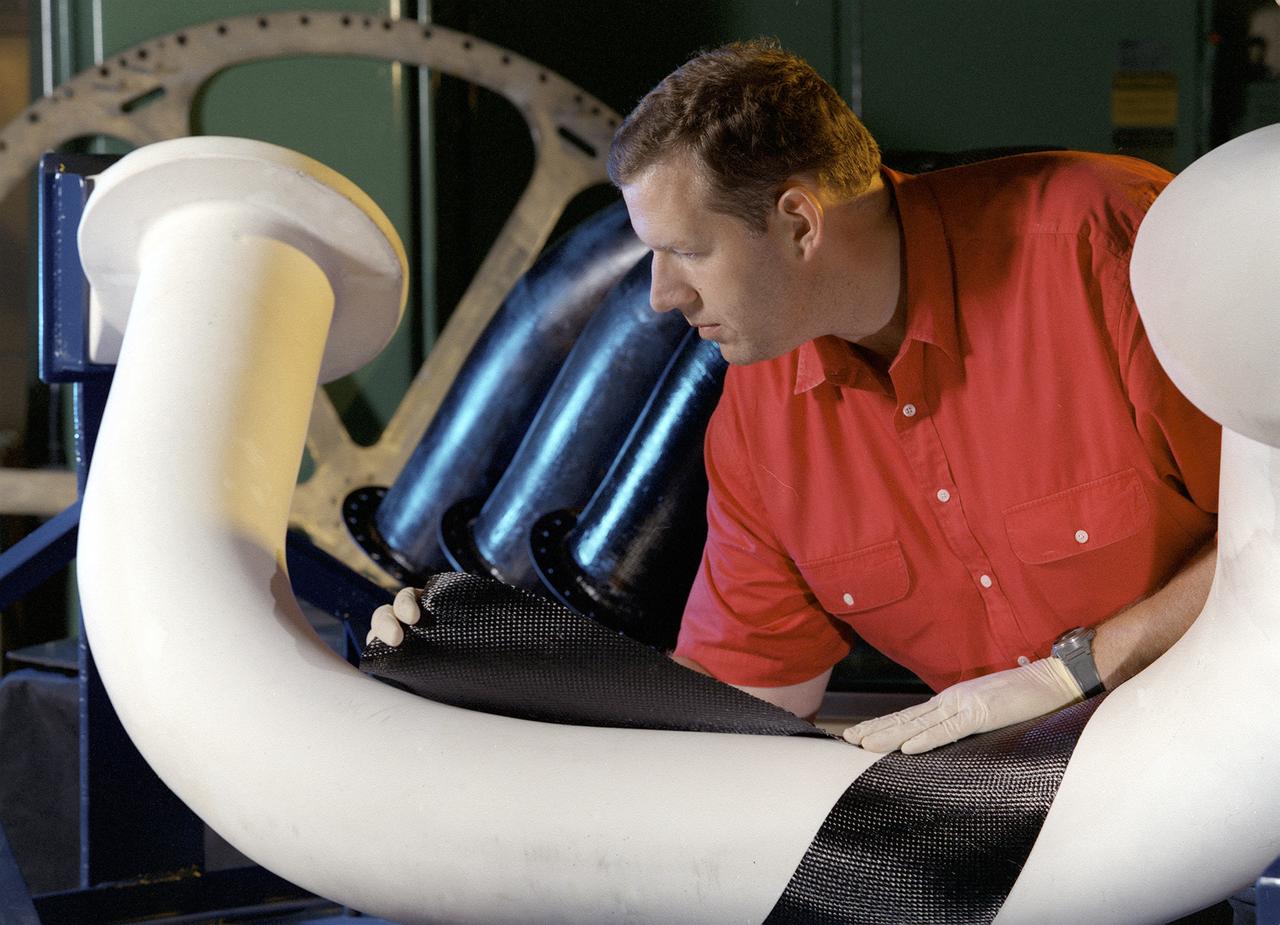

Engineers at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are working with industry partners to develop a new generation of more cost-efficient space vehicles. Lightweight fuel tanks and components under development will be the critical elements in tomorrow's reusable launch vehicles and will tremendously curb the costs of getting to space. In this photo, Tom DeLay, a materials processes engineer for MSFC, uses a new graphite epoxy technology to create lightweight cryogenic fuel lines for futuristic reusable launch vehicles. He is wrapping a water-soluble mandrel, or mold, with a graphite fabric coated with an epoxy resin. Once wrapped, the pipe will be vacuum-bagged and autoclave-cured. The disposable mold will be removed to reveal a thin-walled fuel line. In addition to being much lighter and stronger than metal, this material won't expand or contract as much in the extreme temperatures encountered by launch vehicles.
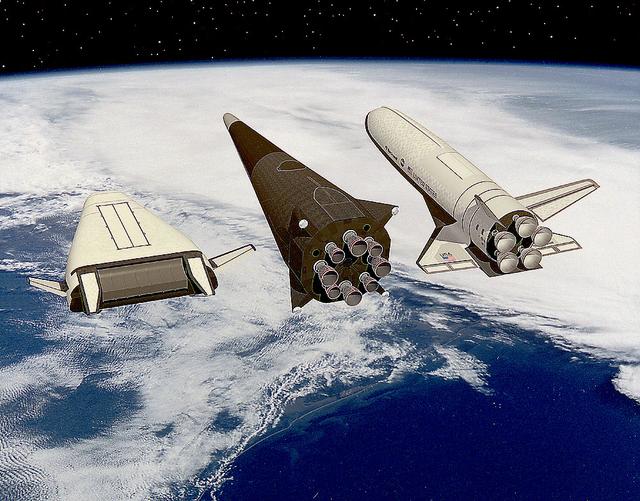

Artist John Frassanito's concept of three Single-Stage-to-Orbit (SSTO) Reusable Launch Vehicles (RLV's). Depicted from the left are: The Lockheed-Martin lifting body configuration that uses an integrated linear aerospike main engine; the McDornell Douglas vertical landing configuration; and the Rockwell wing body configuration that uses liquid oxygen and hydrogen bell engines.
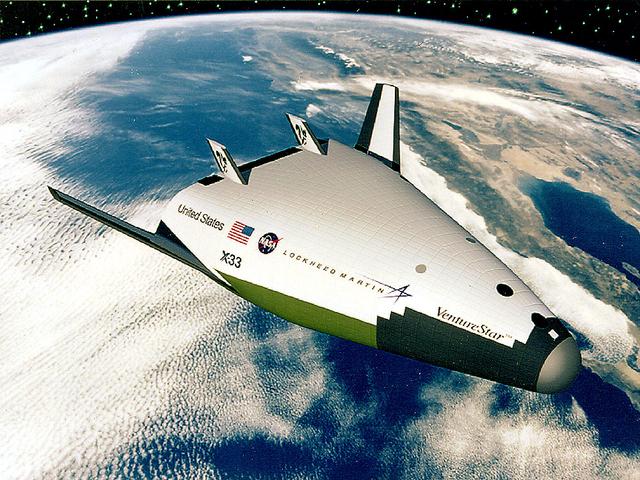

In this artist's concept, the X-33 Venture Star, a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), manufactured by Lockheed Martin Skunk Works, is shown in orbit with a deployed payload. The Venture Star was one of the earliest versions of the RLV's developed to replace the aging shuttle fleet. The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.
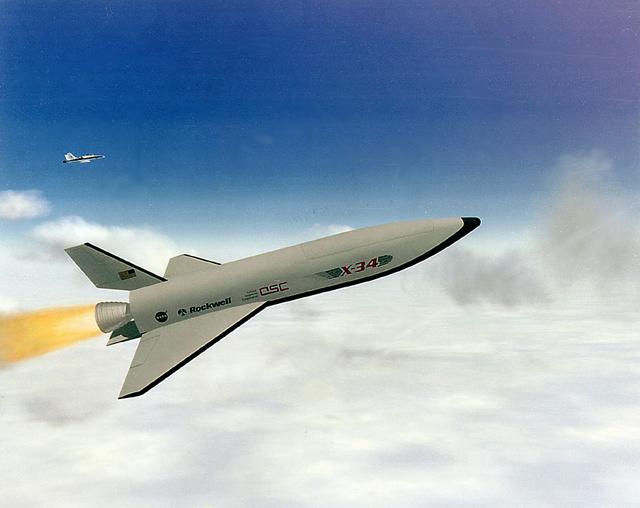

The X-34 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) concept is pictured here. NASA plarned to utilize the X-34 small reusable booster for research of Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) technologies that may be applicable to future larger RLV's. It was being developed cooperatively by Orbital Science Corporation, Rockwell International Corporation, and NASA. The objectives of the X-34 program were to significantly reduce launch costs for small payloads and to provide a test bed for NASA RLV technology. The X-34 would be launched from a 747 shuttle carrier aircraft. After delivering its payload (booster by an upper stage) to orbit, it would land autonomously on the same runway from which the 747 departed. The X-34 vehicle was powered by a liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and an RP-1 liquid Fastrac engine that was designed and built by Marshall Space Flight Center. The X-34 would be capable of speeds up to Mach 8 and altitudes of 250,000 feet. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
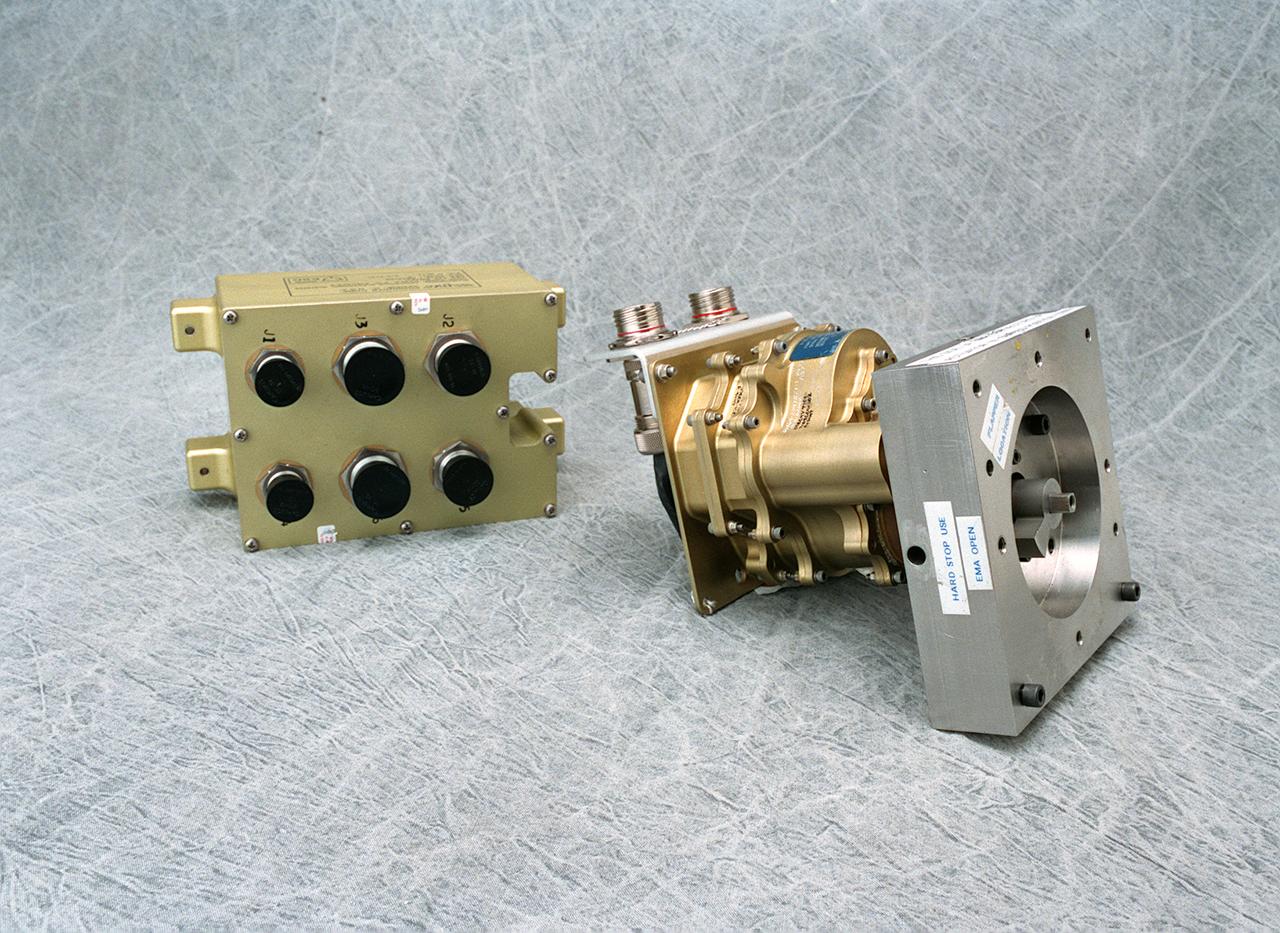
The electro-mechanical actuator, a new electronics technology, is an electronic system that provides the force needed to move valves that control the flow of propellant to the engine. It is proving to be advantageous for the main propulsion system plarned for a second generation reusable launch vehicle. Hydraulic actuators have been used successfully in rocket propulsion systems. However, they can leak when high pressure is exerted on such a fluid-filled hydraulic system. Also, hydraulic systems require significant maintenance and support equipment. The electro-mechanical actuator is proving to be low maintenance and the system weighs less than a hydraulic system. The electronic controller is a separate unit powering the actuator. Each actuator has its own control box. If a problem is detected, it can be replaced by simply removing one defective unit. The hydraulic systems must sustain significant hydraulic pressures in a rocket engine regardless of demand. The electro-mechanical actuator utilizes power only when needed. A goal of the Second Generation Reusable Launch Vehicle Program is to substantially improve safety and reliability while reducing the high cost of space travel. The electro-mechanical actuator was developed by the Propulsion Projects Office of the Second Generation Reusable Launch Vehicle Program at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
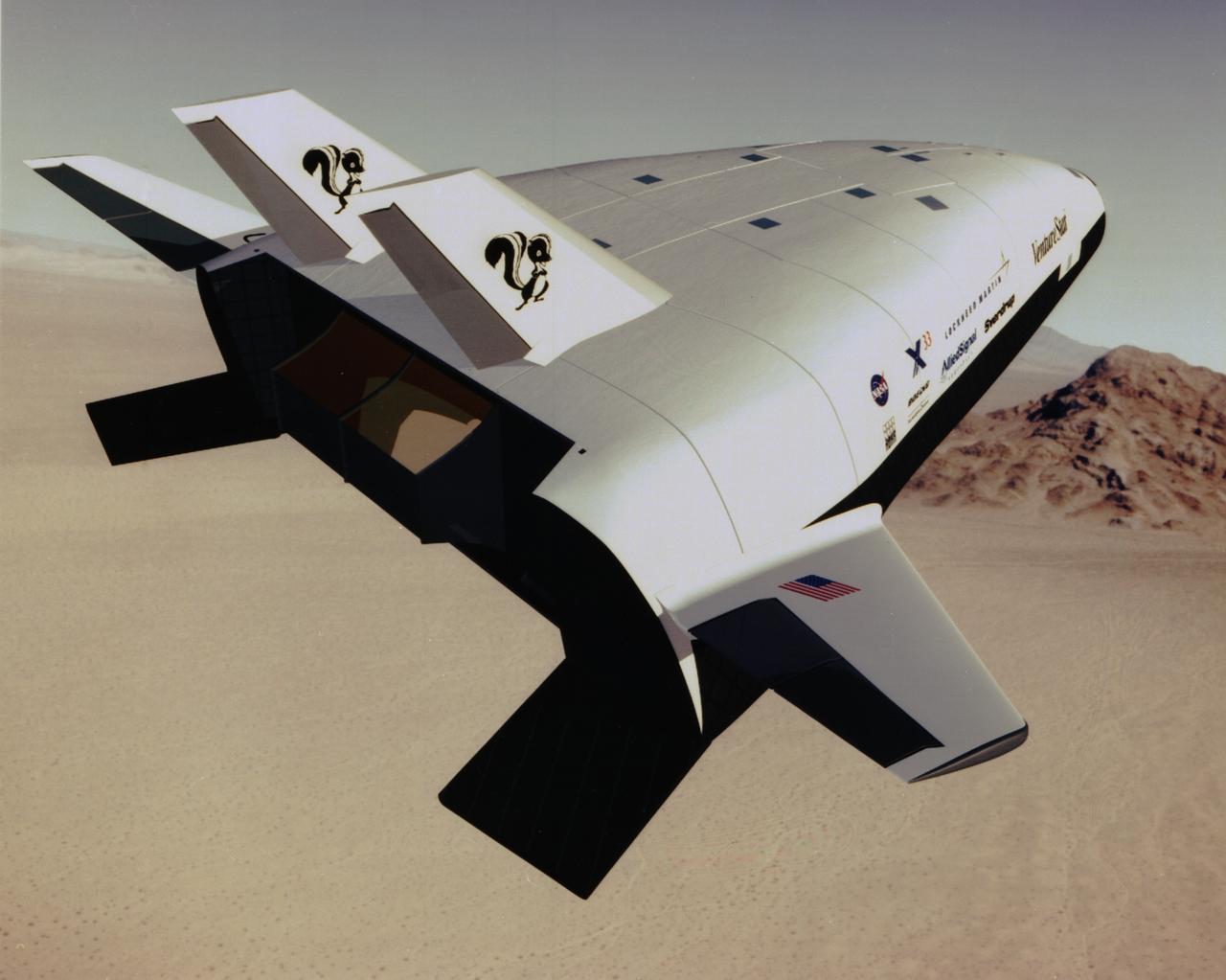

This artist’s concept is of the X-33 Advanced Technology Demonstrator, a subscale prototype Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), in its 1997 configuration. Named the Venture Star, this vehicle manufactured by Lockheed Martin Skunk Works, is shown in orbit with a deployed payload. The Venture Star was one of the earliest versions of the RLV’s developed in attempt to replace the aging shuttle fleet. The X-33 program has been discontinued.
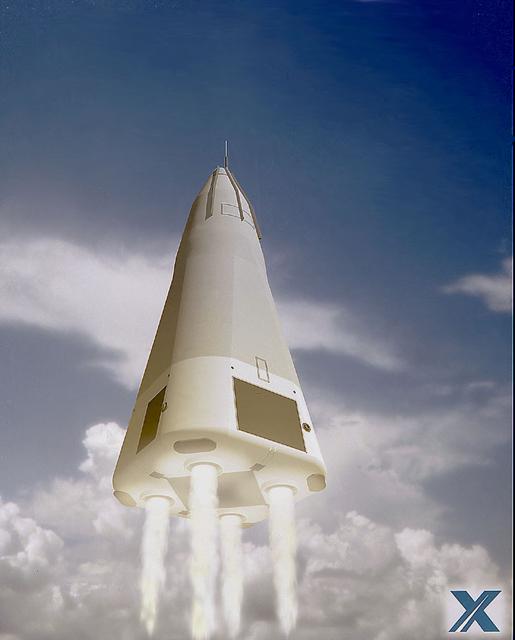

Pictured here is a DC-XA Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) prototype concept with an RLV logo. The Delta Clipper-Experimental (DC-X) was originally developed by McDornell Douglas for the Department of Defense (DOD). The DC-XA is a single-stage-to-orbit, vertical takeoff/vertical landing, launch vehicle concept, whose development is geared to significantly reduce launch costs and will provide a test bed for NASA Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) technology as the Delta Clipper-Experimental Advanced (DC-XA).
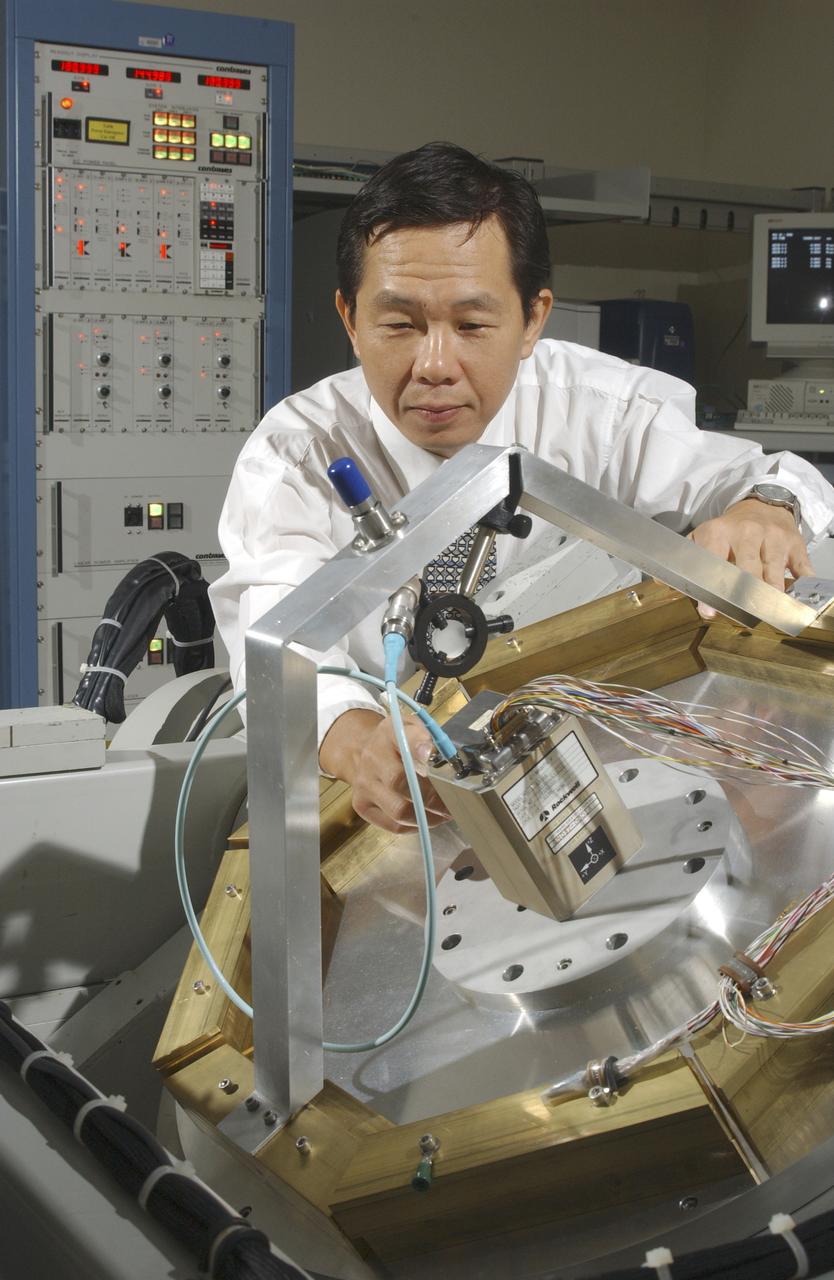
An array of components in a laboratory at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is being tested by the Flight Mechanics Office to develop an integrated navigation system for the second generation reusable launch vehicle. The laboratory is testing Global Positioning System (GPS) components, a satellite-based location and navigation system, and Inertial Navigation System (INS) components, sensors on a vehicle that determine angular velocity and linear acceleration at various points. The GPS and INS components work together to provide a space vehicle with guidance and navigation, like the push of the OnStar button in your car assists you with directions to a specific address. The integration will enable the vehicle operating system to track where the vehicle is in space and define its trajectory. The use of INS components for navigation is not new to space technology. The Space Shuttle currently uses them. However, the Space Launch Initiative is expanding the technology to integrate GPS and INS components to allow the vehicle to better define its position and more accurately determine vehicle acceleration and velocity. This advanced technology will lower operational costs and enhance the safety of reusable launch vehicles by providing a more comprehensive navigation system with greater capabilities. In this photograph, Dr. Jason Chuang of MSFC inspects an INS component in the laboratory.
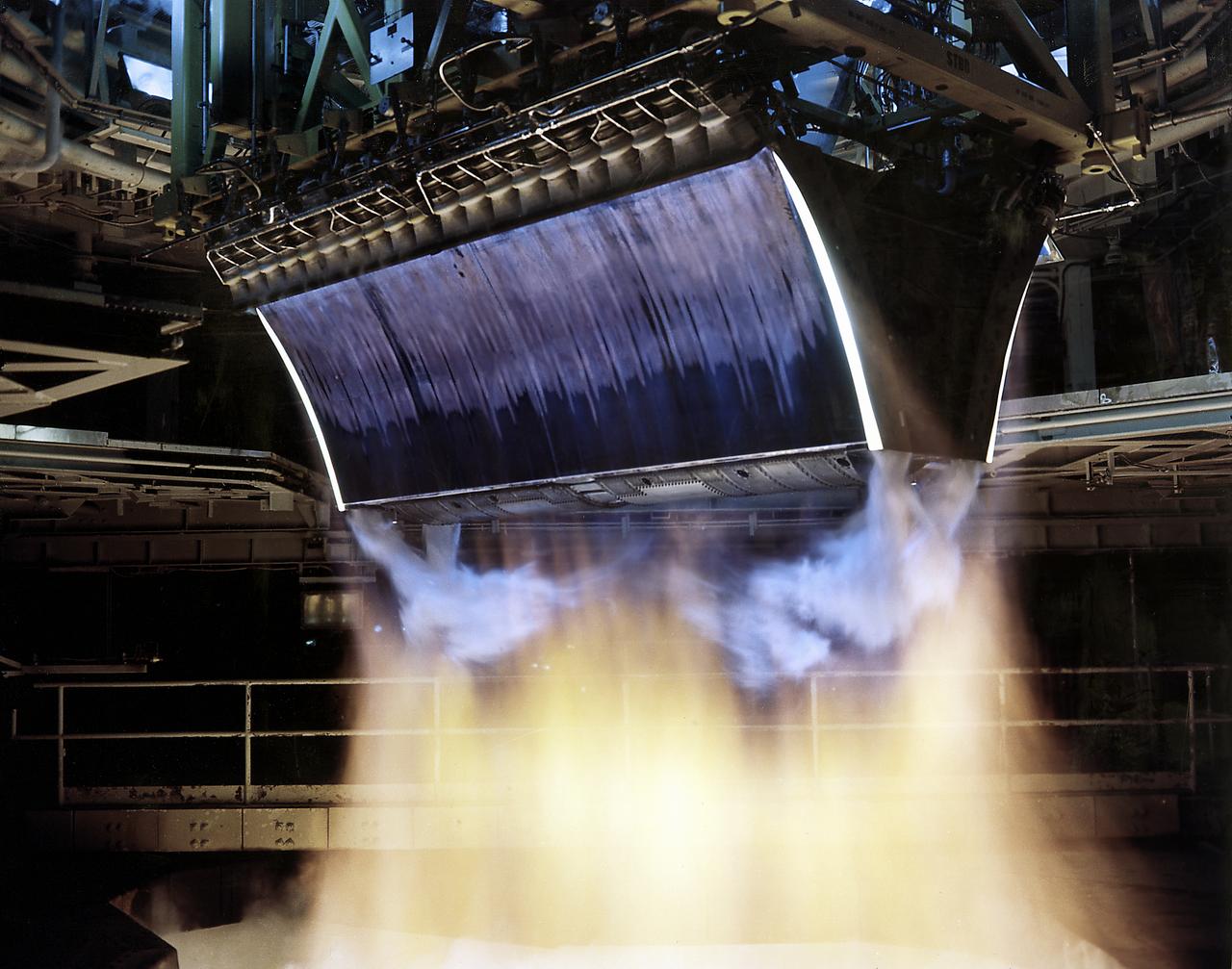

The test of twin Linear Aerospike XRS-2200 engines, originally built for the X-33 program, was performed on August 6, 2001 at NASA's Sternis Space Center, Mississippi. The engines were fired for the planned 90 seconds and reached a planned maximum power of 85 percent. NASA's Second Generation Reusable Launch Vehicle Program , also known as the Space Launch Initiative (SLI), is making advances in propulsion technology with this third and final successful engine hot fire, designed to test electro-mechanical actuators. Information learned from this hot fire test series about new electro-mechanical actuator technology, which controls the flow of propellants in rocket engines, could provide key advancements for the propulsion systems for future spacecraft. The Second Generation Reusable Launch Vehicle Program, led by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, is a technology development program designed to increase safety and reliability while reducing costs for space travel. The X-33 program was cancelled in March 2001.

This is a computer generated image of a Shuttle launch utilizing 2nd generation Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) flyback boosters, a futuristic concept that is currently undergoing study by NASA's Space Launch Initiative (SLI) Propulsion Office, managed by the Marshall Space Fight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, working in conjunction with the Agency's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. Currently, after providing thrust to the Space Shuttle, the solid rocket boosters are parachuted into the sea and are retrieved for reuse. The SLI is considering vehicle concepts that would fly first-stage boosters back to a designated landing site after separation from the orbital vehicle. These flyback boosters would be powered by several jet engines integrated into the booster capable of providing over 100,000 pounds of thrust. The study will determine the requirements for the engines, identify risk mitigation activities, and identify costs associated with risk mitigation and jet engine development and production, as well as determine candidate jet engine options to pursue for the flyback booster.
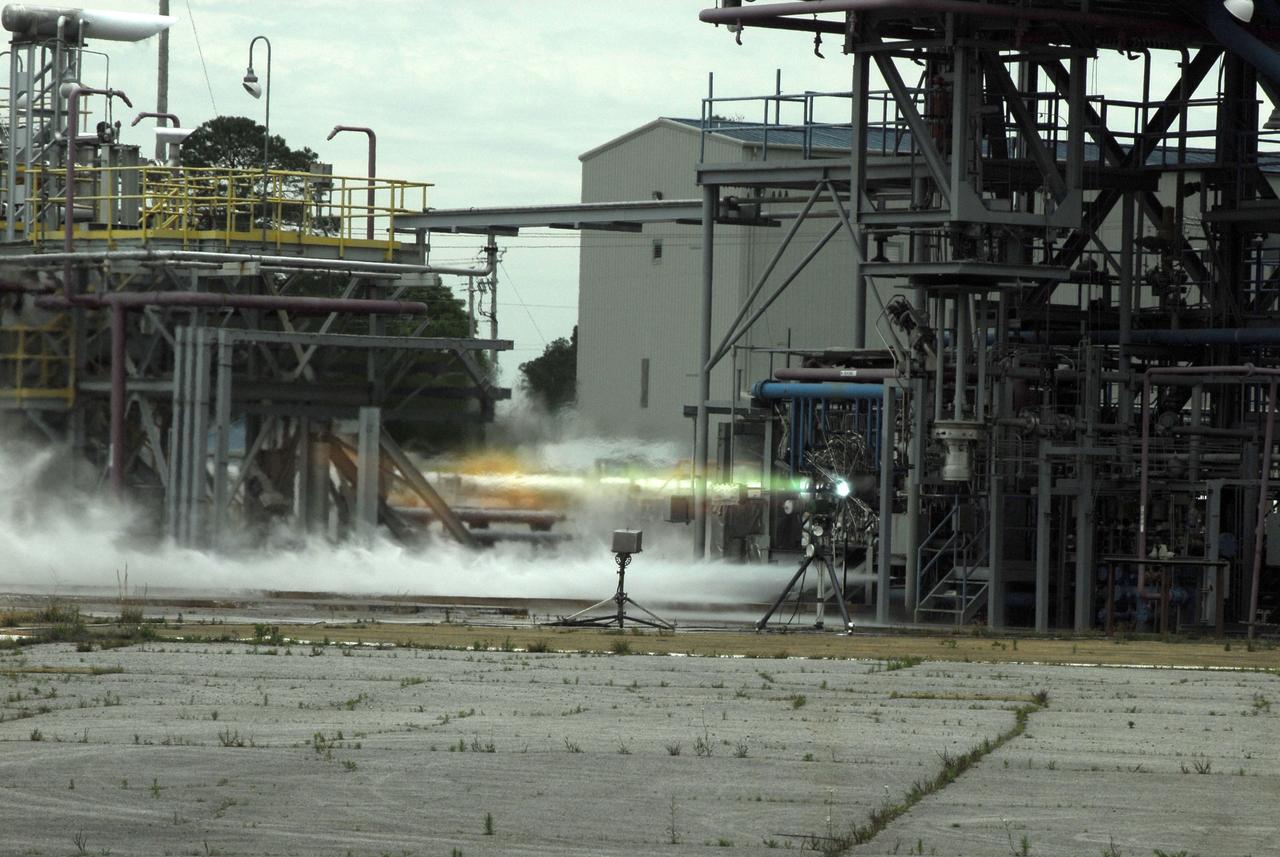

Chosen to power the upper stages of the new Ares I Crew Launch Vehicle (CLV) and the Ares V cargo segment, the J-2X engine is a stepped up version of the hydrogen/oxygen-fuelled Apollo-era J-2 engine. It was developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne (PWR), a business unit of United Technologies Corporation of Canoga Park, California. As seen in this photograph, the engine underwent a series of hot fire tests, performed on sub scale main injector hardware in the Test Stand 116 at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The injector is a major component of the engine that injects and mixes propellants in the combustion chamber, where they are ignited and burned to produce thrust.
This is the McDornell Douglas CD-XA Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) concept. The Delta Clipper-Experimental (DC-X) was originally developed by McDonnell Douglas for the DOD. The DC-XA is a single-stage-to-orbit, vertical takeoff/vertical landing, launch vehicle concept, whose development is geared to significantly reduce launch cost and provided a test bed for NASA Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) technology as the Delta Clipper-Experimental Advanced (DC-XA). The program was discontinued in 2003.
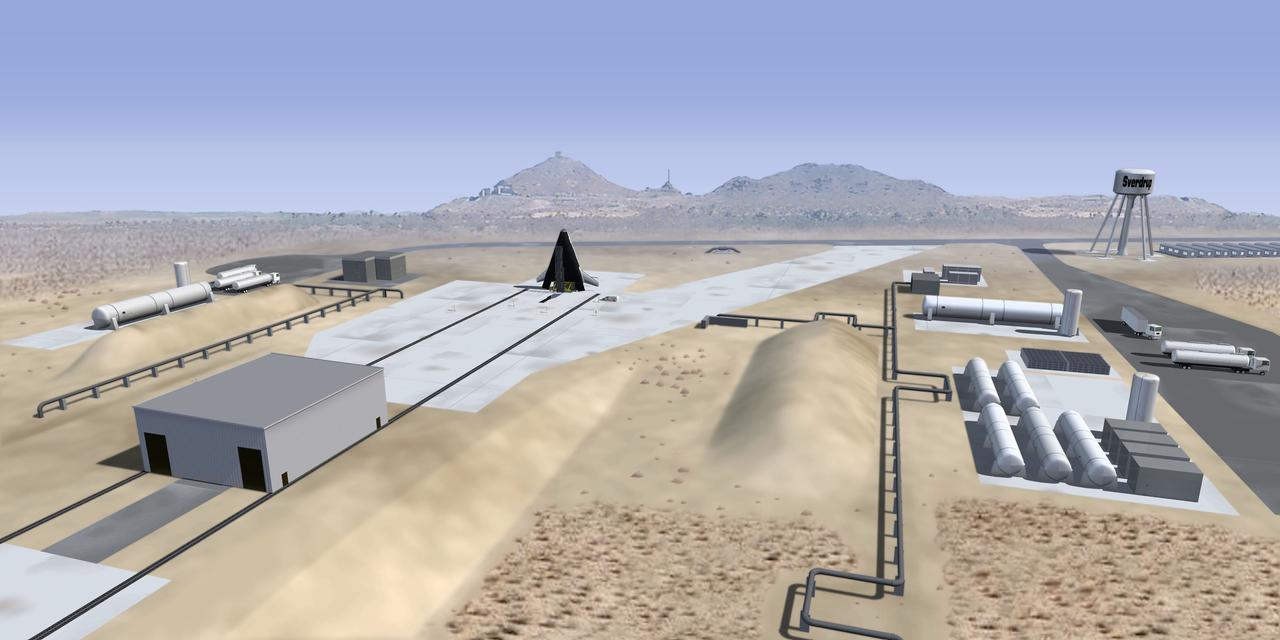

This is an artist's interpretation of a future launch complex for third generation propulsion reusable launch vehicles such as the X-33. The X-33 is a sub-scale technology demonstrator prototype of a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), with a vertical take off / horizontal landing (lifting body) concept, which was manufactured and named as the Venture Star by Lockheed Martin. The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.
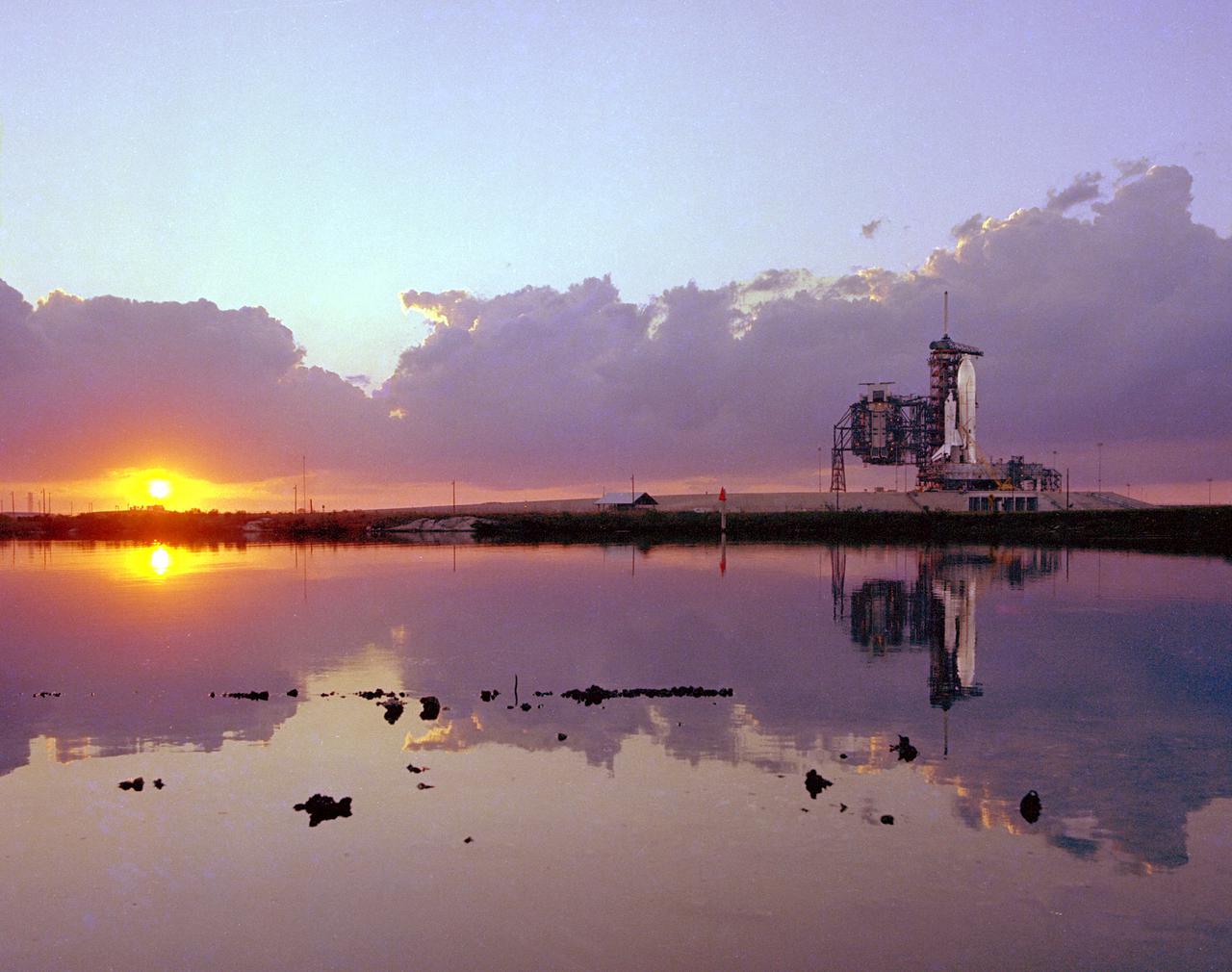

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Dramatically reflected by the waters of the extensive lagoonal sysem adjacent to Launch Pad A, the Space Shuttle, the world's first reusable space vehicle, is lighted by spotlights and the setting sun on the evening prior to Flight Readiness Firing of the orbiter Columbia's main engines. The 20-second firing was a milestone procedure in flight preparation of the world's first reusable space vehicle.
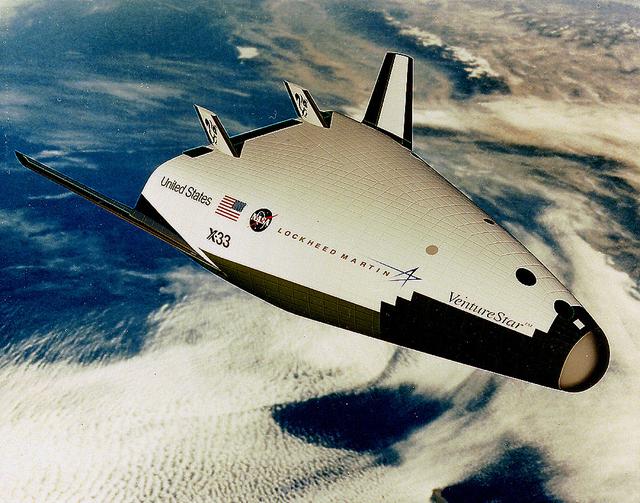

This picture is of a small scale flight demonstrator of the X-33 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), Venture Star, developed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin. The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.

Pictured here is an artist's depiction of Rockwell's Vertical Landing Single-Stage-to-Orbit (SSTO) Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) deploying a satellite concept. The development of the RLV is essential in the cost reduction of future space travel.
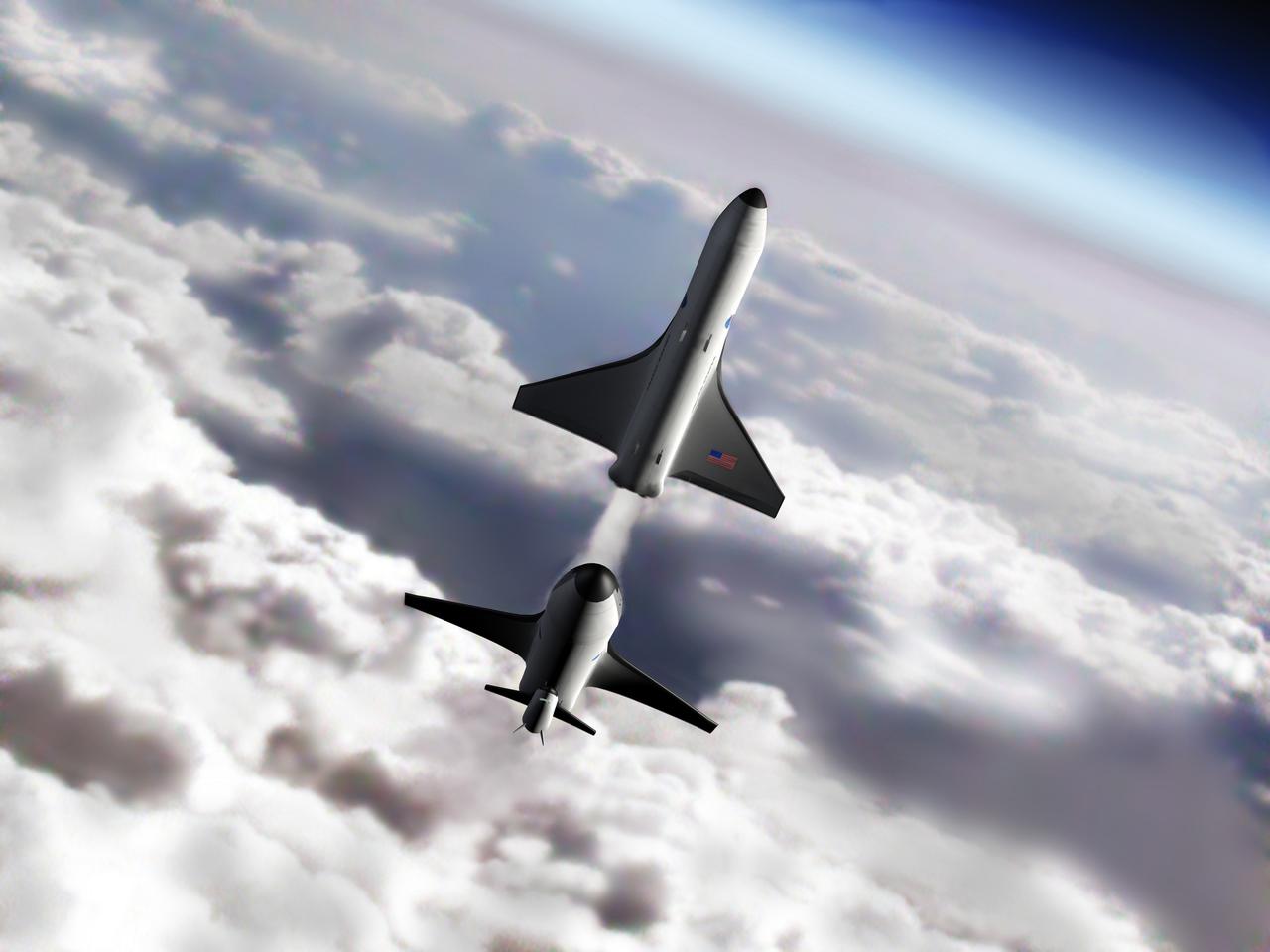

NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Space Launch Initiative (SLI), NASA's priority developmental program focused on empowering America's leadership in space. SLI includes commercial, higher education and defense partnerships and contracts to offer widespread participation in both the risk and success of developing our nation's next-generation reusable launch vehicle. This photo depicts an artist's concept of a future second-generation launch vehicle during separation of stages. For SLI, architecture definition includes all components of the next-generation reusable launch system: Earth-to-orbit vehicles (the Space Shuttle is the first-generation earth-to-orbit vehicle), crew transfer vehicles, transfer stages, ground processing systems, flight operations systems, and development of business case strategies. Three contractor teams have each been funded to develop potential second generation reusable launch system architectures: The Boeing Company of Seal Beach, California; Lockheed Martin Corporation of Denver, Colorado; a team including Northrop Grumman of El Segundo, California; and Orbital Sciences Corporation of Dulles, Virginia.
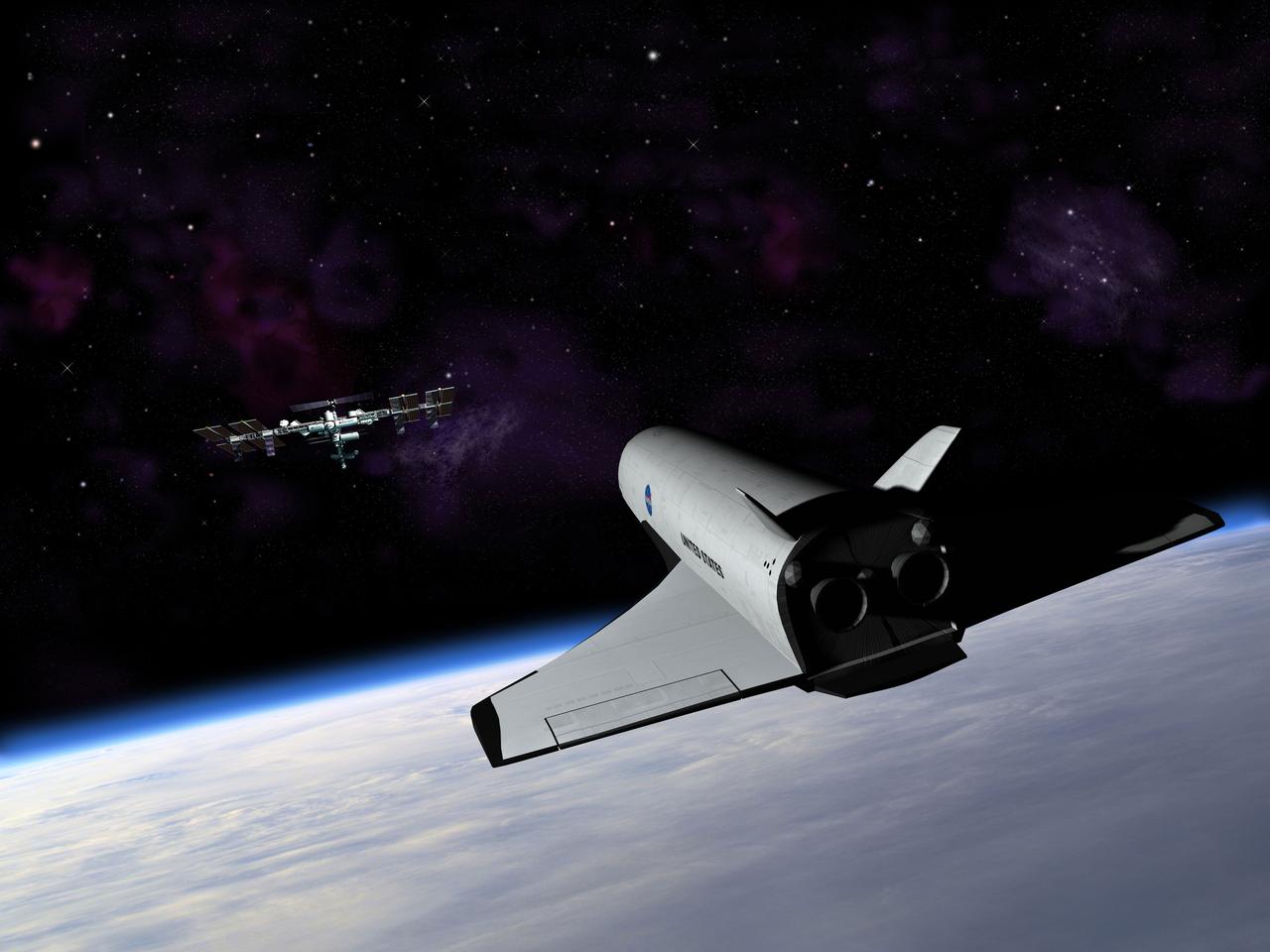

NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Space Launch Initiative (SLI), NASA's priority developmental program focused on empowering America's leadership in space. SLI includes commercial, higher education, and Defense partnerships and contracts to offer widespread participation in both the risk and success of developing our nation's next-generation reusable launch vehicle. This photo depicts an artist's concept of a future second-generation launch vehicle enroute to the International Space Station. For the SLI, architecture definition includes all components of the next-generation reusable launch system: Earth-to-orbit vehicles (the Space Shuttle is the first generation earth-to-orbit vehicle), crew transfer vehicles, transfer stages, ground processing systems, flight operations systems, and development of business case strategies. Three contractor teams have each been funded to develop potential second-generation reusable launch system architectures: The Boeing Company of Seal Beach, California; Lockheed Martin Corporation of Denver, Colorado along with a team including Northrop Grumman of El Segundo, California; and Orbital Sciences Corporation of Dulles, Virginia.
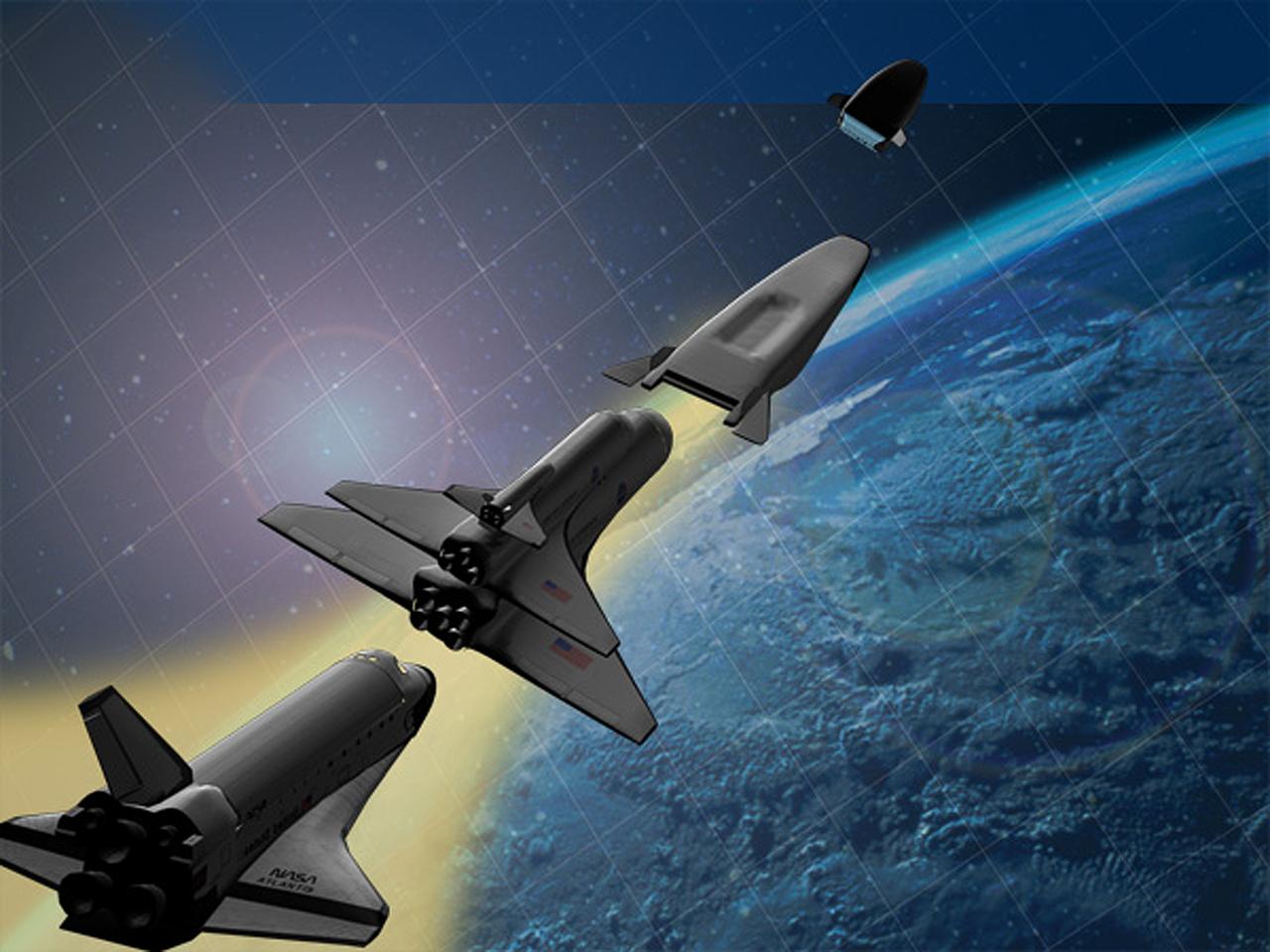

NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Space Launch Initiative (SLI), NASA's priority developmental program focused on empowering America's leadership in space. SLI includes commercial, higher education, and defense partnerships and contracts to offer widespread participation in both the risk and success of developing our nation's next-generation reusable launch vehicle. This photo depicts an artist's concept of a future second-generation launch vehicle. For the SLI, architecture definition includes all components of the next-generation reusable launch system: Earth-to-orbit vehicles (the Space Shuttle is the first generation earth-to-orbit vehicle), crew transfer vehicles, transfer stages, ground processing systems, flight operations systems, and development of business case strategies. Three contractor teams have each been funded to develop potential second- generation reusable launch system architectures: The Boeing Company of Seal Beach, California; Lockheed Martin Corporation of Denver, Colorado along with a team including Northrop Grumman of El Segundo, California; and Orbital Sciences Corporation of Dulles, Virginia.
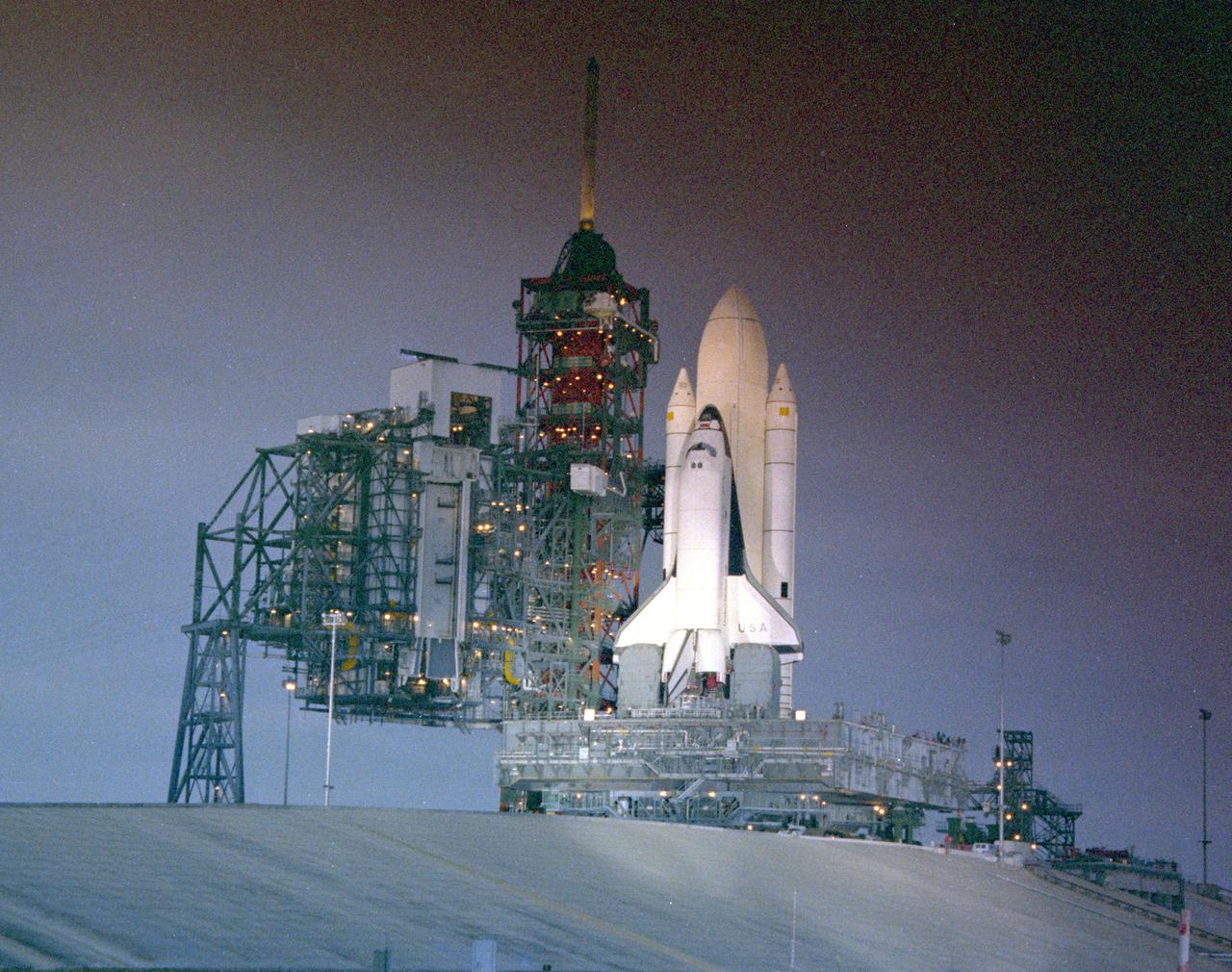
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first Space Shuttle vehicle destined to fly in space arrives at its launch site, Pad A at Complex 39, following a 3.5-mile move from the Vehicle Assembly Building where the vehicle was assembled. The rollout of the STS-1 vehicle - consisting of America's first reusable spaceship, Columbia, the external propellant tank and twin solid rocket boosters - from the VAB to the launch pad is a major milestone in the series of events that will lead to its scheduled liftoff in March 1981.
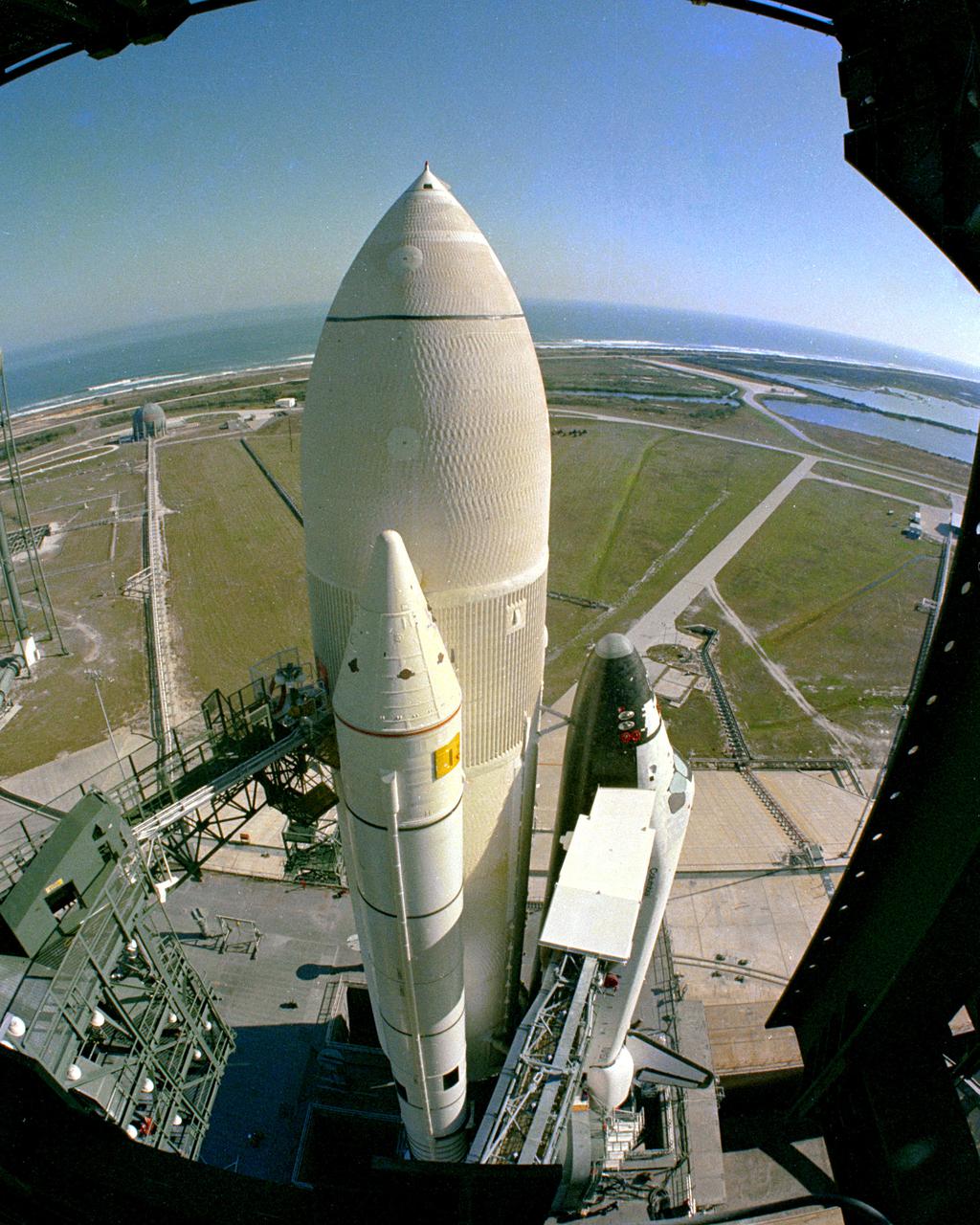

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first Space Shuttle vehicle destined to fly in space arrives at its launch site, Pad A at Complex 39, following a 3.5-mile move from the Vehicle Assembly Building where the vehicle was assembled. The rollout of the STS-1 vehicle - consisting of America's first reusable spaceship, Columbia, the external propellant tank and twin solid rocket boosters - from the VAB to the launch pad is a major milestone in the series of events that will lead to its scheduled liftoff in March 1981.
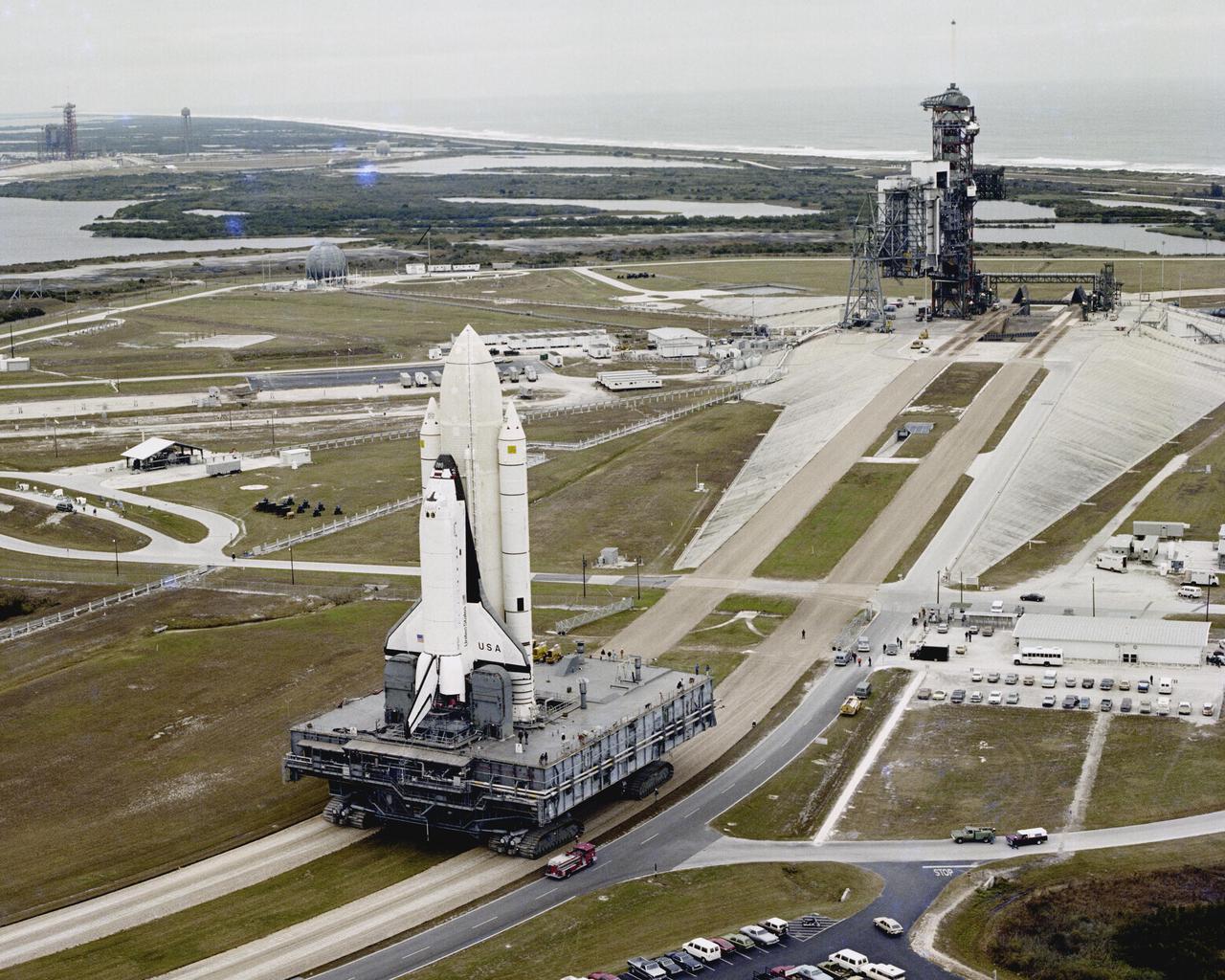

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first Space Shuttle vehicle destined to fly in space moves toward Launch Complex 39A where it will be launched. The STS-1 vehicle, consisting of America’s first reusable space ship - the orbiter Columbia, an external propellant tank and two solid rocket boosters, was assembled on a Mobile Launcher Platform in the Vehicle Assembly Building. A six-million pound tractor, called the Crawler-Transporter, is used to carry the Space Shuttle from the VAB to the launch pad, some 3.5 miles away.
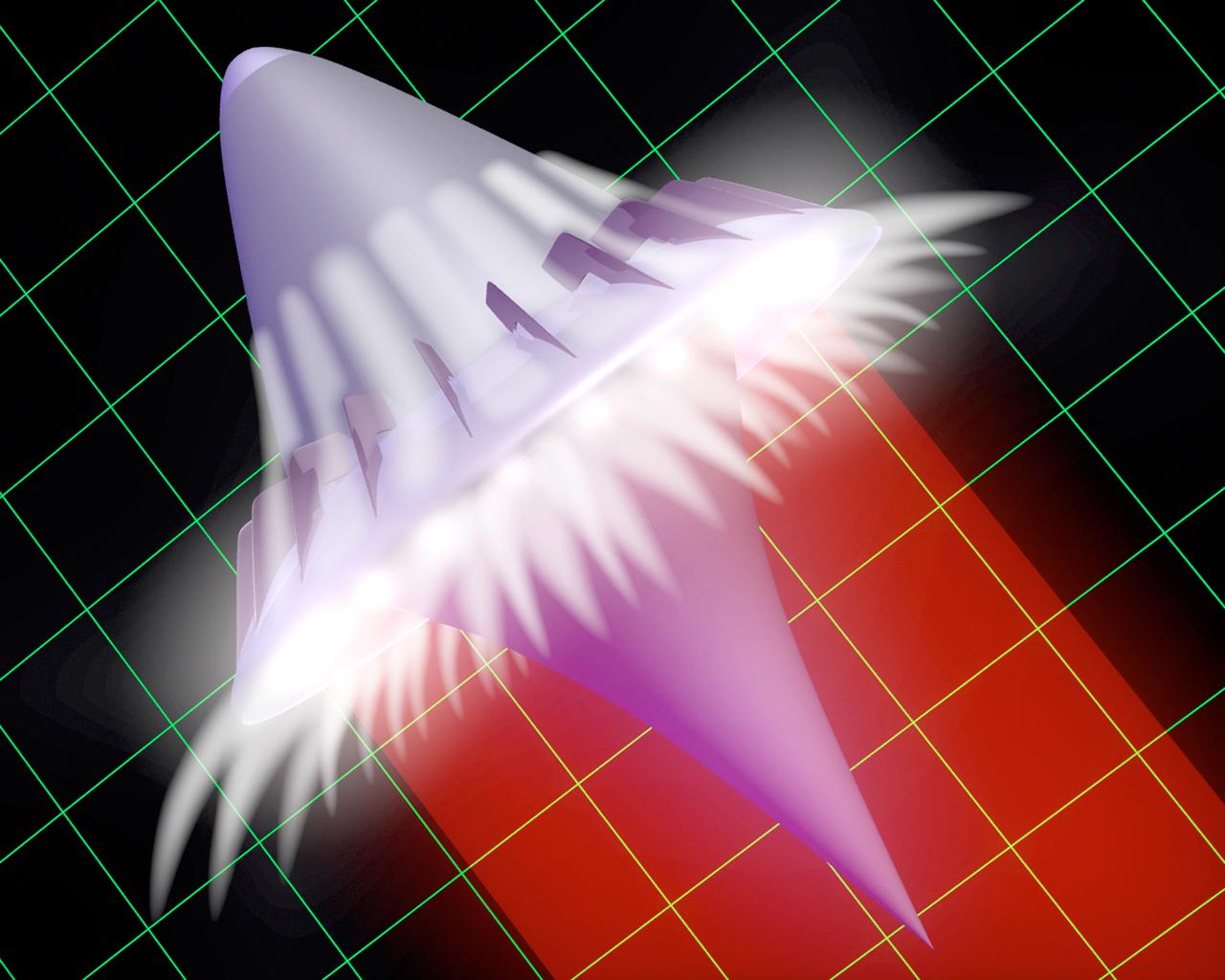

It is predicted that by the year 2040, there will be no distinction between a commercial airliner and a commercial launch vehicle. Fourth Generation Reusable Launch Vehicles (RLVs) will be so safe and reliable that no crew escape system will be necessary. Every year there will be in excess of 10,000 flights and the turn-around time between flights will be just hours. The onboard crew will be able to accomplish a launch without any assistance from the ground. Provided is an artist's concept of these fourth generation space vehicles.
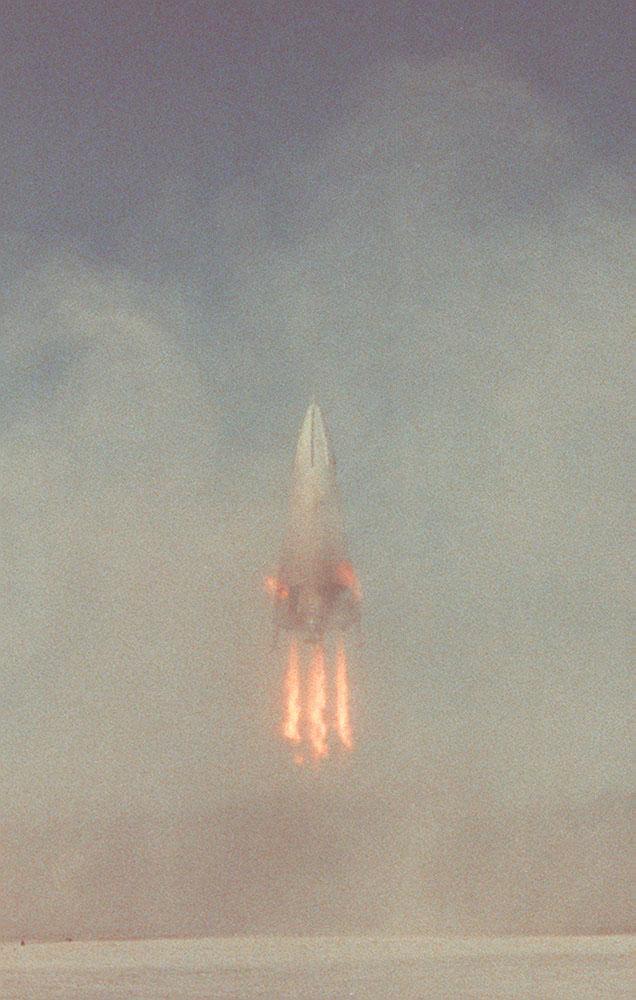

The Delta Clipper-Experimental Advanced (DC-XA) is a single-stage-to-orbit, vertical takeoff / vertical landing launch vehicle concept, whose development was geared to significantly reduce launch cost and provided a test bed for NASA Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) technology. This photograph shows the descending vehicle landing during the first successful test flight at White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico. The program was discontinued in 2003.

Wranglers steadied the X-40A at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, March 14, 2001, as the experimental craft was carried to 15,000 feet for an unpiloted glide flight. The unpiloted X-40 is a risk-reduction vehicle for the X-37, which is intended to be a reusable space vehicle. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala, manages the X-37 project. At Dryden, the X-40A will undergo a series of ground and air tests to reduce possible risks to the larger X-37, including drop tests from a helicopter to check guidance and navigation systems planned for use in the X-37. The X-37 is designed to demonstrate technologies in the orbital and reentry environments for next-generation reusable launch vehicles that will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000 per pound.
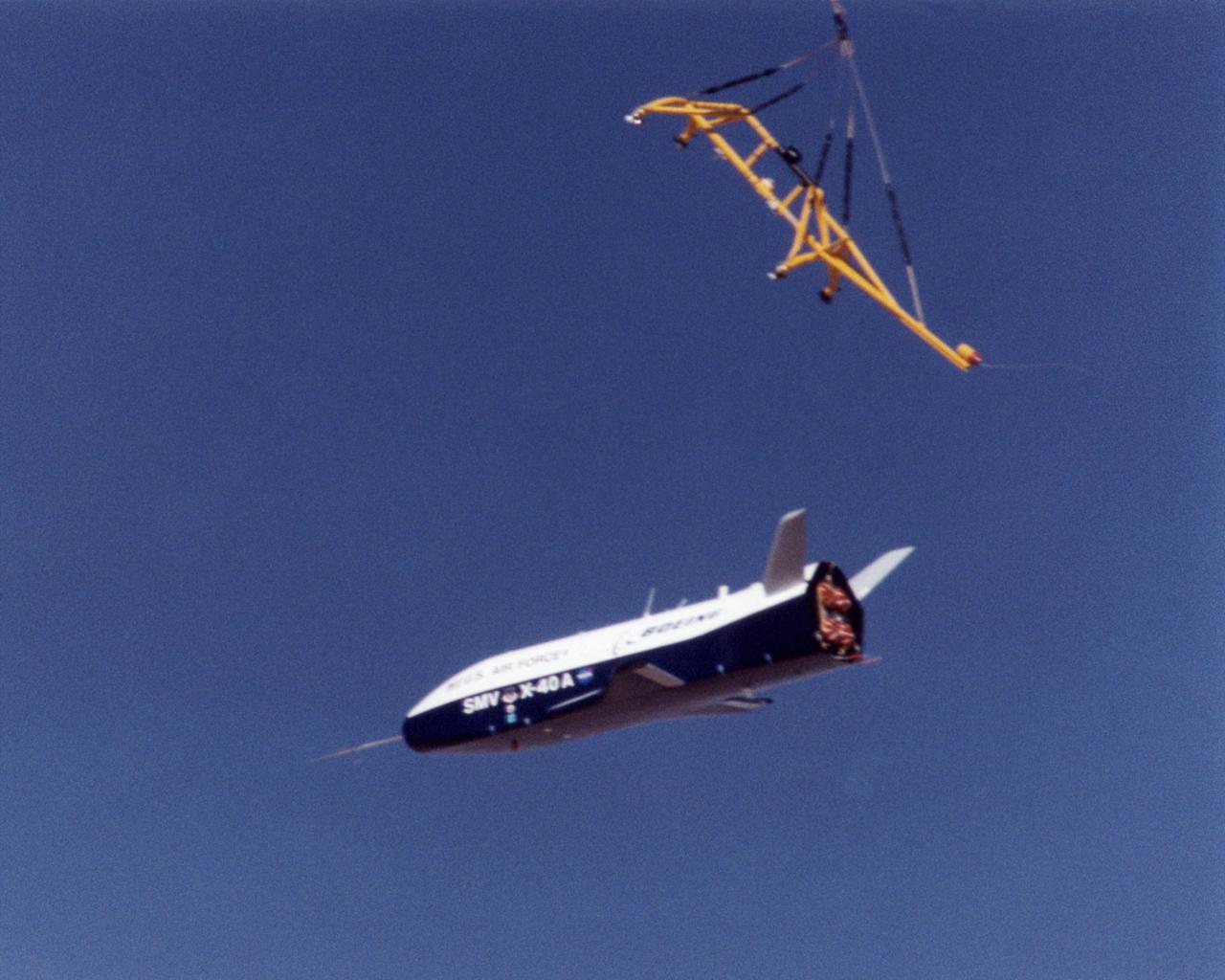

The X-40A immediately after release from its harness suspended from a helicopter 15,000 feet above NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, California, on March 14, 2001. The unpiloted X-40 is a risk-reduction vehicle for the X-37, which is intended to be a reusable space vehicle. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala, manages the X-37 project. At Dryden, the X-40A will undergo a series of ground and air tests to reduce possible risks to the larger X-37, including drop tests from a helicopter to check guidance and navigation systems planned for use in the X-37. The X-37 is designed to demonstrate technologies in the orbital and reentry environments for next-generation reusable launch vehicles that will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000 per pound.
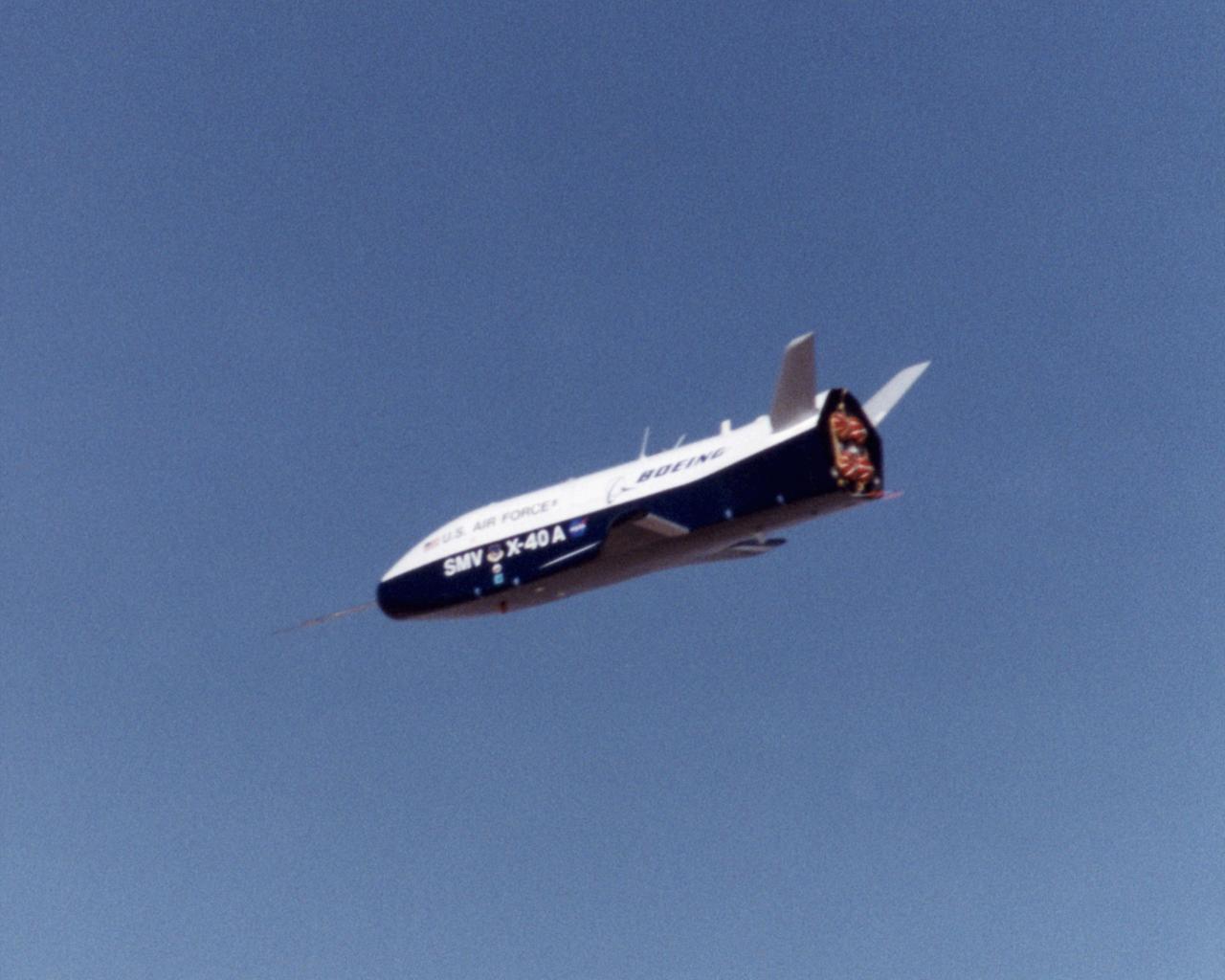

First flight at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center for the X-40A was a 74 second glide from 15,000 feet on March 14, 2001. The unpiloted X-40 is a risk-reduction vehicle for the X-37, which is intended to be a reusable space vehicle. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala, manages the X-37 project. At Dryden, the X-40A will undergo a series of ground and air tests to reduce possible risks to the larger X-37, including drop tests from a helicopter to check guidance and navigation systems planned for use in the X-37. The X-37 is designed to demonstrate technologies in the orbital and reentry environments for next-generation reusable launch vehicles that will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000 per pound.
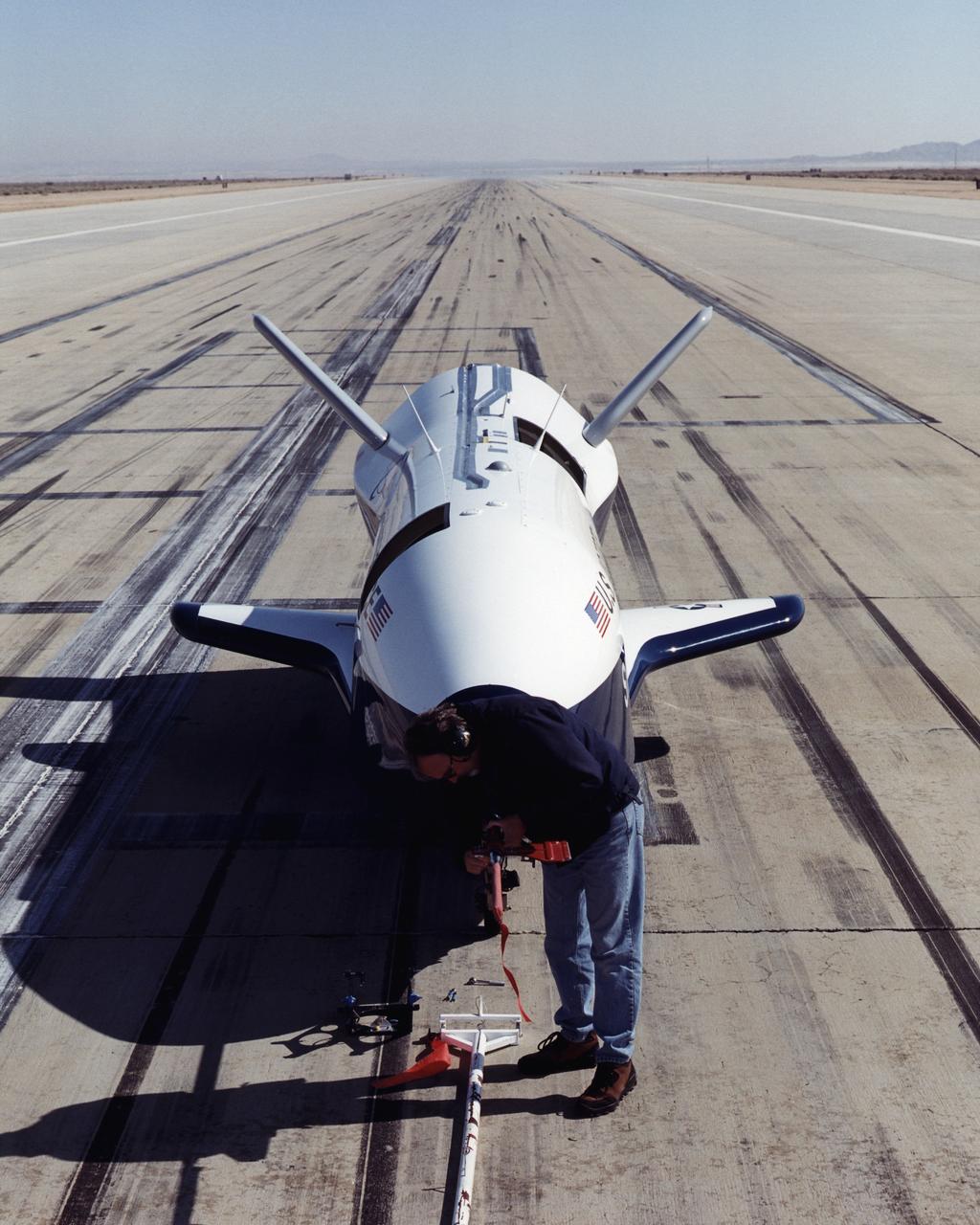

A worker attaches covers for the nose pitot boom before removing the unpiloted X-40 from the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California, following its successful free-flight on March 14, 2001. The unpiloted X-40 is a risk-reduction vehicle for the X-37, which is intended to be a reusable space vehicle. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala, manages the X-37 project. At Dryden, the X-40A will undergo a series of ground and air tests to reduce possible risks to the larger X-37, including drop tests from a helicopter to check guidance and navigation systems planned for use in the X-37. The X-37 is designed to demonstrate technologies in the orbital and reentry environments for next-generation reusable launch vehicles that will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000 per pound.
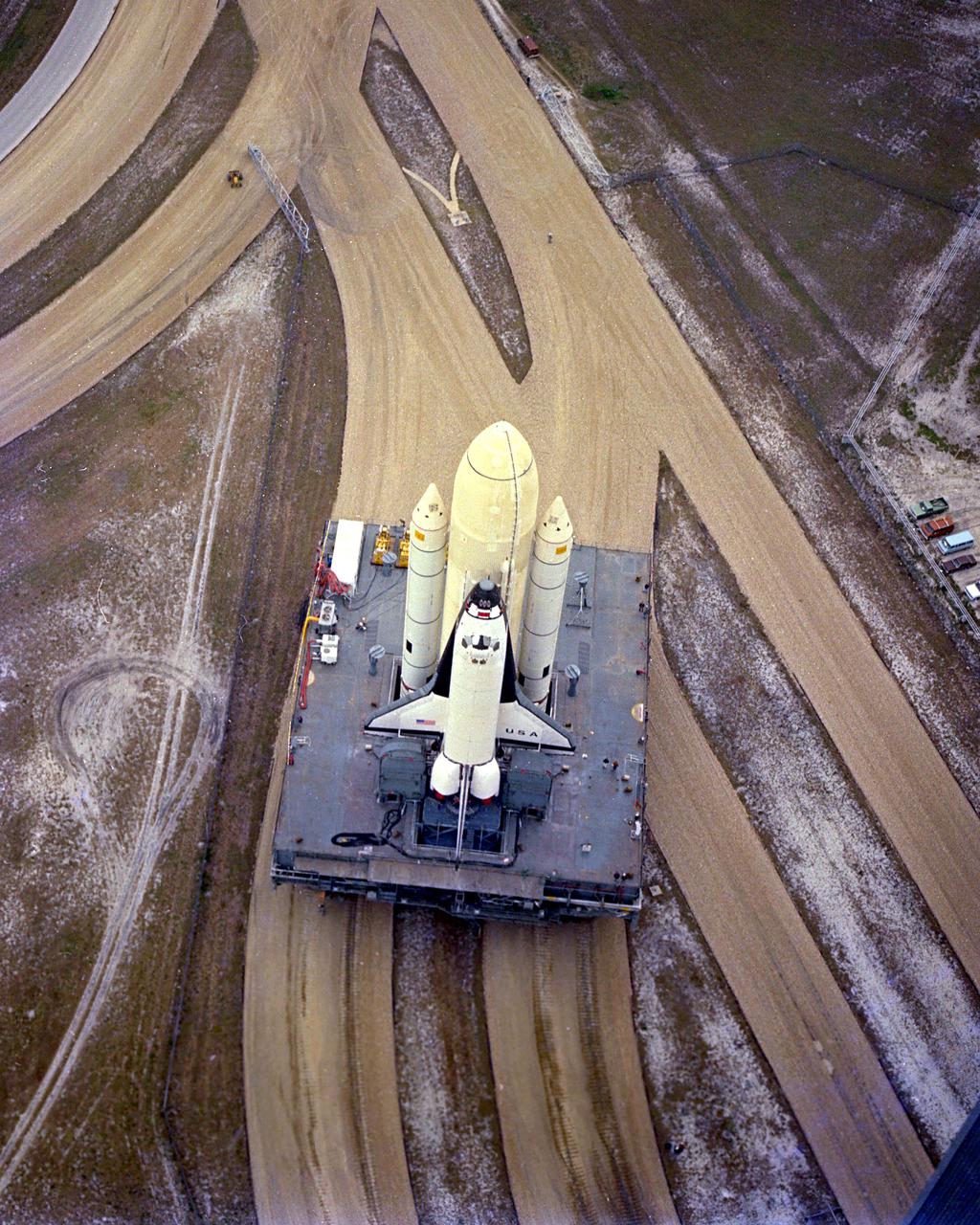

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first Space Shuttle vehicle destined to fly in space moves toward Pad A at Complex 39, where it will be launched. The STS-1 vehicle - consisting of America's first reusable spaceship, Columbia, the external propellant tank and twin solid rocket boosters - was assembled on a Mobile Launcher Platform in the Vehicle Assembly Building. A six-million-pound tractor, called the Crawler-Transporter, is used to carry the Space Shuttle from the VAB to the launch pad, about 3.5 miles away.
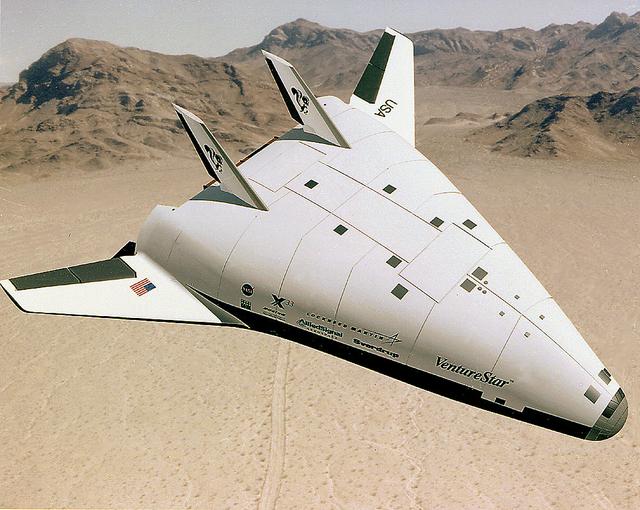

This is an artist's concept of an X-33 Advanced Technology Demonstrator, a subscale protoptye launch vehicle being developed by NASA Lockheed Martin Skunk Works. (Vehicle configuration current as of 10/97) The X-33 is a subscale prototype of a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Lockheed Martin has labeled "Venture Star TM." The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.
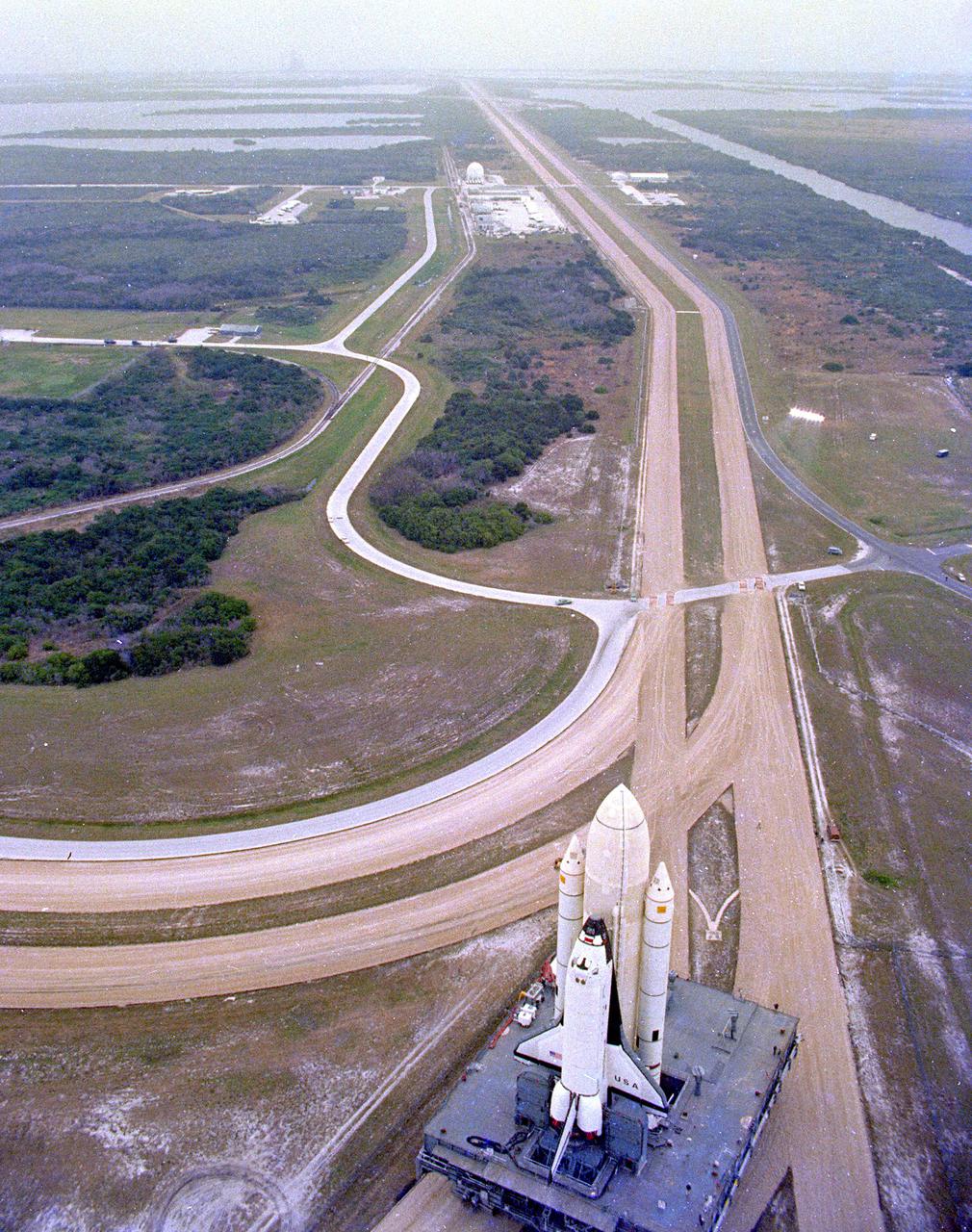

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first Space Shuttle vehicle destined to fly in space moves toward Pad A at Complex 39, where it will be launched. The STS-1 vehicle - consisting of America's first reusable spaceship, Columbia, the external propellant tank and twin solid rocket boosters - was assembled on a Mobile Launcher Platform in the Vehicle Assembly Building. A six-million-pound tractor, called the Crawler-Transporter, is used to carry the Space Shuttle from the VAB to the launch pad, about 3.5 miles away.
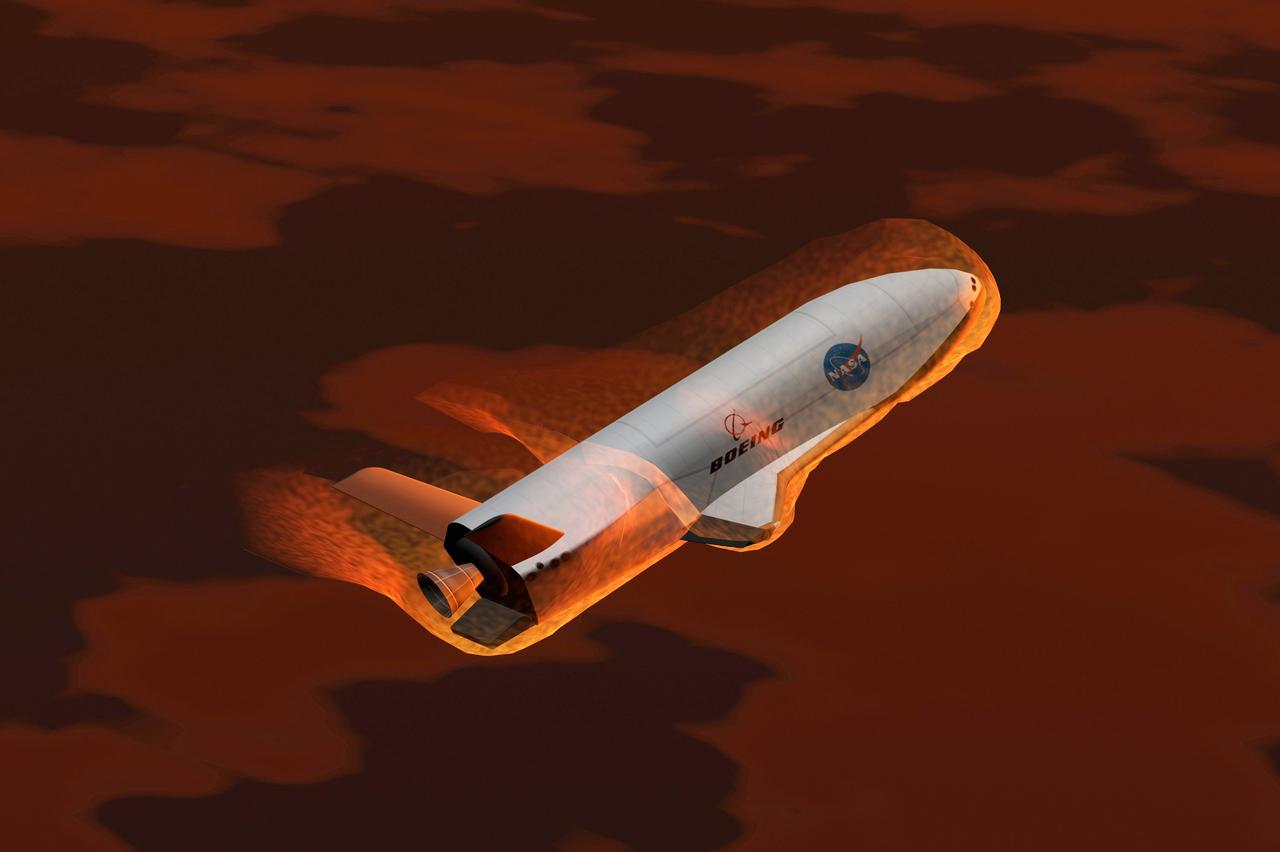

Pictured is an artist's concept of the experimental X-37 Reusable Launch Vehicle re-entering Earth‘s atmosphere. NASA and the Boeing Company entered a cooperative agreement to develop and fly a new experimental space plane called the X-37 that would be ferried into orbit to test new technologies. The reusable space plane incorporated technologies aimed at significantly cutting the cost of space flight. The X-37 would be carried into orbit by the Space Shuttle or be launched by an expendable rocket. After the X-37 was deployed, it would remain in orbit up to 21 days, performing a variety of experiments before re-entering the Earth's atmosphere and landing. The X-37 program was discontinued in 2003.

The Advanced Space Transportation Group takes the future of space travel far into the 21st Century. Pictured is an artist's concept of a third generation Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV). Projected for the year 2025, this third generation RLV will introduce an era of space travel not unlike air travel today.
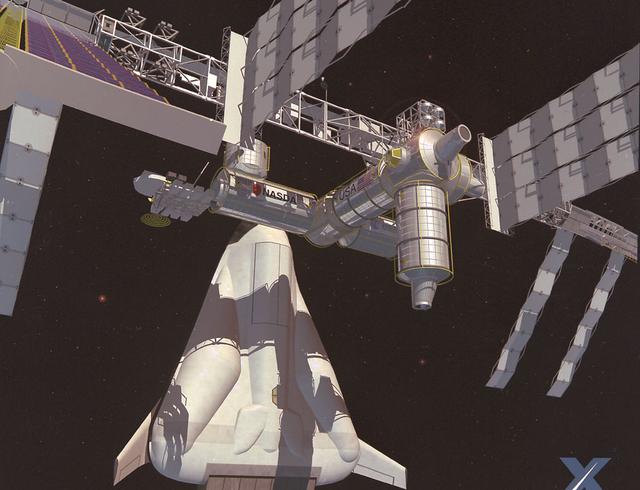

Pictured here is an artist's depiction of Lockheed Martin's Lifting Body Single-Stage-to-Orbit (SSTO) Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) concept servicing the International Space Station. The development of the RLV is essential in the cost reduction of future space travel.
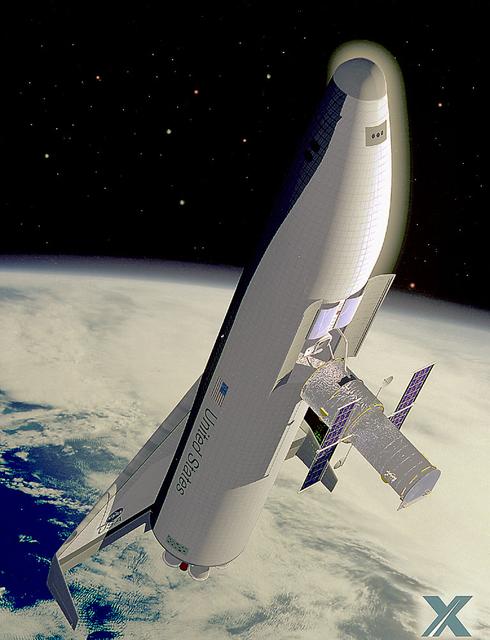

Pictured here is an artist's depiction of the McDornel Douglas' wing body Single-Stage-to-Orbit (SSTO) Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) servicing the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) concept. The development of the RLV is essential in the cost reduction of future space travel.
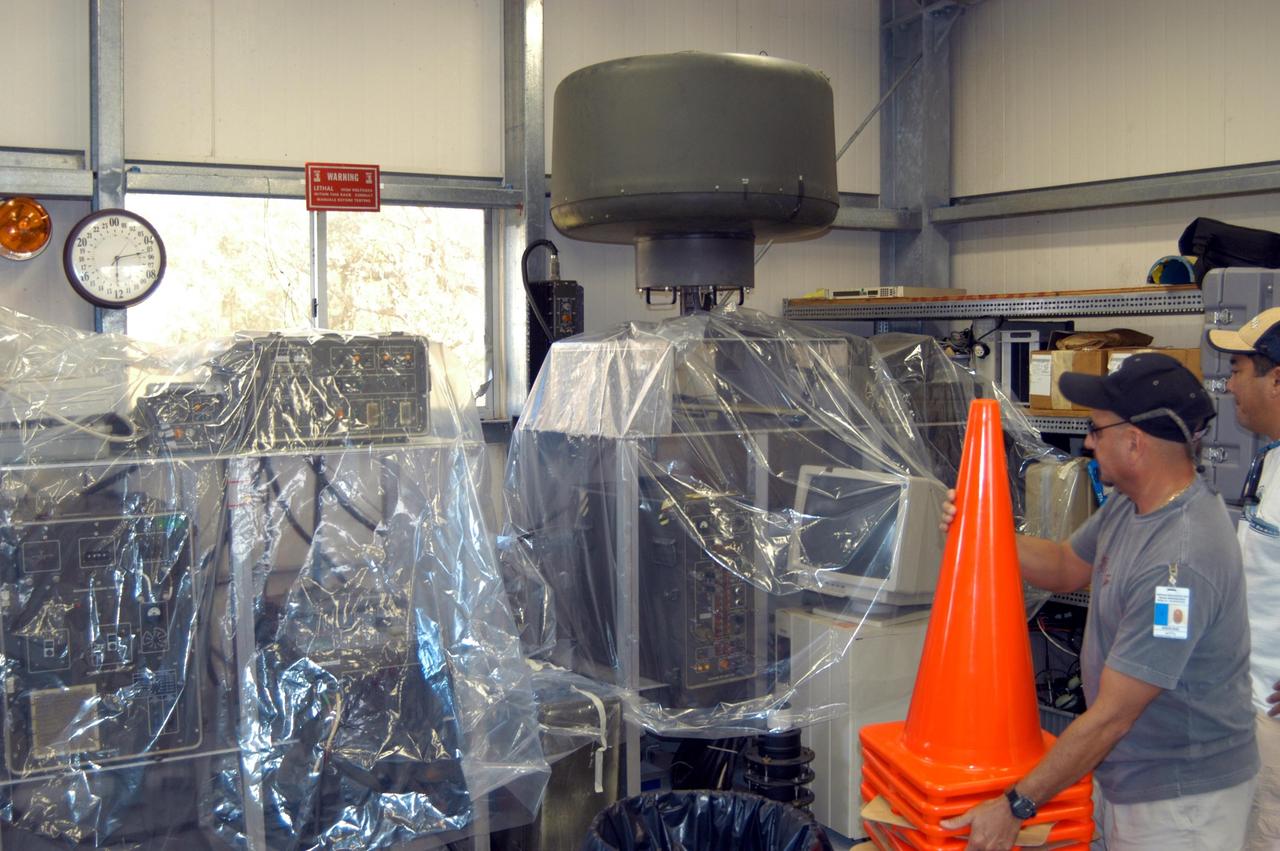

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers place plastic sheets over racks of equipment in the Reusable Launch Vehicle Support Complex in preparation for the arrival of Hurricane Jeanne, expected to impact Central Florida Sunday. This is the fourth hurricane in 45 days to make landfall somewhere in the state.
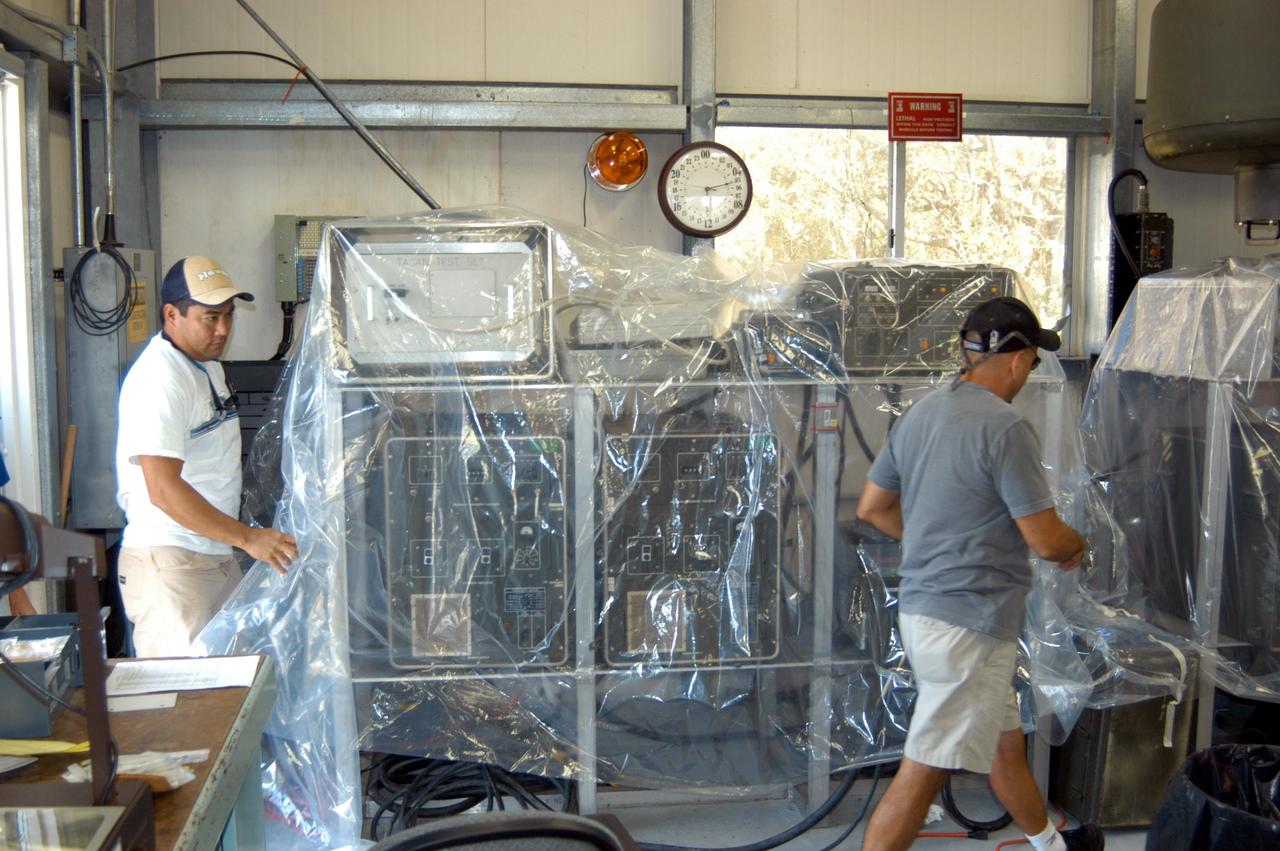

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers place plastic sheets over racks of equipment in the Reusable Launch Vehicle Support Complex in preparation for the arrival of Hurricane Jeanne, expected to impact Central Florida Sunday. This is the fourth hurricane in 45 days to make landfall somewhere in the state.
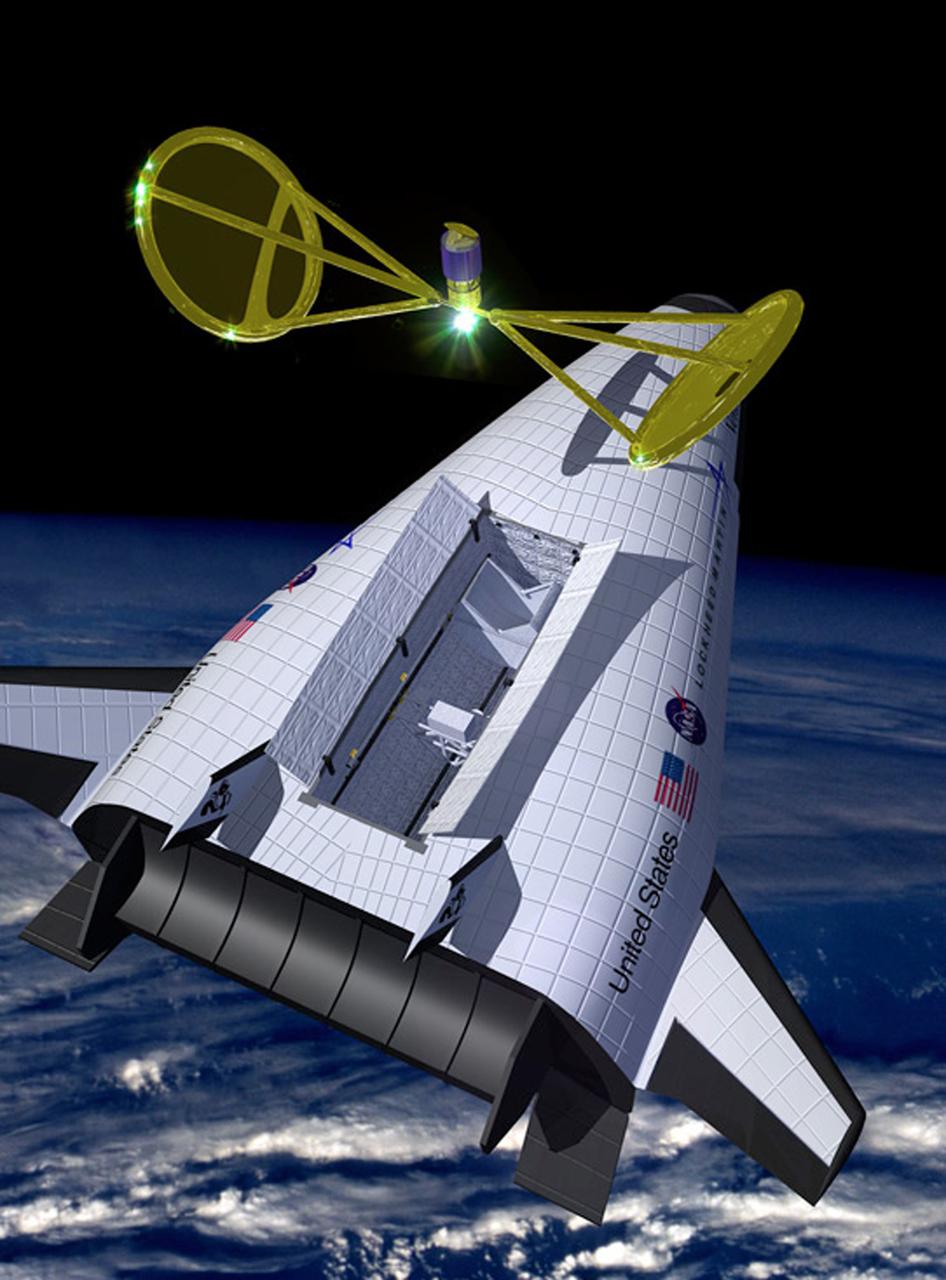

In this artist's concept, the X-33 Venture Star, a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), manufactured by Lockheed Martin Skunk Works, is shown in orbit with a deployed payload. The Venture Star was one of the earliest versions of the RLV's developed to replace the aging shuttle fleet. The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.
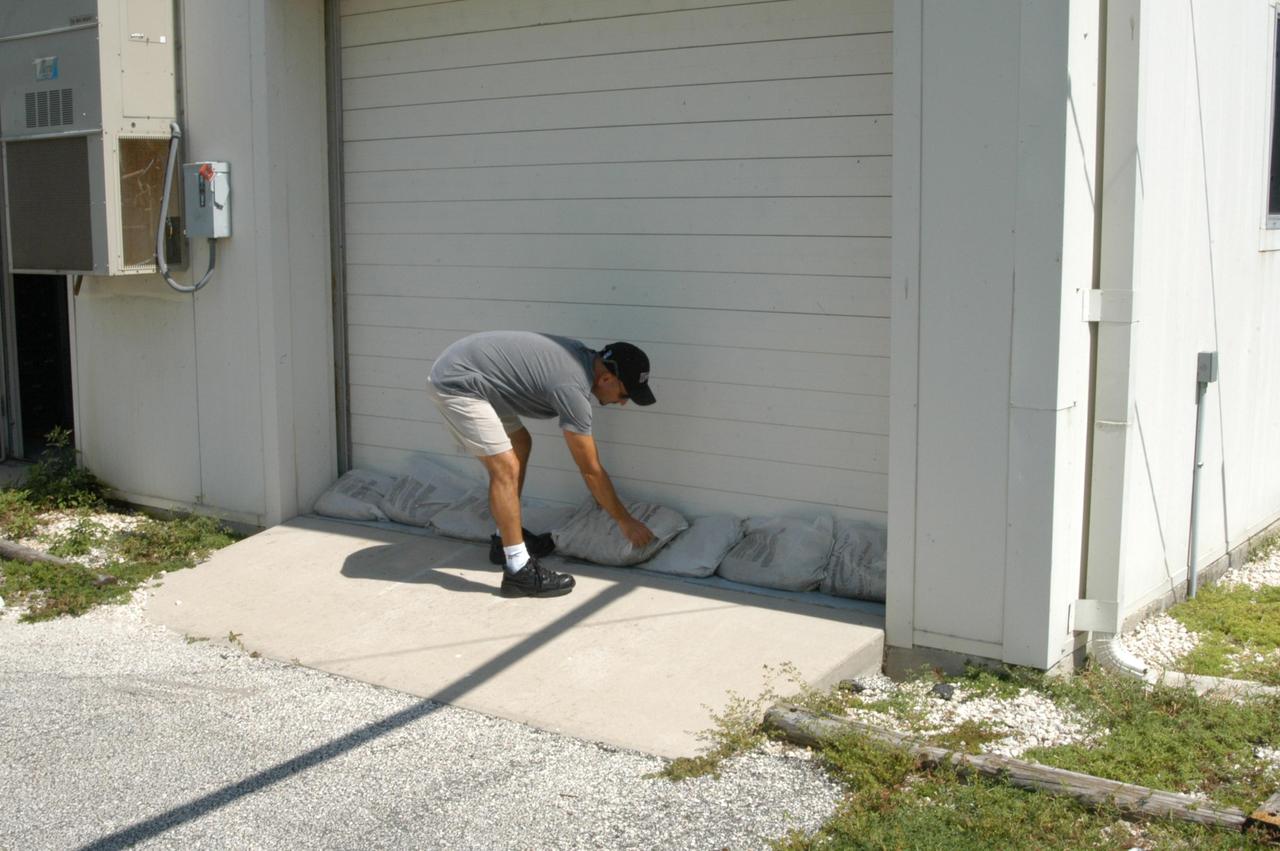

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A worker places sandbags at the bottom of the door into the Reusable Launch Vehicle Support Complex in preparation for the arrival of Hurricane Jeanne, expected to impact Central Florida Sunday. This is the fourth hurricane in 45 days to make landfall somewhere in the state.
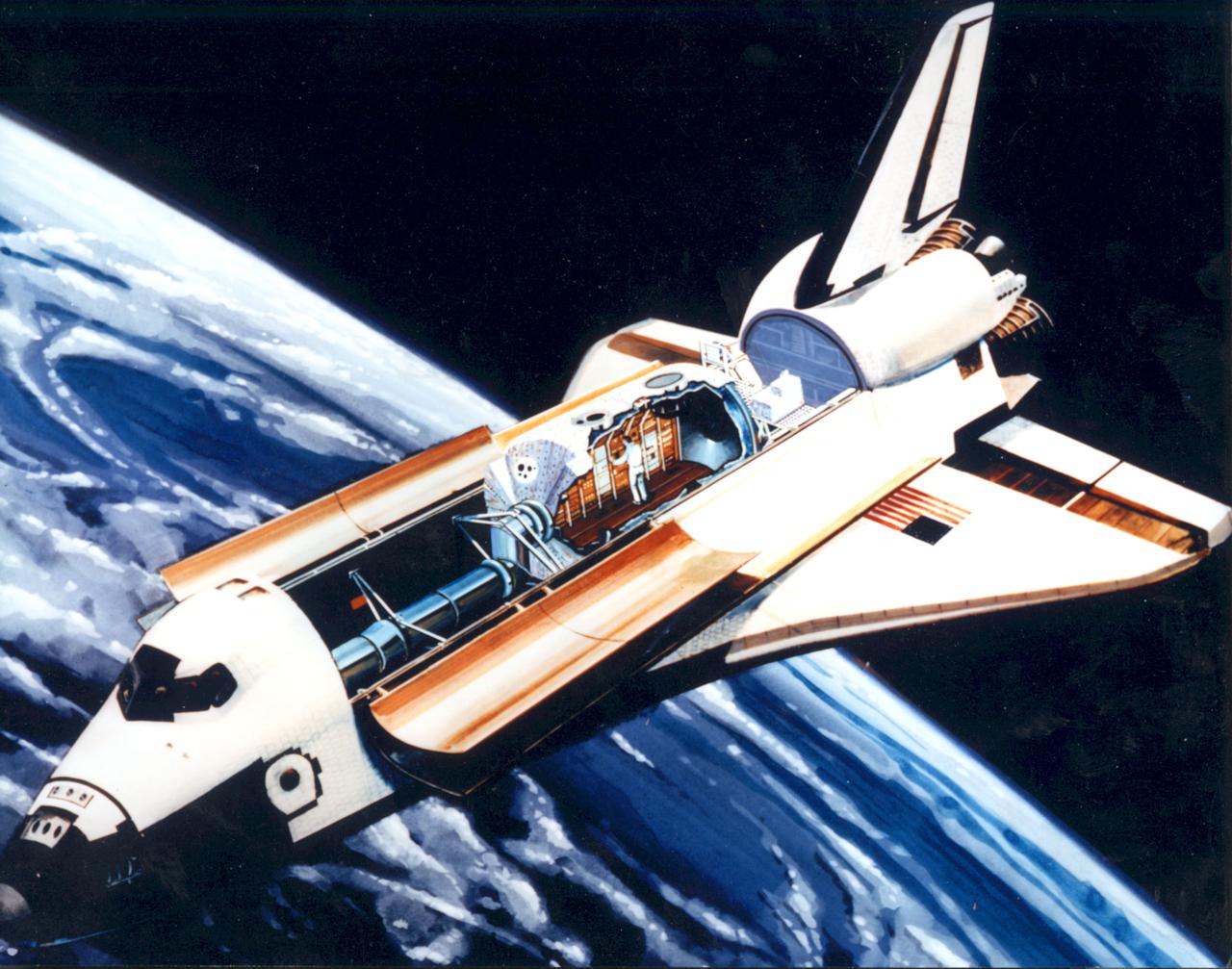
The shuttle is a reusable launch vehicle that can maintain a consistent orbit and provide up to 17 days of high-quality microgravity conditions. The shuttle, which can accomodate a wide range of experiment apparatus, provides a laboratory environment in which scientists can conduct long-term investigations.
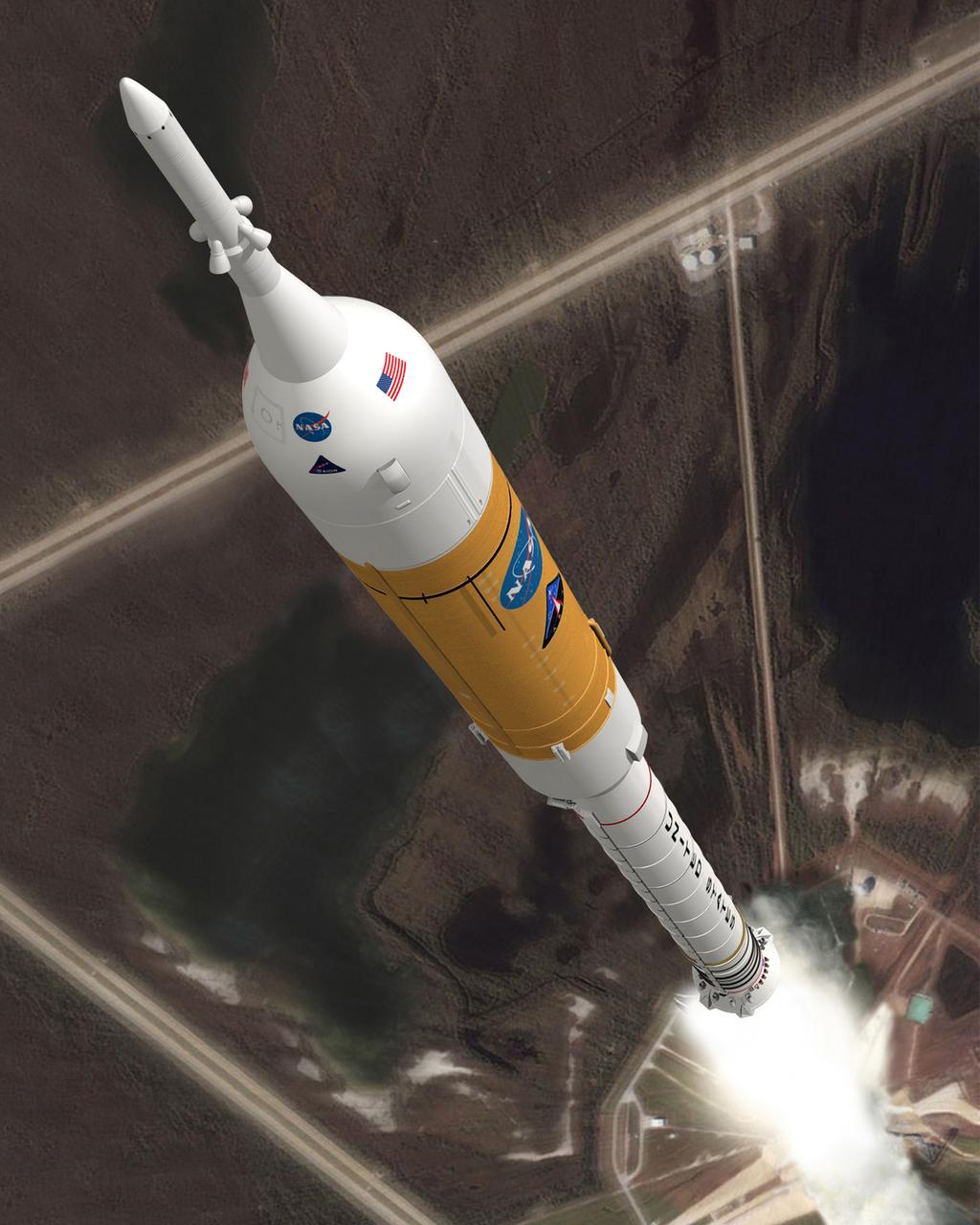

A CONCEPT IMAGE SHOWS THE ARES I CREW LAUNCH VEHICLE DURING ASCENT. ARES I IS AN IN-LINE, TWO-STAGE ROCKET CONFIGURATION TOPED BY THE ORION CREW EXPLORATION VEHICLE AND LAUNCH ABORT SYSTEM. THE ARES I FIRST STAGE IS A SINGLE, FIVE-SEGMENT REUSABLE SOLID ROCKET BOOSTER, DERIVED FROM THE SPACE SHUTTLE. ITS UPPER STAGE IS POWERED BY A J-2X ENGINE. ARES I WILL CARRY THE ORION WITH ITS CRW OF UP TO SIX ASTRONAUTS TO EARTH ORBIT.
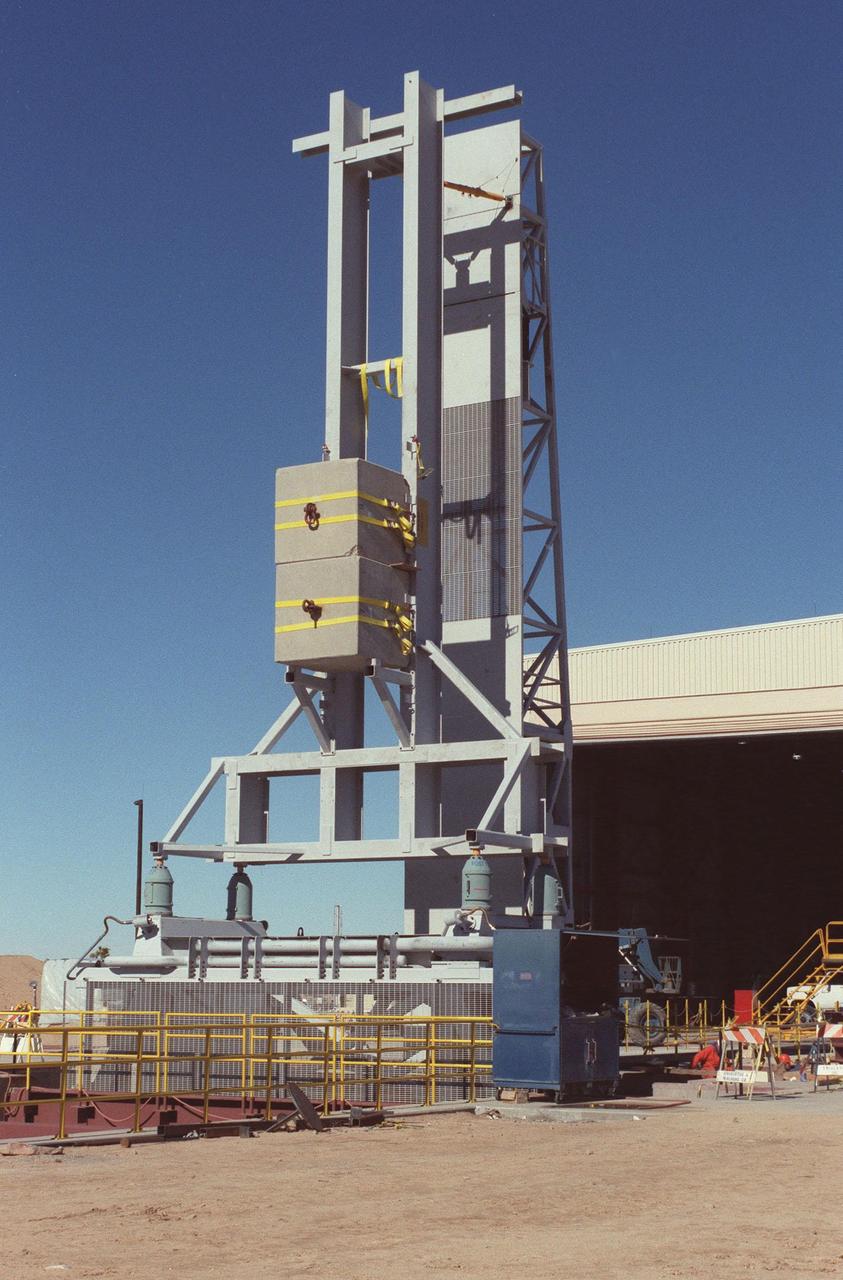

The KSC-developed X-33 weight simulator (left), known as the "iron bird," is fully raised to a vertical position at the X-33 launch site as part of launch equipment testing on Edwards Air Force Base, CA. The simulator matches the 75,000-pound weight and 63-foot height of the X-33 vehicle that will be using the launch equipment. KSC's Vehicle Positioning System (VPS) placed the simulator on the rotating launch platform prior to the rotation. The new VPS will dramatically reduce the amount of manual labor required to position a reusable launch vehicle for liftoff
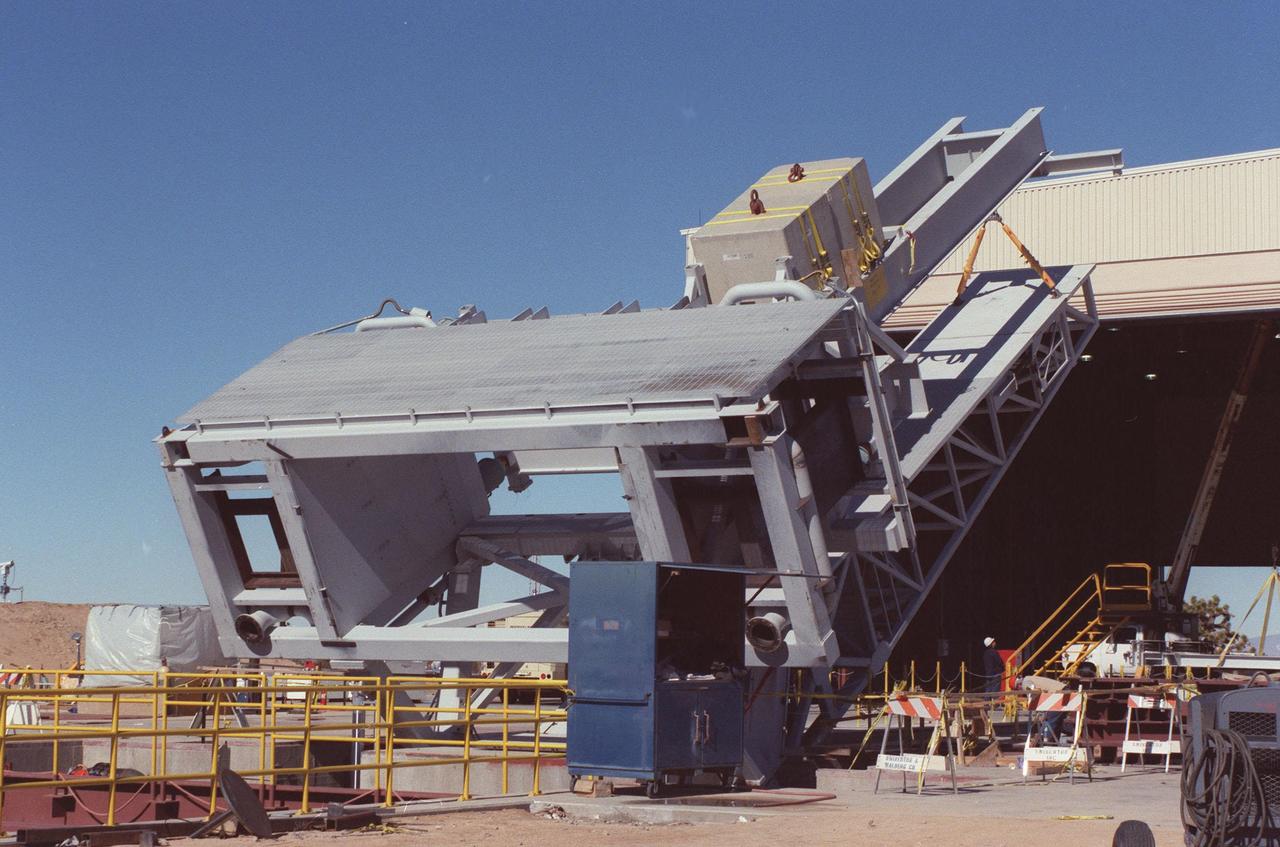

The KSC-developed X-33 weight simulator (top), known as the "iron bird," is lifted to a vertical position at the X-33 launch site as part of launch equipment testing on Edwards Air Force Base, CA. The simulator matches the 75,000-pound weight and 63-foot height of the X-33 vehicle that will be using the launch equipment. KSC's Vehicle Positioning System (VPS) placed the simulator on the rotating launch platform prior to the rotation. The new VPS will dramatically reduce the amount of manual labor required to position a reusable launch vehicle for liftoff

The KSC-developed X-33 weight simulator (top, right), known as the "iron bird," is lifted to a vertical position at the X-33 launch site as part of launch equipment testing on Edwards Air Force Base, CA. The simulator matches the 75,000-pound weight and 63-foot height of the X-33 vehicle that will be using the launch equipment. KSC's Vehicle Positioning System (VPS) placed the simulator on the rotating launch platform prior to the rotation. The new VPS will dramatically reduce the amount of manual labor required to position a reusable launch vehicle for liftoff
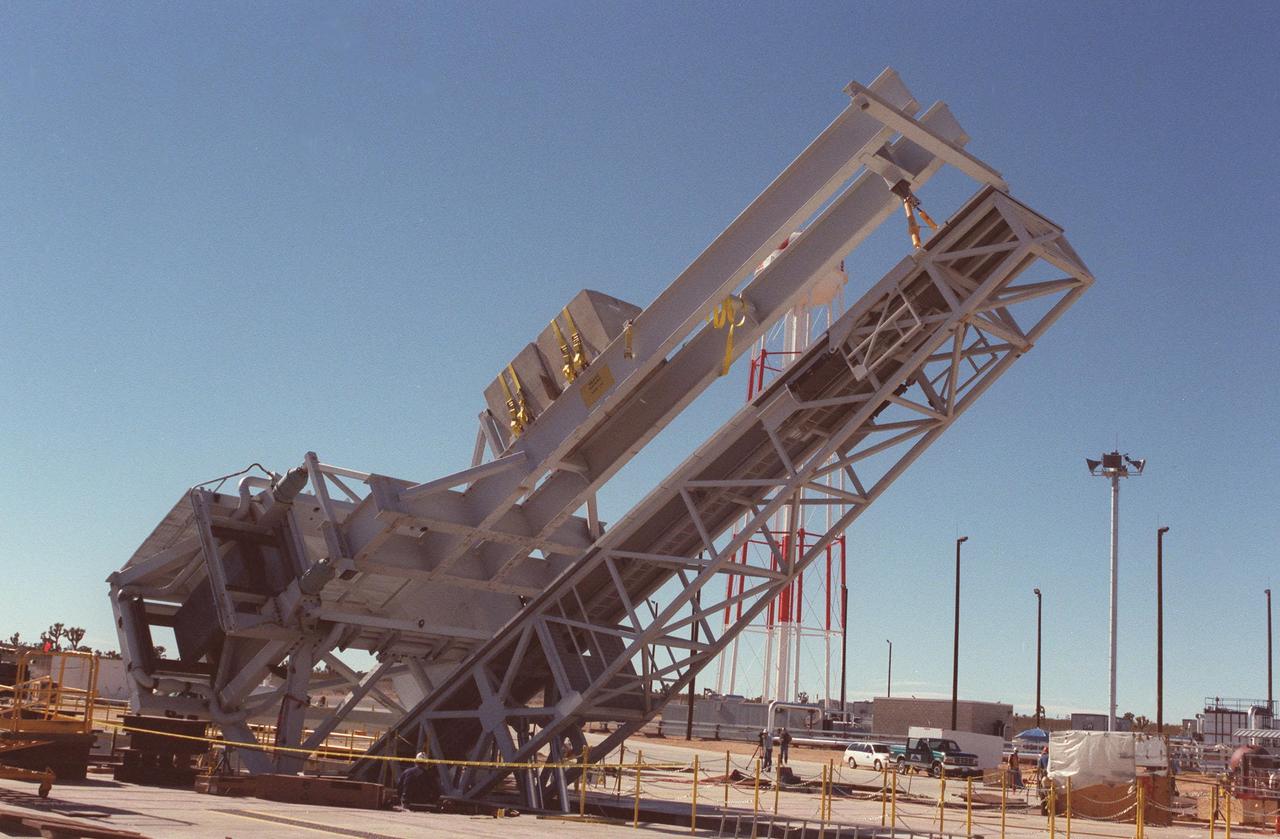

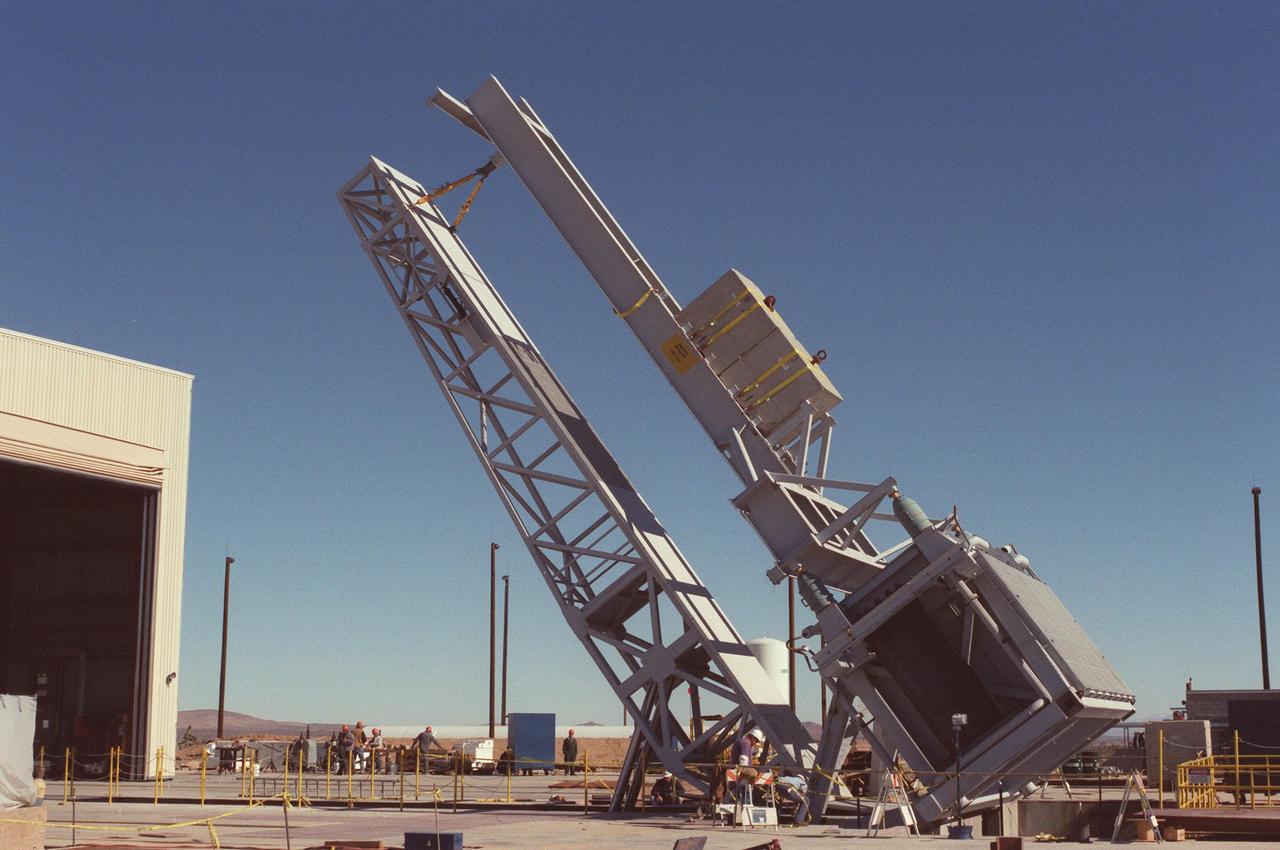
As part of X-33 launch equipment testing at Edwards Air Force Base, CA, the KSC-developed X-33 weight simulator (top), known as the "iron bird," is lifted to a vertical position at the X-33 launch site. The simulator matches the 75,000-pound weight and 63-foot height of the X-33 vehicle that will be using the launch equipment. KSC's Vehicle Positioning System (VPS) placed the simulator on the rotating launch platform prior to the rotation. The new VPS will dramatically reduce the amount of manual labor required to position a reusable launch vehicle for liftoff
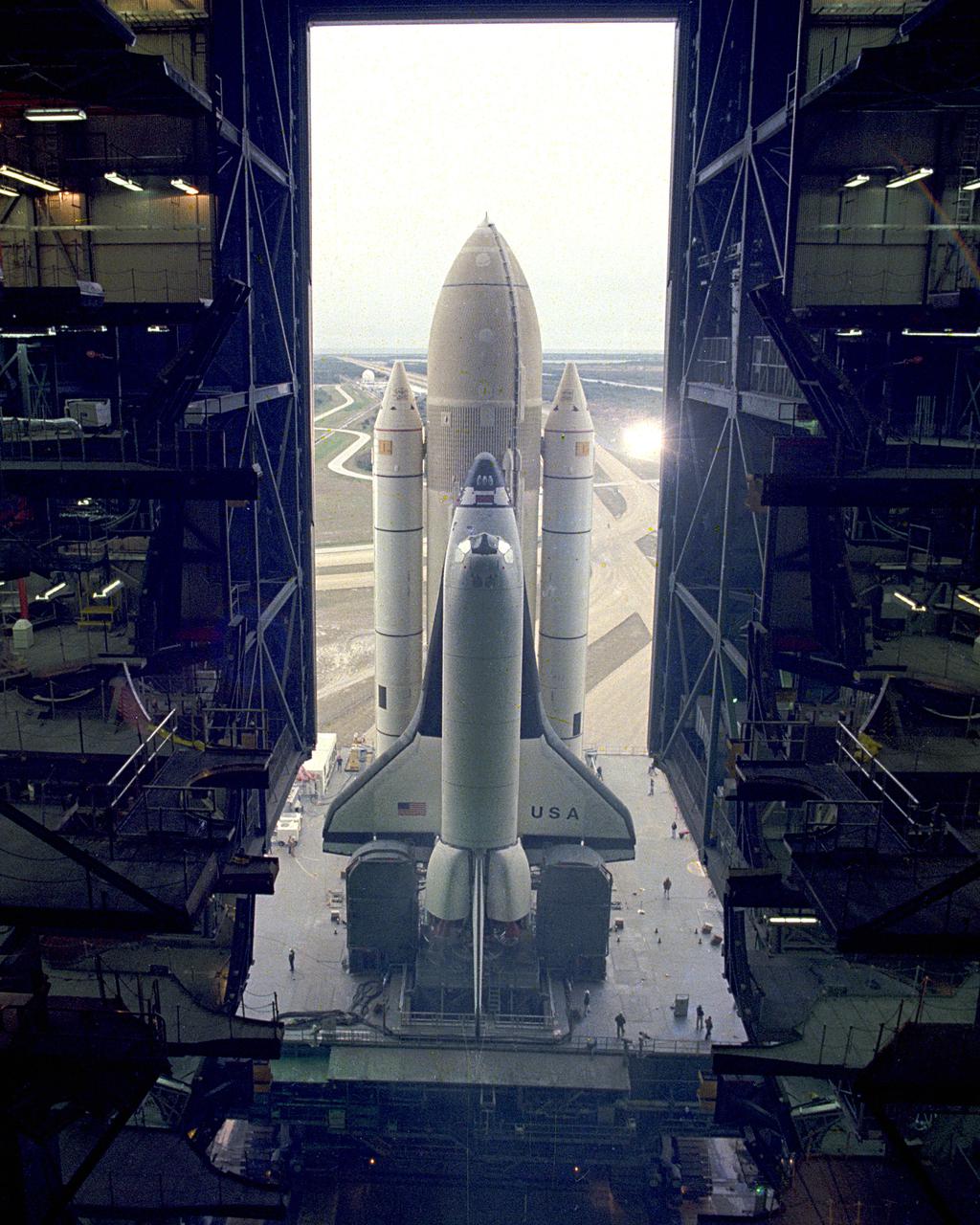

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first Space Shuttle vehicle destined to fly in space inches out of the Vehicle Asembly Building on its way to Pad A at Complex 39, where it will be launched. The STS-1 vehicle - consisting of America's first reusable spaceship, Columbia, the external propellant tank and twin solid rocket boosters - was assembled on a Mobile Launcher Platform in the Vehicle Assembly Building. A six-million-pound tractor, called the Crawler-Transporter, is used to carry the Space Shuttle from the VAB to the launch pad, about 3.5 miles away.
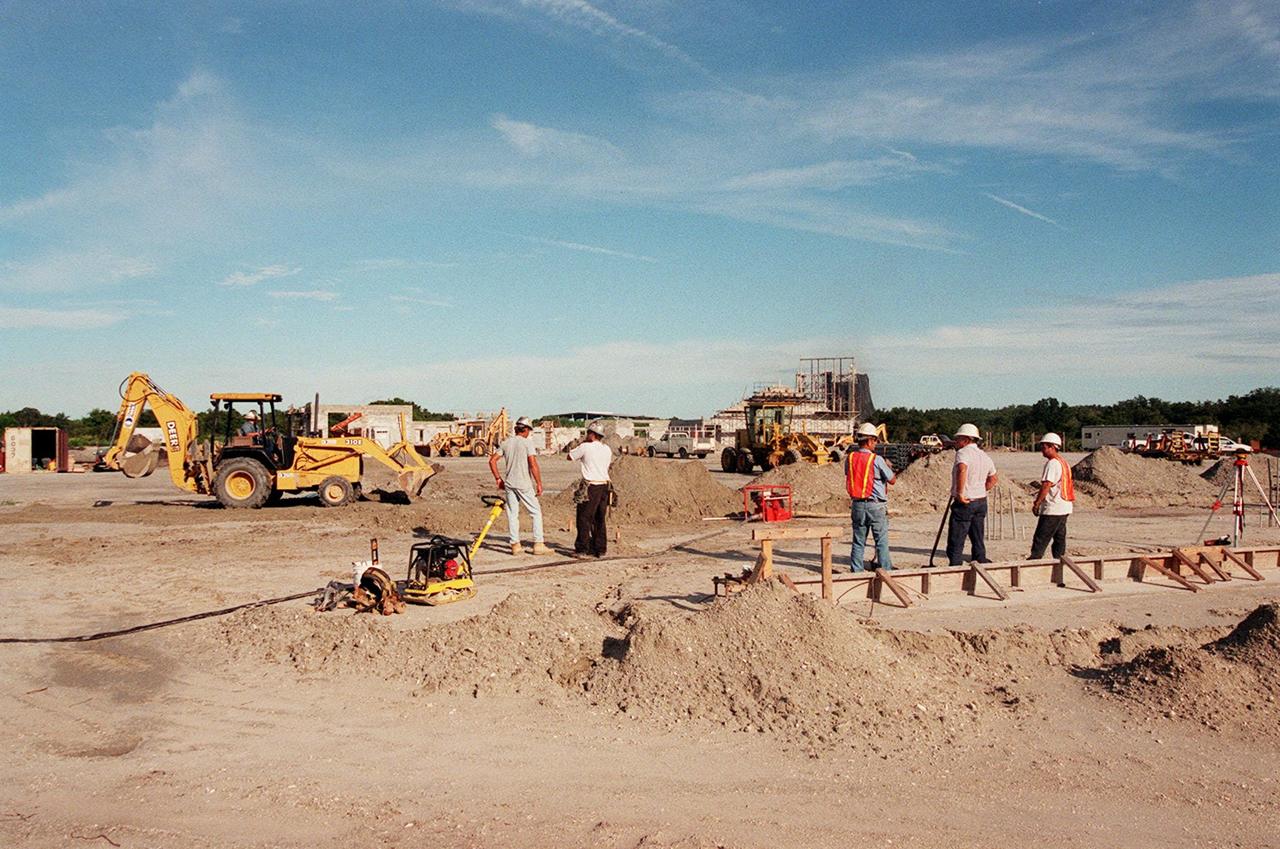

Construction is under way for the X-33/X-34 hangar complex near the Shuttle Landing Facility at KSC. The Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) complex will include facilities for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. It will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
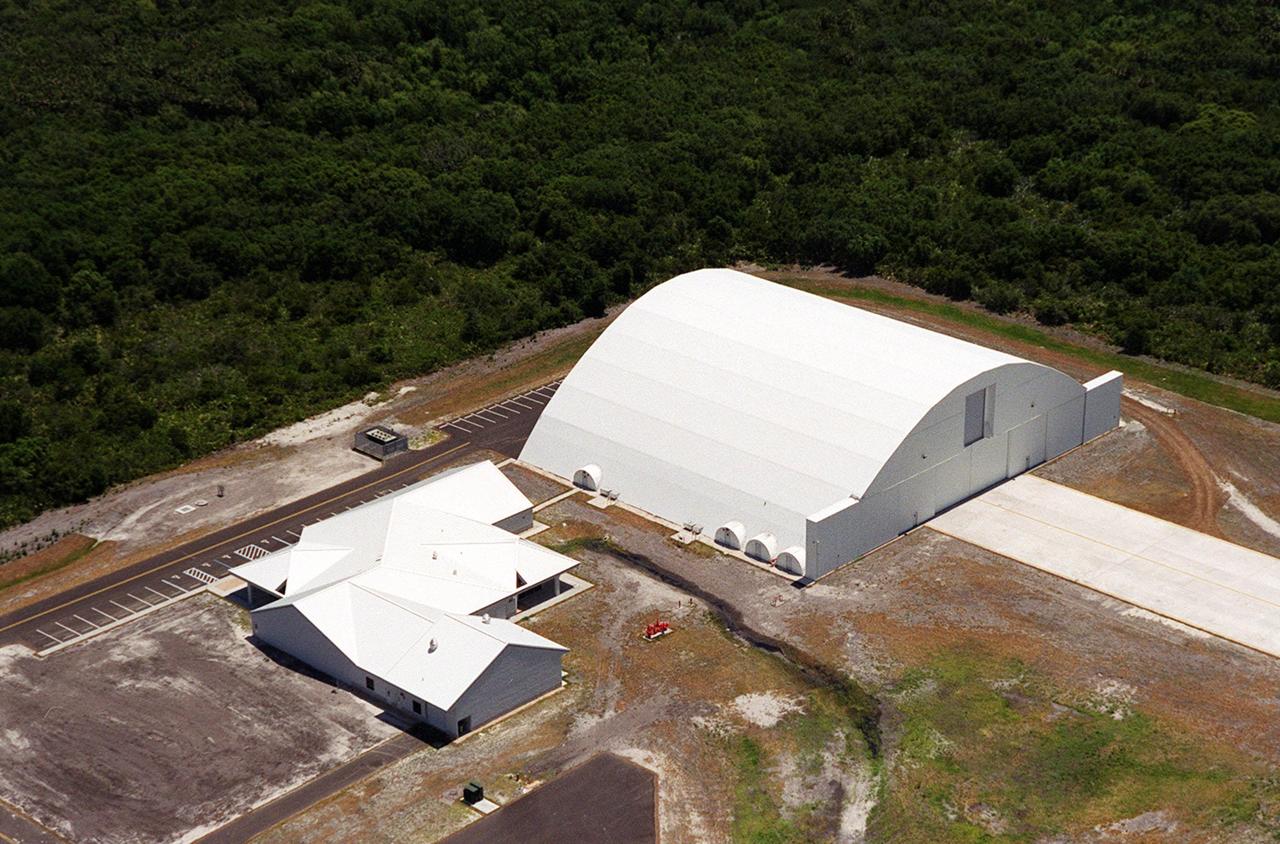

This closeup photo shows the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. At right is a multi-purpose hangar and to the left is a building for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. The complex is situated at the Shuttle Landing Facility. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA’s Space Shuttle Program and KSC
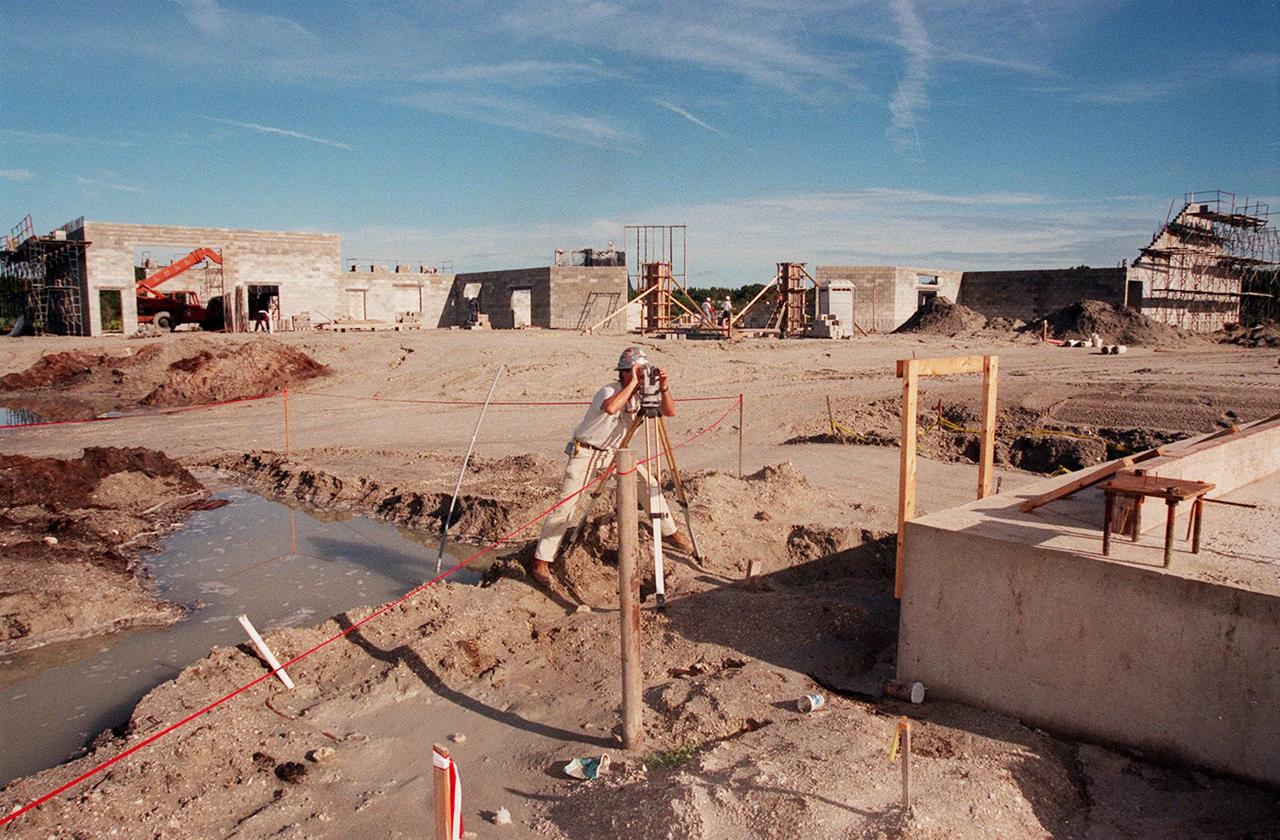

A worker takes a measurement for construction of the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) complex at KSC. Located near the Shuttle Landing Facility, the complex will include facilities for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. It will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
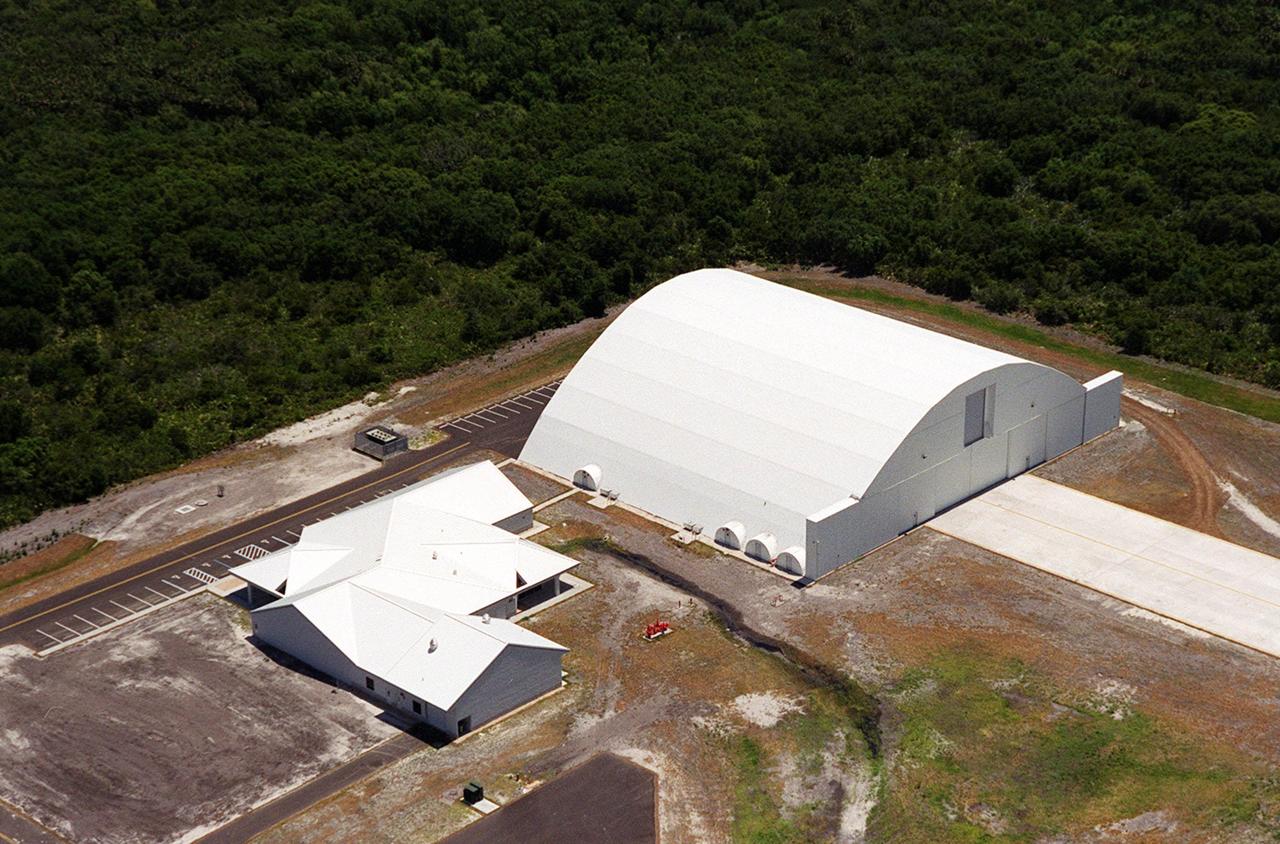

This closeup photo shows the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. At right is a multi-purpose hangar and to the left is a building for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. The complex is situated at the Shuttle Landing Facility. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA’s Space Shuttle Program and KSC
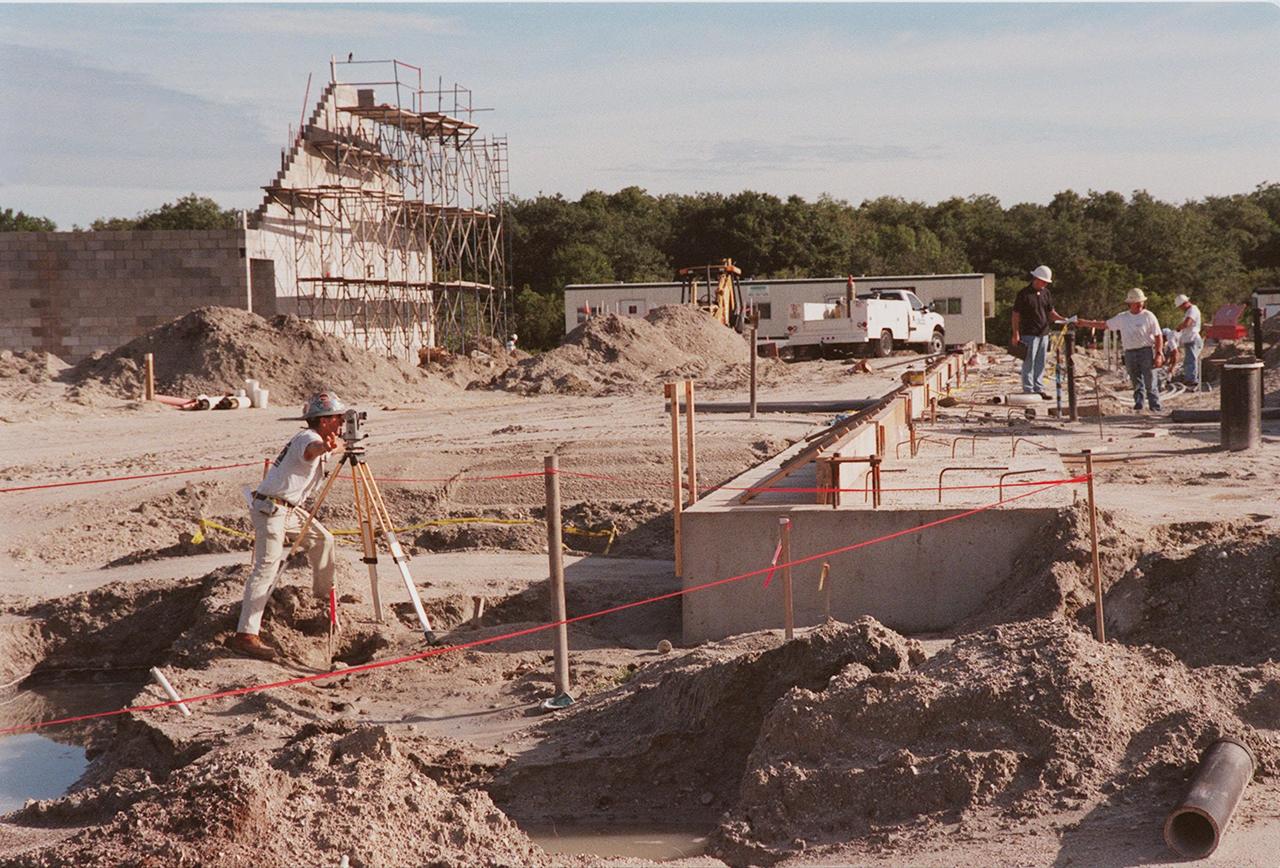

At the construction site of the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) complex at KSC, workers take measurements for one of the buildings. Located near the Shuttle Landing Facility, the complex will include facilities for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. It will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000

At the construction site of the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) complex at KSC, a worker takes a measurement. Located near the Shuttle Landing Facility, the complex will include facilities for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. It will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
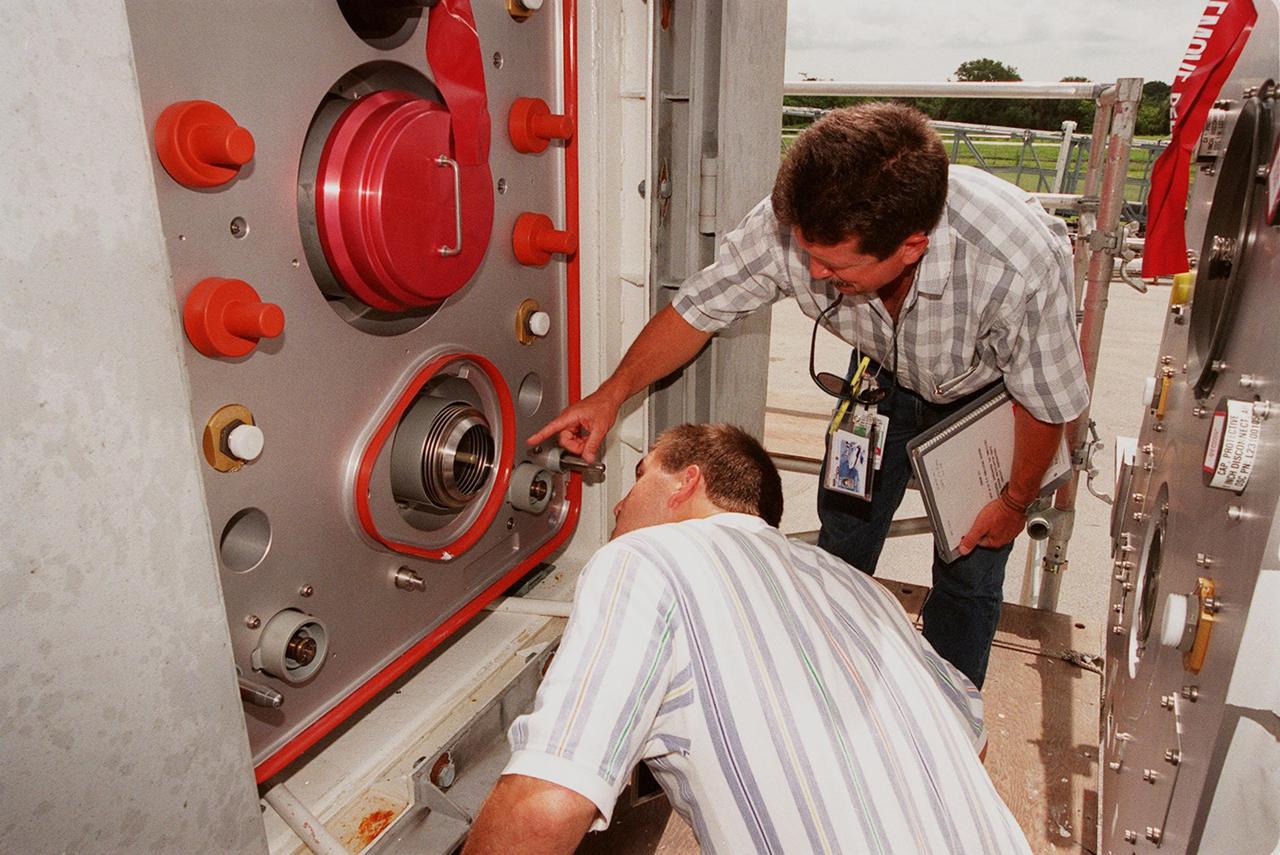

At the Launch Equipment Test Facility, Mike Solomon (left) and Will Reaves (right), both with Lockheed Martin Technical Operations, move in for a close look at part of the X-33 umbilical system. A team of Kennedy Space Center experts developed the umbilical system, comprising panels, valves and hoses that provide the means to load the X-33 with super-cold propellant. The X-33, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, Calif., is a half-scale prototype of the planned operational reusable launch vehicle dubbed VentureStar
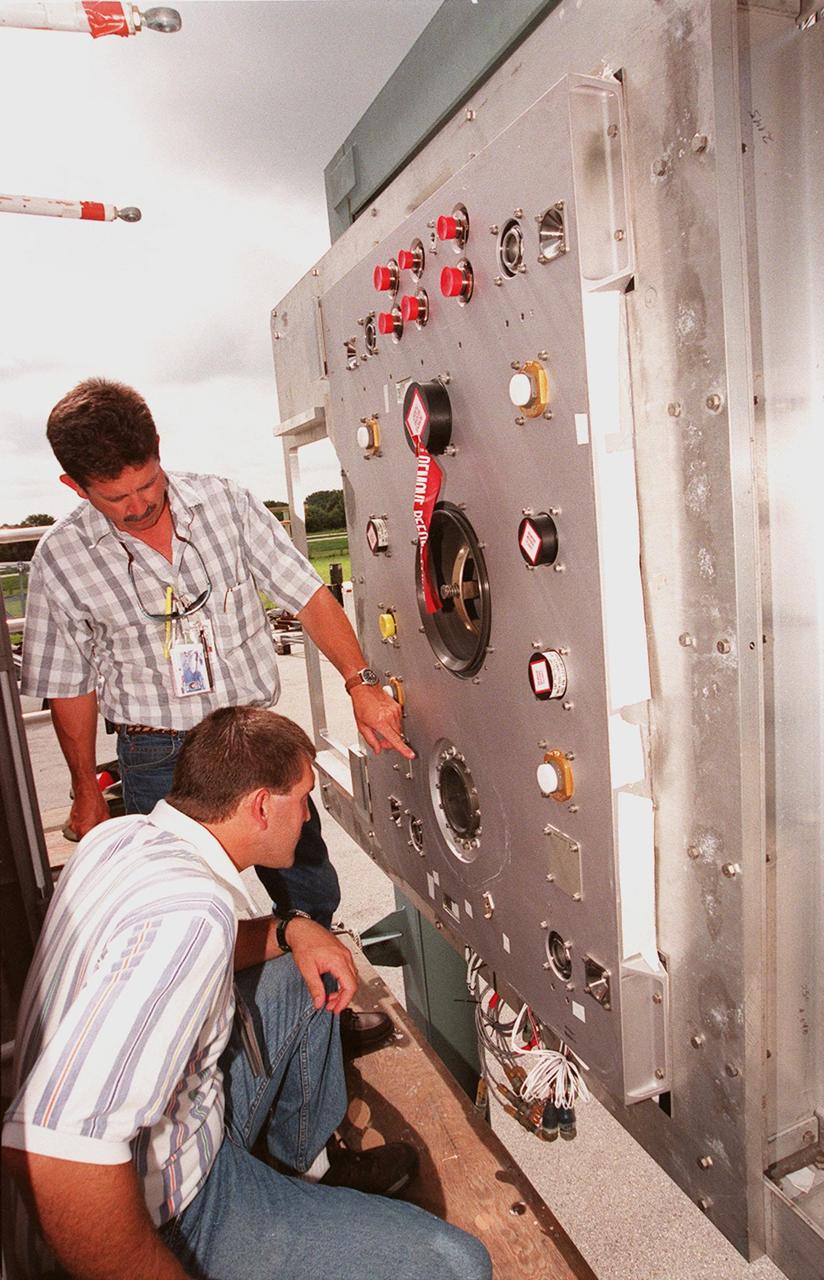

At the Launch Equipment Test Facility, , Will Reaves and Mike Solomon (kneeling), both with Lockheed Martin Technical Operations, observe parts of the X-33 umbilical system during testing. A team of Kennedy Space Center experts developed the umbilical system, comprising panels, valves and hoses that provide the means to load the X-33 with super-cold propellant. The X-33, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, Calif., is a half-scale prototype of the planned operational reusable launch vehicle dubbed VentureStar
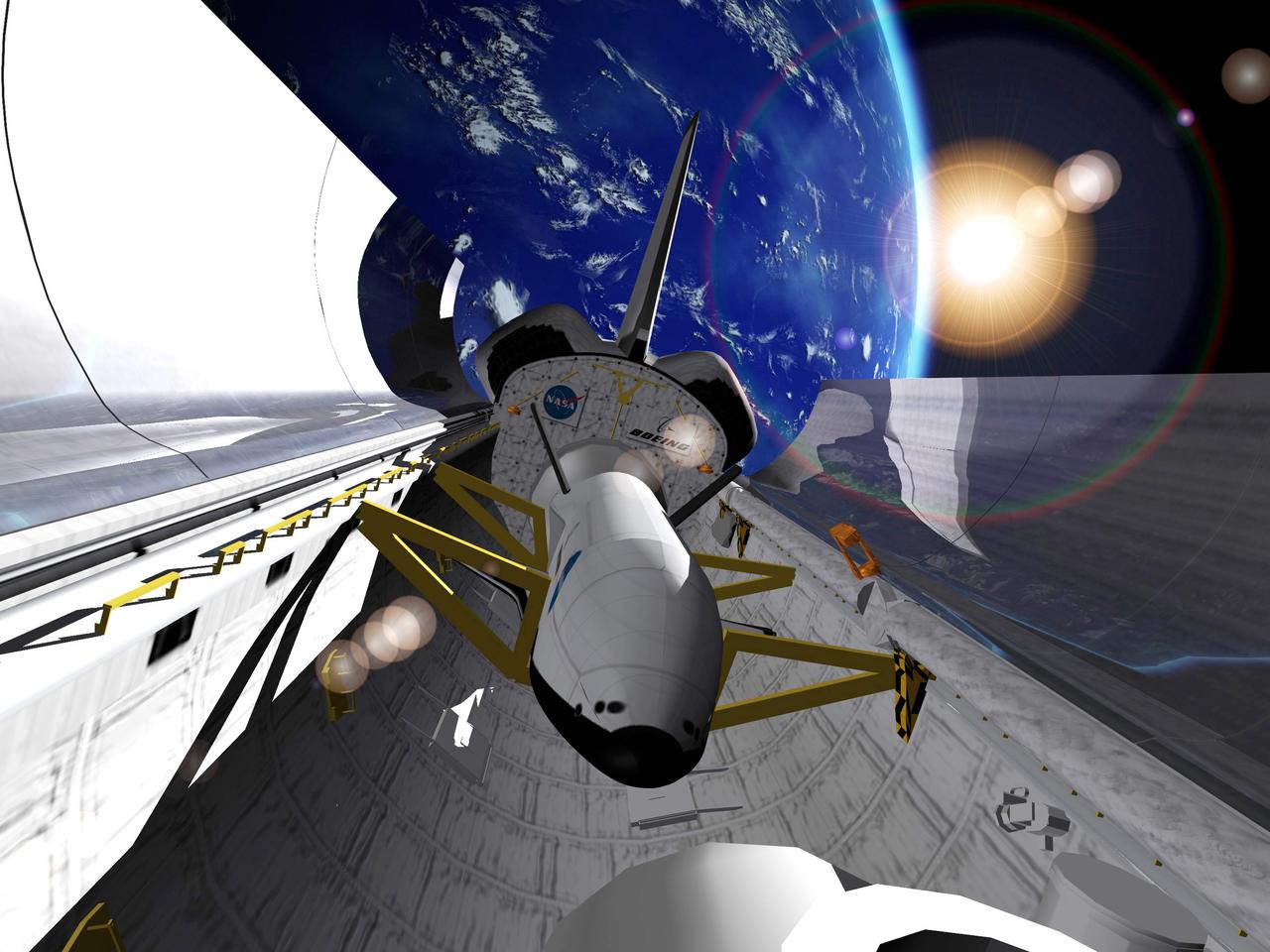

Pictured is an artist's concept of the experimental Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), the X-37 located in the cargo bay of a space shuttle with Earth in the background. The X-37 was designed to launch from the space shuttle's cargo bay as a secondary payload. Once deployed, the X-37 would remain on-orbit up to 21 days performing a variety of experiments before re-entering the Earth's atmosphere and landing. The X-37 program was discontinued in 2003.

At the Launch Equipment Test Facility, Mike Ynclan, with Dynacs, and Greg Melton, a NASA engineer, look at measurements during testing of the X-33 umbilical system. A team of Kennedy Space Center experts developed the umbilical system, comprising panels, valves and hoses that provide the means to load the X-33 with super-cold propellant. The X-33, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, Calif., is a half-scale prototype of the planned operational reusable launch vehicle dubbed VentureStar

At the Launch Equipment Test Facility, Will Reaves (top of stand), with Lockheed Martin Technical Operations, looks over components of the X-33 umbilical system undergoing testing. A team of Kennedy Space Center experts developed the umbilical system, comprising panels, valves and hoses that provide the means to load the X-33 with super-cold propellant. The X-33, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, Calif., is a half-scale prototype of the planned operational reusable launch vehicle dubbed VentureStar
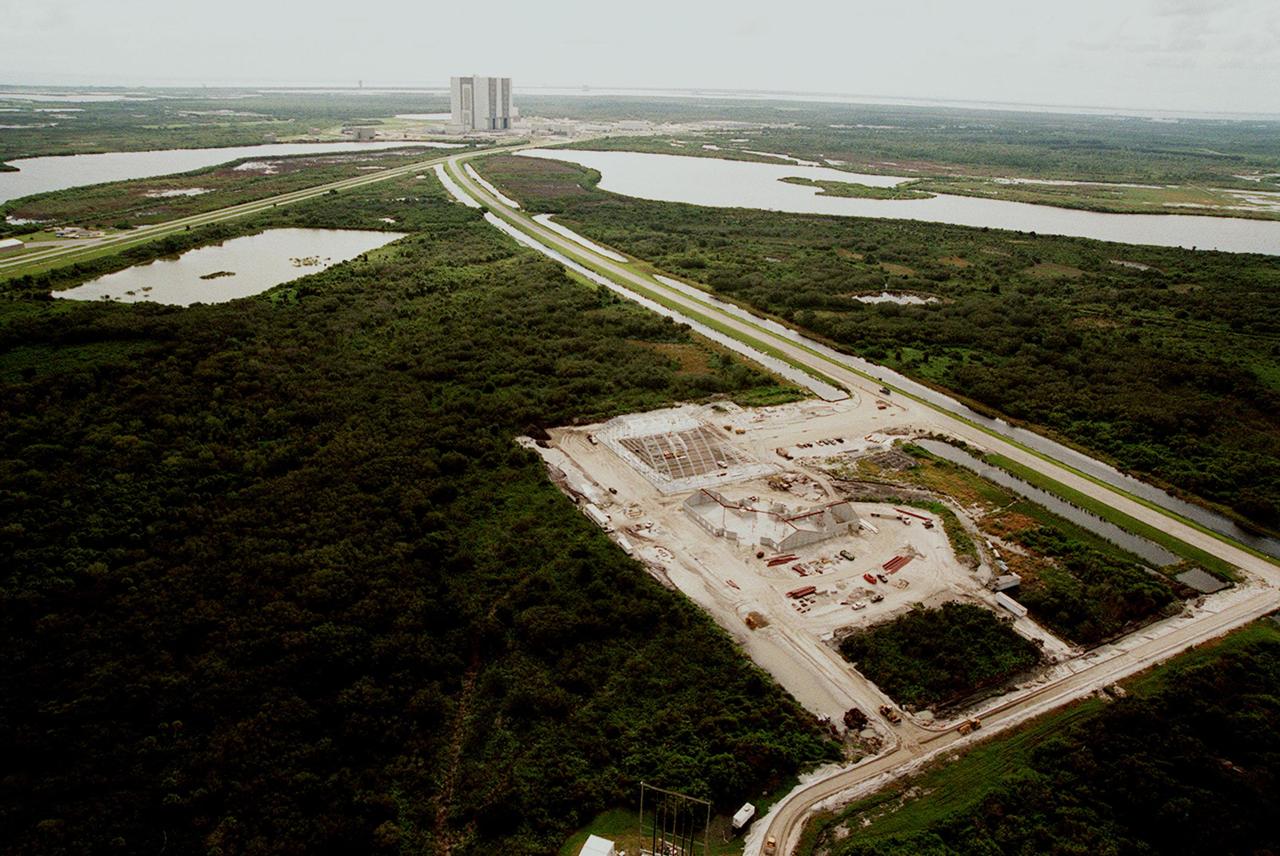

An aerial view reveals (foreground) the ongoing construction of an $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. At left is a multi-purpose hangar and at right a building for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building. The road at right is the tow-way. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000.
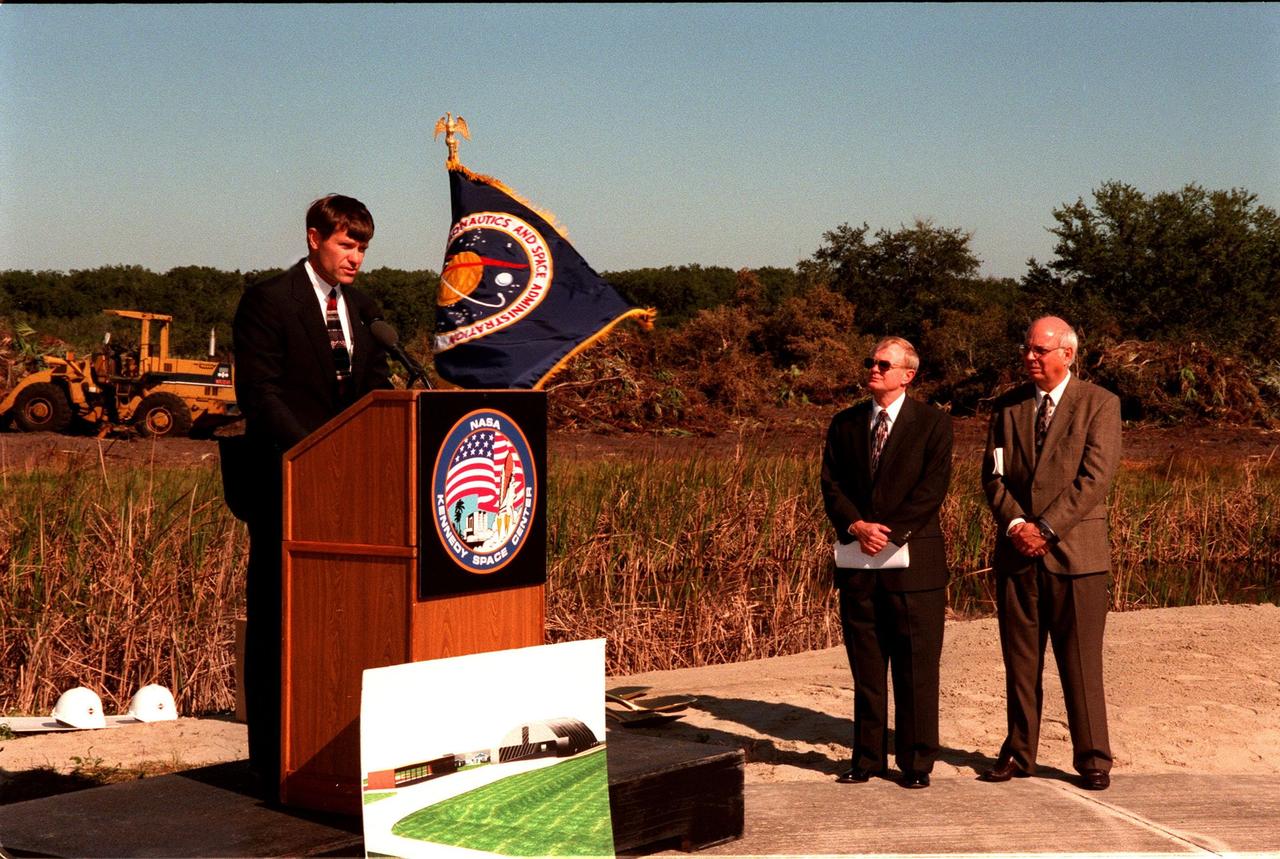

Donald McMonagle (left), manager, Launch Integration, speaks to federal and state elected officials during the ground breaking ceremony for a multi-purpose hangar, phase one of the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex to be built near the Shuttle Landing Facility. At right are Center Director Roy Bridges and Executive Director of the Spaceport Florida Authority (SFA) Ed O'Connor. The new complex is jointly funded by SFA, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and Kennedy Space Center. It is intended to support the Space Shuttle and other RLV land X-vehicle systems. Completion is expected by the year 2000
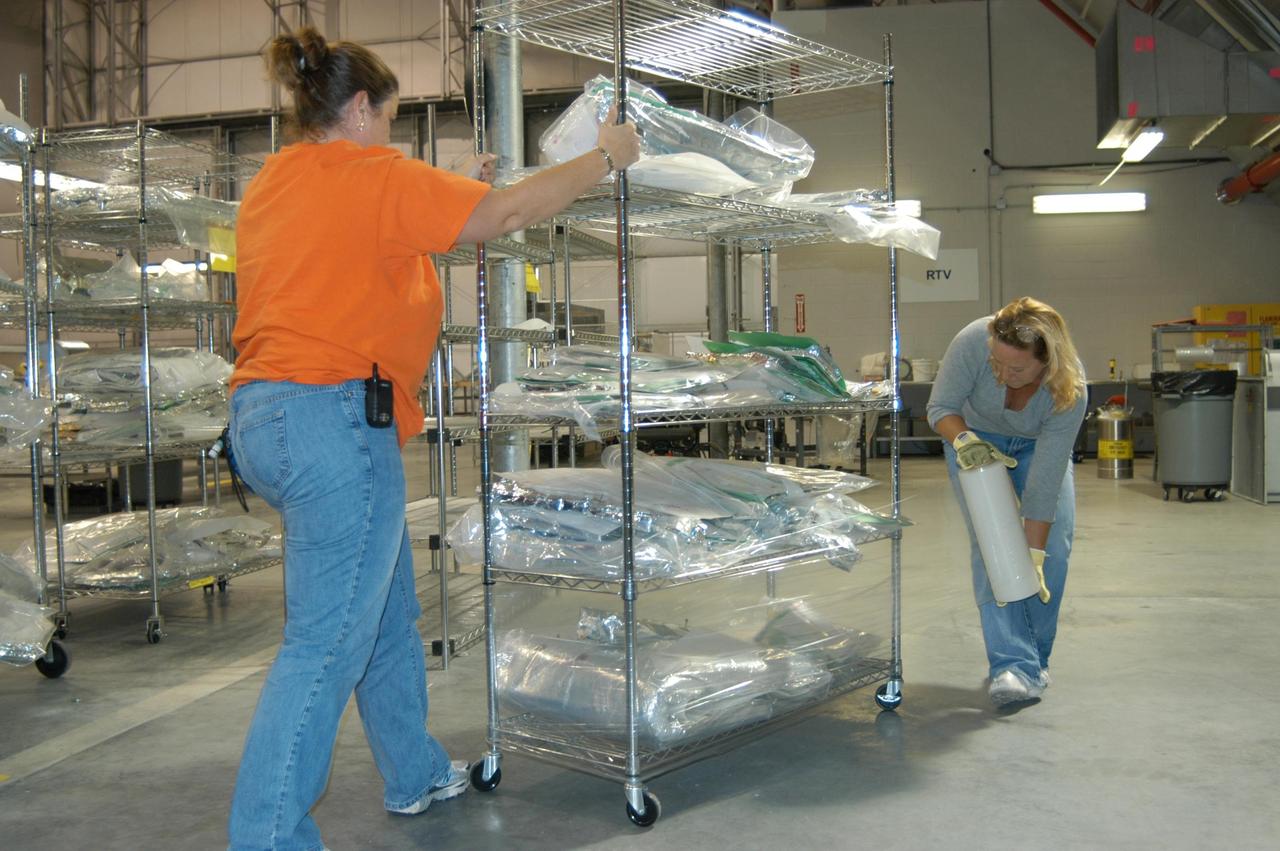

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Hangar, workers begin wrapping racks of equipment in preparation for the arrival of Hurricane Jeanne, expected to impact Central Florida Sunday. This is the fourth hurricane in 45 days to make landfall somewhere in the state. The Thermal Protection System (TPS) Facility suffered extensive damage from Hurricane Frances, causing the relocation of equipment to the RLV.
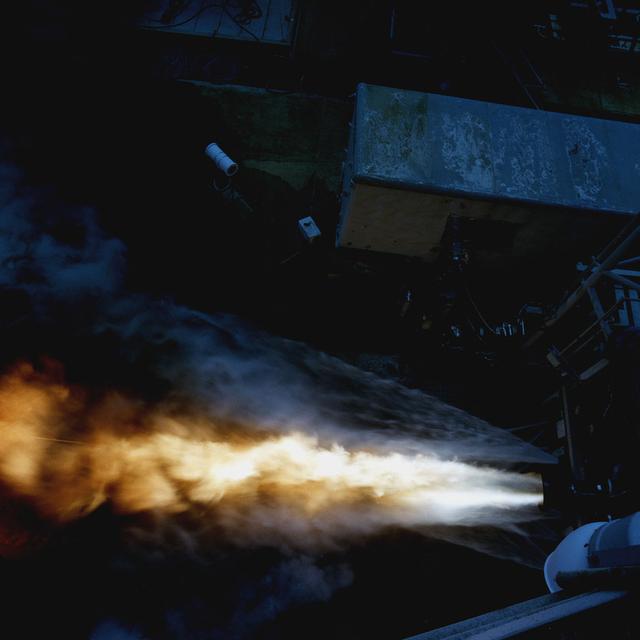

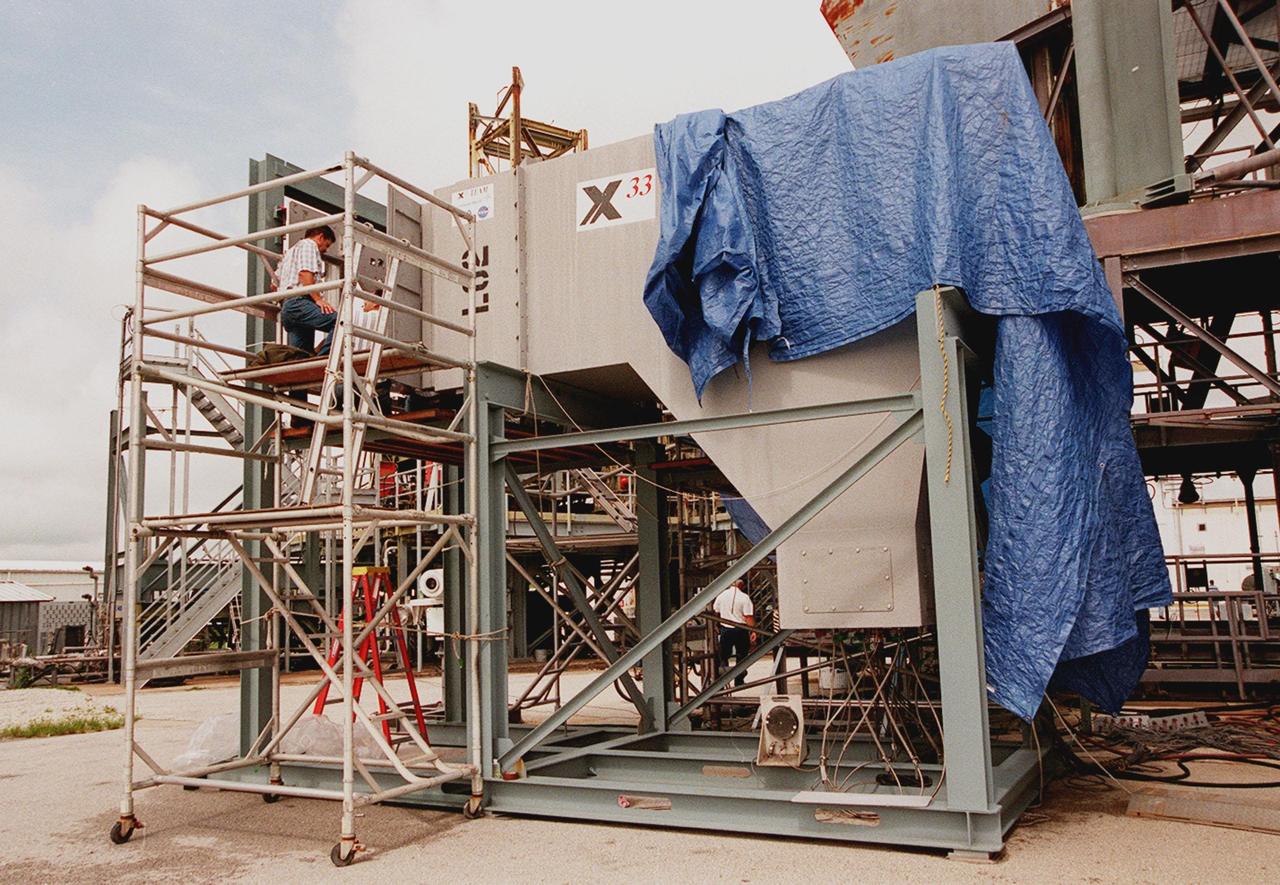
This shot offers a bird's eye-view of a Fastrac II engine duration test at Marshall's Test Stand 116. The Fastrac II engine was designed as a part of the low cost X-34 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV). The purpose for these tests was to test the different types of metal alloys in the nozzle. Beside the engine were six additional nozzels which spray a continuous stream of water onto the test stand to reduce damage to the test stand and the engines. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
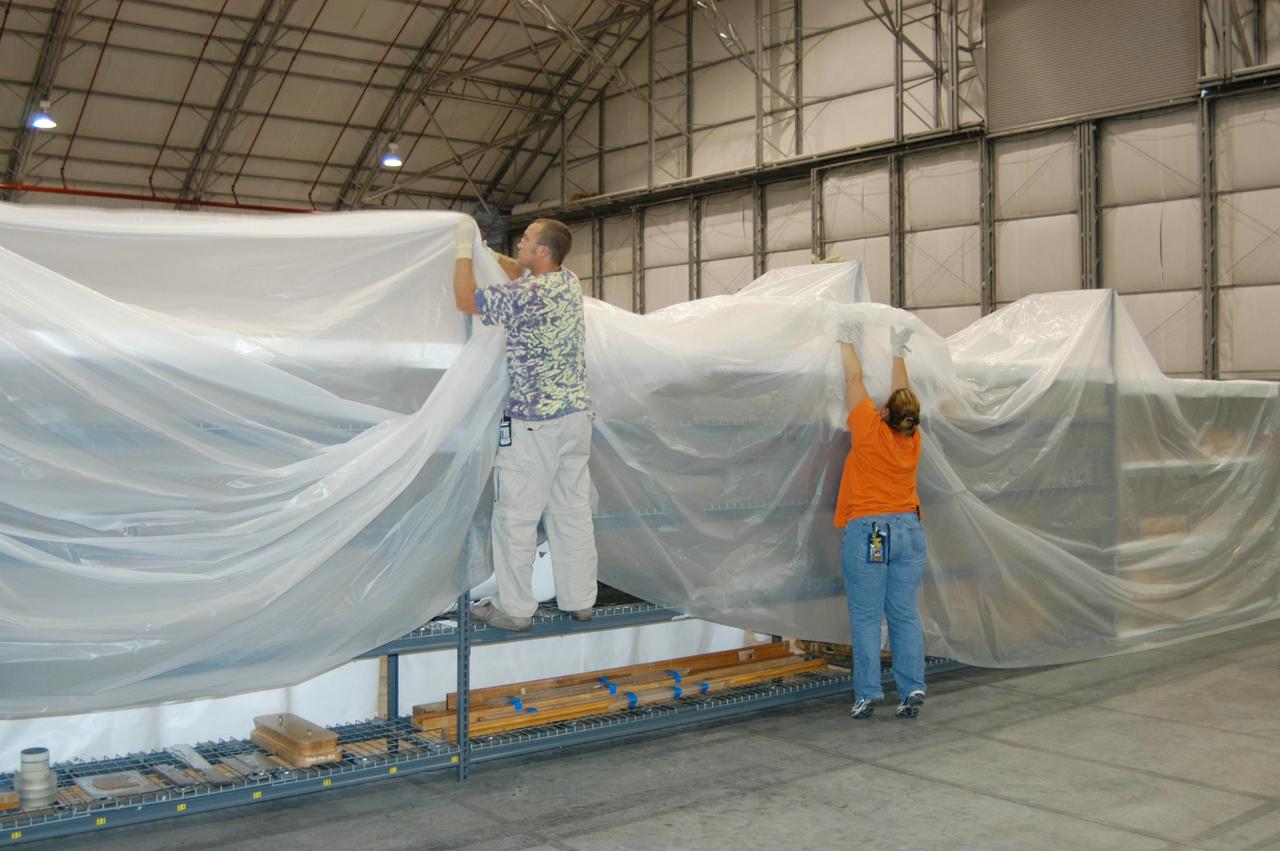

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Hangar, workers secure stretch sheets of plastic over racks of equipment in preparation for the arrival of Hurricane Jeanne, expected to impact Central Florida Sunday. This is the fourth hurricane in 45 days to make landfall somewhere in the state. The Thermal Protection System (TPS) Facility suffered extensive damage from Hurricane Frances, causing the relocation of equipment to the RLV.
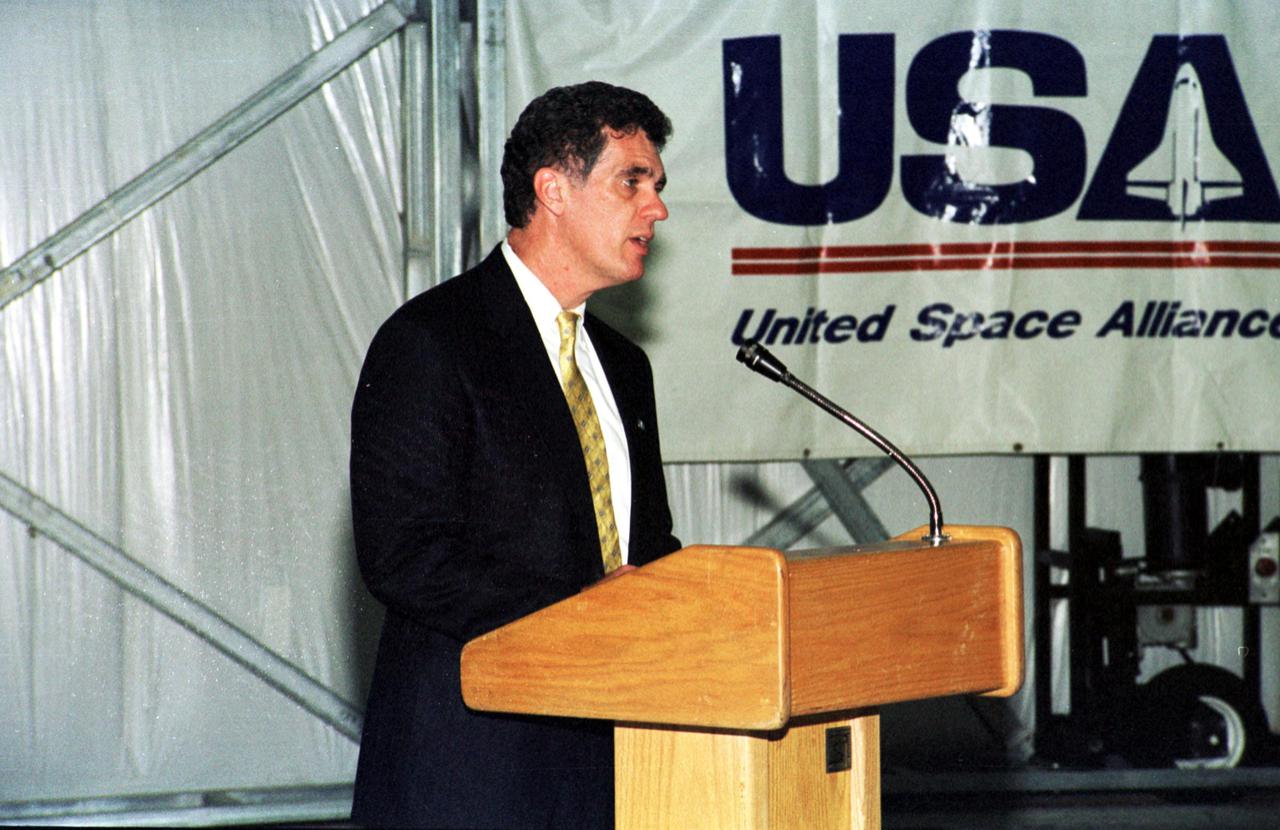

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Congressman Dave Weldon (R-Palm Bay) speaks to attendees at the signing of a lease agreement between Spaceport Florida Authority and United Space Alliance (USA) for the use of a hangar. The hangar was originally developed by the state as part of a joint NASA_ Spaceport Florida Authority (SFA) Reusable Launch Vehicle Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. USA plans to use the state-developed 50,000-square-foot facility to store and maintain Space Shuttle ground equipment
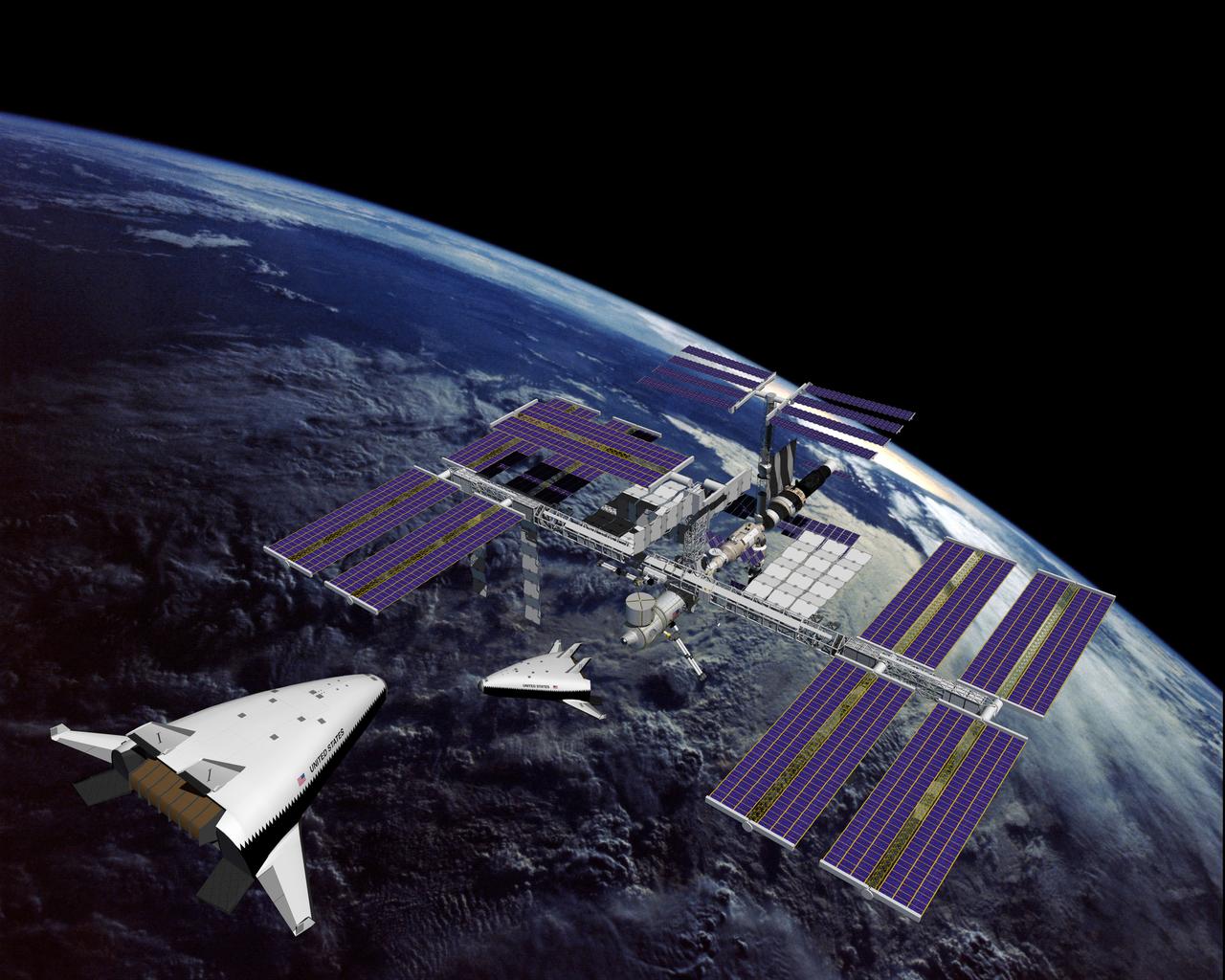

This is an artist's concept of the completely operational International Space Station being approached by an X-33 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV). The X-33 program was designed to pave the way to a full-scale, commercially developed RLV as the flagship technology demonstrator for technologies that would lower the cost of access to space. It is unpiloted, taking off vertically like a rocket, reaching an altitude of up to 60 miles and speeds between Mach 13 and 15, and landing horizontally like an airplane. The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.
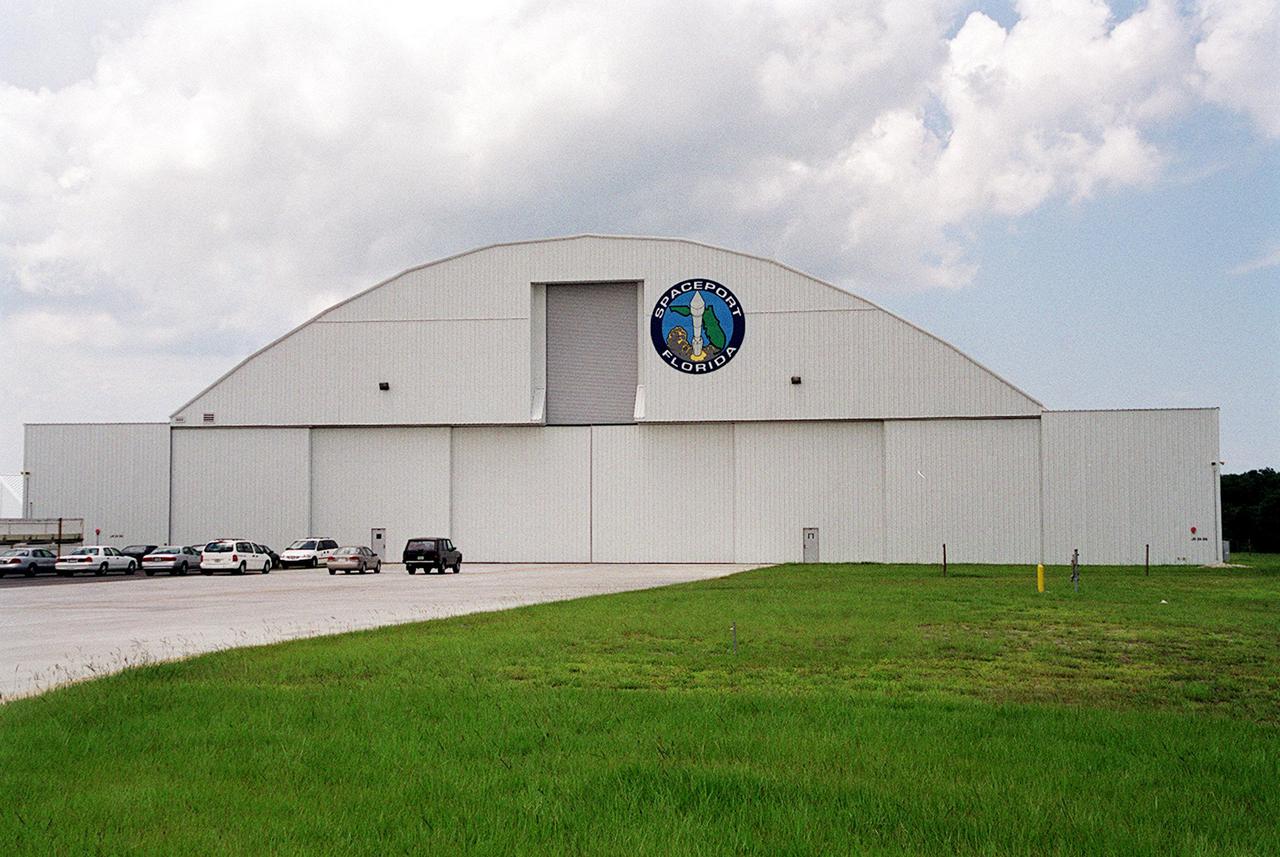

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- This state-developed 50,000-square-foot hangar at Kennedy Space Center is being leased by United Space Alliance (USA) to store and maintain Space Shuttle ground equipment. The hangar was originally developed by the state as part of a joint NASA_ Spaceport Florida Authority (SFA) Reusable Launch Vehicle Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. A ceremony at the site included the signing of a lease agreement between SFA and USA
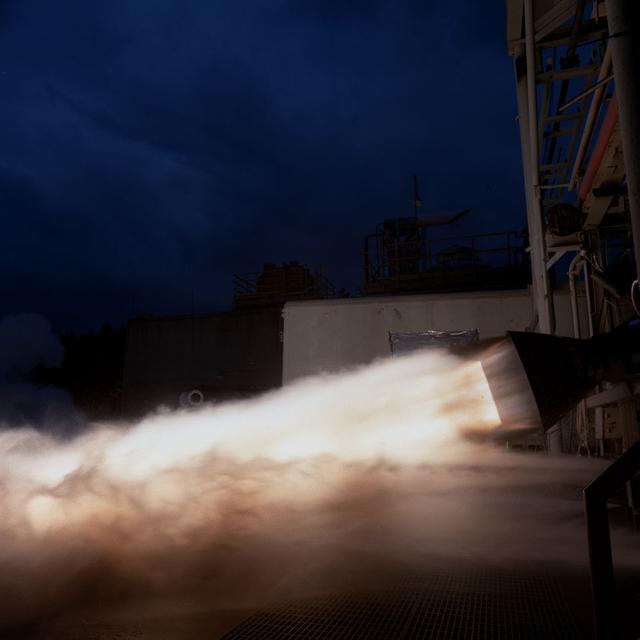

A close-up view of Bantam duration testing of the 40K Fastrac II Engine for X-34 at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) test stand 116. The Bantam test refers to the super lightweight engines of the Fastrac program. The engines were designed as part of the low cost X-34 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV). The testing of these engines at MSFC allowed the engineers to determine the capabilities of these engines and the metal alloys that were used in their construction. The Fastrac and X-34 programs were cancelled in 2001.
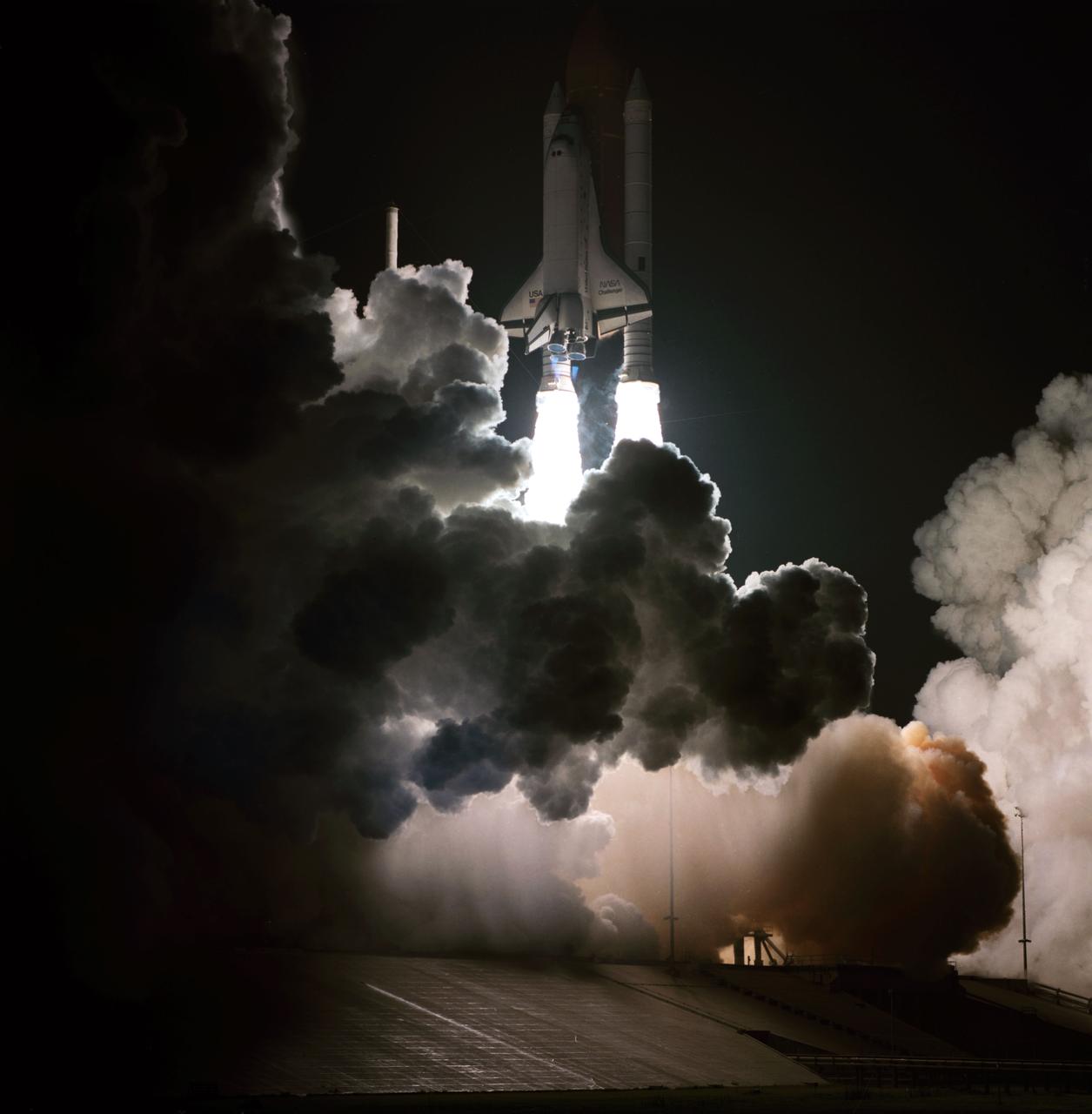

S83-39513 (30 Aug. 1983) --- NASA's eighth space shuttle launch lights up the Florida sky at 2:32 a.m. (EDT), Aug. 30, 1983. The Challenger's third flight is the first to have its beginnings in darkness. Five astronauts and an assortment of experiments are aboard the reusable vehicle. Crew members are astronauts Richard H. Truly, STS-8 commander; Daniel C. Brandenstein, pilot; and Dale A. Gardner, Guion S. Bluford and William E. Thornton, all mission specialists. Photo credit: NASA
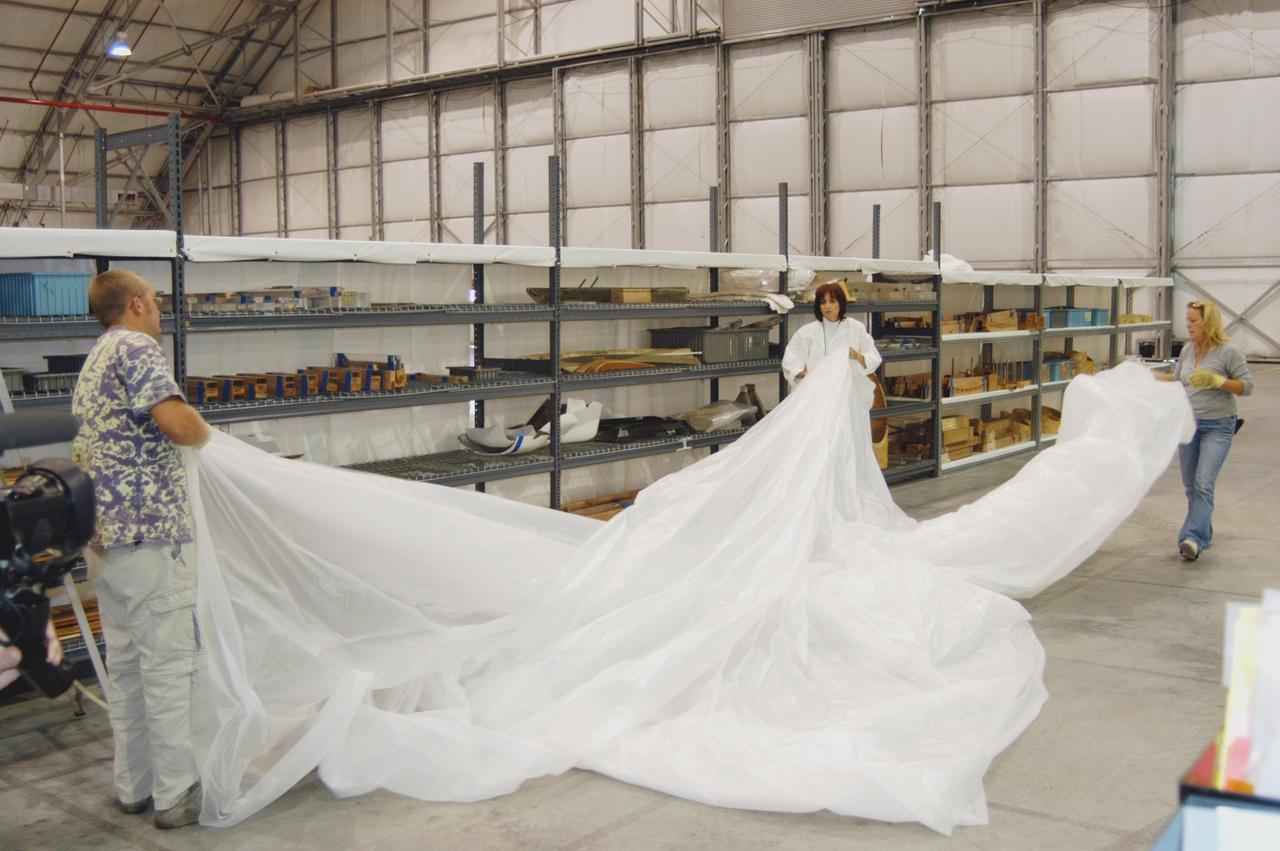

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In preparation for the arrival of Hurricane Jeanne, workers in the Reusable Launch Vehicle Hangar unroll long pieces of plastic to place on shelves holding Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF) equipment. Jeanne is expected to impact Central Florida Sunday. This is the fourth hurricane in 45 days to make landfall somewhere in the state. The TPSF suffered extensive damage from Hurricane Frances, causing the relocation of equipment and materials to the hangar.
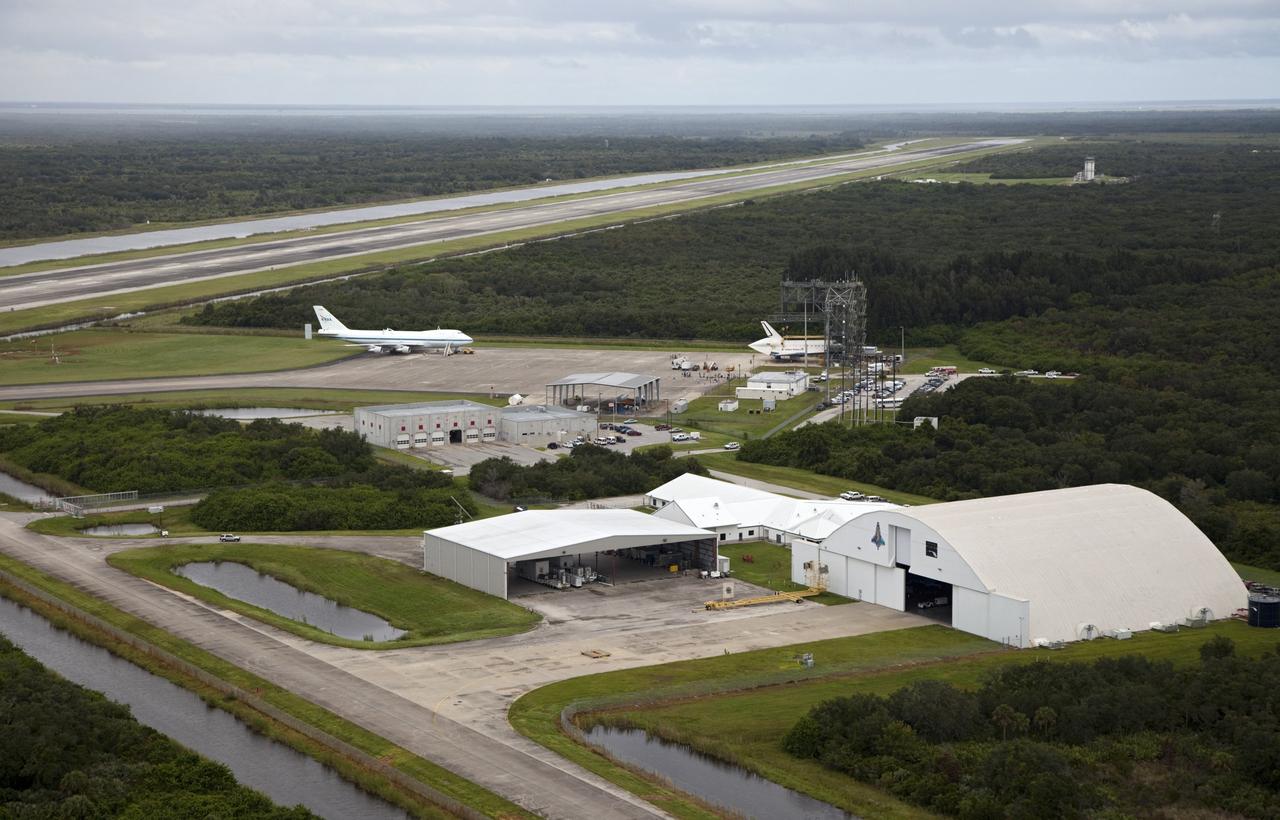

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Endeavour is seen inside the Mate-Demate Device, or MDD, at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, is seen on the ramp. The SCA will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. The center's Reusable Launch Vehicle hangar and other structures at the SLF are also visible. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Hangar, workers stretch sheets of plastic over racks of equipment in preparation for the arrival of Hurricane Jeanne, expected to impact Central Florida Sunday. This is the fourth hurricane in 45 days to make landfall somewhere in the state. The Thermal Protection System (TPS) Facility suffered extensive damage from Hurricane Frances, causing the relocation of equipment to the RLV.
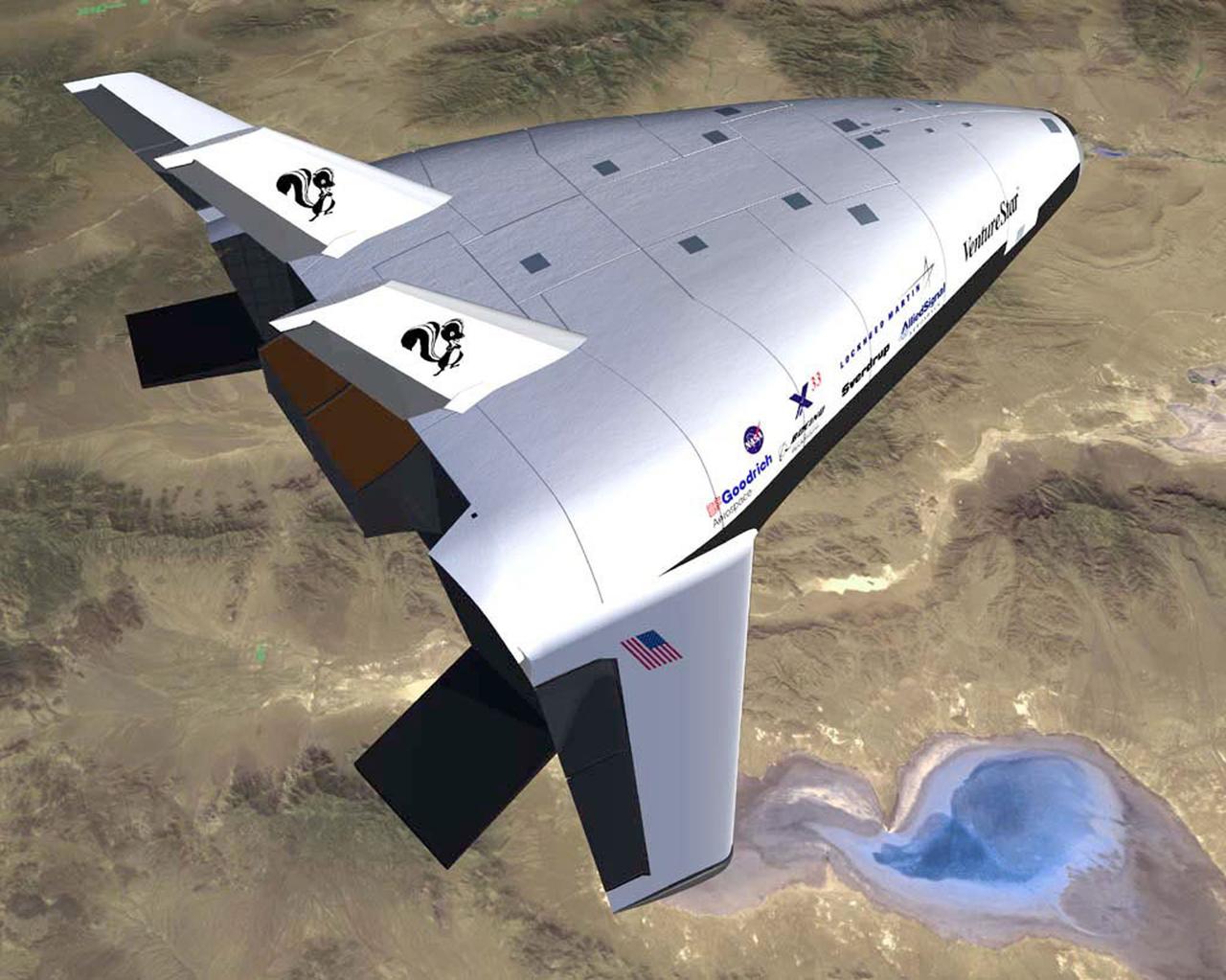

Pictured here is an artist's concept of the experimental X-33 in-flight. The X-33 program was designed to pave the way to a full-scale commercially developed, reusable launch vehicle (RLV). The program that will put the U.S. on a path toward safe, affordable, reliable access to space by providing the latest technology was ready for space flight. The X-33 is the flagship technology demonstrator for technologies that will dramatically lower the cost of access to space. The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.

Managed by Marshall Space Flight Center, the Space Tug was a reusable multipurpose space vehicle designed to transport payloads to different orbital inclinations. Utilizing mission-specific combinations of its three primary modules (crew, propulsion, and cargo) and a variety of supplementary kits, the Space Tug was capable of numerous space applications. This 1970 artist's concept depicts the Tug's propulsion module launching a space probe into lunar orbit.
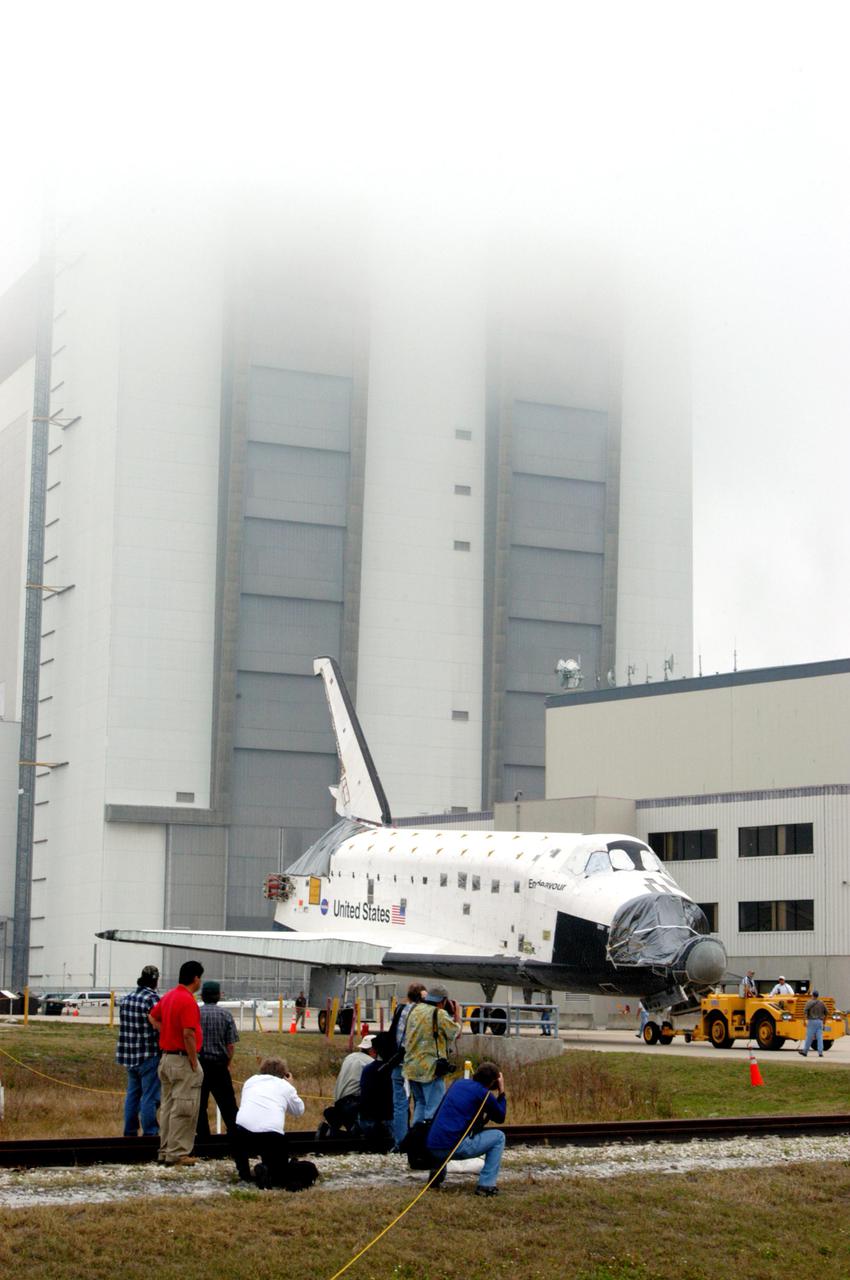

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers watch as the orbiter Endeavour rolls past the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Florida Space Authority’s Reusable Launch Vehicle hangar for temporary storage. Endeavour is being moved from the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) to allow work to be performed in the OPF that can only be accomplished while the bay is empty. Work scheduled in the OPF includes modifications to the bay and platform validation in the bay. Endeavour will remain in the hangar for approximately 30 days, then return to the OPF. Endeavour was pulled out of service in December 2003 for Orbiter Major Modification (OMM). OMMs are scheduled at regular intervals to enhance safety and performance, infuse new technology, and, in this case, perform RTF modifications.
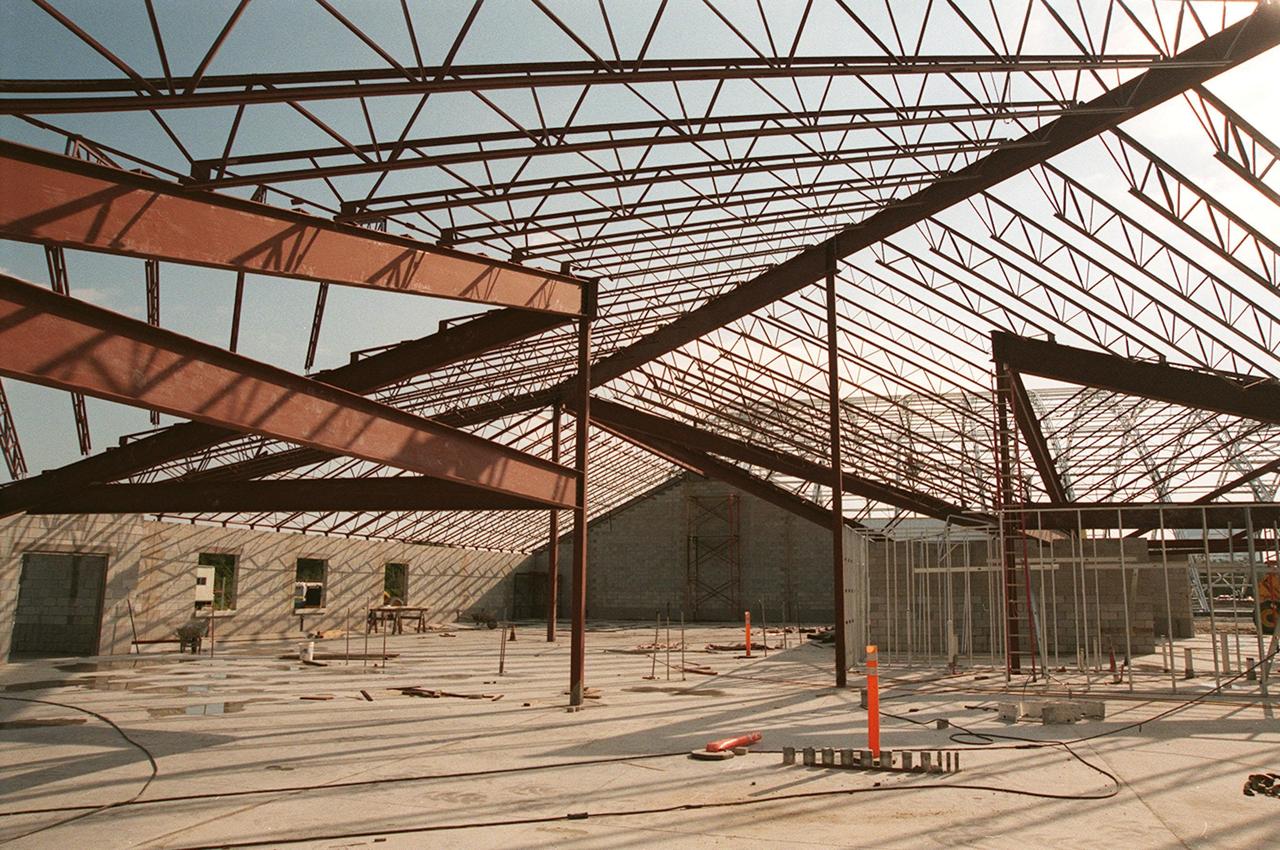

Girders overhead cast shadows on the walls and floor of a support building under construction, part of the new $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. The building is to be used for related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support. The RLV complex also includes a multi-purpose hangar. The complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The facility, jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC, will be operational in early 2000
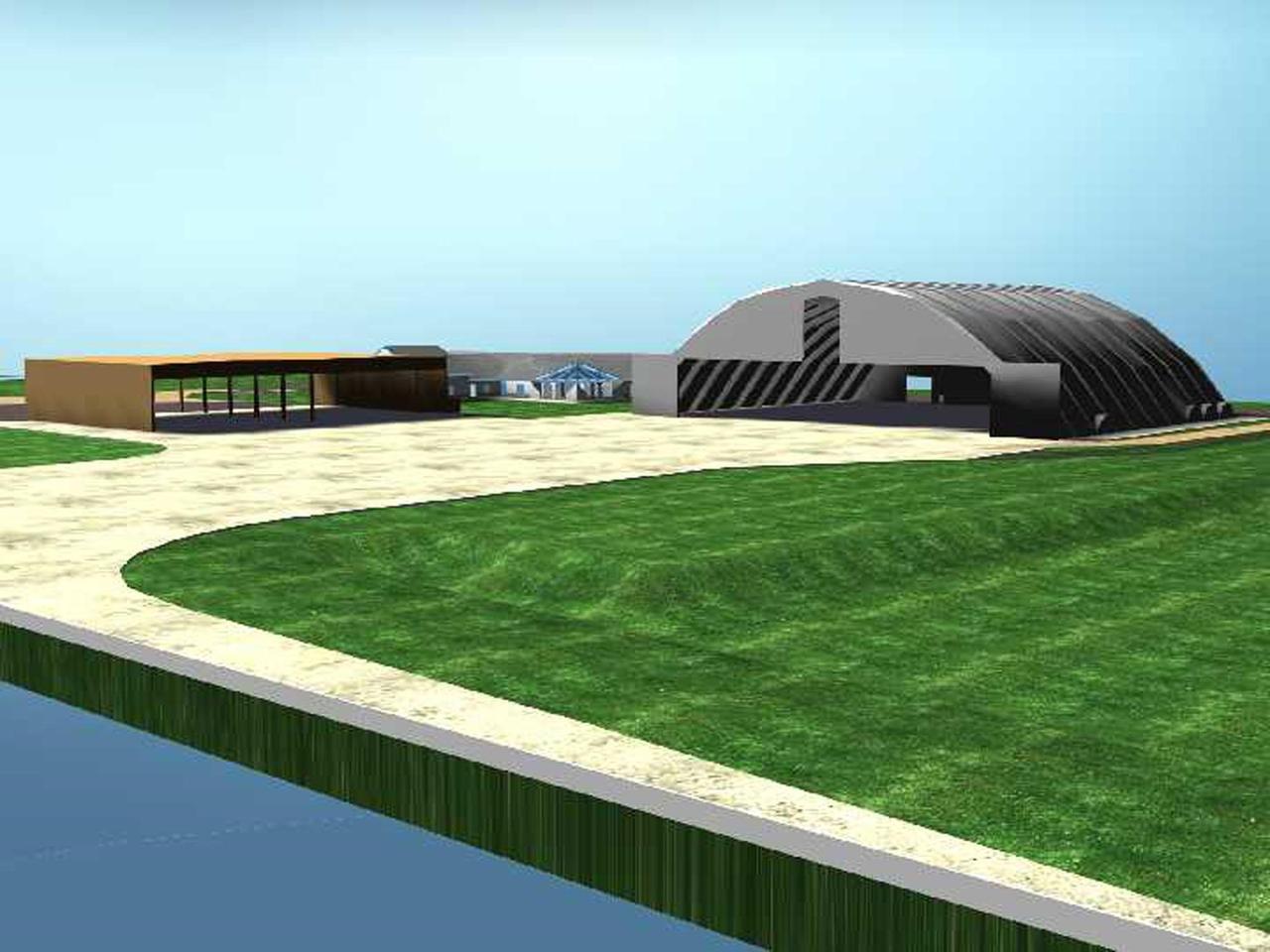

An artist's rendering shows the $8-million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex planned for the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) at Kennedy Space Center. The ground breaking took place today. To be located at the tow-way adjacent to the SLF, the complex will include a multi-purpose RLV hangar and adjacent facilities for related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support. It will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle, the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator, the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34, and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
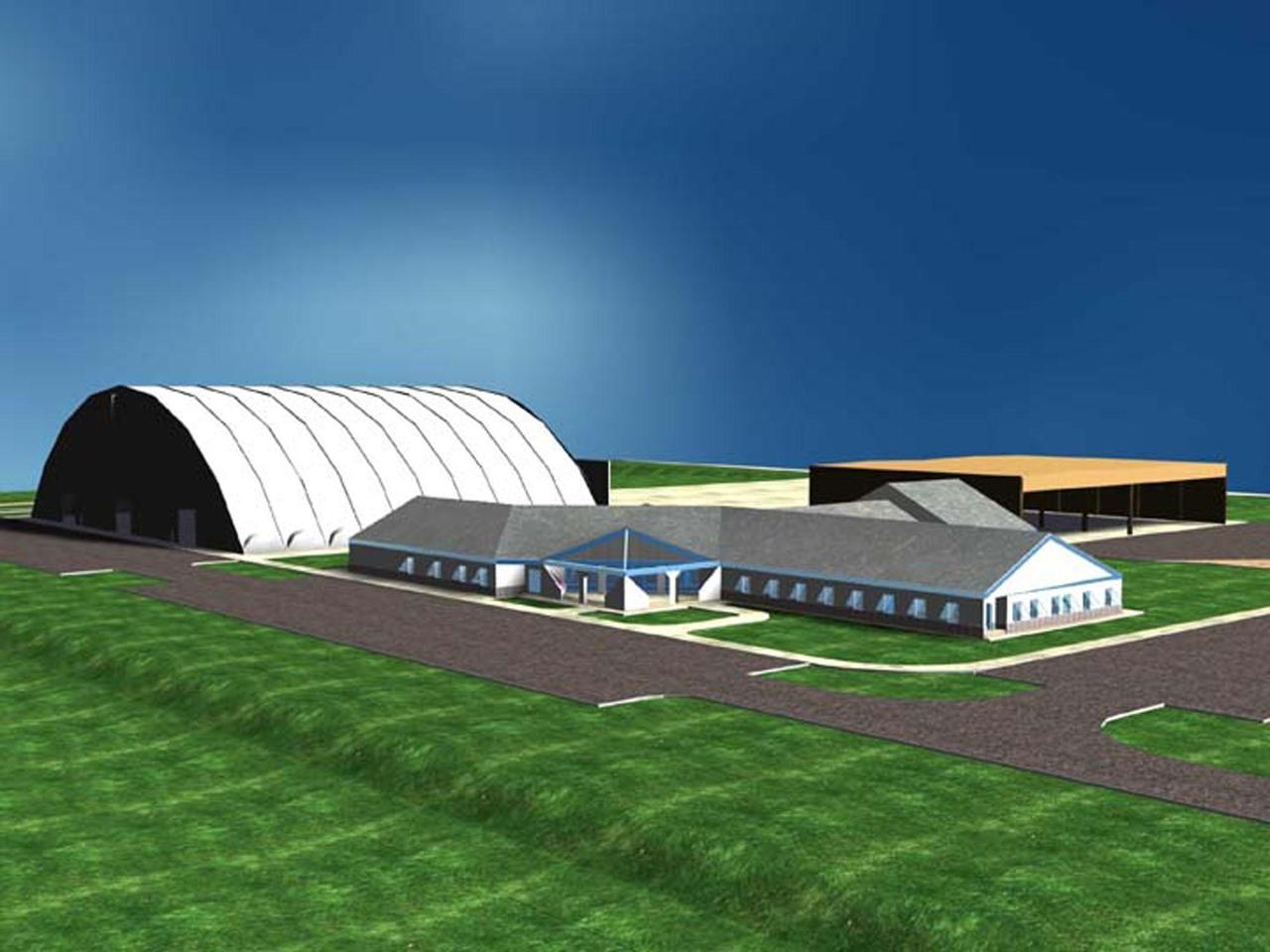

An artist's rendering shows the $8-million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex planned for the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) at Kennedy Space Center. The ground breaking took place today. To be located at the tow-way adjacent to the SLF, the complex will include a multi-purpose RLV hangar and adjacent facilities for related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support. It will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle, the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator, the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34, and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
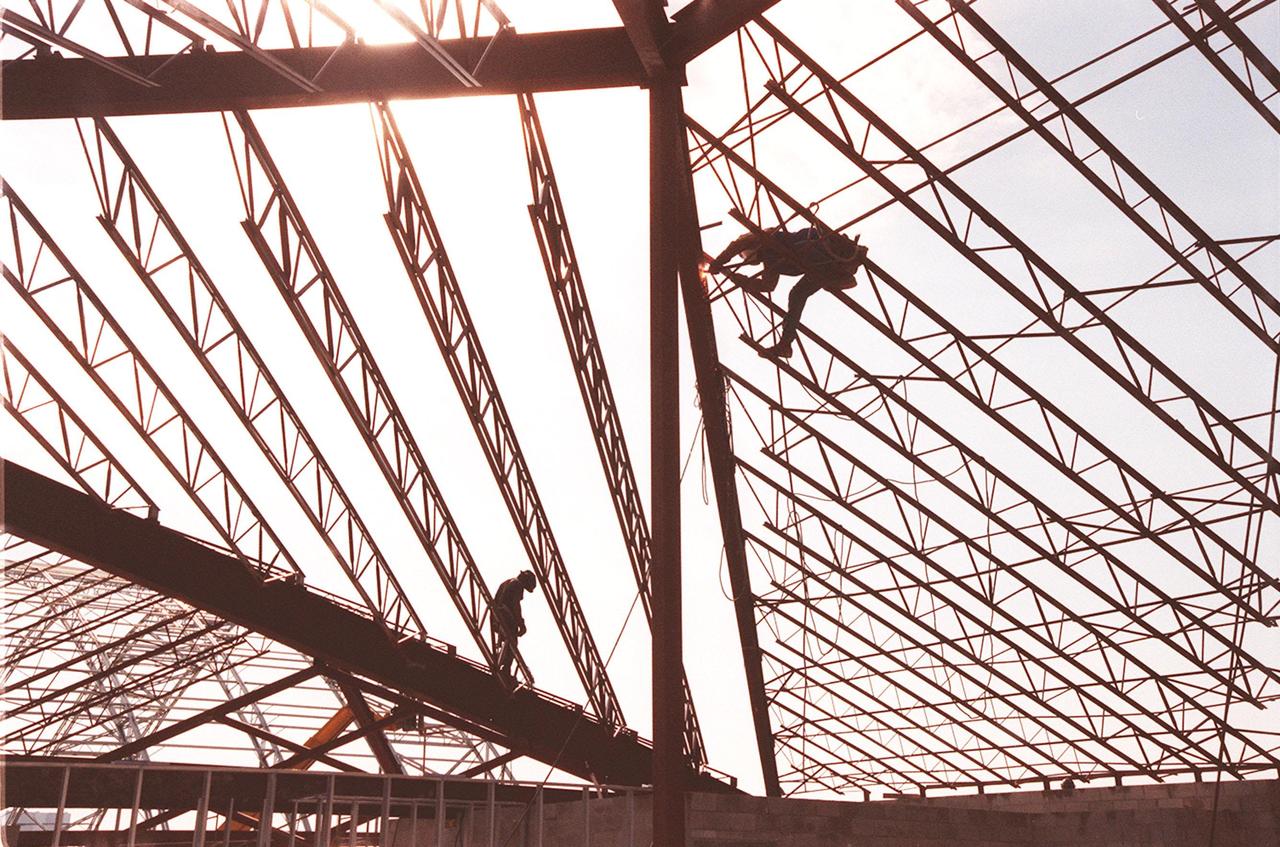

Construction workers are silhouetted against the sky as they work on the girders of a support building, part of the new $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. The building is to be used for related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support. The RLV complex also includes a multi-purpose hangar. The complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The facility, jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC, will be operational in early 2000
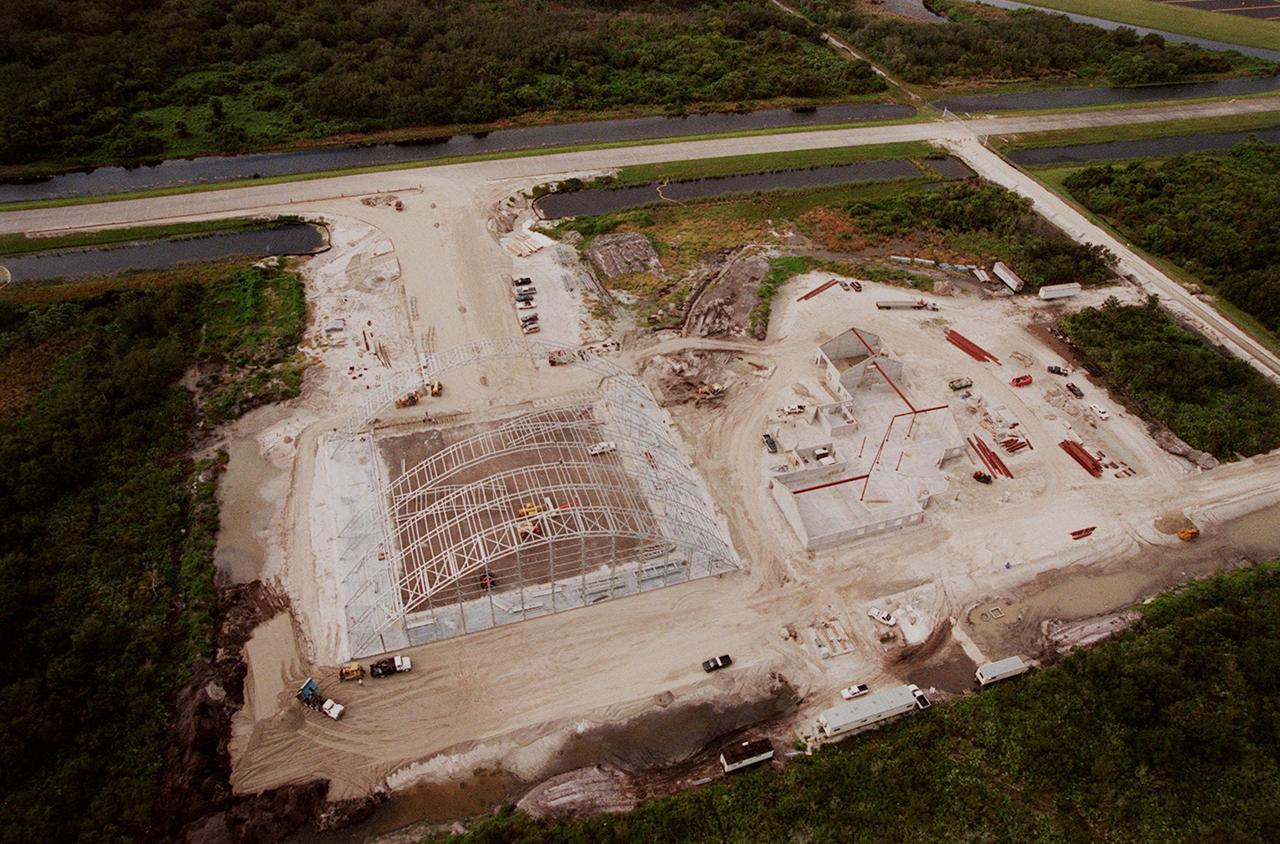

Construction continues on an $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. At left is a multi-purpose hangar and at right a building for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. The complex is situated at the Shuttle Landing Facility (upper right). Near the top of the photo is the tow-way. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
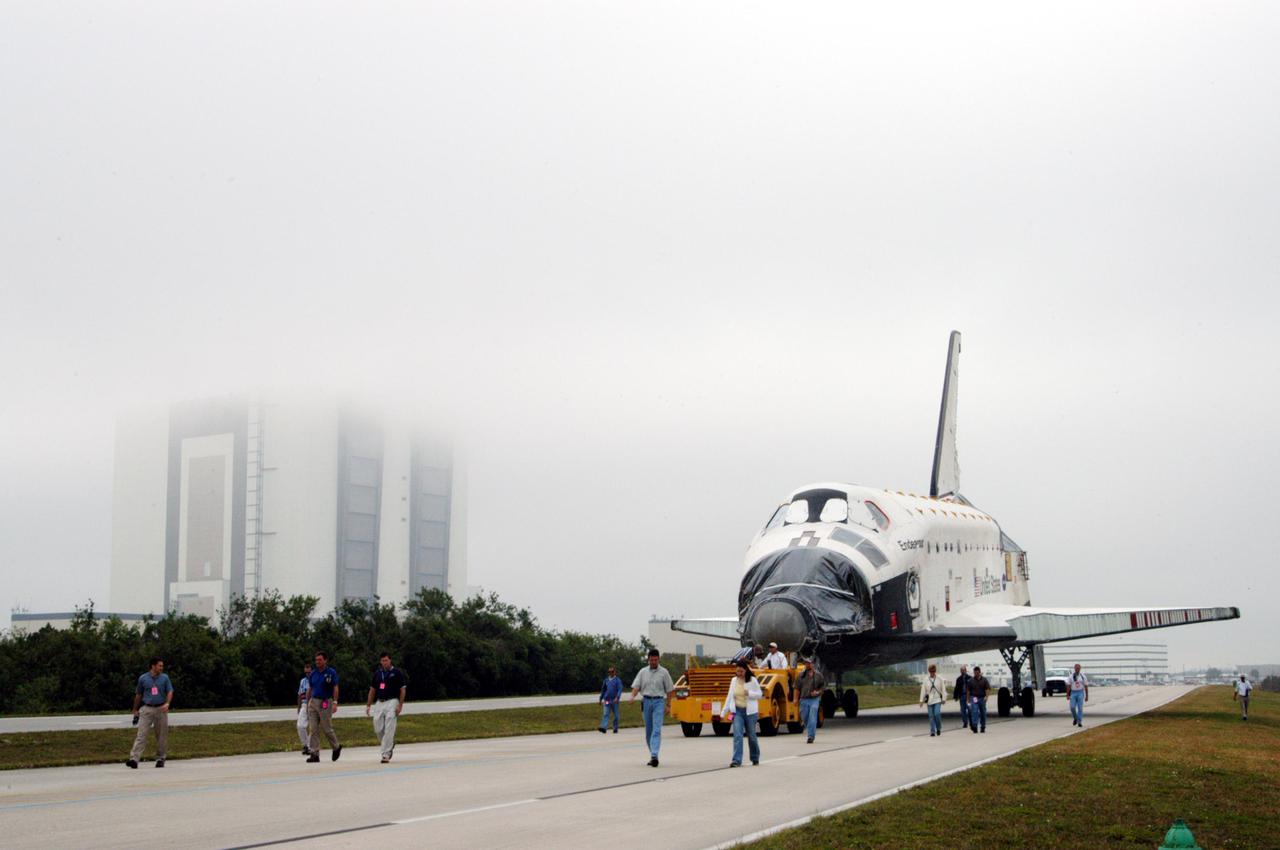

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers accompany the orbiter Endeavour as it rolls past the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Florida Space Authority’s Reusable Launch Vehicle hangar for temporary storage. Endeavour is being moved from the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) to allow work to be performed in the OPF that can only be accomplished while the bay is empty. Work scheduled in the OPF includes modifications to the bay and platform validation in the bay. Endeavour will remain in the hangar for approximately 30 days, then return to the OPF. Endeavour was pulled out of service in December 2003 for Orbiter Major Modification (OMM). OMMs are scheduled at regular intervals to enhance safety and performance, infuse new technology, and, in this case, perform RTF modifications.
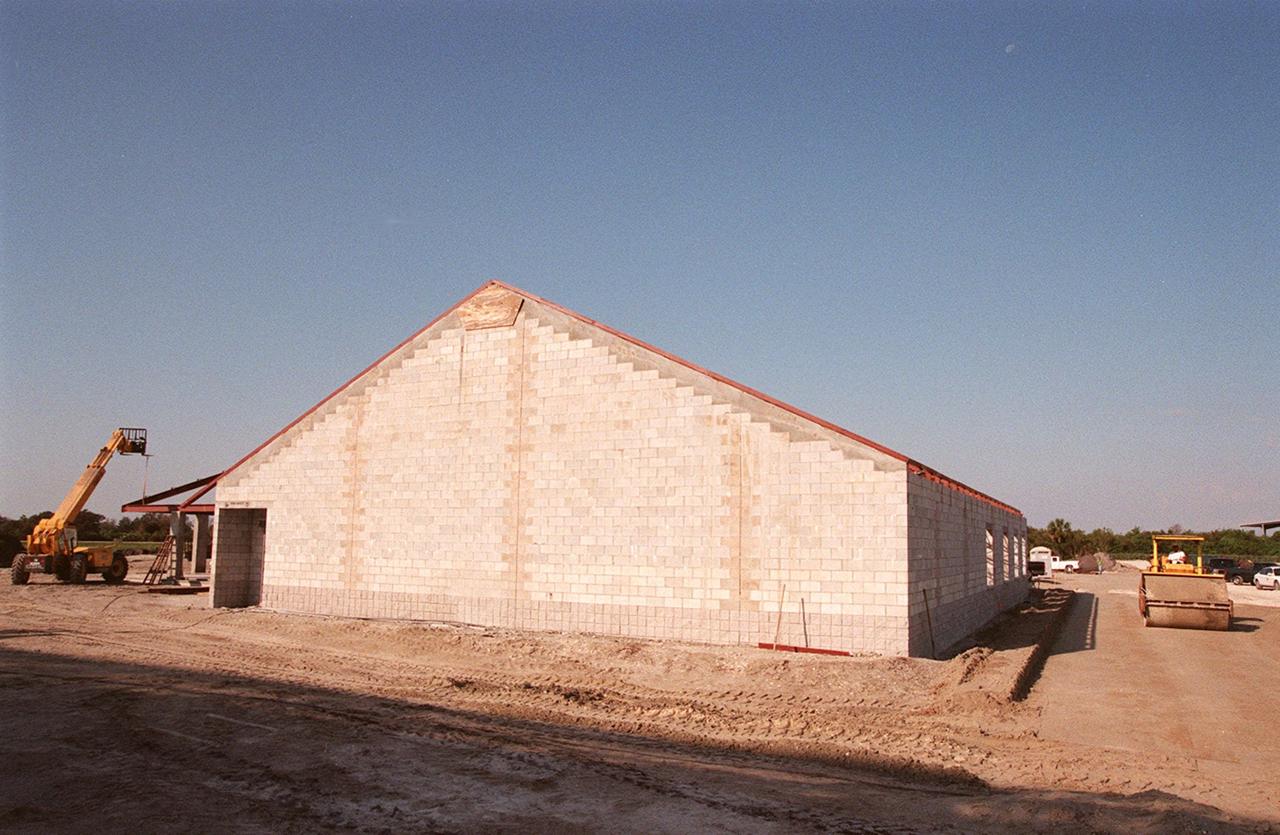

The support building at the $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center takes form. It will house related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support. The RLV complex includes a multi-purpose hangar that will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
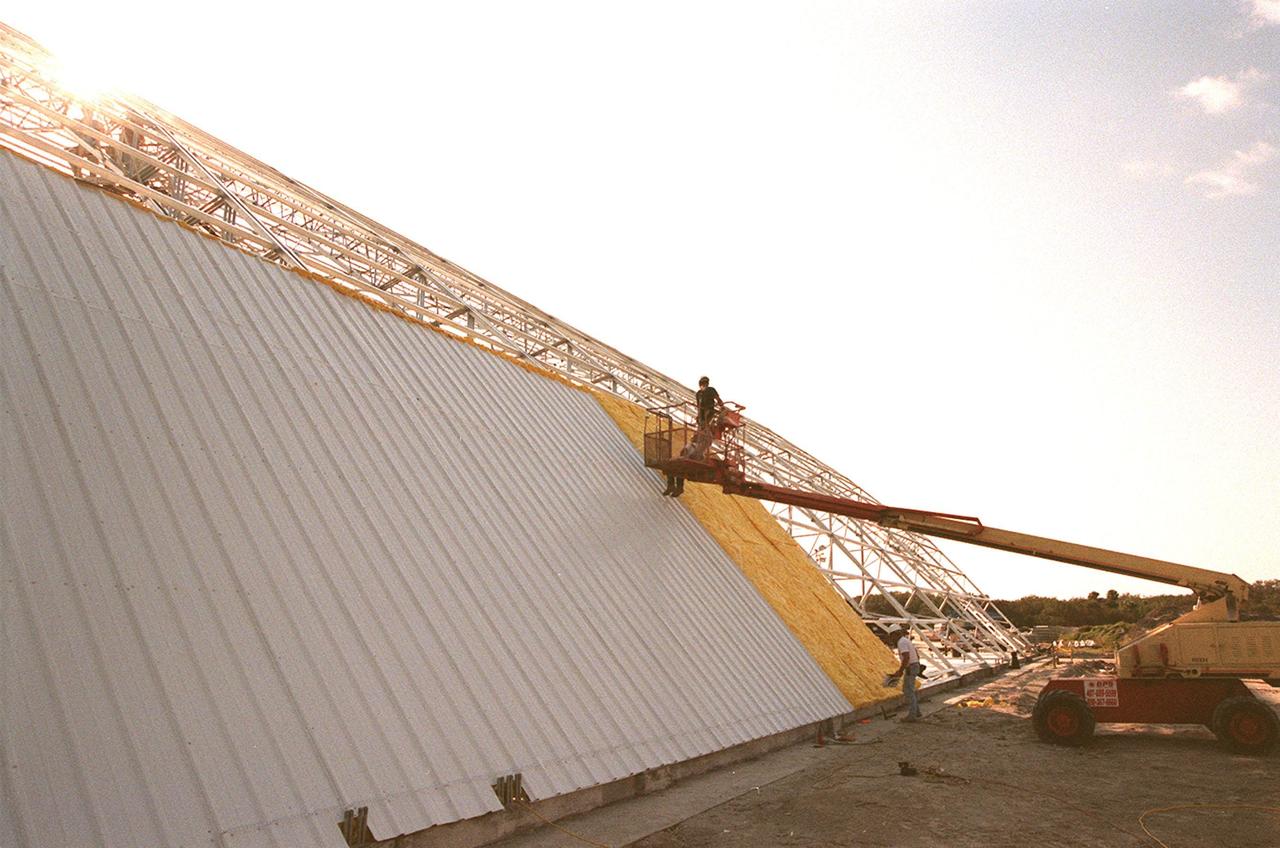

Workers place the first roof panels on the multi-purpose hangar at the site of the $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. The RLV complex, which includes the hangar and a building for related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support, will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
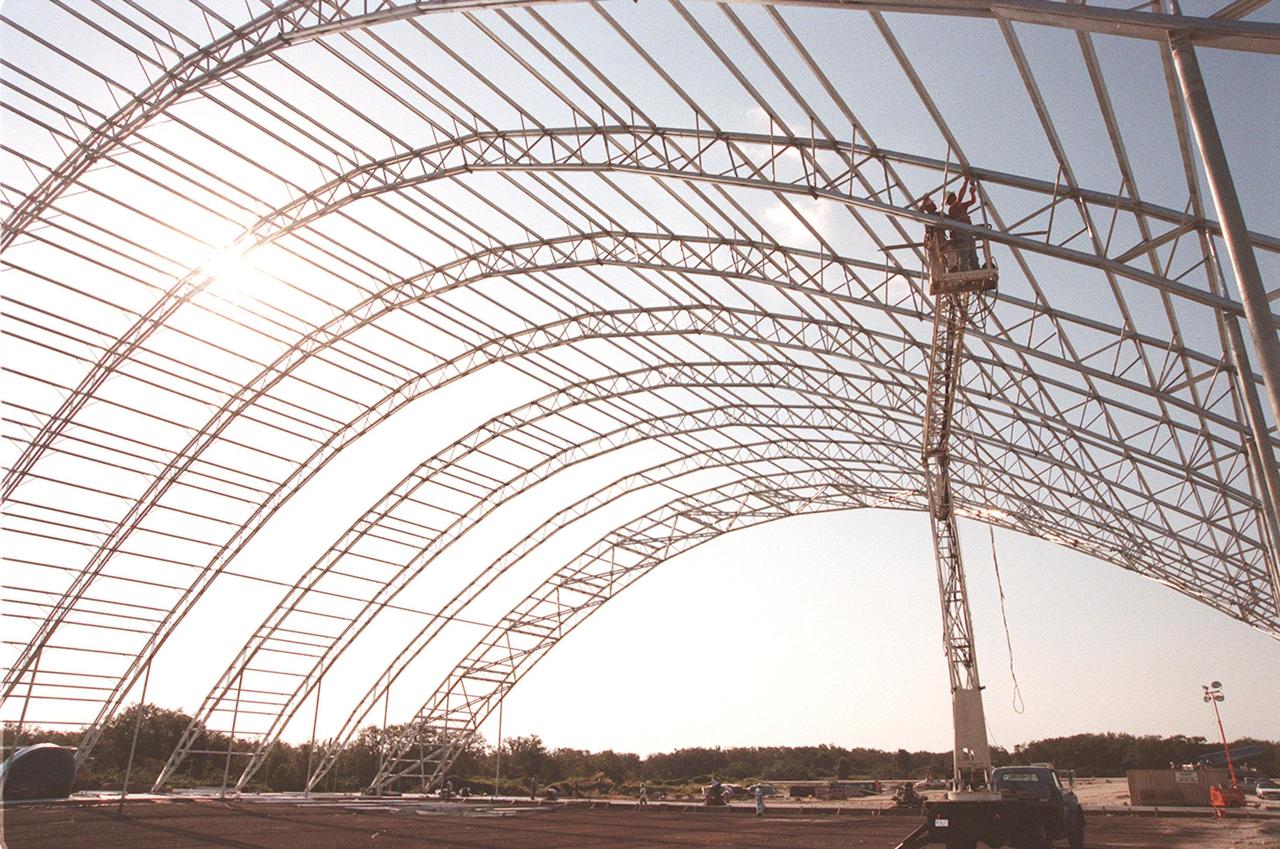

Work continues on the construction of the roof for the multi-purpose hangar at the site of the $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. In the background can be seen the new construction for the building that will house related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
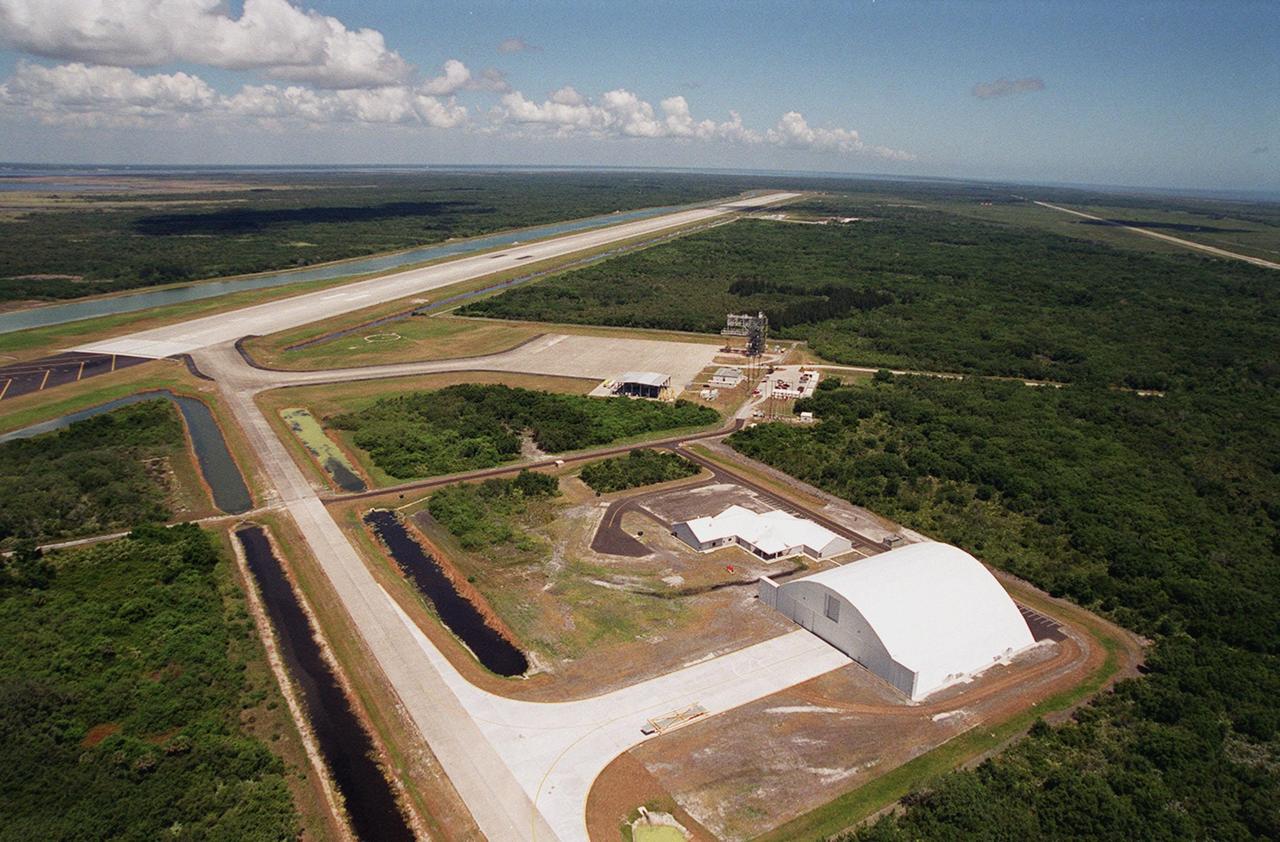

In the foreground of this aerial photo is the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. At right is a multi-purpose hangar and to its left is a building for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. The complex is situated at the Shuttle Landing Facility (center). At the upper left is the runway. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA’s Space Shuttle Program and KSC
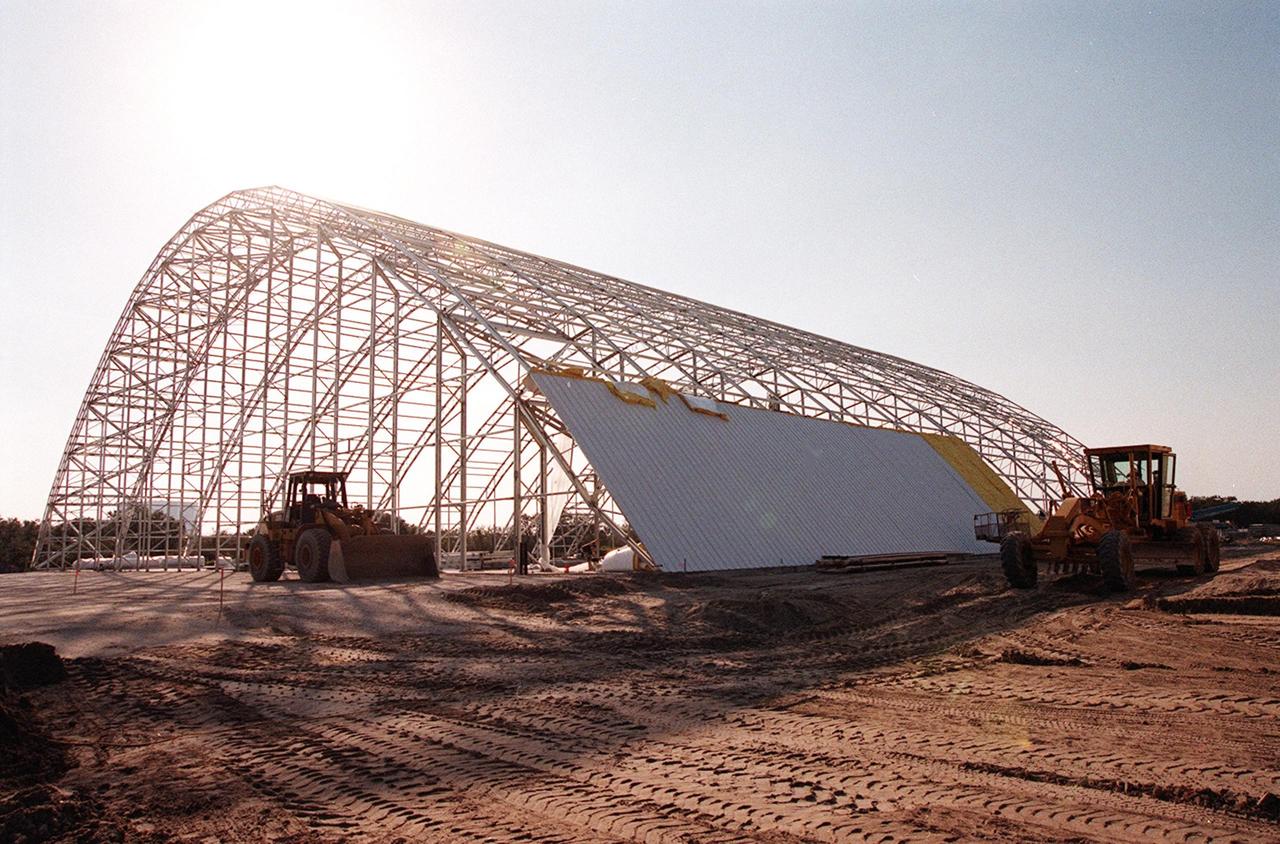

The first roof panels are placed on the multi-purpose hangar at the site of the $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. The RLV complex, which includes the hangar and a building for related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support, will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000

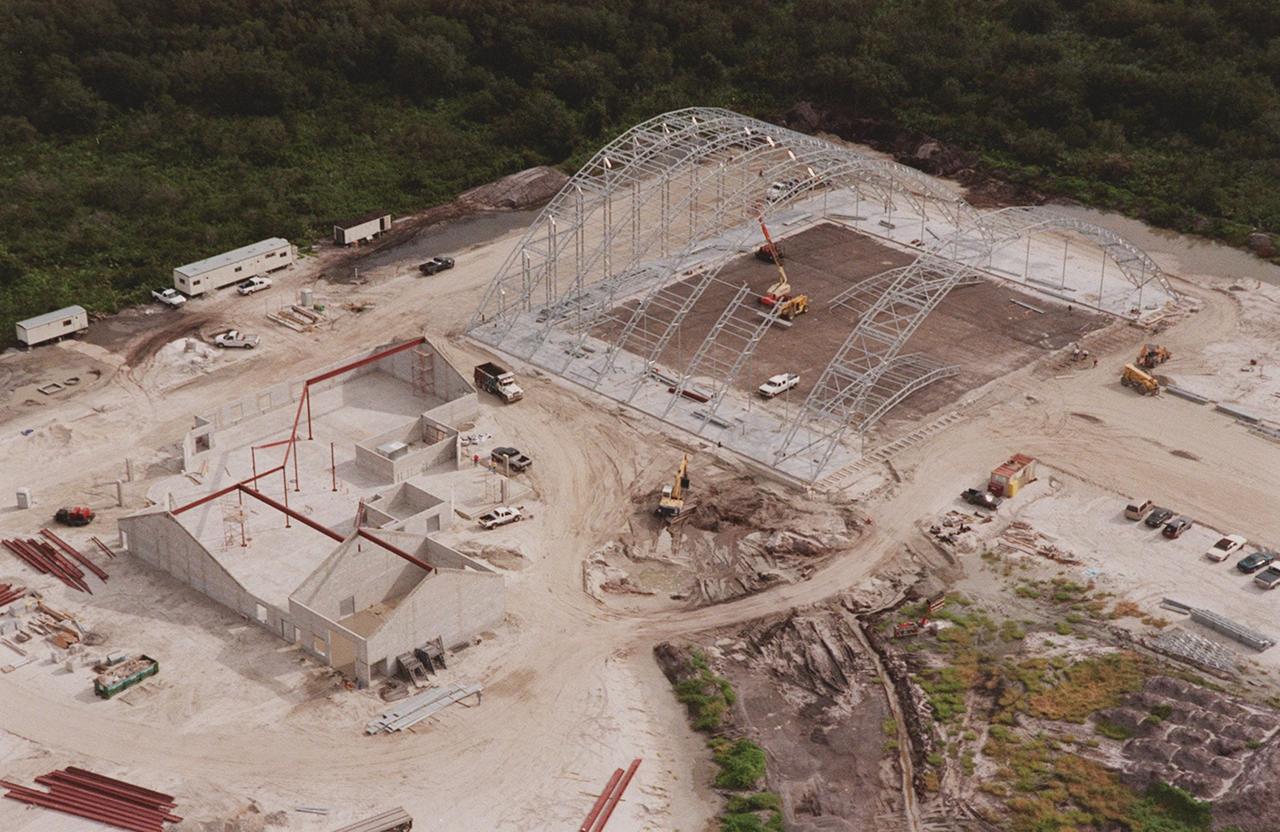
Looking southwest, this view shows ongoing construction of a multi-purpose hangar, which is part of the $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. Edging the construction is Sharkey Road, which parallels the landing strip of the Shuttle Landing Facility nearby. The RLV complex will include facilities for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. It will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000.

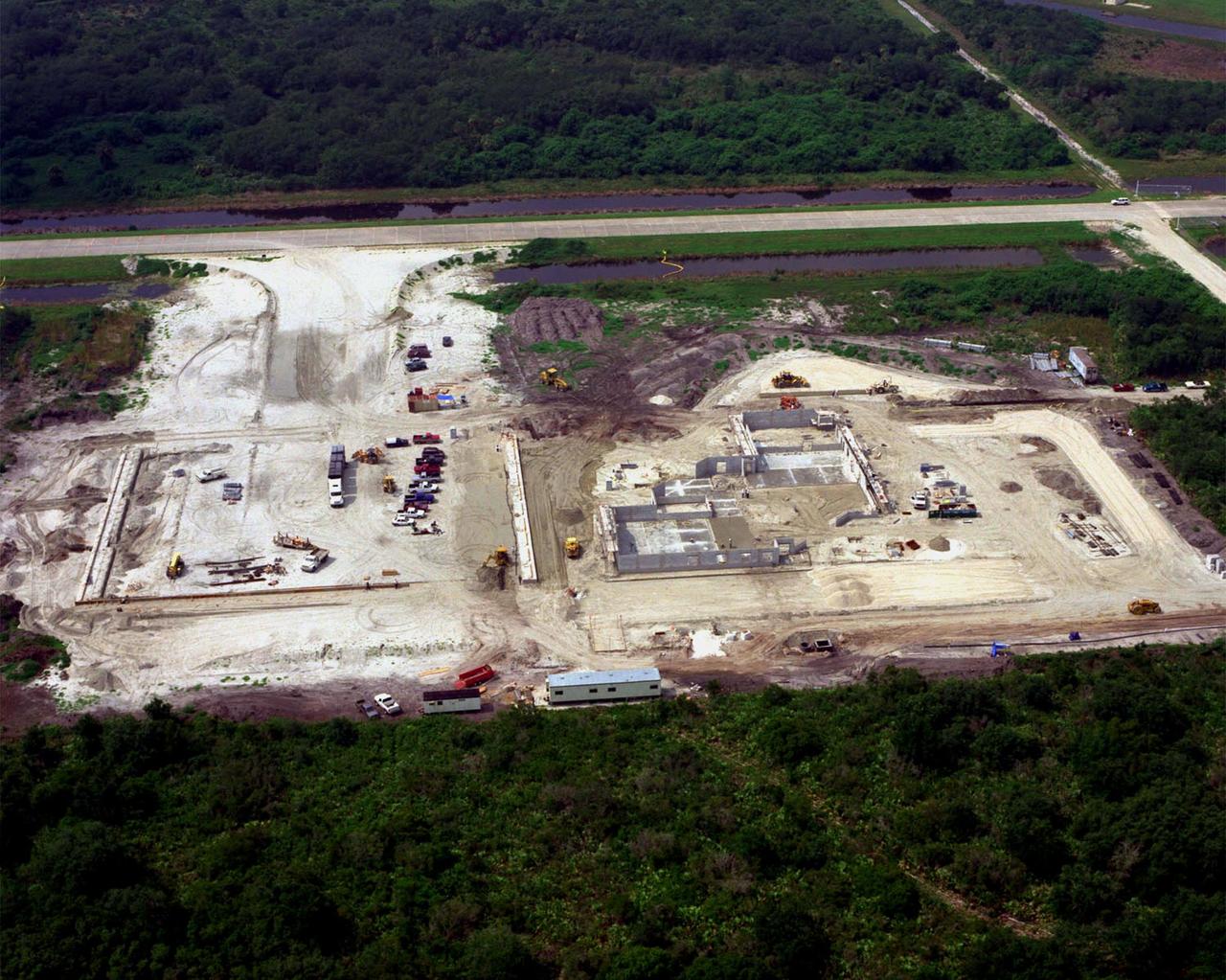
An aerial closeup view reveals the ongoing construction of an $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. At right is a multi-purpose hangar and at left a building for related ground support equipment and administrative/ technical support. The complex is situated at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Near the top of the photo can be seen the tow-way. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
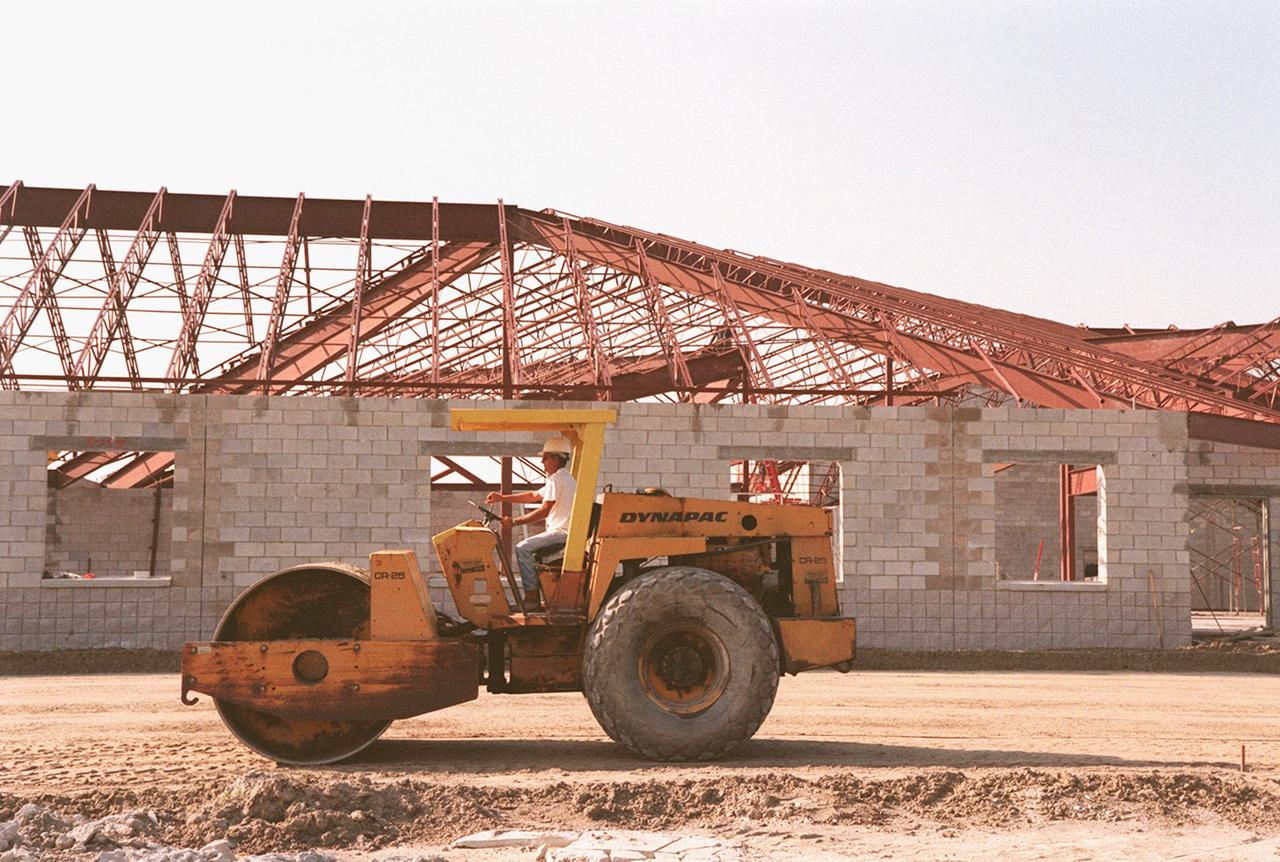

A steam roller packs down the ground next to construction of a support building, part of the $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. The RLV complex, which includes a multi-purpose hangar and the building to be used for related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support, will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
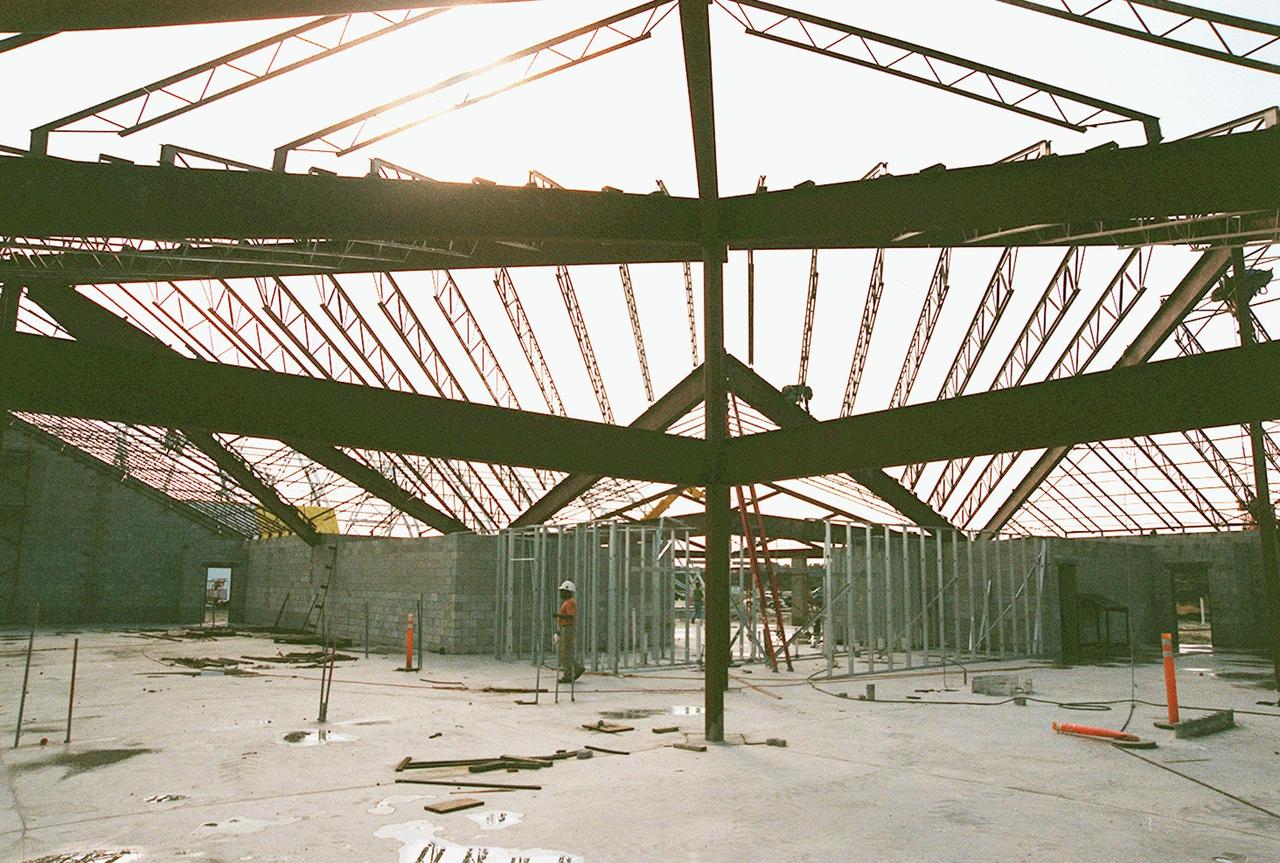

Construction continues on the $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. Shown is the interior of the building to be used for related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support. The RLV complex also includes a multi-purpose hangar. The complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The facility, jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC, will be operational in early 2000
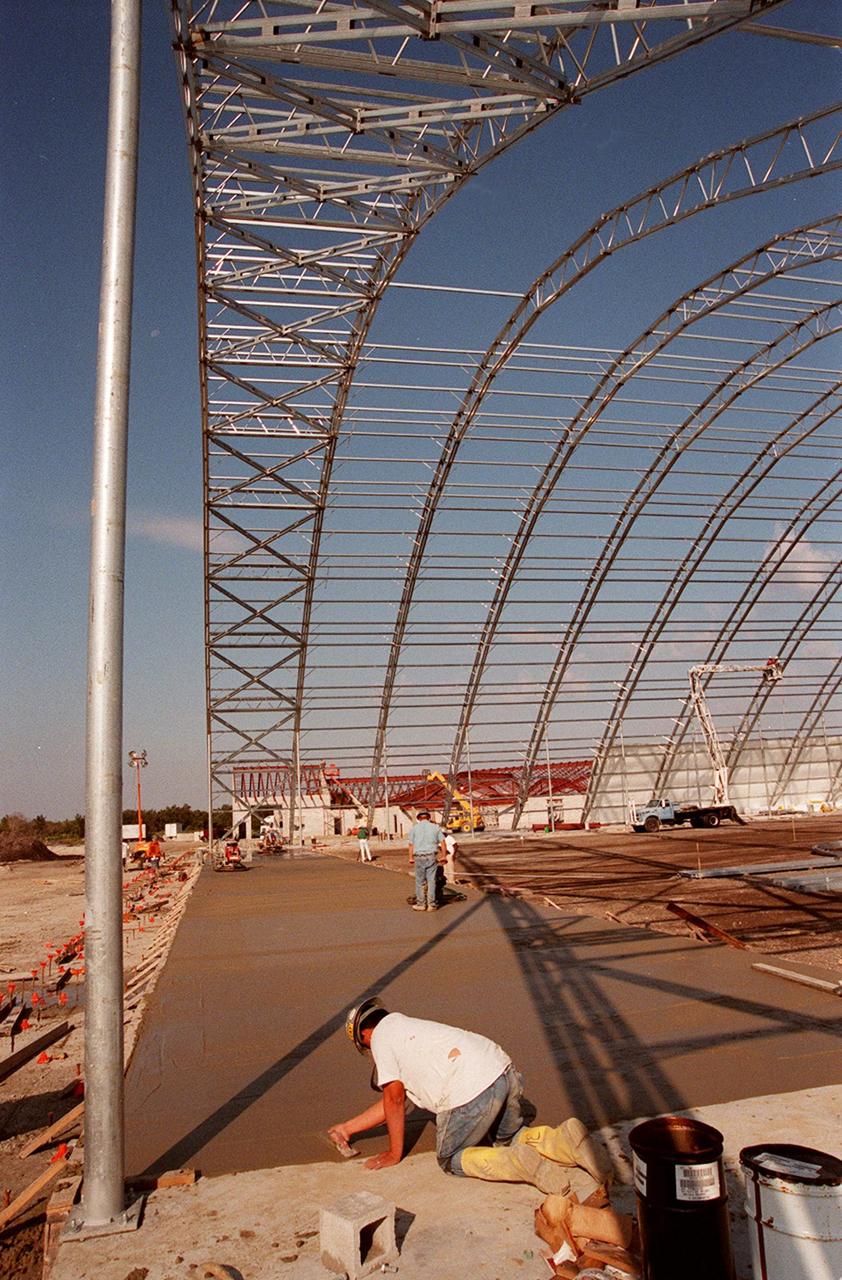

A worker smoothes the recently poured foundation of the multi-purpose hangar at the site of the $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. In the background can be seen the new construction for the building that will house related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
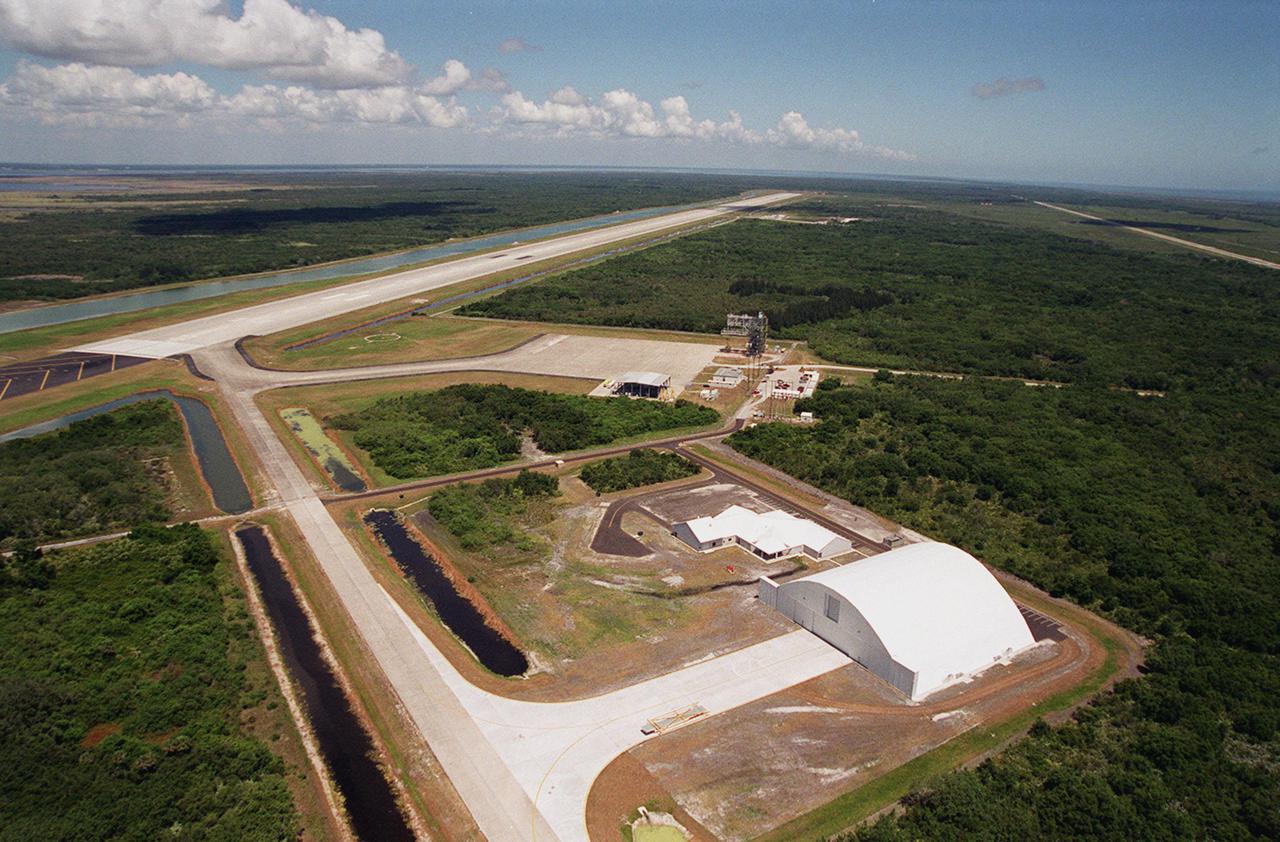

In the foreground of this aerial photo is the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. At right is a multi-purpose hangar and to its left is a building for related ground support equipment and administrative_ technical support. The complex is situated at the Shuttle Landing Facility (center). At the upper left is the runway. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA’s Space Shuttle Program and KSC
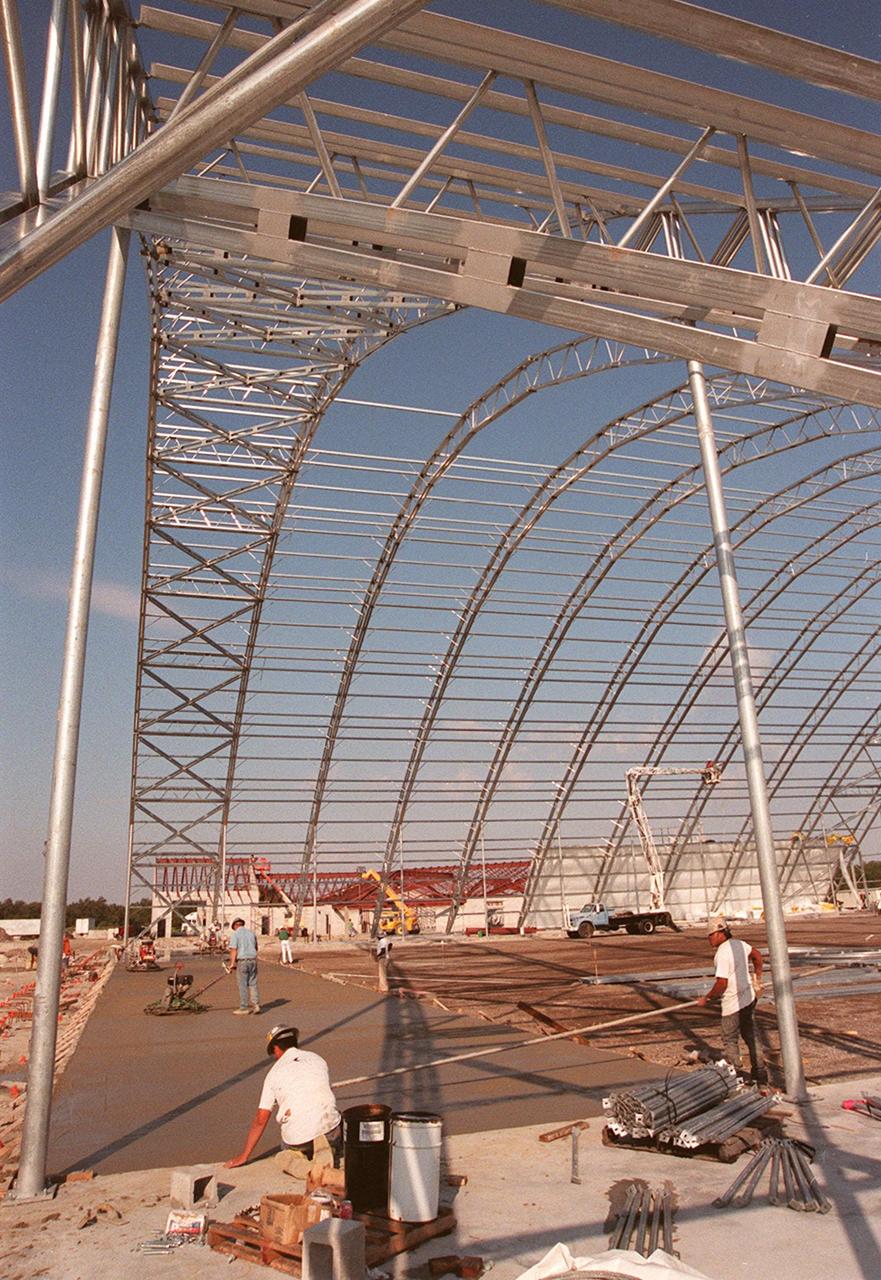

Work continues on construction of the multi-purpose hangar at the site of the $8 million Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex at Kennedy Space Center. In the background can be seen the new construction for the building that will house related ground support equipment and administrative/technical support. The RLV complex will be available to accommodate the Space Shuttle; the X-34 RLV technology demonstrator; the L-1011 carrier aircraft for Pegasus and X-34; and other RLV and X-vehicle programs. The complex is jointly funded by the Spaceport Florida Authority, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and KSC. The facility will be operational in early 2000
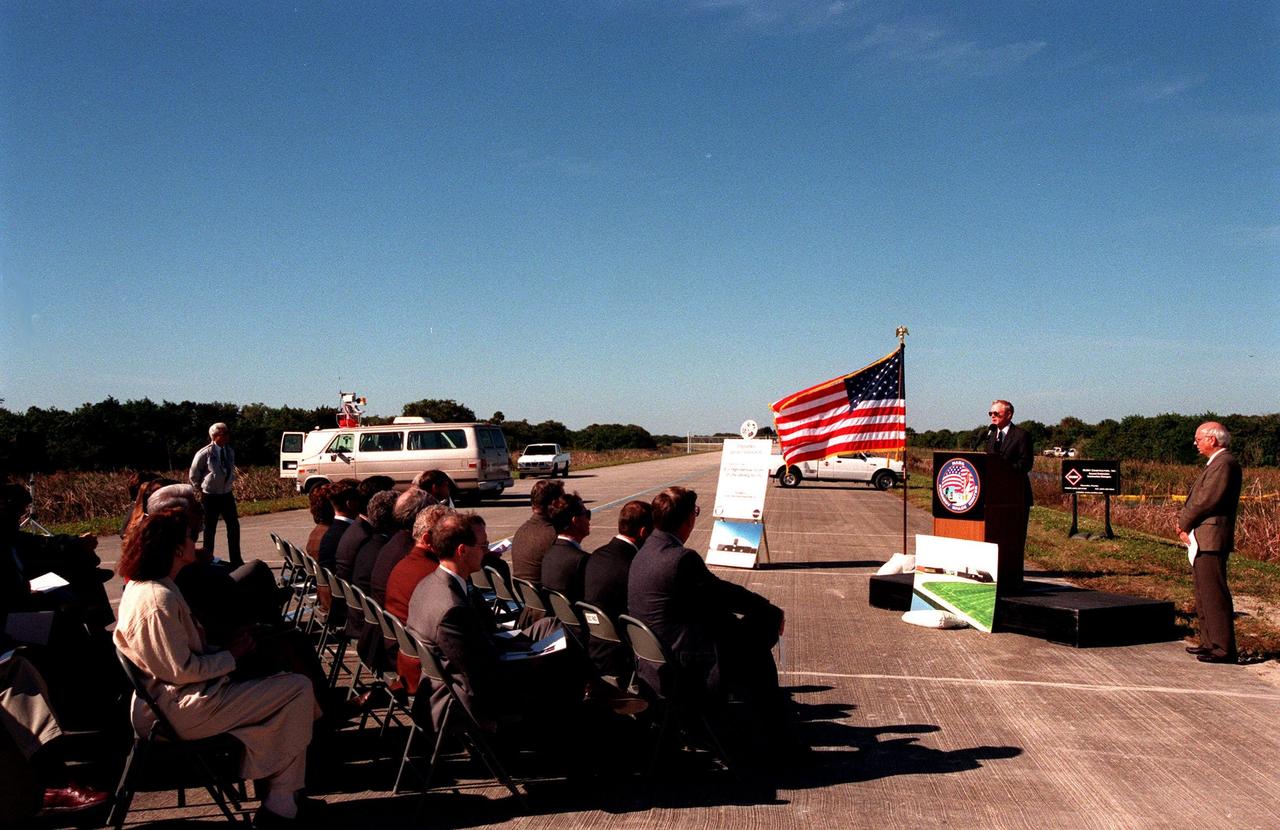

Center Director Roy Bridges, at the podium, speaks to federal and state elected officials during the ground breaking ceremony for a multi-purpose hangar, phase one of the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Support Complex to be built near the Shuttle Landing Facility. At right is Ed O'Connor, executive director of the Spaceport Florida Authority (SFA). The new complex is jointly funded by SFA, NASA's Space Shuttle Program and Kennedy Space Center. It is intended to support the Space Shuttle and other RLV land X-vehicle systems. Completion is expected by the year 2000
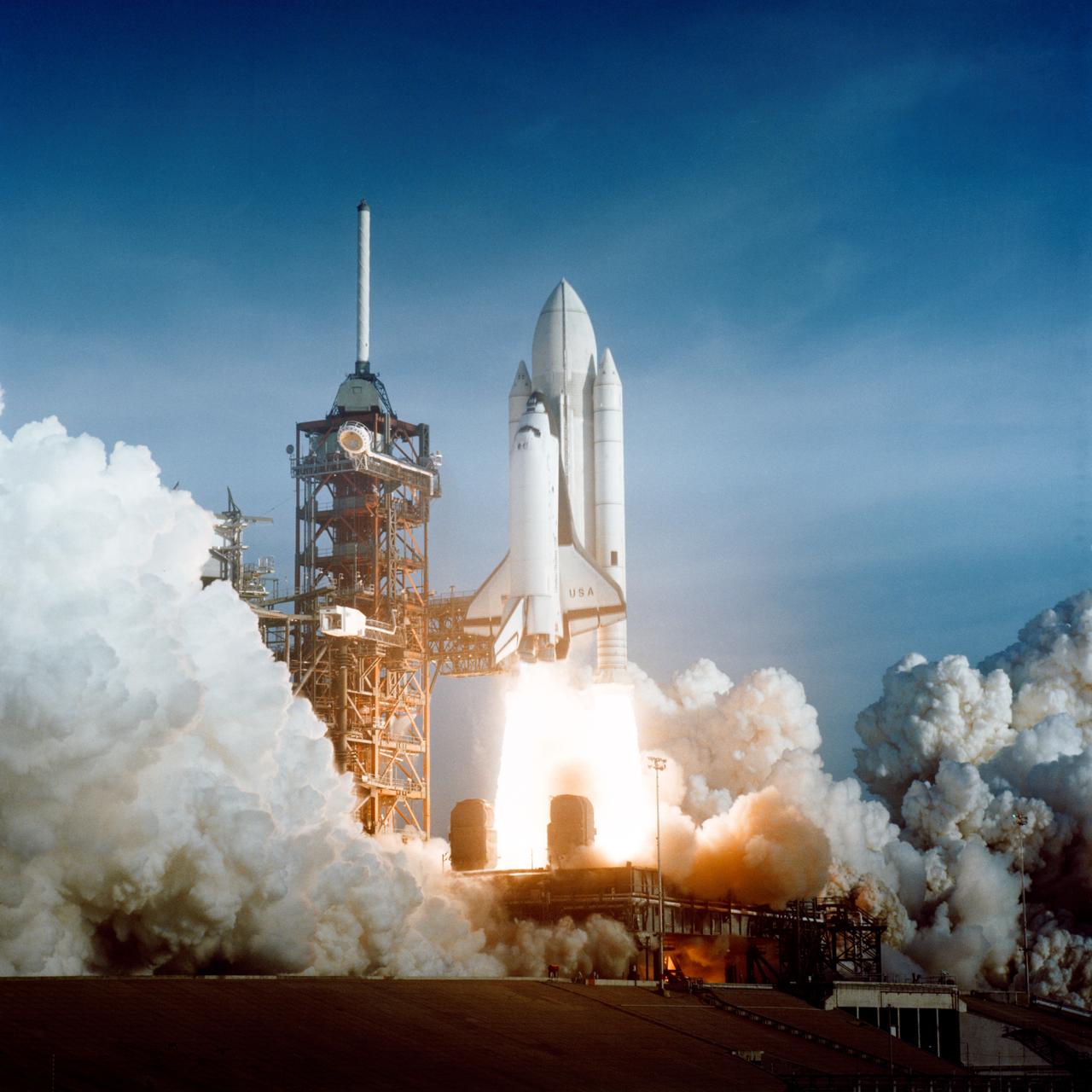

S81-30498 (12 April 1981) --- After six years of silence, the thunder of manned spaceflight is heard again, as the successful launch of the first space shuttle ushers in a new concept in utilization of space. The April 12, 1981 launch, at Pad 39A, just seconds past 7 a.m., carries astronaut John Young and Robert Crippen into an Earth-orbital mission scheduled to last for 54 hours, ending with unpowered landing at Edwards Air Force Base in California. STS-1, the first in a series of shuttle vehicles planned for the Space Transportation System, utilizes reusable launch and return components. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
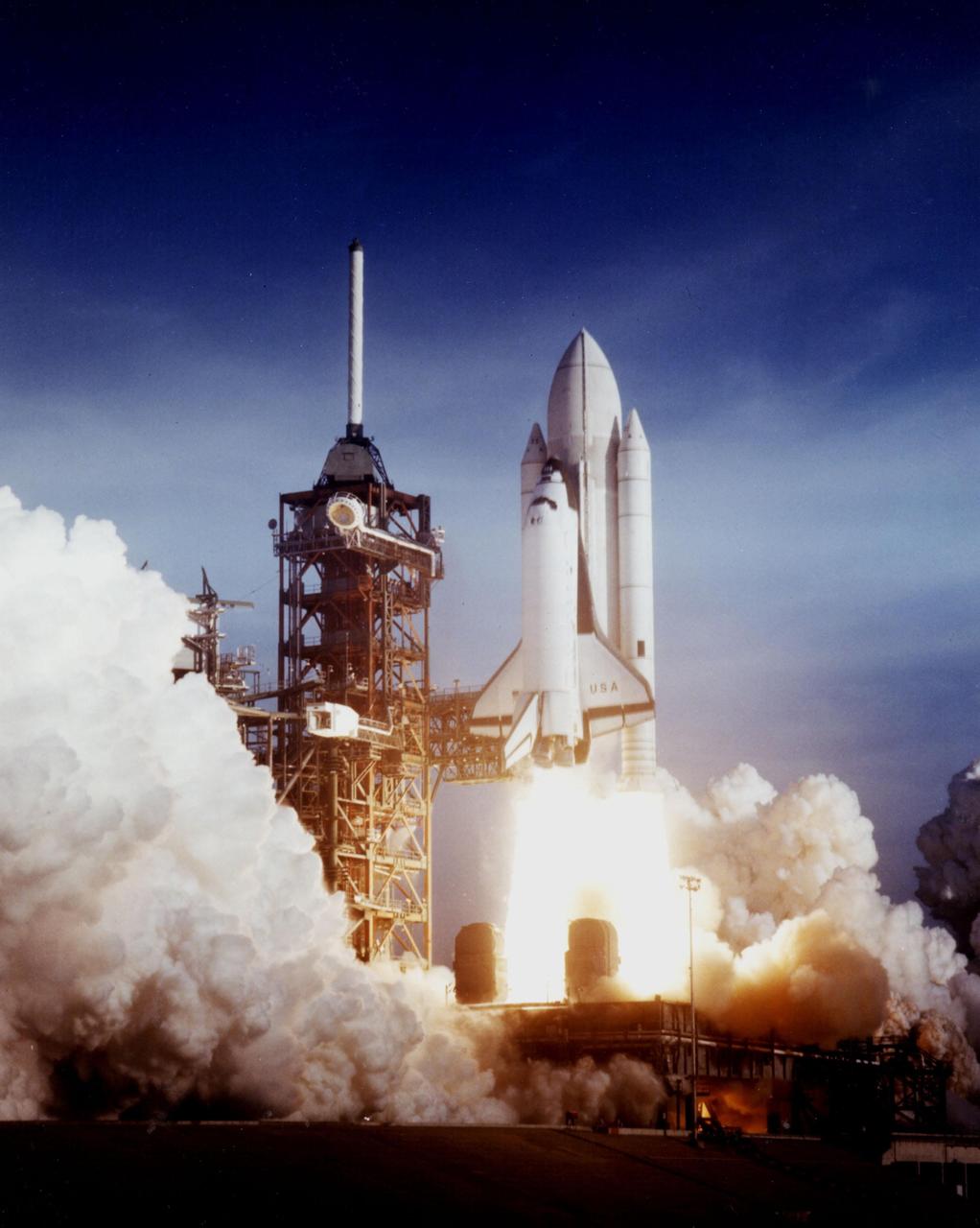

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After six years of silence, the thunder of manned space flight is heard again as the successful launch of the first Space Shuttle ushers in a new concept in utilization of space. The April 12 launch at Pad 39A, just seconds past 7 a.m., carries astronauts John Young and Robert Crippen into an Earth orbital mission scheduled to last for 54 hours, ending with unpowered landing at Edwards Air Force Base in California. STS-1, the first in a series of shuttle vehicles planned for the Space Transportation sysstem, utilizes reusable launch and return components

Space Shuttle Orbiters: From its establishment in 1958, NASA studied aspects of reusable launch vehicles and spacecraft that could return to earth. On January 5, 1972, President Richard Nixon announced that the United States would develop the space shuttle, a delta-winged orbiter about the size of a DC-9 aircraft. Between the first launch on April 12, 1981, and the final landing on July 21, 2011, NASA's space shuttle fleet -- Columbia, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour – launched on 135 missions, helped construct the International Space Station and inspired generations. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
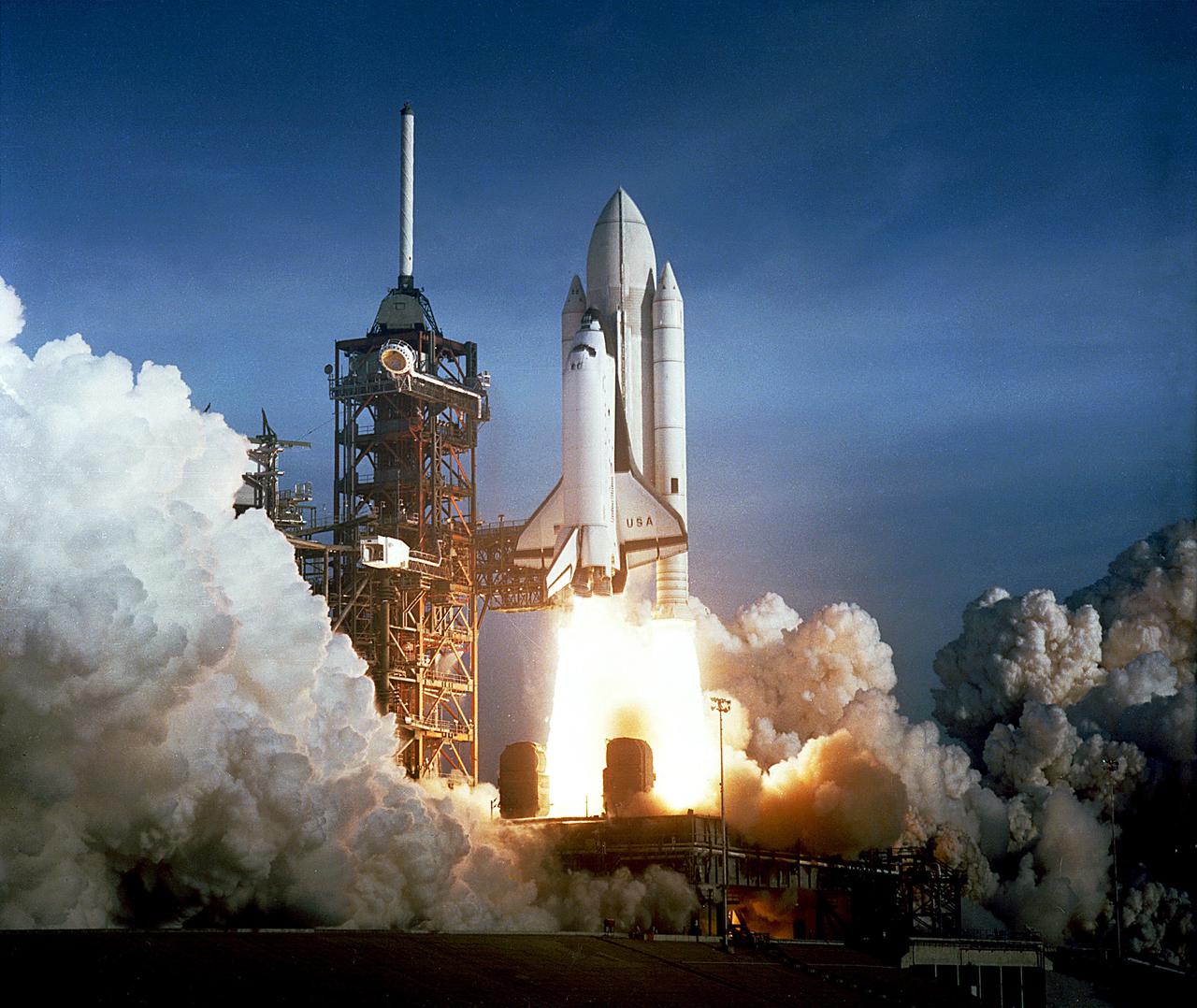

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After six years of silence, the thunder of manned space flight is heard again, as the successful launch of the first Space Shuttle ushers in a new concept in utilization of space. The April 12 launch at Pad 39A, just seconds past 7 a.m., carries astronauts John Young and Robert Crippen into an Earth orbital mission scheduled to last 54 hours, ending with unpowered landing at Edwards Air Force Base in California. STS-1, the first in a series of Shuttle Vehicles planned for the Space Transportation System, utilizes reusable launch and return components.
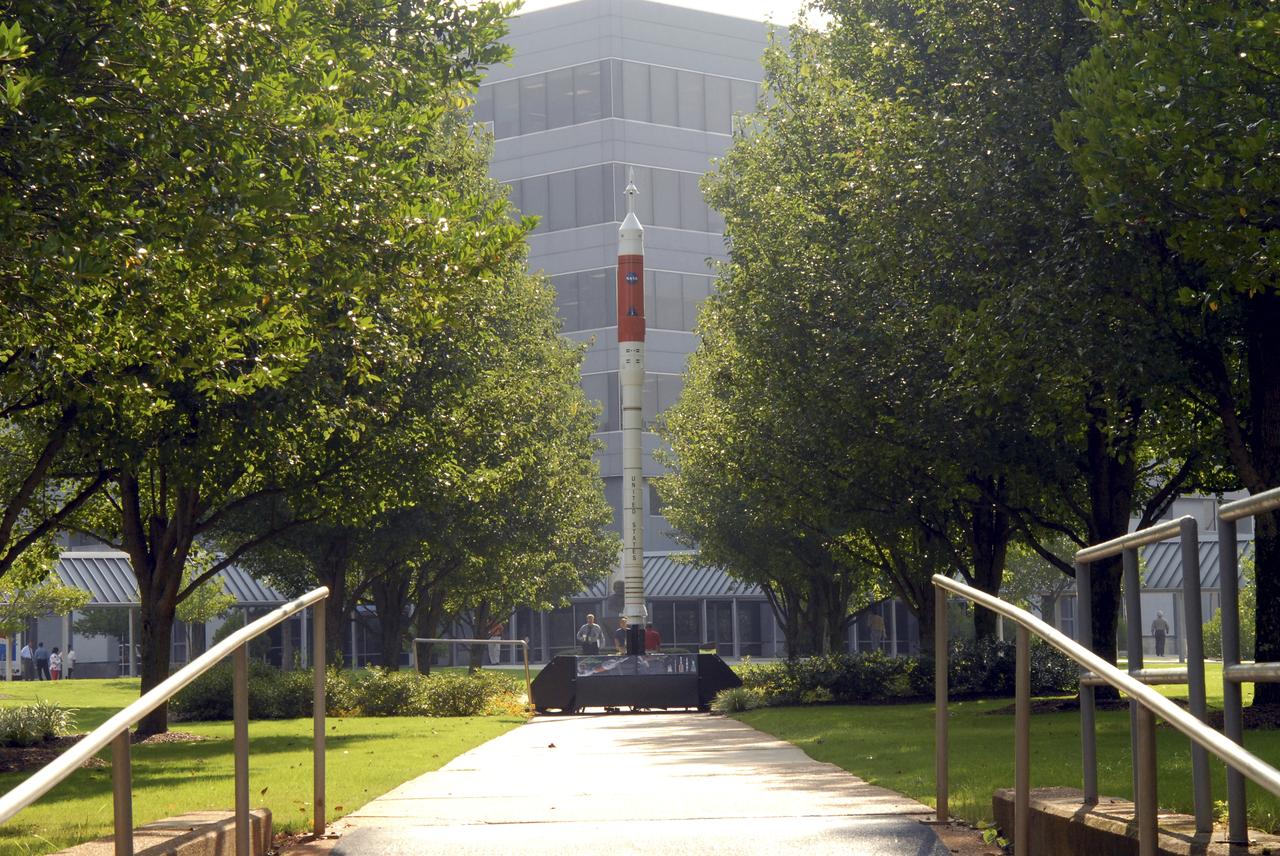

A model of the new Aries I crew launch vehicle, for which NASA is designing, testing and evaluating hardware and related systems, is seen here on display at the Marshall Space Fight Center (MSFC), in Huntsville, Alabama. The Ares I crew launch vehicle is the rocket that will carry a new generation of space explorers into orbit. Under the goals of the Vision for Space Exploration, Ares I is a chief component of the cost-effective space transportation infrastructure being developed by NASA’s Constellation Program. These transportation systems will safely and reliably carry human explorers back to the moon, and then onward to Mars and other destinations in the solar system. The Ares I effort includes multiple project element teams at NASA centers and contract organizations around the nation, and is led by the Exploration Launch Projects Office at NASA’s MFSC. Together, these teams are developing vehicle hardware, evolving proven technologies, and testing components and systems. Their work builds on powerful, reliable space shuttle propulsion elements and nearly a half-century of NASA space flight experience and technological advances. Ares I is an inline, two-stage rocket configuration topped by the Crew Exploration Vehicle, its service module and a launch abort system. The launch vehicle’s first stage is a single, five-segment reusable solid rocket booster derived from the Space Shuttle Program’s reusable solid rocket motor that burns a specially formulated and shaped solid propellant called polybutadiene acrylonitrile (PBAN). The second or upper stage will be propelled by a J-2X main engine fueled with liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen. In addition to its primary mission of carrying crews of four to six astronauts to Earth orbit, the launch vehicle’s 25-ton payload capacity might be used for delivering cargo to space, bringing resources and supplies to the International Space Station or dropping payloads off in orbit for retrieval and transport to exploration teams on the moon. Crew transportation to the space station is planned to begin no later than 2014. The first lunar excursion is scheduled for the 2020 timeframe.
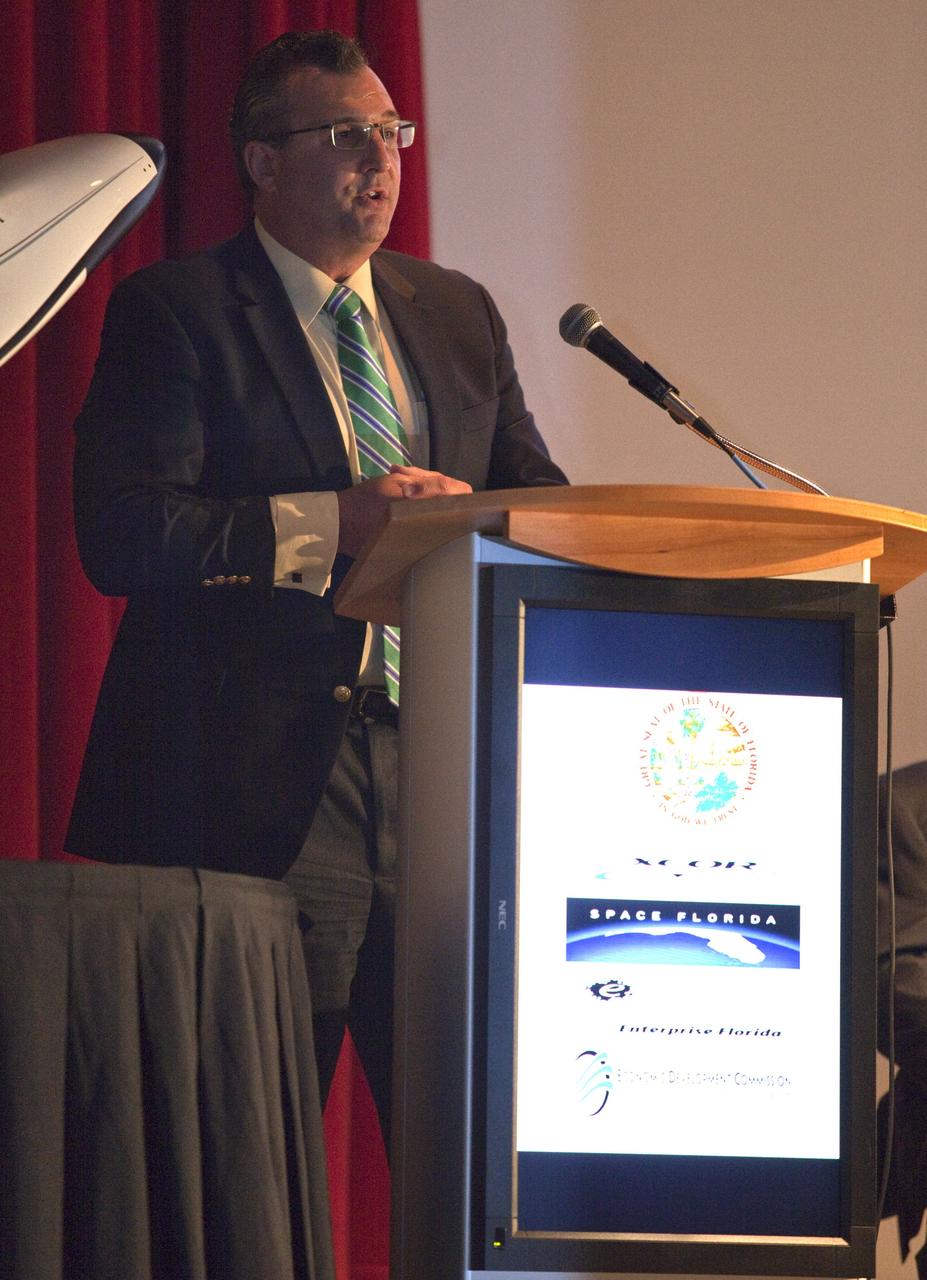

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Todd Lindner, senior manager of Aviation Planning and Spaceport Development for the Jacksonville Aviation Authority, addresses guests at a presentation during which XCOR Aerospace announced plans to open a manufacturing operation in Brevard. The company's suborbital Lynx Mark II spacecraft possibly will take off and land at Kennedy's shuttle landing facility. XCOR Aerospace is a small, privately held California corporation with focus on the research, development, project management and production of reusable launch vehicles, rocket engines and rocket propulsion systems. XCOR will focus on space tourism, experimental flights and launching satellites. Photo credit: NASA/ Frankie Martin
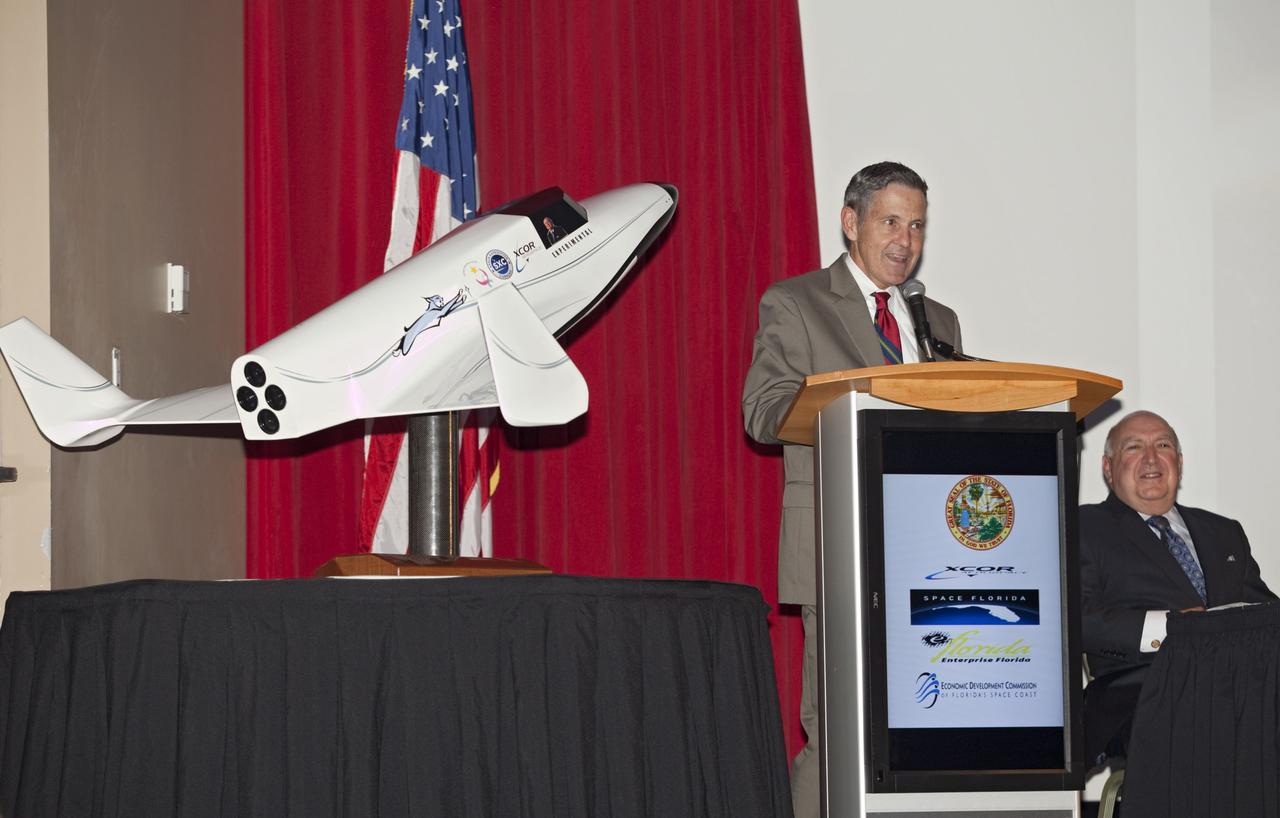

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Bob Cabana addresses guests at a presentation during which XCOR Aerospace announced plans to open a manufacturing operation in Brevard. Space Florida President Frank DiBello is seated to the right. The company's suborbital Lynx Mark II spacecraft possibly will take off and land at Kennedy's shuttle landing facility. XCOR Aerospace is a small, privately held California corporation with focus on the research, development, project management and production of reusable launch vehicles, rocket engines and rocket propulsion systems. XCOR will focus on space tourism, experimental flights and launching satellites. Photo credit: NASA/ Frankie Martin
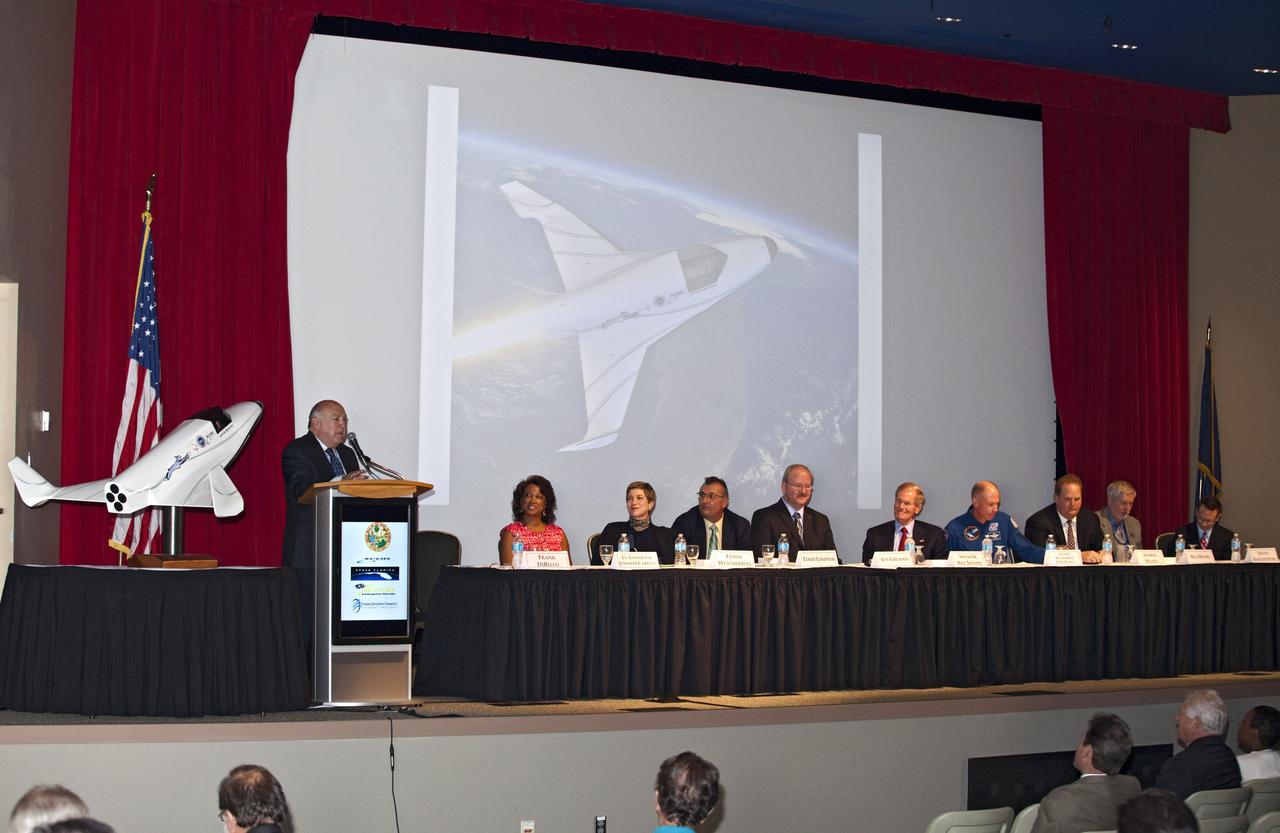

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Space Florida President Frank DiBello joined other space executives and elected officials in addressing guests at a presentation during which XCOR Aerospace announced plans to open a manufacturing operation in Brevard County. The company's suborbital Lynx Mark II spacecraft possibly will take off and land at Kennedy's shuttle landing facility. XCOR Aerospace is a small, privately held California corporation with focus on the research, development, project management and production of reusable launch vehicles, rocket engines and rocket propulsion systems. XCOR will focus on space tourism, experimental flights and launching satellites. Photo credit: NASA/ Frankie Martin