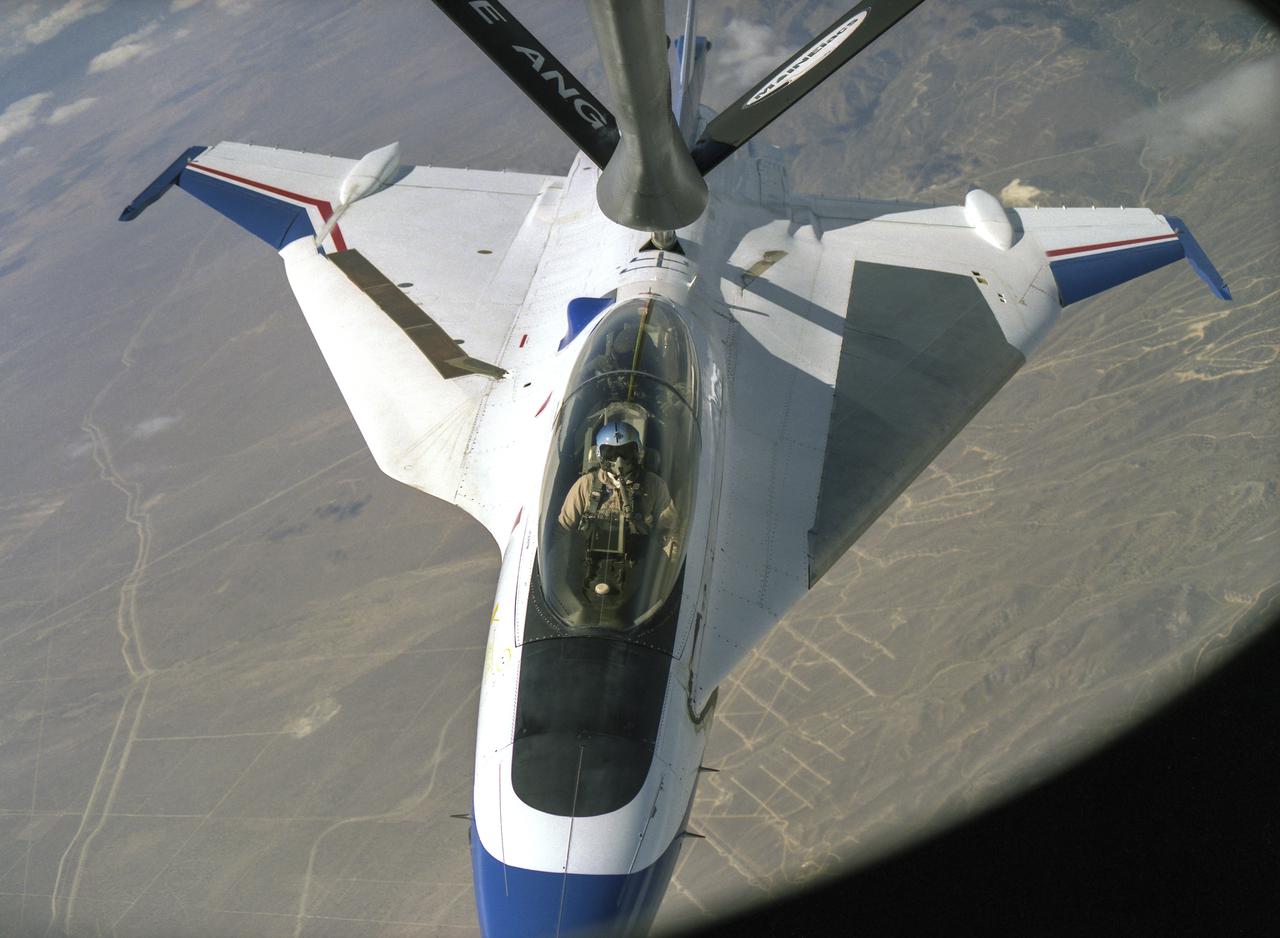

An F-16XL refuels in-flight. Only two XLs were built, and NASA eventually operated both for experimental purposes, including an active supersonic laminar flow experiment.
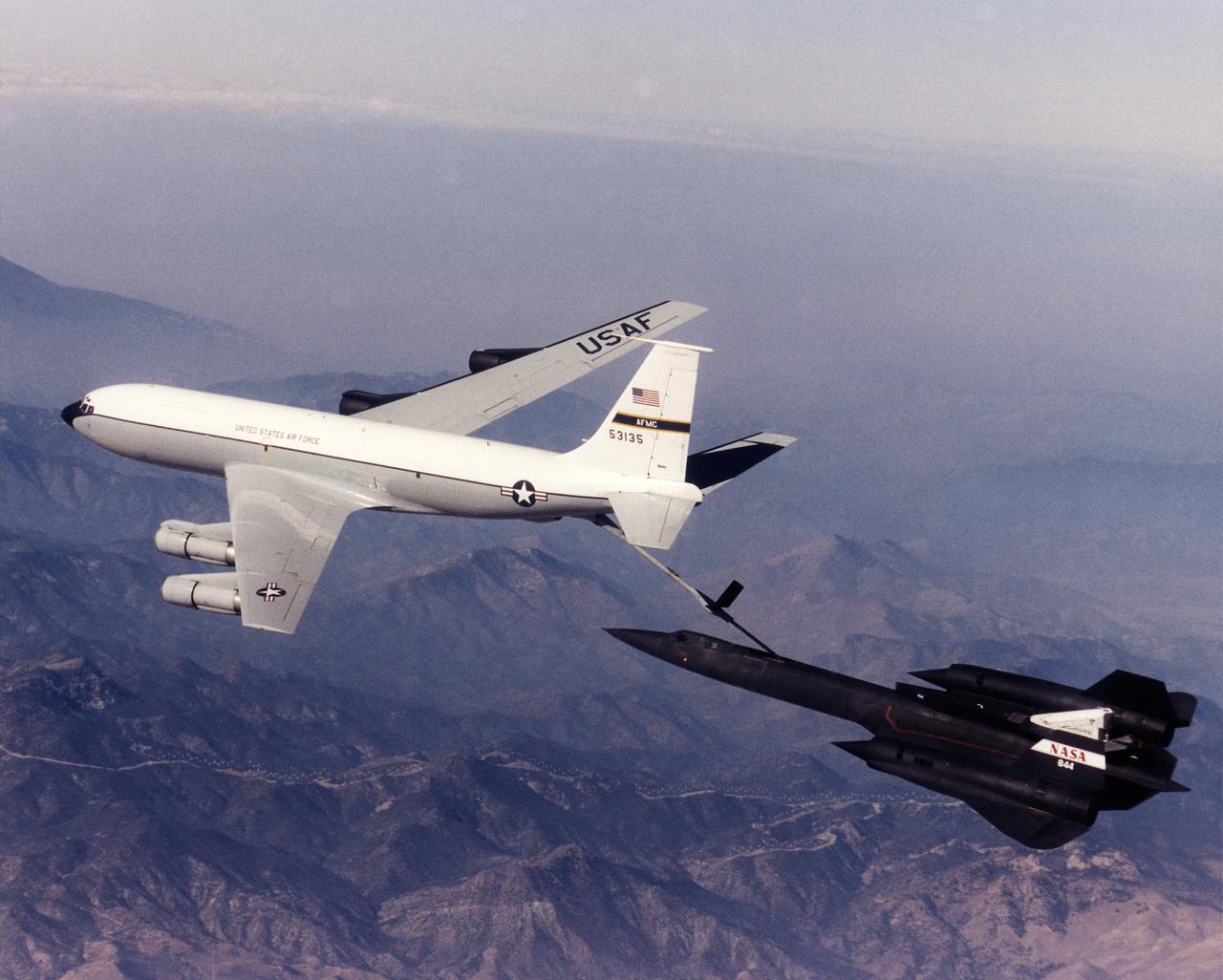

A NASA SR-71 refuels with an Edwards Air Force Base KC-135 during the first flight of the NASA/Rocketdyne/ Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE). The flight took place Oct. 31 at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
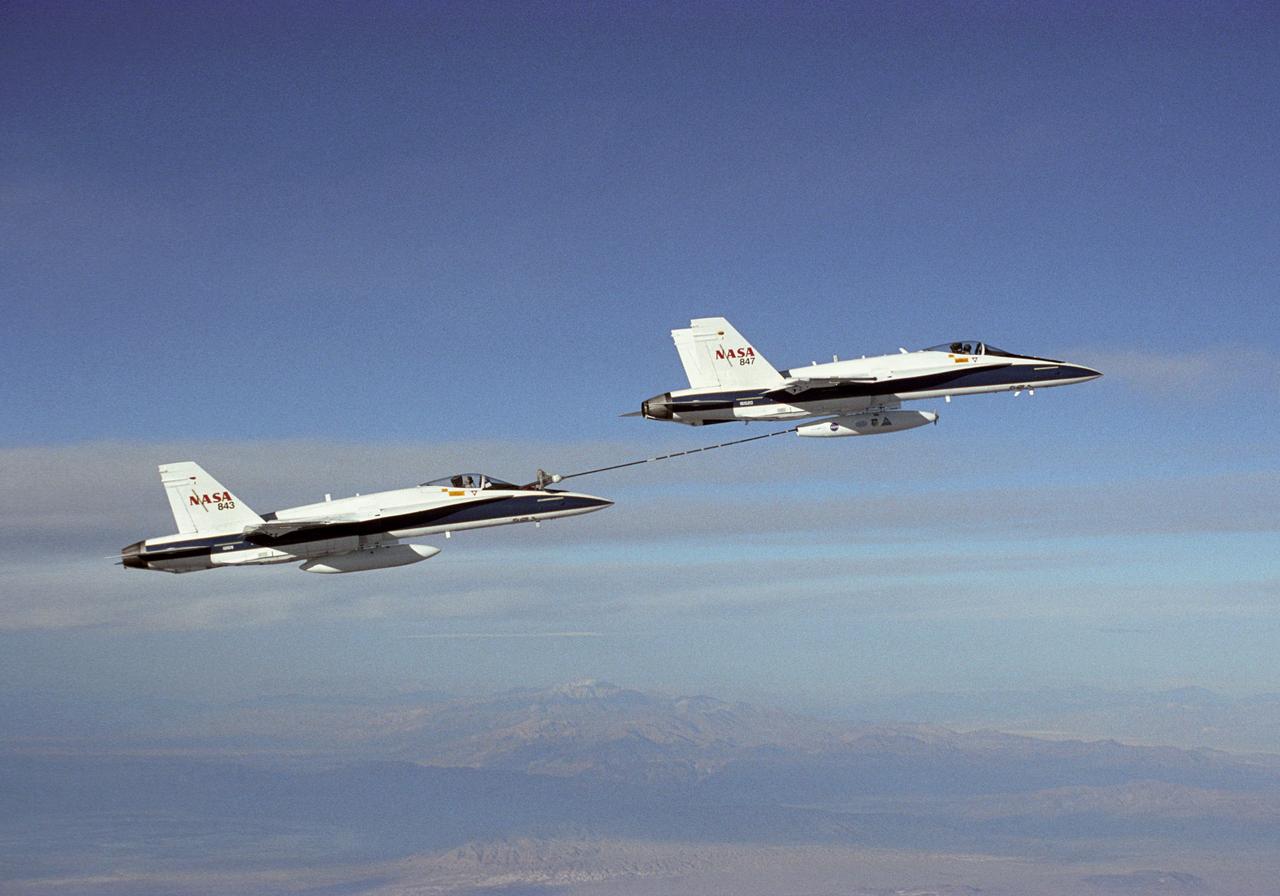

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
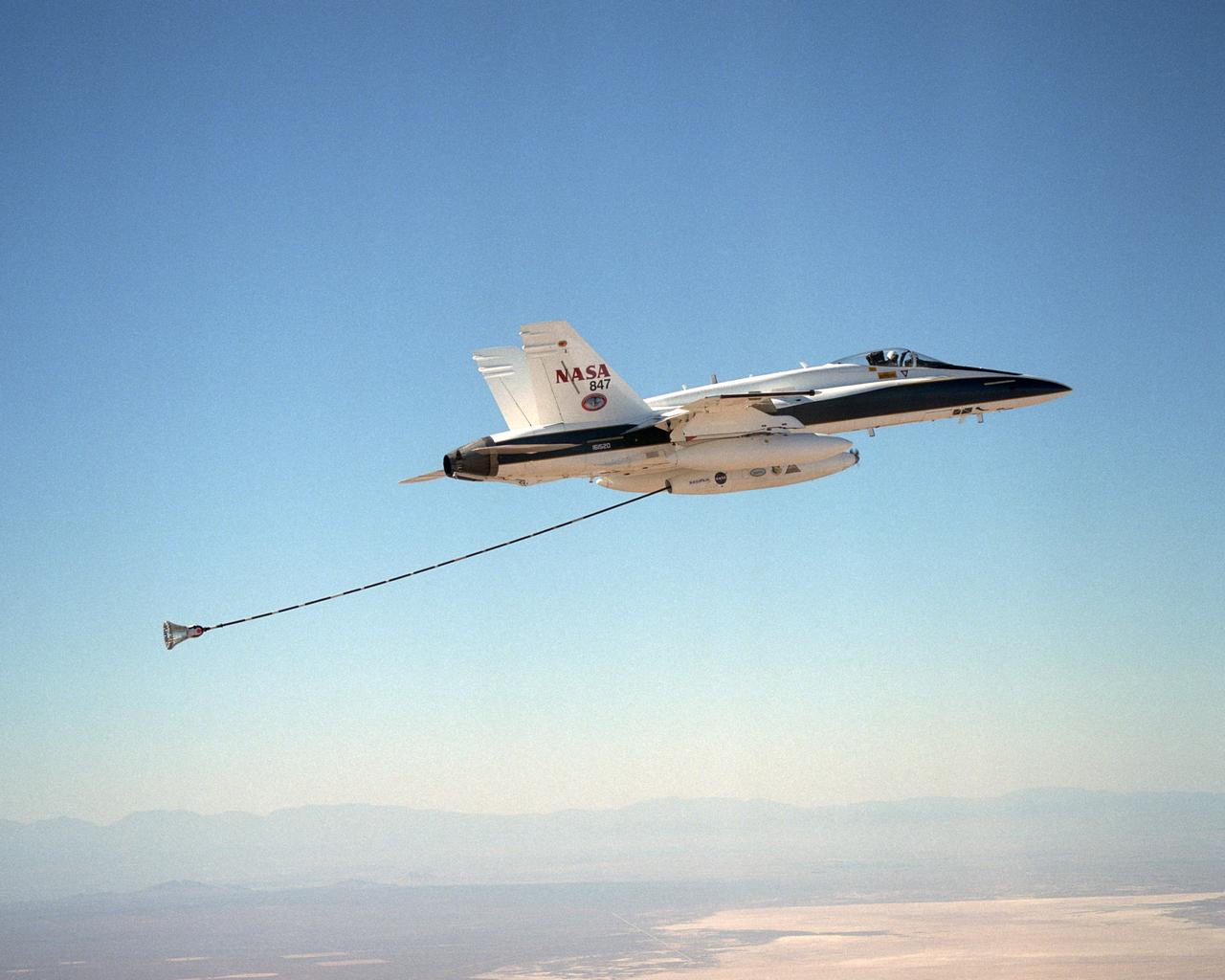

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
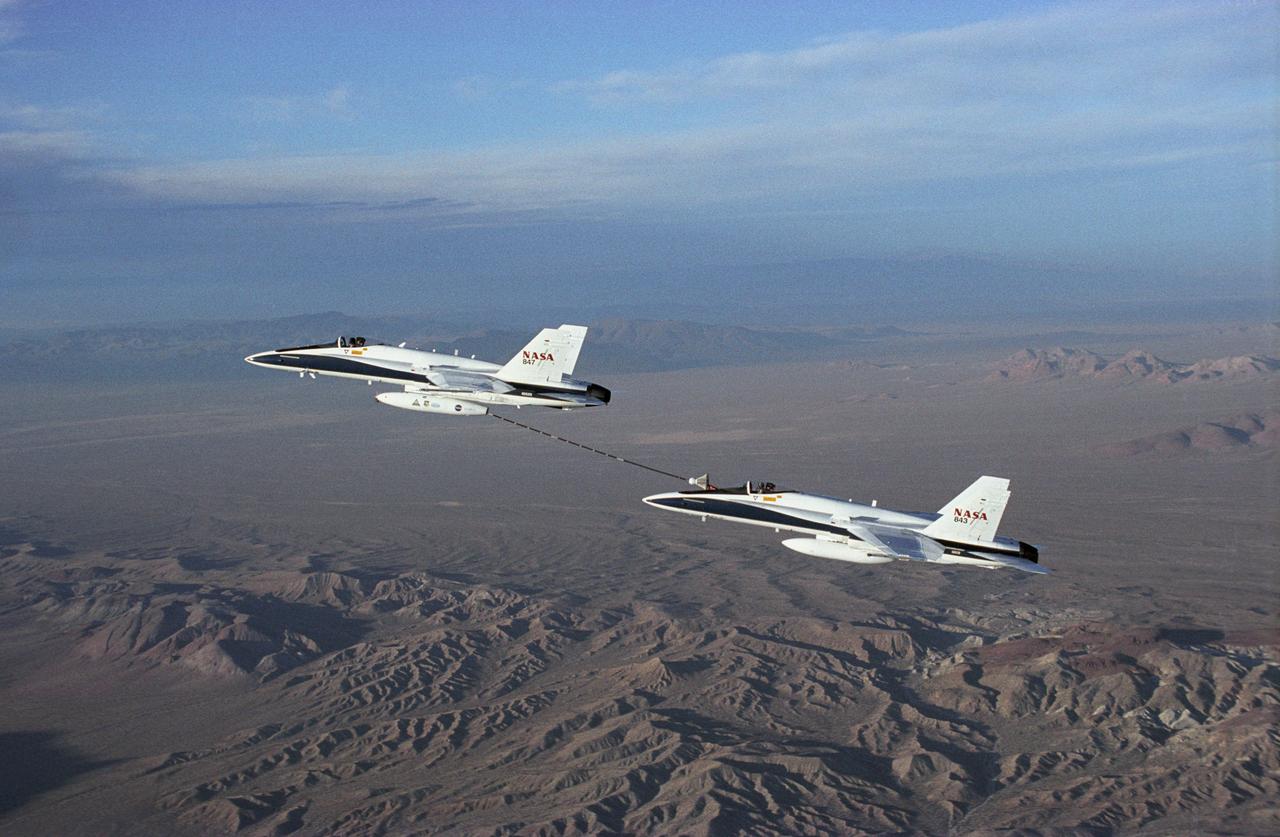

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
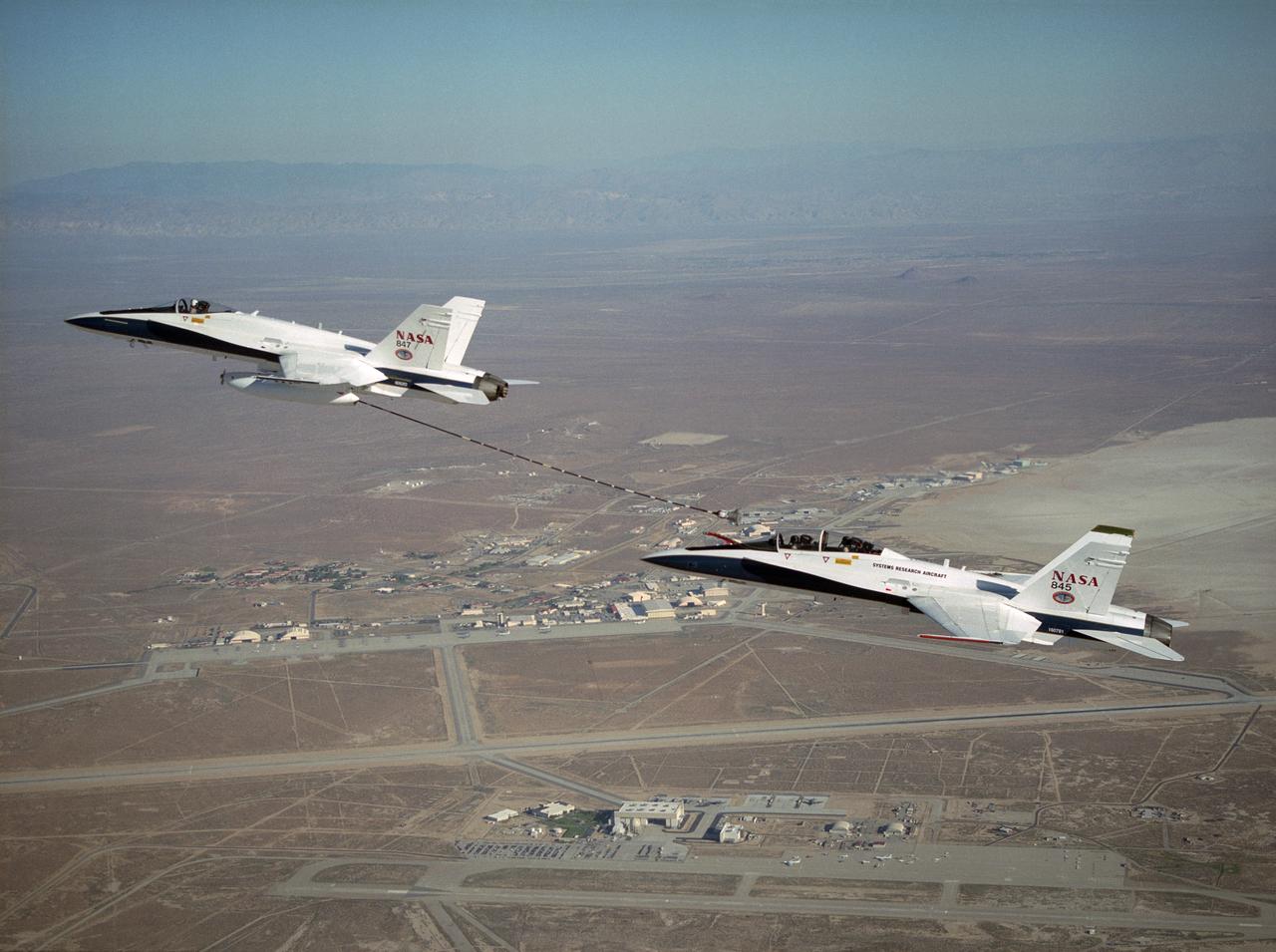

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
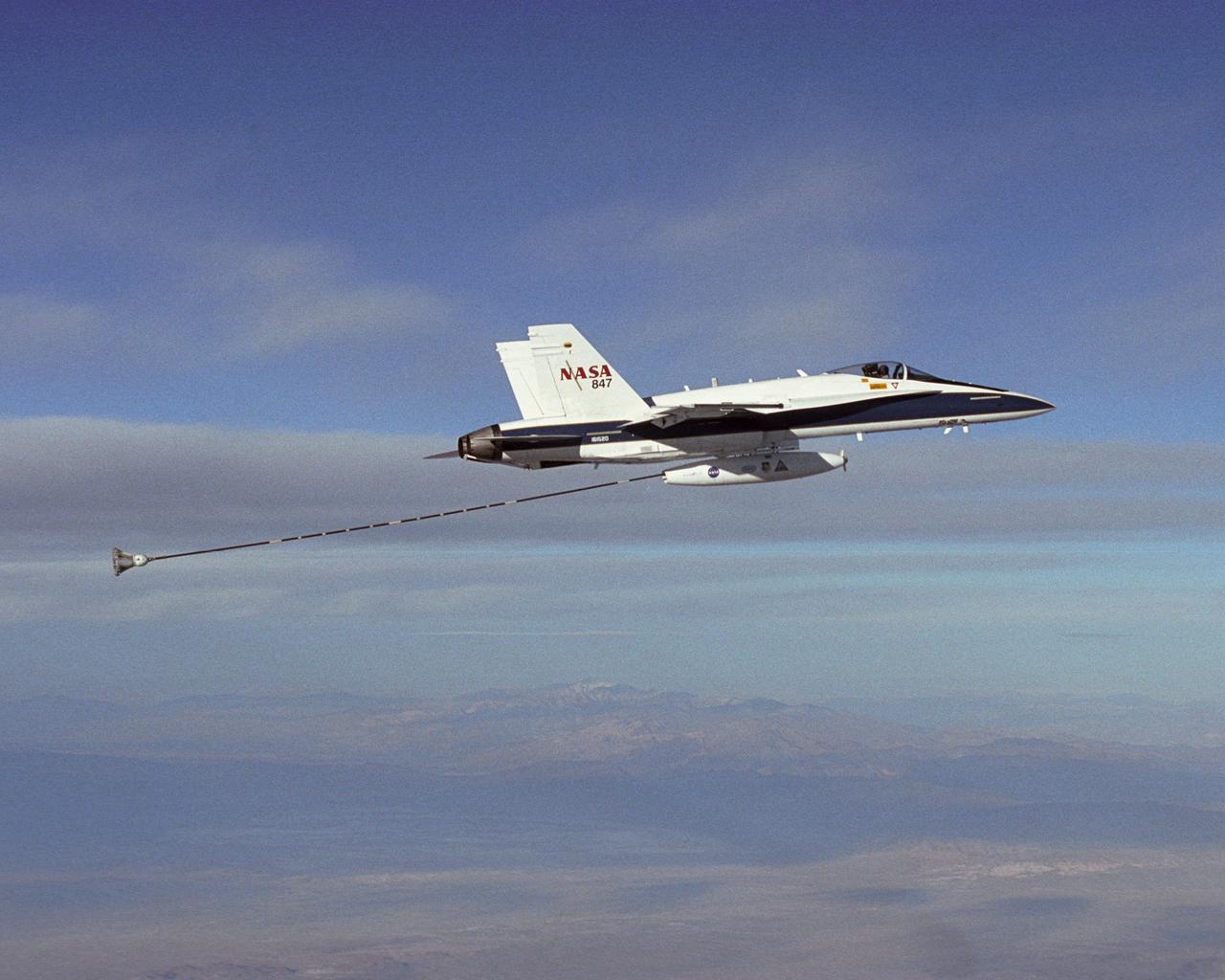

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
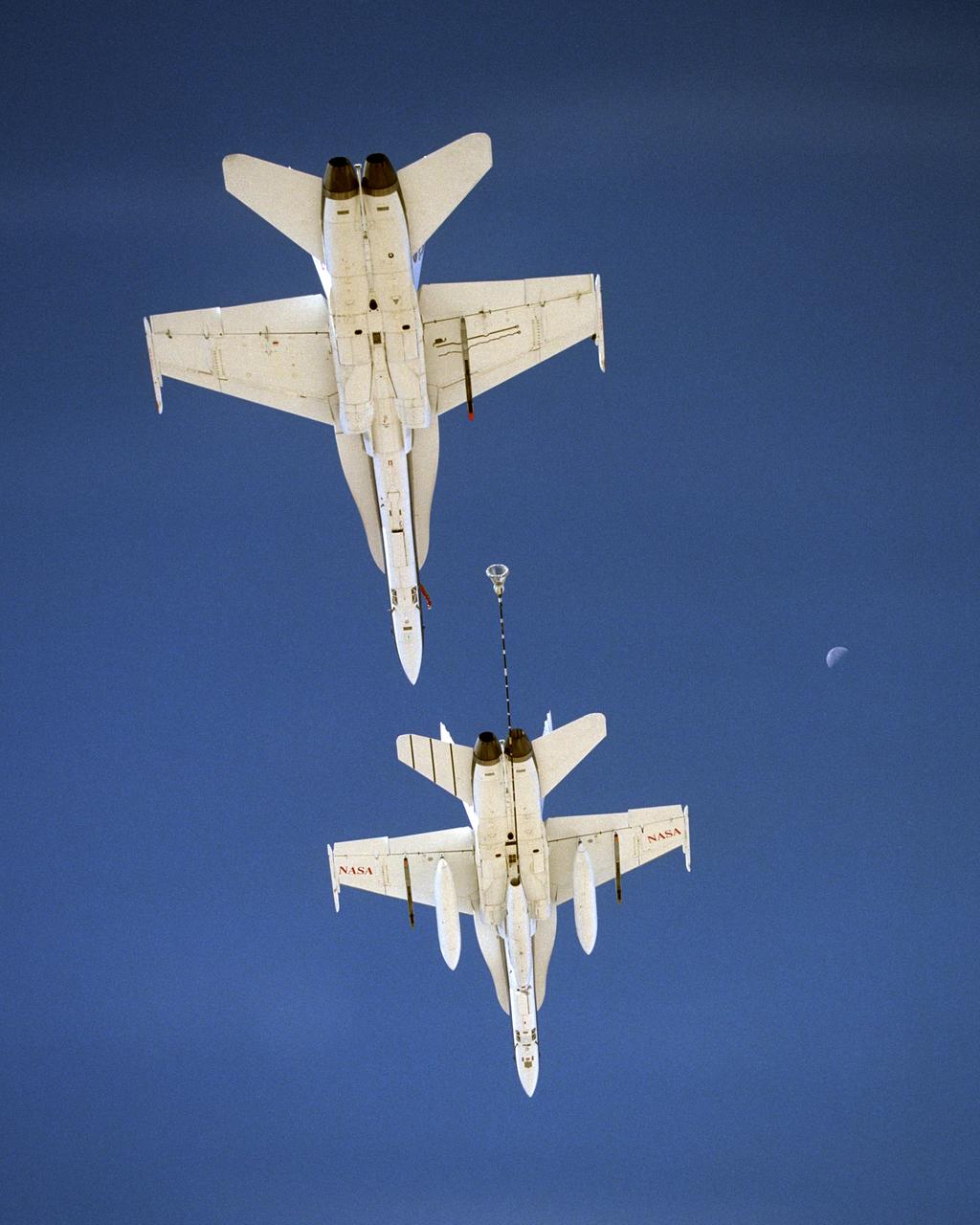

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
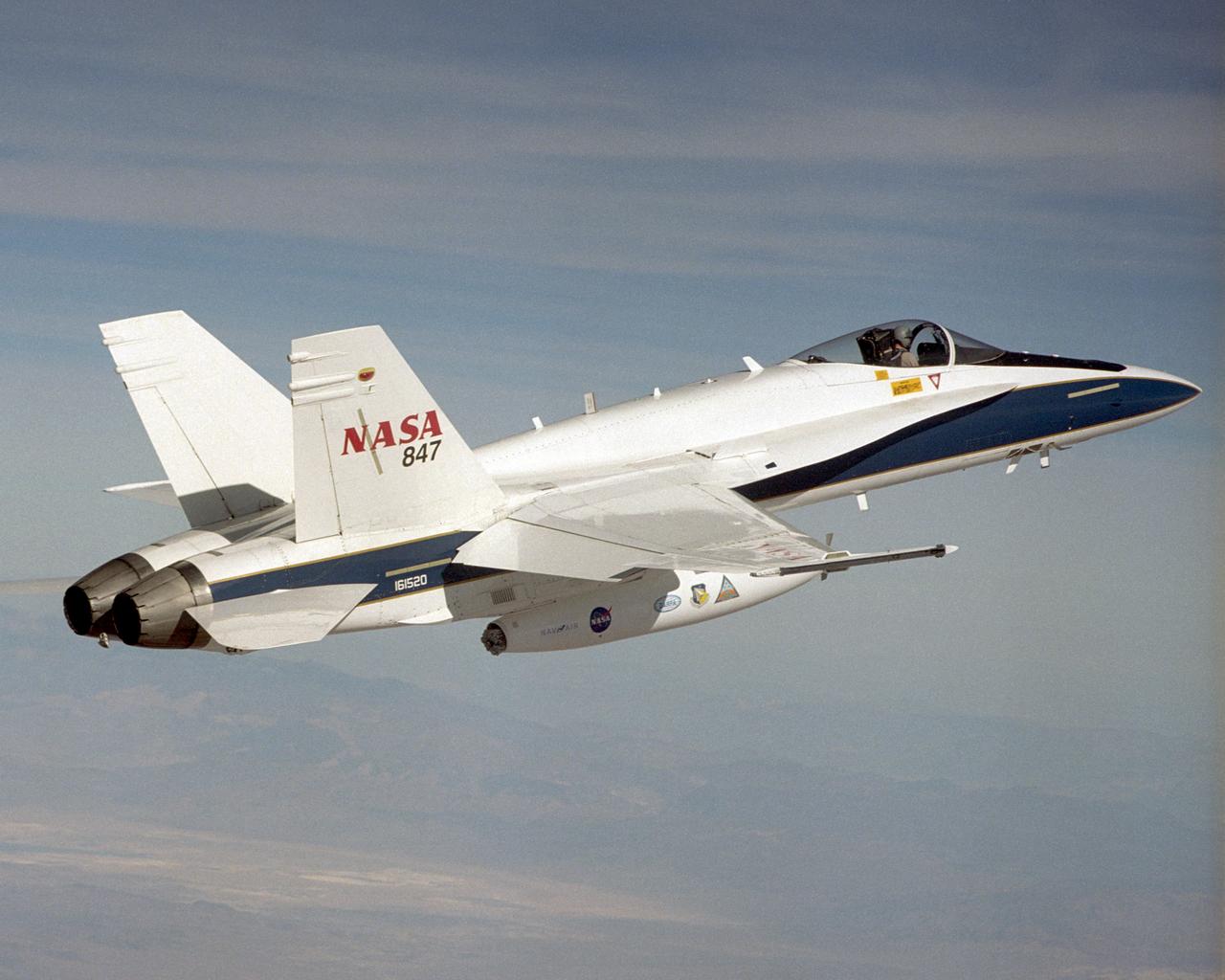

A NASA F/A-18 flies over the Dryden Flight Research Center and Rogers Dry Lake on December 11, 2002. The aircraft participated in the Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project. The 300-gallon aerial refueling store seen on the belly of the aircraft carries fuel and a refueling drogue. This aircraft acted as a tanker in the study to develop an aerodynamic model for future automated aerial refueling, especially of unmanned vehicles.
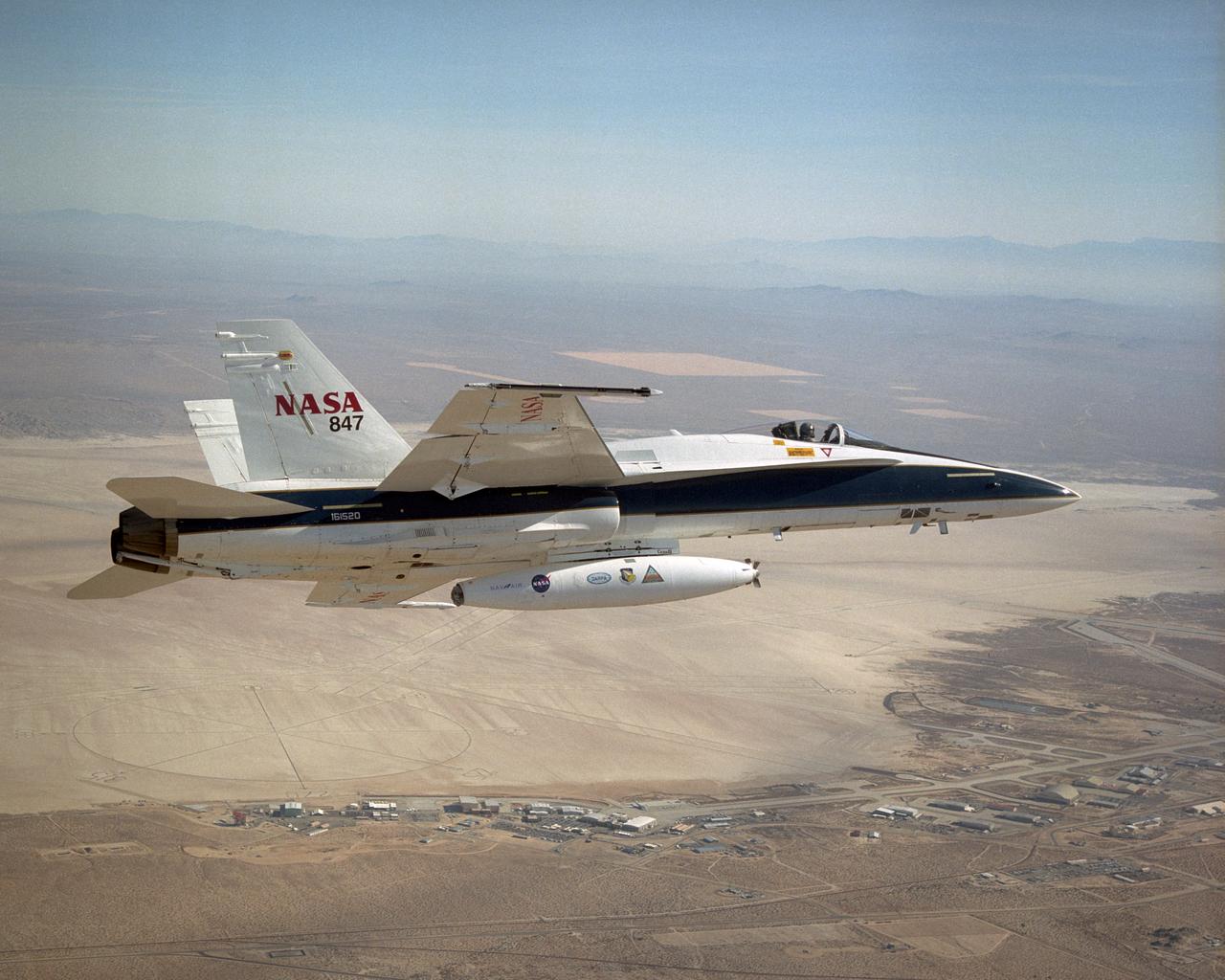

A NASA F/A-18 flies over the Dryden Flight Research Center and Rogers Dry Lake on December 11, 2002. The aircraft participated in the Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project. The 300-gallon aerial refueling store seen on the belly of the aircraft carries fuel and a refueling drogue. This aircraft acted as a tanker in the study to develop an aerodynamic model for future automated aerial refueling, especially of unmanned vehicles.

