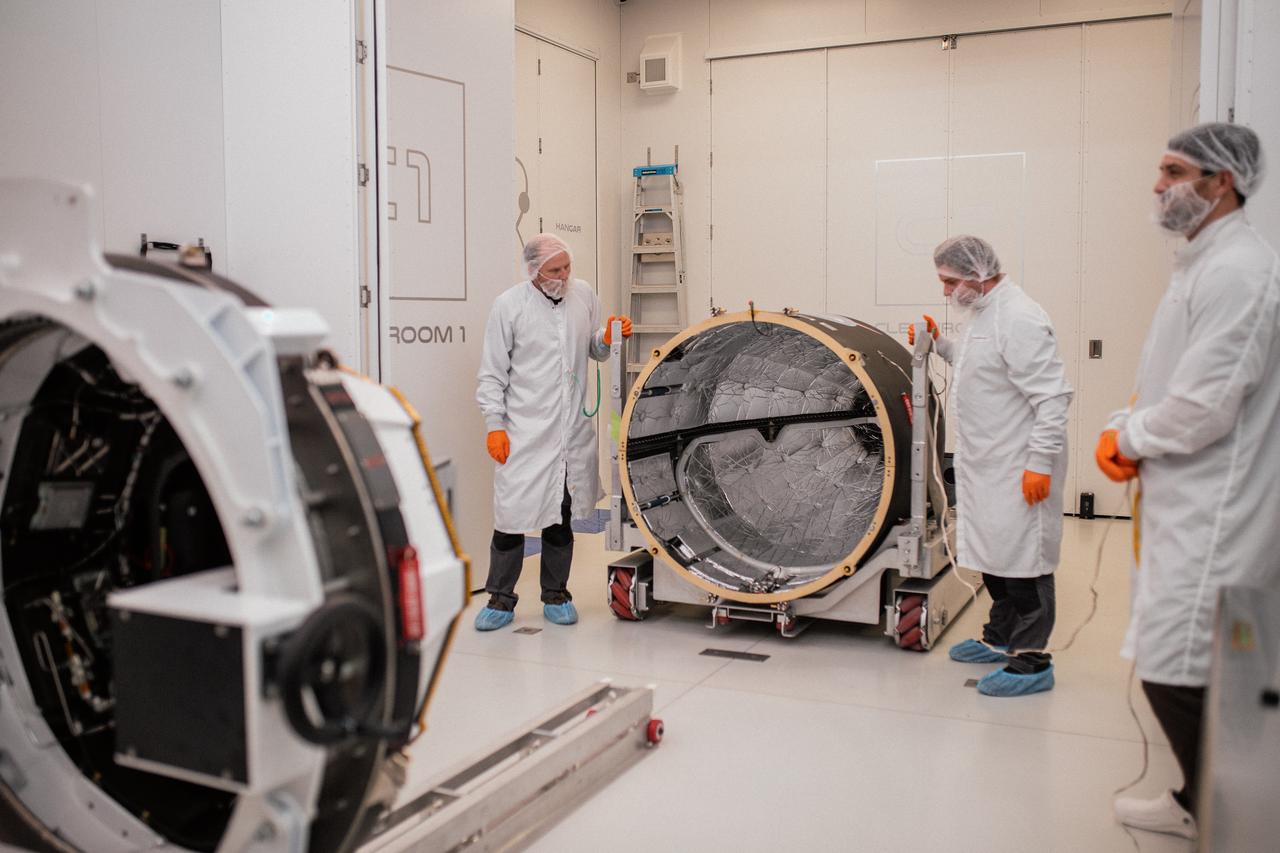

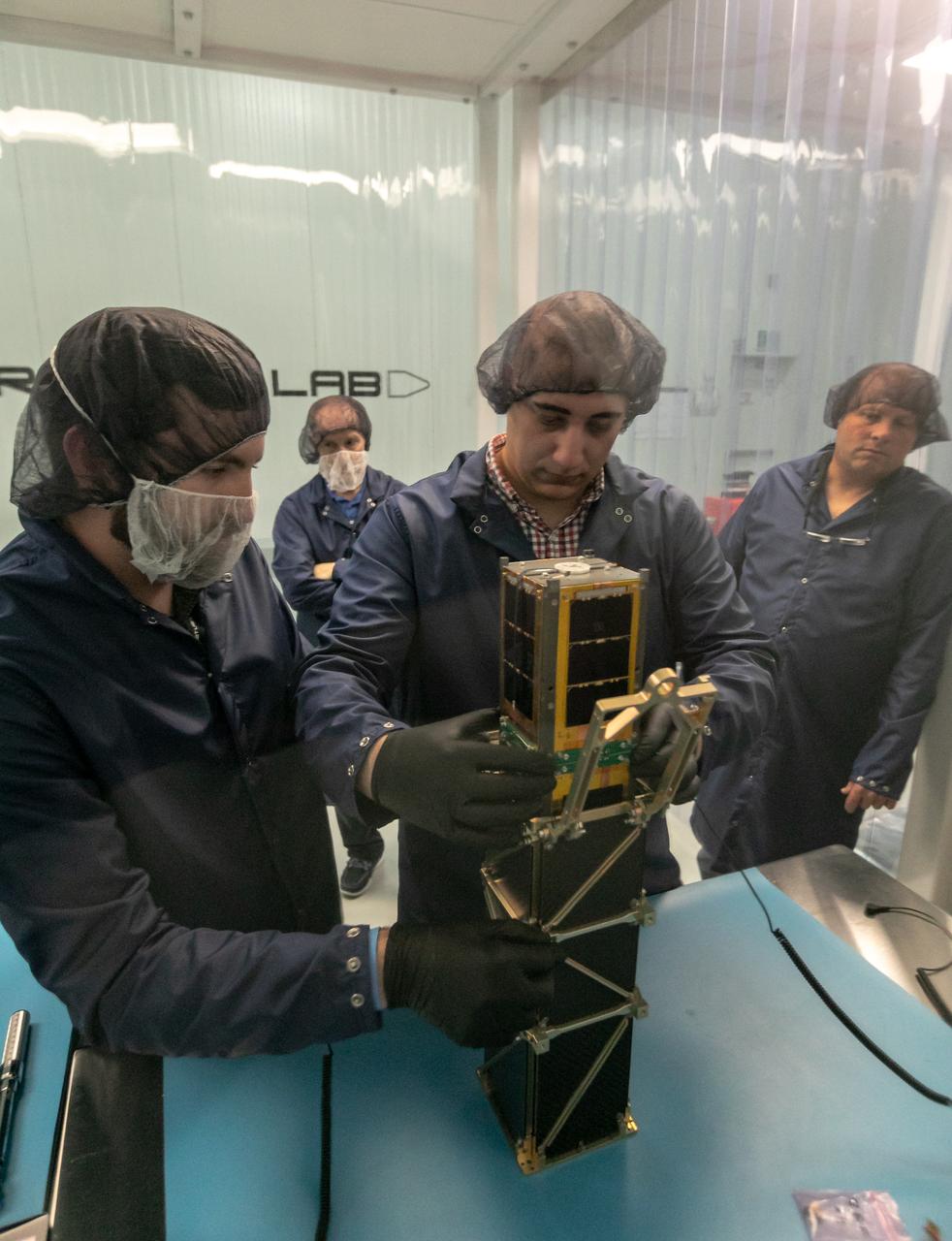
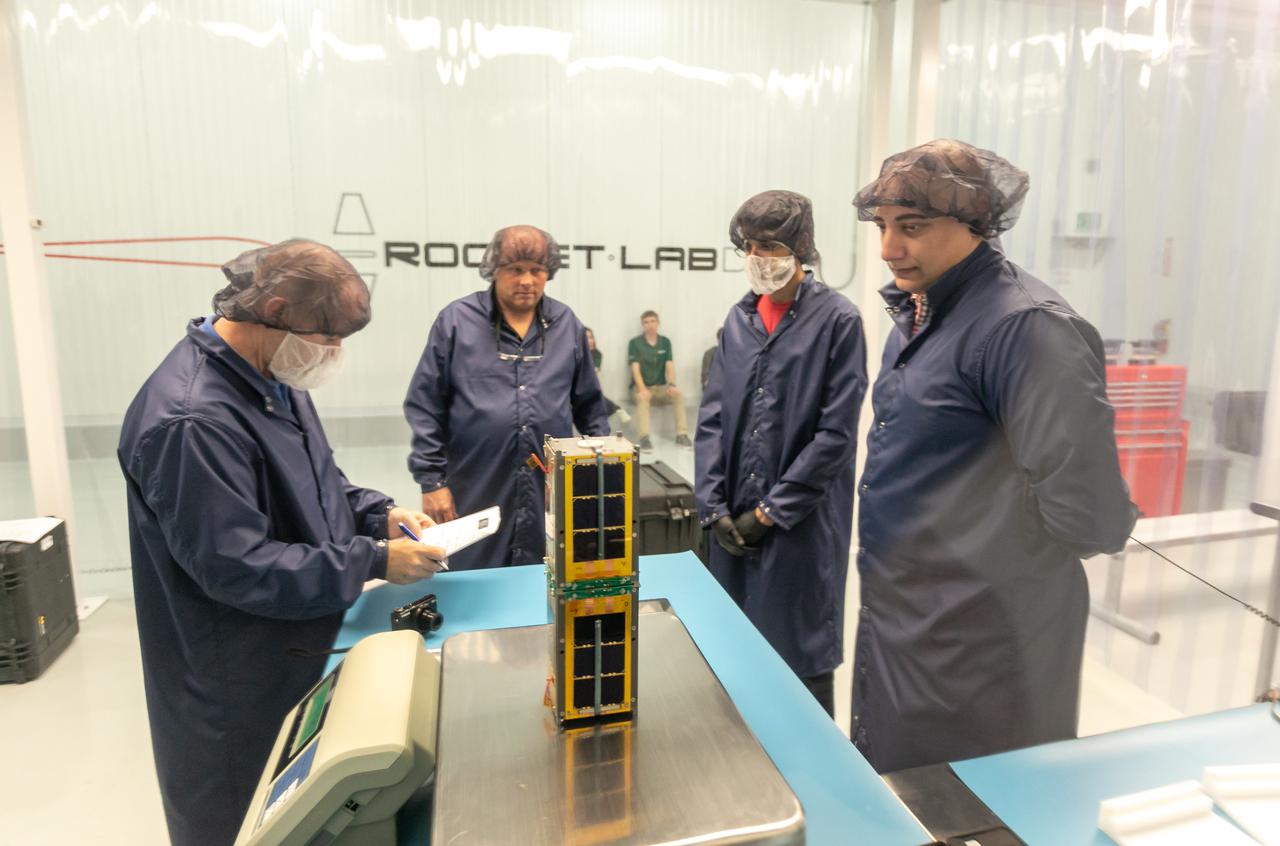
Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
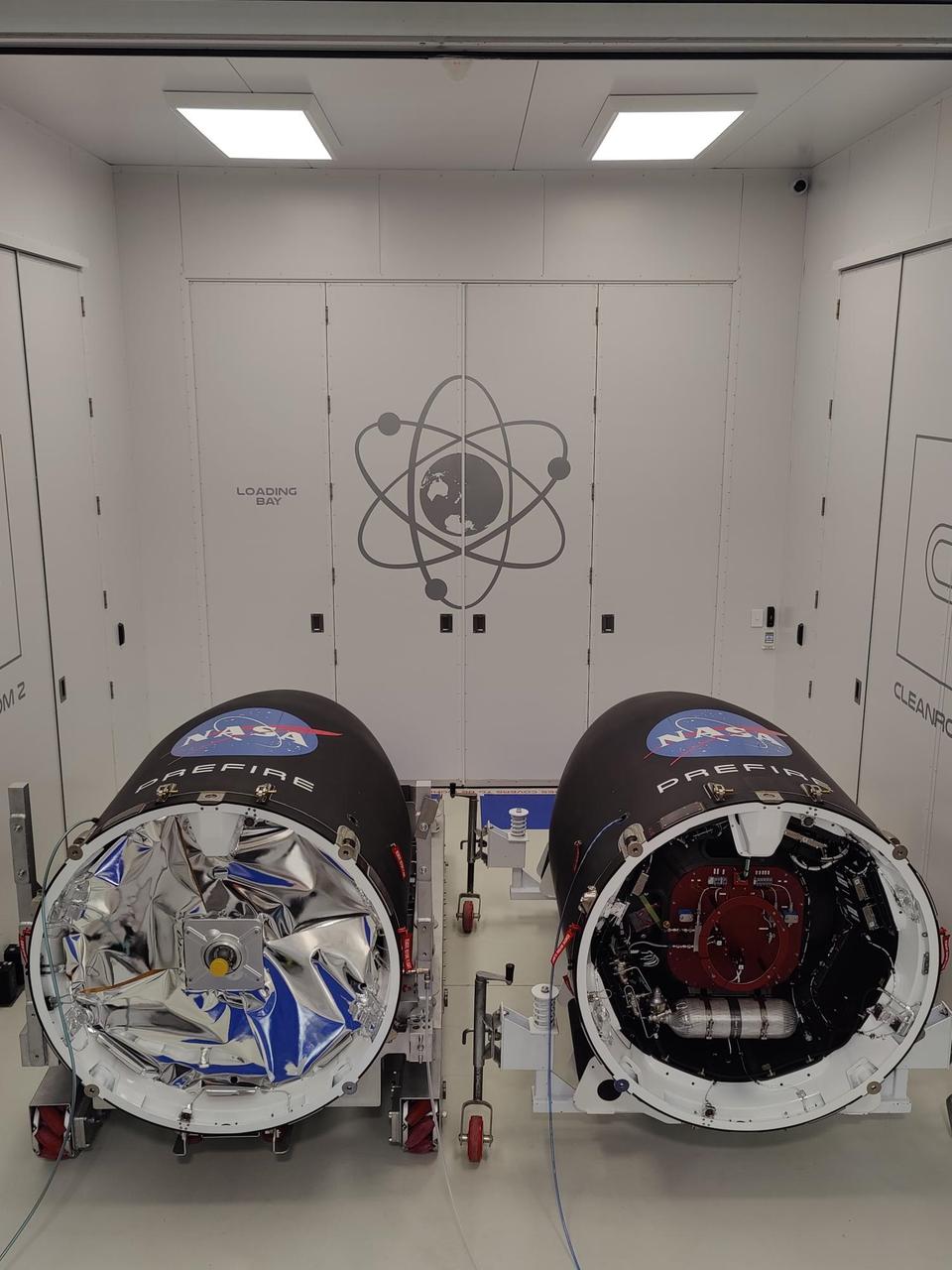

NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) CubeSats are encapsulated inside Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairings on Tuesday, May 21, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
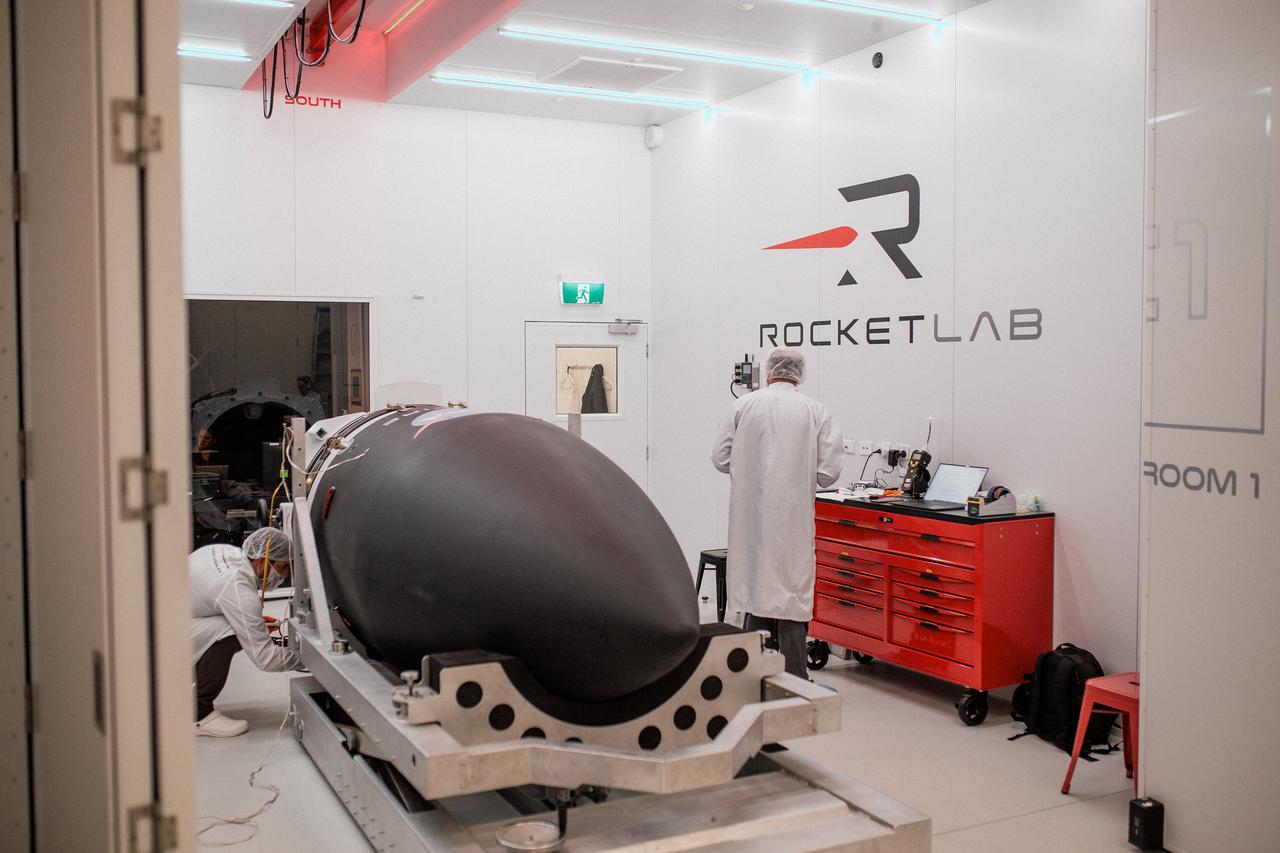

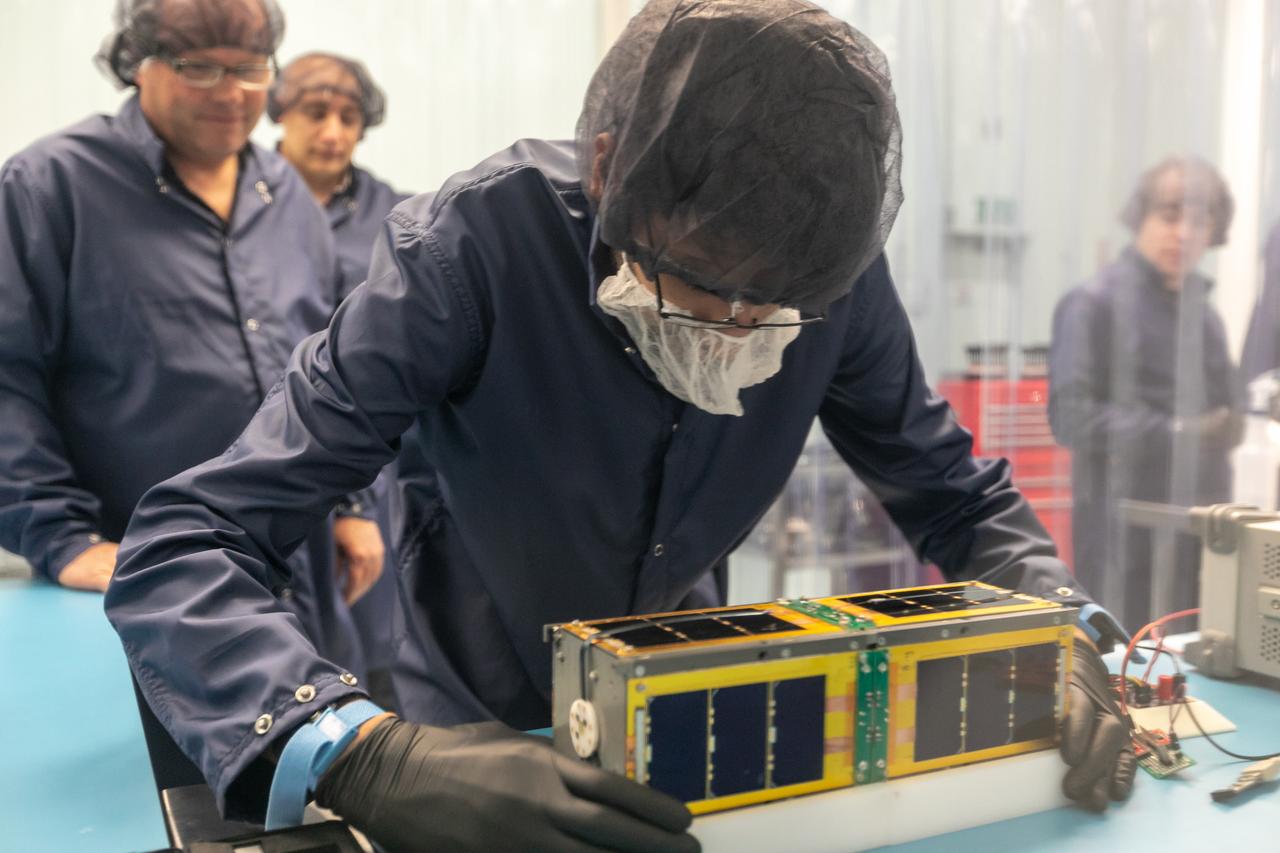
Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
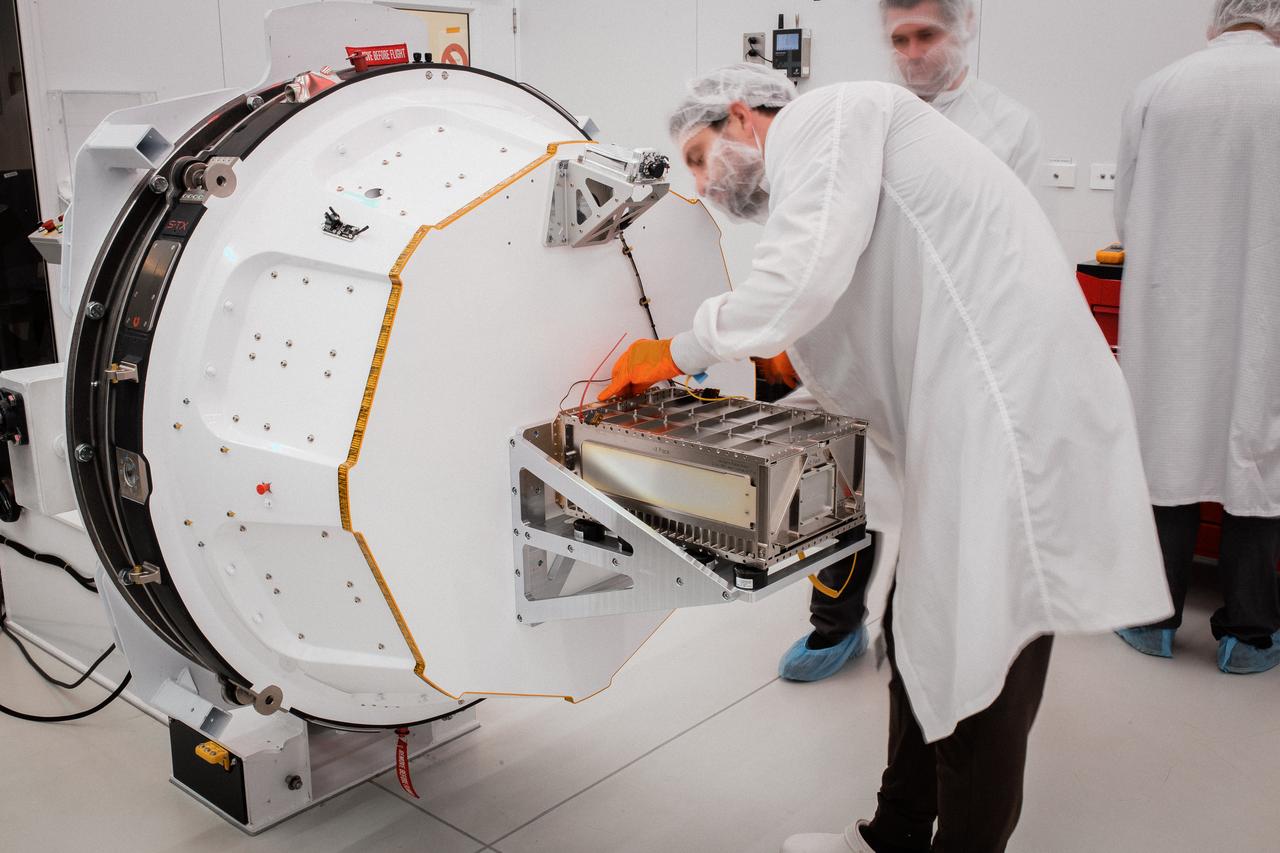

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
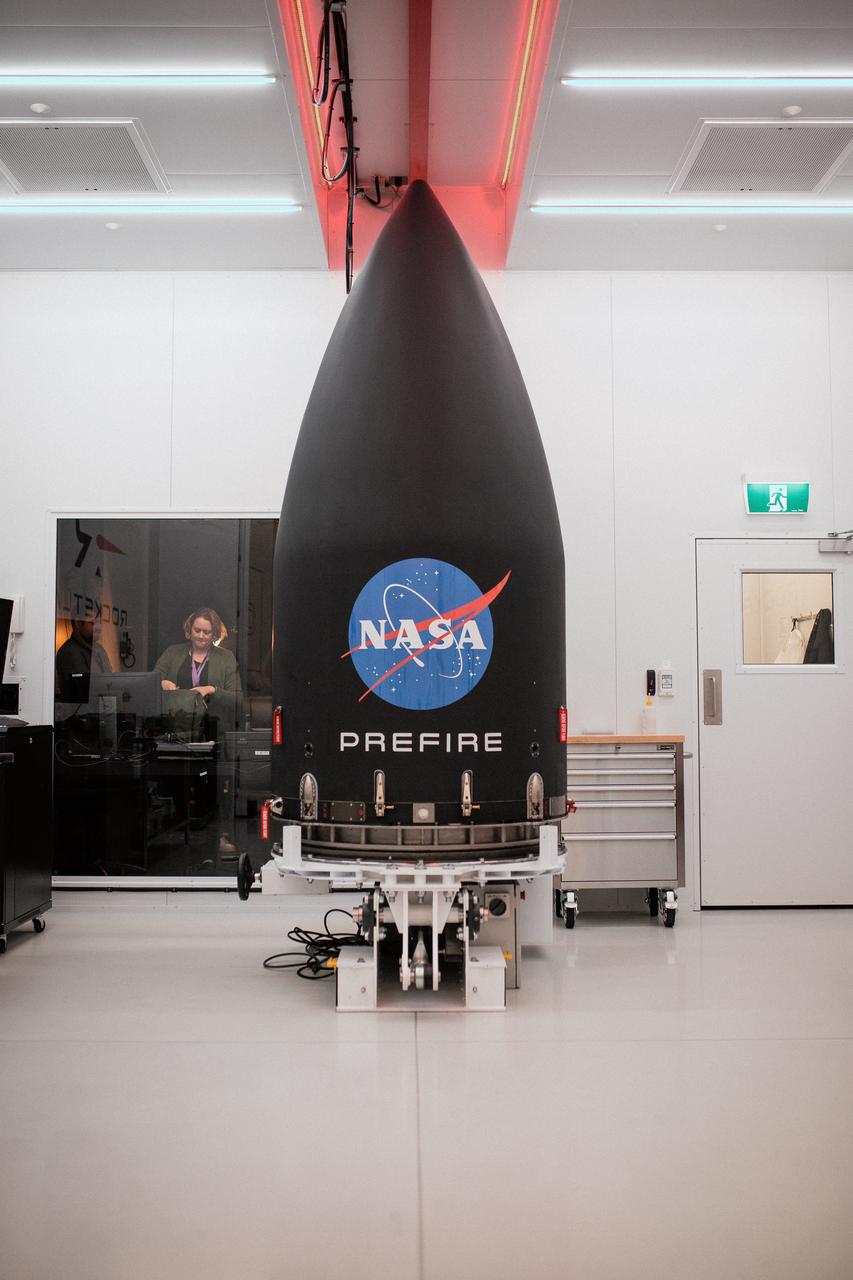

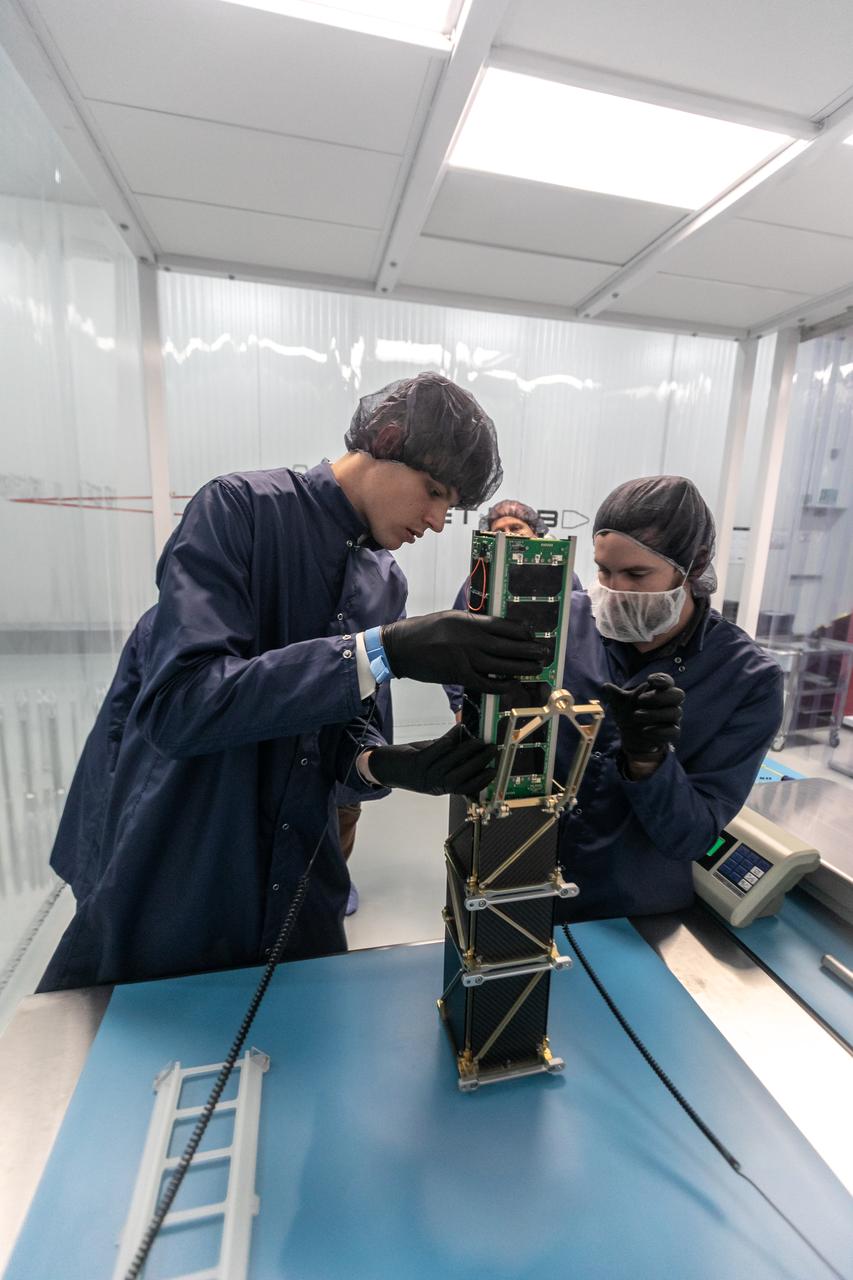
Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
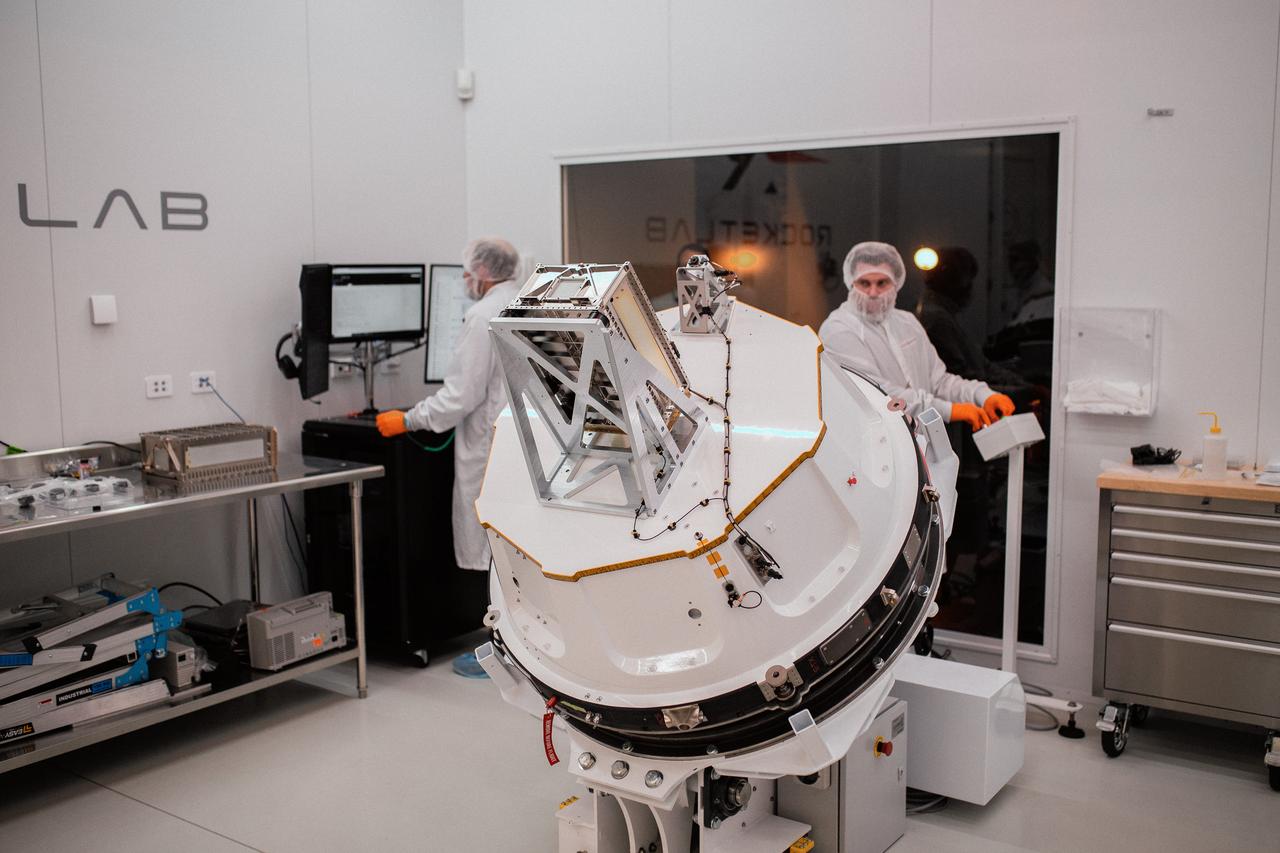

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
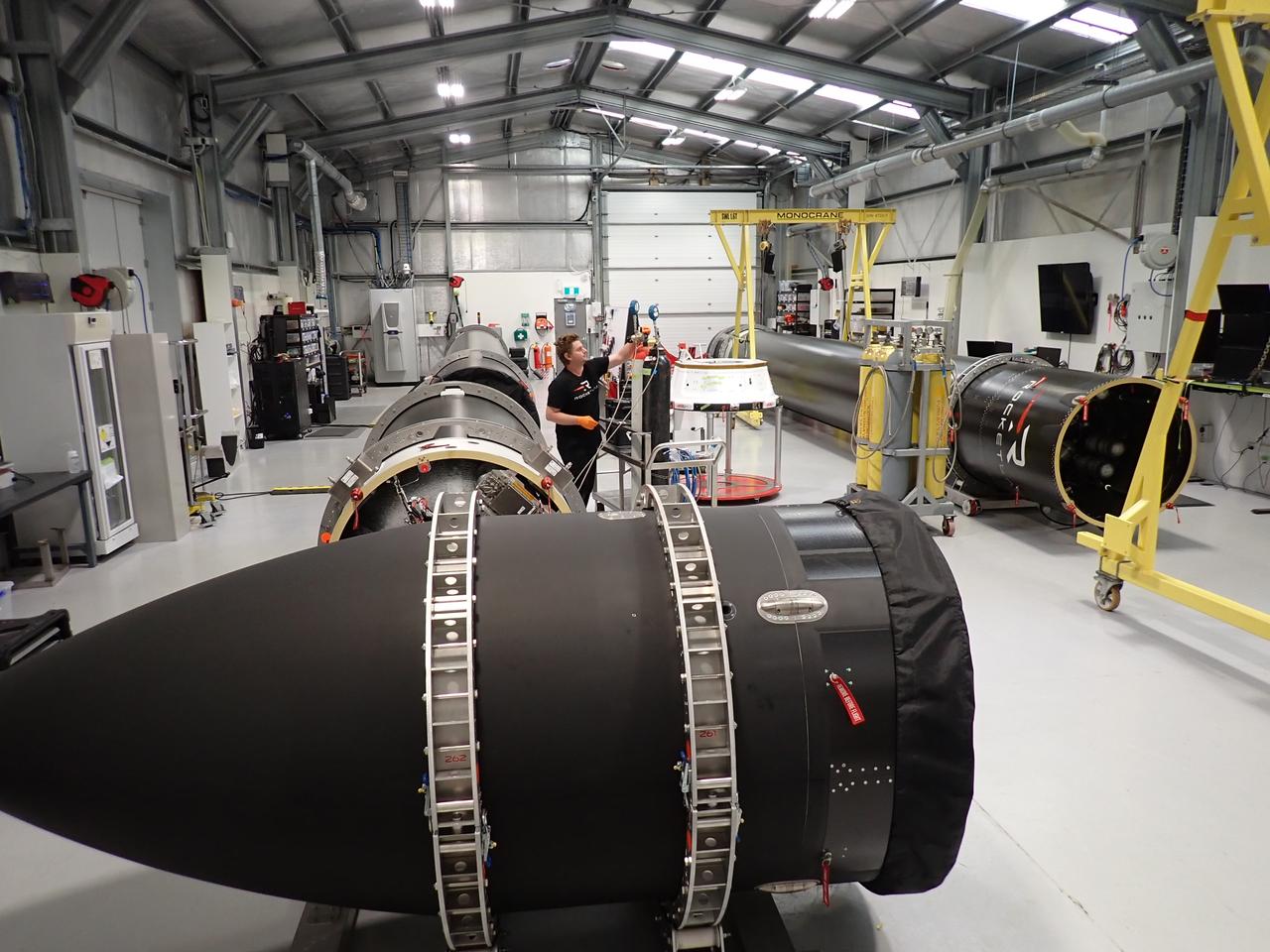

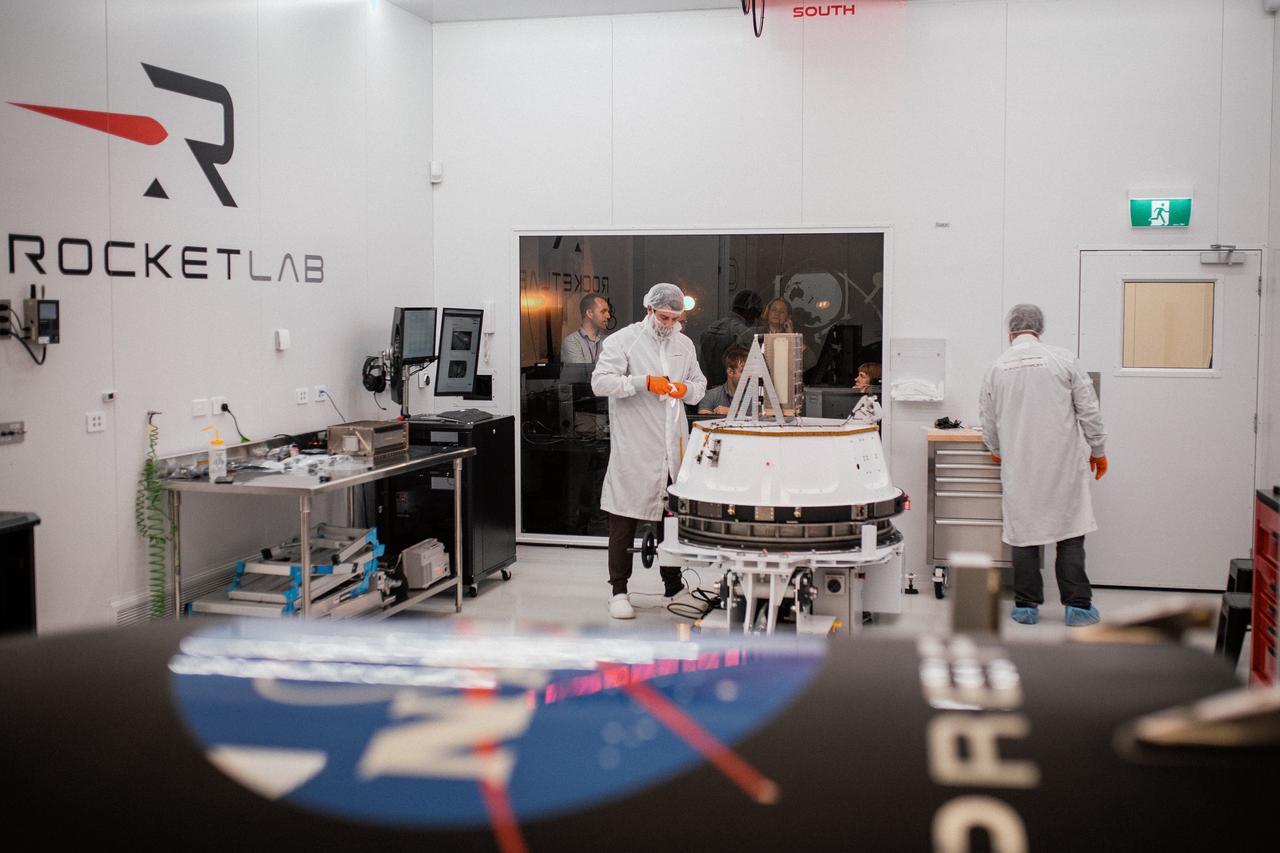
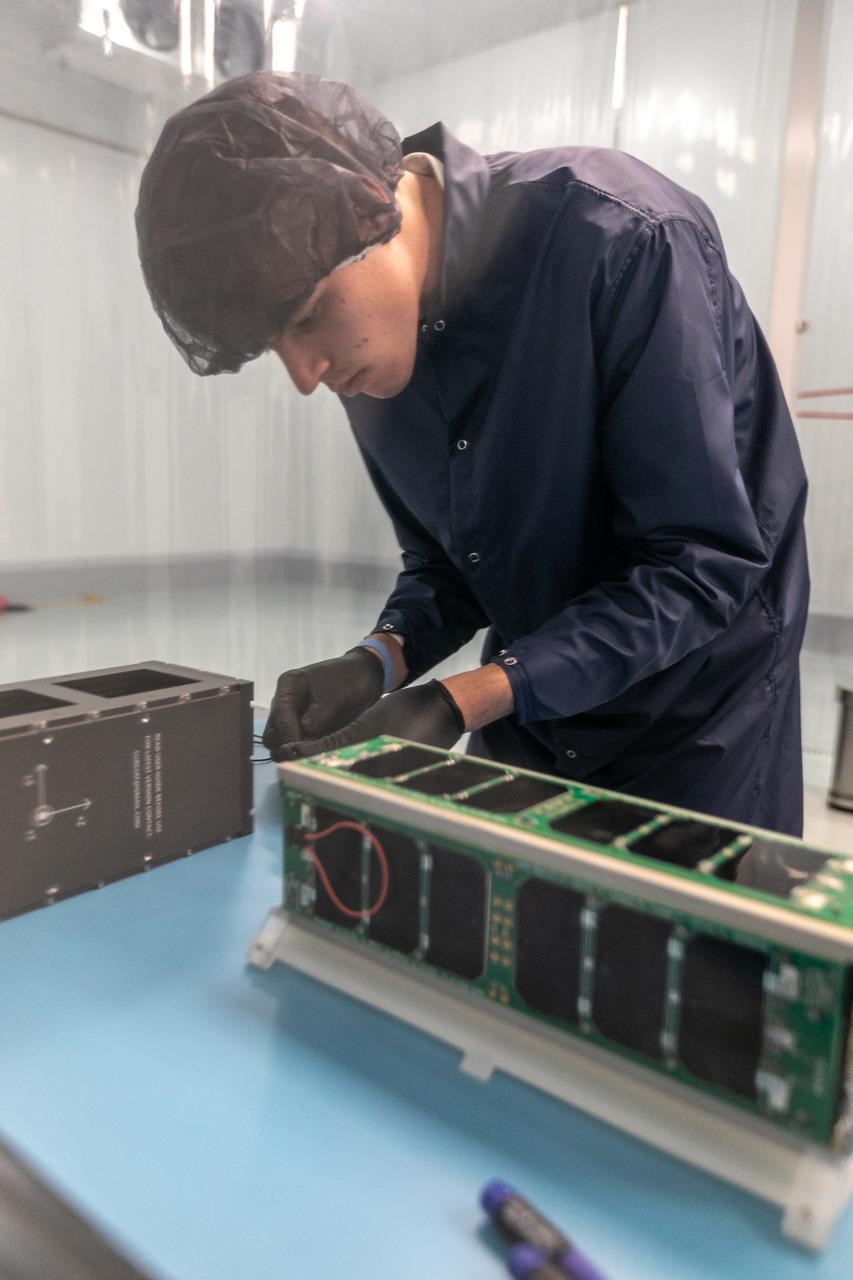
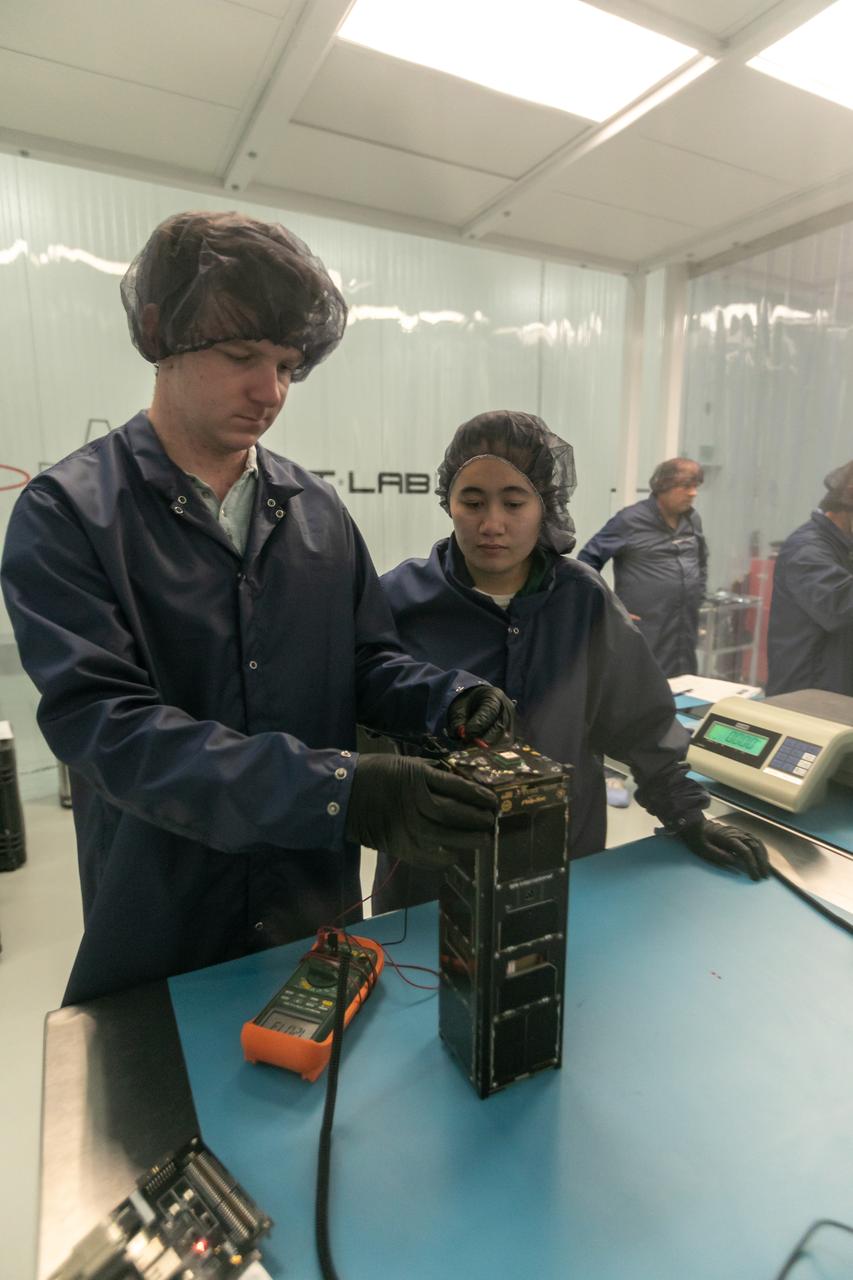
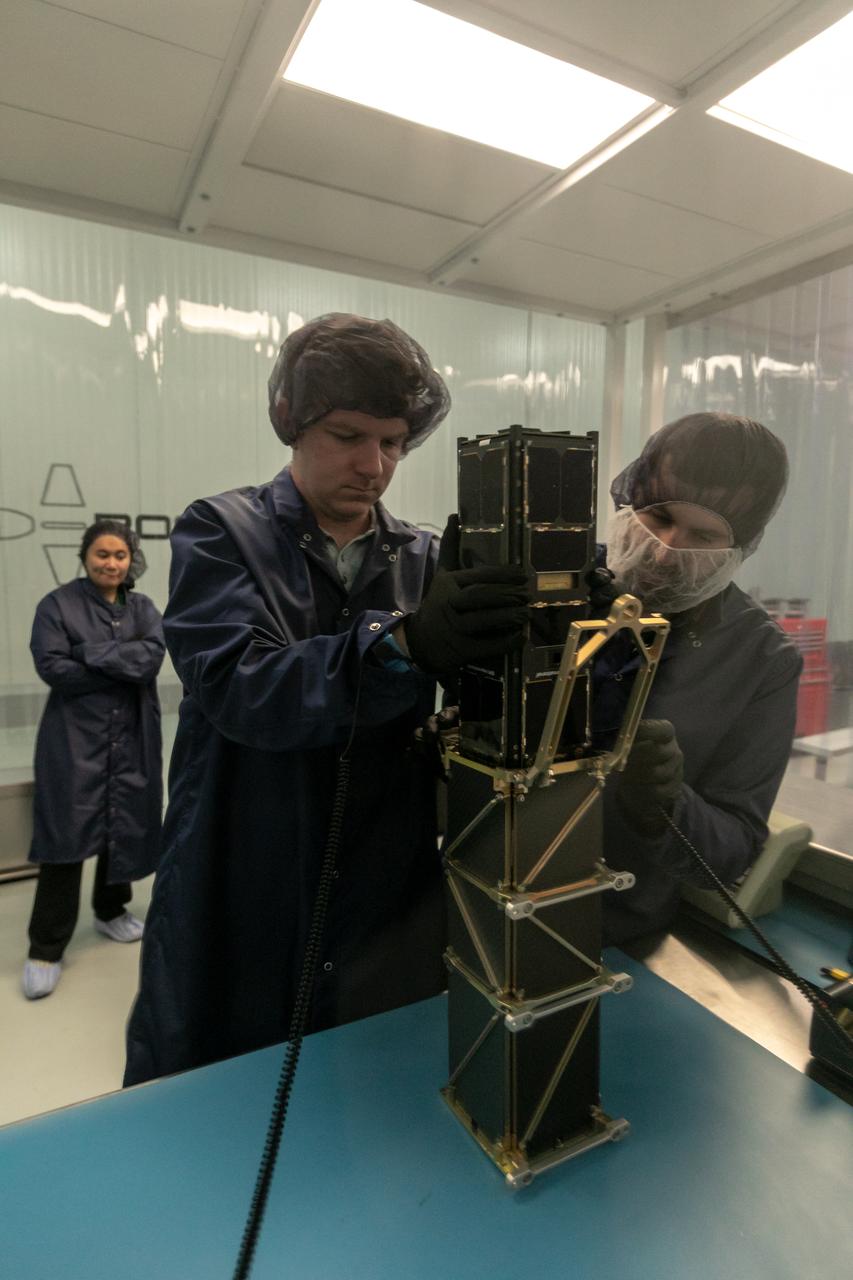
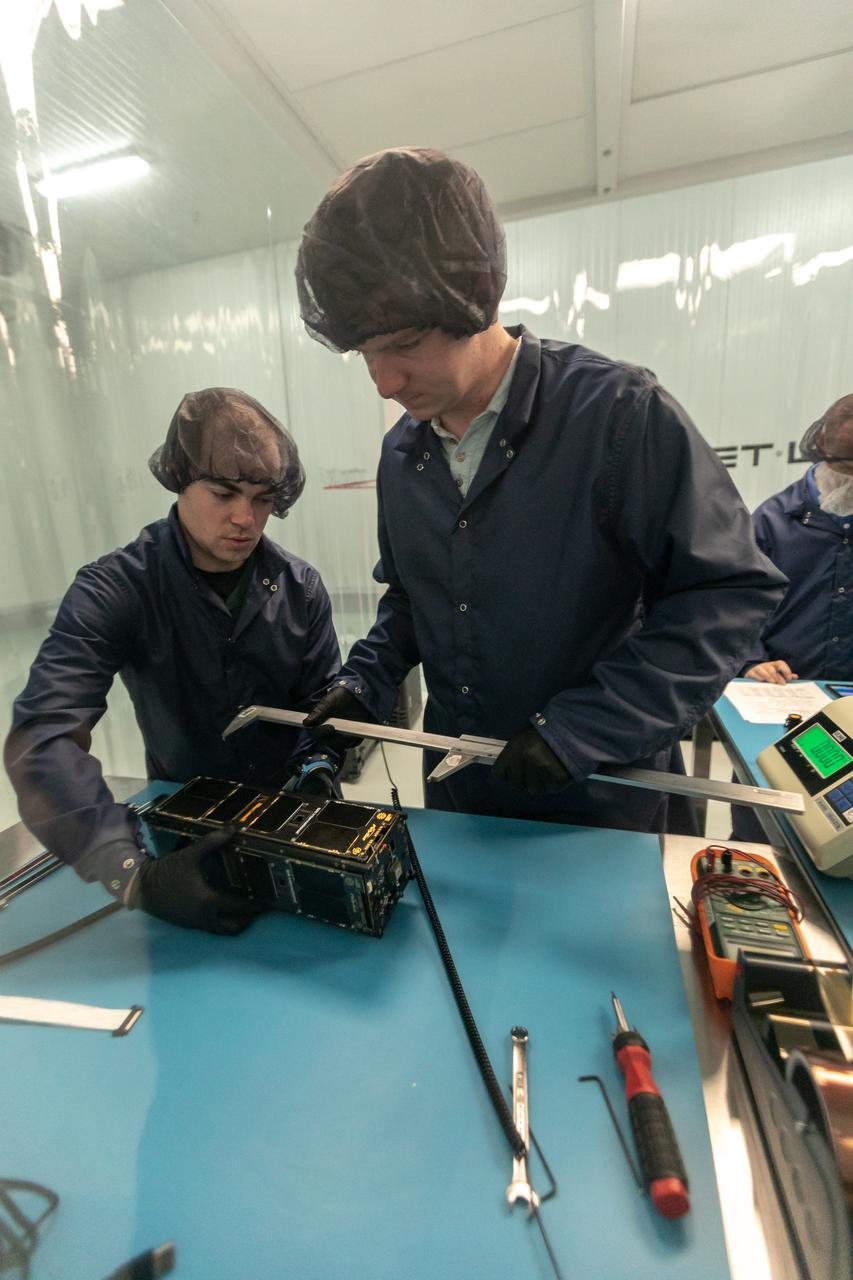
Technicians process NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) ahead of integration with a Rocket Lab Electron rocket on Thursday, May 2, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
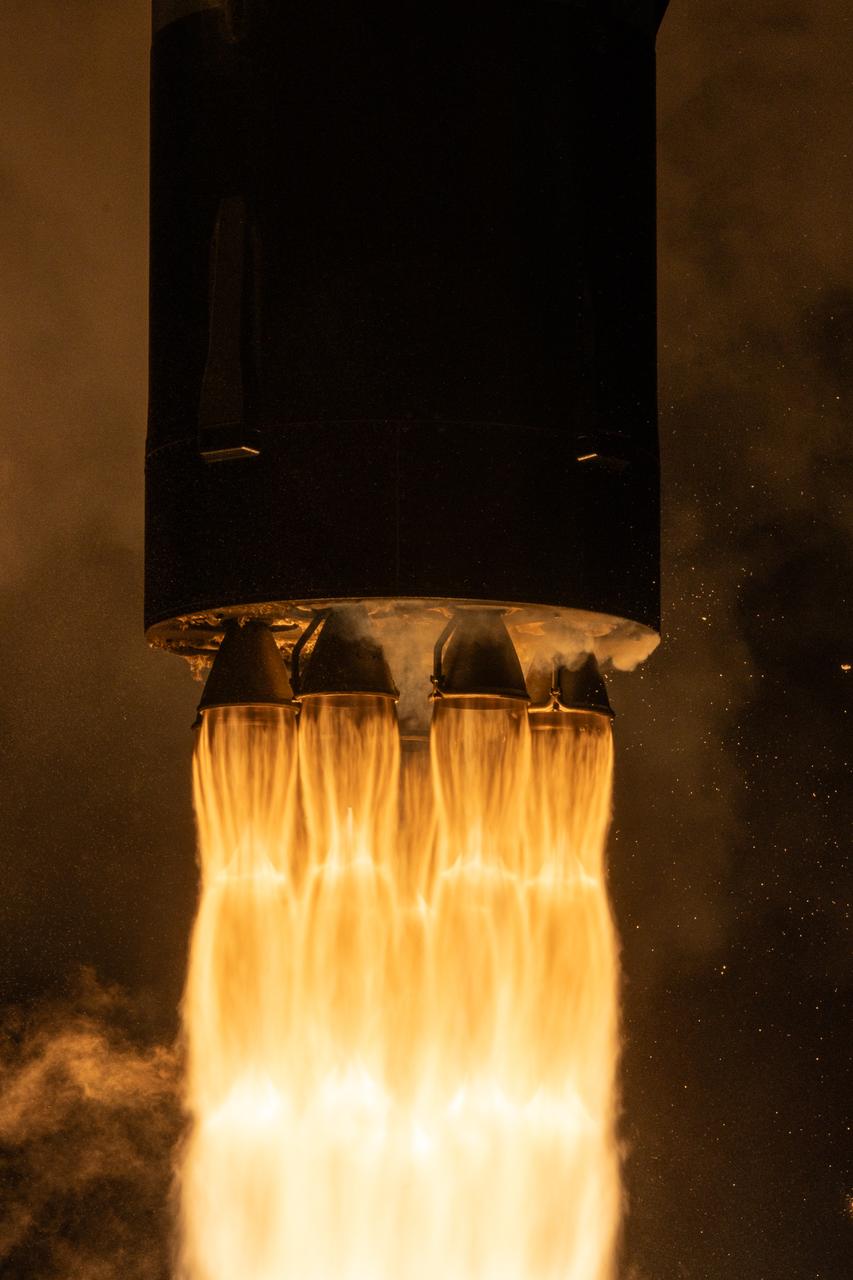

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT) Saturday, May 25, 2024, on the first of two launches which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission. The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
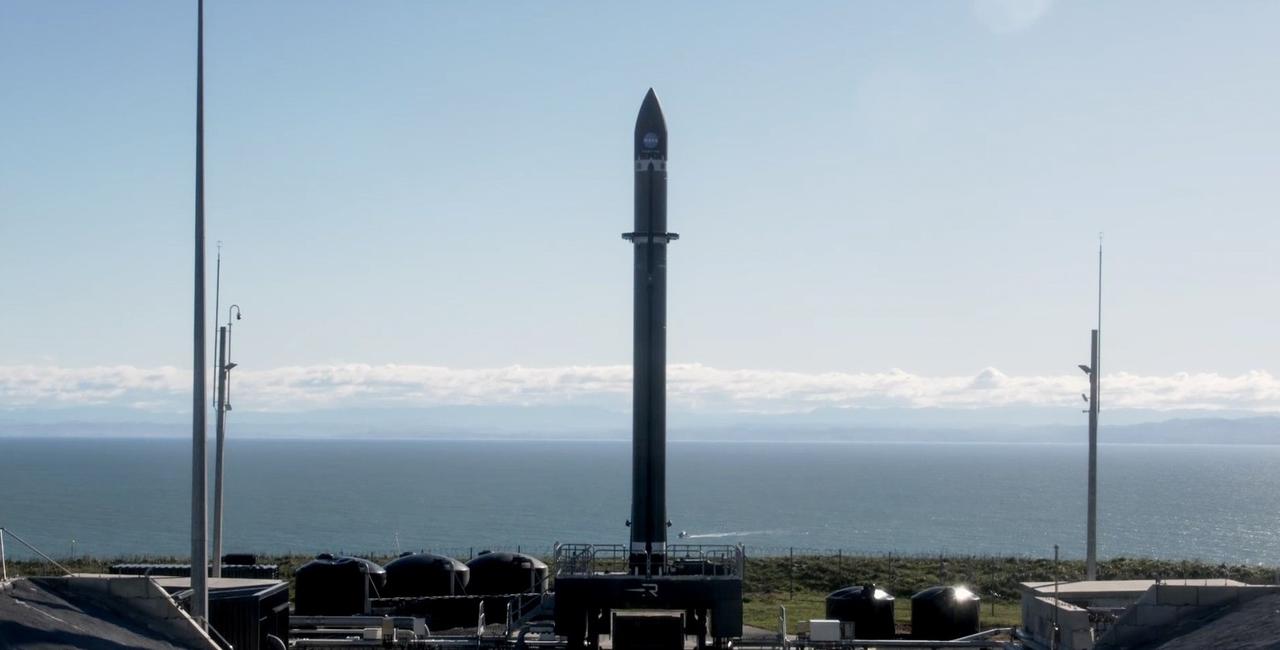

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
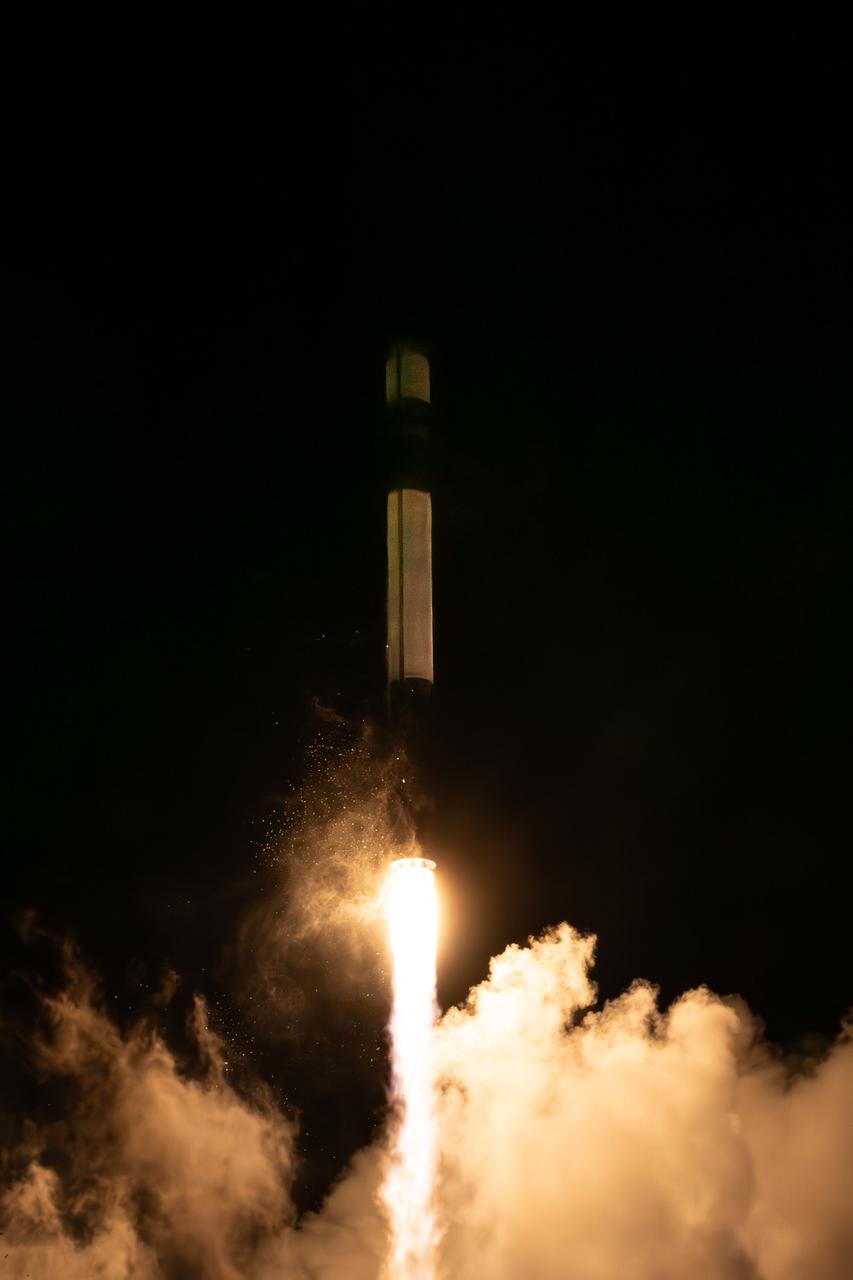

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT) Saturday, May 25, 2024, on the first of two launches which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission. The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
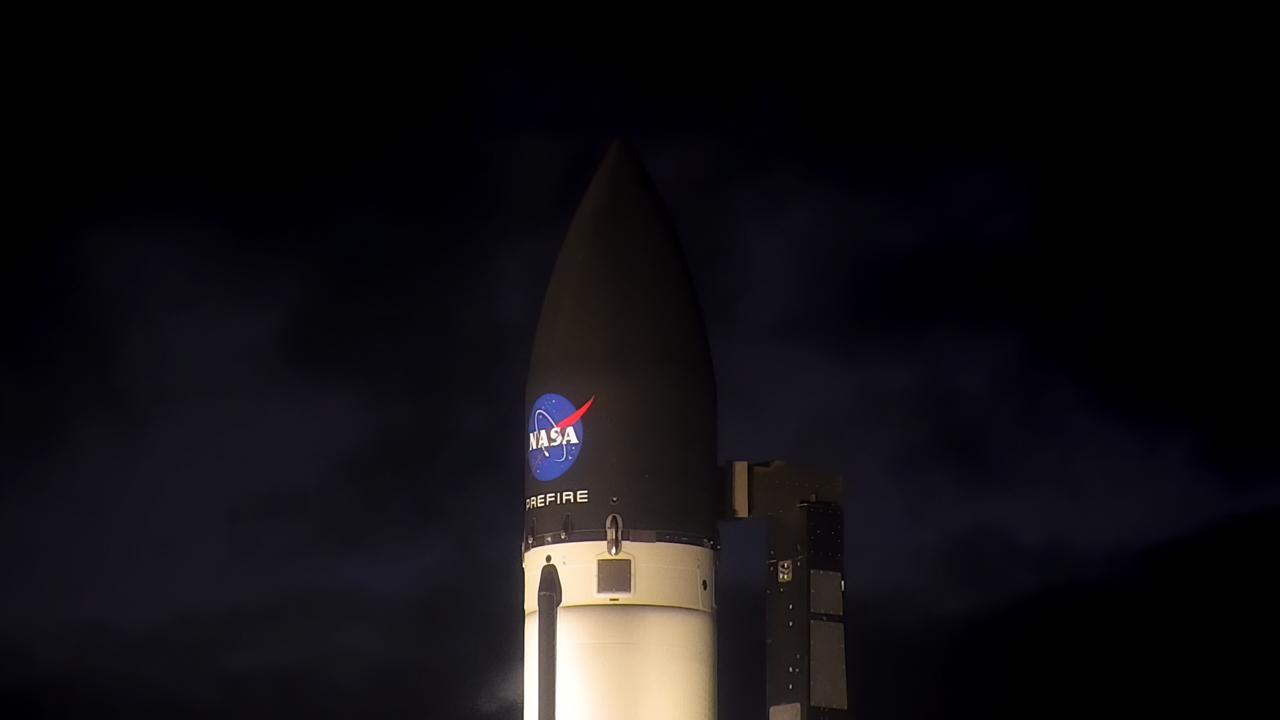

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
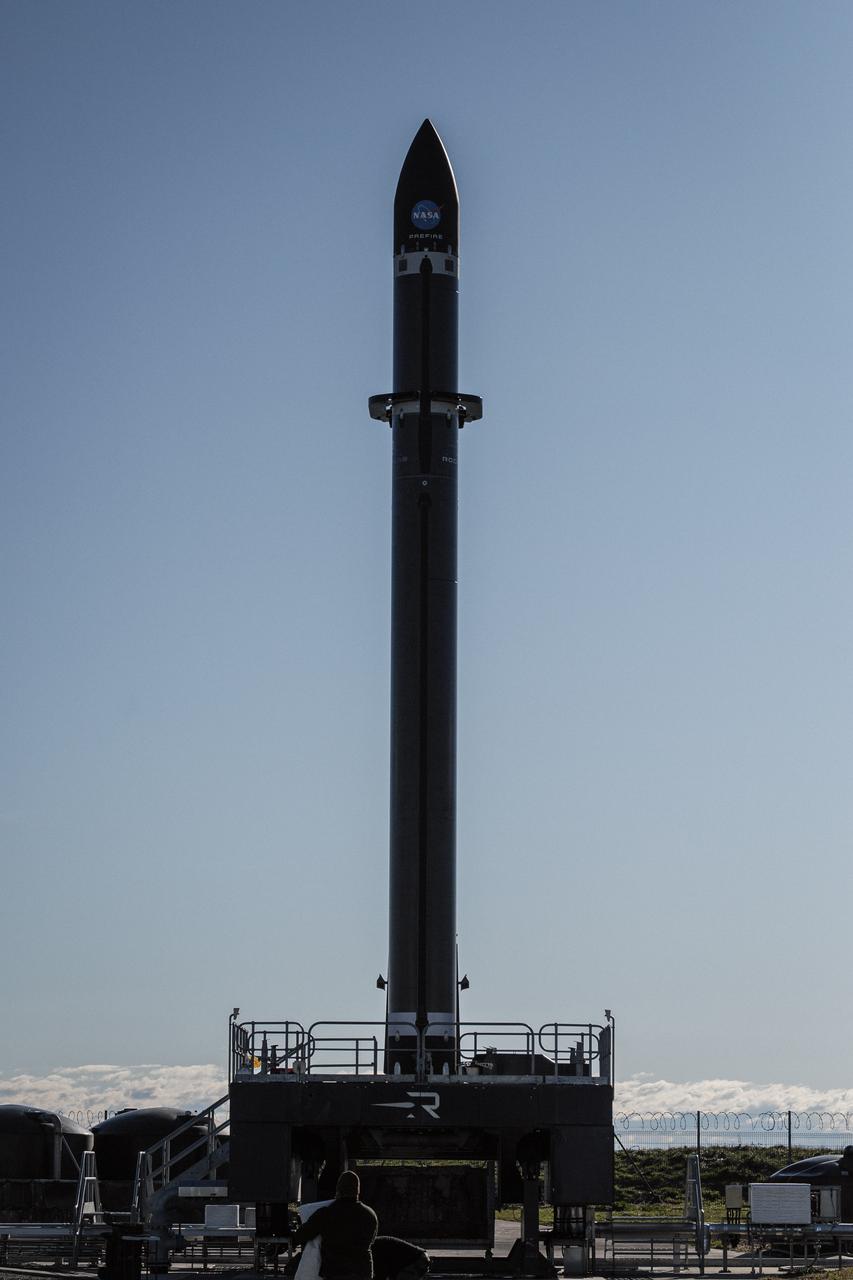

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
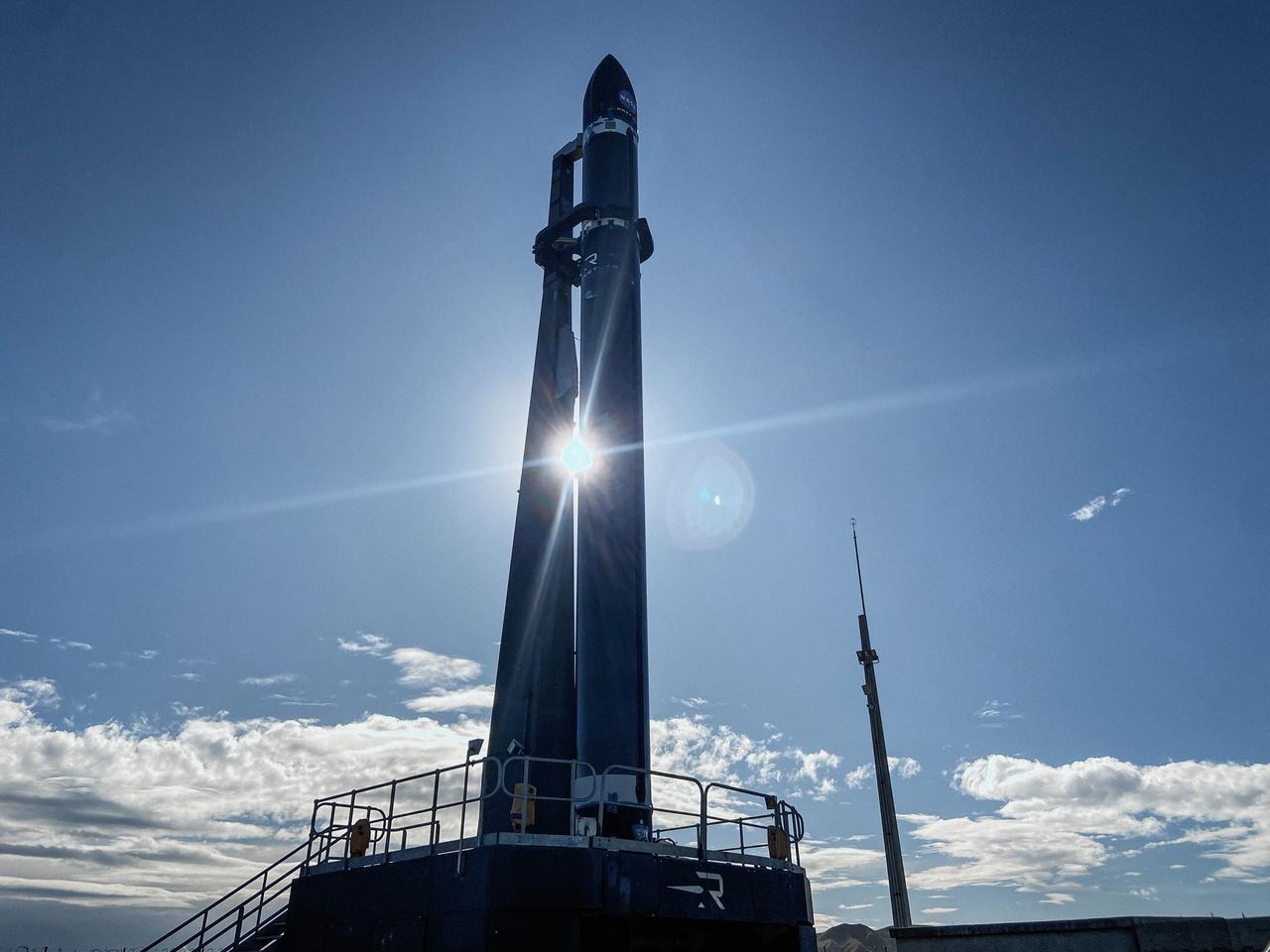

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the second of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the second CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “PREFIRE and Ice” was targeted for Saturday, June 1, 2024, but was scrubbed for the day.
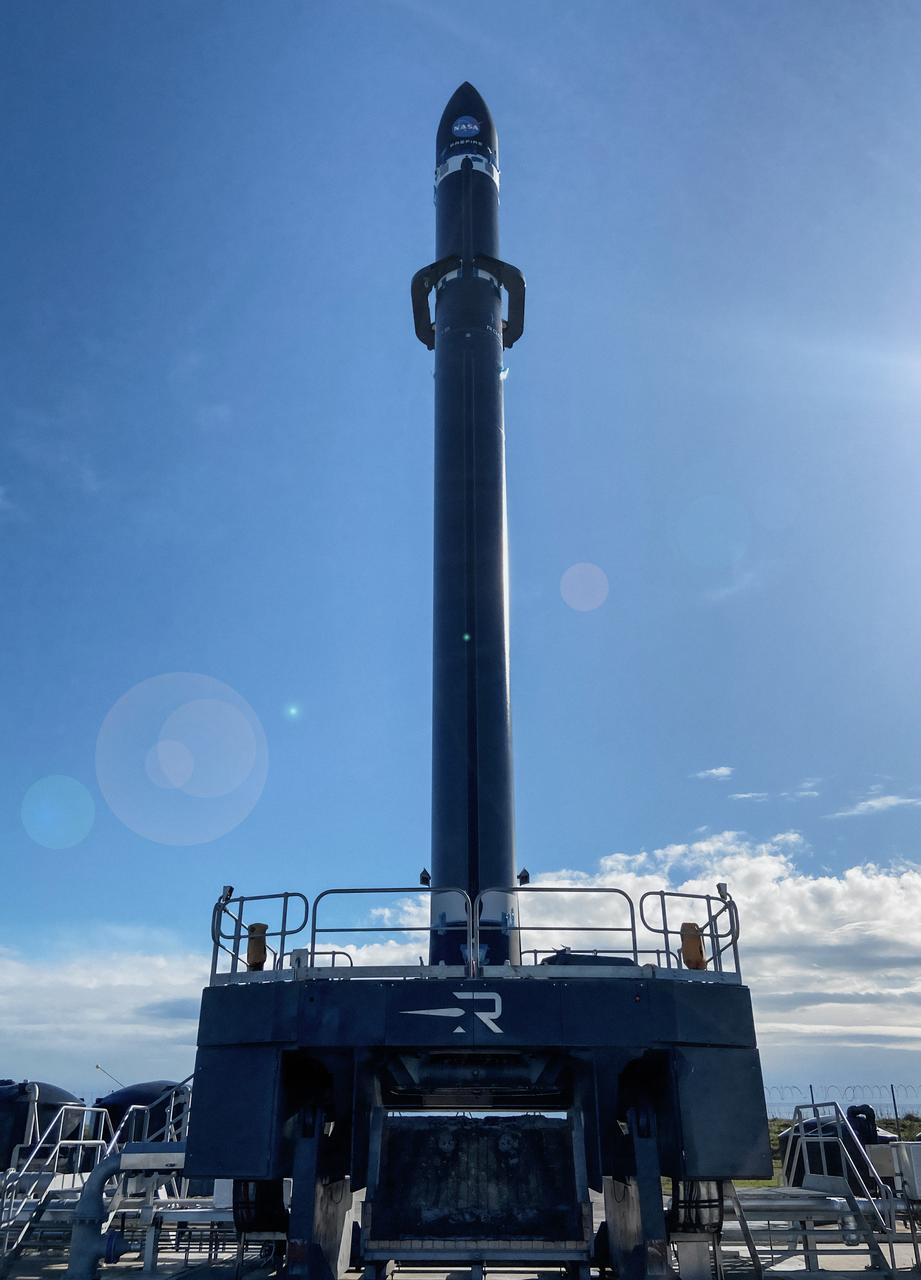

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the second of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the second CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “PREFIRE and Ice” was targeted for Saturday, June 1, 2024, but was scrubbed for the day.
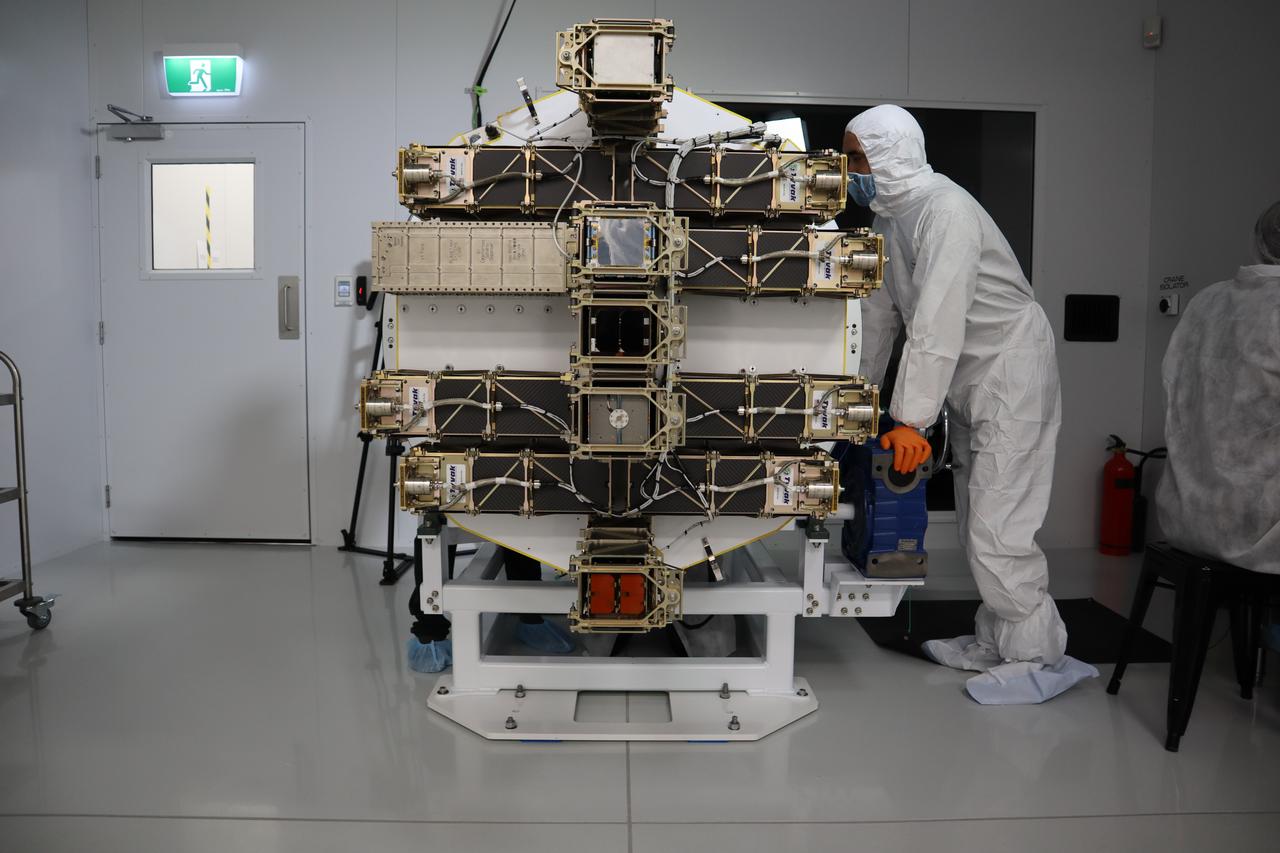

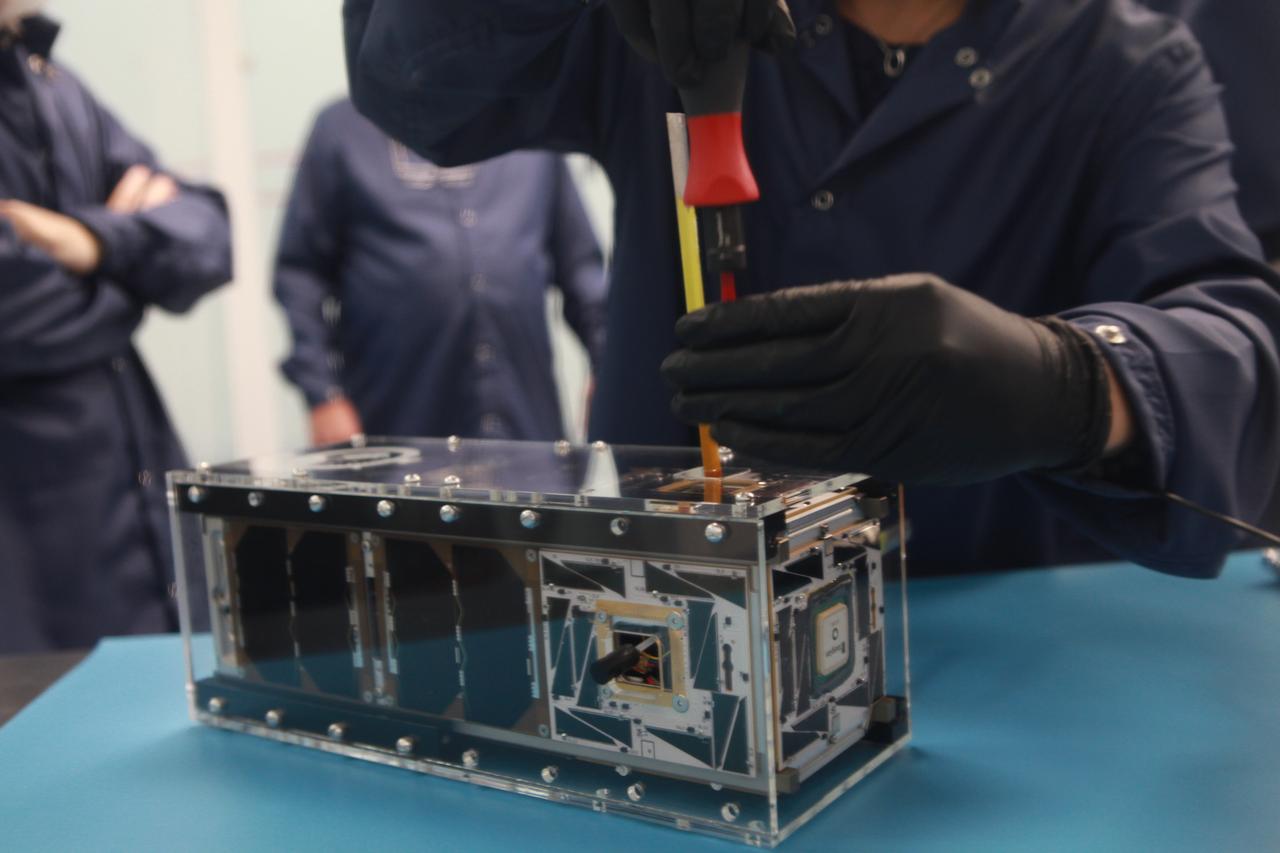
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
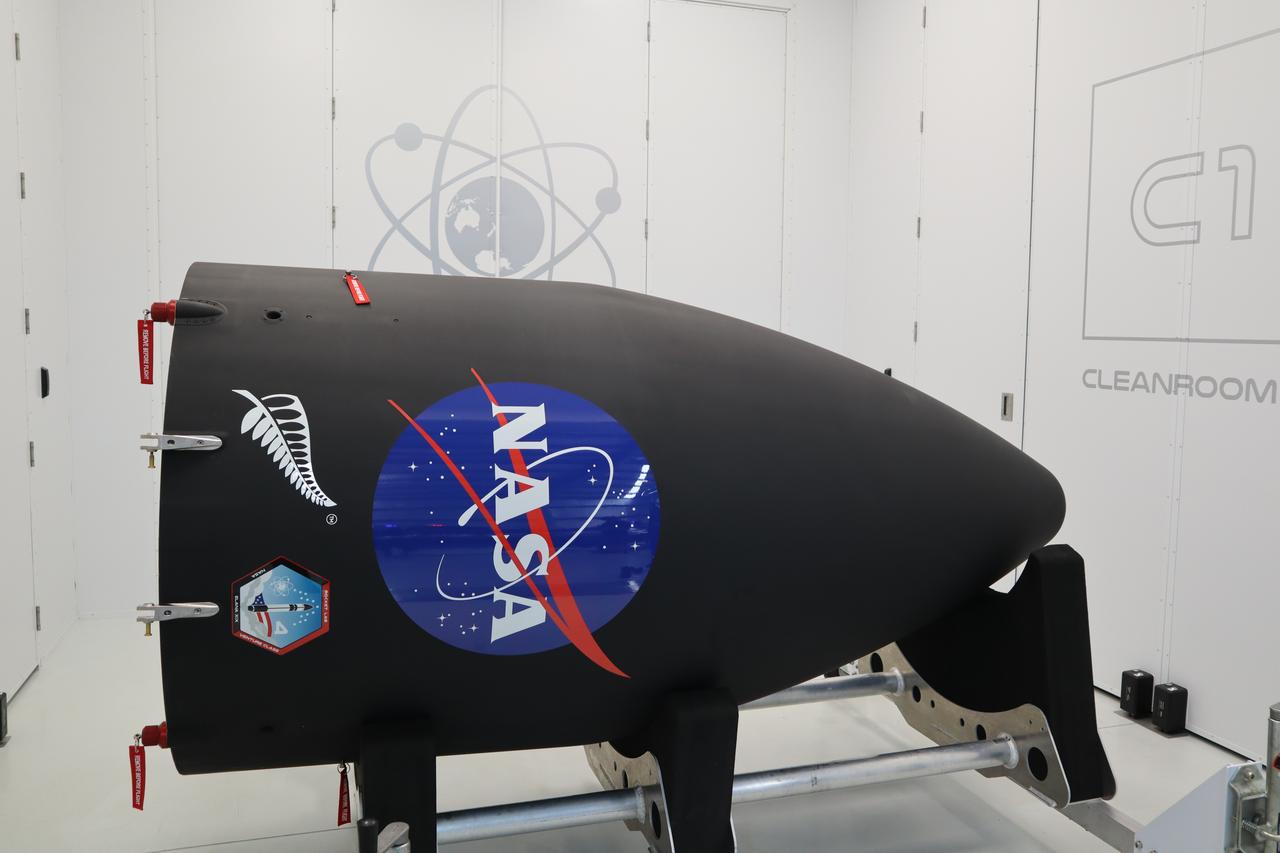
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
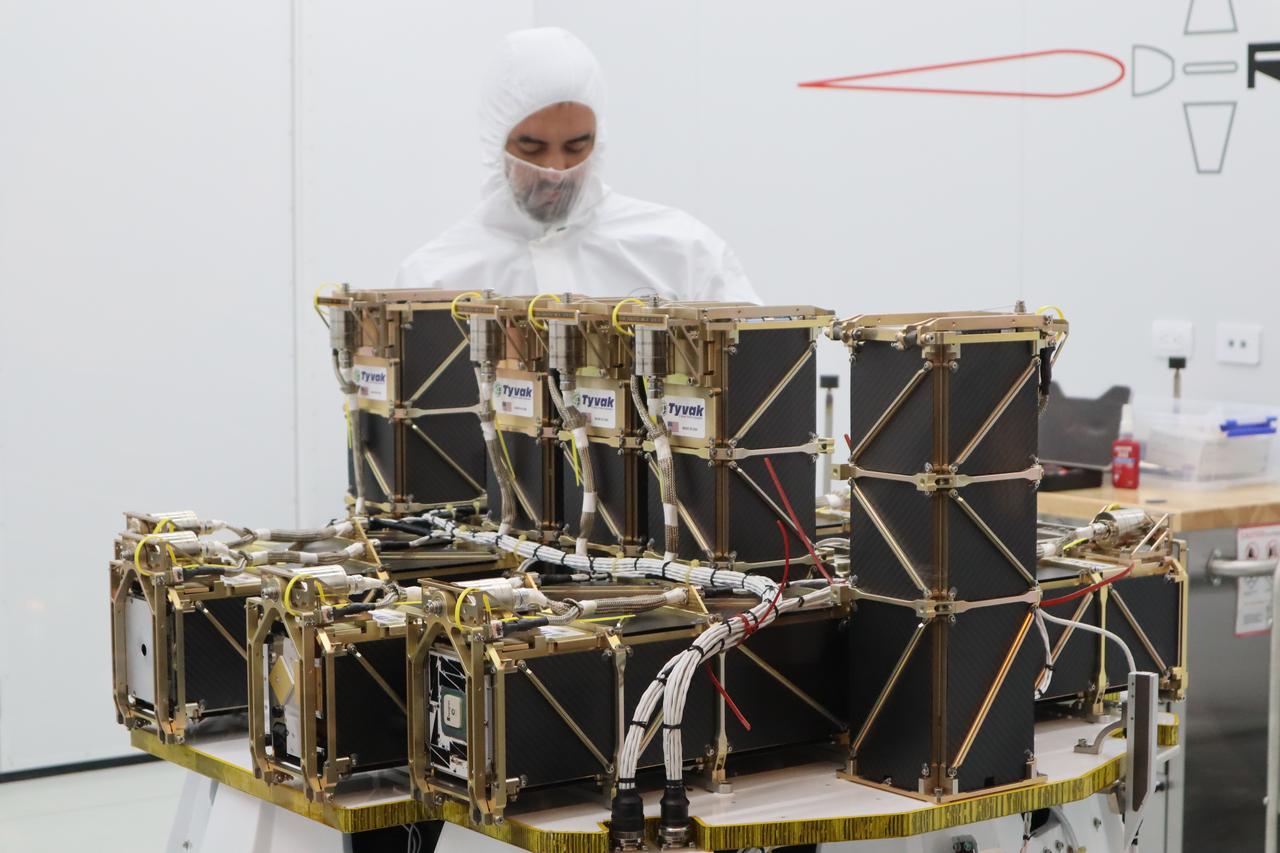

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
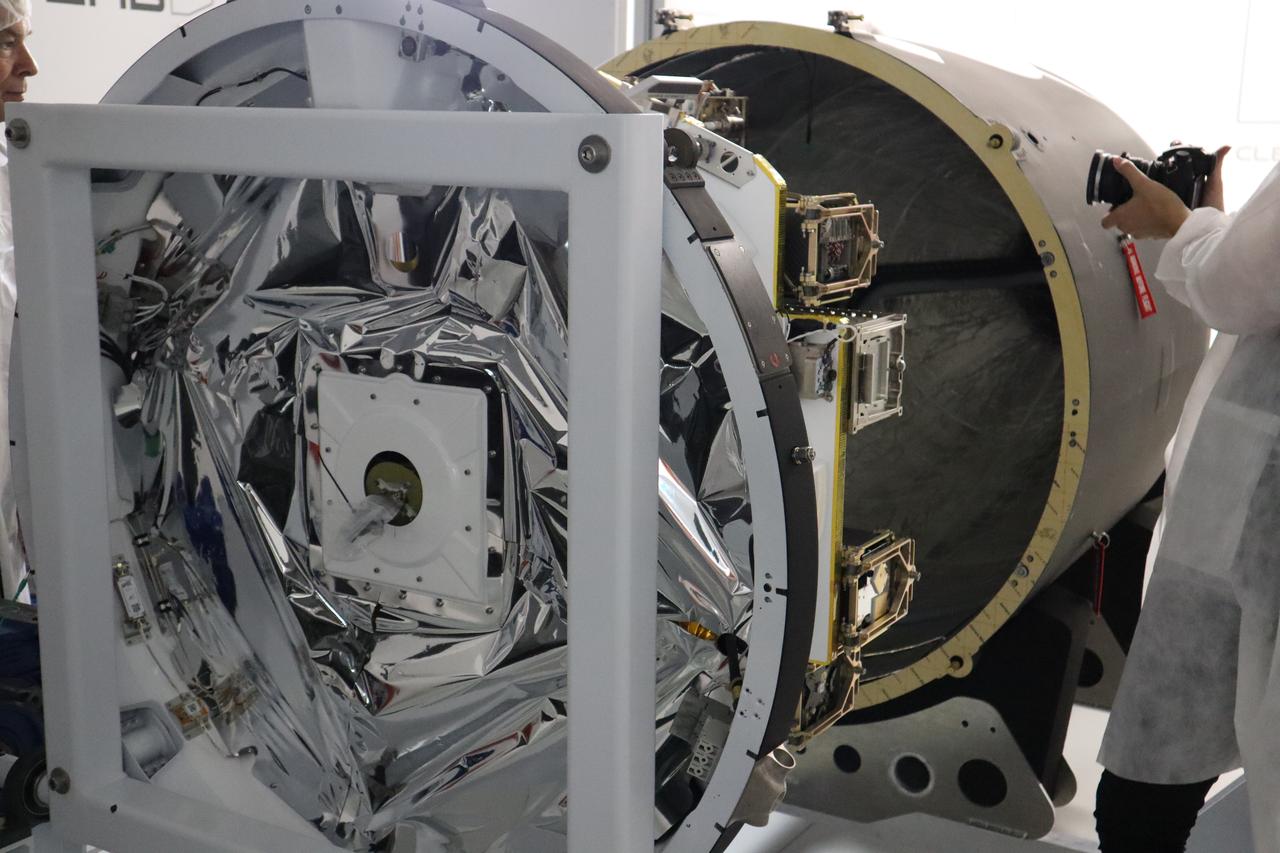
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
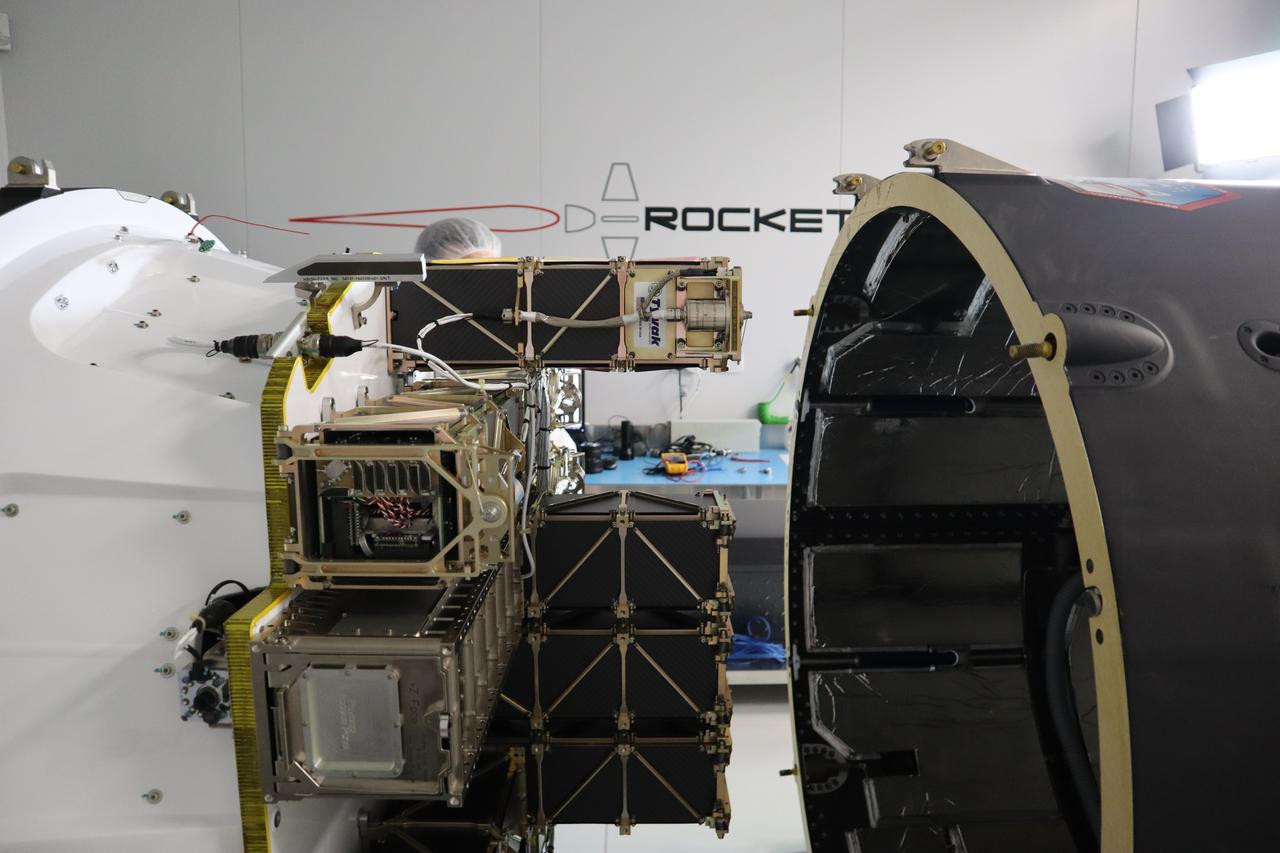

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
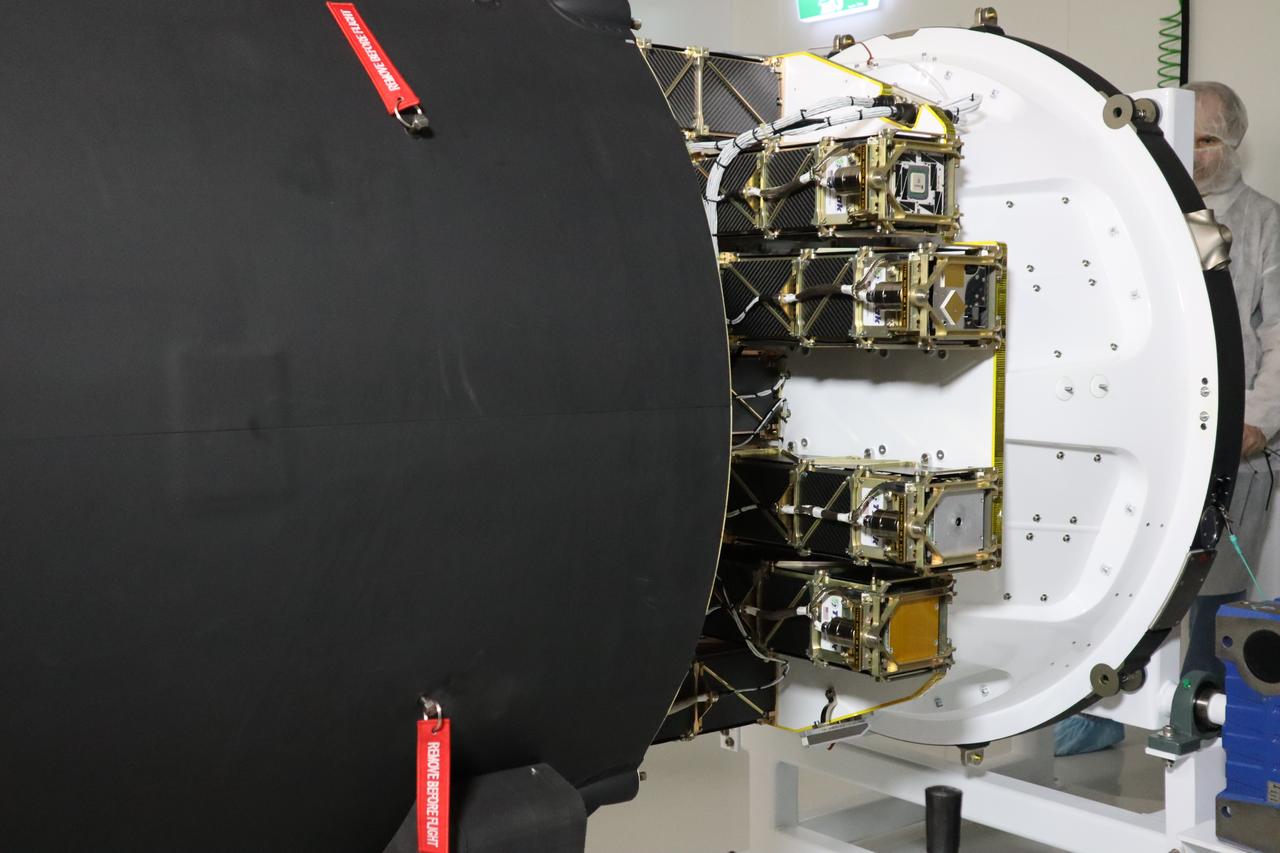

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
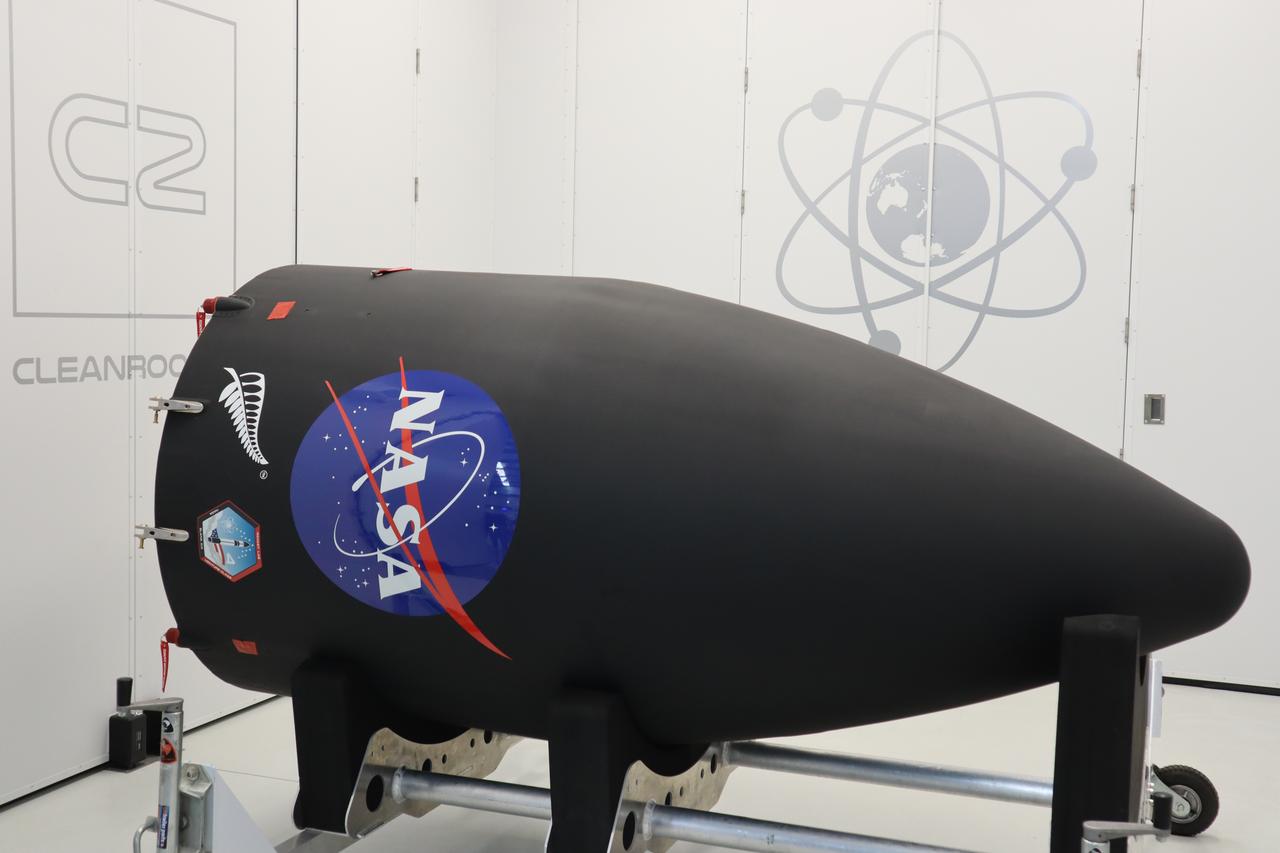
The Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing is prepared for the encapsulation of the Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
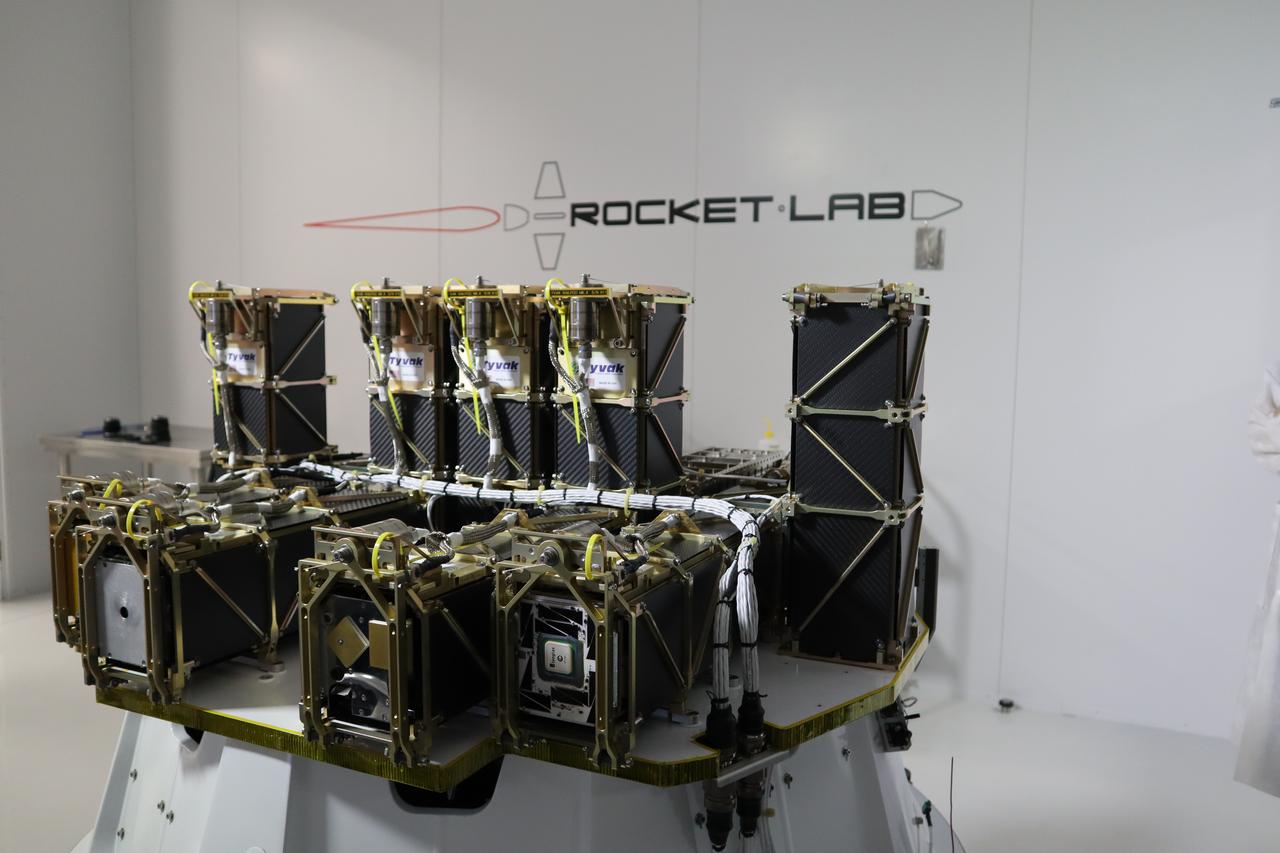

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
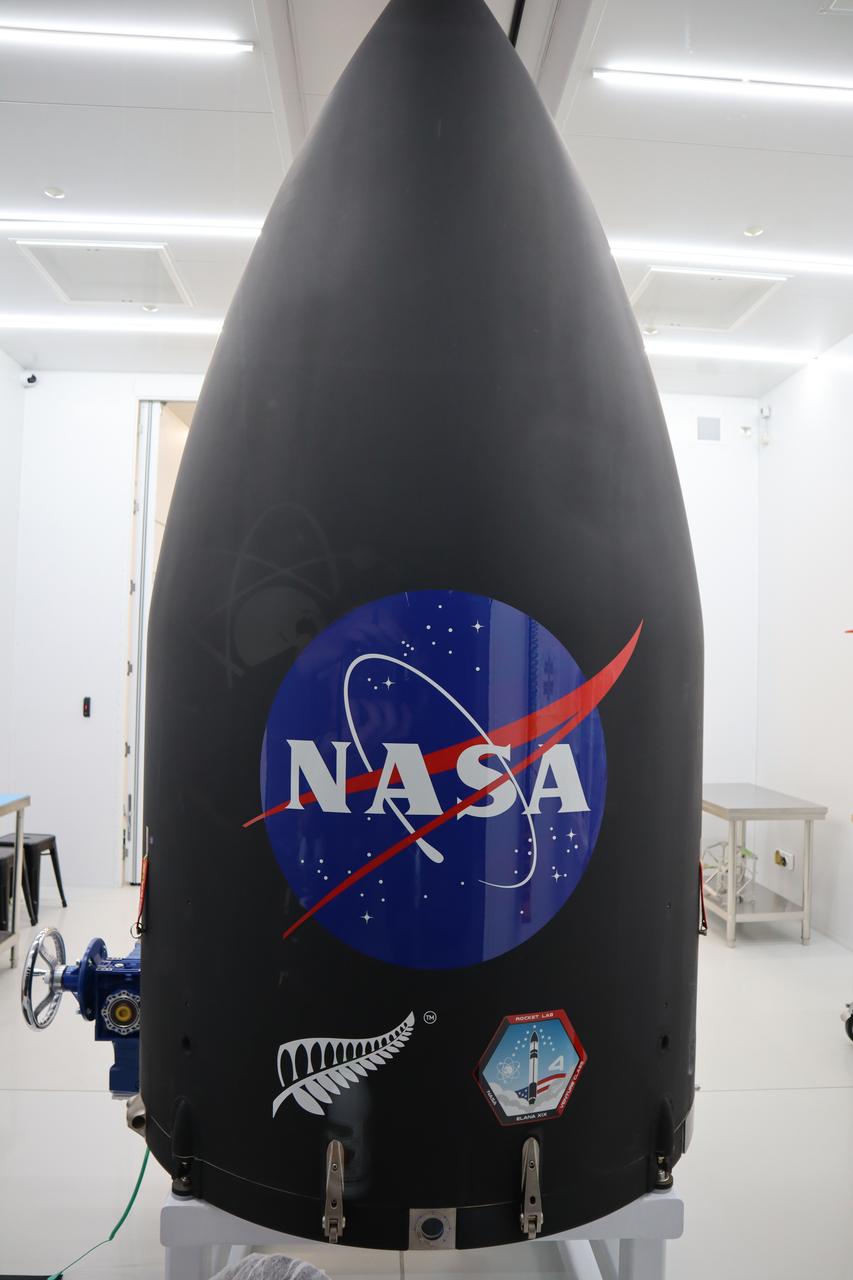

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
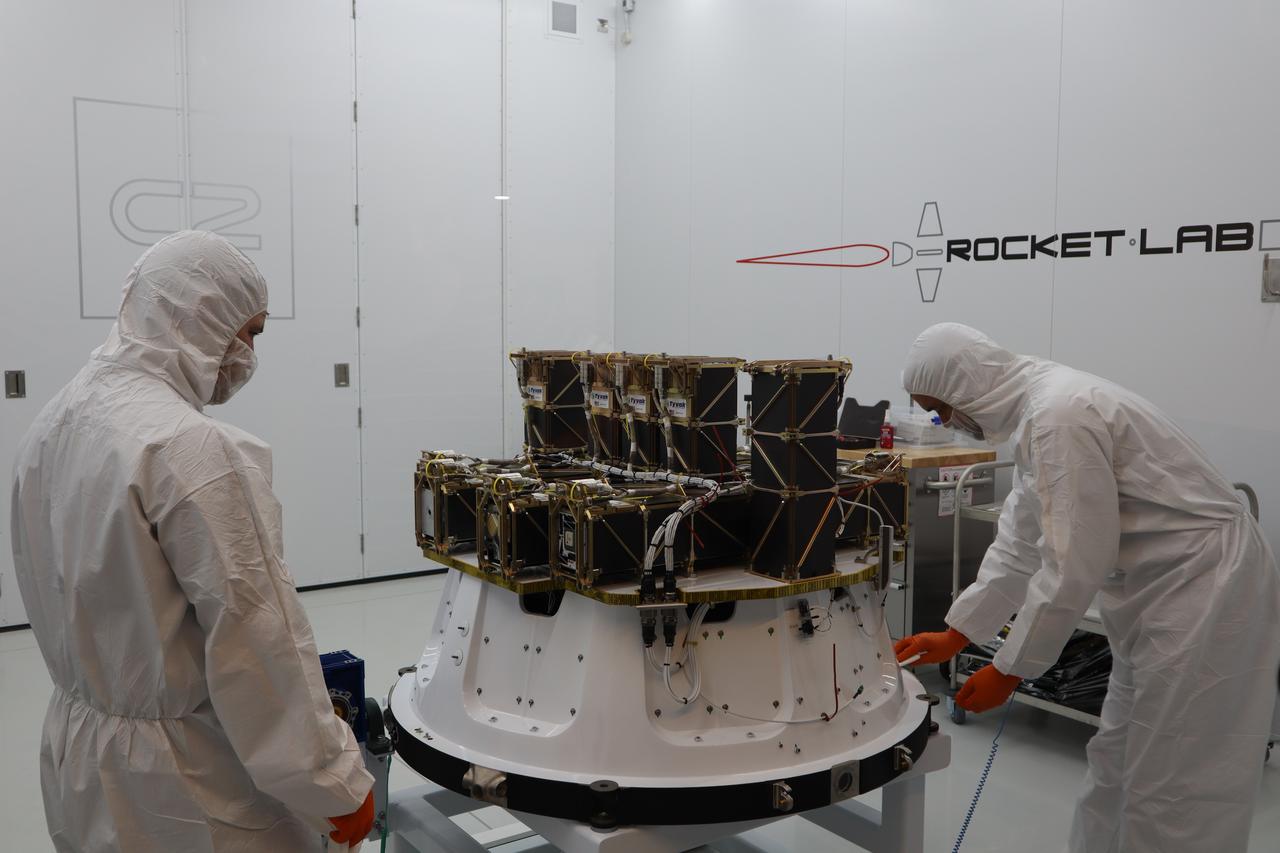

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
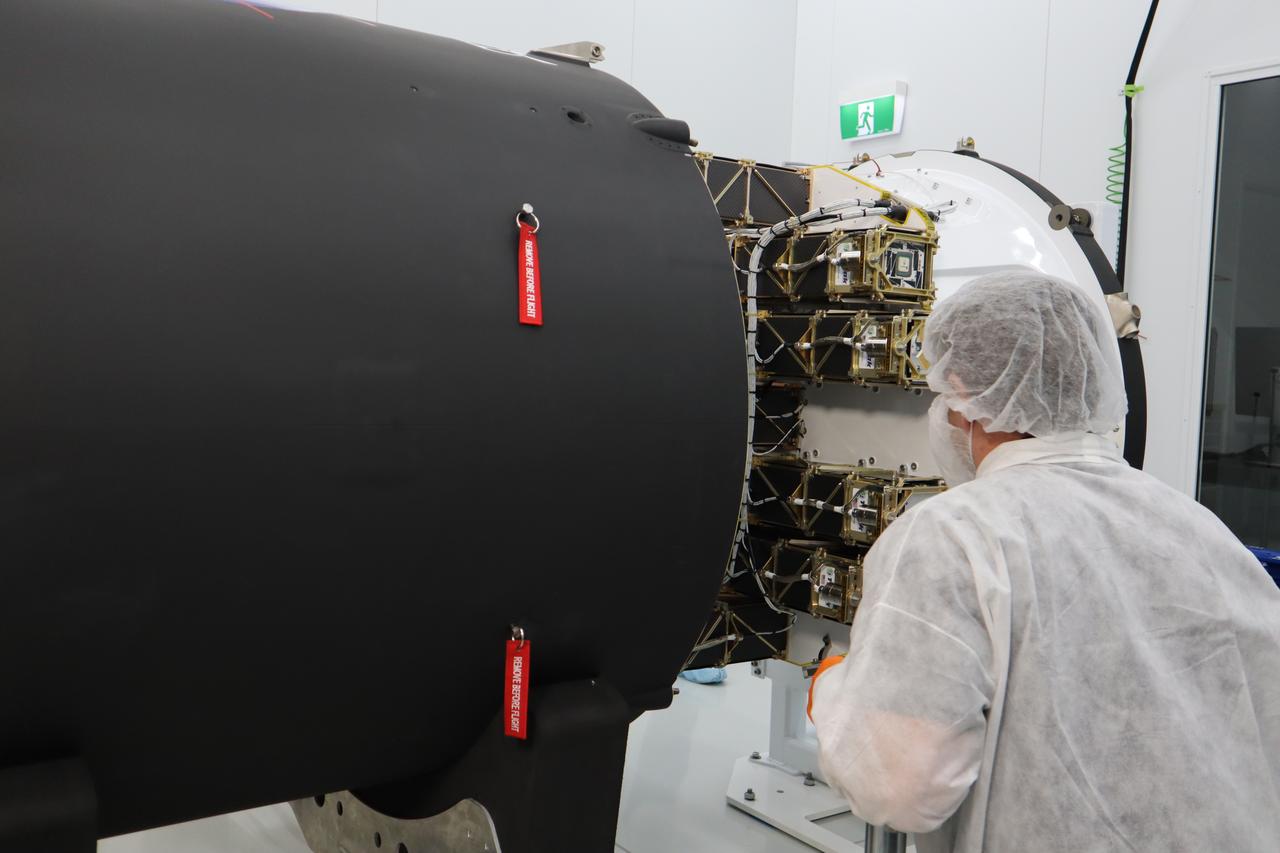

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
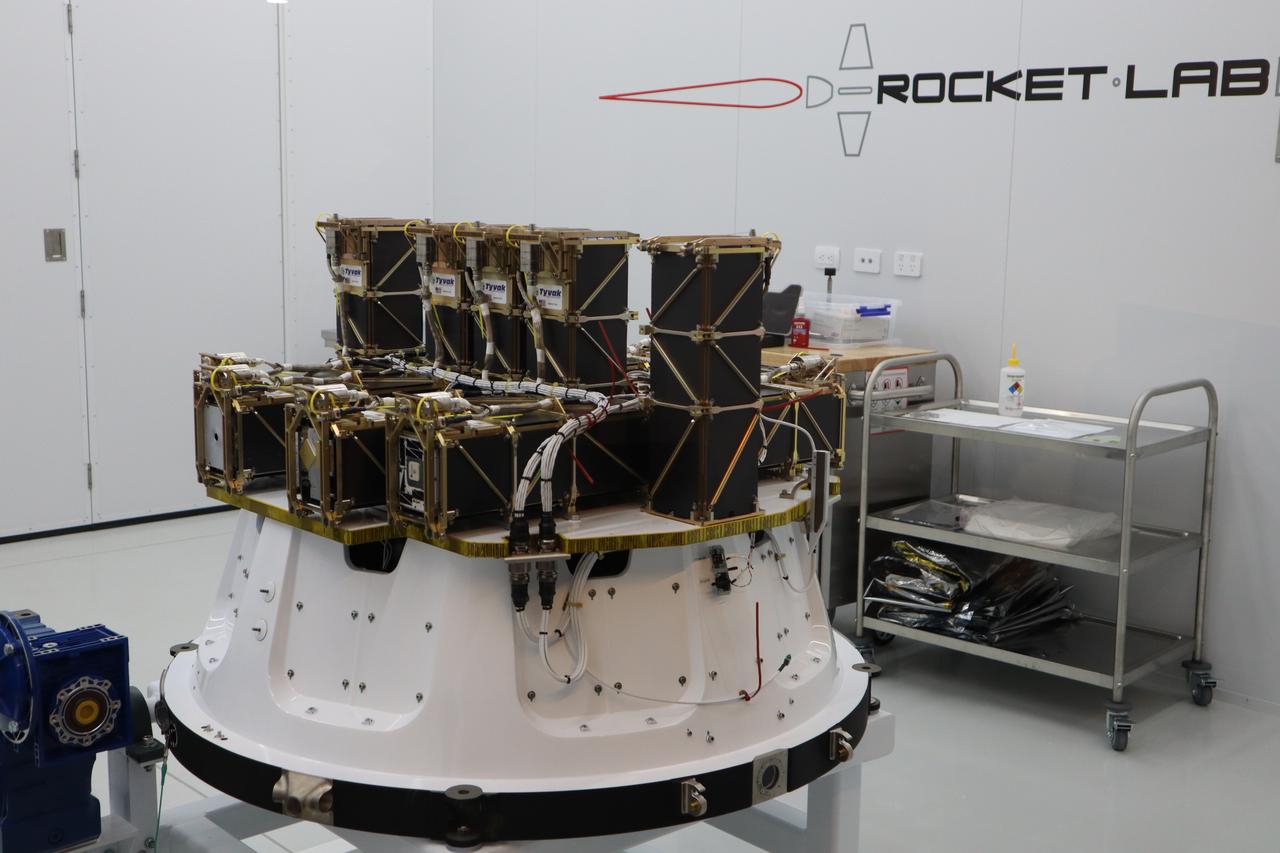

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
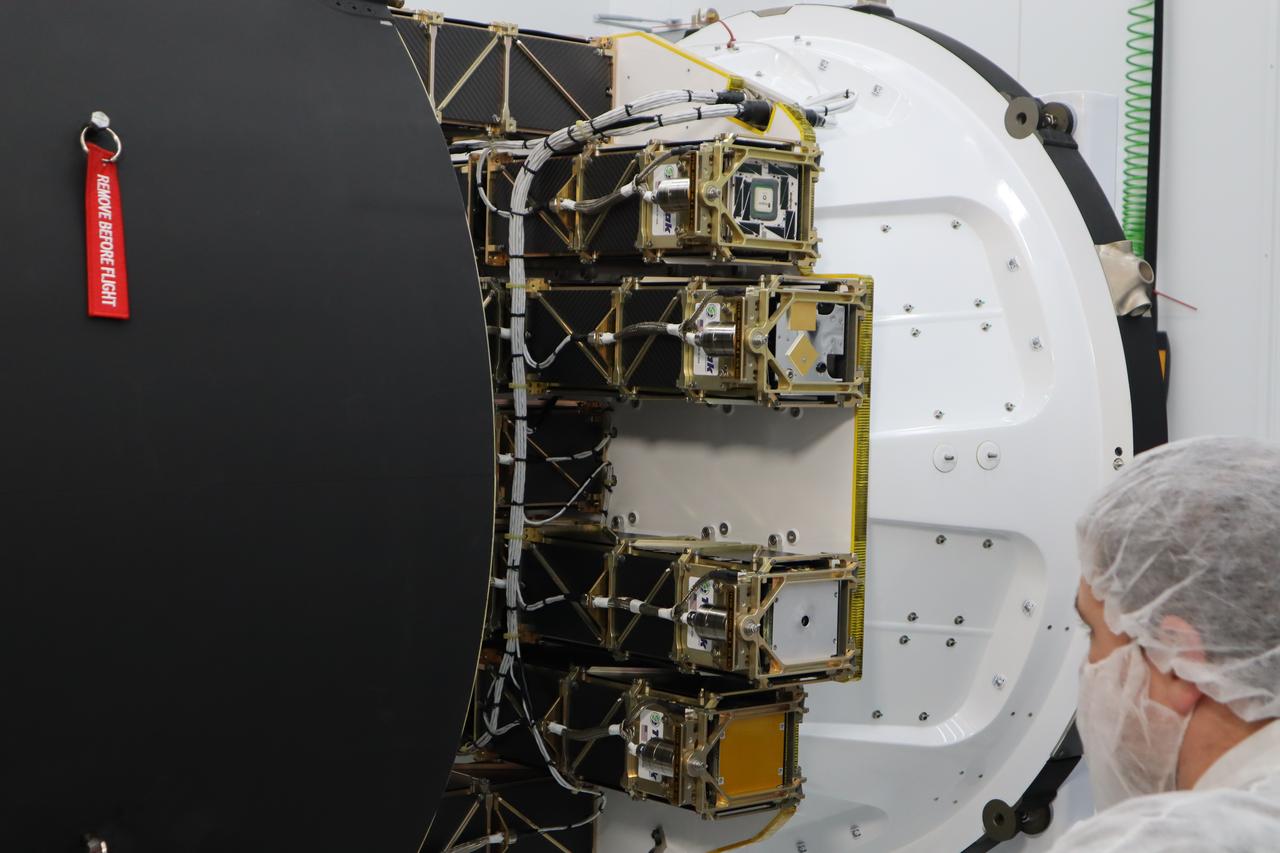
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
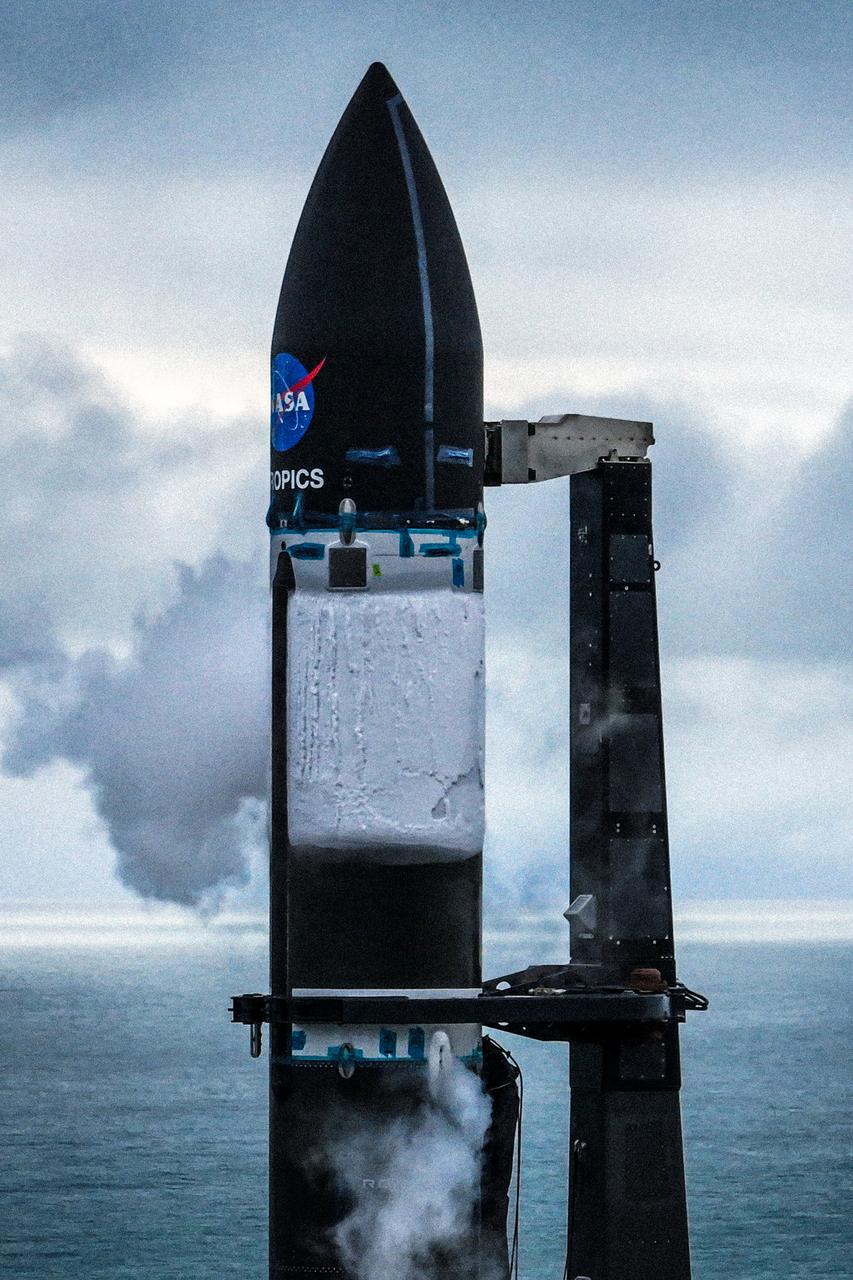

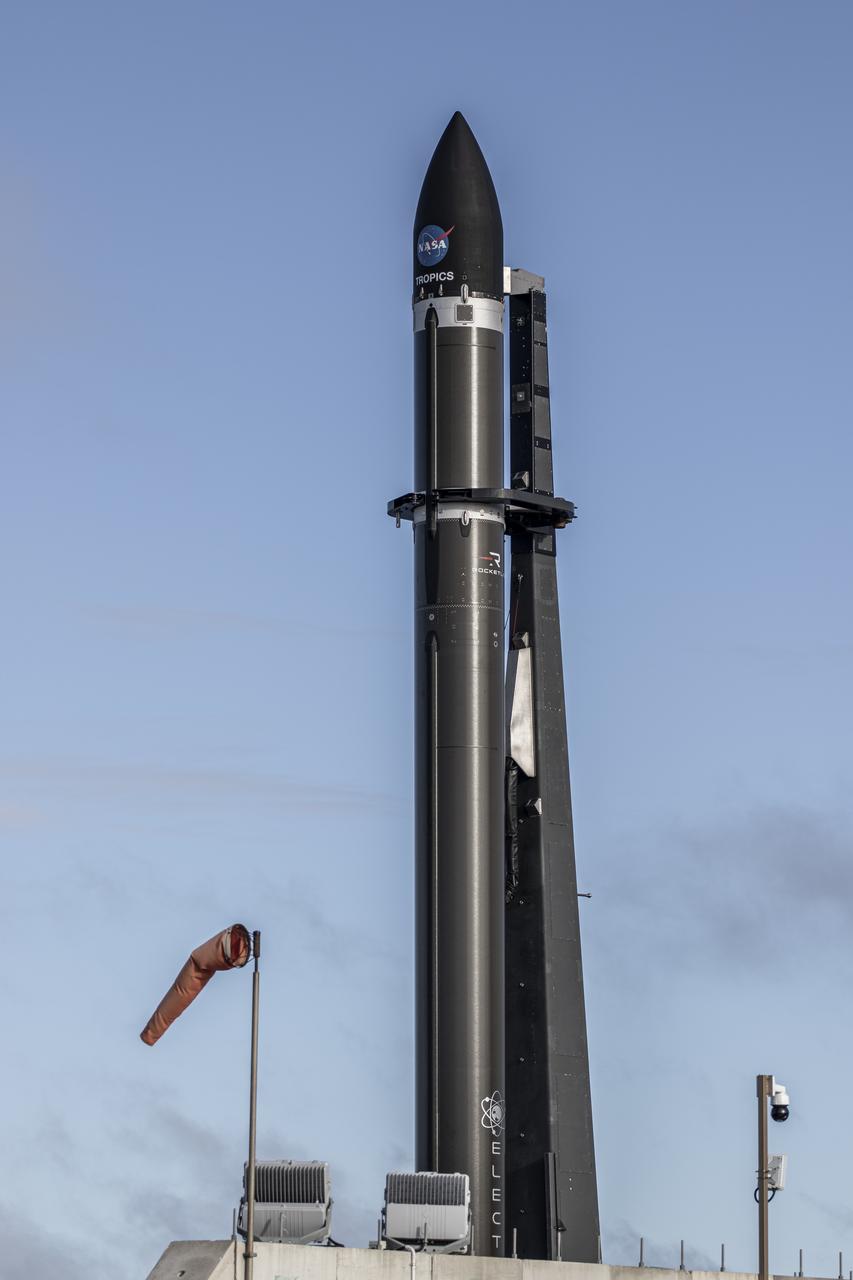
A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
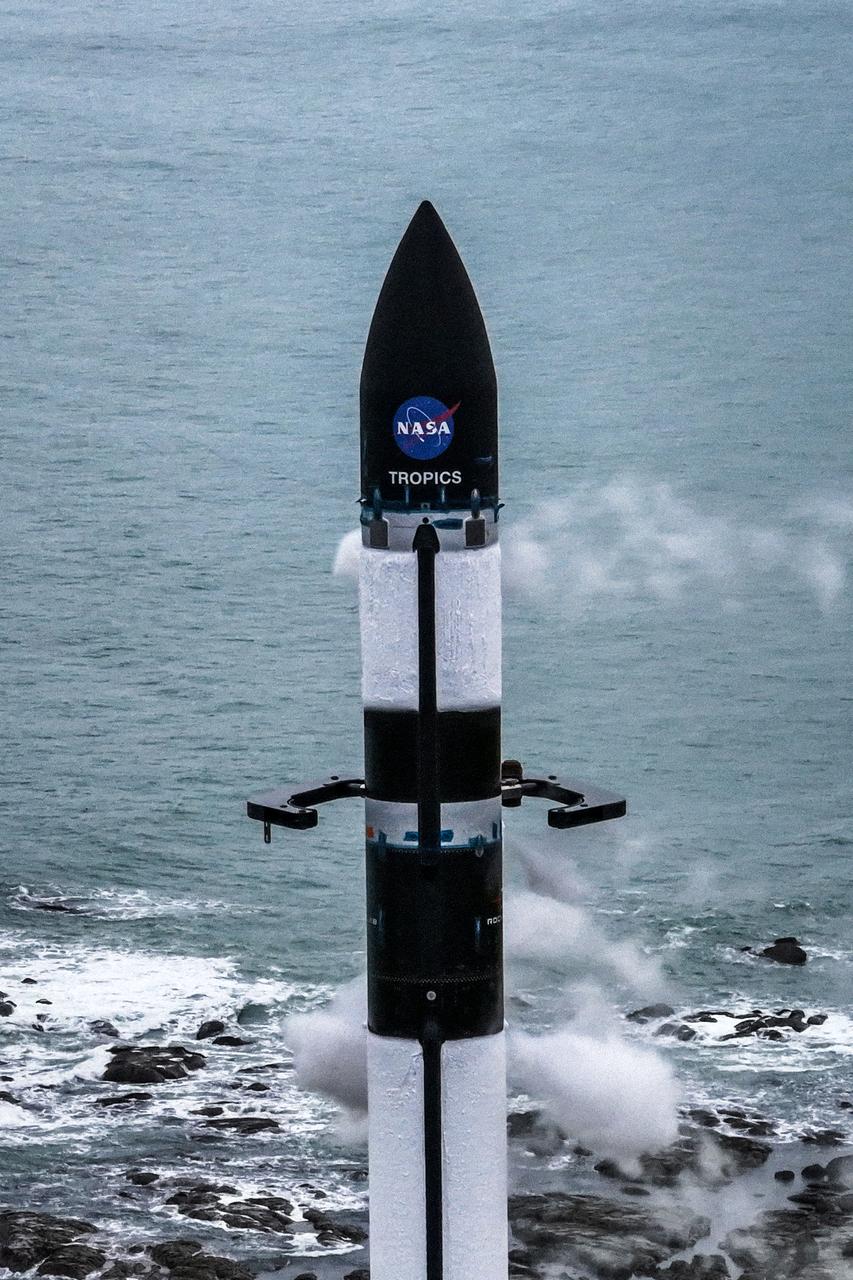

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
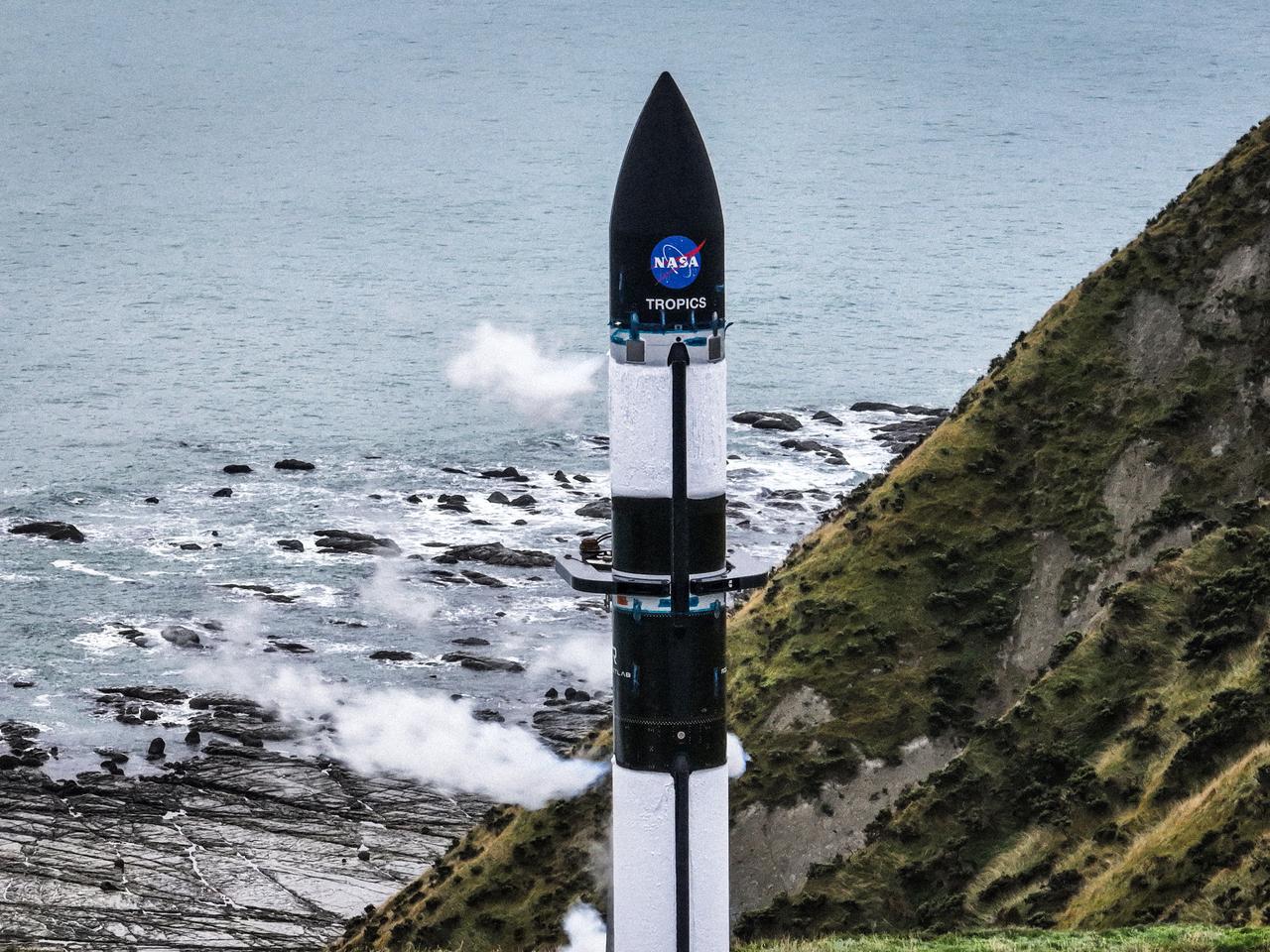

A wet dress rehearsal is underway for Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand on April 28, 2023. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
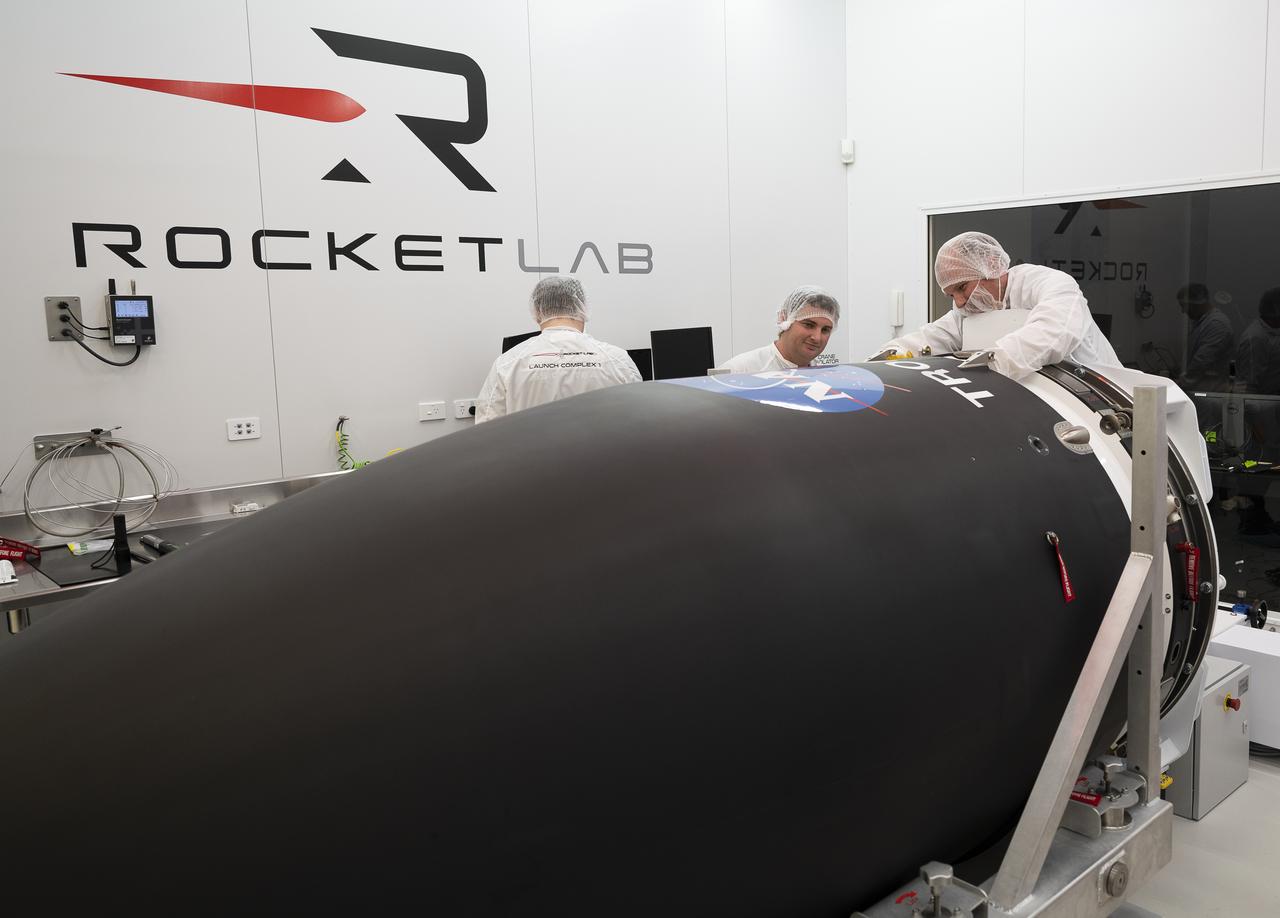

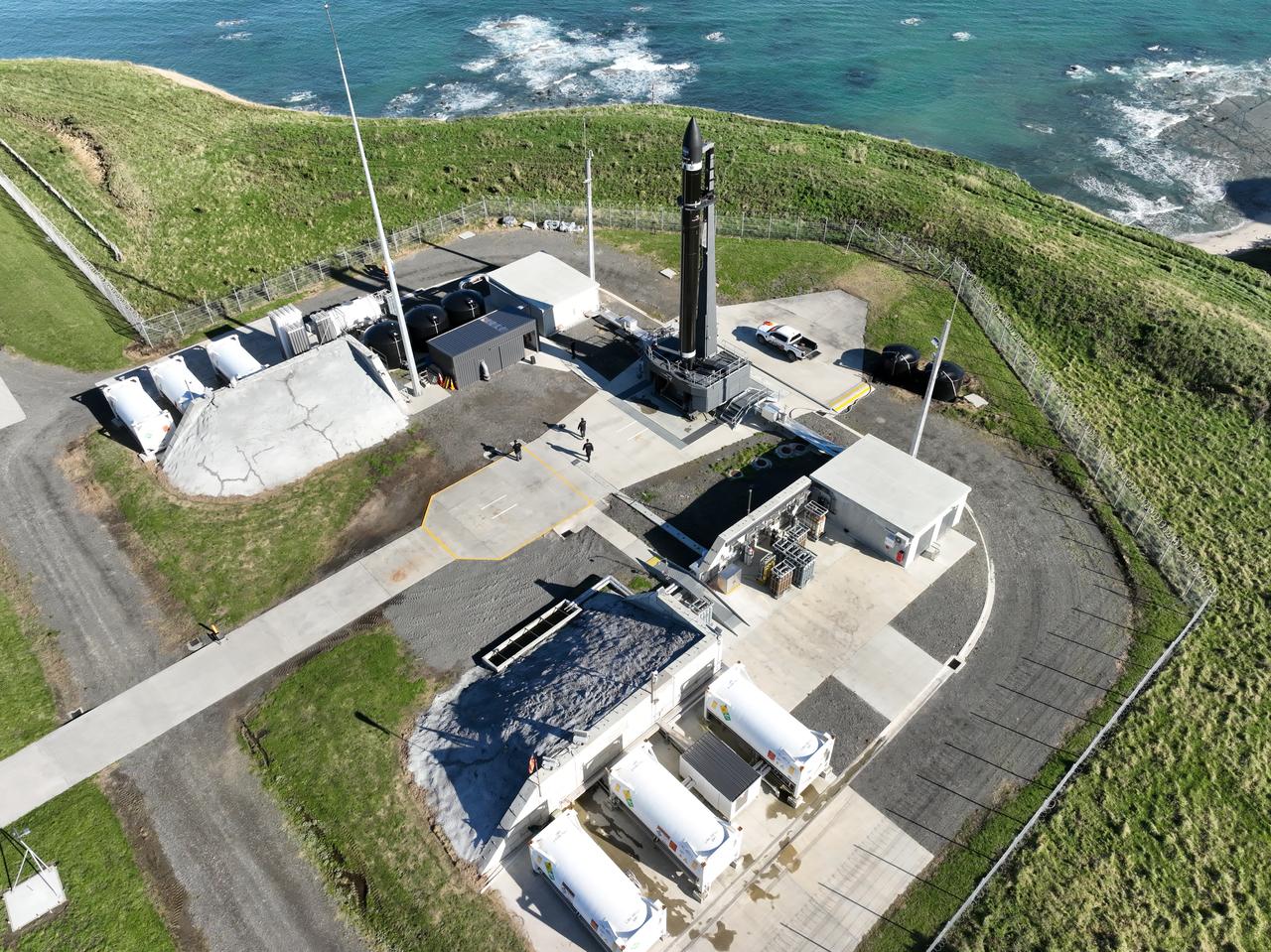
NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are encapsulated inside Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians prepare NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats for encapsulation in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
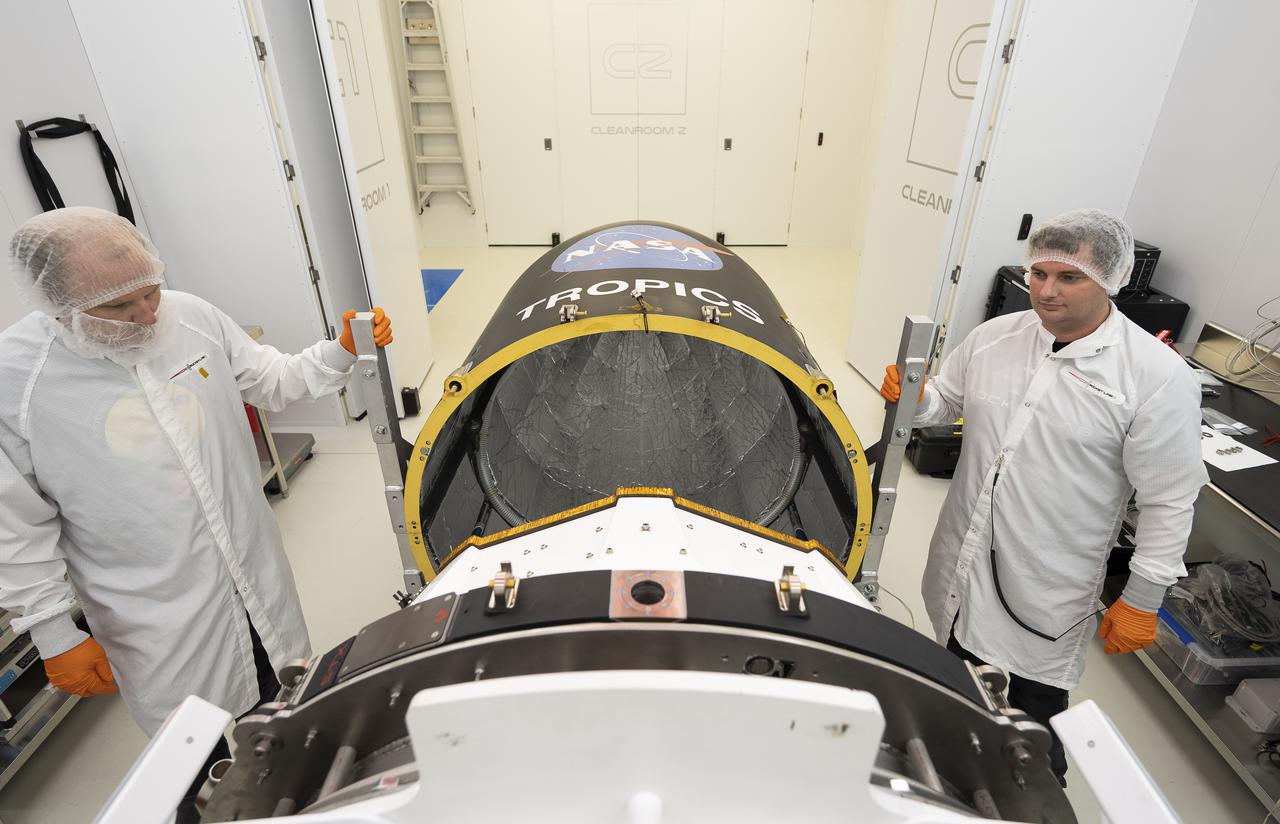

Technicians place NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians check Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
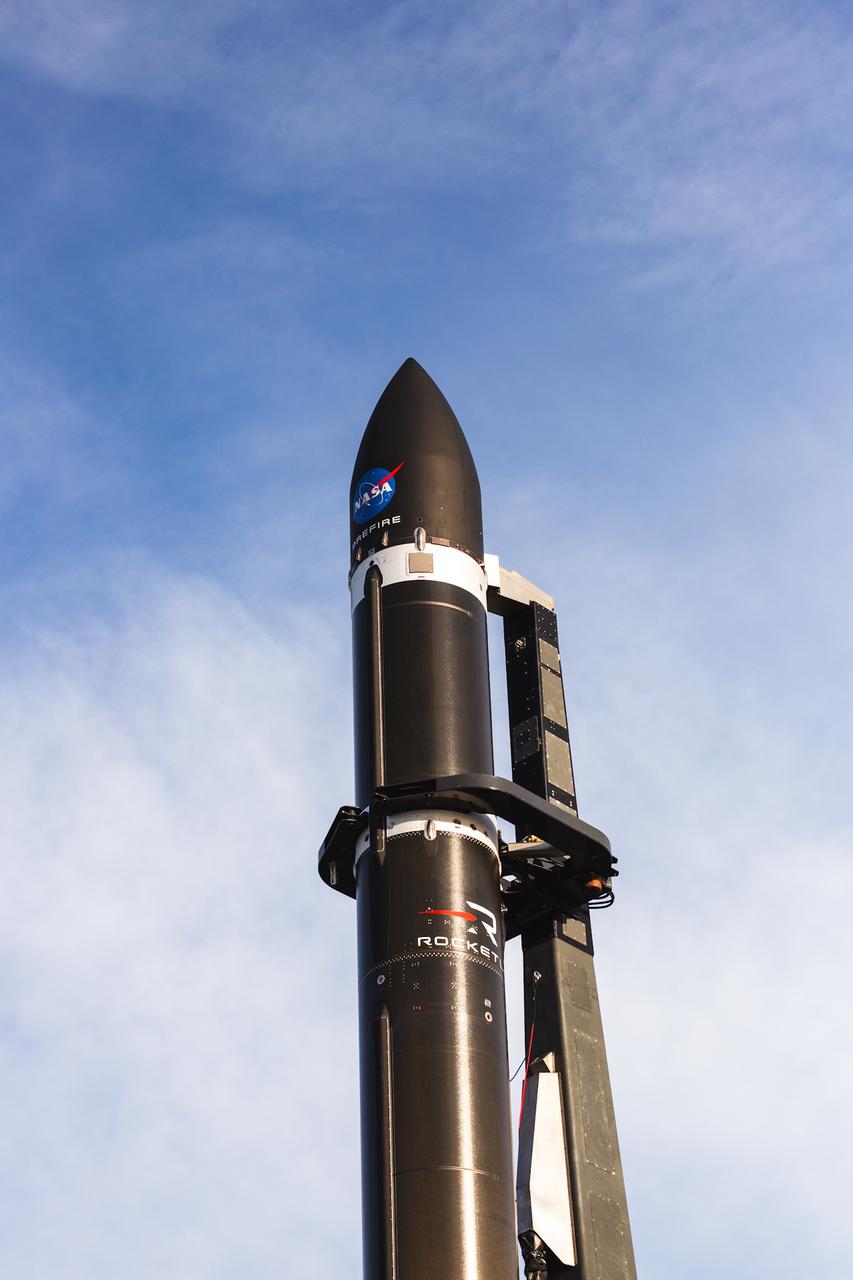

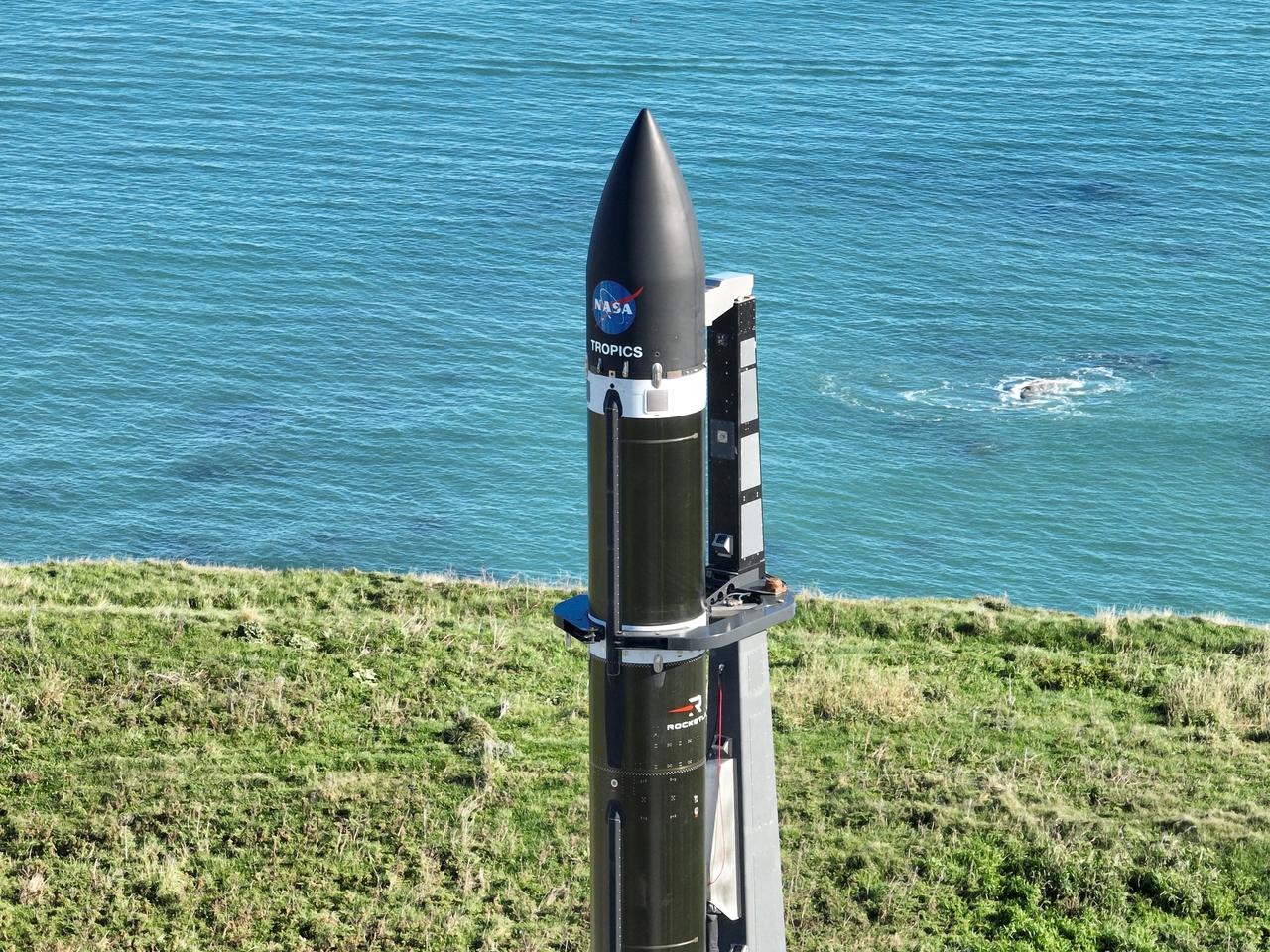
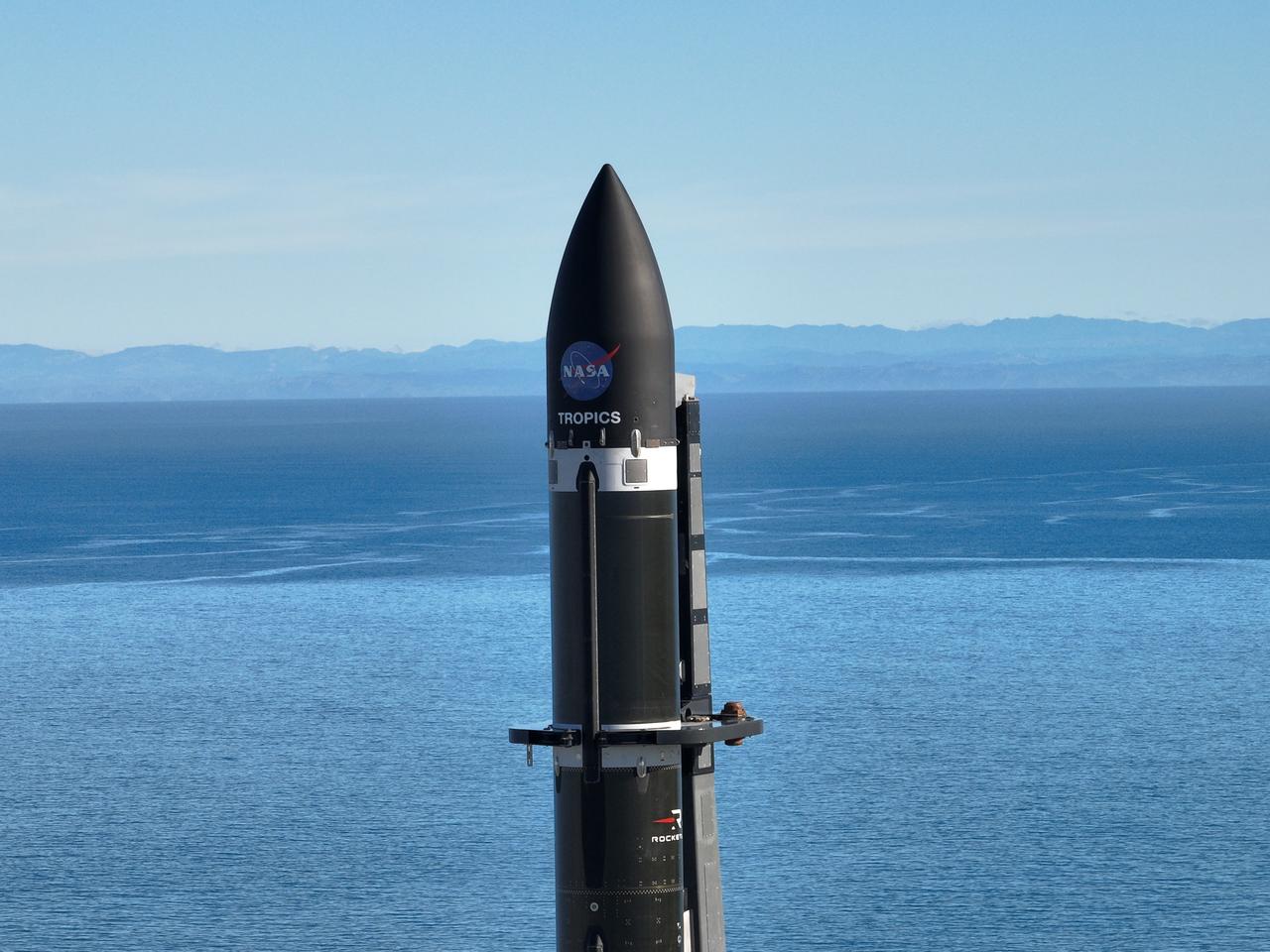
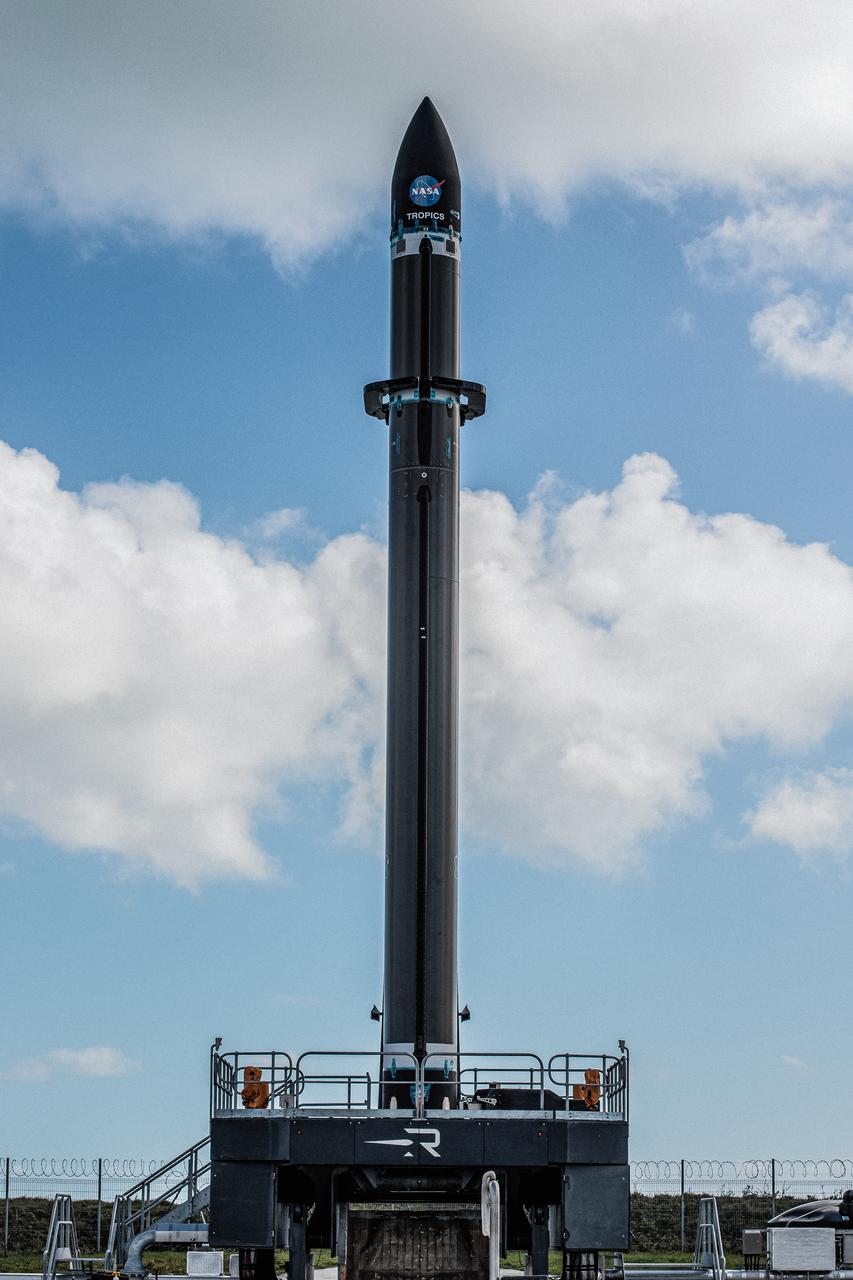
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” is vertical on the pad awaiting liftoff at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, ahead of NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission Wednesday, June 5, 2024. The mission, the second of two launches for NASA’S PREFIRE, features two identical 6U CubeSats in asynchronous, near-polar orbits, will study how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
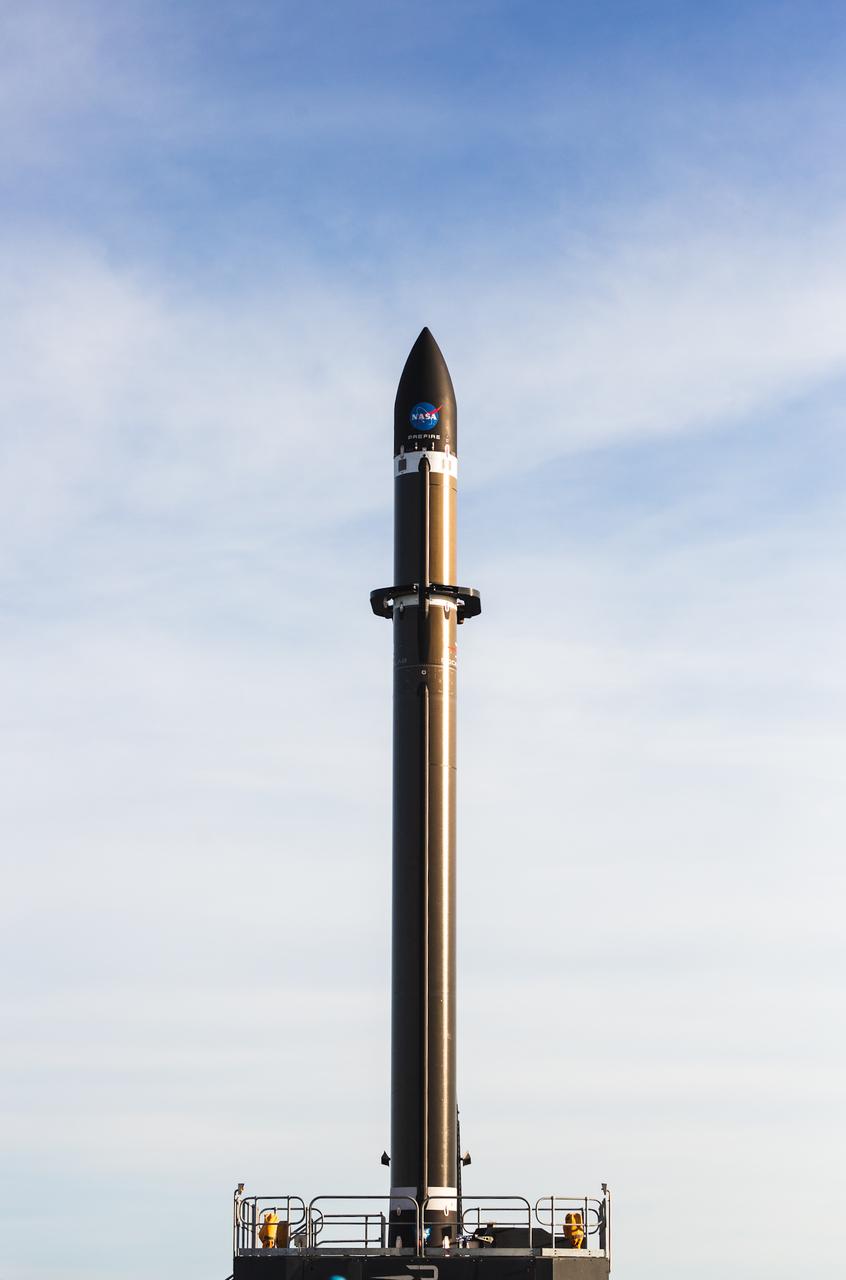

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” is vertical on the pad awaiting liftoff at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, ahead of NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission Wednesday, June 5, 2024. The mission, the second of two launches for NASA’S PREFIRE, features two identical 6U CubeSats in asynchronous, near-polar orbits, will study how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
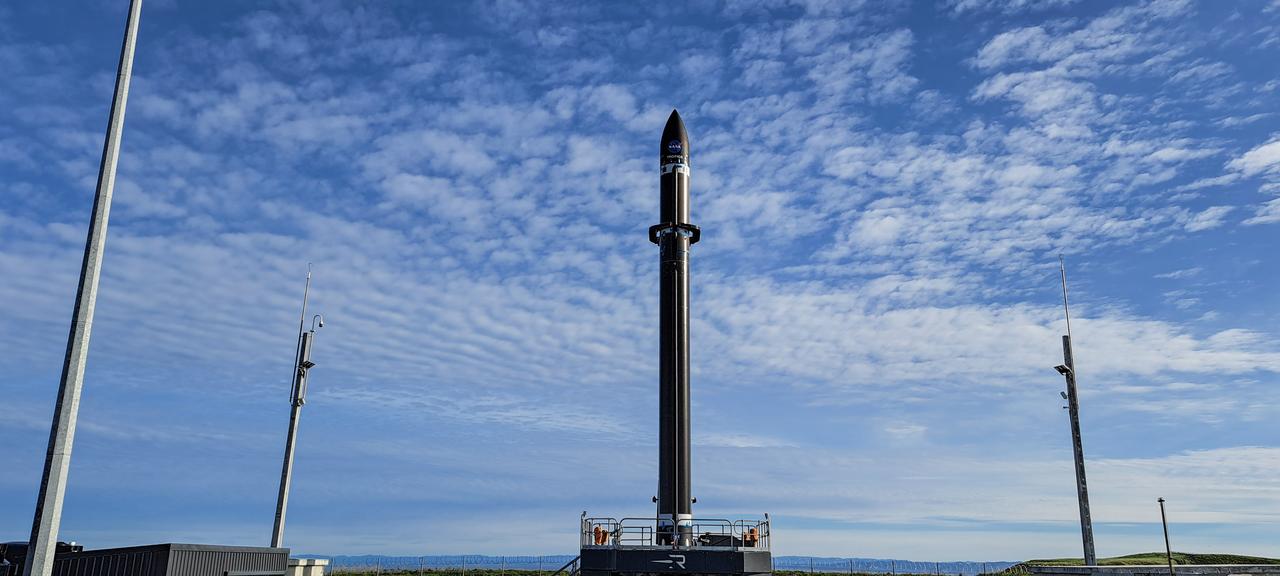

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
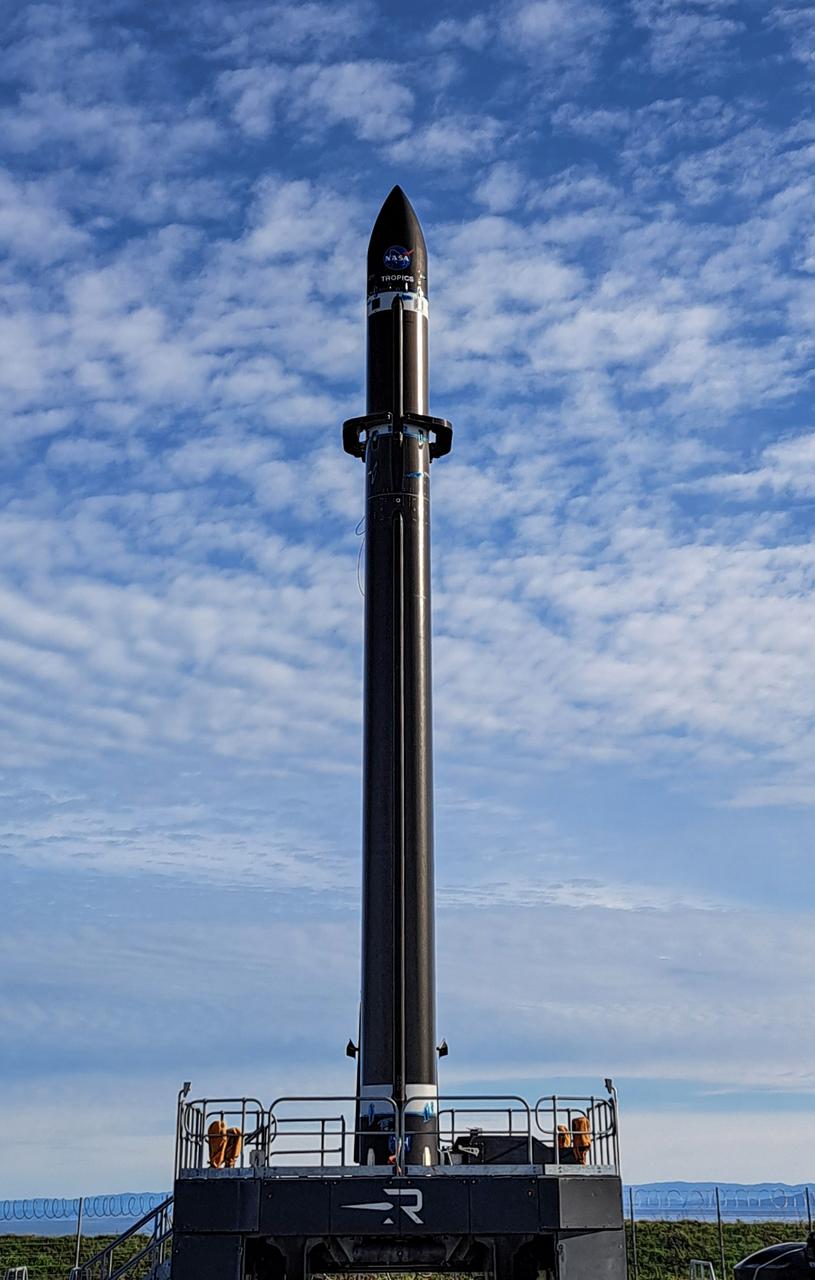

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
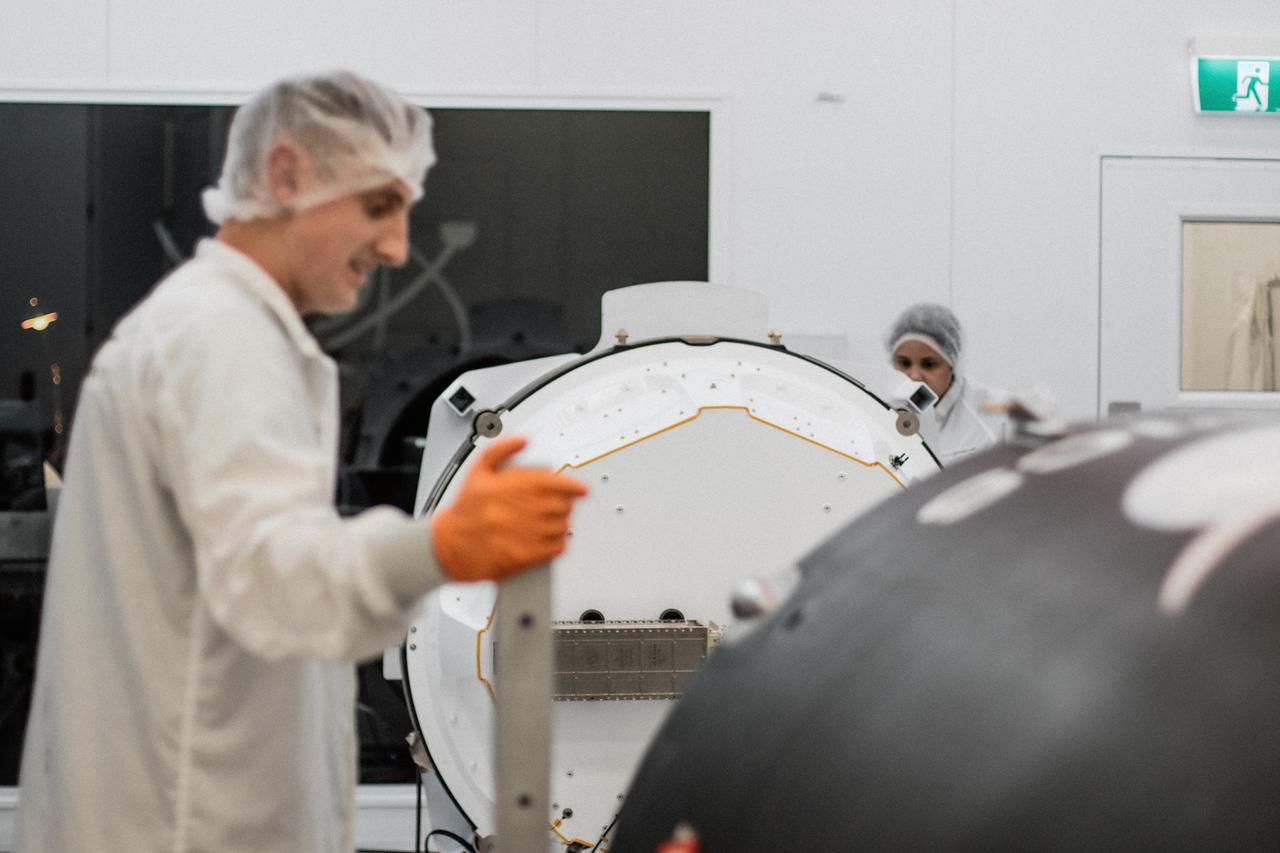

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
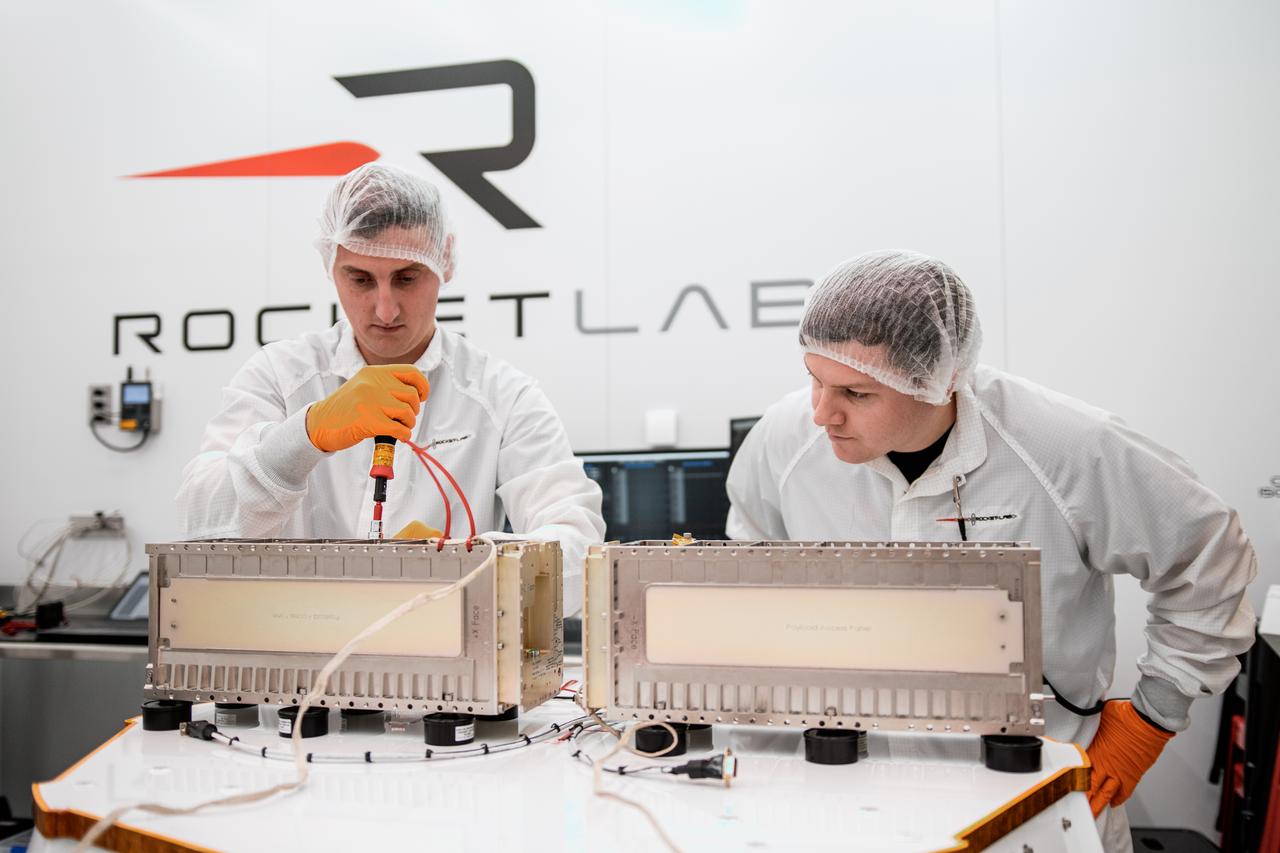

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
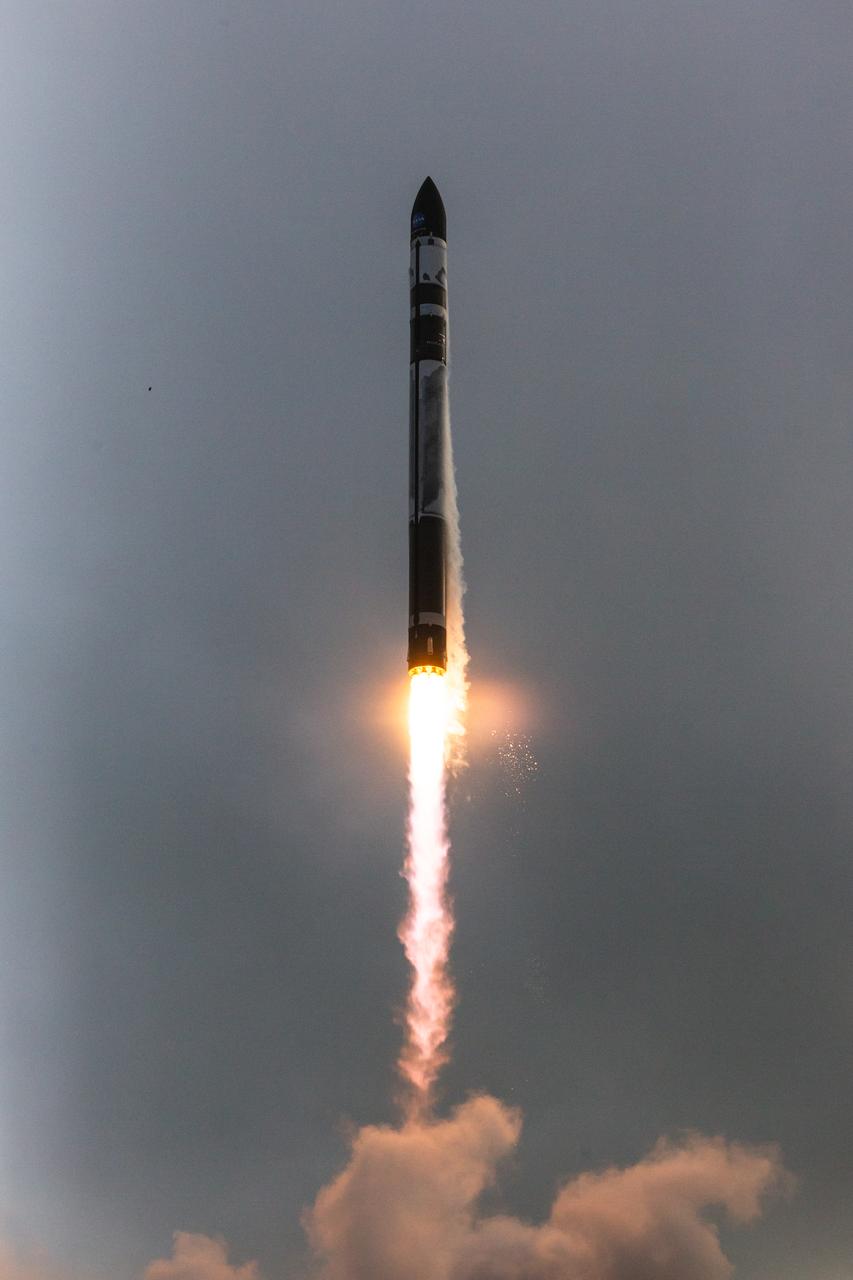

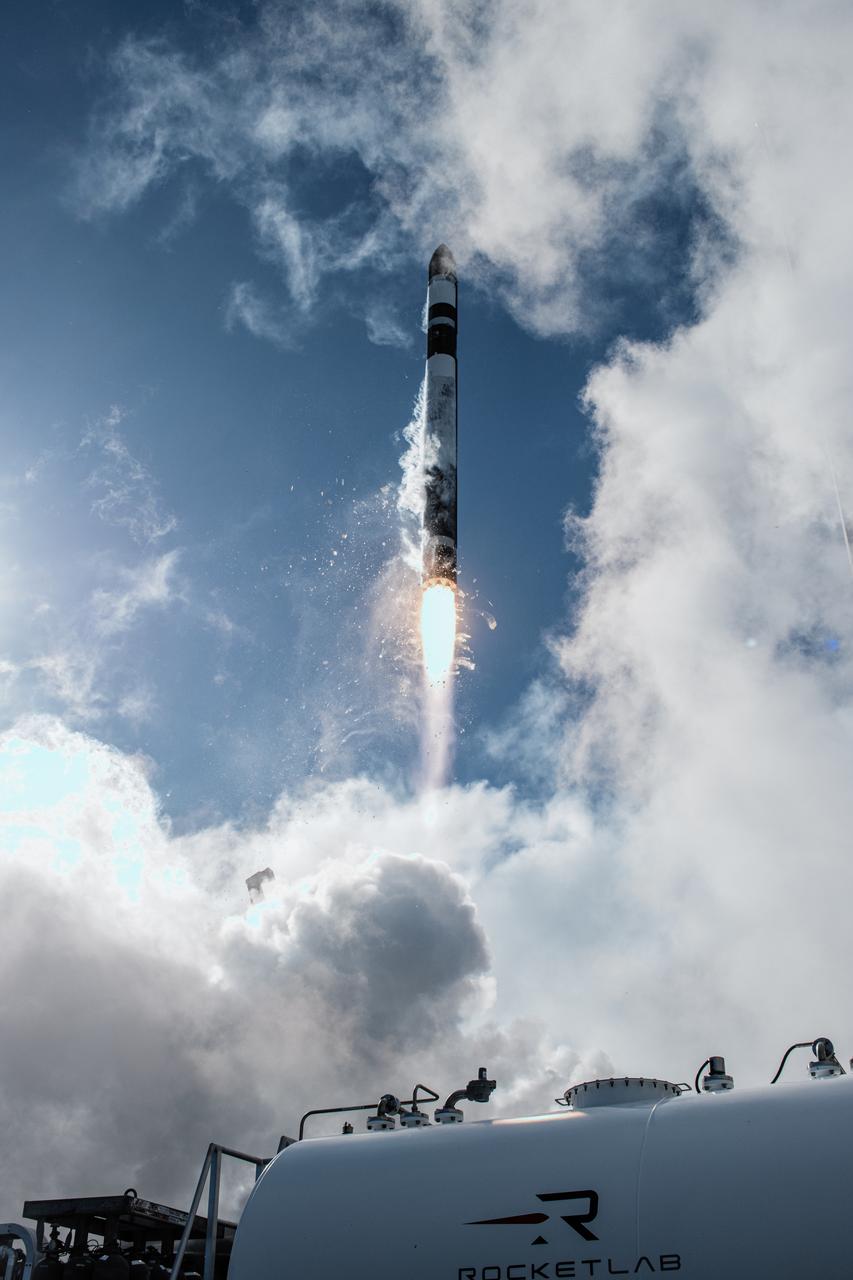
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 3:15 p.m. NZST Wednesday, June 5, 2024 (11:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 4), on the second of two launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment). The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
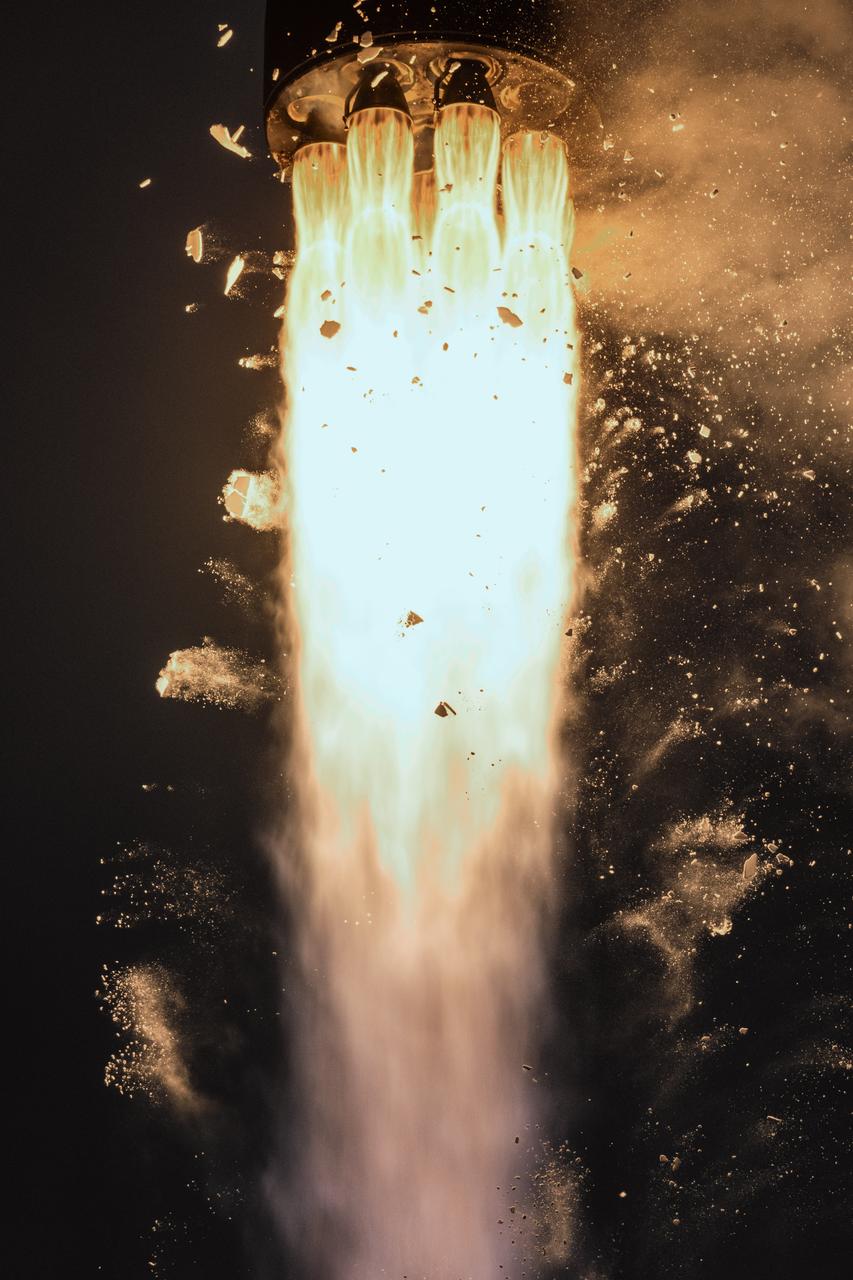

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 3:15 p.m. NZST Wednesday, June 5, 2024 (11:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 4), on the second of two launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment). The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
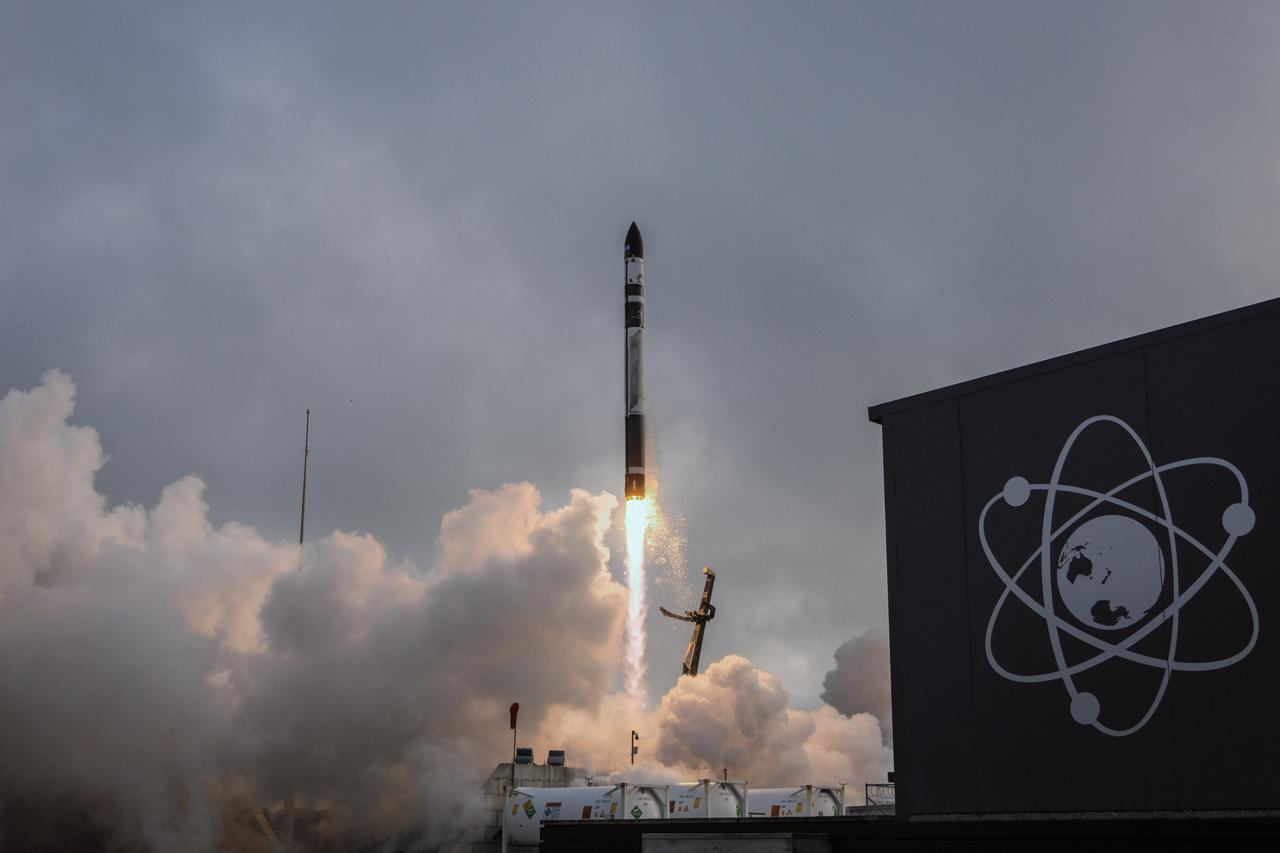

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 3:15 p.m. NZST Wednesday, June 5, 2024 (11:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 4), on the second of two launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment). The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
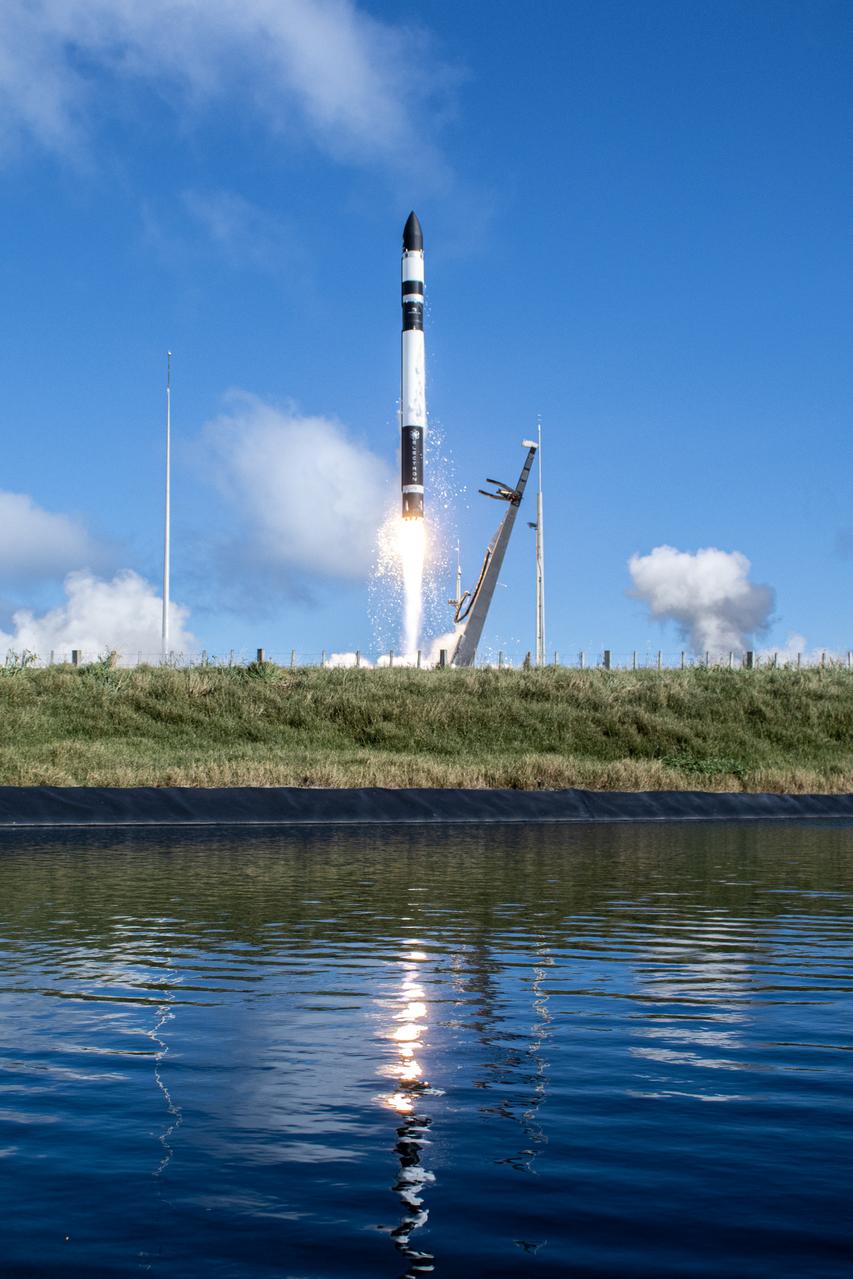

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
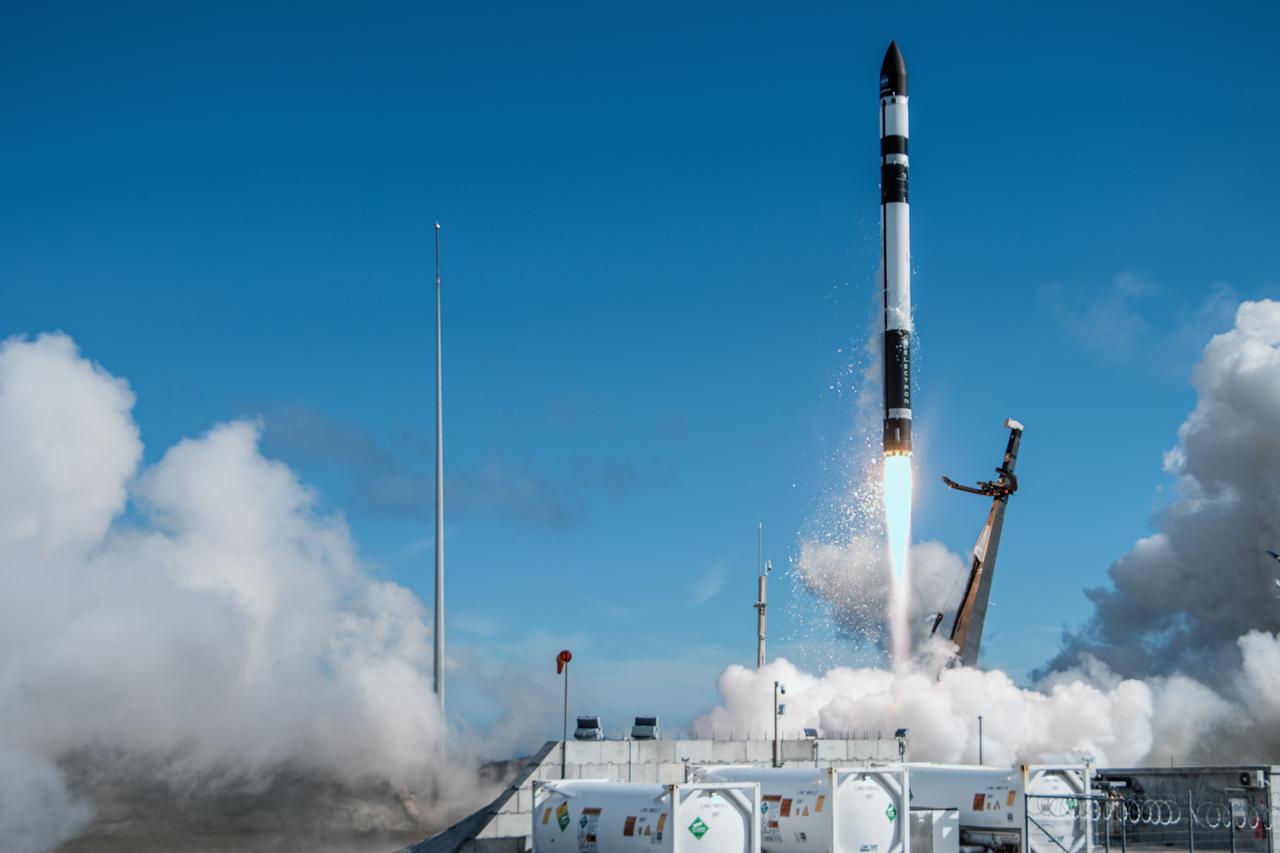

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
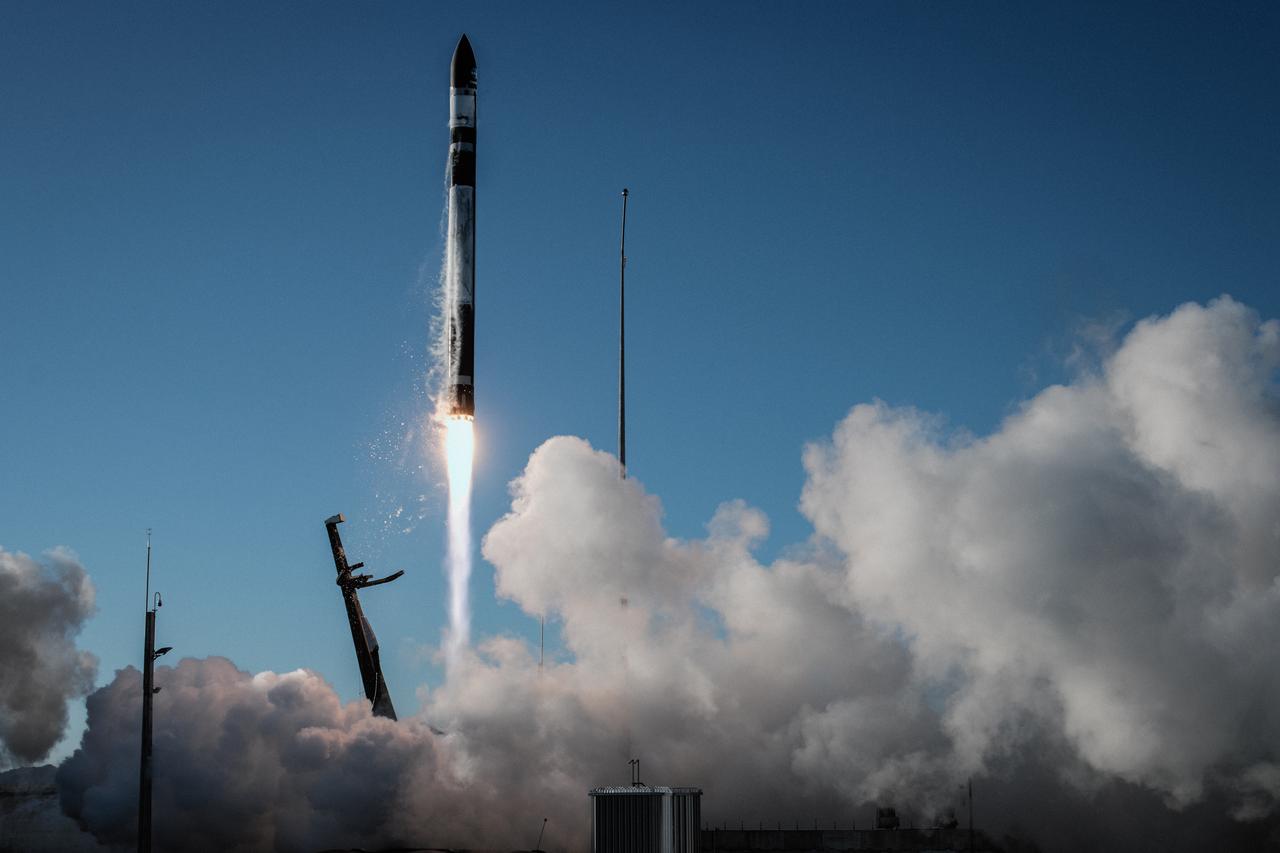

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket is poised for launch atop Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand. Launch time is May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT). The Electron rocket is carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
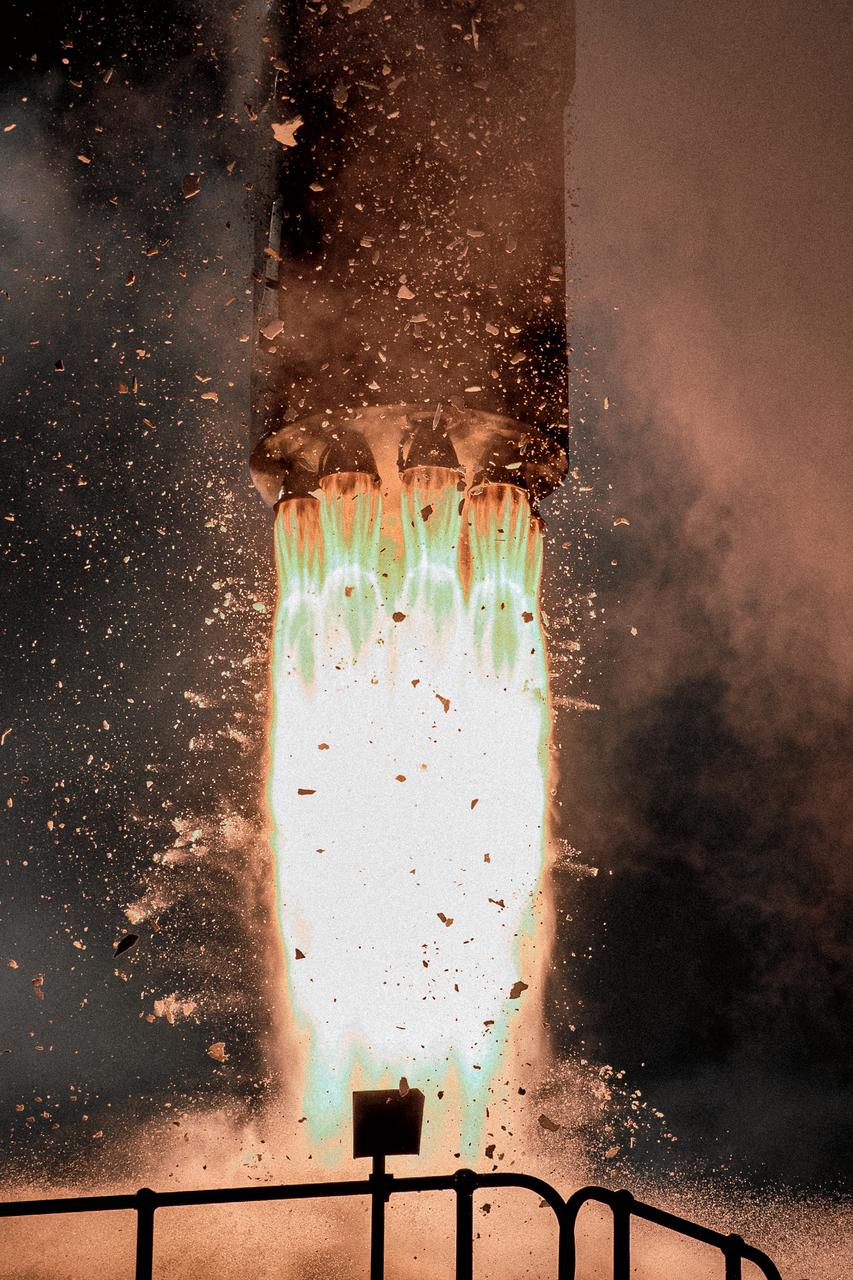

The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
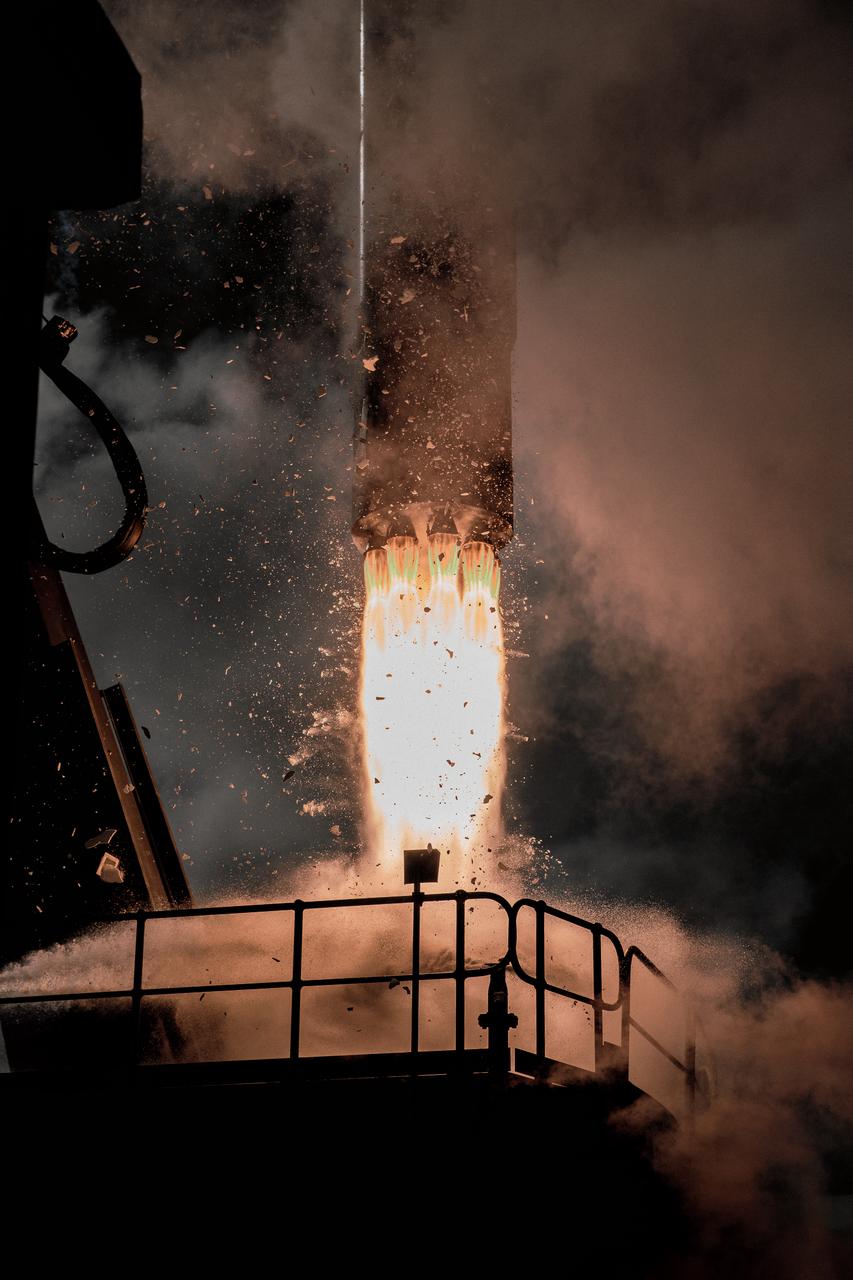

The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
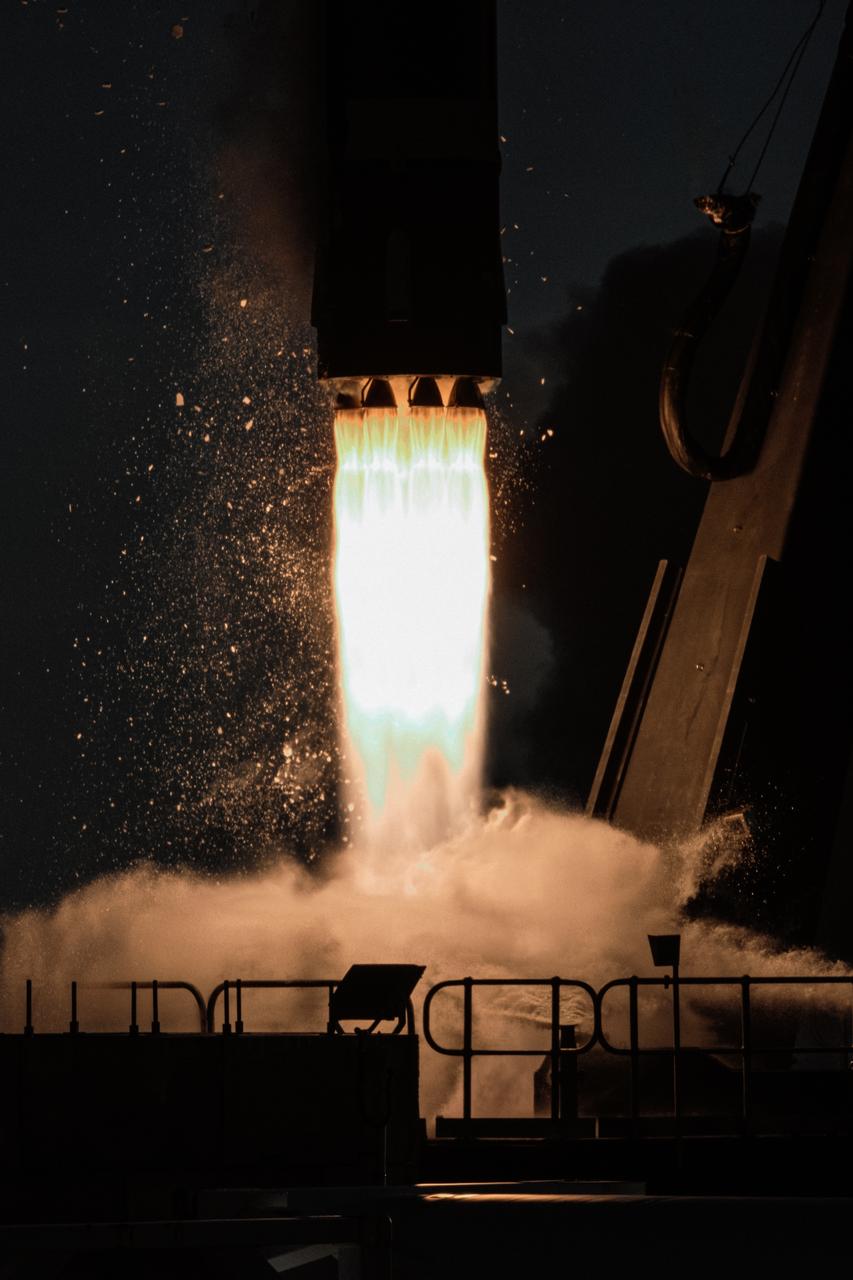

The first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignites at liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
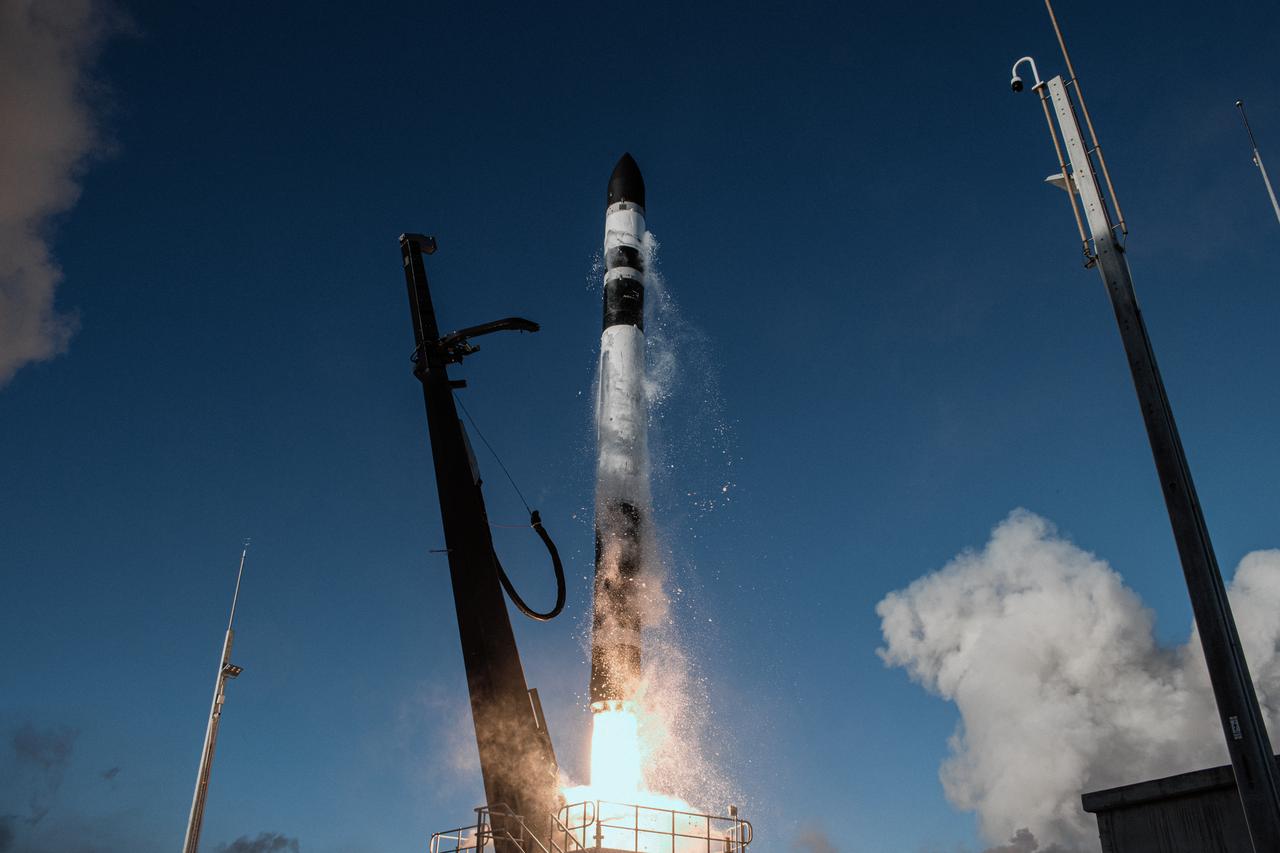

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
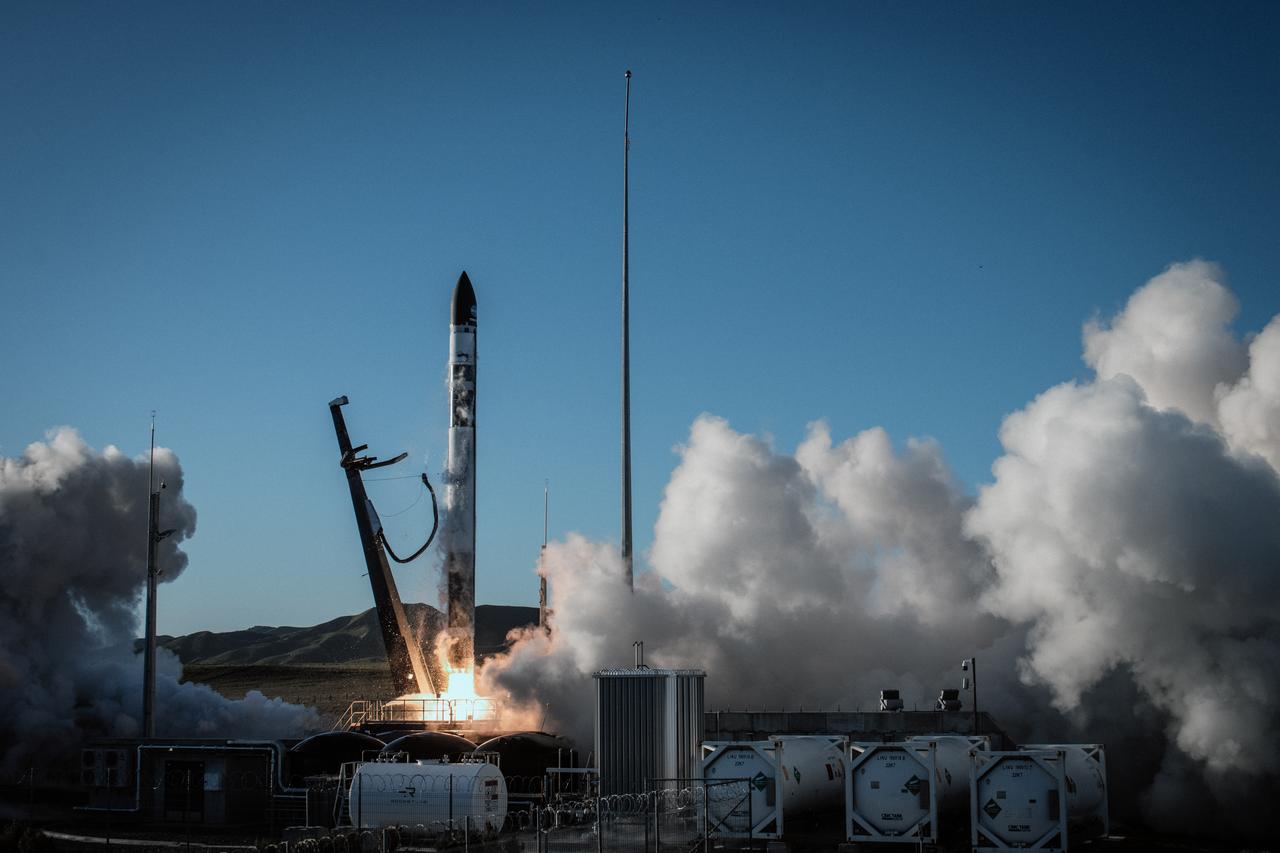

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
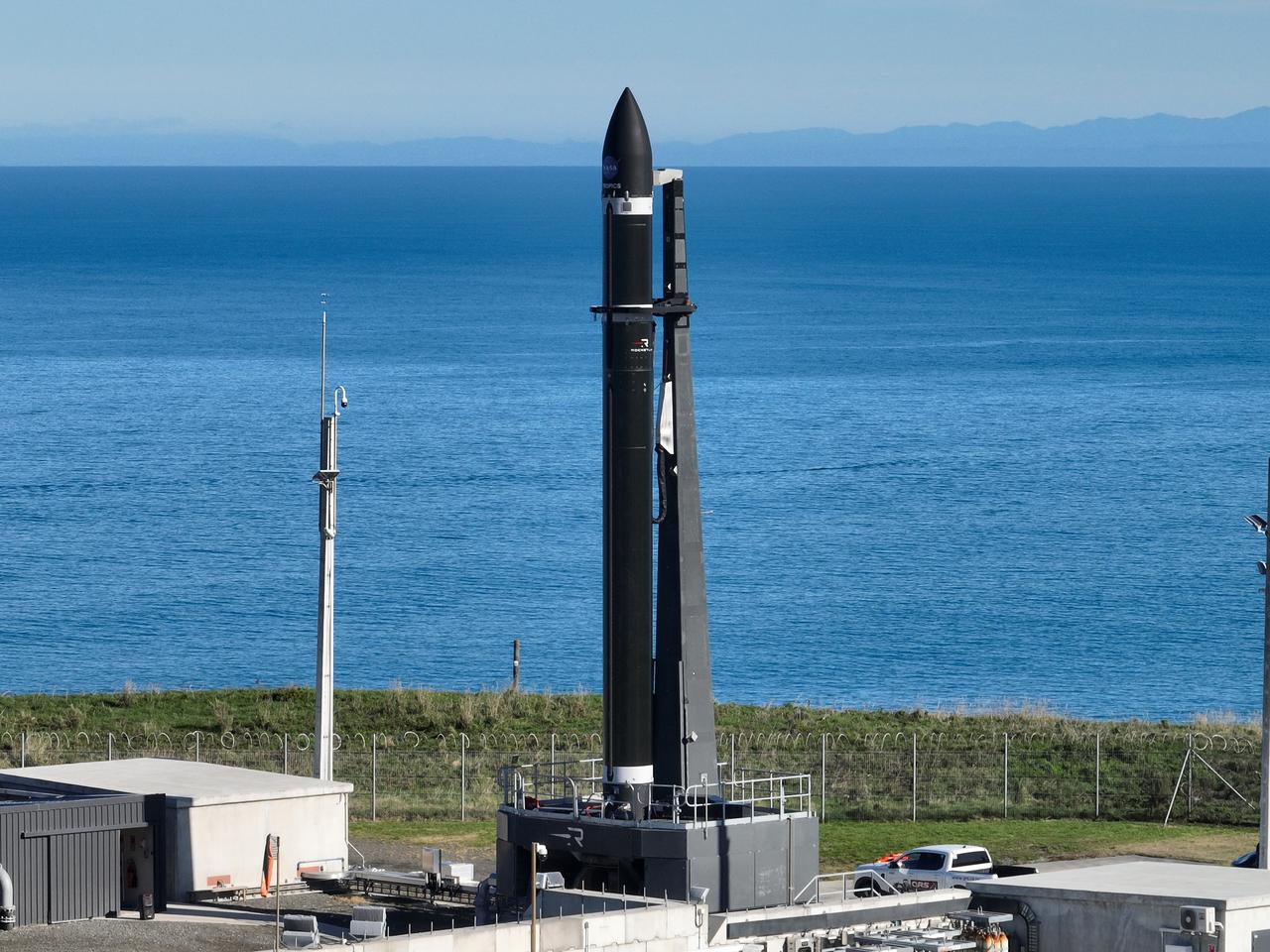

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
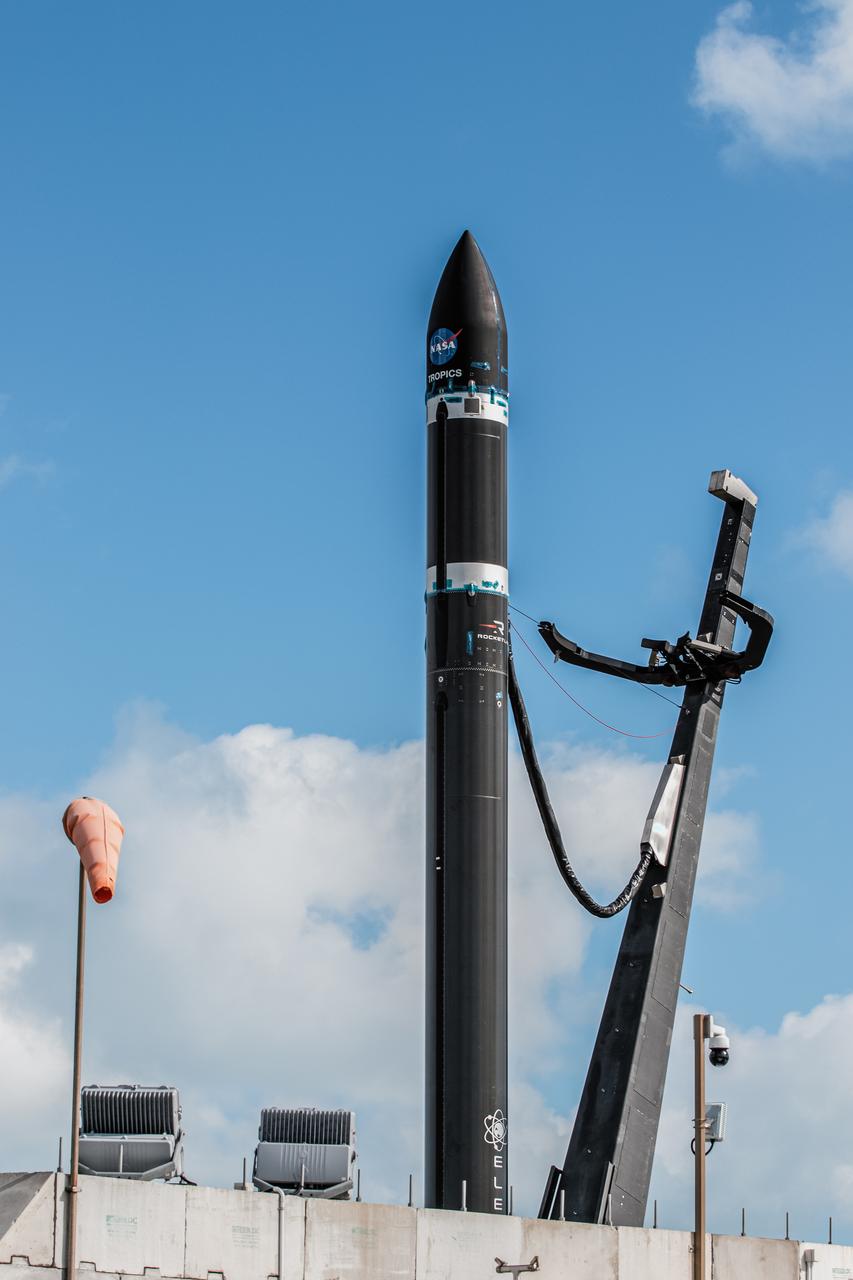

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
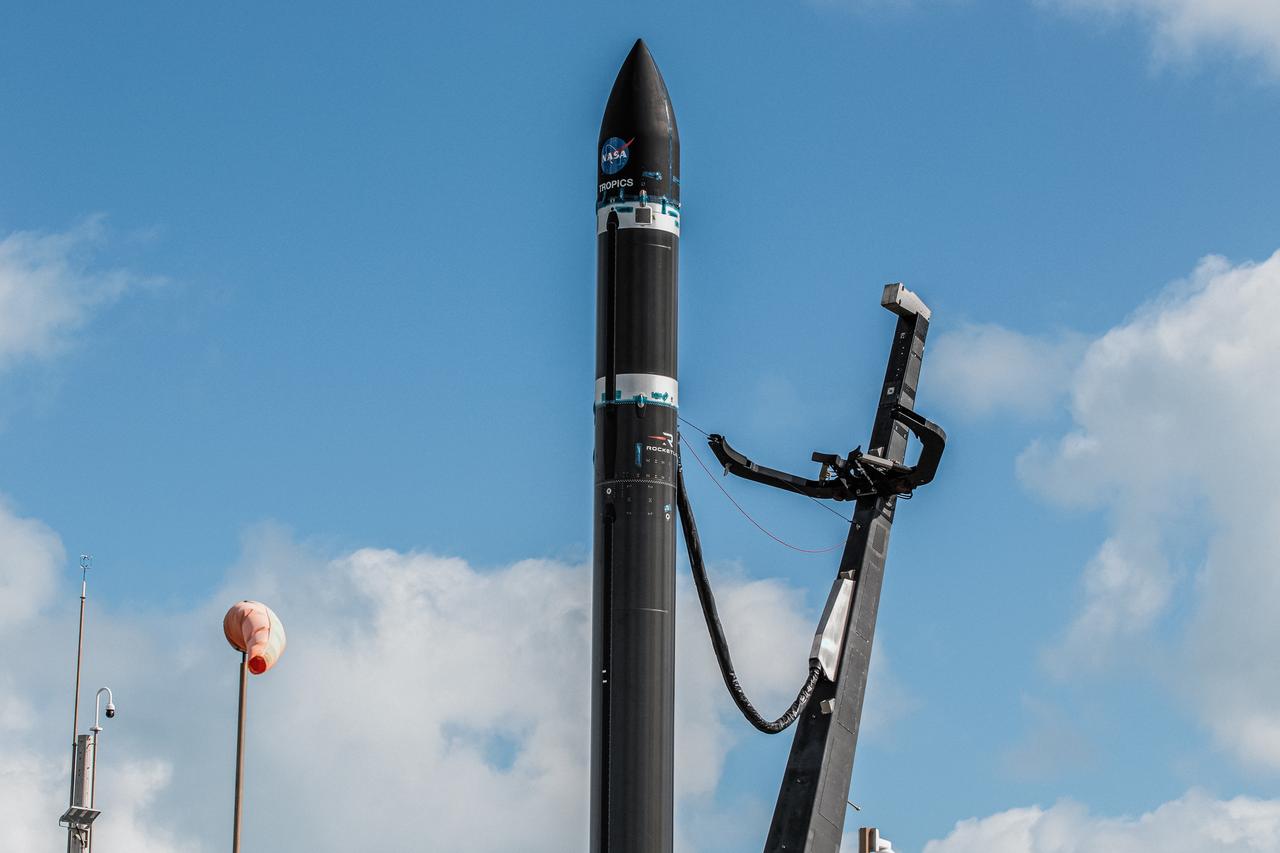

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
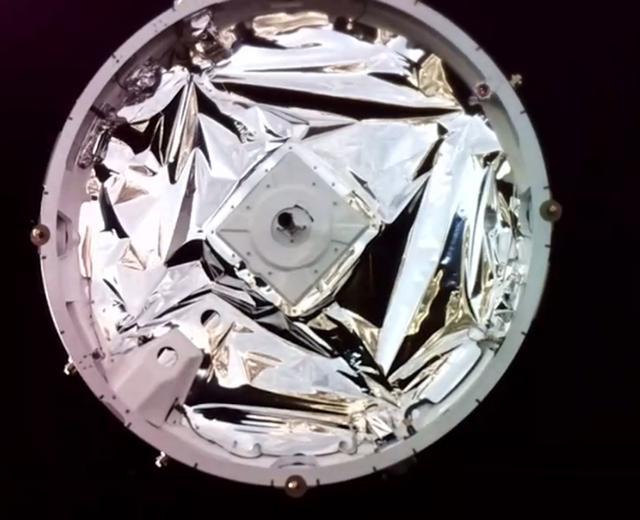

NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites-19 (ELaNa-19) payload after separation from a Rocket Lab Electron rocket after successful liftoff from Launch Complex-1 at Māhia Peninsula in New Zealand. Launched at 6:33 a.m. UTC on Dec. 17 (1:33 p.m. EST on Dec 16), this marks the first flight of a payload under NASA’s Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS). Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to provide increased access to space specifically for payloads like this, carrying small spacecraft called CubeSats. The successful launch and deployment officially begins the venture-class era.
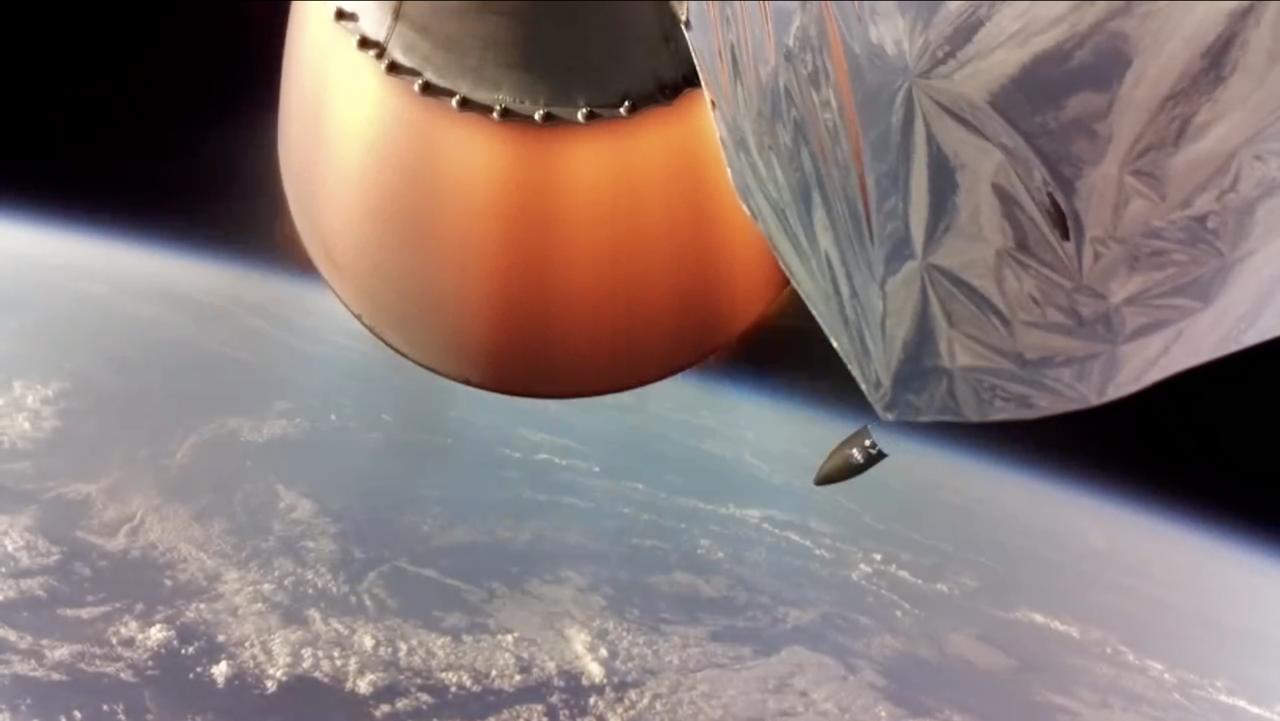

NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites-19 (ELaNa-19) payload separates from the upper stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket after successful liftoff from Launch Complex-1 at Māhia Peninsula in New Zealand. Launched at 6:33 a.m. UTC on Dec. 17 (1:33 p.m. EST on Dec. 16), this marks the first flight of a payload under NASA’s Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS). Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to provide increased access to space specifically for these small spacecraft, called CubeSats.

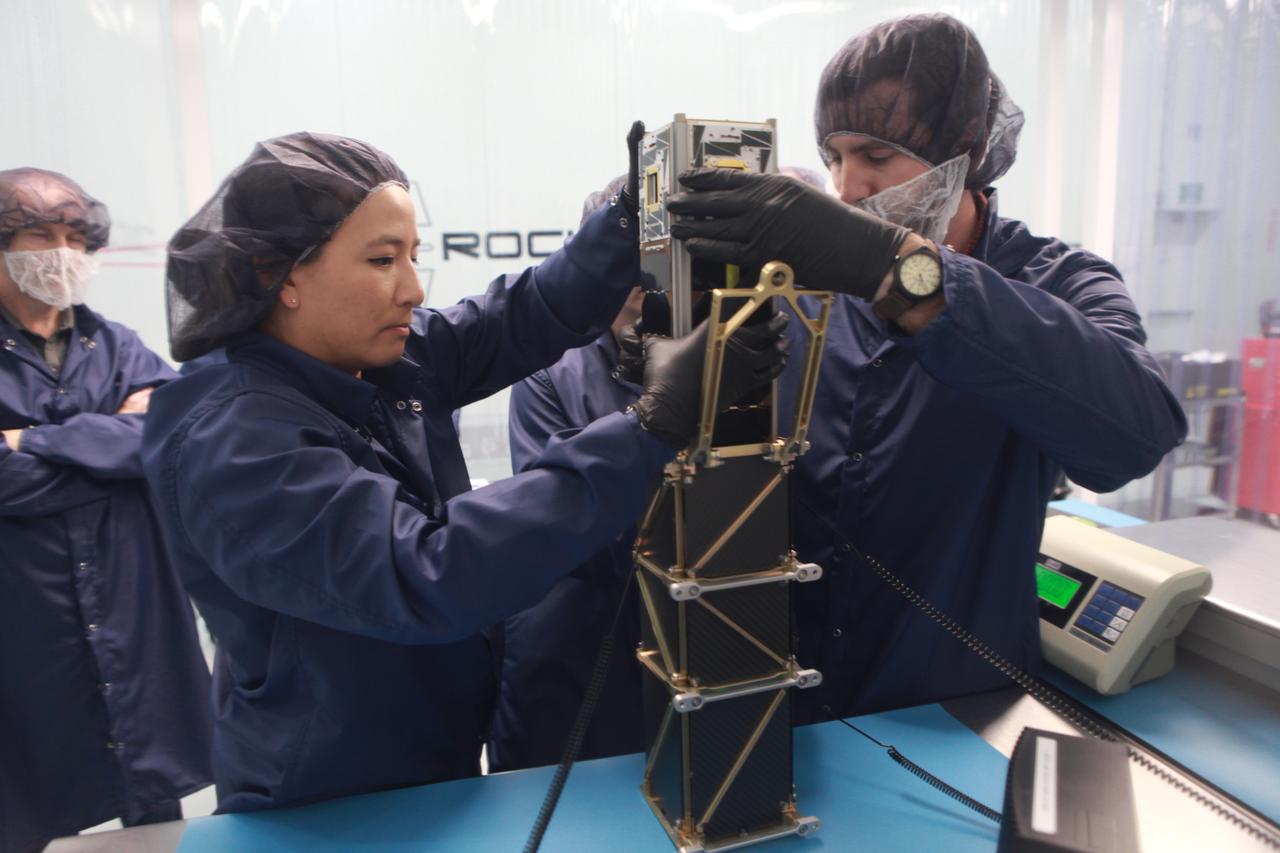
RSat is a 3U CubeSat with two seven degree of freedom robotic arms designed to latch onto a host satellite and maneuver around to image and potentially repair malfunctioning components. RSat is part of the AMODS research project developed by a team of Midshipmen from the United States Naval Academy. The three-year-old program aims to employ a small satellite platform to provide both new and legacy spacecraft with cost-effective on-orbit assessments and repair services. Currently, if a satellite makes it to orbit, there is no guarantee it will work as intended. In these cases, not only is the spacecraft lost, but invaluable experience vanishes with it. RSat takes advantage of cost and profile efficiencies of the small satellite platform to offer satellite developers and operators a fundamentally new way to reduce risk, protect investment and effect design improvements correlated against observed space environment experience. RSat-P is launching as part of ELaNa XIX as a free-flying unit intended to validate the on-orbit effectiveness of compact robotic manipulators.

RSat is a 3U CubeSat with two seven degree of freedom robotic arms designed to latch onto a host satellite and maneuver around to image and potentially repair malfunctioning components. RSat is part of the AMODS research project developed by a team of Midshipmen from the United States Naval Academy. The three-year-old program aims to employ a small satellite platform to provide both new and legacy spacecraft with cost-effective on-orbit assessments and repair services. Currently, if a satellite makes it to orbit, there is no guarantee it will work as intended. In these cases, not only is the spacecraft lost, but invaluable experience vanishes with it. RSat takes advantage of cost and profile efficiencies of the small satellite platform to offer satellite developers and operators a fundamentally new way to reduce risk, protect investment and effect design improvements correlated against observed space environment experience. RSat-P is launching as part of ELaNa XIX as a free-flying unit intended to validate the on-orbit effectiveness of compact robotic manipulators.

CubeSail is a nano-scale flight experiment to demonstrate deployment and control of a single 250-meter (20 m2) solar sail blade as a low-cost risk reduction precursor of the exciting advanced interplanetary UltraSail concept having four 5-kilometer blades (with approximately 100,000 m2 of sail area). CubeSail was built by the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and CU Aerospace, the same team that designed the I-Sail and UltraSail concepts funded by NASA’s SBIR program. CubeSail represents an affordable stepping-stone towards the future development of the UltraSail solar sail concept that would enable very high-energy inner heliosphere and interstellar scientific missions. In addition, near-earth missions such as Heliostorm for early warning of solar storms will provide more warning margin as the solar sail performance is increased with UltraSail technology. Spacecraft design studies show that for sail areal densities below 5 gm/m2, as proposed with UltraSail, that spacecraft payloads can be significantly increased to 50-60% because of the elimination of the propellant, without sacrificing flight time. Furthermore, higher payload fractions will result in dramatically lower total spacecraft mass and consequently much lower launch cost, enabling more missions for the research dollar.

CubeSail is a nano-scale flight experiment to demonstrate deployment and control of a single 250-meter (20 m2) solar sail blade as a low-cost risk reduction precursor of the exciting advanced interplanetary UltraSail concept having four 5-kilometer blades (with approximately 100,000 m2 of sail area). CubeSail was built by the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and CU Aerospace, the same team that designed the I-Sail and UltraSail concepts funded by NASA’s SBIR program. CubeSail represents an affordable stepping-stone towards the future development of the UltraSail solar sail concept that would enable very high-energy inner heliosphere and interstellar scientific missions. In addition, near-earth missions such as Heliostorm for early warning of solar storms will provide more warning margin as the solar sail performance is increased with UltraSail technology. Spacecraft design studies show that for sail areal densities below 5 gm/m2, as proposed with UltraSail, that spacecraft payloads can be significantly increased to 50-60% because of the elimination of the propellant, without sacrificing flight time. Furthermore, higher payload fractions will result in dramatically lower total spacecraft mass and consequently much lower launch cost, enabling more missions for the research dollar.

RSat is a 3U CubeSat with two seven degree of freedom robotic arms designed to latch onto a host satellite and maneuver around to image and potentially repair malfunctioning components. RSat is part of the AMODS research project developed by a team of Midshipmen from the United States Naval Academy. The three-year-old program aims to employ a small satellite platform to provide both new and legacy spacecraft with cost-effective on-orbit assessments and repair services. Currently, if a satellite makes it to orbit, there is no guarantee it will work as intended. In these cases, not only is the spacecraft lost, but invaluable experience vanishes with it. RSat takes advantage of cost and profile efficiencies of the small satellite platform to offer satellite developers and operators a fundamentally new way to reduce risk, protect investment and effect design improvements correlated against observed space environment experience. RSat-P is launching as part of ELaNa XIX as a free-flying unit intended to validate the on-orbit effectiveness of compact robotic manipulators.

CubeSail is a nano-scale flight experiment to demonstrate deployment and control of a single 250-meter (20 m2) solar sail blade as a low-cost risk reduction precursor of the exciting advanced interplanetary UltraSail concept having four 5-kilometer blades (with approximately 100,000 m2 of sail area). CubeSail was built by the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and CU Aerospace, the same team that designed the I-Sail and UltraSail concepts funded by NASA’s SBIR program. CubeSail represents an affordable stepping-stone towards the future development of the UltraSail solar sail concept that would enable very high-energy inner heliosphere and interstellar scientific missions. In addition, near-earth missions such as Heliostorm for early warning of solar storms will provide more warning margin as the solar sail performance is increased with UltraSail technology. Spacecraft design studies show that for sail areal densities below 5 gm/m2, as proposed with UltraSail, that spacecraft payloads can be significantly increased to 50-60% because of the elimination of the propellant, without sacrificing flight time. Furthermore, higher payload fractions will result in dramatically lower total spacecraft mass and consequently much lower launch cost, enabling more missions for the research dollar.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex-1 at Māhia Peninsula in New Zealand carrying NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites-19 (ELaNa-19) payload. Liftoff occurred at 6:33 a.m. UTC on Dec. 17 (1:33 p.m. EST on Dec. 16). The liftoff marks the first flight of a payload under NASA’s Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS). Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to provide increased access to space specifically for these small spacecraft, called CubeSats.
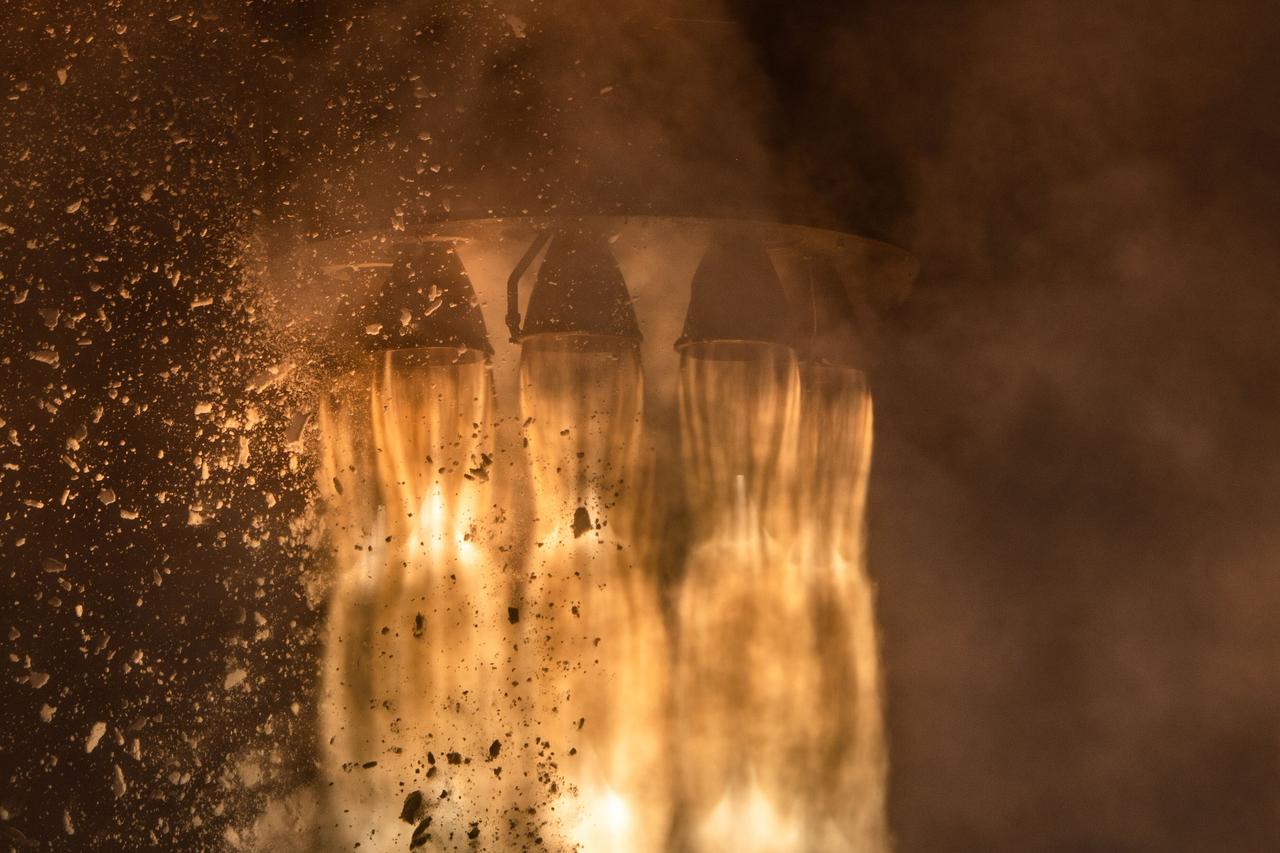
A Rocket Lab Electron rocket’s nine first-stage Rutherford engines ignite as NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites-19 (ELaNa-19) payload lifts off at 6:33 a.m. UTC on Dec. 17 (1:33 p.m. EST on Dec. 16) from Launch Complex-1, located at Māhia Peninsula in New Zealand. The liftoff marks the first flight of a payload under NASA’s Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS). Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to provide increased access to space specifically for these small spacecraft, called CubeSats.

NMTSat is a student-built satellite built by undergraduate and graduates students primarily from New Mexico Tech. NMTSat is designed to operate five sensors in four experiments in space for 3 months of data collection. The experiments will provide data on earth’s magnetic field, high altitude plasma density, atmospheric weather measurements, and an optical beacon experiment. Approximately 50 students have contributed to NMTSat and its design not including the students and groups who have developed the science instruments. NMTSat CubeSat is providing the opportunity for these science experiments to be conducted on orbit and demonstrates the collaborative nature of the Educational Launch of Nano Satellite (ELaNa) Program at NASA. The instruments have been contributed by New Mexico Tech, Turabo University in Puerto Rico, Los Alamos National Laboratory, and Atmospheric and Space Technology Research Associates (ASTRA) in Boulder, CO. Dr. Anders M. Jorgensen, Associate Professor at New Mexico Tech is the PI and Dr. Hien Vo from Vietnamese-German University in Ho Chi Minh University in Vietnam is a Co-Investigator. NMTSat is funded by the New Mexico NASA EPSCoR program as well as New Mexico Tech.

Plasma fluctuations in the upper atmosphere can distort radio signals as they pass into space, damaging radio communication with satellites. The ISX (Ionospheric Scintillation Explorer) mission will study these effects by measuring and comparing digital TV signals produced on the ground. Developed as a collaboration between SRI International and PolySat at Cal Poly, San Luis Obispo, the ISX mission will attempt to improve our understanding of these plasma irregularities and help model space weather predictions in the future.

NMTSat is a student-built satellite built by undergraduate and graduates students primarily from New Mexico Tech. NMTSat is designed to operate five sensors in four experiments in space for 3 months of data collection. The experiments will provide data on earth’s magnetic field, high altitude plasma density, atmospheric weather measurements, and an optical beacon experiment. Approximately 50 students have contributed to NMTSat and its design not including the students and groups who have developed the science instruments. NMTSat CubeSat is providing the opportunity for these science experiments to be conducted on orbit and demonstrates the collaborative nature of the Educational Launch of Nano Satellite (ELaNa) Program at NASA. The instruments have been contributed by New Mexico Tech, Turabo University in Puerto Rico, Los Alamos National Laboratory, and Atmospheric and Space Technology Research Associates (ASTRA) in Boulder, CO. Dr. Anders M. Jorgensen, Associate Professor at New Mexico Tech is the PI and Dr. Hien Vo from Vietnamese-German University in Ho Chi Minh University in Vietnam is a Co-Investigator. NMTSat is funded by the New Mexico NASA EPSCoR program as well as New Mexico Tech.

Plasma fluctuations in the upper atmosphere can distort radio signals as they pass into space, damaging radio communication with satellites. The ISX (Ionospheric Scintillation Explorer) mission will study these effects by measuring and comparing digital TV signals produced on the ground. Developed as a collaboration between SRI International and PolySat at Cal Poly, San Luis Obispo, the ISX mission will attempt to improve our understanding of these plasma irregularities and help model space weather predictions in the future.

NMTSat is a student-built satellite built by undergraduate and graduates students primarily from New Mexico Tech. NMTSat is designed to operate five sensors in four experiments in space for 3 months of data collection. The experiments will provide data on earth’s magnetic field, high altitude plasma density, atmospheric weather measurements, and an optical beacon experiment. Approximately 50 students have contributed to NMTSat and its design not including the students and groups who have developed the science instruments. NMTSat CubeSat is providing the opportunity for these science experiments to be conducted on orbit and demonstrates the collaborative nature of the Educational Launch of Nano Satellite (ELaNa) Program at NASA. The instruments have been contributed by New Mexico Tech, Turabo University in Puerto Rico, Los Alamos National Laboratory, and Atmospheric and Space Technology Research Associates (ASTRA) in Boulder, CO. Dr. Anders M. Jorgensen, Associate Professor at New Mexico Tech is the PI and Dr. Hien Vo from Vietnamese-German University in Ho Chi Minh University in Vietnam is a Co-Investigator. NMTSat is funded by the New Mexico NASA EPSCoR program as well as New Mexico Tech.

Plasma fluctuations in the upper atmosphere can distort radio signals as they pass into space, damaging radio communication with satellites. The ISX (Ionospheric Scintillation Explorer) mission will study these effects by measuring and comparing digital TV signals produced on the ground. Developed as a collaboration between SRI International and PolySat at Cal Poly, San Luis Obispo, the ISX mission will attempt to improve our understanding of these plasma irregularities and help model space weather predictions in the future.
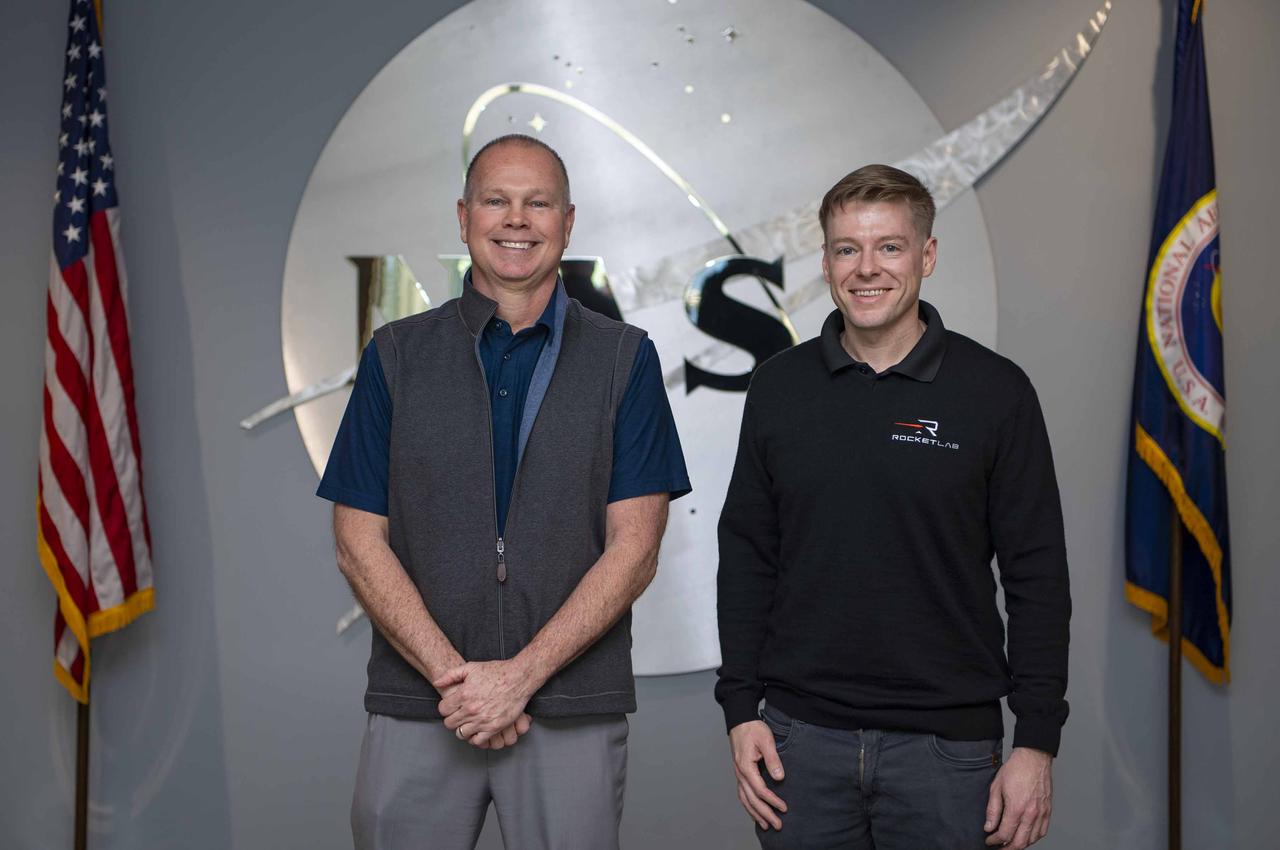

NASA Stennis Director John Bailey, left, welcomes Richard French, Rocket Lab USA, Inc. vice president of business development and strategy of space systems, for a tour of NASA Stennis on Feb. 26. In 2022, NASA and Rocket Lab reached an agreement for the aerospace company to locate its engine test complex at NASA Stennis. The initial 10-year agreement between NASA and Rocket Lab includes an option to extend an additional 10 years. The Archimedes Test Complex includes 24 acres surrounding the site’s A-3 Test Stand. Archimedes is Rocket Lab’s liquid oxygen and liquid methane rocket engine to power its medium-lift Neutron rocket. The company successfully completed the first hot fire of the new Archimedes rocket engine at NASA Stennis in August 2024.
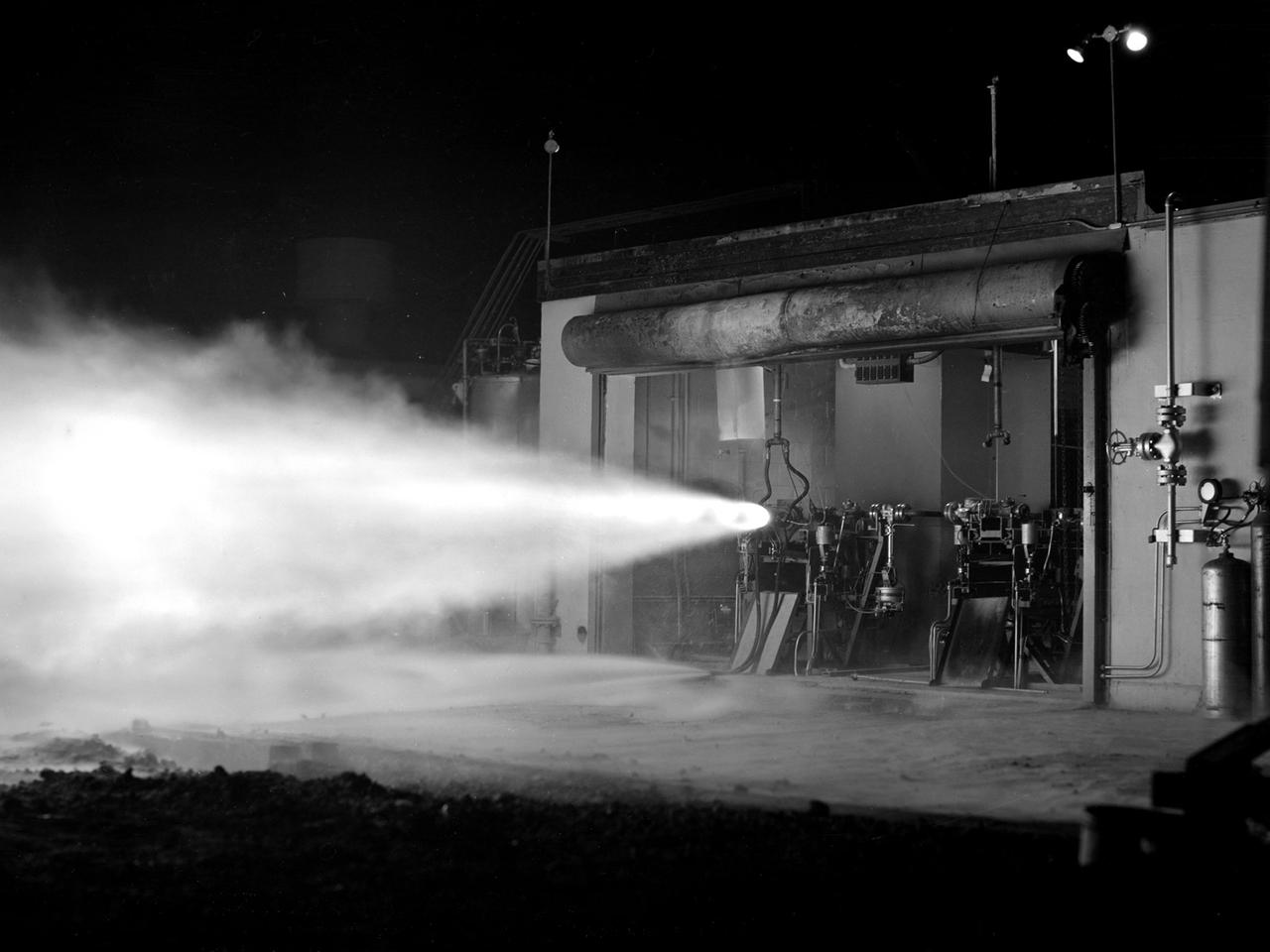

A rocket using high-energy propellant is fired from the Rocket Laboratory at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The Rocket Lab was a collection of ten one-story cinderblock test cells located behind earthen barriers at the western edge of the campus. The rocket engines tested there were comparatively small, but the Lewis researchers were able to study different configurations, combustion performance, and injectors and nozzle design. The rockets were generally mounted horizontally and fired, as seen in this photograph of Test Cell No. 22. A group of fuels researchers at Lewis refocused their efforts after World War II in order to explore high energy propellants, combustion, and cooling. Research in these three areas began in 1945 and continued through the 1960s. The group of rocket researches was not elevated to a division branch until 1952. The early NACA Lewis work led to the development of liquid hydrogen as a viable propellant in the late 1950s. Following the 1949 reorganization of the research divisions, the rocket group began working with high-energy propellants such as diborane, pentaborane, and hydrogen. The lightweight fuels offered high levels of energy but were difficult to handle and required large tanks. In late 1954, Lewis researchers studied the combustion characteristics of gaseous hydrogen in a turbojet combustor. Despite poor mixing of the fuel and air, it was found that the hydrogen yielded more than a 90-percent efficiency. Liquid hydrogen became the focus of Lewis researchers for the next 15 years.
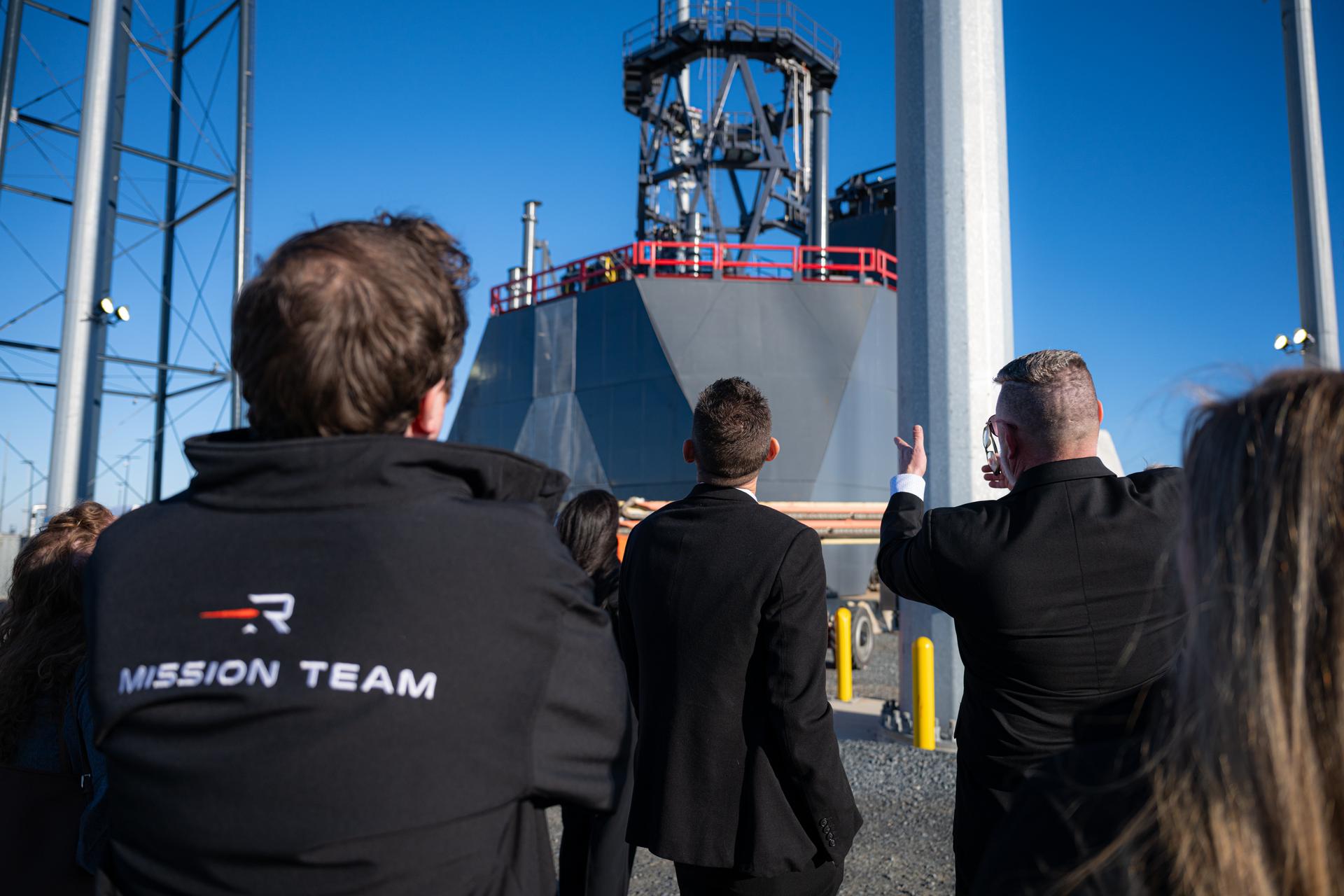

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman, center, and Rocket Lab leadership visit the company's Launch Complex 3, Monday, Jan. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Wallops marks the third stop in Isaacman’s roadshow to visit NASA facilities and engage directly with the agency’s workforce. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

The goal of the CHOMPTT mission is to demonstrate new technologies that could be used for navigation and satellite networking in deep space. For future explorers and colonizers of the Moon or Mars, navigation systems like GPS here on Earth, will be essential. The key idea behind CHOMPTT is to use lasers to transfer time code data over long distances instead of radio waves. Because lasers can be more tightly beamed compared to radio waves, more of the transmitted energy reaches its intended target, making them more power-efficient. CHOMPTT takes advantage of this and of new miniature but very stable atomic clocks to produce a timing system with performance similar to that of GPS, but in a very compact and power efficient form factor. We will use a pulsed laser system, located at the Kennedy Space Center that will be synchronized with an atomic clock. Laser pulses will propagate from the ground to the orbiting CHOMPTT CubeSat and back. By precisely measuring the time of emission and detection of these pulses on the ground and in space we can calculate the time discrepancy between the ground atomic clock and the atomic clock on CHOMPTT. Our goal is to do this with an accuracy of 0.2 billionths of a second, or the time it takes light to travel just 6 centimeters. In the future, we envision using this technology on constellations or swarms of small satellites, for example orbiting the Moon, to equip them with precision navigation, networking, and ranging capabilities. CHOMPTT is a collaboration between the University of Florida and the NASA Ames Research Center. The CHOMPTT precision timing payload was designed and built by the Precision Space Systems Lab at the University of Florida, while the 3U CubeSat bus that has prior flight heritage, was provided by NASA Ames. The CHOMPTT mission has been funded by the Air Force Research Lab and by NASA.
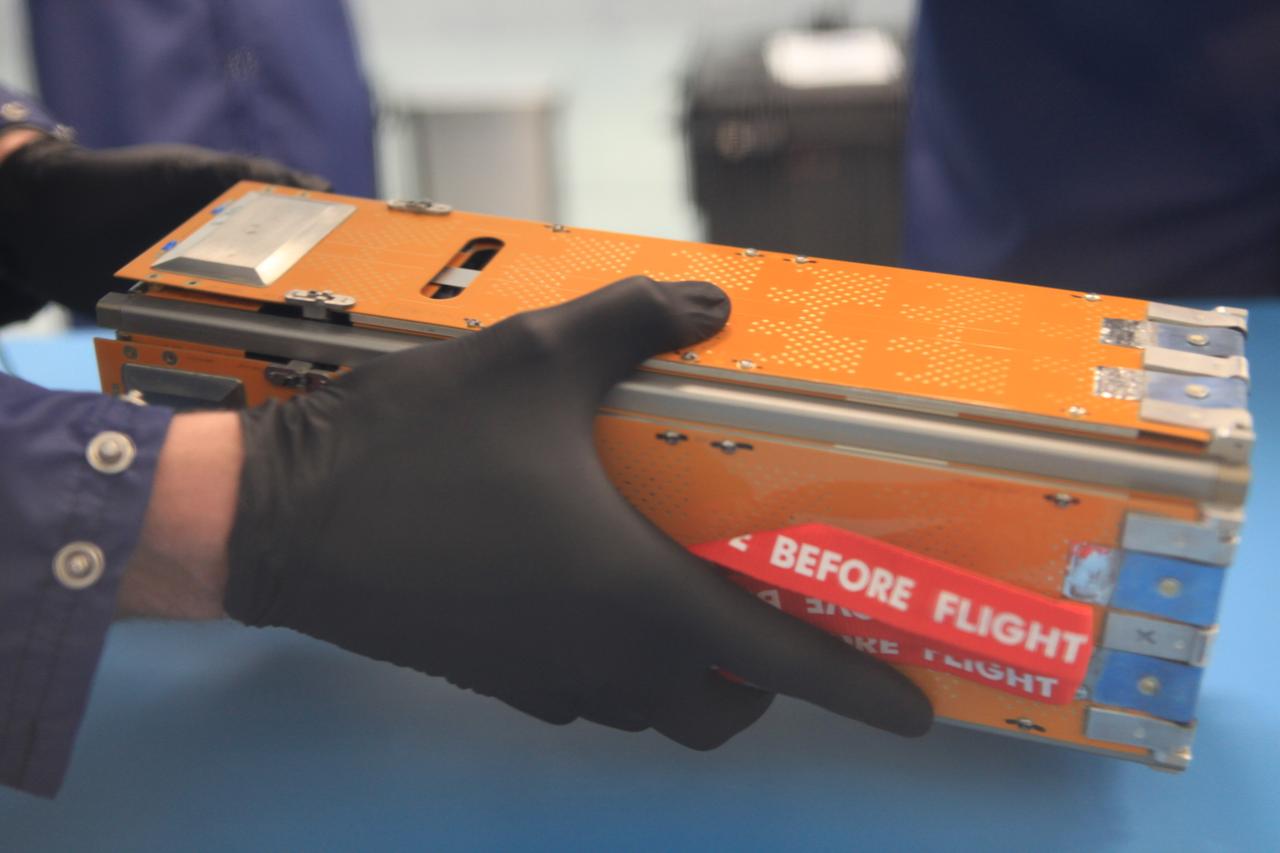

The Advanced Electrical Bus (ALBus) mission is a technology demonstration of resettable Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) mechanisms for deployable solar arrays and a pathfinder for high power density CubeSats. The mission has two primary objectives. The first is to demonstrate the functionality of the novel SMA activated solar array mechanisms in the on-orbit environment. The second objective is to assess the system level ability to charge a high capacity battery, distribute 100 W of electrical power and thermally control the 3-U CubeSat system. Performance from the mission will be used to mature the SMA mechanism designs for CubeSat applications and plan for future high power density CubeSat missions.

The Advanced Electrical Bus (ALBus) mission is a technology demonstration of resettable Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) mechanisms for deployable solar arrays and a pathfinder for high power density CubeSats. The mission has two primary objectives. The first is to demonstrate the functionality of the novel SMA activated solar array mechanisms in the on-orbit environment. The second objective is to assess the system level ability to charge a high capacity battery, distribute 100 W of electrical power and thermally control the 3-U CubeSat system. Performance from the mission will be used to mature the SMA mechanism designs for CubeSat applications and plan for future high power density CubeSat missions.
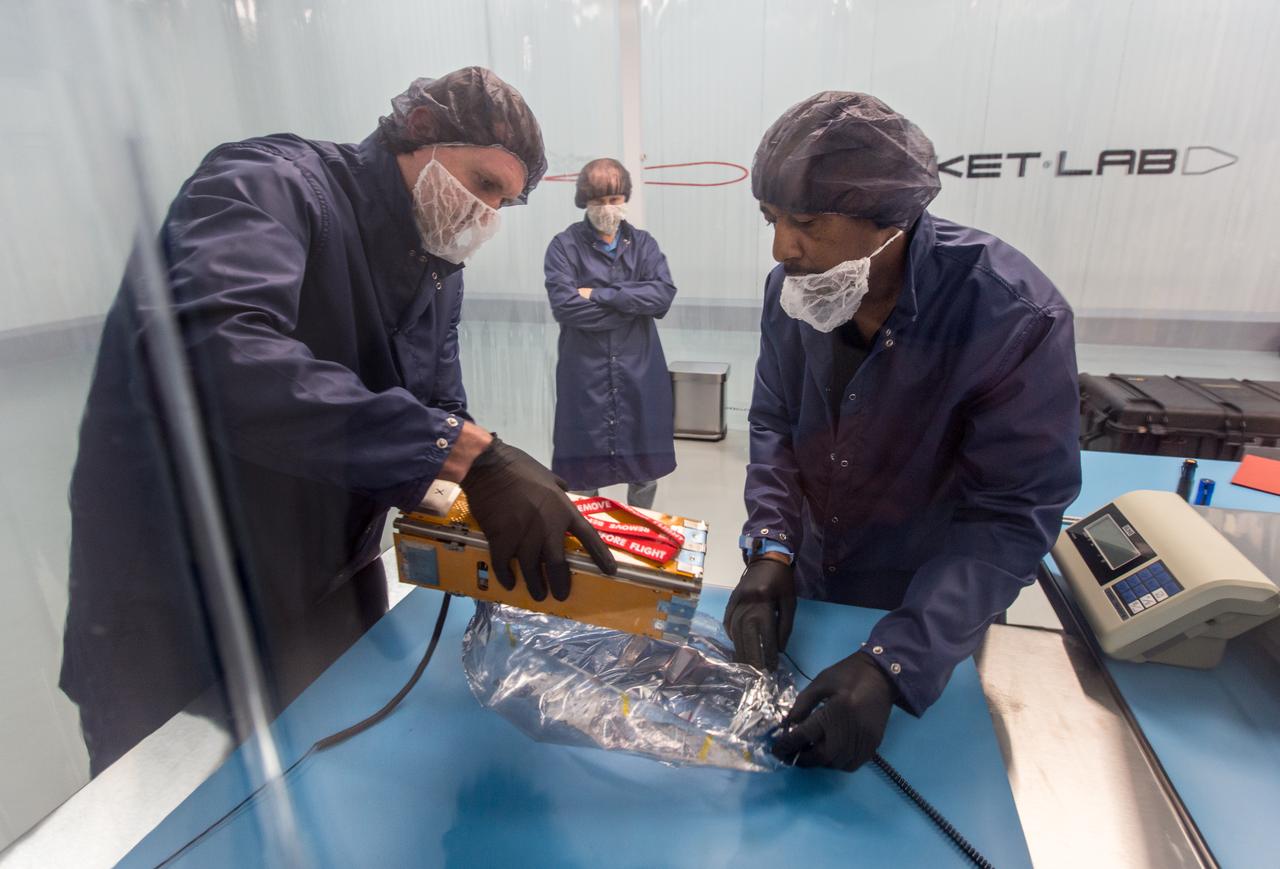
The goal of the CHOMPTT mission is to demonstrate new technologies that could be used for navigation and satellite networking in deep space. For future explorers and colonizers of the Moon or Mars, navigation systems like GPS here on Earth, will be essential. The key idea behind CHOMPTT is to use lasers to transfer time code data over long distances instead of radio waves. Because lasers can be more tightly beamed compared to radio waves, more of the transmitted energy reaches its intended target, making them more power-efficient. CHOMPTT takes advantage of this and of new miniature but very stable atomic clocks to produce a timing system with performance similar to that of GPS, but in a very compact and power efficient form factor. We will use a pulsed laser system, located at the Kennedy Space Center that will be synchronized with an atomic clock. Laser pulses will propagate from the ground to the orbiting CHOMPTT CubeSat and back. By precisely measuring the time of emission and detection of these pulses on the ground and in space we can calculate the time discrepancy between the ground atomic clock and the atomic clock on CHOMPTT. Our goal is to do this with an accuracy of 0.2 billionths of a second, or the time it takes light to travel just 6 centimeters. In the future, we envision using this technology on constellations or swarms of small satellites, for example orbiting the Moon, to equip them with precision navigation, networking, and ranging capabilities. CHOMPTT is a collaboration between the University of Florida and the NASA Ames Research Center. The CHOMPTT precision timing payload was designed and built by the Precision Space Systems Lab at the University of Florida, while the 3U CubeSat bus that has prior flight heritage, was provided by NASA Ames. The CHOMPTT mission has been funded by the Air Force Research Lab and by NASA.

The goal of the CHOMPTT mission is to demonstrate new technologies that could be used for navigation and satellite networking in deep space. For future explorers and colonizers of the Moon or Mars, navigation systems like GPS here on Earth, will be essential. The key idea behind CHOMPTT is to use lasers to transfer time code data over long distances instead of radio waves. Because lasers can be more tightly beamed compared to radio waves, more of the transmitted energy reaches its intended target, making them more power-efficient. CHOMPTT takes advantage of this and of new miniature but very stable atomic clocks to produce a timing system with performance similar to that of GPS, but in a very compact and power efficient form factor. We will use a pulsed laser system, located at the Kennedy Space Center that will be synchronized with an atomic clock. Laser pulses will propagate from the ground to the orbiting CHOMPTT CubeSat and back. By precisely measuring the time of emission and detection of these pulses on the ground and in space we can calculate the time discrepancy between the ground atomic clock and the atomic clock on CHOMPTT. Our goal is to do this with an accuracy of 0.2 billionths of a second, or the time it takes light to travel just 6 centimeters. In the future, we envision using this technology on constellations or swarms of small satellites, for example orbiting the Moon, to equip them with precision navigation, networking, and ranging capabilities. CHOMPTT is a collaboration between the University of Florida and the NASA Ames Research Center. The CHOMPTT precision timing payload was designed and built by the Precision Space Systems Lab at the University of Florida, while the 3U CubeSat bus that has prior flight heritage, was provided by NASA Ames. The CHOMPTT mission has been funded by the Air Force Research Lab and by NASA.
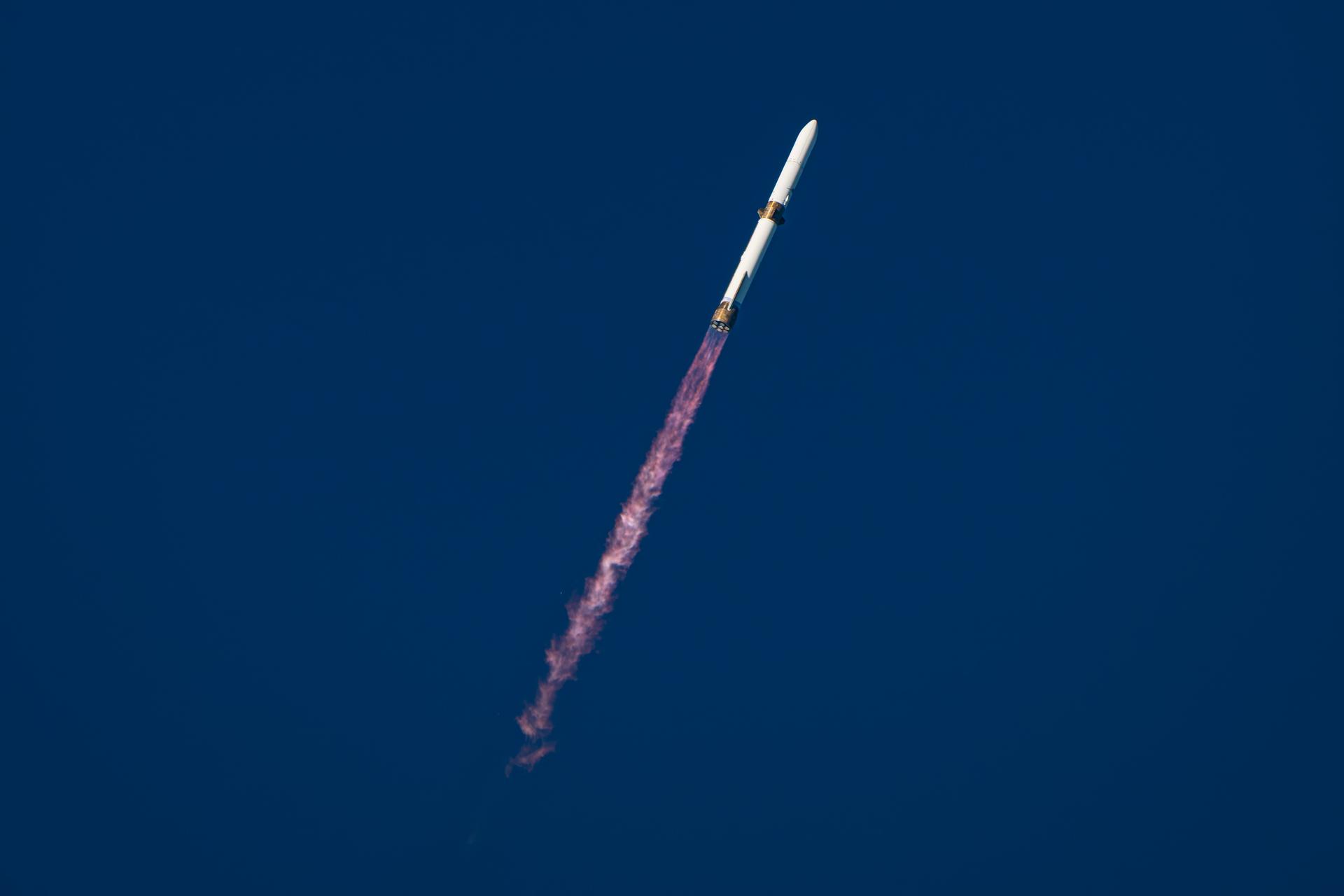

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
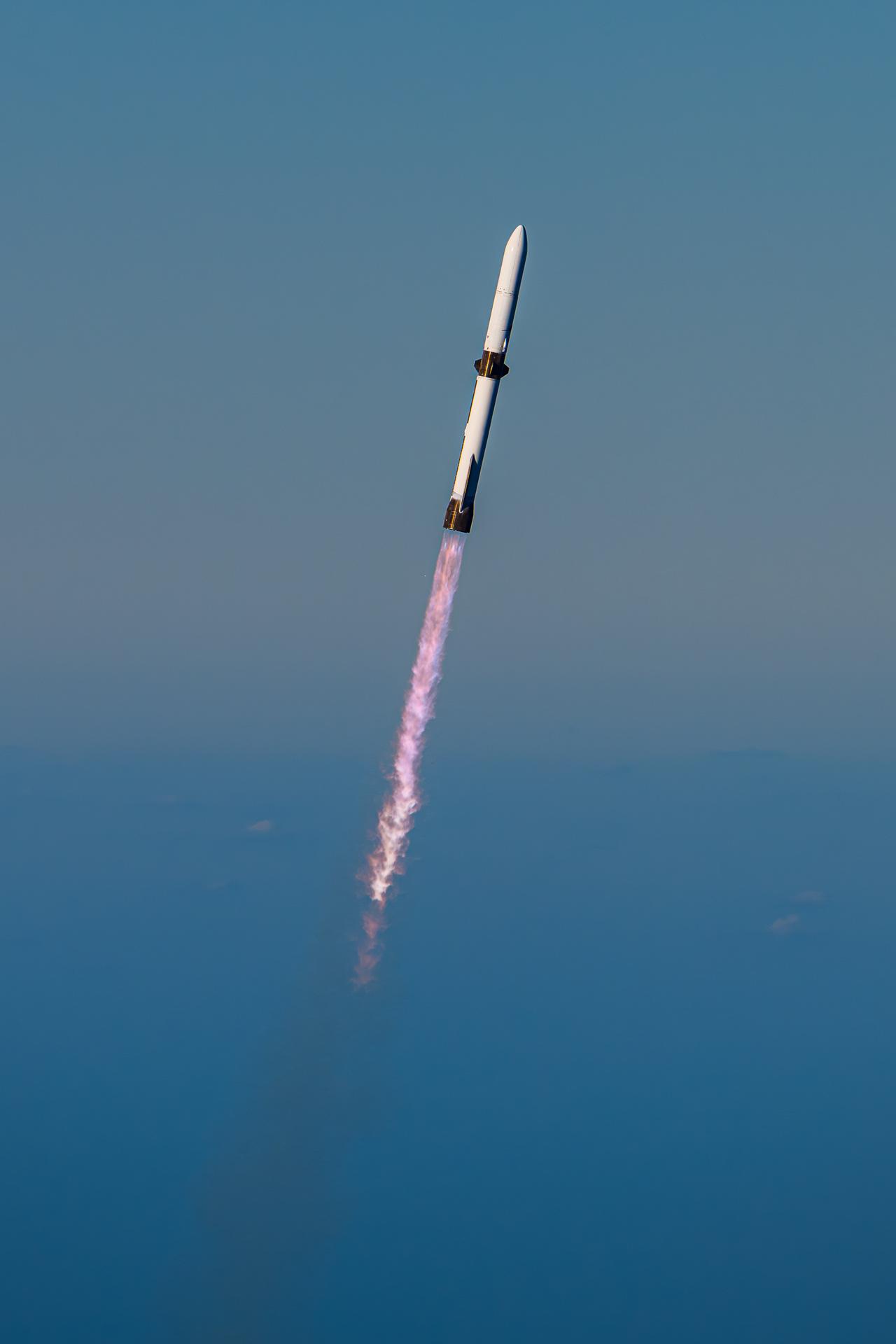

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
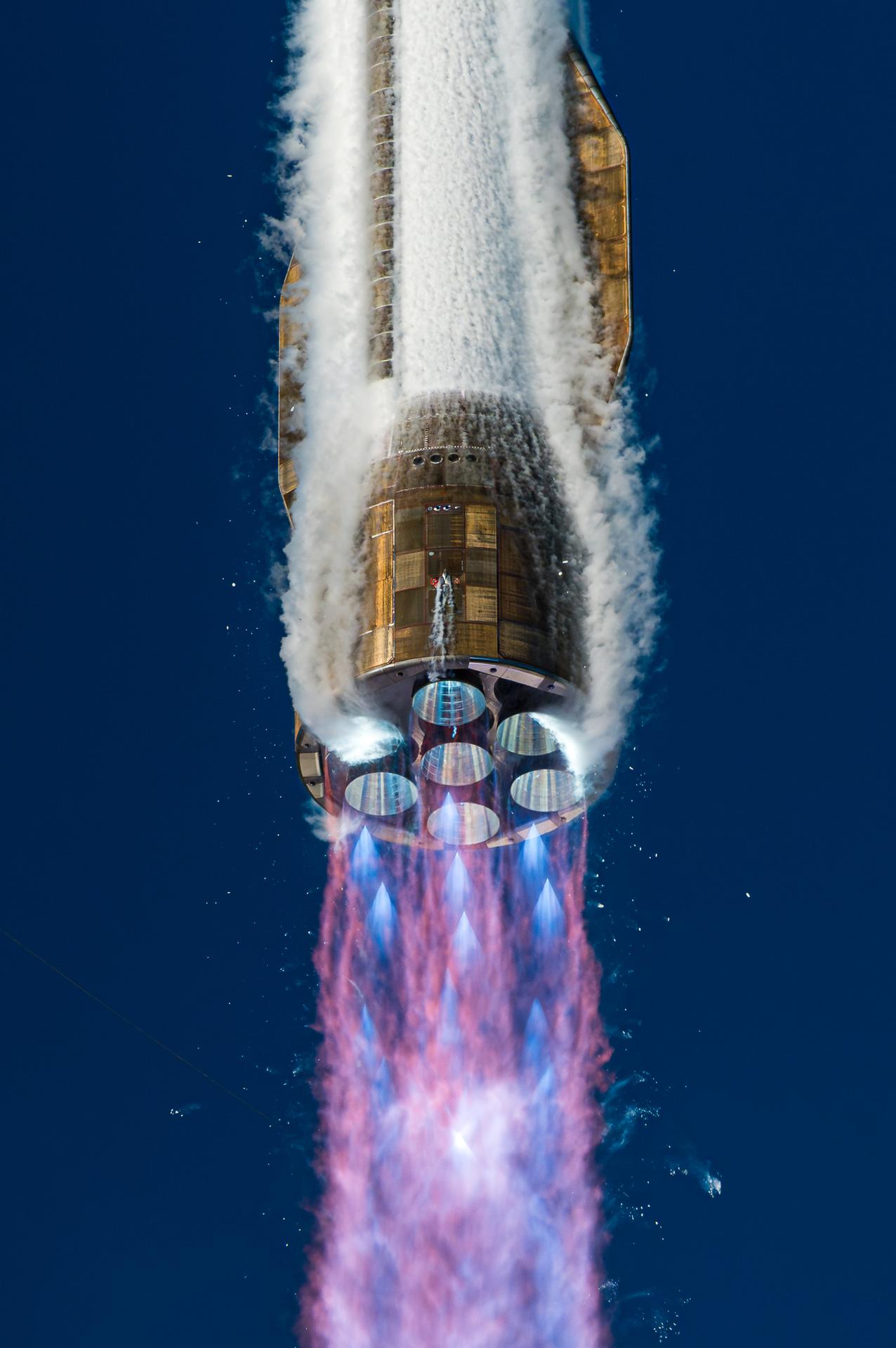

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
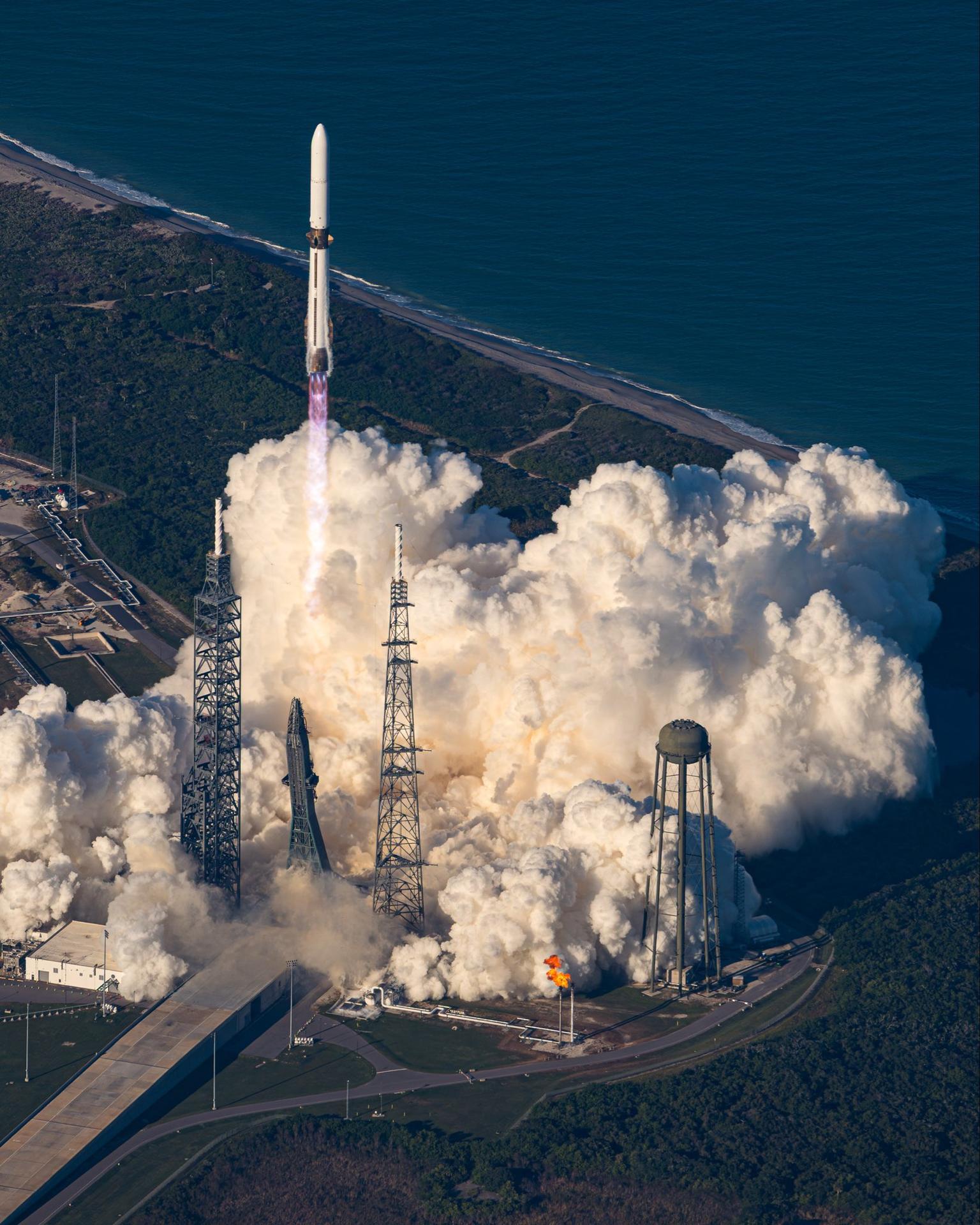

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
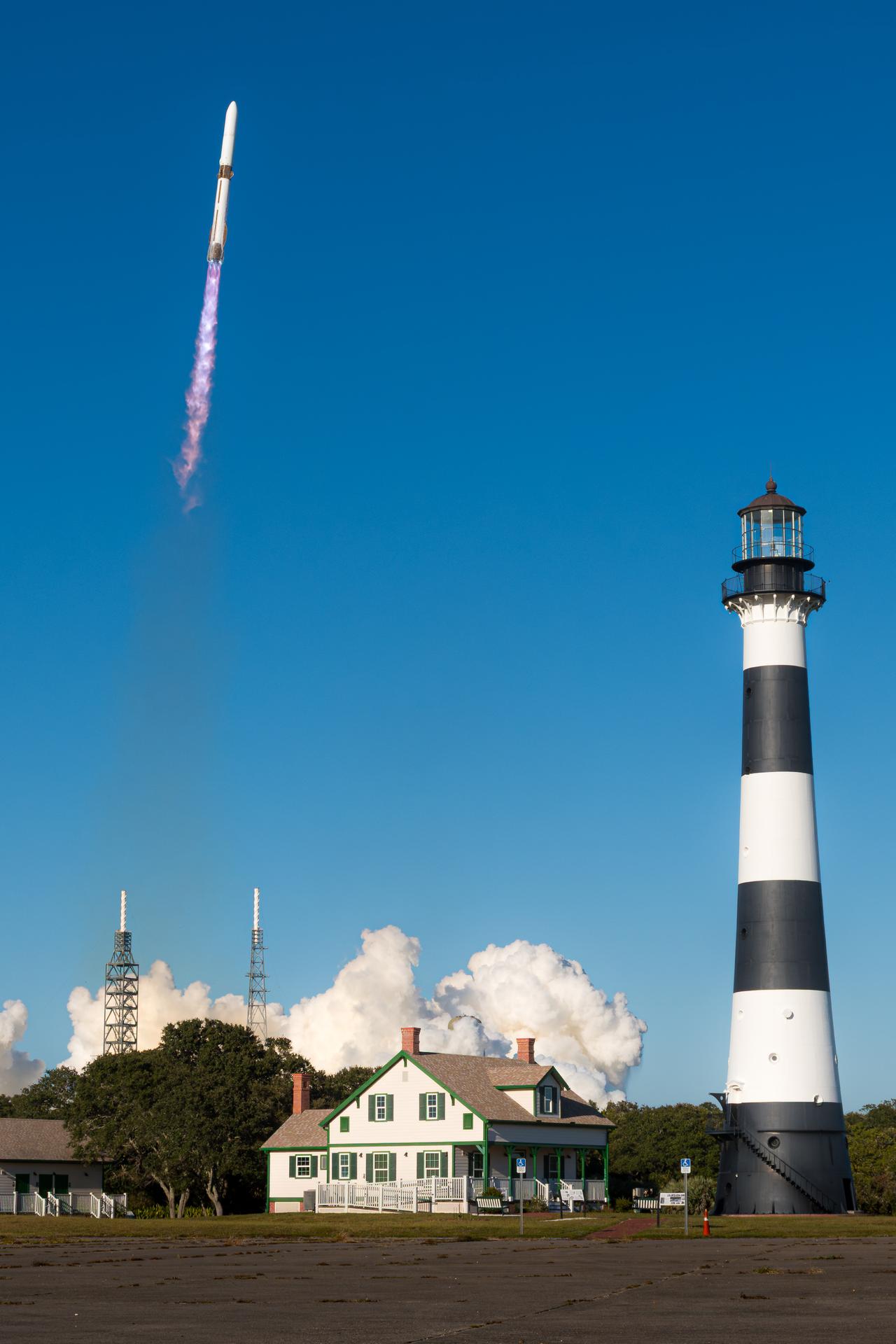

Near Cape Canaveral Lighthouse, Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.