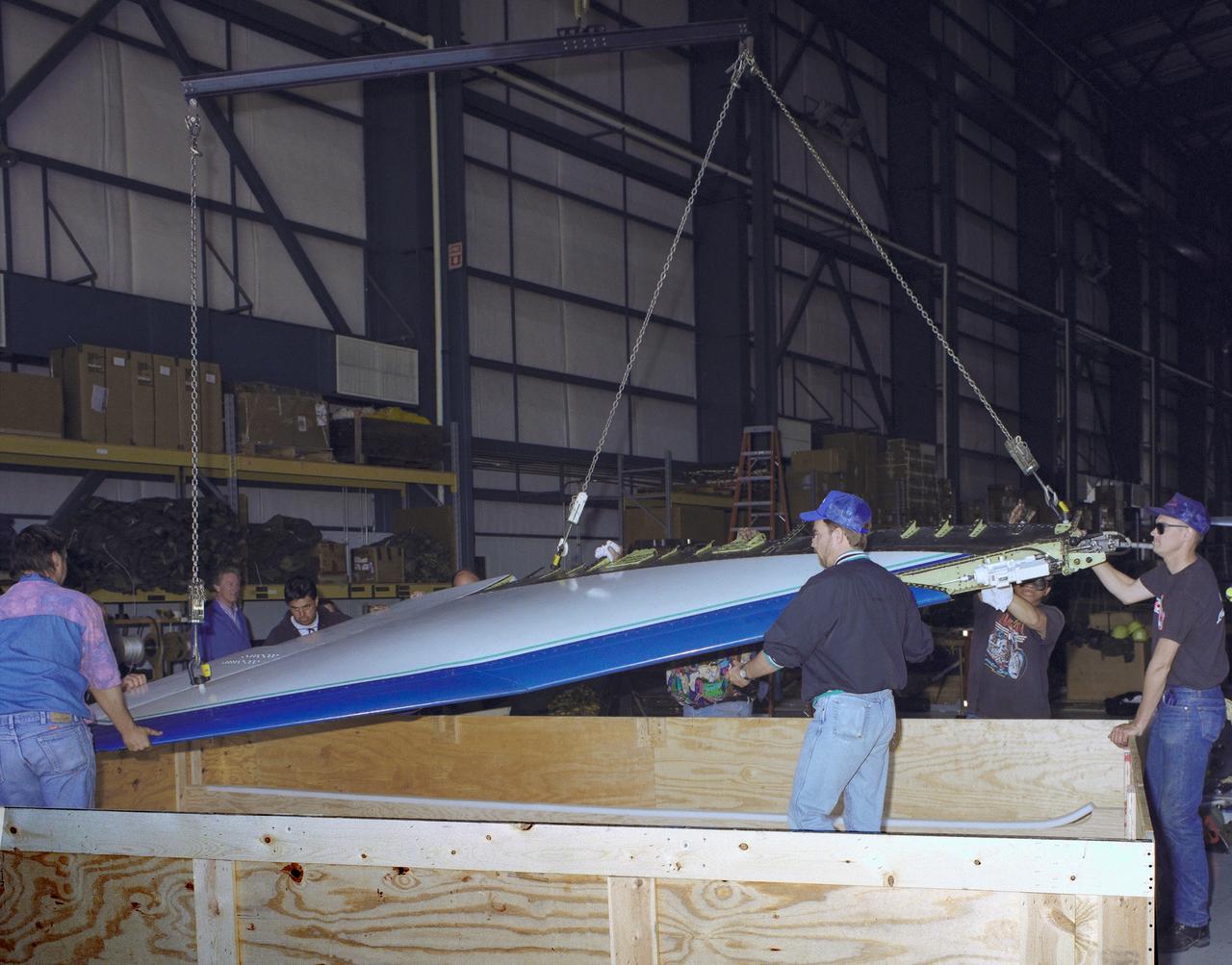

The right wing of the X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator Aircraft is seen here being put into a shipping container May 18, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, by U.S. and German members of the program. To fit inside an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport, which was used to ferry the X-31 to Europe on May 22, 1995, the right wing had to be removed. Manching, Germany, was used as a staging base to prepare the aircraft for participation in the Paris Air Show. At the air show on June 11 through the 18th, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack. The aircraft arrived back at Edwards in an Air Force Reserve C-5 on June 25, 1995, and off loaded at Dryden the 27th. The X-31 aircraft was developed jointly by Rockwell International's North American Aircraft Division (now part of Boeing) and Daimler-Benz Aerospace (formerly Messerschmitt-Bolkow-Blohm), under sponsorship by the U.S. Department of Defense and the German Federal Ministry of Defense.
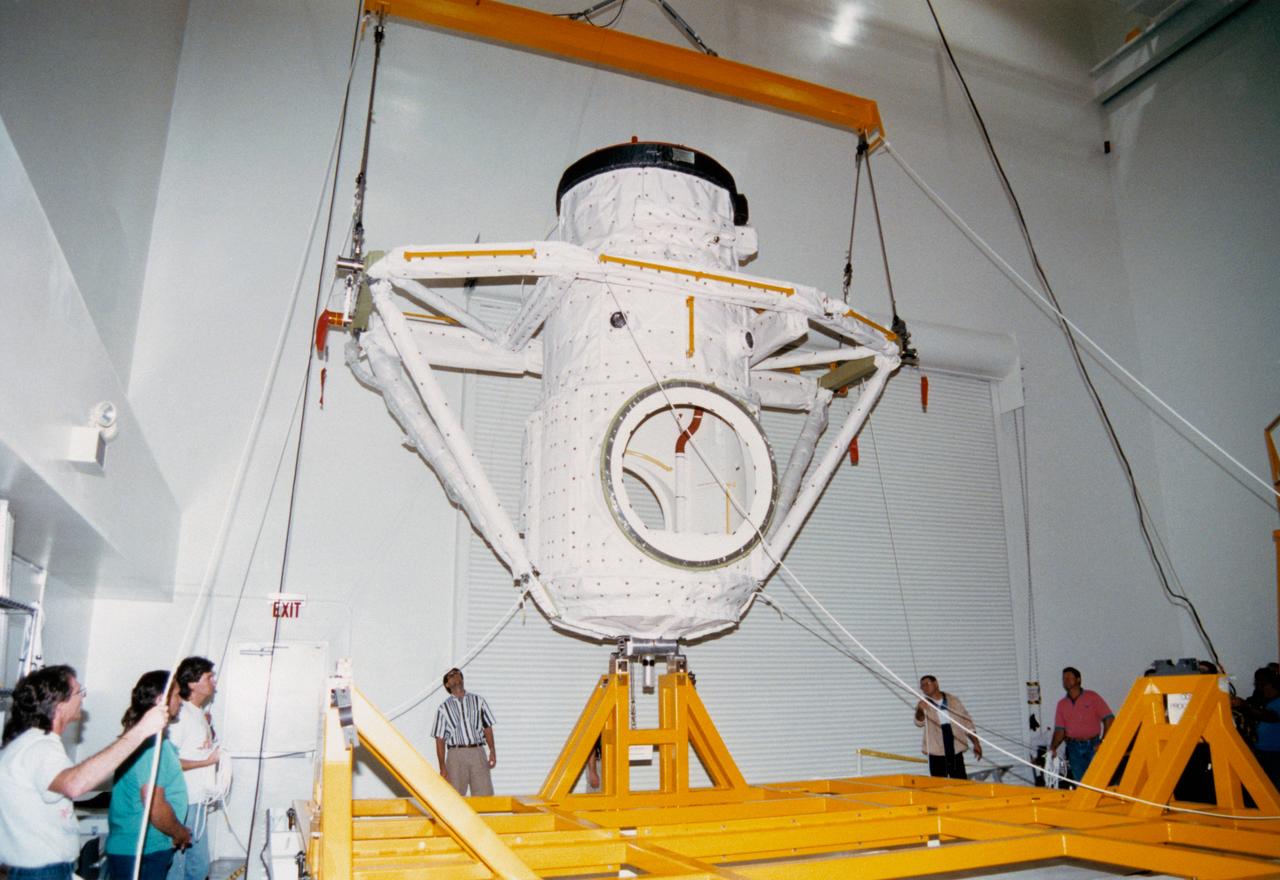
S94-47810 (2 Dec. 1994) --- Lockheed Space Operations Company workers in the Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO) Facility, located inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), carefully hoist the Orbiter Docking System (ODS) from its shipping container into a test stand. The ODS was shipped in a horizontal position to the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) from contractor Rockwell Aerospace's Downey plant. Once the ODS is upright, work can continue to prepare the hardware for the first docking of the United States Space Shuttle and Russian Space Station MIR in 1995. The ODS contains both United States-made and Russian-made hardware. The black band is Russian-made thermal insulation protecting part of the docking mechanism, also Russian-made, called the Androgynous Peripheral Docking System (APDS). A red protective cap covers the APDS itself. Other elements of the ODS, most of it protected by white United States-made thermal insulation, were developed by Rockwell, which also integrated and checked out the assembled Russian-United States system.
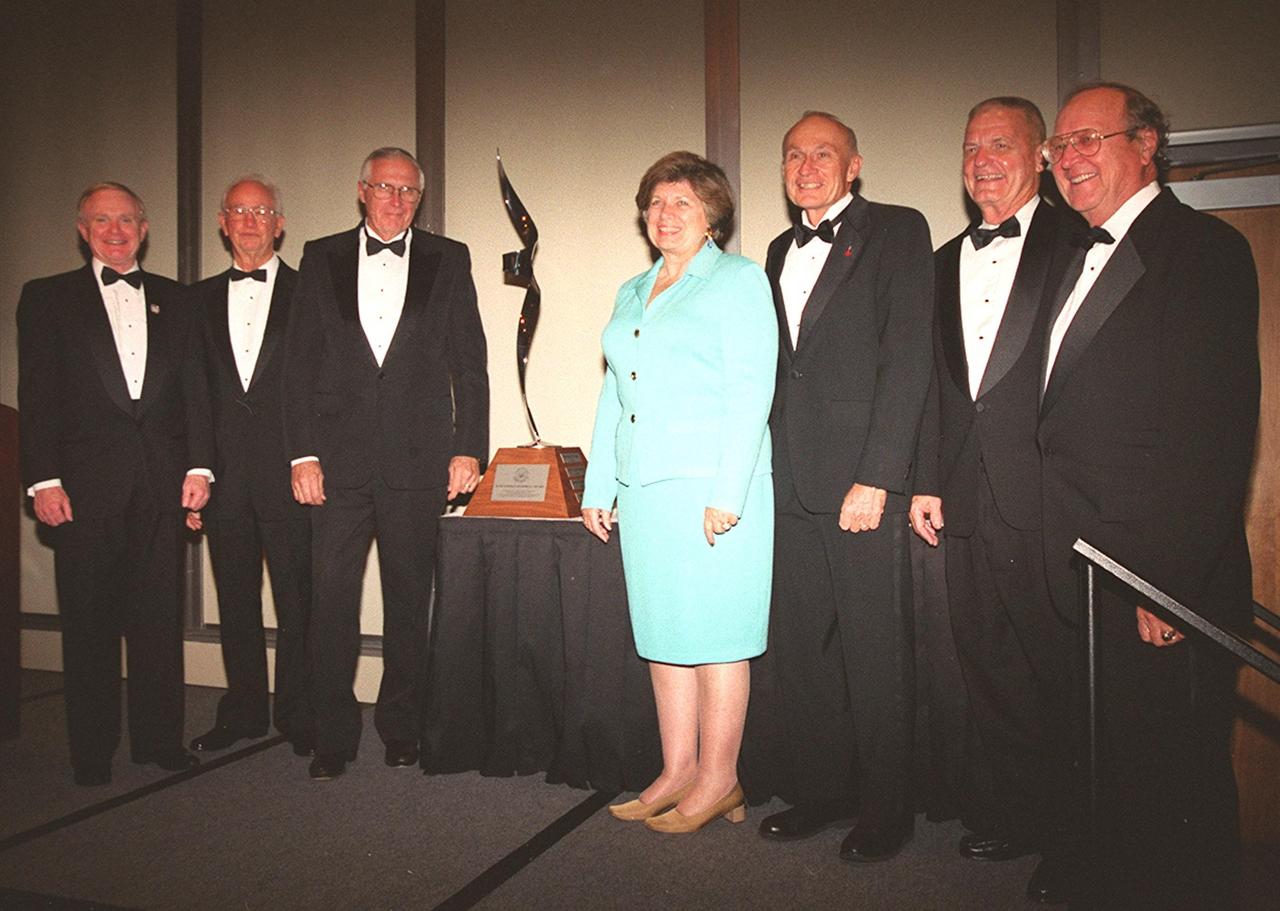

The 12th annual Dr. Kurt H. Debus Award Dinner gathered these distinguished guests: (from left), Center Director Roy Bridges, who received the 2001 Dr. Kurt H. Debus Award, Maxwell King, Lee Solid, JoAnn Morgan, Bob Sieck, Forrest McCartney and Ernie Briel. Solid is the former vice president and general manager of Space Systems Division, Florida Operations, Rockwell International. Morgan is the director of KSC’s External Relations & Business Development Directorate; Bob Sieck is the former director of Shuttle Processing at KSC. McCartney, center director of KSC from 1986-1991, received the first Debus award ever given to a KSC director. Bridges was given the honor for his progressive, visionary leadership and contributions to space technology and exploration. The Florida Committee of the National Space Club presented the award. The Debus Award was first given in 1980. Created to recognize significant achievements and contributions made in Florida to the American aerospace effort, the award is named for the KSC’s first Director, Dr. Kurt H. Debus
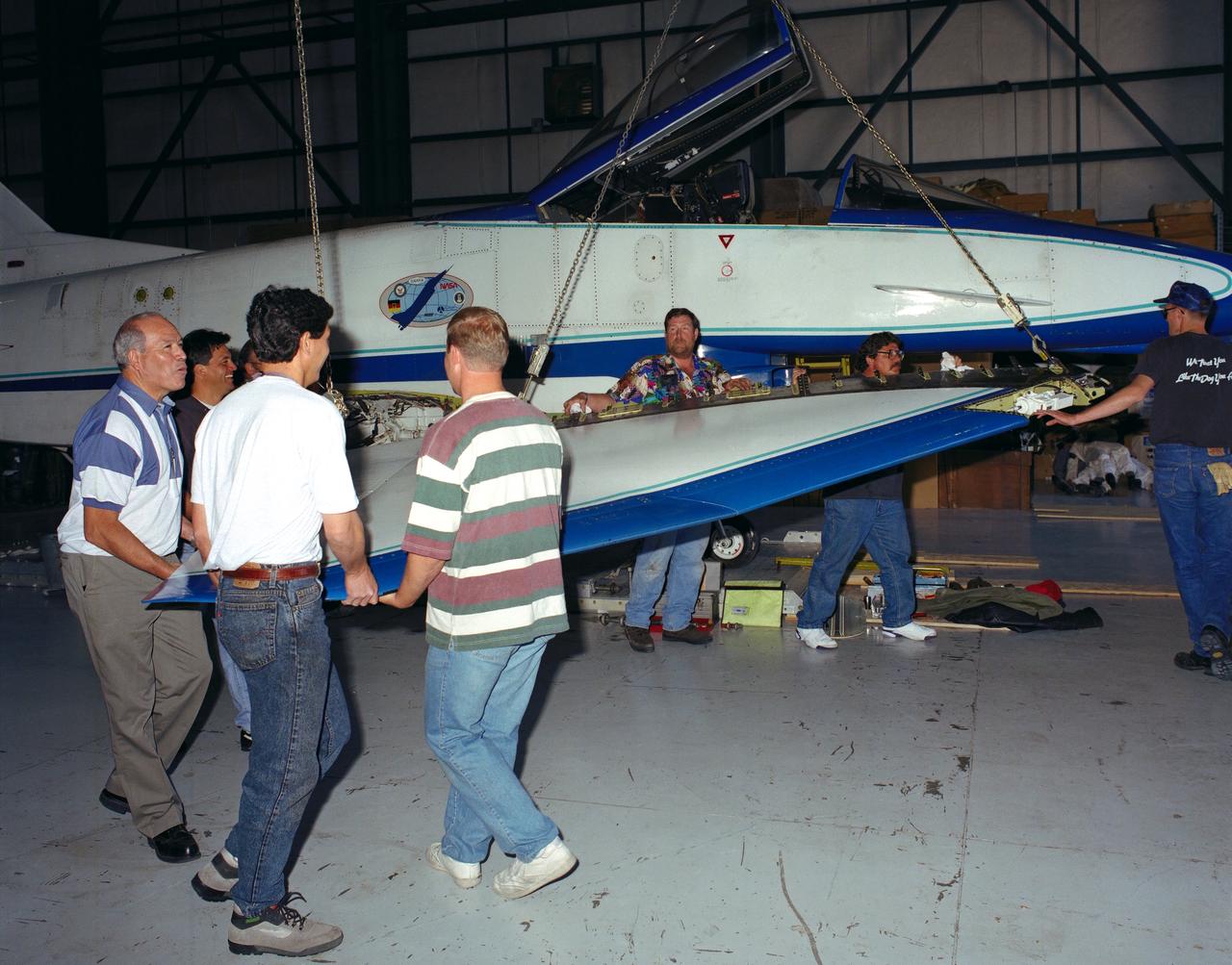

U.S. and German personnel of the X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator aircraft program removing the right wing of the aircraft, which was ferried from Edwards Air Force Base, California, to Europe on May 22, 1995 aboard an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport. The X-31, based at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center was ferried to Europe and flown in the Paris Air Show in June. The wing of the X-31 was removed on May 18, 1995, to allow the aircraft to fit inside the C-5 fuselage. Officials of the X-31 project used Manching, Germany, as a staging base to prepare the aircraft for the flight demonstration. At the air show, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack. The aircraft arrived back at Edwards in a Air Force Reserve C-5 on June 25, 1995 and off loaded at Dryden June 27. The X-31 aircraft was developed jointly by Rockwell International's North American Aircraft Division (now part of Boeing) and Daimler-Benz Aerospace (formerly Messerschmitt-Bolkow-Blohm), under sponsorship by the U.S. Department of Defense and the German Federal Ministry of Defense.
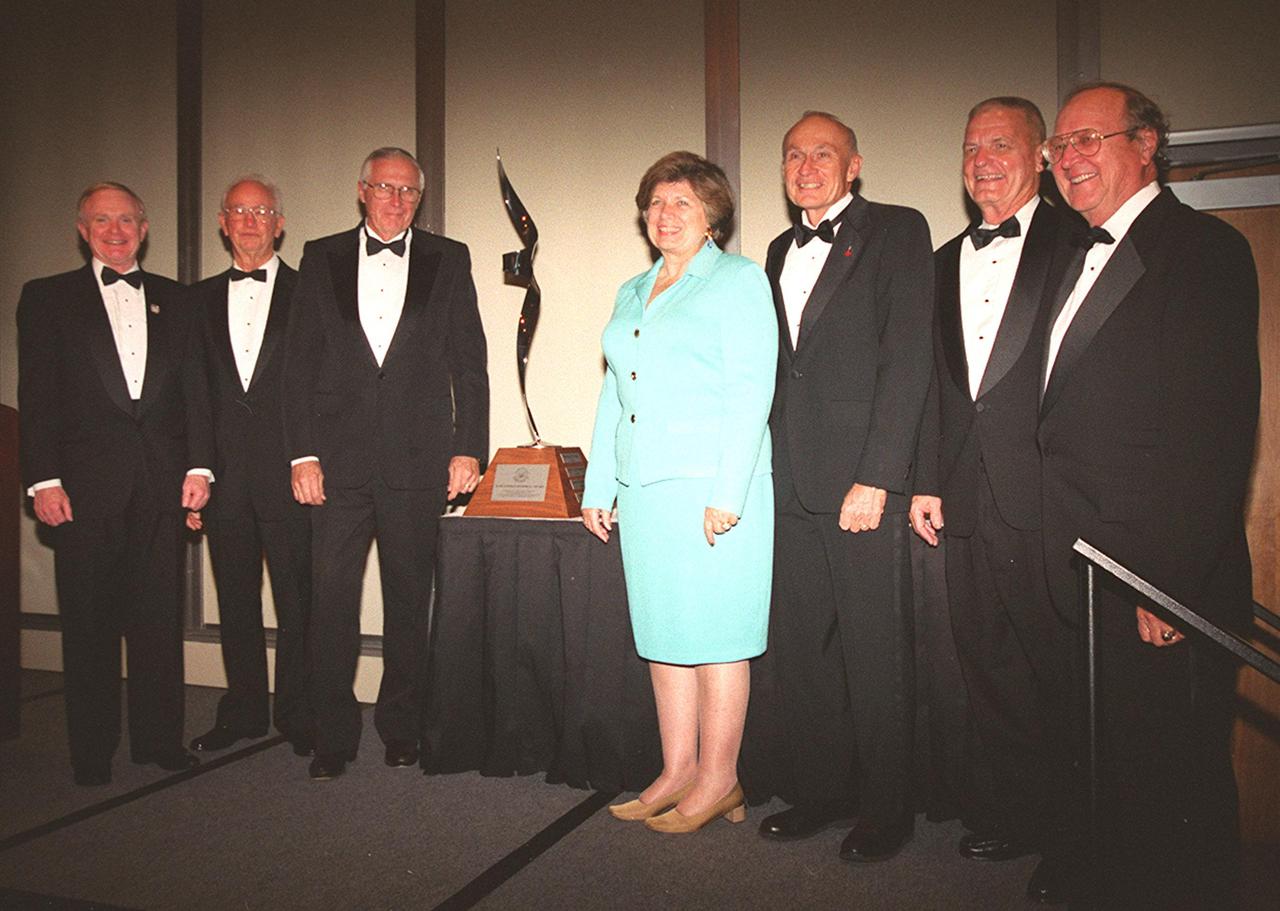

The 12th annual Dr. Kurt H. Debus Award Dinner gathered these distinguished guests: (from left), Center Director Roy Bridges, who received the 2001 Dr. Kurt H. Debus Award, Maxwell King, Lee Solid, JoAnn Morgan, Bob Sieck, Forrest McCartney and Ernie Briel. Solid is the former vice president and general manager of Space Systems Division, Florida Operations, Rockwell International. Morgan is the director of KSC’s External Relations and Business Development Directorate; Bob Sieck is the former director of Shuttle Processing at KSC. McCartney, center director of KSC from 1986-1991, received the first Debus award ever given to a KSC director. Bridges was given the honor for his progressive, visionary leadership and contributions to space technology and exploration. The Florida Committee of the National Space Club presented the award. The Debus Award was first given in 1980. Created to recognize significant achievements and contributions made in Florida to the American aerospace effort, the award is named for the KSC’s first Director, Dr. Kurt H. Debus
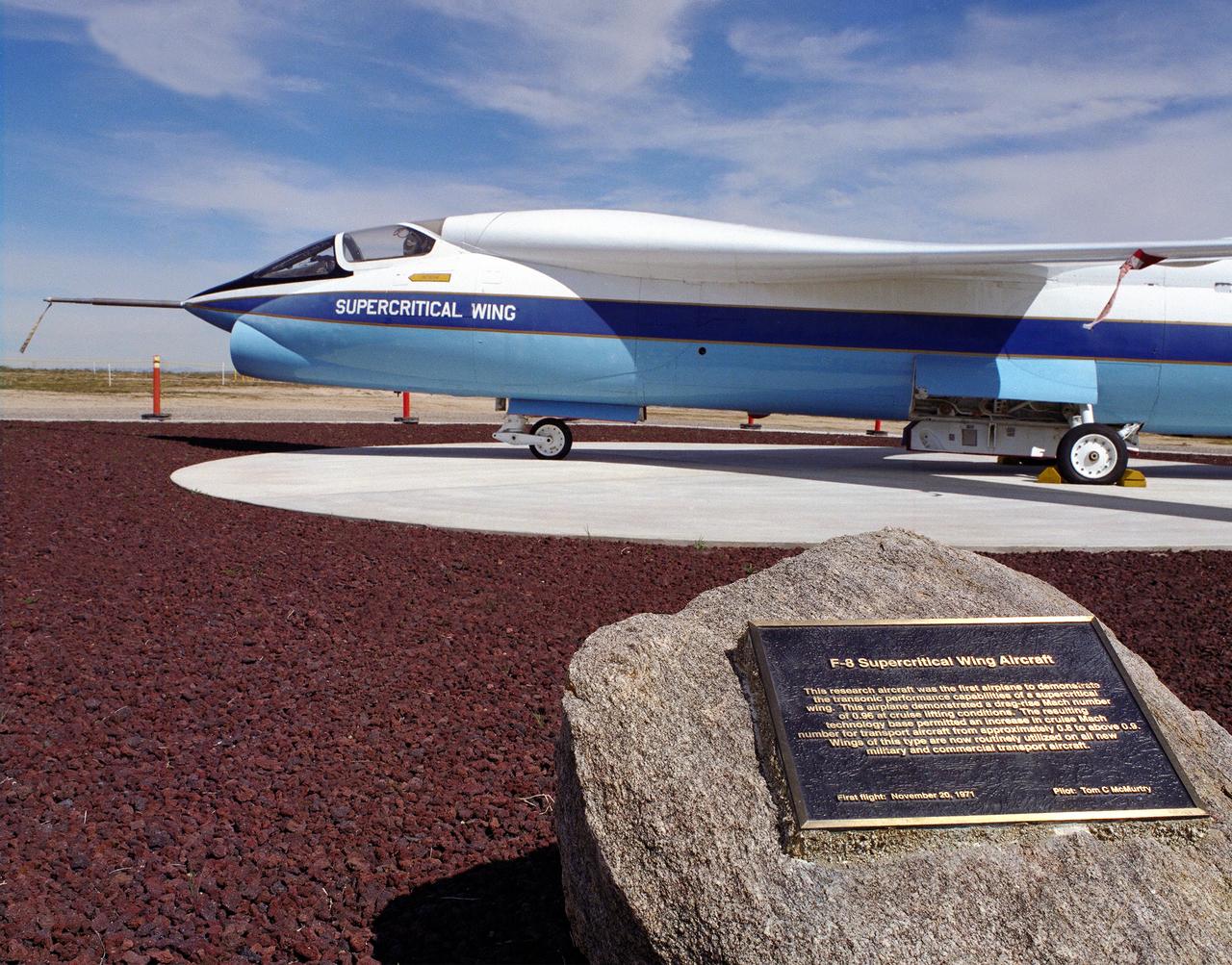

A Vought F-8A Crusader was selected by NASA as the testbed aircraft (designated TF-8A) to install an experimental Supercritical Wing (SCW) in place of the conventional wing. The unique design of the Supercritical Wing reduces the effect of shock waves on the upper surface near Mach 1, which in turn reduces drag. In the photograph the TF-8A Crusader with the Supercritical Wing is shown on static display in front of the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The F-8 SCW aircraft, along with the F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire aircraft were placed on display on May 27, 1992, at a conference marking the 20th anniversary of the start of the two programs.
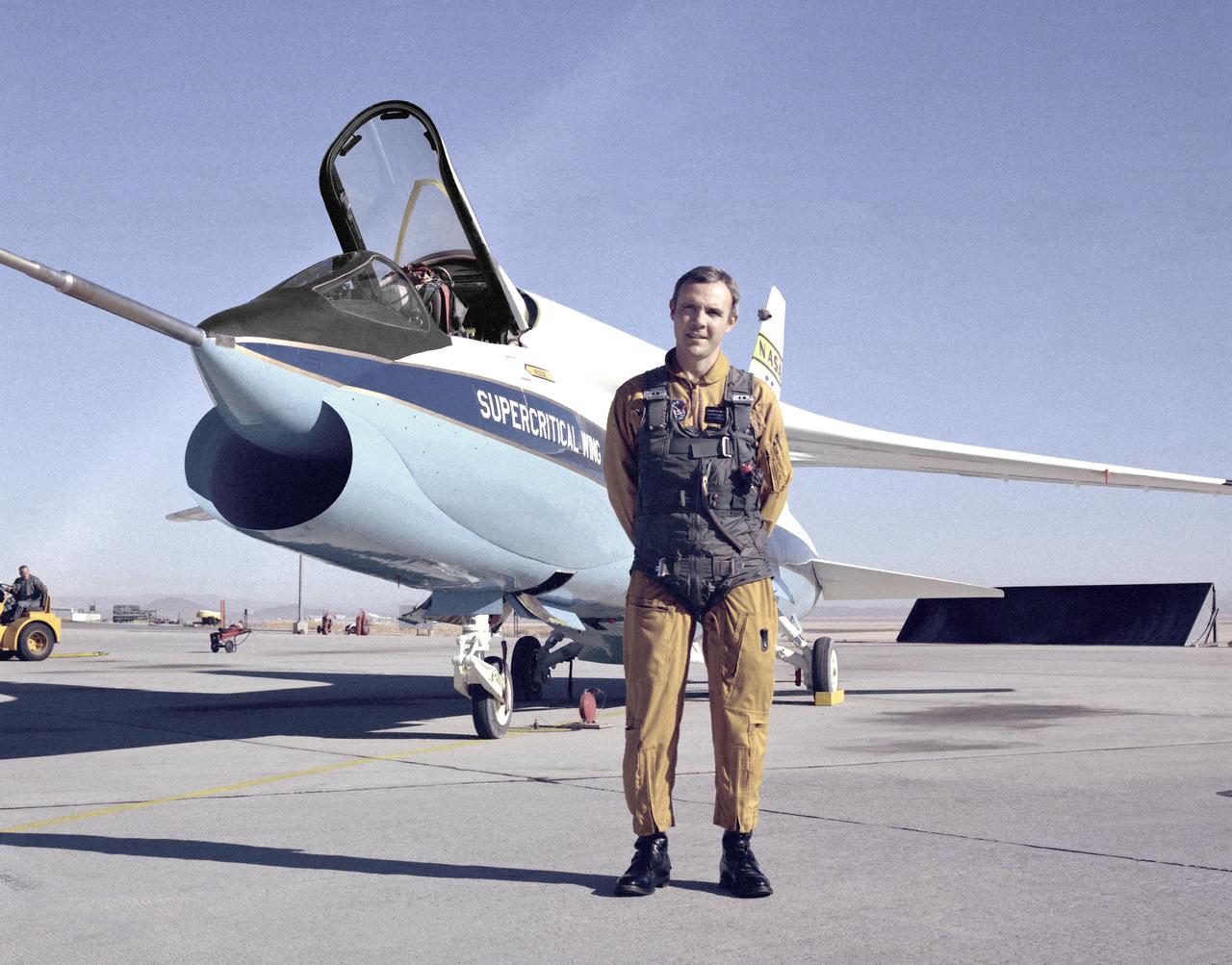

A Vought F-8A Crusader was selected by NASA as the testbed aircraft (designated TF-8A) to install an experimental Supercritical Wing (SCW) in place of the conventional wing. The unique