A NASA F/A-18 flies over the Dryden Flight Research Center and Rogers Dry Lake on December 11, 2002. The aircraft participated in the Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project. The 300-gallon aerial refueling store seen on the belly of the aircraft carries fuel and a refueling drogue. This aircraft acted as a tanker in the study to develop an aerodynamic model for future automated aerial refueling, especially of unmanned vehicles.
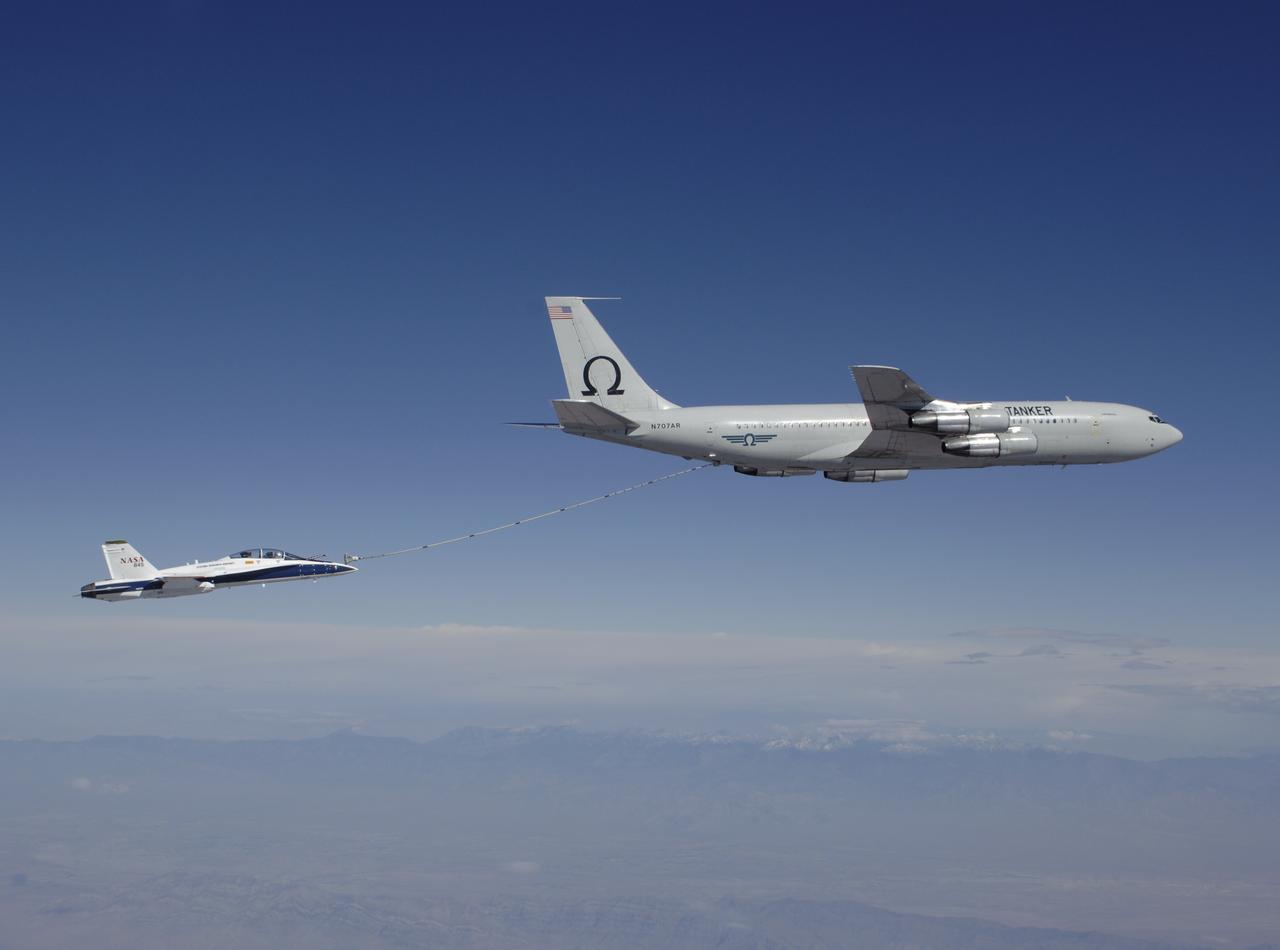

F/A-18 #845 behind an Omega Air Boeing 707 tanker during an Autonomous Airborne Refueling Demonstration (AARD) flight.
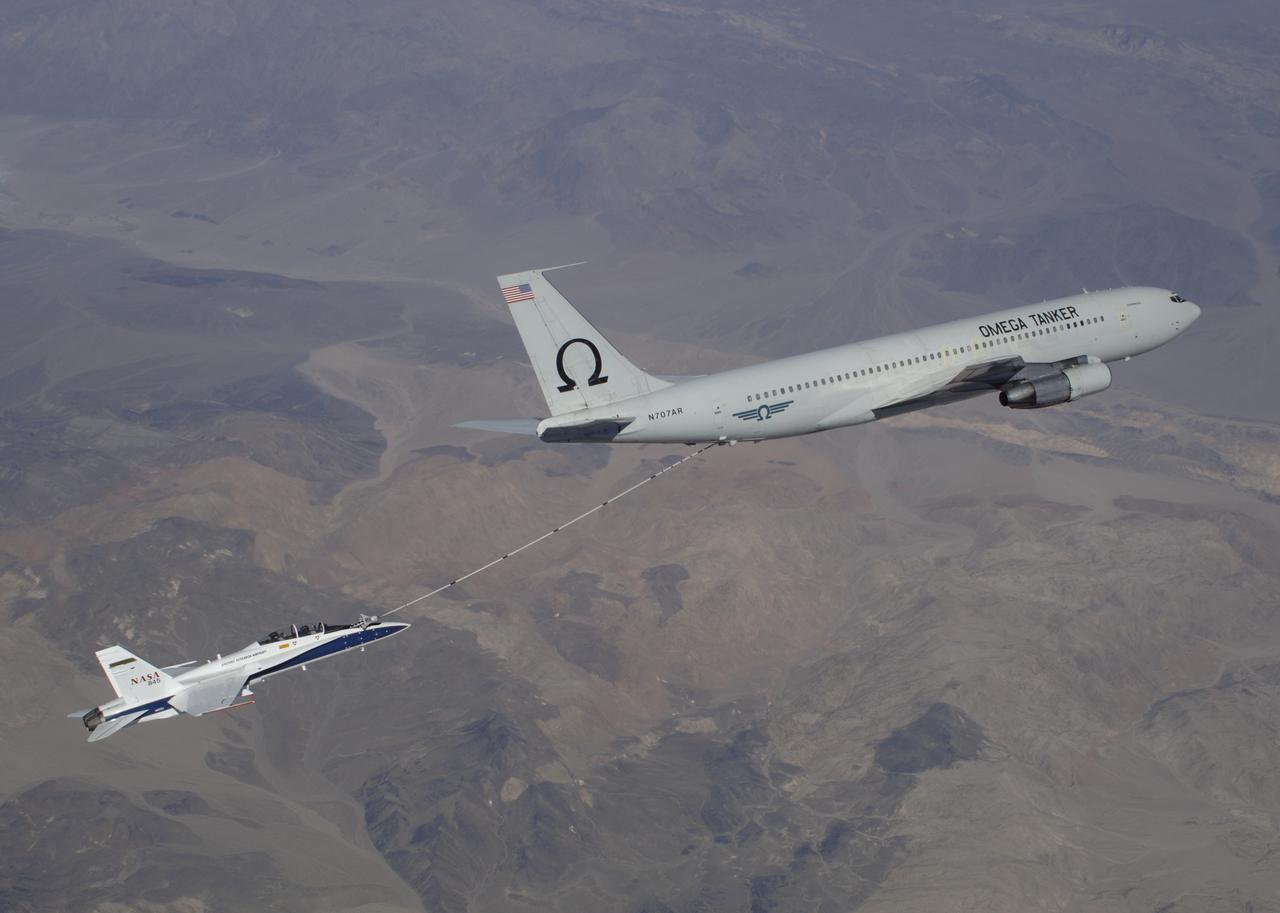

F/A-18 #845 behind an Omega Air Boeing 707 tanker during an Autonomous Airborne Refueling Demonstration (AARD) flight.
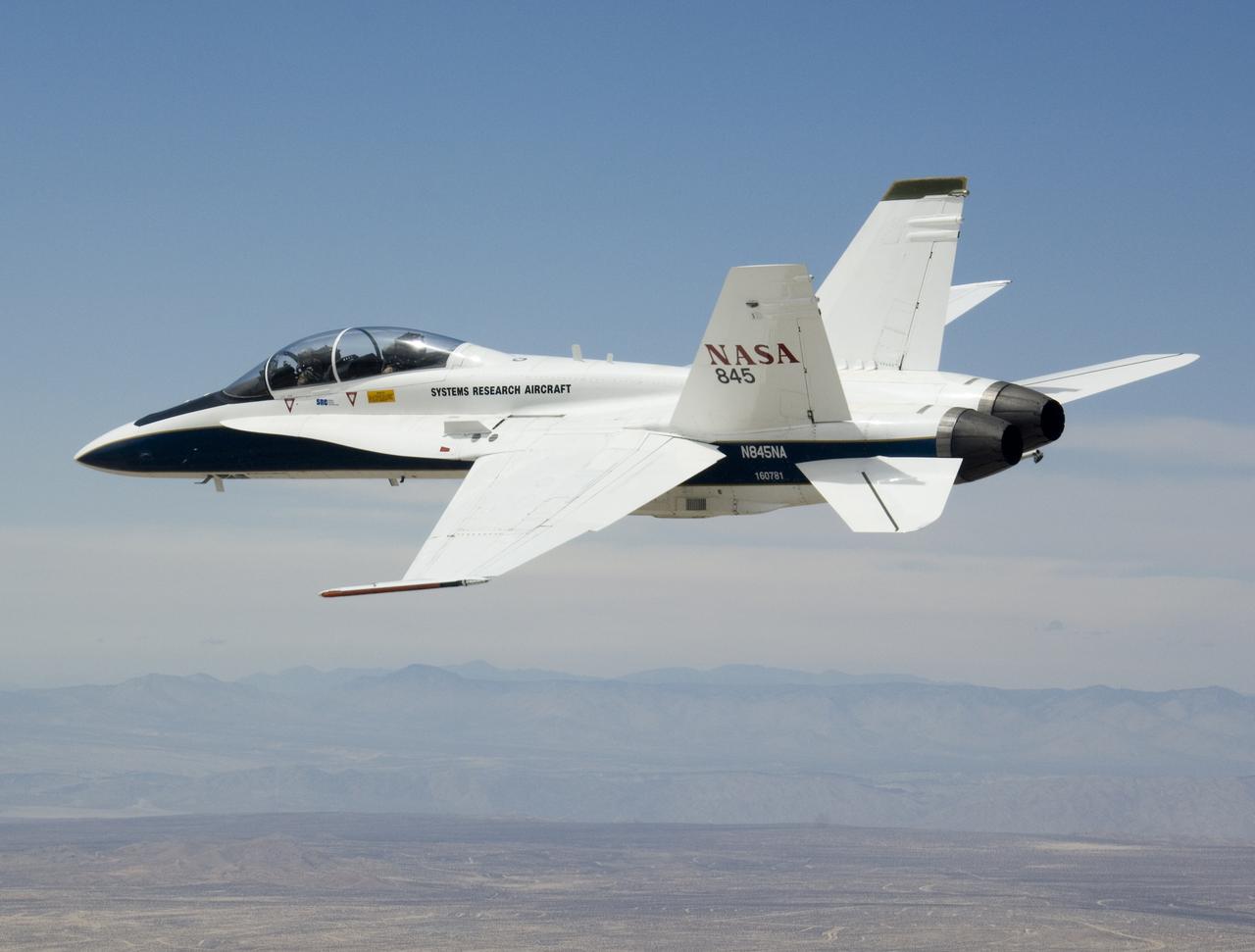

NASA's F/A-18B #845 was captured by the photographer as it returned from its final flight in the Autonomous Airborne Refueling Demonstration research project.
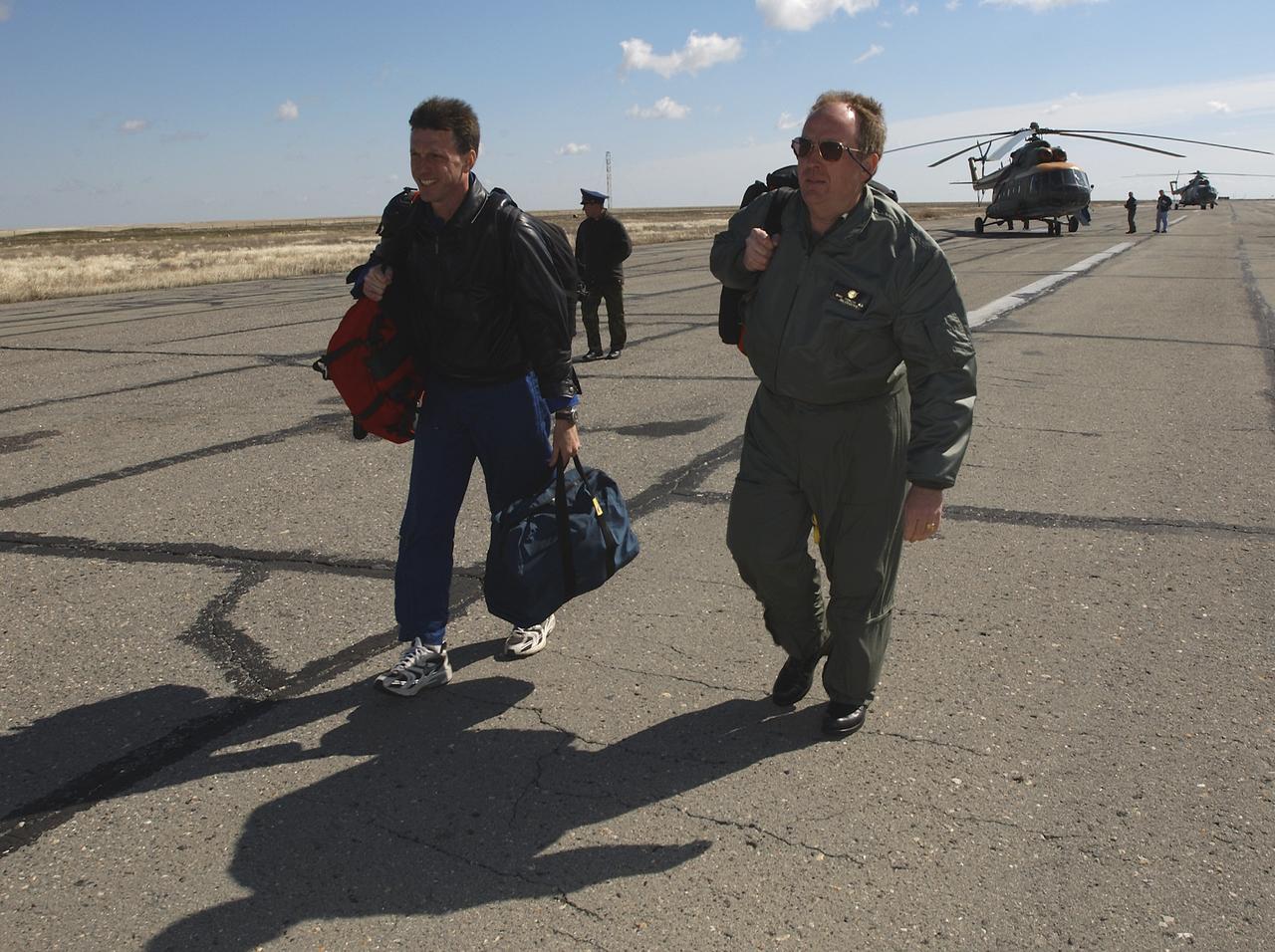

Astronaut Michael Foale, left, and Mike Duncan, Expedition 6 Lead Flight Surgeon, move to another helicopter after the landing team helicopters returned for refueling, Tuesday, May 4, 2003, in Kazakhstan. Foale and Duncan went on from the refueling to meet the crew of Expedition 6 at the landing site. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
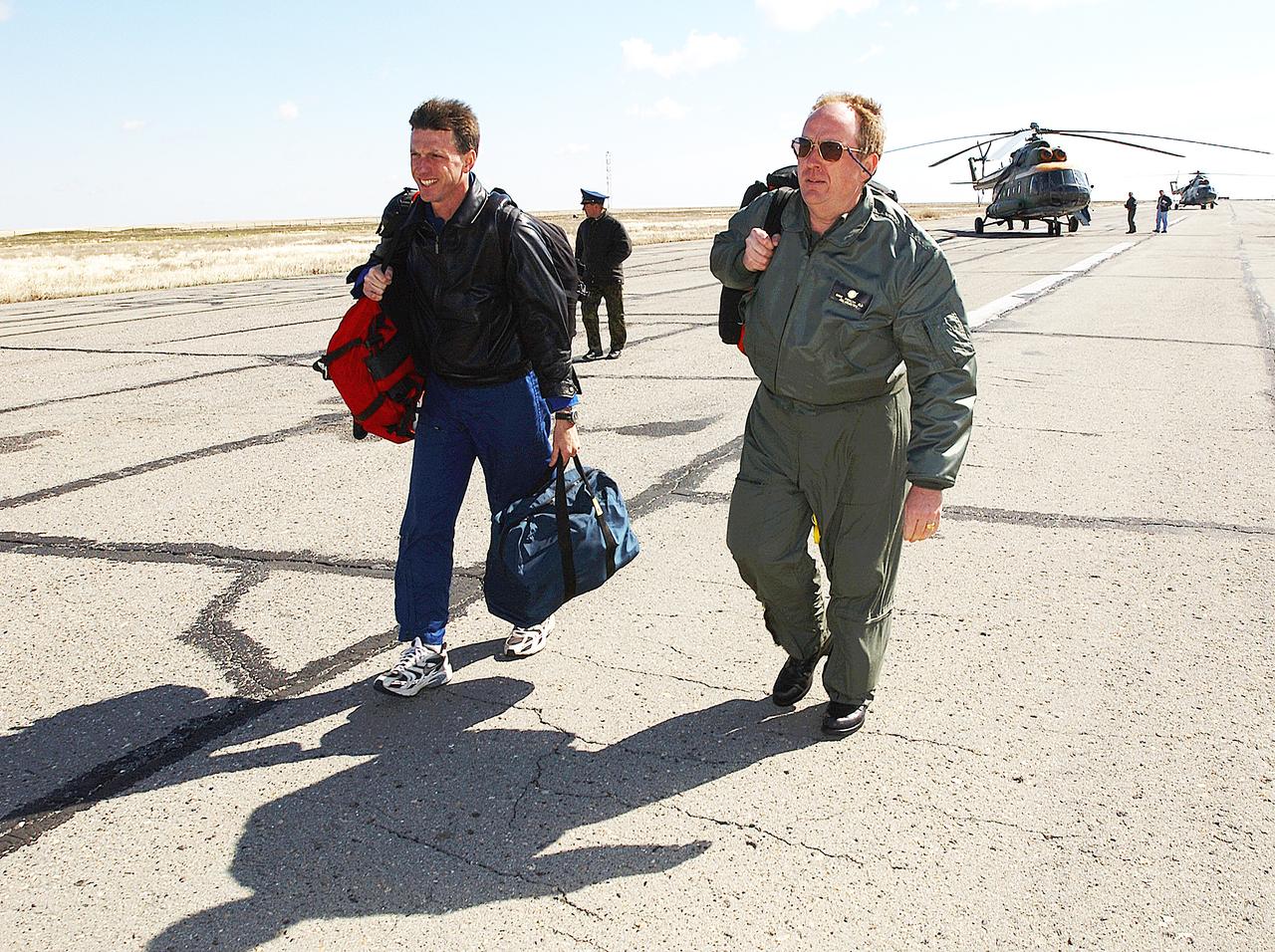

May 4, 2003, Kazakhstan. Astronaut Michael Foale (L) and Mike Duncan (R), Expedition Six Lead Flight Surgeon move to the lead helicopter after the landing team helicopters needed to return for refueling. Foale and Duncan went on from the refueling to meet the crew of Expedition Six at the landing site. Photo Credit: "NASA/Bill Ingalls"
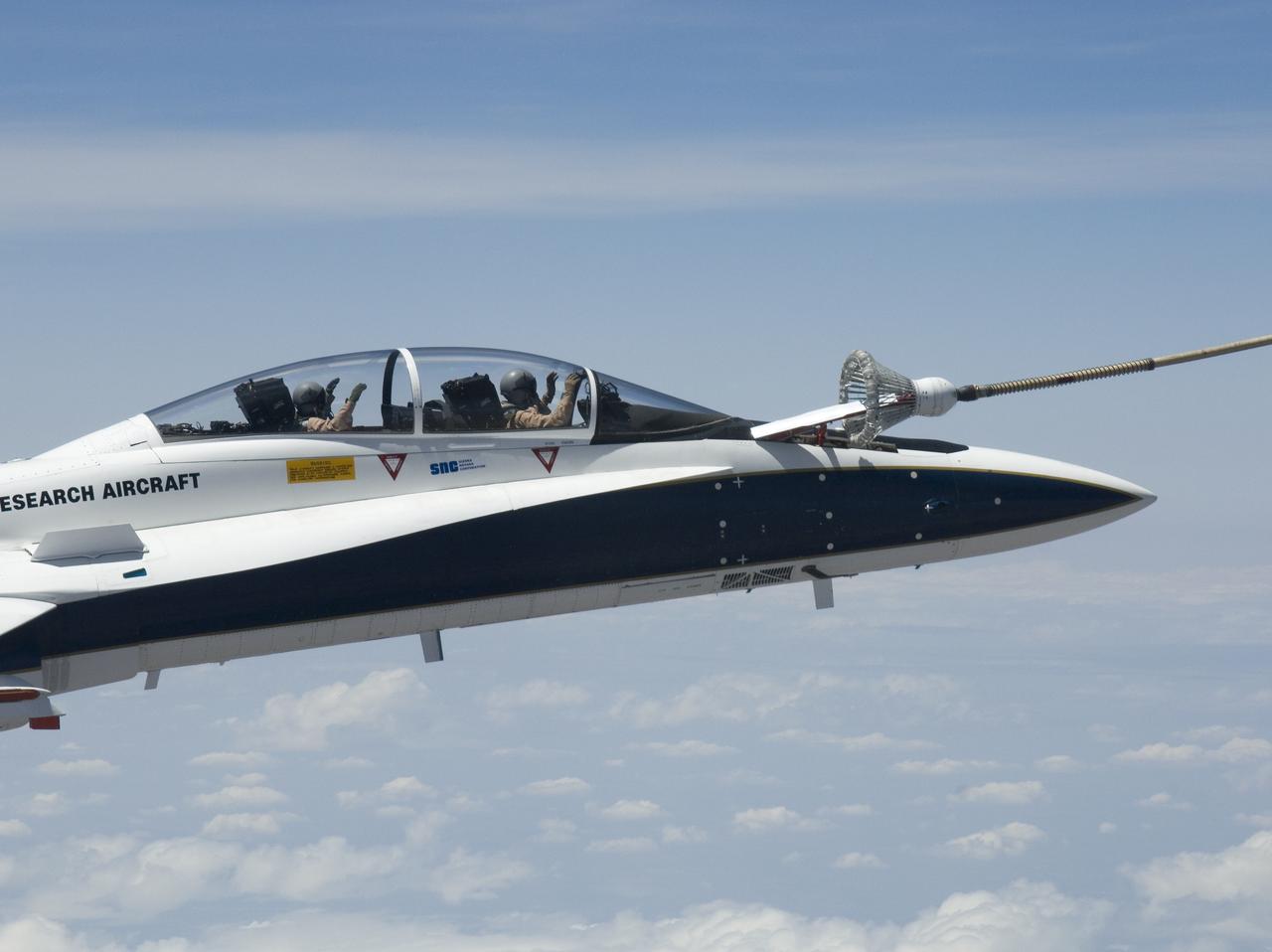

Pilot Dick Ewers and flight test engineer Leslie Molzahn were hands-off as NASA F/A-18 #845 flew itself into the drogue on an autonomous refueling demonstration.
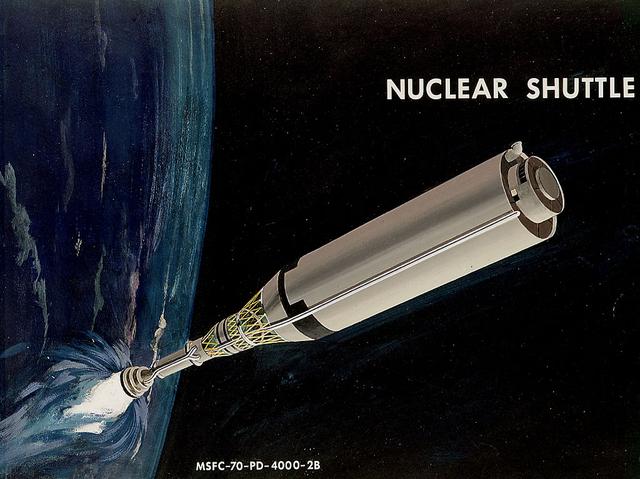

This 1970 artist's concept shows a Nuclear Shuttle in flight. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development engineers, the Nuclear Shuttle would deliver payloads to lunar orbit or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling and additional missions.
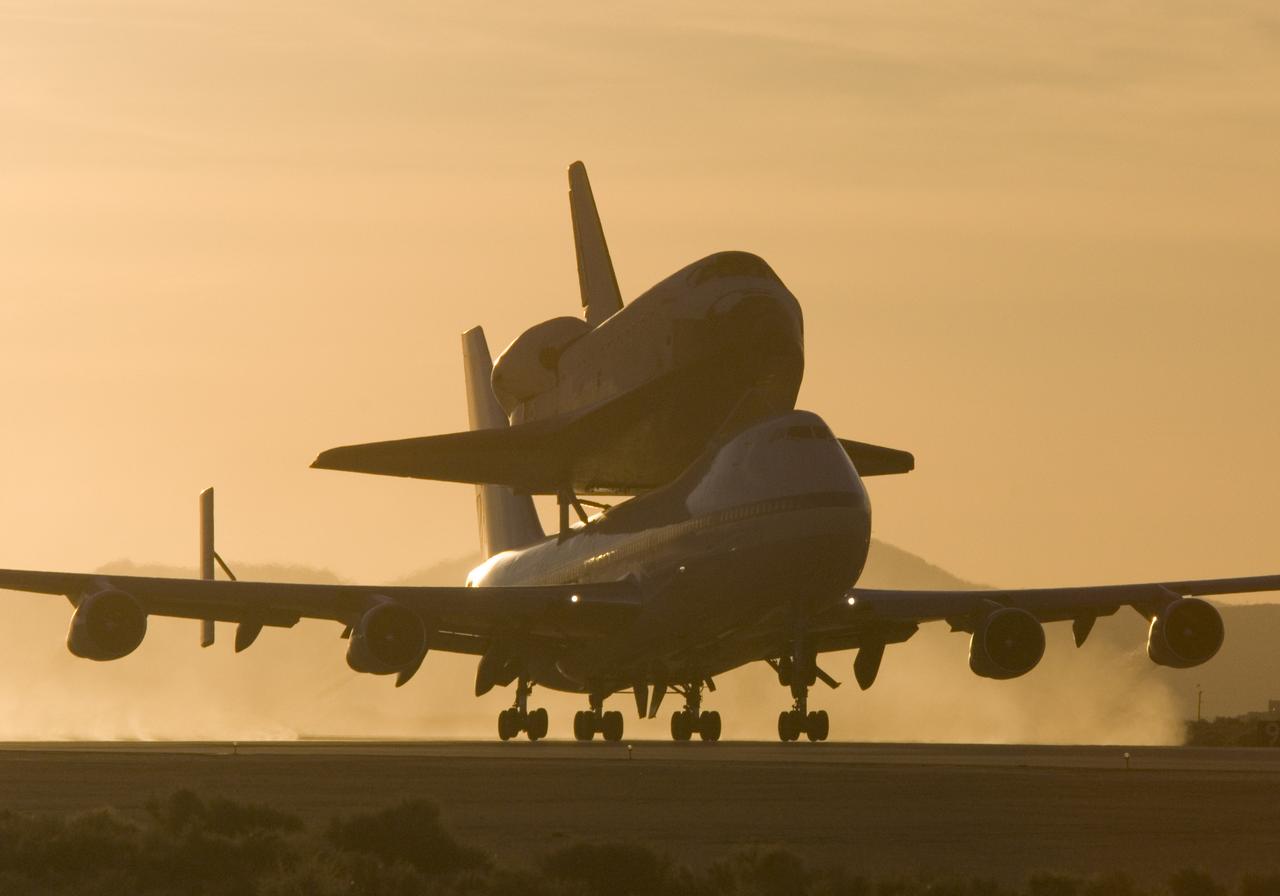

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Atlantis on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take approximately two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling.
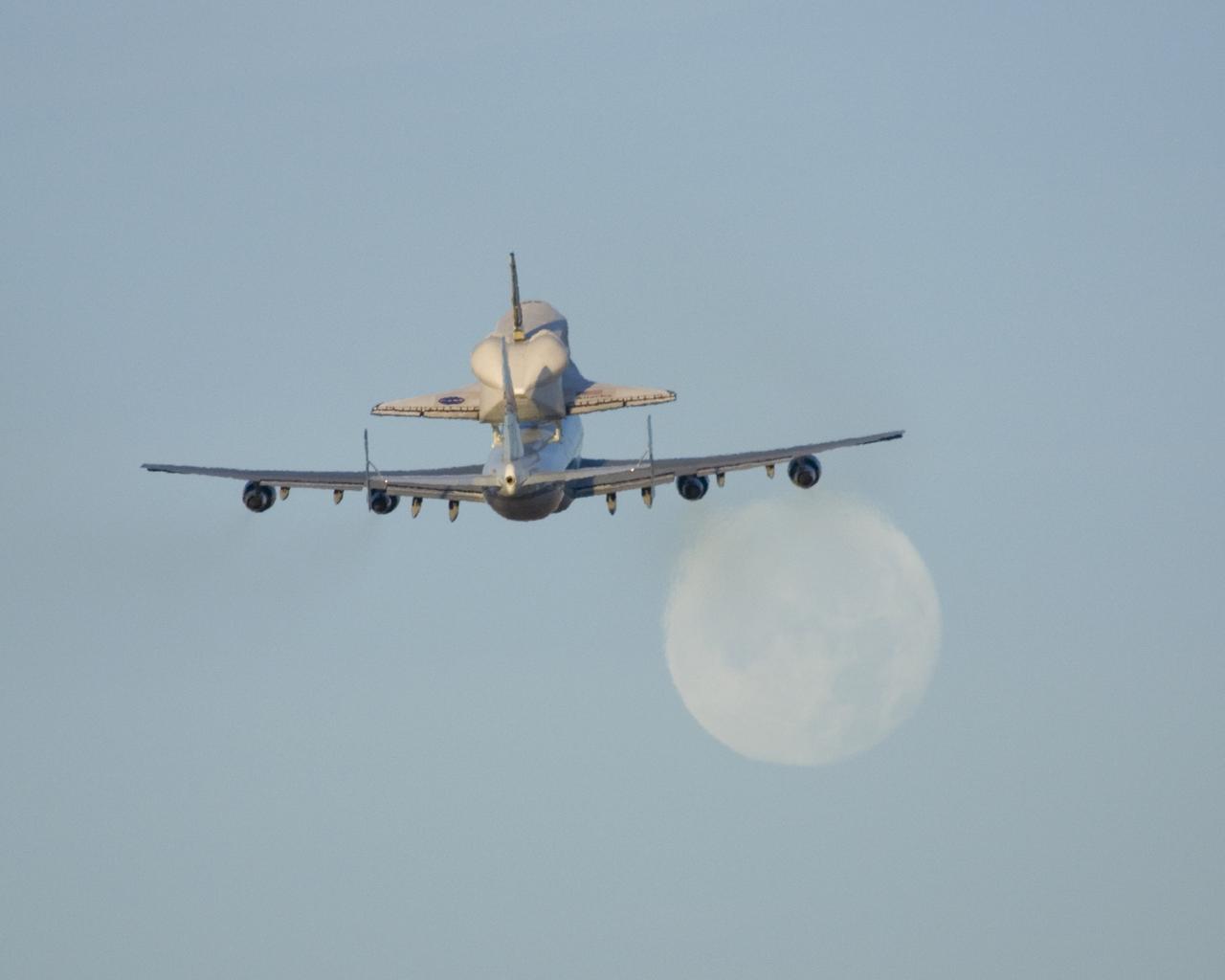

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Atlantis on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take approximately two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling.
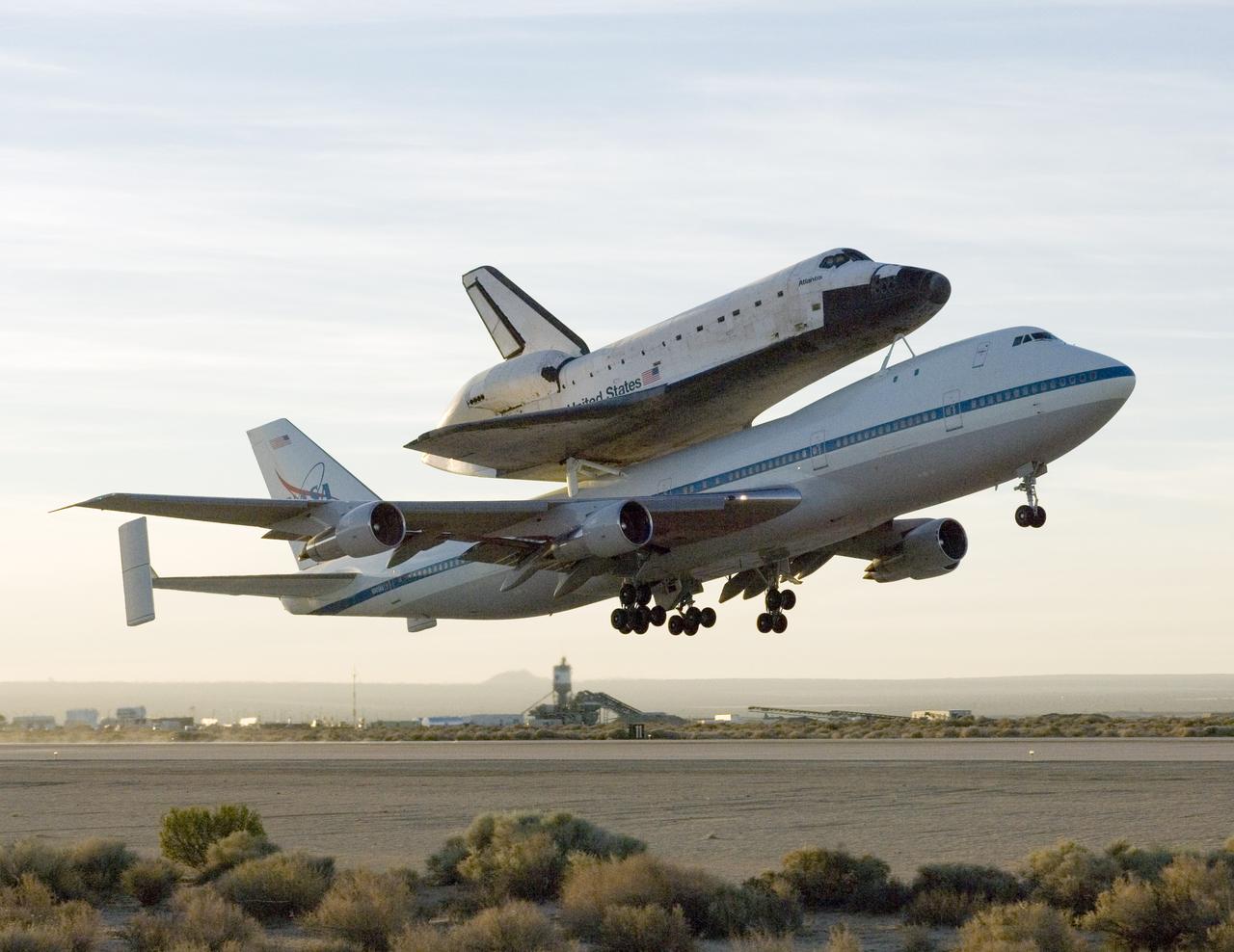

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Atlantis on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take approximately two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling.
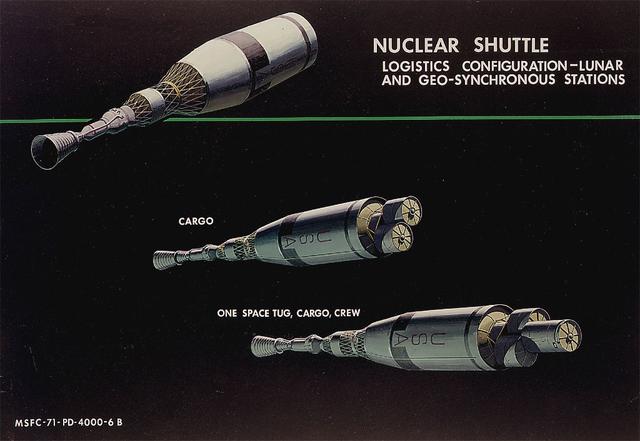
This 1971 artist's concept shows the Nuclear Shuttle in both its lunar logistics configuraton and geosynchronous station configuration. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development persornel, the Nuclear Shuttle would deliver payloads to lunar orbits or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling and additional missions.

As part of the Space Task Group's recommendations for more commonality and integration in America's space program, Marshall Space Flight Center engineers proposed an orbiting propellant storage facility to augment Space Shuttle missions. In this artist's concept from 1969 an early version of the Space Shuttle is shown refueling at the facility.
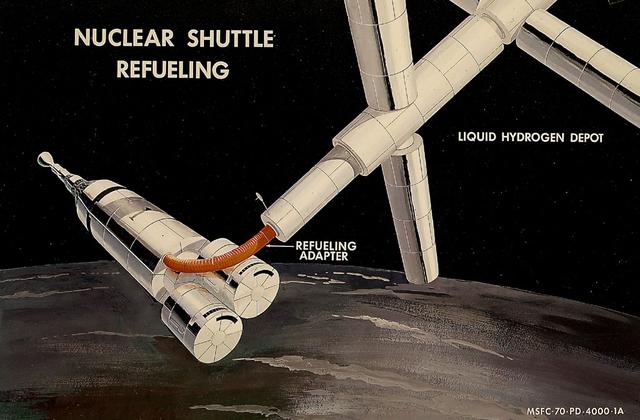
This artist's concept from 1970 shows a Nuclear Shuttle taking on fuel from an orbiting Liquid Hydrogen Depot. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development persornel, the Nuclear Shuttle would deliver payloads to lunar orbit or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling and additional missions.
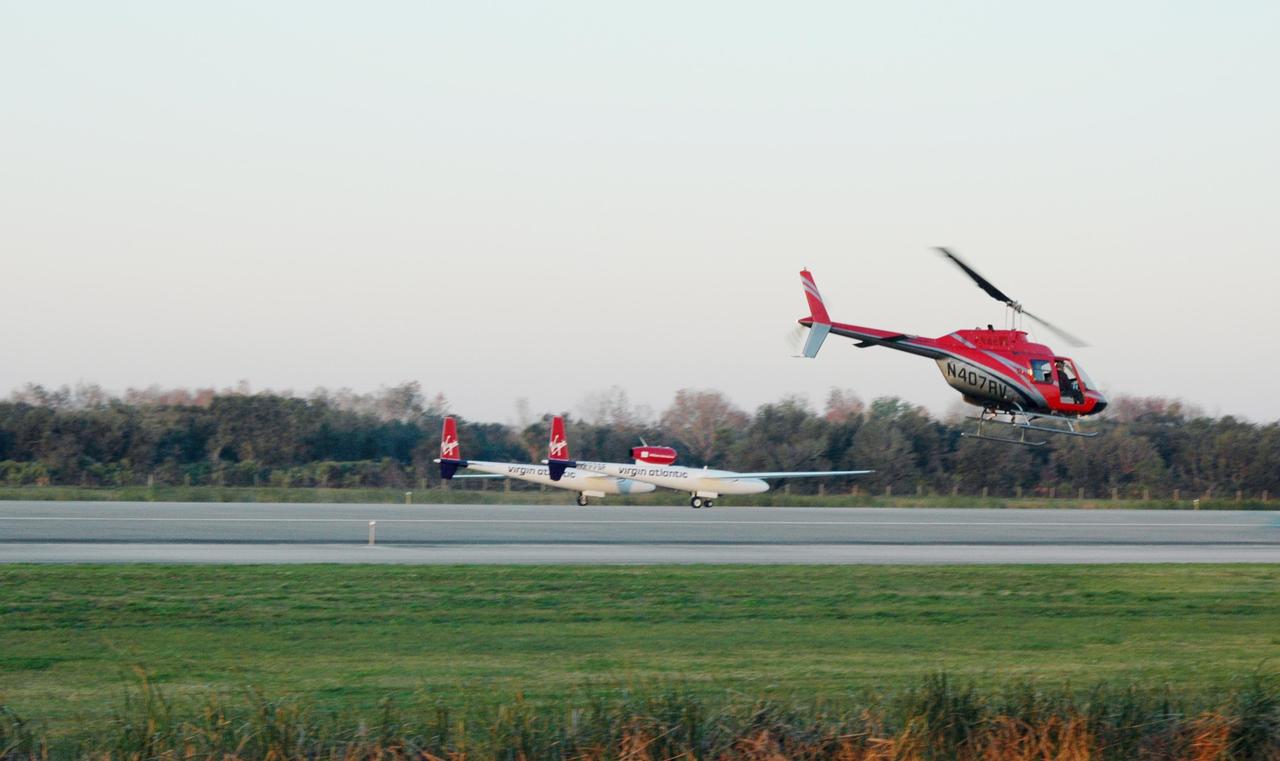

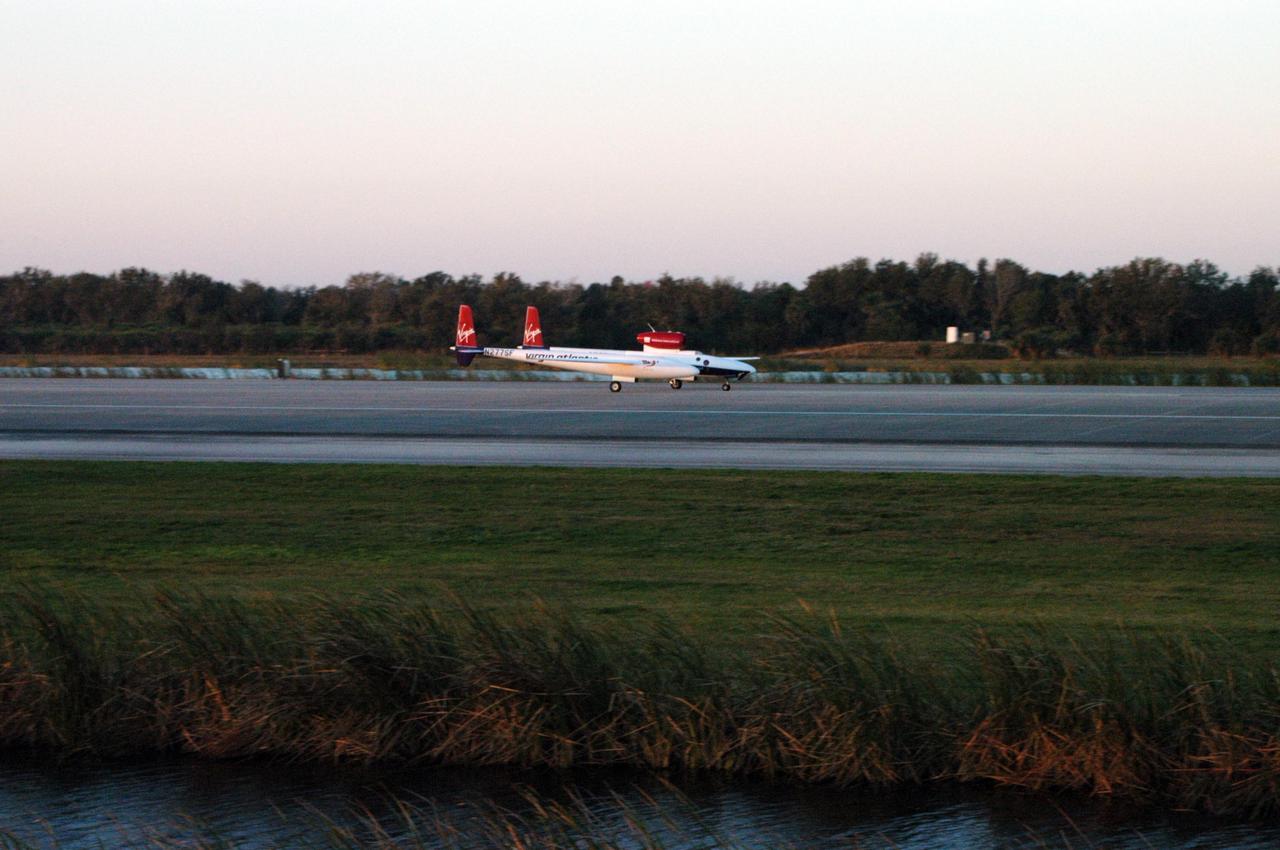
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff as a nearby helicopter films the historic event for audiences in the United Kingdom. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.
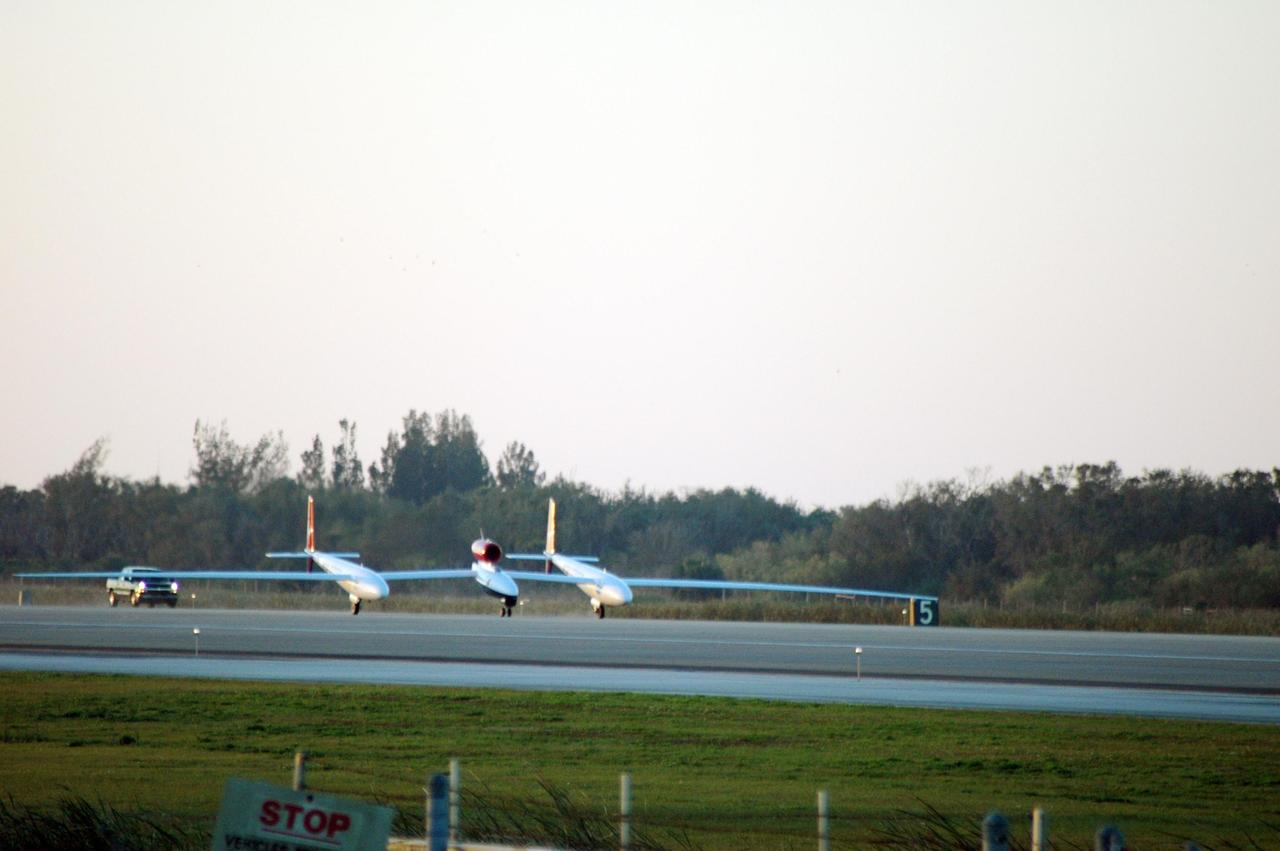

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.
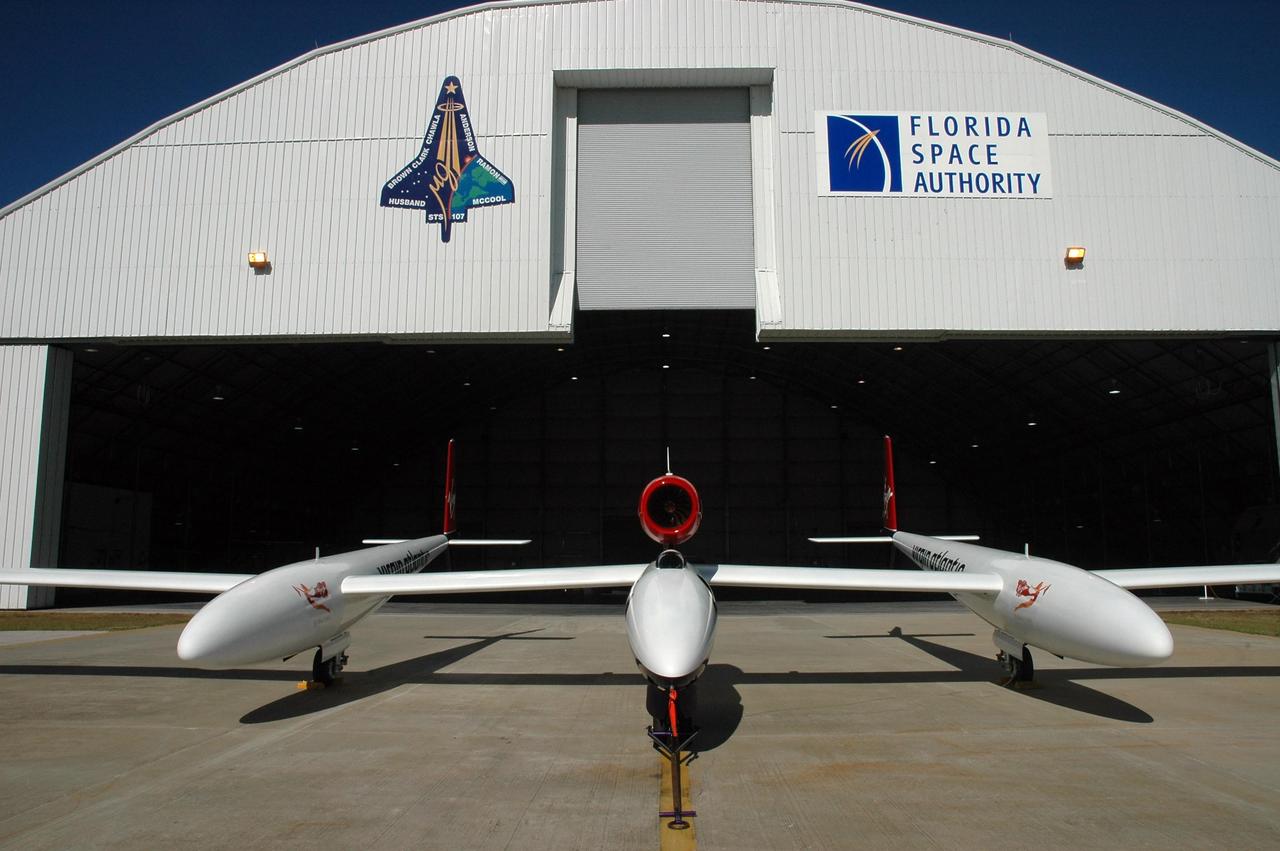

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — The Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer aircraft is on display for employees at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Final preparations are being made at Kennedy before taking off on its record-setting flight, as early as Feb. 1, from Kennedy's Space Shuttle Landing Facility. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff as a nearby helicopter films the event for audiences in the United Kingdom. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.
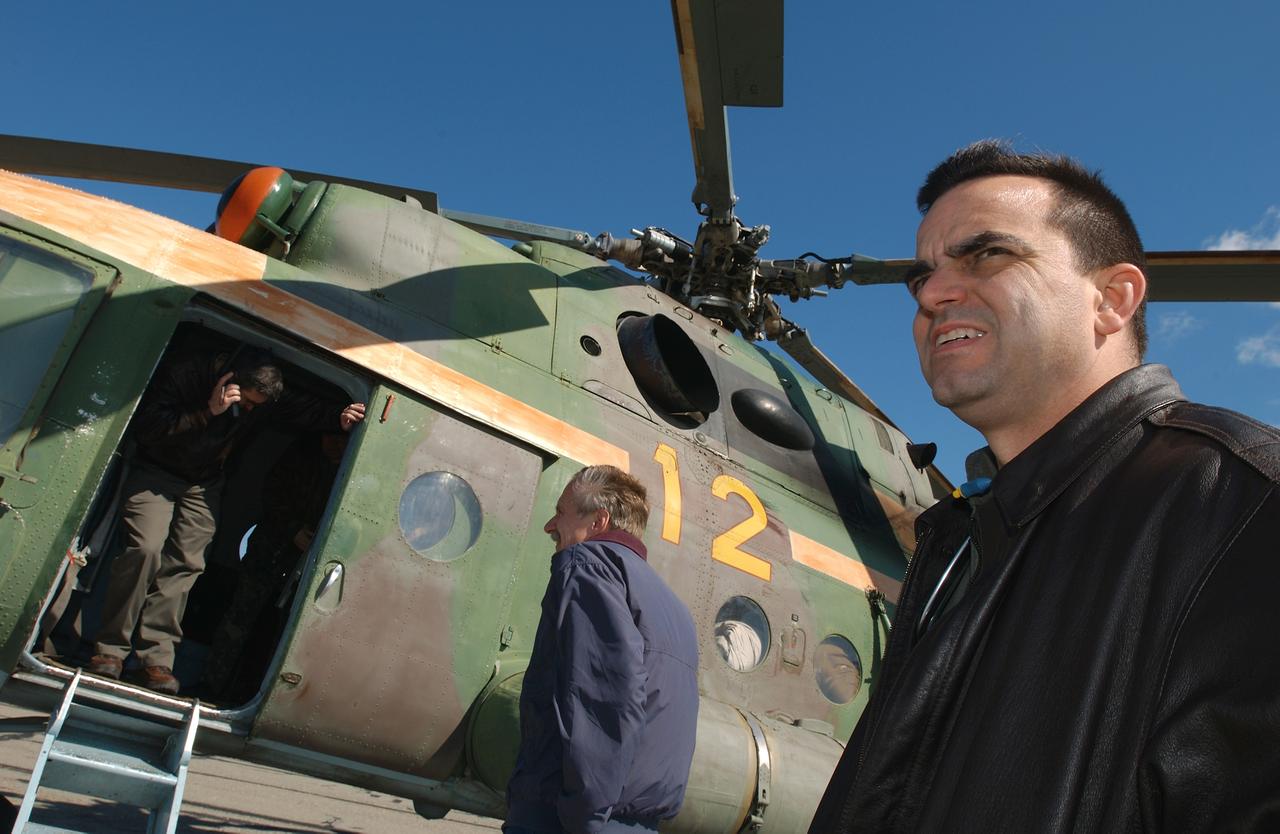

May 4, 2003, Kazakhstan. Bob Cabana (L in door), Director of Flight Crew Operations talks with NASA colleagues on the satellite phone from a Russian helicopter while Bill Gerstenmaier (center), I.S.S. Program Manager and J.D. Polk (R), Expedition Six Flight Surgeon wait to get word if they will be continuing on to the landing site after a refueling stop. Photo Credit: "NASA/Bill Ingalls"
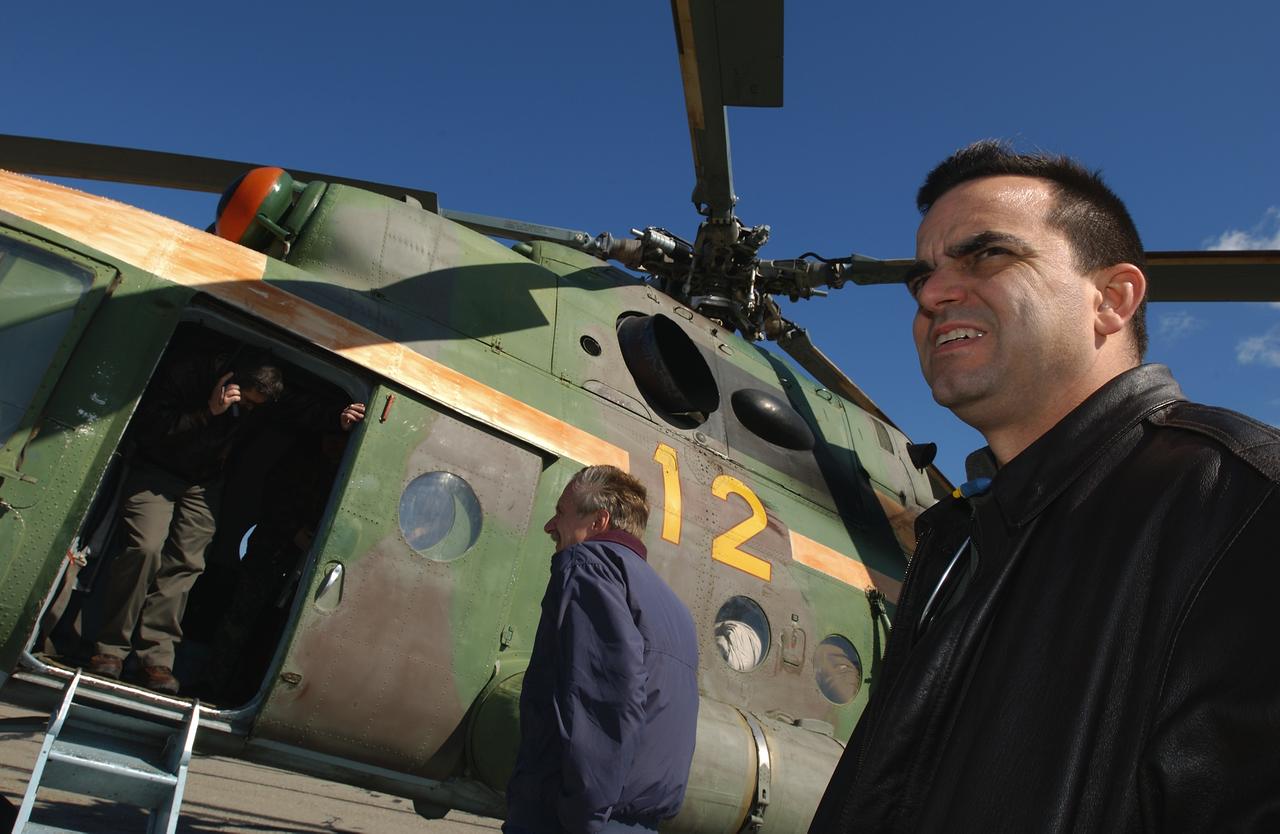

Director of Flight Crew Operations Bob Cabana, upper left, talks with NASA colleagues on the satellite phone from a Russian helicopter while International Space Station Program Manager, William Gerstenmaier and J.D. Polk, Expedition 6 Flight Surgeon, right, wait to get word if they will be continuing on to the landing site after a refueling stop, Tuesday, May 4, 2003 in Kazakhstan. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
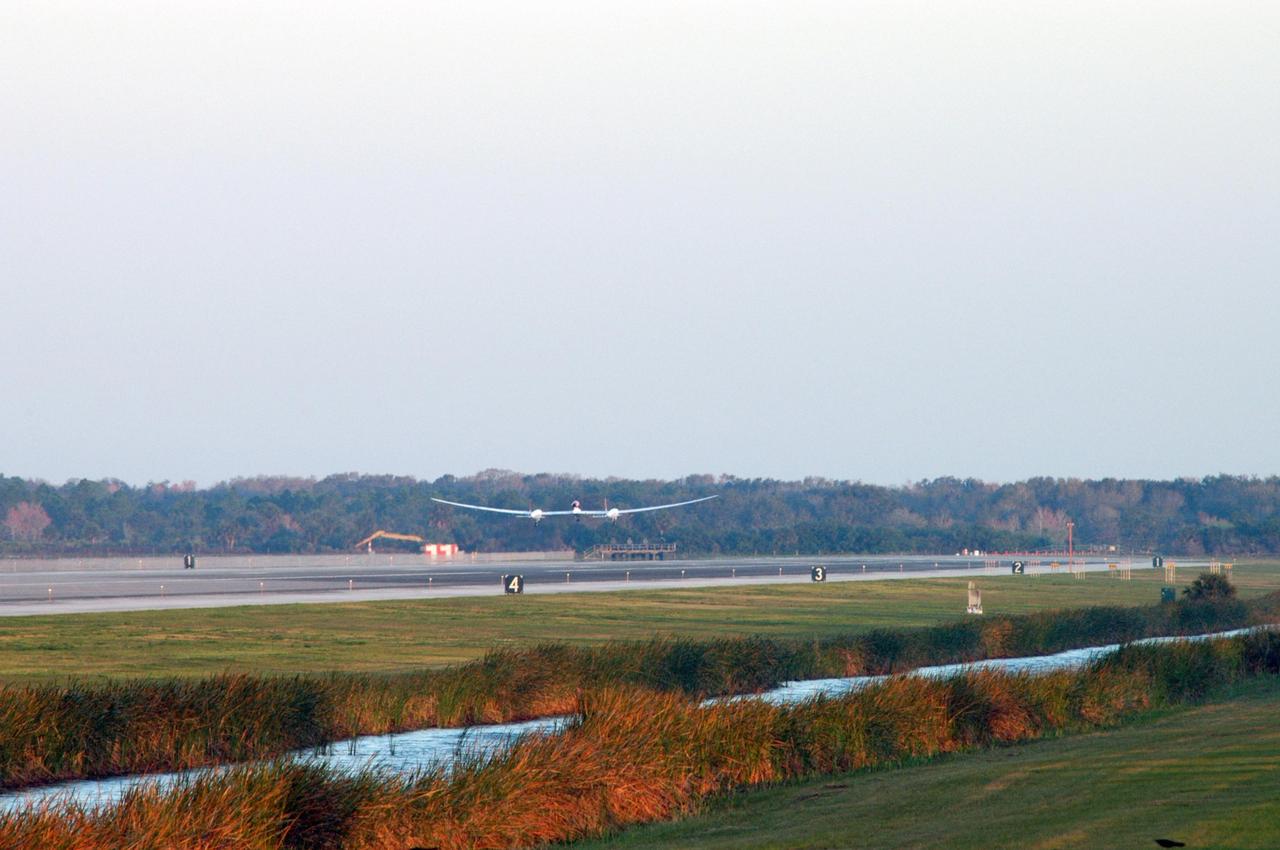

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, lifts off the ground. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
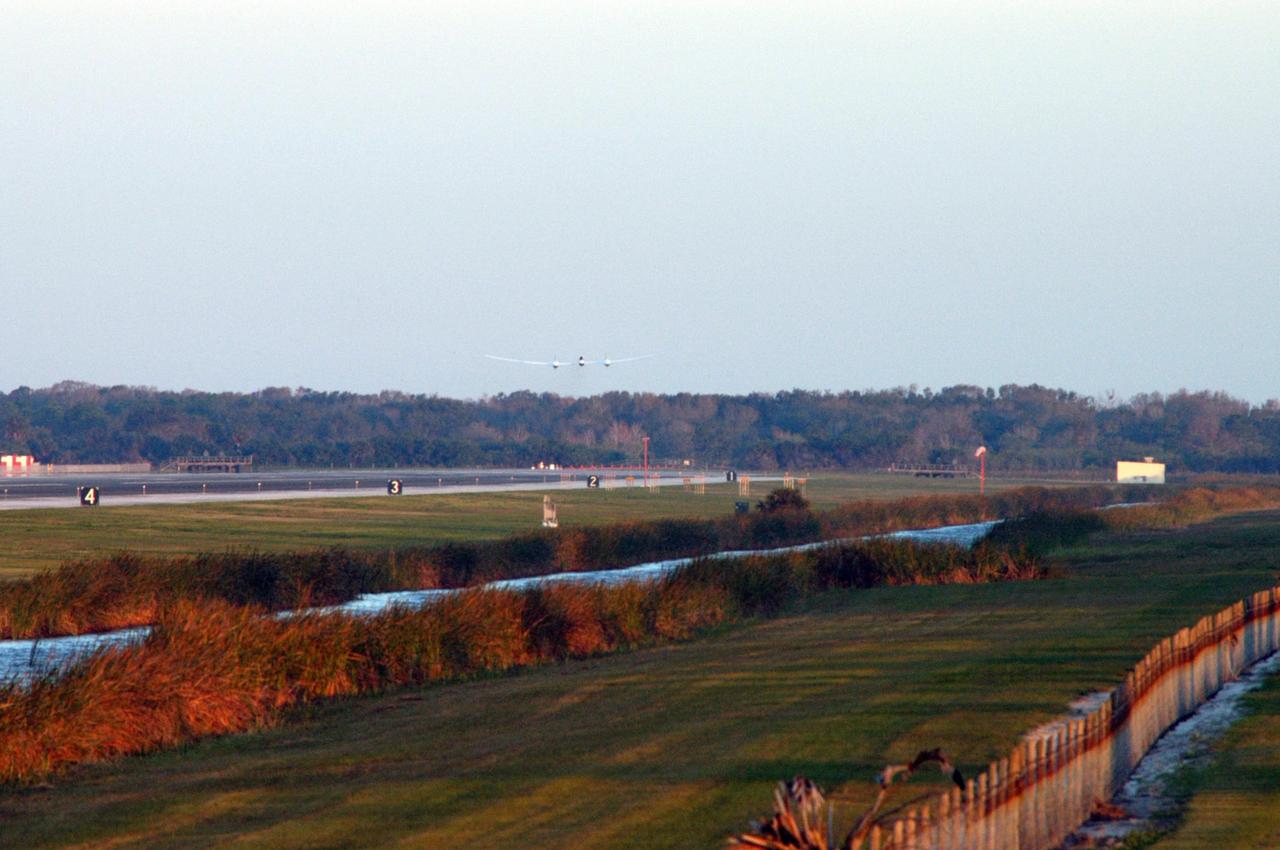

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - From NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, is airborne. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
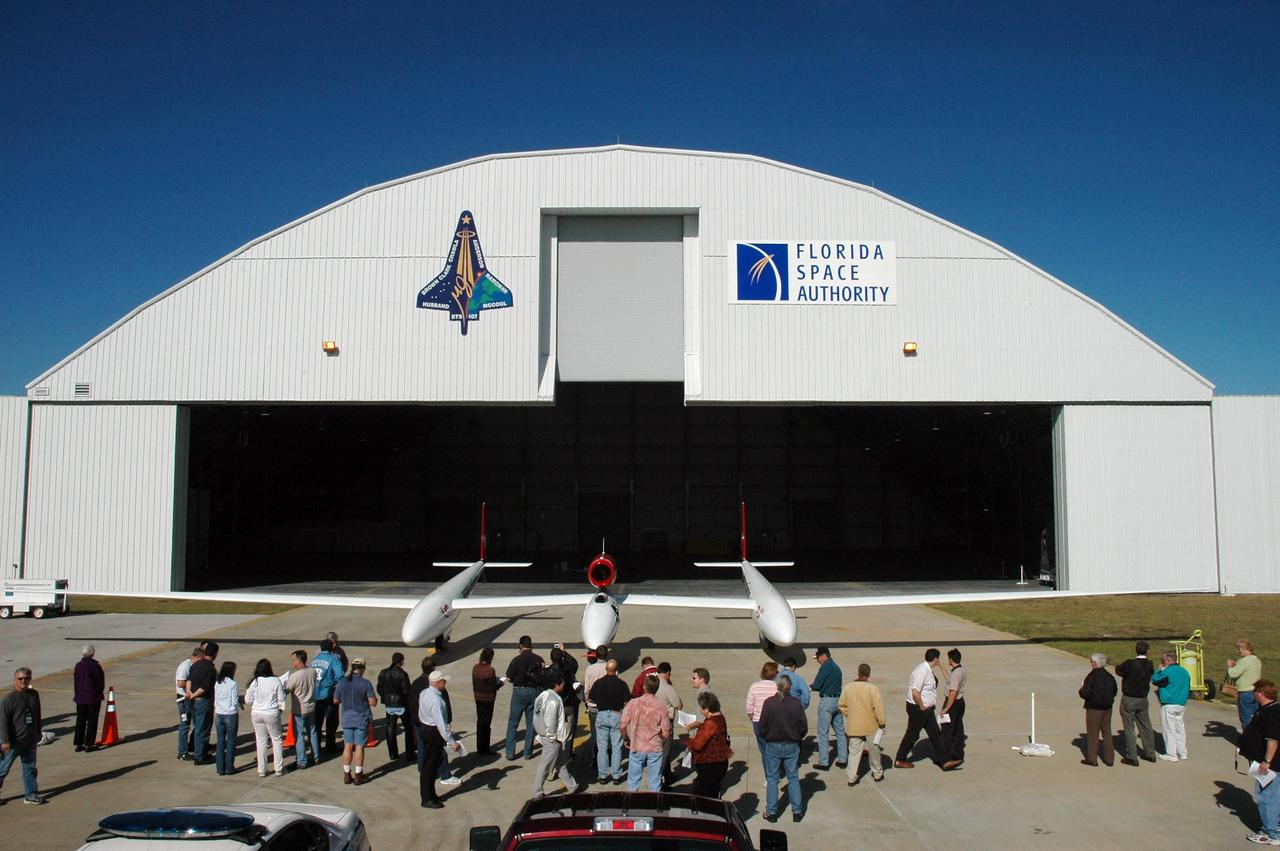

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — The Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer aircraft is on display for employees at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Final preparations are being made at Kennedy before taking off on its record-setting flight, as early as Feb. 1, from Kennedy's Space Shuttle Landing Facility. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
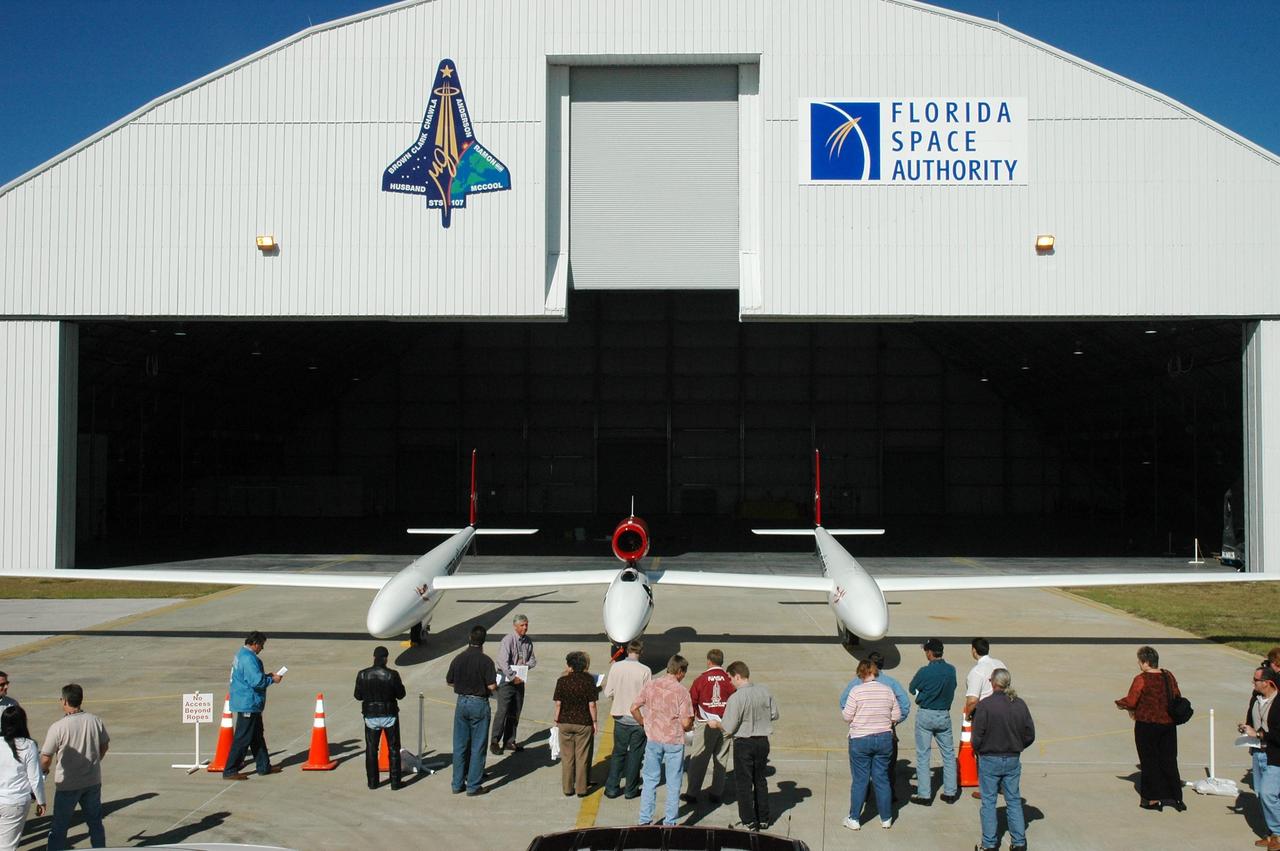

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — The Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer aircraft is on display for employees at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Fla. Steve Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Final preparations are being made at Kennedy before taking off on its record-setting flight, as early as Feb. 1, from Kennedy's Space Shuttle Landing Facility. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
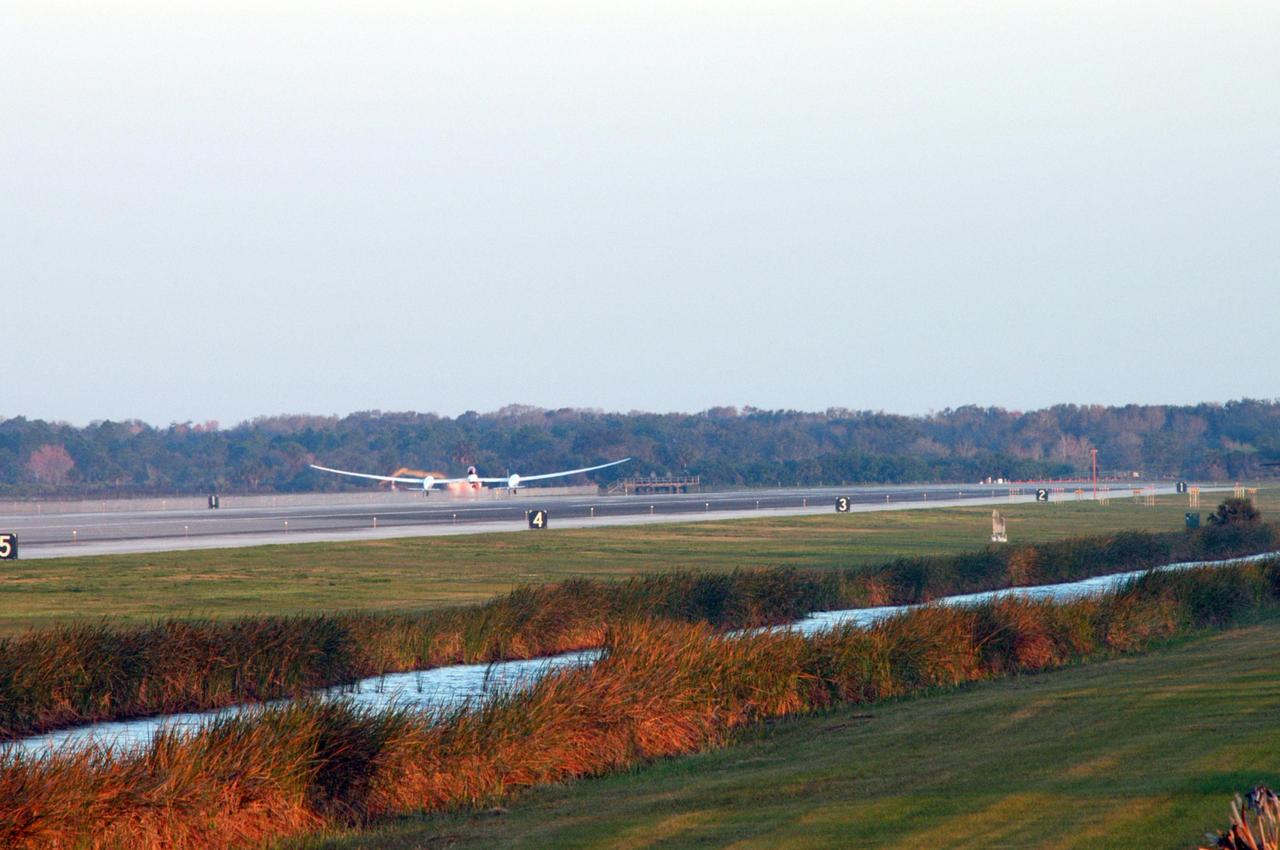

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility runway, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, begins its takeoff. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
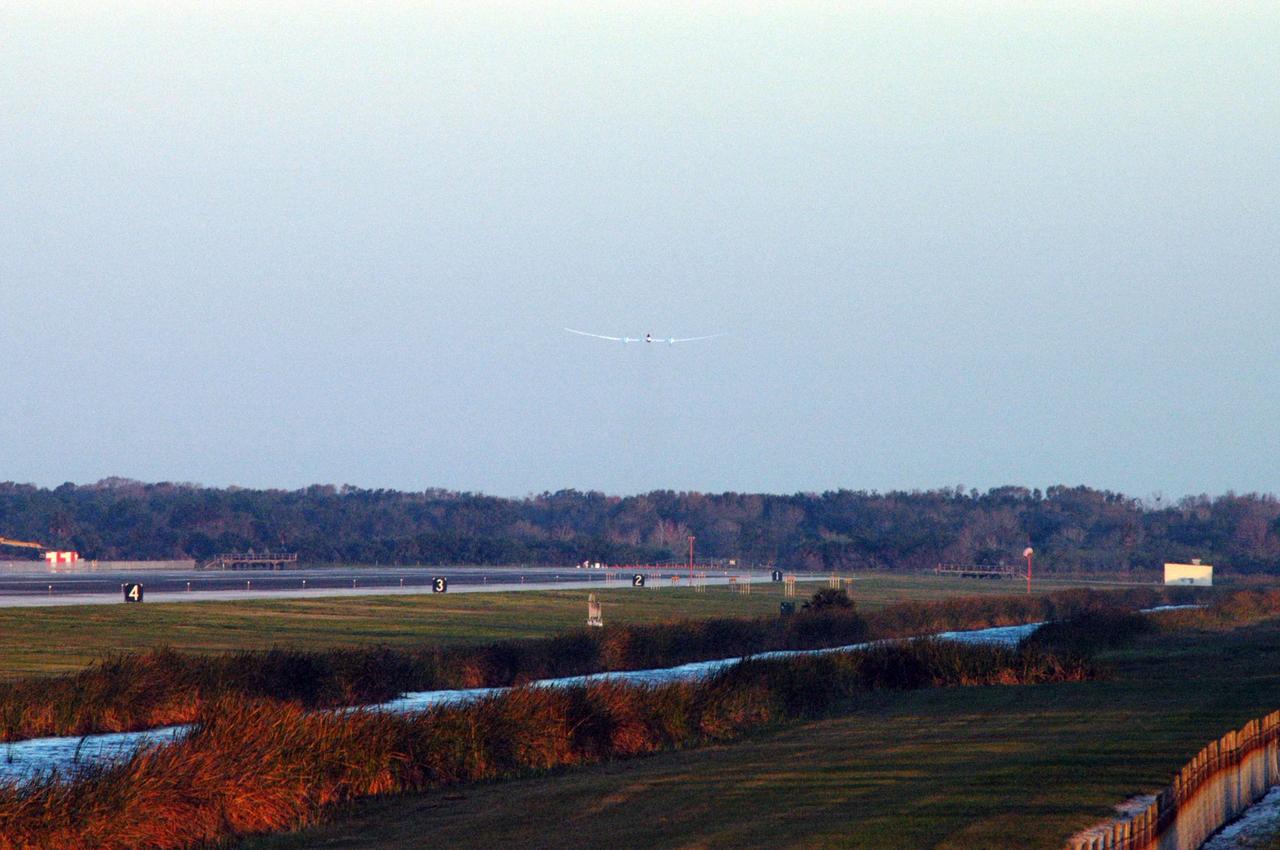

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - With little runway to spare, the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer, piloted by Steve Fossett, is airborne from NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

Cape Canaveral, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis soars into a layer of thin clouds at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida moments after lifting off on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/ Jim Grossmann Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim will lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: Jim Grossmann
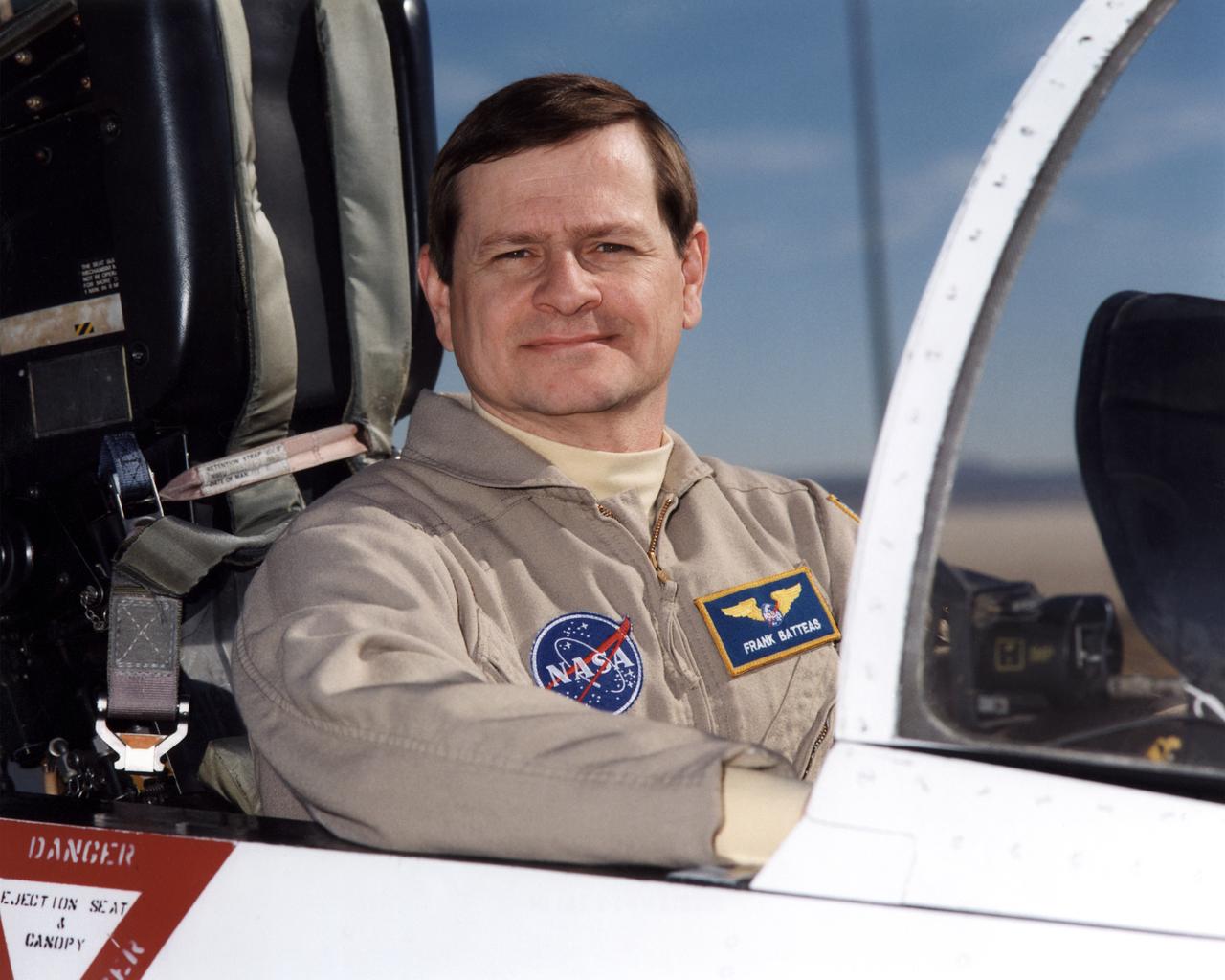

Frank Batteas is a research test pilot in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. He is currently a project pilot for the F/A-18 and C-17 flight research projects. In addition, his flying duties include operation of the DC-8 Flying Laboratory in the Airborne Science program, and piloting the B-52B launch aircraft, the King Air, and the T-34C support aircraft. Batteas has accumulated more than 4,700 hours of military and civilian flight experience in more than 40 different aircraft types. Batteas came to NASA Dryden in April 1998, following a career in the U.S. Air Force. His last assignment was at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio, where Lieutenant Colonel Batteas led the B-2 Systems Test and Evaluation efforts for a two-year period. Batteas graduated from Class 88A of the Air Force Test Pilot School, Edwards Air Force Base, California, in December 1988. He served more than five years as a test pilot for the Air Force's newest airlifter, the C-17, involved in nearly every phase of testing from flutter and high angle-of-attack tests to airdrop and air refueling envelope expansion. In the process, he achieved several C-17 firsts including the first day and night aerial refuelings, the first flight over the North Pole, and a payload-to-altitude world aviation record. As a KC-135 test pilot, he also was involved in aerial refueling certification tests on a number of other Air Force aircraft. Batteas received his commission as a second lieutenant in the U. S. Air Force through the Reserve Officer Training Corps and served initially as an engineer working on the Peacekeeper and Minuteman missile programs at the Ballistic Missile Office, Norton Air Force Base, Calif. After attending pilot training at Williams Air Force Base, Phoenix, Ariz., he flew operational flights in the KC-135 tanker aircraft and then was assigned to research flying at the 4950th Test Wing, Wright-Patterson. He flew extensively modified C-135

iss072e423785 (1/3/2025) — A view of the CLINGERS Cubesat connection mechanism aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Flight Tech Demo of Docking/Undocking Cubesats Inside ISS (CLINGERS) uses the International Space Station’s Astrobee robots to demonstrate an adaptor for docking and close approach sensing to connect both active and passive objects in space. These are critical functions to enable applications such as satellite servicing, orbital refueling, spacecraft repair and upgrade, and in-orbit manufacturing.
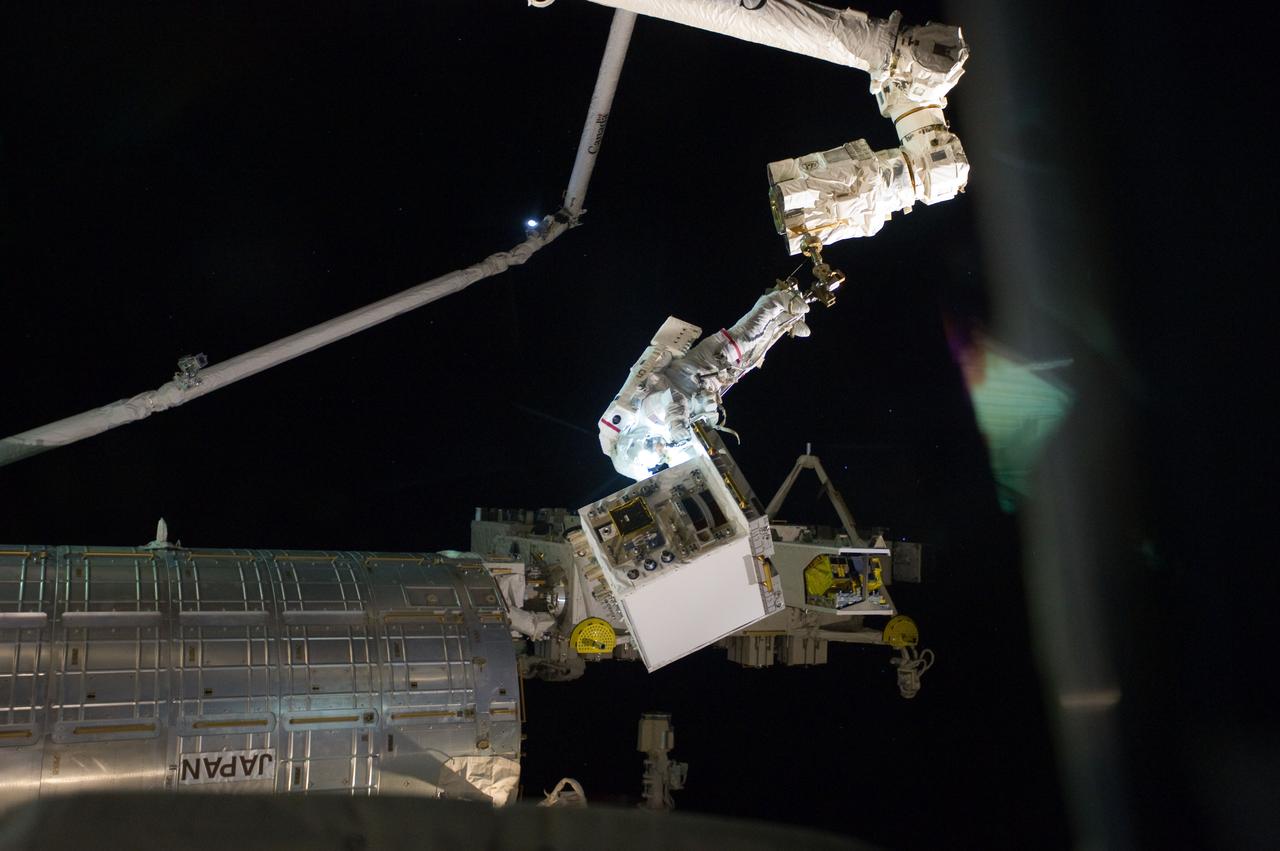

S135-E-007535 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system’s robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum, is holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. NASA astronaut Ron Garan, also a station flight engineer, who shared the spacewalk with Fossum, is out of frame. Photo credit: NASA
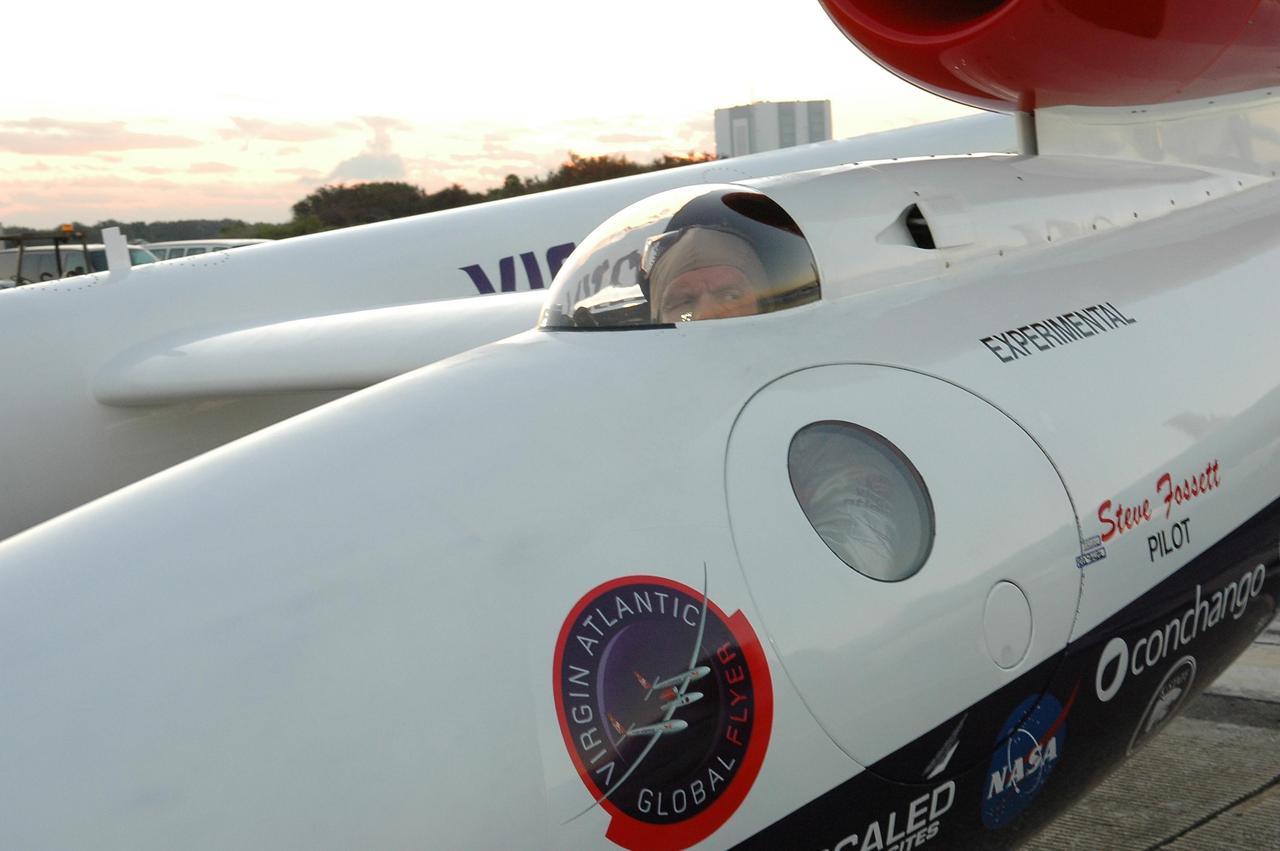

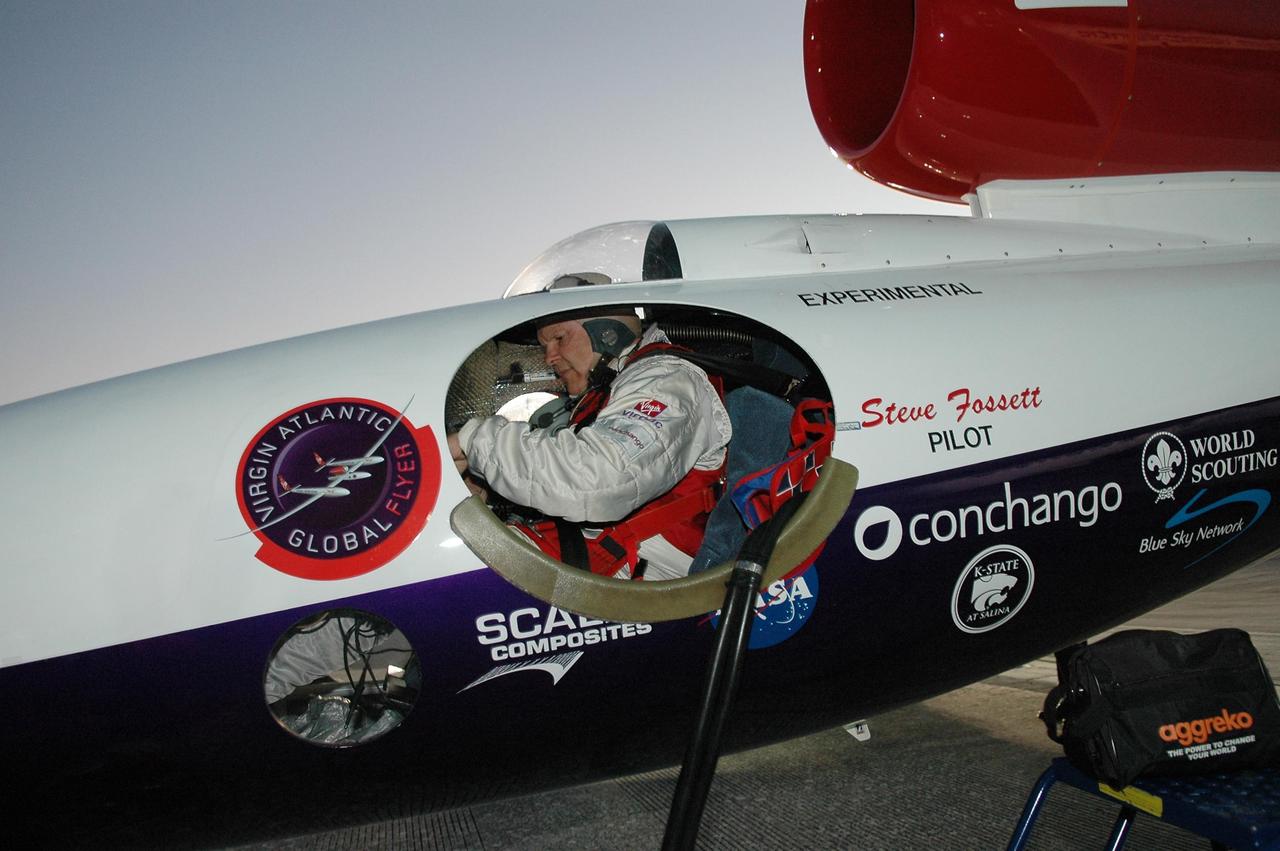
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, the door is closed on the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer as pilot Steve Fossett looks out the cockpit window. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett stands next to the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer aircraft. Fossett will pilot the aircraft on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility early Tuesday morning. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

S84-43433 (11 Oct 1984) --- Photographed through aft flight deck windows, this 70mm frame shows Astronauts David C. Leestma, left, and Kathryn D. Sullivan at the orbital refueling system (ORS) in the aft cargo bay. A wrist camera on the remote manipulator system (RMS) is perched to record the historic extravehicular activity (EVA). Dr. Sullivan's part of the EVA represented the first such feat for an American woman.
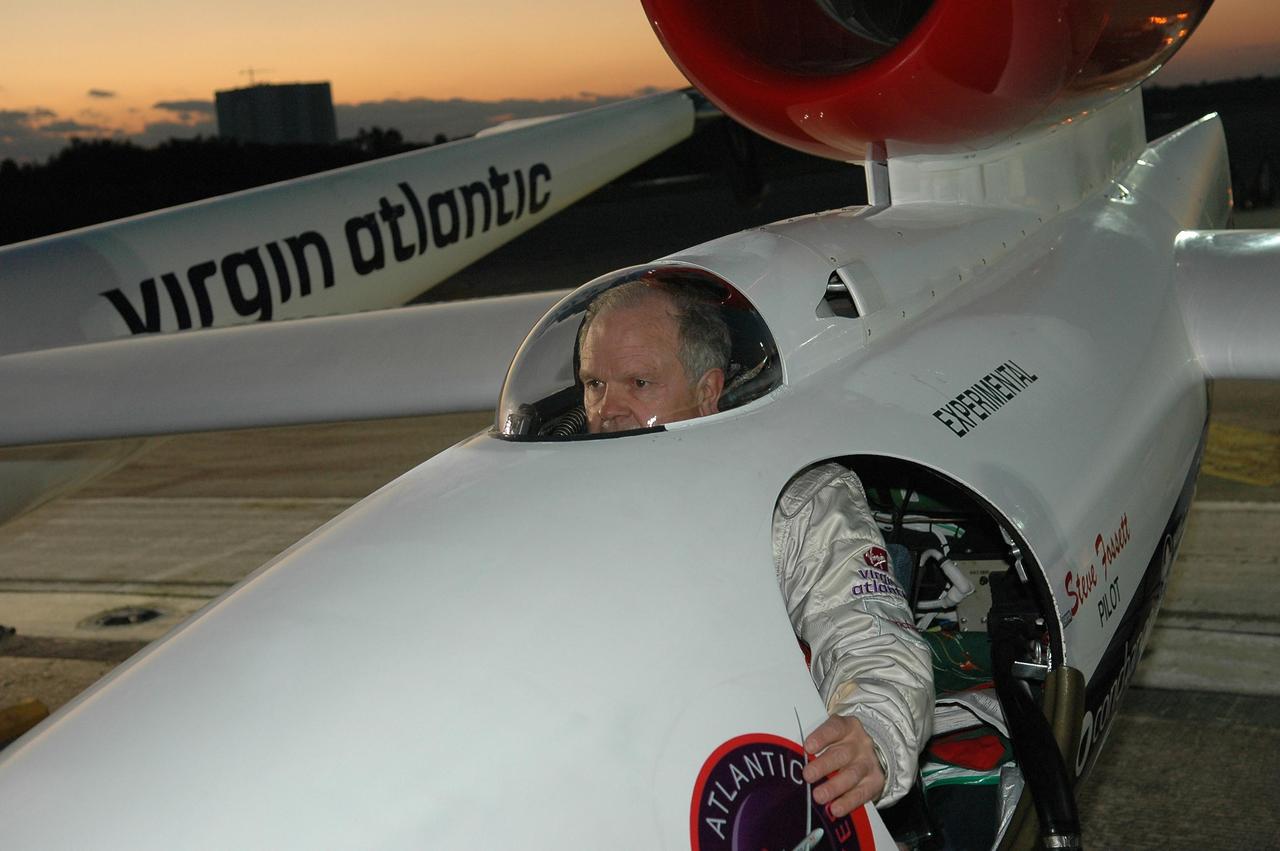

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett, seated in the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer cockpit, checks visibility and head space. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

iss072e747124 (March 18, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers works inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module loading software onto an Astrobee robotic free-flyer. The software is part of a technology investigation demonstrating an adaptor for docking and close approach sensing to connect both active and passive objects in space. Results may enable applications such as satellite servicing, orbital refueling, spacecraft repair and upgrade, and in-orbit manufacturing.
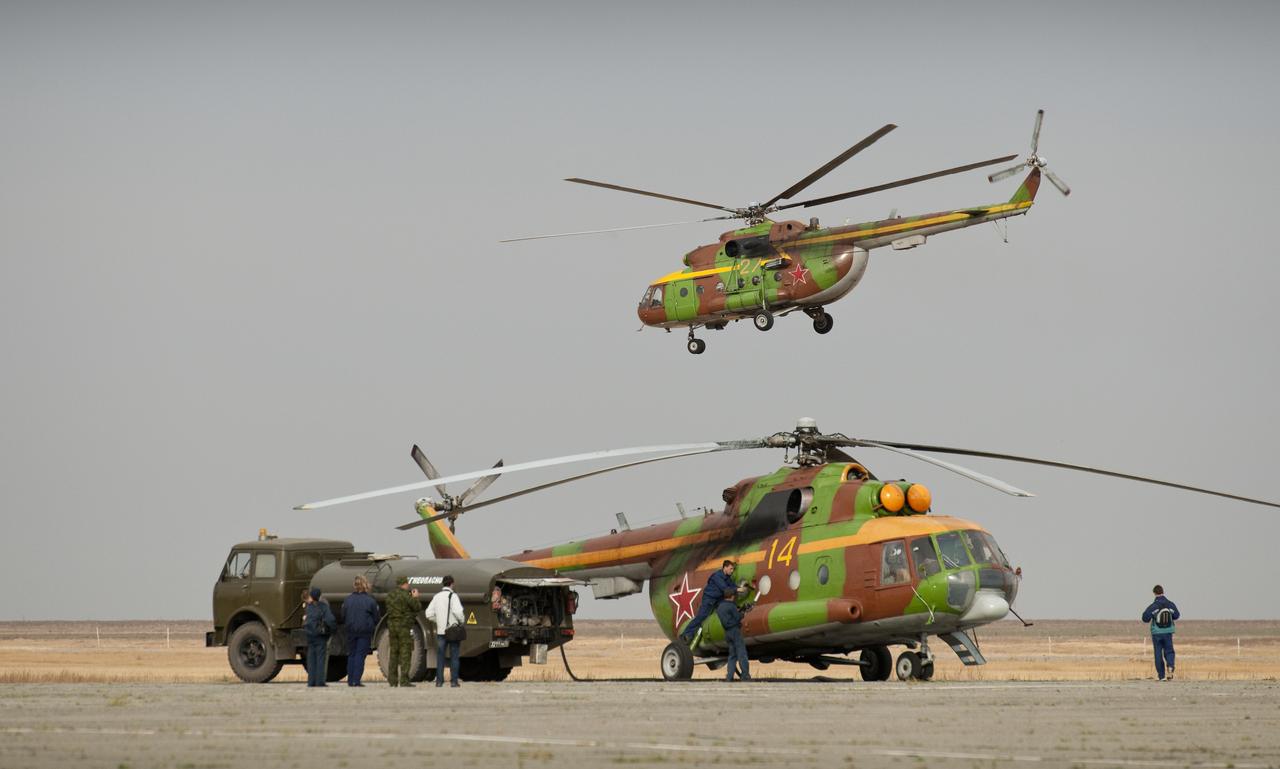

Russian search and rescue helicopters refuel in Arkalyk, Kazakhstan prior to the landing of the Soyuz TMA-18 spacecraft with Expedition 24 Commander Alexander Skvortsov and Flight Engineers Tracy Caldwell Dyson and Mikhail Kornienko on Saturday, Sept. 25, 2010. Russian Cosmonauts Skvortsov and Kornienko and NASA Astronaut Caldwell Dyson, are returning from six months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 23 and 24 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
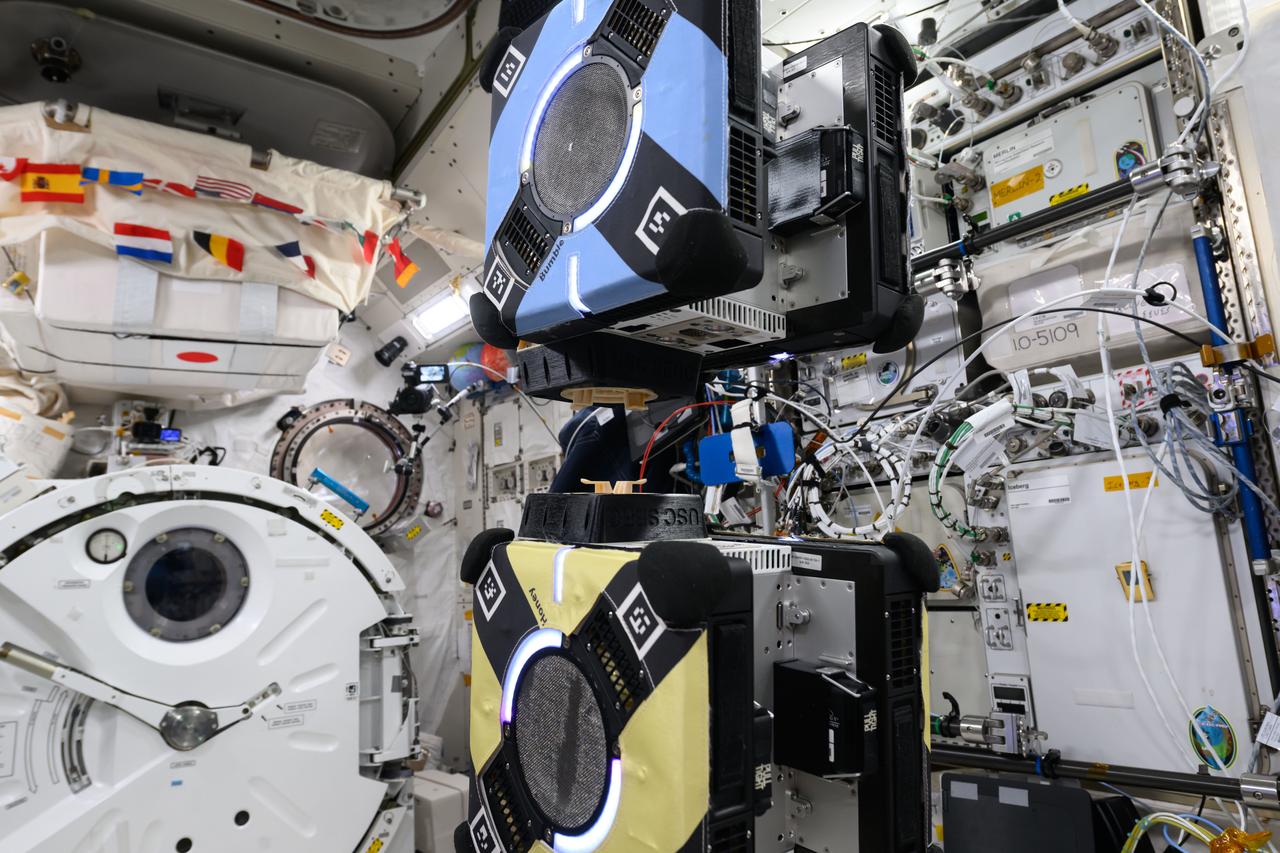

iss072e423875 (1/3/2025) — A view of the CLINGERS Cubesats attached to Astrobee aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Flight Tech Demo of Docking/Undocking Cubesats Inside ISS (CLINGERS) uses the International Space Station’s Astrobee robots to demonstrate an adaptor for docking and close approach sensing to connect both active and passive objects in space. These are critical functions to enable applications such as satellite servicing, orbital refueling, spacecraft repair and upgrade, and in-orbit manufacturing.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at dawn, Steve Fossett (left) gets ready to climb into the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer parked on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
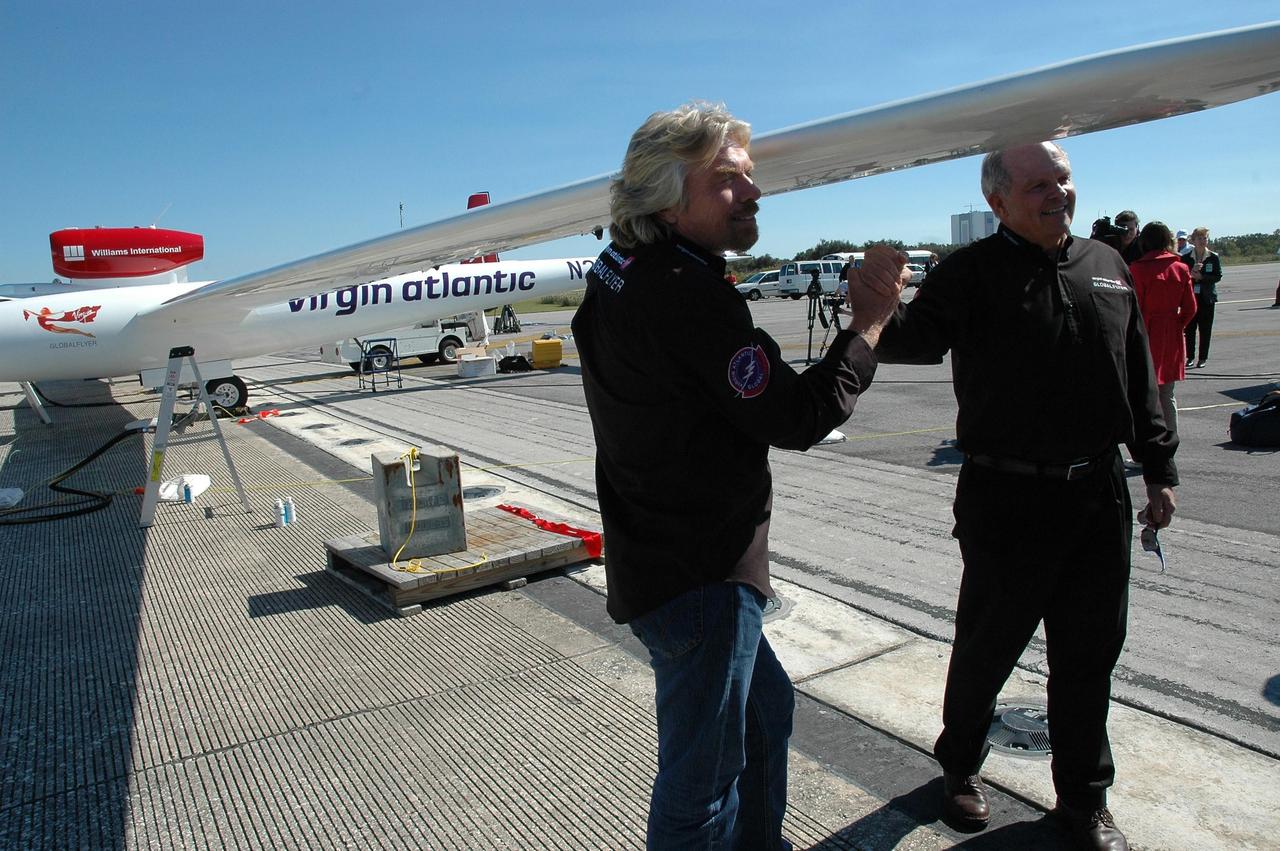

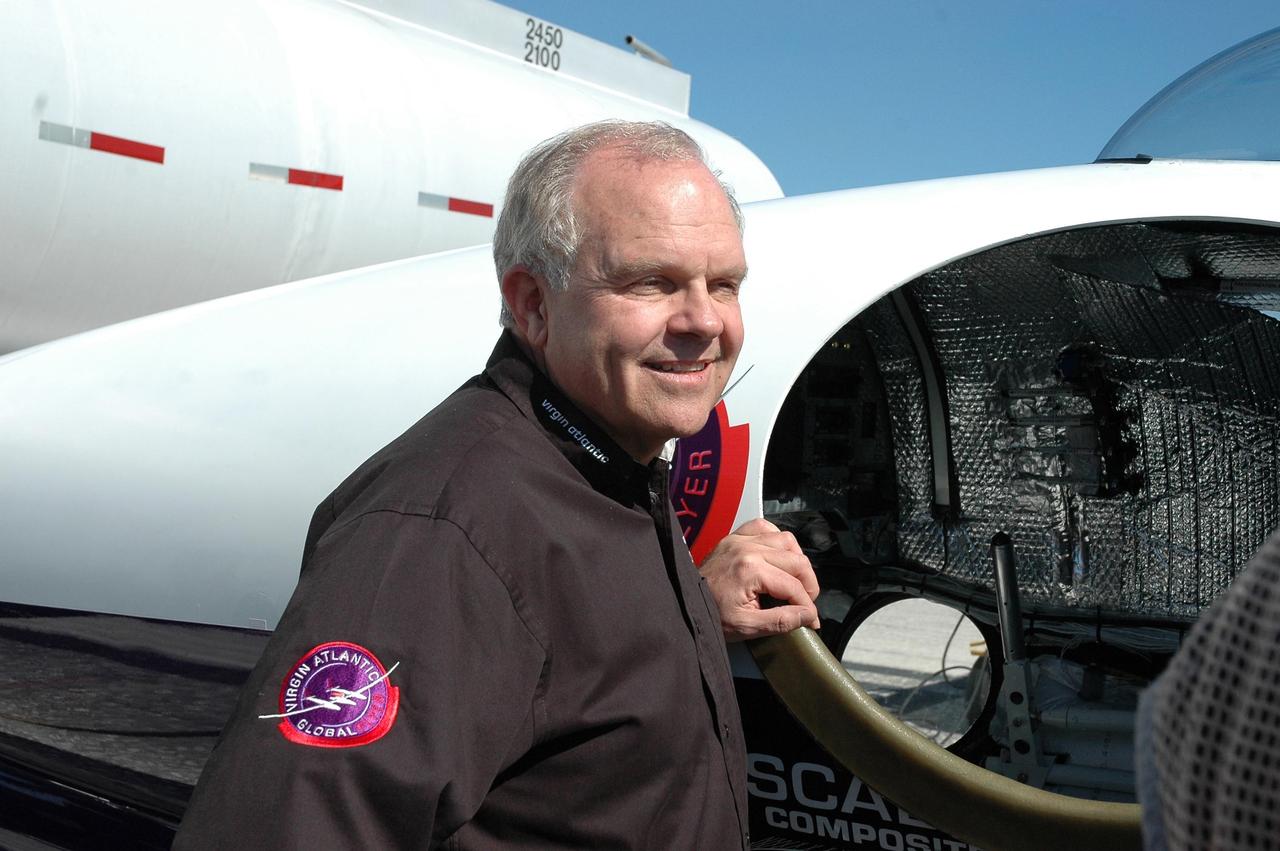
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Sir Richard Branson (left), chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic, talks with Steve Fossett. They are standing next to the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer aircraft, which Fossett will pilot on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility early Tuesday morning. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
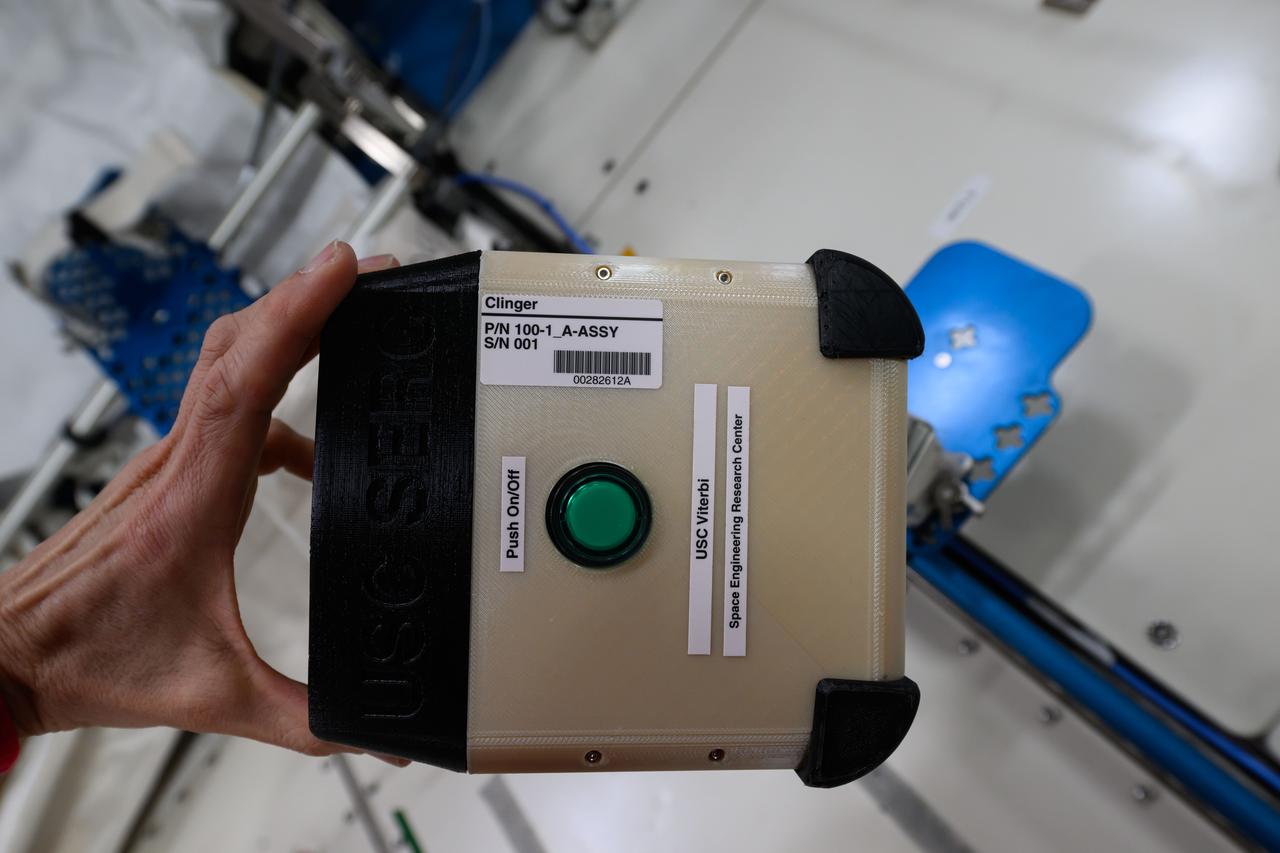

iss072e423784 (1/3/2025) — A view of the CLINGERS Cubesat aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Flight Tech Demo of Docking/Undocking Cubesats Inside ISS (CLINGERS) uses the International Space Station’s Astrobee robots to demonstrate an adaptor for docking and close approach sensing to connect both active and passive objects in space. These are critical functions to enable applications such as satellite servicing, orbital refueling, spacecraft repair and upgrade, and in-orbit manufacturing.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett, seated in the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer cockpit, completes the checkout before takeoff. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
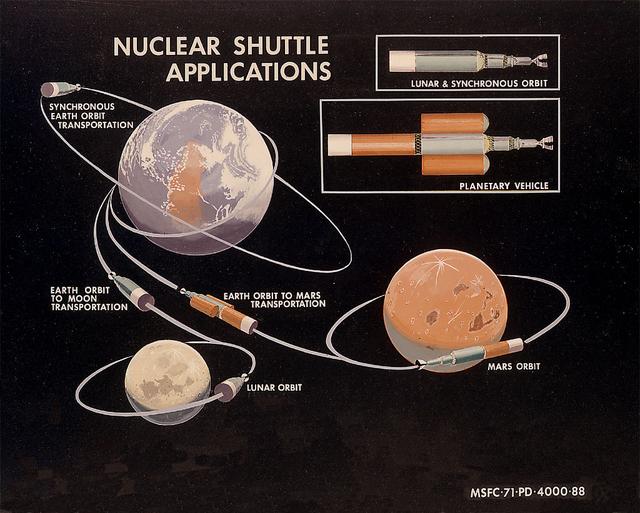
In this 1971 artist's concept, the Nuclear Shuttle is shown in various space-based applications. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development persornel, the Nuclear Shuttle would deliver payloads to geosychronous Earth orbits or lunar orbits then return to low Earth orbit for refueling. A cluster of Nuclear Shuttle units could form the basis for planetary missions.
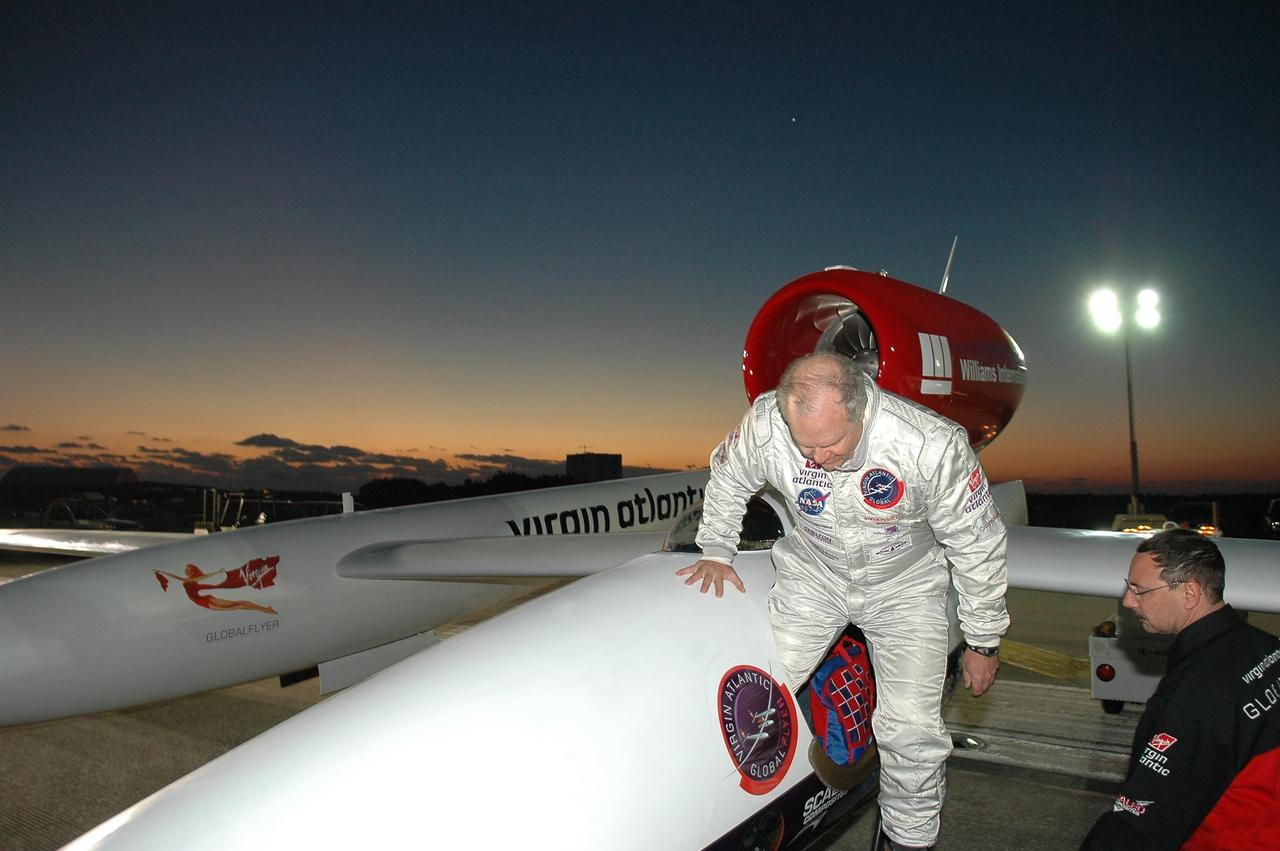

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at dawn, Steve Fossett (left) climbs into the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer parked on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
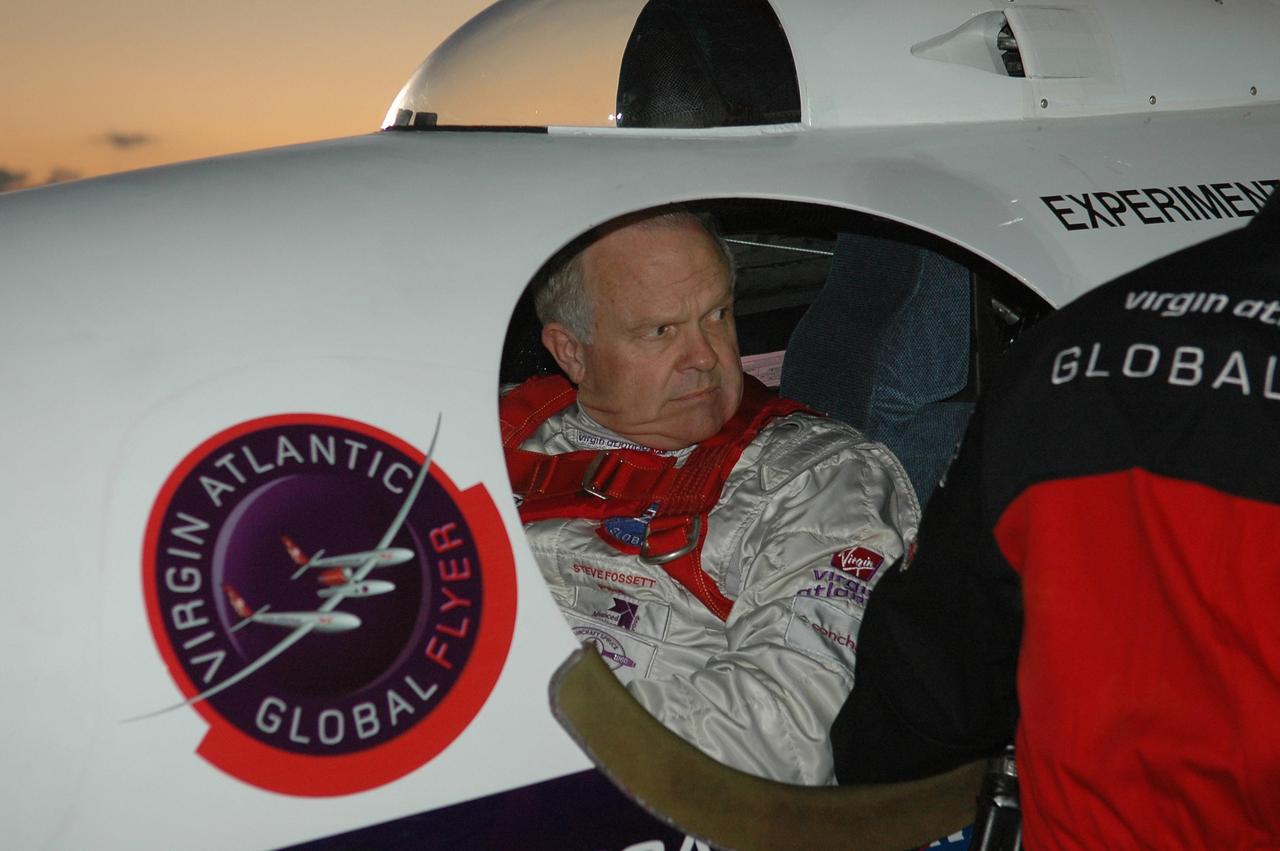

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett is strapped into the cockpit of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer waiting for takeoff. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
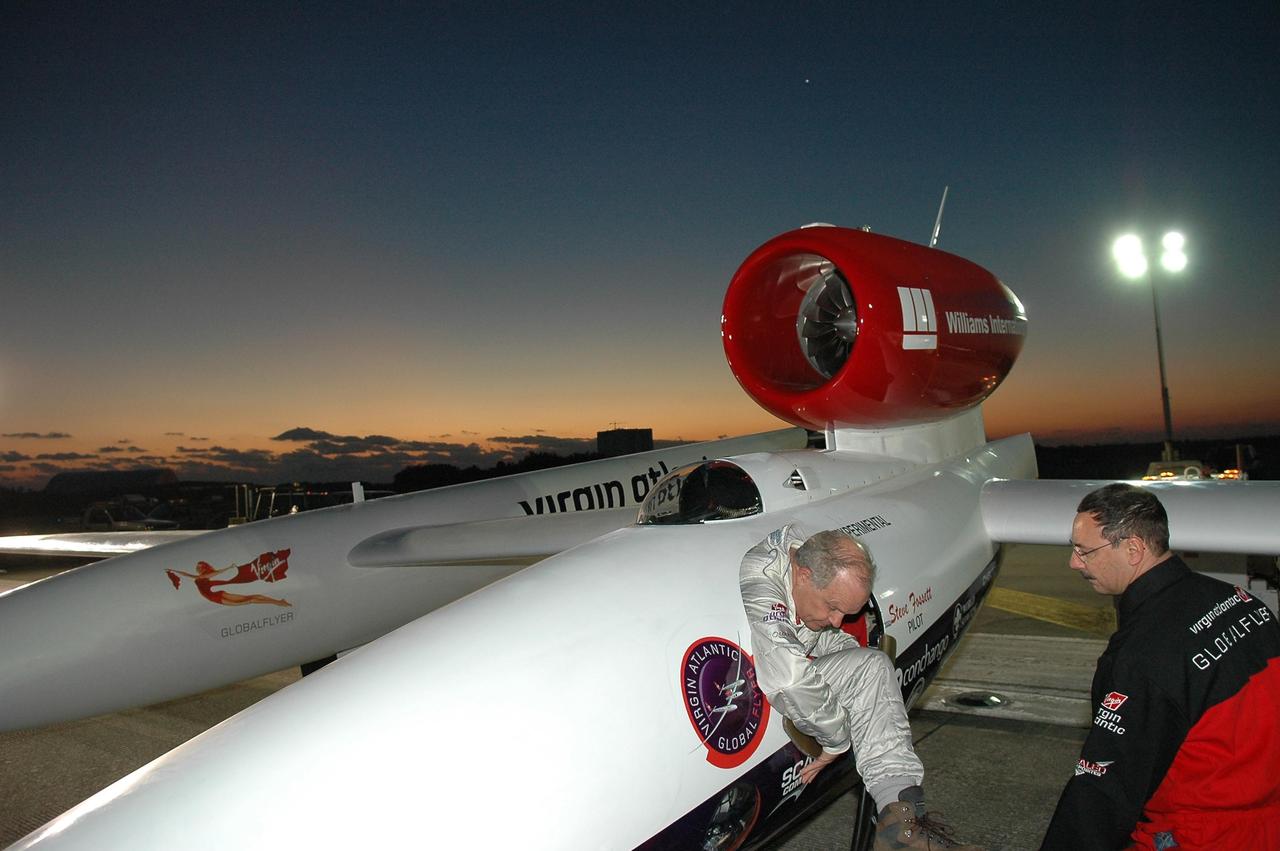

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at dawn, Steve Fossett (left) climbs into the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer parked on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
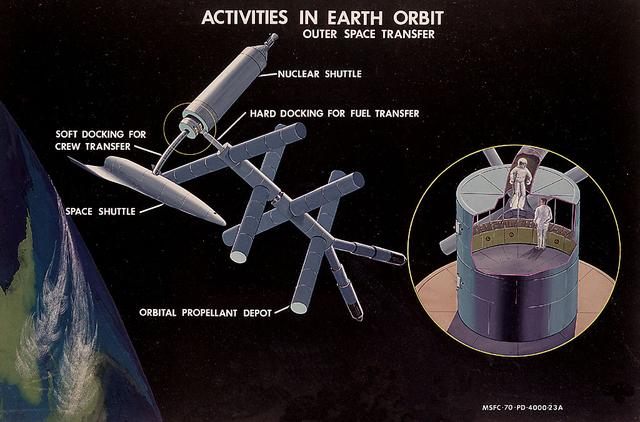
This artist's concept from 1970 shows a Nuclear Shuttle docked to an Orbital Propellant Depot and an early Space Shuttle. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development plarners, the Nuclear Shuttle, in either manned or unmanned mode, would deliver payloads to lunar orbit or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling and additonal missions.
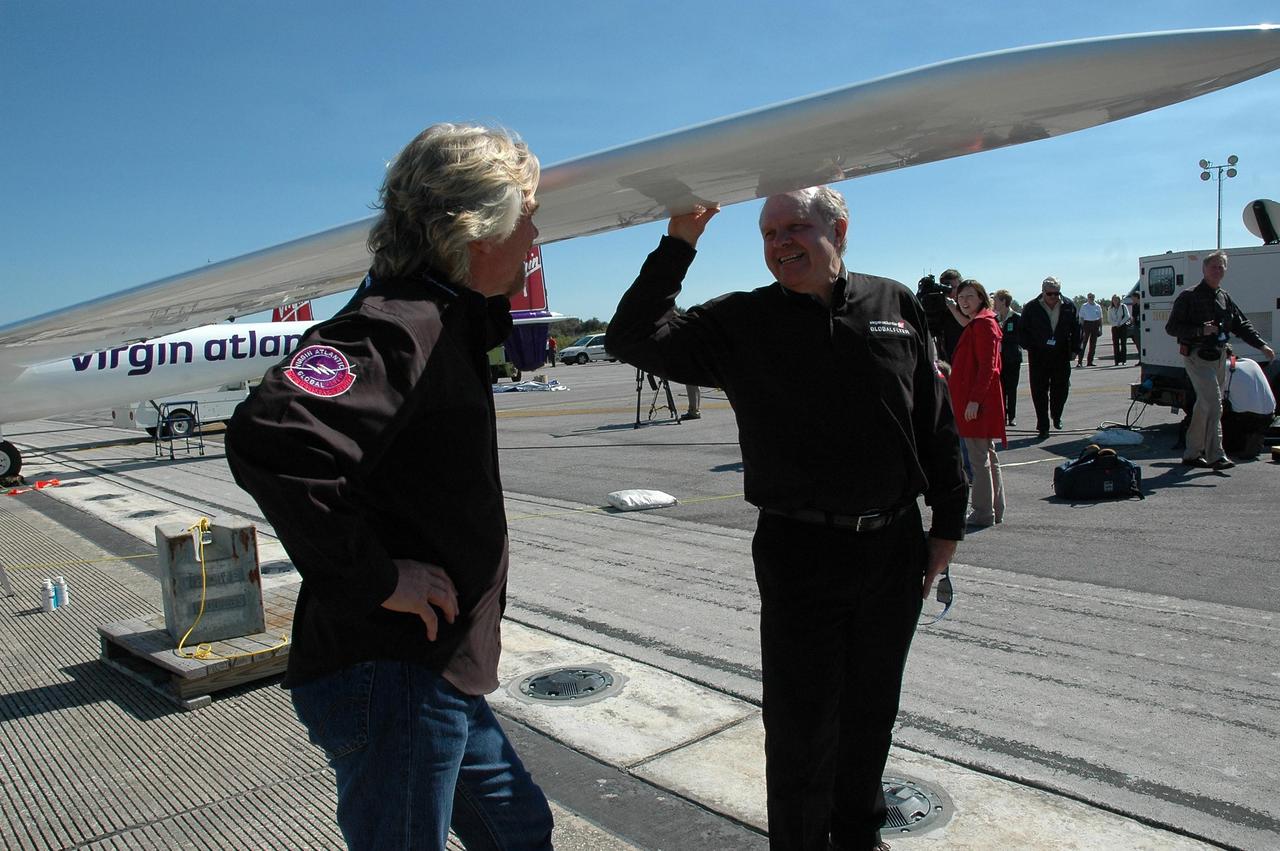

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Sir Richard Branson (left), chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic, talks with Steve Fossett. They are standing next to the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer aircraft, which Fossett will pilot on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility early Tuesday morning. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

In this 1970 artist's concept, the Nuclear Shuttle is shown in its lunar and geosynchronous orbit configuration and in its planetary mission configuration. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development plarners, the Nuclear Shuttle would deliver payloads to lunar orbit or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling. A cluster of Nuclear Shuttle units could form the basis for planetary missions.
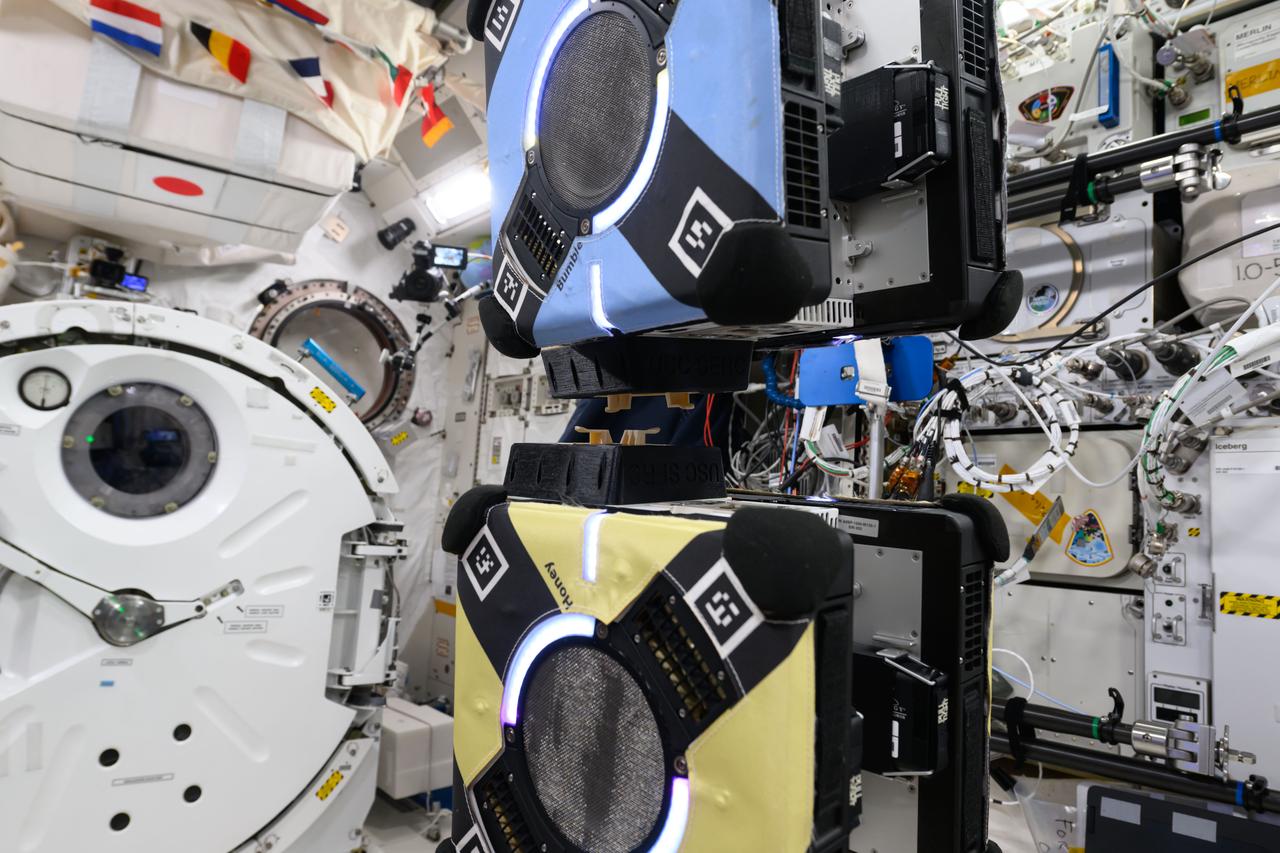
iss072e423864 (1/3/2025) — A view of the CLINGERS Cubesats attached to Astrobee aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Flight Tech Demo of Docking/Undocking Cubesats Inside ISS (CLINGERS) uses the International Space Station’s Astrobee robots to demonstrate an adaptor for docking and close approach sensing to connect both active and passive objects in space. These are critical functions to enable applications such as satellite servicing, orbital refueling, spacecraft repair and upgrade, and in-orbit manufacturing.
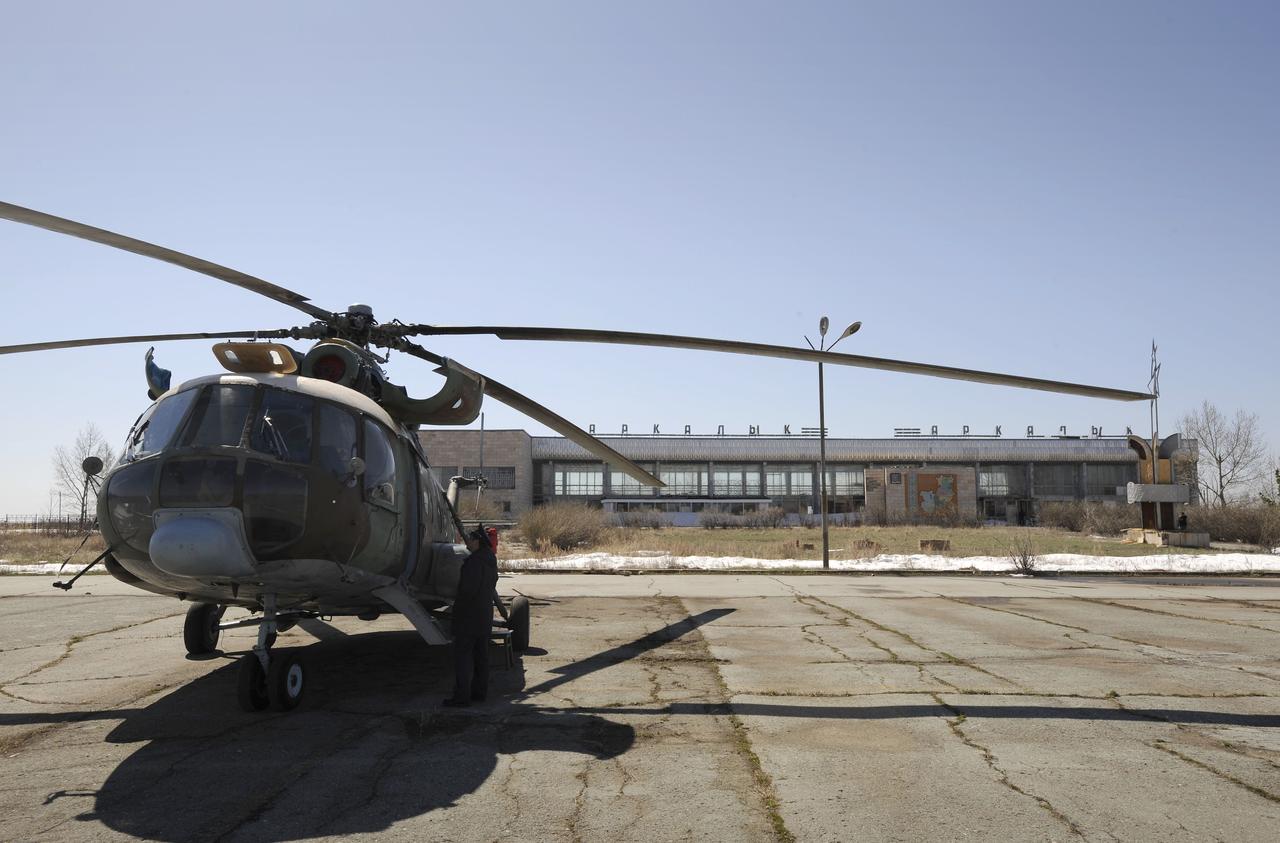

A Russian Search and Rescue helicopter waits for refueling at the Arkalyk airport in Kazakhstan prior to taking off for the landing of the Soyuz TMA-11 spacecraft carrying Expedition 16 Commander Peggy Whitson, Flight Engineer and Soyuz Commander Yuri Malenchenko and South Korean spaceflight participant So-yeon Yi, Friday, April, 19, 2008. The Soyuz made a ballistic landing, touching down more then 400 kilometers short of the intended target in central Kazakhstan. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Sir Richard Branson (left), chairman and founder of Virgin Atlantic, fuels the GlobalFlyer aircraft. At right is the pilot Steve Fossett. Fossett will pilot the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility early Tuesday morning. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
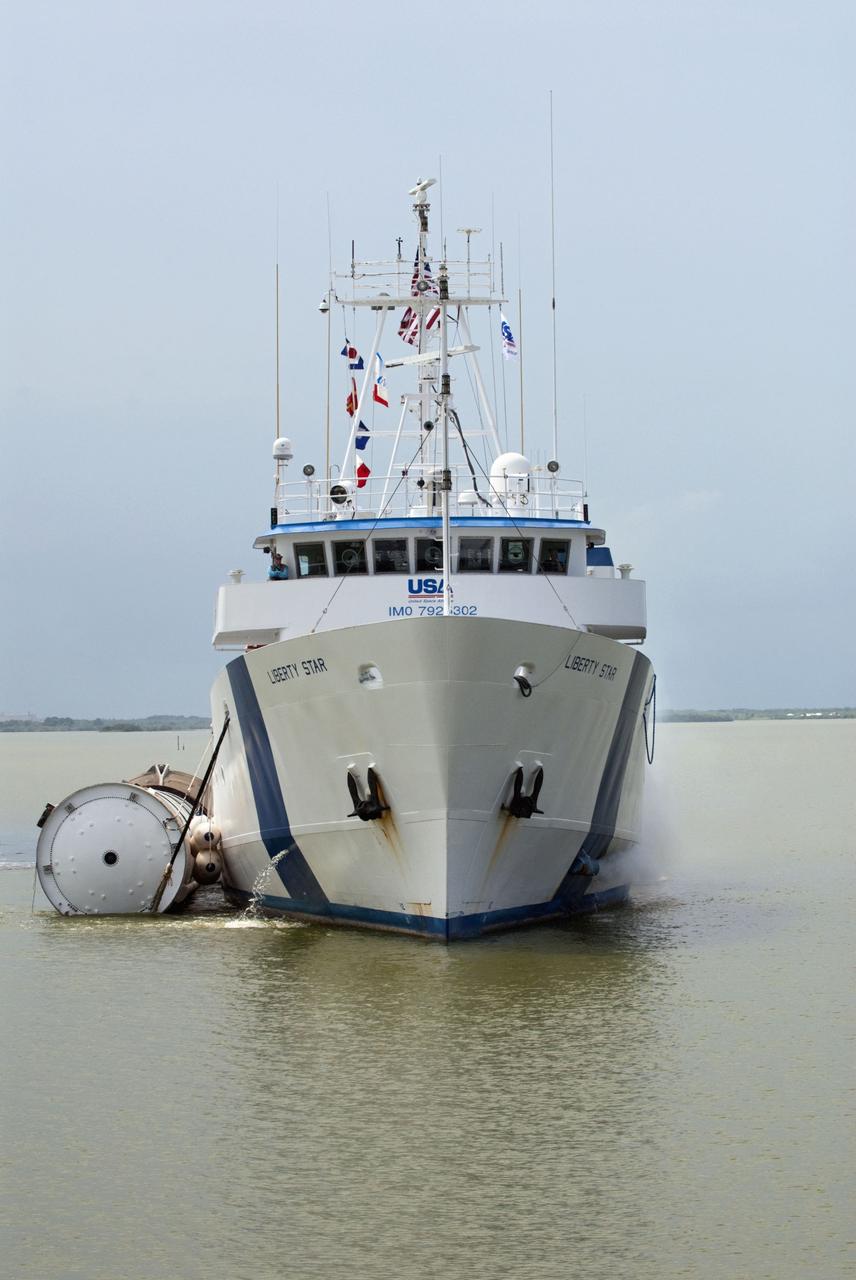

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
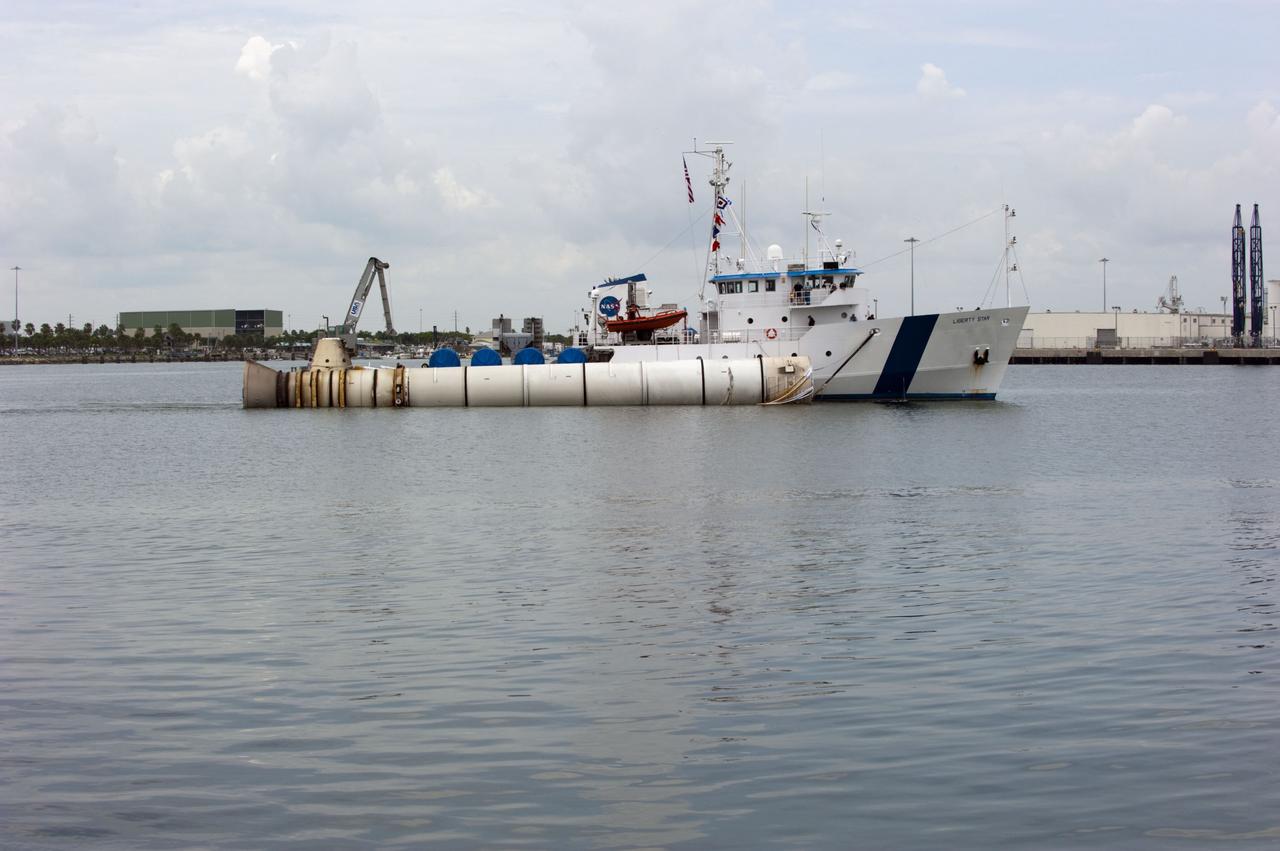

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8. STS-135 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
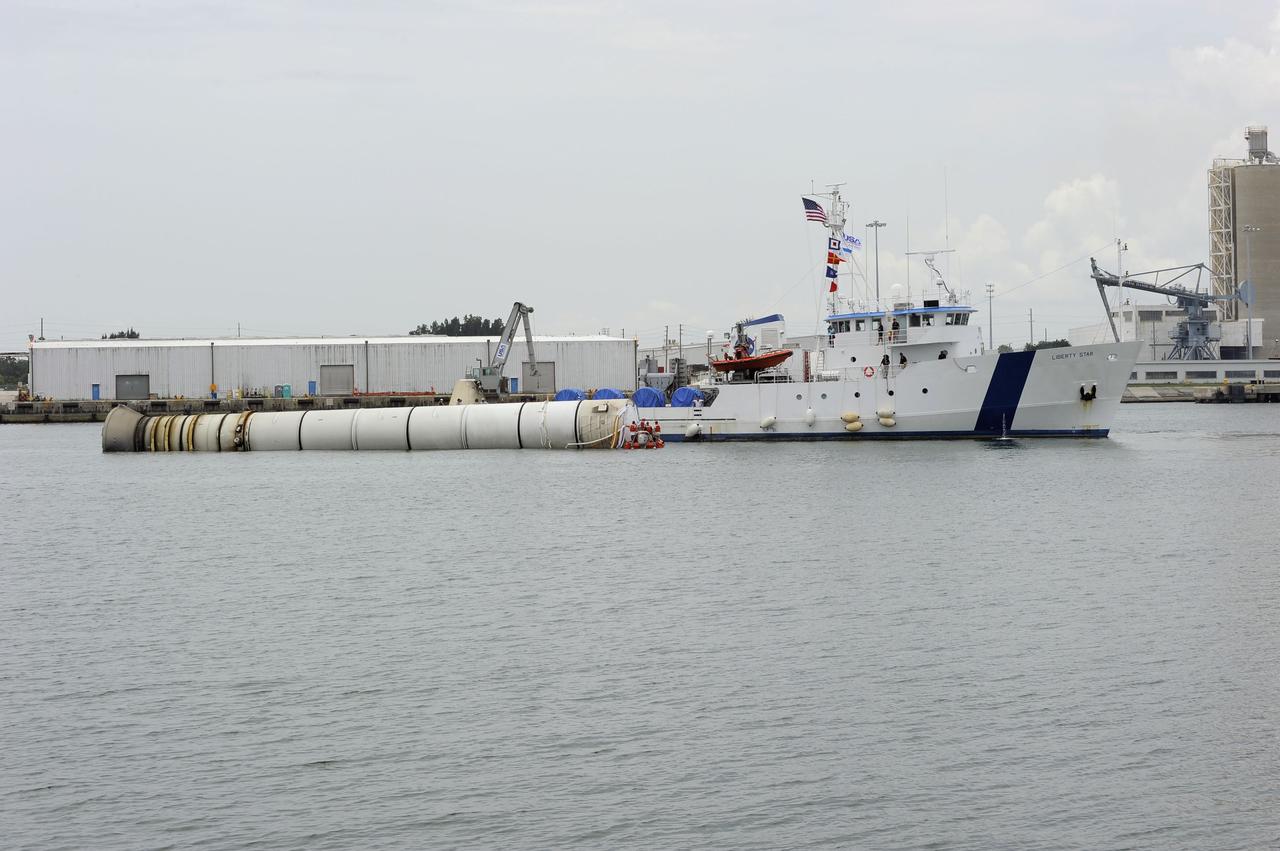

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, maneuvers the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
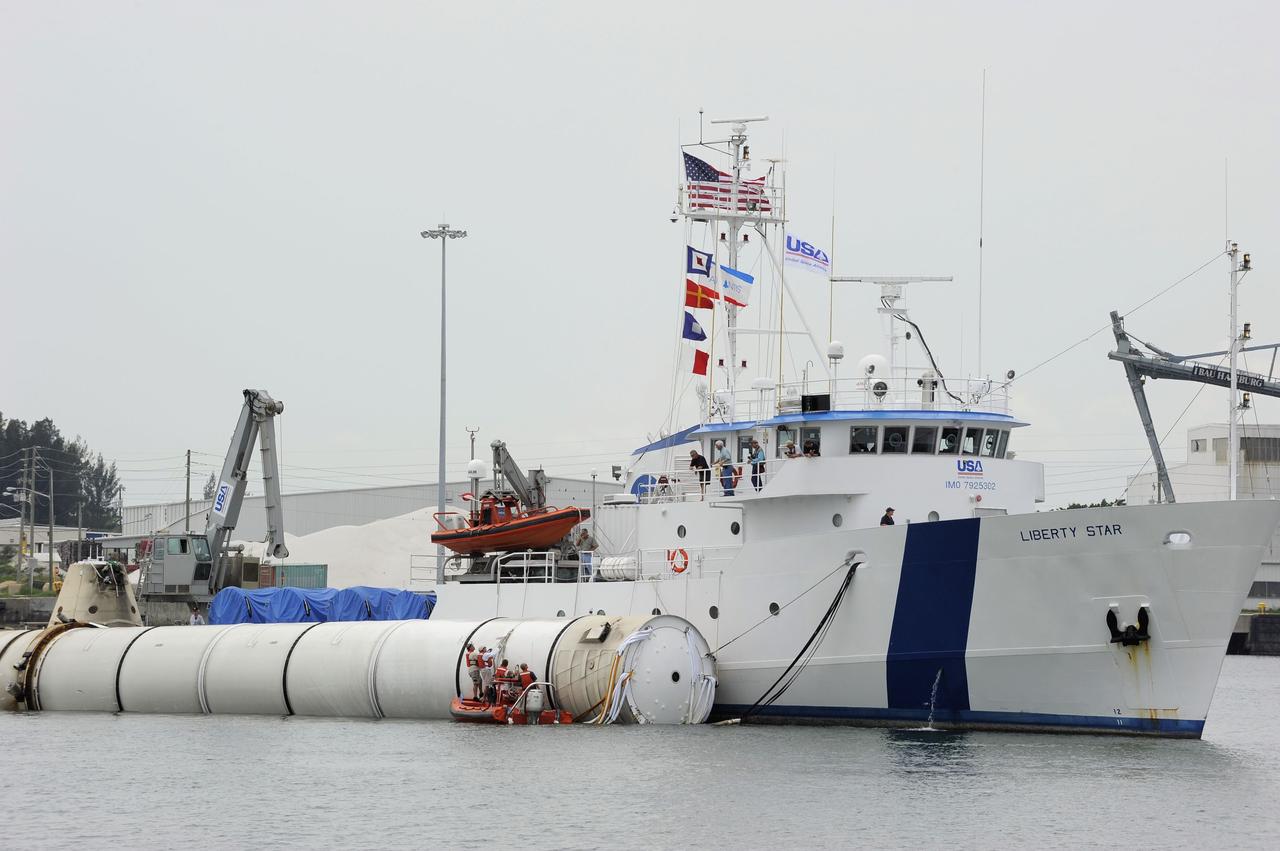

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, maneuvers the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
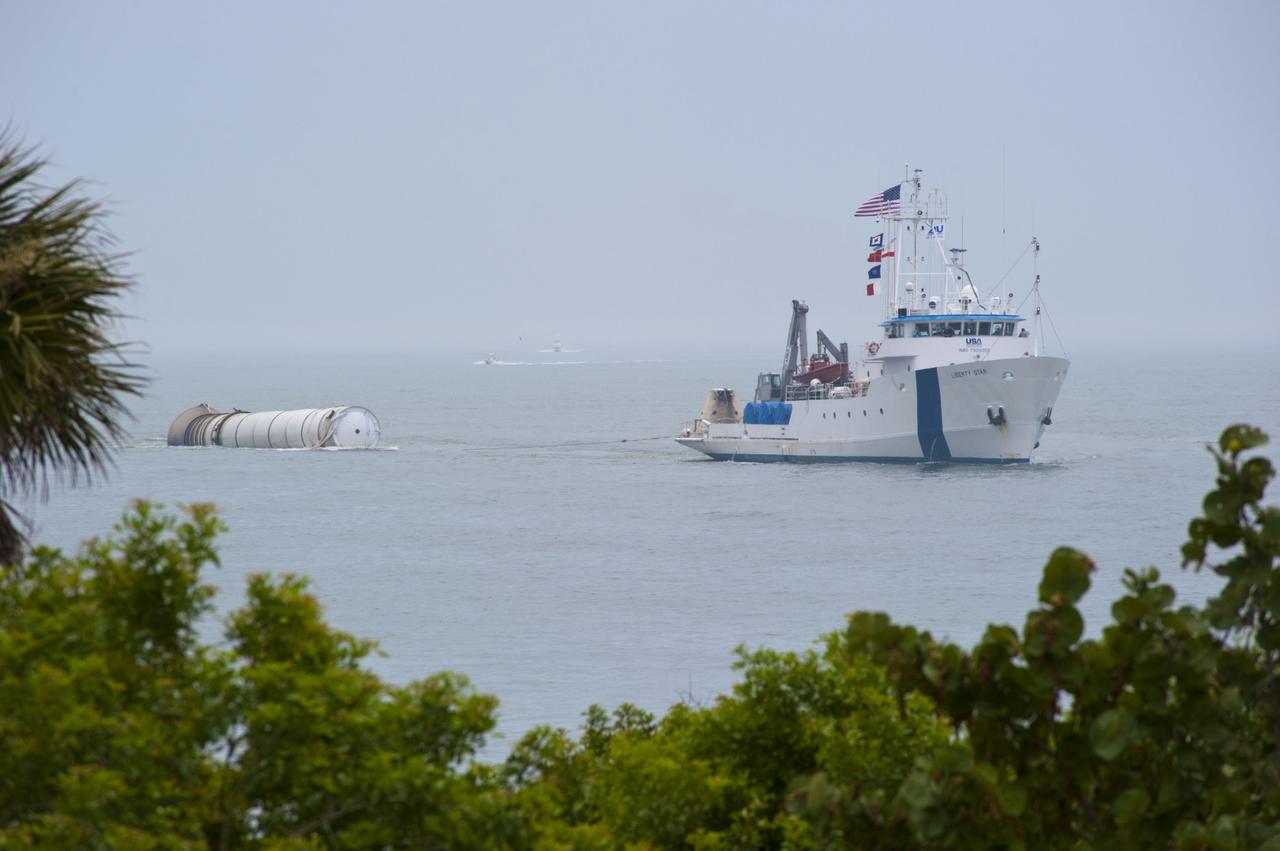

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
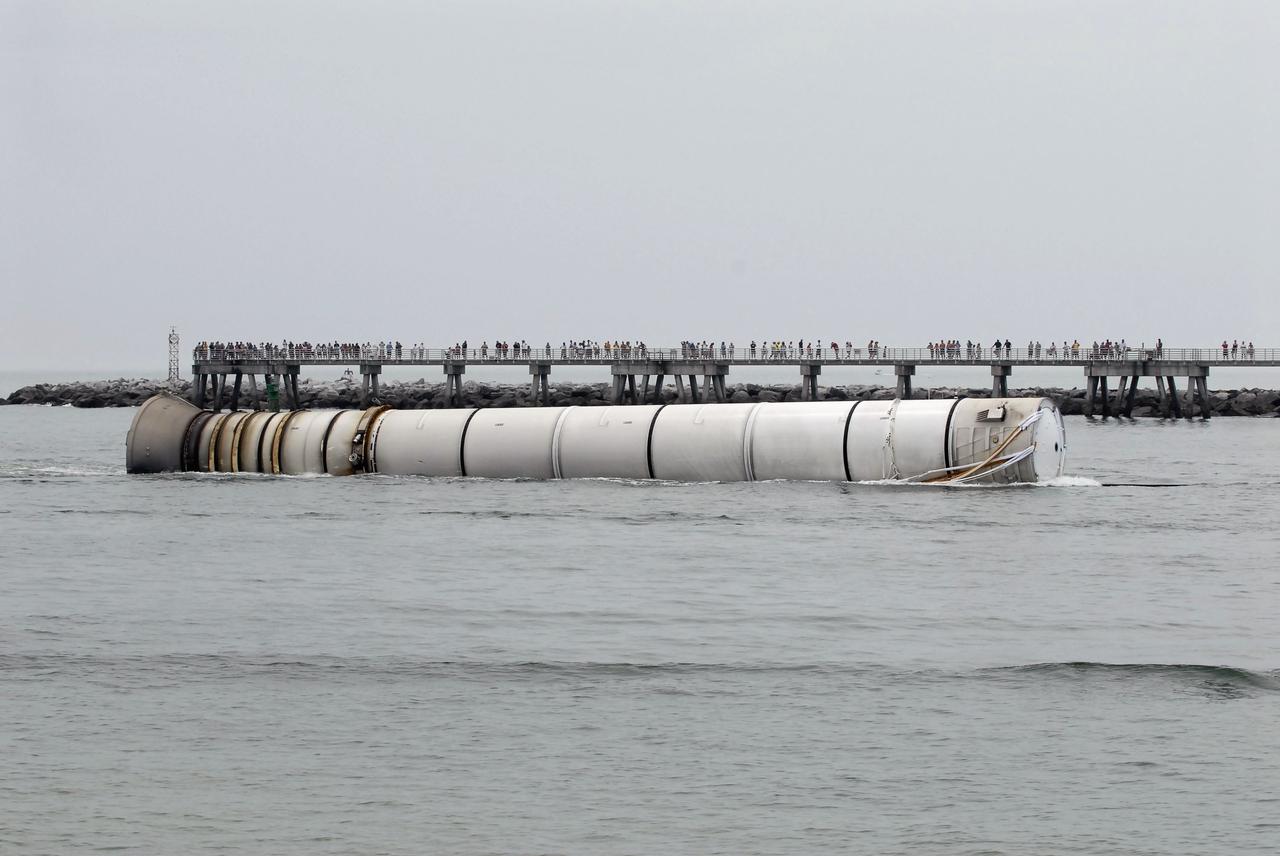

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch is towed by the Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
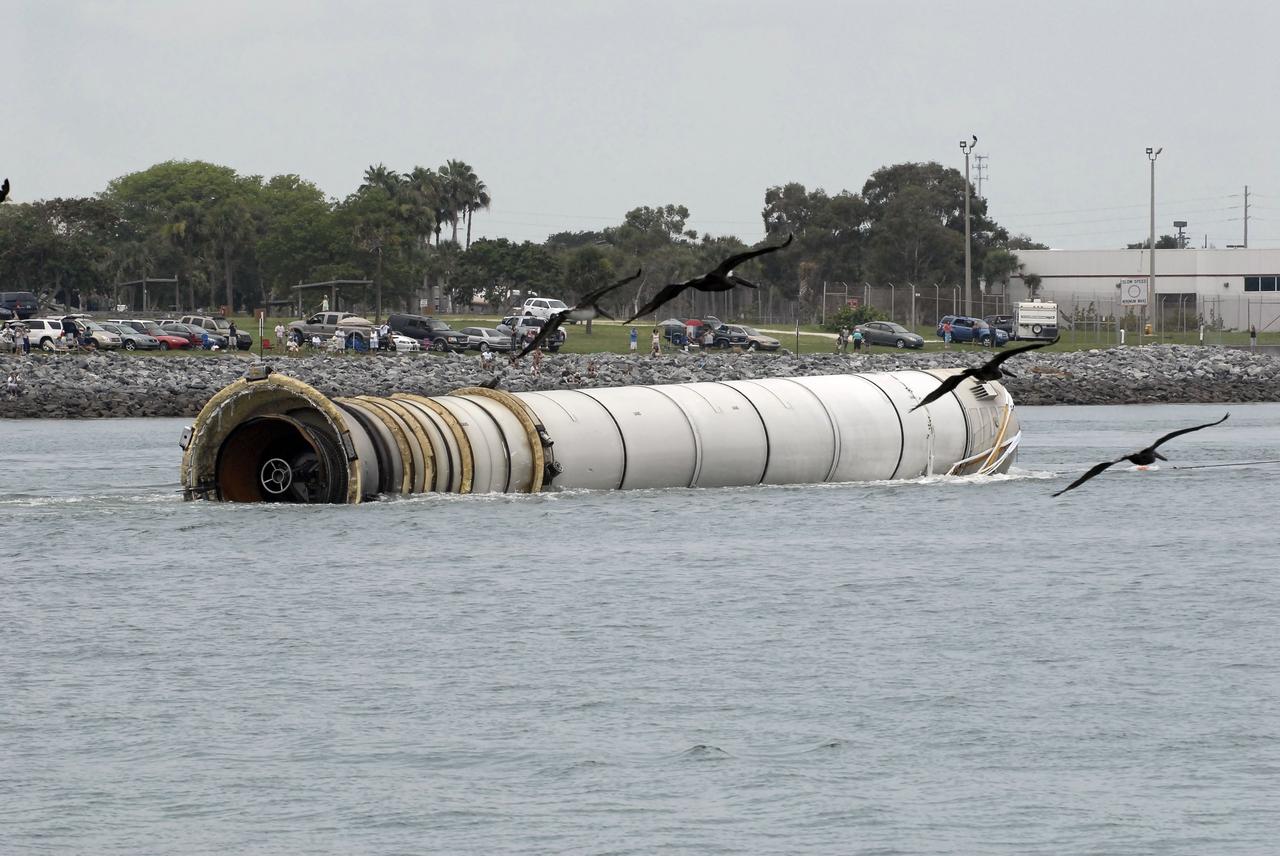

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch is towed by the Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
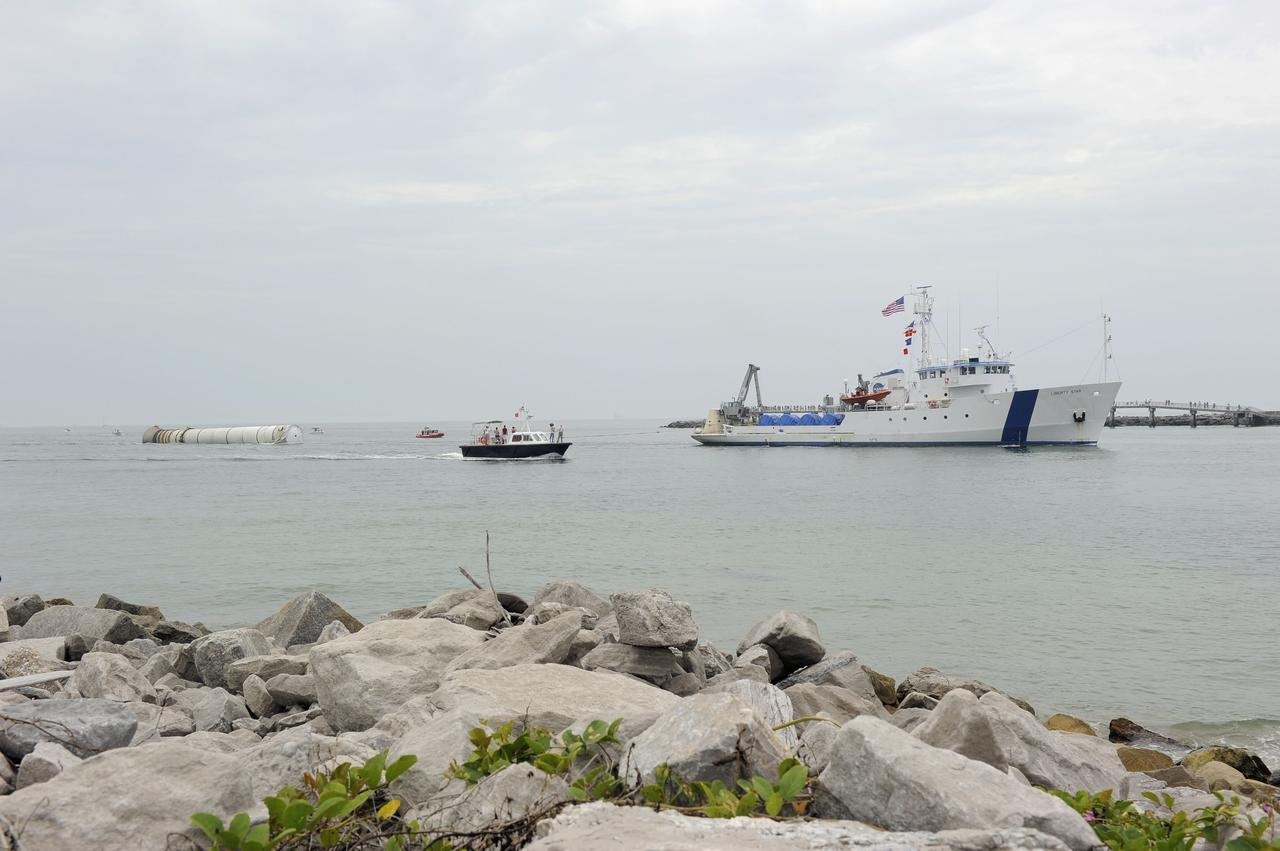

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
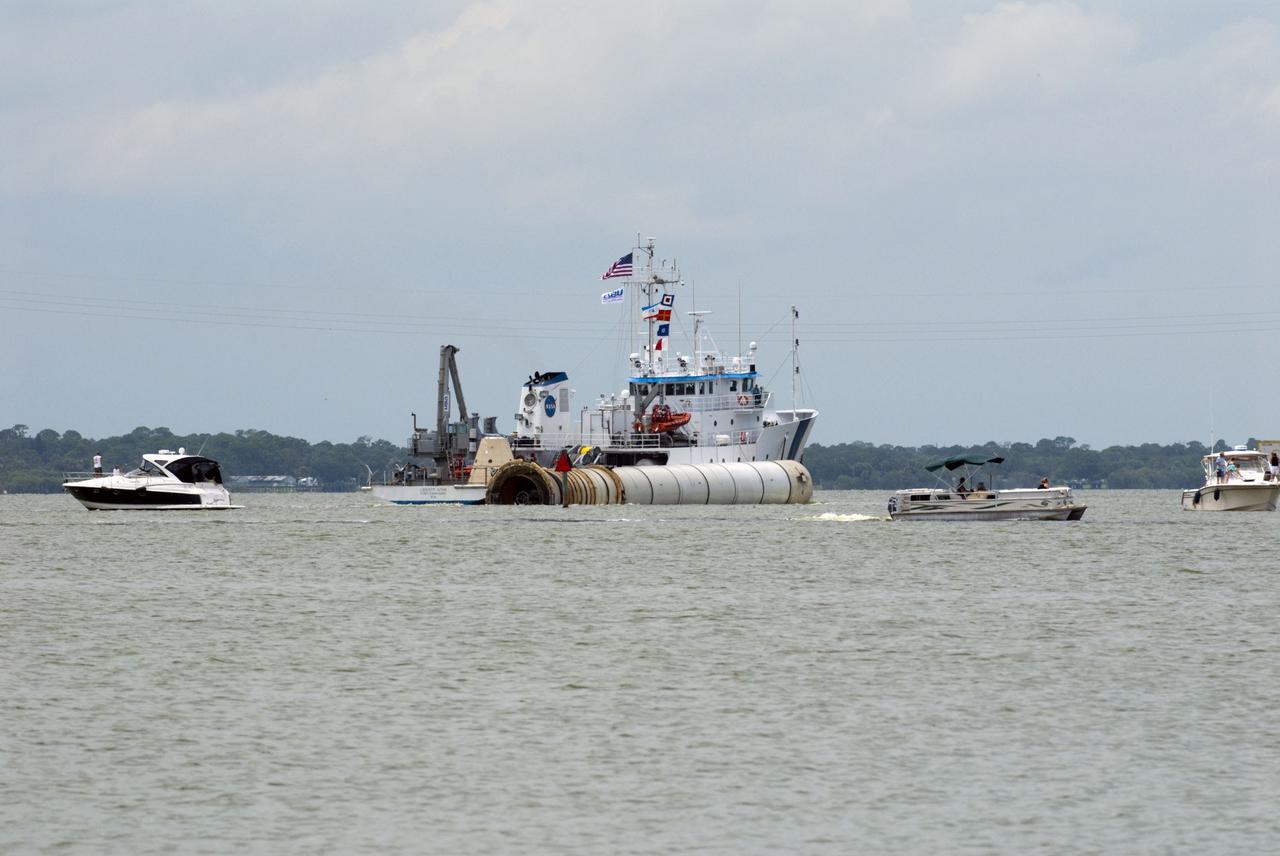

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
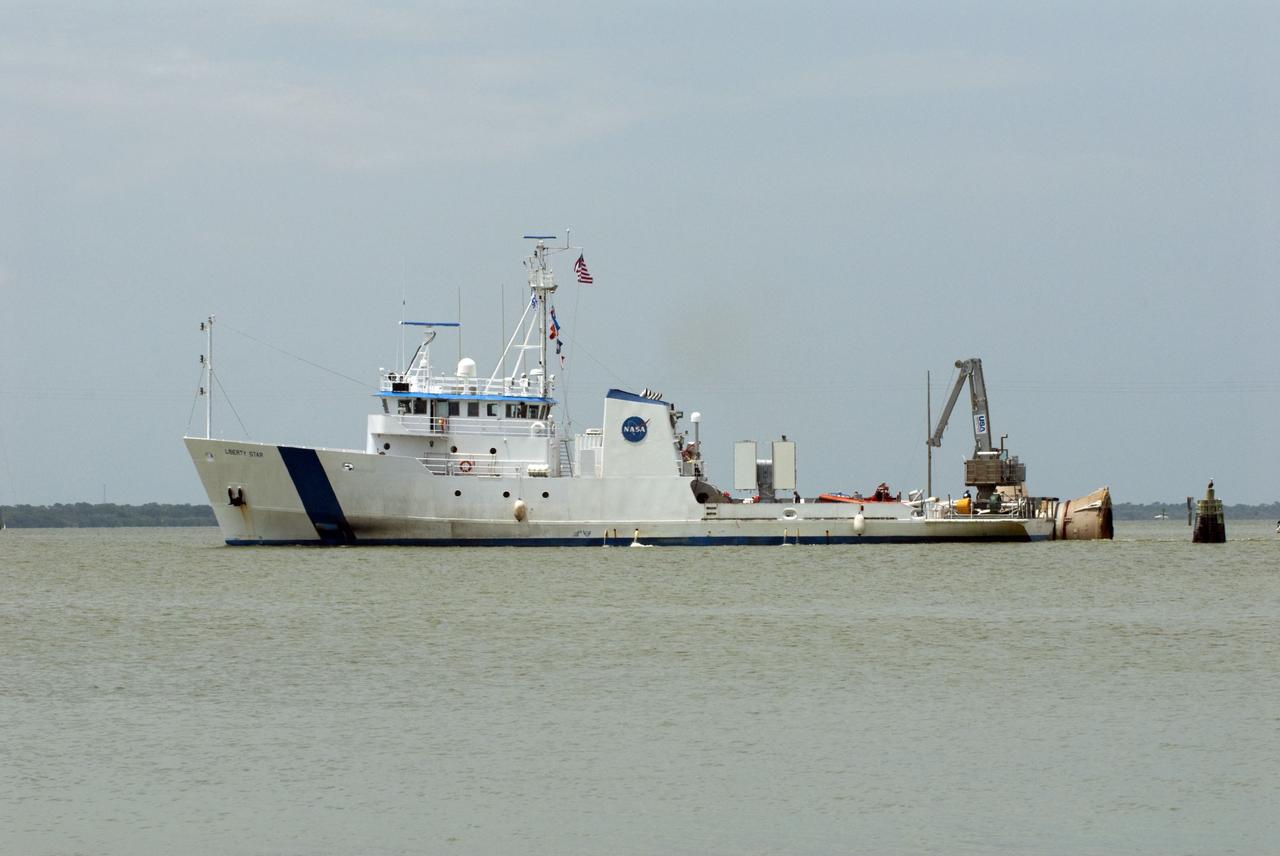

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
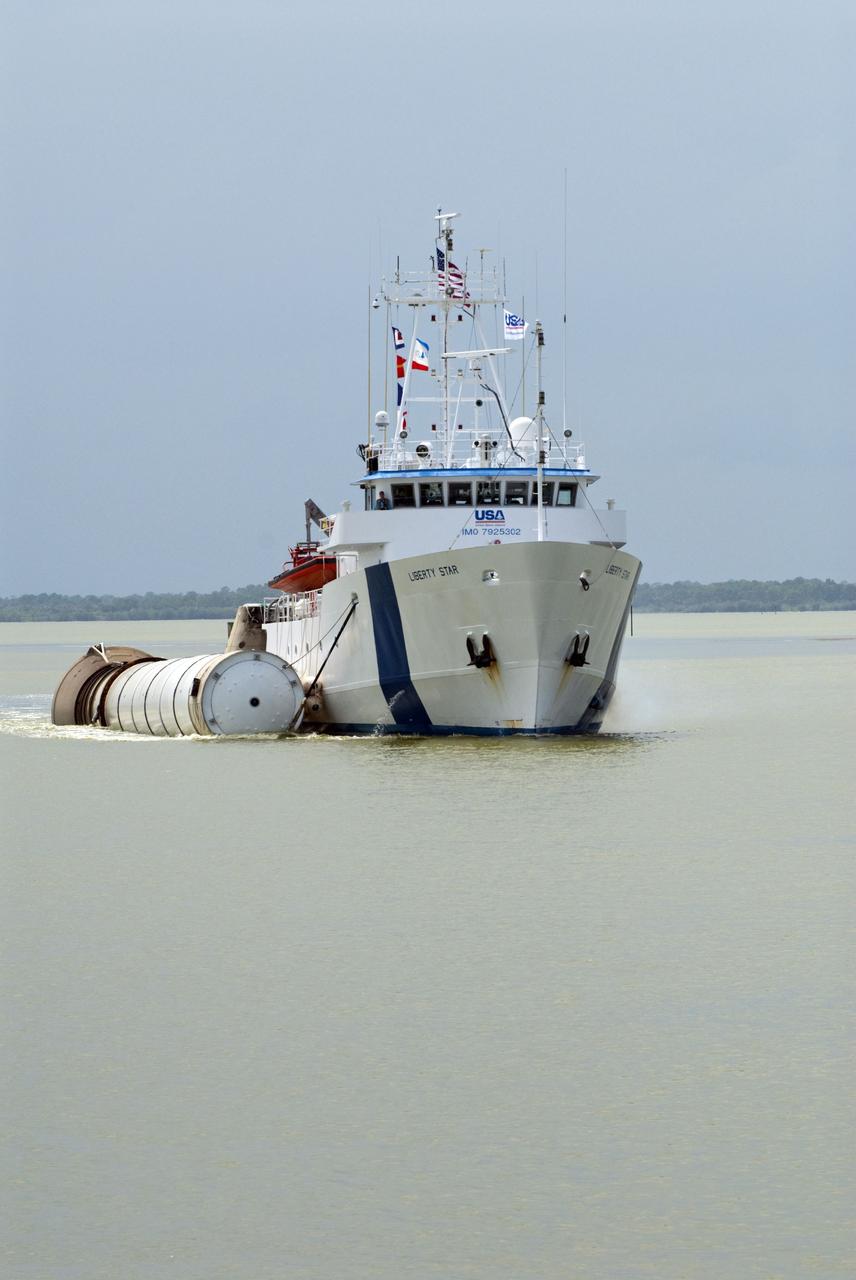

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
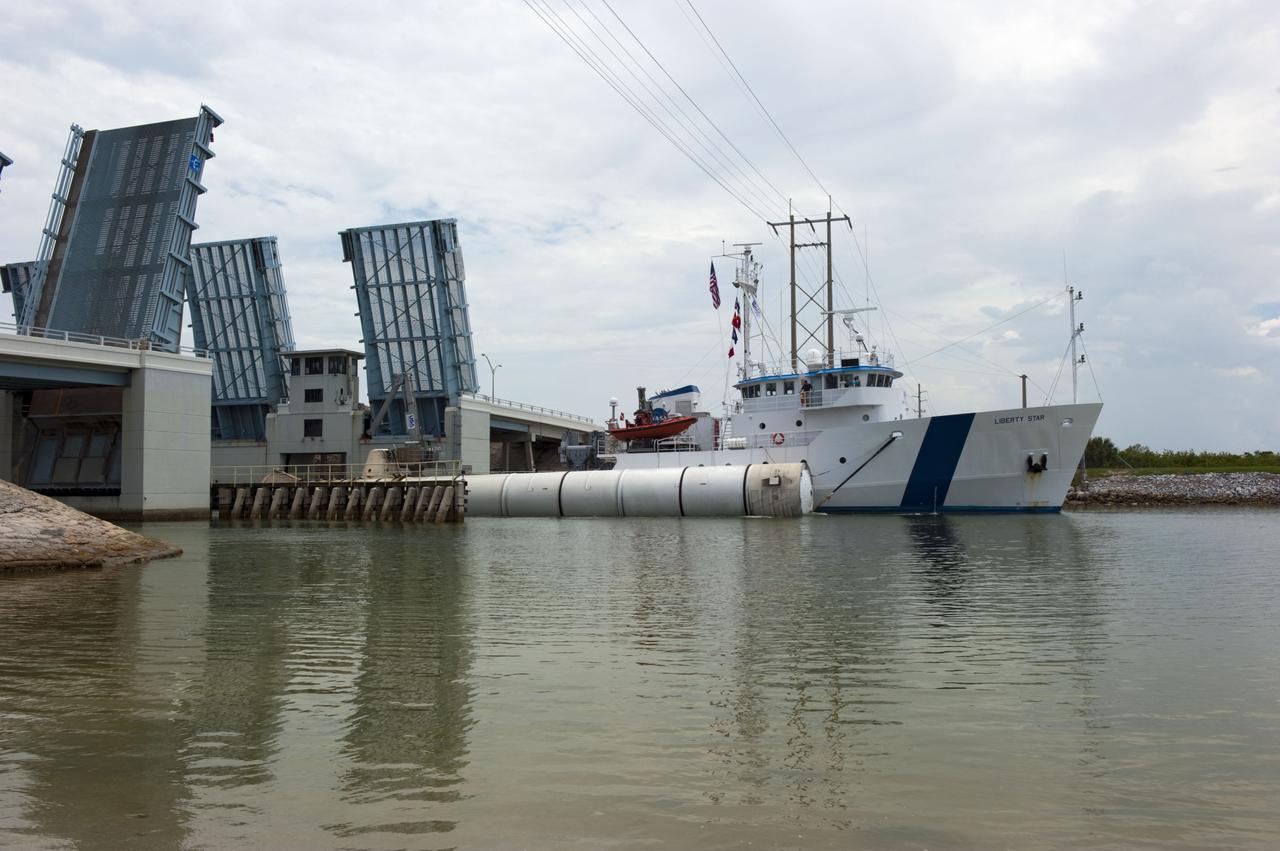

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
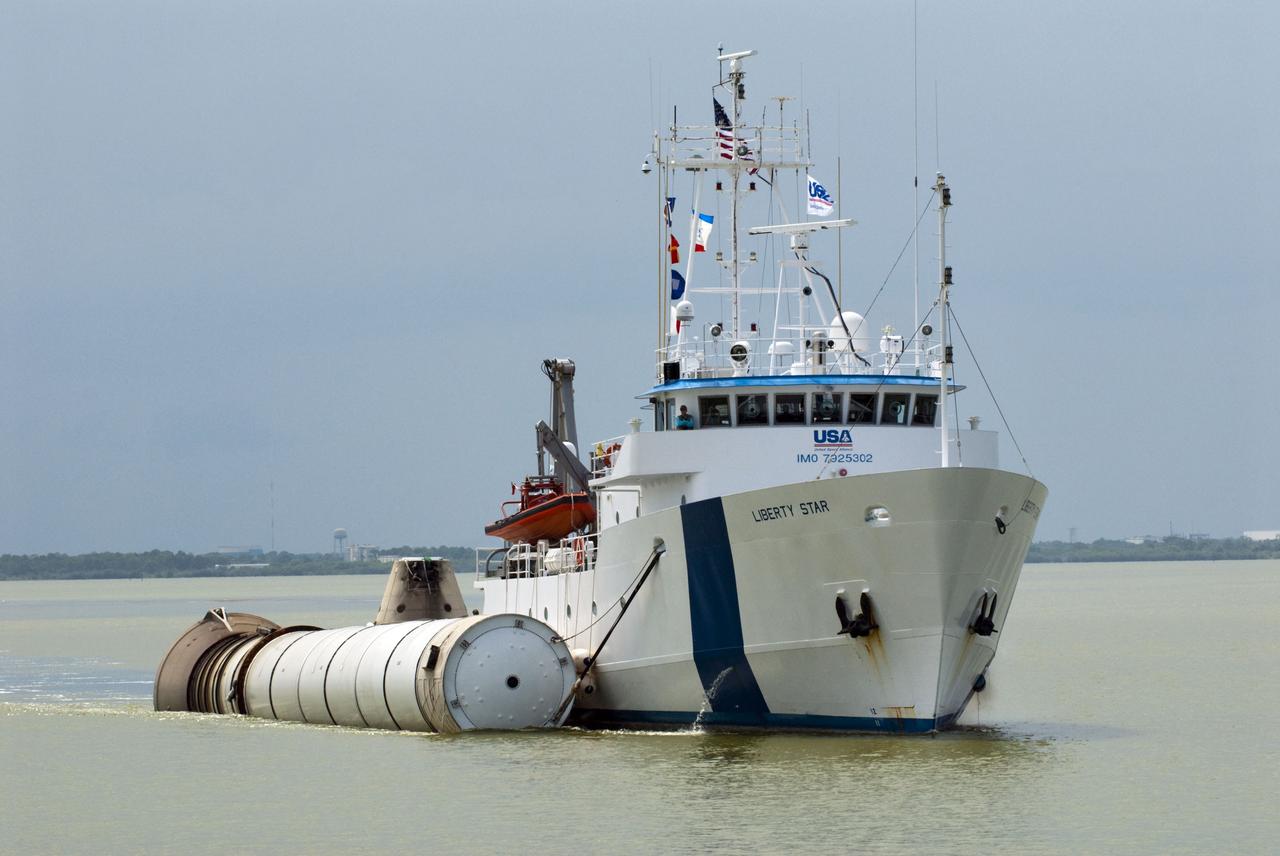

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
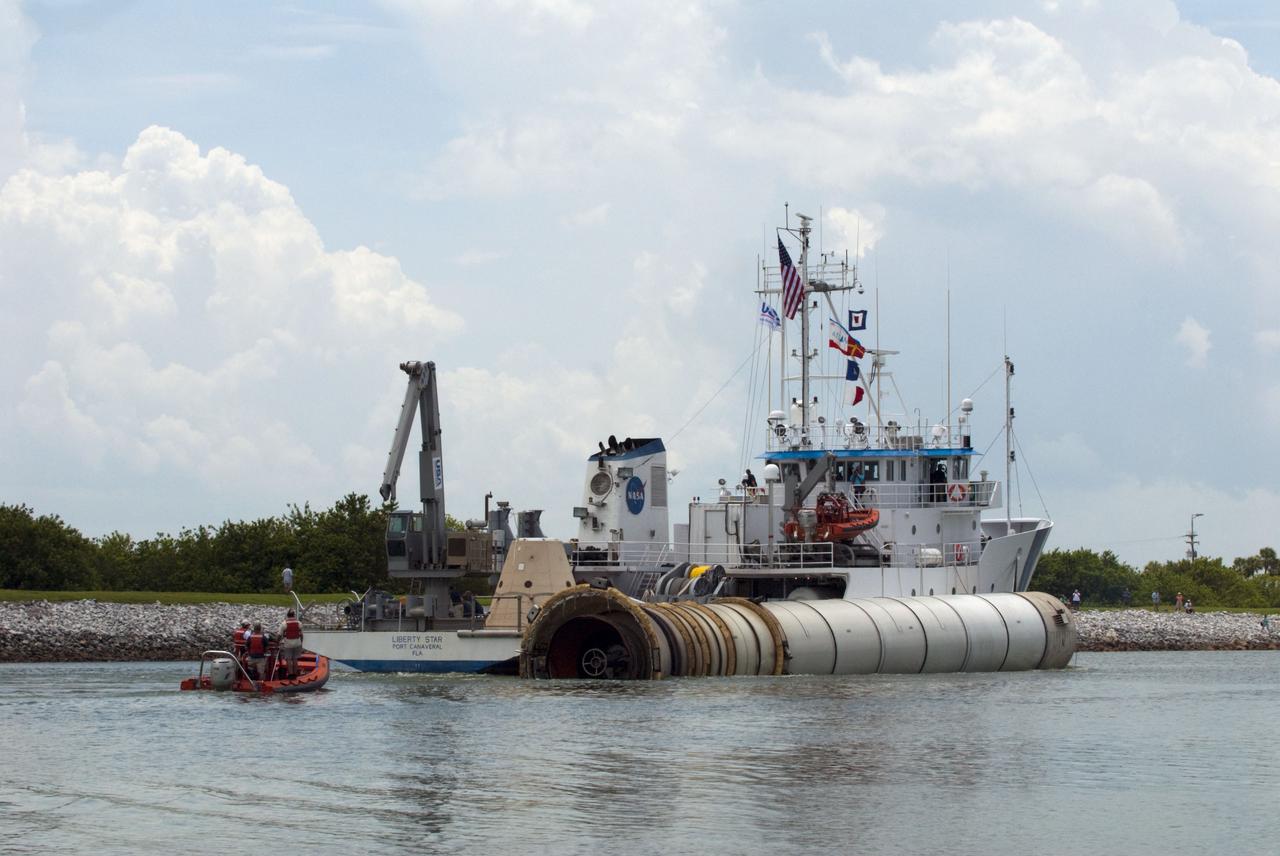

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
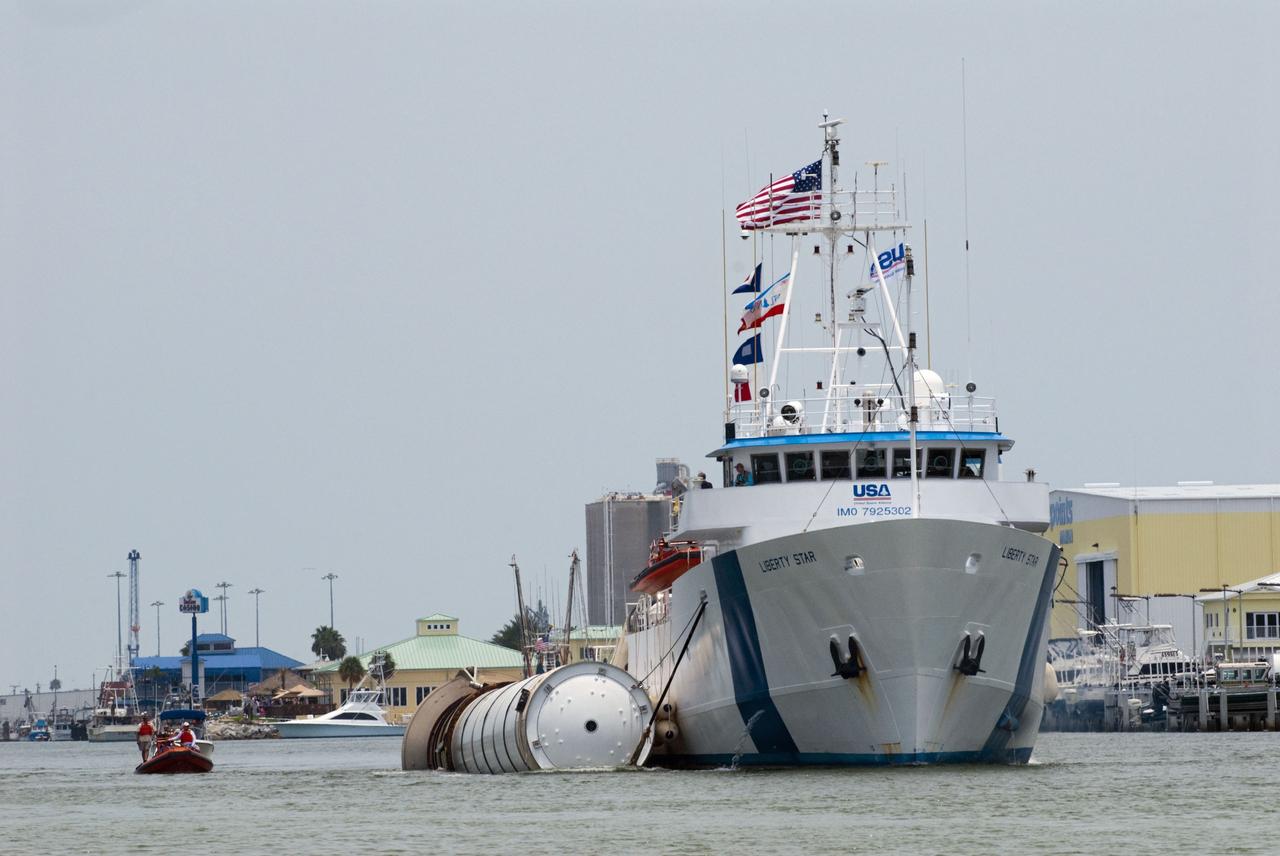

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
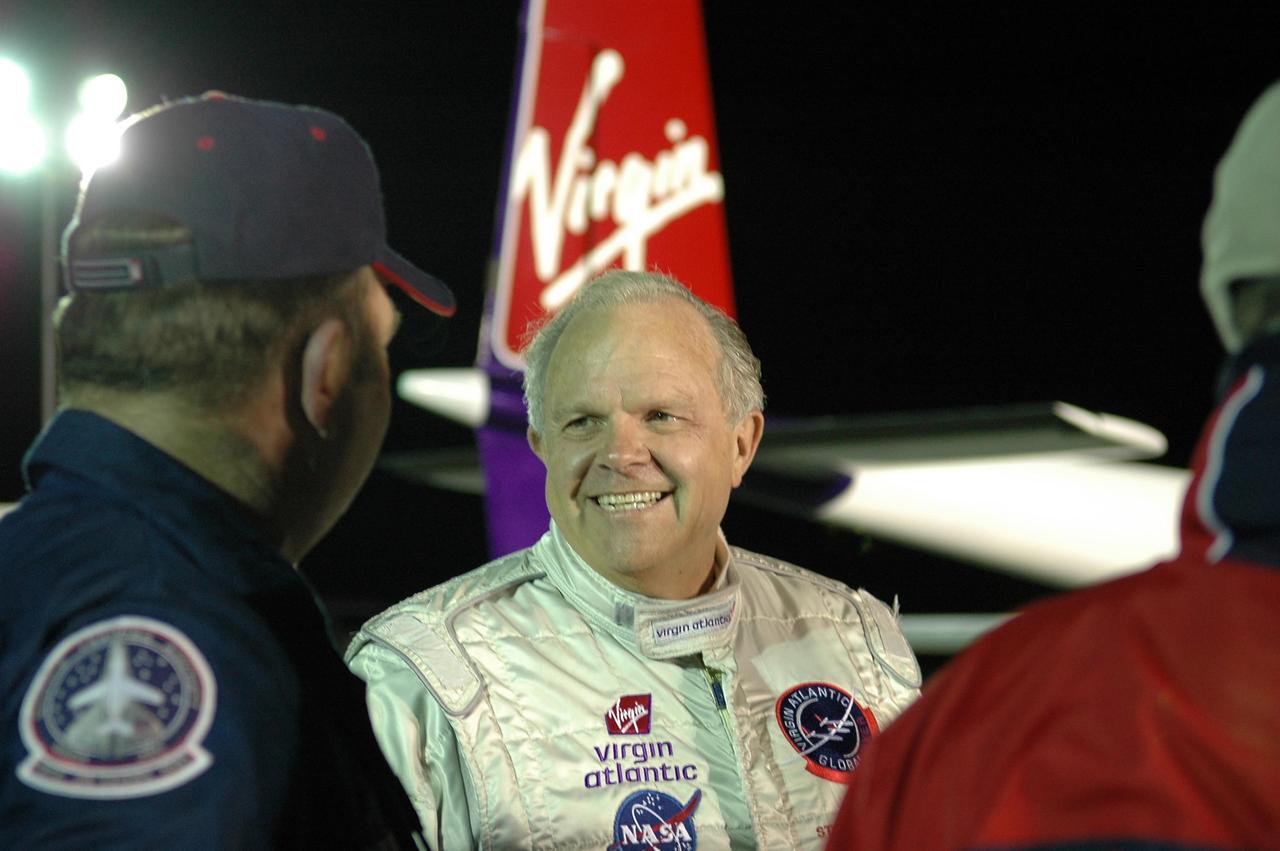

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Before dawn on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF), Steve Fossett talks to the media about the anticipated flight of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
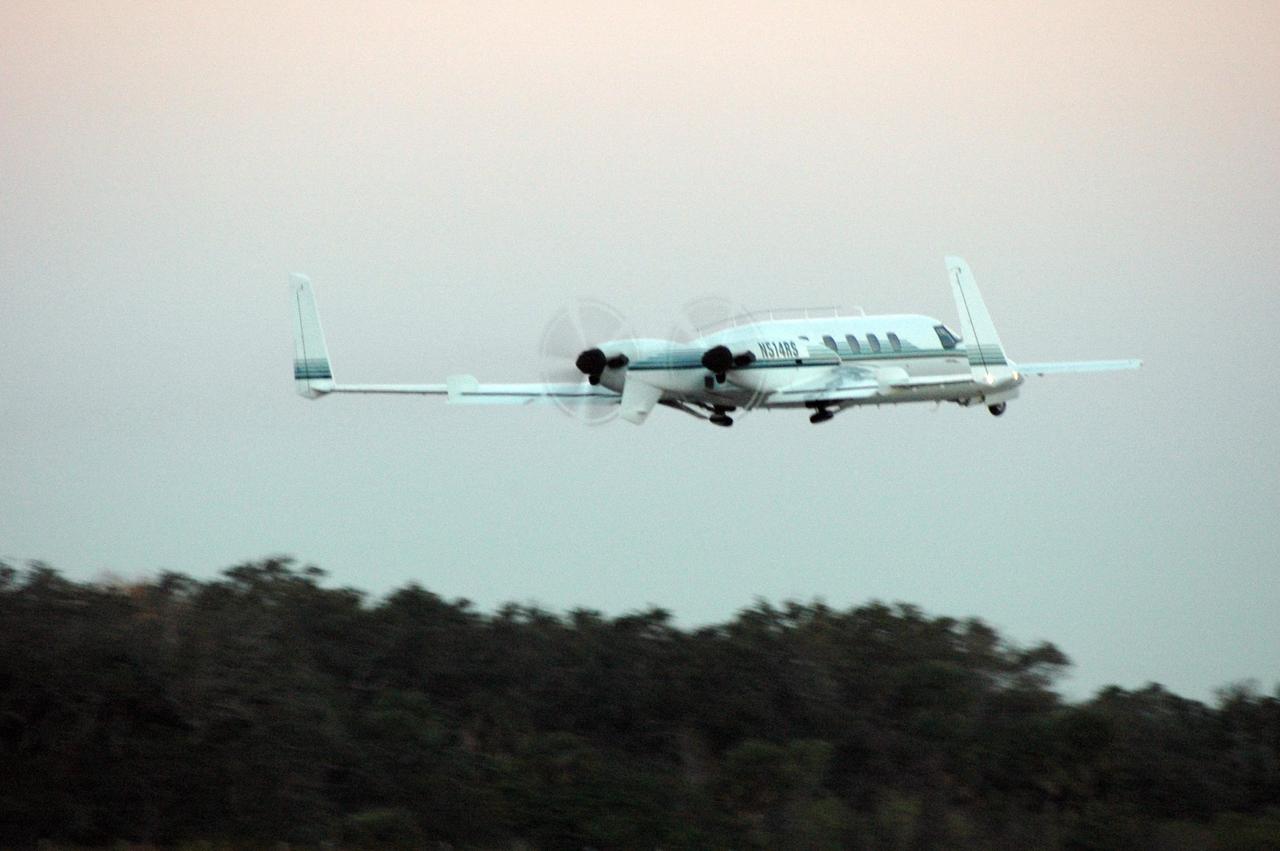

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Beechcraft Starship aircraft precedes the takeoff of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer from NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Photographers on board the Beachcraft will capture the historic event from the air. Pilot Steve Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Before dawn on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF), Steve Fossett looks over the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer in preparation for flight.. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
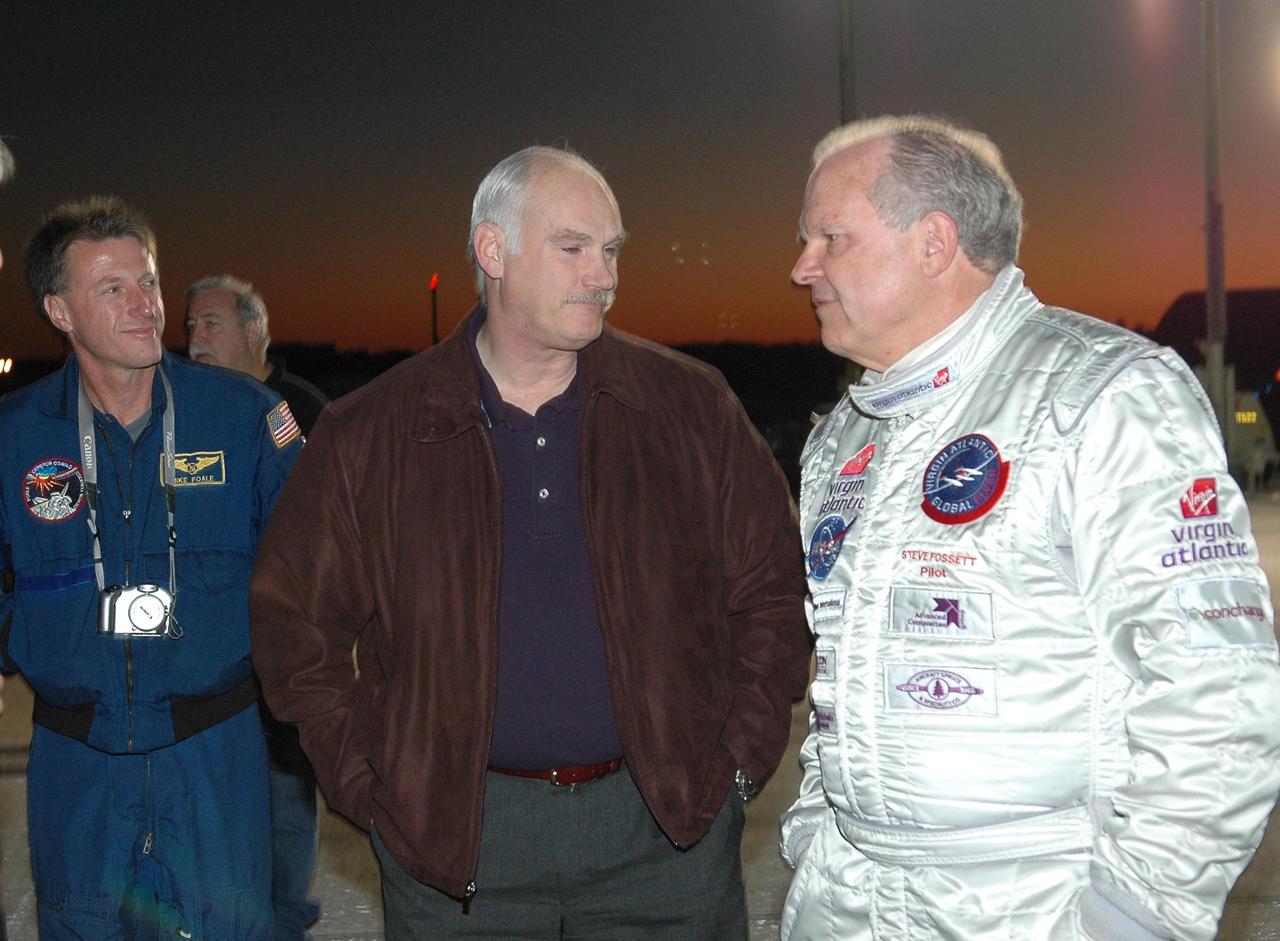

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - As a rosy dawn creeps over the horizon, Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Operations Michael Foale (left) and astronaut Bill Readdy (center) talk to Steve Fossett about the anticipated flight of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. Fossett is expected to take off from the KSC SLF. Later, takeoff of the GlobalFlyer was postponed due to a fuel leak that appeared during the last moments of loading. The next planned takeoff attempt is 7 a.m. Feb. 8 from the SLF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
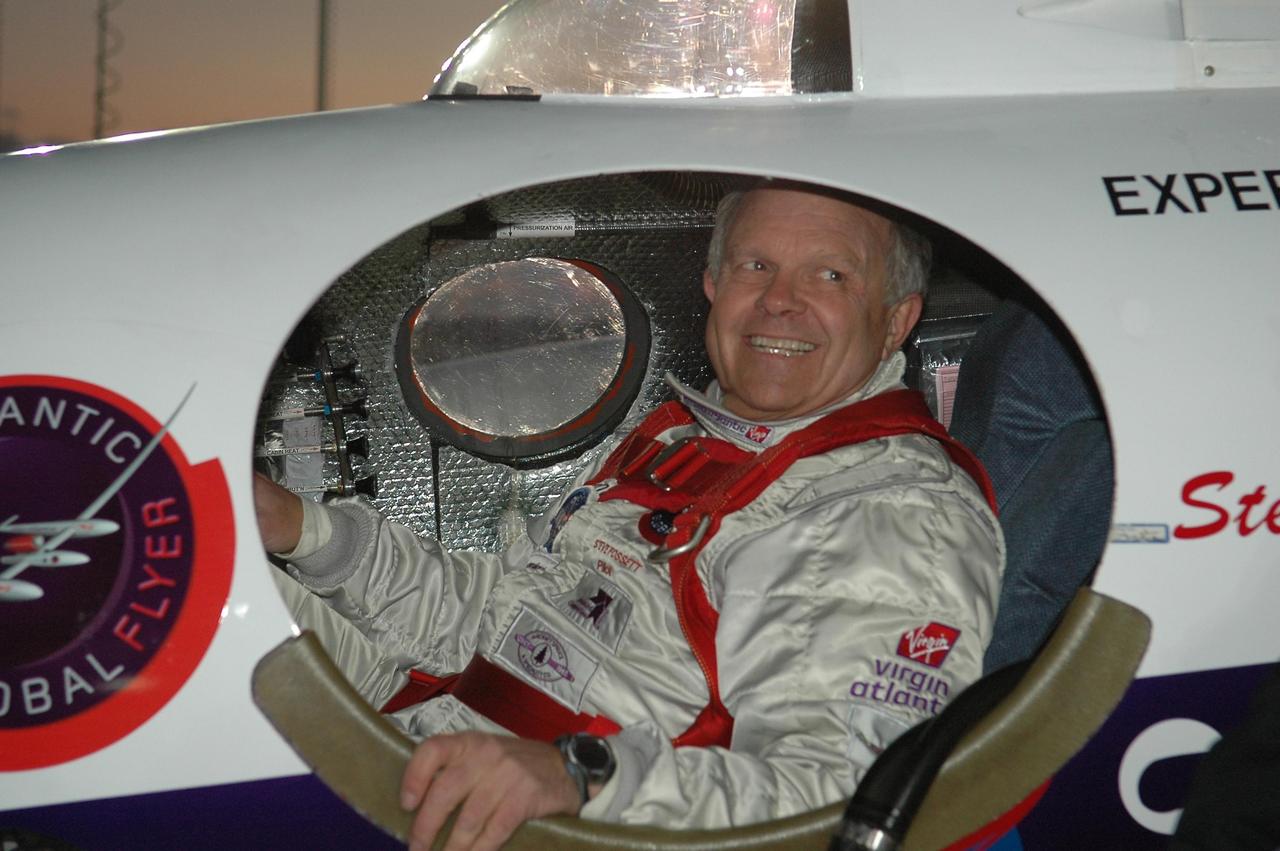

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility, Steve Fossett is happy and eager to start what he hopes will be a historic flight in the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer he is strapped into. Fossett will pilot the GlobalFlyer on a record-breaking attempt by flying solo, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The expected time of takeoff is 7 a.m. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
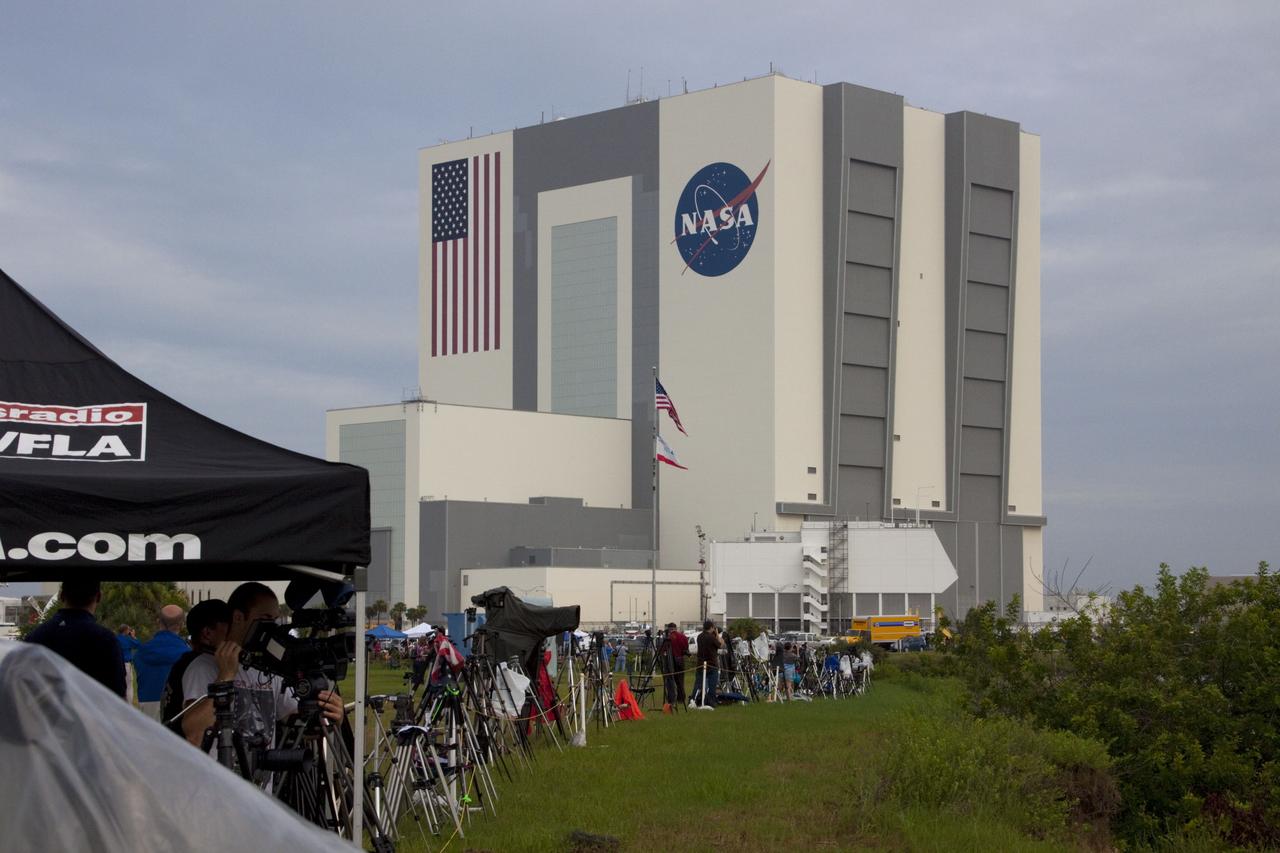

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen towering above is the massive Vehicle Assembly Building. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is moments from liftoff from Launch Pad 39A overlooking the Atlantic Ocean at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Atlantis began its final flight, the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the orbiting laboratory. Atlantis also is flying the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, a failed ammonia pump module will be returned to Earth aboard Atlantis to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather in their respective tents at the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
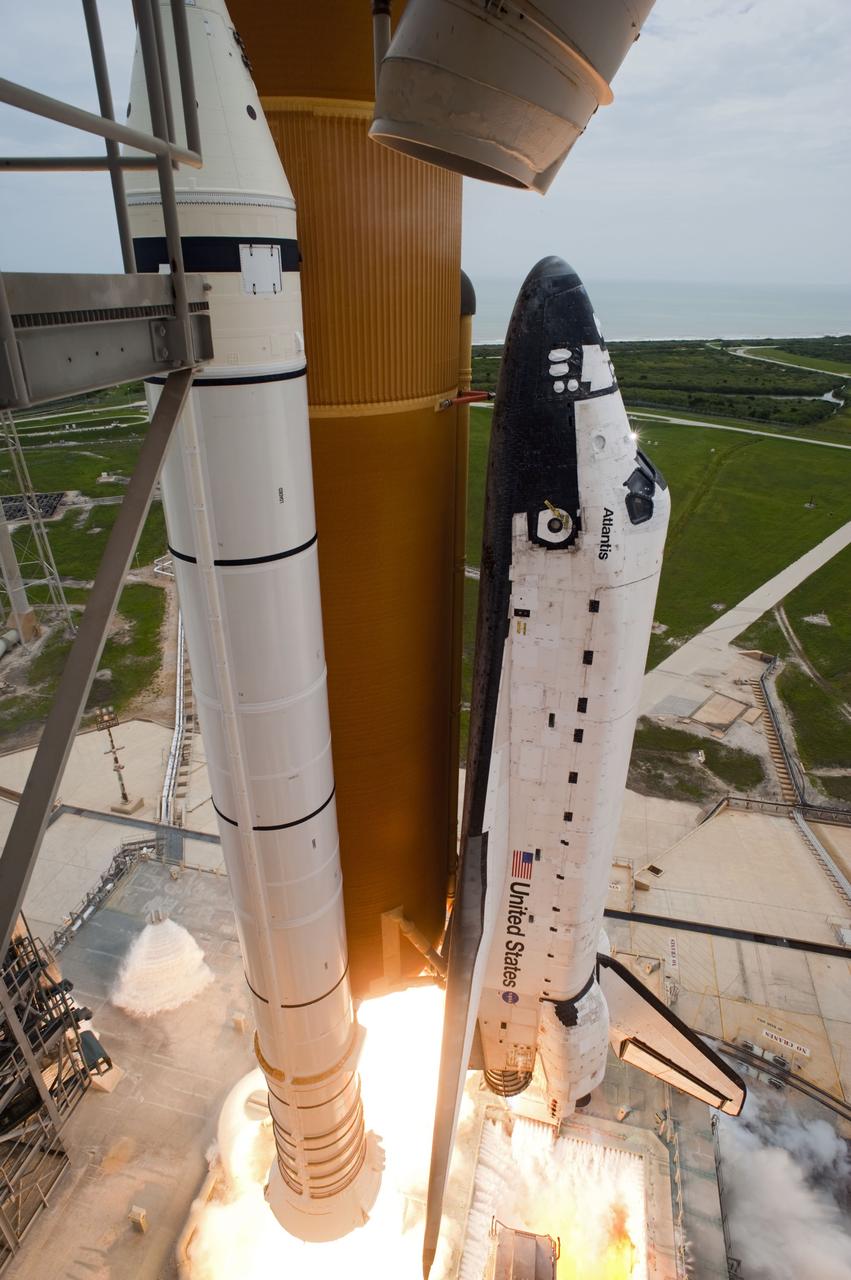

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The engines' glare beneath space shuttle Atlantis heralds liftoff from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Atlantis began its final flight, the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the orbiting laboratory. Atlantis also is flying the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, a failed ammonia pump module will be returned to Earth aboard Atlantis to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
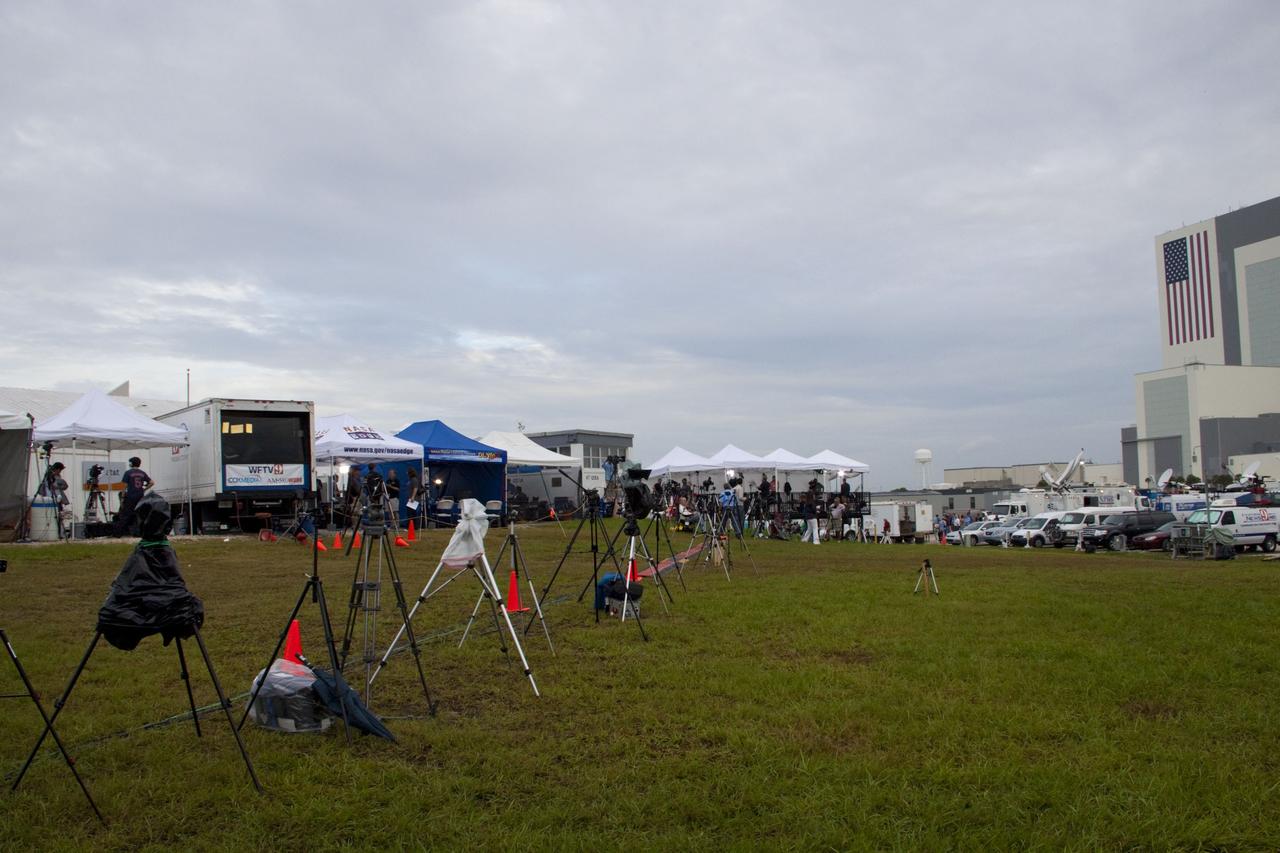

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
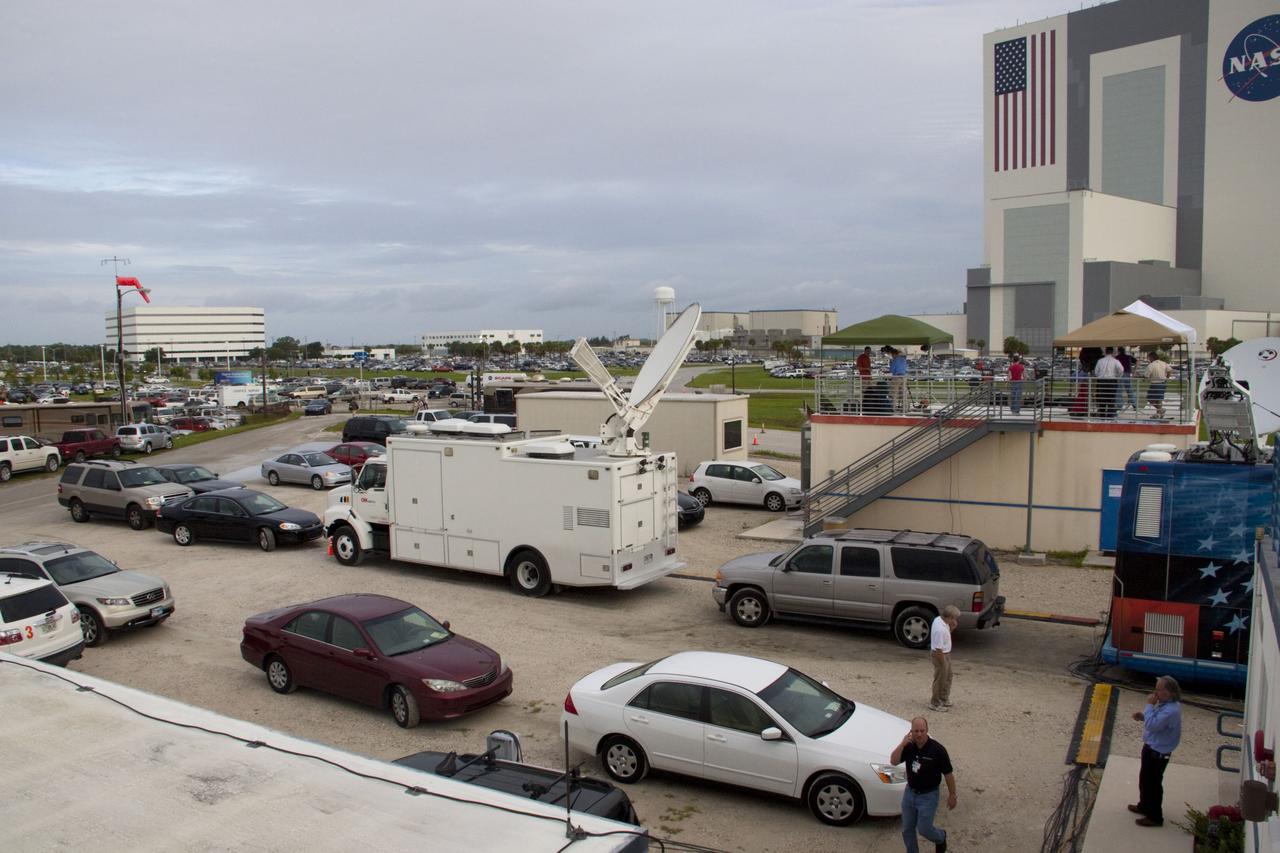

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen towering above is the massive Vehicle Assembly Building. Satellite news trucks, trailers and automobiles can be seen in the parking lot with the massive Vehicle Assembly Building towering above. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
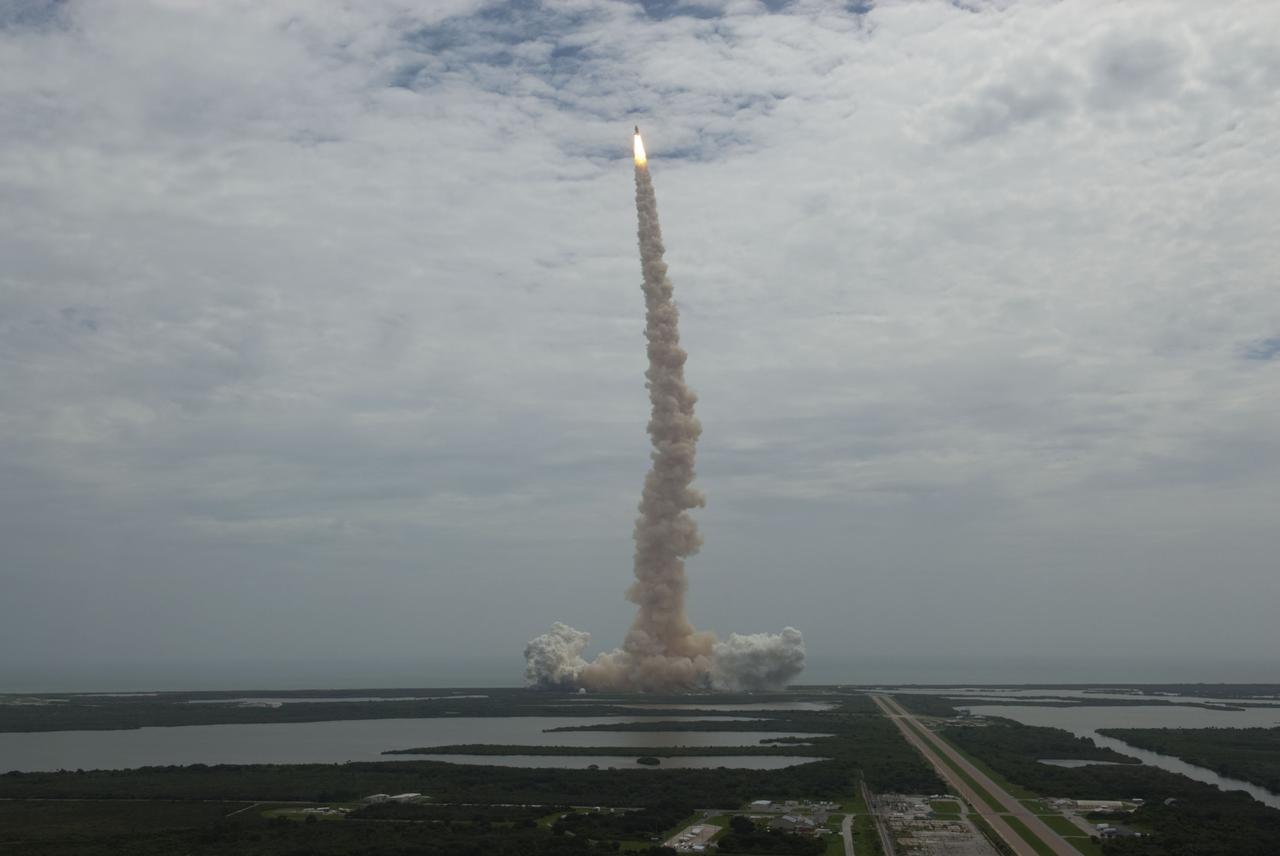

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Seen from the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building, space shuttle Atlantis thunders off Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Atlantis began its final flight, the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jeffrey Marino
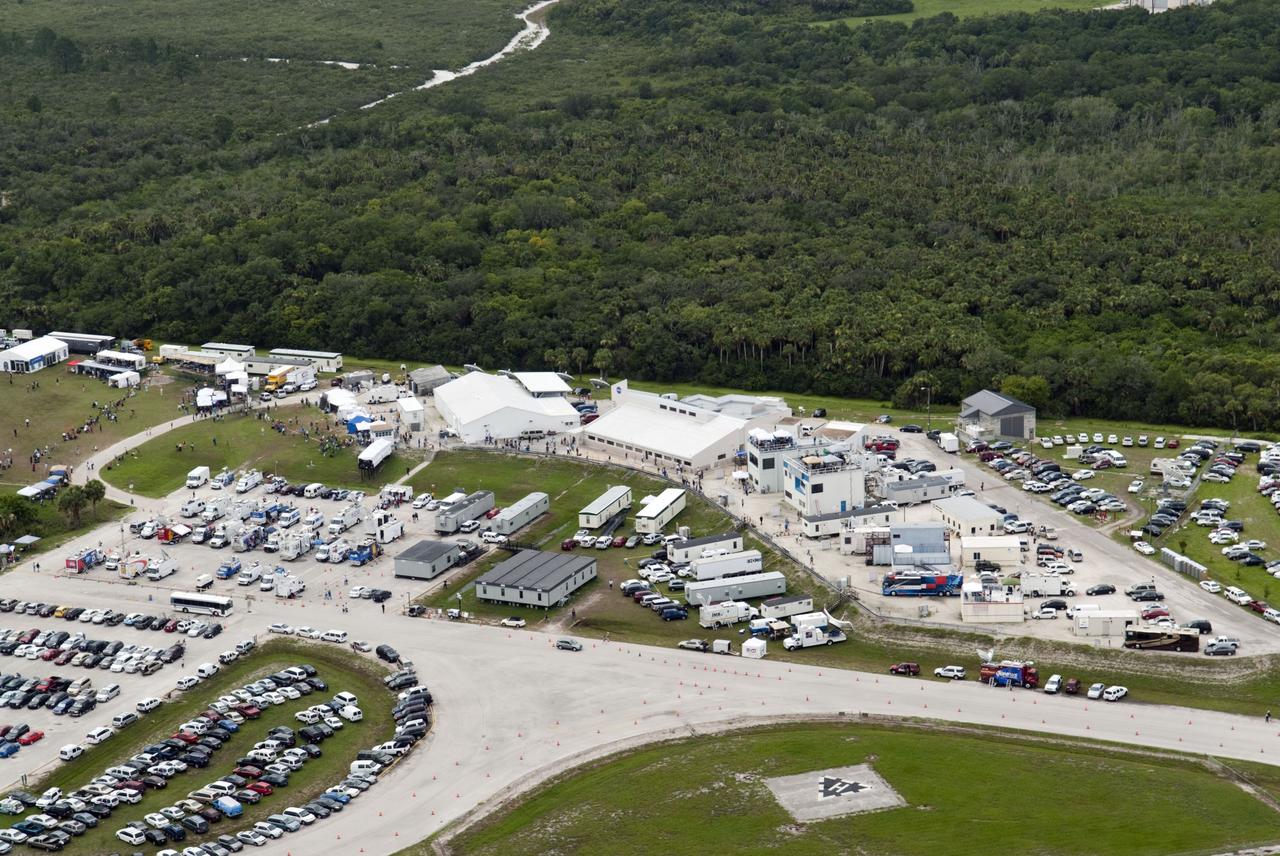

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Taken from the Vehicle Assembly Building roof at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, this image shows the Press Site complex with a myriad of vehicles, satellite trucks and trailers belonging to invited guests and media for the launch of space shuttle Atlantis. Atlantis began its final flight, the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jeffrey Marino
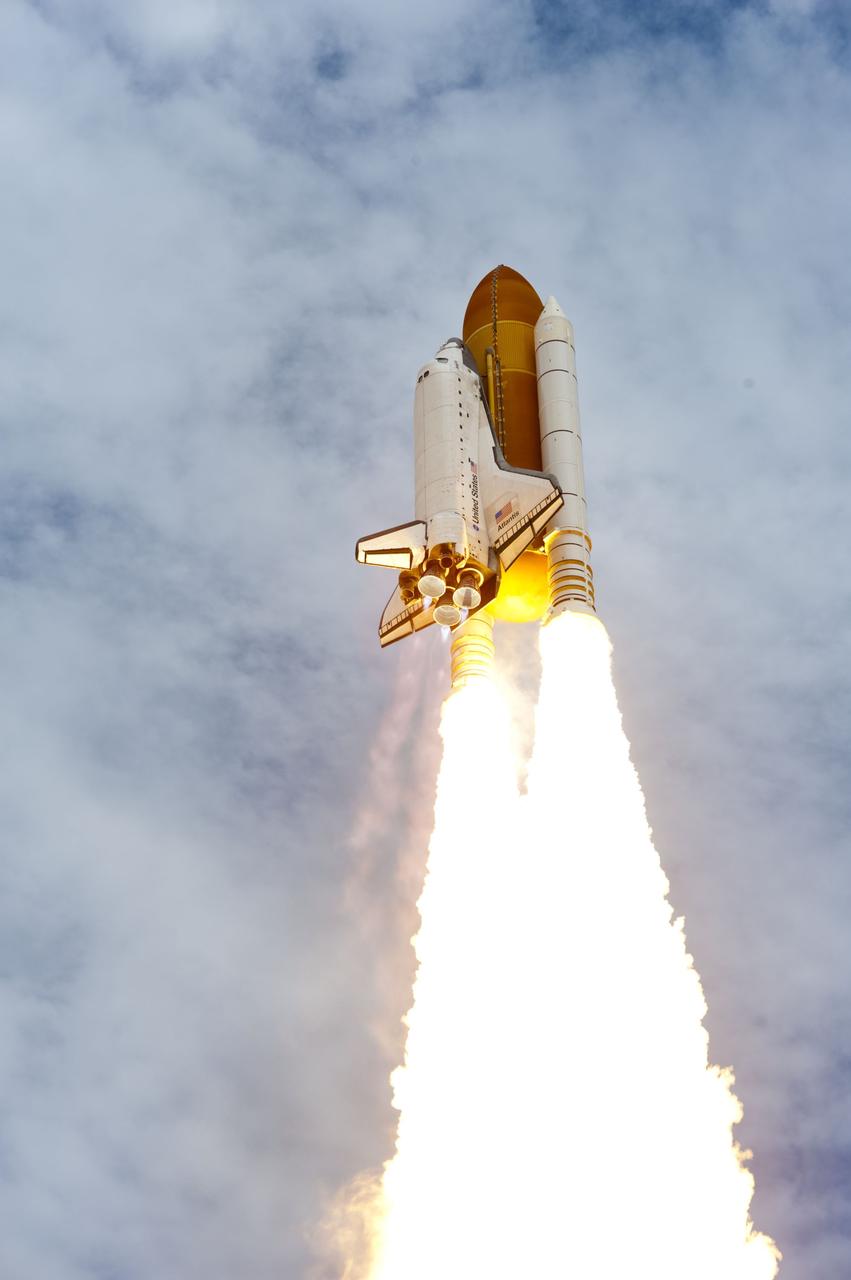

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Solid rocket motors blazing, space shuttle Atlantis heads into the cloud-laden sky over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Atlantis began its final flight, the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the orbiting laboratory. Atlantis also is flying the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, a failed ammonia pump module will be returned to Earth aboard Atlantis to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
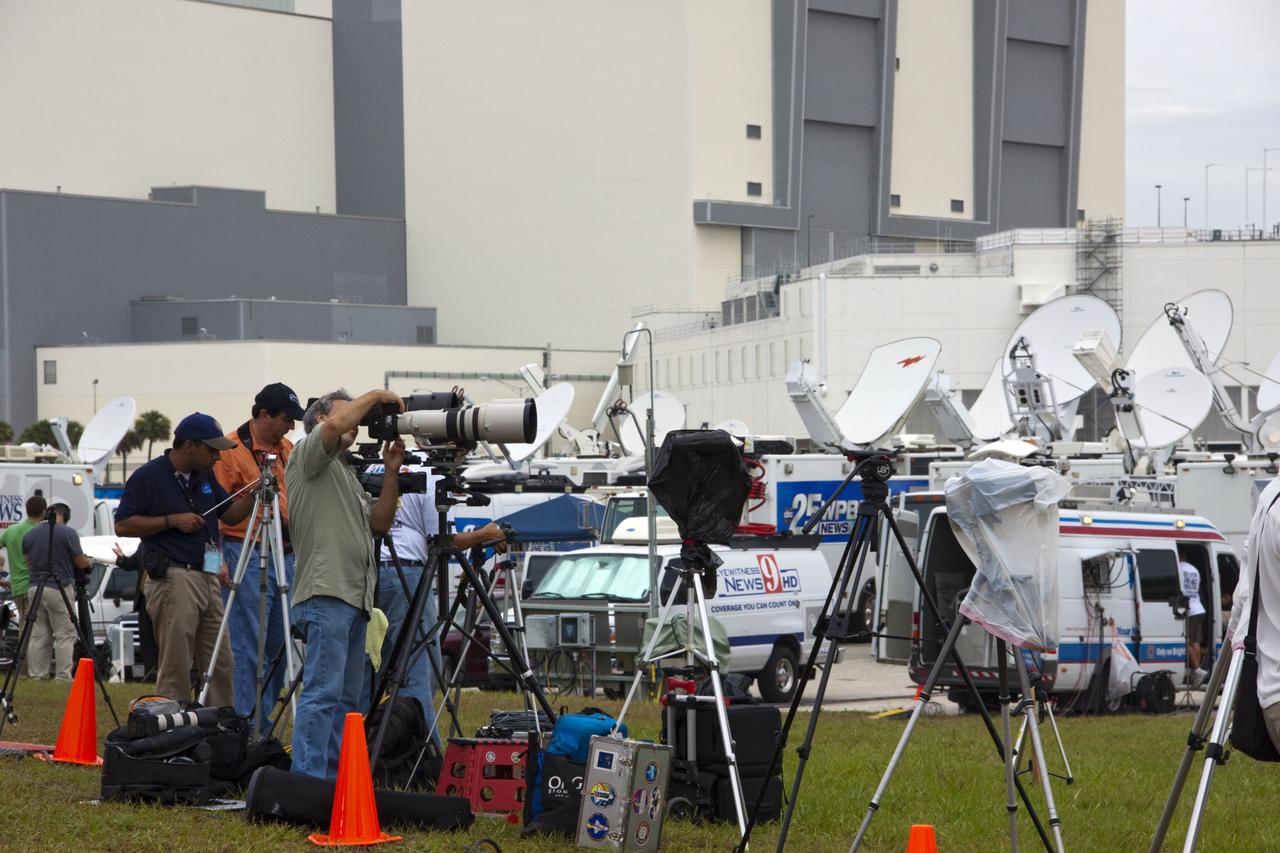

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather at the NASA News Center at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Press Site in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Satellite news trucks, trailers and automobiles can be seen in the parking lot with the massive Vehicle Assembly Building towering above. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana speaks to media and spectators before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen also are Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann (left), Marshall Space Flight Center Director Robert Lightfoot and Johnson Space Center Director Mike Coats. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
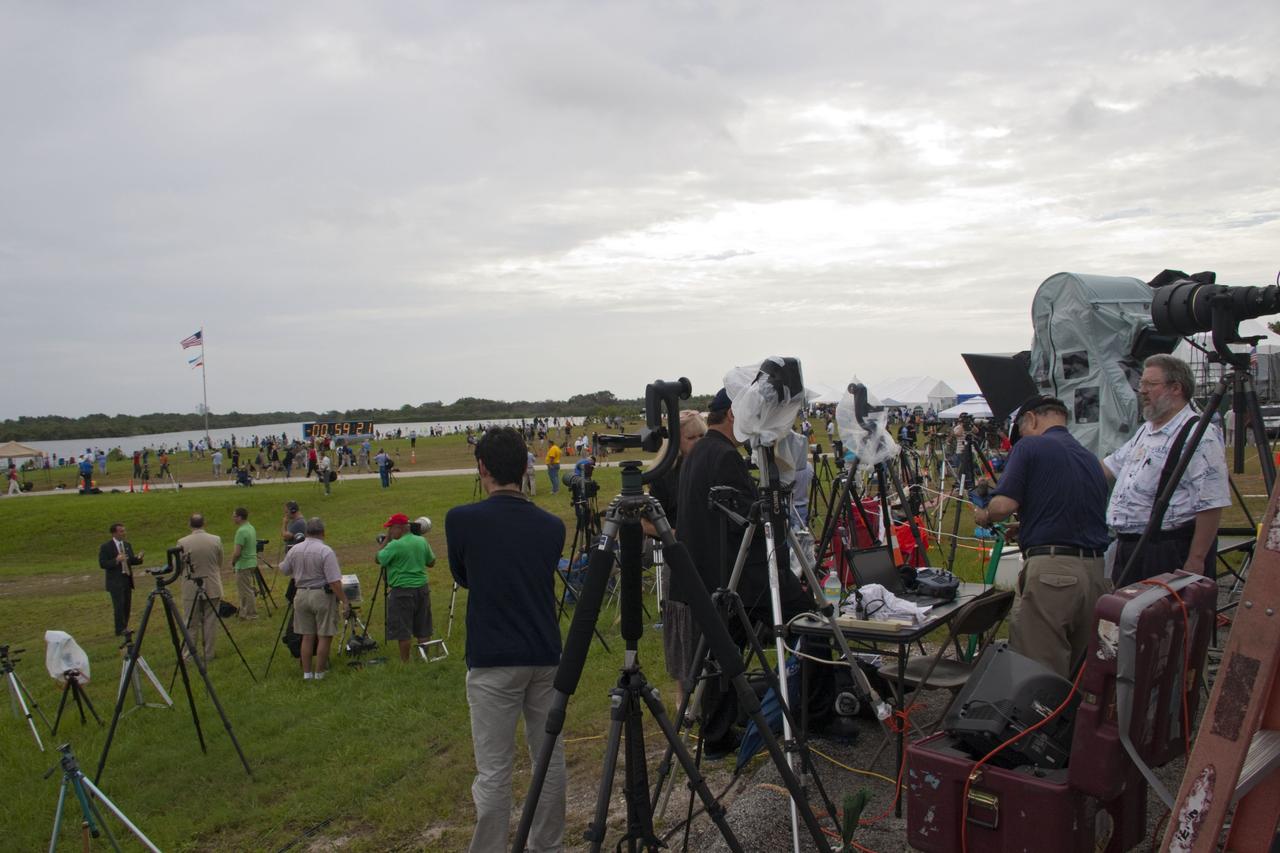

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site and countdown clock at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
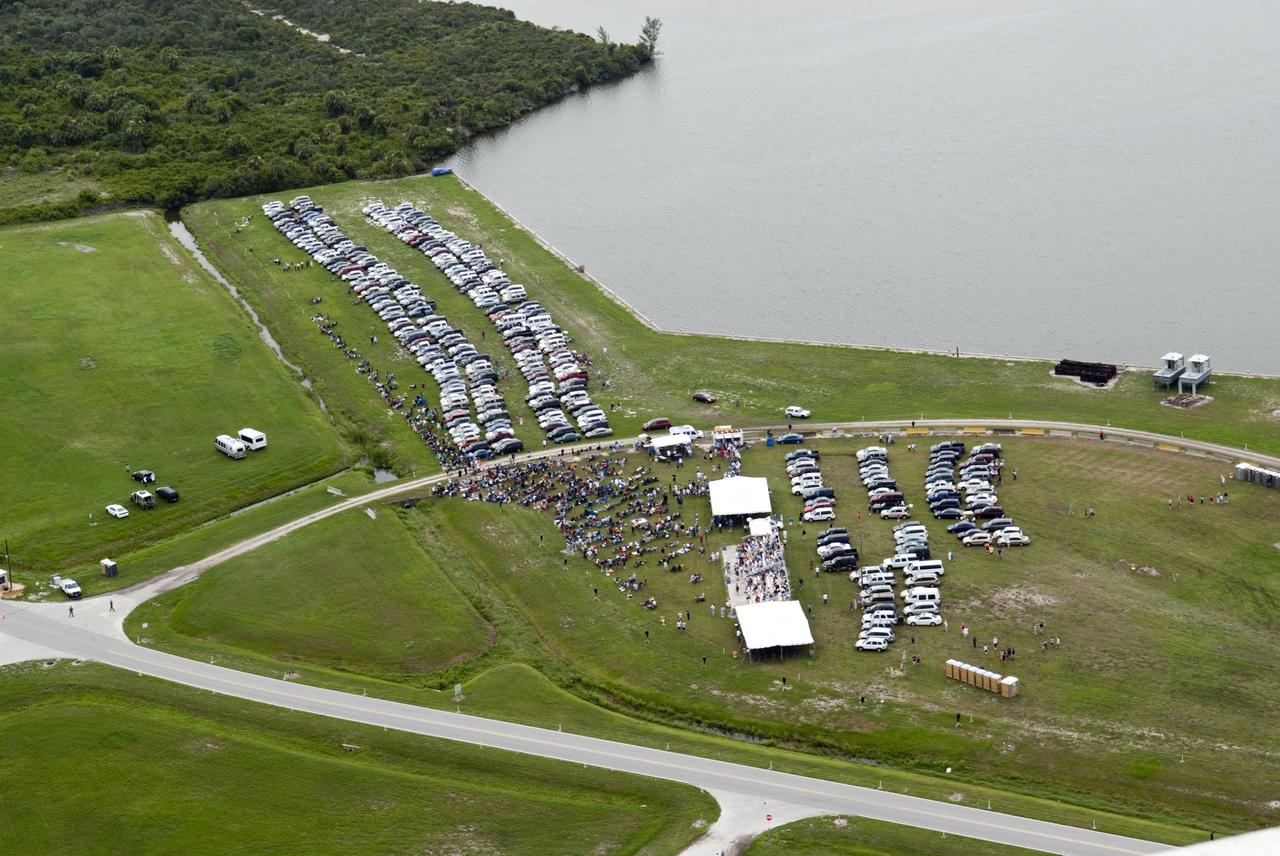

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Taken from the Vehicle Assembly Building roof at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, this image shows the Turn Basin with a myriad of vehicles belonging to invited guests for the launch of space shuttle Atlantis. Atlantis began its final flight, the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jeffrey Marino
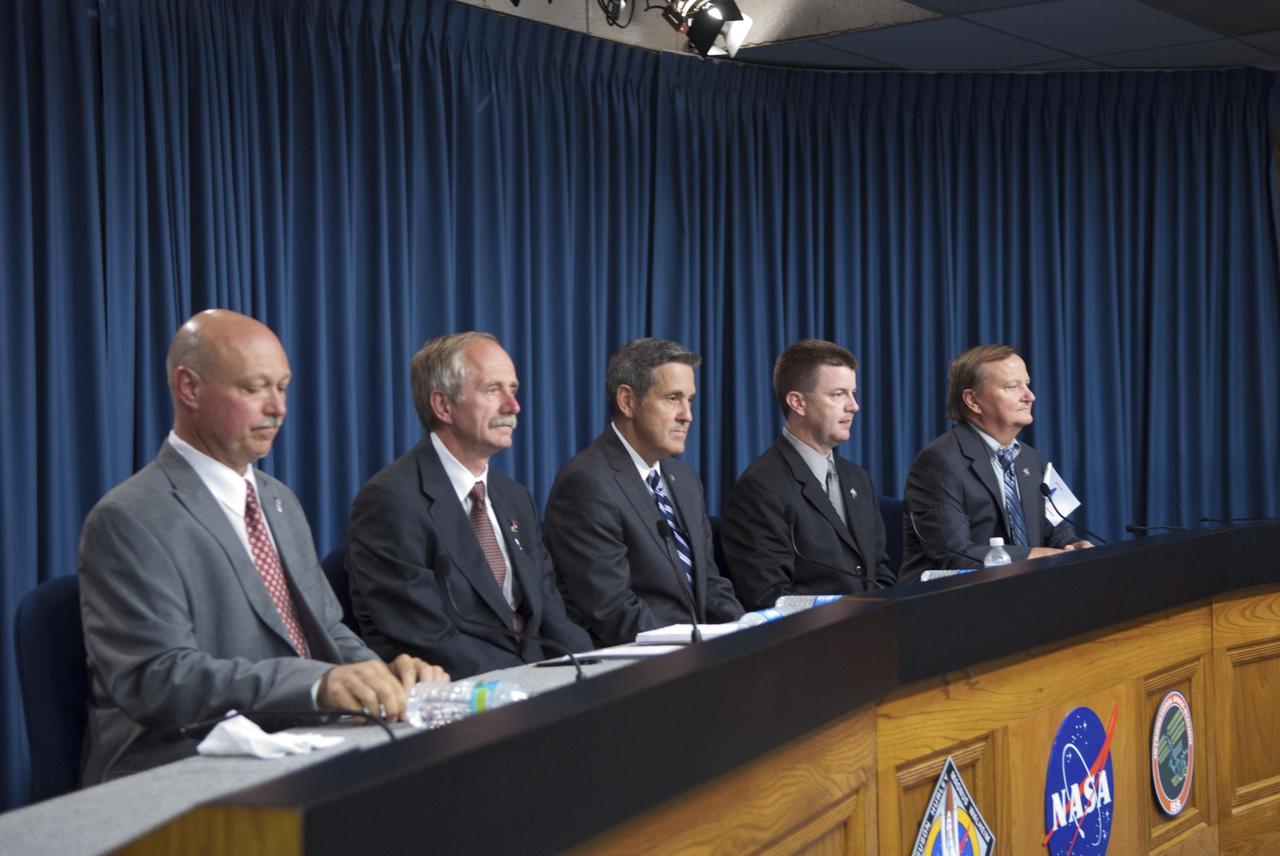

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Members of the media gather for a post-launch news conference held in the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, following the successful launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here are NASA Public Affairs Officer Mike Curie (left) moderator; Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier, Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, Shuttle Program Launch Integration Manager Mike Moses, and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
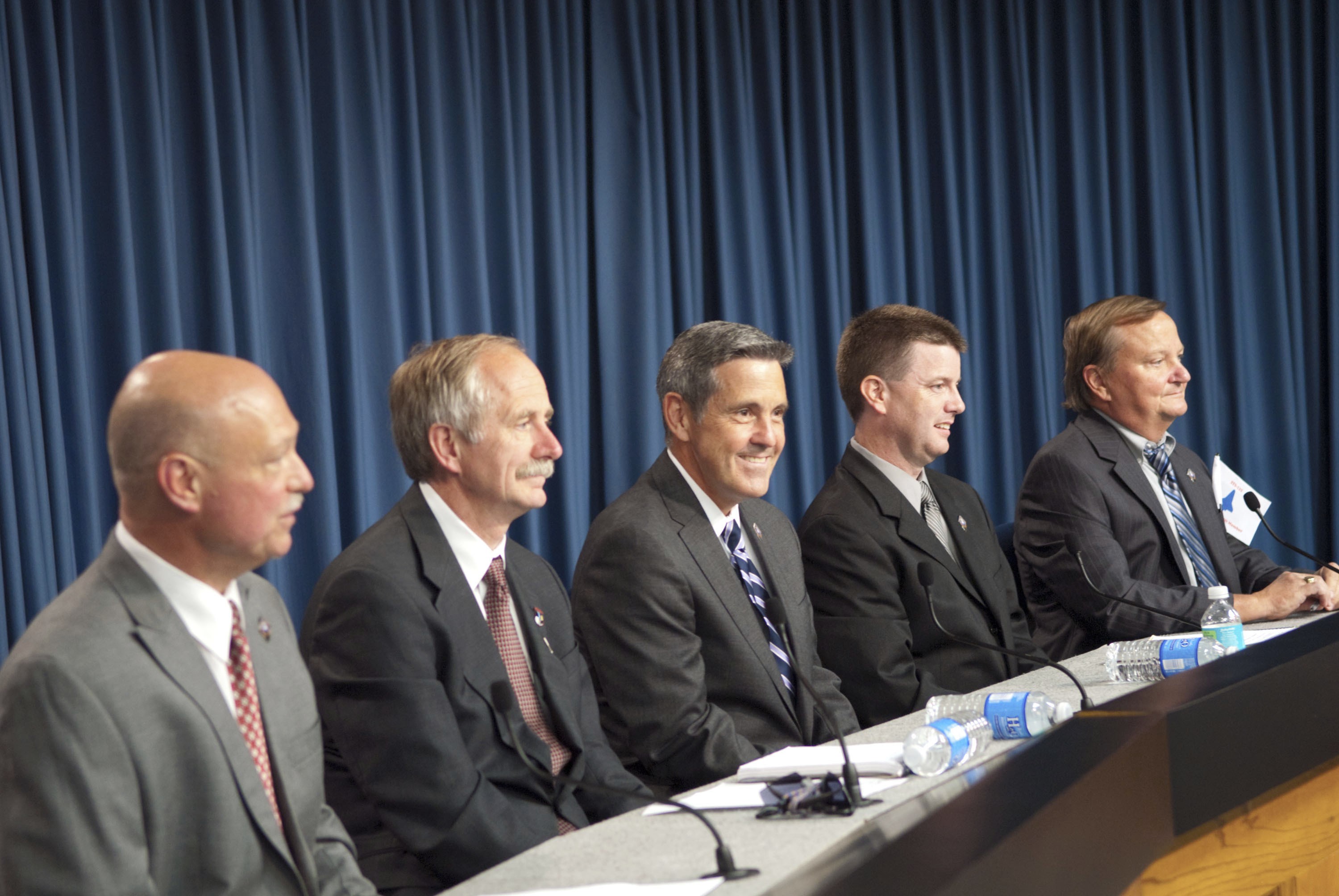

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Members of the media gather for a post-launch news conference held in the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, following the successful launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here are NASA Public Affairs Officer Mike Curie (left) moderator; Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier, Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, Shuttle Program Launch Integration Manager Mike Moses, and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
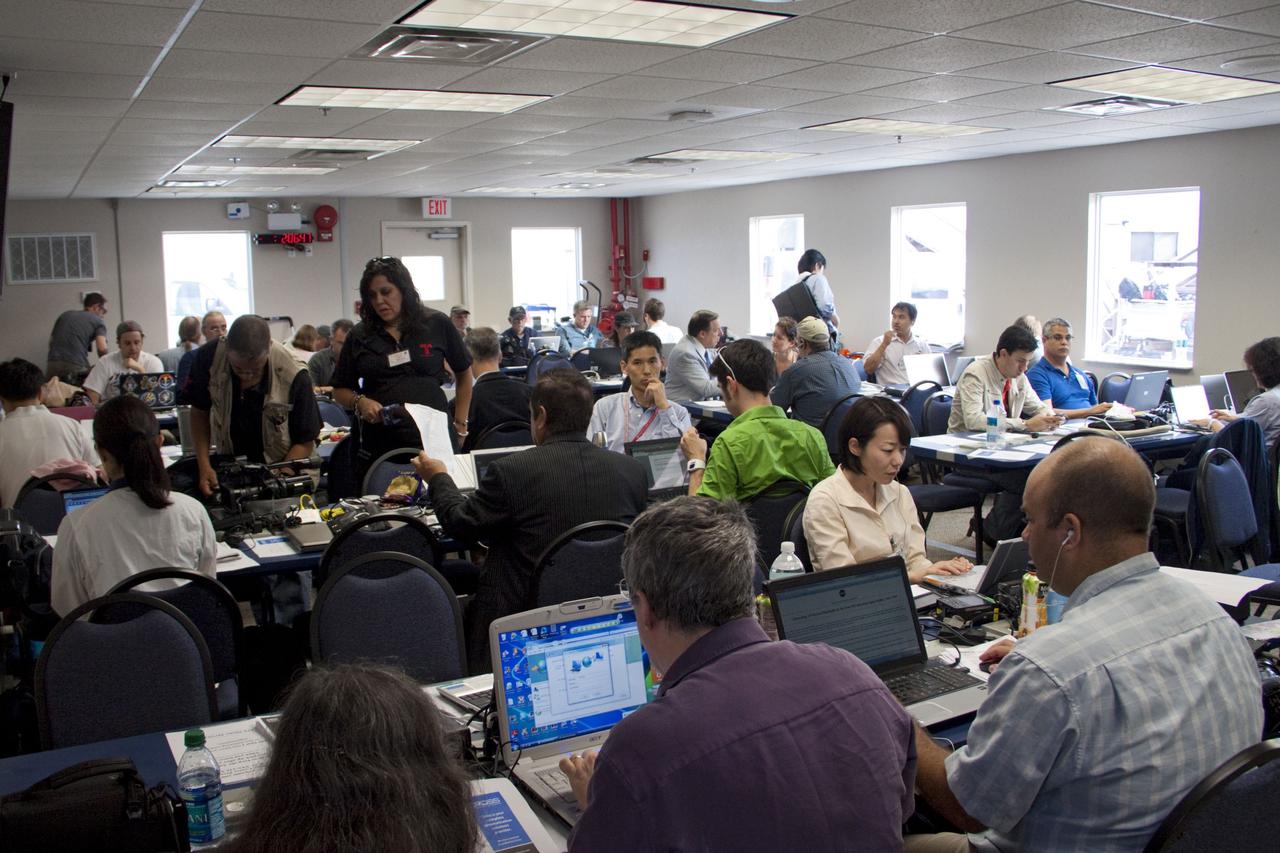

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather at the NASA News Annex at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Press Site in Florida to cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
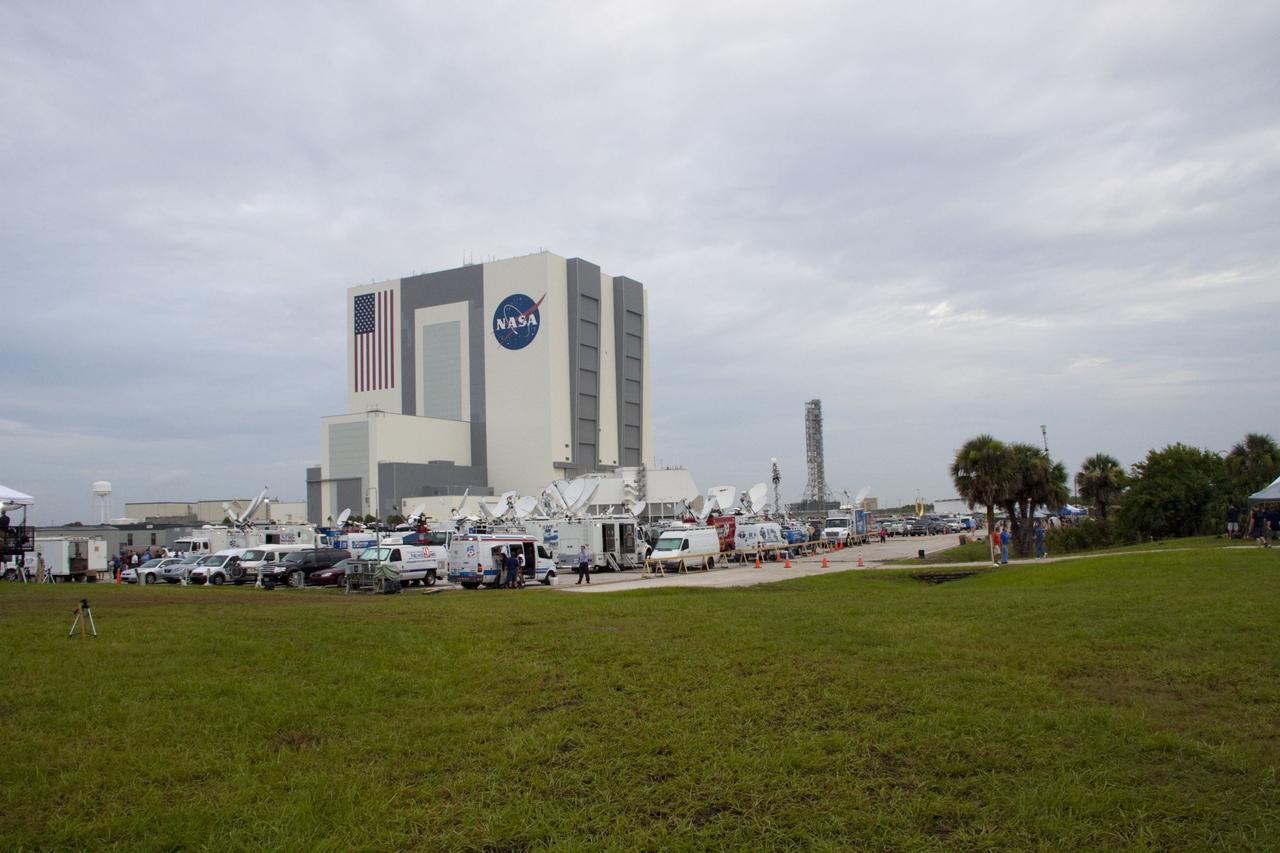

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Dozens of satellite news vehicles can be seen in the parking lot while the massive Vehicle Assembly Building towers above in the background. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
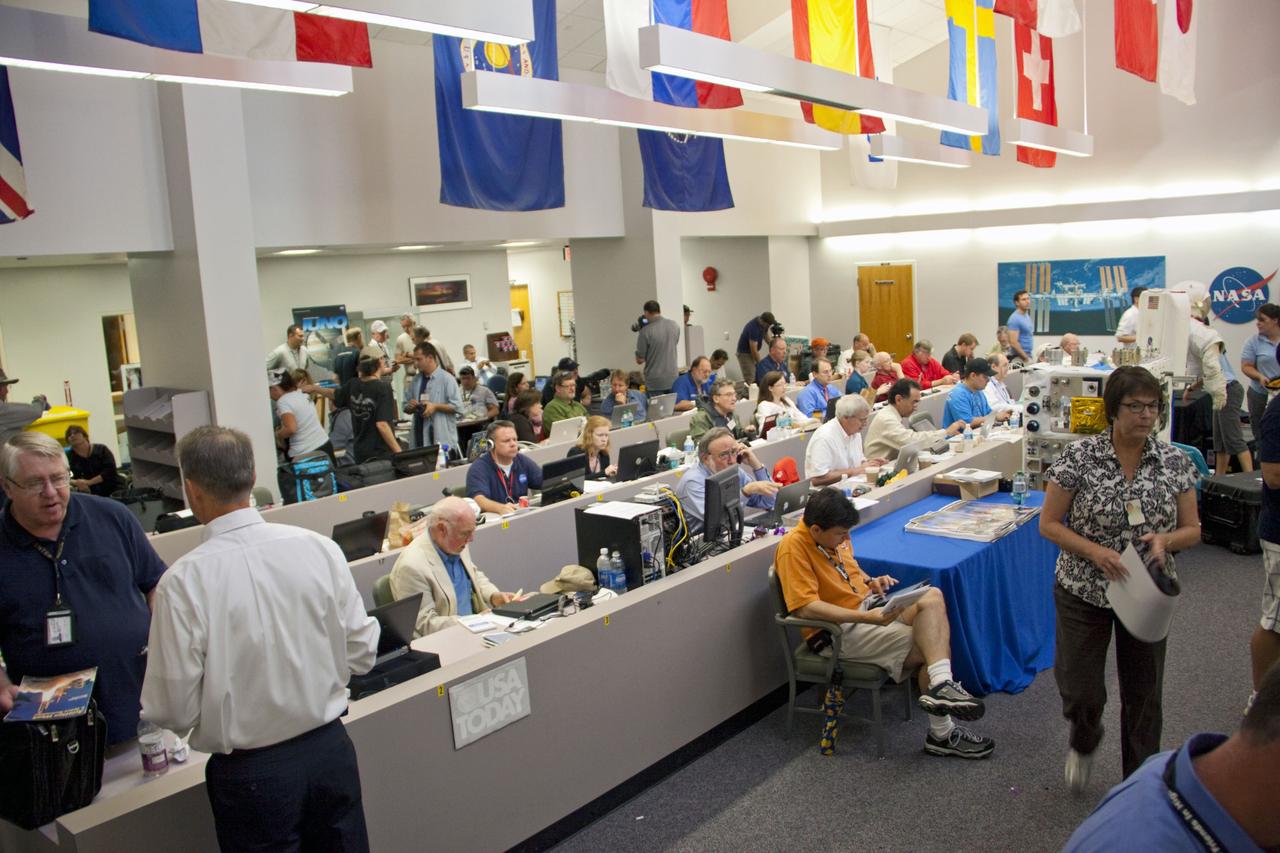

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather at the NASA News Center at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Press Site in Florida to cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann