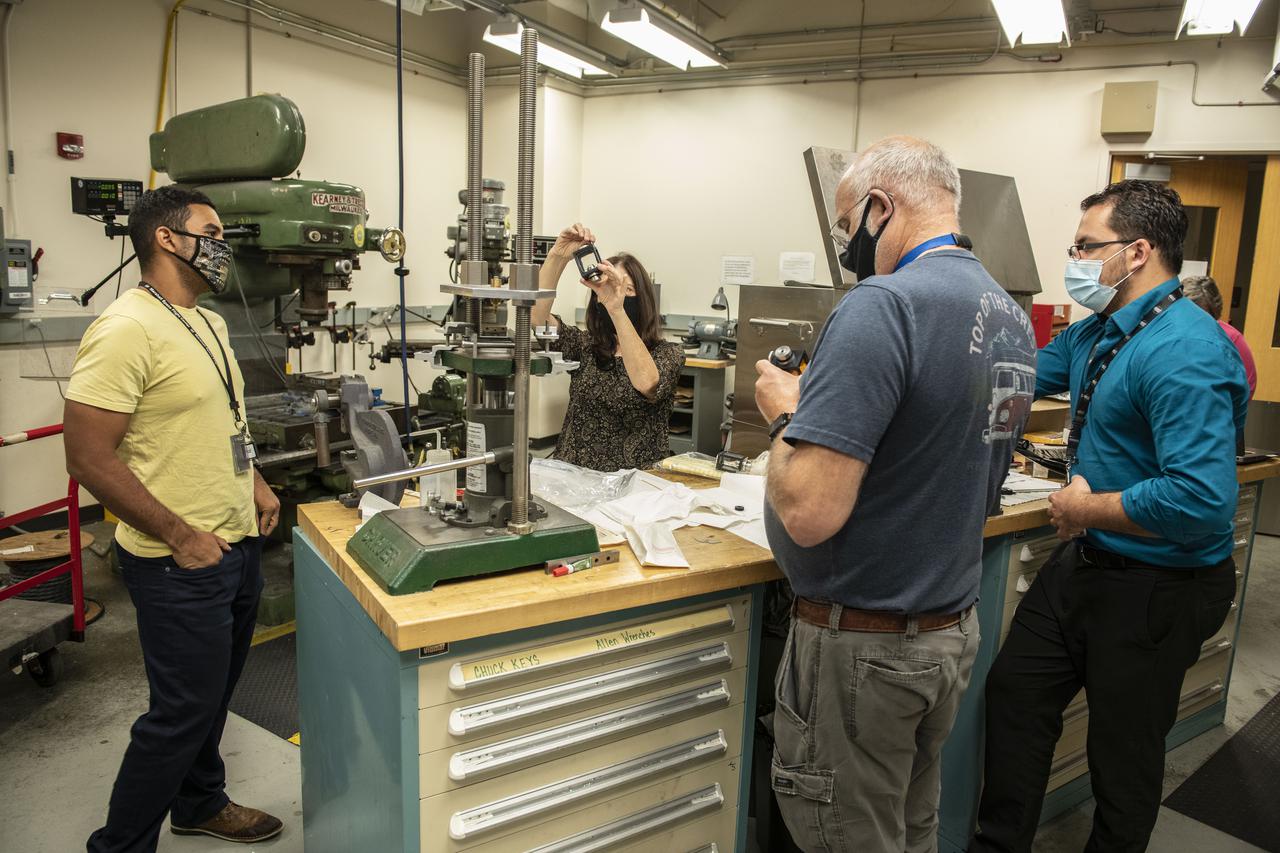

Scientists at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, clean equipment and prepare for shipment of the ring sheared drop payload currently set for launch on Northrop Grumman 16 the first week in August, 2021. The payload studies the formation of potentially destructive amyloid fibrils, or protein clusters, like those found in the brain tissue of patients battling neurodegenerative diseases. Such illnesses may damage neurons, the drivers of the human nervous system. Experimentation in microgravity provides the opportunity to study amyloid fibril formation in conditions more analogous to those found in the human body than can be studied in a ground-based laboratory environment.
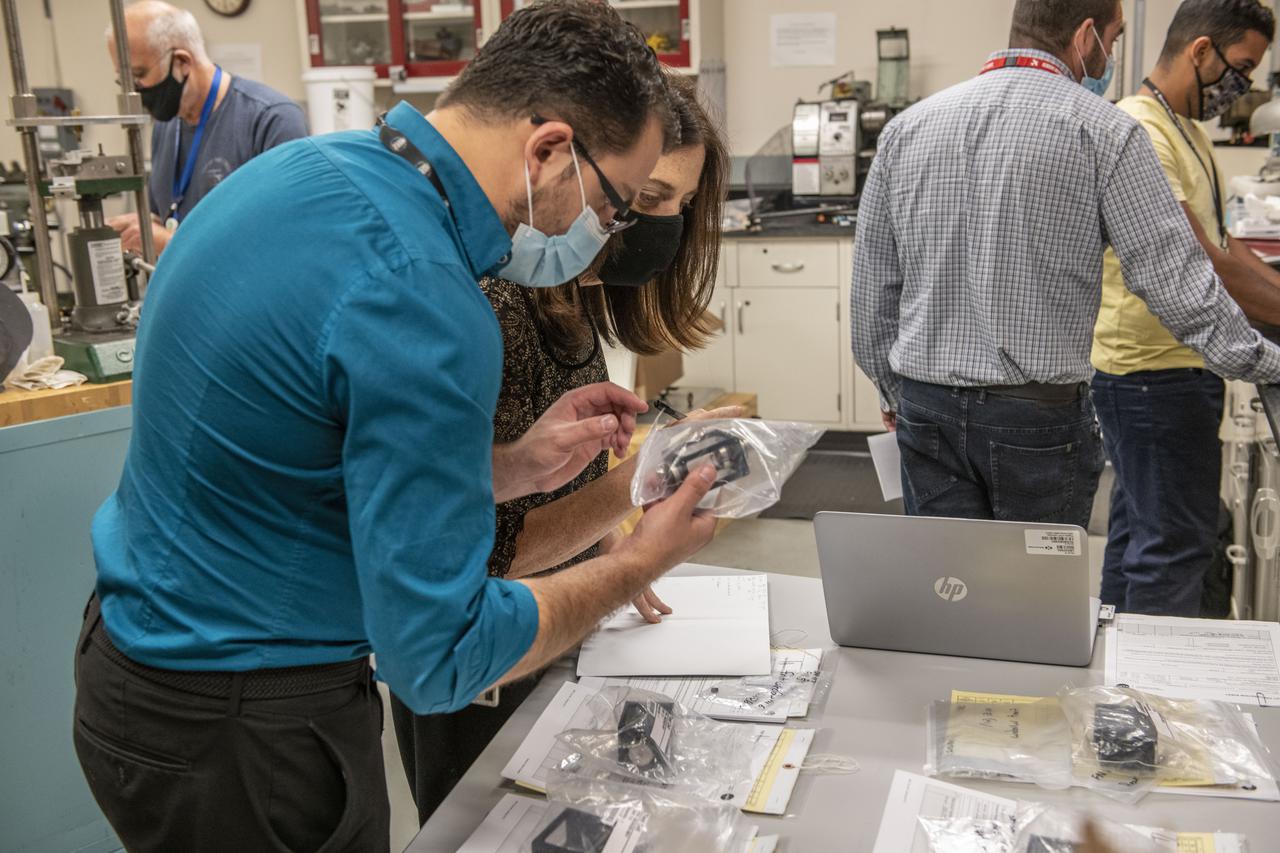

Scientists at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, clean equipment and prepare for shipment of the ring sheared drop payload currently set for launch on Northrop Grumman 16 the first week in August, 2021. The payload studies the formation of potentially destructive amyloid fibrils, or protein clusters, like those found in the brain tissue of patients battling neurodegenerative diseases. Such illnesses may damage neurons, the drivers of the human nervous system. Experimentation in microgravity provides the opportunity to study amyloid fibril formation in conditions more analogous to those found in the human body than can be studied in a ground-based laboratory environment.

