
Goddard's Ritsko Wins 2011 SAVE Award The winner of the 2011 SAVE Award is Matthew Ritsko, a Goddard financial manager. His tool lending library would track and enable sharing of expensive space-flight tools and hardware after projects no longer need them. This set of images represents the types of tools used at NASA. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/people/features/ritsko-save.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/people/features/ritsko-save.html</a> The engineering mockup of the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module is currently on display within the press building at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The RRM mission is a joint effort between NASA and the Canadian Space Agency designed to demonstrate and test the tools, technologies, and techniques needed to robotically refuel satellites in space. Reporters have the opportunity to get a close-up view of the replica module and tools that are a part of the final shuttle mission payload. SSCO engineers test an RRM tool. To learn more about the RRM go to: <a href="http://ssco.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">ssco.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagr.am/p/E_05l/" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on May 8. The mission, which is scheduled to launch to the International Space Station later this year, will advance satellite servicing capabilities that will enable long duration, deep space exploration.

NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) builds on the first two phases of International Space Station (ISS) technology demonstrations that tested tools, technologies and techniques to refuel and repair satellites in orbit. RRM3, which arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on May 8, is planned to launch to the ISS later this year.

NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on May 8. The fluid transfer module will demonstrate innovative methods to store, transfer and freeze standard cryogenic fluid in space. RRM3 is scheduled to launch to the International Space Station later this year.

The technology to replenish crucial satellite supplies in space currently does not exist. NASA is looking to help change that with Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3). The fluid transfer module arrived at Kennedy Space Center on May 8, and is planned to launch to the International Space Station later this year.
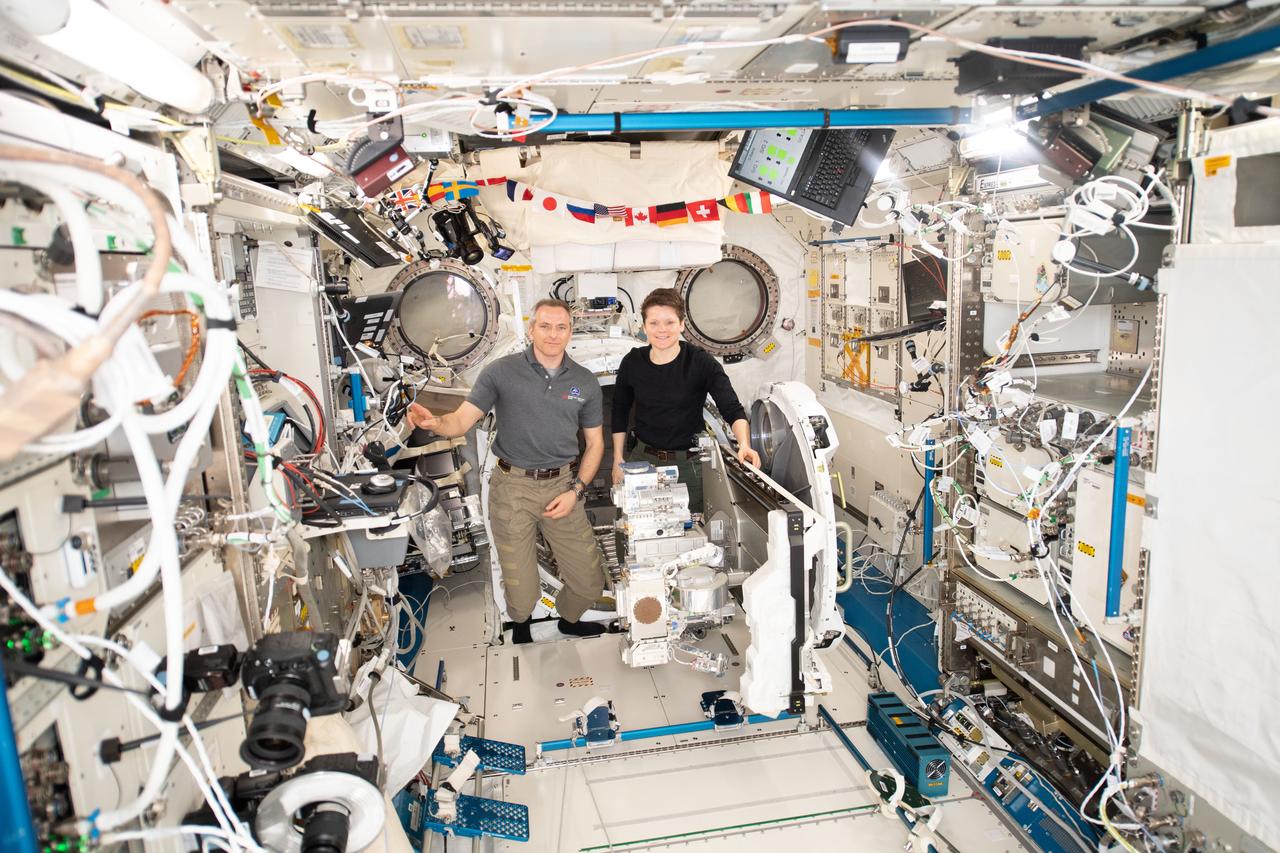

iss058e015664 (2/19/2019) --- NASA astronaut Anne McClain and Canadian Space Agency (CSA) astronaut David Saint-Jacques shown during the installation of the Robotics Refueling Mission (RRM)-3 on the JEM Airlock slide table in the KIBO module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) demonstrates the first transfer and long term storage of liquid methane, a cryogenic fluid, in microgravity. The ability to replenish and store cryogenic fluids, which can function as a fuel or coolant, can help enable long duration journeys to destinations like the Moon and Mars.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module demonstration. Seen here speaking with media are Dewayne Washington from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland, moderator (left); Frank Cepollina, project manager with NASA's Satellite Servicing Capabilities Office and Mathieu Caron, Mission Operations manager with the Canadian Space Agency. Space shuttle Atlantis will fly the RRM on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Once in place the RRM will use the station's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre, to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. Atlantis and its crew of four are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the RRM and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
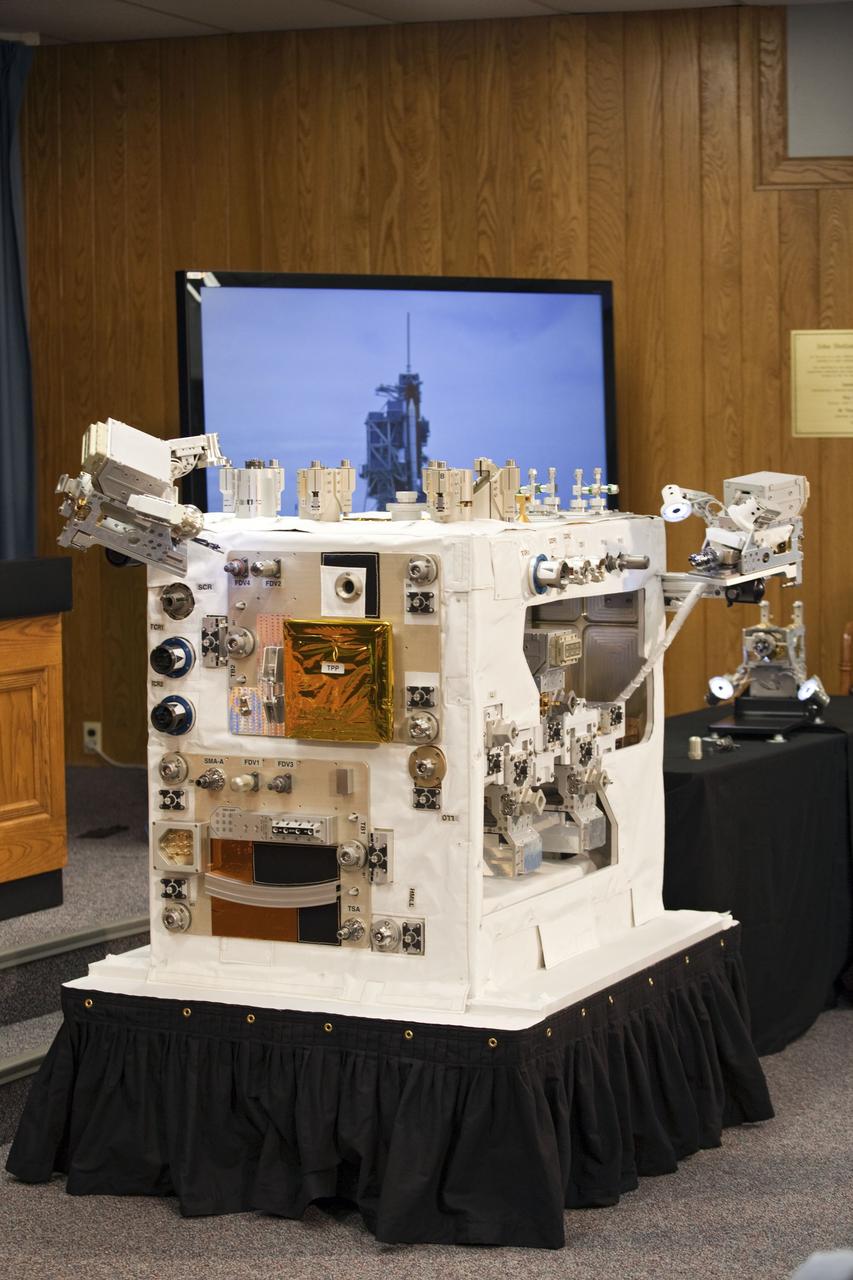

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module demonstration. Seen here is a demo version of the experiment that will fly on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Once in place, the RRM will use the station's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre, to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. Atlantis and its crew of four are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the RRM and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
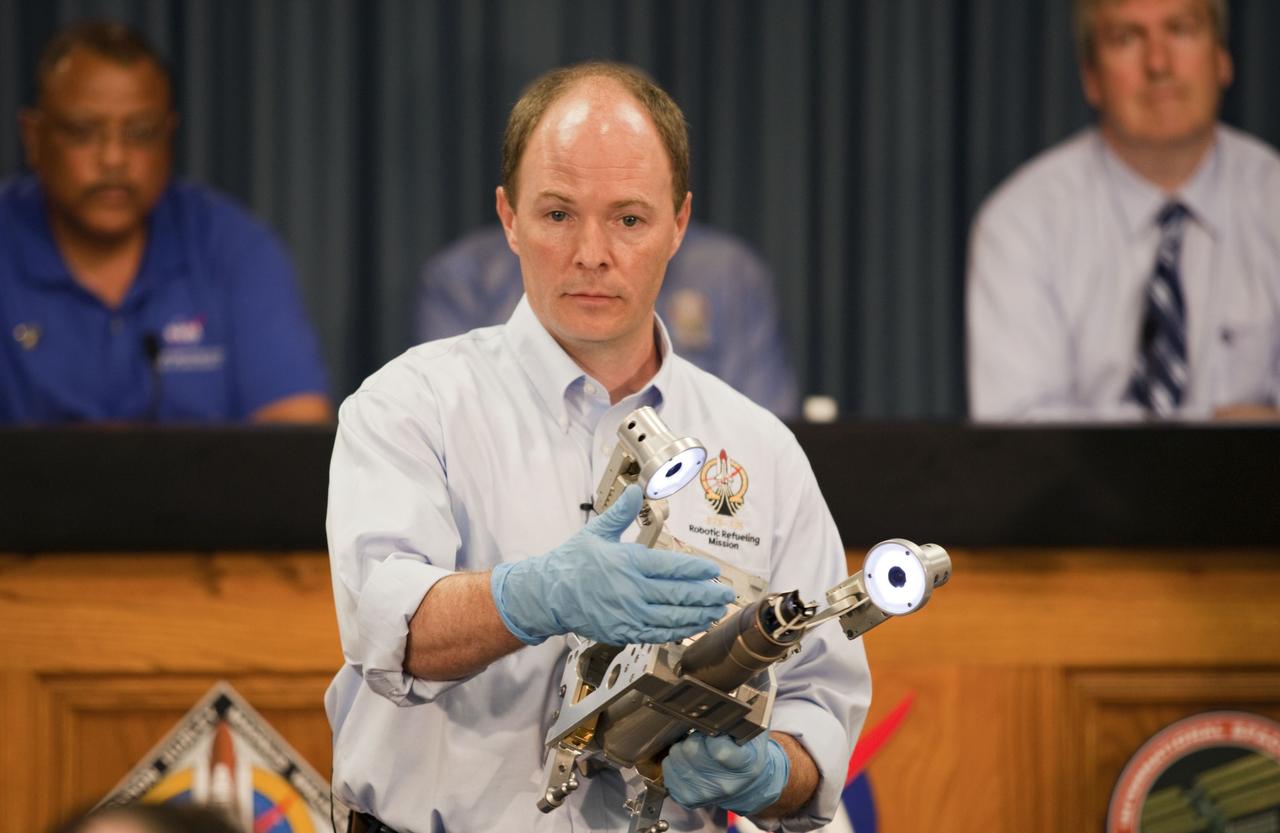

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module demonstration. Seen here is Benjamin Reed, deputy project manager with NASA's Satellite Servicing Capabilities Office, giving media an overview of the RRM. Space shuttle Atlantis will fly the RRM on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Once in place, the RRM will use the station's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre, to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. Atlantis and its crew of four are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the RRM and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
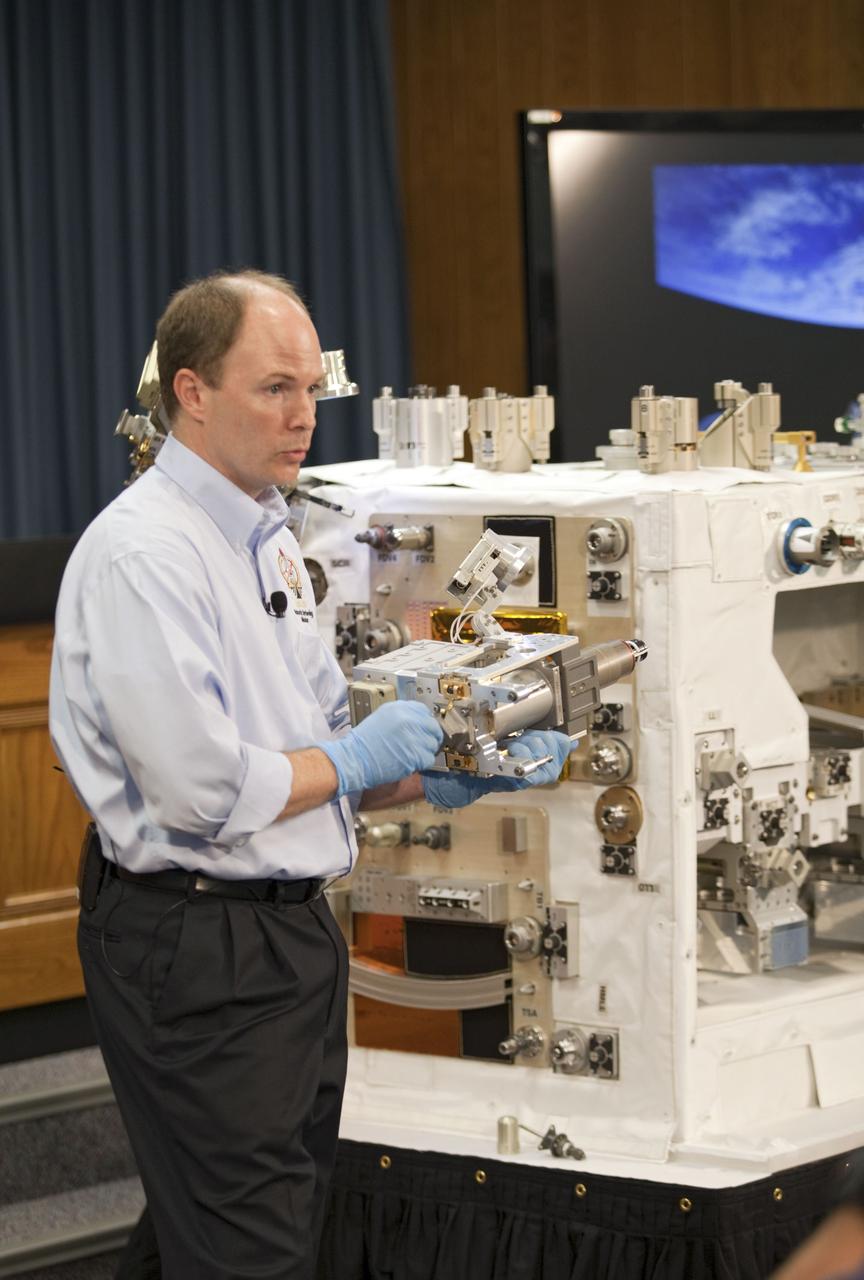

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida hosted a Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) module demonstration. Seen here is Benjamin Reed, deputy project manager with NASA's Satellite Servicing Capabilities Office, giving media an overview of the RRM. Space shuttle Atlantis will fly the RRM on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Once in place, the RRM will use the station's two-armed robotic system, known as Dextre, to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. Atlantis and its crew of four are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the RRM and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
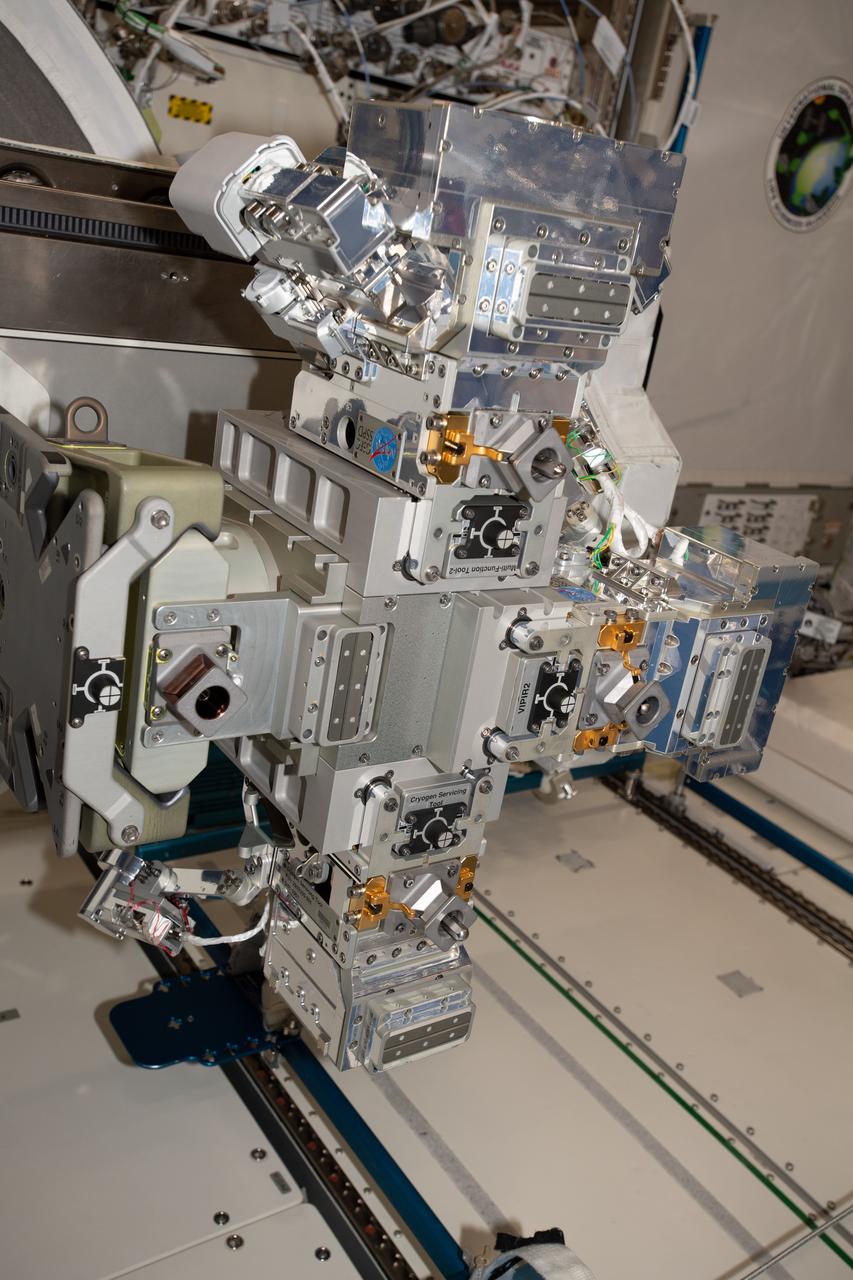

iss058e015157 (2/19/2019) --- Photo documentation of the Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) hardware in the KIBO module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) demonstrates the first transfer and long term storage of liquid methane, a cryogenic fluid, in microgravity. The ability to replenish and store cryogenic fluids, which can function as a fuel or coolant, can help enable long duration journeys to destinations like the Moon and Mars.
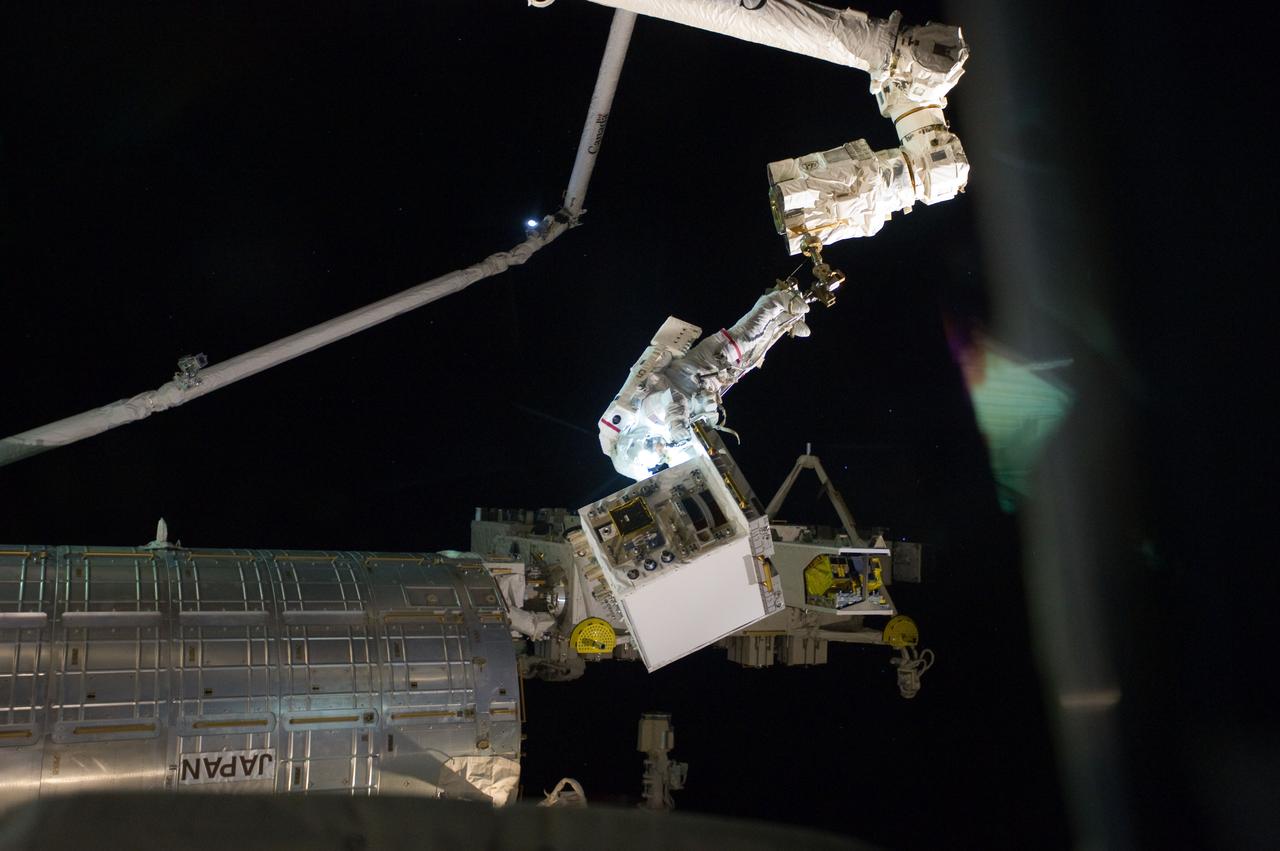

S135-E-007535 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system’s robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum, is holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. NASA astronaut Ron Garan, also a station flight engineer, who shared the spacewalk with Fossum, is out of frame. Photo credit: NASA
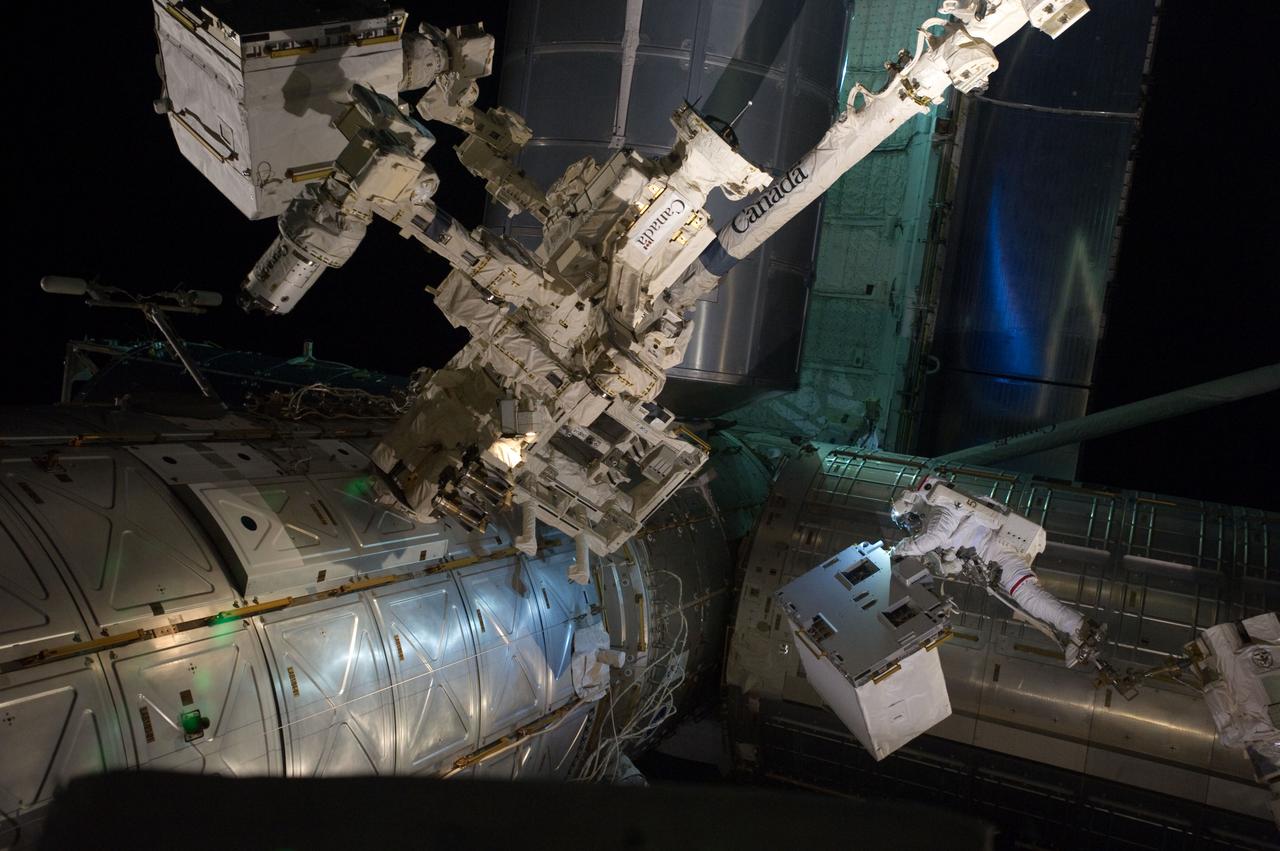

S135-E-007551 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system's robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum (lower right side of frame) holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. The failed pump module is with DEXTRE in the upper left corner of the photo. NASA astronauts Fossum and Ron Garan performed the six-hour, 31-minute spacewalk, which represents the final scheduled extravehicular activity during shuttle missions. Photo credit: NASA
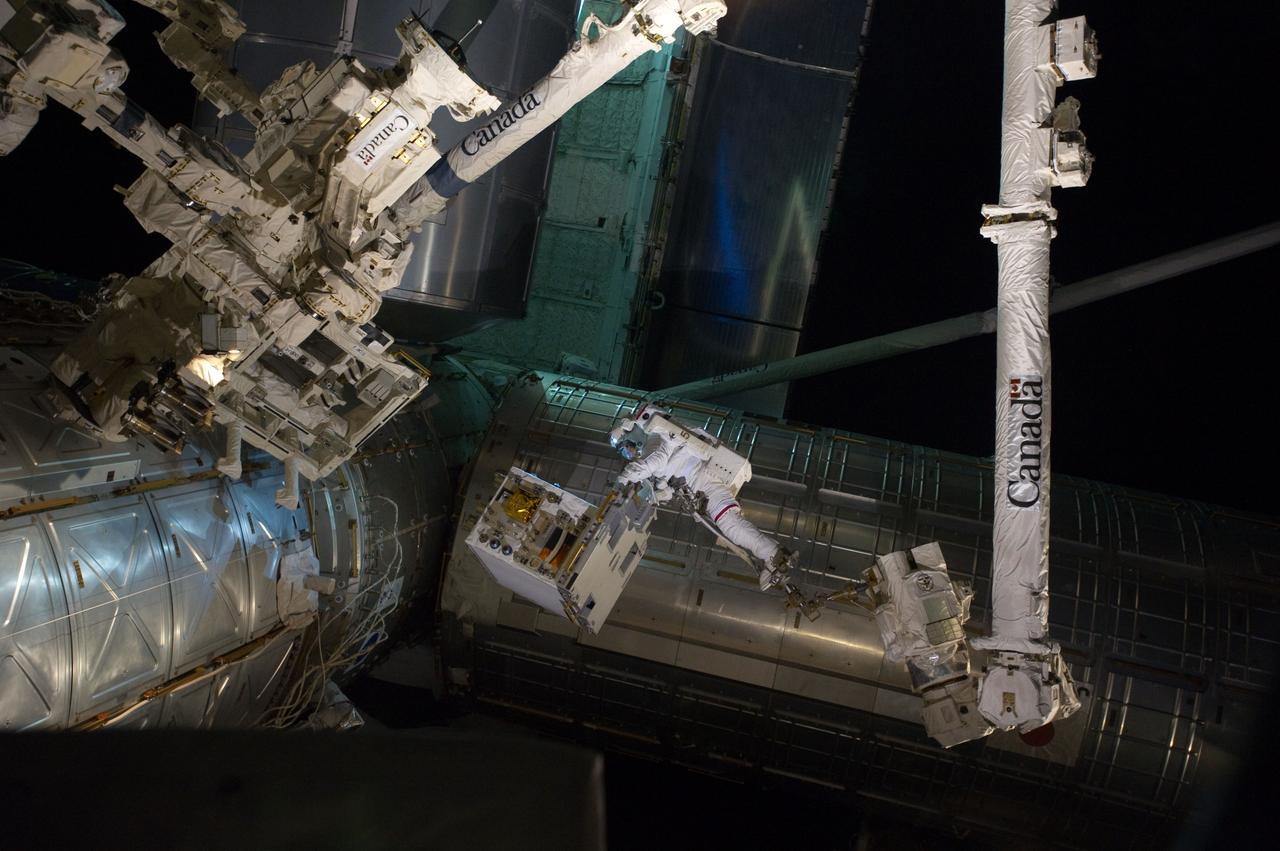

S135-E-007547 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system's robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum (frame center) holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. The failed pump module is with DEXTRE on left side of the photo. NASA astronauts Fossum and Ron Garan performed the six-hour, 31-minute spacewalk, which represents the final scheduled extravehicular activity during shuttle missions. Photo credit: NASA
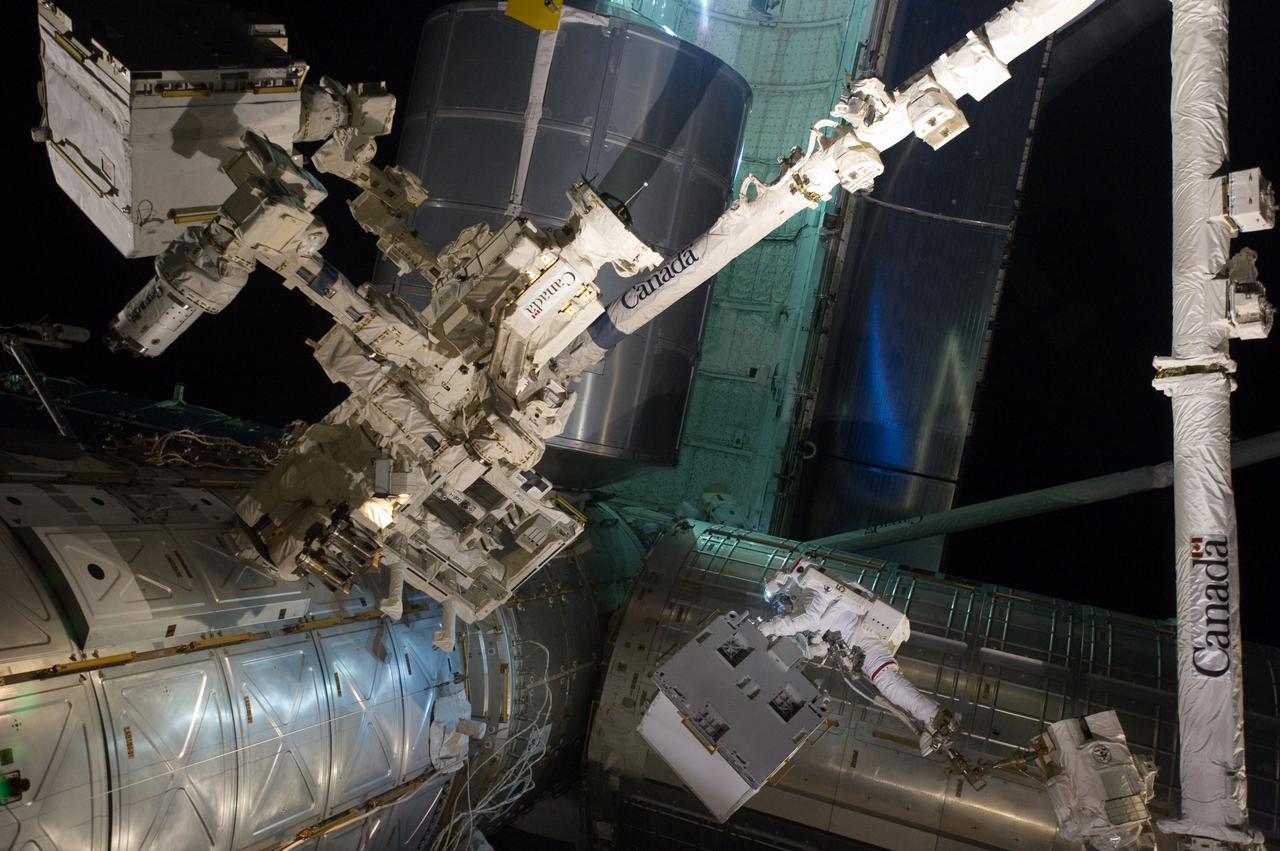
S135-E-007549 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system's robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum (lower right side of frame) holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. The failed pump module is with DEXTRE in the upper left corner of the photo. NASA astronauts Fossum and Ron Garan performed the six-hour, 31-minute spacewalk, which represents the final scheduled extravehicular activity during shuttle missions. Photo credit: NASA
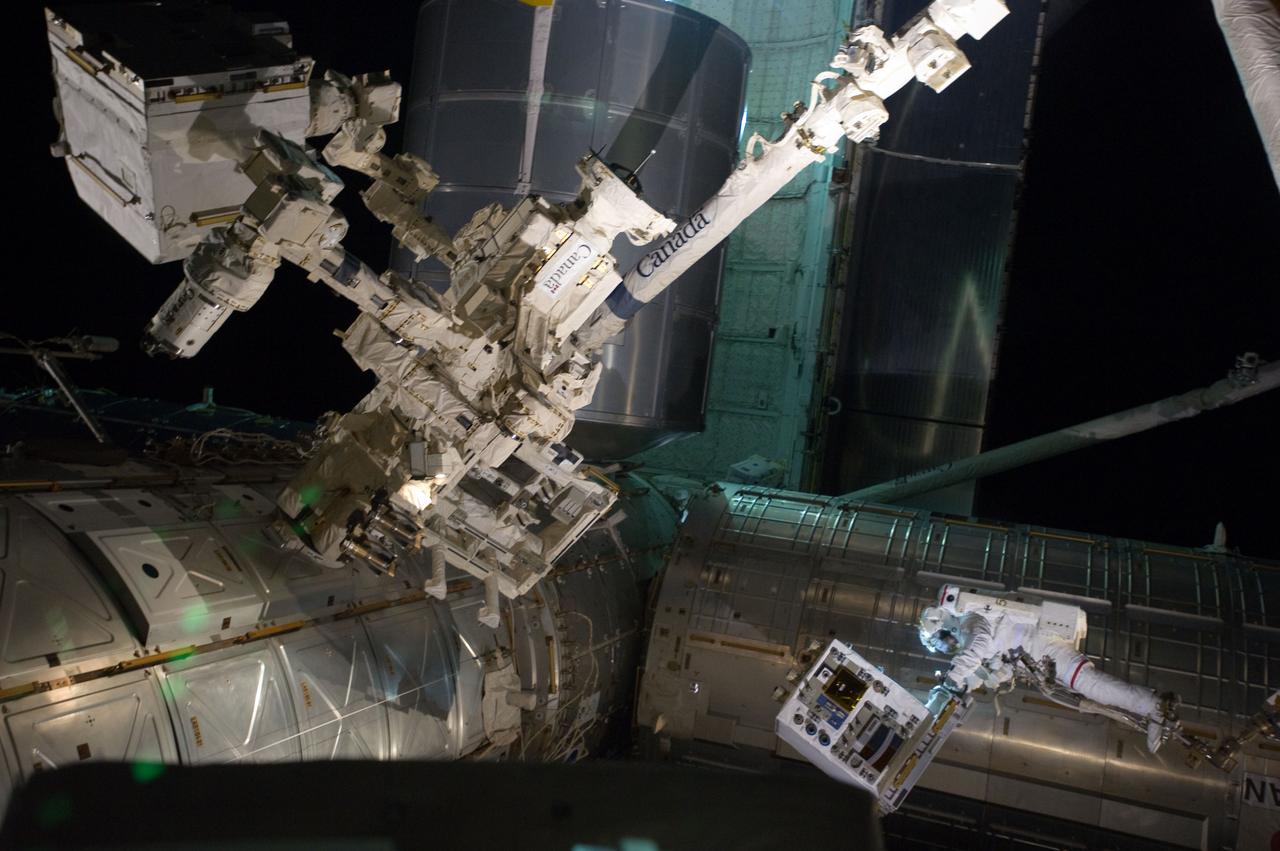

S135-E-007544 (12 July 2011) --- With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system's robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum (lower right side of frame) holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. The failed pump module is with DEXTRE in the upper left corner of the photo. NASA astronauts Fossum and Ron Garan performed the six-hour, 31-minute spacewalk, which represents the final scheduled extravehicular activity during shuttle missions. Photo credit: NASA
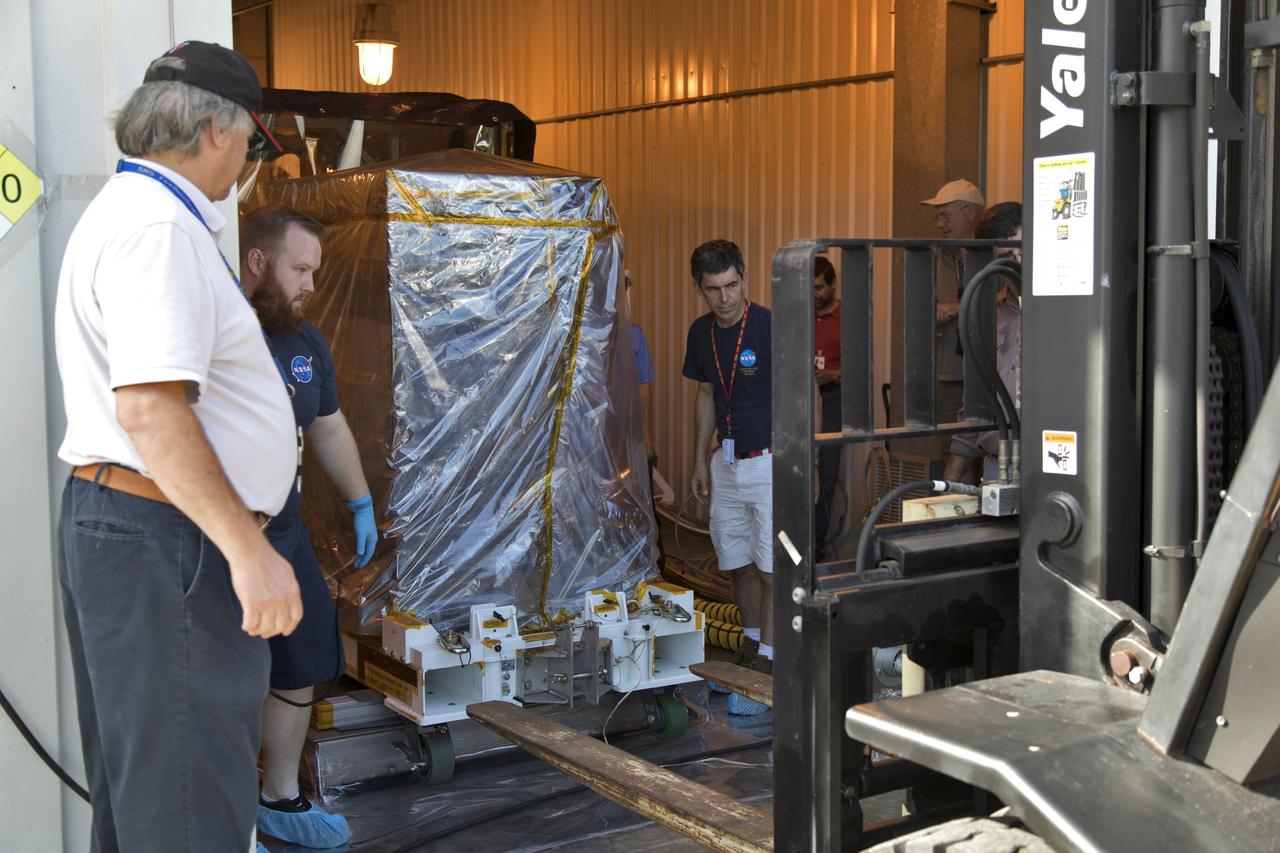

