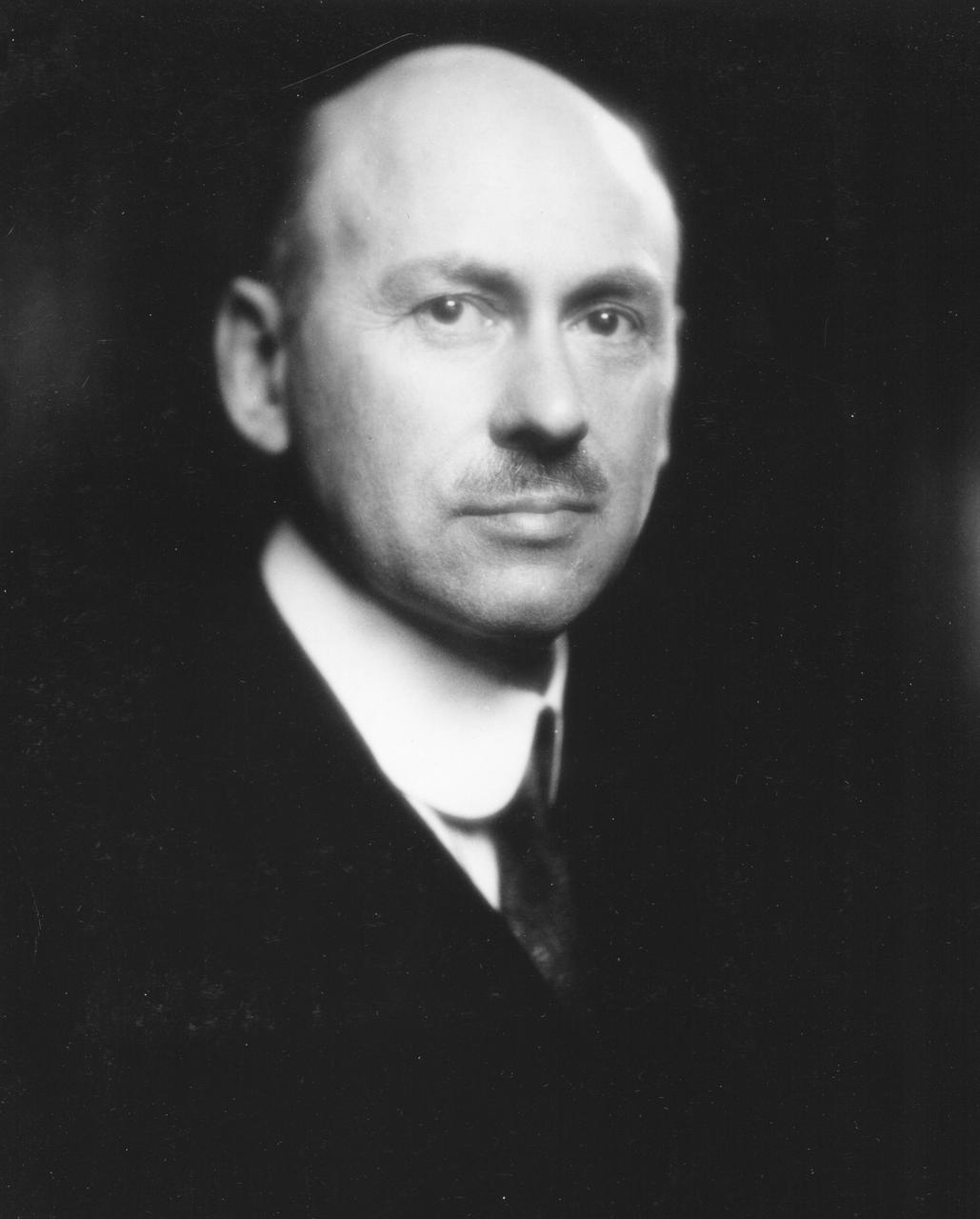

Dr. Robert Hutchings Goddard (1882-1945). Dr. Goddard has been recognized as the father of American rocketry and as one of the pioneers in the theoretical exploration of space. Robert Hutchings Goddard, born in Worcester, Massachusetts, on October 5, 1882, was theoretical scientist as well as a practical engineer. His dream was the conquest of the upper atmosphere and ultimately space through the use of rocket propulsion. Dr. Goddard, died in 1945, but was probably as responsible for the dawning of the Space Age as the Wrights were for the beginning of the Air Age. Yet his work attracted little serious attention during his lifetime. However, when the United States began to prepare for the conquest of space in the 1950's, American rocket scientists began to recognize the debt owed to the New England professor. They discovered that it was virtually impossible to construct a rocket or launch a satellite without acknowledging the work of Dr. Goddard. More than 200 patents, many of which were issued after his death, covered this great legacy. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
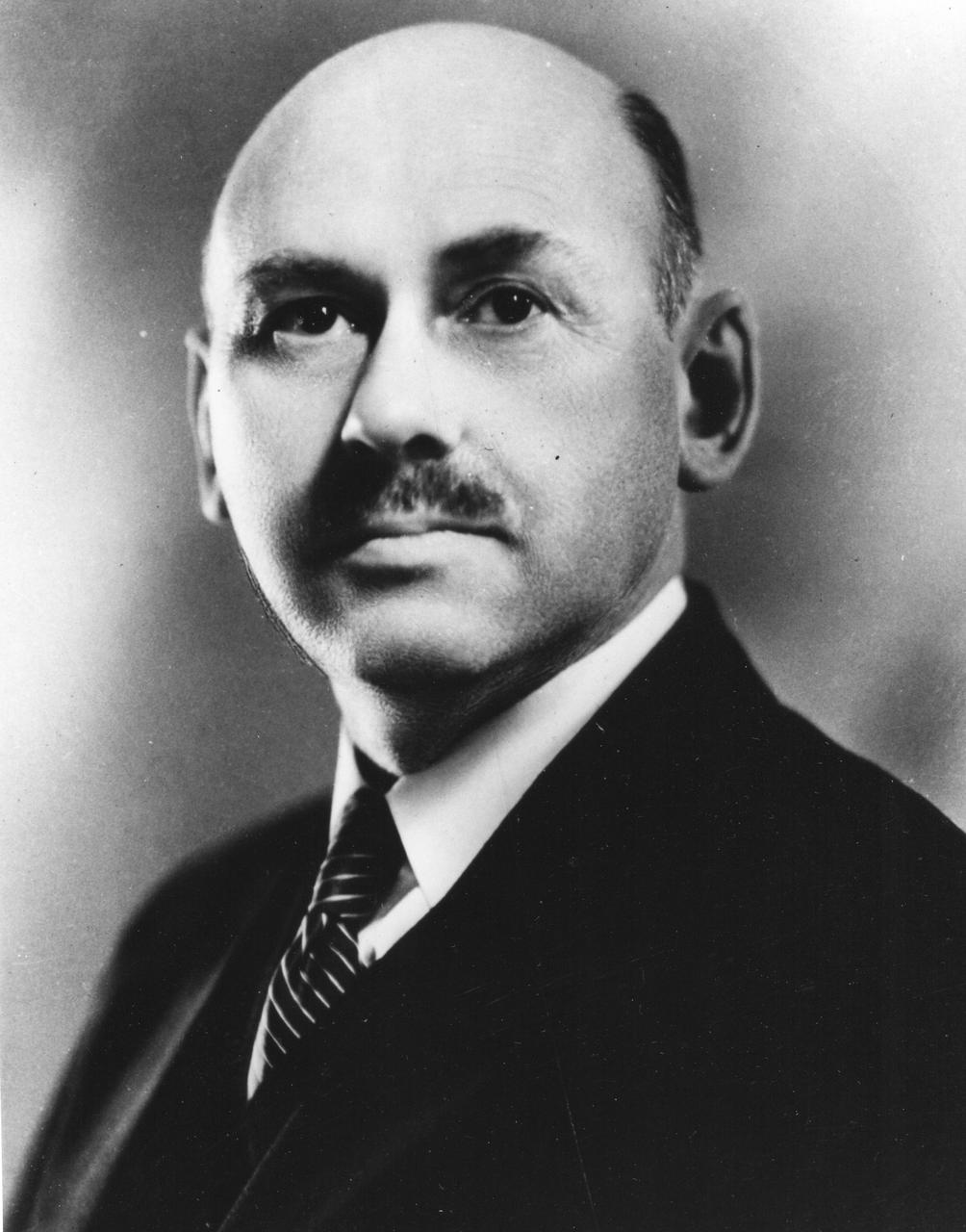

Dr. Robert Hutchings Goddard (1882-1945). Dr. Goddard has been recognized as the father of American rocketry and as one of the pioneers in the theoretical exploration of space. Robert Hutchings Goddard, born in Worcester, Massachusetts, on October 5, 1882, was theoretical scientist as well as a practical engineer. His dream was the conquest of the upper atmosphere and ultimately space through the use of rocket propulsion. Dr. Goddard, died in 1945, but was probably as responsible for the dawning of the Space Age as the Wrights were for the beginning of the Air Age. Yet his work attracted little serious attention during his lifetime. However, when the United States began to prepare for the conquest of space in the 1950's, American rocket scientists began to recognize the debt owed to the New England professor. They discovered that it was virtually impossible to construct a rocket or launch a satellite without acknowledging the work of Dr. Goddard. More than 200 patents, many of which were issued after his death, covered this great legacy. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
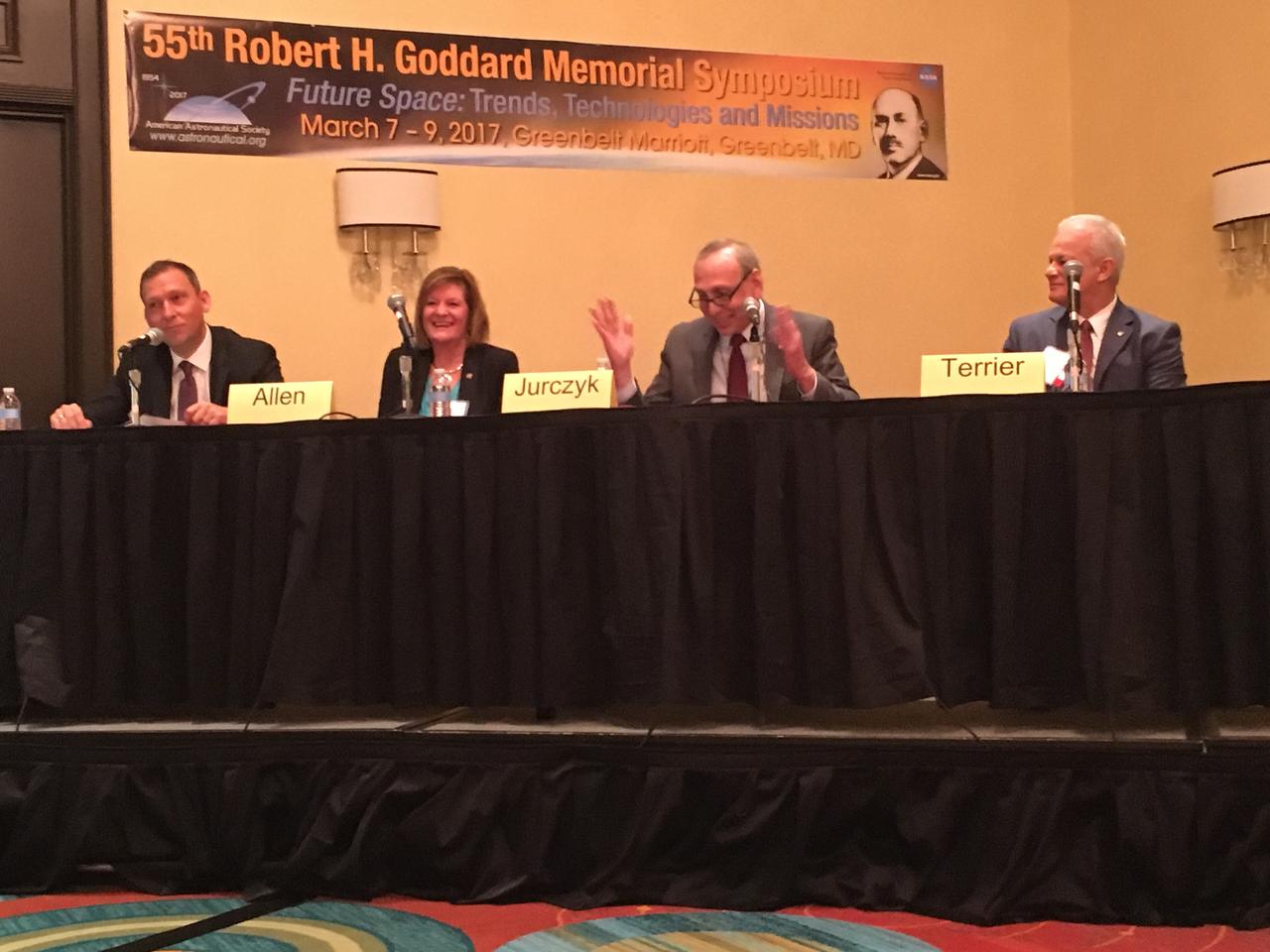

NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier moderated the discussion “NASA Leadership in the Future of Science and Technology" during the AAS 55th Robert H. Goddard Memorial Symposium on March 8, 2017. Terrier was joined by Associate Administrator for Space Technology Steve Jurczyk, Chief Scientist Gale Allen and Associate Administrator for Science Thomas Zurbuchen.
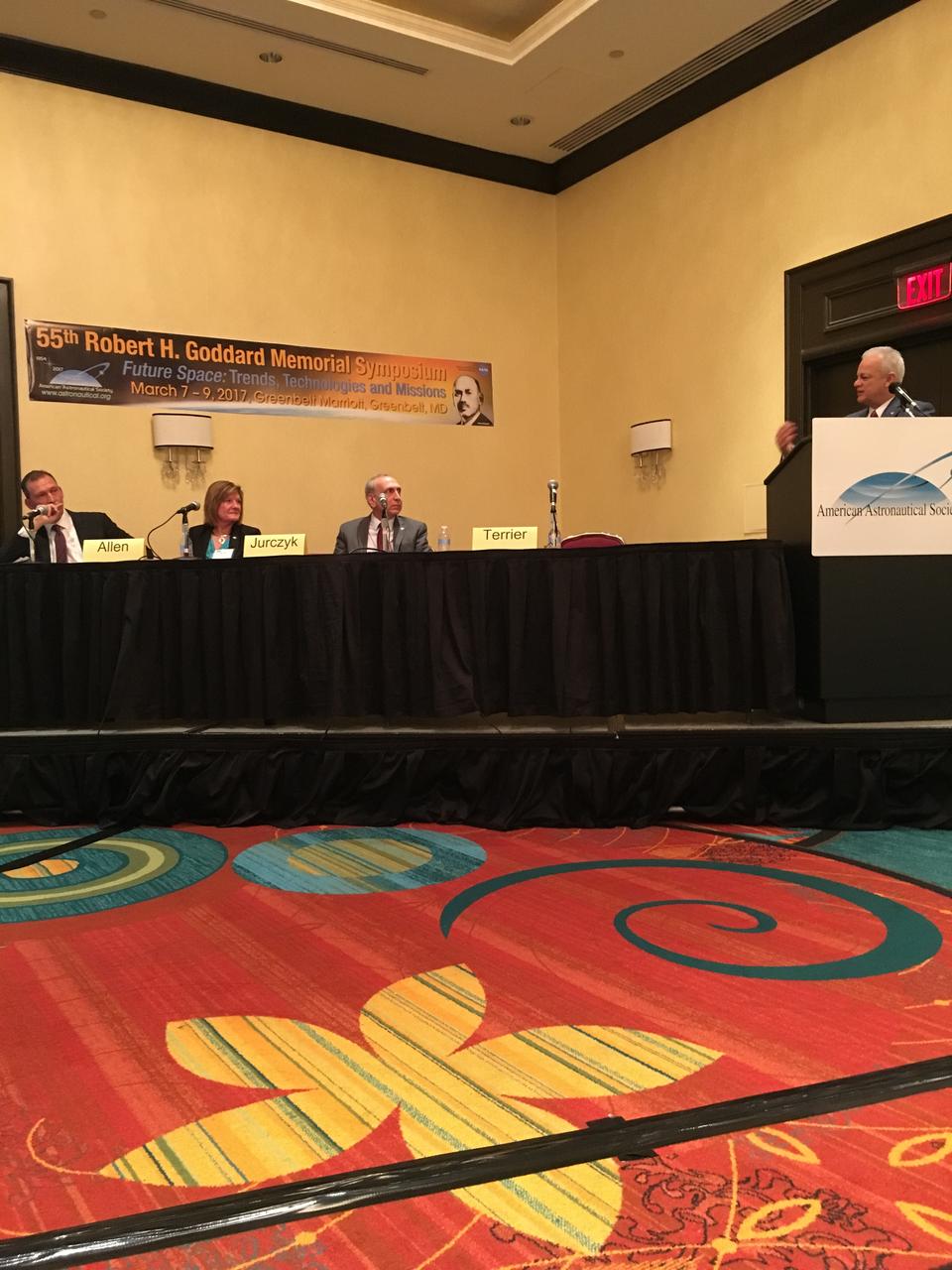

NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier moderated the discussion “NASA Leadership in the Future of Science and Technology" during the AAS 55th Robert H. Goddard Memorial Symposium on March 8, 2017. Terrier was joined by Associate Administrator for Space Technology Steve Jurczyk, Chief Scientist Gale Allen and Associate Administrator for Science Thomas Zurbuchen.
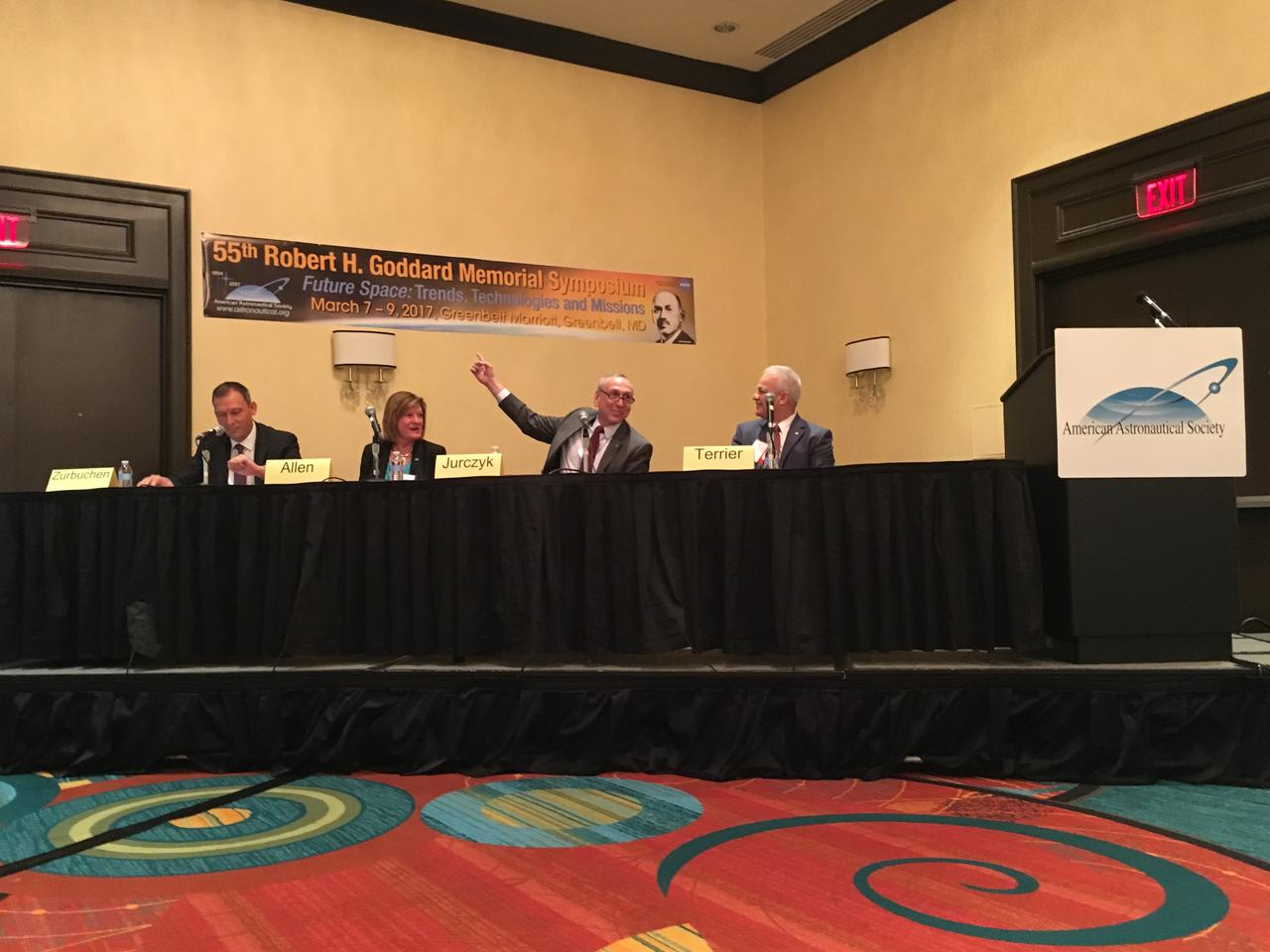

NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier moderated the discussion “NASA Leadership in the Future of Science and Technology" during the AAS 55th Robert H. Goddard Memorial Symposium on March 8, 2017. Terrier was joined by Associate Administrator for Space Technology Steve Jurczyk, Chief Scientist Gale Allen and Associate Administrator for Science Thomas Zurbuchen.
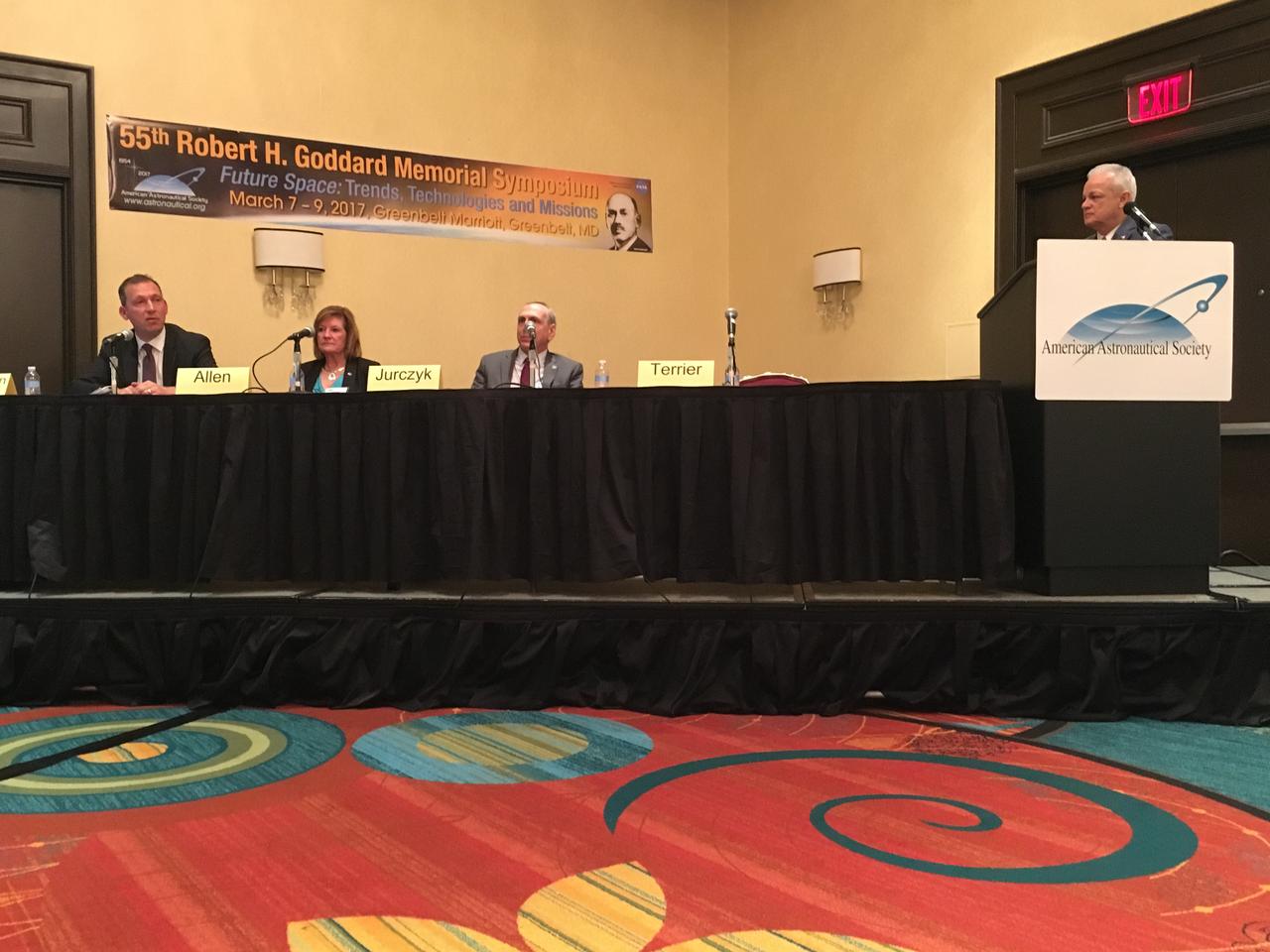

NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier moderated the discussion “NASA Leadership in the Future of Science and Technology" during the AAS 55th Robert H. Goddard Memorial Symposium on March 8, 2017. Terrier was joined by Associate Administrator for Space Technology Steve Jurczyk, Chief Scientist Gale Allen and Associate Administrator for Science Thomas Zurbuchen.

NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier moderated the discussion “NASA Leadership in the Future of Science and Technology" during the AAS 55th Robert H. Goddard Memorial Symposium on March 8, 2017. Terrier was joined by Associate Administrator for Space Technology Steve Jurczyk, Chief Scientist Gale Allen and Associate Administrator for Science Thomas Zurbuchen.
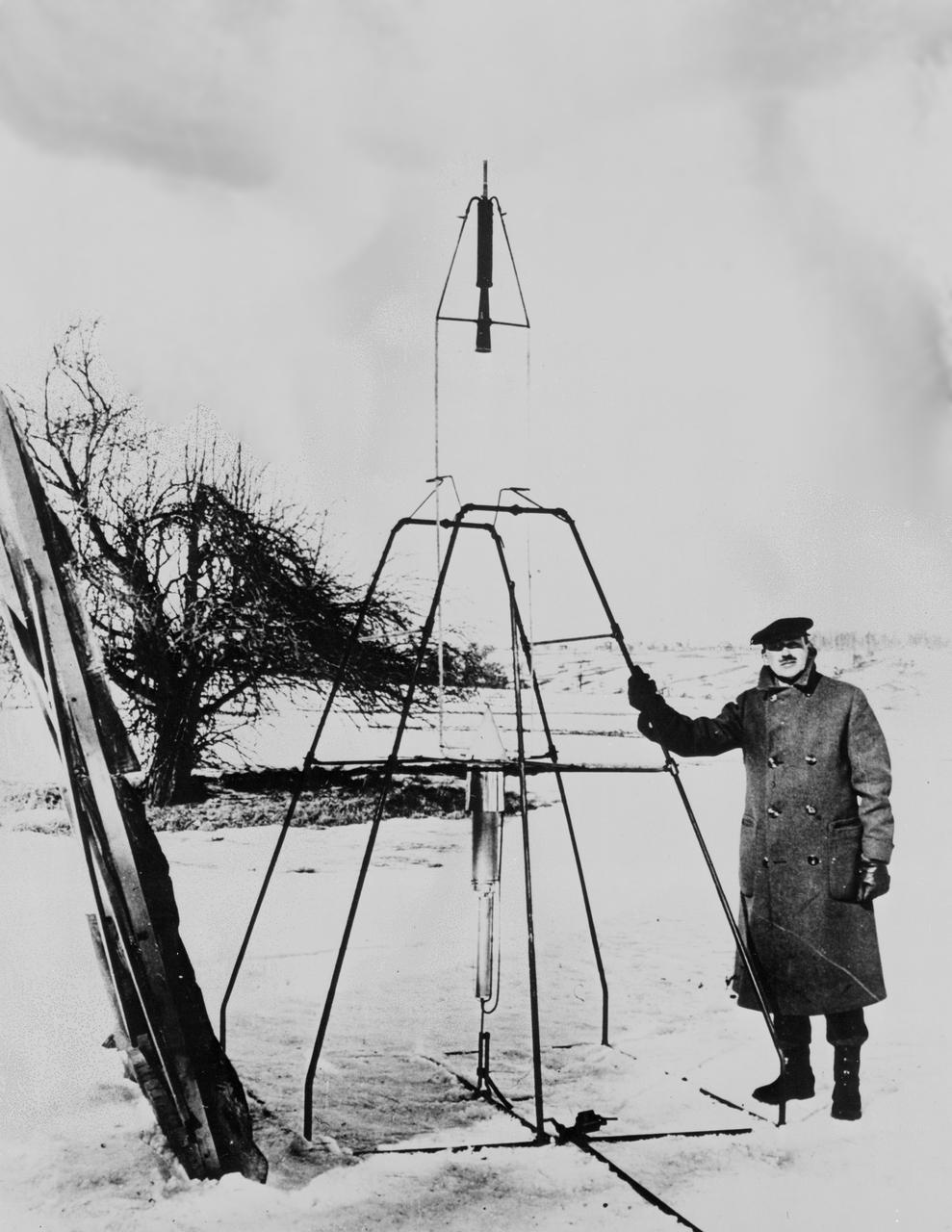

Dr. Robert H. Goddard and liquid oxygen-gasoline rocket in the frame from which it was fired on March 16, 1926, at Auburn, Mass. It flew for only 2.5 seconds, climbed 41 feet, and landed 184 feet away in a cabbage patch. From 1930 to 1941, Dr. Goddard made substantial progress in the development of progressively larger rockets, which attained altitudes of 2400 meters, and refined his equipment for guidance and control, his techniques of welding, and his insulation, pumps, and other associated equipment. In many respects, Dr. Goddard laid the essential foundations of practical rocket technology
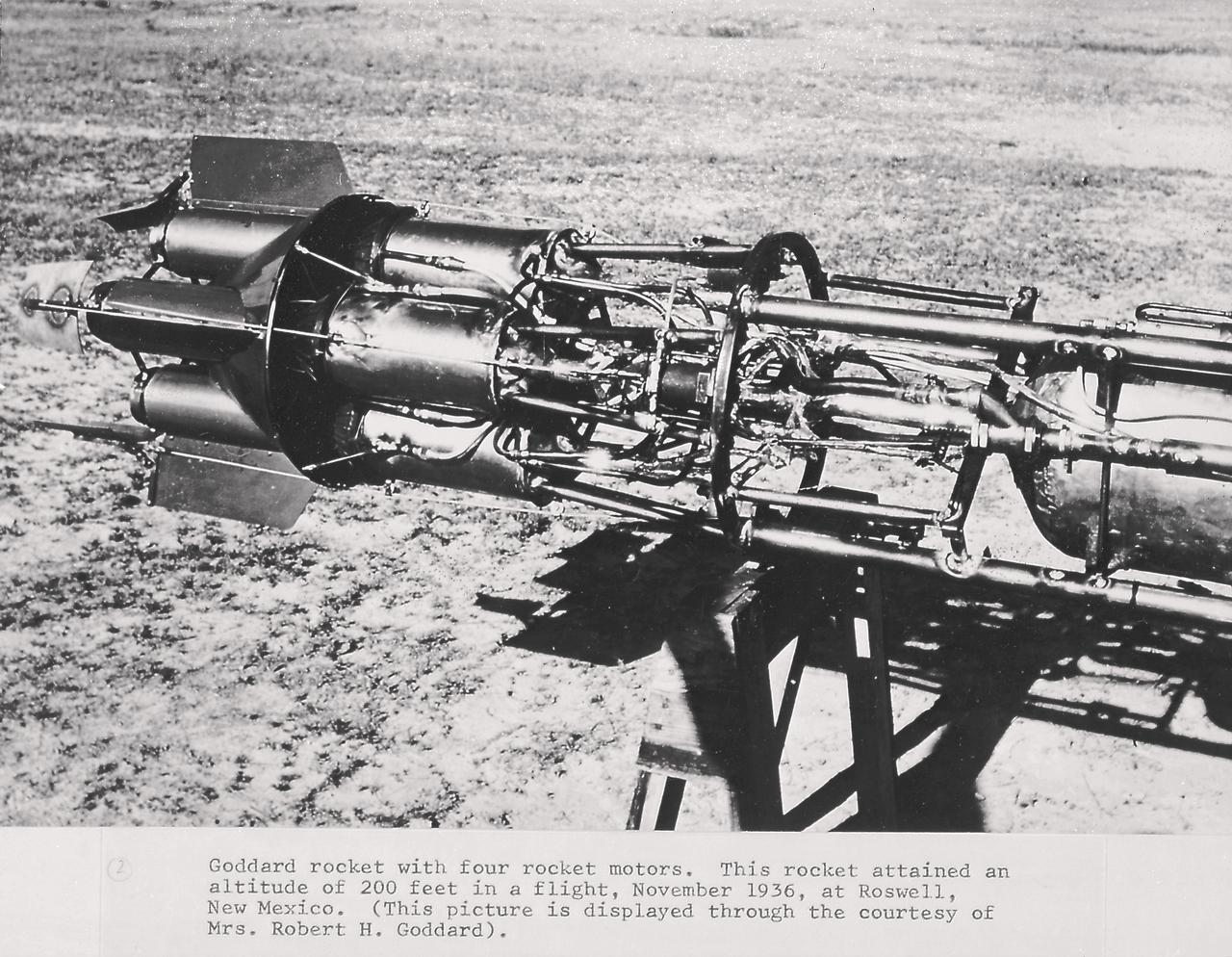
Goddard rocket with four rocket motors. This rocket attained an altitude of 200 feet in a flight, November 1936, at Roswell, New Mexico. From 1930 to 1941, Dr. Goddard made substantial progress in the development of progressively larger rockets which attained altitudes of 2400 meters, and refined his equipment for guidance and control, his techniques of welding, and his insulation, pumps, and other associated equipment. In many respects, Dr. Goddard laid the essential foundations of practical rocket technology
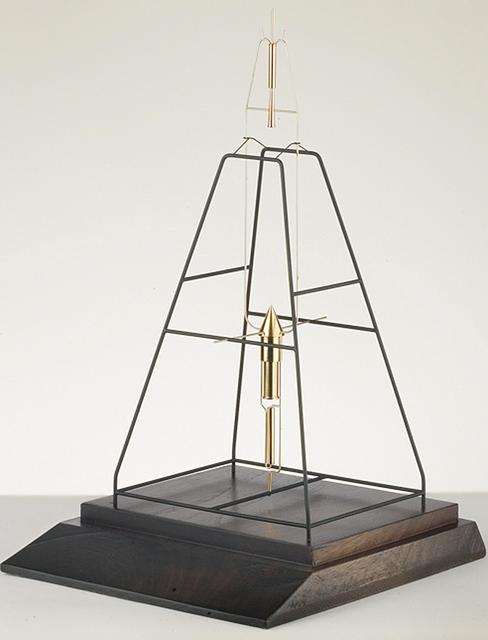

A desktop-sized model of Robert H. Goddard's 1926 liquid-fueled rocket.
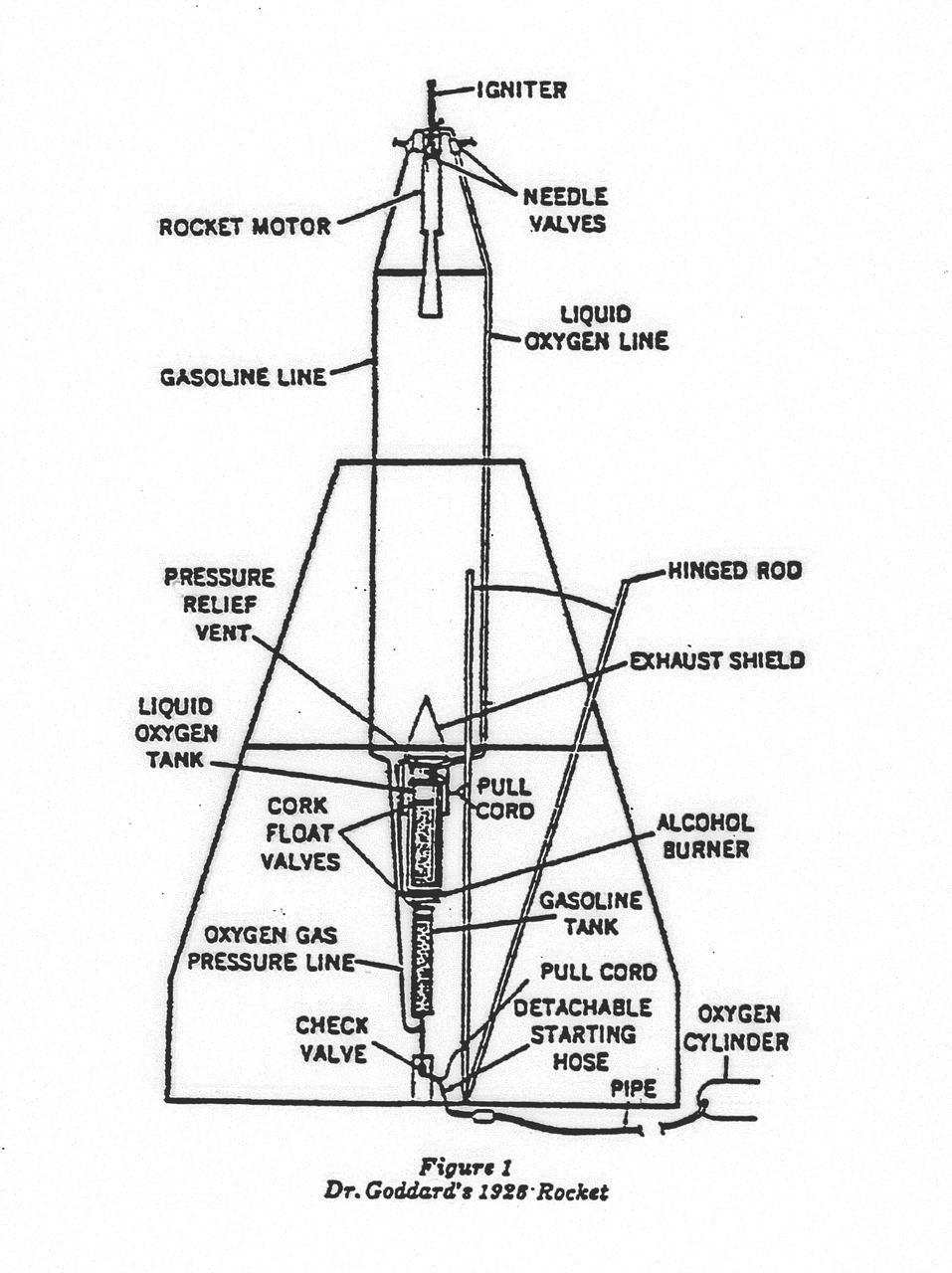
Dr. Goddard's 1926 rocket configuration. Dr. Goddard's liquid oxygen-gasoline rocket was fired on March 16, 1926, at Auburn, Massachusetts. It flew for only 2.5 seconds, climbed 41 feet, and landed 184 feet away in a cabbage patch. From 1930 to 1941, Dr. Goddard made substantial progress in the development of progressively larger rockets, which attained altitudes of 2400 meters, and refined his equipment for guidance and control, his techniques of welding, and his insulation, pumps, and other associated equipment. In many respects, Dr. Goddard laid the essential foundations of practical rocket technology
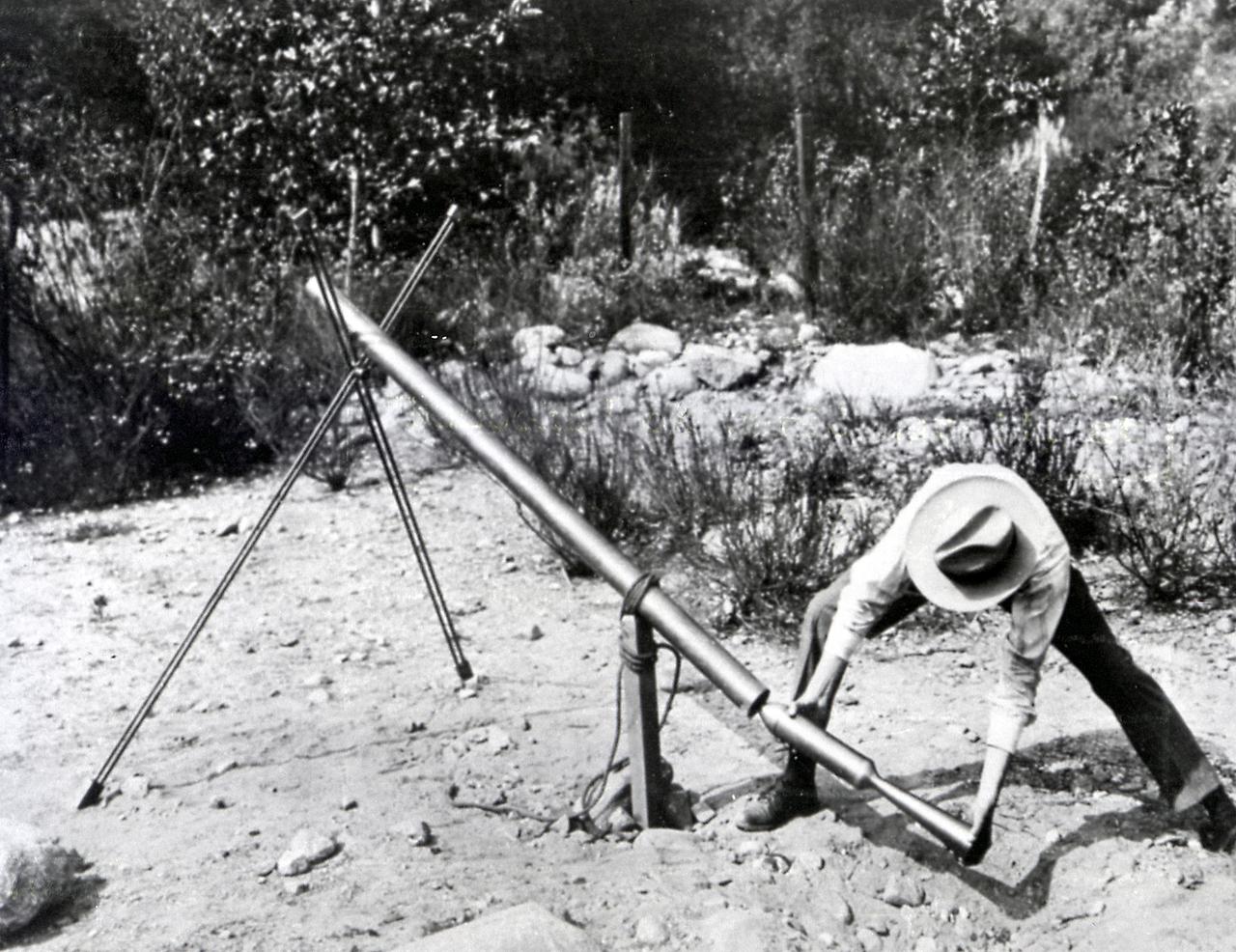

Dr. Robert H. Goddard loading a 1918 version of the Bazooka of World War II. From 1930 to 1941, Dr. Goddard made substantial progress in the development of progressively larger rockets, which attained altitudes of 2400 meters, and refined his equipment for guidance and control, his techniques of welding, and his insulation, pumps, and other associated equipment. In many respects, Dr. Goddard laid the essential foundations of practical rocket technology
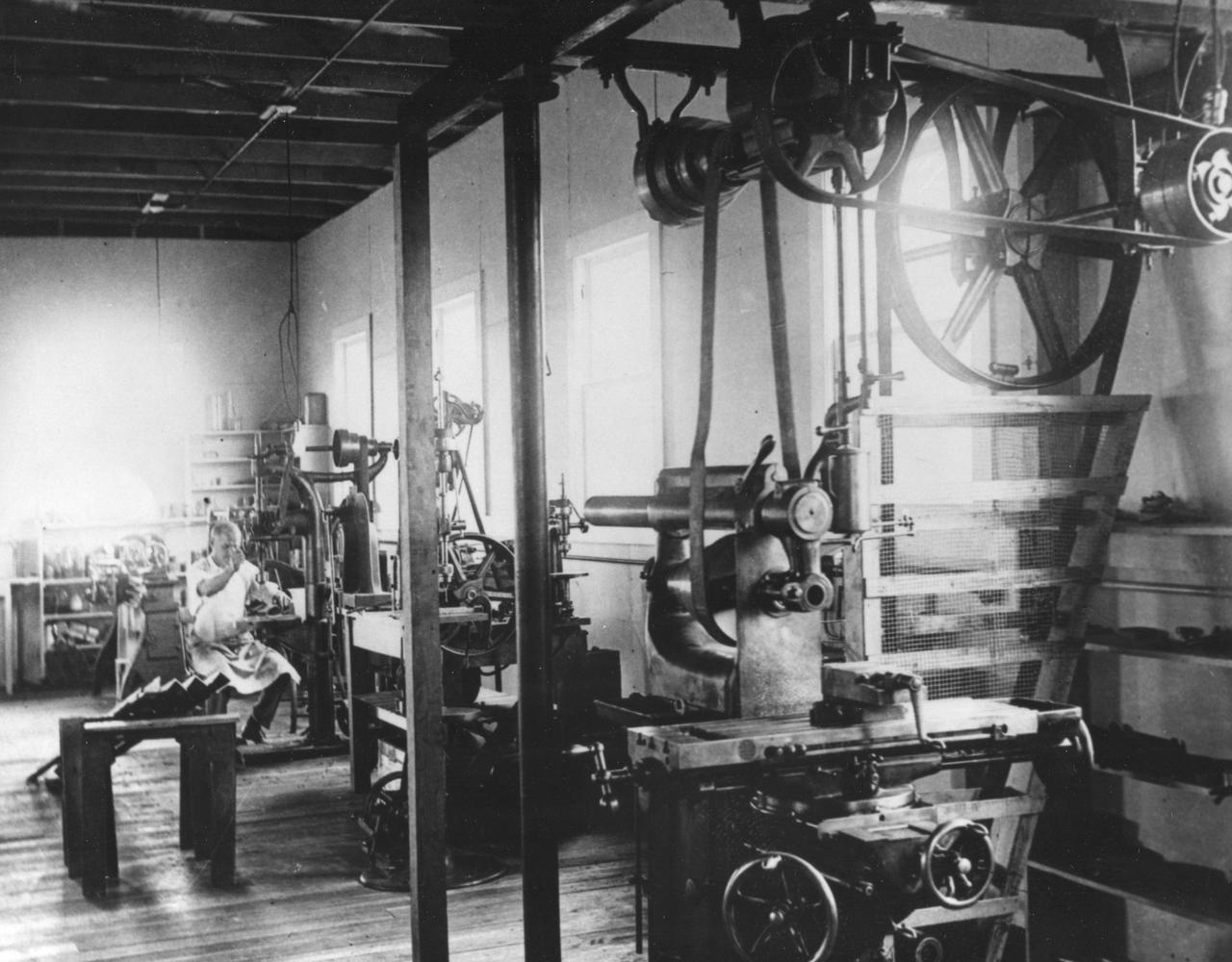
Interior view along the south side of Dr. Robert Goddard’s shop at the Mescalero Ranch in New Mexico. Mr. H. Sachs is shown seated in the rear of the shop. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
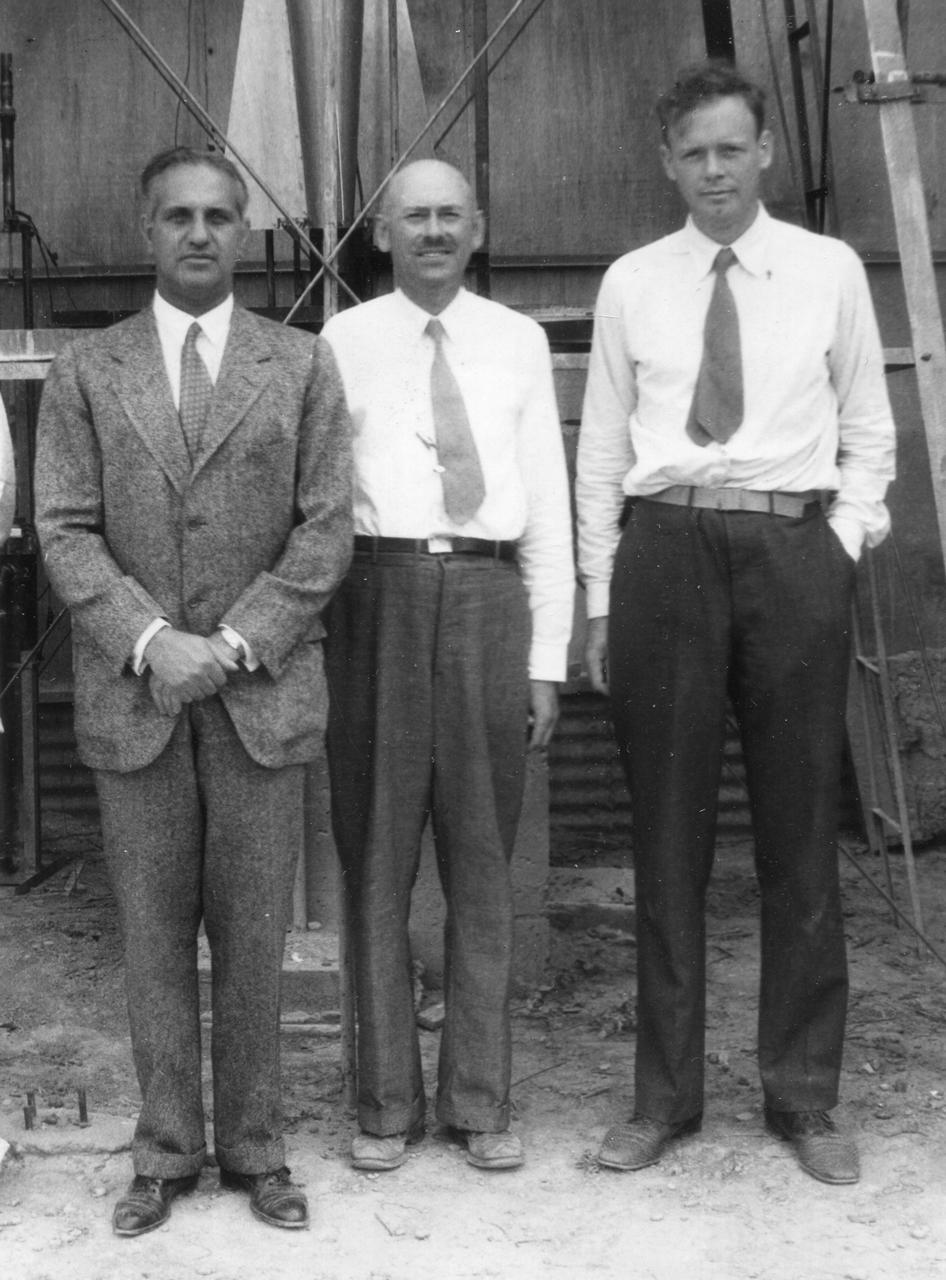

Standing in front of the rocket in the launch tower on September 23, 1935, are (left to right): Harry F. Guggenheim; Dr. Robert H. Goddard; and Col. Charles A. Lindbergh. Charles Lindbergh, an advocate for Goddard and his research, helped secure a grant from the Daniel and Florence Guggenheim Foundation in 1930. With that money Goddard and his wife moved to Roswell, New Mexico, where he could conduct research and launch rockets while avoiding the scrutiny and criticism of his colleagues and the press. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
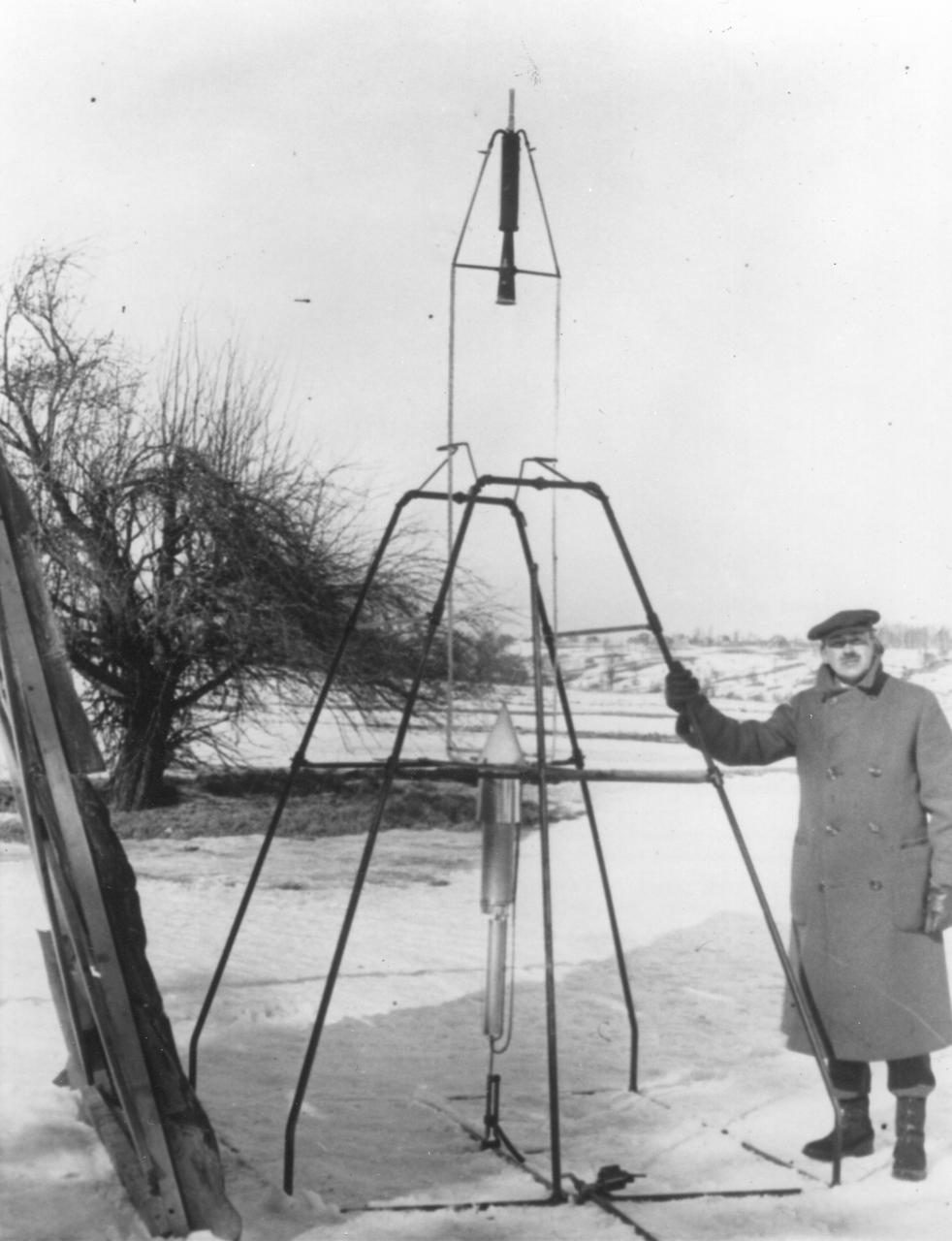

Dr. Robert H. Goddard and a liquid oxygen-gasoline rocket in the frame from which it was fired on March 16, 1926, at Auburn, Massachusetts. From 1930 to 1941, Dr. Goddard made substantial progress in the development of progressively larger rockets, which attained altitudes of 2400 meters, and refined his equipment for guidance and control, his techniques of welding, and his insulation, pumps and other associated equipment. In many respects, Dr. Goddard laid the essential foundations of practical rocket technology. He is considered one of the fathers of rocketry along with Konstantin Tsiolovsky (1857-1935) and Hermann Oberth (1894-1989). <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
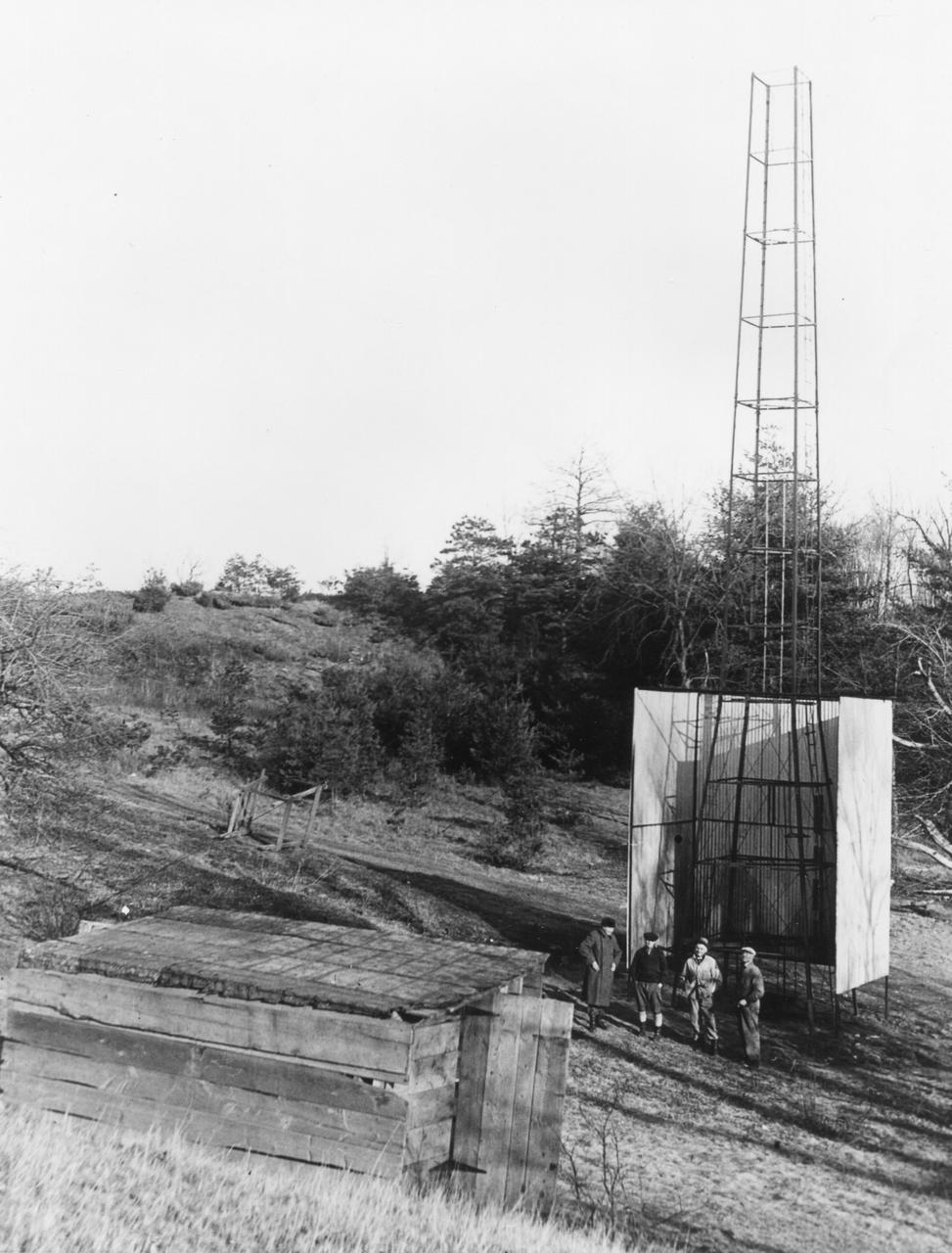

Dr. Robert H. Goddard's tower and shelter at the Army artillery range at Camp Devens, in Ayer, Massachusetts in the winter of 1929-1930. Goddard originally began testing rockets on his aunt's farm in Auburn, Massachusetts until the local police, fire department and townspeople became concerned about the noise and menace to the public the rockets created. Although Goddard maintained that the rockets were not a danger, he soon moved to Camp Devens, Massachusetts. There he was able to launch the rockets without attracting attention. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
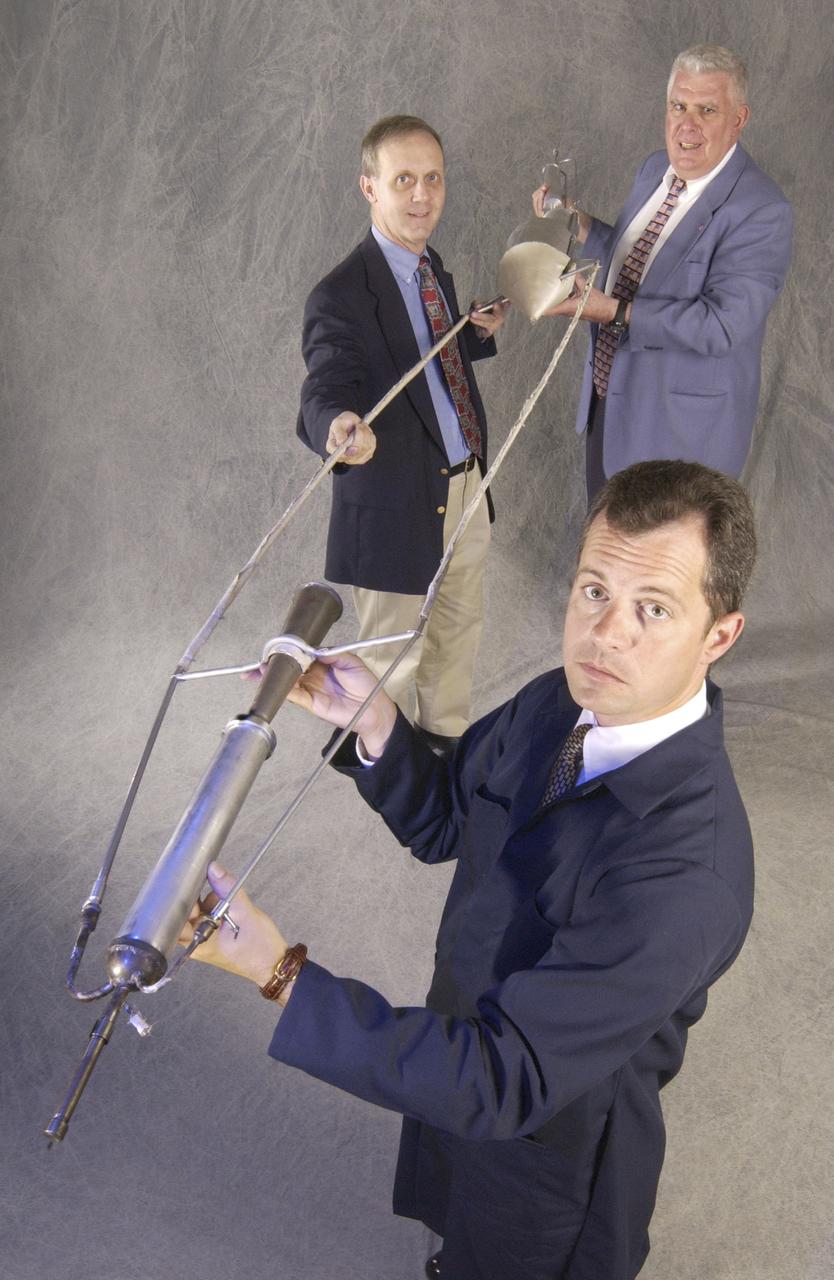

In honor of the Centernial of Flight celebration and commissioned by the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), a team of engineers from Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) built a replica of the first liquid-fueled rocket. The original rocket, designed and built by rocket engineering pioneer Robert H. Goddard in 1926, opened the door to modern rocketry. Goddard's rocket reached an altitude of 41 feet while its flight lasted only 2.5 seconds. The Marshall design team's plan was to stay as close as possible to an authentic reconstruction of Goddard's rocket. The same propellants were used - liquid oxygen and gasoline - as available during Goddard's initial testing and firing. The team also tried to construct the replica using the original materials and design to the greatest extent possible. By purposely using less advanced techniques and materials than many that are available today, the team encountered numerous technical challenges in testing the functional hardware. There were no original blueprints or drawings, only photographs and notes. However, this faithful adherence to historical accuracy has also allowed the team to experience many of the same challenges Goddard faced 77 years ago, and more fully appreciate the genius of this extraordinary man. The replica will undergo ground tests at MSFC this summer.
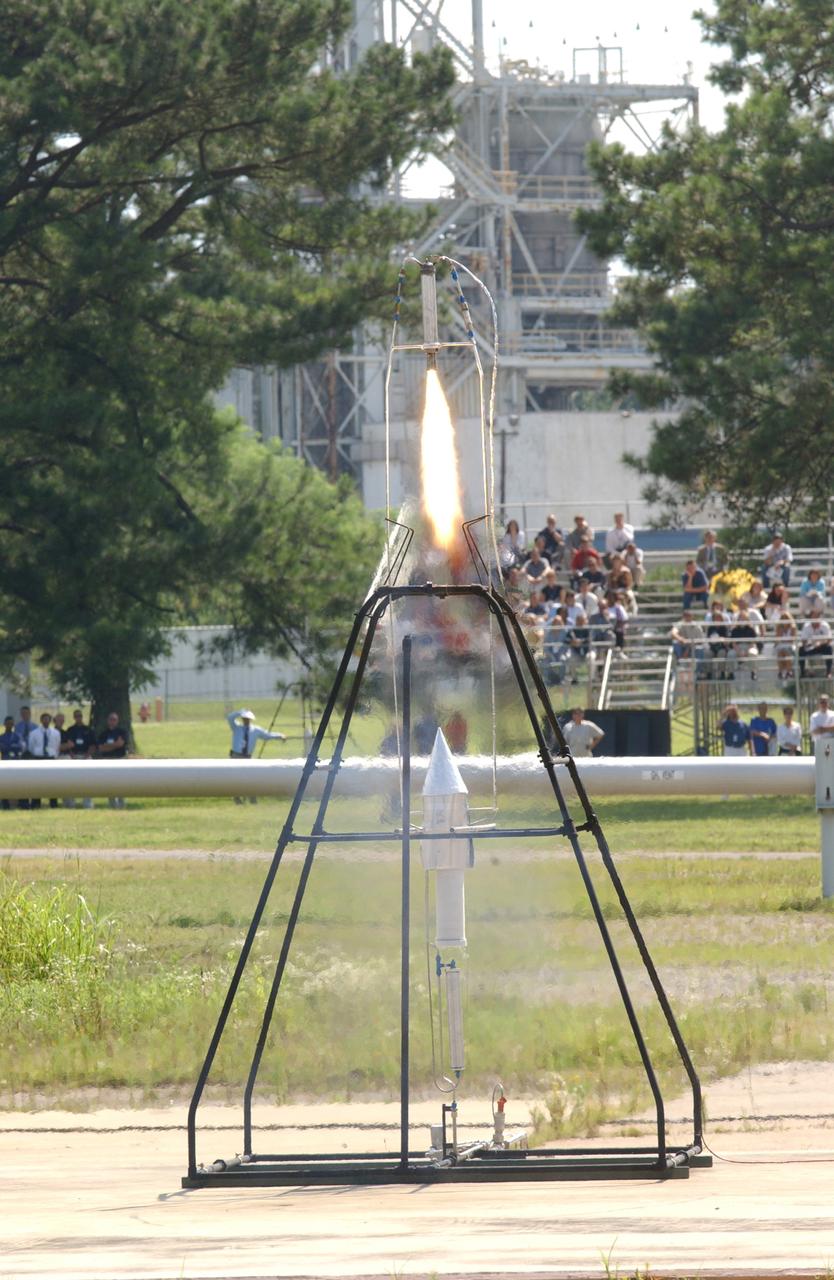
In honor of the Centernial of Flight Celebration and commissioned by the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), a team of engineers from Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) built a replica of the first liquid-fueled rocket. The original rocket, designed and built by rocket engineering pioneer Robert H. Goddard in 1926, opened the door to modern rocketry. Goddard's rocket reached an altitude of 41 feet while its flight lasted only 2.5 seconds. The Marshall design team's plan was to stay as close as possible to an authentic reconstruction of Goddard's rocket. The same propellants were used - liquid oxygen and gasoline - as available during Goddard's initial testing and firing. The team also tried to construct the replica using the original materials and design to the greatest extent possible. By purposely using less advanced techniques and materials than many that are available today, the team encountered numerous technical challenges in testing the functional hardware. There were no original blueprints or drawings, only photographs and notes. However, this faithful adherence to historical accuracy has allowed the team to experience many of the same challenges Goddard faced 77 years ago, and more fully appreciate the genius of this extraordinary man. In this photo, the replica is shown firing in the A-frame launch stand in near-flight configuration at MSFC's Test Area 116 during the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics 39th Joint Propulsion Conference on July 23, 2003.
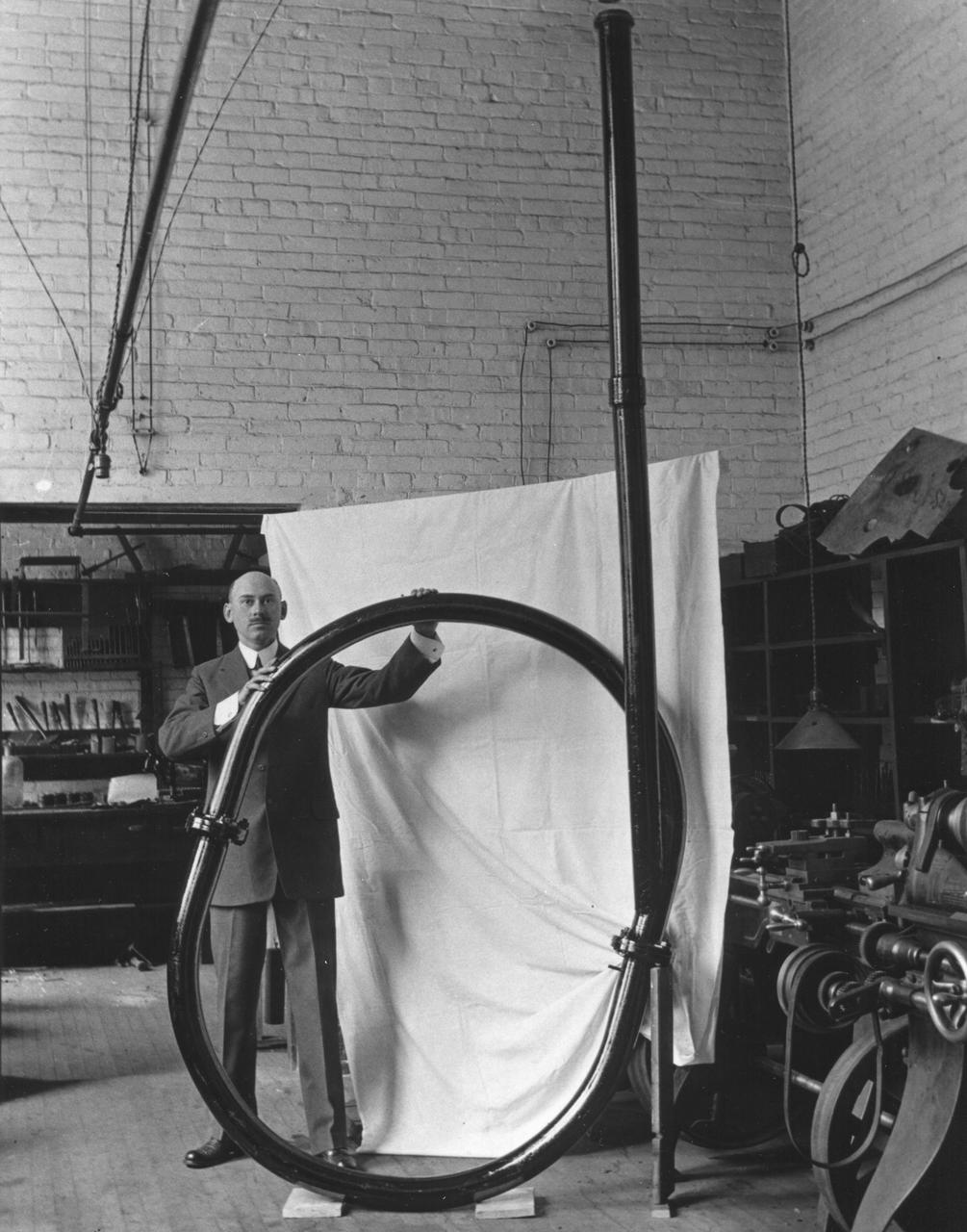

Robert H. Goddard with vacuum tube apparatus he built in 1916 to research rocket efficiency. Dr. Robert Hutchings Goddard is commonly referred to as the father of American rocketry. The same year he built the apparatus, Goddard wrote a study requesting funding from the Smithsonian Institution so that he could continue his rocket research, which he had begun in 1907 while still a student at Worcester Polytechnic Institute. A brilliant physicist, with a unique genius for invention, Goddard may not have succeeded had it not been for the Smithsonian Institution and later the Daniel Guggenheim Foundation and his employer the Worcester Polytechnic Institute of Clark University. The former gave him research monies while the Institute provided leaves of absence so that he could continue his life's work. He was the first scientist who not only realized the potential of missiles and space flight, but also contributed directly to making them a reality. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
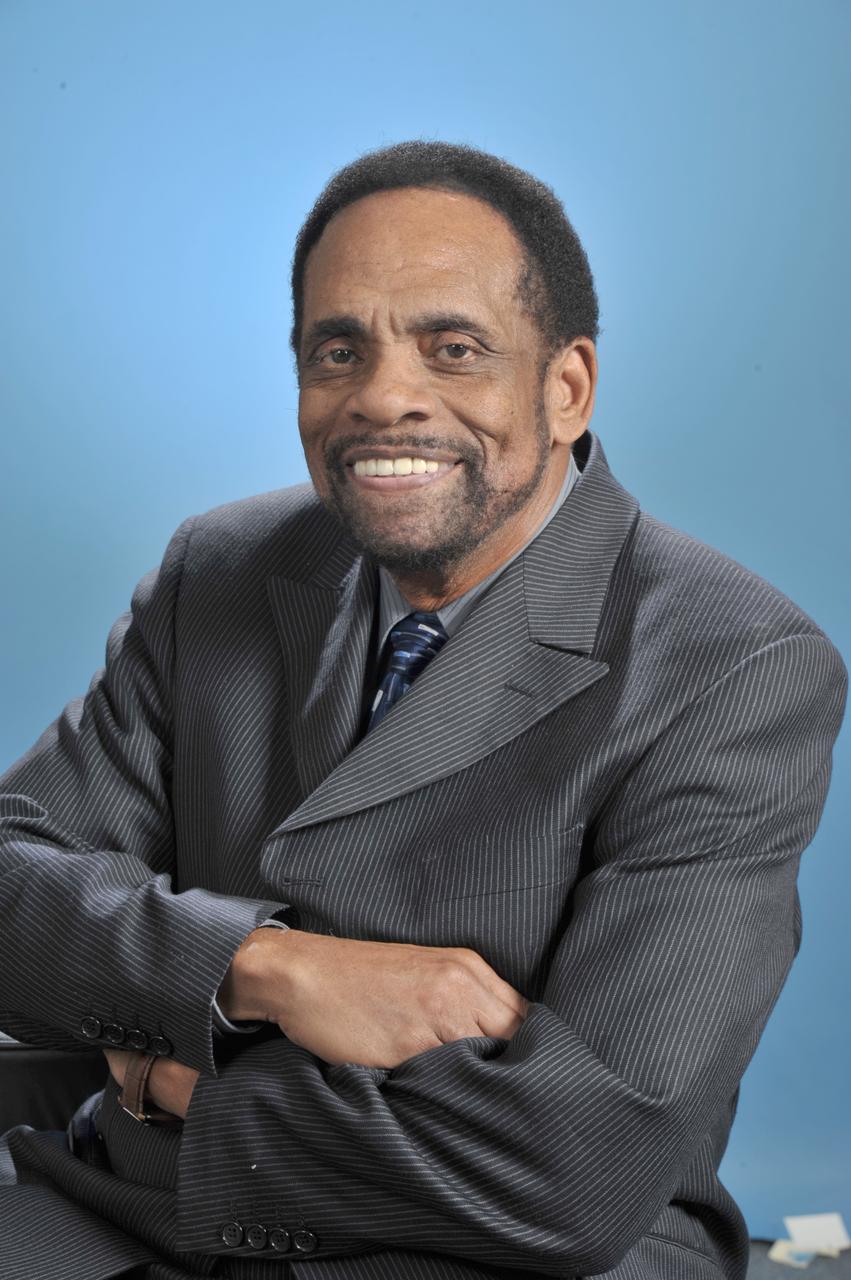

George Edward Alcorn, a pioneering African American physicist and engineer, is credited with dozens of inventions over the course of a distinguished career in private industry and at NASA, for which he earned eight patents. Alcorn joined Goddard Space Flight Center in 1978 and held numerous leadership roles in both research and administration until his retirement in 2012. One of Alcorn’s signature accomplishments at NASA was developing a smaller, more sensitive X-ray spectrometer, changing the way scientists were able to use the powerful tool in deep space exploration missions. His tool, which uses thermomigration of aluminum, can gather information about remote solar systems; for the invention, Alcorn was honored as the NASA Goddard Inventor of the Year in 1984. In addition to his groundbreaking contributions as an inventor and innovator, Alcorn also championed efforts to hire more women and minorities at Goddard, for which he was honored with the NASA Equal Opportunity Medal, and taught students at Howard University and the University of the District of Columbia. He also founded the Saturday Academy, an honors program in math and science for underserved middle school students. He earned many accolades over the years from NASA and beyond. These include, in 2010, the Robert H. Goddard Award for Merit, for his outstanding innovation and significant contributions to space science, technology, and NASA programs, as well as recognition in 1994 at Howard University’s Heritage of Greatness awards ceremony. He was also inducted into the National Inventor’s Hall of Fame in 2015. Alcorn passed away in 2024 at the age of 84.