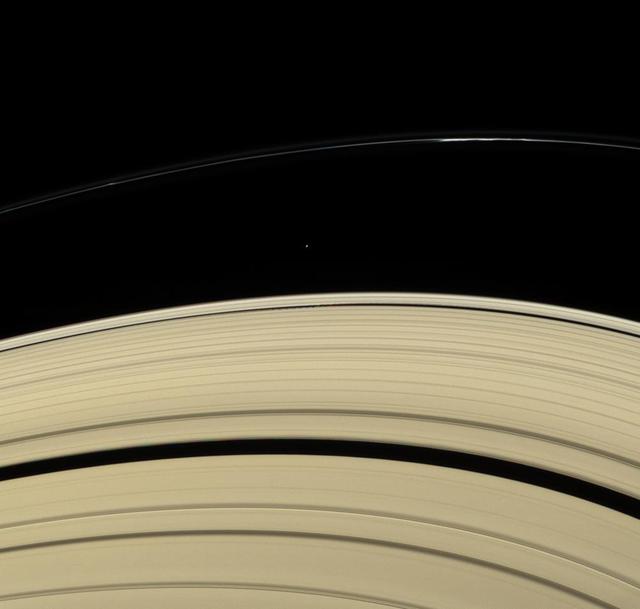
Ring Moon Rendezvous

Ice Moon Rendezvous
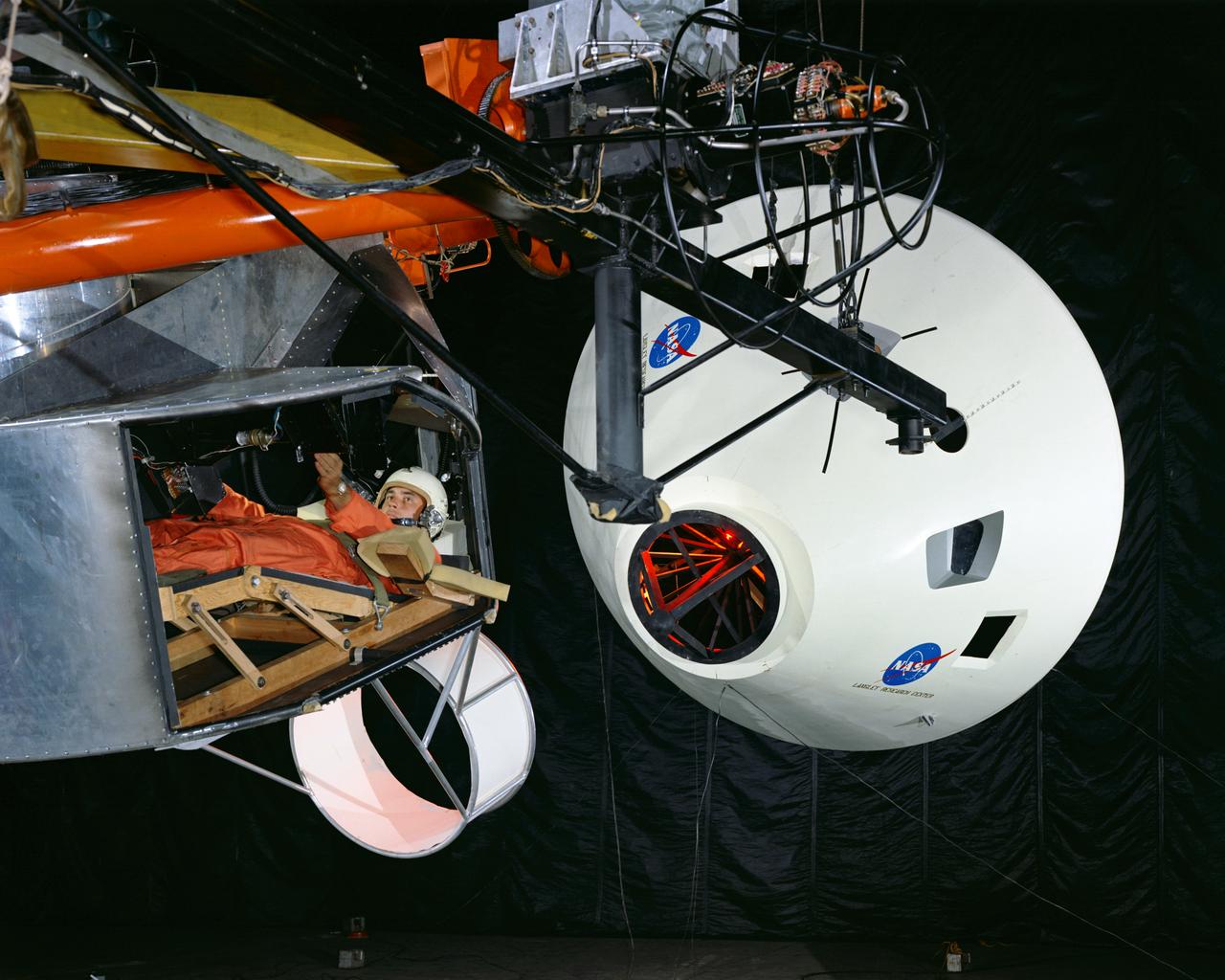
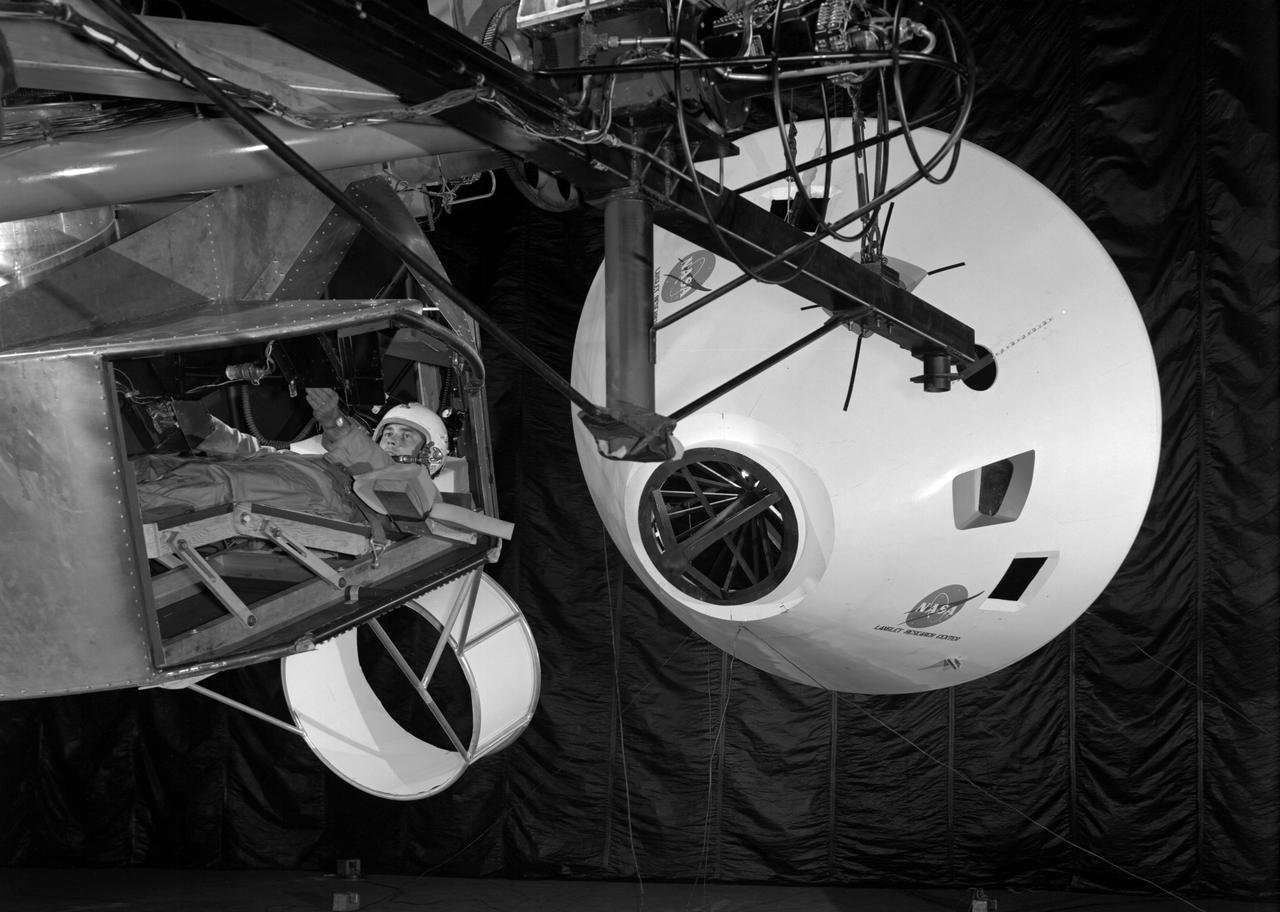
Simulator for Apollo Rendezvous Lunar Excursion Module (LEM)
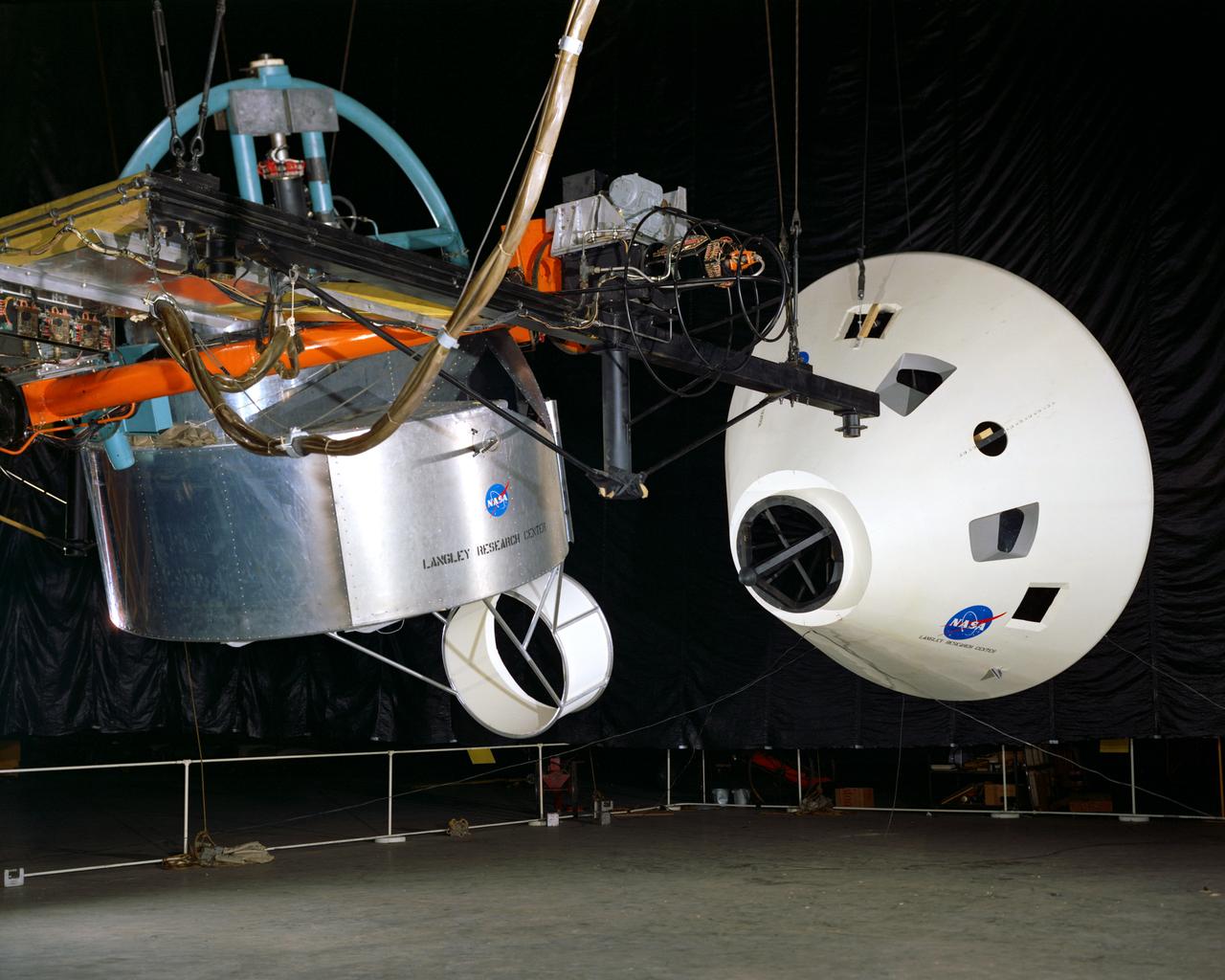
Simulator for Apollo Rendezvous Lunar Excursion Module (LEM)
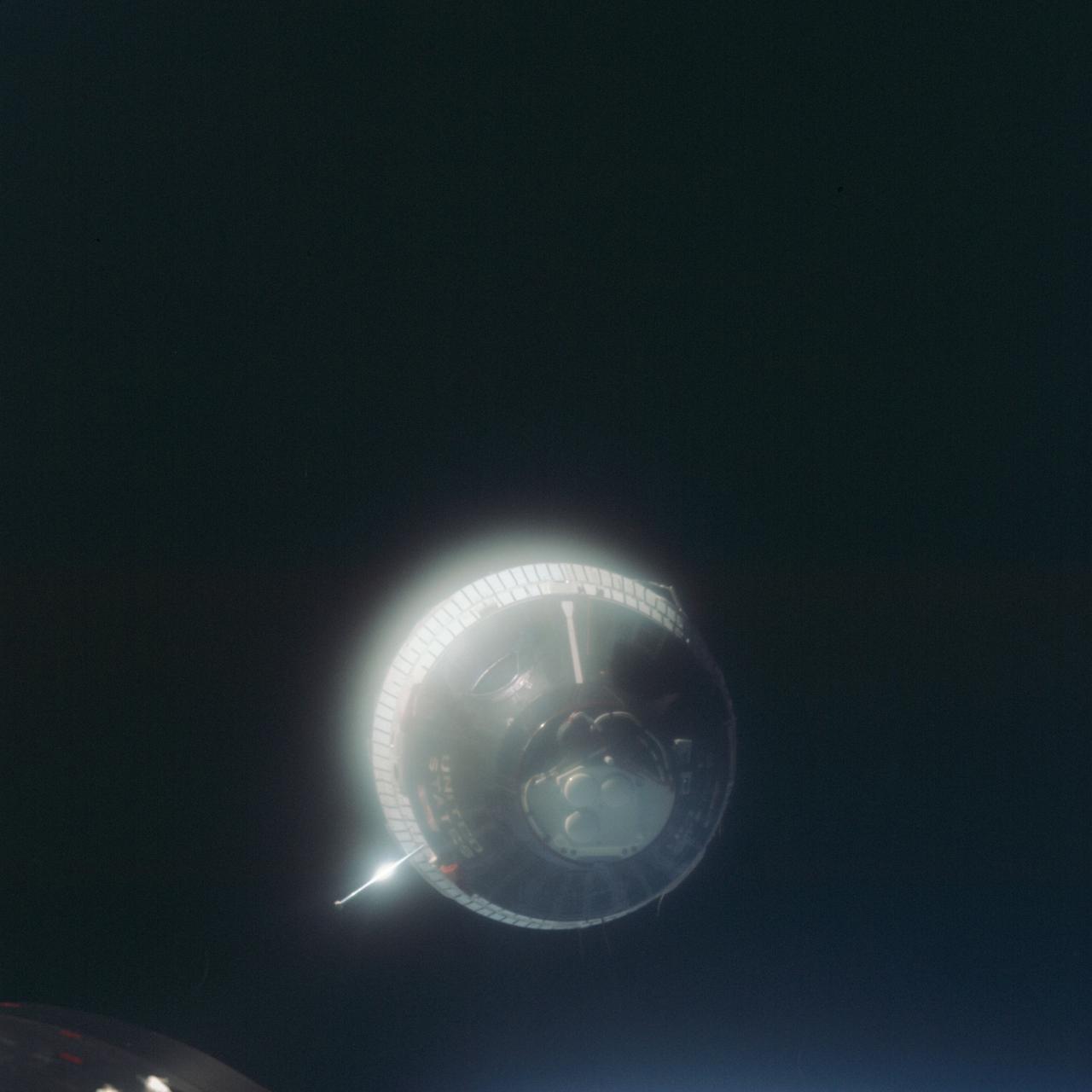

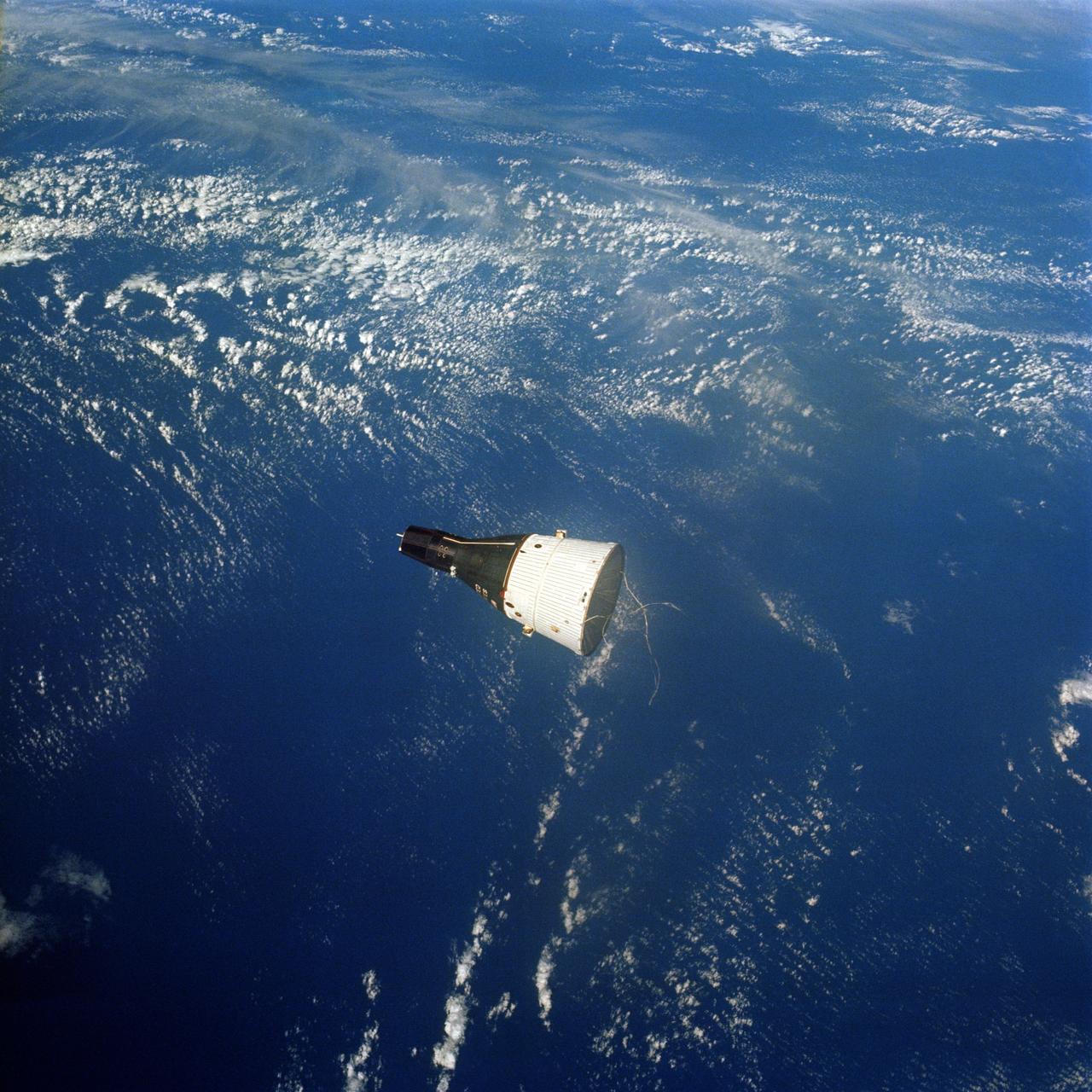
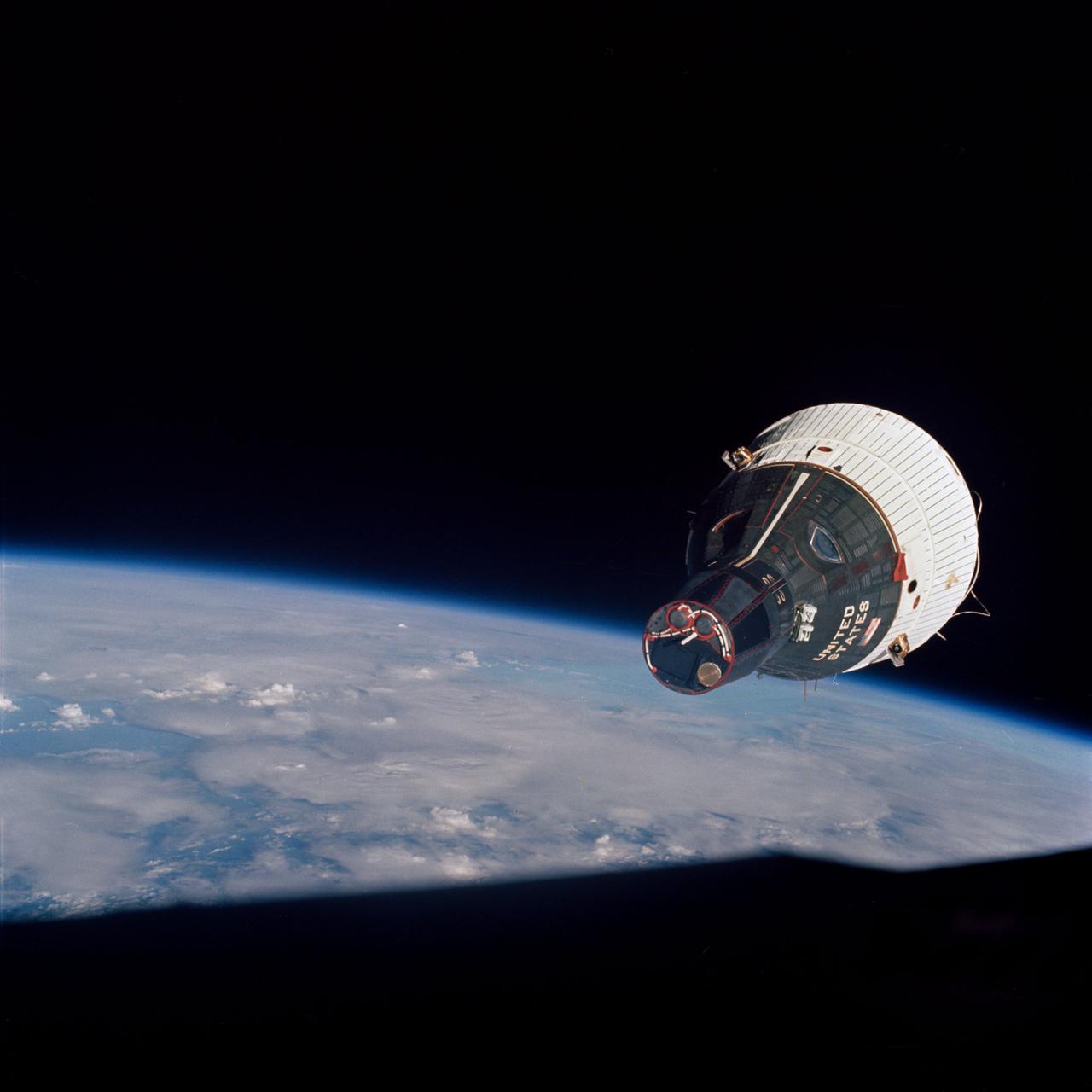
S65-63898 (15 Dec. 1965) --- This picture of the Earth-orbiting Gemini-6 spacecraft against the blackness of space was taken from the Gemini-7 spacecraft during the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's historic rendezvous mission. The two spacecraft are approximately 40 feet apart. This photograph was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Aboard the Gemini-6 spacecraft were astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr. and Thomas P. Stafford. Astronauts Frank Borman and James A. Lovell Jr. were in the Gemini-7 spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA
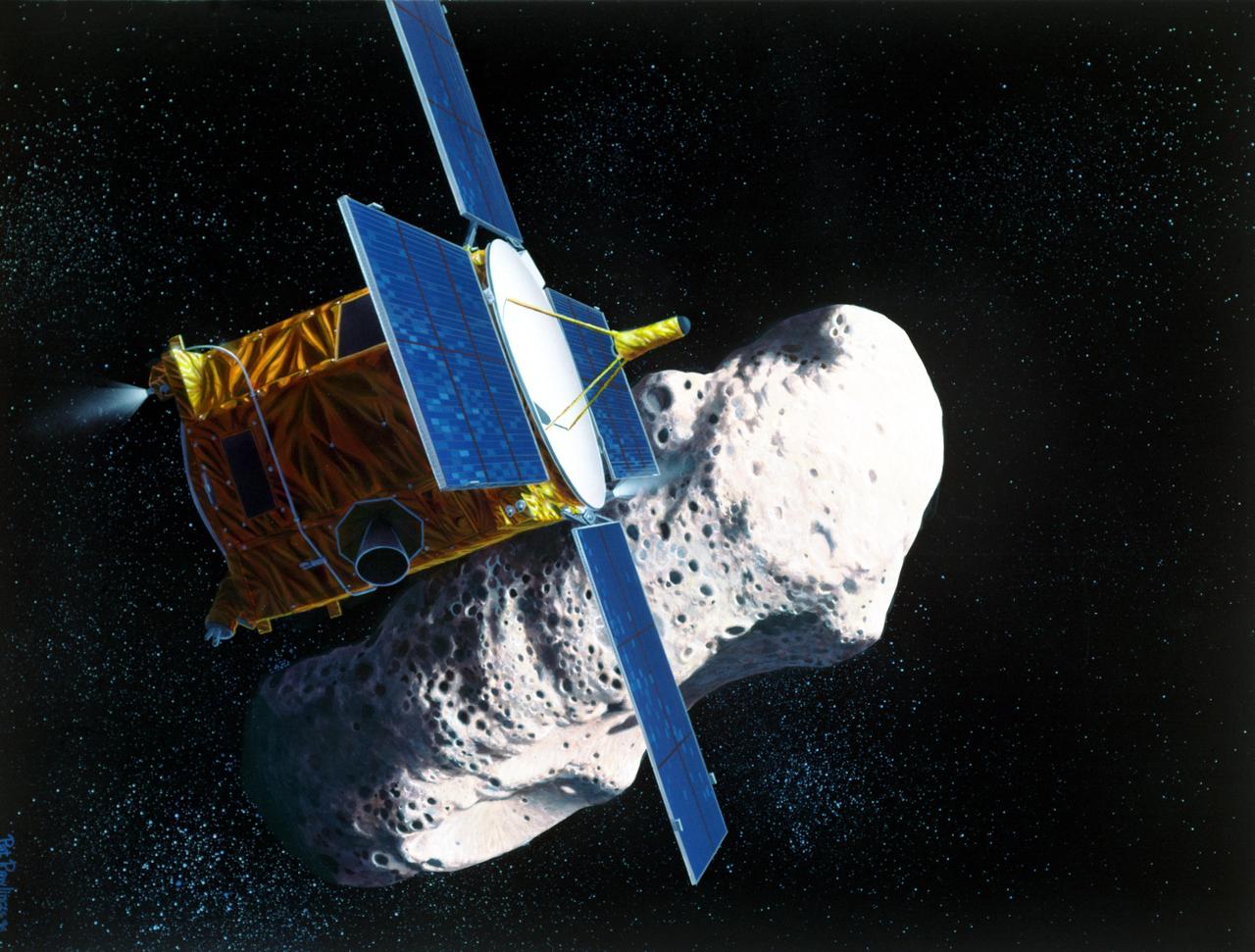

Artist rendering of the the Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous NEAR spacecraft rendezvous with the asteroid Eros.
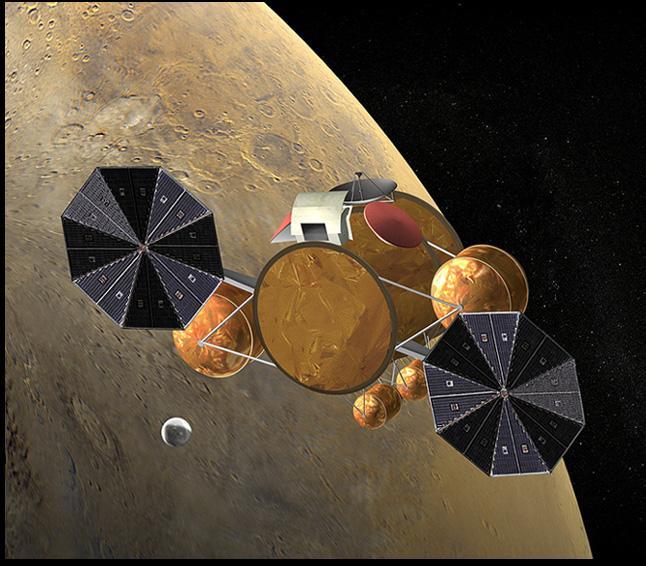
This artist concept of the proposed NASA Mars Sample Return mission shows rendezvous of the orbiting sample container with the Earth return vehicle.

Originally the Rendezvous was used by the astronauts preparing for Gemini missions. The Rendezvous Docking Simulator was then modified and used to develop docking techniques for the Apollo program. The pilot is shown maneuvering the LEM into position for docking with a full-scale Apollo Command Module. From A.W. Vogeley, Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center, Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27 - December 1, 1966. The Rendezvous Docking Simulator and also the Lunar Landing Research Facility are both rather large moving-base simulators. It should be noted, however, that neither was built primarily because of its motion characteristics. The main reason they were built was to provide a realistic visual scene. A secondary reason was that they would provide correct angular motion cues (important in control of vehicle short-period motions) even though the linear acceleration cues would be incorrect. Apollo Rendezvous Docking Simulator: Langley s Rendezvous Docking Simulator was developed by NASA scientists to study the complex task of docking the Lunar Excursion Module with the Command Module in Lunar orbit.
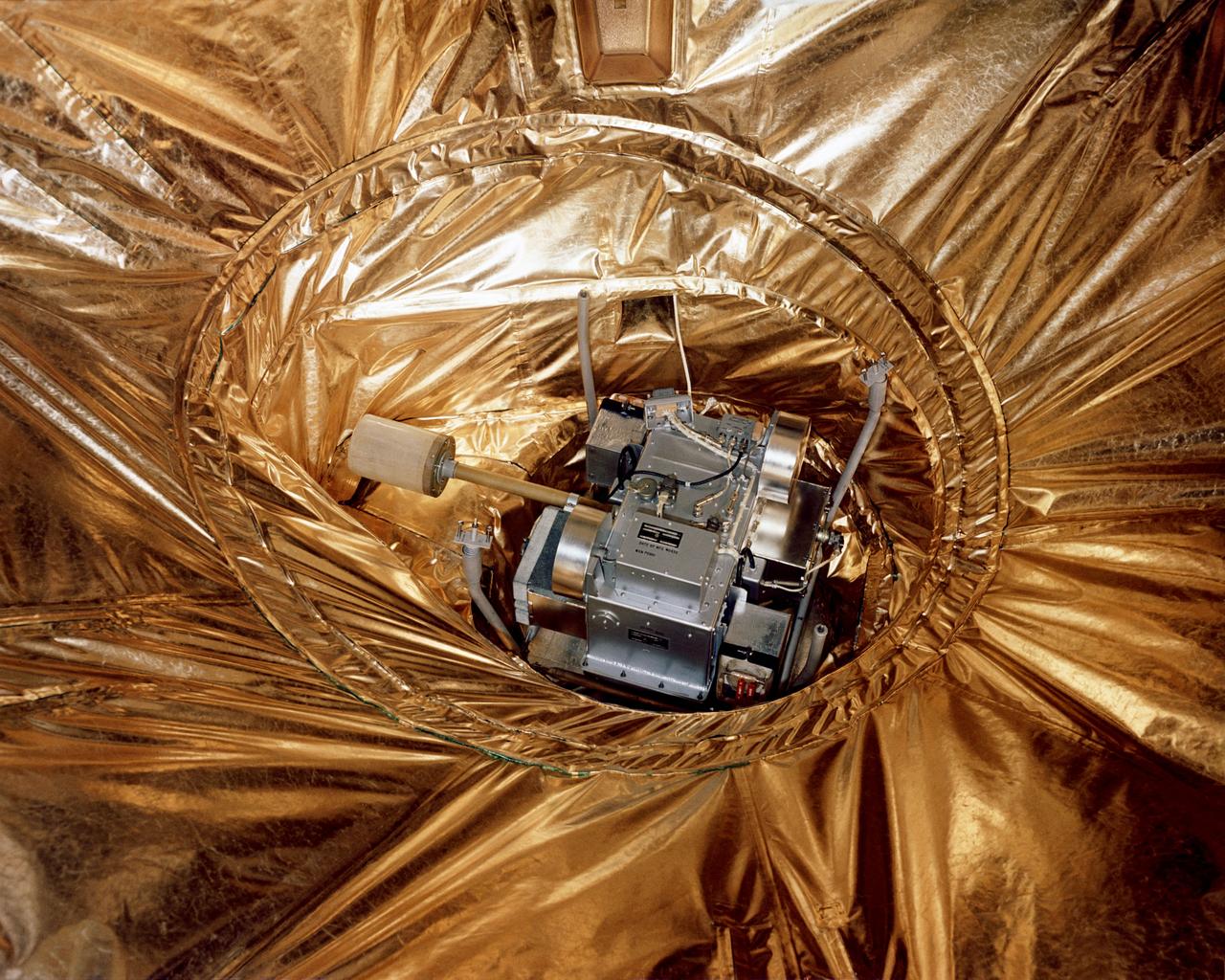

S65-42044 (28 July 1965) --- Close-up view of the Rendezvous Evaluation Pod installed in the equipment section of the Gemini-5 spacecraft at Pad 19.
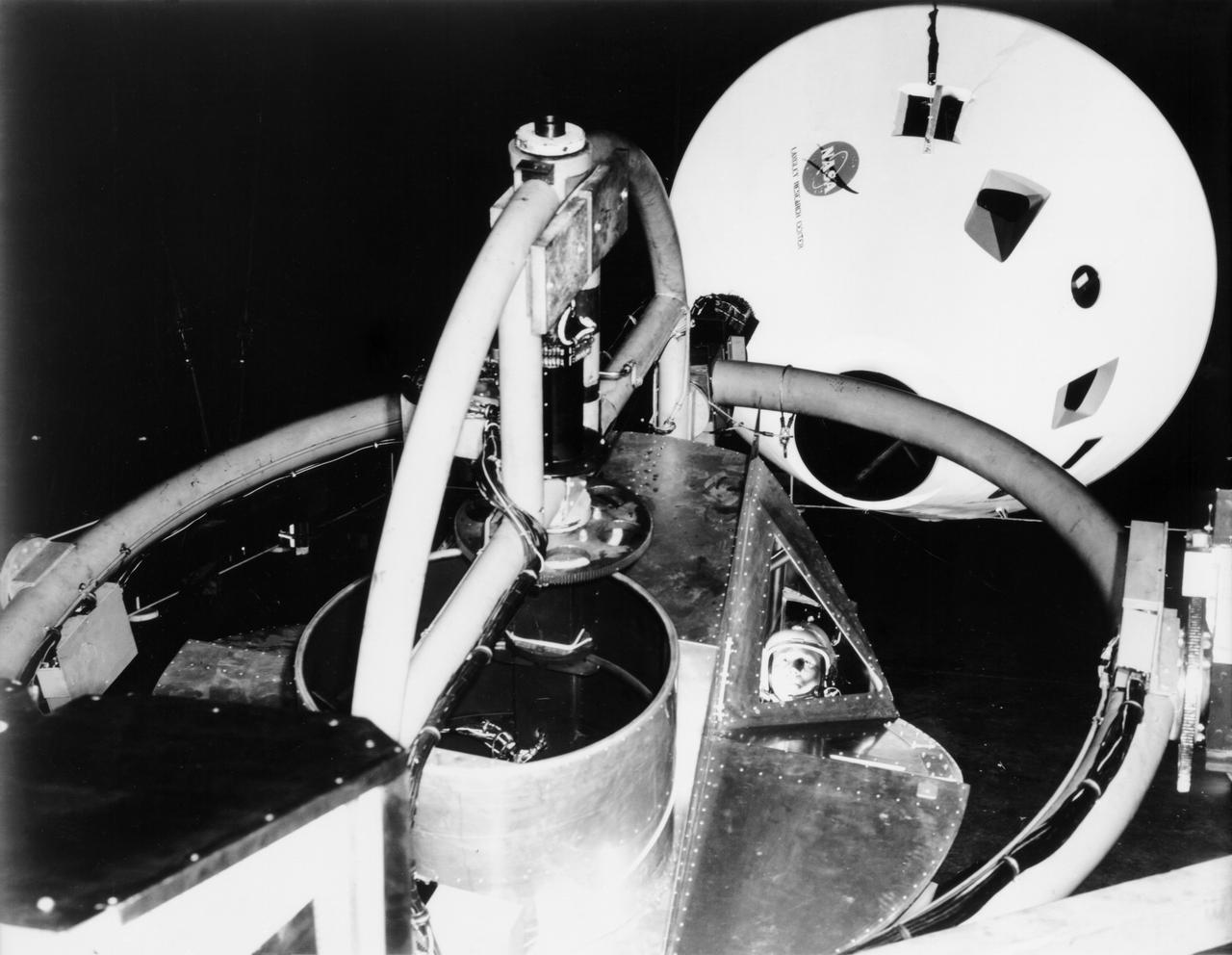

Originally the Rendezvous was used by the astronauts preparing for Gemini missions. The Rendezvous Docking Simulator was then modified and used to develop docking techniques for the Apollo program. "The LEM pilot's compartment, with overhead window and the docking ring (idealized since the pilot cannot see it during the maneuvers), is shown docked with the full-scale Apollo Command Module." A.W. Vogeley described the simulator as follows: "The Rendezvous Docking Simulator and also the Lunar Landing Research Facility are both rather large moving-base simulators. It should be noted, however, that neither was built primarily because of its motion characteristics. The main reason they were built was to provide a realistic visual scene. A secondary reason was that they would provide correct angular motion cues (important in control of vehicle short-period motions) even though the linear acceleration cues would be incorrect." -- Published in A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27 - December 1, 1966;
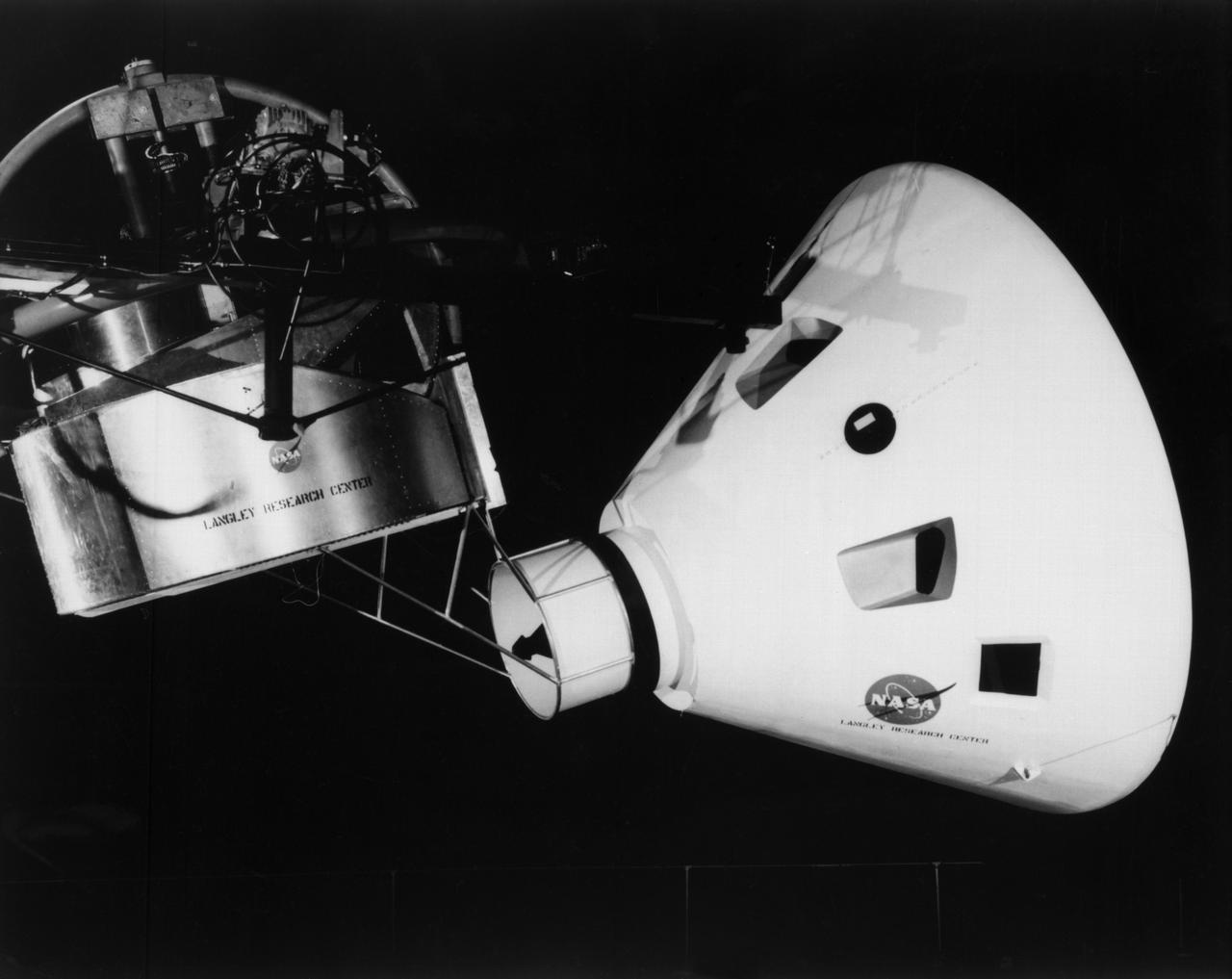
Originally the Rendezvous was used by the astronauts preparing for Gemini missions. The Rendezvous Docking Simulator was then modified and used to develop docking techniques for the Apollo program. "The LEM pilot's compartment, with overhead window and the docking ring (idealized since the pilot cannot see it during the maneuvers), is shown docked with the full-scale Apollo Command Module." A.W. Vogeley described the simulator as follows: "The Rendezvous Docking Simulator and also the Lunar Landing Research Facility are both rather large moving-base simulators. It should be noted, however, that neither was built primarily because of its motion characteristics. The main reason they were built was to provide a realistic visual scene. A secondary reason was that they would provide correct angular motion cues (important in control of vehicle short-period motions) even though the linear acceleration cues would be incorrect." -- Published in A.W. Vogeley, "Piloted Space-Flight Simulation at Langley Research Center," Paper presented at the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1966 Winter Meeting, New York, NY, November 27 - December 1, 1966;
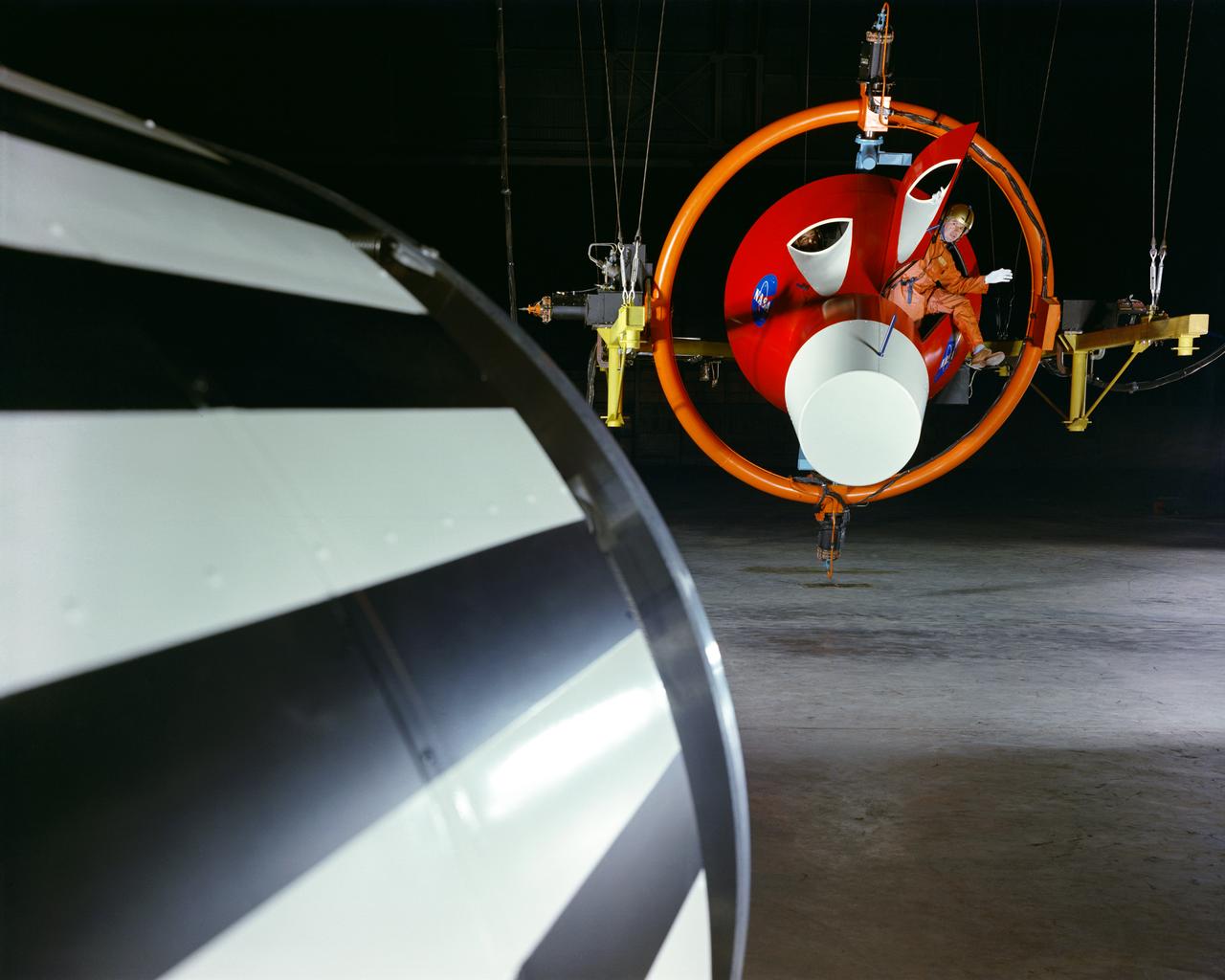

Practicing with a full-scale model of the Gemini Capsule in Langley's Rendezvous Docking Simulator. -- Caption and photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, (page 89), by James Schultz.

S65-63198 (15 Dec. 1965) --- The Gemini-7 spacecraft as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during their rendezvous mission in space. They are approximately 39 feet apart. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

S65-63171 (15 Dec. 1965) --- The Gemini-7 spacecraft as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during their rendezvous mission in space. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
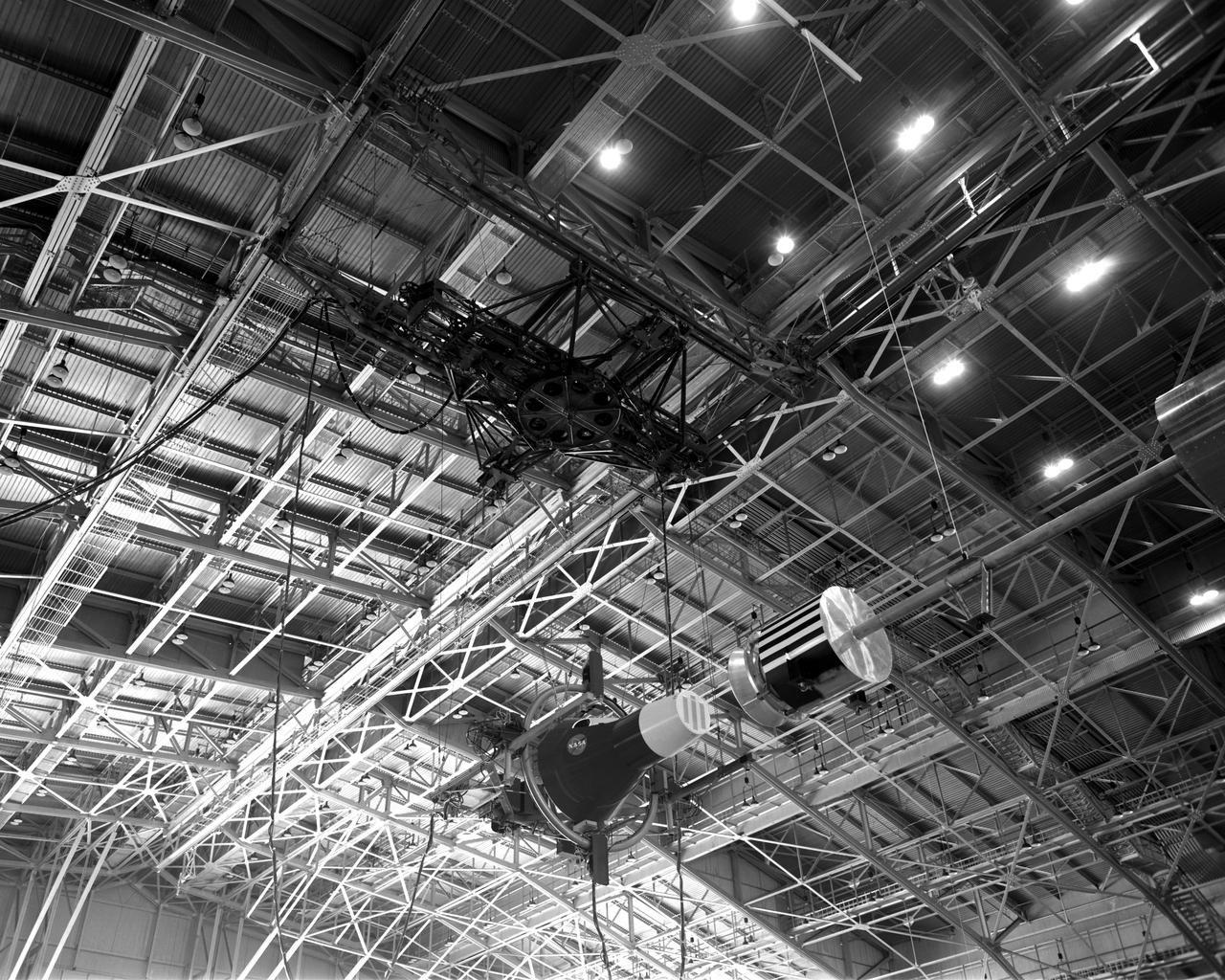

Rendezvous Docking Simulator Suspended From the Roof of the West Area Hangar Image 1963-L-05016 on page 372 of Spaceflight Revolution NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo

S65-63189 (15 Dec. 1965) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Gemini-7 spacecraft as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during their rendezvous mission in space. The two spacecraft are approximately 43 feet apart. This image was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

S65-63113 (15 Dec. 1965) --- This photograph of the Gemini-7 spacecraft was taken from the hatch window of the Gemini-6 spacecraft during rendezvous and station keeping maneuvers at an altitude of approximately 160 miles on Dec. 15, 1965. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
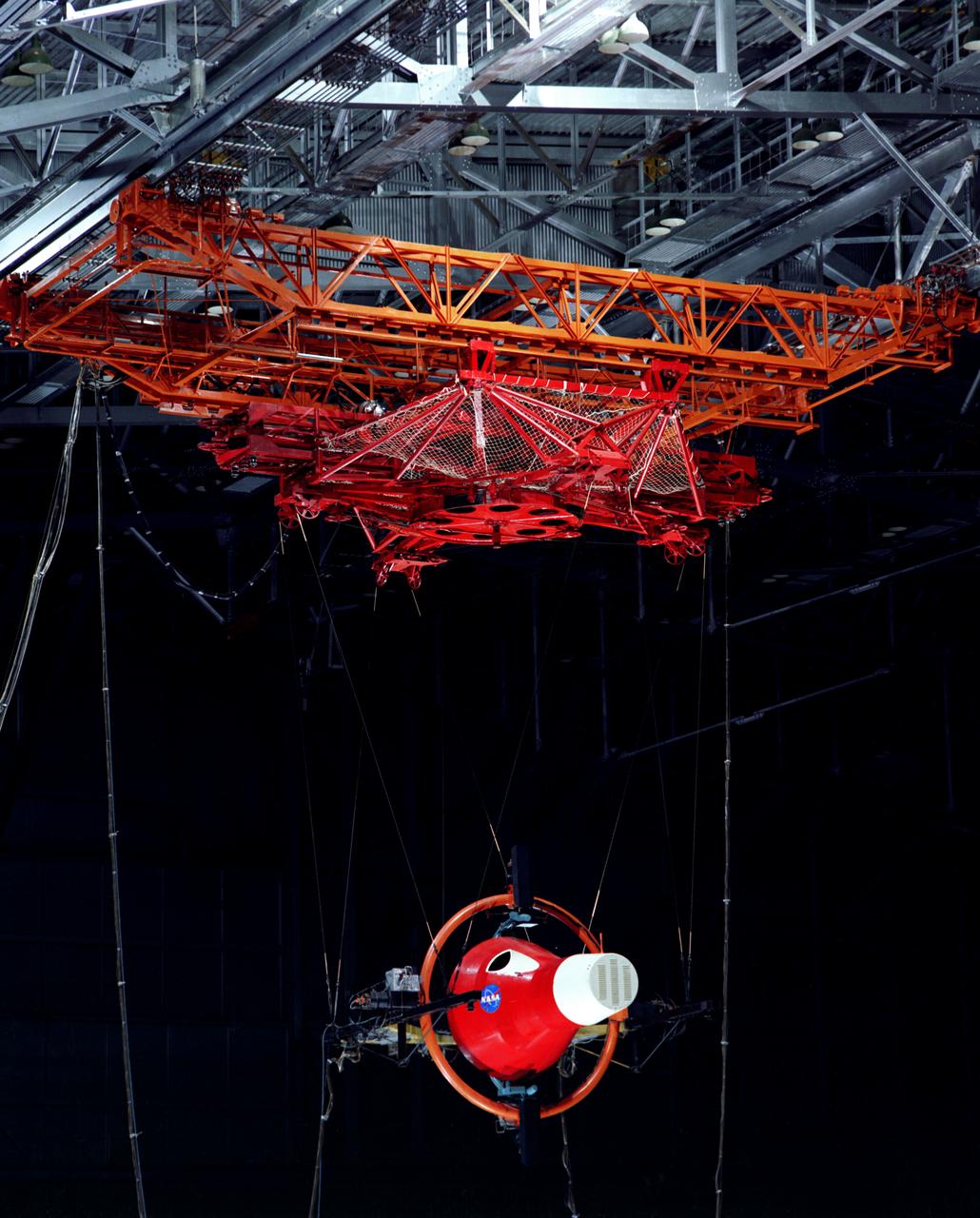

Gemini Rendezvous Docking Simulator suspended from the roof of the Langley Research Center s aircraft hangar. Francis B. Smith wrote: The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. This figure illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft. -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203 Francis B. Smith, Simulators for Manned Space Research, Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966.

S66-62999 (13 Nov. 1966) --- Jettison of the extravehicular life support system (ELSS) and other equipment from the Gemini-12 spacecraft during its rendezvous mission in space. The nose of the Gemini-12 spacecraft is clearly visible at right edge of photo. Photo credit: NASA

S65-63209 (15 Dec. 1965) --- The Gemini-7 spacecraft as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during their rendezvous mission in space. The two spacecrafts are approximately 122 feet apart. This photo was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
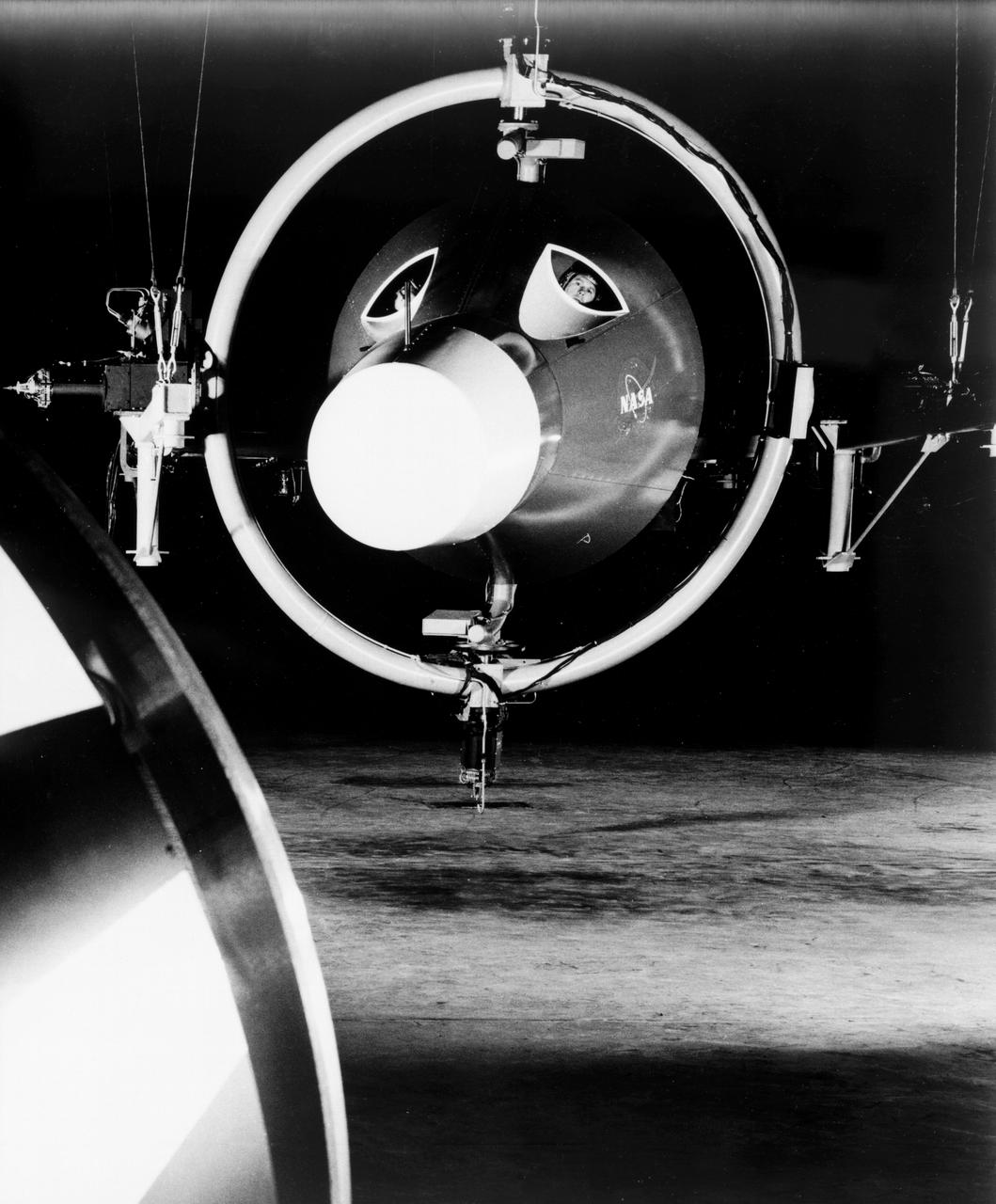
![Multiple exposure of Gemini rendezvous docking simulator. Francis B. Smith wrote in his paper "Simulators for Manned Space Research," "The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. [This figure] illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft." A.W. Vogeley further described the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," "Docking operations are considered to start when the pilot first can discern vehicle target size and aspect and terminate, of course, when soft contact is made. ... This facility enables simulation of the docking operation from a distance of 200 feet to actual contact with the target. A full-scale mock-up of the target vehicle is suspended near one end of the track. ... On [the Agena target] we have mounted the actual Agena docking mechanism and also various types of visual aids. We have been able to devise visual aids which have made it possible to accomplish nighttime docking with as much success as daytime docking." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators for Manned Space Research," Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/LRC-1963-B701_P-08973/LRC-1963-B701_P-08973~medium.jpg)
Multiple exposure of Gemini rendezvous docking simulator. Francis B. Smith wrote in his paper "Simulators for Manned Space Research," "The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. [This figure] illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft." A.W. Vogeley further described the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," "Docking operations are considered to start when the pilot first can discern vehicle target size and aspect and terminate, of course, when soft contact is made. ... This facility enables simulation of the docking operation from a distance of 200 feet to actual contact with the target. A full-scale mock-up of the target vehicle is suspended near one end of the track. ... On [the Agena target] we have mounted the actual Agena docking mechanism and also various types of visual aids. We have been able to devise visual aids which have made it possible to accomplish nighttime docking with as much success as daytime docking." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators for Manned Space Research," Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964.

S65-63220 (15 Dec. 1965) --- This photograph of the Gemini-Titan 7 (GT-7) spacecraft was taken from the Gemini-Titan 6 (GT-6) spacecraft during the historic rendezvous of the two spacecraft on Dec. 15, 1965. The two spacecraft are some 37 feet apart here. Earth can be seen below. Astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., command pilot; and Thomas P. Stafford, pilot, were inside the GT-6 spacecraft, while crewmen for the GT-7 mission were astronauts Frank Borman, command pilot, and James A. Lovell Jr., pilot. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

S65-63188 (15 Dec. 1965) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Gemini-7 spacecraft as seen from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during their rendezvous mission in space. The two spacecraft are approximately 43 feet apart. The image was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
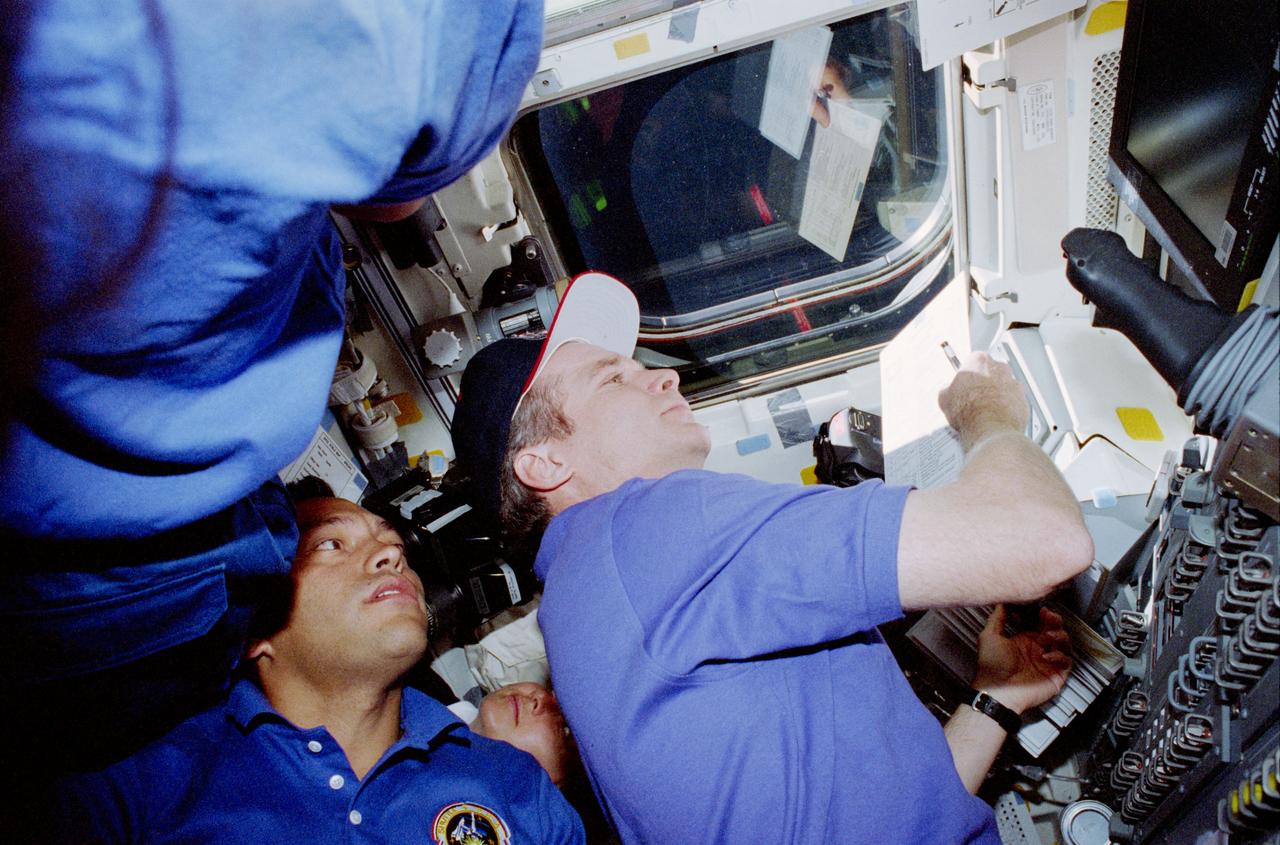

STS084-357-015 (15-24 May 1997) --- Astronaut Charles J. Precourt (right), STS-84 commander, controls the rate of the Space Shuttle Atlantis' approach to Russia's Mir Space Station during rendezvous operations. Carlos I. Noriega (left), Elena V. Kondakova (bottom center) and an unidentified crew member (far left) crowd into the scene -- typical of the busy rendezvous in-cabin scenarios on all Mir-Atlantis missions.
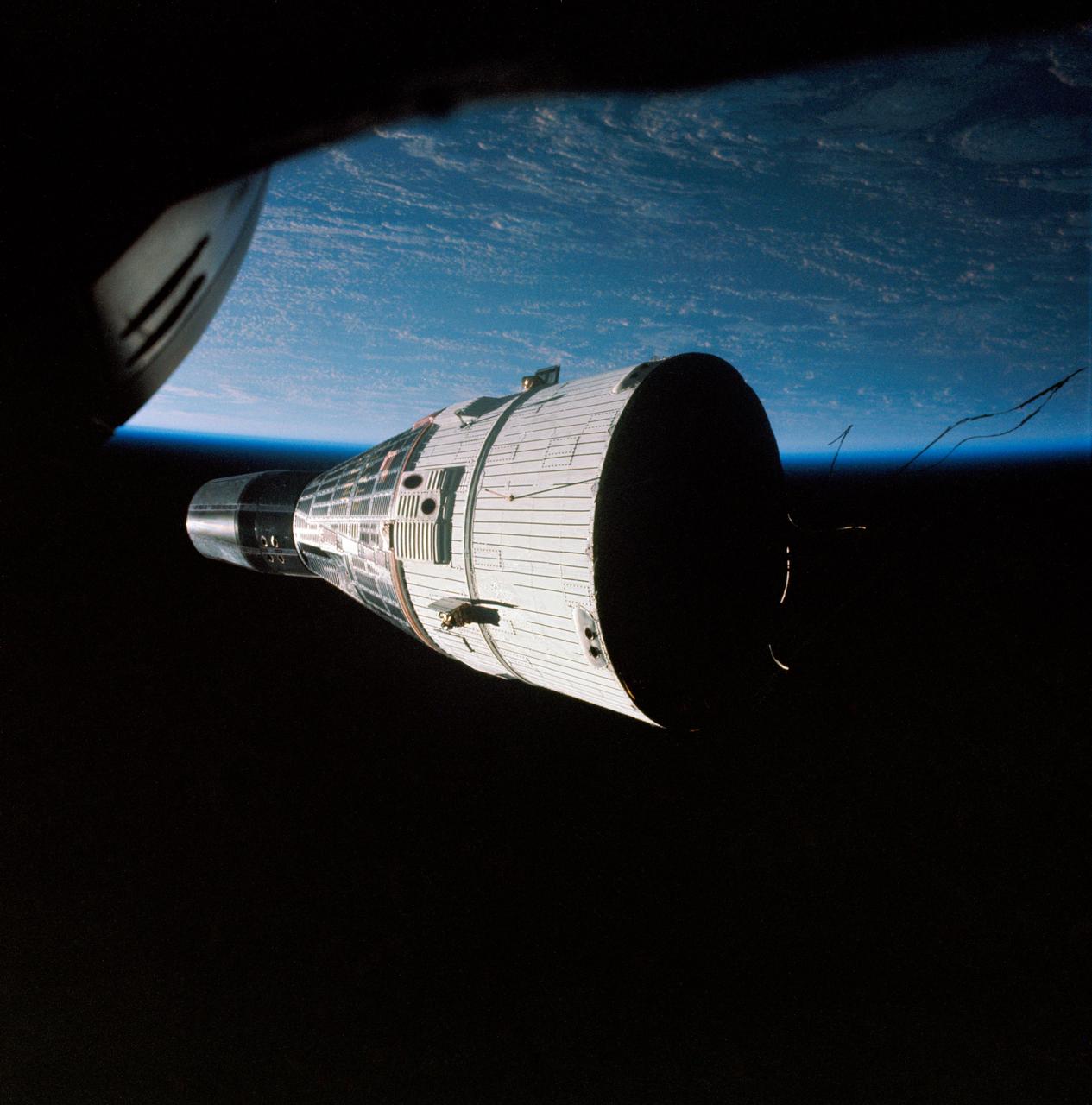

S65-63197 (15 Dec. 1965) --- This historic view of the orbiting Gemini-7 spacecraft was taken from the Gemini-6 spacecraft during their rendezvous mission in space. Astronauts Frank Borman and James A. Lovell Jr. were in the Gemini-7 spacecraft. In the Gemini-6 spacecraft were astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr. and Thomas P. Stafford. This photograph was taken with a modified 70mm Hassleblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (SO 217) color film. The two National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) spacecraft?s are approximately 34 feet apart. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
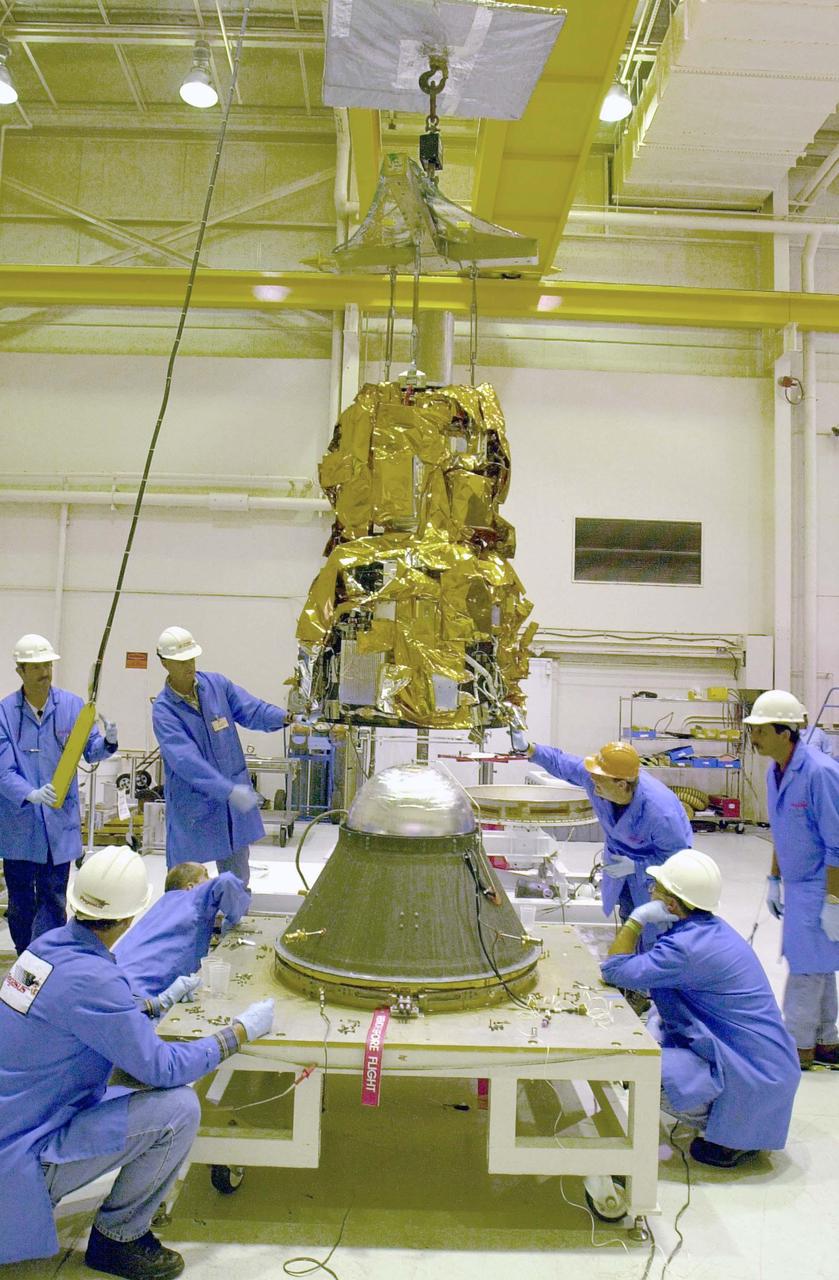

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers maneuver the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, suspended by a crane, over the upper stage in preparation for launch on the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
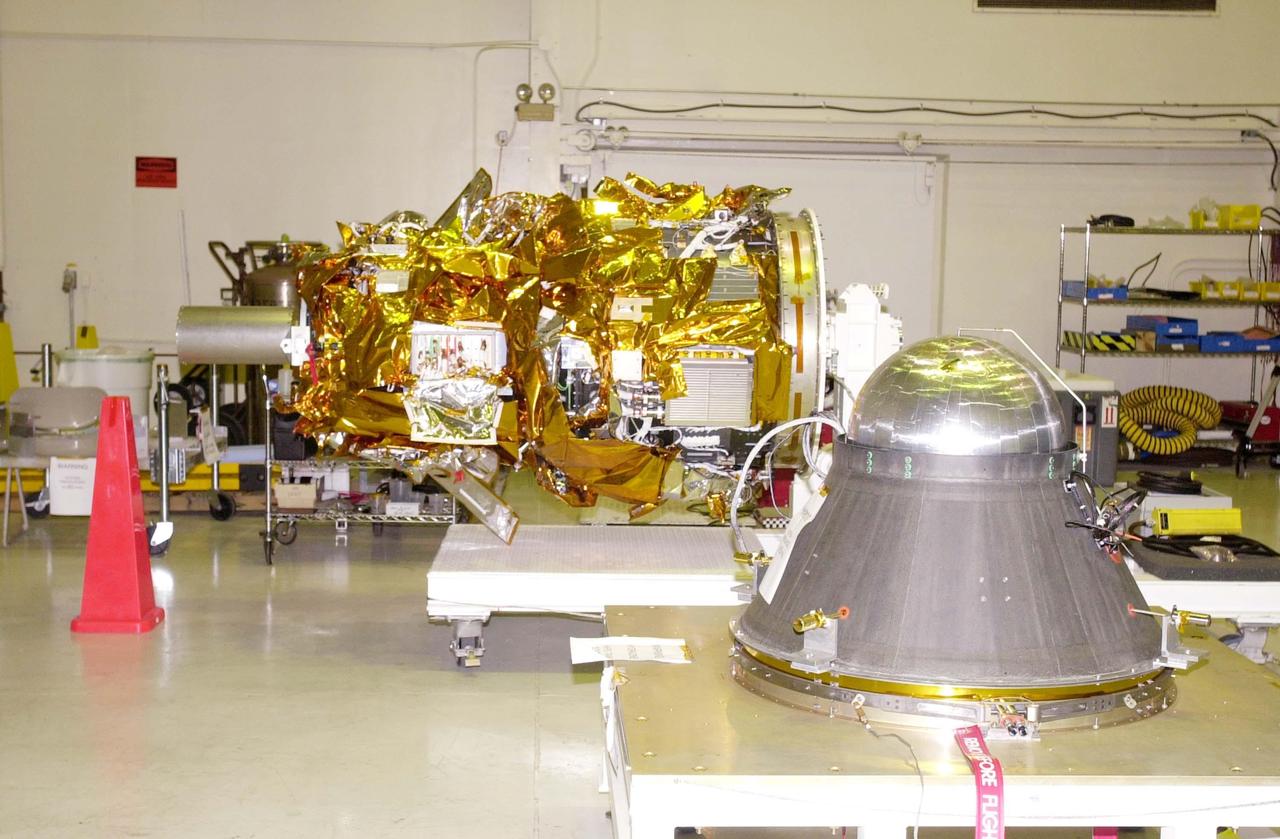

