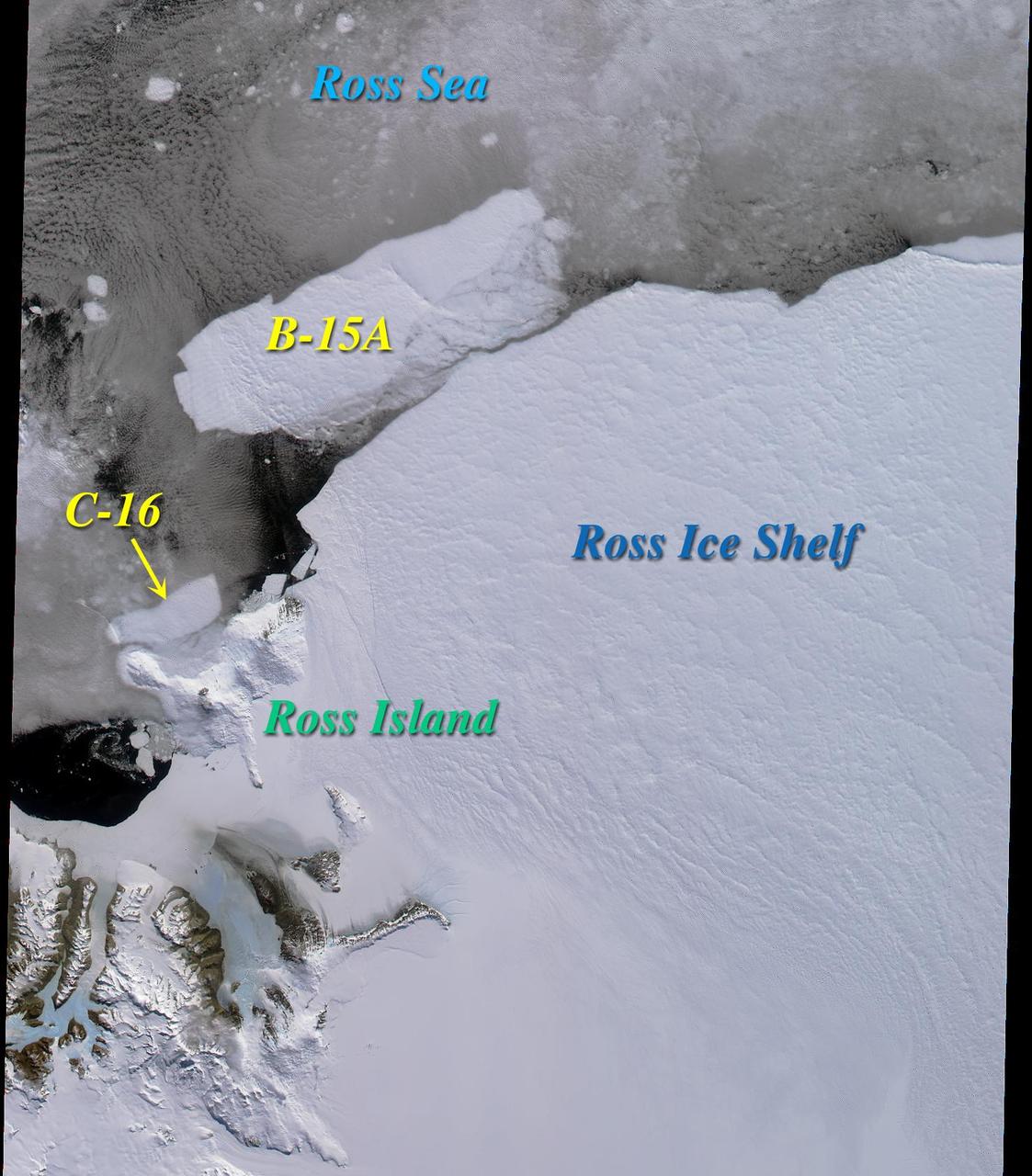
Two large icebergs, designated B-15A and C-16, captured by NASA Terra satellite, are of the Ross Ice Shelf and Ross Sea in Antarctica, acquired on December 10, 2000 during Terra orbit 5220, show
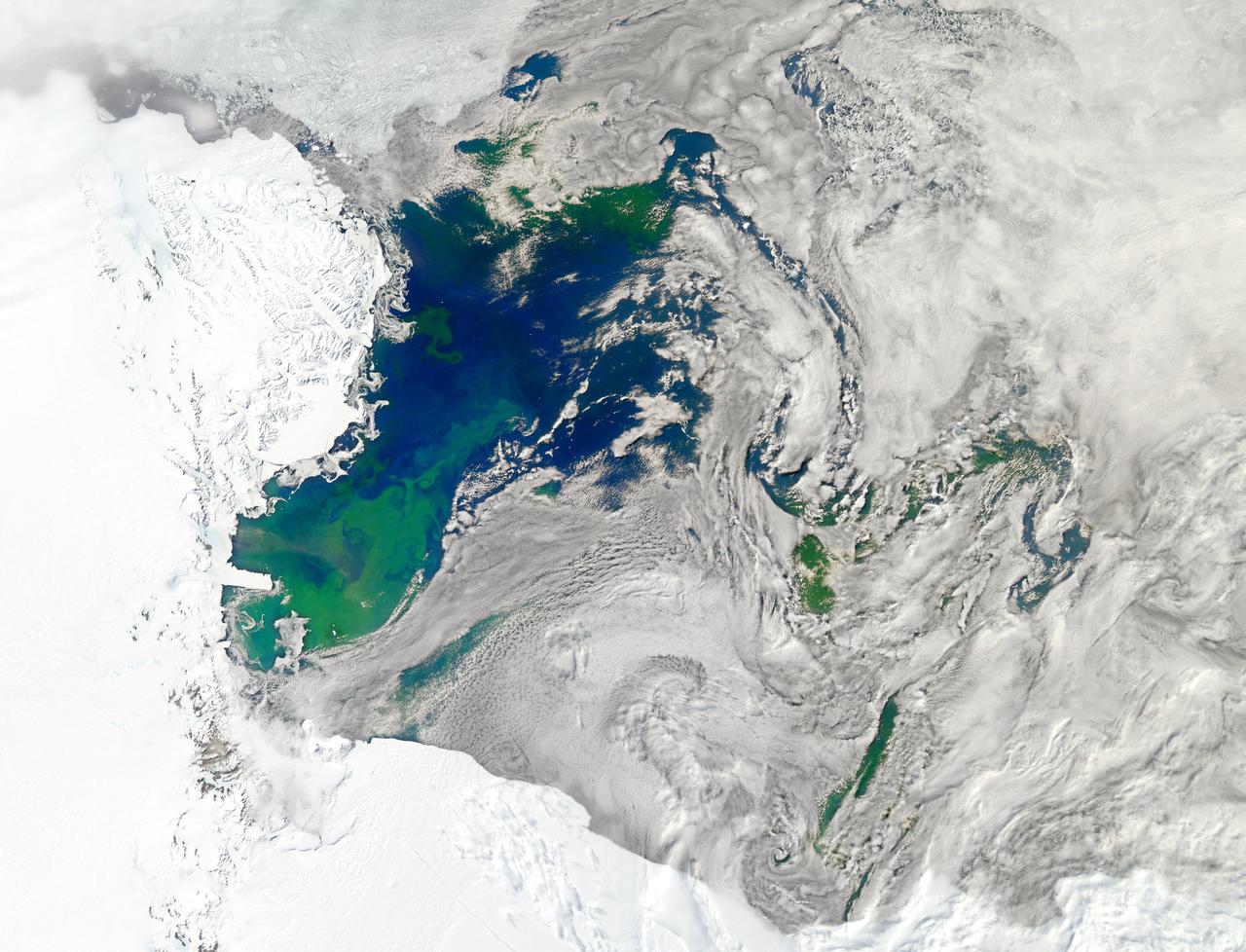
NASA image acquired January 22, 2011 Every southern spring and summer, after the Sun has risen into its 24-hour circuit around the skies of Antarctica, the Ross Sea bursts with life. Floating, microscopic plants, known as phytoplankton, soak up the sunlight and the nutrients stirring in the Southern Ocean and grow into prodigious blooms. Those blooms become a great banquet for krill, fish, penguins, whales, and other marine species who carve out a living in the cool waters of the far south. This true-color image captures such a bloom in the Ross Sea on January 22, 2011, as viewed by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite. Bright greens of plant-life have replaced the deep blues of open ocean water. The Ross Sea is a relatively shallow bay in the Antarctic coastline and due south from New Zealand. As the spring weather thaws the sea ice around Antarctica, areas of open water surrounded by ice—polynyas—open up on the continental shelf. In this open water, sunlight provides the fuel and various current systems provide nutrients from deeper waters to form blooms that can stretch 100 to 200 kilometers (60 to 120 miles). These blooms are among the largest in extent and abundance in the world. Scientists have hypothesized that the Modified Circumpolar Deep Water is the engine behind the blooms, stirring up just the right mix of trace metals and minerals from the deep to sustain plankton growth. This month, researchers aboard the U.S. icebreaking ship Nathaniel B. Palmer are cruising in the Ross Sea in search of the signatures of this current system. NASA image courtesy Norman Kuring, Ocean Color Team at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Mike Carlowicz, with information from Hugh Powell, COSEE-NOW. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS Go here to download the full high res file: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
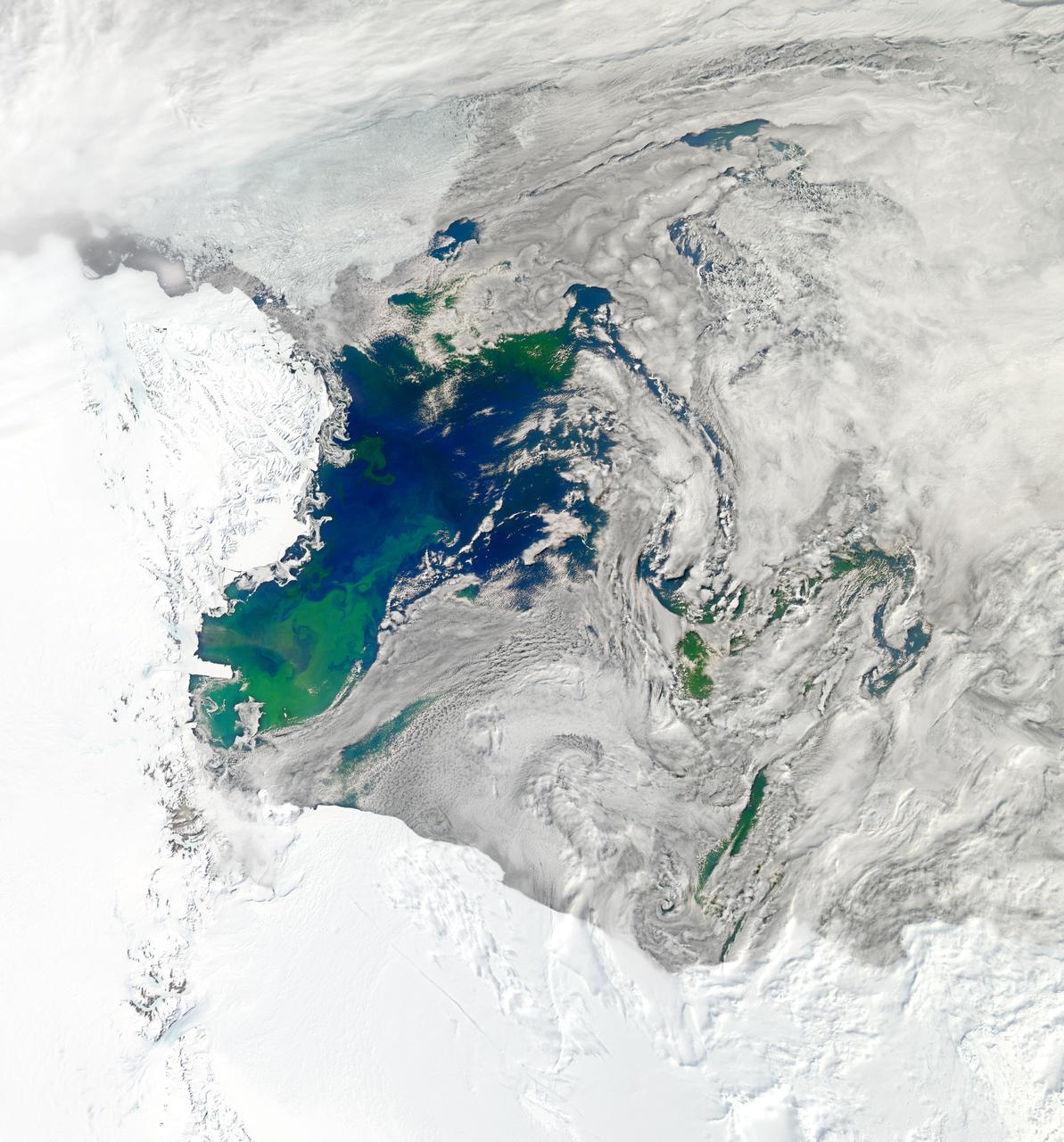

NASA image acquired January 22, 2011 To see a detail of this image go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5398237910">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5398237910</a> Every southern spring and summer, after the Sun has risen into its 24-hour circuit around the skies of Antarctica, the Ross Sea bursts with life. Floating, microscopic plants, known as phytoplankton, soak up the sunlight and the nutrients stirring in the Southern Ocean and grow into prodigious blooms. Those blooms become a great banquet for krill, fish, penguins, whales, and other marine species who carve out a living in the cool waters of the far south. This true-color image captures such a bloom in the Ross Sea on January 22, 2011, as viewed by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite. Bright greens of plant-life have replaced the deep blues of open ocean water. The Ross Sea is a relatively shallow bay in the Antarctic coastline and due south from New Zealand. As the spring weather thaws the sea ice around Antarctica, areas of open water surrounded by ice—polynyas—open up on the continental shelf. In this open water, sunlight provides the fuel and various current systems provide nutrients from deeper waters to form blooms that can stretch 100 to 200 kilometers (60 to 120 miles). These blooms are among the largest in extent and abundance in the world. Scientists have hypothesized that the Modified Circumpolar Deep Water is the engine behind the blooms, stirring up just the right mix of trace metals and minerals from the deep to sustain plankton growth. This month, researchers aboard the U.S. icebreaking ship Nathaniel B. Palmer are cruising in the Ross Sea in search of the signatures of this current system. NASA image courtesy Norman Kuring, Ocean Color Team at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Mike Carlowicz, with information from Hugh Powell, COSEE-NOW. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
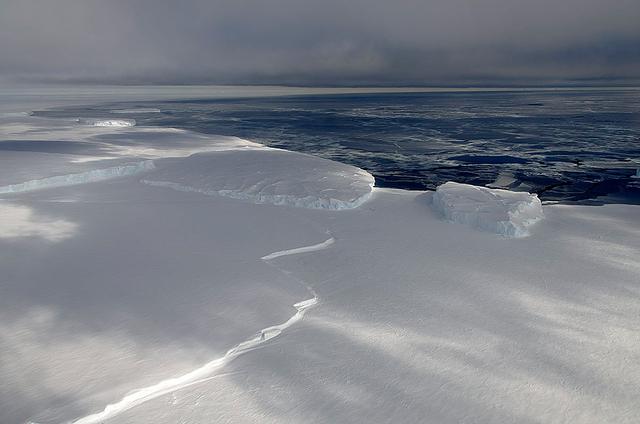

November 21, 2013 - NASA's Operation IceBridge P-3 landed a few minutes ago after a successful survey of sea ice in the Ross Sea. In this photo taken by project scientist Michael Studinger we see icebergs in Sulzberger Bay off of the eastern portion of the Ross Sea. NASA's Operation IceBridge is an airborne science mission to study Earth's polar ice. In 2013, IceBridge is conducting its first field campaign directly from Antarctica. For more information about IceBridge, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/icebridge" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/icebridge</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Michael Studinger <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

While NASA Dryden's Jim Ross outlined his job as an aerial photographer, sixth-grade student Leo Banuelos learned first-hand about the gear Ross wears in the cockpit.
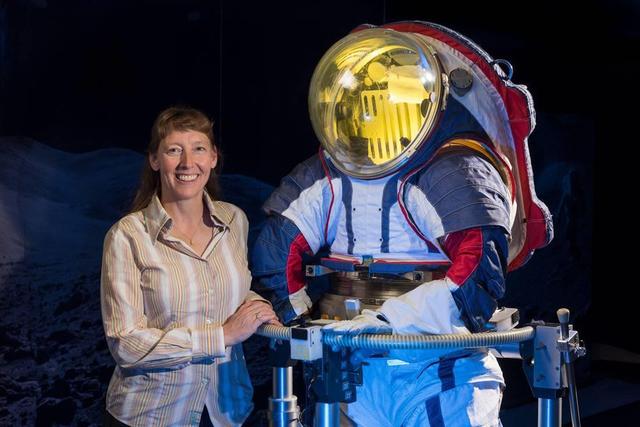

Advanced spacesuit designer Amy Ross of the NASA's Johnson Space Center stands with the Z-2, a prototype spacesuit. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23978
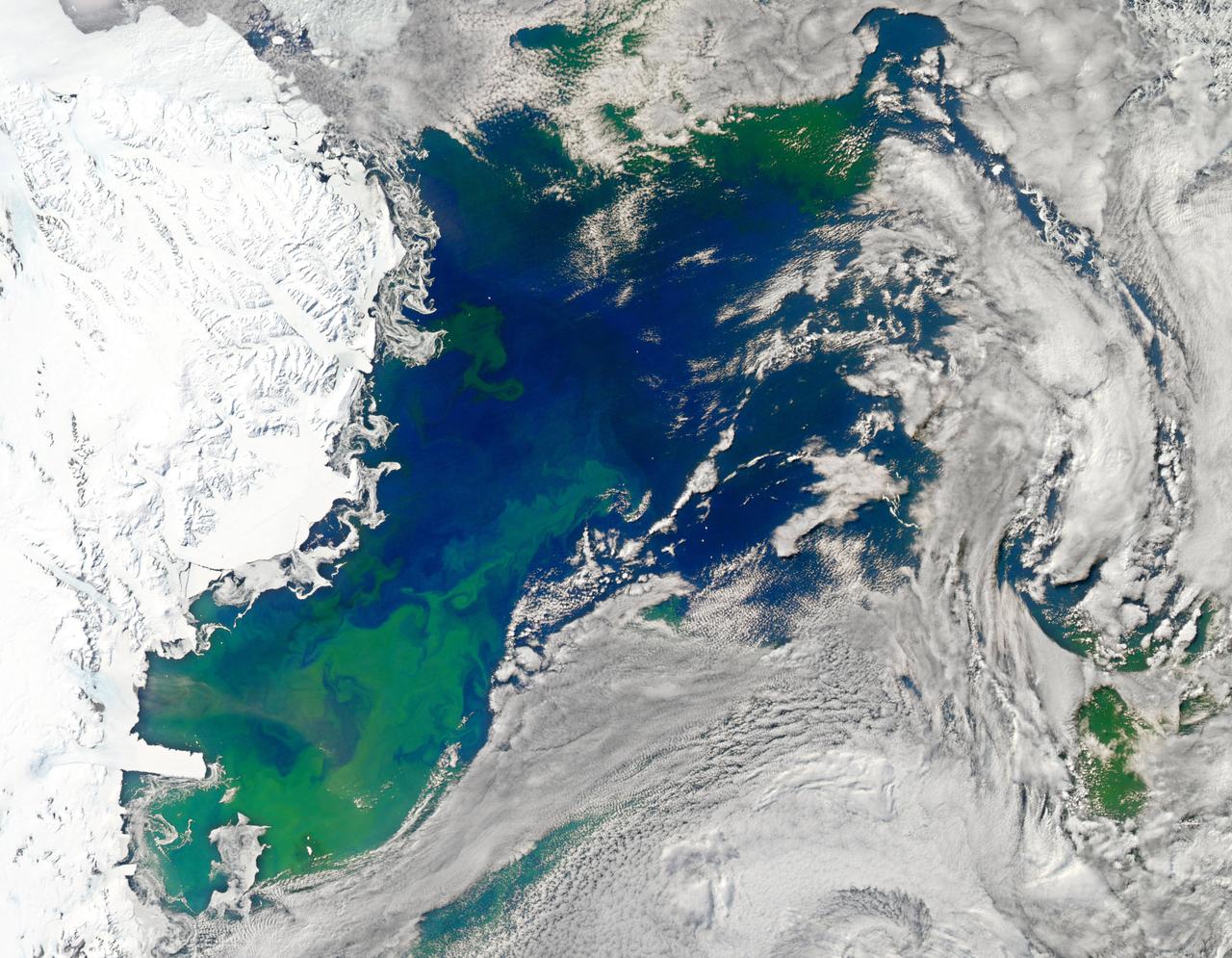
NASA image acquired January 22, 2011 To view the full image go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5397636843">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5397636843</a> Every southern spring and summer, after the Sun has risen into its 24-hour circuit around the skies of Antarctica, the Ross Sea bursts with life. Floating, microscopic plants, known as phytoplankton, soak up the sunlight and the nutrients stirring in the Southern Ocean and grow into prodigious blooms. Those blooms become a great banquet for krill, fish, penguins, whales, and other marine species who carve out a living in the cool waters of the far south. This true-color image captures such a bloom in the Ross Sea on January 22, 2011, as viewed by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite. Bright greens of plant-life have replaced the deep blues of open ocean water. The Ross Sea is a relatively shallow bay in the Antarctic coastline and due south from New Zealand. As the spring weather thaws the sea ice around Antarctica, areas of open water surrounded by ice—polynyas—open up on the continental shelf. In this open water, sunlight provides the fuel and various current systems provide nutrients from deeper waters to form blooms that can stretch 100 to 200 kilometers (60 to 120 miles). These blooms are among the largest in extent and abundance in the world. Scientists have hypothesized that the Modified Circumpolar Deep Water is the engine behind the blooms, stirring up just the right mix of trace metals and minerals from the deep to sustain plankton growth. This month, researchers aboard the U.S. icebreaking ship Nathaniel B. Palmer are cruising in the Ross Sea in search of the signatures of this current system. NASA image courtesy Norman Kuring, Ocean Color Team at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Mike Carlowicz, with information from Hugh Powell, COSEE-NOW. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS For more info go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

This color picture of the Ross Ice Shelf , Antarctica was taken NASA Galileo camera about 6:20 p.m. PST on December 8, 1990. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00074

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows Ross Crater in Aonia Terra. The crater rim is dissected by gullies, however these gullies are much smaller than those in yesterday's image. Orbit Number: 66831 Latitude: -57.6184 Longitude: 251.468 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-01-06 18:28 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21320

Today's VIS image shows part of Ross Crater. Located in Aonia Terra, the impact crater is 82 km (51 miles) in diameter. In addition to the dunes on the crater floor, the crater rim is dissected with numerous gullies, one of which is visible at top of the image. Orbit Number: 83304 Latitude: -57.1209 Longitude: 251.822 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-09-24 12:56 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24254
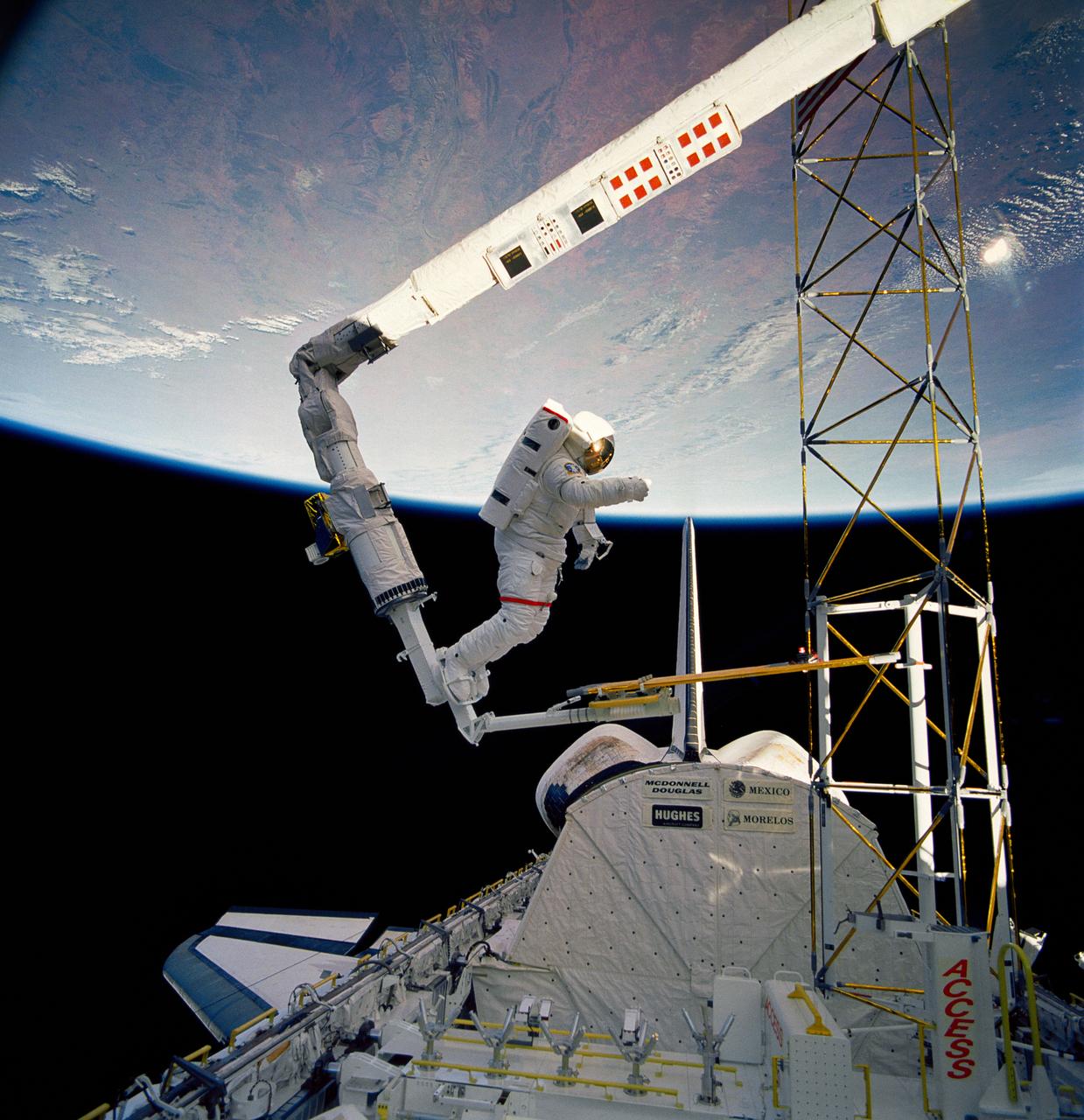

61B-41-019 (26 Nov. ? 3 Dec. 1985) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, one of NASA flight 6l-B's mission specialists, approaches a tower device just erected by Ross and astronaut Sherwood (Woody) C. Spring during the second of two extravehicular activities. The tower was called Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures. Ross is secured on a foot restraint device connected to the Canadian-built remote manipulator system (RMS) arm aboard the Earth orbiting Atlantis.
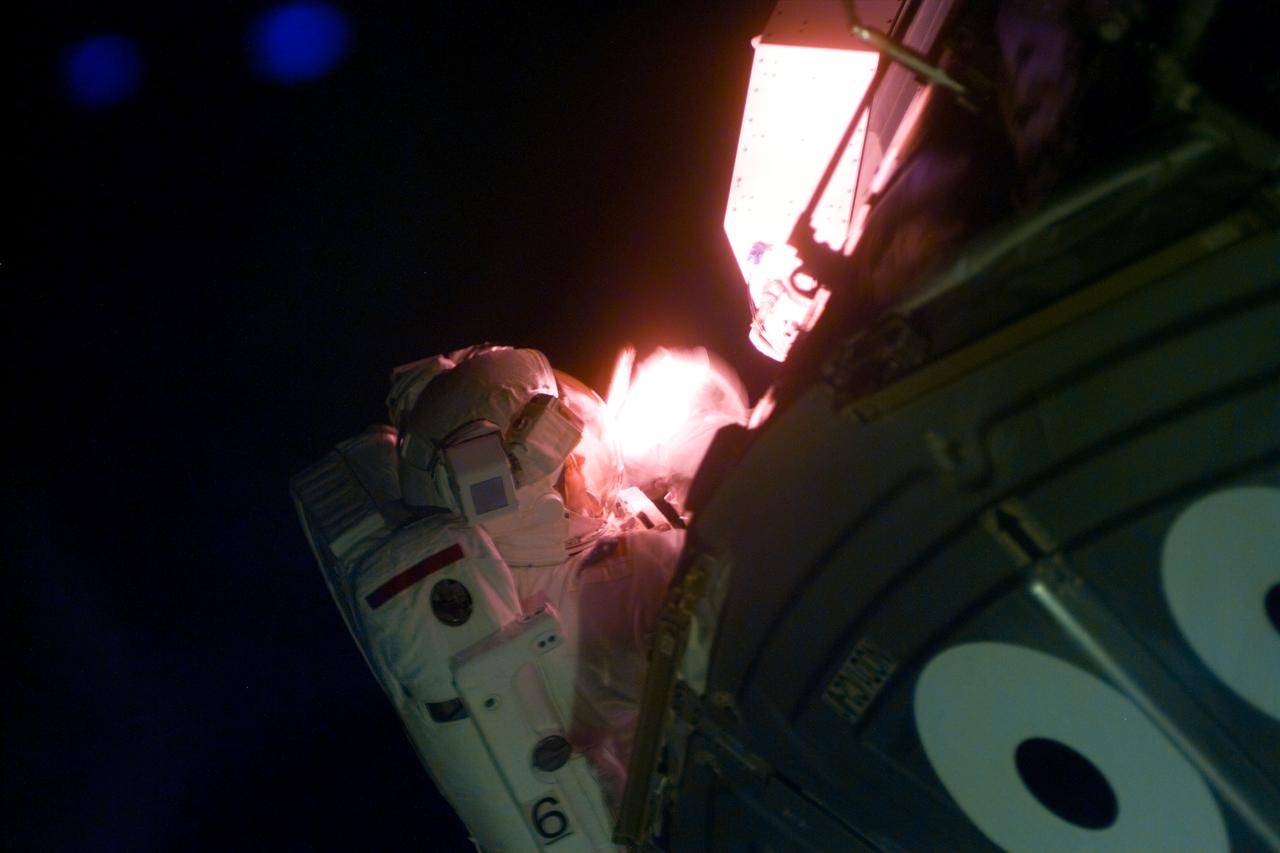

S88-E-5093 (12-09-98) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist, requires artificial light to work during the second STS-88 space walk. Part of a pressurized mating adapter (PMA) is in the foreground. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 23:49:36 GMT, Dec. 9.

James Ross Island captured by NASA photographer James Ross(no relation), from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during an AirSAR 2004 mission over the Antarctic Peninsula. James Ross Island, named for 19th century British polar explorer Sir James Clark Ross, is located at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. The island is about 1500 m high and 40-60 km wide. In recent decades, the area has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
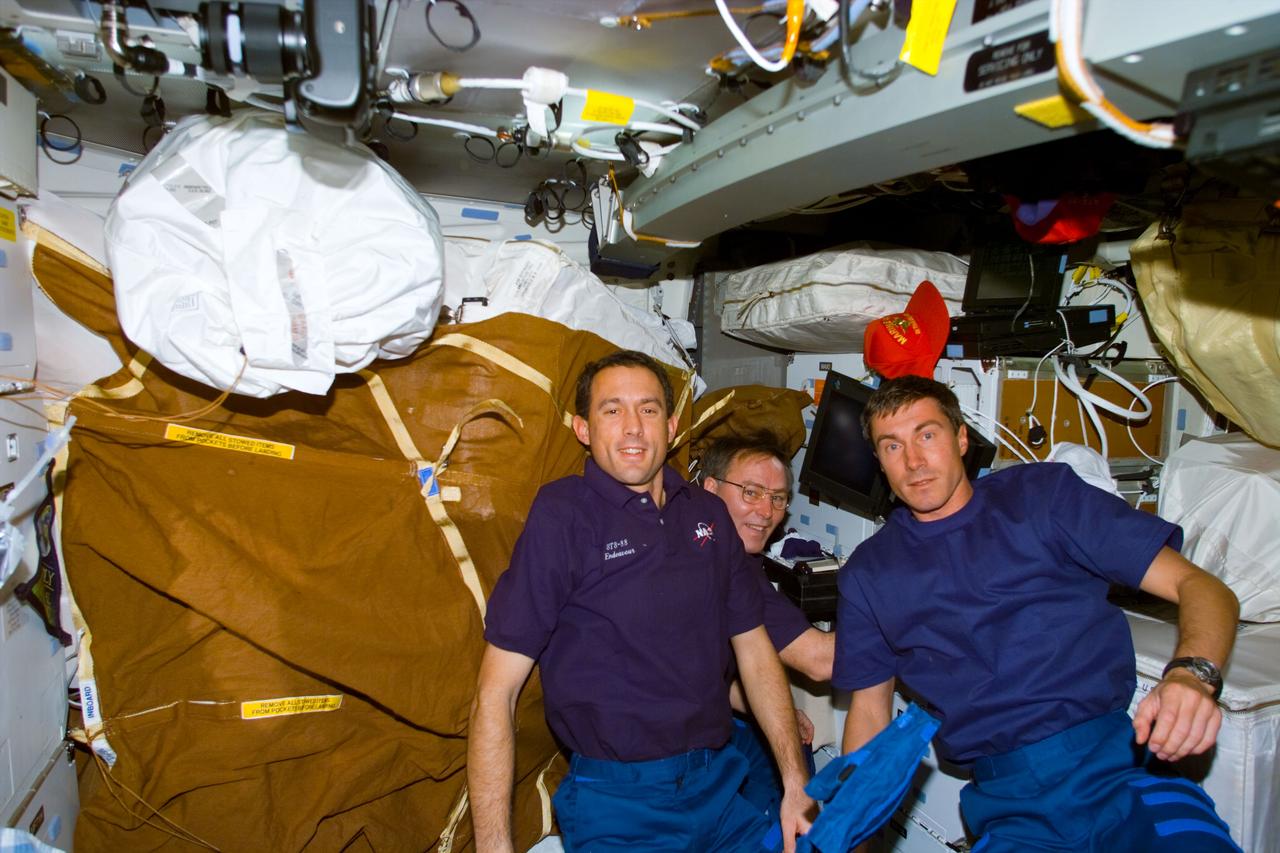

S88-E-5163 (12-08-98) --- Left to right, James H. Newman, Jerry L. Ross and Sergei K. Krikalev--all mission specialists--on Endeavour's middeck. Ross and Newman eventually participated in three space walks as part of the STS-88 work involved in readying the Unity and Zarya modules for their ISS roles. Krikalev, representing the Russian Space Agency, has been named as a member of the first ISS flight crew. This photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 23:14:01 GMT, Dec. 8.