design of the Supercritical Wing reduces the effect of shock waves on the upper surface near Mach 1, which in turn reduces drag. In this photograph the TF-8A Crusader with Supercritical Wing is shown on the ramp with project pilot Tom McMurtry standing beside it. McMurtry received NASA's Exceptional Service Medal for his work on the F-8 SCW aircraft. He also flew the AD-1, F-15 Digital Electronic Engine Control, the KC-130 winglets, the F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire and other flight research aircraft including the remotely piloted 720 Controlled Impact Demonstration and sub-scale F-15 research projects. In addition, McMurtry was the 747 co-pilot for the Shuttle Approach and Landing Tests and made the last glide flight in the X-24B. McMurtry was Dryden’s Director for Flight Operations from 1986 to 1998, when he became Associate Director for Operations at NASA Dryden. In 1982, McMurtry received the Iven C. Kincheloe Award from the Society of Experimental Test Pilots for his contributions as project pilot on the AD-1 Oblique Wing program. In 1998 he was named as one of the honorees at the Lancaster, Calif., ninth Aerospace Walk of Honor ceremonies. In 1999 he was awarded the NASA Distinguished Service Medal. He retired in 1999 after a distinguished career as pilot and manager at Dryden that began in 1967.
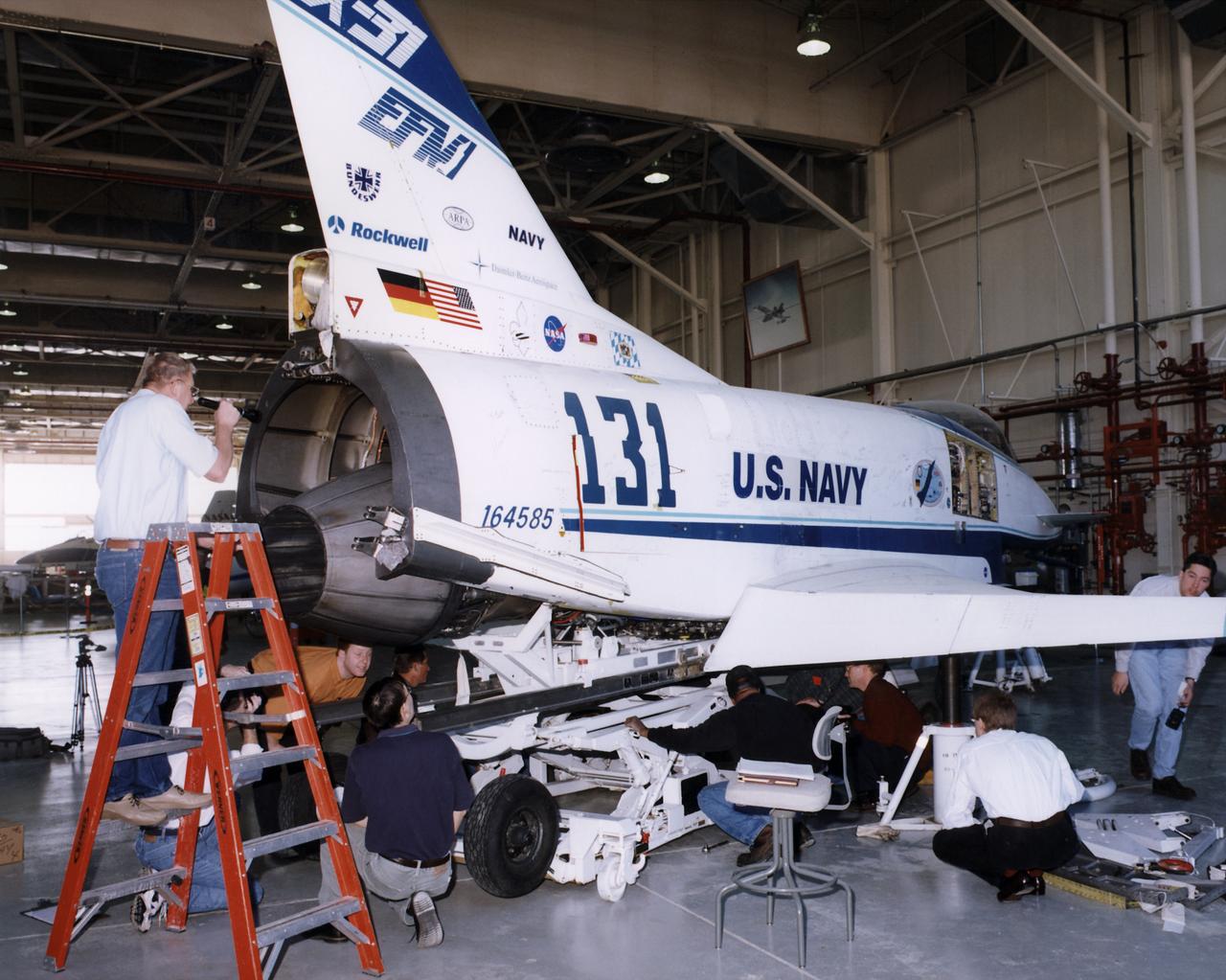

X-31 team members perform an engine fit check on the X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability demonstrator aircraft in a hangar at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
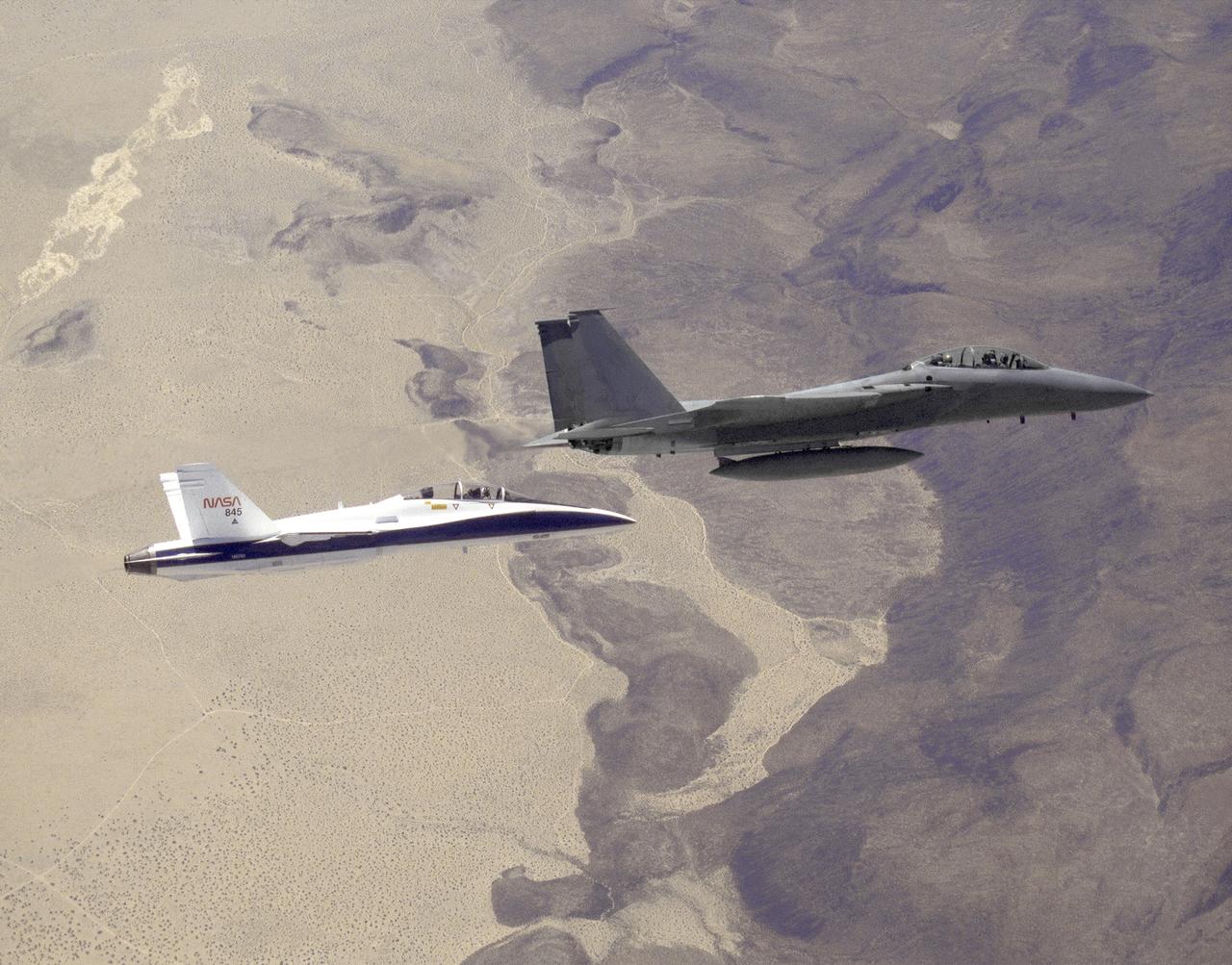

The three thrust-vectoring aircraft at Edwards, California, each capable of flying at extreme angles of attack, cruise over the California desert in formation during flight in March 1994. They are, from left, NASA's F-18 High Alpha Research Vehicle (HARV), flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center; the X-31, flown by the X-31 International Test Organization (ITO) at Dryden; and the Air Force F-16 Multi-Axis Thrust Vectoring (MATV) aircraft.
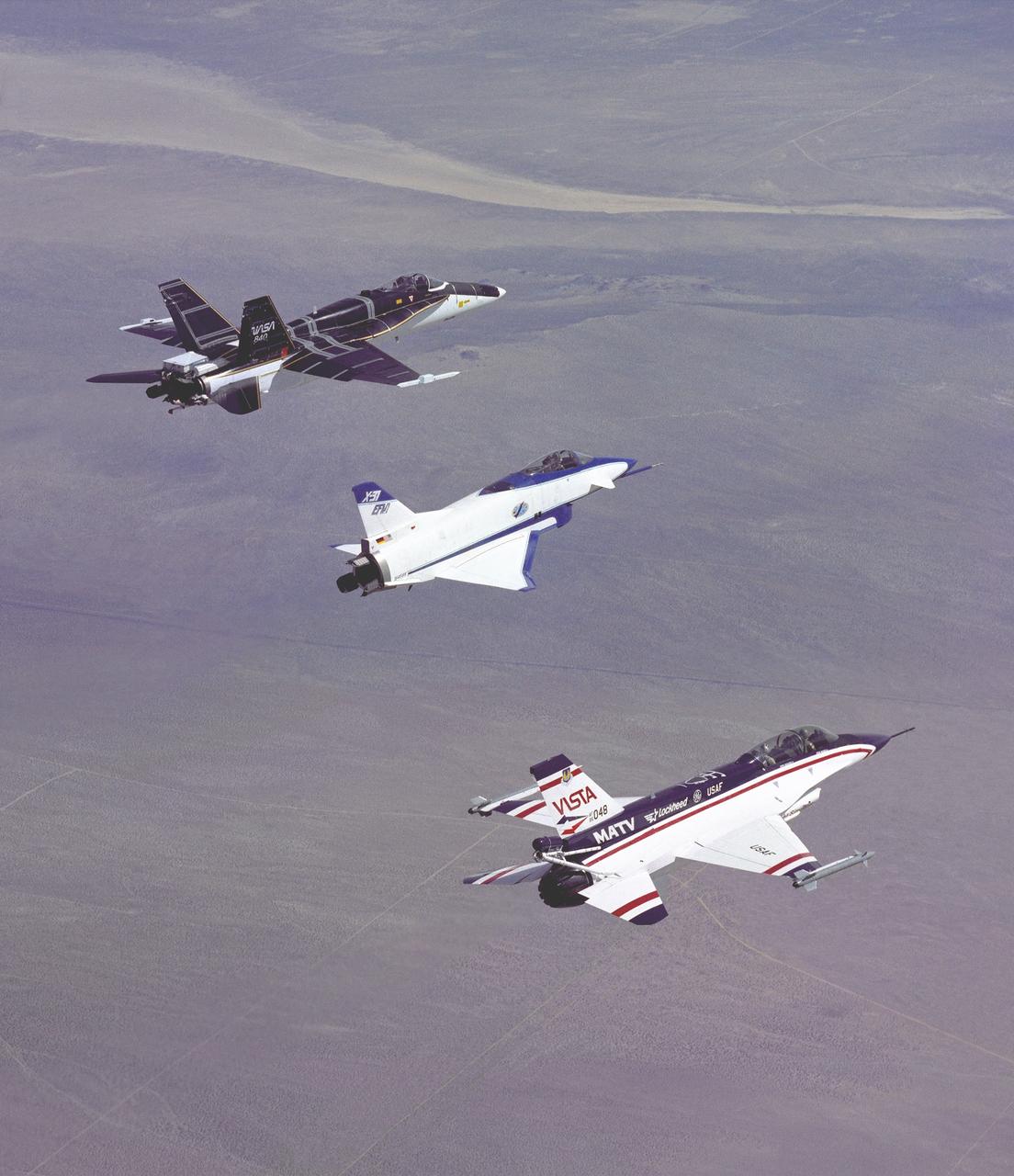

The three thrust-vectoring aircraft at Edwards, California, each capable of flying at extreme angles of attack, cruise over the California desert in formation during flight in March 1994. They are, from left, NASA's F-18 High Alpha Research Vehicle (HARV), flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center; the X-31, flown by the X-31 International Test Organization (ITO) at Dryden; and the Air Force F-16 Multi-Axis Thrust Vectoring (MATV) aircraft.
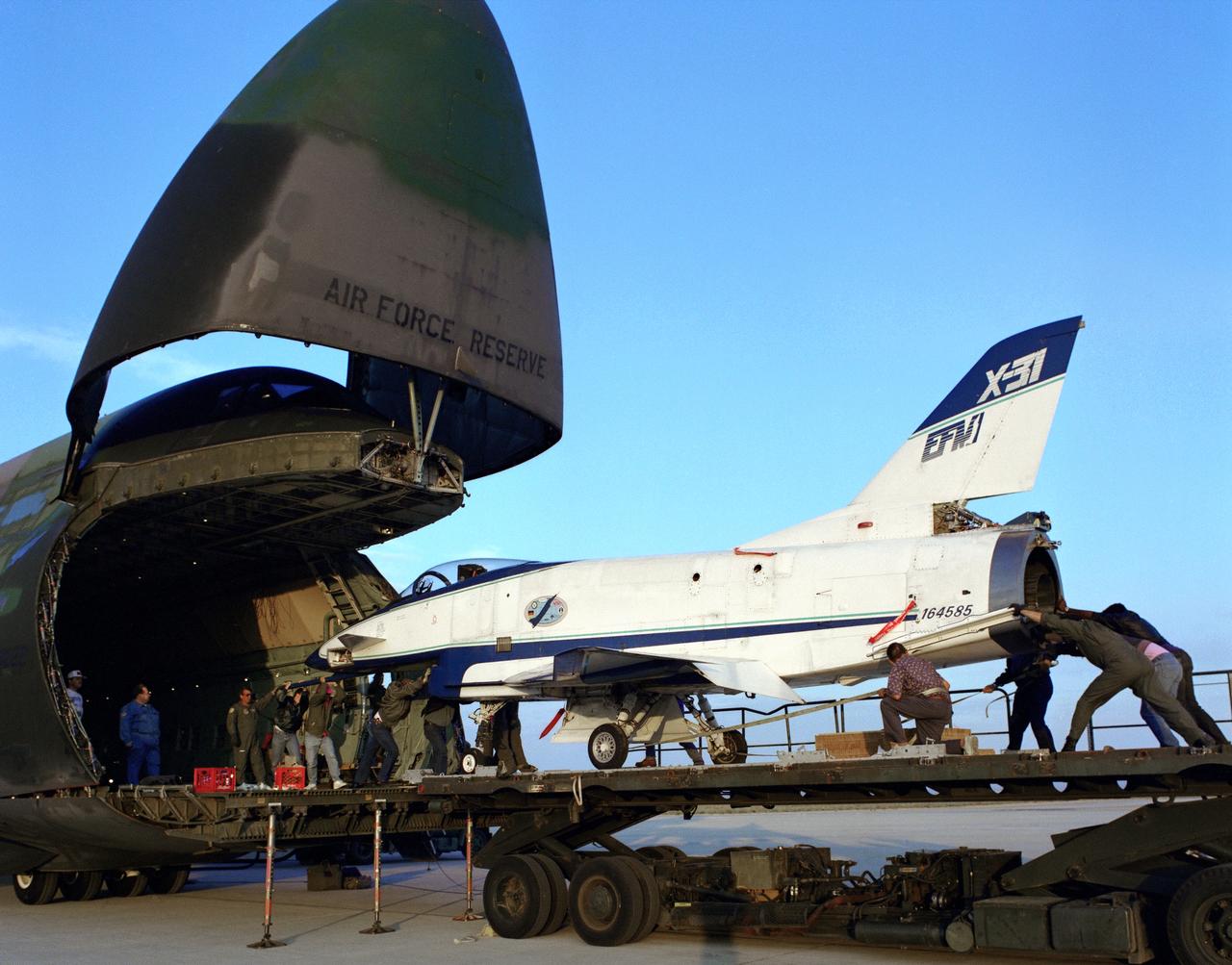

The X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator Aircraft, based at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, begins rolling aboard an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport which ferried it on May 22, 1995 to Europe where it was flown in the Paris Air Show in June 1995. To fit in the C-5 the right wing of the X-31 had to be removed. At the air show, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack.