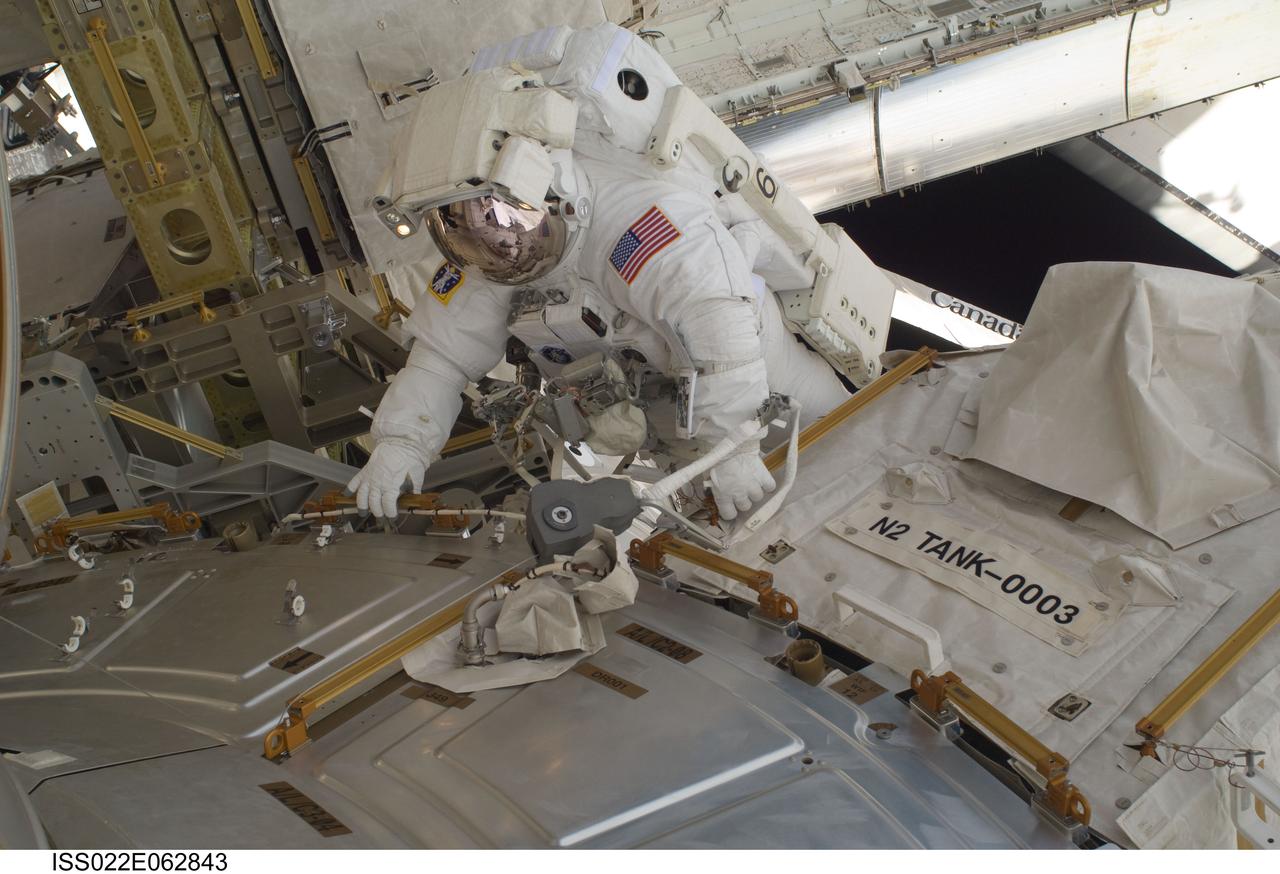

ISS022-E-062843 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Nicholas Patrick, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Patrick and astronaut Robert Behnken (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station?s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station?s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station?s cooling radiators during the mission?s second spacewalk.
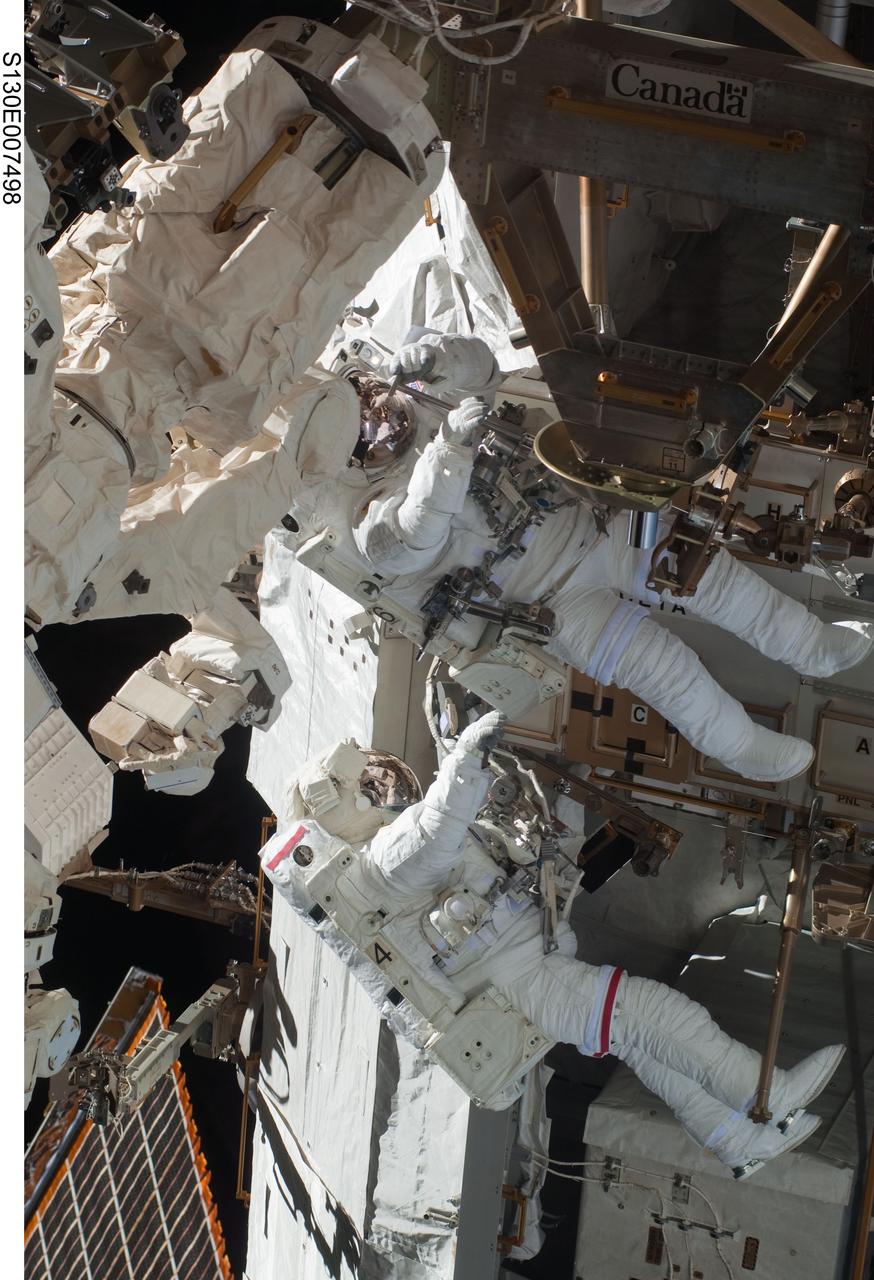

S130-E-007498 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Robert Behnken (bottom) and Nicholas Patrick, both STS-130 mission specialists, participate in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and Patrick relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
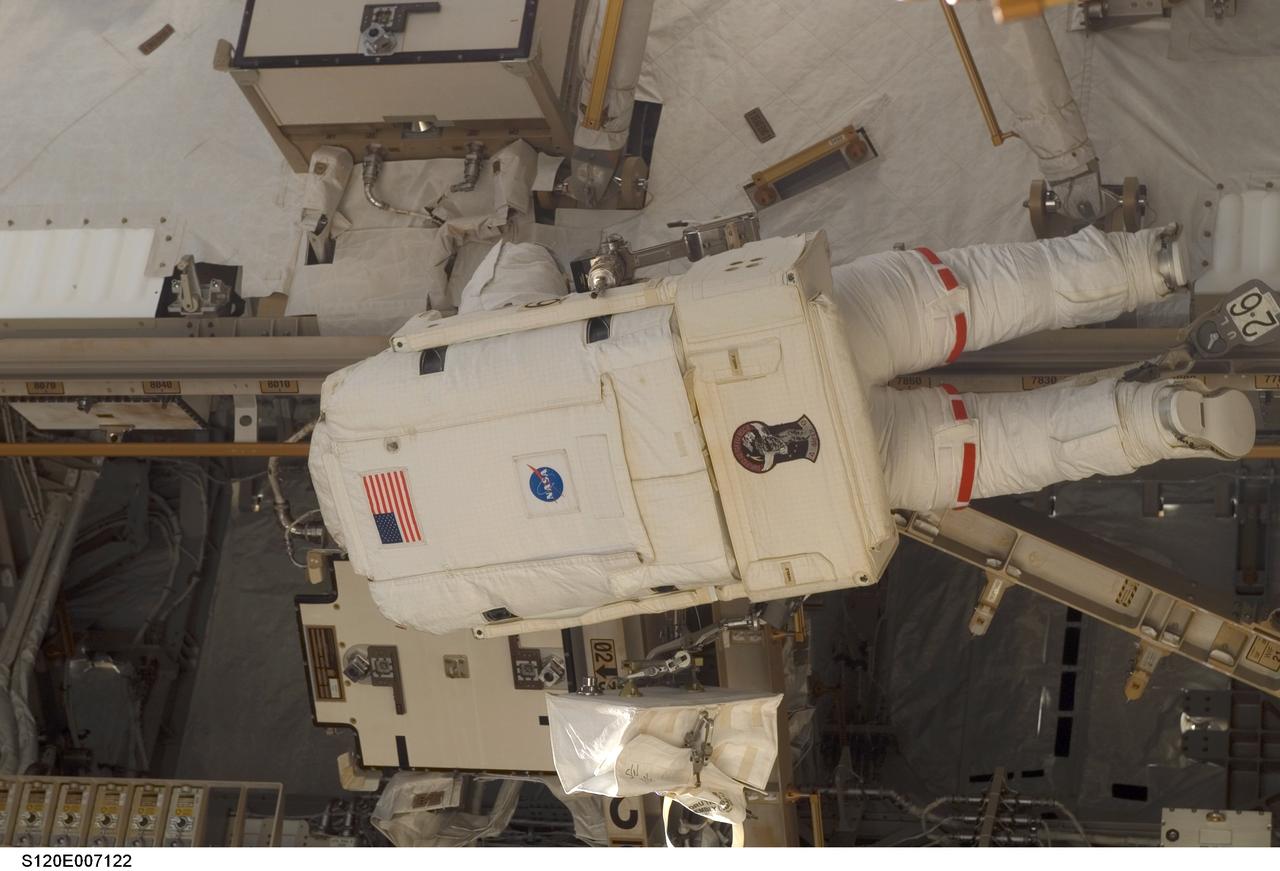

S120-E-007122 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
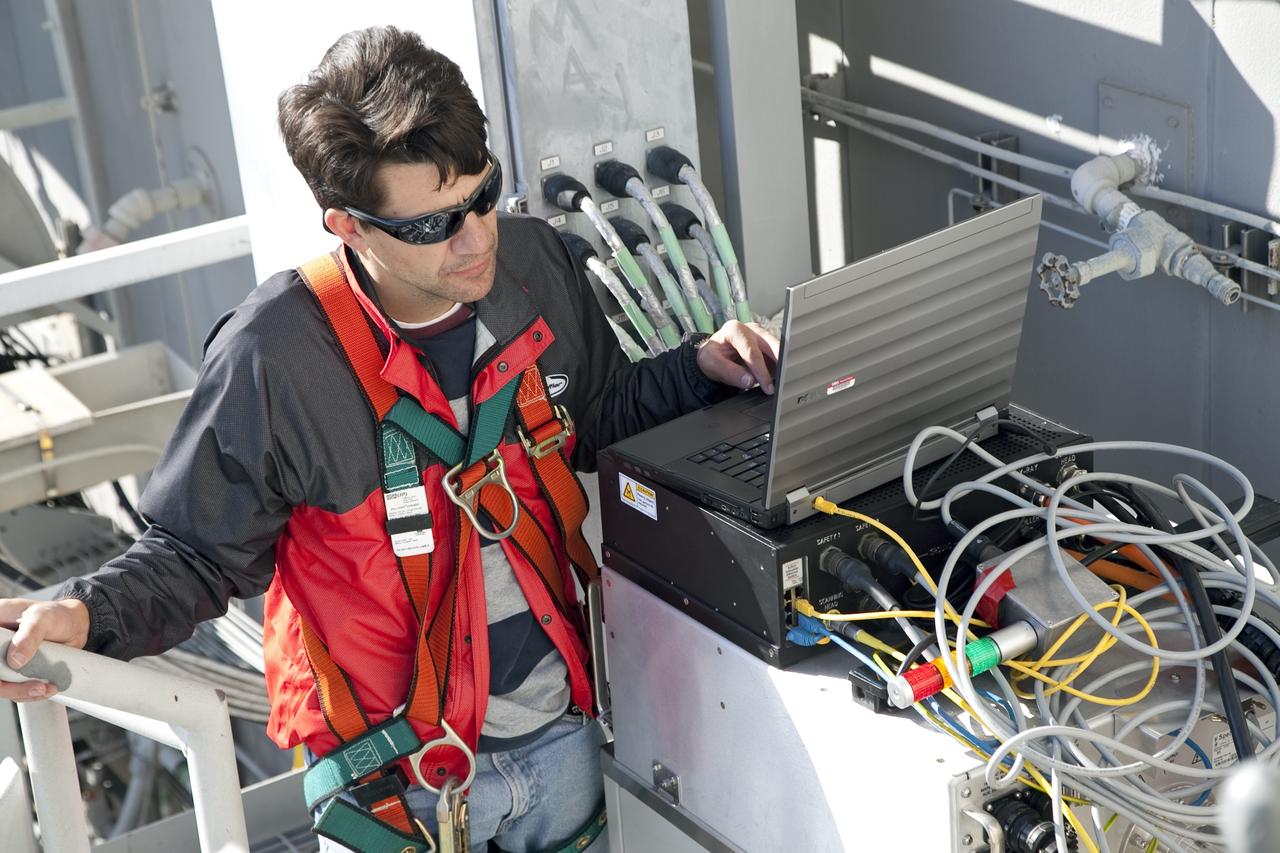

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An engineer examines images of space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank taken from a backscatter device on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
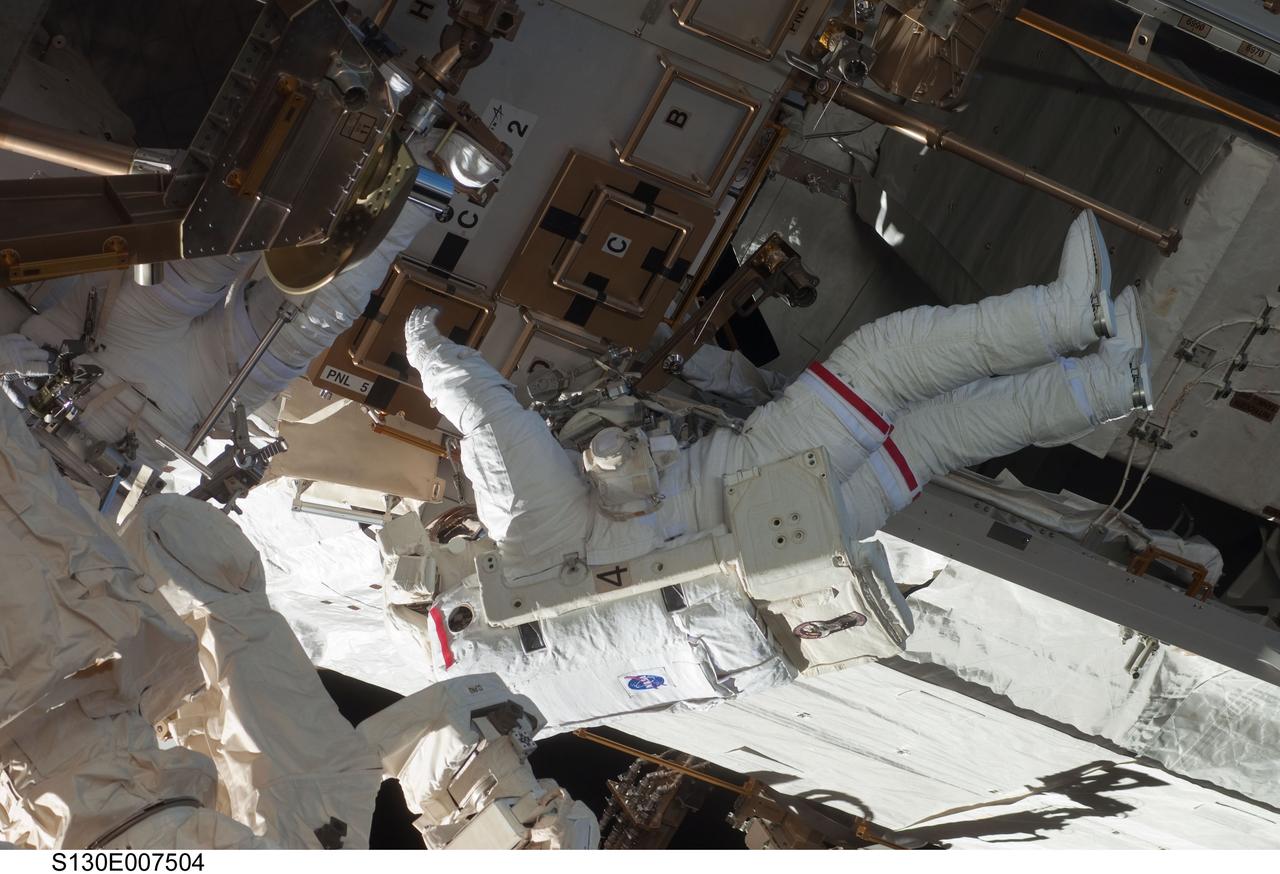

S130-E-007504 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Nicholas Patrick (partially obscured at left), both STS-130 mission specialists, participate in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and Patrick relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
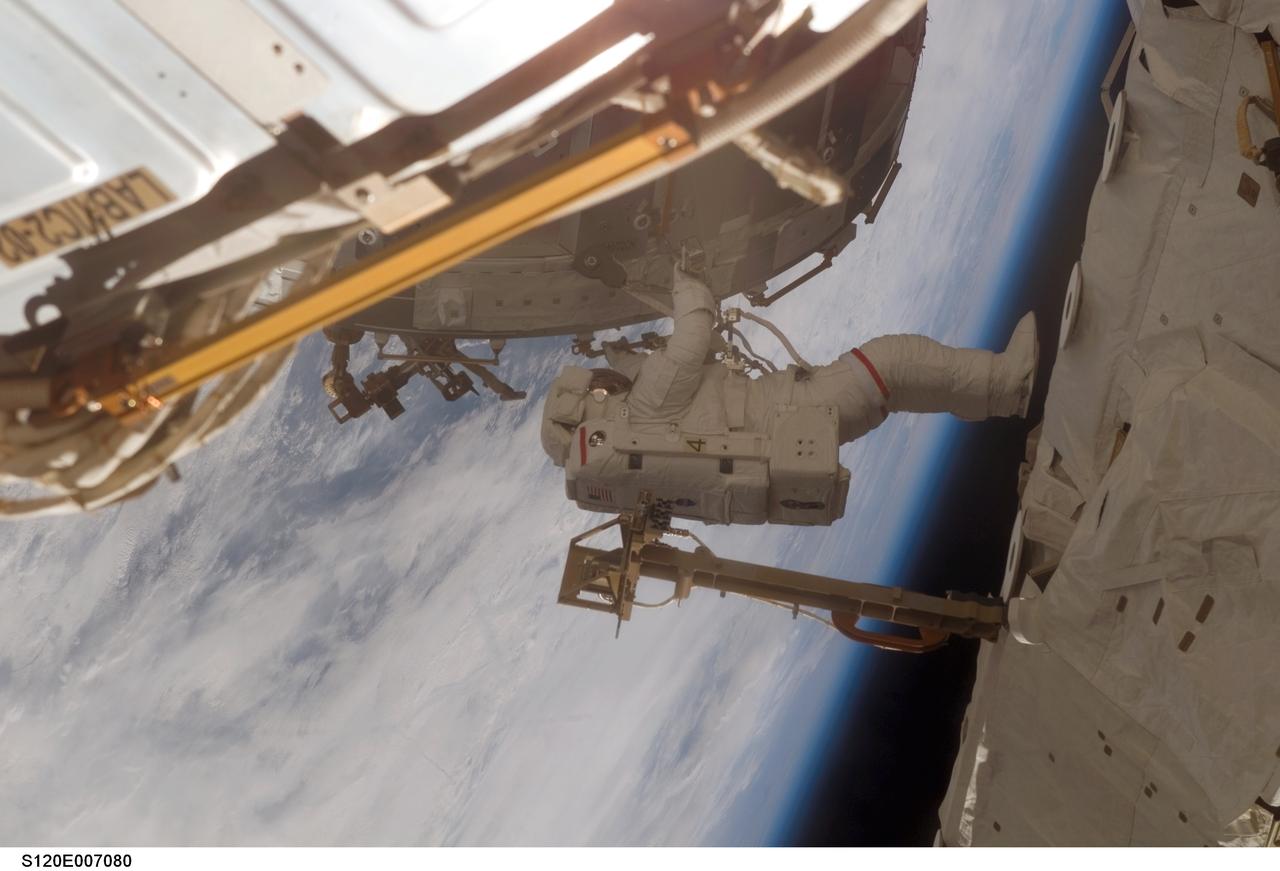

S120-E-007080 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Parazynski and astronaut Daniel Tani (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A backscatter device is being used to examine space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
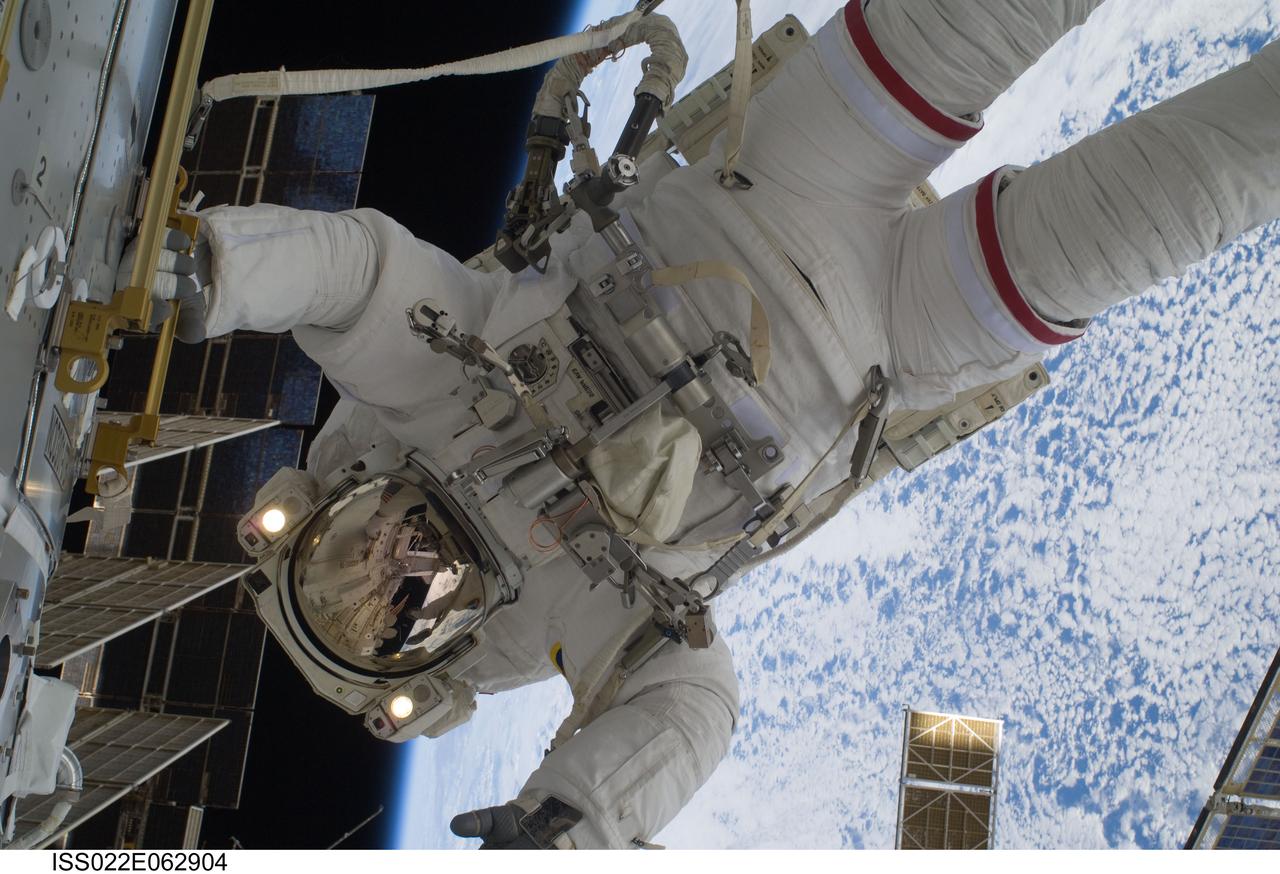

ISS022-E-062904 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Robert Behnken, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and astronaut Nicholas Patrick (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station?s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station?s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station?s cooling radiators during the mission?s second spacewalk.
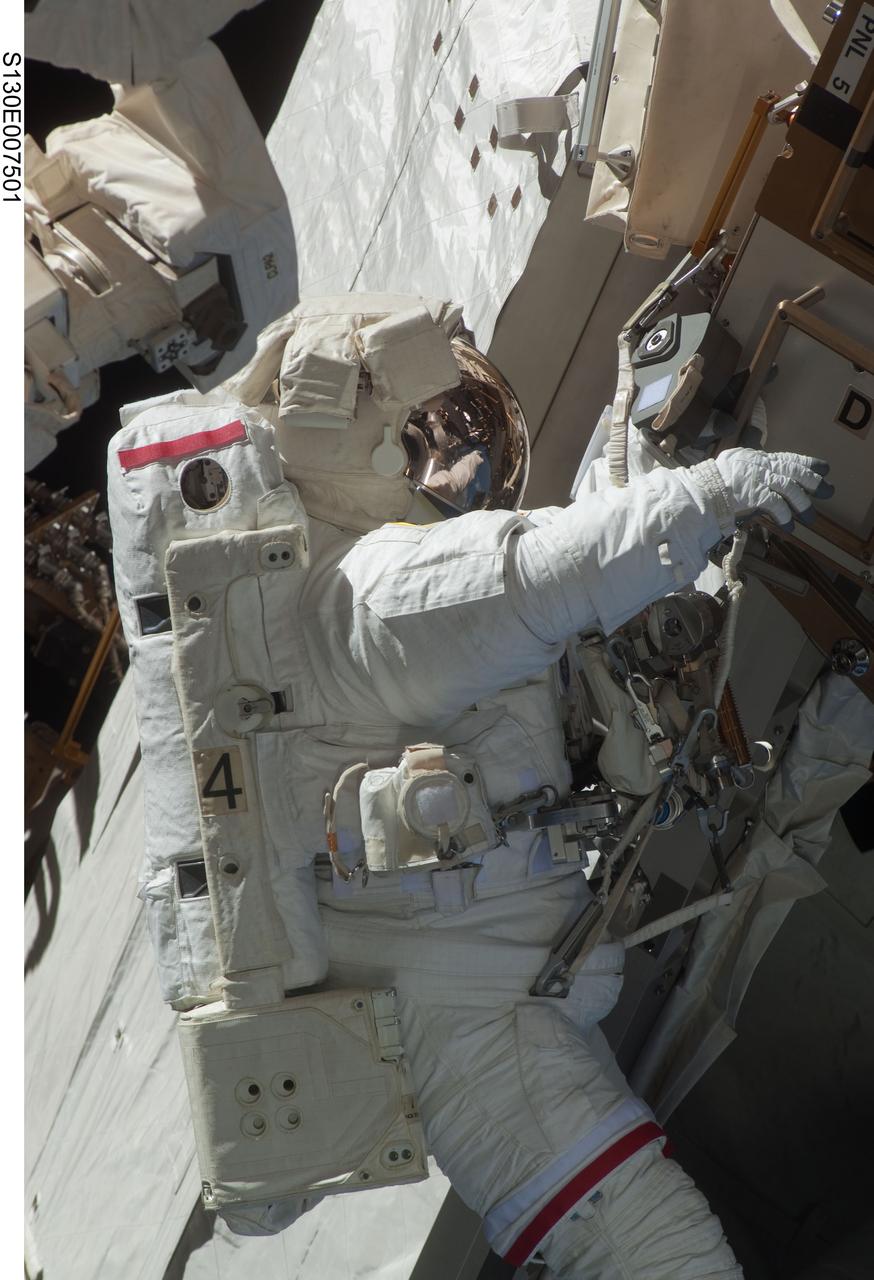

S130-E-007501 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Robert Behnken, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and astronaut Nicholas Patrick (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
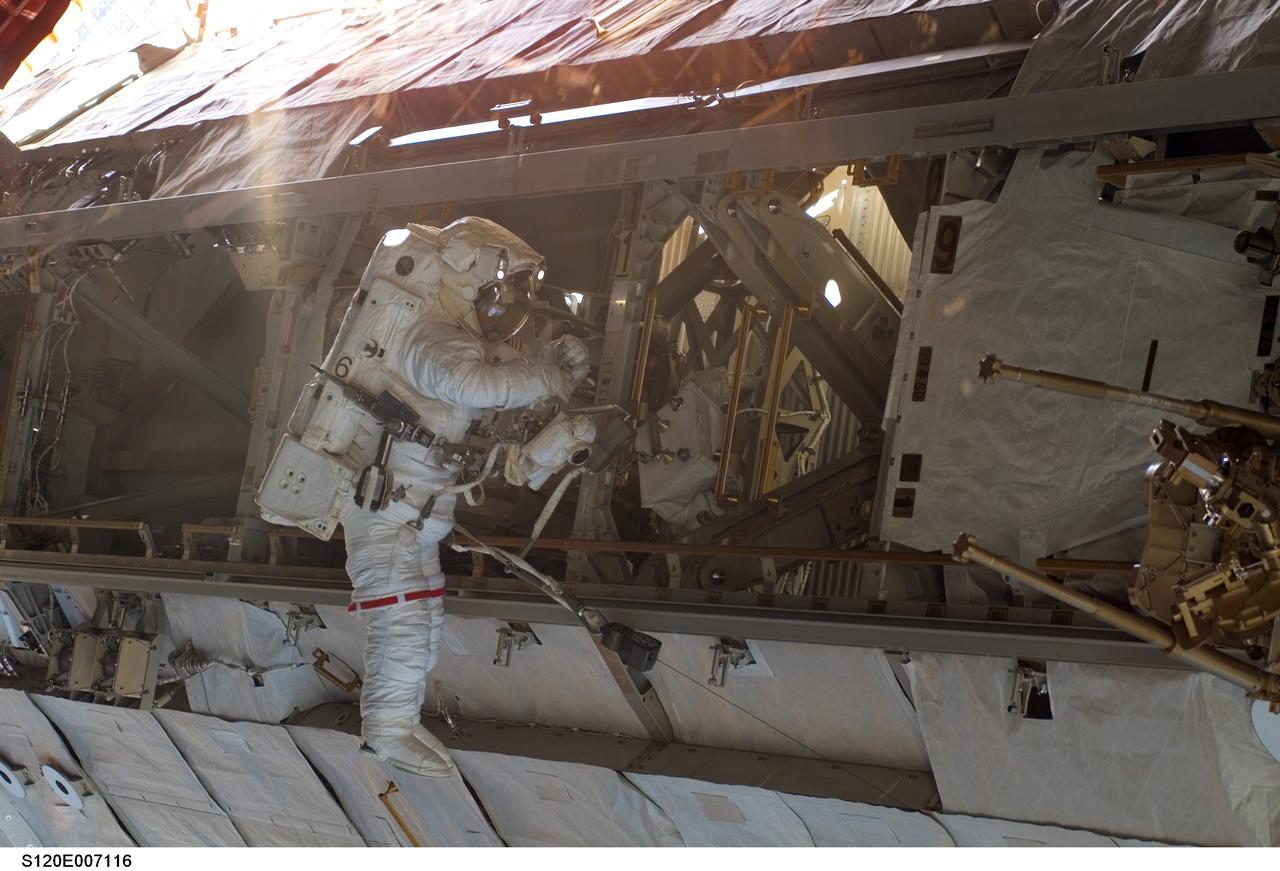

S120-E-007116 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
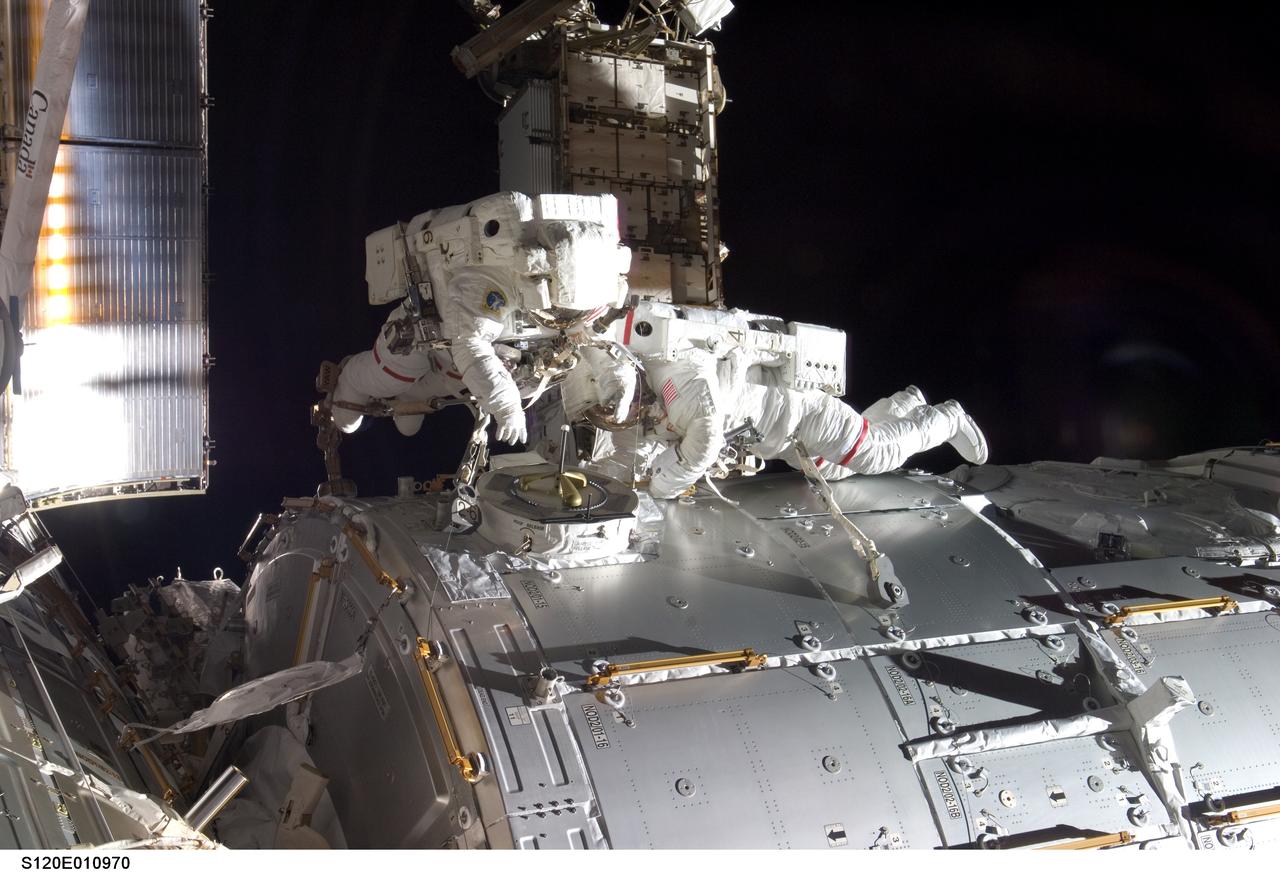

S120-E-010970 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani (left), Expedition 16 flight engineer, and Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participate in the second scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and Parazynski outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. Also the spacewalkers worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers.
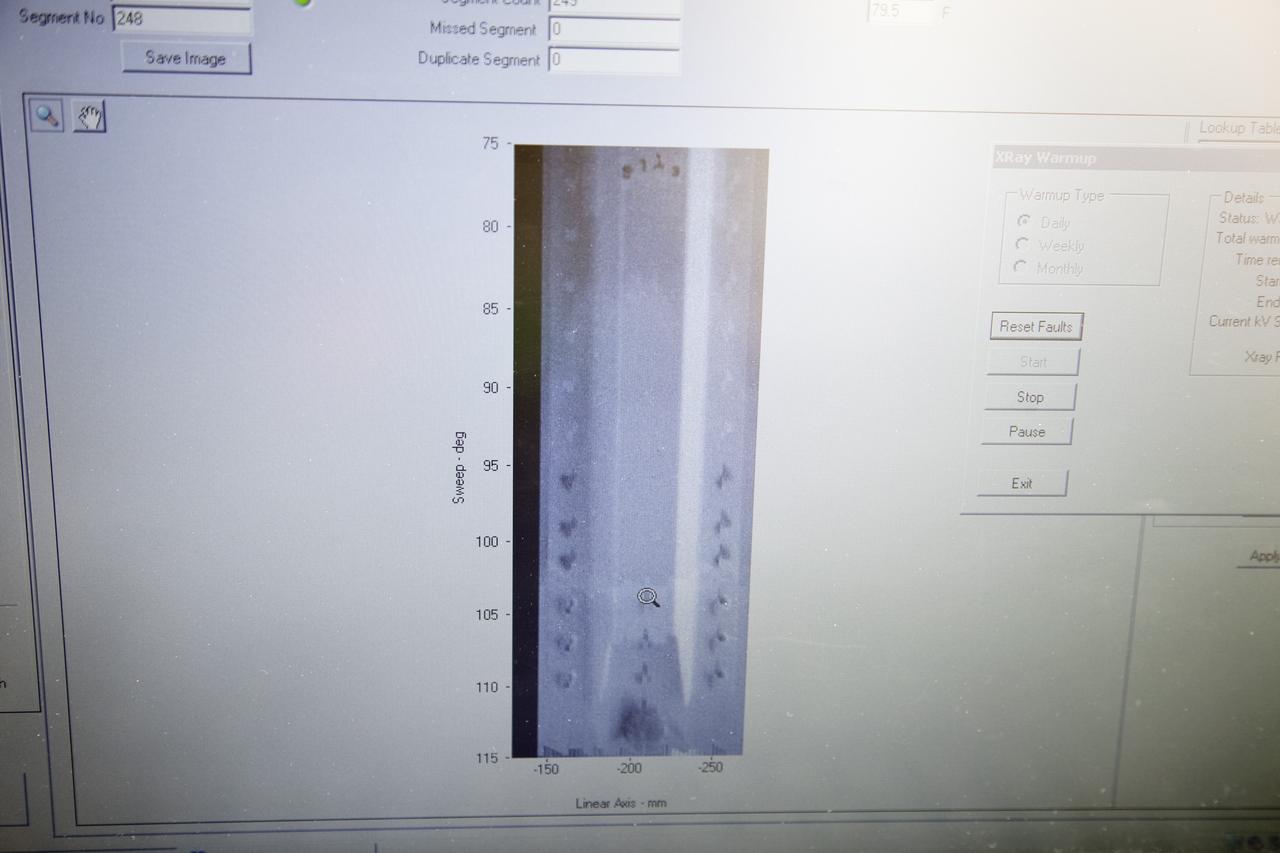
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An engineer examines images of space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank taken from a backscatter device on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
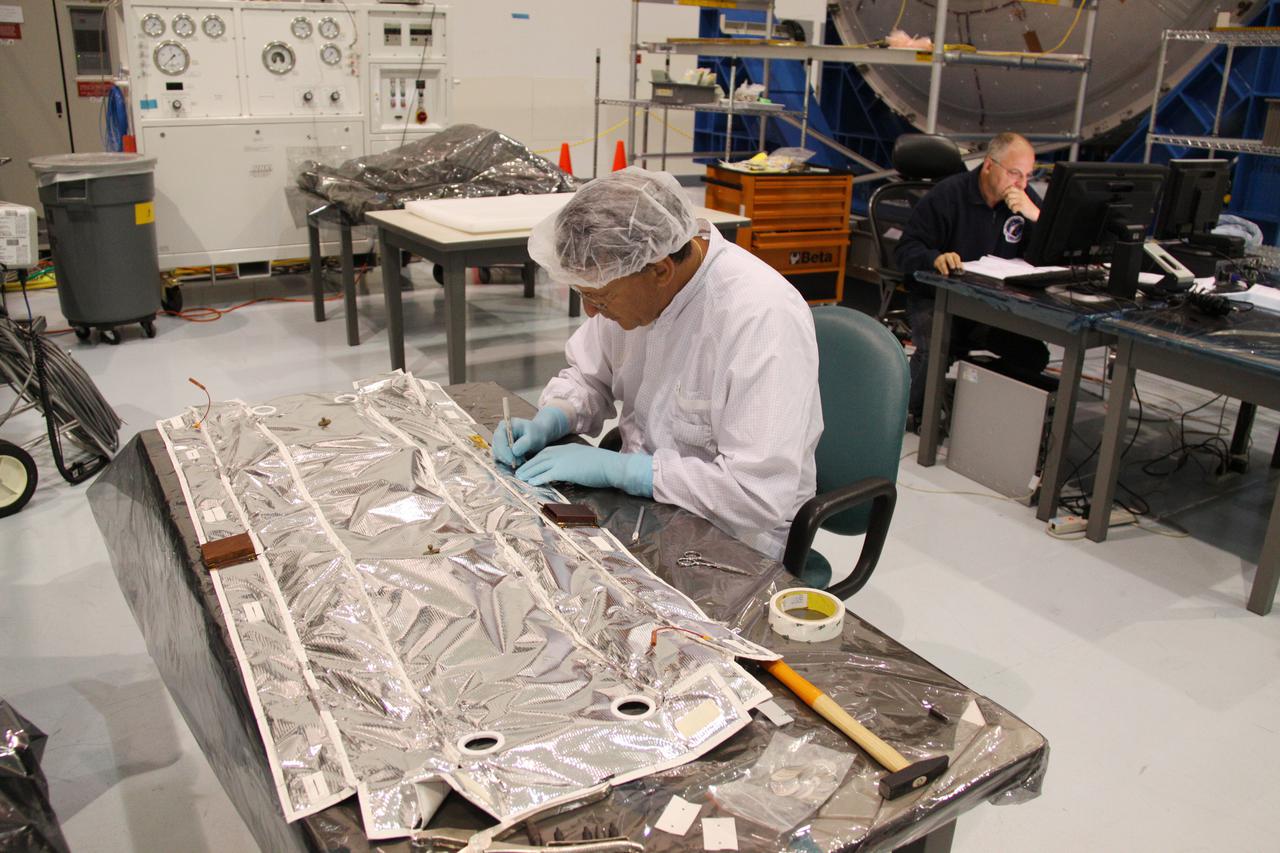

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician inspects multi-layer insulation before it is installed on the Meteoroids and Debris Protective Shield of the Permanent Multipurpose Module, or PMM. The reflective silver mesh is Mylar, which is aluminized to protect hardware aboard the International Space Station from solar thermal radiation. The Leonardo multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, is being modified to become the PMM that will carry supplies and critical spare parts to the station aboard space shuttle Discovery’s STS-133 mission. Discovery, targeted to launch Nov. 1, will leave the module behind so it can be used for microgravity experiments in fluid physics, materials science, biology and biotechnology. Photo credit: NASA_Troy Cryder
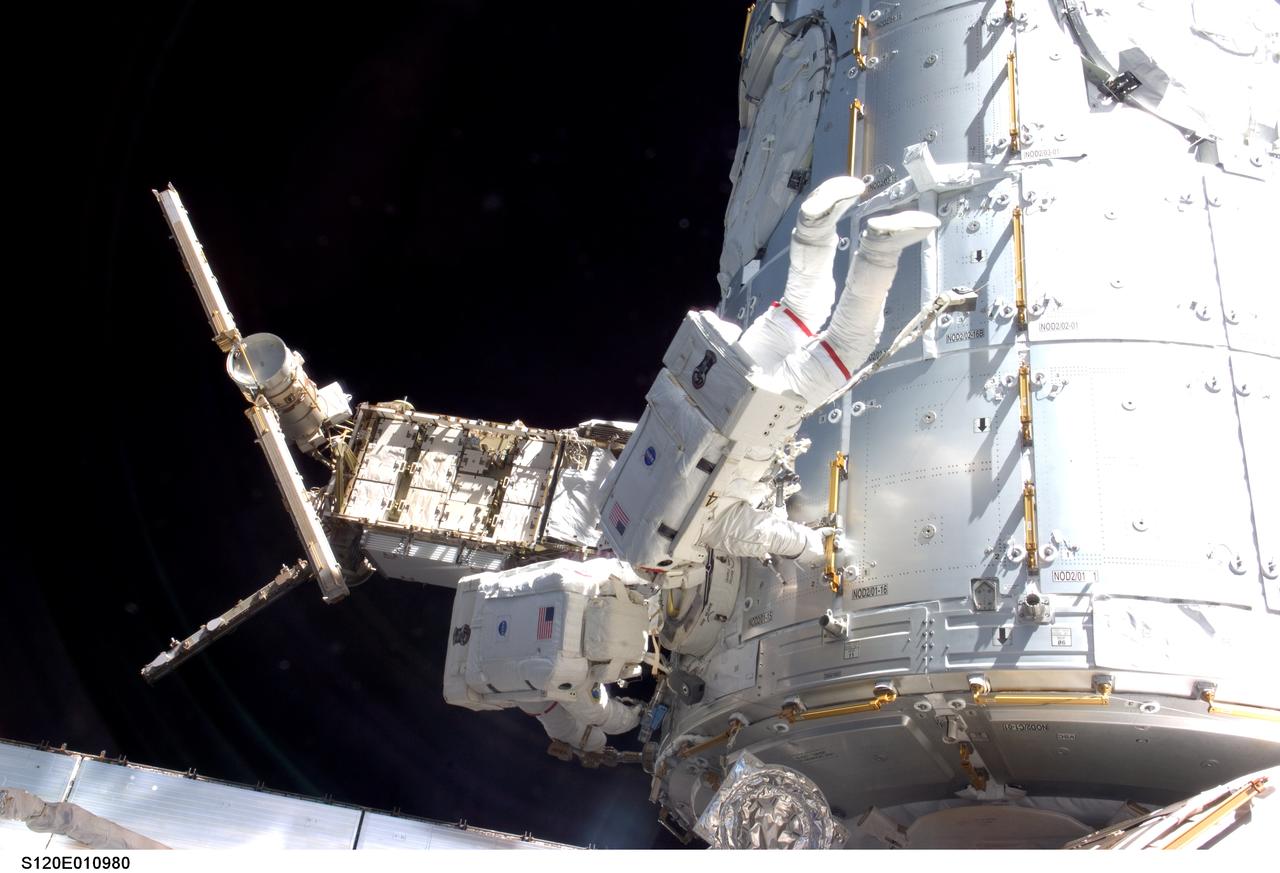

S120-E-010980 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani (left), Expedition 16 flight engineer, and Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participate in the second scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and Parazynski outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. Also the spacewalkers worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers.
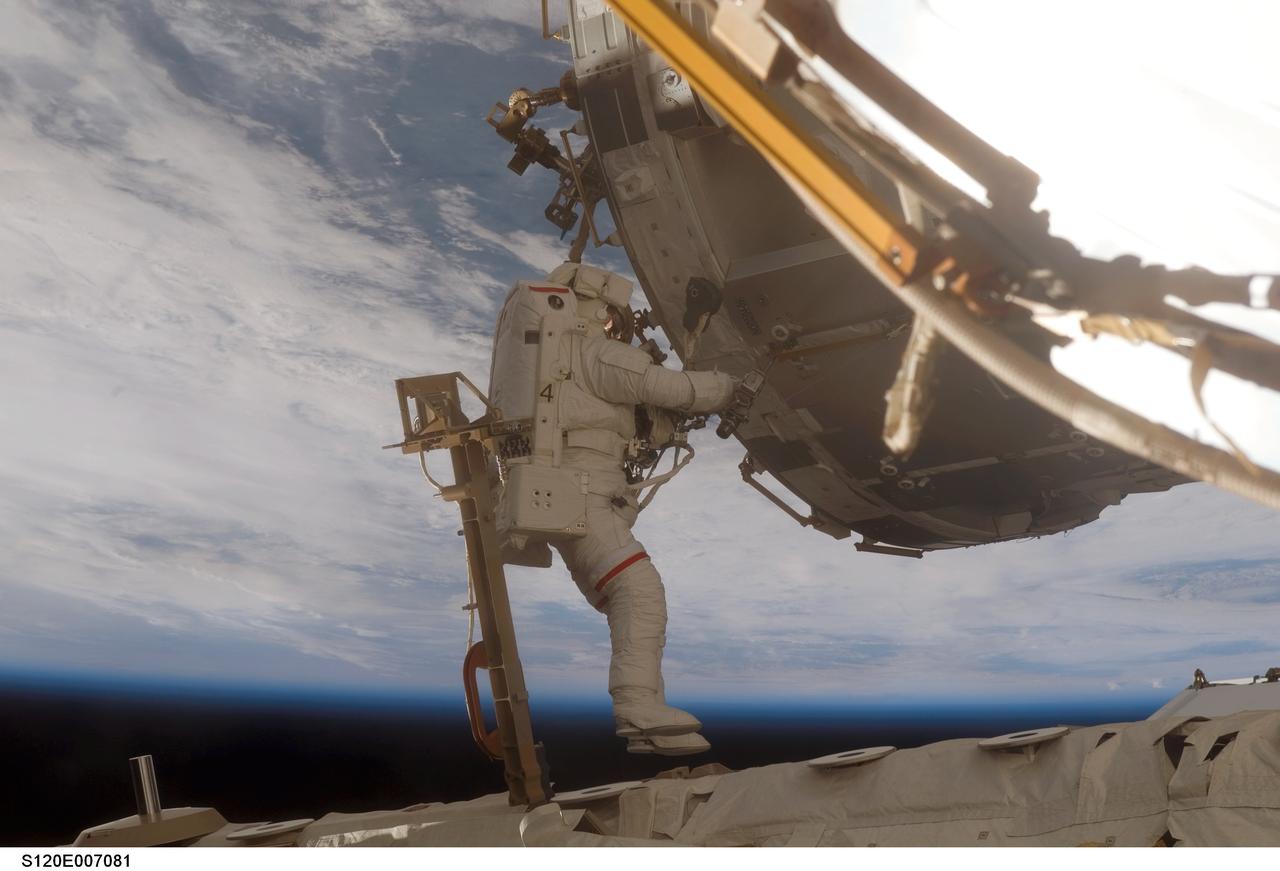

S120-E-007081 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Parazynski and astronaut Daniel Tani (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
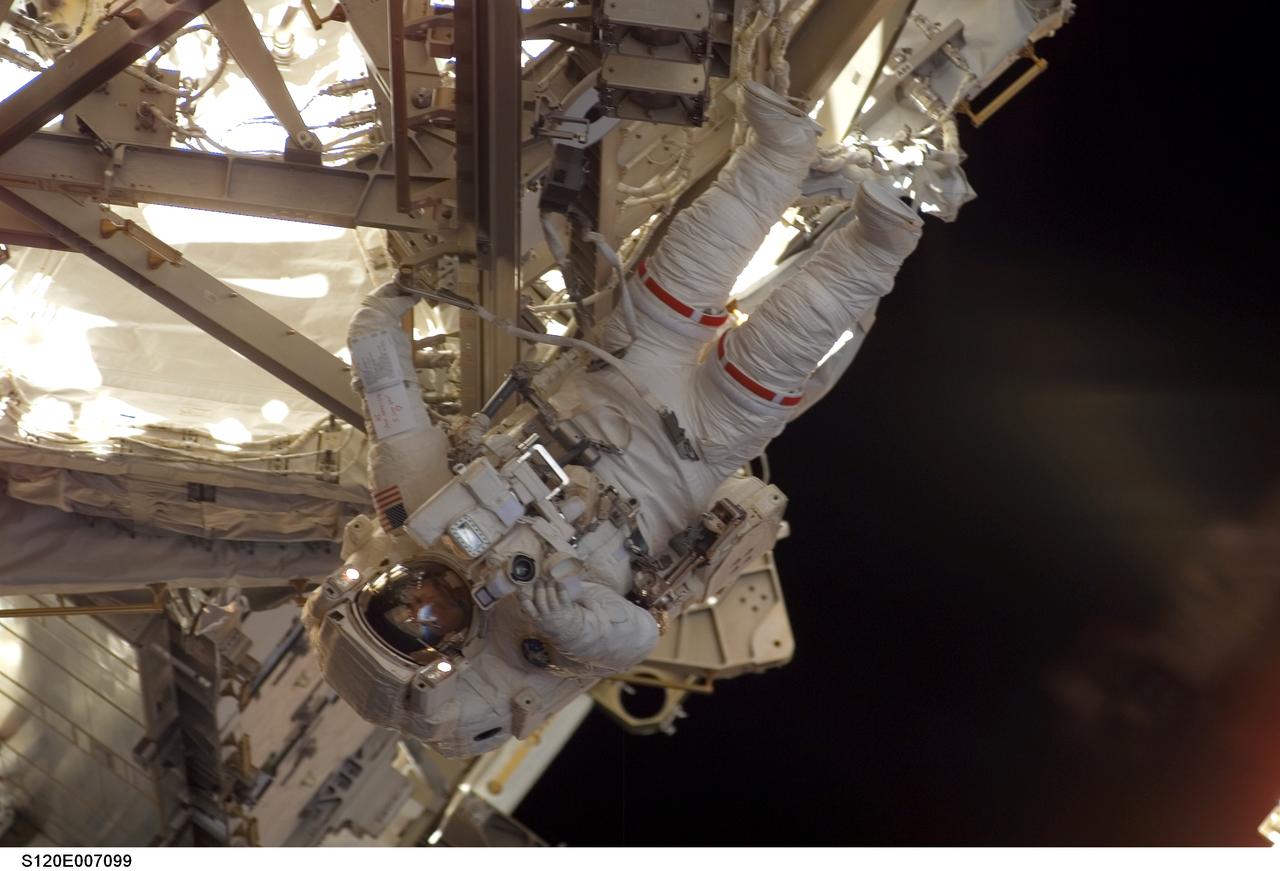

S120-E-007099 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
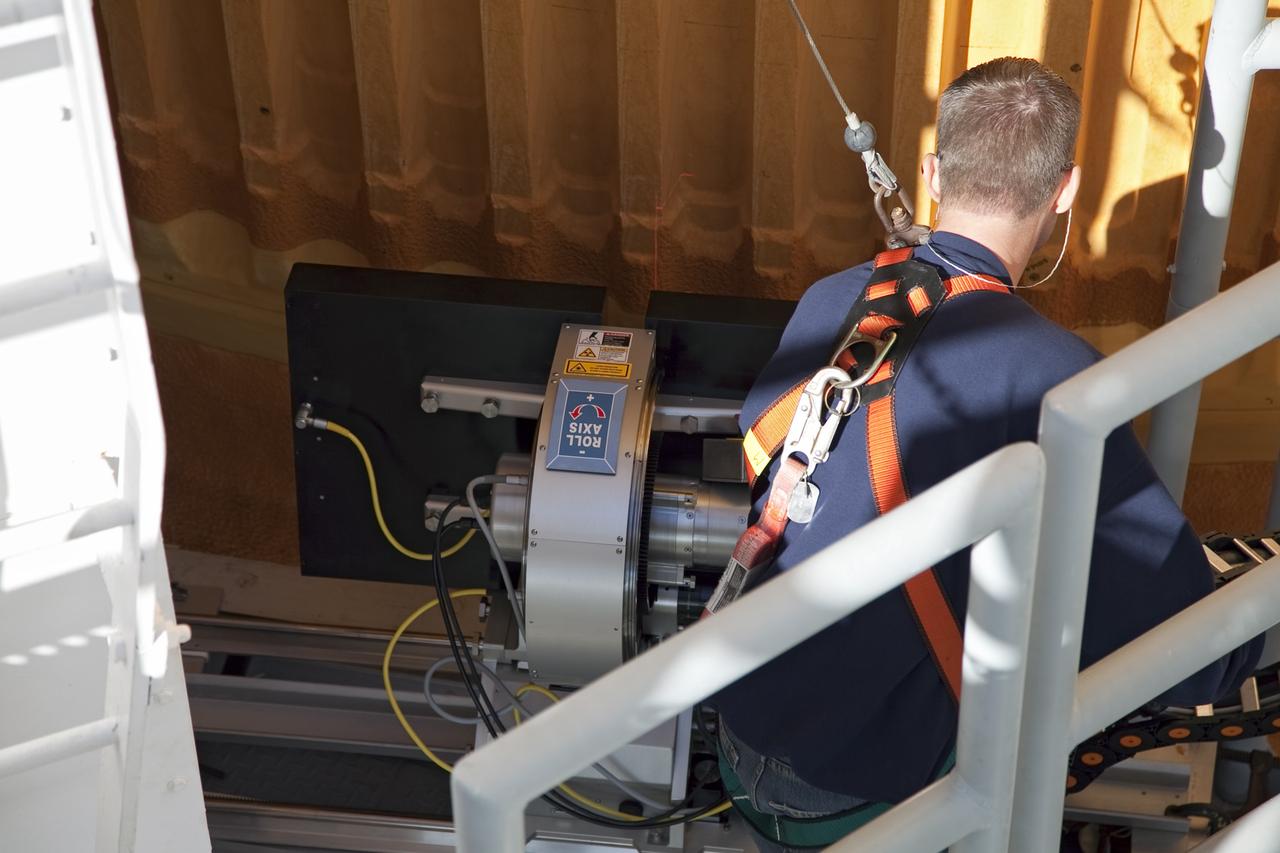

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An engineer uses a backscatter device to examine space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
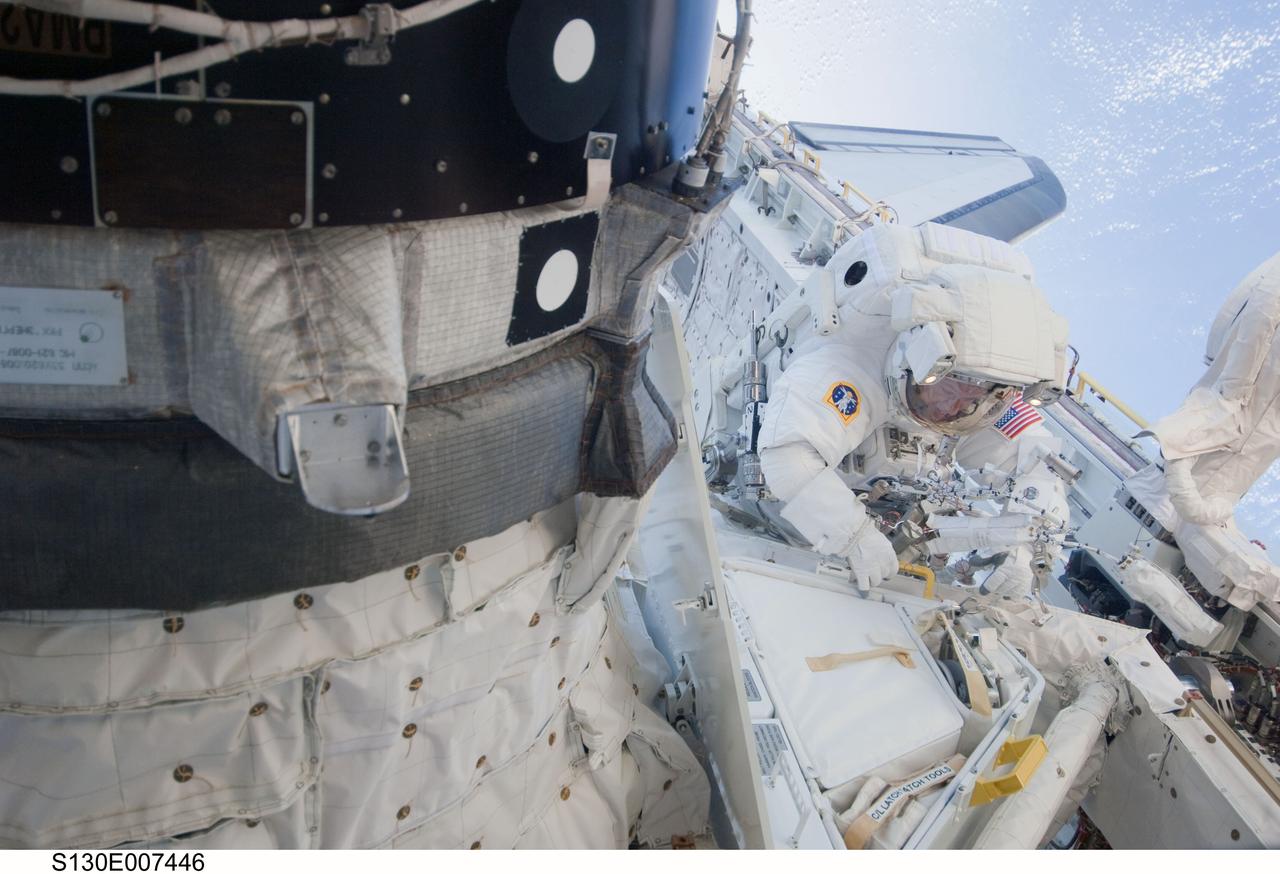

S130-E-007446 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Nicholas Patrick, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Patrick and astronaut Robert Behnken (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
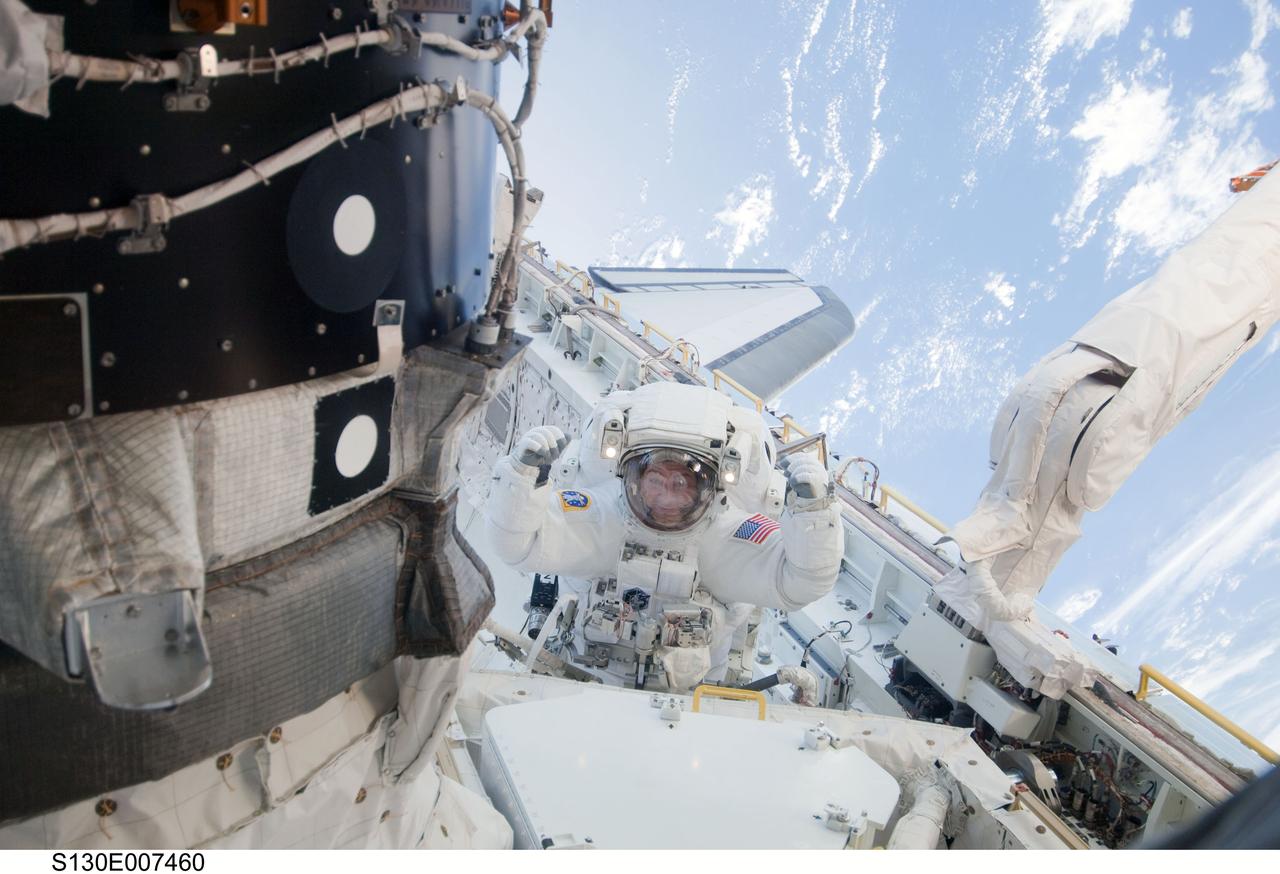

S130-E-007460 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Nicholas Patrick, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Patrick and astronaut Robert Behnken (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
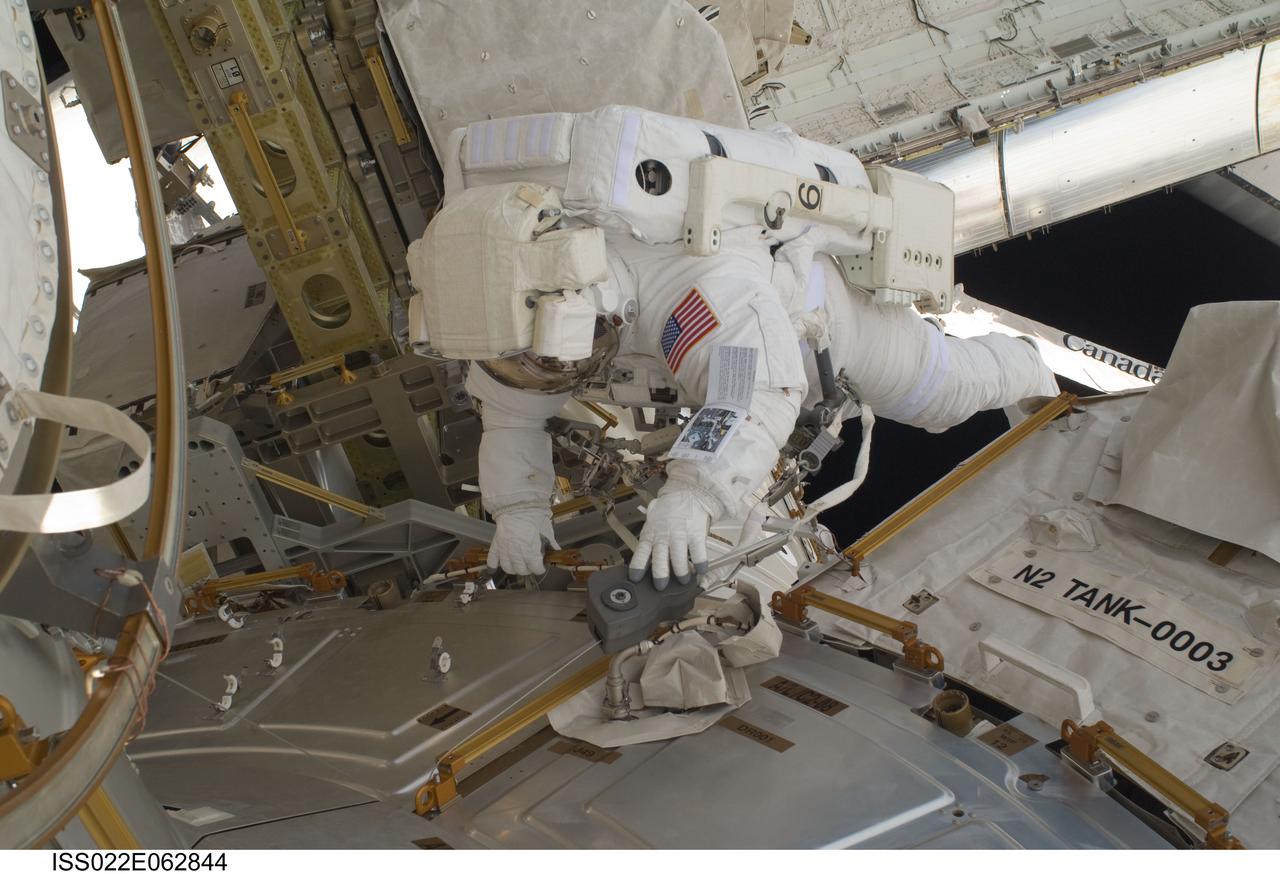

ISS022-E-062844 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Nicholas Patrick, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Patrick and astronaut Robert Behnken (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station?s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station?s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station?s cooling radiators during the mission?s second spacewalk.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A backscatter device is being used to examine space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
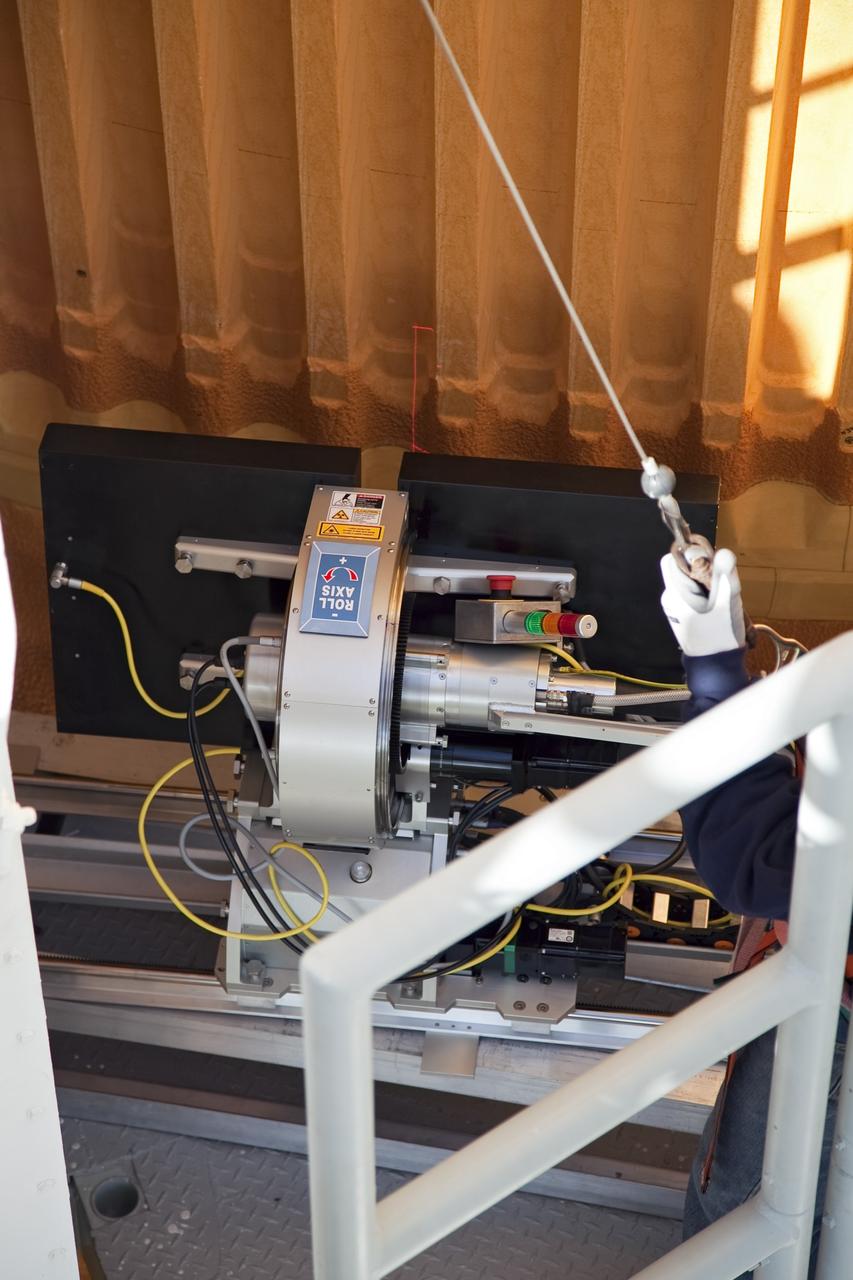
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An engineer uses a backscatter device to examine space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
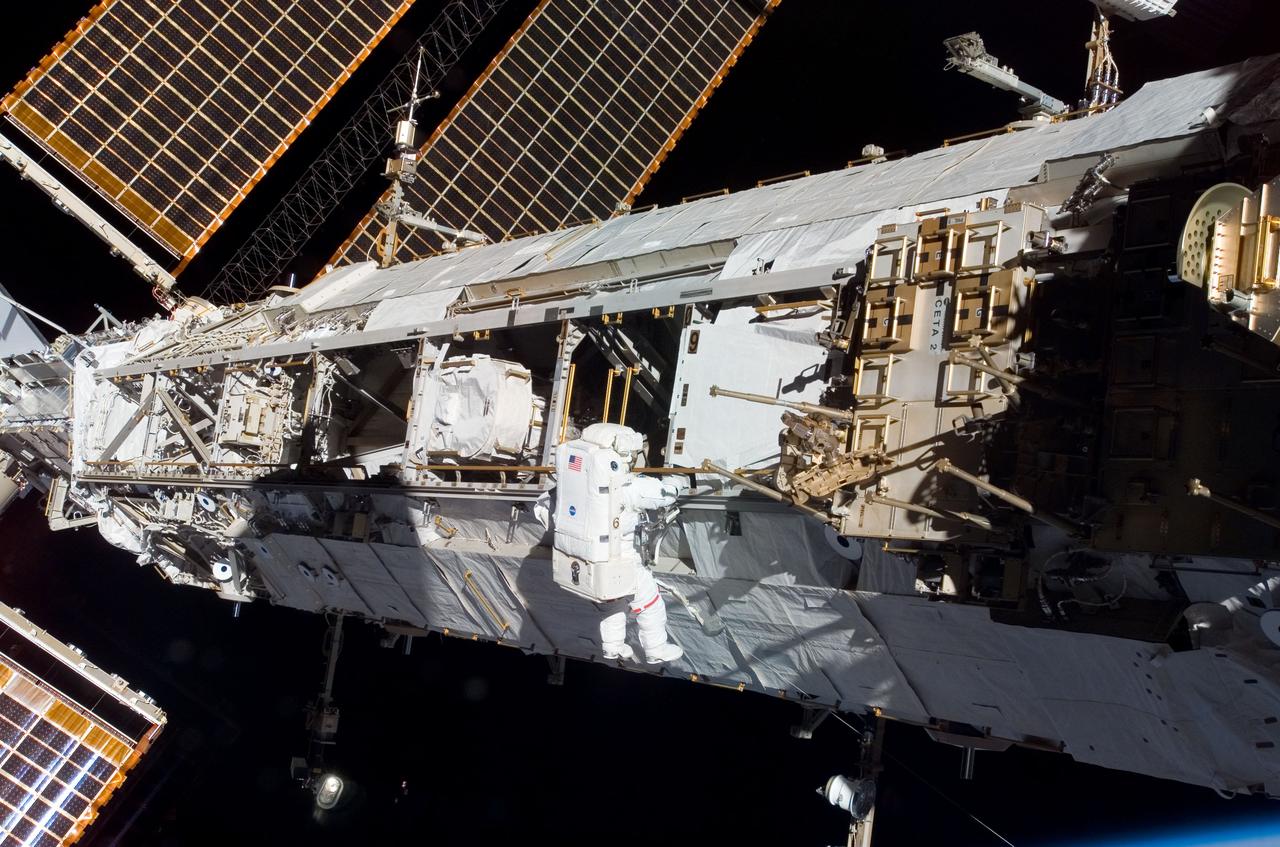

S120-E-007003 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
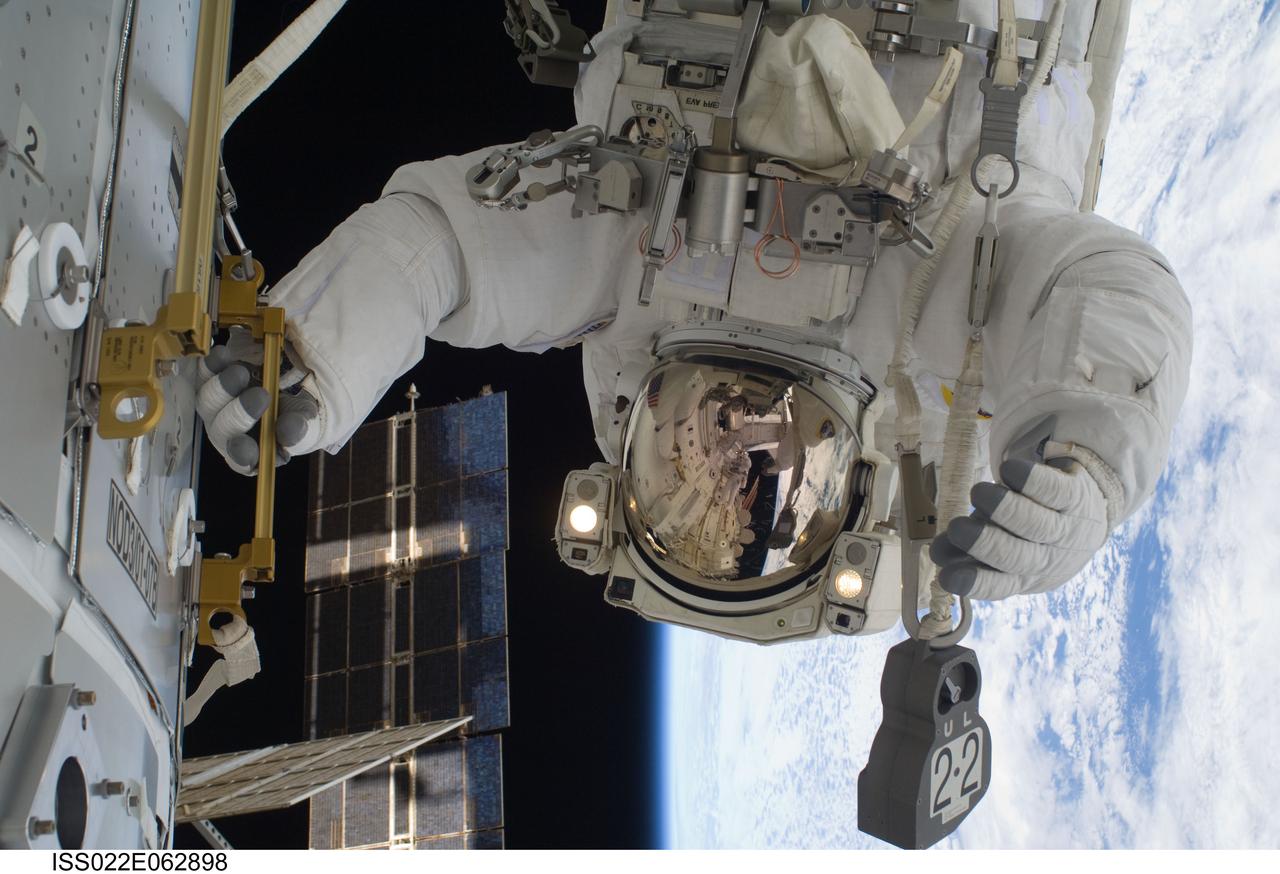

ISS022-E-062898 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Robert Behnken, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and astronaut Nicholas Patrick (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station?s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station?s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station?s cooling radiators during the mission?s second spacewalk.
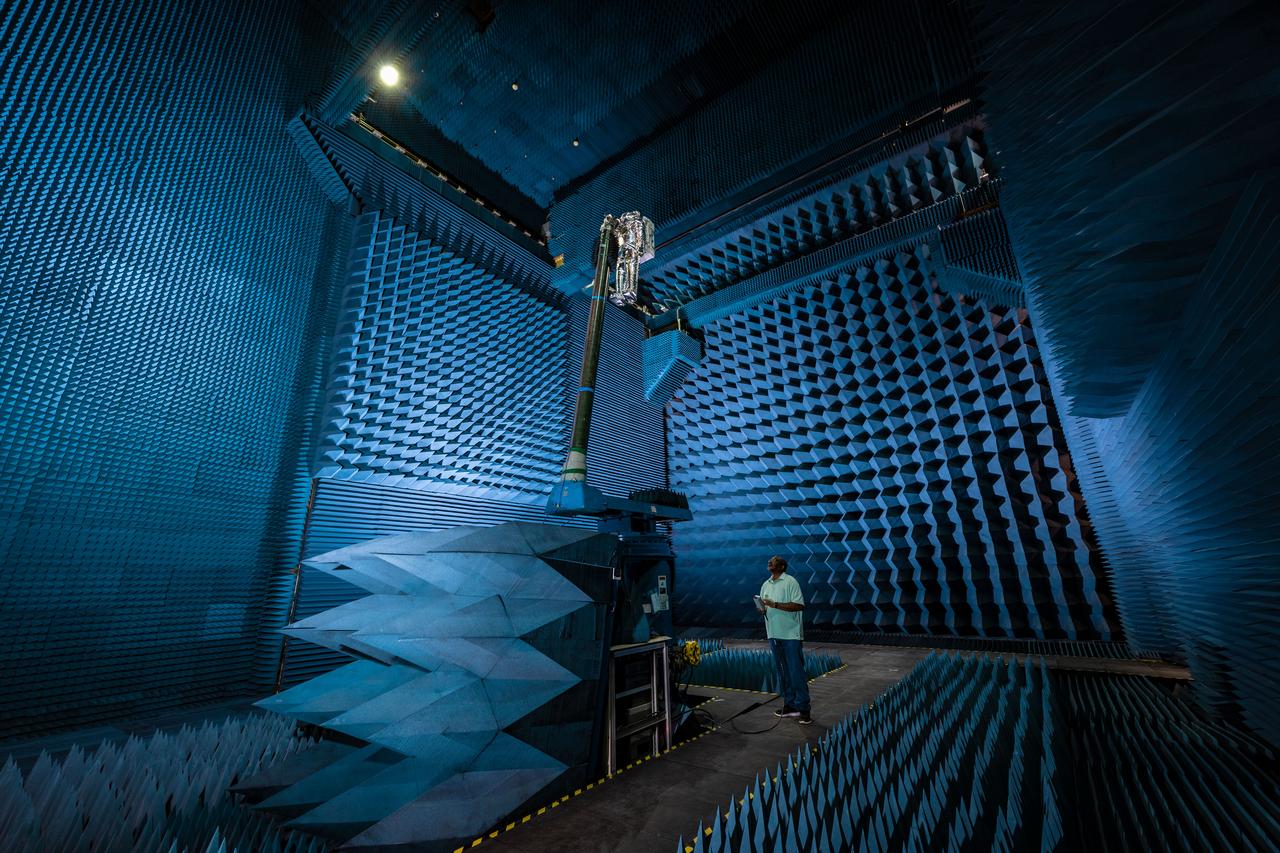

jsc2021e022488 (June 11, 2021) --- NASA’s Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (xEMU) spacesuit undergoes antenna testing in NASA Johnson Space Center’s anechoic chamber to inspect multi-layer insulation keep-out zones for the Wi-Fi and ultra-high-frequency antennas that are part of the spacesuit’s communication system. The xEMU test article is named xGUS, the successor to the Extravehicular Mobility Unit test article (also named GUS), which was named after NASA astronaut Gus Grissom and his iconic silver spacesuit. This image was taken from where the "horn," or source antenna, is located that sends out radio frequency signals to the spacesuit. The anechoic chamber walls are covered with a material that absorbs electromagnetic energy allowing the anechoic chamber to simulate a space environment. The antenna test facility is utilized to test antenna radiation distribution pattern performance for spaceflight applications in electromagnetic environments. Pictured in the photo is antenna test engineer Will Bond.
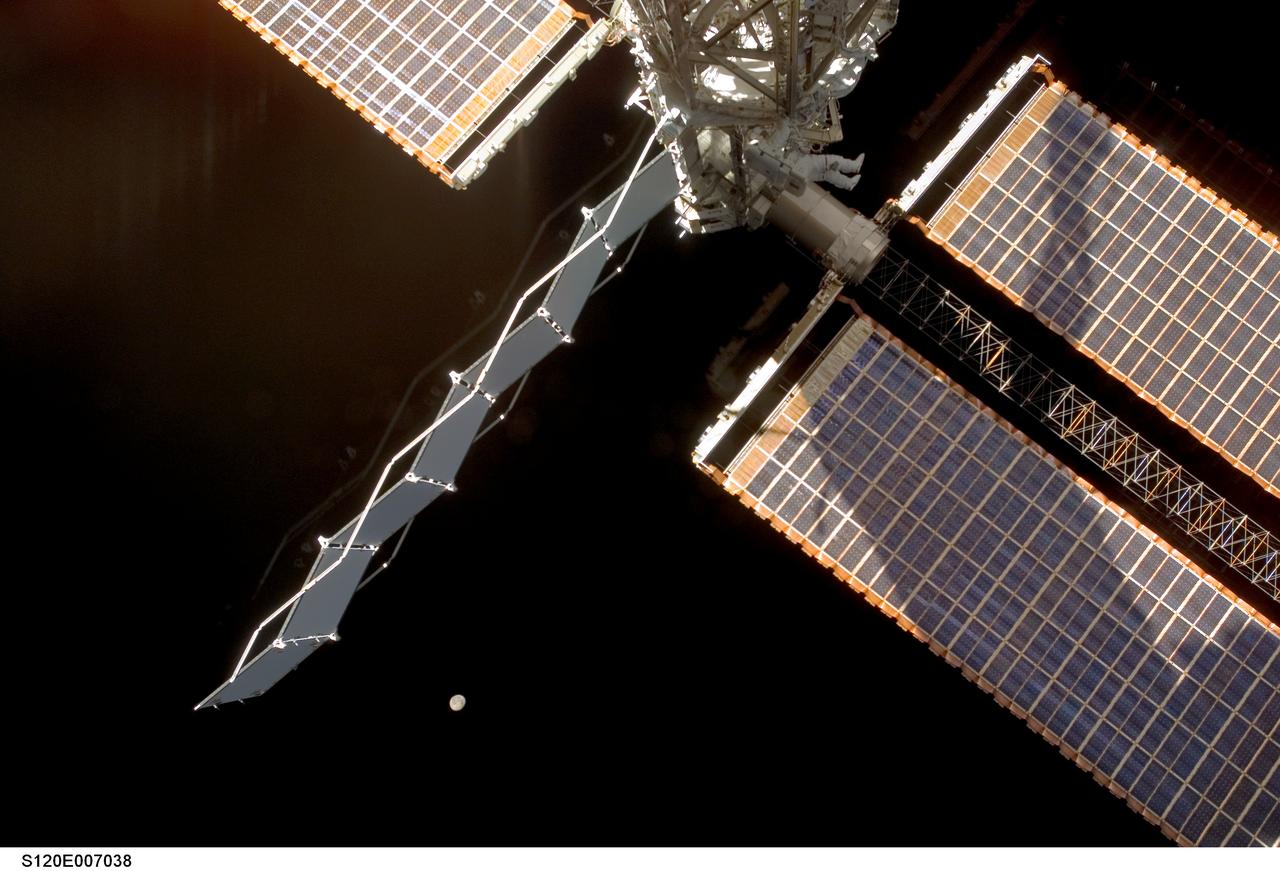

S120-E-007038 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani (top center), Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. The moon is visible at lower center.
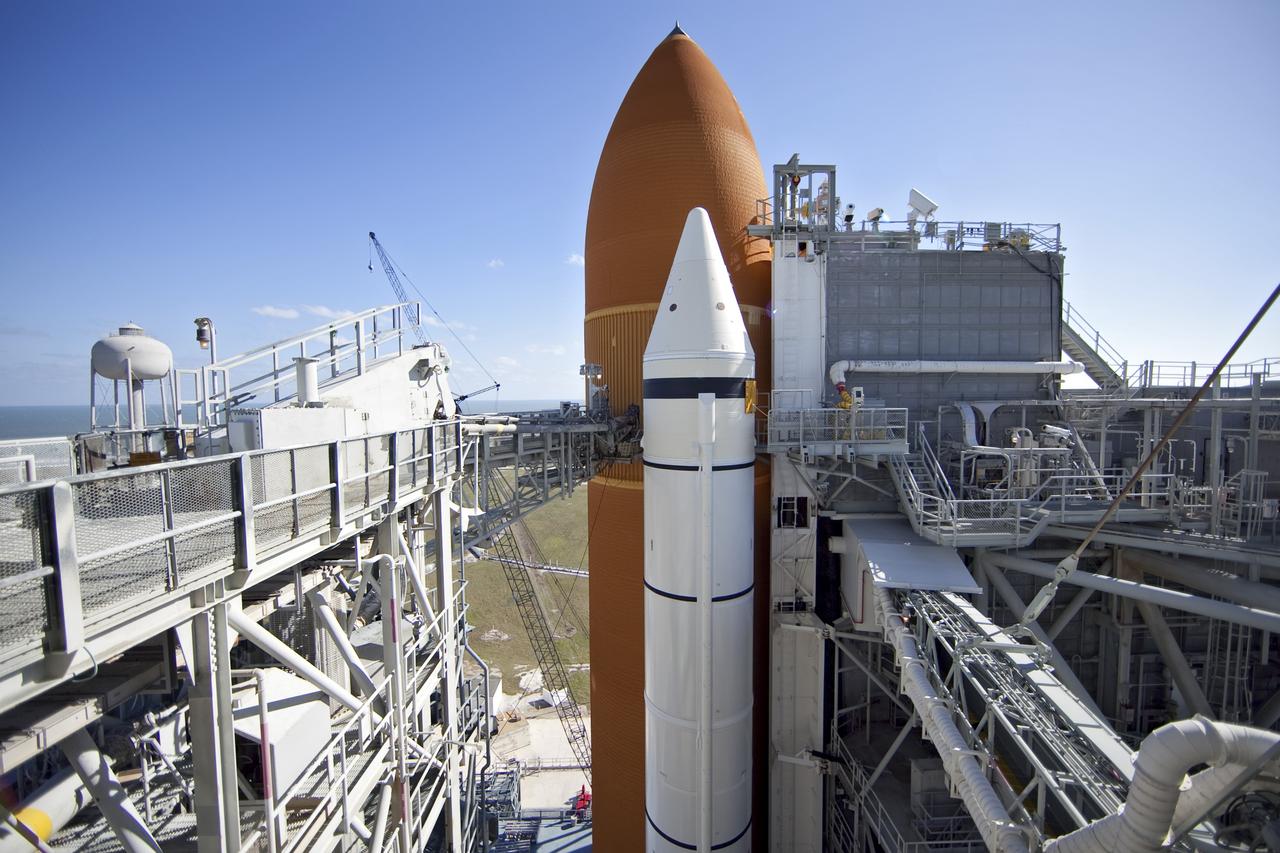

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Engineers will use a backscatter device to examine space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
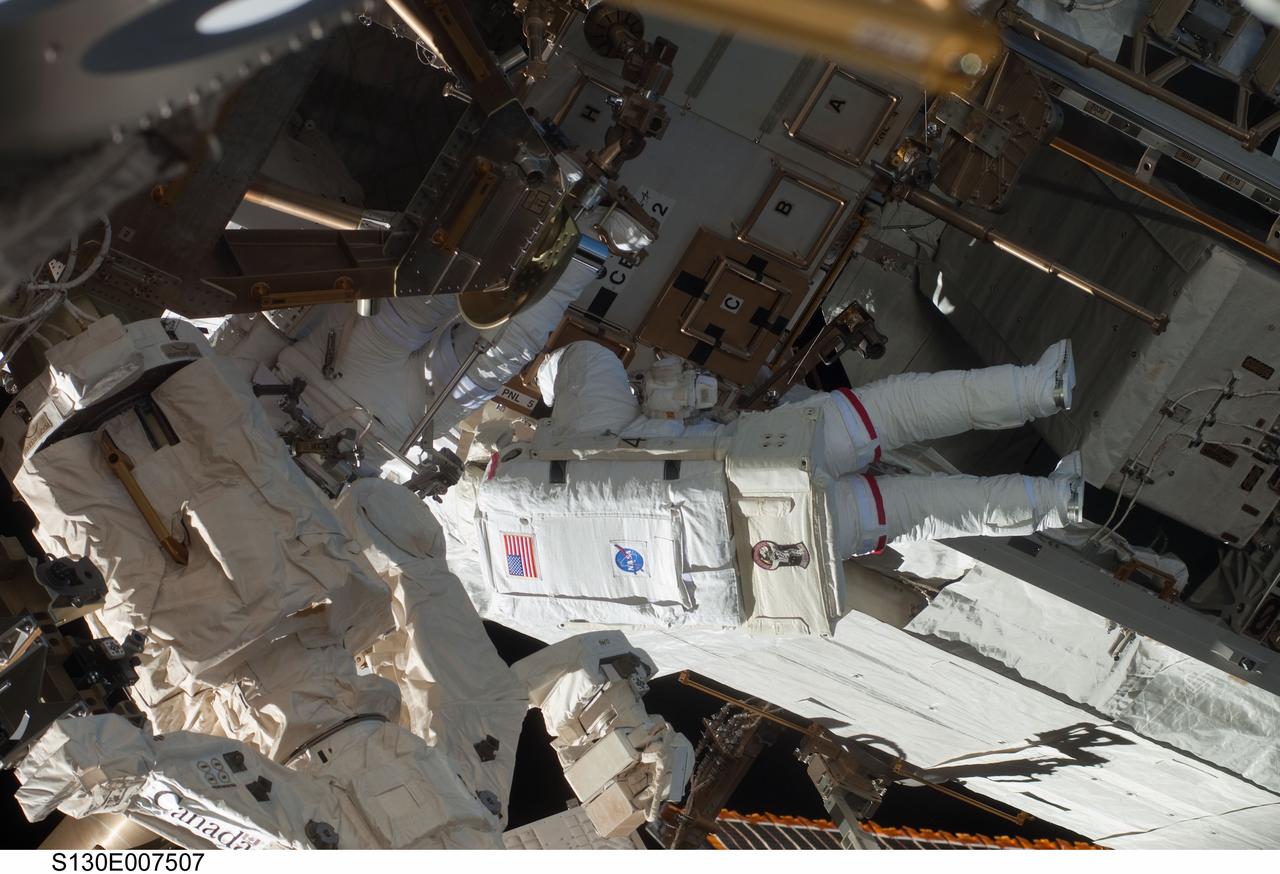

S130-E-007507 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Nicholas Patrick (partially obscured at left), both STS-130 mission specialists, participate in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Behnken and Patrick relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
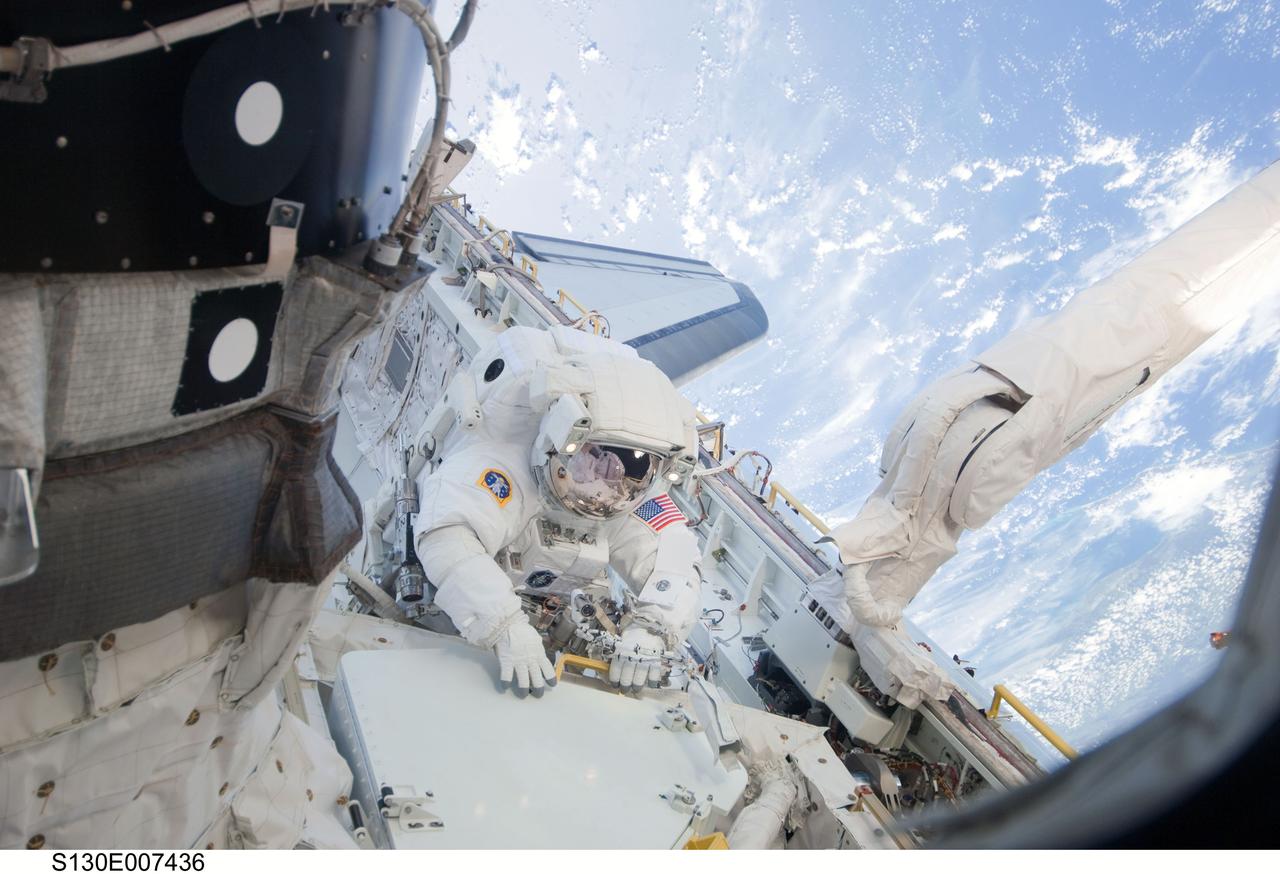

S130-E-007436 (11 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Nicholas Patrick, STS-130 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 32-minute spacewalk, Patrick and astronaut Robert Behnken (out of frame), mission specialist, relocated a temporary platform from the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, or Dextre, to the station’s truss structure and installed two handles on the robot. Once Tranquility was structurally mated to Unity, the spacewalkers connected heater and data cables that will integrate the new module with the rest of the station’s systems. They also pre-positioned insulation blankets and ammonia hoses that will be used to connect Tranquility to the station’s cooling radiators during the mission’s second spacewalk.
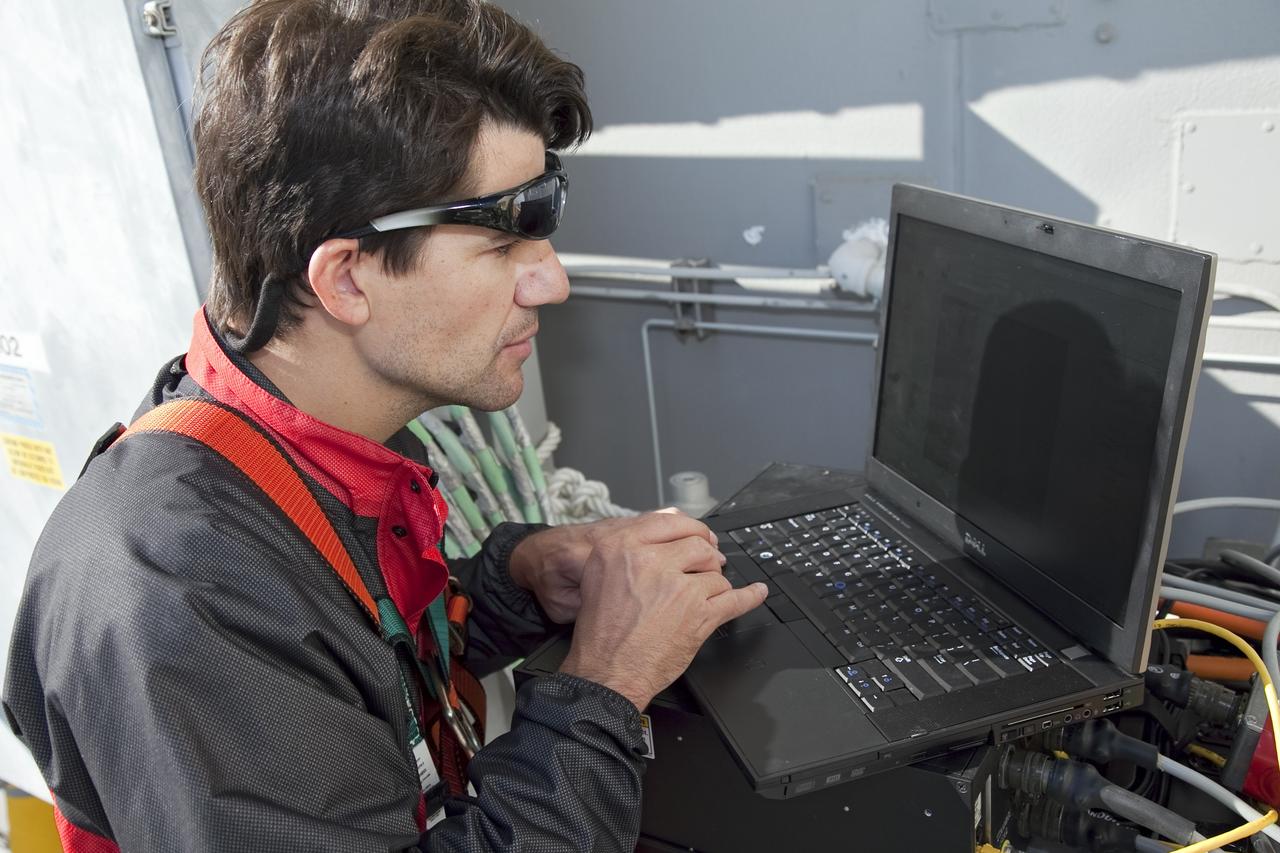

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An engineer examines images of space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank taken from a backscatter device on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
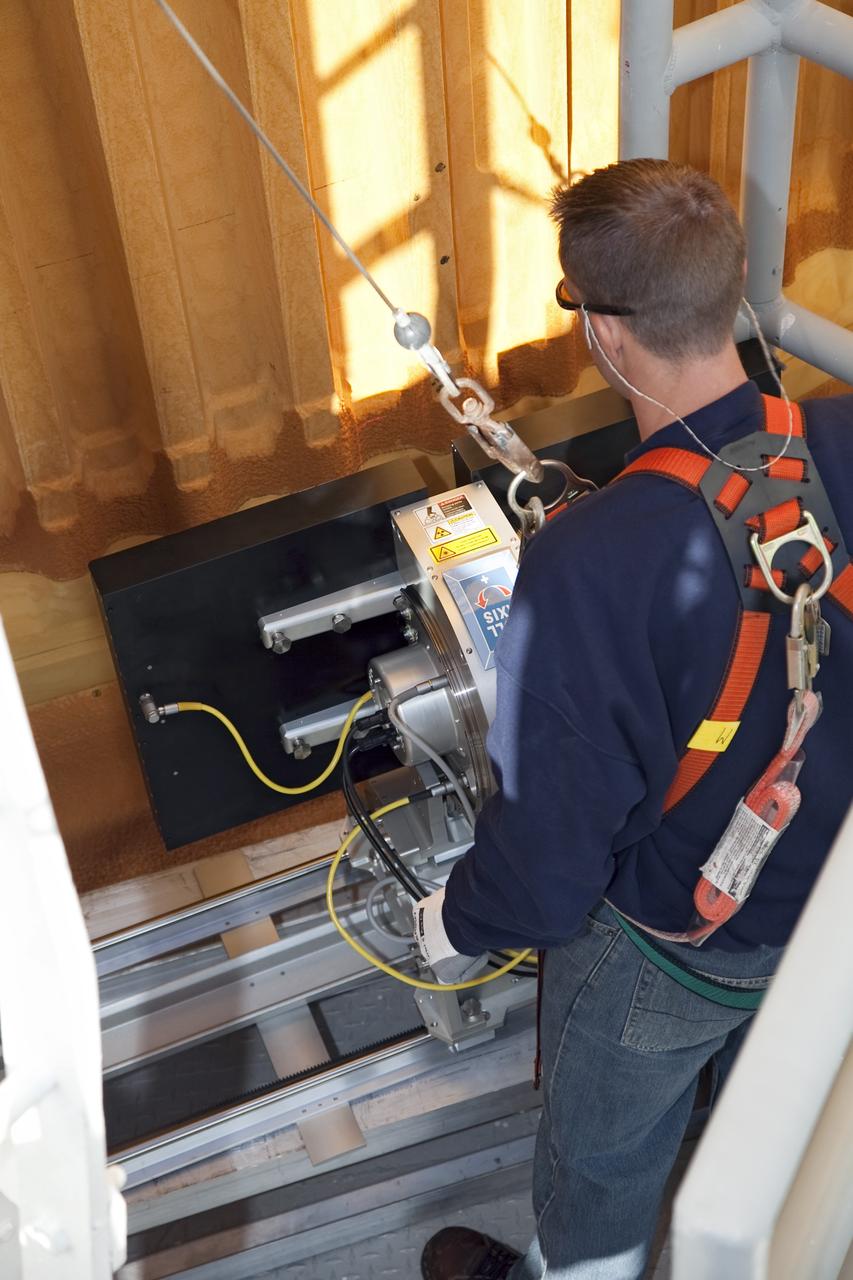

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An engineer uses a backscatter device to examine space shuttle Discovery's external fuel tank on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The device bounces radiation off the tank, allowing technicians to see under the tank's foam insulation. The foam cracked during initial loading operations for Discovery’s STS-133 launch attempt on Nov. 5, and technicians later identified two cracked stringers, which are the composite aluminum ribs located vertically on the tank’s intertank area. Those two stringers have been replaced and reinforced with doublers, which are shaped metal pieces twice as thick as the original stringers. Launch is no earlier than Dec. 17 at 8:51 p.m. EST. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
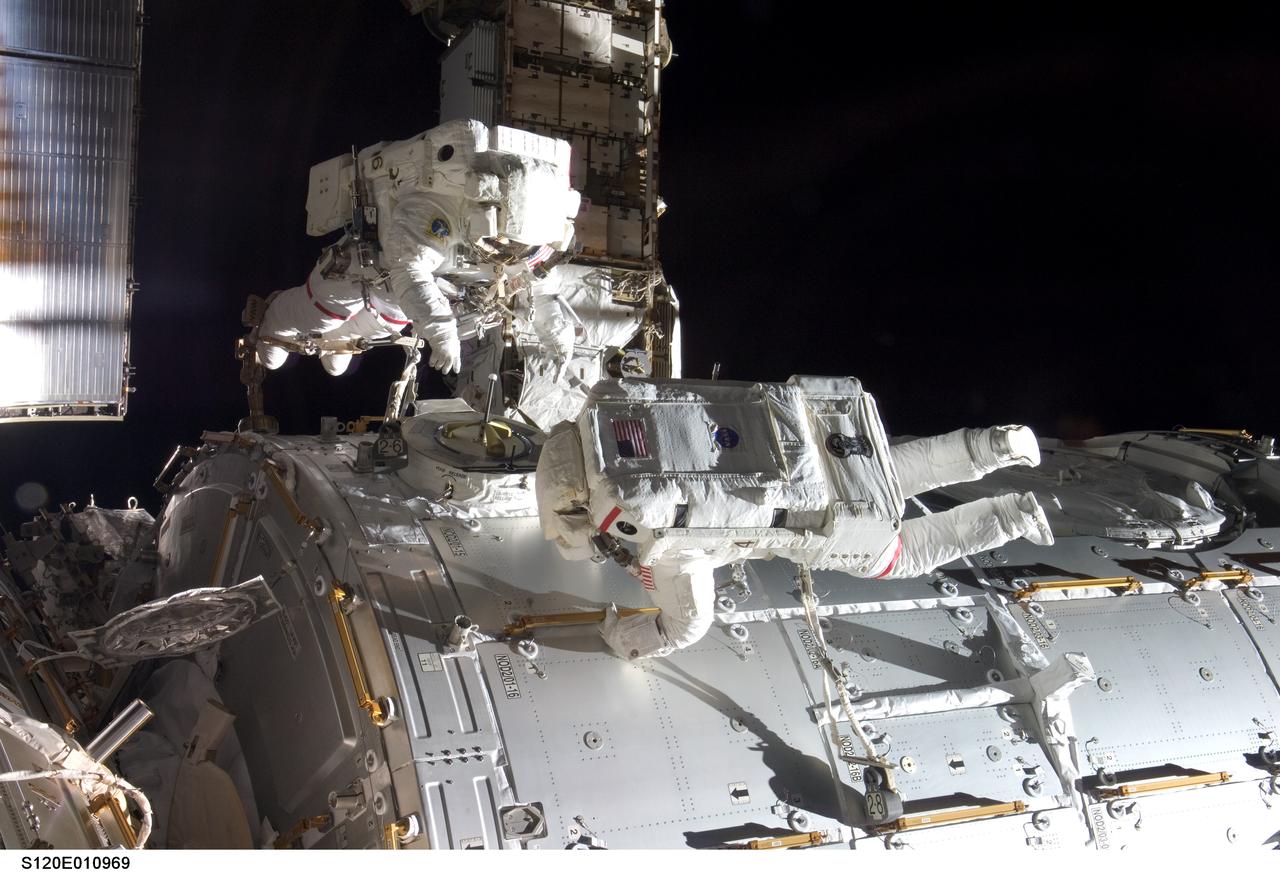

S120-E-010969 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani (left), Expedition 16 flight engineer, and Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participate in the second scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and Parazynski outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. Also the spacewalkers worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers.
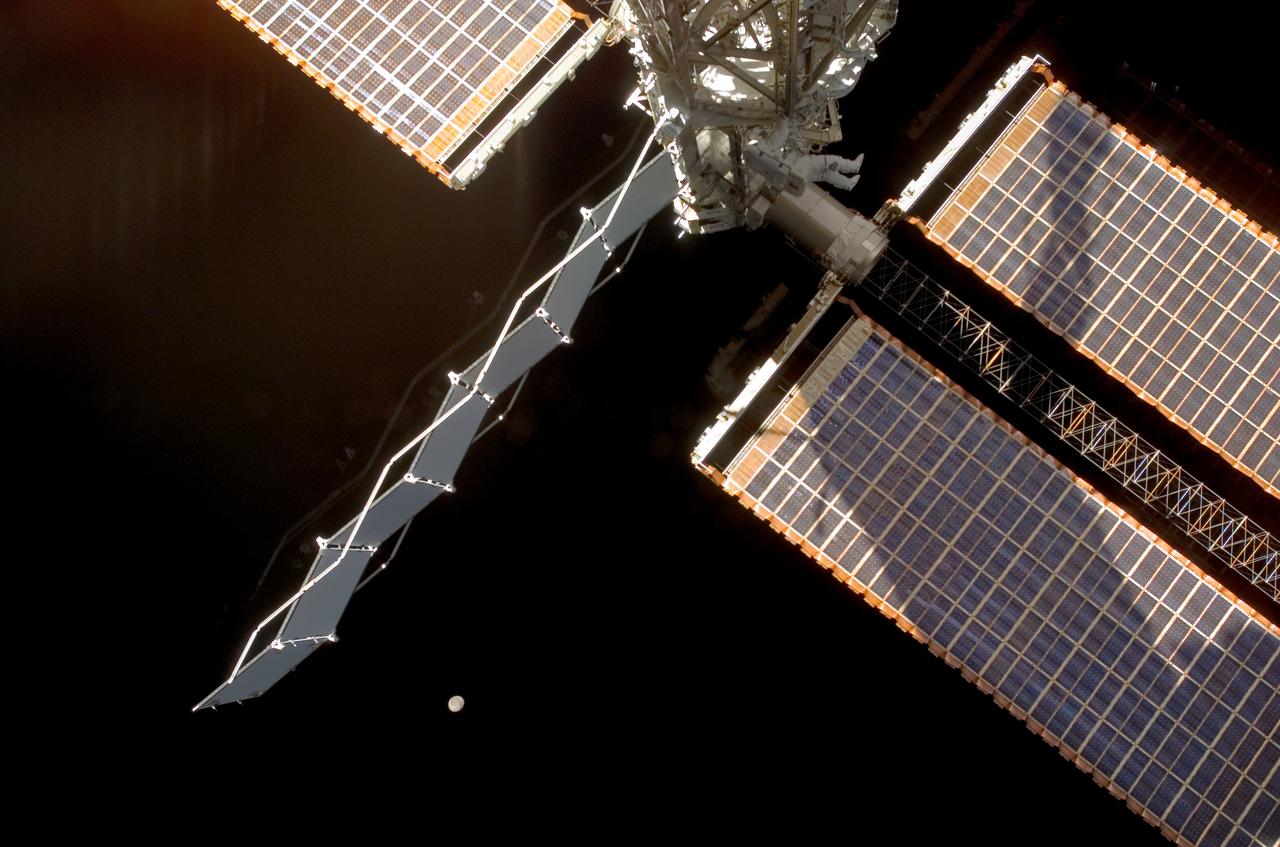

Astronaut Daniel Tani (top center), Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station (ISS). During the 6-hour and 33-minute space walk, Tani and STS-120 mission specialist Scott Parazynski (out of frame), worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multilayer insulation covers. The space walkers also outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. The moon is visible at lower center. The STS-120 mission launched from Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39A at 11:38:19 a.m. (EDT) on October 23, 2007.