Scientists at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, clean equipment and prepare for shipment of the ring sheared drop payload currently set for launch on Northrop Grumman 16 the first week in August, 2021. The payload studies the formation of potentially destructive amyloid fibrils, or protein clusters, like those found in the brain tissue of patients battling neurodegenerative diseases. Such illnesses may damage neurons, the drivers of the human nervous system. Experimentation in microgravity provides the opportunity to study amyloid fibril formation in conditions more analogous to those found in the human body than can be studied in a ground-based laboratory environment.
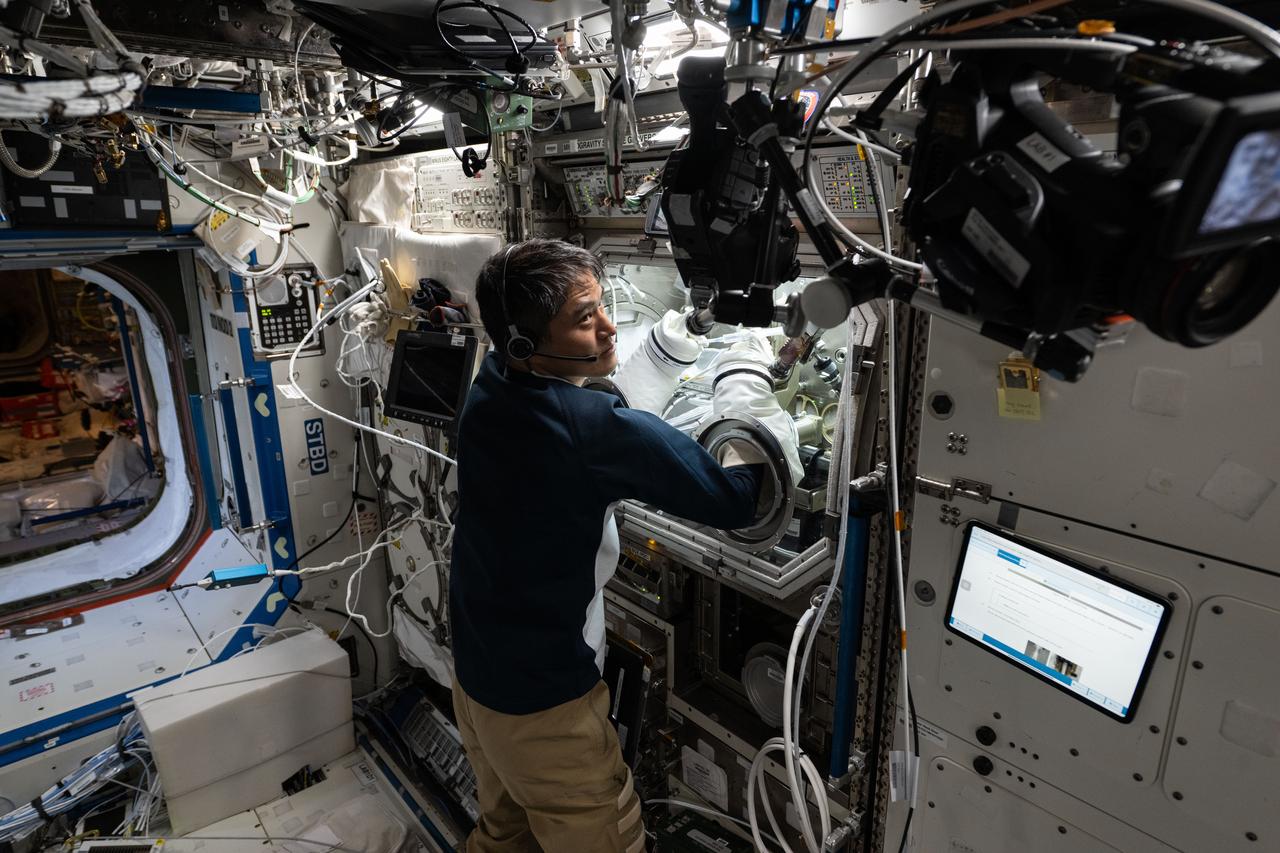

iss073e0177064 (6/11/2025) --- Scientists can study protein solutions without interference from container walls and gravity driven forces present on Earth using the space station’s Ring Sheared Drop module. The device pins a drop of liquid between two rings and holds it in place with surface tension. JAXA astronaut Takuya Onishi sets up for Ring Sheared Drop-IBP-2, a study of the behavior of protein fluids in microgravity. The investigation uses the module to test computer models to predict fluid behavior that could lead to improved processes for manufacturing pharmaceuticals, 3D printing, food processing, and microelectronics.
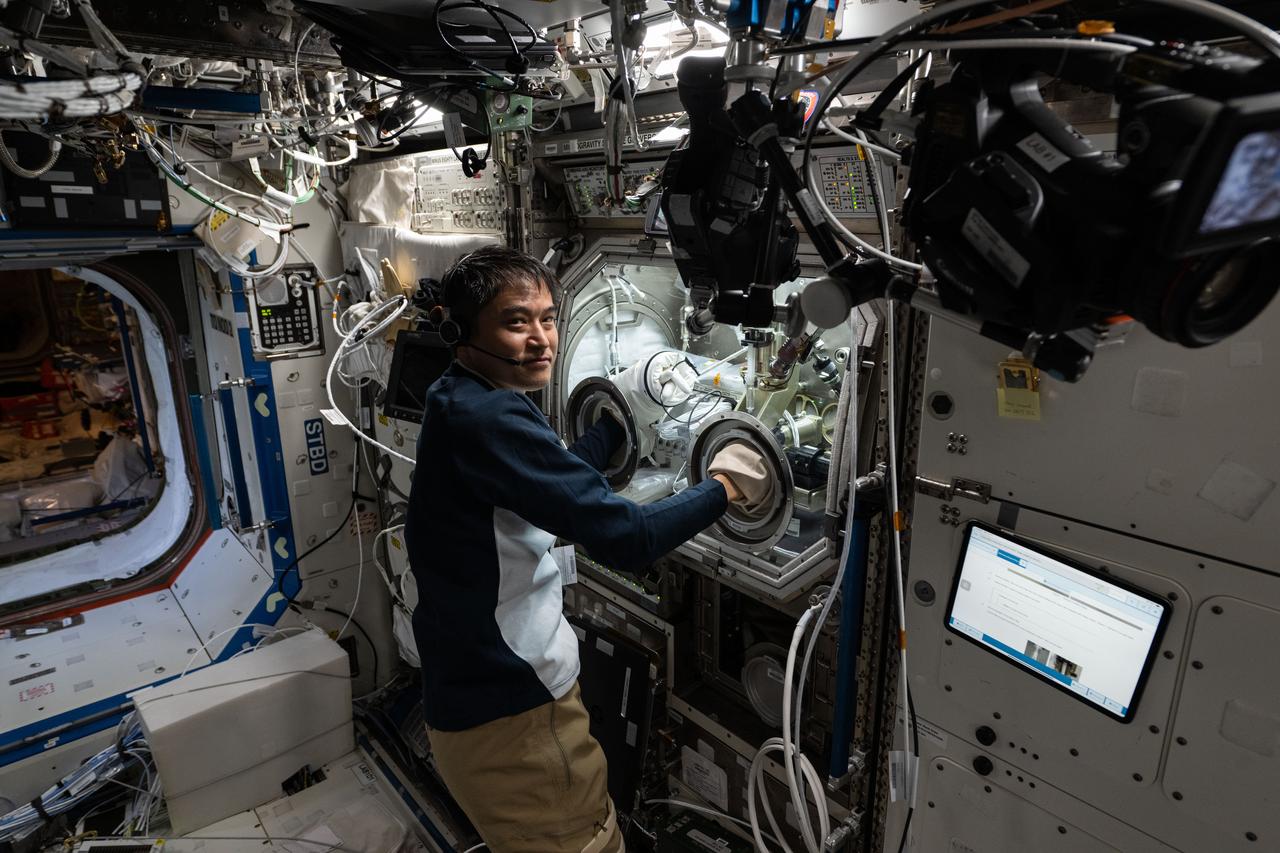

iss073e0177065 (6/11/2025) --- Scientists can study protein solutions without interference from container walls and gravity driven forces present on Earth using the space station’s Ring Sheared Drop module. The device pins a drop of liquid between two rings and holds it in place with surface tension. JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 73 Commander Takuya Onishi sets up for Ring Sheared Drop-IBP-2, a study of the behavior of protein fluids in microgravity. The investigation uses the module to test computer models to predict fluid behavior that could lead to improved processes for manufacturing pharmaceuticals, 3D printing, food processing, and microelectronics.
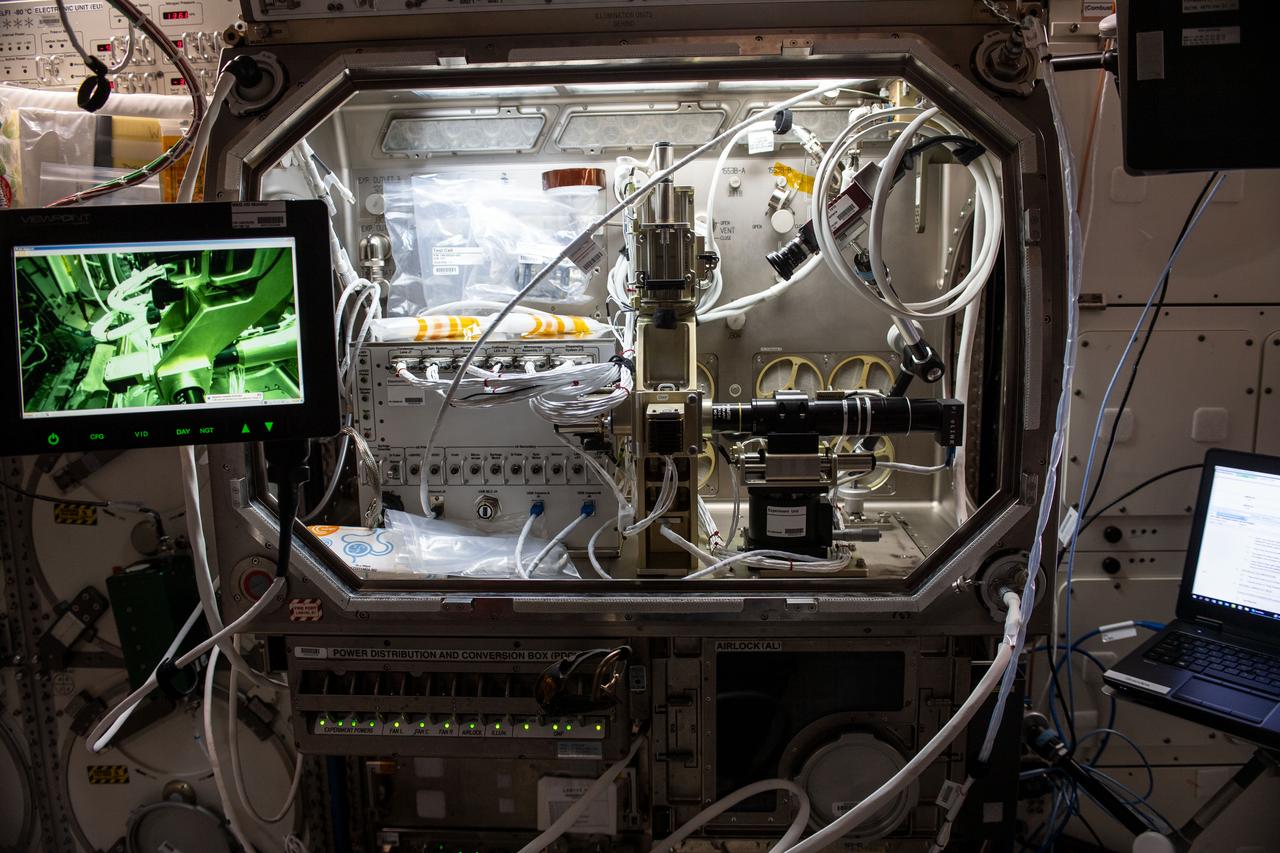

iss060e073382 (9/19/2019) --- Photo documentation of the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) with the Ring Sheared Drop investigation in the Destiny Lab aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Ring Sheared Drop investigation uses microgravity to examine the formation and flow of amyloids in the absence of surface tension and other complications created by the solid walls of a container. Fibrous, extracellular protein deposits found in organs and tissues, amyloids are associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. Results could contribute to better understanding of these diseases as well as to development of advanced materials.
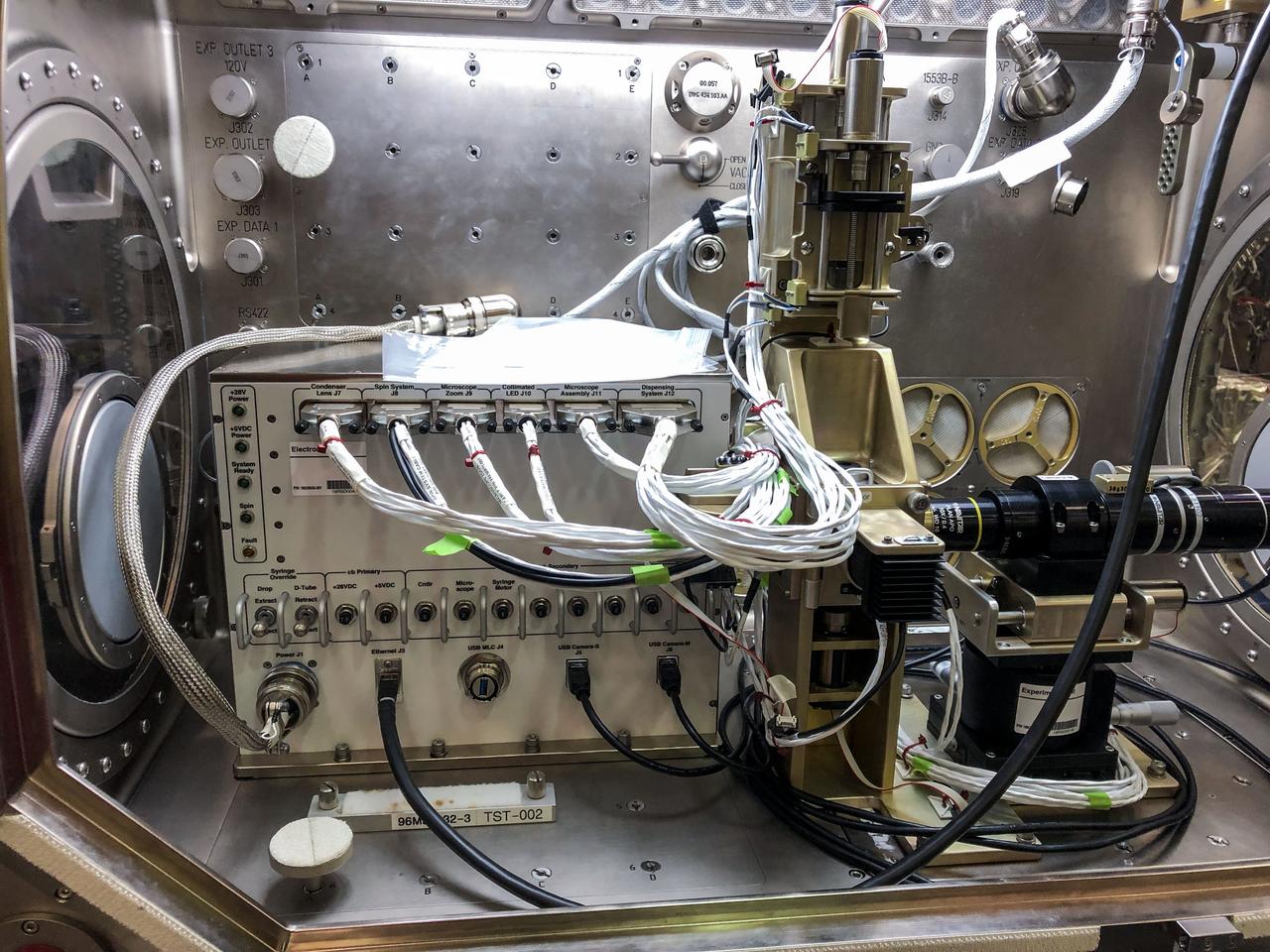
jsc2019e034530 (6/6/2019) --- Preflight photo documentation of the Ring Sheared Drop setup in the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox (MSG). The Ring Sheared Drop investigation uses microgravity to examine the formation and flow of amyloids in the absence of surface tension and other complications created by the solid walls of a container. Amyloids are associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. This investigation may contribute to a better understanding of these diseases and development of potential treatments.
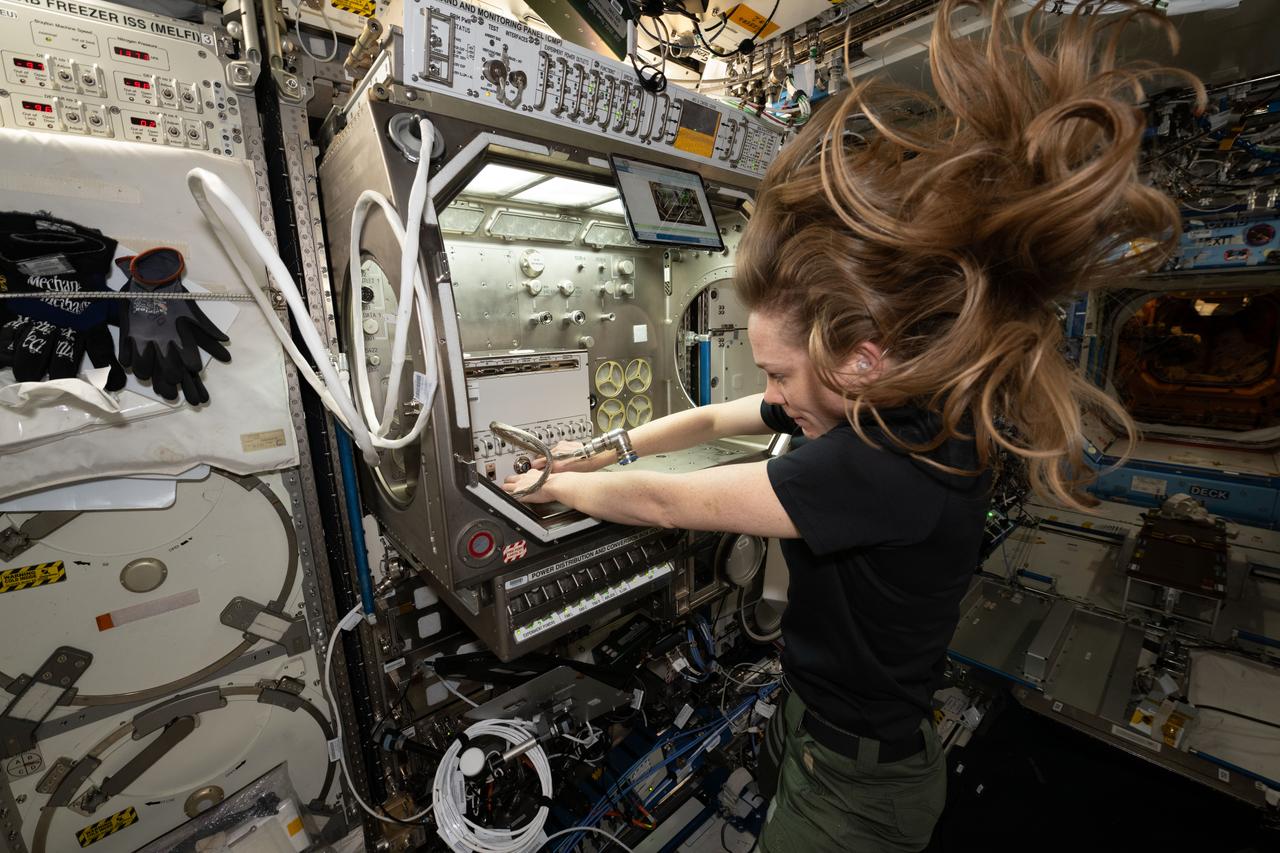

iss073e0134929 (6/9/2025) ---NASA astronaut Nichole Ayers sets up the station’s Ring Sheared Drop module. This system makes it possible to study liquid protein solutions without using containers, eliminating interactions between the solutions and container walls that can affect results. Ring Sheared Drop-IBP-2 studies the behavior of protein fluids in microgravity and tests computer models to predict that fluid’s behavior. Better models could help could advance manufacturing processes in space and on Earth for producing next-generation medicines for treating cancers and other diseases.NASA astronaut Nichole Ayers sets up the station’s Ring Sheared Drop module. This system makes it possible to study liquid protein solutions without using containers, eliminating interactions between the solutions and container walls that can affect results. Ring Sheared Drop-IBP-2 studies the behavior of protein fluids in microgravity and tests computer models to predict that fluid’s behavior. Better models could help could advance manufacturing processes in space and on Earth for producing next-generation medicines for treating cancers and other diseases.
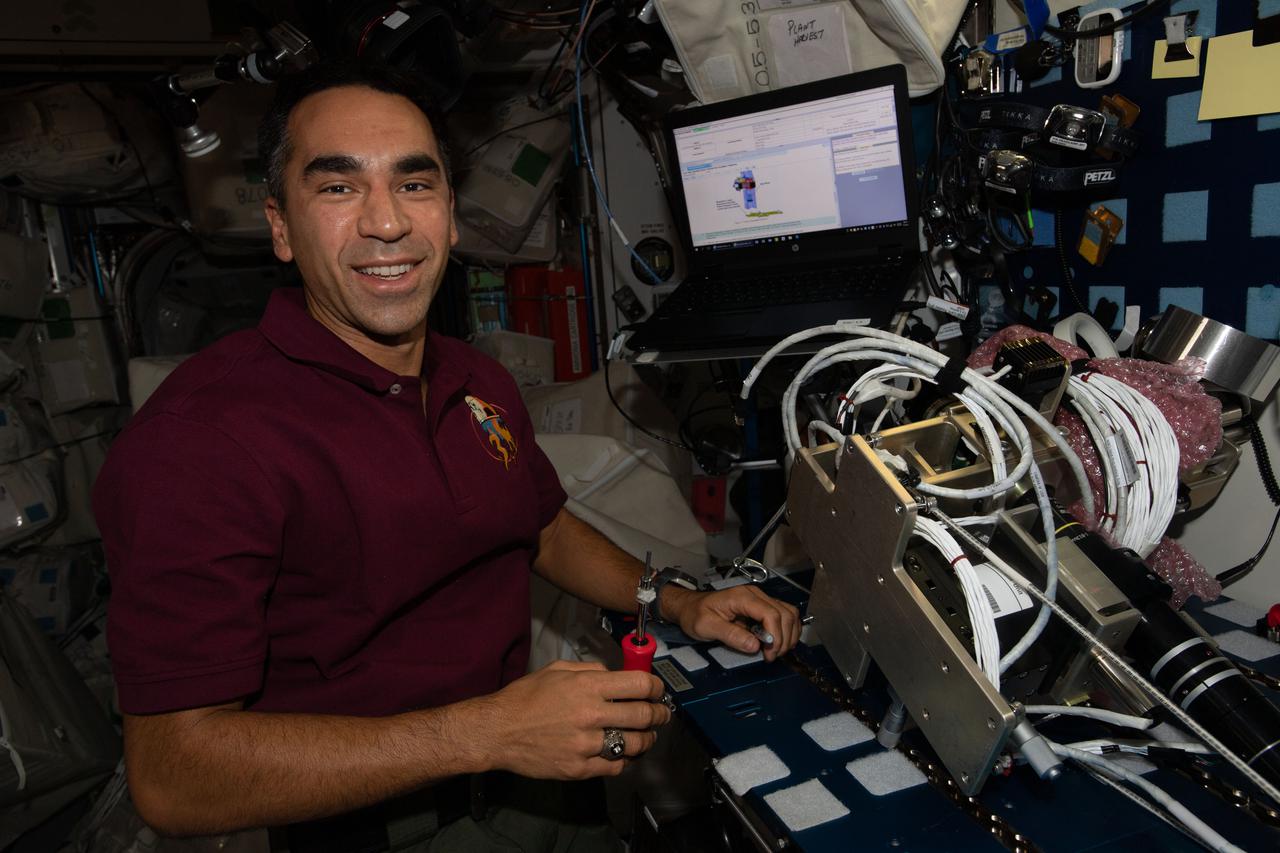

iss066e111006 (Jan. 12, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Raja Chari removes components from the Ring Sheared Drop experiment that could lead to a better understanding of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
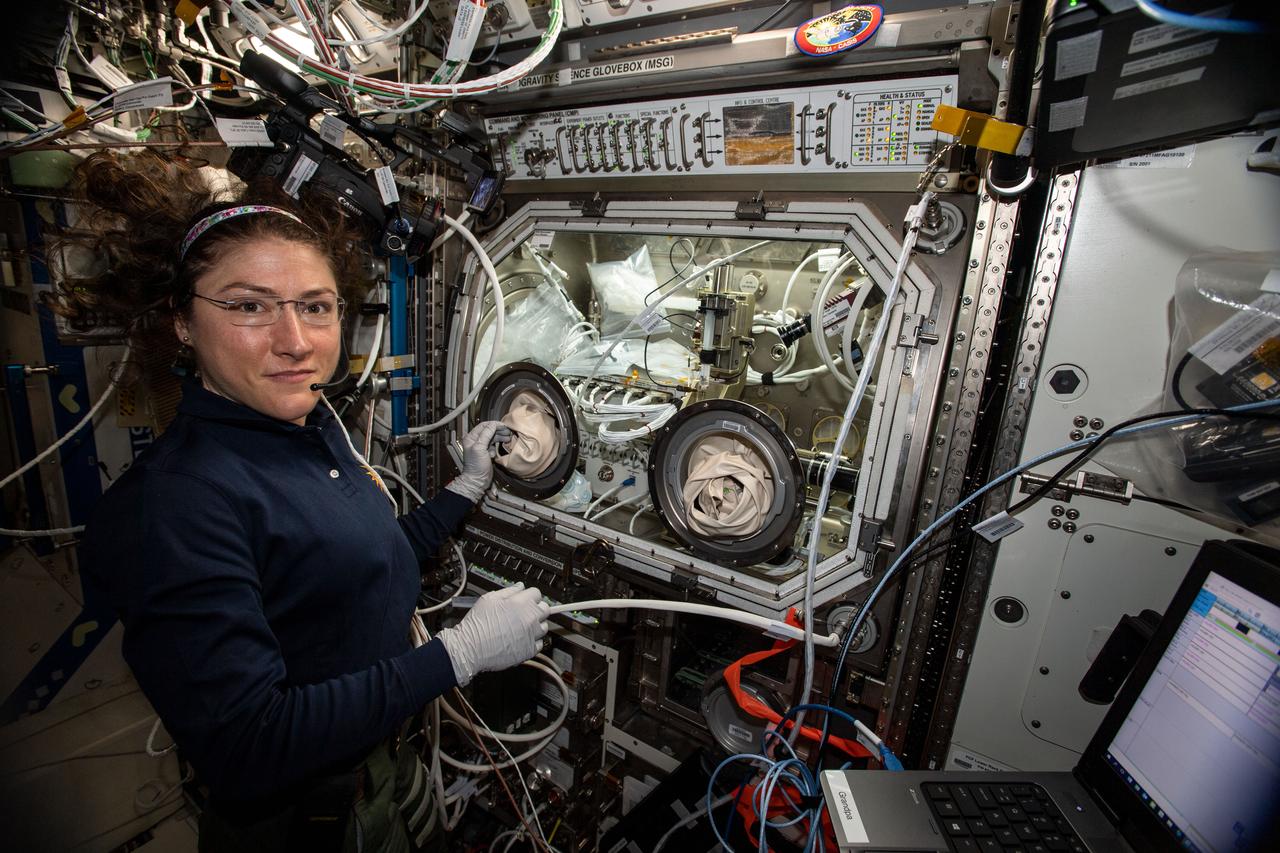

iss061e012803 (Oct. 22, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Christina Koch performs science operations in the Microgravity Science Glovebox for the Ring Sheared Drop human health and advanced materials investigation.
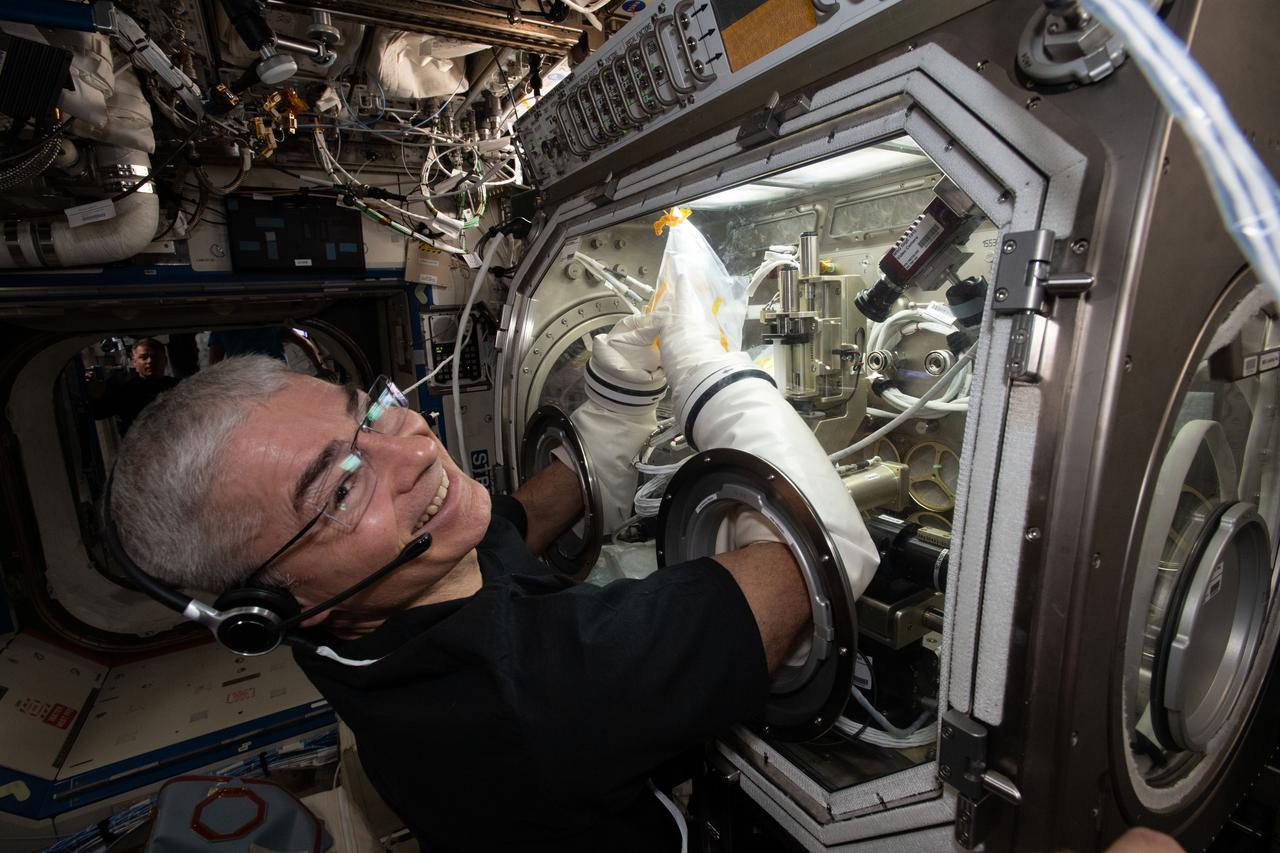

iss065e276849 (Aug. 16, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei works inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox for the Ring Sheared Drop fluid physics study.

iss067e378812 (Sept. 21, 2022) --- Expedition 67 Flight Engineer and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti works inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox removing hardware that supported the Ring Sheared Drop experiment. The fluid physics study observes the formation of destructive protein clusters that may be responsible for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
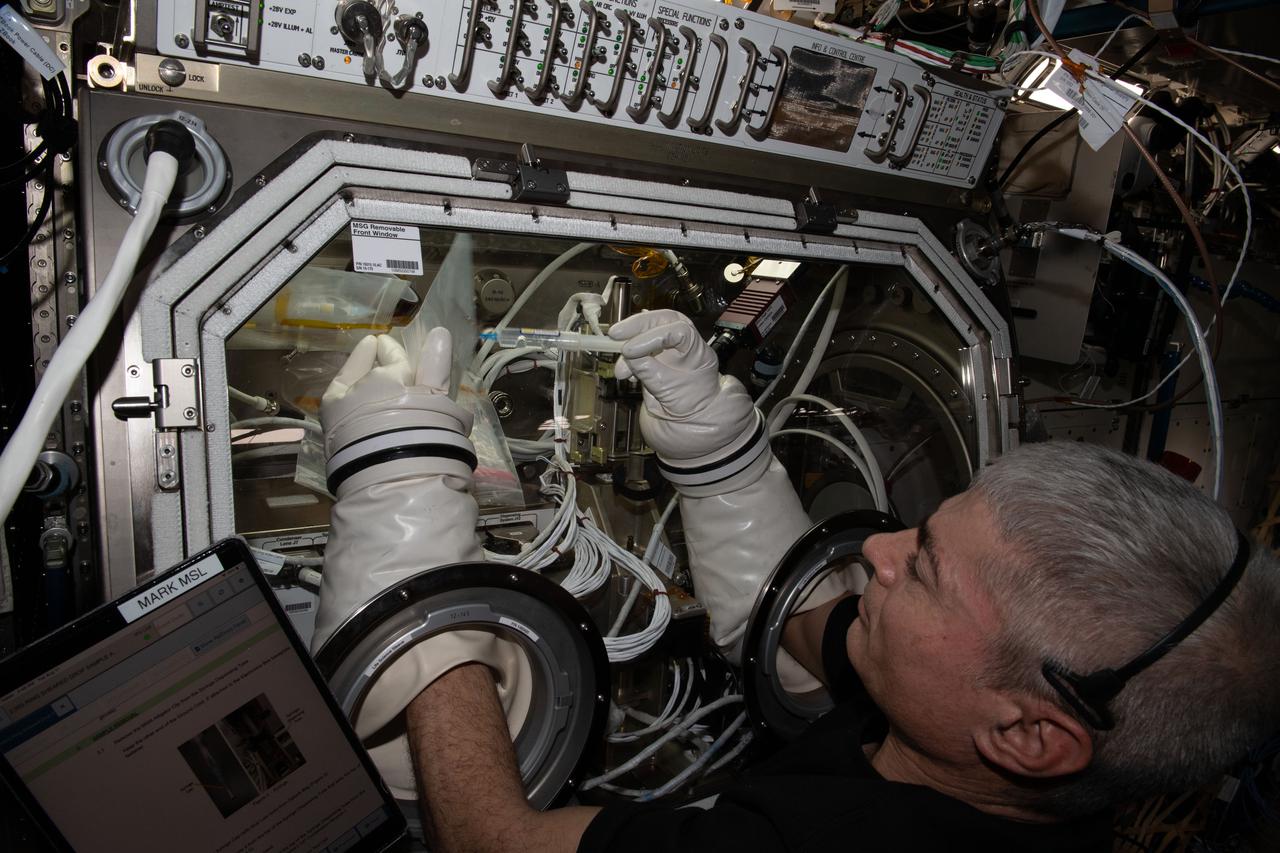

iss065e257449 (Aug. 17, 2021) --- NASA Astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei works on the Ring Sheared Drop investigation in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) aboard the International Space Station. This experiment leverages the microgravity environment of the orbiting laboratory to study proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. The research may contribute to a better understanding of these diseases and development of potential treatments.
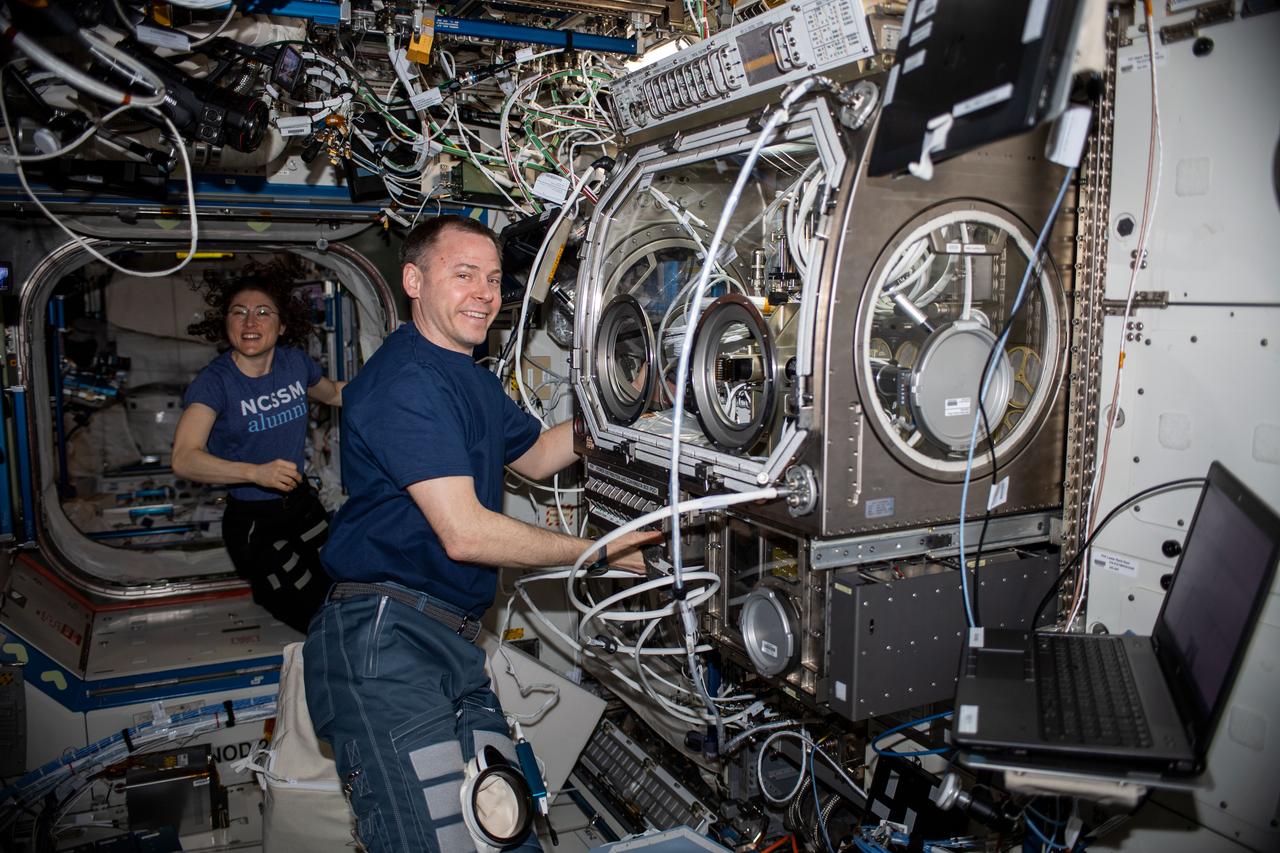

iss060e073417 (Sept. 19, 2019) --- NASA astronauts Christina Koch and Nick Hague are pictured inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module. Hague was setting up the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox to begin operations for the Ring-Sheared Drop experiment to understand how fluids flow in the human body and other materials. Koch had finished an exercise session after jogging on the COLBERT (Combined Operational Load Bearing External Resistance Treadmill).
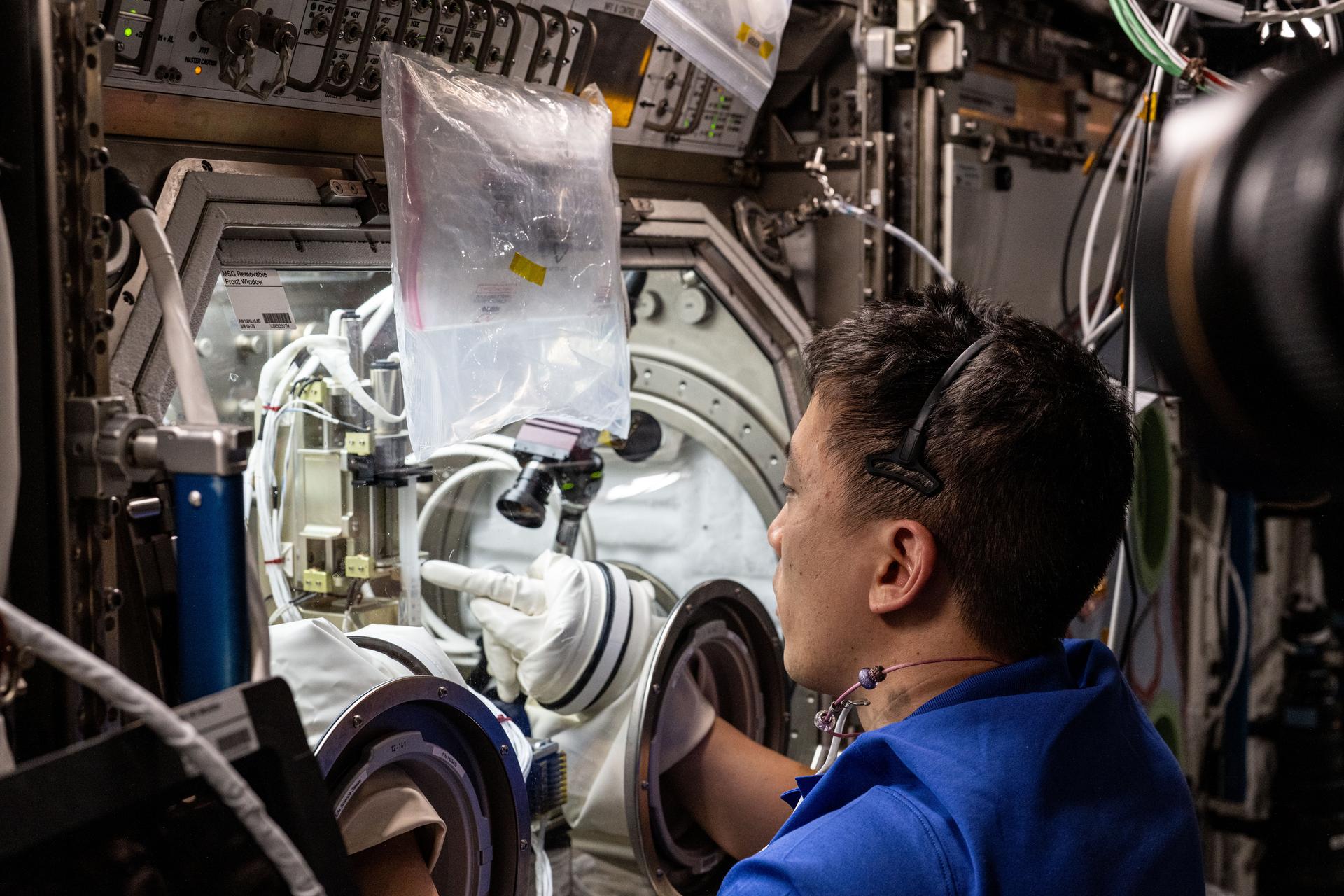

iss073e0177558 (June 12, 2025) -- NASA astronaut Jonny Kim works in the International Space Station’s Microgravity Science Glovebox on Ring Sheared Drop-IBP-2. This investigation studies the behavior of high-concentration protein fluids in microgravity using a special device that holds liquid protein solutions without containers, eliminating interference from interactions with container walls. Results could help advance manufacturing processes and 3D printing in space and for production of medicines, microelectronics, foods, and medical devices on Earth.
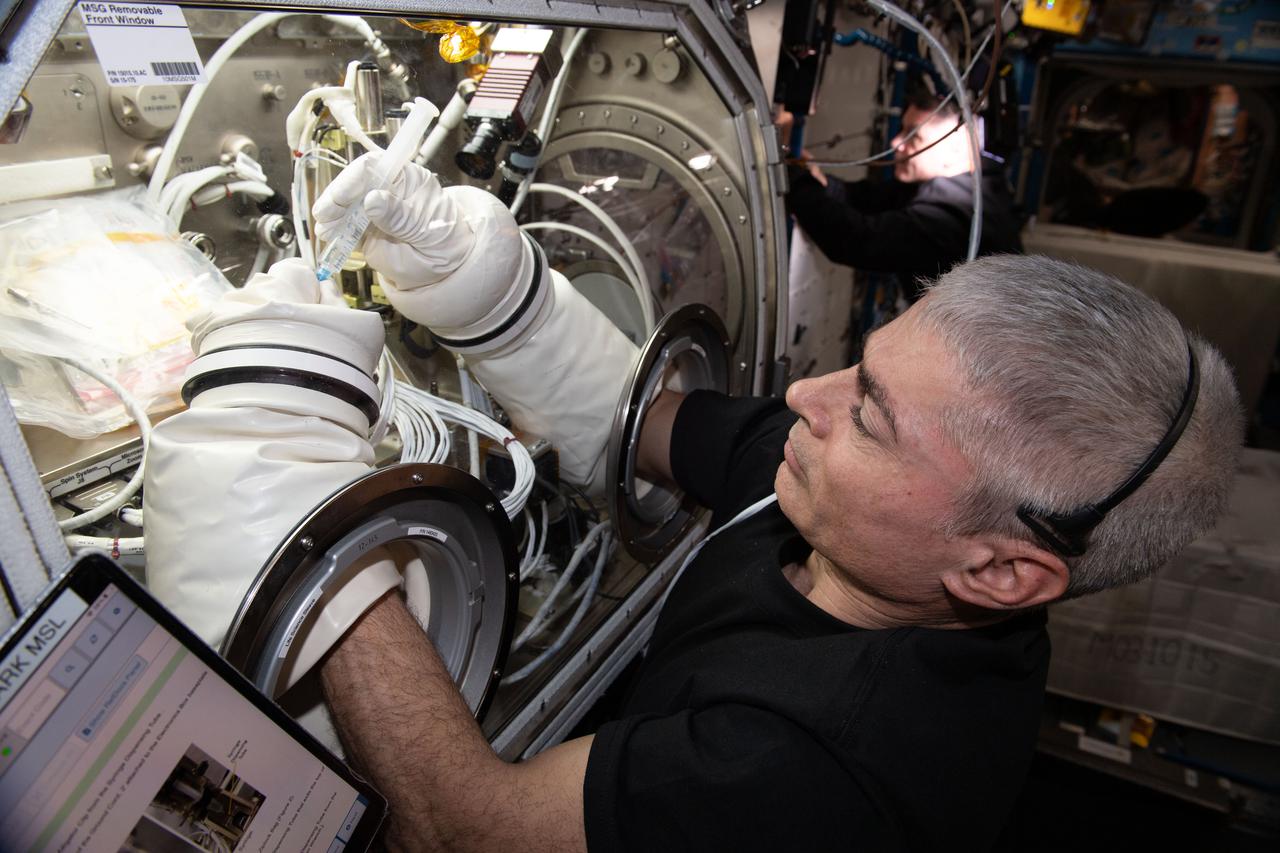

iss065e257447 (Aug. 17, 2021) --- NASA Astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei works on the Ring Sheared Drop investigation in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) aboard the International Space Station. This experiment leverages the microgravity environment of the orbiting laboratory to study proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. The research may contribute to a better understanding of these diseases and development of potential treatments.
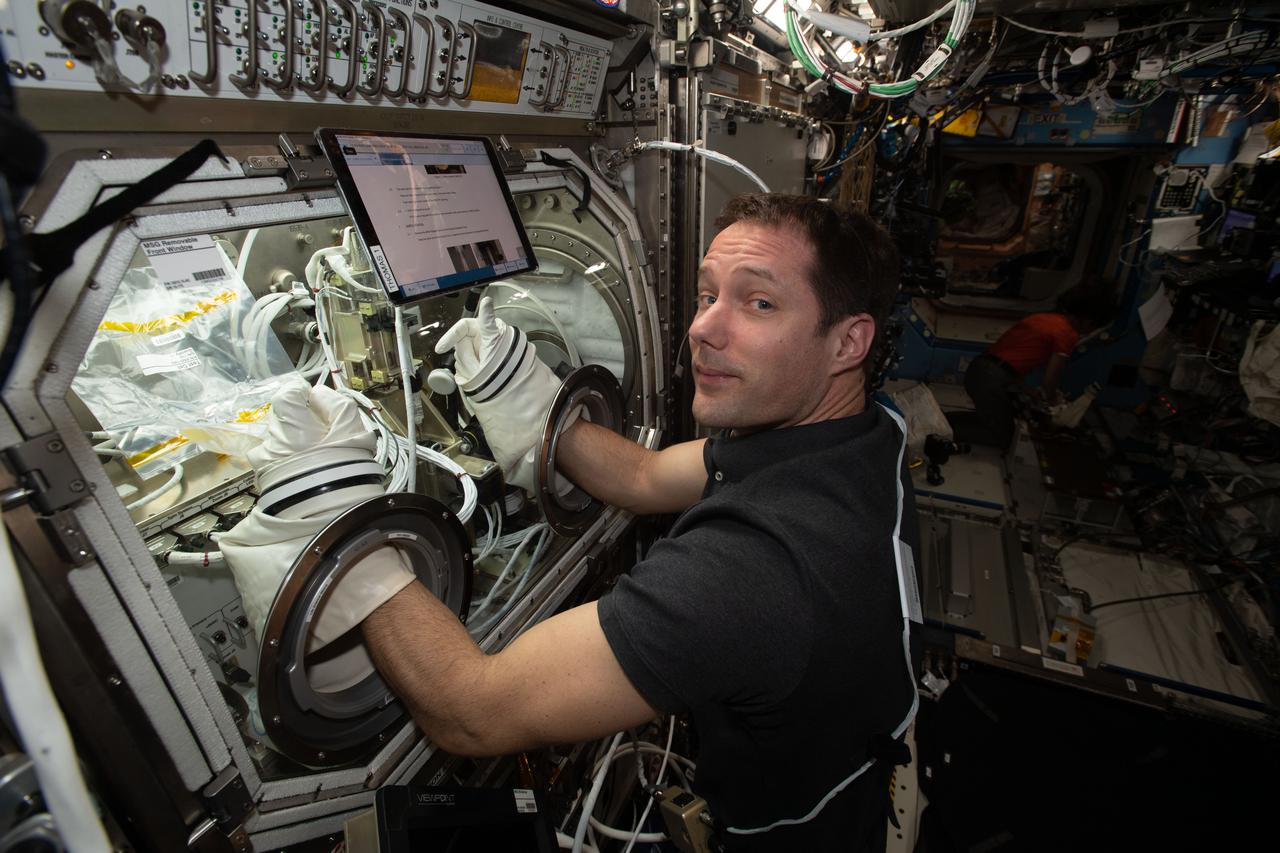

iss065e319336 (Aug. 27, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) works on the Ring-Sheared Drop experiment inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox. Results from the fluid physics study could contribute to a better understanding of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s as well as the development of advanced materials.
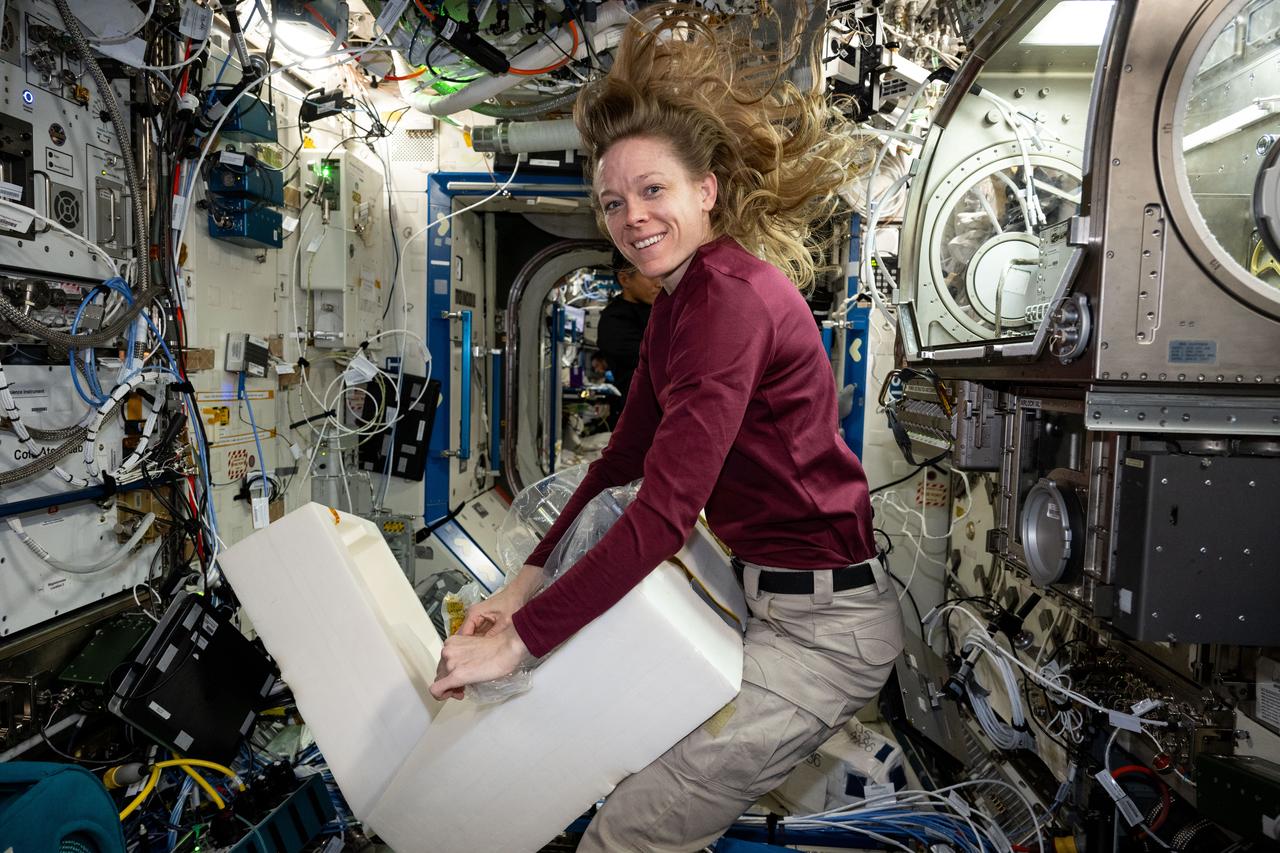

iss073e0253842 (July 1, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers stows physics research hardware from inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox located inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. Ayers was completing operations with the Ring Sheared Drop investigation that may benefit pharmaceutical manufacturing techniques and 3D printing in space.
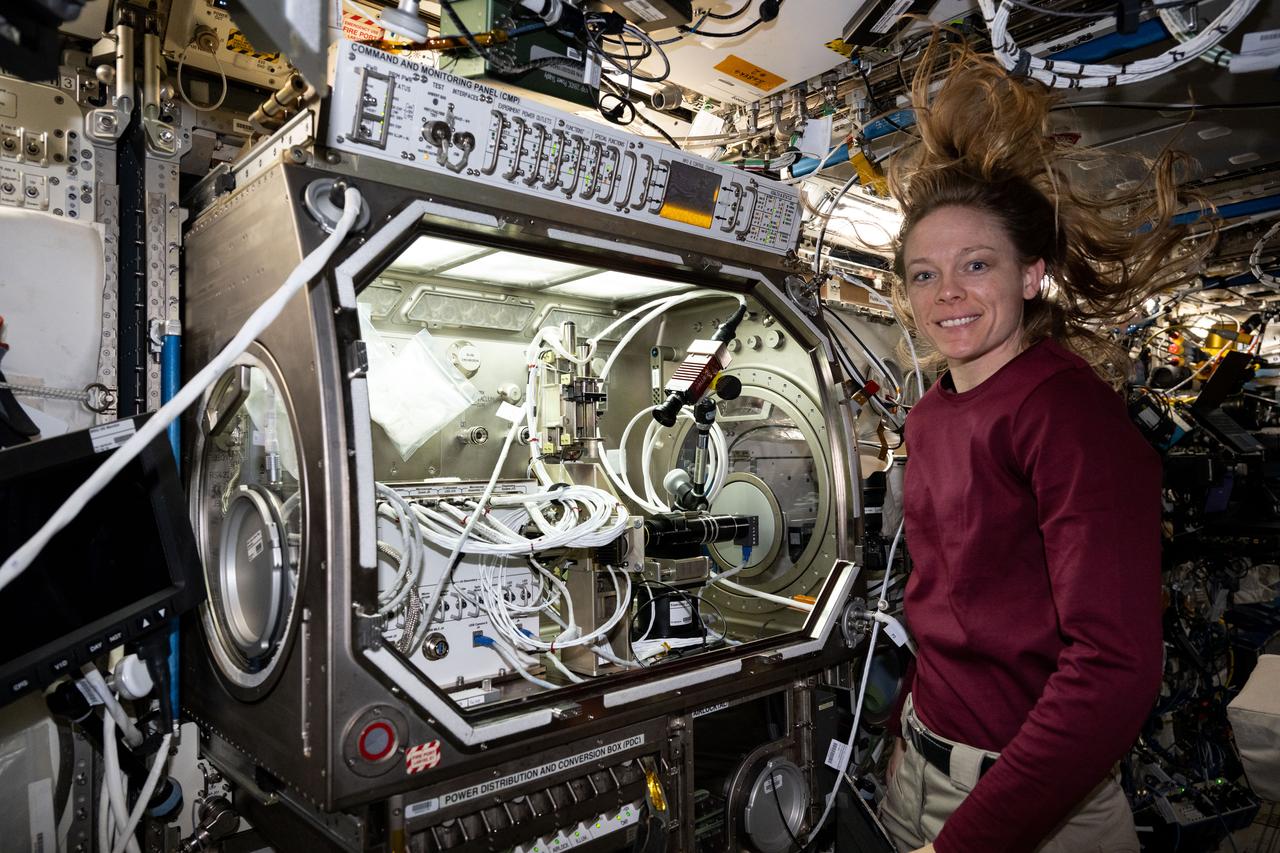

iss073e0253837 (July 1, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers poses for a portrait as she removes physics research hardware from inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox located inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. Ayers was completing operations with the Ring Sheared Drop investigation that may benefit pharmaceutical manufacturing techniques and 3D printing in space.
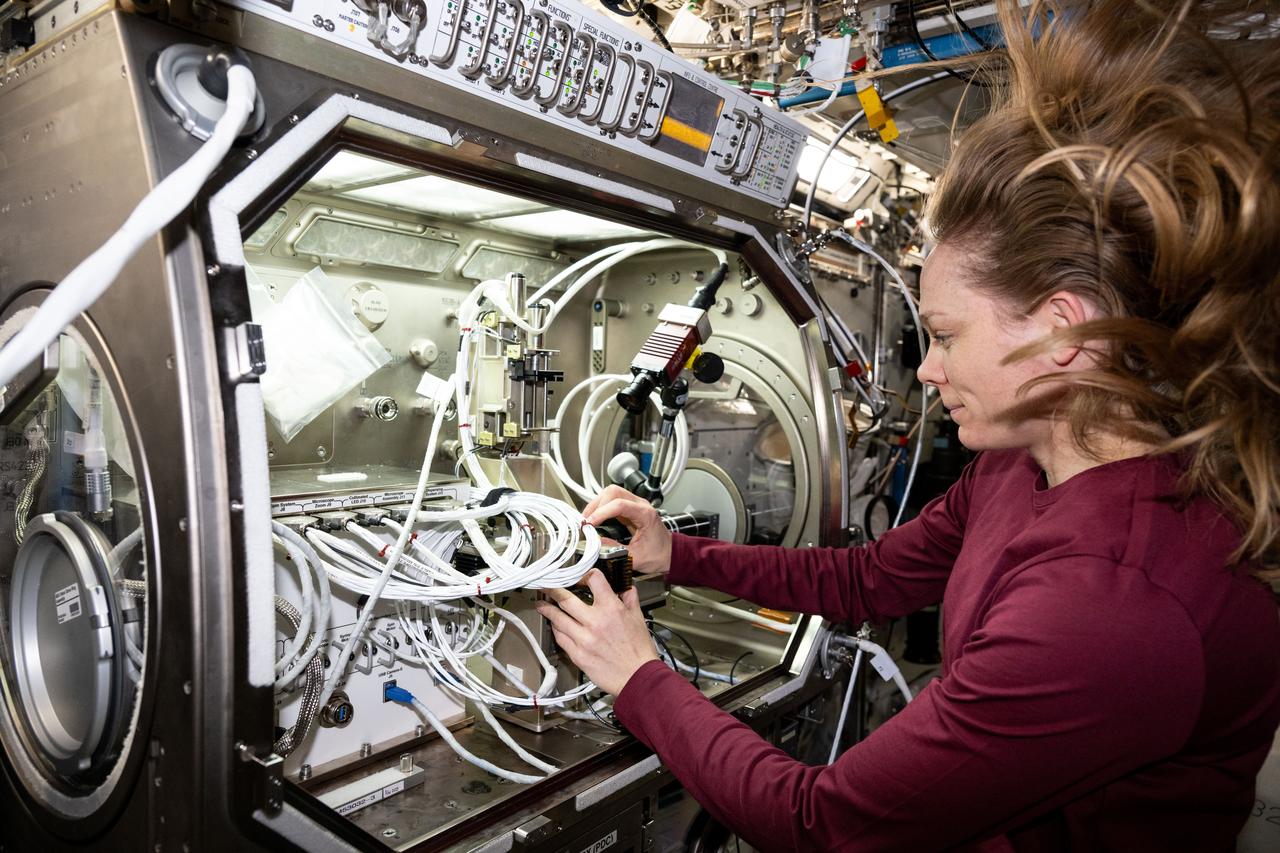

iss073e0253839 (July 1, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers removes physics research hardware from inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox located inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. Ayers was completing operations with the Ring Sheared Drop investigation that may benefit pharmaceutical manufacturing techniques and 3D printing in space.

iss073e0178587 (June 16, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers conducts research operations inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. Ayers swapped syringes containing protein samples and installed test cells inside the glovebox for the Ring-Sheared Drop Interfacial Bioprocessing of Pharmaceuticals investigation that explores using surface tension to contain liquids and study proteins without contacting solid walls. Results may benefit pharmaceutical manufacturing and 3D printing techniques on and off the Earth.
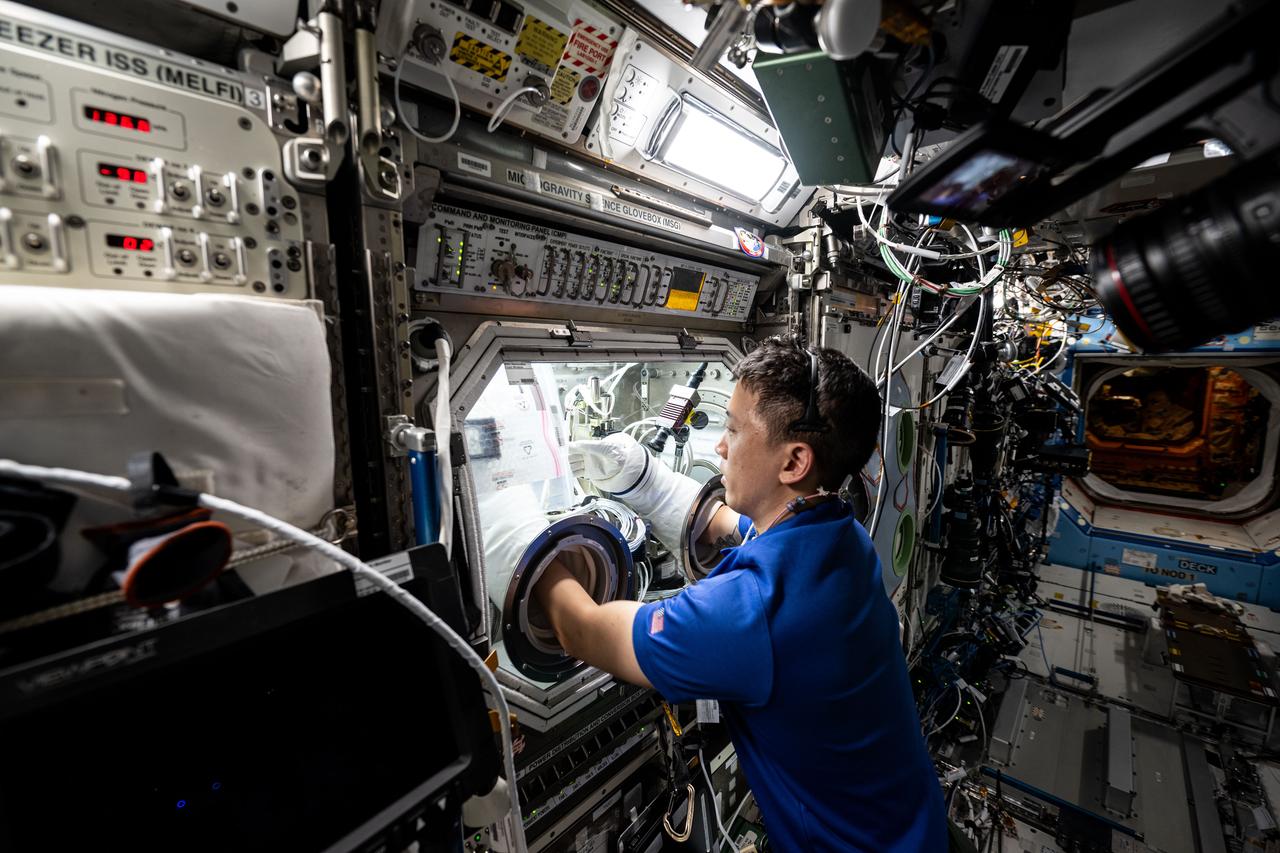

iss073e0177791 (June 12, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim conducts research operations inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. Kim swapped syringes containing protein samples and installed test cells inside the glovebox for the Ring-Sheared Drop Interfacial Bioprocessing of Pharmaceuticals investigation that explores using surface tension to contain liquids and study proteins without contacting solid walls. Results may benefit pharmaceutical manufacturing and 3D printing techniques on and off the Earth.
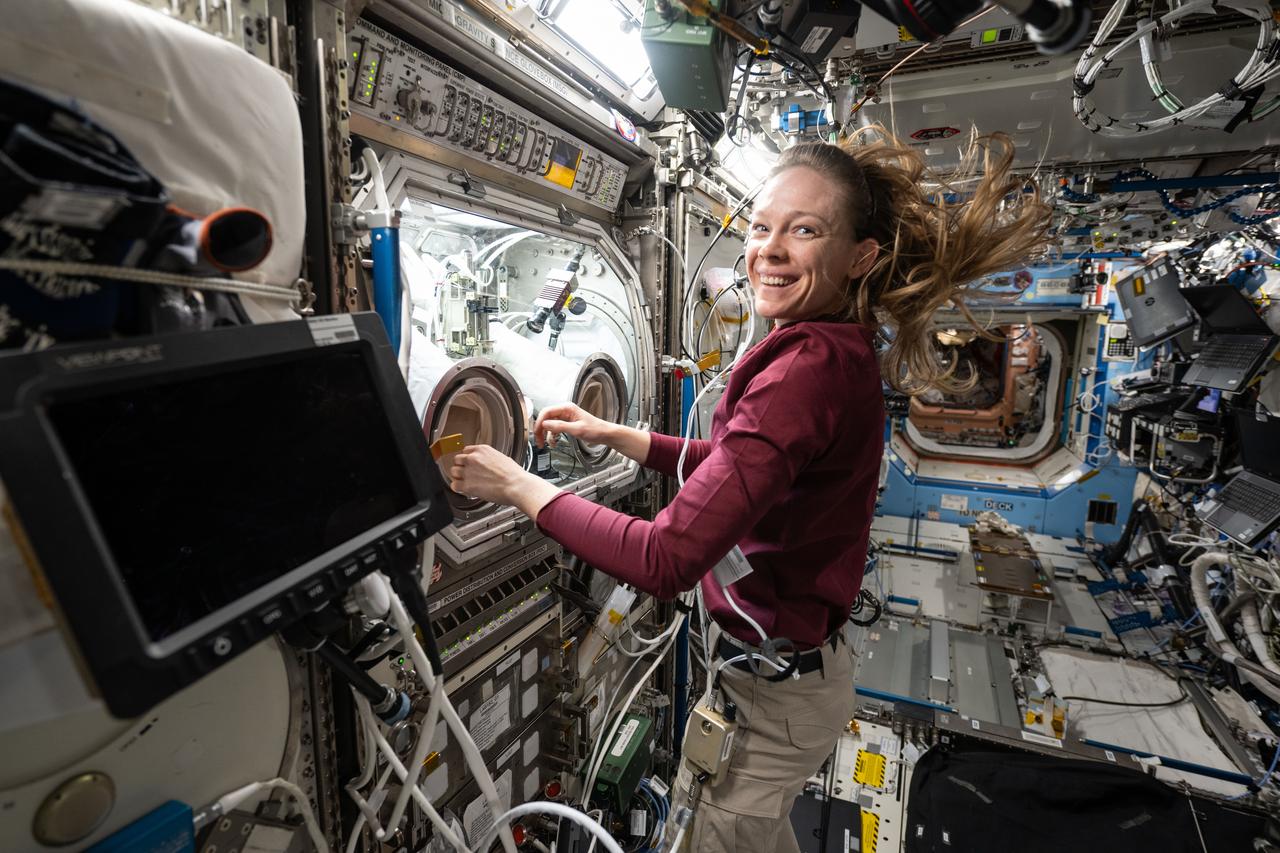

iss073e0248499 (June 25, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers conducts research operations inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. Ayers swapped syringes containing protein samples and installed test cells inside the glovebox for the Ring-Sheared Drop Interfacial Bioprocessing of Pharmaceuticals investigation that explores using surface tension to contain liquids and study proteins without contacting solid walls. Results may benefit pharmaceutical manufacturing and 3D printing techniques on and off the Earth.