S96-00265 (12 Dec. 1995) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist.

Former Center Director, Larry Ross, in the Altitude Wind Tunnel, AWT

Marshall Space Flight Center's Black History Month program featured a panel discussion including Dr. Quentin T. Ross, 15th President of Alabama State University.
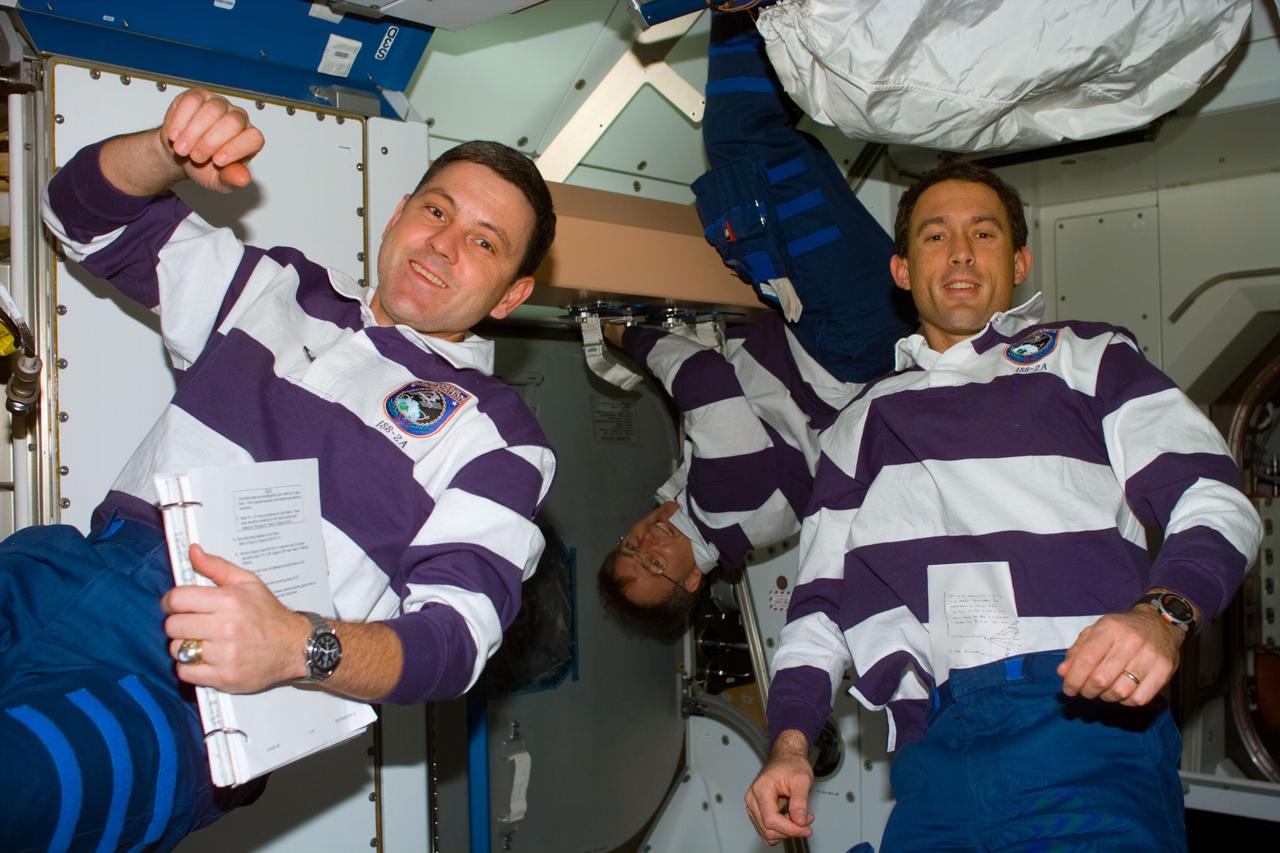

S88-E-5124 (12-11-98) --- From the left, astronauts Robert D. Cabana, Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman are pictured during work to ready the Unity connecting module for its ISS role. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 00:23:27 GMT, Dec. 11.
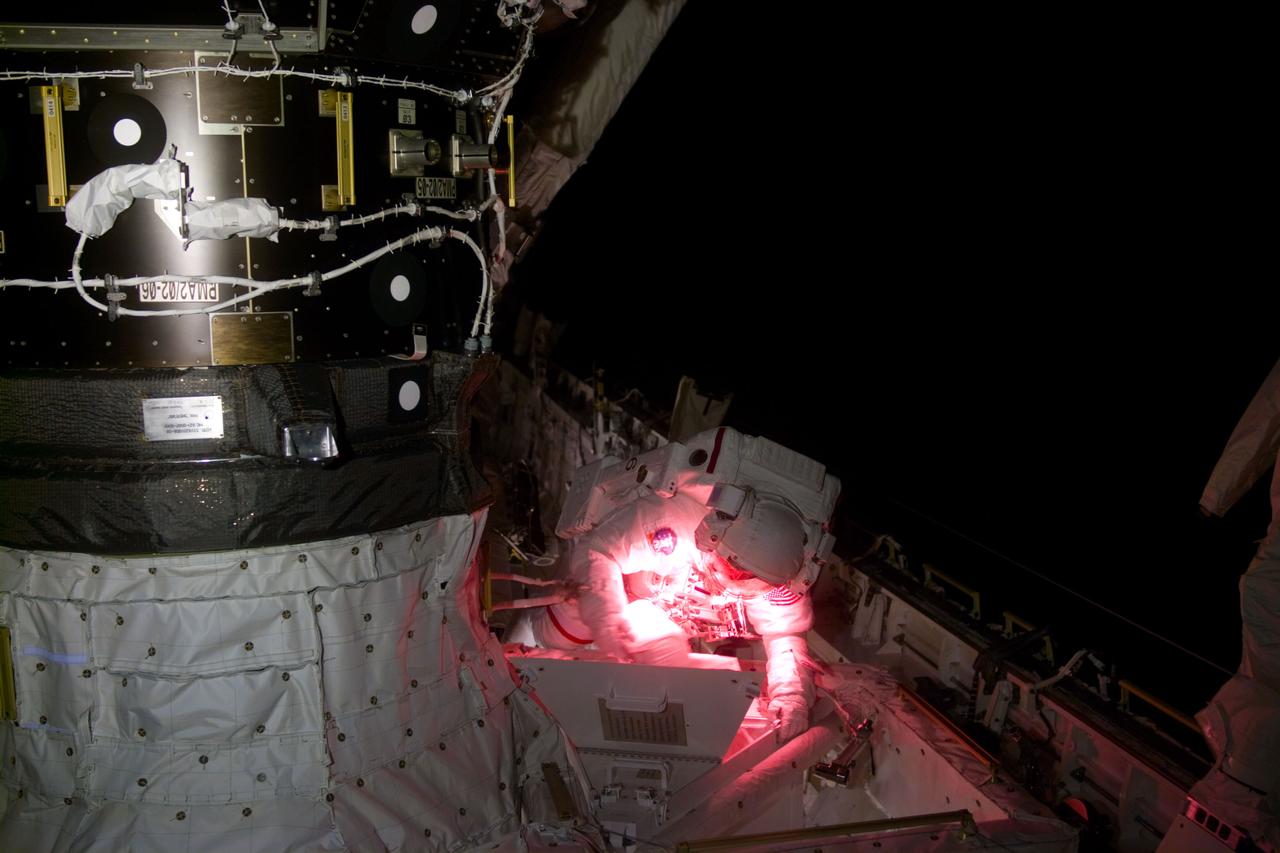
S88-E-5104 (12-10-98) With the Shuttle in a "night side" position, astronaut Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist, uses artificial light during the second STS-88 space walk. Ross is near a pressurized module adapter (PMA) on Endeavour's port side. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 03:10:00 GMT, Dec. 10.
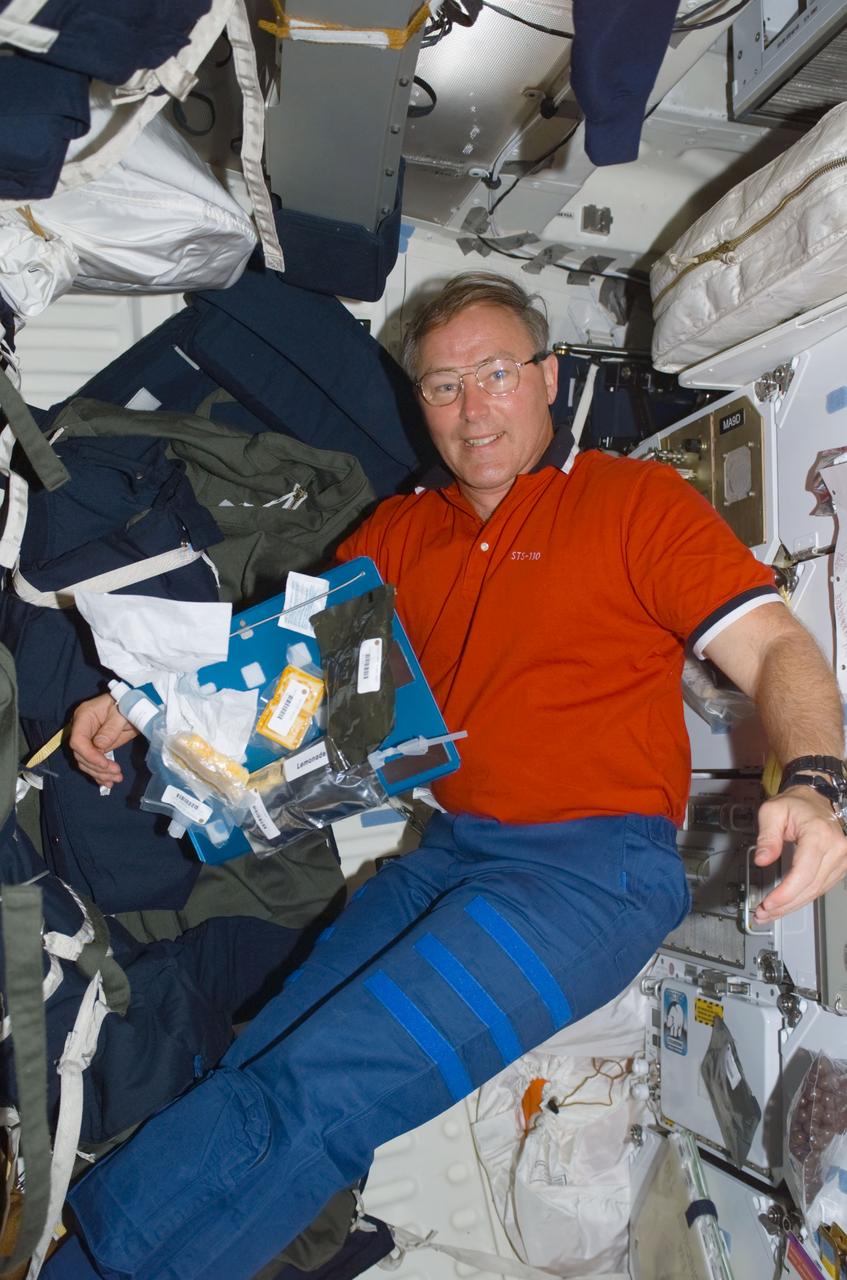

STS110-E-5035 (8 April 2002) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, STS-110 mission specialist, along with a tray of food, floats on the mid deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The image was taken with a digital still camera.
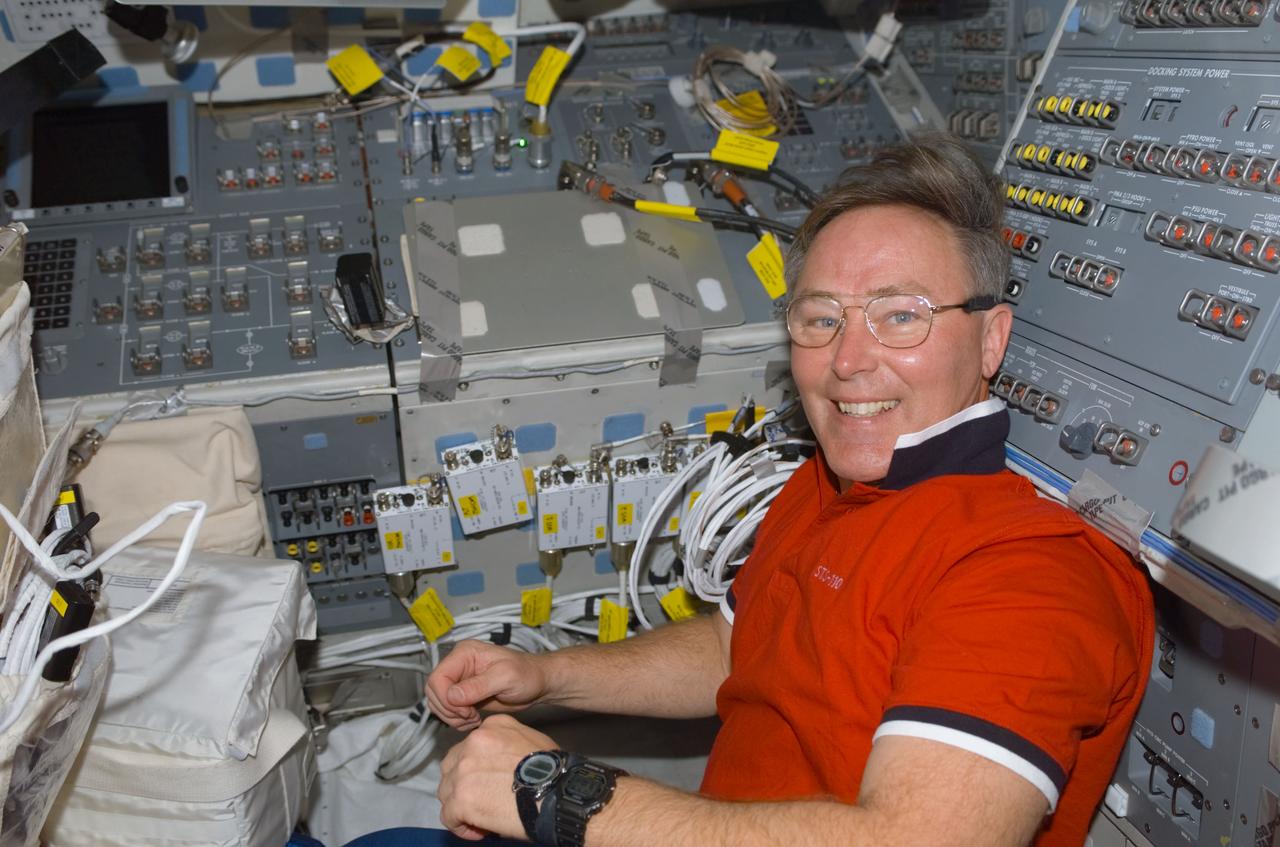

STS110-E-5004 (8 April 2002) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, STS-110 mission specialist, works on the mid deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The image was taken with at digital still camera.

STS110-E-5148 (10 April 2002) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, STS-110 mission specialist, navigates one of the many hatches on the International Space Station (ISS). The image was taken with a digital still camera.
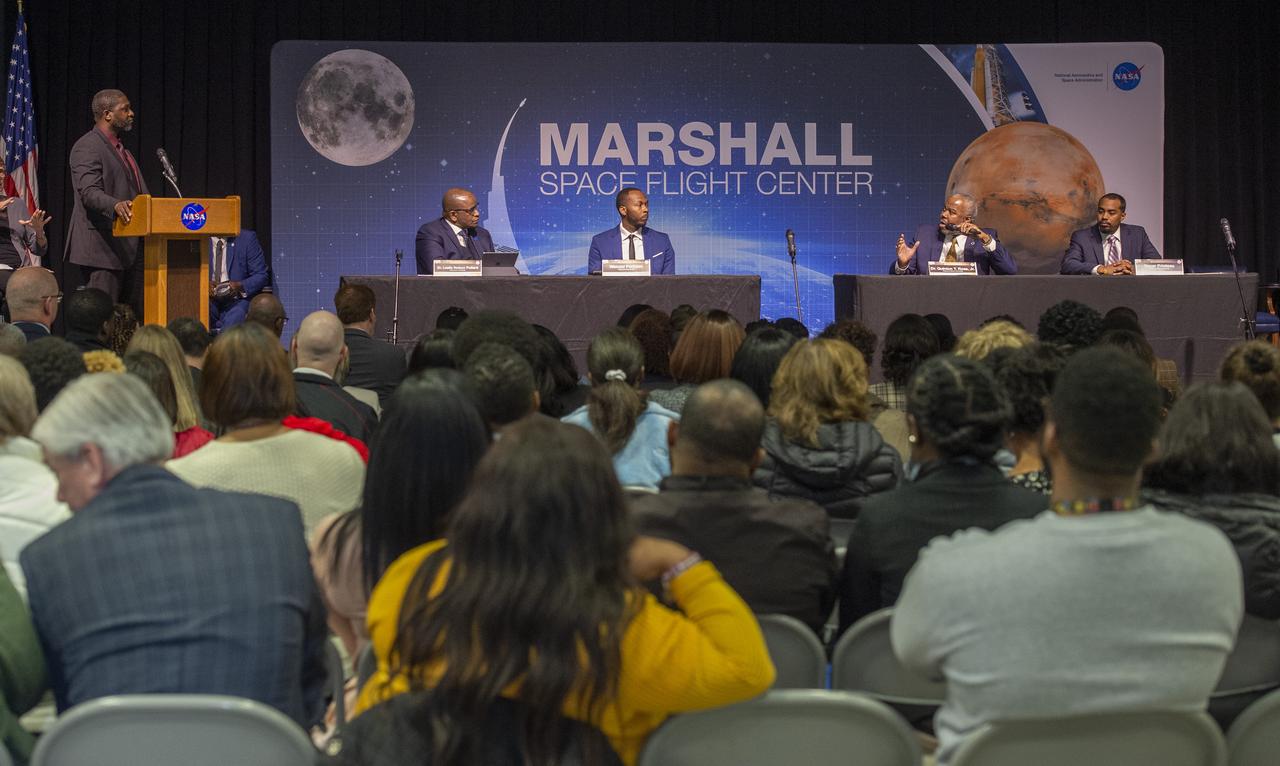

Marshall Space Flight Center's Black History Month program featured a panel discussion including Leslie Pollard, President of Oakwood University and Quinton Ross, President of Alabama State University.
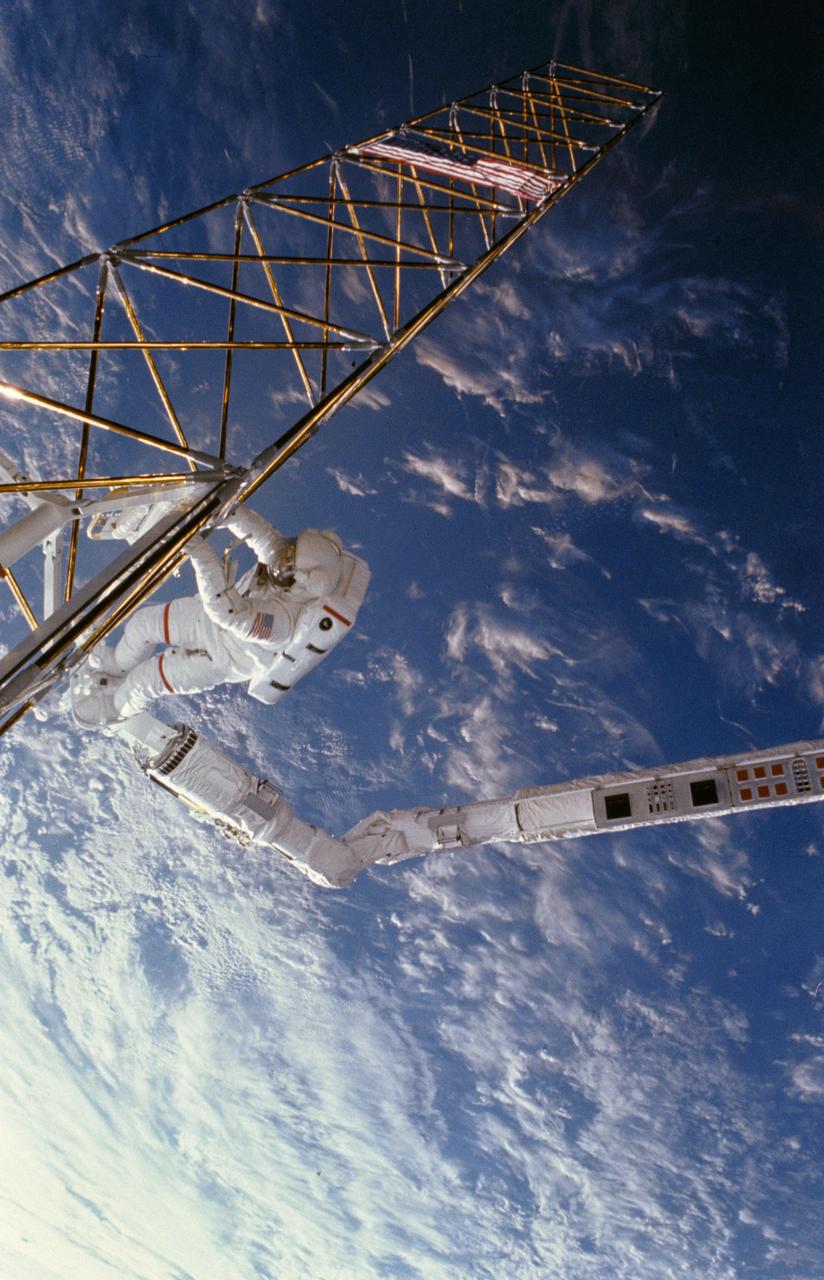

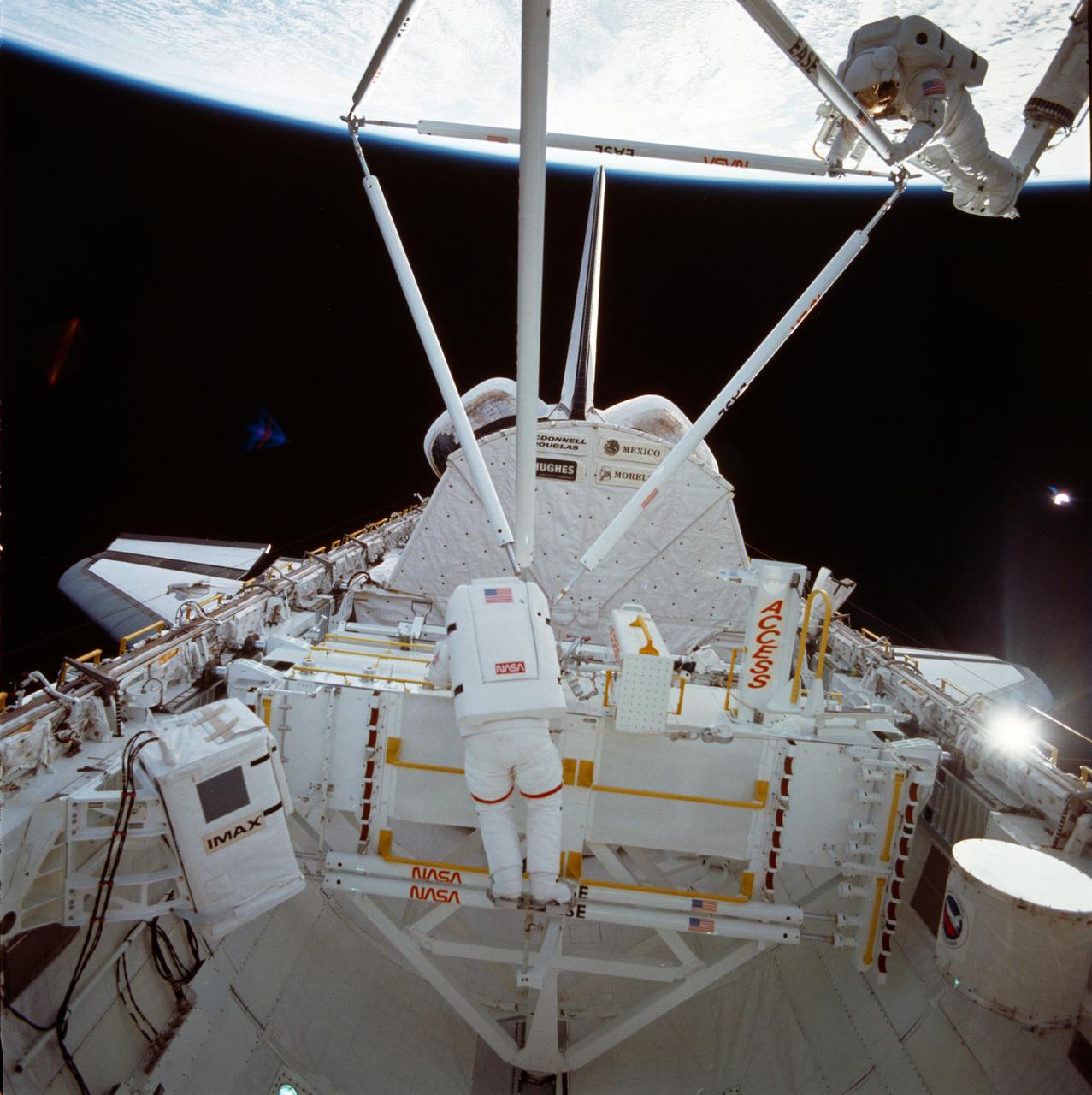
61B-102-022 (1 Dec 1985) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, anchored to the foot restraint on the remote manipulator system (RMS), holds onto the tower-like Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) device, as the Atlantis flies over white clouds and blue ocean waters. The frame was exposed with a negative-equipped camera held by Astronaut Sherwood C. Spring, who was also on the EVA-task.
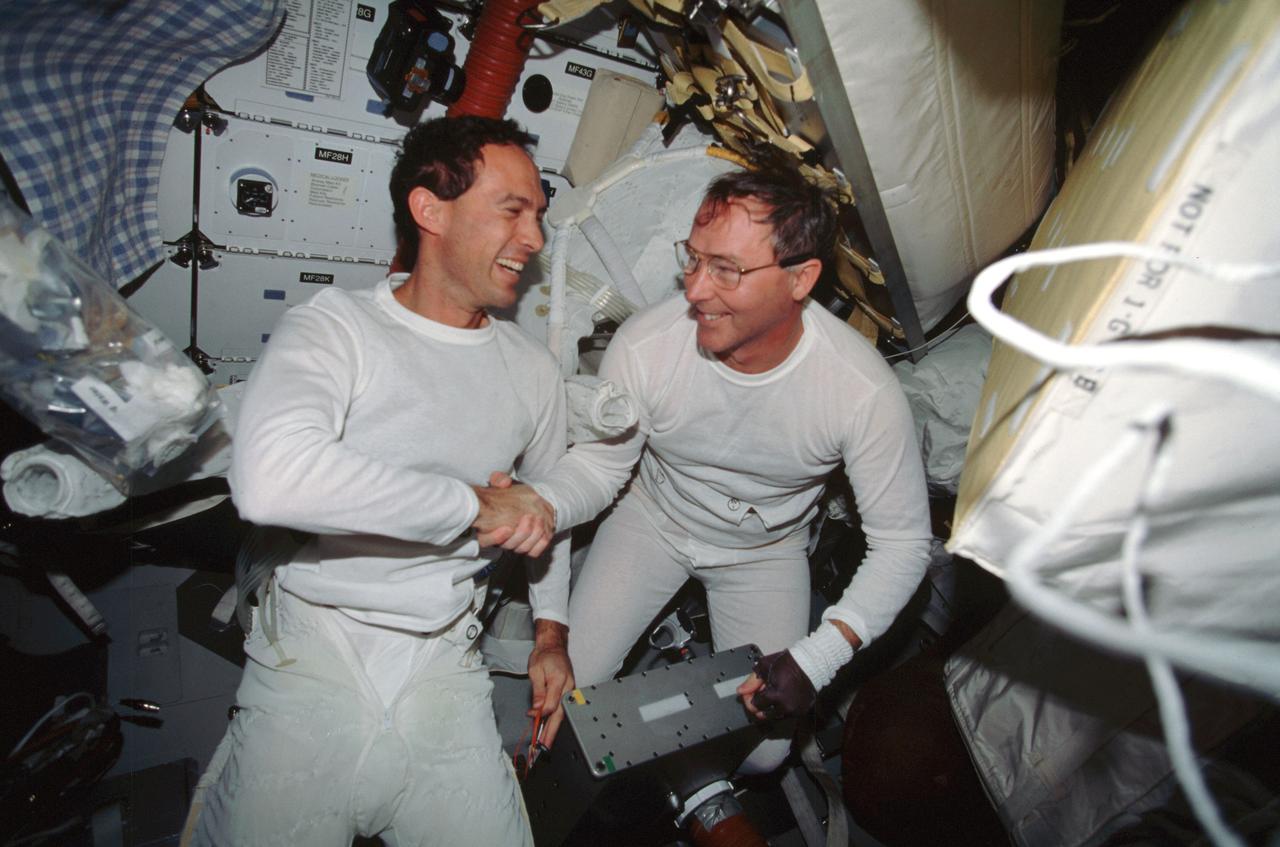

STS088-307-005 (4-15 December 1998) --- Astronauts James H. Newman (left) and Jerry L. Ross, both mission specialists, congratulate each other following one of their three extravehicular activities (EVA). The two had just doffed their Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMU) with the aid of astronaut Frederick W. "Rick" Sturckow (out of frame), pilot.
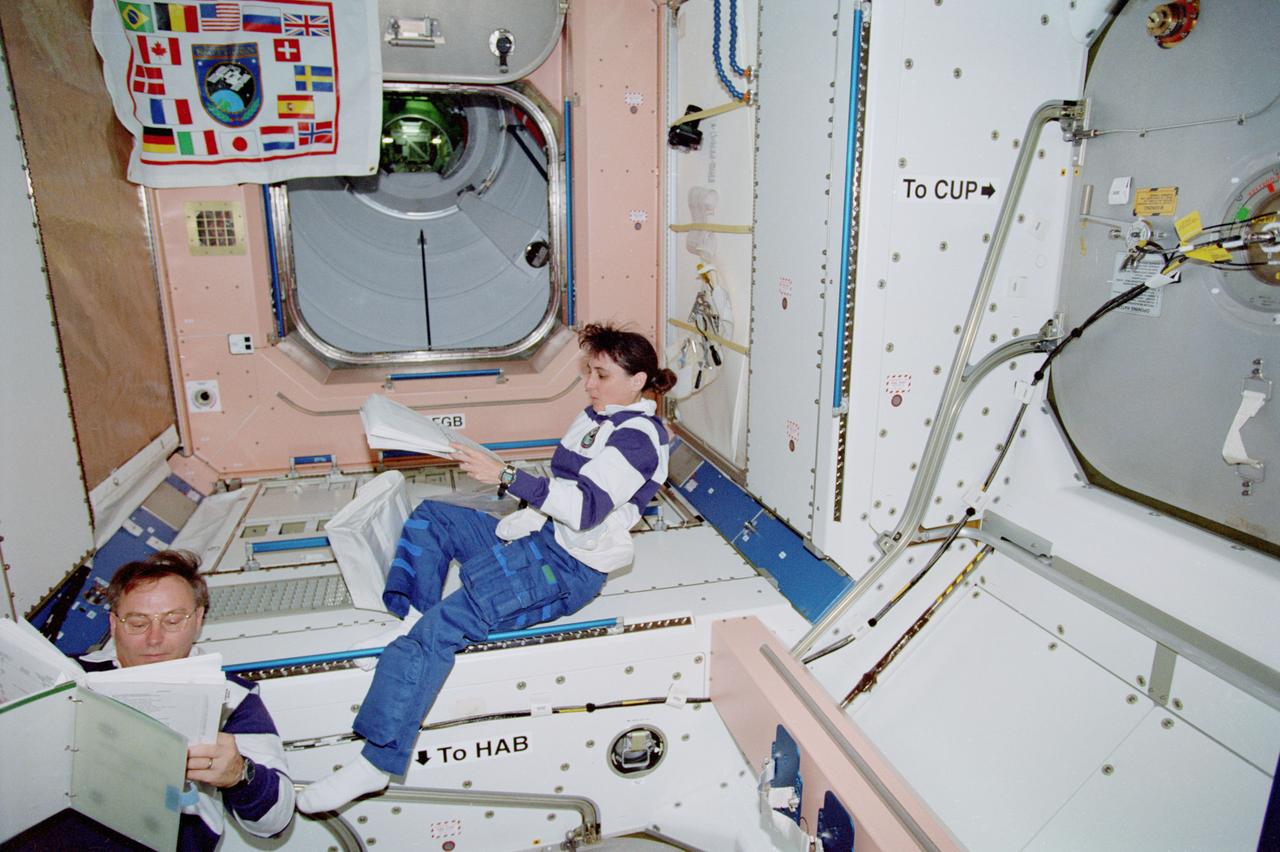

STS088-357-020 (4-15 Dec. 1998) --- Astronauts Jerry L. Ross and Nancy J. Currie, both mission specialists, check procedures list prior to performing a variety of tasks in the United States-built Node 1 or Unity Module. The hatchway in upper left corner accesses the Russian-built FGB or Zarya Module, which had earlier been retrieved with the aid of the Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) and linked with Unity.
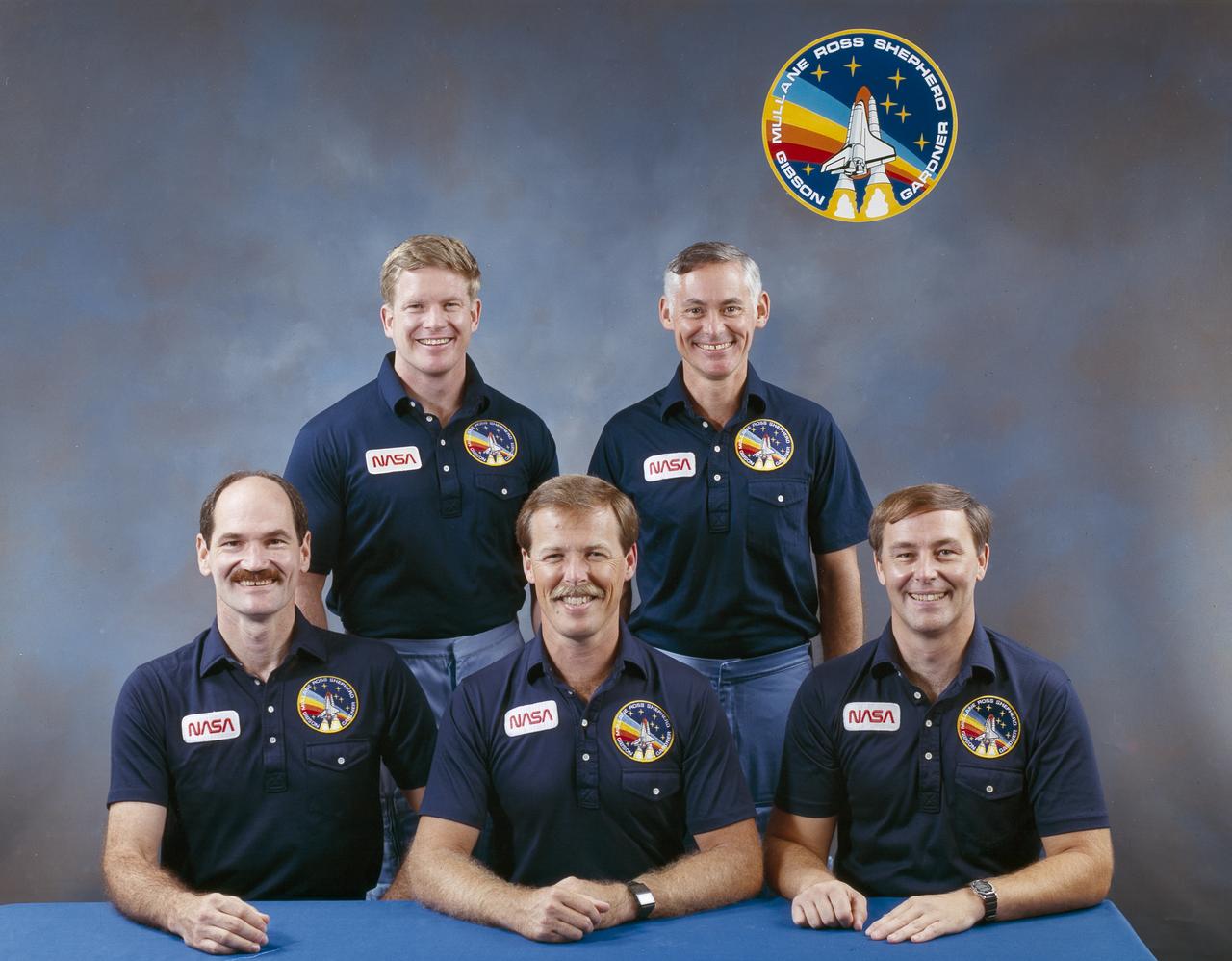

The STS-27 crew portrait features 5 astronauts. Seated, left to right, are Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist; Guy S. Gardner, pilot; and Robert L. Gibson, commander. On the back row, left to right, are mission specialists Richard M. Mullane, and William M. Shepherd. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on December 2, 1988 at 9:30:34 am (EST), the STS-27 mission was the third mission dedicated to the Department of Defense (DOD).
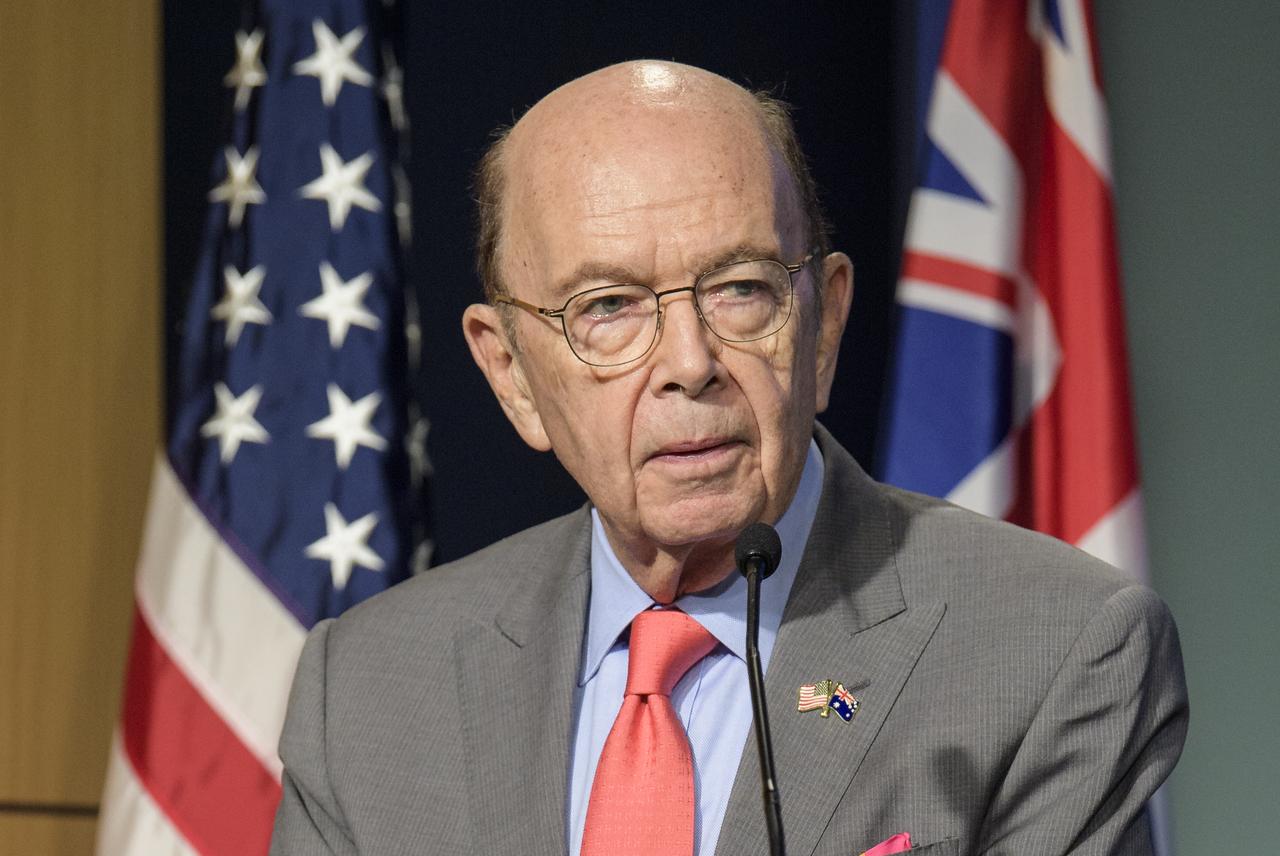

U.S. Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross delivers remarks prior the signing of a letter of intent between NASA and the Australian Space Agency, Saturday, Sept. 21, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA and the Australian Space Agency will build on over 60 years of collaboration in space exploration between the two countries and commit to expanding cooperation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
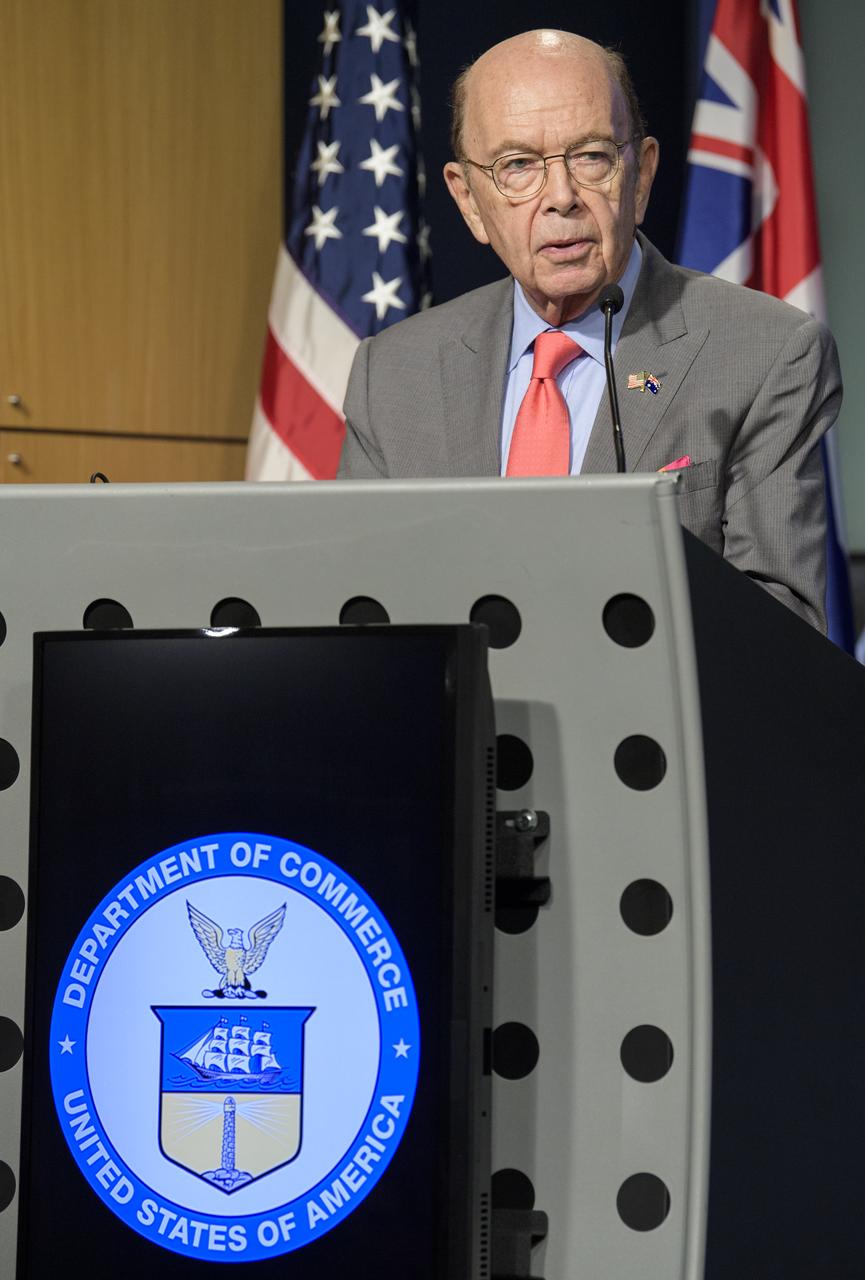

U.S. Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross delivers remarks prior the signing of a letter of intent between NASA and the Australian Space Agency, Saturday, Sept. 21, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA and the Australian Space Agency will build on over 60 years of collaboration in space exploration between the two countries and commit to expanding cooperation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
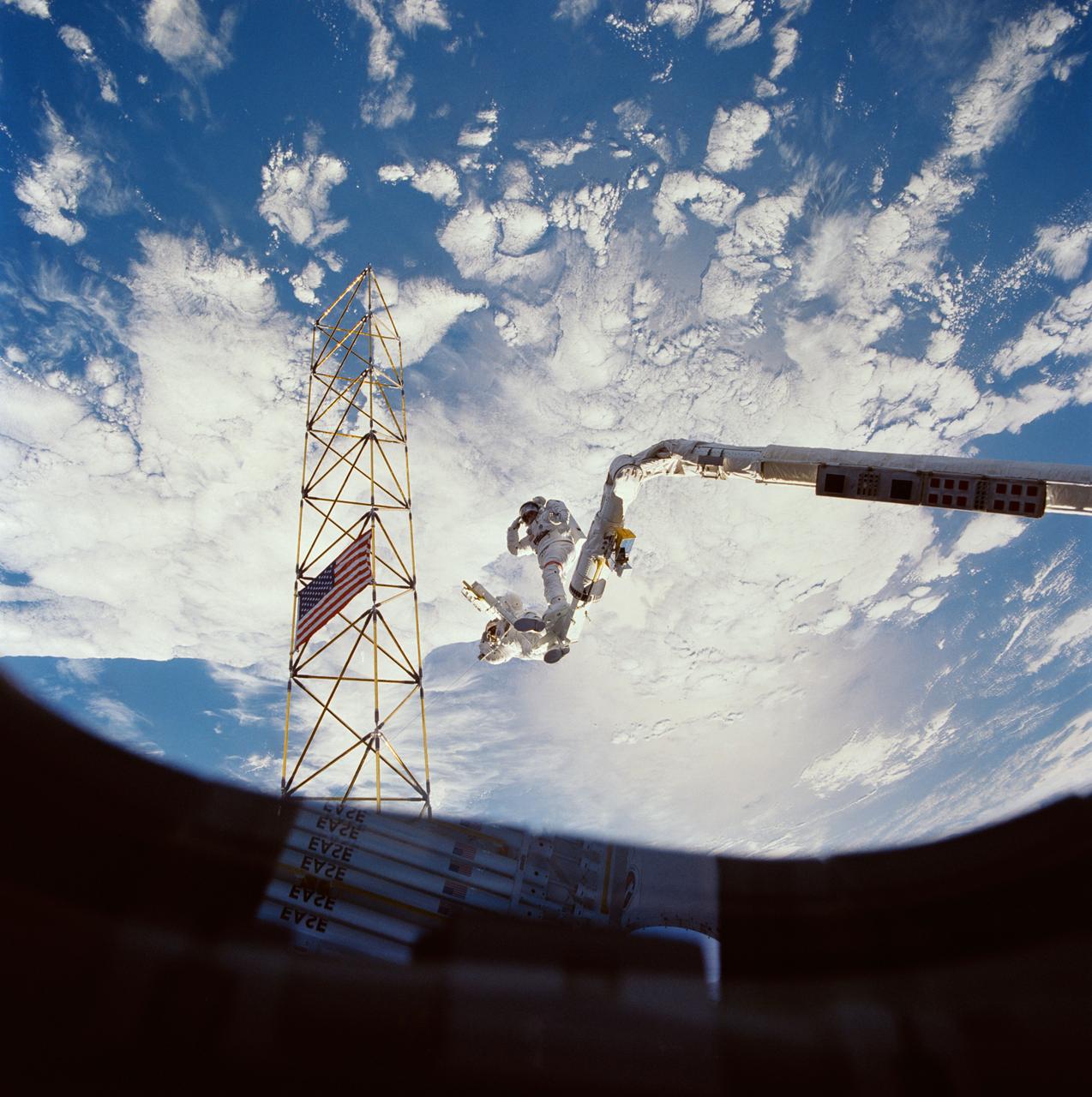

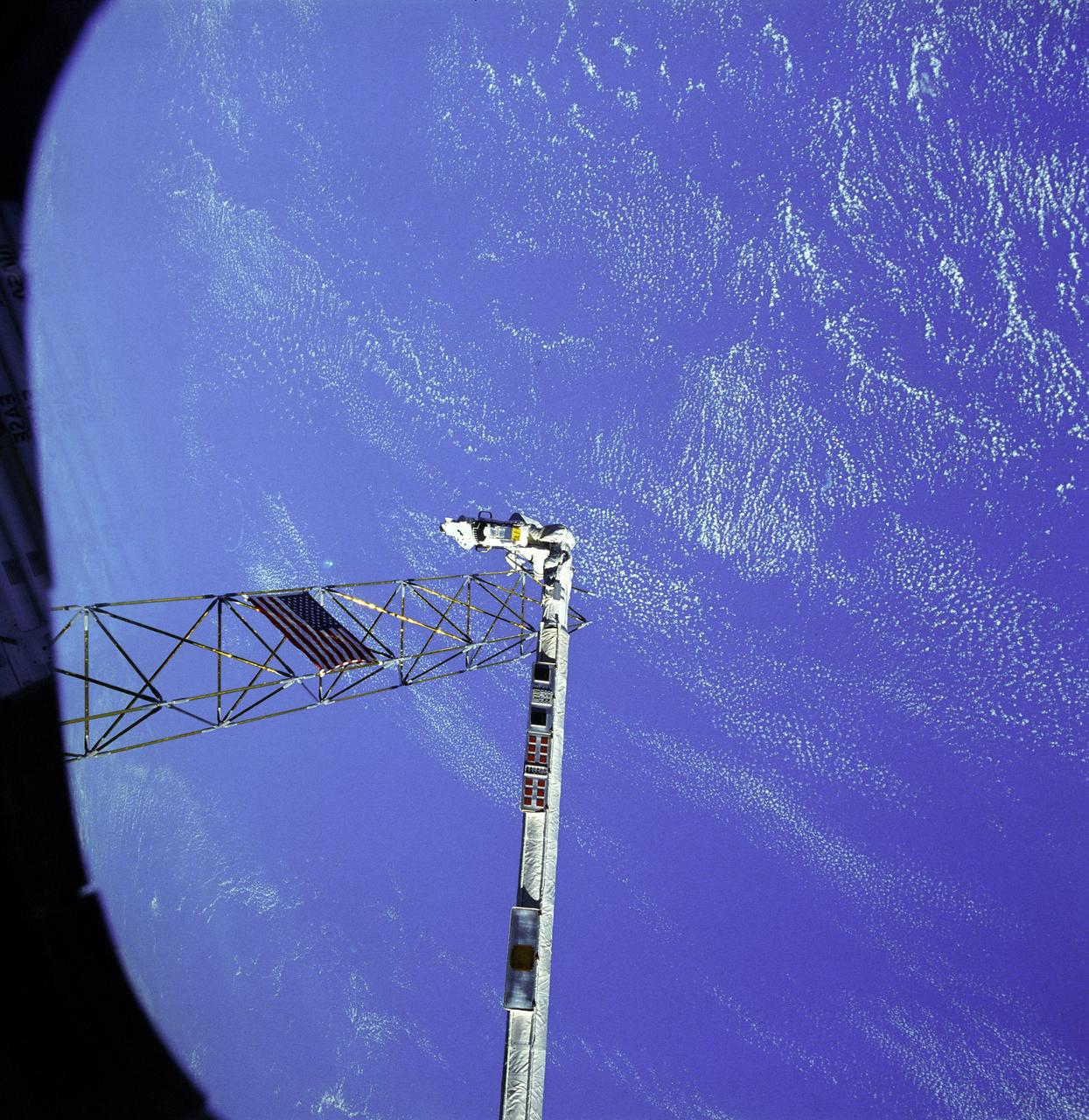
Astronauts Jerry L. Ross (right) and Sherwood C. (Woody) Spring (left) share a foot restraint as they survey the assembled ACCESS components after a lengthy extravehicular activity. Both men salute the American flag placed on the assembled ACCESS tower. Stowed EASE pieces are reflected in the window through which the photo was taken.
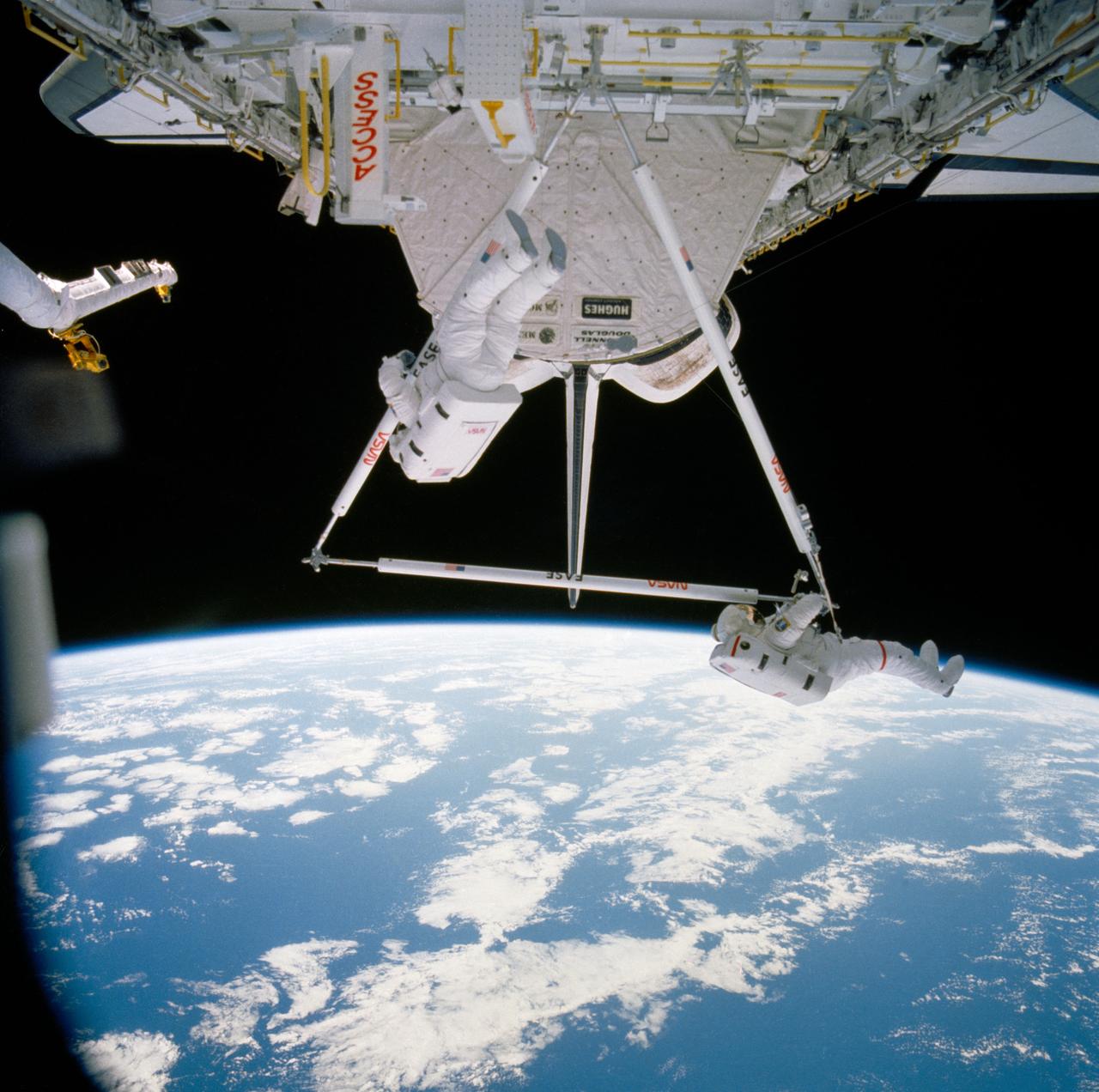

Astronauts Jerry L. Ross (left) and Sherwood C. (Woody) Spring are photographed as they assemble pieces of the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activities (EASE) device in the open payload bay. The Canadian-built remote manipulator system (RMS) arm (partially obscured in the right portion of the frame) is in position to allow television cameras to record the activity.

The crew assigned to the STS-61B mission included Bryan D. O’Conner, pilot; Brewster H. Shaw, commander; Charles D. Walker, payload specialist; mission specialists Jerry L. Ross, Mary L. Cleave, and Sherwood C. Spring; and Rodolpho Neri Vela, payload specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis November 28, 1985 at 7:29:00 pm (EST), the STS-61B mission’s primary payload included three communications satellites: MORELOS-B (Mexico); AUSSAT-2 (Australia); and SATCOM KU-2 (RCA Americom). Two experiments were conducted to test assembling erectable structures in space: EASE (Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity), and ACCESS (Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structure). In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, and the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), EASE and ACCESS were developed and demonstrated at MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). In this STS-61B onboard photo, astronaut Ross works on ACCESS high above the orbiter. The primary objective of these experiments was to test the structural assembly concepts for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction.
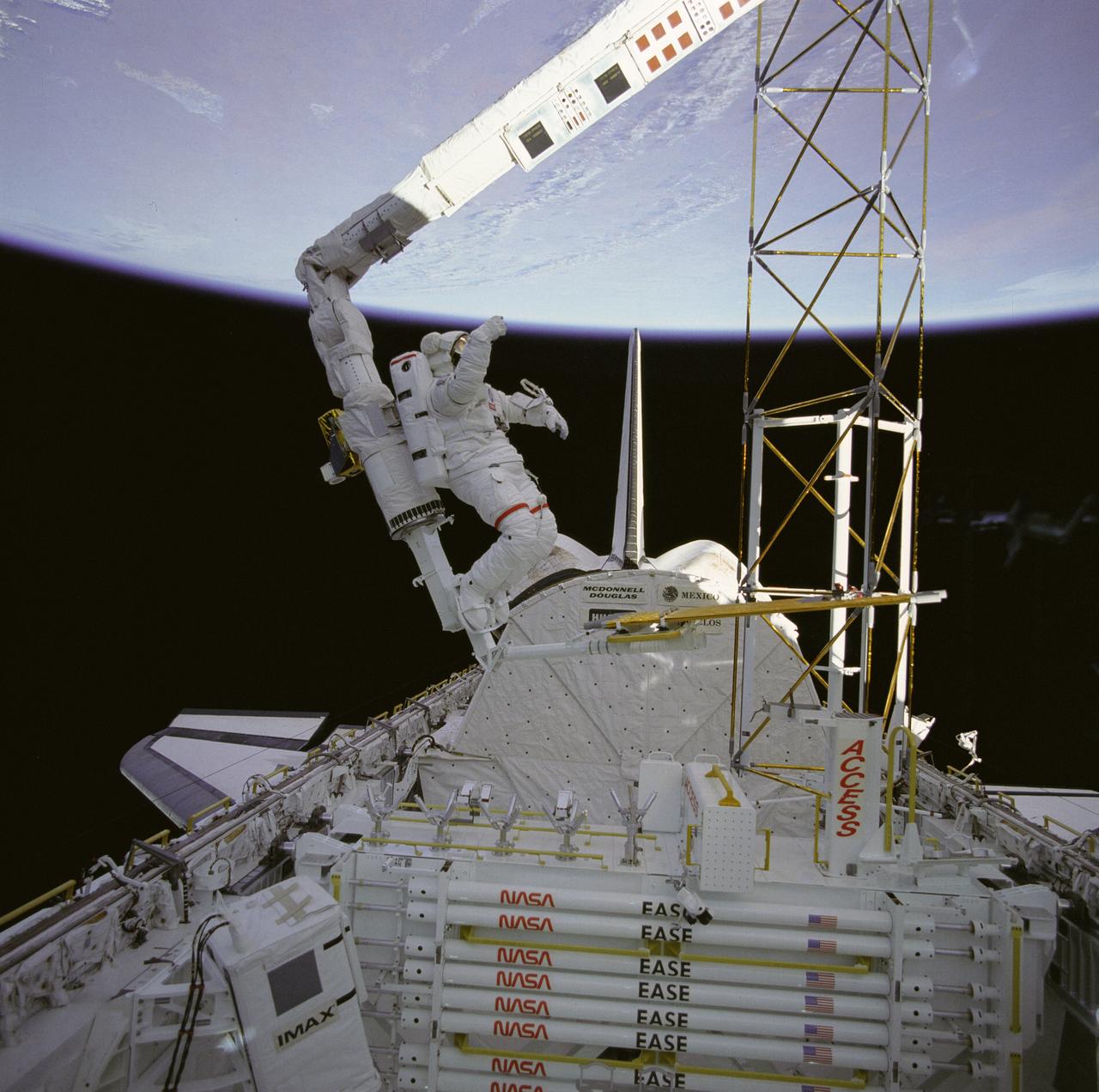

The crew assigned to the STS-61B mission included Bryan D. O’Conner, pilot; Brewster H. Shaw, commander; Charles D. Walker, payload specialist; mission specialists Jerry L. Ross, Mary L. Cleave, and Sherwood C. Spring; and Rodolpho Neri Vela, payload specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis November 28, 1985 at 7:29:00 pm (EST), the STS-61B mission’s primary payload included three communications satellites: MORELOS-B (Mexico); AUSSAT-2 (Australia); and SATCOM KU-2 (RCA Americom). Two experiments were conducted to test assembling erectable structures in space: EASE (Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity), and ACCESS (Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structure). In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia and the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), EASE and ACCESS were developed and demonstrated at MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). In this STS-61B onboard photo astronaut Ross, located on the Manipulator Foot Restraint (MFR) over the cargo bay, erects ACCESS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the structural assembly concepts for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction.

STS037-18-032 (7 April 1991) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist, peers into Space Shuttle Atlantis' cabin and is photographed by a fellow crew member using a 35mm camera. Ross was in the space shuttle's cargo bay to join astronaut Jerome (Jay) Apt in accomplishing a repair task on the Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO), seen in left frame. The two had been called upon to manually extend the high-gain antenna on GRO.

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, second from left, is seen with Washington Aerospace Scholars Brenna Tuller-Ross, far left, and Alec Lindsey as they escort him on a tour of the Museum of Flight, Tuesday, Jan. 15, 2013 in Seattle, Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Kenton Ross, DEVELOP's National Science Advisor, speaks about SICA during the 2019 Annual Earth Science Applications Showcase, Thursday, Aug. 1, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters and present their research projects. DEVELOP is a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisers from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
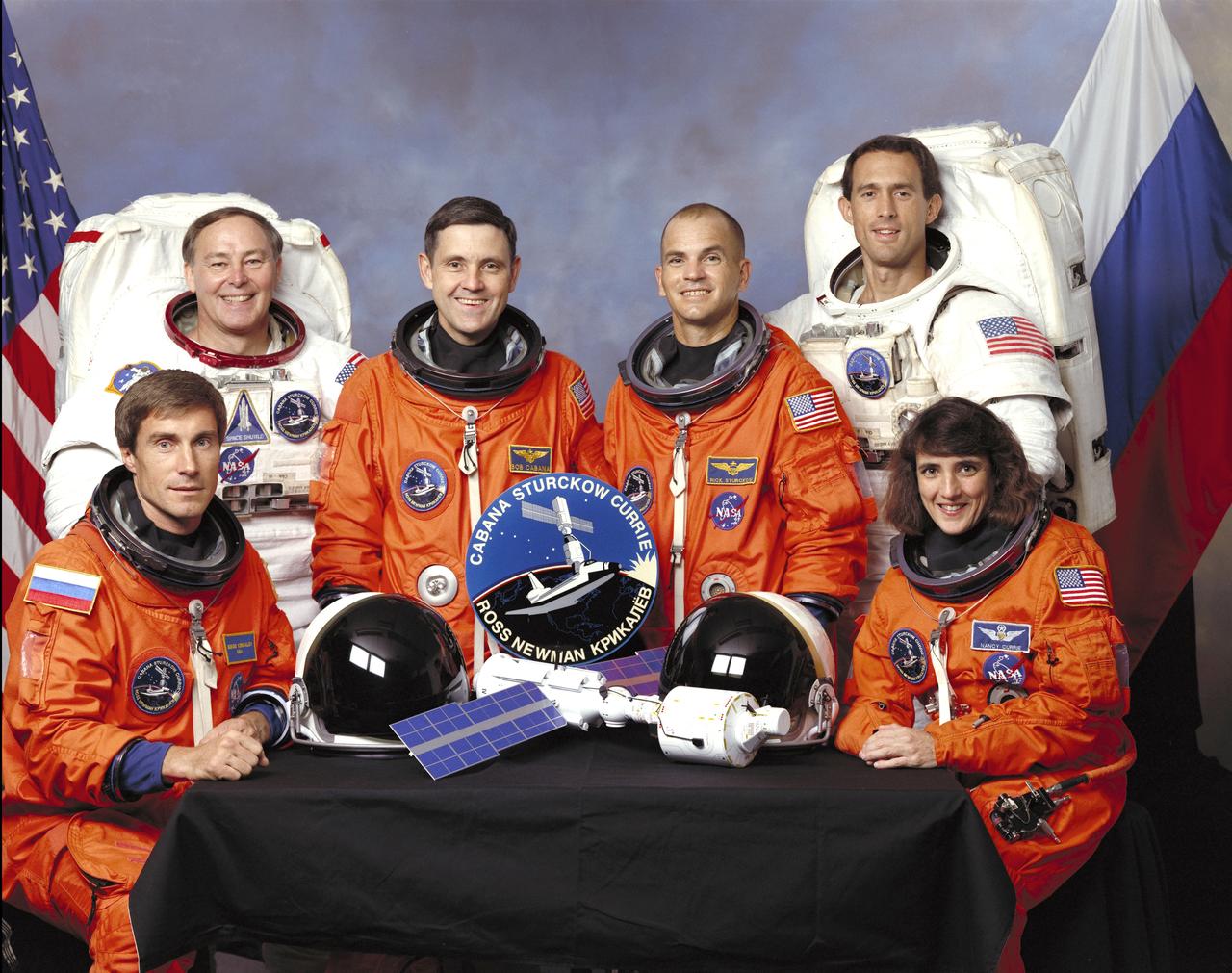

Five NASA astronauts and a Russian cosmonaut assigned to the STS-88 mission pose for a crew portrait. Seated in front (left to right) are mission specialists Sergei K. Krikalev, representing the Russian Space Agency (RSA), and astronaut Nancy J. Currie. In the rear from the left, are astronauts Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist; Robert D. Cabana, mission commander; Frederick W. “Rick” Sturckow, pilot; and James H. Newman, mission specialist. The STS-88 mission launched aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavor on December 4, 1998 at 2:35 a.m. (CST) to deliver the Unity Node to the International Space Station (ISS).
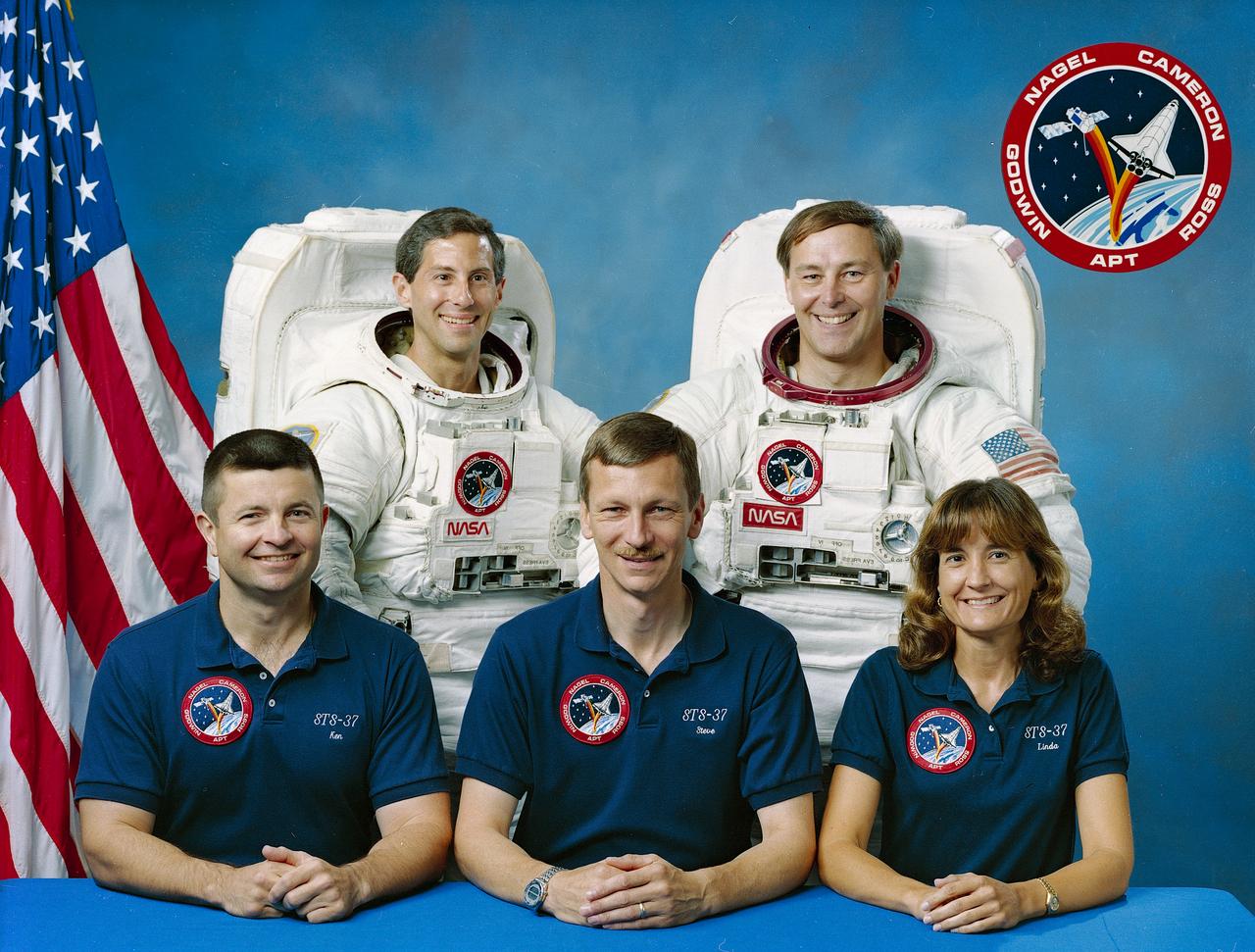

This is the STS-37 Crew portrait. Pictured from left to right are Kenneth D. (Ken) Cameron, pilot; Jay Apt, mission specialist; Steven R. Nagel, commander; and Jerry L. Ross and Linda M. Godwin, mission specialists. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on April 5, 1991 at 9:22:44am (EST), the crew’s major objective was the deployment of the Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO). Included in the observatory were the Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE); the Imaging Compton Telescope (COMPTEL); the Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope (EGRET); and the Oriented Scintillation Spectrometer Telescope (OSSEE).
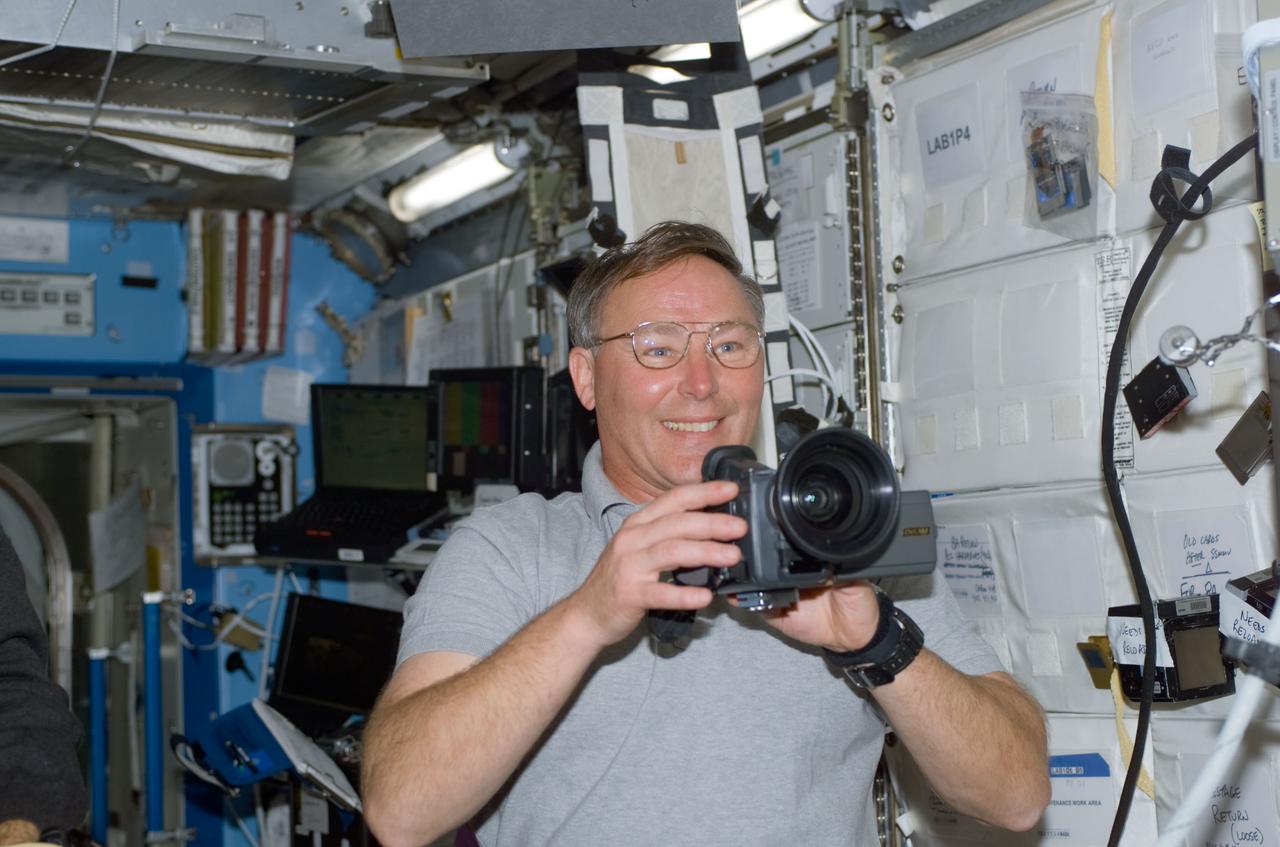

STS110-E-5110 (10 April 2002) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, STS-110 mission specialist, holds a still camera in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). The image was taken with a digital still camera.
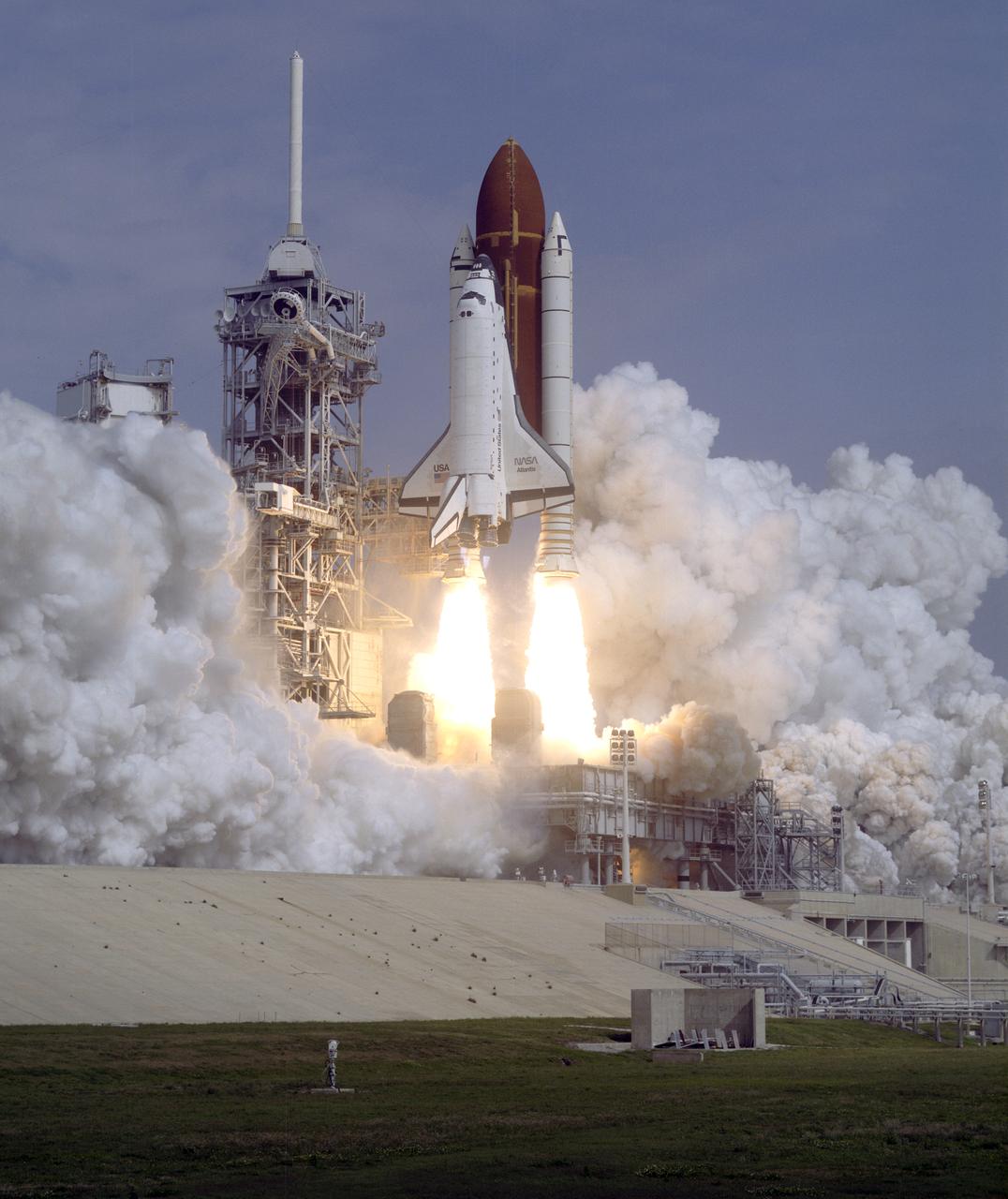

Aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis, the STS-37 mission launched April 5, 1991 from launch pad 39B at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and landed back on Earth April 11, 1991. The 39th shuttle mission included crew members: Steven R. Nagel, commander; Kenneth D. Cameron, pilot; Jerry L,. Ross, mission specialist 1; Jay Apt, mission specialist 2; and Linda M. Godwin, mission specialist 3. The primary payload for the mission was the Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO). The GRO included the Burst and Transient Experiment (BATSE); the Imaging Compton Telescope (COMPTEL); the Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope (EGRET); and the Oriented Scintillation Spectrometer Experiment (OSSEE). Secondary payloads included Crew and Equipment Translation Aids (CETA); the Ascent Particle Monitor (APM); the Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment II (SAREXII), the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG); the Bioserve Instrumentation Technology Associates Materials Dispersion Apparatus (BIMDA); Radiation Monitoring Equipment III (RMEIII); and Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS).
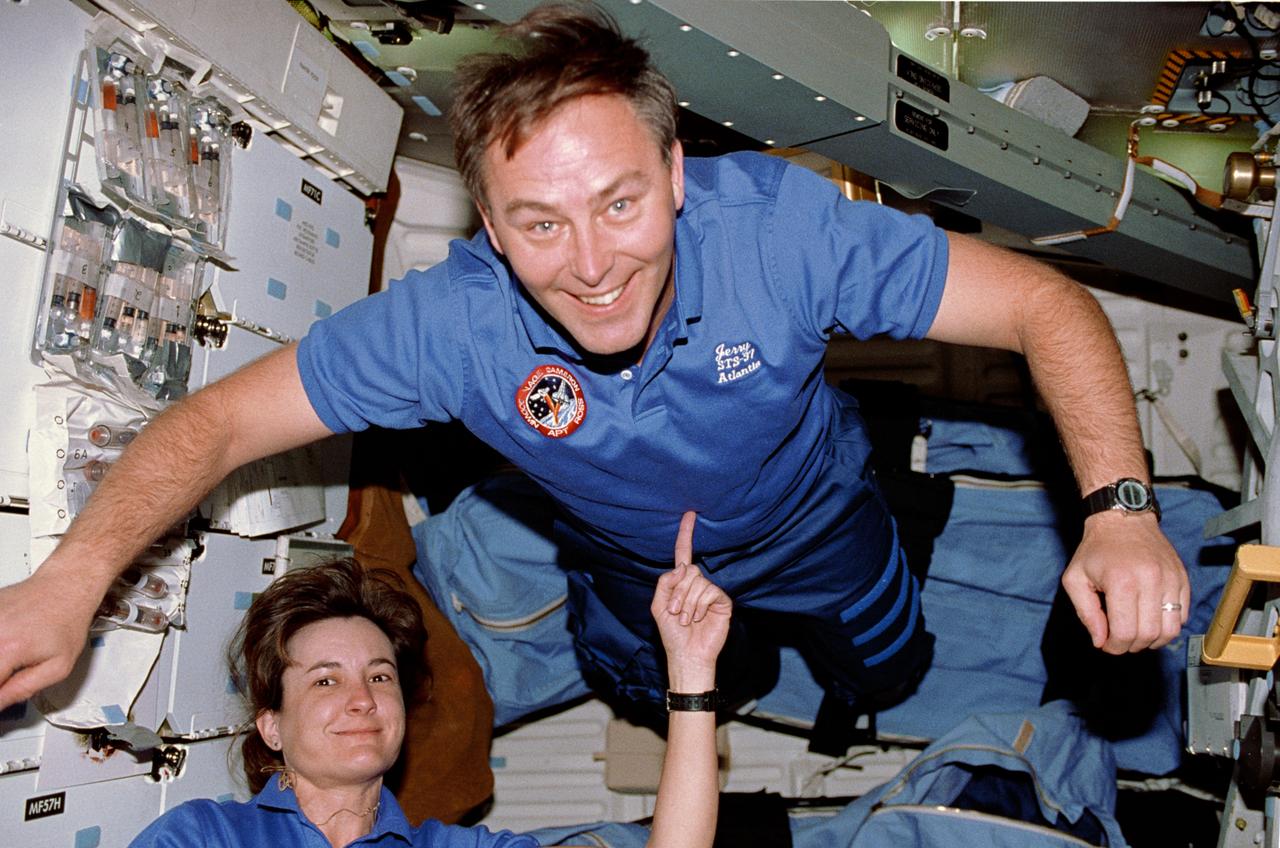

STS037-29-002 (5-11 April 1991) --- Astronauts Linda M. Godwin and Jerry L. Ross perform a balancing act on Atlantis' middeck. With little effort Godwin is able to hold Ross up near the ceiling with her index finger. Although the area the two occupy is very small, a number of articles are seen, including two sleep restraints, the escape pole and Bioserve ITA Materials Dispersion Apparatus bioprocessing test bed (attached to stowage lockers at left). This was one of the visuals used by the STS-37 crewmembers during their April 19 post-flight press conference at the Johnson Space Center (JSC).

61B-41-047 (1 Dec 1985) --- Astronauts Jerry L. Ross (left) and Sherwood C. (Woody) Spring are photographed by Astronaut Bryan D. O'Connor as they continue to assemble more pieces of the EASE (Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activities) device during the week-long STS 61-B mission. This frame is one of a series covering the structure's build-up.
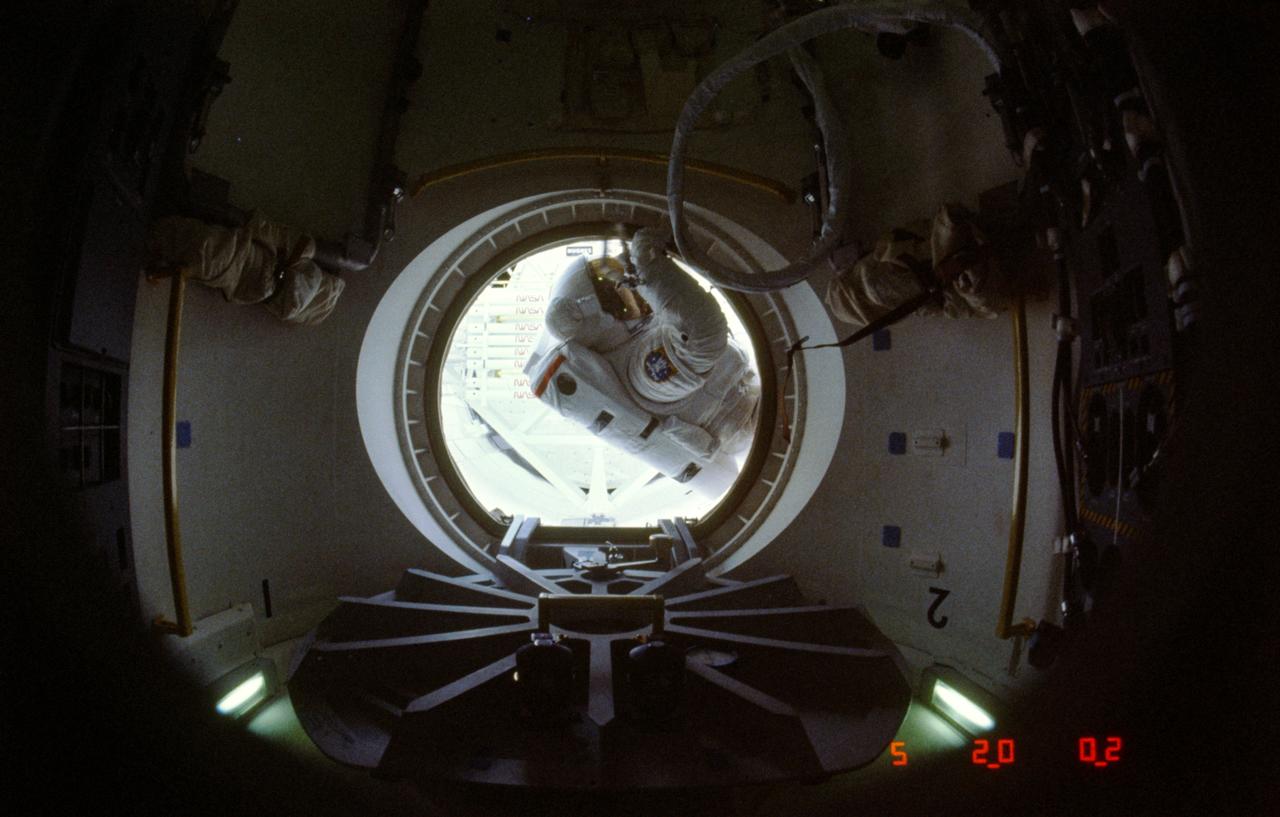

61B-08-026 (1 Dec 1985) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross was photographed by astronaut Bryan D. O'Connor through Atlantis's airlock as the mission specialist, fully equipped with his red-striped, white extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), moved out into the cargo bay to begin one of two lengthy extravehicular activities (EVA) on the week-long STS 61-B mission.

S93-43752 (1 Sept 1993) --- Astronauts Jerry L. Ross and Susan J. Helms are pictured at the Spacecraft Communicators Console during joint integrated simulations for the STS-61 mission. Astronauts assigned to extravehicular activity (EVA) tasks with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) were simultaneously rehearsing in a Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) tank at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Alabama.

STS088-334-033 (4-15 Dec. 1998) --- Astronauts Jerry L. Ross (on left with camera) and James H. Newman, both mission specialists, work in the Unity Module (Node 1). This task was designed to complete the assembly of an early S-band communications system that will allow flight controllers in Houston, Texas, to send commands to Unity's systems and to keep tabs on the health of the station with a more extensive communications capability than exists through Russian ground stations.
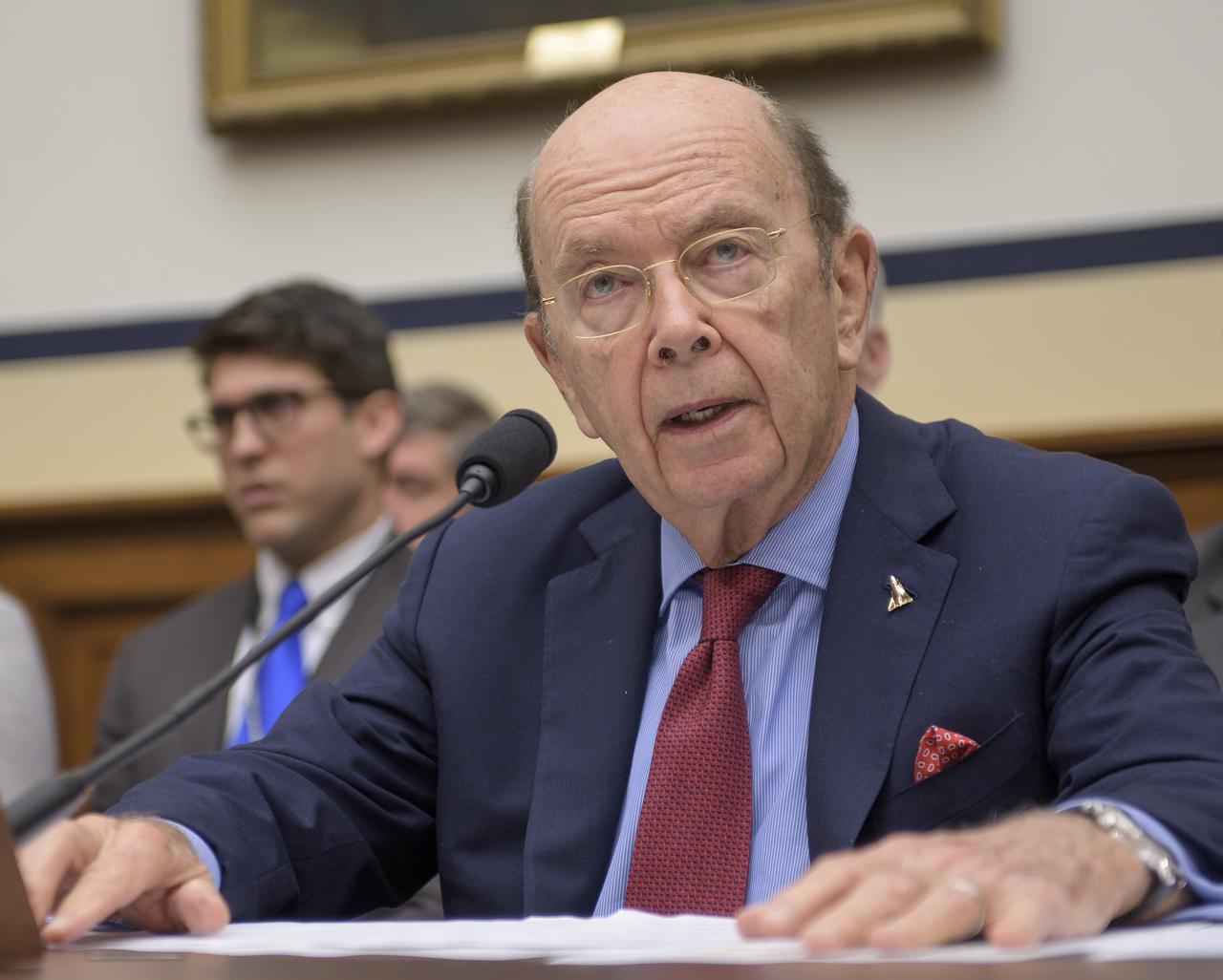

Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross testifies before the House Subcommittee on Strategic Forces during a hearing on Space Situational Awareness: Whole of Government Perspectives on Roles and Responsibilities, Friday, June 22, 2018 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
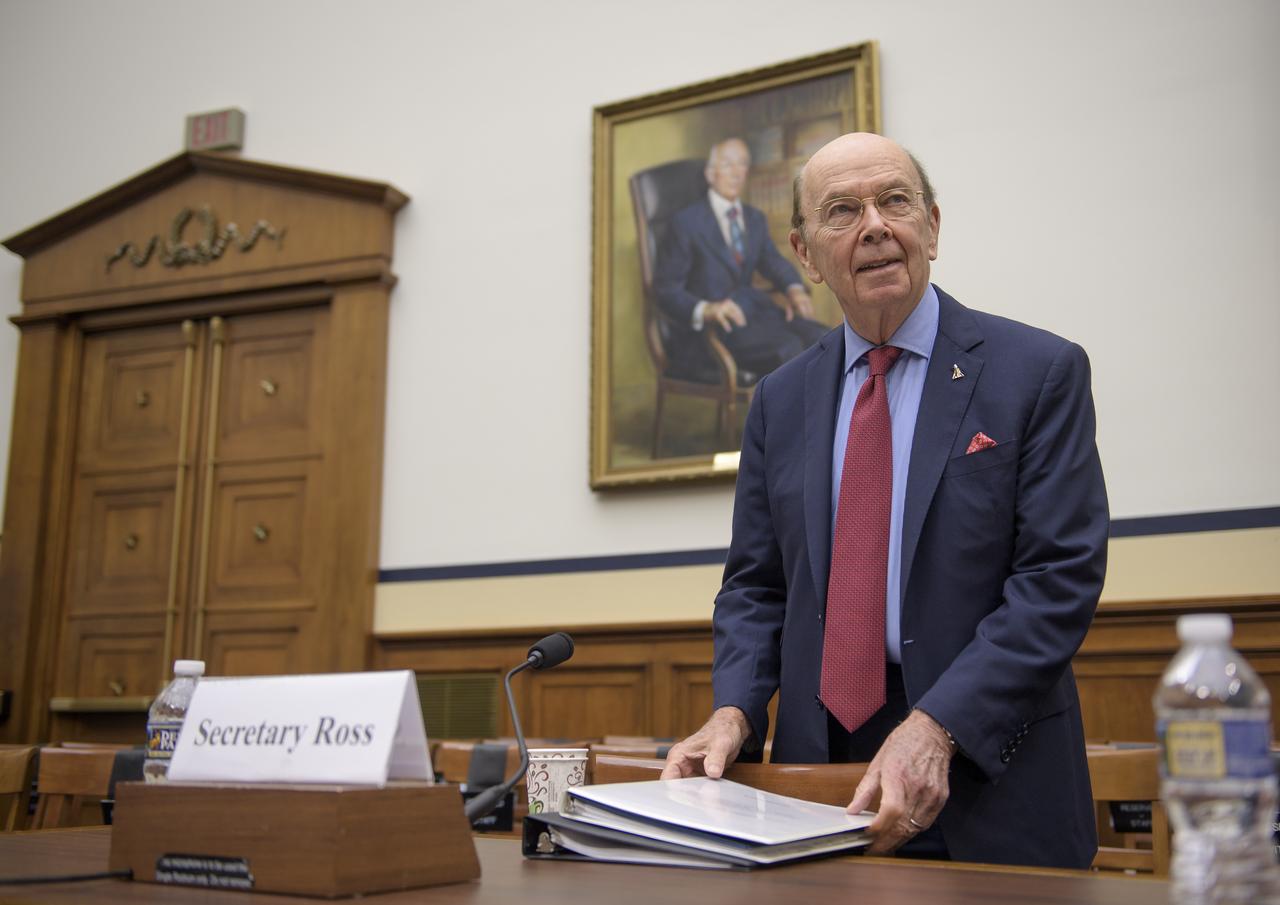

Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross prepares to testify before the House Subcommittee on Strategic Forces during a hearing on Space Situational Awareness: Whole of Government Perspectives on Roles and Responsibilities, Friday, June 22, 2018 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
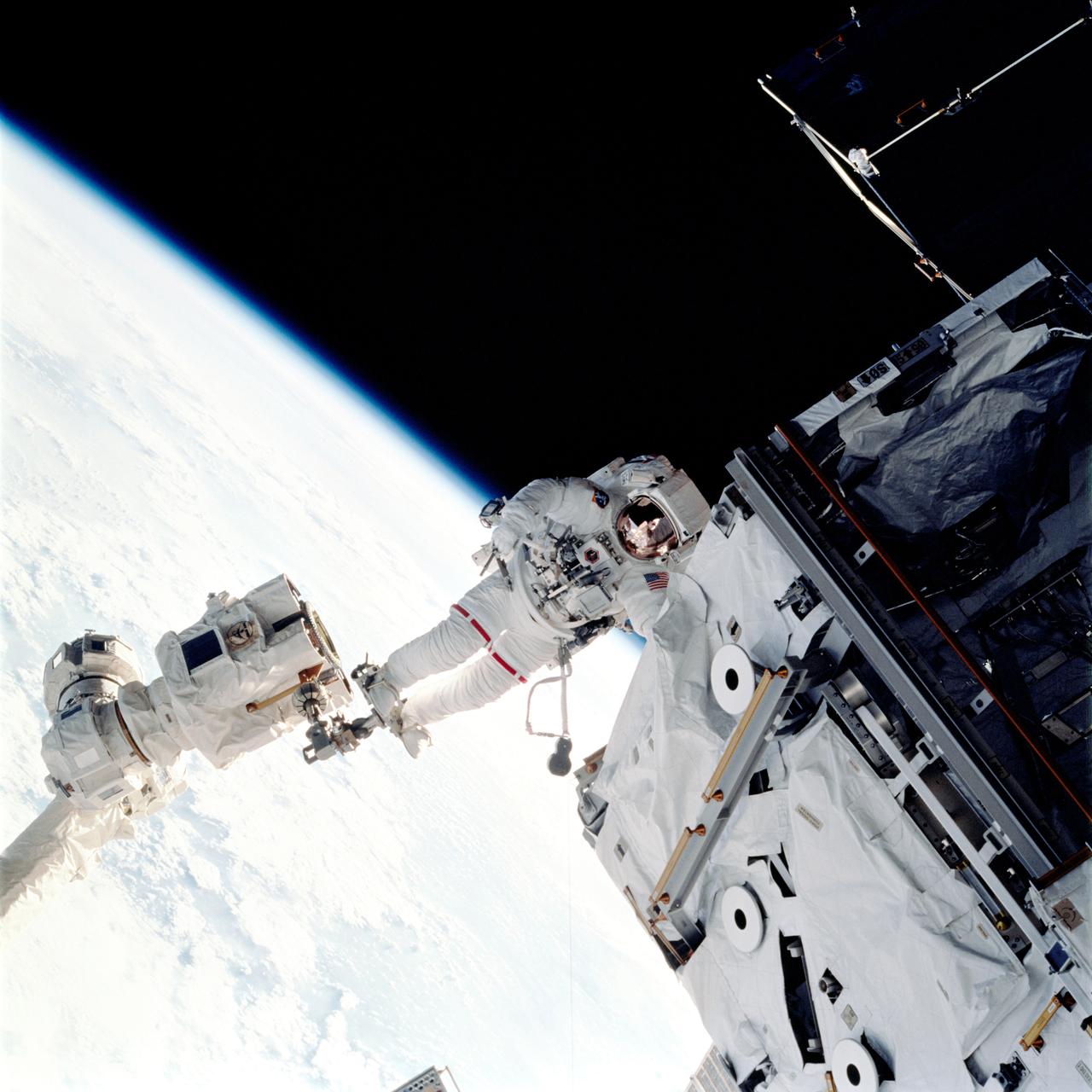

Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis on April 8, 2002, the STS-110 mission prepared the International Space Station (ISS) for future space walks by installing and outfitting the 43-foot-long Starboard side S0 (S-zero) truss and preparing the first railroad in space, the Mobile Transporter. The 27,000 pound S0 truss was the first of 9 segments that will make up the Station's external framework that will eventually stretch 356 feet (109 meters), or approximately the length of a football field. This central truss segment also includes a flatcar called the Mobile Transporter and rails that will become the first "space railroad," which will allow the Station's robotic arm to travel up and down the finished truss for future assembly and maintenance. The completed truss structure will hold solar arrays and radiators to provide power and cooling for additional international research laboratories from Japan and Europe that will be attached to the Station. STS-110 Extravehicular Activity (EVA) marked the first use of the Station's robotic arm to maneuver space walkers around the Station and was the first time all of a shuttle crew's space walks were based out of the Station's Quest Airlock. In this photograph, Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist, anchored on the end of the Canadarm2, moves near the newly installed S0 truss. Astronaut Lee M. E. Morin, mission specialist, (out of frame), worked in tandem with Ross during this fourth and final scheduled session of EVA for the STS-110 mission. The final major task of the space walk was the installation of a beam, the Airlock Spur, between the Quest Airlock and the S0. The spur will be used by space walkers in the future as a path from the airlock to the truss.
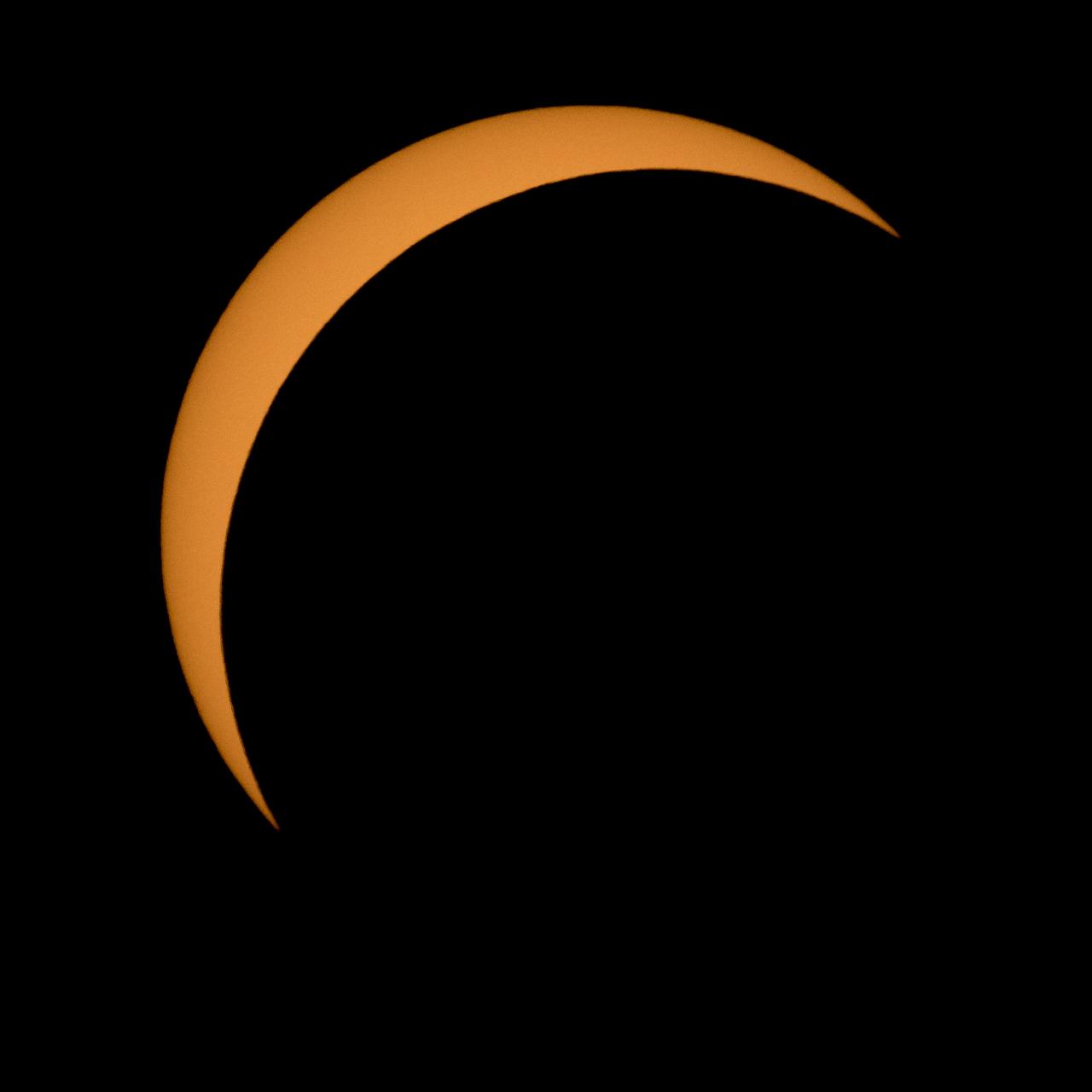

The Moon is seen passing in front of the Sun during a solar eclipse from Ross Lake, Northern Cascades National Park, Washington on Monday, Aug. 21, 2017. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
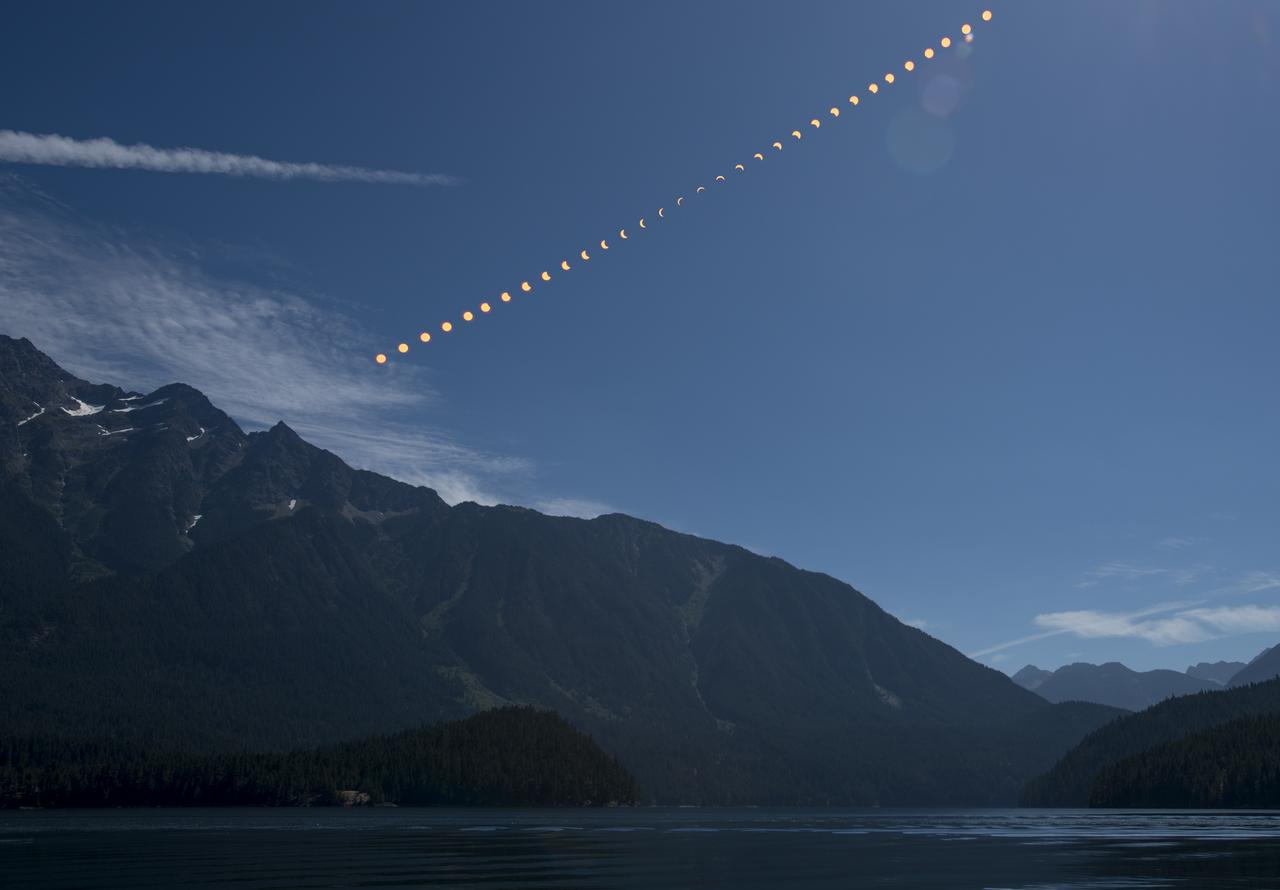

This composite image shows the progression of a partial solar eclipse over Ross Lake, in Northern Cascades National Park, Washington on Monday, Aug. 21, 2017. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
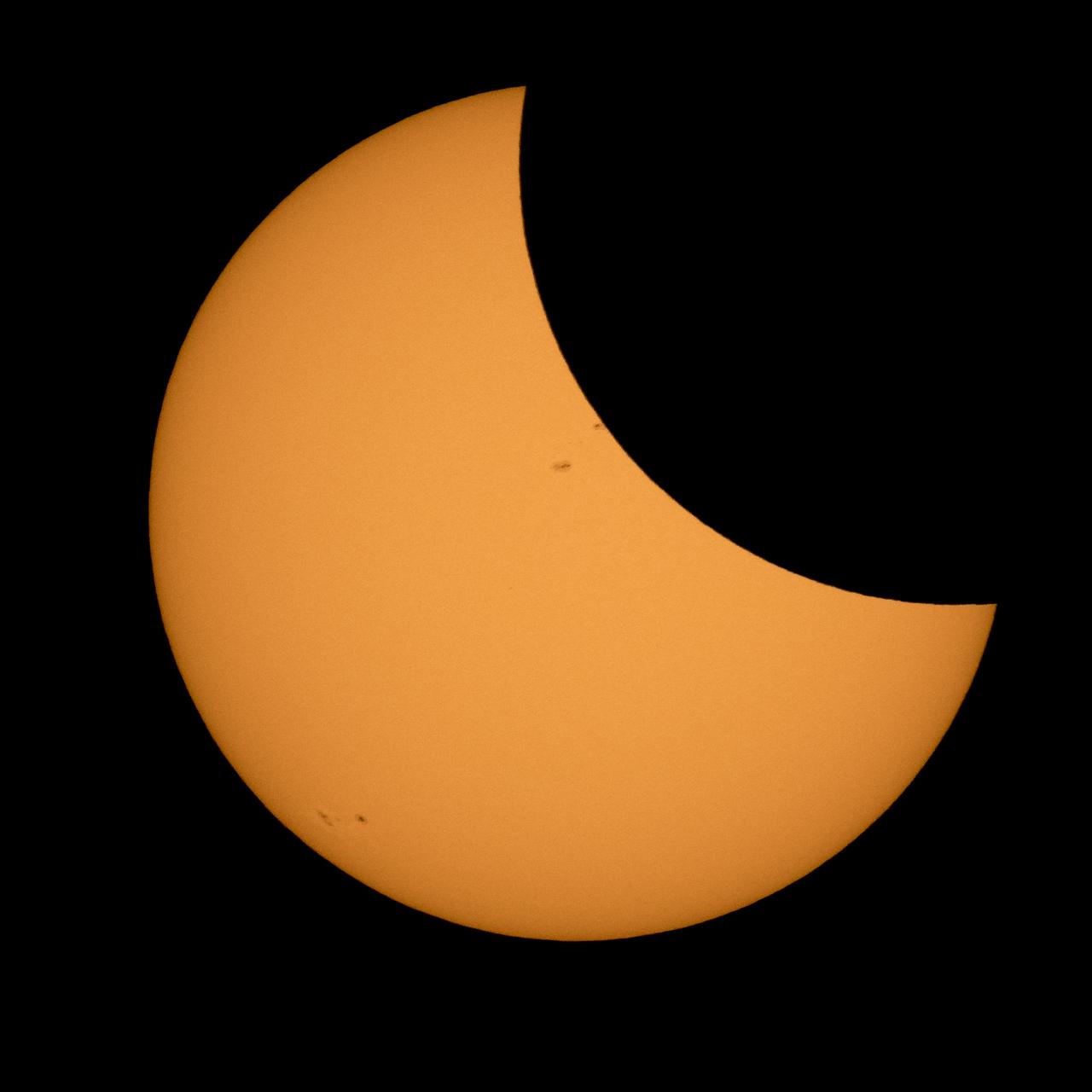

The Moon is seen passing in front of the Sun during a solar eclipse from Ross Lake, Northern Cascades National Park, Washington on Monday, Aug. 21, 2017. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
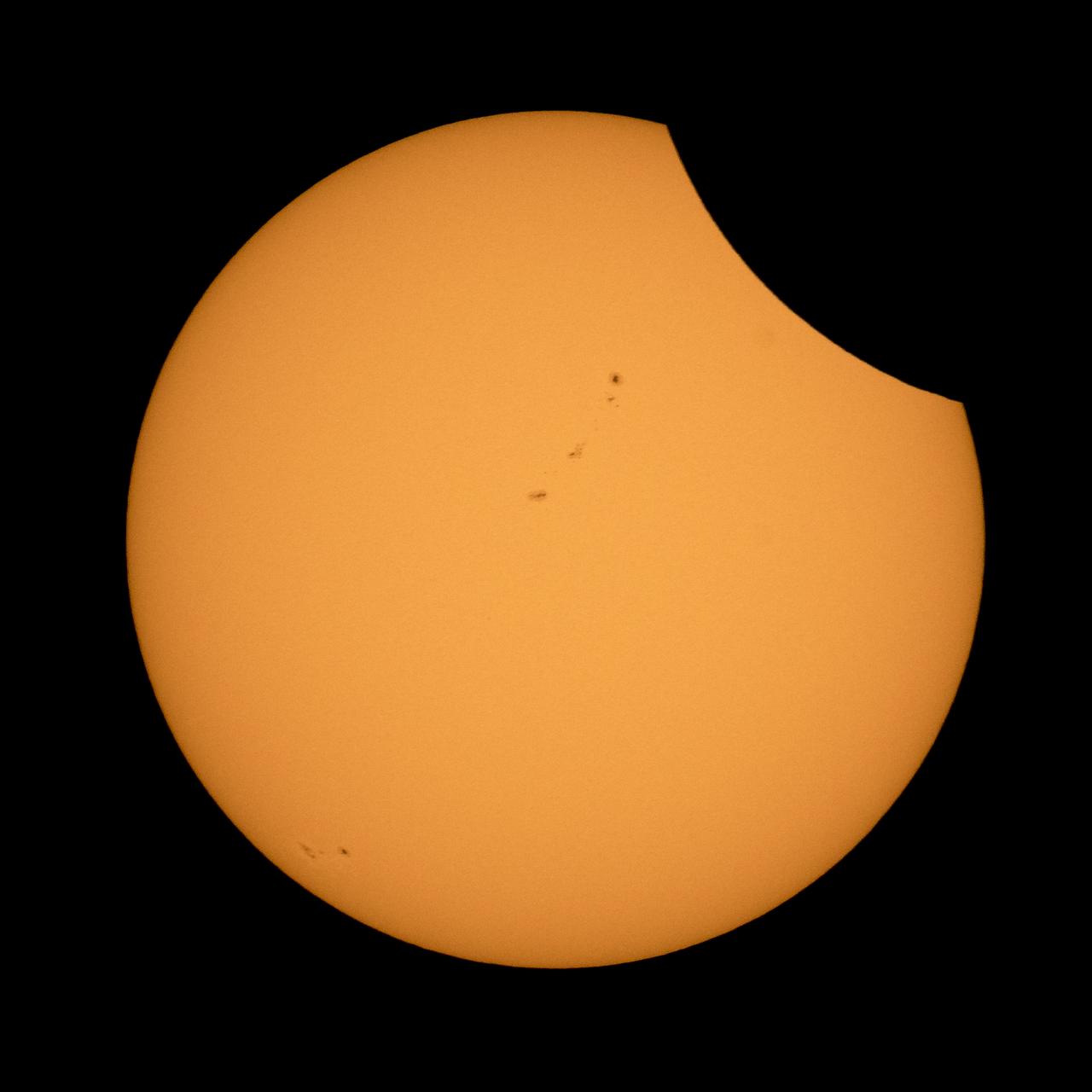

The Moon is seen as it starts passing in front of the Sun during a solar eclipse from Ross Lake, Northern Cascades National Park, Washington on Monday, Aug. 21, 2017. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
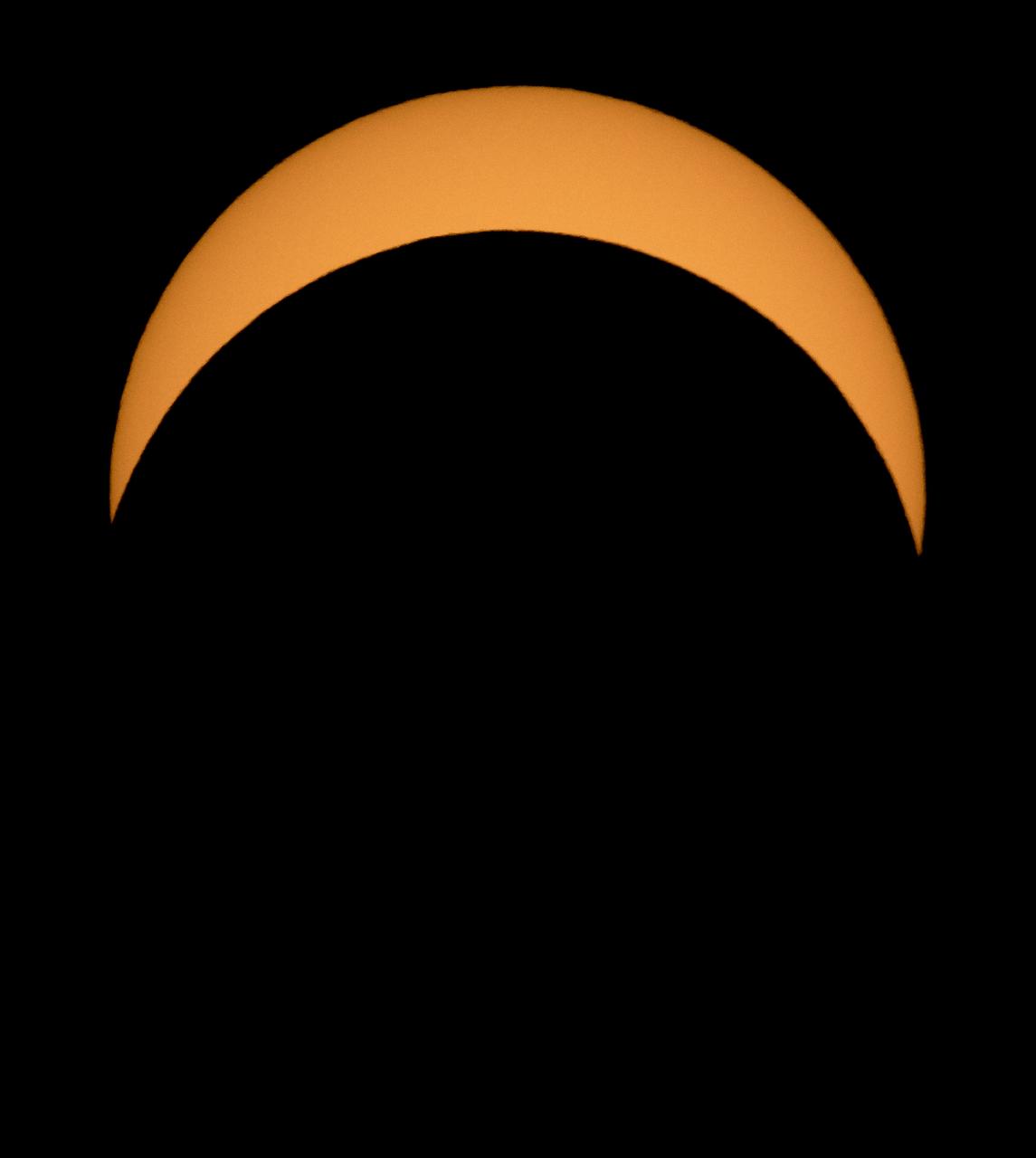

The Moon is seen passing in front of the Sun during a solar eclipse from Ross Lake, Northern Cascades National Park, Washington on Monday, Aug. 21, 2017. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
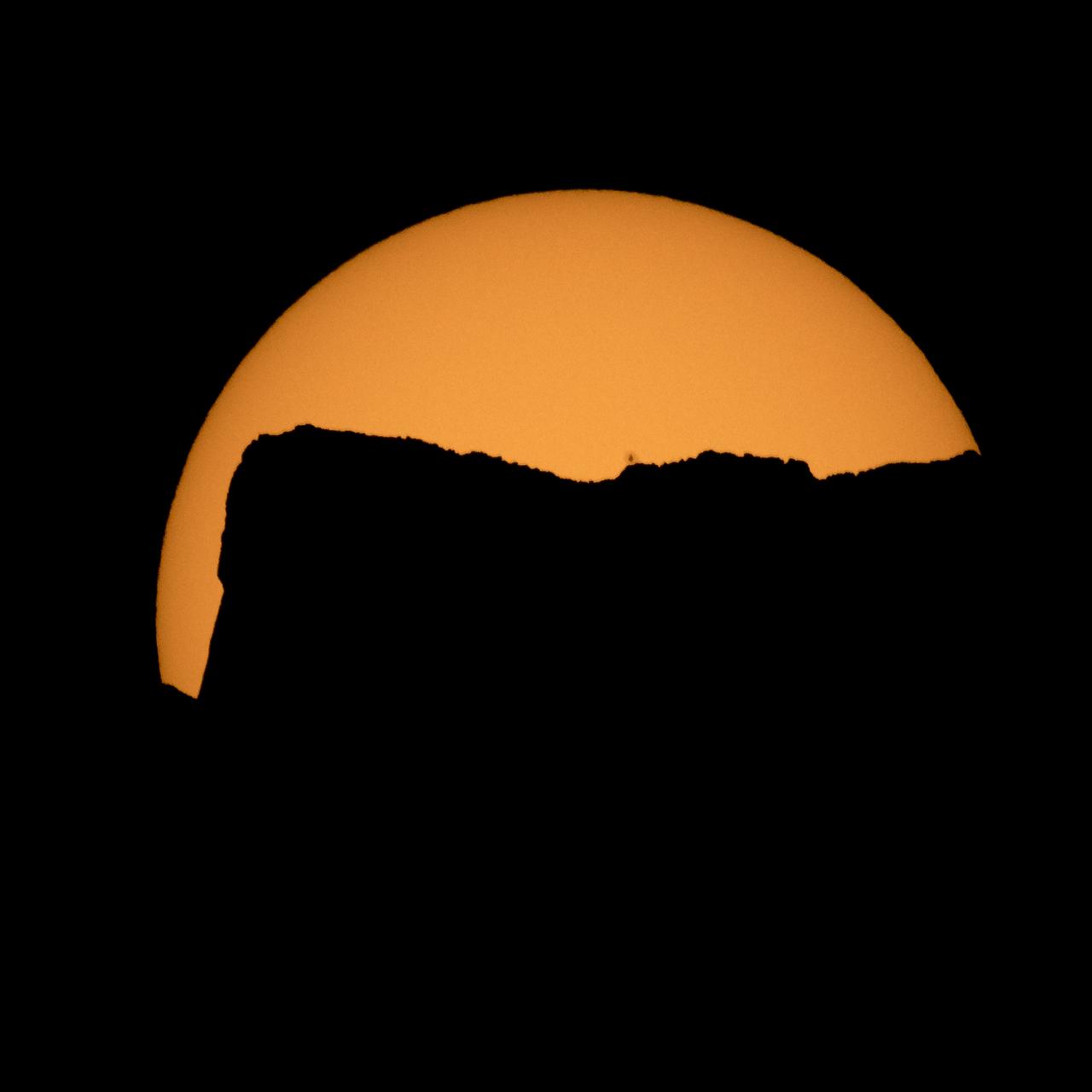

The Sun is seen as it rises behind Jack Mountain head of the solar eclipse, Monday, Aug. 21, 2017, Ross Lake, Northern Cascades National Park, Washington. A total solar eclipse will sweep across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
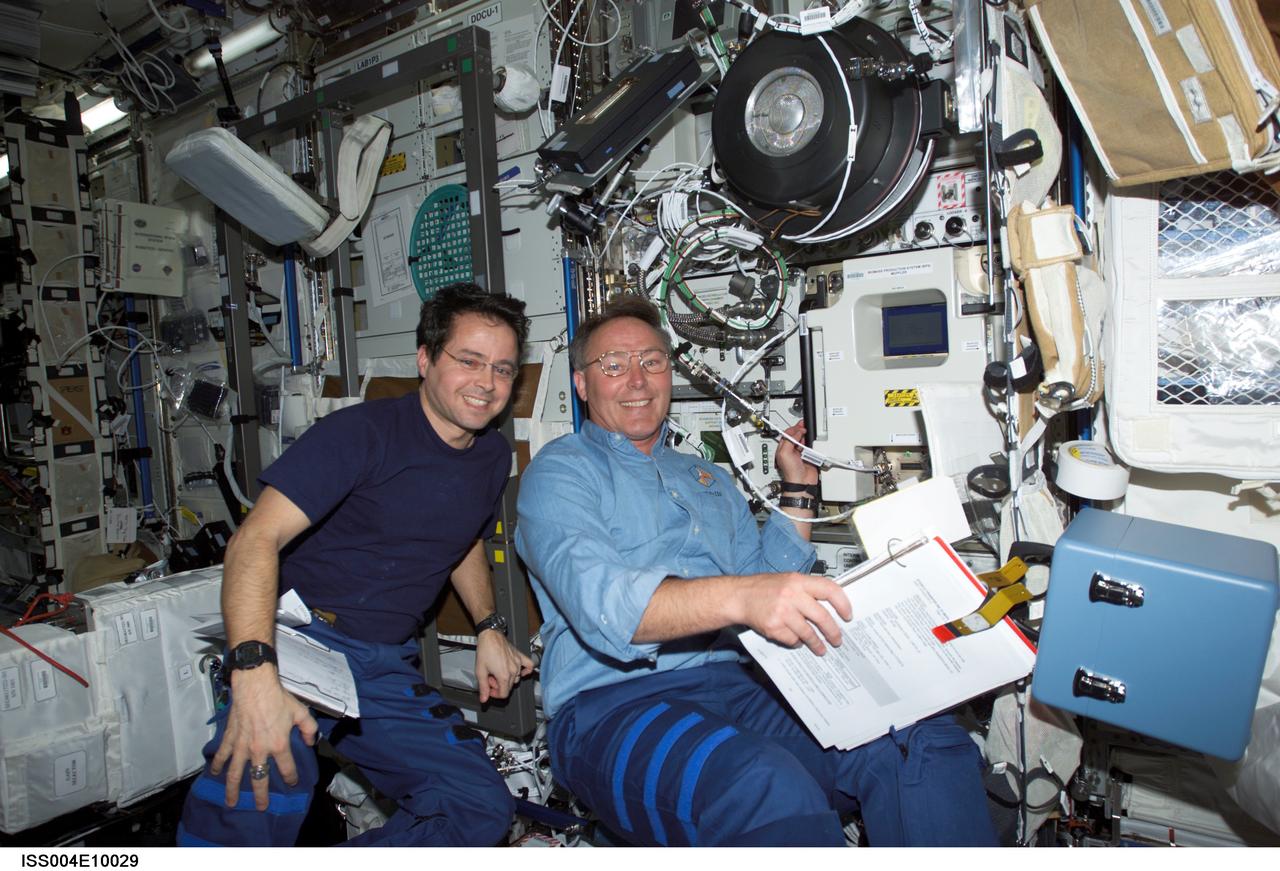

ISS004-E-10029 (12 April 2002) --- Astronauts Daniel W. Bursch (left), Expedition Four flight engineer, and Jerry L. Ross, STS-110 mission specialist, work in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
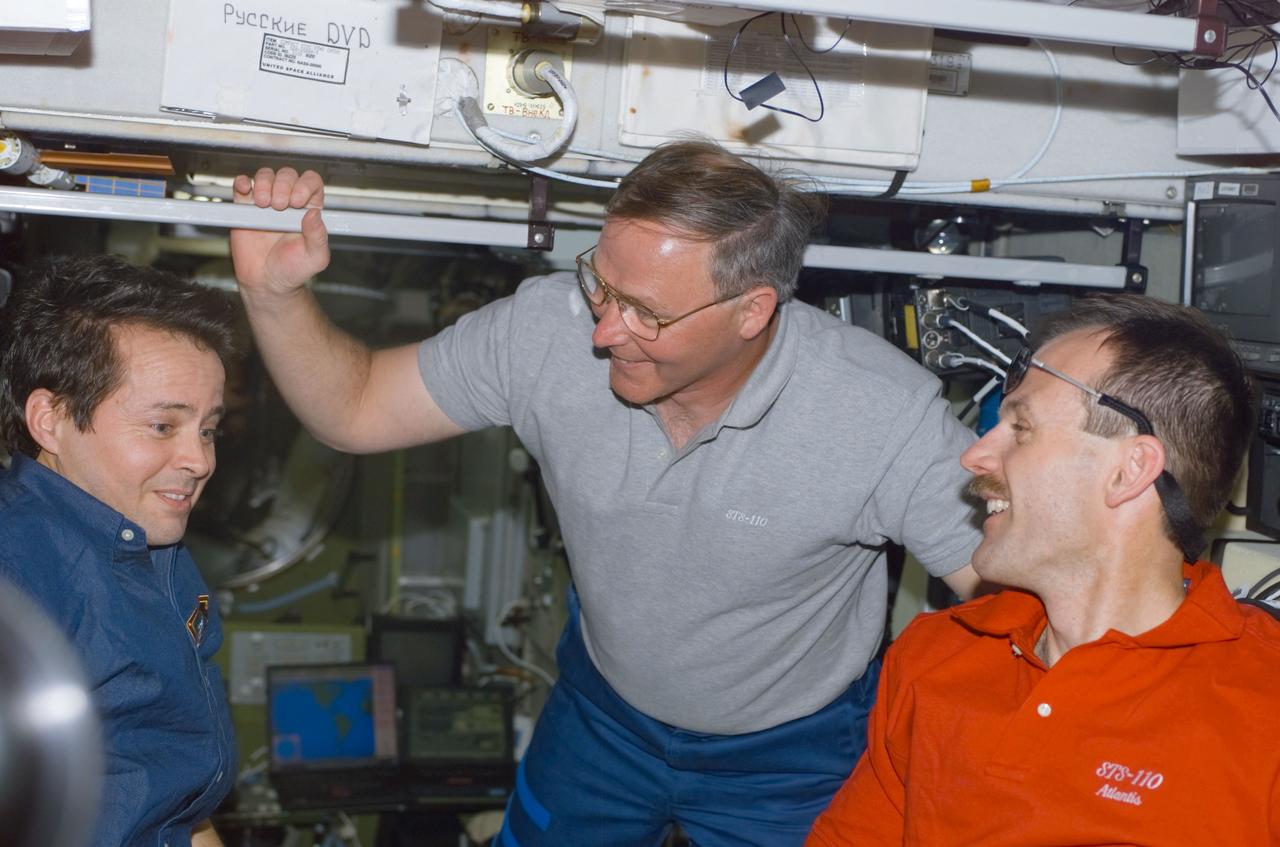

STS110-E-5122 (10 April 2002) --- Astronauts Daniel W. Bursch (left), Expedition Four flight engineer, Jerry L. Ross and Steven L. Smith, both STS-110 mission specialists, converse in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The image was taken with a digital still camera.
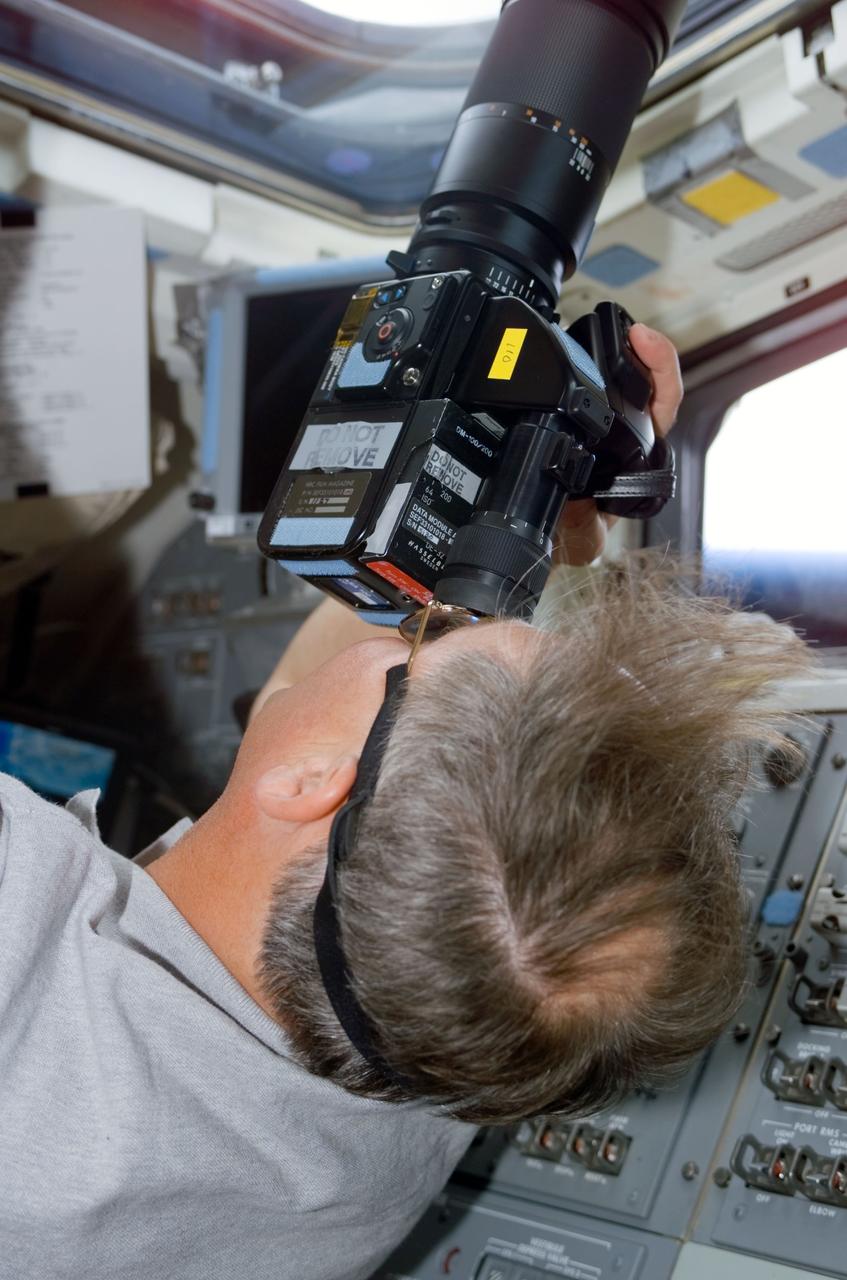

STS110-E-5050 (9 April 2002) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, STS-110 mission specialist, takes photos out of an aft flight deck overhead window using a 70mm hand-held camera. The image was taken with a digital still camera.
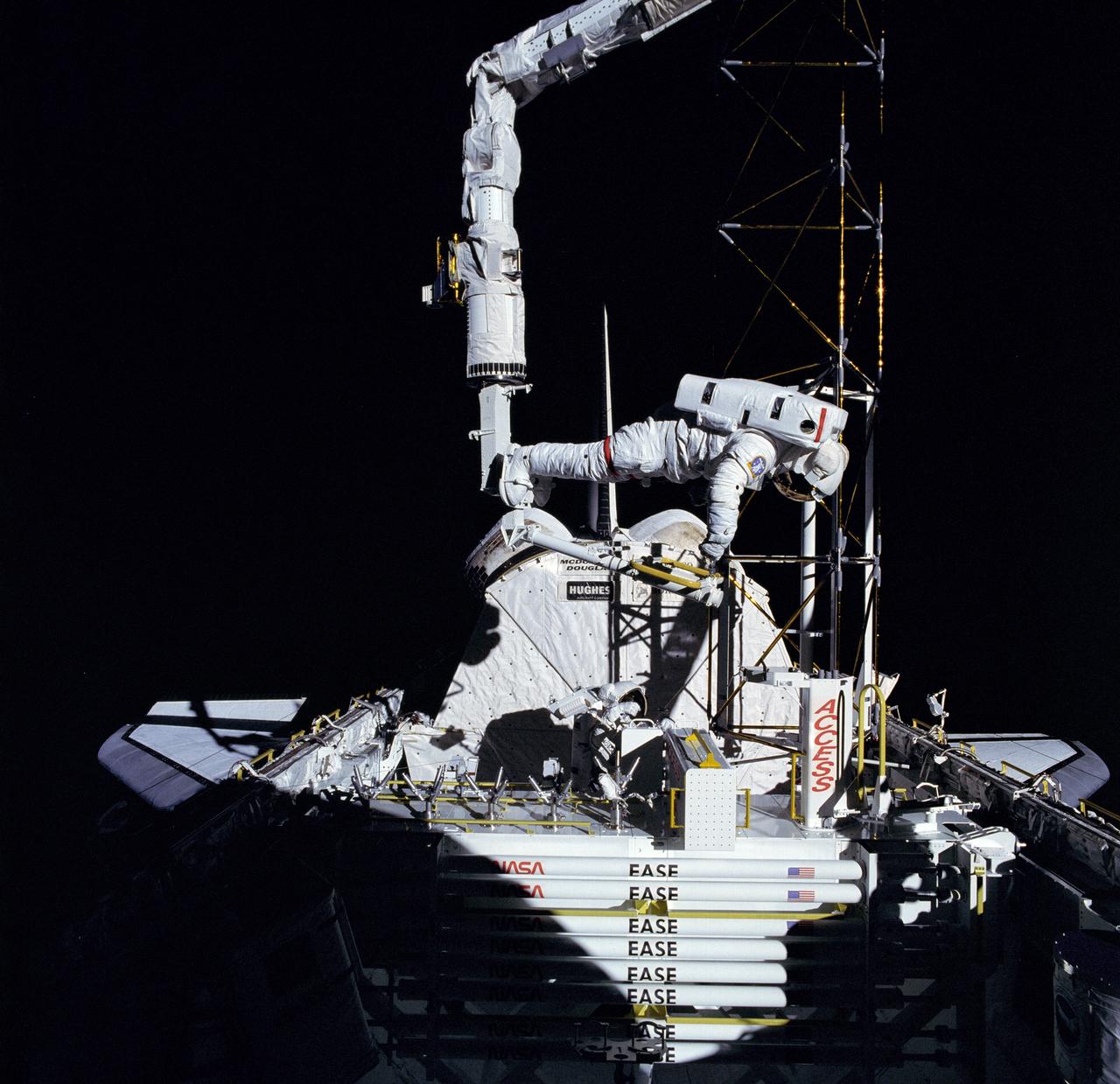

The crew assigned to the STS-61B mission included Bryan D. O’Conner, pilot; Brewster H. Shaw, commander; Charles D. Walker, payload specialist; mission specialists Jerry L. Ross, Mary L. Cleave, and Sherwood C. Spring; and Rodolpho Neri Vela, payload specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis November 28, 1985 at 7:29:00 pm (EST), the STS-61B mission’s primary payload included three communications satellites: MORELOS-B (Mexico); AUSSAT-2 (Australia); and SATCOM KU-2 (RCA Americom). Two experiments were conducted to test assembling erectable structures in space: EASE (Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity), and ACCESS (Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structure). In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia and the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), EASE and ACCESS were developed and demonstrated at MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). The primary objective of this experiment was to test the structural assembly concepts for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. In this STS-61B onboard photo, astronaut Ross was working on the ACCESS experiment during an Extravehicular Activity (EVA).

NASA photographer Jim Ross captured this shot while pilot Troy Asher flew inverted in an F-15D. The F-15B is seen here flying over the mirror farm, AKA the Abengoa Mojave Solar Project, east of Four Corners off of Highway 58 in Southern California.
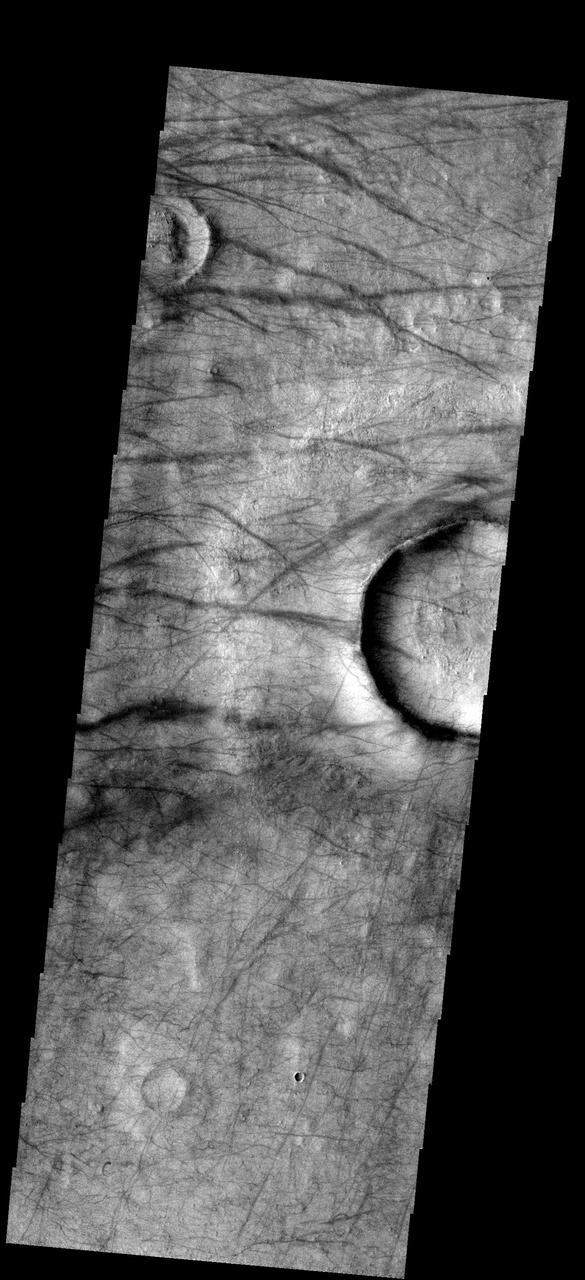
Dust Devil activity in this region between Brashear and Ross Craters is very common. Large regions of dust devil tracks surround the south polar region of Mars
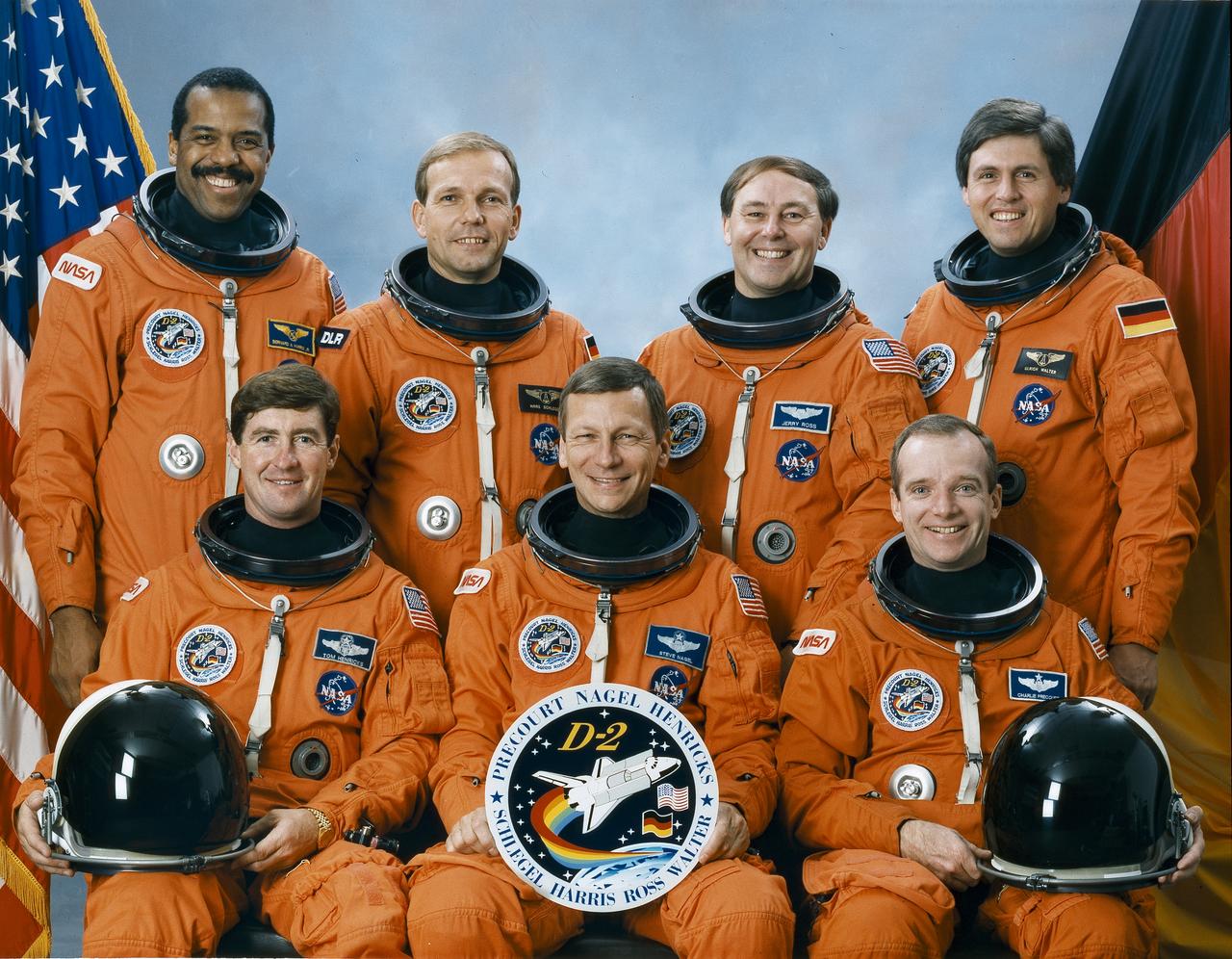

The seven astronauts included in the STS-55 crew portrait are: (front left to right) Terence (Tom) Henricks, pilot; Steven R. Negal, commander; and Charles J. Precourt, mission specialist. On the back row, from left to right, are Bernard A. Harris, mission specialist; Hans Schlegel, payload specialist; Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist; and Ulrich Walter, payload specialist. The crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on April 26, 1993 at 10:50:00 am (EDT). The major payload was the German Dedicated Spacelab, D2.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, and Amy Ross, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, left, are seen with Kristine Davis, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, wearing a ground prototype of NASA’s new Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (xEMU), during a demonstration of the suit, Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The xEMU suit improves on the suits previous worn on the Moon during the Apollo era and those currently in use for spacewalks outside the International Space Station and will be worn by first woman and next man as they explore the Moon as part of the agency’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
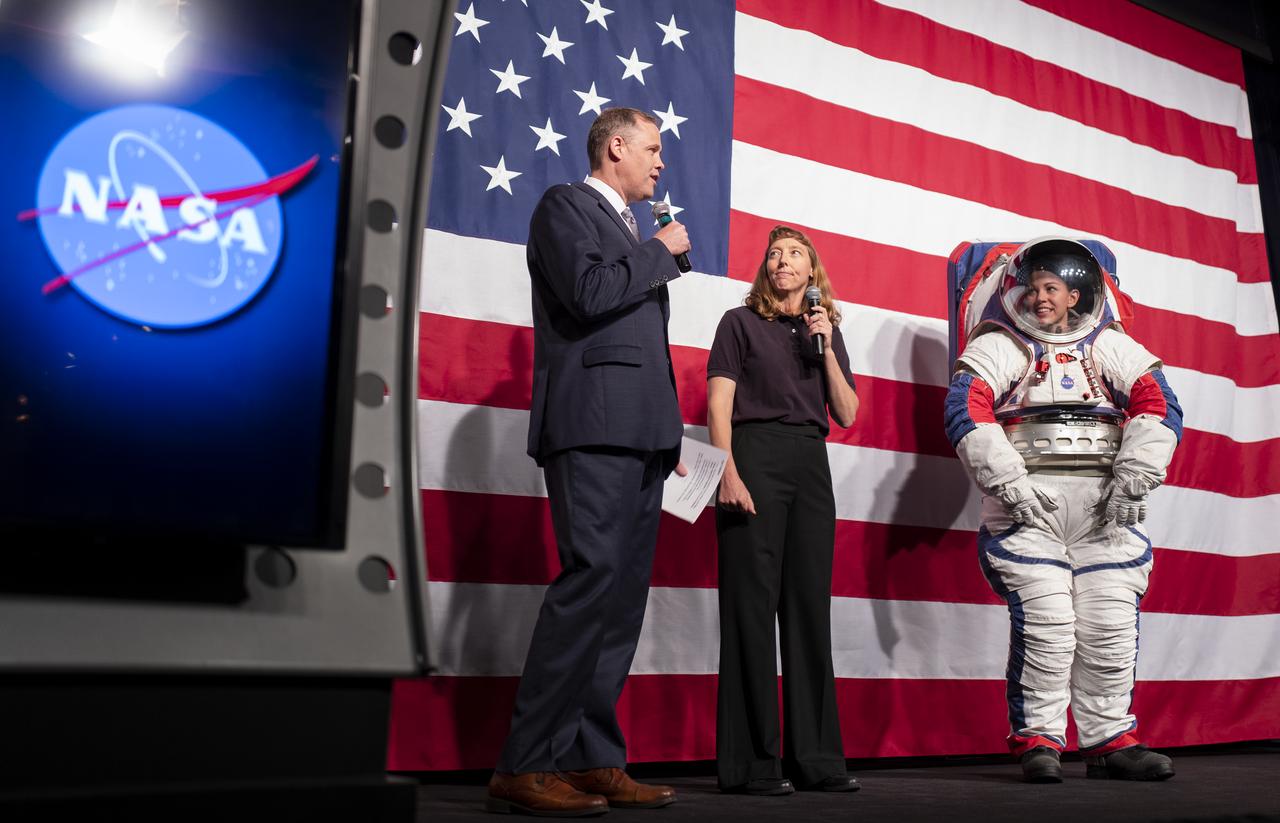

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, and Amy Ross, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, left, are seen with Kristine Davis, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, wearing a ground prototype of NASA’s new Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (xEMU), during a demonstration of the suit, Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The xEMU suit improves on the suits previous worn on the Moon during the Apollo era and those currently in use for spacewalks outside the International Space Station and will be will be worn by first woman and next man as they explore the Moon as part of the agency’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, and Amy Ross, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, left, are seen with Kristine Davis, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, wearing a ground prototype of NASA’s new Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (xEMU), during a demonstration of the suit, Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The xEMU suit improves on the suits previous worn on the Moon during the Apollo era and those currently in use for spacewalks outside the International Space Station and will be worn by first woman and next man as they explore the Moon as part of the agency’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, gives a thumbs up as Amy Ross, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, center, high fives Kristine Davis, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, wearing a ground prototype of NASA’s new Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (xEMU), after a demonstration of the suits enhanced mobility, Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The xEMU suit improves on the suits previous worn on the Moon during the Apollo era and those currently in use for spacewalks outside the International Space Station and will be will be worn by first woman and next man as they explore the Moon as part of the agency’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Amy Ross, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, is seen with Kristine Davis, a spacesuit engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, wearing a ground prototype of NASA’s new Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (xEMU), during a demonstration of the suit, Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The xEMU suit improves on the suits previous worn on the Moon during the Apollo era and those currently in use for spacewalks outside the International Space Station and will be worn by first woman and next man as they explore the Moon as part of the agency’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA research pilot Nils Larson and photographer Jim Ross complete aerobatic maneuvers in a NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California owned T-34C aircraft during a proficiency flight.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, left, talks with Col Douglas “Beaker” Wickert, Cadet First Class Gavin Ross, and Cadet First Class Grant Schlichting, right, during a tour of the aeronautics lab at the United States Air Force Academy, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, north of Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, 4th from left, along with Cadet First Class Grant Schlichting, left, Cadet Second Class Colt Crowson, and Cadet First Class Gavin Ross listen to Col Douglas “Beaker” Wickert, right, during a tour of the aeronautics lab at the United States Air Force Academy, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, north of Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
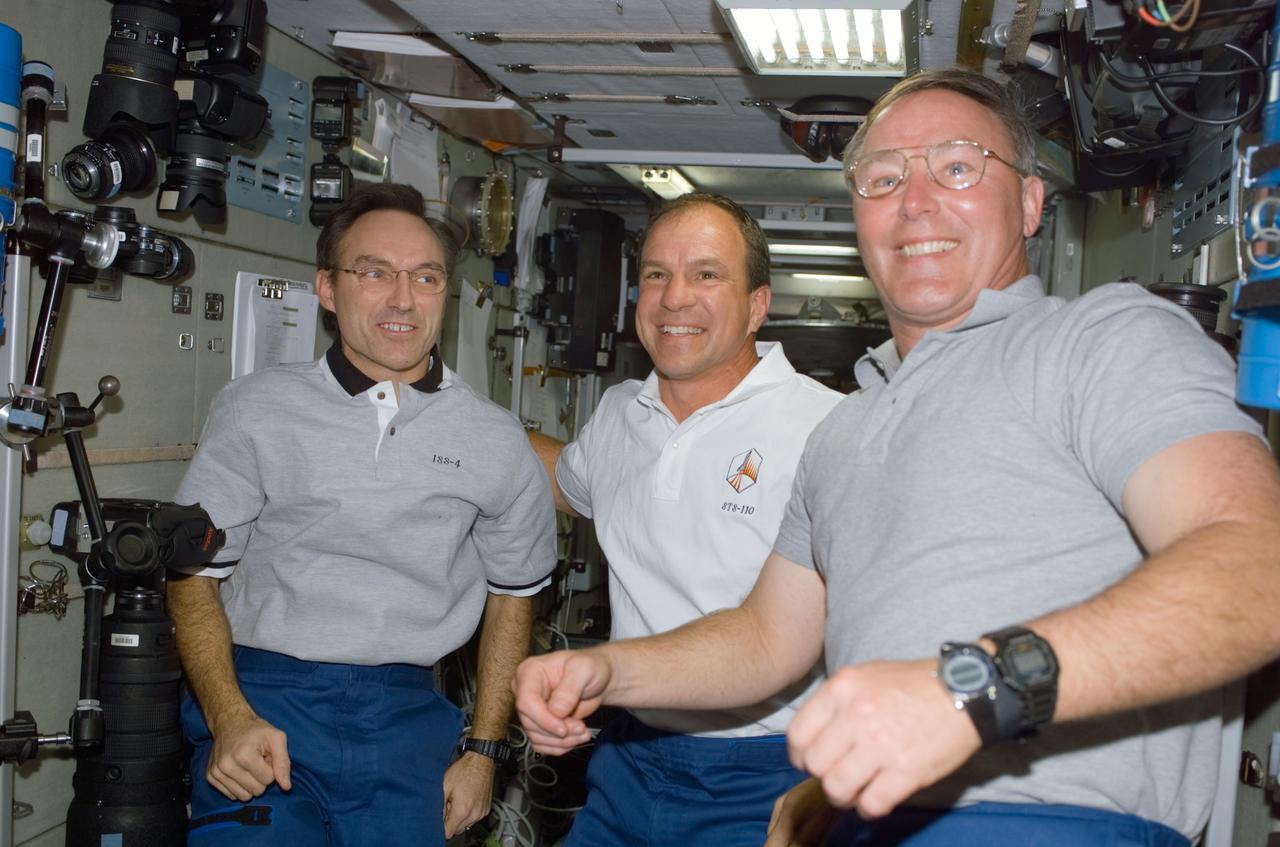

STS110-E-5126 (10 April 2002) --- Astronauts Carl E. Walz (left), Expedition Four flight engineer, Michael J. Bloomfield and Jerry L. Ross, STS-110 mission commander and mission specialist, respectively, are photographed in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The image was taken with a digital still camera.
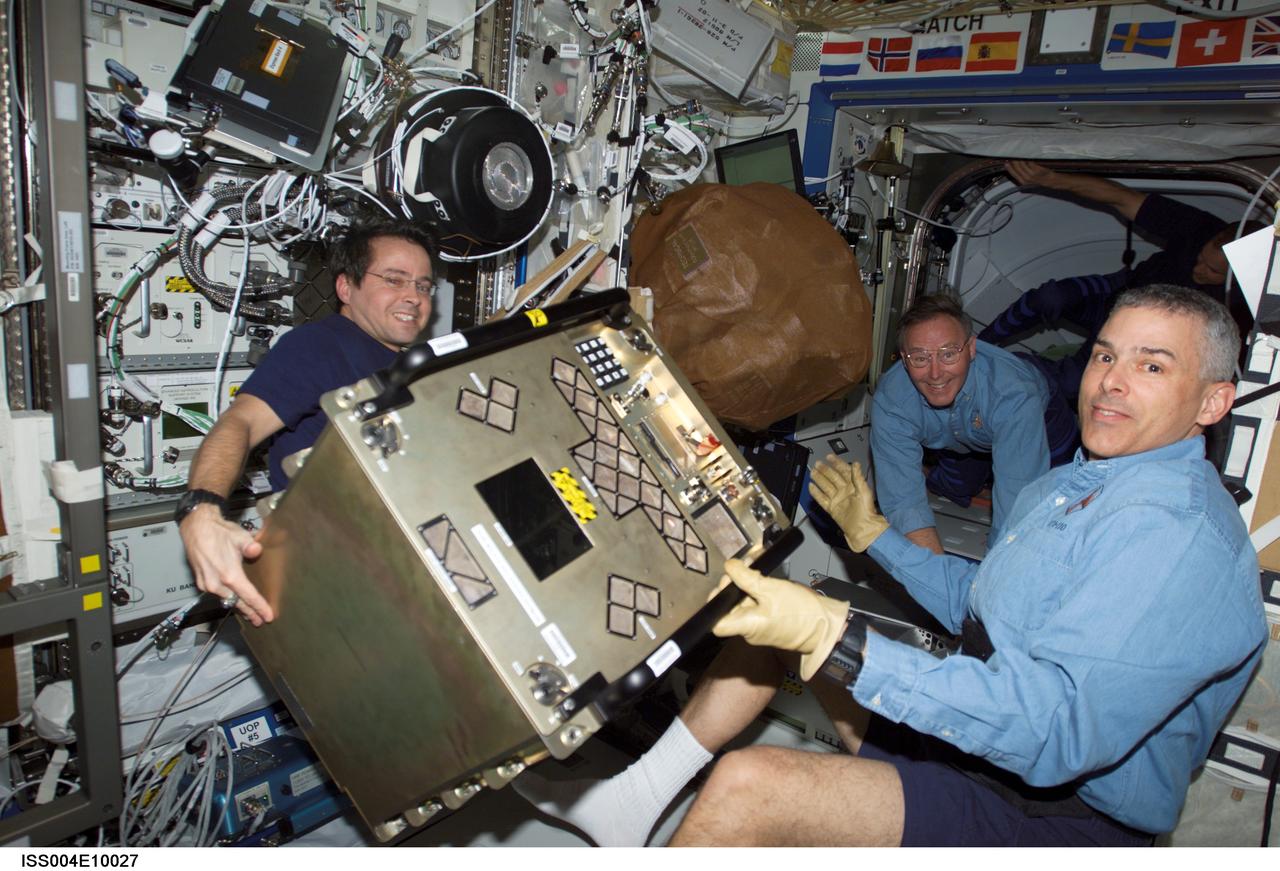

ISS004-E-10027 (12 April 2002) --- Astronauts Daniel W. Bursch (left), Expedition Four flight engineer, and Lee M. E. Morin, STS-110 mission specialist, move equipment in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, STS-110 mission specialist, is visible in the background.
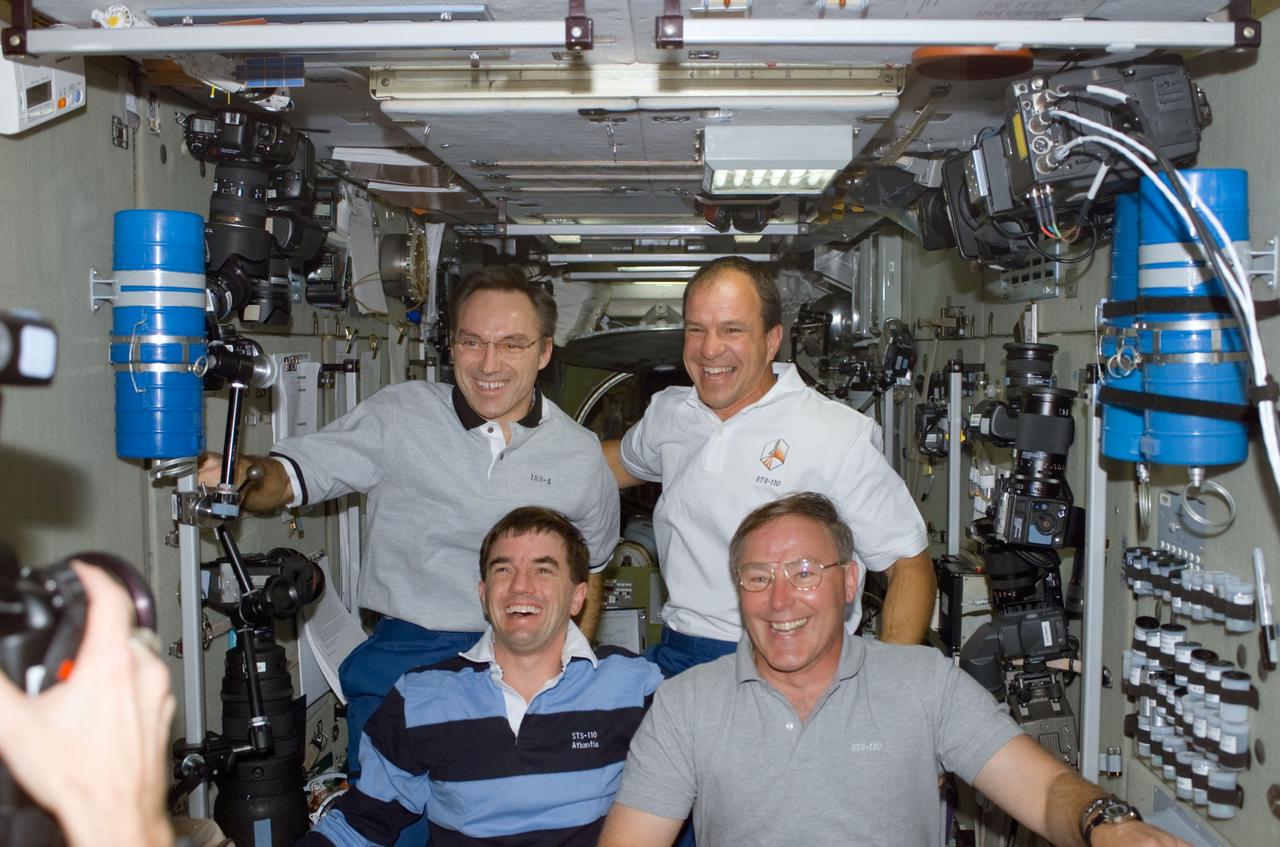

STS110-E-5127 (10 April 2002) --- Astronauts Carl E. Walz (top left), Expedition Four flight engineer, Michael J. Bloomfield, STS-110 mission commander, and Rex J. Walheim (bottom left) and Jerry L. Ross, both STS-110 mission specialists, gather for an informal photo in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The image was taken with a digital still camera.
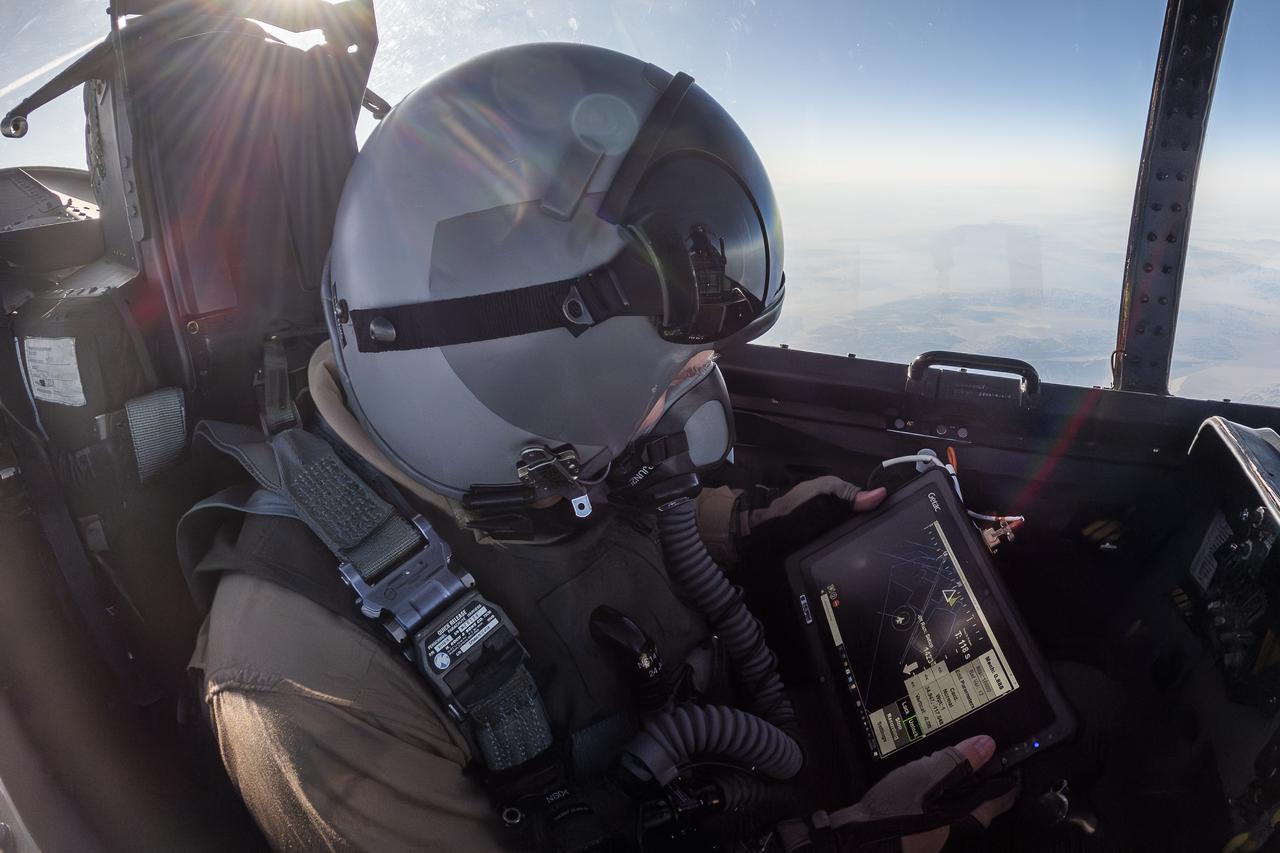

NASA photographer James Ross monitors the Airborne Location Integrating Geospatial Navigation System (ALIGNS) from the backseat of an F-15 near NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The ALIGNS provides real-time positioning guidance between aircraft for shock wave probing and schlieren imagery capture.
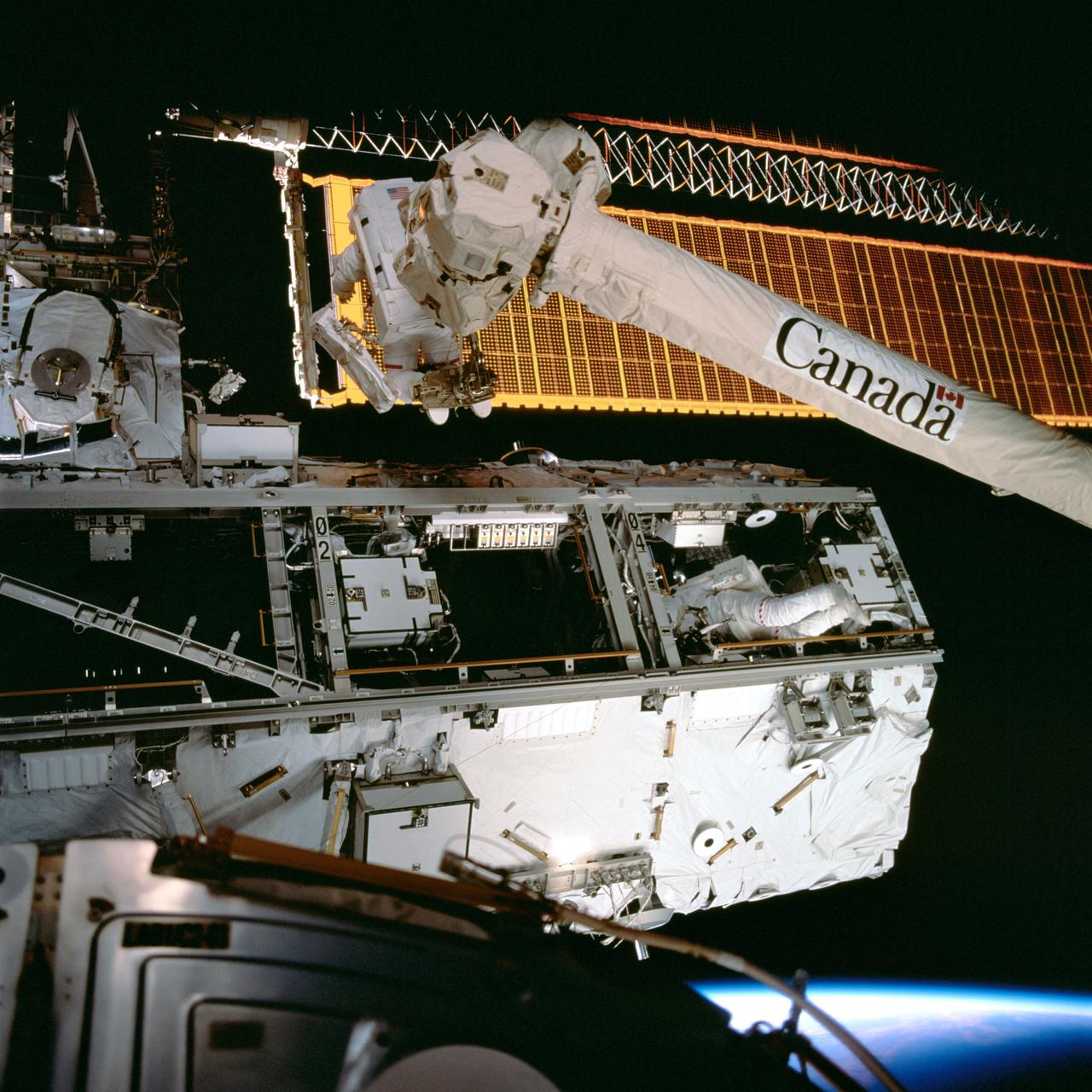
STS-110 Mission Specialists Jerry L. Ross and Lee M.E. Morin work in tandem on the fourth scheduled EVA session for the STS-110 mission aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis. Ross is anchored on the mobile foot restraint on the International Space Station's (ISS) Canadarm2, while Morin works inside the S0 (S-zero) truss. The STS-110 mission prepared the Station for future spacewalks by installing and outfitting a 43-foot-long S0 truss and preparing the Mobile Transporter. The 27,000 pound S0 Truss was the first of 9 segments that will make up the Station's external framework that will eventually stretch 356 feet (109 meters), or approximately the length of a football field. This central truss segment also includes a flatcar called the Mobile Transporter and rails that will become the first "space railroad," which will allow the Station's robotic arm to travel up and down the finished truss for future assembly and maintenance. The completed truss structure will hold solar arrays and radiators to provide power and cooling for additional international research laboratories from Japan and Europe that will be attached to the Station. Milestones of the S-110 mission included the first time the ISS robotic arm was used to maneuver spacewalkers around the Station and marked the first time all spacewalks were based out of the Station's Quest Airlock. It was also the first Shuttle to use three Block II Main Engines. The Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis, STS-110 mission, was launched April 8, 2002 and returned to Earth April 19, 2002.
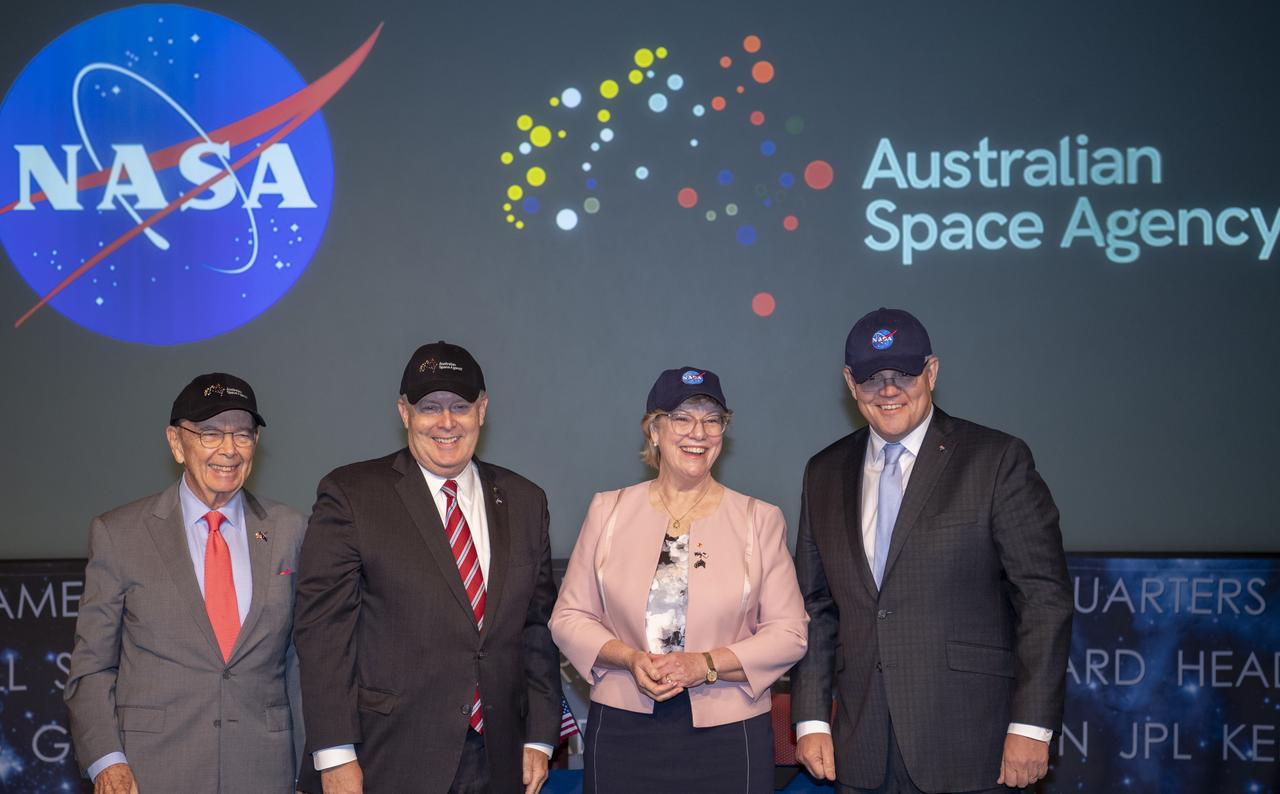

U.S. Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard, second from left, Dr. Megan Clark, Head of the Australian Space Agency, second from right, and Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison, right, pose for a picture after exchanging space agency hats following the signing of a letter of intent between NASA and the Australian Space Agency, Saturday, Sept. 21, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA and the Australian Space Agency will build on over 60 years of collaboration in space exploration between the two countries and commit to expanding cooperation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

U.S. Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard, second from left, Dr. Megan Clark, Head of the Australian Space Agency, second from right, and Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison, right, pose for a picture after exchanging space agency hats following the signing of a letter of intent between NASA and the Australian Space Agency, Saturday, Sept. 21, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA and the Australian Space Agency will build on over 60 years of collaboration in space exploration between the two countries and commit to expanding cooperation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

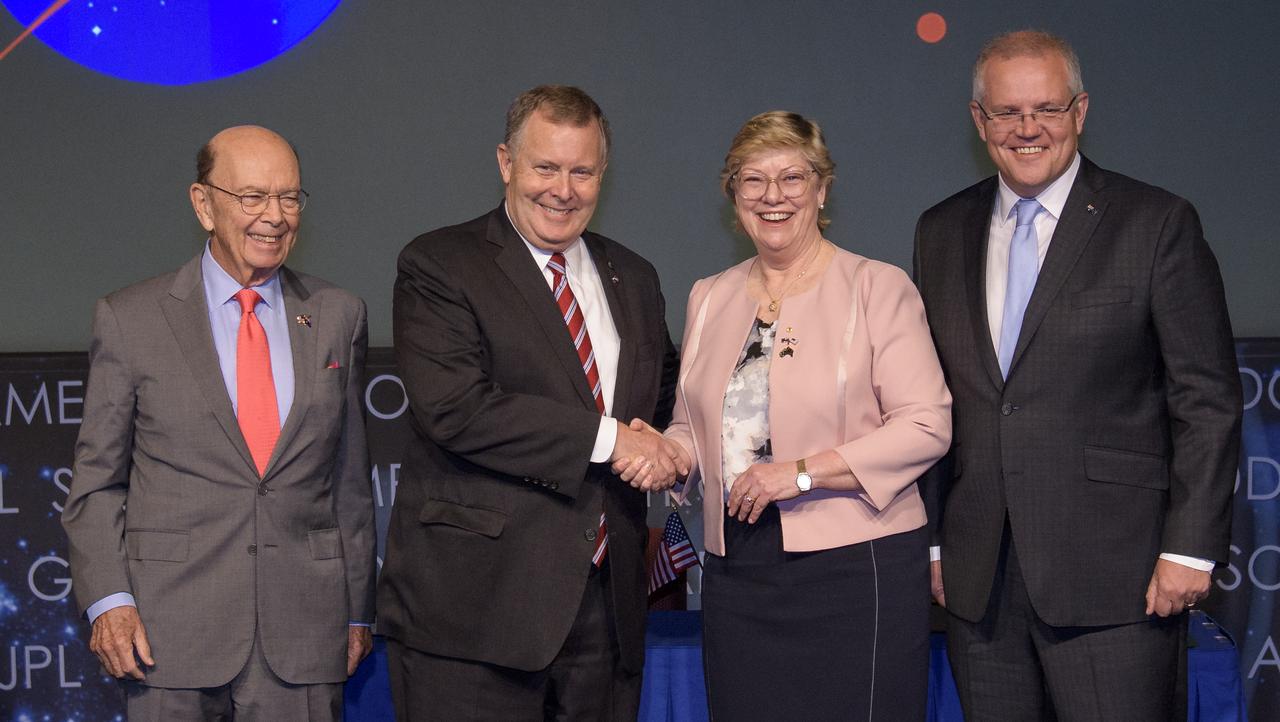
U.S. Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, top left, and Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison, top right, witness the signing of a letter of intent between NASA and the Australian Space Agency by NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard, left, and Dr. Megan Clark, Head of the Australian Space Agency, right, Saturday, Sept. 21, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA and the Australian Space Agency will build on over 60 years of collaboration in space exploration between the two countries and commit to expanding cooperation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

U.S. Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, top left, and Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison, top right, witness the signing of a letter of intent between NASA and the Australian Space Agency by NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard, left, and Dr. Megan Clark, Head of the Australian Space Agency, right, Saturday, Sept. 21, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA and the Australian Space Agency will build on over 60 years of collaboration in space exploration between the two countries and commit to expanding cooperation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

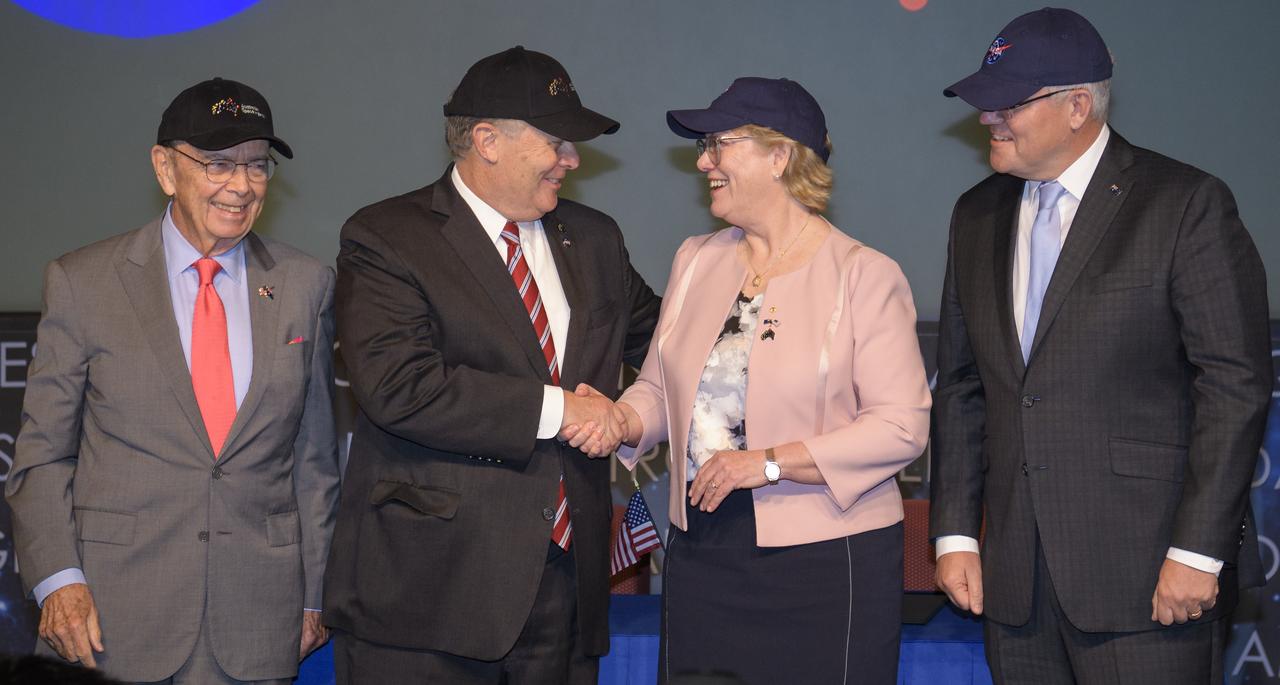
NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard, second from left, shakes hands with Dr. Megan Clark, Head of the Australian Space Agency, second from right, as they pose for a photo with U.S. Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, left, and Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison, right, following the signing of a letter of intent between NASA and the Australian Space Agency, Saturday, Sept. 21, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA and the Australian Space Agency will build on over 60 years of collaboration in space exploration between the two countries and commit to expanding cooperation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
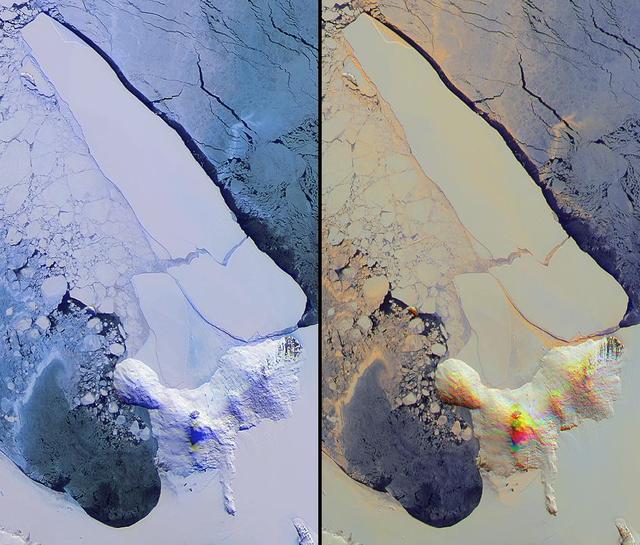

NASA Terra spacecraft imaged Iceberg B-15A, the largest iceberg in the world measuring about 11,000 square kilometers when it broke away from Western Antarctica Ross Ice Shelf in March 2000.
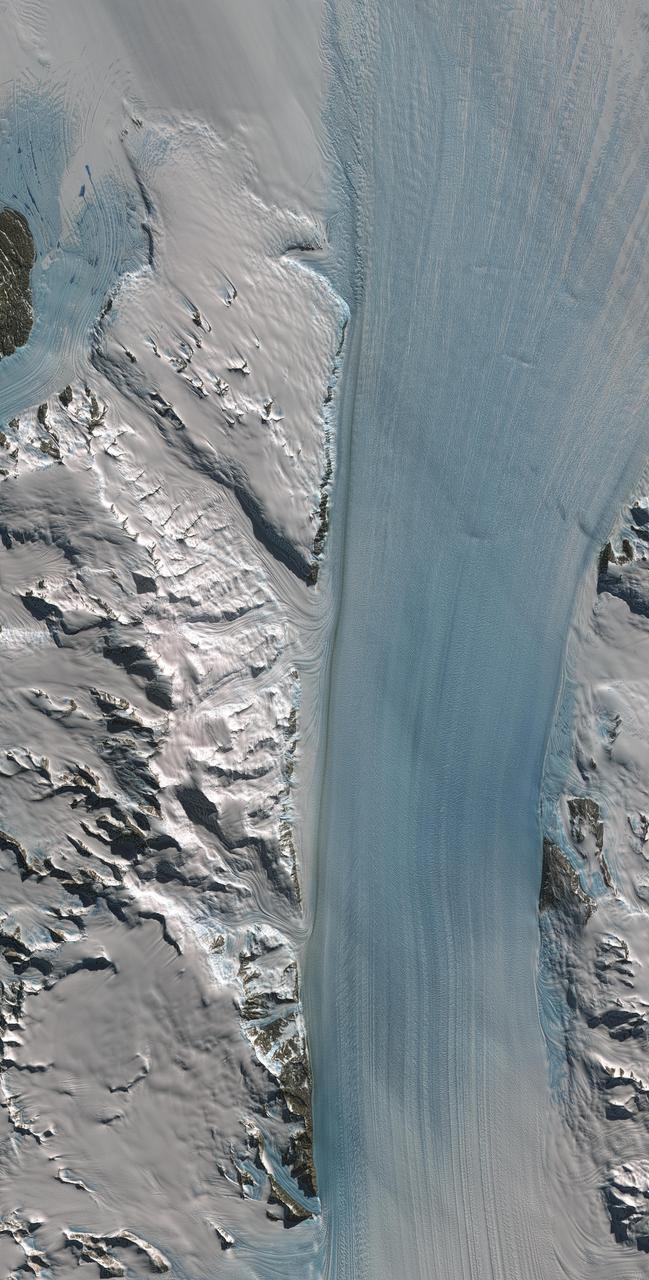

Byrd Glacier is a major glacier in Antarctica; it drains an extensive area of the polar plateau and flows eastward between the Britannia Range and the Churchill Mountains to discharge into the Ross Ice Shelf. This image is from NASA Terra satellite.

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, third from left, is seen as he is escorted on a tour of the Space Shuttle Trainer Crew Compartment in the Charles Simonyi Space Gallery at the Museum of Flight, Tuesday, Jan. 15, 2013 in Seattle, Washington. Bolden is joined by Washington Aerospace Scholars Alec Lindsey, far left, Brenna Tuller-Ross and Doug King, far right, president and CEO of the museum. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

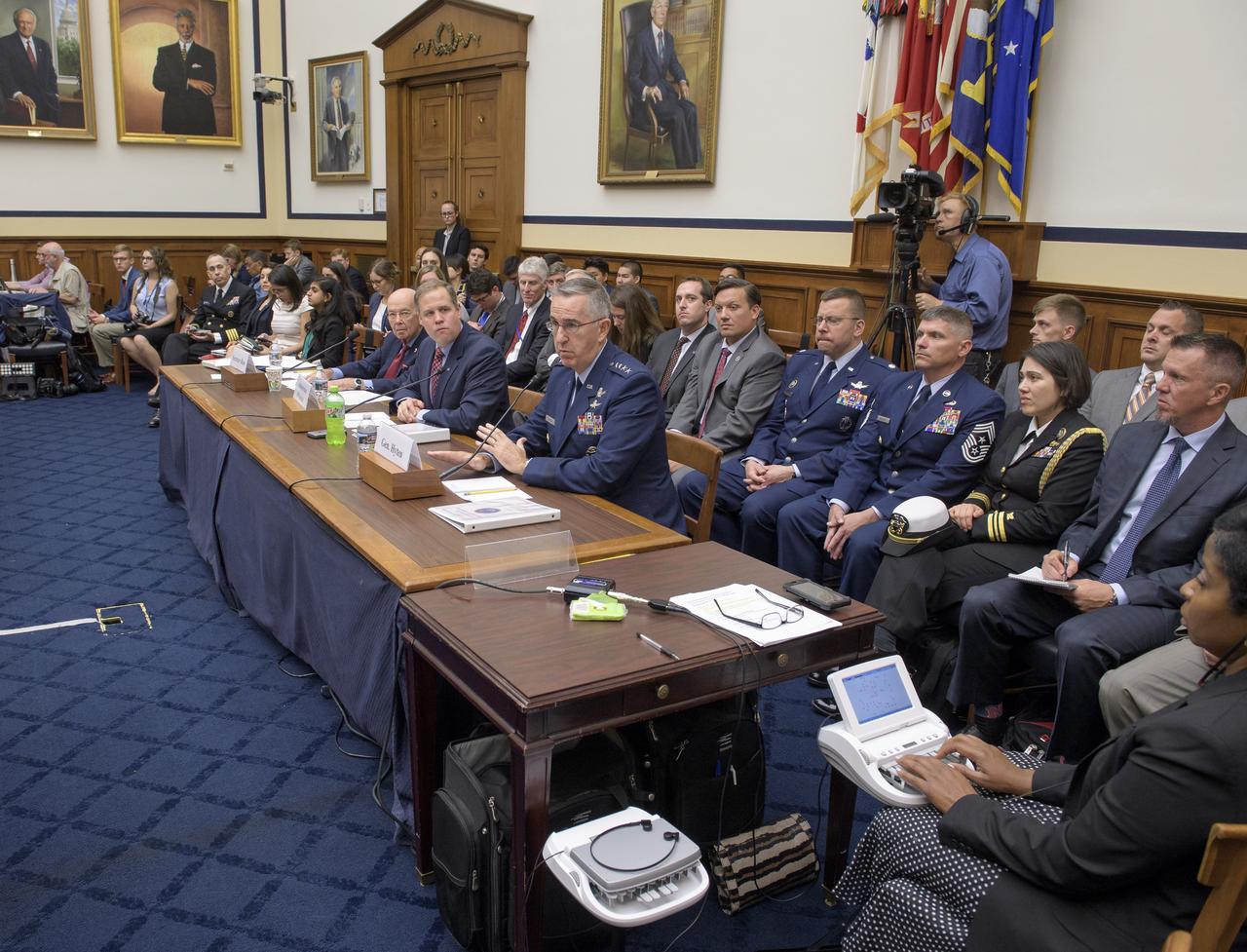
Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, left, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, center, and Commander, U.S. Strategic Command, General John Hyten prepare to testify before the House Subcommittee on Strategic Forces during a hearing on Space Situational Awareness: Whole of Government Perspectives on Roles and Responsibilities, Friday, June 22, 2018 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, left, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, center, and Commander, U.S. Strategic Command, General John Hyten testify before the House Subcommittee on Strategic Forces during a hearing on Space Situational Awareness: Whole of Government Perspectives on Roles and Responsibilities, Friday, June 22, 2018 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
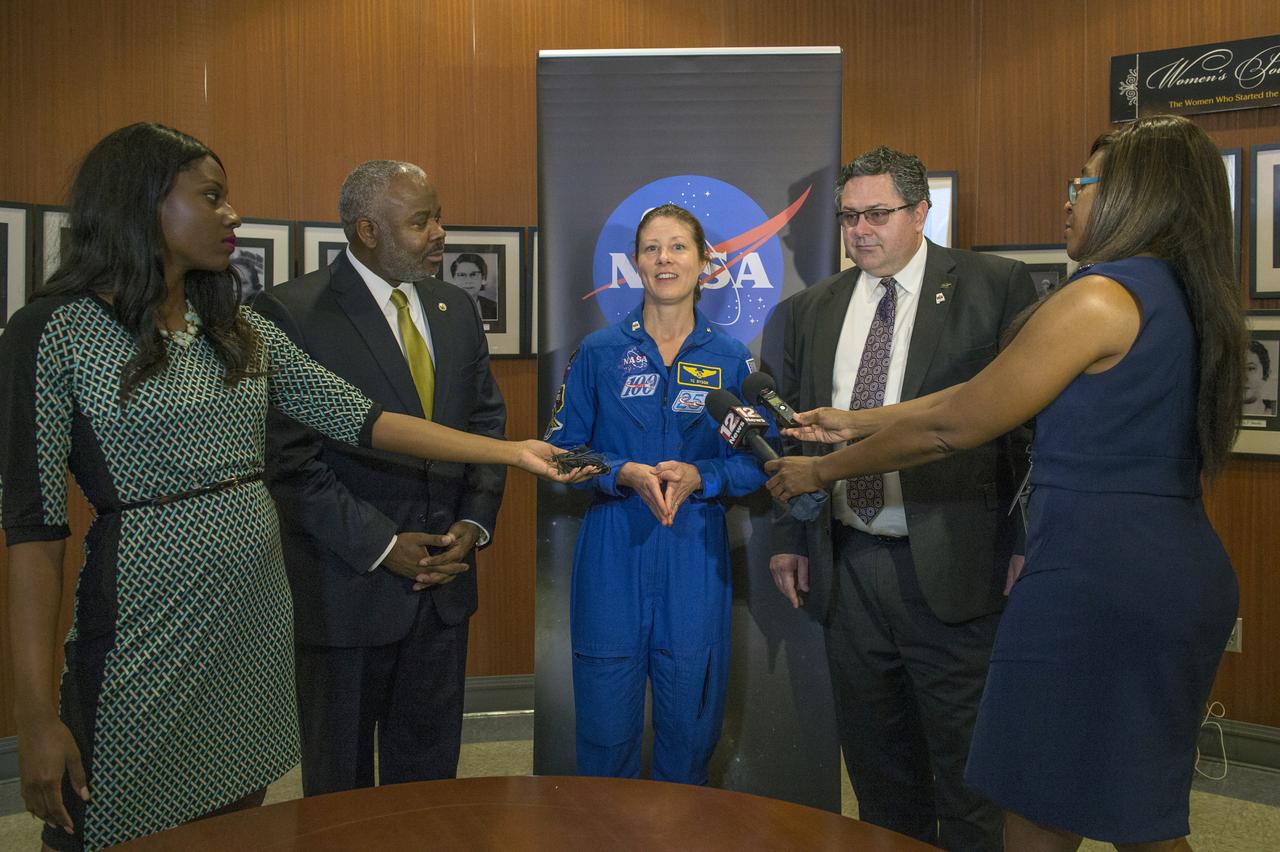

Officials from Marshall Space Flight Center discussed the state's role in leading America back to the Moon and on to Mars with elected officials, industry leaders, students and the public during the Aerospace States Association’s Alabama Aerospace Week in Montgomery, Ala. NASA was honored by the Alabama legislature with a resolution and proclamation from Gov. Kay Ivey recognizing the agency's achievements. Dr. Quentin T. Ross, Jr., President, Alabama State University, Astronaut Tracy Dyson, and MSFC Director Todd May talk to members of the media at Alabama State University.

Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, left, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, center, and Commander, U.S. Strategic Command, General John Hyten testify before the House Subcommittee on Strategic Forces during a hearing on Space Situational Awareness: Whole of Government Perspectives on Roles and Responsibilities, Friday, June 22, 2018 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
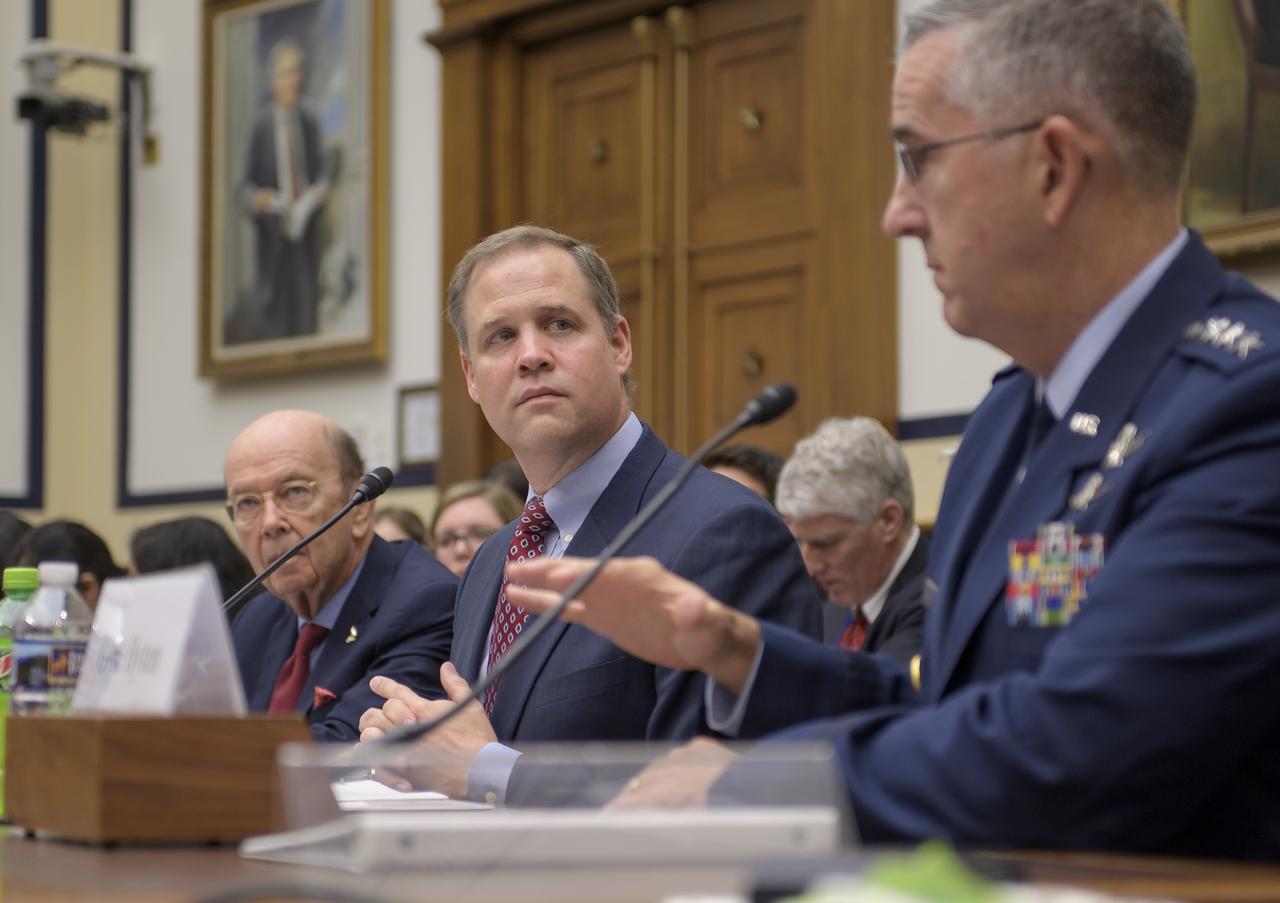

Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, left, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, center, and Commander, U.S. Strategic Command, General John Hyten testify before the House Subcommittee on Strategic Forces during a hearing on Space Situational Awareness: Whole of Government Perspectives on Roles and Responsibilities, Friday, June 22, 2018 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
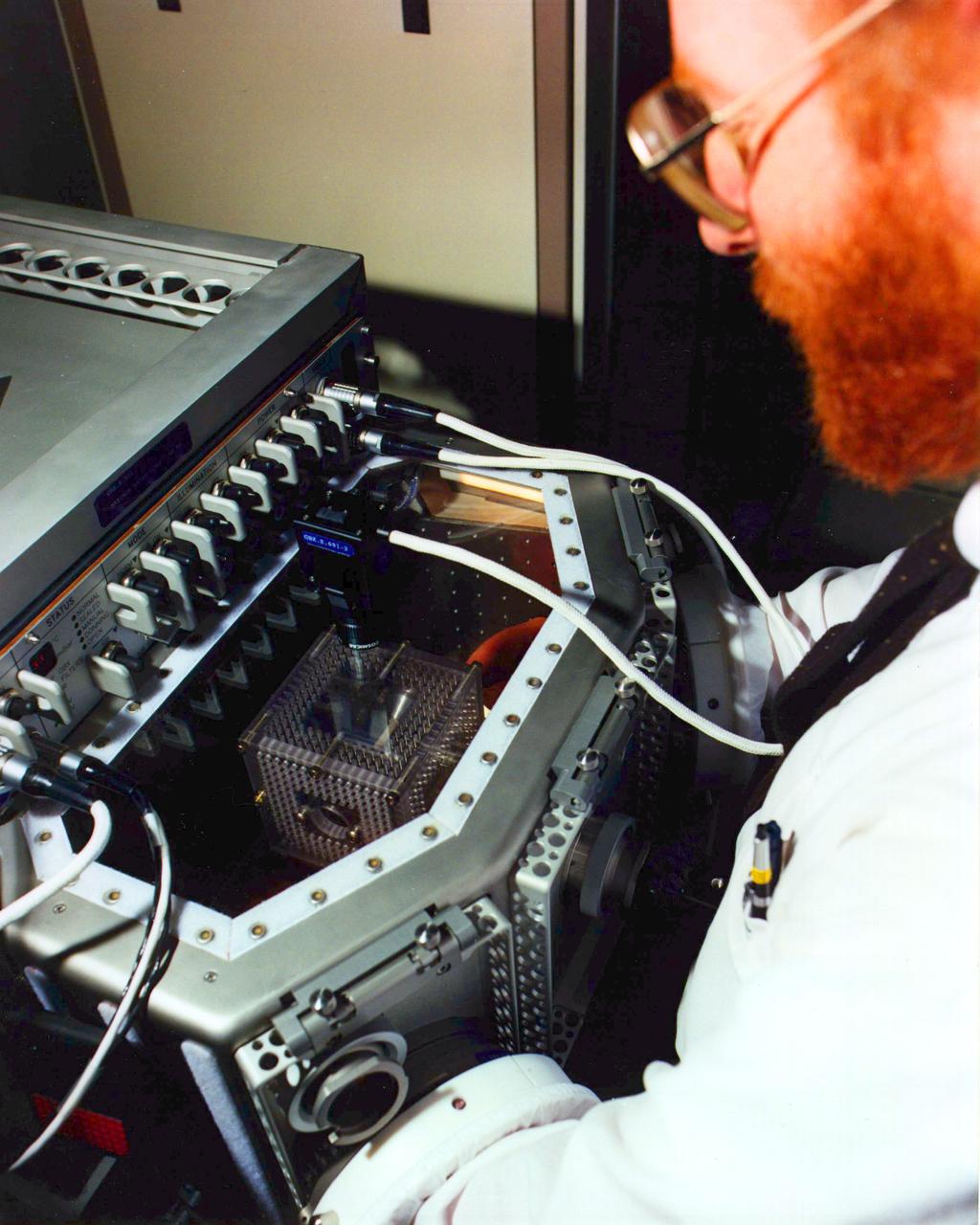

USML-1, Howard Ross working with the Glovebox Module

The International Space Station, with a crew of six onboard, is seen in silhouette as it transits the Sun at roughly five miles per second during a partial solar eclipse, Monday, Aug. 21, 2017 from Ross Lake, Northern Cascades National Park, Washington. Onboard as part of Expedition 52 are: NASA astronauts Peggy Whitson, Jack Fischer, and Randy Bresnik; Russian cosmonauts Fyodor Yurchikhin and Sergey Ryazanskiy; and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Paolo Nespoli. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
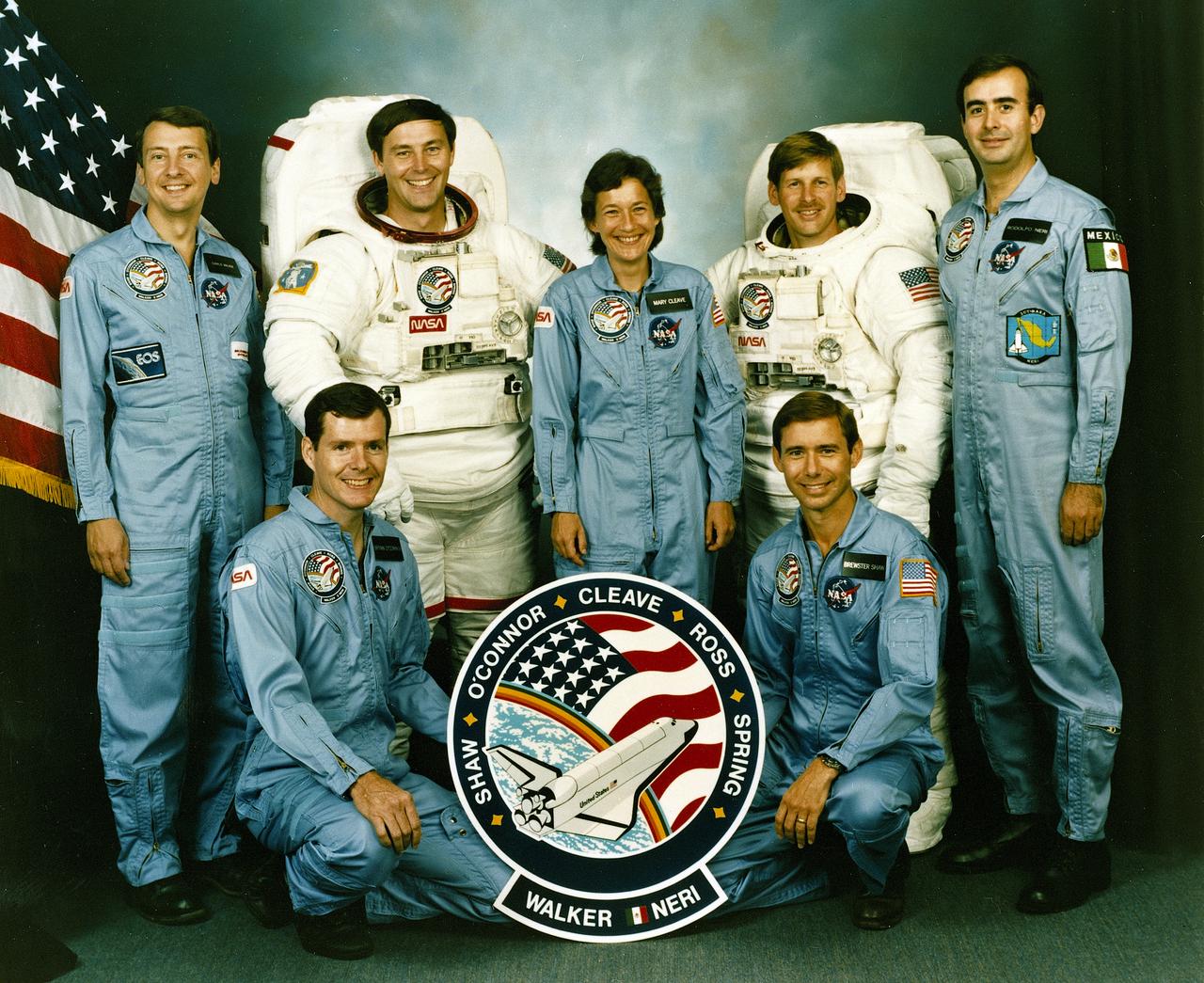

The crew assigned to the STS-61B mission included (kneeling left to right) Bryan D. O’conner, pilot; and Brewster H. Shaw, commander. On the back row, left to right, are Charles D. Walker, payload specialist; mission specialists Jerry L. Ross, Mary L. Cleave, and Sherwood C. Spring; and Rodolpho Neri Vela, payload specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis November 28, 1985 at 7:29:00 pm (EST), the STS-61B mission’s primary payload included three communications satellites: MORELOS-B (Mexico); AUSSAT-2 (Autralia); and SATCOM KU-2 (RCA Americom. Two experiments were conducted to test assembling erectable structures in space: EASE (Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity), and ACCESS (Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structure). In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA and Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction.
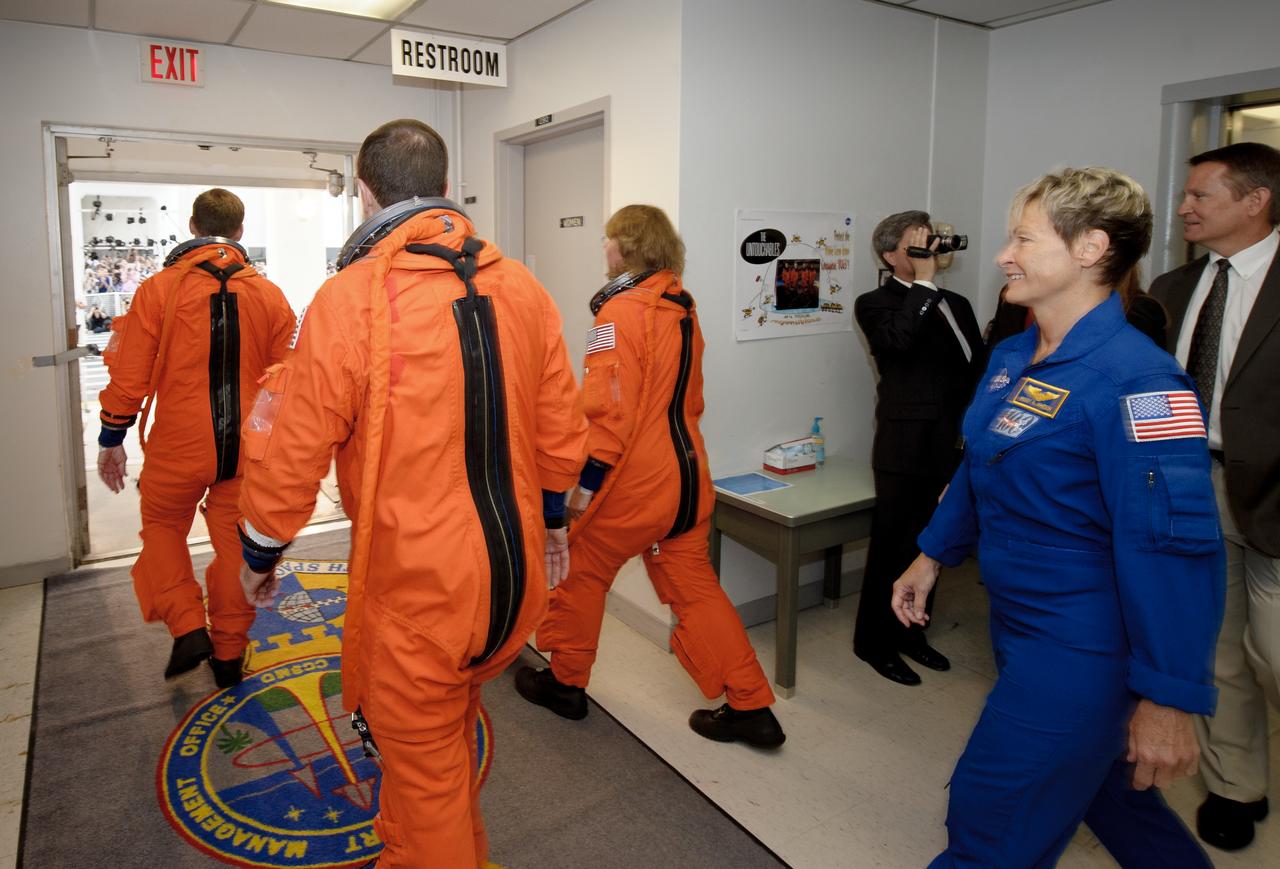

The crew of STS-135 is seen as they depart the NASA Kennedy Space Center, Operations and Checkout Building and get into the Astrovan for launch pad 39A, on Friday, July 8, 2011 in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The launch of Atlantis, STS-135, is the final flight of the shuttle program, a 12-day mission to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jerry Ross)

Crowds are seen out the front window of the Astrovan carrying the STS-135 crew as it departs the NASA Kennedy Space Center, Operations and Checkout Building for launch pad 39A, on Friday, July 8, 2011 in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The launch of Atlantis, STS-135, is the final flight of the shuttle program, a 12-day mission to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jerry Ross)
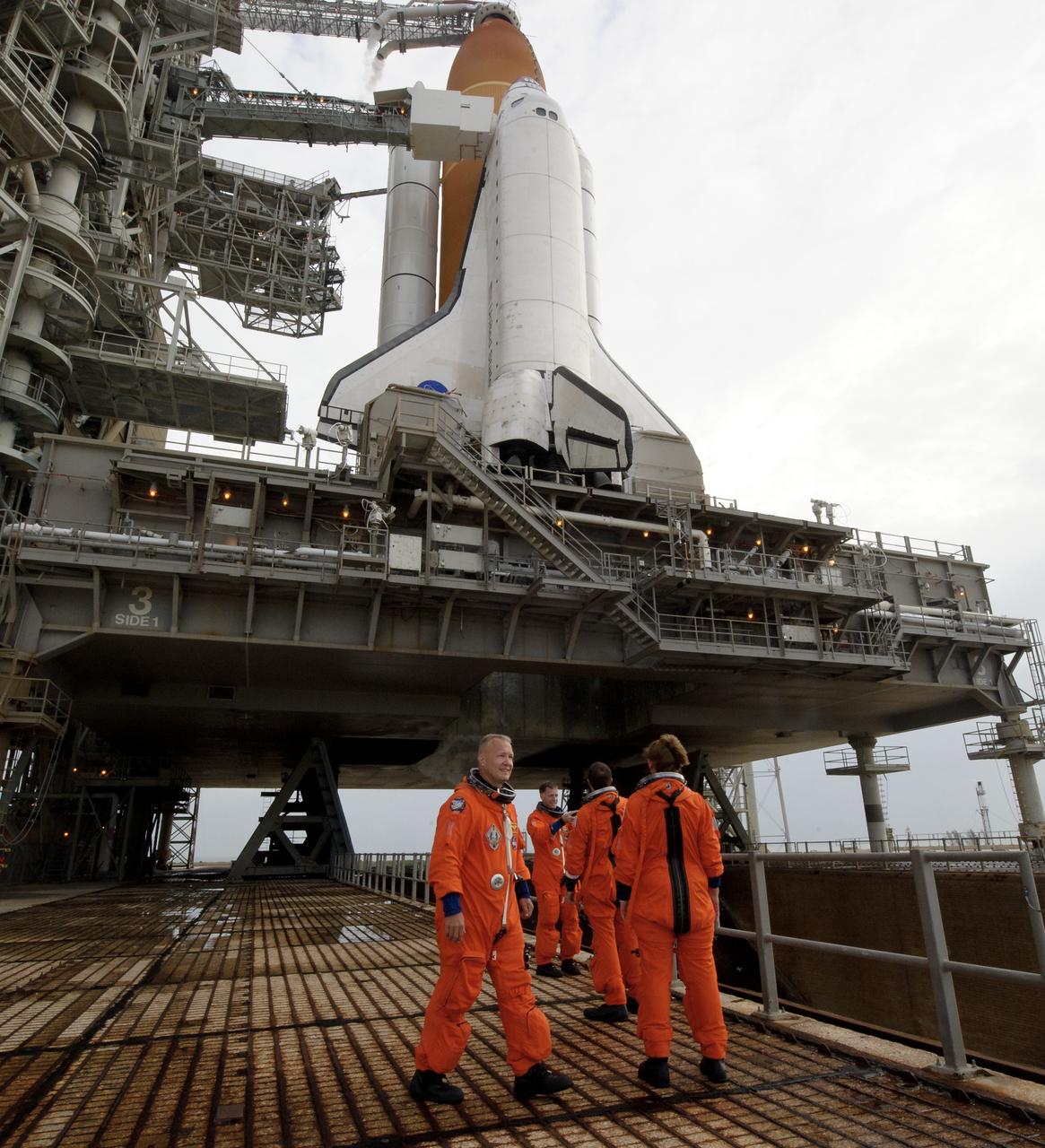

The STS-135 crew; Chris Ferguson, commander; Doug Hurley, pilot;, left, Rex Walheim and Sandy Magnus, both mission specialists are seen before boarding space shuttle Atlantis at launch pad 39A prior to launch, Friday, July 8, 2011 at the NASA Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The launch of Atlantis, STS-135, is the final flight of the shuttle program, a 12-day mission to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jerry Ross)
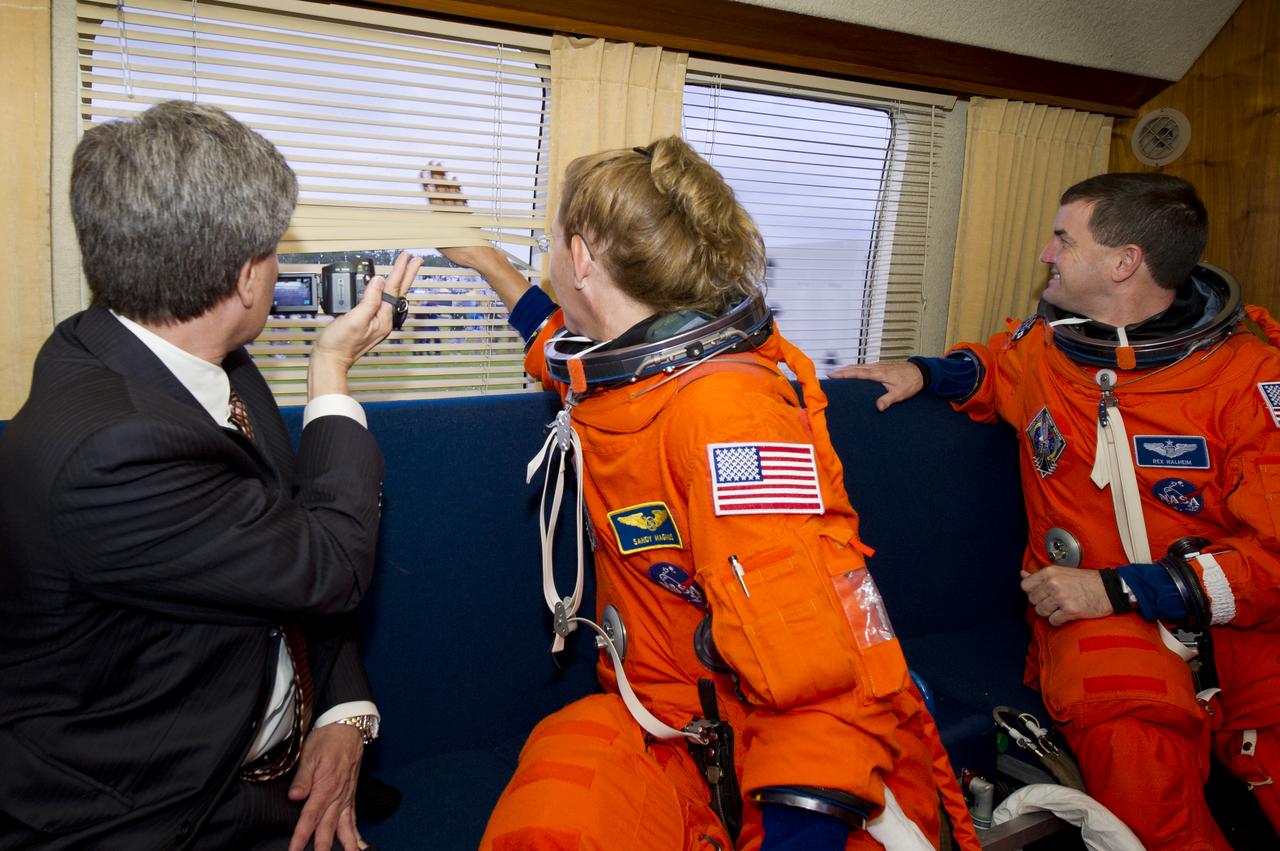

James Branson of United Space Alliance, far left; Sandra Magnus, STS-135 mission specialist and Rex Walheim, STS-135 mission specialist, far right, are seen in the Astrovan as they ride to launch pad 39A to board space shuttle Atlantis on Friday, July 8, 2011, at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The launch of Atlantis, STS-135, is the final flight of the shuttle program, a 12-day mission to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jerry Ross)
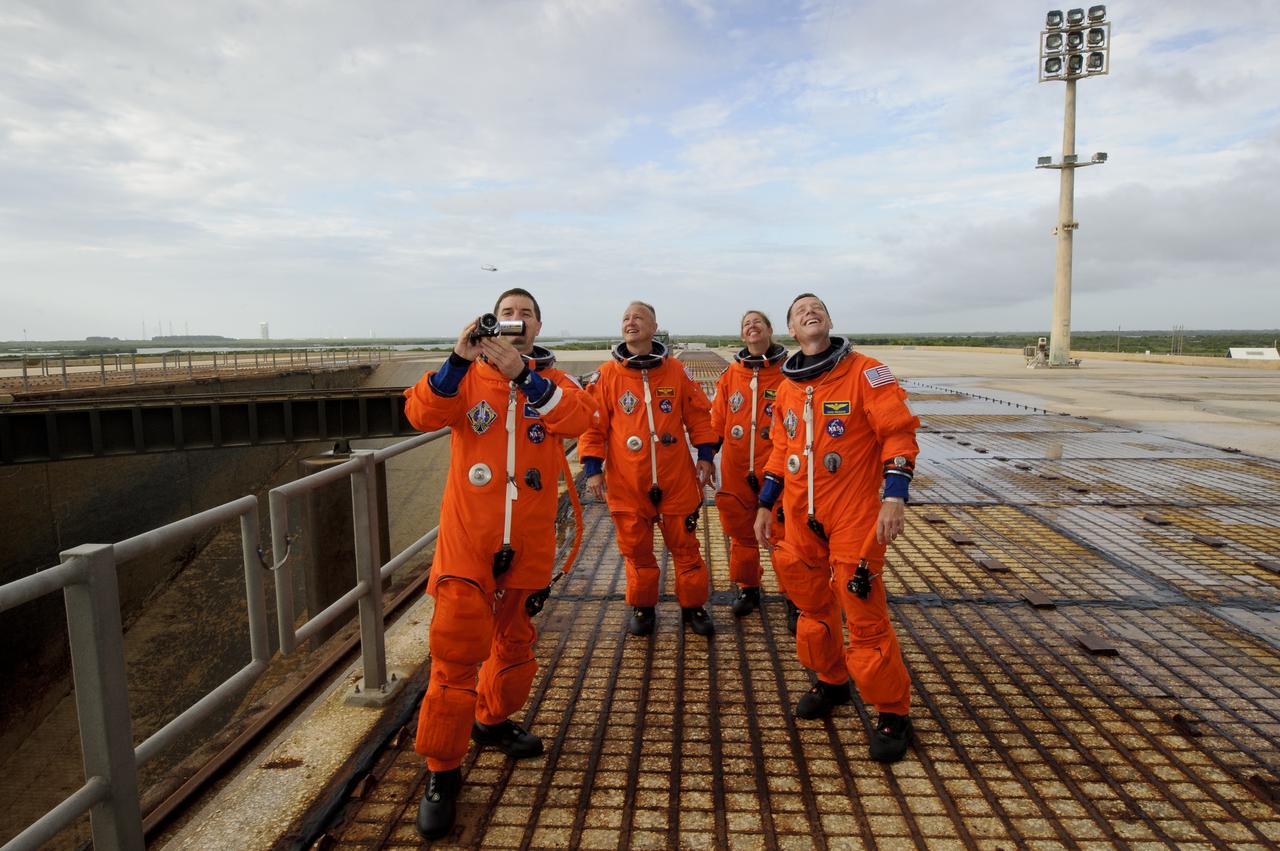

The STS-135 mission specialist Rex Walheim, left, Doug Hurley, pilot; second from left, Sandy Magnus, mission specialist; and Chris Ferguson, commander, right, stop and take a moment to look up at the space shuttle Atlantis prior to boarding at launch pad 39A, Friday, July 8, 2011 at the NASA Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The launch of Atlantis, STS-135, is the final flight of the shuttle program, a 12-day mission to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jerry Ross)
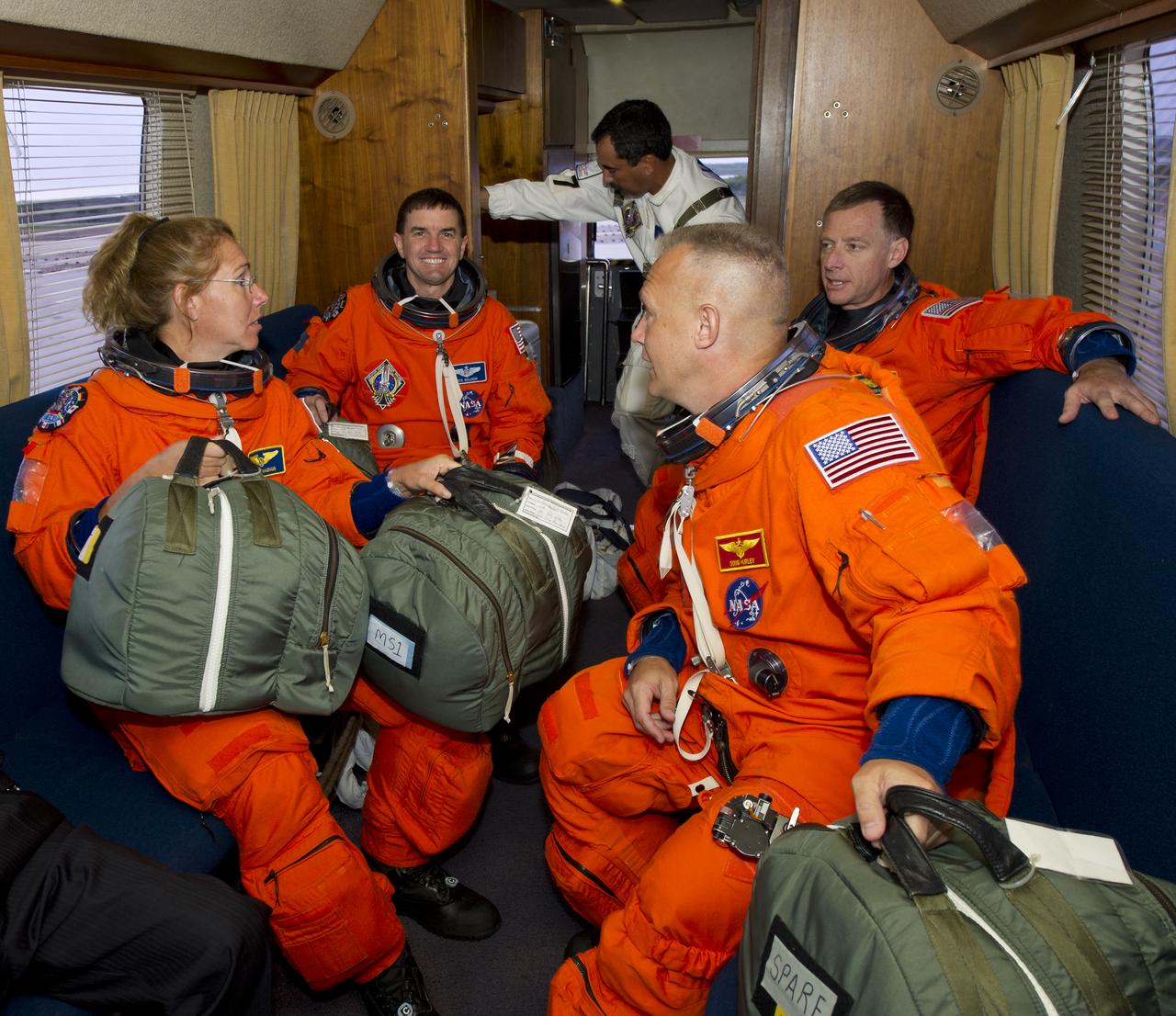

The STS-135 crew, clockwise: Sandra Magnus, mission specialist; Rex Walheim, mission specialist; Chris Ferguson, commander and Doug Hurley, pilot are seen in the Astrovan as they ride to launch pad 39A to board space shuttle Atlantis on Friday, July 8, 2011, at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The launch of Atlantis, STS-135, is the final flight of the shuttle program, a 12-day mission to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jerry Ross)

This composite image of seven pictures shows the progression of a partial solar eclipse near from Ross Lake, Northern Cascades National Park, Washington on Monday, Aug. 21, 2017. The second to the last frame shows the International Space Station, with a crew of six onboard, in silhouette as it transits the Sun at roughly five miles per second. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the contiguous United States from Lincoln Beach, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of South America, Africa, and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
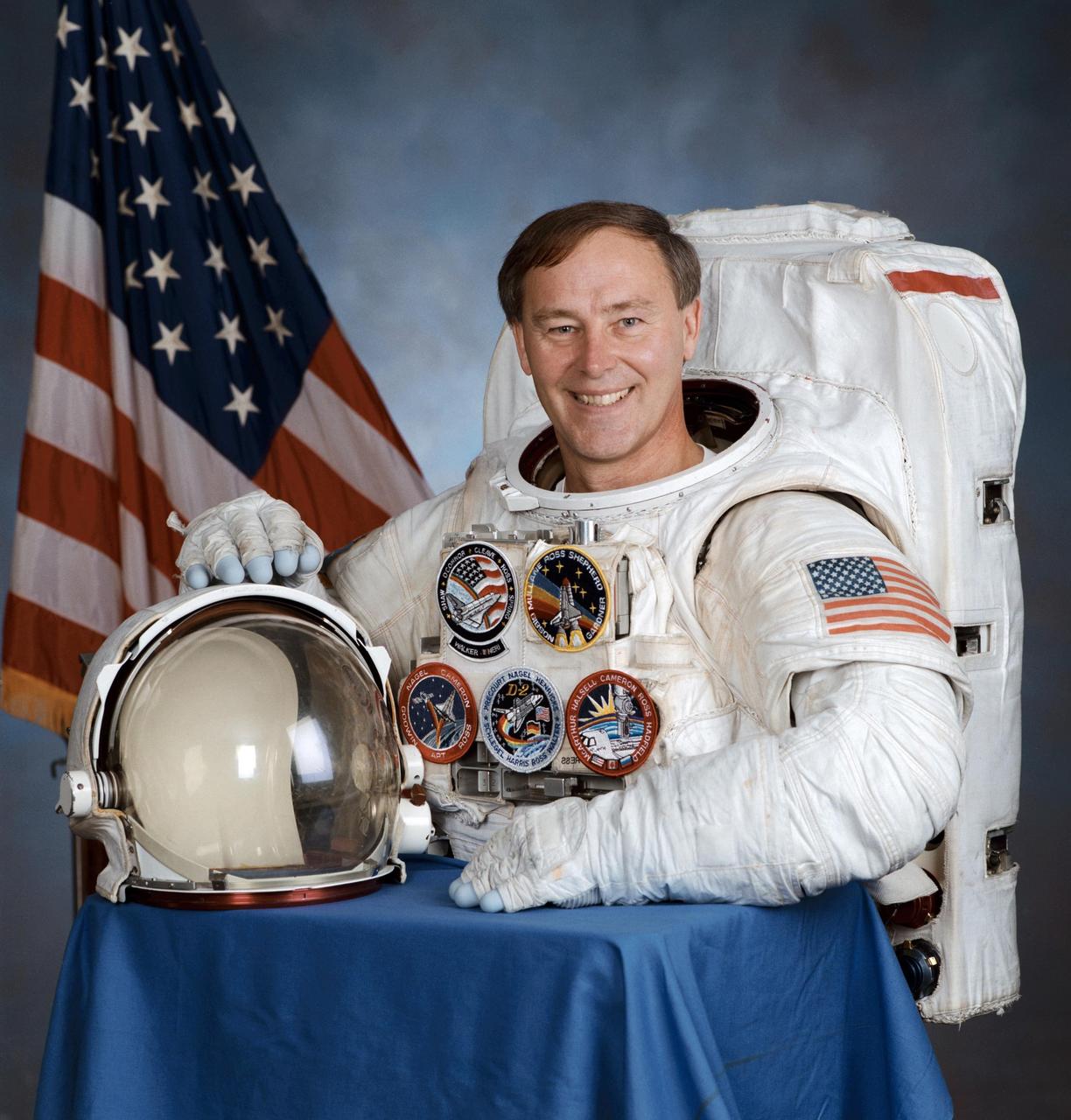

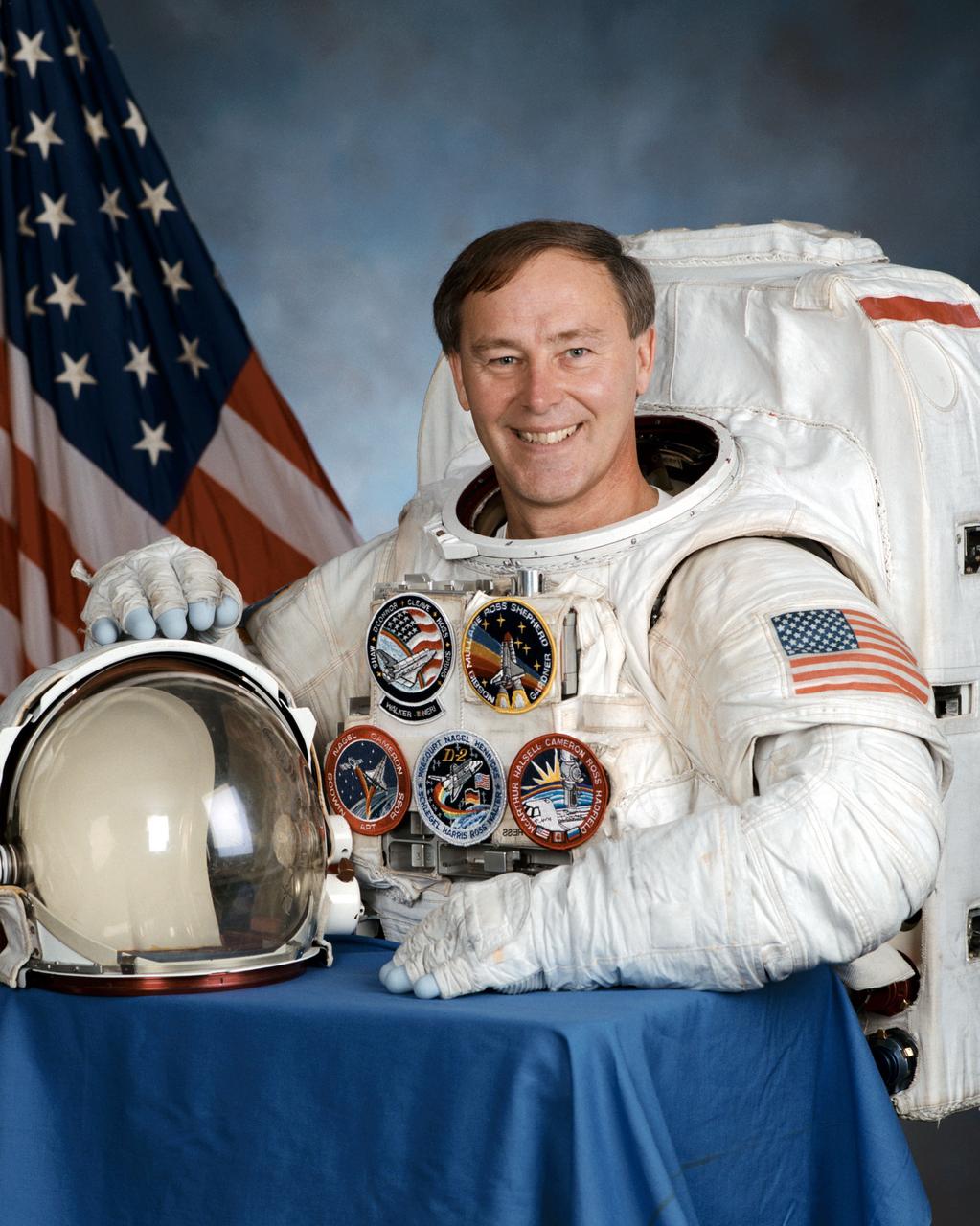
JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS. -- (JSC 596-00265) -- Official portrait of astronaut Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist
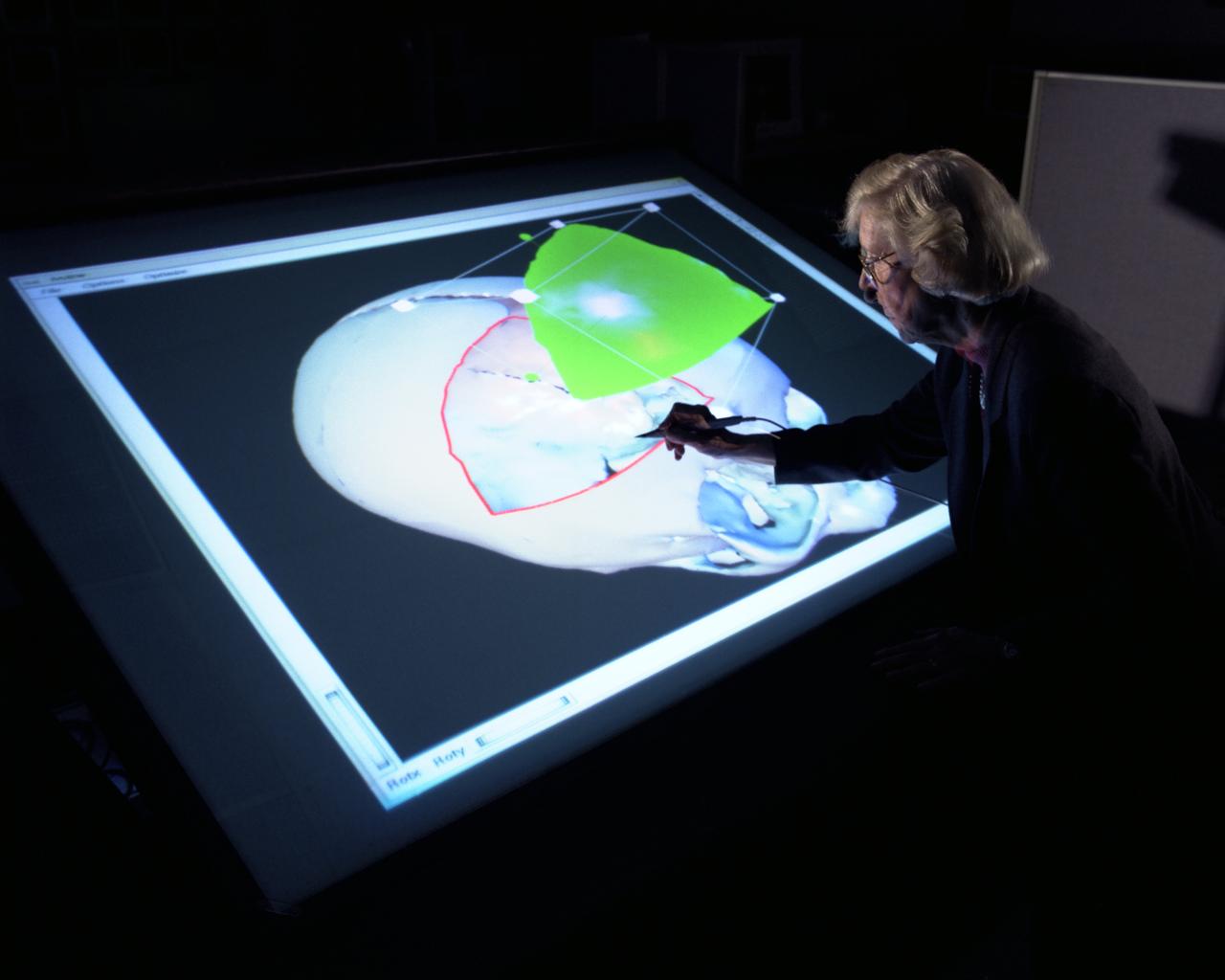

Biocomputation Lab: Fake Space Immersible Workbench Research; software scalpel with Dr Murial Ross
Life Sceince Division Facilities, Labs and Personnel (Code-SL) Dr. Muriel Ross