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (in background) has been rotated from vertical to horizontal and is ready for mating with the upper stage (foreground). DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
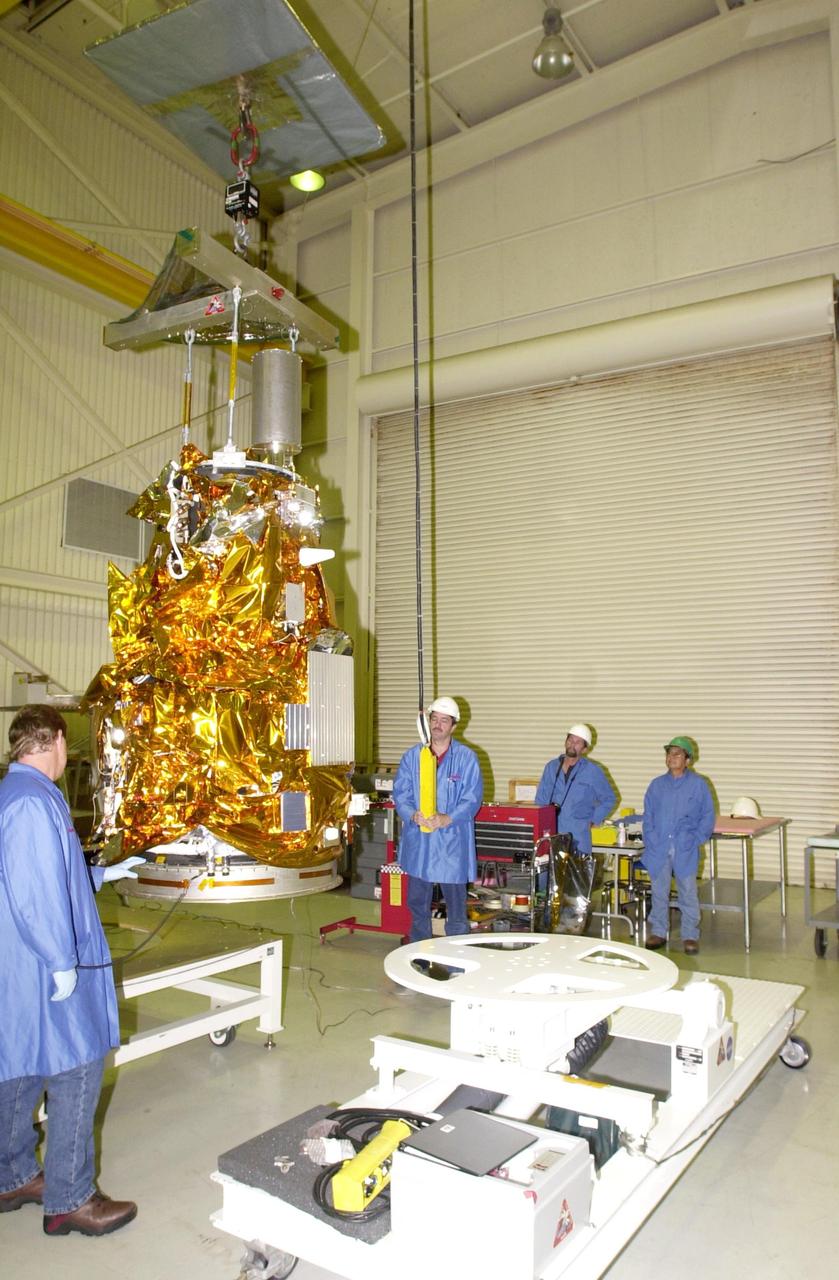

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers stand by while an overhead crane moves the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft onto the mobile stand at right. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (right) is ready for mating with the upper stage (foreground) in preparation for launch on the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
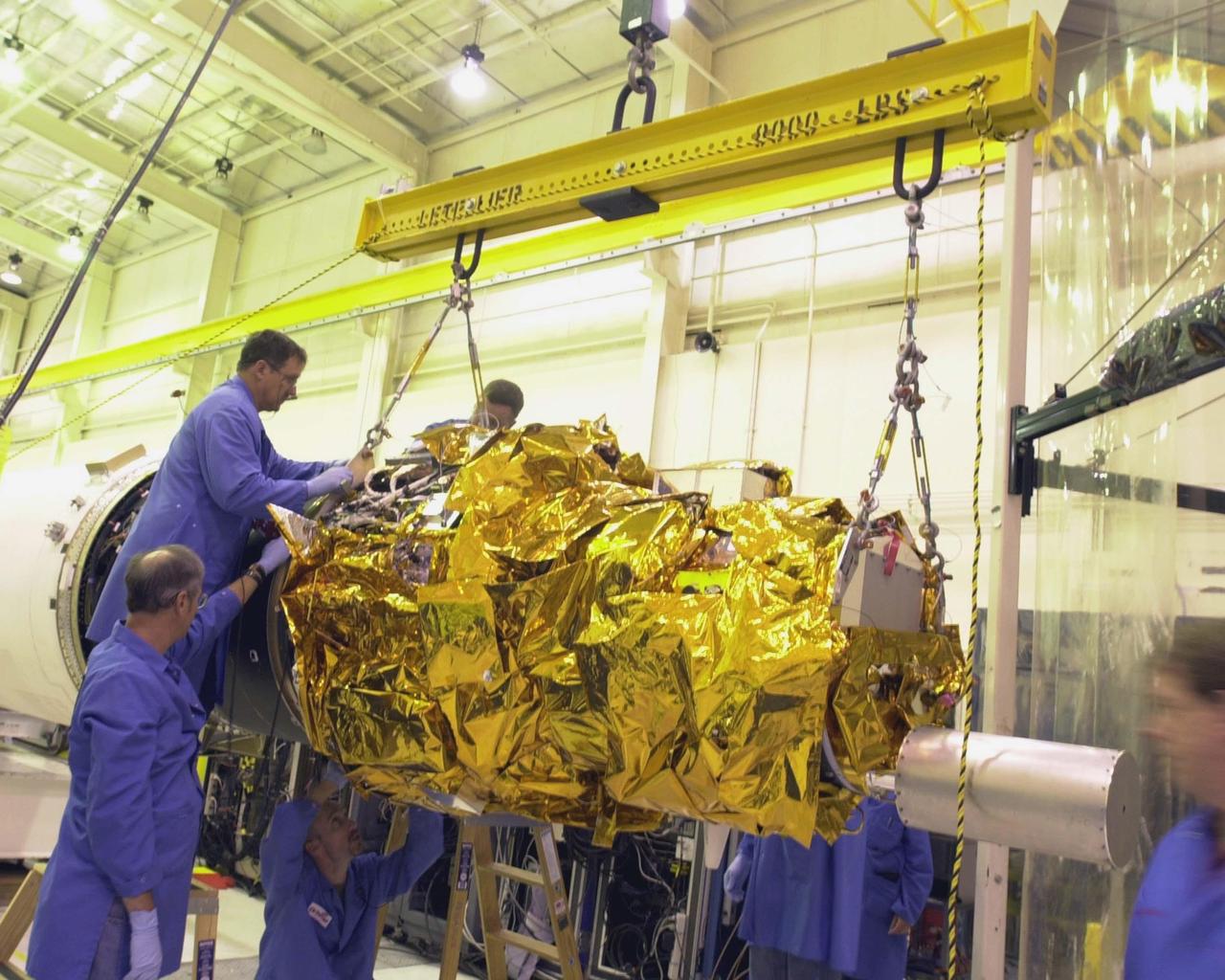

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers maneuver the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and mated upper stage toward the second stage behind them in preparation or launch aboard the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Pegasus will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers maneuver the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and mated upper stage toward the second stage at right in preparation or launch aboard the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Pegasus will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
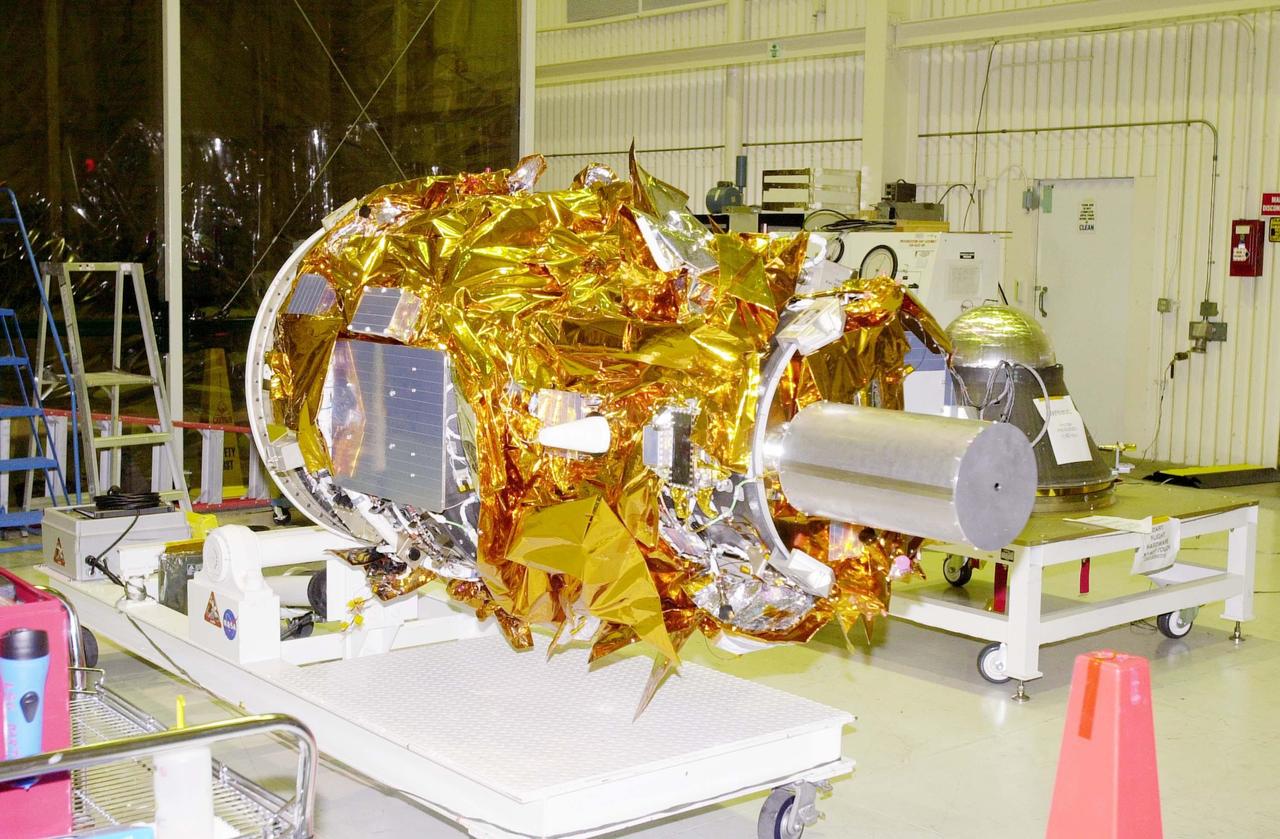

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is ready for mating with the upper stage of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL behind it (right). DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
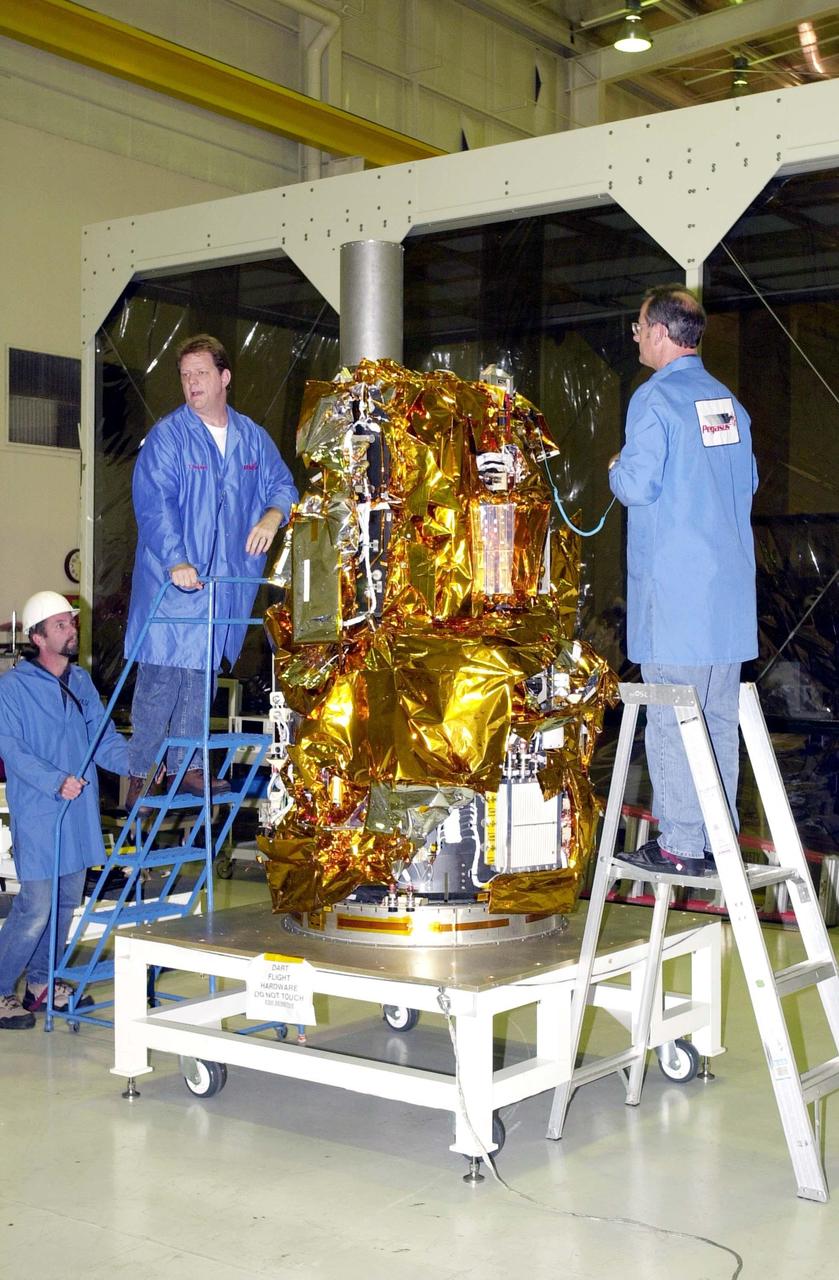

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft for launch. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
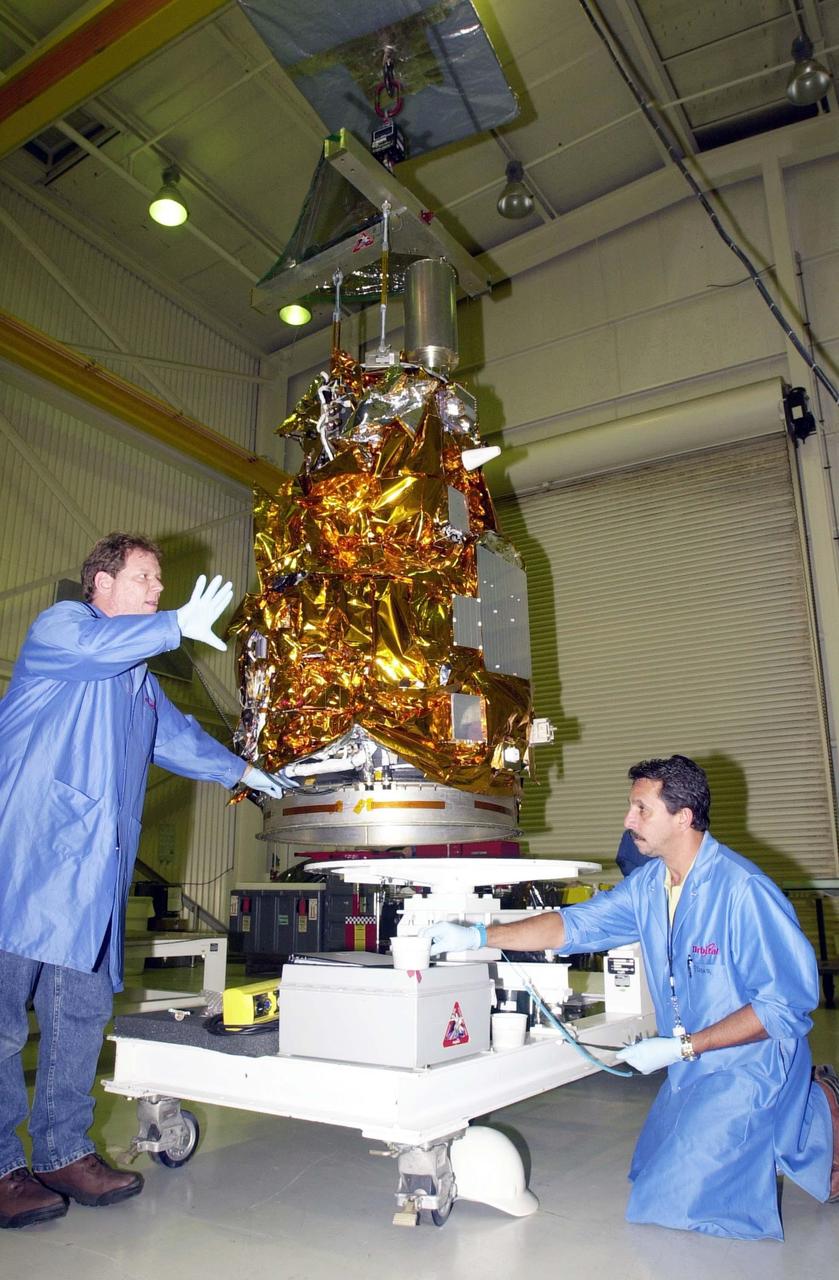

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers help guide the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft onto the mobile stand below. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
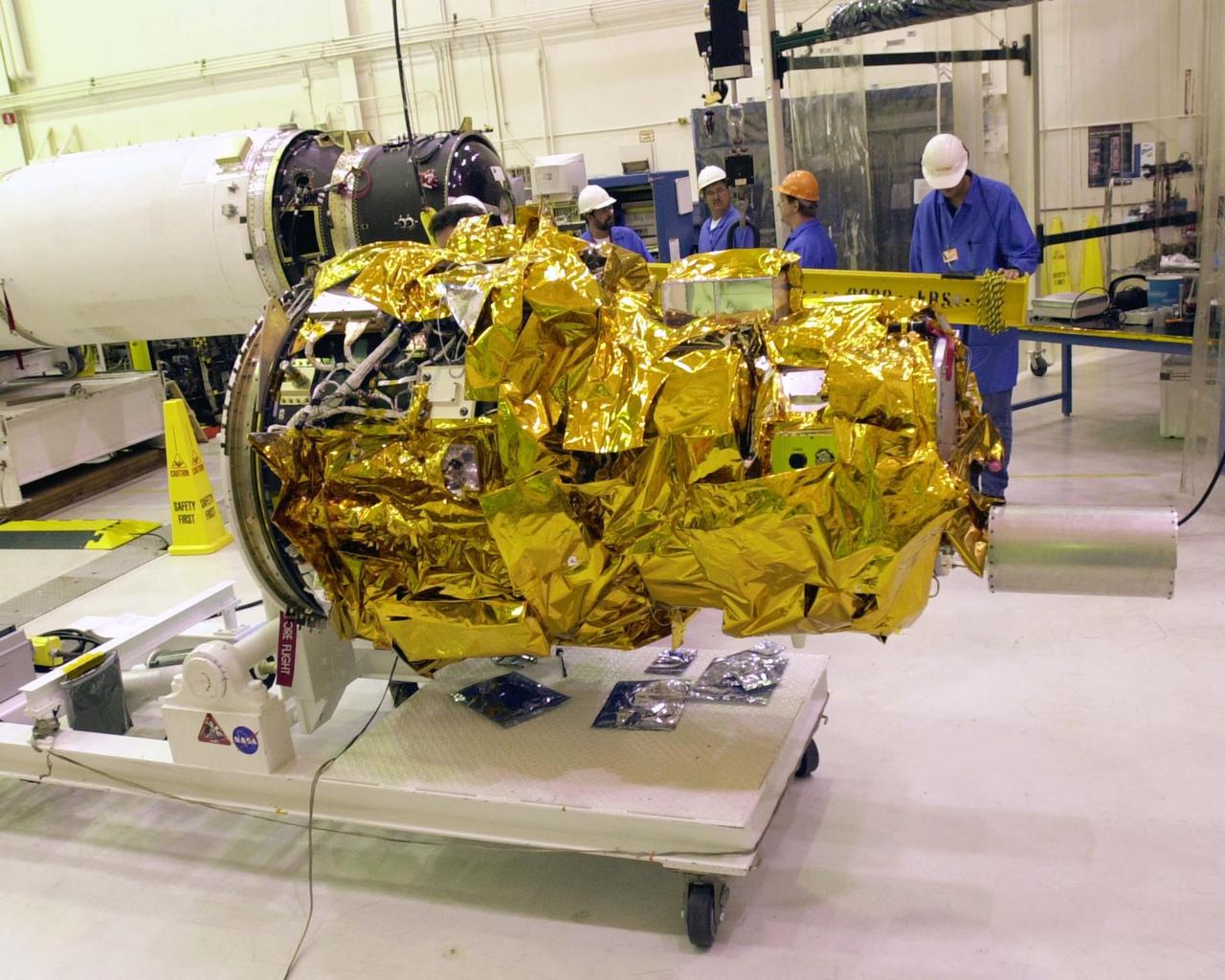

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (foreground) is ready to be mated to second and third stages in preparation for the launch aboard the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Pegasus will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (right) is ready for mating with the upper stage (behind it) in preparation for launch on the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers begin mating the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle that will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
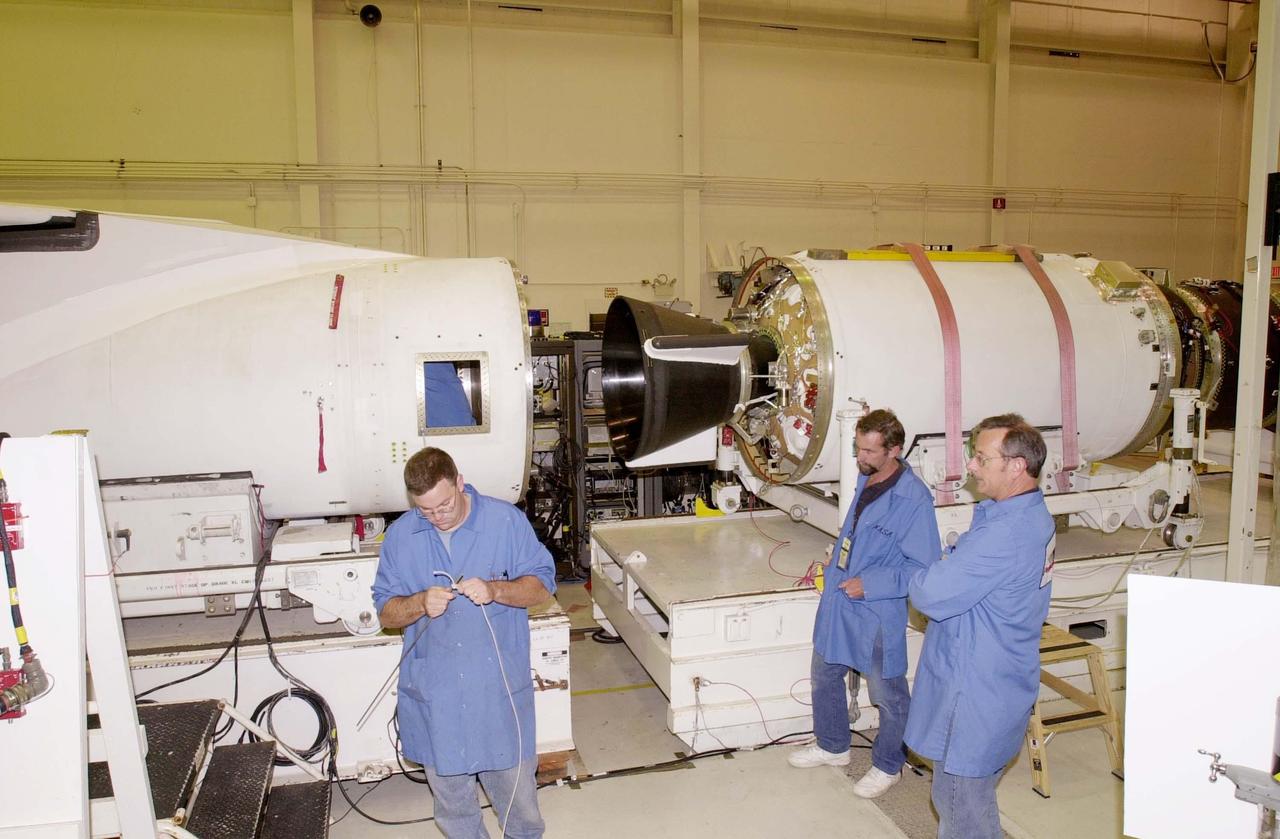

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare to mate the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle that will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
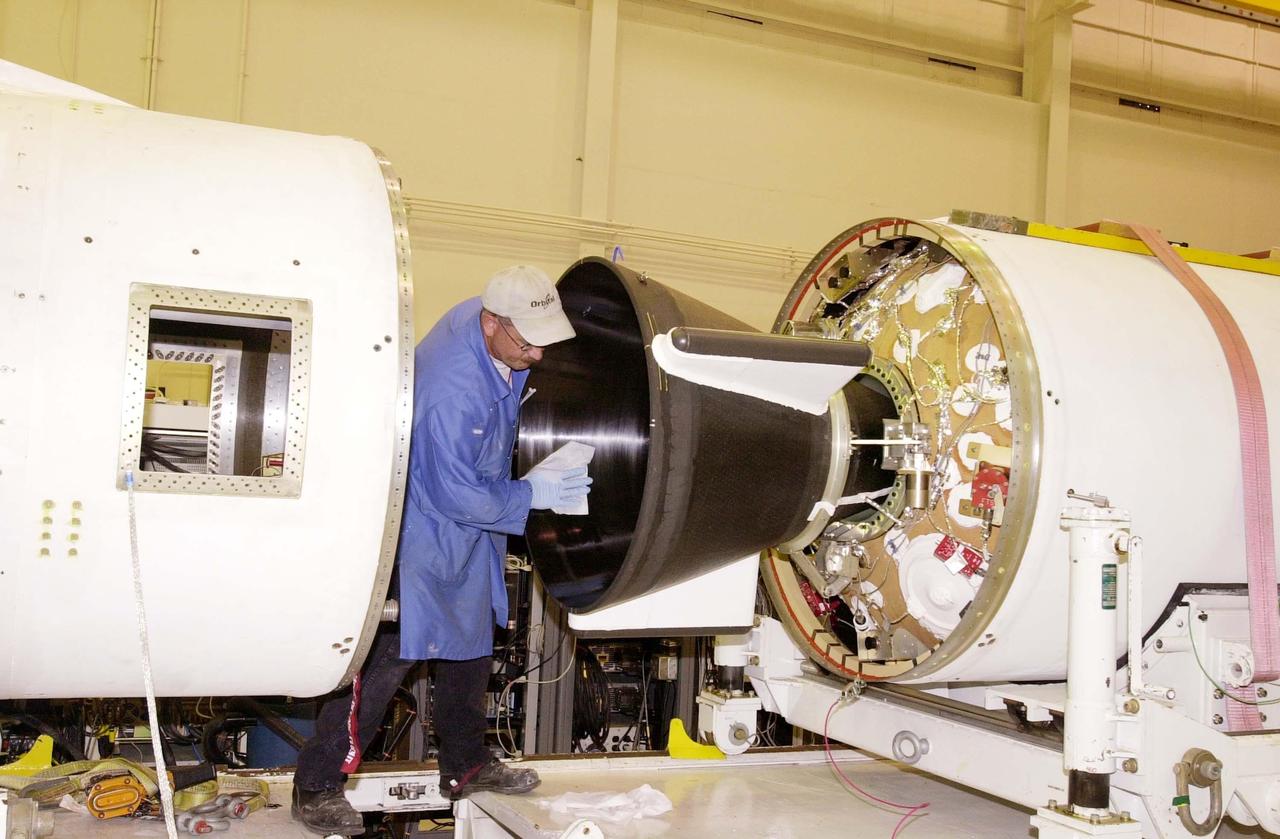
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker prepares the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle for mating. The Pegasus XL will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
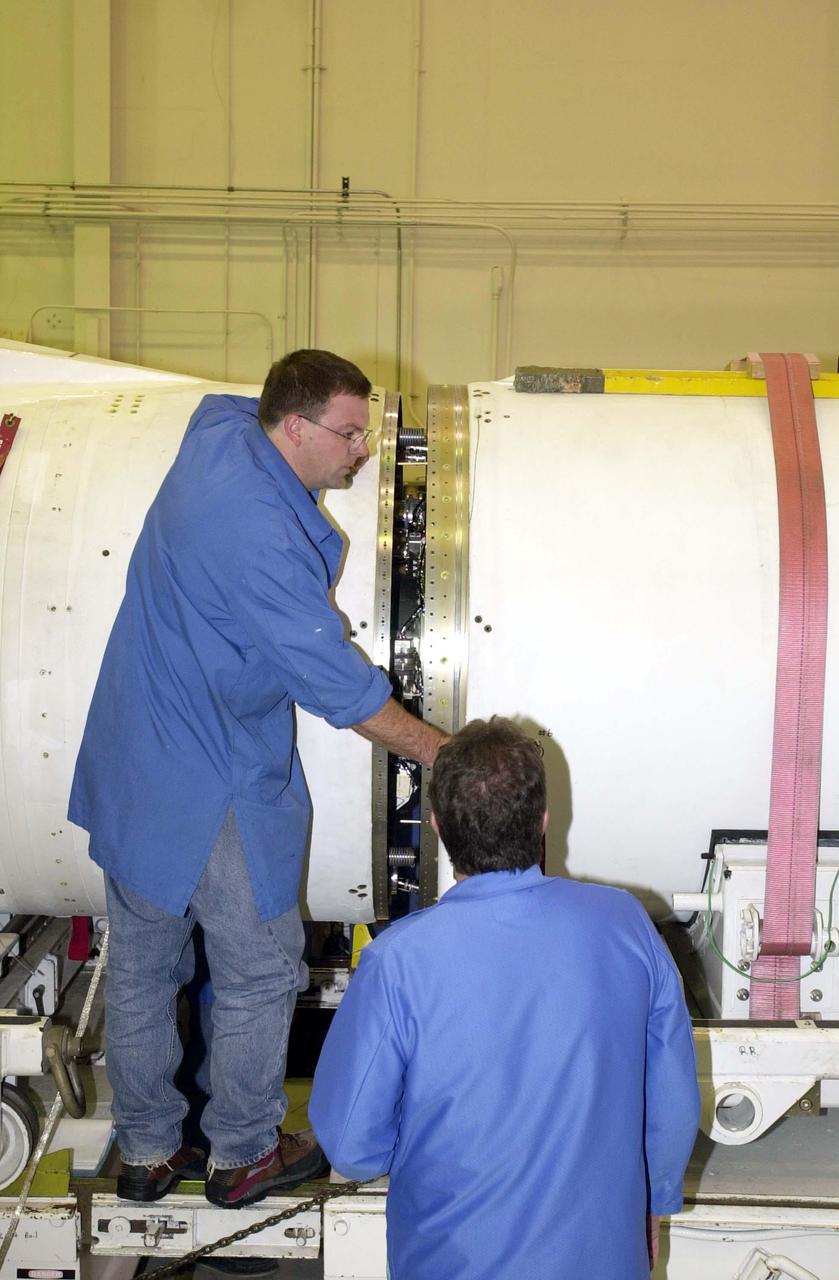

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers begin closing the gap between the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle that will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
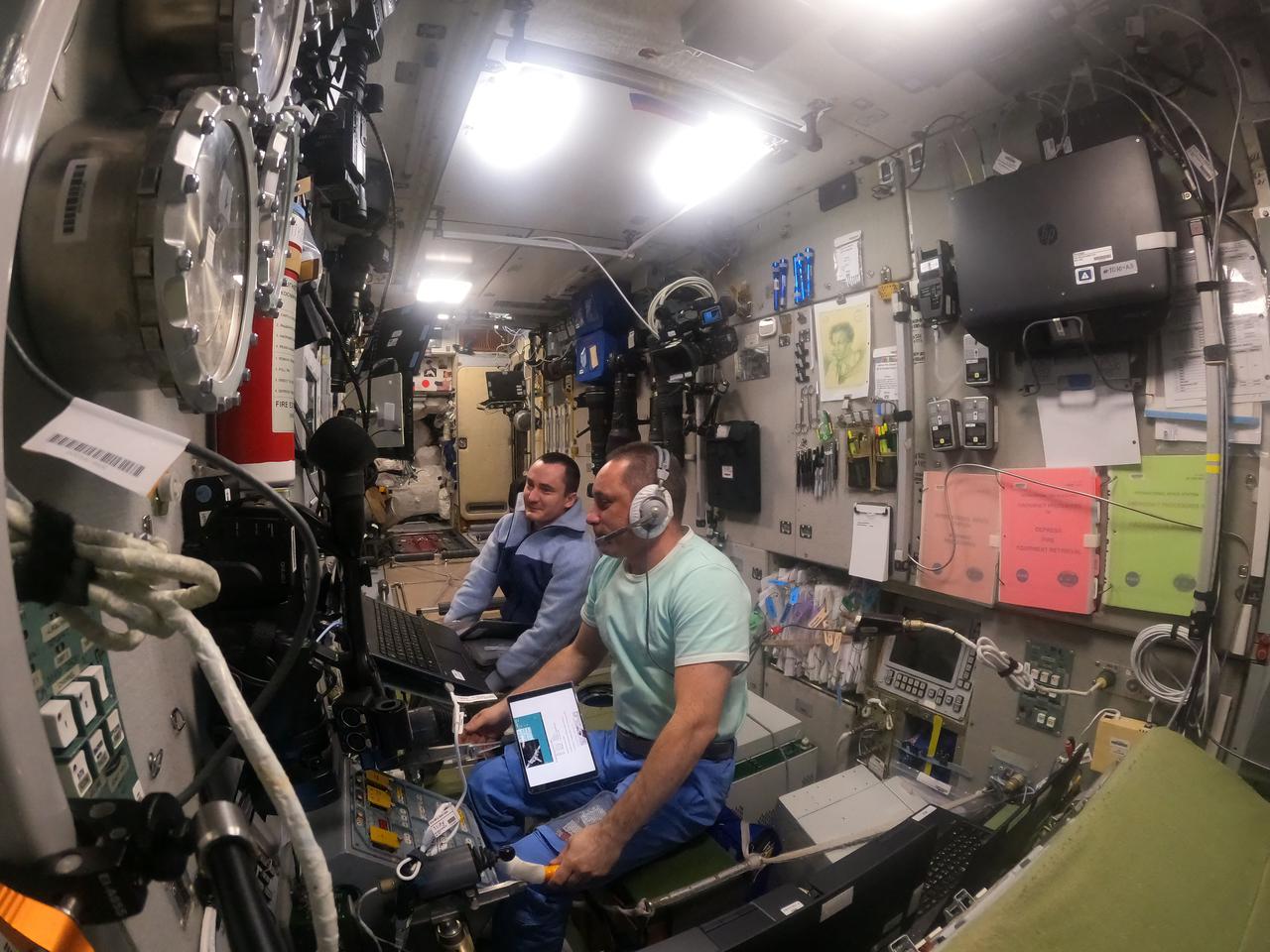

iss066e012273 (Oct. 25, 2021) --- Roscosmos cosmonauts Anton Shkaplerov (foreground) and Pyotr Dubrov were inside the International Space Station's Zvezda service module training for the arrival of the ISS Progress 79 cargo craft. The duo practiced rendezvous maneuvers on the tele-robotically operated rendezvous unit (TORU) ahead of the Progress 79's automated approach, rendezvous and docking that took place on Oct. 29, 2021.
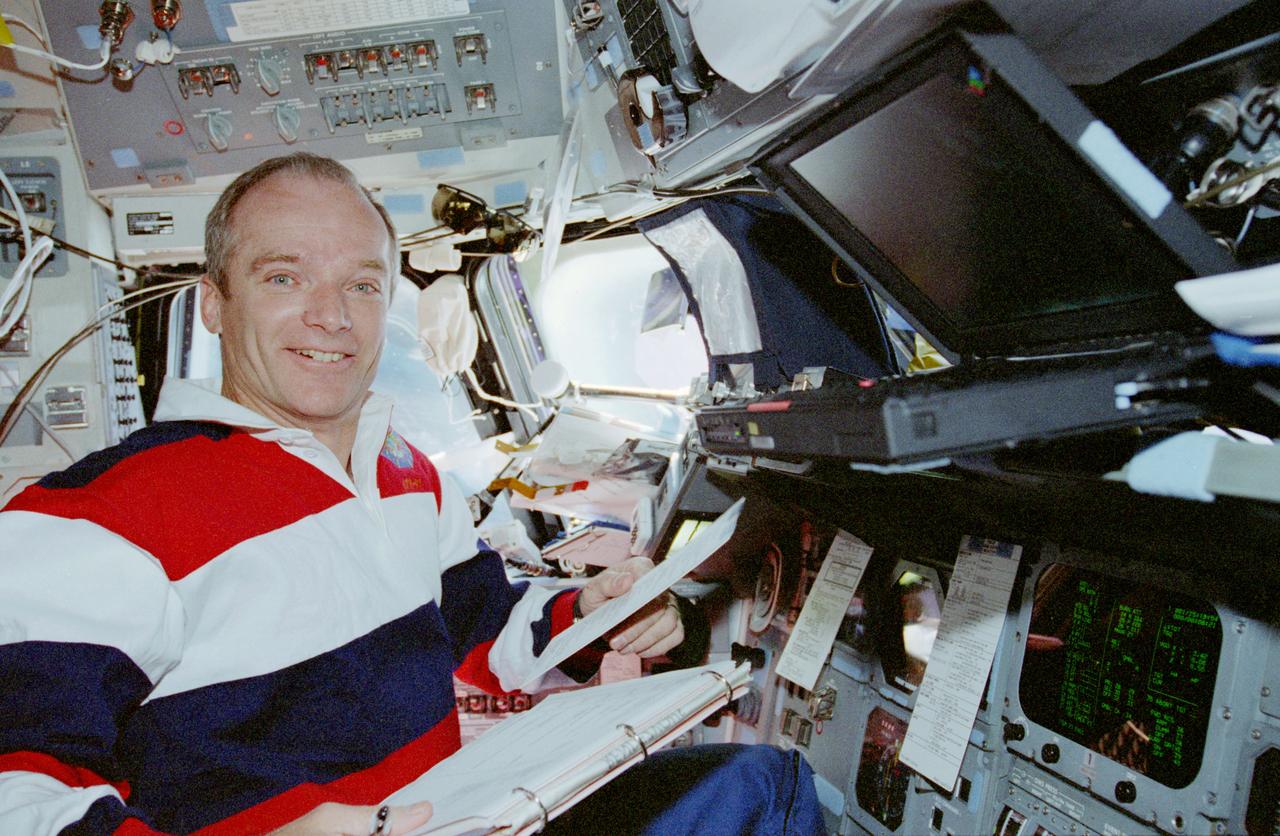

STS091-360-014 (2-12 June 1998) --- Astronaut Charles J. Precourt mans the commander's station on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery during NASA's scheduled final rendezvous operations with Russia's Mir space station. The veteran astronaut holds checklists related to the rendezvous activities.
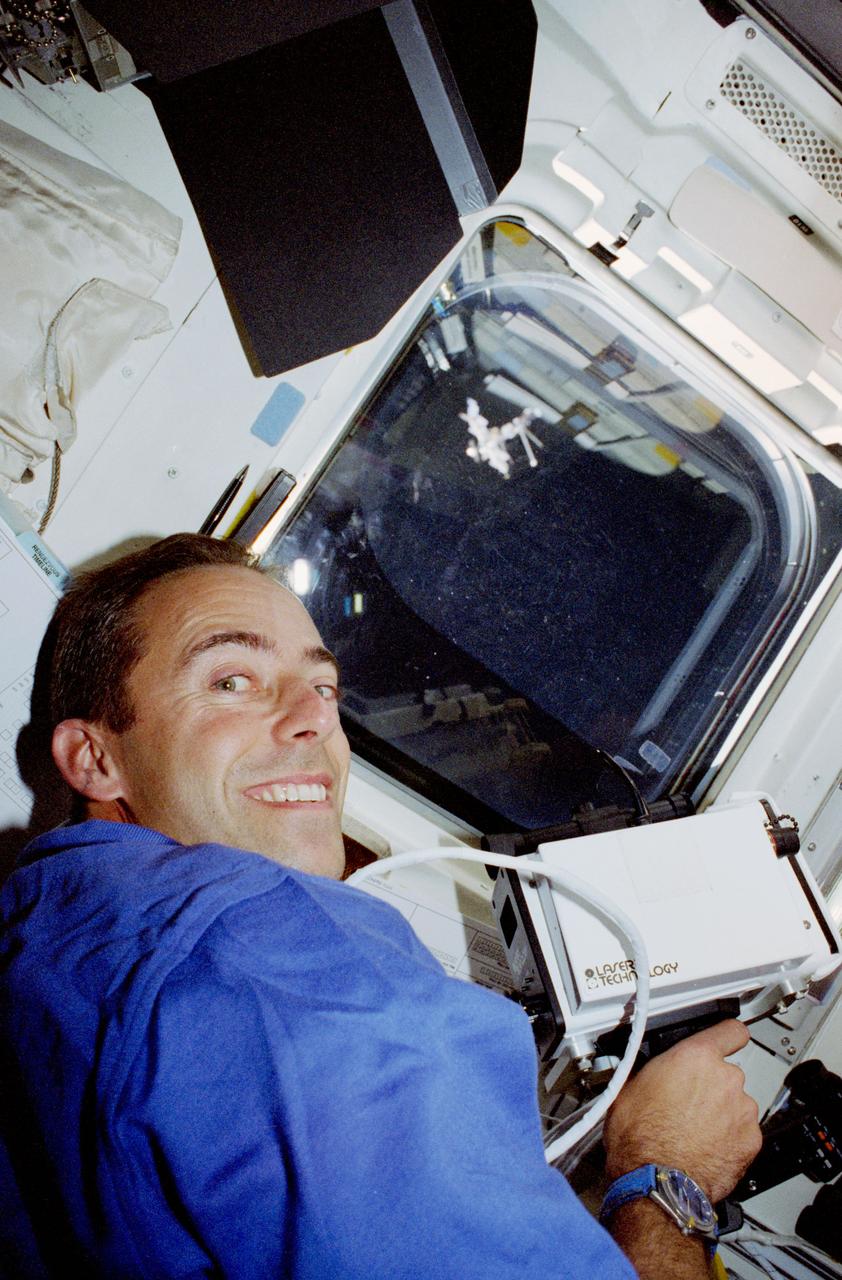

STS084-357-009 (15-24 May 1997) --- Astronaut Jean-Fran?ois Clervoy, STS-84 payload commander, uses a hand held laser range finder during rendezvous operations with Russia's Mir Space Station (seen just above center through the Space Shuttle Atlantis' overhead window).
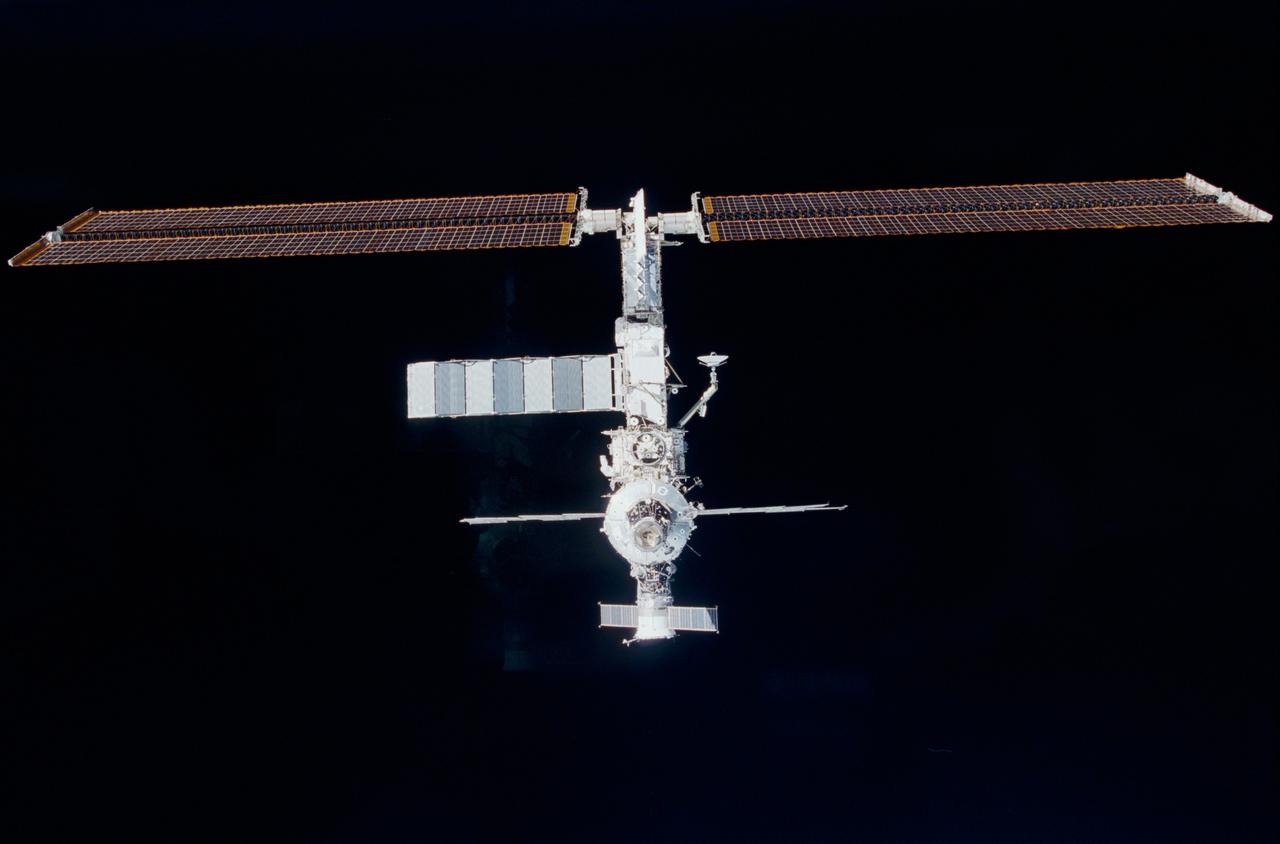

STS102-326-034 (10 March 2001) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the International Space Station (ISS) is lined up for rendezvous with the Space Shuttle Discovery. One of the astronauts aboard Discovery took this 35mm photograph from the aft flight deck.
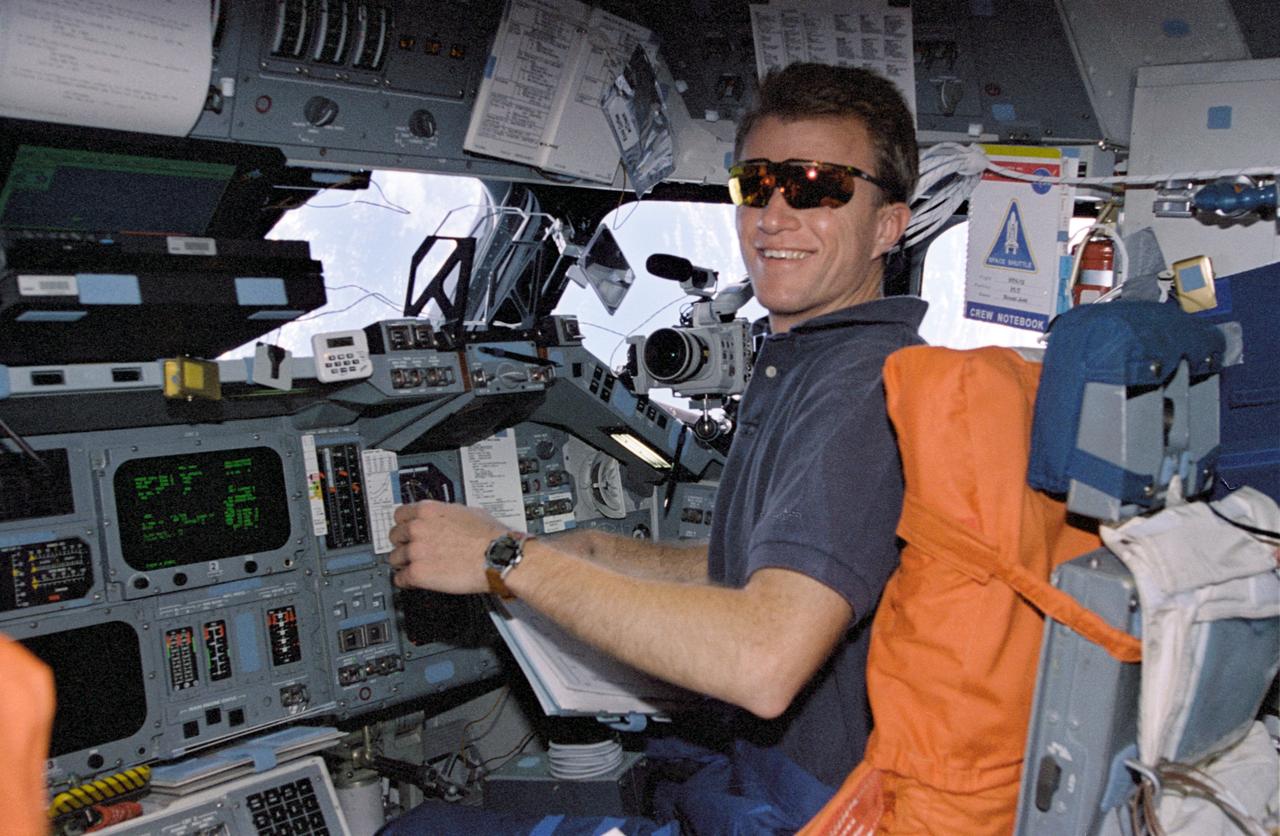

STS072-302-029 (11-20 Jan. 1996) --- Astronaut Brent W. Jett Jr. mans the pilot’s station aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour during rendezvous operations with the Japanese Space Flyer Unit (SFU). The pilot joined five other astronauts for a week a half aboard Endeavour in Earth-orbit.

MR. AND MRS. ROBERT LIGHTFOOT POSE WITH ASTRONAUT NEIL ARMSTRONG AND DR. GEORG VON TIESENHAUSEN AT THE TRANQUILITY BASE RENDEZVOUS EVENT AT THE DAVIDSON CENTER AT THE U.S. SPACE AND ROCKET CENTER.

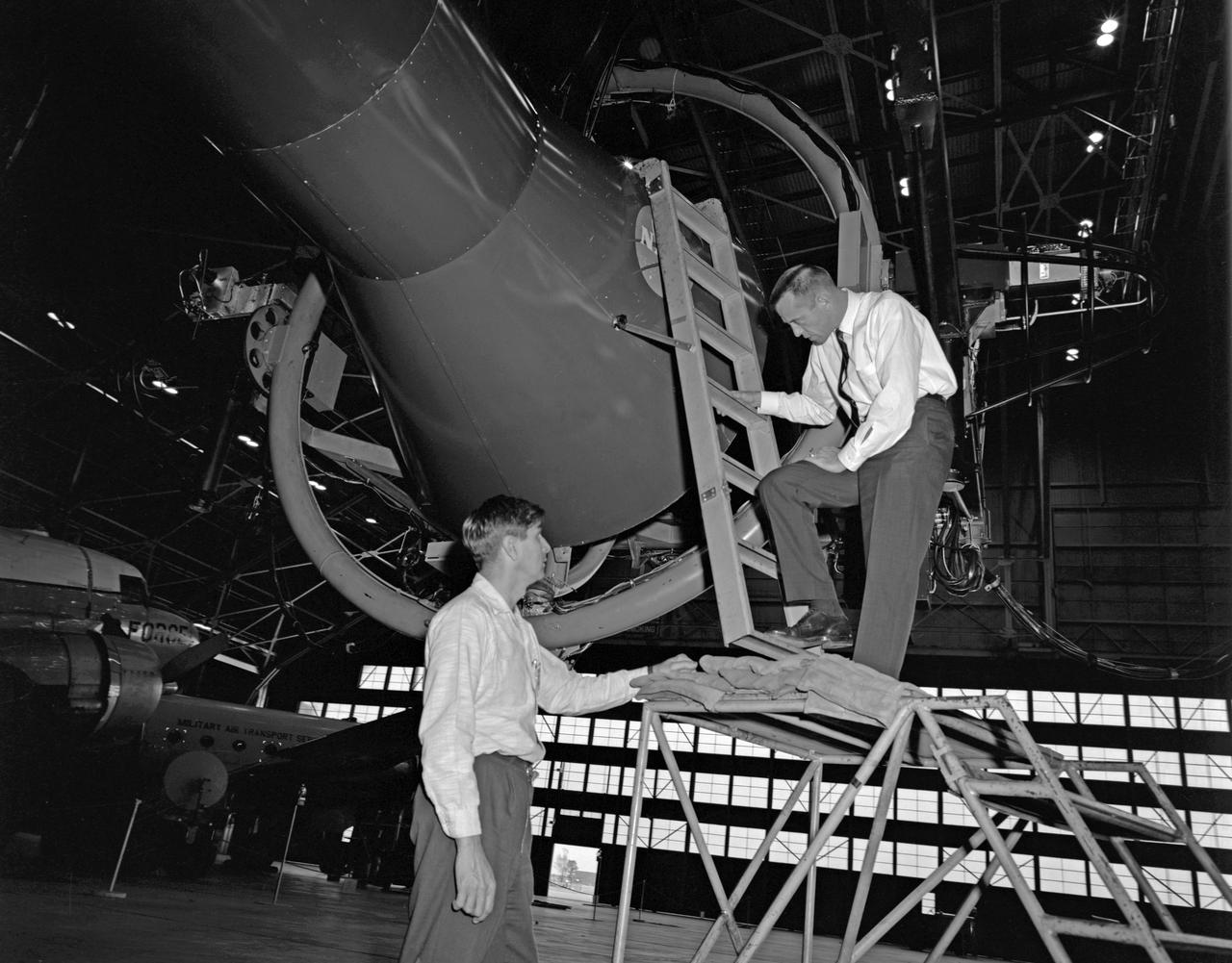
Unidentified Pilot eyeballs his way to a docking by peering through the portal in his capsule. Photo published in Spaceflight Revolution, NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo. By James R. Hansen. NASA SP-4308, 1995, p. 372.

Astronaut Alan Shepard (right) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Shepard flew the simulator on November 14, 1963. A.W. Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden noted that: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." Shepard commented: "I had the feeling tonight - a couple of times - that I was actually doing the space mission instead of the simulation. As I said before, I think it is a very good simulation." Shepard also commented on piloting techniques. Most astronauts arrived at this same preferred technique: Shepard: "I believe I have developed the preferred technique for these conditions and the technique appeared to me to be best was to come in slightly above the target so that I was able to use the longitudinal marks on the body of the target as a reference, particularly for a lateral translation and, of course, I used the foreshortening effect for a vertical translation, and this appeared to give me the best results. By that I mean the least number of control motions and the lowest fuel usage and the best end techniques, or the best end conditions, I should say." Engineer: "When you started to run you didn't start thrusting immediately I don't believe. It looked like you started working on your attitudes, then started closing in." Shepard: "That is correct. I did that because I felt that I wanted to get the X-axis translation in the most effective vector and for minimum fuel usage that wouldn't introduce any other lateral or vertical offsets that did not already exist." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.

Astronaut Alan Shepard (right) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Shepard flew the simulator on November 14, 1963. A.W. Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden noted that: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." Shepard commented: "I had the feeling tonight - a couple of times - that I was actually doing the space mission instead of the simulation. As I said before, I think it is a very good simulation." Shepard also commented on piloting techniques. Most astronauts arrived at this same preferred technique: Shepard: "I believe I have developed the preferred technique for these conditions and the technique appeared to me to be best was to come in slightly above the target so that I was able to use the longitudinal marks on the body of the target as a reference, particularly for a lateral translation and, of course, I used the foreshortening effect for a vertical translation, and this appeared to give me the best results. By that I mean the least number of control motions and the lowest fuel usage and the best end techniques, or the best end conditions, I should say." Engineer: "When you started to run you didn't start thrusting immediately I don't believe. It looked like you started working on your attitudes, then started closing in." Shepard: "That is correct. I did that because I felt that I wanted to get the X-axis translation in the most effective vector and for minimum fuel usage that wouldn't introduce any other lateral or vertical offsets that did not already exist." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.
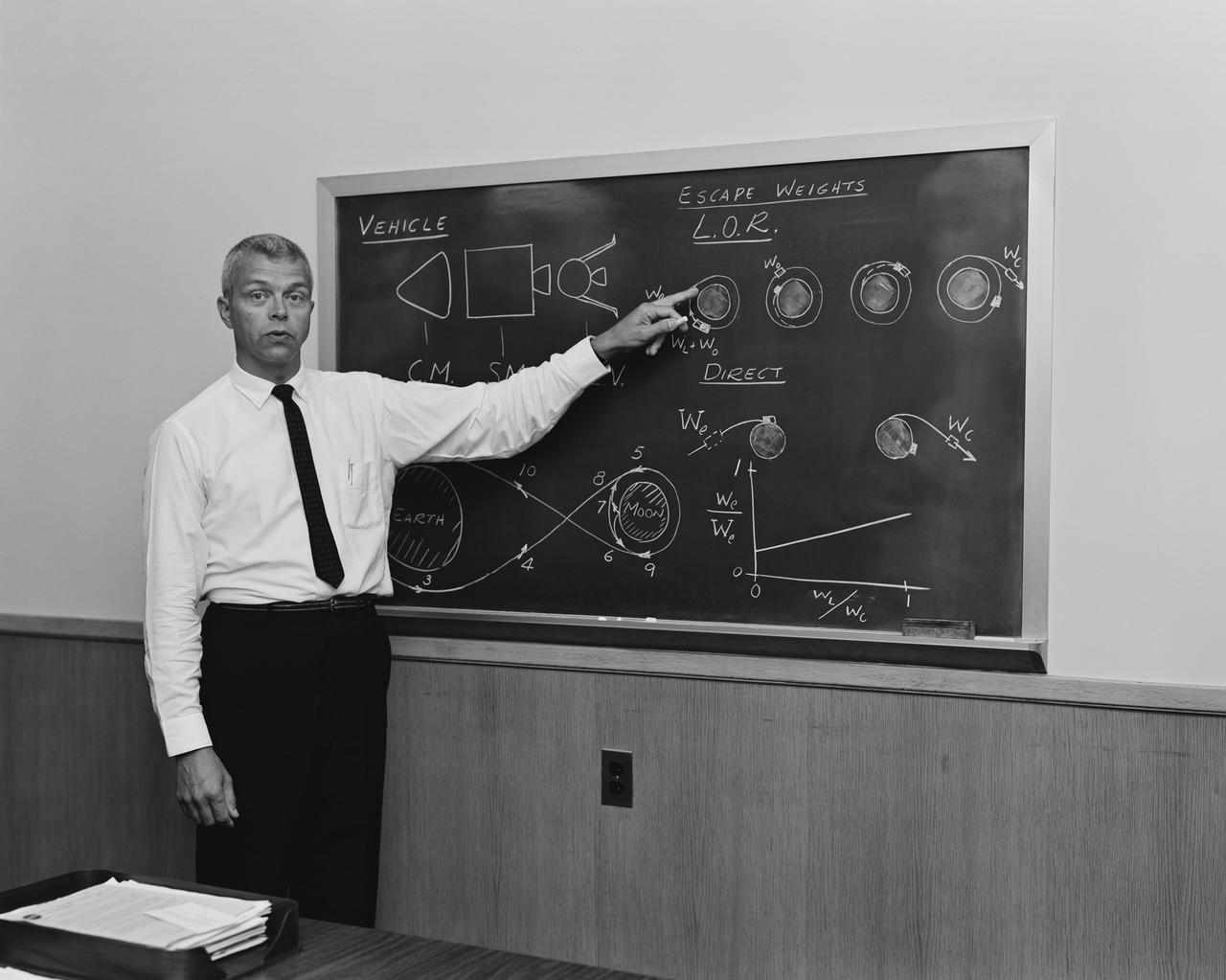

At blackboard, showing his space rendezvous concept for lunar landings. Lunar Orbital Rendezvous (LOR) would be used in the Apollo program. Photograph published in Space Flight Revolution - NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo (page 247), by James R. Hansen.
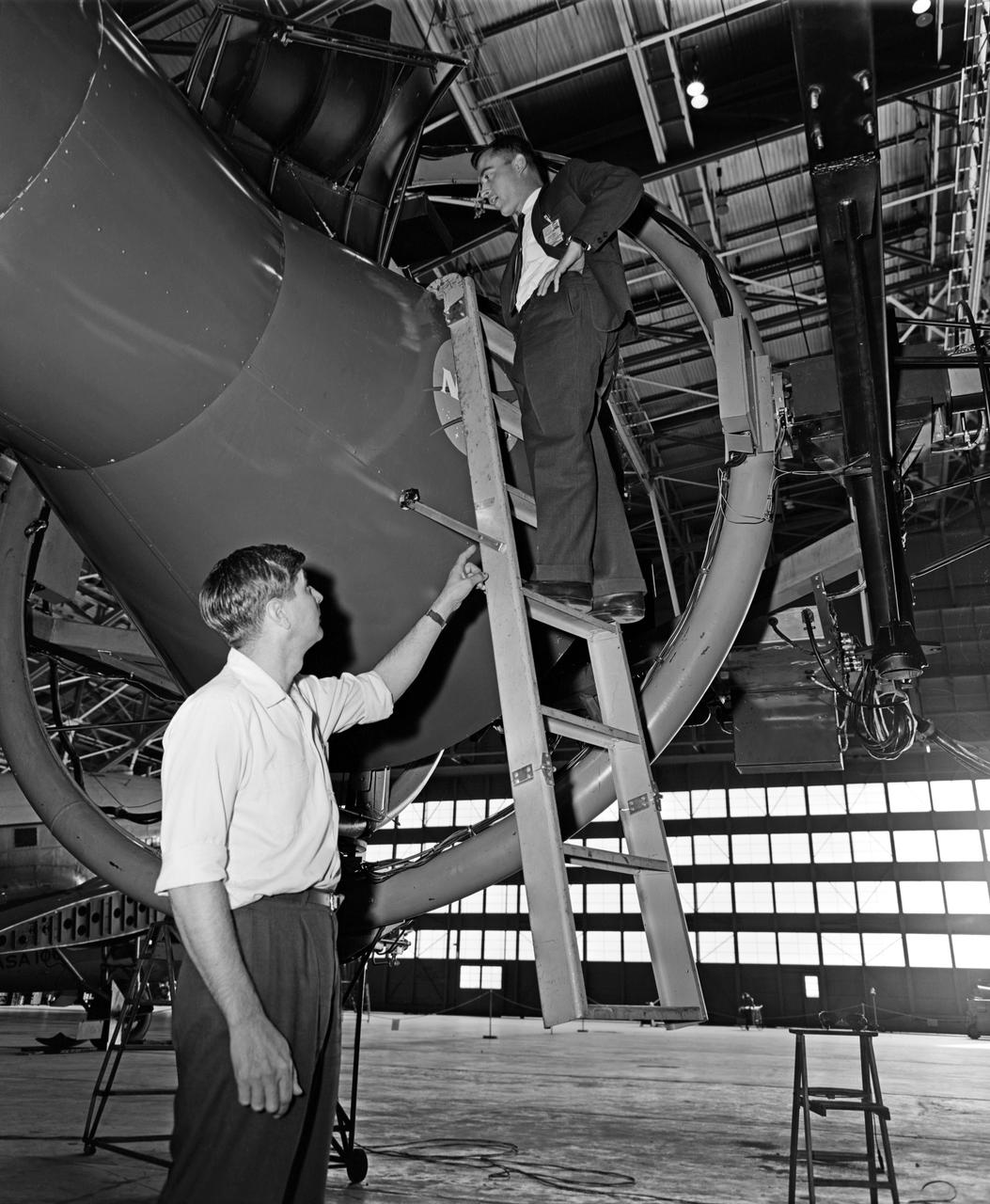

Astronaut John Young (above) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Young piloted the simulator on November 12, 1963 Arthur Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden wrote: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.
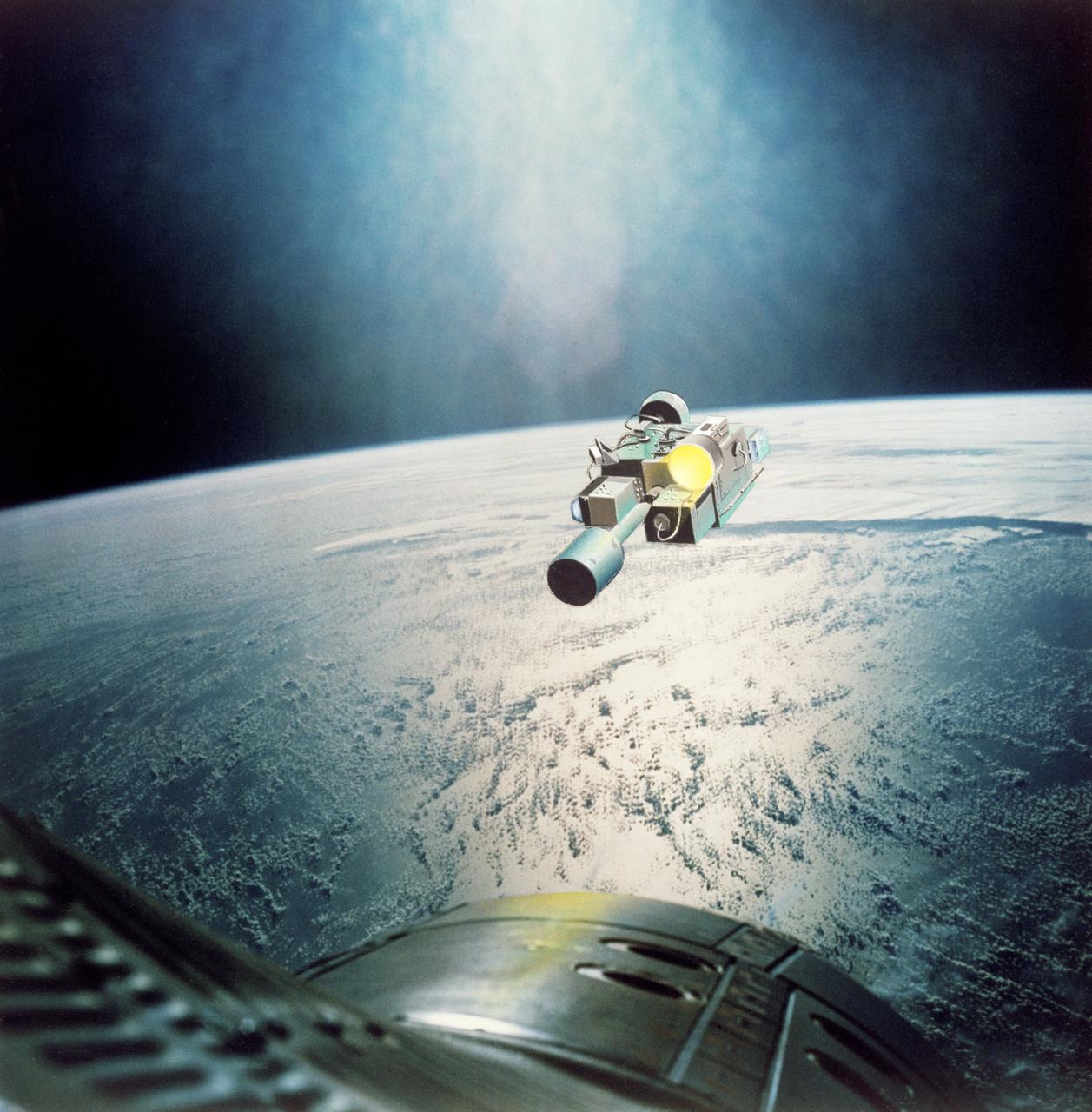

S65-28653 (August 1965) --- Rendezvous Evaluation Pod (REP) in orbit is approached by Gemini spacecraft as seen in this artist's concept using an actual photograph taken on the Gemini-4 mission. The REP is superimposed over a Gemini-4 Earth-sky picture of cloud formations over an ocean. The REP will be used by the crew of the Gemini-5 spacecraft to practice rendezvous techniques.

ISS022-E-059171 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This 800mm lens's image of part of space shuttle Endeavour's starboard wing, displaying the orbiter's name and the U.S. flag, was photographed during the rendezvous operations between the shuttle and the International Space Station, which included a back-flip by the shuttle.
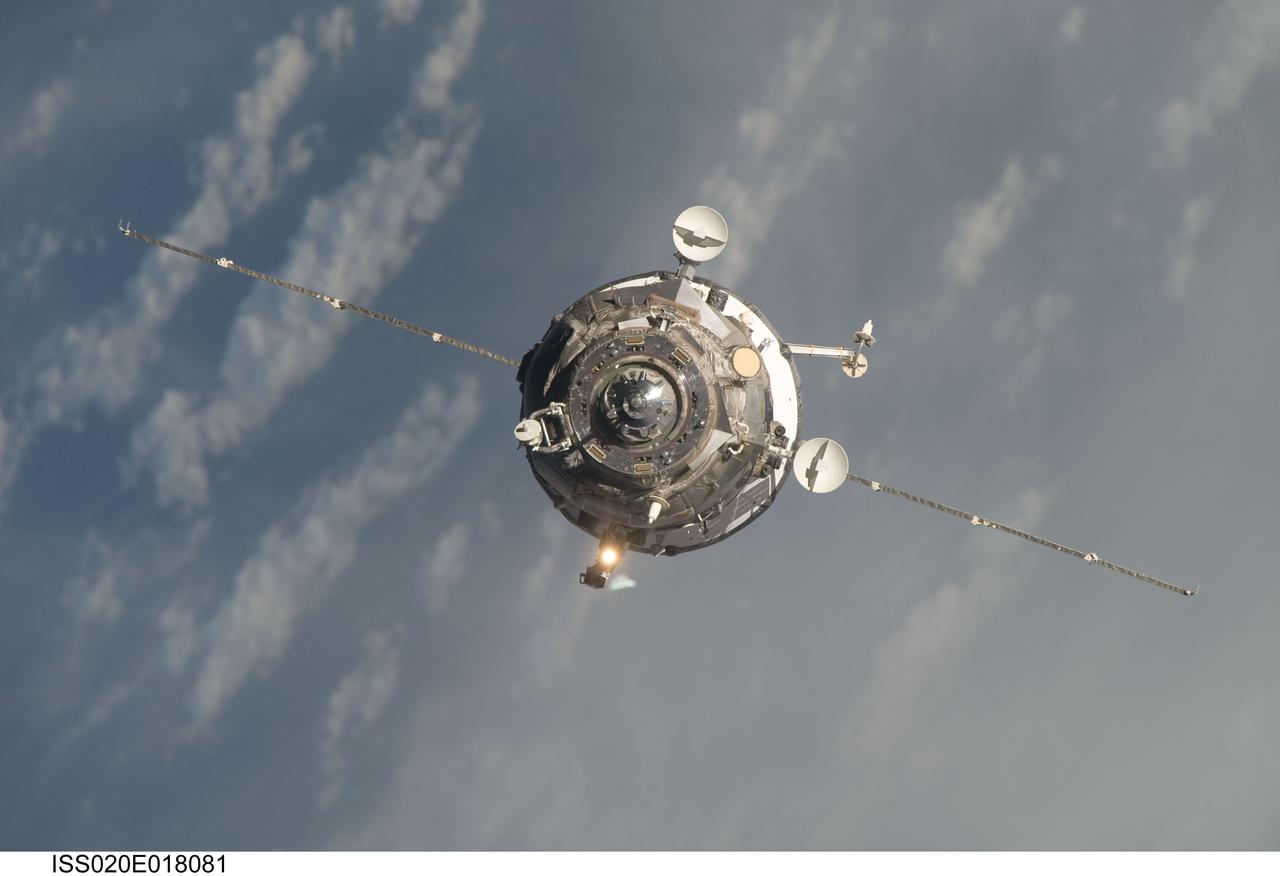

ISS020-E-018081 (12 July 2009) --- An unpiloted ISS Progress 33 cargo craft approaches the International Space Station. On June 30, the Progress undocked from the station and was commanded into a parking orbit for its re-rendezvous with the ISS on July 12, approaching to within 10-15 meters of the Zvezda Service Module to test new automated rendezvous equipment mounted on Zvezda during a pair of spacewalks earlier this month by Gennady Padalka and Mike Barratt that will be used to guide the new Mini-Research Module-2 (MRM2) to an unpiloted docking to the zenith port of Zvezda later this year. MRM2 will serve as a new docking port for Russian spacecraft and an additional airlock for spacewalks conducted out of the Russian segment.

ISS020-E-018069 (12 July 2009) --- An unpiloted ISS Progress 33 cargo craft approaches the International Space Station. On June 30, the Progress undocked from the station and was commanded into a parking orbit for its re-rendezvous with the ISS on July 12, approaching to within 10-15 meters of the Zvezda Service Module to test new automated rendezvous equipment mounted on Zvezda during a pair of spacewalks earlier this month by Gennady Padalka and Mike Barratt that will be used to guide the new Mini-Research Module-2 (MRM2) to an unpiloted docking to the zenith port of Zvezda later this year. MRM2 will serve as a new docking port for Russian spacecraft and an additional airlock for spacewalks conducted out of the Russian segment.
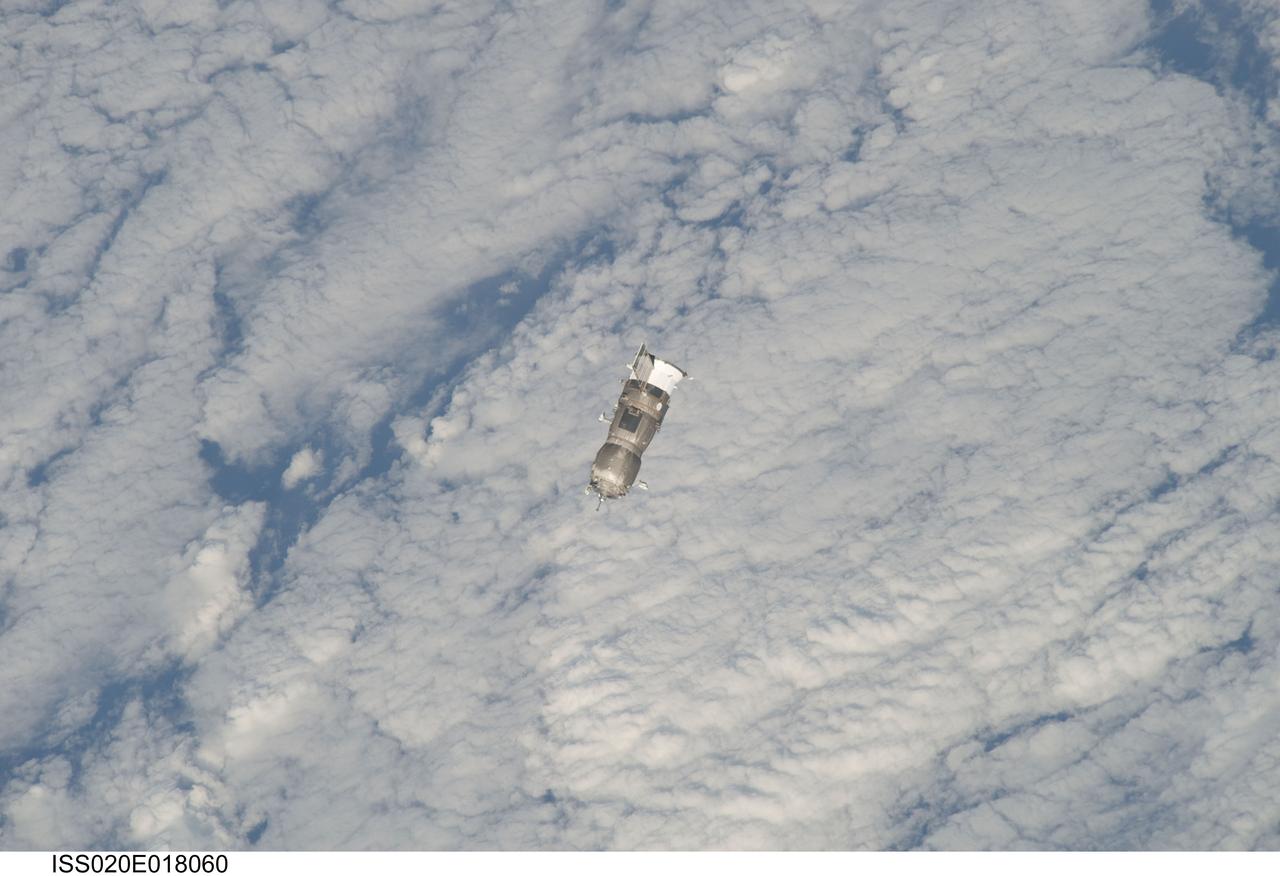

ISS020-E-018060 (12 July 2009) --- An unpiloted ISS Progress 33 cargo craft approaches the International Space Station. On June 30, the Progress undocked from the station and was commanded into a parking orbit for its re-rendezvous with the ISS on July 12, approaching to within 10-15 meters of the Zvezda Service Module to test new automated rendezvous equipment mounted on Zvezda during a pair of spacewalks earlier this month by Gennady Padalka and Mike Barratt that will be used to guide the new Mini-Research Module-2 (MRM2) to an unpiloted docking to the zenith port of Zvezda later this year. MRM2 will serve as a new docking port for Russian spacecraft and an additional airlock for spacewalks conducted out of the Russian segment.
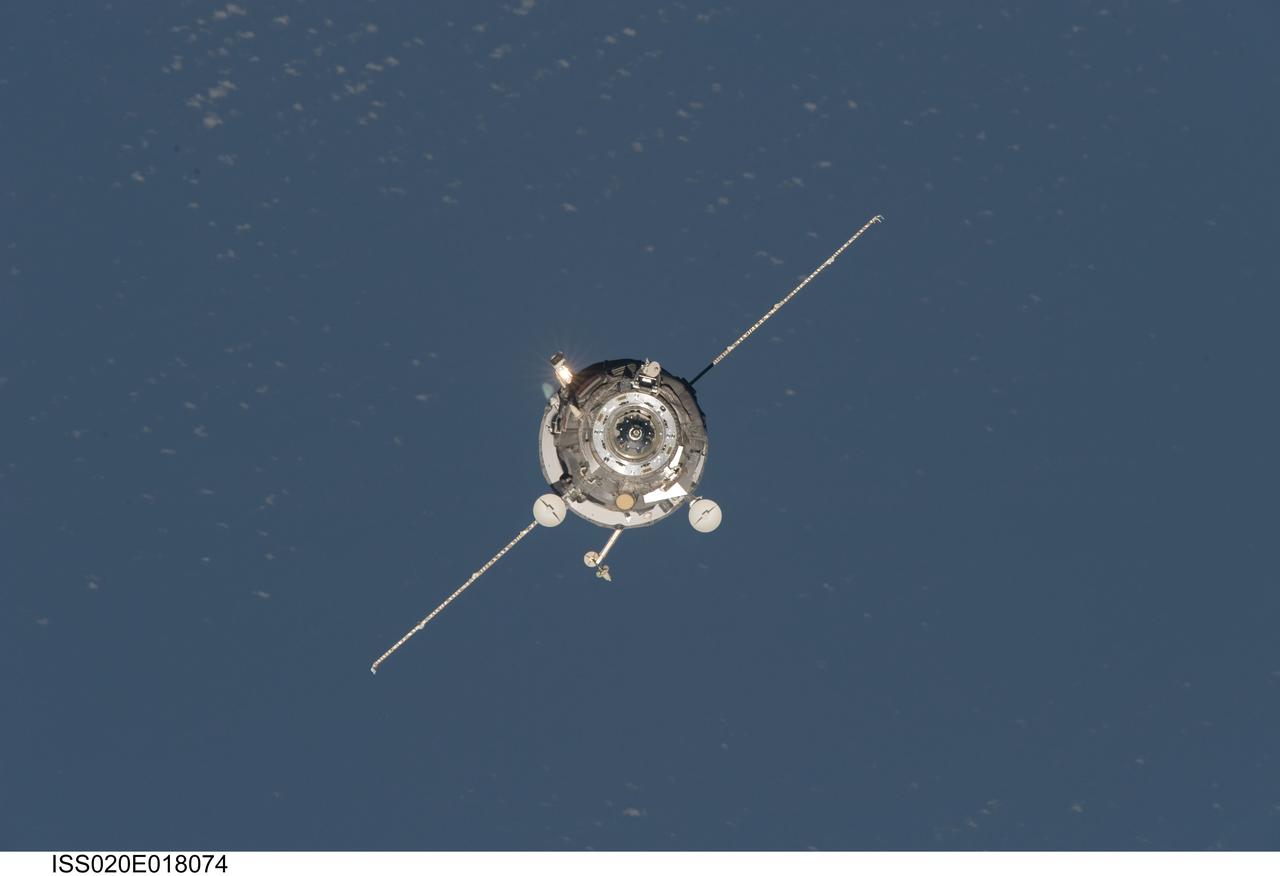

ISS020-E-018074 (12 July 2009) --- An unpiloted ISS Progress 33 cargo craft approaches the International Space Station. On June 30, the Progress undocked from the station and was commanded into a parking orbit for its re-rendezvous with the ISS on July 12, approaching to within 10-15 meters of the Zvezda Service Module to test new automated rendezvous equipment mounted on Zvezda during a pair of spacewalks earlier this month by Gennady Padalka and Mike Barratt that will be used to guide the new Mini-Research Module-2 (MRM2) to an unpiloted docking to the zenith port of Zvezda later this year. MRM2 will serve as a new docking port for Russian spacecraft and an additional airlock for spacewalks conducted out of the Russian segment.
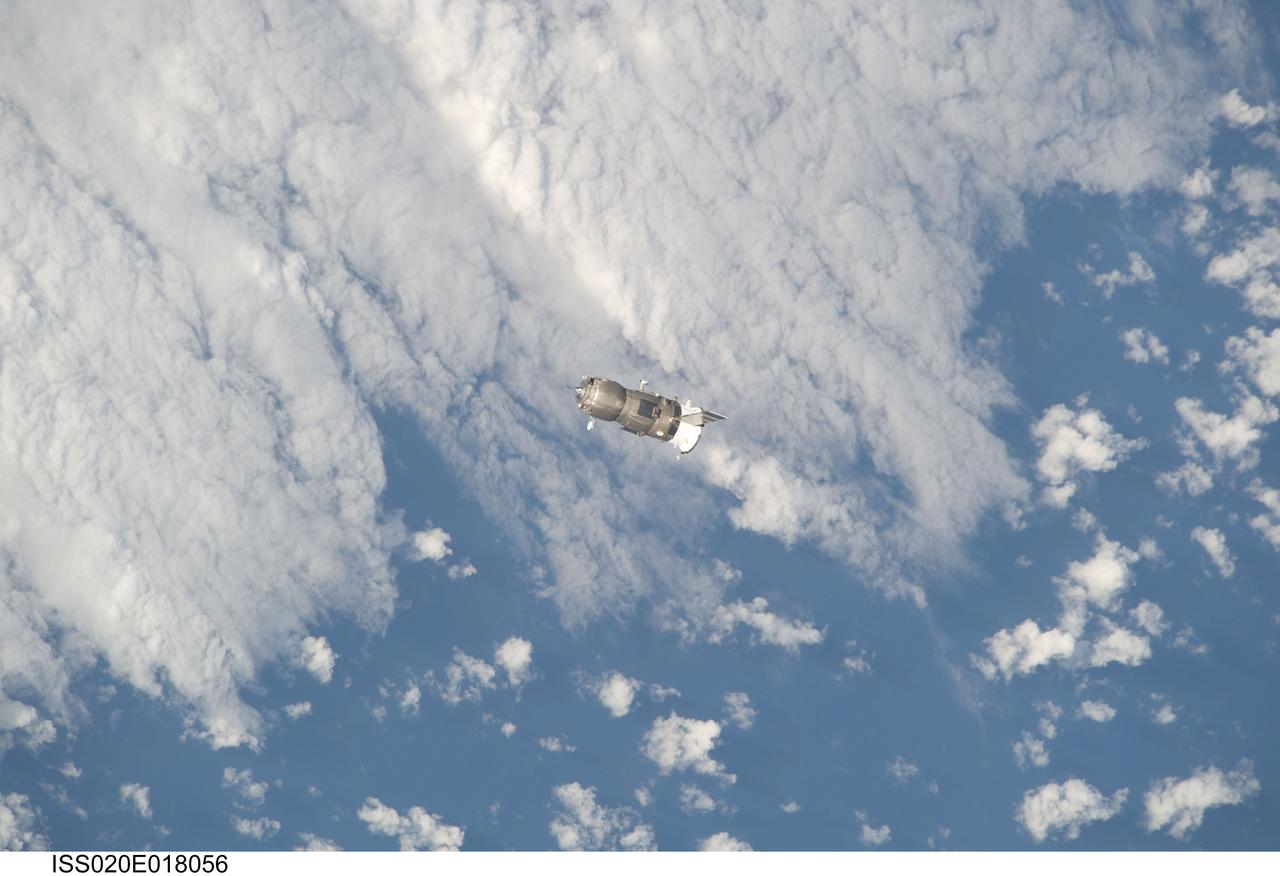

ISS020-E-018056 (12 July 2009) --- An unpiloted ISS Progress 33 cargo craft approaches the International Space Station. On June 30, the Progress undocked from the station and was commanded into a parking orbit for its re-rendezvous with the ISS on July 12, approaching to within 10-15 meters of the Zvezda Service Module to test new automated rendezvous equipment mounted on Zvezda during a pair of spacewalks earlier this month by Gennady Padalka and Mike Barratt that will be used to guide the new Mini-Research Module-2 (MRM2) to an unpiloted docking to the zenith port of Zvezda later this year. MRM2 will serve as a new docking port for Russian spacecraft and an additional airlock for spacewalks conducted out of the Russian segment.
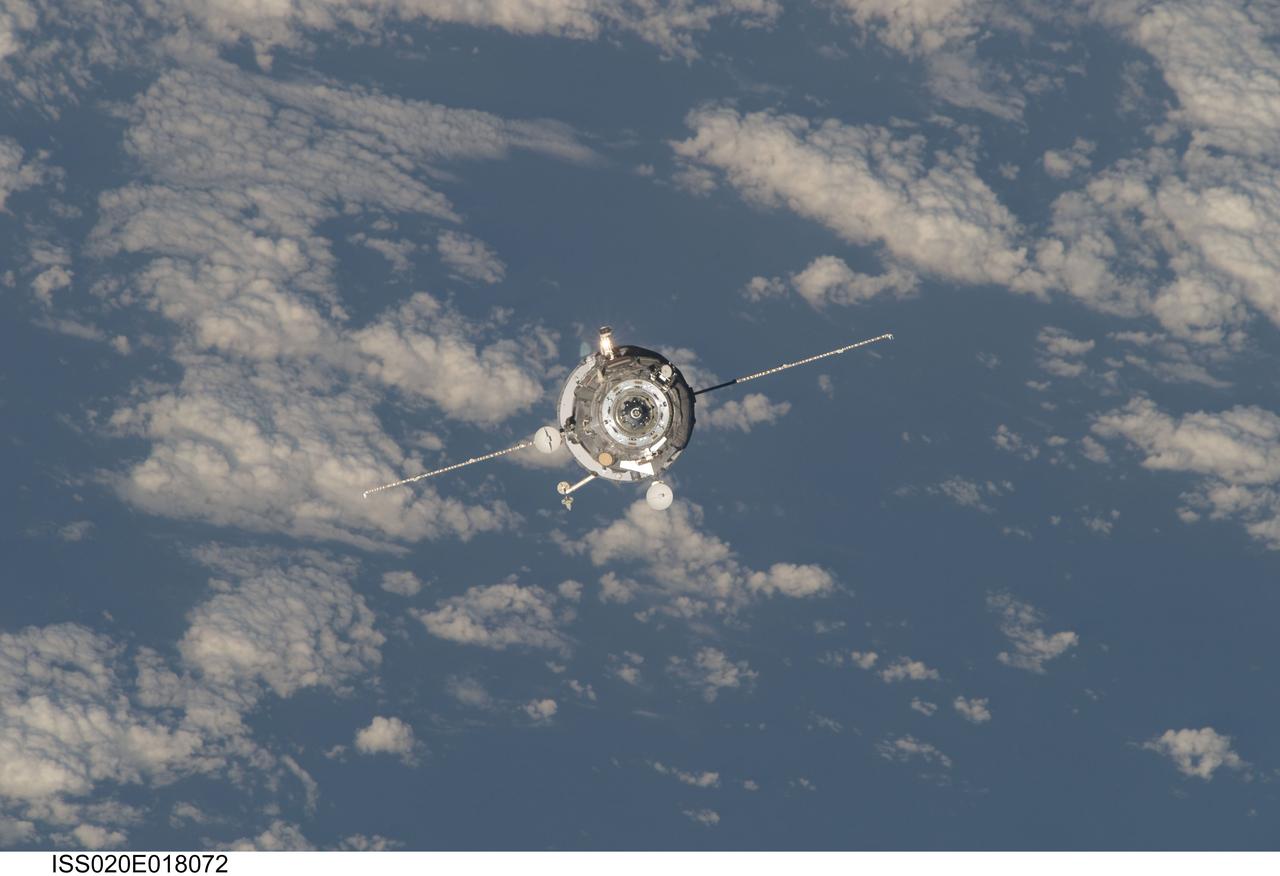

ISS020-E-018072 (12 July 2009) --- An unpiloted ISS Progress 33 cargo craft approaches the International Space Station. On June 30, the Progress undocked from the station and was commanded into a parking orbit for its re-rendezvous with the ISS on July 12, approaching to within 10-15 meters of the Zvezda Service Module to test new automated rendezvous equipment mounted on Zvezda during a pair of spacewalks earlier this month by Gennady Padalka and Mike Barratt that will be used to guide the new Mini-Research Module-2 (MRM2) to an unpiloted docking to the zenith port of Zvezda later this year. MRM2 will serve as a new docking port for Russian spacecraft and an additional airlock for spacewalks conducted out of the Russian segment.
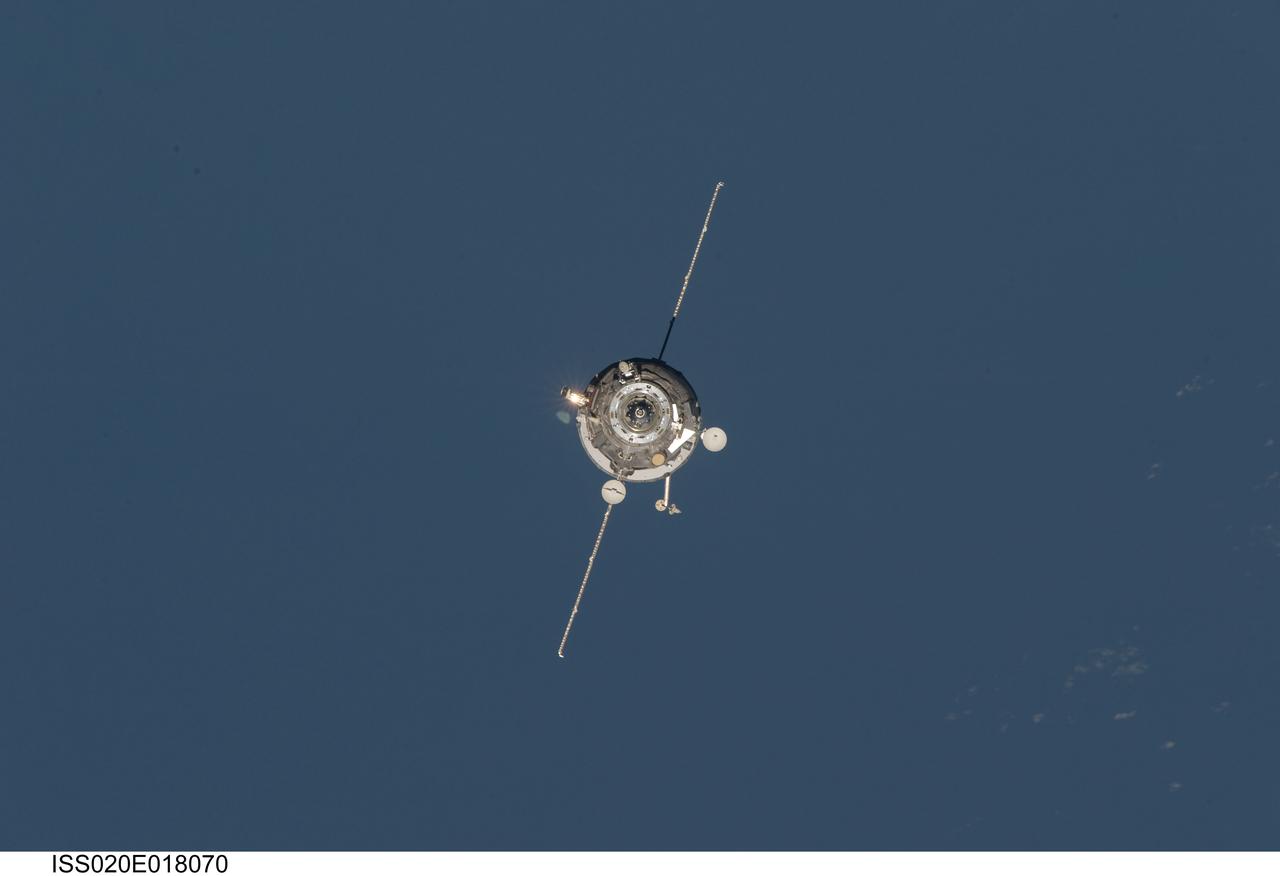

ISS020-E-018070 (12 July 2009) --- An unpiloted ISS Progress 33 cargo craft approaches the International Space Station. On June 30, the Progress undocked from the station and was commanded into a parking orbit for its re-rendezvous with the ISS on July 12, approaching to within 10-15 meters of the Zvezda Service Module to test new automated rendezvous equipment mounted on Zvezda during a pair of spacewalks earlier this month by Gennady Padalka and Mike Barratt that will be used to guide the new Mini-Research Module-2 (MRM2) to an unpiloted docking to the zenith port of Zvezda later this year. MRM2 will serve as a new docking port for Russian spacecraft and an additional airlock for spacewalks conducted out of the Russian segment.
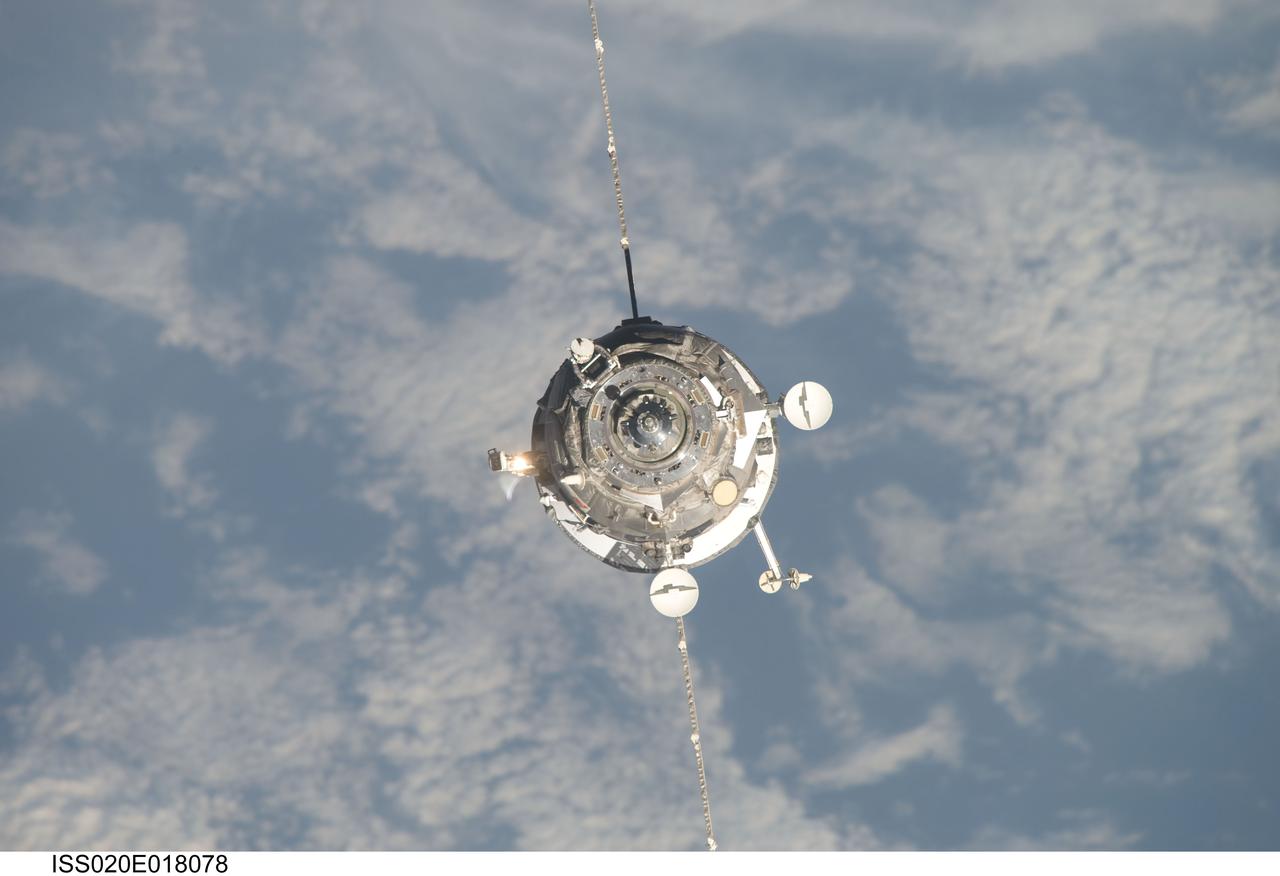

ISS020-E-018078 (12 July 2009) --- An unpiloted ISS Progress 33 cargo craft approaches the International Space Station. On June 30, the Progress undocked from the station and was commanded into a parking orbit for its re-rendezvous with the ISS on July 12, approaching to within 10-15 meters of the Zvezda Service Module to test new automated rendezvous equipment mounted on Zvezda during a pair of spacewalks earlier this month by Gennady Padalka and Mike Barratt that will be used to guide the new Mini-Research Module-2 (MRM2) to an unpiloted docking to the zenith port of Zvezda later this year. MRM2 will serve as a new docking port for Russian spacecraft and an additional airlock for spacewalks conducted out of the Russian segment.
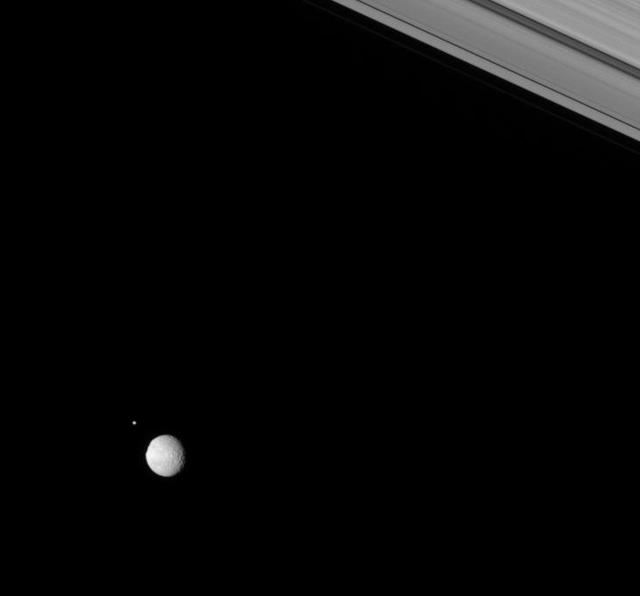

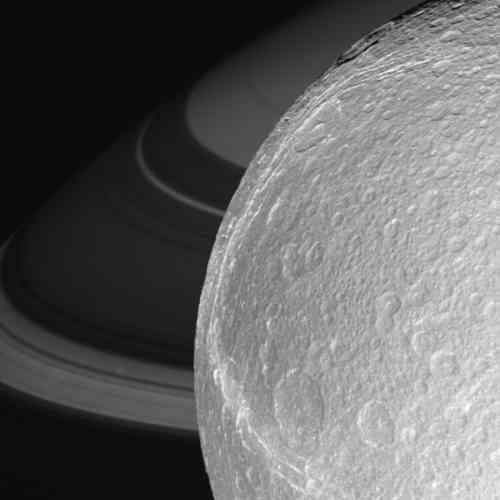
Two moons of Saturn rendezvous in the Saturnian skies above the Cassini spacecraft
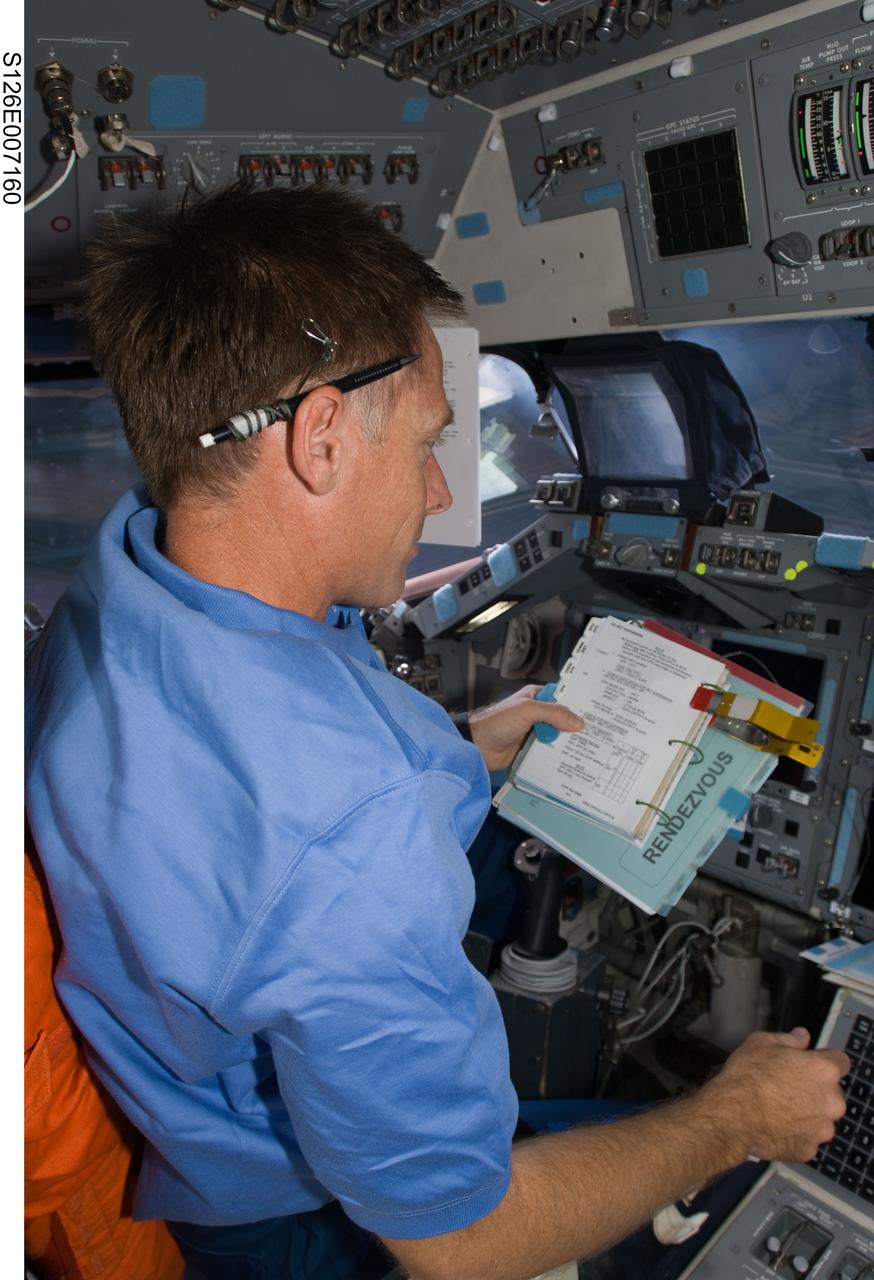

S126-E-007160 (16 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Chris Ferguson, STS-126 commander, occupies the commander's station on the forward flight deck of Space Shuttle Endeavour during rendezvous and docking operations with the International Space Station.
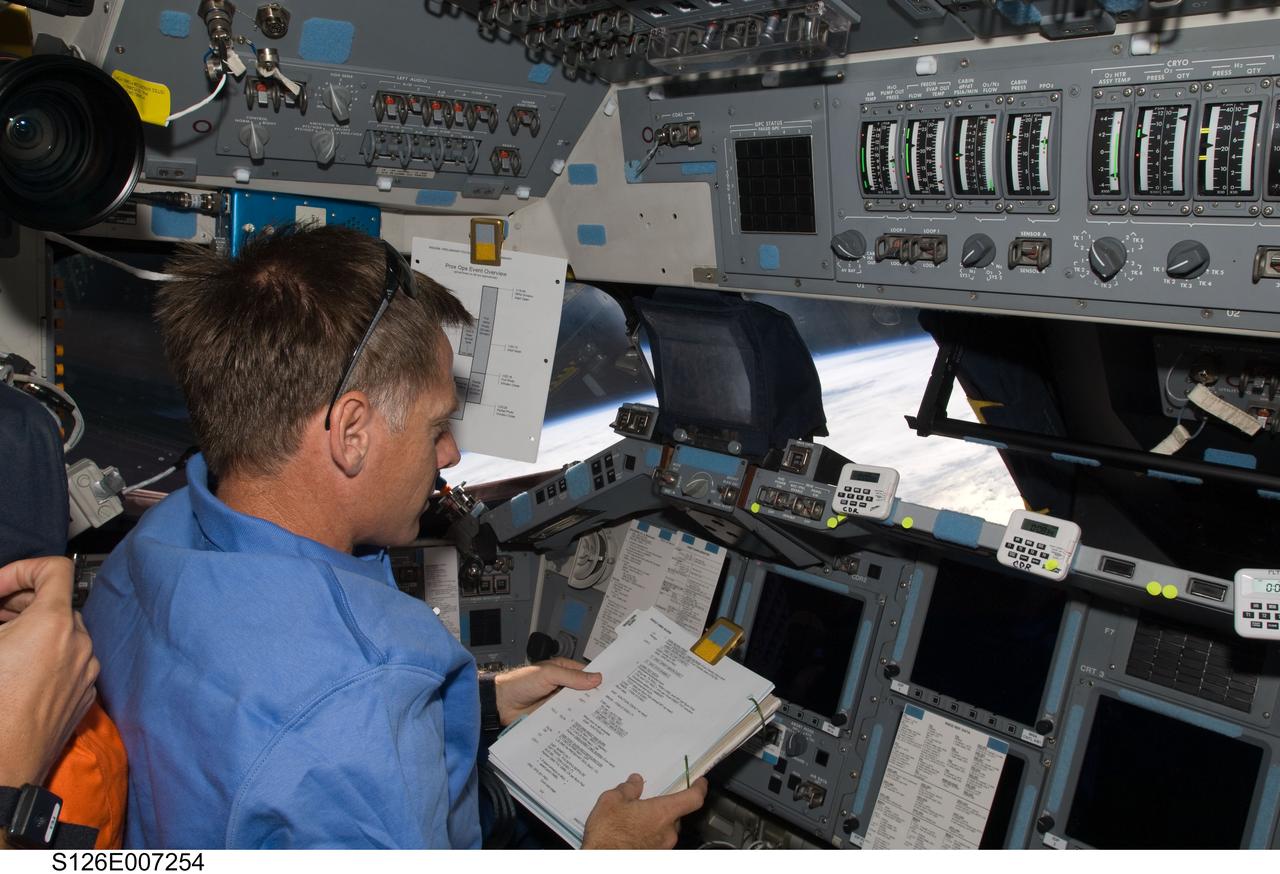

S126-E-007254 (16 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Chris Ferguson, STS-126 commander, occupies the commander's station on the forward flight deck of Space Shuttle Endeavour during rendezvous and docking operations with the International Space Station.
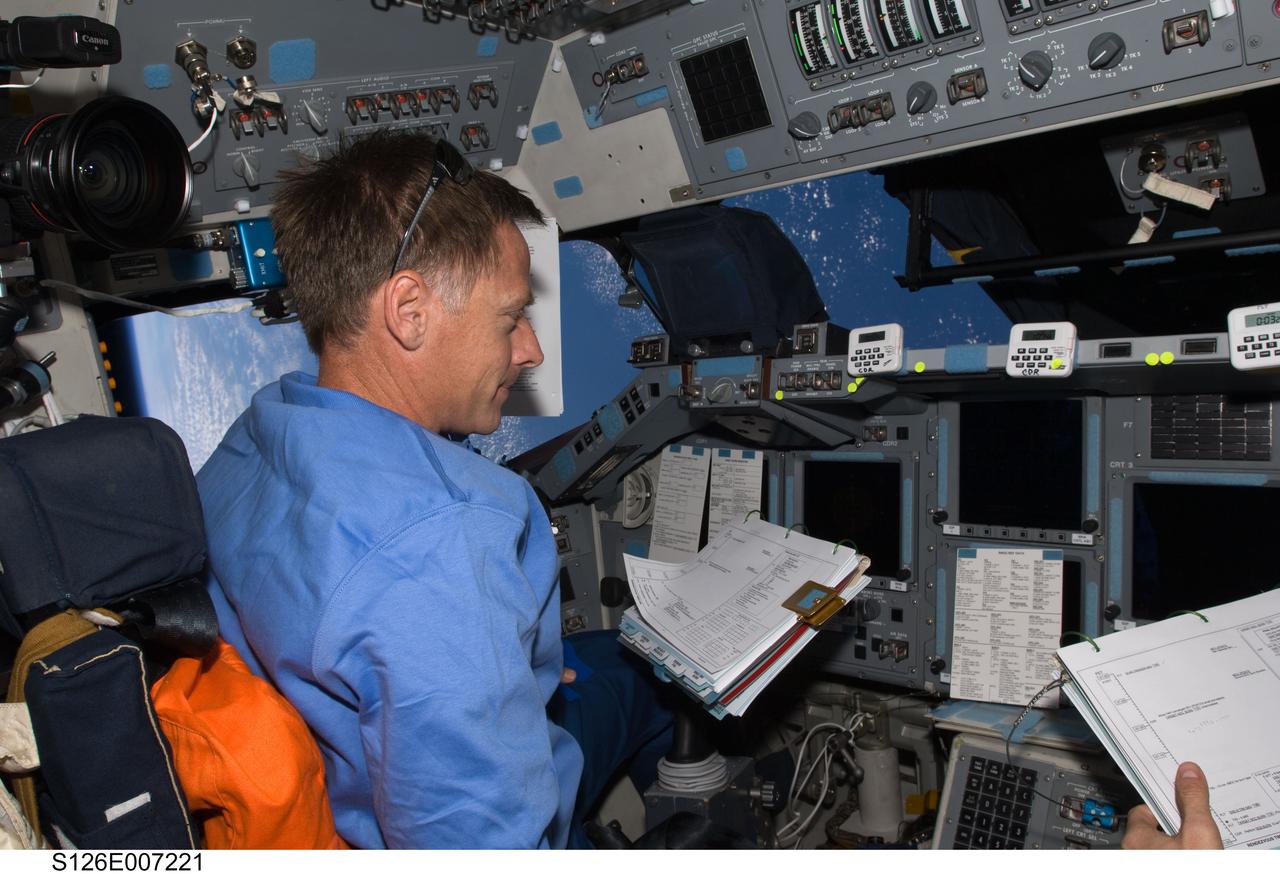

S126-E-007221 (16 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Chris Ferguson, STS-126 commander, occupies the commander's station on the forward flight deck of Space Shuttle Endeavour during rendezvous and docking operations with the International Space Station.
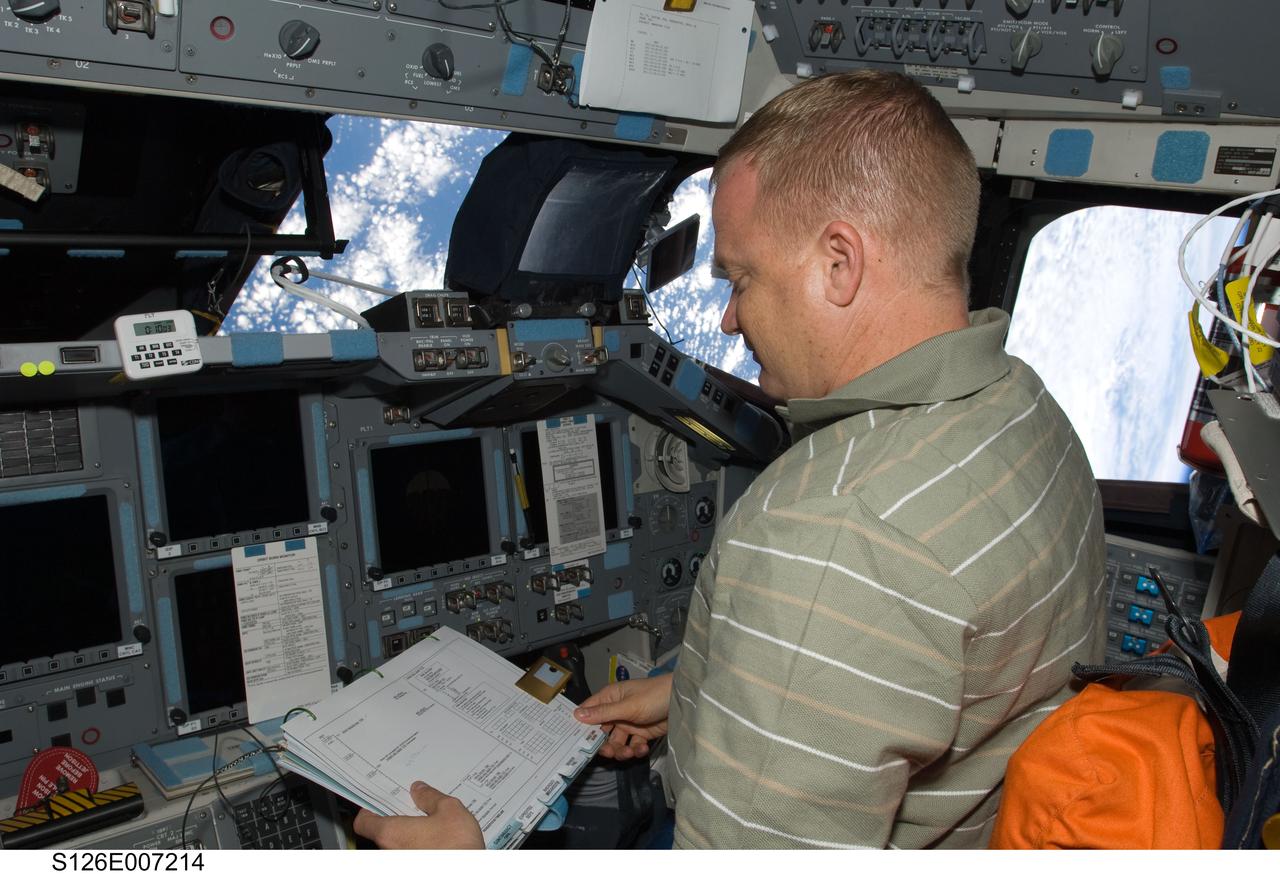

S126-E-007214 (16 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Eric Boe, STS-126 pilot, occupies the pilot's station on the forward flight deck of Space Shuttle Endeavour during rendezvous and docking operations with the International Space Station.

S66-25781 (16-17 March 1966) --- Closer view of the Agena Target Docking vehicle seen from the Gemini-8 spacecraft during rendezvous in space. Photo credit: NASA
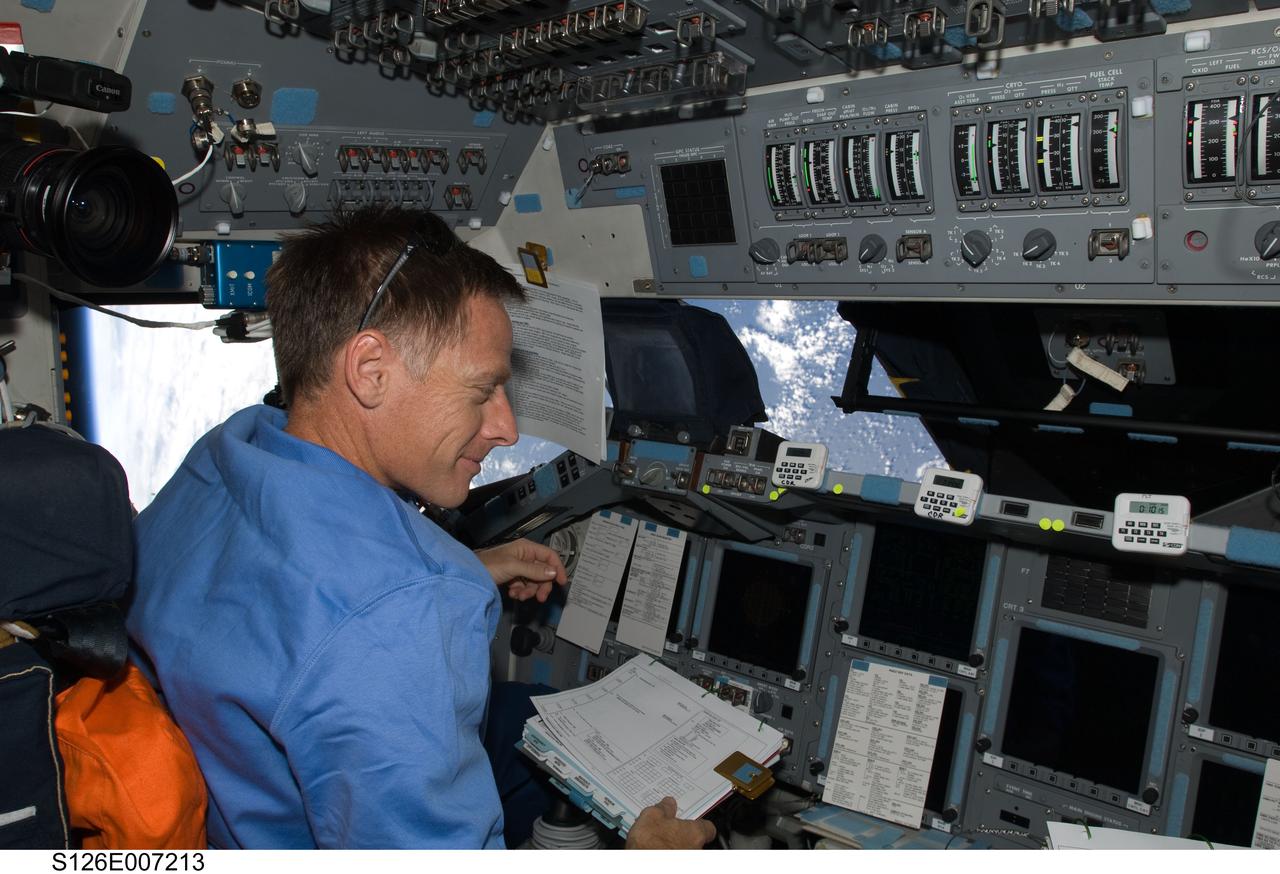

S126-E-007213 (16 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Chris Ferguson, STS-126 commander, occupies the commander's station on the forward flight deck of Space Shuttle Endeavour during rendezvous and docking operations with the International Space Station.
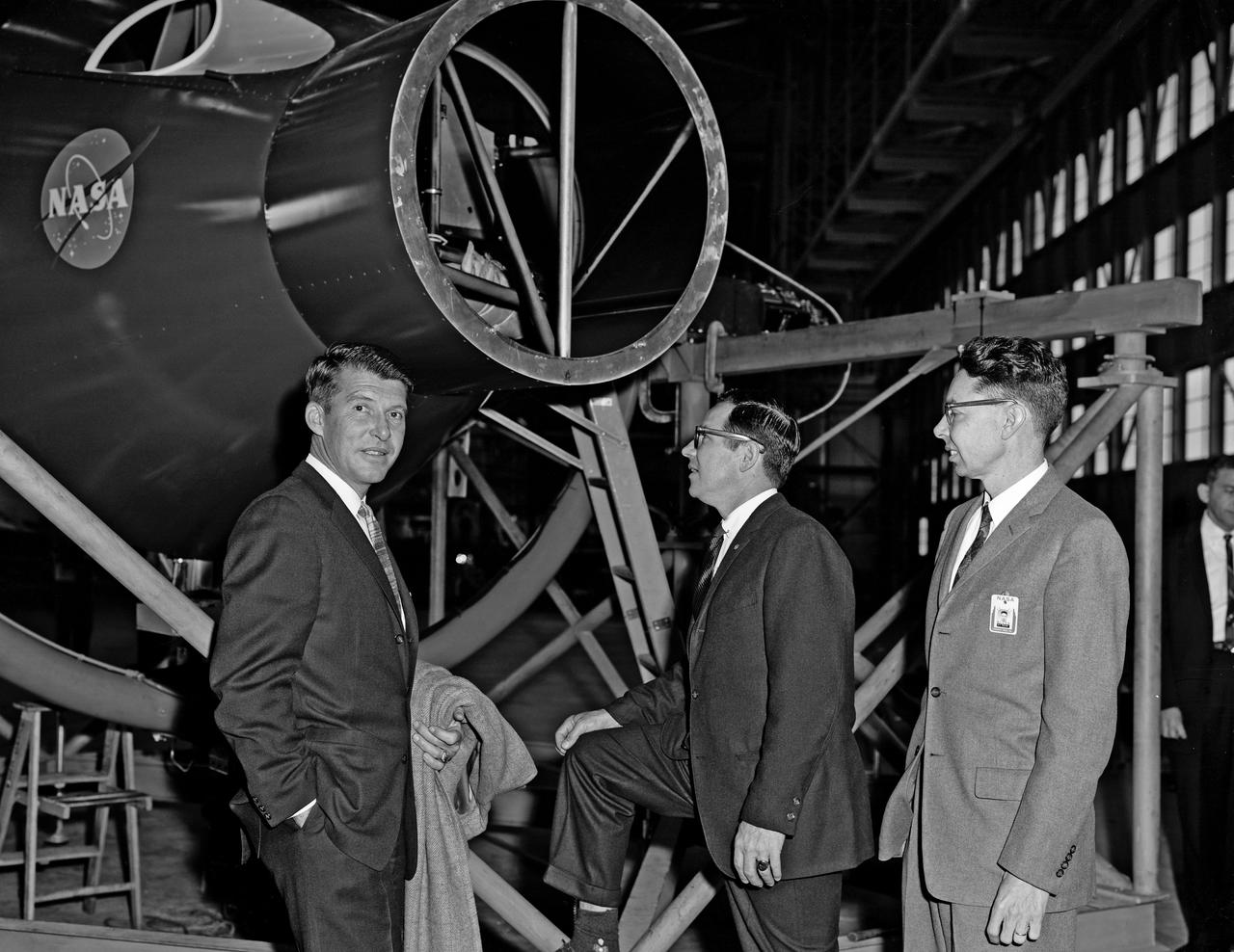

Walter (Wally) M. Schirra Visit to Langley Research Center to the Rendezvous Docking Simulator.
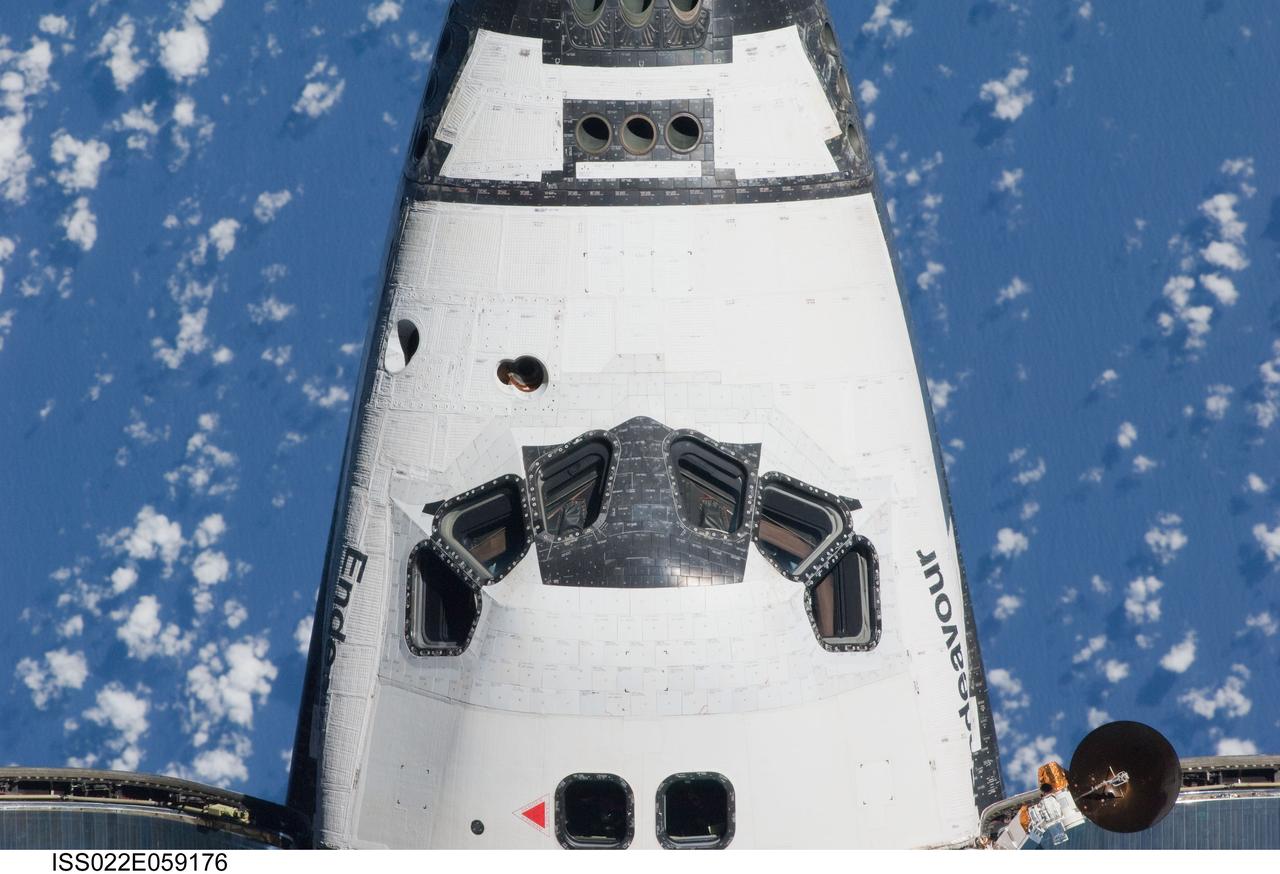

ISS022-E-059176 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This view of the crew cabin of the space shuttle Endeavour was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, the STS-130 Endeavour crew performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
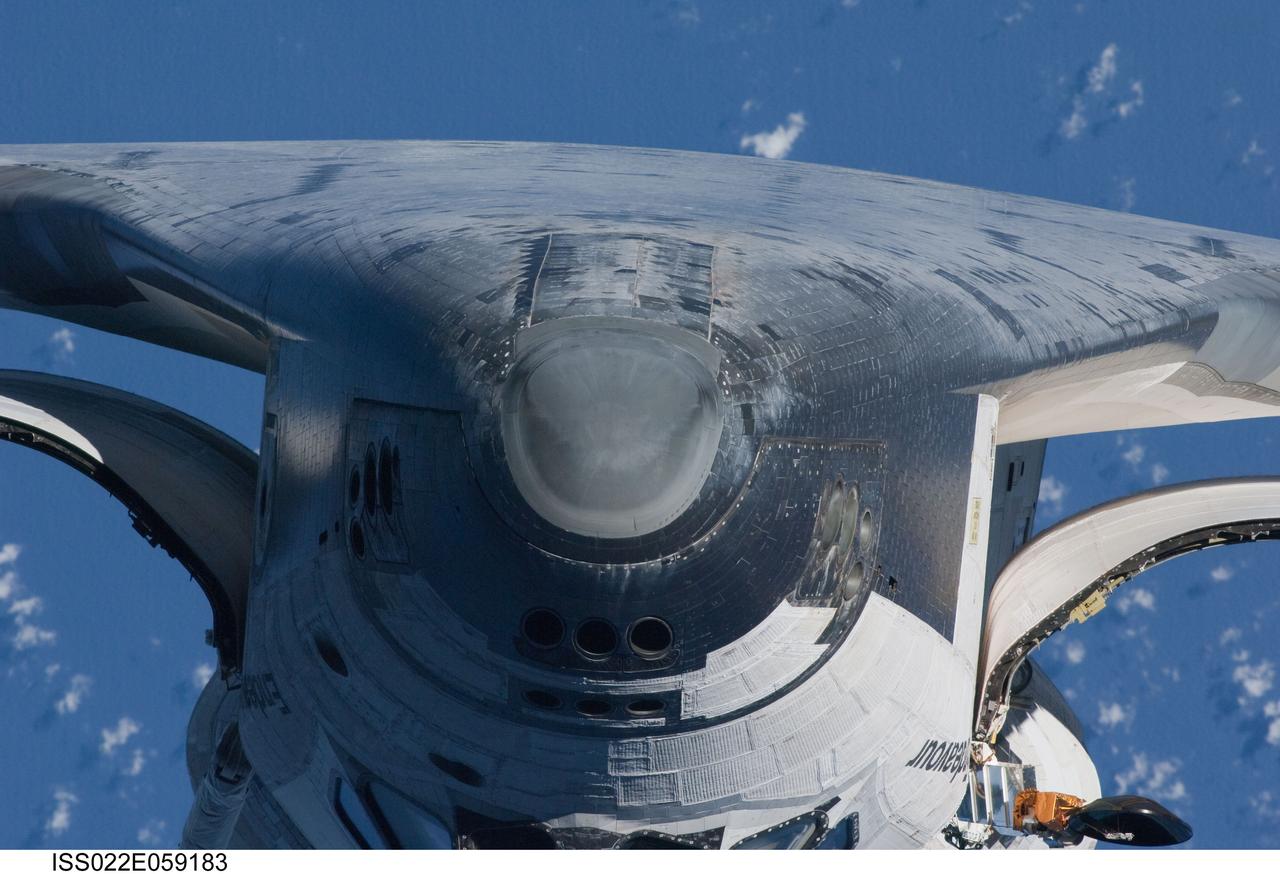

ISS022-E-059183 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This view of the underside of the crew cabin of the space shuttle Endeavour was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-130 crew to the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
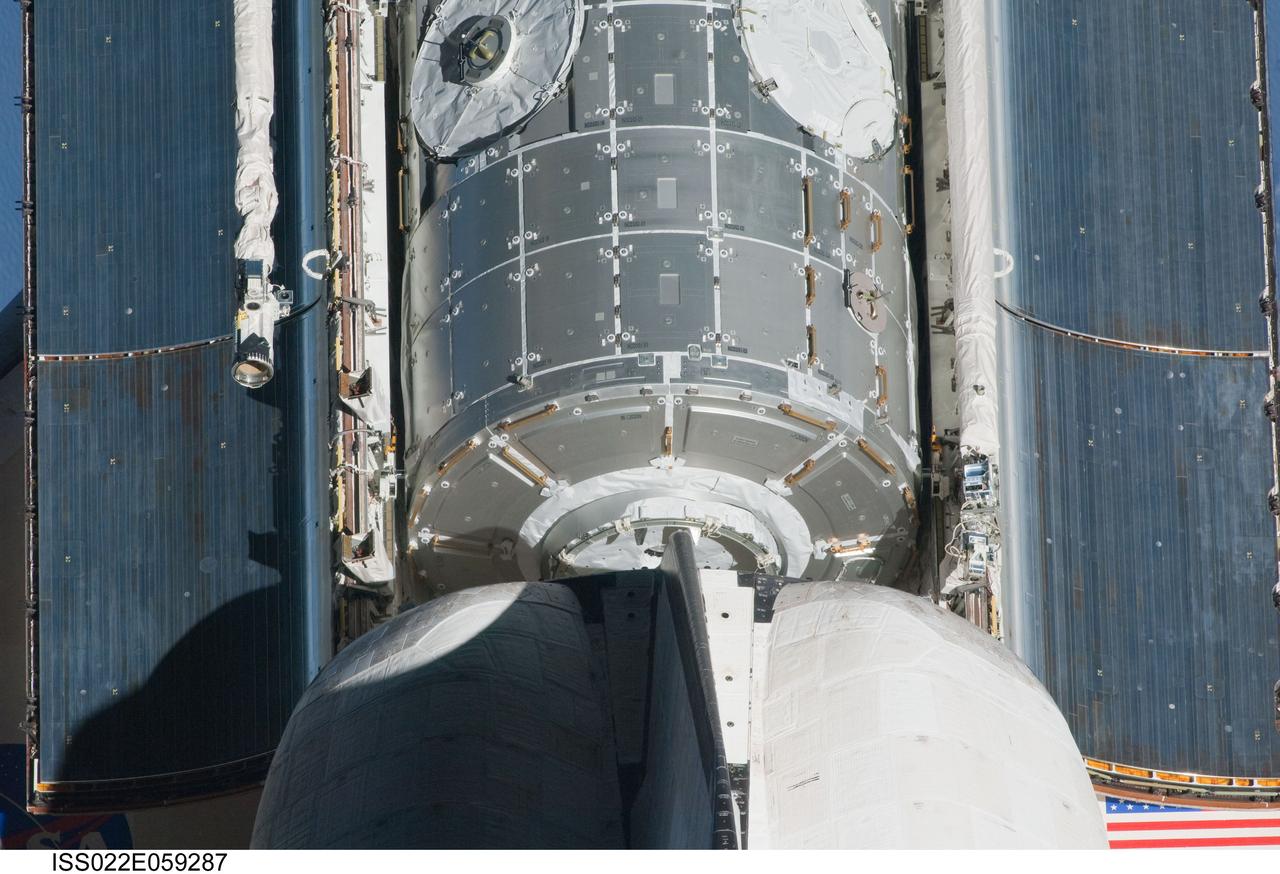

ISS022-E-059287 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This partial view of the space shuttle Endeavour?s payload bay featuring the Tranquility node was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-130 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
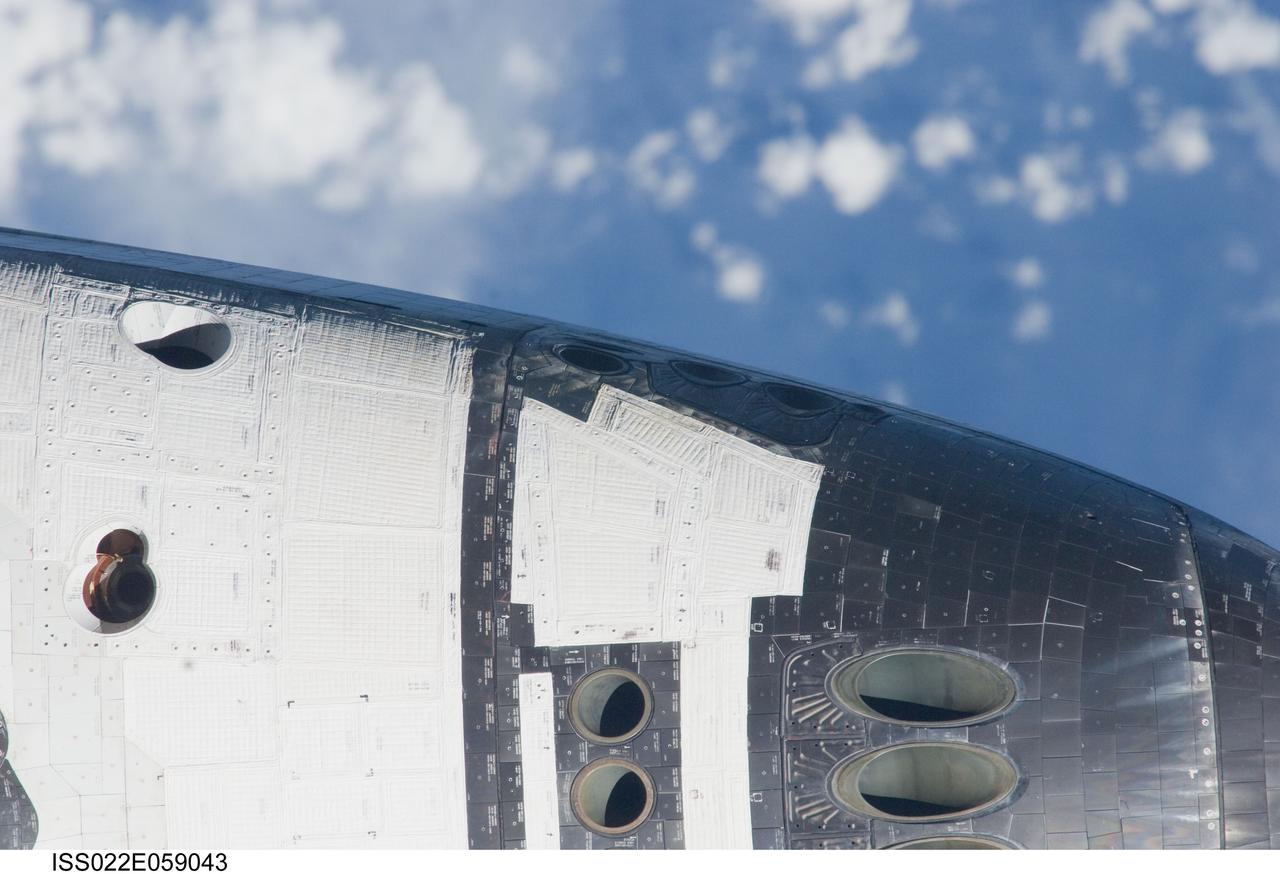

ISS022-E-059043 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This nadir image showing mostly the port side of space shuttle Endeavour's crew cabin was photographed with a digital camera?s 800mm lens by one of the Expedition 22 crew members aboard the International Space Station. The two spacecraft were in the midst of rendezvous operations, which included a back-flip by the shuttle.
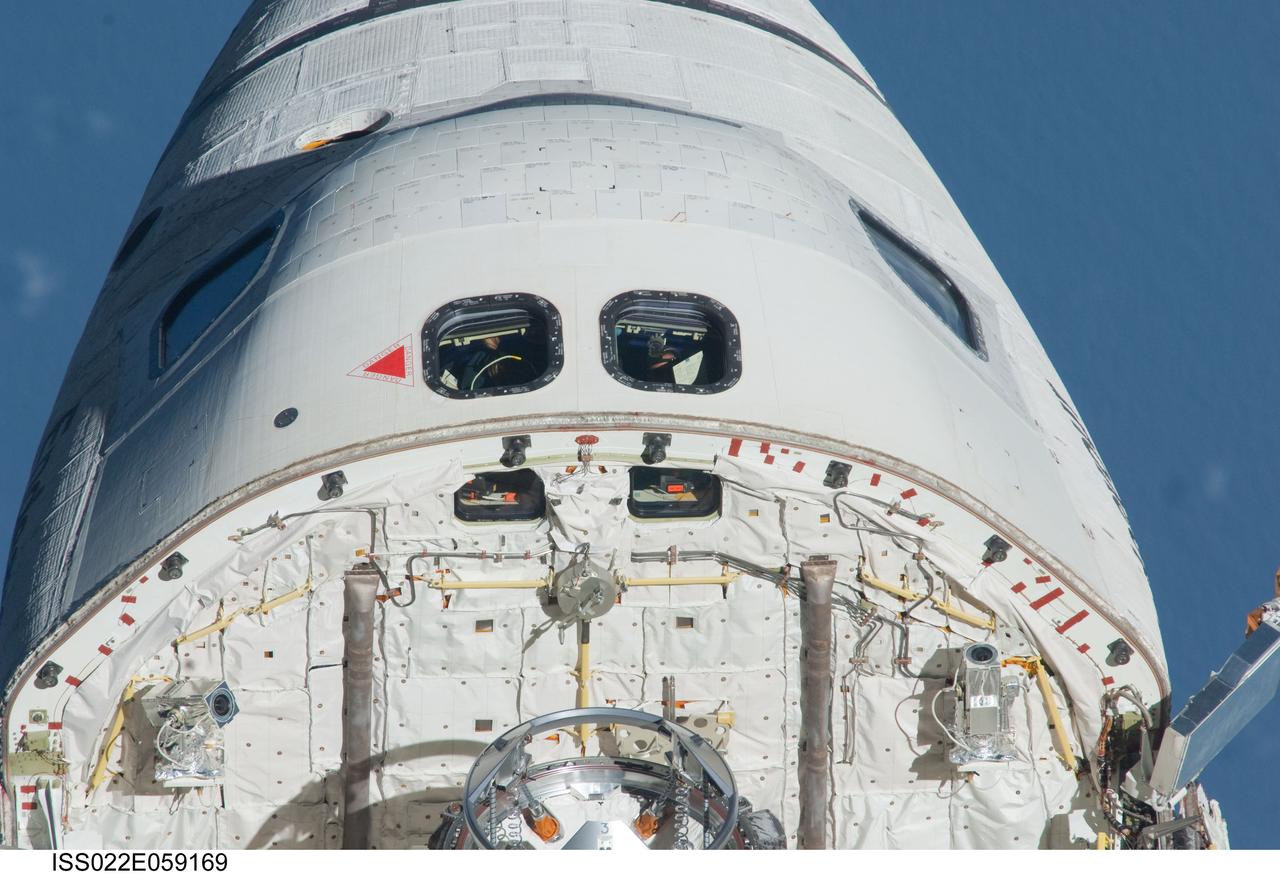

ISS022-E-059169 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This image, showing the top of space shuttle Endeavour's crew cabin, its firewall and part of the docking mechanism in the cargo bay, was photographed by one of the Expedition 22 crew members aboard the International Space Station. The two spacecraft were in the midst of rendezvous operations, which included a back-flip by the shuttle for the purposes of inspecting and photographing it from a number of angles.
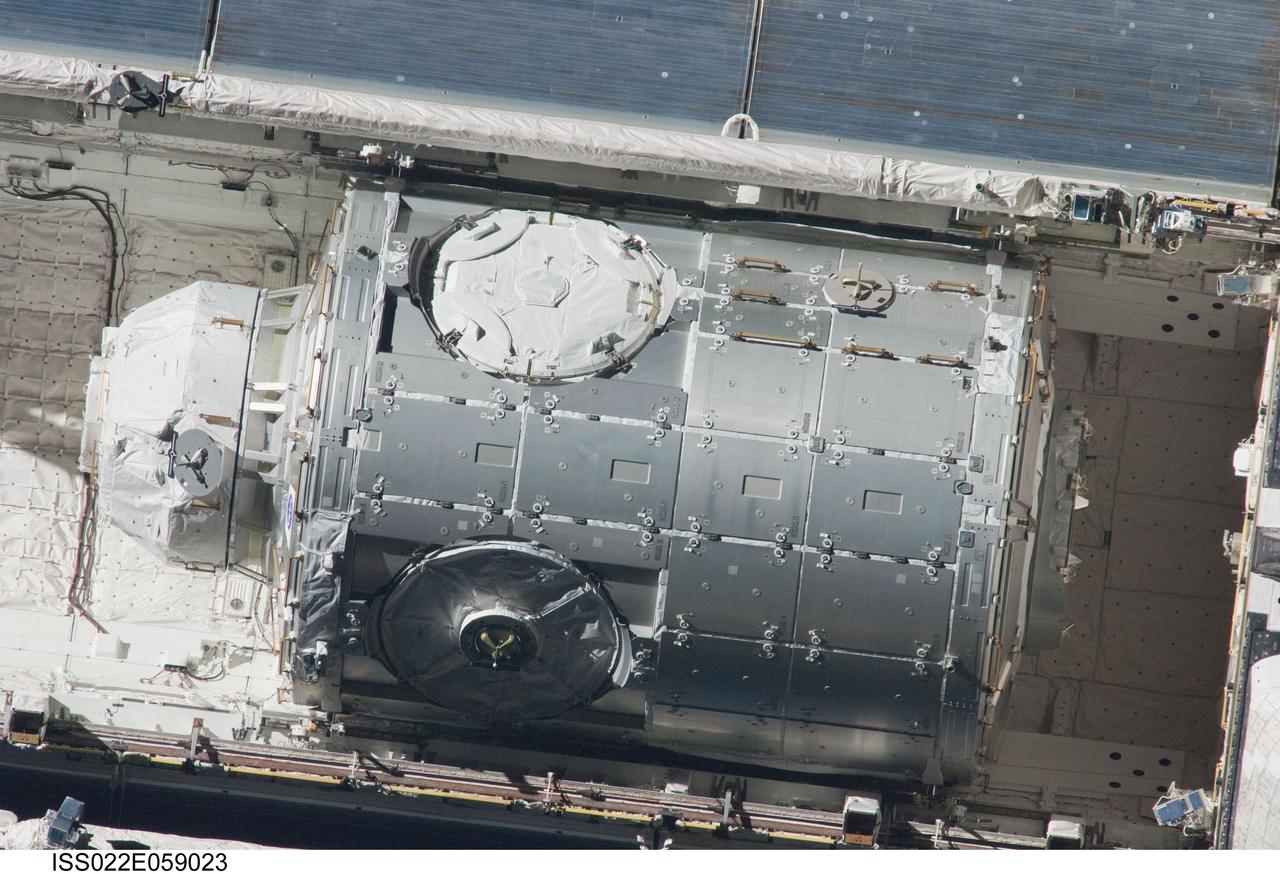

ISS022-E-059023 (9 Feb. 2009) --- This high- angle 800mm image of the Tranquility node in space shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay was photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member aboard the International Space Station. The two spacecraft were in the process of their rendezvous activities which included a back-flip by Endeavour. Tranquility will be installed as the third node for the orbital outpost.
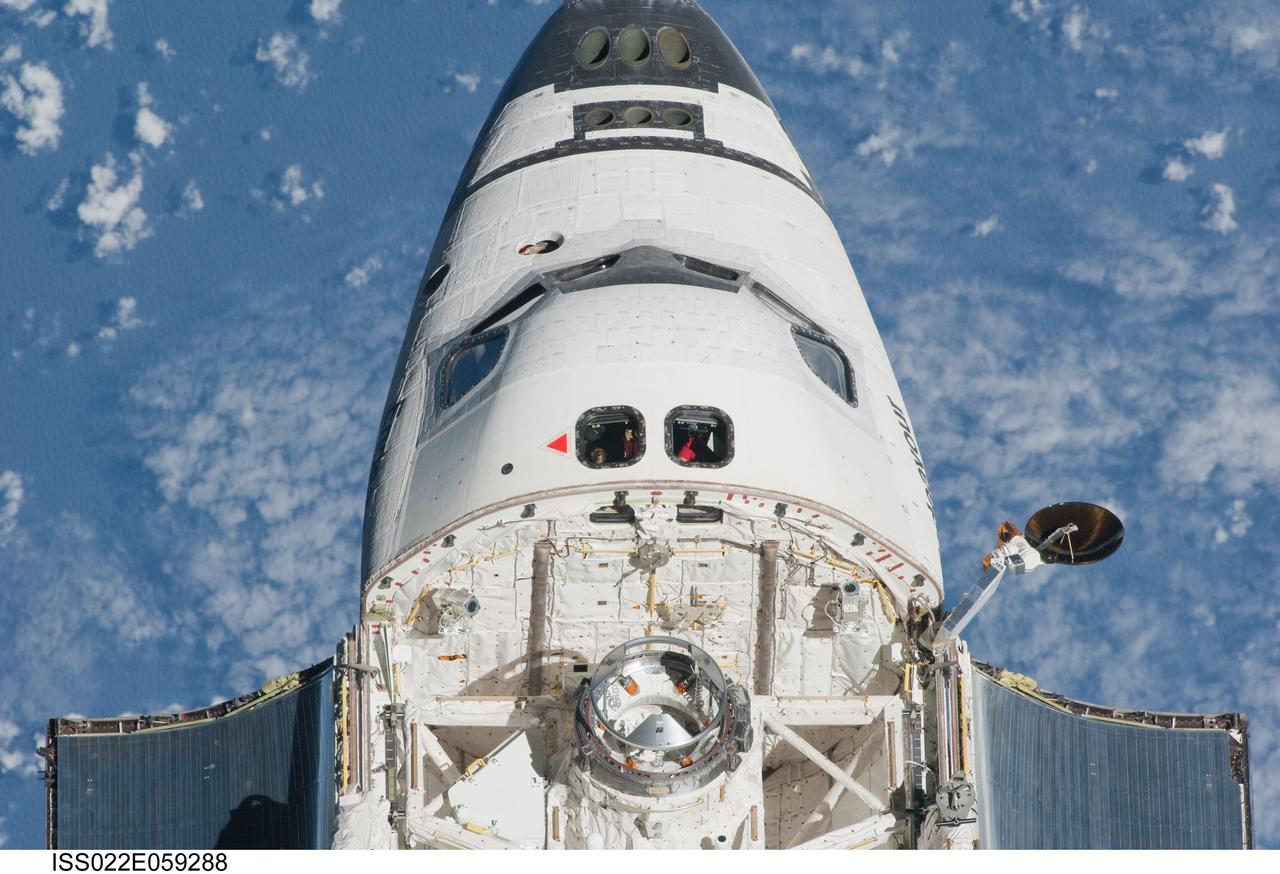

ISS022-E-059288 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This partial view of the crew cabin and forward payload bay of the space shuttle Endeavour was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, the STS-130 Endeavour crew performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
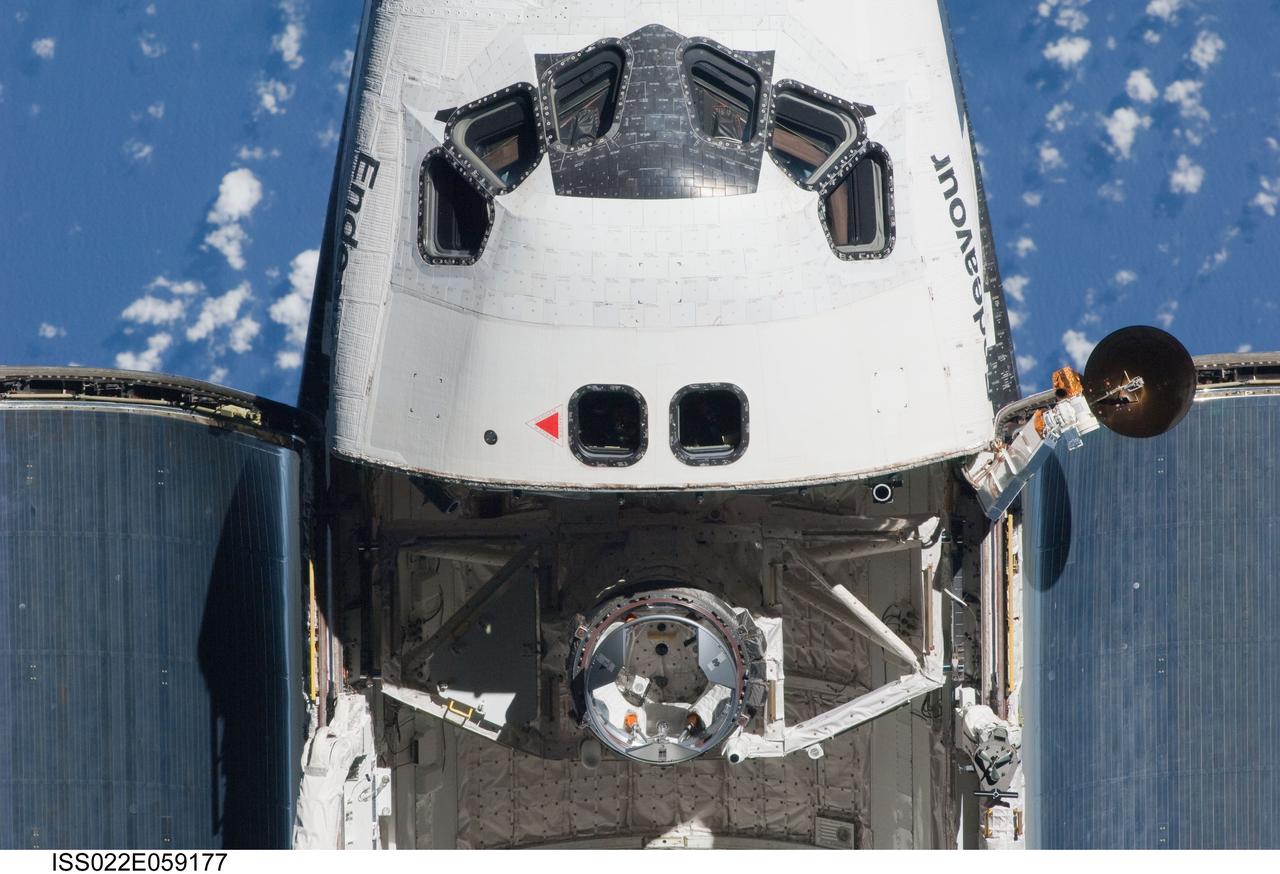

ISS022-E-059177 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This partial view of the crew cabin and forward payload bay of the space shuttle Endeavour was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, the STS-130 Endeavour crew performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
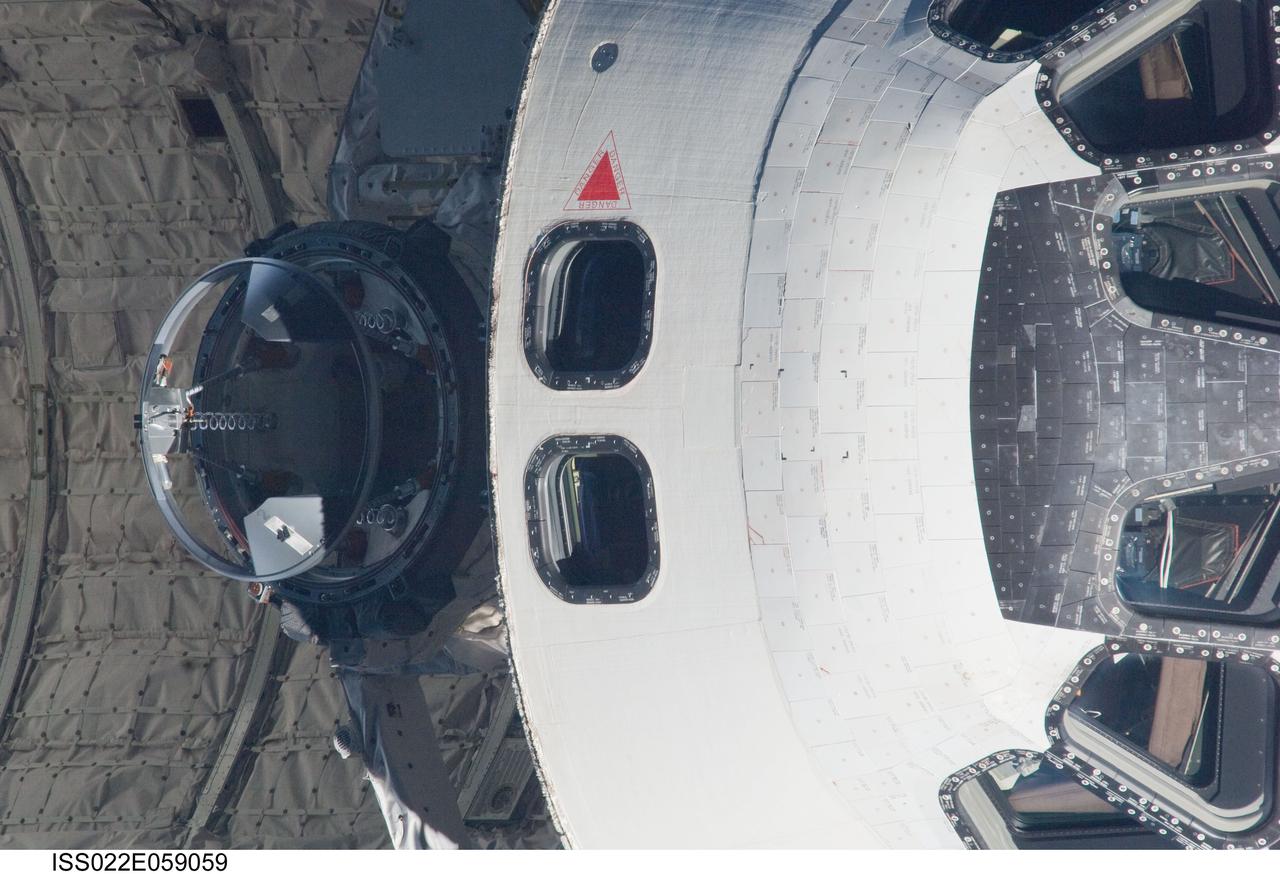

ISS022-E-059059 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This 800mm image showing the top of space shuttle Endeavour's crew cabin and the docking mechanism was photographed by one of the Expedition 22 crew members aboard the International Space Station. The two spacecraft were in the midst of rendezvous operations, which included a back-flip by the shuttle for the purposes of inspecting and photographing it from a number of angles.
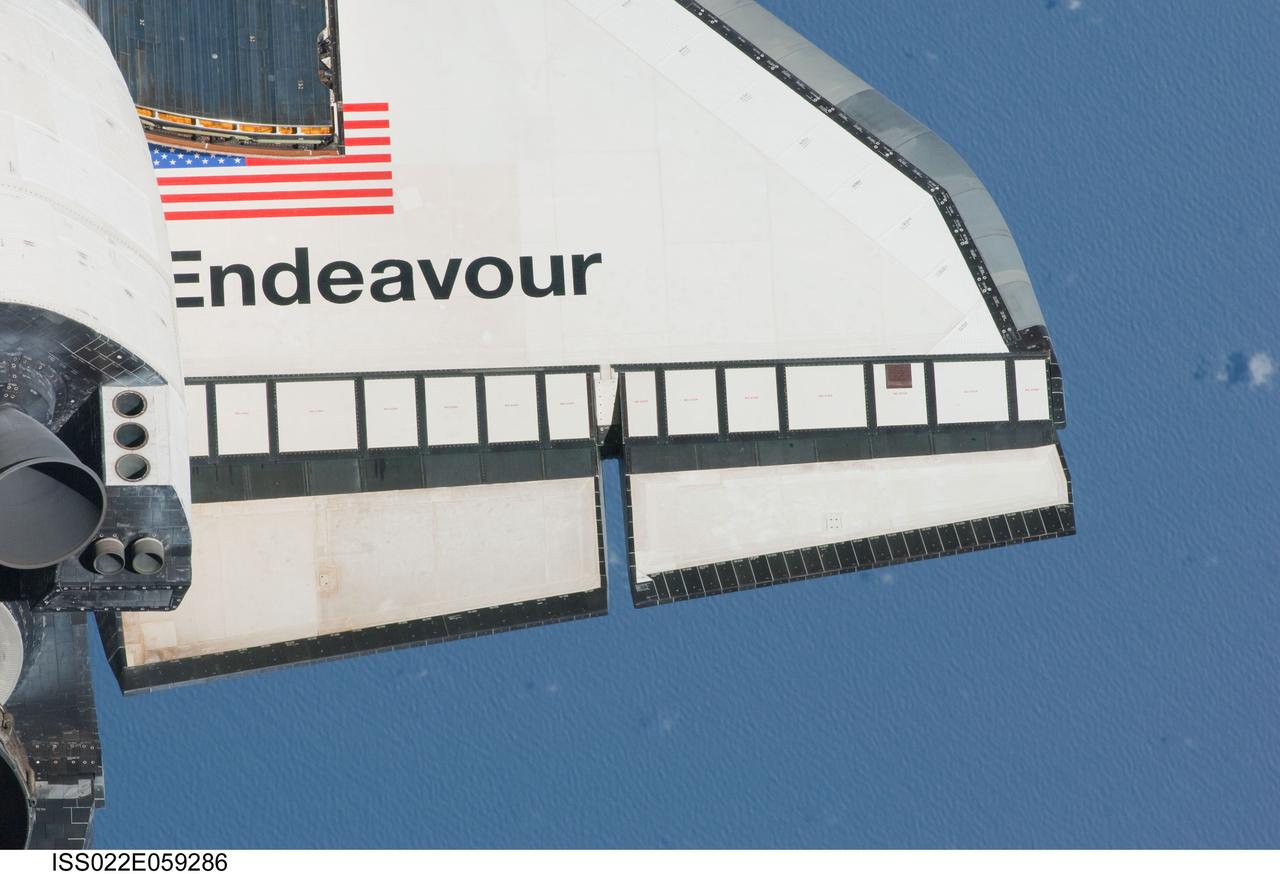

ISS022-E-059286 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This partial view of the starboard wing of the space shuttle Endeavour was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-130 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
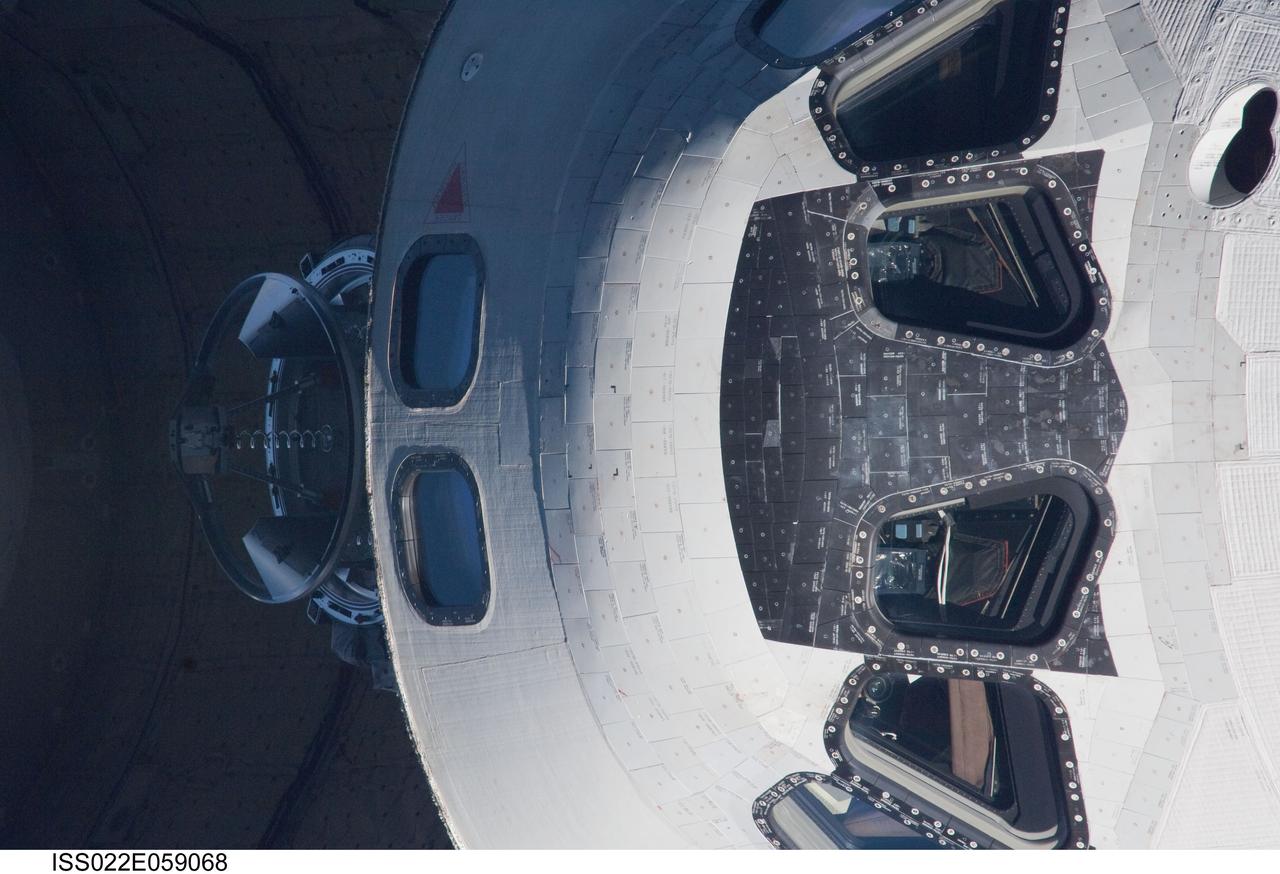

ISS022-E-059068 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This 800mm image showing a head-on view of space shuttle Endeavour's crew cabin, was photographed by one of the Expedition 22 crew members aboard the International Space Station. The two spacecraft were in the midst of rendezvous operations, which included a back-flip by the shuttle for the purposes of inspecting and photographing it from a number of angles.
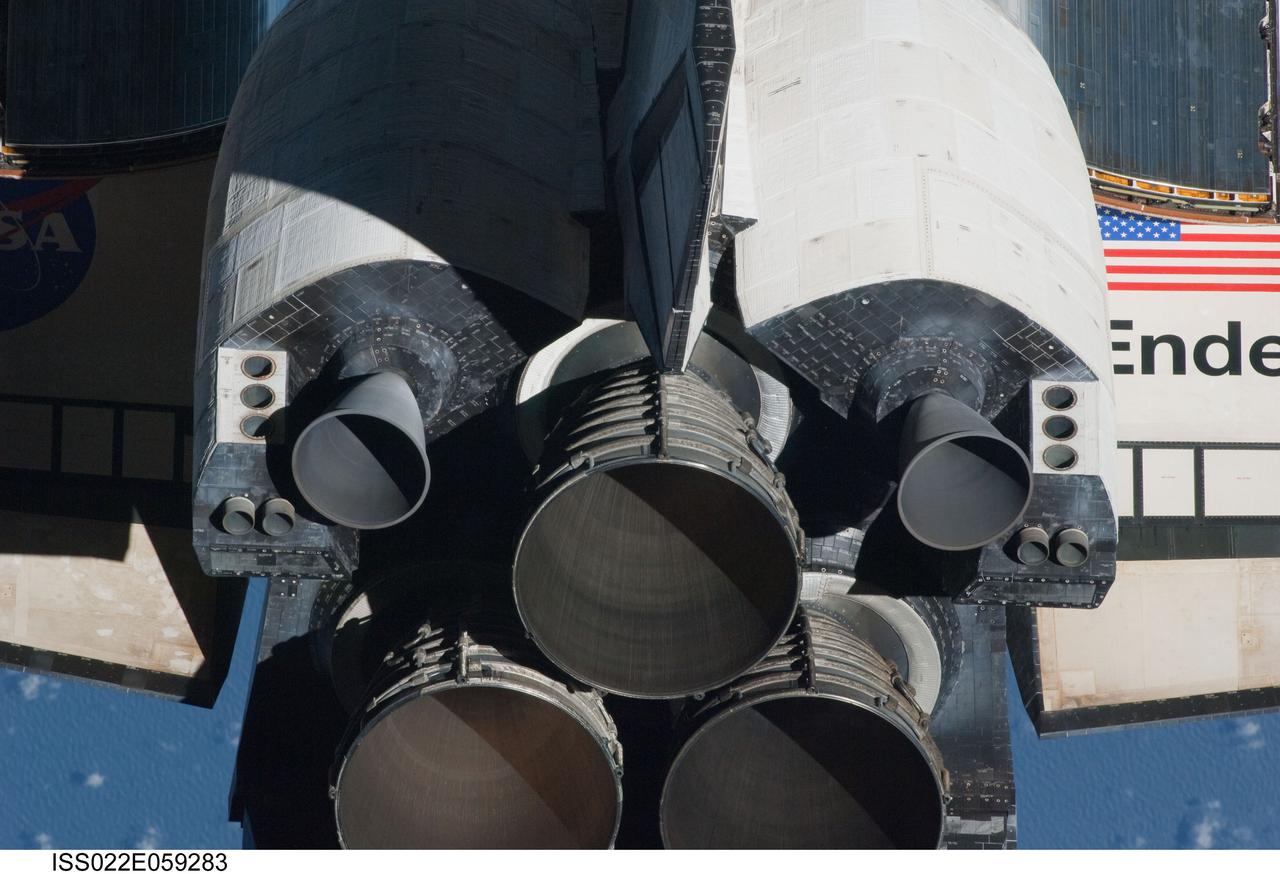

ISS022-E-059283 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This view of the aft portion of the space shuttle Endeavour, including the three main engines and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods, was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
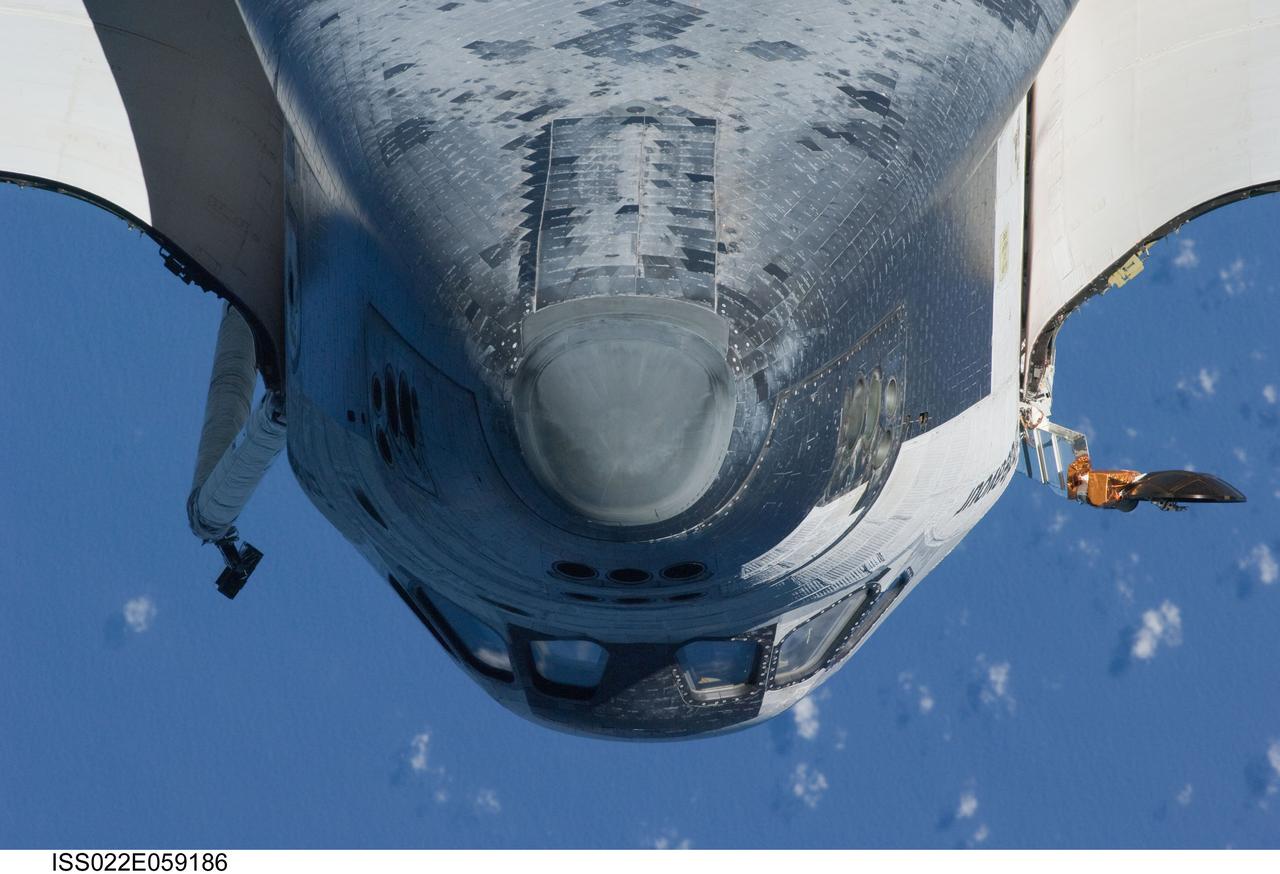

ISS022-E-059186 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This view of the underside of the crew cabin of the space shuttle Endeavour was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-130 crew to the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
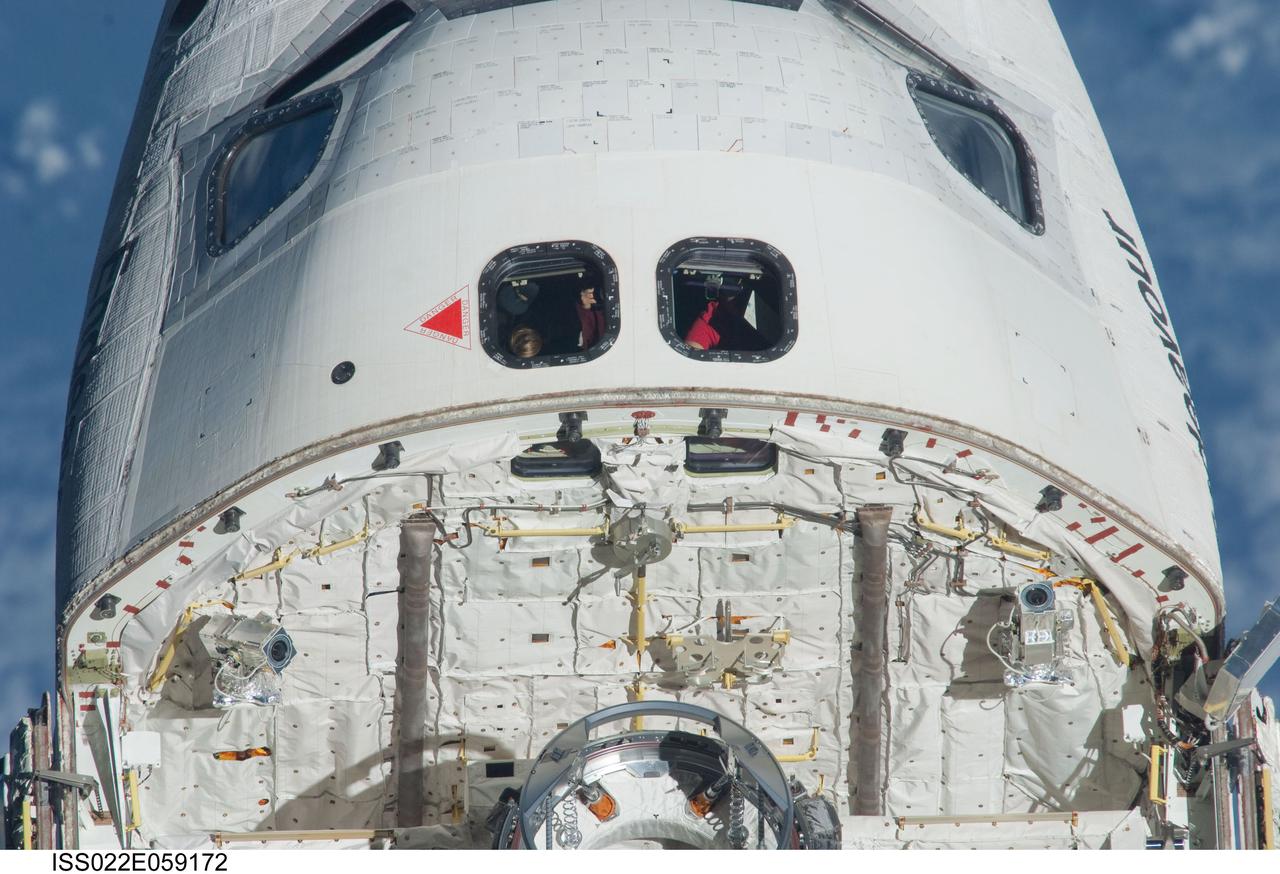

ISS022-E-059172 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This 800mm image, showing the top of space shuttle Endeavour's crew cabin, its firewall and part of the docking mechanism in the cargo bay, was photographed by one of the Expedition 22 crew members aboard the International Space Station. The two spacecraft were in the midst of rendezvous operations, which included a back-flip by the shuttle for the purposes of inspecting and photographing it from a number of angles.

ISS022-E-059237 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This partial view of the starboard wing of the space shuttle Endeavour was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-130 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
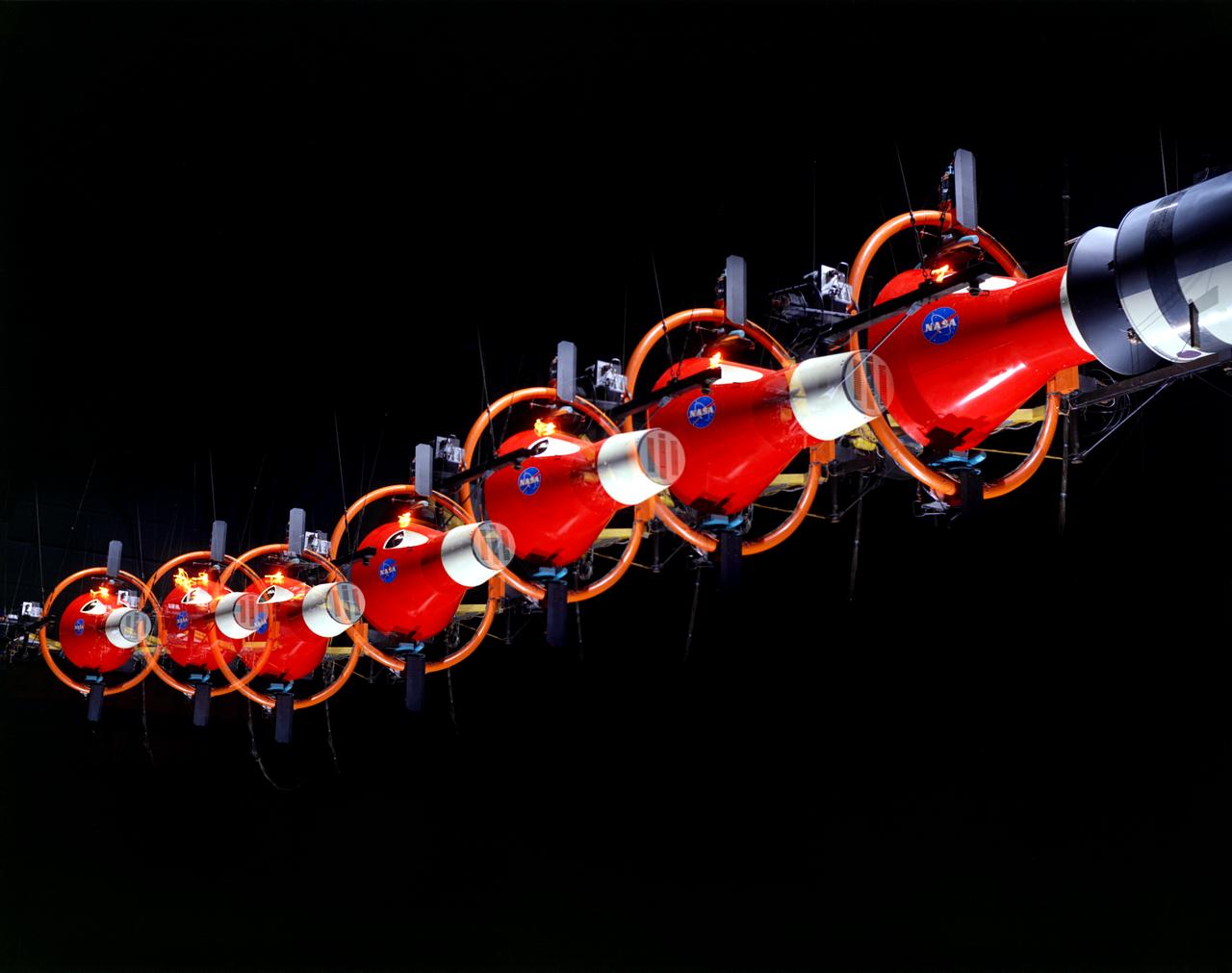

Multiple exposure of Rendezvous Docking Simulator. Francis B. Smith, described the simulator as follows: The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. This figure illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft. -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203 Francis B. Smith, Simulators for Manned Space Research, Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966.
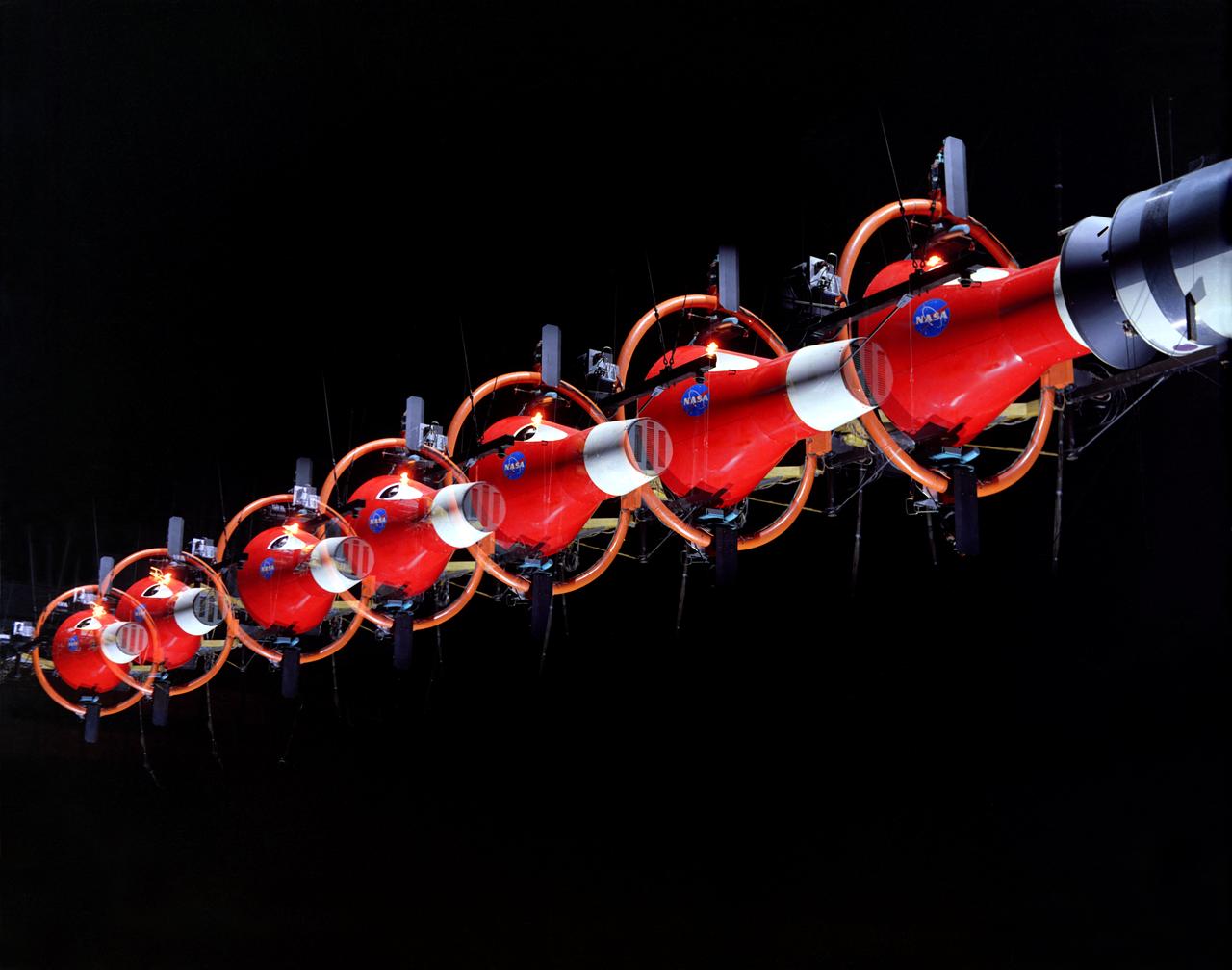

Multiple exposure of Rendezvous Docking Simulator. Francis B. Smith, described the simulator as follows: The rendezvous and docking operation of the Gemini spacecraft with the Agena and of the Apollo Command Module with the Lunar Excursion Module have been the subject of simulator studies for several years. This figure illustrates the Gemini-Agena rendezvous docking simulator at Langley. The Gemini spacecraft was supported in a gimbal system by an overhead crane and gantry arrangement which provided 6 degrees of freedom - roll, pitch, yaw, and translation in any direction - all controllable by the astronaut in the spacecraft. Here again the controls fed into a computer which in turn provided an input to the servos driving the spacecraft so that it responded to control motions in a manner which accurately simulated the Gemini spacecraft. -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203 Francis B. Smith, Simulators for Manned Space Research, Paper presented at the 1966 IEEE International convention, March 21-25, 1966.
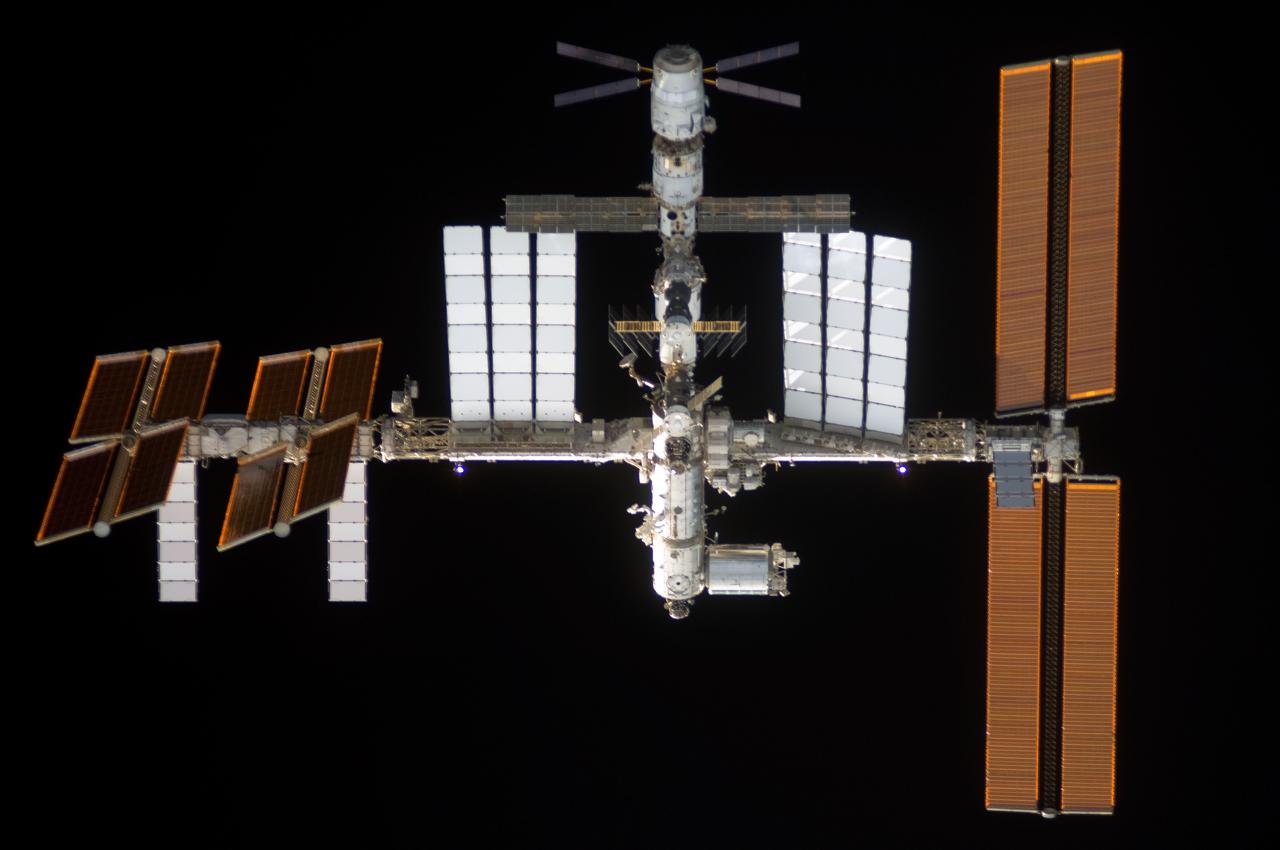

S124-E-005522 (2 June 2008) --- The International Space Station is featured in this image photographed by an STS-124 crewmember as Space Shuttle Discovery approaches the station during rendezvous and docking activities on flight day three. Docking occurred at 2:03 p.m. (EDT) on June 2, 2008.
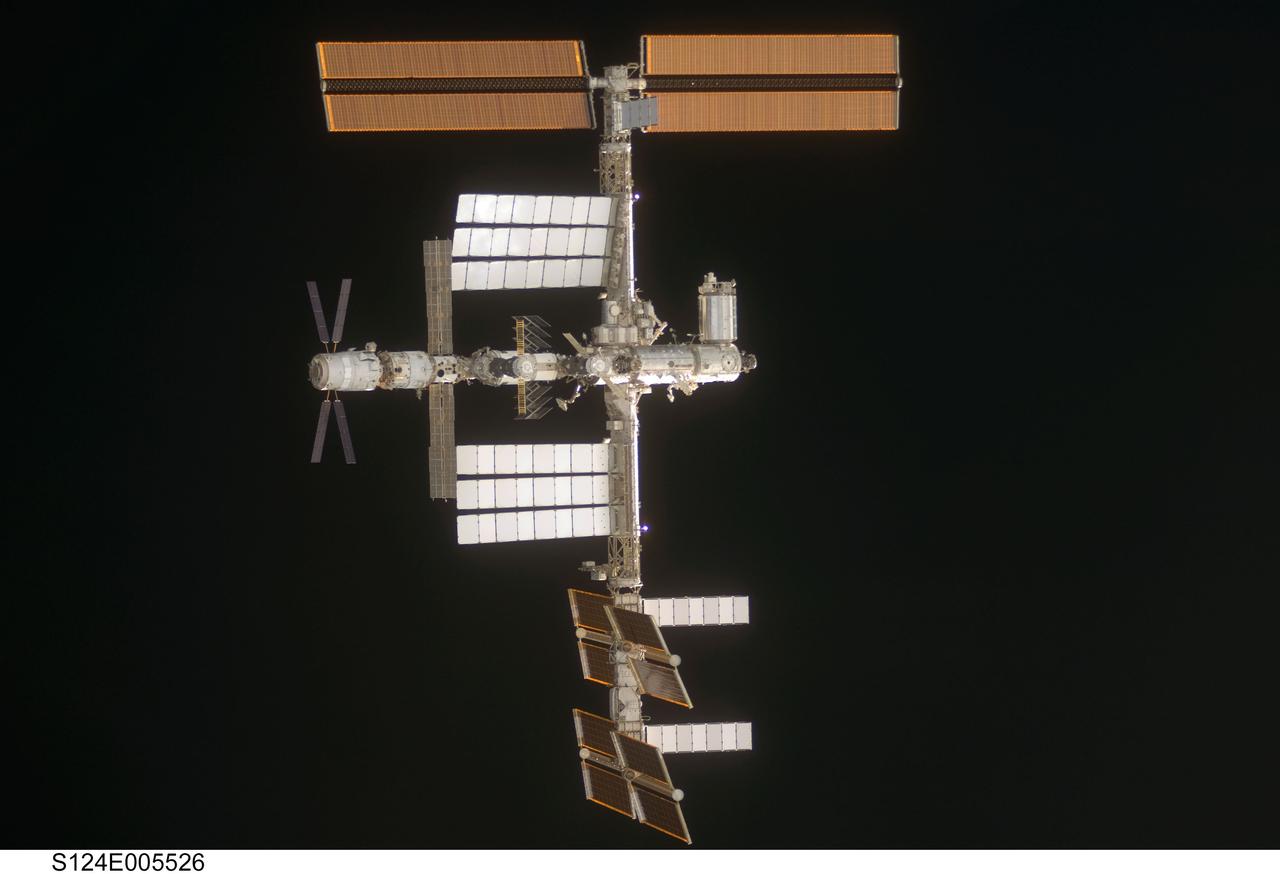

S124-E-005526 (2 June 2008) --- The International Space Station is centered in this image photographed by an STS-124 crewmember as Space Shuttle Discovery approaches the station during rendezvous and docking activities on flight day three. Docking occurred at 2:03 p.m. (EDT) on June 2, 2008.
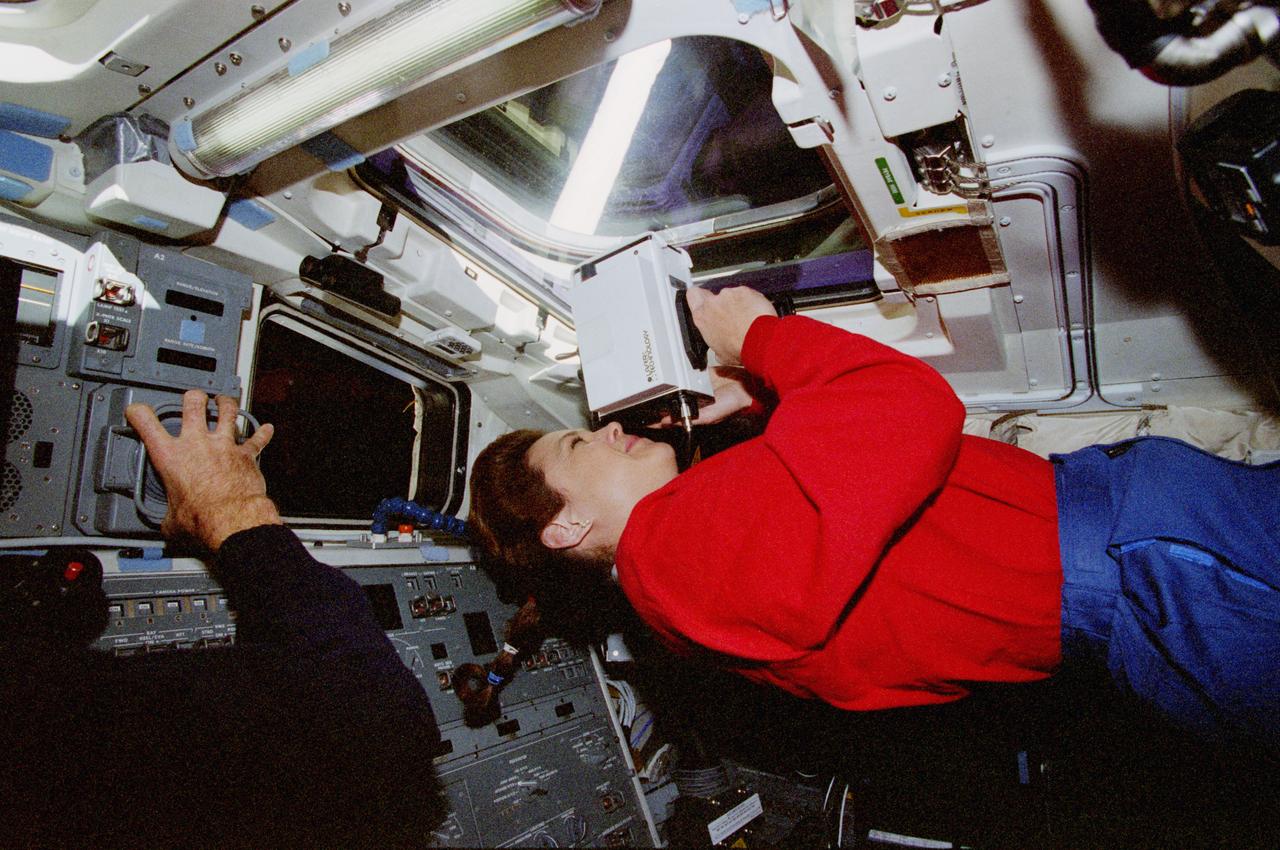

STS080-370-022 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Astronaut Tamara E. Jernigan, STS-80 mission specialist, uses a laser ranging device during the space shuttle Columbia's rendezvous operations with the Orbiting Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer - Shuttle Pallet Satellite (ORFEUS-SPAS).
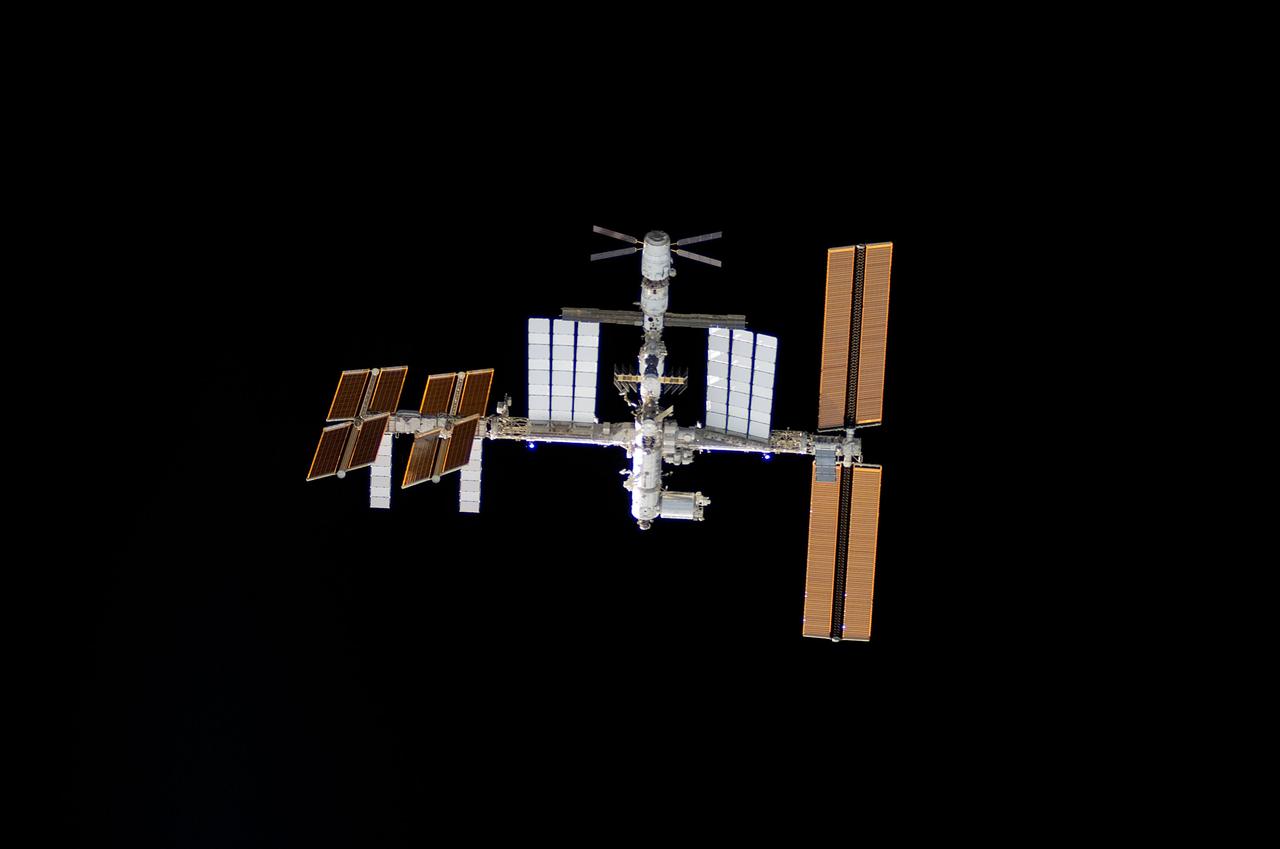

S124-E-005521 (2 June 2008) --- The International Space Station is centered in this image photographed by an STS-124 crewmember as Space Shuttle Discovery approaches the station during rendezvous and docking activities on flight day three. Docking occurred at 2:03 p.m. (EDT) on June 2, 2008.
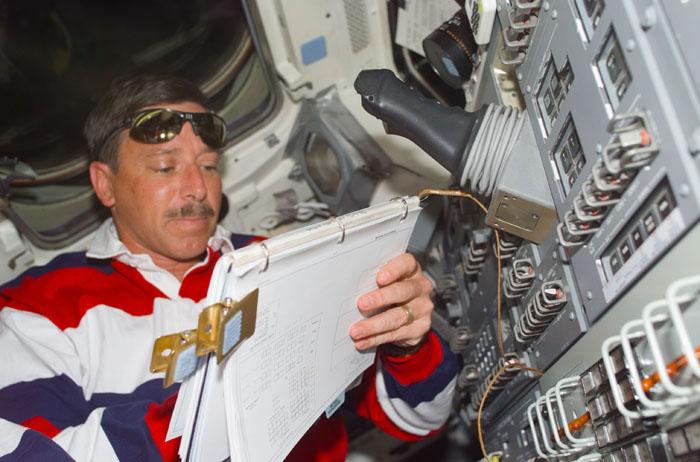

STS105-E-5061 (12 August 2001) --- Astronaut Scott J. Horowitz, STS-105 mission commander, looks over a checklist on the aft flight deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery during rendezvous operations with the International Space Station (ISS). The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
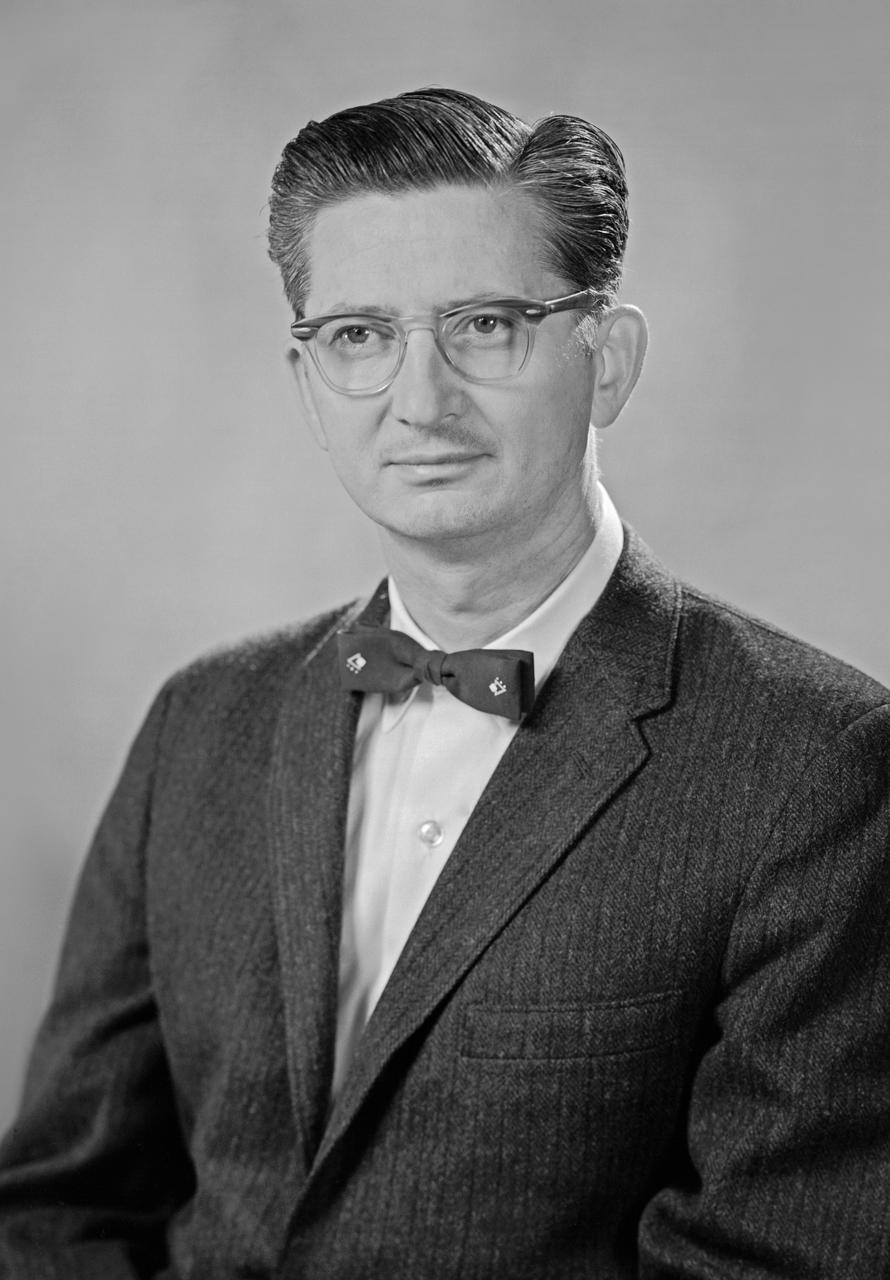

Portrait of John D. Bird "Jaybird" designed the LOR Lunar Orbit Rendezvous. Published in NASA SP-4308 Page 229.
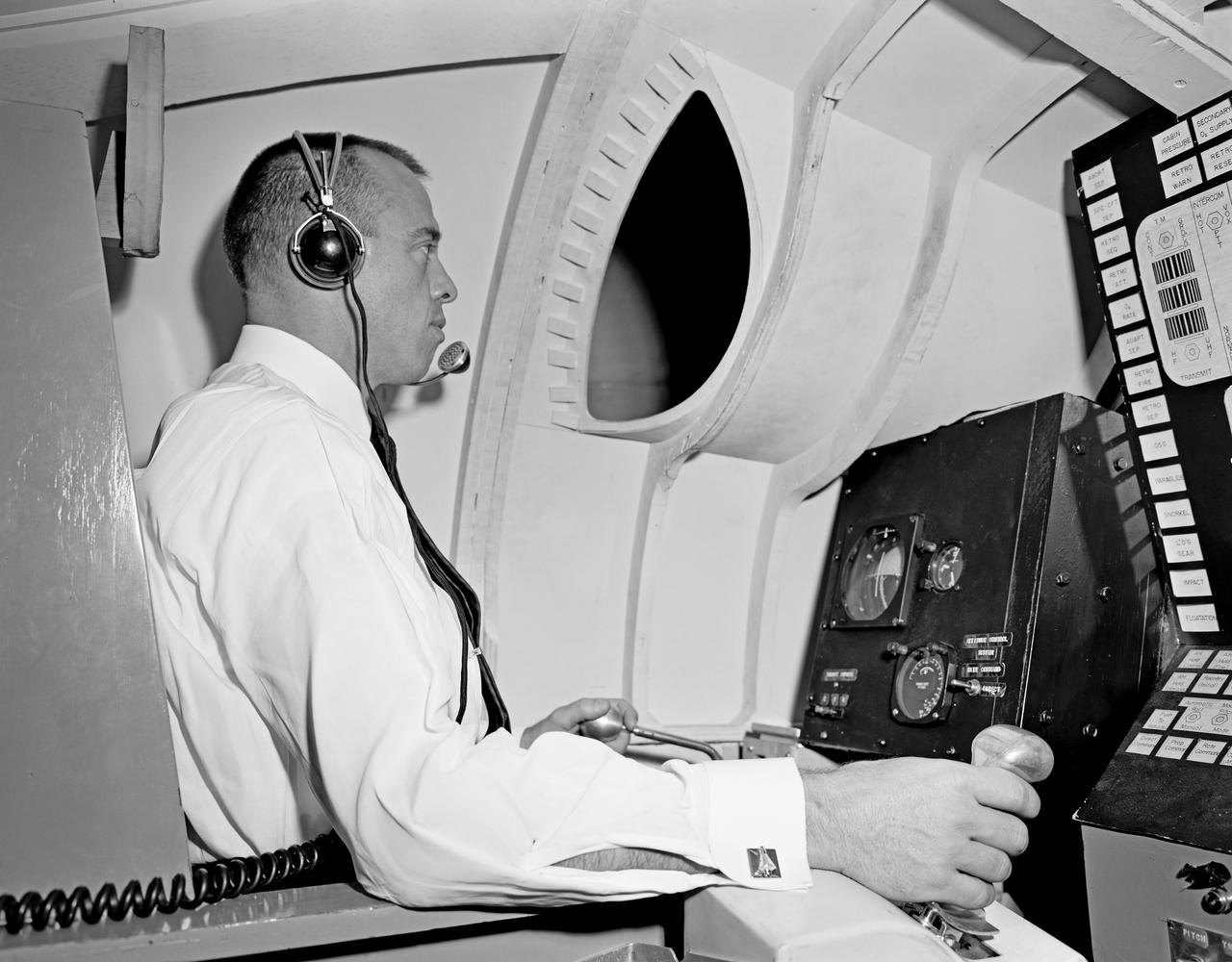

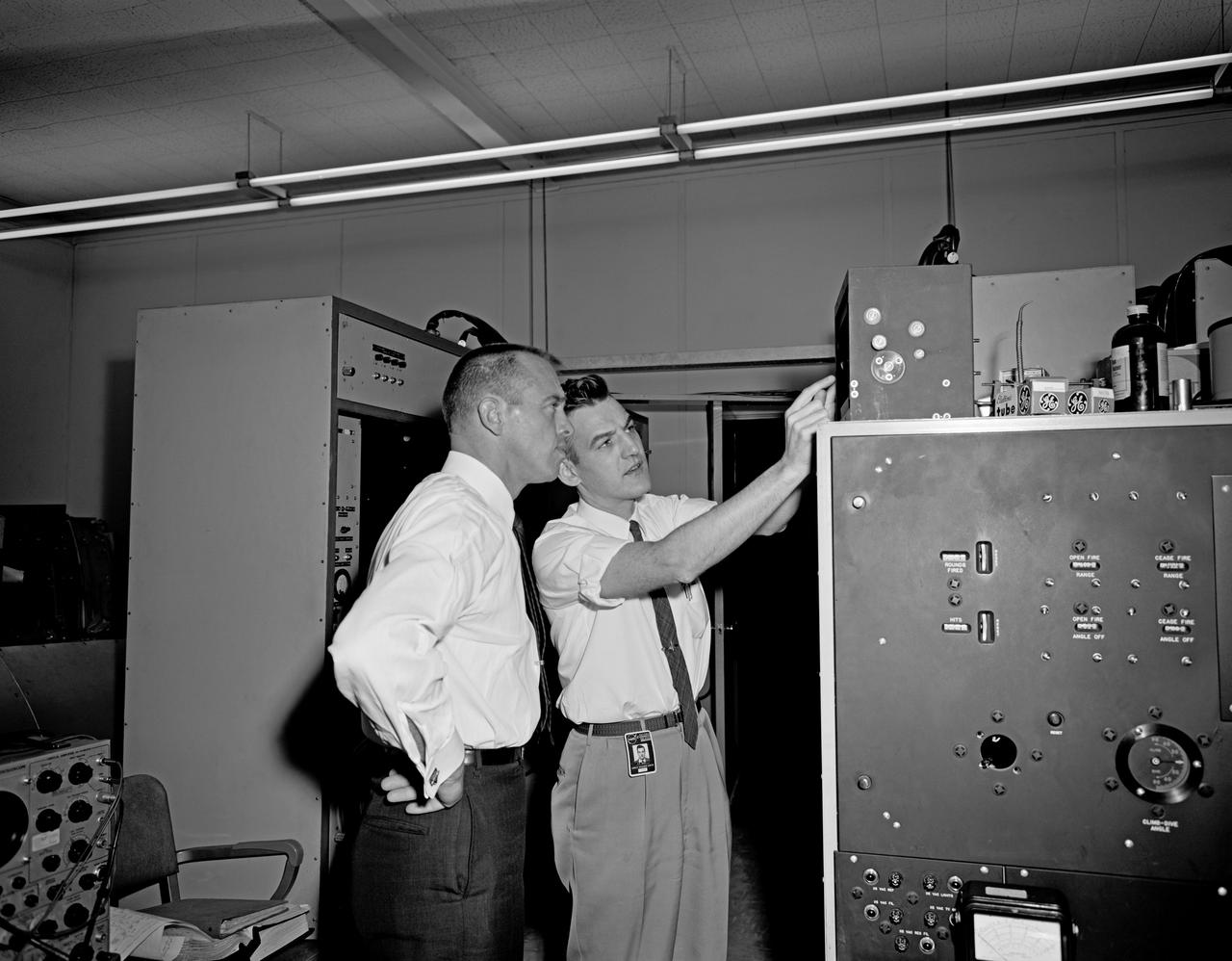
Alan Shepard and engineer looking at equipment, alone in Visual Docking Simulator, with engineers in Visual Docking Simulator.
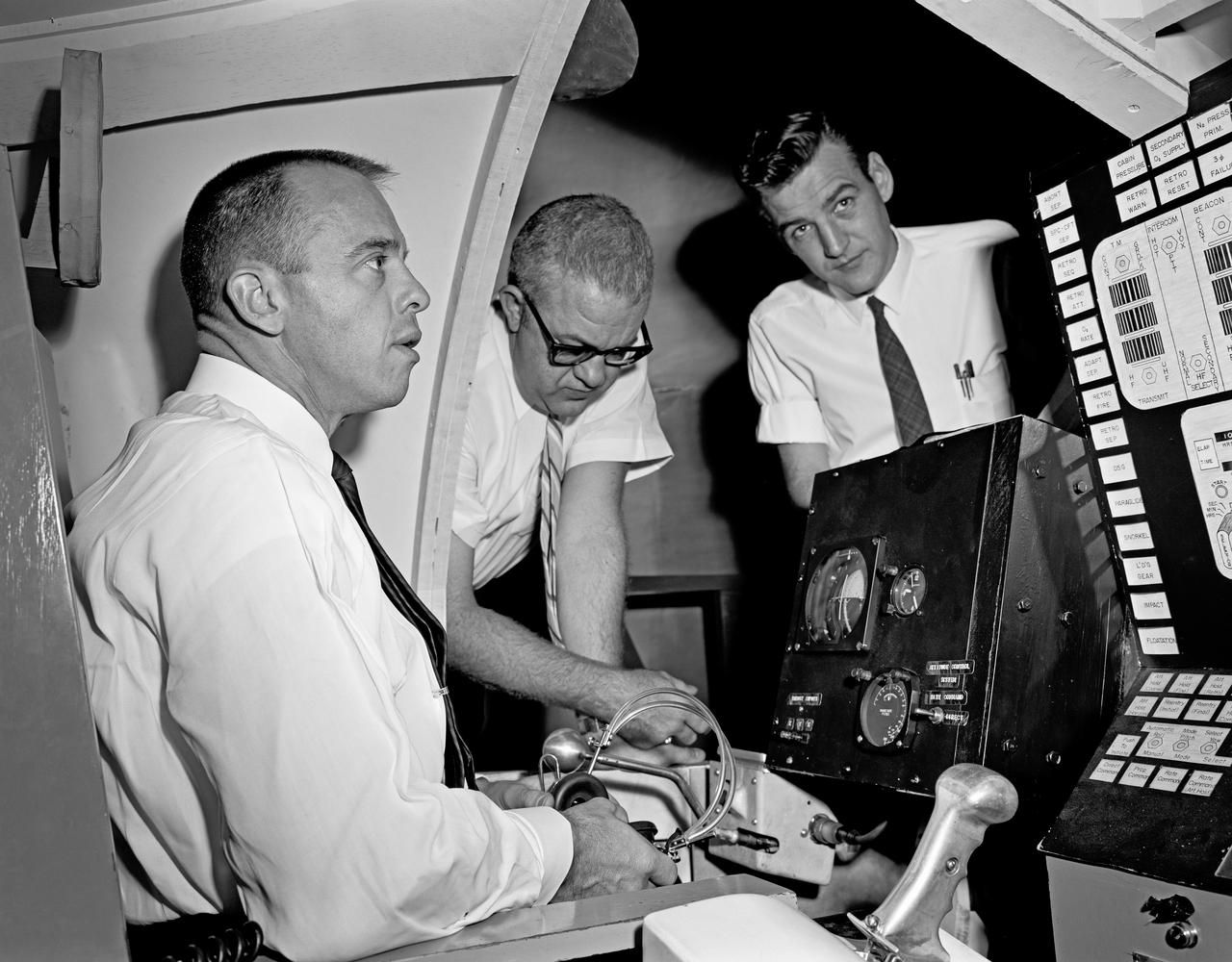

Alan Shepard and engineer looking at equipment, alone in Visual Docking Simulator, with engineers in Visual Docking Simulator.
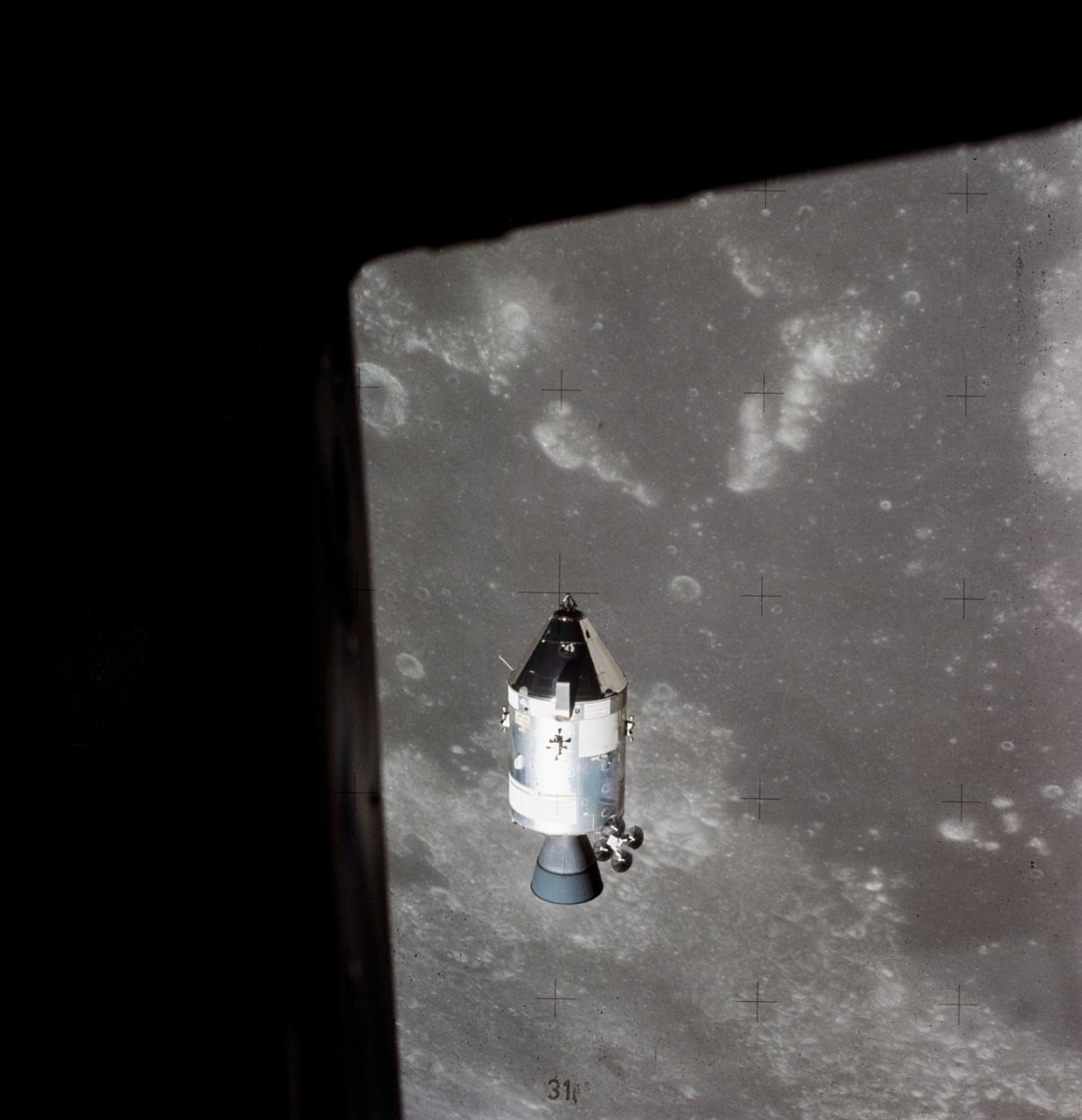
AS15-88-11974 (30 July 1971) --- A view of the Apollo 15 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit as photographed from the Lunar Module (LM) just after rendezvous. The lunar nearside is in the background. This view is looking southeast into the Sea of Fertility. The crater Taruntius is at the right center edge of the picture.

S65-59952 (1 Nov. 1965) --- Artist's concept depicting the approximate positions which the Gemini 6 and 7 spacecrafts will be oriented at the terminal phase of the proposed rendezvous mission. Photo credit: NASA

STS113-E-5037 (25 November 2002) --- The International Space Station (ISS) is backdropped against the blackness of space as the Space Shuttle Endeavour quickly closes the distance to the orbital outpost for a Nov. 25 rendezvous. Endeavour went on to dock with the International Space Station at 3:59 p.m. (CST), bringing a new crew and another segment of the station's backbone, the Port One (P1)segment of the Integrated Truss System. The rendezvous and docking of Endeavour with astronaut James D. Wetherbee, mission commander, at the controls, occurred about 248 statute miles above the South Pacific off the southeastern coast of Australia.
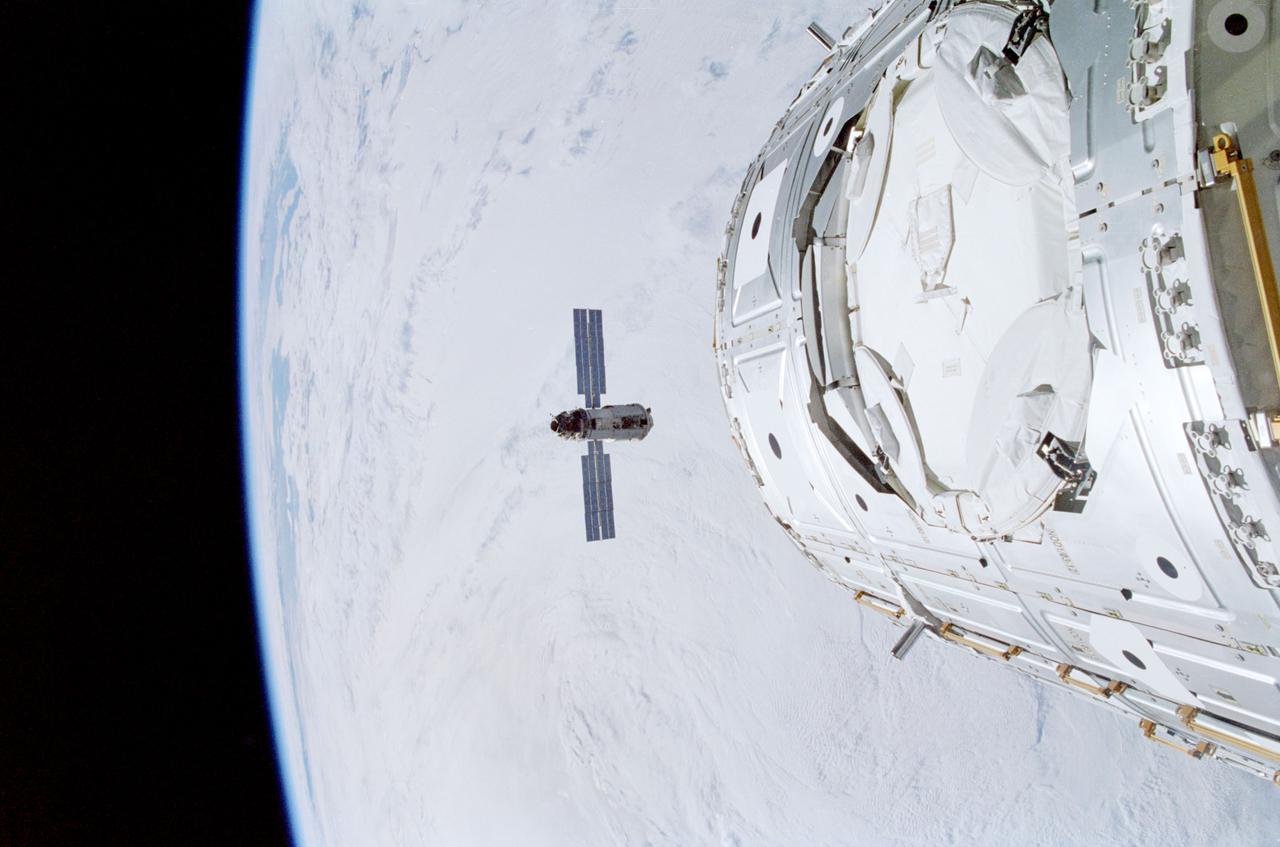

STS088-341-015 (6 Dec. 1998) --- Backdropped against a blanket of heavy cloud cover, the Russian-built FGB, also called Zarya, approaches the Space Shuttle Endeavour and the U.S.-built Node 1, also called Unity (foreground). Inside Endeavour's cabin, the STS-88 crew readied the remote manipulator system (RMS) for Zarya capture as they awaited the rendezvous.
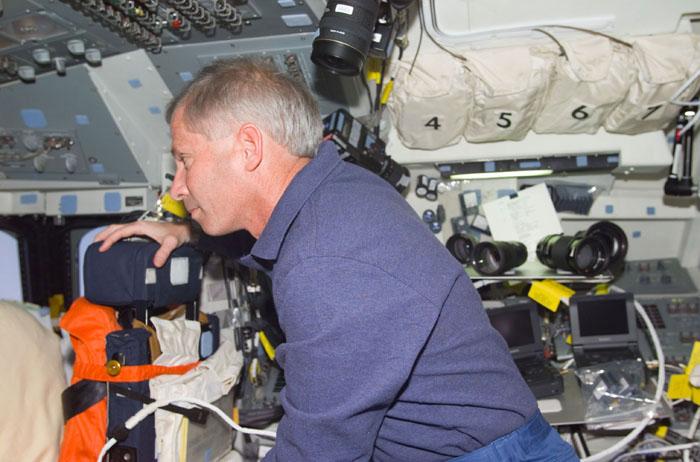

STS98-E-5028 (9 February 2001) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Cockrell, STS-98 mission commander, looks at displays (out of frame) on the forward flight deck as he stands behind the pilot's station on the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The crew was preparing for its rendezvous and docking with the International Space Station (ISS). The scene was recorded with a digital still camera.
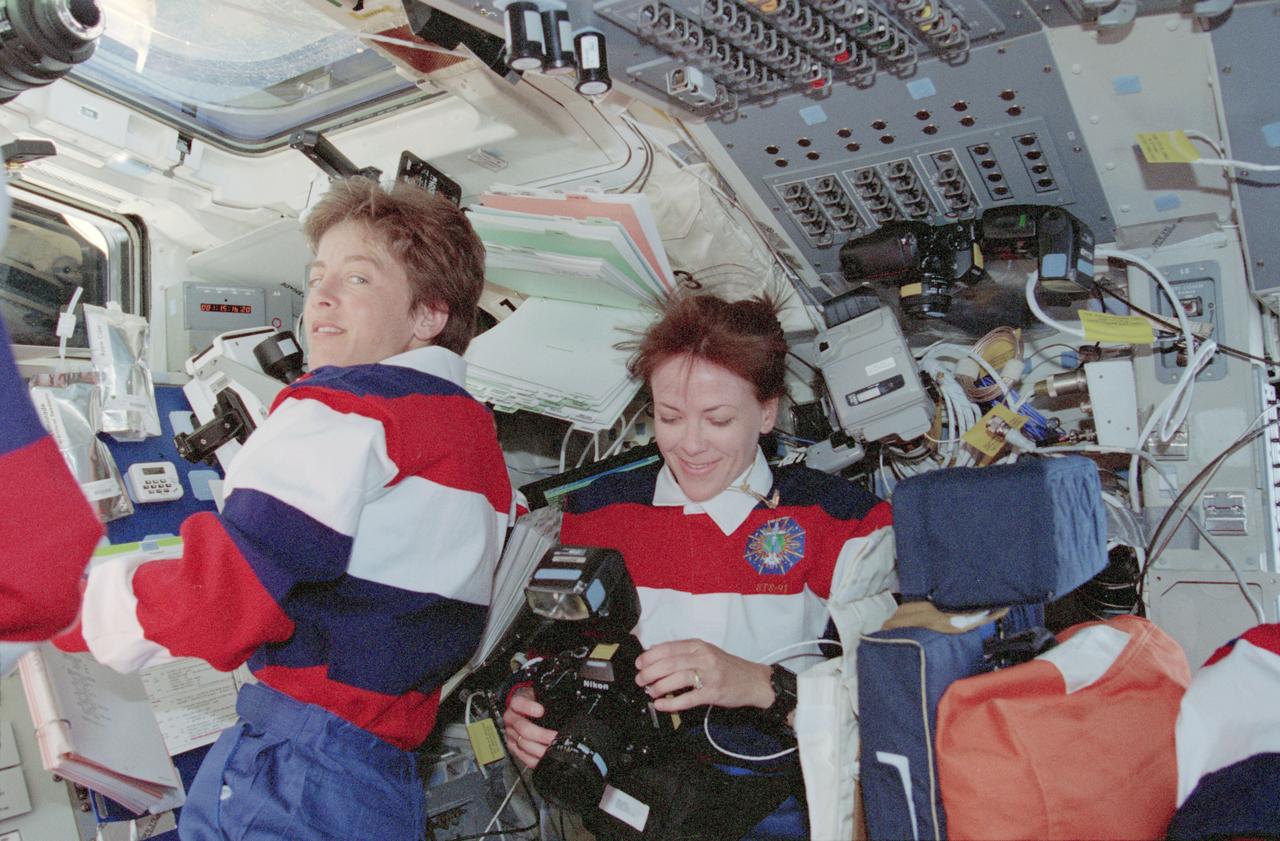

STS091-360-010 (2-12 June 1998) --- Astronauts Wendy B. Lawrence (left) and Janet L. Kavandi are pictured on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery during rendezvous operations with Russia's Mir space station. Kavandi prepares to use a 35mm still camera. The two mission specialists joined four other Discovery crew members for the flight to Mir, from which they later retrieved astronaut Andrew S.W. Thomas.