
NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. Through a partnership with Jacobs Technology, Inc., teams have constructed a bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – as an eco-friendly way to filter zinc out of rainwater runoff. Photographed on Sept. 29, 2020, at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower, the bio-filter catches water that runs off of this location’s galvanized roof, which contains a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the Indian River Lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.
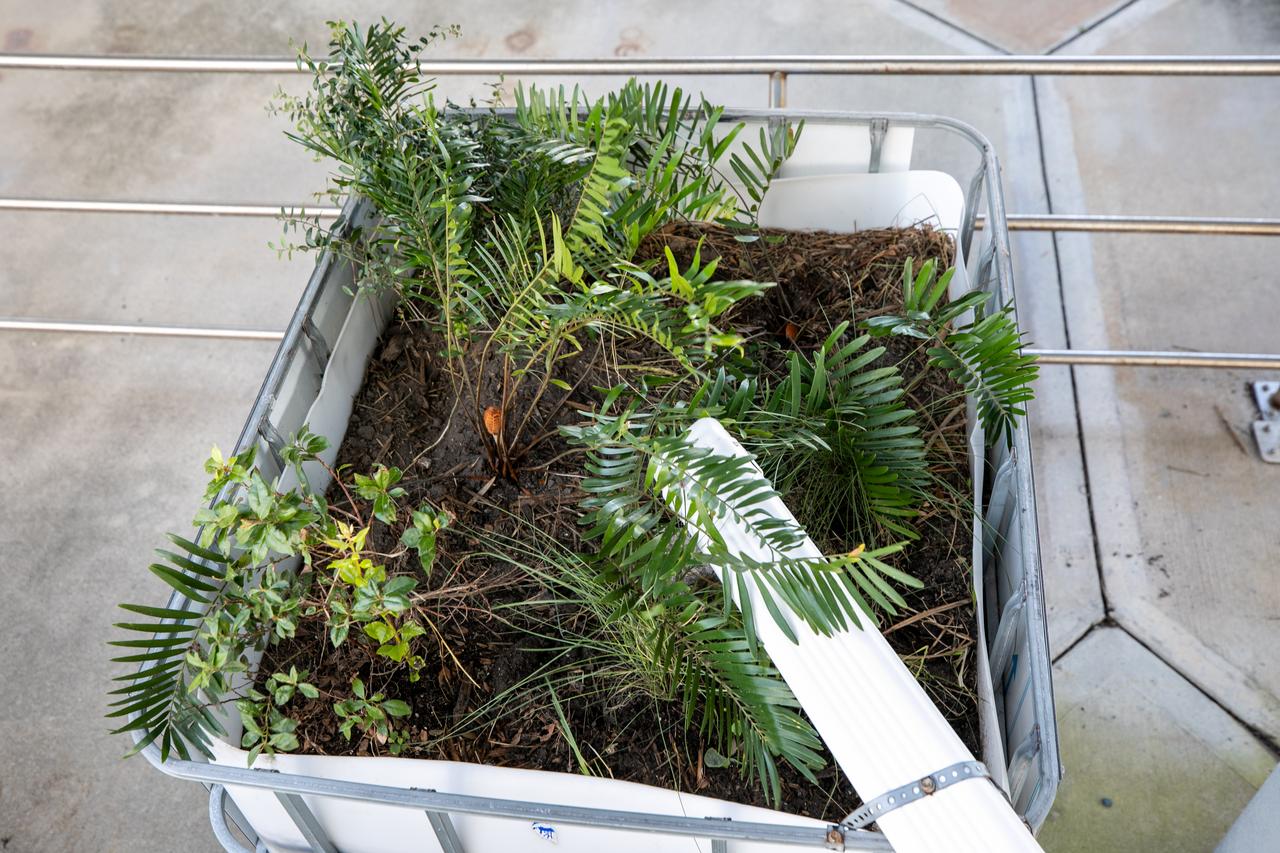

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. Through a partnership with Jacobs Technology, Inc., teams have constructed a bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – as an eco-friendly way to filter zinc out of rainwater runoff. Photographed on Sept. 29, 2020, at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower, the bio-filter catches water that runs off of this location’s galvanized roof, which contains a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the Indian River Lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.
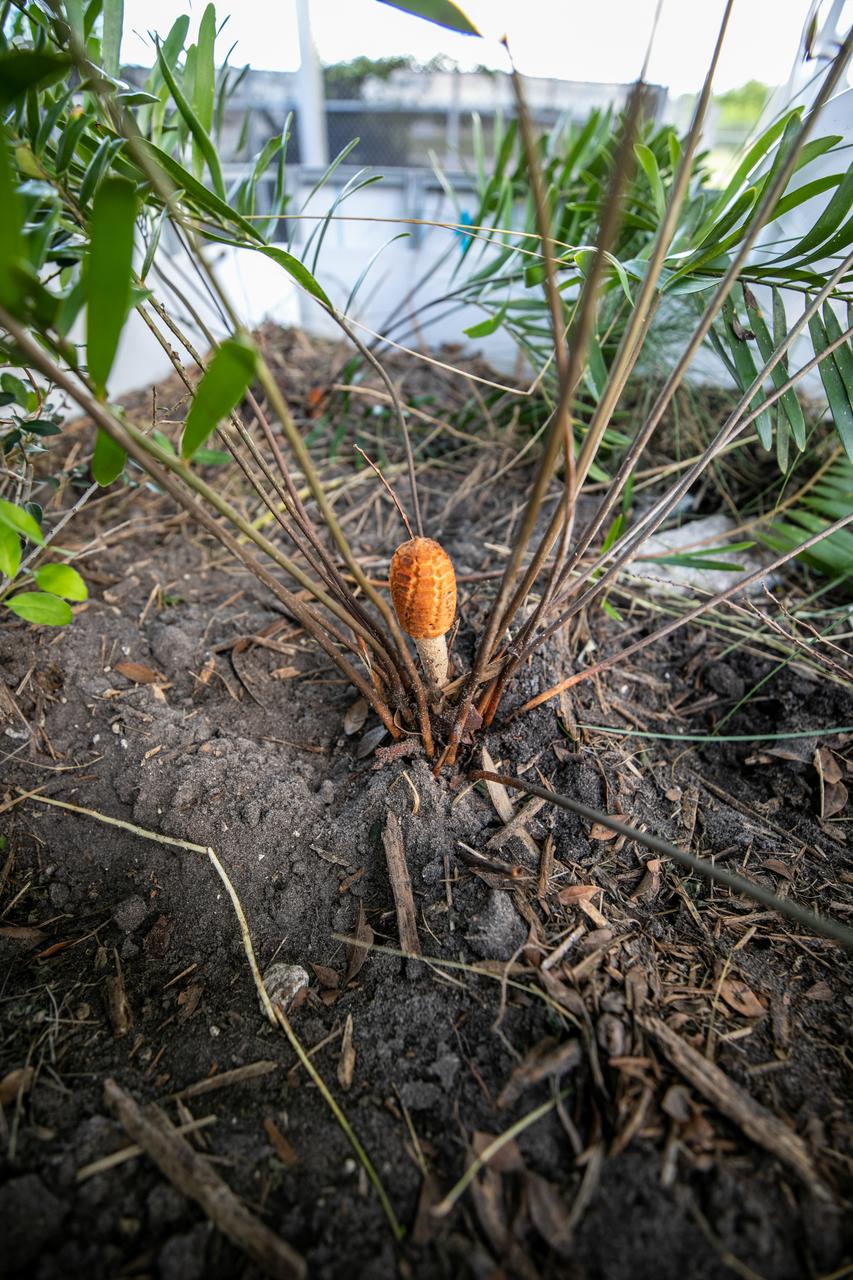

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. An up-close view of the plants that make up a bio-filter constructed by teams with Kennedy and Jacobs Technology, Inc. is shown on Sept. 29, 2020. The bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – is used to catch and filter zinc out of rainwater that runs off of the roof at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower. Many facilities at Kennedy have galvanized roofs, which contain a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion but can have serious effects on fish and other aquatic life if it runs into the Indian River Lagoon. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.
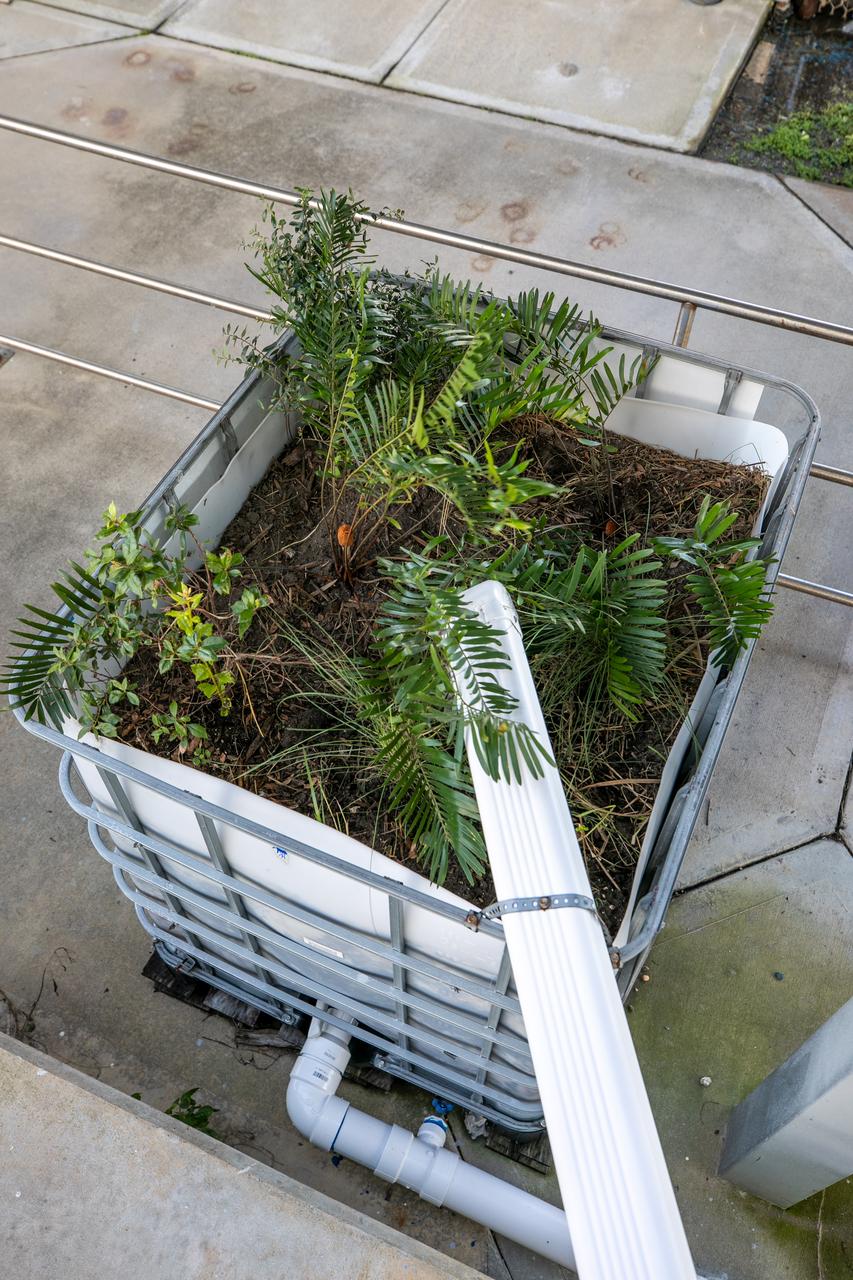

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. Through a partnership with Jacobs Technology, Inc., teams have constructed a bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – as an eco-friendly way to filter zinc out of rainwater runoff. Photographed on Sept. 29, 2020, at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower, the bio-filter catches water that runs off of this location’s galvanized roof, which contains a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the Indian River Lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.
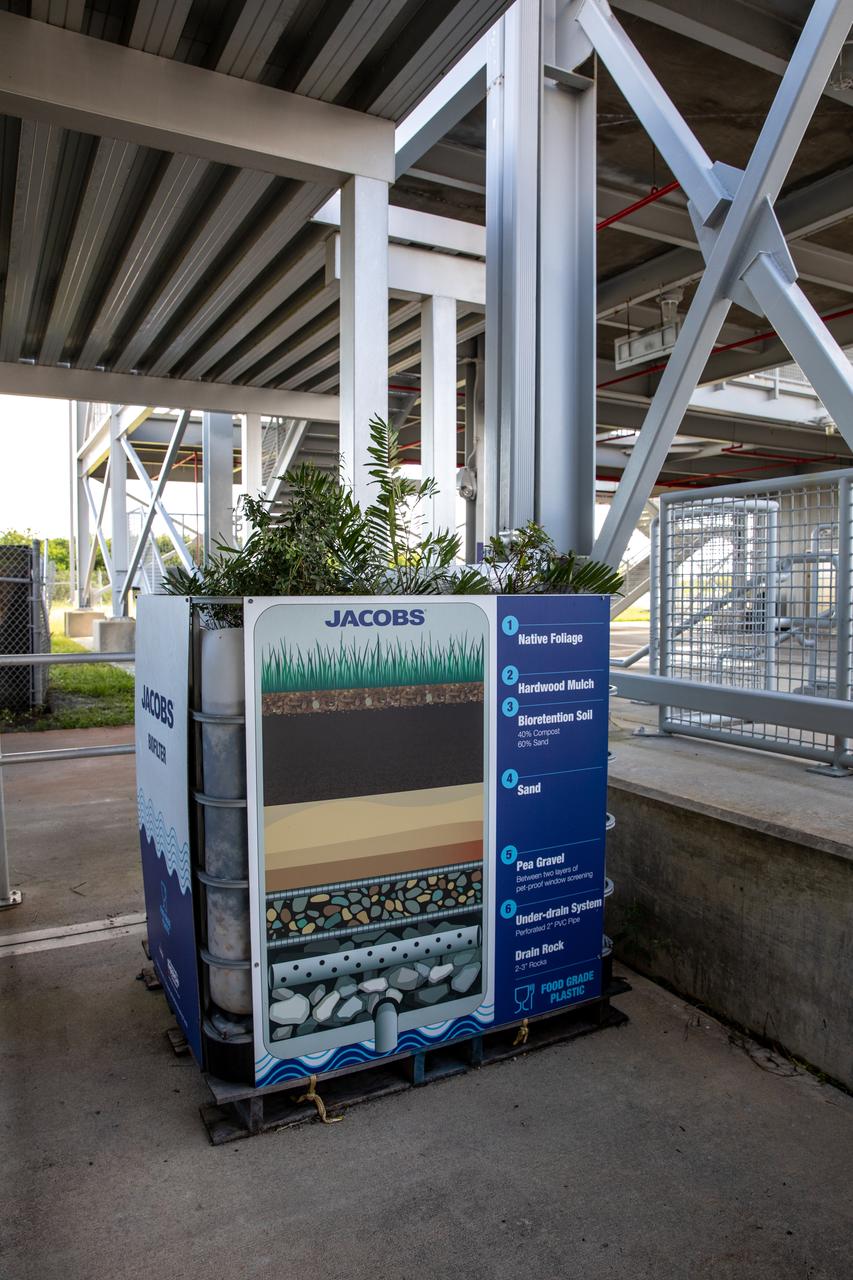

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. Through a partnership with Jacobs Technology, Inc., teams have constructed a bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – as an eco-friendly way to filter zinc out of rainwater runoff. Photographed on Sept. 29, 2020, at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower, the bio-filter catches water that runs off of this location’s galvanized roof, which contains a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the Indian River Lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.
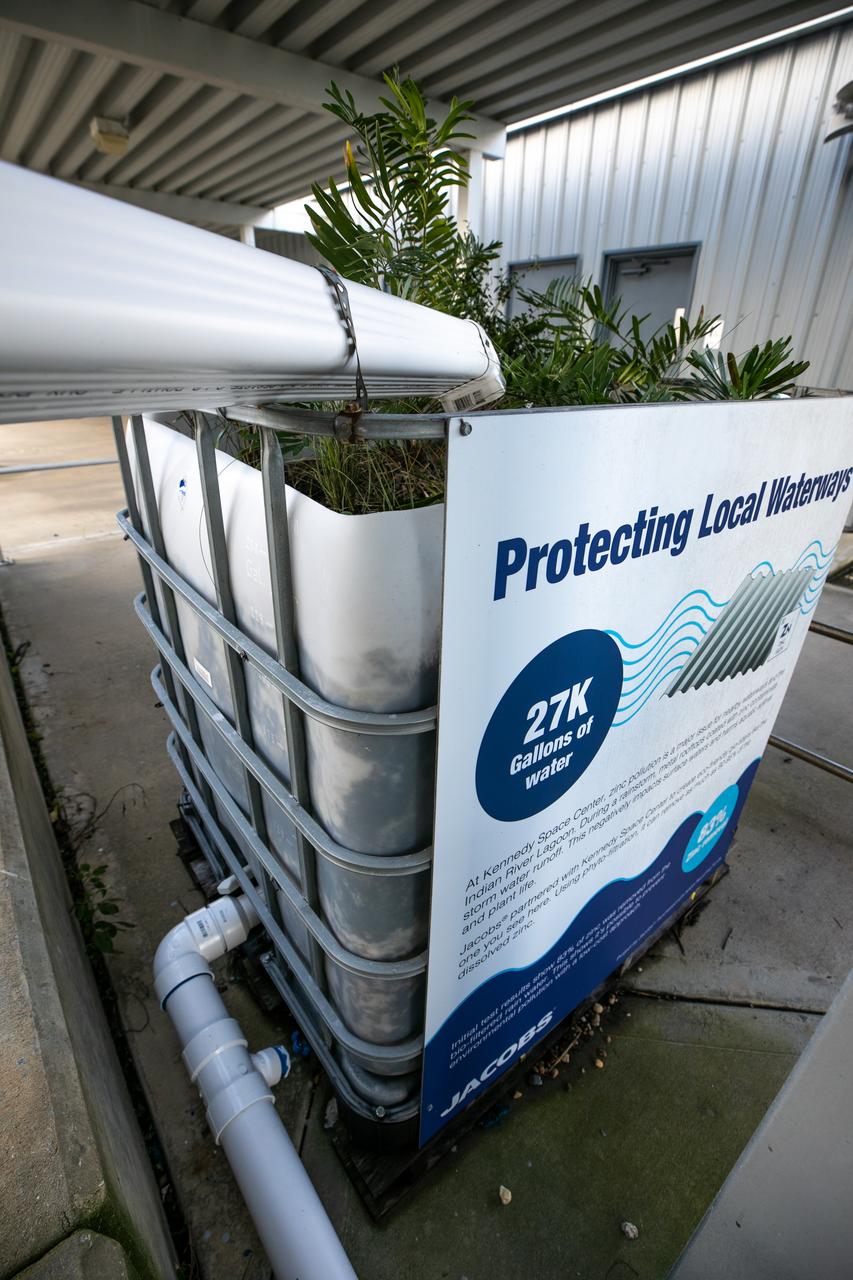

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. Through a partnership with Jacobs Technology, Inc., teams have constructed a bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – as an eco-friendly way to filter zinc out of rainwater runoff. Photographed on Sept. 29, 2020, at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower, the bio-filter catches water that runs off of this location’s galvanized roof, which contains a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the Indian River Lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.
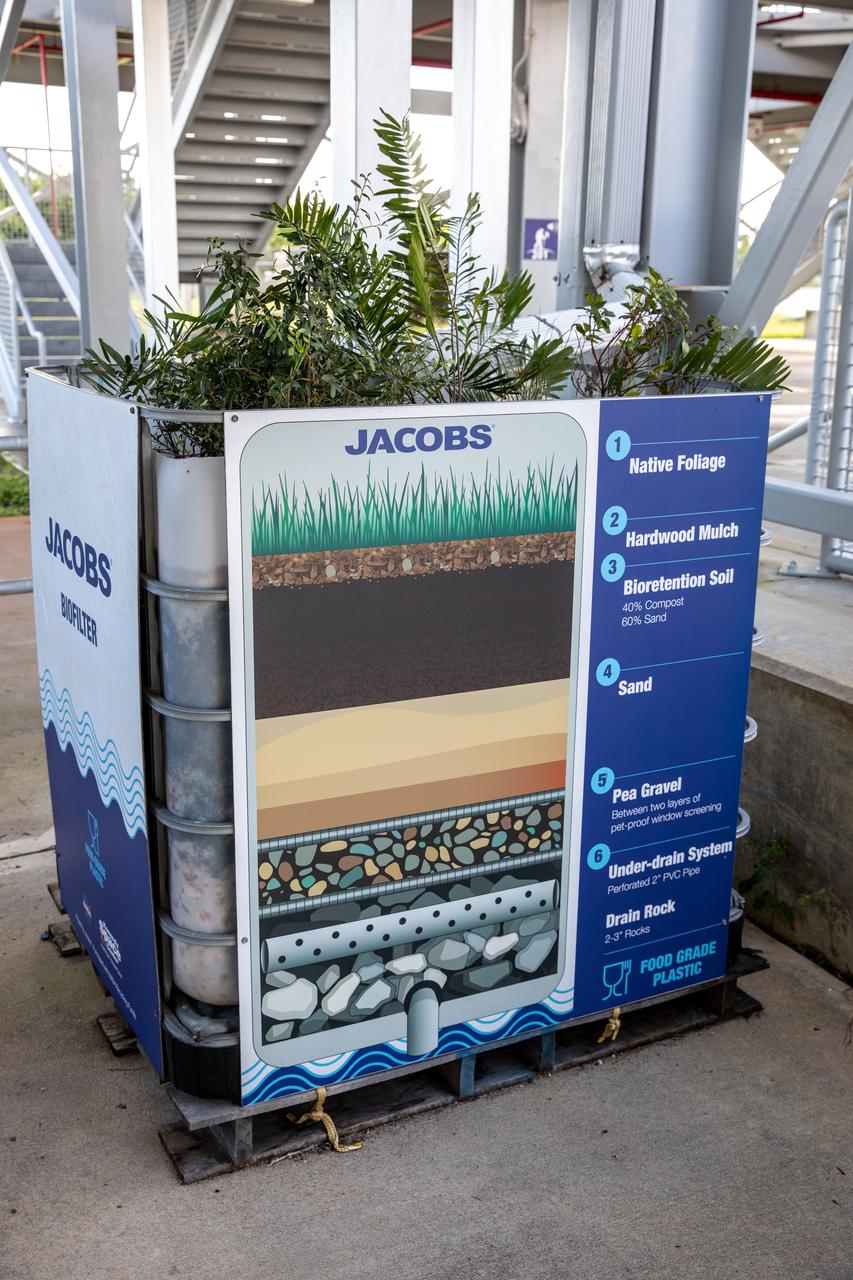

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. Through a partnership with Jacobs Technology, Inc., teams have constructed a bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – as an eco-friendly way to filter zinc out of rainwater runoff. Photographed on Sept. 29, 2020, at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower, the bio-filter catches water that runs off of this location’s galvanized roof, which contains a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the Indian River Lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.
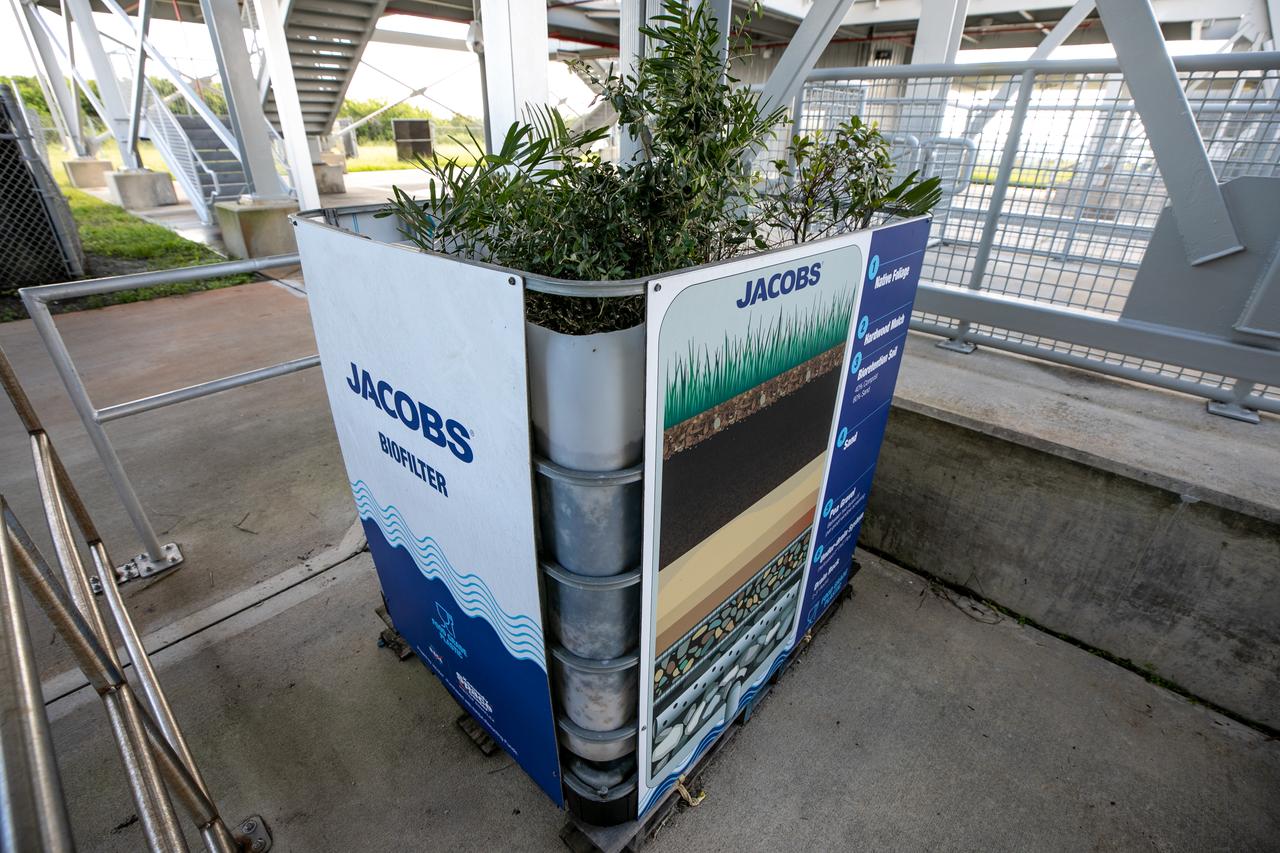

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. Through a partnership with Jacobs Technology, Inc., teams have constructed a bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – as an eco-friendly way to filter zinc out of rainwater runoff. Photographed on Sept. 29, 2020, at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower, the bio-filter catches water that runs off of this location’s galvanized roof, which contains a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the Indian River Lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.
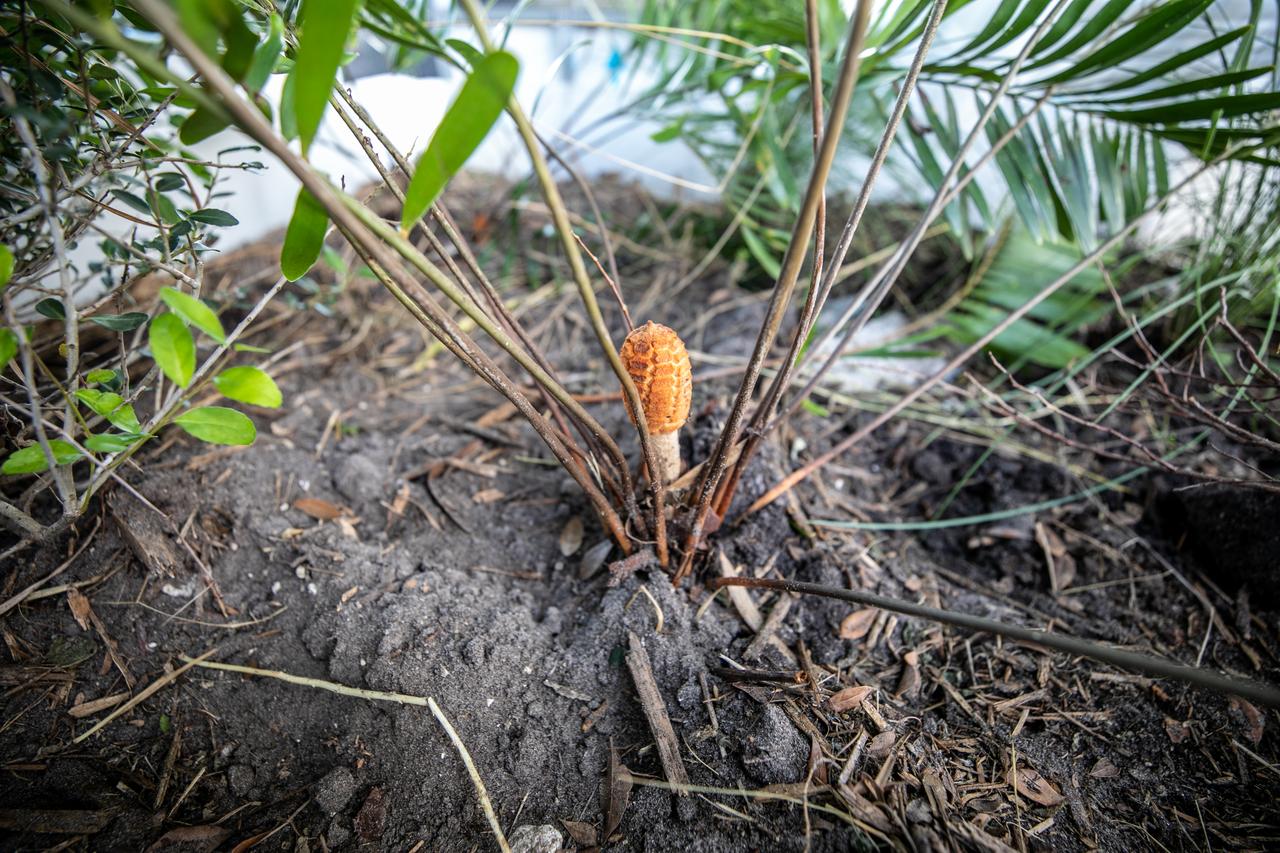

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. An up-close view of the plants that make up a bio-filter constructed by teams with Kennedy and Jacobs Technology, Inc. is shown on Sept. 29, 2020. The bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – is used to catch and filter zinc out of rainwater that runs off of the roof at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower. Many facilities at Kennedy have galvanized roofs, which contain a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion but can have serious effects on fish and other aquatic life if it runs into the Indian River Lagoon. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s unrivaled dedication to the environment is highlighted through a variety of environmental programs and projects. Through a partnership with Jacobs Technology, Inc., teams have constructed a bio-filter – made of layered rock, soil, and native plants – as an eco-friendly way to filter zinc out of rainwater runoff. Photographed on Sept. 29, 2020, at the Florida spaceport’s Launch Complex 39 observation tower, the bio-filter catches water that runs off of this location’s galvanized roof, which contains a coating of zinc to help protect the metal from rust or corrosion. The plants in the bio-filter bind to the zinc so that when the water comes out of the bottom, it’s clean and safe to go into the Indian River Lagoon – its waterline located about 20 to 30 feet away.
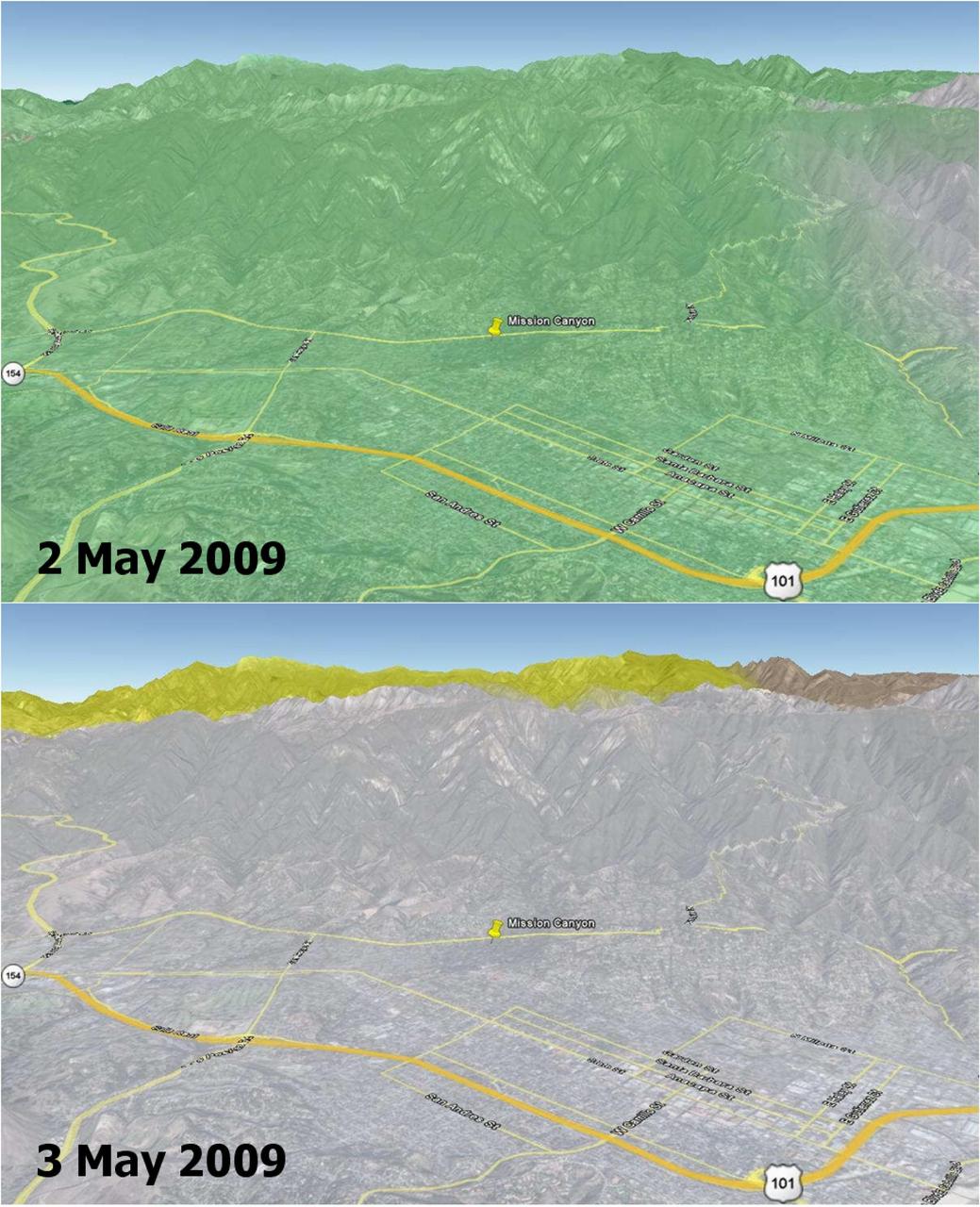
Wildfires are a recurring natural hazard faced by Californians. In Santa Barbara County, a wildfire, called the Jesusita fire, ignited on May 5, 2009 in the Cathedral Peak area northwest of Mission Canyon. As of midday May 8, the fire, which was 10-percent contained, had scorched 3,500 acres, damaged or destroyed 75 structures, and had forced the evacuation of tens of thousands of residents. This image shows soil moisture change in the top soil layer (2-inches deep) on 2 and 3 May 2009, as measured by the NASA QuikSCAT satellite scatterometer (radar). Rainwater increased the amount of moisture in the soil by a moderate 4 percent (represented by the green color) on May 2, which rapidly dried up on the next day (0 percent, as depicted by the grey color on May 3). Son Nghiem of JPL is leading a science team to develop wildfire applications using QuikScat data. “Information critical to assessing the conditions leading to wildfires can be obtained from NASA’s SeaWinds scatterometer, a stable and accurate radar aboard the QuikScat satellite,” says Dr. Son Nghiem, a JPL scientist in remote sensing. This is accomplished by using QuikScat data to map moisture changes in the topsoil. As such, QuikScat can detect rainwater that actually reaches the land surface and accumulates on it, rather than raindrops in the air. While rain radars may detect a significant rain rate, rainwater may evaporate in part before reaching the surface. For example, in the case of dry thunderstorm (known as virga), raindrops disappear on the way down, leaving the land dry, while the associated lightning ignites fires. For the case of the current fire in Santa Barbara, QuikScat detected a moderate increase of 4 percent in soil moisture on May 2, while rain radar data seemed to indicate a significant and extensive rain. The next day, QuikScat revealed that whatever rainwater that had accumulated earlier quickly dried up over the whole area. The maximum temperature in Santa Barbara approached 90 degrees Fahrenheit and broke the record set in 1984. An important characteristic of QuikScat measurements is that they represent the average conditions over the whole area, rather than some disparate data collected at a few localized points. The rapid dry-up in Santa Barbara together with high temperatures and high winds led to the devastating Jesusita fire. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12006
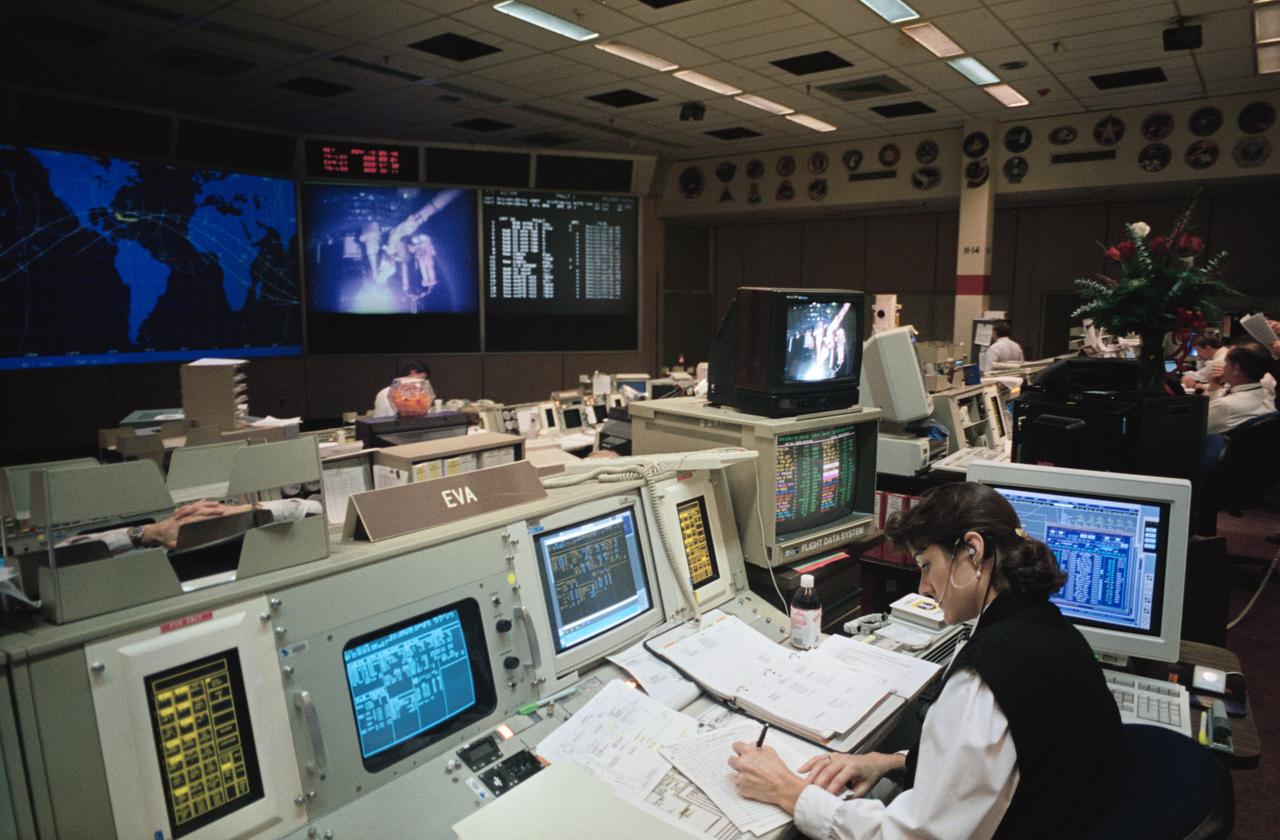

Flight controller Susan P. Rainwater observes as two astronauts work through a lengthy period of extravehicular activity (EVA) in the cargo bay of the Earth-looking Space Shuttle Endeavour. Rainwater's EVA console was one of Mission Control's busiest during this eleven-day Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission in Earth orbit.
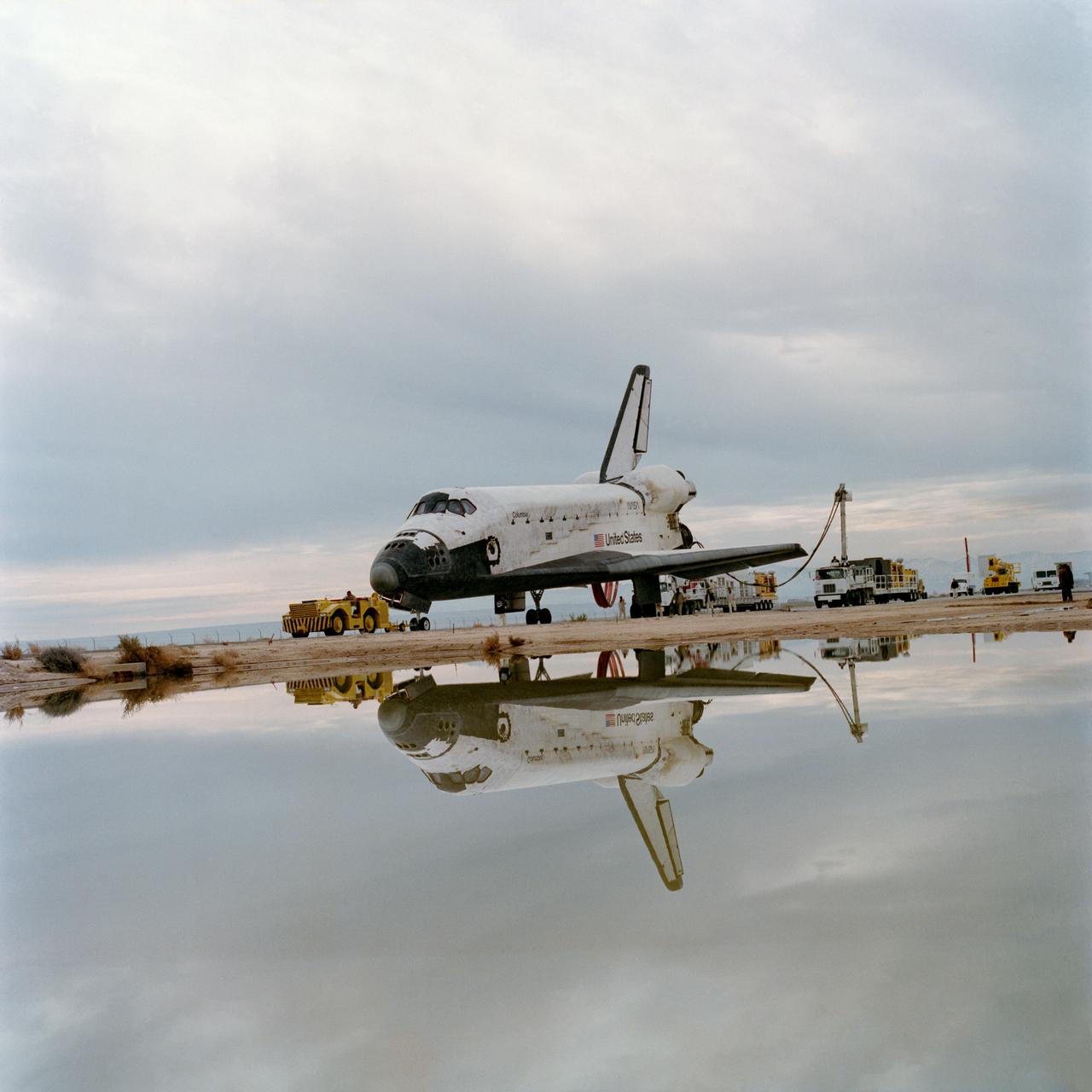

S82-39888 (16 Nov. 1982) --- Post-landing processing of the space shuttle Columbia is seen in double in this rare scene at the Dryden Flight Research Facility (DFRF) in southern California. Uncommon rainwater has given a mirror effect to the normally dry lakebed. Columbia, with its first four-member crew aboard, touched down earlier today to complete a successful five-day, two-hour mission. The runway used was Number 22 at Edwards Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA
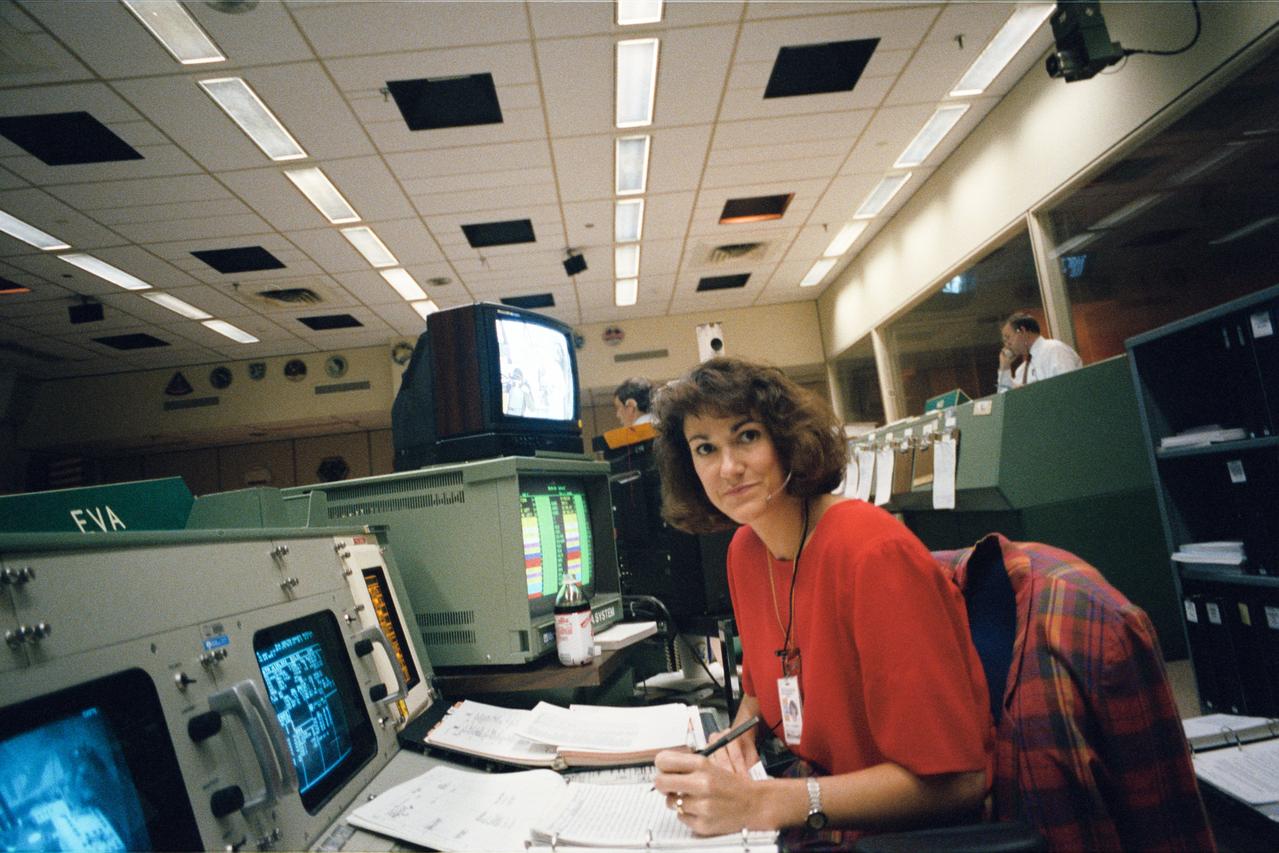

Susan P. Rainwater monitors an extravehicular activity (EVA) simulation from the EVA console at JSC's Mission Control Center (MCC) during joint integrated simulations for the STS-61 mission. Astronauts assigned to extravehicular activity (EVA) tasks with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) were simultaneously rehearsing in a neutral buoyancy tank at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Alabama.
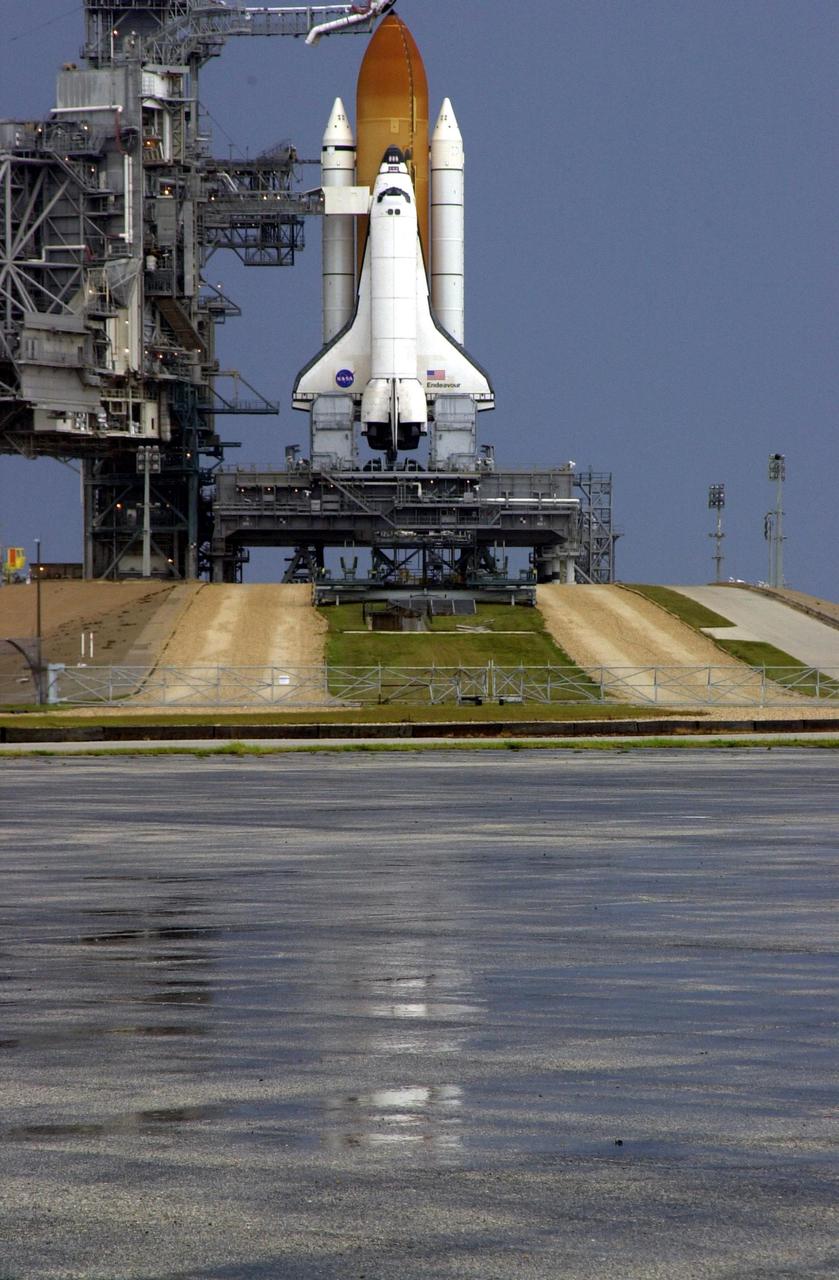

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour sits poised for launch at Pad 39A after mission managers postponed today's launch of mission STS-111. Forecasters' predictions that weather would prohibit a launch attempt due to severe thunderstorms and rain showers within the vicinity of the launch pad were accurate as depicted by the rainwater on the pavement in the foreground. STS-111 is the second Utilization Flight to the International Space Station, carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the Mobile Base System (MBS), and a replacement wrist/roll joint for the Canadarm 2. Also on board will be the Expedition Five crew who will replace Expedition Four on the Station. Launch has been rescheduled for Monday, June 3, between 4 and 8 p.m. EDT
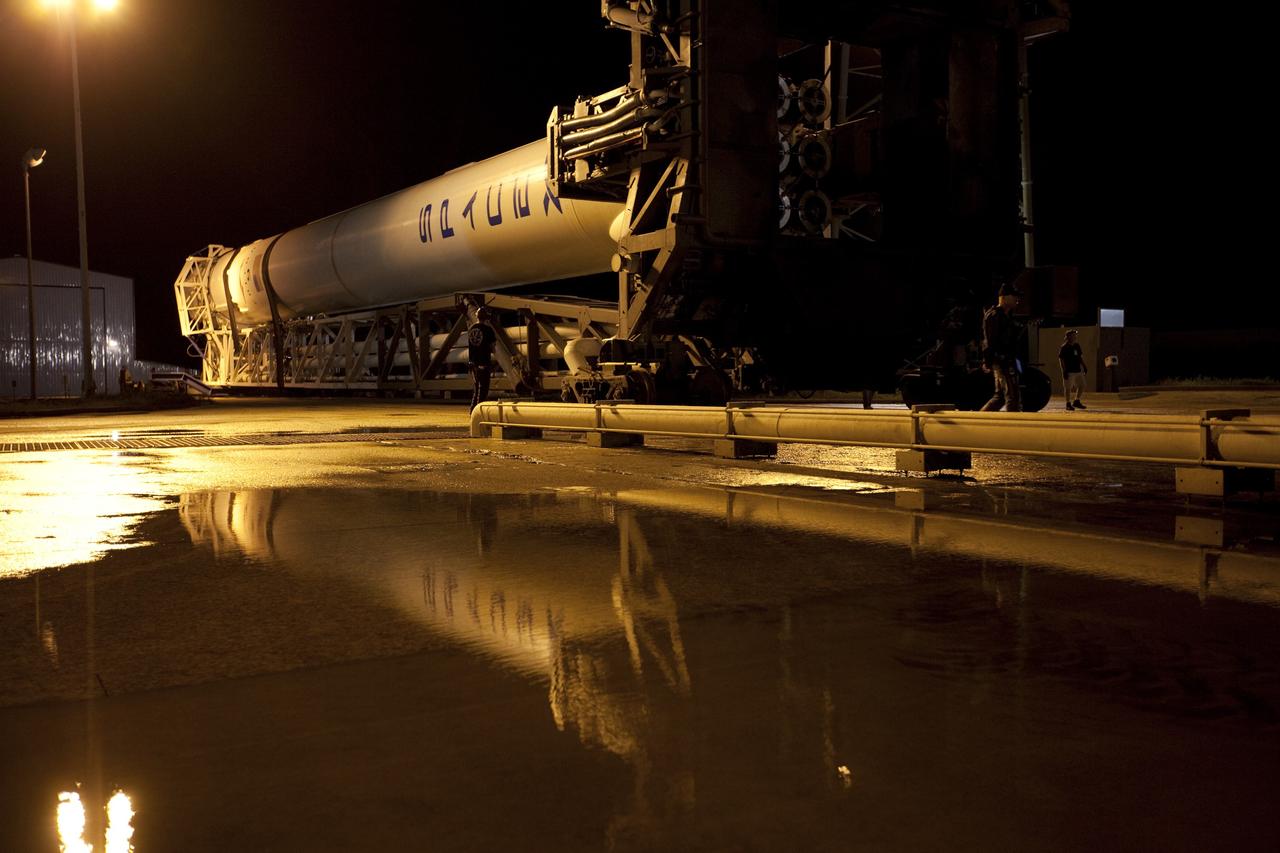

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Falcon 9 rocket with a Dragon capsule secured atop is reflected in the rainwater standing on the surface of Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida as it rolls from the processing hangar to the pad. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. Rollout was complete at 9:55 p.m. EDT. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. Launch is scheduled for 8:35 p.m. EDT on Oct. 7. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

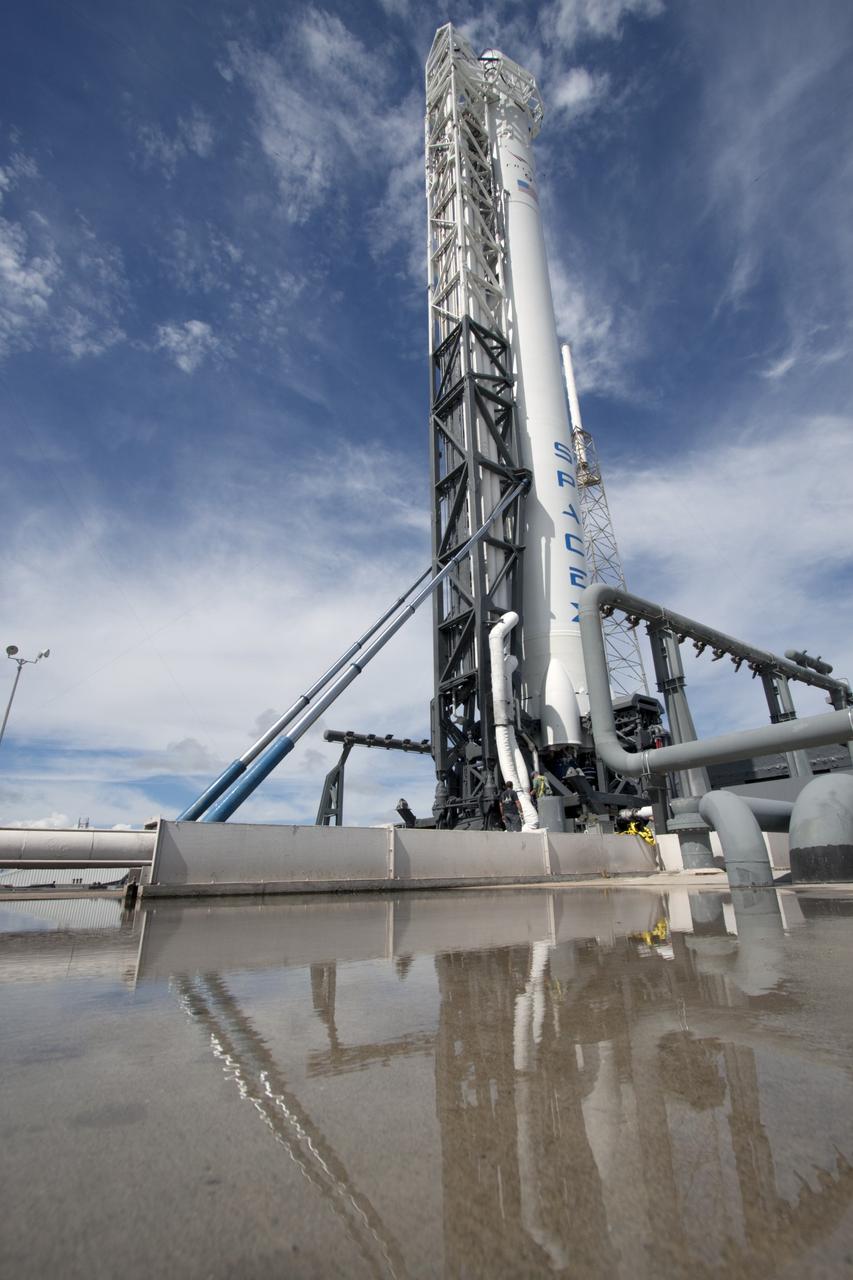
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Falcon 9 rocket with a Dragon capsule secured atop is reflected in the rainwater standing on the surface of Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida as it rolls from the processing hangar to the pad. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. Rollout was complete at 9:55 p.m. EDT. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. Launch is scheduled for 8:35 p.m. EDT on Oct. 7. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

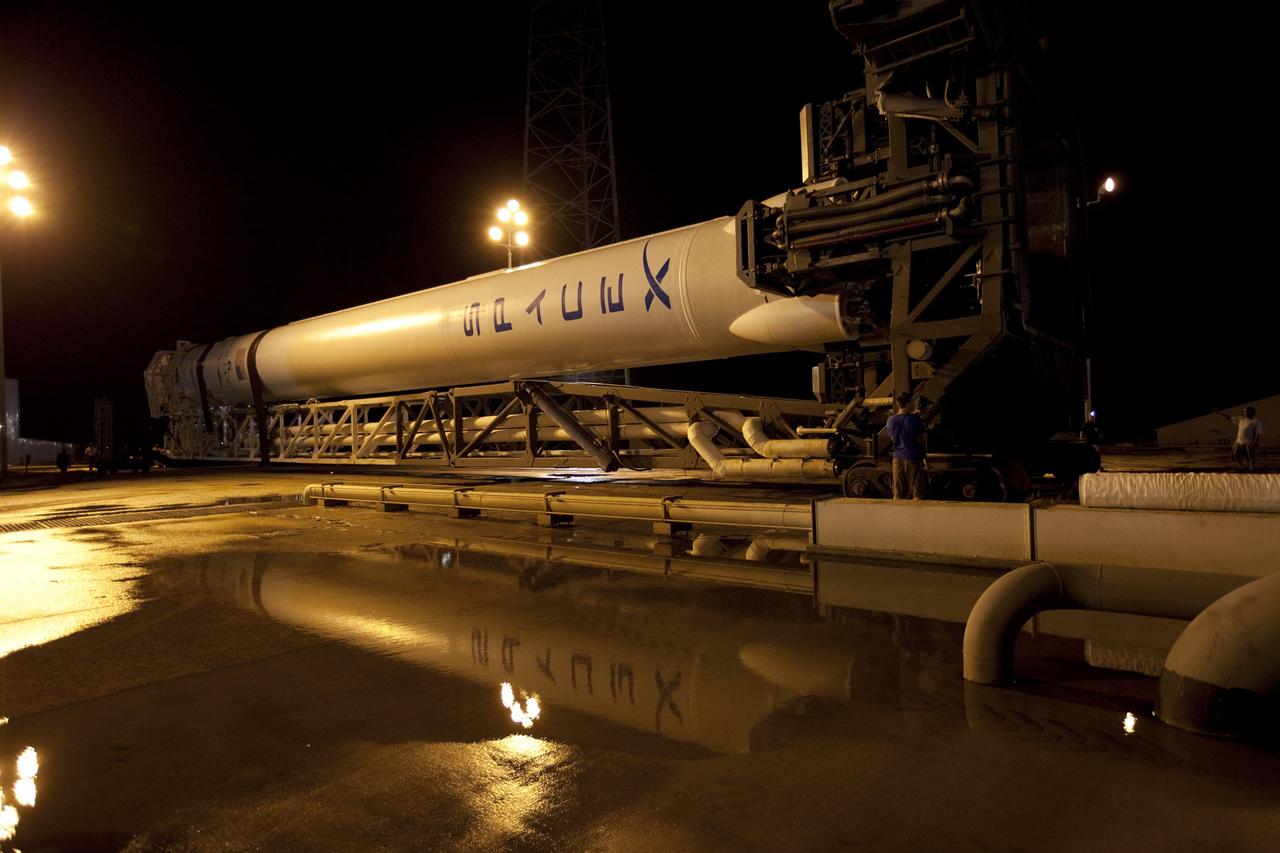
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Falcon 9 rocket with a Dragon capsule secured atop is reflected in the rainwater standing on the surface of the pad of Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida following its lift into a vertical position. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. The vertical lift was complete at 1 p.m. EDT. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. Launch is scheduled for 8:35 p.m. EDT on Oct. 7. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
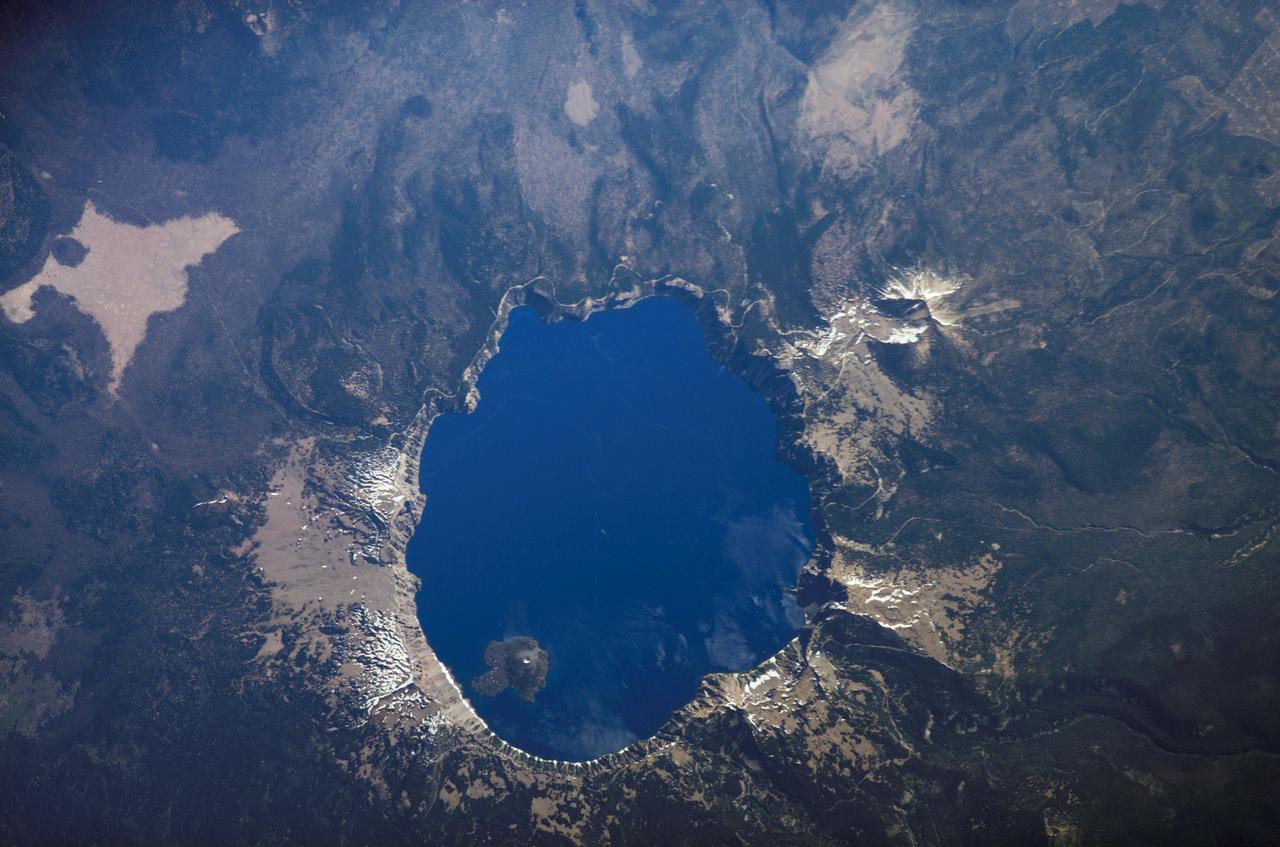

ISS013-E-54243 (19 July 2006) --- Crater Lake, Oregon is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. Crater Lake is formed from the caldera (collapsed magma chamber) of a former volcano known as Mount Mazama. Part of the Cascades volcanic chain, Mount Mazama is situated between the Three Sisters volcanoes to the north and Mount Shasta to the south. While considered a dormant volcano, Crater Lake is part of the United States Geological Survey Cascades Volcano Observatory seismic monitoring network. The dark blue water coloration is typical of the 592 meter (1943 feet) deep Crater Lake; light blue-green areas to the southeast of Wizard Island (along the southern crater rim) most probably correspond to particulates either on or just below the water surface. A light dusting of snow fills the summit cone of Wizard Island. Some of the older lava flows in the area are associated with Mount Scott to the east-southeast of the Lake. Water is lost only by evaporation and seepage, and is only replenished by rainwater and snowmelt from the surrounding crater walls. These processes help maintain minimal sediment input into the lake and exceptional water clarity. The Crater Lake ecosystem is of particular interest to ecologists because of its isolation from the regional landscape, and its overall pristine quality is important to recreational users of Crater Lake National Park (447,240 visitors in 2005). The United States National Park Service maintains programs to monitor changes (both natural and human impacts) to Crater Lake.