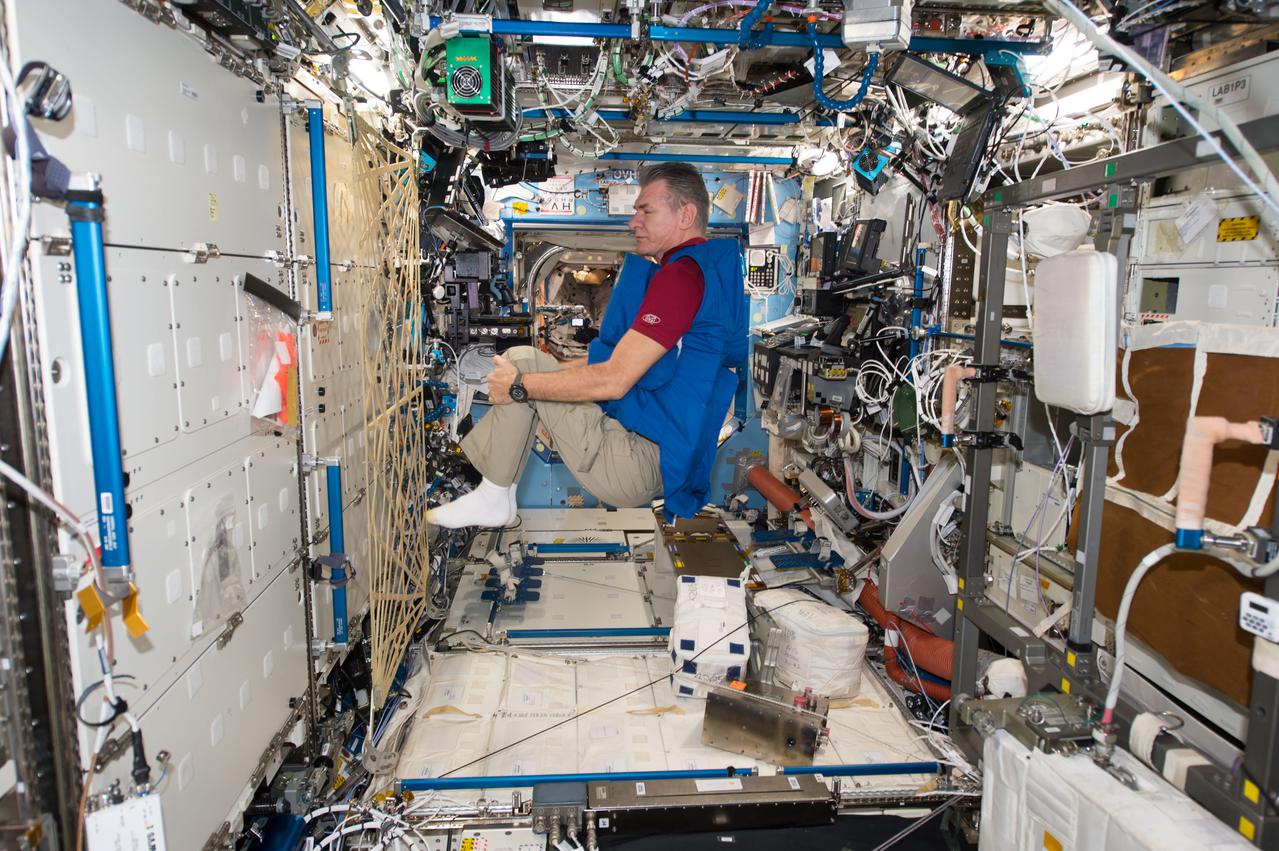

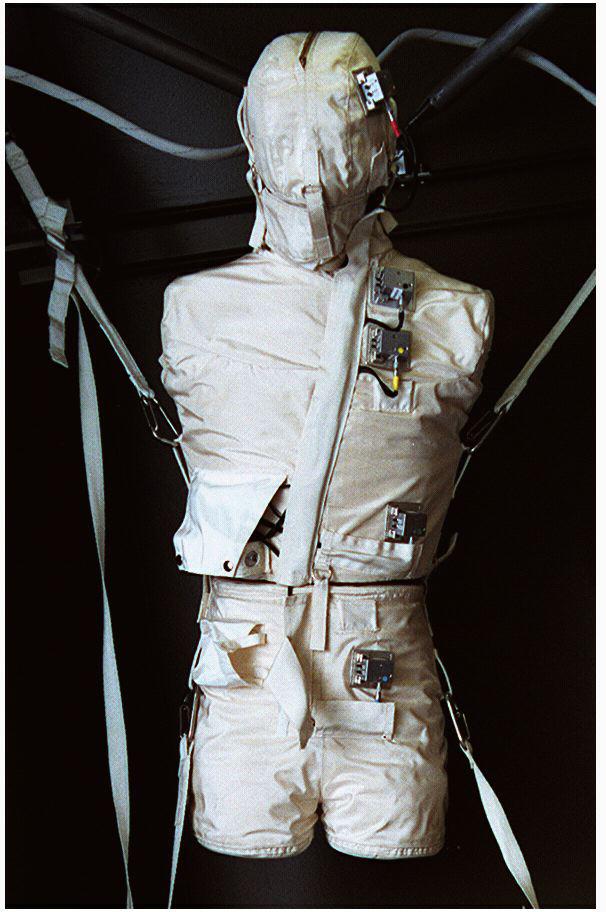
iss053e238888 (Nov. 7, 2017) --- Expedition 53 Flight Engineer Paolo Nespoli, from the European Space Agency, tests a personal radiation shielding garment. Water is used for its shielding properties and filled inside garment containers covering organs that are especially sensitive to cosmic radiation.
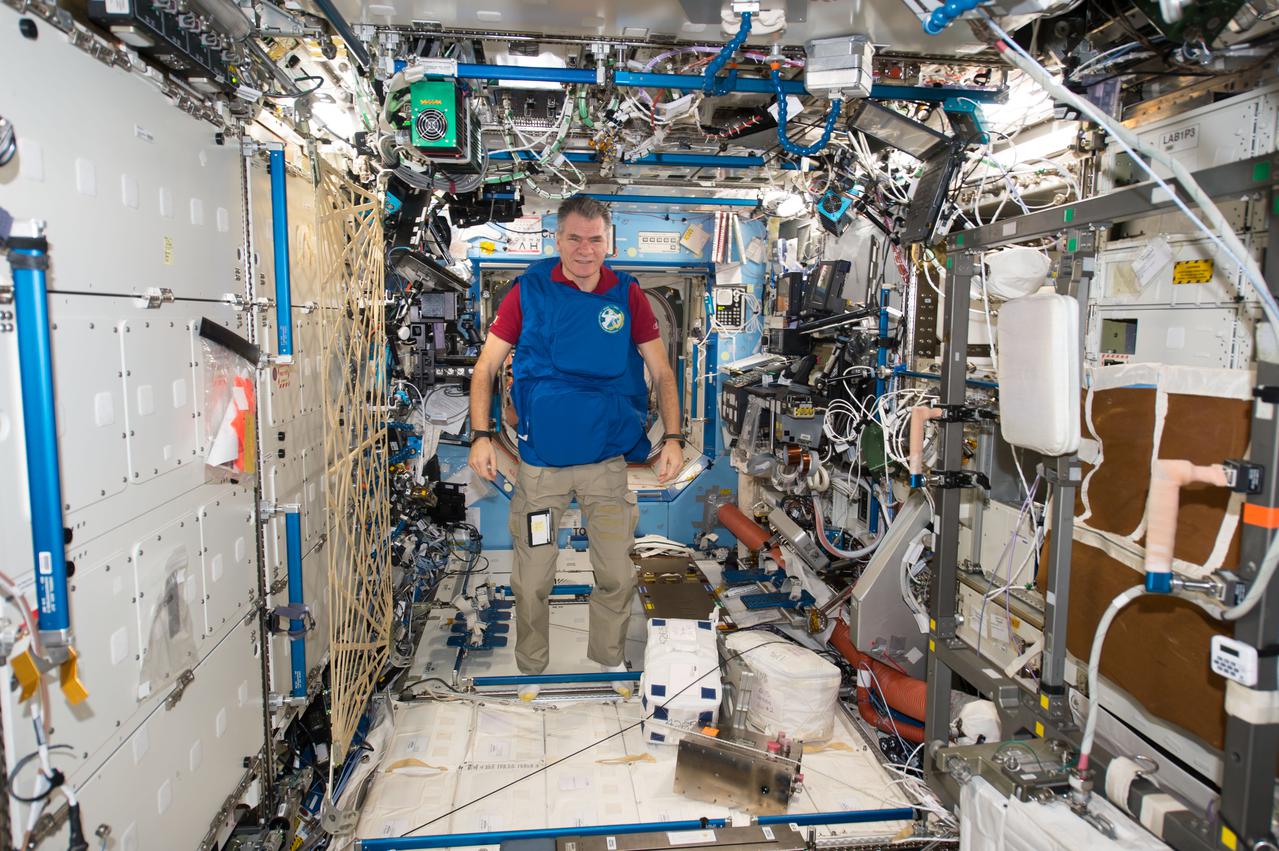

iss053e238886 (Nov. 7, 2017) --- Expedition 53 Flight Engineer Paolo Nespoli, from the European Space Agency, tests a personal radiation shielding garment. Water is used for its shielding properties and filled inside garment containers covering organs that are especially sensitive to cosmic radiation.
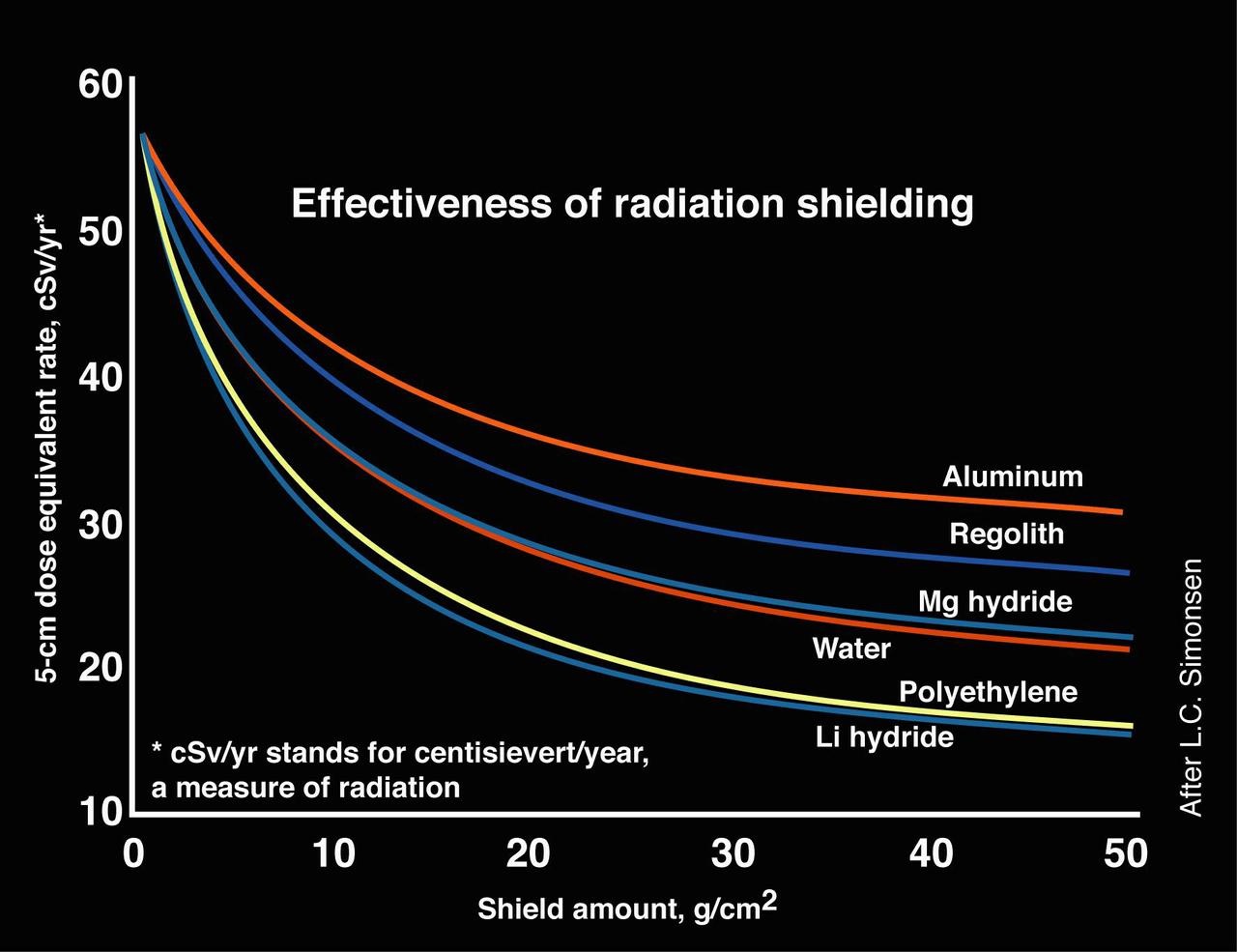
Materials with a smaller mean atomic mass, such as lithium (Li) hydride and polyethylene, make the best radiation shields for astronauts. The materials have a higher density of nuclei and are better able to block incoming radiation. Also, they tend to produce fewer and less dangerous secondary particles after impact with incoming radiation.
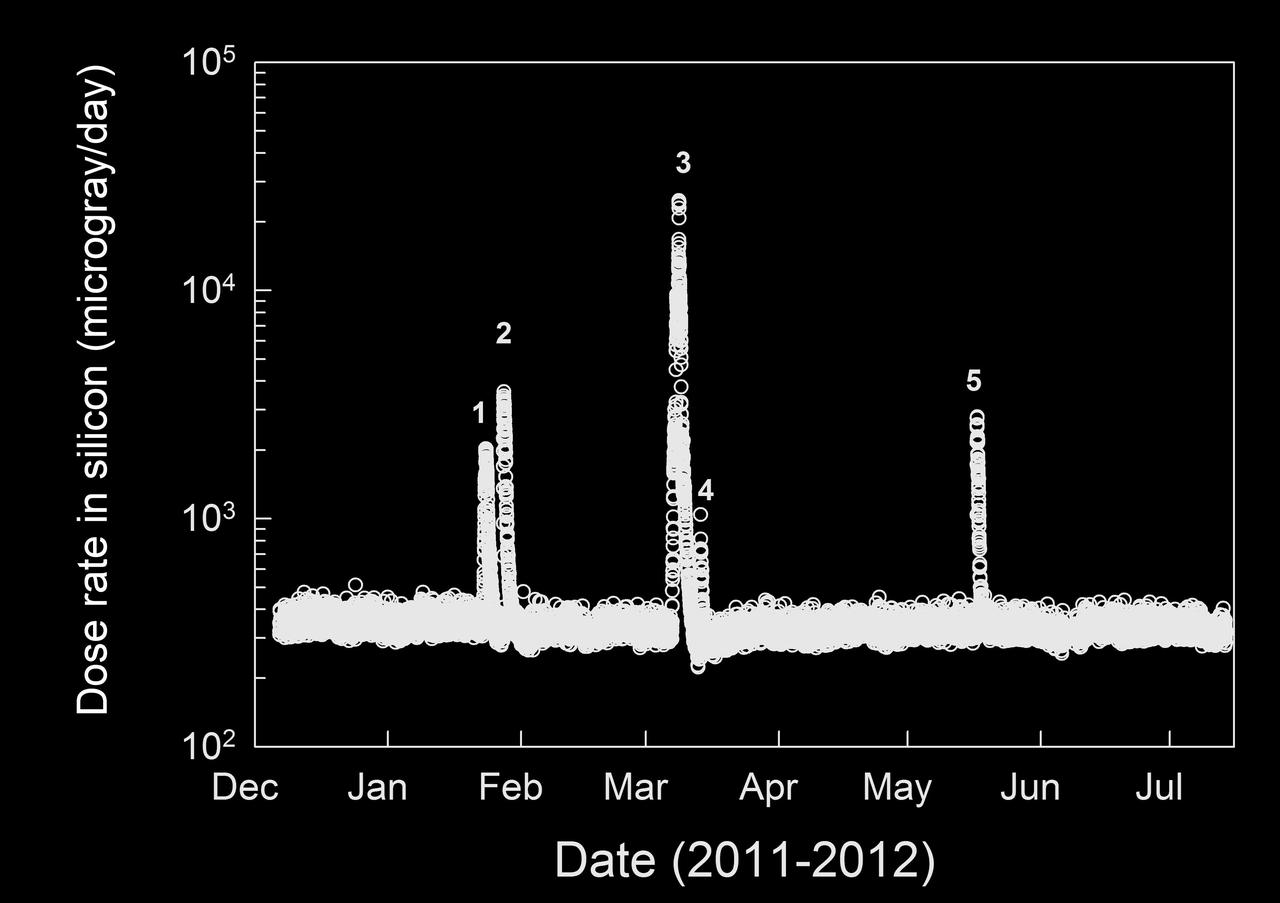
This graphic shows the level of natural radiation detected by the Radiation Assessment Detector shielded inside NASA Mars Science Laboratory on the trip from Earth to Mars from December 2011 to July 2012.
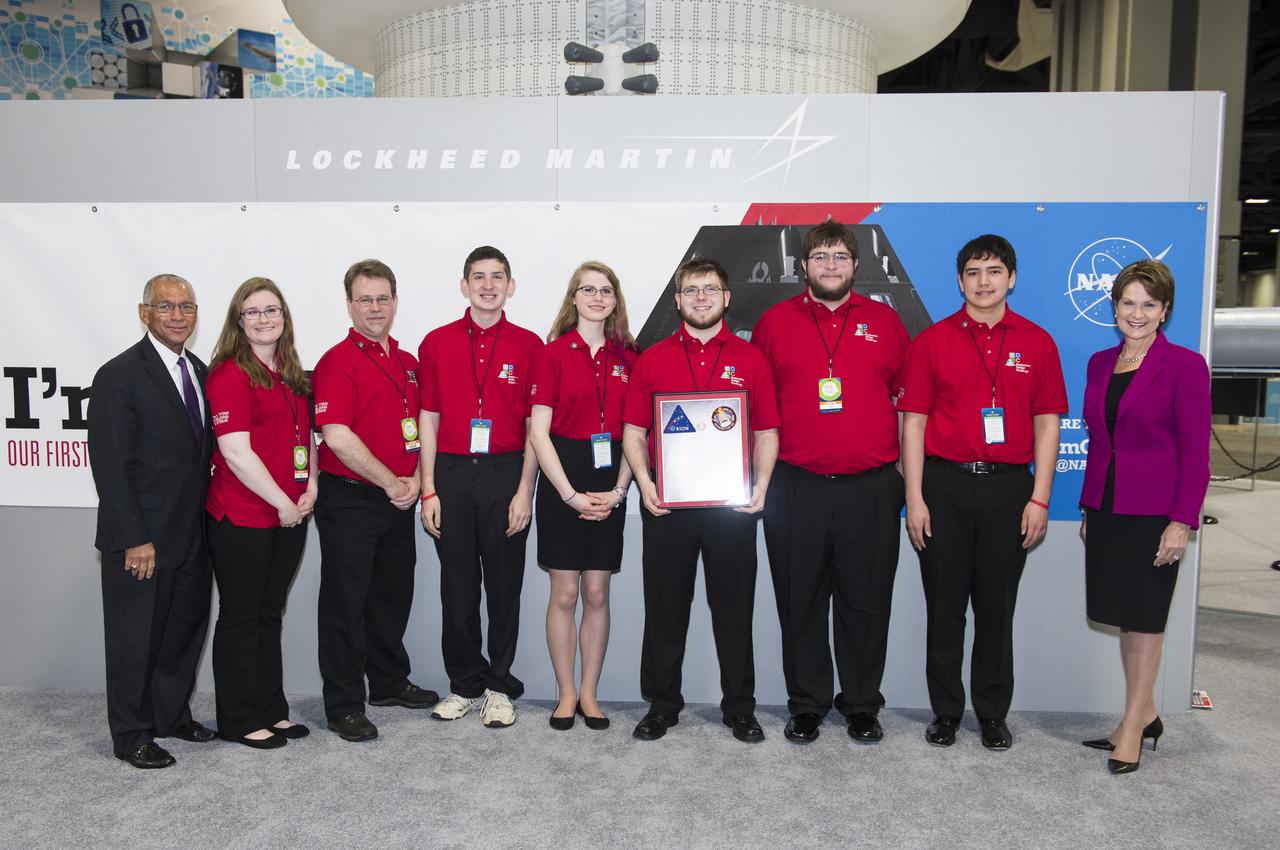

Team Titan Shielding Systems poses with NASA Administrator Charles Bolden and Lockheed Martin CEO, Marillyn Hewson. Team Titan Shielding Systems was one of the semi-finalists in the Exploration Design Challenge. The goal of the Exploration Design Challenge is for students to research and design ways to protect astronauts from space radiation. The winner of the challenge was announced on April 25, 2014 at the USA Science and Engineering Festival at the Washington Convention Center in Washington, DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
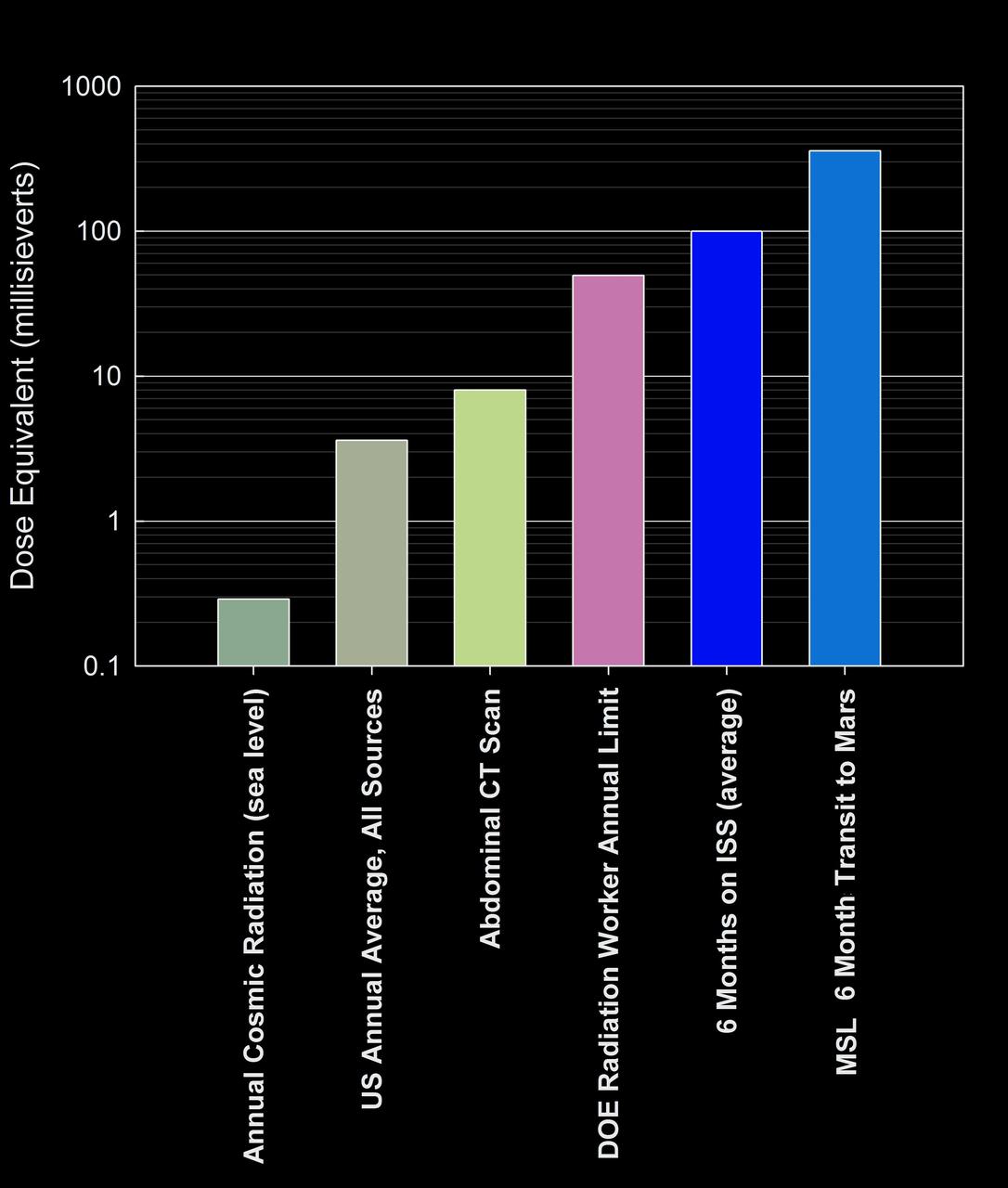
This graphic compares the radiation dose equivalent for several types of experiences, including a calculation for a trip from Earth to Mars based on measurements made by the RAD instrument shielded inside NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft.
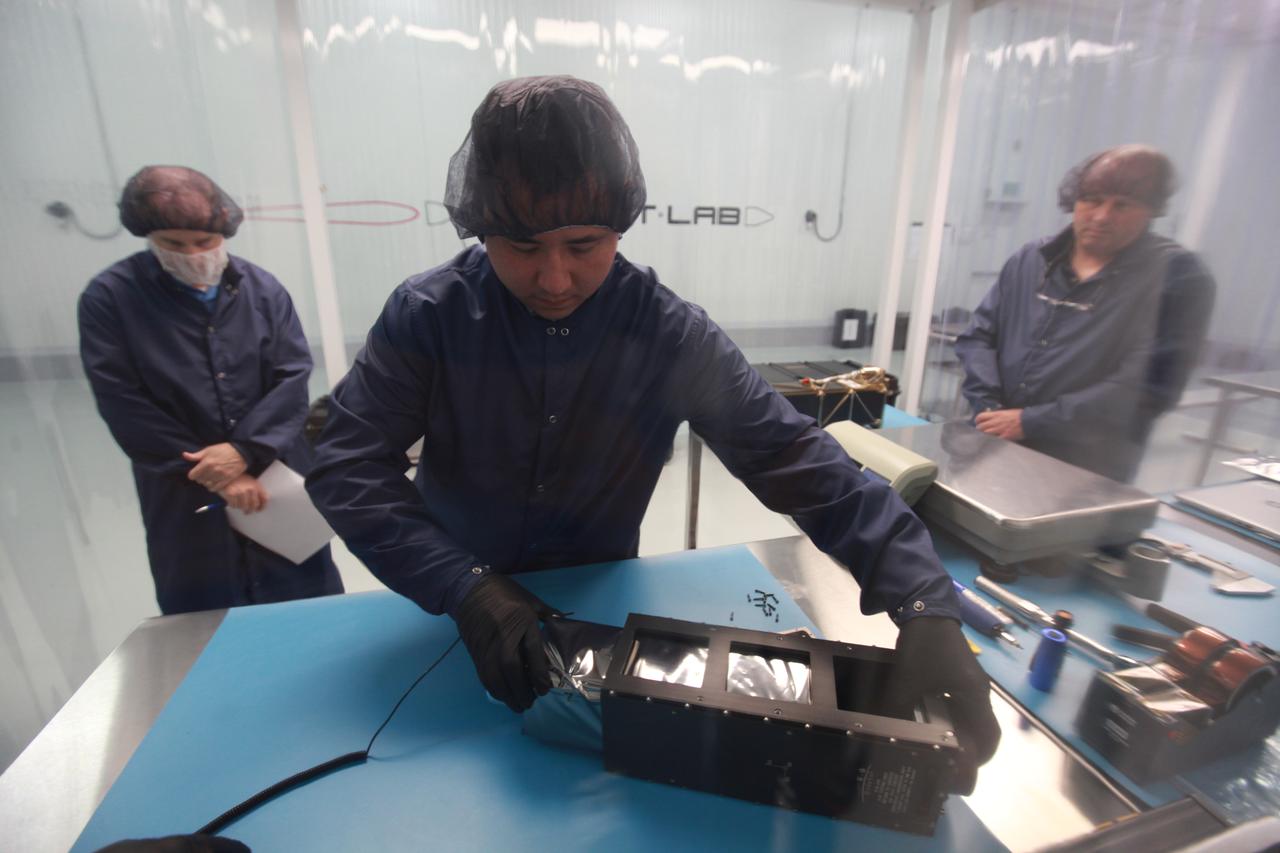

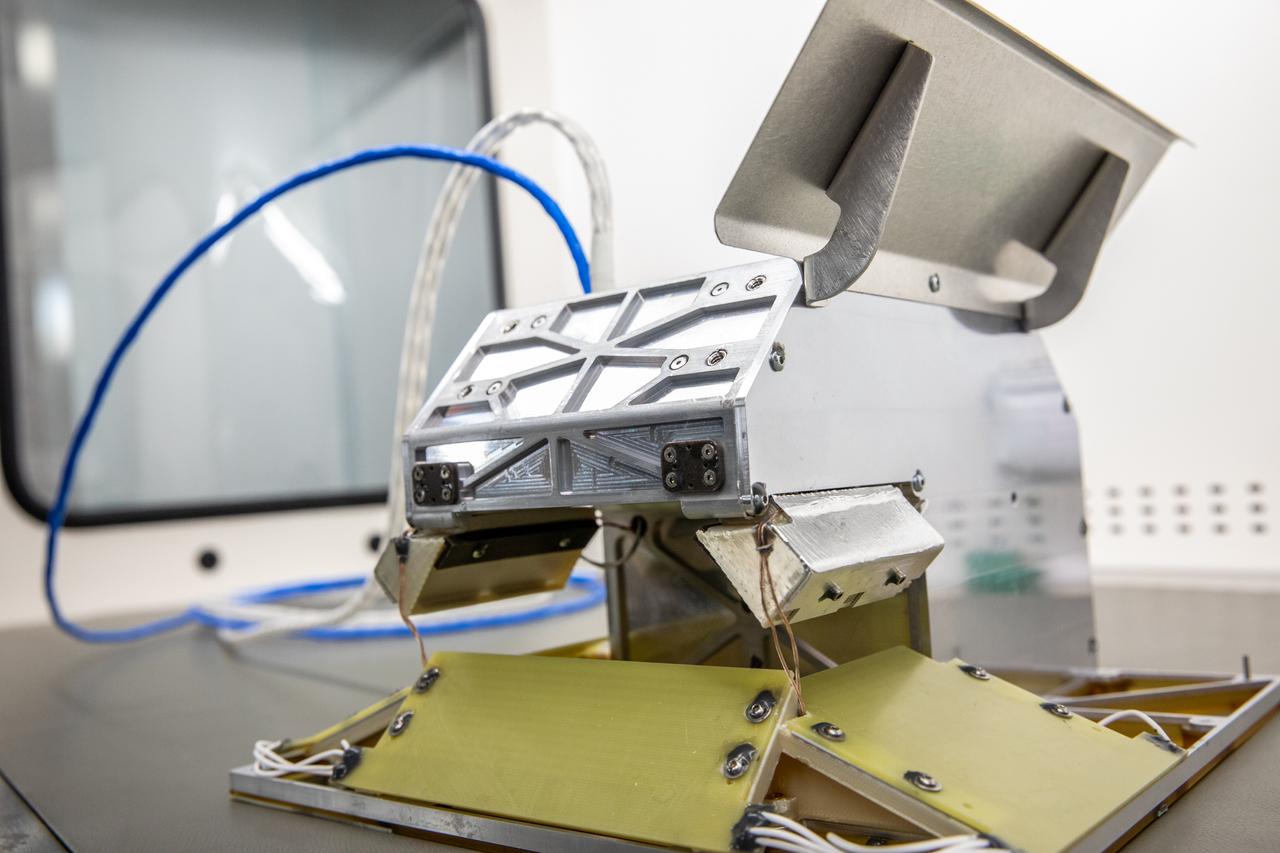
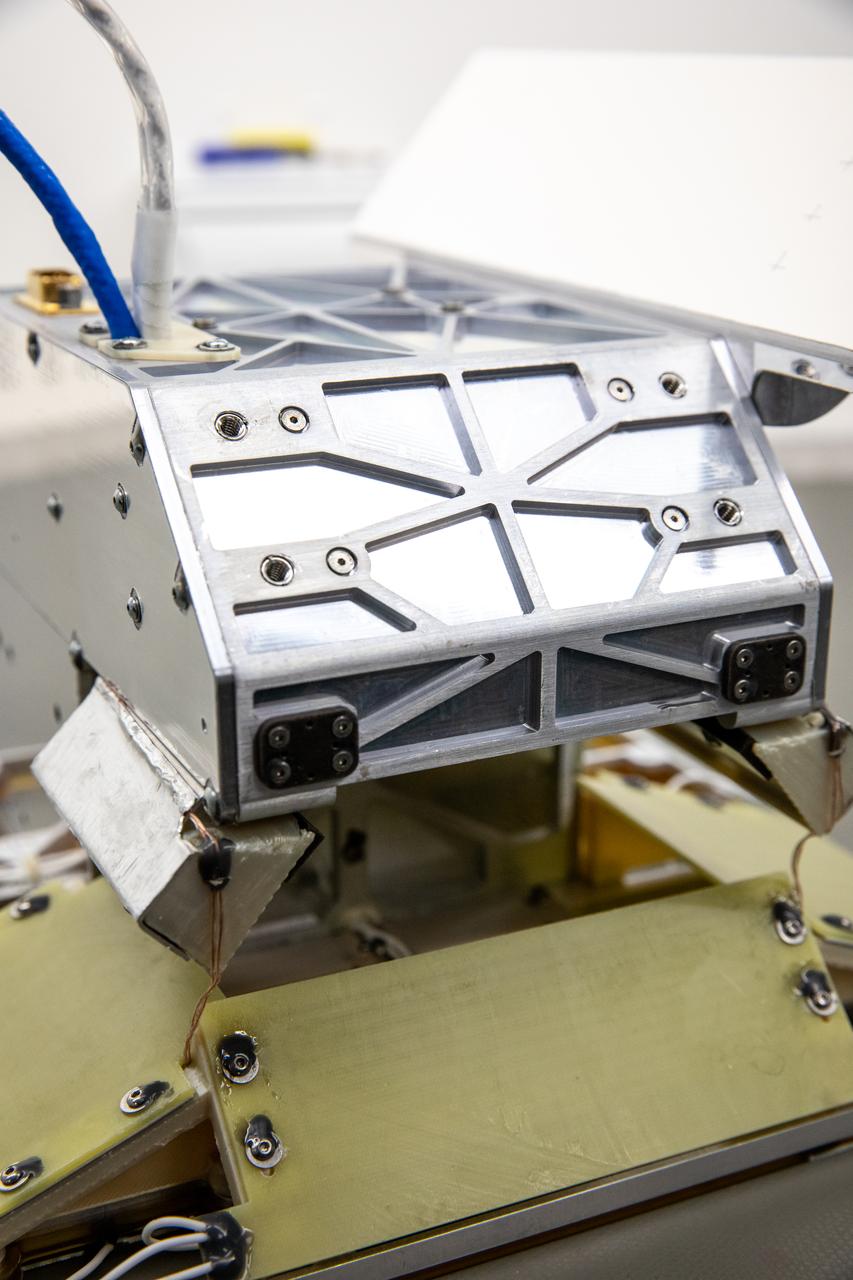
The NASA Langley Research Center (LaRC) Shields-1 CubeSat will demonstrate a research payload with materials durability experiments on emerging radiation shielding technologies. Shields-1 incorporates eight mdosimeters for radiation shielding experiments: one in the atomic number (Z)-grade radiation shielding vault, three behind experimental Z-grade radiation shielding samples developed at NASA LaRC, three behind baseline aluminum shielding samples, and one deep inside the research payload. The Z-grade is defined as an atomic number gradient of shielding materials using a low atomic number metal, such as aluminum, with a high atomic number material, like tantalum. The metals are fabricated into the vault structure. Also, Shields-1 measures a charge dissipation film resistance for technology development. The Shields-1 mission contributes to the SmallSat community with the development of technologies to increase the lifetimes of CubeSat missions from months to years in multiple radiation environments and increase the return on investment for scientific and commercial spacecraft.
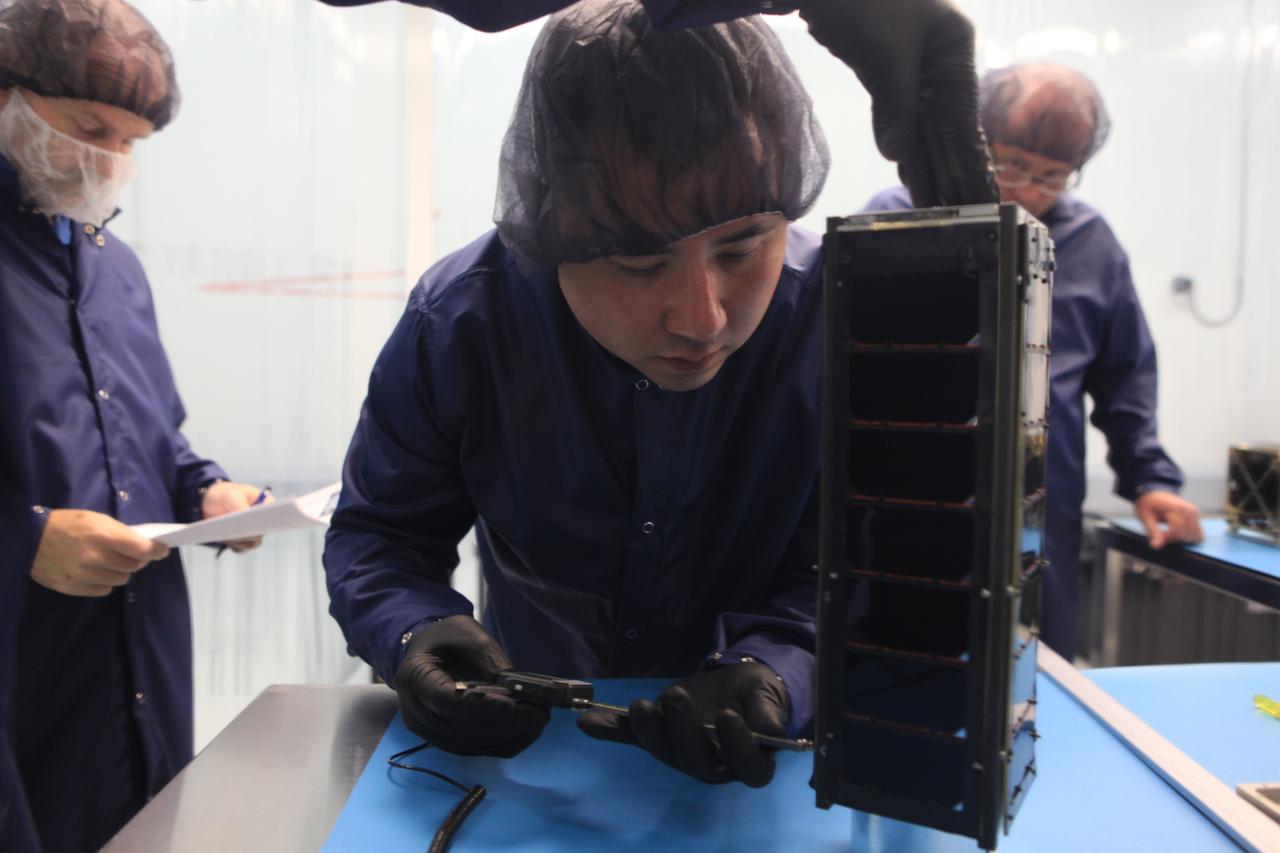

The NASA Langley Research Center (LaRC) Shields-1 CubeSat will demonstrate a research payload with materials durability experiments on emerging radiation shielding technologies. Shields-1 incorporates eight mdosimeters for radiation shielding experiments: one in the atomic number (Z)-grade radiation shielding vault, three behind experimental Z-grade radiation shielding samples developed at NASA LaRC, three behind baseline aluminum shielding samples, and one deep inside the research payload. The Z-grade is defined as an atomic number gradient of shielding materials using a low atomic number metal, such as aluminum, with a high atomic number material, like tantalum. The metals are fabricated into the vault structure. Also, Shields-1 measures a charge dissipation film resistance for technology development. The Shields-1 mission contributes to the SmallSat community with the development of technologies to increase the lifetimes of CubeSat missions from months to years in multiple radiation environments and increase the return on investment for scientific and commercial spacecraft.

The NASA Langley Research Center (LaRC) Shields-1 CubeSat will demonstrate a research payload with materials durability experiments on emerging radiation shielding technologies. Shields-1 incorporates eight mdosimeters for radiation shielding experiments: one in the atomic number (Z)-grade radiation shielding vault, three behind experimental Z-grade radiation shielding samples developed at NASA LaRC, three behind baseline aluminum shielding samples, and one deep inside the research payload. The Z-grade is defined as an atomic number gradient of shielding materials using a low atomic number metal, such as aluminum, with a high atomic number material, like tantalum. The metals are fabricated into the vault structure. Also, Shields-1 measures a charge dissipation film resistance for technology development. The Shields-1 mission contributes to the SmallSat community with the development of technologies to increase the lifetimes of CubeSat missions from months to years in multiple radiation environments and increase the return on investment for scientific and commercial spacecraft.
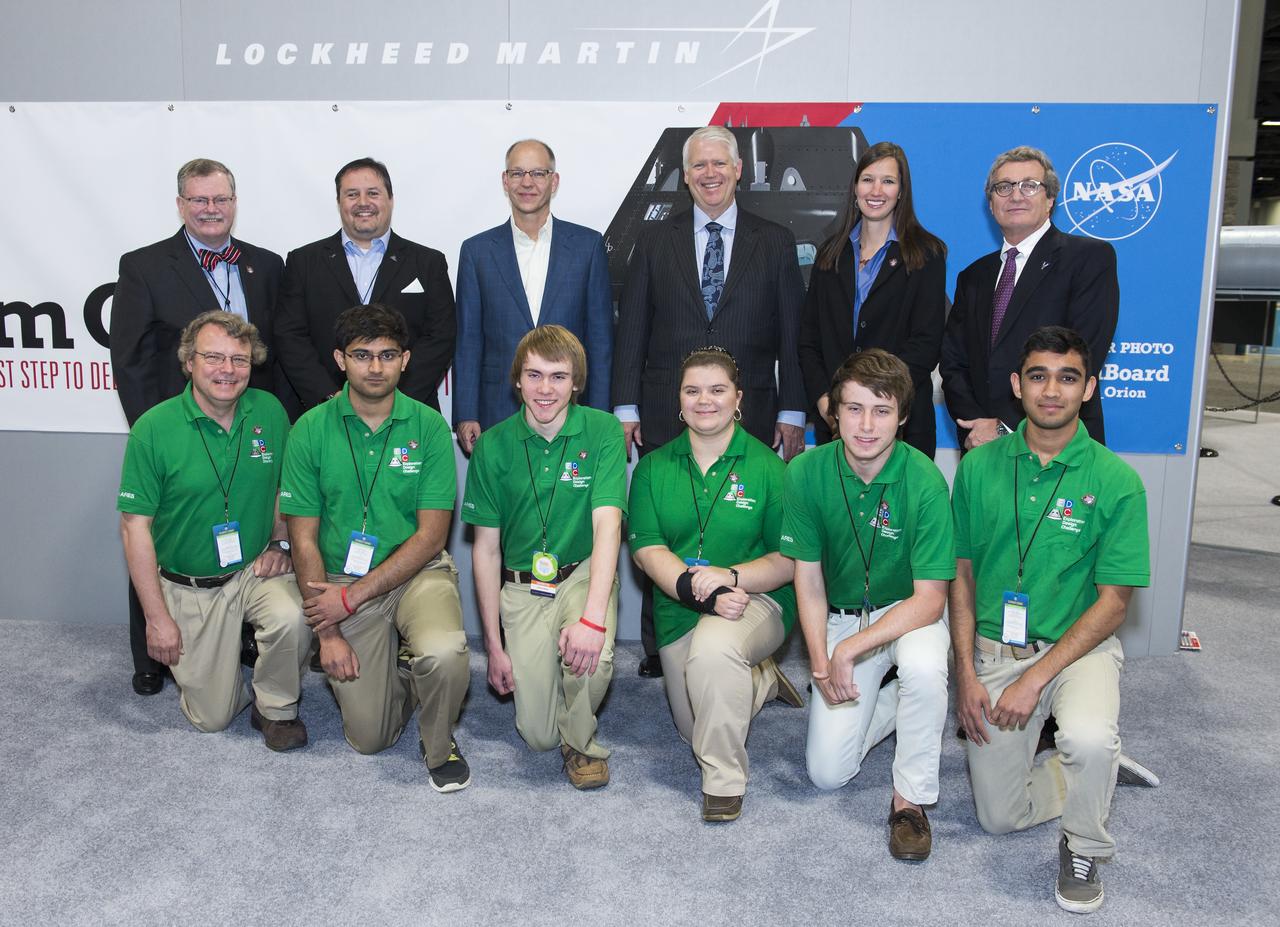

Sponsors of Team ARES pose for a group photo with the winning high school team in the Exploration Design Challenge. Team ARES from the Governors School for Science and Technology in Hampton, Va. won the challenge with their radiation shield design, which will be built and flown aboard the Orion/EFT-1. The award was announced at the USA Science and Engineering Festival on April 25, 2014 at the Washington Convention Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
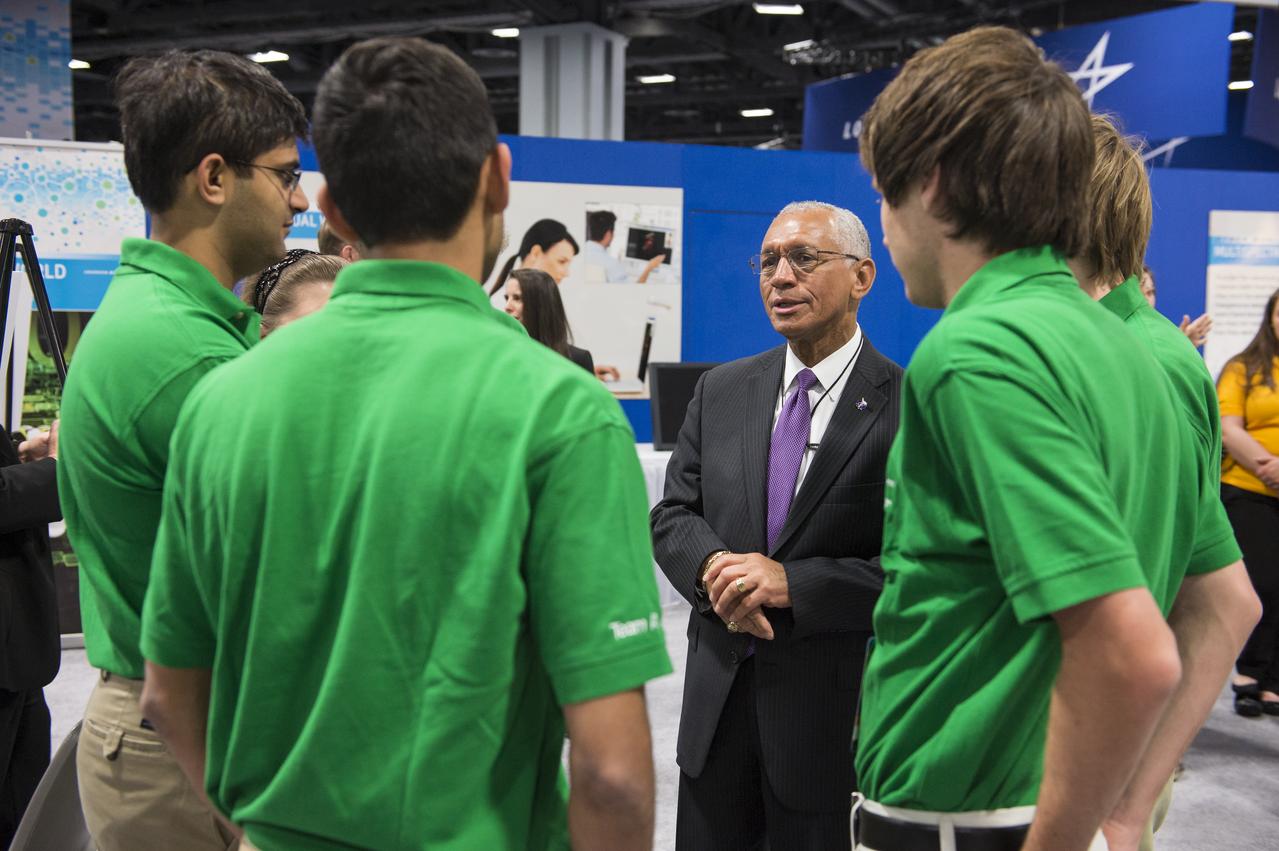

NASA’s Administrator, Charles Bolden speaks with the winning high school team in the Exploration Design Challenge prior to the award ceremony. Team ARES from the Governors School for Science and Technology in Hampton, Va. won the challenge with their radiation shield design, which will be built and flown aboard the Orion/EFT-1. The award was announced at the USA Science and Engineering Festival on April 25, 2014 at the Washington Convention Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
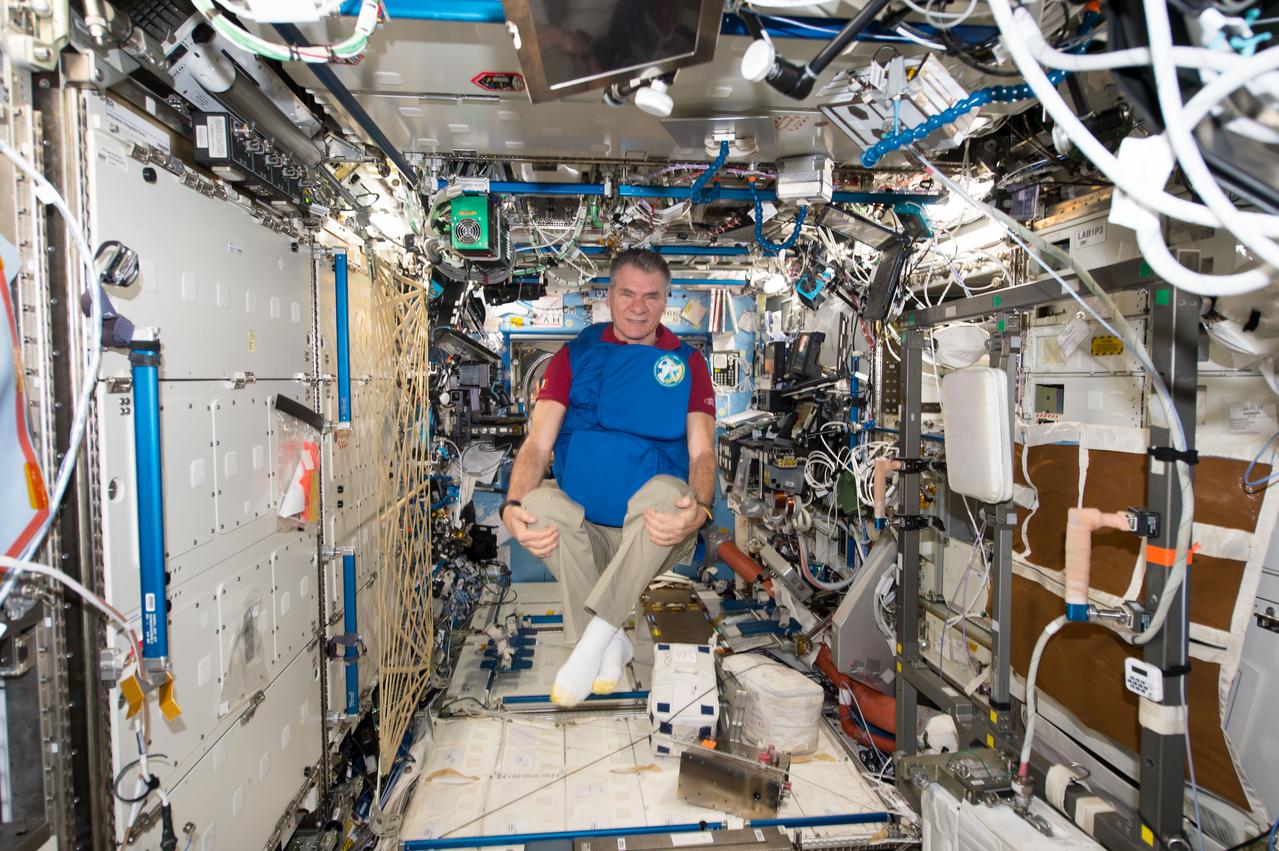

iss053e238891 (Nov. 7, 2017) --- Expedition 53 Flight Engineer Paolo Nespoli, from the European Space Agency, tests a personal radiation shielding garment. Water is used for its shielding properties and filled inside garment containers covering organs that are especially sensitive to cosmic radiation.
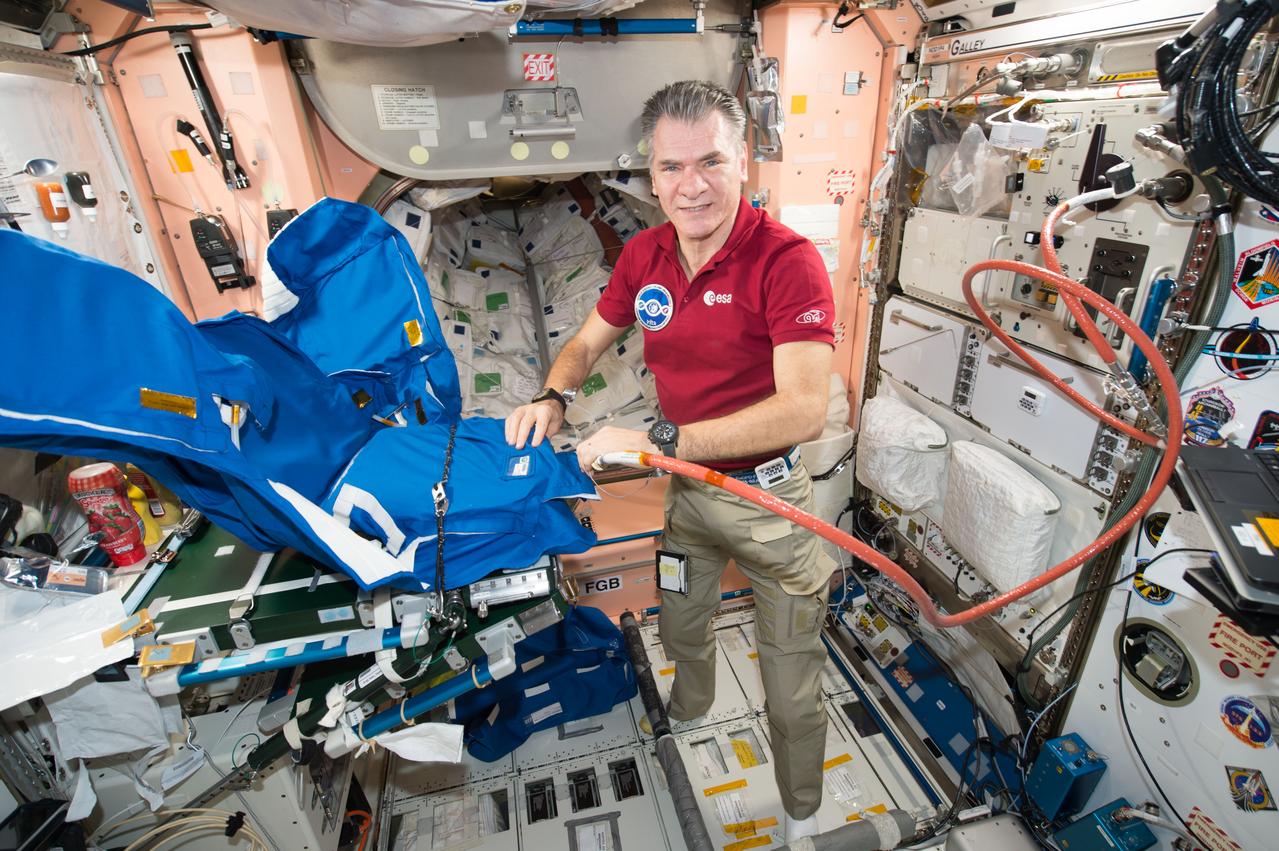

iss053e238877 (Nov. 7, 2017) --- Expedition 53 Flight Engineer Paolo Nespoli, from the European Space Agency, fills a personal radiation shielding garment with water. Water is used for its shielding properties and filled inside garment containers covering organs that are especially sensitive to cosmic radiation.

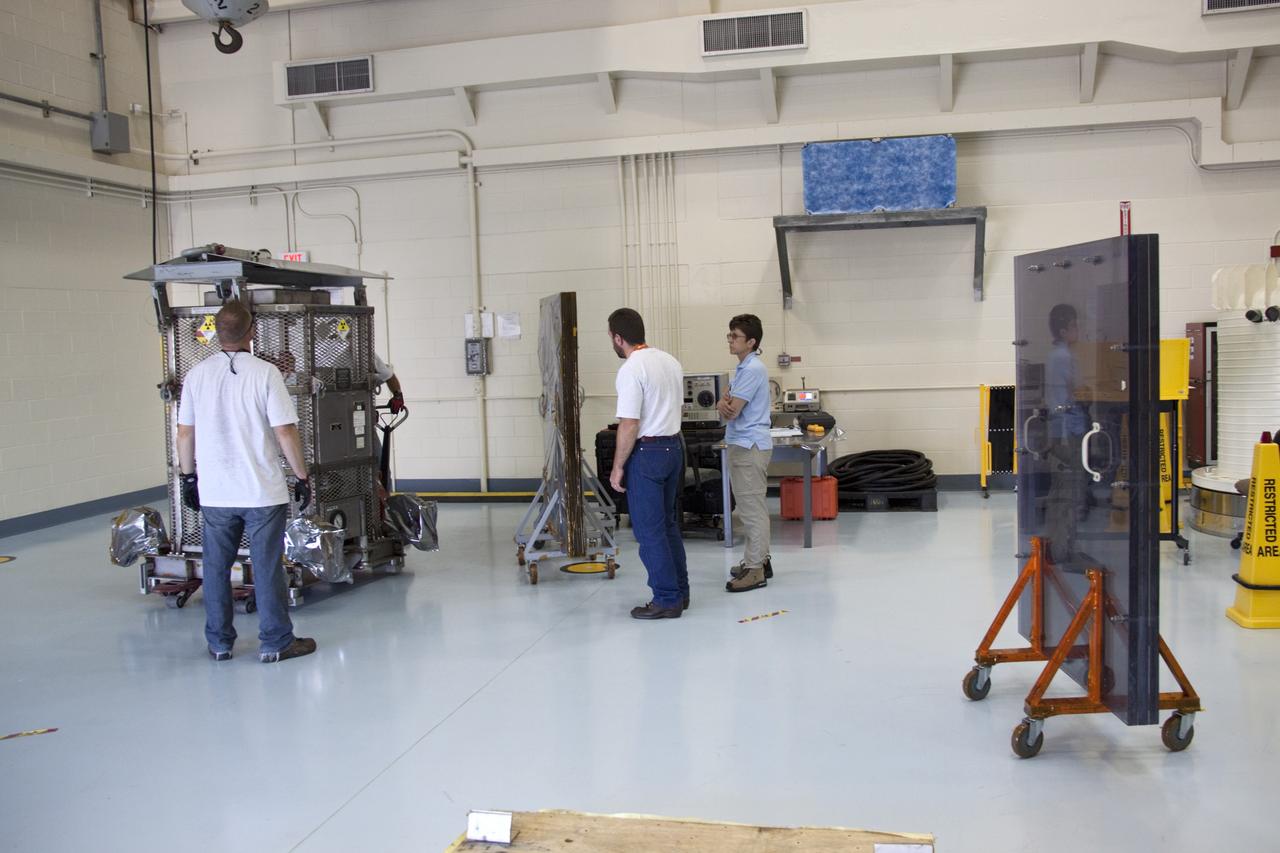
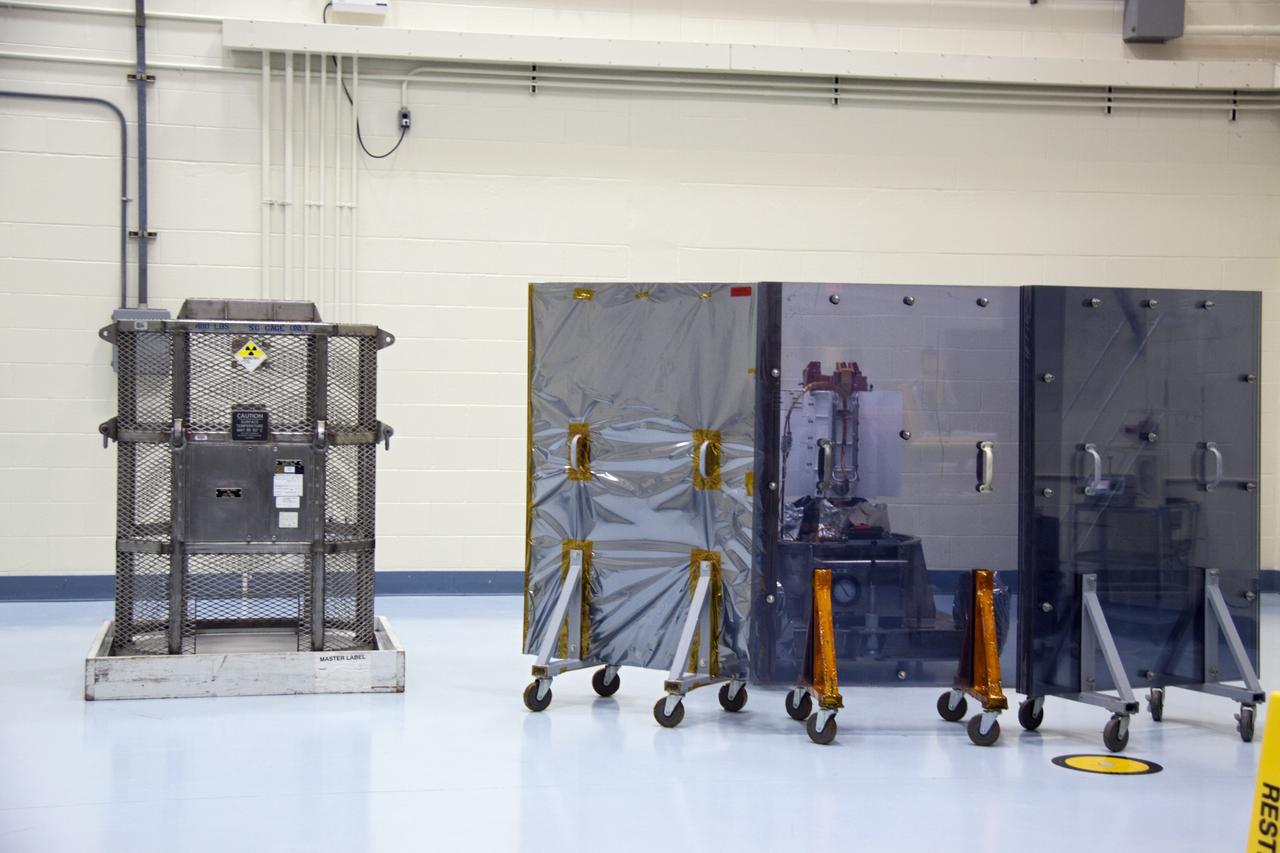
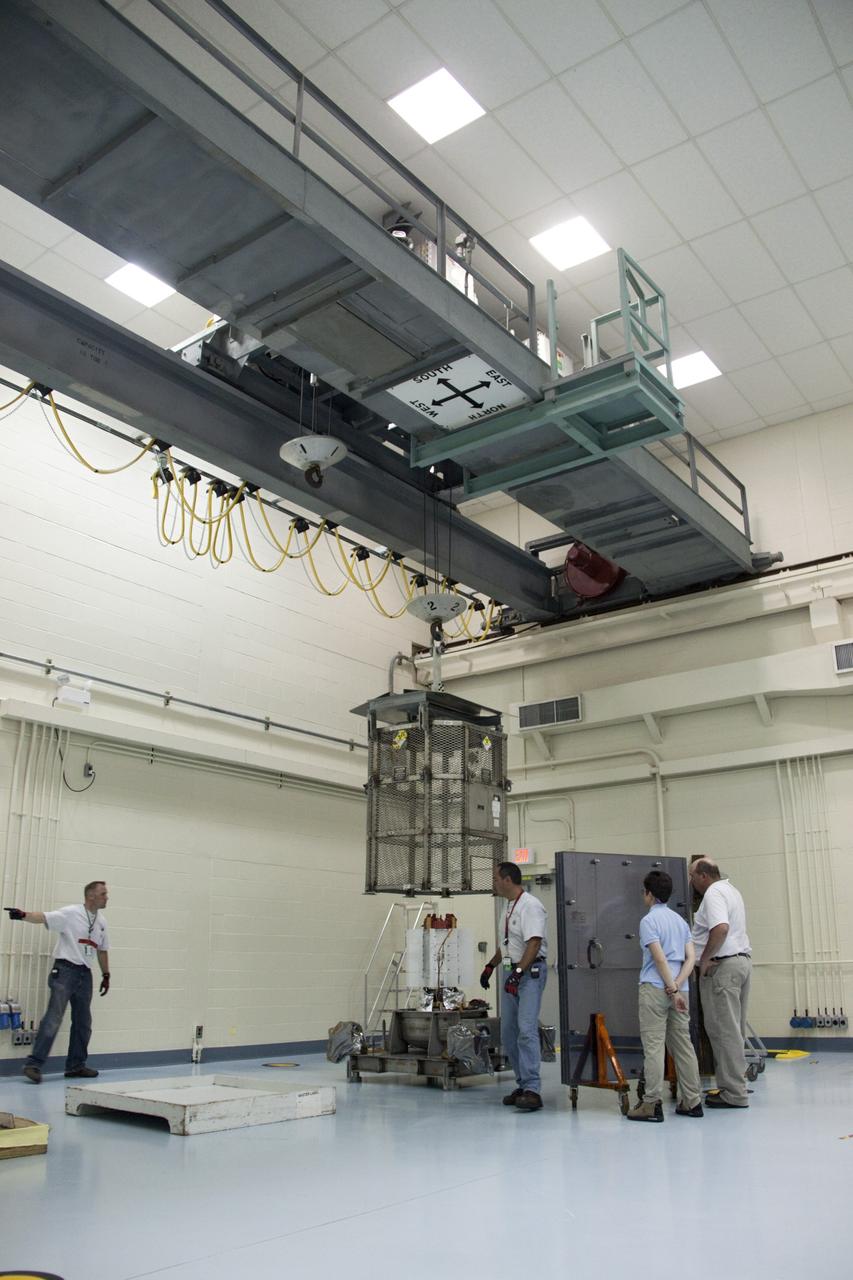
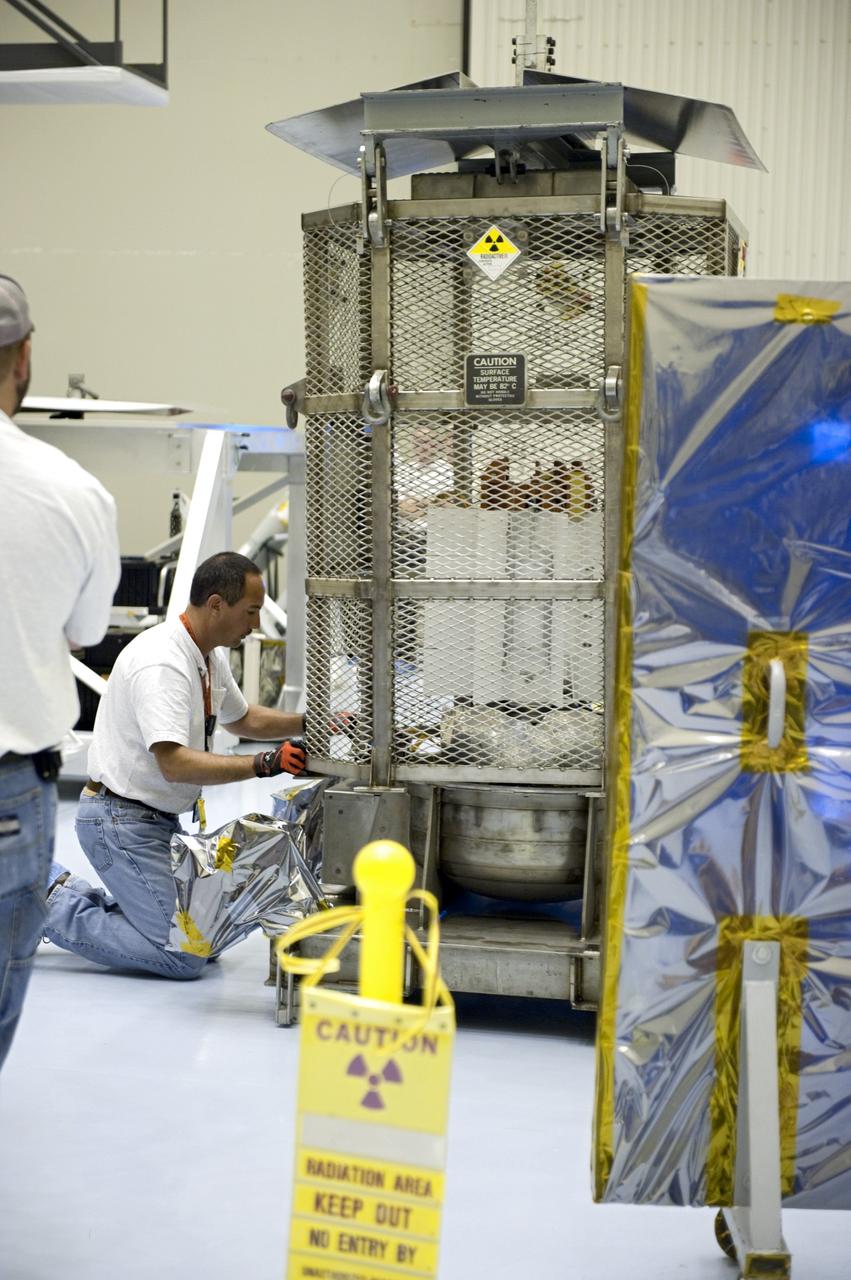
jsc2011e080236 (8/25/2011) --- A preflight view of Hi Shielding Mass Single Event Environment (HiMassSEE) Kit 1 within plastic bag. Spacecraft Single Event Environments at High Shielding Mass (HiMassSEE) measures space radiation interactions with spacecraft structure and shielding using several passive track detector technologies to provide a more accurate definition of International Space Station (ISS) payload accommodations, radiation transport model validation, and flight demonstration data on advanced microelectronics and chemical dosimeters.
iss032e016954 (8/11/2012) --- A view of Spacecraft Single Event Enviroments at High Shielding Mass (HiMassSEE) kit 4 in U.S. Lab aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Spacecraft Single Event Environments at High Shielding Mass (HiMassSEE) measures space radiation interactions with spacecraft structure and shielding using several passive track detector technologies to provide a more accurate definition of International Space Station (ISS) payload accommodations, radiation transport model validation, and flight demonstration data on advanced microelectronics and chemical dosimeters.
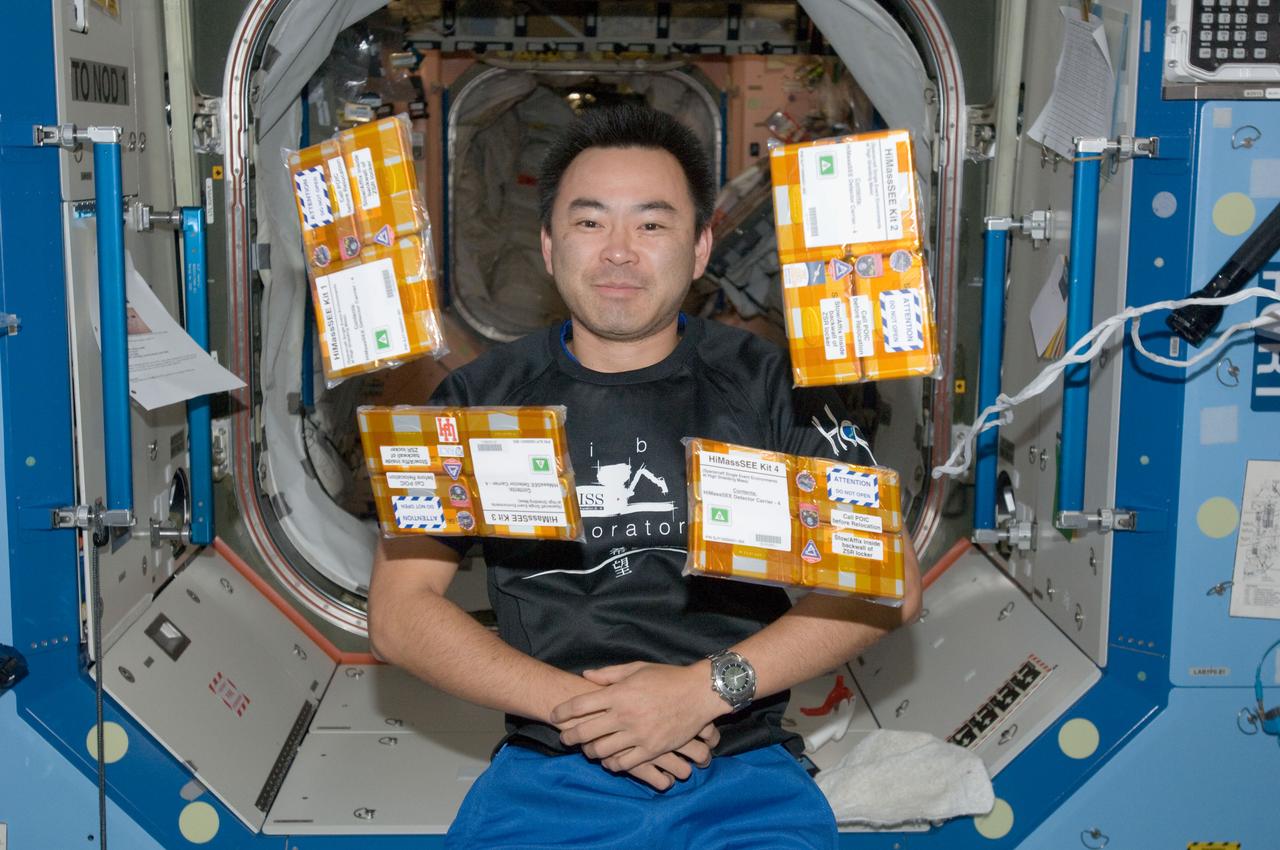

iss032e016946 (8/11/2012) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Akihiko Hoshide poses with the HiMassSEE (Spacecraft Single Event Environments at High Shielding Mass) kits 1,2,3 and 4 in the U.S. Lab aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Spacecraft Single Event Environments at High Shielding Mass (HiMassSEE) measures space radiation interactions with spacecraft structure and shielding using several passive track detector technologies to provide a more accurate definition of International Space Station (ISS) payload accommodations, radiation transport model validation, and flight demonstration data on advanced microelectronics and chemical dosimeters.
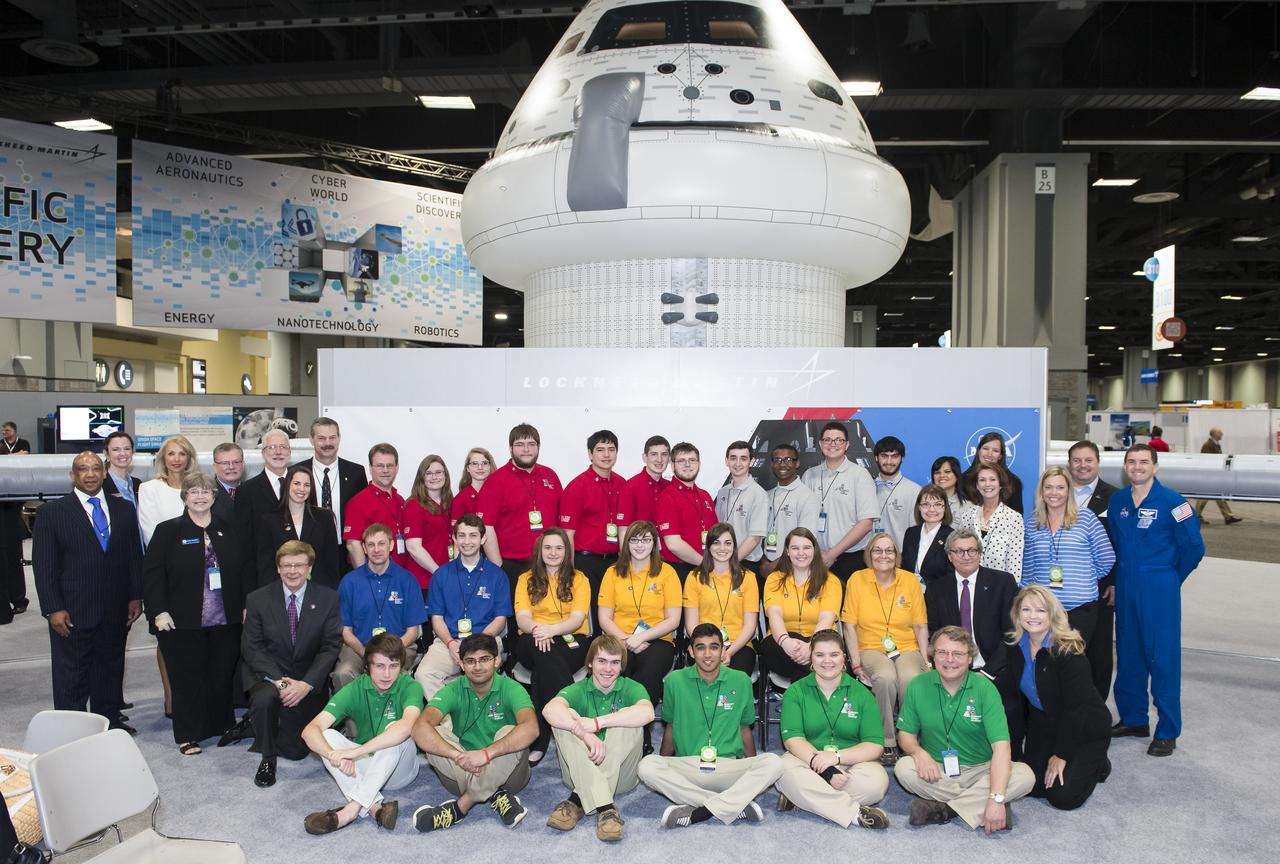

Sponsors of all of the semi-finalist teams in the Exploration Design Challenge pose for a group photo with the teams. Team ARES from the Governors School for Science and Technology in Hampton, Va. won the challenge with their radiation shield design, which will be built and flown aboard the Orion/EFT-1. The award was announced at the USA Science and Engineering Festival on April 25, 2014 at the Washington Convention Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
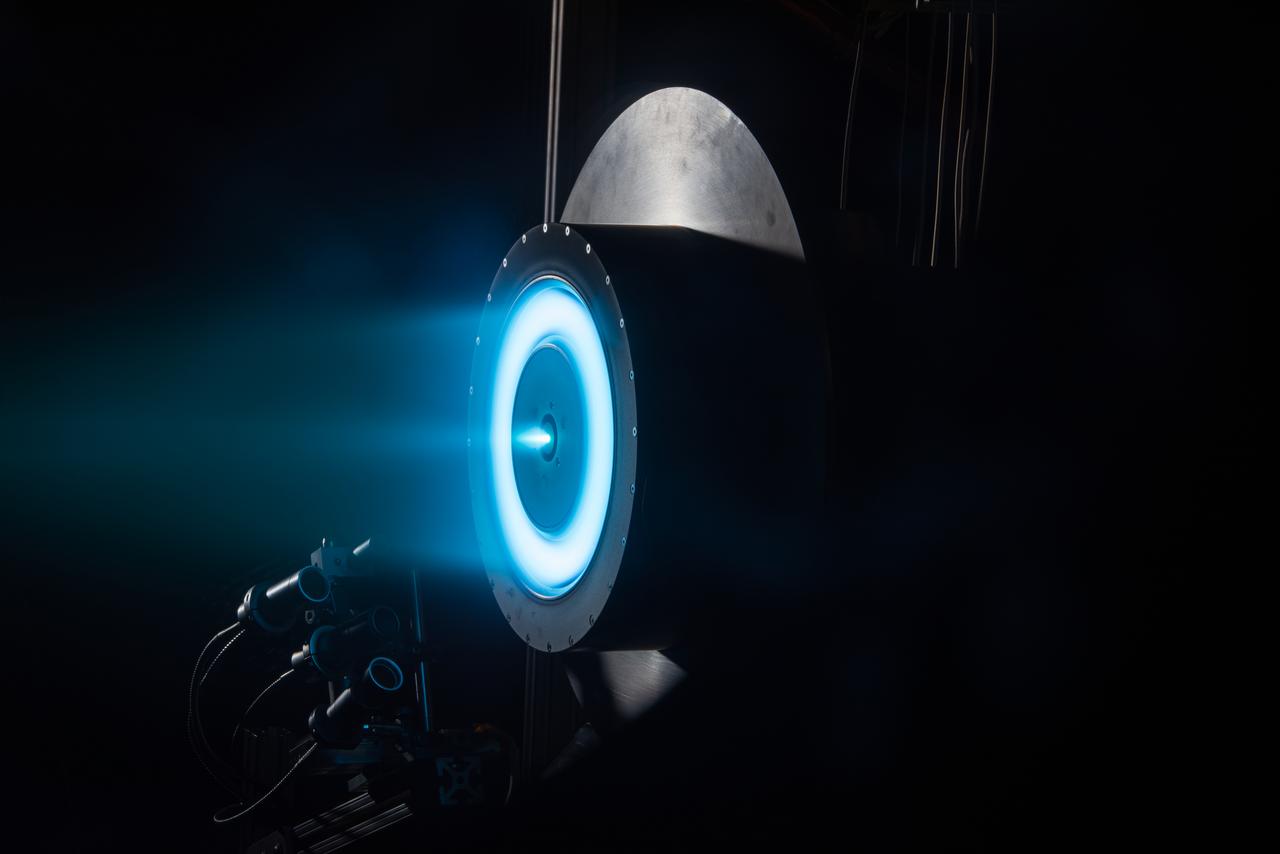
Hall Effect Rocket with Magnetic Shielding Technology Development Unit 1 with Large Radiator working in conjunction with High Power 300 Volt Silicon Carbide Power Processing Unit
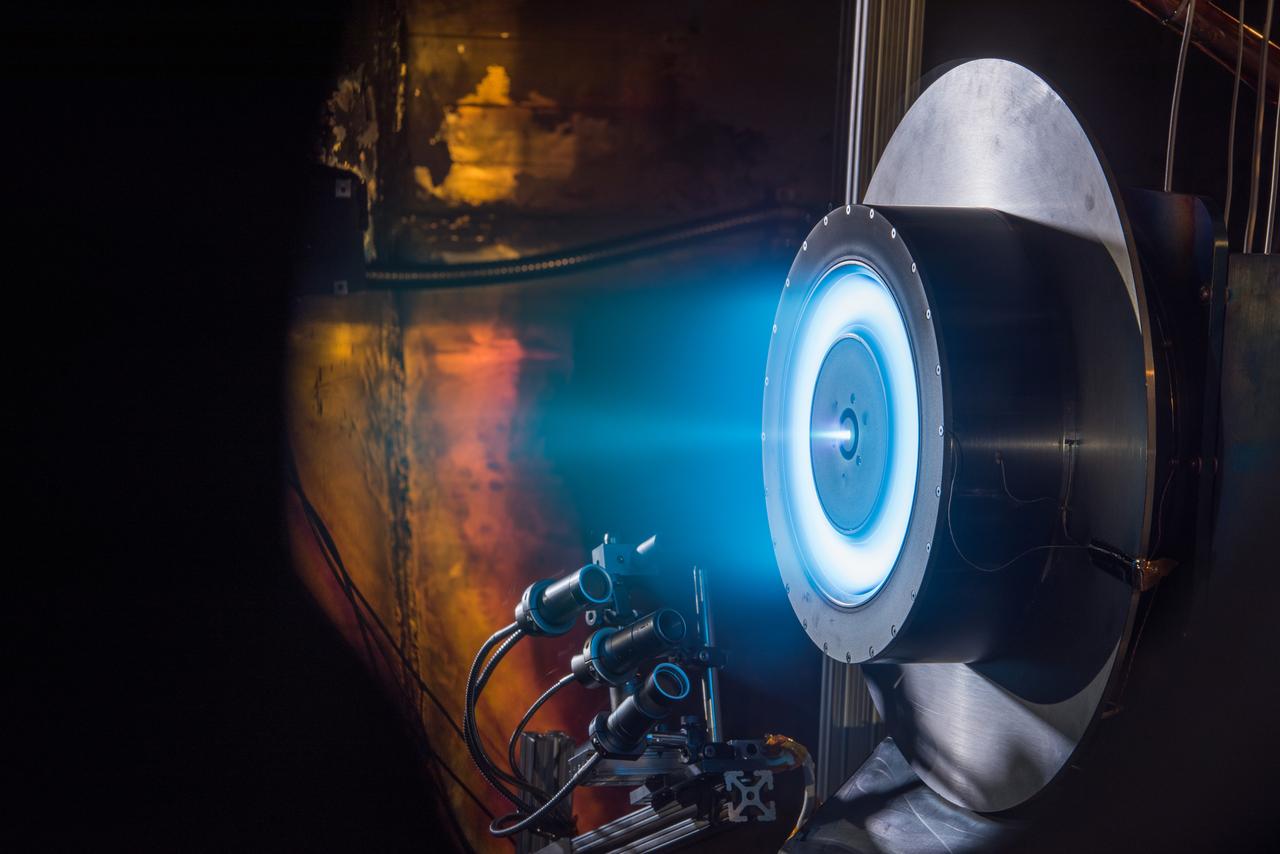
Hall Effect Rocket with Magnetic Shielding Technology Development Unit 1 with Large Radiator working in conjunction with High Power 300 volt Silicon Carbide Power Processing Unit
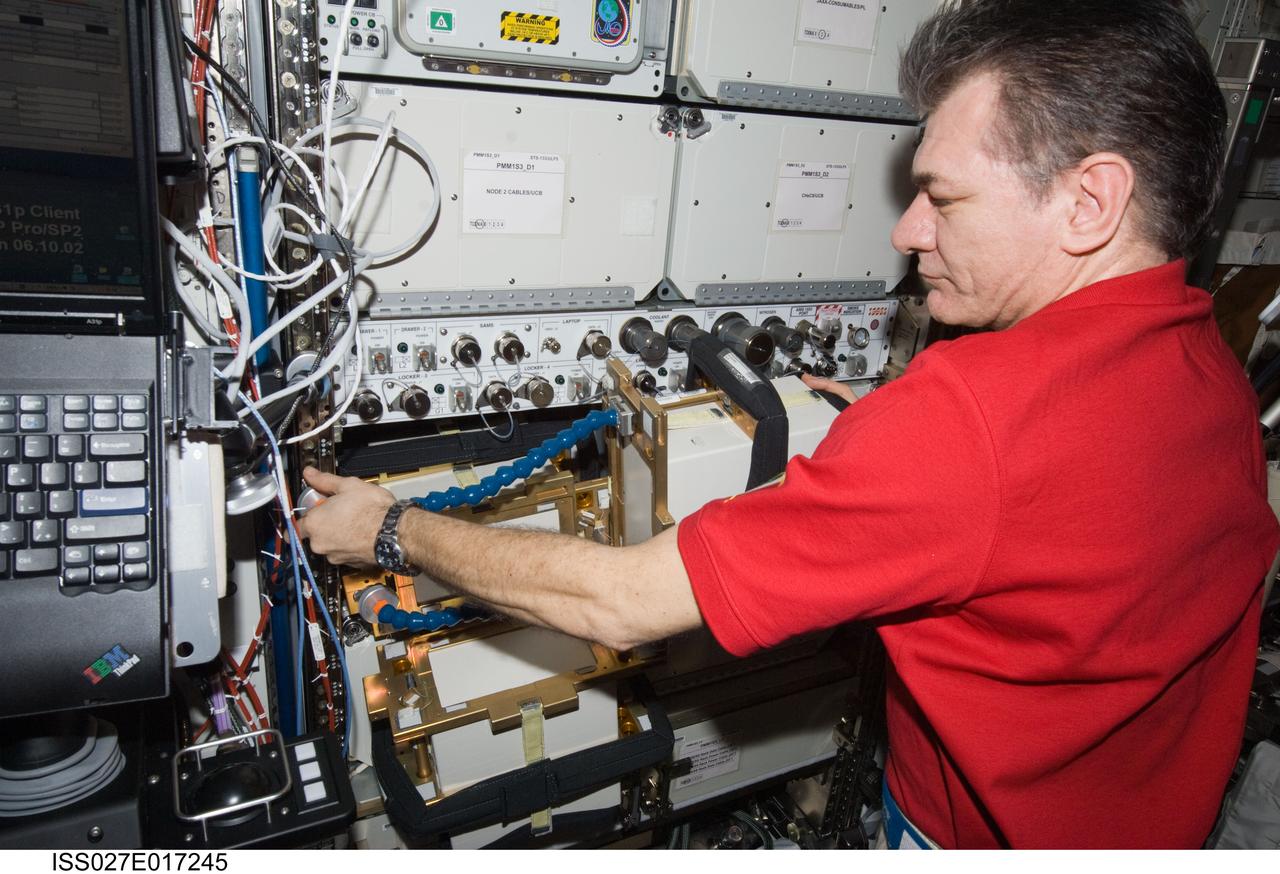

ISS027-E-017245 (23 April 2011) --- European Space Agency astronaut Paolo Nespoli, Expedition 27 flight engineer, works with Anomalous Long Term Effects on Astronauts (ALTEA) Shield isotropic equipment in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. ALTEA-Shield isotropic dosimetry uses existing ALTEA hardware to survey the radiation environment in the Destiny laboratory in 3D. It also measures the effectiveness and shielding properties of several materials with respect to the perception of anomalous light flashes.
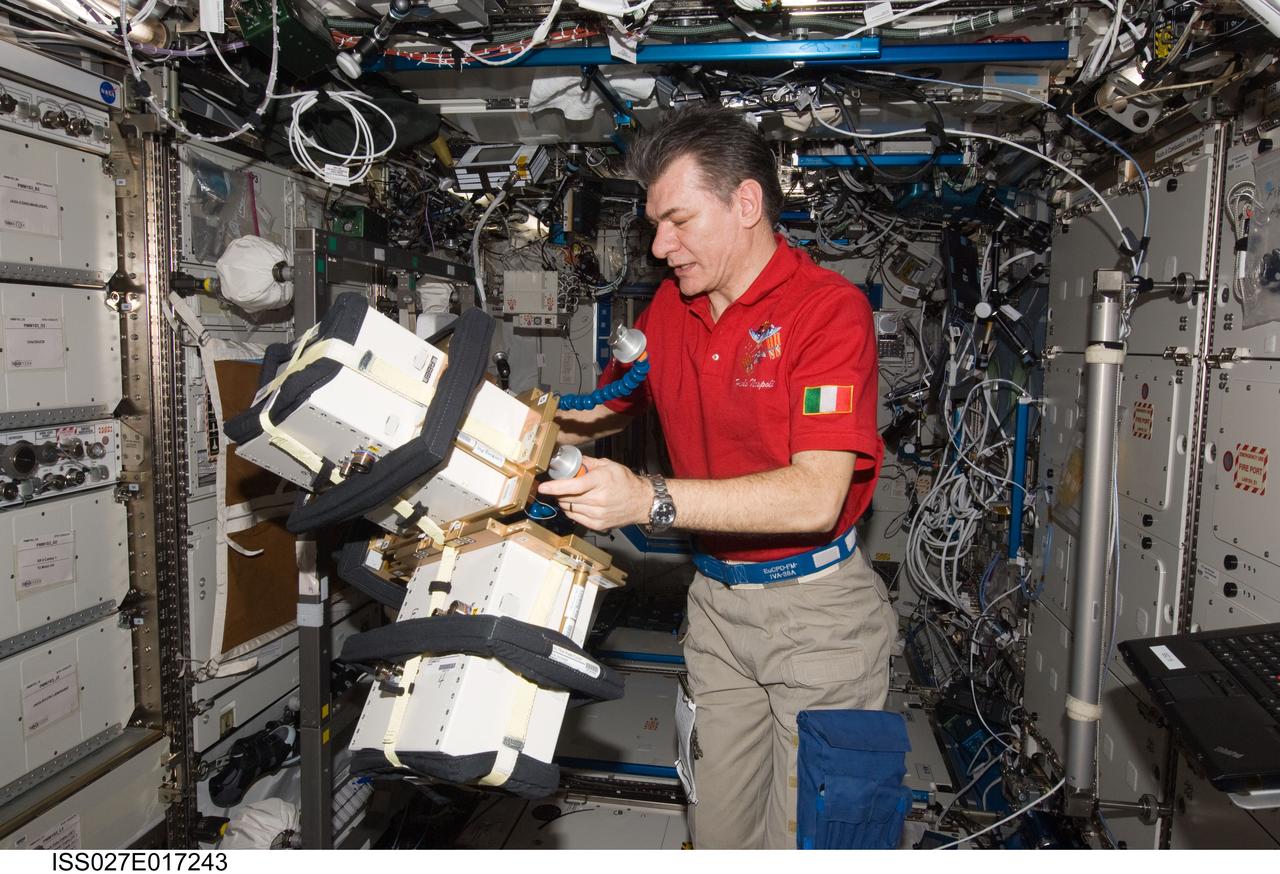

ISS027-E-017243 (23 April 2011) --- European Space Agency astronaut Paolo Nespoli, Expedition 27 flight engineer, works with Anomalous Long Term Effects on Astronauts (ALTEA) Shield isotropic equipment in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. ALTEA-Shield isotropic dosimetry uses existing ALTEA hardware to survey the radiation environment in the Destiny laboratory in 3D. It also measures the effectiveness and shielding properties of several materials with respect to the perception of anomalous light flashes.
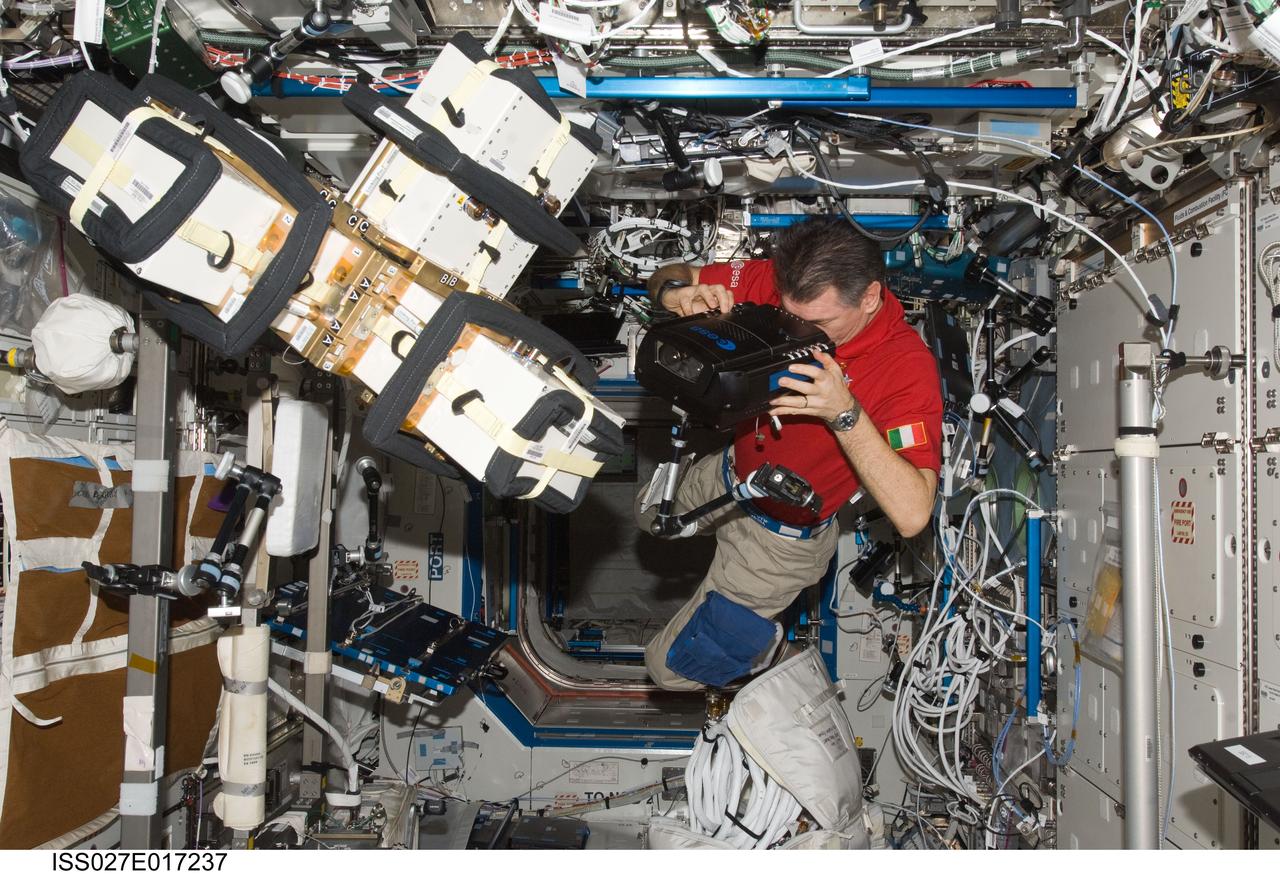

ISS027-E-017237 (23 April 2011) --- European Space Agency astronaut Paolo Nespoli, Expedition 27 flight engineer, works with Anomalous Long Term Effects on Astronauts (ALTEA) Shield isotropic equipment in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. ALTEA-Shield isotropic dosimetry uses existing ALTEA hardware to survey the radiation environment in the Destiny laboratory in 3D. It also measures the effectiveness and shielding properties of several materials with respect to the perception of anomalous light flashes.
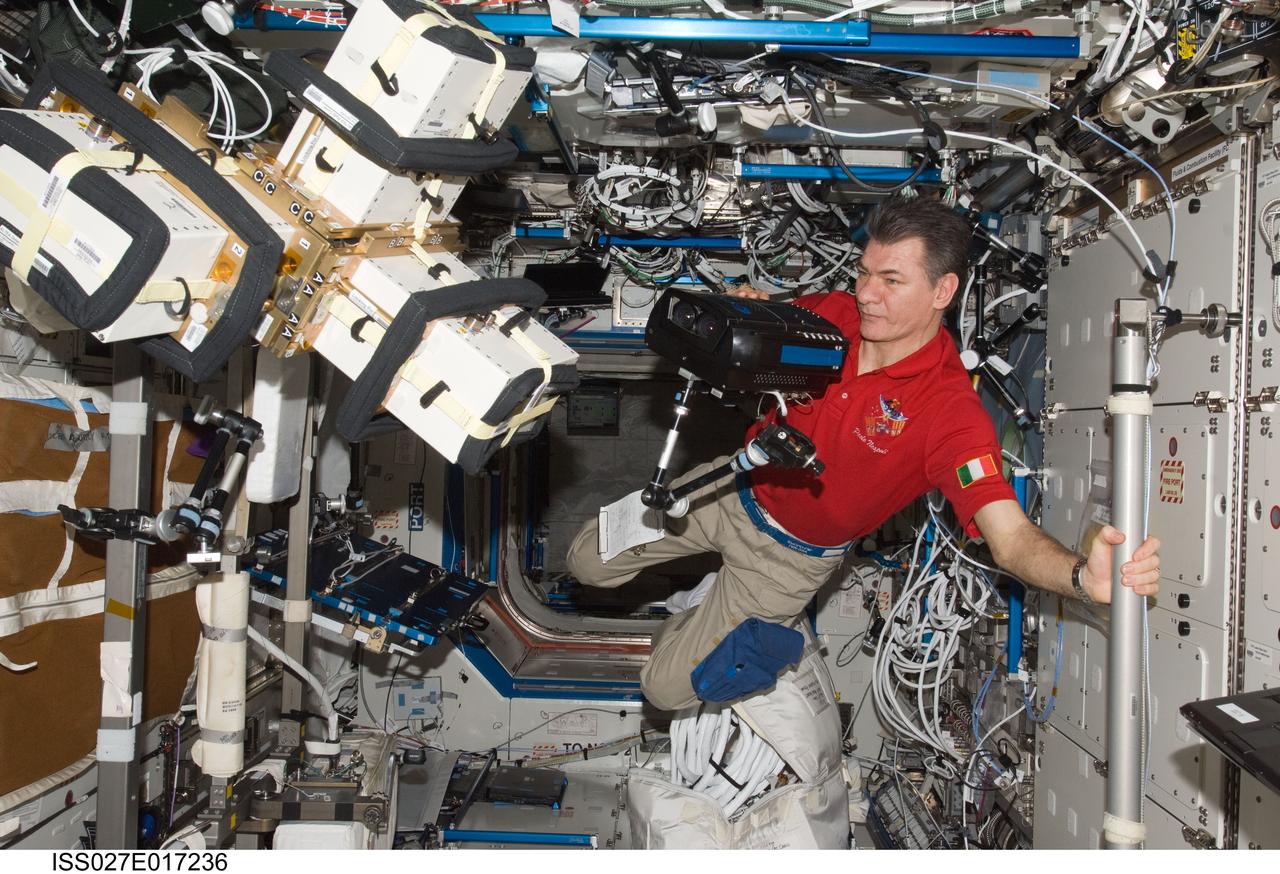

ISS027-E-017236 (23 April 2011) --- European Space Agency astronaut Paolo Nespoli, Expedition 27 flight engineer, works with Anomalous Long Term Effects on Astronauts (ALTEA) Shield isotropic equipment in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. ALTEA-Shield isotropic dosimetry uses existing ALTEA hardware to survey the radiation environment in the Destiny laboratory in 3D. It also measures the effectiveness and shielding properties of several materials with respect to the perception of anomalous light flashes.
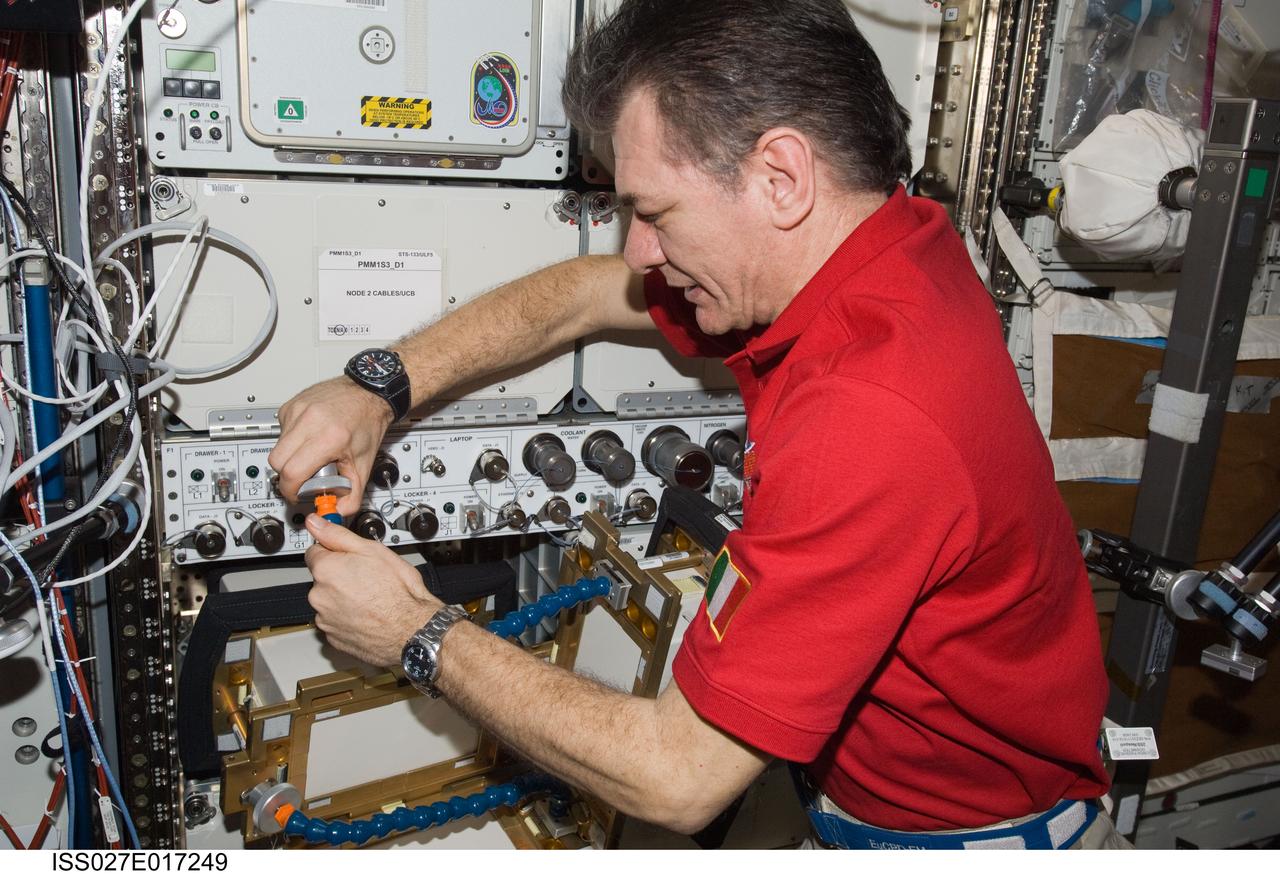

ISS027-E-017249 (23 April 2011) --- European Space Agency astronaut Paolo Nespoli, Expedition 27 flight engineer, works with Anomalous Long Term Effects on Astronauts (ALTEA) Shield isotropic equipment in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. ALTEA-Shield isotropic dosimetry uses existing ALTEA hardware to survey the radiation environment in the Destiny laboratory in 3D. It also measures the effectiveness and shielding properties of several materials with respect to the perception of anomalous light flashes.
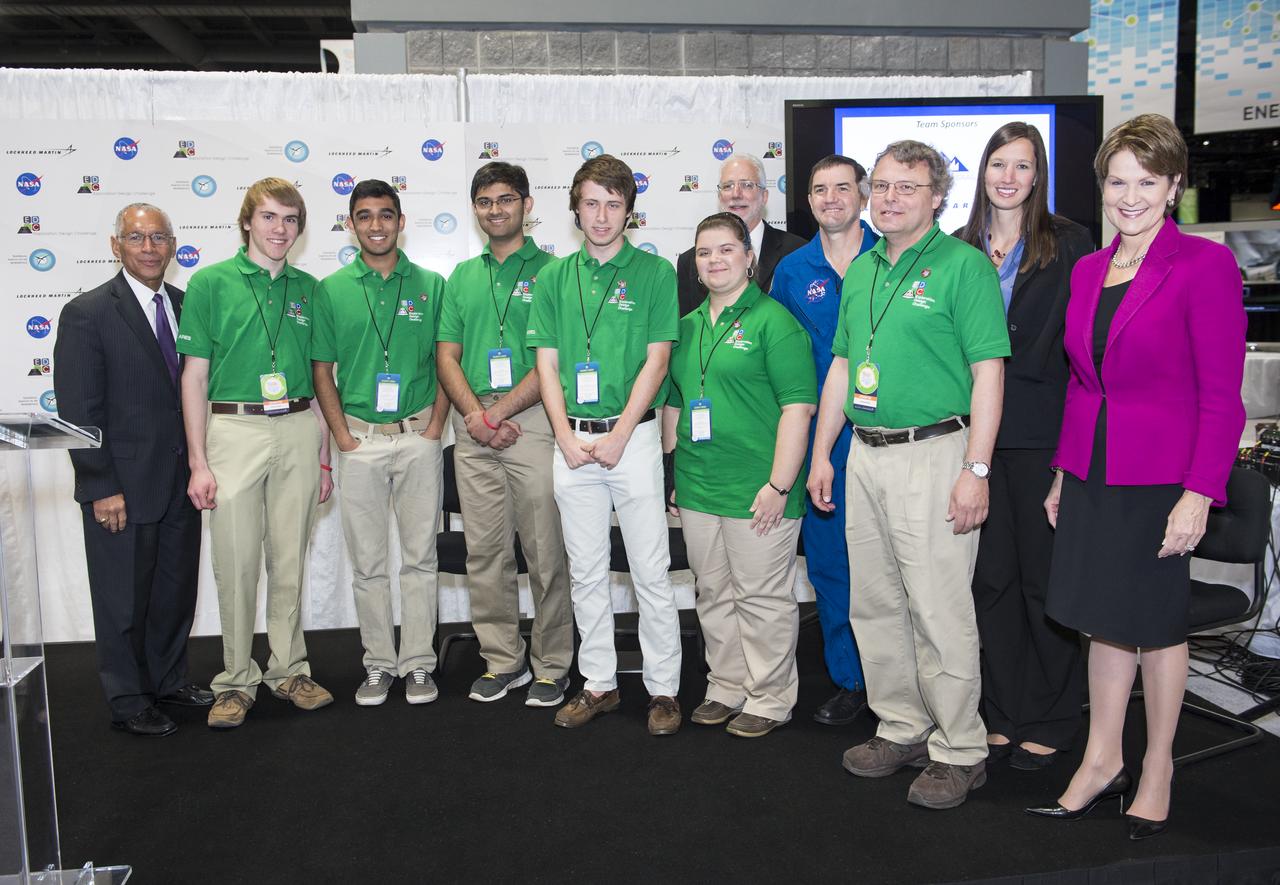

NASA’s Administrator, Charles Bolden (left), President/CEO of Lockheed Martin, Marillyn Hewson (right), and astronaut Rex Walheim (back row) pose for a group photo with the winning high school team in the Exploration Design Challenge. Team ARES from the Governors School for Science and Technology in Hampton, Va. won the challenge with their radiation shield design, which will be built and flown aboard the Orion/EFT-1. The award was announced at the USA Science and Engineering Festival on April 25, 2014 at the Washington Convention Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
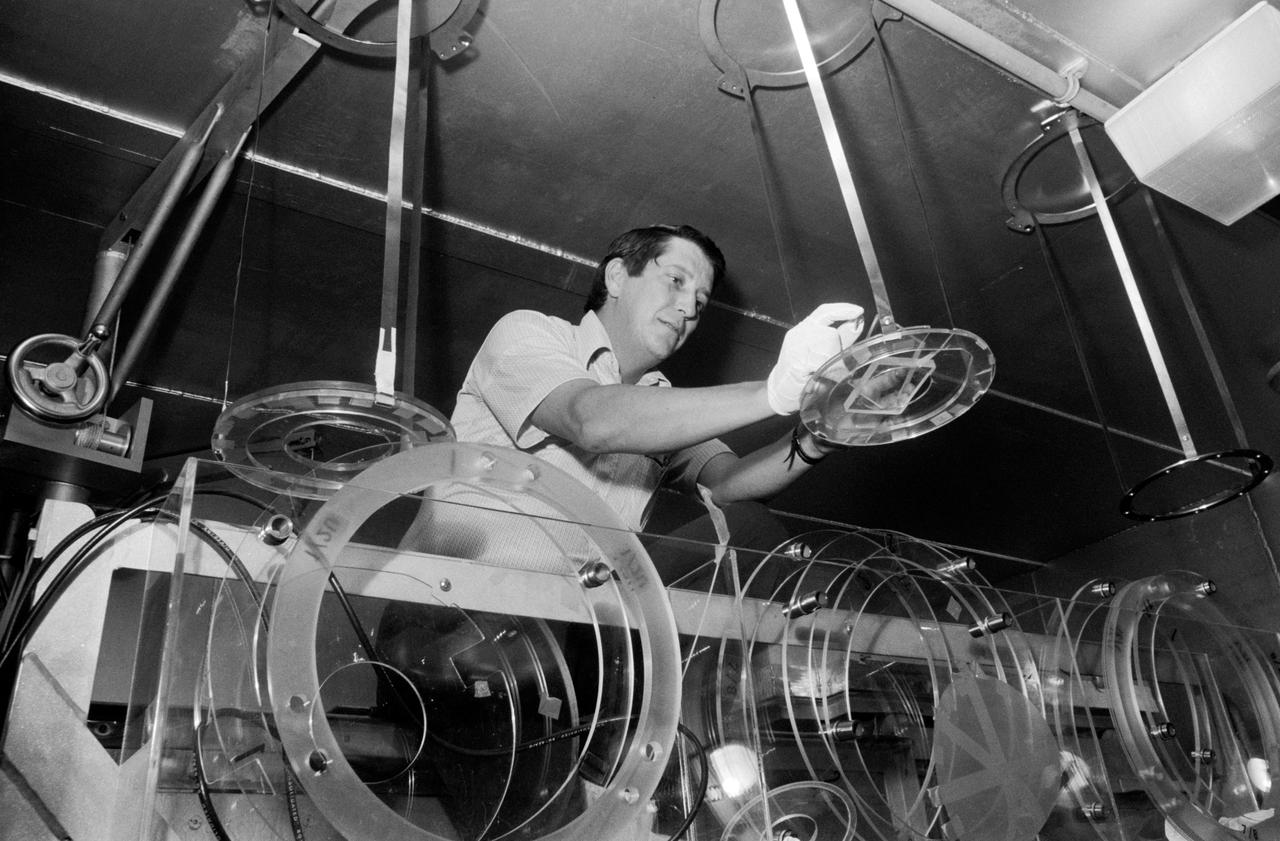

S73-36161 (November 1973) --- In the Radiation Counting Laboratory sixty feet underground at JSC, Dr. Robert S. Clark prepares to load pieces of iridium foil -- sandwiched between plastic sheets -- into the laboratory's radiation detector. The iridium foil strips were worn by the crew of the second Skylab flight in personal radiation dosimeters throughout their 59 1/2 days in space. Inside the radiation detector assembly surrounded by 28 tons of lead shielding, the sample will be tested to determine the total neutron dose to which the astronauts were exposed during their long stay aboard the space station. Photo credit: NASA
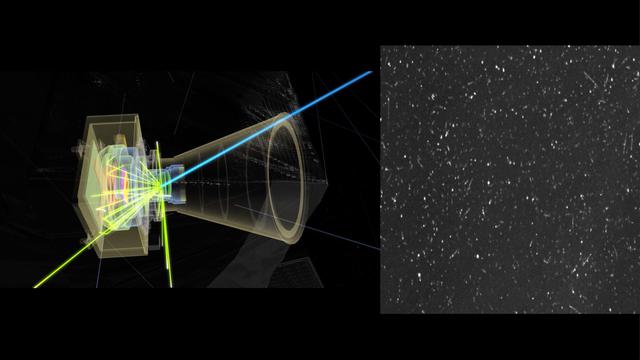
This animation gives an X-ray view of the Juno spacecraft's Stellar Reference Unit (SRU) star camera (left) as it is bombarded by high-energy particles in Jupiter's inner radiation belts. Even though the SRU camera head is six times more heavily shielded than Juno's radiation vault, the highest-energy particles in Jupiter's extreme radiation environment can still penetrate, striking the imaging sensor inside. The signatures from high-energy electron and ion hits appear as dots, squiggles, and streaks (right) in the images collected by the SRU, like static on a television screen. Juno's Radiation Monitoring Investigation collects SRU images and uses image processing to extract these radiation-induced noise signatures to profile the radiation levels encountered by Juno during its close flybys of Jupiter. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24436
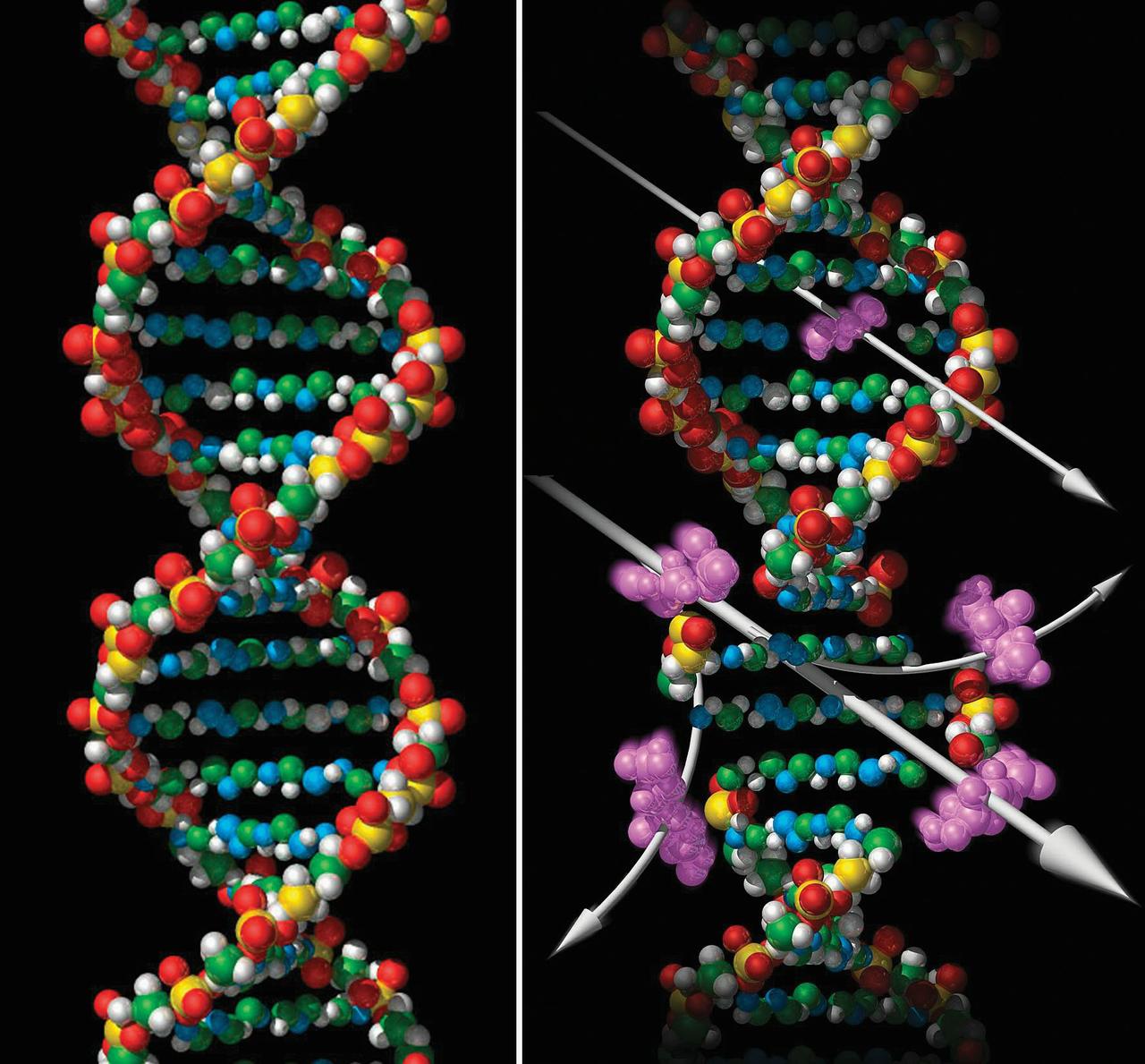
The blueprint of life, DNA's double helix is found in the cells of everything from bacteria to astronauts. Exposure to radiation(depicted at right) such as X-rays (upper) or heavy ion particles (lower), can damage DNA and cause dire consequences both to the organism itself and to future generations. One of NASA's main goals is to develop better radiation shielding materials to protect astronauts from destructive radiation in space. This is particularly important for long space missions. NASA has selected researchers to study materials that provide better shielding. This research is managed by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research and is supported by the Microgravity Science and Applications Department at NASA's Marshall Center. During International Space Station Expedition Six, the Extravehicular Activity Radiation Monitoring (EVARM) will continue to measure radiation dosage encountered by the eyes, internal organs and skin during specific spacewalks, and relate it to the type of activity, location and other factors. An analysis of this information may be useful in mitigating potential exposure to space walkers in the future. (Illustration by Dr. Frank Cucinotta, NASA/Johnson Space Center, and Prem Saganti, Lockheed Martin)
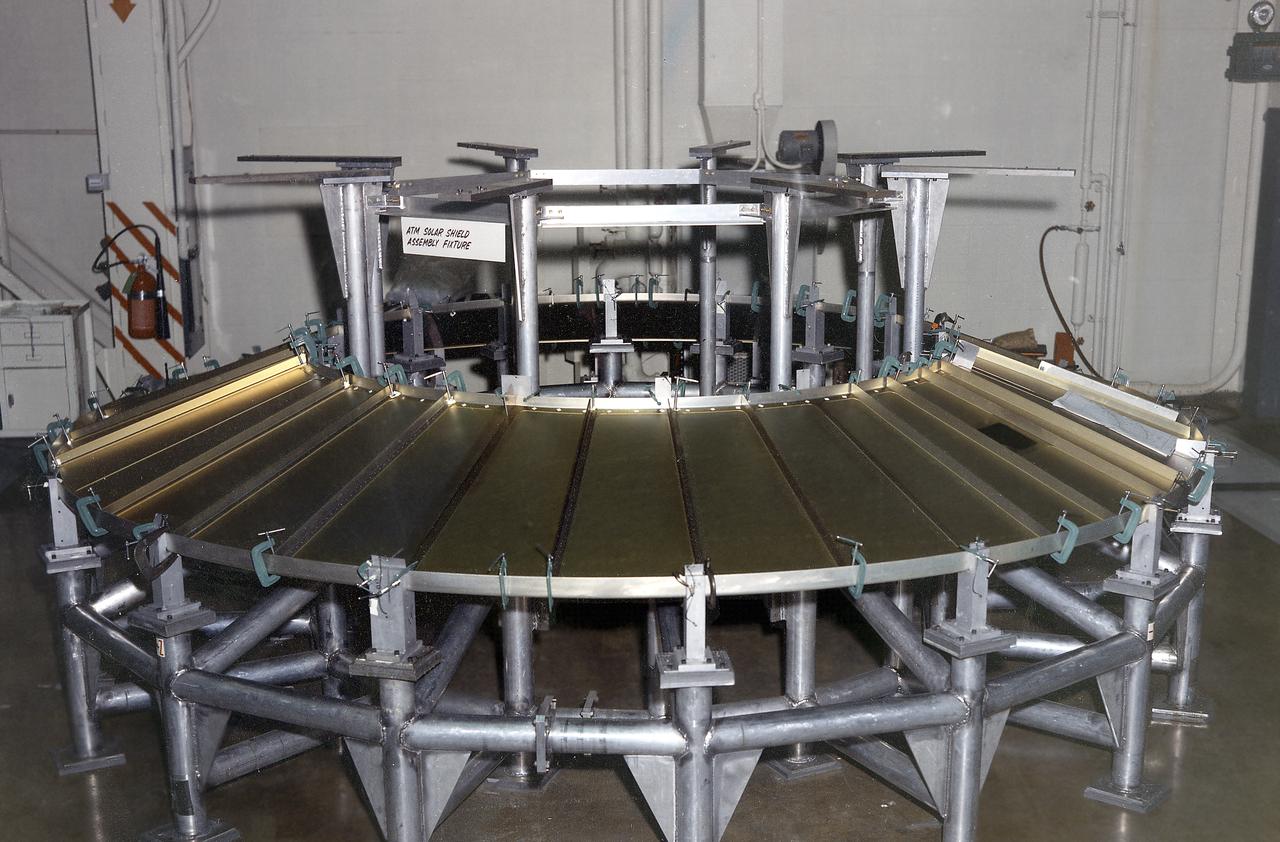
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. One scientific instrument was the ATM solar shield that formed the base for the rack/frame instrument and the instrument canister. The solar shield contained aperture doors for each instrument to protect against solar radiation and space contamination.
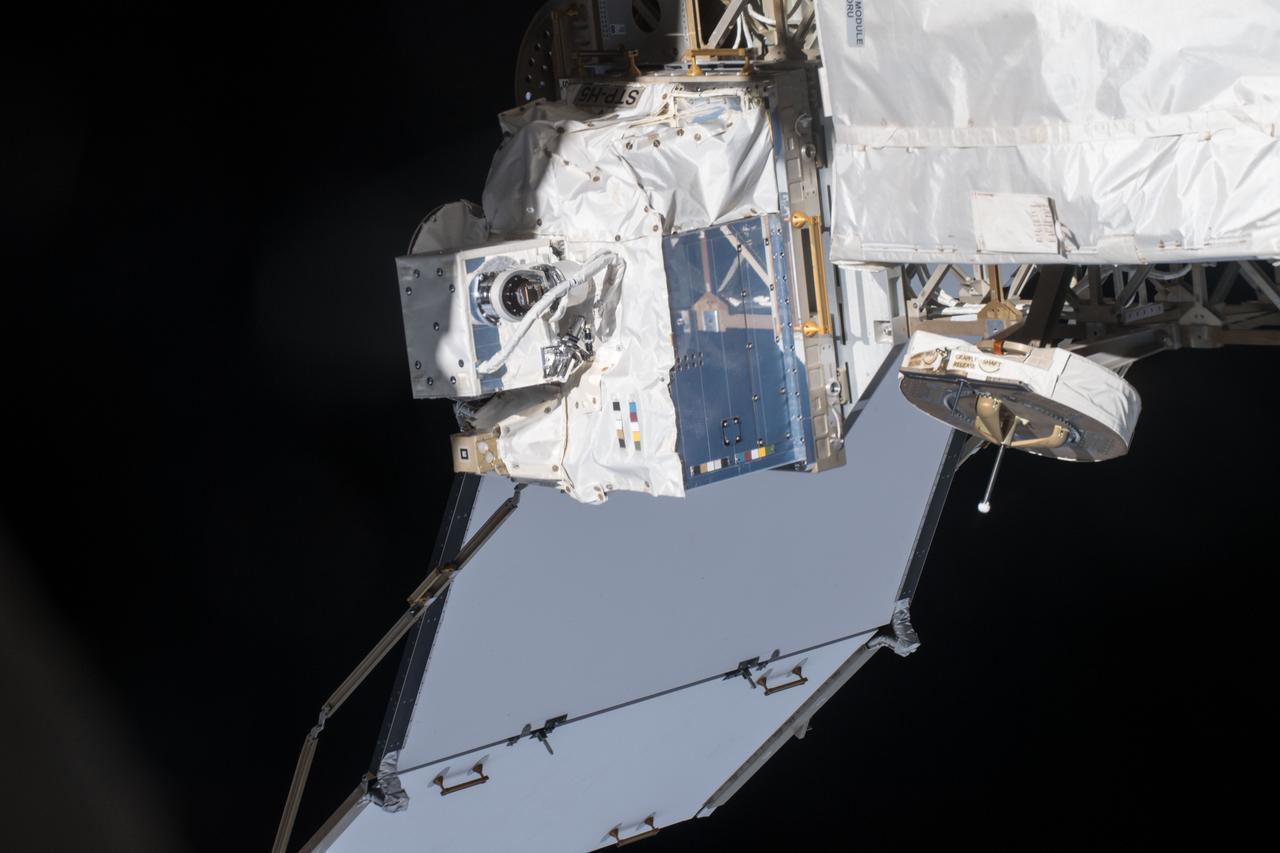

iss054e004116 (Dec. 26, 2017) --- Space Test Program - Houston 5 - Innovative Coatings Experiment (STP-H5-ICE) in front of International Space Station (ISS) radiator. A spacecraft’s exterior coating protects against extreme temperatures, shields the spacecraft from radiation, prevents contamination, and guides cameras that help robots or humans capture and service the spacecraft. STP-H5-ICE studies different paints and coatings that protect spacecraft exteriors.
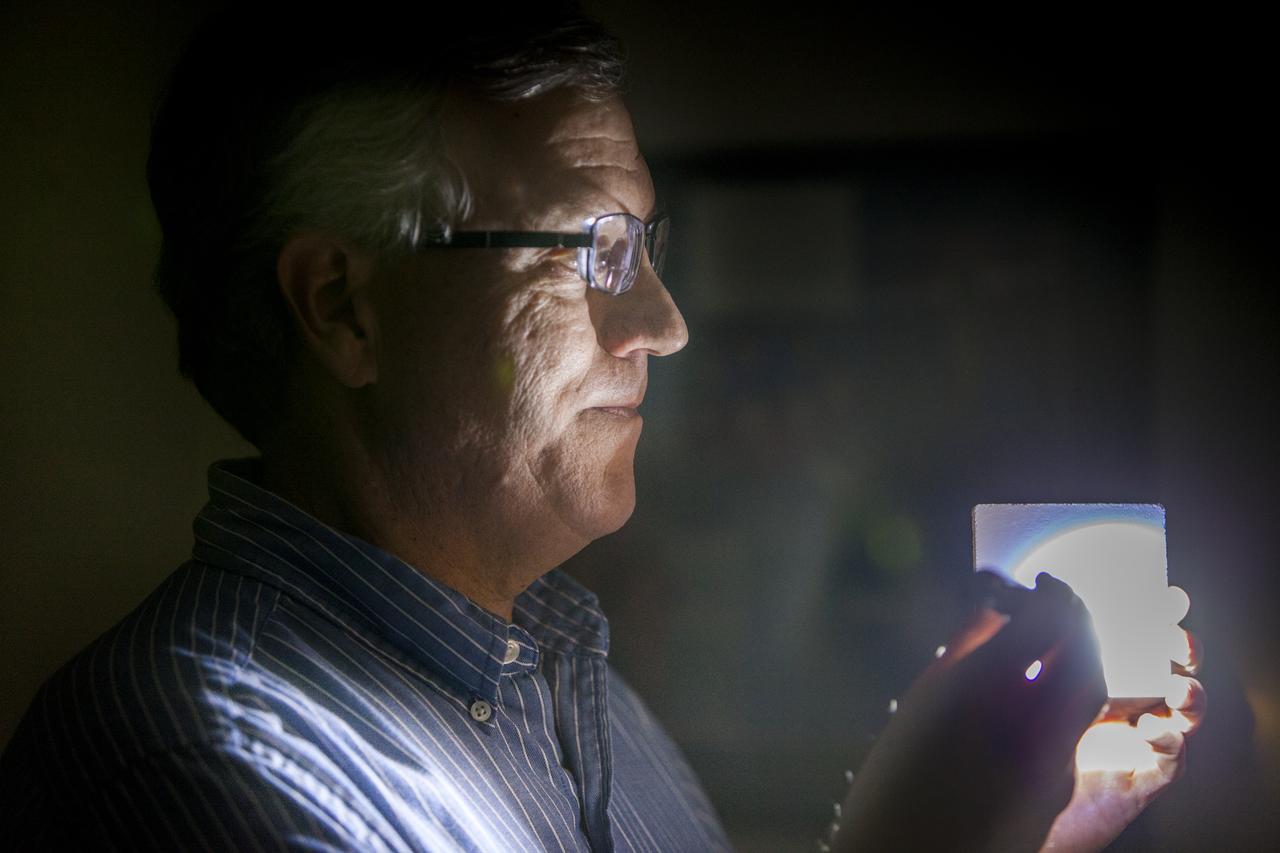

Robert Youngquist, Ph.D., tests a sample disk with a "Solar White" cryogenic selective surface coating with a flash light, demonstrating the coating’s reflective properties. The innovative coating is predicted to reflect more than 99.9 percent of the simulated solar infrared radiation. This technology could enable storing super-cold, or cryogenic, liquids and support systems that shield astronauts against radiation during the Journey to Mars.
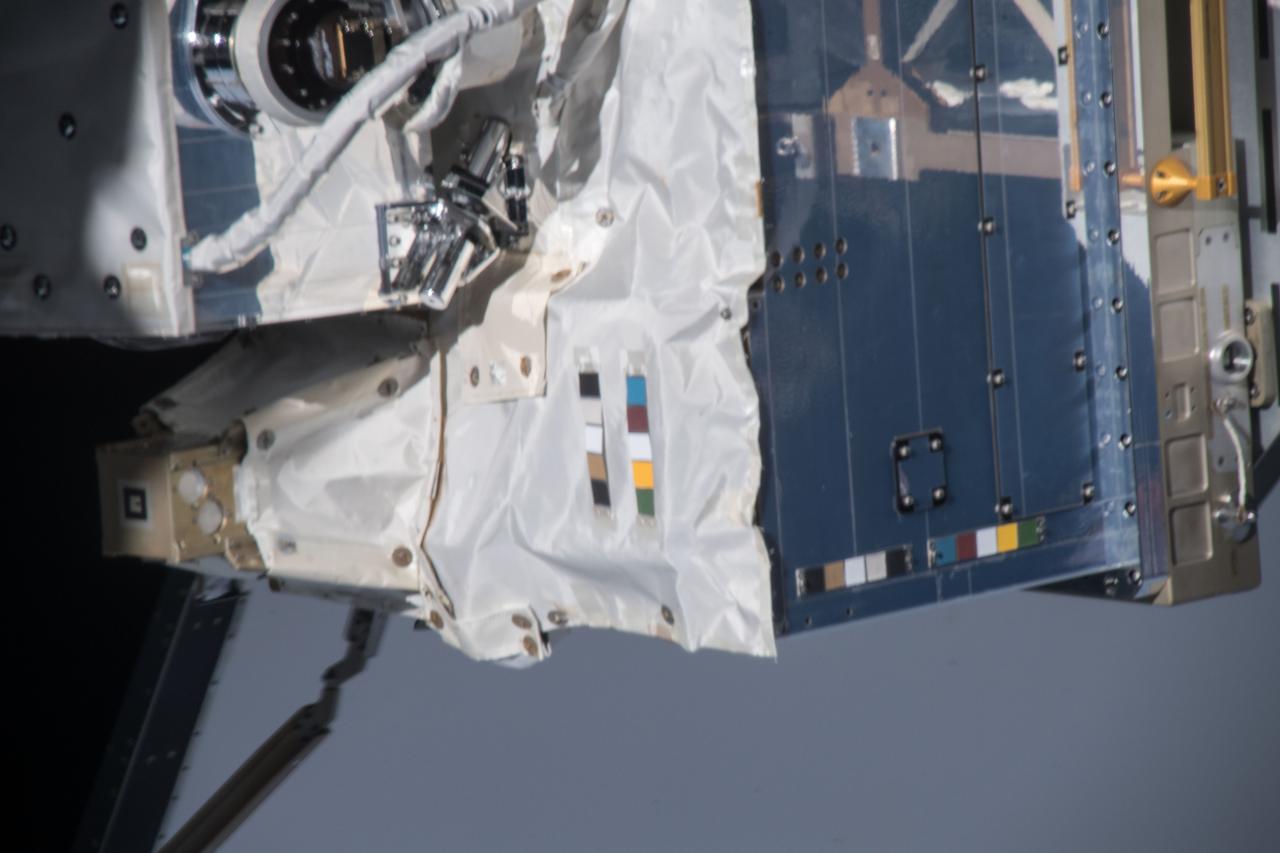

iss054e004119 (Dec. 26, 2017) --- Space Test Program - Houston 5 - Innovative Coatings Experiment (STP-H5-ICE) with International Space Station (ISS) radiator in the background. A spacecraft’s exterior coating protects against extreme temperatures, shields the spacecraft from radiation, prevents contamination, and guides cameras that help robots or humans capture and service the spacecraft. STP-H5-ICE studies different paints and coatings that protect spacecraft exteriors.
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dust particles scatter during an experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fabricated material is designed to mimic the dust on the lunar surface. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are underway to conduct a dust particle experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities.
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are underway to conduct a dust particle experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are underway to conduct a dust particle experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities.
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dust particles are readied for an experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fabricated material is designed to mimic the dust on the lunar surface. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are underway to conduct a dust particle experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities.
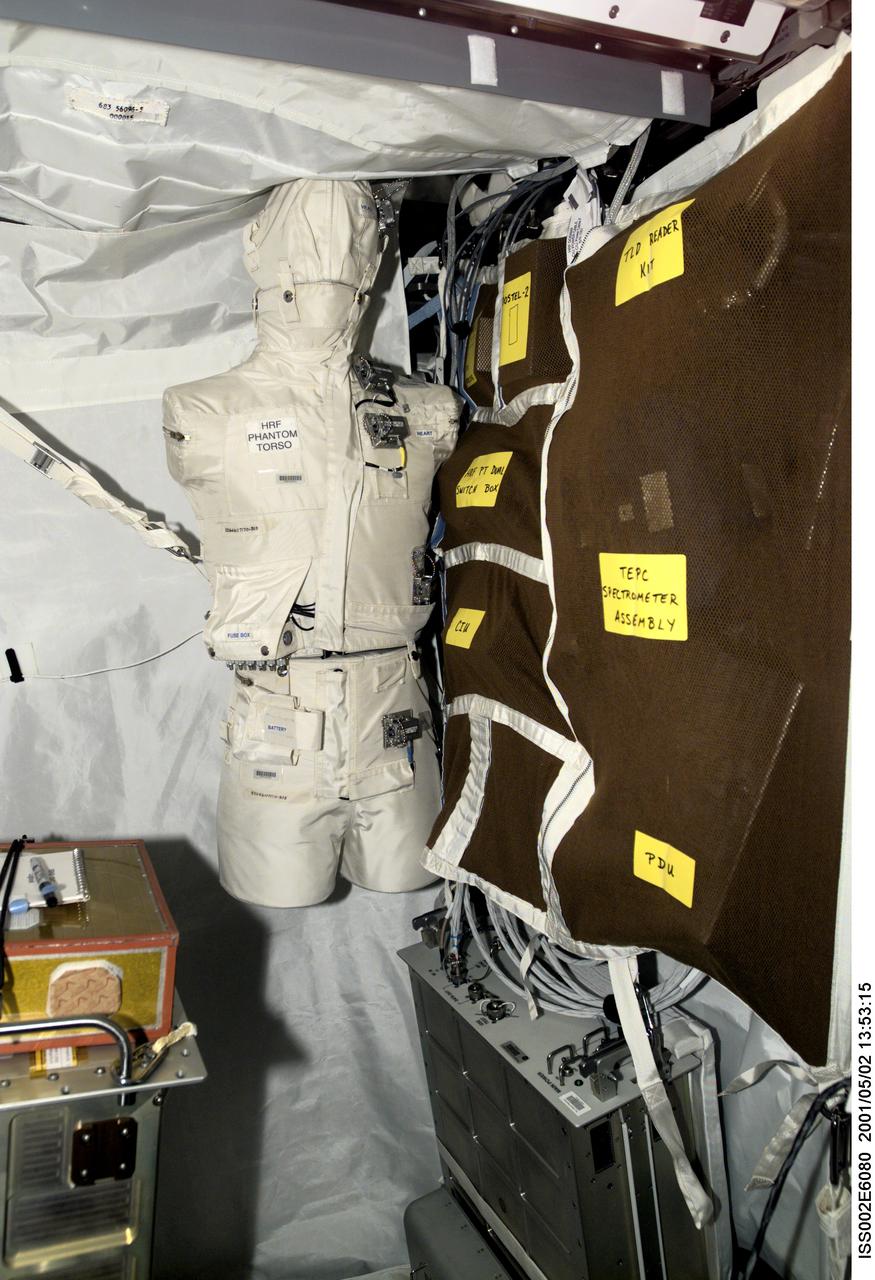

ISS002-E-6080 (2 May 2001) --- The Phantom Torso, seen here in the Human Research Facility (HRF) section of the Destiny/U.S. laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS), is designed to measure the effects of radiation on organs inside the body by using a torso that is similar to those used to train radiologists on Earth. The torso is equivalent in height and weight to an average adult male. It contains radiation detectors that will measure, in real-time, how much radiation the brain, thyroid, stomach, colon, and heart and lung area receive on a daily basis. The data will be used to determine how the body reacts to and shields its internal organs from radiation, which will be important for longer duration space flights. The experiment was delivered to the orbiting outpost during by the STS-100/6A crew in April 2001. Dr. Gautam Badhwar, NASA JSC, Houston, TX, is the principal investigator for this experiment. A digital still camera was used to record this image.
The Phantom Torso is a tissue-muscle plastic anatomical model of a torso and head. It contains over 350 radiation measuring devices to calculate the radiation that penetrates internal organs in space travel. The Phantom Torso is one of three radiation experiments in Expedition Two including the Borner Ball Neutron Detector and Dosimetric Mapping.
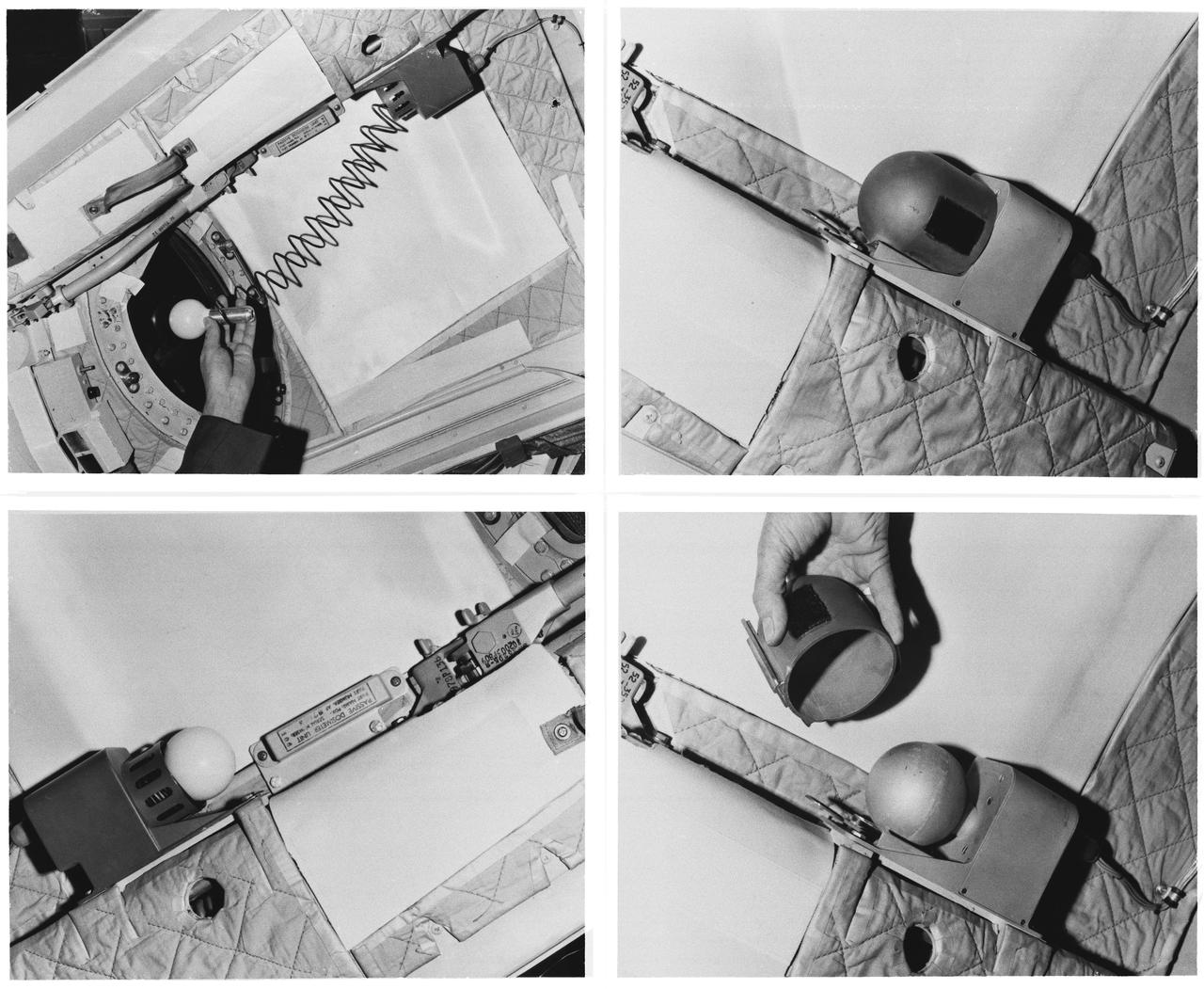
S65-61788 (For release: 11 Dec. 1965) --- Close-up view of equipment which will be used in the D-8 (Radiation in Spacecraft) experiment on the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Gemini-6 spaceflight. This experiment is designed to make highly accurate measurements of the absorbed dose rate of radiation which penetrates the Gemini spacecraft, and determine the spatial distribution of dose levels inside the spacecraft particularly in the crew area. This is experimentation of the U.S. Air Force Weapons Laboratory, Kirtland AFB, N.M. LOWER LEFT: The second ionization chamber, this one is unshielded. This chamber can be removed from its bracket by the astronaut who will periodically take measurements at various locations in the spacecraft. Nearby is Passive Dosimeter Unit which is one of five small packets each containing a standard pocket ionization chamber, gamma electron sensitive film, glass needles and thermo luminescent dosimeters which are mounted at various locations in the cabin. UPPER LEFT: Photo illustrates how ionization chamber can be removed from bracket for measurements. LOWER RIGHT: Shield of bulb-shaped chamber will be removed (shown in photo) as the spacecraft passes through the South Atlantic anomaly, the area where the radiation belt dips closest to Earth's surface. UPPER RIGHT: Dome-shaped object is shield covering one of two Tissue Equivalent Ionization Chambers (sensors) which will read out continuously the instantaneous rate at which dose is delivered during the flight. This chamber is mounted permanently. The information will be recorded aboard the spacecraft, and will also be received directly by ground stations. This chamber is shielded to simulate the amount of radiation the crew members are receiving beneath their skin. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
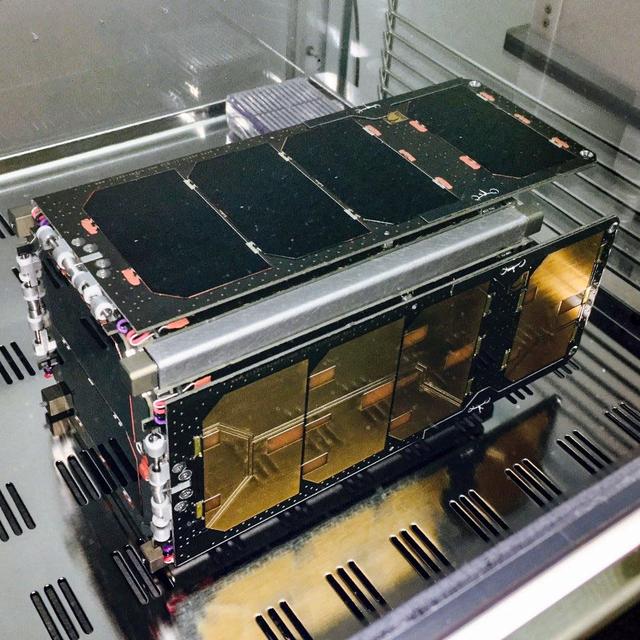
Jsc2020e004942(2/7/2020) — A preflight view of the CryoCube BUS. CryoCube demonstrates on-orbit thermal management technology. Such technology has a variety of potential applications, including storing rocket propellants in space, cooling instruments to improve their signal-to-noise ratios, and supporting future cryogenic experiments in microgravity. The small satellite uses a deployable shield to block radiation from the Sun and Earth and an attitude control system to point its experiment into deep space. Image courtesy of: Sierra Lobo Inc.
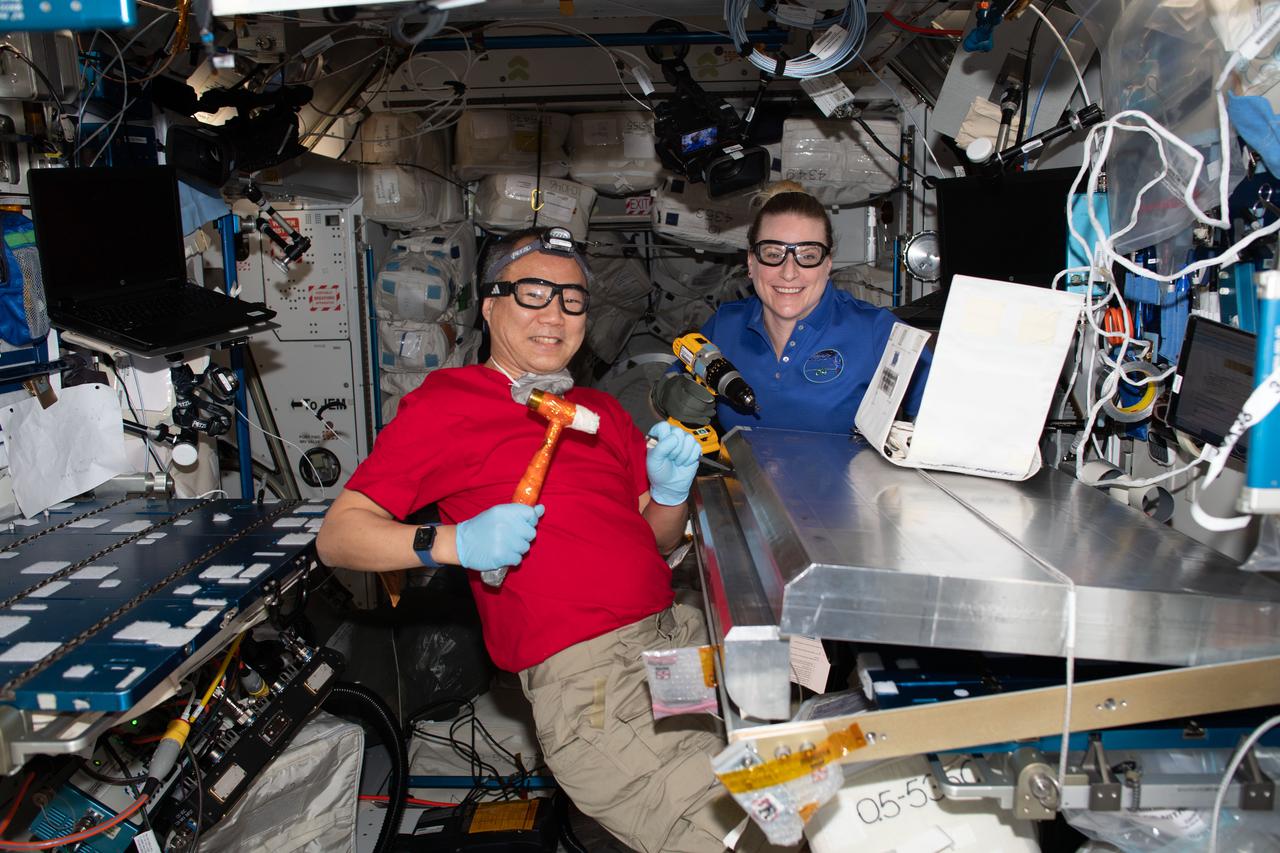

iss064e053432 (April 6, 2021) --- Expedition 64 Flight Engineers Soichi Noguchi of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency and Kate Rubins of NASA configure a radiation shield for temporary sleeping quarters, or the Crew Alternate Sleep Accommodation (CASA). The CASA will allow extra space for the short period when up to 11 crew members will be occupying the International Space Station in April.
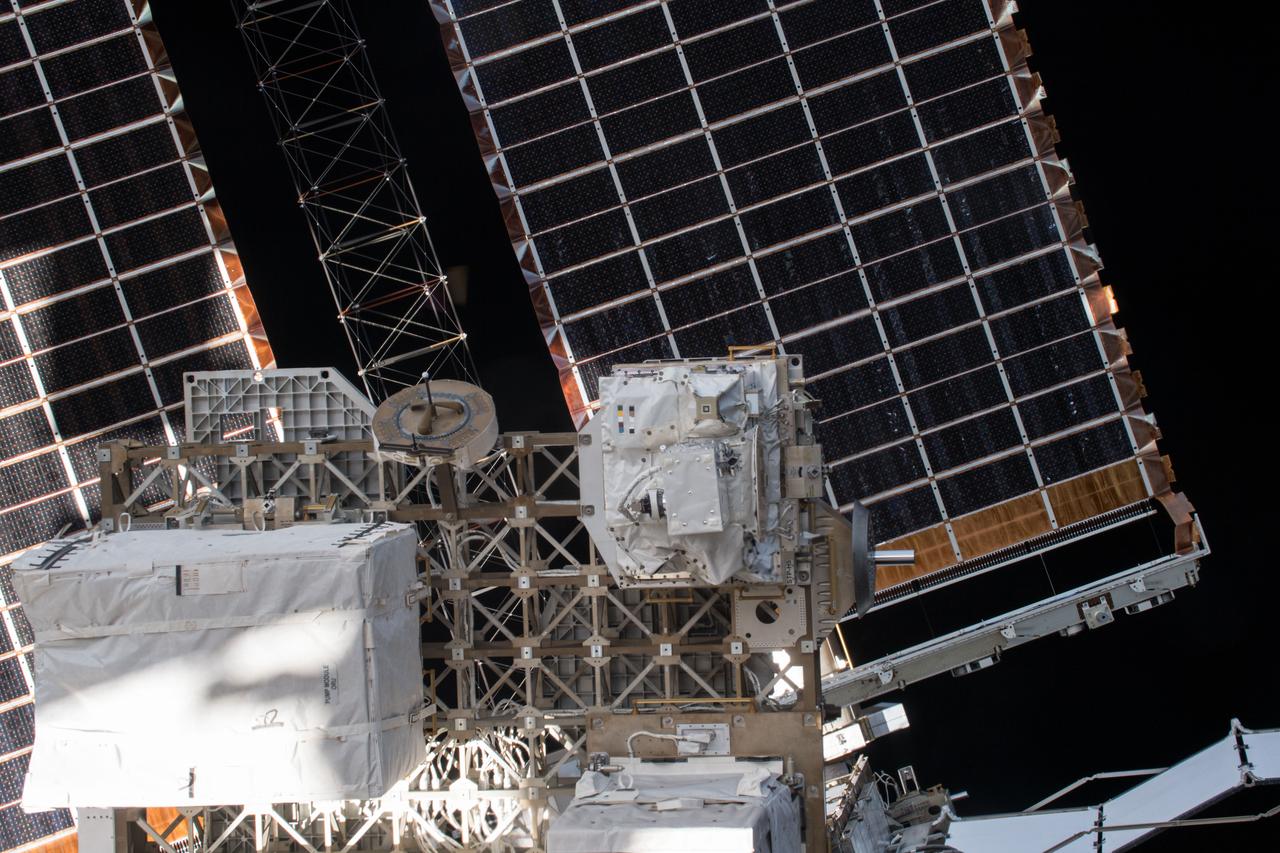

iss054e004101 (Dec. 26, 2017) --- Space Test Program - Houston 5 - Innovative Coatings Experiment (STP-H5-ICE) in front of International Space Station (ISS) solar panels. A spacecraft’s exterior coating protects against extreme temperatures, shields the spacecraft from radiation, prevents contamination, and guides cameras that help robots or humans capture and service the spacecraft. STP-H5-ICE studies different paints and coatings that protect spacecraft exteriors.
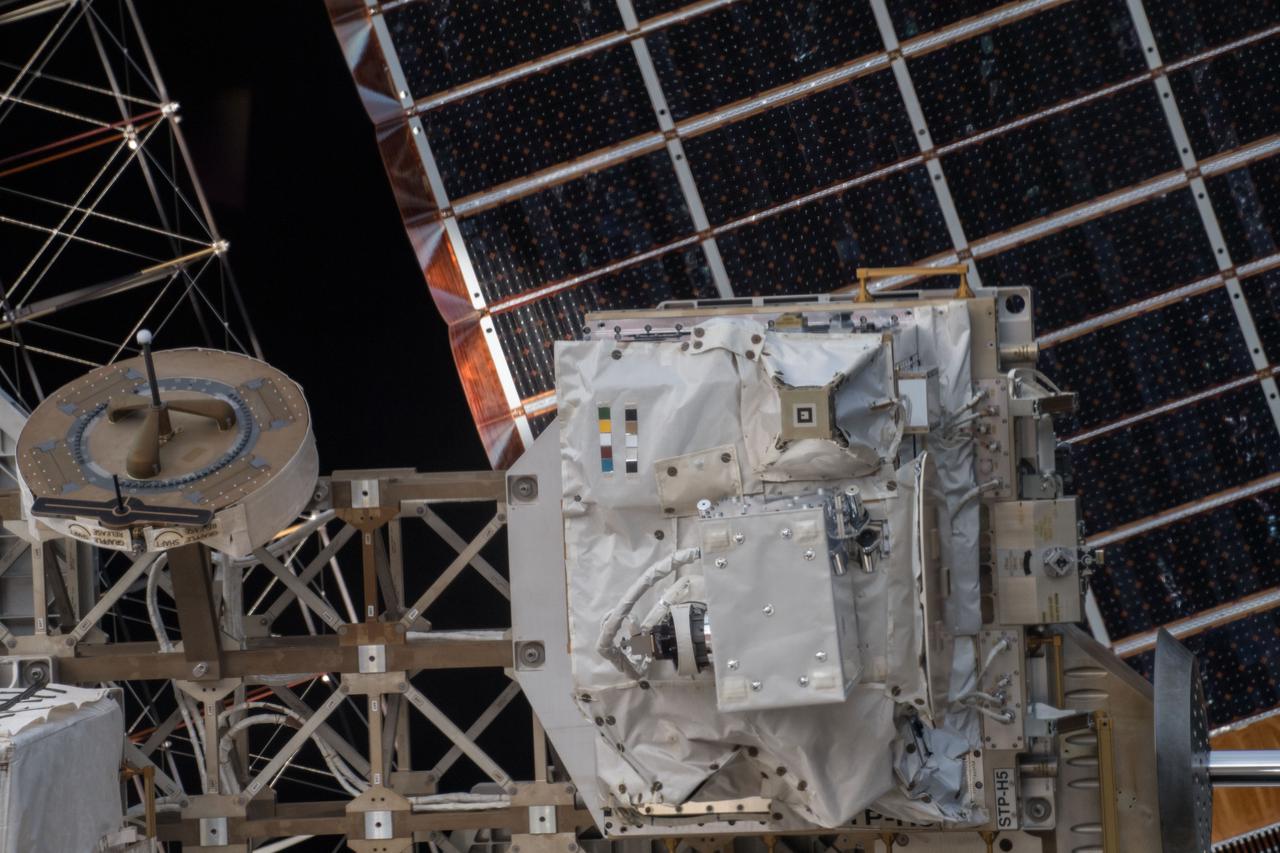

iss054e004105 (Dec. 26, 2017) --- Space Test Program - Houston 5 - Innovative Coatings Experiment (STP-H5-ICE) in front of International Space Station (ISS) solar panels. A spacecraft’s exterior coating protects against extreme temperatures, shields the spacecraft from radiation, prevents contamination, and guides cameras that help robots or humans capture and service the spacecraft. STP-H5-ICE studies different paints and coatings that protect spacecraft exteriors.
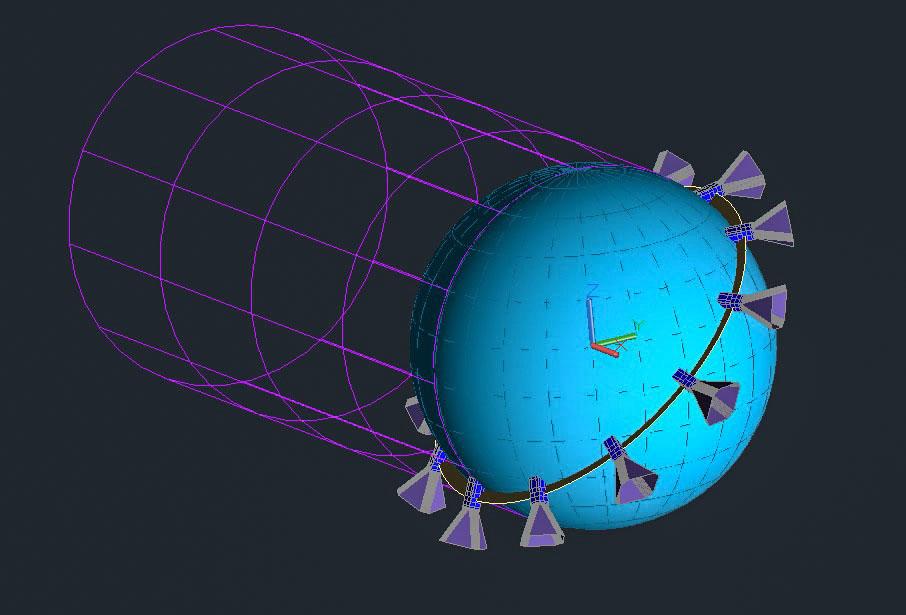
Jsc2020e004943 (2/7/2020) — A computer model showing CryoCube’s orbital orientation. CryoCube demonstrates on-orbit thermal management technology. Such technology has a variety of potential applications, including storing rocket propellants in space, cooling instruments to improve their signal-to-noise ratios, and supporting future cryogenic experiments in microgravity. The small satellite uses a deployable shield to block radiation from the Sun and Earth and an attitude control system to point its experiment into deep space. Image courtesy of : Kennedy Space Center
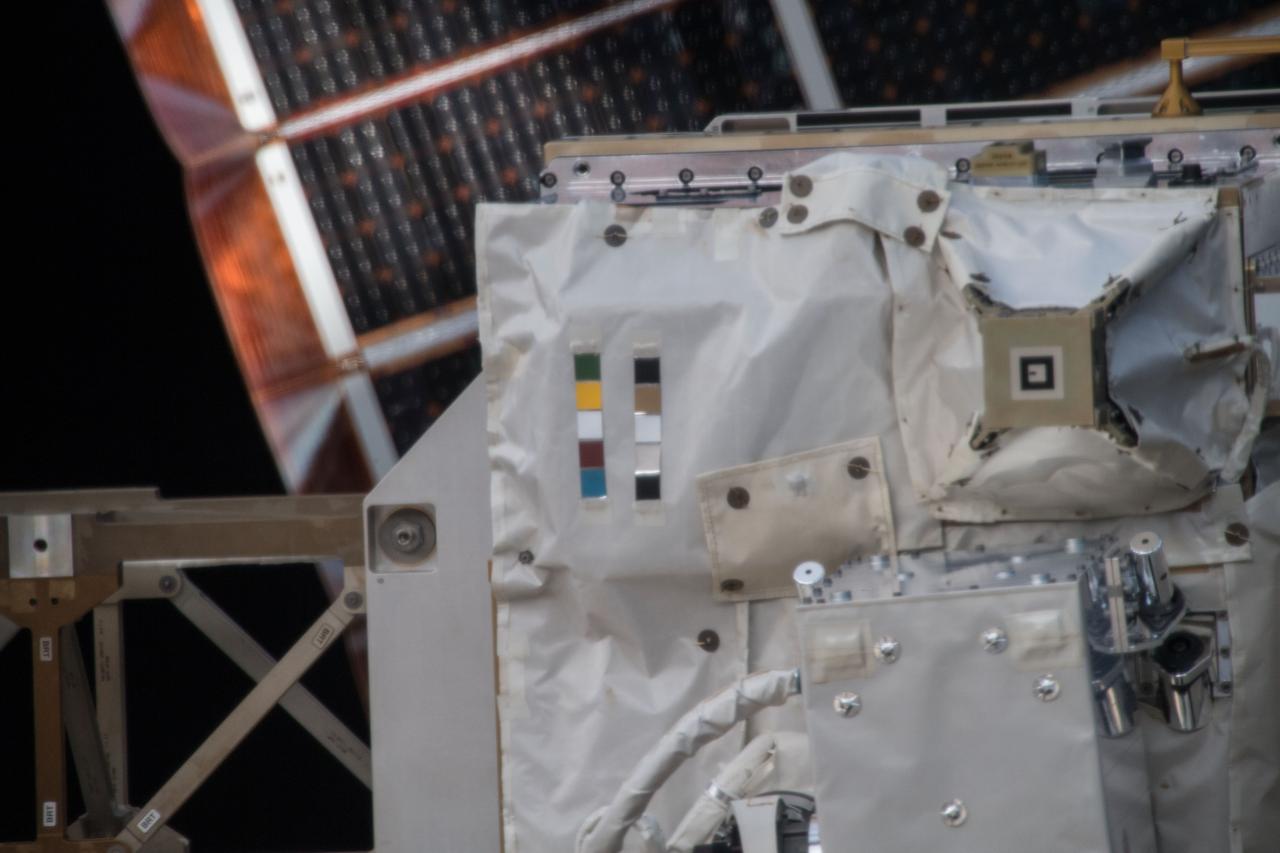

iss054e004111 (Dec. 26, 2017) --- Space Test Program - Houston 5 - Innovative Coatings Experiment (STP-H5-ICE) with International Space Station (ISS) solar panels in the background. A spacecraft’s exterior coating protects against extreme temperatures, shields the spacecraft from radiation, prevents contamination, and guides cameras that help robots or humans capture and service the spacecraft. STP-H5-ICE studies different paints and coatings that protext spacecraft exteriors.
Inside of the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an electrodynamic dust shield (EDS) is in view on Jan. 18, 2023. The dust shield is one of the payloads that will fly aboard Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative. During the mission, EDS will generate a non-uniform electric field using varying high voltage on multiple electrodes. This traveling field, in turn, carries away the particles and has potential applications in thermal radiators, spacesuit fabrics, visors, camera lenses, solar panels, and many other technologies. The CLPS initiative is a key part of NASA’s Artemis lunar exploration efforts. The science and technology payloads sent to the Moon’s surface as part of the initiative will help lay the foundation for human missions and a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
Inside of the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an electrodynamic dust shield (EDS) is in view on Jan. 18, 2023. The dust shield is one of the payloads that will fly aboard Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative. During the mission, EDS will generate a non-uniform electric field using varying high voltage on multiple electrodes. This traveling field, in turn, carries away the particles and has potential applications in thermal radiators, spacesuit fabrics, visors, camera lenses, solar panels, and many other technologies. The CLPS initiative is a key part of NASA’s Artemis lunar exploration efforts. The science and technology payloads sent to the Moon’s surface as part of the initiative will help lay the foundation for human missions and a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
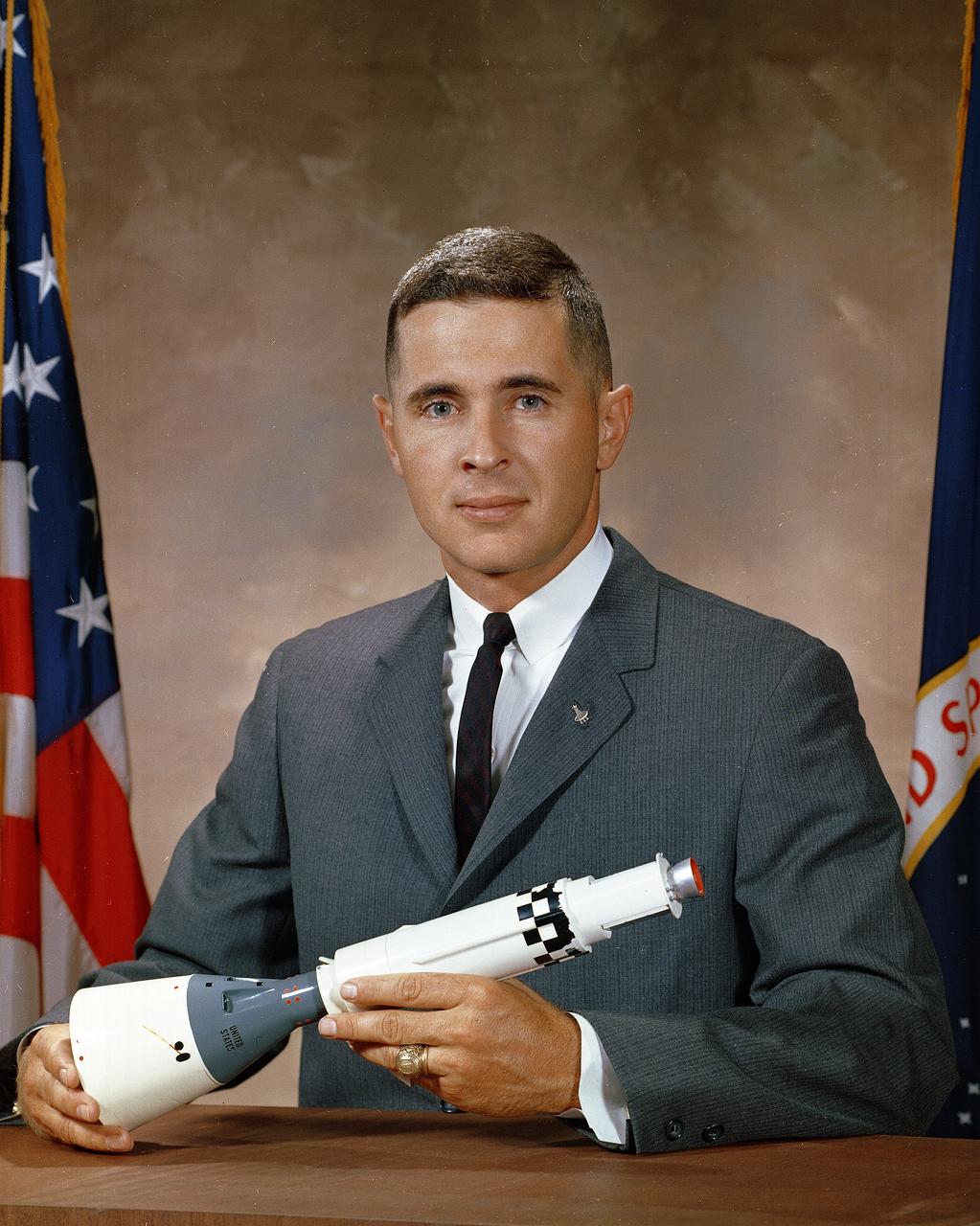

This is the official NASA portrait of astronaut William Anders. Anders was commissioned in the air Force after graduation from the Naval Academy and served as a fighter pilot in all-weather interception squadrons of the Air Defense Command. Later he was responsible for technical management of nuclear power reactor shielding and radiation effects programs while at the Air Force Weapons Laboratory in New Mexico. In 1964, Anders was selected by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as an astronaut with responsibilities for dosimetry, radiation effects and environmental controls. He was backup pilot for the Gemini XI, Apollo 11 flights, and served as lunar module (LM) pilot for Apollo 8, the first lunar orbit mission in December 1968. He has logged more than 6,000 hours flying time.
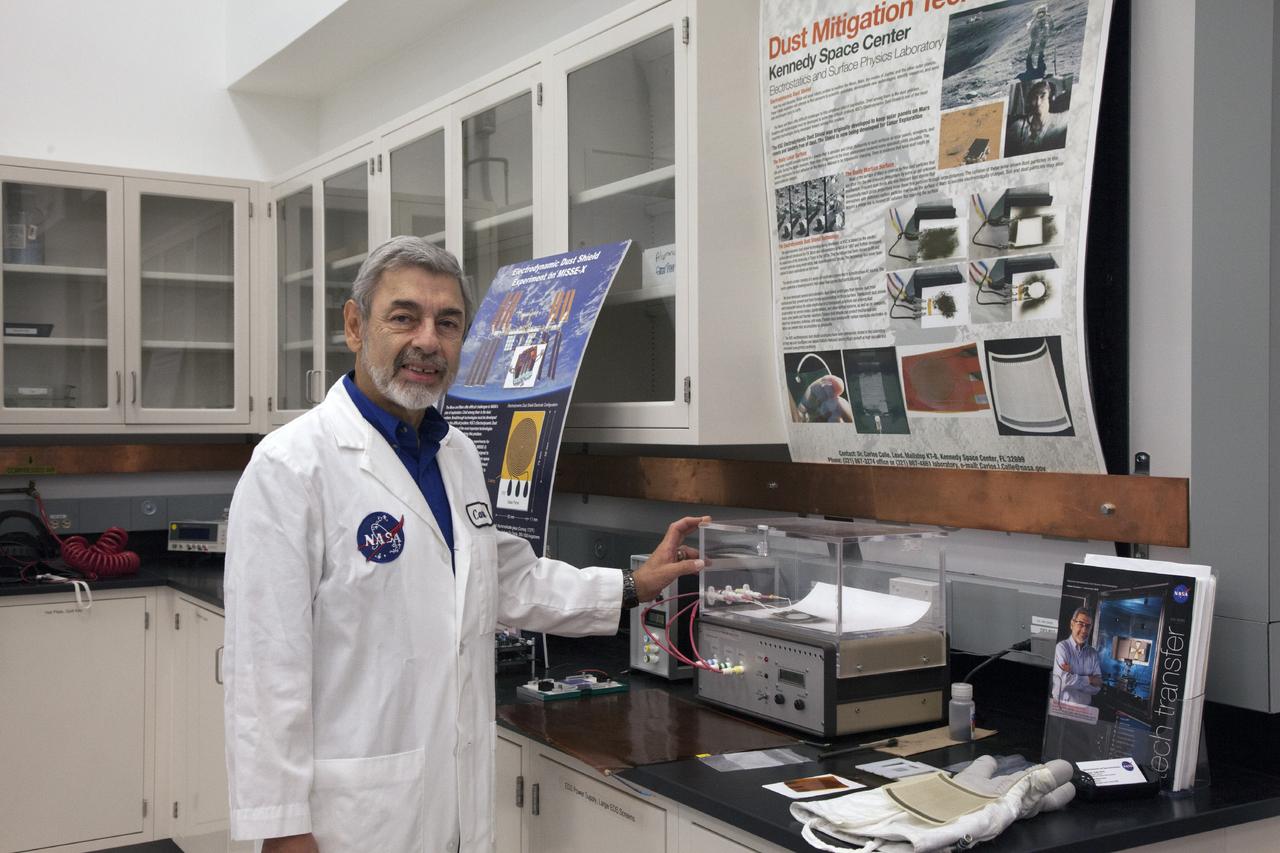

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dr. Carlos Calle, senior research scientist on the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project, demonstrates a dust particle experiment in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. Electrodynamic dust shield, or EDS, technology is based on concepts originally developed by NASA as early as 1967 and later by the University of Tokyo. In 2003, NASA, in collaboration with the University of Arkansas at Little Rock, started development of the EDS for dust particle removal from solar panels to be used on future missions to the moon, an asteroid or Mars. A flight experiment to expose the dust shields to the space environment currently is under development. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/content/scientists-developing-ways-to-mitigate-dust-problem-for-explorers/ Photo credit: NASA/Dan Casper
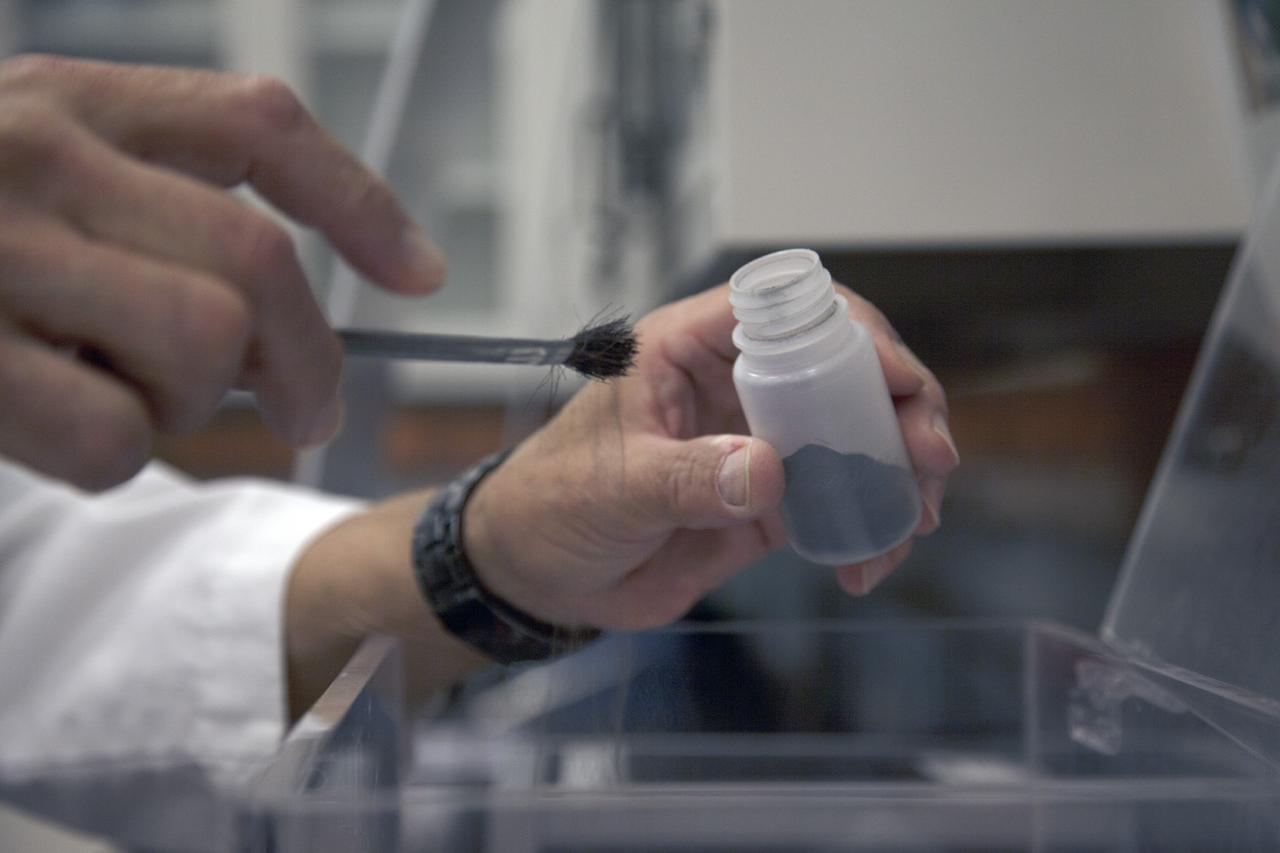

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dr. Carlos Calle, senior research scientist on the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project, works with dust fabricated for use in his experiments in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fabricated material is designed to mimic the dust on the lunar surface. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. Electrodynamic dust shield, or EDS, technology is based on concepts originally developed by NASA as early as 1967 and later by the University of Tokyo. In 2003, NASA, in collaboration with the University of Arkansas at Little Rock, started development of the EDS for dust particle removal from solar panels to be used on future missions to the moon, an asteroid or Mars. A flight experiment to expose the dust shields to the space environment currently is under development. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/content/scientists-developing-ways-to-mitigate-dust-problem-for-explorers/ Photo credit: NASA/Dan Casper
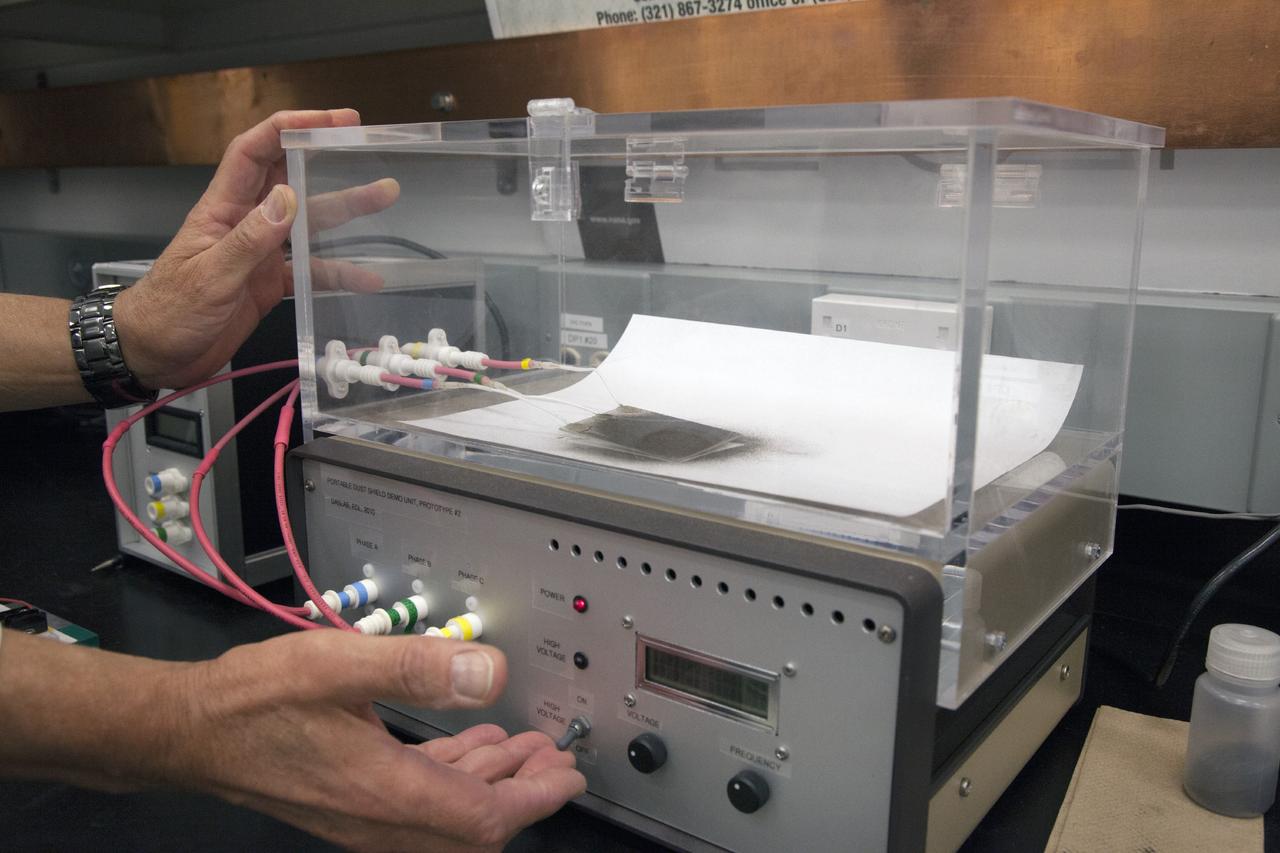
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dr. Carlos Calle, senior research scientist on the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project, demonstrates a dust particle experiment in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. Electrodynamic dust shield, or EDS, technology is based on concepts originally developed by NASA as early as 1967 and later by the University of Tokyo. In 2003, NASA, in collaboration with the University of Arkansas at Little Rock, started development of the EDS for dust particle removal from solar panels to be used on future missions to the moon, an asteroid or Mars. A flight experiment to expose the dust shields to the space environment currently is under development. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/content/scientists-developing-ways-to-mitigate-dust-problem-for-explorers/ Photo credit: NASA/Dan Casper
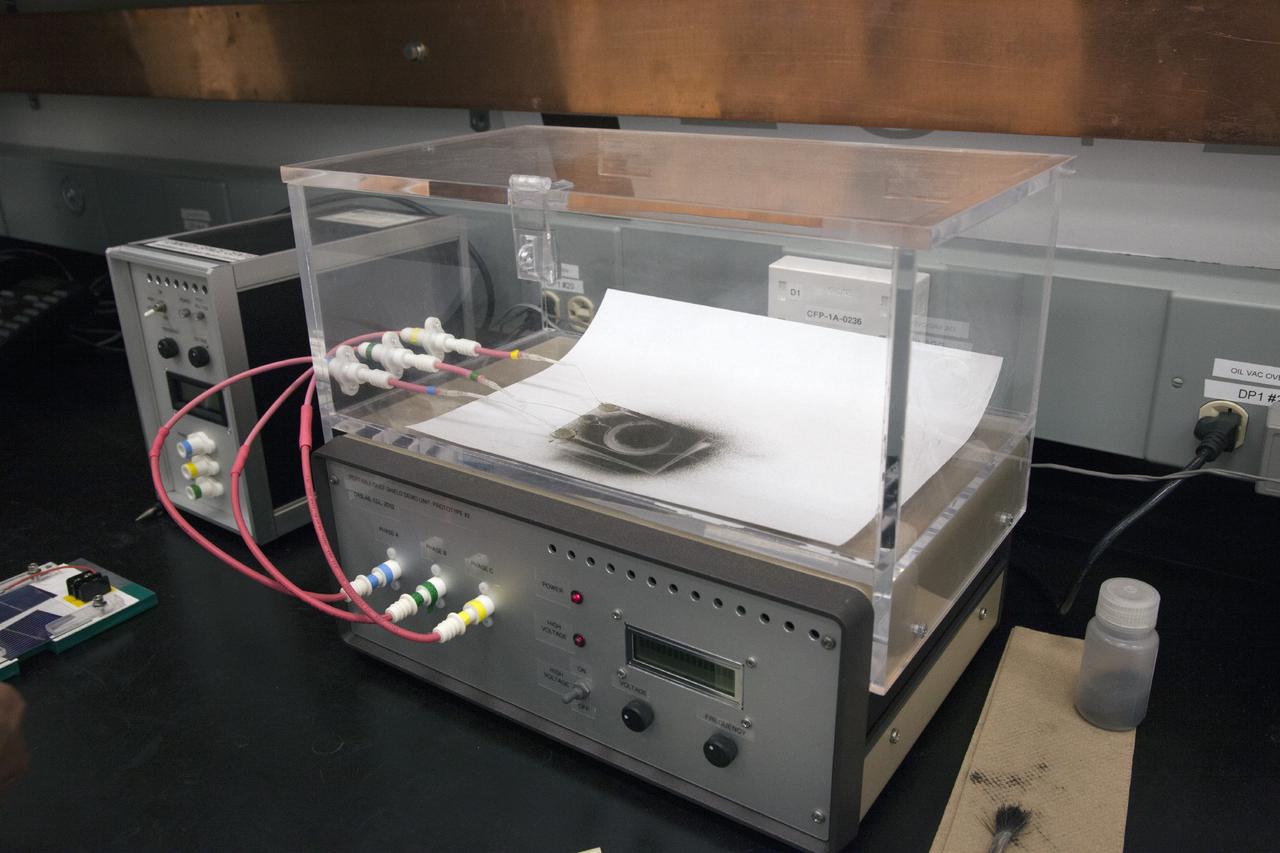
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dust particle experiments are conducted for Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. Electrodynamic dust shield, or EDS, technology is based on concepts originally developed by NASA as early as 1967 and later by the University of Tokyo. In 2003, NASA, in collaboration with the University of Arkansas at Little Rock, started development of the EDS for dust particle removal from solar panels to be used on future missions to the moon, an asteroid or Mars. A flight experiment to expose the dust shields to the space environment currently is under development. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/content/scientists-developing-ways-to-mitigate-dust-problem-for-explorers/ Photo credit: NASA/Dan Casper

Sara Susca, deputy payload manager and payload systems engineer for the NASA's SPHEREx mission, looks up at one of the spacecraft's photon shields at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in October 2023. Short for Specto-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other, imaging the entire sky and gathering information about millions of galaxies. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, the history of galaxy evolution, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. Three concentric photon shields will surround the SPHEREx telescope to protect it from nearby light sources that could overwhelm its detectors. The shields will primarily block light from the Sun and the Earth. They also block heat; SPHEREx needs to be kept cold – below minus 350 degrees Fahrenheit (about minus 210 degrees Celsius). That's because SPHEREx detects infrared light, which is sometimes called heat radiation because it's emitted by anything warm. The heat from SPHEREx's own detectors could overwhelm their ability to image faint cosmic objects, so the spacecraft needs a way to cool the detectors down. The spacecraft stands almost 8.5 feet tall (2.6 meters) and stretches nearly 10.5 feet (3.2 meters) wide. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25784

Part of one of the protective photon shields for NASA's SPHEREx telescope are shown here being assembled at Applied Aerospace Structures in Stockton, California, in July 2023. Short for Specto-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other, imaging the entire sky and gathering information about millions of galaxies. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, the history of galaxy evolution, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. The three concentric photon shields will surround the SPHEREx telescope to protect it from nearby light sources that could overwhelm its detectors. The shields will primarily block light from the Sun and the Earth. They also block heat, because SPHEREx needs to be kept cold – below minus 350 degrees Fahrenheit (about minus 210 degrees Celsius). That's because SPHEREx detects infrared light, which is sometimes called heat radiation because it's emitted by anything warm. The heat from SPHEREx's own detectors could overwhelm their ability to detect faint cosmic objects if they aren't cooled down. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25785
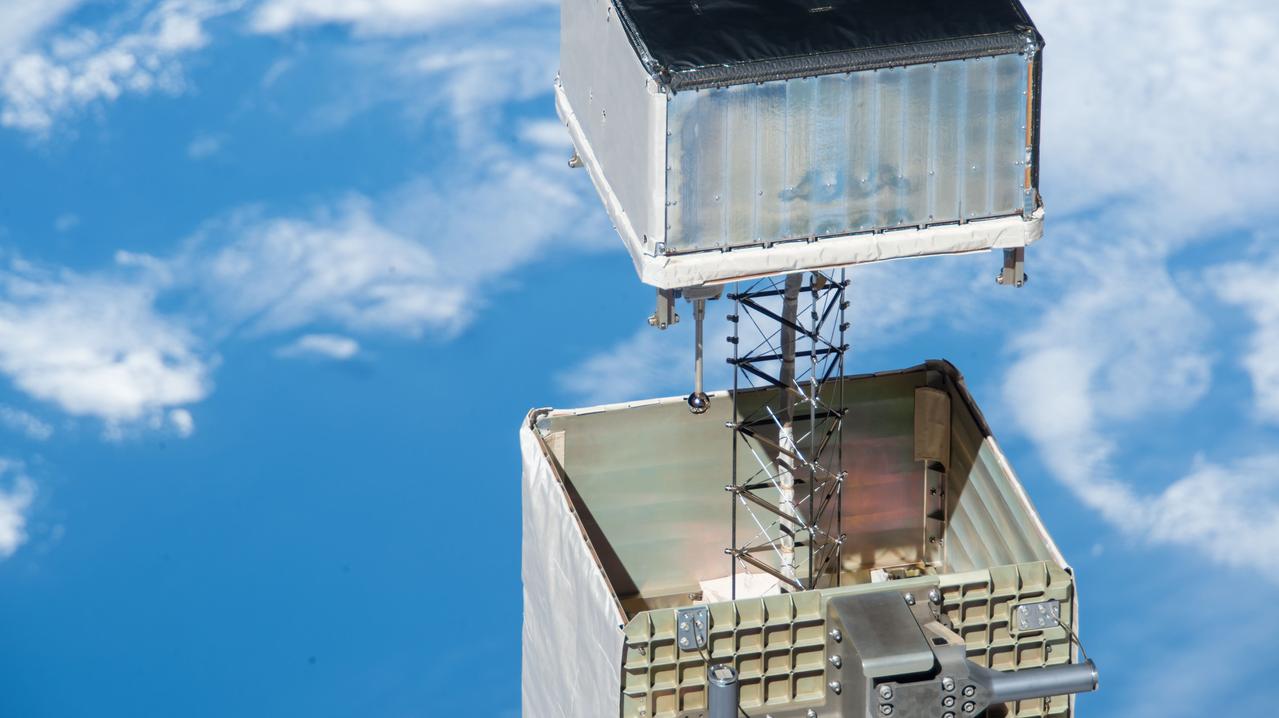

iss057e080455 (11/12/2018) --- A view of the Space Environment Data Acquisition Equipment - Attached Payload (SEDA-AP) located on the Japanese Experiment Module - Exposed Facility (JEM-EF). The SEDA-AP investigation consists of eight small instruments designed to measure the space environment. Five radiation and particle monitors, an electronic device performance monitor, a micro-particle capture , and a space environment exposure device will provide data to help researchers characterize the environment around space vehicles in low-Earth orbit, which will be used to develop shielding to ensure future spacecraft are safe.

Amelia Quan, the mechanical integration lead for NASA's SPHEREx mission, is seen with a V-groove radiator, a piece of hardware that will help keep the space telescope cold, at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in May 2023. Short for Specto-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other, imaging the entire sky and gathering information about millions of galaxies. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, the history of galaxy evolution, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. SPHEREx will detect infrared light, a range of wavelengths longer than the visible light human eyes can see. Infrared light is also sometimes called heat radiation because all warm objects emit it. Even the telescope itself can create infrared light, which would interfere with its detectors. So the telescope has to be kept cold – below minus 350 degrees Fahrenheit (about minus 210 degrees Celsius). The V-groove radiator consists of three conical mirrors, each like an upside-down umbrella, stacked atop one another. They sit below the photon shields, and each is composed of a series of wedges that redirect infrared light so it bounces through the gaps between the shields and out into space. This removes heat carried through the supports from the room temperature spacecraft bus that contains the spacecraft computer and electronics. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25786
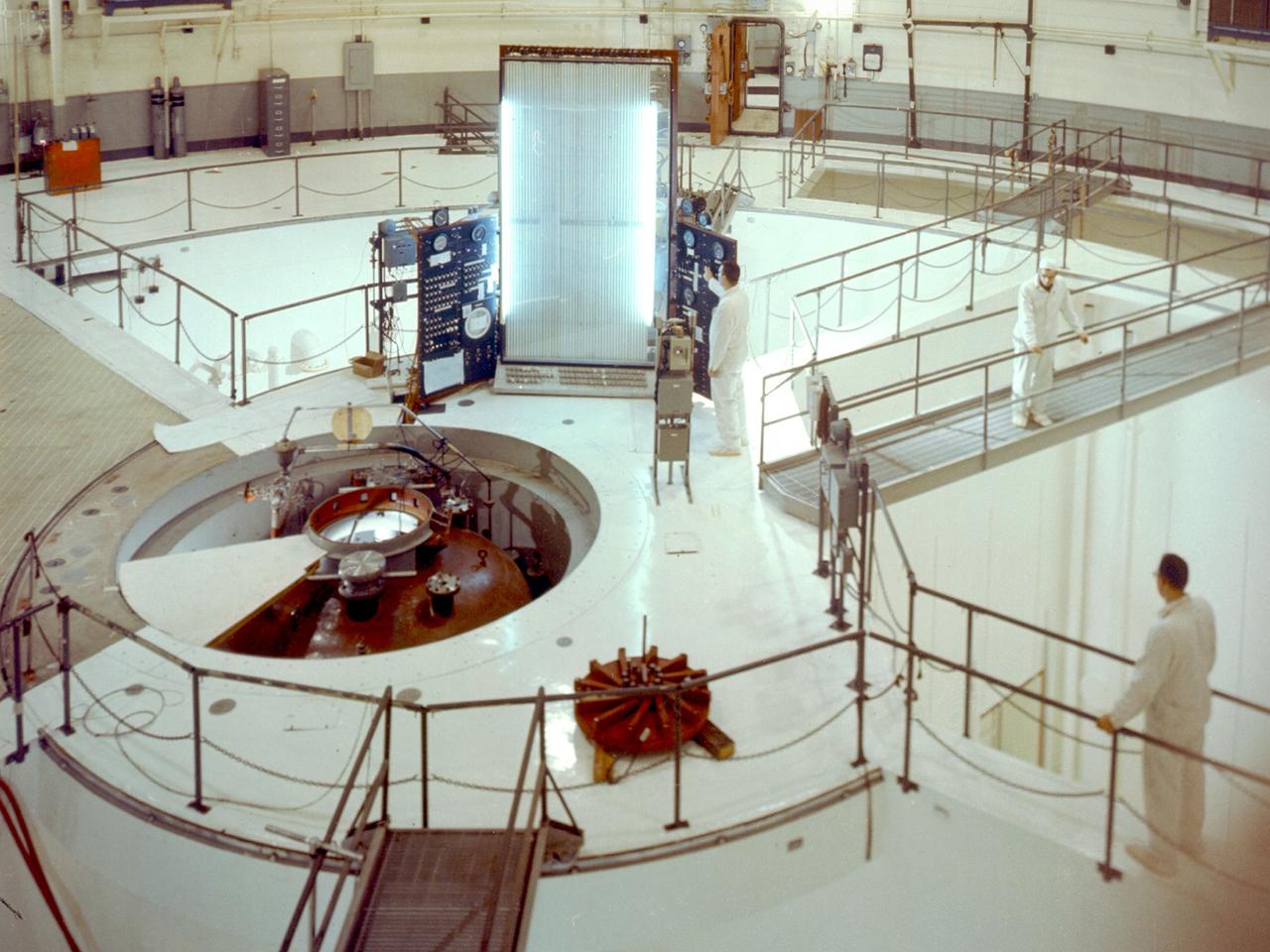

A view inside the 55-foot high containment vessel of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Plum Brook Reactor Facility in Sandusky, Ohio. The 60-megawatt test reactor went critical for the first time in 1961 and began its full-power research operations in 1963. From 1961 to 1973, this reactor performed some of the nation’s most advanced nuclear research. The reactor was designed to determine the behavior of metals and other materials after long durations of irradiation. The materials would be used to construct a nuclear-powered rocket. The reactor core, where the chain reaction occurred, sat at the bottom of the tubular pressure vessel, seen here at the center of the shielding pool. The core contained fuel rods with uranium isotopes. A cooling system was needed to reduce the heat levels during the reaction. A neutron-impervious reflector was also employed to send many of the neutrons back to the core. The Plum Brook Reactor Facility was constructed from high-density concrete and steel to prevent the excess neutrons from escaping the facility, but the water in the pool shielded most of the radiation. The water, found in three of the four quadrants served as a reflector, moderator, and coolant. In this photograph, the three 20-ton protective shrapnel shields and hatch have been removed from the top of the pressure tank revealing the reactor tank. An overhead crane could be manipulated to reach any section of this room. It was used to remove the shrapnel shields and transfer equipment.
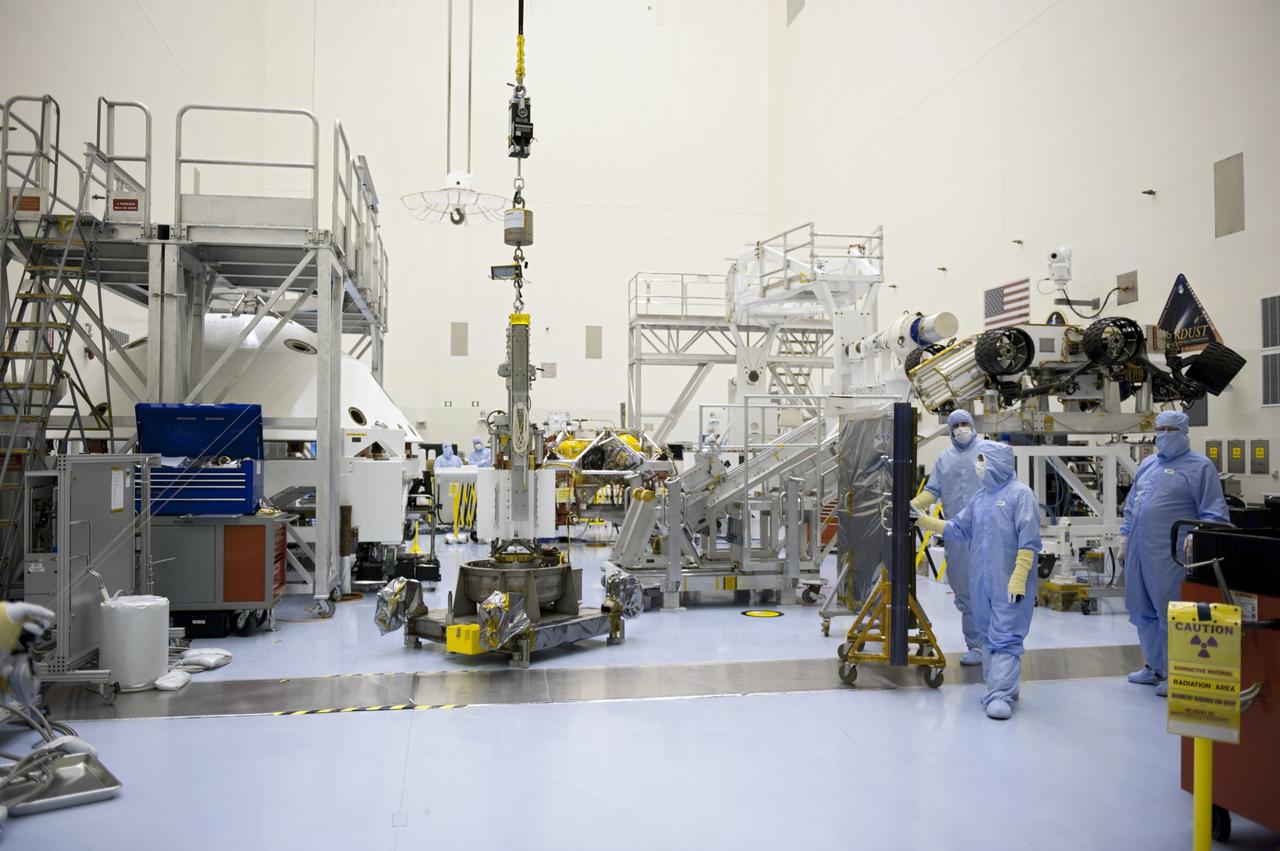

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, still connected to the turning fixture, rests on a support base following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. A mobile plexiglass radiation shield is in place between the MMRTG and the spacecraft technicians, at right, to help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
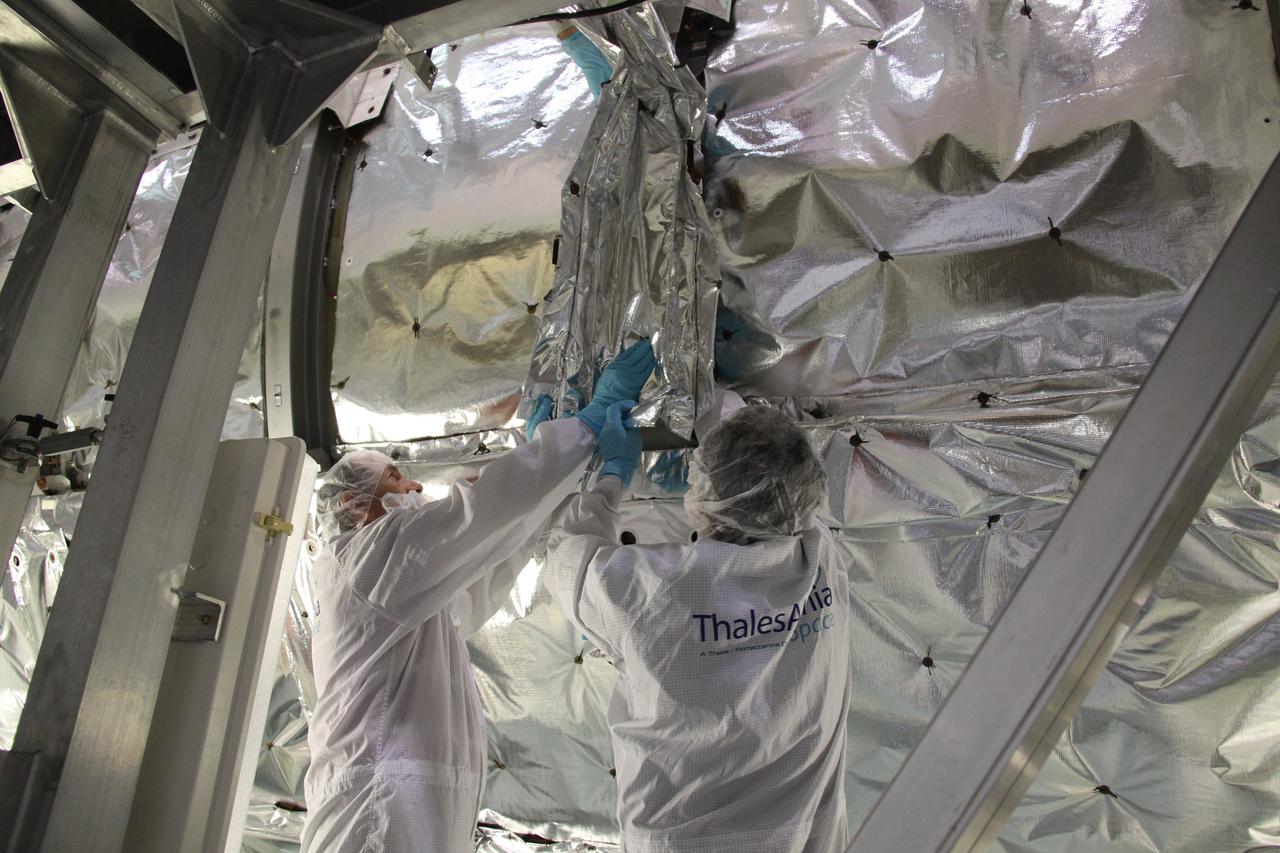

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Meteoroids and Debris Protective Shield of the Permanent Multipurpose Module, or PMM. The reflective silver mesh is Mylar, which is aluminized to protect hardware aboard the International Space Station from solar thermal radiation. The Leonardo multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, is being modified to become the PMM that will carry supplies and critical spare parts to the station aboard space shuttle Discovery’s STS-133 mission. Discovery, targeted to launch Nov. 1, will leave the module behind so it can be used for microgravity experiments in fluid physics, materials science, biology and biotechnology. Photo credit: NASA_Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician inspects multi-layer insulation before it is installed on the Meteoroids and Debris Protective Shield of the Permanent Multipurpose Module, or PMM. The reflective silver mesh is Mylar, which is aluminized to protect hardware aboard the International Space Station from solar thermal radiation. The Leonardo multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, is being modified to become the PMM that will carry supplies and critical spare parts to the station aboard space shuttle Discovery’s STS-133 mission. Discovery, targeted to launch Nov. 1, will leave the module behind so it can be used for microgravity experiments in fluid physics, materials science, biology and biotechnology. Photo credit: NASA_Troy Cryder

Team Lore listens in the audience as NASA Administrator Charles Bolden speaks at the event to announce the winner of the Exploration Design Challenge. Team Lore was one of the semi-finalists in the challenge. The goal of the Exploration Design Challenge is for students to research and design ways to protect astronauts from space radiation. The winner of the challenge was announced on April 25, 2014 at the USA Science and Engineering Festival at the Washington Convention Center in Washington, DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Department of Energy workers position mobile plexiglass radiation shields around the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission upon its arrival in the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The shields are designed to minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The MMRTG is enclosed in a mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," which protects it during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG is returning to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is position behind mobile plexiglass radiation shields in the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG was returned to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The generator will remain in the RTGF until is moved to the pad for integration on the rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted from around the MMRTG. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The cage is being removed following the return of the MMRTG to the RTGF from a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The workers at right are observing the operation from behind a mobile plexiglass radiation shield to minimize their radiation exposure. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Department of Energy employee positions the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," on the support base of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The mobile plexiglass radiation shields, in the foreground at right, helps minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Transport of the MMRTG to the RTG storage facility follows the completion of the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
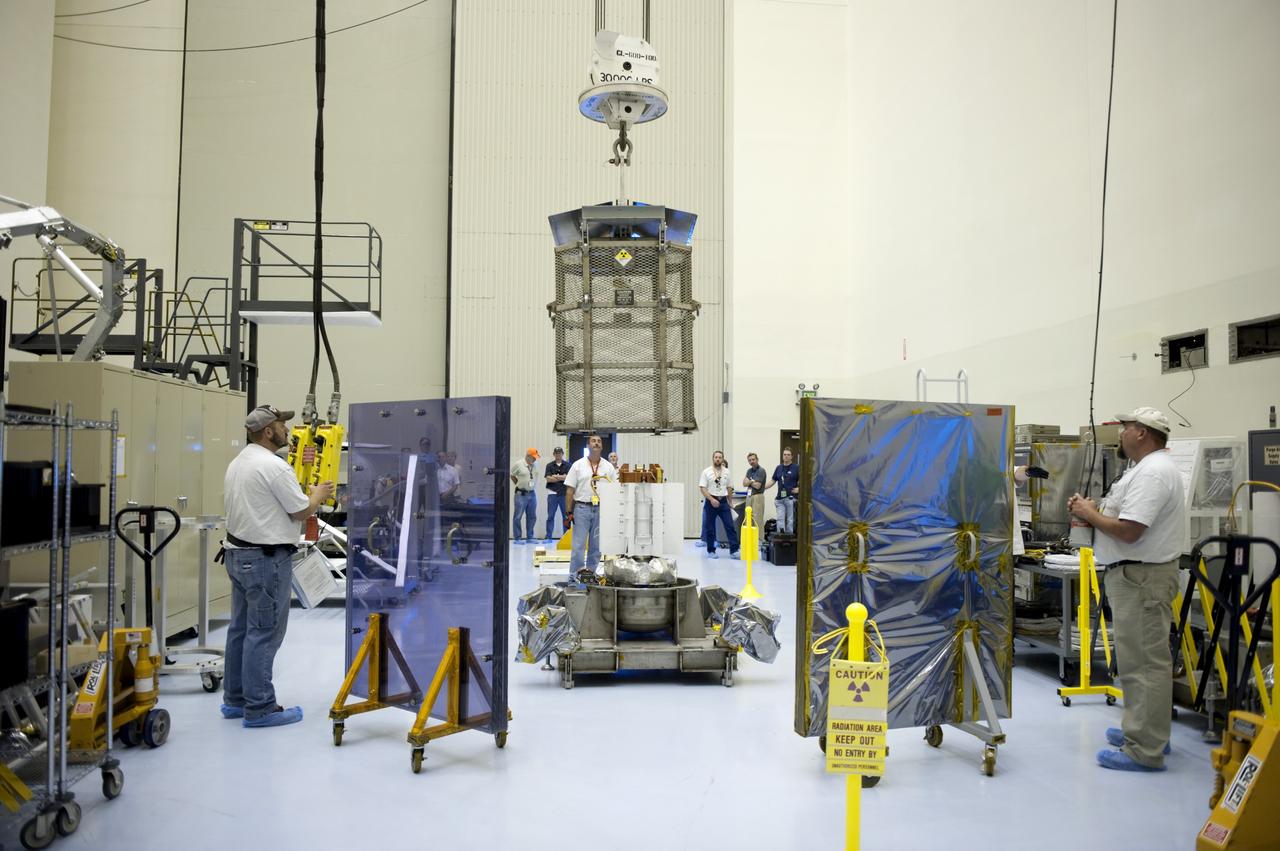

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Department of Energy employees lower the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," toward the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The employees are standing behind mobile plexiglass radiation shields to help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Transport of the MMRTG to the RTG storage facility follows the completion of the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
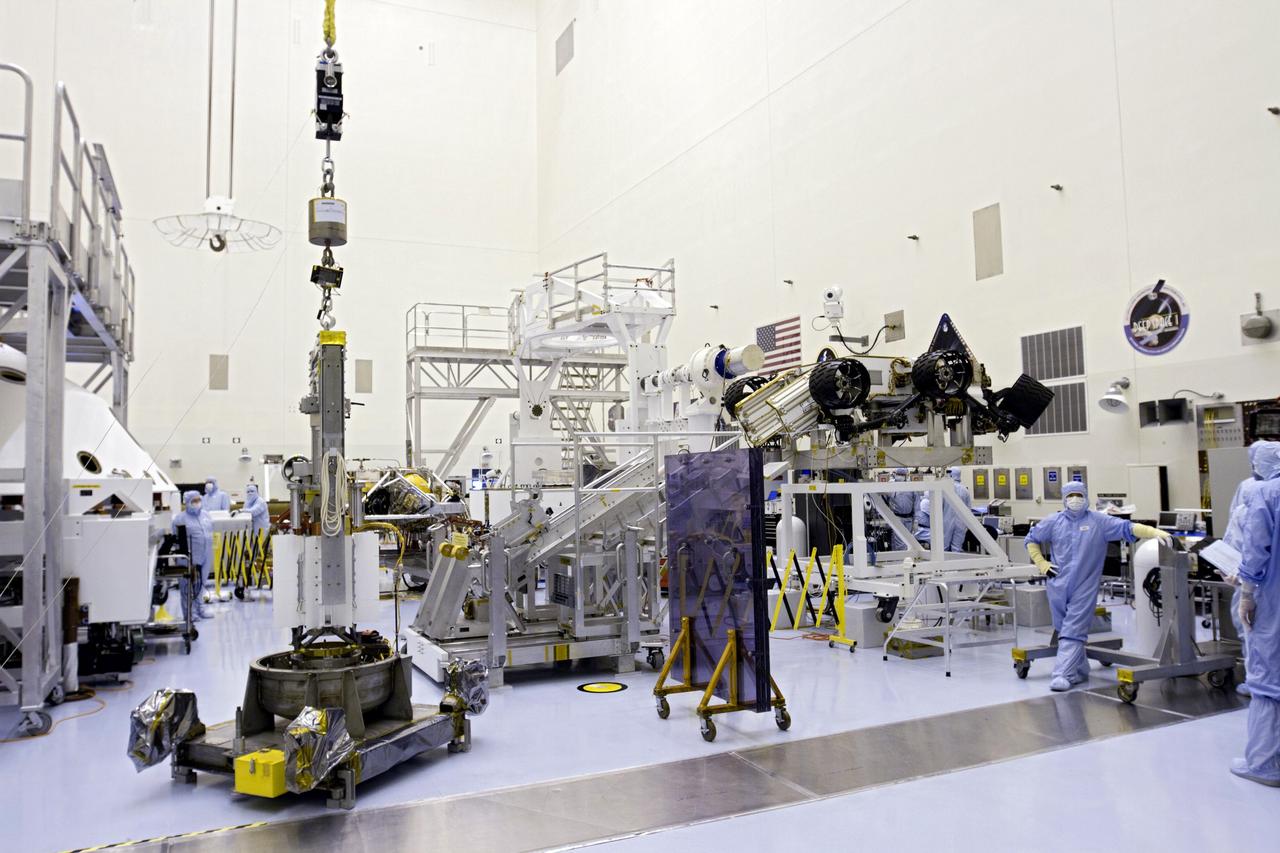

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are under way for a crane to lift the turning fixture connected to the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission from its support base. Between the MMRTG and the spacecraft technicians at right is a mobile plexiglass radiation shield to help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The turning fixture will lift and lower the MMRTG onto the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on Curiosity for a fit check. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
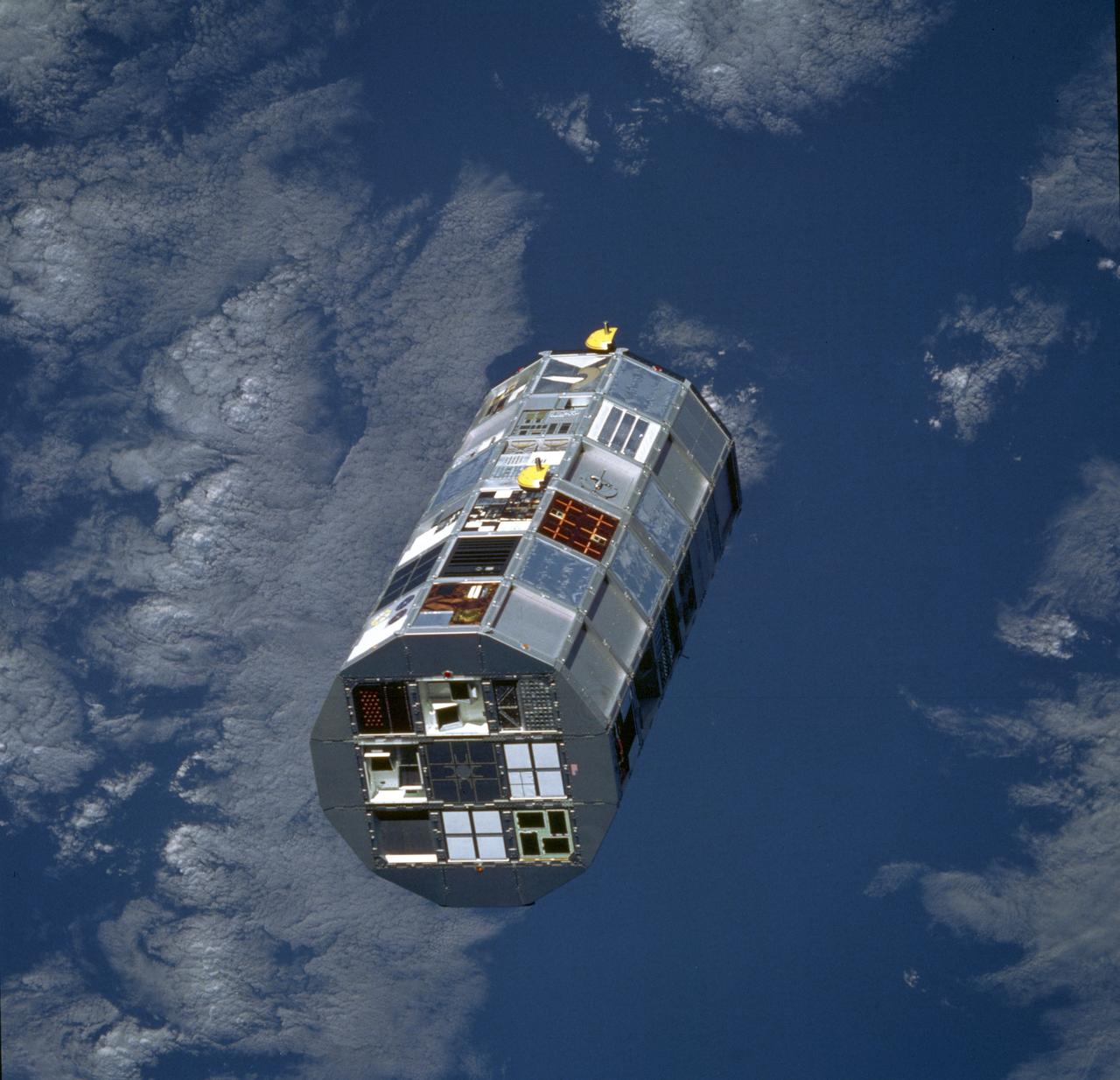

The Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) was designed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) to test the performance of spacecraft materials, components, and systems that have been exposed to the environment of micrometeoroids and space debris for an extended period of time. The LDEF proved invaluable to the development of future spacecraft and the International Space Station (ISS). The LDEF carried 57 science and technology experiments, the work of more than 200 investigators. MSFC`s experiments included: Trapped Proton Energy Determination to determine protons trapped in the Earth's magnetic field and the impact of radiation particles; Linear Energy Transfer Spectrum Measurement Experiment which measures the linear energy transfer spectrum behind different shielding configurations; Atomic oxygen-Simulated Out-gassing, an experiment that exposes thermal control surfaces to atomic oxygen to measure the damaging out-gassed products; Thermal Control Surfaces Experiment to determine the effects of the near-Earth orbital environment and the shuttle induced environment on spacecraft thermal control surfaces; Transverse Flat-Plate Heat Pipe Experiment, to evaluate the zero-gravity performance of a number of transverse flat plate heat pipe modules and their ability to transport large quantities of heat; Solar Array Materials Passive LDEF Experiment to examine the effects of space on mechanical, electrical, and optical properties of lightweight solar array materials; and the Effects of Solar Radiation on Glasses. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger's STS-41C mission April 6, 1984, the LDEF remained in orbit for five years until January 1990 when it was retrieved by the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia STS-32 mission and brought back to Earth for close examination and analysis.
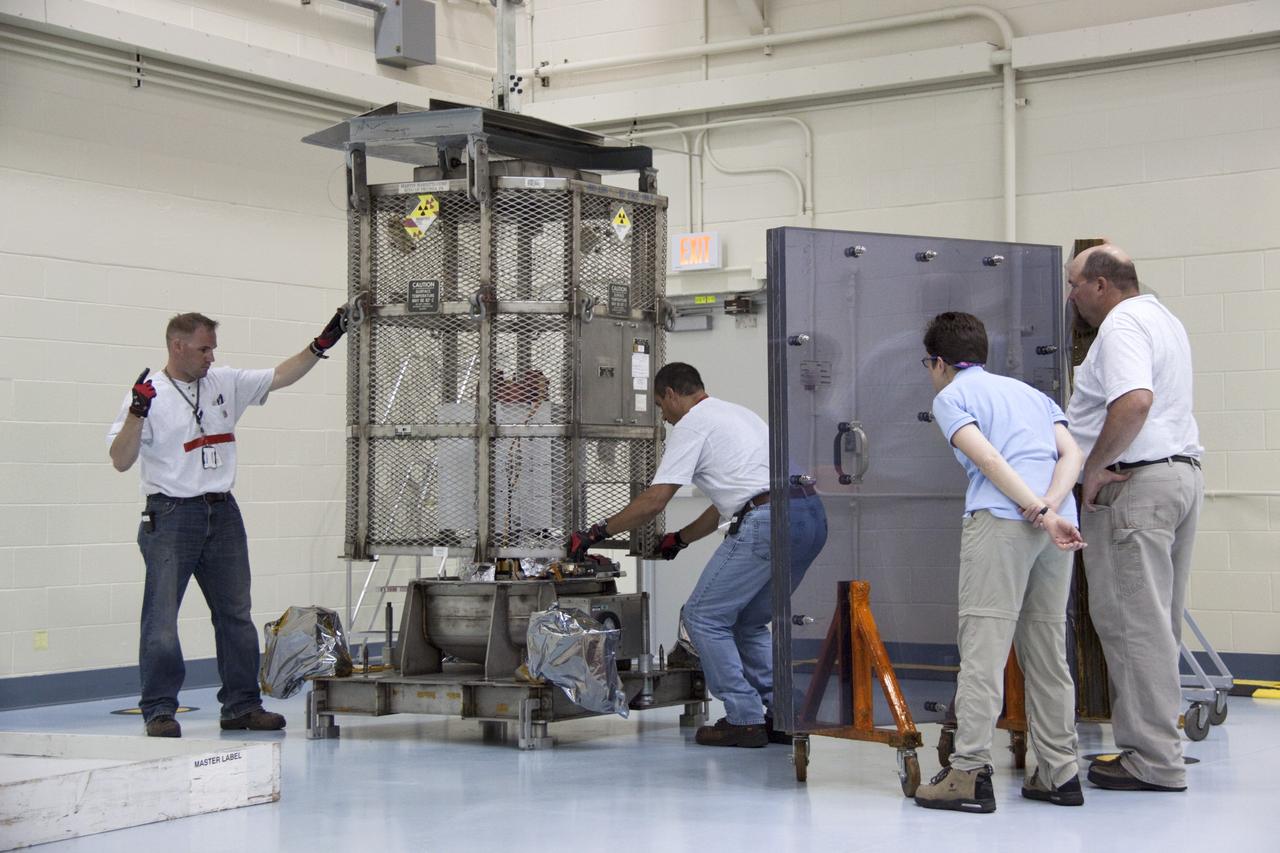

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Department of Energy workers guide the mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission as it is lifted by a crane. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The cage is being removed from around the MMRTG following it return to the RTGF from a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The workers at right are observing the operation from behind a mobile plexiglass radiation shield to minimize their radiation exposure. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
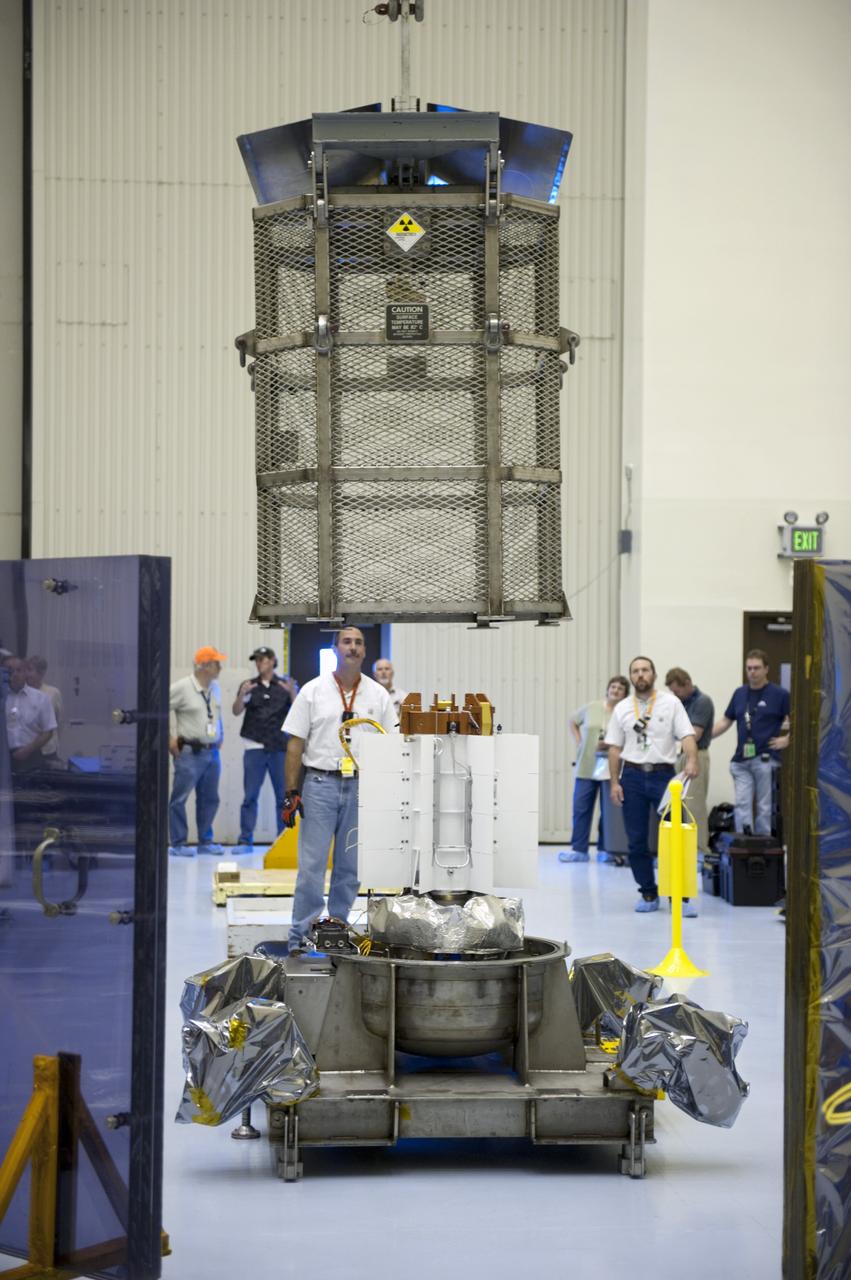

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Department of Energy employees lower the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," toward the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The mobile plexiglass radiation shields in the foreground help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Transport of the MMRTG to the RTG storage facility follows the completion of the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
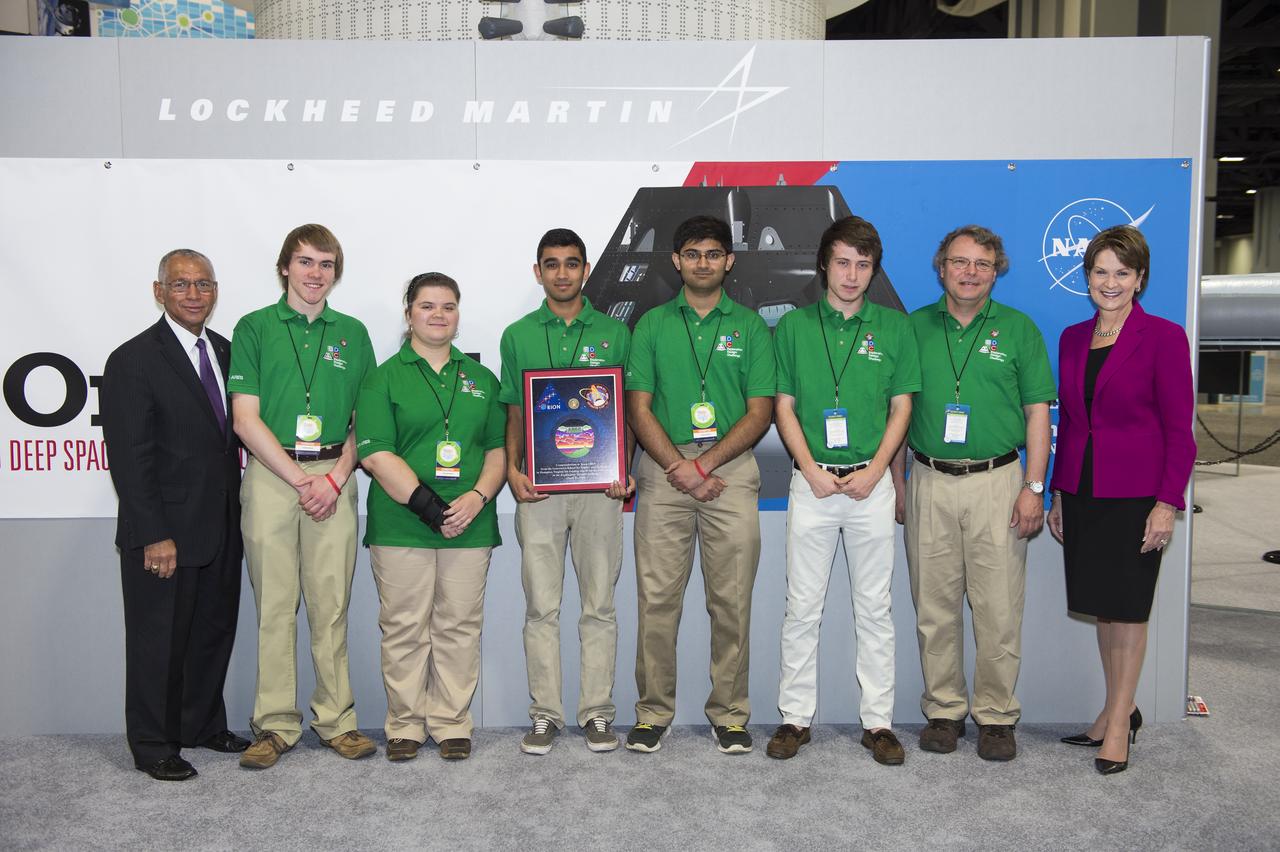

Team ARES poses with NASA Administrator Charles Bolden and Lockheed Martin CEO, Marillyn Hewson. Team ARES was the winner of the Exploration Design Challenge. The goal of the Exploration Design Challenge is for students to research and design ways to protect astronauts from space radiation. The winning team was announced on April 25, 2014 at the USA Science and Engineering Festival at the Washington Convention Center in Washington, DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
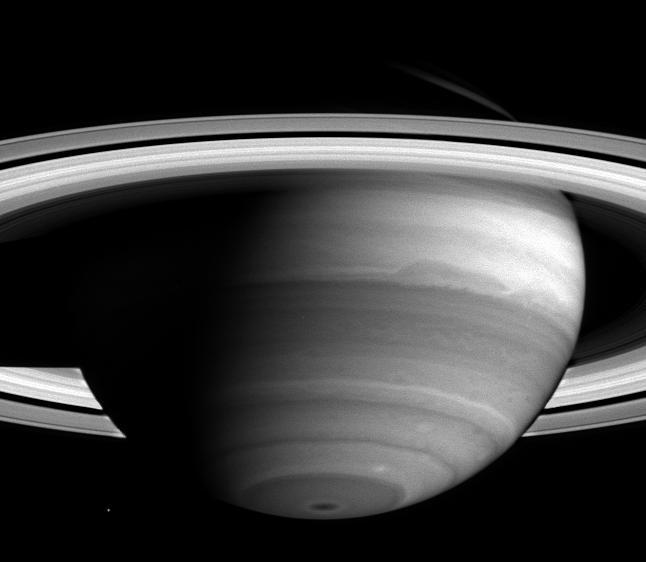

As Cassini nears its rendezvous with Saturn, new detail in the banded clouds of the planet's atmosphere are becoming visible. Cassini began the journey to the ringed world of Saturn nearly seven years ago and is now less than two months away from orbit insertion on June 30. Cassini’s narrow-angle camera took this image on April 16, 2004, when the spacecraft was 38.5 million kilometers (23.9 million miles) from Saturn. Dark regions are generally areas free of high clouds, and bright areas are places with high, thick clouds which shield the view of the darker areas below. A dark spot is visible at the south pole, which is remarkable to scientists because it is so small and centered. The spot could be affected by Saturn's magnetic field, which is nearly aligned with the planet's rotation axis, unlike the magnetic fields of Jupiter and Earth. From south to north, other notable features are the two white spots just above the dark spot toward the right, and the large dark oblong-shaped feature that extends across the middle. The darker band beneath the oblong-shaped feature has begun to show a lacy pattern of lighter-colored, high altitude clouds, indicative of turbulent atmospheric conditions. The cloud bands move at different speeds, and their irregularities may be due to either the different motions between them or to disturbances below the visible cloud layer. Such disturbances might be powered by the planet's internal heat; Saturn radiates more energy than it receives from the Sun. The moon Mimas (396 kilometers, 245 miles across) is visible to the left of the south pole. Saturn currently has 31 known moons. Since launch, 13 new moons have been discovered by ground-based telescopes. Cassini will get a closer look and may discover new moons, perhaps embedded within the planet’s magnificent rings. This image was taken using a filter sensitive to light near 727 nanometers, one of the near-infrared absorption bands of methane gas, which is one of the ingredients in Saturn's atmosphere. The image scale is approximately 231 kilometers (144 miles) per pixel. Contrast has been enhanced to aid visibility of features in the atmosphere. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05391
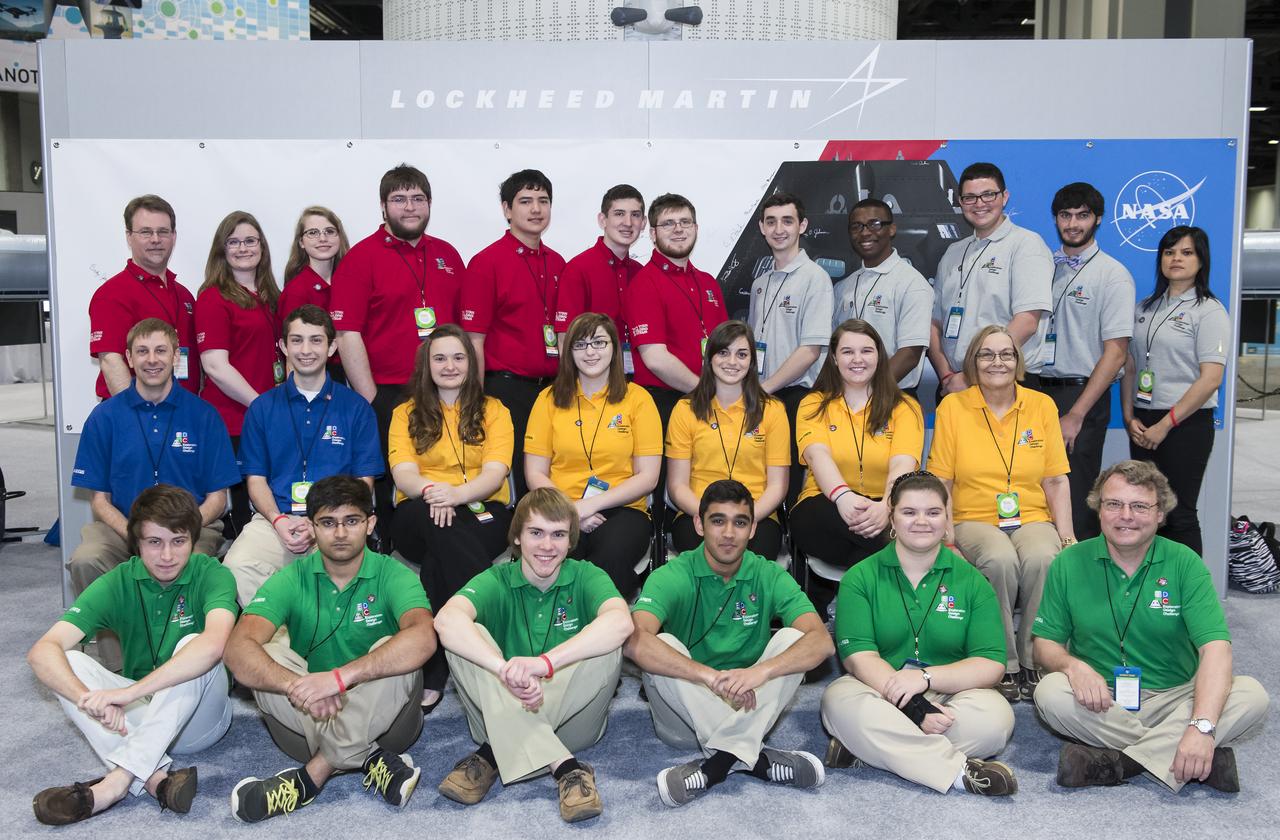

Pictured are all Semi-finalist teams in the Exploration Design Challenge. NASA Administrator, Charles Bolden and Lockheed Martin CEO, Marillyn Hewson announced the winner of the Exploration Design Challenge at the USA Science and Engineering Festival on April 25, 2014. The goal of the challenge was for students to research and design ways to protect astronauts from space radiation. The winning team's design will be built and flown aboard the Orion/EFT-1. The USA Science and Engineering Festival is taking place at the Washington Convention Center in Washington, DC on April 26 and 27, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)