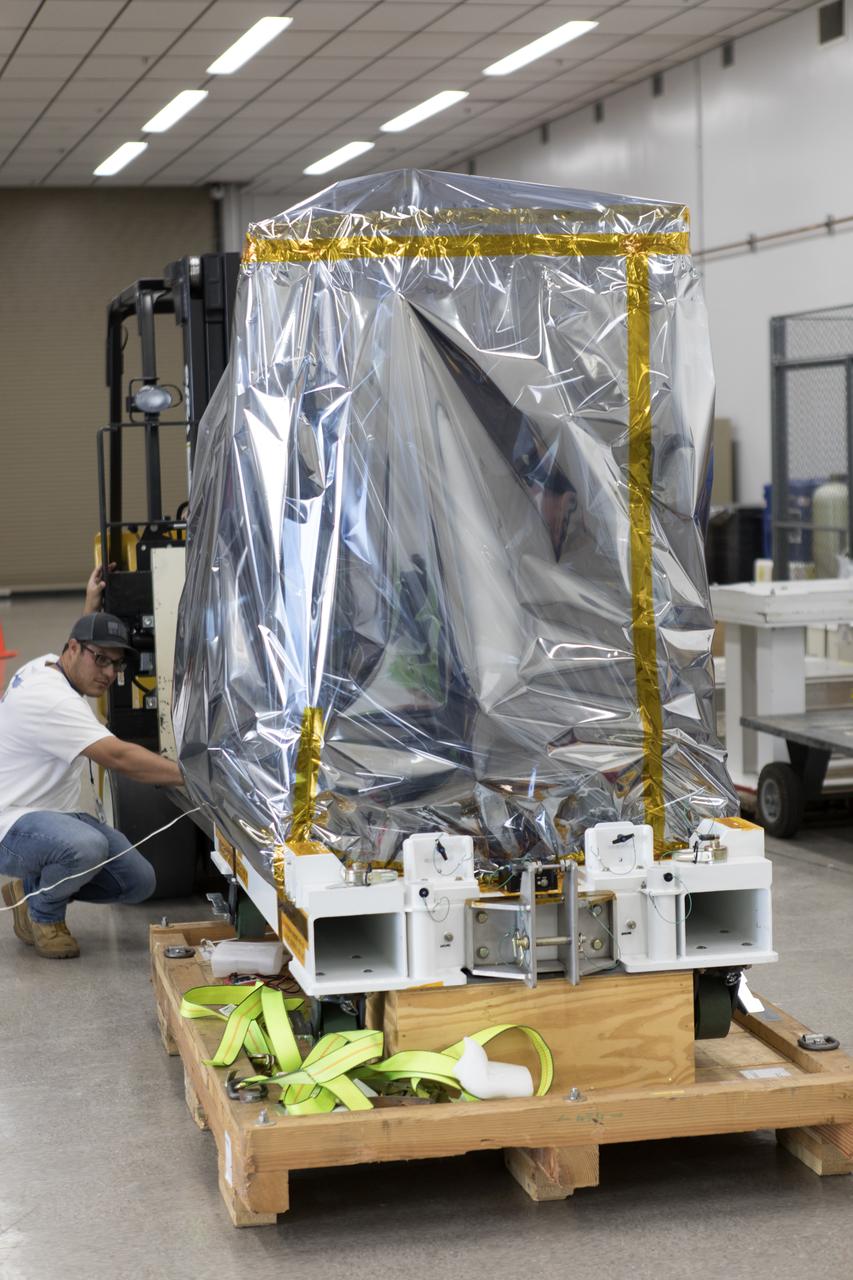
The Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload is unloaded from a forklift inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
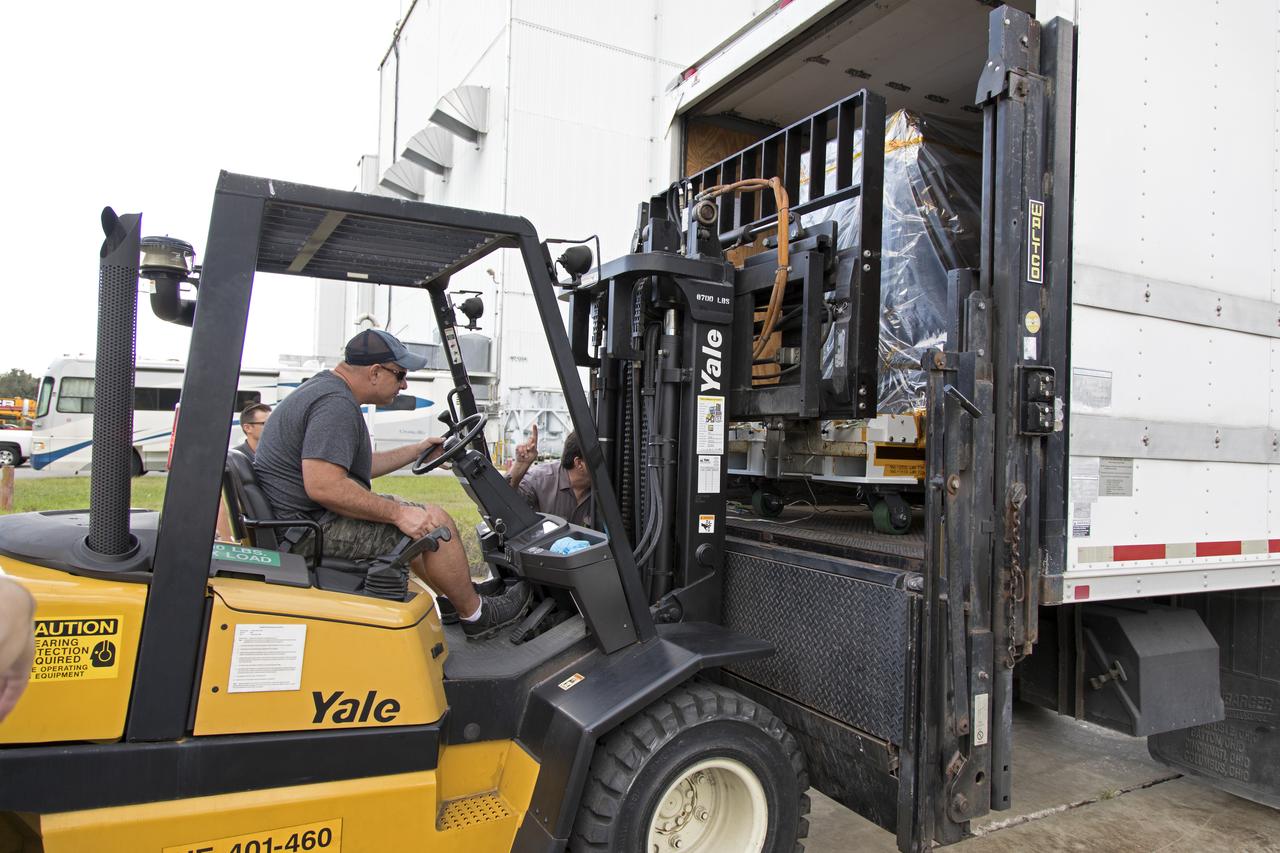

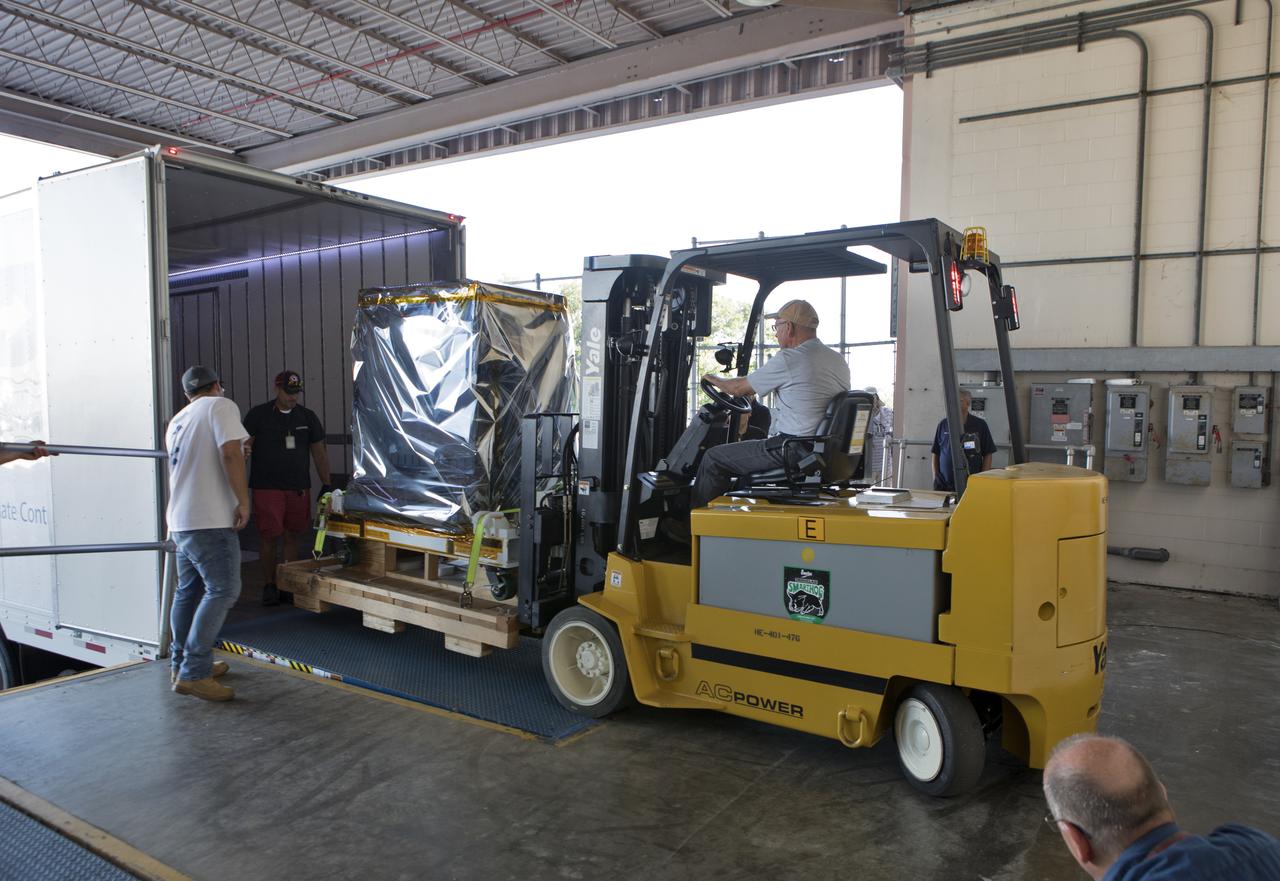
A worker uses a forklift to unload the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload from a truck at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
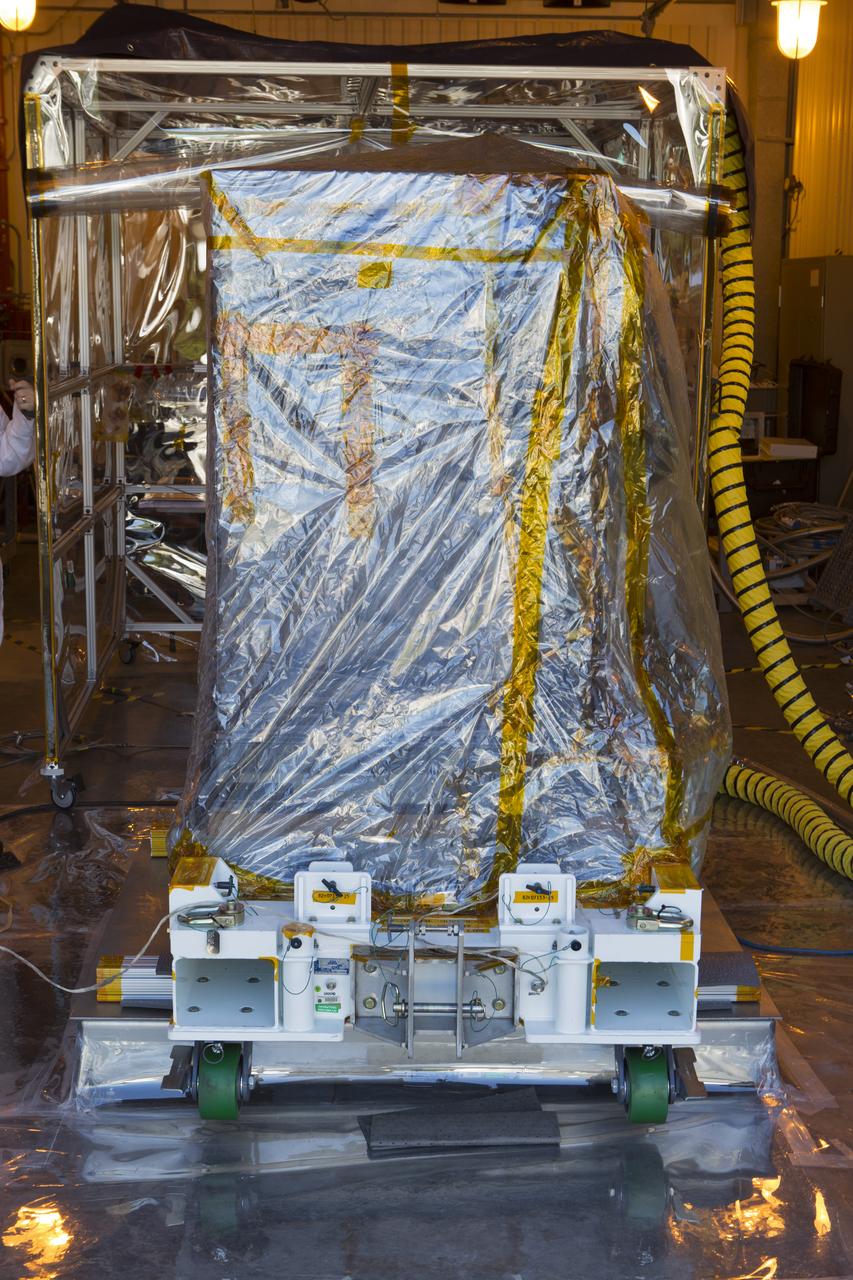

The Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload is being prepared to be moved from the Fuel Transfer Building to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
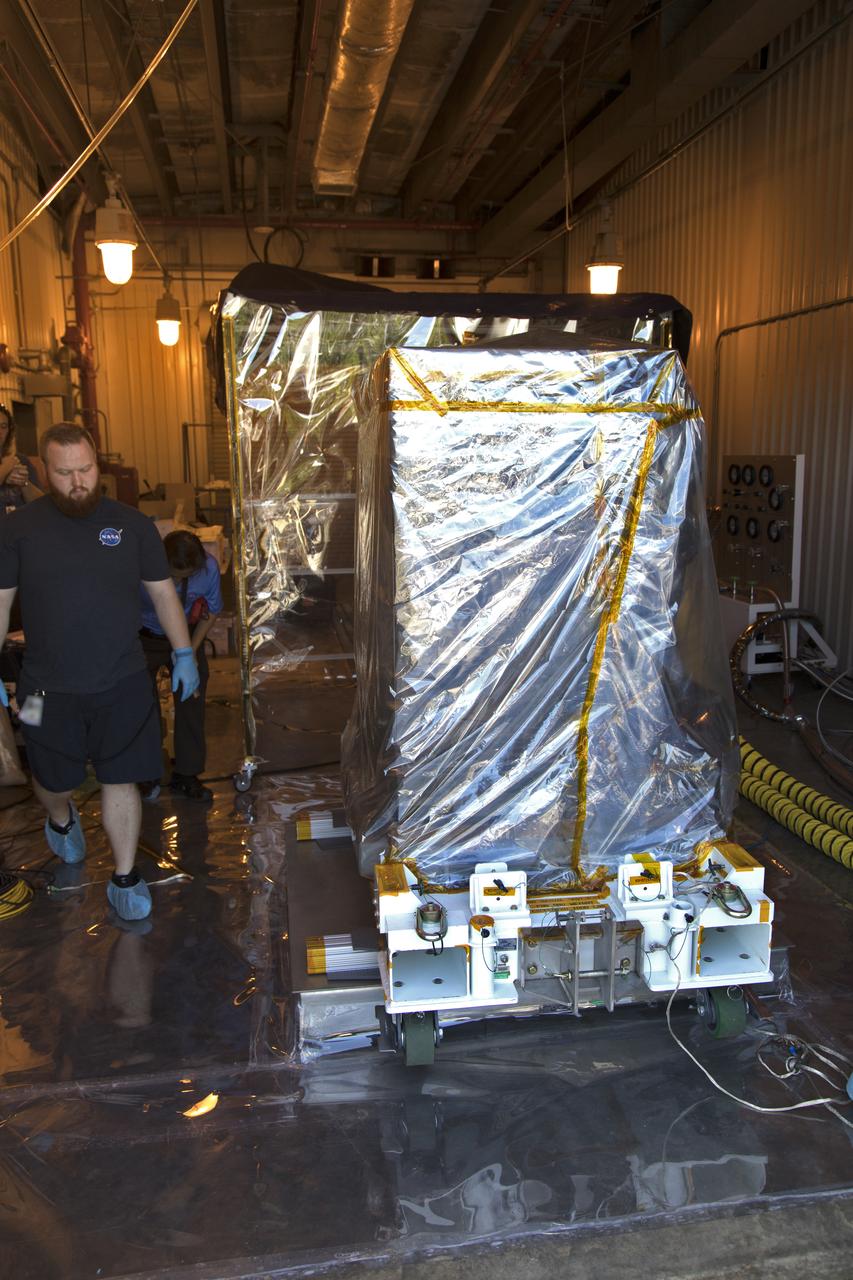

The Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload is inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

Workers prepare the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload for transport from the Fuel Transfer Building to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

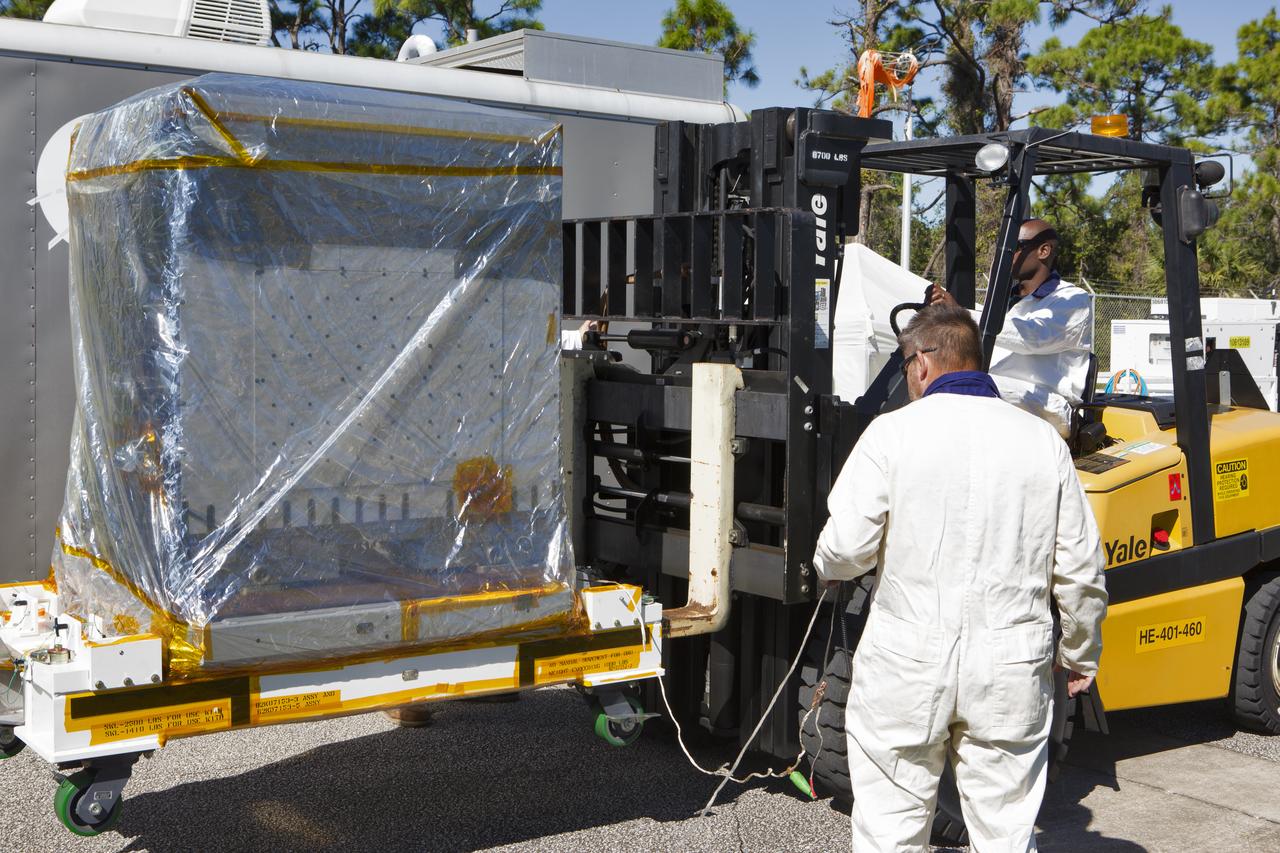
A worker uses a forklift to unload the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload from a truck at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
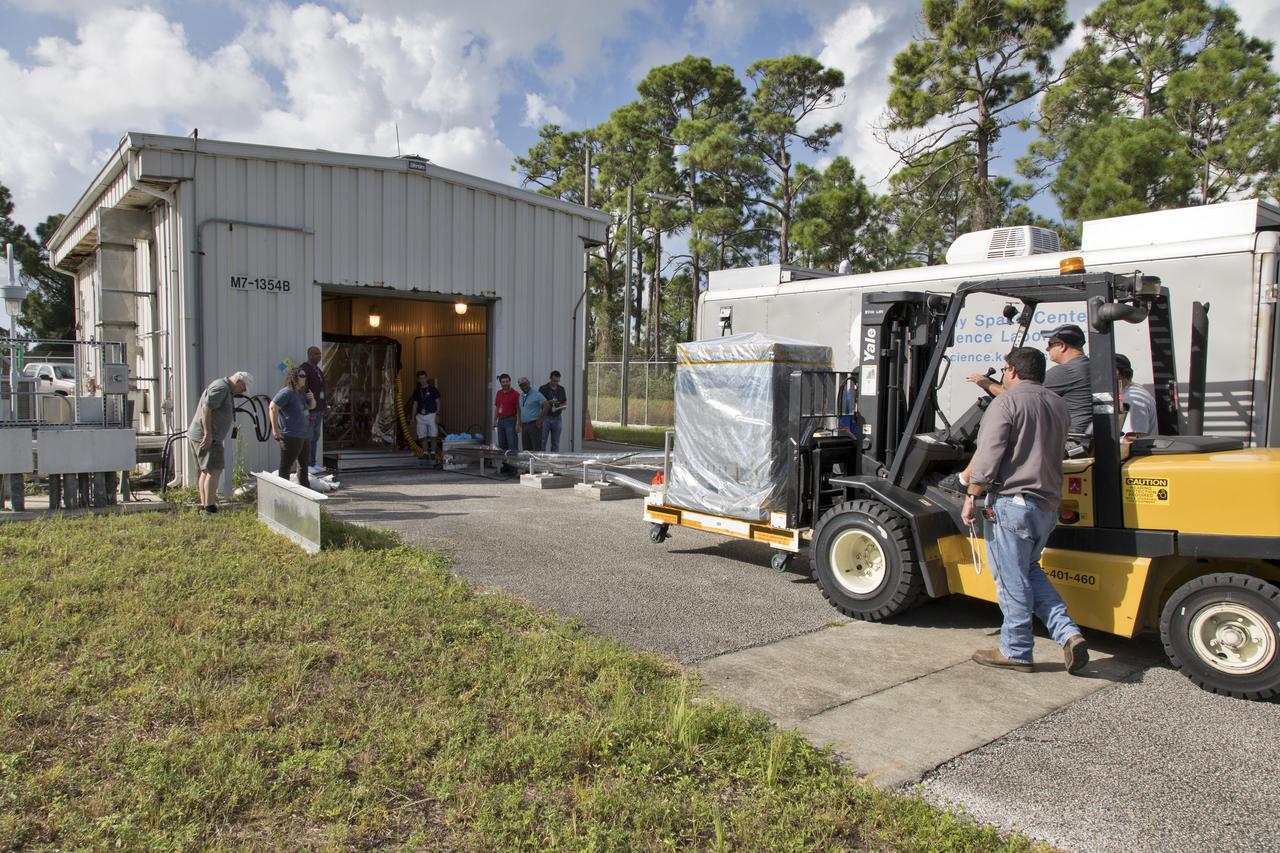

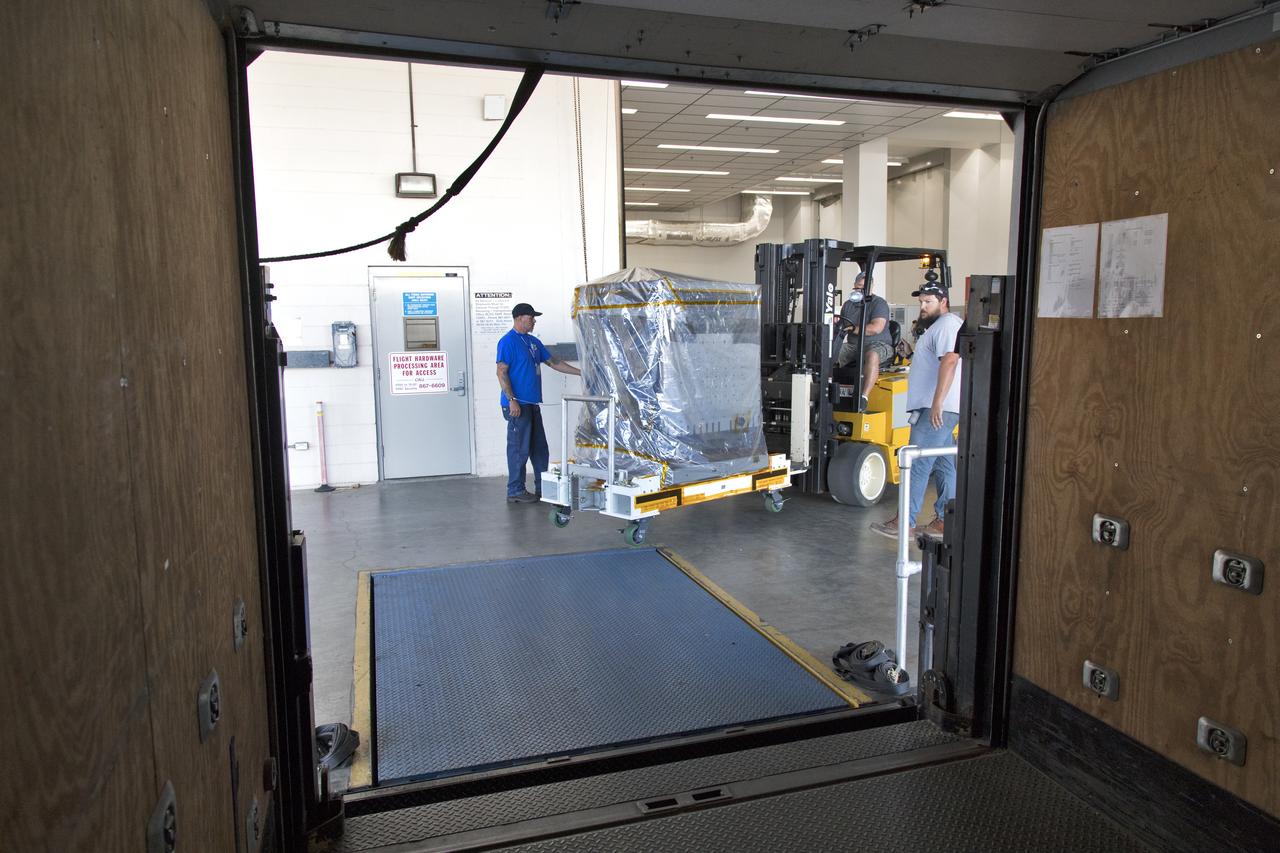
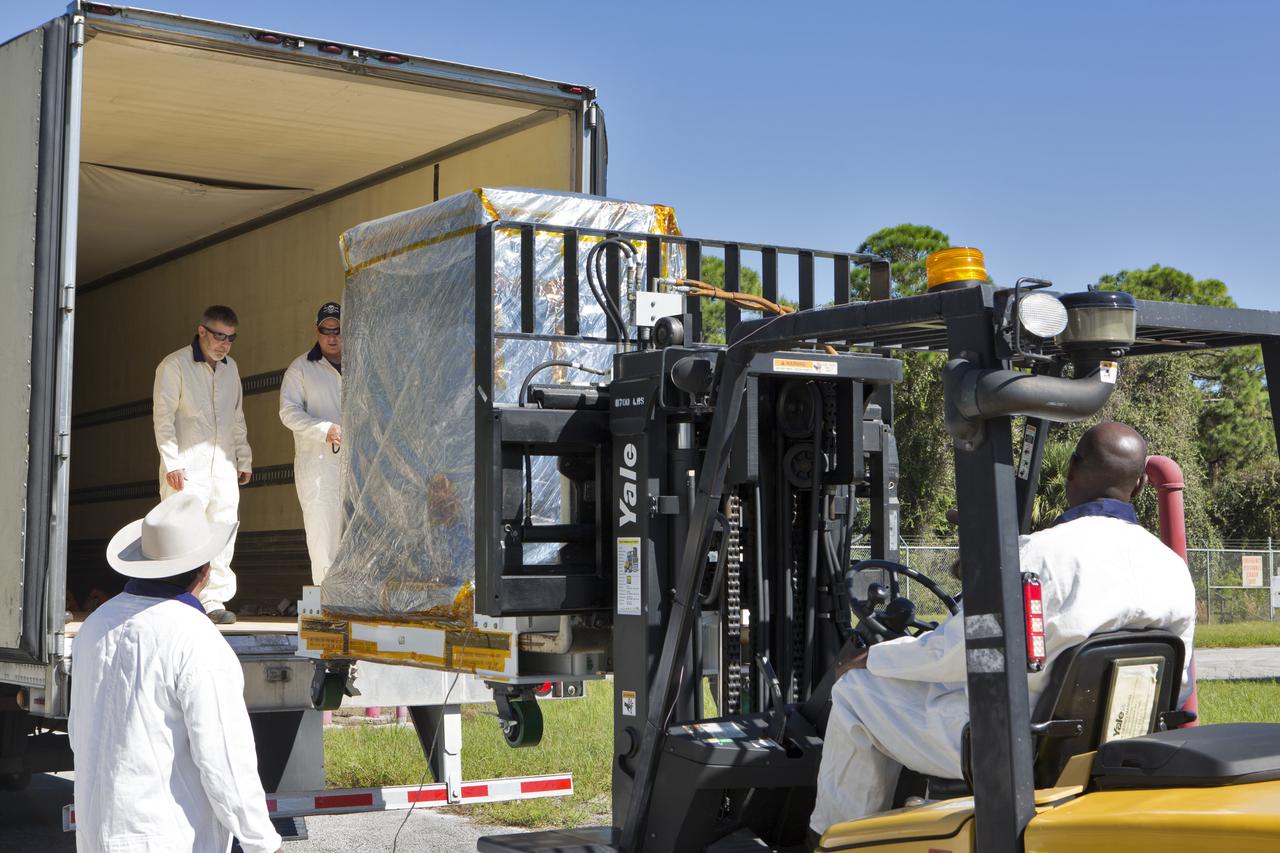
A worker uses a forklift to carry the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload to the entrance of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
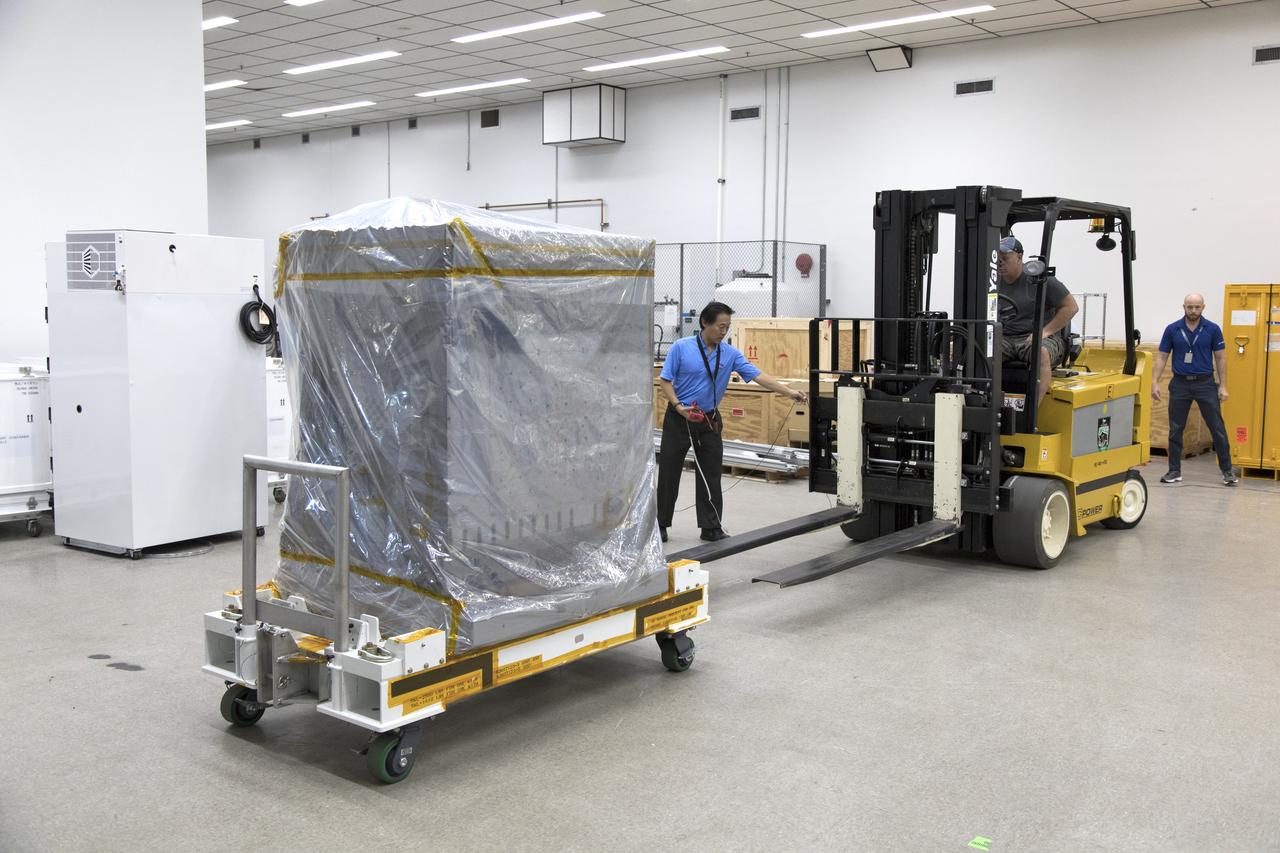

Workers prepare the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload to be transferred from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

Workers prepare to transfer the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
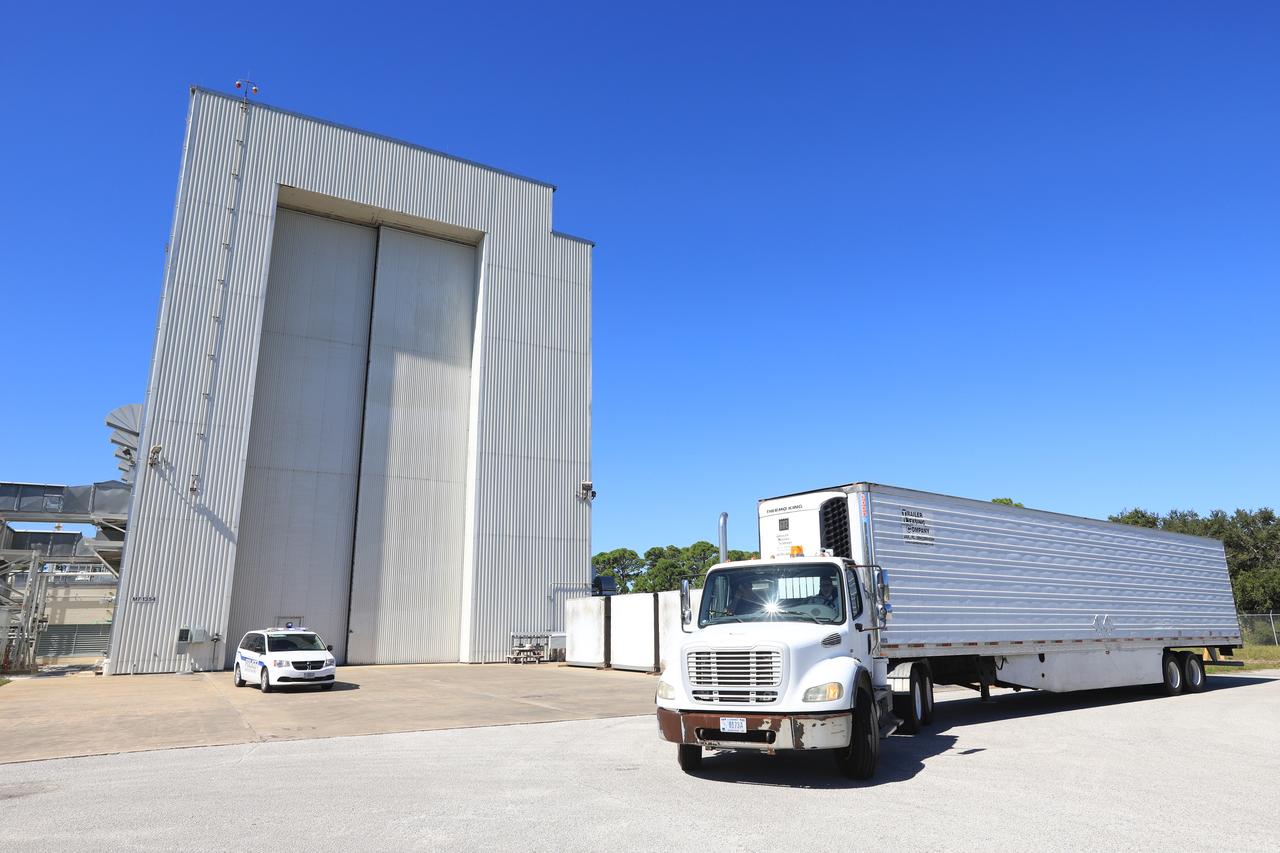

A truck containing the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload departs the Fuel Transfer Building near the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for transport to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
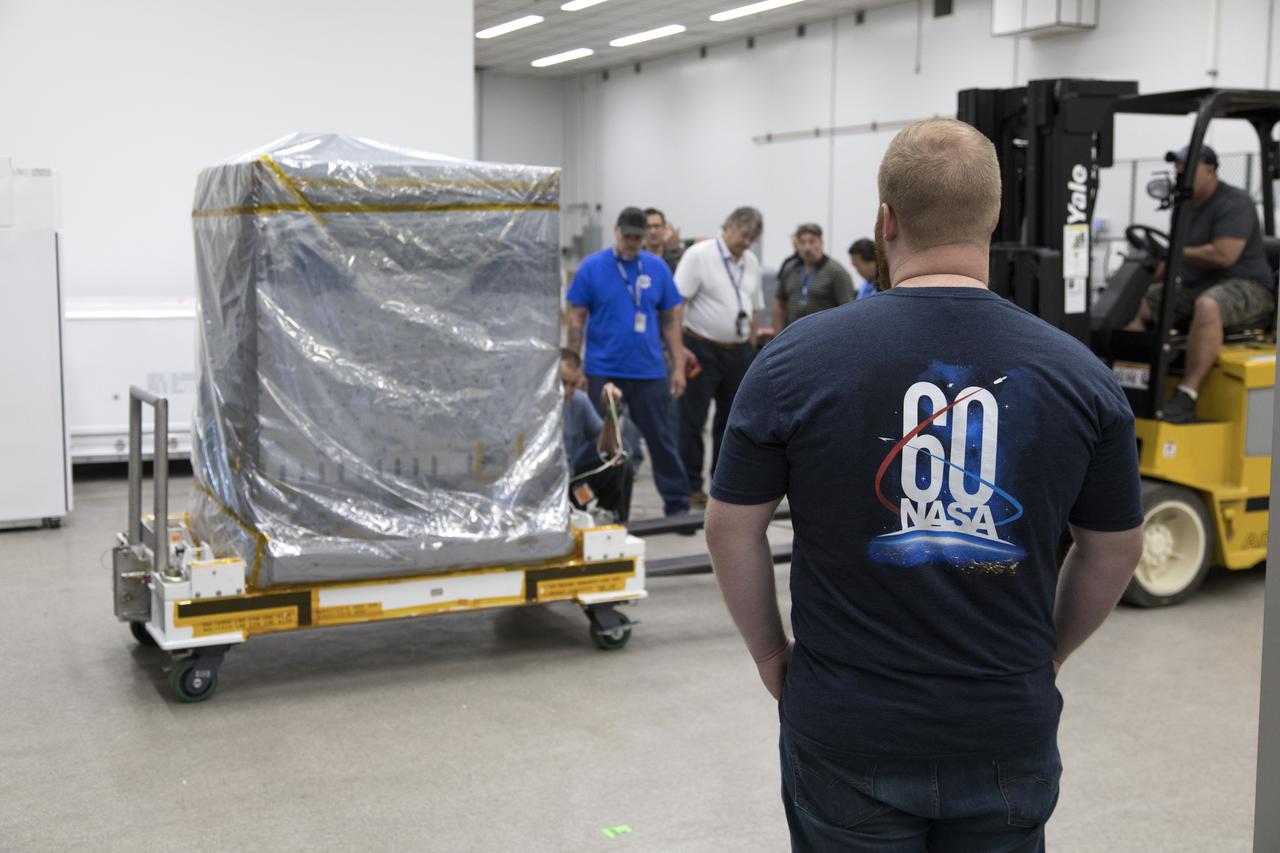

Workers prepare the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload to be transferred from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
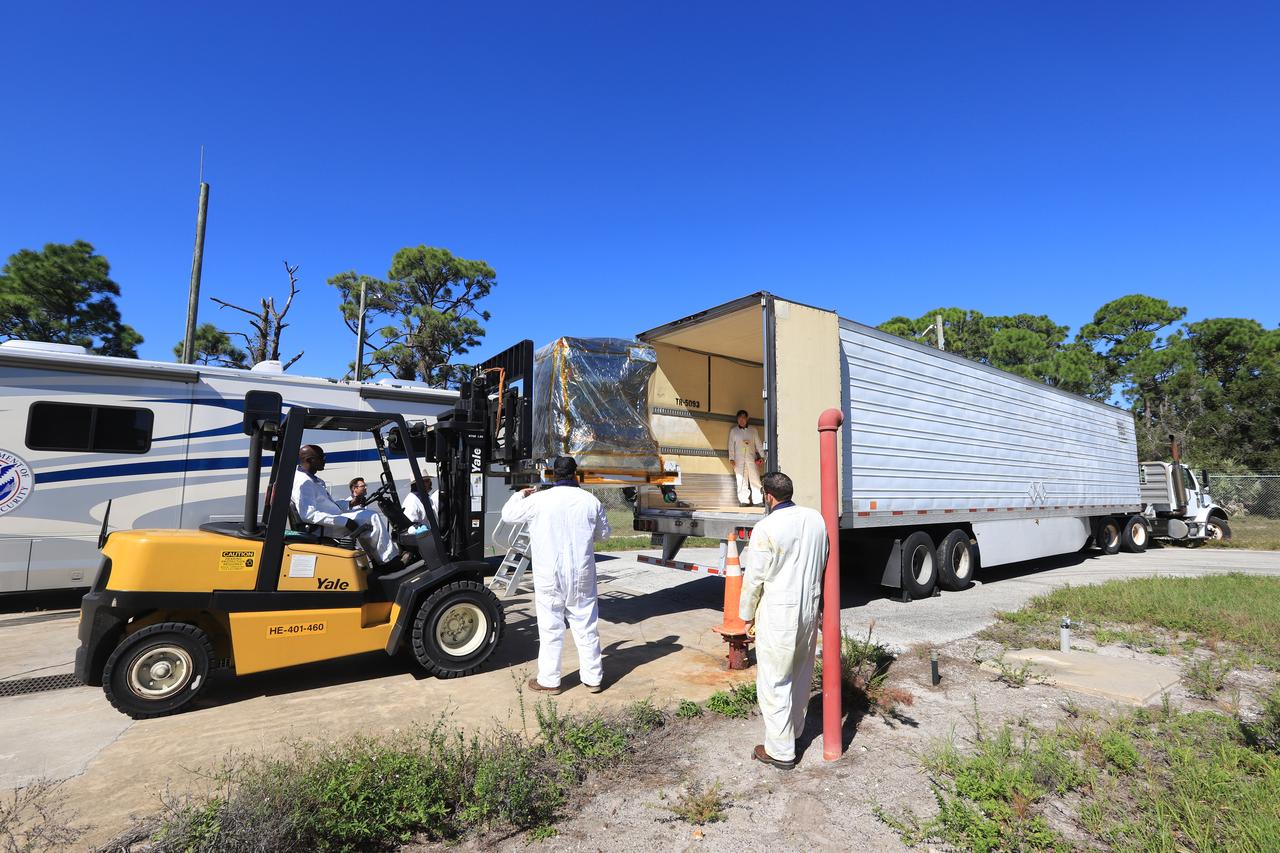

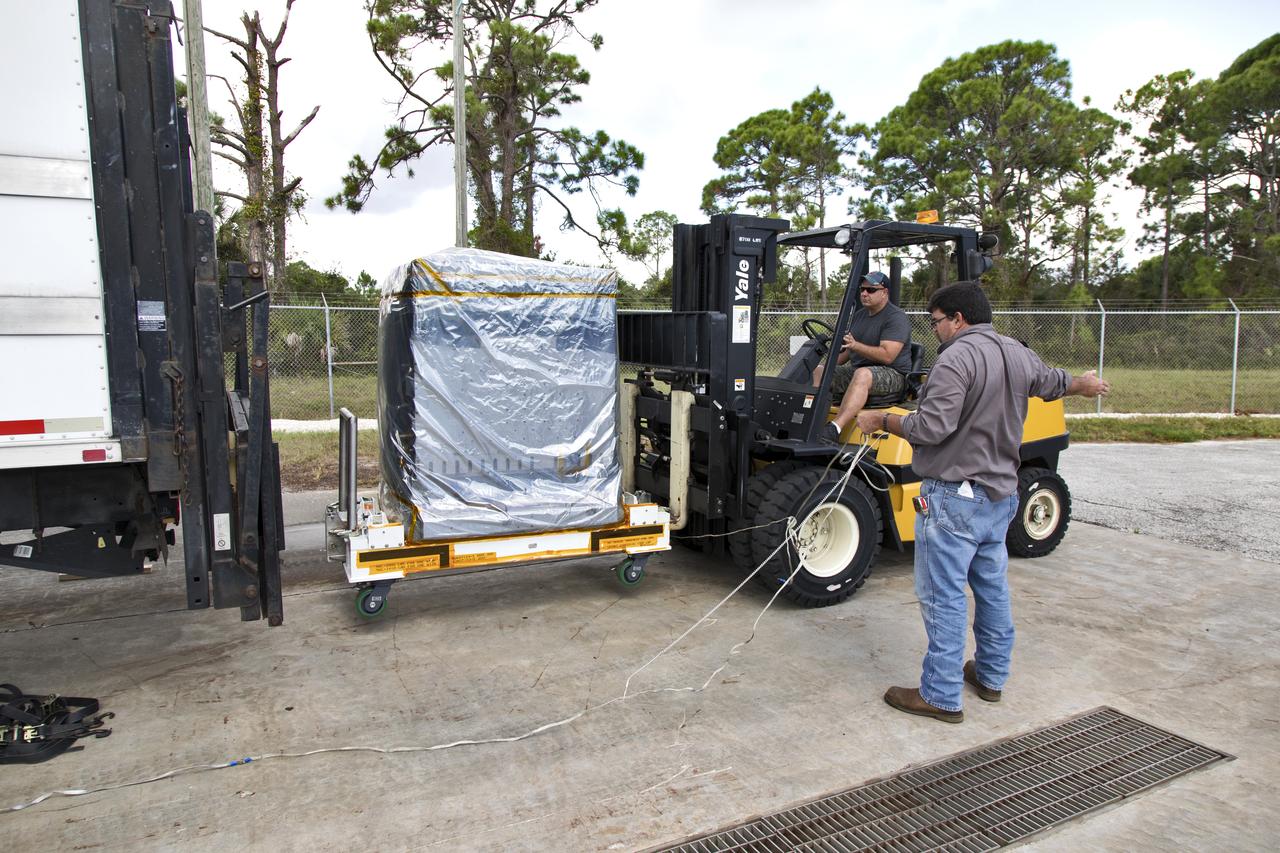
A forklift is used to load the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload onto a truck at the Fuel Transfer Building for transport to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
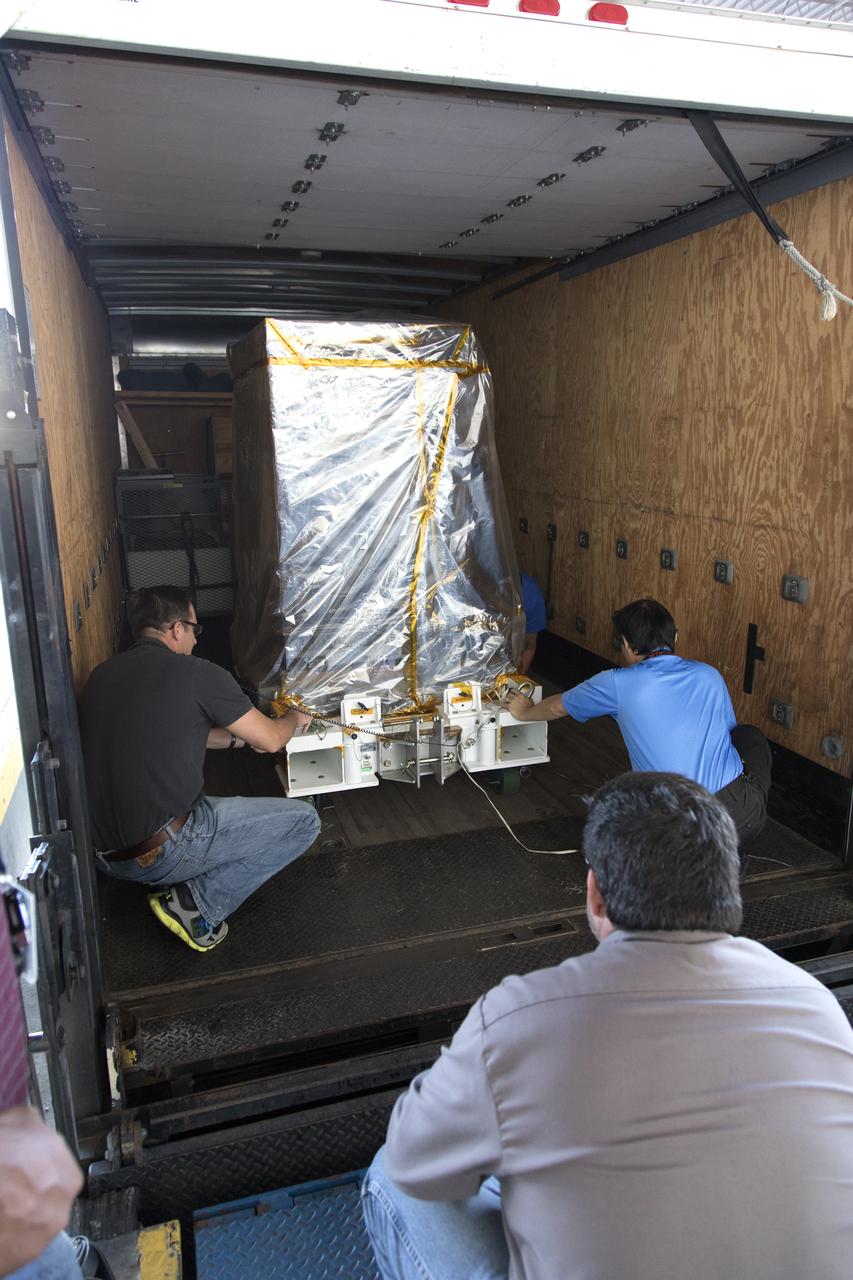

Workers load the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload onto a truck at the Space Station Processing Facility for transfer to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
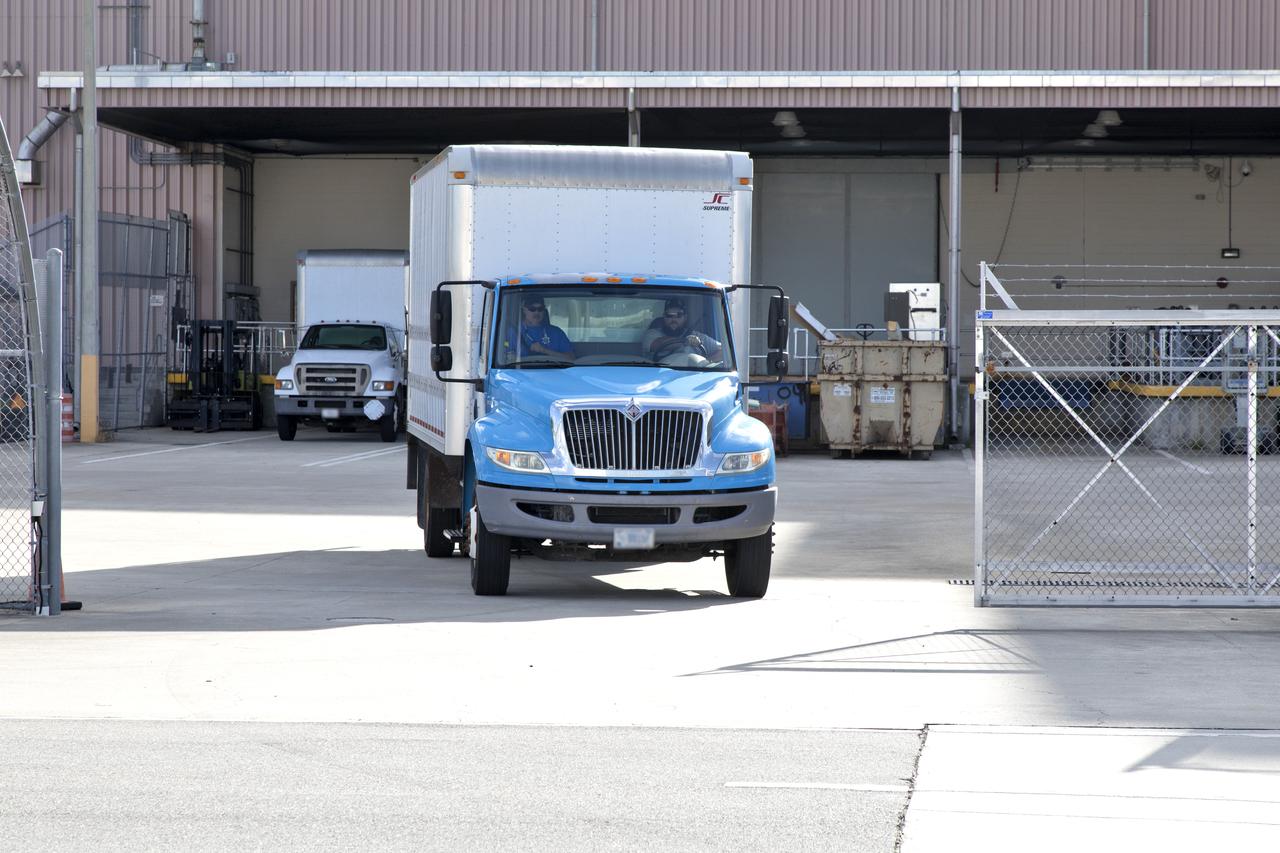

A truck carrying the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload departs from the Space Station Processing Facility on its way to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on Oct. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.

A forklift is used to load the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload onto a truck at the Fuel Transfer Building for transport to the SpaceX facility on Oct. 30, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
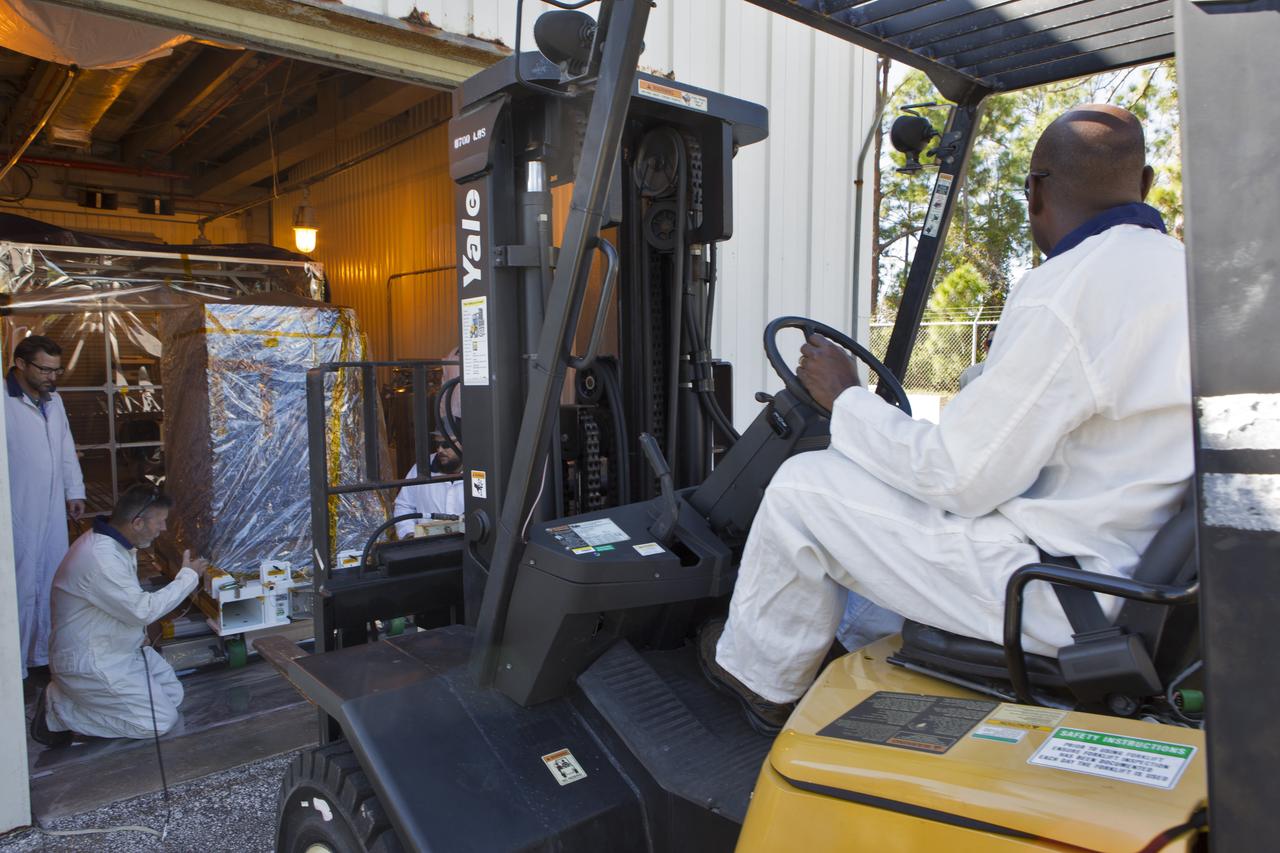

A forklift is being used to lift the Robotic Refueling Mission-3 (RRM3) payload out of the Fuel Transfer Building on Oct. 30, 2018, to be transported to the SpaceX facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The payload will be carried to the International Space Station on SpaceX's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission. RRM3 demonstrates the transfer of xenon gas and liquid methane in microgravity, and advances technologies for storing and manipulating these cryogenic fuels robotically. RRM3 also supports development of technology for the Restore-L mission, a robotic spacecraft equipped to service satellites in-orbit.
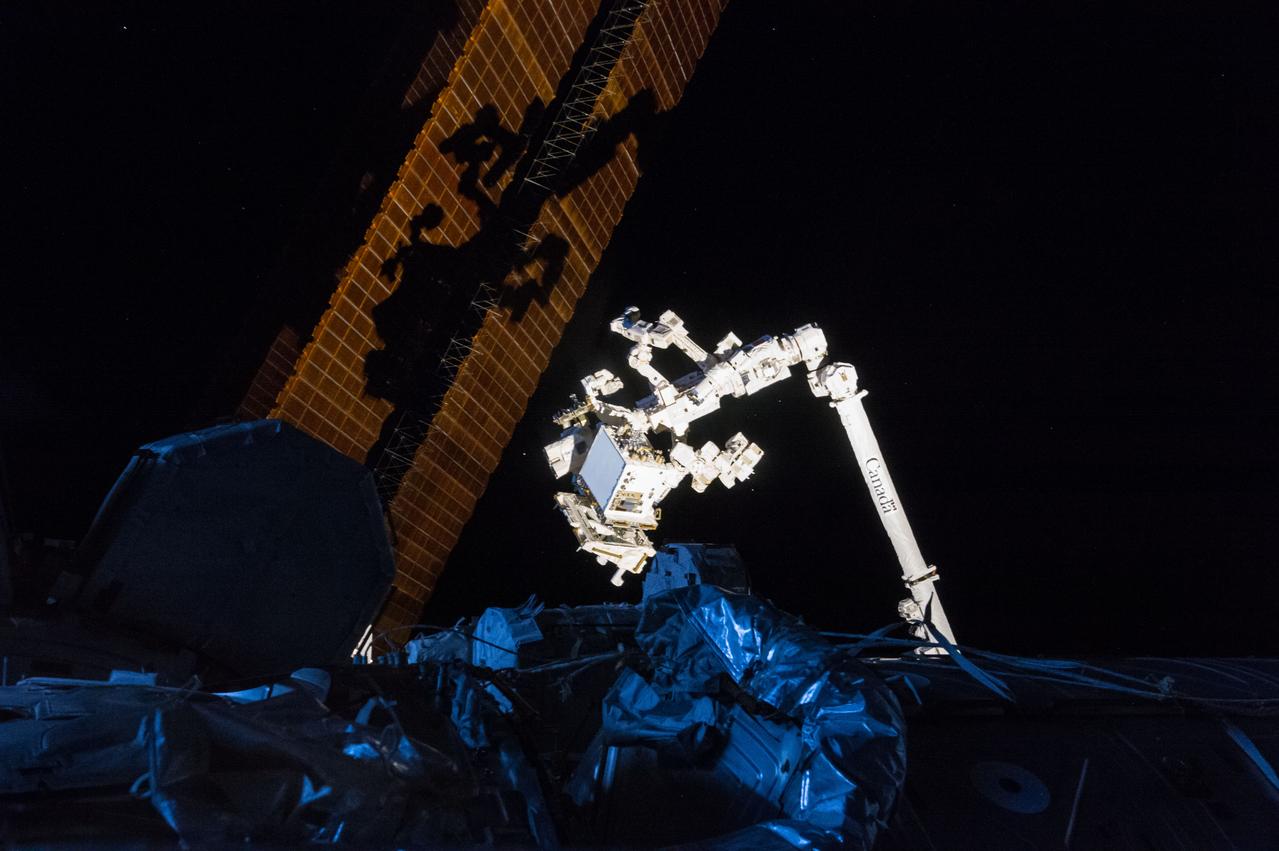

iss050e056301 (3/8/2017) --- A view of the Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS) during Robotic Refueling Mission-Phase 2 (RRM-P2) operations. NASA's Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) is an external International Space Station (ISS) investigation that demonstrates and tests the tools, technologies and techniques needed to robotically refuel, repair, and upgrade satellites in space, especially satellites that were not designed to be serviced. A joint effort between NASA and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), RRM is the first in-orbit attempt to test robotic refueling and servicing techniques for spacecraft not built with in-orbit servicing in mind.

Cape Canaveral, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis soars into a layer of thin clouds at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida moments after lifting off on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/ Jim Grossmann Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim will lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: Jim Grossmann
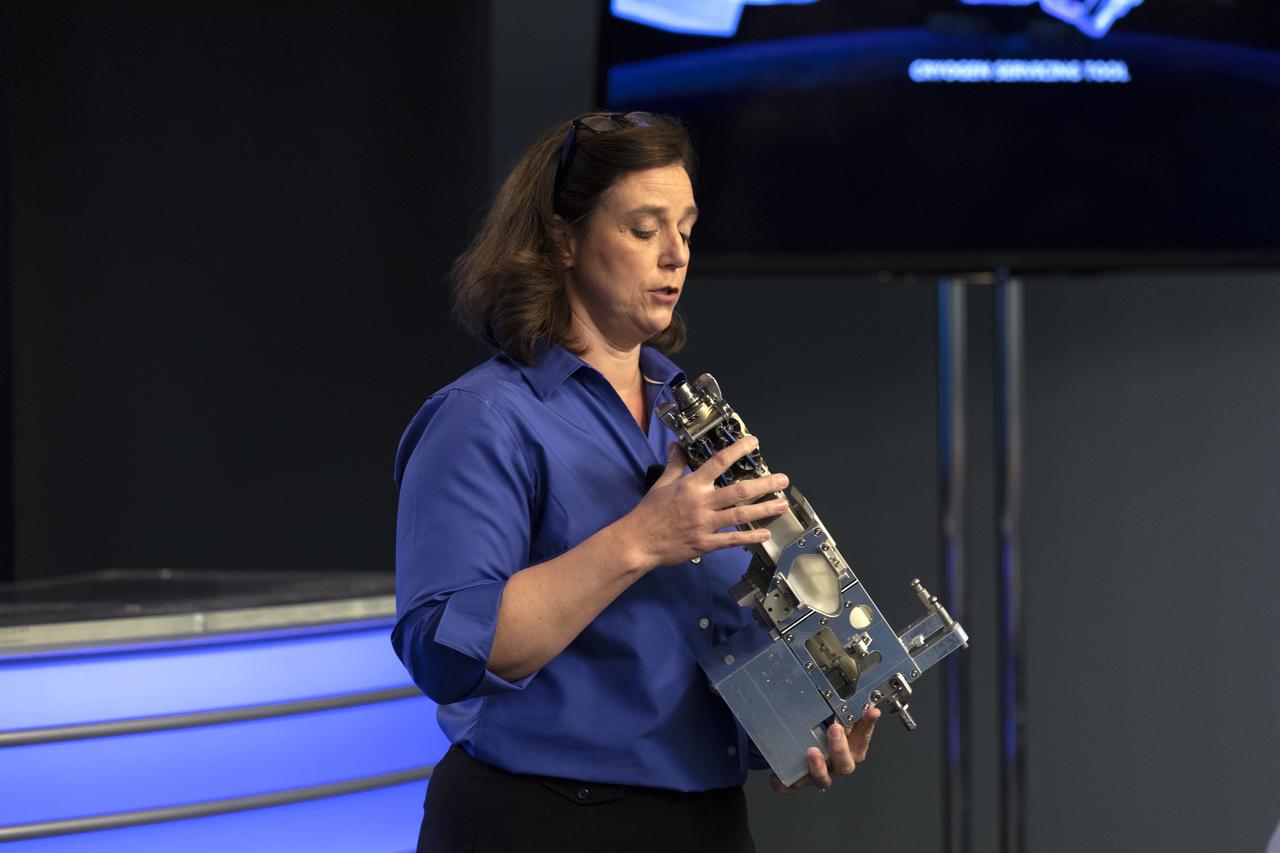

Jill McGuire, project manager for the Robotic Refueling Mission 3, or RRM3, experiment, describes RRM3 hardware for members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.

Jill McGuire, project manager for the Robotic Refueling Mission 3, or RRM3, experiment, describes RRM3 hardware for members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
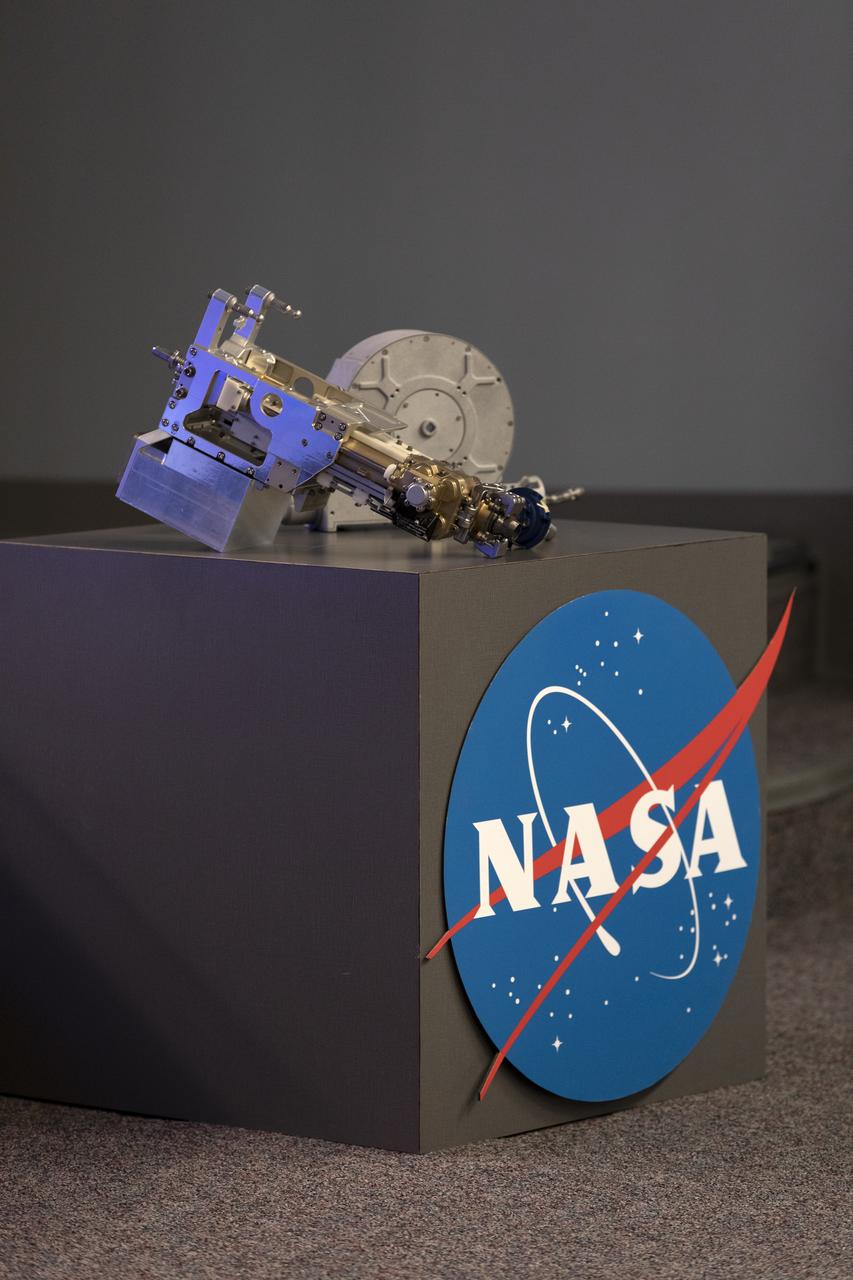

Hardware associated with the Robotic Refueling Mission 3, or RRM3, experiment, ws on display for members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
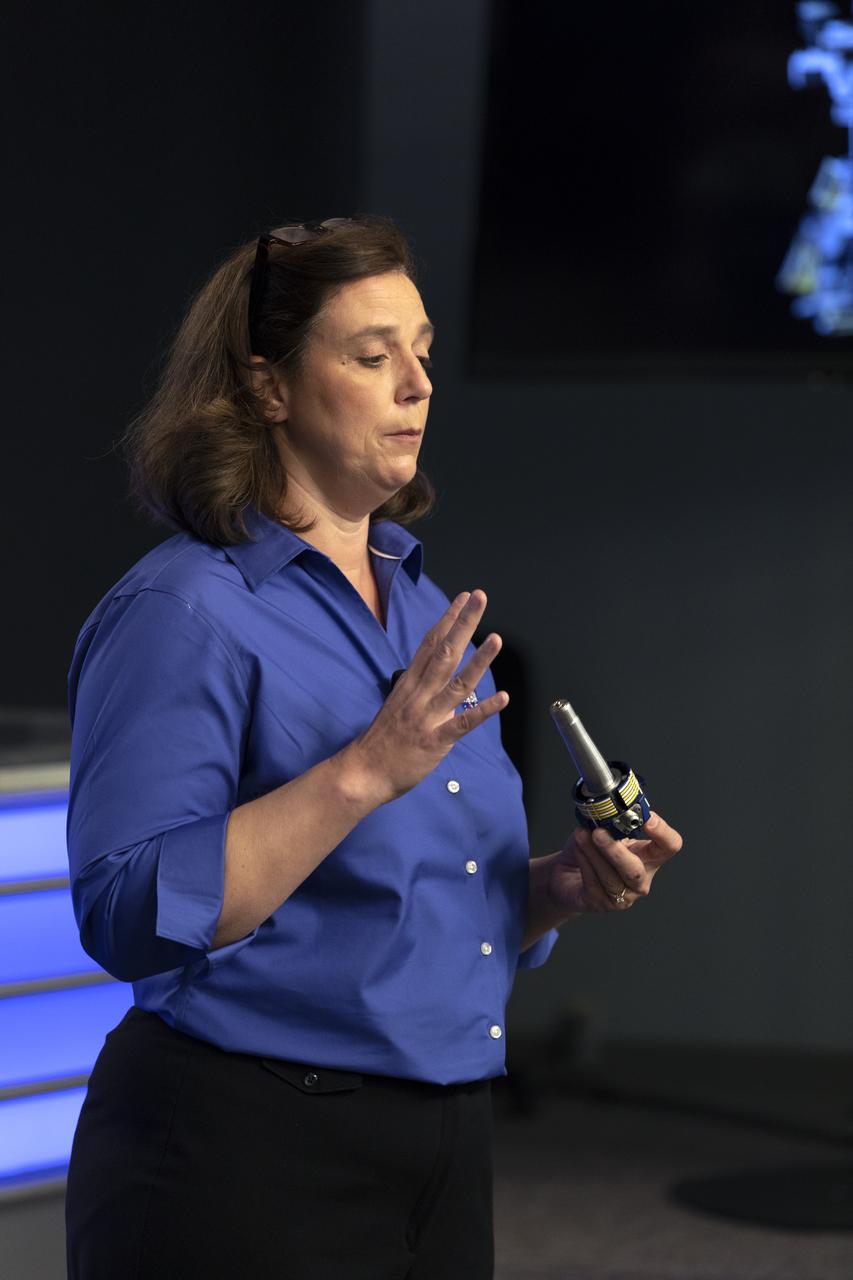

Jill McGuire, project manager for the Robotic Refueling Mission 3, or RRM3, experiment, describes RRM3 hardware for members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
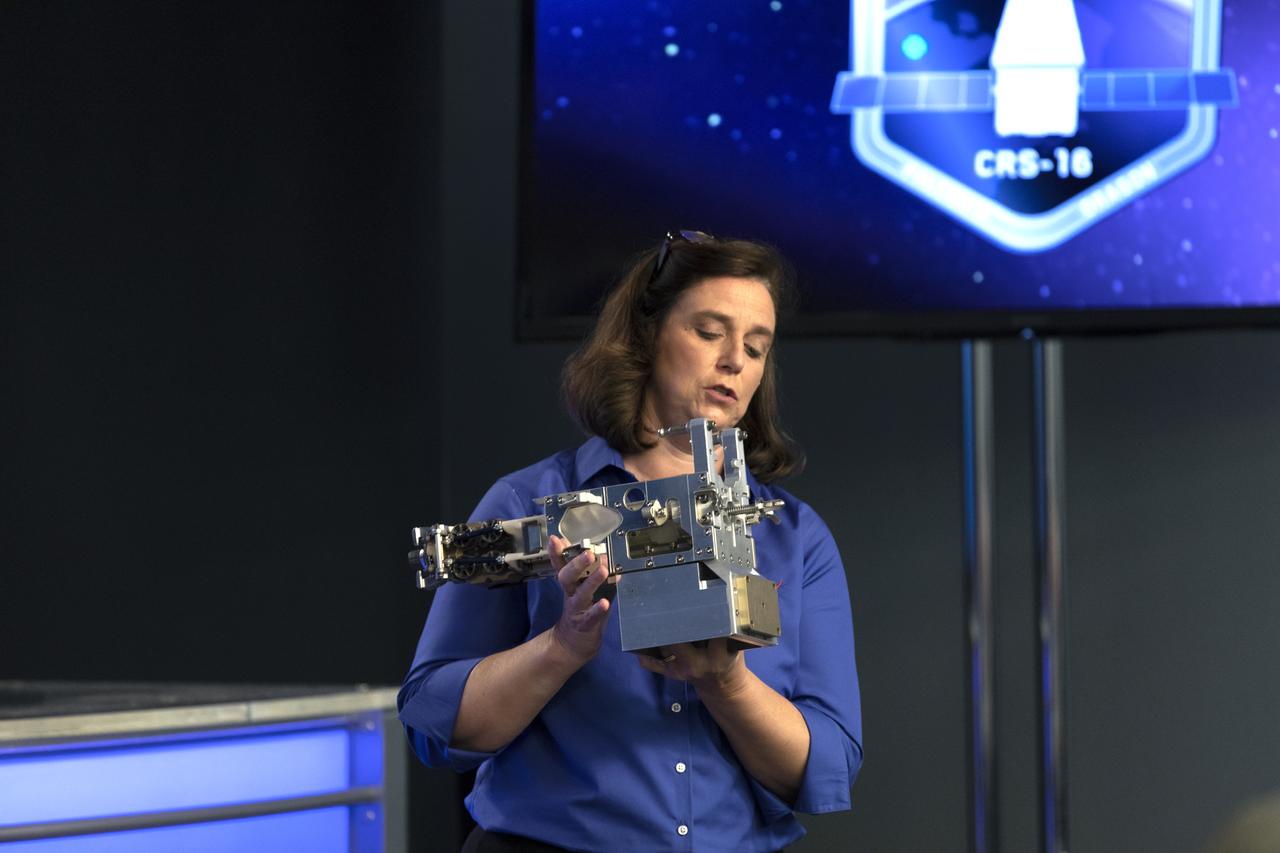

Jill McGuire, project manager for the Robotic Refueling Mission 3, or RRM3, experiment, describes RRM3 hardware for members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
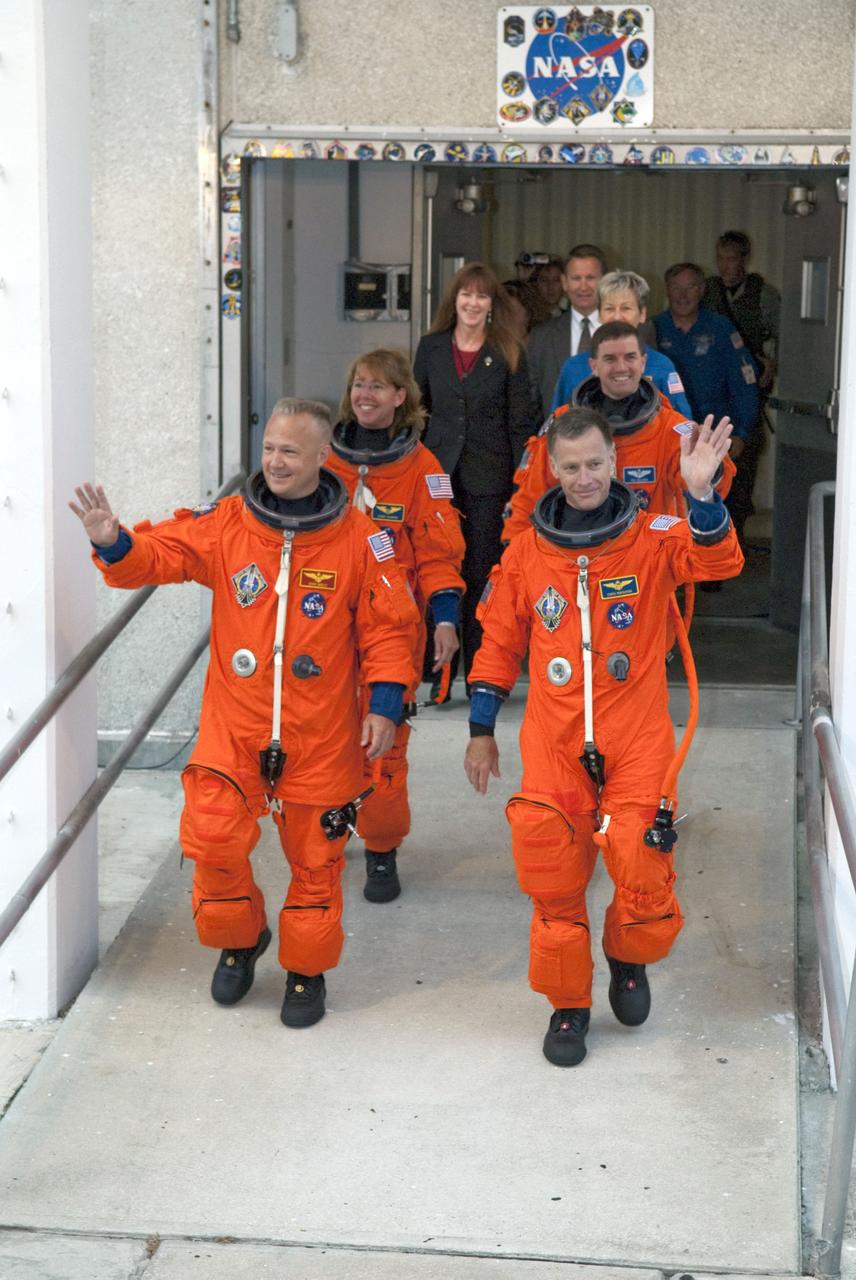

STS135-S-022 (8 July 2011) --- After suiting up, the STS-135 crew members exit the Operations and Checkout Building to board the Astrovan, which will take them to launch pad 39A for the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission. On the right (front to back) are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, commander; and Rex Walheim, mission specialist. On the left (front to back) are NASA astronauts Doug Hurley, pilot; and Sandy Magnus, mission specialist. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. (EDT) on July 8 for its mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA
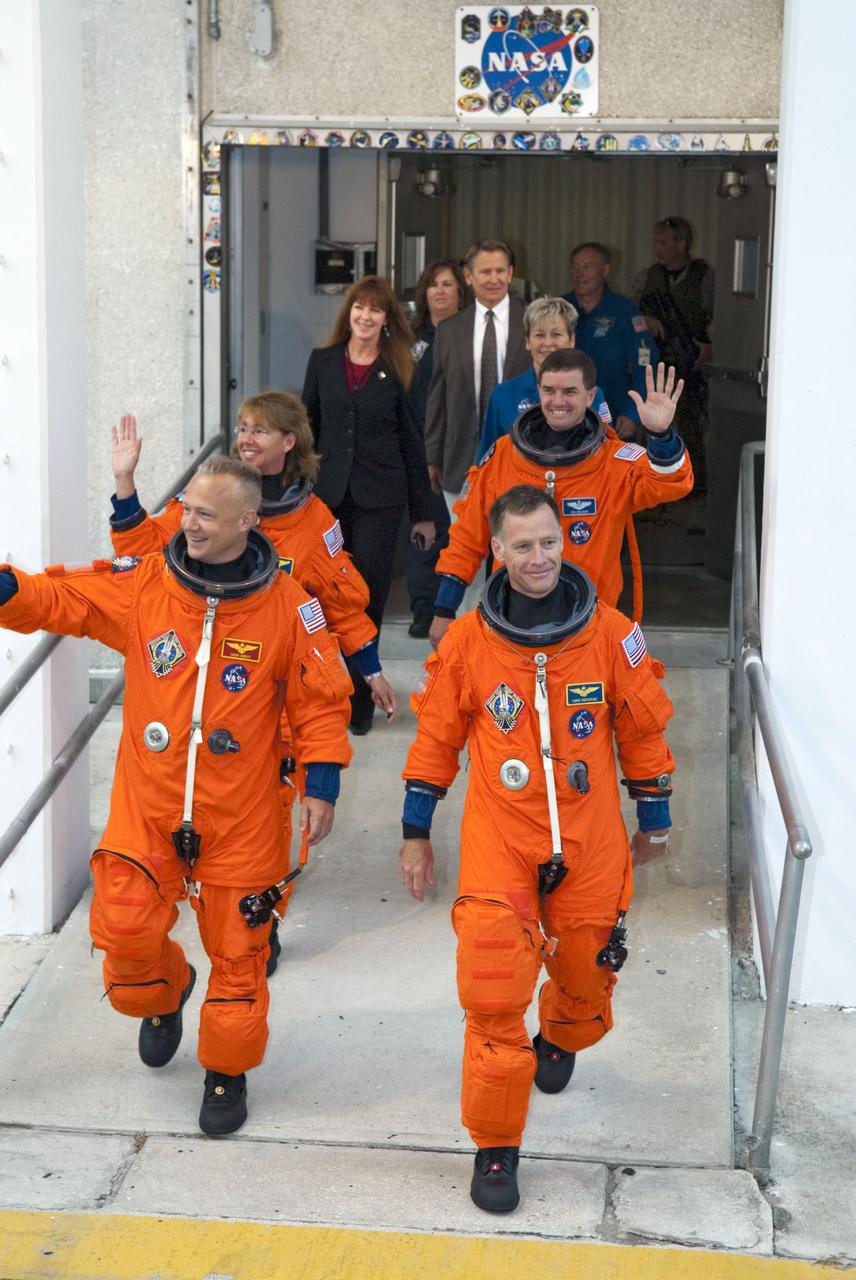

STS135-S-023 (8 July 2011) --- After suiting up, the STS-135 crew members exit the Operations and Checkout Building to board the Astrovan, which will take them to launch pad 39A for the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission. On the right (front to back) are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, commander; and Rex Walheim, mission specialist. On the left (front to back) are NASA astronauts Doug Hurley, pilot; and Sandy Magnus, mission specialist. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. (EDT) on July 8 for its mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA
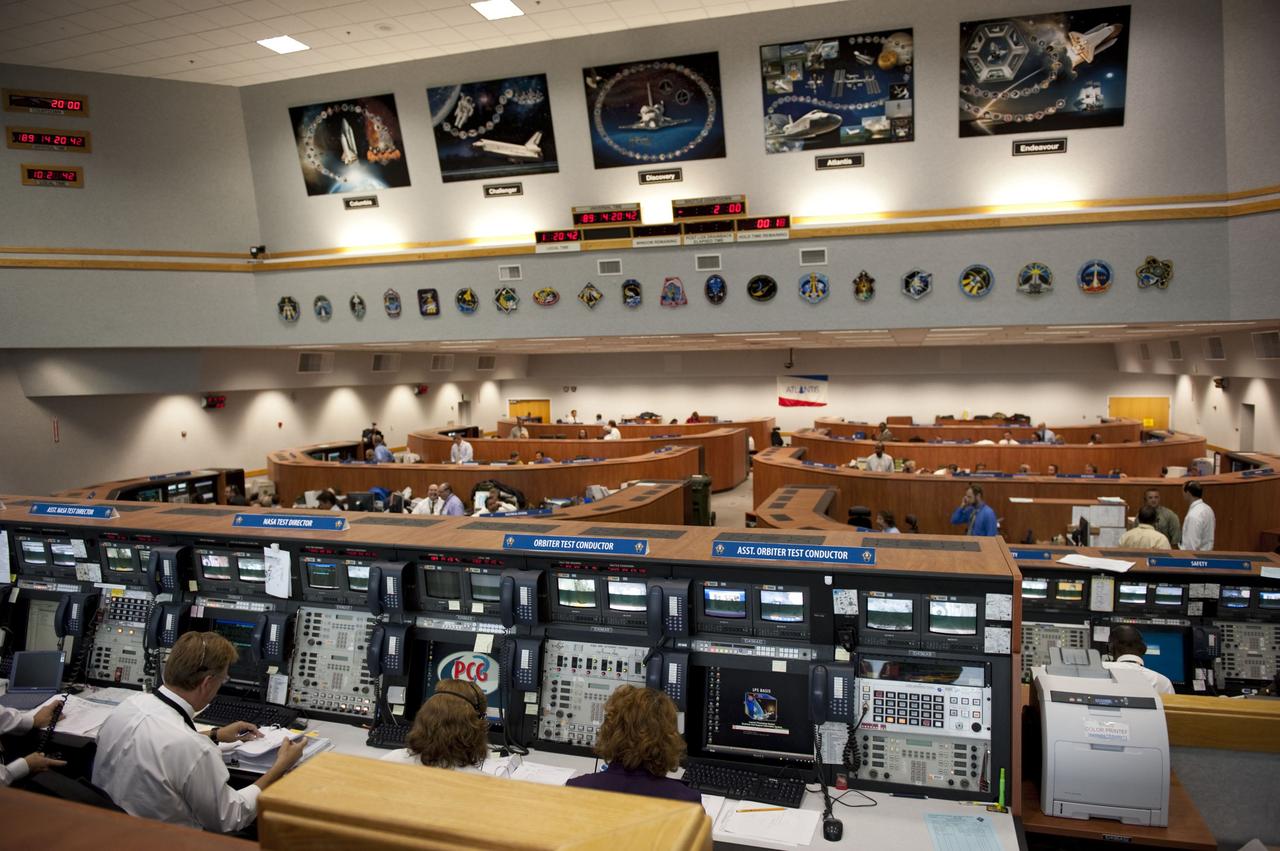

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Above the space shuttle countdown clock are five orbiter tributes on display. The tributes feature major accomplishments and significant achievements made by each shuttle, as well as mission patches and processing milestones. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
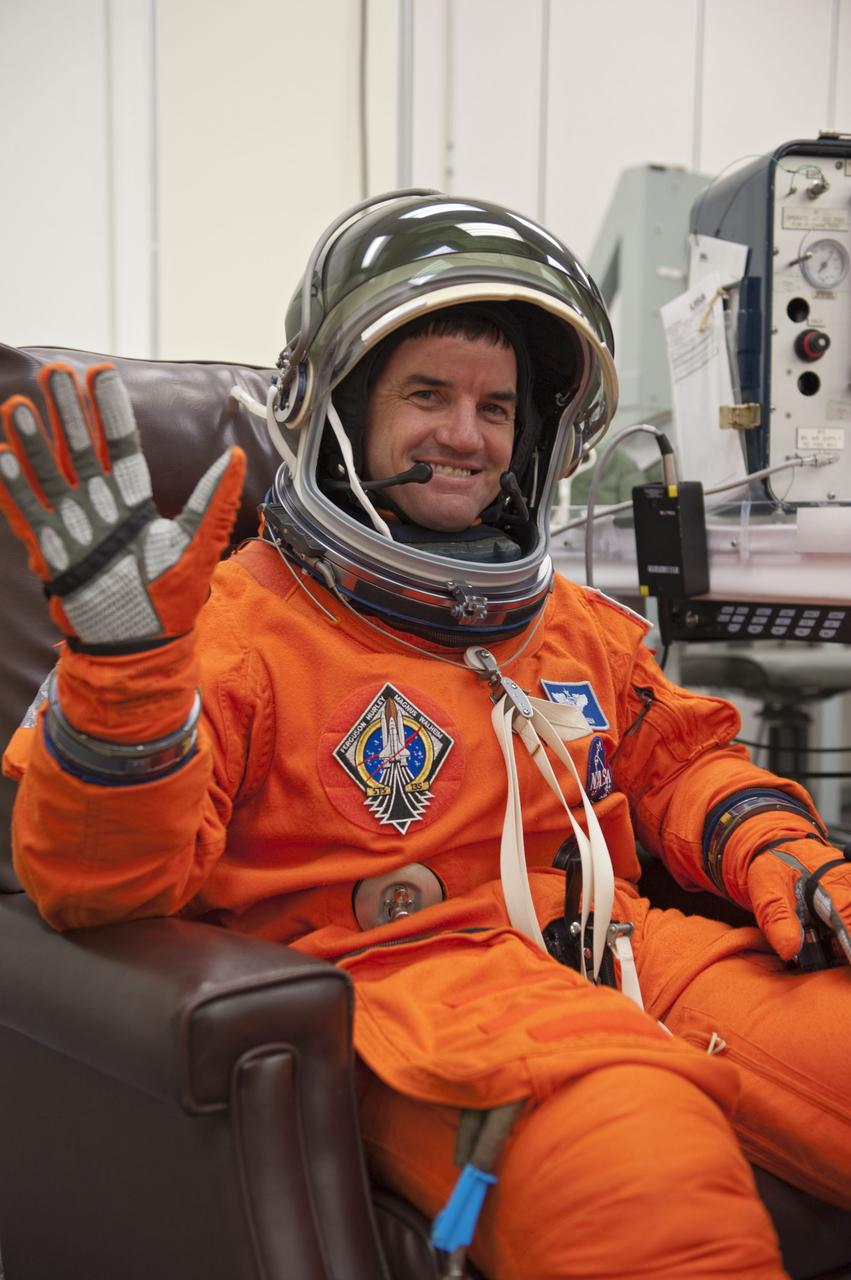

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- STS-135 Mission Specialist Rex Walheim waves as he dons his launch-and-entry suit and helmet in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Walheim is one of the final four astronauts to launch aboard a space shuttle. All three of Walheim's missions -- STS-110, STS-122 and now STS-135 -- will have been aboard space shuttle Atlantis. STS-135 is scheduled to lift off aboard Atlantis at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for a mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
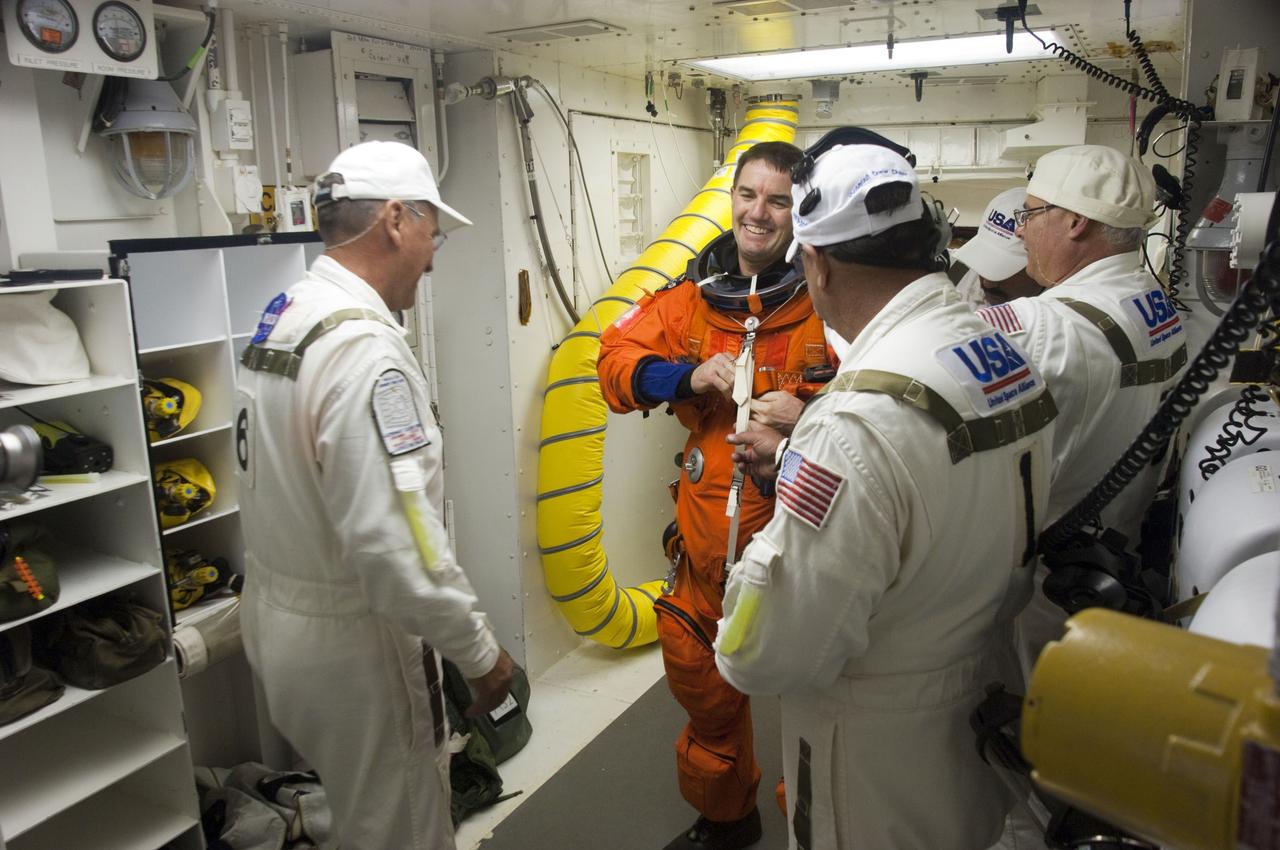

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The final astronaut to board a space shuttle for flight, STS-135 Mission Specialist Rex Walheim, bids farewell to the Closeout Crew in the White Room of Launch Pad 39A. All three of Walheim's missions -- STS-110, STS-122 and now STS-135 -- will have been aboard space shuttle Atlantis. Four STS-135 crew members are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for a mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
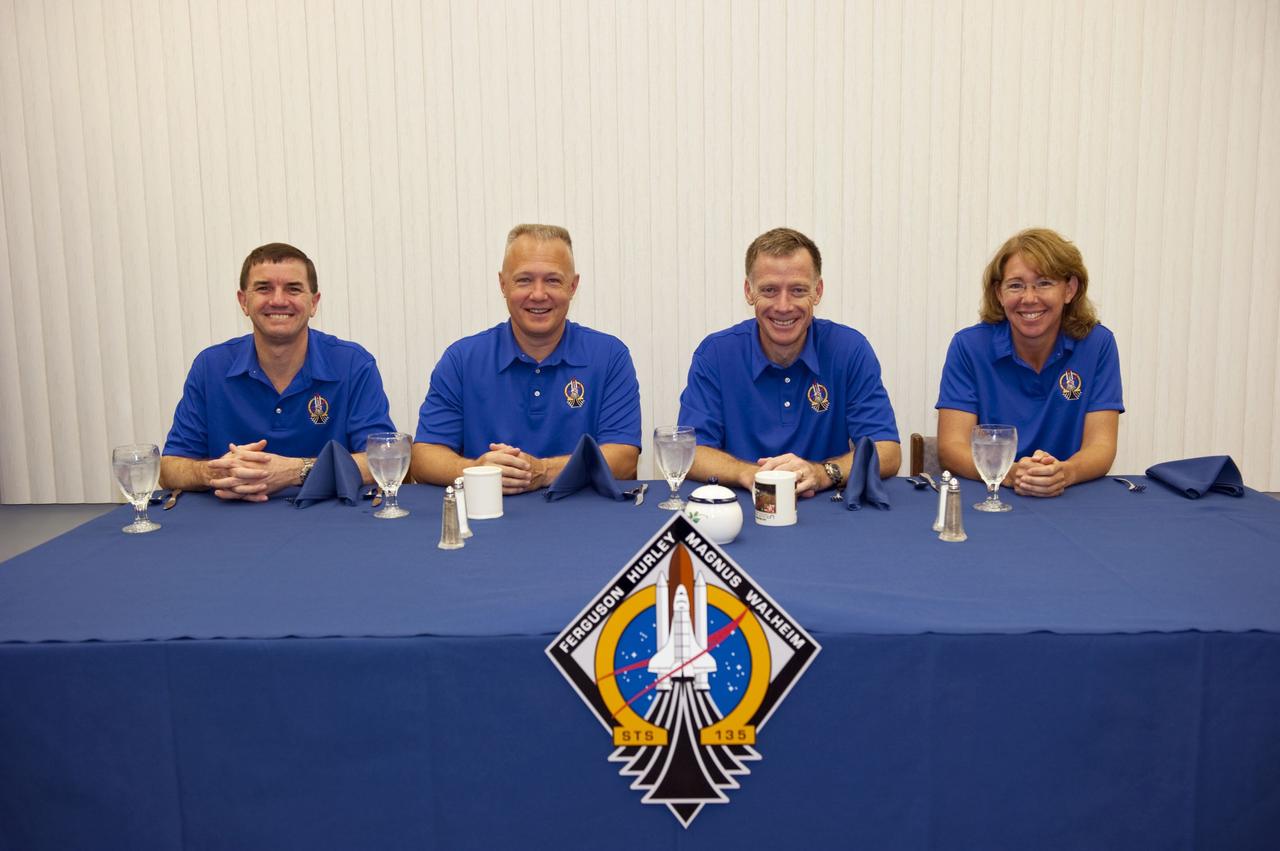

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The final four astronauts to launch aboard a space shuttle await breakfast in their Astronaut Crew Quarters in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left, are STS-135 Mission Specialist Rex Walheim, Pilot Doug Hurley, Commander Chris Ferguson, and Mission Specialist Sandy Magnus. The astronauts are scheduled to lift off aboard space shuttle Atlantis at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for their mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
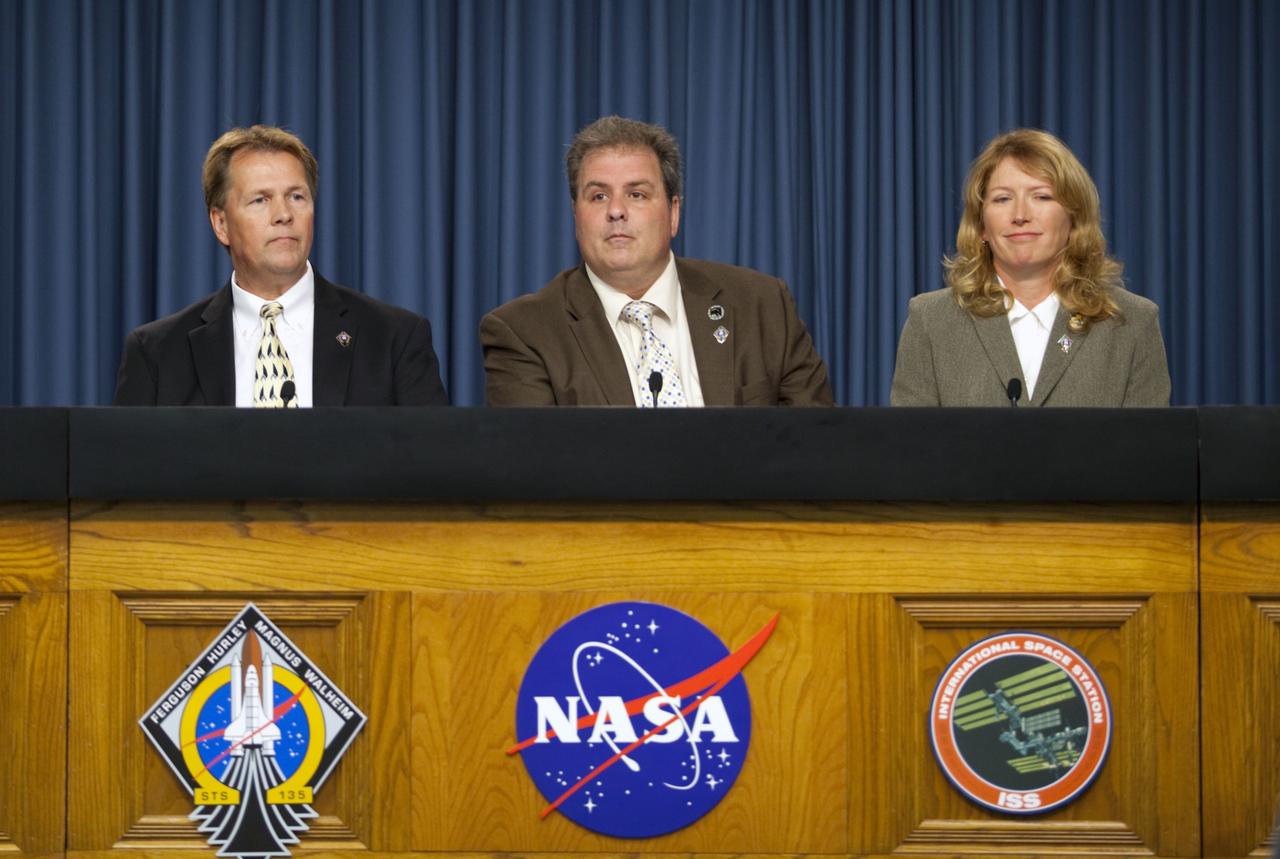

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA managers brief media about the payload and launch status of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here are NASA Test Director Jeff Spaulding (left), Payload Mission Manager Joe Delai and Shuttle Weather Officer Kathy Winters. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
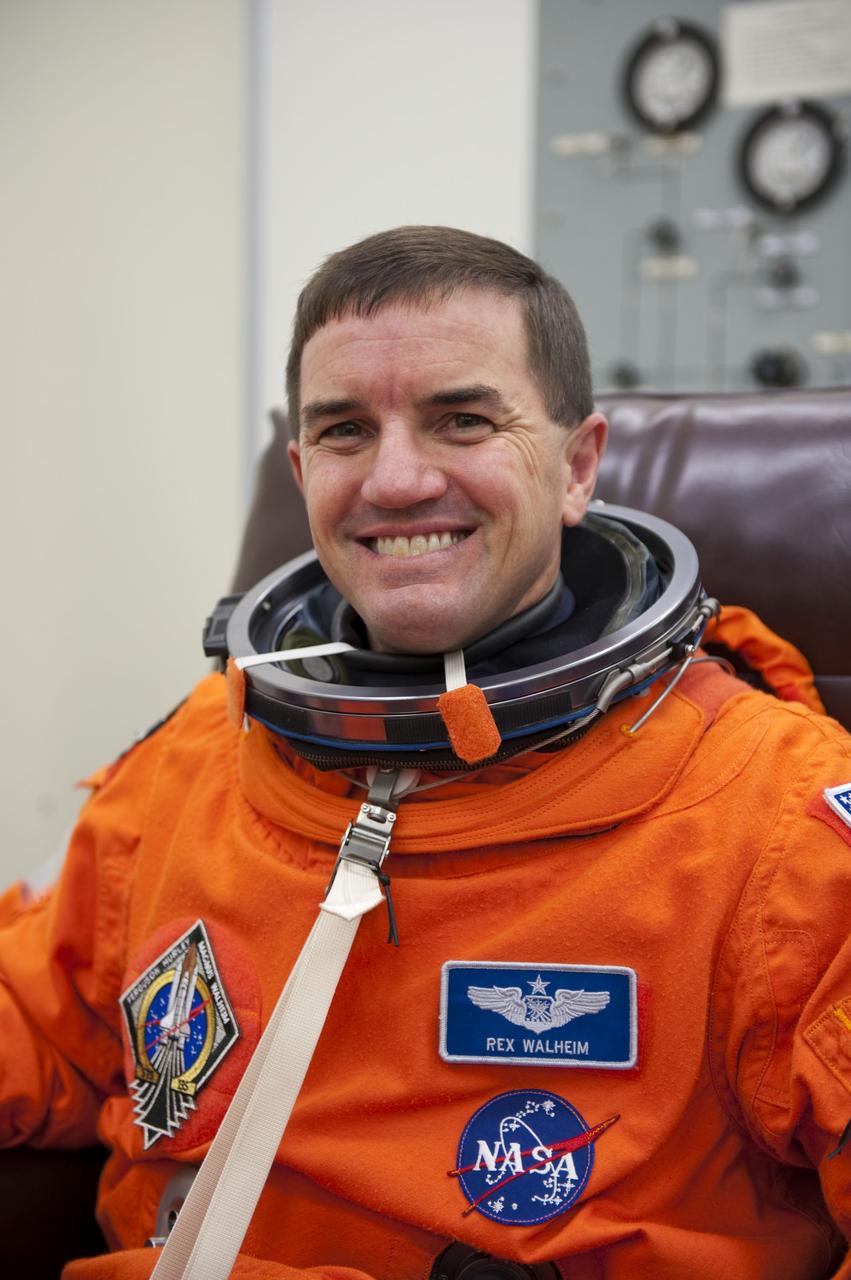

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- STS-135 Mission Specialist Rex Walheim dons his launch-and-entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Walheim is one of the final four astronauts to launch aboard a space shuttle. All three of Walheim's missions -- STS-110, STS-122 and now STS-135 -- will have been aboard space shuttle Atlantis. STS-135 is scheduled to lift off aboard Atlantis at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for a mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
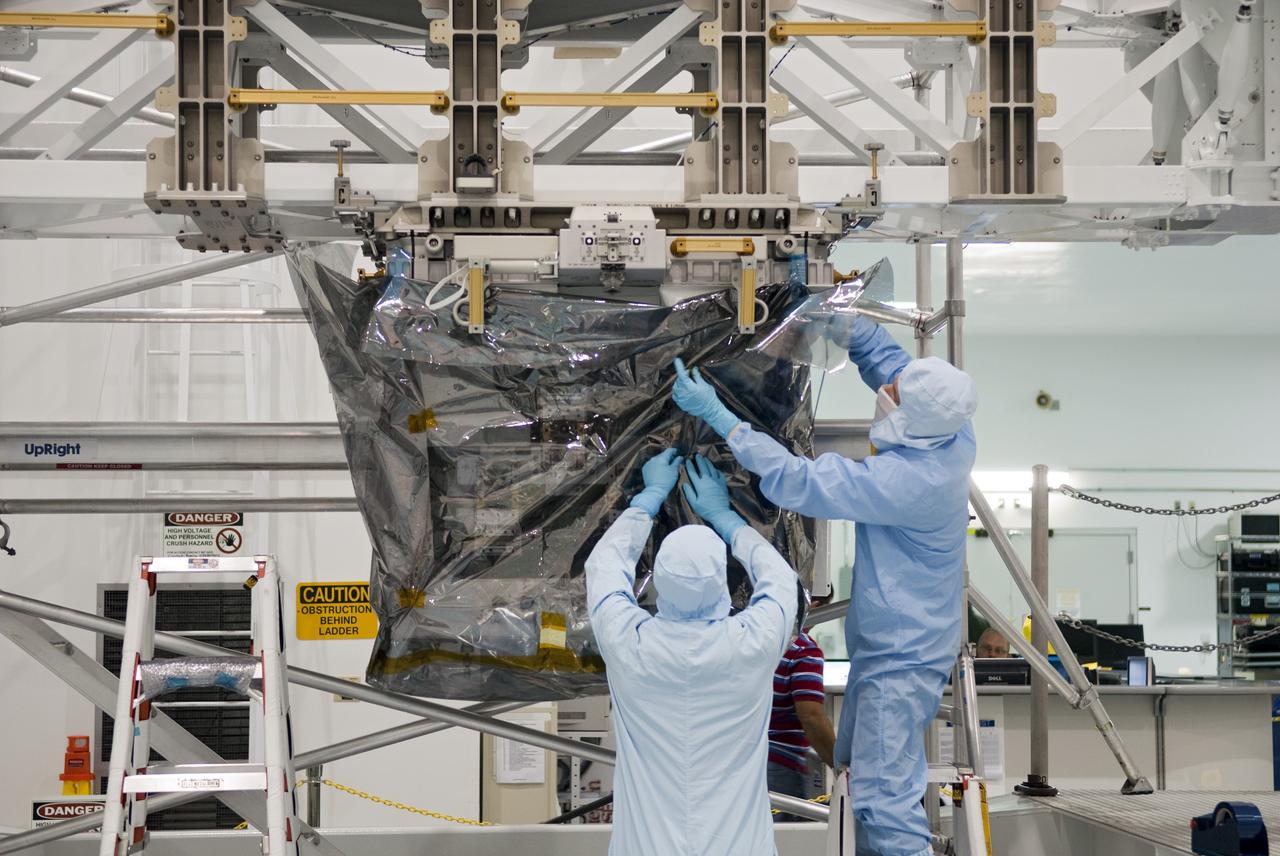

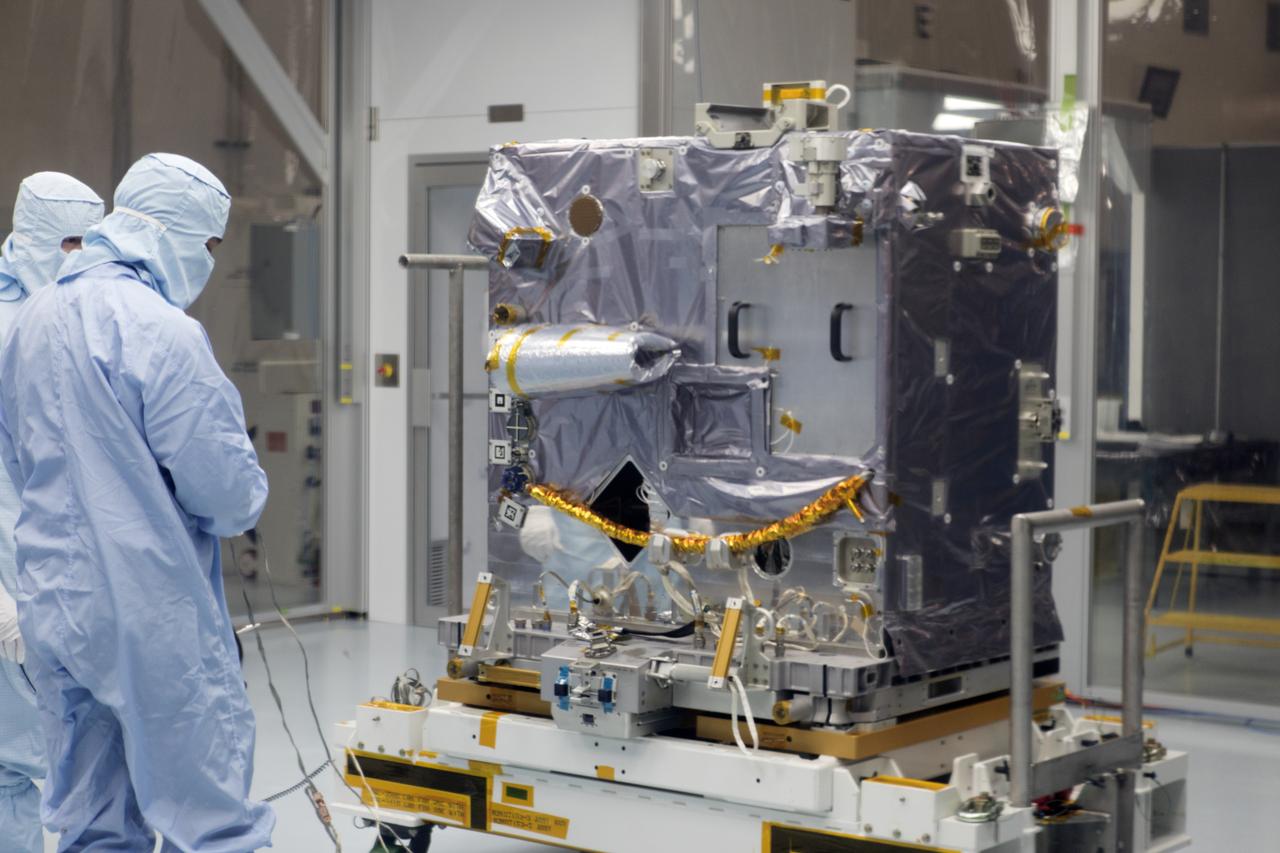
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians install a protective cover around the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) before its move into a payload canister. The RRM is being processed to fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to launch in early July, taking with them the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
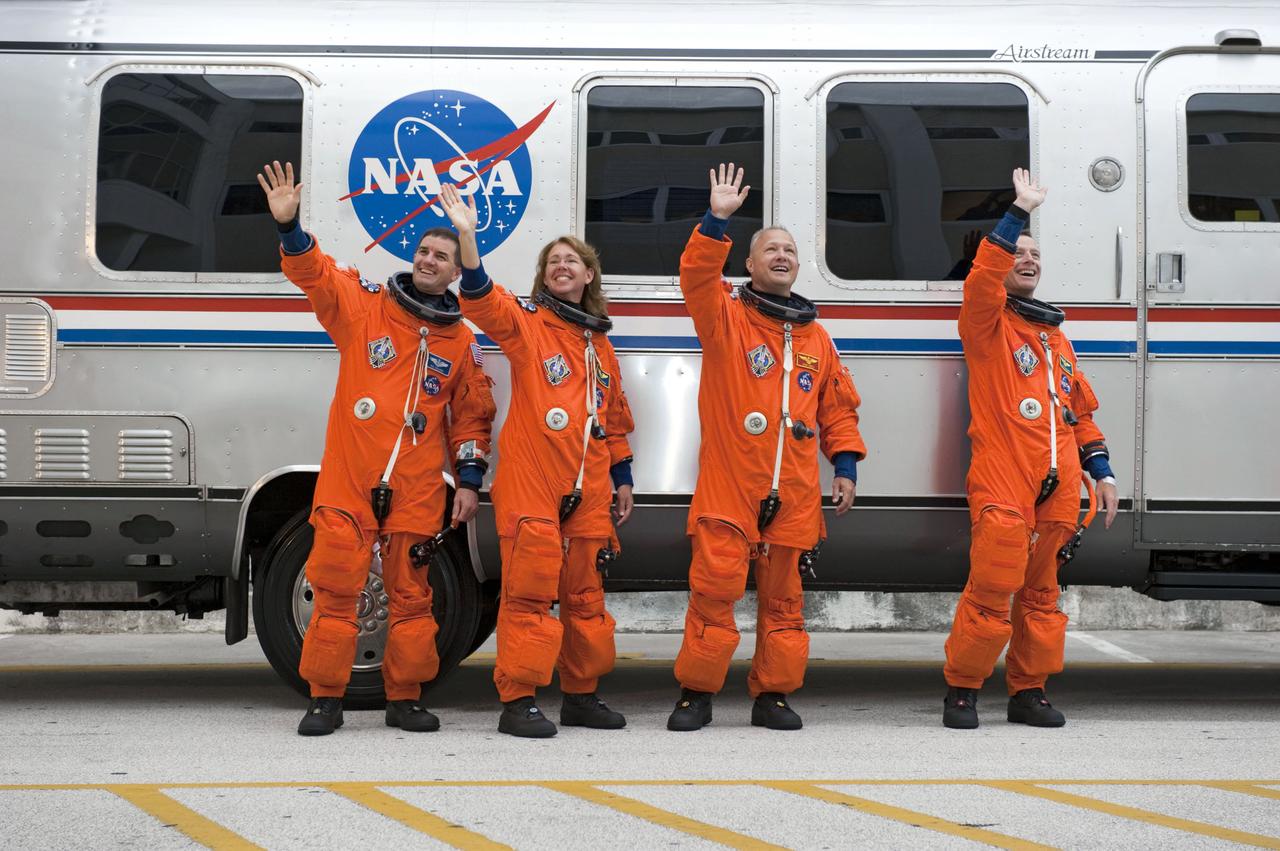

STS135-S-025 (8 July 2011) --- After suiting up, the STS-135 crew members pause alongside the Astrovan to wave farewell to onlookers before heading for launch pad 39A for the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission. From the right are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, commander; Doug Hurley, pilot; Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, both mission specialists. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. (EDT) on July 8 for its mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA
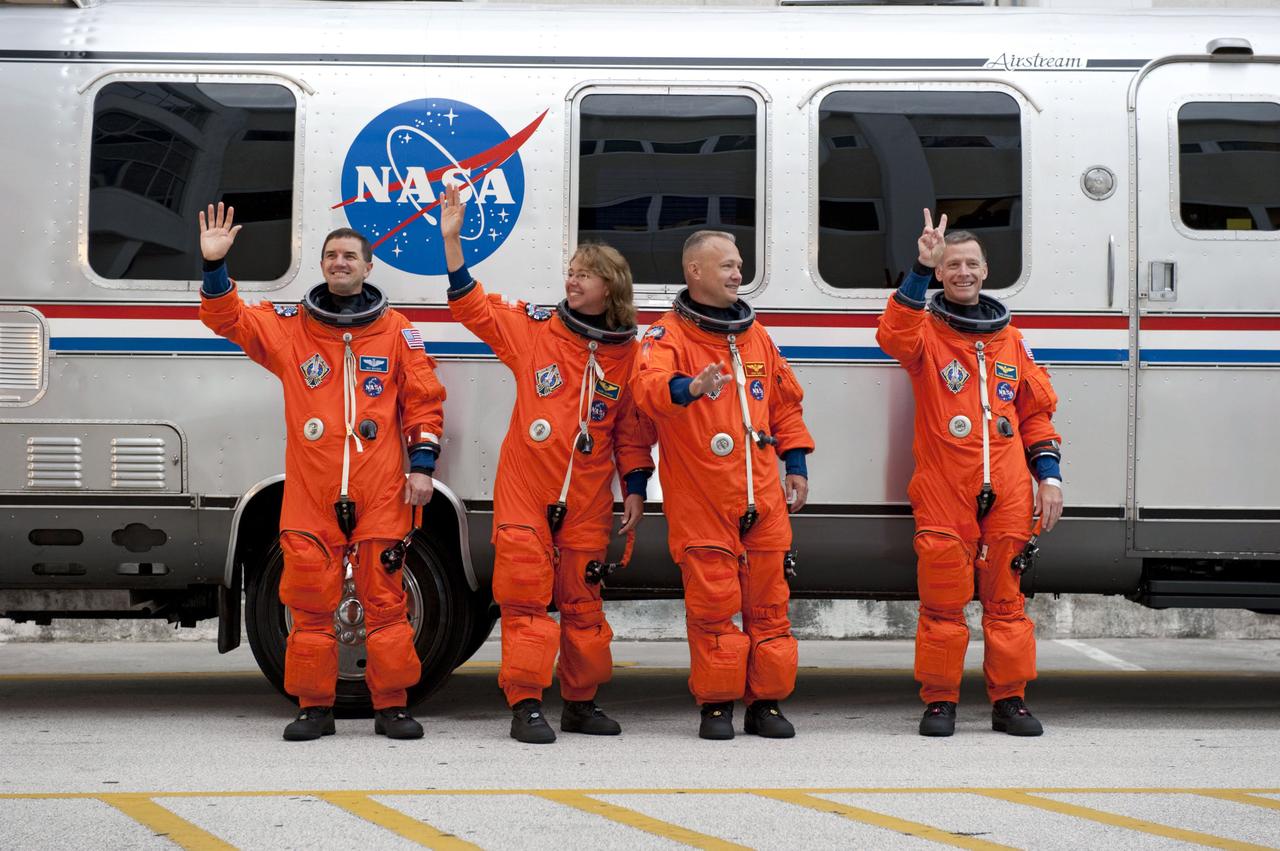

STS135-S-026 (8 July 2011) --- After suiting up, the STS-135 crew members pause alongside the Astrovan to wave farewell to onlookers before heading for launch pad 39A for the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission. From the right are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, commander; Doug Hurley, pilot; Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, both mission specialists. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. (EDT) on July 8 for its mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA
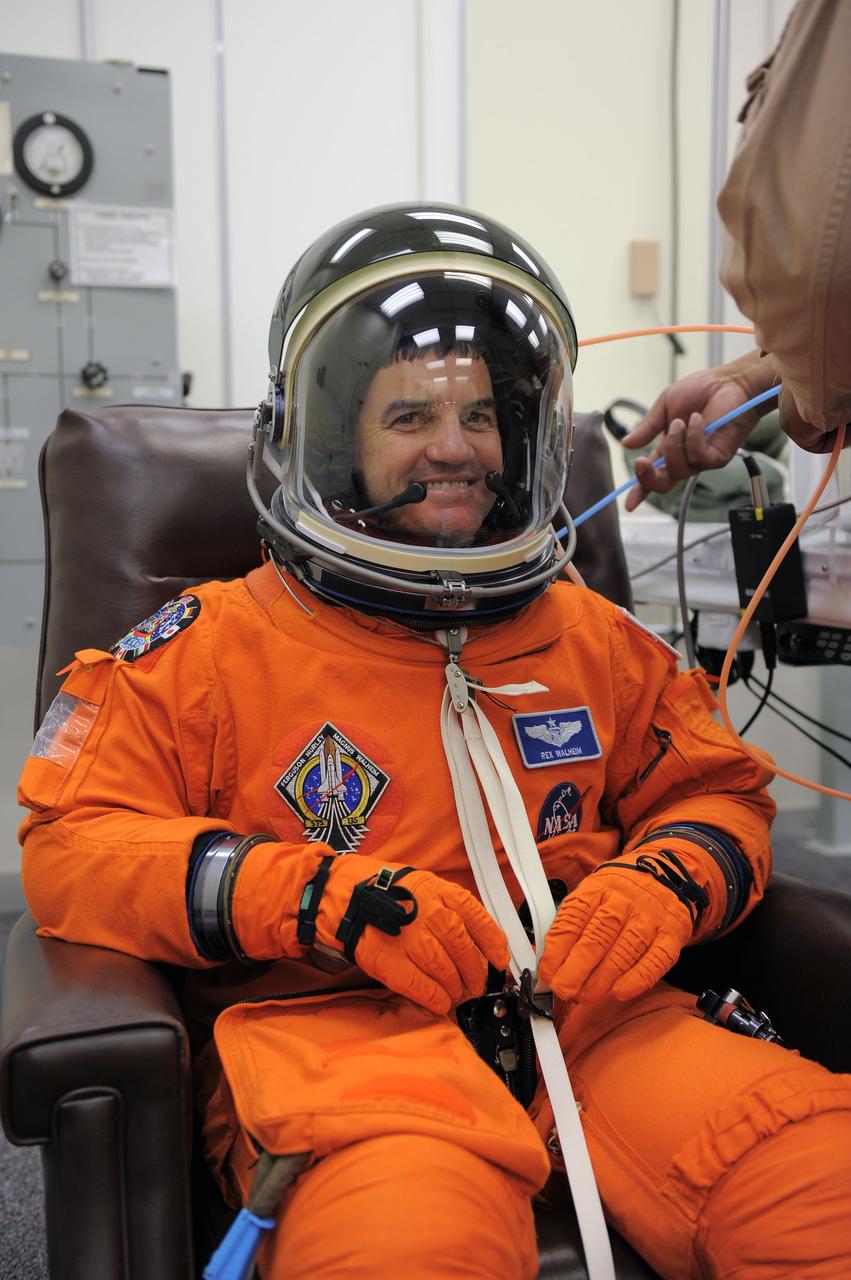

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- STS-135 Mission Specialist Rex Walheim dons his launch-and-entry suit and helmet in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Walheim is one of the final four astronauts to launch aboard a space shuttle. All three of Walheim's missions -- STS-110, STS-122 and now STS-135 -- will have been aboard space shuttle Atlantis. STS-135 is scheduled to lift off aboard Atlantis at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for a mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
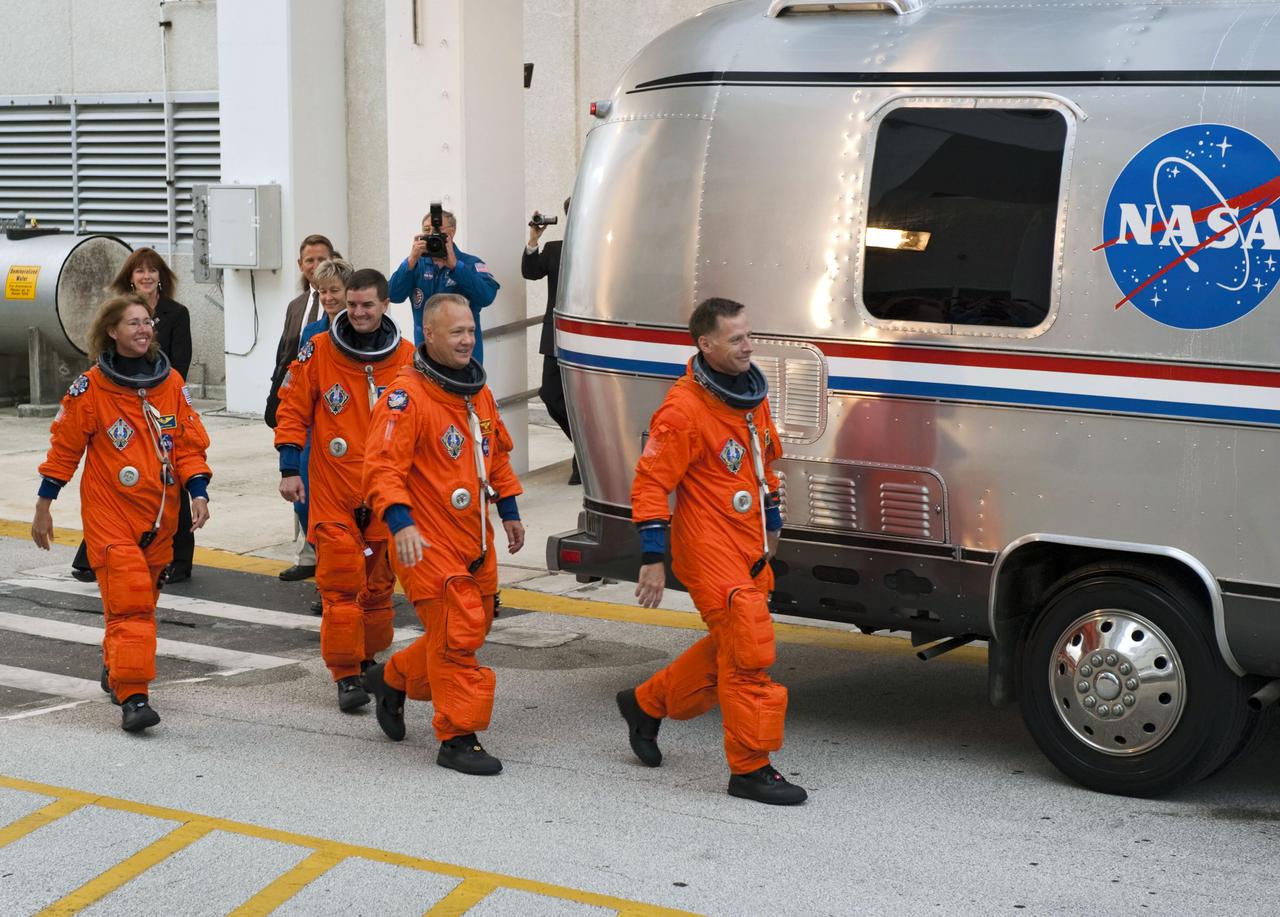

STS135-S-024 (8 July 2011) --- After suiting up, the STS-135 crew members exit the Operations and Checkout Building to board the Astrovan, which will take them to launch pad 39A for the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission. From the right are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, commander; Doug Hurley, pilot; Rex Walheim and Sandy Magnus, both mission specialists. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. (EDT) on July 8 for its mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA
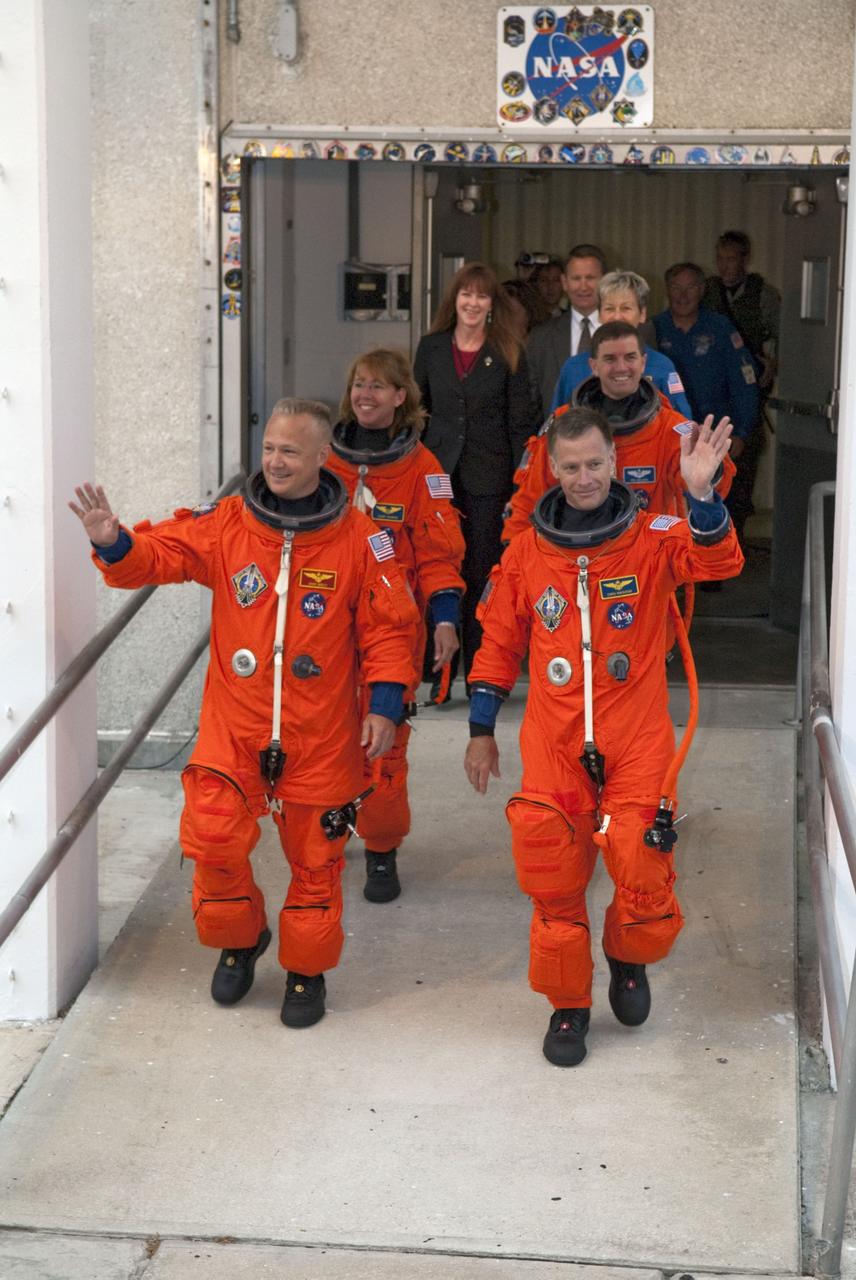

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dressed in their bright-orange launch-and-entry suits, the final four astronauts to launch aboard a space shuttle exit the Astronaut Crew Quarters in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the left row, STS-135 Pilot Doug Hurley is followed by Mission Specialist Sandy Magnus. In the right row, Commander Chris Ferguson is followed by Mission Specialist Rex Walheim. The astronauts, who will head to Launch Pad 39A aboard the silver Astrovan, are scheduled to lift off aboard space shuttle Atlantis at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for their mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
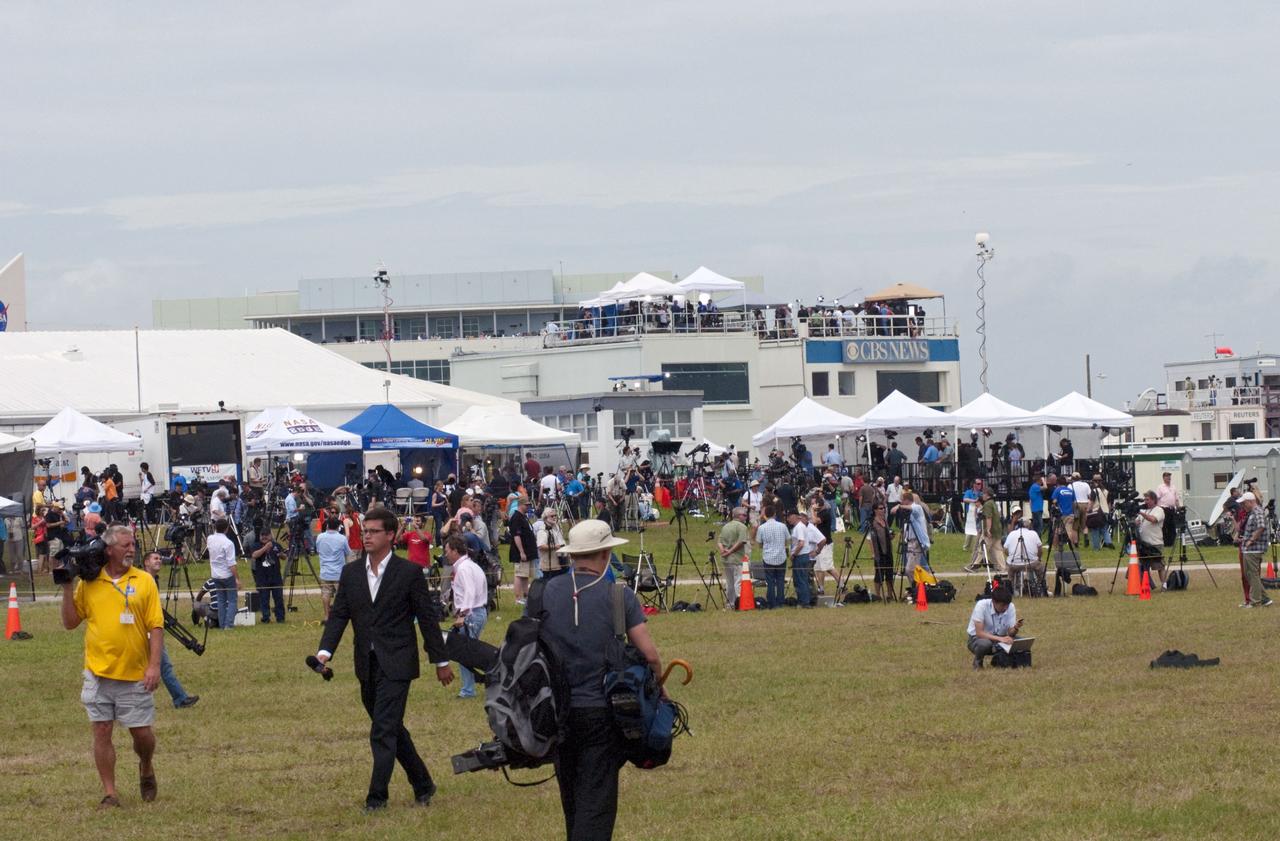

Cape Canaveral, Fla. – Shortly after launch, members of the news media continue the coverage of space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Working from the NASA News Center at Kennedy Space Center, news media from television, World Wide Web and newspaper outlets from around the world relayed the launch and mission details for the final flight of the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/ Jim Grossmann
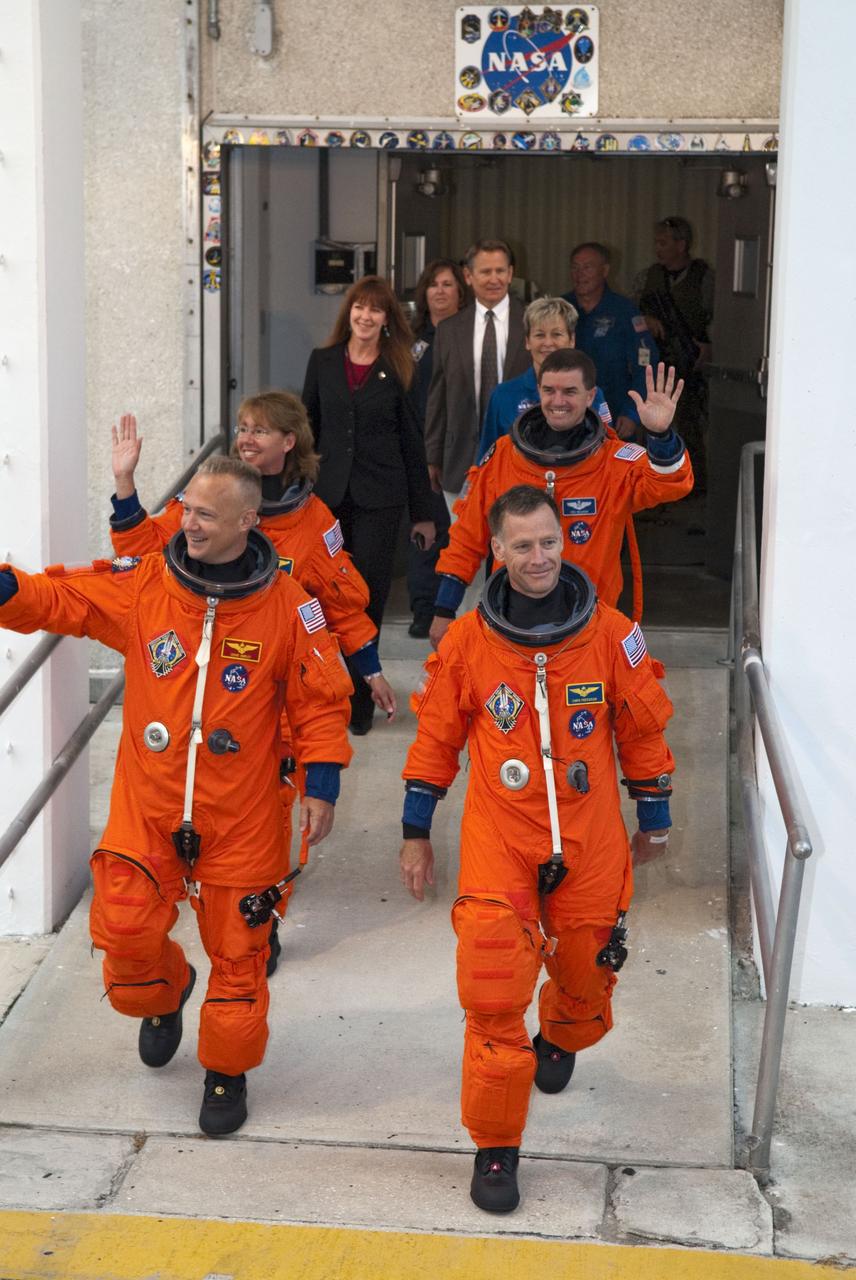

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dressed in their bright-orange launch-and-entry suits, the final four astronauts to launch aboard a space shuttle exit the Astronaut Crew Quarters in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the left row, STS-135 Pilot Doug Hurley is followed by Mission Specialist Sandy Magnus. In the right row, Commander Chris Ferguson is followed by Mission Specialist Rex Walheim. The astronauts, who will head to Launch Pad 39A aboard the silver Astrovan, are scheduled to lift off aboard space shuttle Atlantis at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for their mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
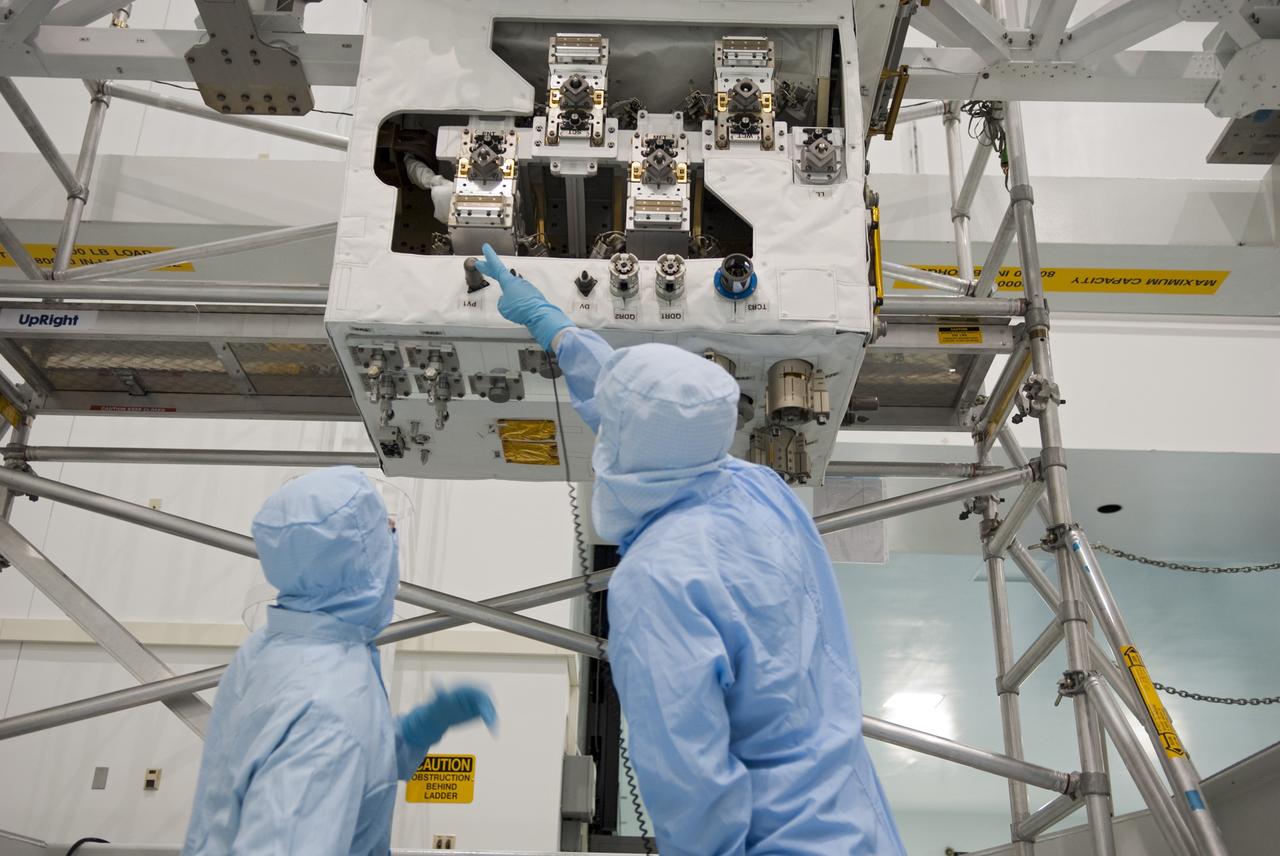

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians inspect the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) before installing its protective cover and later move it into a payload canister. The RRM is being processed to fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to launch in early July, taking with them the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
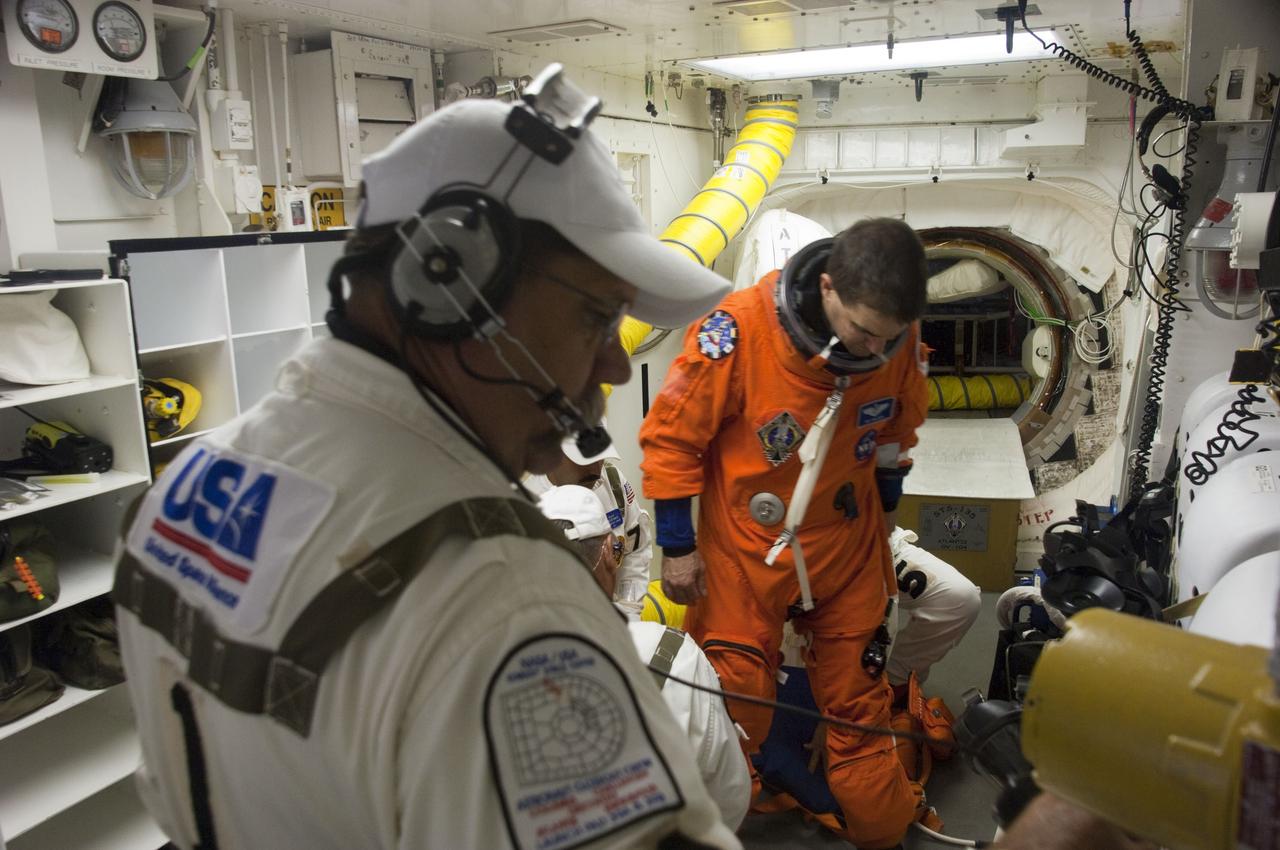

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The final astronaut to board a space shuttle for flight, STS-135 Mission Specialist Rex Walheim, is assisted by the Closeout Crew in the White Room of Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. All three of Walheim's missions -- STS-110, STS-122 and now STS-135 -- will have been aboard space shuttle Atlantis. Four STS-135 crew members are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for a mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
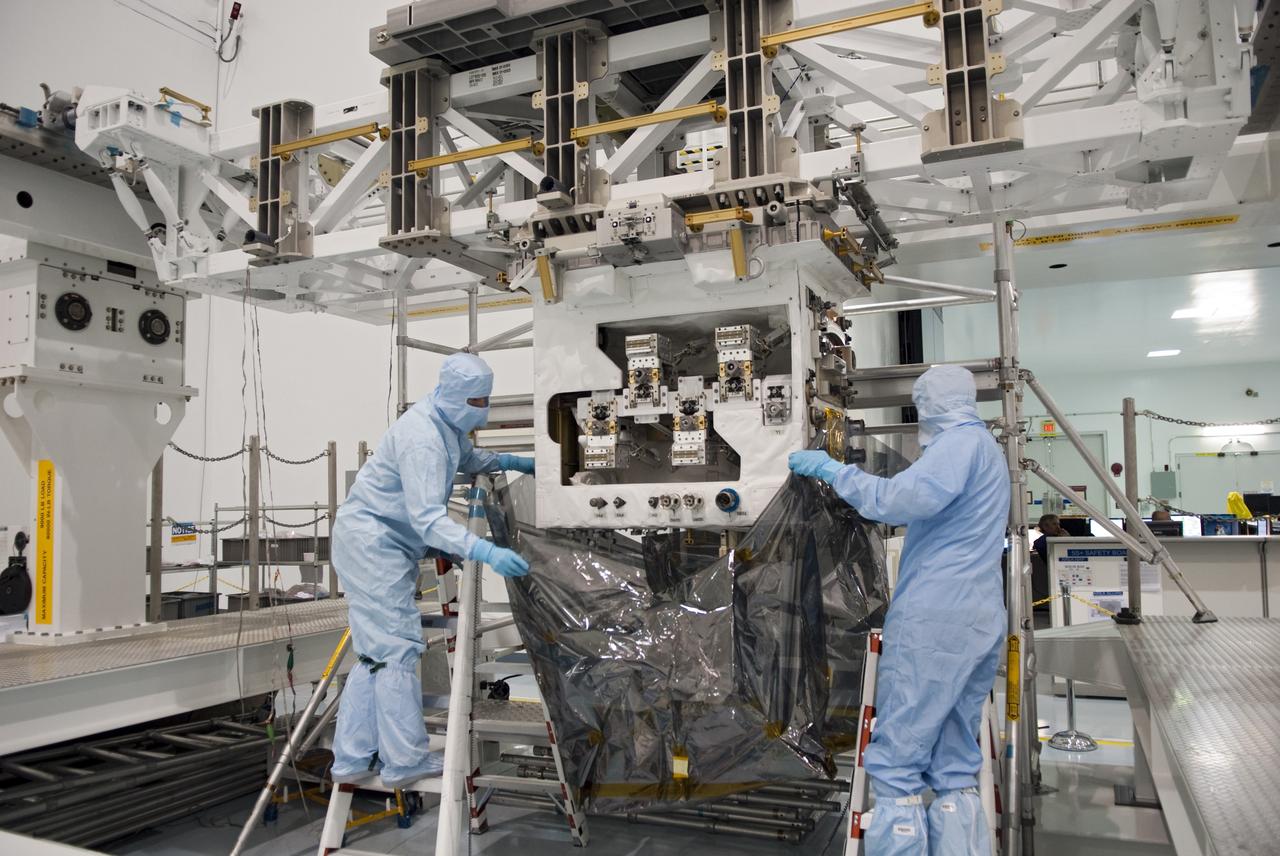

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians install a protective cover around the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) before its move into a payload canister. The RRM is being processed to fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to launch in early July, taking with them the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
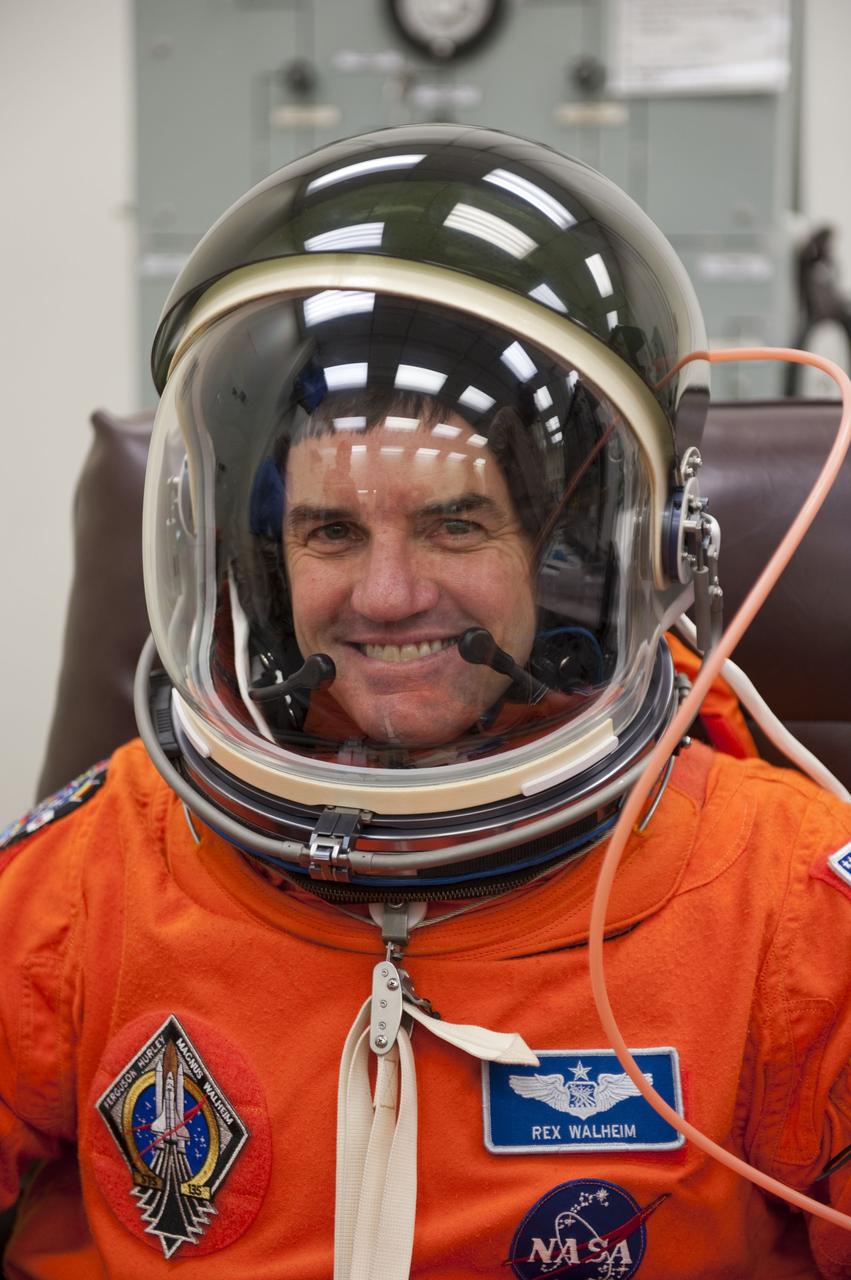

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- STS-135 Mission Specialist Rex Walheim dons his launch-and-entry suit and helmet in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Walheim is one of the final four astronauts to launch aboard a space shuttle. All three of Walheim's missions -- STS-110, STS-122 and now STS-135 -- will have been aboard space shuttle Atlantis. STS-135 is scheduled to lift off aboard Atlantis at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for a mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
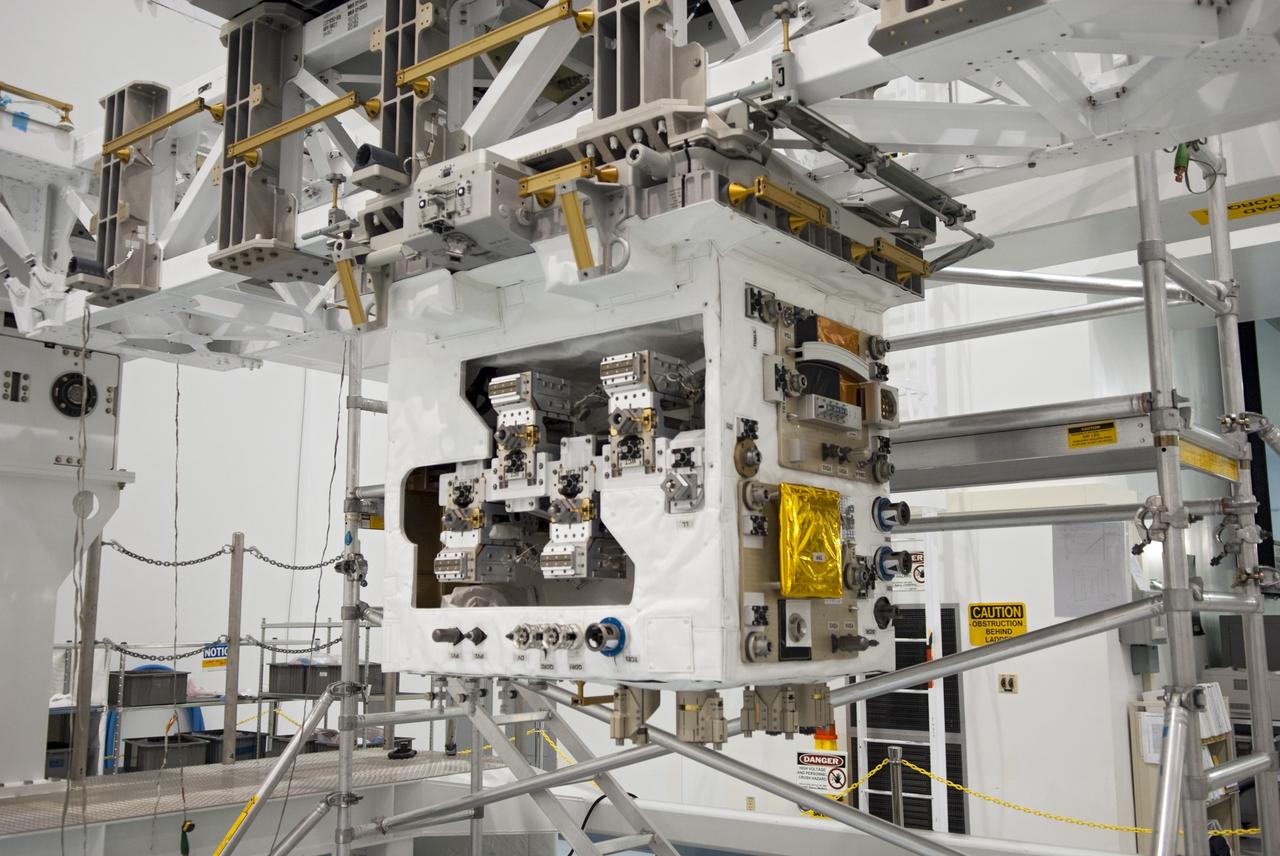

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM) is installed on the Lightweight Multi- Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier, or LMC . Technicians are preparing it for its protective cover installation prior to its move into a payload canister. The RRM is being processed to fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to launch in early July, taking with them the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
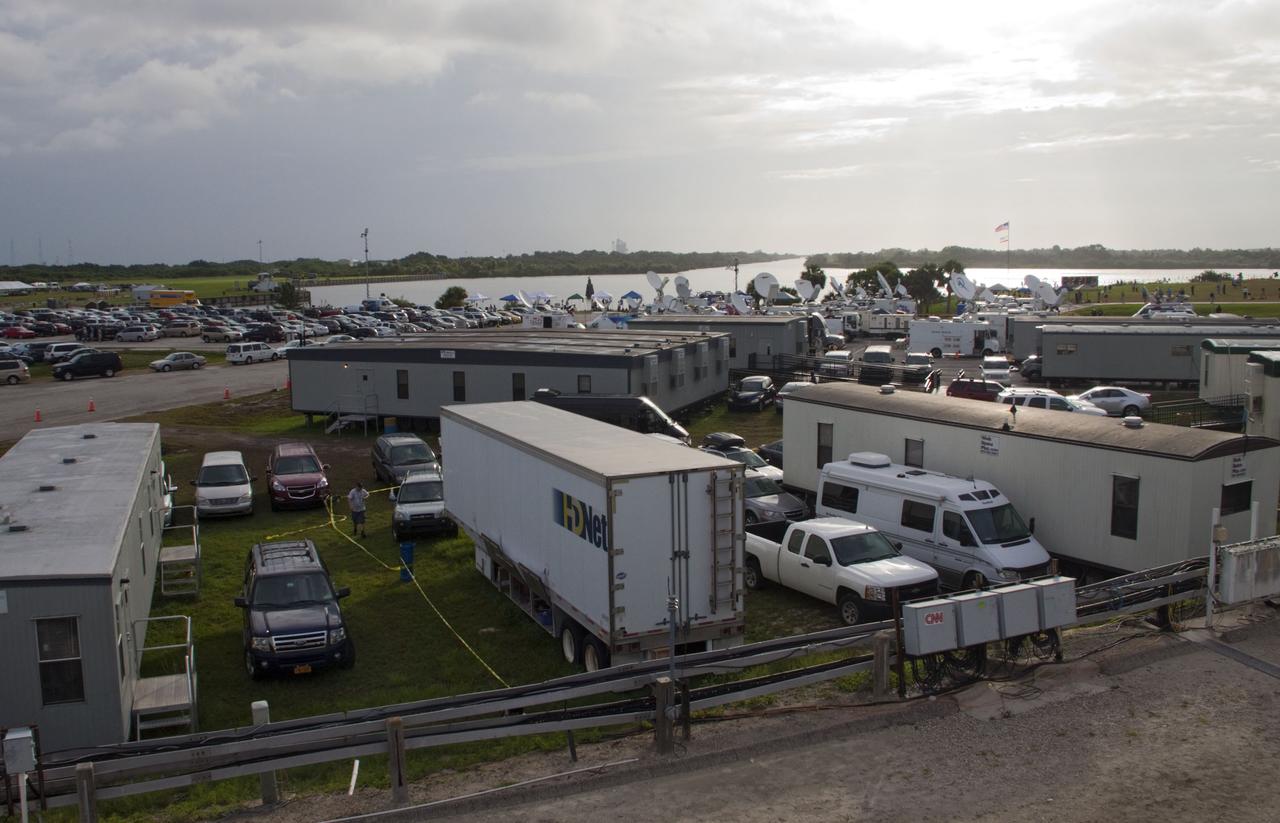

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen towering above is the massive Vehicle Assembly Building. Dozens of satellite news vehicles and trailers can be seen in the parking lot. In the background is the Turn Basin where NASA's Pegasus barge delivered the final external tank for the mission. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
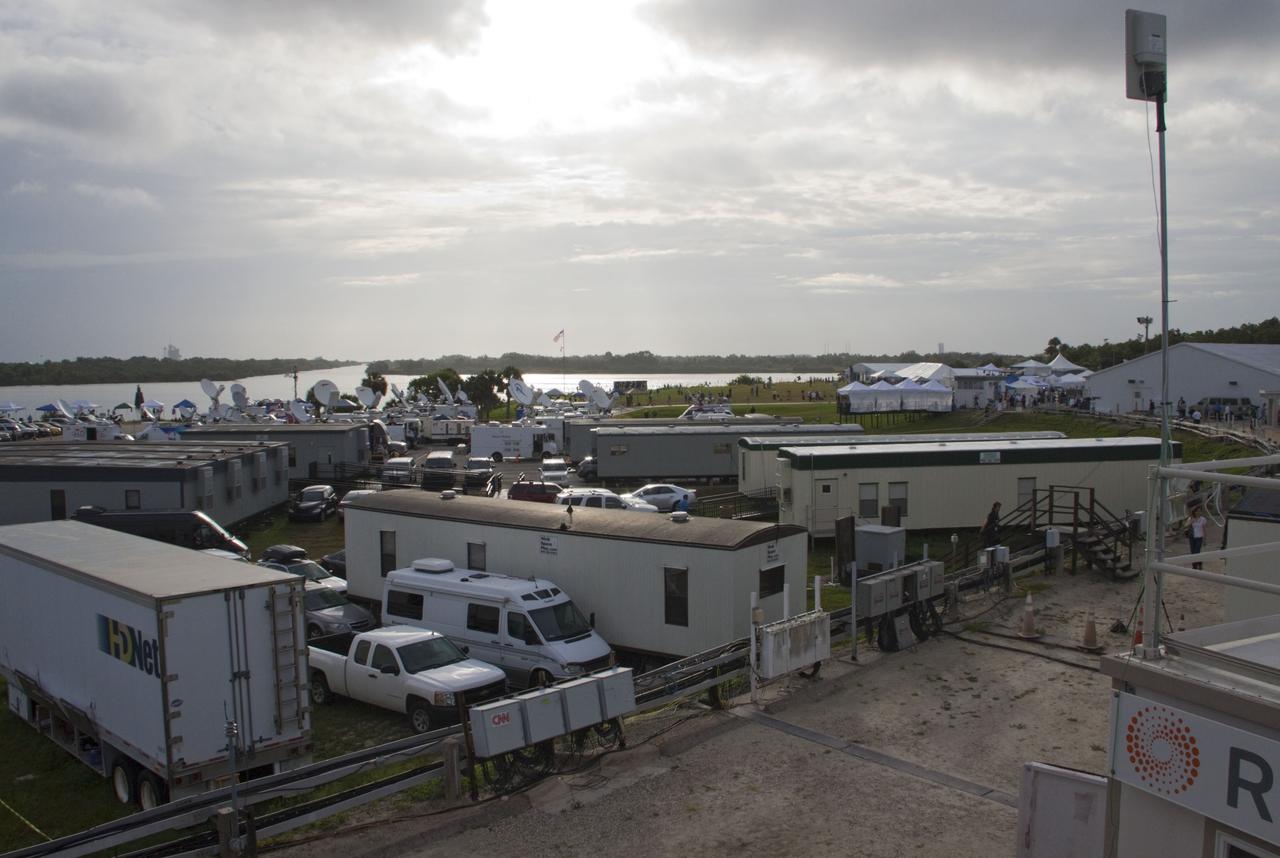

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen towering above is the massive Vehicle Assembly Building. Dozens of satellite news vehicles and trailers can be seen in the parking lot. In the background is the Turn Basin where NASA's Pegasus barge delivered the final external tank for the mission. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
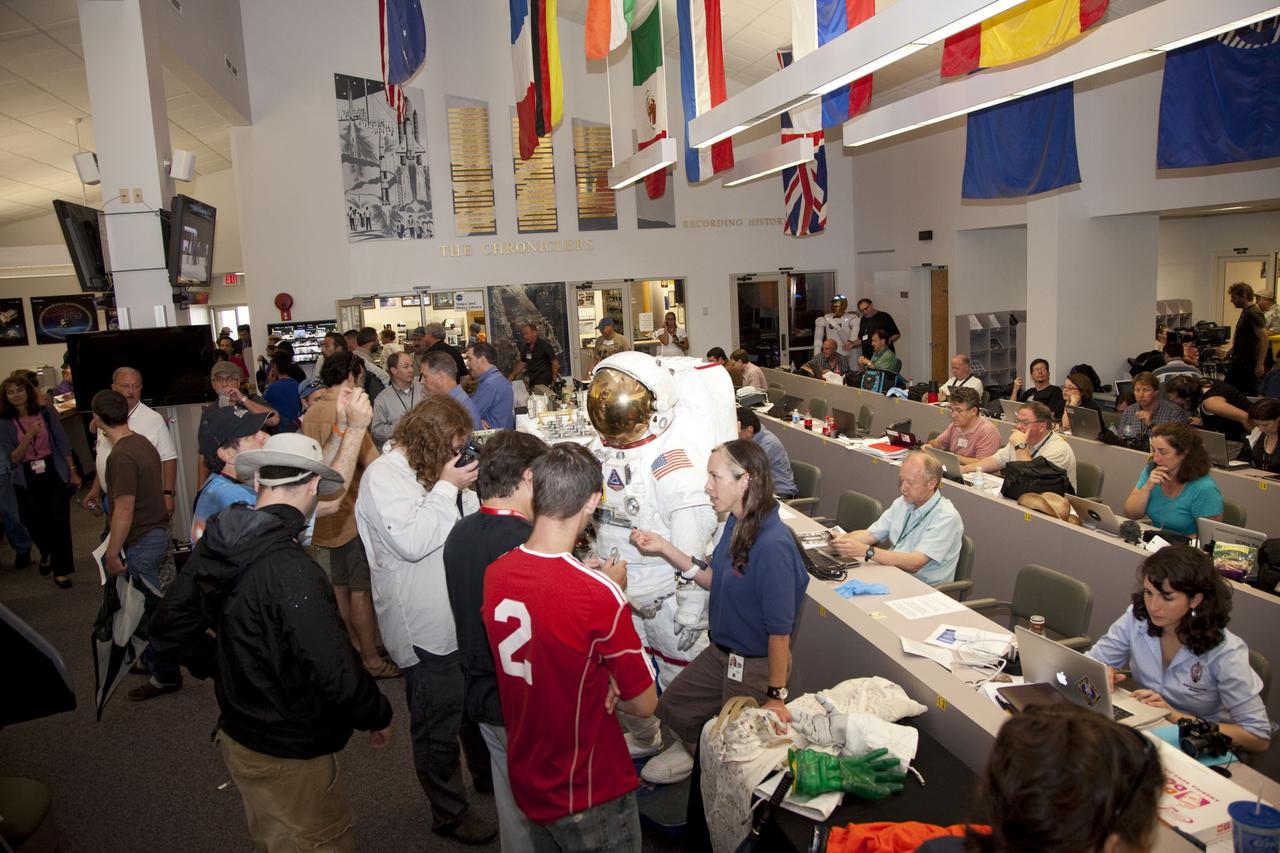

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather at the Press Site bull pen at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
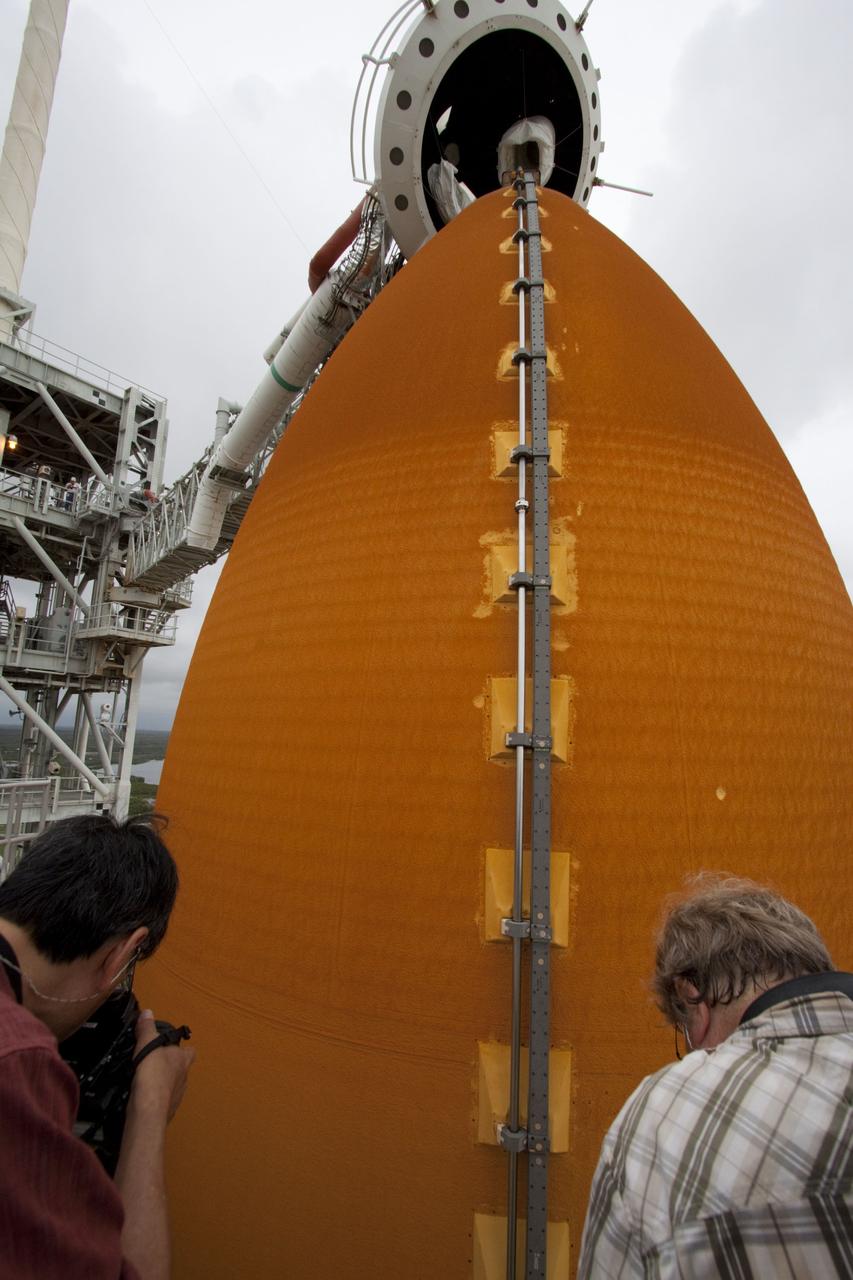

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Photographers Stan Hernda of AFP News, left, and Scott Andrews of Canon record space shuttle Atlantis as it is revealed on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the move of the rotating service structure (RSS). The structure provides weather protection and access to the shuttle while it awaits liftoff on the pad. RSS "rollback" marks a major milestone in Atlantis' STS-135 mission countdown. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
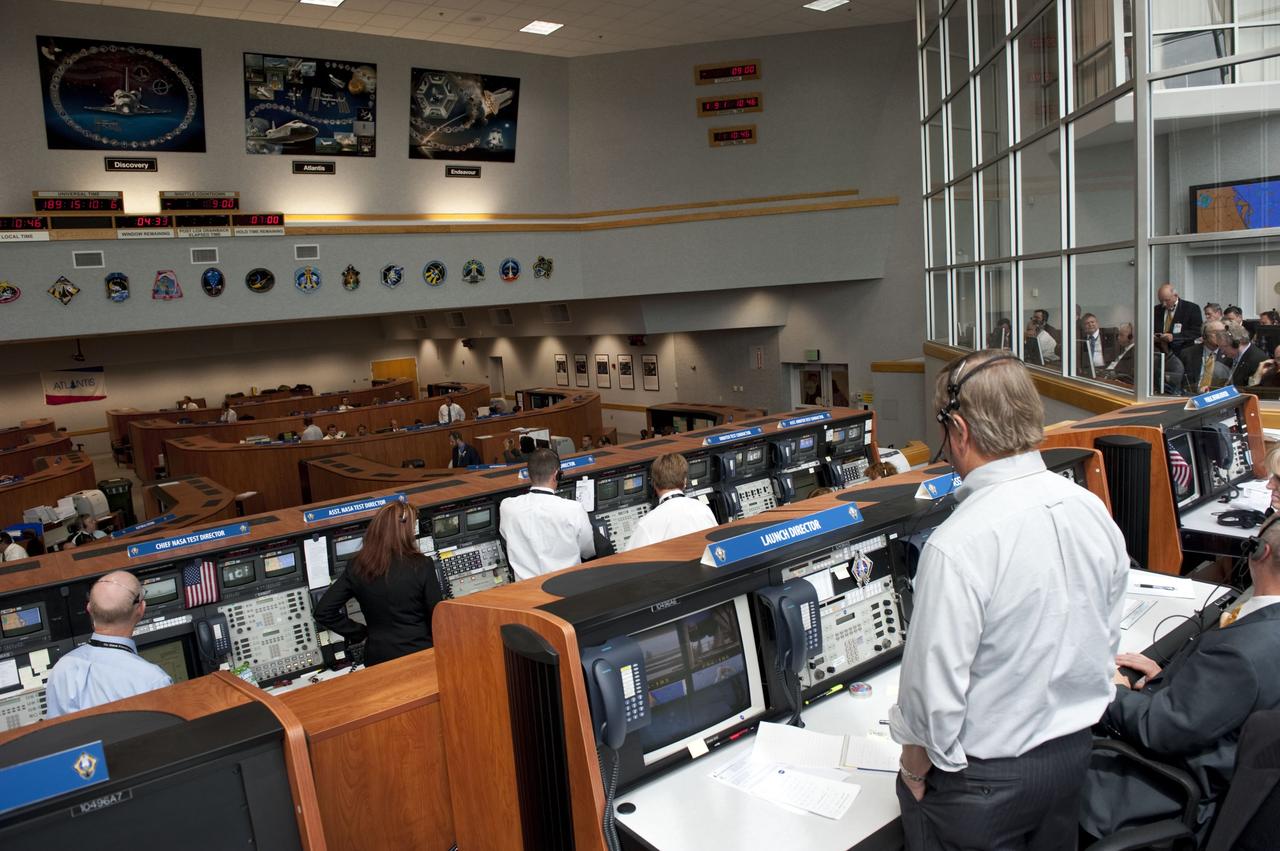

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach oversees the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
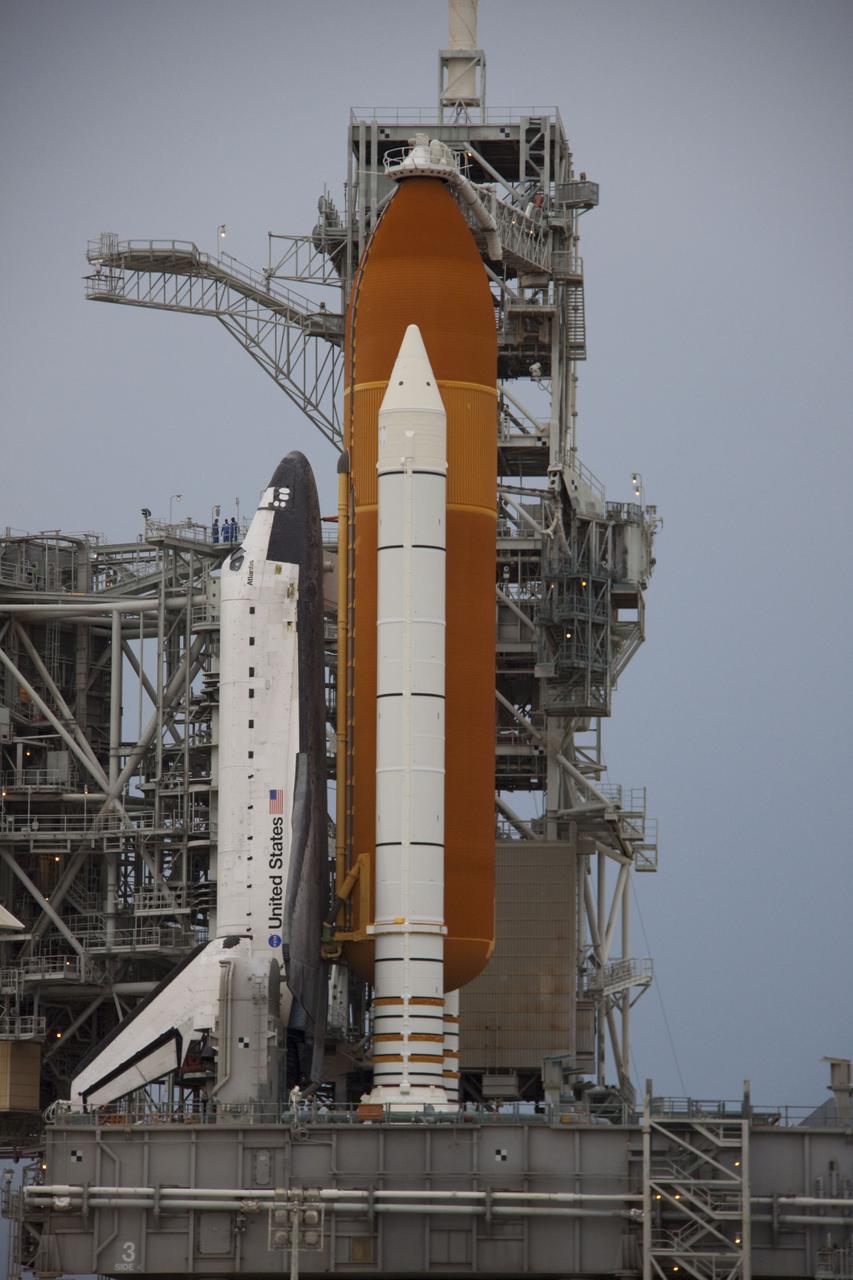

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is revealed on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the move of the rotating service structure (RSS). The structure provides weather protection and access to the shuttle while it awaits liftoff on the pad. RSS "rollback" marks a major milestone in Atlantis' STS-135 mission countdown. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
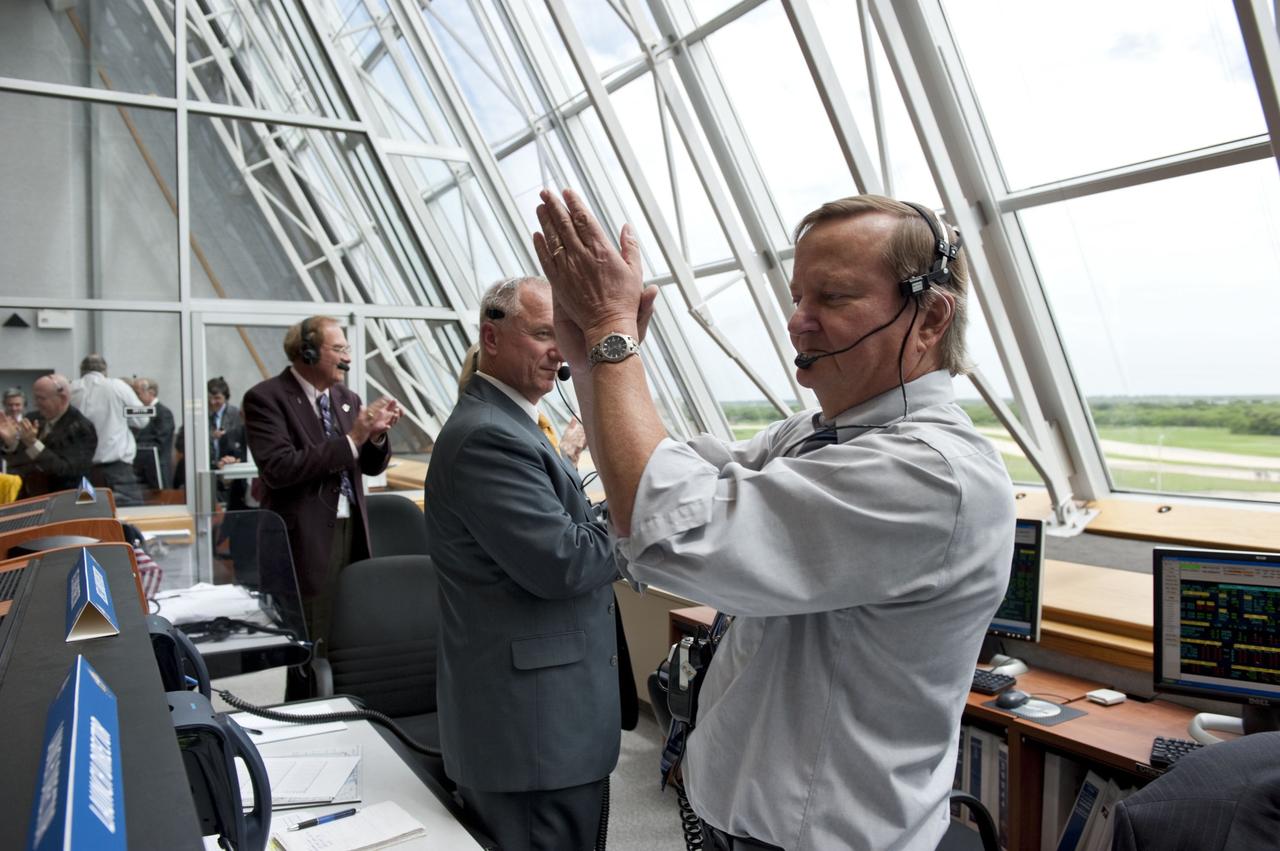

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach (right), Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko and NASA Commentator and Public Affairs Officer George Diller applaud the successful launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
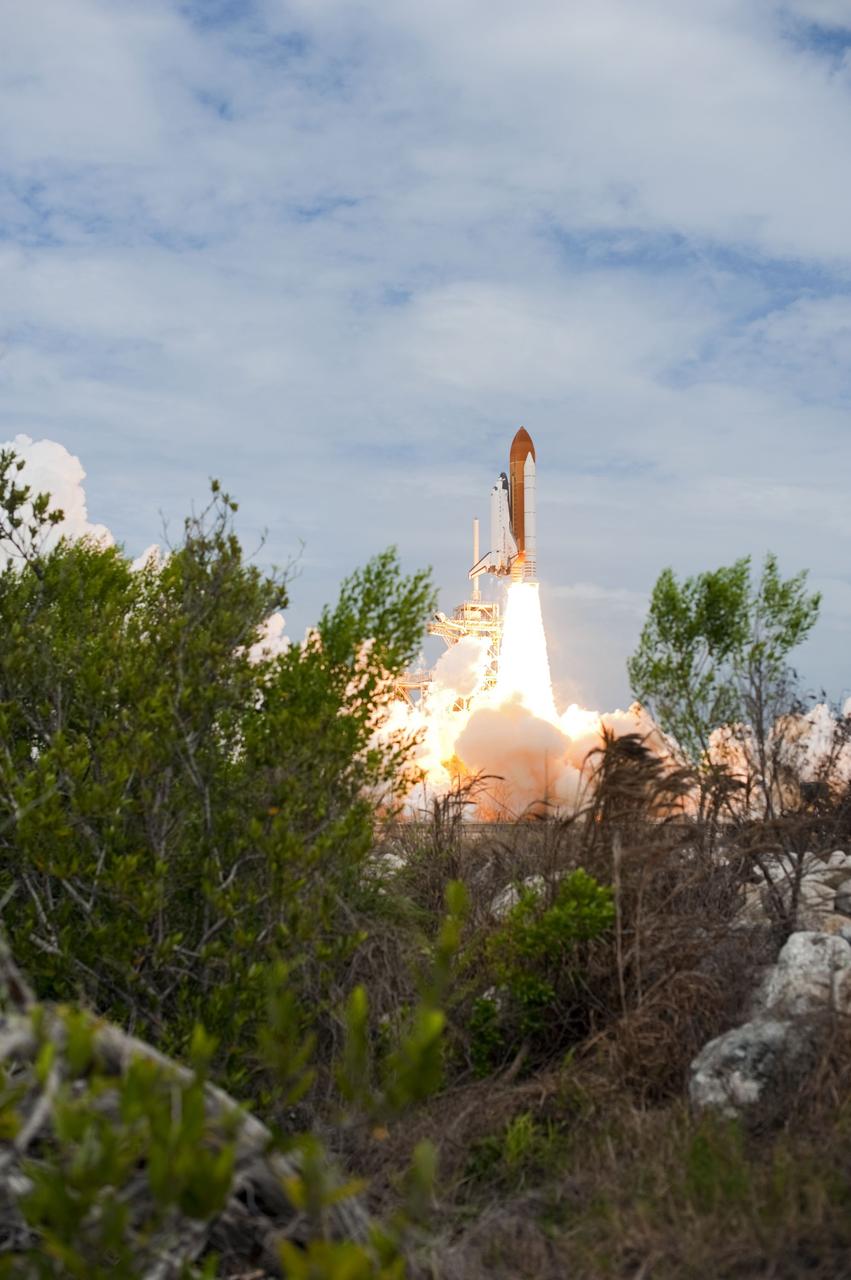

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis lifts off of Launch Pad 39A leaving behind a billow of steam and smoke as it heads upwards past the tower on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis' main engines and solid rocket boosters ignite on Launch Pad 39A producing billows of steam and smoke as it lifts off on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
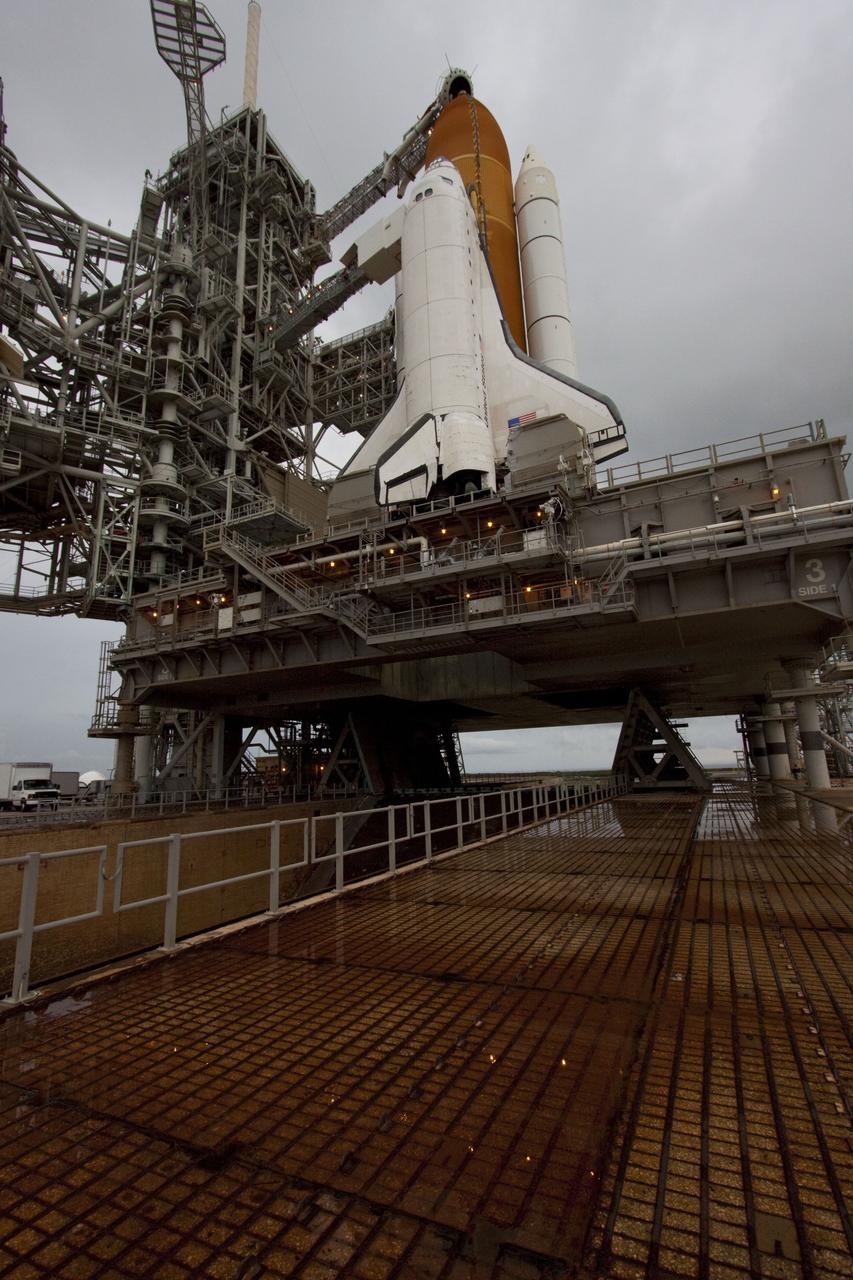

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is revealed on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the move of the rotating service structure (RSS). The structure provides weather protection and access to the shuttle while it awaits liftoff on the pad. RSS "rollback" marks a major milestone in Atlantis' STS-135 mission countdown. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
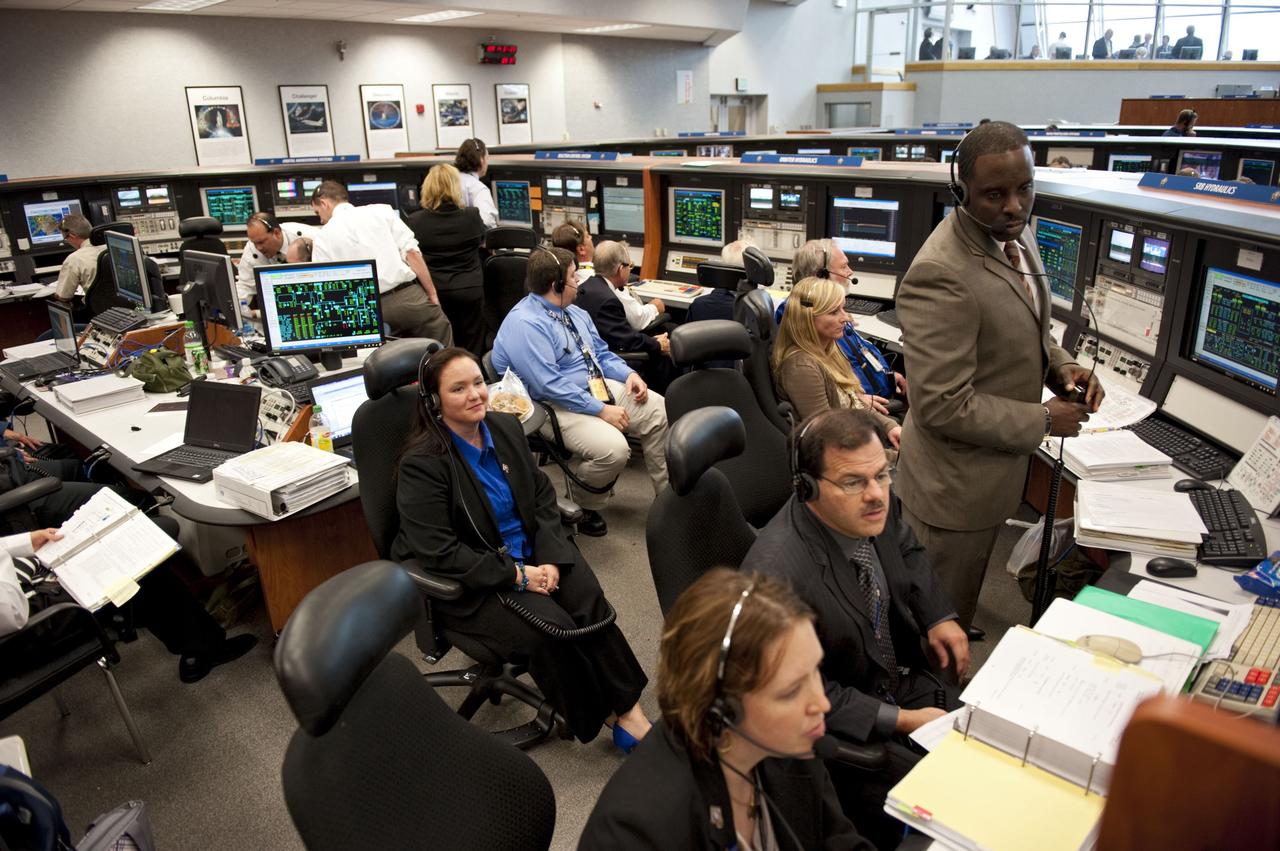

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
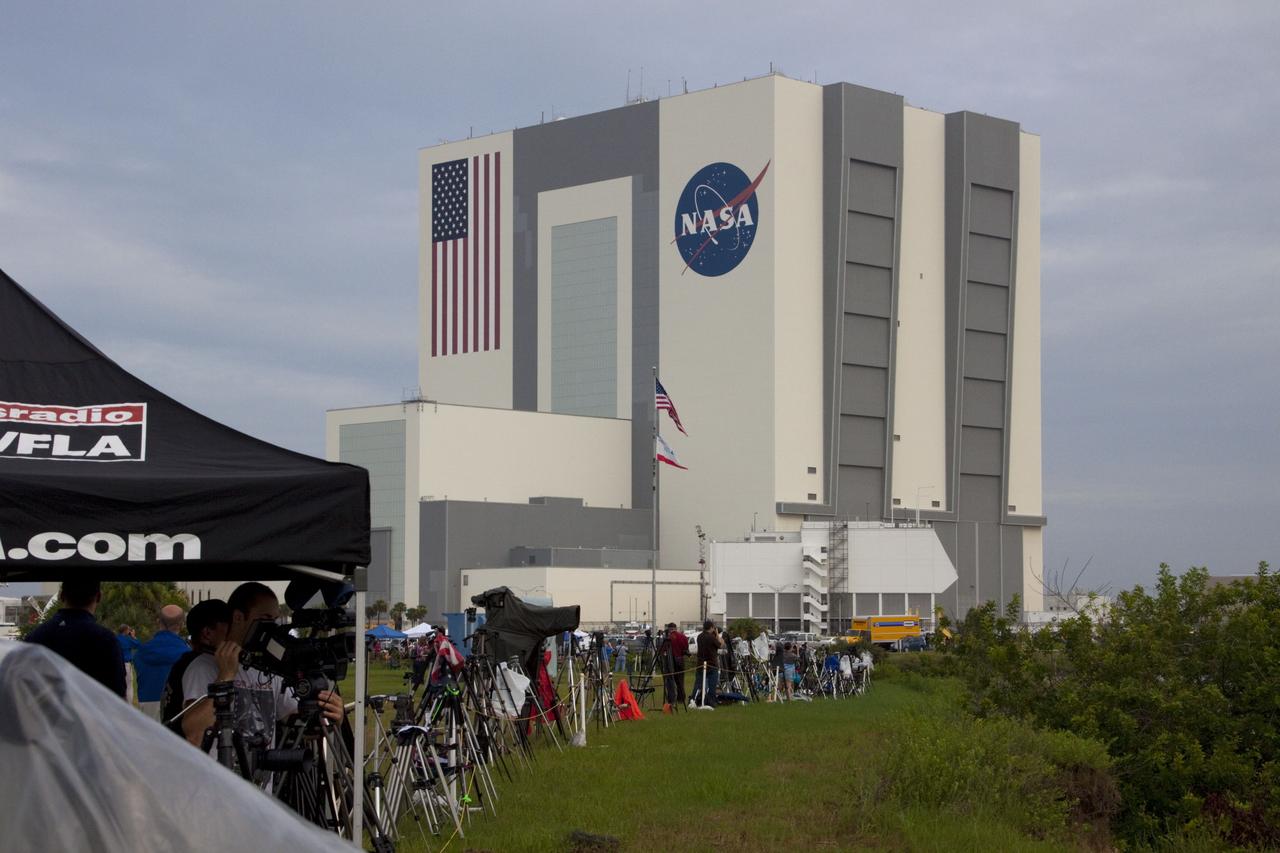

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen towering above is the massive Vehicle Assembly Building. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
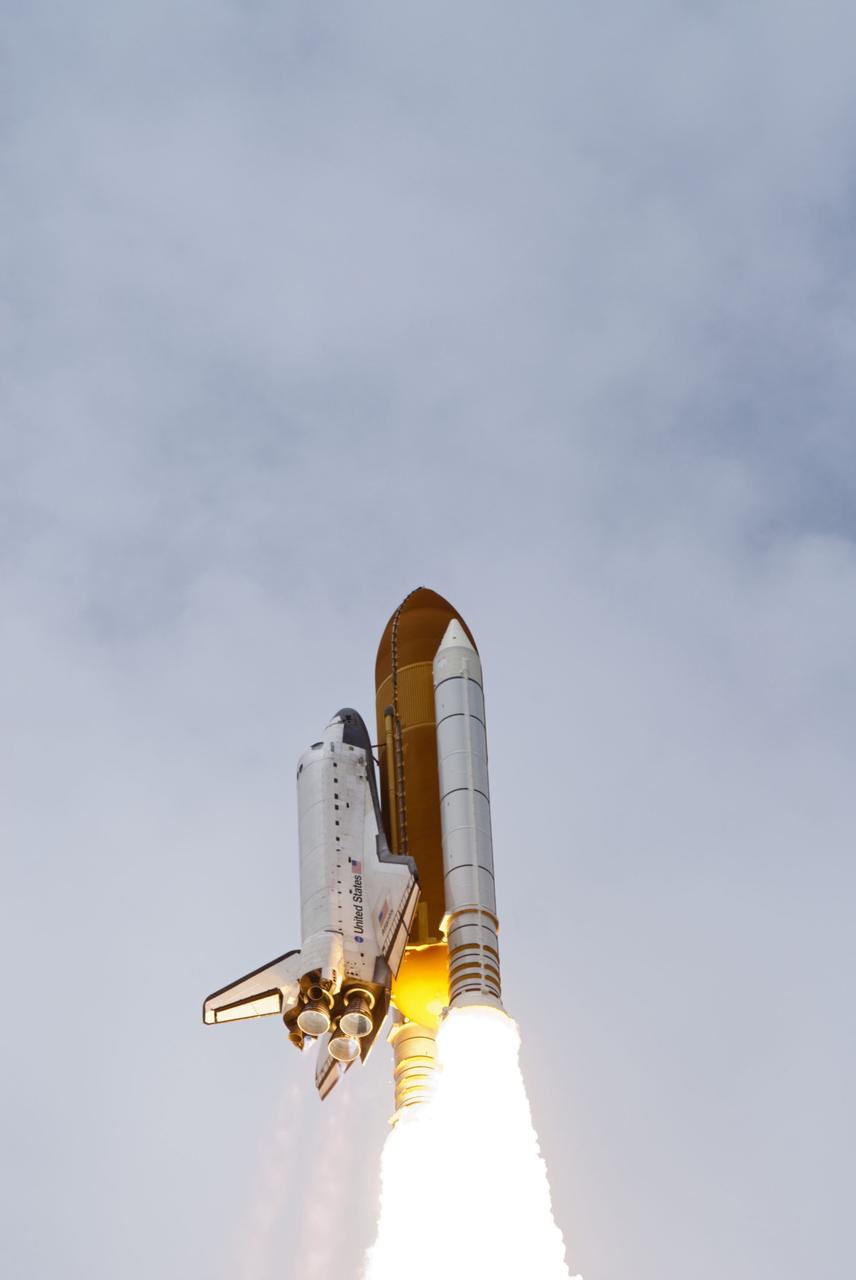

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis soars into the clouds on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer and Mike Gayle
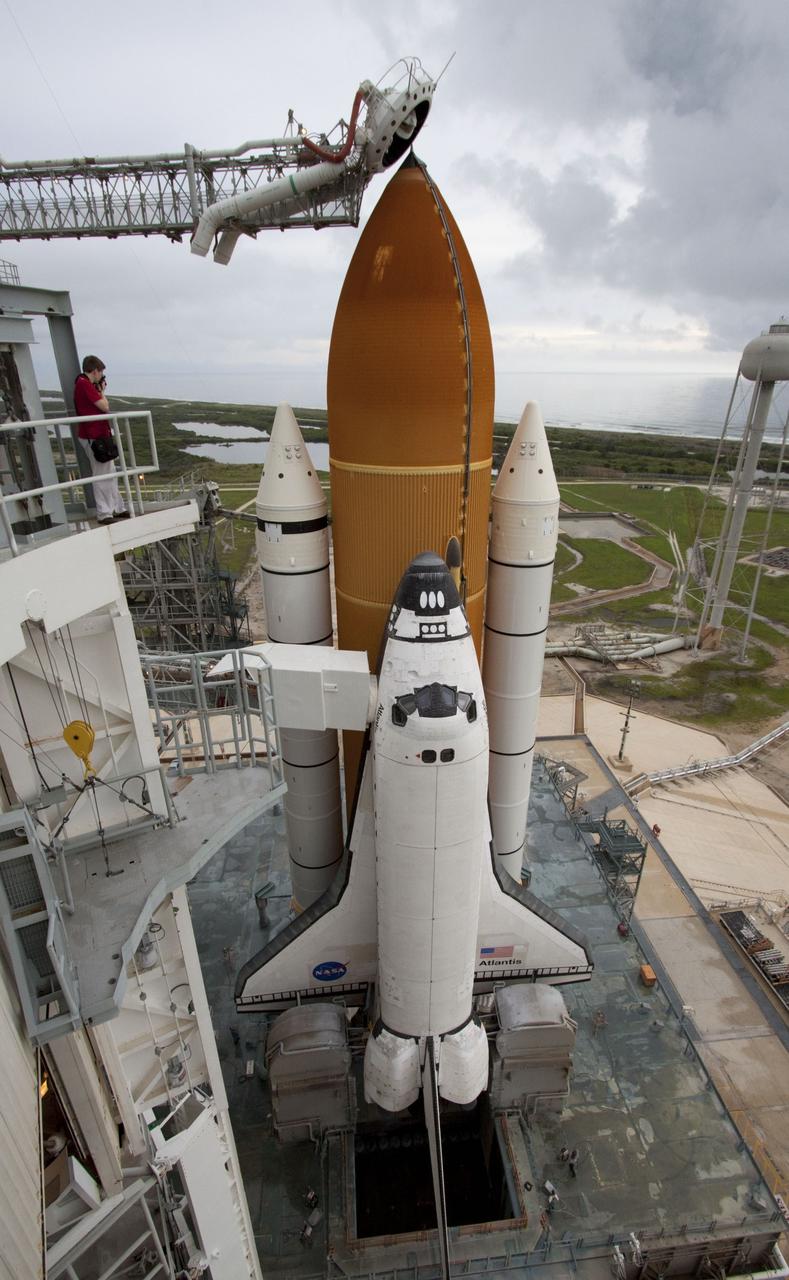

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is revealed on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the move of the rotating service structure (RSS). The structure provides weather protection and access to the shuttle while it awaits liftoff on the pad. RSS "rollback" marks a major milestone in Atlantis' STS-135 mission countdown. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
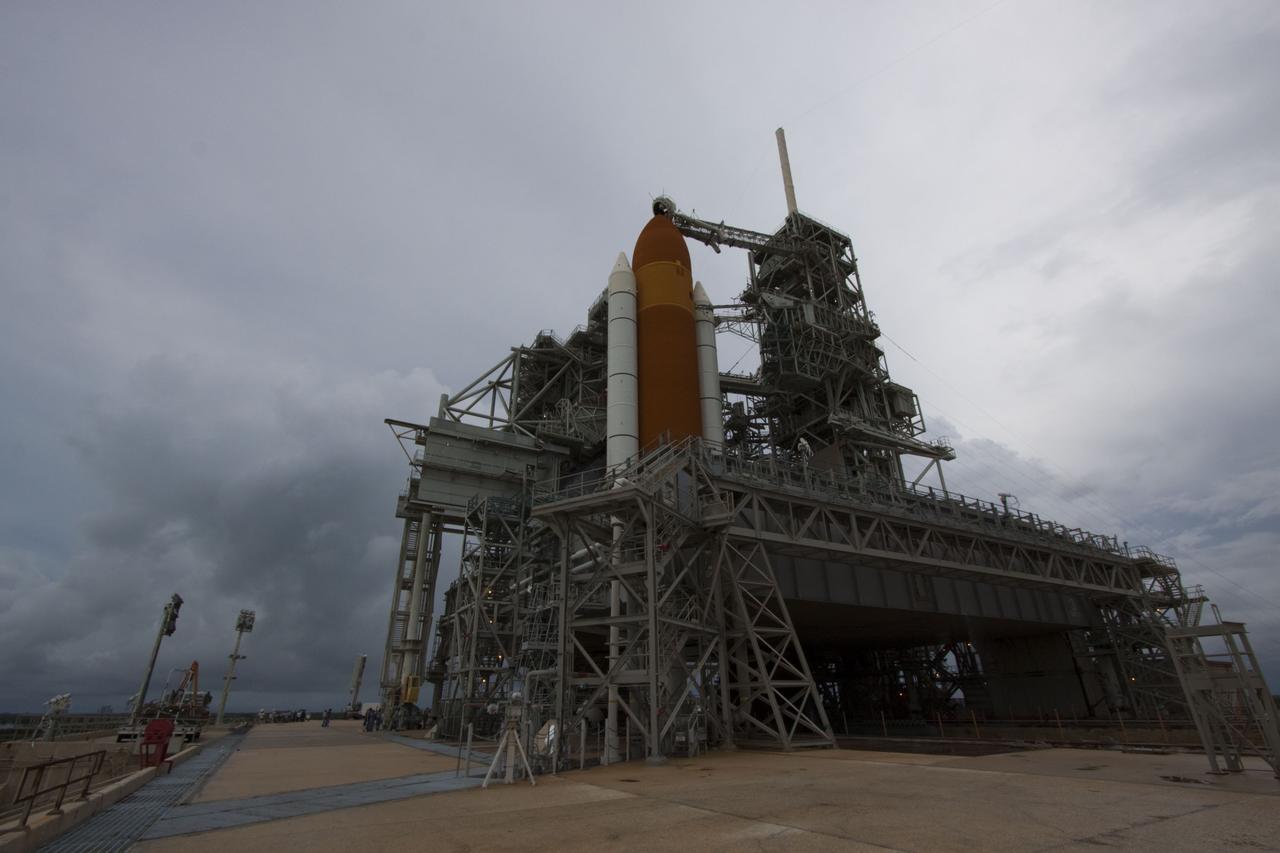

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On a cloudy and overcast day on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers prepare to roll the rotating service structure (RSS) away from space shuttle Atlantis. The RSS provides weather protection and access to the shuttle while it awaits liftoff. RSS "rollback" marks a major milestone in Atlantis' STS-135 mission countdown. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
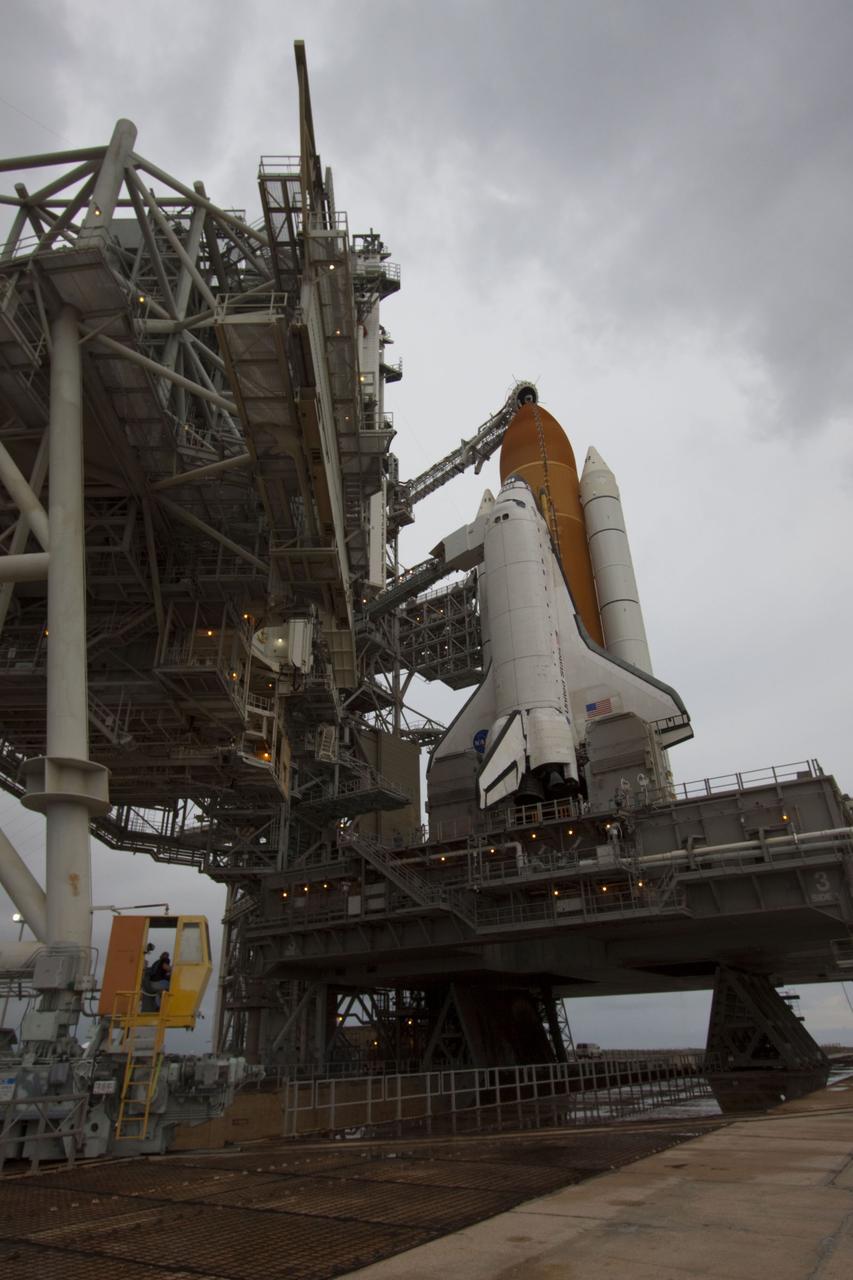

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A worker in a control booth on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida monitors the progress of the rotating service structure (RSS) as it is rolled back revealing space shuttle Atlantis. The structure provides weather protection and access to the shuttle while it awaits liftoff on the pad. RSS "rollback" marks a major milestone in Atlantis' STS-135 mission countdown. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
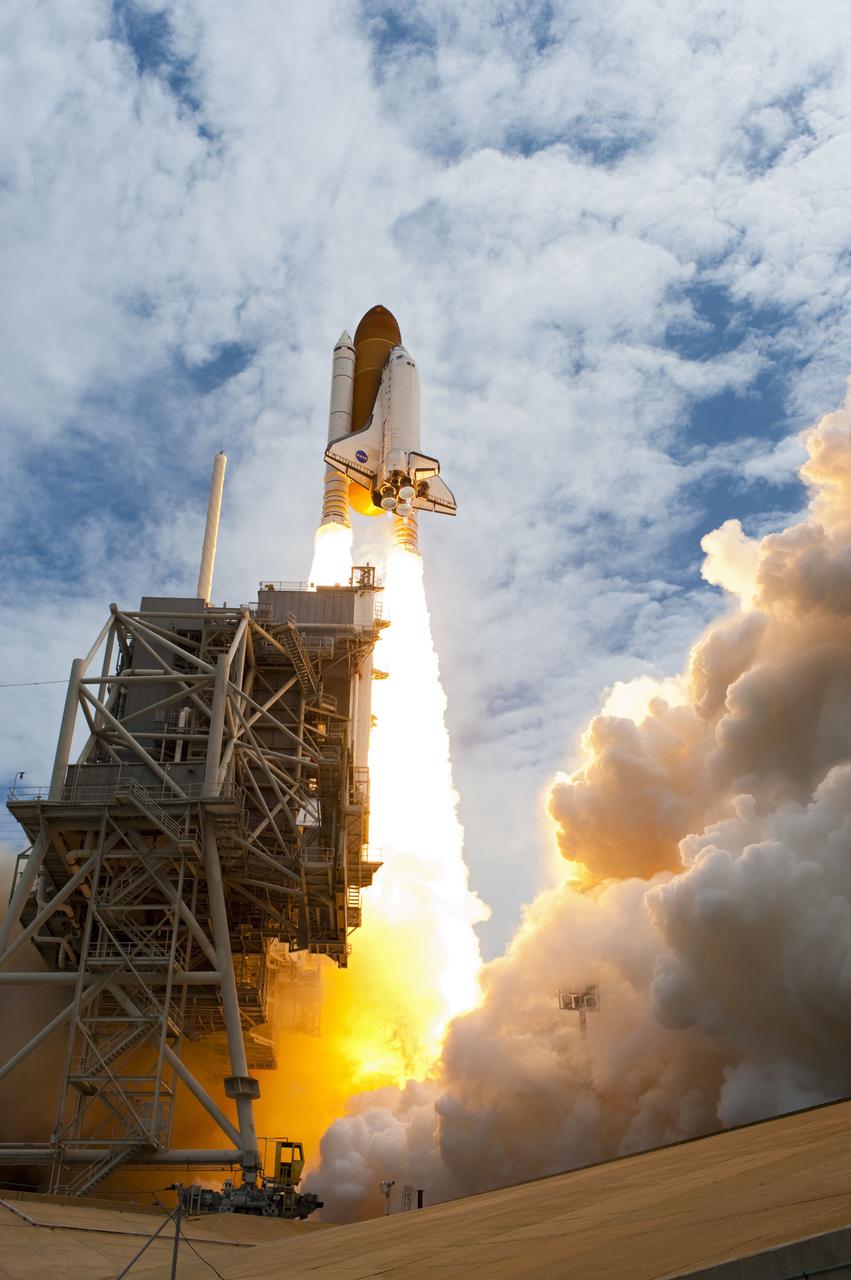

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis' main engines and solid rocket boosters ignite on Launch Pad 39A leaving behind a billow of steam and smoke as it lifts off past the tower on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
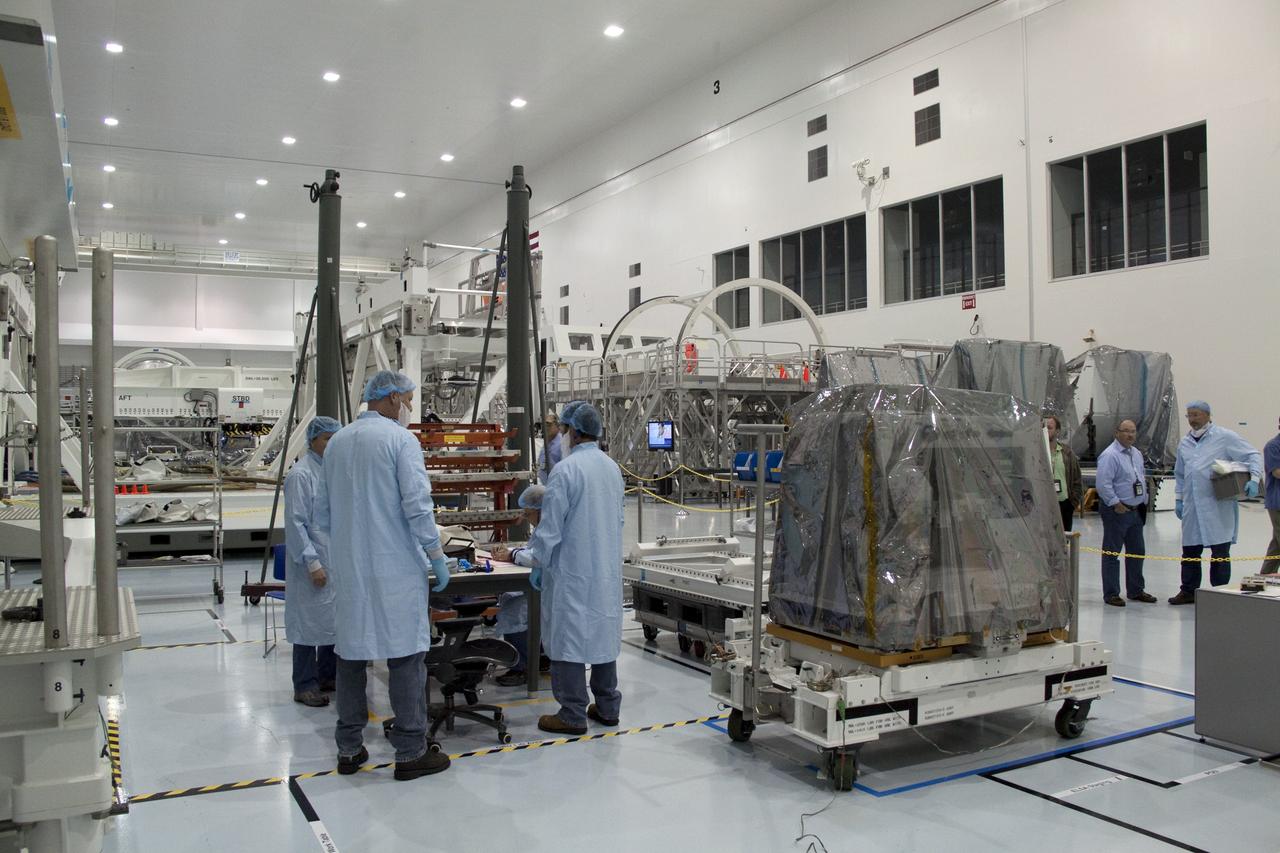

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians move a system that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft in orbit from a processing lab to a high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The move prepares the system for its lift into the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC), which will carry it into orbit. Called the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM), the system will be processed to fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Also going up will be the Raffaello multipurpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The mission also will return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135, targeted to launch June 28, will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
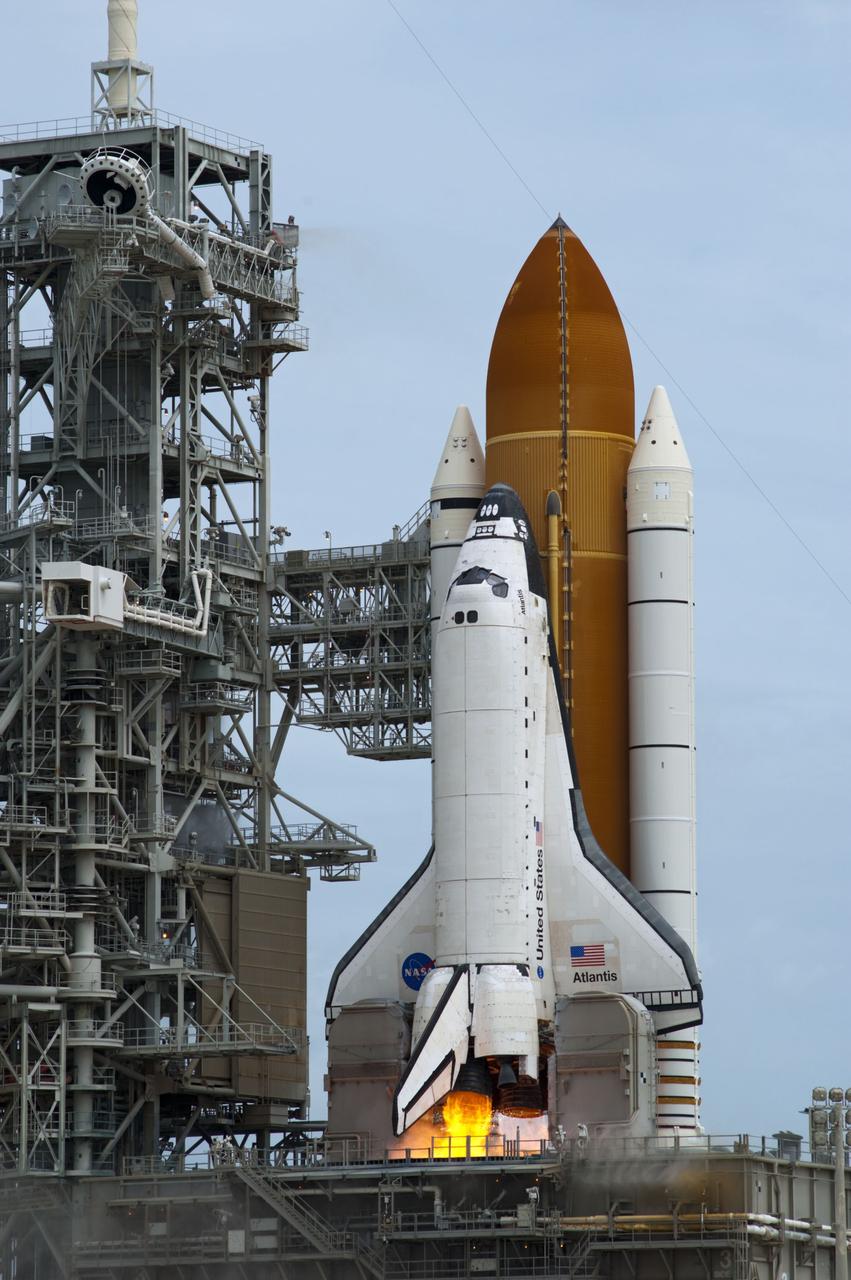

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis' main engines ignite on Launch Pad 39A as it lifts off on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
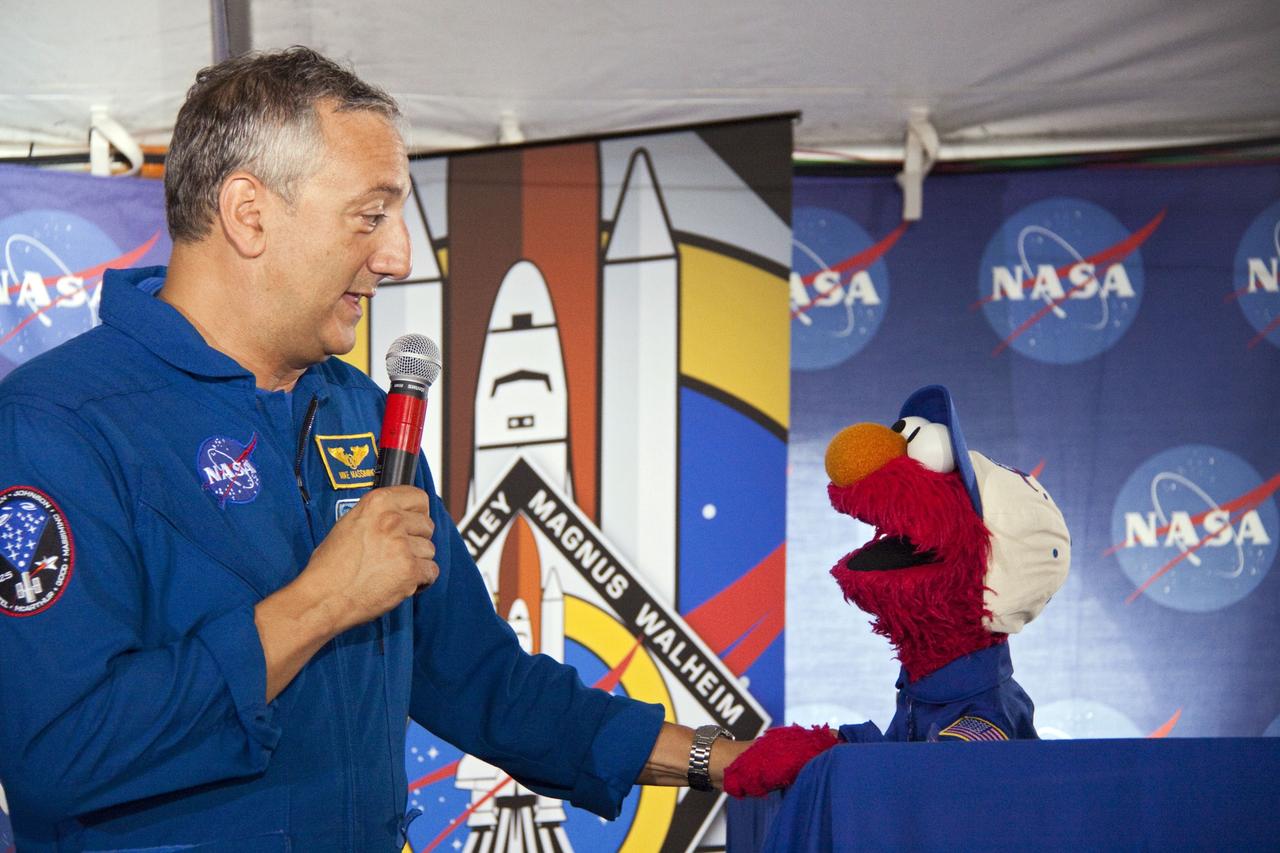

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA is hosting a Tweetup for 150 Twitter followers of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station, selected from more than 5,500 online registrants. A Tweetup is an informal meeting of people who use the social messaging medium Twitter. Here, NASA astronaut Mike Massimino talks with Sesame Street's Elmo. Sesame Street also is at Kennedy to film Elmo, as he learns about space exploration at NASA. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here is Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
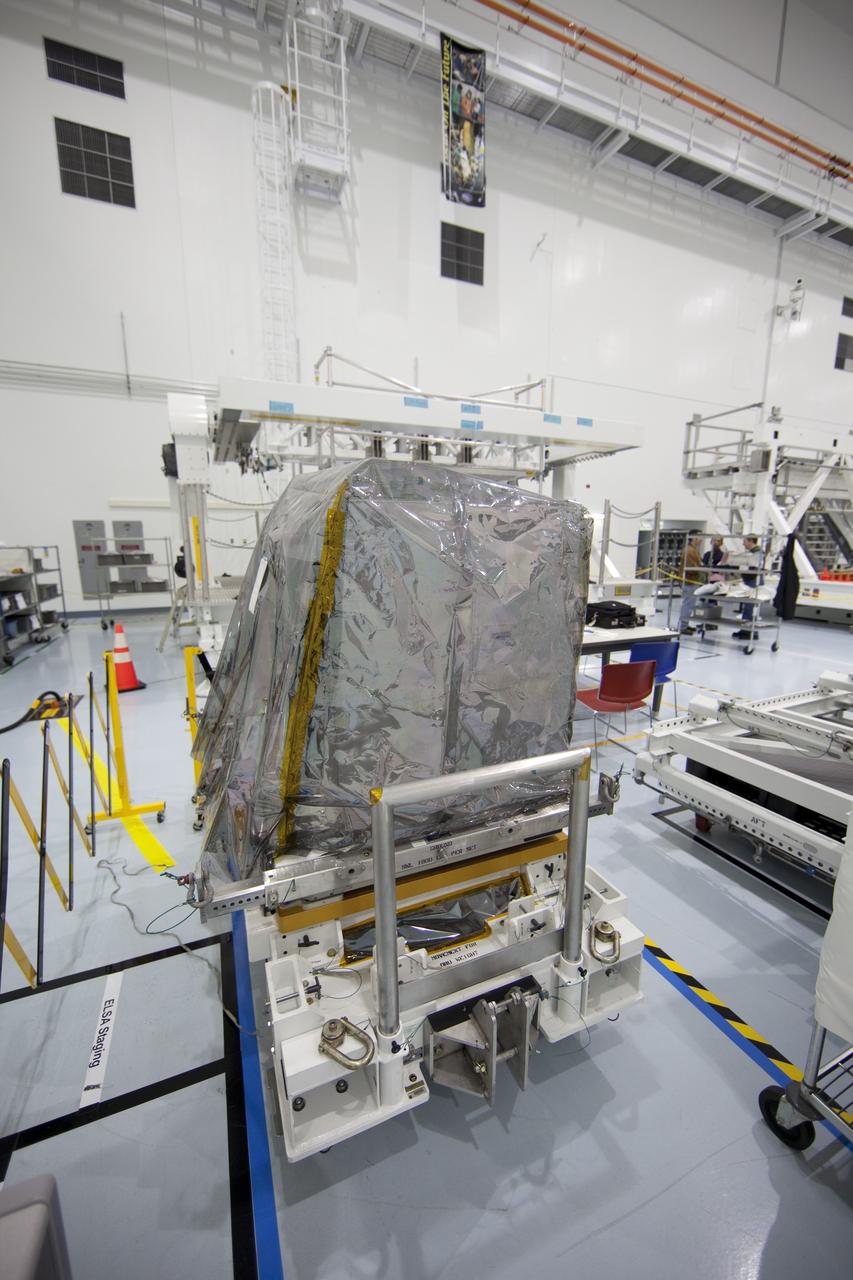

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a system that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft in orbit will be moved into the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC). Called the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM), the system is being processed to fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis in the LMC on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Also going up will be the Raffaello multipurpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The mission also will return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135, targeted to launch June 28, will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
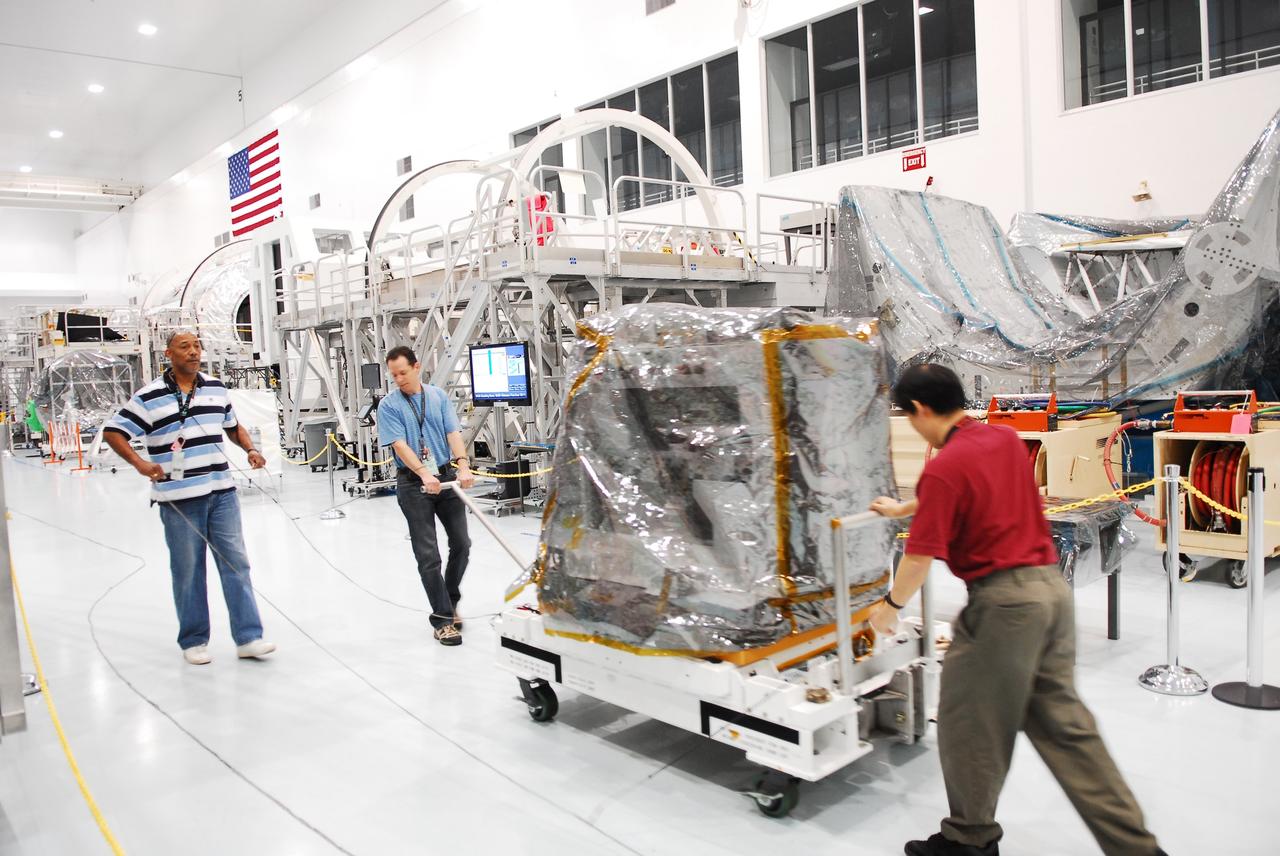

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians transport a system that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft in orbit to a low bay test cell in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Called the Robotic Refueling Mission RRM, the system will be processed to fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis and its STS-135 crew are scheduled to carry the Raffaello multipurpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the space station. The mission also will return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135, targeted to launch June 28, will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather in their respective tents at the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
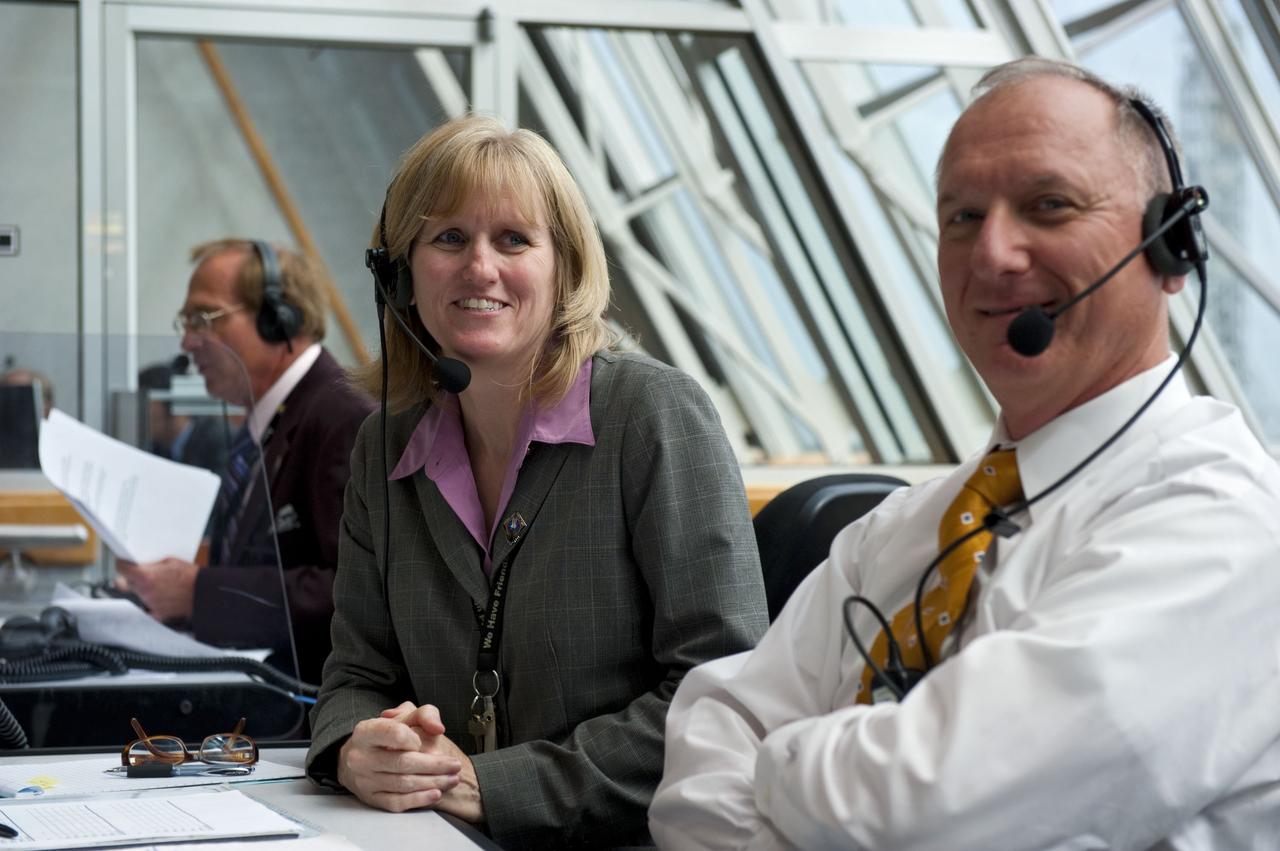

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here are Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko (right), Atlantis NASA Flow Director Angie Brewer and NASA Commentator and Public Affairs Officer George Diller. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
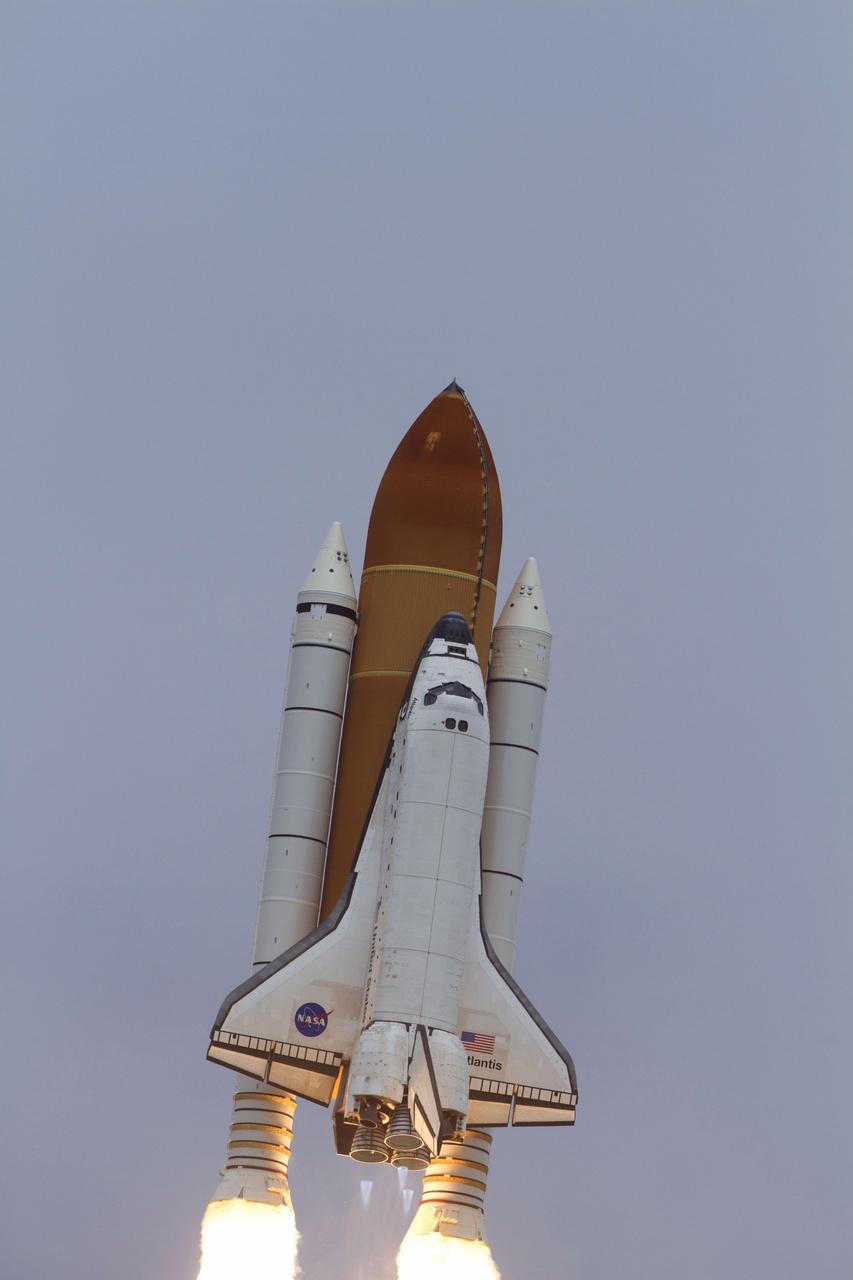

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space shuttle Atlantis makes its last reach for the sky, rising above Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to begin the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis, with its crew of Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kenny Allen and George Roberts
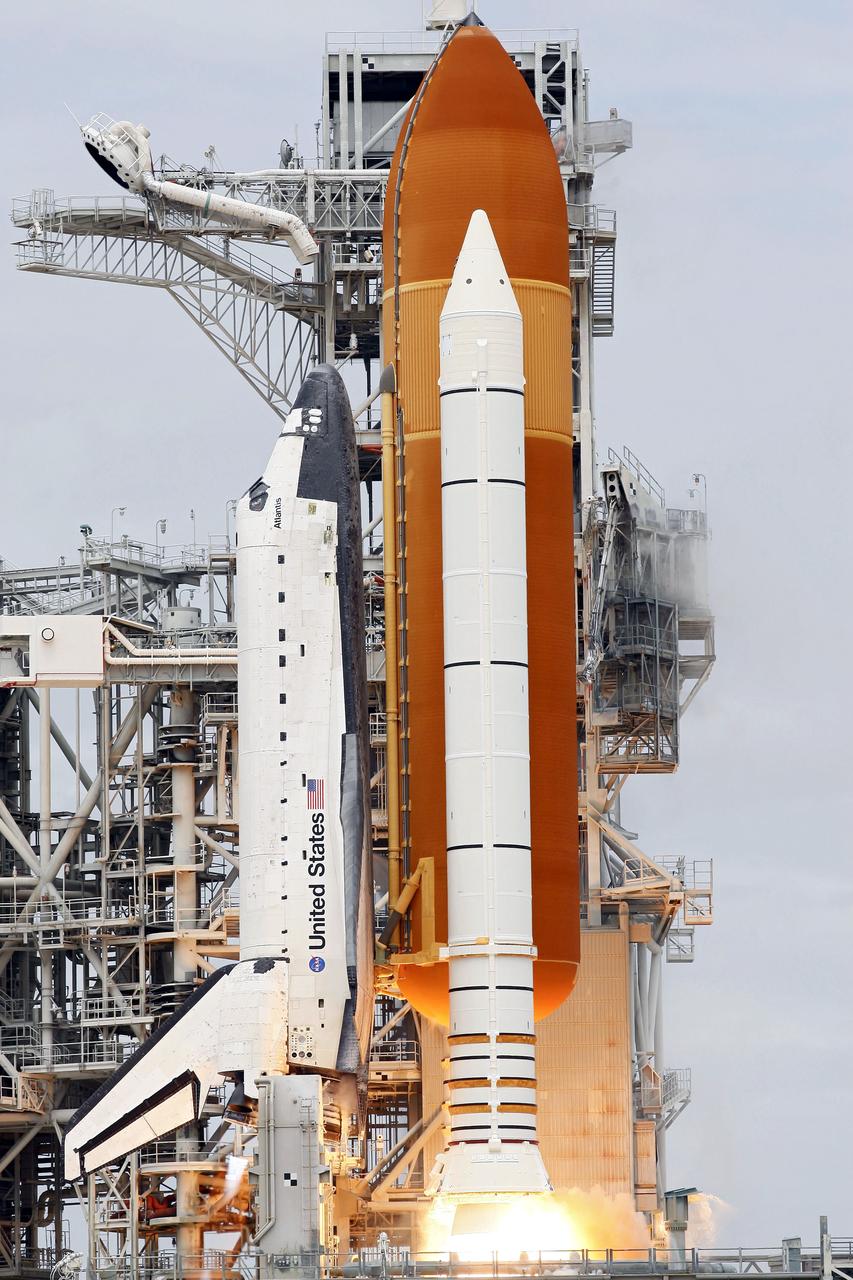

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis' main engines ignite and solid rocket boosters ignite on Launch Pad 39A leaving behind a twin stream of flame as it lifts off on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer and Mike Gayle
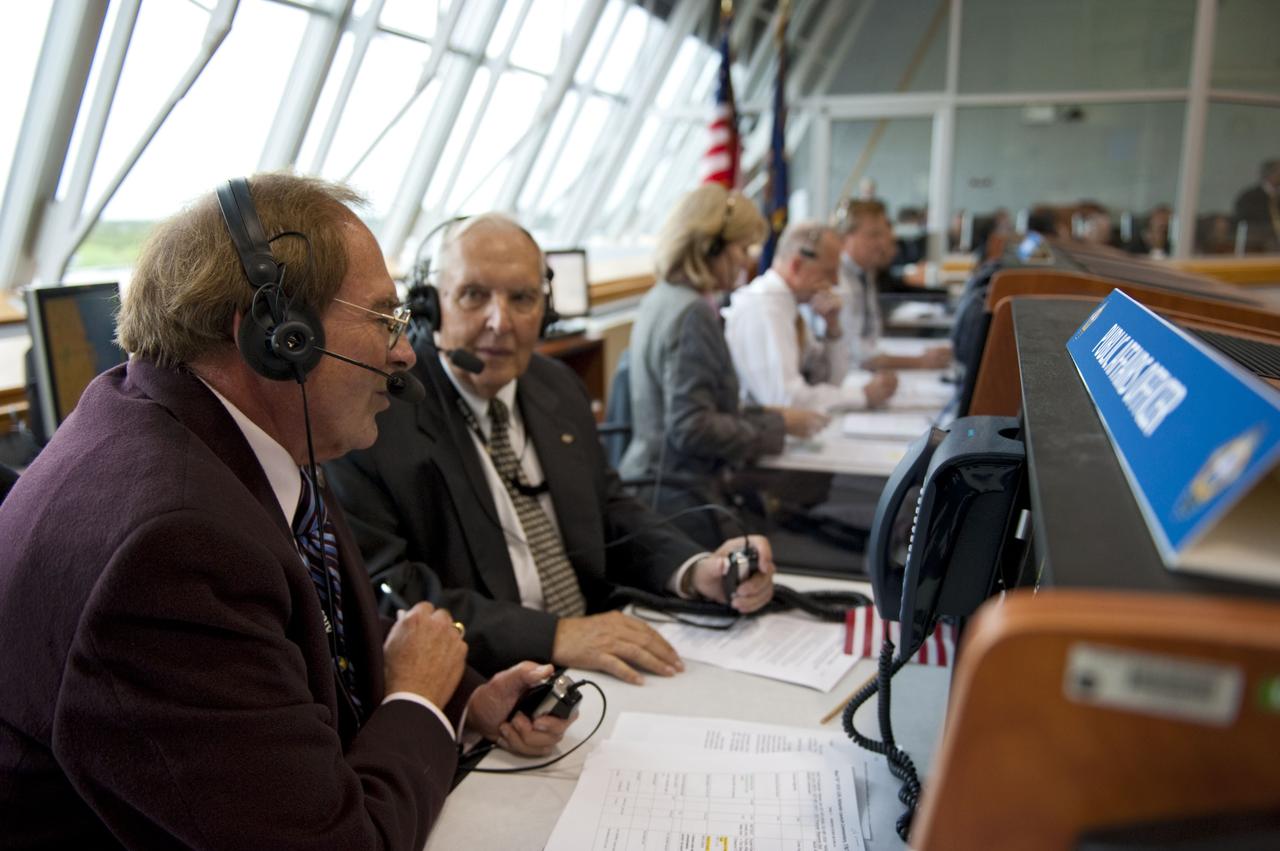

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Launch Commentator and Public Affairs Officer George Diller interviews former Kennedy Director of Public Affairs Hugh Harris during prelaunch activities before liftoff of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
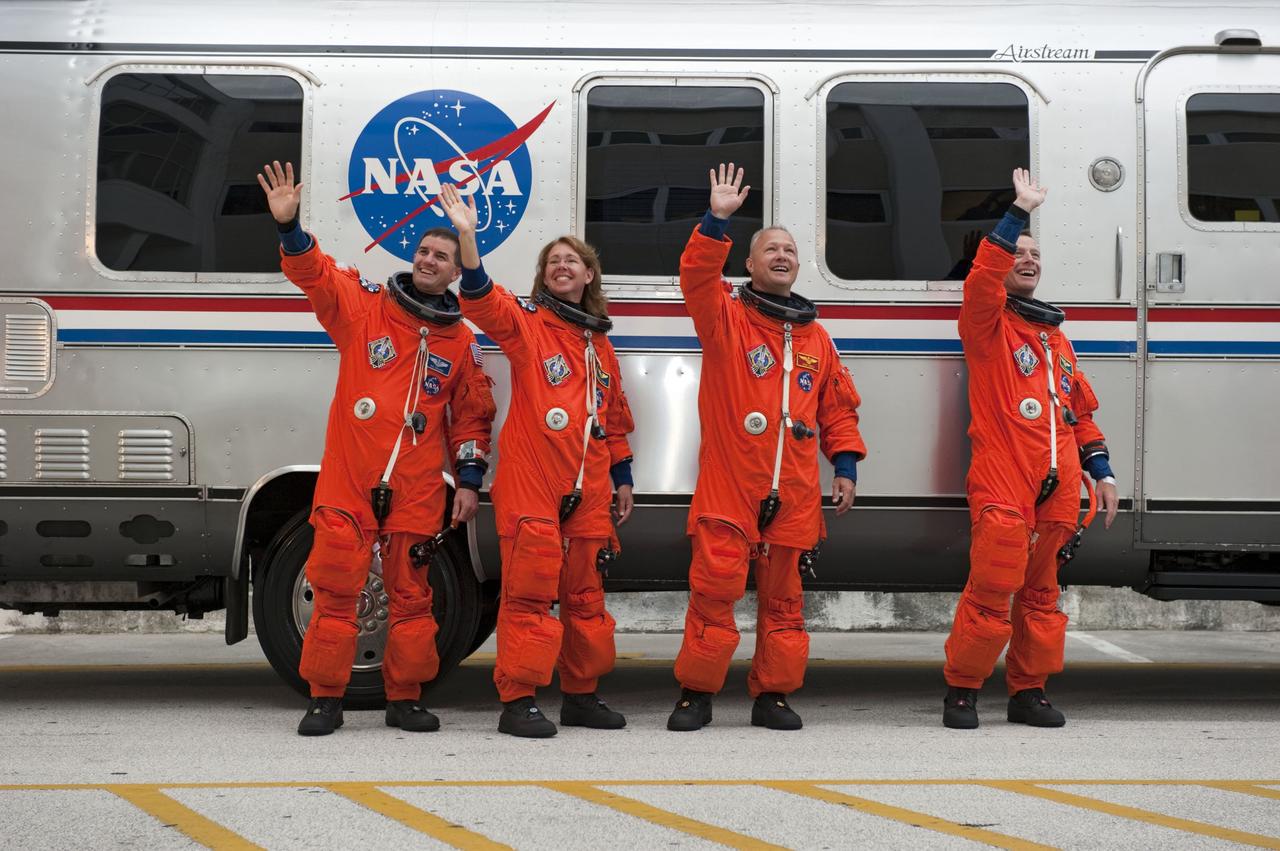

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dressed in their bright-orange launch-and-entry suits, the final four astronauts to launch aboard a space shuttle wave to media and employees cheering them on in front of the Astronaut Crew Quarters in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left, are STS-135 Mission Specialists Rex Walheim and Sandy Magnus, Pilot Doug Hurley, and Commander Chris Ferguson. The silver Astrovan will take the astronauts to Launch Pad 39A, where they will board space shuttle Atlantis for a scheduled liftoff at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 for their mission to the International Space Station. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the orbiting outpost. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
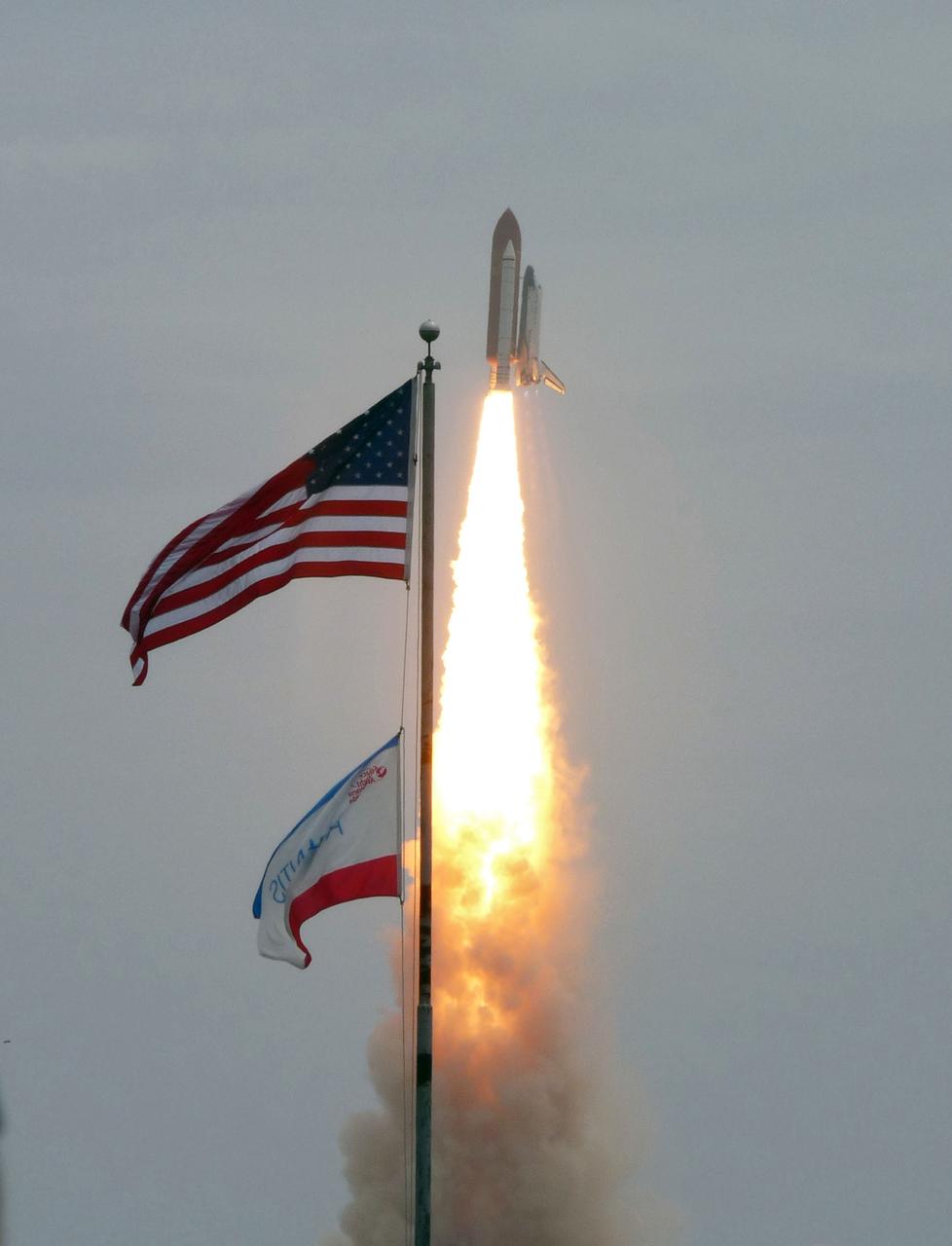

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- After 30 years and 135 missions, residents and visitors to Florida's Space Coast see this rocket's red glare for the last time as space shuttle Atlantis soars past the American flag after lifting off Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8. On board are four experienced astronauts -- STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Fletcher Hildreth

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis soars above its billowing exhaust from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/ Kenny Allen
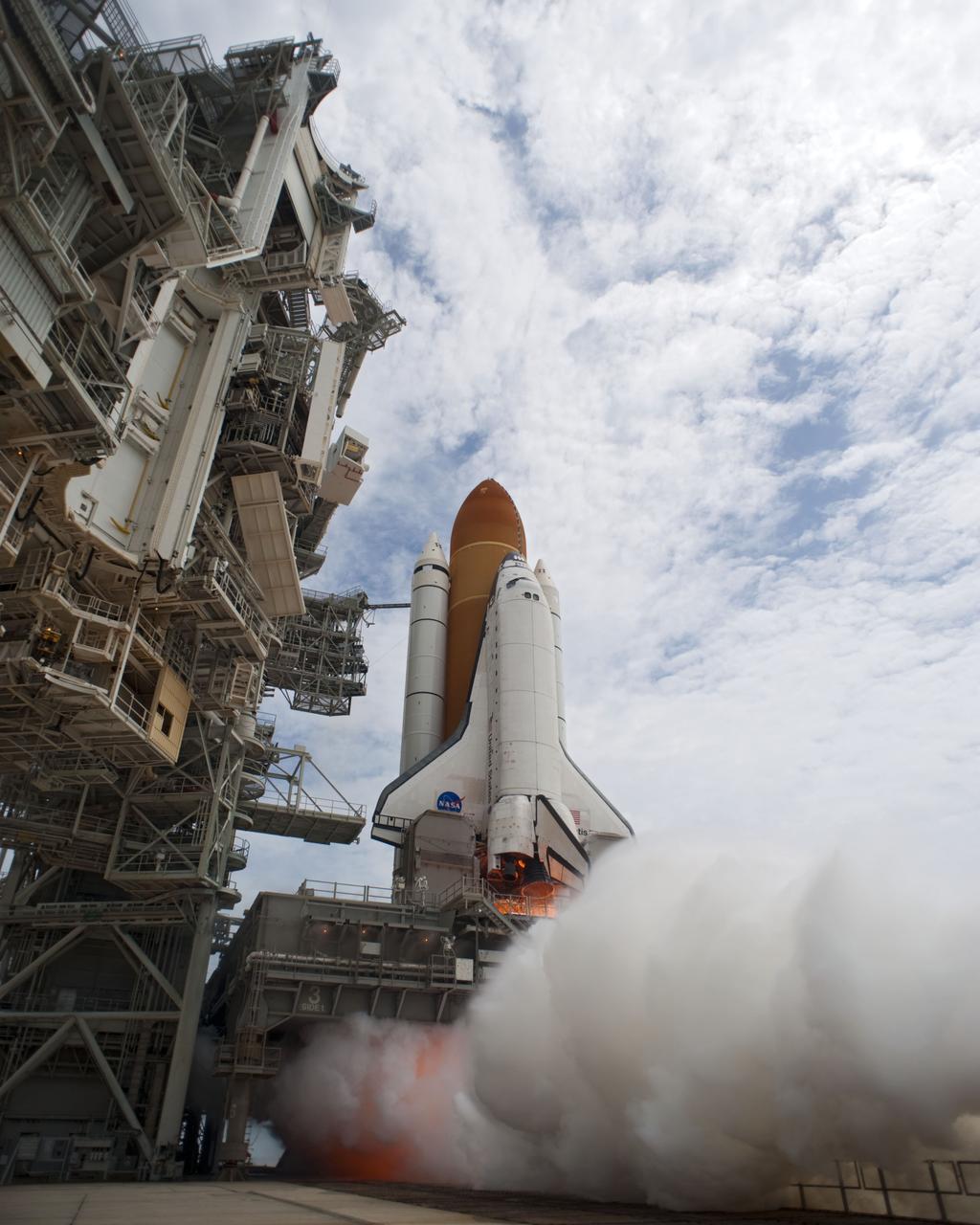

STS135-S-101 (8 July 2011) --- Smoke and steam begin to billow outward as space shuttle Atlantis' main engines are ignited for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida as it begins its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:29 a.m. (EDT) on July 8, 2011. Onboard are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, commander; Doug Hurley, pilot; Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, both mission specialists. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the space station. Atlantis also carries the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA
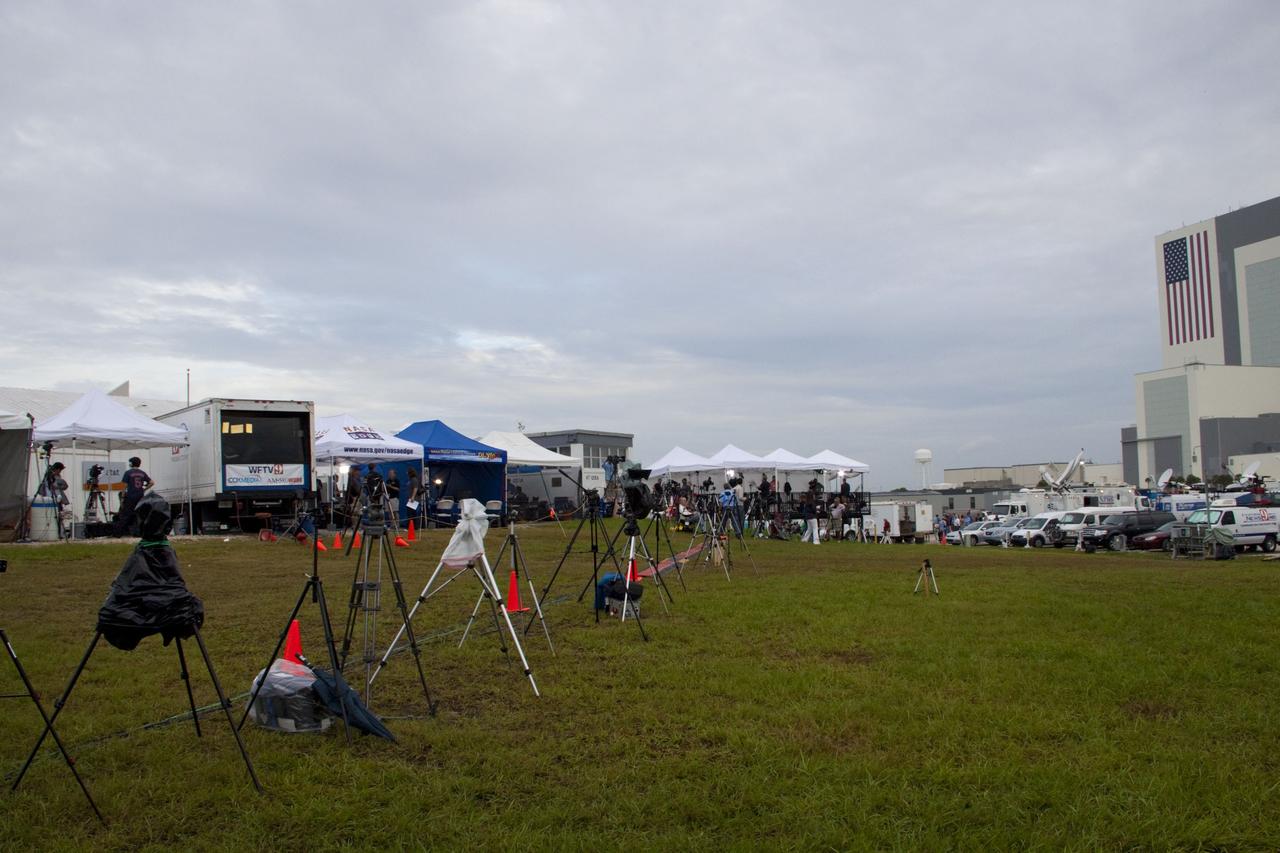

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
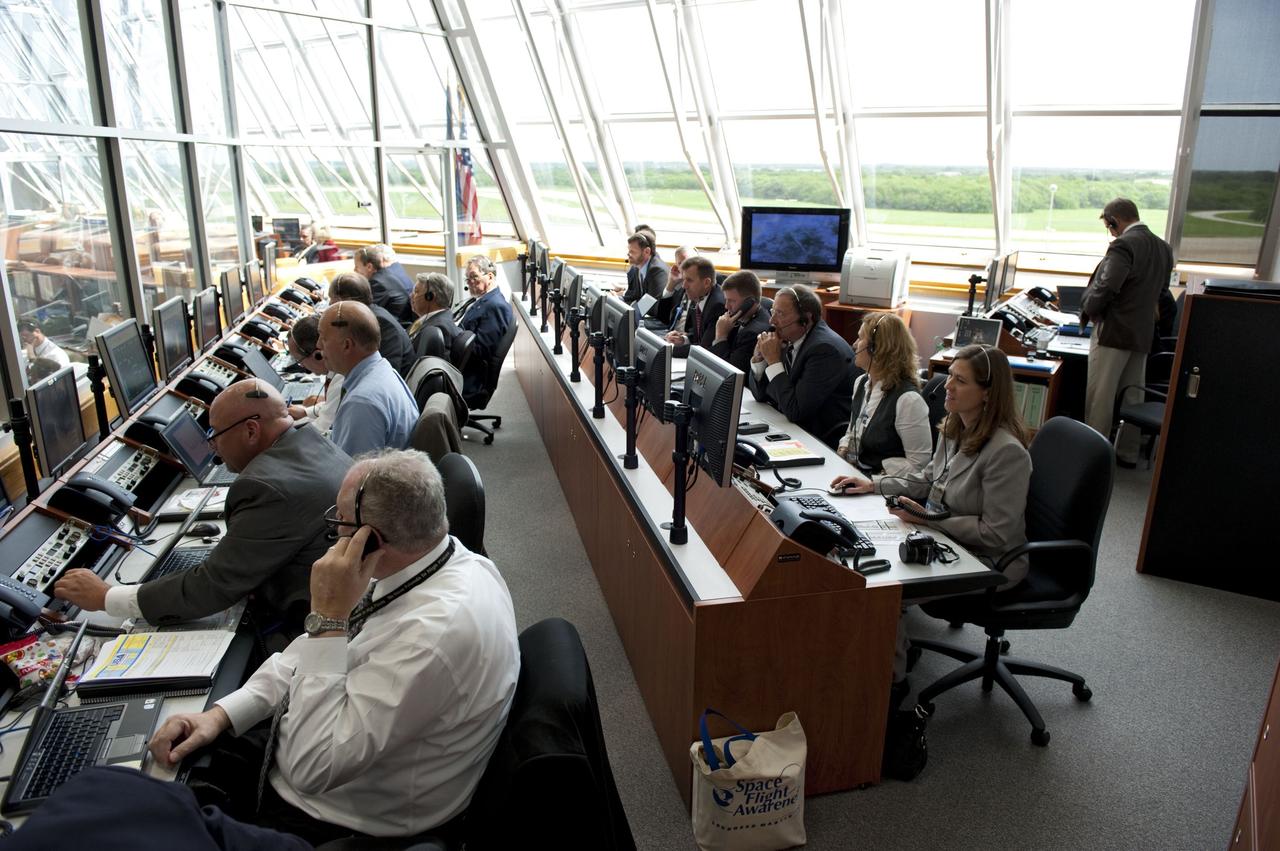

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
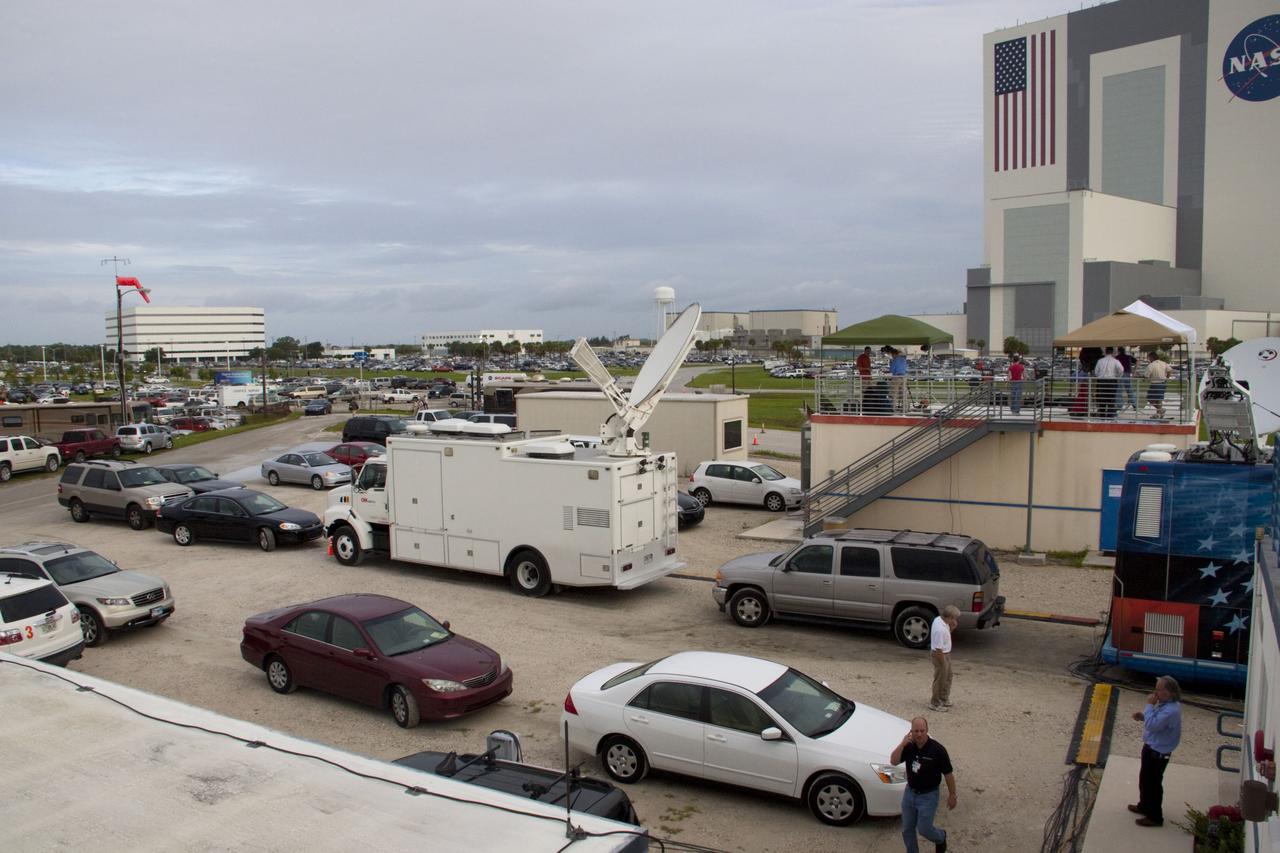

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen towering above is the massive Vehicle Assembly Building. Satellite news trucks, trailers and automobiles can be seen in the parking lot with the massive Vehicle Assembly Building towering above. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
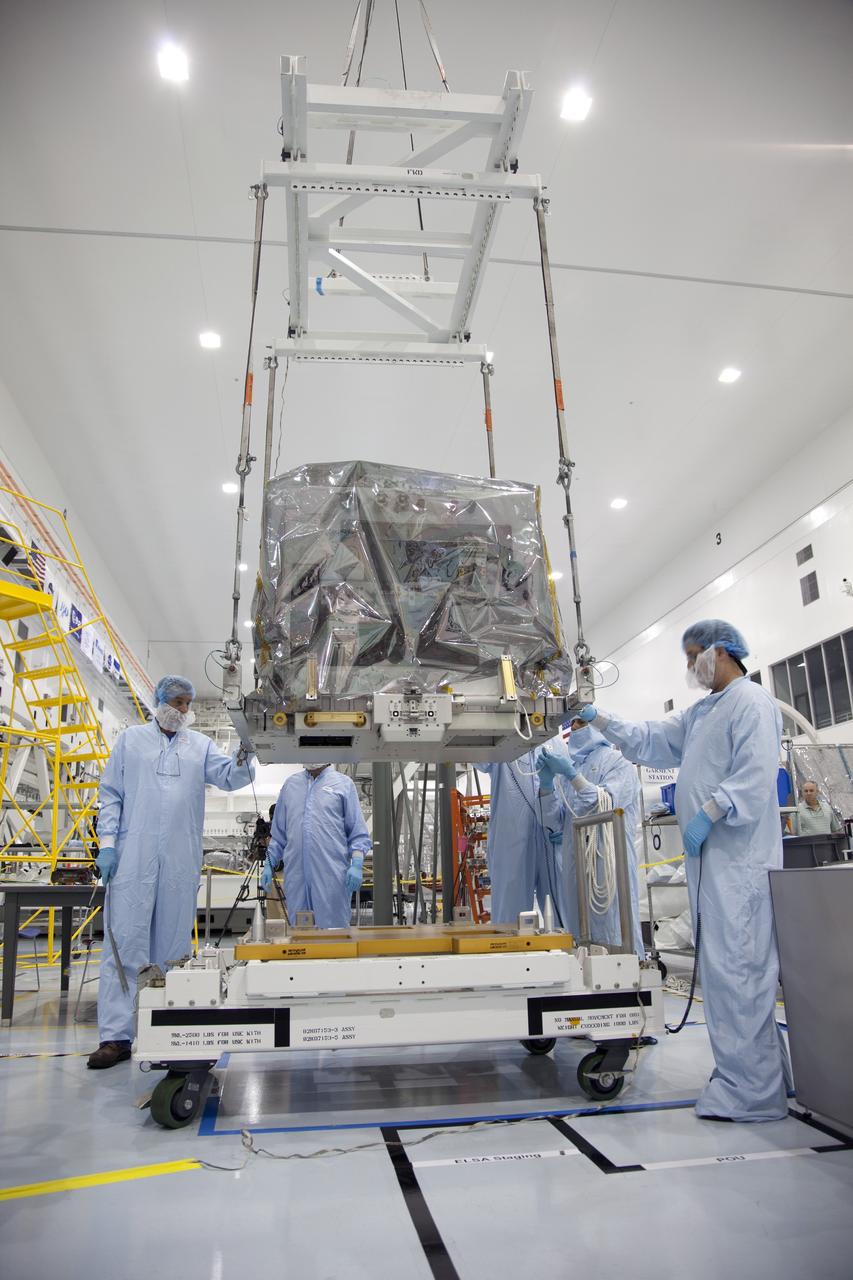

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin to move a system that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft in orbit into the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC). Called the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM), the system is being processed to fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis in the LMC on the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Also going up will be the Raffaello multipurpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The mission also will return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135, targeted to launch June 28, will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
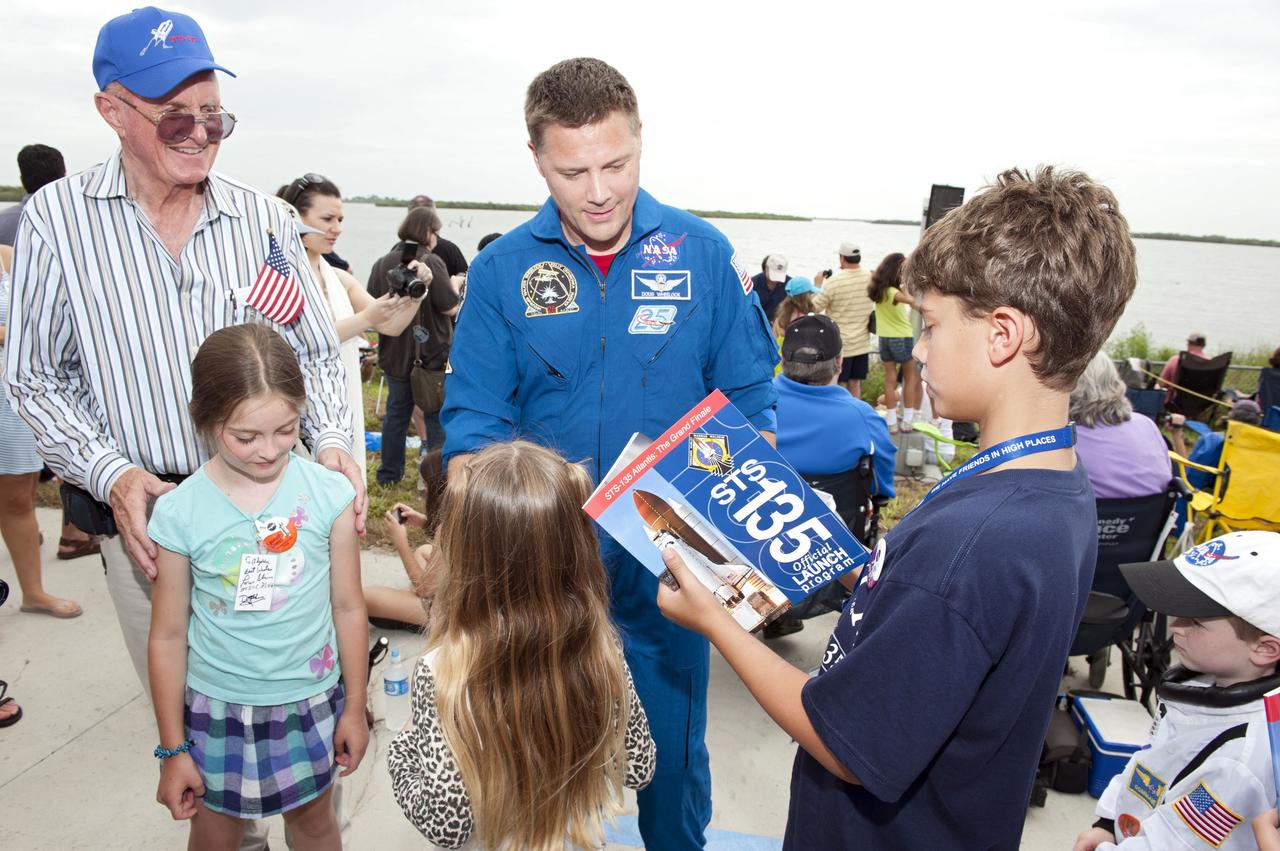

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Banana River Creek VIP viewing area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, youngsters delight in meeting NASA astronaut Doug Wheelock before the launch of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
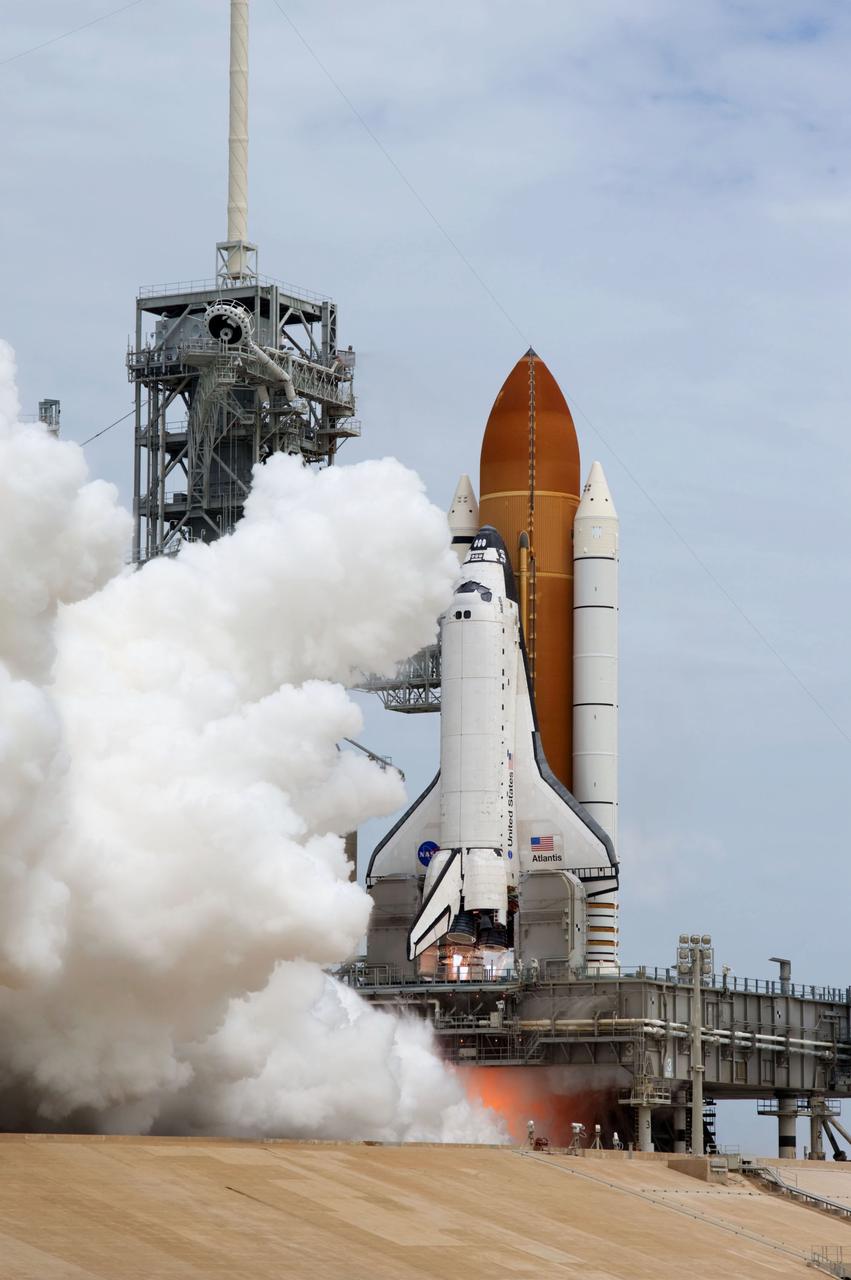

STS135-S-123 (8 July 2011) --- Smoke and steam billow outward as space shuttle Atlantis' main engines are ignited for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida as it begins its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 11:29 a.m. (EDT) on July 8, 2011. Onboard are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, commander; Doug Hurley, pilot; Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, both mission specialists. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the space station. Atlantis also carries the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA
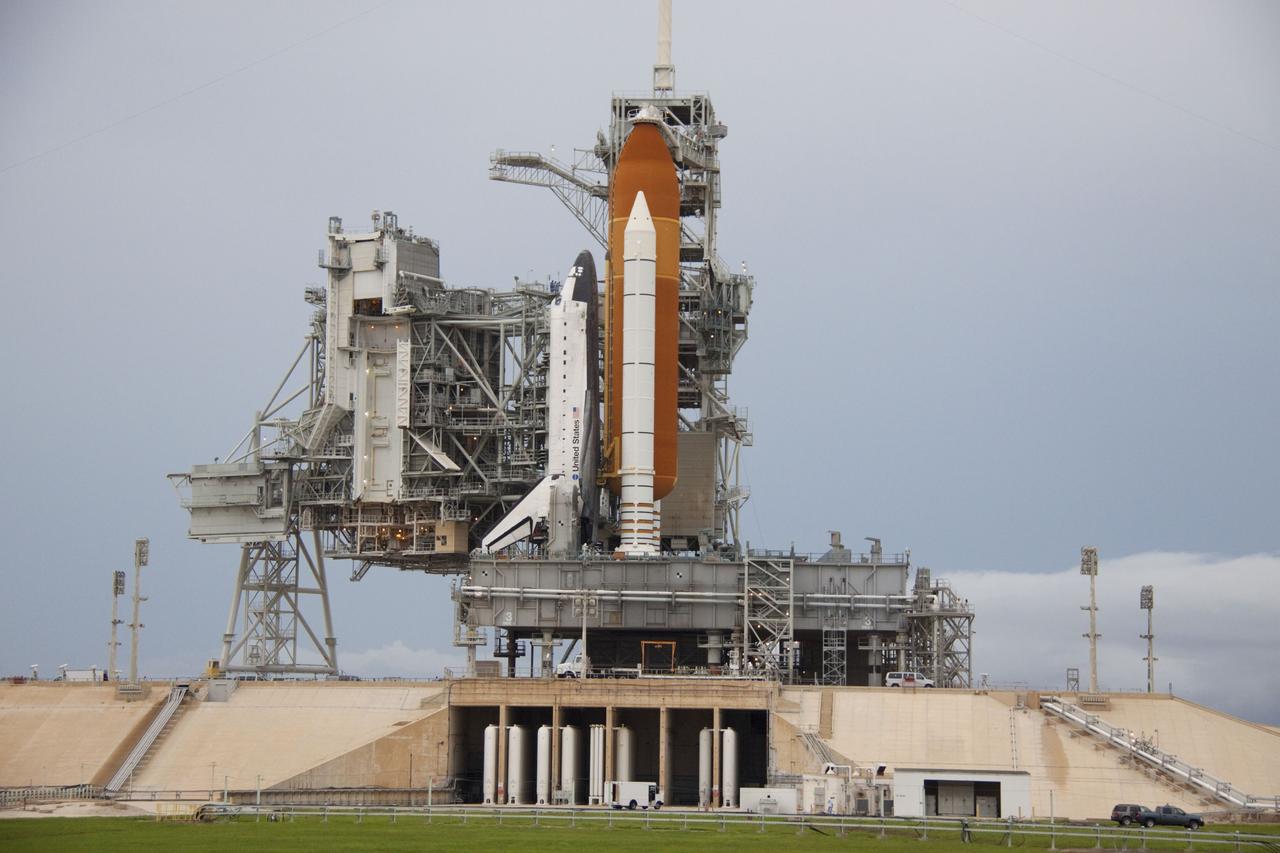

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is revealed on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the move of the rotating service structure (RSS). The structure provides weather protection and access to the shuttle while it awaits liftoff on the pad. RSS "rollback" marks a major milestone in Atlantis' STS-135 mission countdown. Atlantis and its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, are scheduled to lift off at 11:26 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
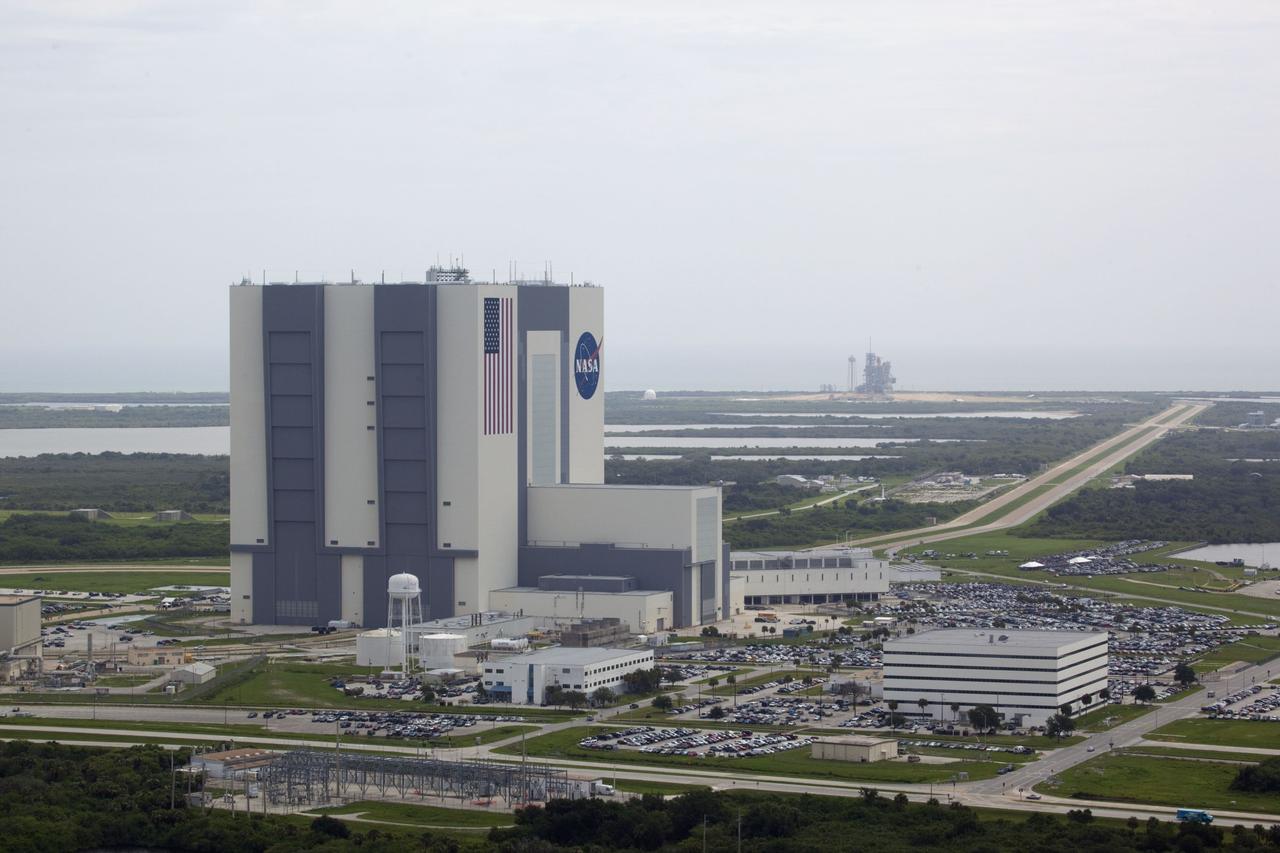

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- After 30 years and 135 missions, employees and invited guests crowd the Launch Complex 39 area of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to see the rocket's red glare of NASA's Space Shuttle Program soar for the last time. Space shuttle Atlantis is scheduled to liftoff at 11:26 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A. On board will be four experienced astronauts -- STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim. STS-135 will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux